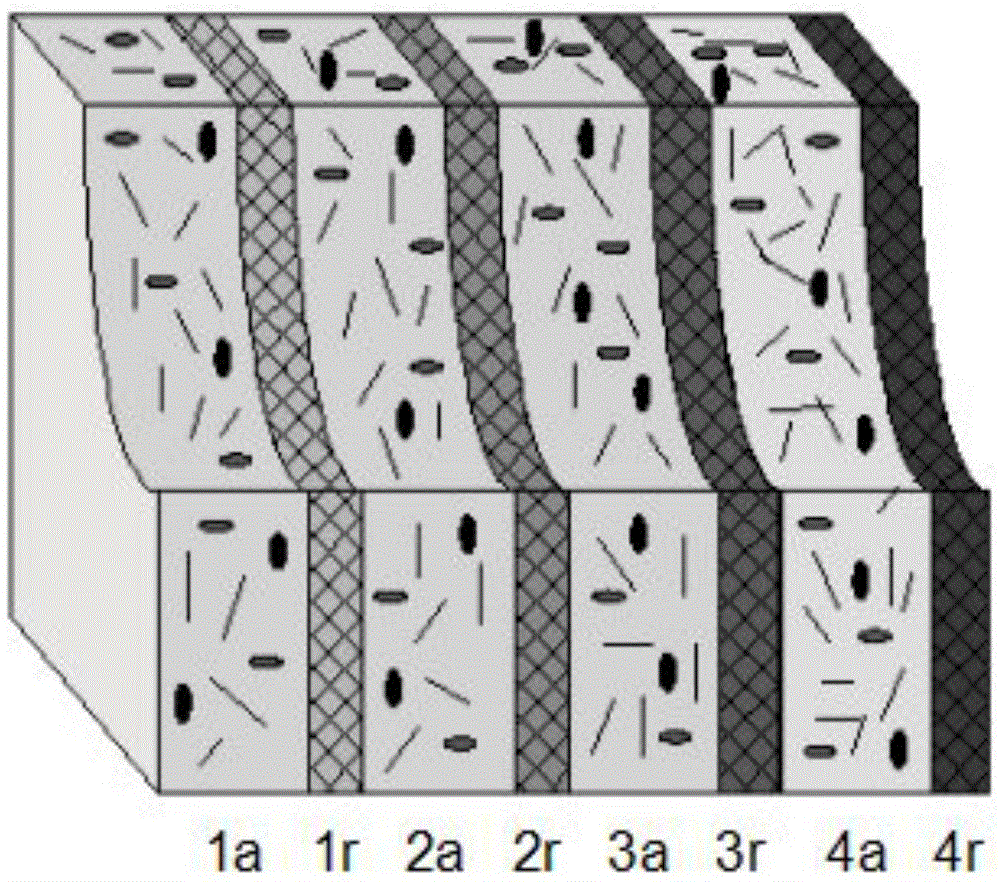
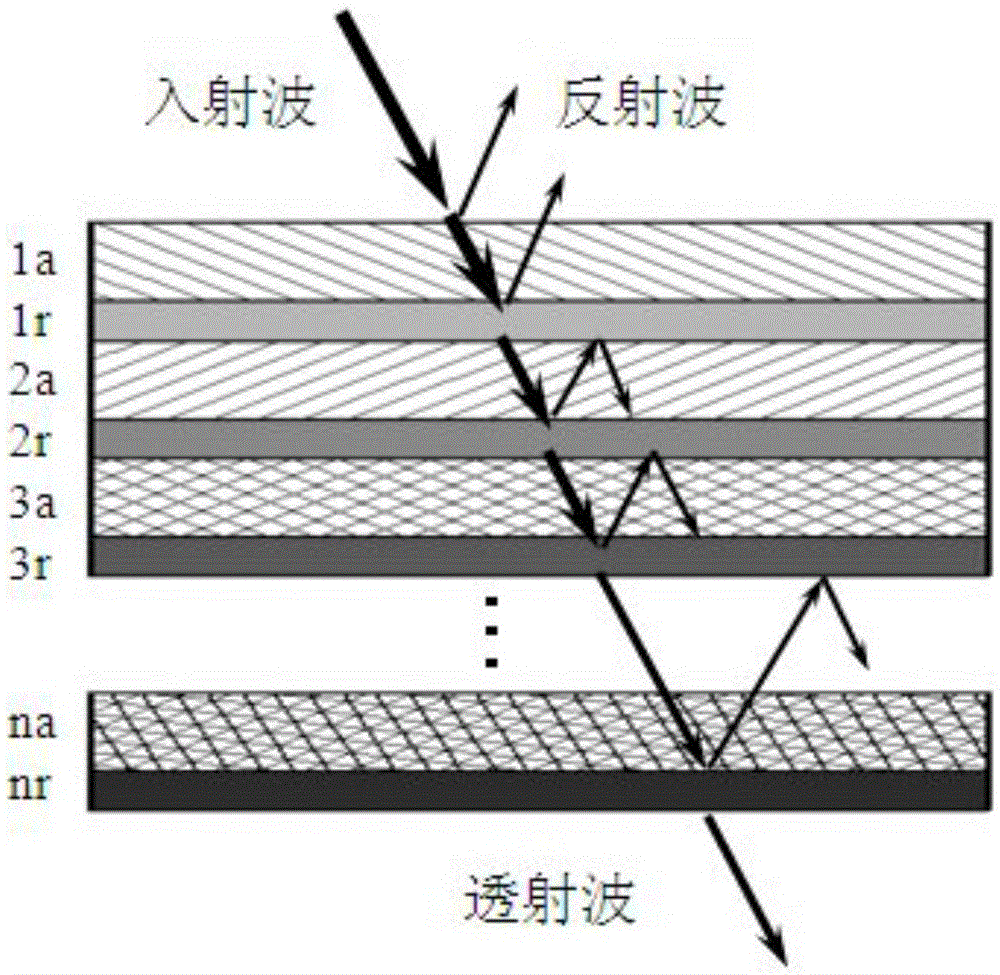
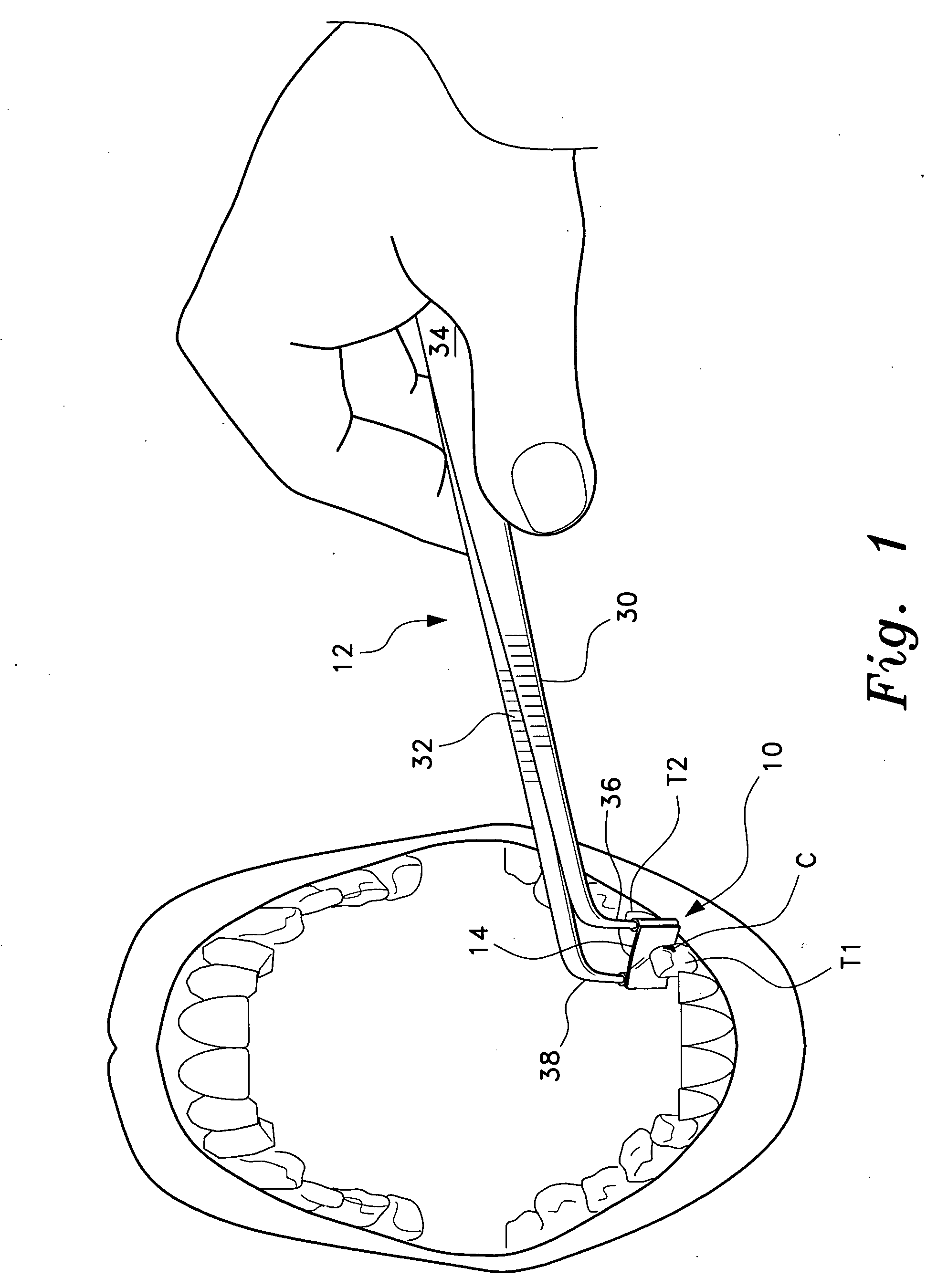
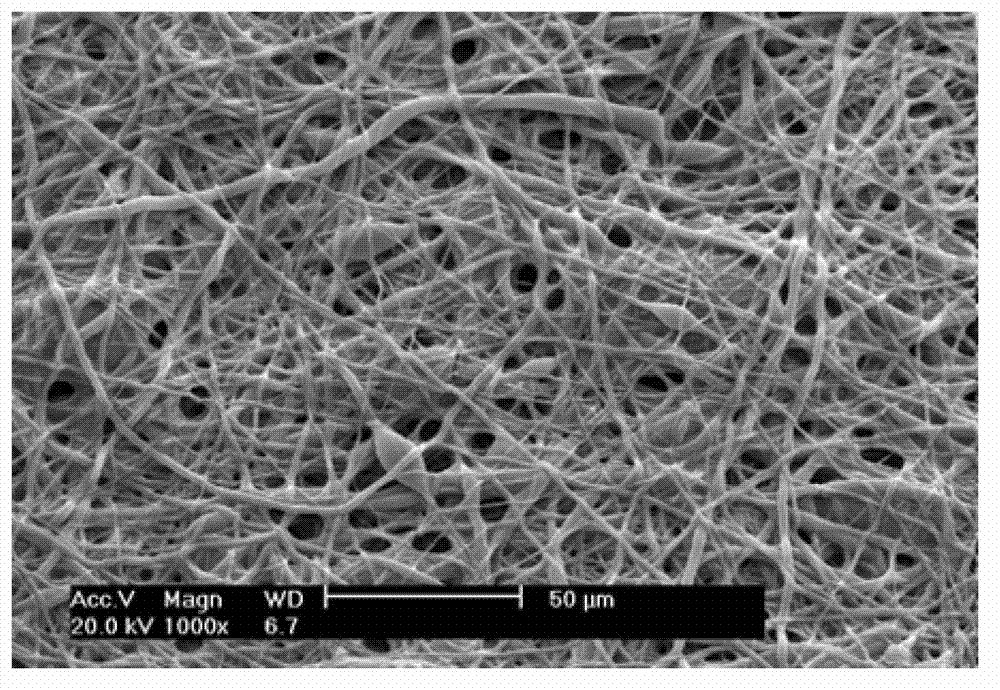
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
396 results about "Composite matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
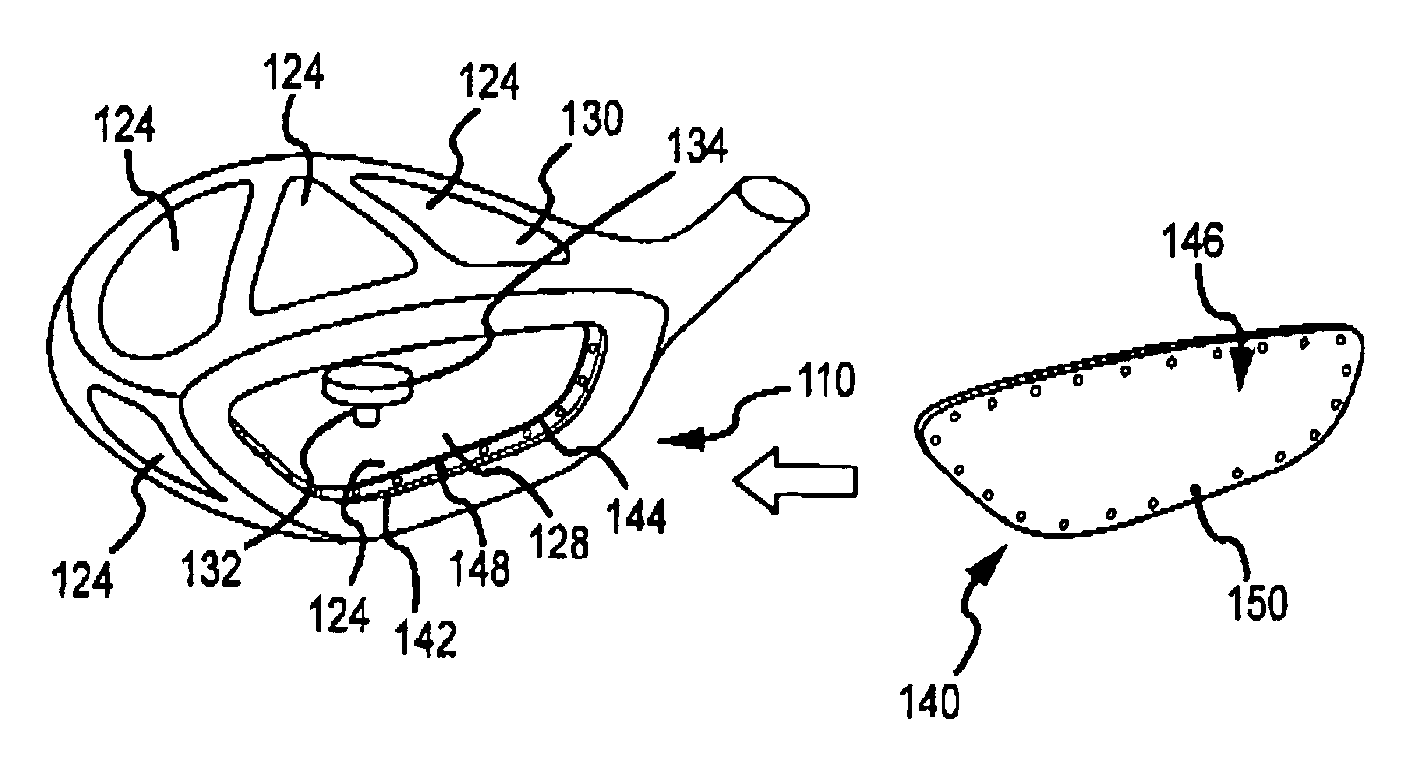
Multi-material golf club head
ActiveUS7338390B2Increase volumeStrong characteristicGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialMoment of inertia
A golf club head in accordance with various aspects of the present invention, may have a higher volume and / or higher strength. The golf club head may comprise a frame structure with a composite matrix. The golf club head may also comprise a detachable face, allowing various faces of differing materials to be attached to the body. A detachable face further allows the head to be tuned via placement / rearrangement of weights within the head to change the center of gravity and moment of inertia.
Owner:DICK'S SPORTING GOODS
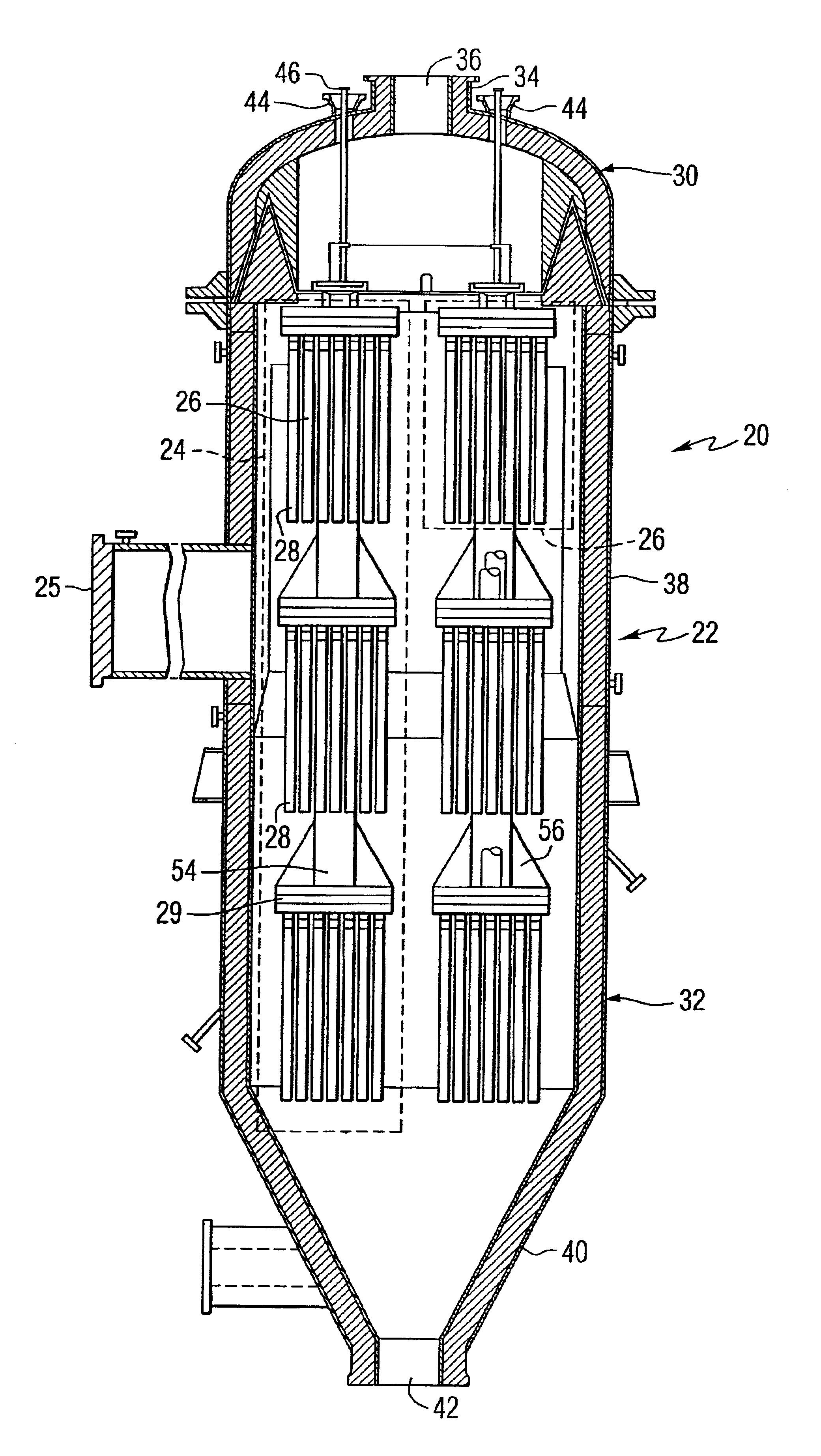
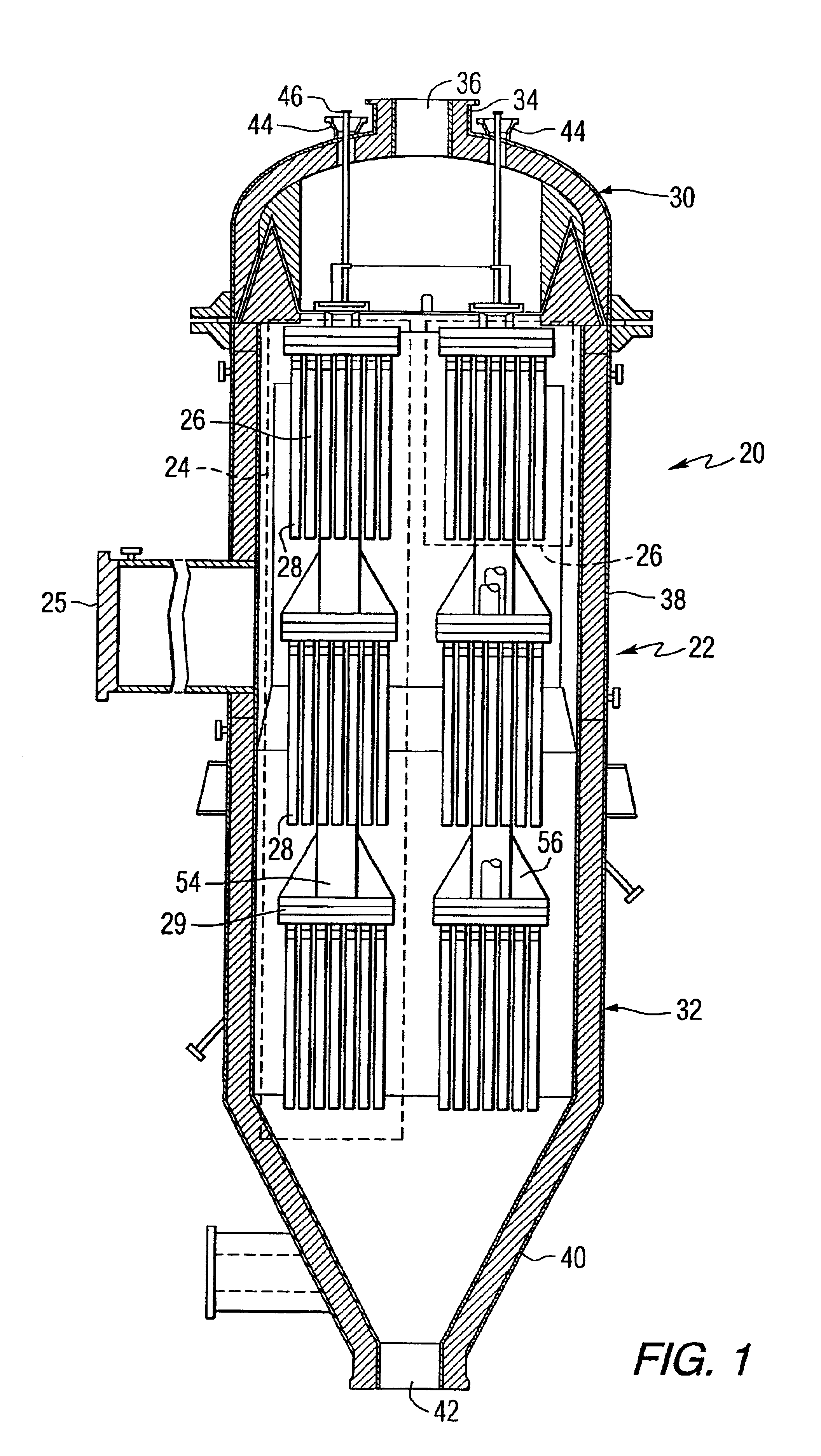
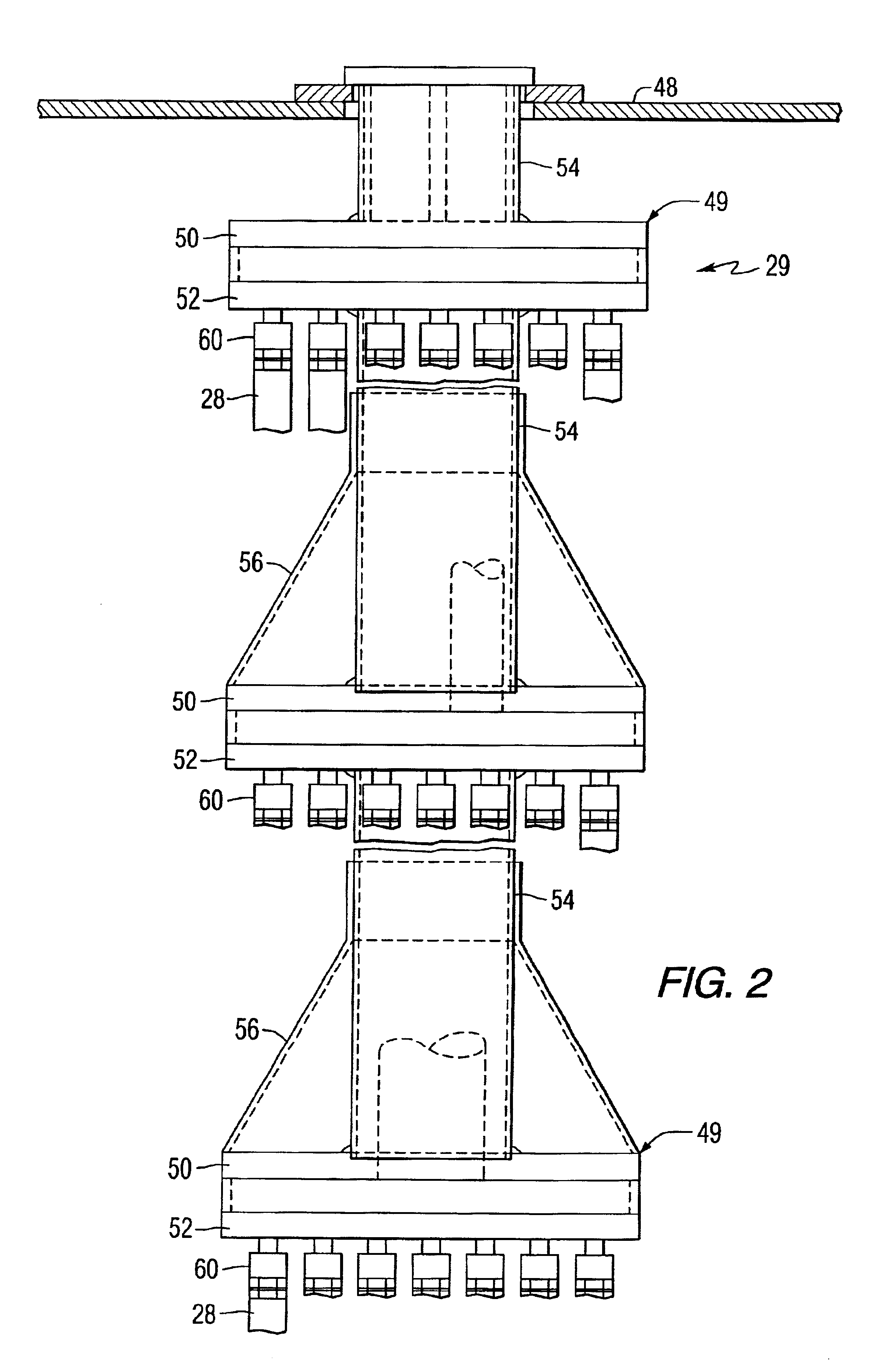
Catalytically enhanced filtration apparatus
A hot gas filtration apparatus includes a vessel, a plurality of filter elements mounted within the vessel and positioned such that hot gas flows through said filter elements, with each of said filter elements having a porous body, and a catalytic layer on surfaces of the porous body. The porous body of the filter element may include one of: a porous ceramic monolithic matrix, a continuous fiber reinforced ceramic composite (CFCC) matrix, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, and a metal-ceramic composite matrix. When the porous body is a nonoxide ceramic, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, or a metal-ceramic composite matrix, the invention further includes an oxidative resistant layer coating surfaces within the porous body, and the catalytic layer is on the oxidative resistant layer. A porous particulate removal membrane can be positioned on one or more surfaces of the filter element. The porous membrane can also provide a surface for one or more catalysts. The catalysts on the porous surface of the membrane(s) can be the same as or different from the catalysts on surfaces within the porous body.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Biodegradable biocompatible implant
ActiveUS20060136071A1Overcomes drawbackPrevent removalDental implantsBone implantBiological bodyBone defect
There is described a biocompatible implant for the filling of a cavity in a living organism if such as, for example, a bone defect or an extraction wound, comprising an open porous scaffold and / or a composite matrix comprising a plurality of inorganic or synthetic granules and a synthetic polymer matrix, and further comprising a biodegradable membrane which is interconnectibly sealed to a surface portion of the scaffold or composite matrix such, that the scaffold or composite matrix and the membrane form a single piece of matter. In one embodiment, the implant is biodegradable.
Owner:COLLAGEN MATRIX
Hand-held microwave polymerization system for dentistry
InactiveUS20050011885A1Improve physical propertiesLess energyTooth crownsOhmic-resistance heatingHand heldEngineering
A hand-held microwave system for intra-oral dentistry utilizes microwave energy to cure polymer materials intra-orally so as to produce dental composites having improved physical characteristics, and also utilizes microwave energy to detect the presence of and to preferentially heat caries or cavities, thereby disinfecting and therapeutically treating the caries in a potentially non-invasive manner. The intra-oral polymerization process can be accomplished with less overall energy and with composite-matrices that maximally absorb the microwave energy so as to reduce heating of adjacent tissue. The antenna of a hand-held version of the intra-oral microwave system is also advantageously designed to detect the presence of and to preferentially heat caries or cavities, thereby disinfecting and therapeutically treating the caries in a potentially non-invasive manner. A method and product by process for the system are also disclosed.
Owner:SEGHATOL MARC +1
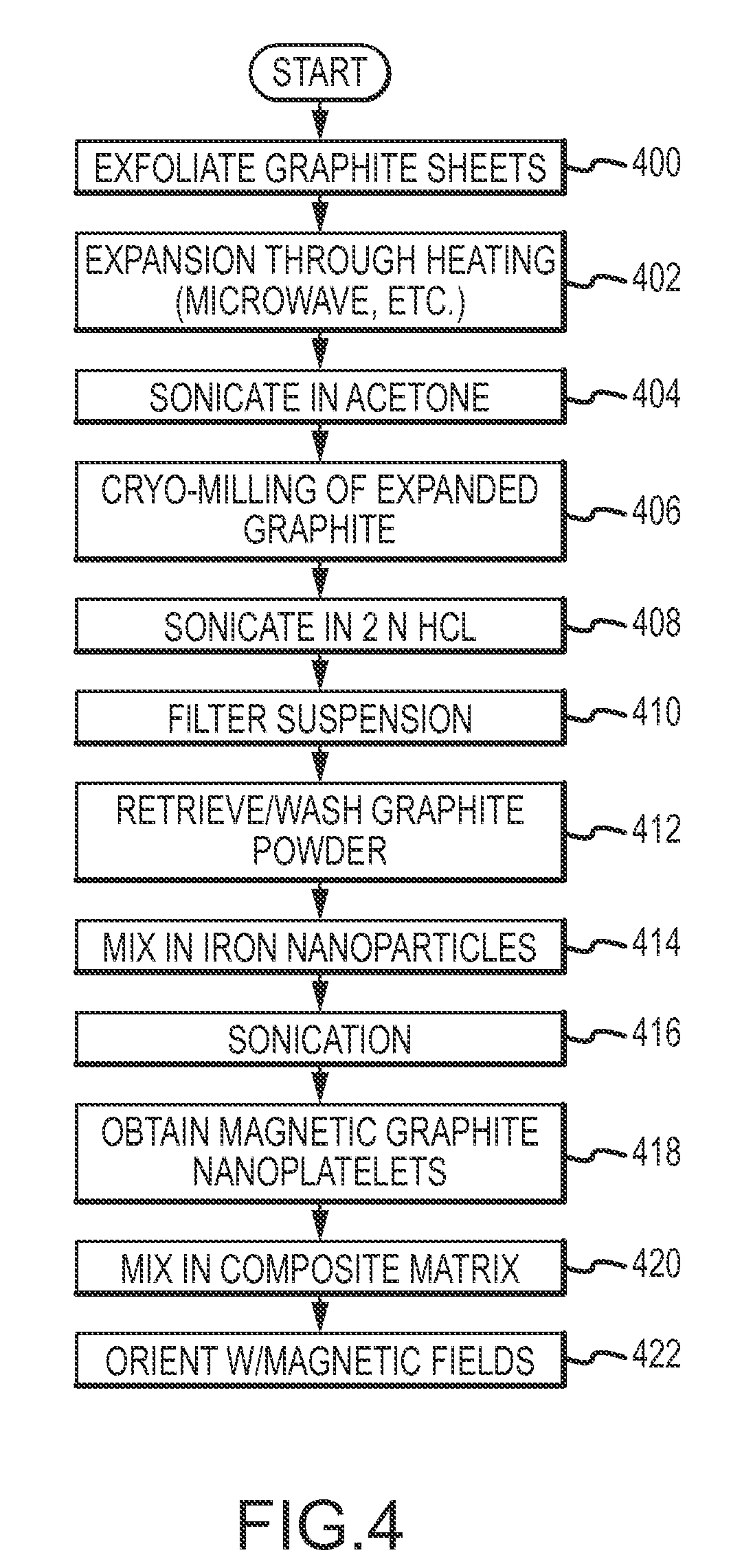
Magnetic Graphite Nanoplatelets
Provided is a magnetic graphite nanoplatelet, and a method of manufacturing nanocomposites by introducing the magnetic nanoplatelets into a composite matrix. Expanded crystalline graphite, in the form of graphite nanoplatelets, is mixed with magnetic particles to adhere the particles to the nanoplatelets. The magnetic graphite nanoplatelets are combined with a composite matrix, typically a polymer, to form a nanocomposite. In the presence of an applied magnetic field, the magnetic graphite nanoplatelets orient and align consistent with the magnetic field to yield a composite having enhance mechanical, electrical and thermal properties
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
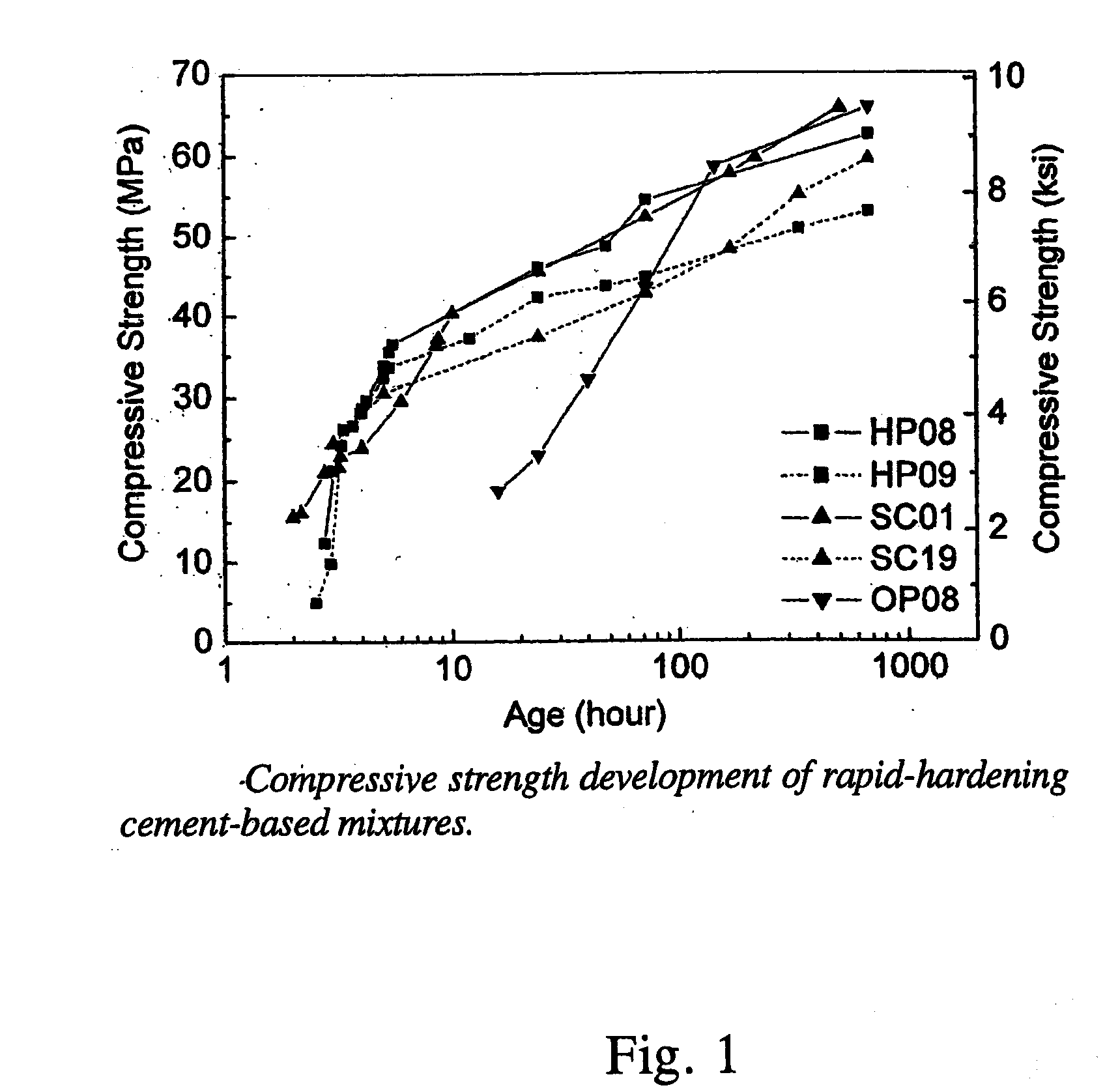
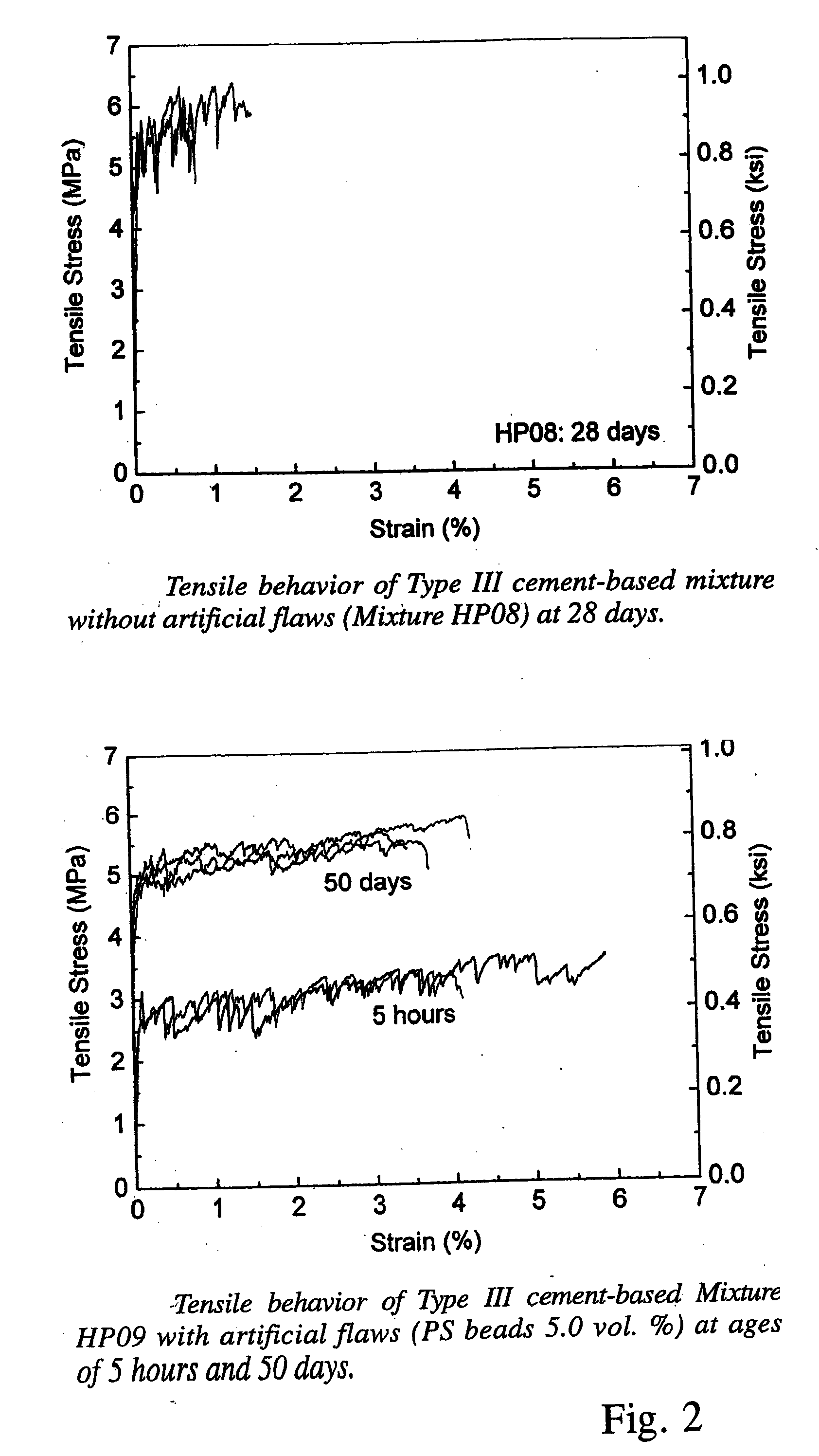
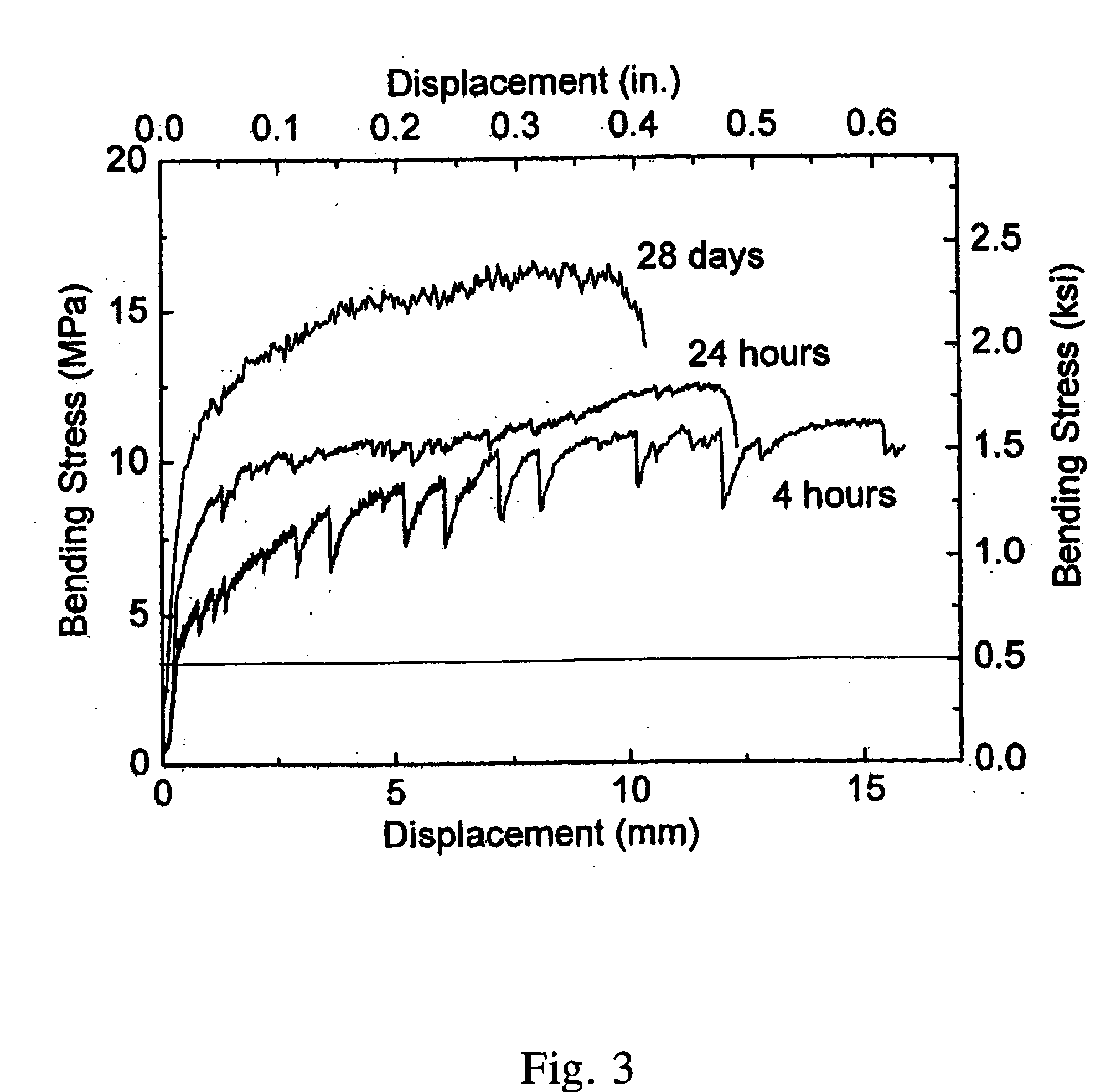
High Early Strength Engineered Cementitious Composites
ActiveUS20070181040A1High early-strengthLarge capacitySolid waste managementClimate change adaptationTensile strainCement composites
Rapid repair and retrofit of existing infrastructures demand durable high early strength materials that not only deliver sufficient strength within a few hours of placement but also significantly prolong the maintenance interval. The invention comprises a class of newly developed polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber-reinforced high early strength engineered cementitious composites (ECC) materials featuring extraordinary ductility. The tailoring of preexisting flaw size distribution through non-matrix interactive crack initiators in the composite matrix results in high tensile ductility. The resulting high early strength ECC materials are capable of delivering a compressive strength of 21 MPa (3.0 ksi) within 4 hours after placement and retaining long-term tensile strain capacity above 2%.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method to prepare processable polyimides with reactive endogroups using 1,3-bis(3-aminophenoxy)benzene
InactiveUS6288209B1Improved solvent resistance and modulus and elevated use temperatureImproved melt processabilityNon-fibrous pulp additionSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceBackbone chain
Polyimide copolymers were obtained containing 1,3-bis(3-aminophenoxy)benzene (APB) and other diamines and dianhydrides and terminating with the appropriate amount of reactive endcapper. The reactive endcappers studied include but should not be limited to 4-phenylethynyl phthalic anhydride (PEPA), 3-aminophenoxy-4'-phenylethynylbenzophenone (3-APEB), maleic anhydride (MA) and nadic anhydride (5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride, NA). Homopolymers containing only other diamines and dianhydrides which are not processable under conditions described previously can be made processable by incorporating various amounts of APB, depending on the chemical structures of the diamines and dianhydrides used. By simply changing the ratio of APB to the other diamine in the polyimide backbone, a material with a unique combination of solubility, Tg, Tm, melt viscosity, toughness and elevated temperature mechanical properties can be prepared. The copolymers that result from using APB to enhance processability have a unique combination of properties that include low pressure processing (200 psi and below), long term melt stability (several hours at 300° C. for the phenylethynyl terminated polymers), high toughness, improved solvent resistance, improved adhesive properties, and improved composite mechanical properties. These copolyimides are eminently suitable as adhesives, composite matrices, moldings, films and coatings.
Owner:NASA
Method to prepare processable polyimides with reactive endgroups using 1,3-bis (3-aminophenoxy) benzene
InactiveUS6133401AImprove adhesionImprove composite effectSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingSolubilityAdhesive
Polyimide copolymers were obtained containing 1,3-bis(3-aminophenoxy)benzene (APB) and other diamines and dianhydrides and terminating with the appropriate amount of reactive endcapper. The reactive endcappers studied include but should not be limited to 4-phenylethynyl phthalic anhydride (PEPA), 3-aminophenoxy-4'-phenylethynylbenzophenone (3-APEB), maleic anhydride (MA) and nadic anhydride (5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride, NA). Homopolymers containing only other diamines and dianhydrides which are not processable under conditions described previously can be made processable by incorporating various amounts of APB, depending on the chemical structures of the diamines and dianhydrides used. By simply changing the ratio of APB to the other diamine in the polyimide backbone, a material with a unique combination of solubility, Tg, Tm, melt viscosity, toughness and elevated temperature mechanical properties can be prepared. The copolymers that result from using APB to enhance processability have a unique combination of properties that include low pressure processing (200 psi and below), long term melt stability (several hours at 300 DEG C. for the phenylethynyl terminated polymers), high toughness, improved solvent resistance, improved adhesive properties, and improved composite mechanical properties. These copolyimides are eminently suitable as adhesives, composite matrices, moldings, films and coatings.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINSTRATION NASA THE
Biodegradable biocompatible implant
ActiveUS7731756B2Overcomes drawbackPrevent removalDental implantsBone implantBiological bodyBone defect
There is described a biocompatible implant for the filling of a cavity in a living organism such as, for example, a bone defect or an extraction wound, comprising an open porous scaffold and / or a composite matrix comprising a plurality of inorganic or synthetic granules and a synthetic polymer matrix, and further comprising a biodegradable membrane which is interconnectibly sealed to a surface portion of the scaffold or composite matrix such, that the scaffold or composite matrix and the membrane form a single piece of matter. In one embodiment, the implant is biodegradable.
Owner:COLLAGEN MATRIX
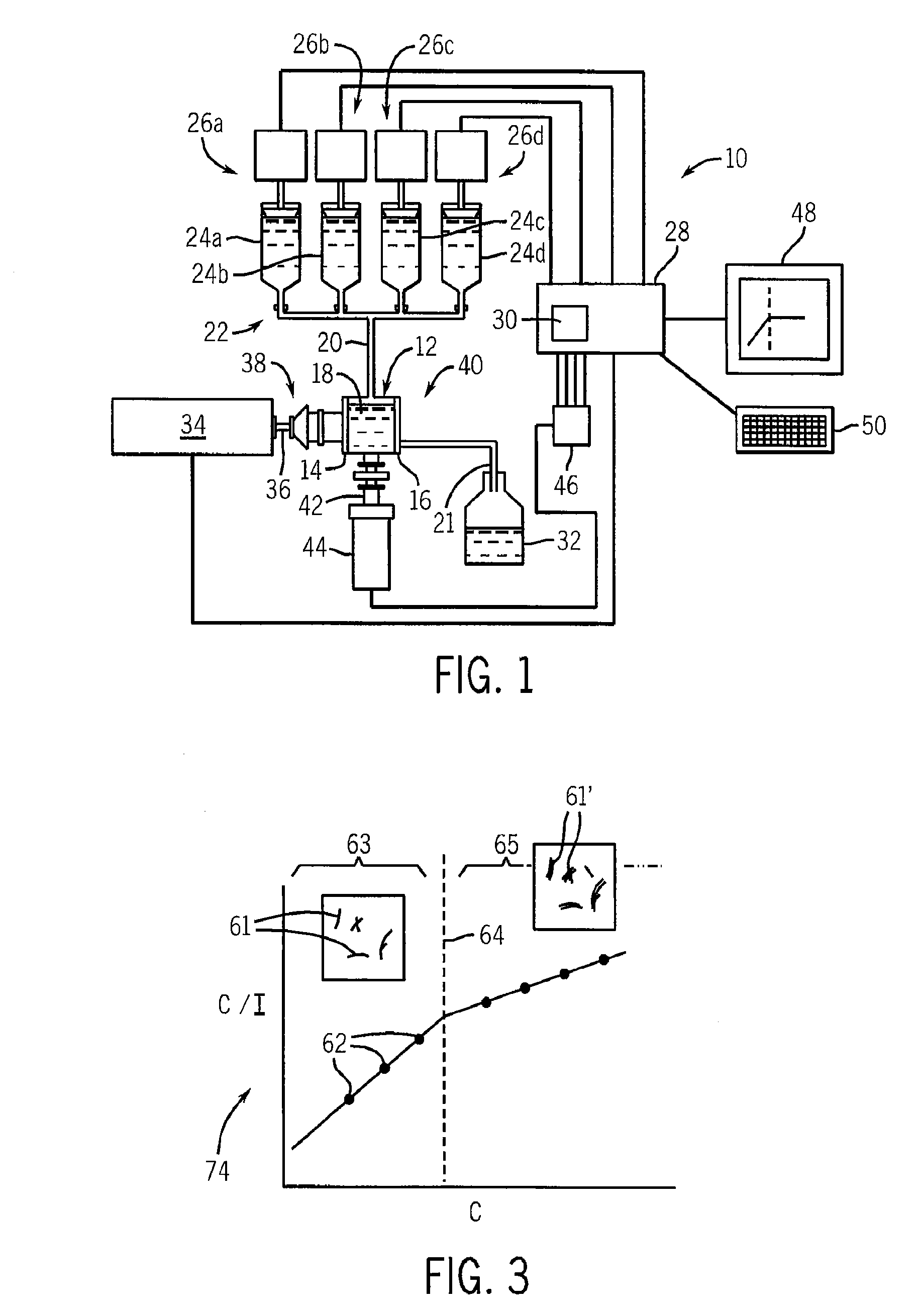
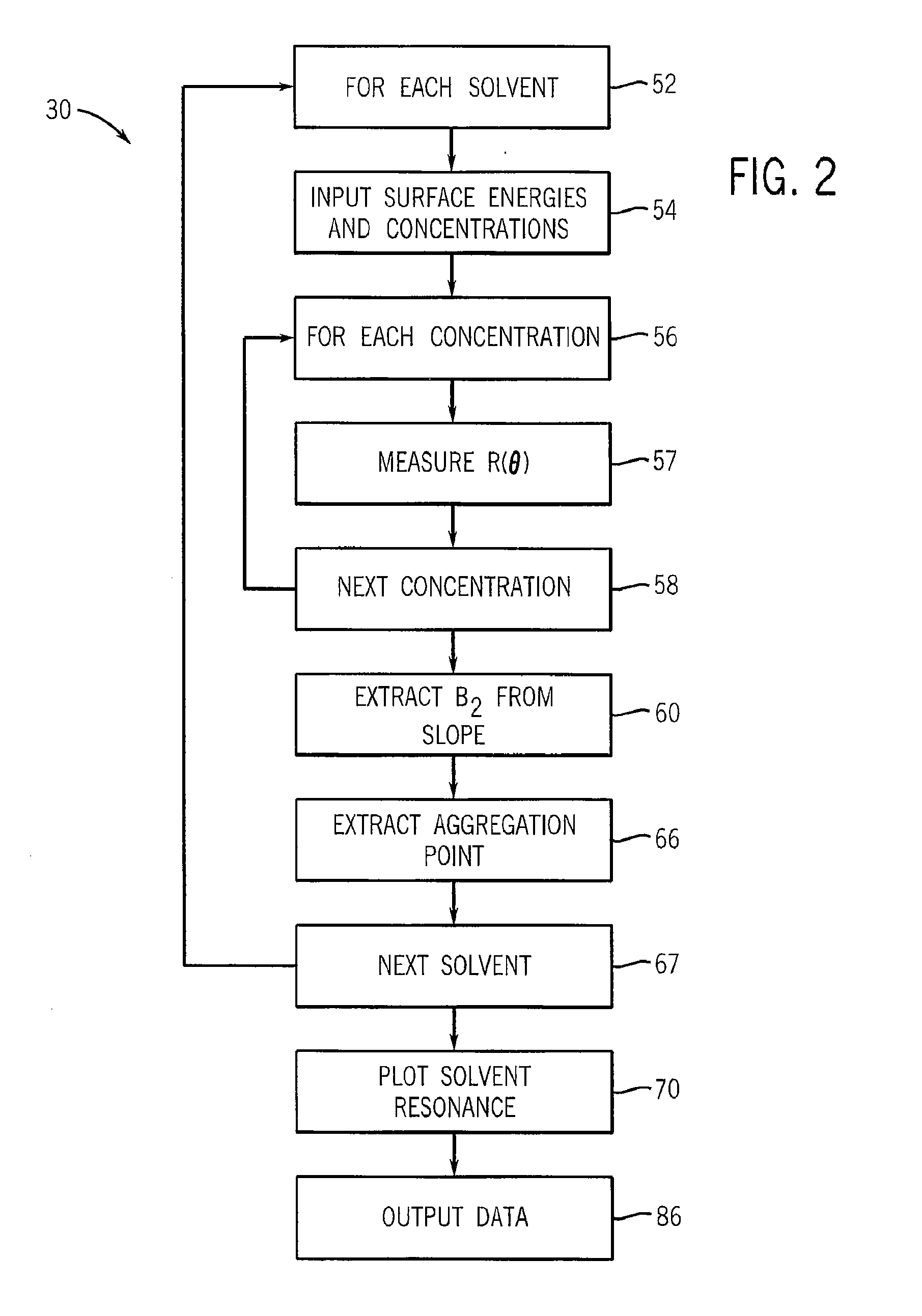
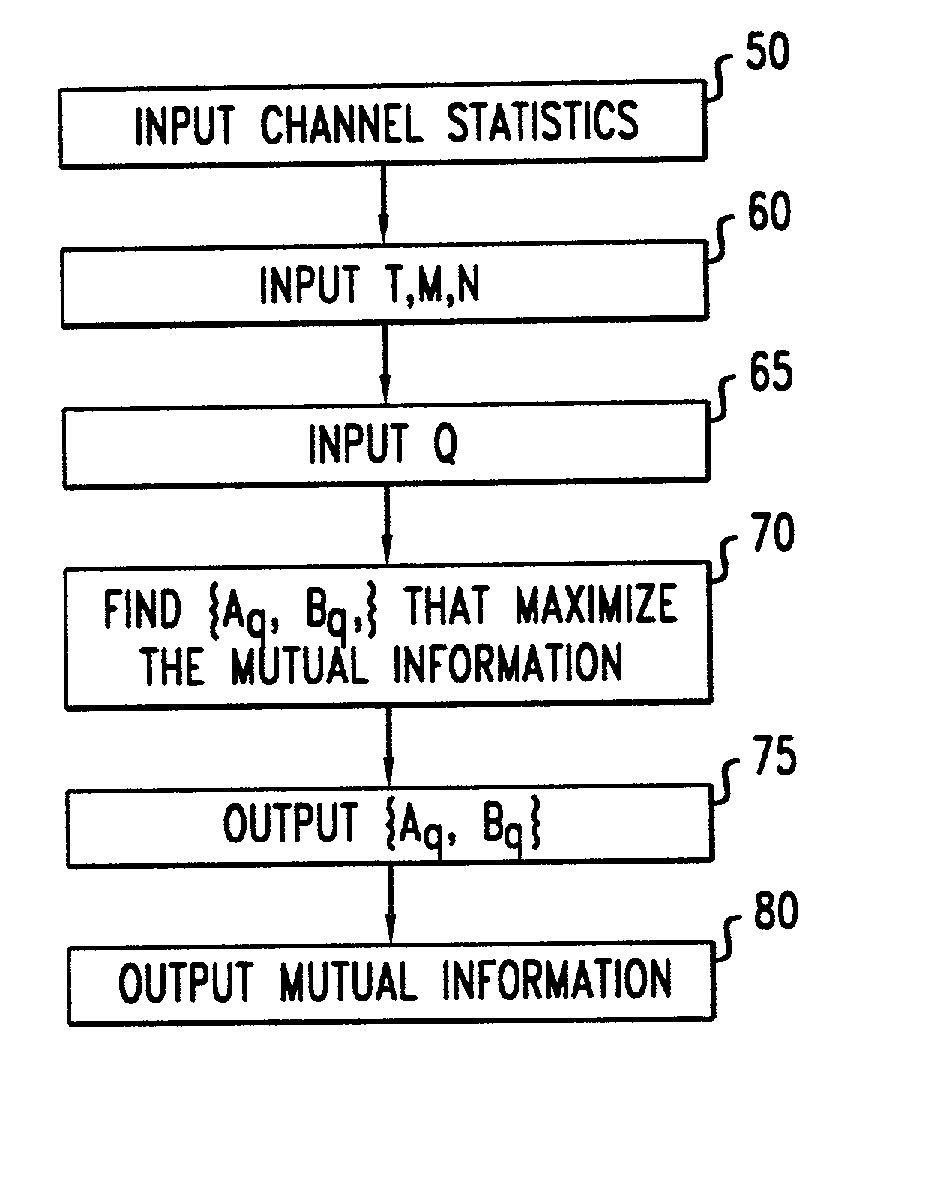
Method And Apparatus For Identifying And Characterizing Material Solvents And Composited Matrices And Methods Of Using Same
ActiveUS20110117361A1High composite strengthMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Solvents for macromolecules generally believed to be insoluble in their pristine form are identified by generation of a ‘solvent resonance’ in the relationship between solvent quality (deduced by Rayleigh scattering) and an intrinsic property of solvents. A local extreme of the solvent resonance identifies the ideal intrinsic property of an ideal solvent which may then be used to select a particular solvent or solvent combination. A solvent for graphene is used in the production of transparent conductive electrodes.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
Light ground mass industrial machine-shaping process technology
InactiveCN101253845AReduce labor intensityProtect environmentBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsEcological environmentEngineering
A technology for industrialized processing and molding of a light matrix includes the steps of crushing agricultural and forest waste first, composting the waste with beneficial microbes, namely EM bacteria for fermentation, conducting rational sifting and matrix matching, using a light-matrix processing and molding machine to process the scattered matrix into an enteroid matrix container with a diameter of 35mm to 50mm, and then cutting the matrix container into small sections, namely matrix sections in the length of 80mm to 100mm, thereby suiting both the cultivation of eucalyptus grafts and the upper bag of the seedling container for tissue-culture rooting. The technology, which can be used for industrialized matrix production, greatly reduces labor intensity and protects ecological environment. The matrix, belonging to composite matrix, can be used for seeding, cuttage and transplant of plants and for the cultivation of other seedlings for greening purpose, with a high survival rate and robust root systems.
Owner:CHINA EUCALYPT RES CENT
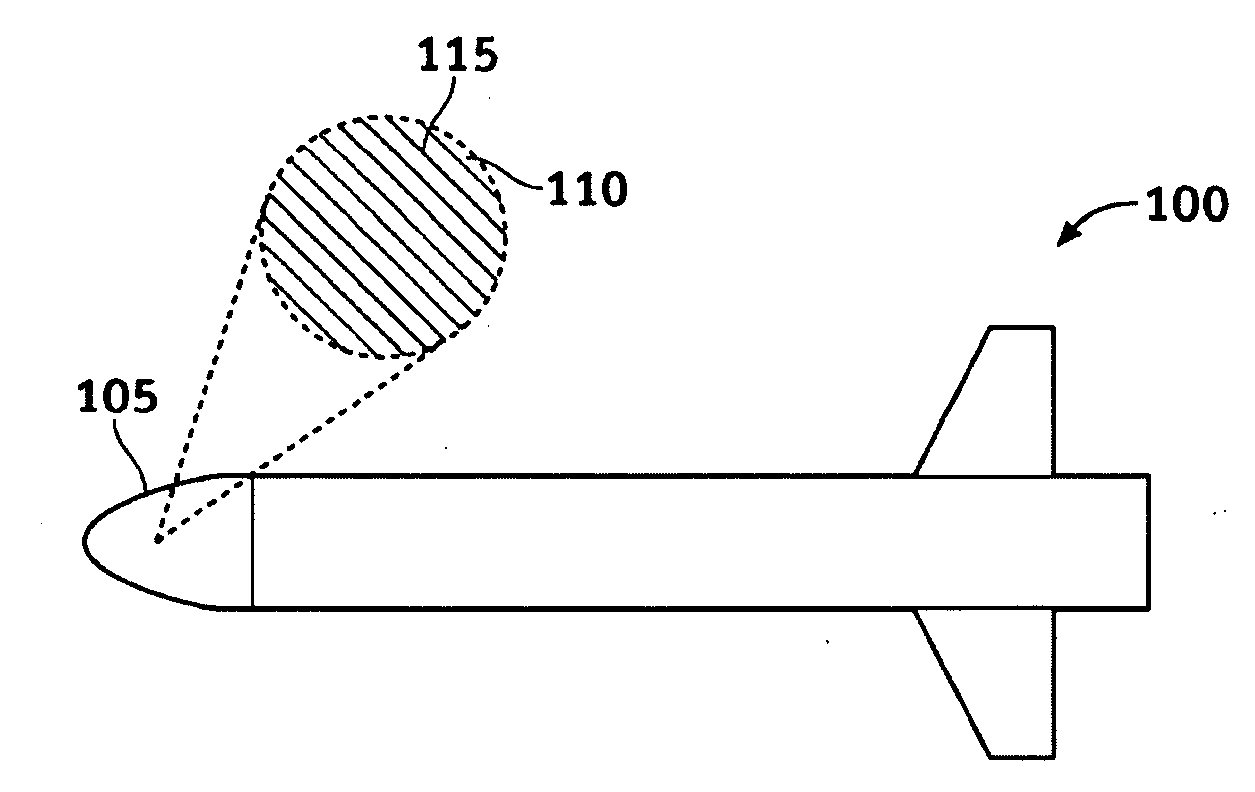
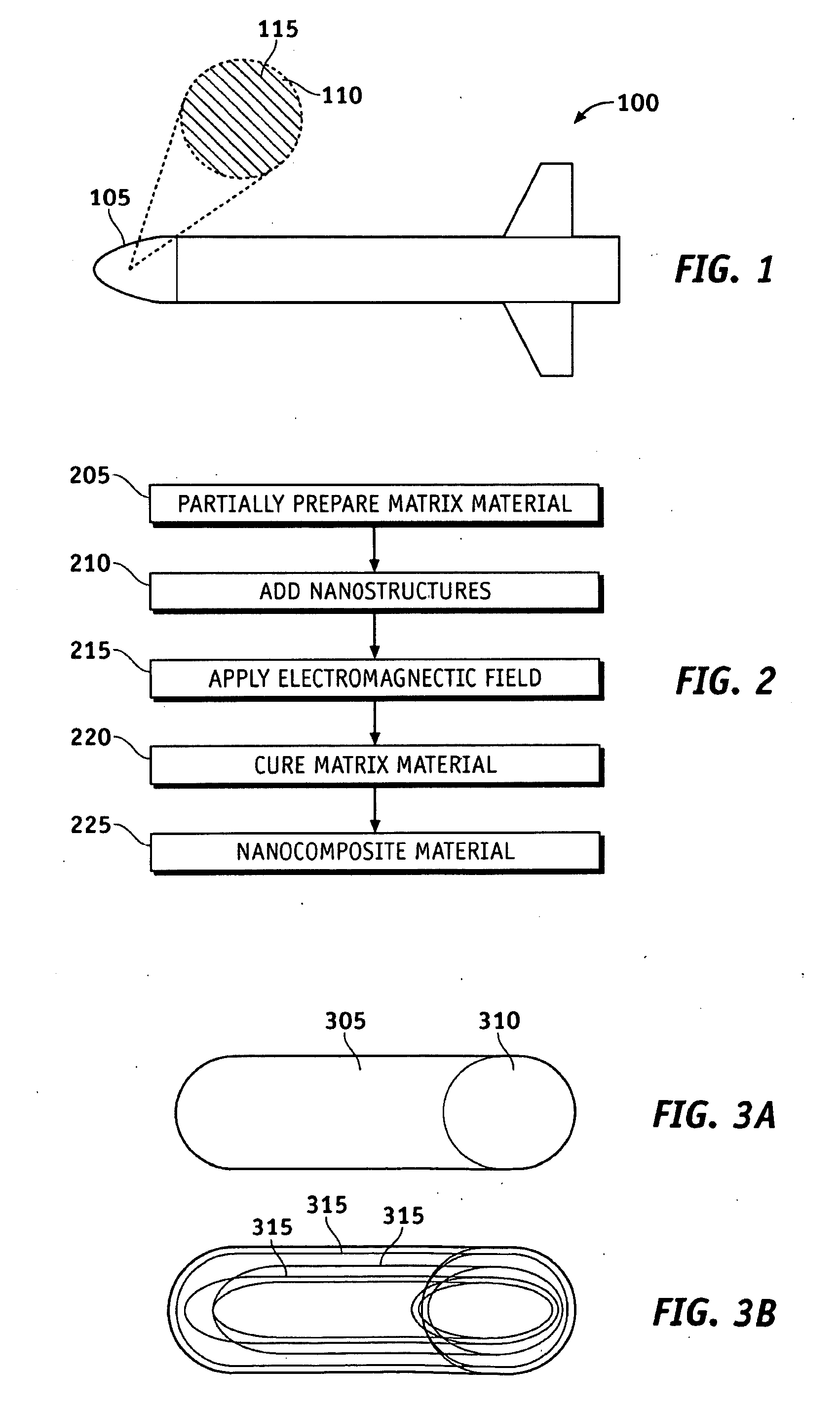
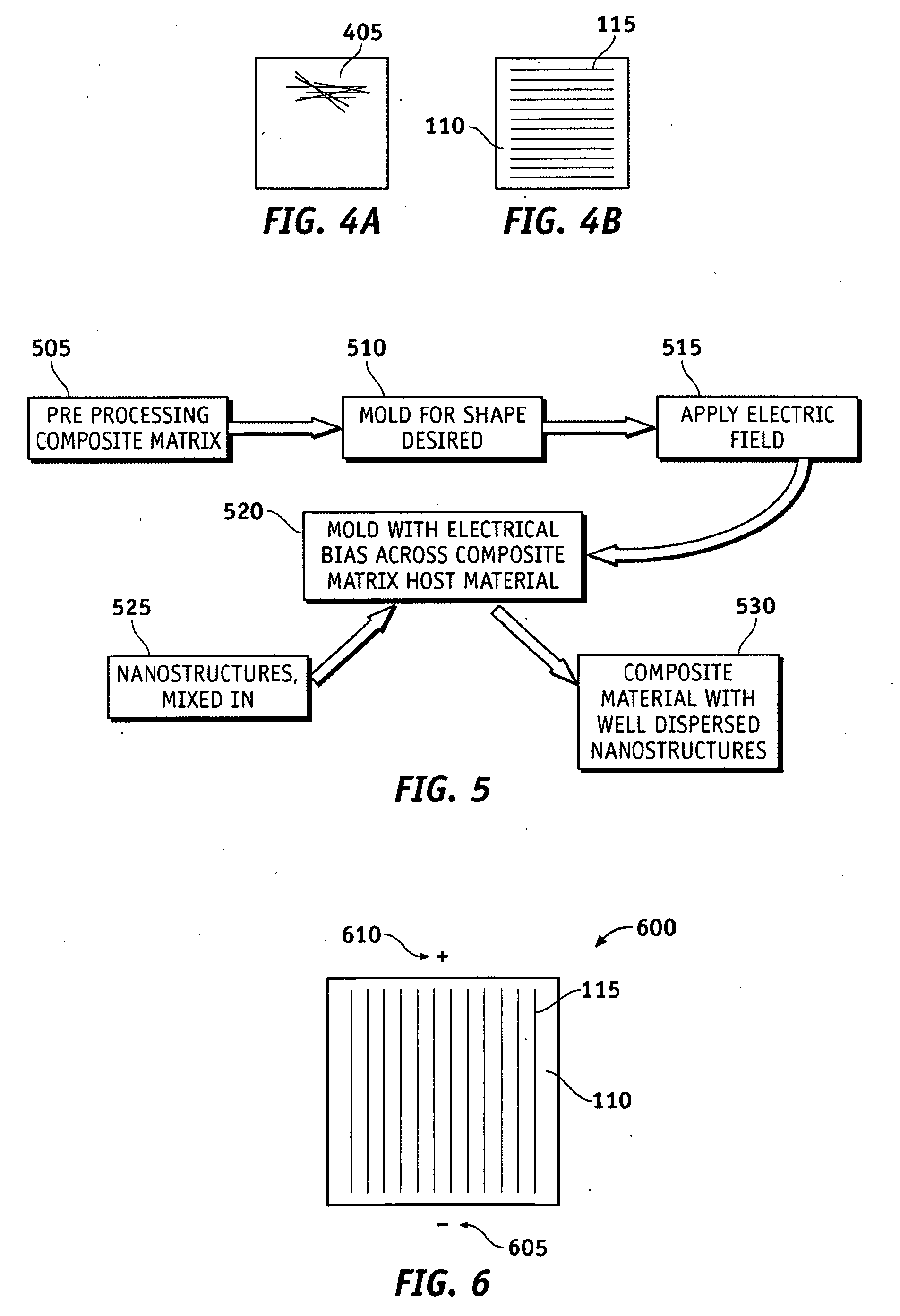
System and methods of dispersion of nanostructures in composite materials
Apparatus and methods according to various aspects of the present invention may operate in conjunction with composite matrix material and reinforcement material, such as nanostructures. The nanostructures may be evenly dispersed and / or aligned in the matrix material through application of an electromagnetic field, resulting in a nanocomposite material. In one embodiment, the nanocomposite material is suitable for large scale processing.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
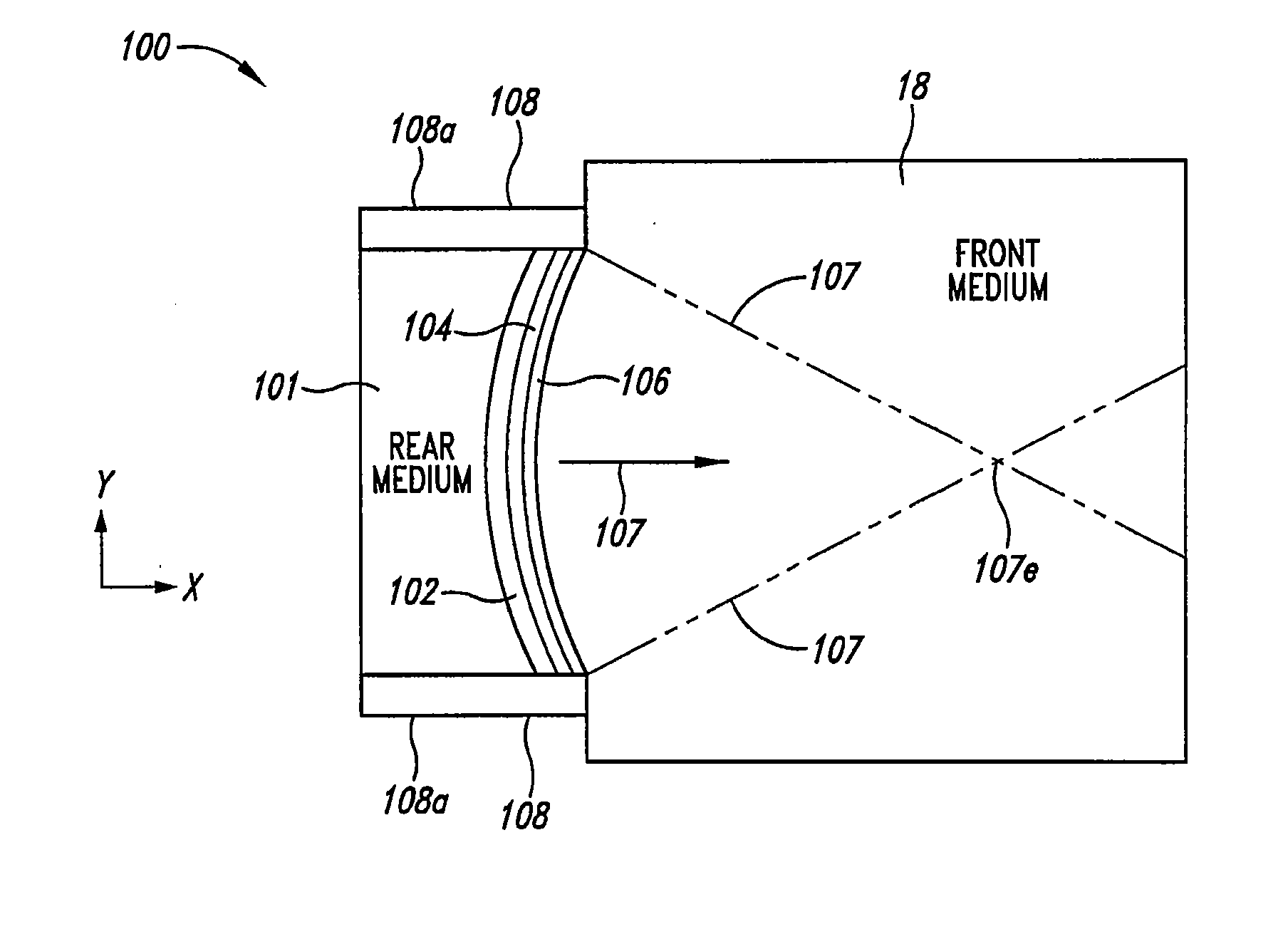
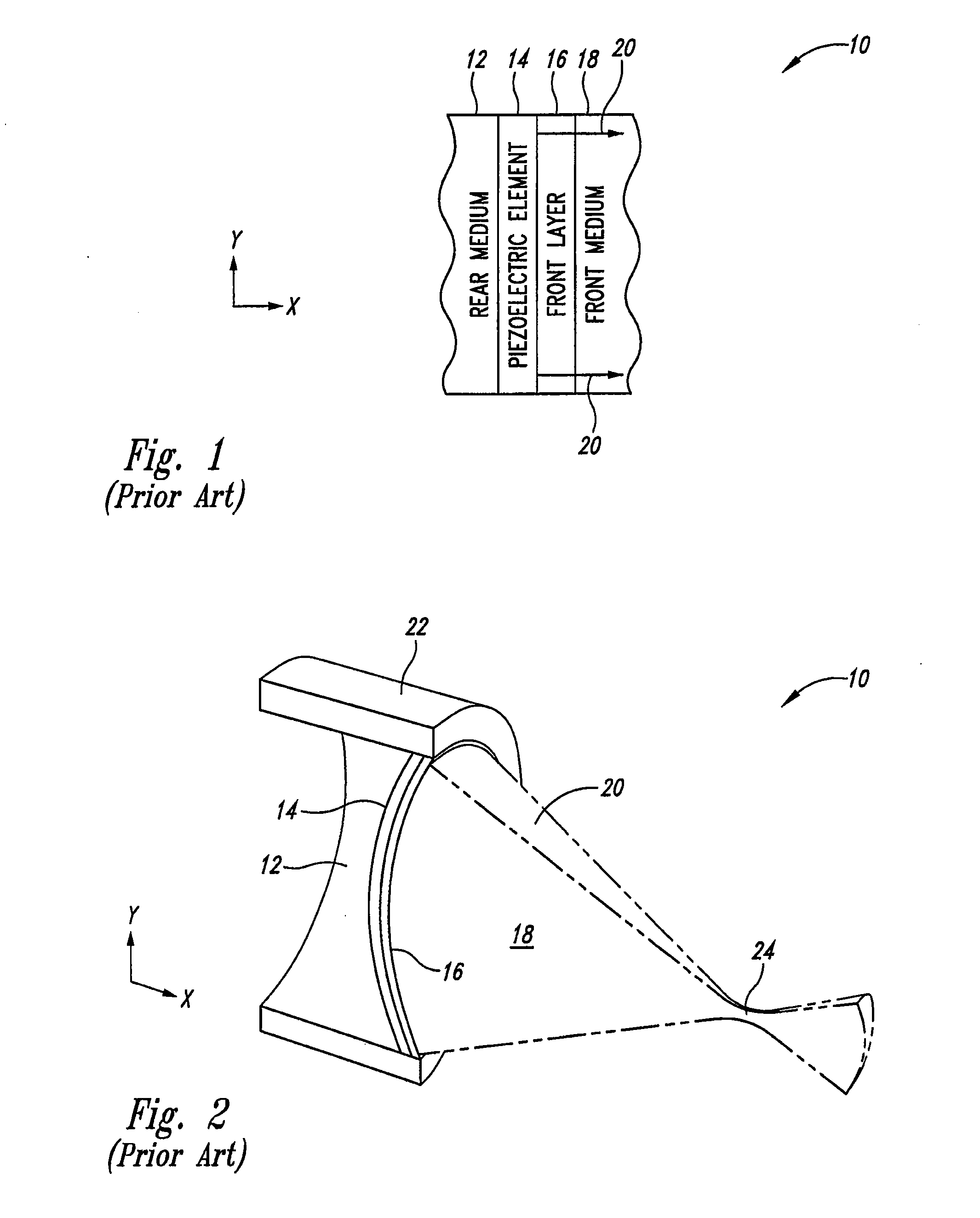
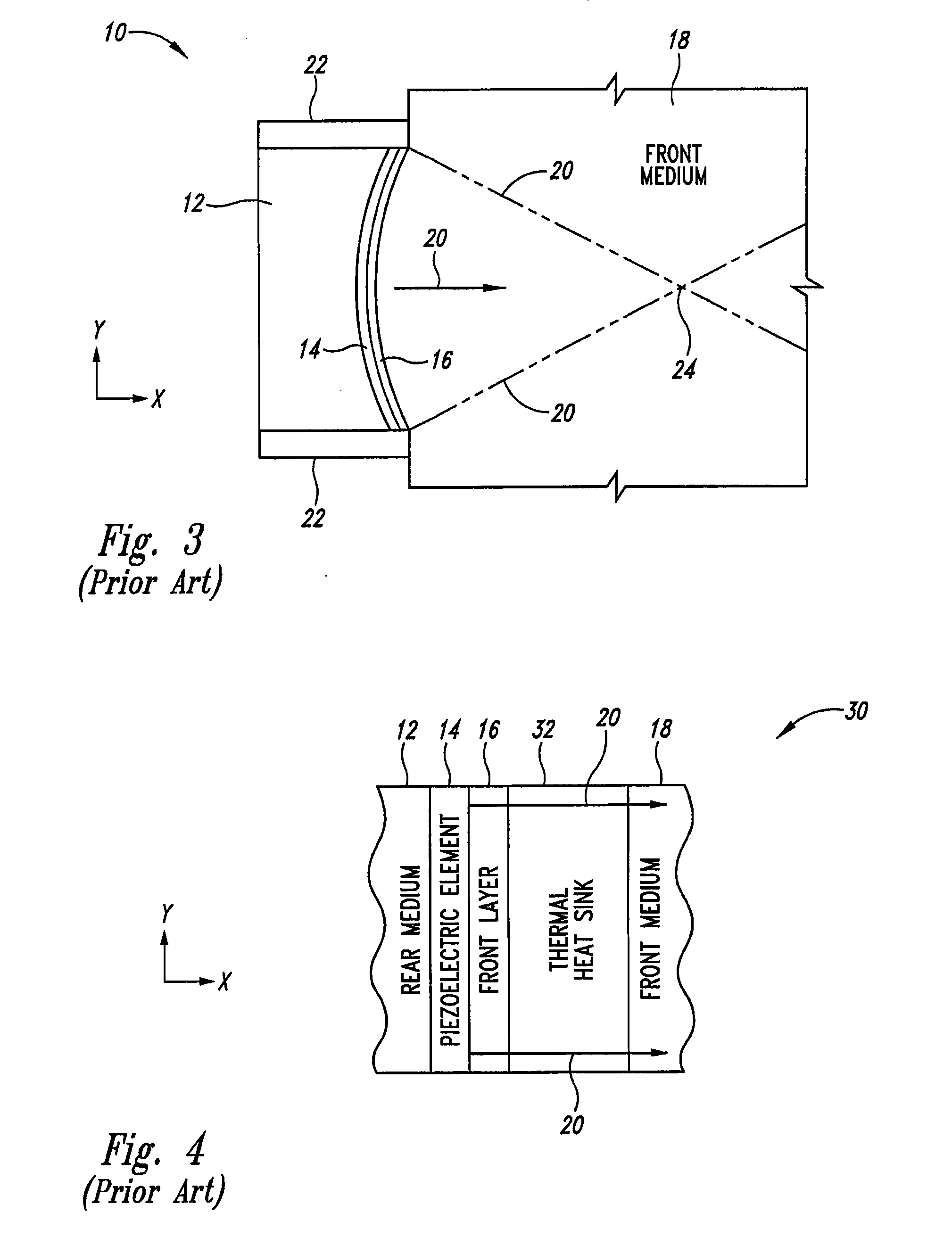
Thermally enhanced piezoelectric element
InactiveUS20070049829A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricityUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for removing unwanted heat generated by a piezoelectric element of an ultrasound transducer. Some implementations have high thermal conductivity (HTC) material placed adjacent to the piezoelectric element. The HTC material can be thermally coupled to one or more heat sinks. Use of HTC material in conjunction with these piezoelectric element surfaces is managed to avoid degradation of propagating acoustic energy. Use of the HTC material in conjunction with heat sinks allows for creation of thermal paths away from the piezoelectric element. Active cooling of the heat sinks with water or air can further draw heat from the piezoelectric element. Further implementations form a composite matrix of thermally conductive material or interleave thermally conductive layers with piezoelectric material.
Owner:UST INC
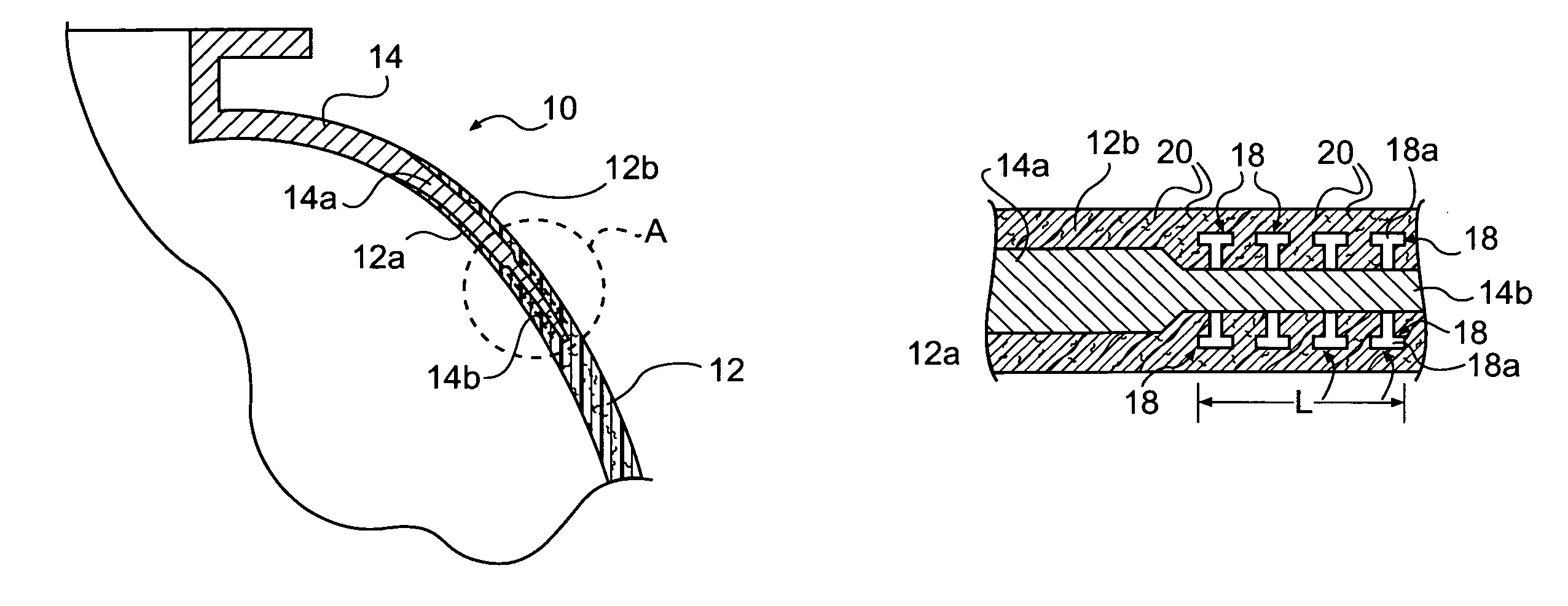
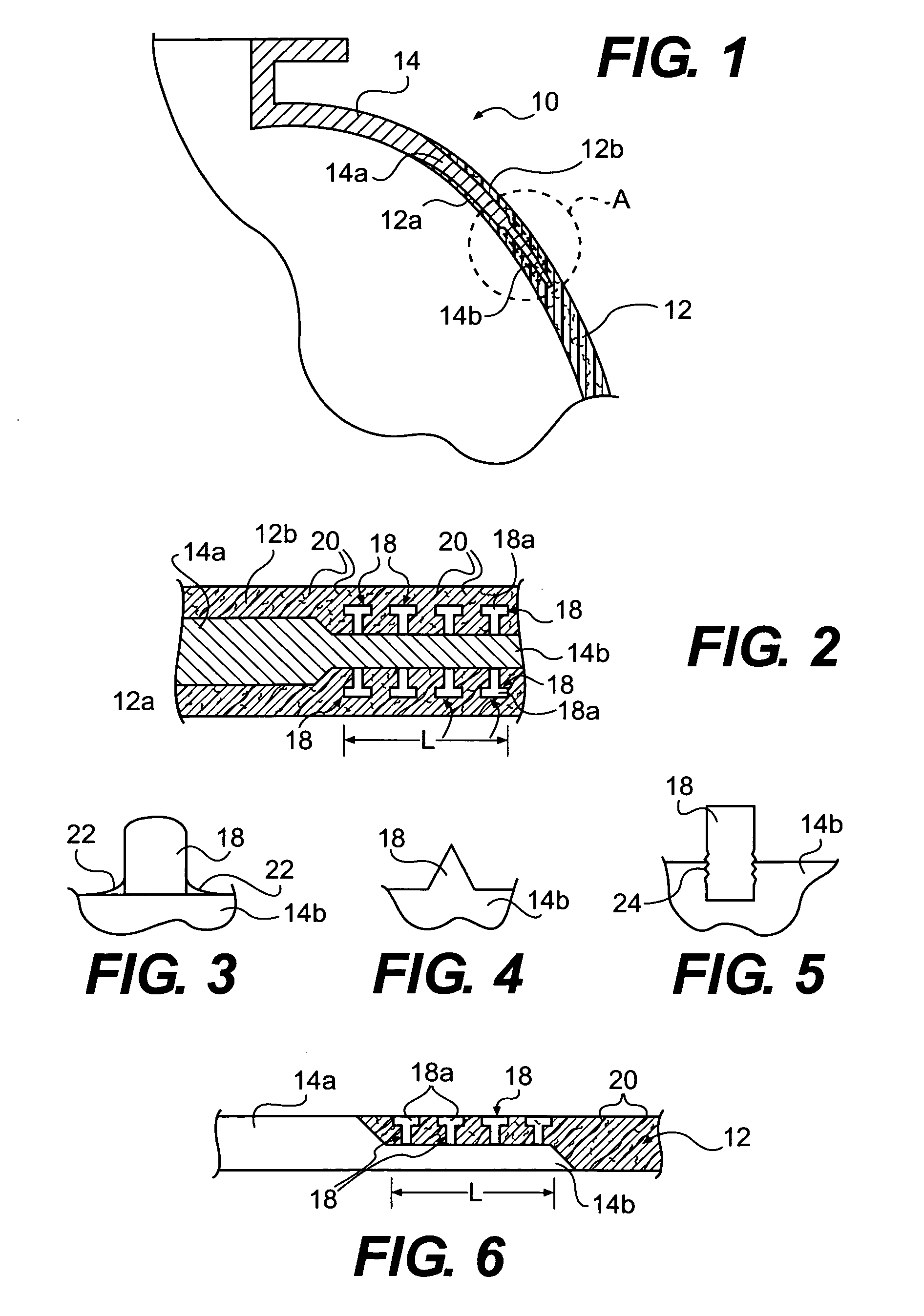
Method of joining metallic and composite components
A method is provided for joining a metallic member to a structure made of a composite matrix material. One or more surfaces of a portion of the metallic member that is to be joined to the composite matrix structure is provided with a plurality of outwardly projecting studs. The surface including the studs is brought into engagement with a portion of an uncured composite matrix material so that fibers of the composite matrix material intertwine with the studs, and the metallic member and composite structure form an assembly. The assembly is then companion cured so as to join the metallic member to the composite matrix material structure.
Owner:NASA
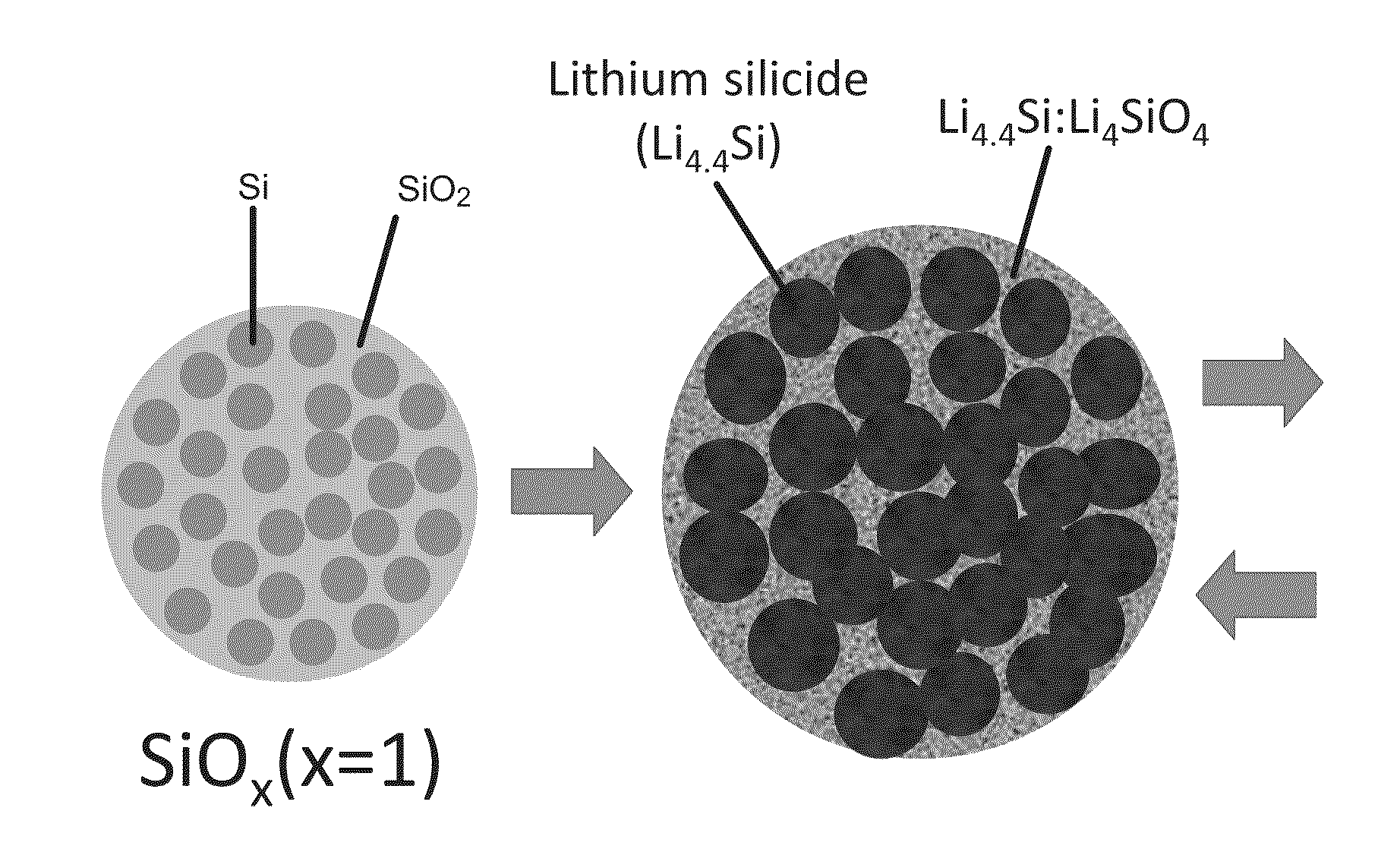
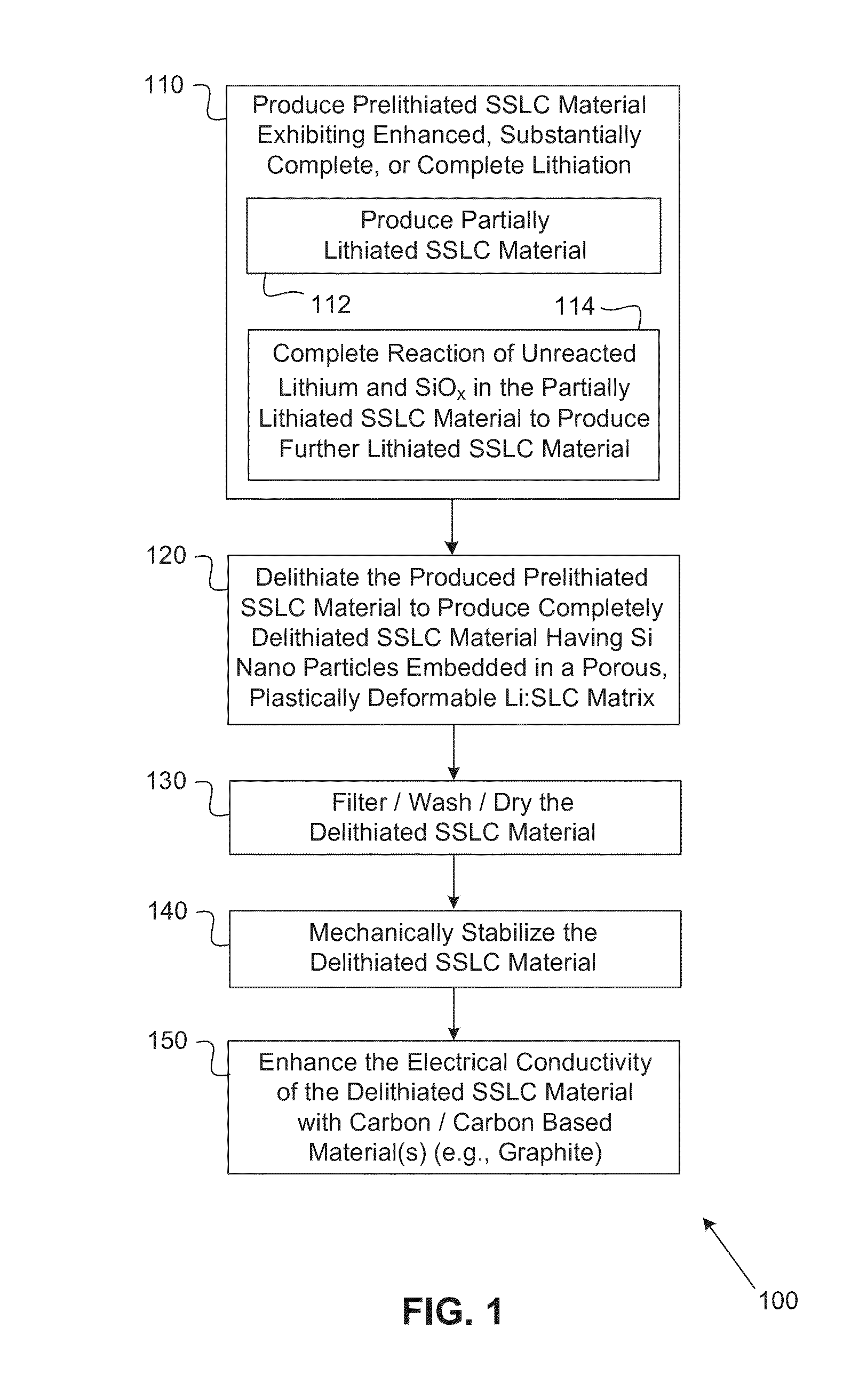
Silicon-silicon oxide-lithium composite material having NANO silicon particles embedded in a silicon:silicon lithium silicate composite matrix, and a process for manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20160260967A1Easy to useGood laminated electrode structureElectrode manufacturing processesSecondary cellsCapacity lossNano silicon
A process for producing a silicon:silicon oxide: lithium composite (SSLC) material useful as a negative electrode active material for non-aqueous battery cells includes: producing a partially lithiated SSLC material by way of mechanical mixing; subsequently producing a further prelithiated SSLC material by way of spontaneous lithiation procedure; and subsequently producing a delithiated SSLC material by way of reacting lithium silicide within the dispersed prelithiated SSLC material with organic solvent(s) to extract lithium from the prelithiated SSLC material, until reactivity of lithium silicide within the prelithiated SSLC material with the organic solvent(s) ceases. The delithiated SSLC material is a porous plastically deformable matrix having nano silicon embedded therein. The delithiated SSLC material can have a lithium silicide content of less than 0.5% by weight. A battery cell having as its negative electrode active material an SSLC material as set forth herein can exhibit an irreversible capacity loss of less than 10%.
Owner:EOCELL LTD
Composite yarn
InactiveUS20030205041A1Excellent chemical adhesionExcellent mechanical adhesionAdhesivesYarnYarnFiber
A composite matrix yarn (Y) including a cover yarn (80) formed of a plurality of twisted fibers, a core strand (70) positioned within the cover yarn (80) and around which the fibers of the cover yarn (80) are twisted to provide mechanical adhesion between the cover yarn (80) and the core strand (70), and an adhesive binder (75) carried on the core strand (70) for providing enhanced adhesion between the core strand (70) and the cover yarn (80).
Owner:BAKER JR PAUL W
Ambient temperature rapid self-polymerization compositions of high cross-linked or linear type beta-amino-ester alternative co-polymers and their applications
InactiveUS20070299211A1Self-polymerization can be very rapidSelf-polymerization rate can be controlledCross-linkAmino esters
Self-polymerization of mono-aziridine (or azetidine) and multi-aziridine (or azetidine) containing compounds with vinyl group containing organic acid, such as acrylic acid (AA), 2-methylenesuccinic acid, 2,3-dimethylenesuccinic acid and etc, at ambient temperature results in the new type of cross-linked and linear type copolymers, respectively.The polymerization of multi-functional aziridine (or azetidine) containing compounds with vinyl group containing organic acid results in the formation of high cross-linked polymers. The self-polymerization takes place at ambient temperature and the resultants, cross-linked polymeric networked materials, are solvent insoluble and potential for adhesive, composite matrix and other applications. These insoluble materials are hydrolyzed in an acidic or basic condition to form the water soluble β-amino acids.A linear poly(β-aminoester) is obtained from the self-polymerization of vinyl group containing organic acid with mono-aziridine (or azetidine) containing compound at ambient temperature. poly(β-aminoester) is applicable for gene transfer, controlled drug release and other applications. This self-polymerization process offers a convenient route for preparing poly(β-aminoesters).
Owner:TAMKANG UNIVERSITY
Electromagnetic shielding composite material
InactiveCN105555112AImprove shielding effectExtended propagation pathShielding materialsFiberReflection loss
The invention discloses an electromagnetic shielding composite material. Electromagnetic wave absorption layers and electromagnetic wave reflection layers are alternately overlapped to form electromagnetic shielding function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin, fiber carriers and electromagnetic absorption function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin and electromagnetic gradient reflection function bodies; in the overlapped electromagnetic wave reflection layers, the mass percentage compositions of short cut carbon fibers increase in gradient along the incident directions of the electromagnetic waves. According to the electromagnetic shielding composite material of the invention, the incident electromagnetic waves generate multi-reflection; the propagation paths of the electromagnetic waves in the material are increased; increase of the multi-reflection loss and absorption loss enables the shielding efficiency of the material to be increased; in adoption of the reflection layers of gradient structure, the electromagnetic waves will not escape away from the shielding material rapidly for reflection; more electromagnetic waves can enter the next shielding unit; therefore, the shielding efficiency of the material is further improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Quasi-as-cast bainite gray cast iron cylinder jacket and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a quasi-cast bainite gray cast iron cylinder liner and a preparation method thereof. The chemical composition weight percentage of the cylinder liner matrix is as follows: carbon 2.9-3.3%, silicon 2.2-2.6%, manganese 0.7-1.3%, Phosphorus is not more than 0.1%, sulfur is not more than 0.1%, copper is 0.5-1.0%, chromium is 0.2-0.5%, and the balance is Fe. The method is as follows: prepare raw materials according to the weight percentage of each component; smelt the raw materials to obtain high-temperature molten iron, control the temperature of the molten iron to be 1500-1550° C. Cylinder liner castings were prepared by wet paint centrifugal casting process; quasi-cast bainitic cylinder liners were obtained by cooling the cylinder liner castings. The composite matrix of the cylinder liner of the invention has good wear resistance; the mechanical properties including tensile strength and hardness are equivalent to those of the existing cylinder liner, but the production cost is reduced and the cost performance is high.
Owner:ZYNP GRP
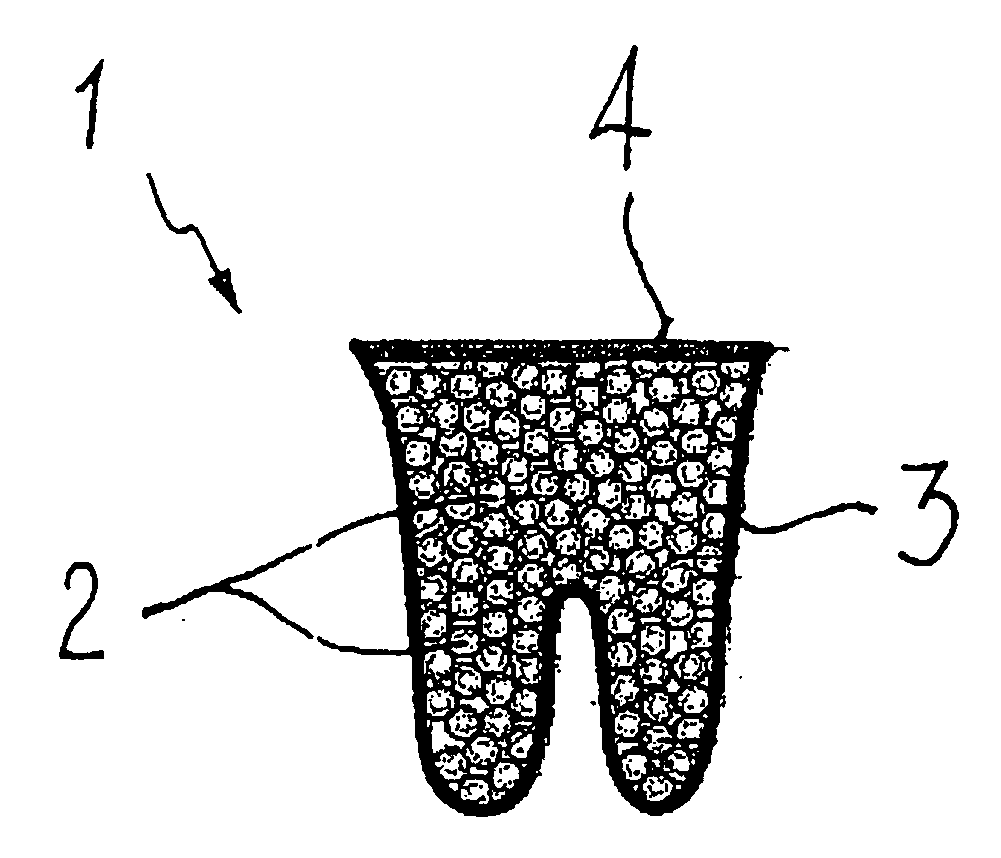
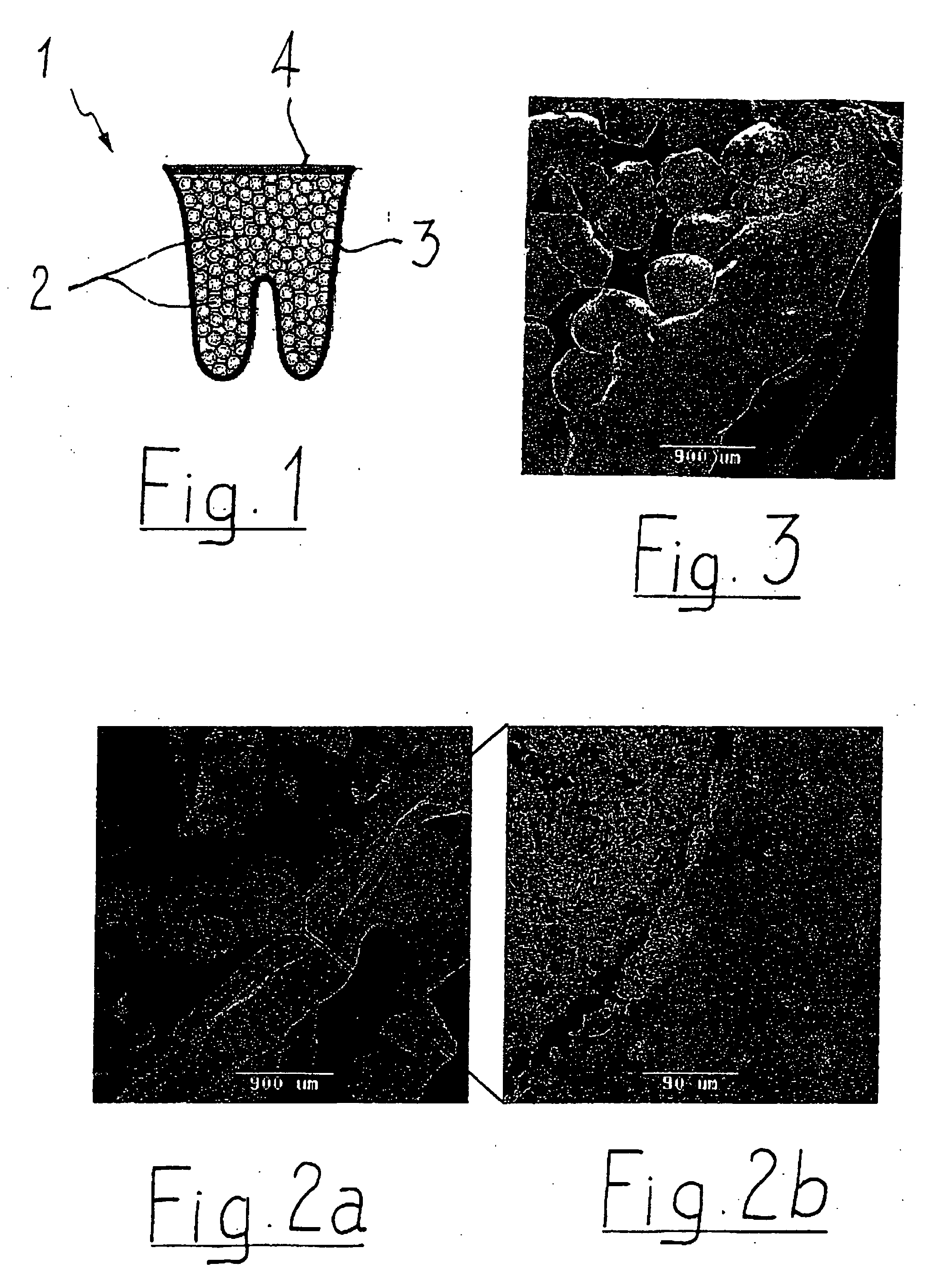
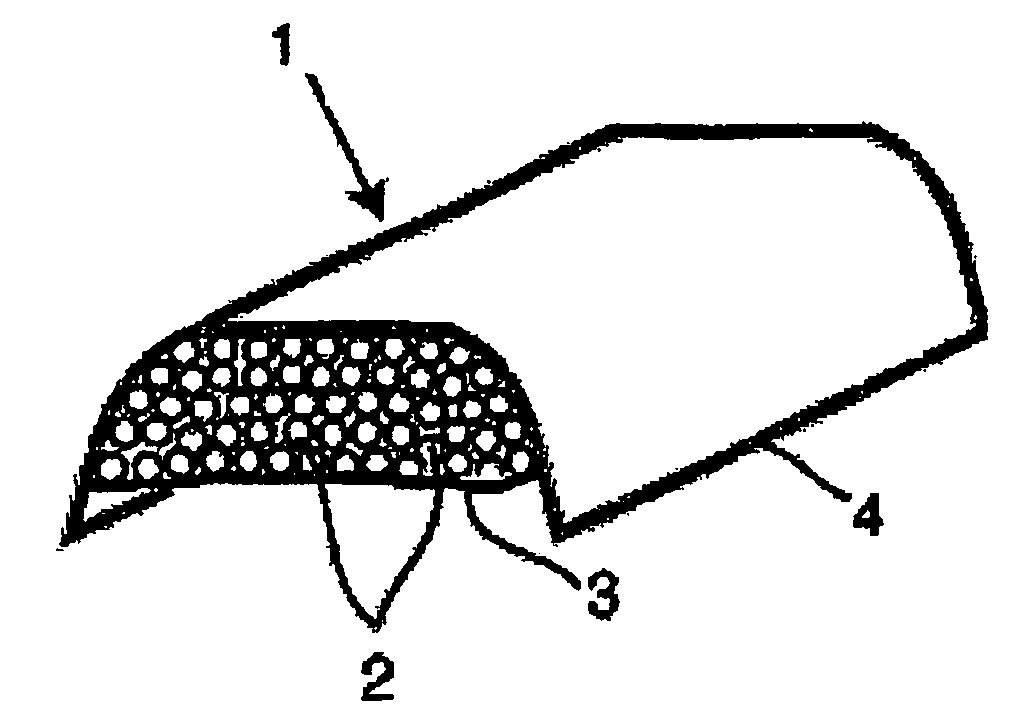
Anterior composite matrix dental restoration system
The anterior composite matrix dental restoration system provides a matrix for holding a composite filling material in place as it cures, and a tool for holding the matrix in place during the curing of the filling material. The matrix comprises a thin, flat, flexible, and transparent sheet of plastic material with parallel tubular extensions on the opposite ends. The distal ends of the specialized forceps tool are inserted into the tubular ends of the matrix and used to install, hold, and remove the matrix. The relatively small and narrow tool greatly increases the comfort of both patient and dentist or dental technician by precluding need to insert and hold the fingers in the mouth of the patient to install, hold, and remove the matrix. The matrices may be provided in different sizes, with at least the tubular end components being optionally color coded to indicate the corresponding size.
Owner:YATES DAVID W
Preparation of polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nano-fiber scaffold and application of PLGA nano-fiber scaffold to tissue engineering
The invention discloses preparation of a polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nano-fiber scaffold and application of the PLGA nano-fiber scaffold to tissue engineering, and belongs to the field of the tissue engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a fiber film containing two materials by taking PLGA and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a raw material through electrostatic blended spinning, and dissolving and removing the PVP in an aqueous solution to obtain the PLGA nano-fiber scaffold with certain microstructures. A cell / PLGA nano-fiber scaffold composite matrix is obtained by the following steps of: inoculating seed cells on the PLGA nano-fiber scaffold, culturing in vitro, folding a cell / PLGA nano-fiber scaffold composite, and culturing for 7 to 14 days in a spinner cultivation mode. The composite matrix can be taken as a tissue engineering material with a specific tissue repair function and implanted into an animal model. The preparation process is simple and feasible, is high in repeatability, and can be widely applied to the field of the tissue engineering.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
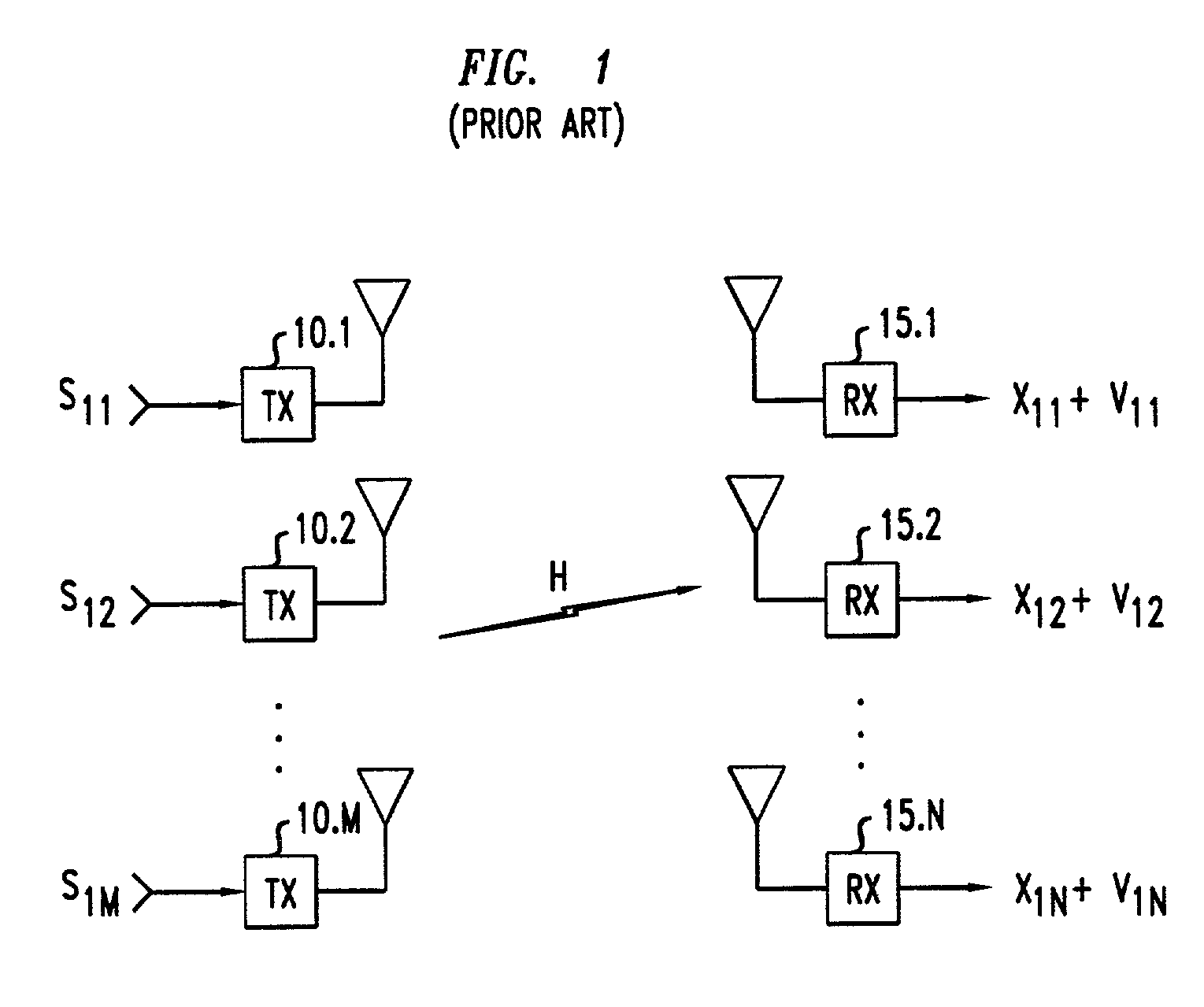
Method of multiple-antenna wireless communication using space-time codes
InactiveUS20020044611A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsComplex amplitudeWireless transmission
In a method of wireless transmission, space time matrices are used to spread the transmission of data over two or more transmit antennas and / or over two or more symbol intervals. Initially, blocks of data are encoded as symbols, each being a complex amplitude selected from a symbol constellation. A finite set of space-time matrices, referred to as "dispersion matrices," is predetermined. In transmission, a group of symbols are transmitted concurrently. Each of the symbols to be transmitted is multiplied by a respective dispersion matrix. Thus, a composite matrix, proportional to a sum of dispersion matrices multiplied by their corresponding symbols, is modulated onto a carrier and transmitted. In reception, knowledge of the dispersion matrices is used to recover the transmitted symbols from the received signals corresponding to the composite matrix that was transmitted.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Reconfigurable S box circuit structure
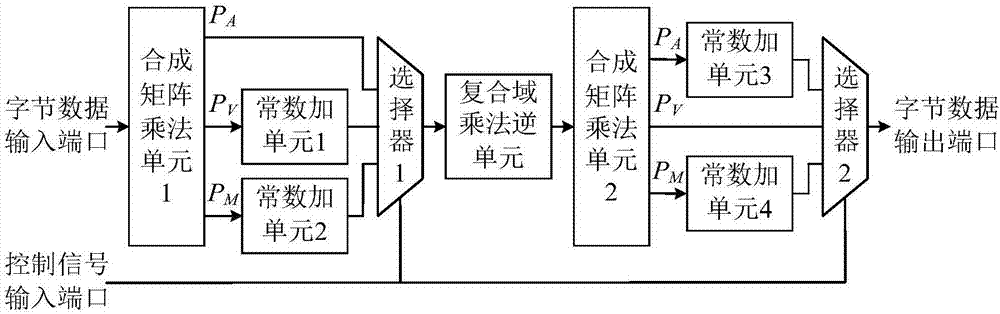
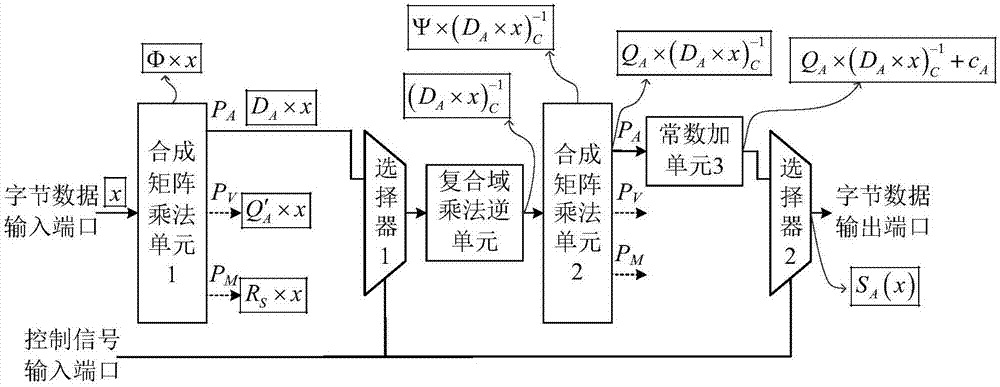
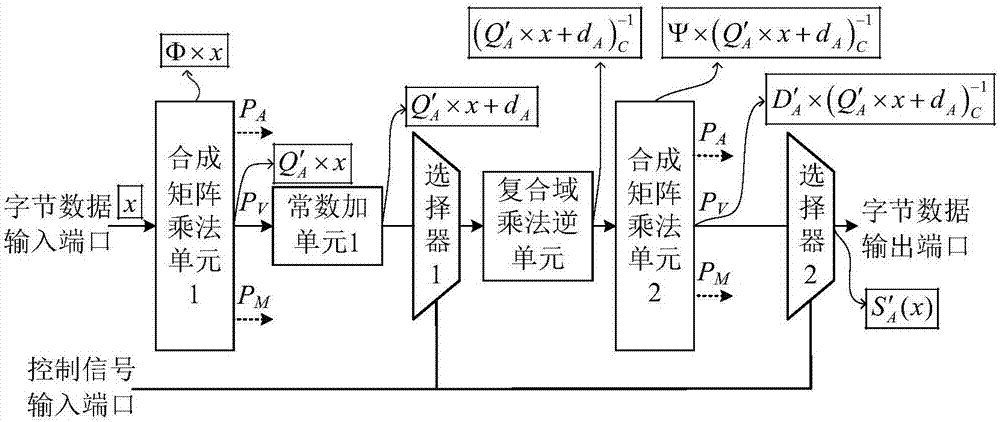
ActiveCN106921487AReduce areaImprove optimization efficiencyEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMultiplexingControl signal
The invention provides a reconfigurable S box circuit structure, comprising a first composite matrix multiplication unit, a second composite matrix multiplication unit, a first constant addition unit, a second constant addition unit, a third constant addition unit, a fourth constant addition unit, a composite domain multiplication unit, a first selector, a second selector, a byte data input port, a byte data output port and a control signal input port. The first selector and the second selector are three-in-one selectors. According to the reconfigurable S box circuit structure provided by the invention, in a mode of multiplexing composite domain multiplication inversion unit, reconfigurable functions of AES (Almost Blank Subframe) encryption S box operation, AES decryption S box operation and SM4S box operation are realized. Through multiplexing of composite domain multiplication inversion, a circuit area is greatly reduced; a composite matrix structure in the reconfigurable S box is beneficial for the improvement of the circuit optimization efficiency; and the circuit area is further reduced.
Owner:WUHU INST OF TECH
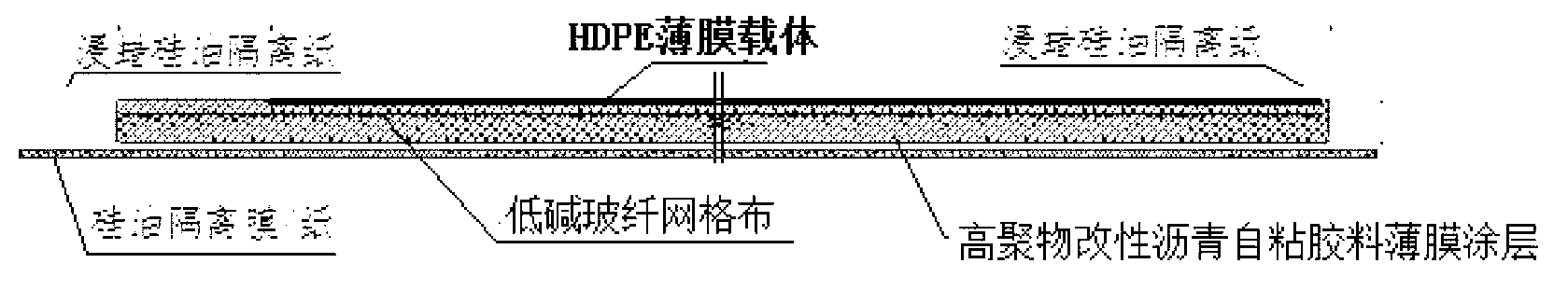
Composite matrix based carrier modified asphalt self-adhesive waterproof coiled material
ActiveCN103223747AReduce resource consumptionImprove waterproof performanceRoof covering using flexible materialsSynthetic resin layered productsGlass fiberNatural resource
The invention discloses a composite matrix based carrier modified asphalt self-adhesive waterproof coiled material, which is composed of three parts. Specifically, the first part is an HDPE film carrier, the second part is a high polymer modified asphalt self-adhesive glue film coating, and the third part is a low-alkaline glass fiber mesh cloth embedded and fixed in a high polymer modified asphalt self-adhesive material. The three parts are sticked and compounded together by the high polymer modified asphalt self-adhesive glue film coating to form the waterproof coiled material. The composite matrix based carrier modified asphalt self-adhesive waterproof coiled material disclosed in the invention can be made into an efficient waterproof material on the basis of maximumly reducing natural resource consumption, thus providing safety guarantee for engineering waterproofing.
Owner:JINZHOU DONGFANG YUHONG BUILDING MATERIALS +2
Distortional composite matrix
InactiveUS20070149725A1High distortional loadReduce high loadSynthetic resin layered productsMechanical propertyMaterials science
Owner:THE BOEING CO +1
Wear bars for impellers
The present invention is particularly, but not exclusively, useful for reducing wear of component parts of impact-type rock-crushing machines caused by earth aggregate flows during operation of impact crushers. The present invention includes a central feed body and impeller shoe that has hard material insert bars fixed therein to reduce wear. The exposed top surface of the central feed body and front face of the impeller shoe are impregnated with a plurality of cemented carbide insert bars. The cemented carbide insert bars form an upper composite matrix that helps to reduce wear and the premature wash out of the hard material insert bars integrally cast within the central feed body.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Rigidified non-conduited electrical harnesses
InactiveUS20140076628A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce weightElectrically conductive connectionsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsEngineeringFlexible cable
A rigidified flexible cable including flexible portions and one or more rigid segments, including a primary flexible cable with ends and end fittings, and at least one rigid medial section integral with the flexible portion and formed by coating the flexible cable material with a composite matrix material. Lateral transitions can be incorporated into the cable run and customized to the installation site specifications.
Owner:ICORE INT
Polyurethane composite matrix material and composite thereof
InactiveUS20100116179A1High strengthSimple waySynthetic resin layered productsConstructions elementsInorganic particleInorganic particles
The present invention provides a composite matrix material which has (a) polyurethane; (b) inorganic particles which have outer surfaces and an aspect ratio of from at least about 1.5 to about 30; and (c) a silane coupling agent; wherein at least a portion of outer surfaces of the inorganic particles are in contact with the silane coupling agent. Also provided is a composite in which a composite matrix material is a polymeric matrix core which has a surface, and a thermoset layer is bonded to at least a portion of the surface of the polymeric matrix core. The composite is a high strength, durable part that may be used, for example, in manufacturing pallets and building or construction materials such as deck boards and siding and roofing panels, etc.
Owner:ADVANCED BUILDING COMPOSITES
Thermally enhanced ultrasound transducer system
InactiveUS20070167803A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricityUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for removing unwanted heat generated by a piezoelectric element of an ultrasound transducer. Some implementations have high thermal conductivity (HTC) material placed adjacent to the piezoelectric element. The HTC material can be thermally coupled to one or more heat sinks. Use of HTC material in conjunction with these piezoelectric element surfaces is managed to avoid degradation of propagating acoustic energy. Use of the HTC material in conjunction with heat sinks allows for creation of thermal paths away from the piezoelectric element. Active cooling of the heat sinks with water or air can further draw heat from the piezoelectric element. Further implementations form a composite matrix of thermally conductive material or interleave thermally conductive layers with piezoelectric material.
Owner:UST INC
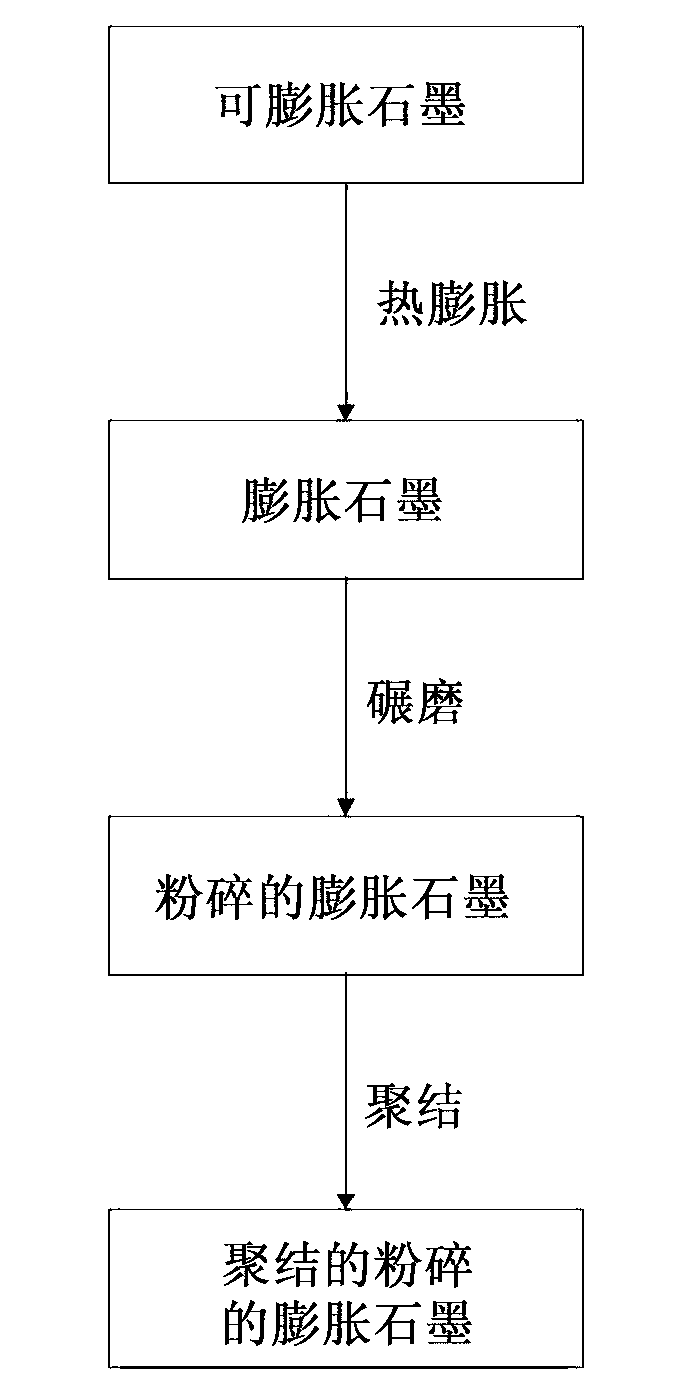
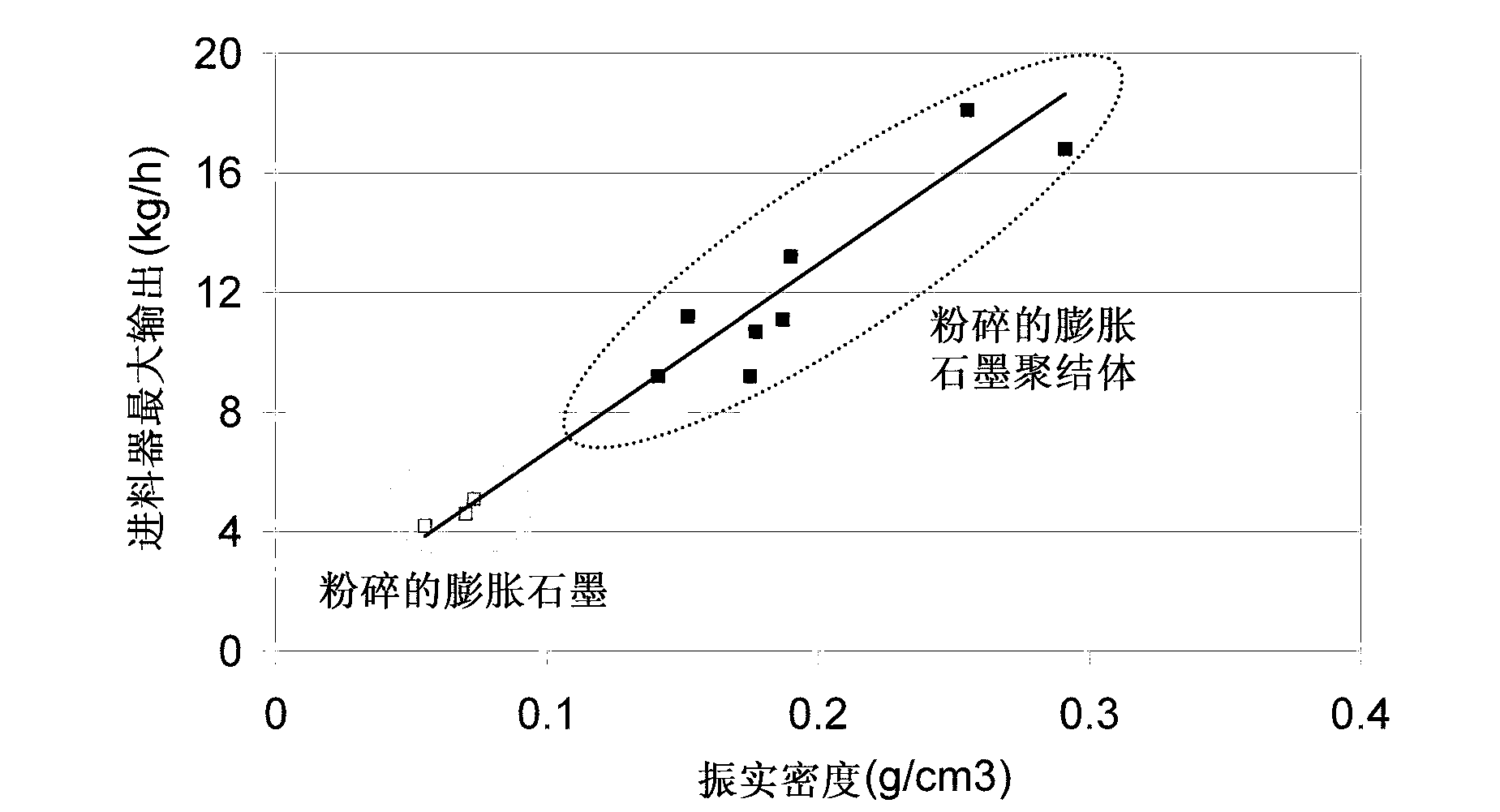
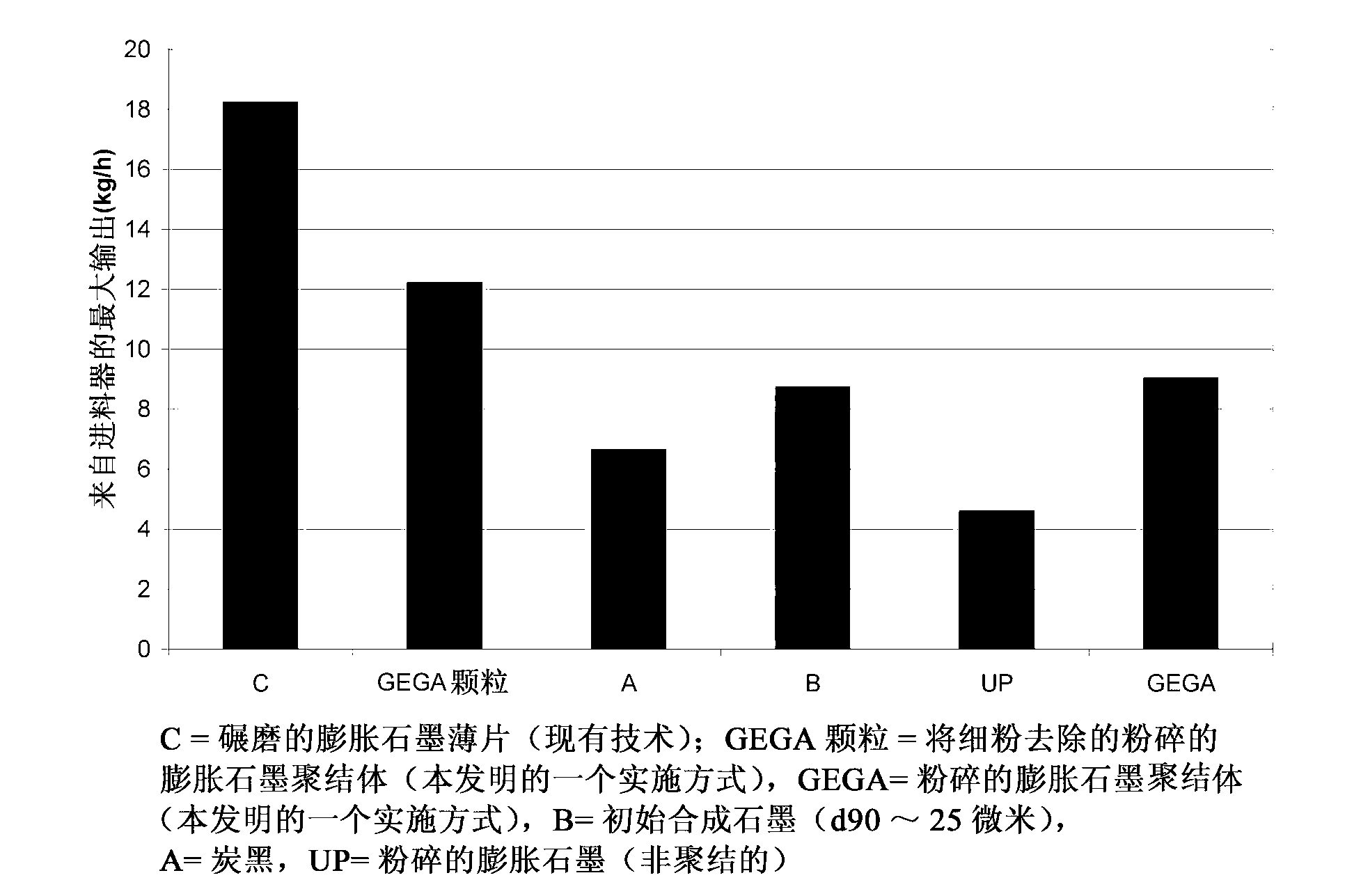
Ground expanded graphite agglomerates, methods of making, and applications of the same
ActiveCN103140441AGraphiteNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialConductive materialsGraphite
The present disclosure relates to ground expanded graphite agglomerate compositions, methods for making such agglomerates, their use as conductive additive, and conductive composites comprising such ground expanded graphite agglomerates. The disclosure also pertains to methods for making such composites and the use of such composites in preparing thermally conductive materials. The agglomerates are characterized by a certain softness allowing the agglomerates to dissolve, e.g., through shear forces applied during compounding, thereby leading to an improved feedability and a highly homogenous distribution of the expanded graphite material in the composite matrix.
Owner:IMERYS GRAPHITE & CARBON SWITZERLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com