Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1059results about "Tooth crowns" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
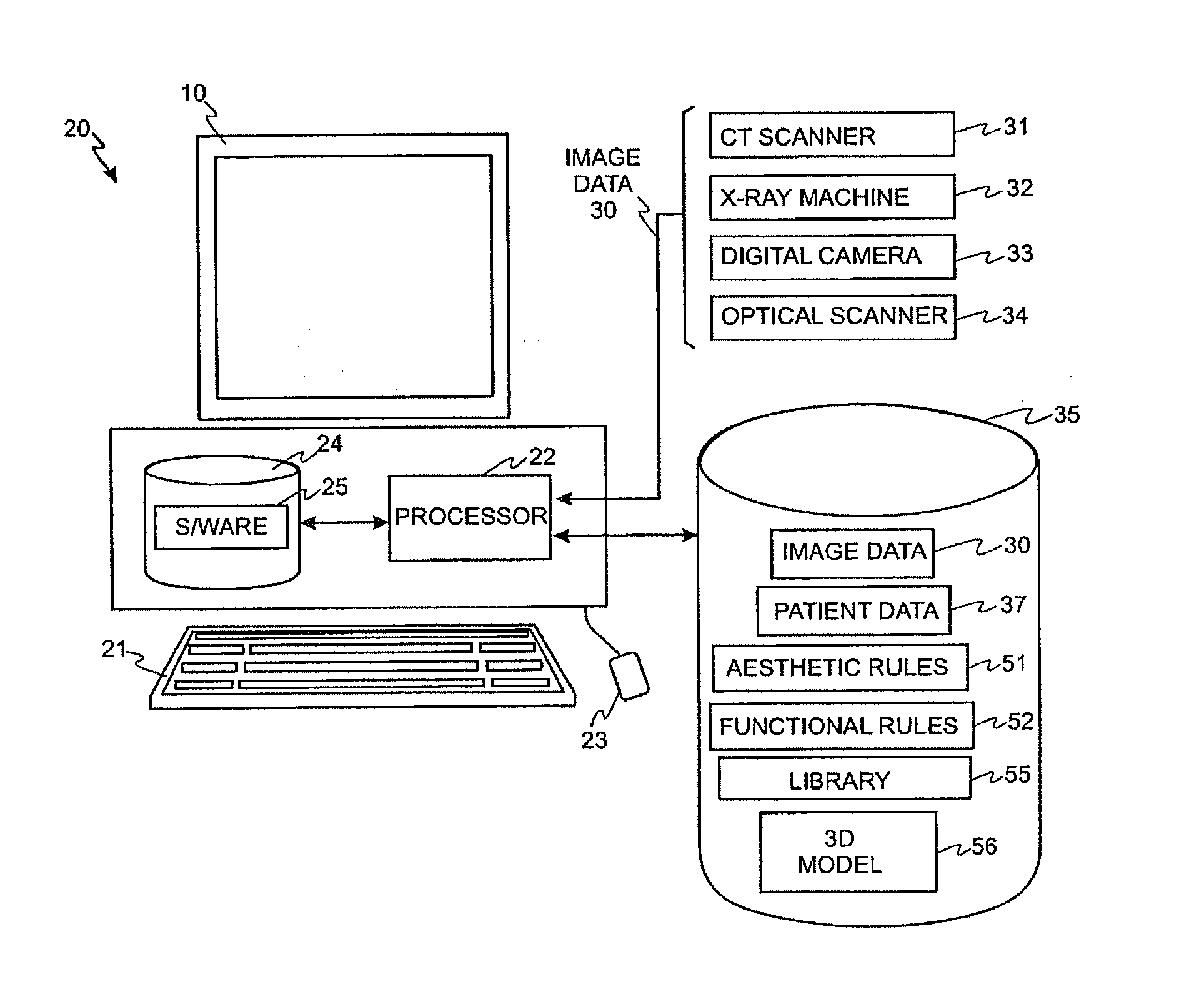
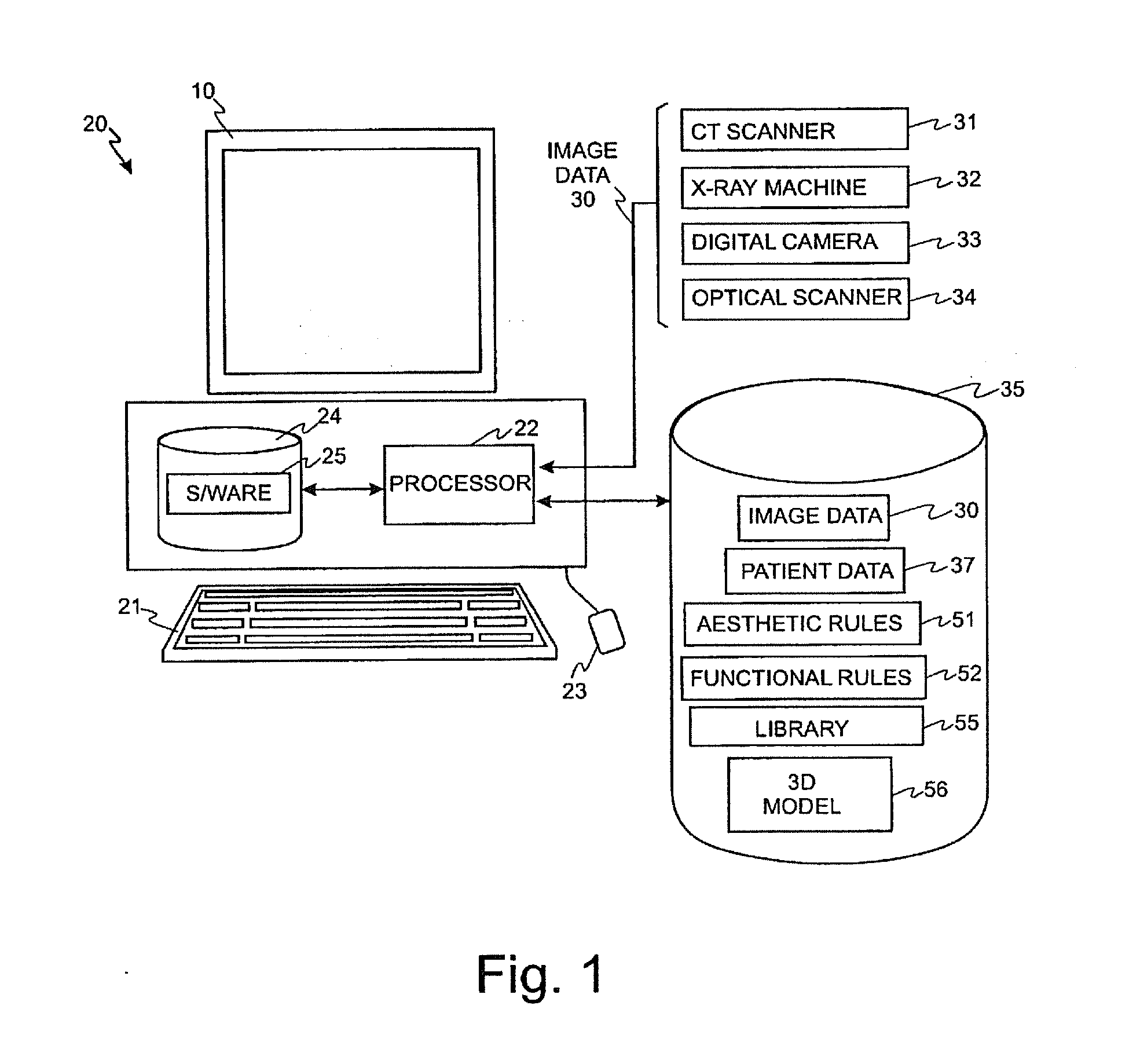
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
InactiveUS20050023710A1Improve bindingImpression capsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceFree form
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
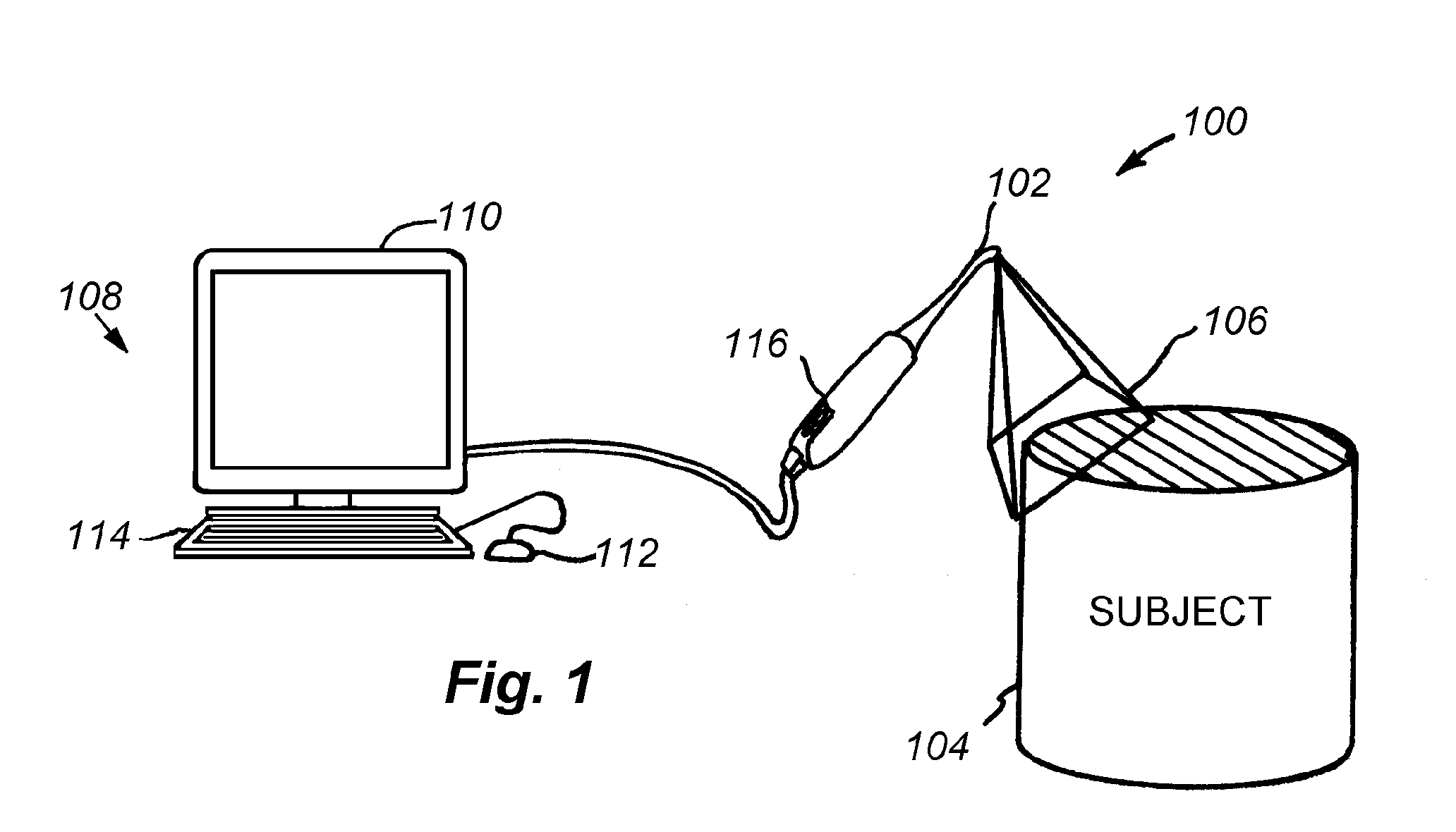
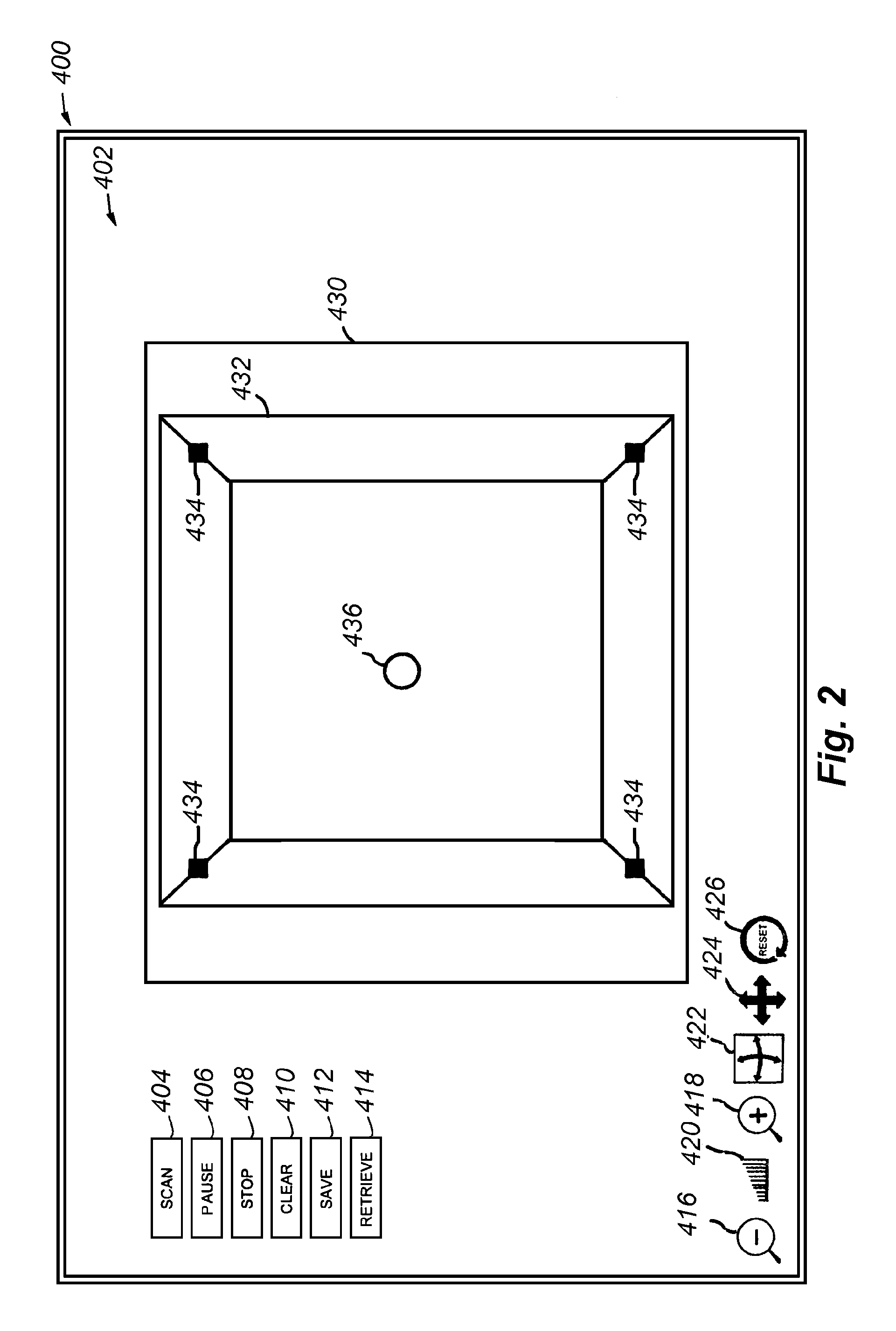
Visual feedback of 3D scan parameters
ActiveUS20070172112A1Impression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapies3d scanningVisual perception
The systems and methods disclosed herein provide visual feedback concerning one or more scanning parameters to a user during acquisition of a three dimensional scan.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
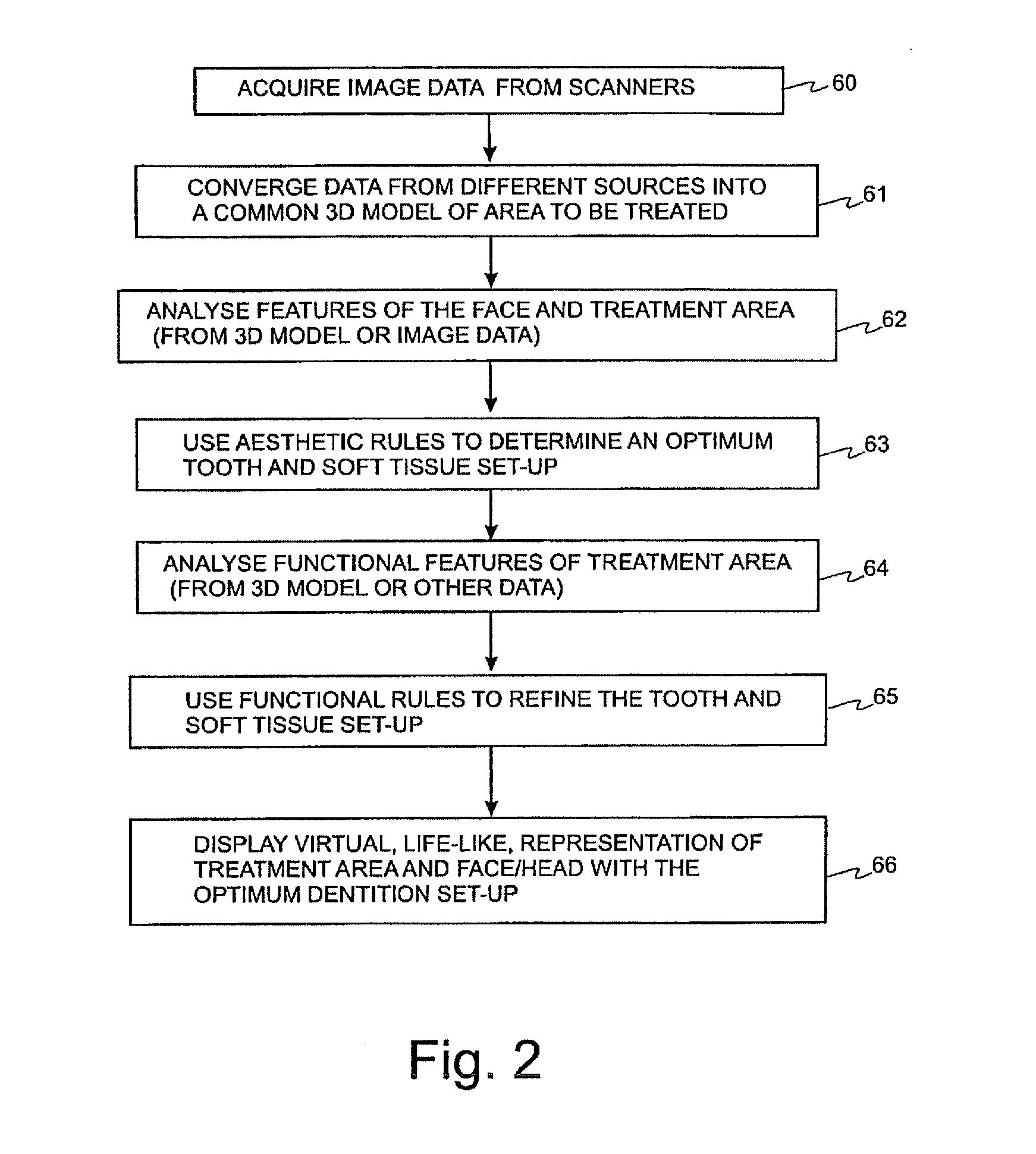
Computer-assisted creation of a custom tooth set-up using facial analysis
A method for automatic, or semi-automatic, planning of dental treatment for a patient comprises: (a) obtaining data about an area which is to be treated and data about a face of a patient; (b) performing a computer-assisted analysis of the data to determine properties of at least the face of the patient; (c) creating a modified tooth set-up using a set of stored rules which make use of the determined facial properties. A three-dimensional representation simulates the appearance of the modified tooth set-up and the patient's face surrounding the treatment area. The method also determines properties of existing teeth and creates a modified tooth set-up which is also based on the existing teeth of the patient. The method can be implemented as software running on a workstation.
Owner:DENTSPLY IMPLANTS NV
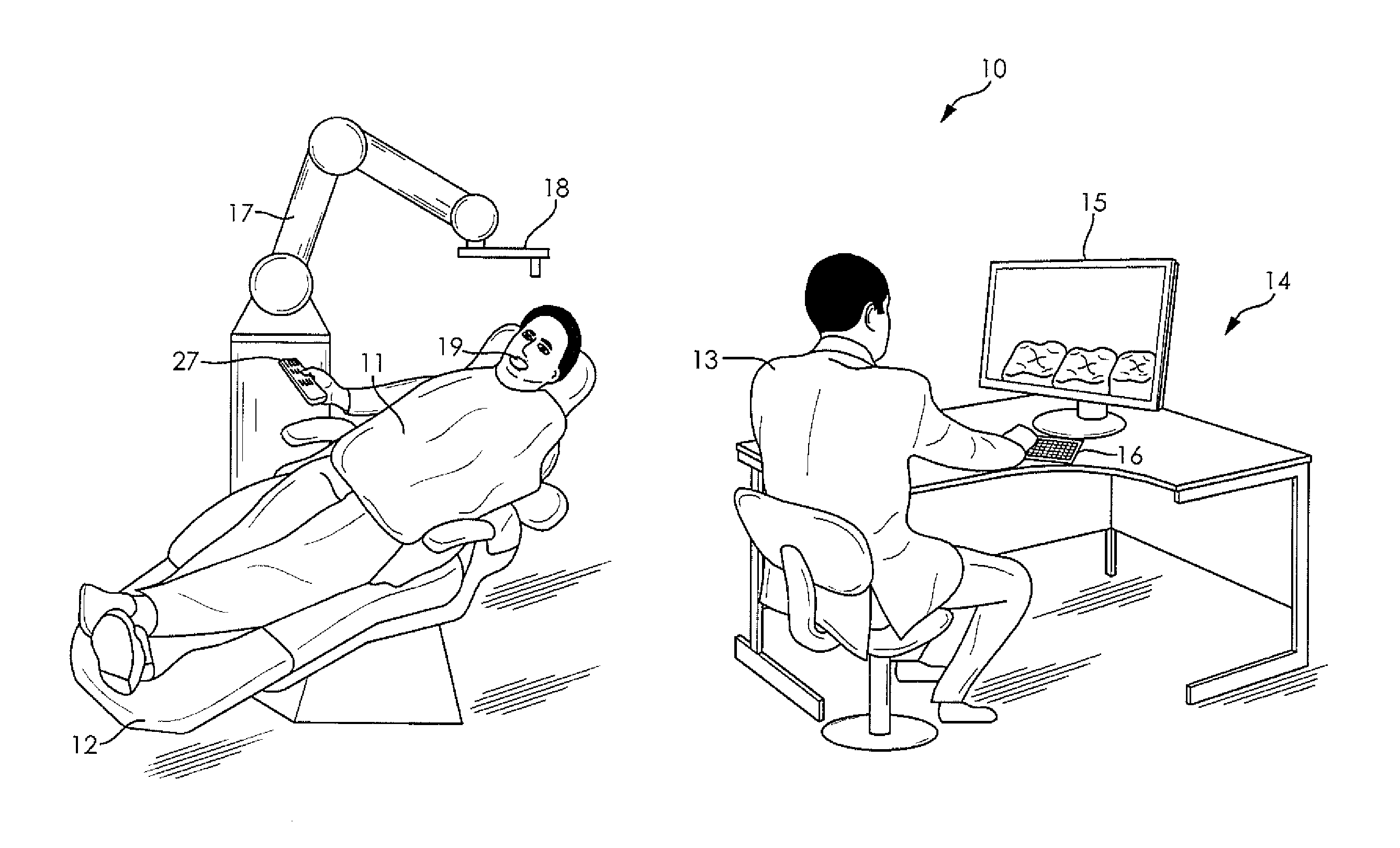
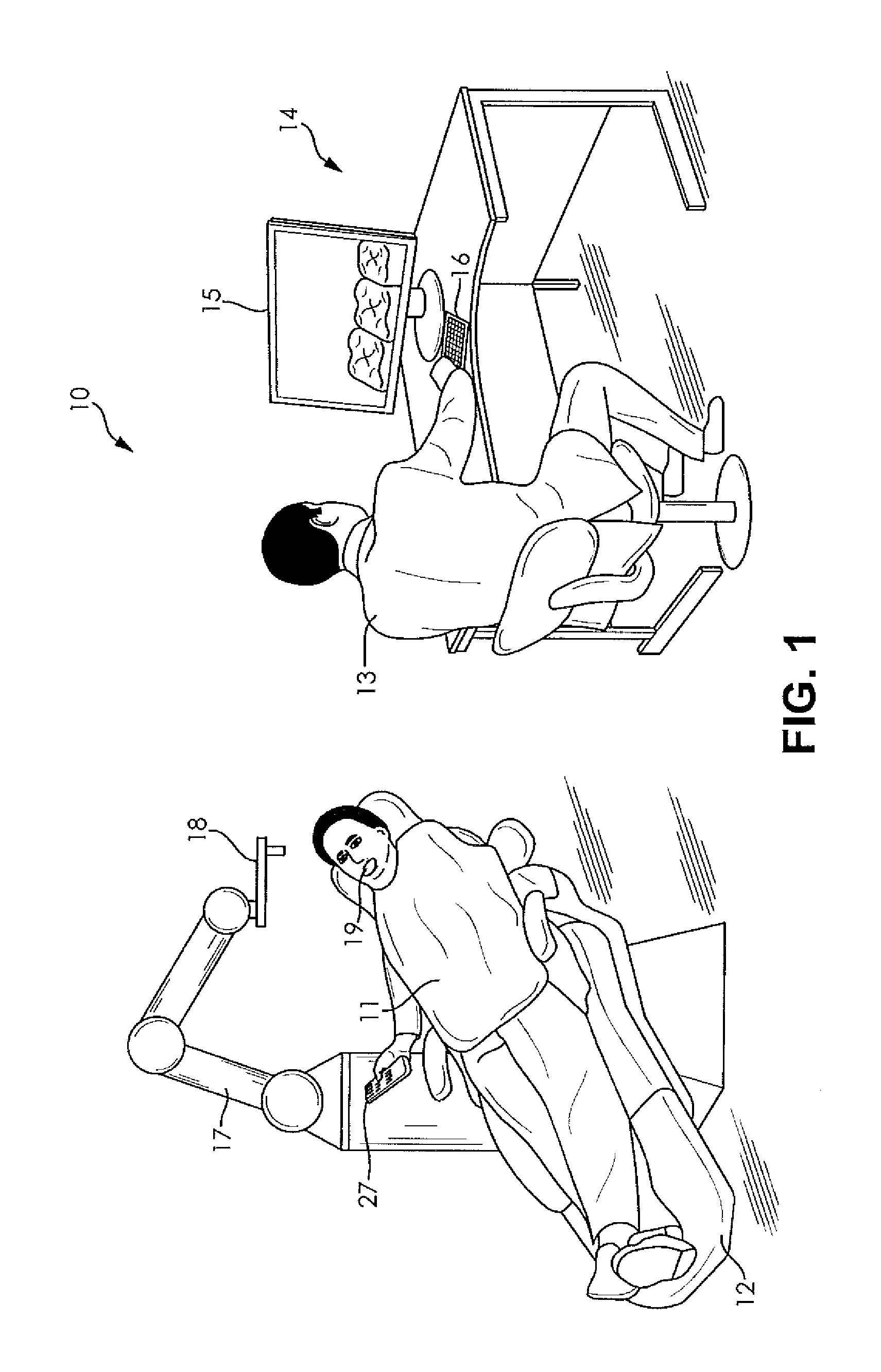
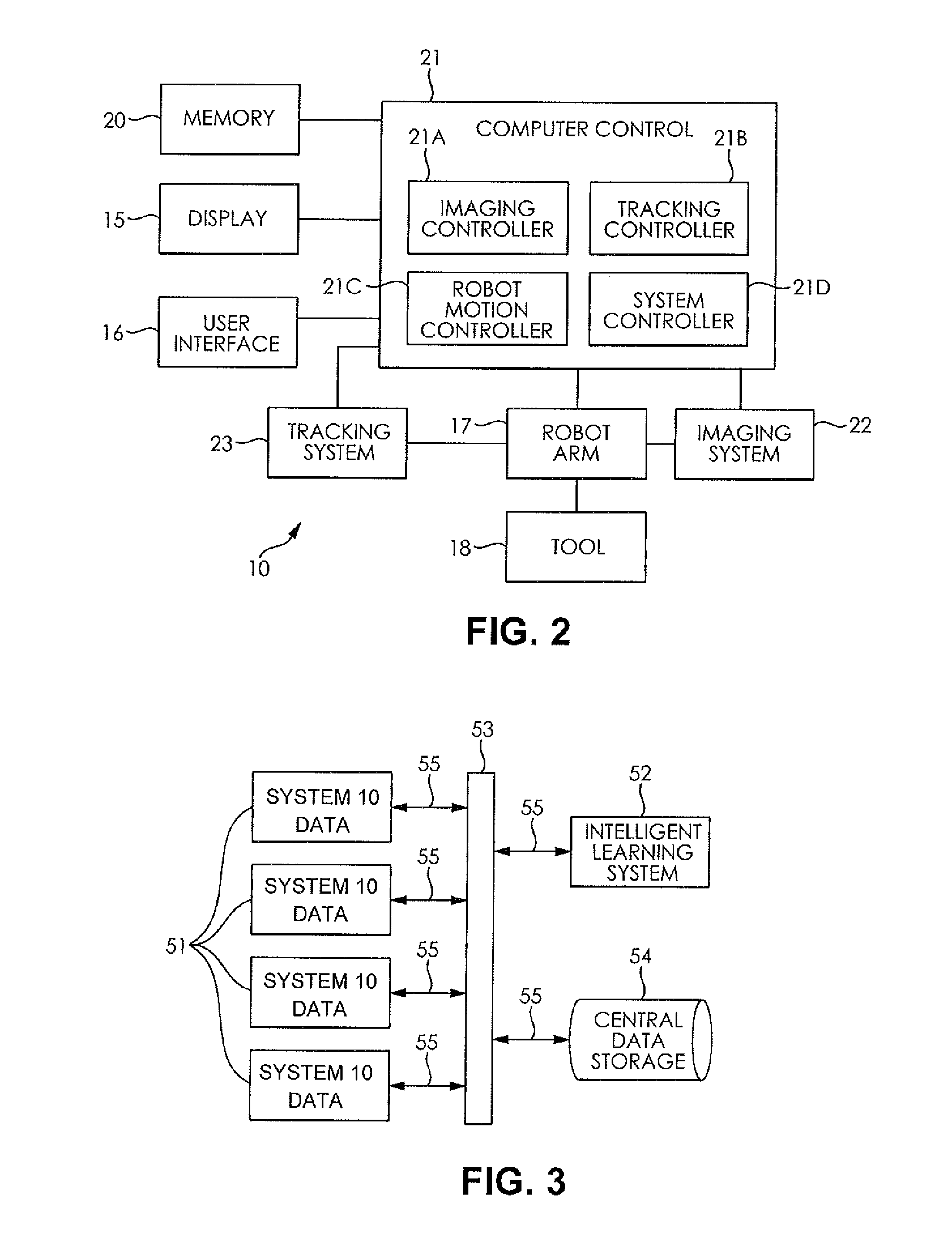
System and method for automating medical procedures
ActiveUS20150057675A1Most comfortMinimum durationDental implantsDiagnosticsDisplay deviceVisual perception
A system and a method for automating a medical process including a memory storing a software program, a computer connected to the memory for running the software program, a display connected to the computer for generating a visual representation of output data generated by the computer running the program, a user interface connected to the computer for obtaining image data representing a configuration of a patient treatment space and fixed markers in the treatment space and storing the image data in the memory, a robot arm connected to the computer, and a medical tool mounted on the robot arm wherein when a human inputs a selected treatment procedure into the computer, the computer runs the software program to generate a tool path based upon the treatment procedure and the image data, and the computer operates the robot arm to move the medical tool along the tool path without human guidance, and wherein the data generated during the treatment procedure is stored, analyzed, and shared among collaborating computer systems.
Owner:BRACHIUM
Mill blank library and computer-implemented method for efficient selection of blanks to satisfy given criteria
ActiveUS20050008887A1Easy to manufactureReduce material wasteDental implantsPerson identificationEngineeringInventory management
The present invention relates generally to mill blank constructions to facilitate the manufacture of dental restorations. A given mill blank is formed in a shape (i.e. with a given geometry) that has been predetermined to reduce material waste when the mill blank is machined into the final part. A set of two or more blanks each having such characteristics comprise a smart blank “library.” In one embodiment, a smart blank library includes a sufficient number of unique blanks such that, when the geometry of the designed restoration is known, the smart blank with a highest yield can be selected for use in milling the restoration. The “yield” of a given smart blank represents the amount of material of the smart blank that is actually used in the final restoration. Automated processes for smart blank inventory management and smart blank selection are also described.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
Method and system for dental planning and production
ActiveUS20110008751A1Reduce dosageEliminate needMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDental articulatorsComputed tomographyData set
A method and system useful for planning a dental restorative procedure of a patient and for producing at least one dental restoration or product related thereto to be used in said dental restorative procedure are disclosed. Input data from different sources, e.g. 3D data from a CT scan of a patient with a dental impression tray including a previously prepared dental impression of the patient in the patient's mouth, is matched with data from a high resolution 3D scan of the same dental impression. The resulting data is for instance matched by means of fiducial markers arranged at the dental impression tray. Thus reliable planning and production are enabled by means of the same, matched data set. In this manner the dosage to which the patient is exposed to may be reduced in comparison to previous methods.
Owner:NOBEL BIOCARE SERVICES AG
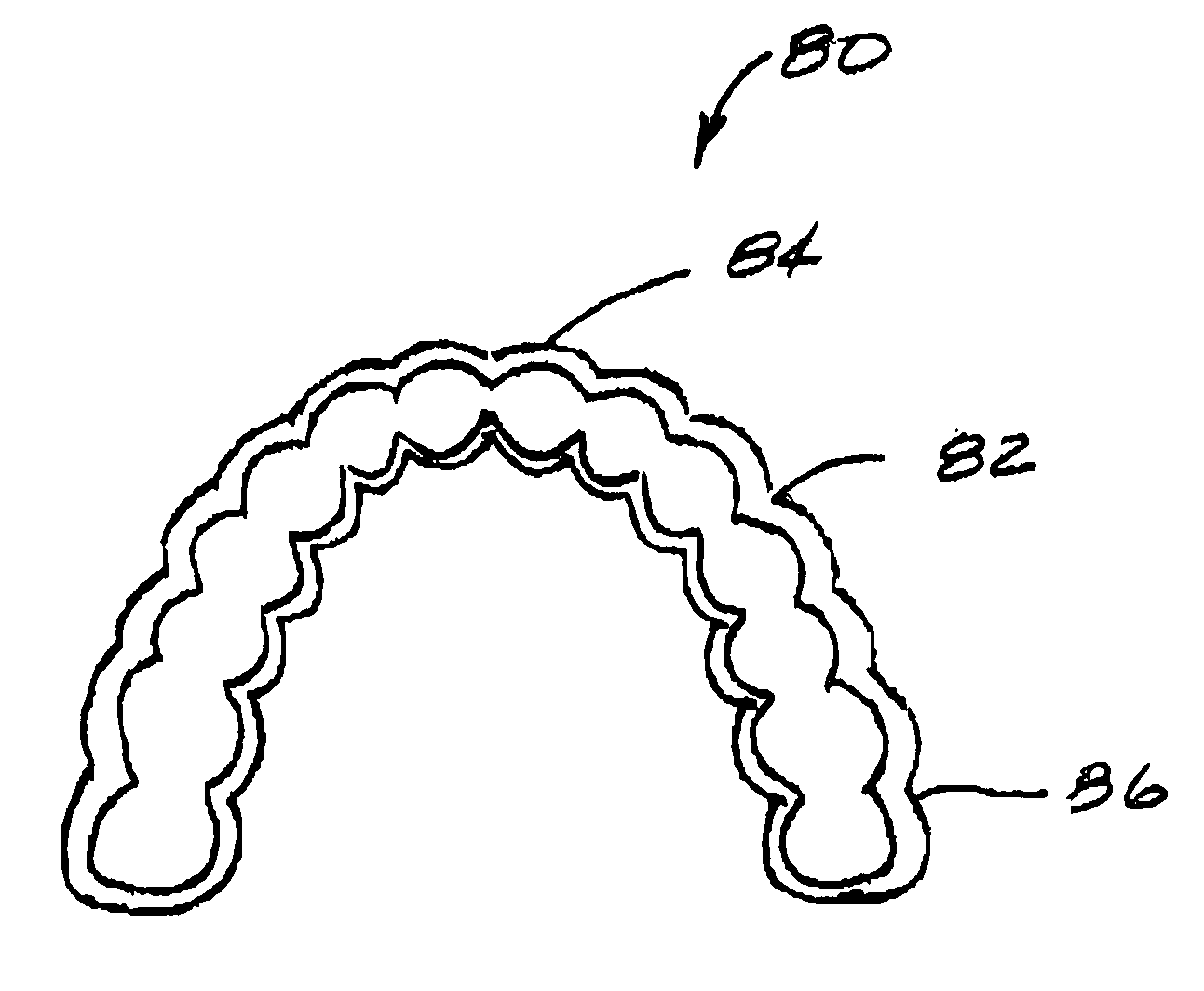
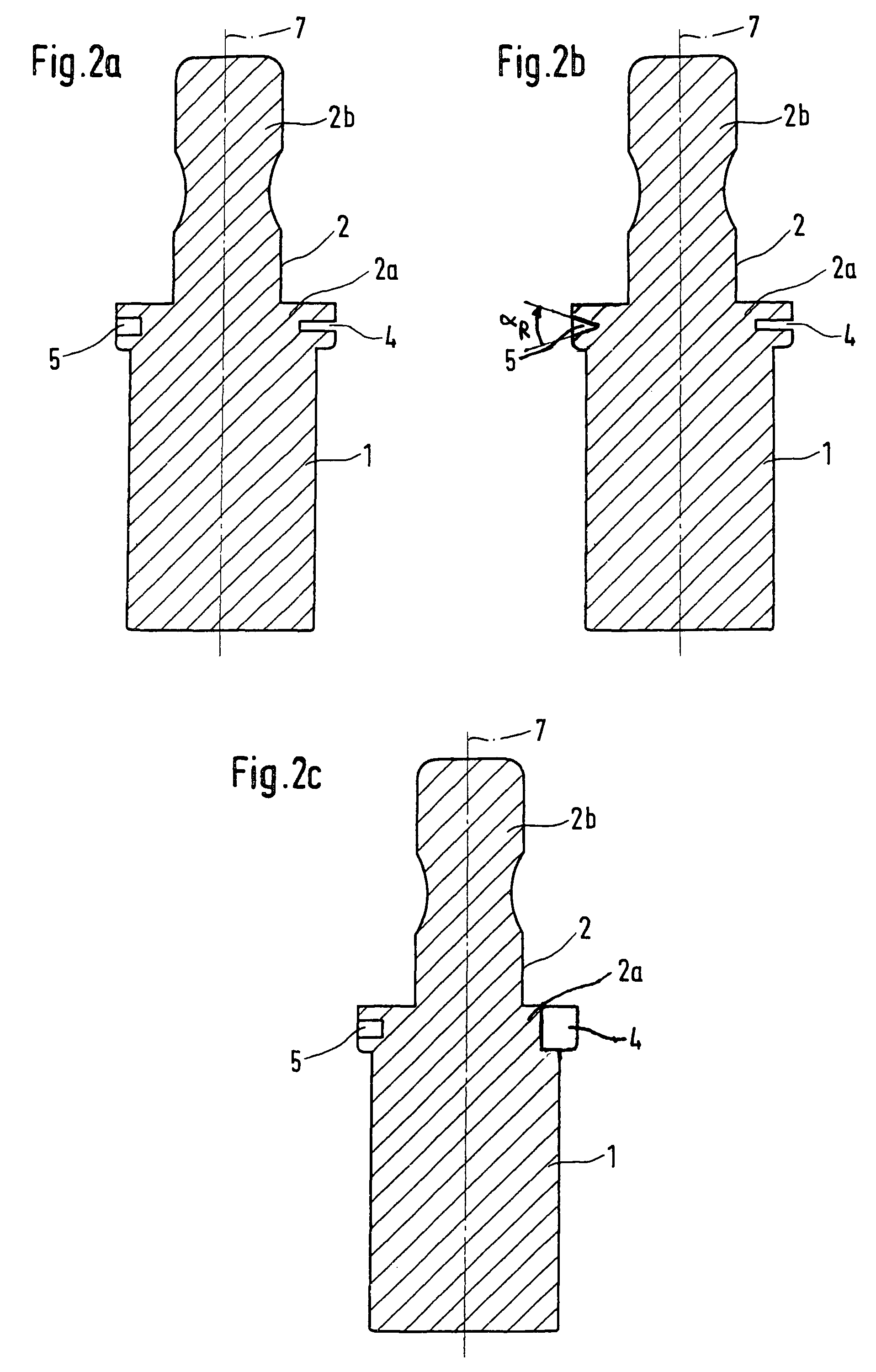
Material for a dental prosthesis, method and device for determining the shape of a remaining tooth area to be provided with a dental prosthesis, method and arrangement for producing a dental prosthesis and use of the arrangement
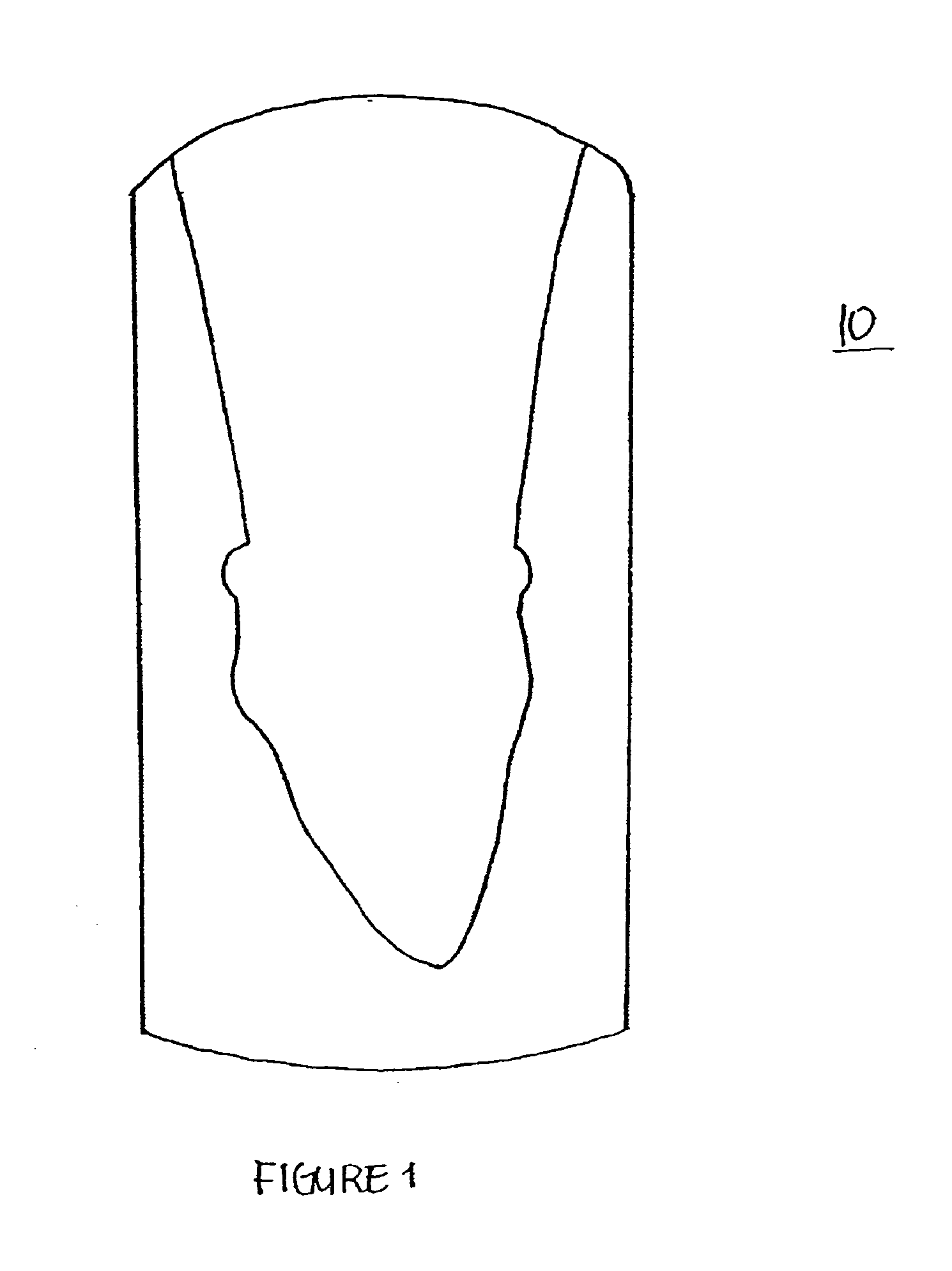
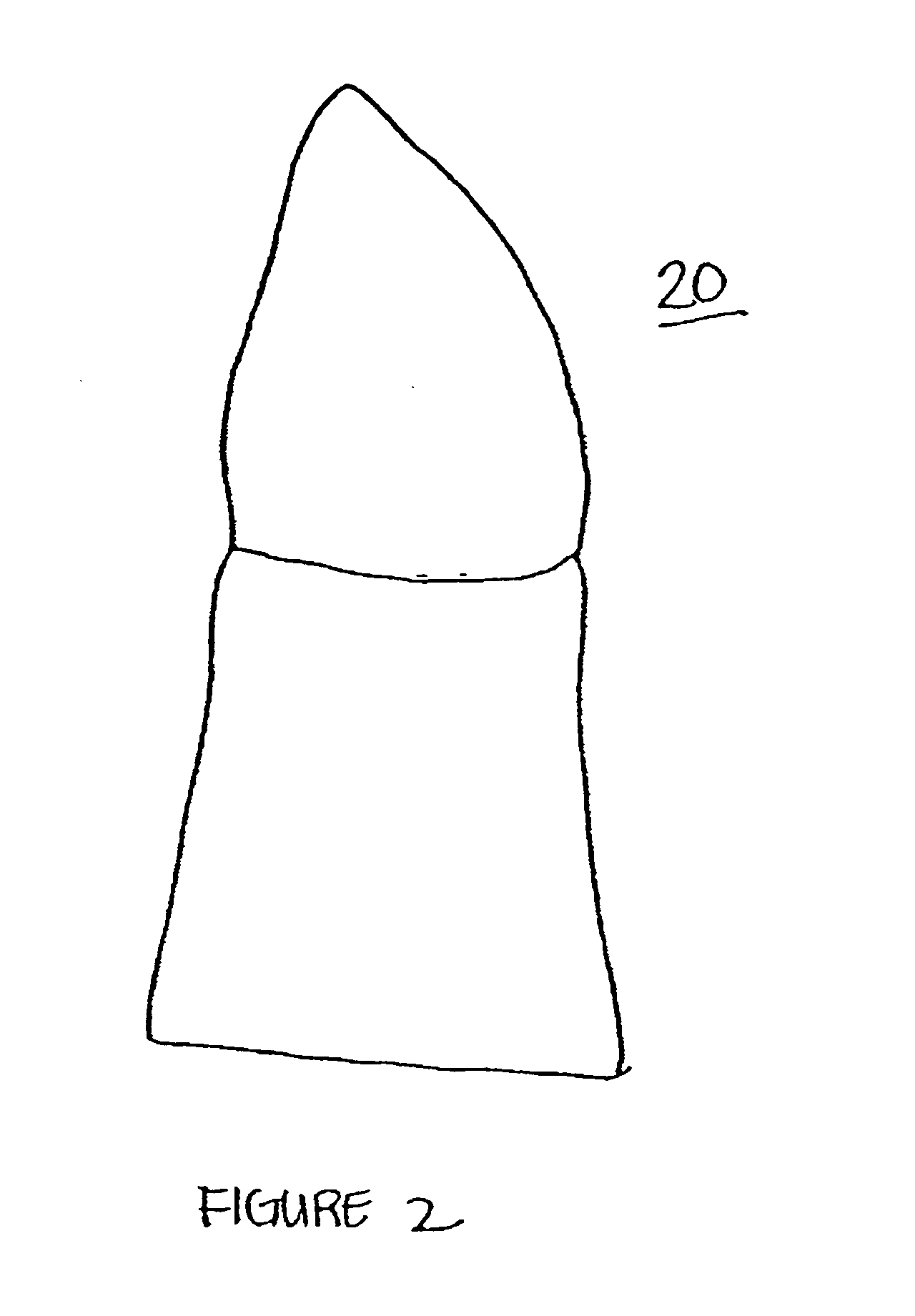
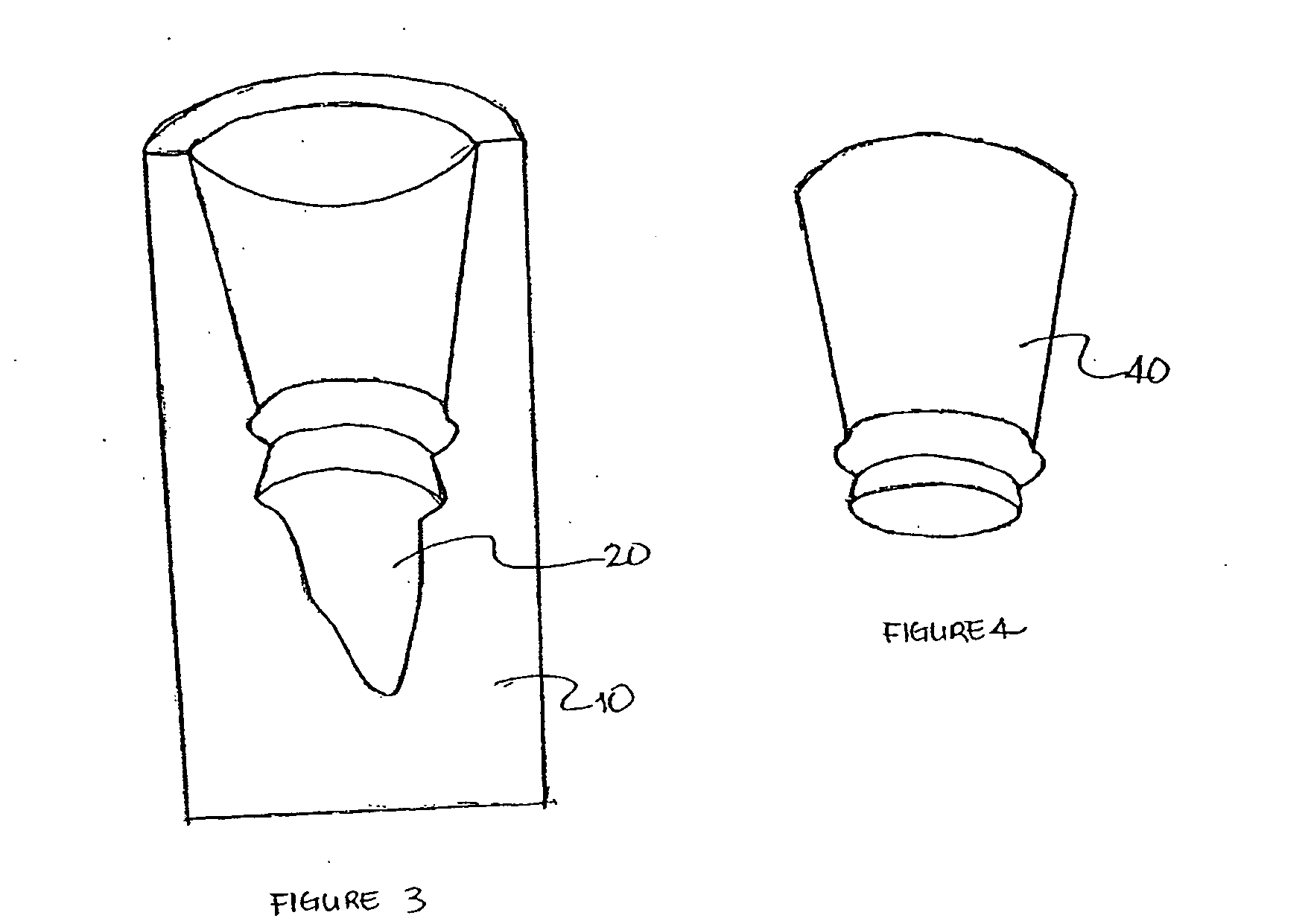
InactiveUS6287121B1Improve accuracySuitable for processingImpression capsTooth crownsDigital dataGlass fiber
Material for a dental prosthesis consisting of fiber glass reinforced plastic. The material is used to produce a blank by means of a special injection-molding process, which can be worked by means of a machining process. A method and a device for determining the shape of a duplicate of a remaining tooth area to be provided with a dental prosthesis. The shape of the duplicate is determined, as is the shape of duplicate sections into which the duplicate has been divided, the determined data are stored and combined. A method and arrangement for producing a dental prosthesis. The shape of a duplicate (42) of a remaining tooth area to be provided with the dental prosthesis is determined by means of a shape determination device (110), the determined data are stored in the form of digital data (DD), and the dental prosthesis (143) is produced in a production machine (114), which is controlled by means of production data (FD). The shape determination device (110) and the production machine (114) are coupled by means of an EDP installation (118), which contains a memory unit for storing the digital data (DD) and performs the calculation of the production data (FD).
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG +2
Video-assisted margin marking for dental models
InactiveUS20100281370A1Simple production processSpeed up the processInput/output for user-computer interactionImpression capsInteractive modelingAmbiguity
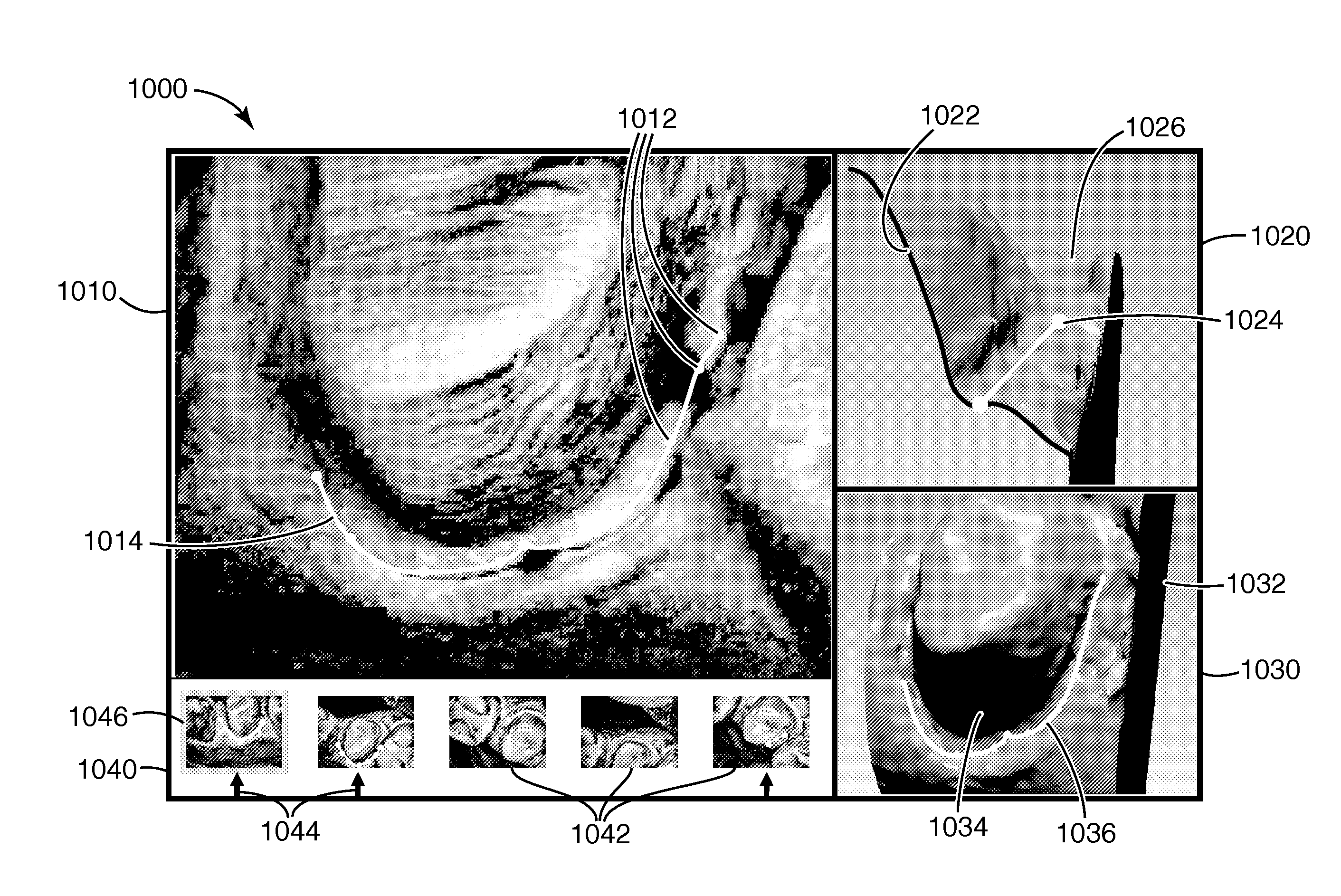
Tools are described for preparing digital dental models for use in dental restoration production processes, along with associated systems and methods. Dental modeling is improved by supplementing views of three-dimensional models with still images of the modeled subject matter. Video data acquired during a scan of the model provides a source of still images that can be displayed alongside a rendered three-dimensional model, and the two views (model and still image) may be synchronized to provide a common perspective of the model's subject matter. This approach provides useful visual information for disambiguating surface features of the model during processing steps such as marking a margin of a prepared tooth surface for a restoration. Interactive modeling tools may be similarly enhanced. For example, tools for margin marking may synchronize display of margin lines between the still image and the model so that a user can interact with either or both of the visual representations, with changes to a margin reflected in both displays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
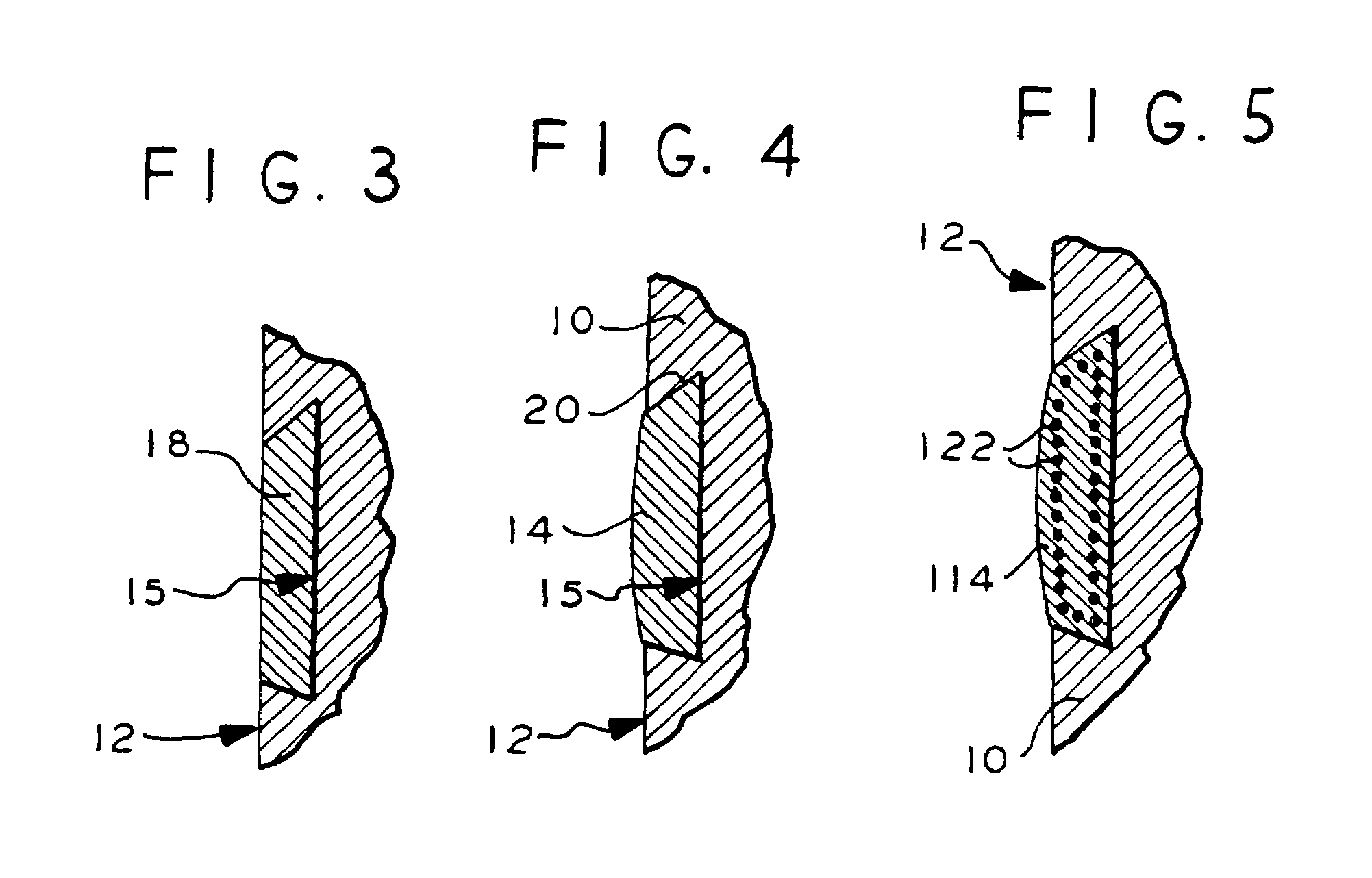
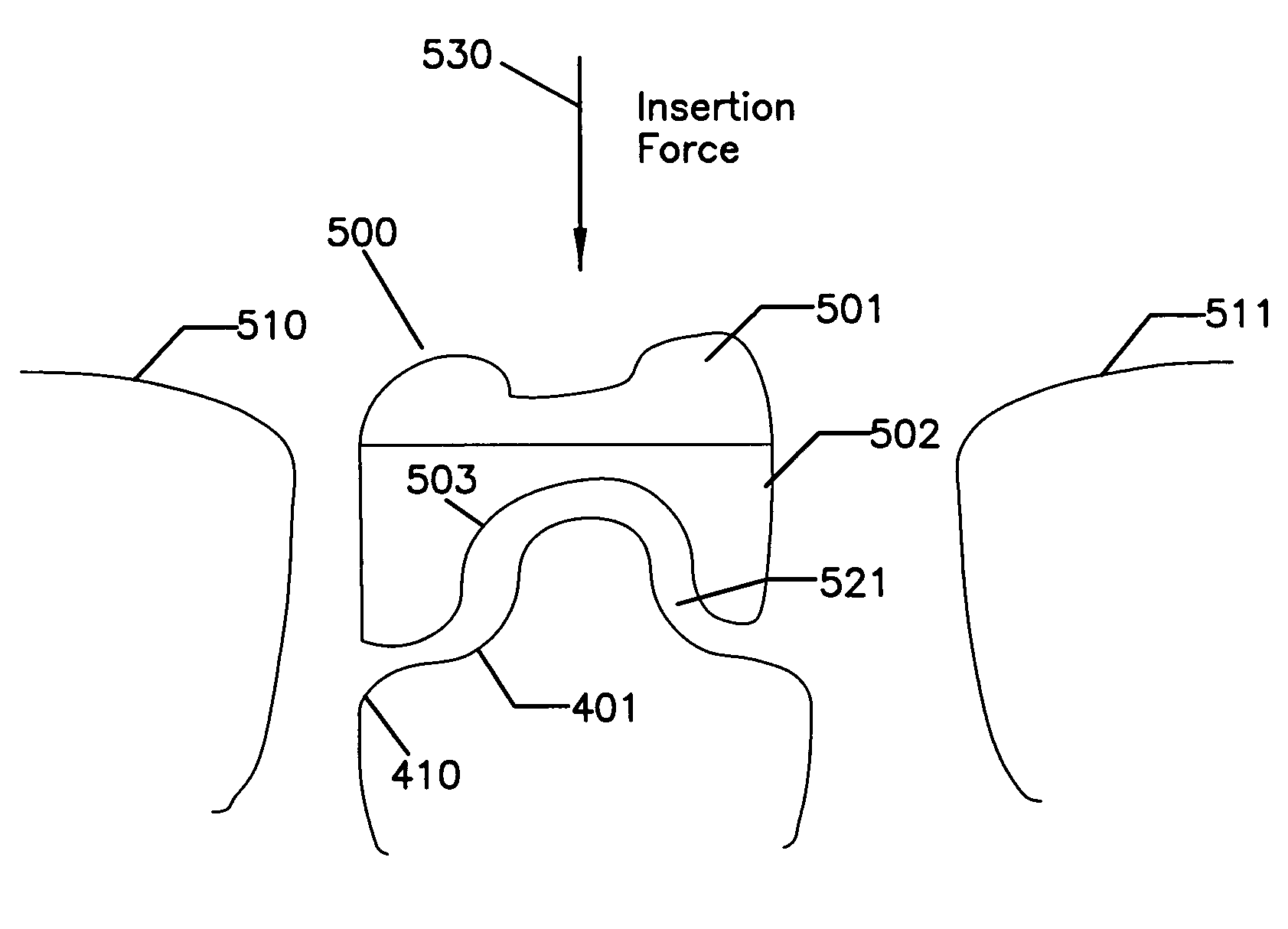
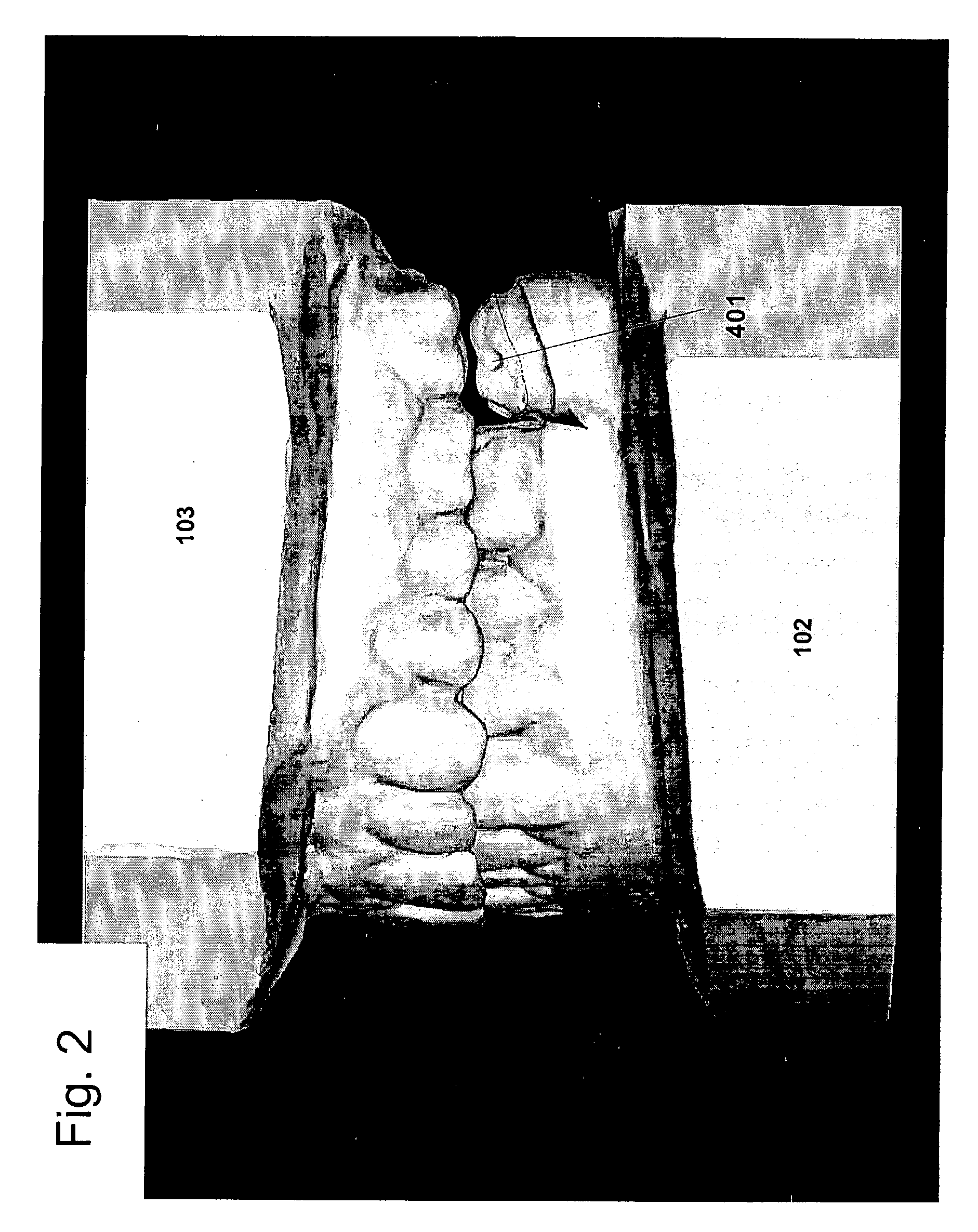
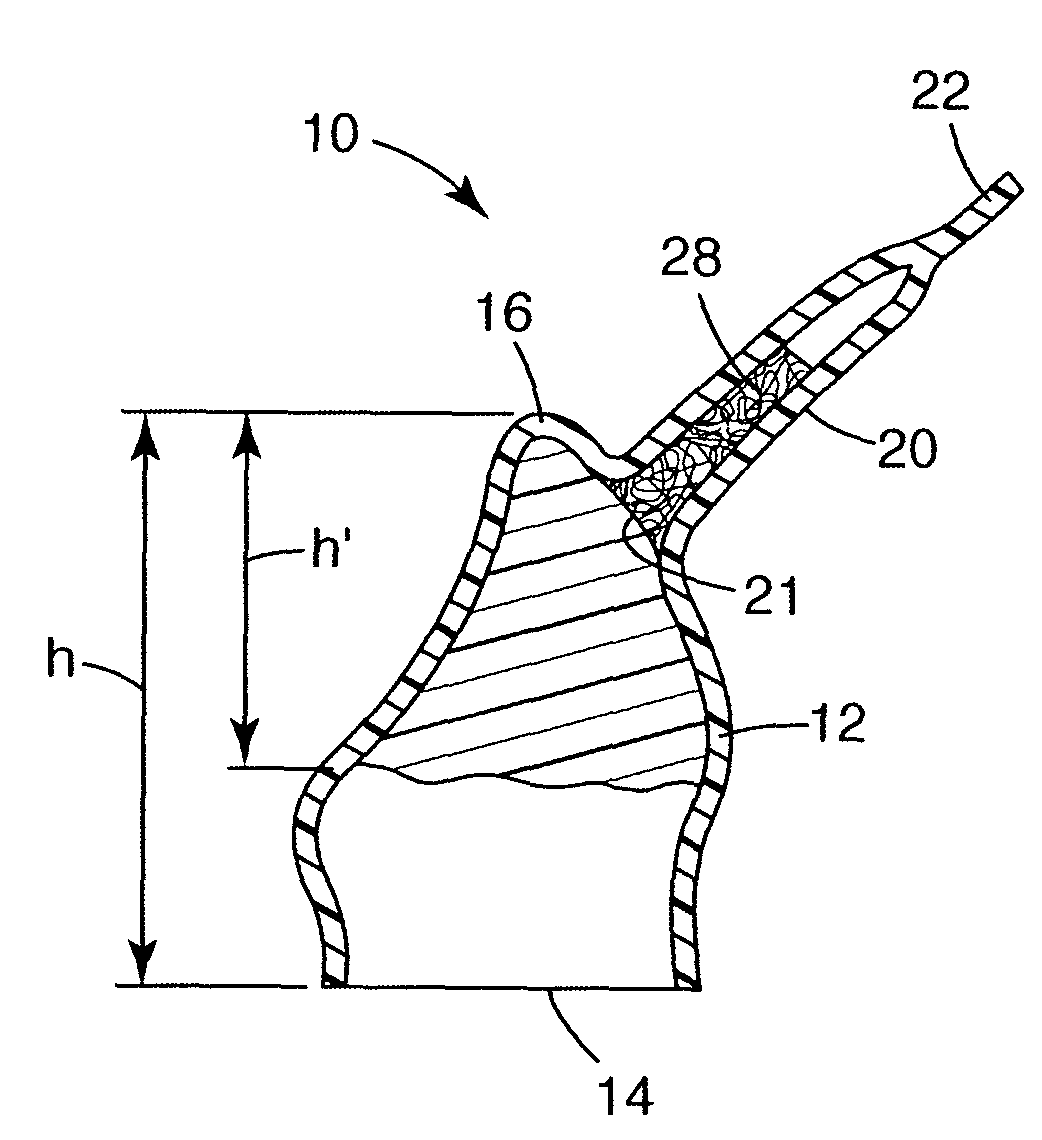
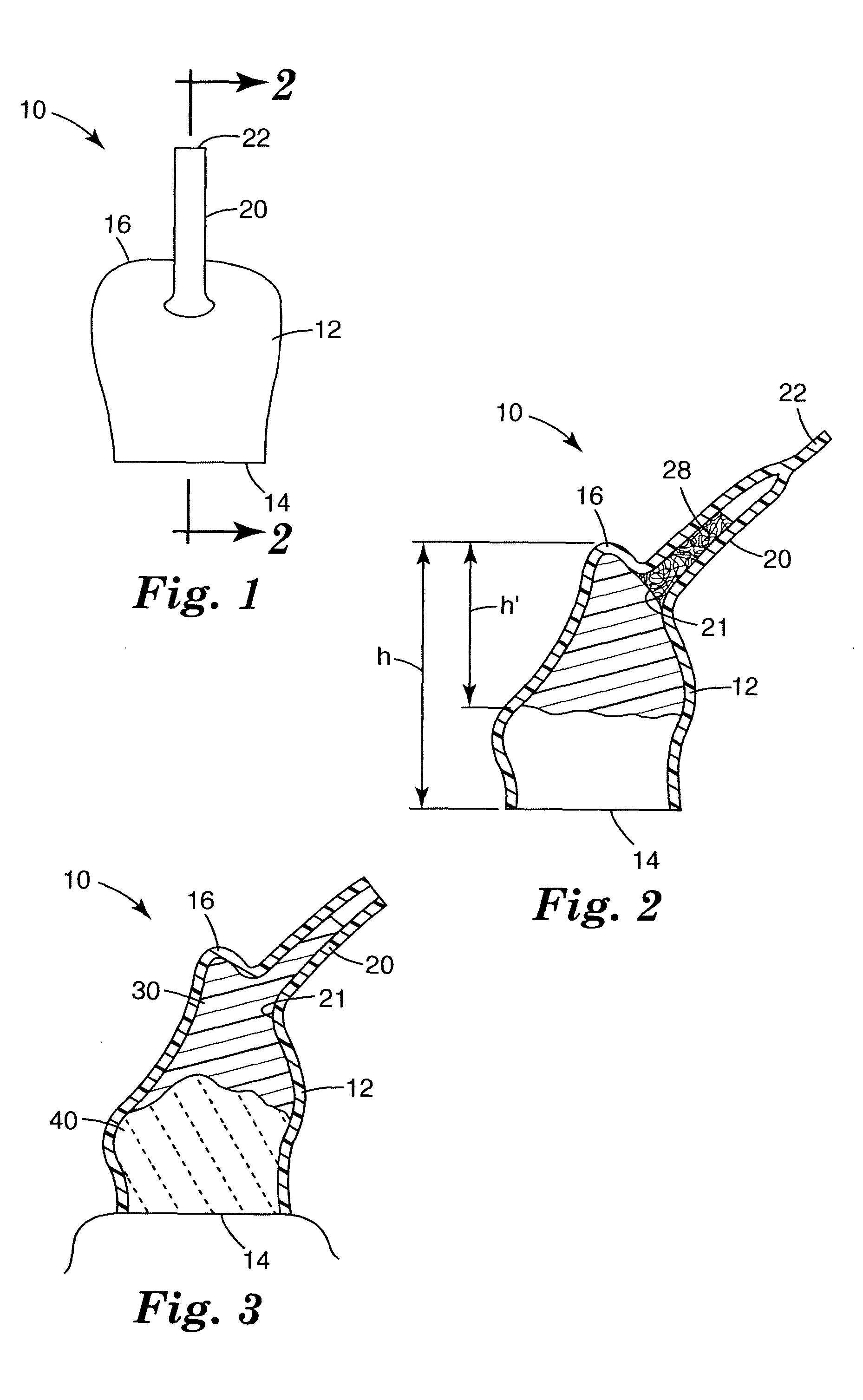
Preparation for being fastened on a natural tooth part or tooth and corresponding fastening method
ActiveUS6955540B2Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsRelieve stressDental implantsImpression capsStress concentrationNatural tooth
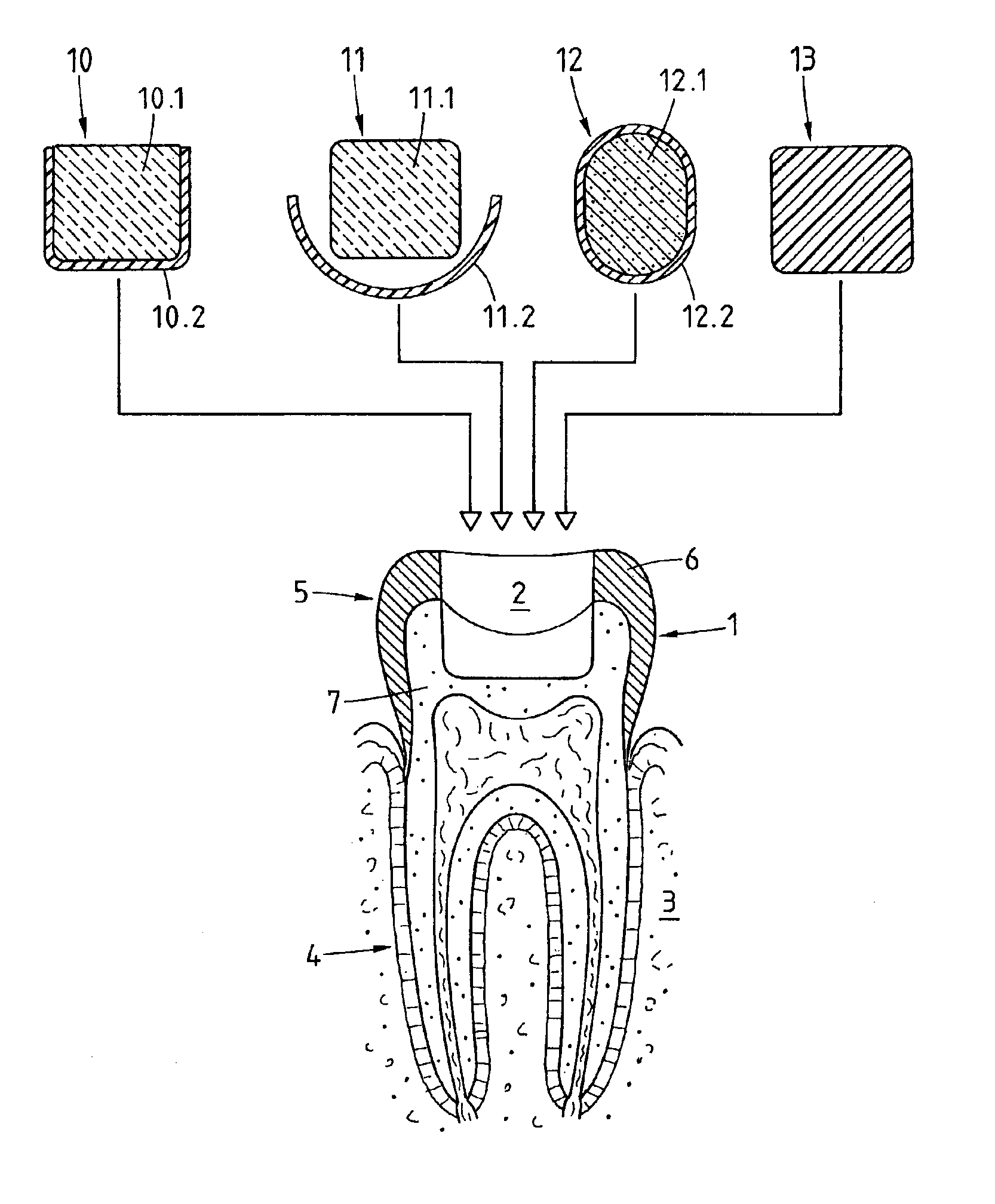
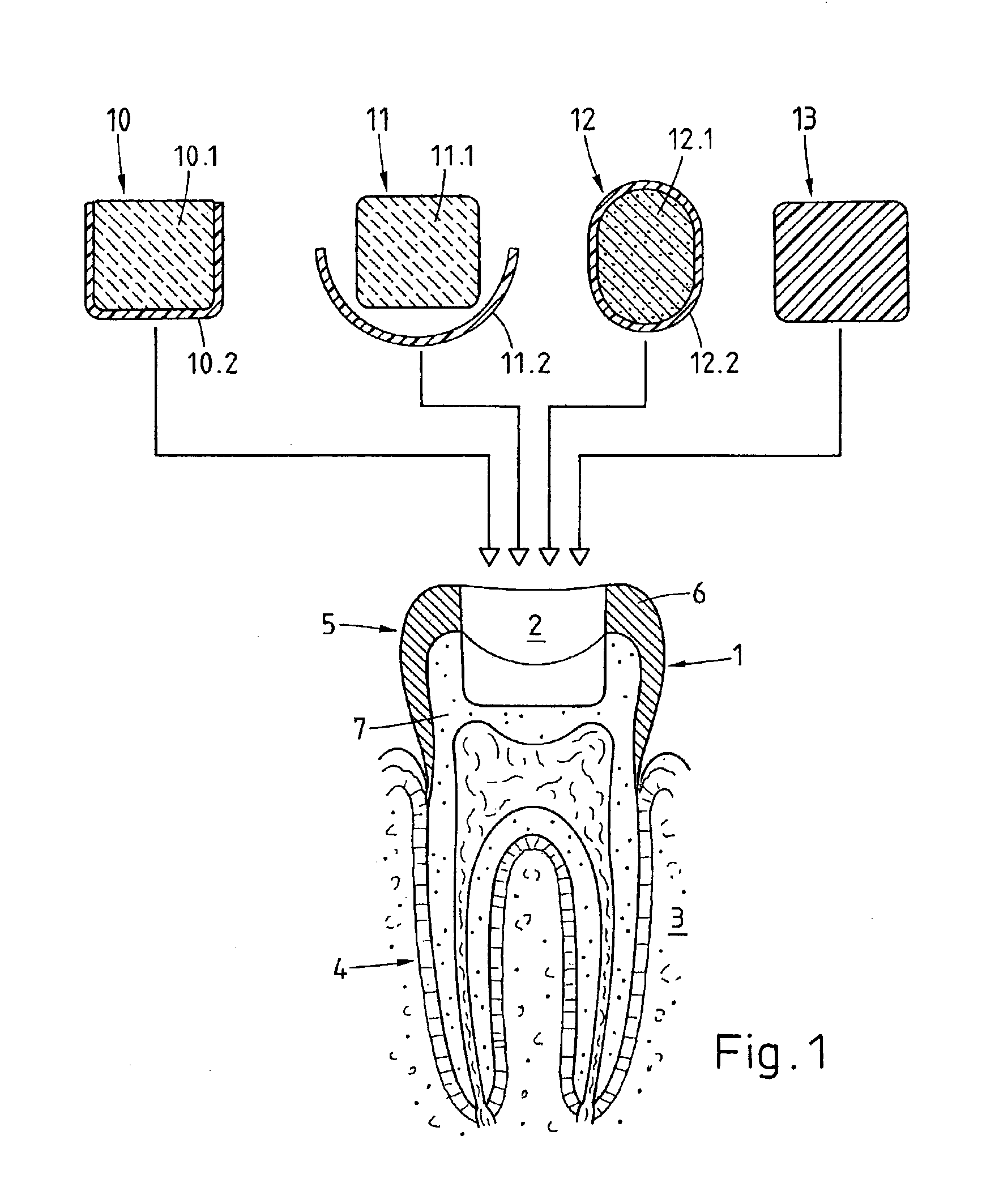
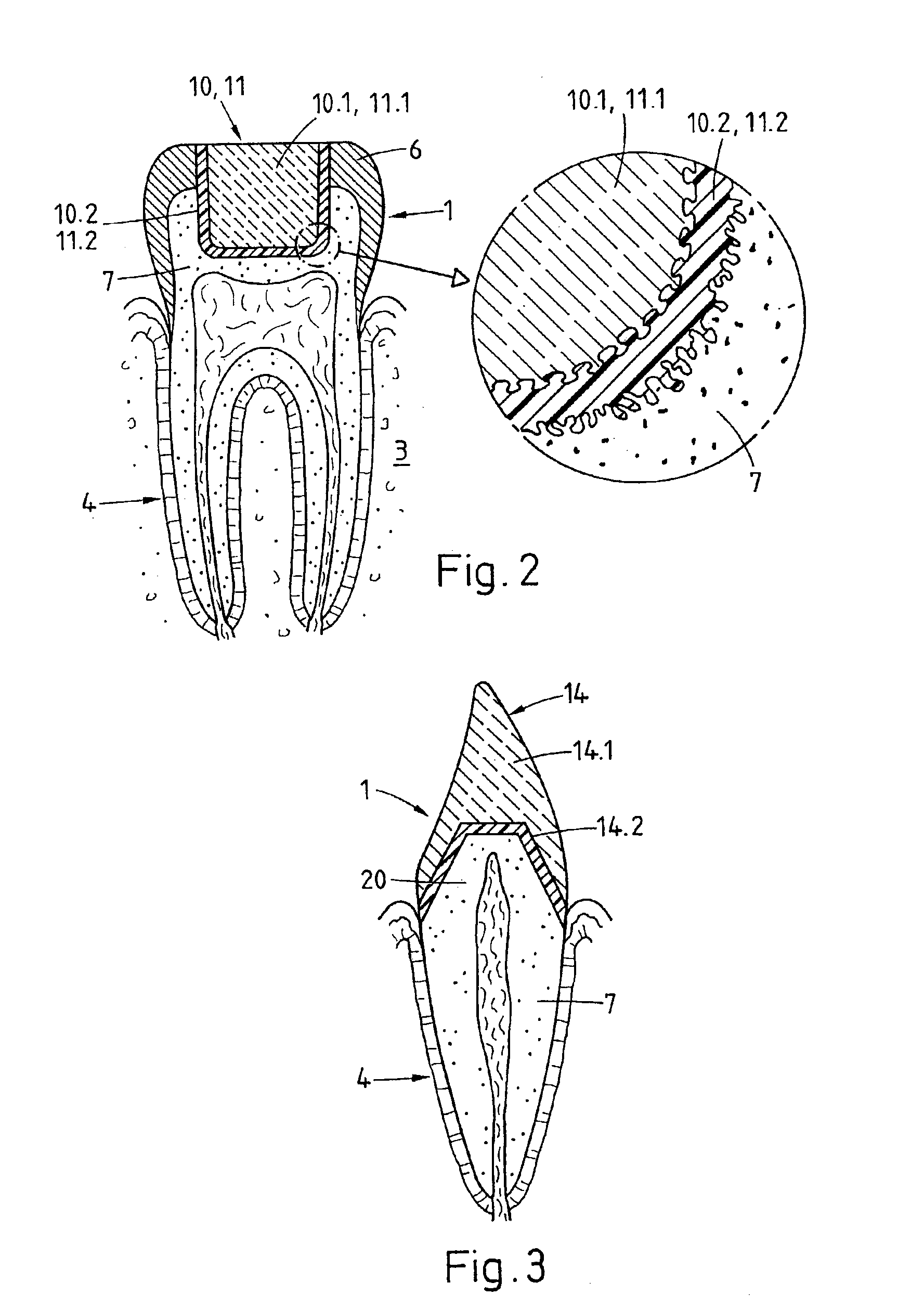
A preparation (10, 11,12,13) to be fixed to a natural tooth part or tooth, in particular for the replacement of a load-bearing tooth part, is for example a filling for a drilled-out tooth (1), a crown, bridge or prosthesis to be placed on a tooth stub, or a tooth pin to be fixed in a tooth root for fastening an artificial tooth, a bridge or a prosthesis. The preparation has surface regions which consist of a material with thermoplastic properties. The preparation (10, 11, 12,13) is designed in a manner such that it has oscillation properties with such low damping losses that for a liquefaction of the material with thermoplastic properties by way of oscillations there are local stress concentrations required, and in a manner such that such stress concentrations only occur in the region of the preparation surface. The preparation is positioned on a suitably prepared natural tooth part in a manner such that the material with the thermoplastic properties is in contact or may be brought into contact with the dentin surface and / or enamel surface. The preparation is then made to mechanically oscillate and is simultaneously pressed against the natural tooth part, whereby the material with the thermoplastic properties is at least partly liquefied and brought into intimate contact with the dentin or enamel surface in a manner such that after solidification it forms a positive fit and / or material fit connection. Teeth restored with such preparations have a high stability and a long life, which in particular is attributed to the fact that the thermoplastic material, in contrast to cements used for the same purpose, shrinks less and has the ability to relieve internal stress by creeping.
Owner:WOODWELDING
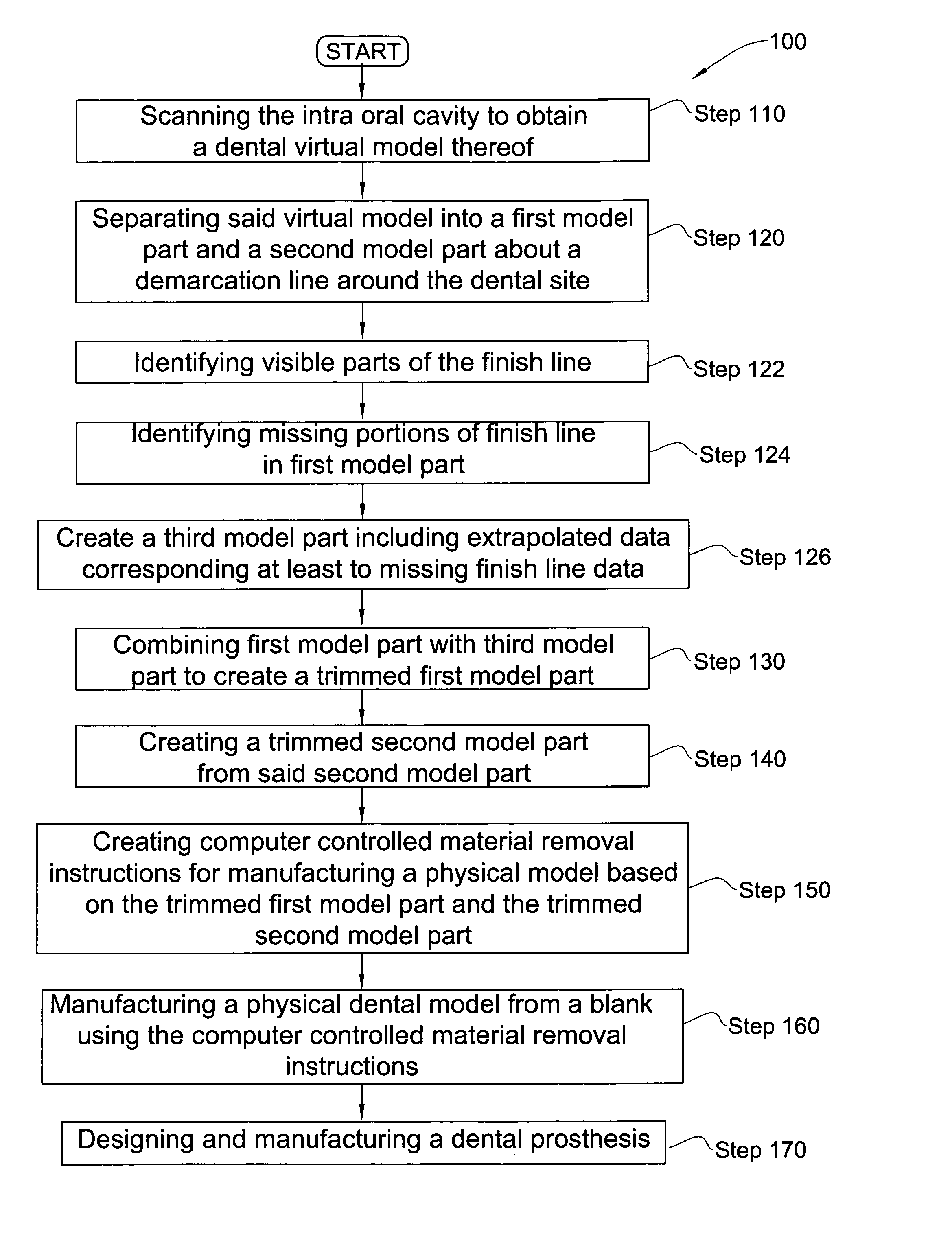
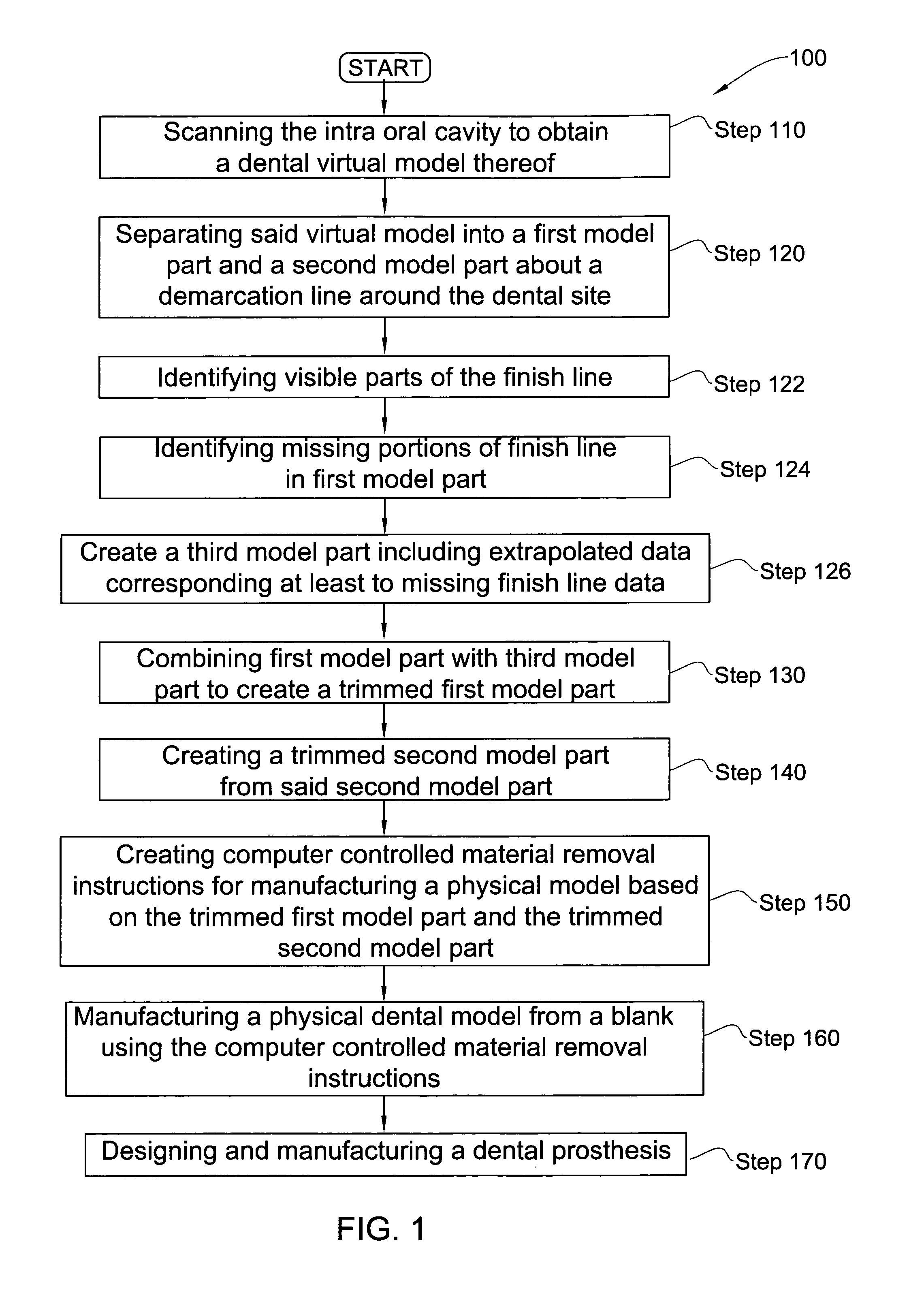
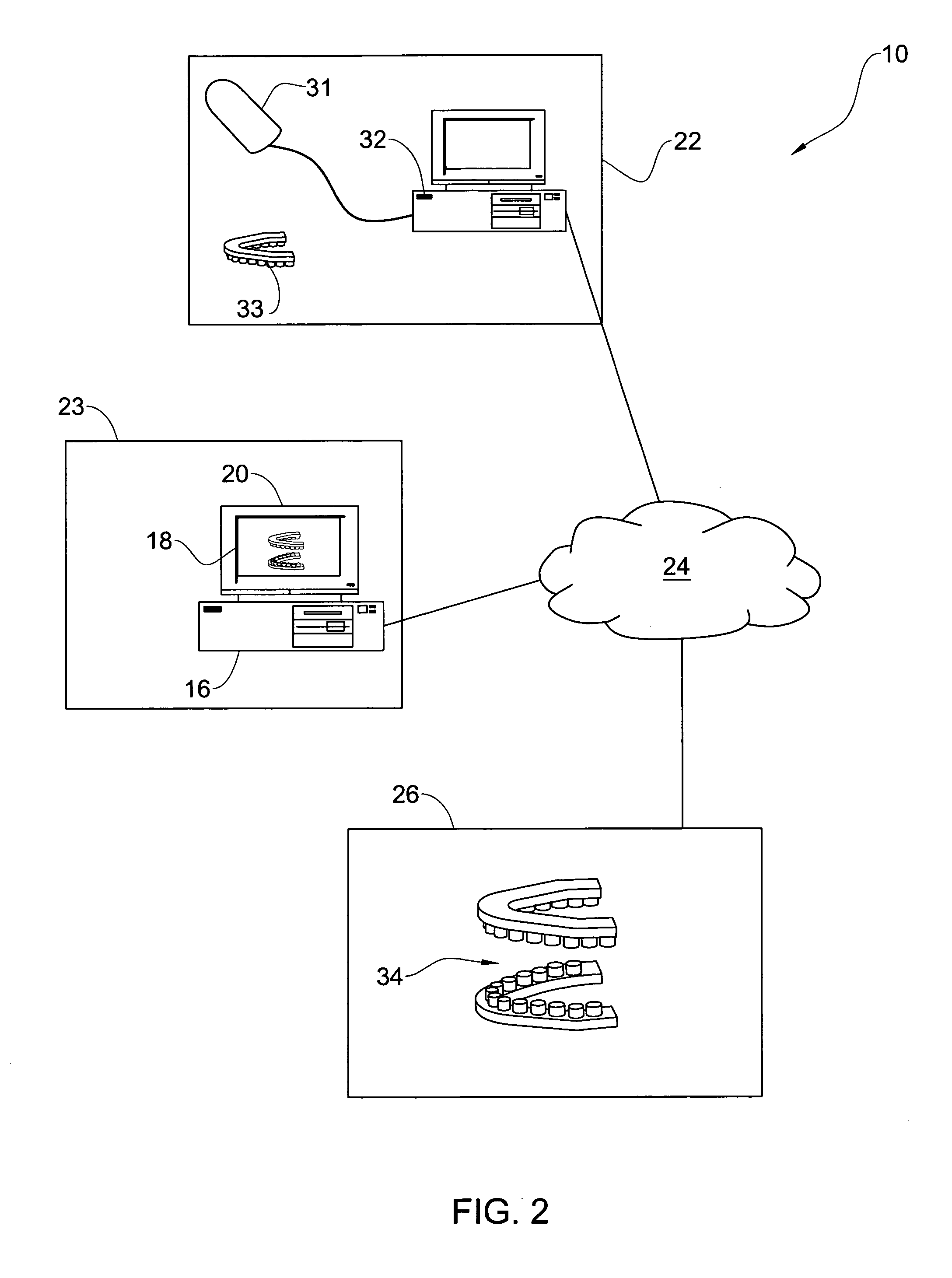
Method for manipulating a dental virtual model, method for creating physical entities based on a dental virtual model thus manipulated, and dental models thus created
A 3D virtual model of an intra oral cavity in which at least a part of a finish line of a preparation is obscured is manipulated in virtual space by means of a computer or the like to create, recreate or reconstruct finish line data and other geometrical corresponding to the obscured part. Trimmed virtual models, and trimmed physical models, can then be created utilizing data thus created. The virtual models and / or the physical models may be used in the design and manufacture of copings or of prostheses.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Dental restorations using nanocrystalline materials and methods of manufacture
Dental articles are produced using relatively low sintering temperatures to achieve high density dental articles exhibiting strengths equal to and greater than about 700 MPa. Ceramic powders comprised of nanoparticulate crystallites are used to manufacture dental articles. The ceramic powders may include sintering agents, binders and other similar additives to aid in the processing of the ceramic powder into a dental article. The ceramic powders may be processed into dental articles using various methods including, but not limited to, injection molding, gel-casting, slip casting, or electroforming, hand, cad / camming and other various rapid prototyping methods. The ceramic powder may be formed into a suspension, pellet, feedstock material or a pre-sintered blank prior to forming into the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Haptically enabled dental modeling system
InactiveUS20090248184A1Minimal distortionGood choiceInput/output for user-computer interactionAdditive manufacturing apparatusDigital dentistryEngineering
The invention provides a digital dentistry system that utilizes a haptic interface and features a computer-based design application configured to allow the intuitive construction of irregular, amorphous three-dimensional structures typically seen in dental restorations, utilizing, where appropriate, the design skills of a user. In certain embodiments, the system provides a comprehensive digital solution for dental labs in the business of creating dental restorations such as partial frameworks, crowns, copings, bridge frameworks, implants and the like, with a sense of touch provided by a haptic interface device.
Owner:SENSABLE TECH
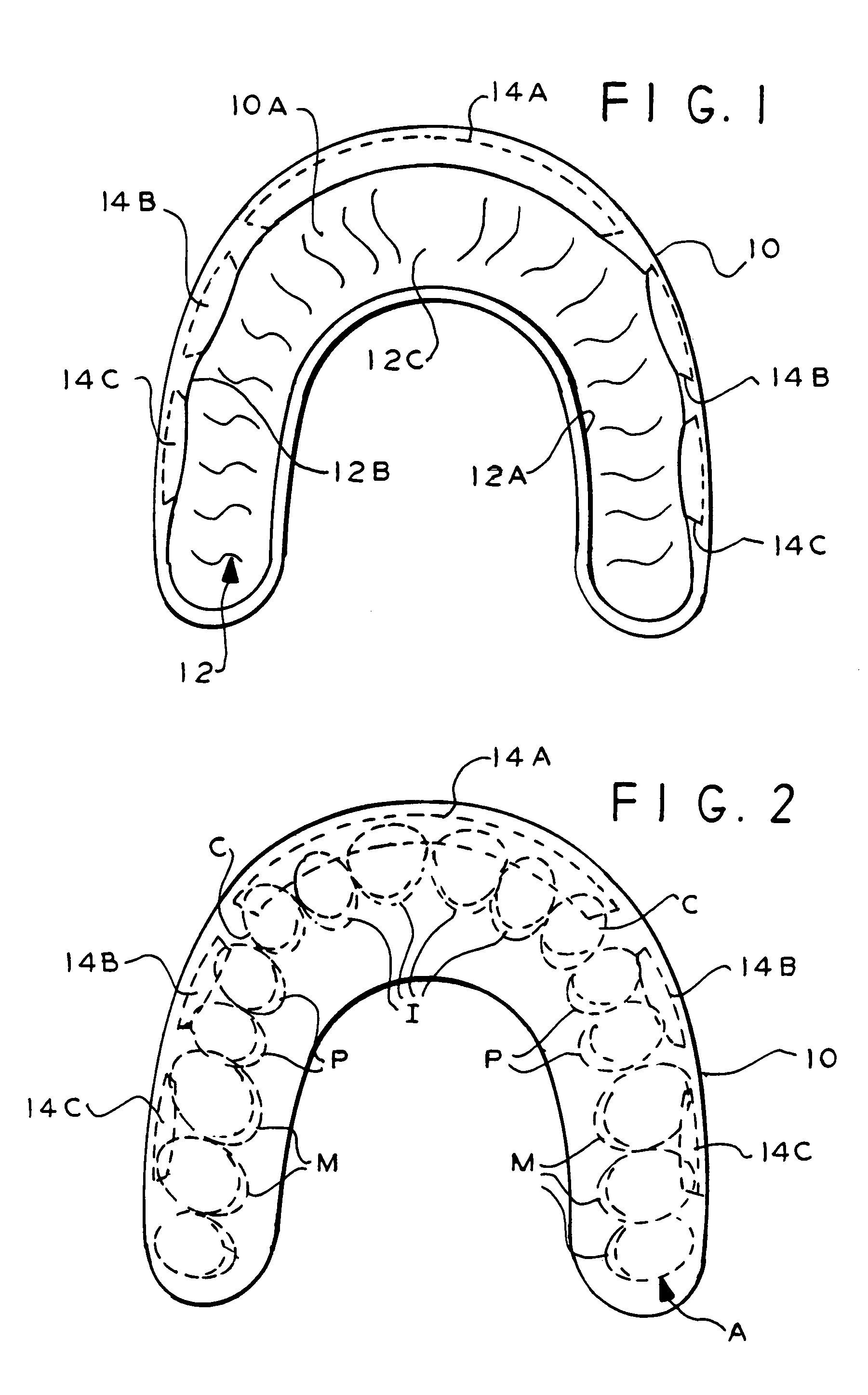
Dental appliance
ActiveUS7357637B2Efficient use ofBeautiful smileOthrodonticsTooth crownsInterior spaceCosmetic appearance
An appliance fabricated to improve the appearance of a patient's smile includes a plurality of simulated teeth. The interior surfaces of each of the teeth closely fits and conforms to the surface of a patient's real teeth while the outer surfaces of each of the simulated teeth has an ideal surface configuration. The dental appliance provides the patient with the appearance of a perfect set of teeth and an ideal smile without a need to alter the dental structure of the patient's teeth.
Owner:DEN MAT HLDG
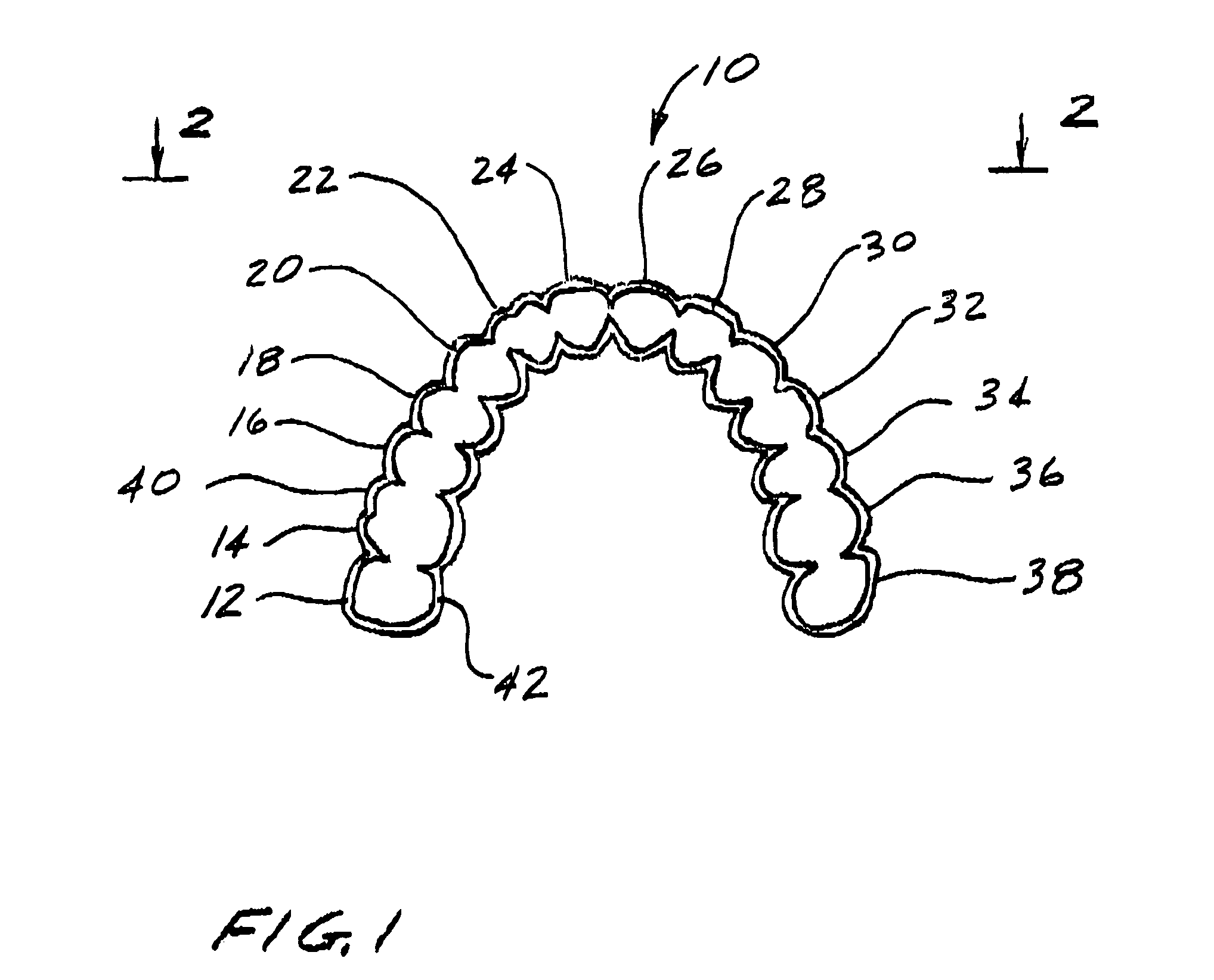
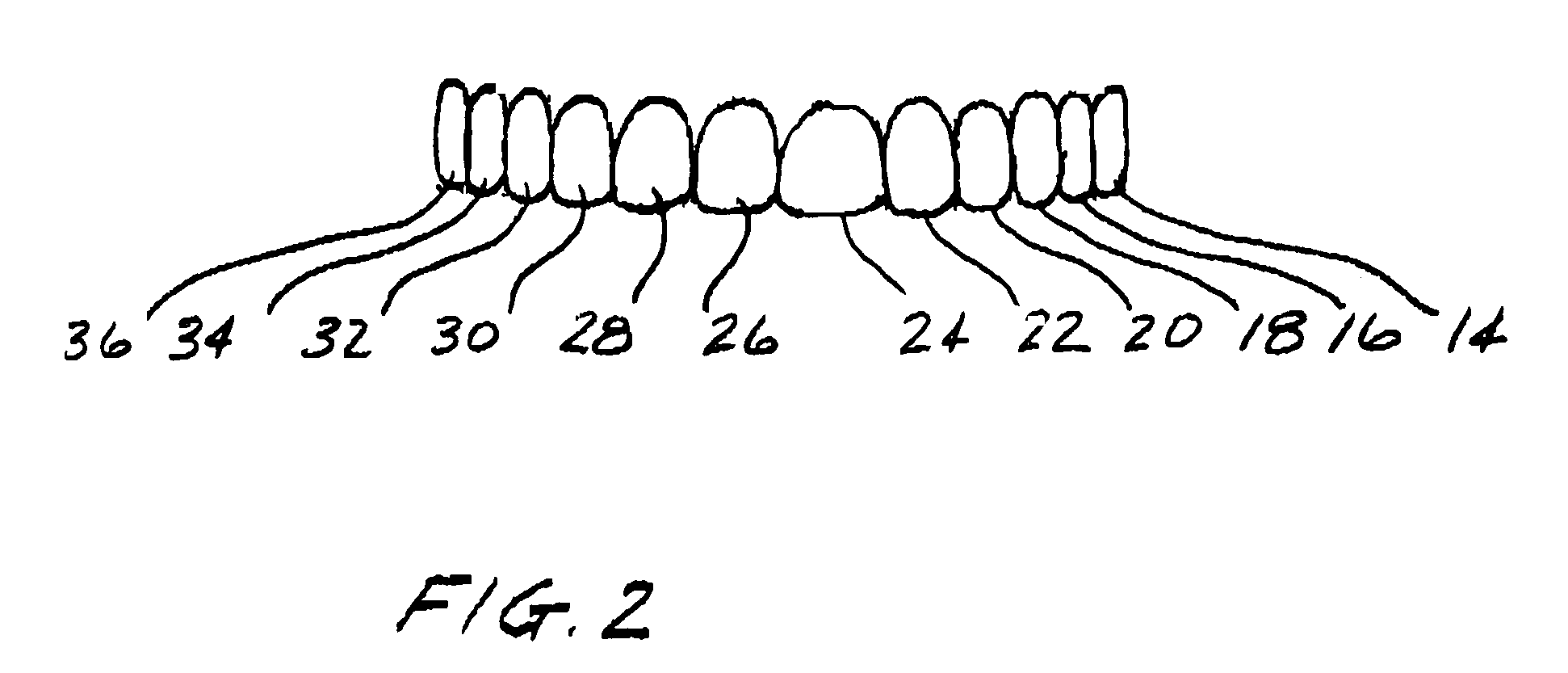
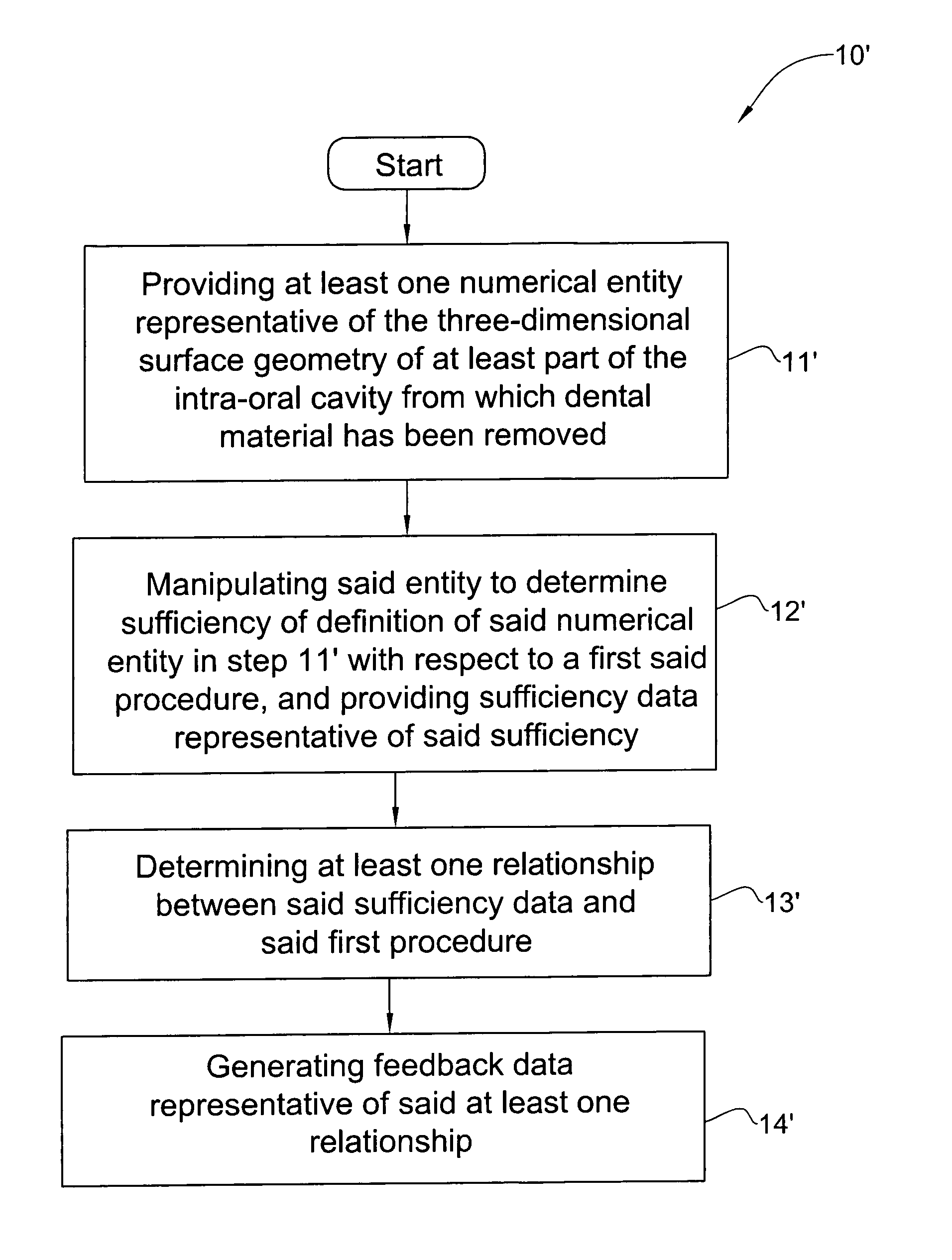
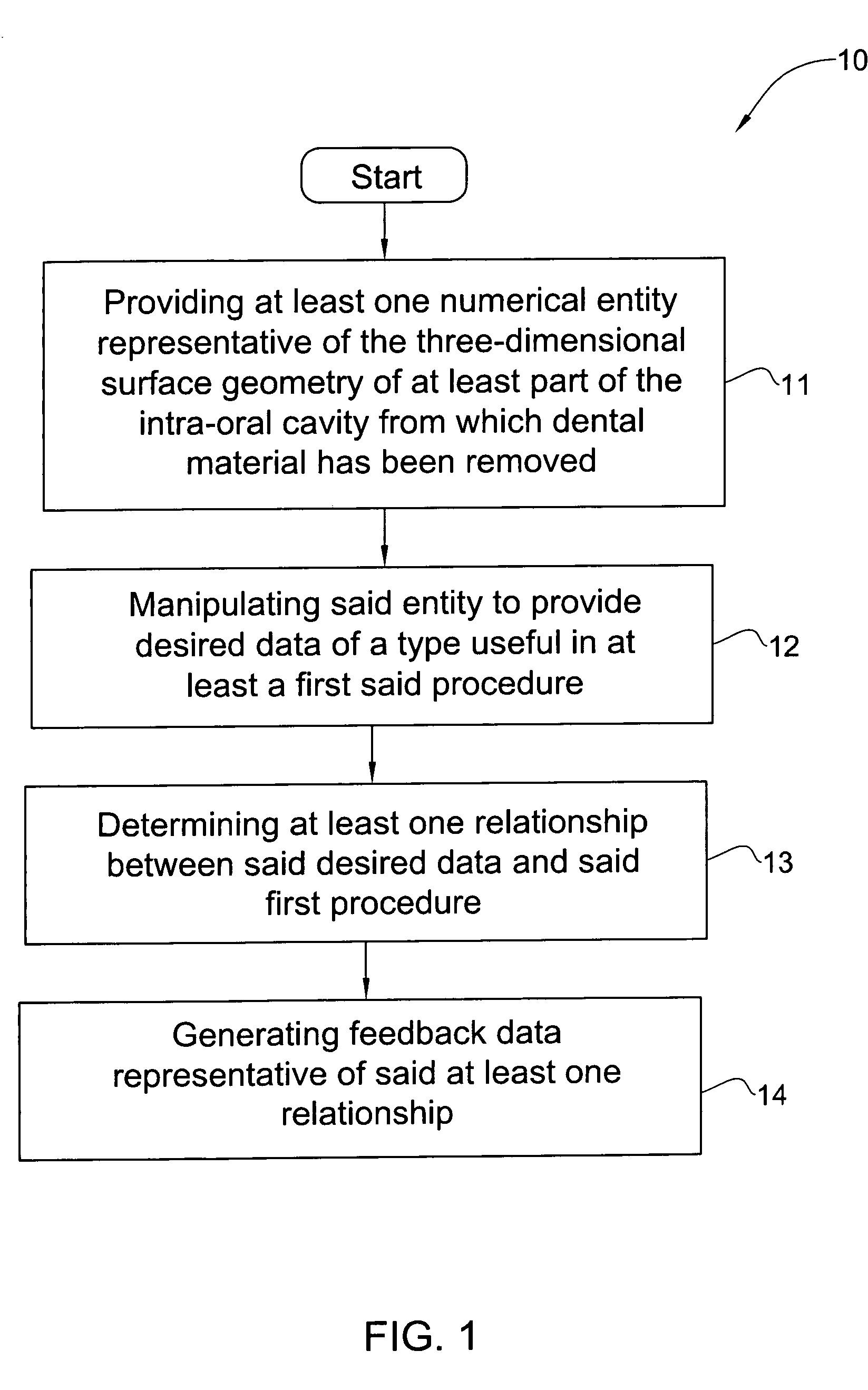
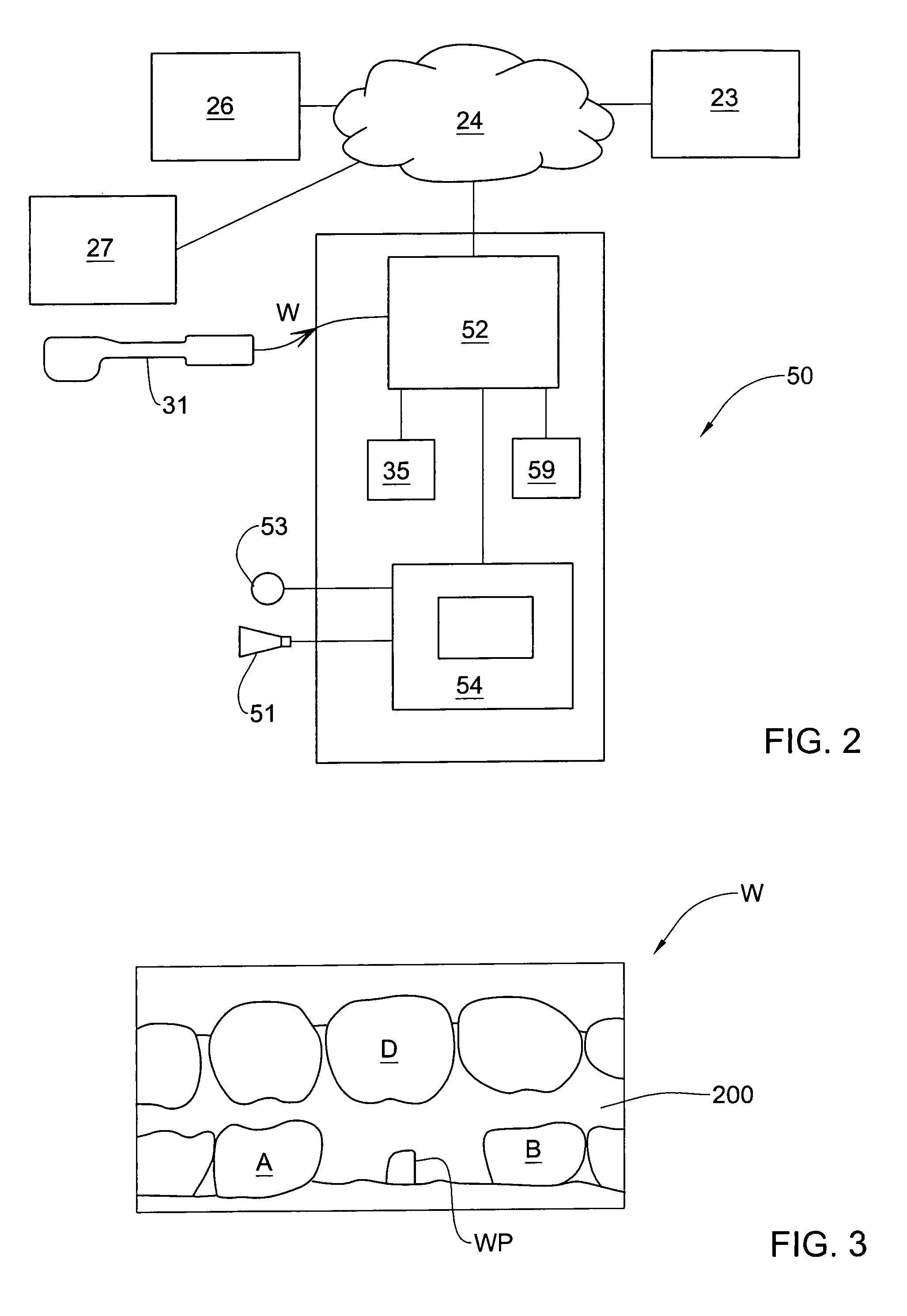
Method and system for providing feedback data useful in prosthodontic procedures associated with the intra oral cavity
ActiveUS7862336B2Impression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNumerical modelsComputer science
Feedback data useful in prosthodontic procedures associated with the intra oral cavity is provided. First, a 3D numerical model of the target zone in the intra oral cavity is provided, and this is manipulated so as to extract particular data that may be useful in a particular procedure, for example data relating to the finish line or to the shape and size of a preparation. The relationship between this data and the procedure is then determined, for example the clearance between the preparation and the intended crown. Feedback data, indicative of this relationship, is then generated, for example whether the preparation geometry is adequate for the particular type of prosthesis.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
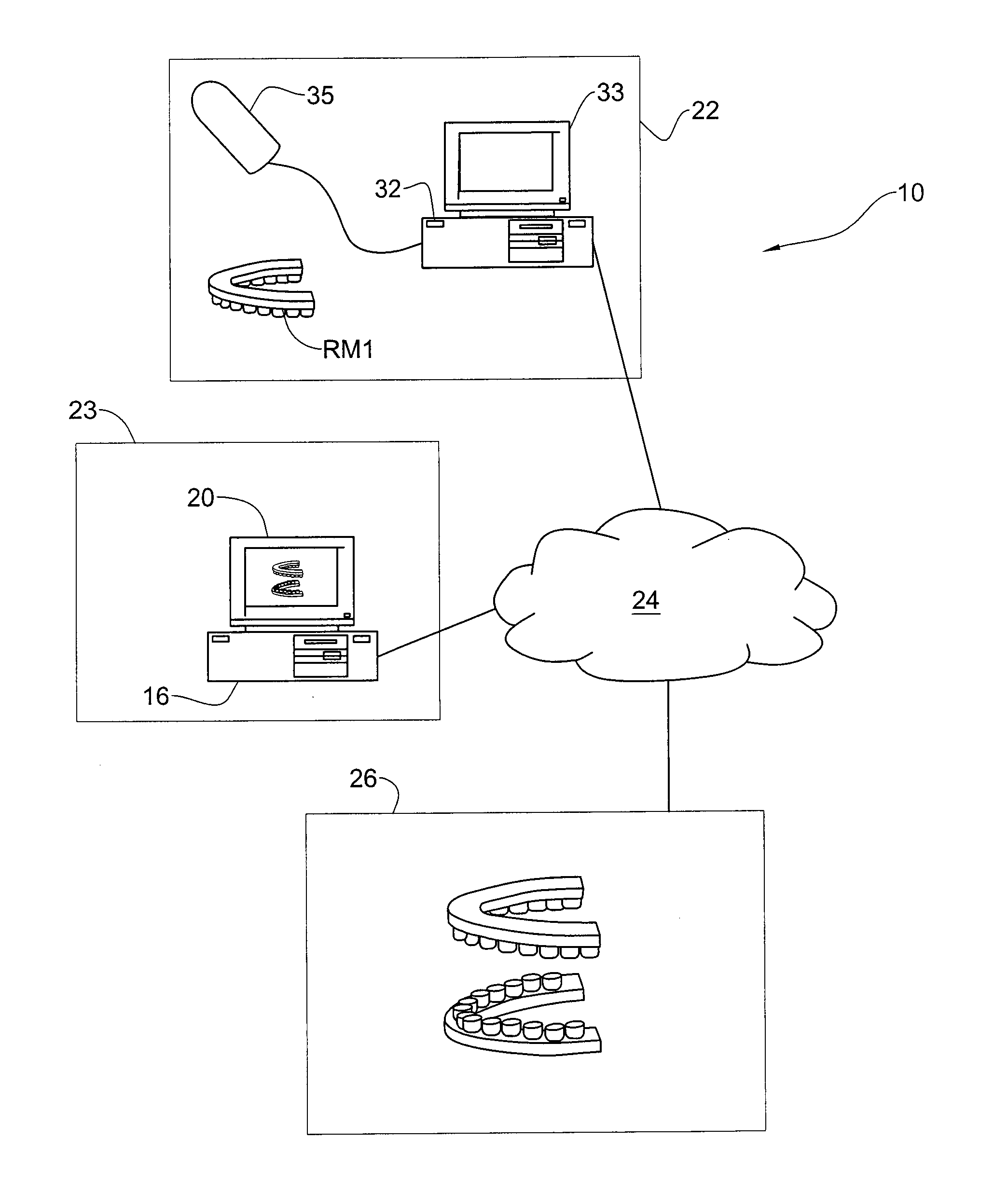
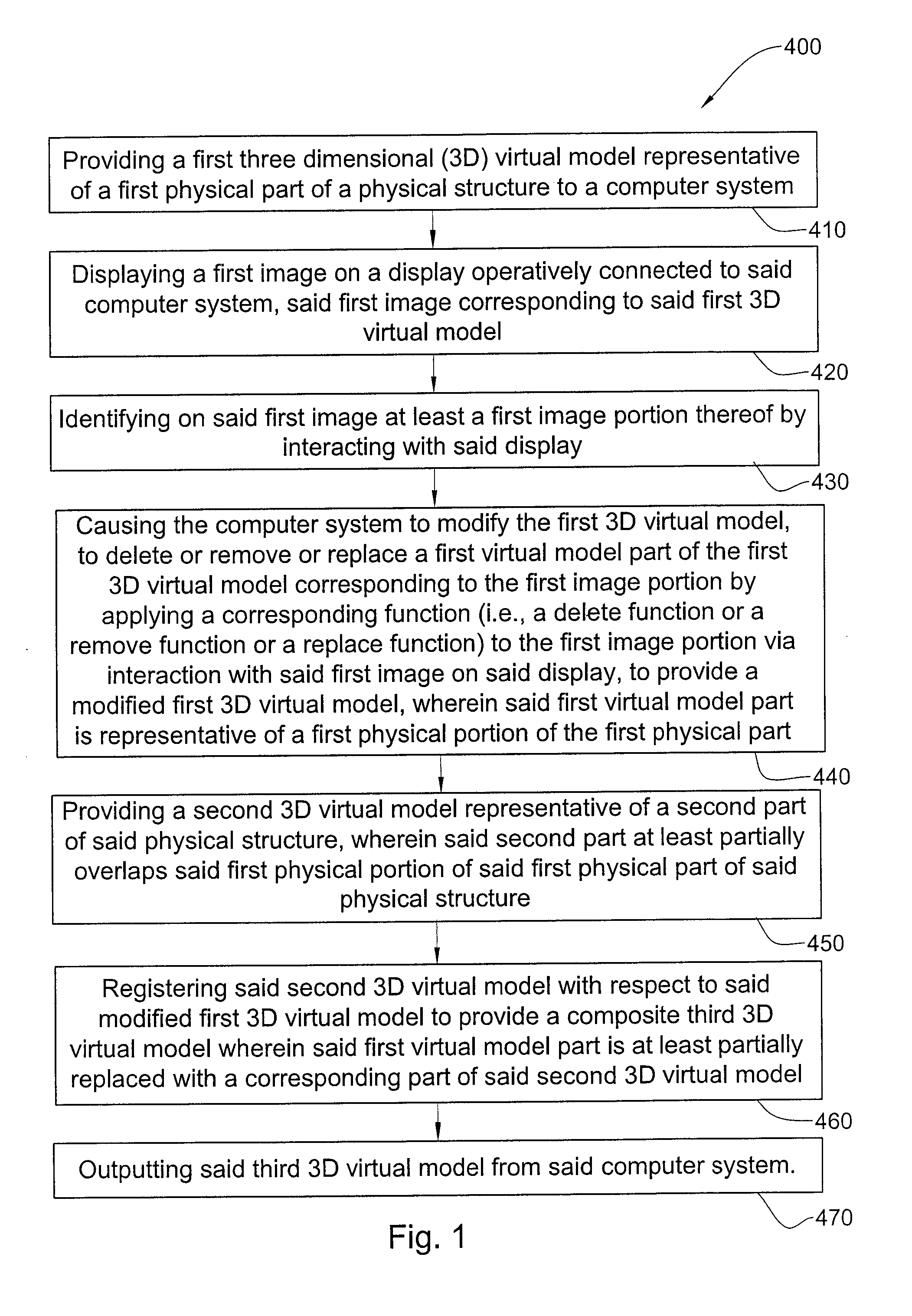
Methods and systems for creating and interacting with three dimensional virtual models
ActiveUS20130110469A1The process is convenient and fastImage enhancementImpression capsComputer graphics (images)Virtual model
Systems and methods are provided for modifying a virtual model of a physical structure with additional 3D data obtained from the physical structure to provide a modified virtual model.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
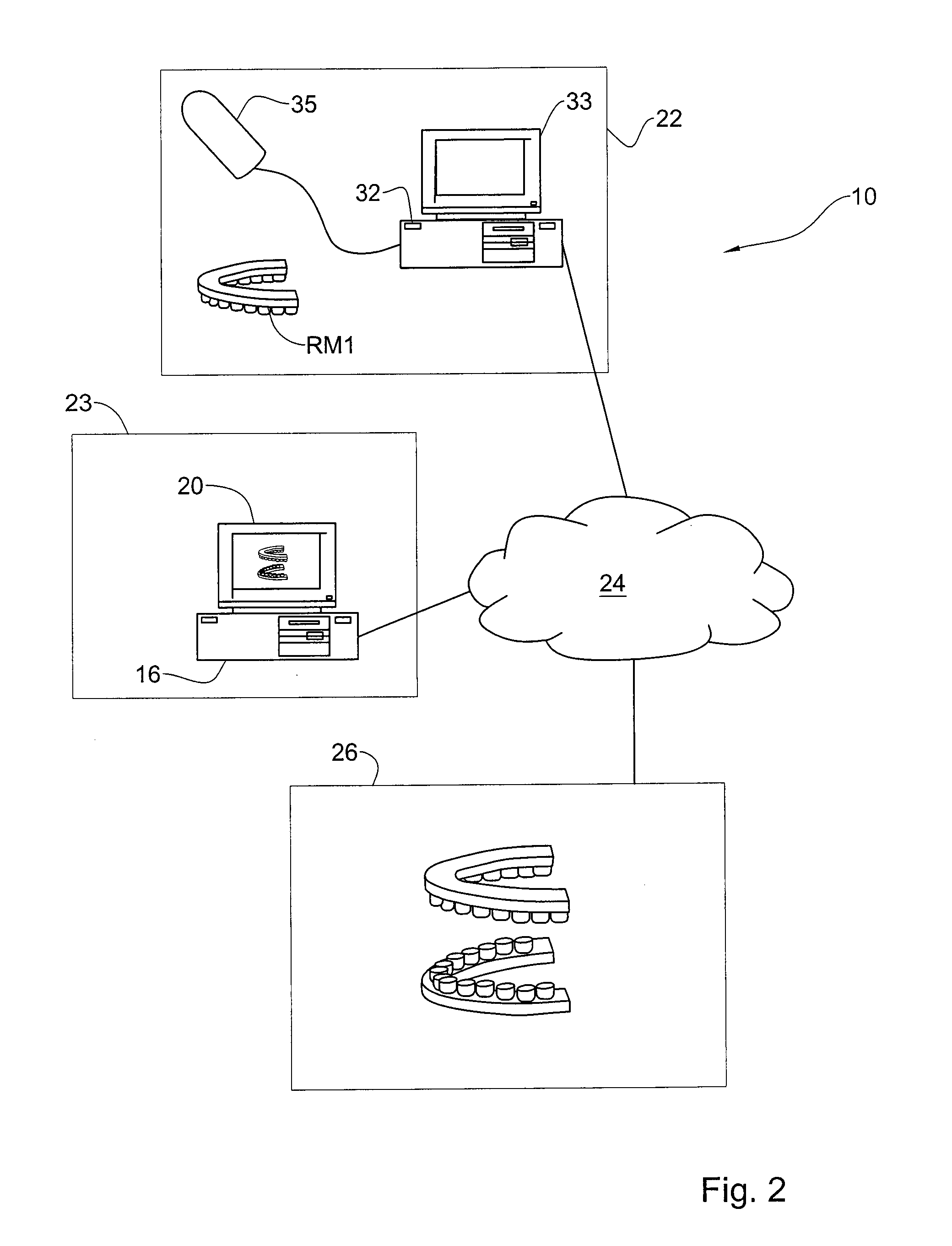
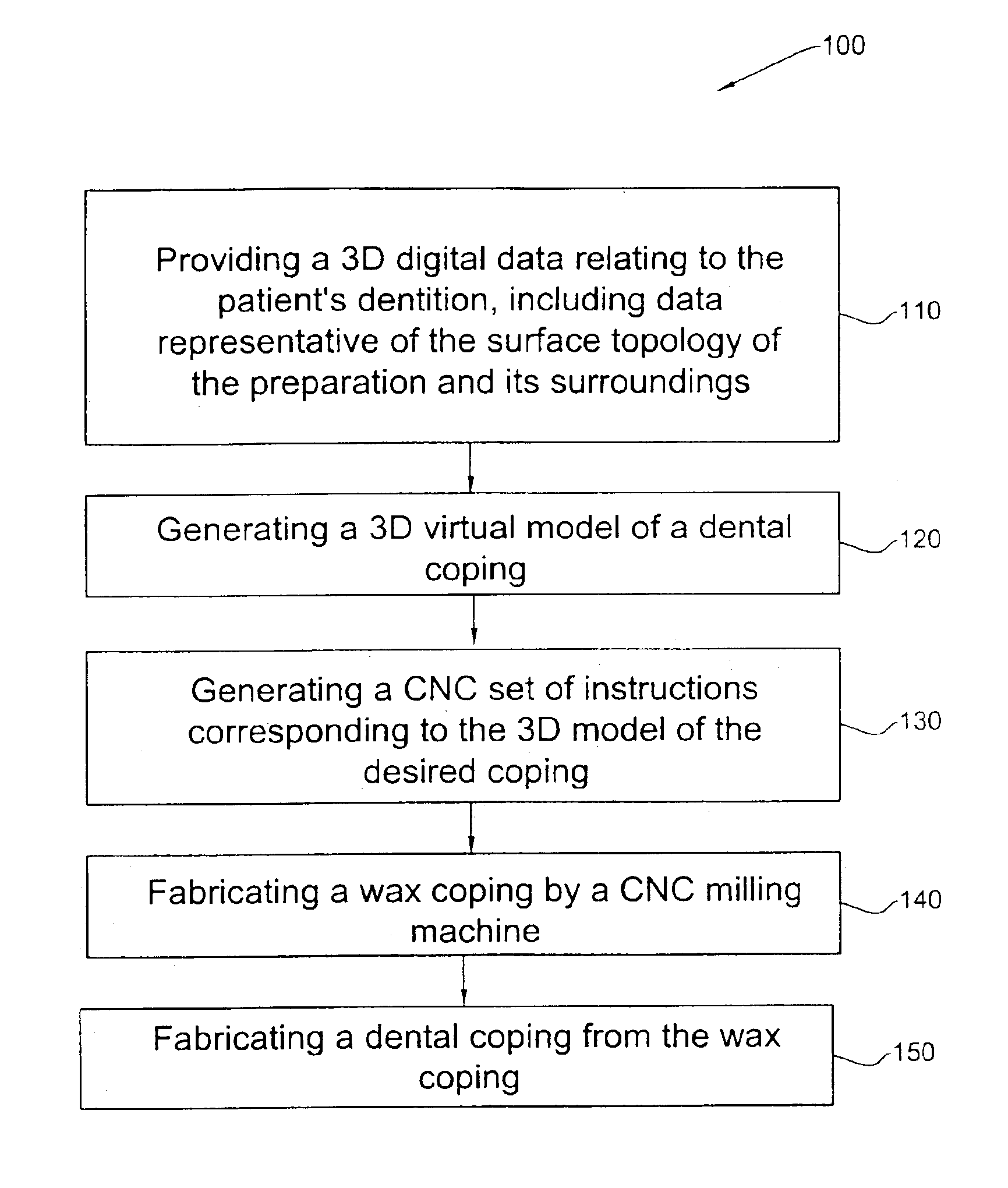
Method and system for fabricating a dental coping, and a coping fabricated thereby
A wax model of a required coping is produced using CNC machining techniques based on a virtual model of the coping created from digital data obtained from the intraoral cavity. The dental coping is then fabricated from the wax model.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
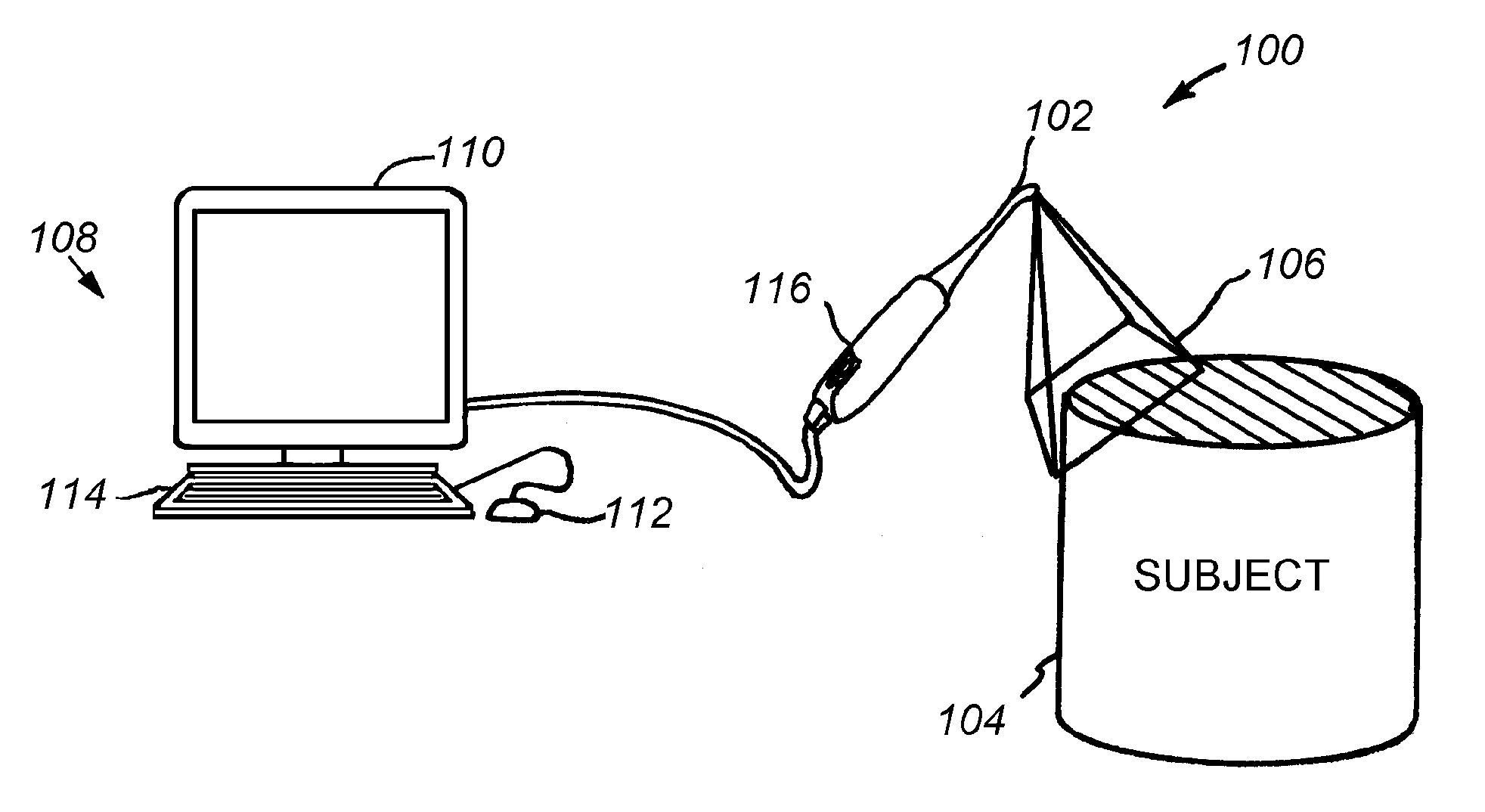
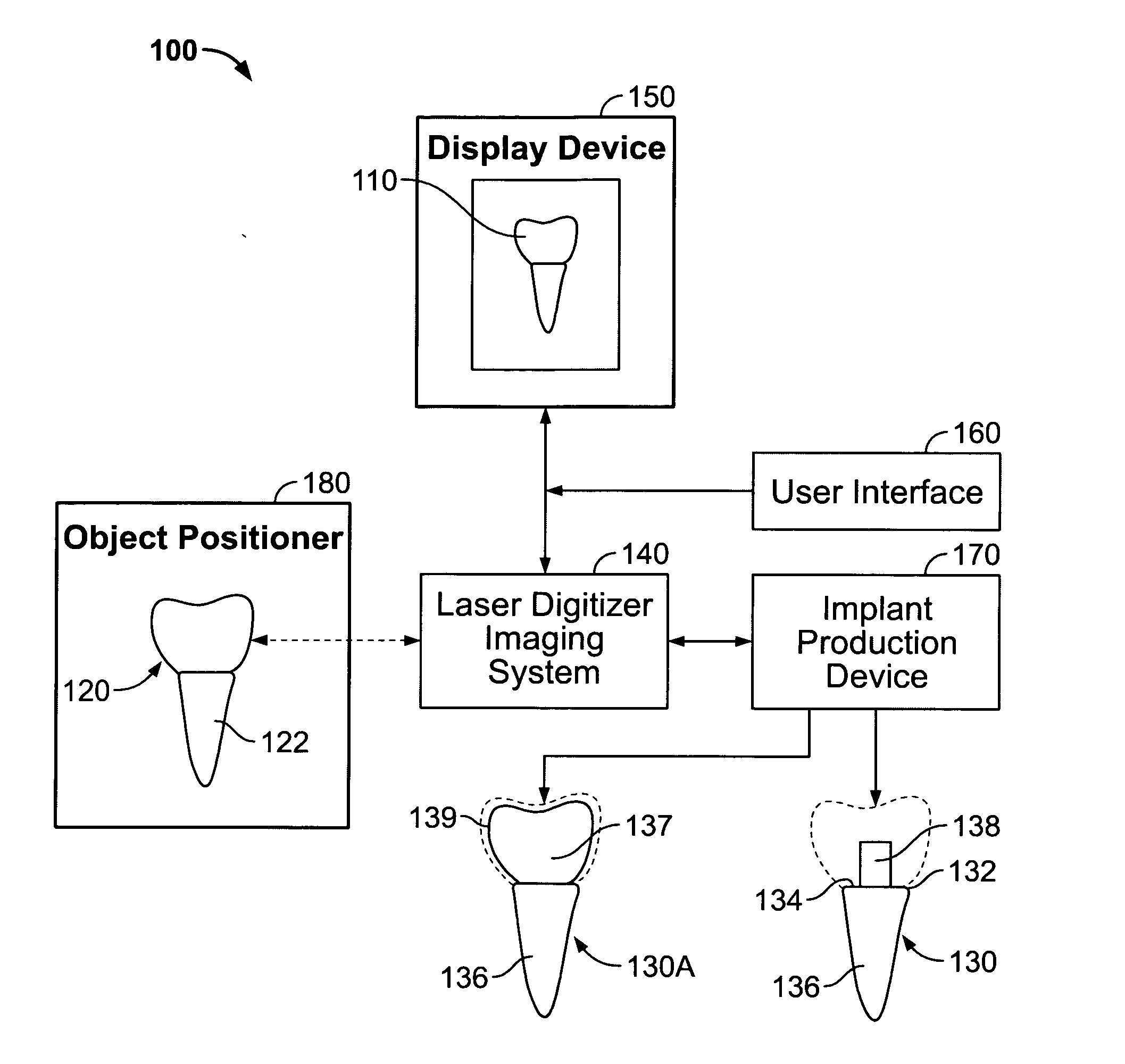
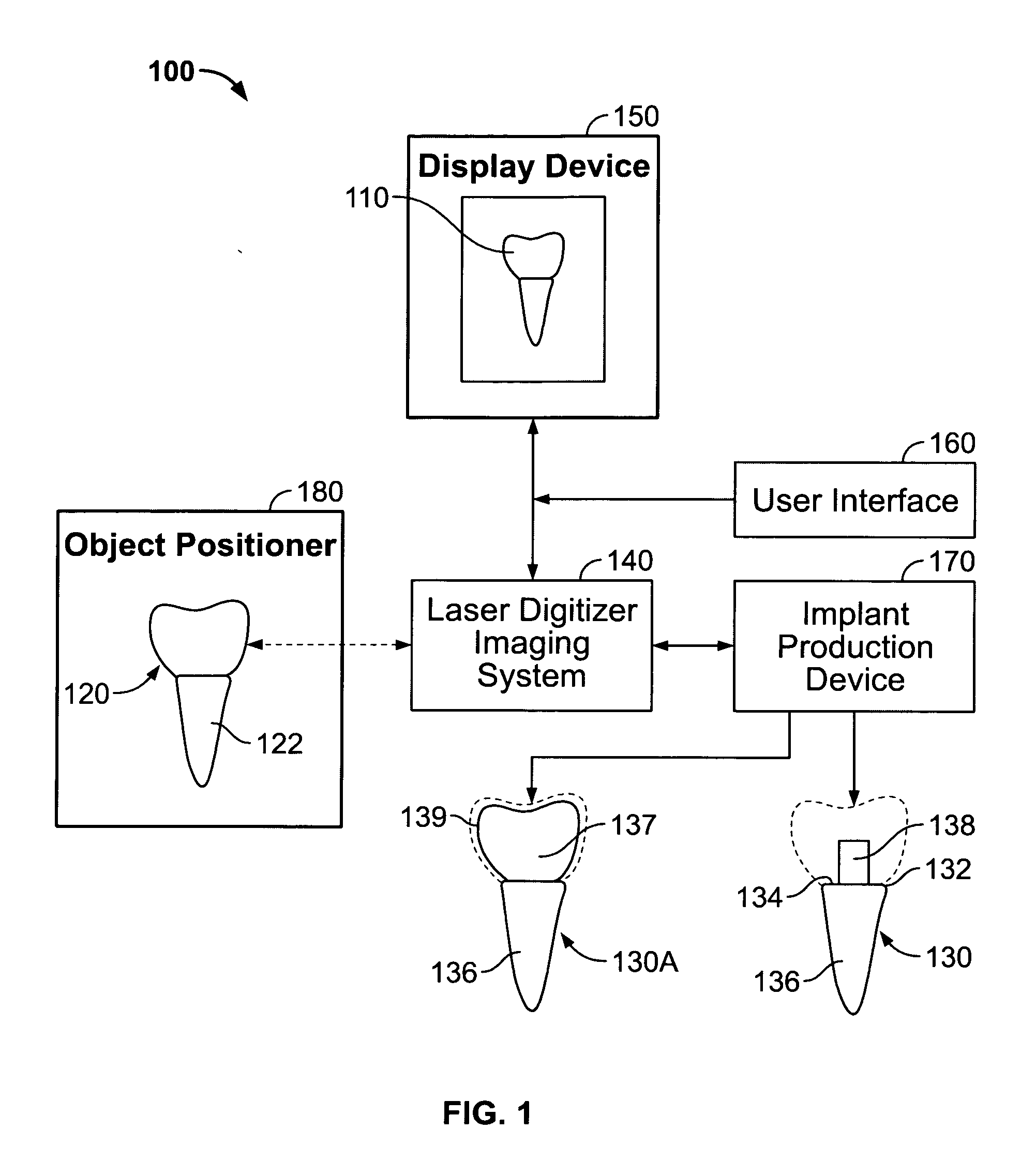
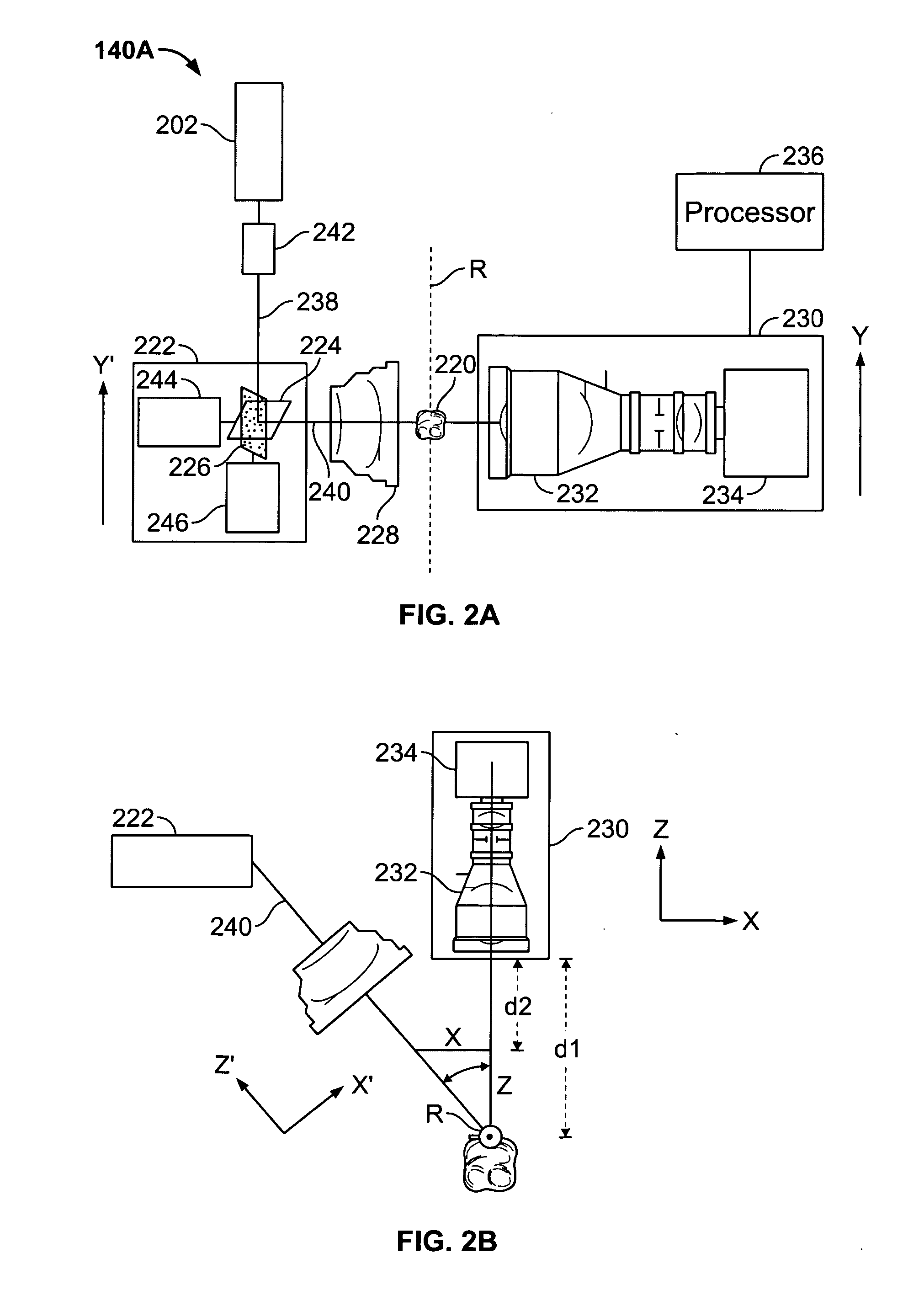
System for producing a dental implant and method
A system and method for producing a dental fixture are provided. A laser digitizer imaging system creates a visual three-dimensional image of a dental item such as a tooth or a dental impression. The three-dimensional image may be displayed and the size and shape of the image may be selectively modified by the user of the system. Digital data associated with the three-dimensional image of the dental item is sent to an implant production device. A dental implant is produced in response to receipt of the data associated with the three-dimensional image such that the implant is insertable into a socket of the jawbone from where a tooth was extracted.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
2d image arrangement
ActiveUS20130218530A1Good for comparisonDetection is slightImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed is a method of designing a dental restoration for a patient, wherein the method includes providing one or more 2D images, where at least one 2D image includes at least one facial feature; providing a 3D virtual model of at least part of the patient's oral cavity; arranging at least one of the one or more 2D images relative to the 3D virtual model in a virtual 3D space such that the 2D image and the 3D virtual model are aligned when viewed from a viewpoint, whereby the 3D virtual model and the 2D image are both visualized in the 3D space; and modeling a restoration on the 3D virtual model, where the restoration is designed to fit the facial feature of the at least one 2D image.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Method, blank, assortment of blanks, dental database and blank database comprising prefabricated partial end surfaces of partial dentures
ActiveUS20090181346A1Simple designSimple processMedical simulationDental implantsDenturesCentral region
The invention relates to a process, a blank, an assortment of blanks, a tooth database, and a database of blanks, for the production of a dental prosthetic item. The method comprises the provision of a 3D model of a dental prosthetic item and the selection of a suitable blank from a plurality of possible blanks. The provision of the 3D model of the dental prosthetic item comprises the determination of an esthetically relevant designed subregion of the 3D model of the dental prosthetic item as part of an exterior surface of said dental prosthetic item, and a blank is specified from a plurality of blanks having a prefabricated esthetically relevant terminal subsurface of a surface of the tooth, the terminal subsurface of said blank being such that it at least approximates the thus specified designed subregion. The 3D model of said dental prosthetic item is carved from the selected blank such that the prefabricated terminal subsurface of said blank remains unmachined in at least a central region thereof.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
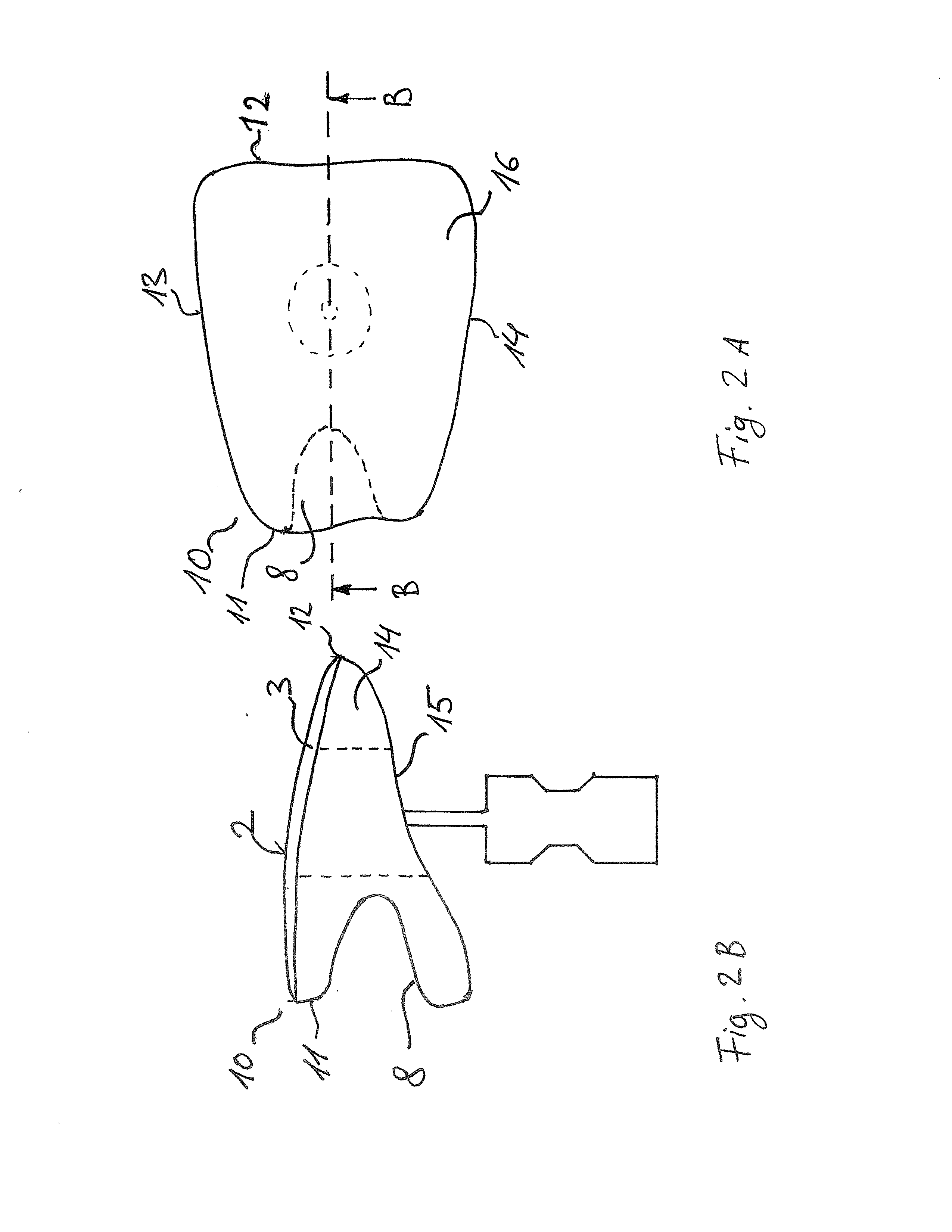
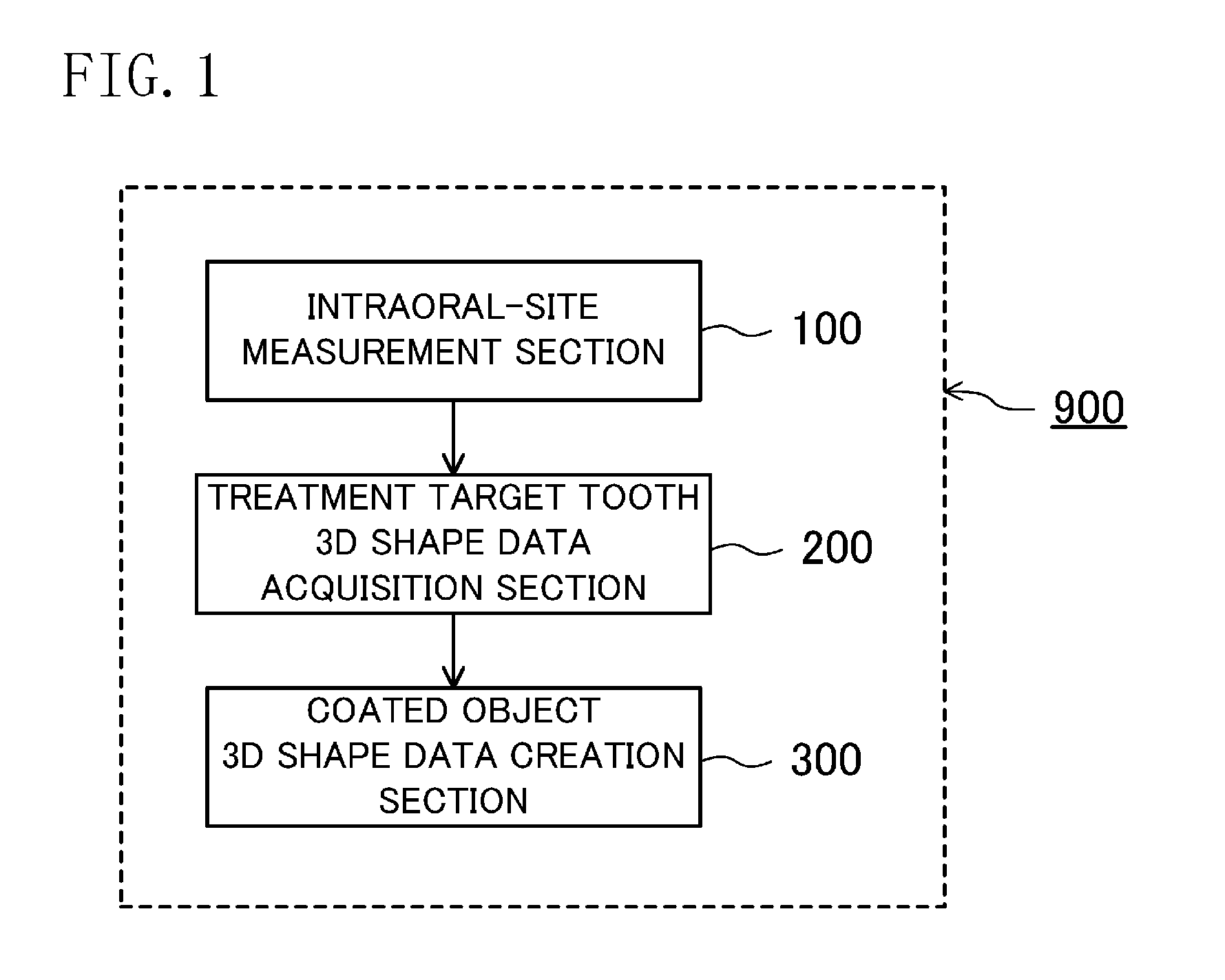
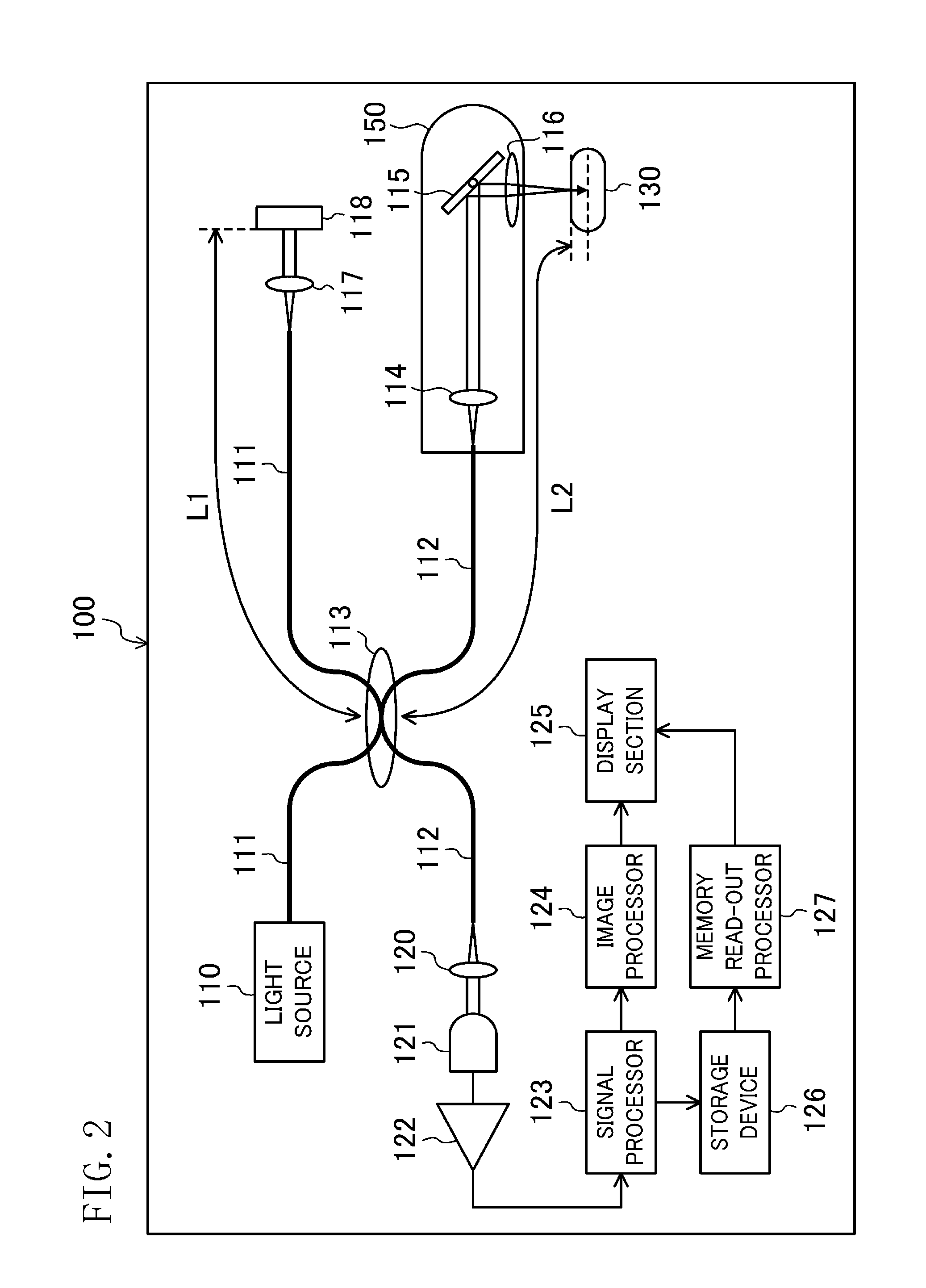
Method for forming dental coating and dental cad/cam device
A dental CAD / CAM device capable of accurately forming a dental coating is provided. The device includes: an intraoral-site measurement section 100 configured to measure 3D shape data on an intraoral site 130 with an OCT probe 150 for obtaining a tomogram of an object using near-ultraviolet light; a treatment-target-tooth 3D shape data acquisition section 200 configured to acquire shape data of a treatment target tooth from 3D shape data obtained by the intraoral-site measurement section 100; and a coating object 3D shape data creation section 300 configured to create 3D shape data on a dental coating such that the dental coating matches the 3D shape data of the treatment target tooth obtained by the treatment target tooth 3D shape data acquisition section 200.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
2D image arrangement
ActiveUS9336336B2Accurate modelingGood for comparisonImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed is a method of designing a dental restoration for a patient, wherein the method includes providing one or more 2D images, where at least one 2D image includes at least one facial feature; providing a 3D virtual model of at least part of the patient's oral cavity; arranging at least one of the one or more 2D images relative to the 3D virtual model in a virtual 3D space such that the 2D image and the 3D virtual model are aligned when viewed from a viewpoint, whereby the 3D virtual model and the 2D image are both visualized in the 3D space; and modeling a restoration on the 3D virtual model, where the restoration is designed to fit the facial feature of the at least one 2D image.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
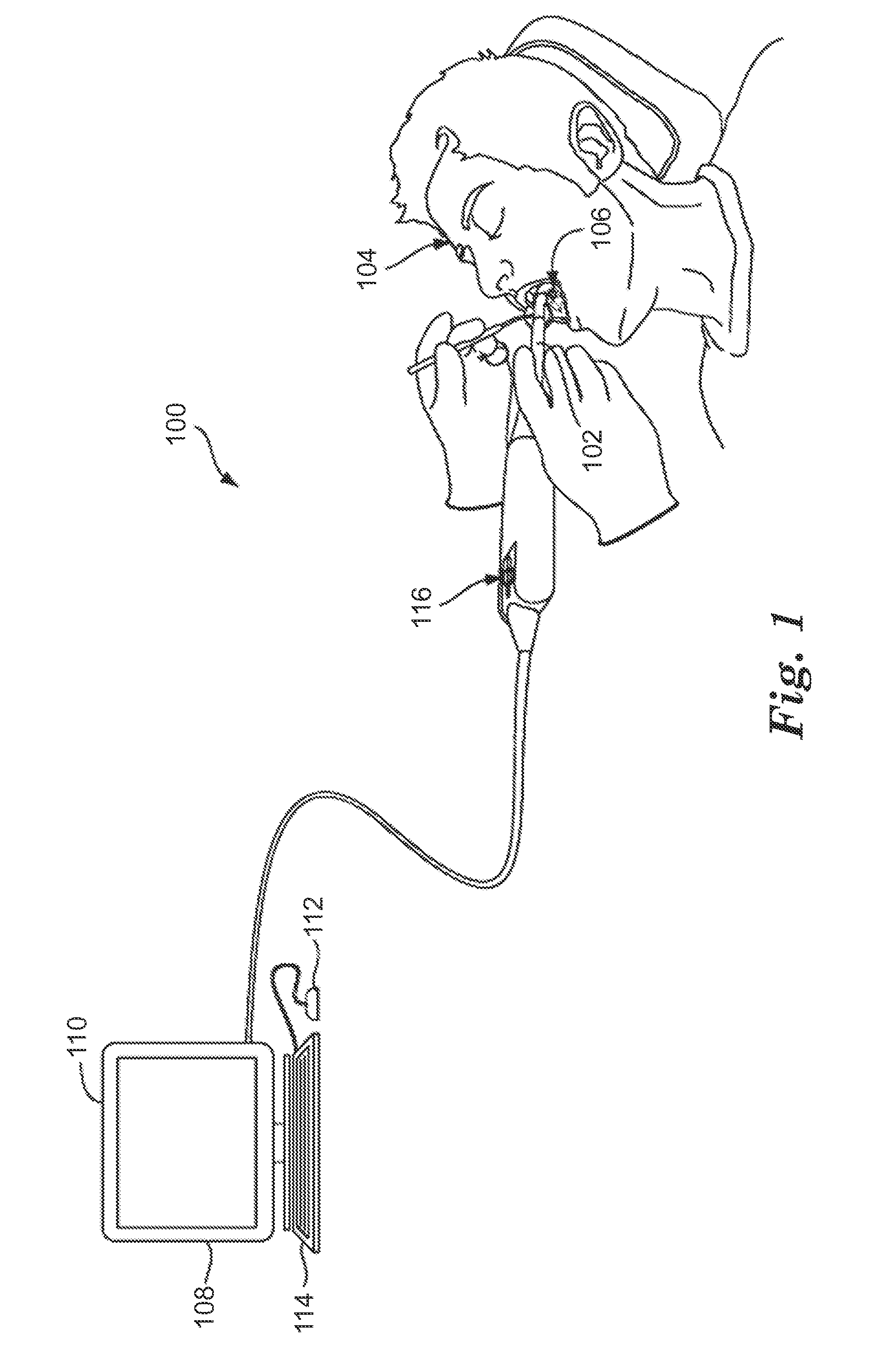
Therapeutic and protective dental device useful as an intra-oral delivery system
InactiveUS7328706B2Promote absorptionMaximize of contactCosmetic preparationsImpression capsOral regionMouthguard
A dental device has a U-shaped carrier with at least one channel for embracing an arch of teeth. The carrier has recessed insets in the channel. Discrete inserts carrying a beneficial agent can fit into the insets and release the agent gradually. When the device is used in a primarily therapeutic application, the inserts may be installed into all or less than all of the insets to form various insert patterns. Thus, different oral regions can be affected by different insert patterns. When the device is used as an athletic mouthguard, temporary blanks may be initially fitted in the insets, while a portion of the mouthguard is softened before an arch of teeth is pressed into the channel to make a custom impression. The inserts that are later installed in the insets possess different physical properties than the carrier and may be positioned and shaped to mechanically buffer teeth of the arch from mechanical shocks as well as release beneficial agents. The inserts may be replaced or refreshed to maintain the beneficial agent, which may be xylitol, remineralizing agents, moisturizing agents, desensitizing agents, flavoring agents, breath fresheners, chemical and biological indicators, nutraceuticals, antibiotics, probiotics, other medications and chemotherapeutics, or other agents.
Owner:DYNAMIC MOUTH DEVICES
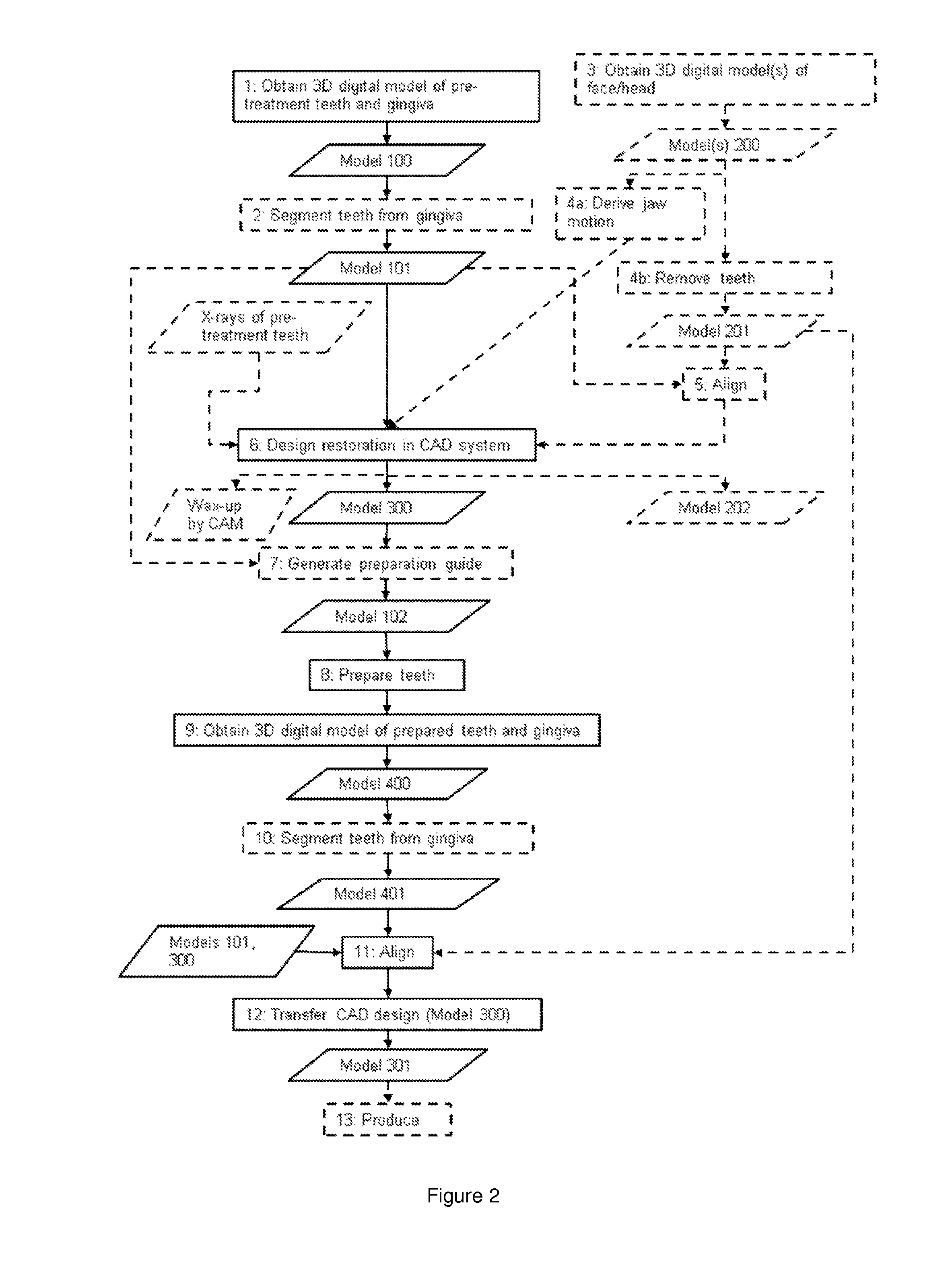
System and method for effective planning, visualization, and optimization of dental restorations
ActiveUS20120095732A1High level of detailLower levelMedical simulationTooth crownsDental restorationDental Restoration Failure
Disclosed is a method for planning, visualizing, and / or optimizing dental restoration on at least a part of the pre-prepared teeth of a patient, wherein said method comprises the steps of:providing at least one 3D digital model of at least a part of the pre-prepared teeth;designing at least one dental restoration CAD model based on the 3D digital model of at least a part of the pre-prepared teeth;providing at least one 3D digital model of at least a part of the prepared teeth, where the prepared teeth are provided by preparing the pre-prepared teeth by dental restorative work, at least partly based on the dental restoration CAD model; andaligning the 3D models of the pre-prepared and the prepared teeth.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
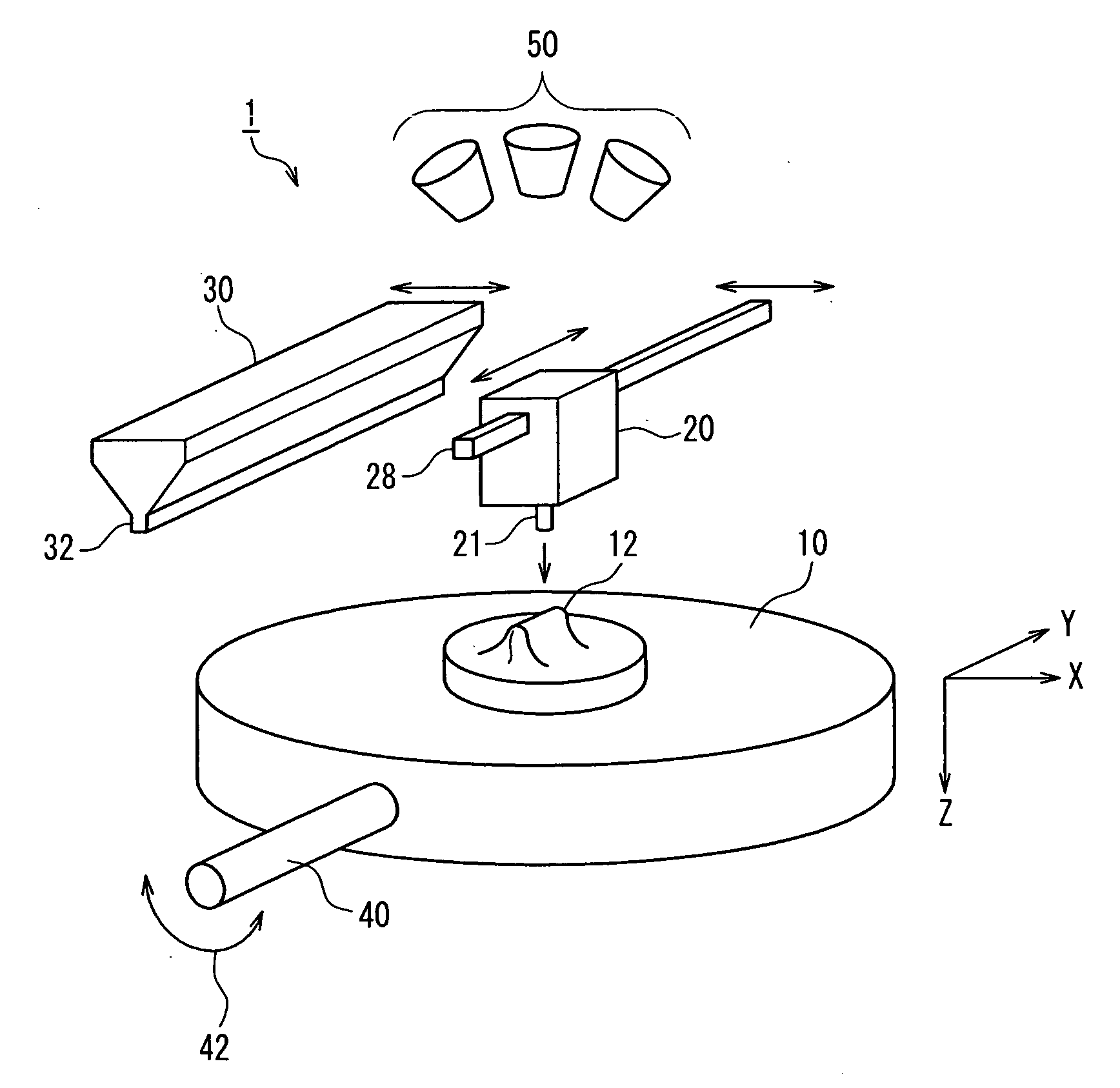
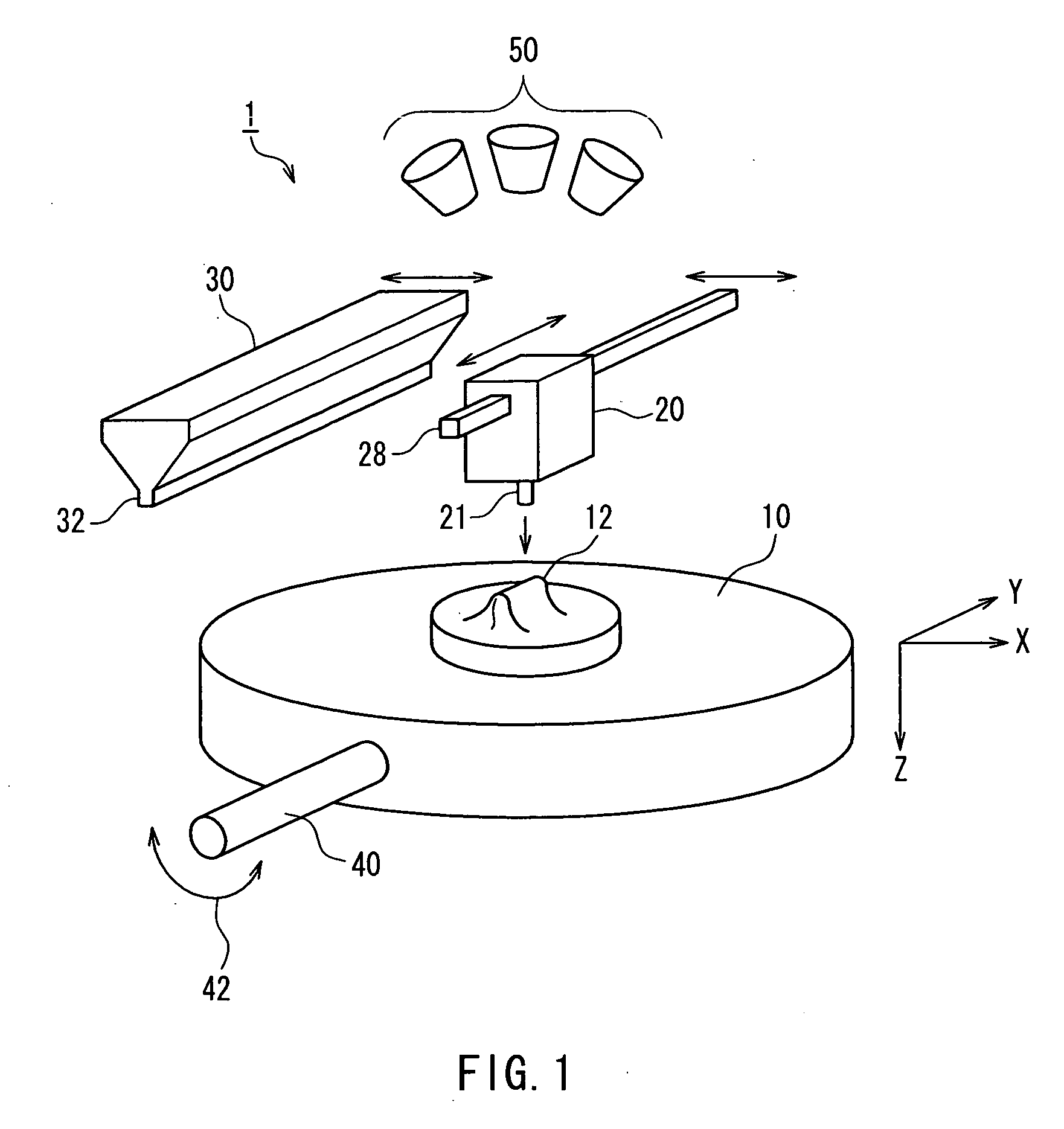
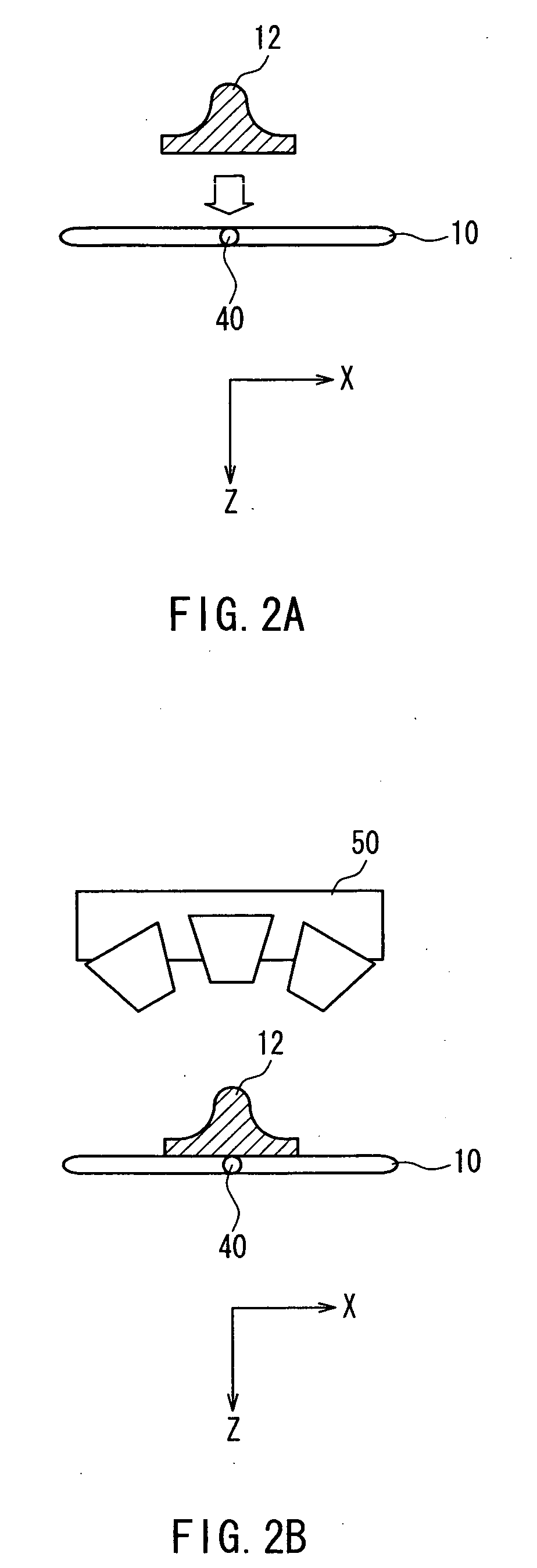
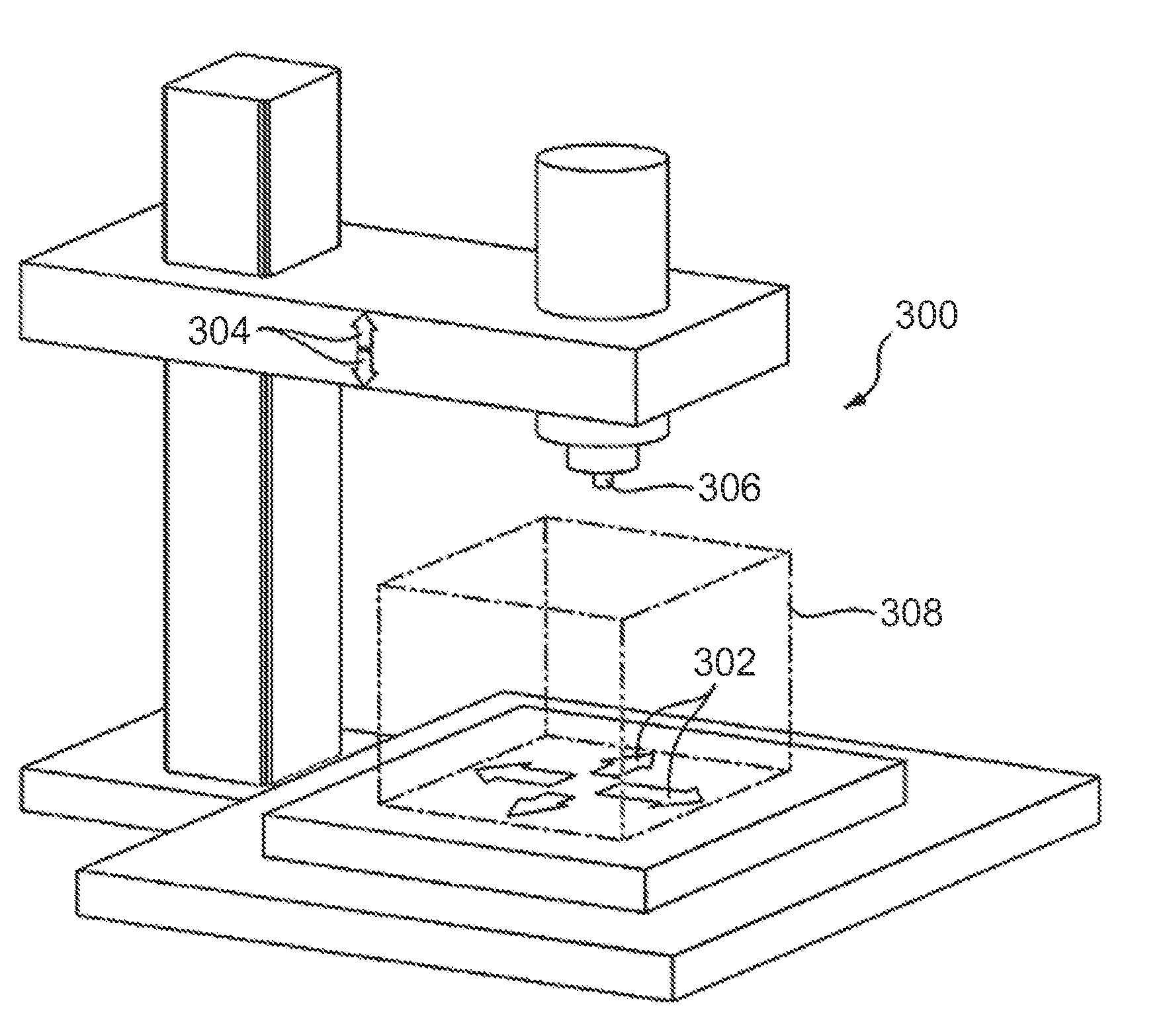
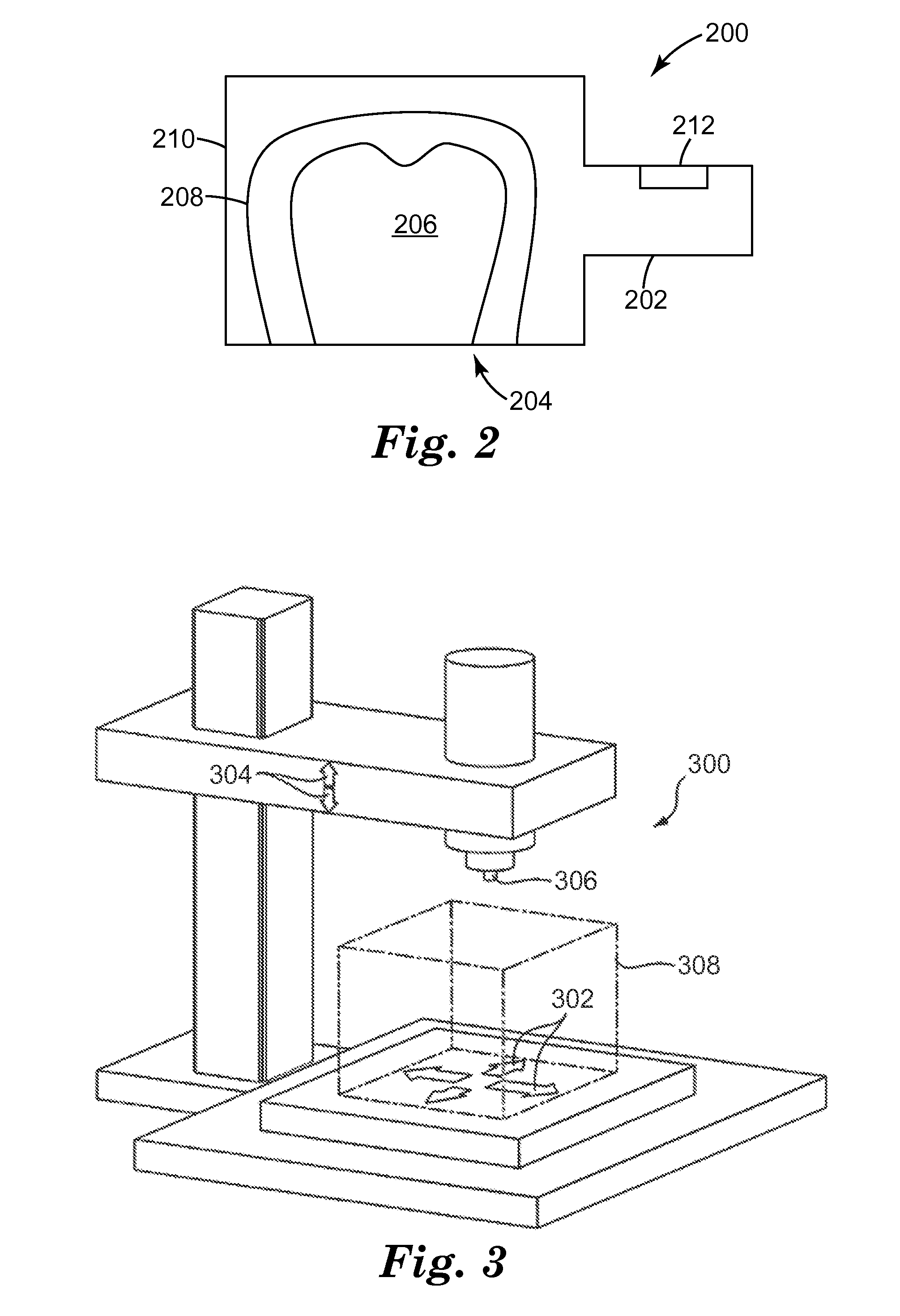
Apparatus for Forming Layered Object
InactiveUS20090025638A1Reduce irregularitiesReduce stepsLiquid surface applicatorsConfectioneryBiomedical engineeringSmooth surface
A layered-object forming apparatus (1) includes a holding mechanism (10) that holds a base (12), a liquid applying device (20) that applies a liquid to a predetermined position from above the base, a powder applying device (30) that allows a powder to fall from above the base, and a powder removing device that removes an unconsolidated powder on the base. Then, a process of applying the liquid by the liquid applying device, subsequently applying the powder by the powder applying device, subsequently consolidating the liquid and the powder applied onto the liquid and then removing the powder that has not been consolidated with the liquid by the powder removing device is repeated, thereby forming a three-dimensional structure on the base. Thus, it is possible to produce a three-dimensional structure that at least partially has a smooth surface, thus allowing omission or simplification of a surface smoothing treatment.
Owner:SHOFU INC
Method and apparatus for constructing crowns, bridges and implants for dental use
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture is disclosed for providing a dental crowns using electronic models, and more particularly to a method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for creating dental crowns using a lost-wax manufacturing process from electronic model files corresponding to patient teeth impressions and corresponding electronic models for tooth crowns. The system and method permit the electronic generation and specification of crown, bridge, and implant dental appliances that may be specified in an industry standard file specification. This specification is utilized in a rapid prototyping process to generate a wax impression for the appliance that may then be fabricated using standard lost-wax fabrication techniques.
Owner:NAT DENTEX LLC
Dental crown forms and methods
Dental crown forms and methods of using them are disclosed. The dental crown forms may include one or more of the following features: a handle attached to the dental crown form at a location removed from the base of the dental crown form; a vented handle through which excess amounts of hardenable dental material can pass during placement of the crown form; and one or more lines of weakness that may be separated to remove a dental crown form from hardenable dental material after placement of the filled crown form. The dental crown forms may also be located in packages with hardenable dental material located within the dental crown forms as packaged.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Production of replacement teeth from a three-dimensionally determined and digitized positive model
InactiveUS6970760B2High strengthSufficient aesthetic effectImpression capsDental articulatorsMachine toolOrthodontics
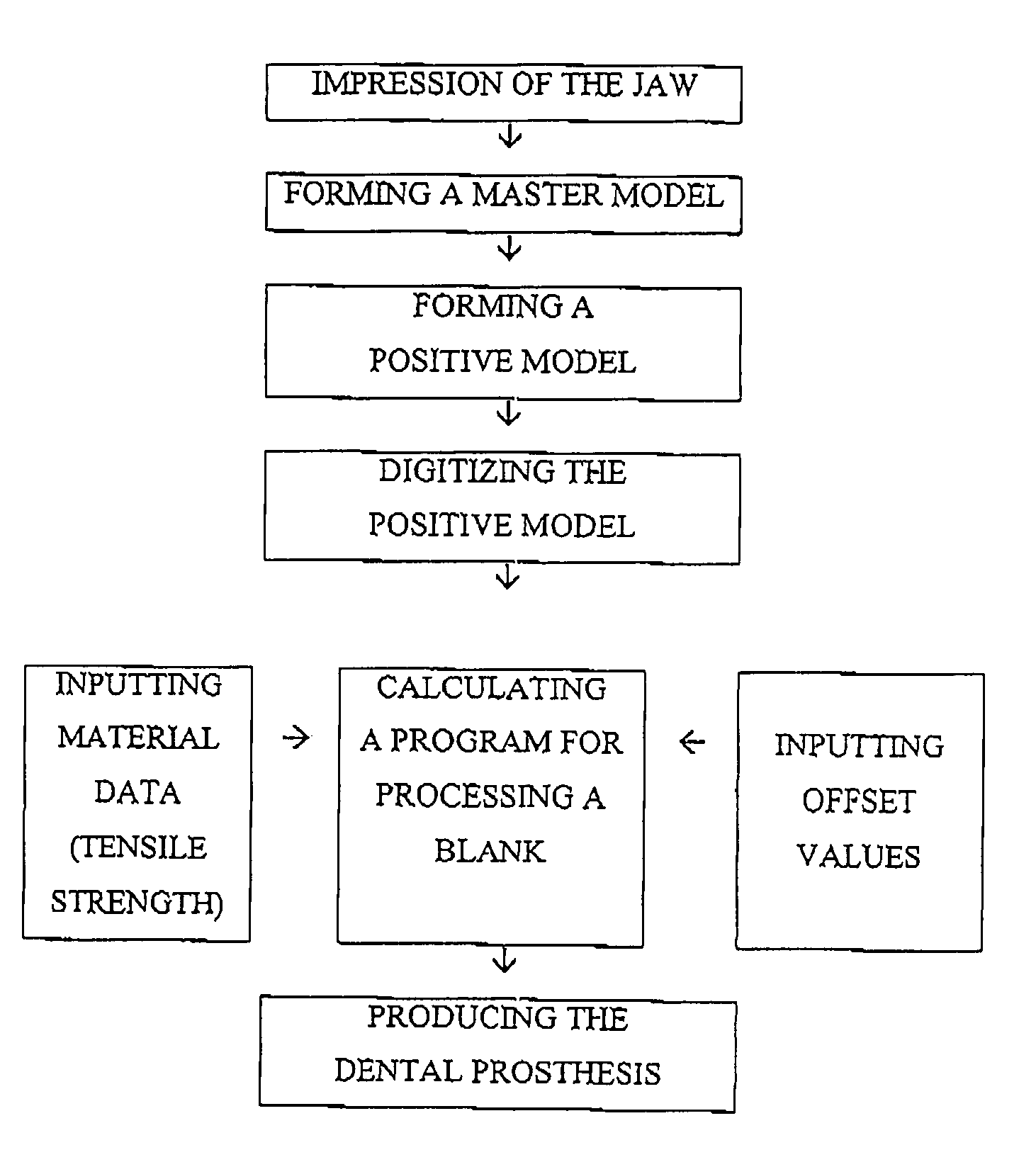
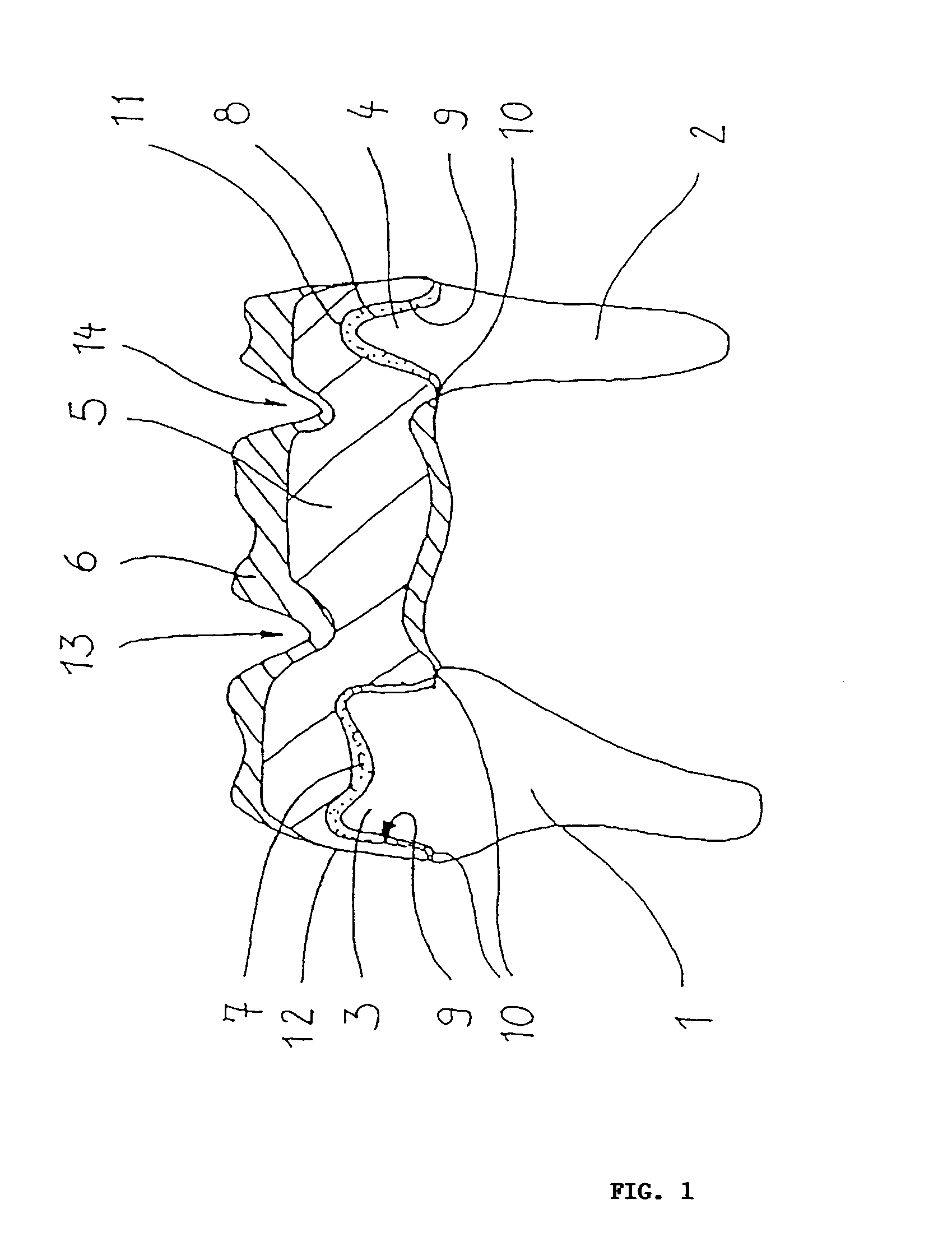
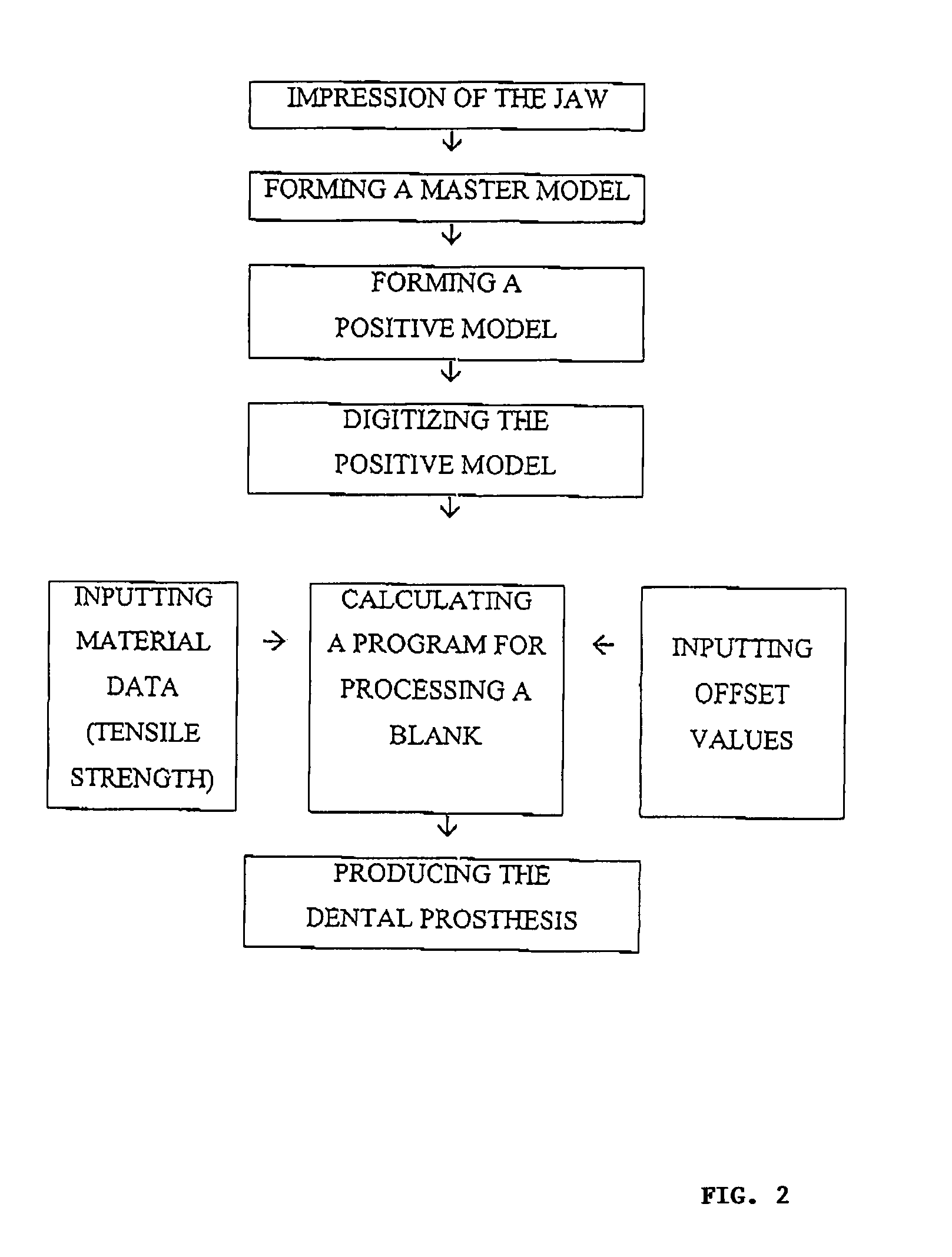
A method for the production of replacement teeth (5) from a three-dimensionally determined and digitized model, whereby for improved handling, cost and quality of the produced replacement tooth (5) a method including the following steps is carried out: inputting the data for the digitized model, treating the inner surface (9) of the surface model with a given offset value to generate a cement gap (7, 8) between the tooth replacement (5) to be made and tooth stump (1, 2) and calculation of a program for machining the blank or a mold by means of a machine tool.
Owner:DEGUDENT
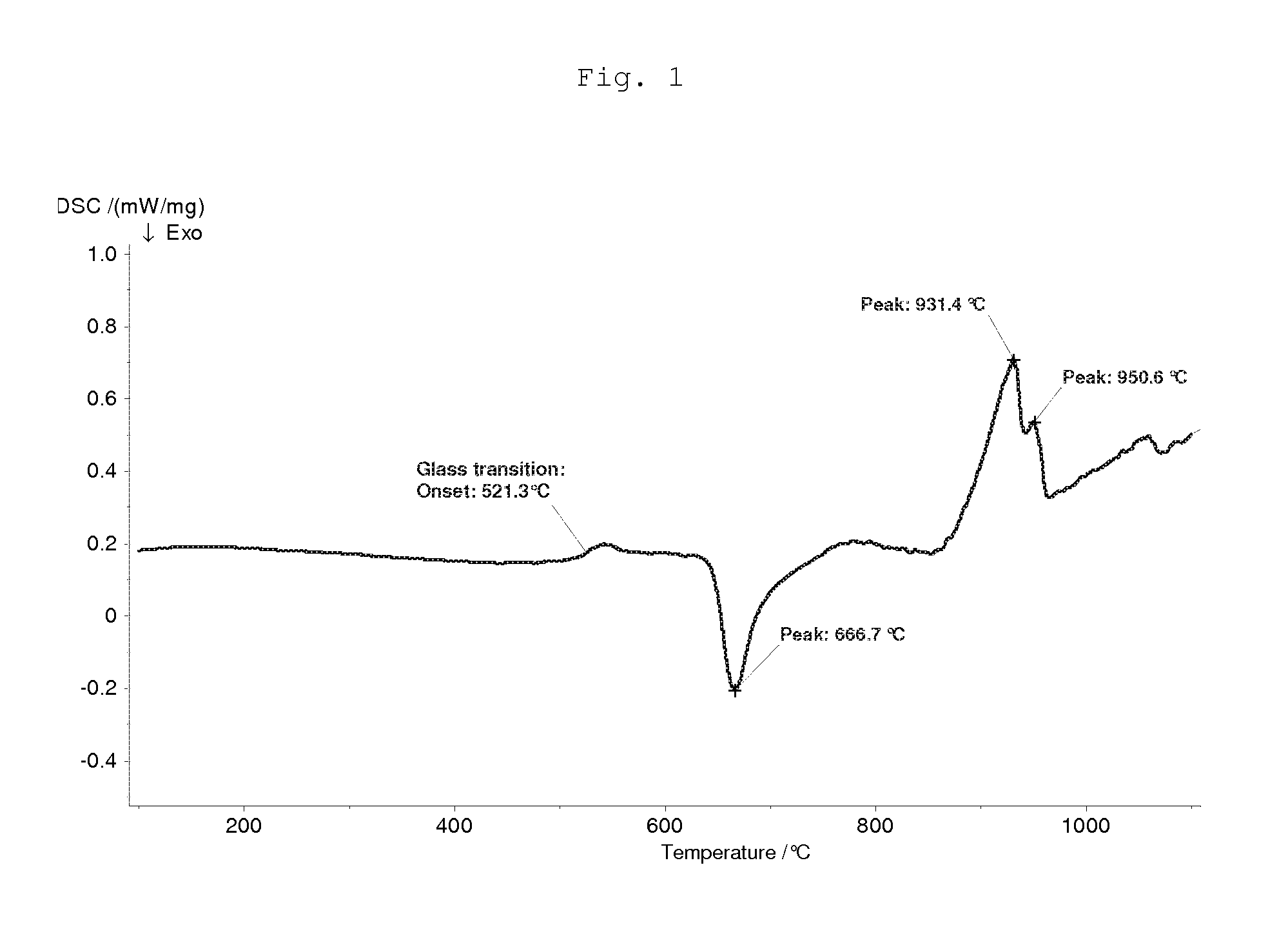
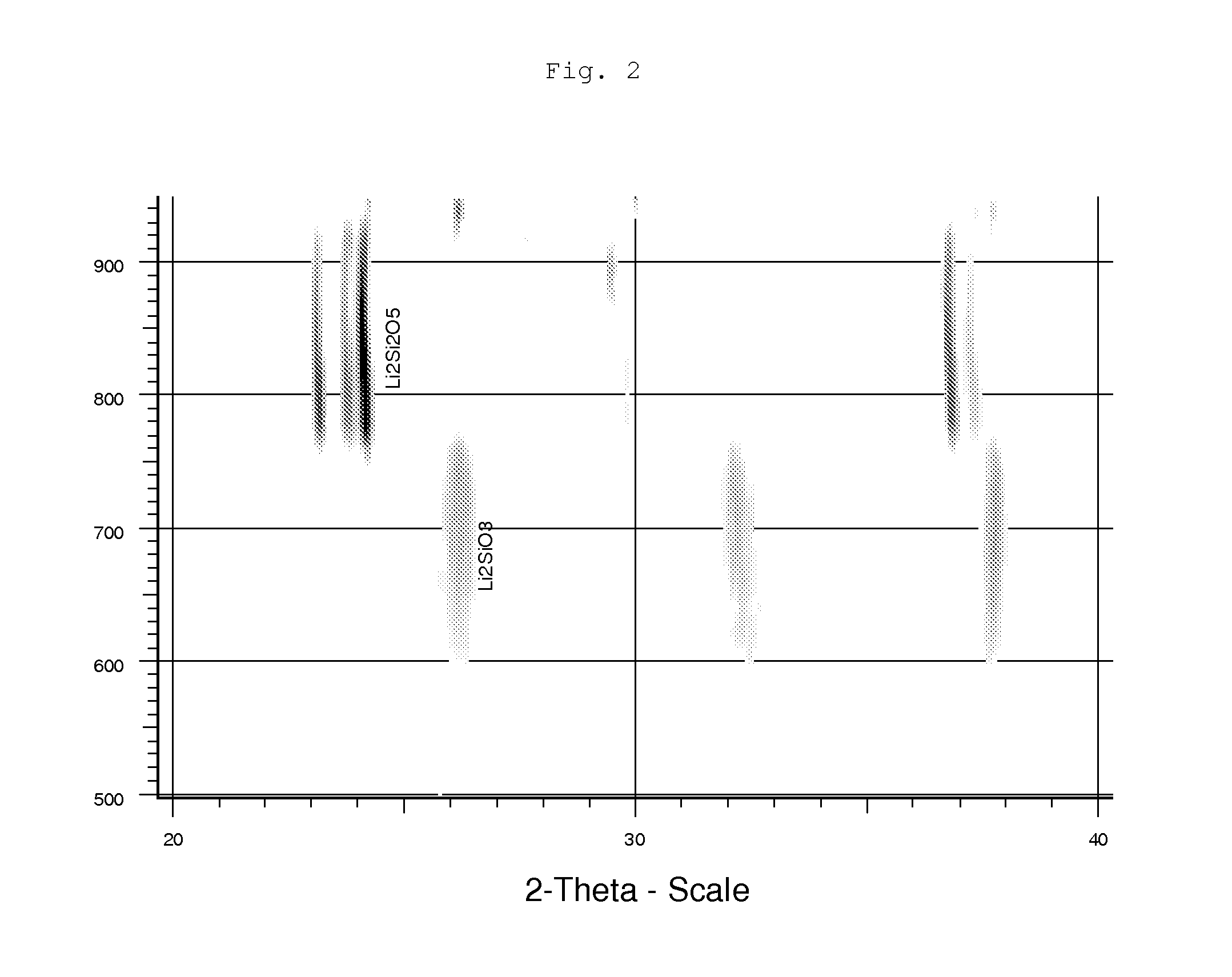
Lithium Silicate Glass Ceramic and Glass With ZrO2 Content
ActiveUS20110256409A1Substantial deterioration in translucencyInhibition formationPretreated surfacesTooth crownsLithiumSolid Bond
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
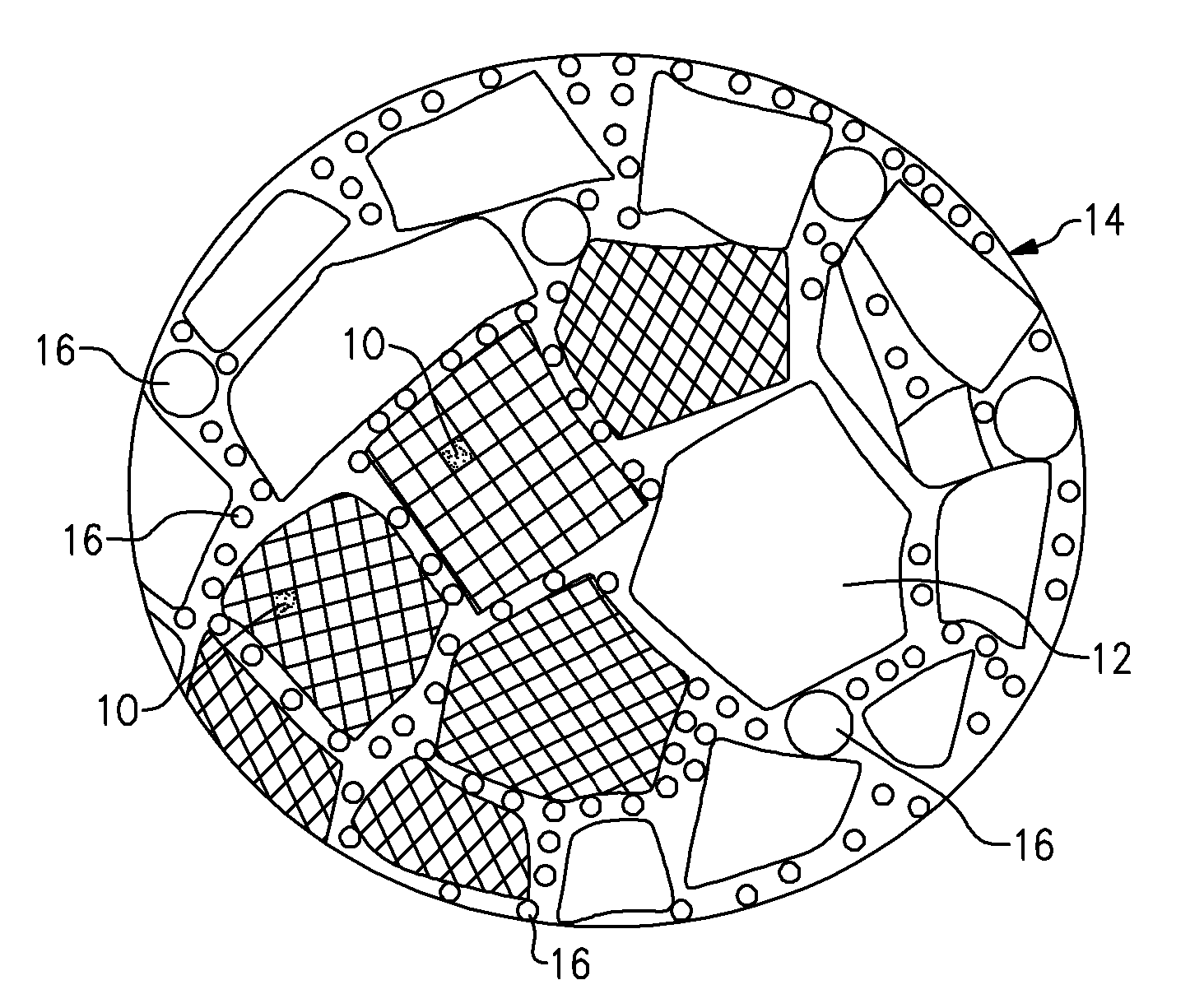
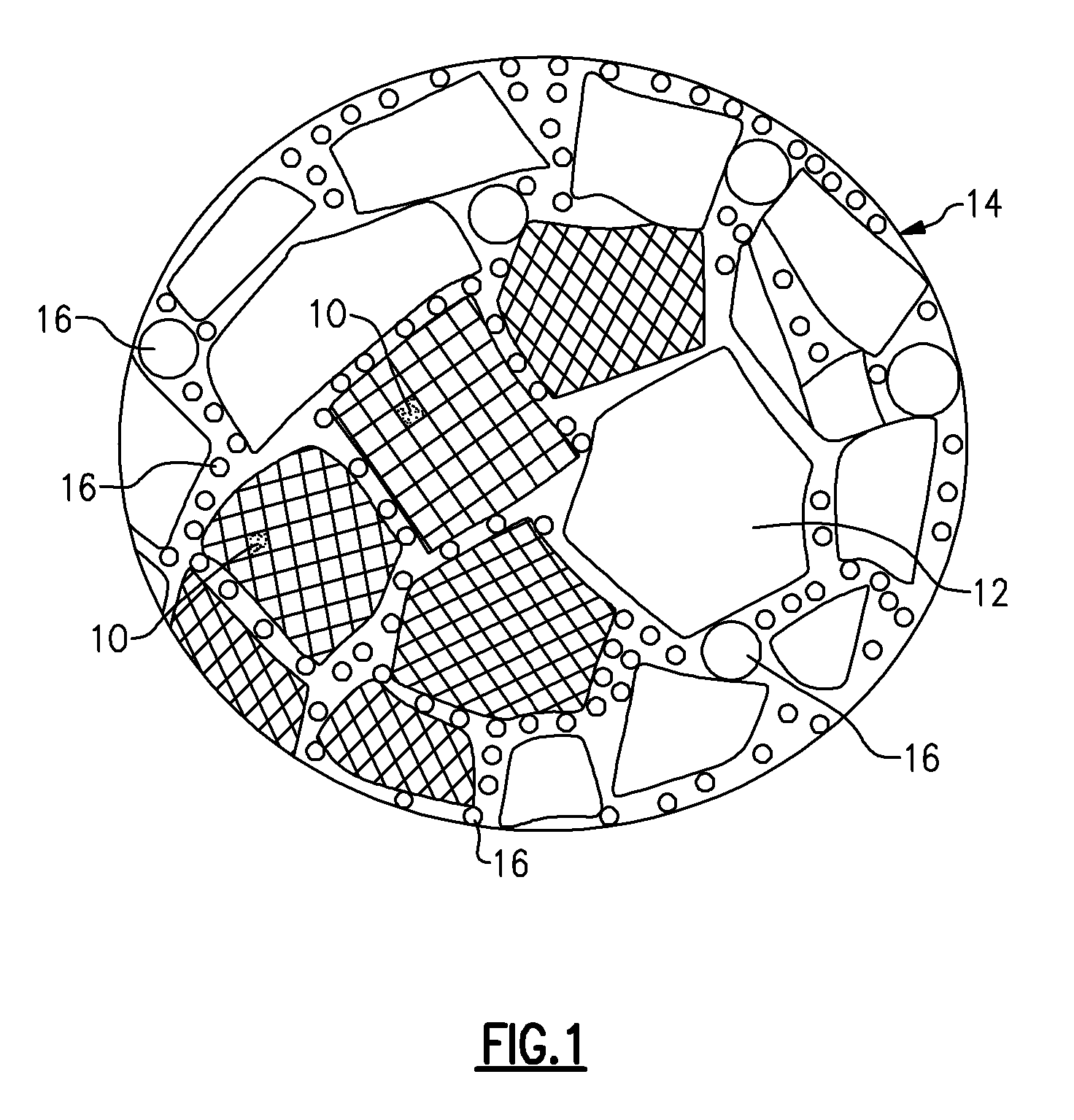
Blank for the production of a dental shaped body and method of producing said shaped body
ActiveUS7985119B2Considerable timeImprove shape qualityGrinding feed controlTooth crownsMaterial removalDental restorative materials
A blank and method for the production of dental shaped bodies in machining equipment having at least two tools located in the machining chamber of the machining equipment, including a corpus of tooth restoration material, from which the shaped body can be carved by means of at least one of at least two tools by material removal. The blank exhibits at least two gages, each of which is in the form of a recess, the geometry of which is such that the tool selected for the cutting operation can be recognized by means of at least one of the gages by reference to its outer contour, the at least two gages being disposed on the blank in such a way that they can be simultaneously engaged by the at least tools when the blank is clamped in the machining equipment for carving purposes.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Digitally-machined smc dental articles
InactiveUS20100268363A1Sufficient malleabilityCompensation for shrinkageProgramme controlComputer controlComputer Aided DesignEngineering
A dental article is fabricated from an SMC material using three-dimensional data captured from natural dentition to guide a computer-controlled milling machine. The three-dimensional data may include scans of an original tooth structure and a prepared tooth surface to characterize all surfaces of a dental article, or certain features may be created within a computer-assisted design environment taking account of occlusion, proximal contacts, and the like. In addition the model applied to a computer-controlled milling machine may account for shrinkage of the SMC material during any post-milling curing steps in order to ensure an accurate fit to the prepared tooth surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com