Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about How to "Save component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Display comprising and integrated loudspeaker and method for recognizing the touching of the display
InactiveUS20050226455A1Reliably recognizeLimited in purposePlane diaphragmsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDisplay deviceEngineering
A combination is provided which consists of a loudspeaker and a display in which at least a portion of a sound-emitting surface of the loudspeaker forms the display that is touch-sensitive, and at least one recognition part is provided for recognizing the touching of the display.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Cell contact-making system for an electrochemical device
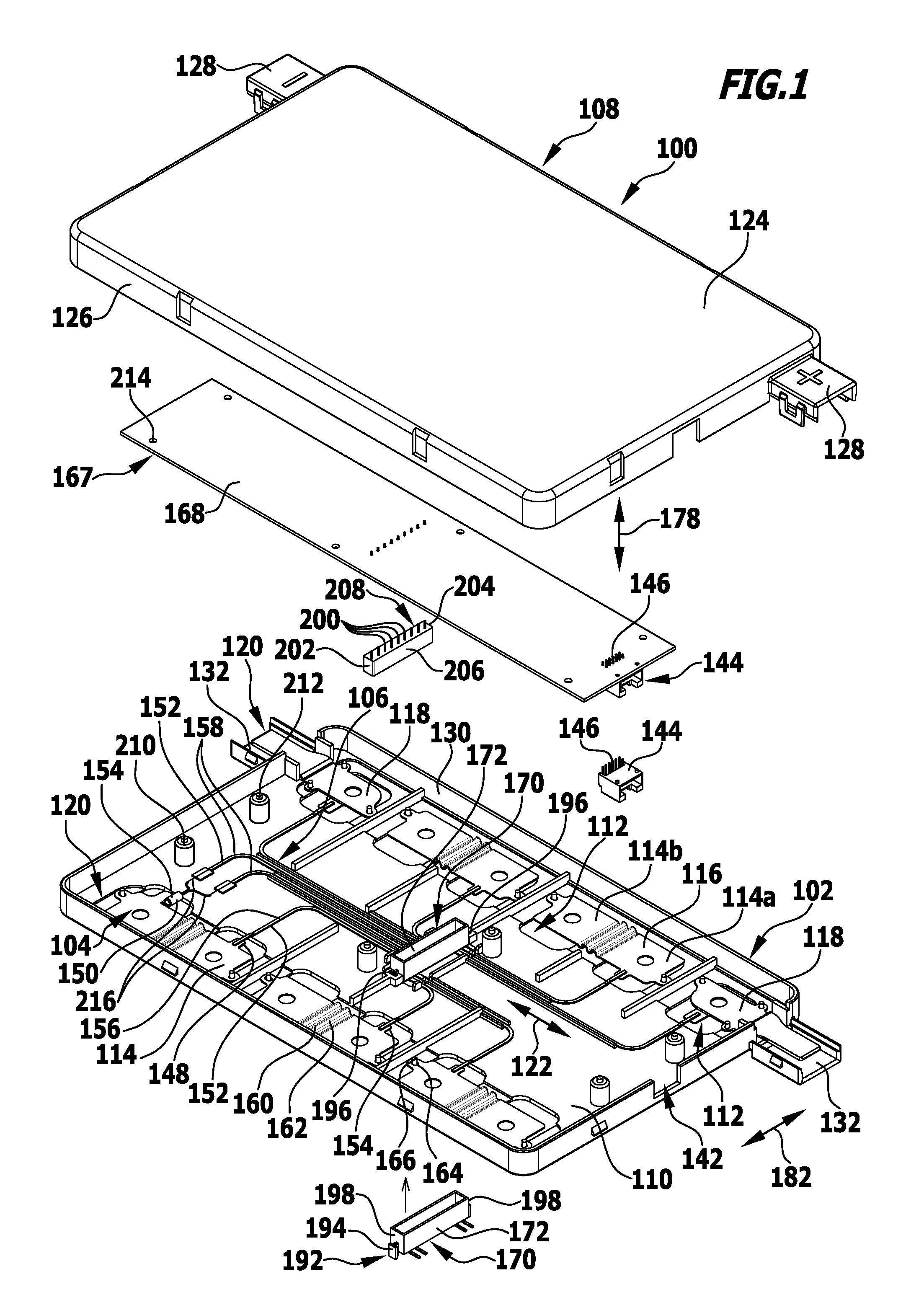
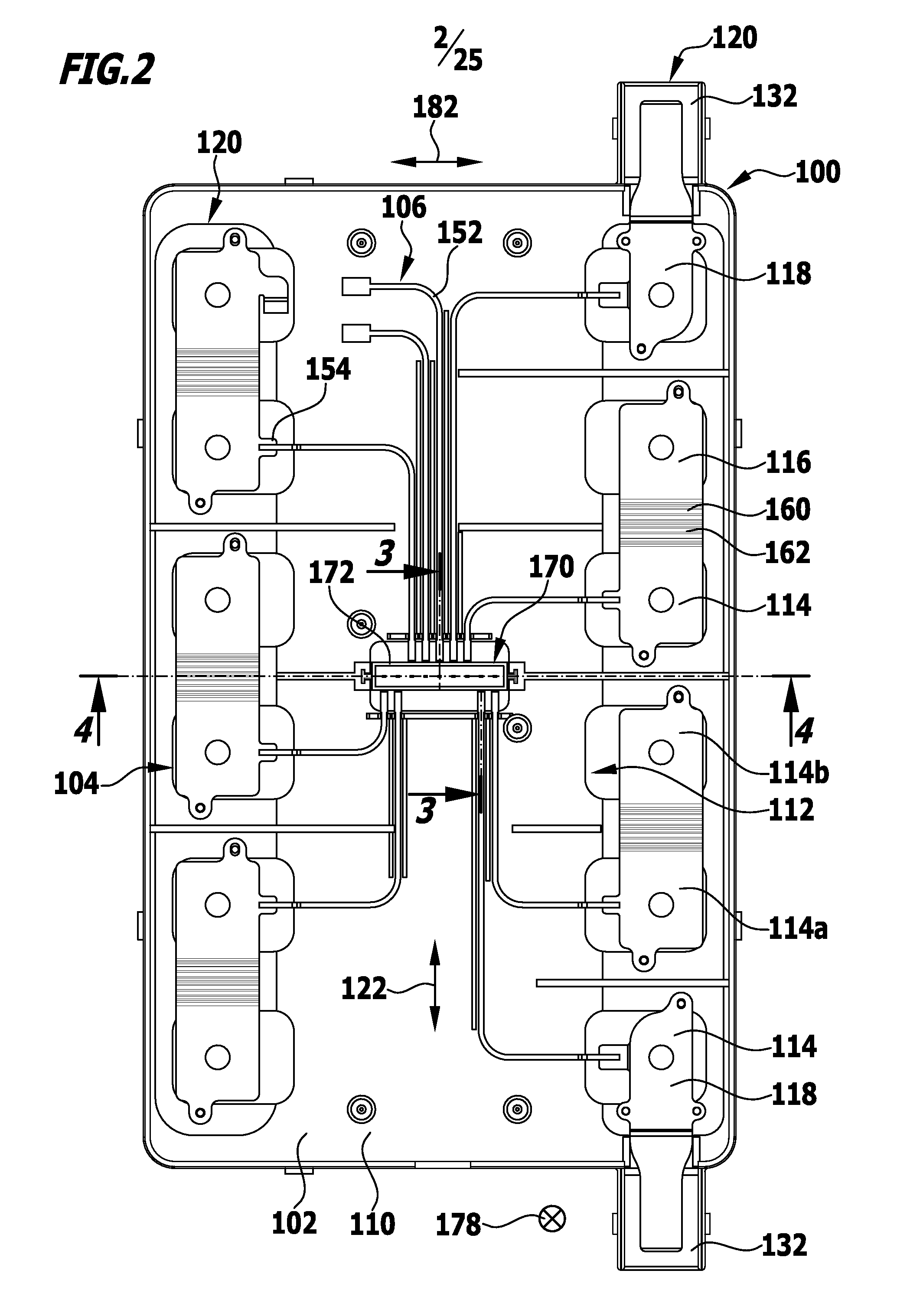
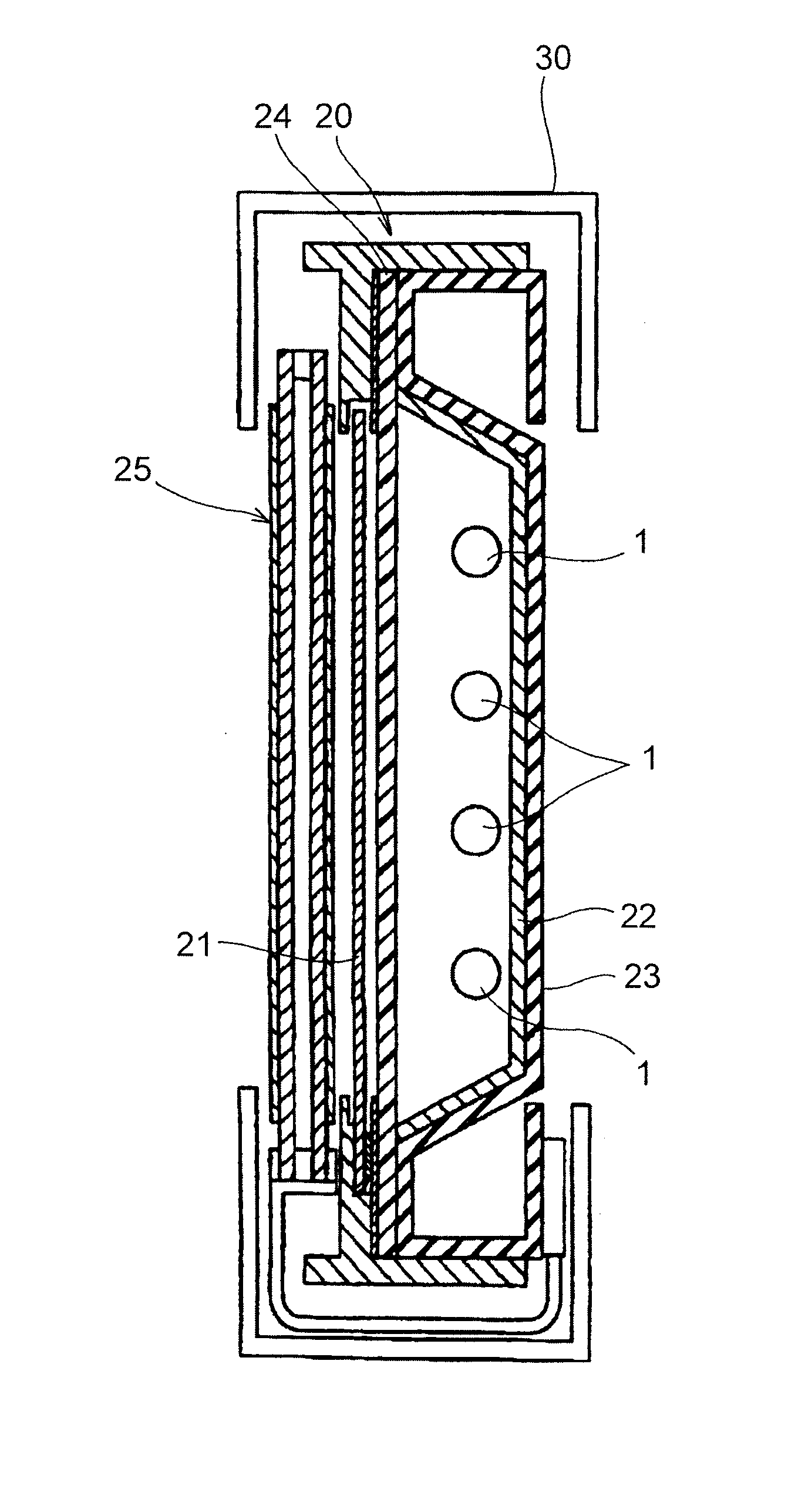
ActiveUS20160043446A1Compact structureLow costCoupling device detailsCells structural combinationElectrochemical cellElectrical conductor
In order to provide a cell contact-making system for an electrochemical device which includes a plurality of electrochemical cells, wherein the cell contact-making system includes a current conductor system having one or more cell connectors, for electrically conductively connecting cell terminals of different electrochemical cells, a signal conductor system having one or more signal conductors for electrically conductively connecting a respective signal source to a signal conductor terminal connector of the cell contact-making system, and a monitoring unit for monitoring signals from the signal sources, which is of compact construction and is assemblable from a relatively small number of parts, it is proposed that the monitoring unit should include a plug contact terminal connector which is directly connectable by a plug connection to the signal conductor terminal connector of the signal conductor system.
Owner:ELRINGKLINGER AG
Microcontroller, switched-mode power supply, ballast for operating at least one electric lamp, and method of operating at least one electric lamp
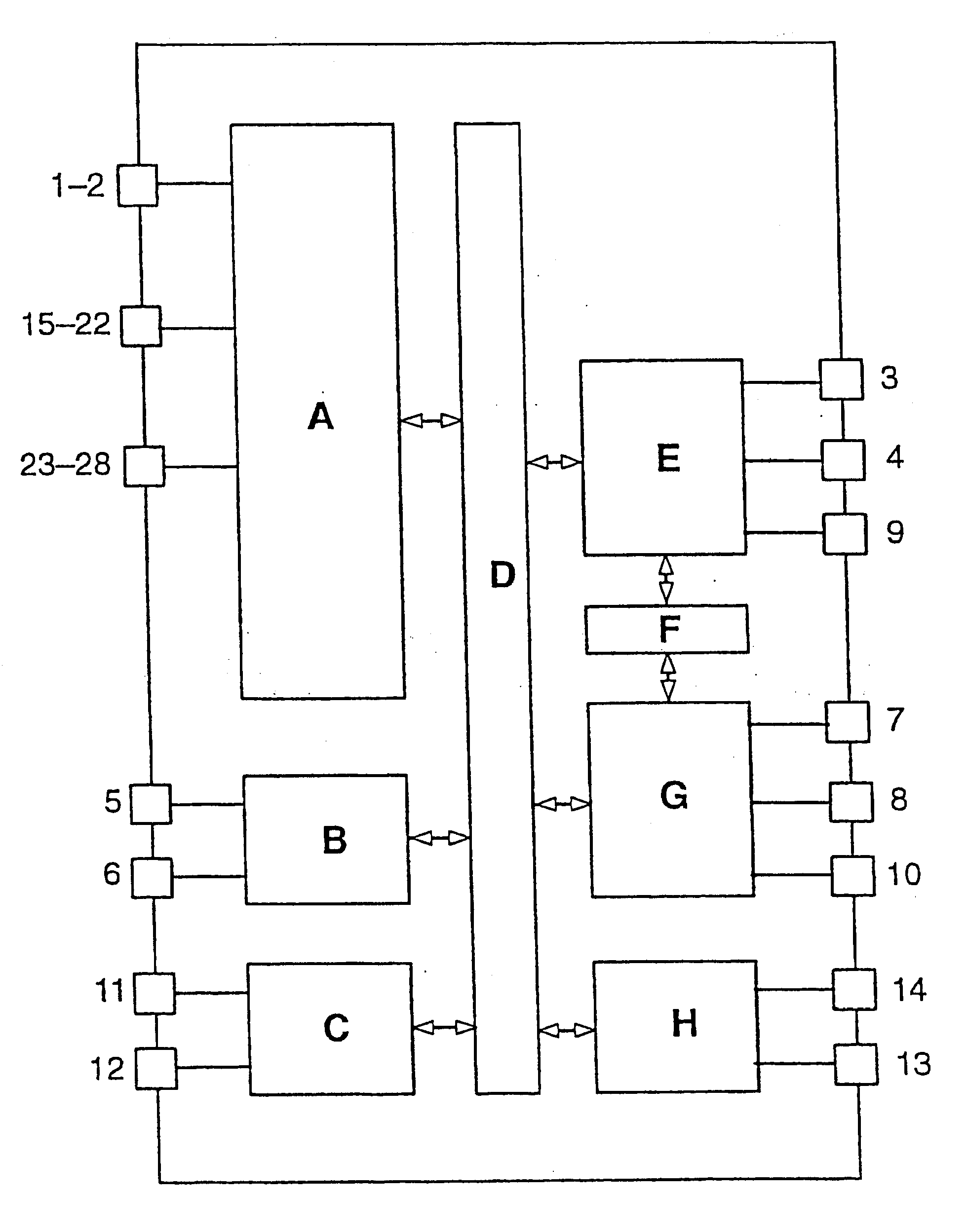
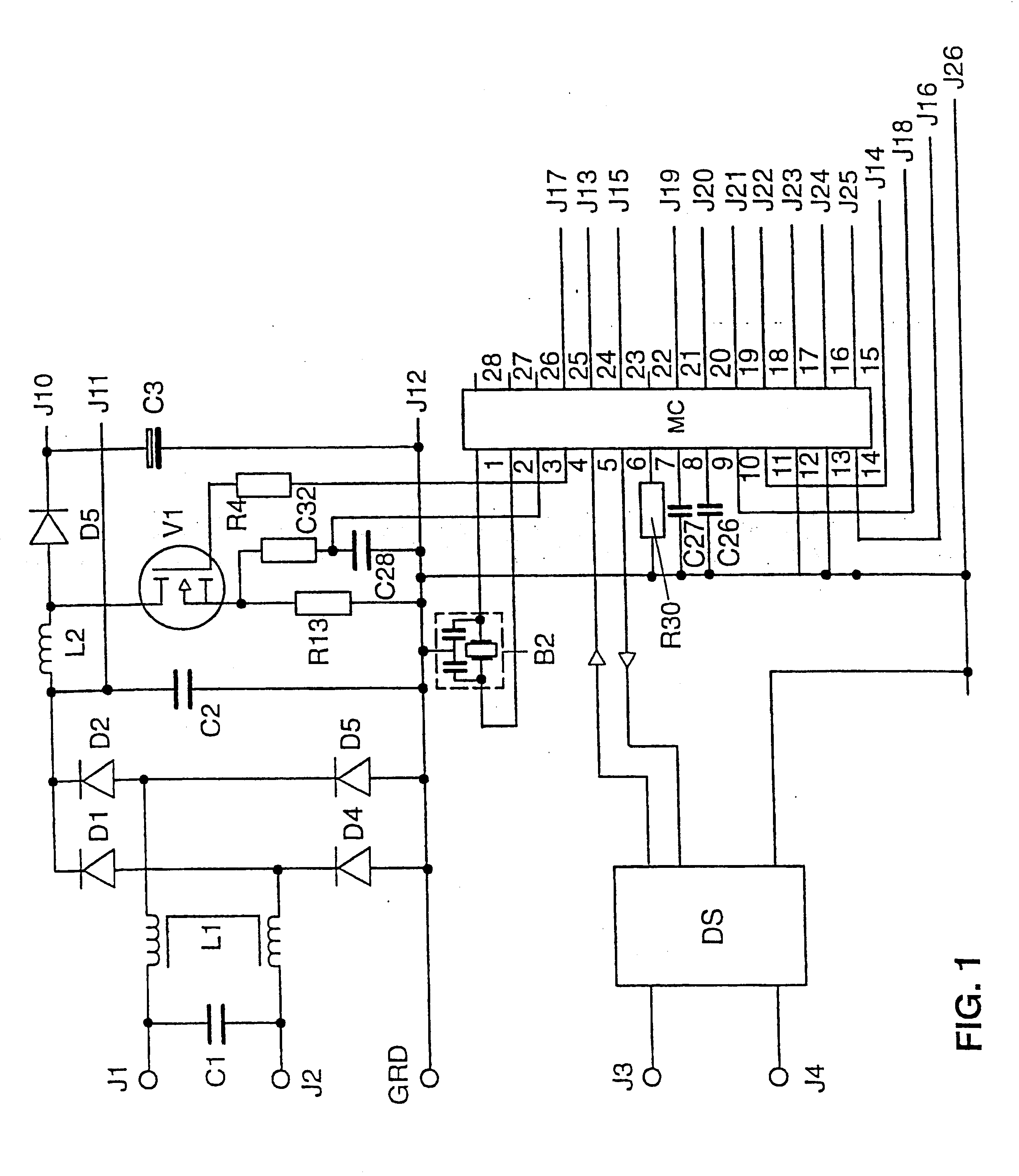
InactiveUS6717374B2Increase motivationEasy to switchElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMicrocontrollerControl signal
The invention relates to a microcontroller (MC) having at least one device (G) for generating pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals for a switched-mode power supply. The device (G) has a further device (SQ1, SS1) for the alternate charging and discharging an electric charge store (C27) that can be connected to the microcontroller (MC), control means for this device (SQ1, SS1) for controlling the charging and discharging operations, and an evalutor for evaluating the time periods which are needed for the individual charging and discharging operations to generate pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals. The microcontroller (MC) generates finely graduated, frequency modulated or pulse-width modulated control signals which are independent of the operating cycle frequency of the microcontroller (MC).
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
Drive system for a motor vehicle having an electric machine
InactiveUS7026733B2Avoid the needMultiple cooling circuits can advantageously be avoidedCooling/ventillation arrangementSupports/enclosures/casingsMobile vehicleElectric machine
A drive system for a transportation device having an electric machine. The electric machine has a converter unit and a cooling unit with the converter unit being embodied at least partially in the shape of a ring and surrounding the electric machine or components of the electric machine.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
Footwear with sealed sole construction and method for producing same
Footwear with an upper and a sole construction having an outsole, in which the upper is constructed with an outer material and with a waterproof functional layer at least partially lining the outer material on the inner side of the latter and having an upper end region on the sole side with an outer-material end region and a functional-layer end region, the outsole (19) is joined to the upper end region, the functional-layer end region has an overhang projecting beyond the outer-material end region and an adhesive zone which is closed in the direction of the sole periphery and comprises a reactive hot-melt adhesive which brings about waterproofness when in the fully reacted state is applied to the overhang.
Owner:HAIMERL FRANZ
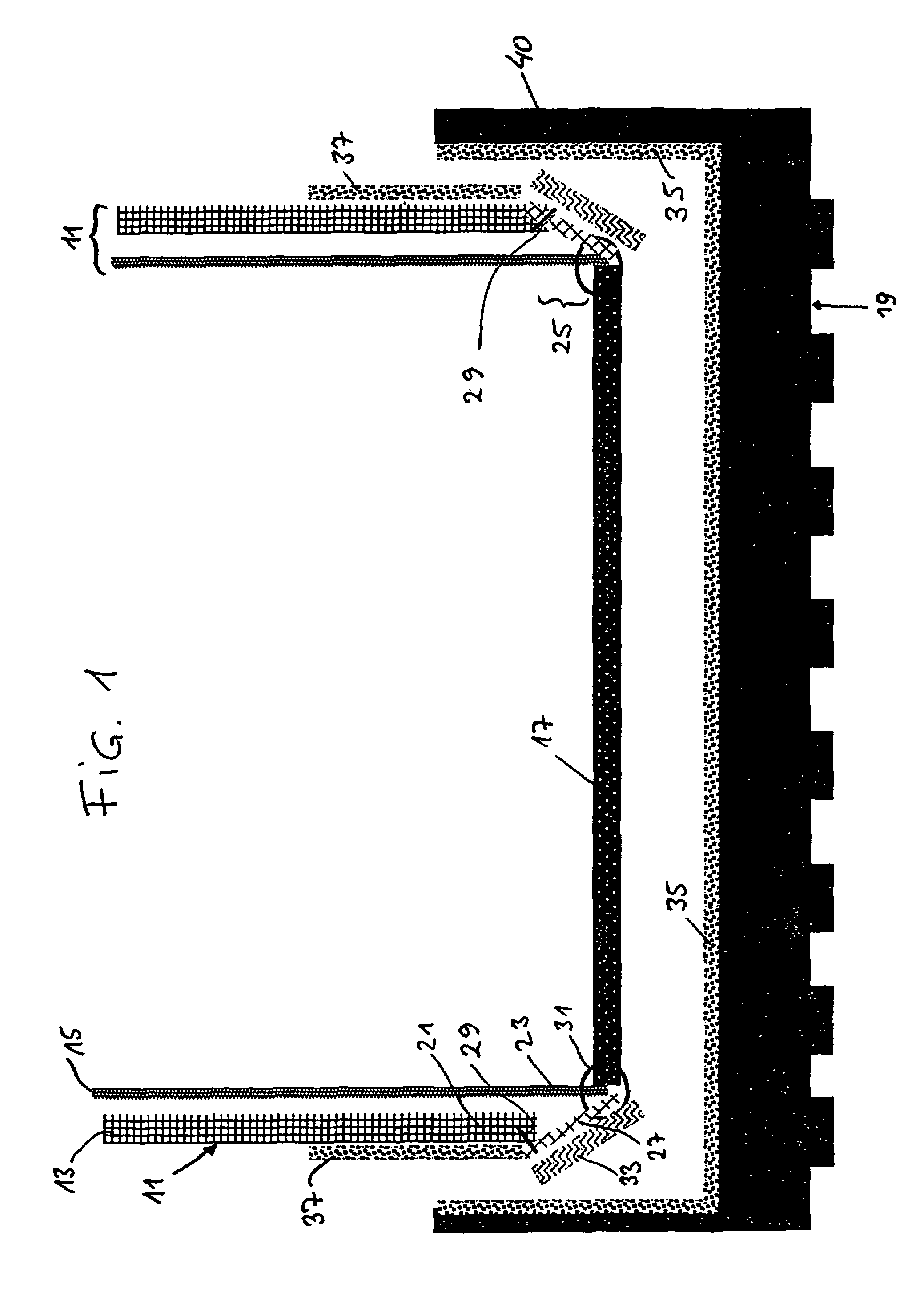
Dual clutch transmission
ActiveUS20100269611A1Low production costIncrease the number ofToothed gearingsTransmission elementsIdler-wheelClutch
A dual-clutch transmission comprising clutches with input sides coupled to an input shaft and output sides respectively coupled to two transmission input shafts. Toothed idler gearwheels are mounted to rotate on countershafts while toothed fixed gearwheels are connected to the first and the second transmission input shafts and engage with the idler gearwheels. Coupling devices are provided for connecting the idler gearwheels to the countershaft, and drive output gearwheels are fixed to the countershafts and couple an output shaft, while a shifting element couples the input shafts such that eight forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be engaged. Four wheel planes are arranged in the transmission such that at least one winding gear can be engaged by the shifting element.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
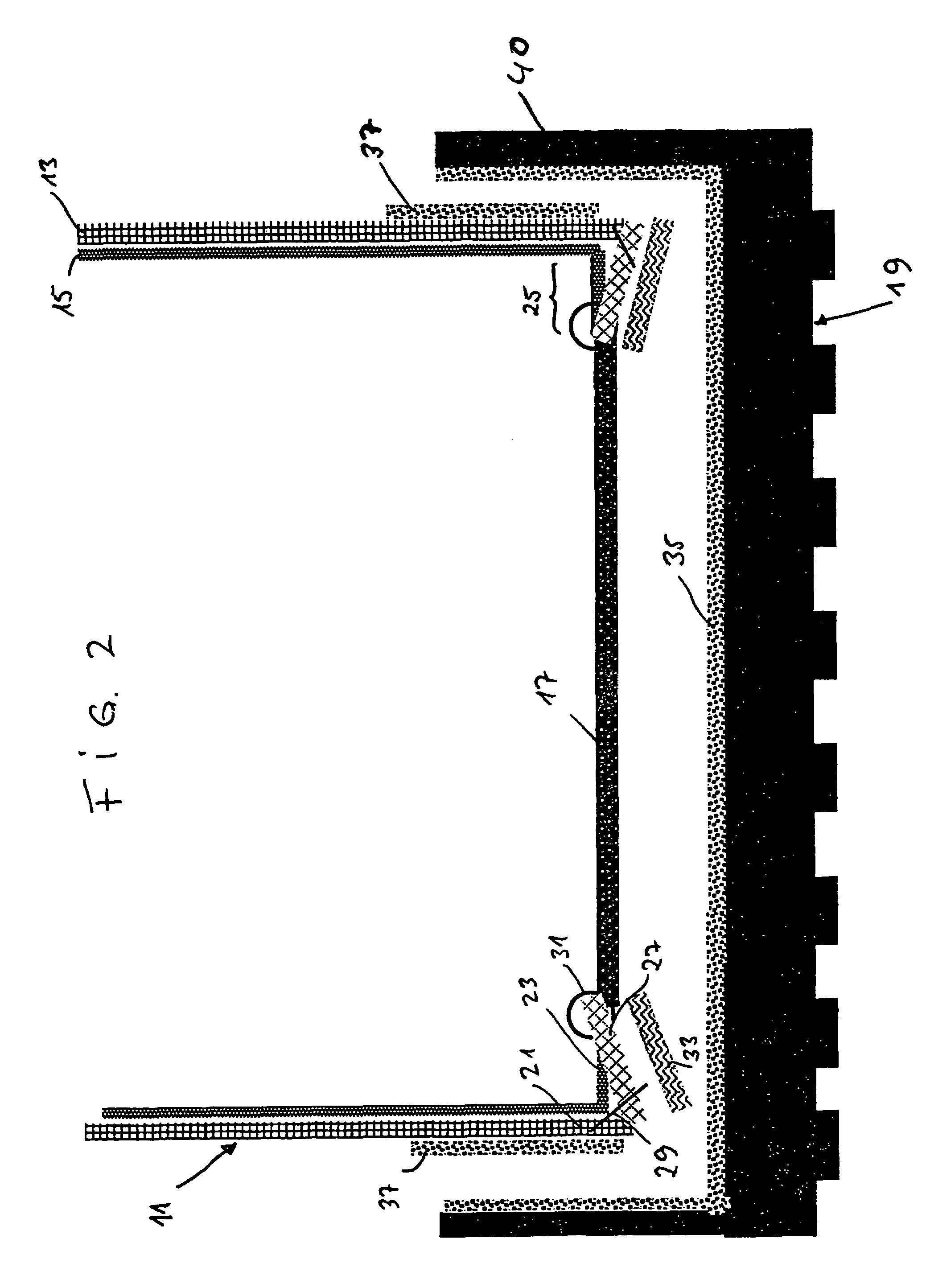
Dual clutch transmission
ActiveUS20100218627A1Low production costIncrease the number ofToothed gearingsTransmission elementsEngineeringIdler-wheel
A dual-clutch transmission comprising clutches with input sides coupled to an input shaft and output sides respectively coupled to first and second transmission input shafts, countershafts on which toothed idler gearwheels are mounted to rotate, toothed fixed gearwheels are coupled to the first and the second transmission input shafts and engage the idler gearwheels, coupling devices connect the idler gearwheel to one of the countershafts, drive output gearwheels are fixed to countershafts and drive an output shaft, and a shifting element couples the input shafts, such that eight forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be engaged. Five wheel planes are arranged in the transmission such that at least one winding gear can be engaged by the shifting element.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Dual clutch transmission
ActiveUS8166842B2Low production costIncrease the number ofToothed gearingsTransmission elementsEngineeringClutch
A dual-clutch transmission comprising clutches with input sides coupled to an input shaft and output sides respectively coupled to two transmission input shafts. Toothed idler gearwheels are mounted to rotate on countershafts while toothed fixed gearwheels are connected to the first and the second transmission input shafts and engage with the idler gearwheels. Coupling devices are provided for connecting the idler gearwheels to the countershaft, and drive output gearwheels are fixed to the countershafts and couple an output shaft, while a shifting element couples the input shafts such that eight forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be engaged. Four wheel planes are arranged in the transmission such that at least one winding gear can be engaged by the shifting element.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Aroma diffuser using an aroma capsule
ActiveUS20160375168A1Quick placementSimply and smoothly combinedRespiratorsLighting and heating apparatusAroma aromaHOLDING CHAMBER
An aroma diffuser using an aroma capsule is disclosed to include a hollow housing including a first opening on a top side thereof, a second opening on a bottom side thereof and an integrated holder member downwardly inwardly extended from a top side thereof and defining therein a holding chamber facing toward the first opening, a heat conduction device mounted in the holding chamber, and a heating element mounted at a bottom side of the heat conduction device and kept in contact with the heat conduction device. Thus, an aroma capsule can be placed in the holding chamber and heated by the heating element to release fragrant vapor. After the aroma contained in the aroma capsule is used up, the aroma capsule can be replaced conveniently and rapidly.
Owner:HSIAO MING JEN
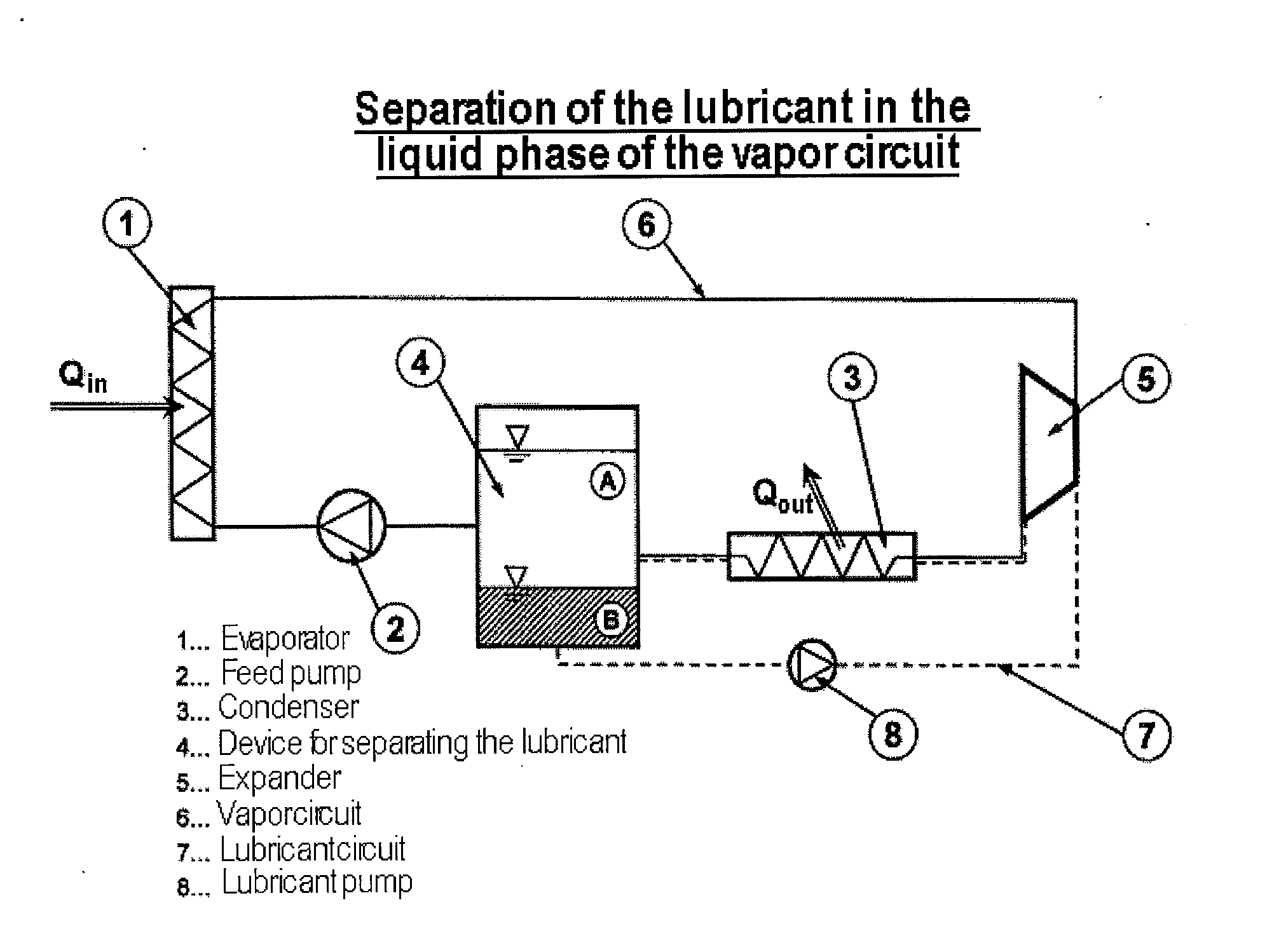
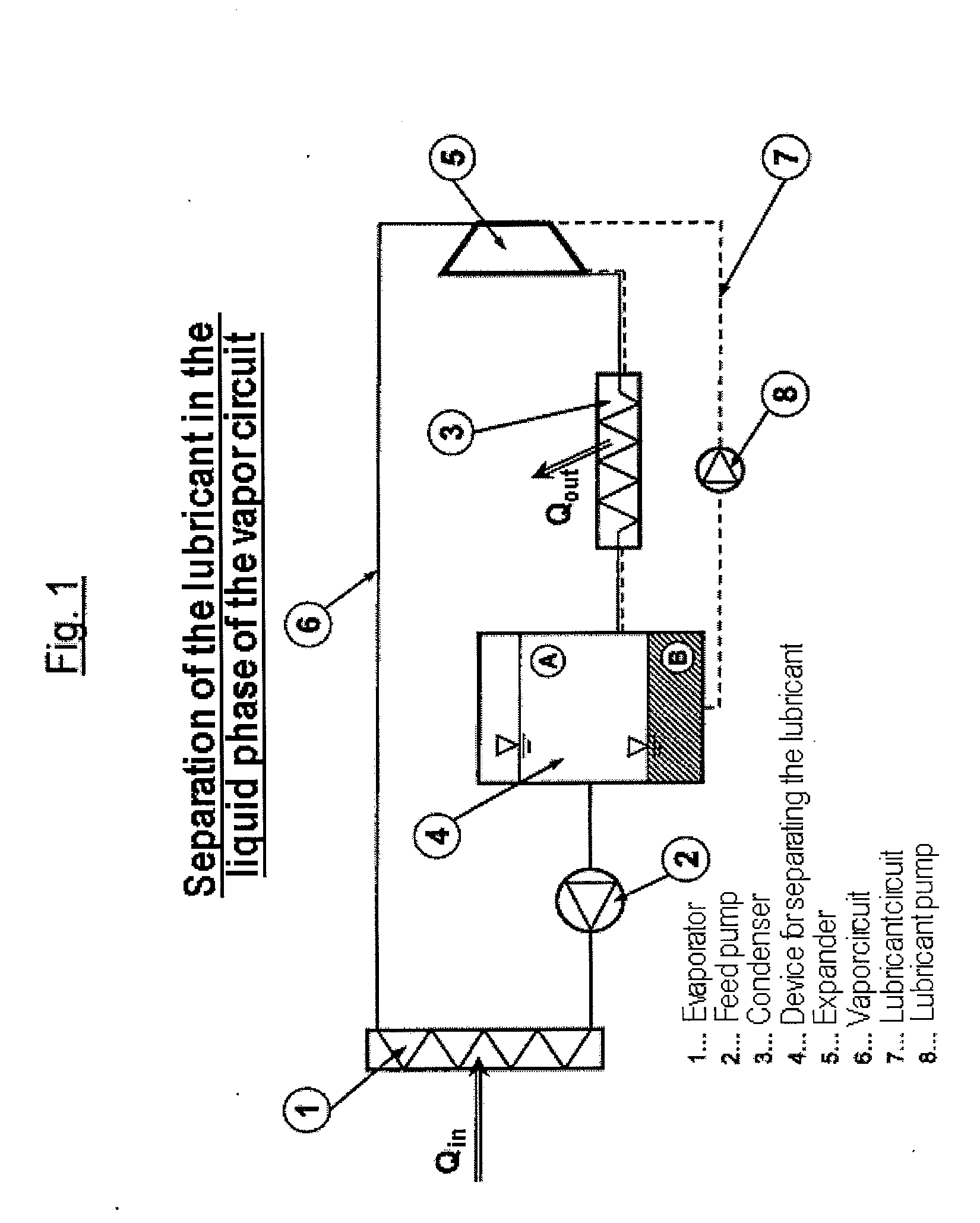
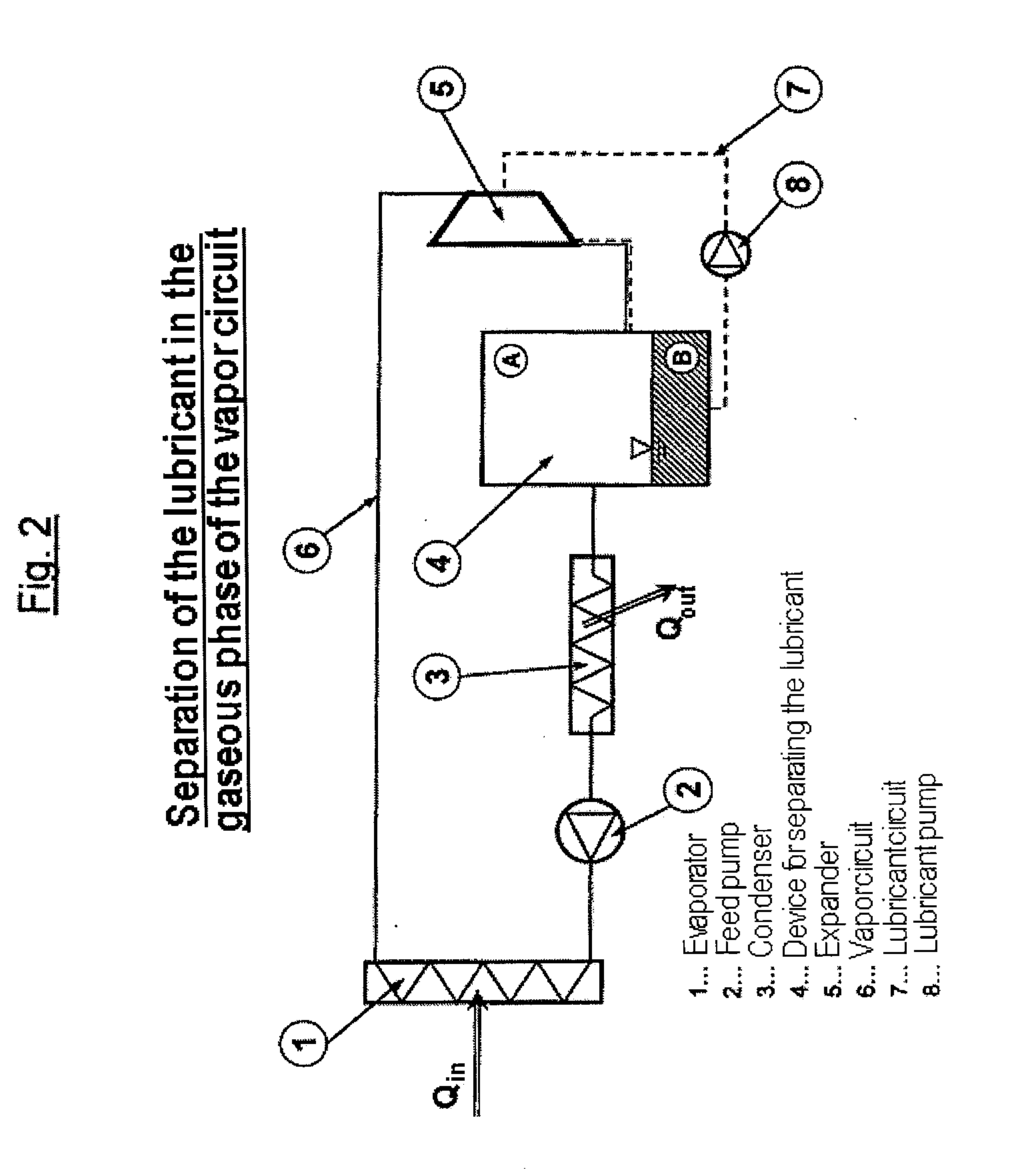
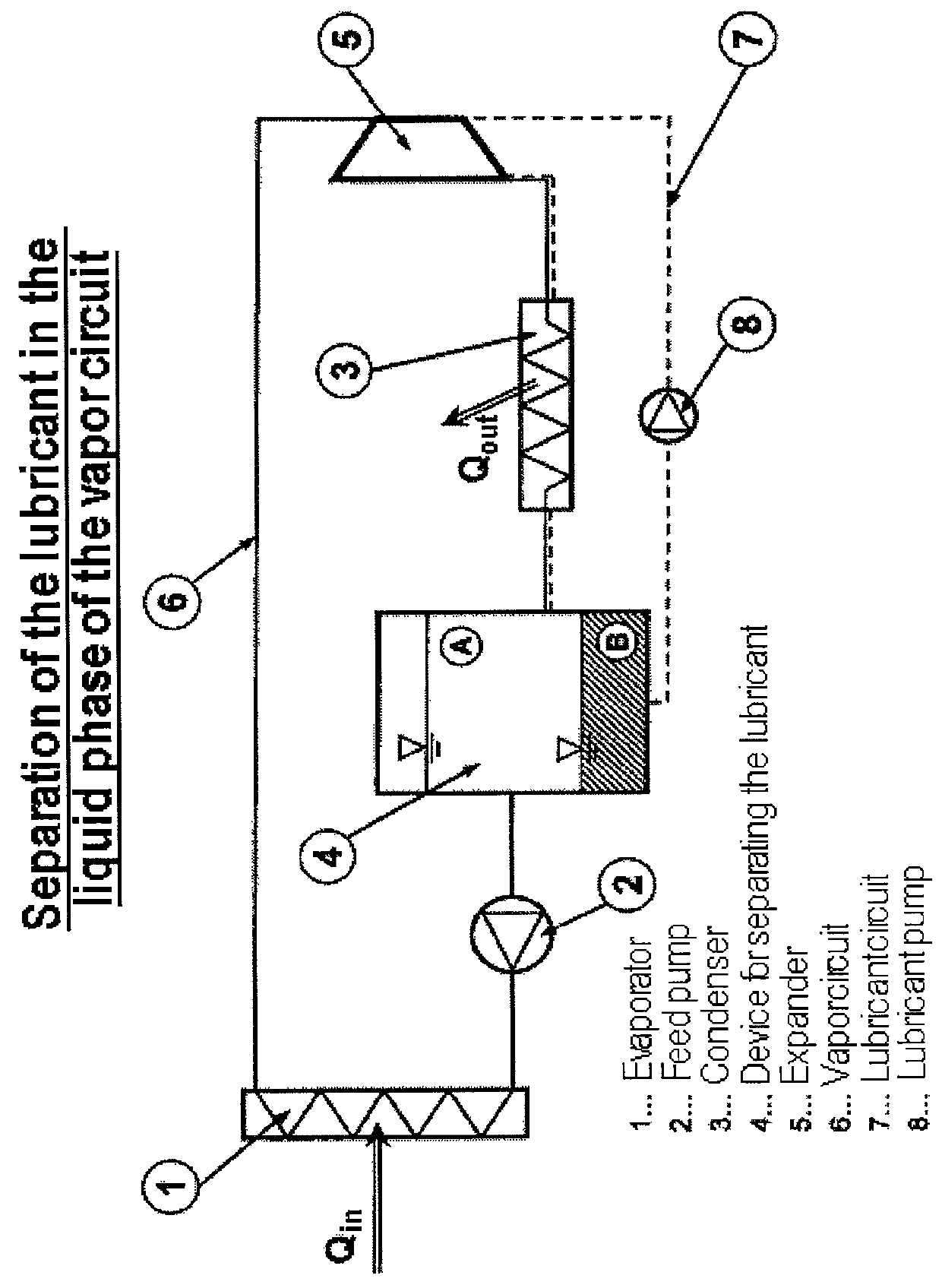
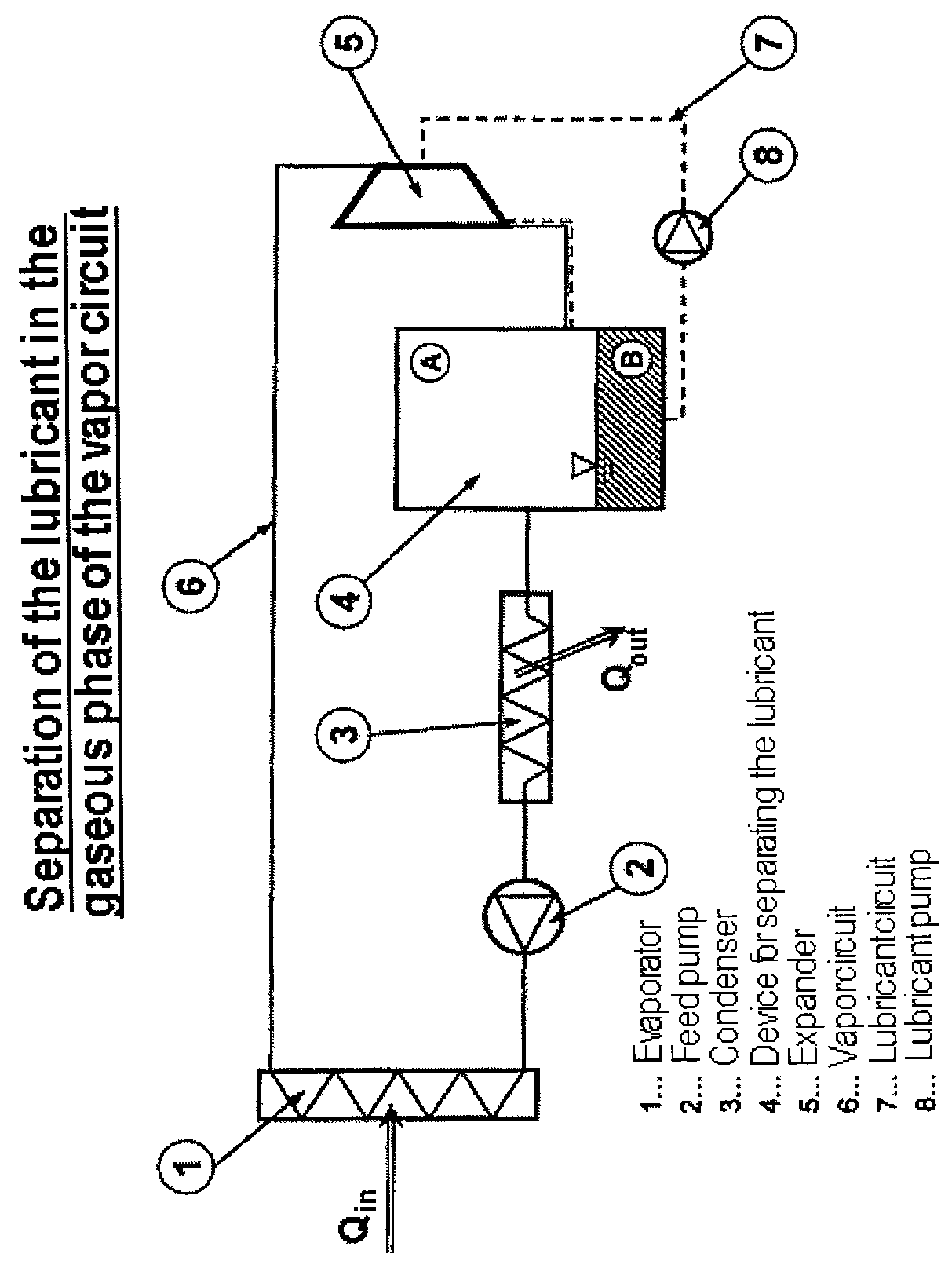
Method and Apparatus for Operating a Steam Cycle Process with a Lubricated Expander
ActiveUS20130263598A1Long operationEfficient separationSteam engine plantsLubricant compositionCyclic processEvaporation
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method for operating a steam cycle process performed in an apparatus having an evaporator or steam generator for the evaporation of a liquid working medium and an expander, which is lubricated by a lubricant, for the performance of mechanical work. The method comprises a) supplying the liquid working medium to the evaporator, in which it evaporates and is fed to the expander in the form of steam; b) supplying an ionic liquid, which at room temperature forms two liquid phases with the liquid working medium, to the expander as a lubricant; and c) separating the ionic liquid forming the lubricant for the expander from the working medium upstream of the evaporator.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
Dual clutch transmission
ActiveUS8342048B2Low production costIncrease the number ofToothed gearingsTransmission elementsIdler-wheelClutch
A dual-clutch transmission comprising clutches with input sides coupled to an input shaft and output sides respectively coupled to first and second transmission input shafts, countershafts on which toothed idler gearwheels are mounted to rotate, toothed fixed gearwheels are coupled to the first and the second transmission input shafts and engage the idler gearwheels, coupling devices connect the idler gearwheel to one of the countershafts, drive output gearwheels are fixed to countershafts and drive an output shaft, and a shifting element couples the input shafts, such that eight forward gears and at least one reverse gear can be engaged. Five wheel planes are arranged in the transmission such that at least one winding gear can be engaged by the shifting element.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Automatic vehicle gearshift transmission
InactiveUS20070049444A1Save componentSimplify the generatorToothed gearingsGas pressure propulsion mountingElectric machineEngineering
An automatic gearshift transmission with a drive input shaft and a drive output, a mechanical gearshift with first and second planetary gearsets, the first planetary gearset being a single planetary gearset downstream from which is connected a double planetary gearset, with several shift elements, including clutches and brakes and with an electric machine provided as a starter and / or generator and / or for the at least partial electric operation of a vehicle, such that the electric machine can be connected by way of a fourth clutch to the combustion engine and by way of a fifth clutch to a first shaft of the first planetary gearset. The combustion engine can be connected by way of the fourth and fifth clutches to the annular gear of the first planetary gearset and / or the electric machine can be connected by way of the fifth clutch to the annular gear of the first planetary gearset.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
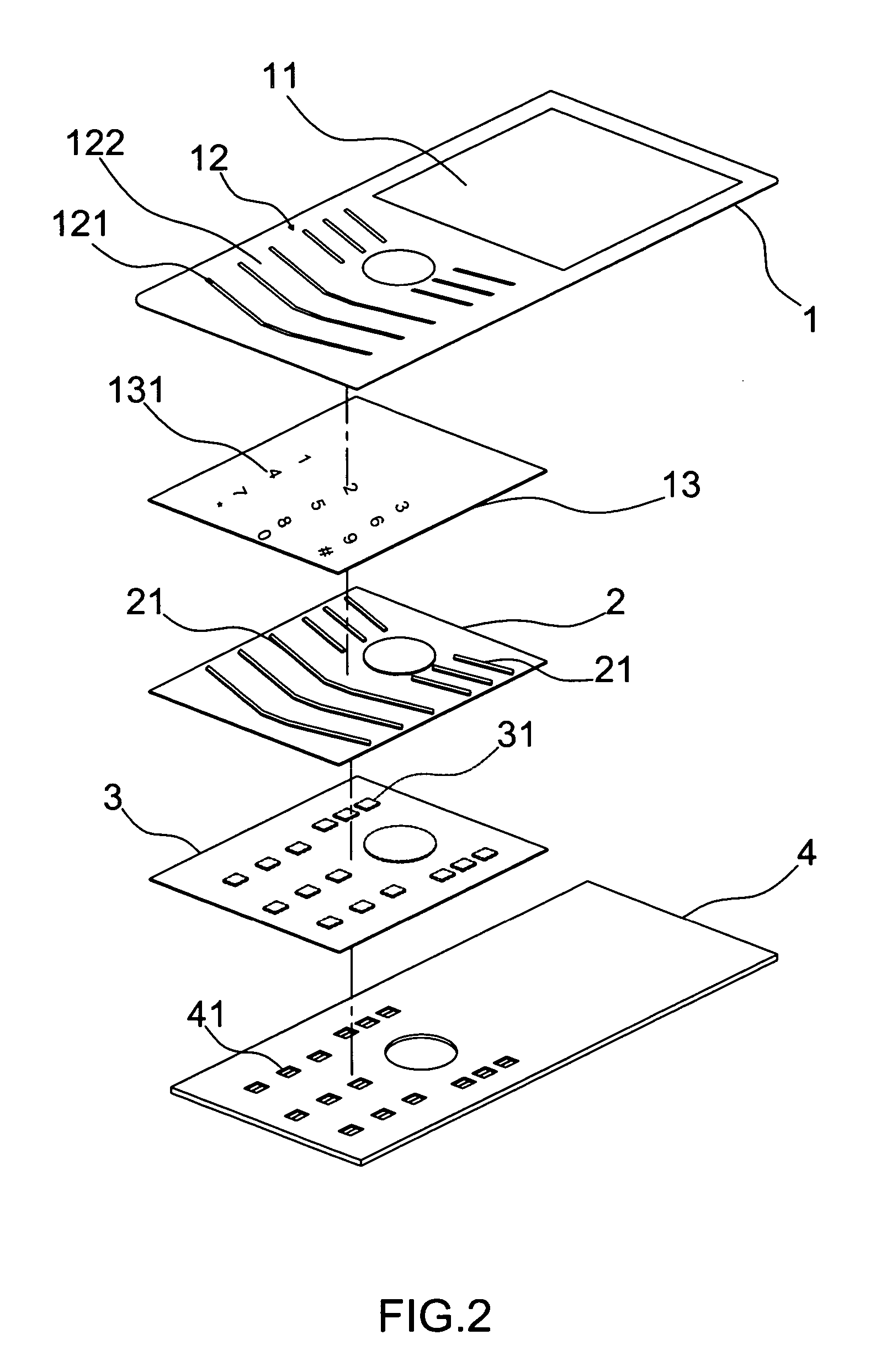
Faceplate having keys for mobile phone
InactiveUS20070275751A1Easily assembleSave componentTelephone set constructionsEngineeringMobile phone
Owner:SPEED TECH
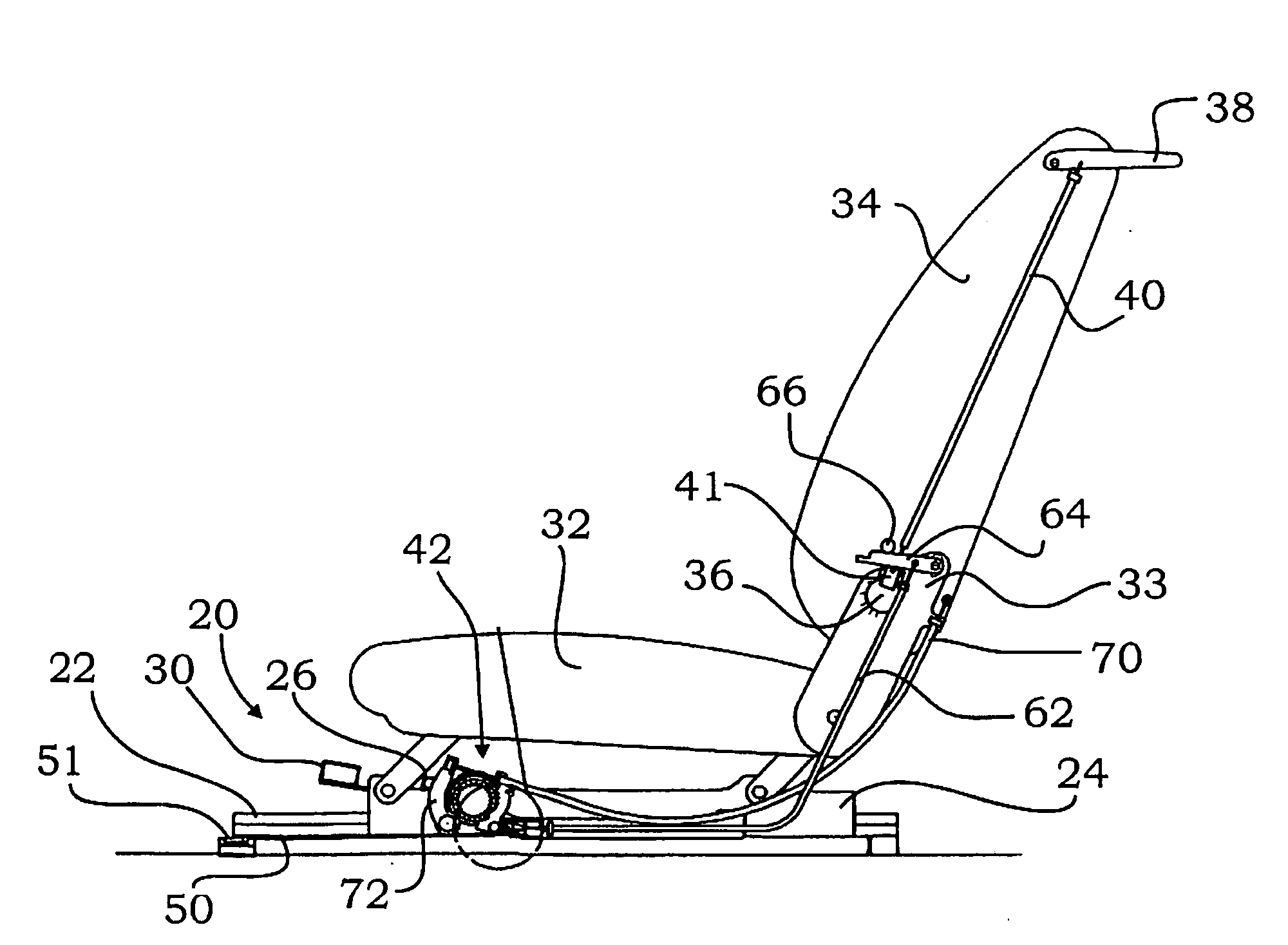
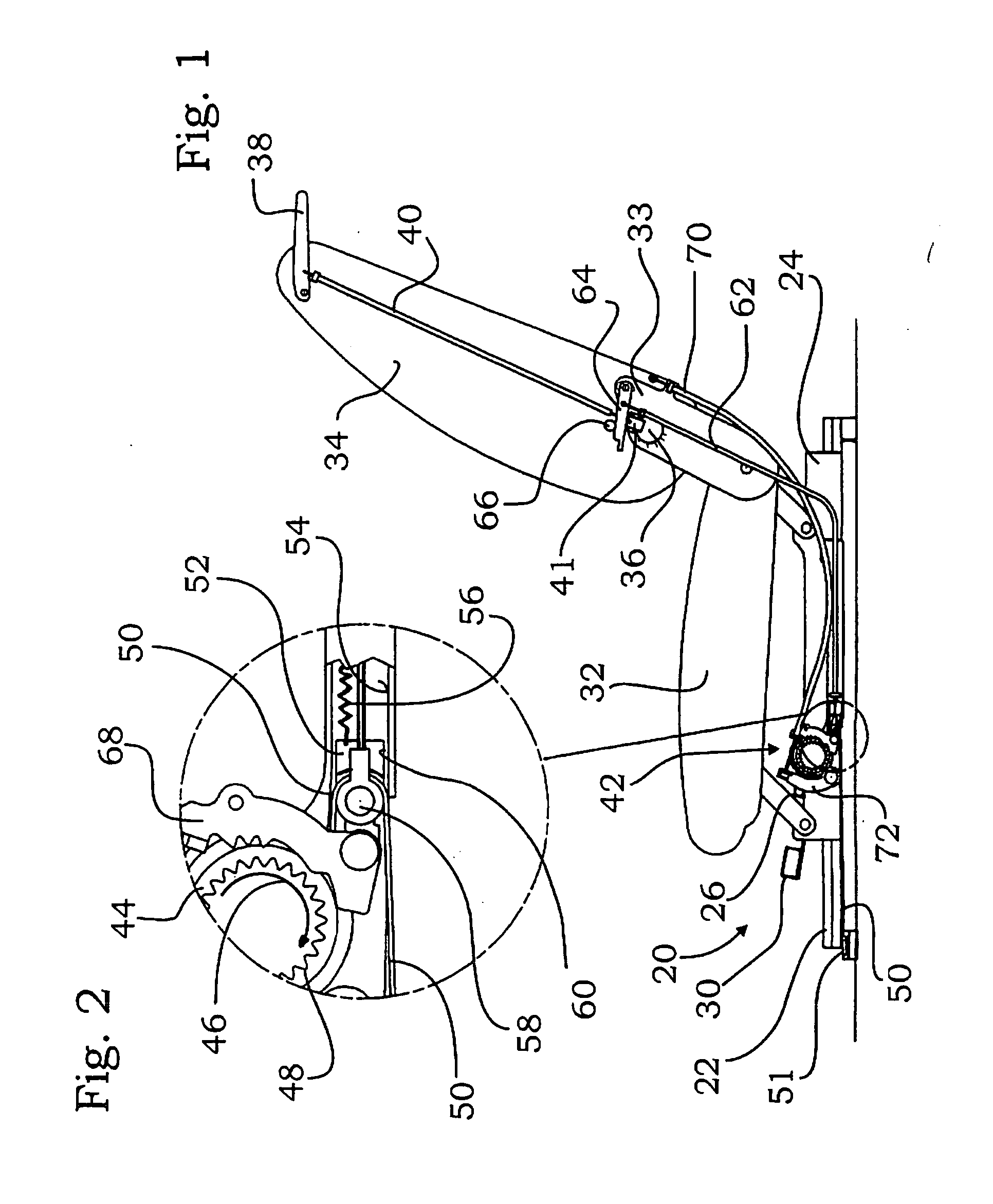
Forwardly movable vehicle seat with an underframe and two pairs of rails
Owner:ADIENT US LLC
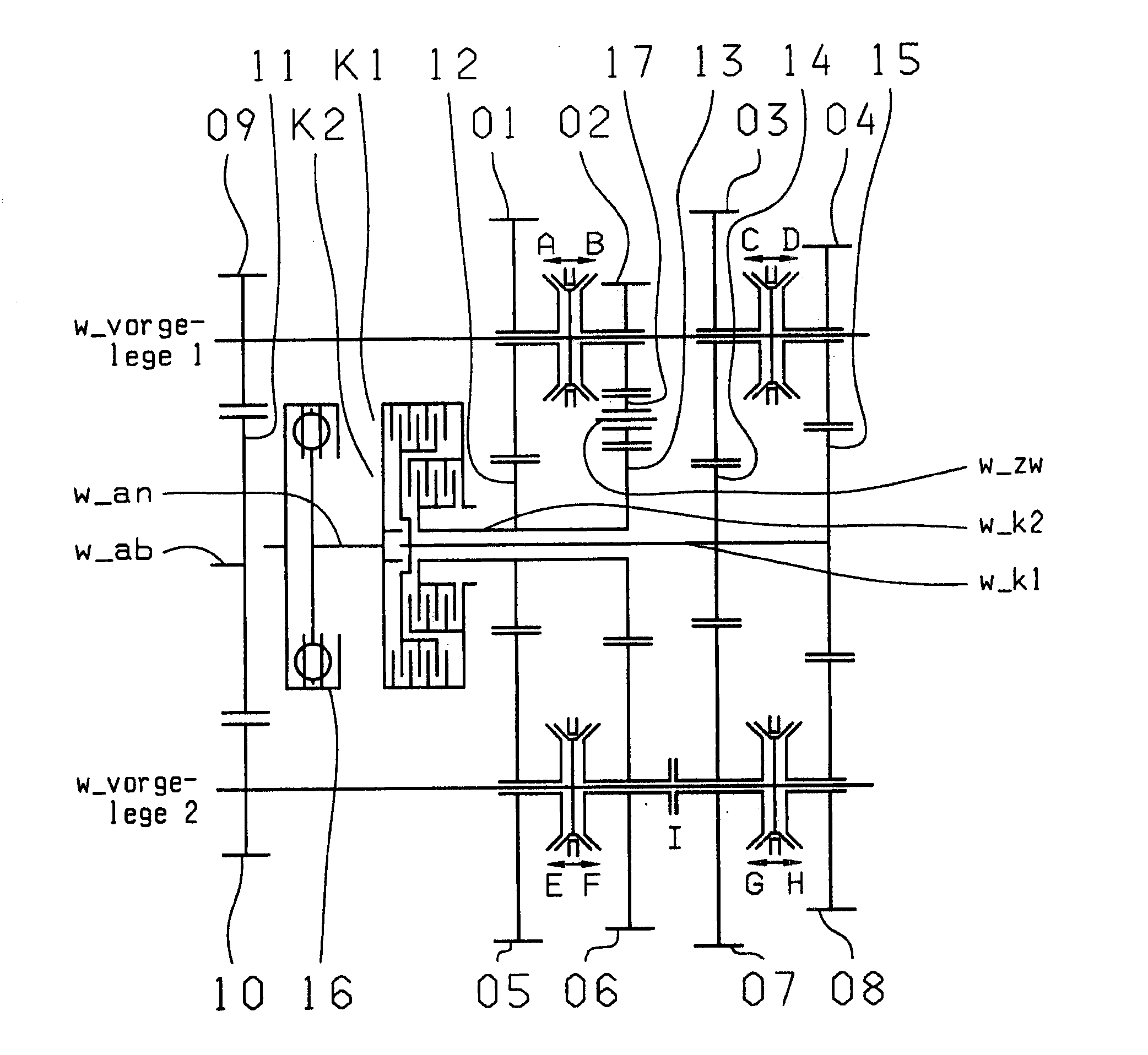
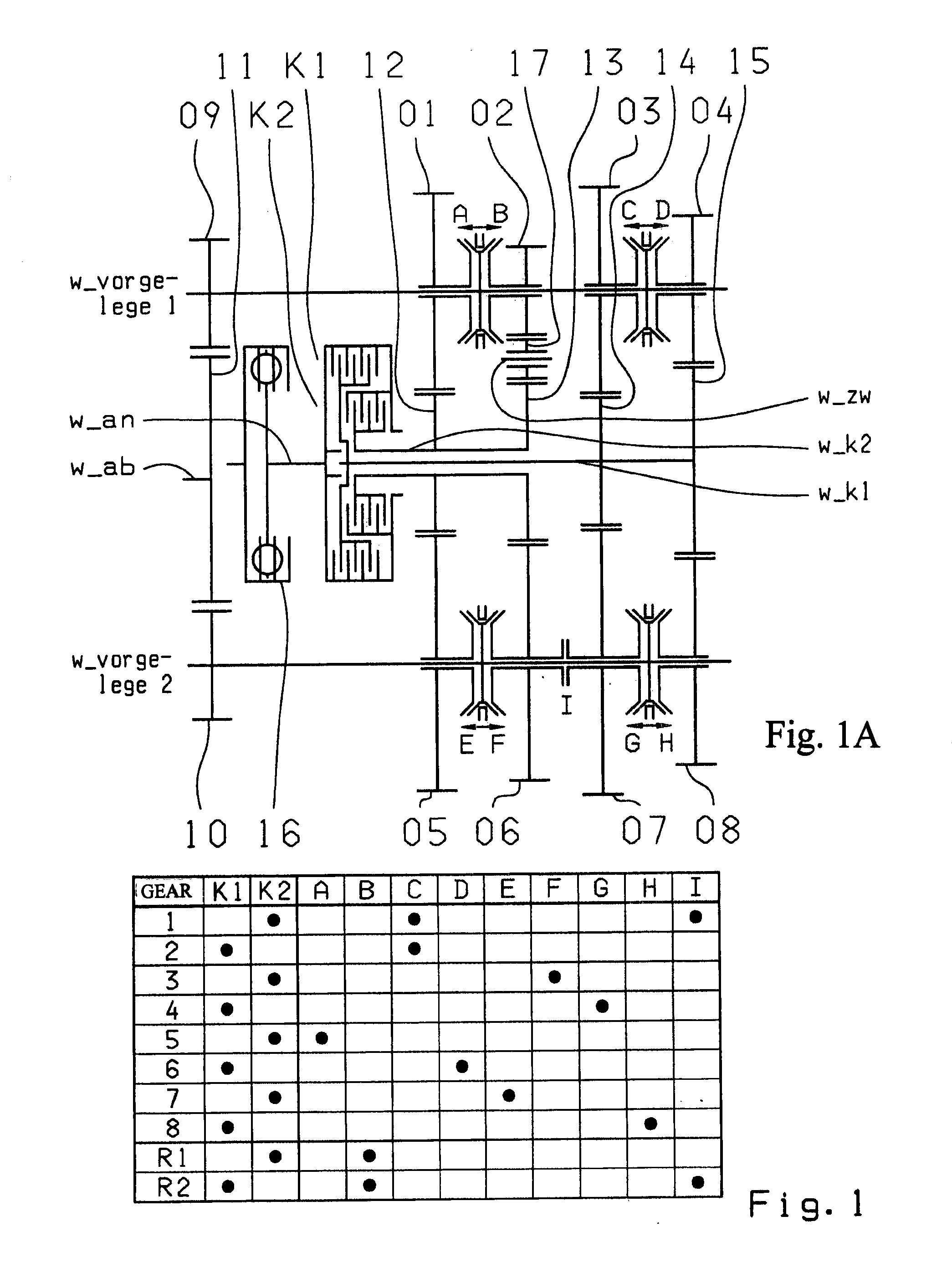
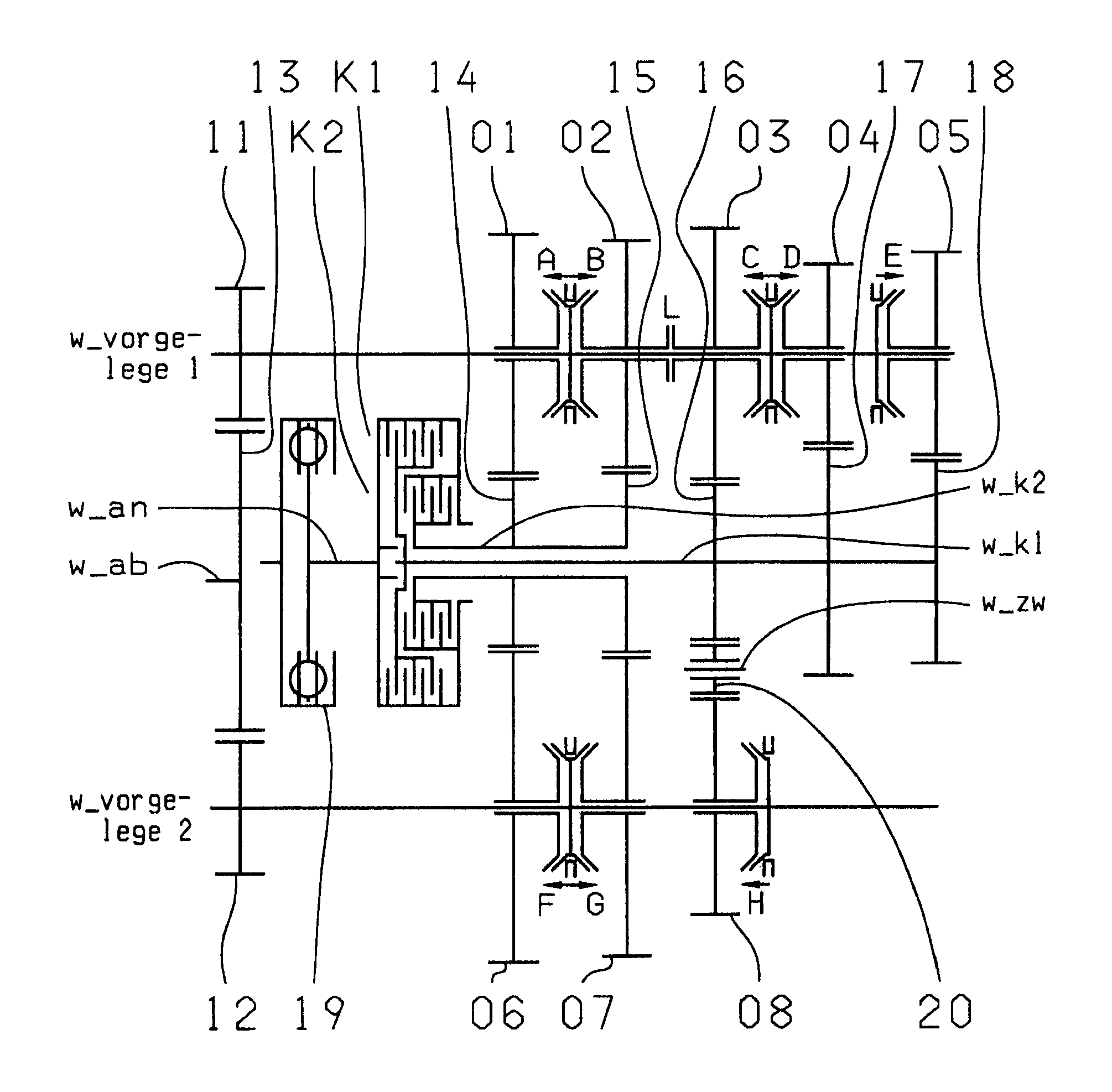
Double clutch transmission
ActiveUS20100282019A1Low production costIncrease the number ofToothed gearingsTransmission elementsCouplingConductor Coil
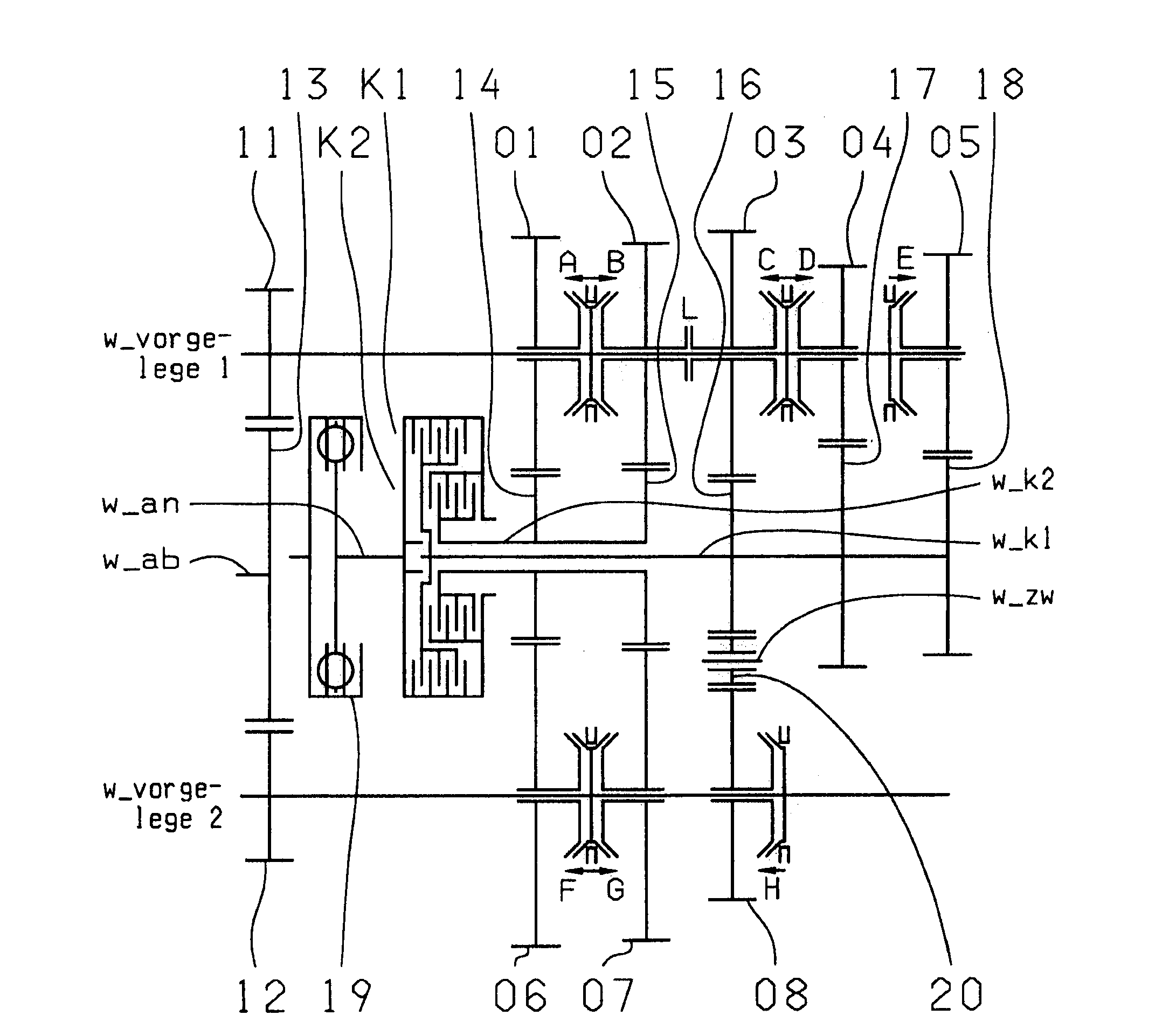
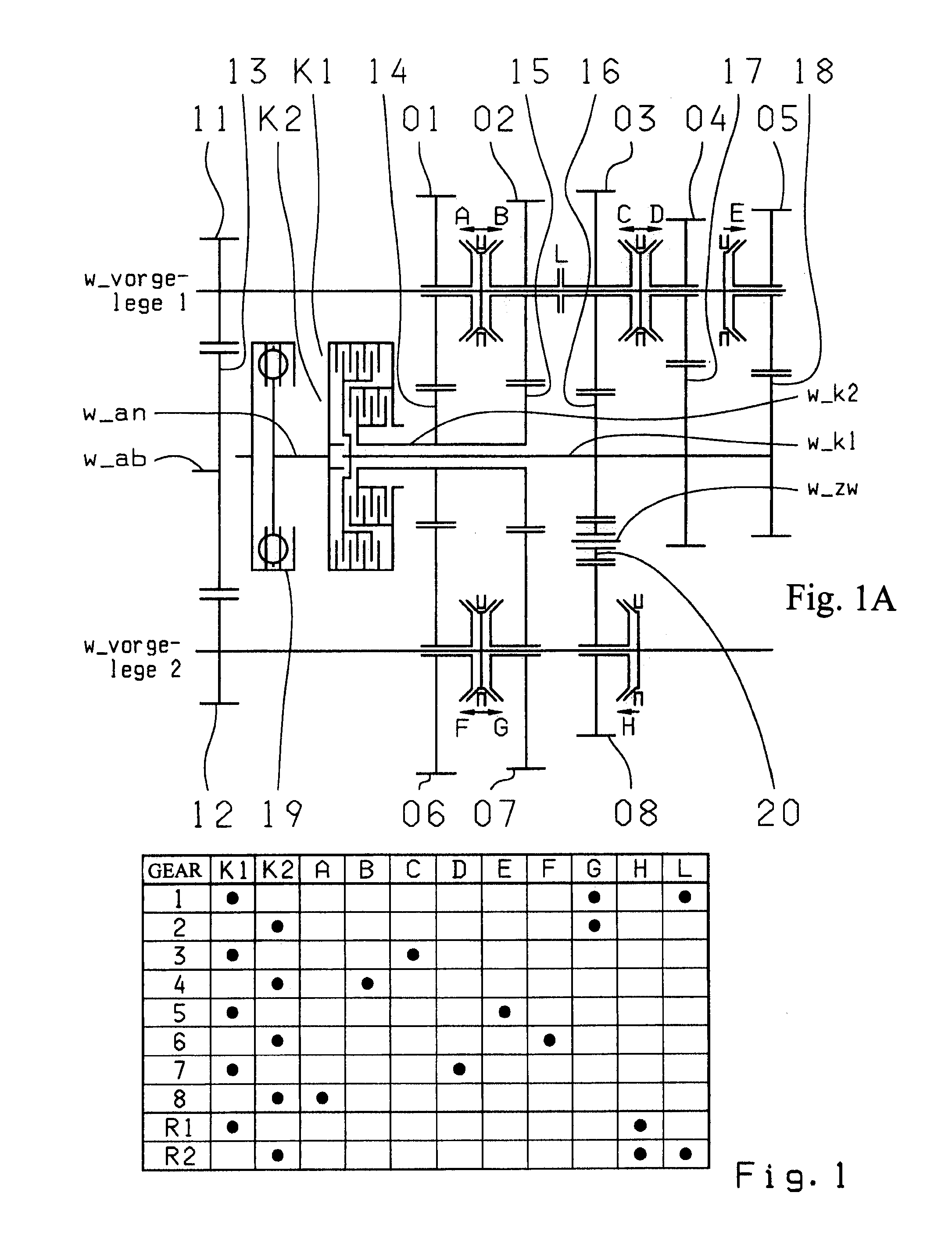
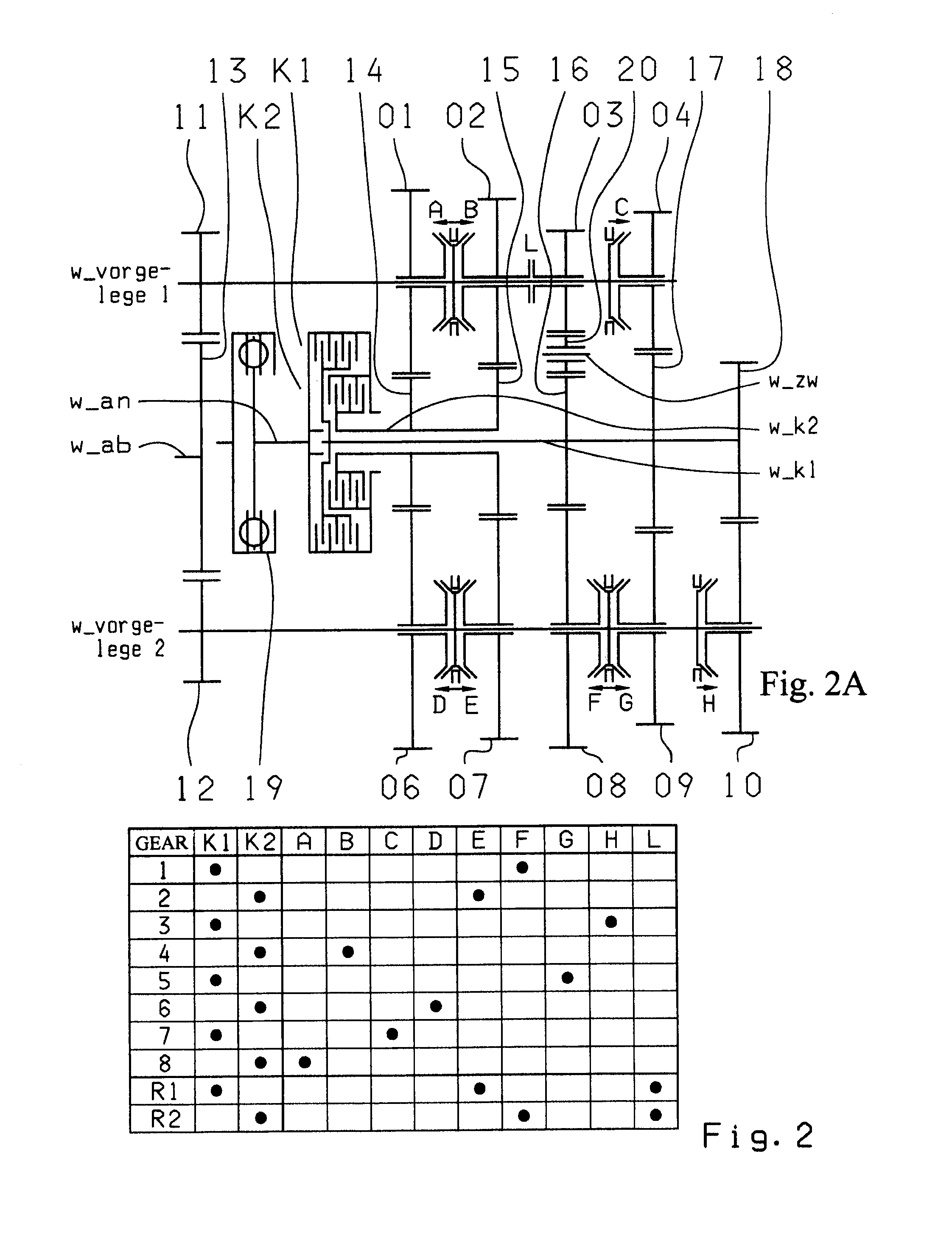
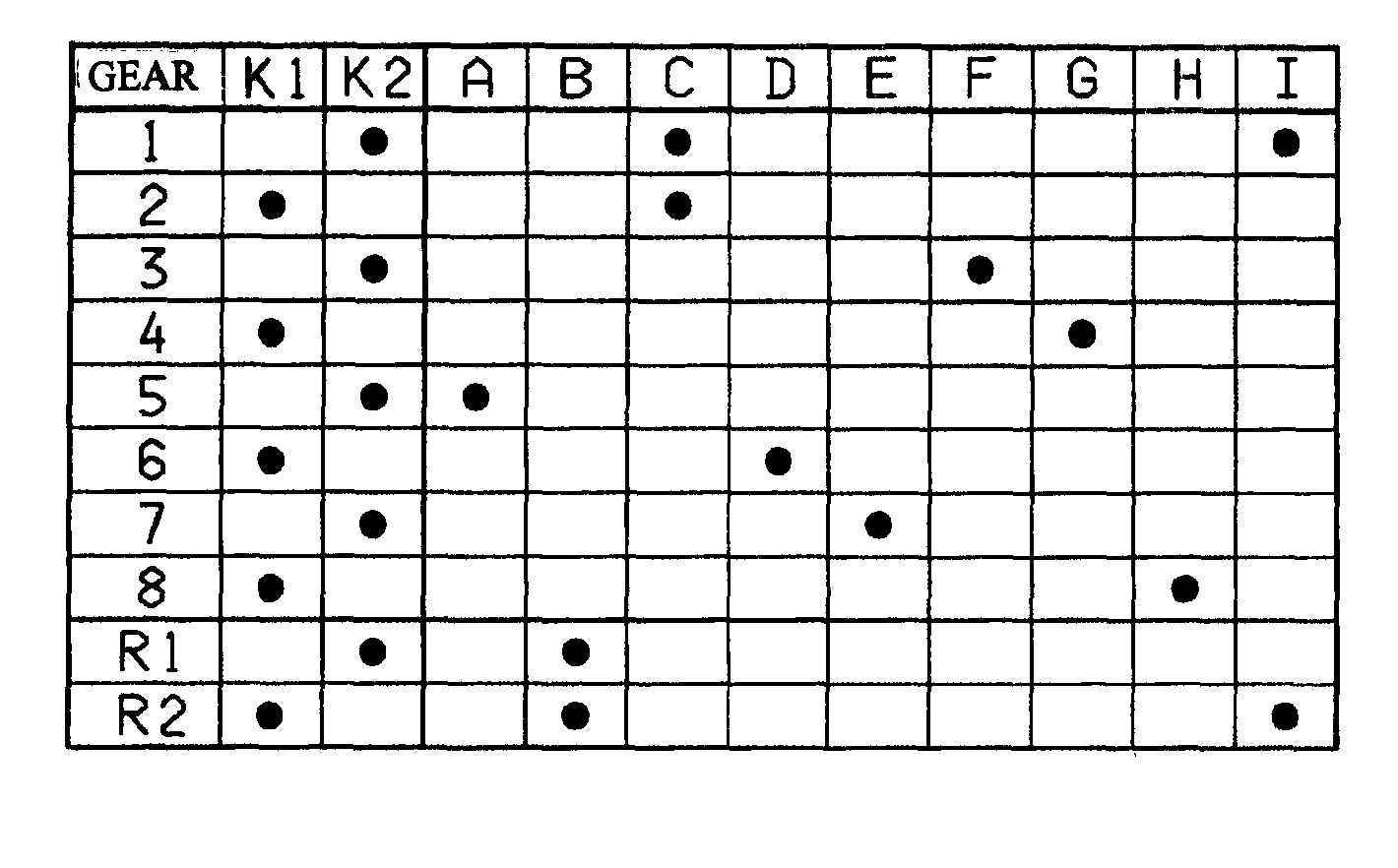
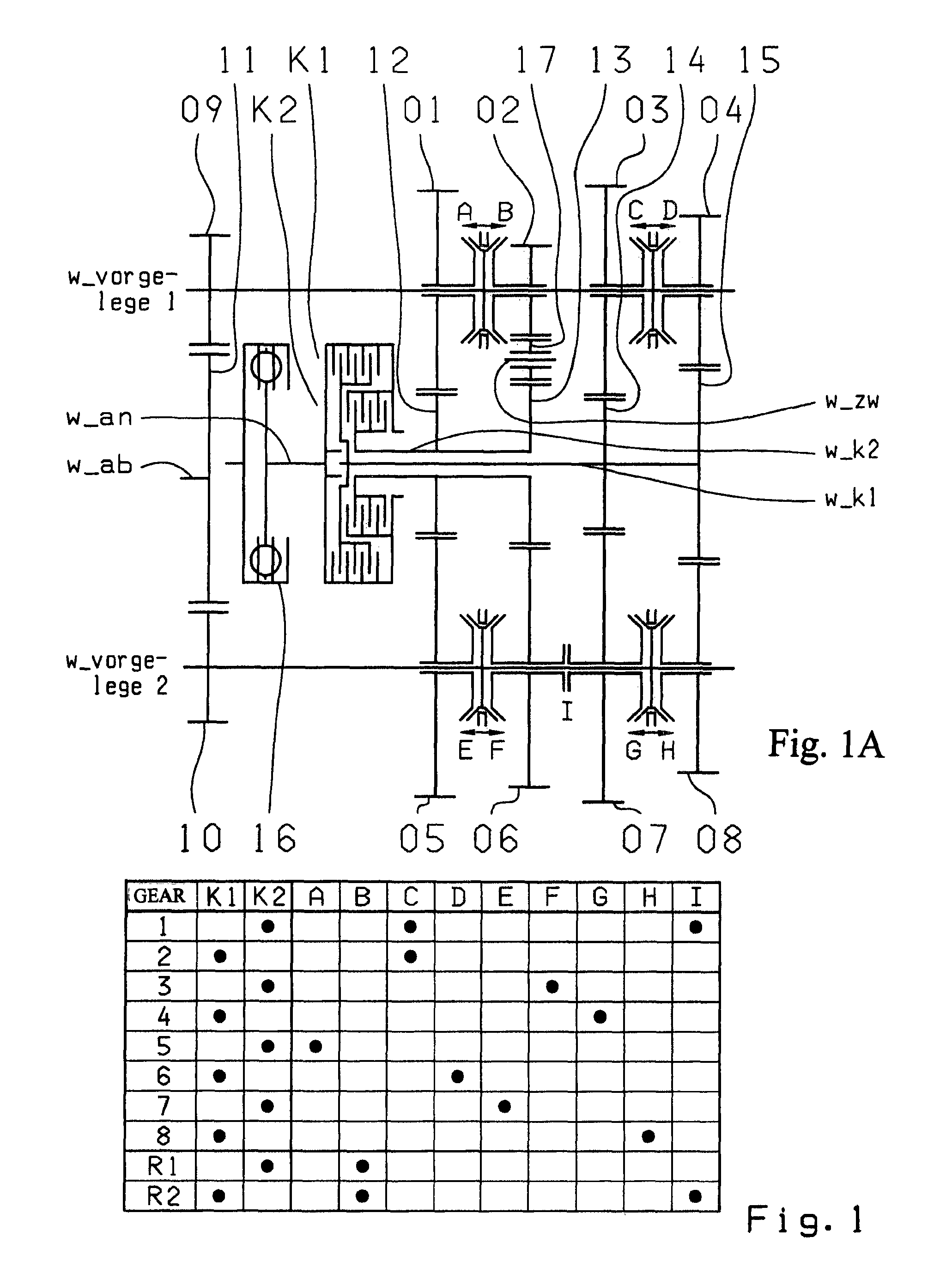
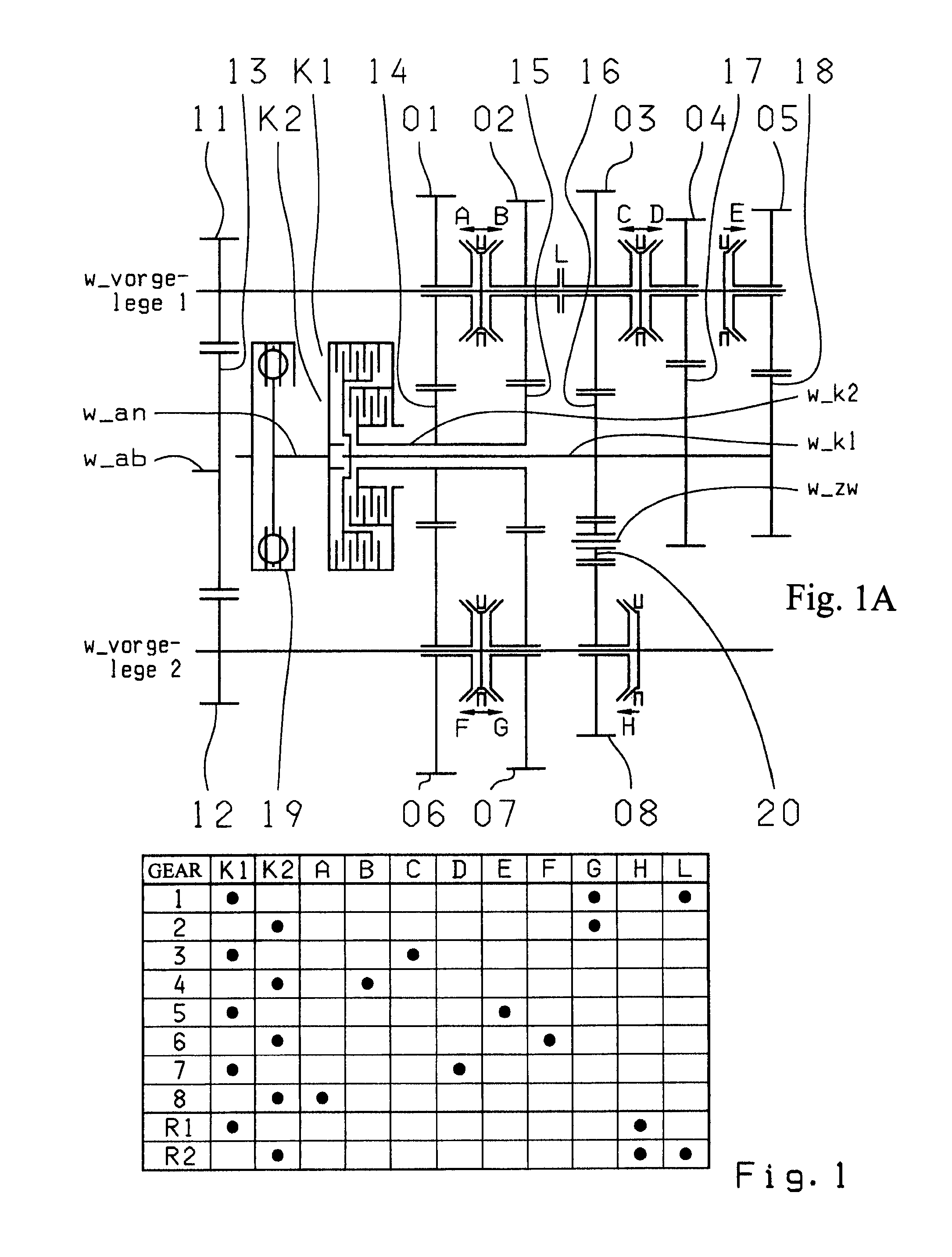
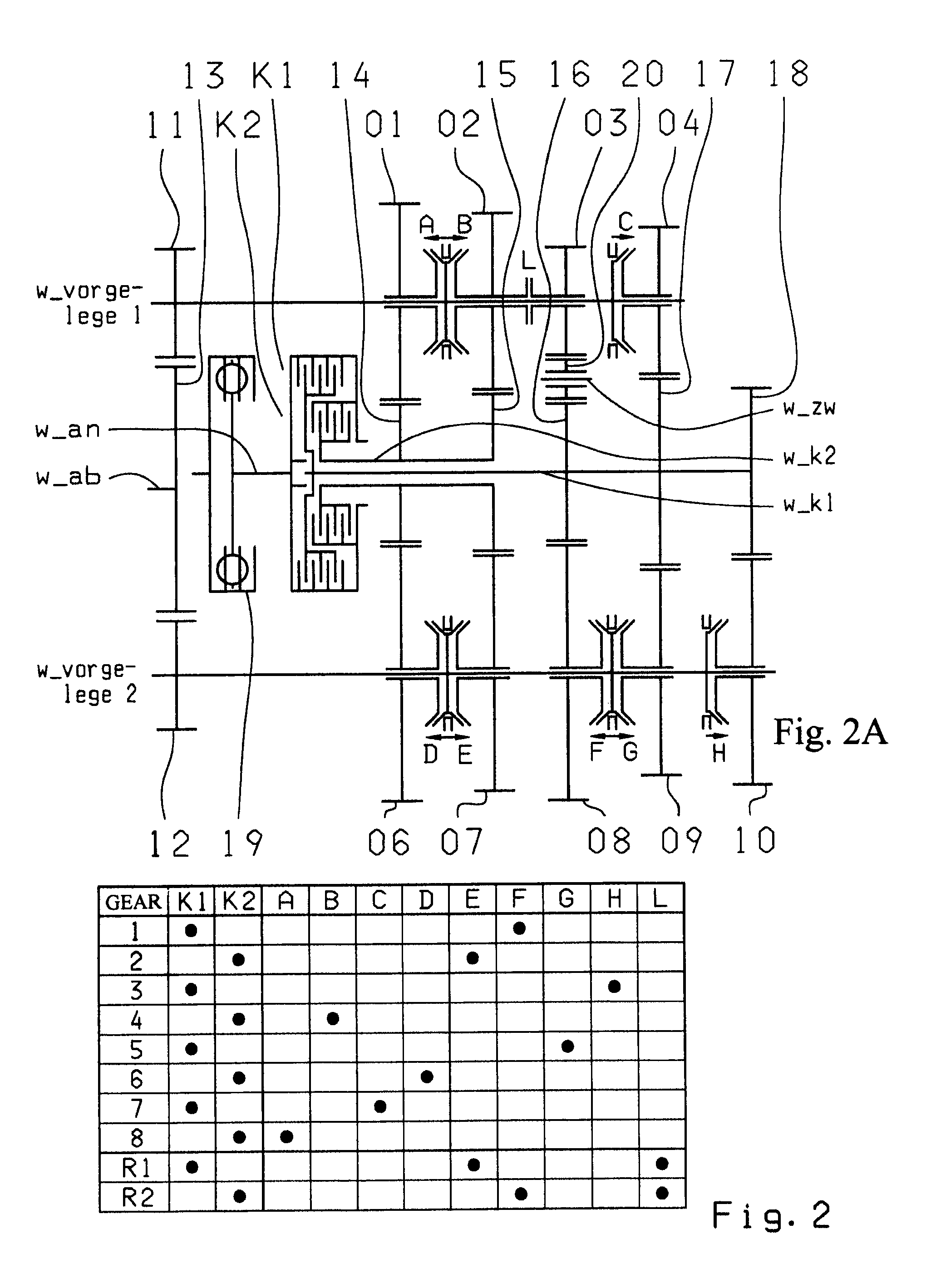
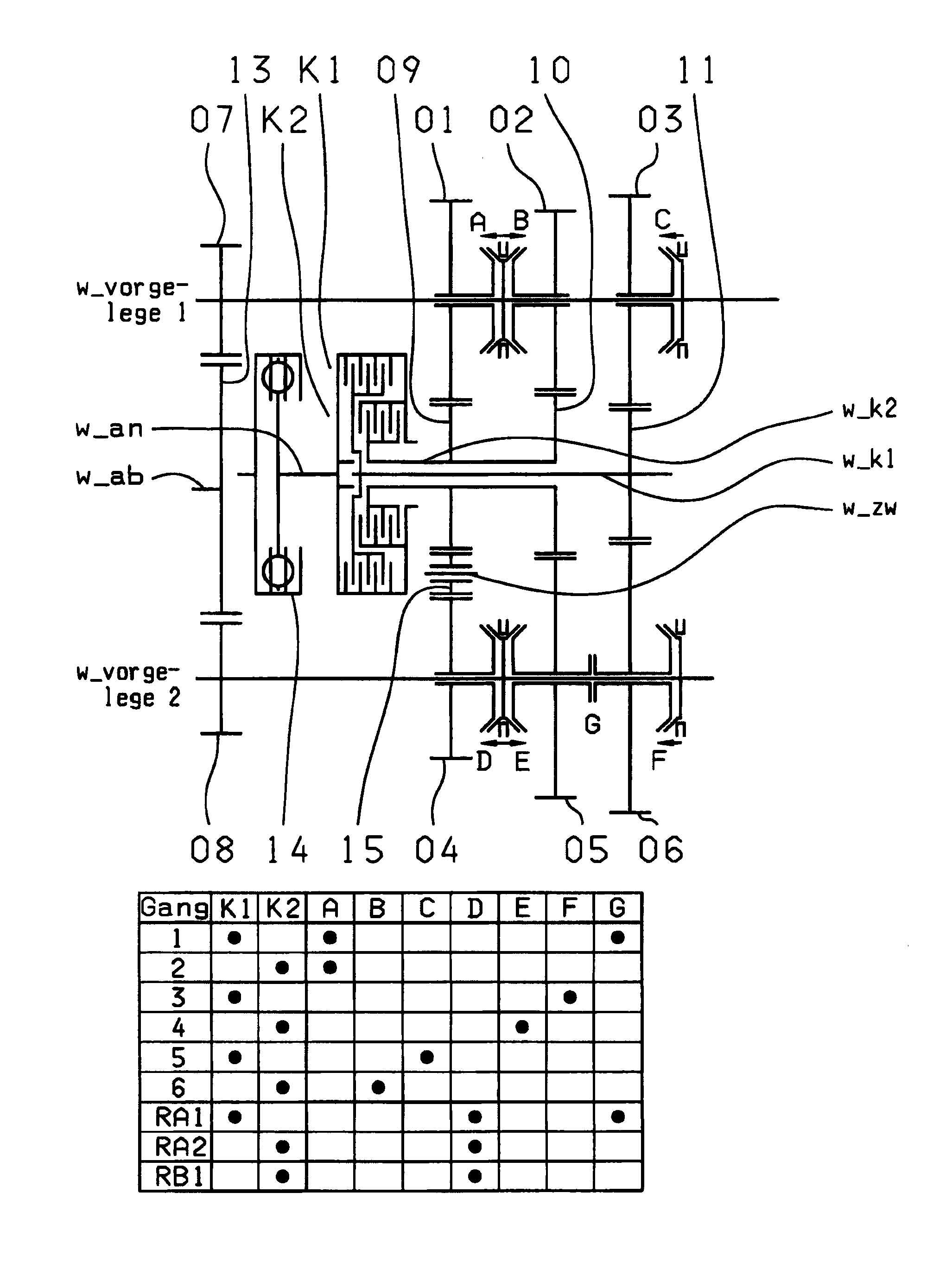
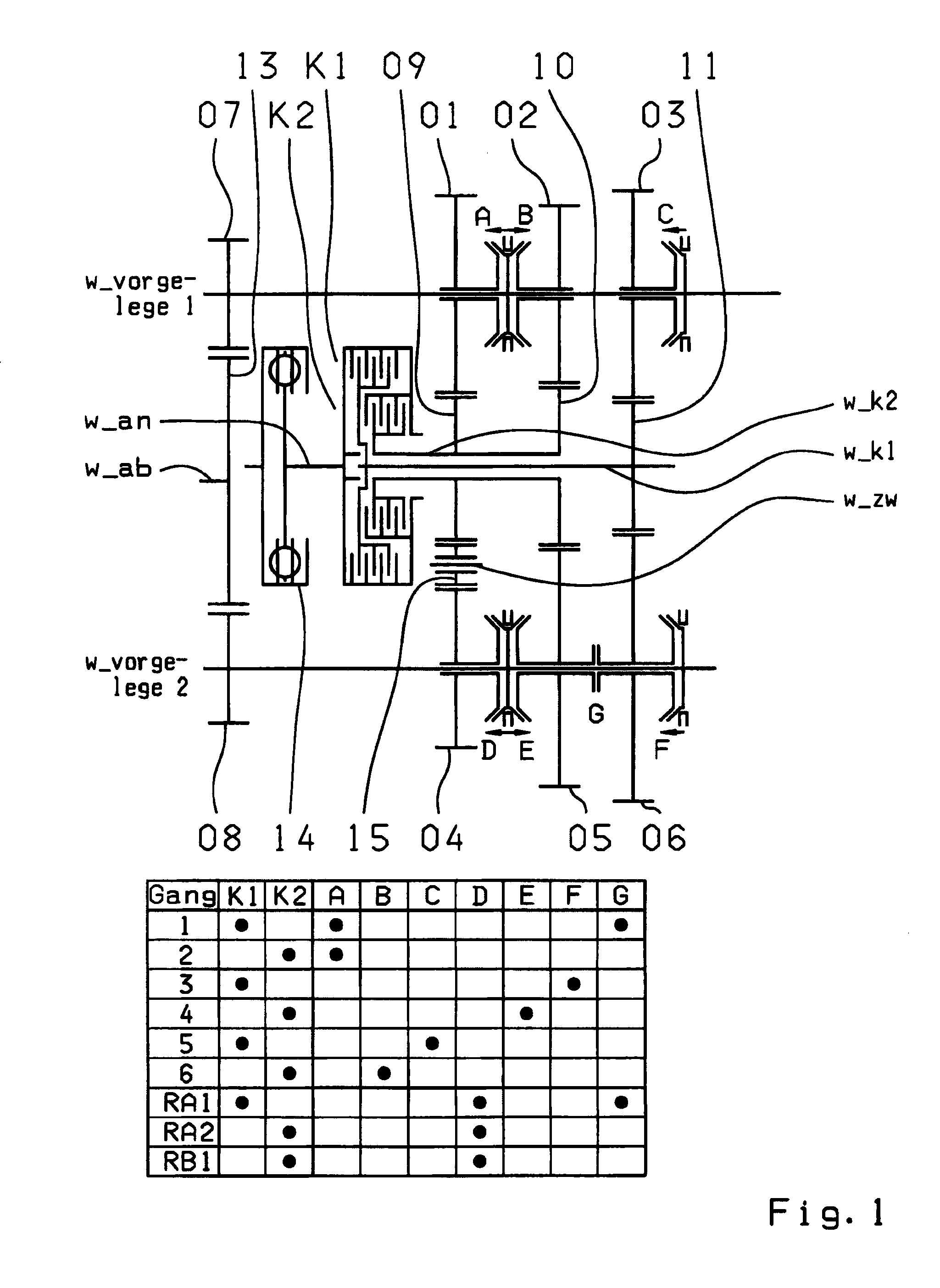
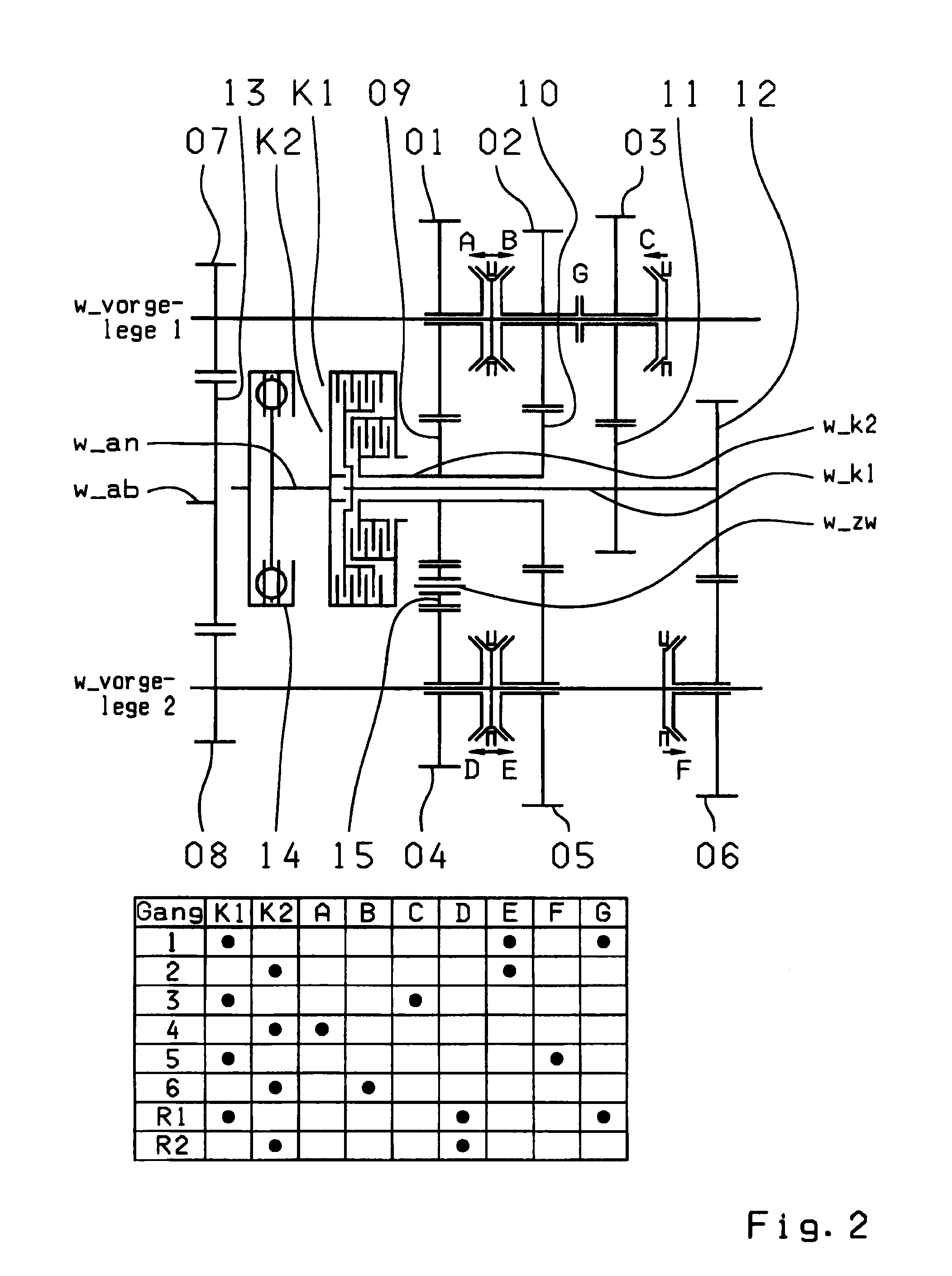
A dual-clutch transmission with two clutches (K1, K2) whose input sides are connected to a drive input shaft (w_an) and whose output sides are respectively connected to one of two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2) arranged coaxially with one another. Idler gearwheels (01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06) are mounted to rotate on at least two countershafts (w_vorgelege1, w_vorgelege2) while fixed gearwheels (09, 10, 11) are rotationally fixedly connected on the two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2). A plurality of coupling devices (A-B, C, D-E, D, E-F, F) connect the idler gearwheels (01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06) of the two countershafts (w_vorgelege1, w_vorgelege2) with a respective drive output gearwheel (07, 08) fixed on each of the two countershafts (w_vorgelege1, w_vorgelege2). At least one shifting element (G) couples the two transmission input shafts (w_K1, w_K2) such that at least six shift-under-load forward gears (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) and at least one reverse gear (RA1, R1) can be engaged. The transmission has three wheel planes (01-04; 02-05; 03-06) or four wheel planes (01-04, 01-09; 02-05, 02-04; 03-11, 03-05; 12-06) arranged in such manner that at least one shift-under-load winding gear can be engaged by the shifting element (G).
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
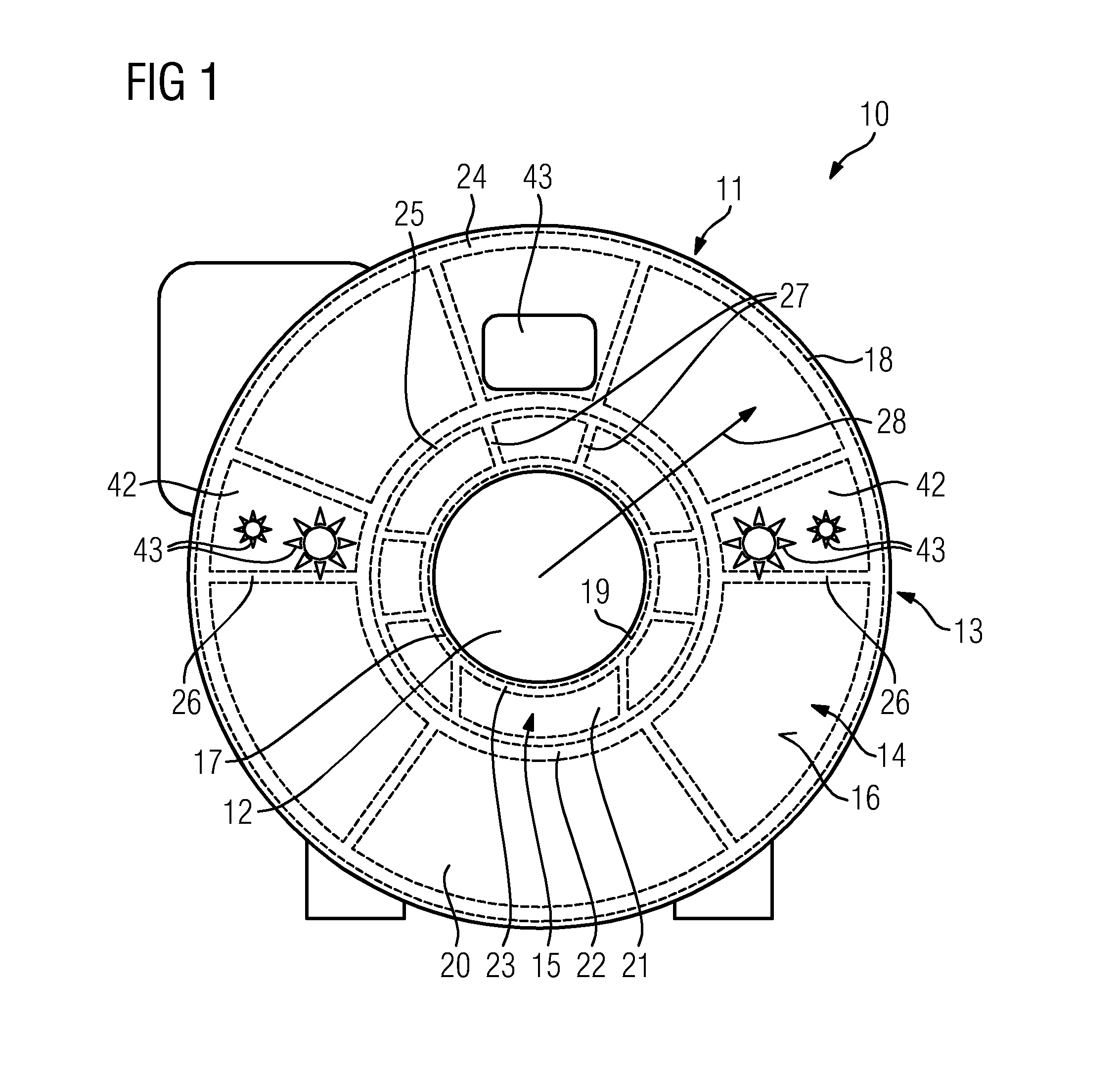
Medical imaging device comprising a housing unit that has a casing shell and method for producing a casing shell of the medical imaging device
ActiveUS20130200896A1Effective noise damping noiseEffective noise noise separationTomographyElectric/magnetic detectionMedical imagingStructural unit
A medical imaging device includes a detection unit and a housing unit that surrounds the detection unit and has at least one casing shell The at least one casing shell includes a netlike supporting structure unit and an elastic spring-mass unit.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
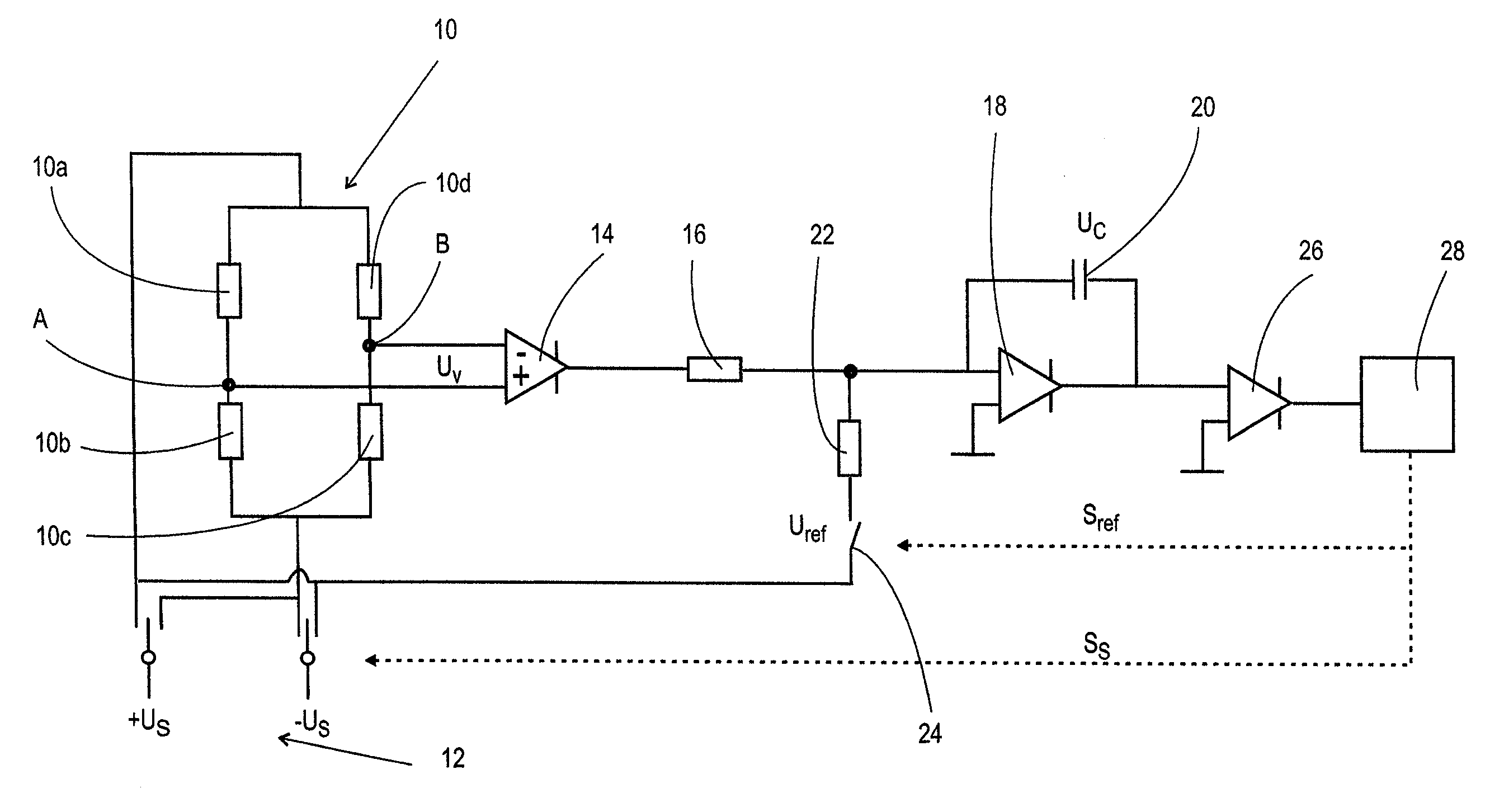
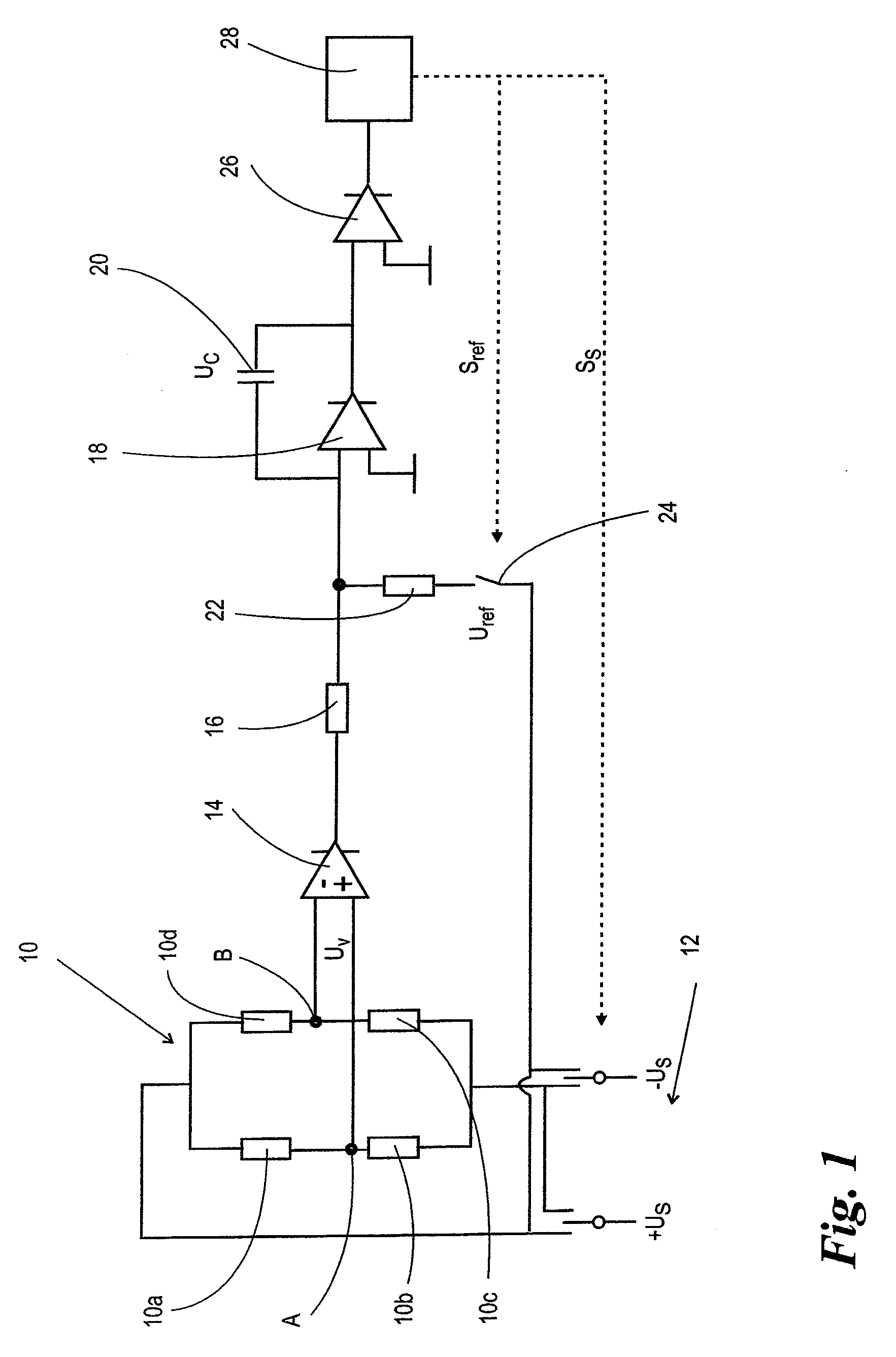
Measurement amplification device and method
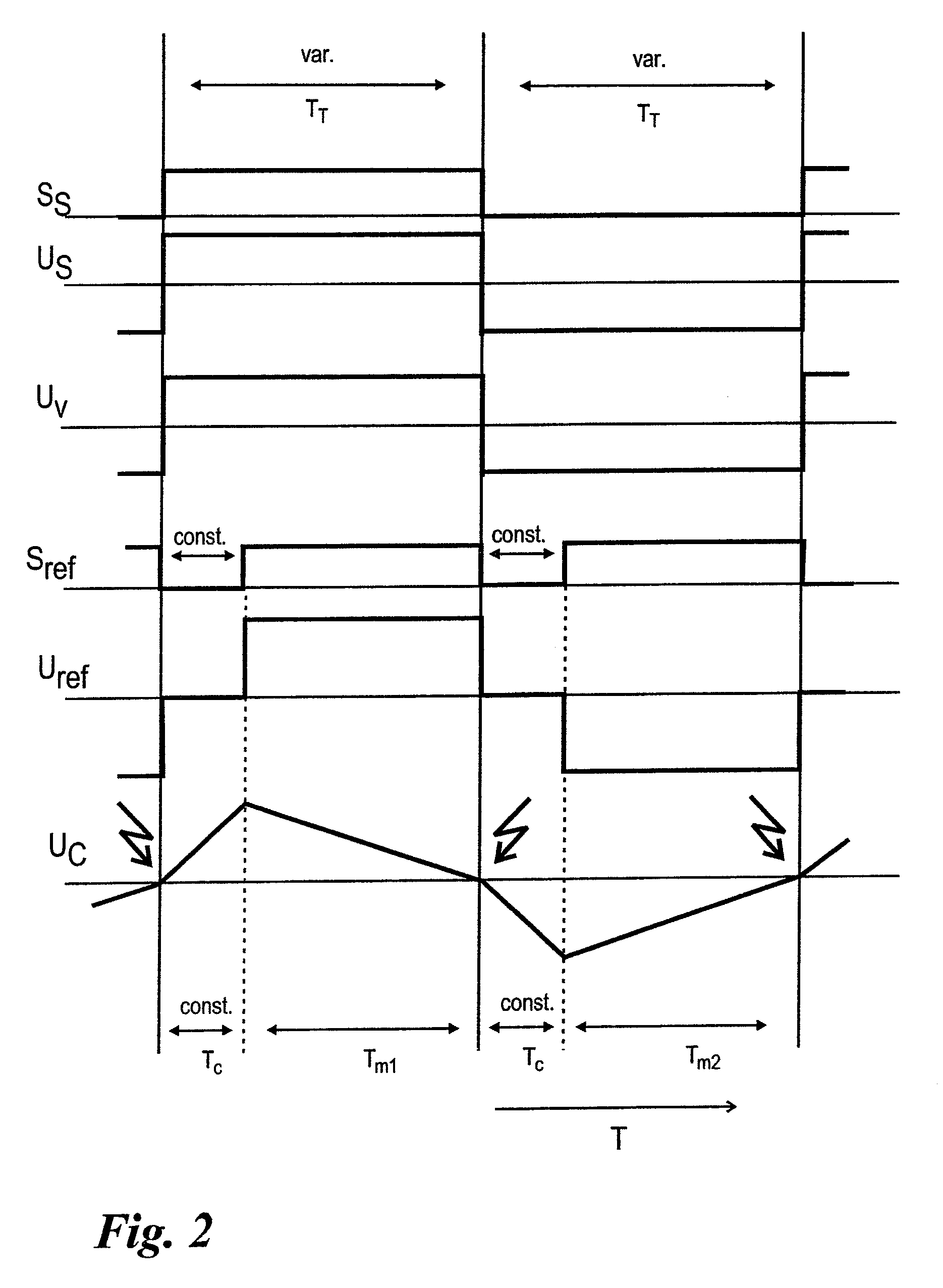
InactiveUS20090207064A1Save componentAvoid necessityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersVoltage referenceEngineering
Measurement amplification methods and devices for detecting the detuning of a measurement bridge (10) to which a bipolar, rectangular supply voltage (Us) is supplied. The methods and devices use integrating A / D conversion and are characterized in that a reference voltage (Uref) used for the A / D conversion undergoes polarity changes synchronized with the polarity changes of the supply voltage (Us). Offset and drift are eliminated by totaling an even number of individual measurements.
Owner:SARTORIUS LAB INSTR GMBH & CO KG
Aroma diffuser using an aroma capsule
ActiveUS9844609B2Simply and smoothly combinedEasy to replaceGaseous substancesFlash distillationEngineeringHOLDING CHAMBER
Owner:HSIAO MING JEN
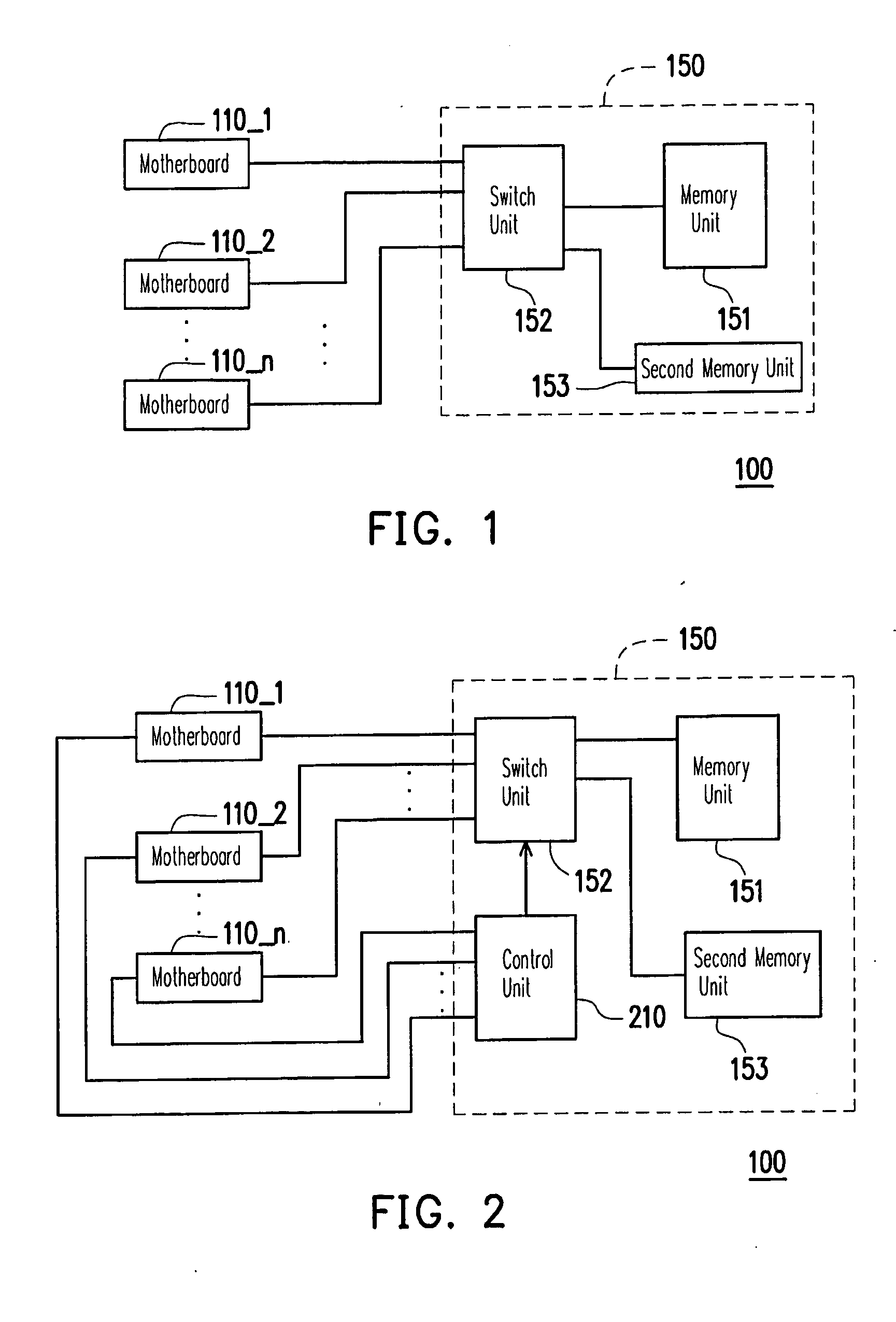
Method of sharing basic input output system, and blade server and computer using the same
InactiveUS20090276613A1Improve efficiencySave componentDigital computer detailsProgram controlBIOSBlade server
A blade server is provided. The blade server includes at least one motherboard, and a backplane. The backplane is coupled to the at least one motherboard, and includes a memory unit and a switch unit. The memory unit is adapted for storing a BIOS. The switch unit is coupled between the motherboard and the memory unit, for coupling the memory unit to one of the at least one motherboard. The present invention is adapted for using less memory units when configuring a blade server.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
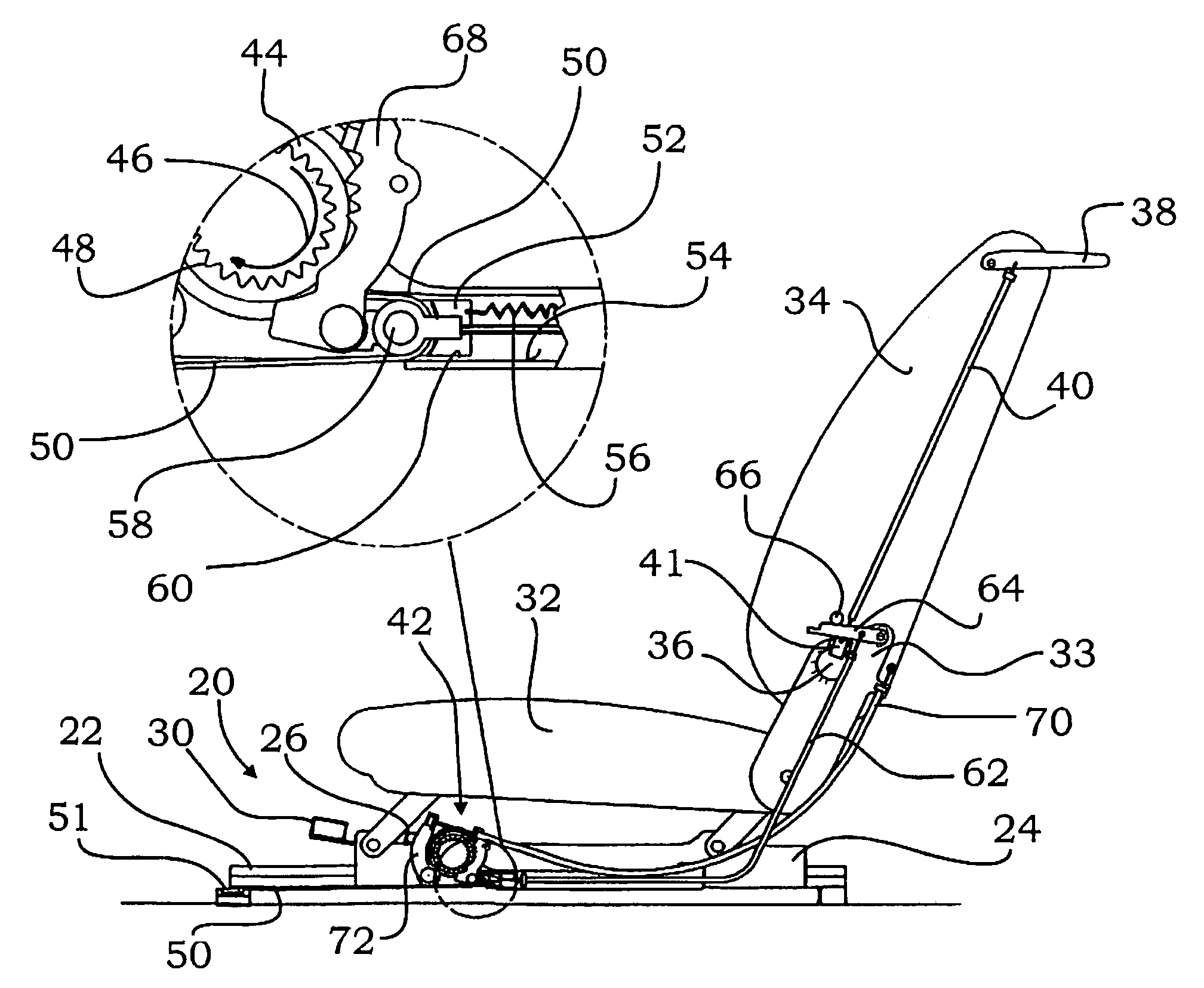
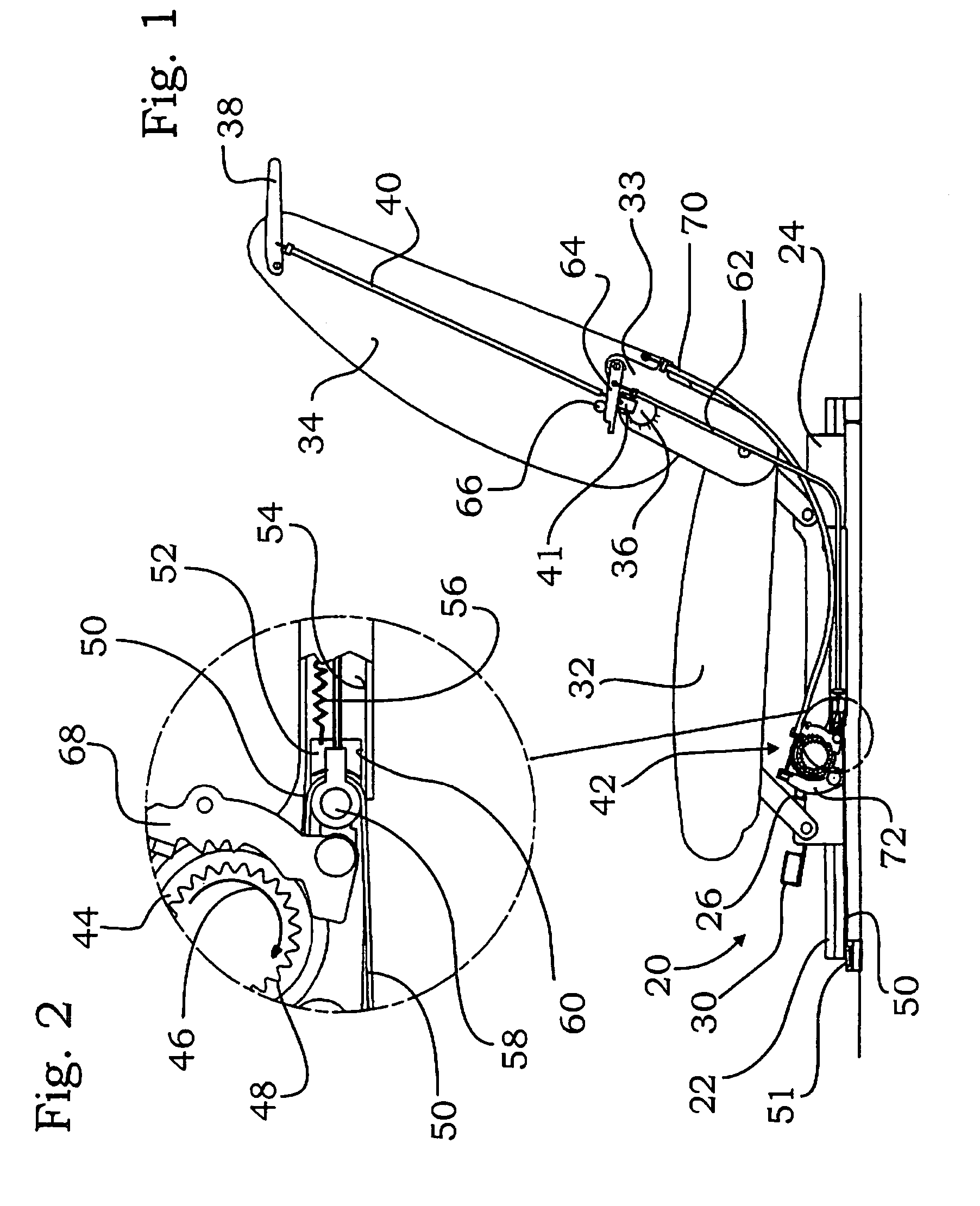
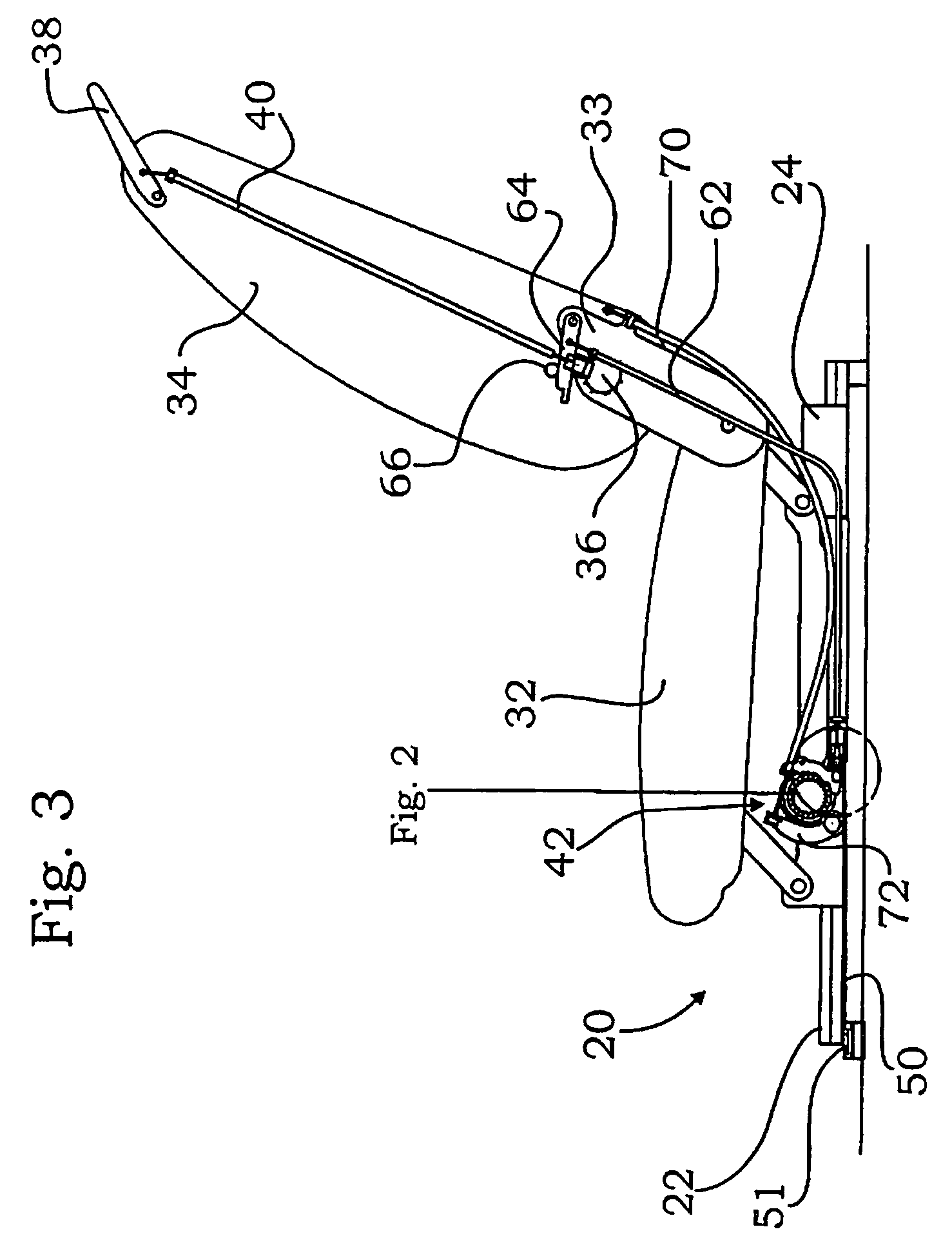
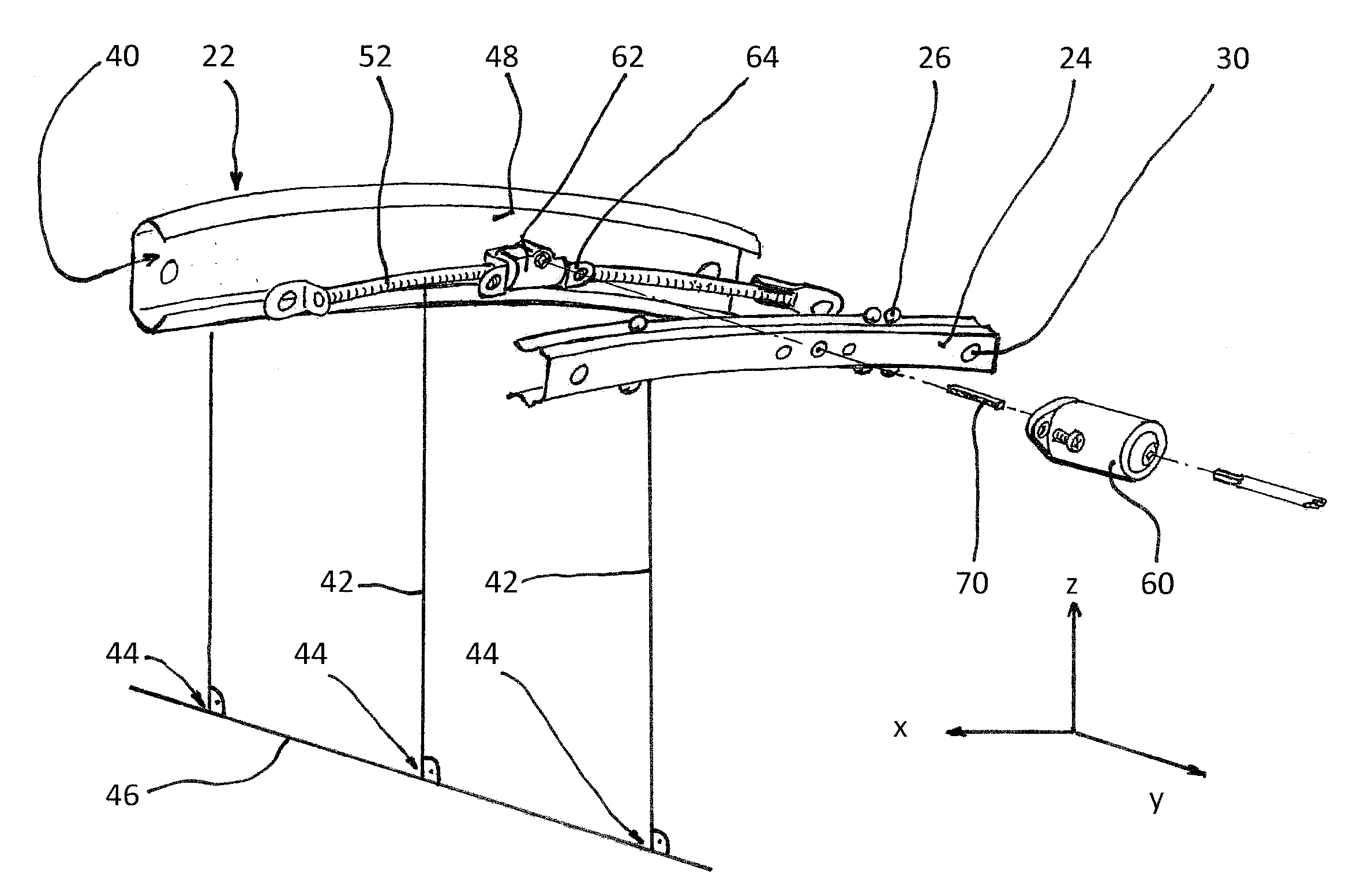
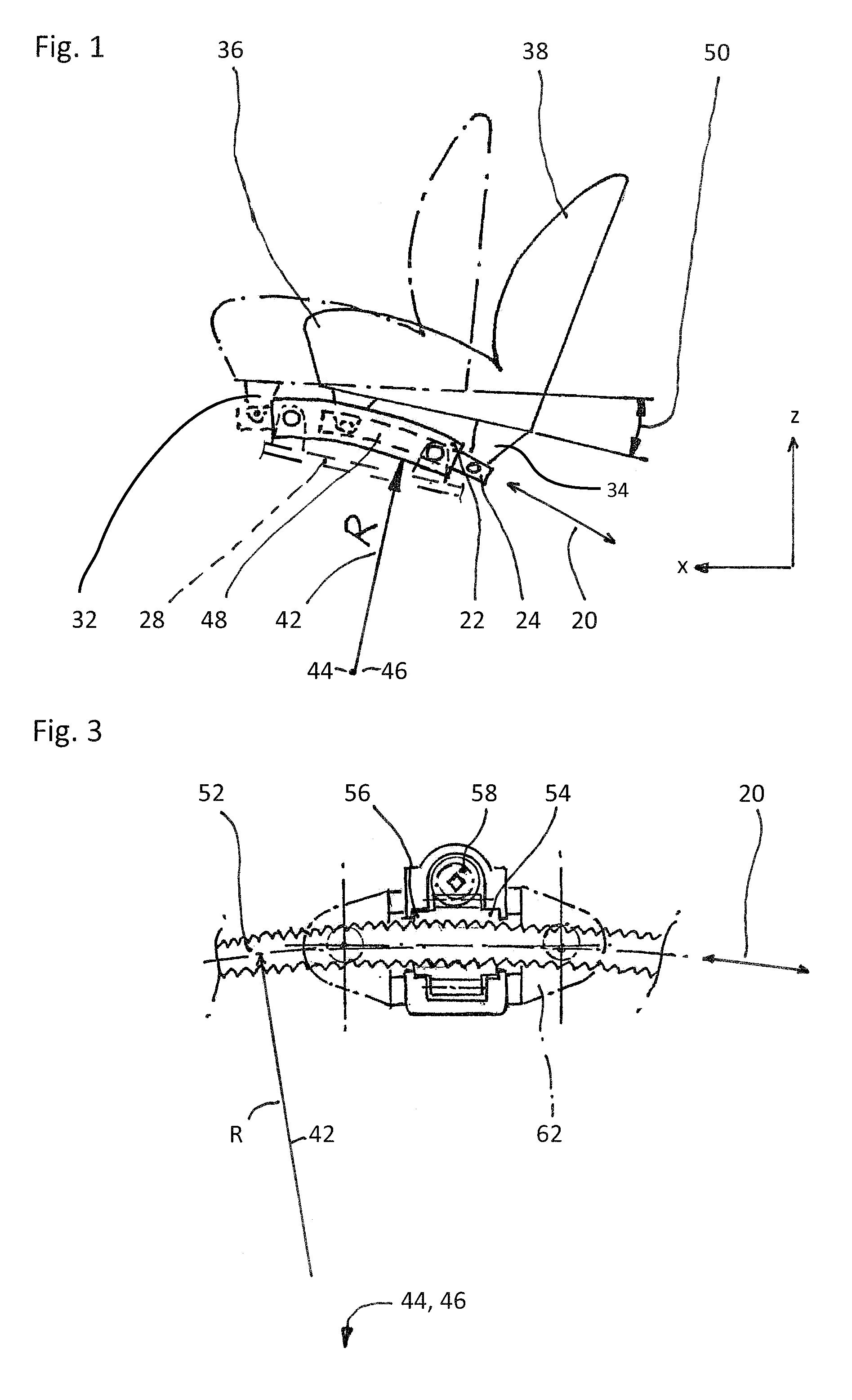
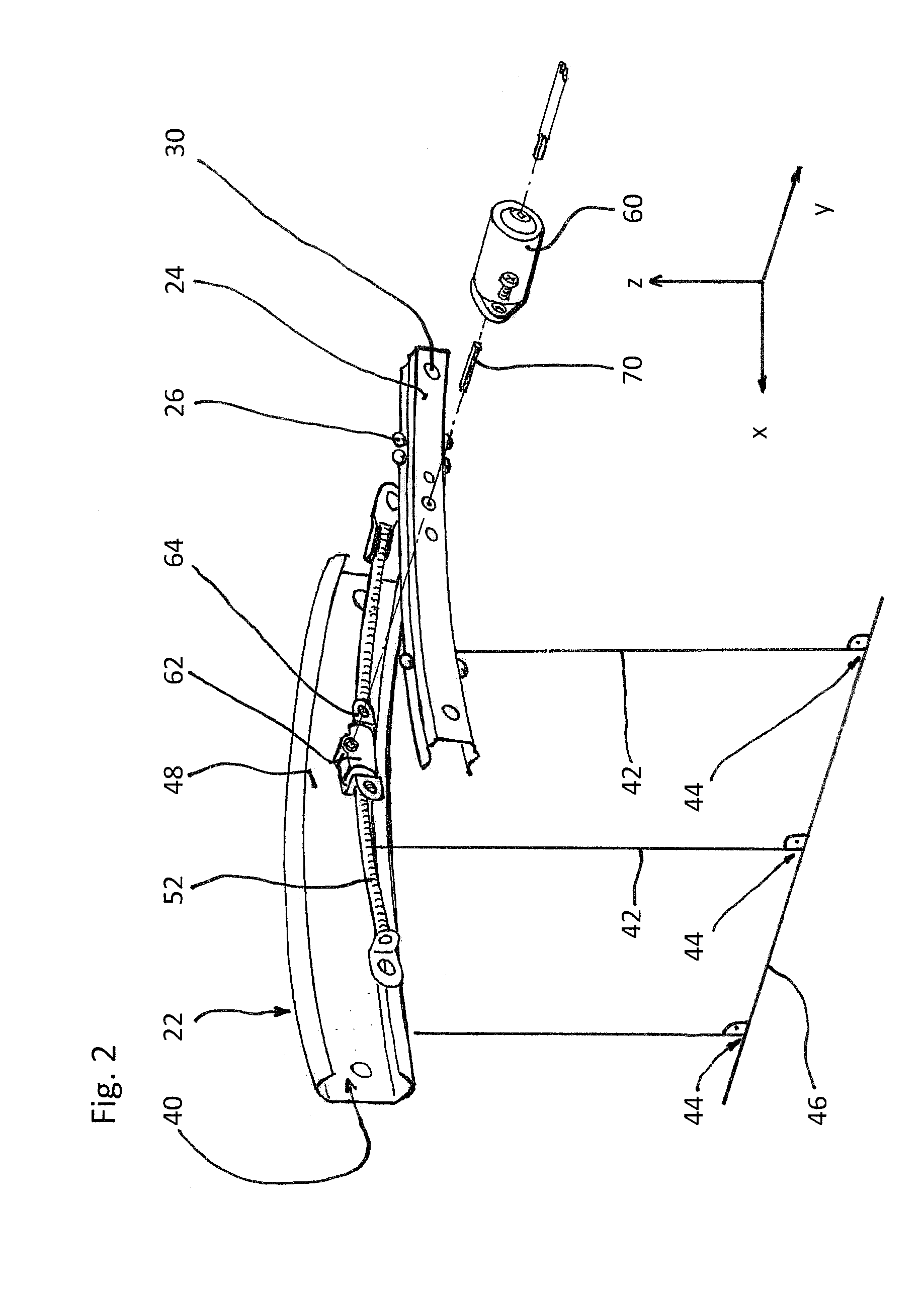
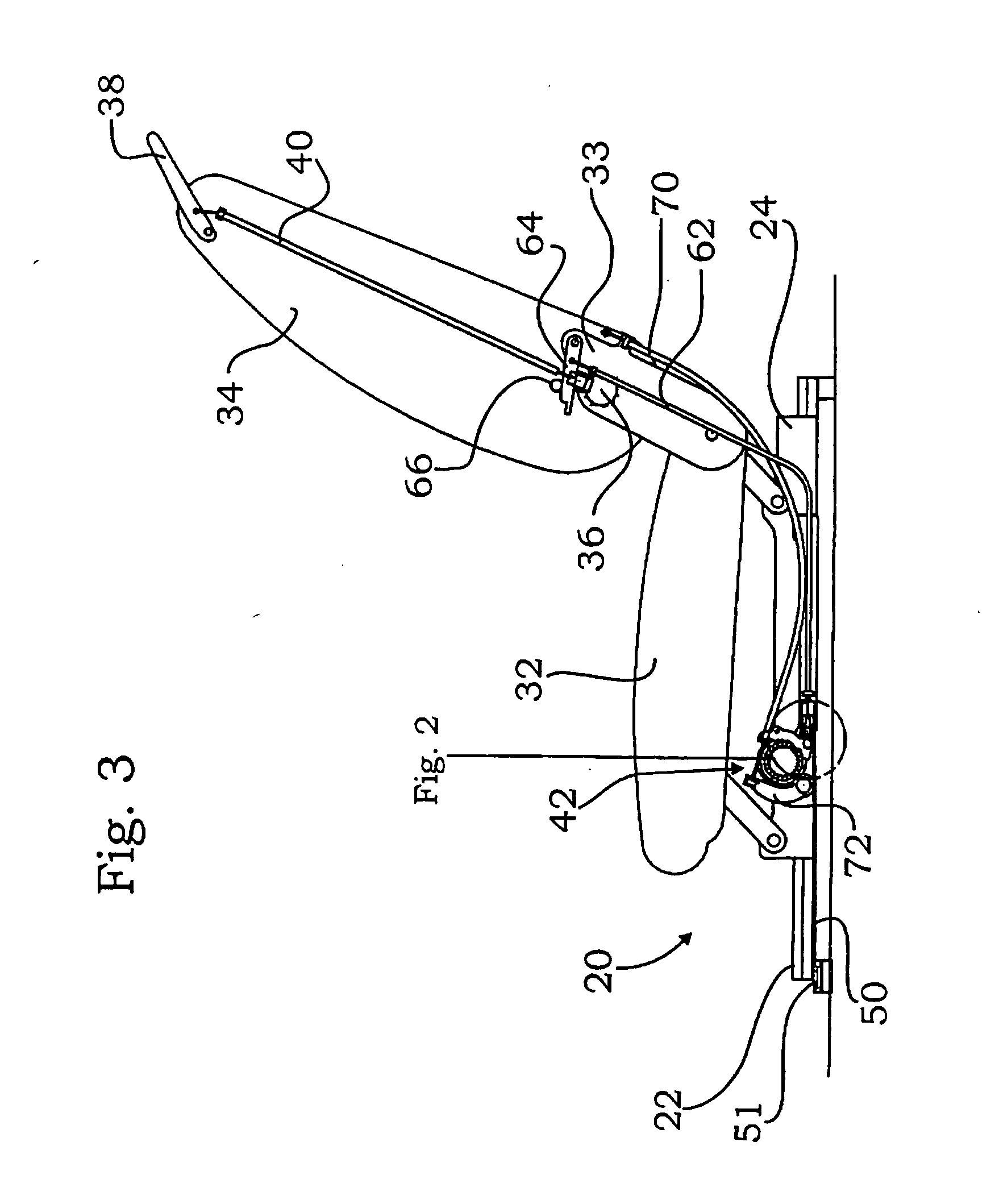
Rail guide for a longitudinal adjustment of a motor vehicle seat and method for producing such a rail guide
ActiveUS20140175249A1Big advantageSave componentStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentControl theoryMechanical engineering
A rail guide that has at least one rail pair consisting of a floor rail (22) and a seat rail (24). The seat rail (24) has means (30) for fastening a seat frame to be arranged above the rail pair. The rails can be moved relative to each other in a longitudinal direction along a movement path (20). The floor rail (22) and the seat rail (24) are curved by the same circular radius of curvature (42) that ranges between 1,500 and 3,000 mm, in particular between 1,800 and 2,500 mm. The center point of curvature (44) is on the side of the rail pair facing away from the seat frame. The rail guide is a longitudinal adjustment device having a stationary spindle (52) and an associated spindle nut (54) that is longitudinally movable thereon, the spindle (52) being curved at the same circular radius of curvature (42). Also disclosed is a suitable method for producing said curved rails by means of at least one stamping mold (68) or by means of bending strips (96).
Owner:KEIPER SEATING MECHANISMS CO LTD
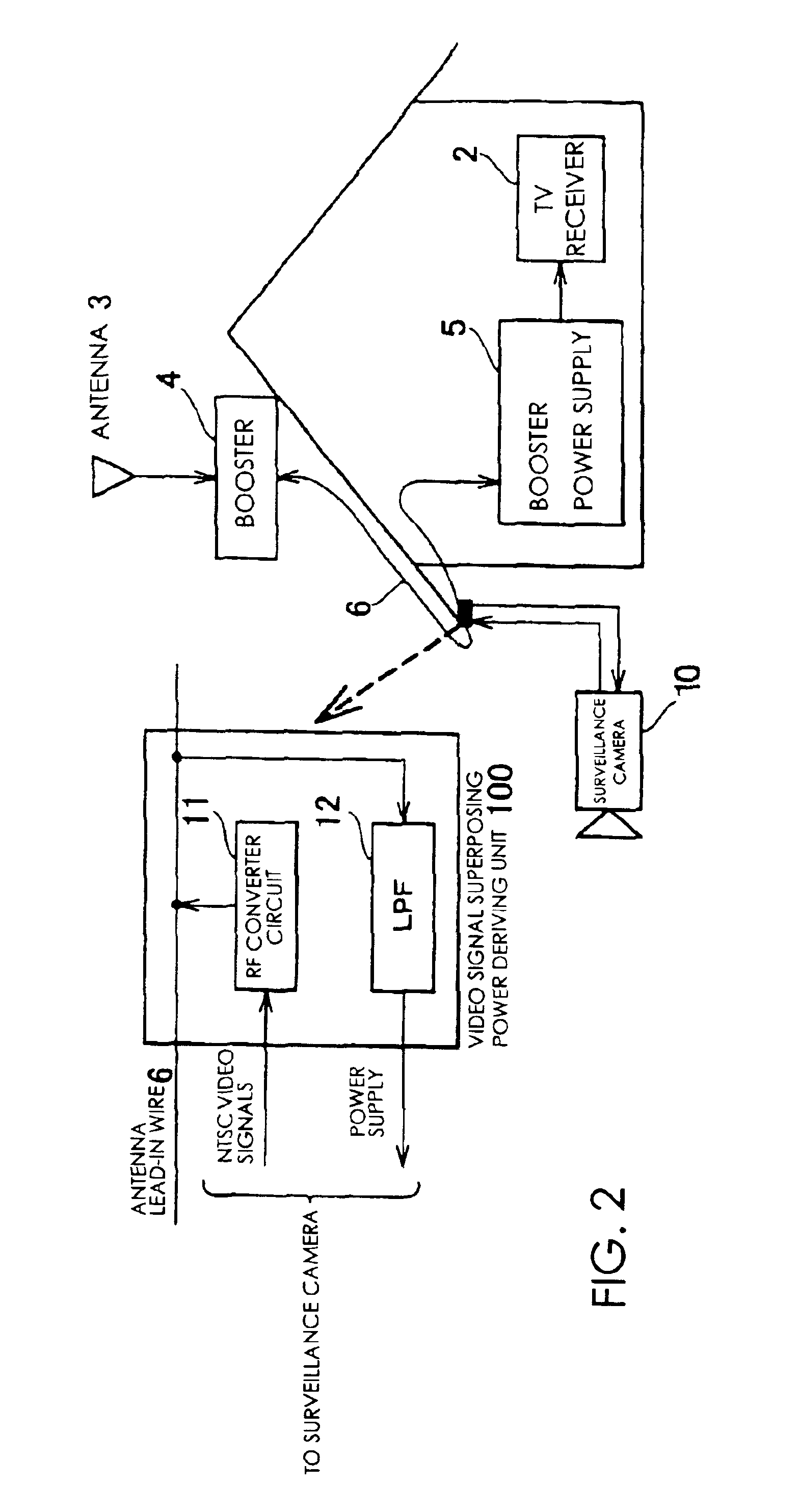
Transmitter for surveillance camera, and surveillance system
InactiveUS6940404B2Simplify wiring workSecurity functionality is enhancedMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelevision receiversRadio frequency signal
An RF converter circuit 11 that constitutes a video signal superposing / power deriving unit 100 converts video signals generated from images taken by a surveillance camera 10, which derives a direct current voltage as a driving power from an antenna lead-in wire 6 through a filter circuit (LPF circuit 12), to radio-frequency signals. The radio-frequency signals are transmitted through the antenna lead-in wire 6 to a television receiver 2. Images taken by the surveillance camera 1 can be viewed on the television receiver 2 only by selecting the channel assigned to the surveillance camera 1. Accordingly, the driving power for the surveillance camera 1 is not relied upon a solar battery or secondary batteries, and wiring work therefor may be simplified.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP
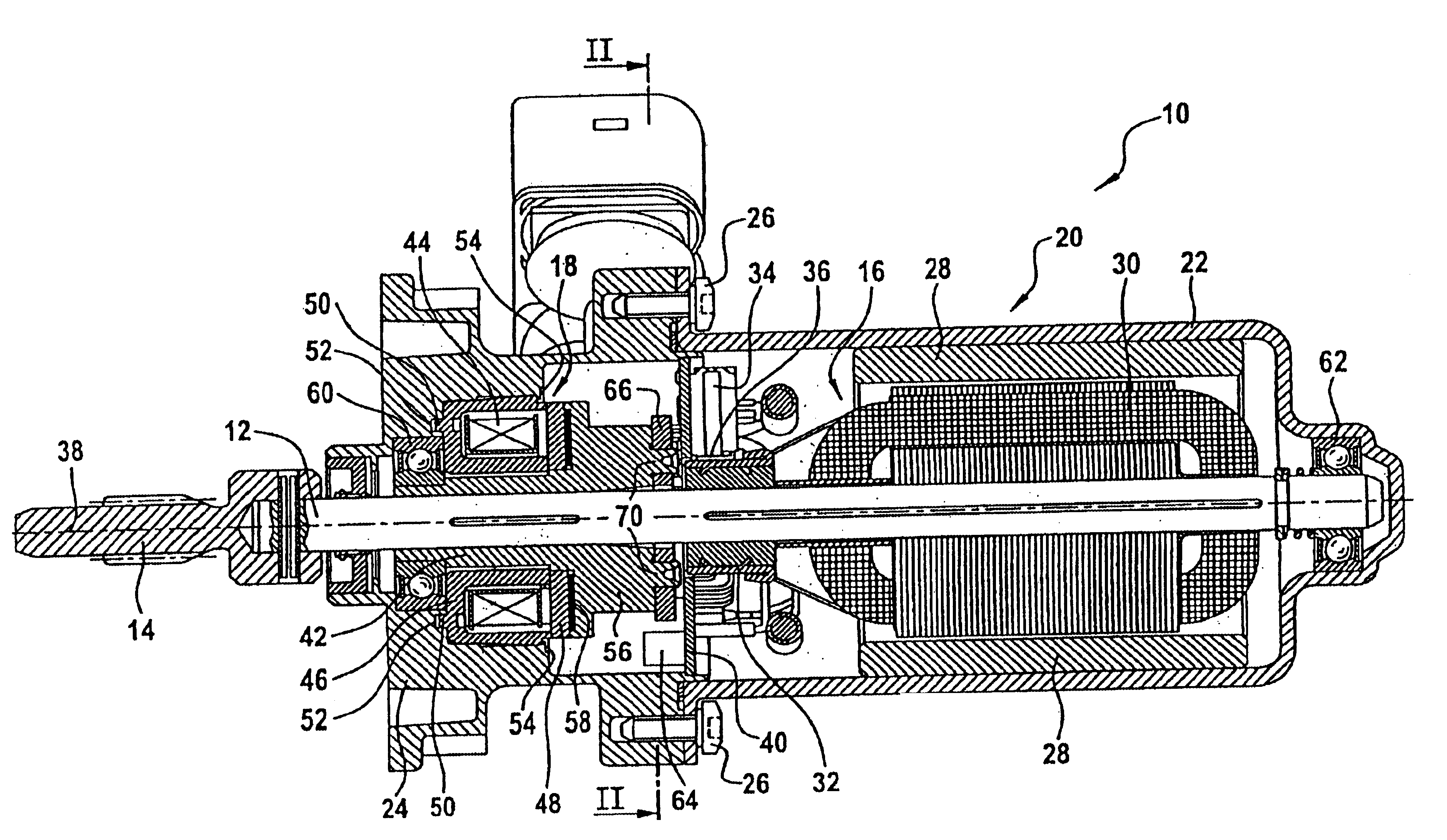
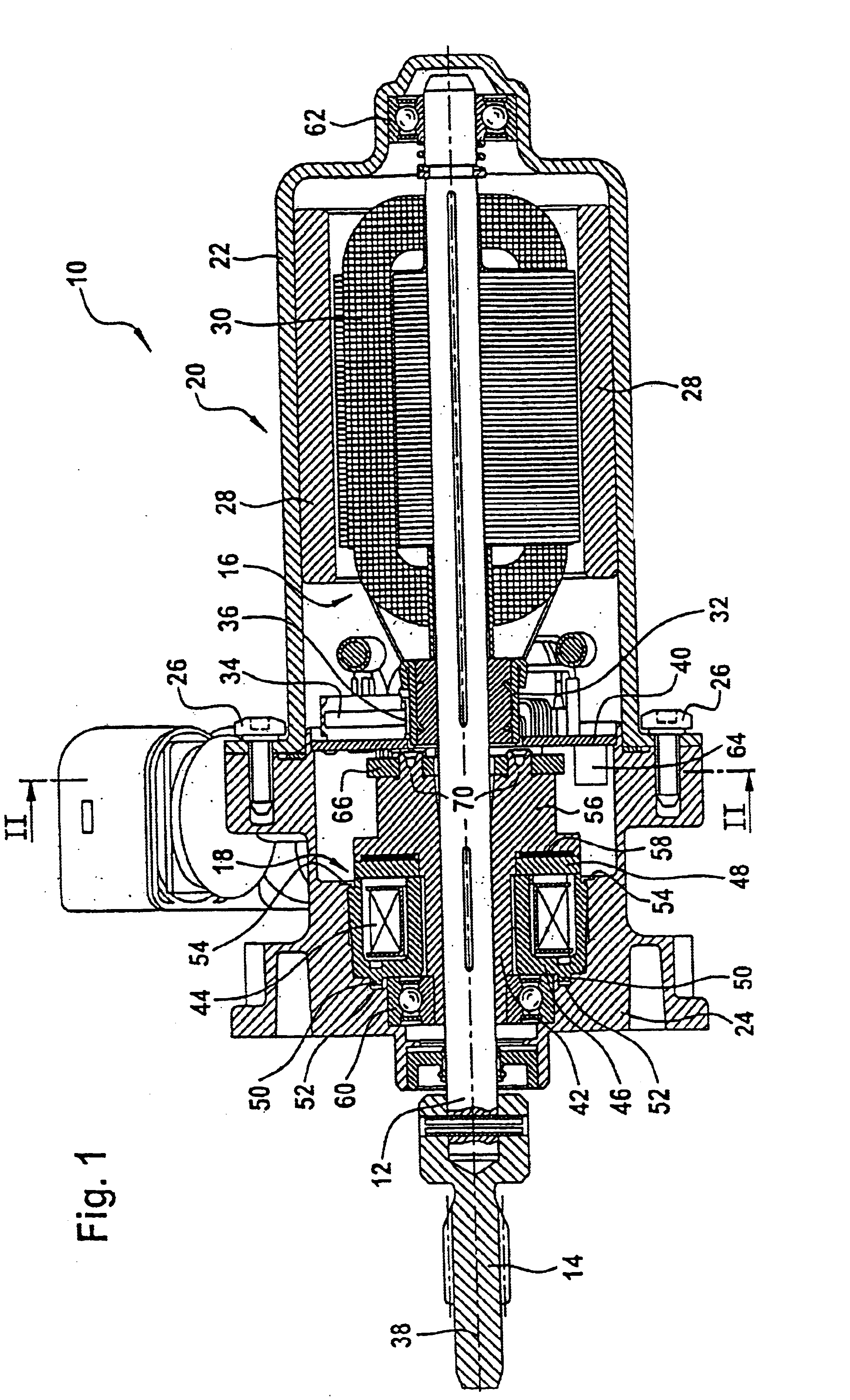
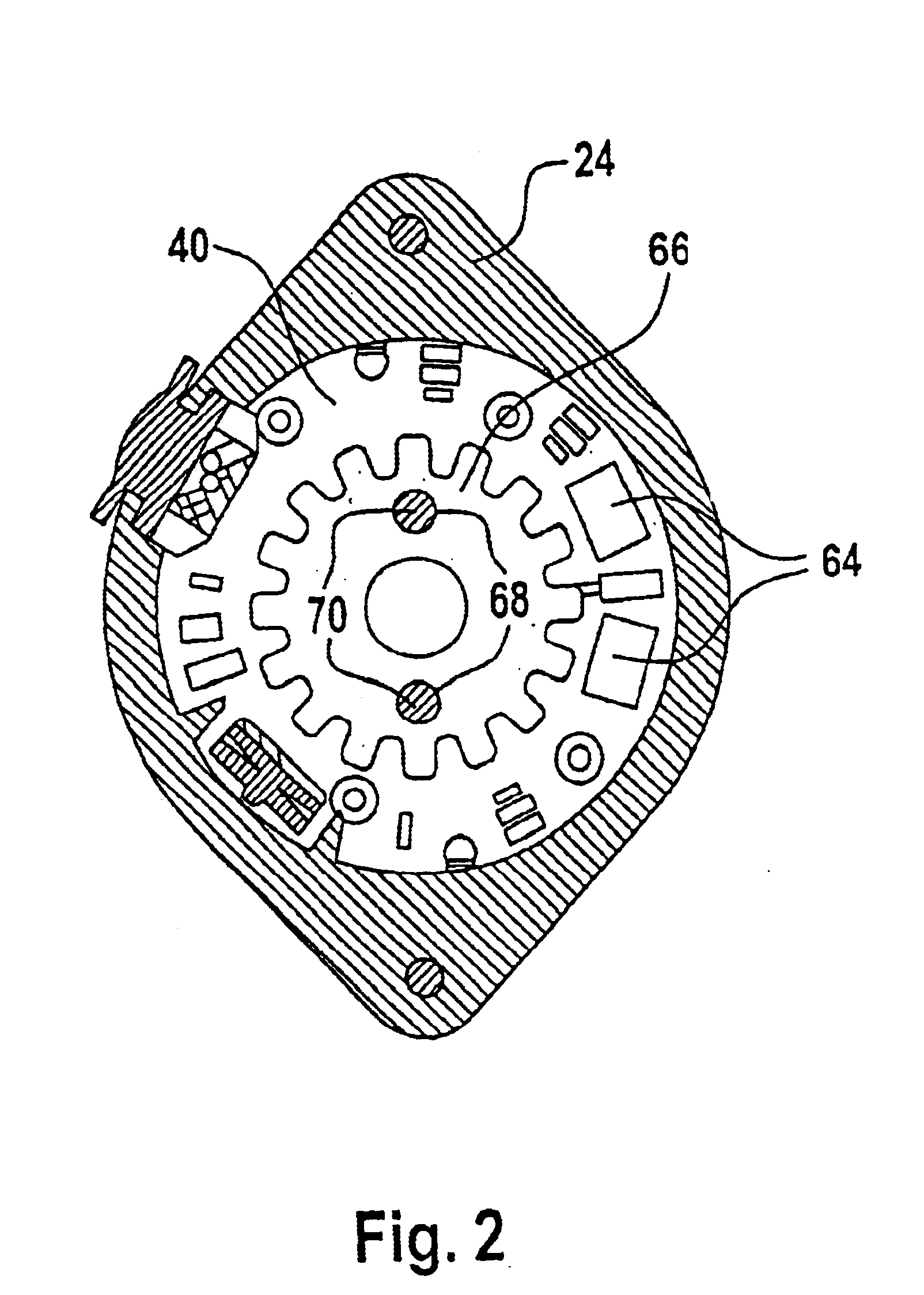
Actuating device, particularly for actuating locking differentials on vehicles
InactiveUS6879072B2Low production costSave componentStructural associationElectrically actuated clutchesAngle of rotationElectromagnetic brake
An actuating device, specifically for actuating locking differentials on vehicles, having an actuating shaft, a drive unit to drive the actuating shaft, where the drive unit comprises an armature core mounted to the actuating shaft so as not to rotate, and a commutator mounted to the actuating shaft so as not to rotate and / or with an electromagnetic brake unit to slow and / or stop the actuating shaft, where the brake unit includes a brake hub flange mounted on the armature so as not to rotate and having a single- or multi-piece housing tightly enclosing the drive unit and the brake unit, where the free end of the actuating shaft extends from the housing and with a sensor to measure the angle of rotation of the shaft, where the sensor unit includes at least one trigger wheel indirectly coupled to the shaft and at least one sensor scanning the trigger wheel position and coupled indirectly to the housing.
Owner:VALEO MOTOREN & AKTUATOREN
External Electrode Flourescent Lamp, Lighting Device, And Display Device
InactiveUS20080012498A1Save componentEasy to assembleSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
An external electrode fluorescent lamp has external electrodes at opposite ends. The portions provided with the external electrodes are bent so that their axes are orthogonal to the axis of a light emitting sections. A conventional external electrode fluorescent lamp is not bent in its portions provided with external electrodes. Since the external electrodes of the external electrodes fluorescent lamps serve concurrently as holding sections for the fluorescent lamps the axial length is made greater than the outer diameter so as to provide sufficient strength. The width of the frame section of the fluorescent lamp of the invention when mounted on a backlight unit is smaller than the width of the frame section of conventional fluorescent lamp. Therefore, the effective light emitting area of the backlight unit can be enlarged.
Owner:SHARP KK
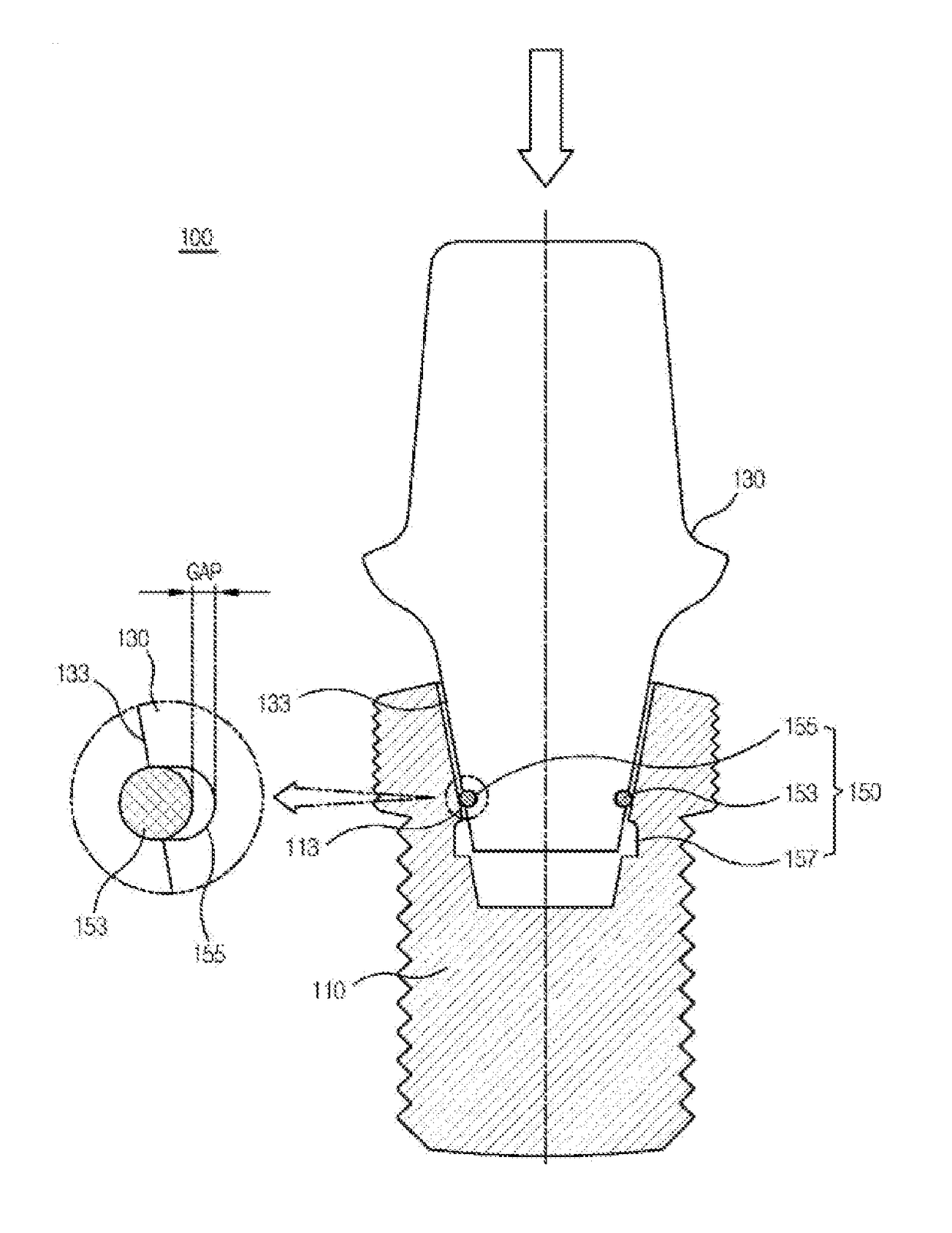
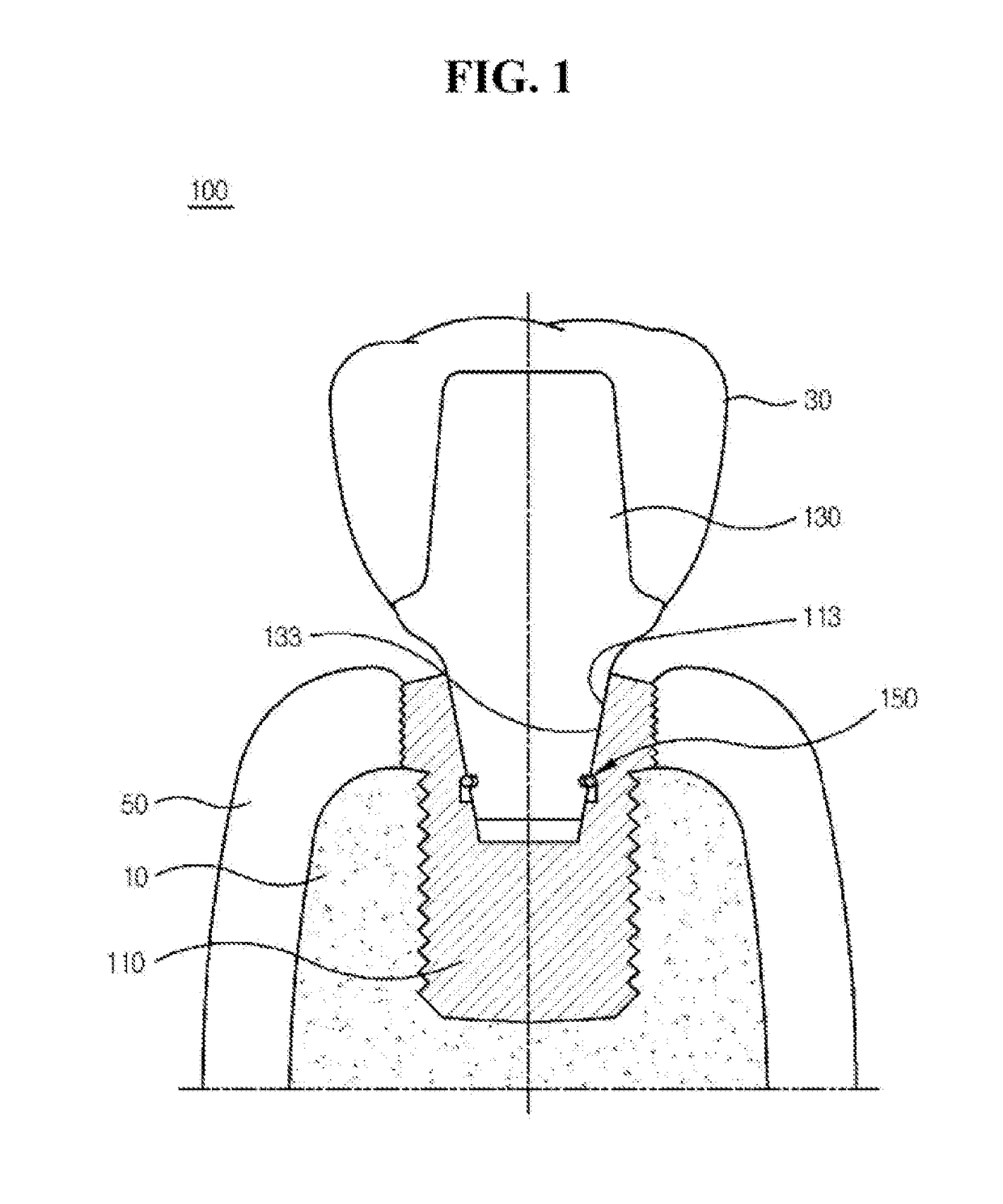
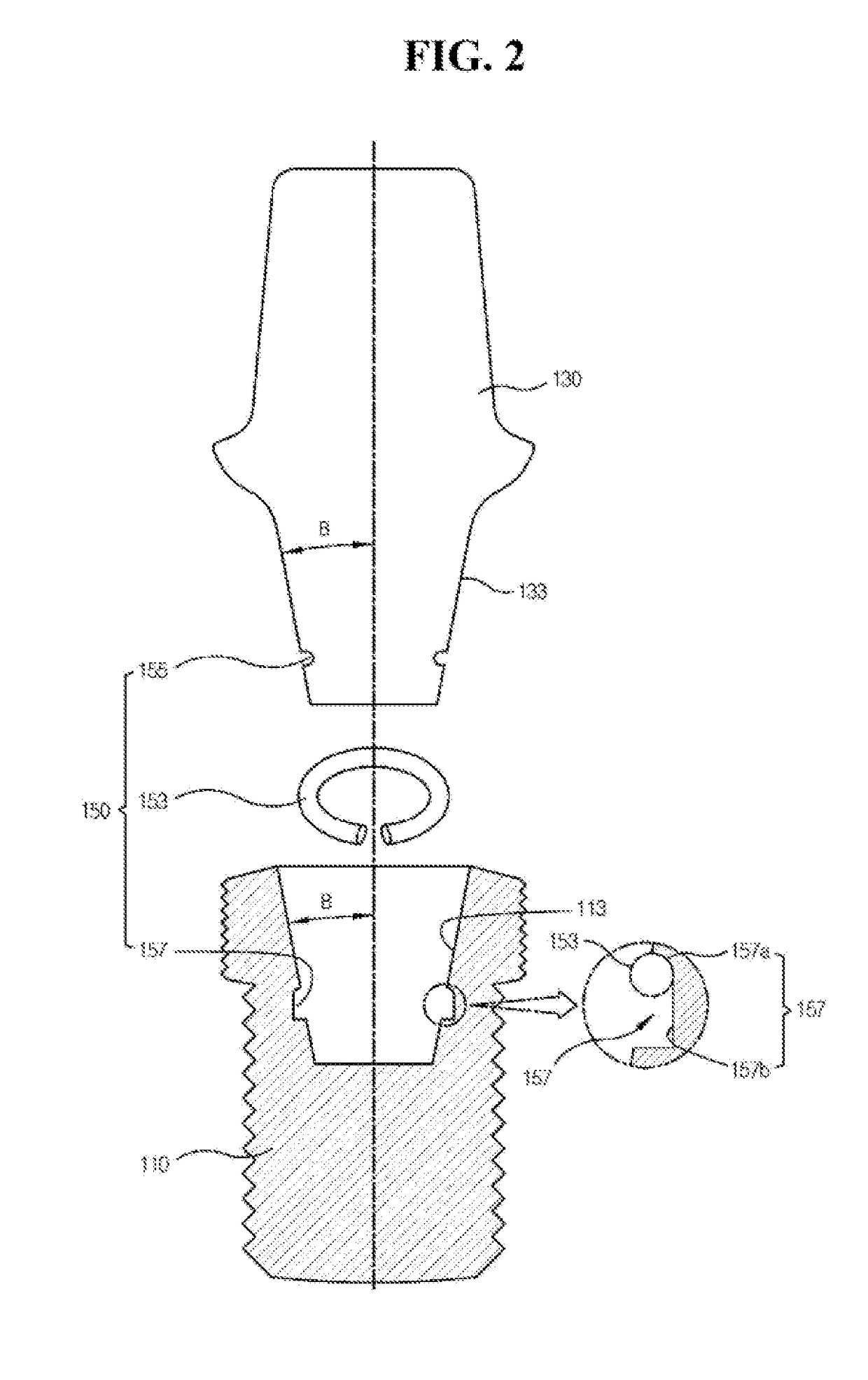
Easily retrievable implant-abutment device
The present invention relates to an implant-abutment comprising: a fixture, which is coupled to an alveolar bone and comprises on the inside thereof a female tapered part having a tapered shape; an abutment, which has one side comprising a male tapered part, which has a shape corresponding to the female tapered part so as to be coupled to the female tapered part in an engaging manner, and the other side having a prosthesis coupled thereto; and an elastic part provided between the female tapered part, and the male tapered part so as for the abutment to move between a locking position, in which the abutment stays coupled to the fixture and is inhibited from moving away from the alveolar bone, and a sinking position, in which the abutment moves and sinks toward the alveolar bone by the occlusal force of occluding teeth. Configured as such, the present invention allows slight movement under a predetermined external, force by the occlusal force of teeth while stably maintaining the state of being coupled to the fixture and allows the abutment to be separated and easily retrieved from the fixture, if necessary, by the application of an external force equal to or greater than a target coupling force whereby the fixture and abutment stay coupled.
Owner:ACRODENT
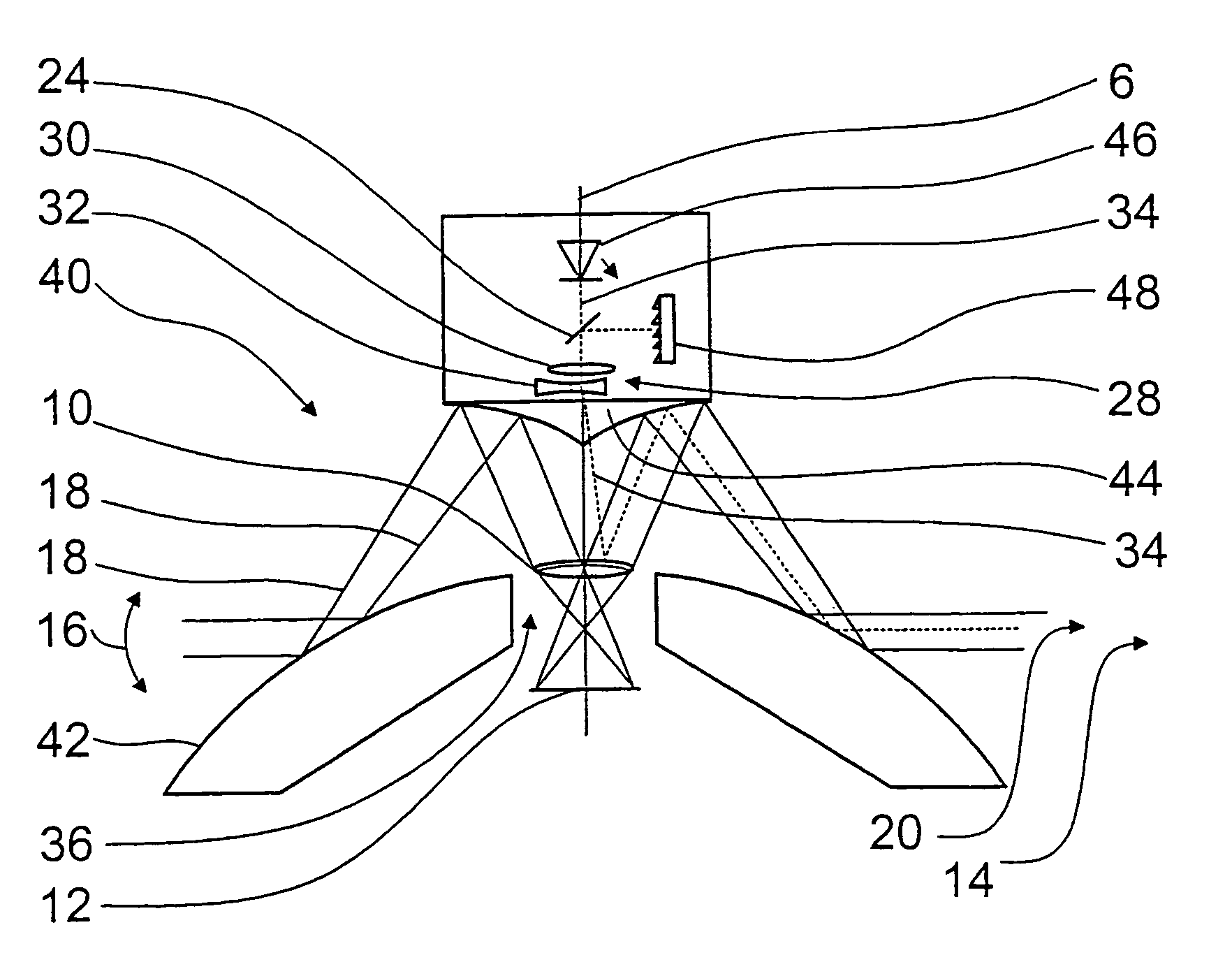
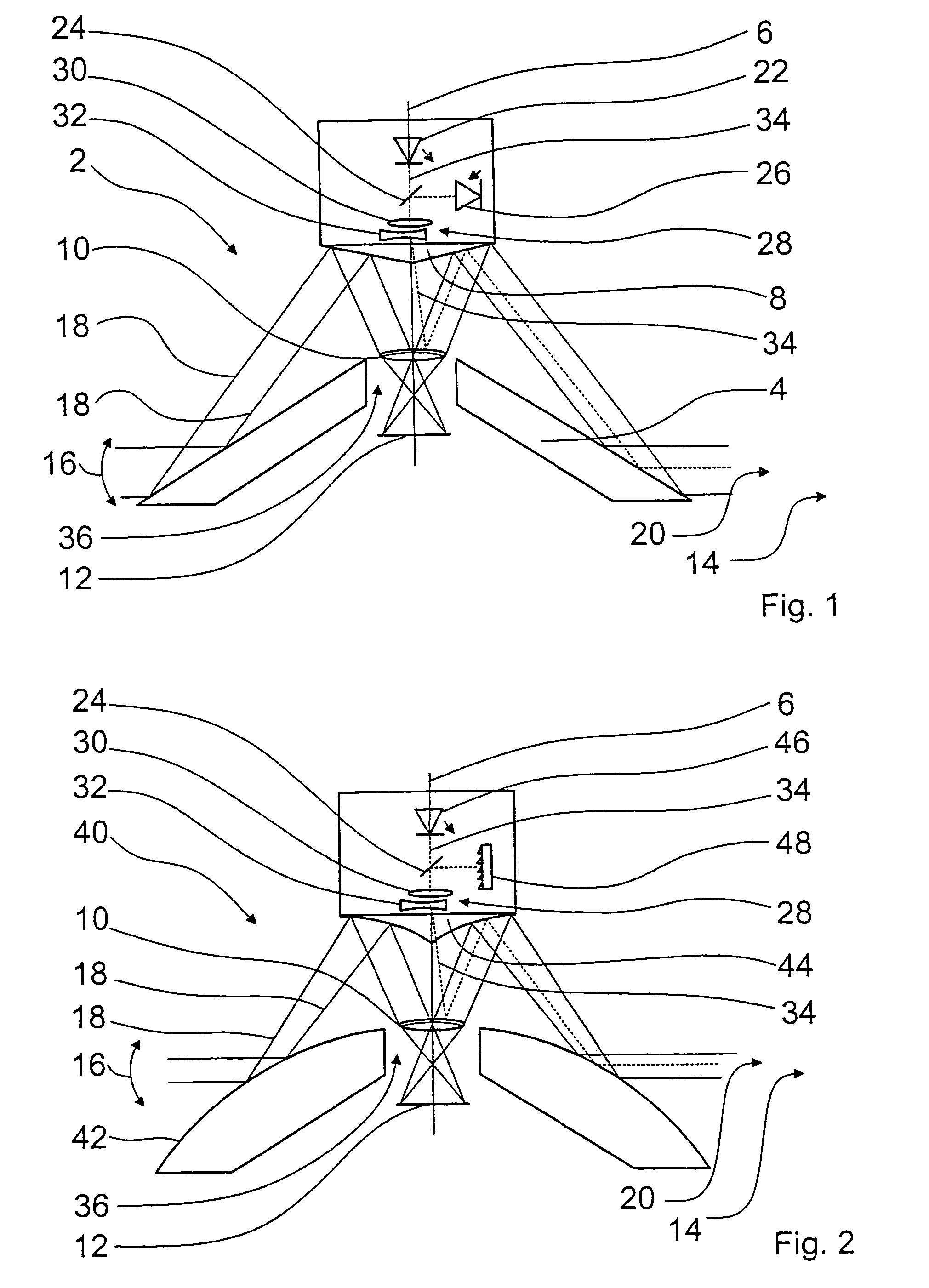
Camera system for monitoring a solid angle region and for detection of detailed information from the solid angle region
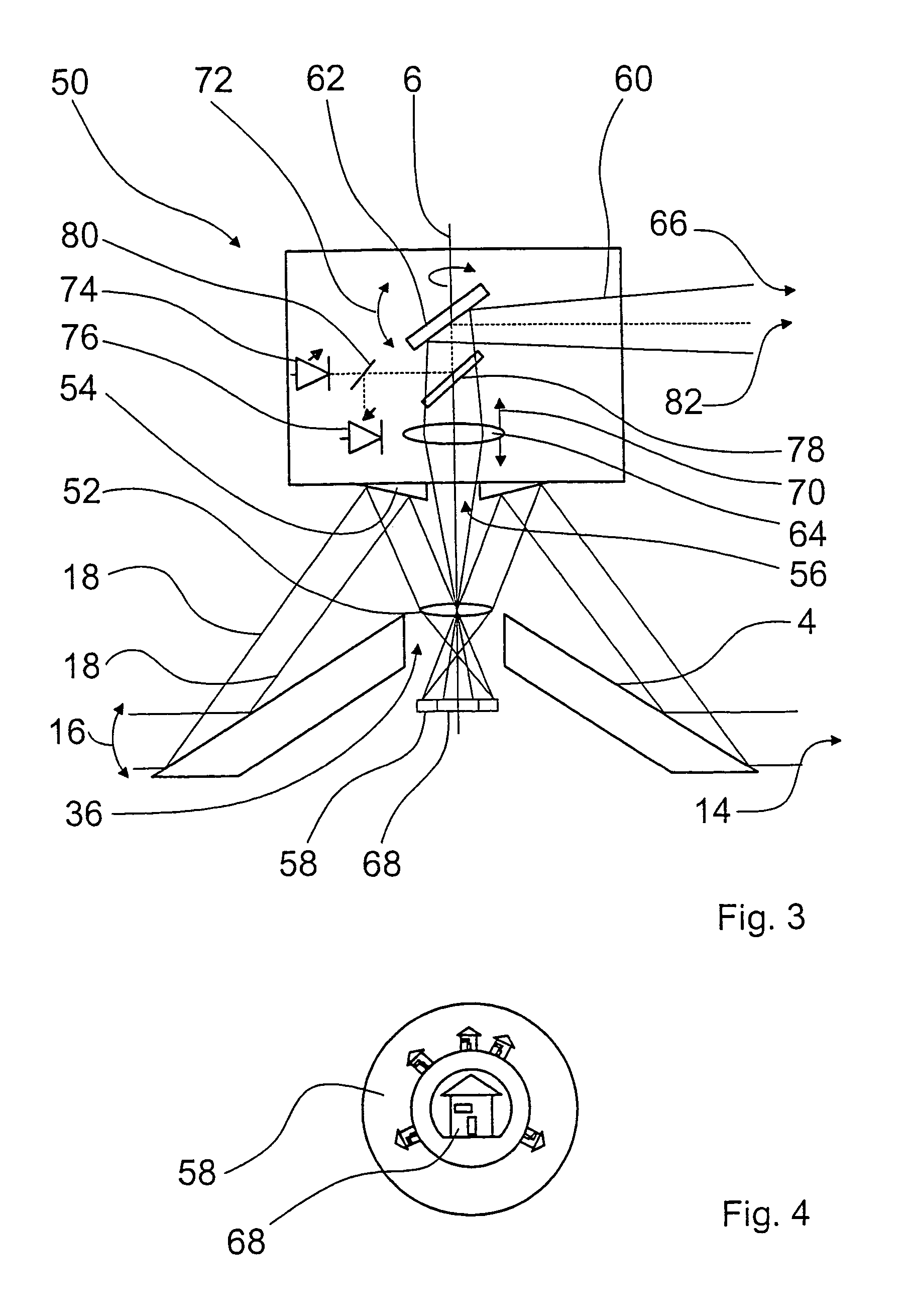
InactiveUS7400347B2Precise positioningSave componentTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsSolid angleOptics
A camera system (2, 40, 50) including a sensor (12, 58) and a first optical system which includes a convex mirror (4, 42) and through which the image of a solid angle region (14) is producible on the sensor (12, 58) by way of a first beam path (18). In order, in addition to producing an image of a large solid angle region (14), to permit scanning or detailed representation of a smaller partial region (20, 66, 82) of the solid angle region (14), the camera system (2, 40, 50) includes a second optical system through which a partial region (20, 66, 82) of the solid angle region (14) is detectable by way of a second beam path (34, 60) on a detail sensor (68), wherein the detail region (20, 66, 82) is selectable by an optical element (28) which is movable relative to the sensors (12, 58, 68).
Owner:METHYIGENE +1
Backlight module and liquid crystal display including the same
ActiveUS20150212257A1Narrow frameImprove cooling effectMechanical apparatusLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
The present disclosure relates to a backlight module and a liquid crystal display using the backlight module. The backlight module comprises an outer frame, a glue frame, a bending heat dissipating plate, and a light guide plate all amounted within the outer frame, a light source lamp facing the light guide plate being arranged on the side wall of the heat dissipating plate at the light-incoming side of the light guide plate. An inserting port is formed on the glue frame, a first positioning hole corresponding to the inserting port is formed on the side wall of the heat dissipating plate at the light-incoming side of the light guide plate, and a second positioning hole corresponding to the first positioning hole is formed on the outer frame. The portion of the outer frame around the second positioning hole is depressed inwards and extends into the inserting port to position the glue frame. The outer frame, the glue frame, and the heat dissipating plate are fixed together by a fixing bolt passing through the first positioning hole and the second positioning hole. The backlight module according to the present disclosure is able to greatly narrow the frame of the liquid crystal display without causing other problems to the liquid crystal display.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Milling Machine and Blank for a Dental Component
ActiveUS20170319303A1Reduce productionReduce failureSleeve/socket jointsTooth crownsAbutmentMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a milling machine for producing a dental component, such as a crown or an abutment for example, from a blank. The milling machine includes a stop and a holder for the blank. The invention is characterized in that the holder is designed such that the holder can be surrounded by a mounting, which surrounds the holder, of the blank, and the surrounding mounting of the blank can be brought into contact with the stop for positioning purposes. The invention further relates to a corresponding blank.
Owner:AMANN GIRRBACH
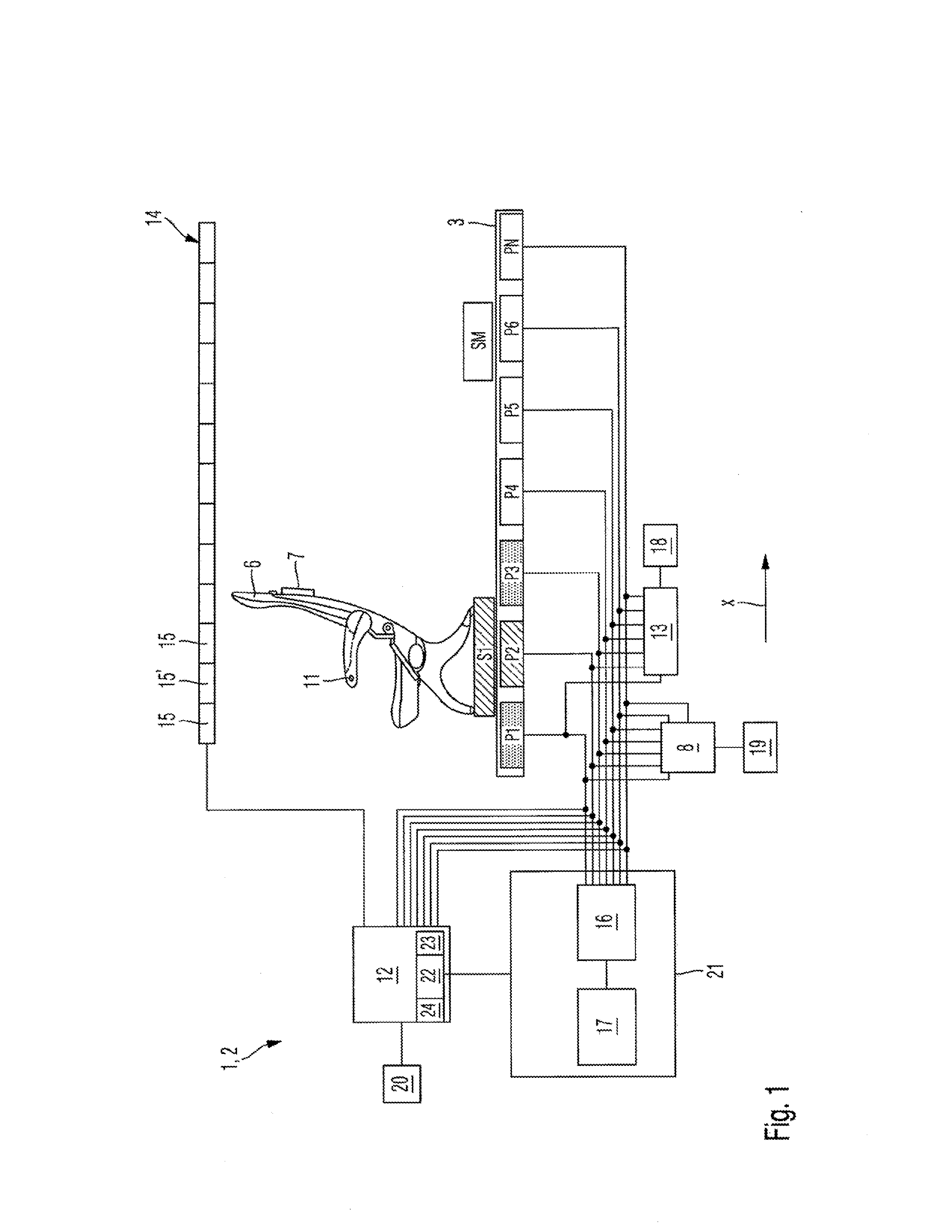
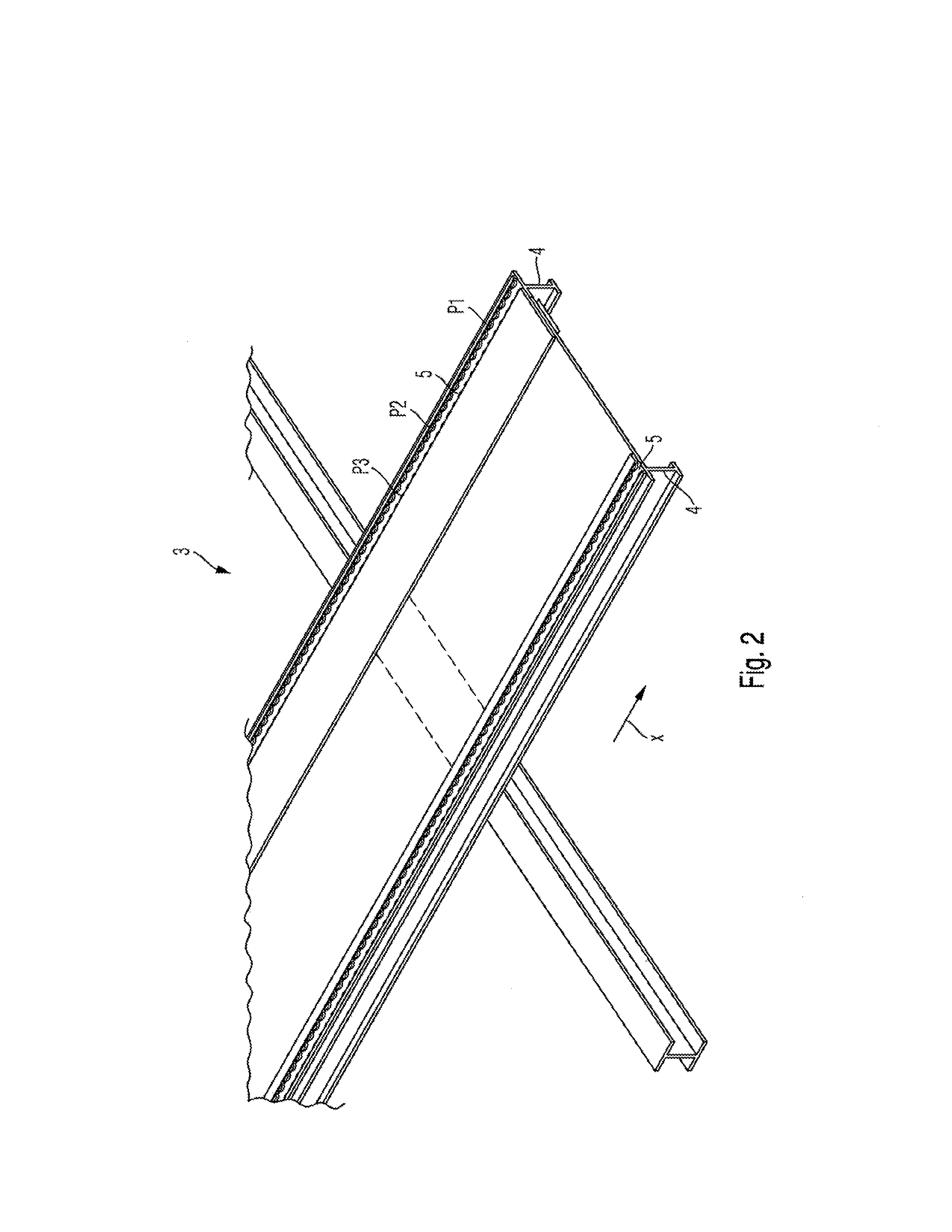
System, aircraft or spacecraft, and method for measuring a current position of a second vehicle part relative to a first vehicle part
ActiveUS20130176019A1Work lessSave componentSeating arrangementsUsing electrical meansFlight vehicleEngineering
An arrangement for transmitting data and / or power between a chassis and a seat that is movably disposed on said chassis by means of a guide rail. Several primary iron half-cores that support at least one primary winding are arranged in a fixed manner within the guide rail while at least one secondary iron half-core comprising at least one secondary winding is placed on the seat. The primary half-cores are disposed within the guide rail in such a way that at least one primary and one secondary iron half-core are positioned relative to each other so as to transmit data and / or power.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Forwardly movable vehicle seat with an underframe and two pairs of rails
Owner:ADIENT US LLC
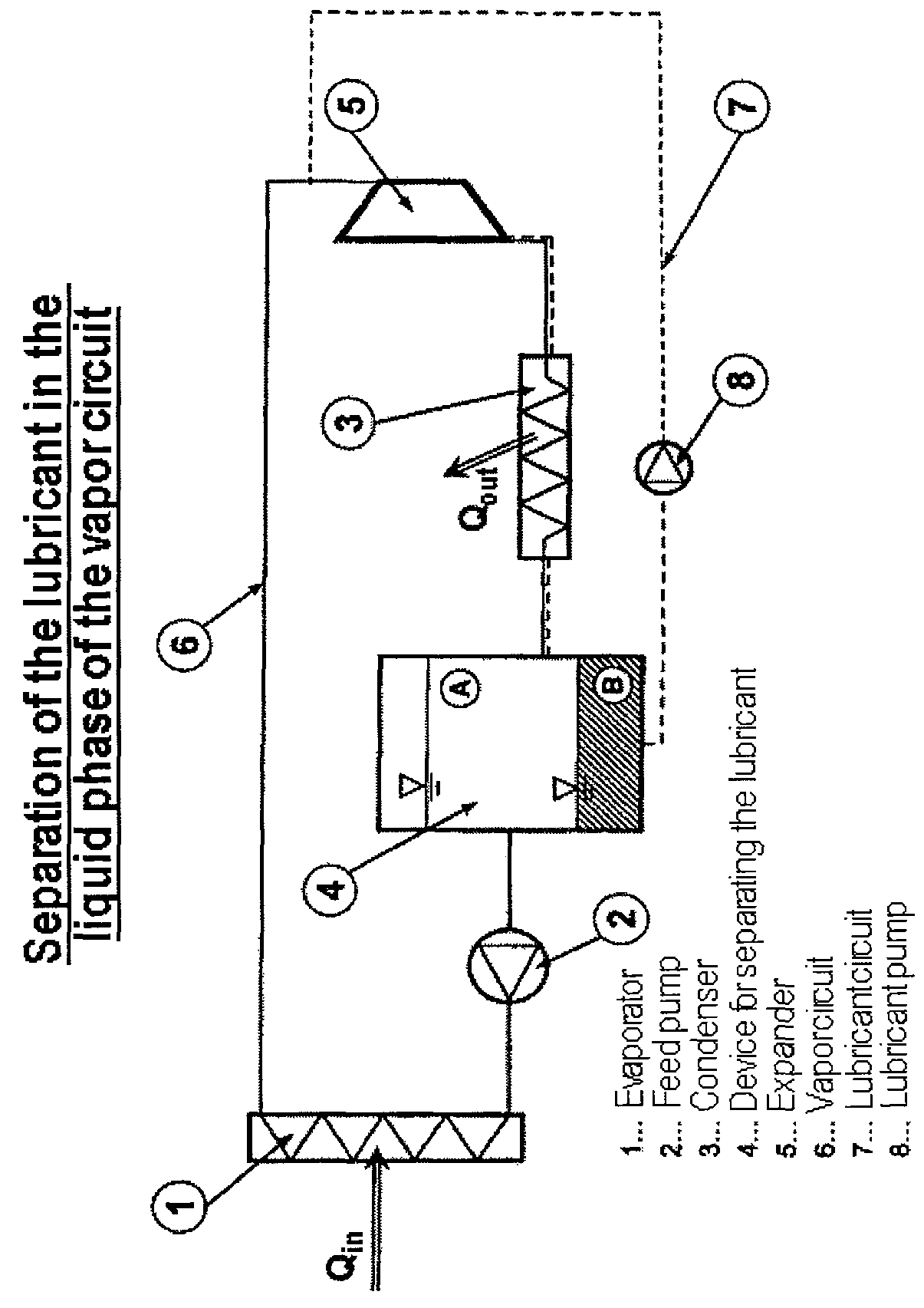
Method and apparatus for operating a steam cycle process with a lubricated expander
ActiveUS9382816B2Highly effectiveMaintain good propertiesSteam engine plantsLubricant compositionCyclic processEvaporation
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method for operating a steam cycle process performed in an apparatus having an evaporator or steam generator for the evaporation of a liquid working medium and an expander, which is lubricated by a lubricant, for the performance of mechanical work. The method comprises a) supplying the liquid working medium to the evaporator, in which it evaporates and is fed to the expander in the form of steam; b) supplying an ionic liquid, which at room temperature forms two liquid phases with the liquid working medium, to the expander as a lubricant; and c) separating the ionic liquid forming the lubricant for the expander from the working medium upstream of the evaporator.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com