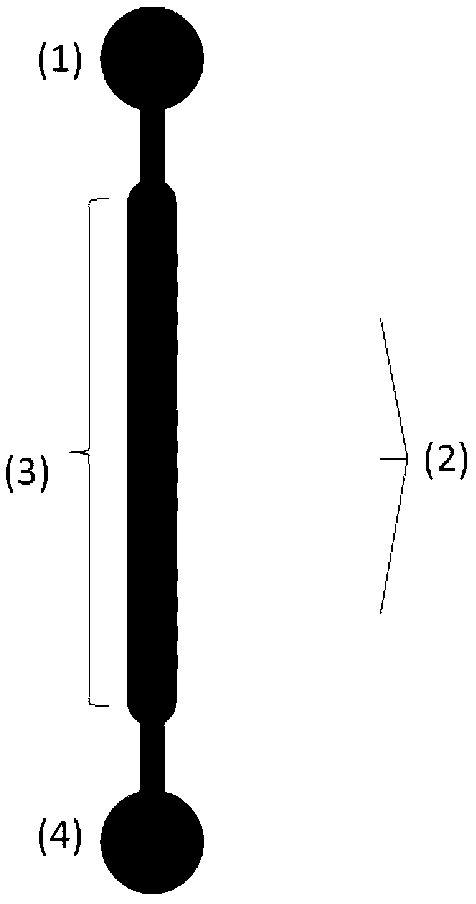Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
735 results about "Square Centimeter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A unit of area measurement equal to a square measuring one centimeter on each side. One square centimeter is equal to 10E-4 square meter.(NCI)
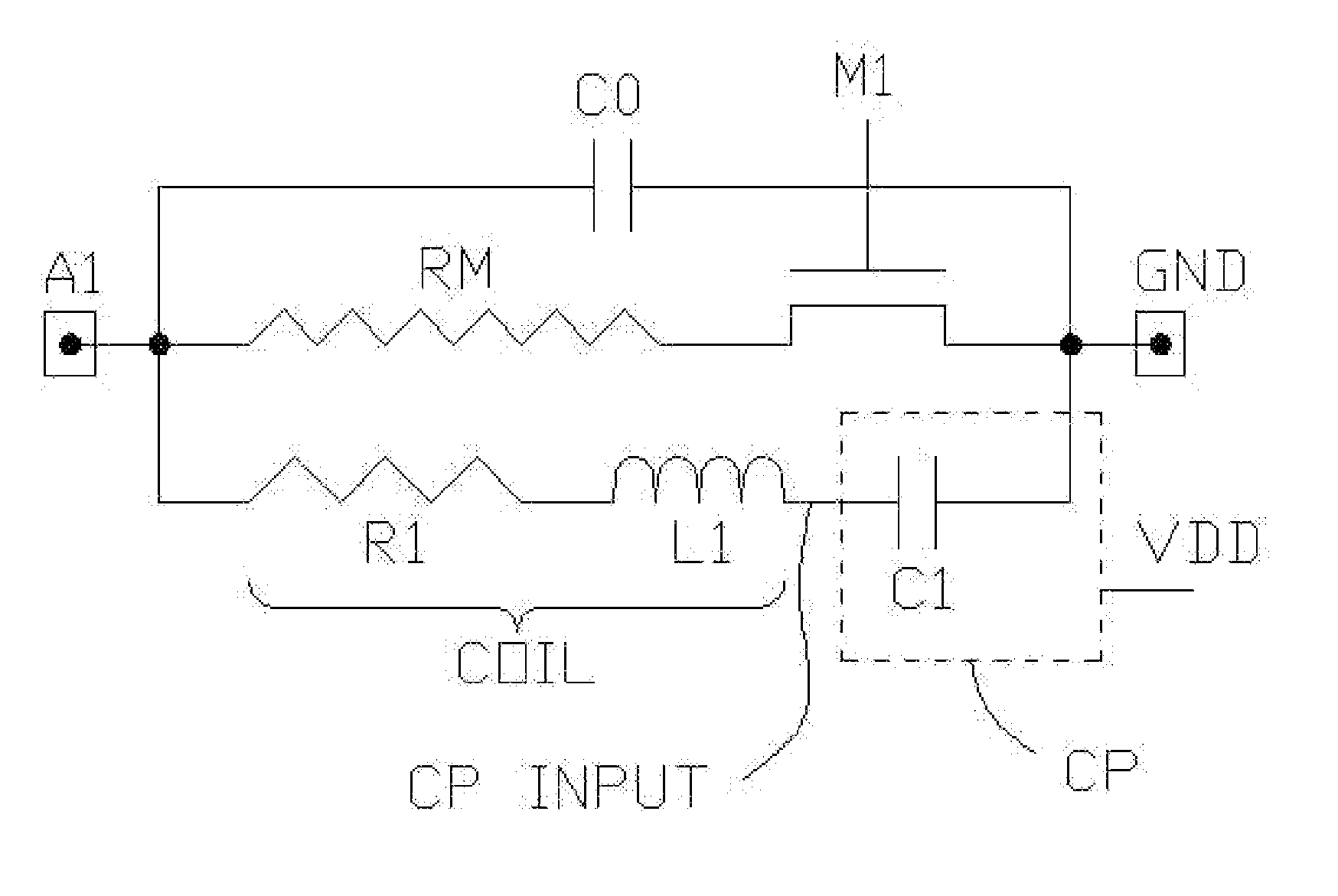
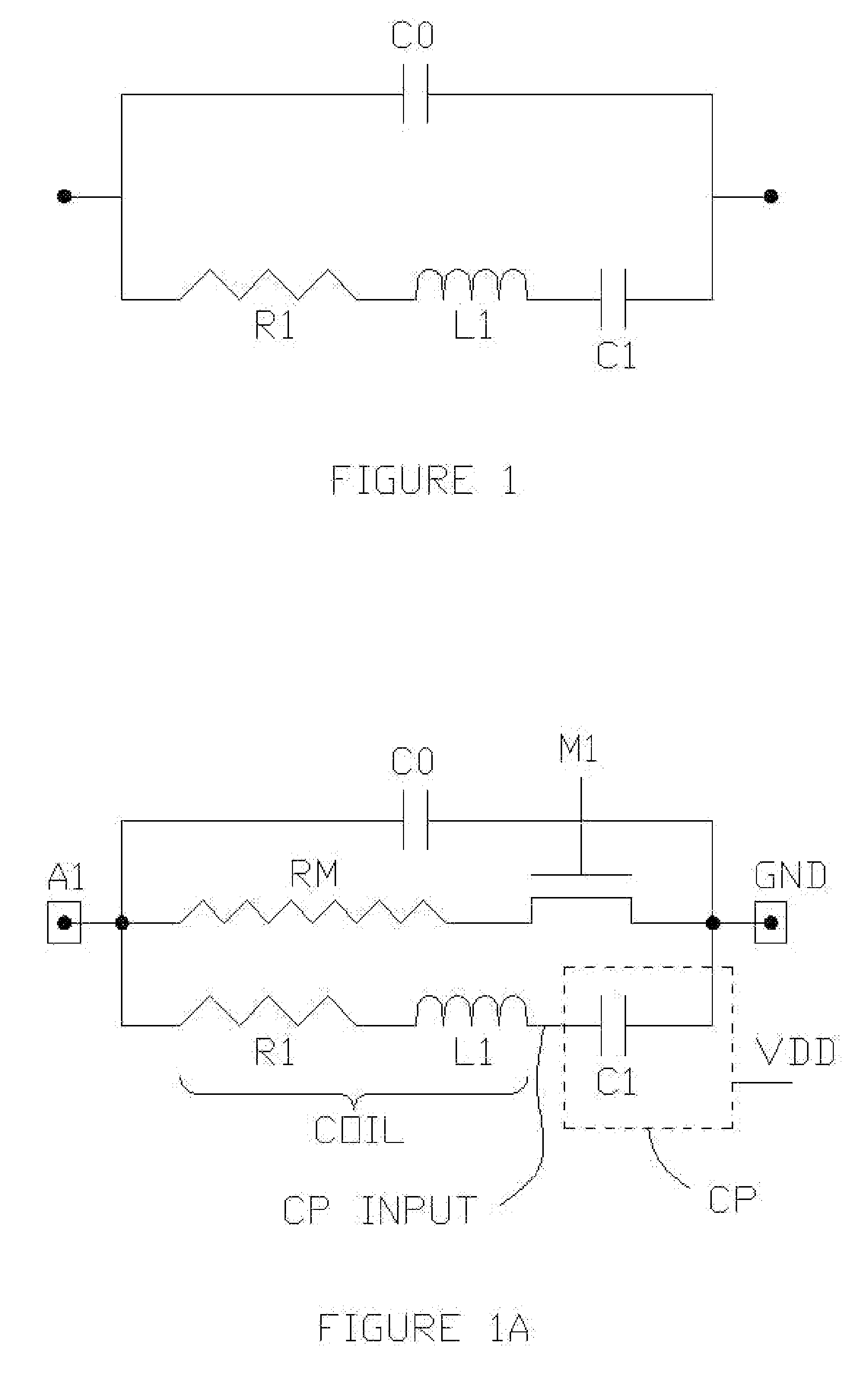
High Sensitivity RFID TAG Integrated Circuits
InactiveUS20070046369A1Reduce the required powerMore sensitiveCharge amplifiersRecord carriers used with machinesElectricityTag antenna
A method and apparatus for an ultra-high sensitivity, low cost, passive (no battery) low-power energy harvesting data transmitting circuit energy, such as a RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) tag integrated circuit “chip.” By using combinations of special purpose design enhancements, the low-power energy harvesting passive data transmitting circuit, such as the RFID tag chip, operates in the sub-microwatt power range. The chip power should be derived from a low-microwatt per square centimeter RF field radiated to the RFID tag antenna from the tag reader (interrogator) or derived from a suitable low signal source, such as a sonic transducer (e.g., a piezoelectric transducer or a low level DC source, such as a bimetallic or chemical source).
Owner:INNURVATION IP LLC
Non-Volatile Resistive-Switching Memories
ActiveUS20090272959A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLeakage current densitySquare Centimeter
Non-volatile resistive-switching memories are described, including a memory element having a first electrode, a second electrode, a metal oxide between the first electrode and the second electrode. The metal oxide switches using bulk-mediated switching, has a bandgap greater than 4 electron volts (eV), has a set voltage for a set operation of at least one volt per one hundred angstroms of a thickness of the metal oxide, and has a leakage current density less than 40 amps per square centimeter (A / cm2) measured at 0.5 volts (V) per twenty angstroms of the thickness of the metal oxide.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Colored web material comprising a plurality of discrete extended elements
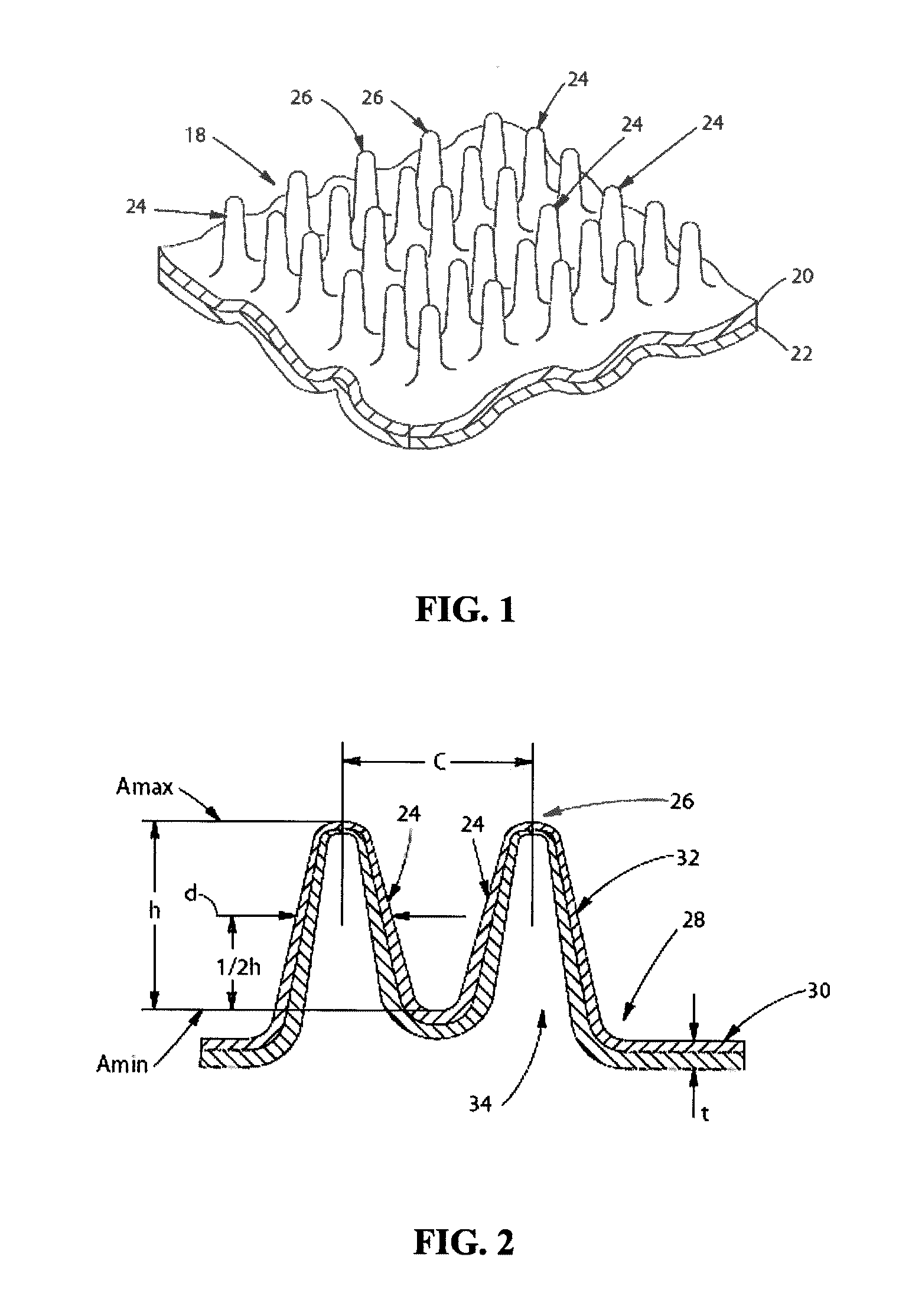
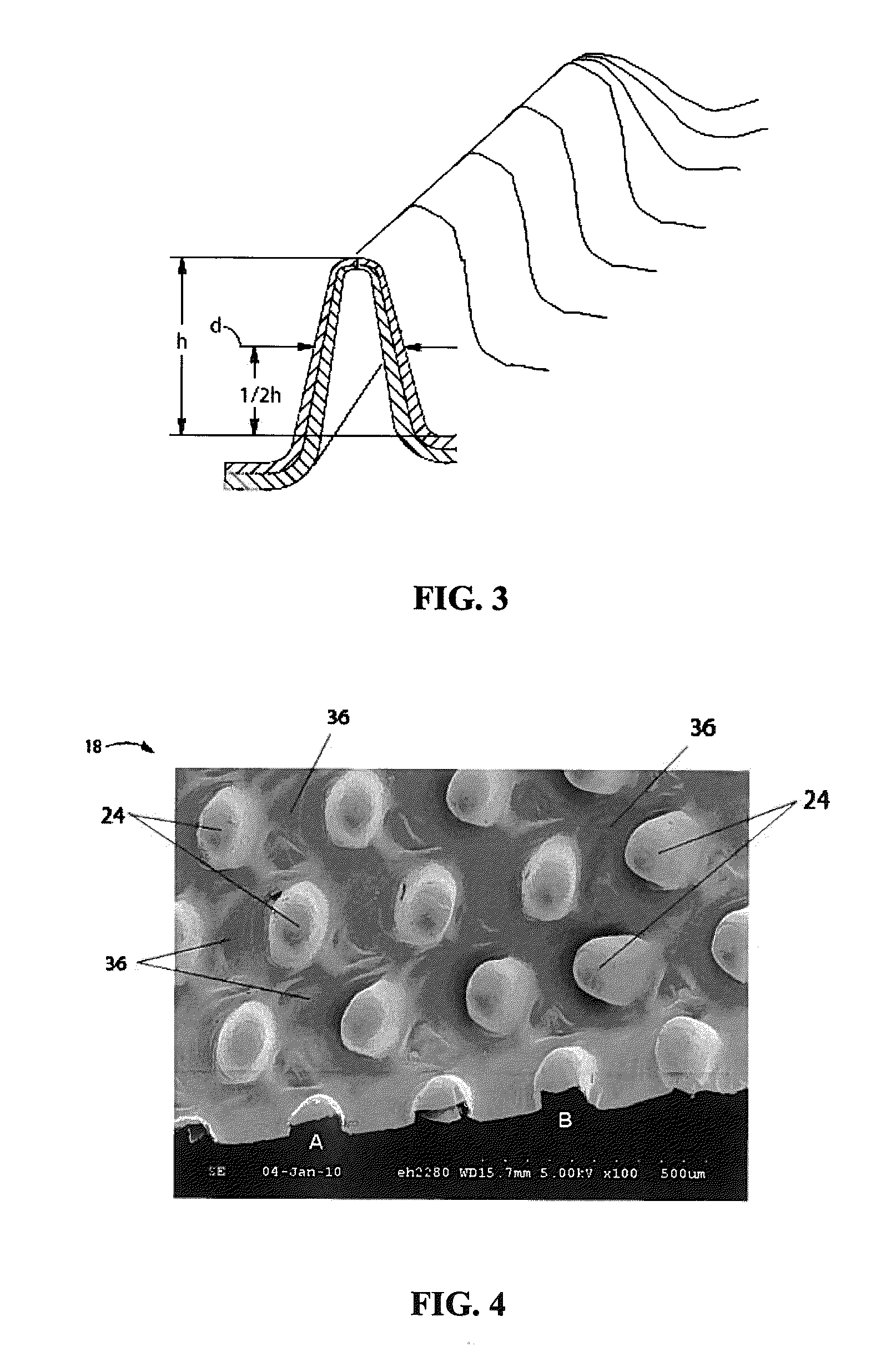
A colored web material comprising a plurality of discrete extended elements. The colored web material comprises a colorant incorporated in the material itself or a colorant disposed on at least one surface of the web material. The discrete extended elements comprise thinned portions at the distal ends and / or along the sidewalls of the discrete extended elements. In one embodiment, the discrete extended elements have a diameter of less than about 500 microns. In one embodiment, the colored web material comprises at least about 95 discrete extended elements per square centimeter. In one embodiment, the discrete extended elements have an aspect ratio of at least about 0.2.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Thin silicon or germanium sheets and photovoltaics formed from thin sheets
Thin semiconductor foils can be formed using light reactive deposition. These foils can have an average thickness of less than 100 microns. In some embodiments, the semiconductor foils can have a large surface area, such as greater than about 900 square centimeters. The foil can be free standing or releasably held on one surface. The semiconductor foil can comprise elemental silicon, elemental germanium, silicon carbide, doped forms thereof, alloys thereof or mixtures thereof. The foils can be formed using a release layer that can release the foil after its deposition. The foils can be patterned, cut and processed in other ways for the formation of devices. Suitable devices that can be formed form the foils include, for example, photovoltaic modules and display control circuits.
Owner:NANOGRAM
System and method for treating exposed tissue with light emitting diodes
The invention comprises a system and method for treating an exposed tissue of a patient with a light energy. A plurality of light emitting diodes are disposed over an area of a supporting structure. The light emitting diodes emit light energy. The light energy comprises a substantial band of wavelengths between about 380 and 800 nm. The light emitting diodes are optically coupled to the exposed tissue of the patient. A driver circuit is electrically coupled to the light emitting diodes for driving a current through the plurality of light emitting diodes. An average irradiance of the light energy emitted from the area by the light emitting diodes is at least about 30 mW per square centimeter during a treatment. In some embodiments, the light energy emitted from a first light emitting diode substantially overlaps with light energy emitted from several adjacent light emitting diodes as the light energy propagates toward the tissue. A substantially uniform irradiance profile distribution forms near a surface of the tissue.
Owner:CUTERA
Surface textured microporous polishing pads
InactiveUS20050276967A1Reduce unevennessHigh removal rateLayered productsFlexible-parts wheelsCompound (substance)Surface roughness
A surface-textured polishing pad suitable for chemical-mechanical polishing comprises a porous polymeric foam having an average pore cell size in the range of about 60 μm or less. At least about 75% of the pores in the foam have a pore cell size within about 30 μm of the average pore cell size. The pad has at least one textured surface that includes divots having a depth in the range of about 25 μm to about 1150 μm, a width in the range of about 0.25 μm to about 380 μm, and a length-to-width aspect ratio of about 1 to about 1000. In addition, the at least one textured surface of the pad includes at least about 10 divots per square centimeter of surface area, and has an average surface roughness of at least about 5 μm. Preferably, at least one textured surface has at least one pattern of spaced, parallel grooves imprinted thereon.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
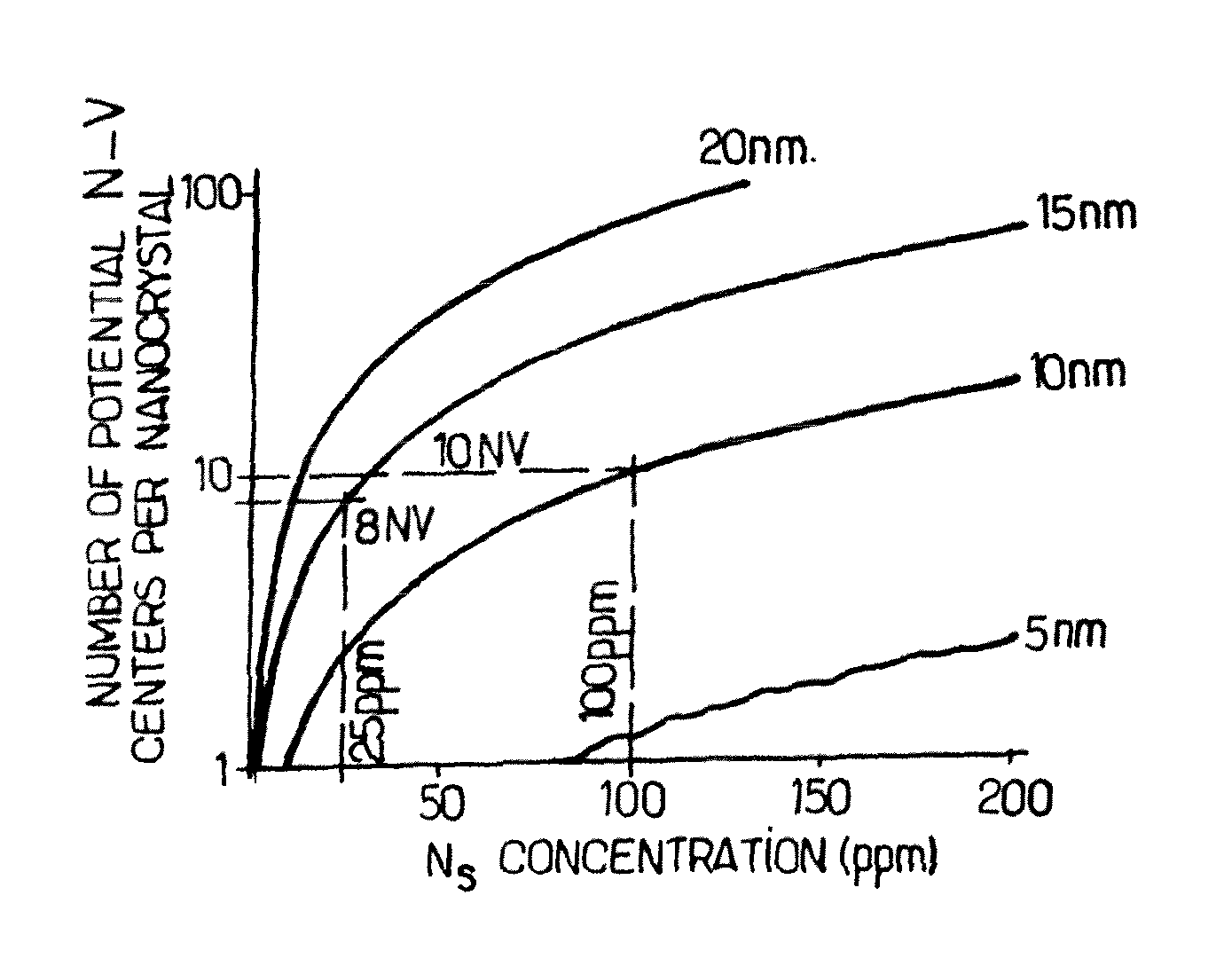
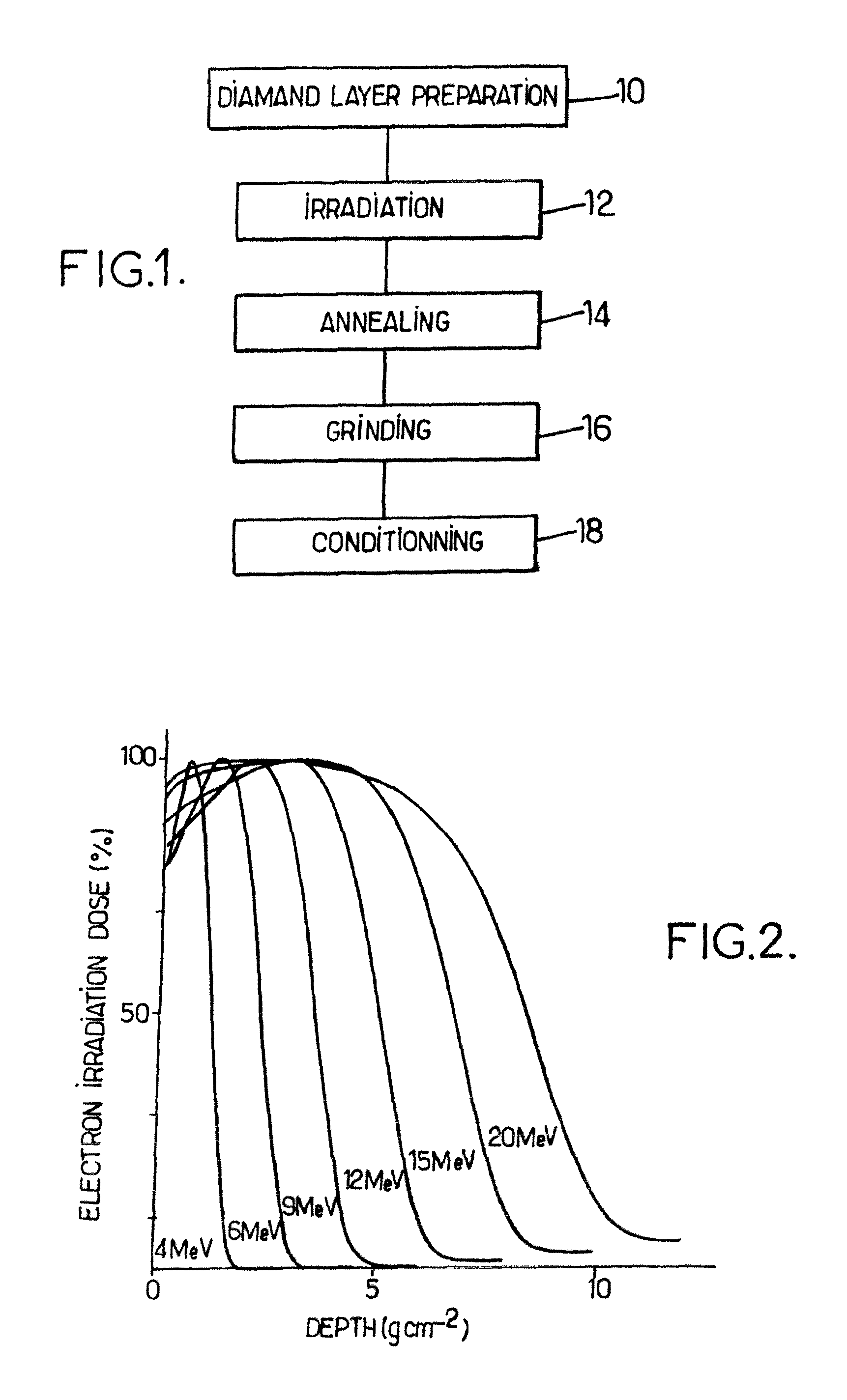
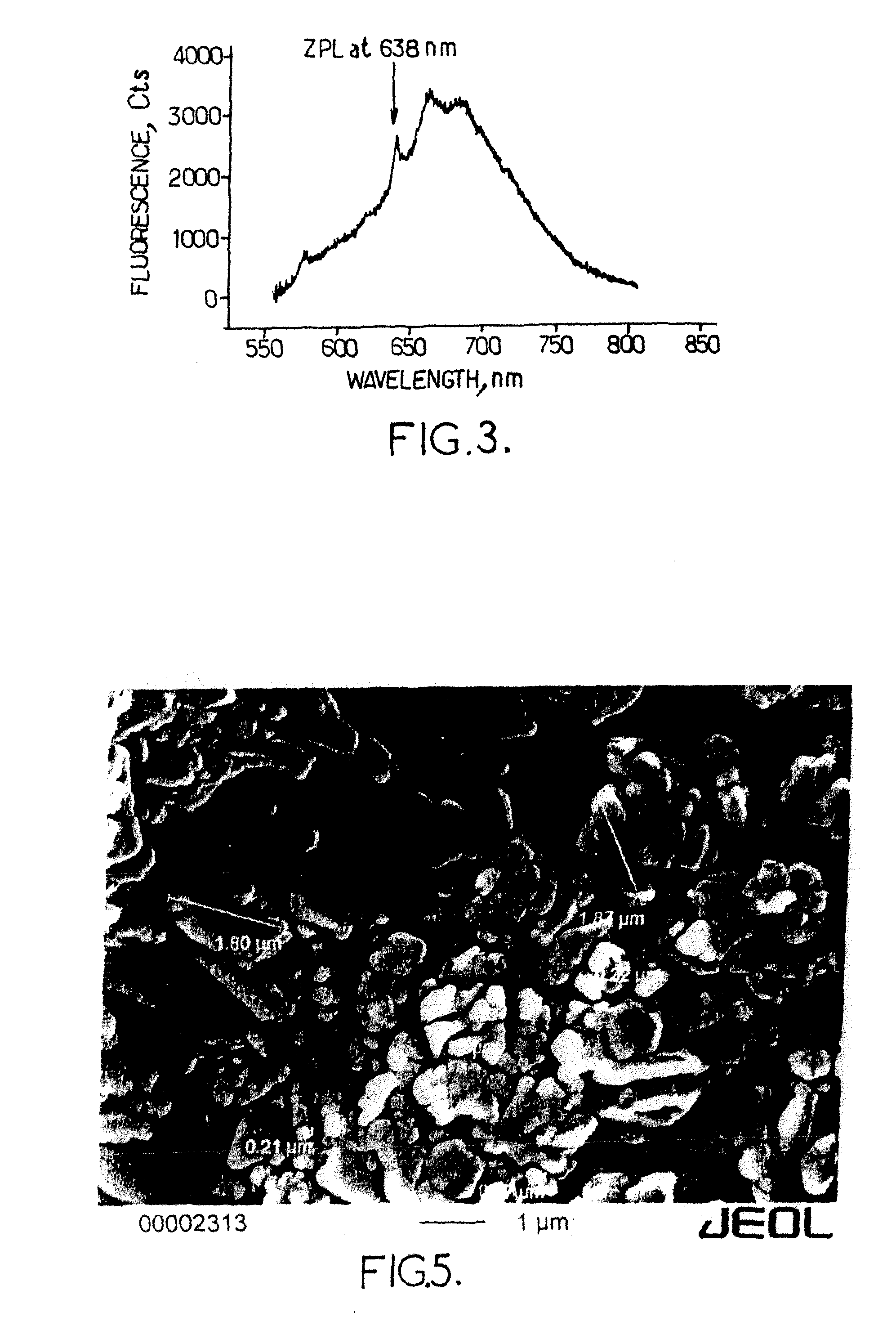
Method to produce light-emitting nano-particles of diamond
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Rotary friction power generator, voltage stabilization output circuit and power supply device
ActiveCN103825489AIncrease output currentIncrease powerFriction generatorsPotential differenceMechanical energy
The invention discloses a rotary friction power generator, a voltage stabilization output circuit and a power supply device. The rotary friction power generator comprises two electrode units which are arranged in the same plane in a spaced mode and a first component which is alternately in contact with the two electrode units. Under the action of external mechanical energy, friction static electricity carried by the first component is alternately in contact with the two electrode units along with rotation of the first component, then the induction potential difference between the two electrode units is alternately changed, a drive electron flows through an external circuit, and then alternating-current signals are formed to be output. According to the rotary friction power generator, a nanostructure layer is not needed to be arranged on the friction surface, and milliwatt-level power output density per square centimeter can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Silicon MEMS based two-phase heat transfer device
InactiveUS20070095507A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicron scaleVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention is a MEMS-based two-phase LHP (loop heat pipe) and CPL (capillary pumped loop) using semiconductor grade silicon and microlithographic / anisotrophic etching techniques to achieve a planar configuration. The principal working material is silicon (and compatible borosilicate glass where necessary), particularly compatible with the cooling needs for electronic and computer chips and package cooling. The microloop heat pipes (μLHP™) utilize cutting edge microfabrication techniques. The device has no pump or moving parts, and is capable of moving heat at high power densities, using revolutionary coherent porous silicon (CPS) wicks. The CPS wicks minimize packaging thermal mismatch stress and improves strength-to-weight ratio. Also burst-through pressures can be controlled as the diameter of the coherent pores can be controlled on a sub-micron scale. The two phase planar operation provides extremely low specific thermal resistance (20-60W / cm2). The operation is dependent upon a unique micropatterened CPS wick which contains up to millions per square centimeter of stacked uniform micro-through-capillaries in semiconductor-grade silicon, which serve as the capillary “engine,” as opposed to the stochastic distribution of pores in the typical heat pipe wick. As with all heat pipes, cooling occurs by virtue of the extraction of heat by the latent heat of phase change of the operating fluid into vapor. In the cooling of a laptop computer processor the device could be attached to the processor during laptop assembly. Consistent with efforts to miniaturize electronics components, the current invention can be directly integrated with a unpackaged chip. For applications requiring larger cooling surface areas, the planar evaporators can be spread out in a matrix and integrally connected through properly sized manifold systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Web material exhibiting viewing-angle dependent color and comprising a plurality of discrete extended elements
A colored web material exhibiting viewing-angle dependent color and comprising a plurality of discrete extended elements. In one embodiment, the colored web material comprises a first web material and a second web material, wherein the first web material comprises a first polymer having first refractive properties and the second web material comprises a second polymer having second refractive properties, wherein said first refractive properties of said first polymer are different than said second refractive properties of said second polymer. In one embodiment, the colored web material comprises an interference pigment incorporated in at least one layer of the colored web material. In one embodiment, the discrete extended elements have a diameter of less than about 500 microns. In one embodiment, the colored web material comprises at least about 95 discrete extended elements per square centimeter. In one embodiment, the discrete extended elements have an aspect ratio of at least about 0.2.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
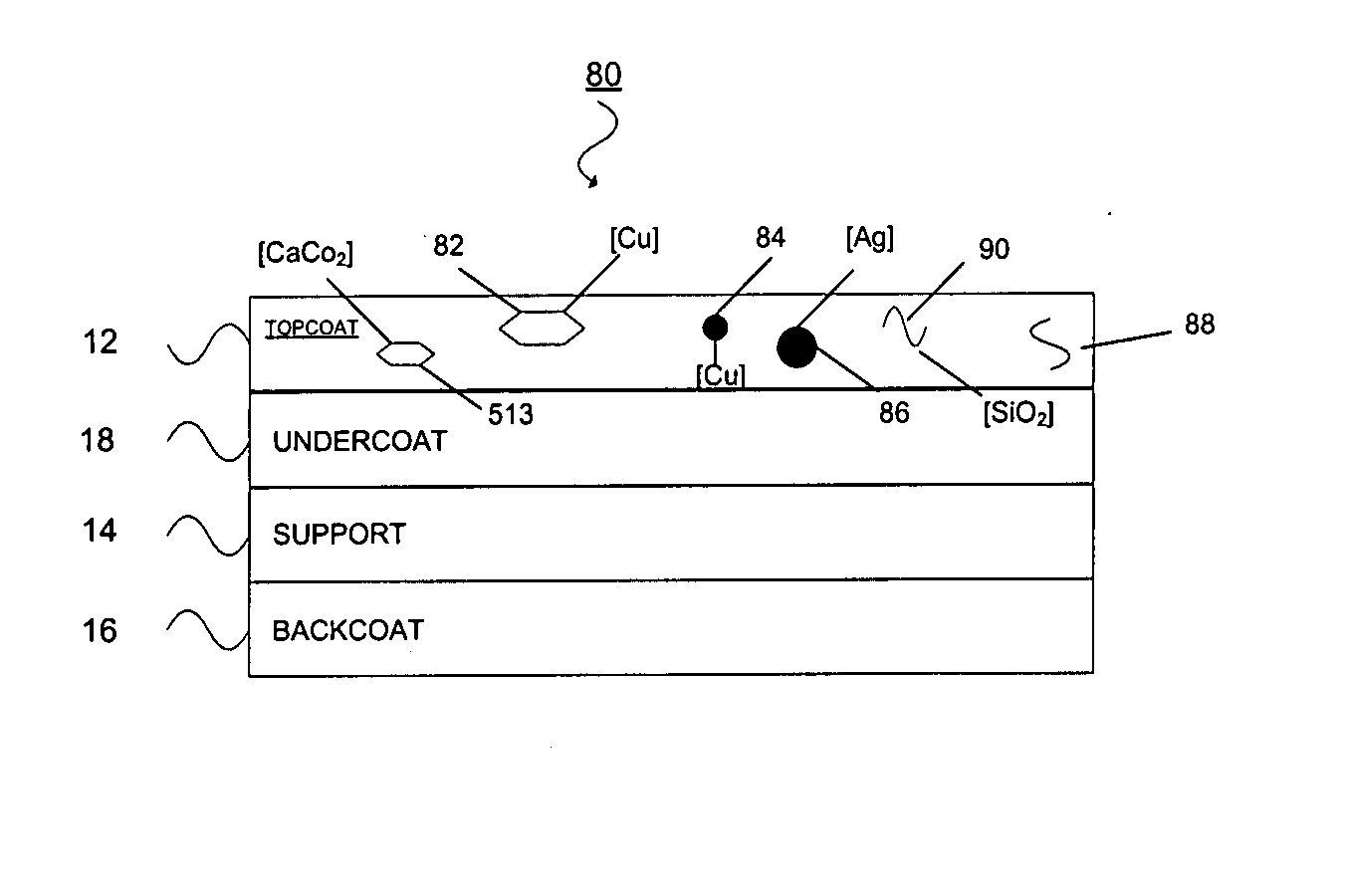
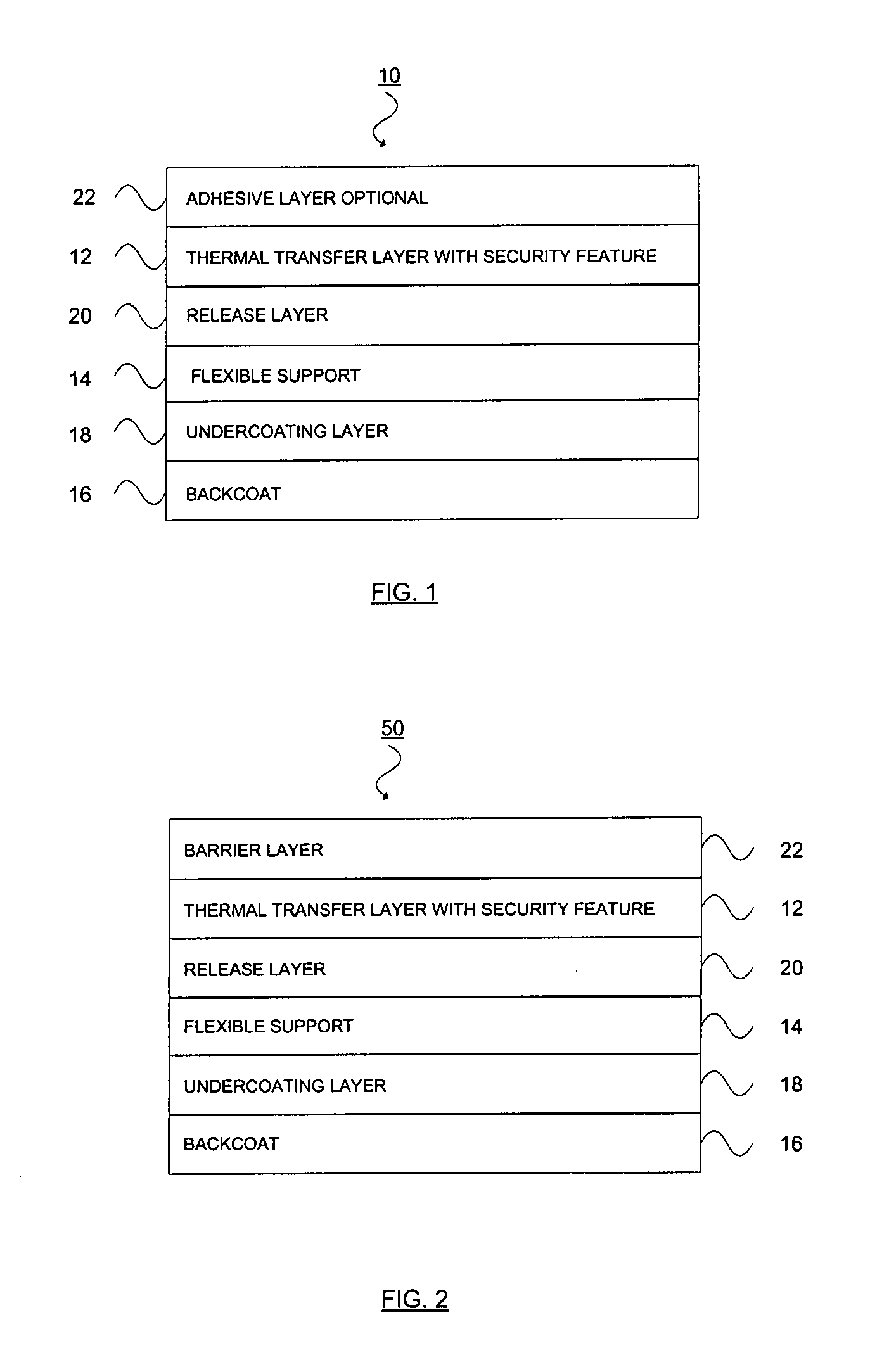
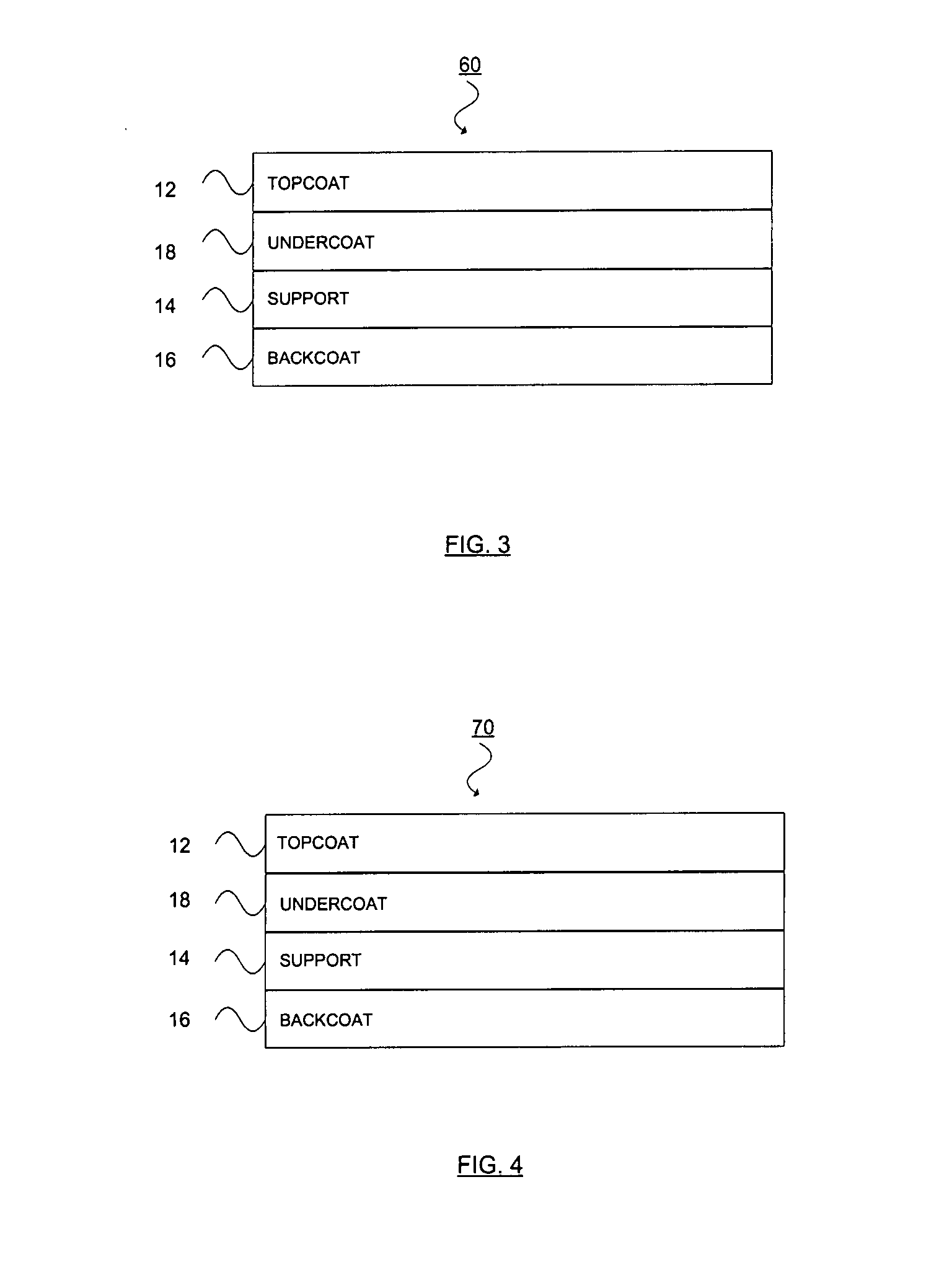
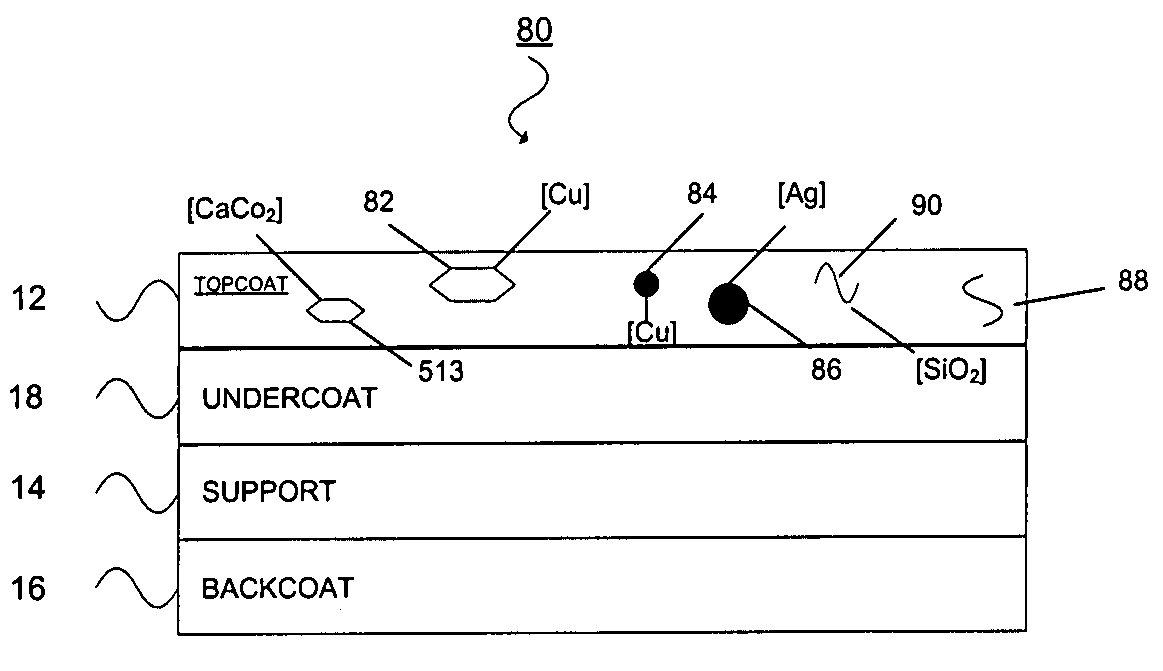
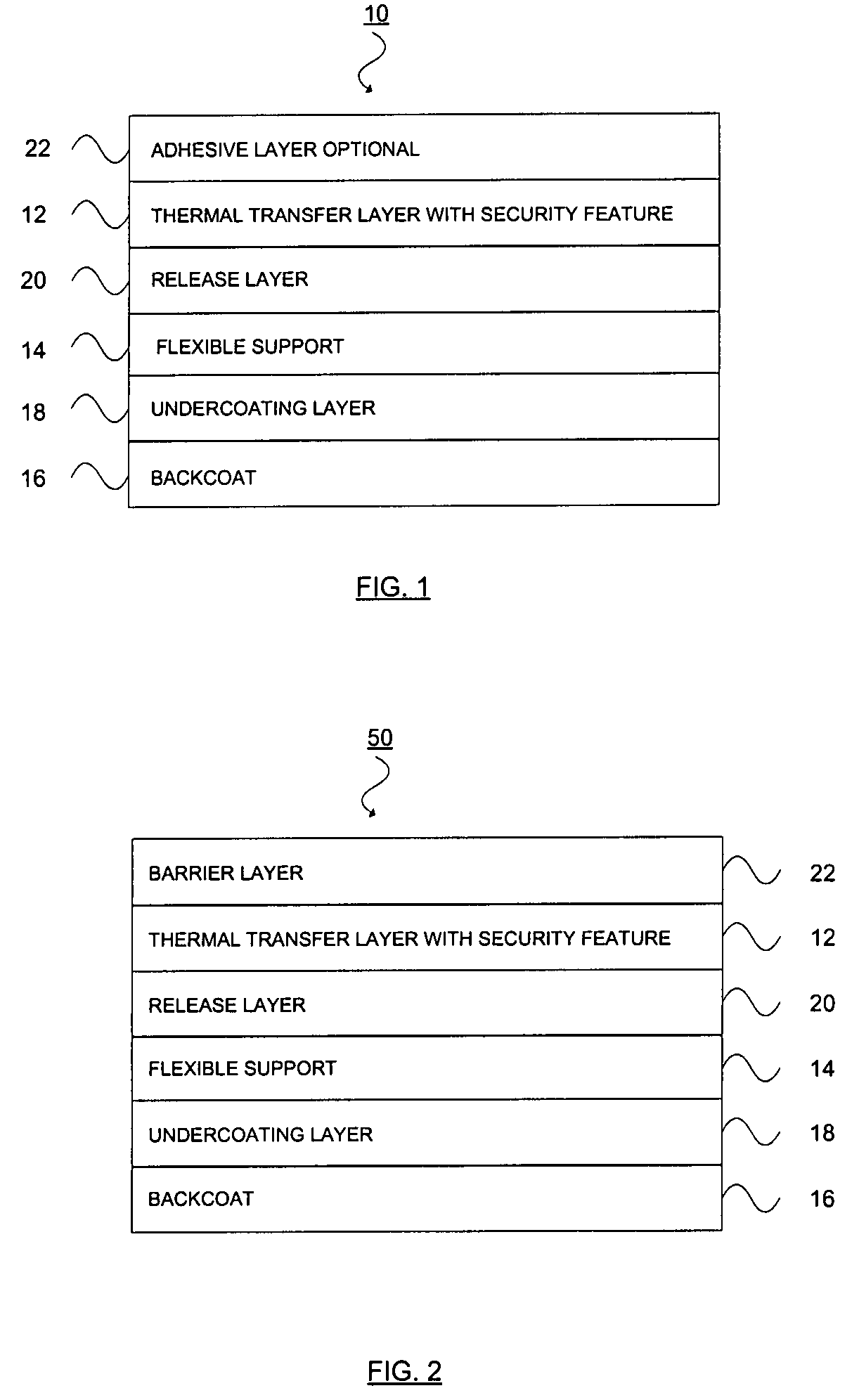
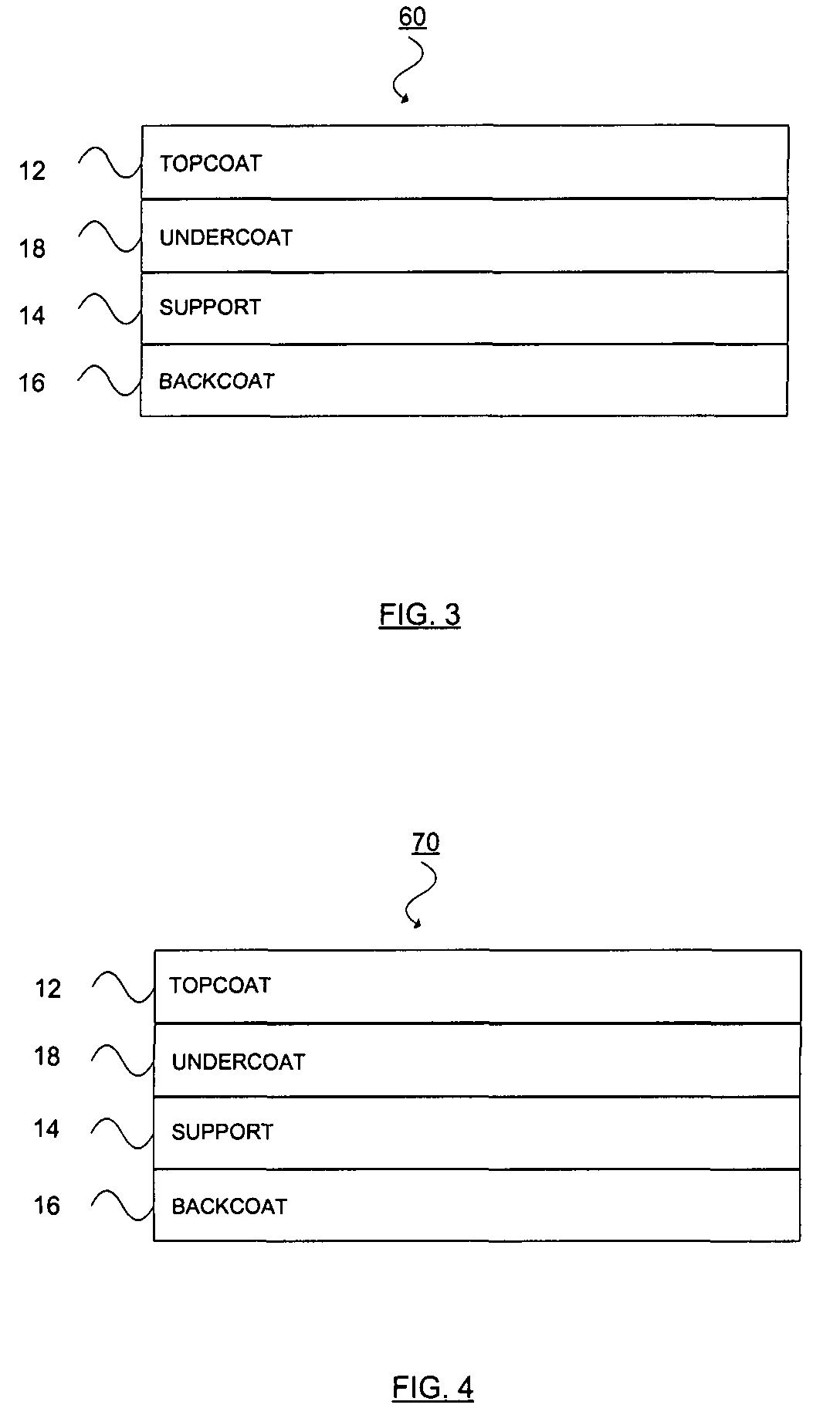
Thermal transfer ribbon
A thermal transfer printing medium that contains a thermal transfer layer which contains a first taggant and colorant, wherein: the first taggant comprises a fluorescent compound with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths of greater than 700 nanometers. When the thermal transfer layer is printed onto a white polyester substrate with a gloss of at least about 84, a surface smoothness Rz value of 1.2, and a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of 1.91 and (b) of −6.79 and a lightness (L) of 95.63, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system, and when such printing utilizes a printing speed of 2.5 centimeters per second and a printing energy of 3.2 joules per square centimeter, a printed substrate with certain properties is produced. The printed substrate has a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of from −15 to 15 and (b) from −18 to 18, and the printed substrate has a lightness (L) of less than about 35, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system. When the printed substrate is illuminated with light source that excites the first taggant with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths greater than 700 nanometers, the printed substrate produces a light fluorescence with a wavelength of from about 300 to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:INT IMAGING MATERIALS
Towel with quality wet scrubbing properties at relatively low basis weight and an apparatus and method for producing same
ActiveUS9719213B2Improve the level ofLose weightLamination ancillary operationsLaminationGramAdhesive
A multi-ply absorbent product having a wet scrubbing resistance greater than 120 revolutions and a basis weight of between 30 and 50 grams per square meter. A heated adhesive is applied between two single plies / webs, the multiple plies are embossed according to particular parameters, and the embossed webs are compressed with a marrying roll. The adhesive is heated to a temperature of between approximately 32 degrees C. to 66 degrees C. for application between the multiple plies. For each ply, the embossed area generally occupies between approximately 5 to 15% of the total surface area of a surface of the ply, the depth of embossment of the surface is generally between approximately 0.28 and 0.43 centimeters deep, and the embossment of the surface is generally between approximately 0.04 to 0.08 square centimeters in size.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY TISSUE LLC
Towel with quality wet scrubbing properties at relatively low basis weight and an apparatus and method for producing same
ActiveUS20160160448A1Improve the level ofLose weightPaper after-treatmentOrnamental structuresFiberAdhesive
A multi-ply absorbent product having a wet scrubbing resistance greater than 120 revolutions and a basis weight of between 30 and 50 grams per square meter. A heated adhesive is applied between two single plies / webs, the multiple plies are embossed according to particular parameters, and the embossed webs are compressed with a marrying roll. The adhesive is heated to a temperature of between approximately 32 degrees C. to 66 degrees C. for application between the multiple plies. For each ply, the embossed area generally occupies between approximately 5 to 15% of the total surface area of a surface of the ply, the depth of embossment of the surface is generally between approximately 0.28 and 0.43 centimeters deep, and the embossment of the surface is generally between approximately 0.04 to 0.08 square centimeters in size.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY TISSUE
Cellular Honeycomb Ultracapacitors and Hybrid Capacitors and Methods for Producing
InactiveUS20090021890A1High densityHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesNon oxide ceramicsSupercapacitor
An ultracapacitor or hybrid capacitor includes an electrically non-conductive rigid or semi-rigid porous honeycomb structure (12) having cells extending along a common direction and having an average density per unit area within in a plane perpendicular to the common direction exceeding 15.5 per square centimeter, desirably formed of a material that is stable at temperatures of 300° or more, such that high temperatures processing can be used to help ensure high purity of the final product. The material may desirably be an oxide or non-oxide ceramic, such as cordierite, silicon nitride, alumina, aluminum titanate, zircon, glass, or glass-ceramic.
Owner:CORNING INC
Laser Modification and Functionalization of Substrates
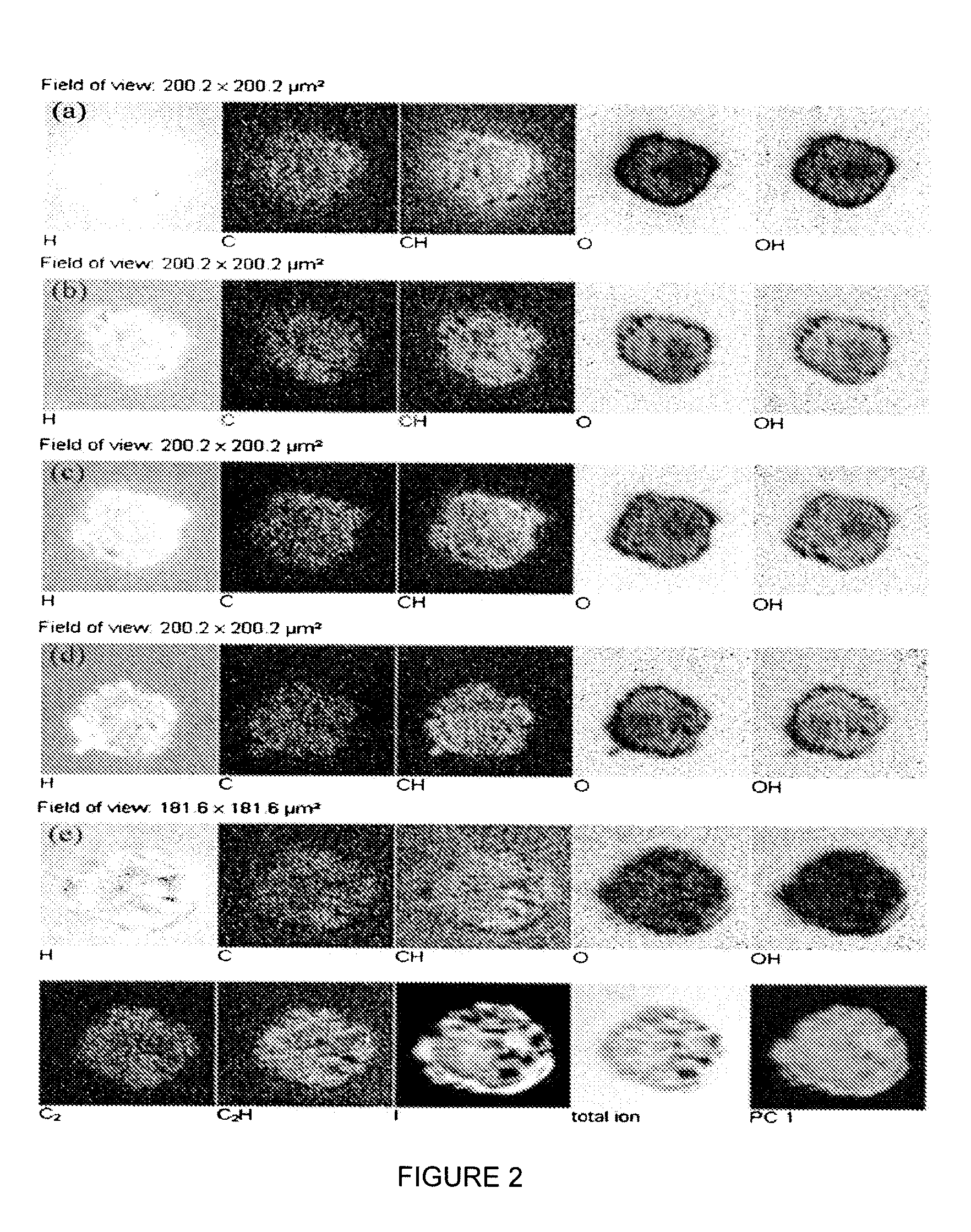
InactiveUS20060234269A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsBiologySquare Centimeter
Assay devices comprising substrates functionalized to comprise probe species on multiple separate regions are provided. Ten thousand to a hundred thousand separate regions can be provided in a substrate of one square centimeter. The separate regions can comprise separate probe species, or in another embodiment, multiple different probe species can be present on each single functionalized region. The probe species are selected to be specific for binding to target species of interest in a sample. Methods and systems for making these devices are also provided. The devices are useful, for example for assaying molecules in a human sample that are reactive to a large number of different allergens placed on the substrate.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Close-packed array of light emitting devices
ActiveUS8415704B2Efficient productionEfficient thermal managementPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceLight emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Microporous balloon catheter
InactiveUS20110160575A1Reduce harmReduce stressStentsBalloon catheterVolumetric Mass DensityBalloon catheter
A method and system for delivering a medicament into tissue, for example via a balloon with small pores. Optionally, the pressure used is high enough to cause jetting, but the pore sizes, pore density, pressure and / or delivery time are such that the jetting do not cause unacceptable tissue damage. Optionally, the pores are smaller than 2 microns, are between 300 and 600 per square centimeter and the pressure is above 8 atmospheres.
Owner:BY PASS
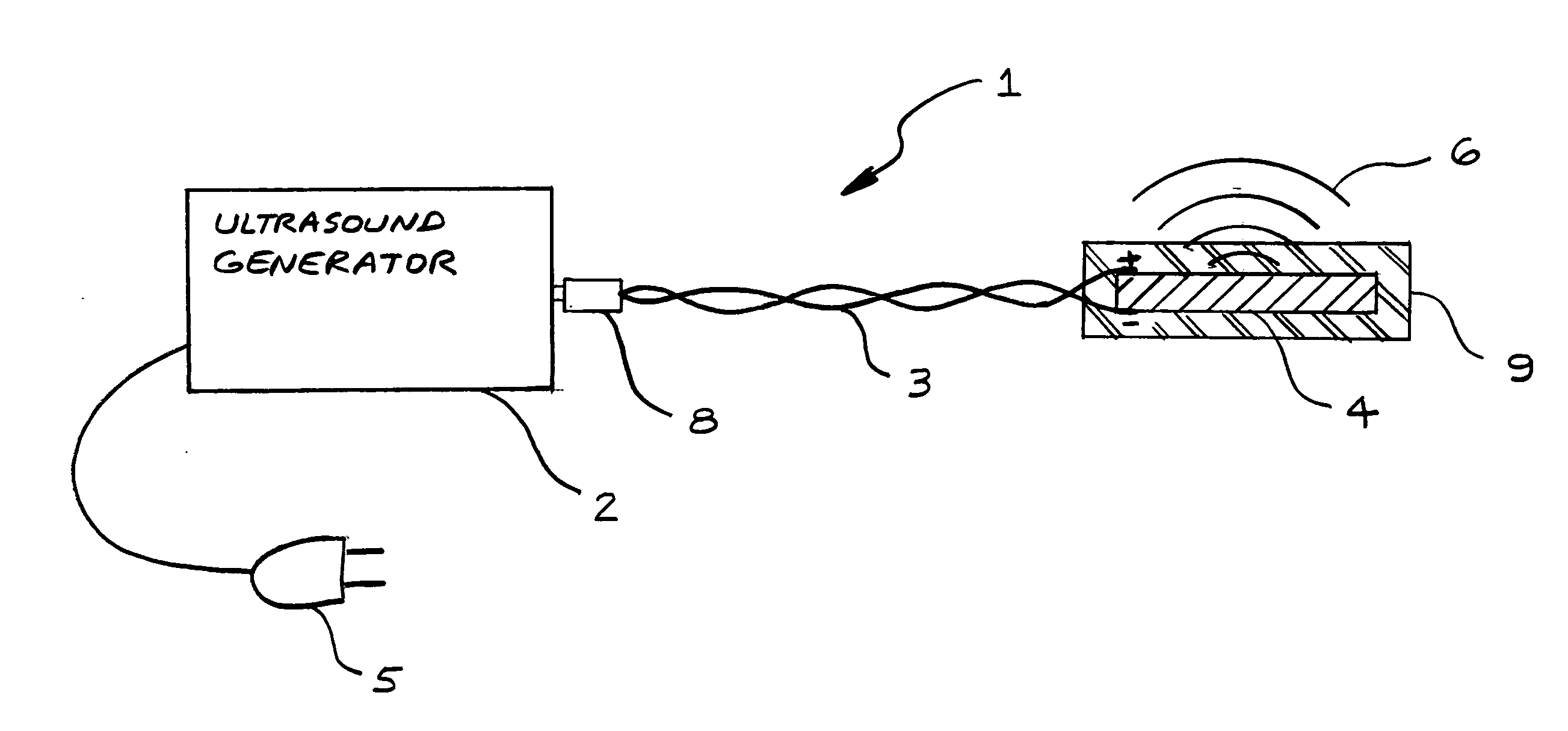
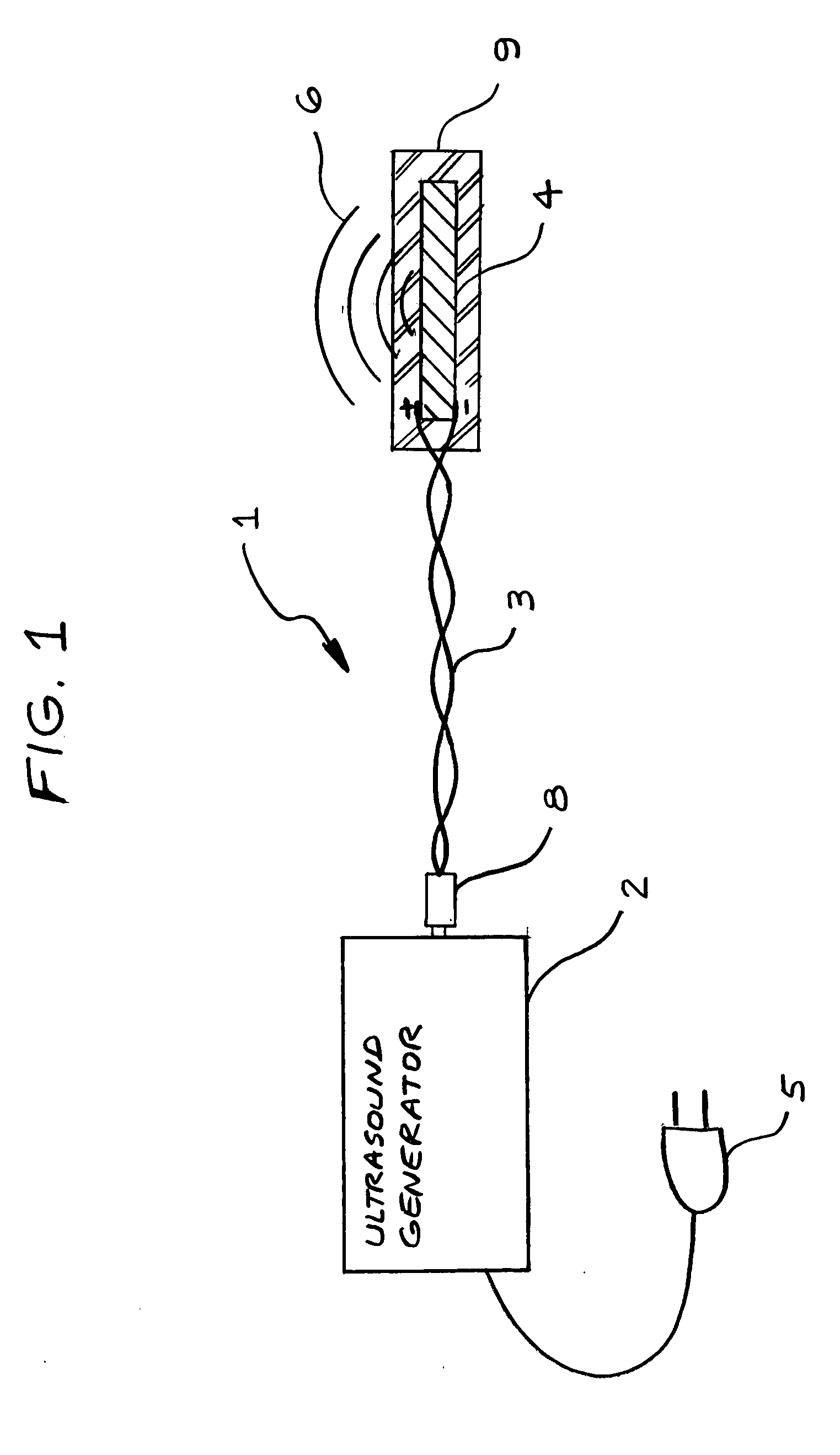
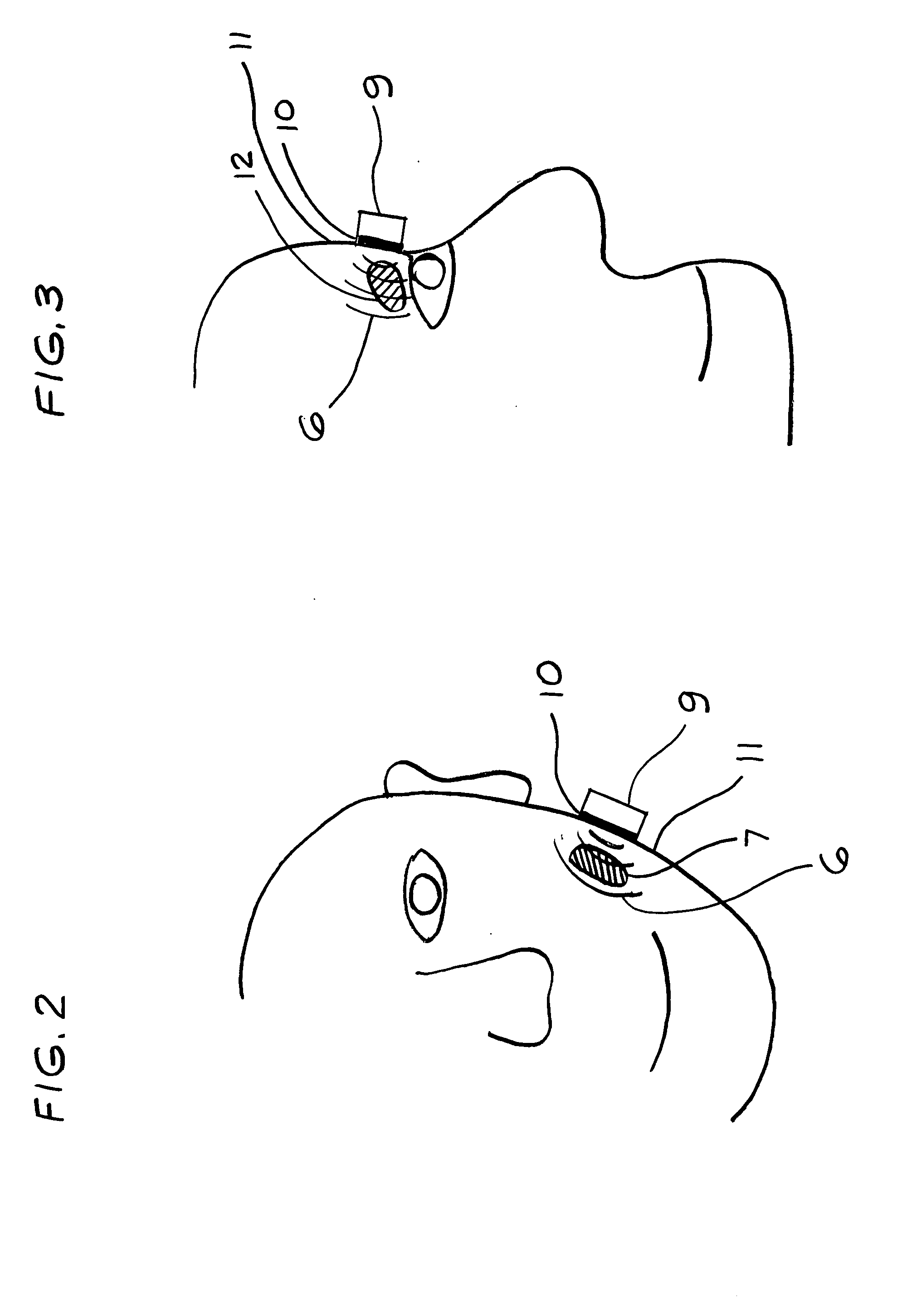
Method for increasing saliva and tear production with ultrasound
InactiveUS20080269648A1Avoid side effectsIncrease tear productionUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesSonificationTissue heating
A non-invasive apparatus and method for increasing saliva and tear production from the salivary and lacrimal glands with the application of high frequency low intensity ultrasound. An ultrasound transducer coated with connecting gel placed in contact with the facial tissues transmitting 1.5 MHz frequency ultrasound pressure waves into the tissues and into the glands. The time-averaged intensity of the ultrasound pressure waves is typically limited to approximately 30 milliwatts per square centimeter to avoid tissue heating.
Owner:ROBERT T BOCK CONSULTANCY
Thermal transfer ribbon
A thermal transfer printing medium that contains a thermal transfer layer which contains a first taggant and colorant, wherein: the first taggant comprises a fluorescent compound with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths of greater than 700 nanometers. When the thermal transfer layer is printed onto a white polyester substrate with a gloss of at least about 84, a surface smoothness Rz value of 1.2, and a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of 1.91 and (b) of −6.79 and a lightness (L) of 95.63, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system, and when such printing utilizes a printing speed of 2.5 centimeters per second and a printing energy of 3.2 joules per square centimeter, a printed substrate with certain properties is produced. The printed substrate has a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of from −15 to 15 and (b) from −18 to 18, and the printed substrate has a lightness (L) of less than about 35, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system. When the printed substrate is illuminated with light source that excites the first taggant with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths greater than 700 nanometers, the printed substrate produces a light fluorescence with a wavelength of from about 300 to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:INT IMAGING MATERIALS
Method of making a thick and smooth embossed tissue
A paper tissue such as a facial tissue or a disposable handkerchief and a method for making a tissue paper product from a tissue paper web. The method comprises the steps of passing the tissue paper web through an embossing nip formed between a first and a second embossing roll, wherein at least one of the embossing rolls comprises at least 30 embossing elements per square centimeter; and passing the tissue paper web through a calendering nip formed between a first and a second calendering roll, wherein the first and the second calendering roll are in contact with the tissue paper web over a contact length measured parallel to the direction of the axis of the first calendering roll exert a pressure onto the paper web of at least 50 N per centimeter of the contact length.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Pipes, systems, and methods for transporting hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20060186023A1Little strengthFlow propertiesFluid removalWall shearHydrocotyle bowlesioides
There is disclosed a method of transporting a produced fluid through a pipe while limiting deposits at a desired pipe inner-wall location comprising providing a pipe having an inner surface roughness Ra less than 2.5 micrometers at said desired pipe inner-wall location, forcing the produced fluid through the pipe, wherein the produced fluid has a wall shear stress of at least 1 dyne per centimeter squared at said desired pipe inner-wall location.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
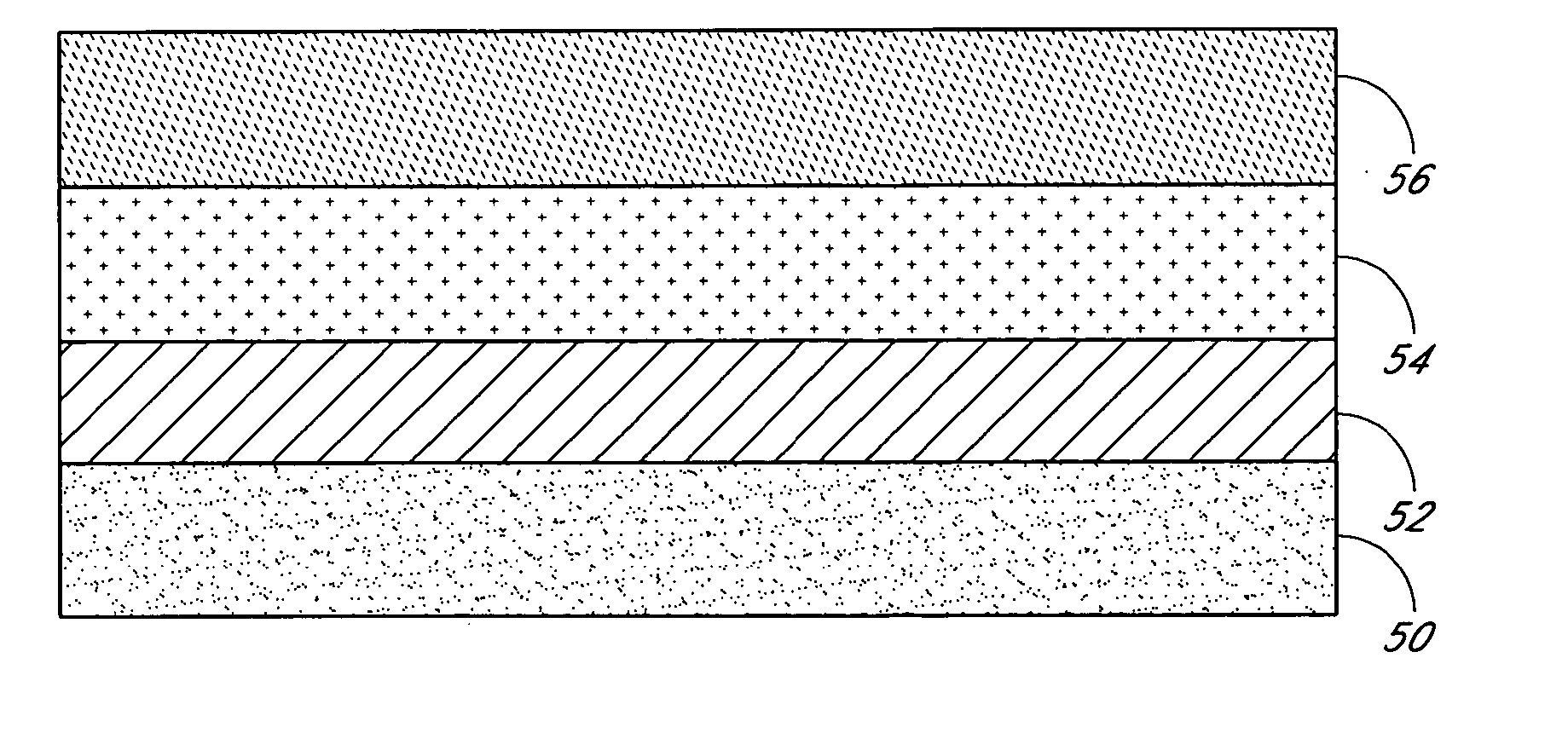
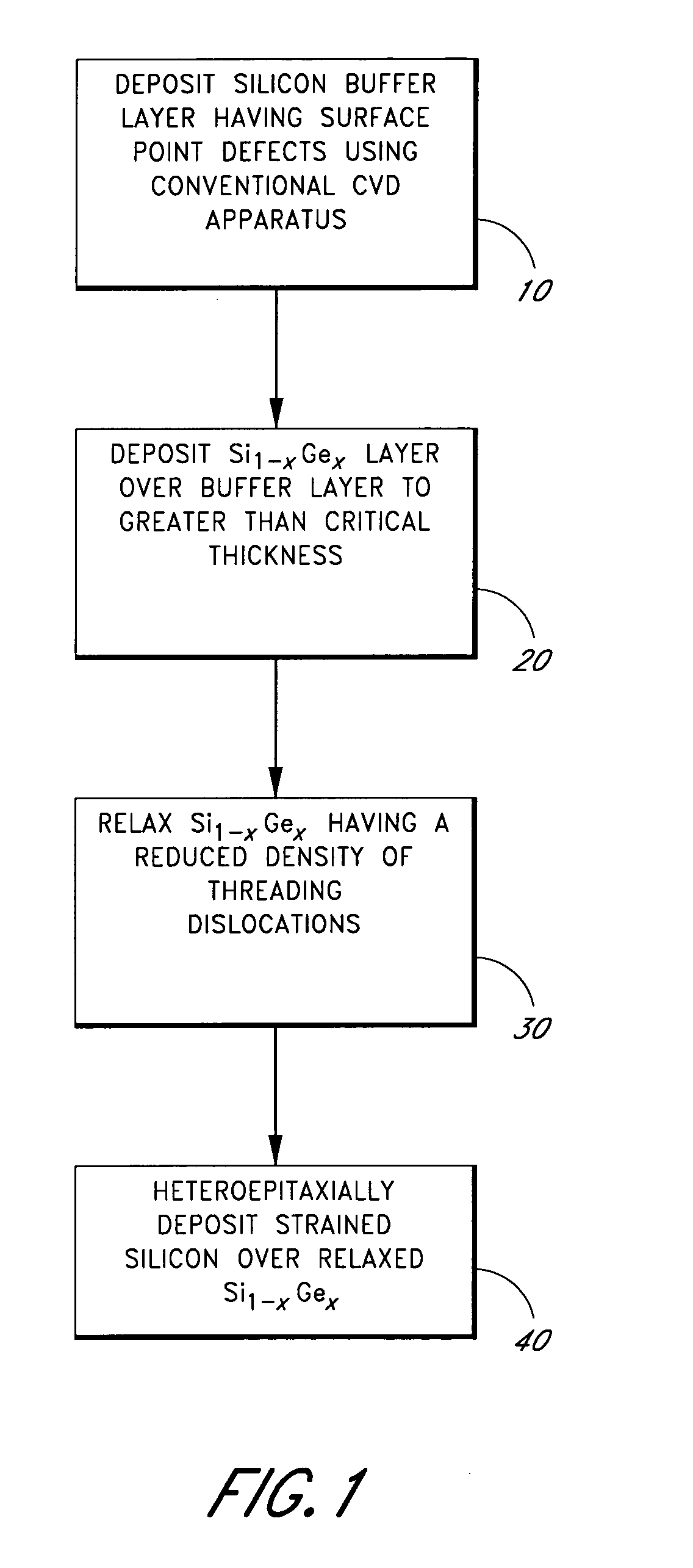
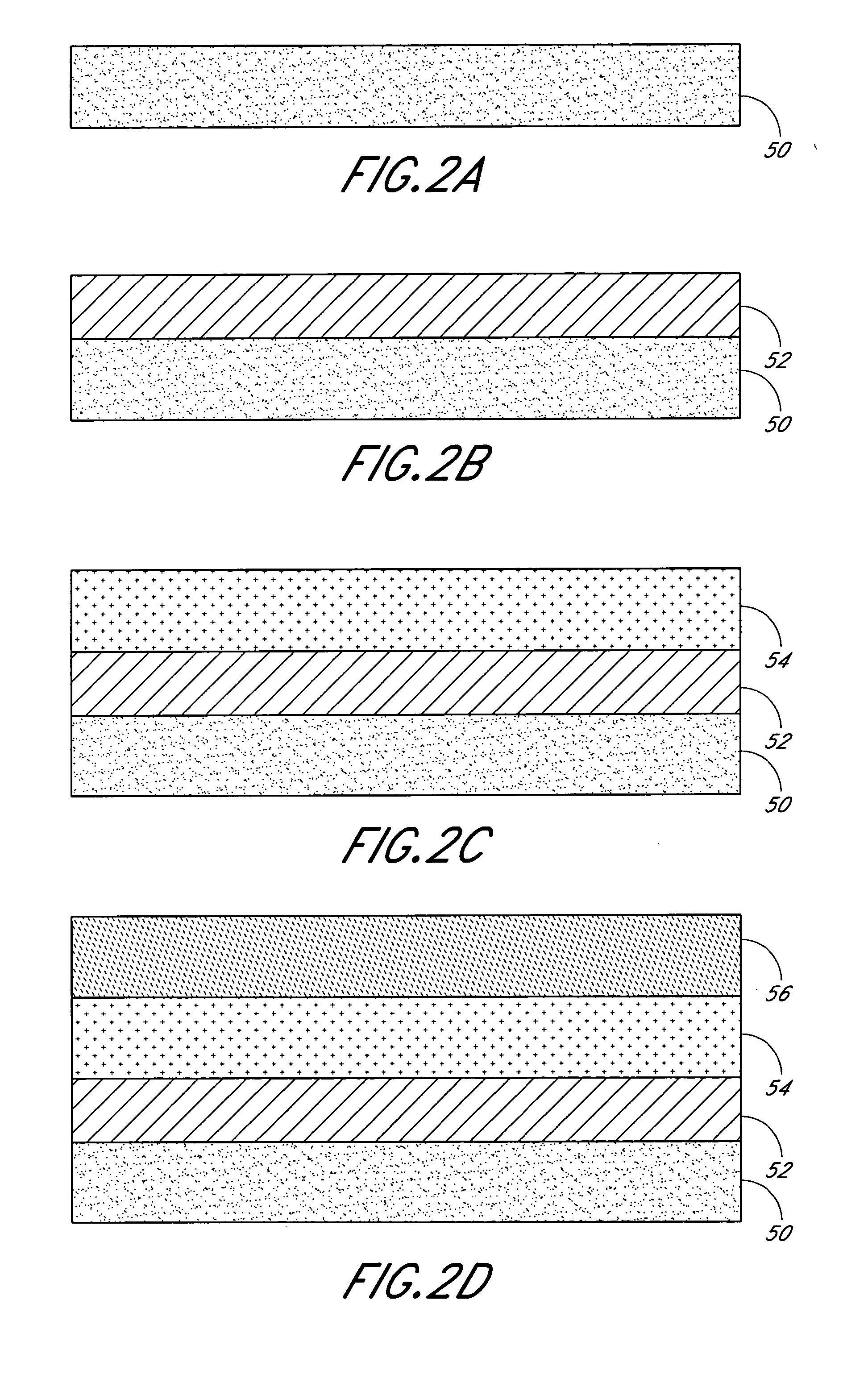
Epitaxial growth of relaxed silicon germanium layers
ActiveUS20050051795A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThreading dislocationsGas phase
A relaxed silicon germanium structure comprises a silicon buffer layer produced using a chemical vapor deposition process with an operational pressure greater than approximately 1 torr. The relaxed silicon germanium structure further comprises a silicon germanium layer deposited over the silicon buffer layer. The silicon germanium layer has less than about 107 threading dislocations per square centimeter. By depositing the silicon buffer layer at a reduced deposition rate, the overlying silicon germanium layer can be provided with a “crosshatch free” surface.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Dandelion health-care tea and preparing process thereof
The invention discloses a dandelion health care tea which consists of the following components and mass percentage of the components is: dandelion leaves: 50 to 70 percent; dandelion rootlets: 25 to 35 percent; ganoderma lucidum rootlets: 2 to 8 percent; and wild chrysanthemum: 2 to 8 percent. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the health care tea which comprises the following steps: first cleaning the dandelion, and cutting the leaves and the root off by a knife, dipping the leaves in warm water for 3 minutes and drying after cutting the leaves into lumps of 1 square centimeter; cutting the root into threads by a blanket machine and drying; cutting the ganoderma lucidum into threads by the blanket machine and drying, and drying the wild chrysanthemum directly, then the health care tea is obtained by mixing and sterilizing the raw materials according to the mass percentage. The health care tea of the invention can effectively prevent and treat hyperplasia of mammary glands at the same time when satisfying the needs of drinking tea. After drinking the health care tea, the occurrence of mammary gland diseases such as hyperplasia of mammary glands of the female can be prevented; the female who suffer from the mammary gland diseases such as hyperplasia of mammary glands can also have good treatment effect after drinking the health care tea without side effects, risk of operation or scar.
Owner:钟伟珍
Preserving a hemoglobin blood substitute with a transparent overwrap
InactiveUS7041800B1High purityExtended shelf lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetal layered productsPolyolefinMedicine
Owner:OPK BIOTECH
Large scale nanoelement assembly method for making nanoscale circuit interconnects and diodes
InactiveUS20110024719A1Final product manufactureVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisCurrent voltage
Nanoelements such as single walled carbon nanotubes are assembled in three dimensions into a nanoscale template on a substrate by means of electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis at ambient temperature. The current-voltage relation indicates that strong substrate-nanotube interconnects carrying mA currents are established inside the template pores. The method is suitable for large-scale, rapid, three-dimensional assembly of 1,000,000 nanotubes per square centimeter area using mild conditions. Circuit interconnects made by the method can be used for nanoscale electronics applications.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Establishment and characterization method of in-vitro blood brain barrier model based on microfluidic chip
InactiveCN102978109AReduce consumptionResolve the secondary inoculationArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsVaccinationEngineering
The present invention provides an establishment and characterization method of in-vitro blood brain barrier model based on microfluidic chip. The microfluidic chip mainly comprises a cell inlet pool (1), collagen inlet pools (2), a cell culture chamber (3) and a waste liquid pool (4). The upper of the cell culture chamber (3) is connected with the cell inlet pool (1). The lower of the cell culture chamber (3) is connected with the waste liquid pool (4). Each collagen inlet pool respectively includes four observation chambers. The collagen inlet pools are communicated with the cell culture chamber (3). According to the invention, construction and characterization of the in-vitro blood brain barrier model and evaluation of the barrier function are integrated into a chip of a few square centimeters, and the chip can be used for in-vitro simulation and subsequent applications of the blood-brain barrier model. Compared the present invention with a Transwell small chamber co-culture model, the cell co-culture model secondary vaccination and time-consuming problems are solved, the flow conditions are added, the chip is closer to the true in-vivo microenvironment, the cell and reagent consumption are significantly reduced, and a plurality of experiment parameters can be obtained once and simultaneously.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High current density electropolishing in the preparation of highly smooth substrate tapes for coated conductors
ActiveUS20050016867A1Electrolysis componentsDecorative surface effectsHigh current densityElectrical conductor
A continuous process of forming a highly smooth surface on a metallic tape by passing a metallic tape having an initial roughness through an acid bath contained within a polishing section of an electropolishing unit over a pre-selected period of time, and, passing a mean surface current density of at least 0.18 amperes per square centimeter through the metallic tape during the period of time the metallic tape is in the acid bath whereby the roughness of the metallic tape is reduced. Such a highly smooth metallic tape can serve as a base substrate in subsequent formation of a superconductive coated conductor.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for synthesizing sec-butyl acetate from acetic acid and linear butylene
InactiveCN101121656AOvercome intractabilityOvercoming the problem of increased consumptionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCelsius DegreeHeteropoly acid
The invention relates to a synthetic method of the sec-butyl acetate with the acetic acid and linear butylene. The invention is characterized in that a fixed-bed reactor is used; the solid catalyst is used; when the butylenes pressure is between 2 and 15 kilograms per square centimeters and the reaction temperature is between 90 and 160 Celsius system, the acetic acid and olefin react and compose the sec-butyl acetate under the gas-liquid-solid reaction condition; therein, the ratio between the cetic acid and olefin is from 1 to 1.15 to 1 to 1.80; the material feeding airspeed of the acetic acid is 1.0 to 1.8 liters per hour; the solid catalyst is the modified resin catalyst, silica gel loading heteropoly acid catalyst, silica gel loading phosphoric acid catalyst or super acid catalyst. The invention overcomes the erosion of the equipment, the side reaction, the difficult treatment of the waste liquid of the reaction, and the difficult separation of water in the traditional process, which may cause the increase of the energy consumption; the invention can greatly lower the production cost of the product.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis of YBa2Cu3O7 using sub-atmospheric processing
InactiveUS20030050195A1Conductive materialVacuum evaporation coatingWater vaporVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention is a method of forming thick films of crystalline YBa2Cu3O7 that includes forming a precursor film comprising barium fluoride (BaF2), yttrium (Y) and copper (Cu). The precursor film is heat-treated at a temperature above 500° C. in the presence of oxygen, nitrogen and water vapor at sub-atmospheric pressure to form a crystalline structure. The crystalline structure is then annealed at about 500° C. in the presence of oxygen to form the crystalline YBa2Cu3O7 film. The YBa2Cu3O7 film formed by this method has a resistivity of from about 100 to about 600 muOhm-cm at room temperature and a critical current density measured at 77 K in a magnetic field of 1 Tesla of about 1.0x105 Ampere per square centimeter (0.1 MA / cm2) or greater.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Copper-graphene composite material and preparation method thereof
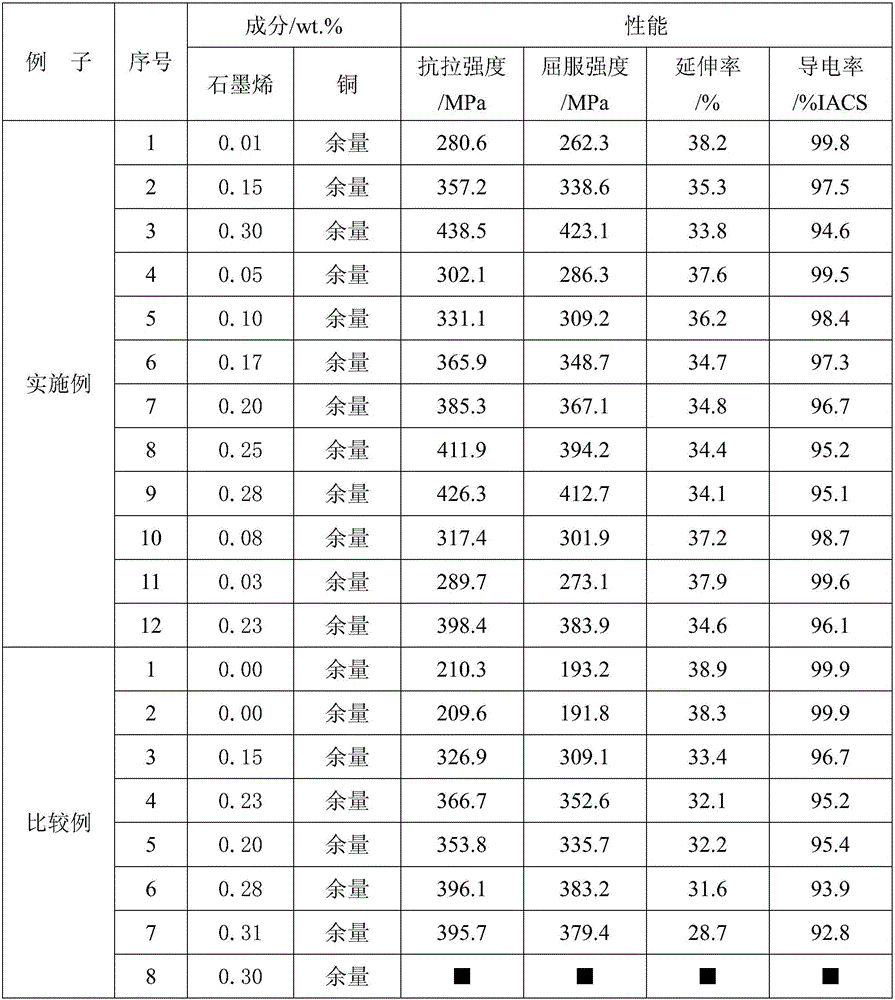
ActiveCN105714139APrevent oxidationControllable distribution densityLead frameUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a copper-graphene composite material and a preparation method thereof. The copper-graphene composite material comprises graphene and copper, and is characterized in that the graphene is evenly distributed in a copper matrix in a sheet structure; distribution density of the graphene is 100 sheets per square centimeter to 3000 sheets per square centimeter; and preferably, the content of the graphene is 0.01 wt% to 0.30 wt%, and the balance is Cu. The copper-graphene composite material disclosed by the invention is prepared by adding the graphene into the copper; the copper matrix can be served as an electrical conduction main body to enable electrical conductivity of the composite material to be close to pure copper, and the graphene is served as a reinforcement phase, so that tensile strength performance and yield strength performance are both increased; therefore the copper-graphene composite material can be widely applied to the fields of consumer electronics, electrics, aeronautics and astronautics, high-speed rails, lead frames, electronic connector preparation; and the preparation method provided by the invention is suitable for industrial and scale production.
Owner:NINGBO POWERWAY ALLOY MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com