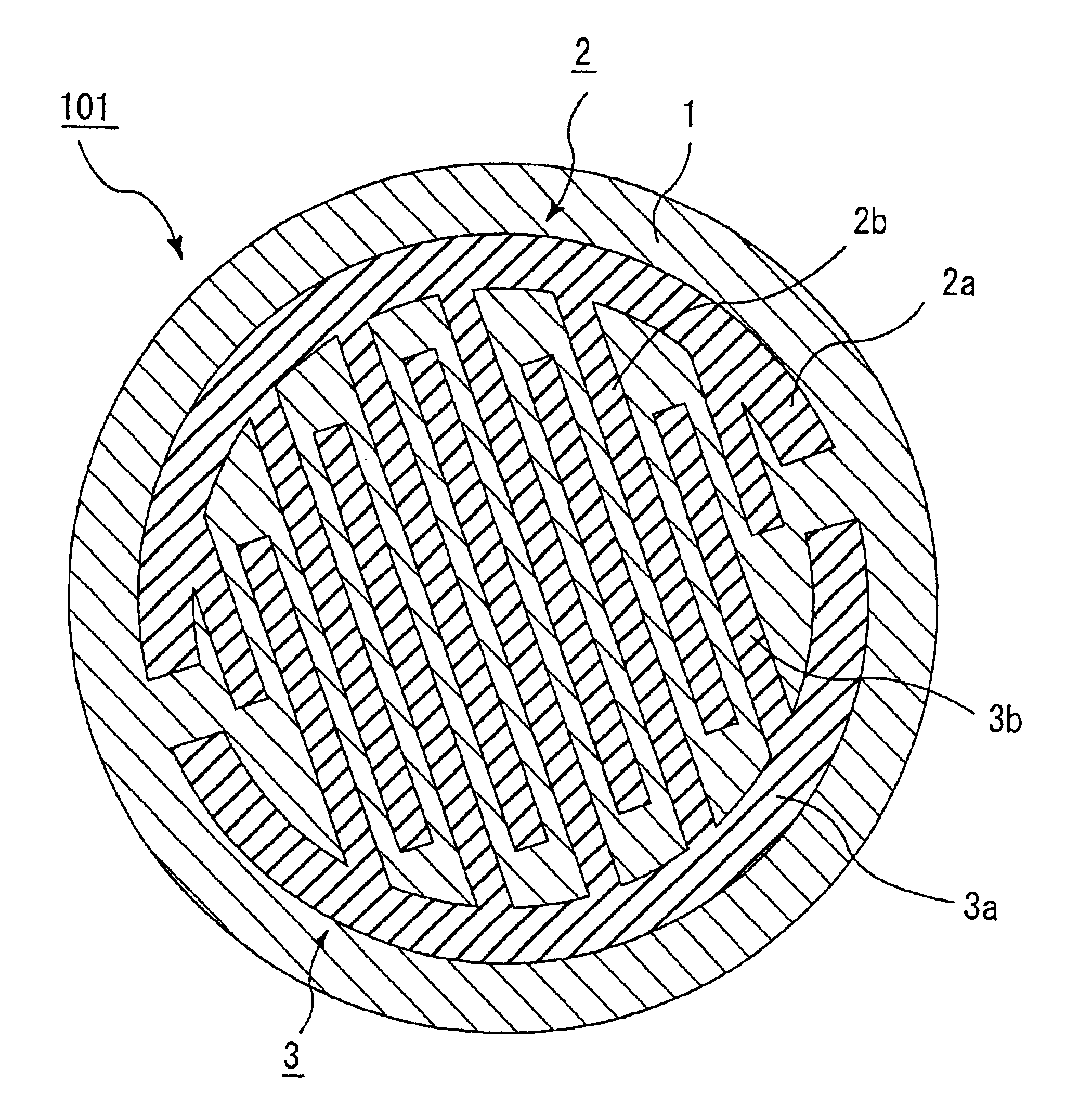
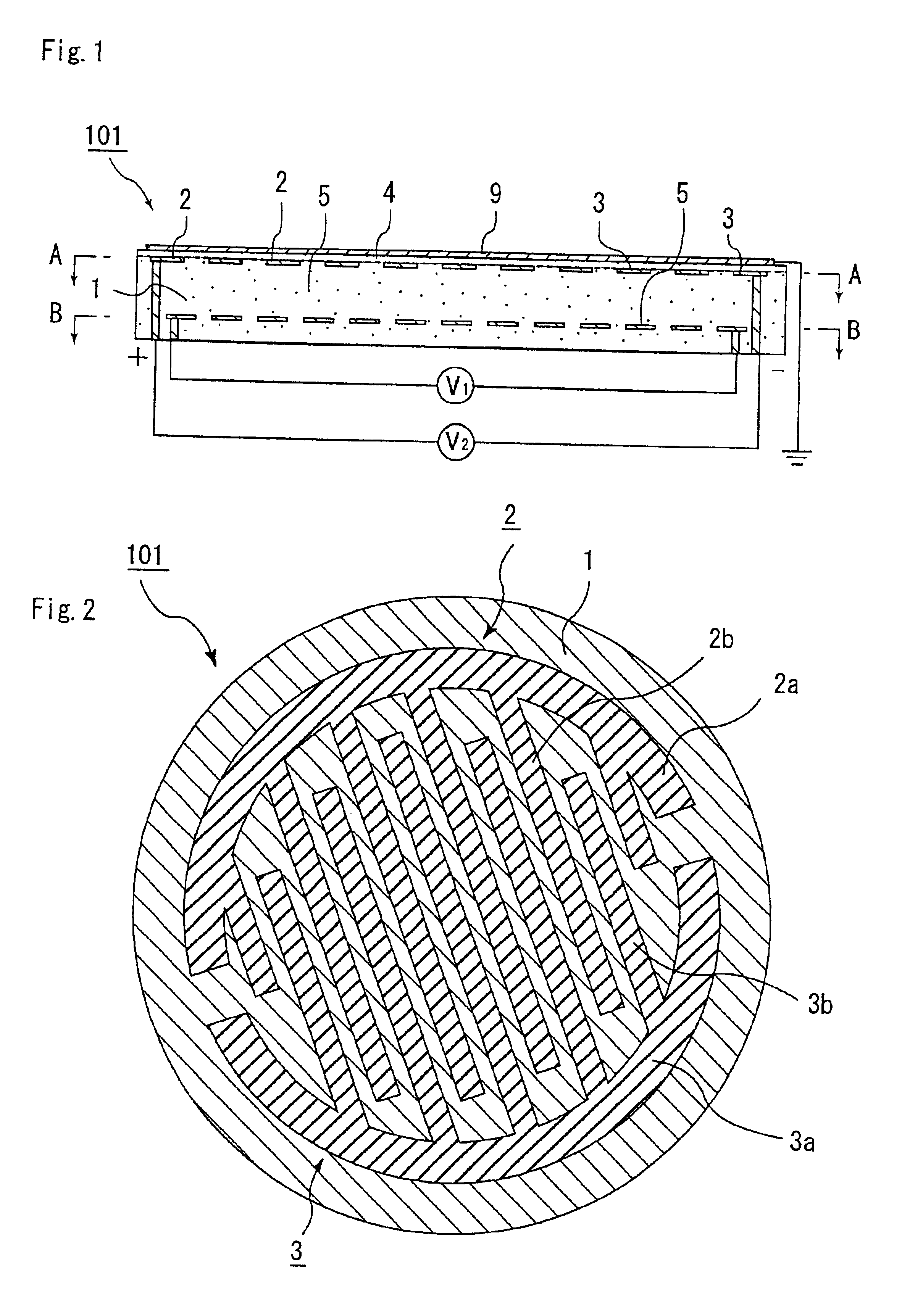
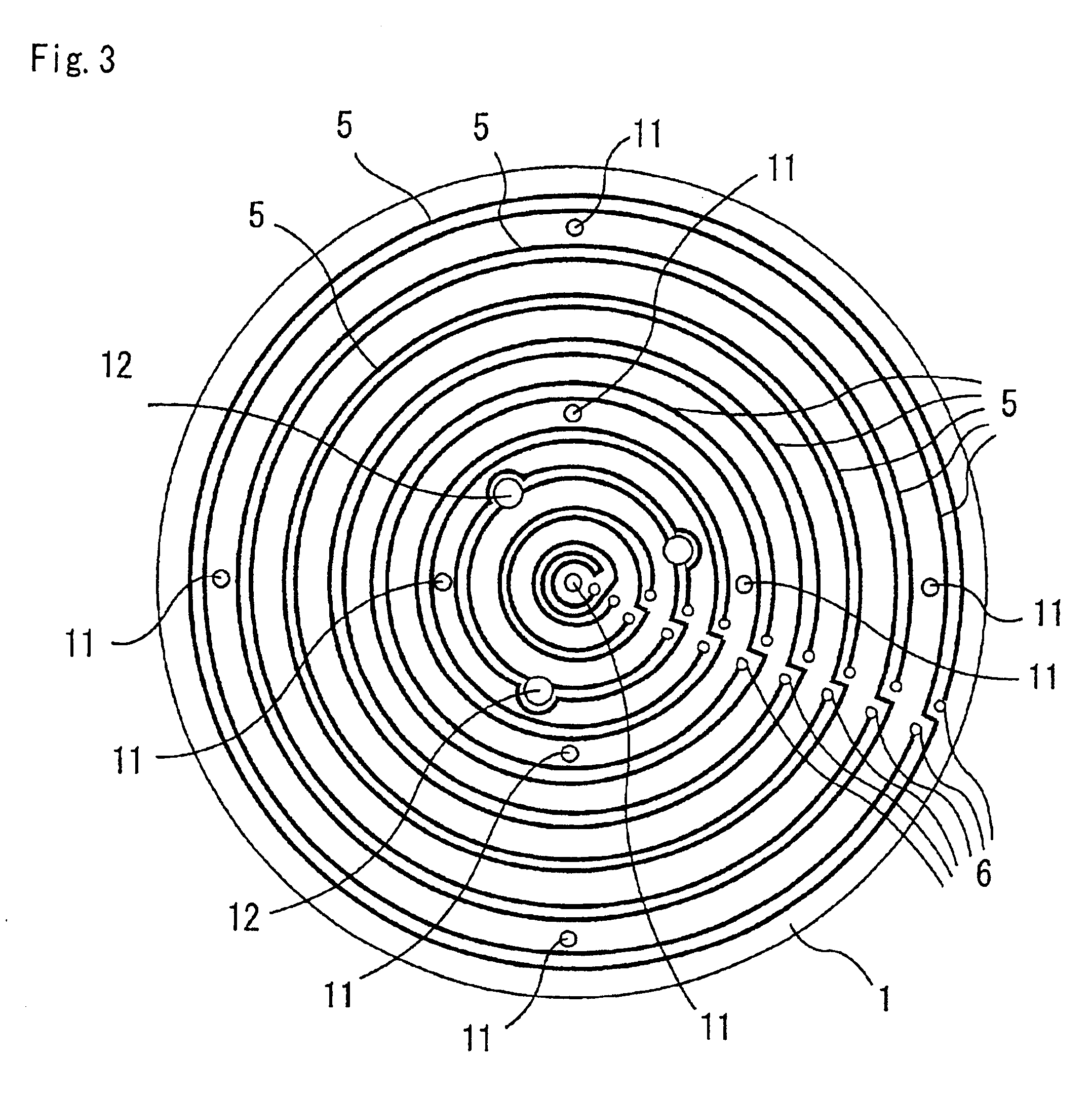
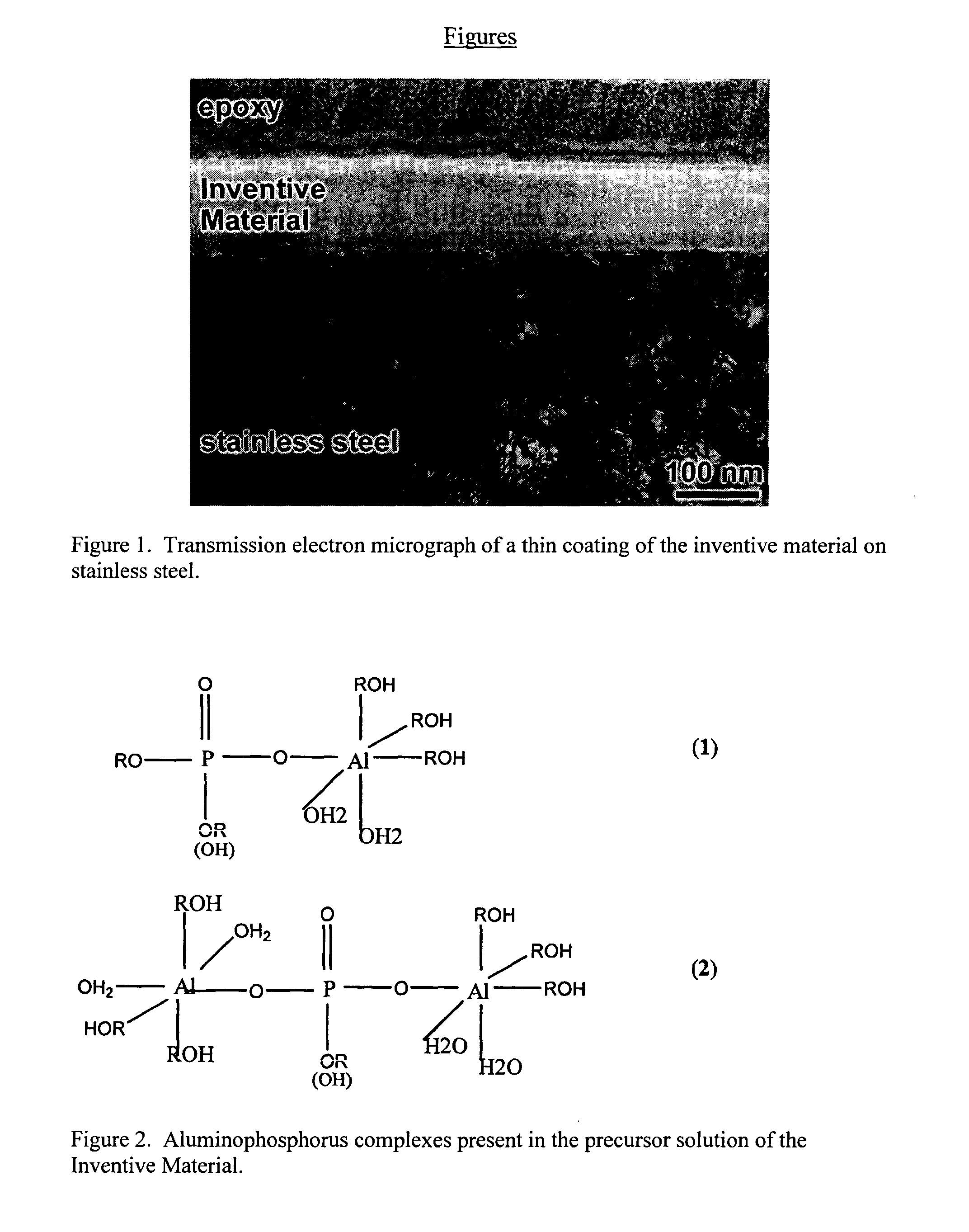
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Non oxide ceramics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ceramic armor apparatus for multiple bullet protection
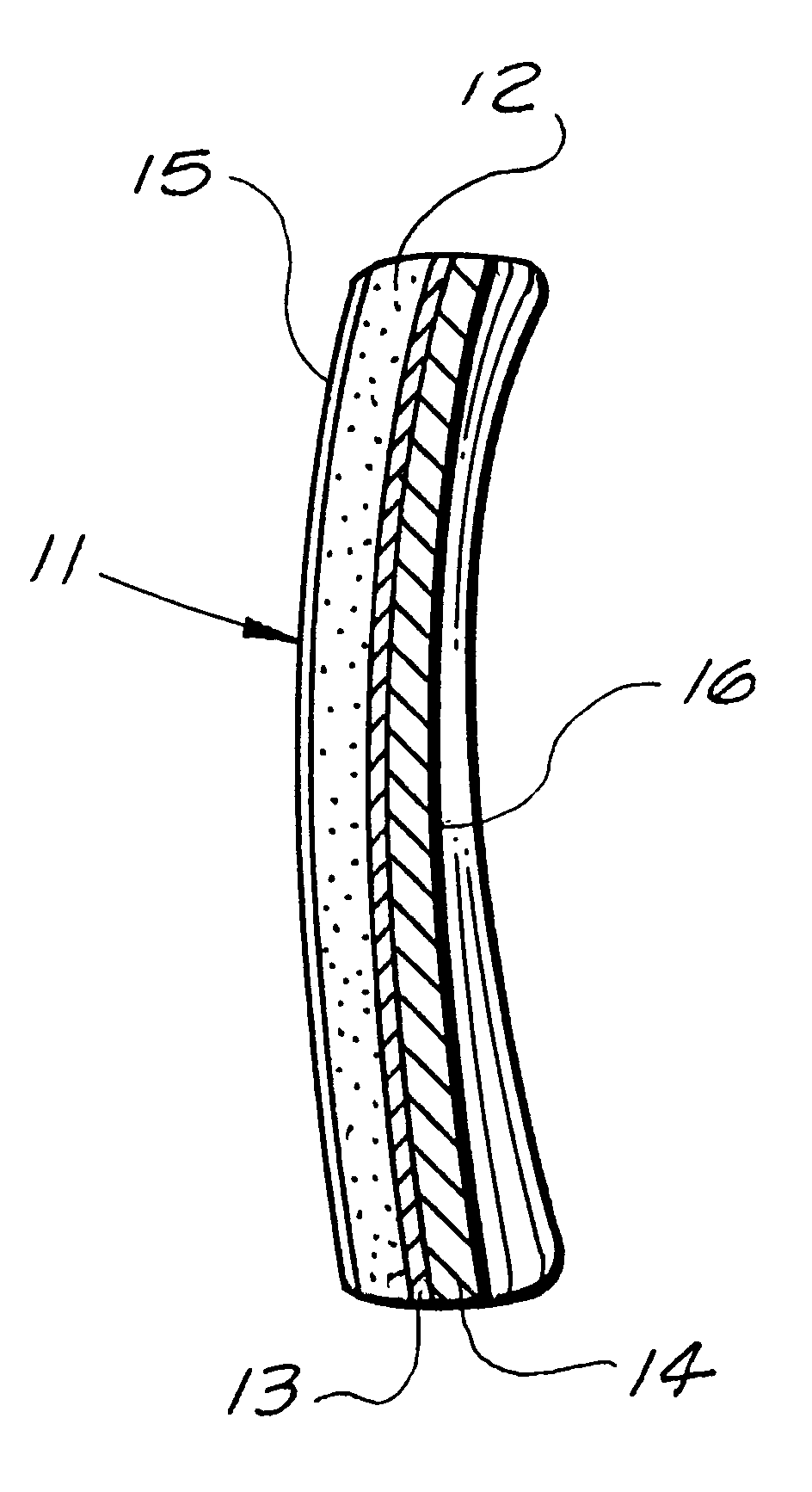
Armor apparatus comprising a non-oxide ceramic element bounded to an aramid fiber composite baking. A special ceramic and a novel aramid fiber substrate are combined in a unique arrangement that permits a single armor system to provide protection against multiple types of ballistic attack. The armor apparatus may be used alone or as a supplementary armor system to provide increased protection from ballistic attack.
Owner:ARMORWORKS ENTERPRISES
Catalytically enhanced filtration apparatus
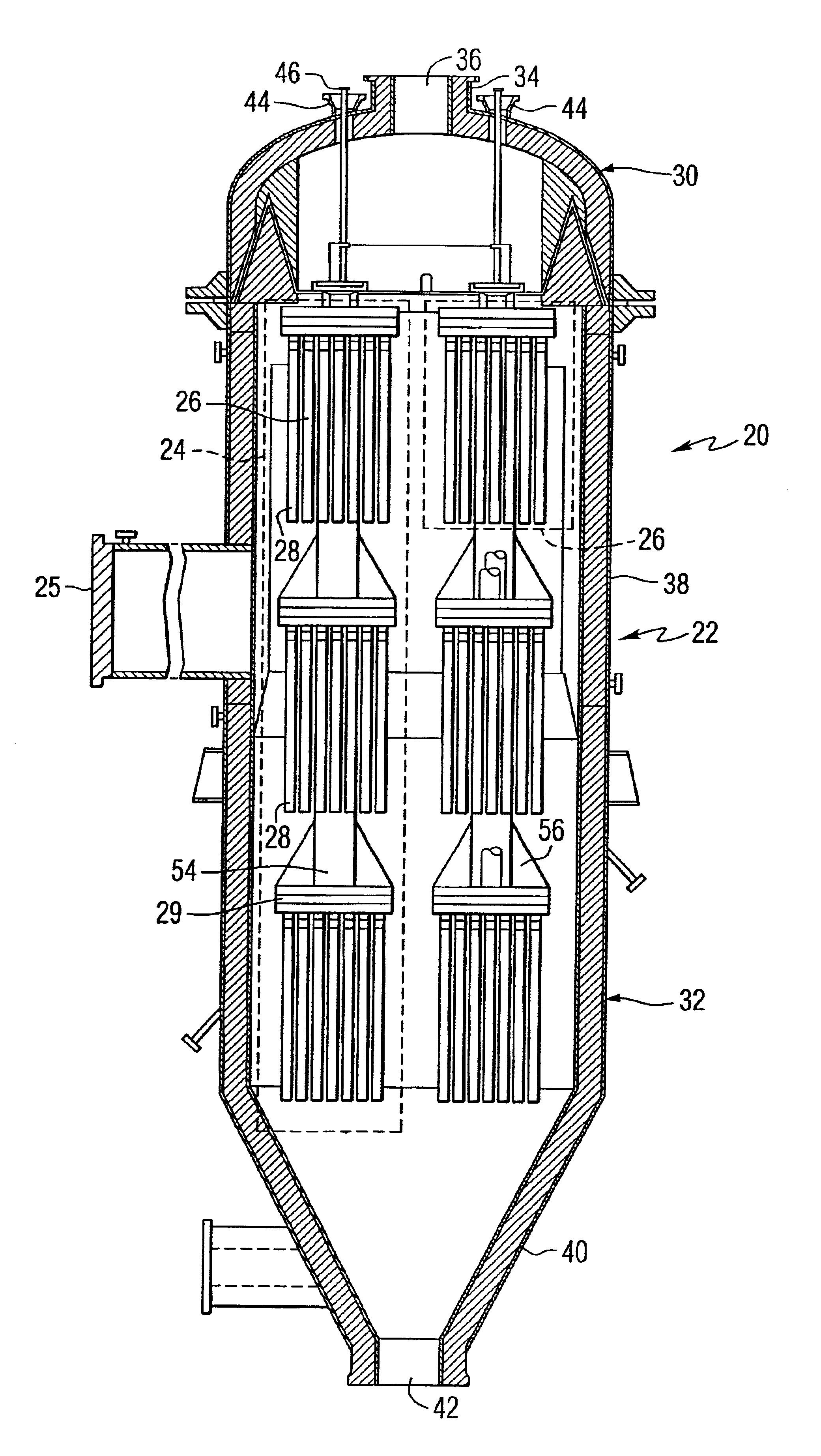
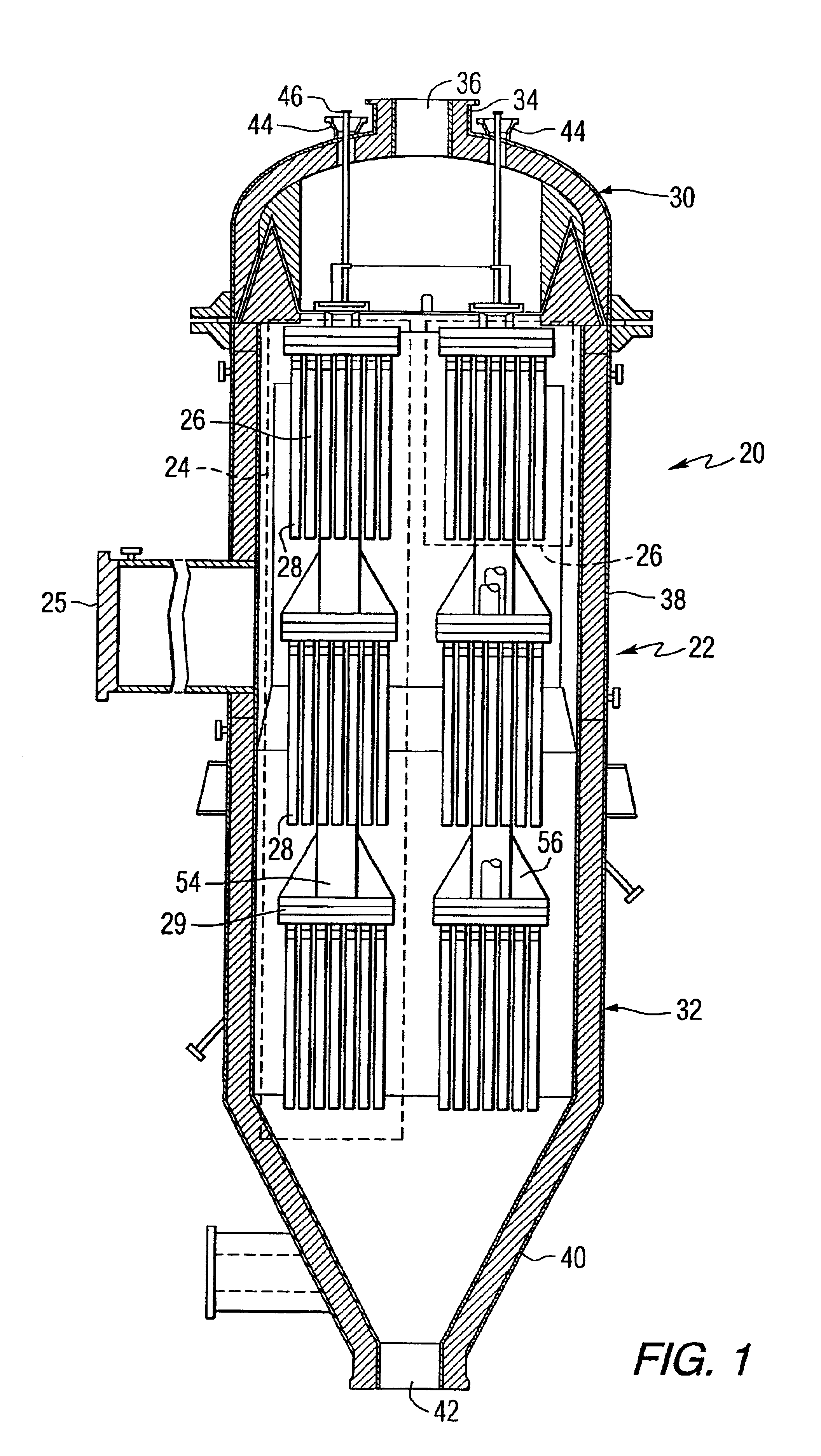
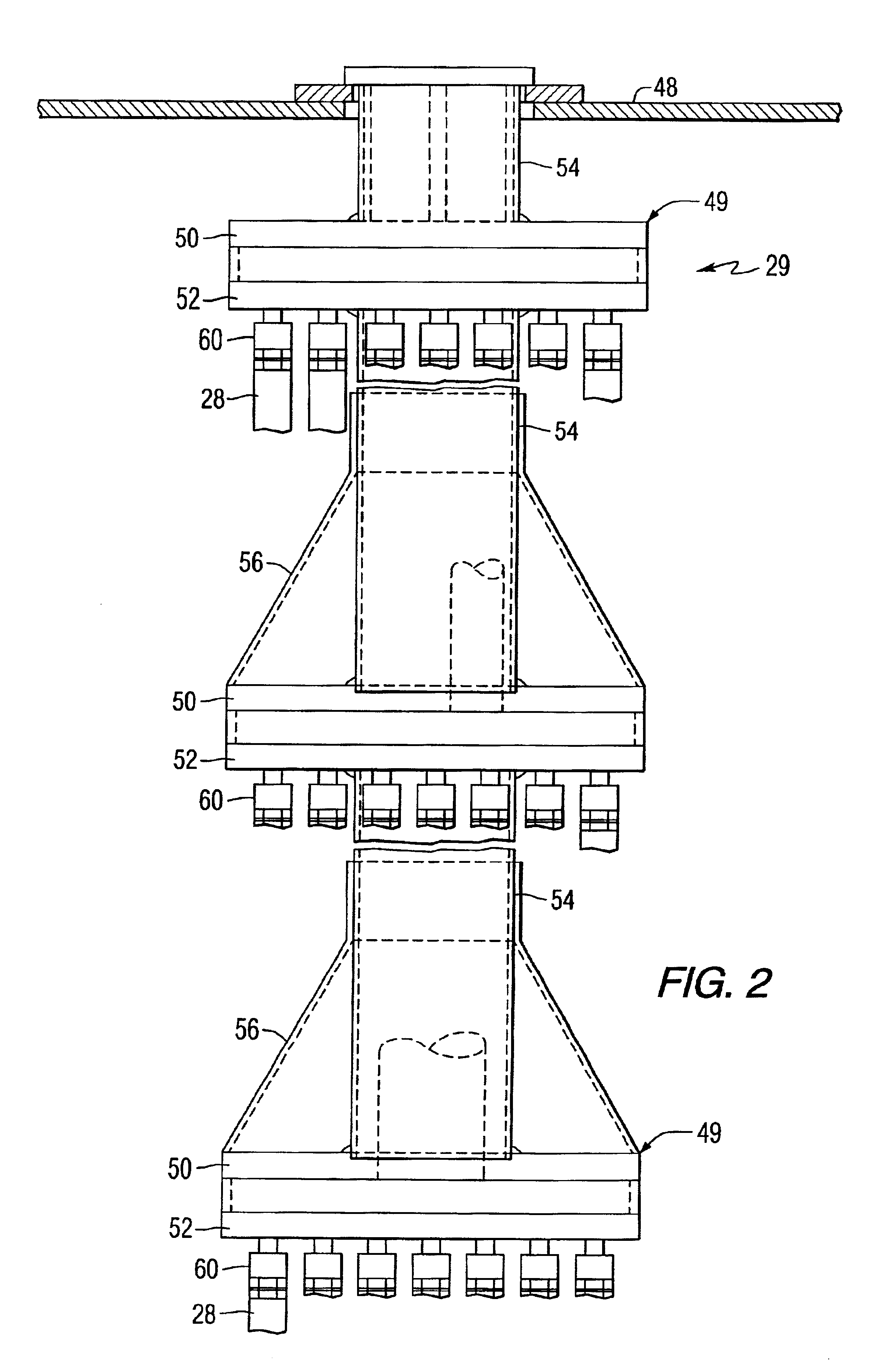
A hot gas filtration apparatus includes a vessel, a plurality of filter elements mounted within the vessel and positioned such that hot gas flows through said filter elements, with each of said filter elements having a porous body, and a catalytic layer on surfaces of the porous body. The porous body of the filter element may include one of: a porous ceramic monolithic matrix, a continuous fiber reinforced ceramic composite (CFCC) matrix, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, and a metal-ceramic composite matrix. When the porous body is a nonoxide ceramic, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, or a metal-ceramic composite matrix, the invention further includes an oxidative resistant layer coating surfaces within the porous body, and the catalytic layer is on the oxidative resistant layer. A porous particulate removal membrane can be positioned on one or more surfaces of the filter element. The porous membrane can also provide a surface for one or more catalysts. The catalysts on the porous surface of the membrane(s) can be the same as or different from the catalysts on surfaces within the porous body.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Ceramic substrate for a semiconductor production/inspection device
InactiveUS6891263B2Increase the number ofLower volume resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNon oxide ceramicsElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a ceramic substrate which can keep a sufficiently large breakdown voltage even if the pore diameter of its maximum pore is 50 μm or less to be larger than that of conventional ceramic substrates, can give a large fracture toughness value because of the presence of pores, can resist thermal impact, and can give a small warp amount at high temperature. The ceramic substrate of the present invention is a ceramic substrate for a semiconductor-producing / examining device having a conductor formed on a surface of the ceramic substrate or inside the ceramic substrate, wherein: the substrate is made of a non-oxide ceramic containing oxygen; and the pore diameter of the maximum pore thereof is 50 μm or less.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
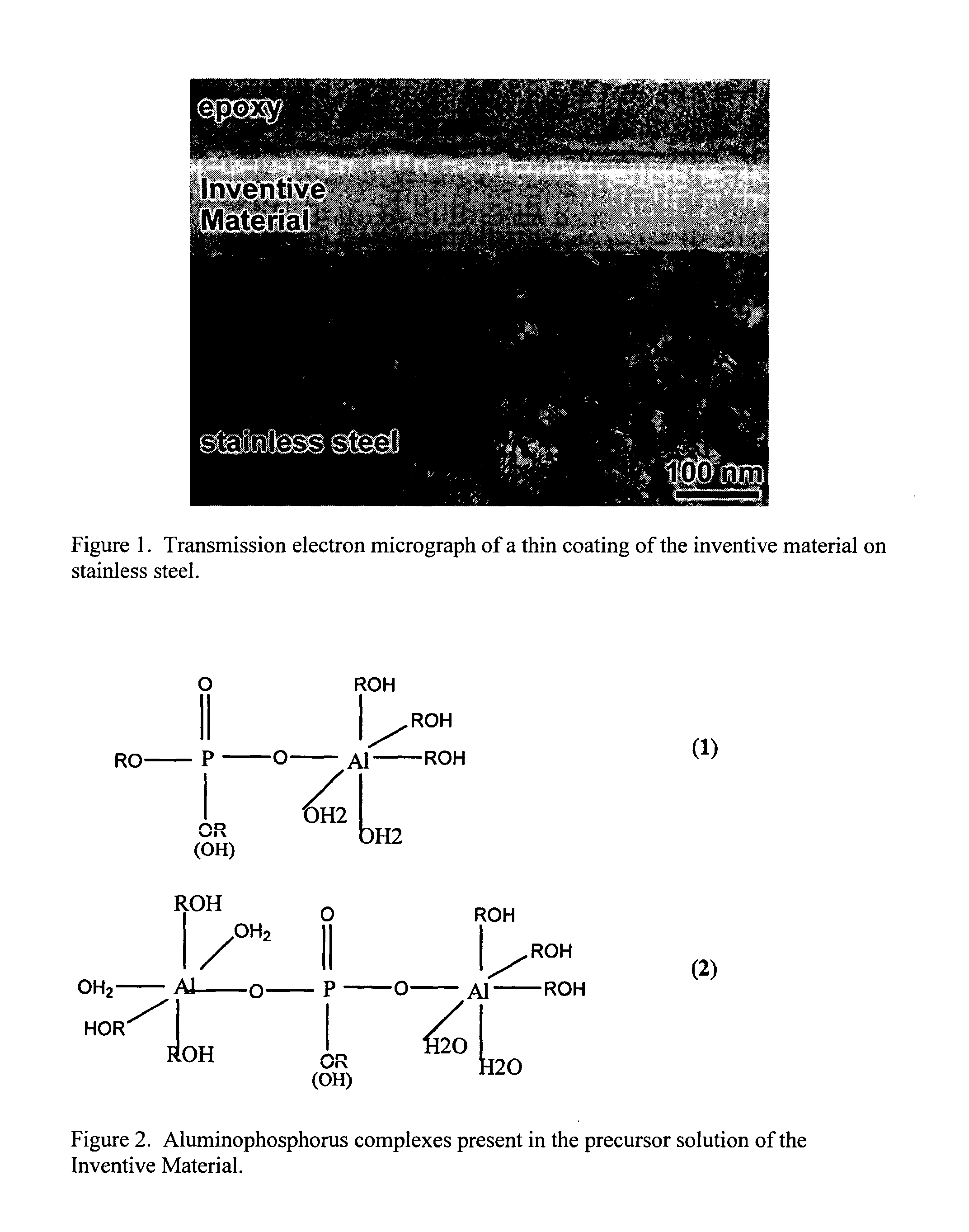
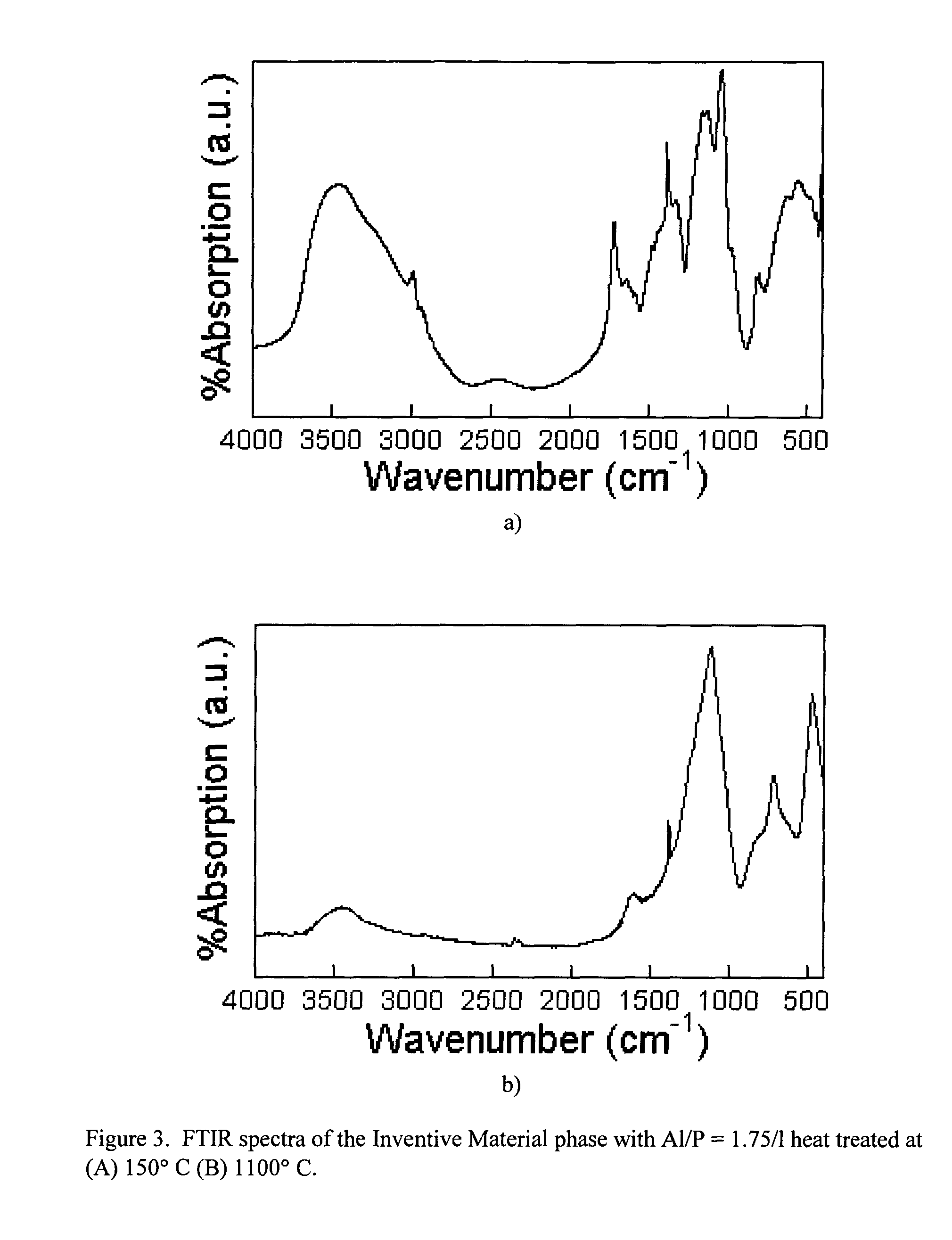
Aluminum phosphate compounds, compositions, materials and related composites
InactiveUS20050106384A1Control spreadImprove adhesionFilm/foil adhesivesPretreated surfacesNon oxide ceramicsMetallurgy
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Cellular Honeycomb Ultracapacitors and Hybrid Capacitors and Methods for Producing
InactiveUS20090021890A1High densityHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesNon oxide ceramicsSupercapacitor
An ultracapacitor or hybrid capacitor includes an electrically non-conductive rigid or semi-rigid porous honeycomb structure (12) having cells extending along a common direction and having an average density per unit area within in a plane perpendicular to the common direction exceeding 15.5 per square centimeter, desirably formed of a material that is stable at temperatures of 300° or more, such that high temperatures processing can be used to help ensure high purity of the final product. The material may desirably be an oxide or non-oxide ceramic, such as cordierite, silicon nitride, alumina, aluminum titanate, zircon, glass, or glass-ceramic.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for preparing ultra-fine diamond grinding wheel of vitrified bond
InactiveCN101870091AReduce surface roughness valueReduce depthAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesPotassiumUltra fine
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
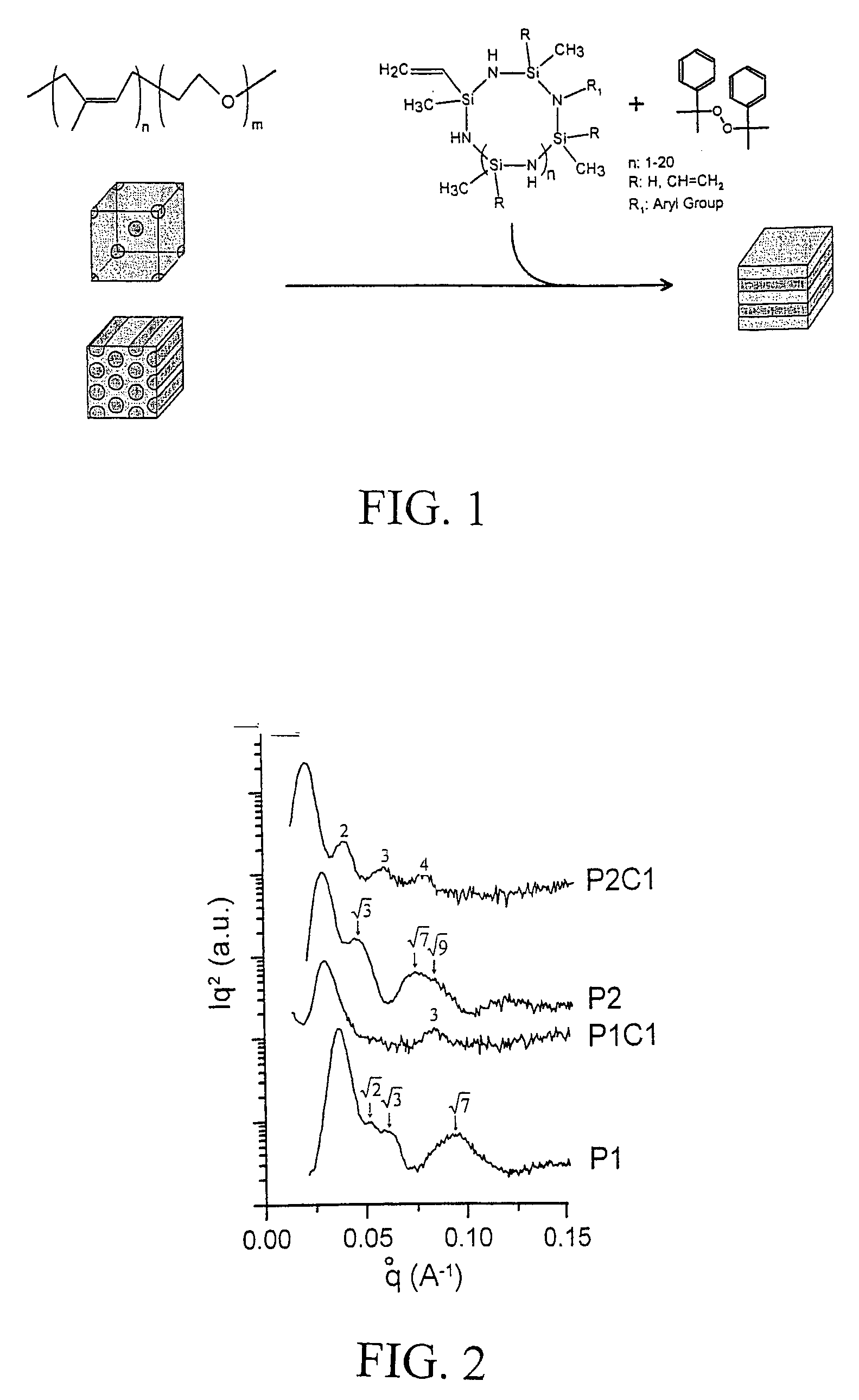
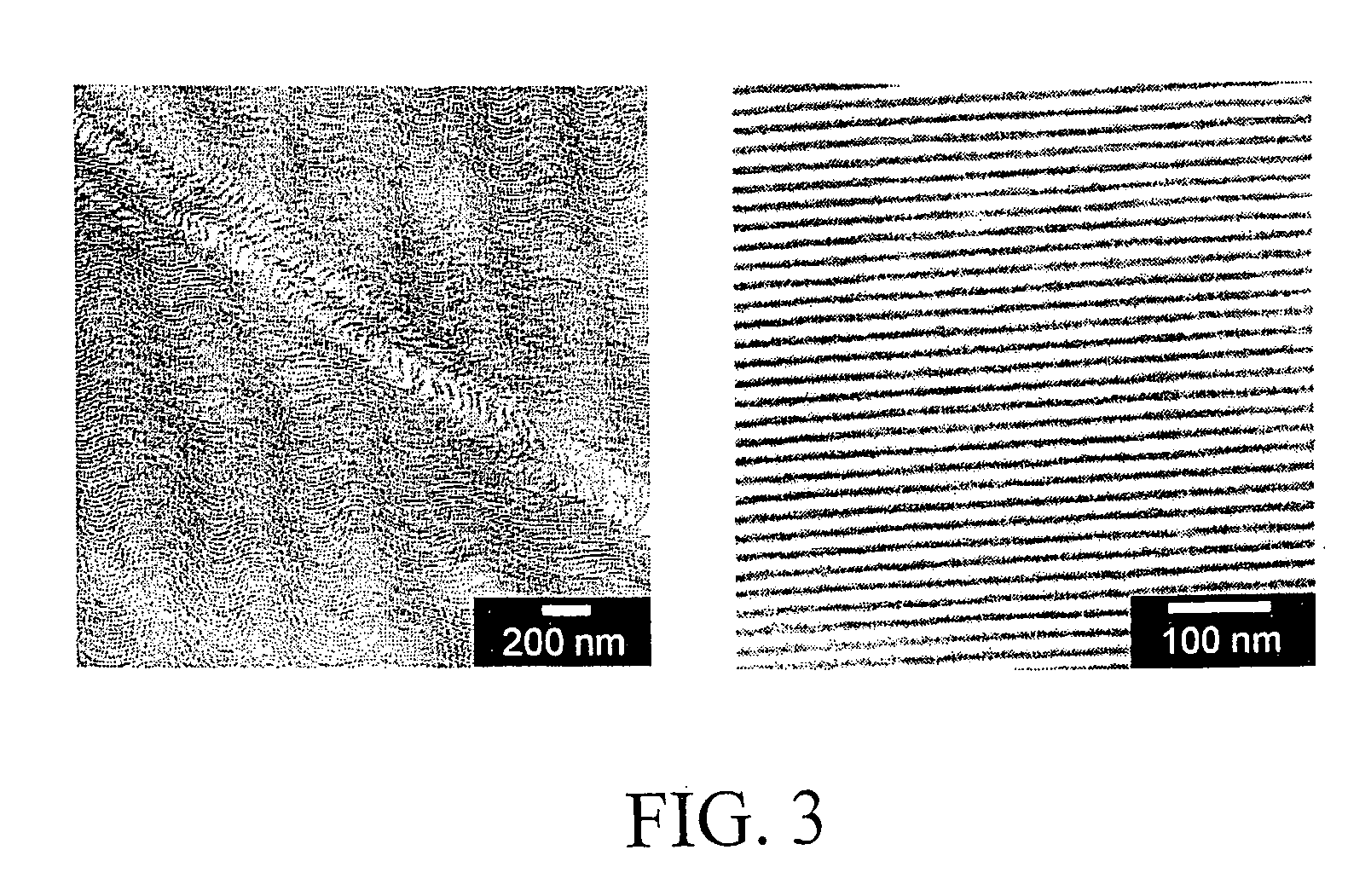
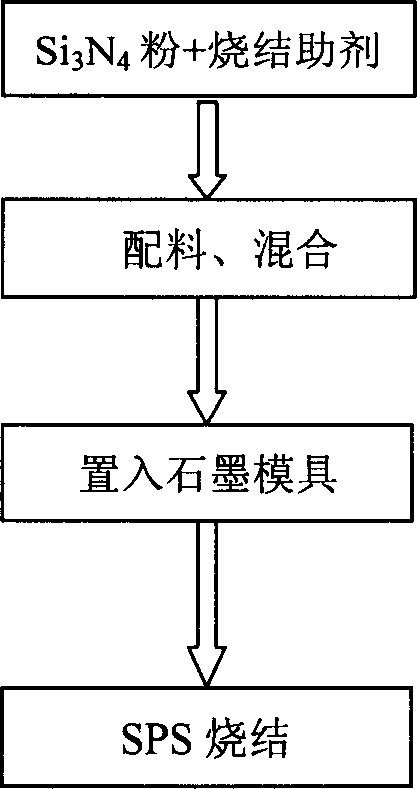
High temperature SiCN and SiC-type nanostructured ceramic material from block copolymer mesophases
InactiveUS20050036931A1Simple and easily controlled pathwayCarbon compoundsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsNon oxide ceramicsPolymer science
A block copolymer, preferably a block copolymer such as poly(isoprene-block-ethylene oxide), PI-b-PEO, is used as a structure directing agent for a polymer derived ceramic (PDC) precursor, preferably a silazane, most preferably a silazane commercially known as Ceraset. The PDC precursor is preferably polymerized after mixing with the block copolymer to form a nanostructured composite material. Through further heating steps, the nanostructured composite material can be transformed into a nanostructured non-oxide ceramic material, preferably a high temperature SiCN or SiC material.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Carbon-based polymer composite material capable of being ceramized and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a carbon-based polymer composite material capable of being ceramized and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-based polymer composite material is formed by mixing and pressing carbon-based resin, a fiber-reinforced material, a high temperature-resistant coupling agent, aluminium silicate mineral powder and non-oxide ceramic powder, and the carbon-based polymer composite material specifically comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-50 parts of the carbon-based resin, 10-40 parts of the fiber-reinforced material, 0.5-2 parts of the high temperature-resistant coupling agent, 10-50 parts of the aluminium silicate mineral powder and 1-10 parts of the non-oxide ceramic powder. Compared with the prior art, the composite material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good thermal protection performance and anti-scour performance; a forming process of the composite material is simple, and aerobic thermal protection and ceramic formationare integrated; the ceramization temperature is lower and the ceramic conversion rate is higher; and the polymer composite material further has the advantages of capability of being formed by the polymer composite material process, strong designability, good mechanical properties at medium and low temperature, high ceramic conversion rate, low thermal weight loss rate, high retention rate of high-temperature strength and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Crosslinkable elastomer composition and formed product comprising the same
ActiveUS20050070637A1Reduce weightGeneration amountFibre treatmentConductive materialElastomerNon oxide ceramics
The present invention provides a crosslinkable elastomer composition, in which generation of HF under high temperature conditions is reduced, the decrease in weight to both NF3 plasma treatment and O3 treatment in the semiconductor manufacturing process is small and generation of foreign substances (particles) in these treatments is suppressed significantly. Specifically, the present invention relates to a crosslinkable elastomer composition comprising a crosslinkable elastomer and a filler having a specific surface area of at least 0.5 m2 / g and containing a synthetic polymer having a thermally and chemically stable aromatic ring in the main chain, a crosslinkable elastomer composition comprising a crosslinkable elastomer and nonoxide ceramics and a crosslinkable elastomer composition wherein the decrease in weight by NF3 plasma irradiation is at most 0.20%.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
High-entropy brazing filler metal for brazing non-oxide ceramics and non-oxide ceramic composite material and preparation method of brazing filler metal
ActiveCN102689109AImprove performanceGood compatibilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaNon oxide ceramicsCeramic composite
The invention relates to a high-entropy brazing filler metal and a preparation method thereof, and particularly relates to a high-entropy brazing filler metal for brazing non-oxide ceramics and the composite material of the non-oxide ceramics and the preparation method of the brazing filler metal, aiming to solve the problem that the brazing filler metal at the joint of the non-oxide ceramics and the ceramic composite material which are soldered together is unreliable in performance at a temperature higher than 500 DEG C in the prior art. The brazing filler metal comprises the following components in parts by weight: 18 to 24 parts of Ni, 14.3 to 19 parts of Cr, 16.8 to 22.5 parts of Co, 15.9 to 21 parts of Fe, 10.1 to 13.5 parts of Cu, and 0 to 24.9 parts of Ti or TiH2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out vacuum melting on the weighed components at the temperature of 1200 to 1800 DEG C, performing linear cutting and carrying out foiling or composite tabletting on the components, so as to obtain the brazing filler metal; or the preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out ball-milling on the components in a ball material mass ratio of (12-16):1, and then tabletting and cleaning the components to obtain the brazing filler metal. The strength of the alloy joint obtained by using the method reaches 35 to 71 MPa, and the strength retention of the alloy joint at a high temperature of 800 DEG C exceeds 67%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wear resistant ceramic composite coatings and process for production thereof
InactiveCN101248144AMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesOxide ceramicNon oxide ceramics
Owner:STANDARD AERO SAN ANTONIO
Heat-resistant coated member
InactiveUS7157148B2Highly non-reactiveIncrease resistanceMolten spray coatingCharge supportsOxide ceramicsRare earth
A heat-resistant coated member comprises a substrate composed of a material selected from among molybdenum, tantalum, tungsten, zirconium, aluminum, titanium, carbon, and alloys, oxide ceramics, non-oxide ceramics and carbide materials thereof, which is covered with a layer composed primarily of a rare earth-containing oxide. In addition to heat resistance, the coated member has good corrosion resistance and non-reactivity, making it highly suitable as a part for sintering or heat-treating metals and ceramics in a vacuum, an inert atmosphere or a reducing atmosphere.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for preparing ceramic body
The invention discloses a method for preparing a ceramic body. The method comprises the following steps: water is used as a solvent, and water-soluble polybutadiene vinyl polymer is added to the solvent to prepare ceramic slurry; the prepared ceramic slurry is injected into a forming mold, and self-gel in-situ solidification is conducted at the temperature of 15 DEG C-40 DEG C in the air; and demolding and drying are conducted after sufficient solidification. Due to the fact that the self-gel in-situ solidification is carried out on the water-soluble polybutadiene vinyl polymer which has the functions of a dispersing agent and a gel reagent at the same time, and is low in toxicity, low in cost and easy to obtain to prepare the ceramic body, preparation cost is greatly reduced and pollution is reduced. Moreover, the method is simple in preparation technology, free of oxygen inhibition, capable of being operated in the air and free of harsh operating conditions and equipment requirements. Besides, the prepared ceramic body is high in intensity, good in toughness, bright and clean in surface, free of exfoliation and suitable for preparation of various oxide ceramics, oxide ceramics, composite ceramics and ceramics with complex shapes, and thus the method for preparing the ceramic body has industrial application prospects.
Owner:PINGXIANG SHUNPENG NEW MATERIALS
Method for making amorphous particles using a uniform melt-state in a microwave generated plasma torch
ActiveUS8951496B2Improve thermal performanceImprove toleranceCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsMolten stateNon oxide ceramics
Feed material comprising uniform solution precursor droplets is processed in a uniform melt state using microwave generated plasma. The plasma torch employed is capable of generating laminar gas flows and providing a uniform temperature profile within the plasma. Plasma exhaust products are quenched at high rates to yield amorphous products. Products of this process include spherical, highly porous and amorphous oxide ceramic particles such as magnesia-yttria (MgO—Y2O3). The present invention can also be used to produce amorphous non oxide ceramic particles comprised of Boron, Carbon, and Nitrogen which can be subsequently consolidated into super hard materials.
Owner:6K INC
Member having composite coating and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6129994AImprove adhesionAdequate unevennessMolten spray coatingLaminationOxide ceramicsNon oxide ceramics
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 00546 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 3, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 3, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 6, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 27694 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 12, 1996A composite steel sheet including a steel base member; an undercoat having opposed surfaces and a thickness of 10-750 mu m obtained by spraying one or more spraying materials selected from metals, non-oxide ceramics, oxide ceramics and cermets onto the steel base member. The undercoat has an oxide layer of not less then 0.5 mu m in thickness on one of the opposed surfaces positioned away from said steel base member. A fired topcoat is formed on the oxide layer of the undercoat from a vitreous coating having a linear expansion coefficient of 4-11x10-6 / DEG C.
Owner:TOCALO CO LTD
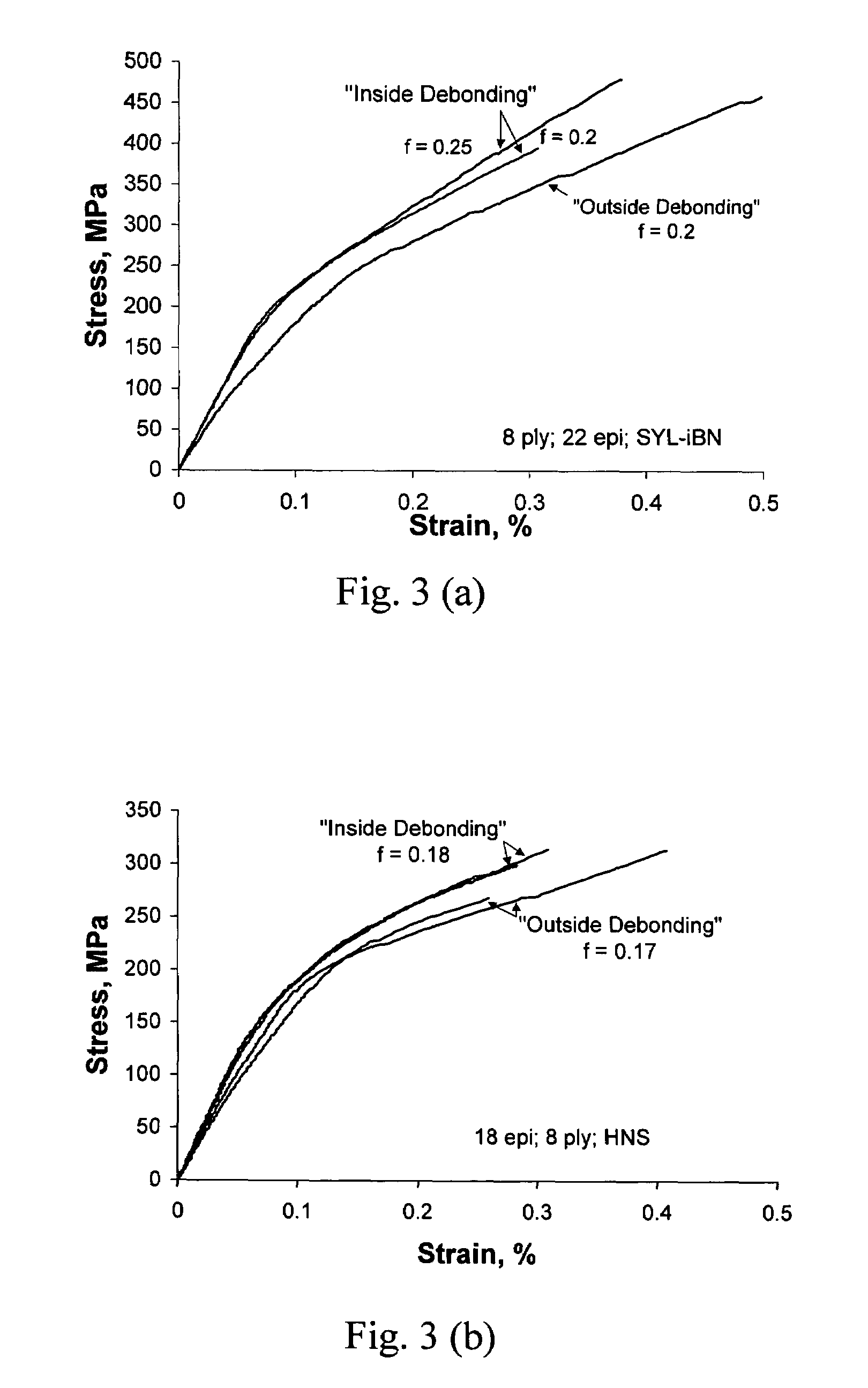
Interphase for ceramic matrix composites reinforced by non-oxide ceramic fibers
ActiveUS7427428B1Improve the oxidative durability of ceramic matrix composite materialsMaintain reliabilityLayered productsPretreated surfacesOxide ceramicNon oxide ceramics
A ceramic matrix composite material is disclosed having non-oxide ceramic fibers, which are formed in a complex fiber architecture by conventional textile processes; a thin mechanically weak interphase material, which is coated on the fibers; and a non-oxide or oxide ceramic matrix, which is formed within the interstices of the interphase-coated fiber architecture. During composite fabrication or post treatment, the interphase is allowed to debond from the matrix while still adhering to the fibers, thereby providing enhanced oxidative durability and damage tolerance to the fibers and the composite material.
Owner:NASA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE
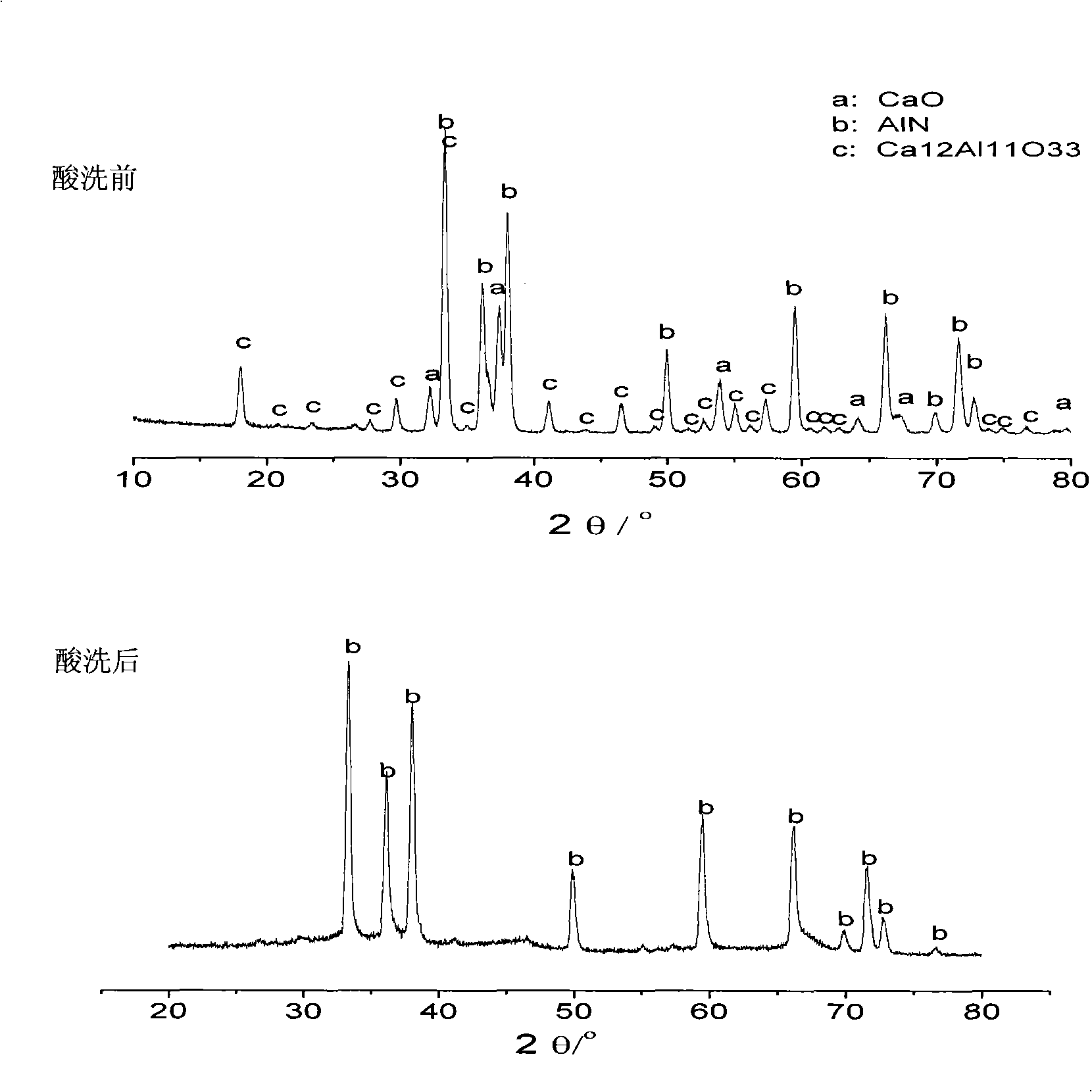
Preparation method for low-oxygen spherical aluminum nitride powder
ActiveCN101525238AEasy to separateTo achieve the purpose of deoxygenationNon oxide ceramicsMaterials preparation
The invention provides a preparation method for low-oxygen spherical aluminum nitride powder and pertains to the field of non-oxide ceramic powder material preparation technology. The low-oxygen spherical aluminum nitride powder can be obtained through the following steps: ball-grinding, evenly mixing and then drying aluminum nitride powder and appropriate amount of spherical auxiliary materials for deoxidation; placing the mixture in a graphite crucible with certain loading density, heating to 1,550 to 1,900 DEG C in N2 or Ar and preserving for 0 to 20 hours, and then cooling with the crucible; mechanically crashing the product and heating to 600 DEG C in a muffle furnace for carbon emission, then washing in a hydrochloric acid solution with 5 to 20 mass percent concentration and fully washing the product after acid cleaning in de-ionized water for 2 to 10 times; after drying, obtaining the aluminum nitride powder with 3 to 15mum median particle diameter, more than 90 percent sphericity and less than 1wt percent oxygen content. The preparation method provided by the invention can achieve spherical particle morphology and granulation at the same time required by the high thermal-conductivity aluminum nitride filling.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Reparative coating and application thereof in repairing coating of silicon carbide-based composite material
The invention relates to a reparative coating and the application thereof in repairing the coating of a silicon carbide-based composite material, and belongs to the technical field of repairing the anti-oxidation coating on the surface of the silicon carbide-based composite material. The reparative coating is prepared through the brush-coating process, wherein a non-oxide ceramic precursor is adopted as an adhesive and ceramic powders are adopted as fillings. In a high-temperature service environment, the precursor inside the coating is pyrolyzed to generate ceramics. In this way, the oxidation resistance and the cohesive property of the coating are further improved. The ceramic precursor can be cured by using a hand-held heating device, so that the dependence on equipment is greatly reduced. Therefore, the reparative coating and the application thereof have a very important role in simply repairing the anti-oxidation coating on the surface of a heterogenic thermal structural component made of the silicon carbide-based composite material.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH +1
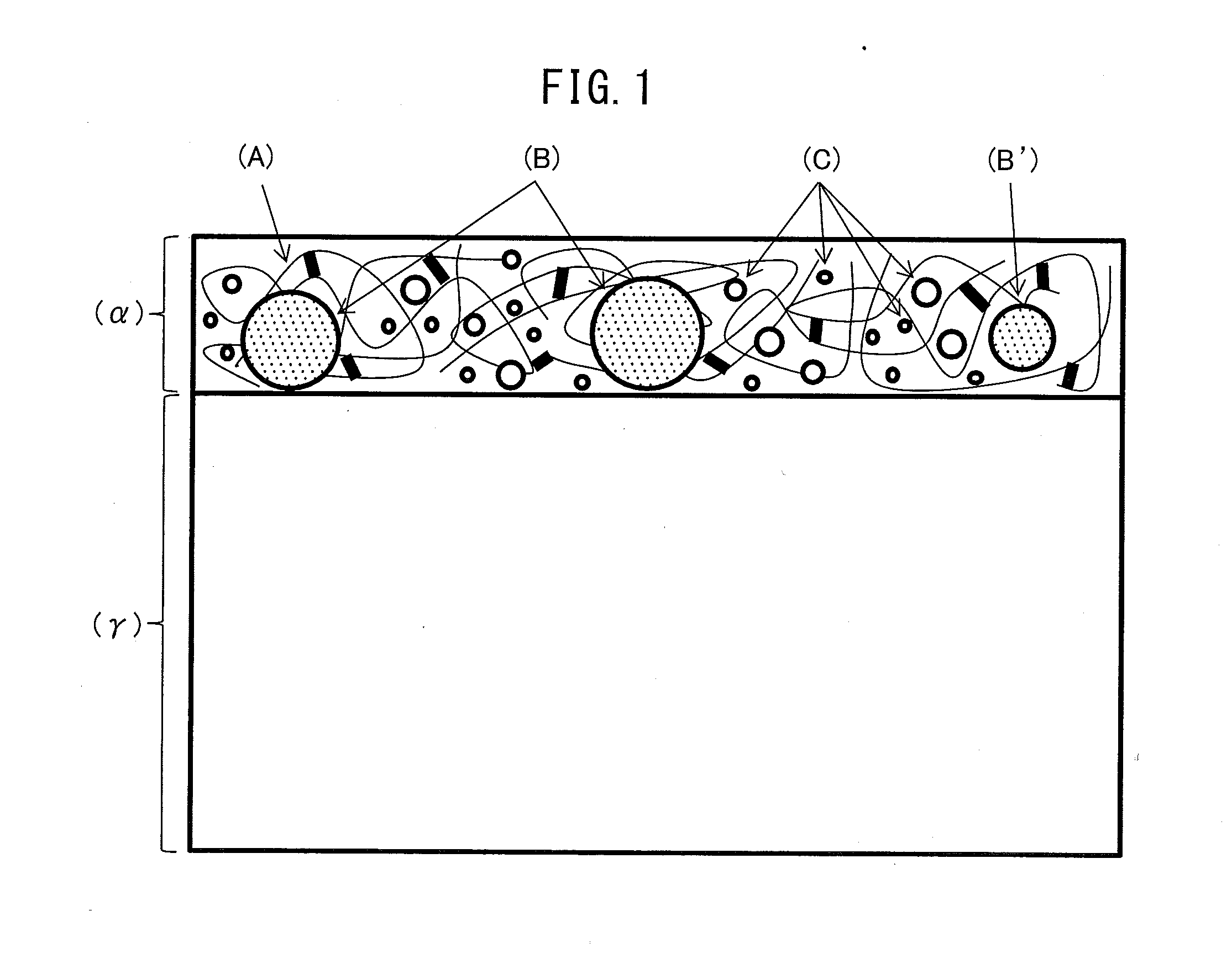
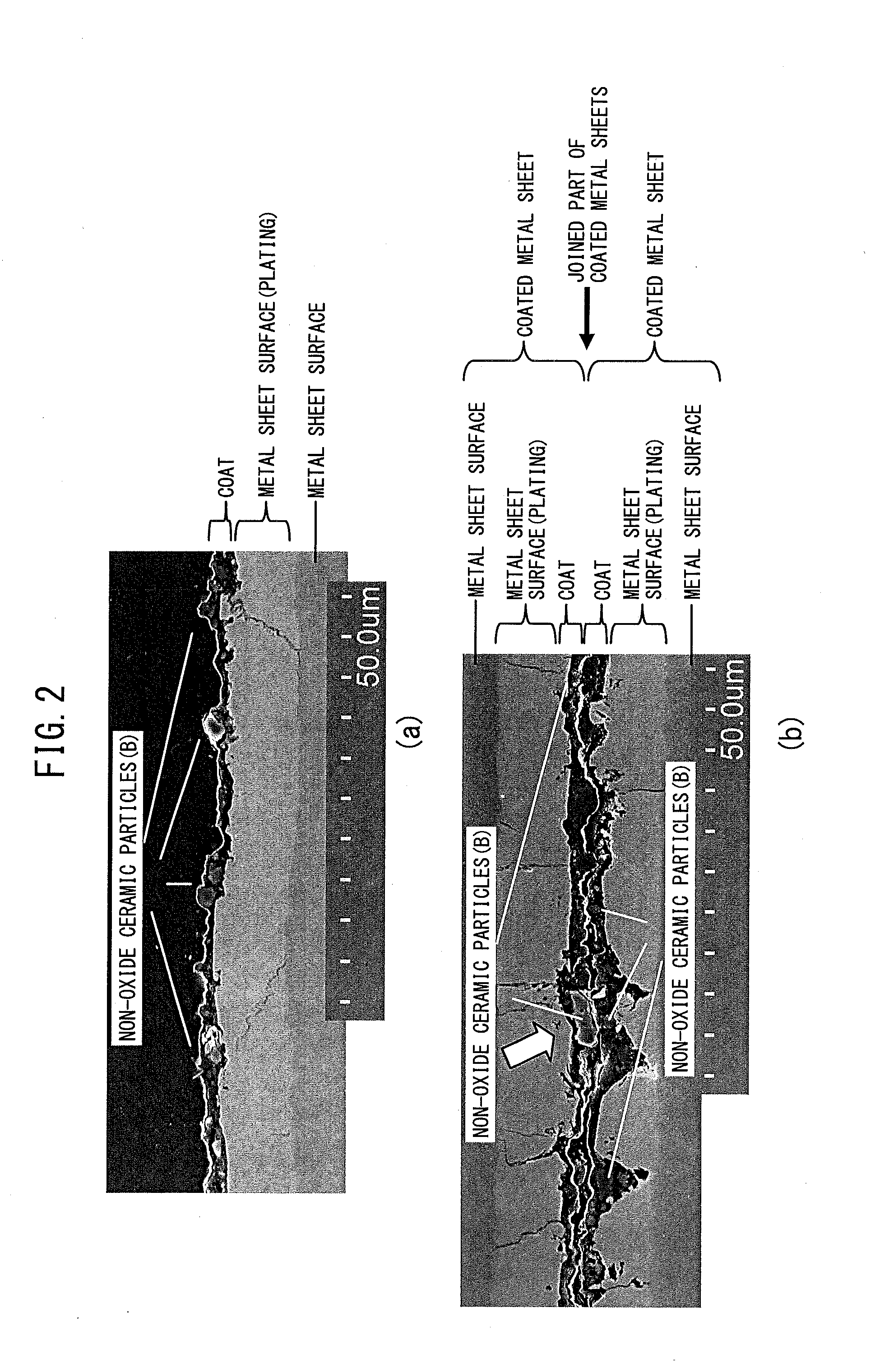
Precoated metal sheet for automobile use excellent in resistance weldability, corrosion resistance, and formability
InactiveUS20150044450A1Improve corrosion resistanceGood formabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsNon oxide ceramicsBoride
Precoated metal sheet for automobile use which is excellent in resistance weldability, corrosion resistance, and formability is provided. The present invention provides precoated metal sheet for automobile use comprising a metal sheet and a coat (α) on at least one surface of the metal sheet, wherein the coat (α) comprising an organic resin (A), non-oxide ceramic particles (B) selected from at least one type of borides, carbides, nitrides, and silicides and which have an electrical resistivity at 25° C. of 0.1×10−6 to 185×10−6 Ωcm, and an anti-corrosive pigment (C).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method for making amorphous particles using a uniform melt-state in a microwave generated plasma torch
ActiveUS20140155249A1Improve thermal performanceImprove toleranceCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsNon oxide ceramicsMolten state
Feed material comprising uniform solution precursor droplets is processed in a uniform melt state using microwave generated plasma. The plasma torch employed is capable of generating laminar gas flows and providing a uniform temperature profile within the plasma. Plasma exhaust products are quenched at high rates to yield amorphous products. Products of this process include spherical, highly porous and amorphous oxide ceramic particles such as magnesia-yttria (MgO—Y2O3). The present invention can also be used to produce amorphous non oxide ceramic particles comprised of Boron, Carbon, and Nitrogen which can be subsequently consolidated into super hard materials.
Owner:6K INC
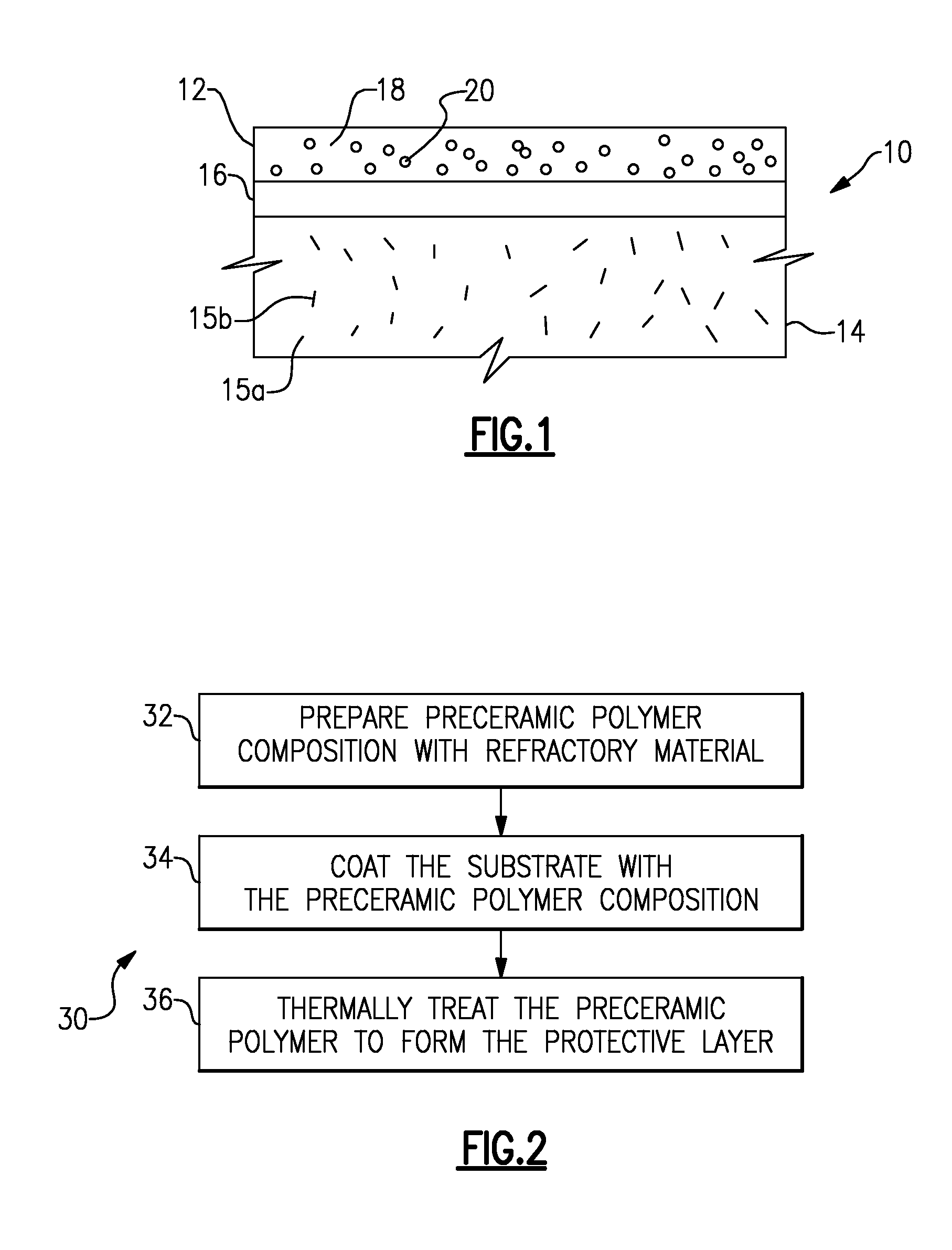
High temperature refractory coatings for ceramic substrates
ActiveUS20090130446A1Ceramic layered productsGlass/slag layered productsNon oxide ceramicsRefractory
A composite article includes a substrate and a protective layer on the substrate. The protective layer includes a non-oxide ceramic matrix and a refractory phase within the non-oxide ceramic matrix.
Owner:RTX CORP
Aluminum phosphate compounds, compositions, materials and related composites
InactiveUS7682700B2Control spreadImprove adhesionFilm/foil adhesivesPretreated surfacesNon oxide ceramicsMetallurgy
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Inorganic binder, preparation method and its application in preparation of porous ceramics
The invention relates to an inorganic bond, a preparation method thereof and an application for the preparation of a porous ceramic thereof. The bond consists of alumina and / or aluminum hydroxide, phosphoric acid and boric acid, wherein, the weight percentage content of the alumina and / or the aluminum hydroxide is 70 percent to 99.5 percent, the weight percentage content of the phosphoric acid is 30 percent to 0.5 percent, and additionally the weight percentage content of the boric acid is 0 percent to 15 percent. The weight percentage content of the aluminum hydroxide is converted into Al2O3. The mol ratio of phosphor and aluminum is less than one. When the bond is used for preparing for the porous ceramic, firstly the granular diameter of the alumina or the aluminum hydroxide used for preparing for the bond is confirmed, and the granular diameter of the alumina or the aluminum hydroxide for using is 0.01 time to 0.5 time of the granular diameter of ceramic powder material; non-oxide ceramic powder material is mixed uniformly and mixed uniformly with pore-forming agent or vesicant to be molded and sintered, the sintering temperature is between 900 DEG C to 1600 DEG C. The sintering atmosphere is processed in air or under the inert atmosphere.
Owner:江西高环陶瓷科技股份有限公司
High temperature SiCN and SiC-type nanostructured ceramic material from block copolymer mesophases
InactiveUS7087656B2Simple and easily controlled pathwayCarbon compoundsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsNon oxide ceramicsPolymer science
A block copolymer, preferably a block copolymer such as poly(isoprene-block-ethylene oxide), PI-b-PEO, is used as a structure directing agent for a polymer derived ceramic (PDC) precursor, preferably a silazane, most preferably a silazane commercially known as Ceraset. The PDC precursor is preferably polymerized after mixing with the block copolymer to form a nanostructured composite material. Through further heating steps, the nanostructured composite material can be transformed into a nanostructured non-oxide ceramic material, preferably a high temperature SiCN or SiC material.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for preparing titanium nitride ceramic powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing titanium nitride ceramic powder, which belongs to the field of the preparation of ceramic powder. A titanium source comprises soluble titanium salt, namely titanium tetrachloride or titanium tetrabromide, and a carbon source comprises glucose, sucrose, citric acid and soluble starch. Nitric acid is used as an oxidizing agent, and urea is used as a fuel; and ammonium nitrate is used as a preparing agent. The mol ratio Ti ;C of the titanium source to the carbon source is 1 to (4-16), and the mol ratio of the nitric acid with the ammonium nitrate to the urea with the ammonium nitrate is (1-12) ;2. Various raw materials are dissolved in water and then are heated at a temperature of between 100 and 600 DEG C, and a solution undergoes a combustion reaction to generate precursors; the precursors are pulverized and then are pretreated for 0 to 10 hours at a temperature of between 200 and 800 DEG C, and then a carbon thermal reduction is carried out for 1 to 10 hours in the atmosphere of flowing nitrogen at a temperature of between 800 and 1,800 DEG C. Follow-up treatment is carried out on products to obtain titanium nitride powder. The titanium source and the carbon source in the precursors of the invention have fine granularity and are uniformly mixed; therefore, the method has good reaction activity and also has the advantages of lowering the temperature of the carbon thermal reduction reaction and improving the reaction rate. The method can prepare nanometer-level non-oxidized ceramic powder with good decentrality.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Spray granulation method of non-oxide ceramic powder
InactiveCN103172380AIncrease productionImprove granulation effectSpray GranulationNon oxide ceramics
The invention discloses a spray granulation method of non-oxide ceramic powder. The spray granulation method specifically comprises the following steps of: step one. material blending, to be specific, blending 35%-65% of non-oxide powder, 0%-3% of carbon powder, 0%-4% of dispersing agent, 0.05%-4.5% of binder and 30%-60% of deionized water in percentage by weight: and step two. preparing the raw materials in the step one into stable ceramic slurry by adopting ball-milling, high-speed stirring or ultrasonic dispersion, wherein the viscosity of the obtained slurry is not more than 5dpa.s; and step three. spray-drying and pelleting, to be specific, controlling the feed rate of the slurry prepared in the step two through a peristaltic pump, adding the slurry to a spray-drying granulator, and obtaining boron carbide pelleting materials by controlling the inlet and outlet temperature and pressure of the slurry, wherein the solid content of the obtained slurry for spray granulation can reach 65wt%.
Owner:常熟佳合高级陶瓷材料有限公司
Prepn process of SiN ceramic with high heat conductivity
The preparation process of Si3N4 ceramic with high heat conductivity features the SPS low temperature quick sintering with nitride as sintering assistant to prepare Si3N4 ceramic with high heat conductivity as one kind one non-oxide ceramic. The Si3N4 ceramic with high heat conductivity is prepared with alpha Si3N4 powder and sintering assistant in the ratio of 100 to 2-10, and through mixing and SPS low temperature quick sintering. During the preparation, the material is filled into graphite mold and quickly SPS sintered at 10-100 MPa pressure and 1500-1700 deg.c for 3-30 min. The Si3N4 ceramic has high heat conductivity up to 120W / m.K and high strength including three point breaking strength over 750 MPa.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiphase eutectic ceramic coatings
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Environmental barrier-infrared stealth integrated coating, composite material containing coating and preparation method of composite material
The invention discloses an environmental barrier-infrared stealth integrated coating capable of coating the surface of a non-oxide fiber reinforced non-oxide ceramic matrix composite material. The coating has a multi-layer superposition structure, and the multi-layer superposition structure comprises a silicon bonding layer, an anti-oxidation layer and a low infrared emissivity / encapsulation layerin sequence from the inside to the outside, wherein the anti-oxidation layer is a mullite single coating or a mullite / BSAS composite coating, and the low infrared emissivity / encapsulation layer is aBi2O3-ZnO-based glass coating containing a noble metal filler. The invention also provides a composite material containing the coating and a preparation method of the composite material. The environmental barrier-infrared stealth integrated coating provided by the invention adopts the multi-layer superposition structure, thermal expansion coefficients of each functional layer gradually and slowlychange, so that thermal mismatch among the layers is weakened, and the coating has excellent thermal shock resistance.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com