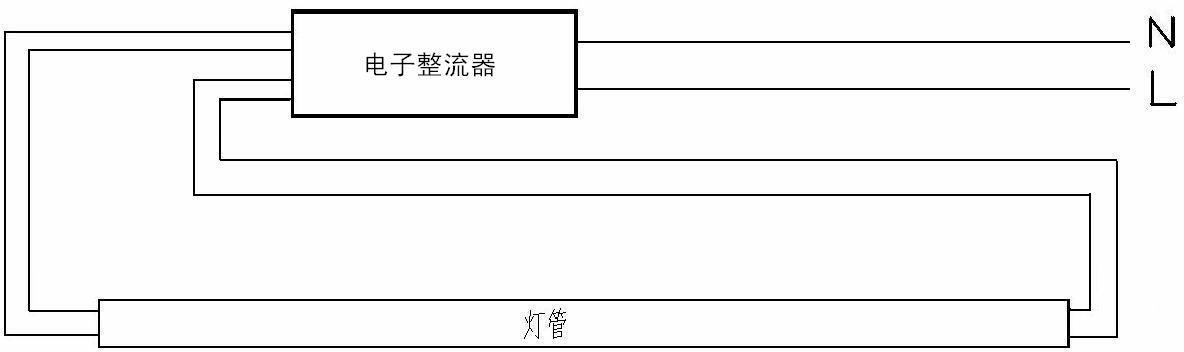
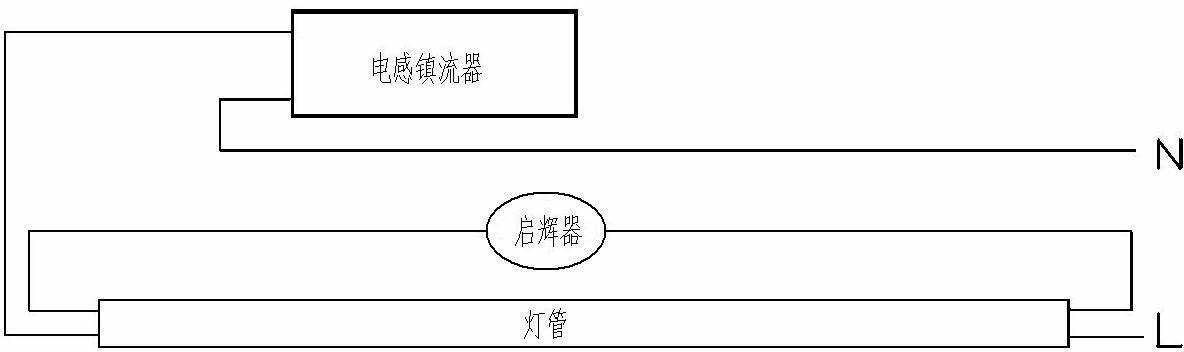
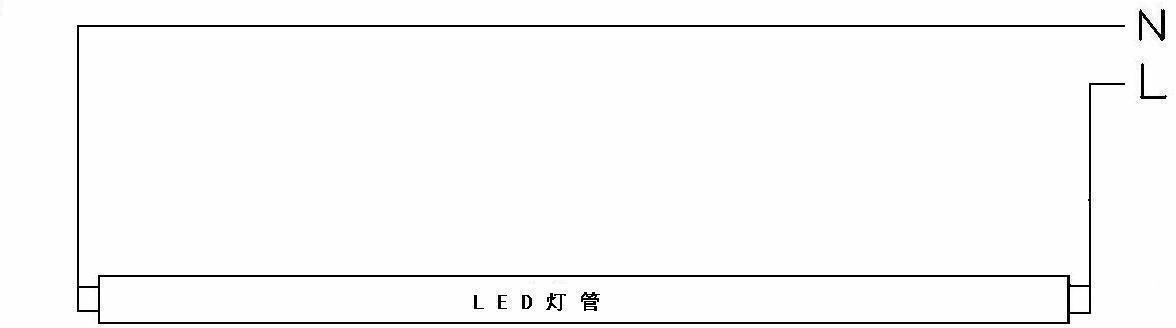
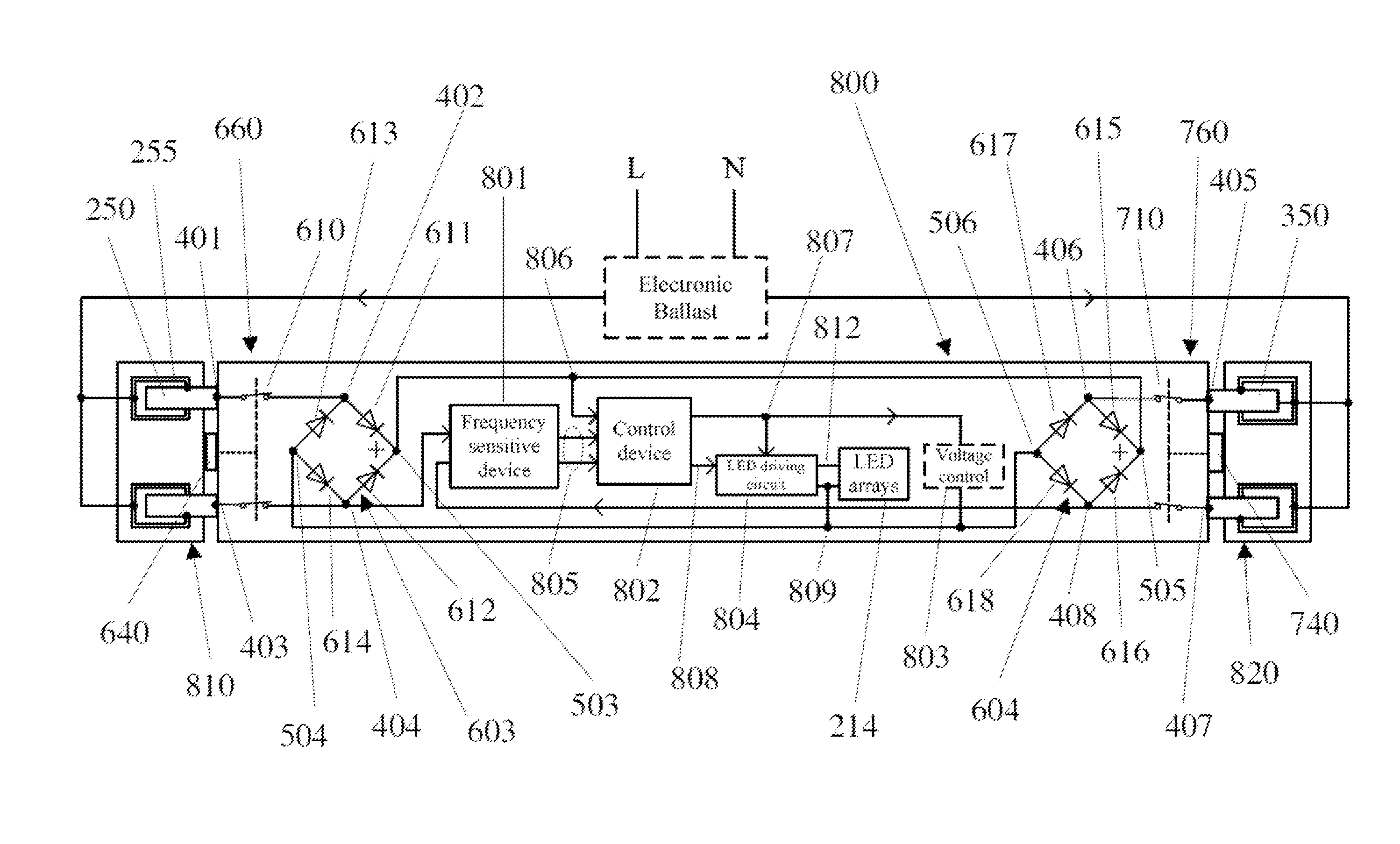
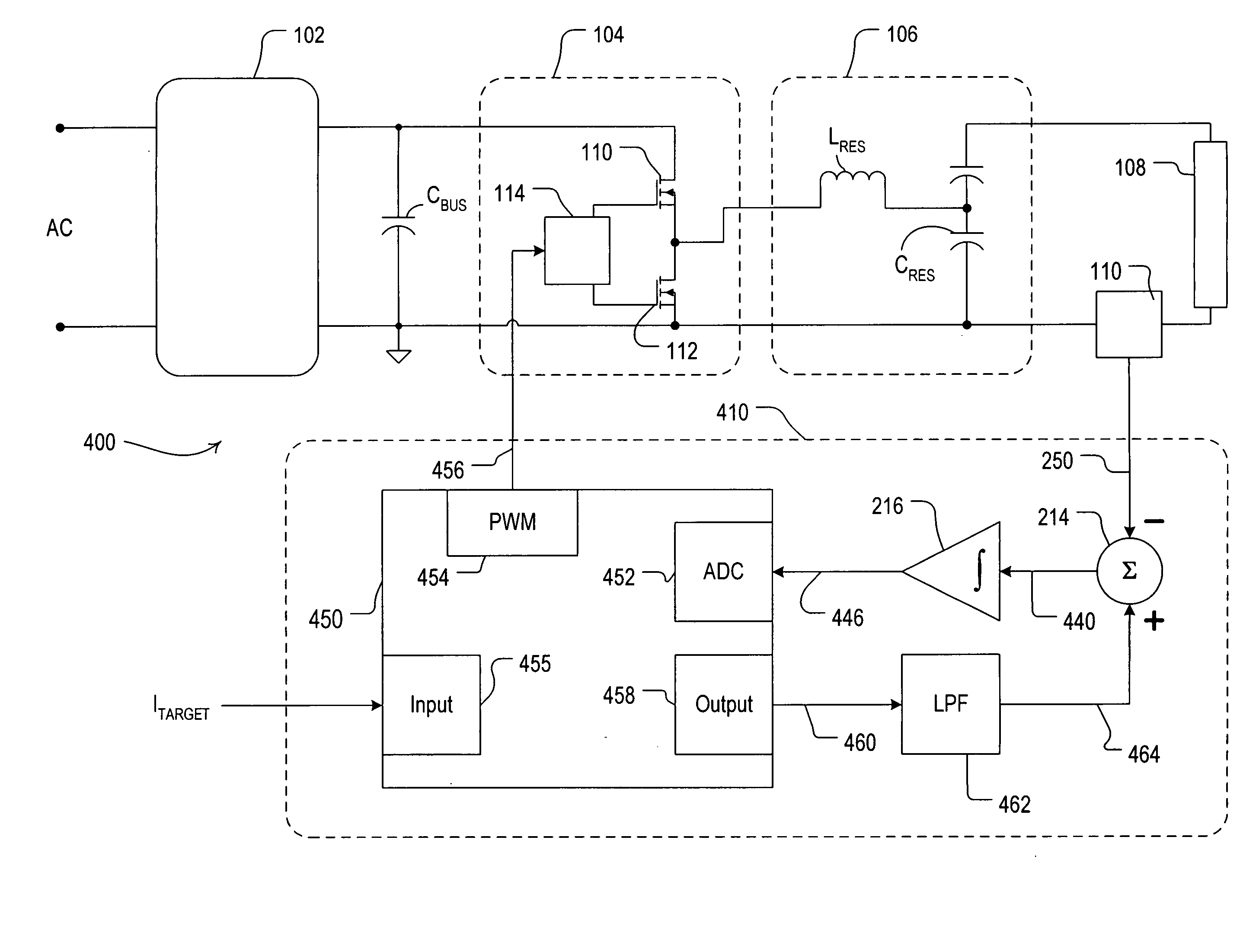
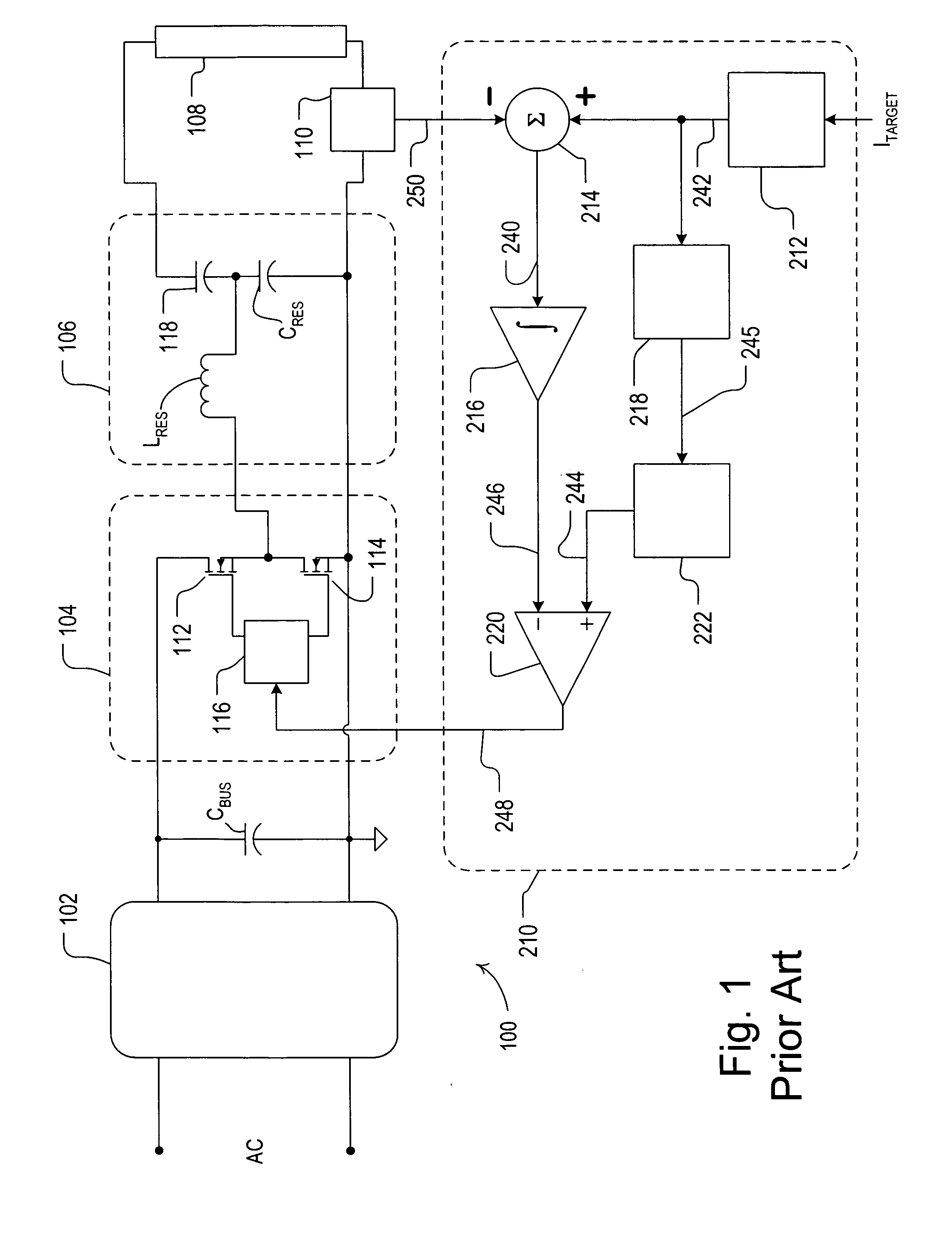
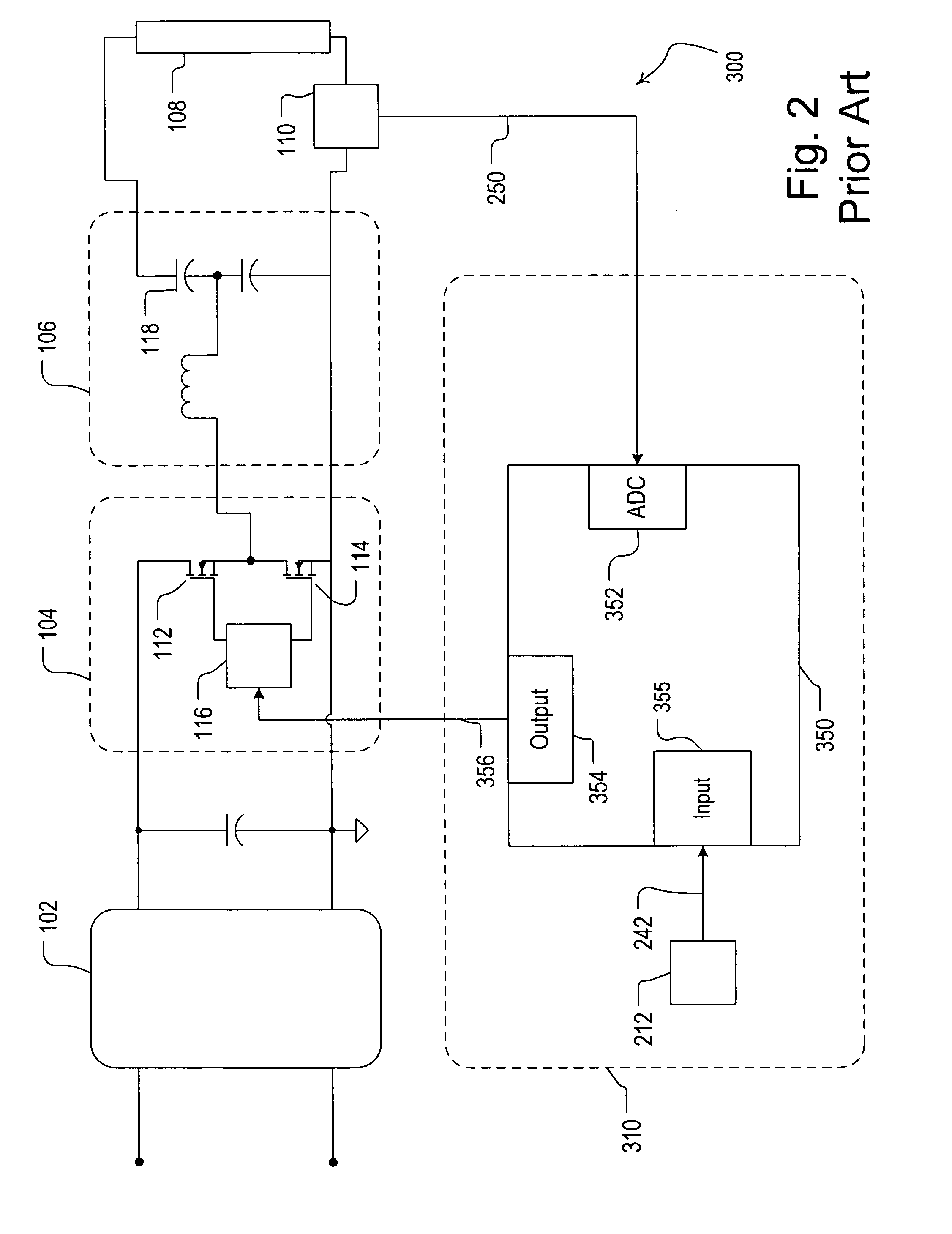
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
838 results about "Electrical ballast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
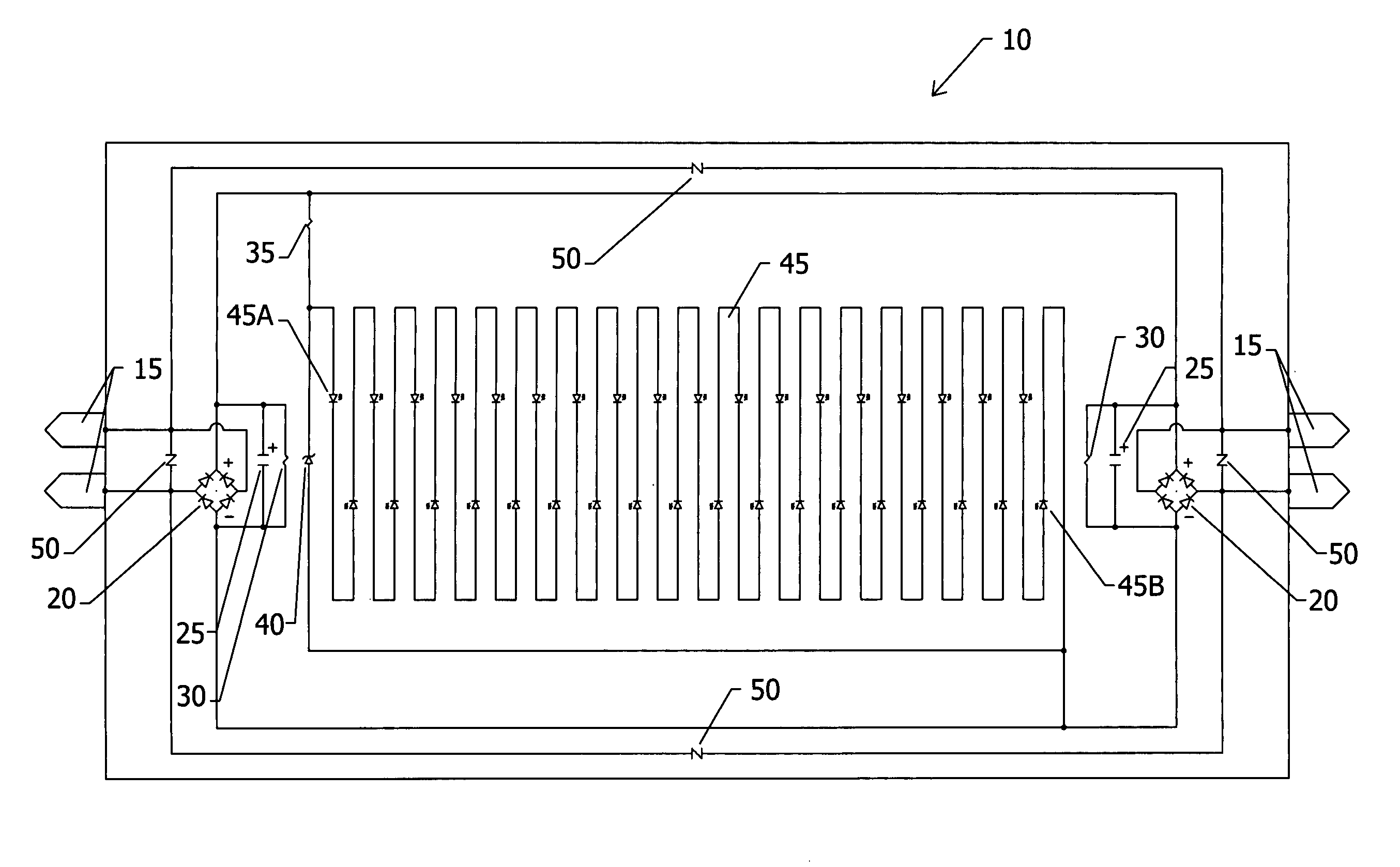
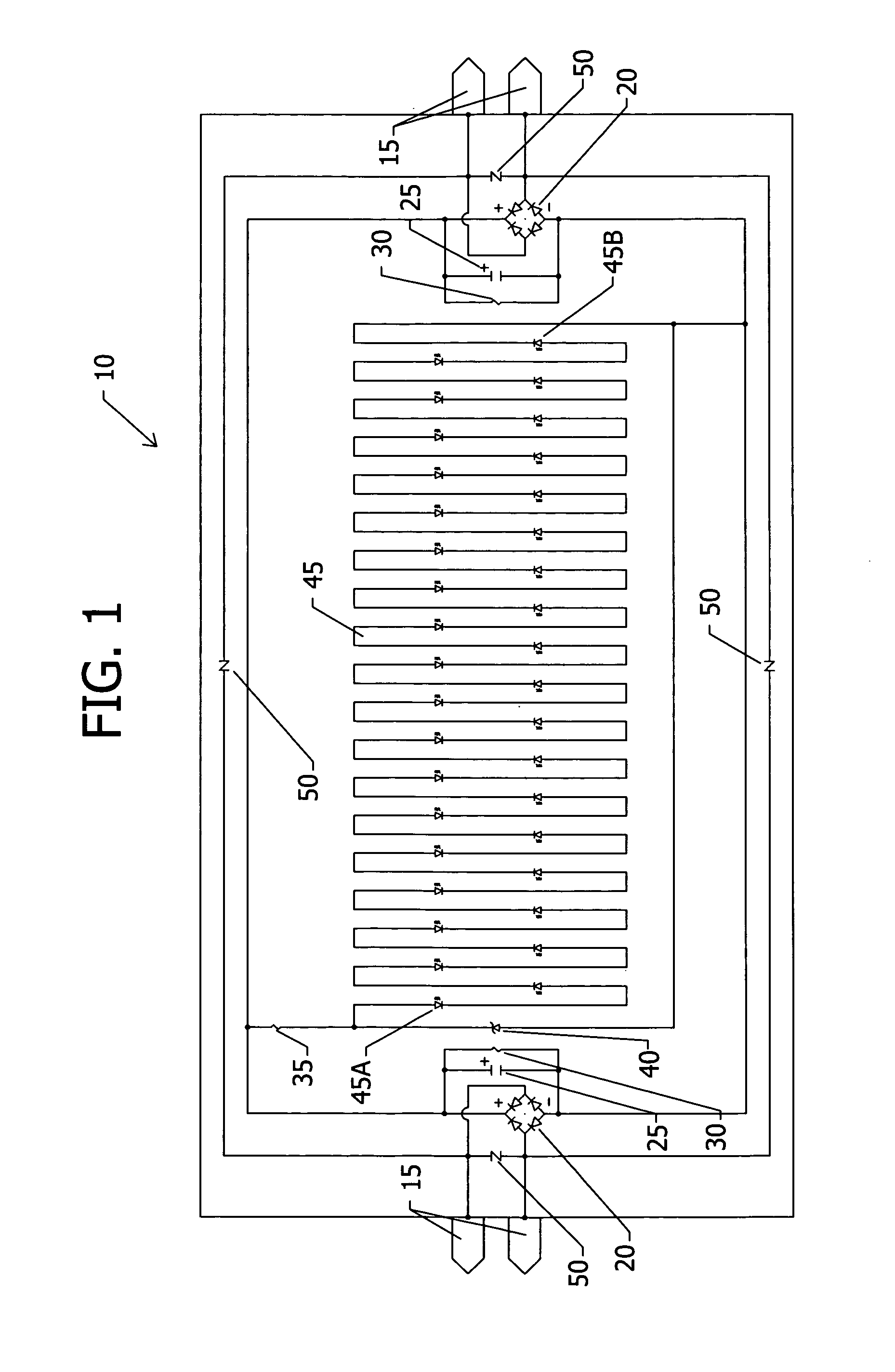
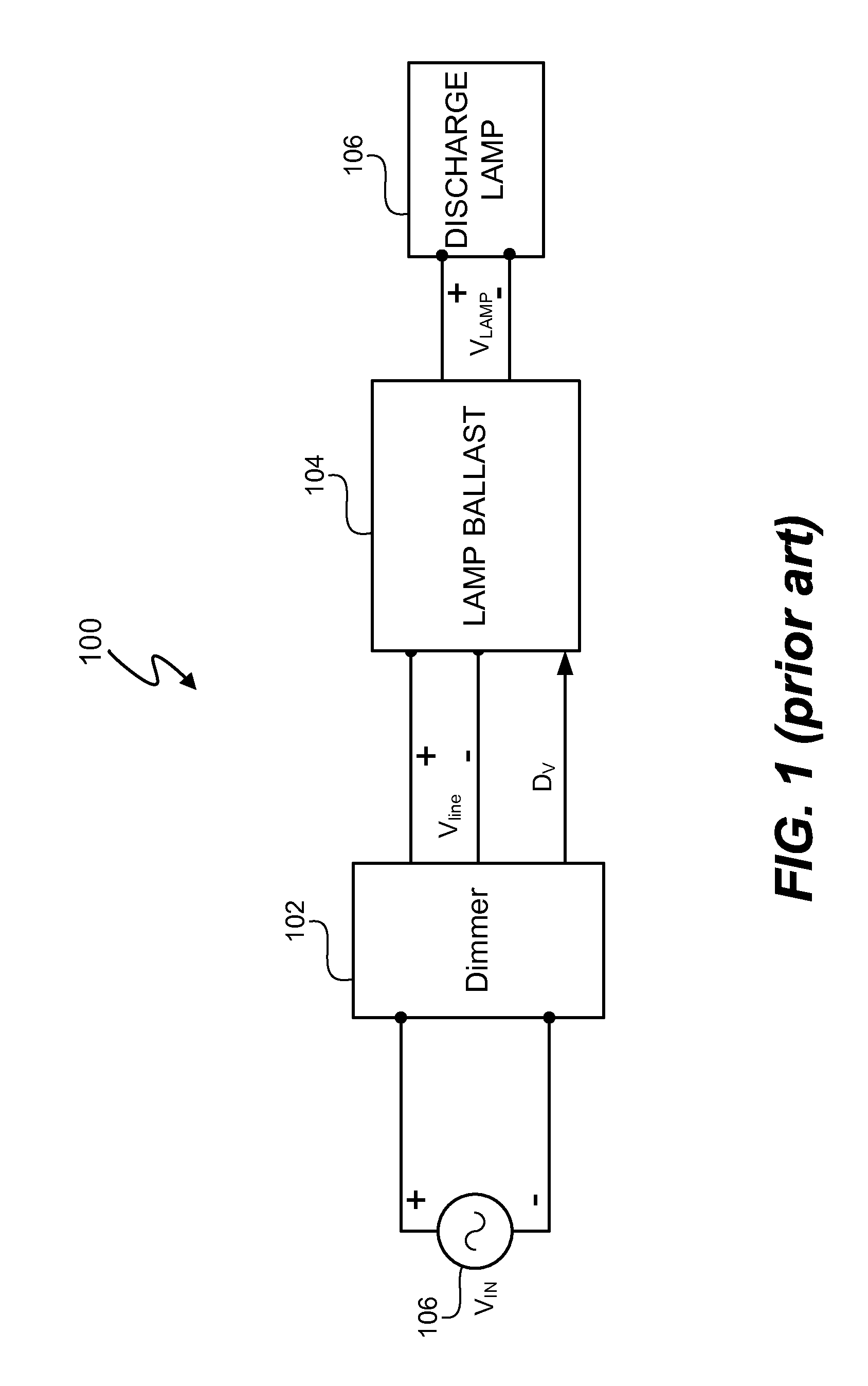
An electrical ballast is a device placed in series with a load to limit the amount of current in an electrical circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to a destructive level due to the negative differential resistance of the tube's voltage-current characteristic.
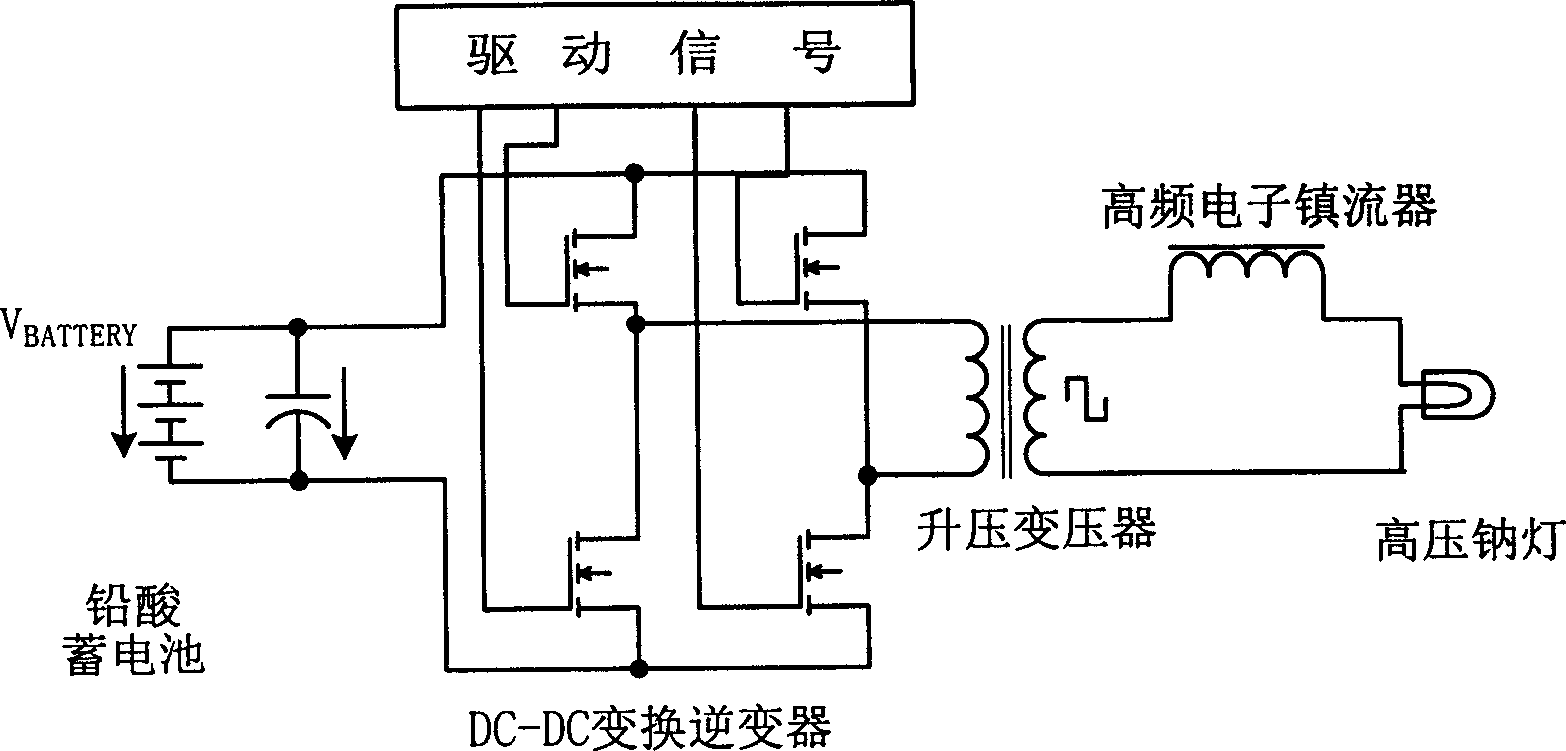
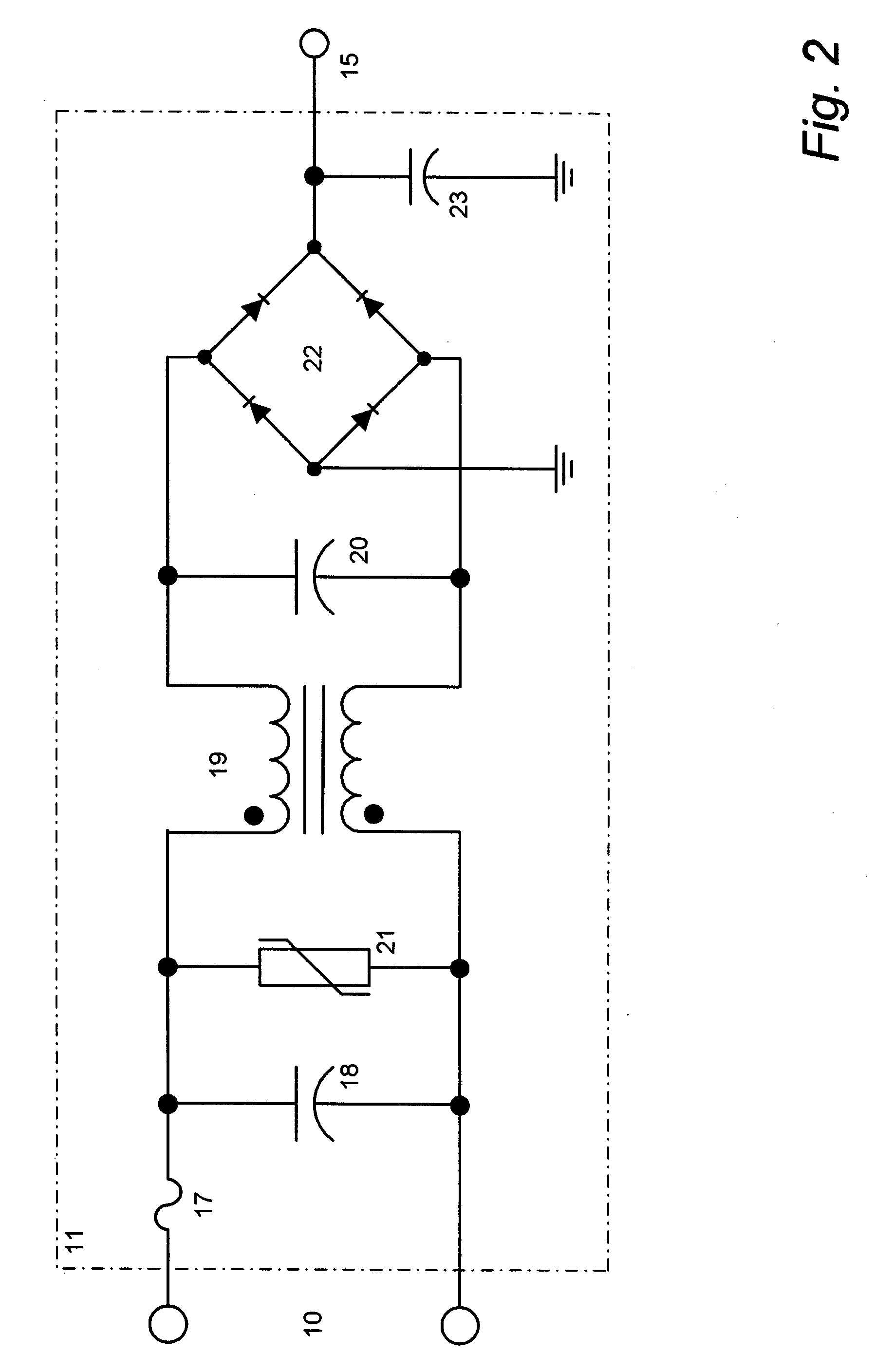
Inductively coupled ballast circuit
InactiveUS20050093475A1Small region of changeInefficient power transferWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCurrent limitingElectrical ballast
A ballast circuit is disclosed for inductively providing power to a load. The ballast circuit includes an oscillator, a driver, a switching circuit, a resonant tank circuit and a current sensing circuit. The current sensing circuit provides a current feedback signal to the oscillator that is representative of the current in the resonant tank circuit. The current feedback signal drives the frequency of the ballast circuit causing the ballast circuit to seek resonance. The ballast circuit preferably includes a current limit circuit that is inductively coupled to the resonant tank circuit. The current limit circuit disables the ballast circuit when the current in the ballast circuit exceeds a predetermined threshold or falls outside a predetermined range.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
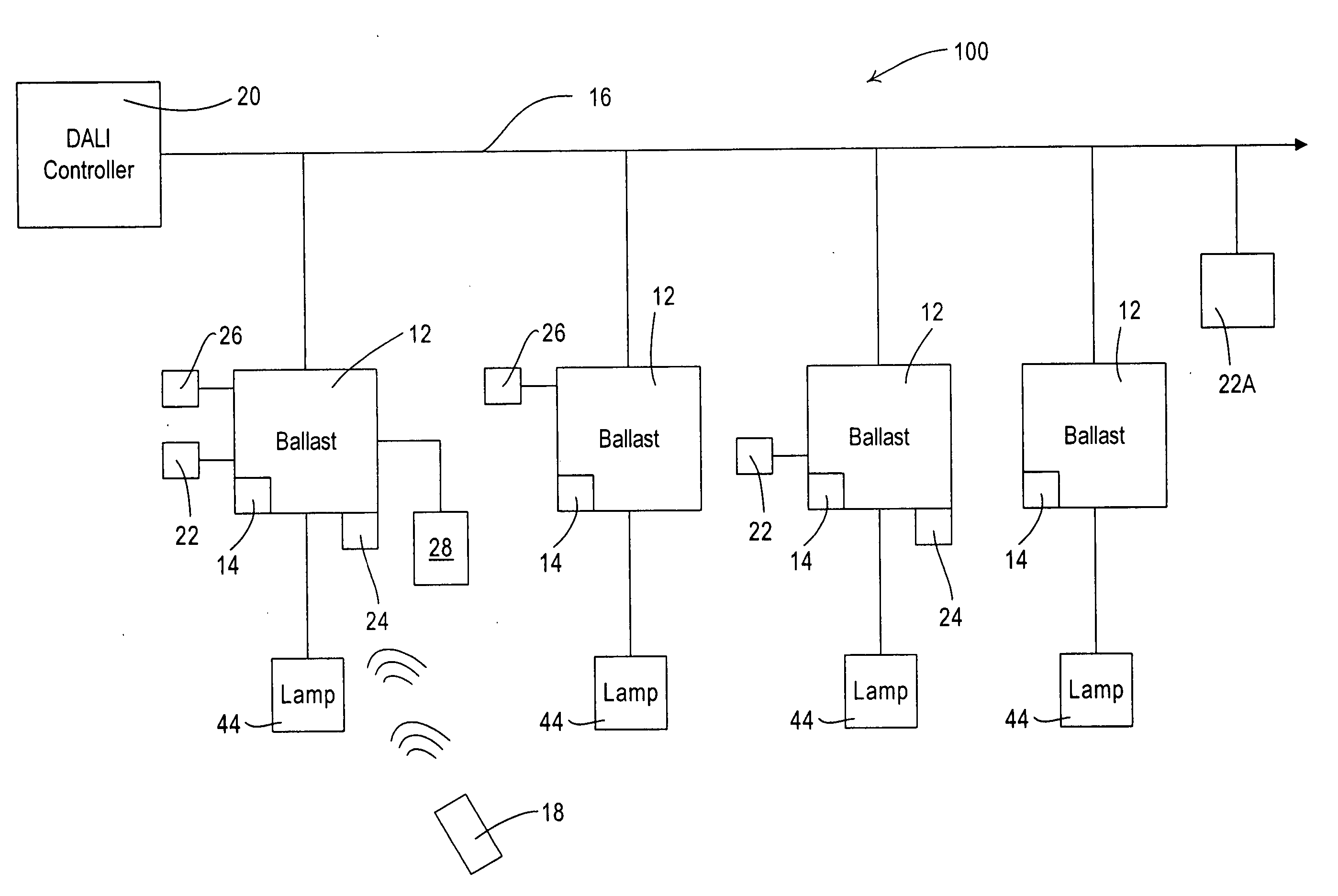
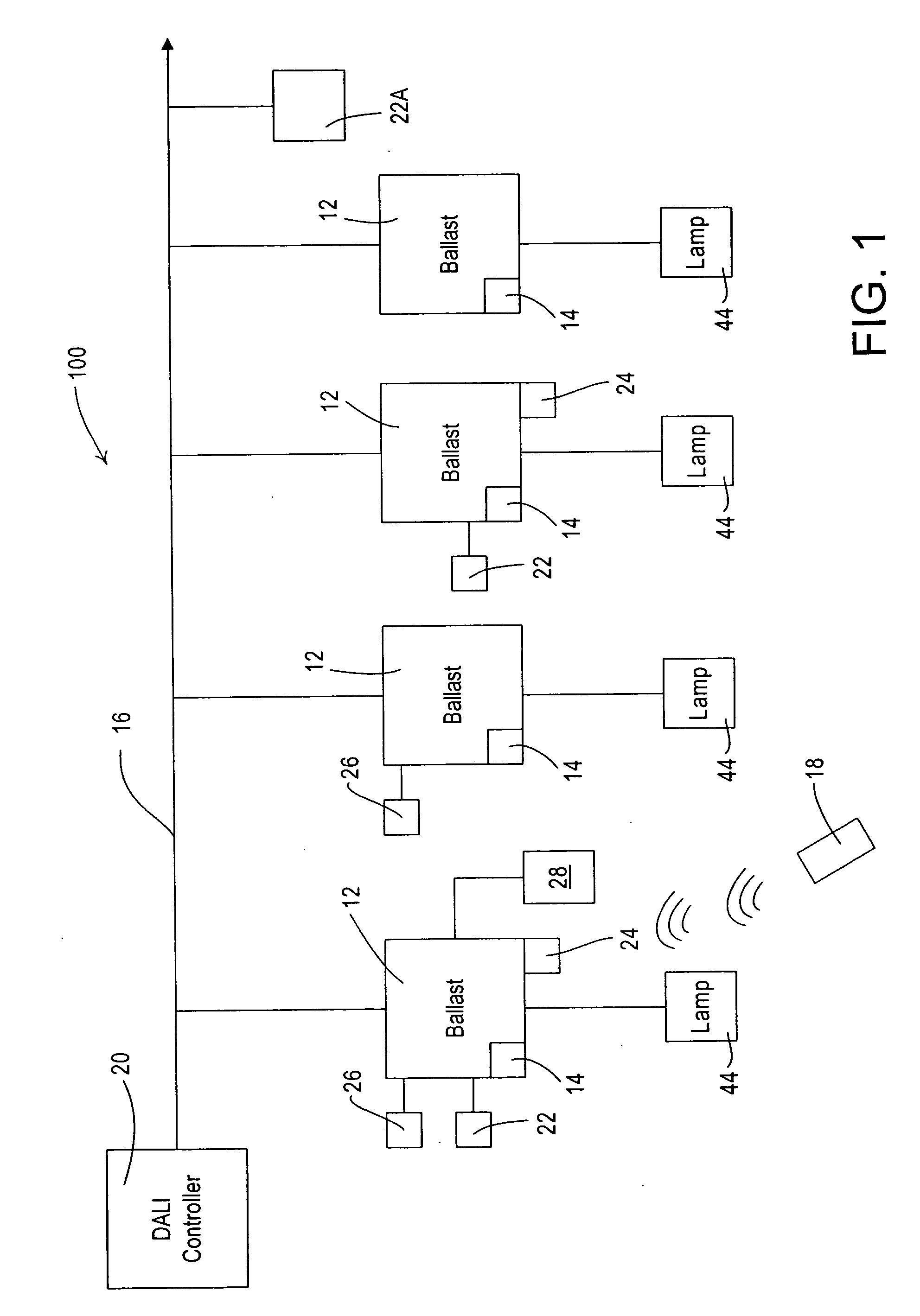
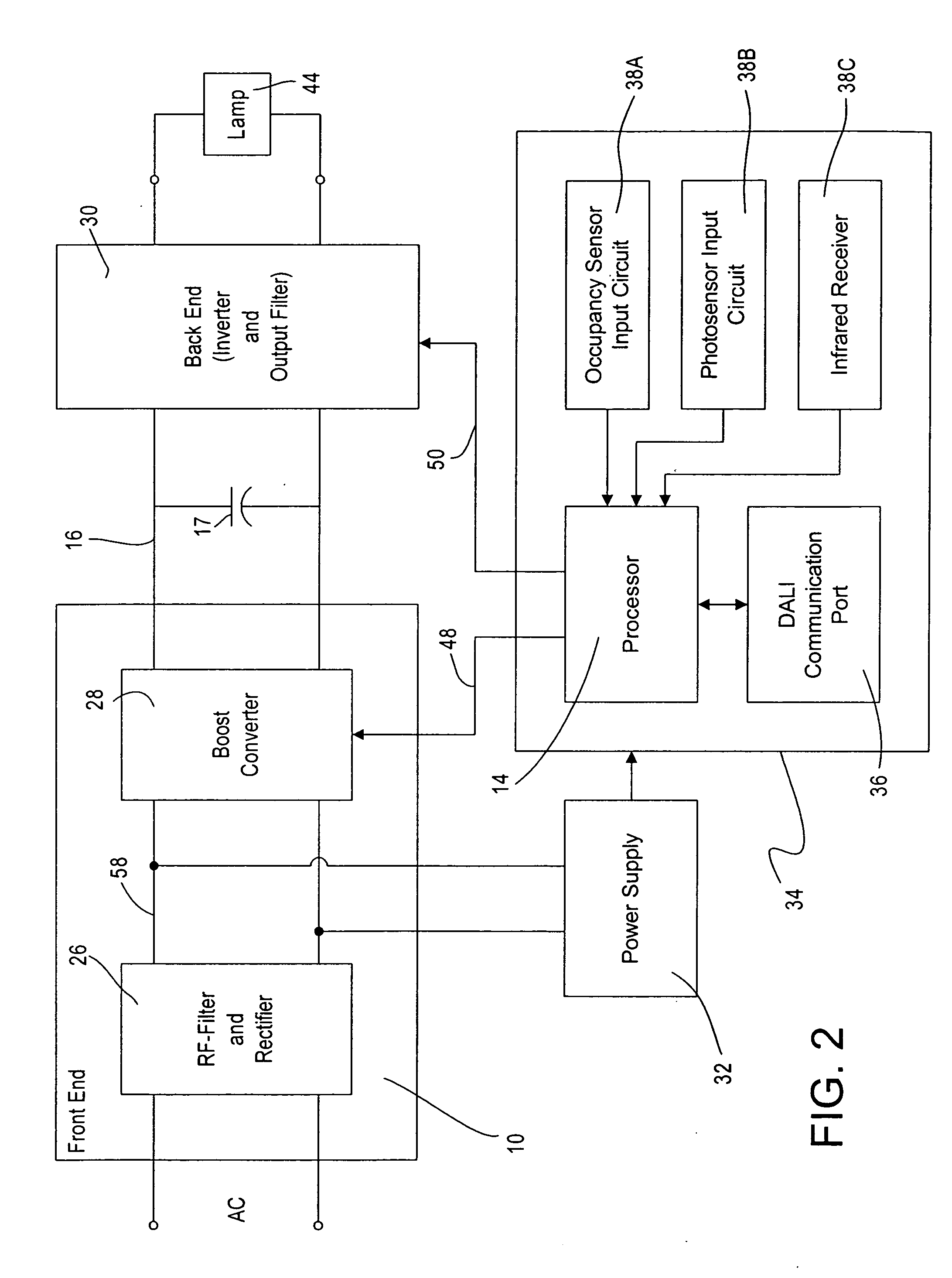
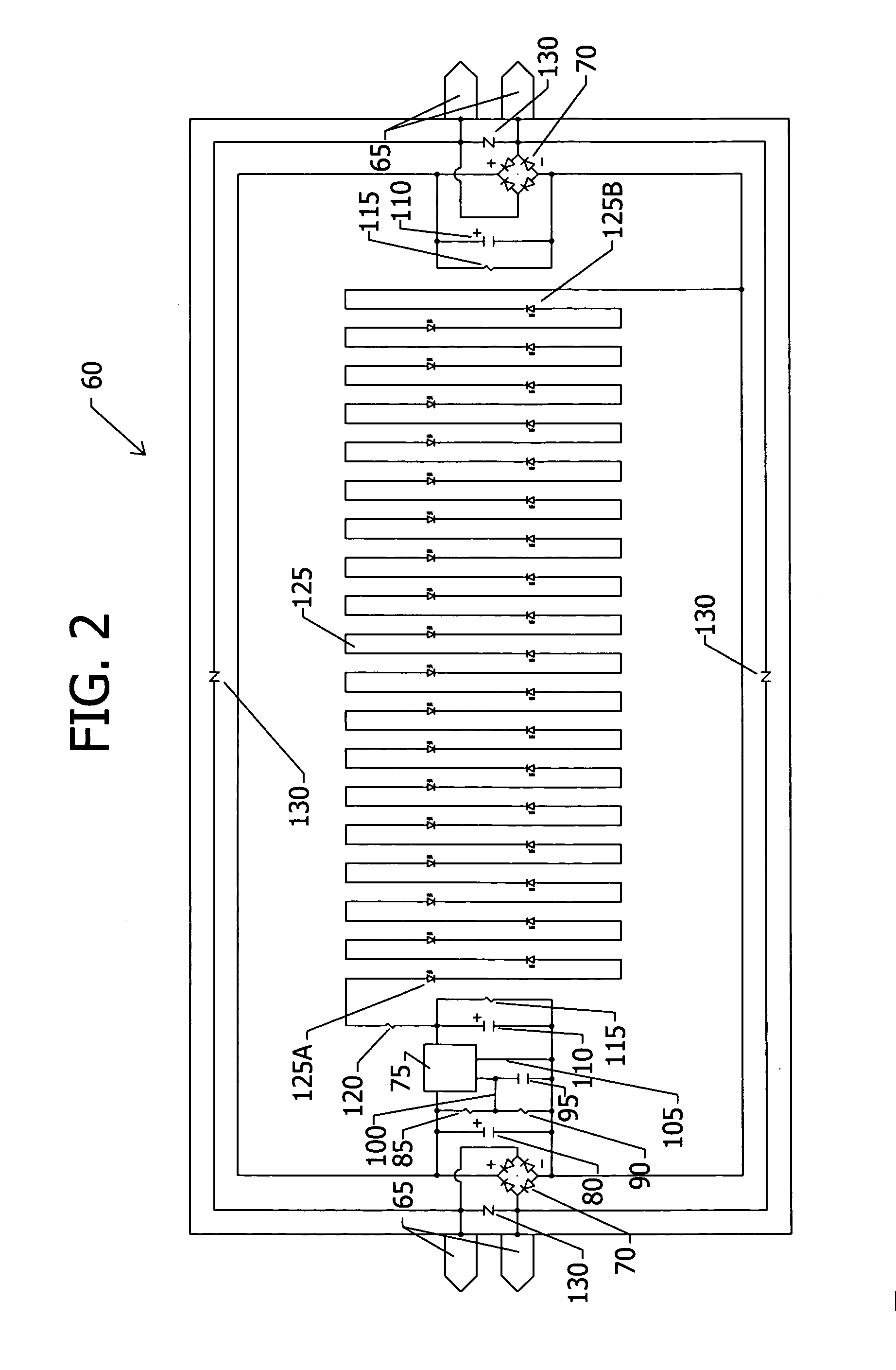
Distributed intelligence ballast system and extended lighting control protocol
ActiveUS20060125426A1Improve responsivenessImprove functionalityElectric signal transmission systemsComputer controlDistributed intelligenceControl signal
A ballast for use in a multi-ballast lighting system wherein the ballasts are coupled together by a digital communication network. The ballast comprises a power circuit portion for providing an electrical current to power a lamp. The ballast further includes a sensor input circuit for receiving at least one sensor input from a sensor device, a processor receiving an input from the sensor input circuit and providing control signals to control the operation of the ballast, and a communication port coupled to the processor and to the communication network for exchanging data. The ballast processor is operative to receive a serial data that has a portion defining whether the message is in a first or a second format, the first format comprising a DALI standard format and the second format comprising a format providing extended functionality. The ballast processor is capable of processing messages in either the first or second formats.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
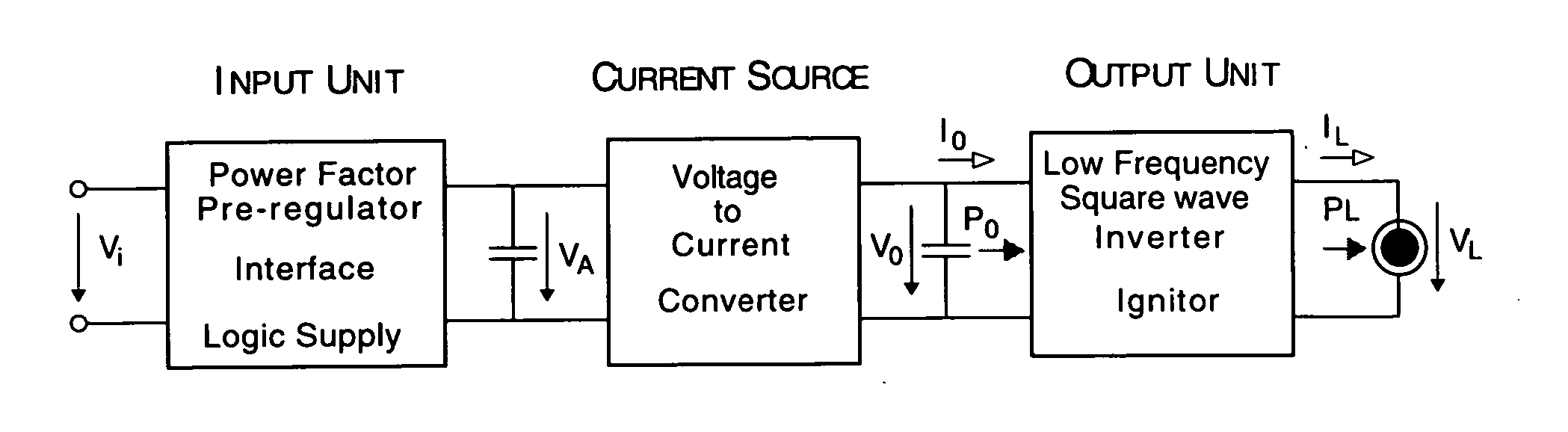
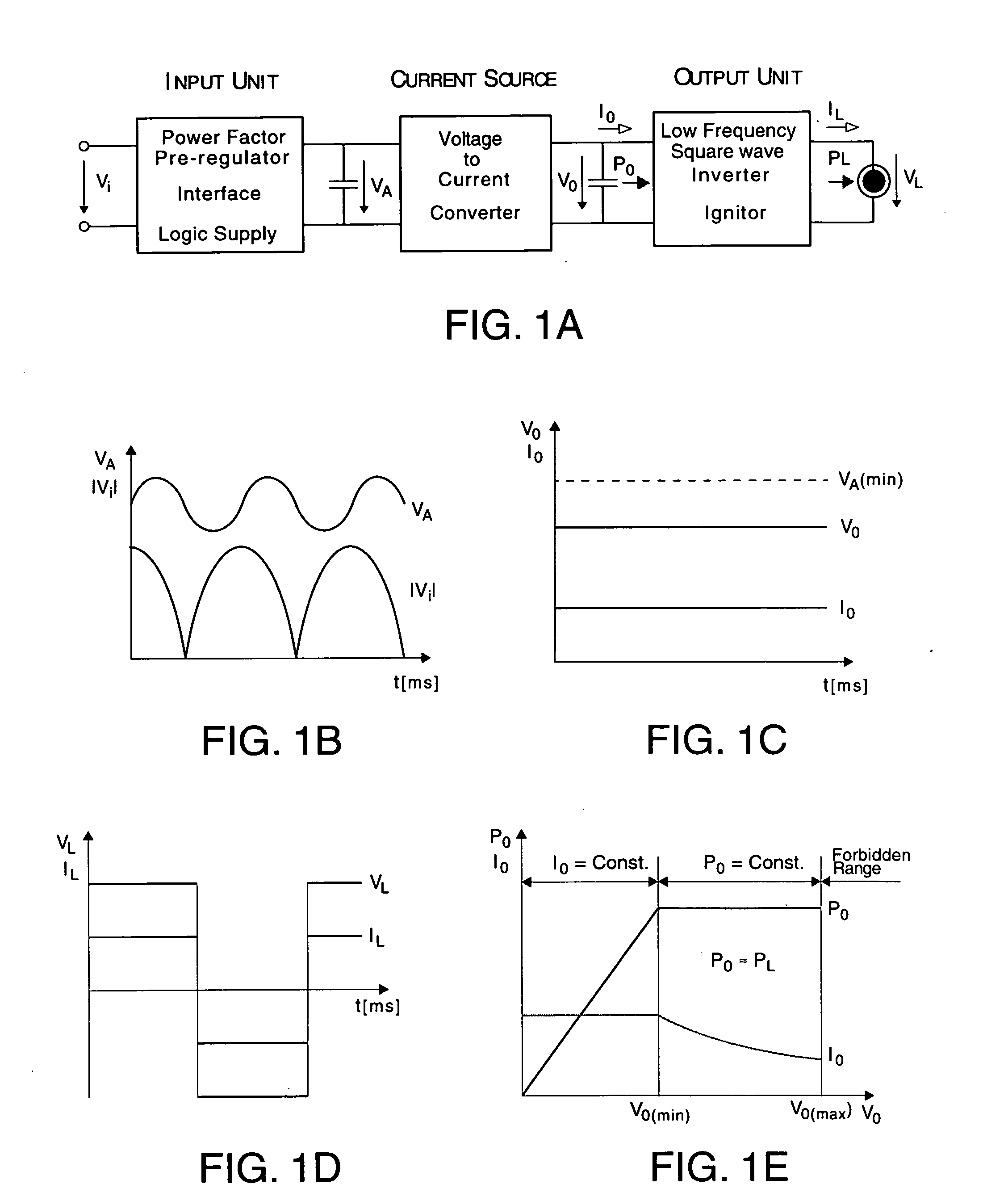
Low frequency electronic ballast for gas discharge lamps
InactiveUS20060232220A1Improve efficiencyEasy to operateElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringLamp current
An electronic ballast for high intensity gas discharge lamps where the wave form of the lamp current is square wave providing acoustic resonance and flickering free operation. The circuit, having high efficiency, operates in a wide temperature range providing ideal ballast curve and reliable ignition for the lamps. Furthermore, significant energy saving can be achieved by its externally controlled built in dimming capability.
Owner:BALLASTRONIC
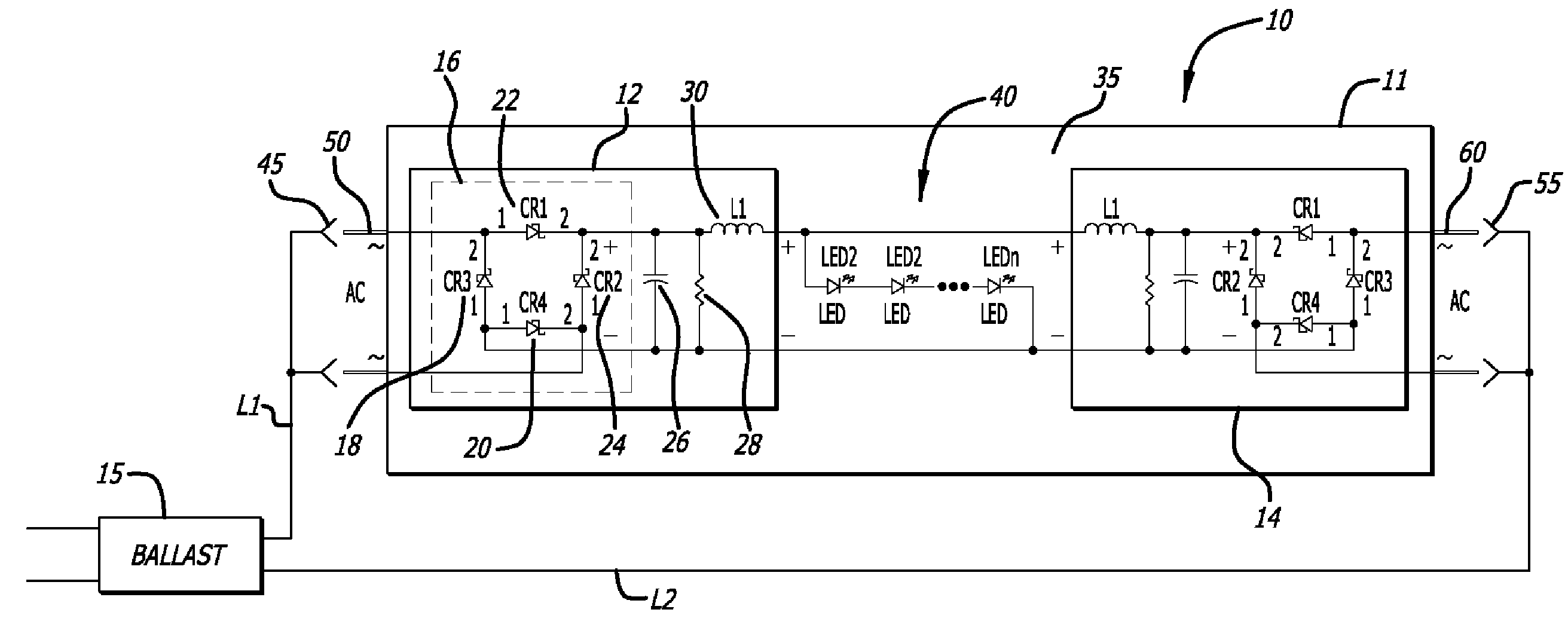
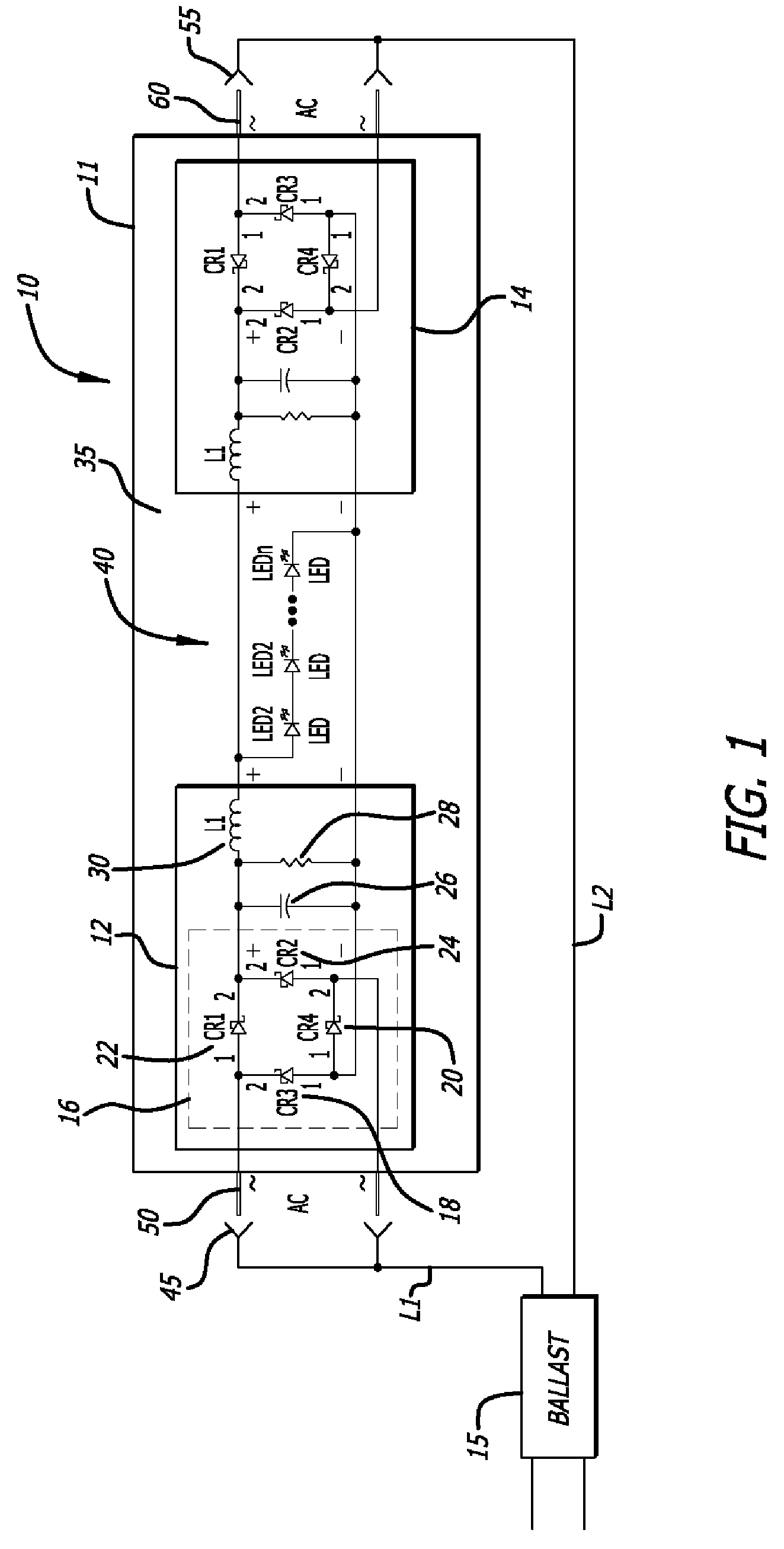
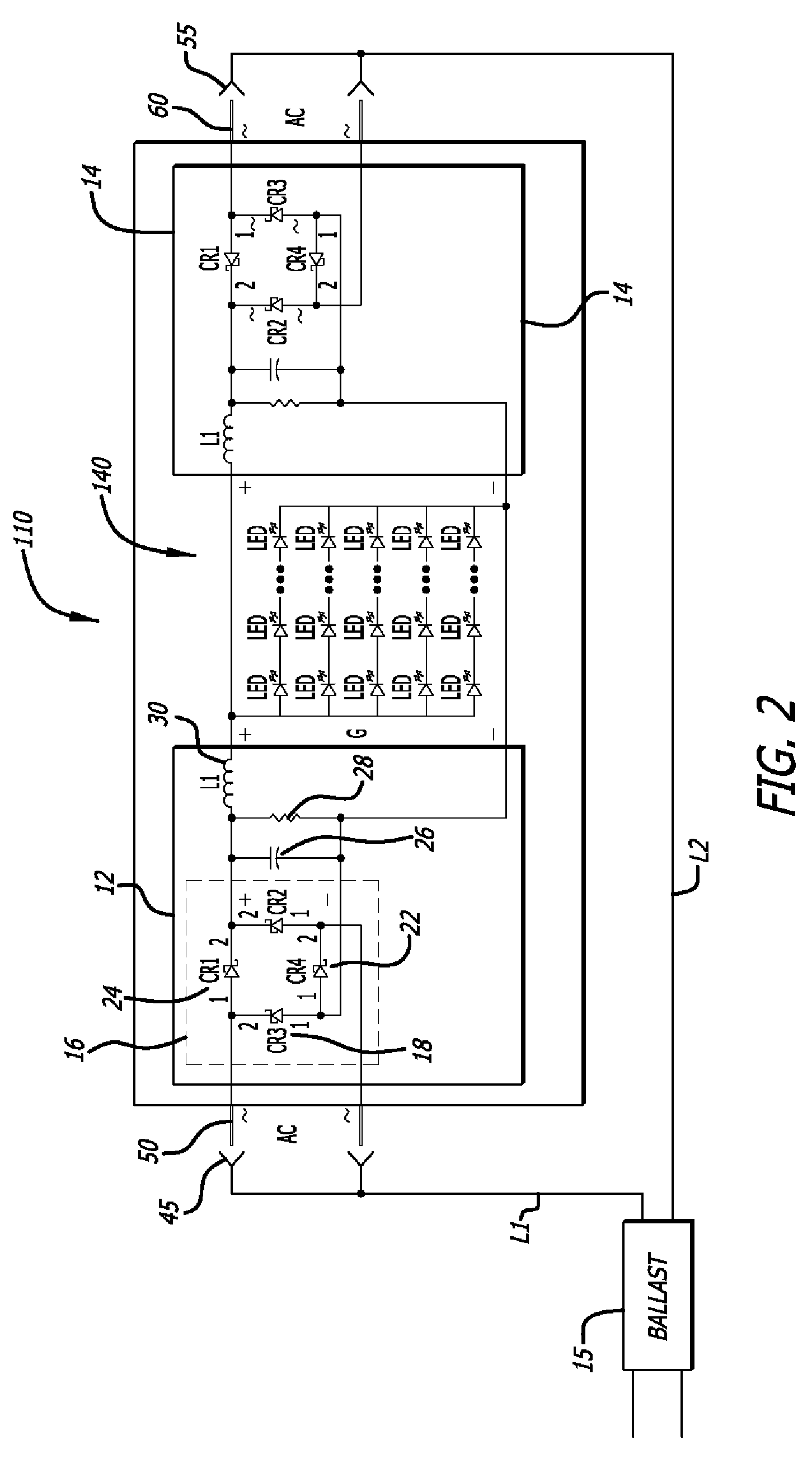
Fluorescent Light Fixture Assembly with LED Lighting Element and Converter Modules
ActiveUS20110121756A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical ballastFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a fluorescent light fixture assembly including a ballast and a novel lighting element that includes an array of LEDs and at least one converter module that enables the existing ballast providing an AC power input to supply DC power to the LED array. The lighting element includes a body that contains the LED array and the converter modules and shares the configuration of the lighting element that is to be retrofitted. The lighting element receives power from the pre-existing ballast, wherein the converter module provides a constant current source to power the LED array. Thus, the lighting element, including the converter module, replaces the conventional fluorescent light tube in a cost-effective retrofit manner with the existing ballast.
Owner:ELECTRALED
Voltage regulating devices in LED lamps with multiple power sources
ActiveUS20110057572A1Reduce materialReduce inventory costsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesZener diodeVoltage regulation
LED driver circuits containing voltage reducing devices, voltage regulating devices, and voltage converting devices are disclosed as the main components to provide power to LEDs. The LED driver circuits are designed to work with a ballast, mains alternating current voltage, direct current voltage, and electromagnetic induction power. The voltage regulating devices can be a resistor in series with at least one zener diode or a voltage regulator both in parallel with and providing power to the LEDs. The LEDs can also be anti-parallel diode pairs consisting of one diode and one LED or two LEDs, or the LEDs can be anti-parallel diode string pairs consisting of diodes and LEDs or all LEDs. The LED driver circuits will be incorporated into LED replacement lamps, and in particular to LED lamps to replace fluorescent lamps for use with existing ballasts and other power sources where the ballast may be removed or bypassed.
Owner:DENOVO LIGHTING
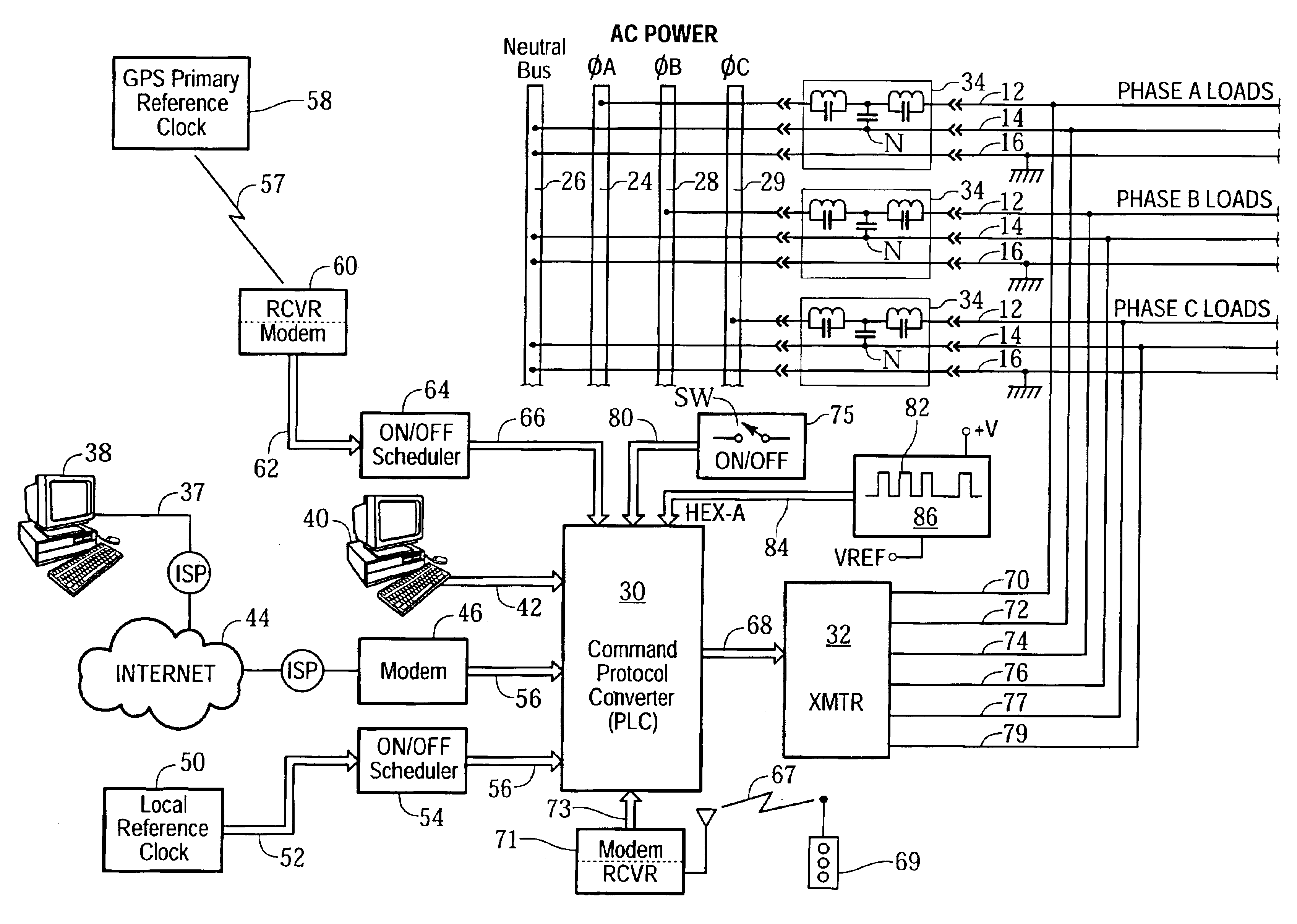
Remotely accessible power controller for building lighting
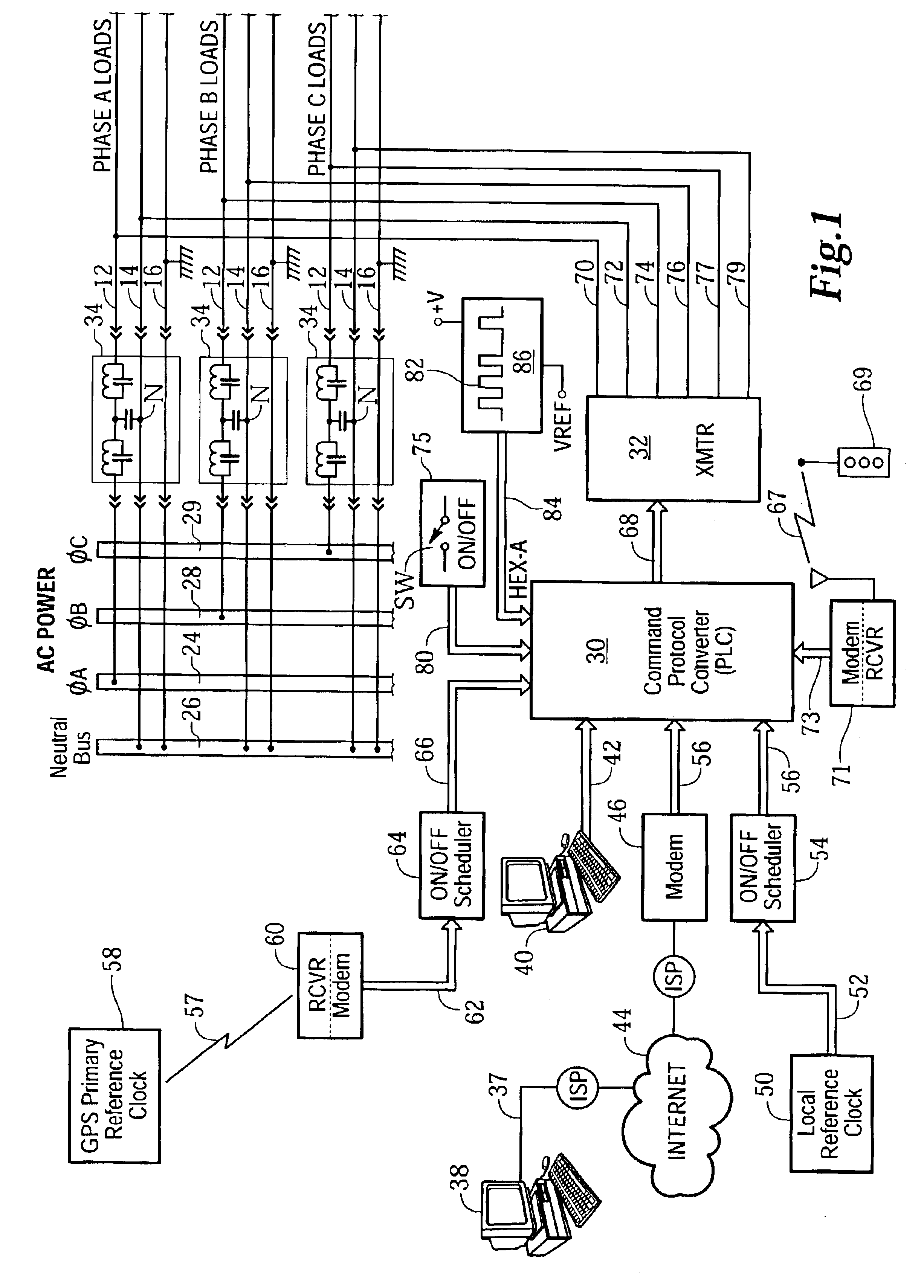
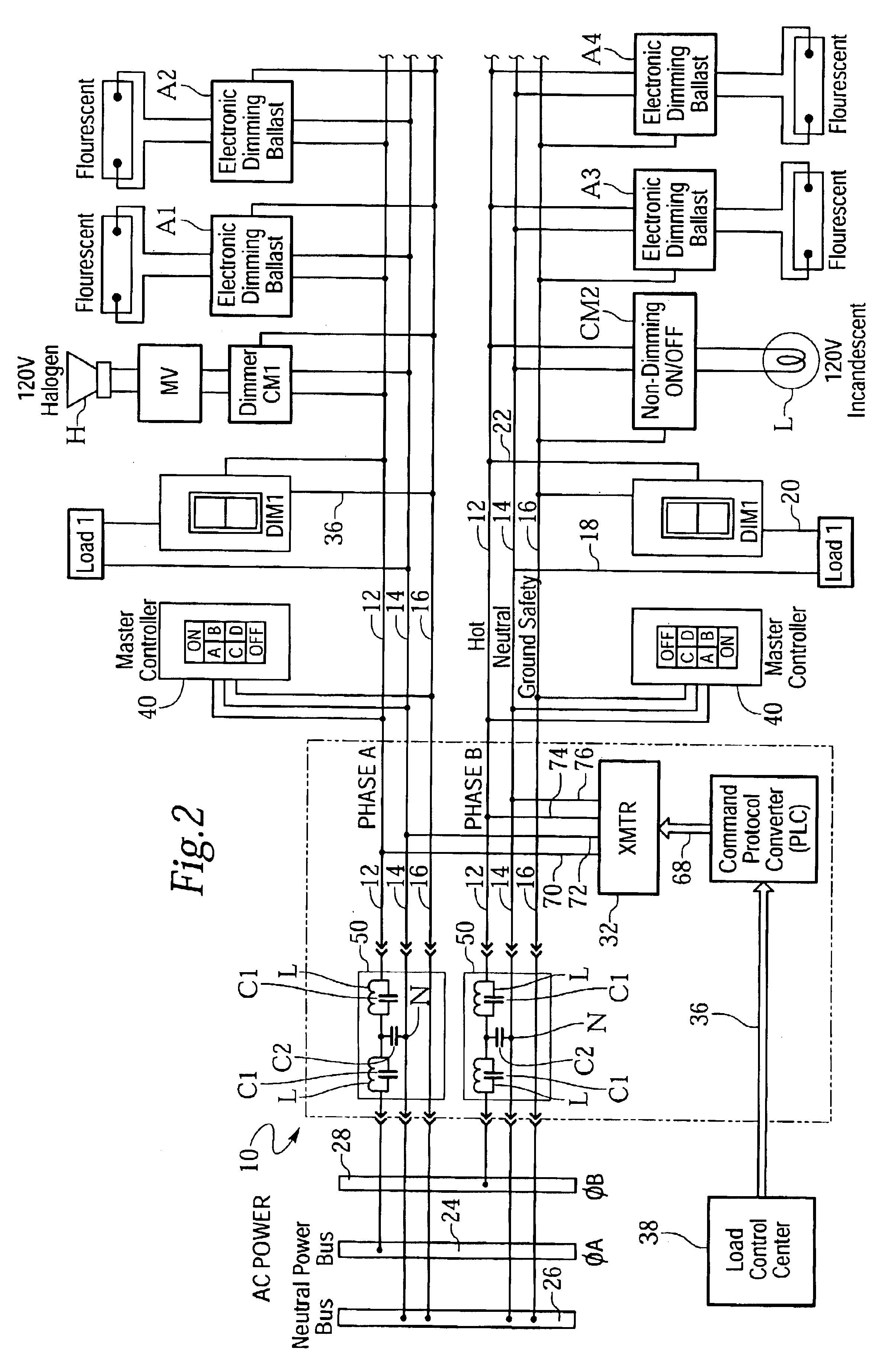
InactiveUS6842668B2Improve reliabilityPrevent external noiseElectric signal transmission systemsLevel controlElectrical conductorEffect light
A remotely accessible power controller communicates power reduction command signals by power line carrier (PLC) signaling over existing AC power distribution conductors for automatically disconnecting building lighting loads. Turn-off command signals from a local or remote controller automatically disconnect building lighting loads according to a time-of-day schedule to comply with mandated energy consumption codes applicable to the automatic shutoff of electrical lighting. Load shedding (selective turn off and / or dimming) command signals transmitted from public or private utility companies automatically disconnect or reduce building lighting loads in accordance with load curtailment agreements to limit total connected power consumption below an agreed level. The power controller is connected by a minimum amount of retrofit wiring into an existing end-user alternating current power distribution network, for example, a building power distribution network having AC power conductors that service multiple lighting loads interconnected in one or more power phase groups. Each dimming lighting load is equipped with an addressable dimming module for decoding and executing dimming and turn-on and turn-off power reduction commands. Fluorescent lamps are equipped with addressable electronic dimming ballasts.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
Solar energy high voltage sodium lamp controller based on single stage inverter
InactiveCN1787717ARealize intelligent controlImproved and enhanced charge and discharge capabilitiesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric lighting sourcesMicrocontrollerEngineering
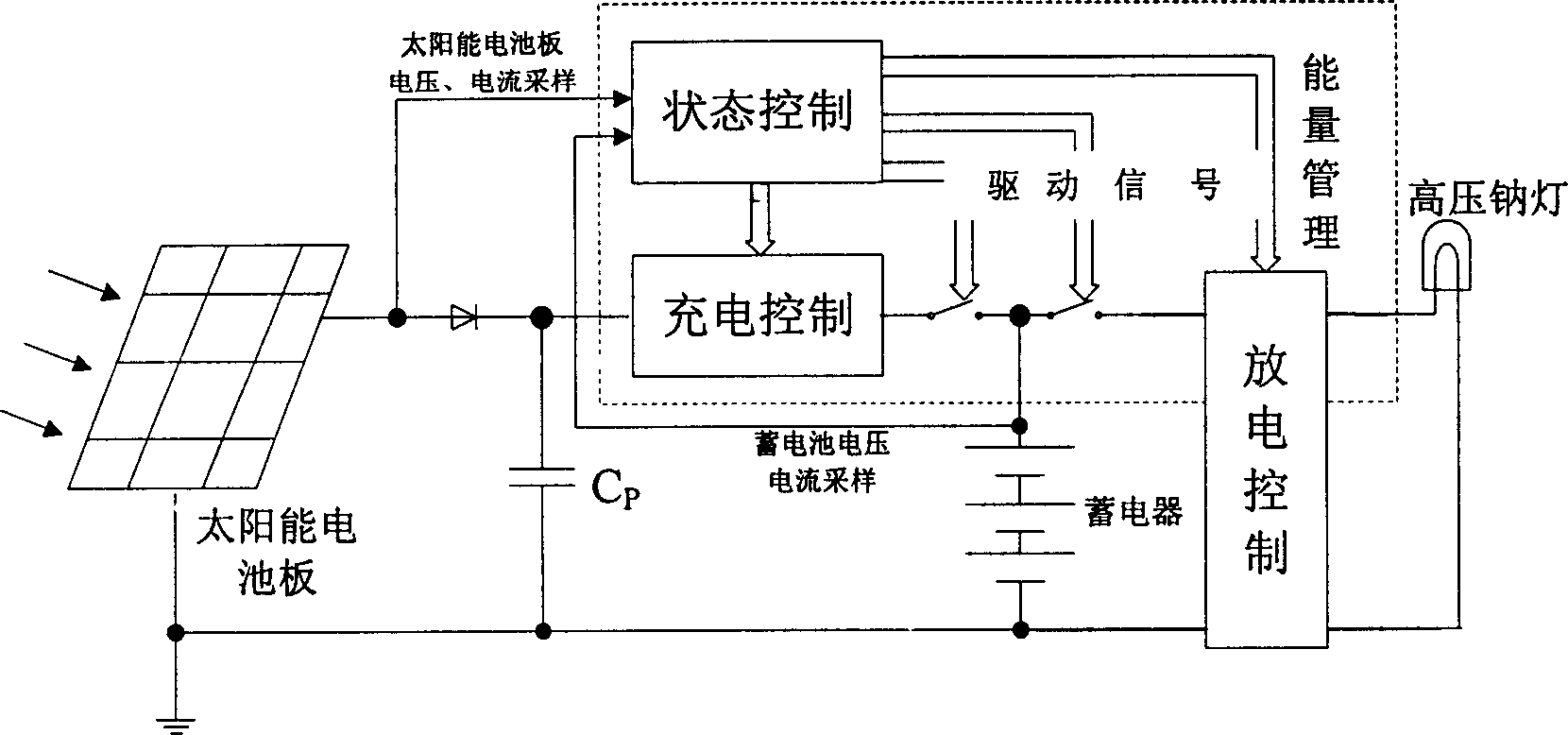
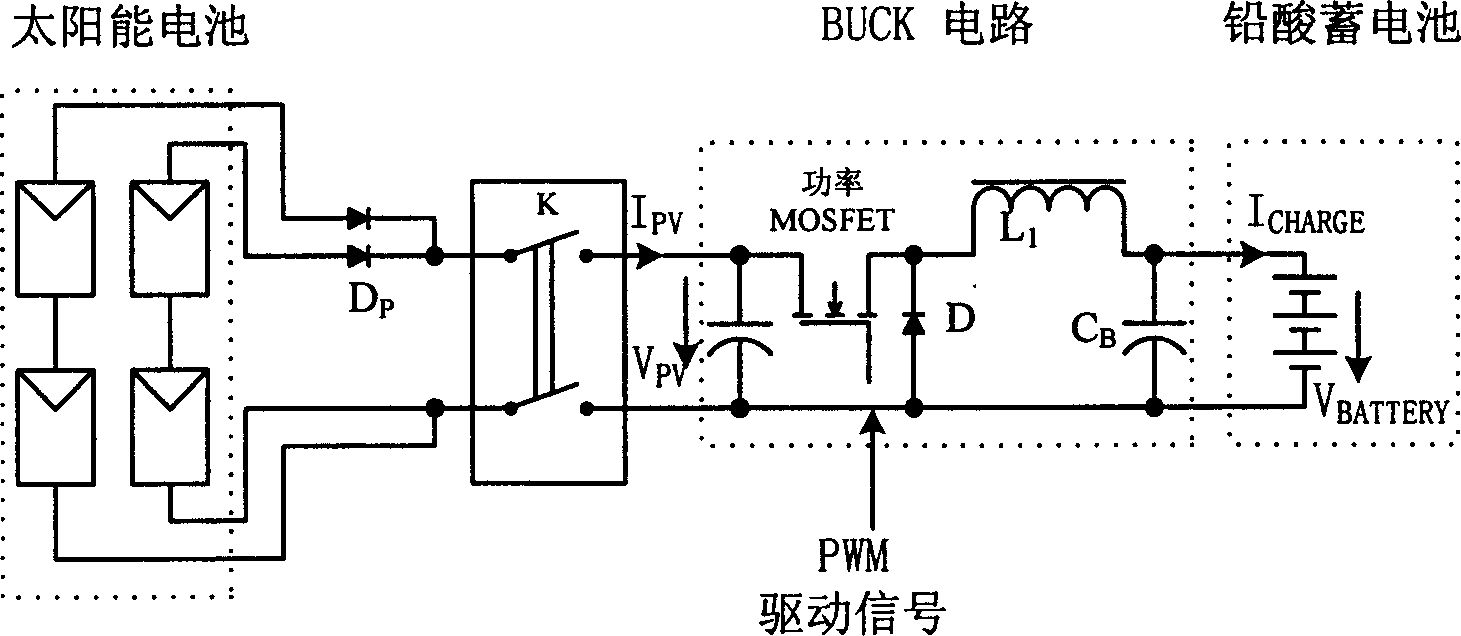
This invention relates to a solar energy high pressure Na-lamp controller based on a single stage inverter characterizing in applying a sectional charge control and a frequency conversion output control, in which, the hardware includes a singlechip control circuit, a single-stage total bridge inversion circuit, a storage battery charge circuit, a high frequency electronic ballast circuit, a solar energy cell, storage batteries and luminaries, the controller is charged by MPPT to increase the system efficiency and applies frequency conversion output to control the current of the lamp, besides, a design of machine-card separation is applied to the controller on the structure to meet the needs of different luminaries and lamination, the control structure is integrated in a control card suitable for software upgrading.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
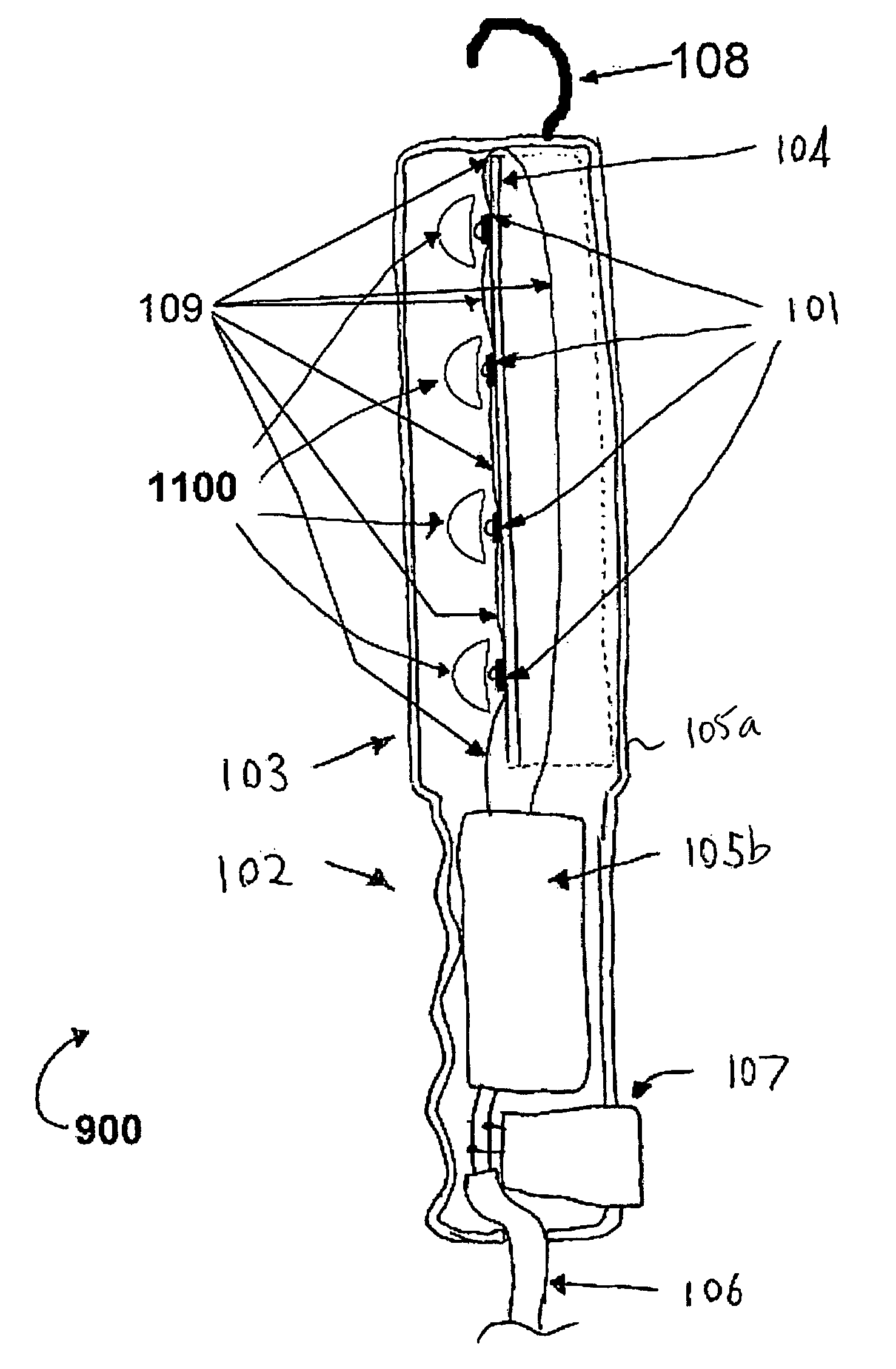
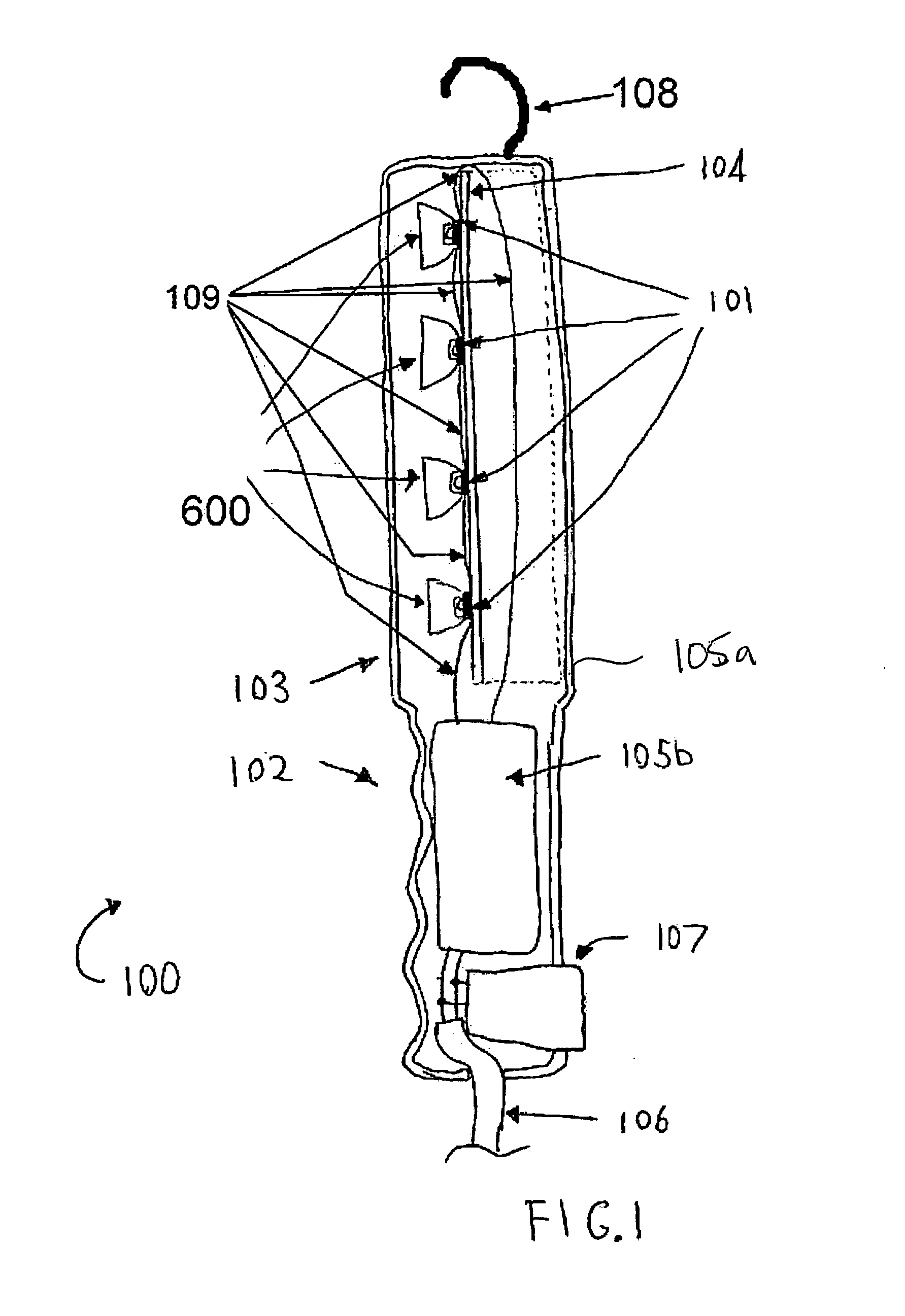
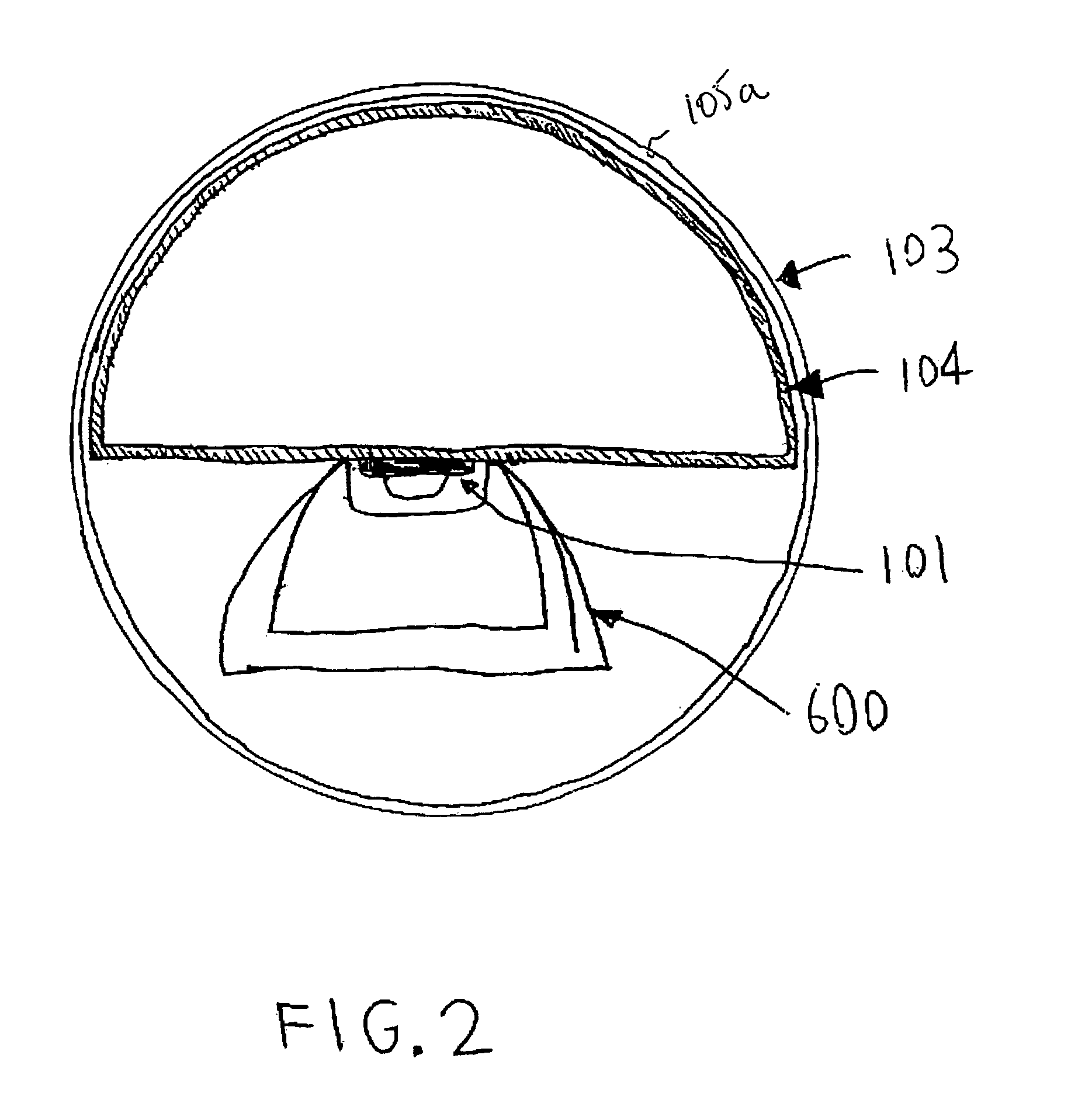
LED work light
ActiveUS7553051B2Preserve useful working lifeUseful working lifeElectric lighting for hand-held useLighting support devicesElectrical ballastElectrical battery
Work light has LEDs that require heatsink. Desired radiation pattern achieved by using optical components designed to produce beam or LEDs may have beams in different directions. Radiation pattern of LEDs may be changed by refractive-reflective optics or by convex lenses. Convex lenses may be hemispheres, other planoconvex shapes, concavo-convex shapes, or other shapes. Curved surfaces on any lenses may be spherical or aspheric. Ballast to operate the LEDs from line voltage AC or low voltage DC. Work light may contain batteries. The work light may be mounted on a stand. May have accessory mount. May have charging station. May have a paging transmitter to activate a paging receiver in work light. May have openings for heat transfer from heatsink to ambient air external to light.
Owner:ALLTEMP PROD CO LTD
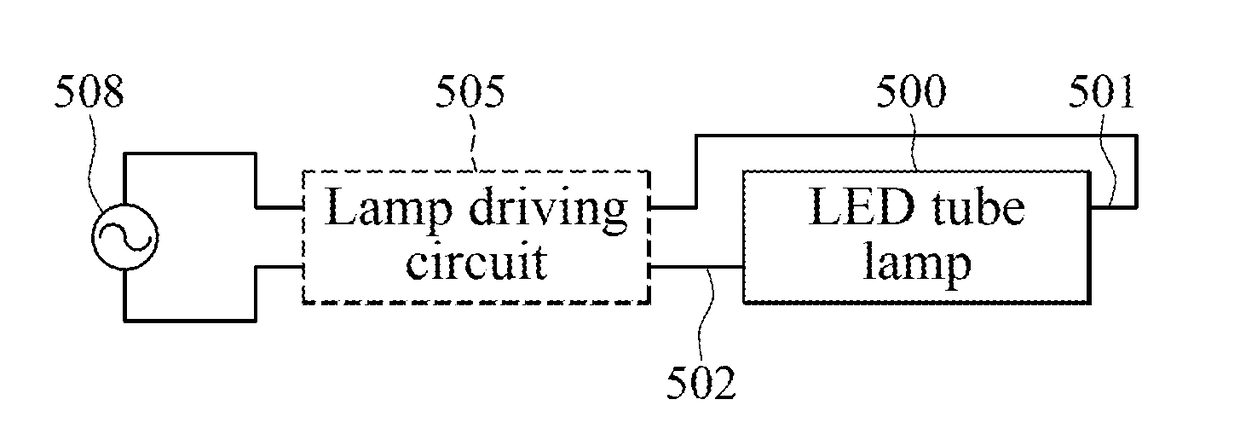
LED (light-emitting diode) tube and drive circuit thereof
InactiveCN102355780AValid conversionSimple structureElectric light circuit arrangementElectrical ballastFluorescent lamp
The invention discloses an LED (light-emitting diode) tube and a drive circuit thereof.The drive circuit comprises an input unit, a rectification filter unit and an LED constant current drive unit, and further comprises a high frequency detection unit and a control unit. The LED tube disclosed by the invention includes the drive circuit of the LED tube and an LED light source plate, and has simple structure and convenience in use when the LED fluorescent lamp is exchanged with a traditional electronic ballast fluorescent lamp and an inductive ballast fluorescent lamp, without needs of line adjustment and component disassembly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GLOBRIGHT OPTICAL TECH
Linear Solid-State Lighting With Frequency Sensing Free Of Fire And Shock Hazards
ActiveUS20150181661A1Safe installationEliminate riskElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical ballastElectric shock
A linear light-emitting diode (LED)-based solid-state universal lamp using a frequency sensing and control mechanism operates normally with both an electronic ballast and the AC mains. The frequency sensing and control mechanism automatically detects voltage types associated with output voltages from the ballast and the AC mains in a single-ended or a double-ended lamp fixture and makes proper management so that the universal lamp works for either case and in either fixture without operational uncertainty. When two shock protection switches are used in two lamp bases, the universal lamp fully protects a person from possible electric shock during initial installation and re-lamping.
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
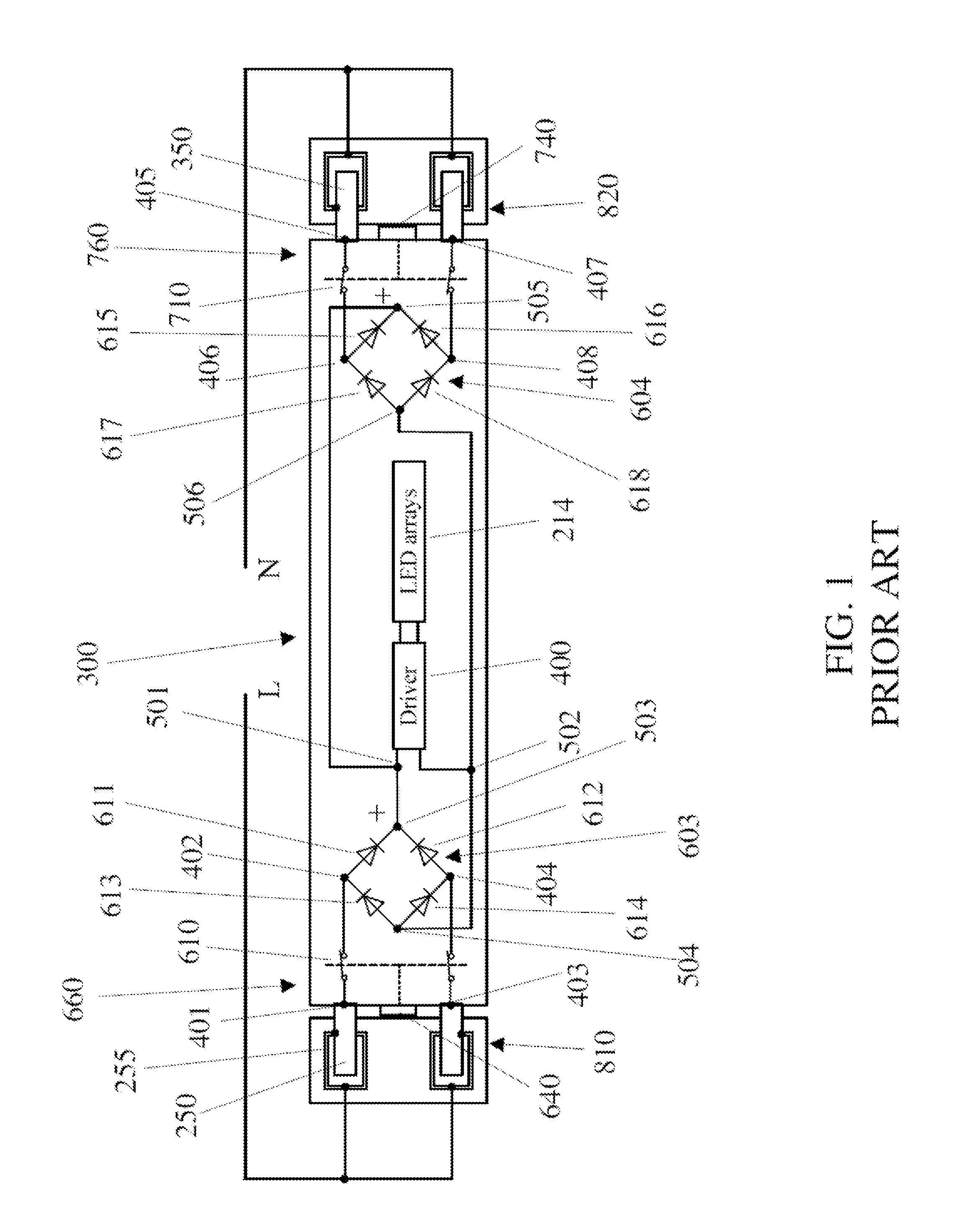
LED tube lamp with operating modes compatible with electrical ballasts
ActiveUS20160381760A1Improve power stabilityImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical ballastEngineering
An LED tube lamp having an LED unit is disclosed. The LED tube lamp includes a control circuit that selectively determines whether to perform a first mode or a second mode of lighting operation according to a state of a property of an external driving signal and a switching circuit coupled to the control circuit and the LED unit. When the control circuit determines to perform the first mode of lighting operation, the control circuit controls the second circuit in a manner such that the switching circuit maintains its on state to allow continual current to flow through the LED unit, until the external driving signal is disconnected from the LED tube lamp, and when the control circuit determines to perform the second mode of lighting operation, the control circuit controls the switching circuit in a manner to regulate the continuity of current to flow through the LED unit by alternately turning on and off the switching circuit.
Owner:JIAXING SUPER LIGHTING ELECTRIC APPLIANCE
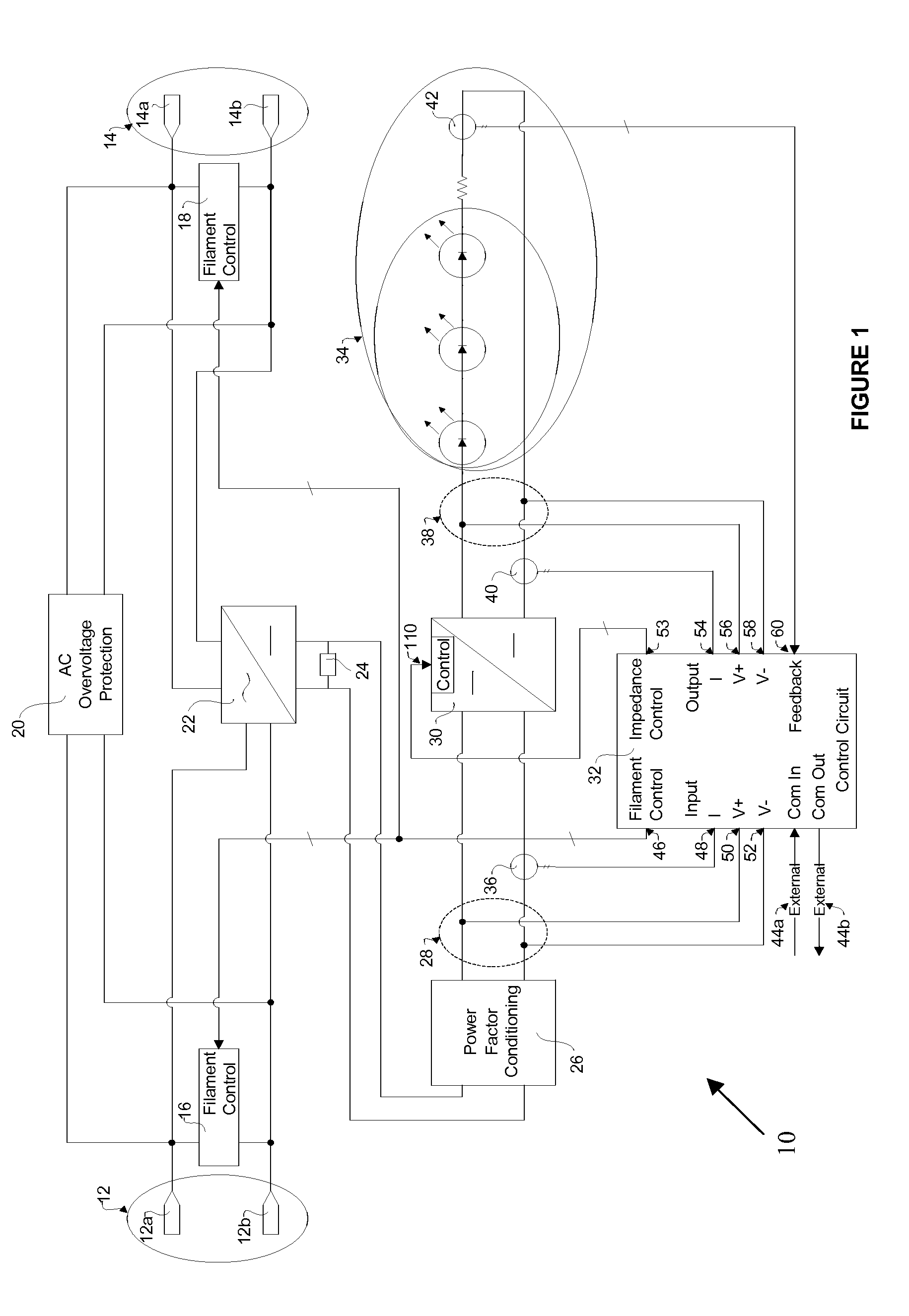
Impedance controlled electronic lamp circuit
InactiveUS20080197786A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical ballastEngineering
There is provided lamp ballast impedance controlled electronic lamp circuit, powered by a lamp ballast, for controlling a set of light emitting devices and being, comprising at least one connector, for connecting to the lamp ballast; and for receiving an AC signal; at least one filament control, associated with one of the at least one connector; a circuit for transforming the AC signal to a DC signal; a power convertor circuit; for receiving the DC signal and for processing the DC signal to provide a signal to power to the set of light emitting devices; a control and monitoring circuit; wherein the control and monitoring circuit monitors the DC signal and controls the impedance of either the at least one filament control or the power convertor circuit to control the set of light emitting devices.
Owner:MARLEX ENG
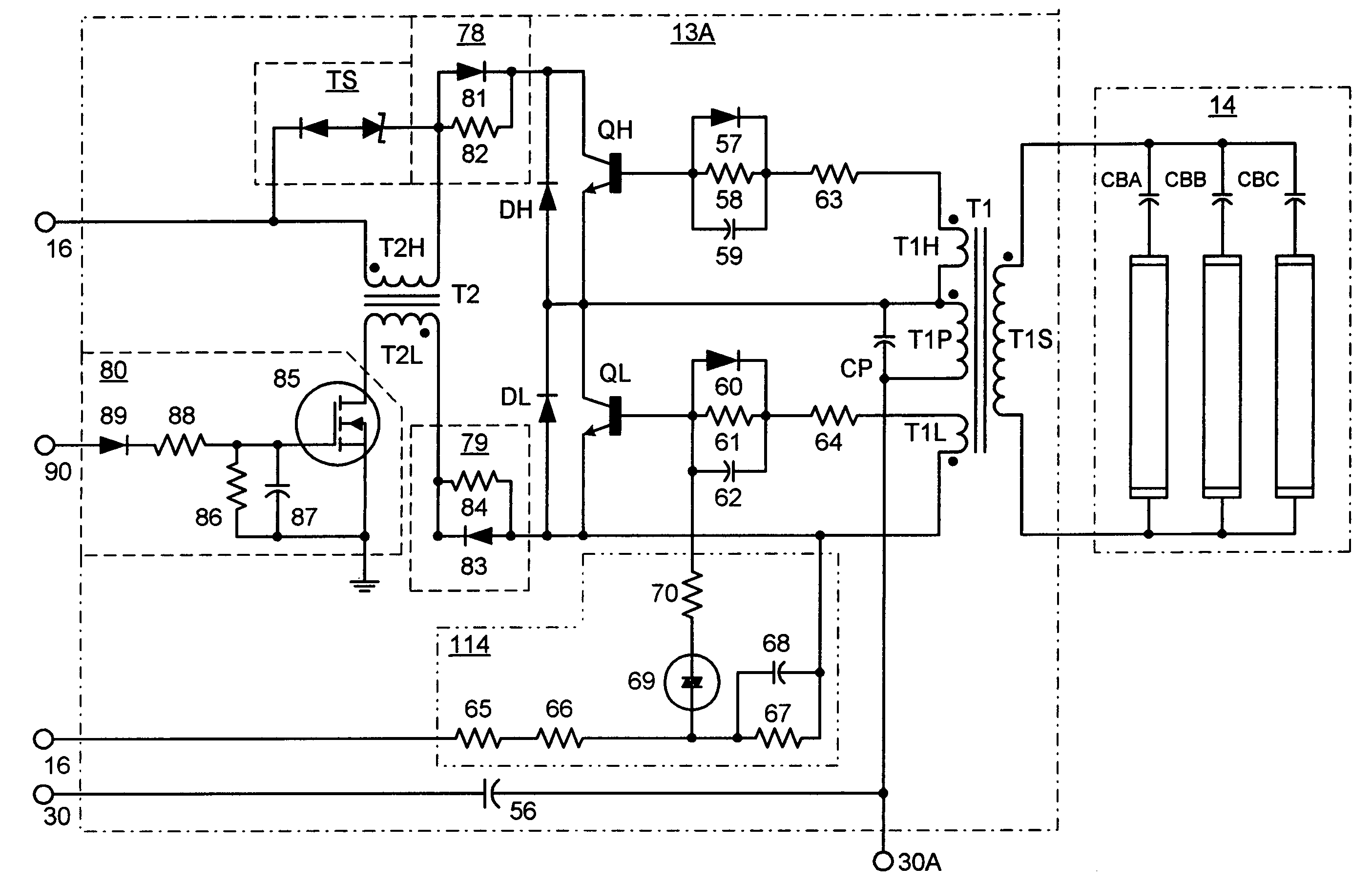
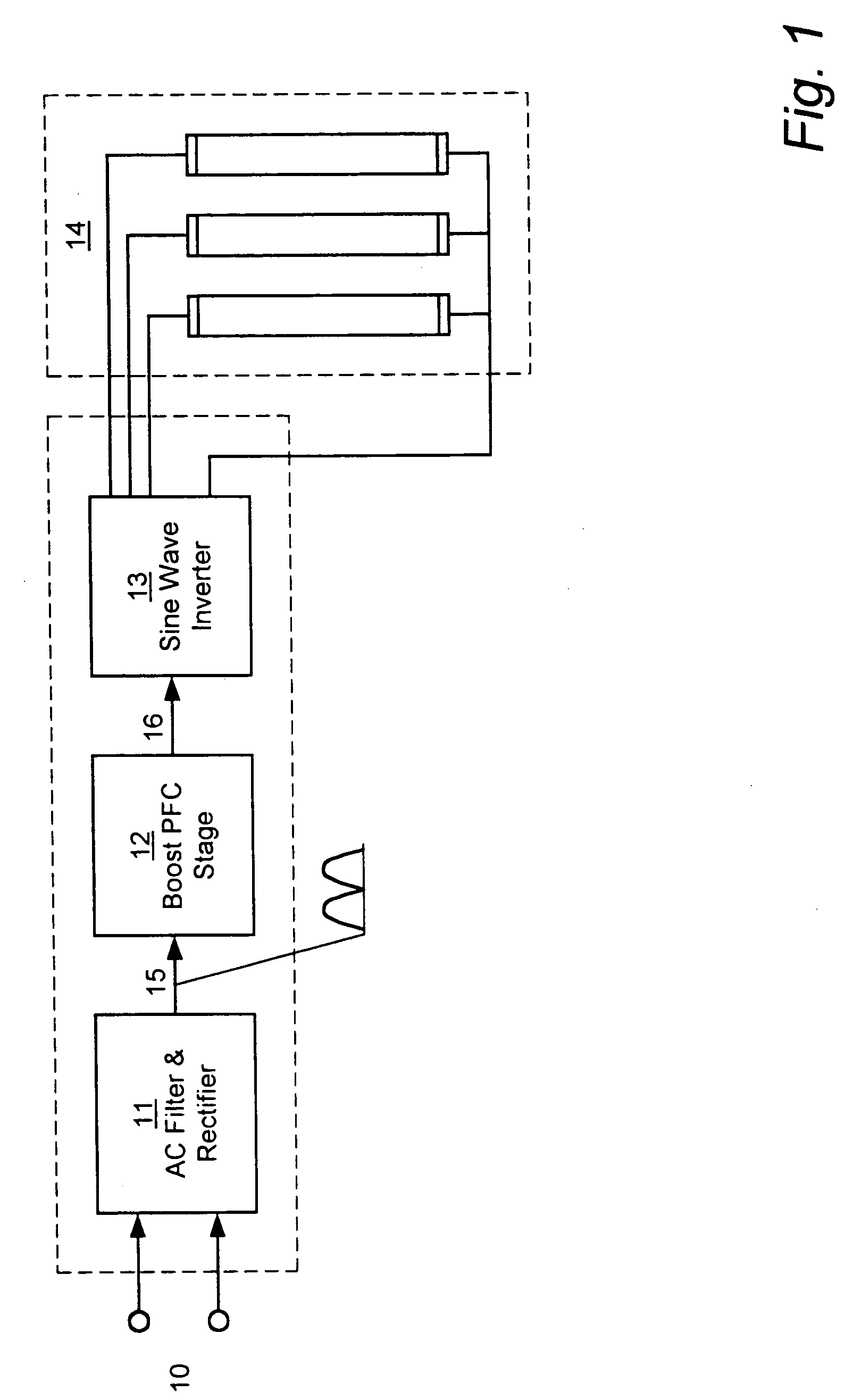
Instant start electronic ballast with universal AC input voltage
InactiveUS7061188B1Improve unit efficiencyLimit power lossElectric heatingElectric light circuit arrangementZener diodeEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic ballast that energizes fluorescent lamps connected in a parallel configuration. The ballast employs a power factor correcting boost converter that can be used over a wide range of AC line voltages to provide regulated power to a self-oscillating sine wave inverter that drives the fluorescent lighting load at high frequencies. The inverter employs special networks that limit a certain type of shoot-through current, and thus improve the efficiency of the unit. Also included is a restart circuit that limits power losses during the zero lamp condition, by periodically interrupting the inverter operation when the zero lamp state is detected. To improve operation of the power factor correcting circuitry over the wide range of AC line voltages, a DC offset is added to the sampled AC voltage at the higher AC line voltages by Zener diode based coupling circuit.
Owner:TECHN CONSUMER PRODS
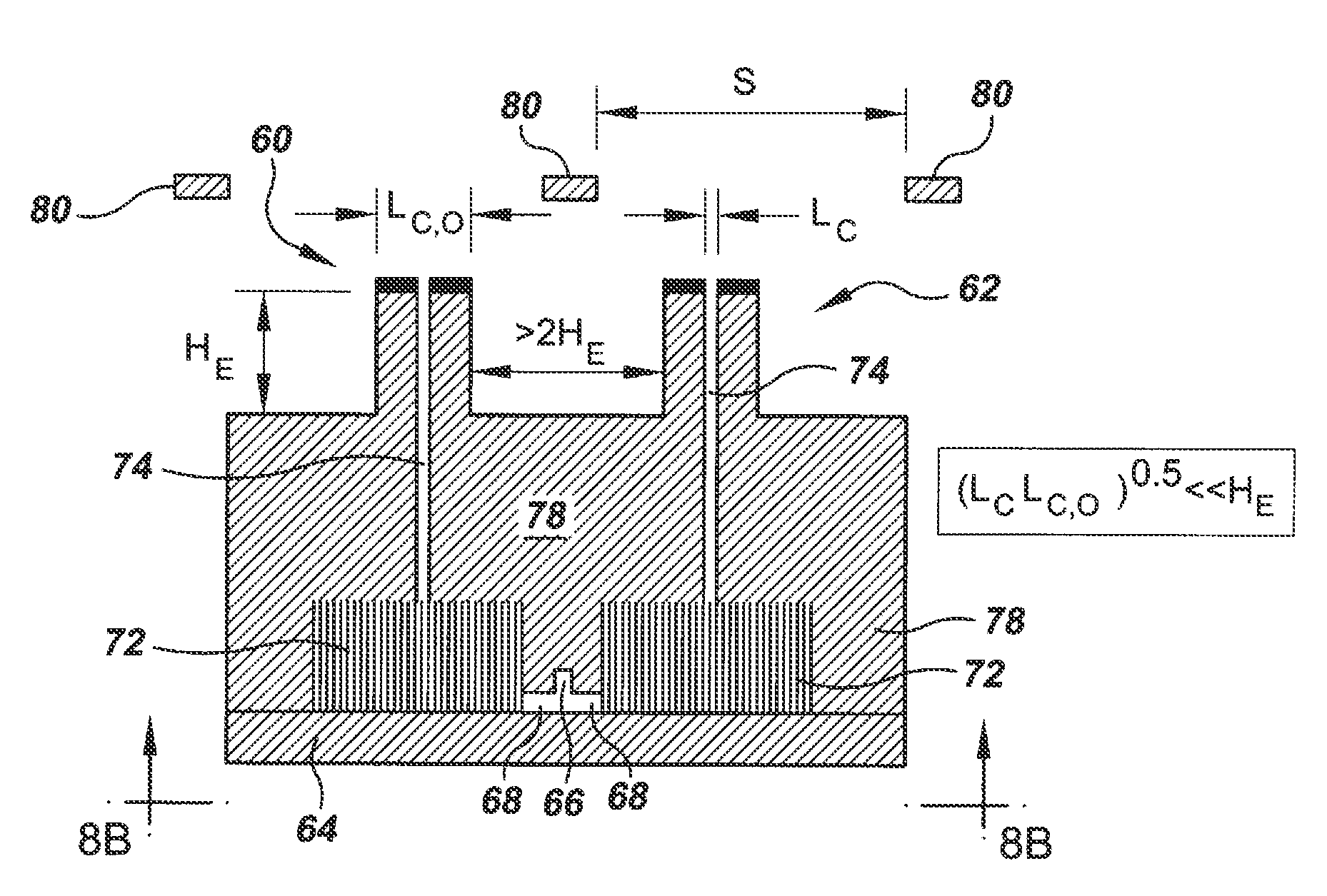
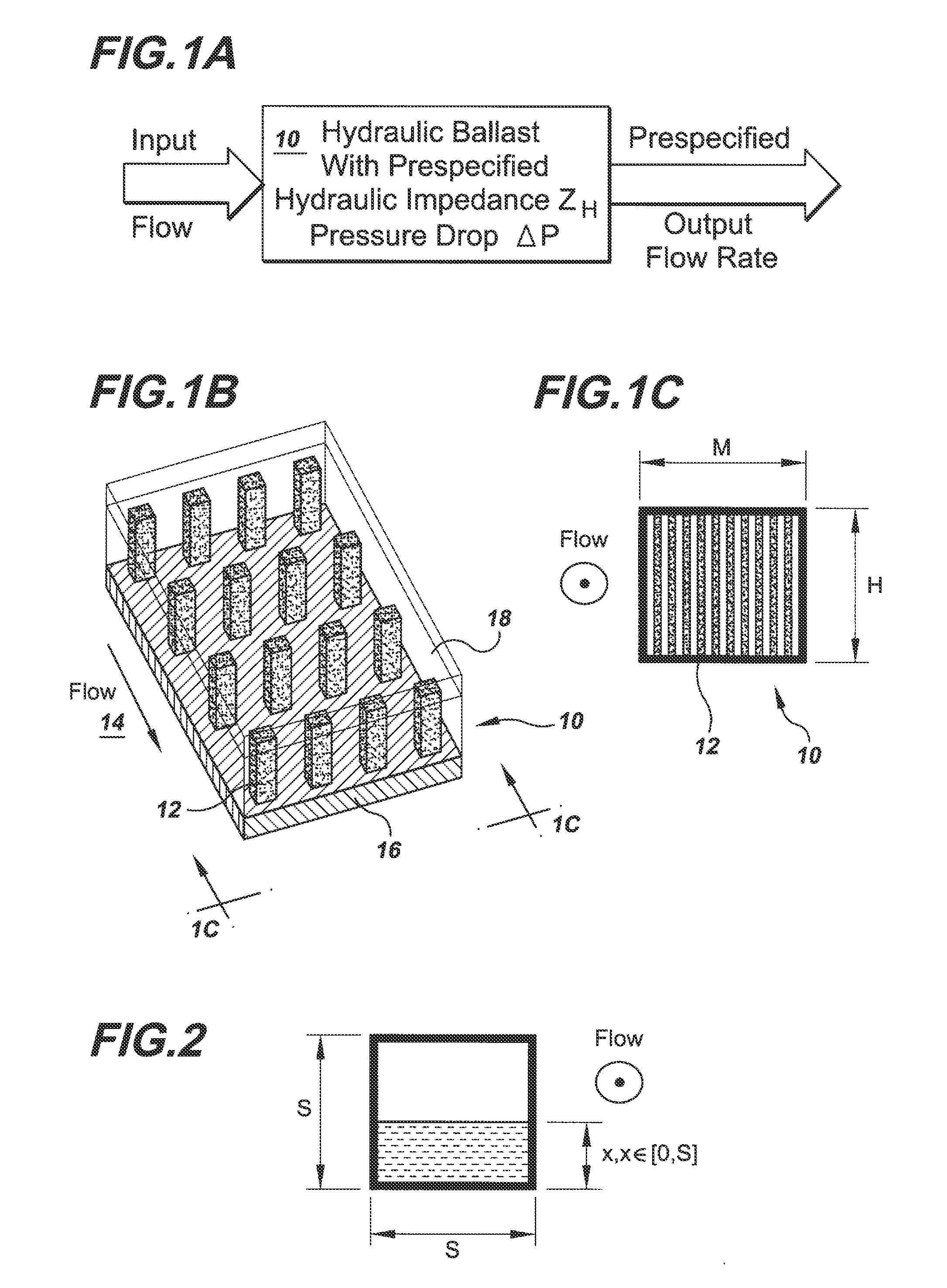
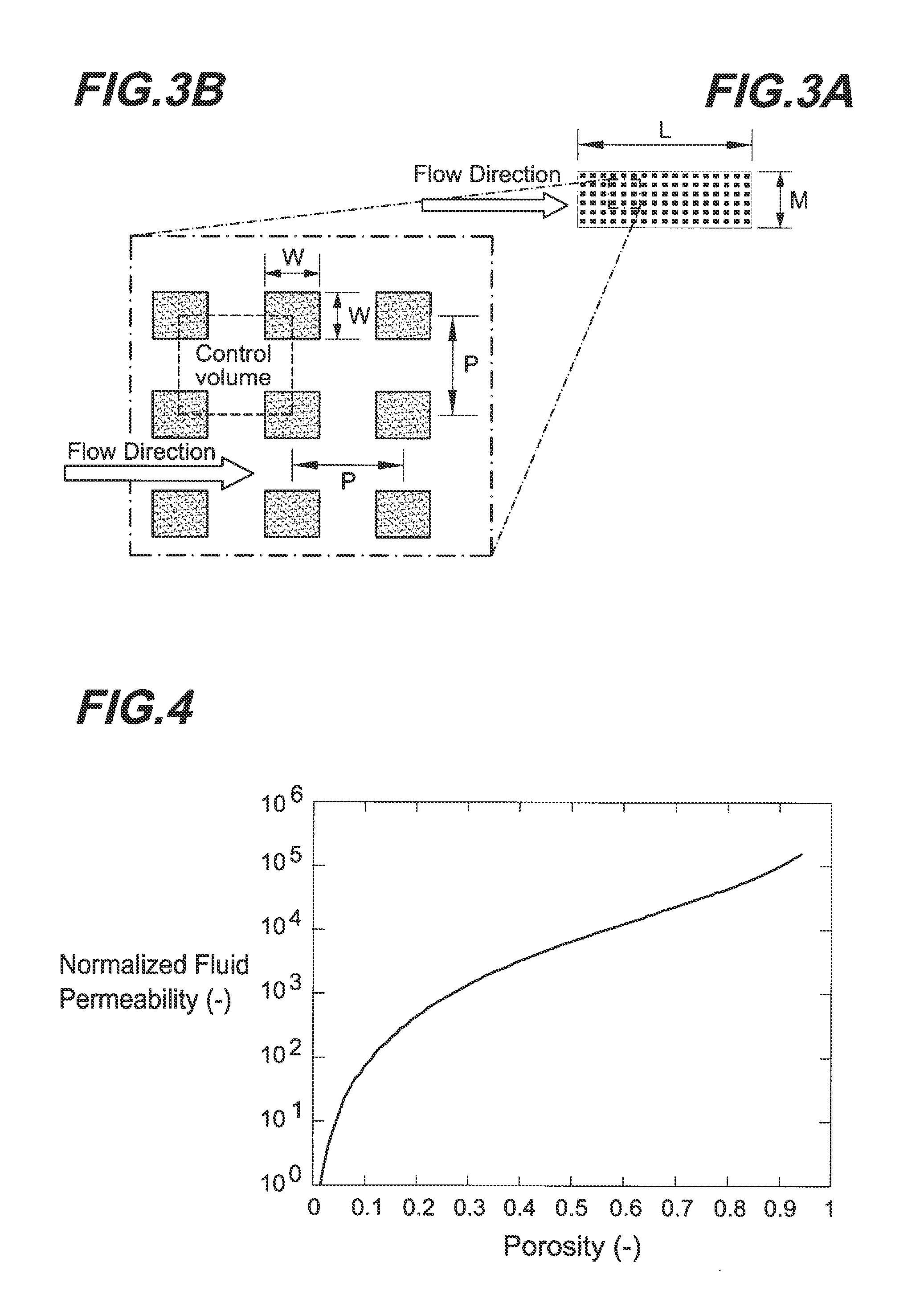
Microstructures For Fluidic Ballasting and Flow Control
InactiveUS20110126929A1Pipe supportsReactant parameters controlElectrical ballastControl engineering
In one example hydraulic ballast of the invention there is provided an input port and an output port through which a prespecified output flow rate is required. There is provided between the input and output ports a ballasting array of columns having a cross-sectional column extent, W, a column pitch, P, and an array length, L, selected based on the required output flow rate, to produce a prespecified pressure drop that enforces the required output flow rate.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Full digital dimming ballast for a fluorescent lamp
ActiveUS20050156534A1Electric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageSignal responseLoop control
A lamp control circuit is described, containing a power factor corrector, coupled to it a digitally controlled ballast, having power devices. The digitally controlled ballast is capable of powering a lamp. The ballast is controlled by a current feedback loop, coupled between the power devices and the digitally controlled ballast, and a voltage feedback loop, coupled between the lamp and the digitally controlled ballast. Further, a method of operating a lamp-control circuit is presented, the circuit containing a digital controller, an output stage, a current feedback loop, and a voltage feedback loop. In operation the digital controller receives a current feedback signal or a voltage feedback signal from the output stage and the lamp. In response to the received signal the digital controller generates a digital control signal and powers a lamp through the output stage according to the generated digital control signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Thermal management for fluorescent ballast and fixture system
InactiveUS20080285266A1Electric circuit arrangementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectrical ballastEngineering
A fluorescent lamp assembly includes a fixture which supports at least one fluorescent lamp. A ballast is mounted to the fixture for controlling a supply of electrical current to the fluorescent lamp. A thermal transfer material is interposed between the ballast and a portion of the fixture whereby heat is transferred between the ballast and the fixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
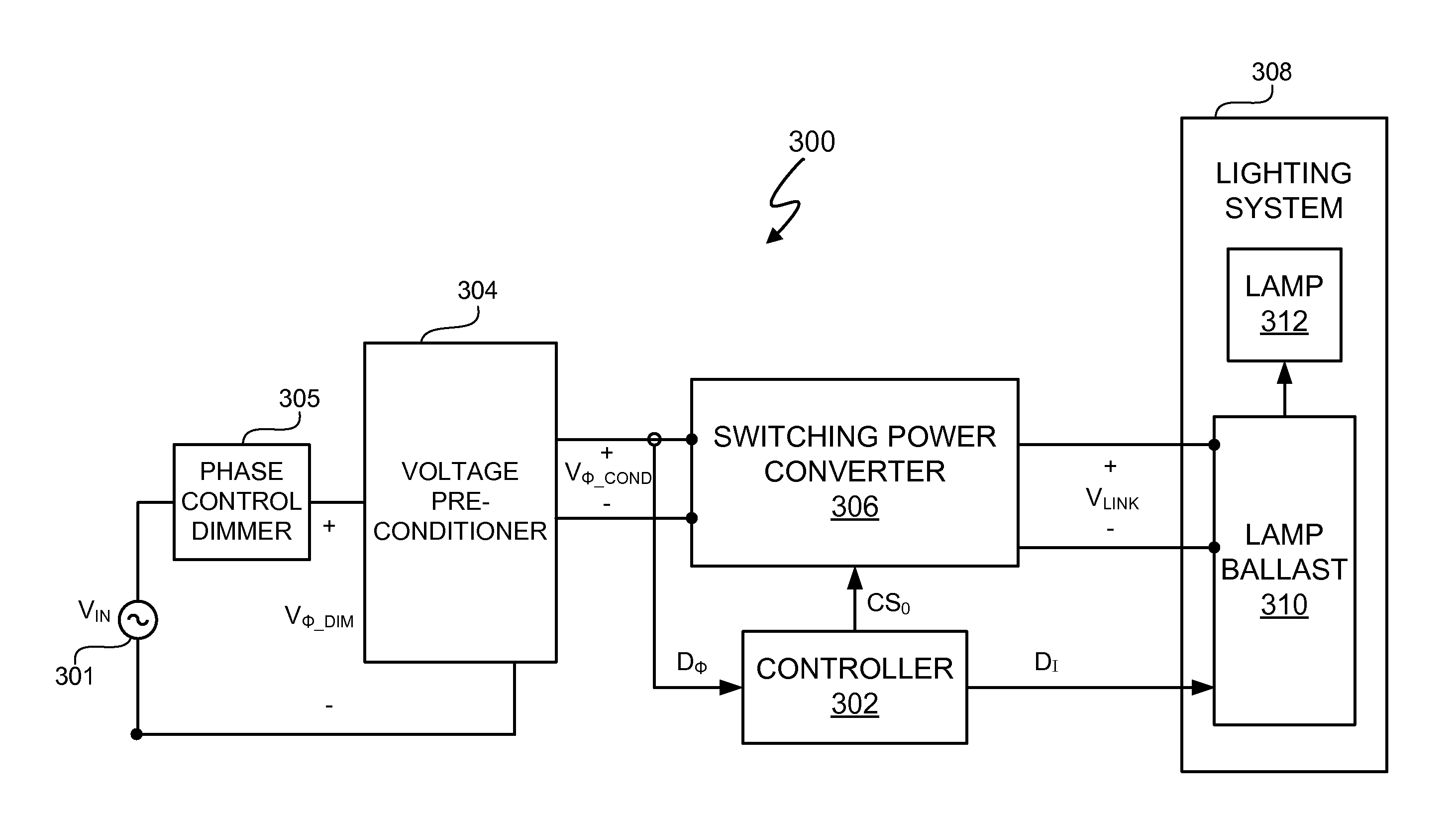
Phase Control Dimming Compatible Lighting Systems
InactiveUS20110074302A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementGas-discharge lampCombined use
A power control / lighting system includes a controller to provide compatibility between a lamp ballast configured to receive a dedicated dimmer signal and a phase control dimmer. In at least one embodiment, the controller converts a phase control dimming signal into dimming information useable by a lamp ballast of a gas discharge lamp based lighting system. Additionally, in at least one embodiment, the controller also controls power factor correction of the power control / lighting system. In at least one embodiment, the controller provides dimming information based on the phase control dimming signal that allows the lamp ballast to be used in conjunction with a phase control dimmer.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
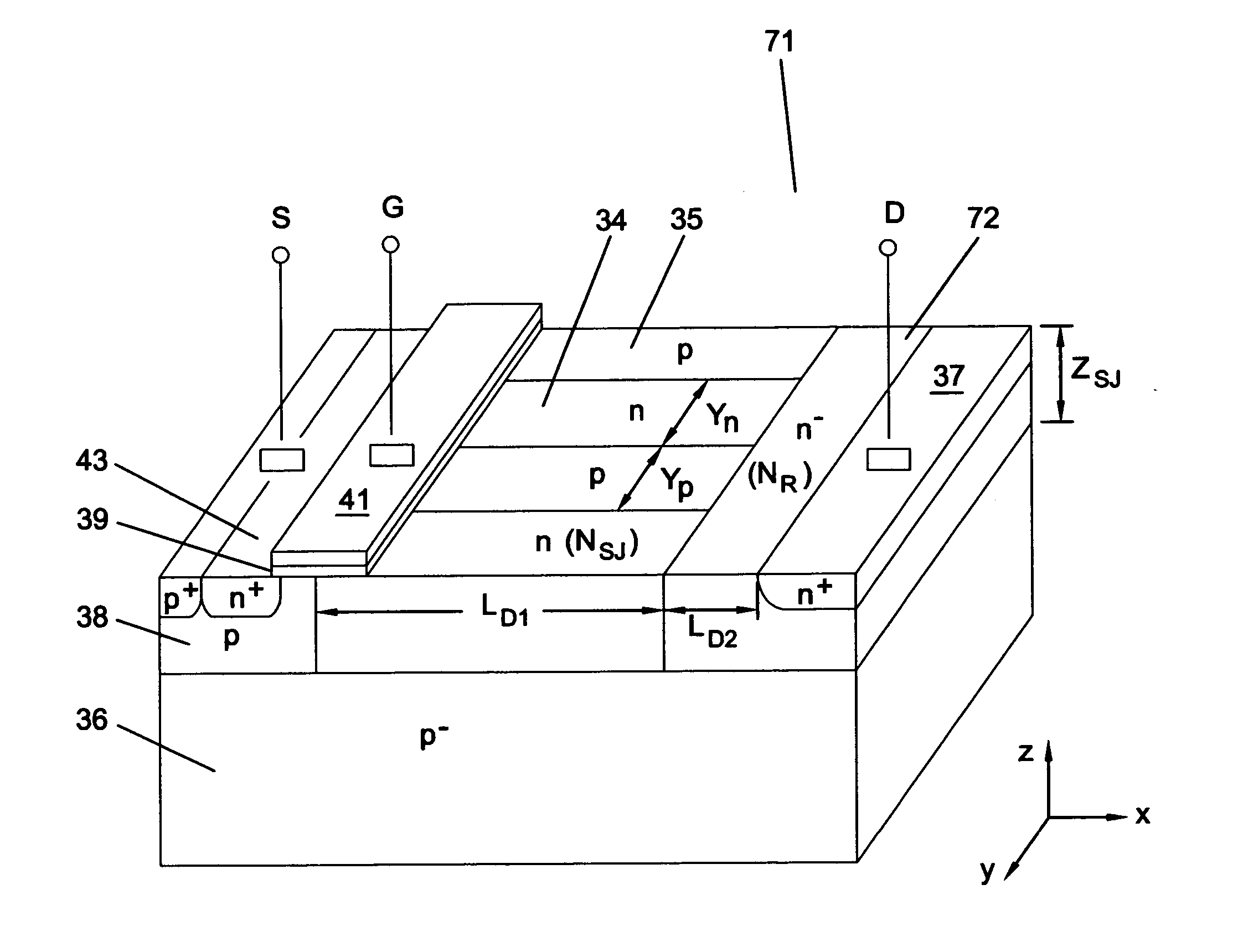
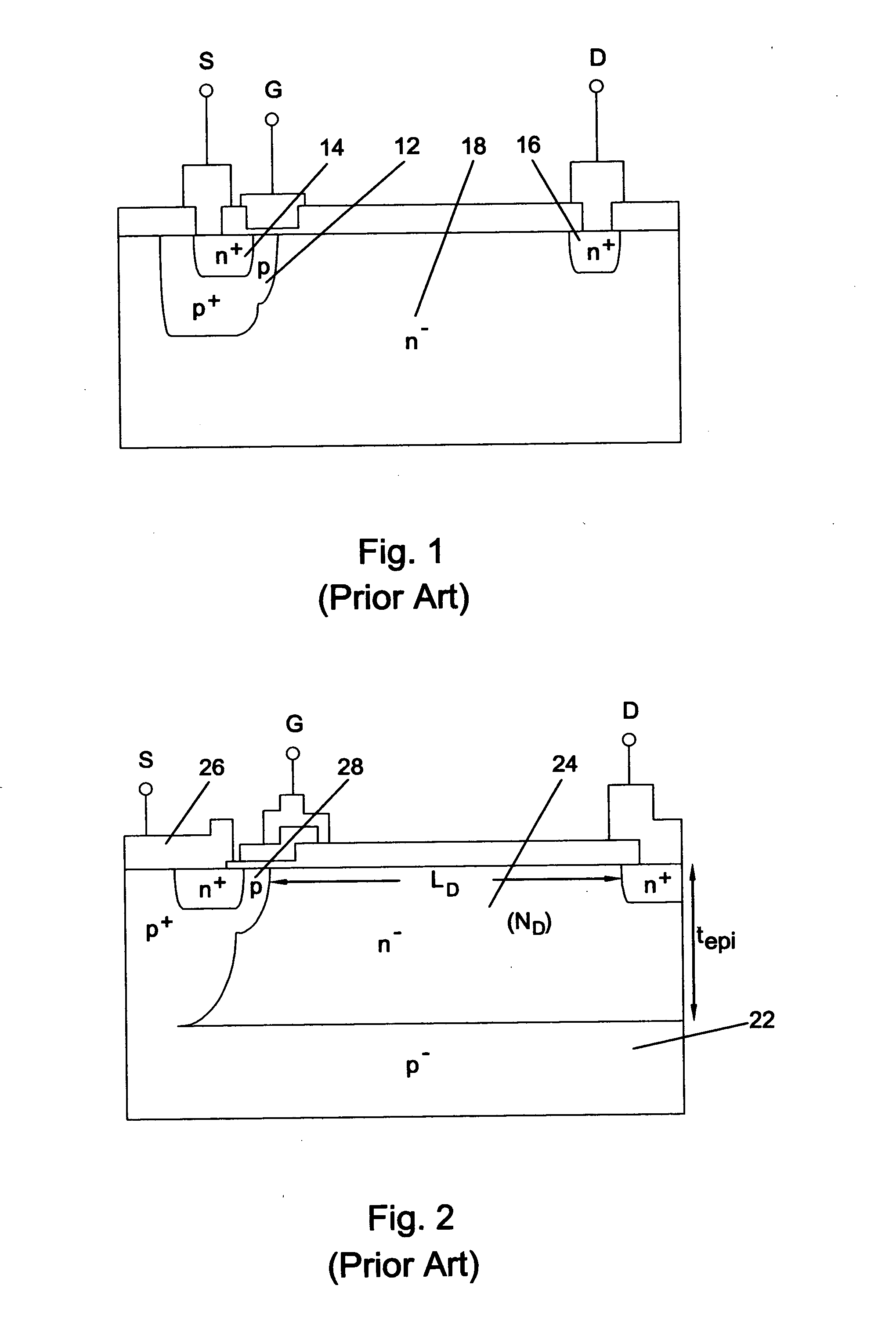
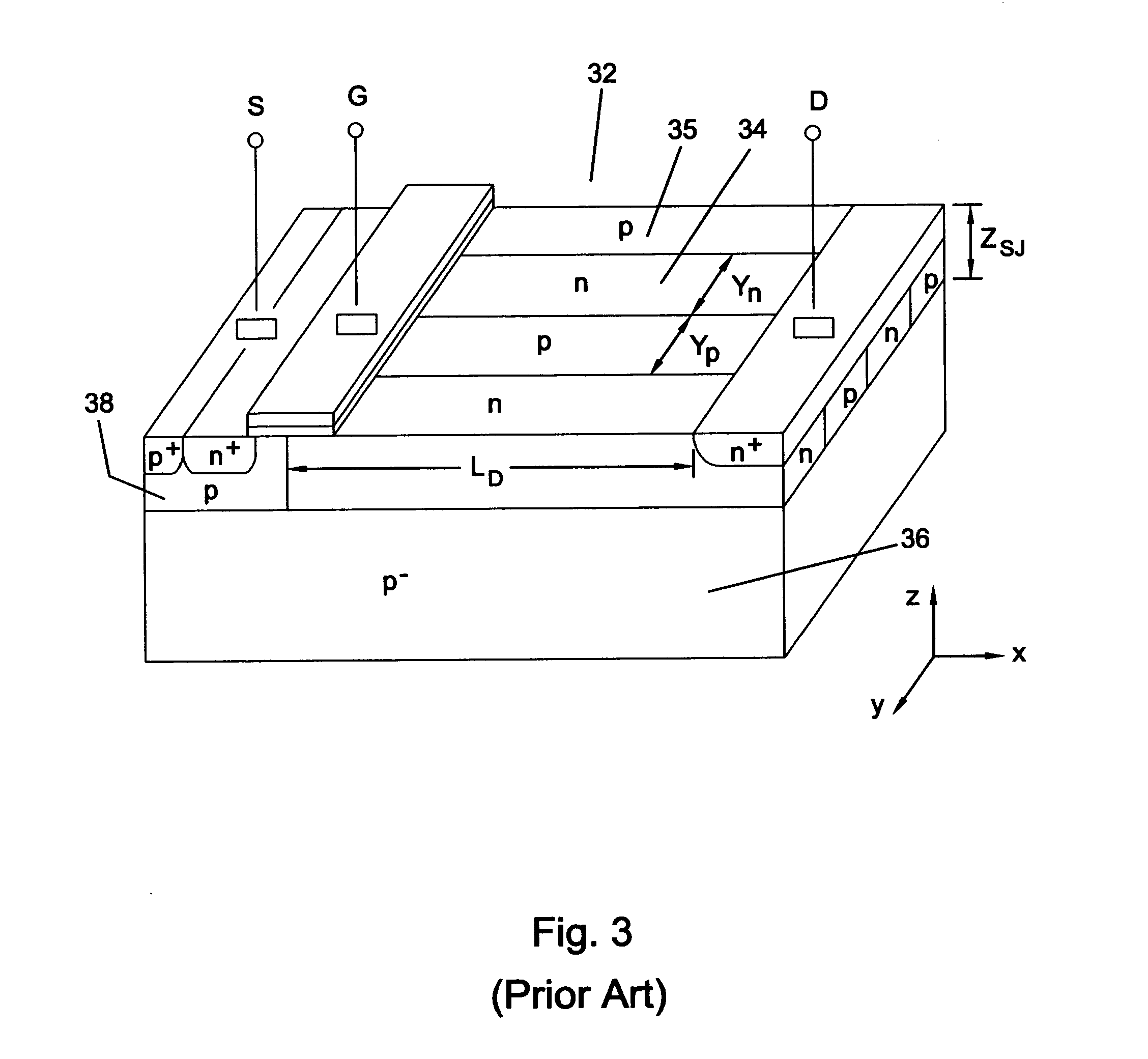
Super junction / resurf ldmost (sjr-LDMOST)
InactiveUS20050017300A1Reduce doping concentrationBreakdown voltage of deviceSemiconductor devicesMOSFETElectrical ballast
A lateral double diffused MOSFET (LDMOST) incorporates both the reduced surface field (RESURF) and super junction (SJ) in a split-drift region to significantly improve the on-state, off-state and switching characteristics in junction-isolated (JI) technology. The structure effectively suppresses substrate-assisted-depletion which is the main problem encountered when applying the SJ concept to lateral power devices. The device structure features a split-drift region formed of two parts: a SJ structure that extends over most of the drift region, and a terminating RESURF region occupying a portion of the drift region next to the drain. The structure offers improved breakdown voltage and reduced specific on resistance as compared to convention structures, and is useful in power integrated circuits suitable for a variety of applications including flat plasma panel display, automotive electronics, motor control, power supply and high voltage lamp ballasts.
Owner:SALAMA C ANDRE T +1
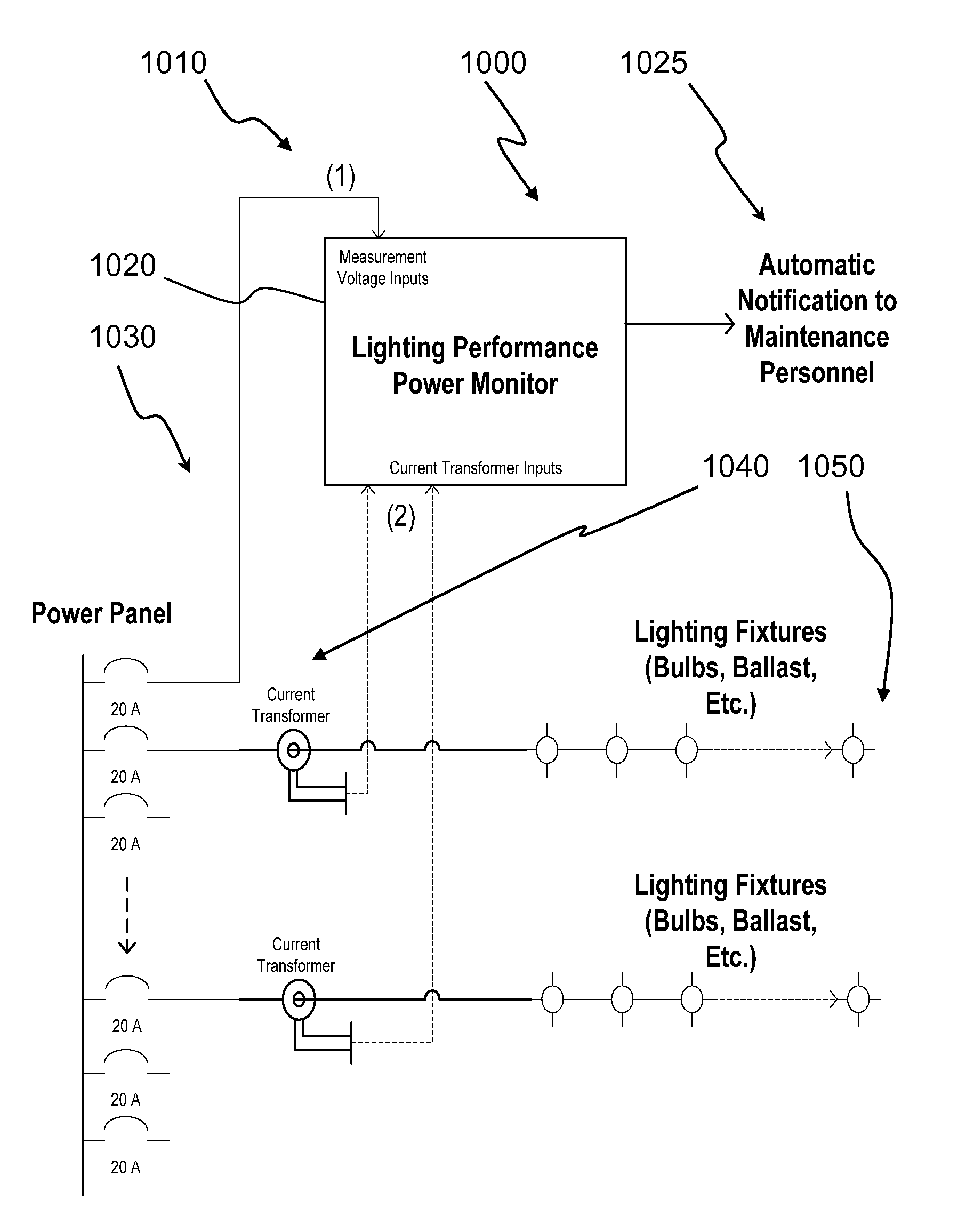
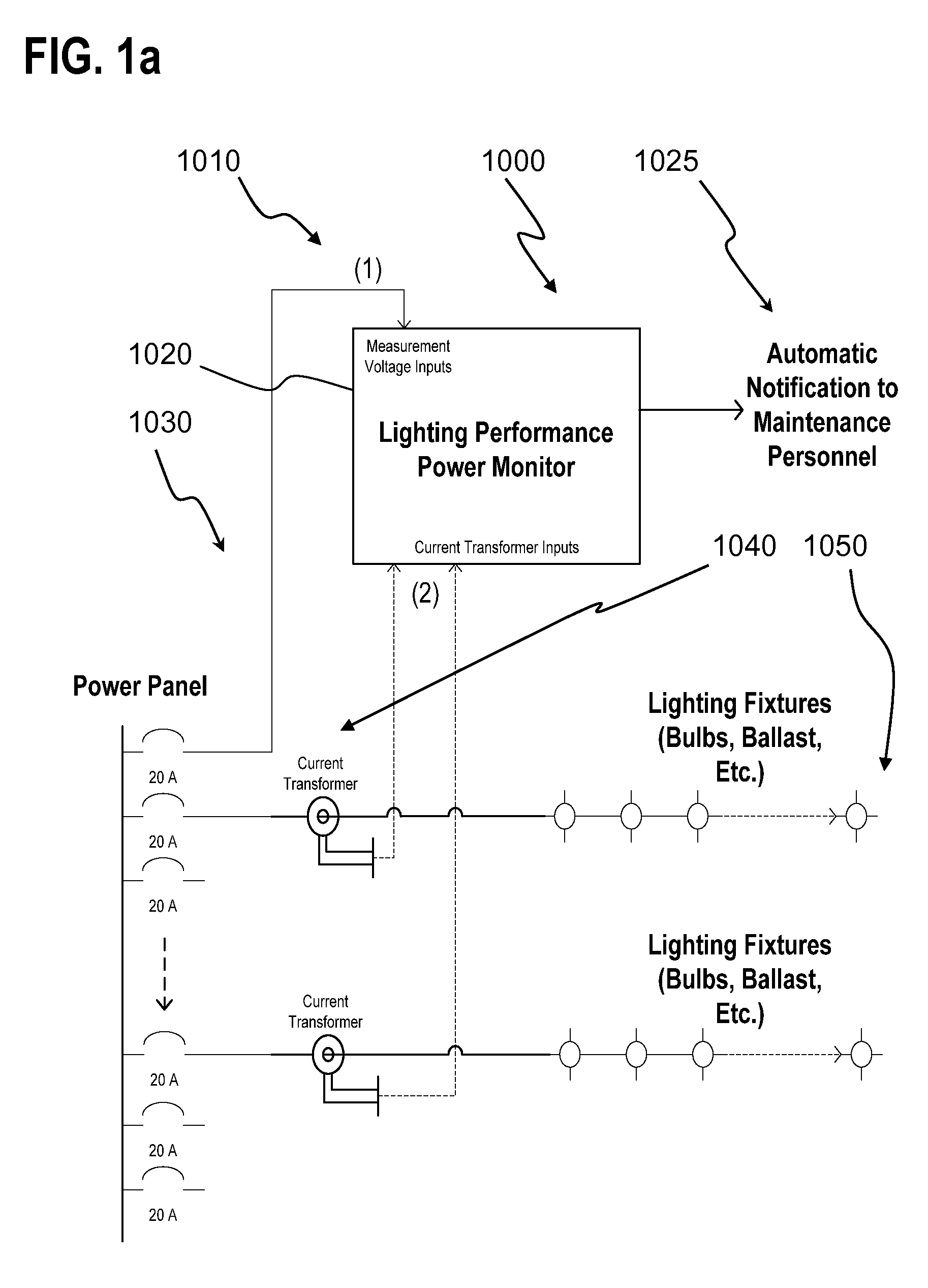
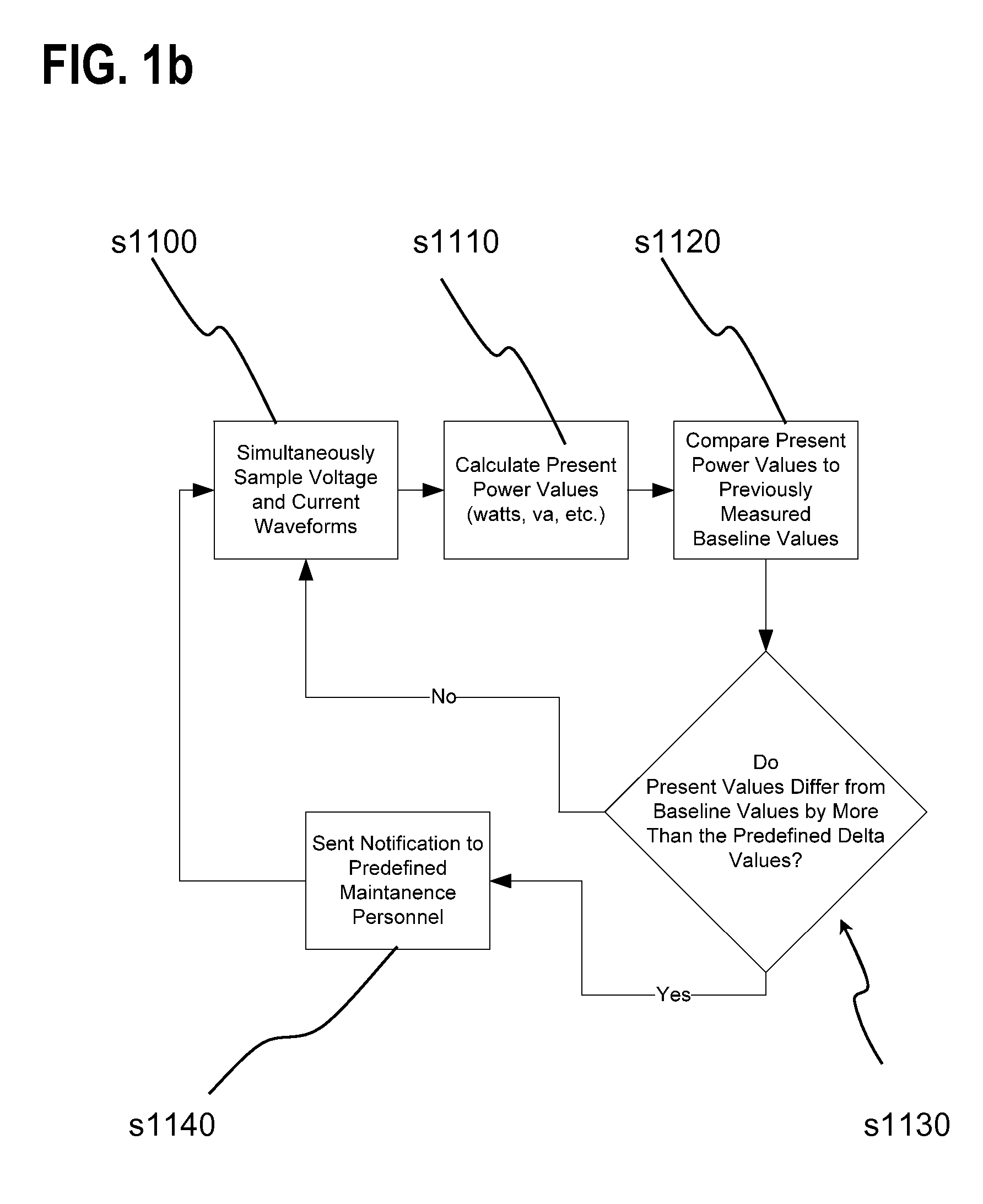
Lighting performance power monitoring system and method with optional integrated light control
ActiveUS20070282547A1Save energyReduce materialLevel controlPower measurement by digital techniqueEngineeringElectric power
A light performance monitoring device and optionally integrated controller includes a monitor module that directly monitors energy usage of at least one energy load to generate at least one measurement of energy usage; a storage module stores a series of baseline values of energy usage of the energy load, a comparator module compares energy measurements made at predetermined intervals with the baseline values, and a notification module notifies a designated recipient that there is a deviation from the baseline values consistent with a burned out or non-operational light fixture, including but not limited to light bulbs or ballast devices. A control module optionally integrated with the light performance monitoring device can be operatively coupled to the monitor module to control energy usage by the at least one energy load via a data link in a pre-determined manner that is based on the at least one measurement of energy usage.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Switching circuit and lamp compatible with fluorescent lamp ballast
InactiveCN104735873AImprove work efficiencyEasy to replaceElectric light circuit arrangementElectrical ballastLED lamp
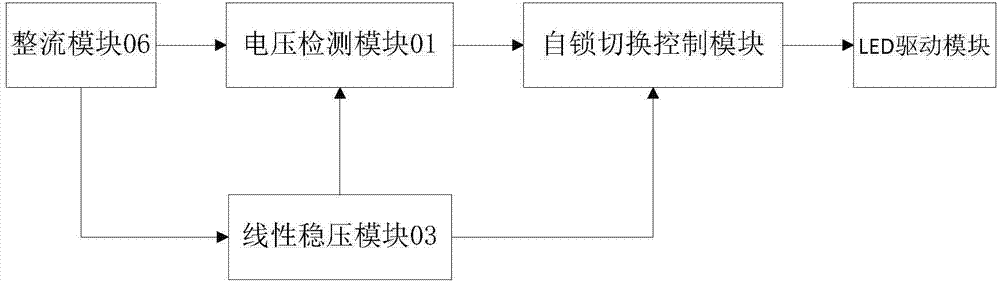
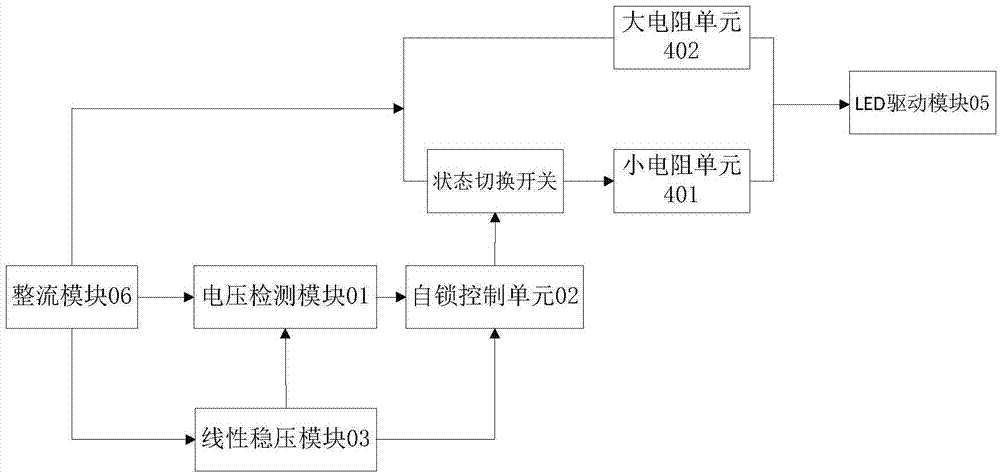
The invention discloses a switching circuit which is compatible with fluorescent lamp ballast. The switching circuit comprises a rectifying module, a switching module and an LED driving module. The output end of the rectifying module is connected with the input end of the switching module. The output end of the switching module is connected with the input end of the LED driving module. The rectifying module is used for converting an alternating current of an external power supply into a direct current, and then outputting the direct current. When a voltage value output by the rectifying module is lower than a preset threshold value, impedance switching is carried out on the switching module, and equivalent impedance of the switching circuit is increased. The invention further discloses an LED lamp which is compatible with the fluorescent lamp ballast. The LED lamp comprises an LED module and the switching circuit which is compatible with the fluorescent lamp ballast. The output end of the LED driving module is connected with the LED module. The LED lamp which adopts the switching circuit can be fully compatible with direct power connection and one-with-one-type and one-with-more-type ballast of a current fluorescent lamp, and has the advantages of being simple and efficient in design, convenient to replace, and low in cost.
Owner:JINGSAM ILLUMINATION
Electronic ballast having adaptive frequency shifting
InactiveUS20070188111A1Minimize the differenceOperating duty cycleElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectrical ballastClosed loop
An electronic ballast for driving a gas discharge lamp avoids mercury pumping in the lamp by adaptively changing an operating frequency of an inverter of the ballast when operating near high-end. The inverter of the ballast generates a high-frequency AC voltage, which is characterized by the operating frequency and an operating duty cycle. The ballast also comprises a resonant tank for coupling the high-frequency AC voltage to the lamp to generate a present lamp current through the lamp, and a current sense circuit for determining the magnitude of the present lamp current. A hybrid analog / digital control circuit controls both the operating frequency and the operating duty cycle of the inverter with closed-loop techniques. The control circuit adjusts the duty cycle of the inverter in response to a target lamp current and the present lamp current. To avoid mercury pumping, the control circuit attempts to maximize the duty cycle of the inverter when operating at high-end. Specifically, the control circuit adjusts the operating frequency of the inverter in response to the target lamp current signal, the duty cycle of the inverter, and a target duty cycle in order to drive the operating duty cycle toward the target duty cycle.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
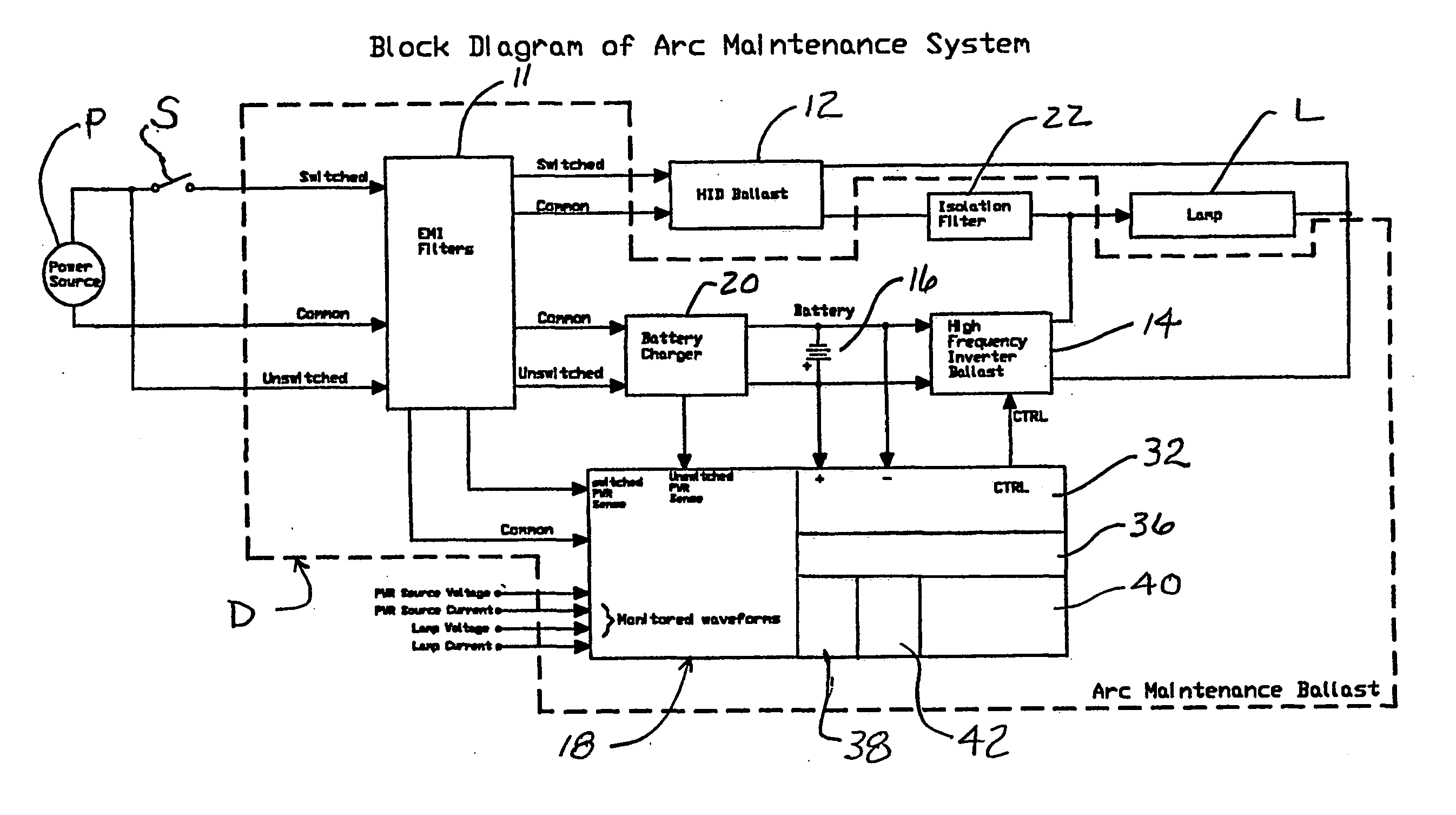
Arc maintenance device for high density discharge lamps including an adaptive wave form monitor
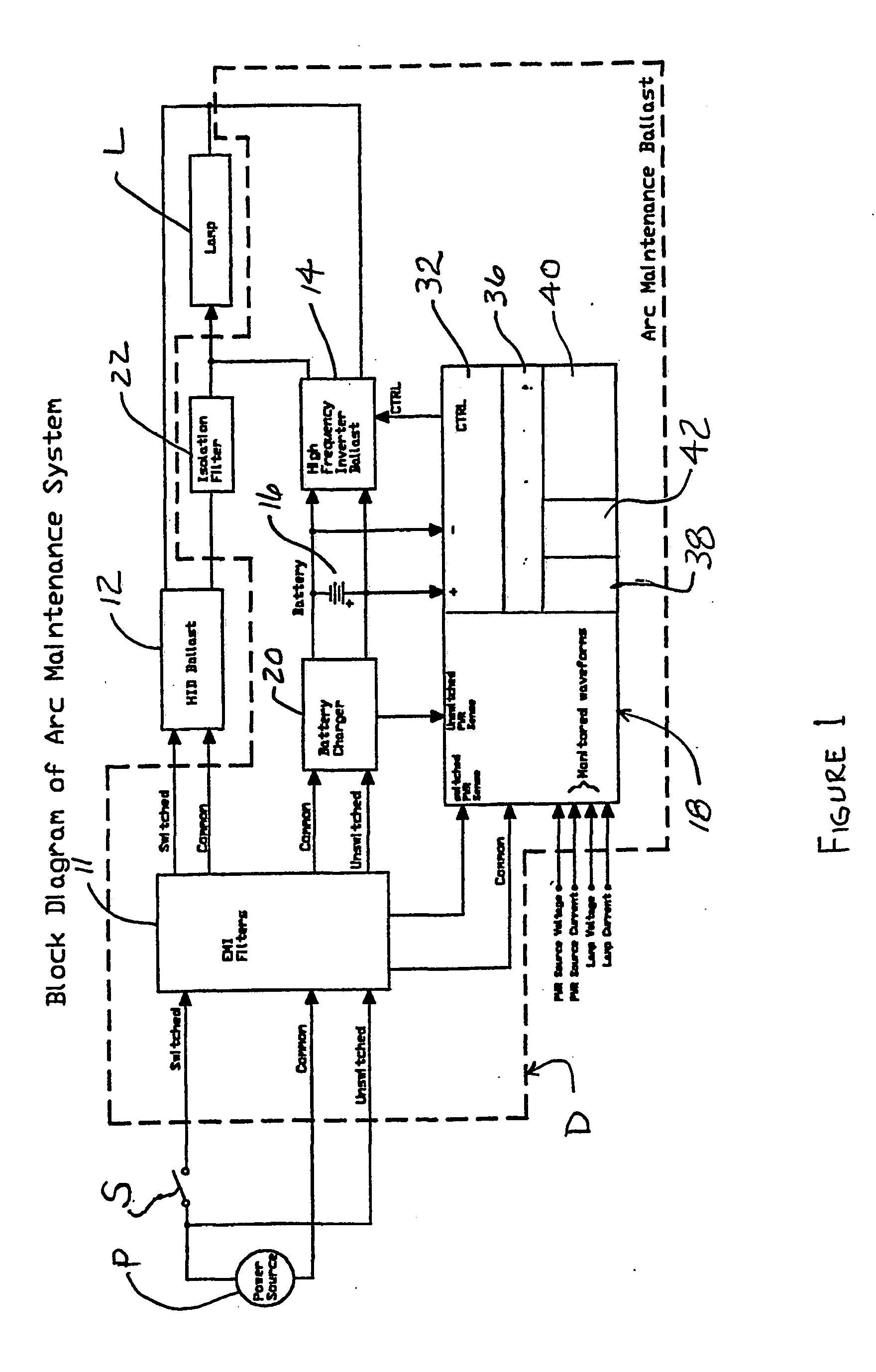
InactiveUS20050258765A1Electric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageInstabilityEngineering
A supplemental arc maintenance electrical supply for a high density discharge (HID) lamp (L) for applying a high frequency supplemental arc voltage to maintain the arc during a period of unstable or intermittent AC supply in addition to or in lieu of the voltage or current being supplied to the lamp by the HID ballast (12). AC supply instability is identified in less time than the unstable or intermittent power will cause the lamp to arc to extingish and energize a supplemental arc maintenance electrical supply to maintain the arc of the lamp during the period of instability or interruption, so long as its internal, rechargeable battery is operational. The monitoring system (18) also recognizes the re-establishment of a stable (as by being a persistently repeating cycle but not necessarily a sinusoidal AC supply) repeating electrical power supply which is also of sufficient energy level to maintain operation of the HID lamp.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Compact fluorescent lamp and method for manufacturing
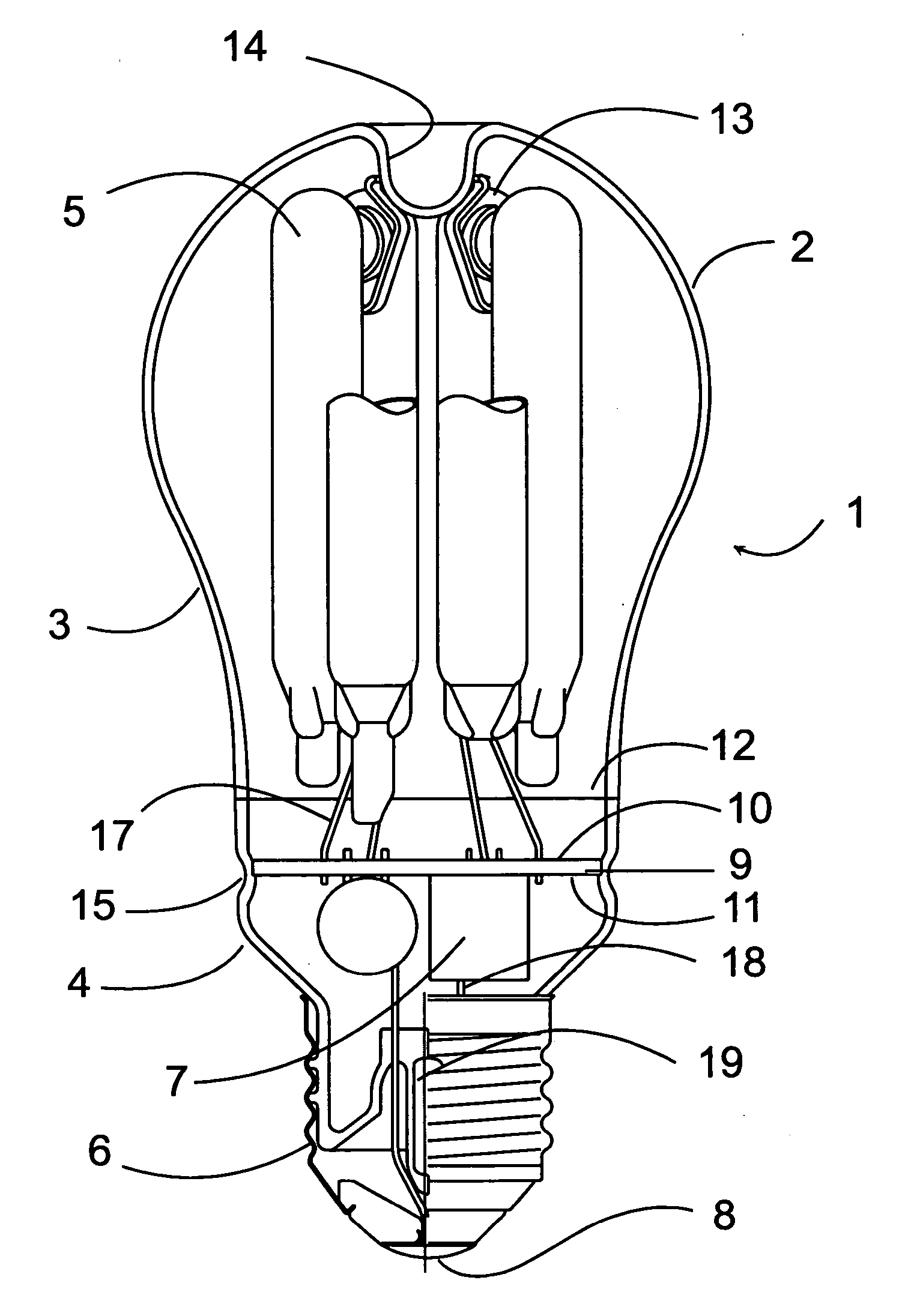
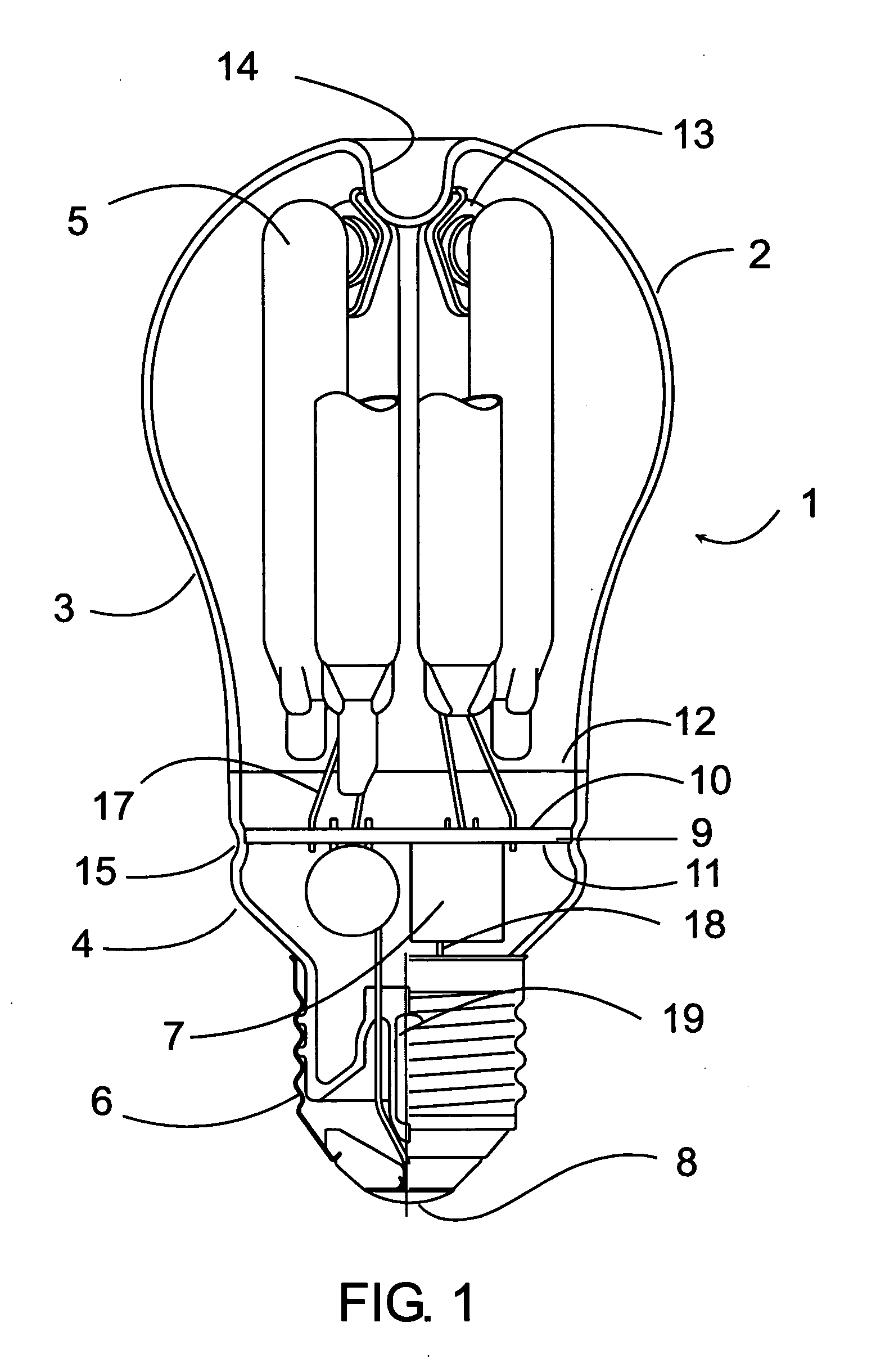
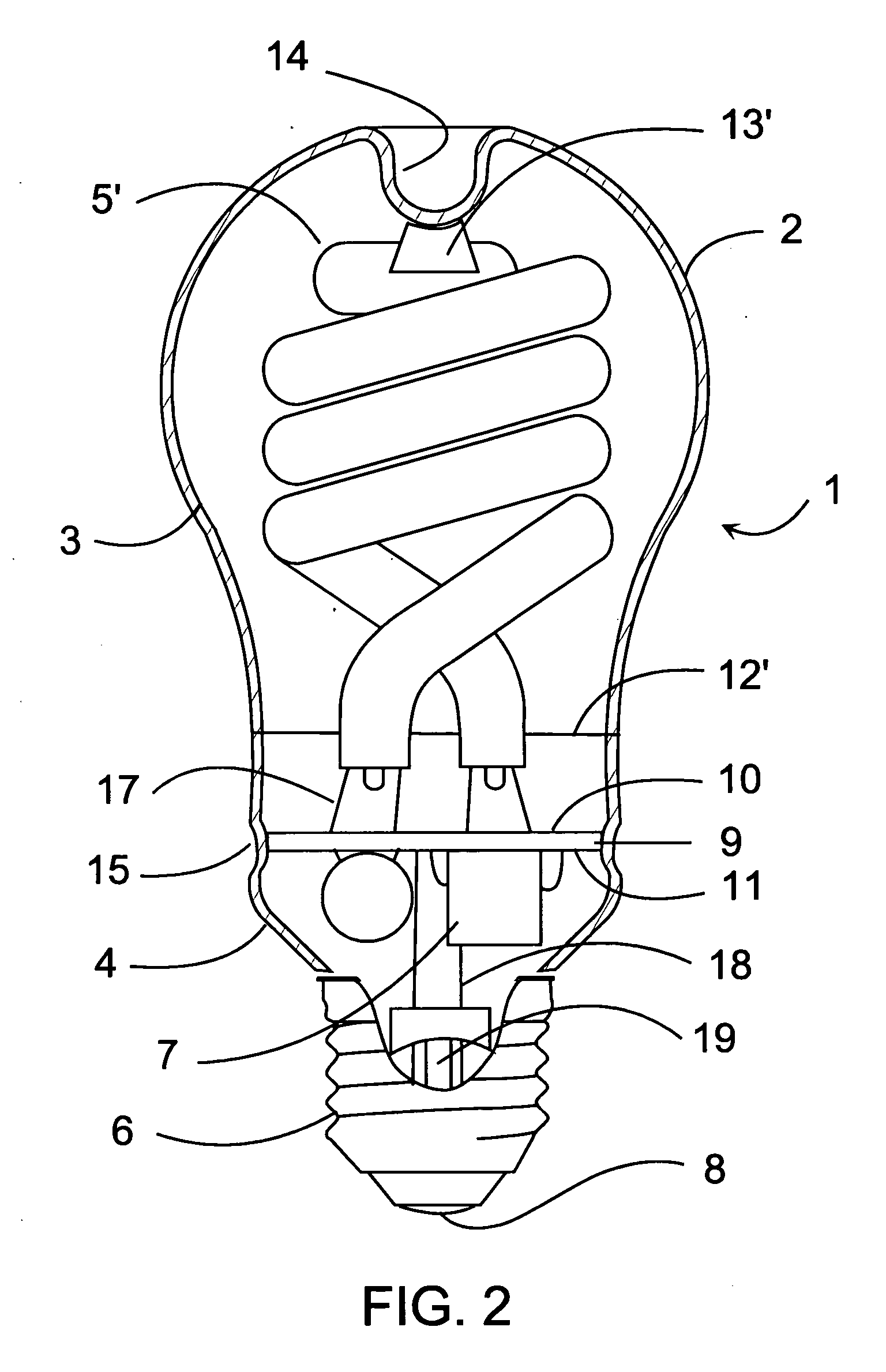
InactiveUS20070063656A1More to mechanical vibrationSimplify manufacturing stepsGas discharge lamp usageSolid cathode detailsElectrical ballastFluorescence
This compact fluorescent lamp comprises a discharge tube arrangement with at least one discharge tube. The tube is formed of glass, encloses a discharge volume filled with a discharge gas and has a fluorescent phosphor coating disposed on the inner surface of the tube. The tube forms a continuous arc path and the tube is provided with electrodes disposed at each end of the arc path. The lamp also comprises a ballast circuit connected to the electrodes for controlling the current in the tube and a lamp base for connecting said lamp to a power supply through a socket. The lamp is enclosed in an outer envelope comprising a substantially spherical portion enclosing the tube arrangement and an elongated end portion enclosing the ballast circuit. The end portion of the outer envelope is closed and sealed by a sealing means of the same material as the material of the outer envelope. The sealing means is connected to the envelope in a hermetically sealing way. A method for manufacturing a compact fluorescent lamp as described above is also disclosed. In the method, an outer envelope with an open end on the base side is provided. The open end of the envelope is closed and sealed with a sealing means to provide a hermetic seal. The envelope is separated by cutting along a circumferential line into an upper part and a lower part. The ballast circuit is introduced into the lower part and respective connection points of the ballast circuit are connected to power supply lead-out wires. The discharge tube arrangement is connected to respective connection points of the ballast circuit by lead-in wires. The lead-in wires and the lead-out wires are short and need not be insulated. The ballast circuit and the discharge tube arrangement are held and supported in the outer envelope by the connecting wires and fixing means.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
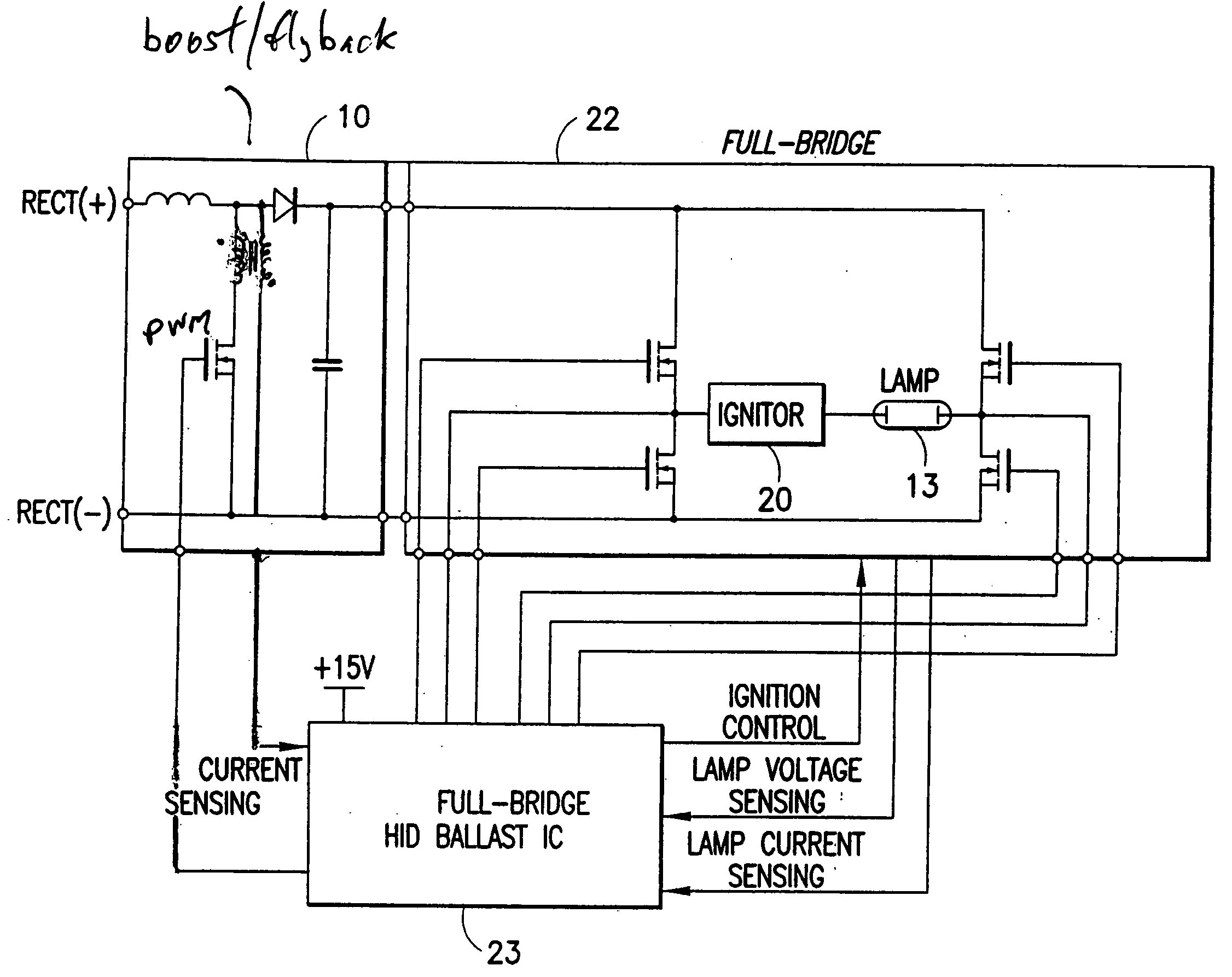
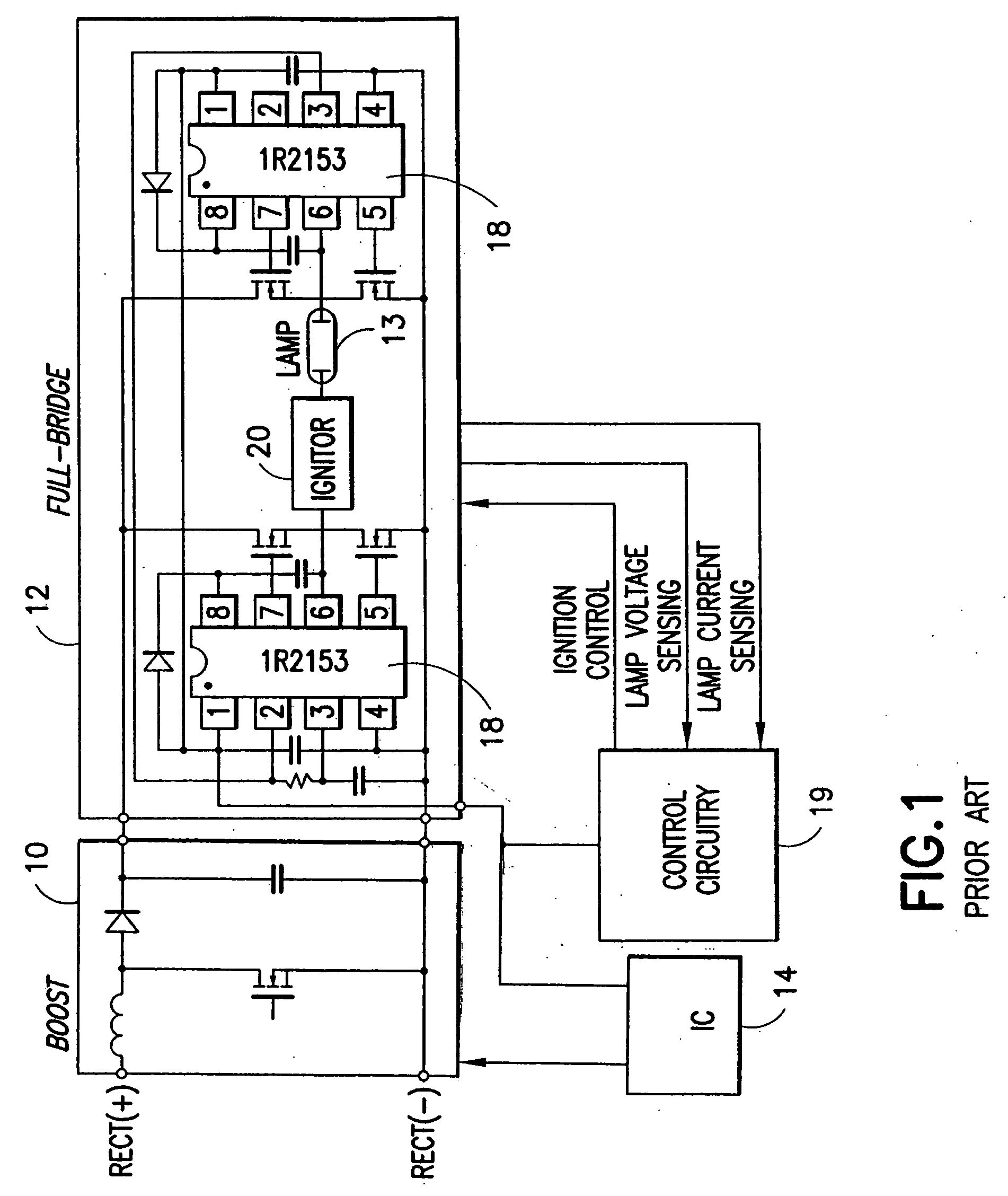
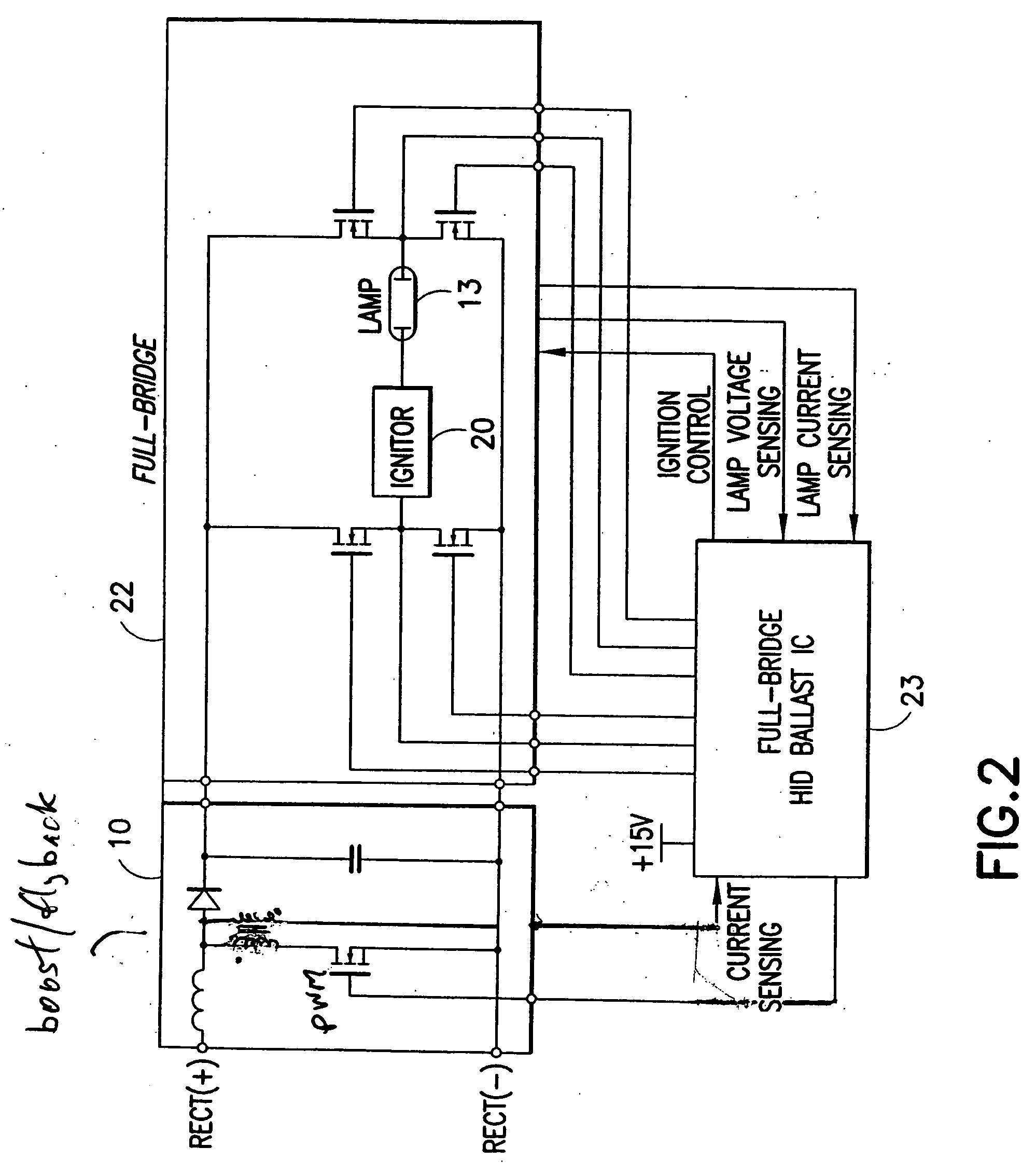
Automotive high intensity discharge lamp ballast circuit
ActiveUS20060197470A1Improve light outputElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMaximum levelElectrical ballast
An electronic ballast for driving a high intensity discharge (HID) lamp is provided. The electronic ballast includes a voltage boost stage for receiving a DC input voltage and outputting a boosted DC output voltage with a controlled current. It further includes a switching stage for converting the boosted DC output voltage to a switched AC voltage capable of driving the HID lamp. An integrated circuit (IC) is coupled to the voltage boost stage and the switching stage for controlling both. The IC includes a lamp power control circuit comprising a sensing circuit for sensing an output current from the switching stage and the boosted DC output voltage, a current control loop which controls the lamp power if the lamp current is at a maximum level and a power control loop which controls the lamp power if the lamp current is below a maximum level. The IC also includes a controller unit interface and provides an ignition mode and a regular operation mode.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS
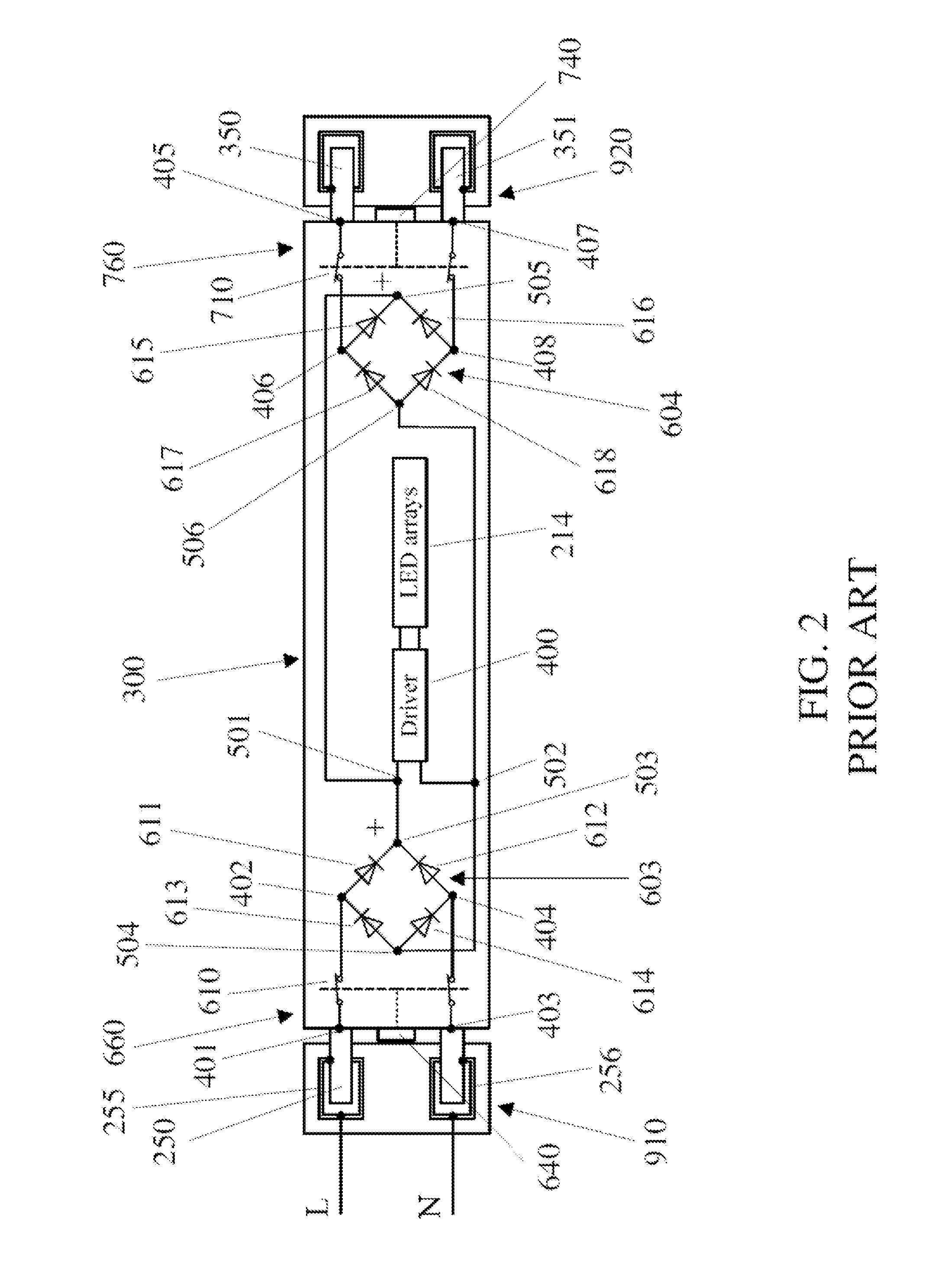
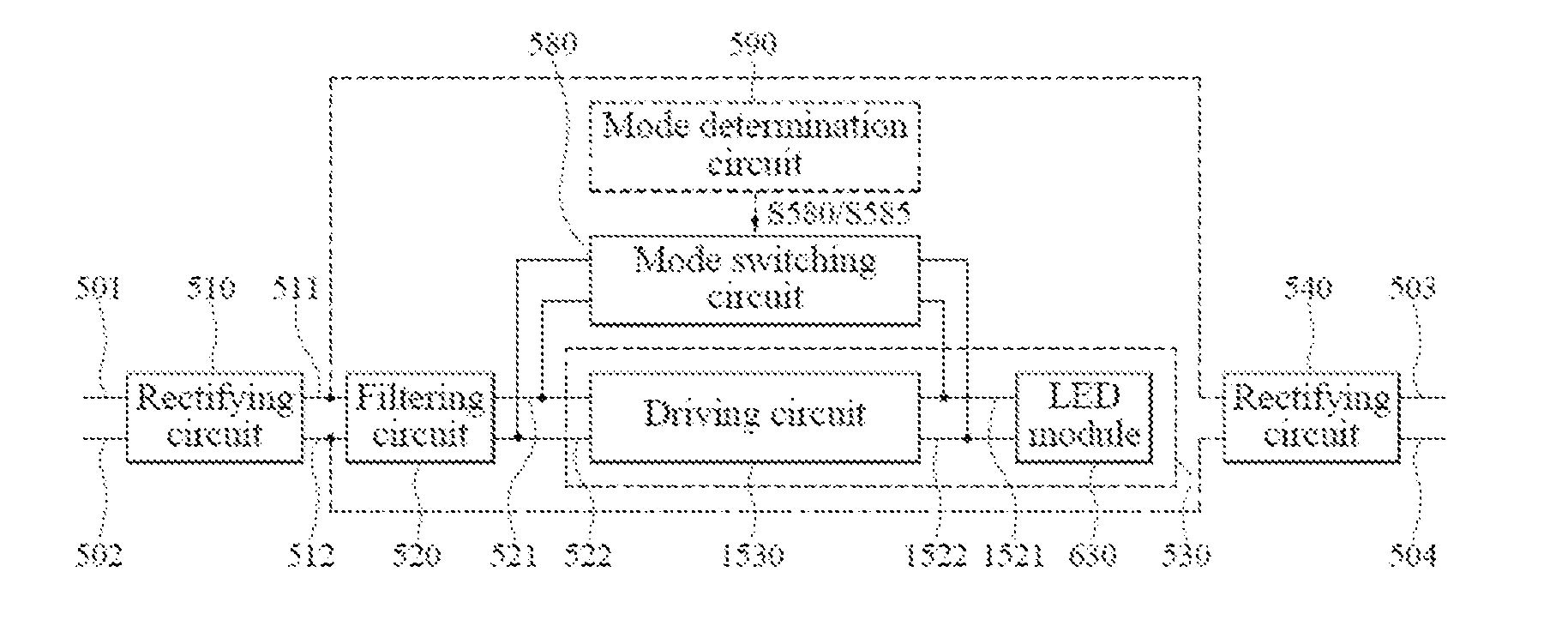
LED tube lamp with two operating modes compatible with electrical ballasts
ActiveUS20170094746A1Improve power stabilityImprove stabilityElongate light sourcesElectric circuit arrangementsElectrical ballastPower flow
An LED tube lamp is disclosed. The LED tube lamp includes an LED module for emitting light, the LED module comprising an LED unit comprising an LED; a rectifying circuit for rectifying an external driving signal to produce a rectified signal; and a mode determination circuit configured to detect a state of a property of the rectified signal, for selectively determining on performing a first mode or a second mode of lighting according to the state of the property of the rectified signal; wherein when the LED tube lamp performs the first mode of lighting, the mode determination circuit allows continual current to flow through the LED unit until the external driving signal is disconnected from the LED tube lamp; and when the LED tube lamp performs the second mode of lighting, the mode determination circuit regulates the continuity of current to flow through the LED unit.
Owner:JIAXING SUPER LIGHTING ELECTRIC APPLIANCE
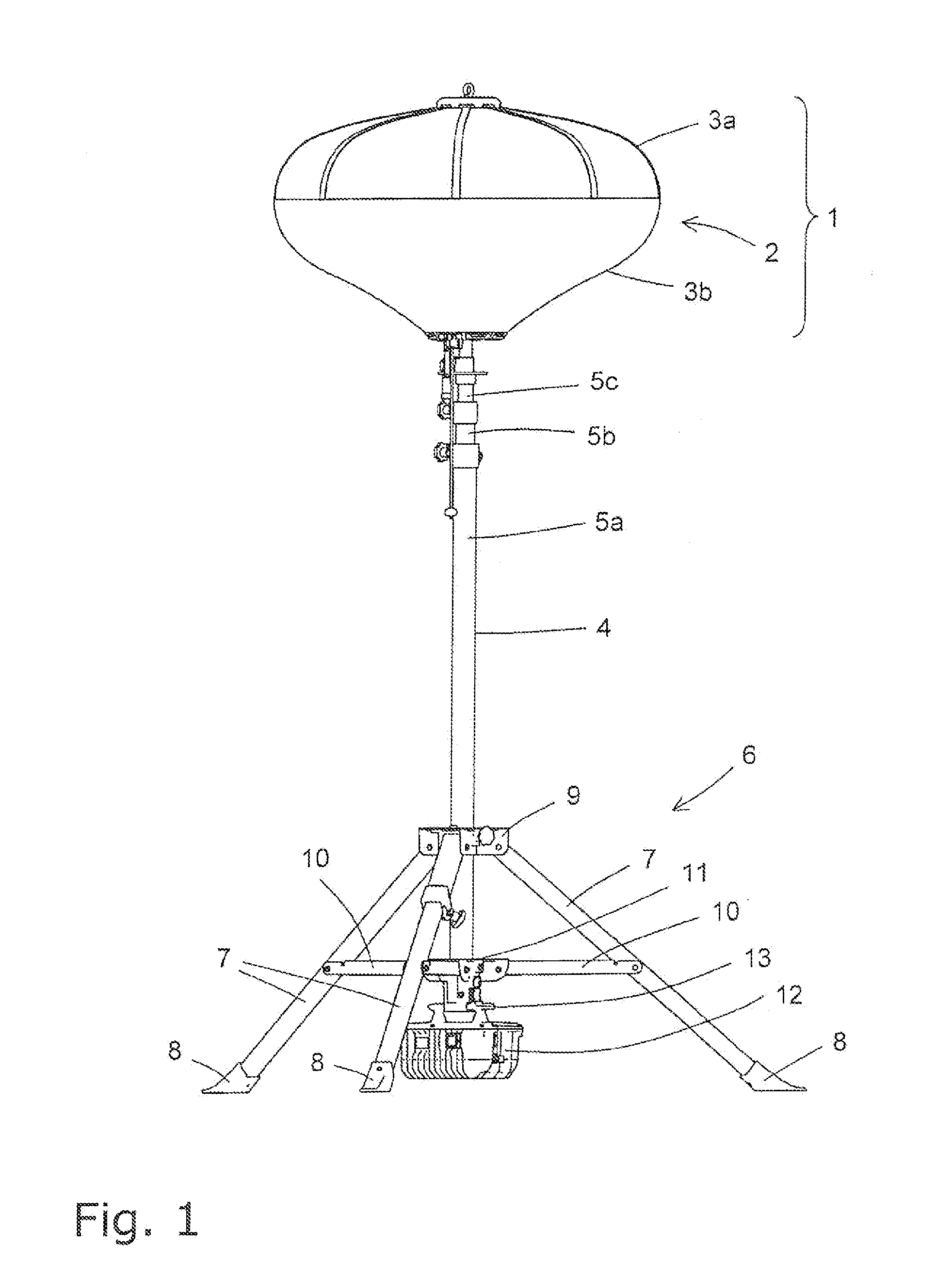
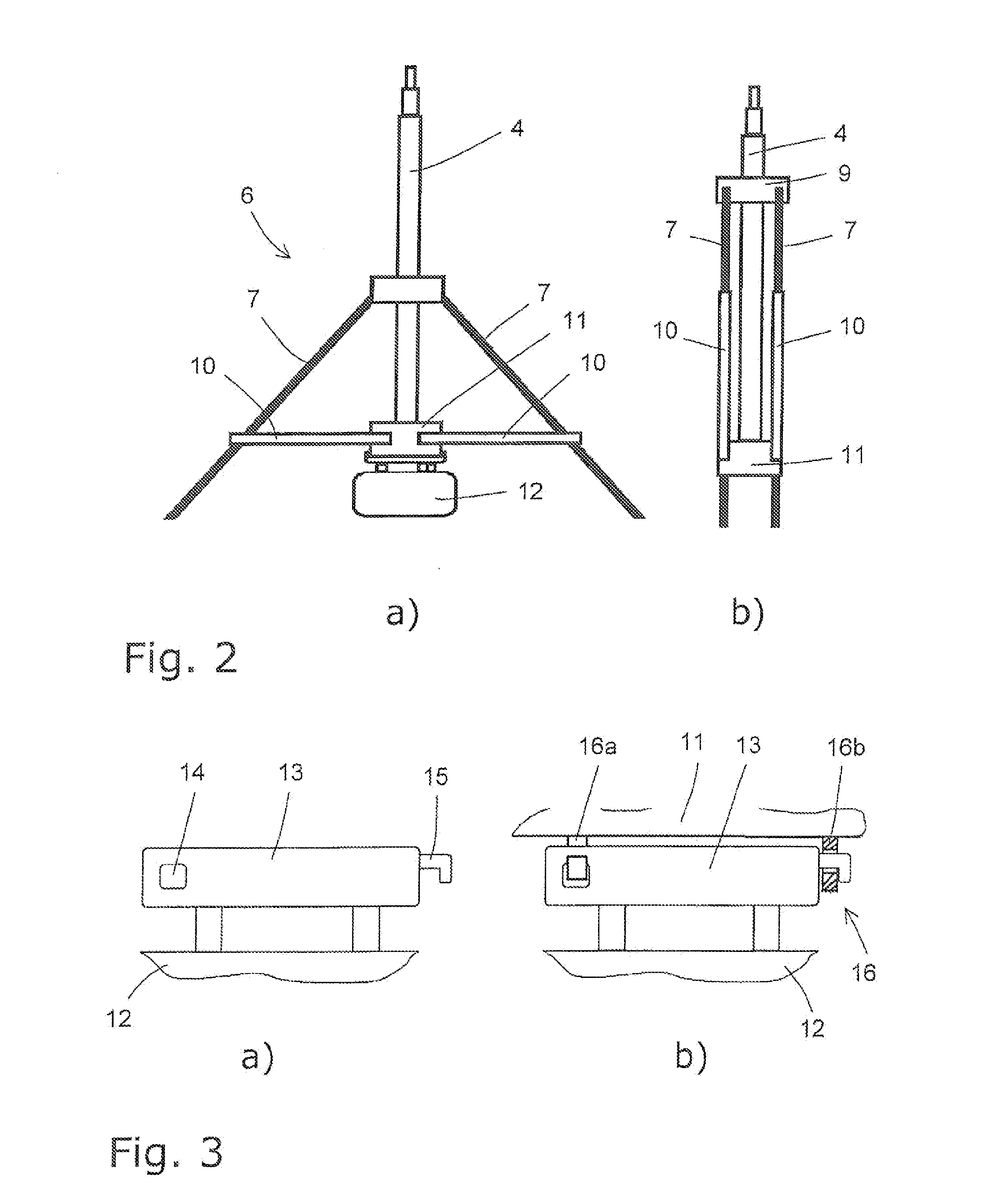
Transportable lighting device
InactiveUS20140218936A1Reduce overall constructive outlayCompact constructionNon-electric lightingMechanical apparatusEngineeringGravitation
A transportable lighting device has a light apparatus, a column device that bears the light apparatus and that extends in a longitudinal direction, and a stand device that bears the column device. In order to provide electrical power for the light apparatus, a ballast is provided that is situated on the column device, underneath the column device in the longitudinal direction. In this way, the overall center of gravity of the transportable lighting device can be shifted significantly downward, This results in improved stability against falling.
Owner:WACKER NEUSON SE
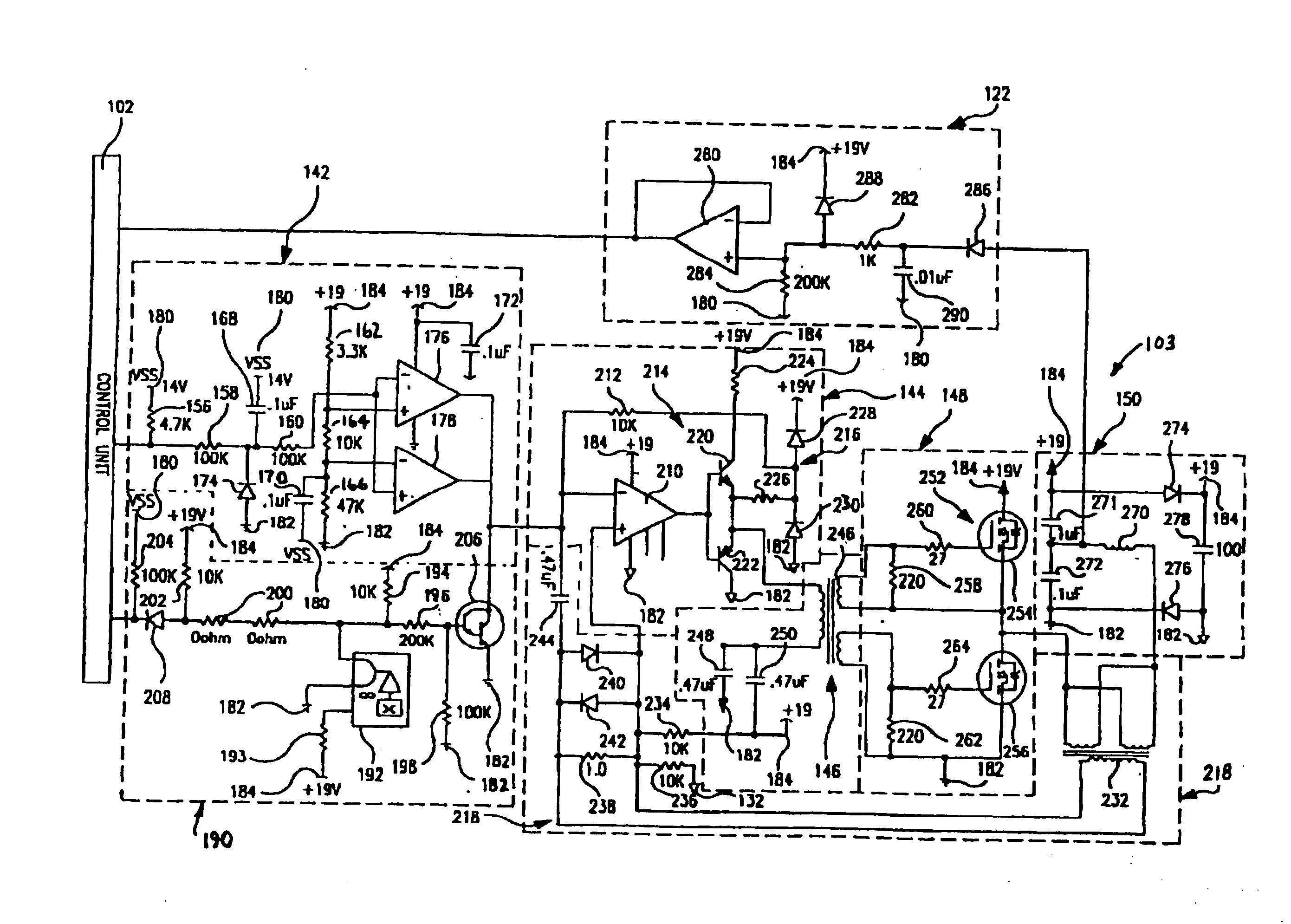
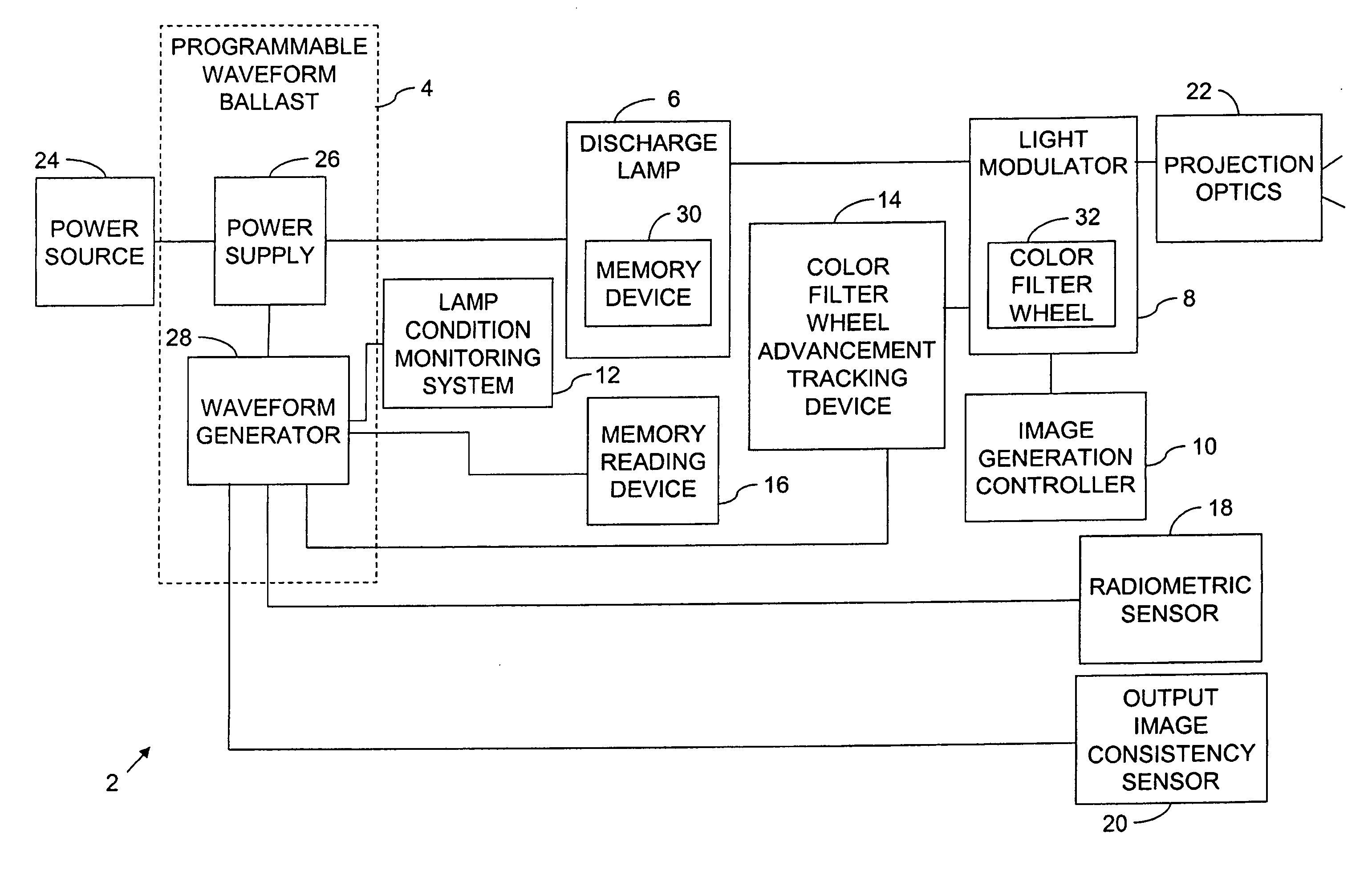
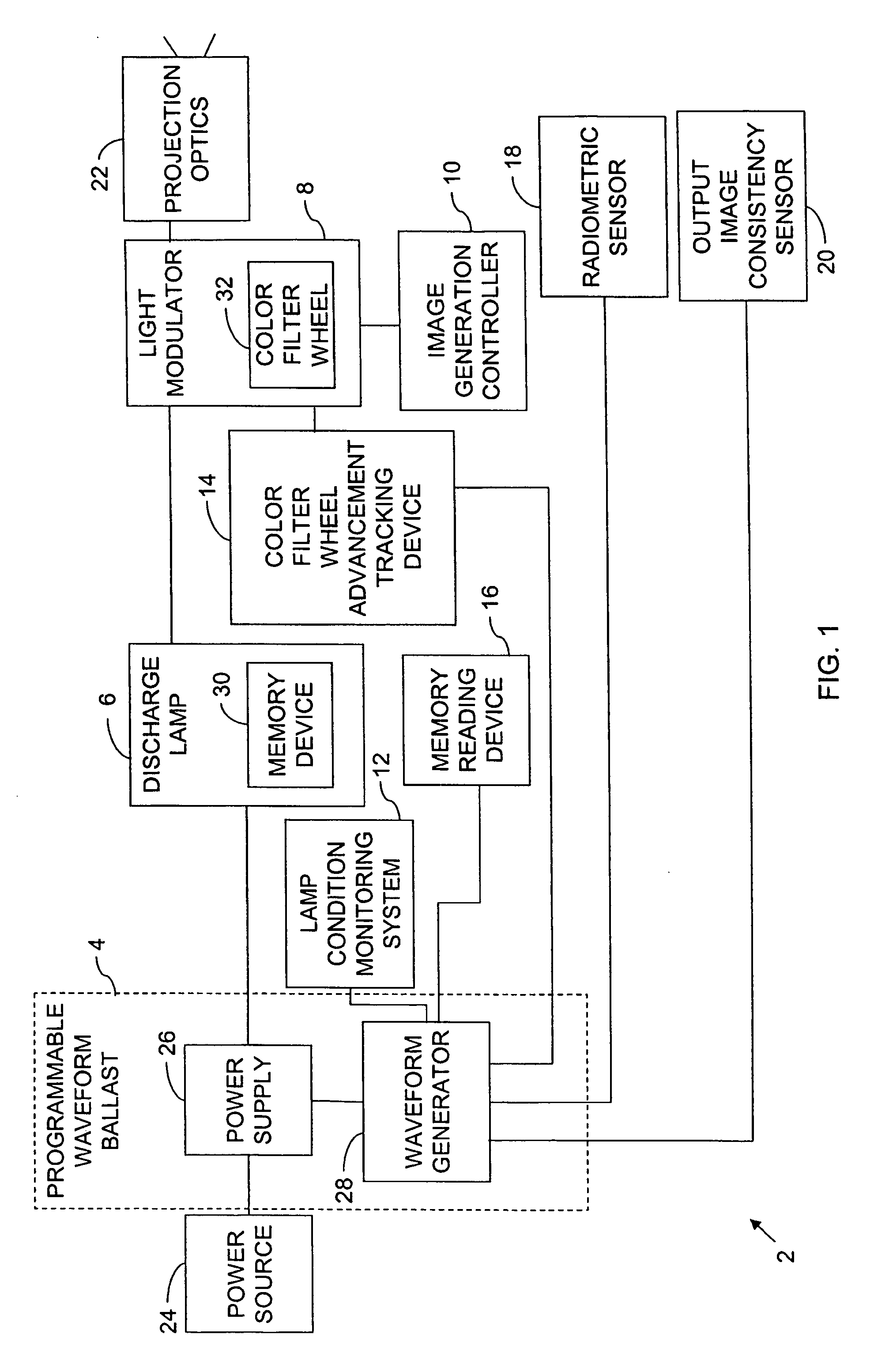
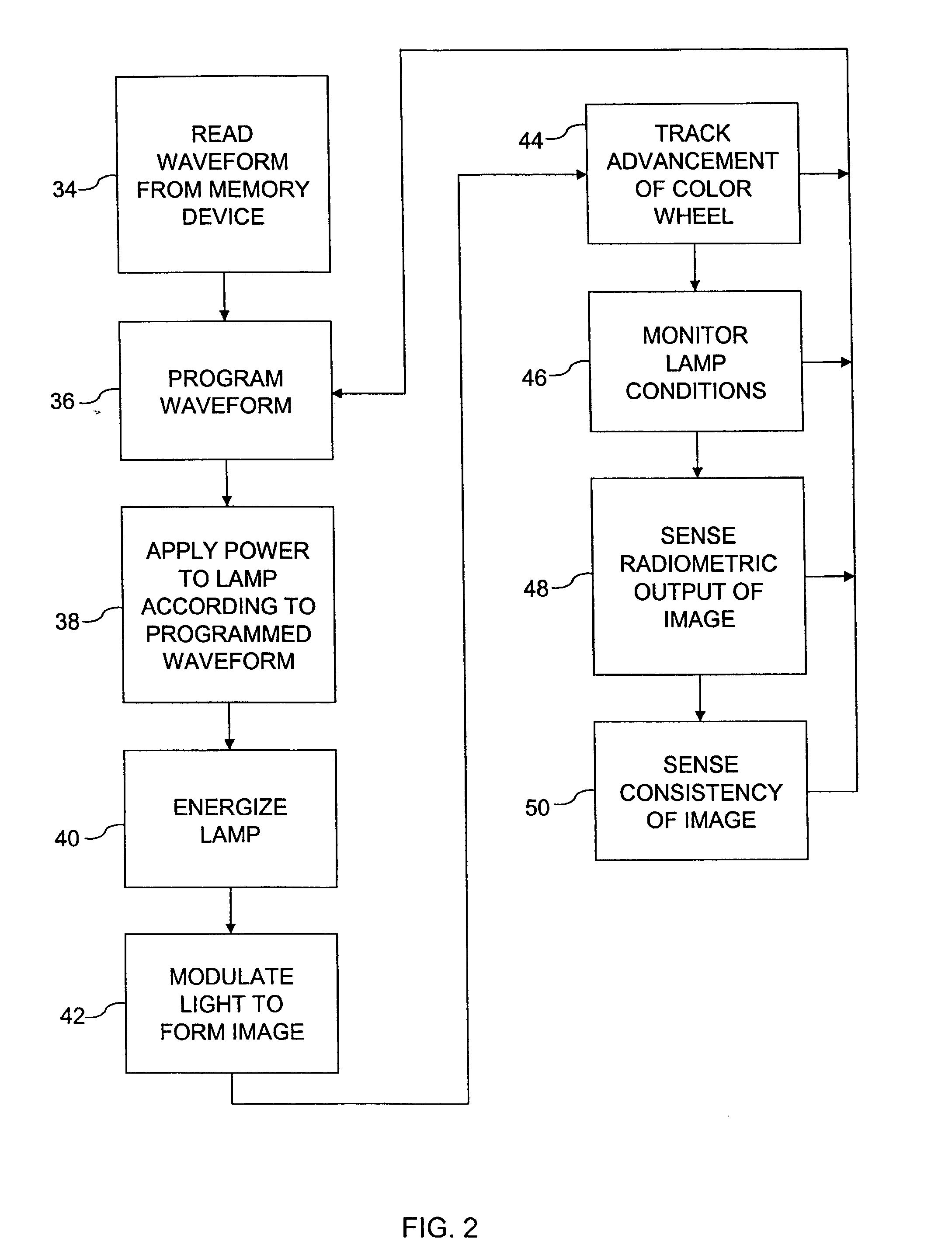
Programmable waveform for lamp ballast
A programmable waveform ballast has a power supply and a waveform generator. The power supply provides, from a power source, a variable power to a discharge lamp. The waveform generator is coupled to the power supply and is programmable to produce a plurality of waveforms. The waveform generator controls the power supply to apply the variable power to the discharge lamp in accordance with a programmed waveform.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
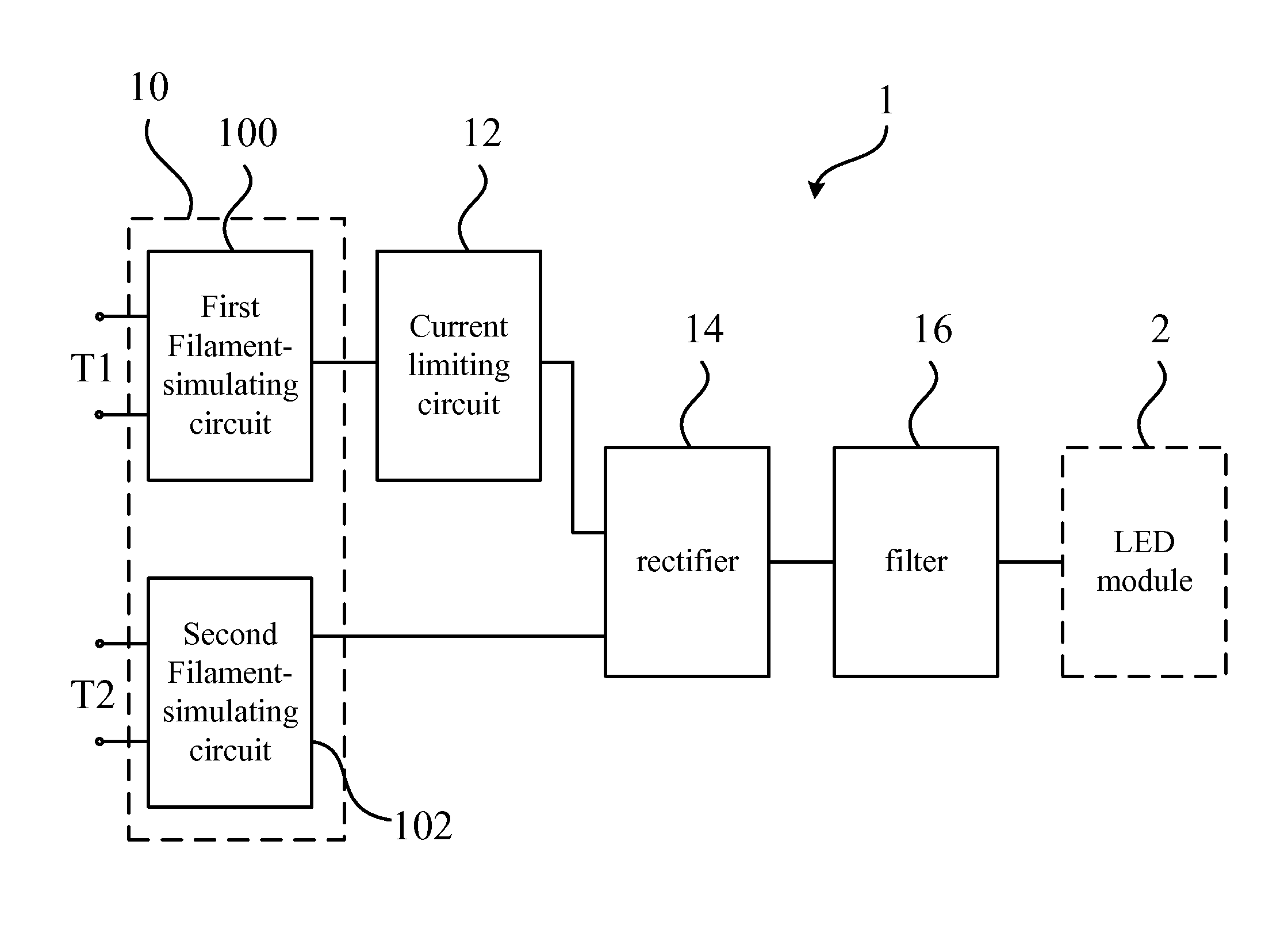
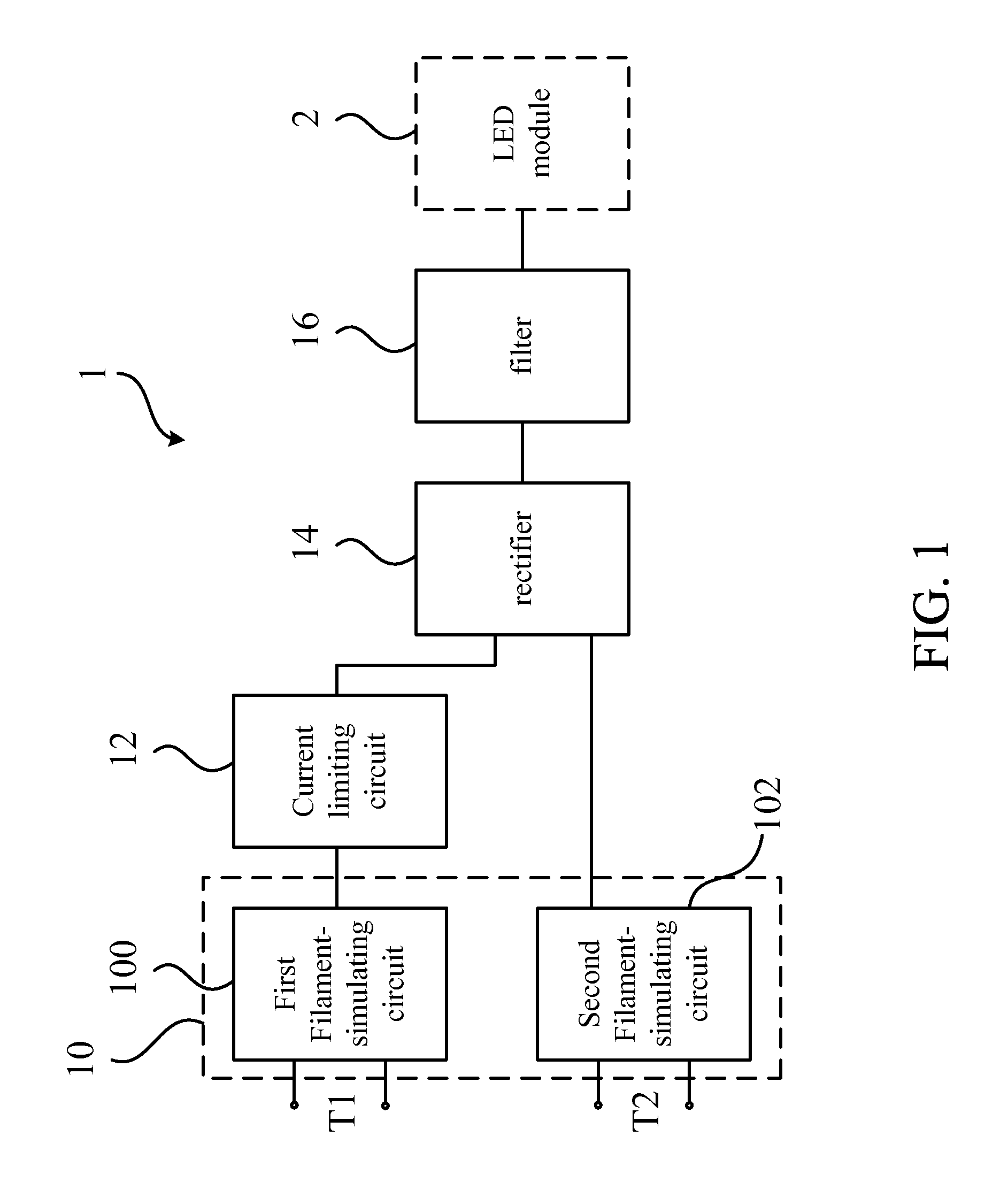
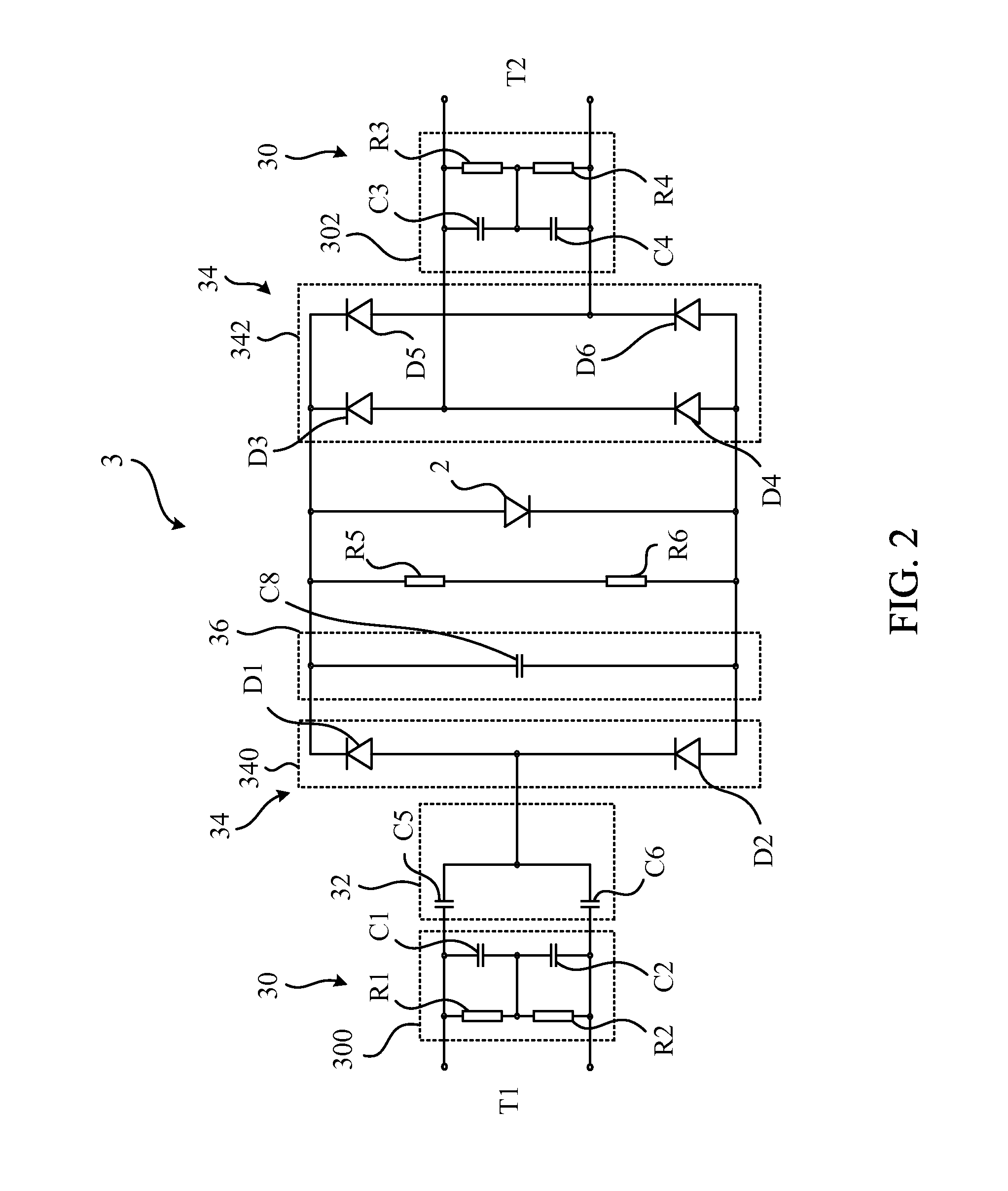
Power source module for LED lamp
ActiveUS20160102813A1Guaranteed uptimeAvoid flickeringElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsElectricityPower flow
A power source module for a LED lamp includes a filament-simulating circuit, a current limiting circuit, a rectifier, a filter, and a discharging circuit electrically connected to each other and a LED in the LED lamp. The filament-simulating circuit simulates a filament before the LED to pass through the pre-heating process of the electrical ballast in a fluorescent lamp base. The current limiting circuit, the rectifier, and the filter limit, rectify and filter the current from an external power source in the fluorescent lamp base to output a high frequency, direct current to drive the LED. The discharging circuit discharges the energy after turning the power switch off to prevent the LED lamp from flicker. Therefore, the power source module enables the LED lamp to be installed on the traditional fluorescent lamp base without modifying the circuit in the base.
Owner:JIAXING SUPER LIGHTING ELECTRIC APPLIANCE
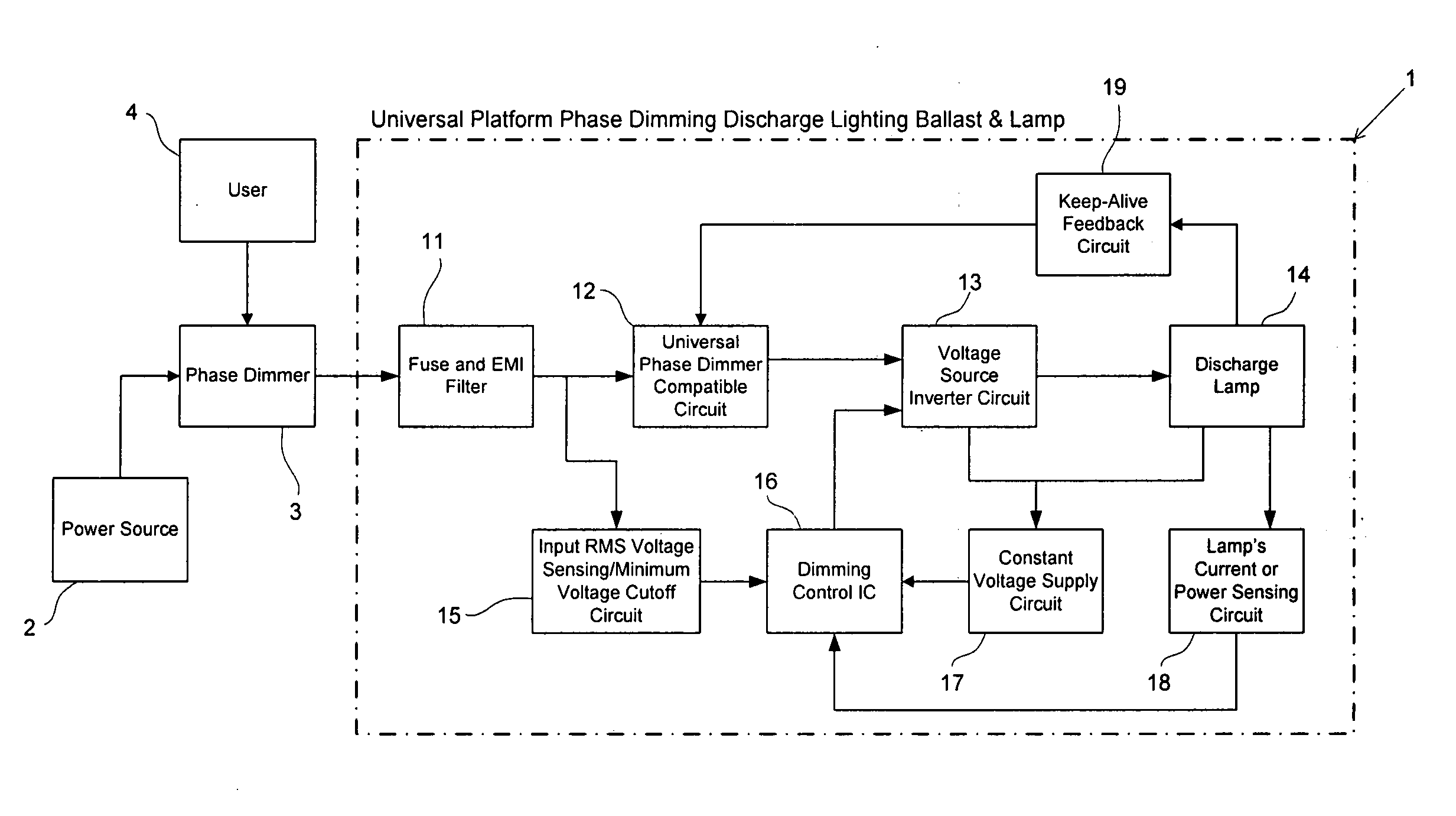
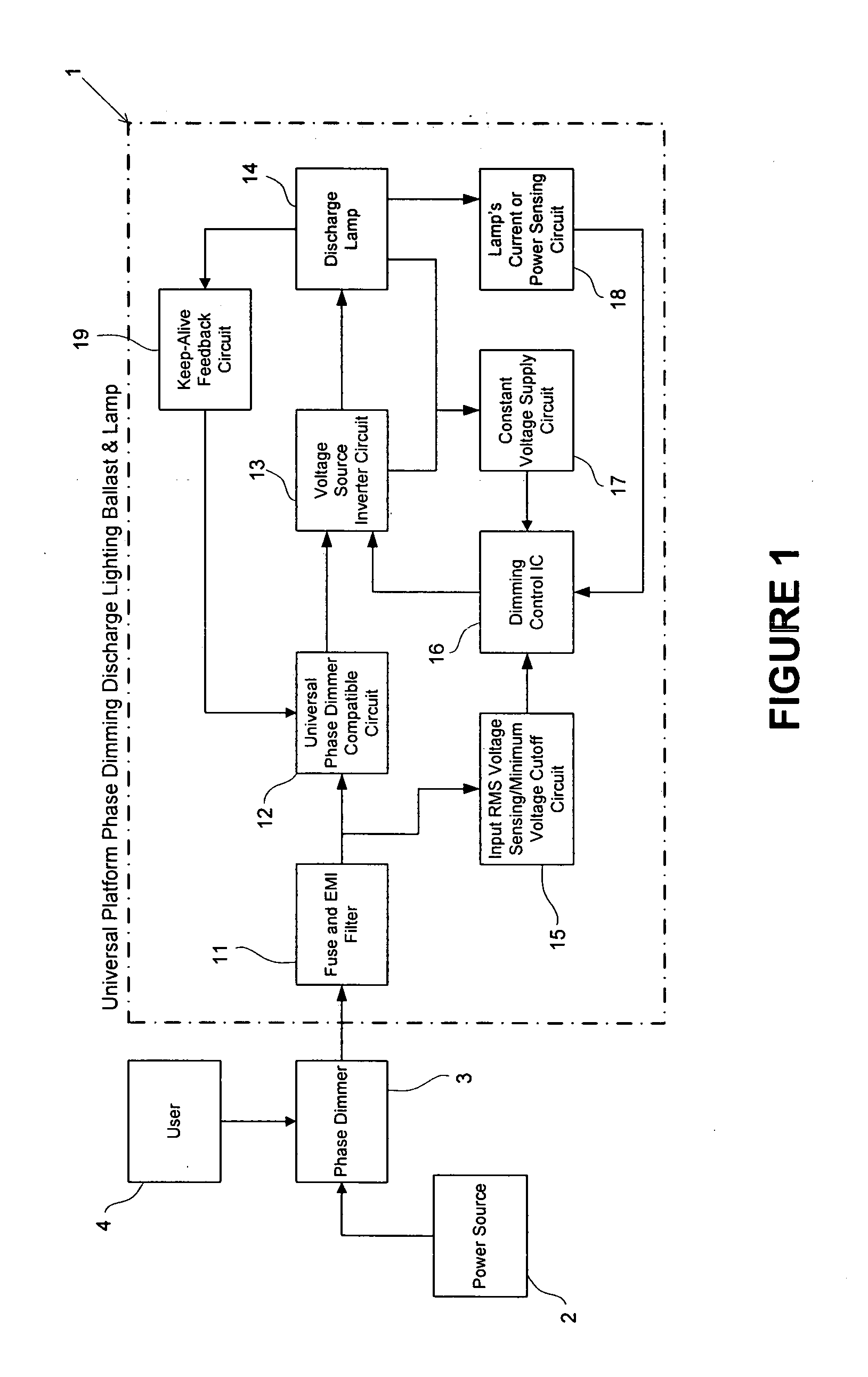
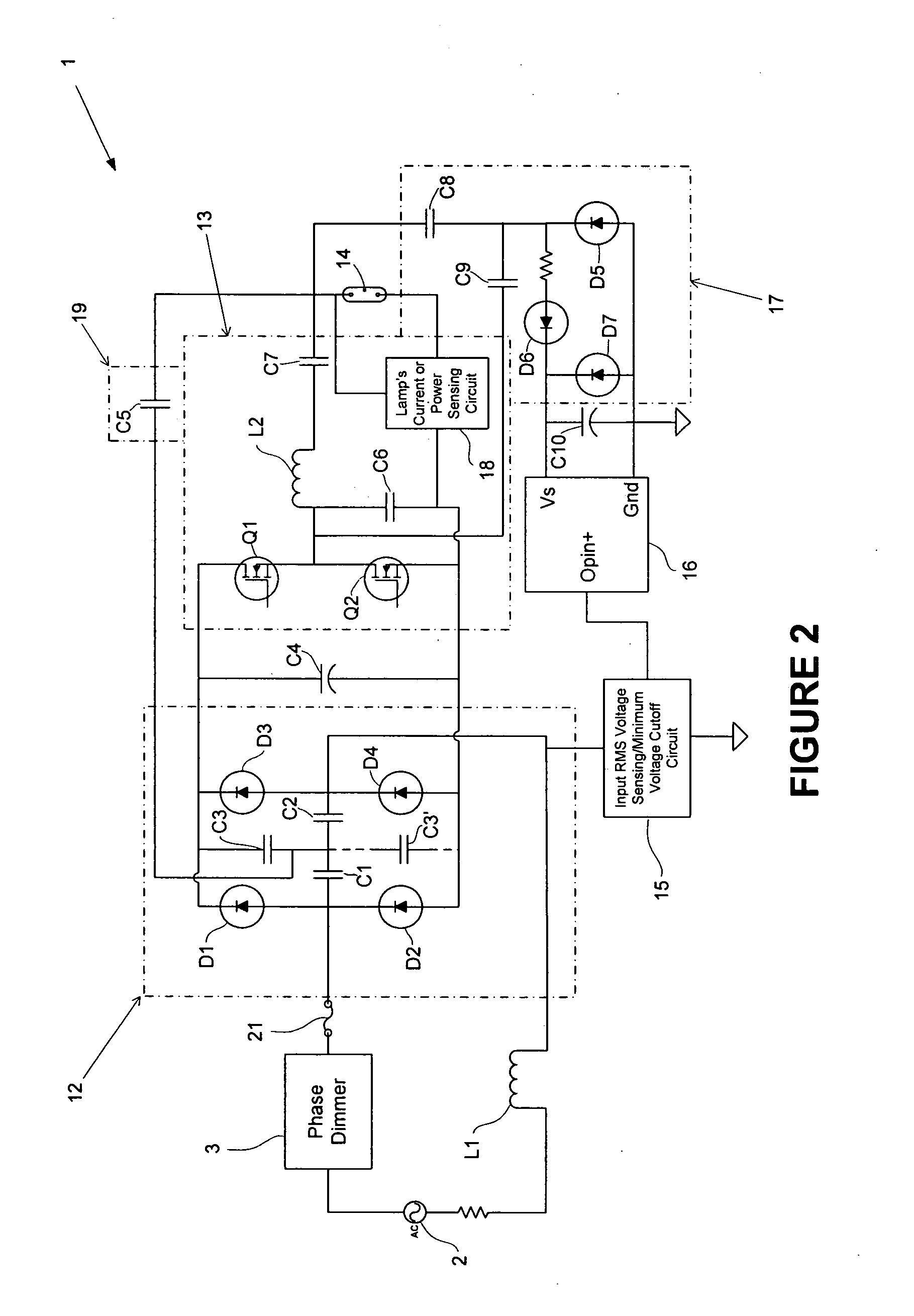
Universal platform for phase dimming discharge lighting ballast and lamp
InactiveUS20050122057A1High dimming operationHigh operating requirementsElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementGas-discharge lampDriver circuit
A ballast, or power supply circuit, for gas discharge lamps of the type using IC control based gate-drive circuitry for controlling a pair of serially connected switches of a d.c.-a.c. inverter. More particularly, the invention relates to a ballast having a resonant feedback circuit drawing continuous input current from a wide range of source voltages to satisfy requirements of phase control dimmers. Even more particularly, the invention relates to a universal platform for phase dimming discharge lighting using the Ballast and a discharge Lamp with a phase dimming circuit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
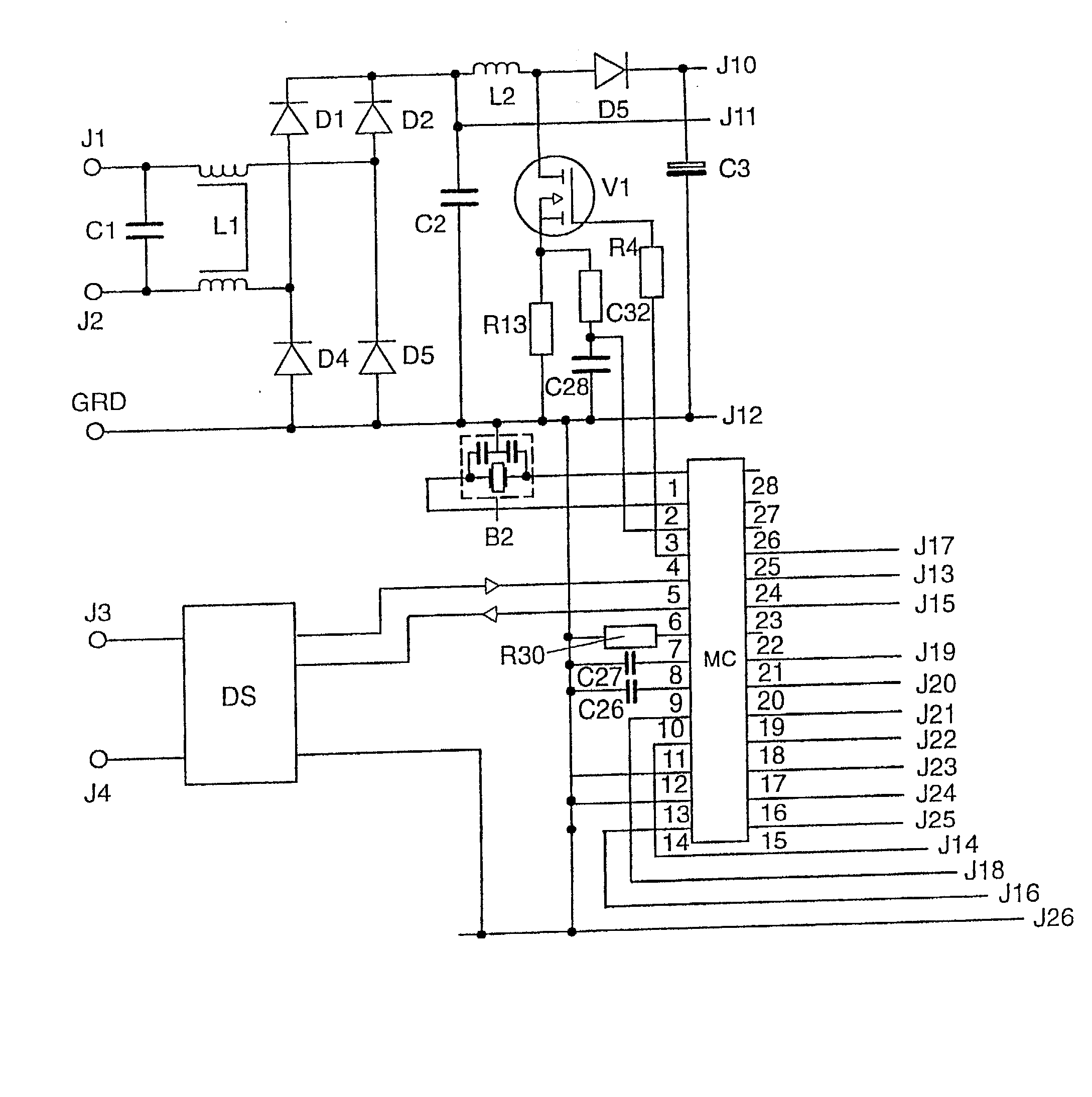
Microcontroller, switched-mode power supply, ballast for operating at least one electric lamp, and method of operating at least one electric lamp
InactiveUS20020097008A1Save componentSimple meansElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMicrocontrollerControl signal
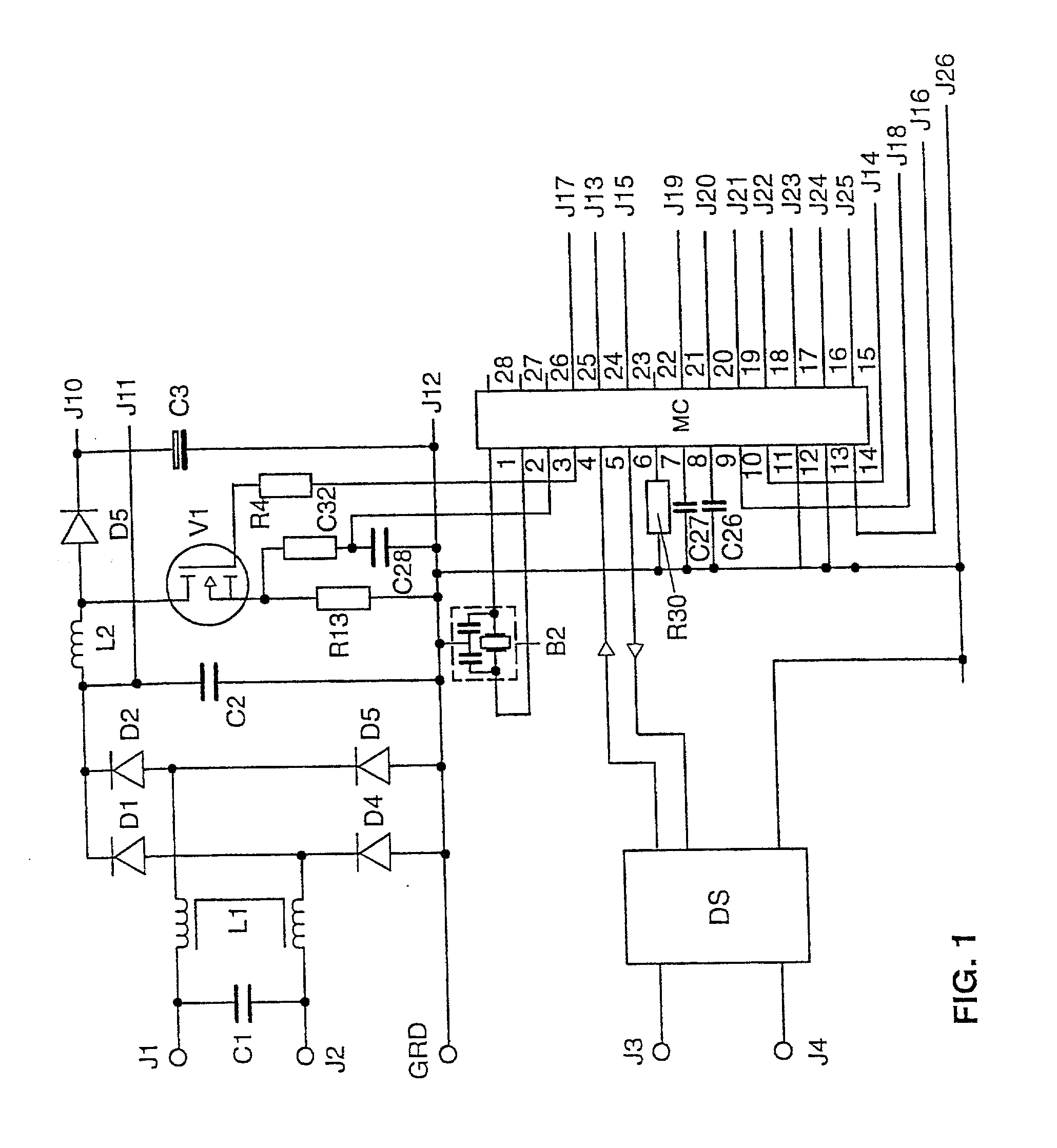
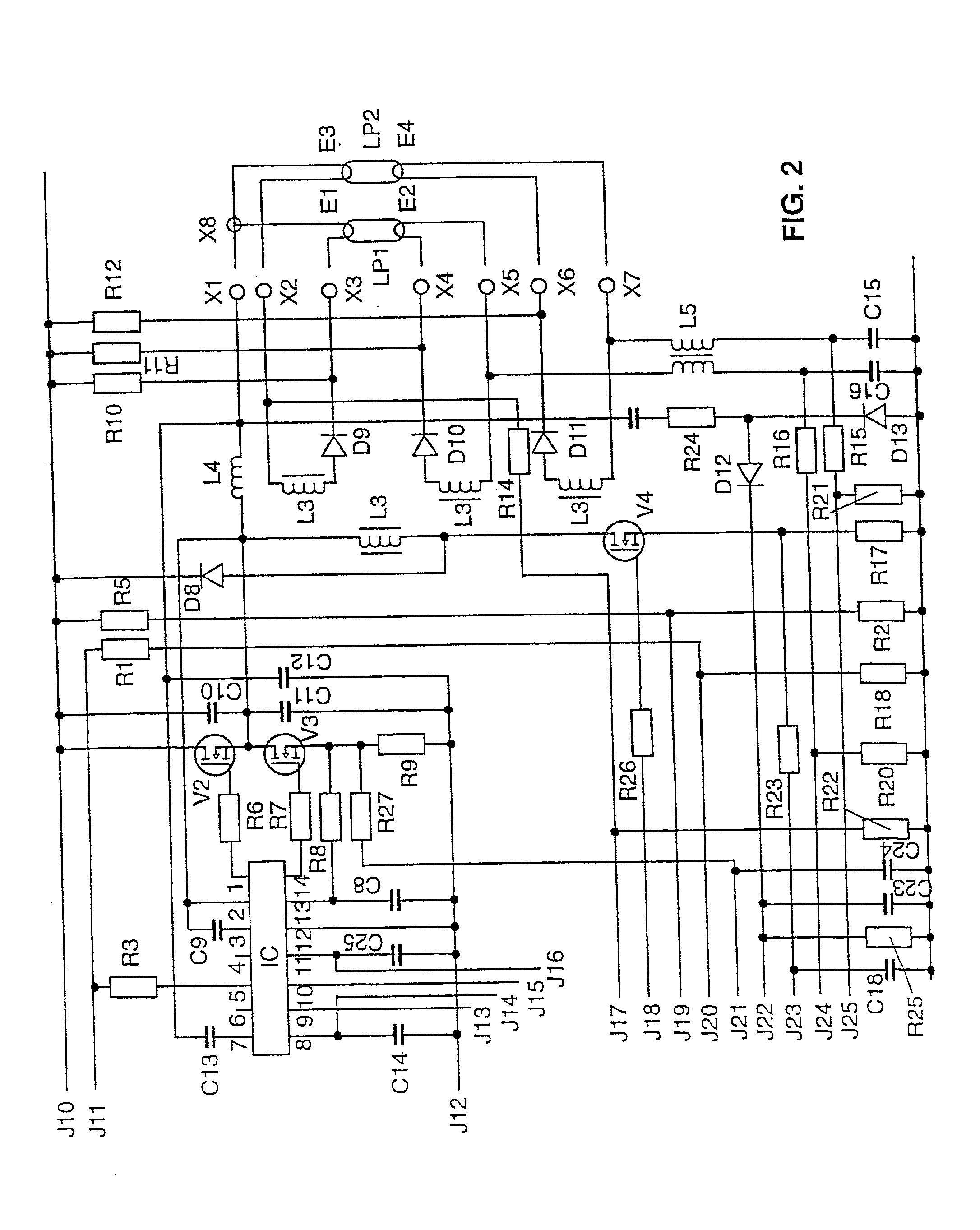
The invention relates to a microcontroller (MC) having at least one device (G) for generating pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals for a switched-mode power supply. According to the invention, this device (G) has a device (SQ1, SS1) for the alternate charging and discharging of an electric charge store (C27) that can be connected to the microcontroller (MC), control means for this device (SQ1, SS1) for controlling the charging and discharging operations, and evaluation means in order to evaluate the time periods which are needed for the individual charging and discharging operations; to generate pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals. The microcontroller (MC) according to the invention generates finely graduated, frequency modulated or pulse-width modulated control signals which are independent of the operating cycle frequency of the microcontroller (MC). The invention further relates to a switched-mode power supply having such a microcontroller (MC) and an electronic ballast for operating at least one electric lamp, and also to an operating method for electric lamps. The frequency modulated or pulse-width modulated control signals for the inverter transistors (V2, V3), for the step-up converter transistor (V1) and for the transistor (V4) of the lamp electrode heating device of the ballast are generated directly by the microcontroller (MC).
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com