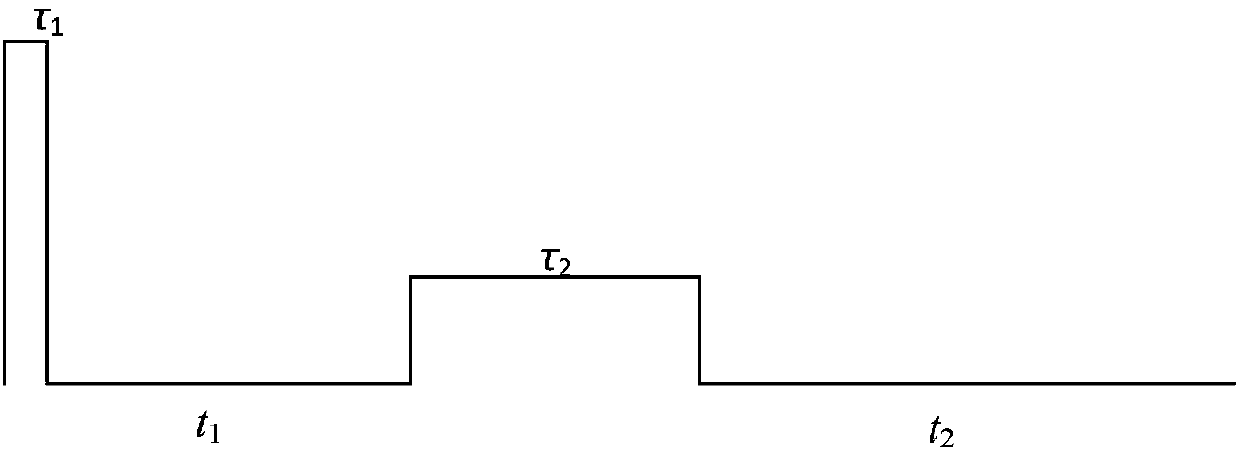
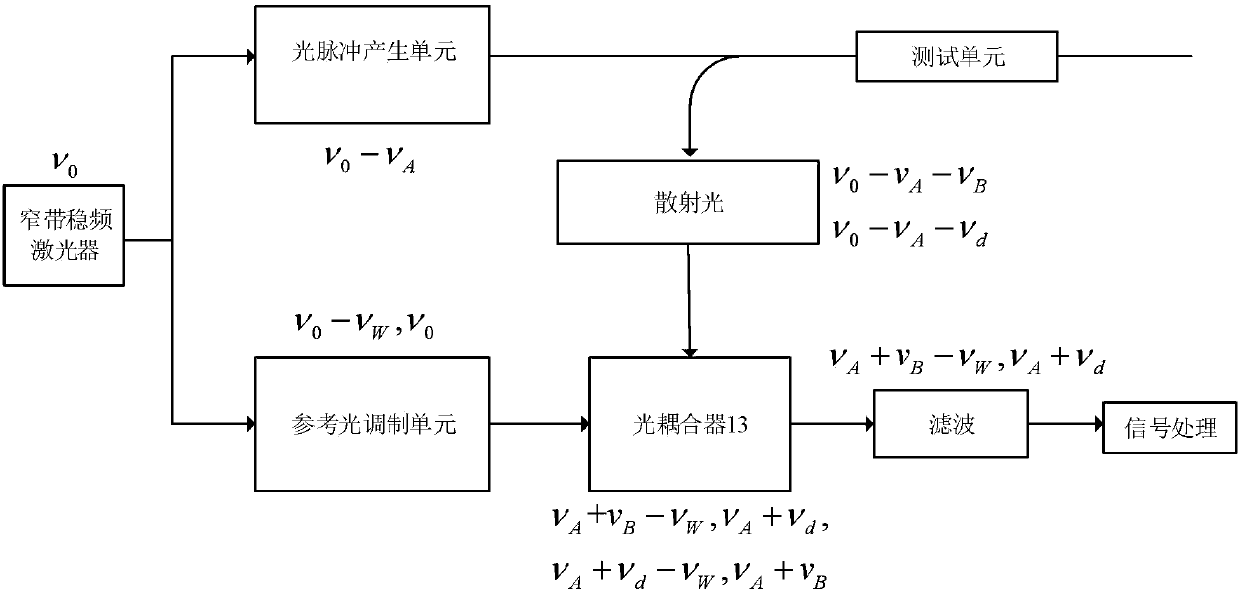
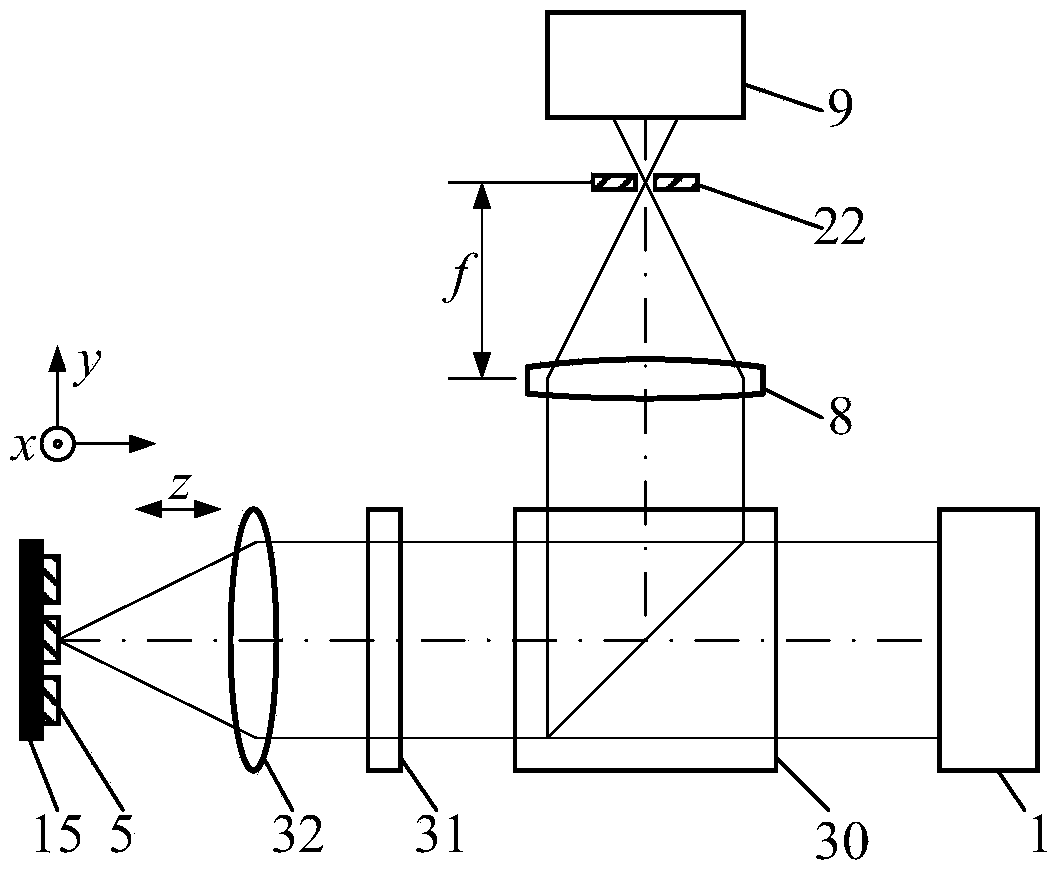
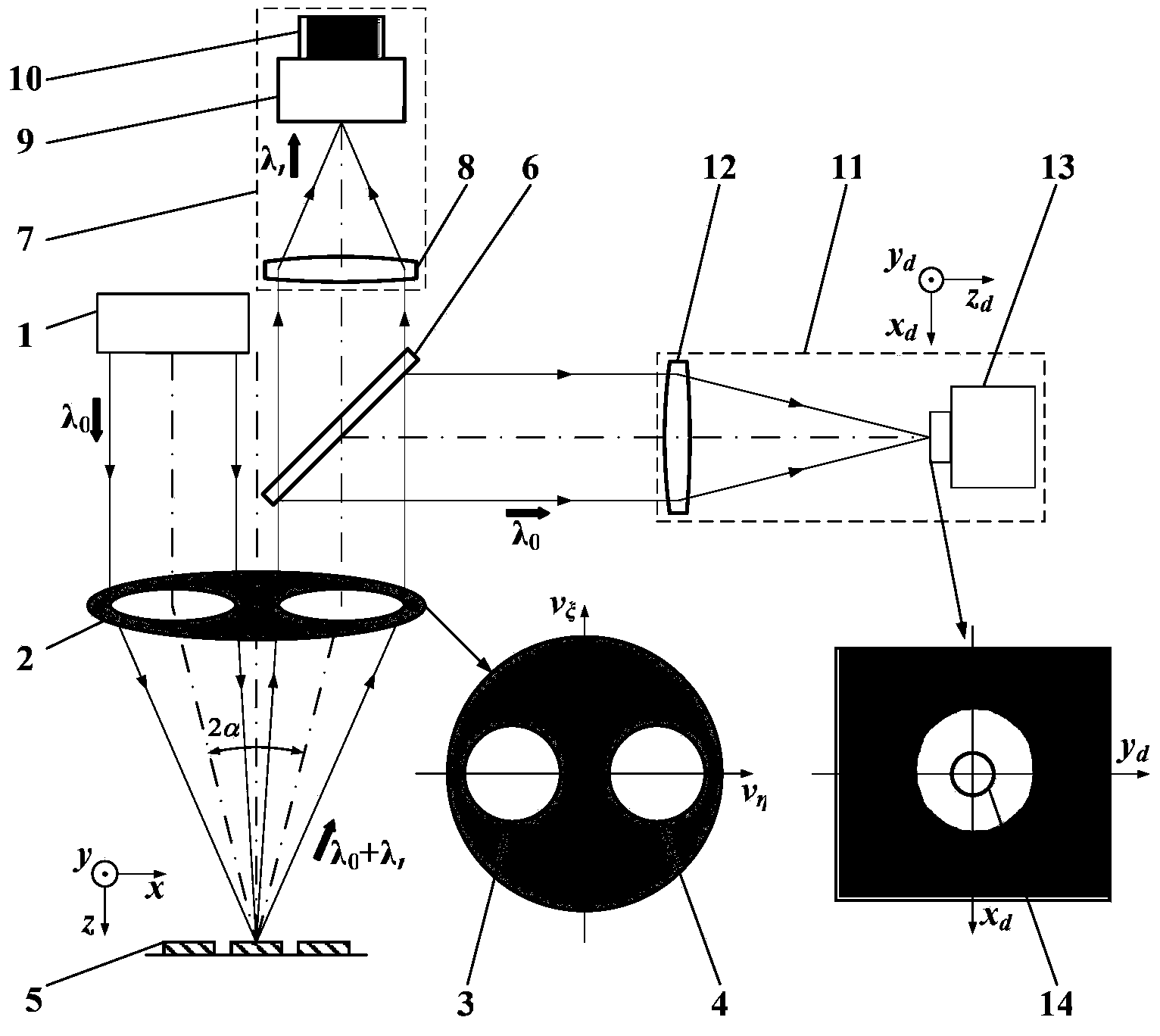
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
943 results about "Rayleigh Light Scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
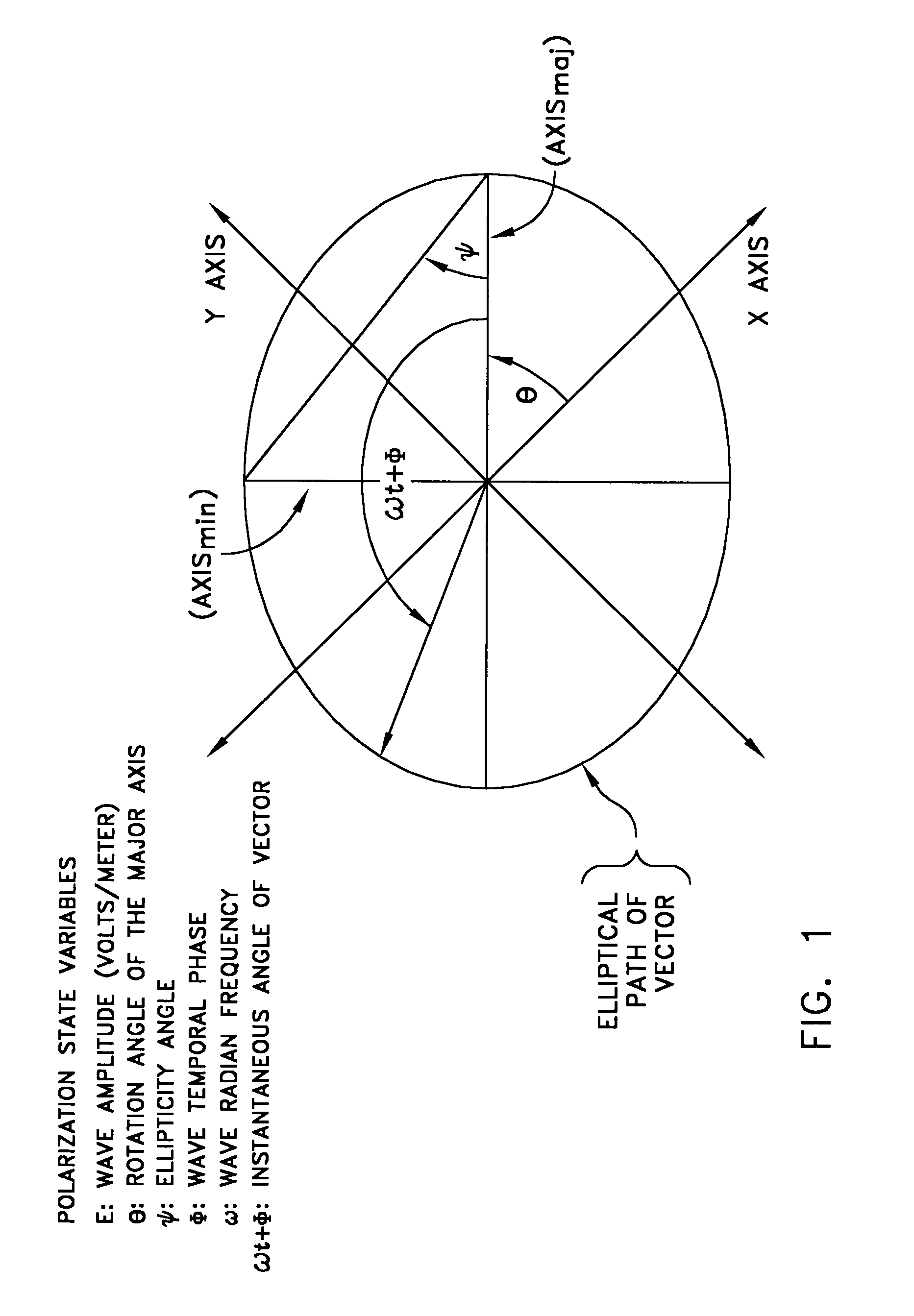
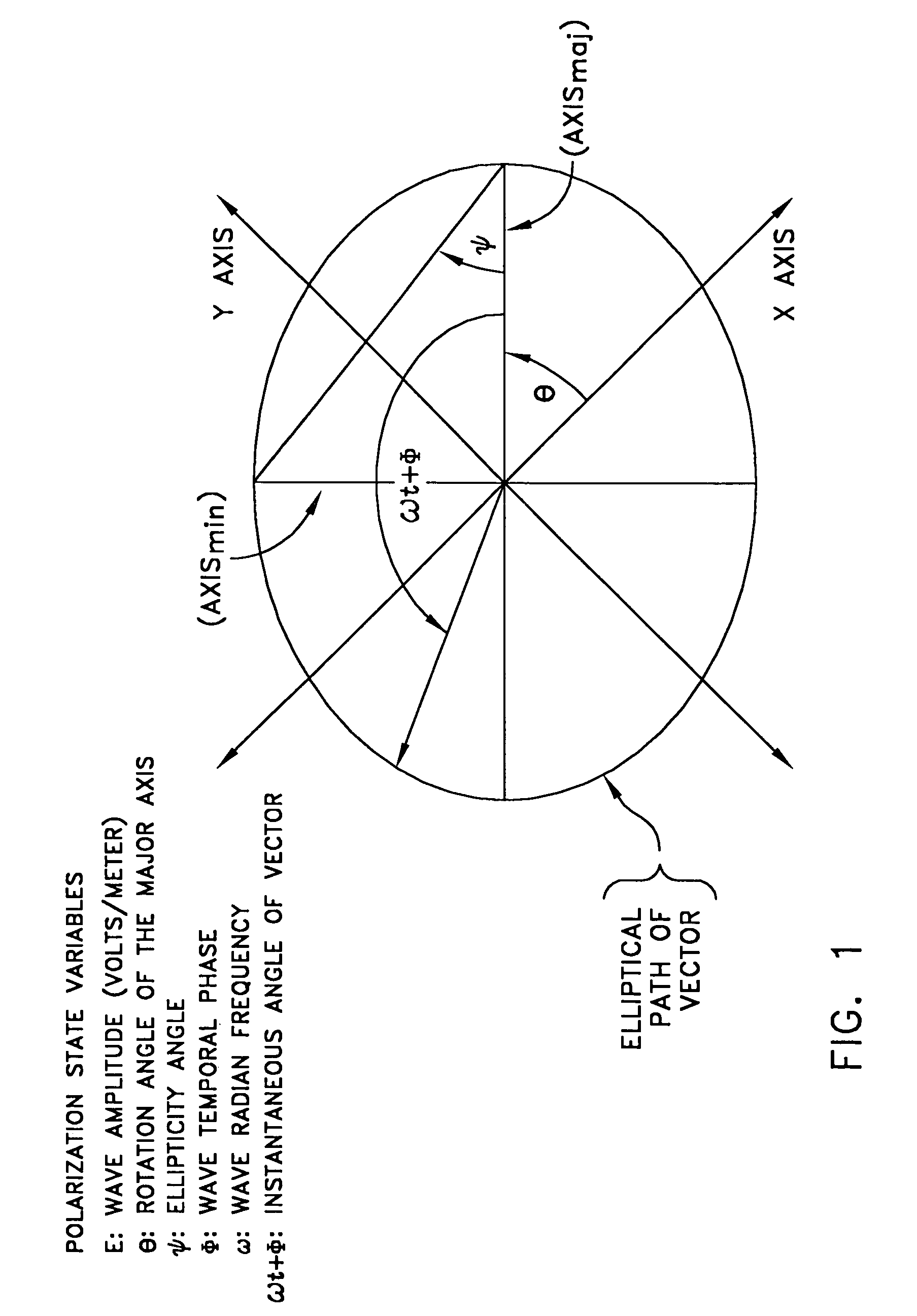
Rayleigh scattering (pronounced /ˈreɪli/ RAY-lee), named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the (dominantly) elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation.
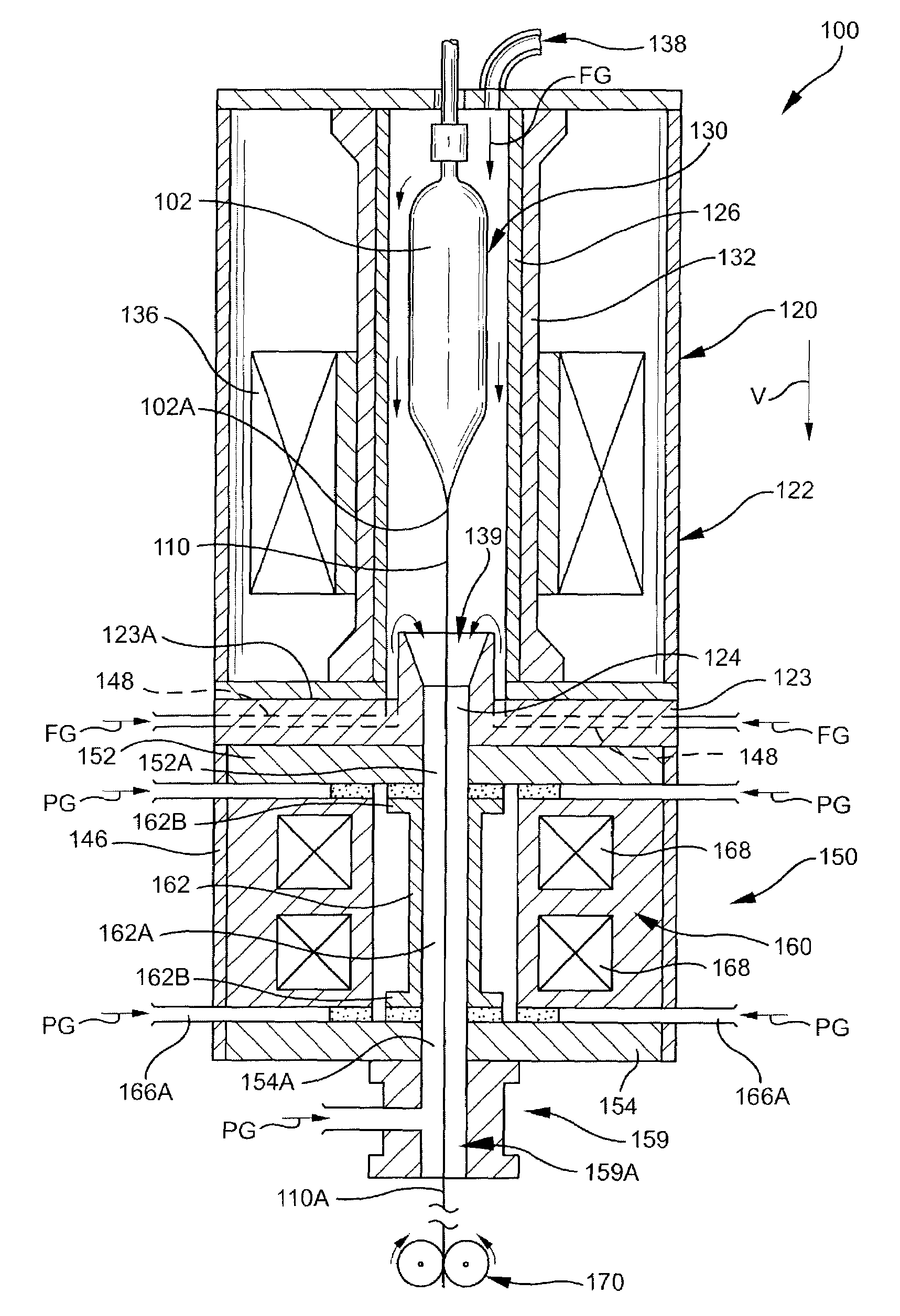
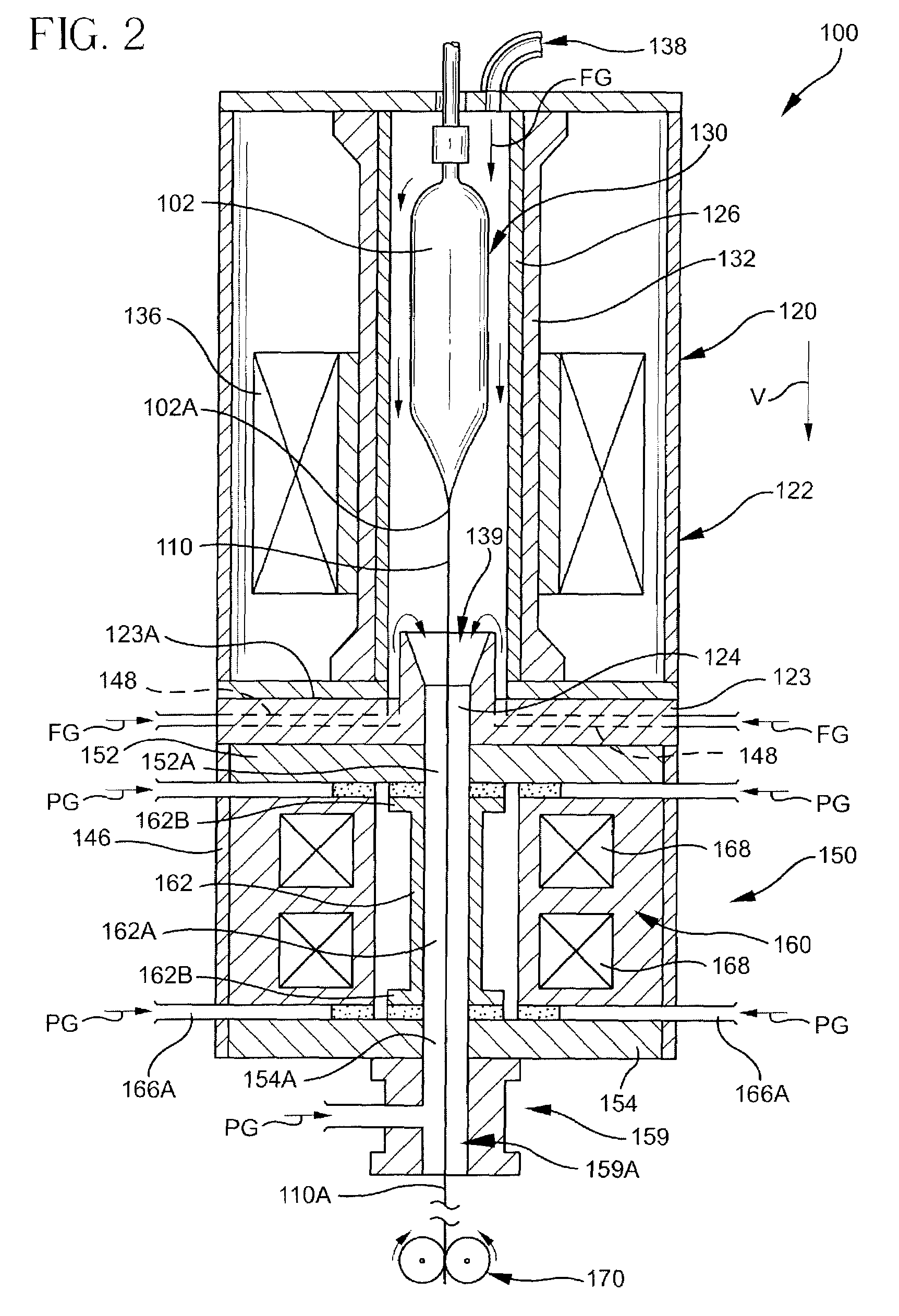
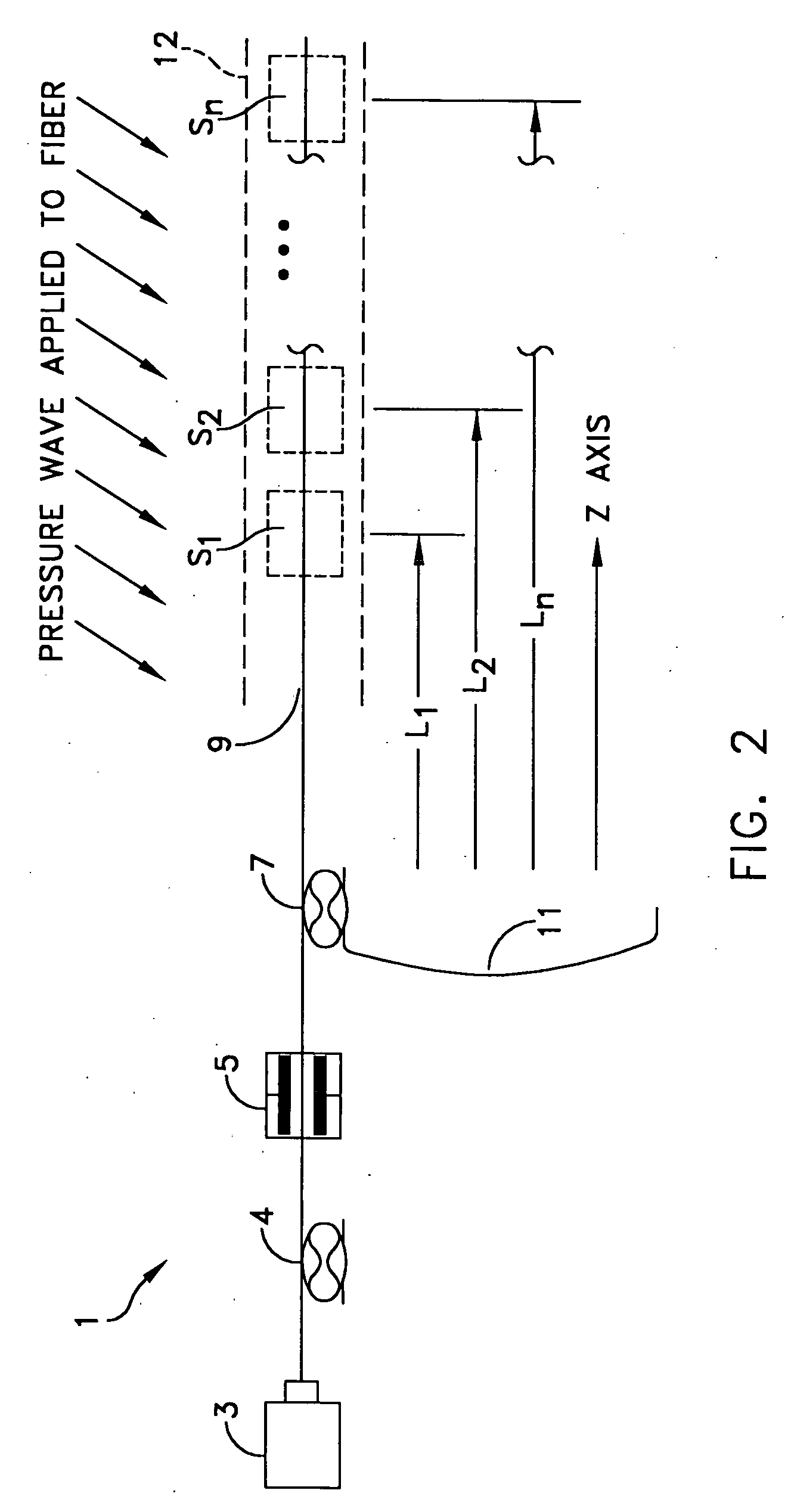
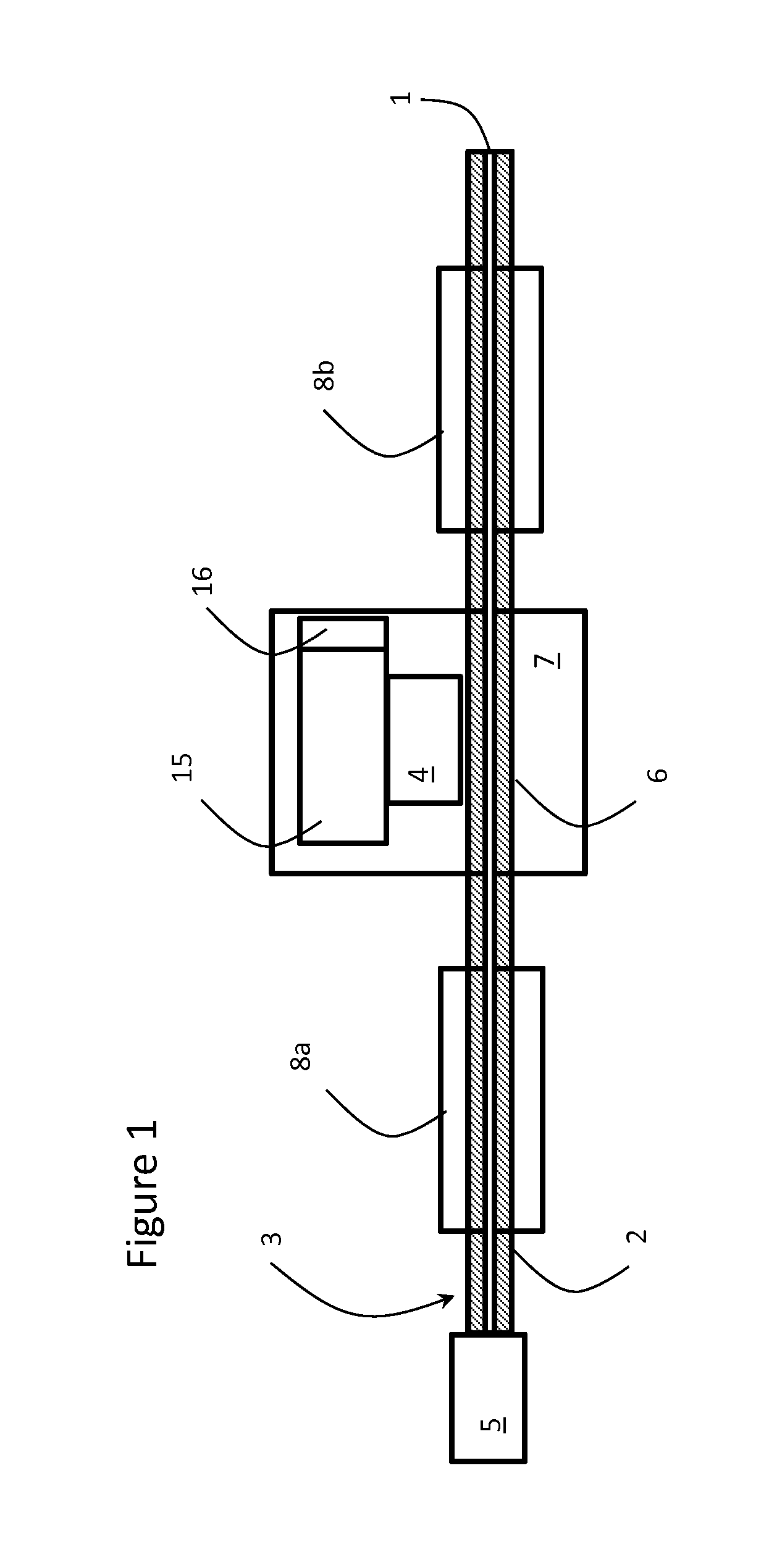
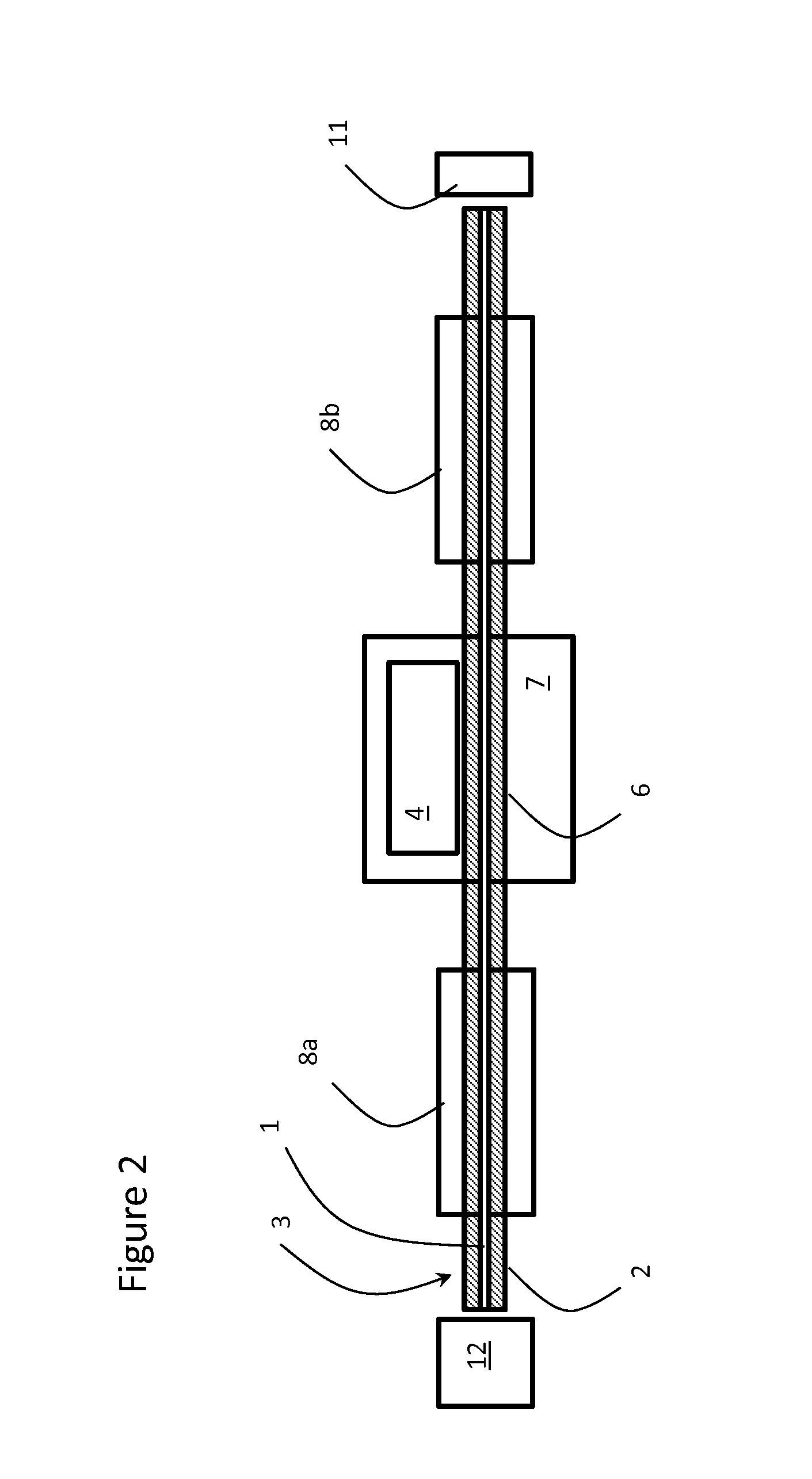
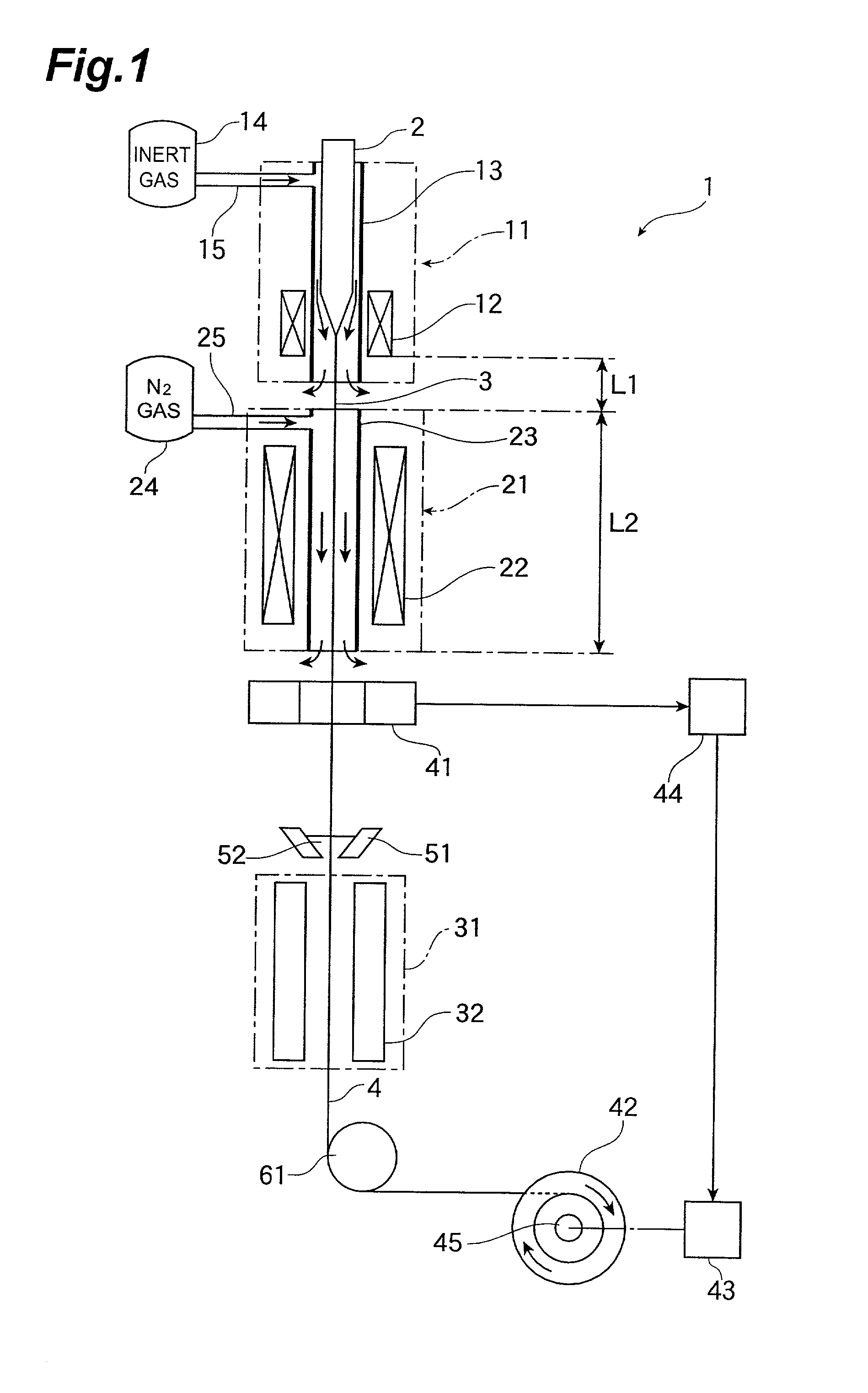
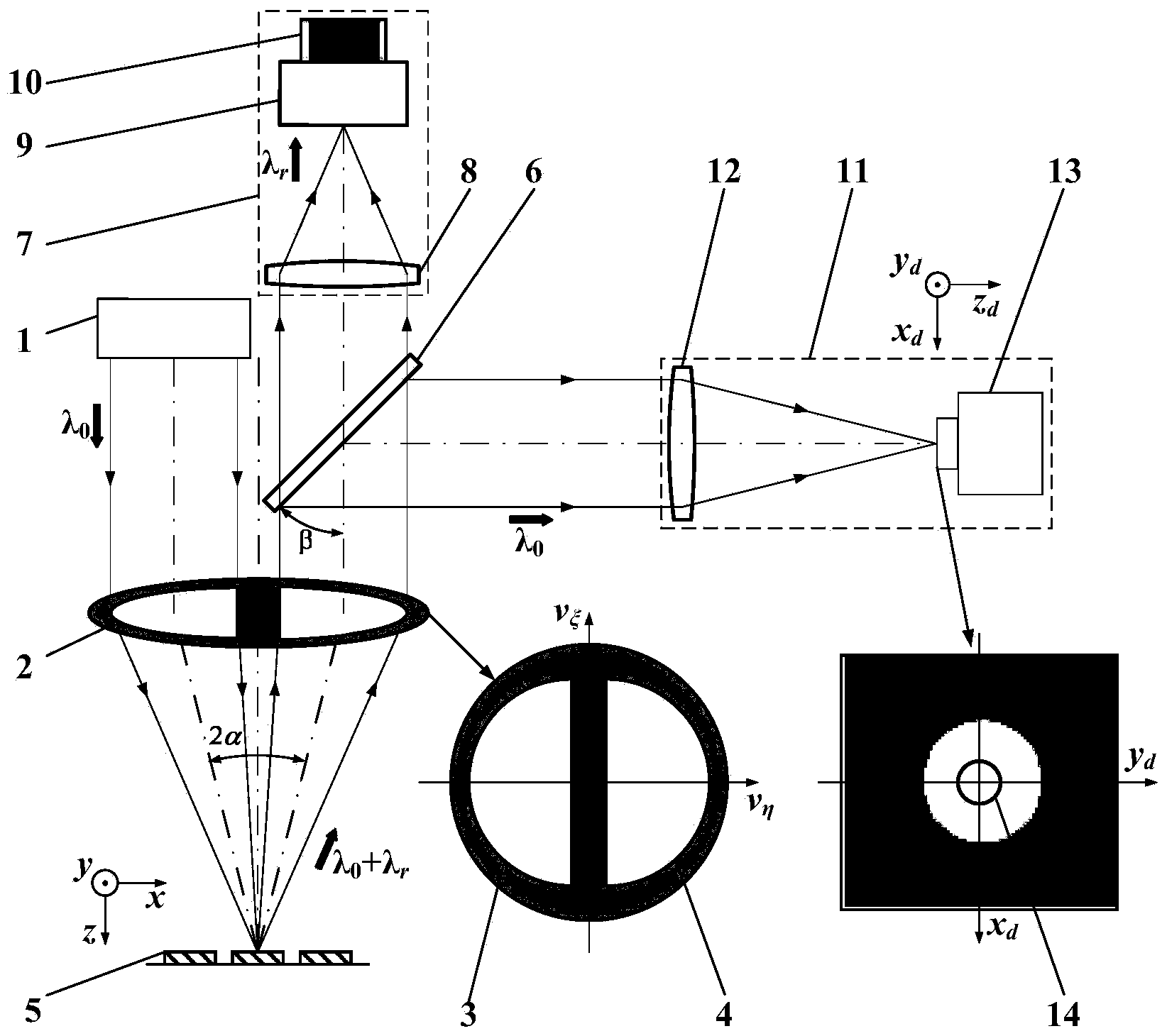
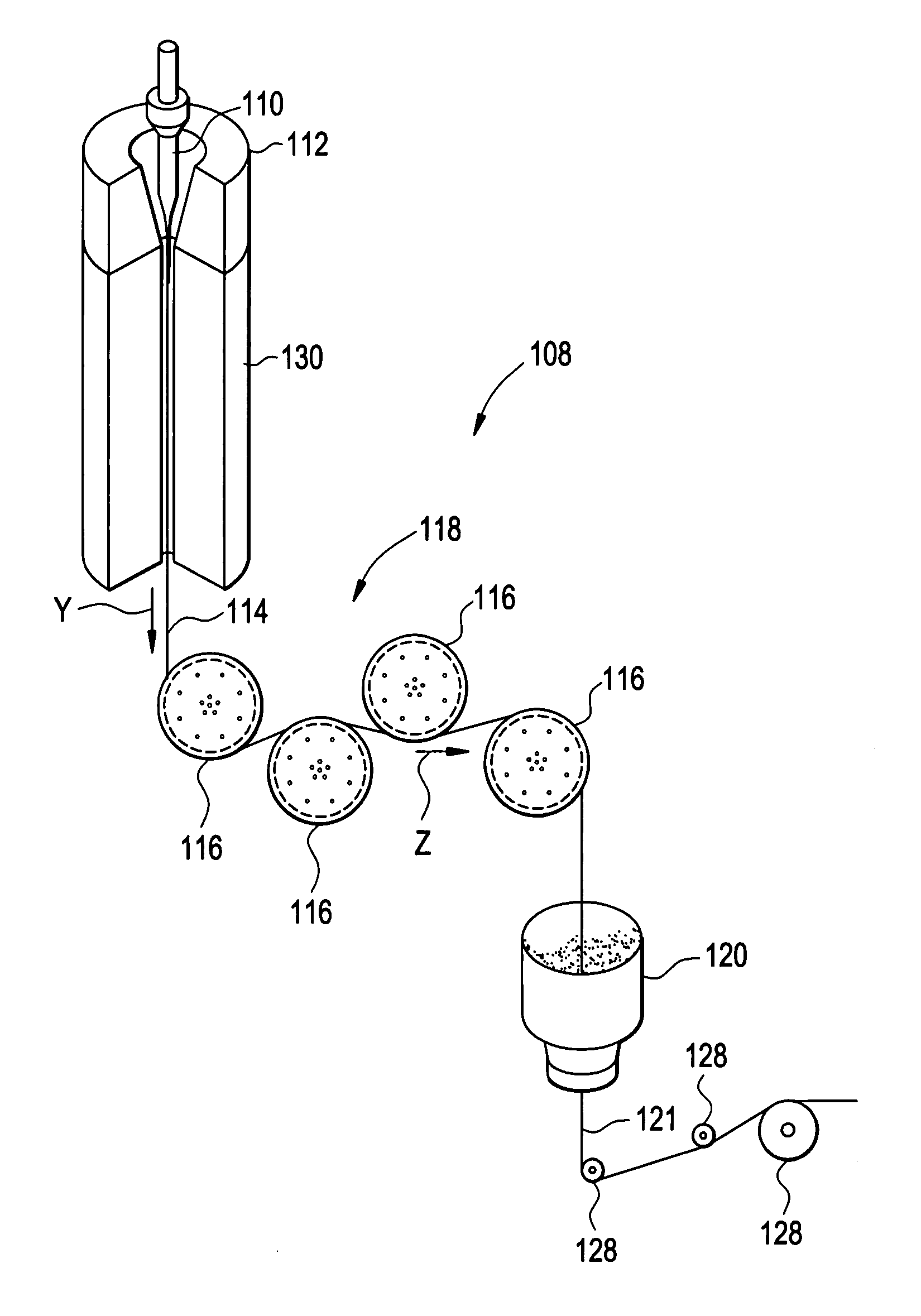
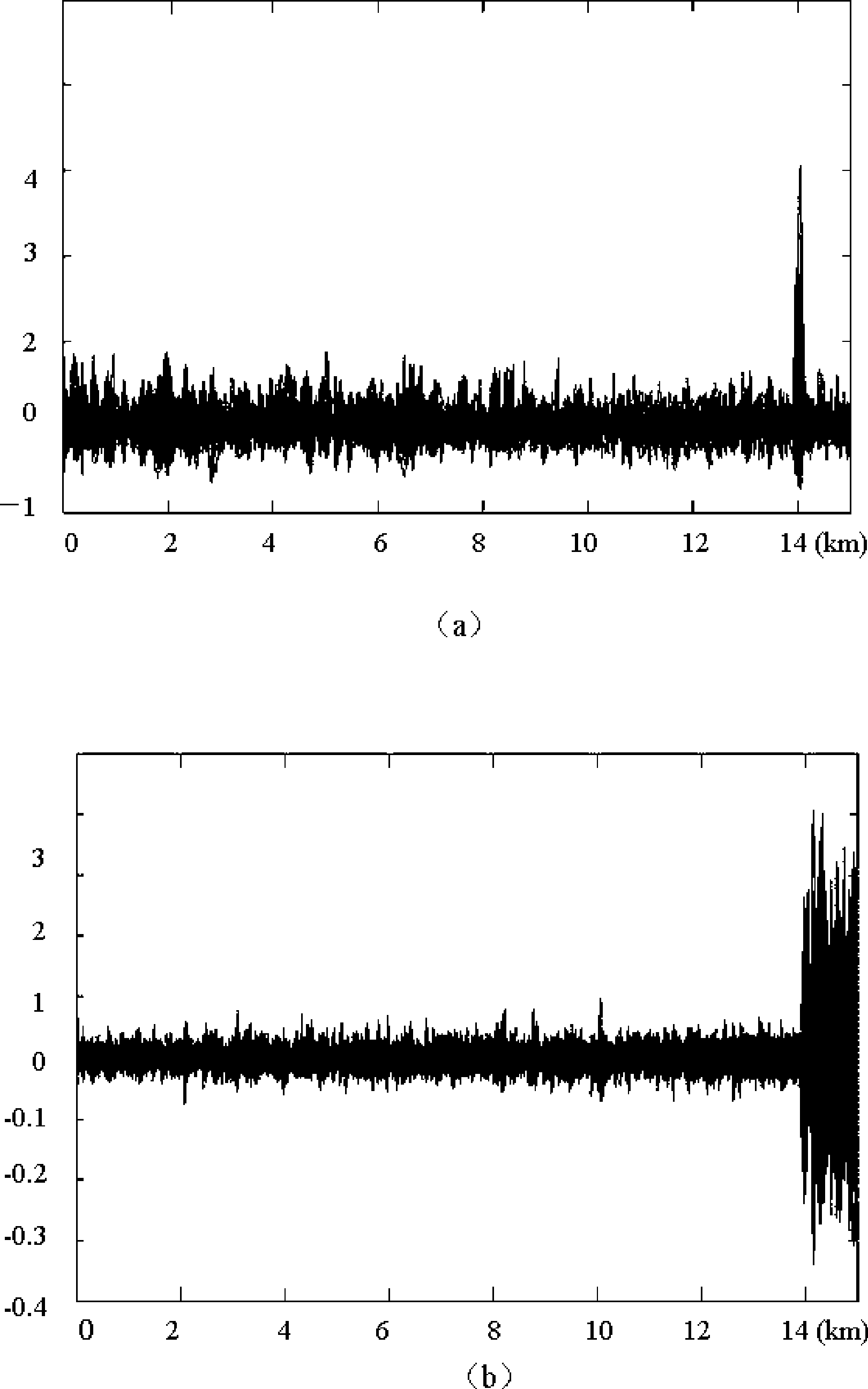
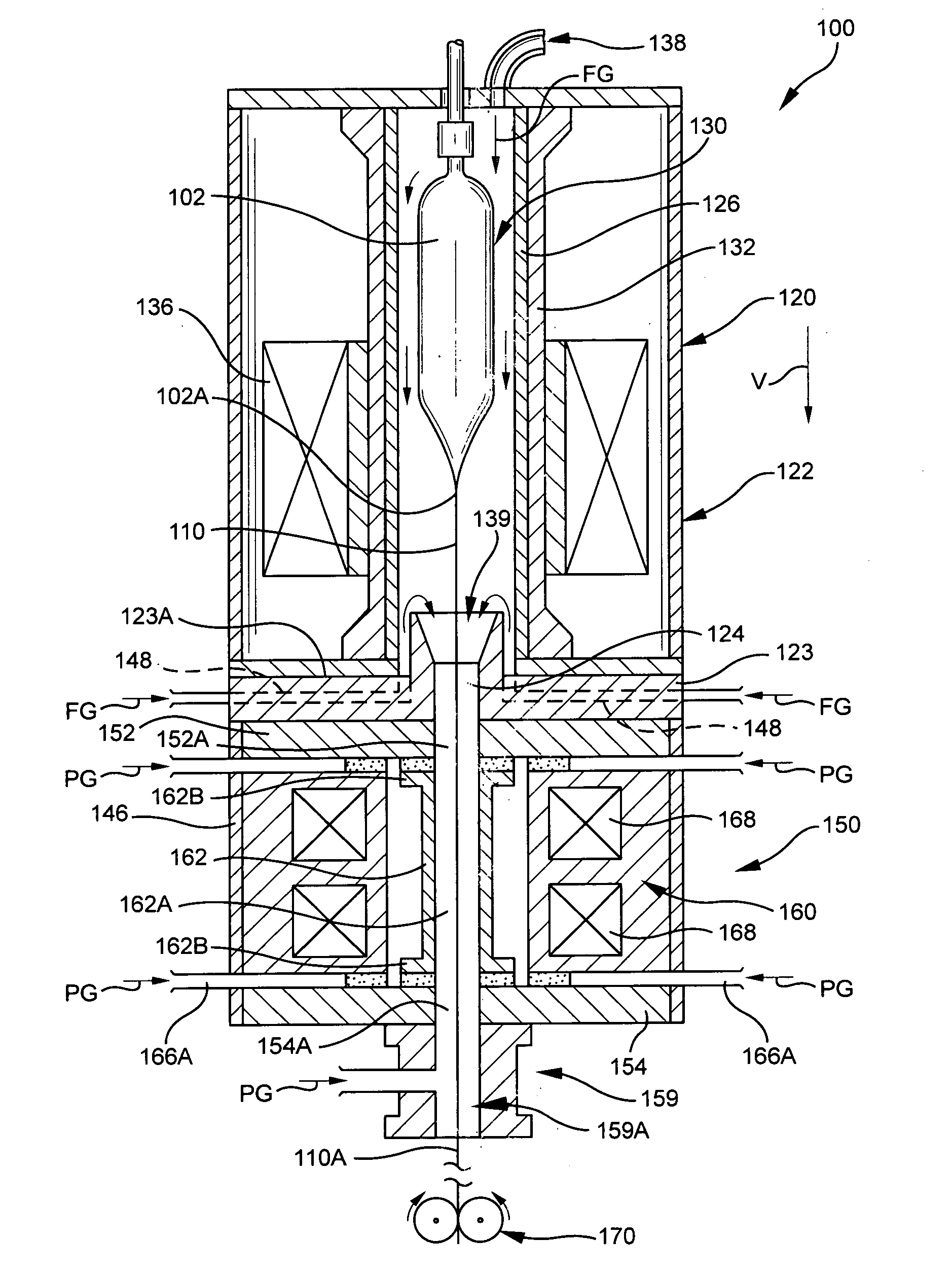
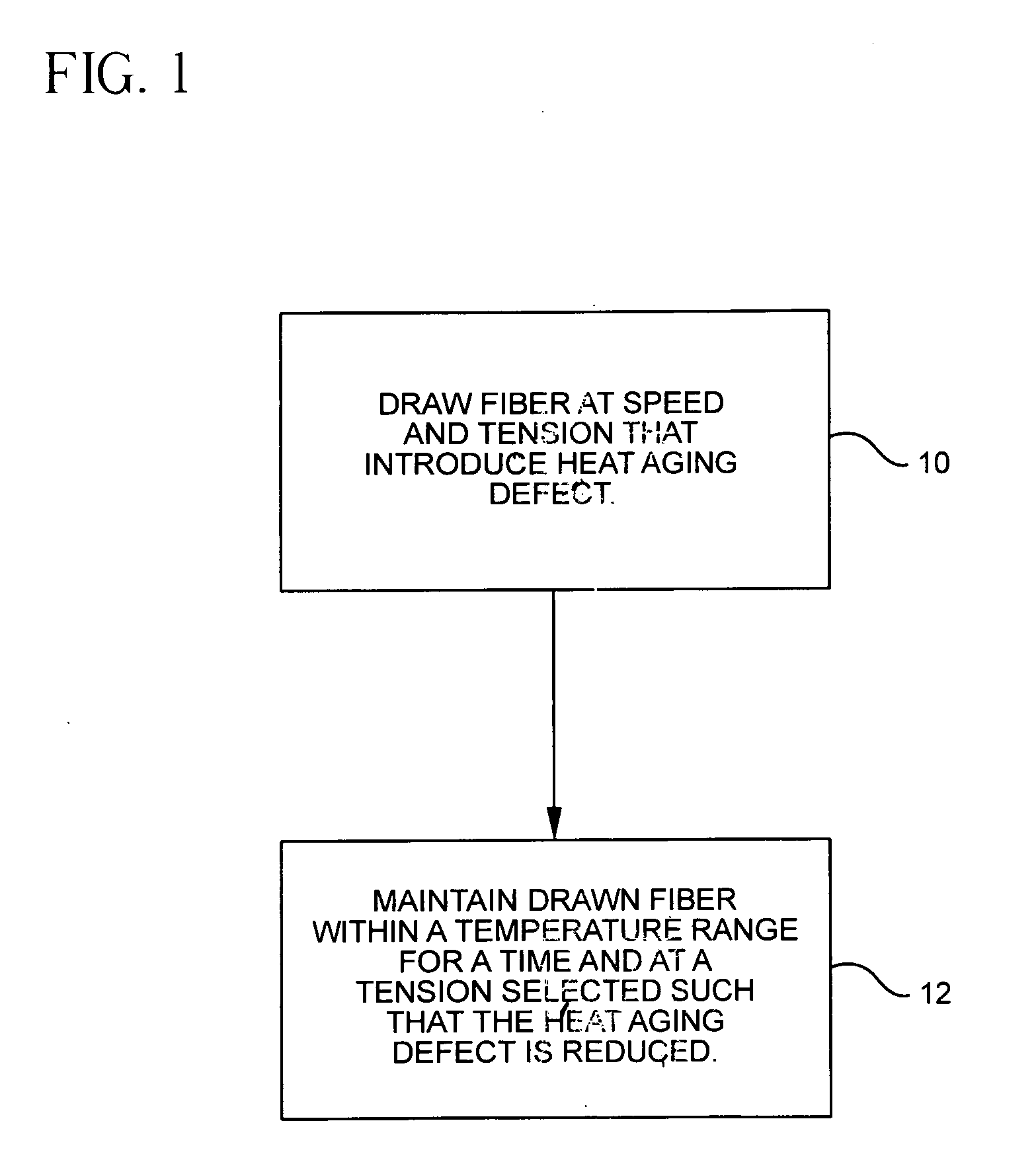
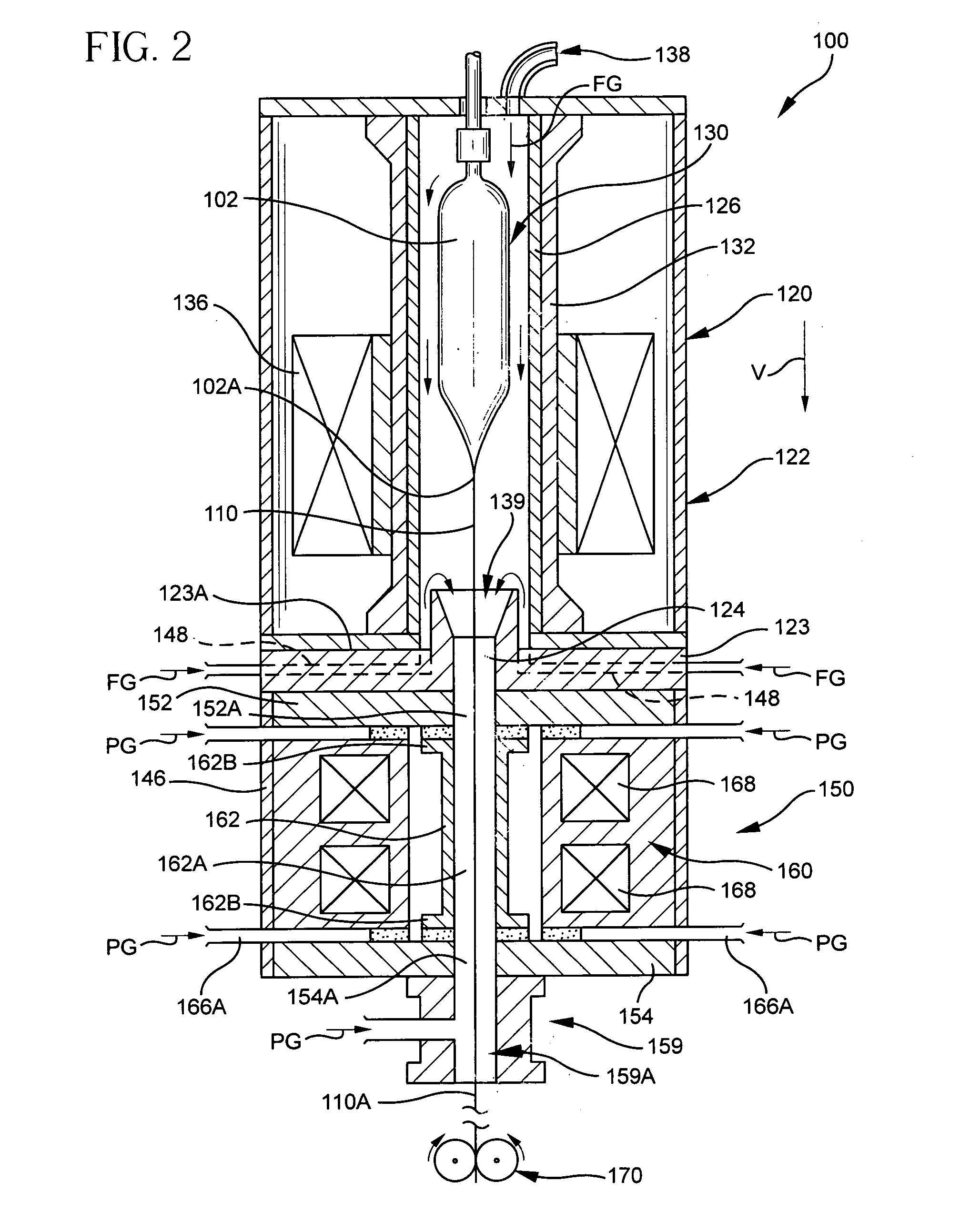
Methods and apparatus for forming heat treated optical fiber
InactiveUS7565820B2Trend downDecreases micro-density variationGlass fibre drawing apparatusNon-linear opticsUltrasound attenuationRayleigh scattering
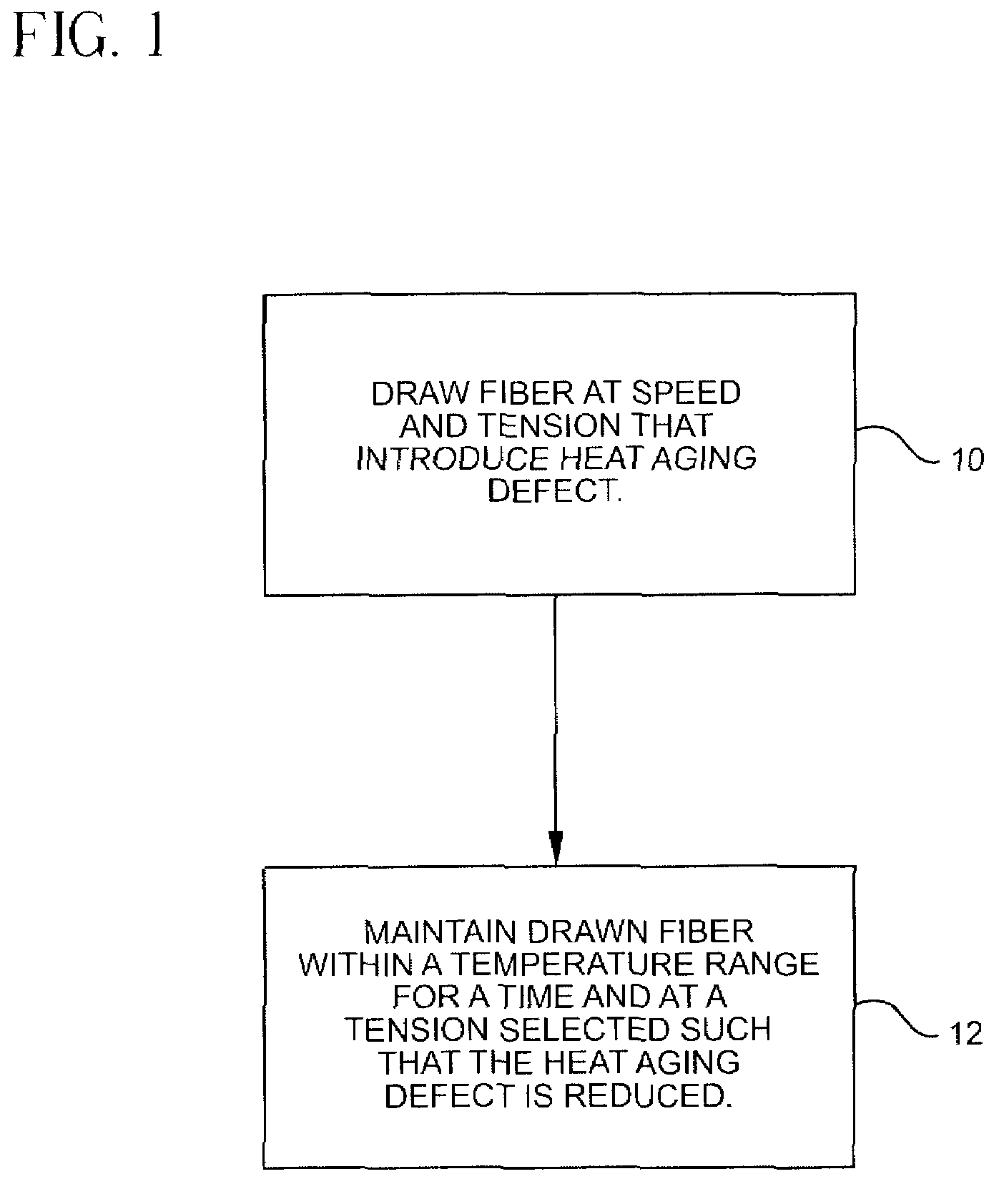
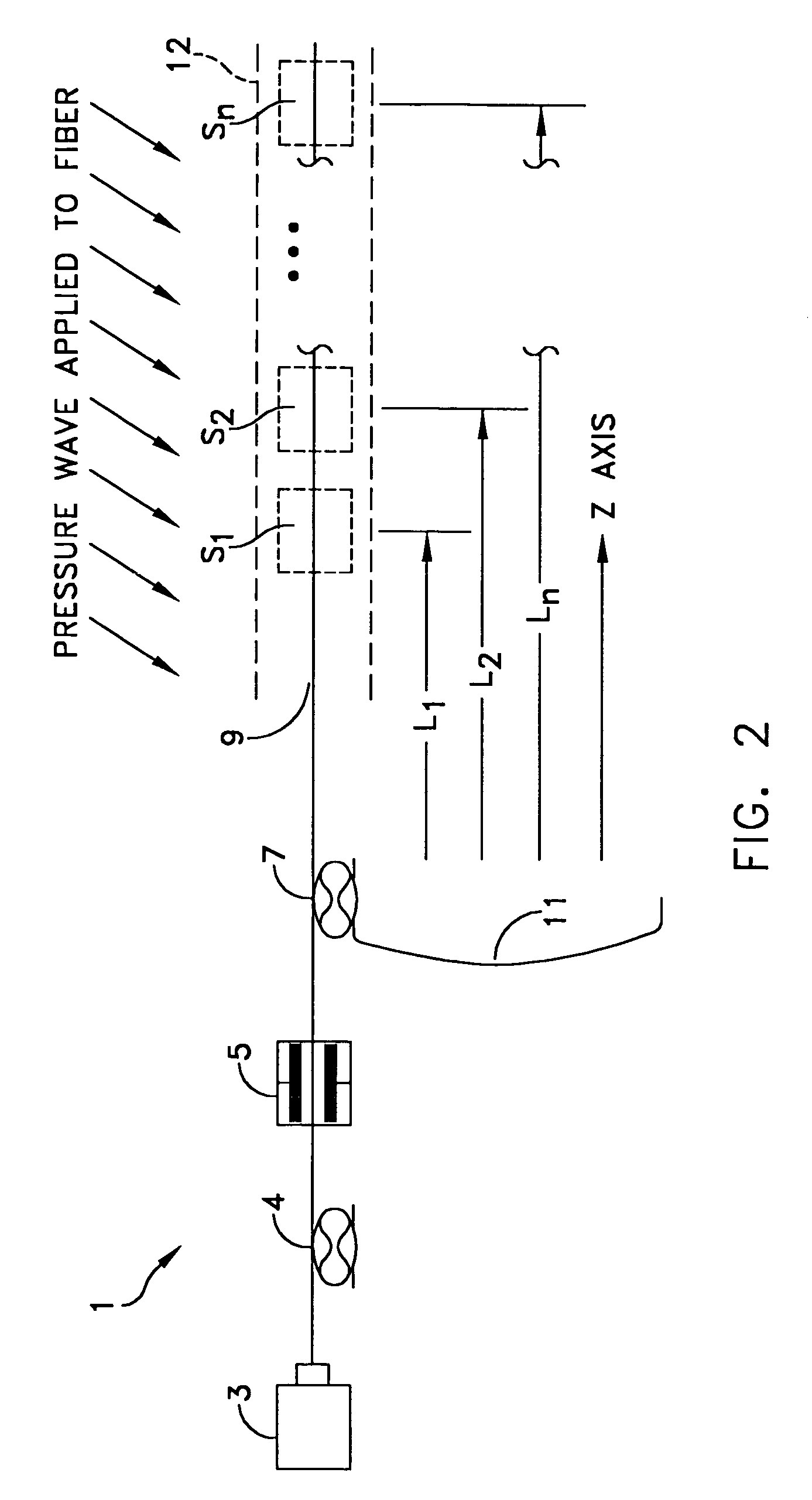
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber within a treatment temperature range for a treatment time. Preferably also, the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Apparatus are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
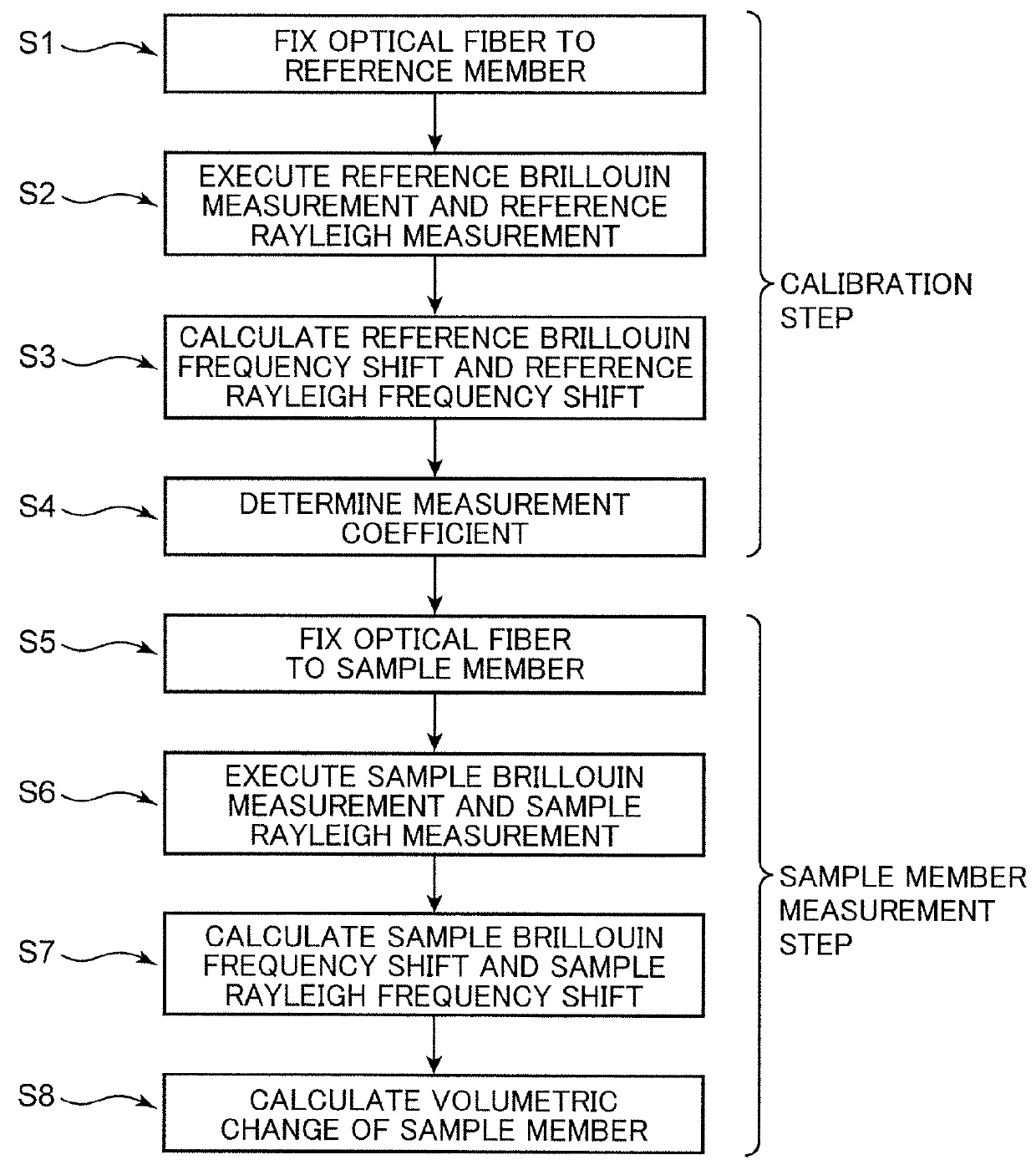
Method for measuring volumetric changes of object
ActiveUS9360304B2Accurate measurementOptical detectionUsing optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Under a known pressure is externally applied to a reference member to which an optical fiber is fixed, test light is allowed to enter the optical fiber, and at least one of a reference Brillouin measurement for determining a reference Brillouin frequency shift amount based on the Brillouin scattering phenomenon, and a reference Rayleigh measurement for determining a reference Rayleigh frequency shift amount based on the Rayleigh scattering phenomenon is performed. A Brillouin measurement coefficient or a Rayleigh measurement coefficient is determined from these calculation results. An optical fiber is fixed to a sample member, the volumetric change of which is unknown, and the same sample Brillouin measurement or sample Rayleigh measurement is performed to determine the frequency shift amount. The volumetric change of the sample member is determined from the sample Brillouin or the sample Rayleigh frequency shift amount, and from the Brillouin or the Rayleigh measurement coefficient.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
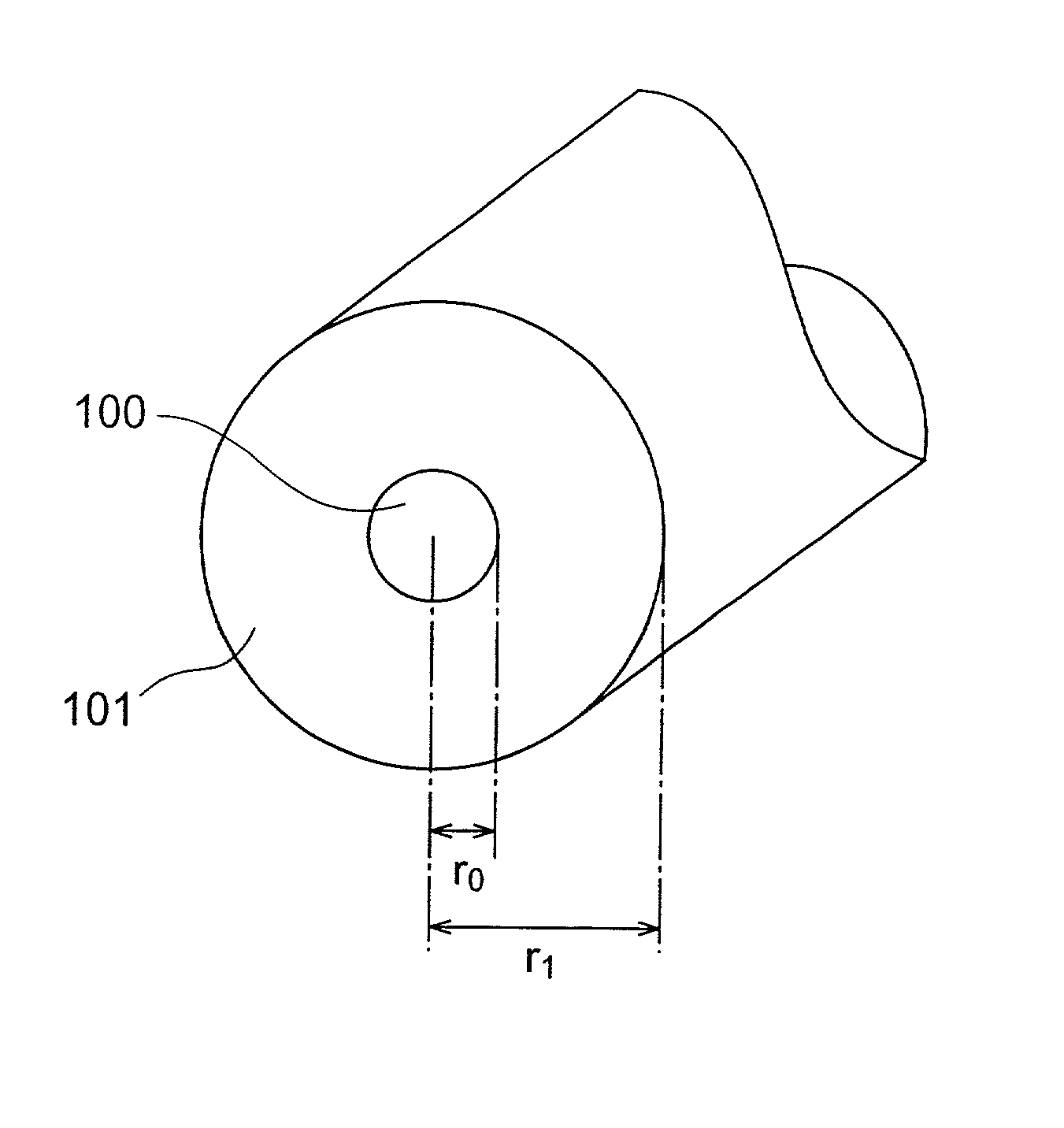
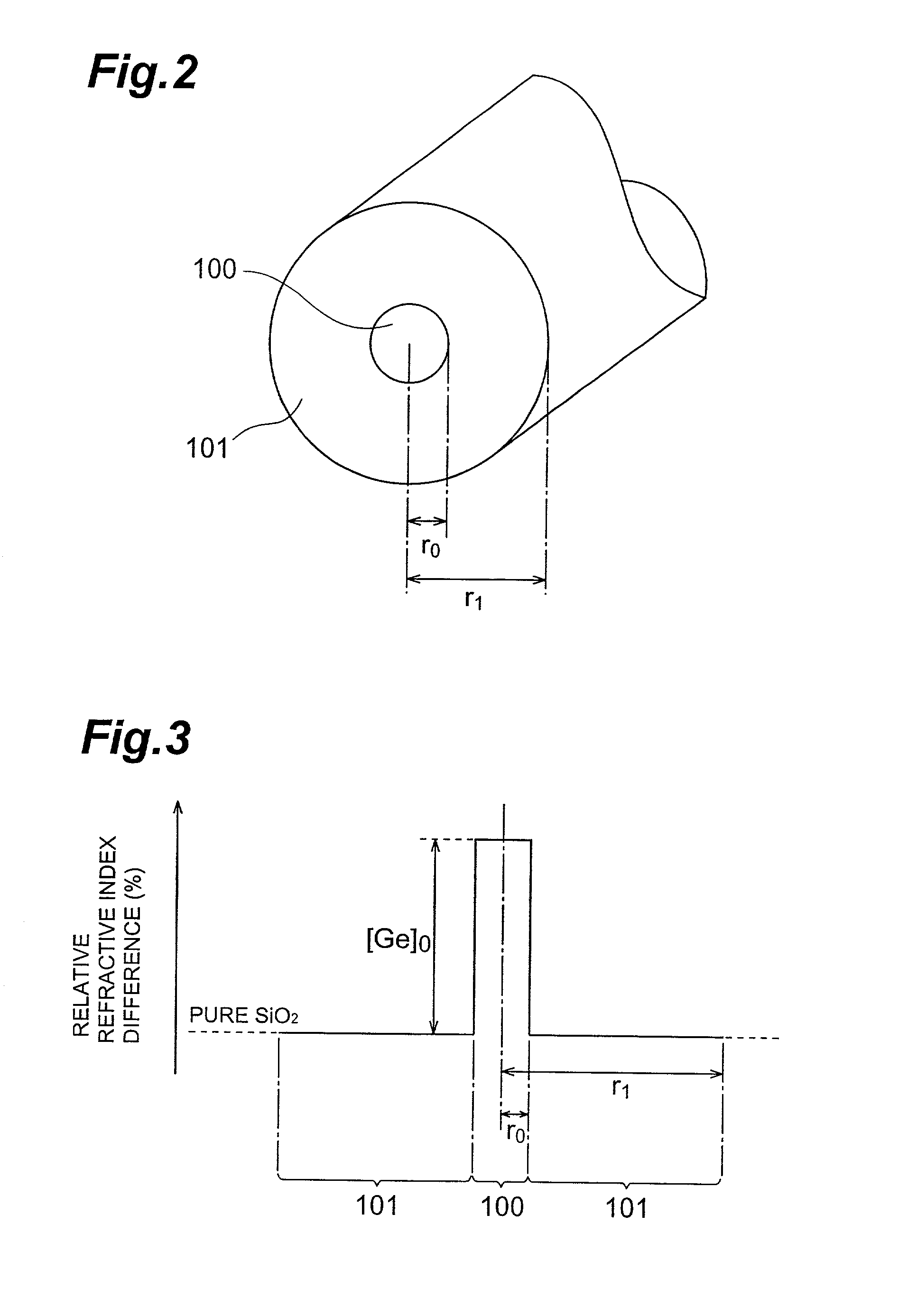
Dispersion-Shifted Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20090252469A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
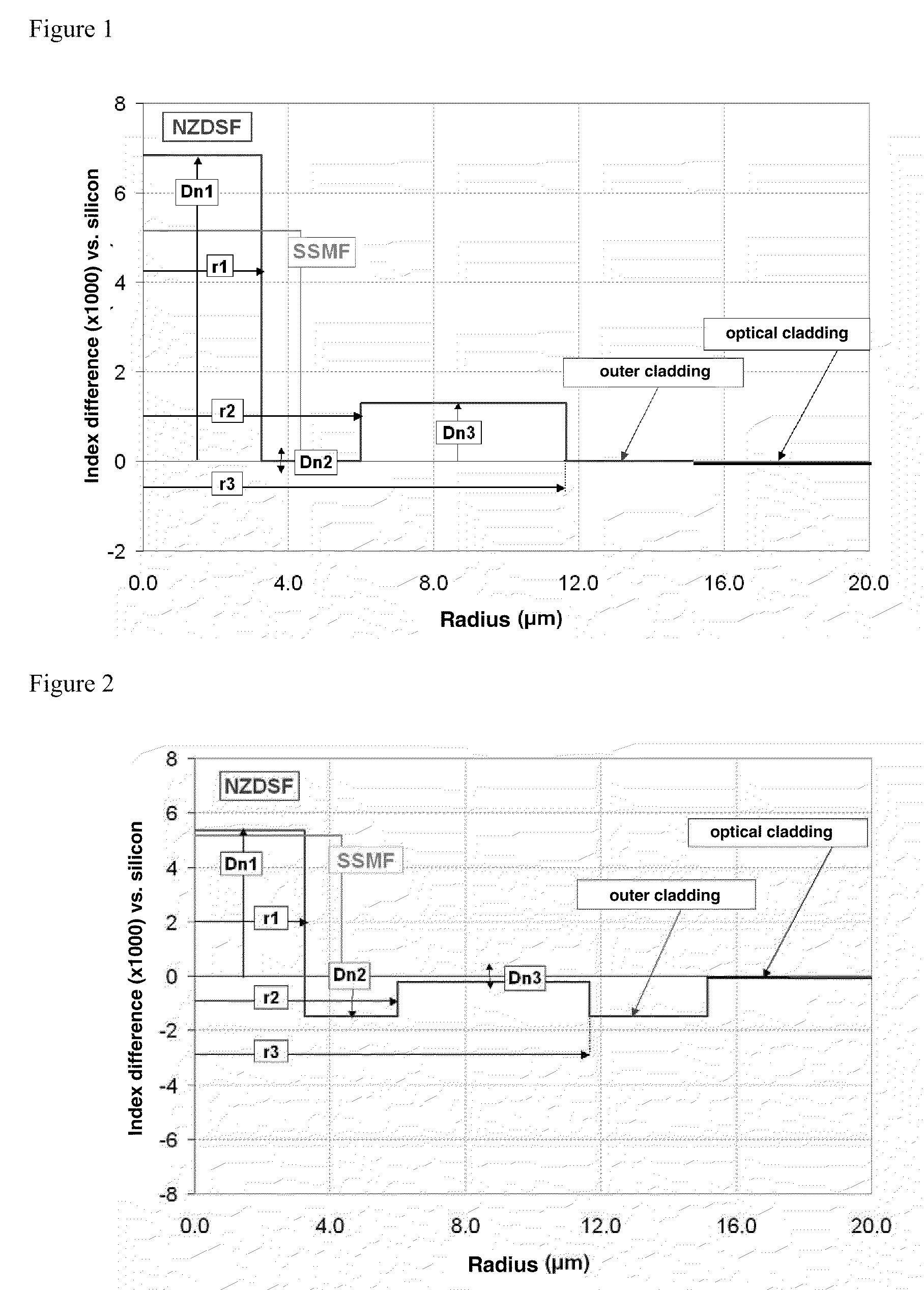
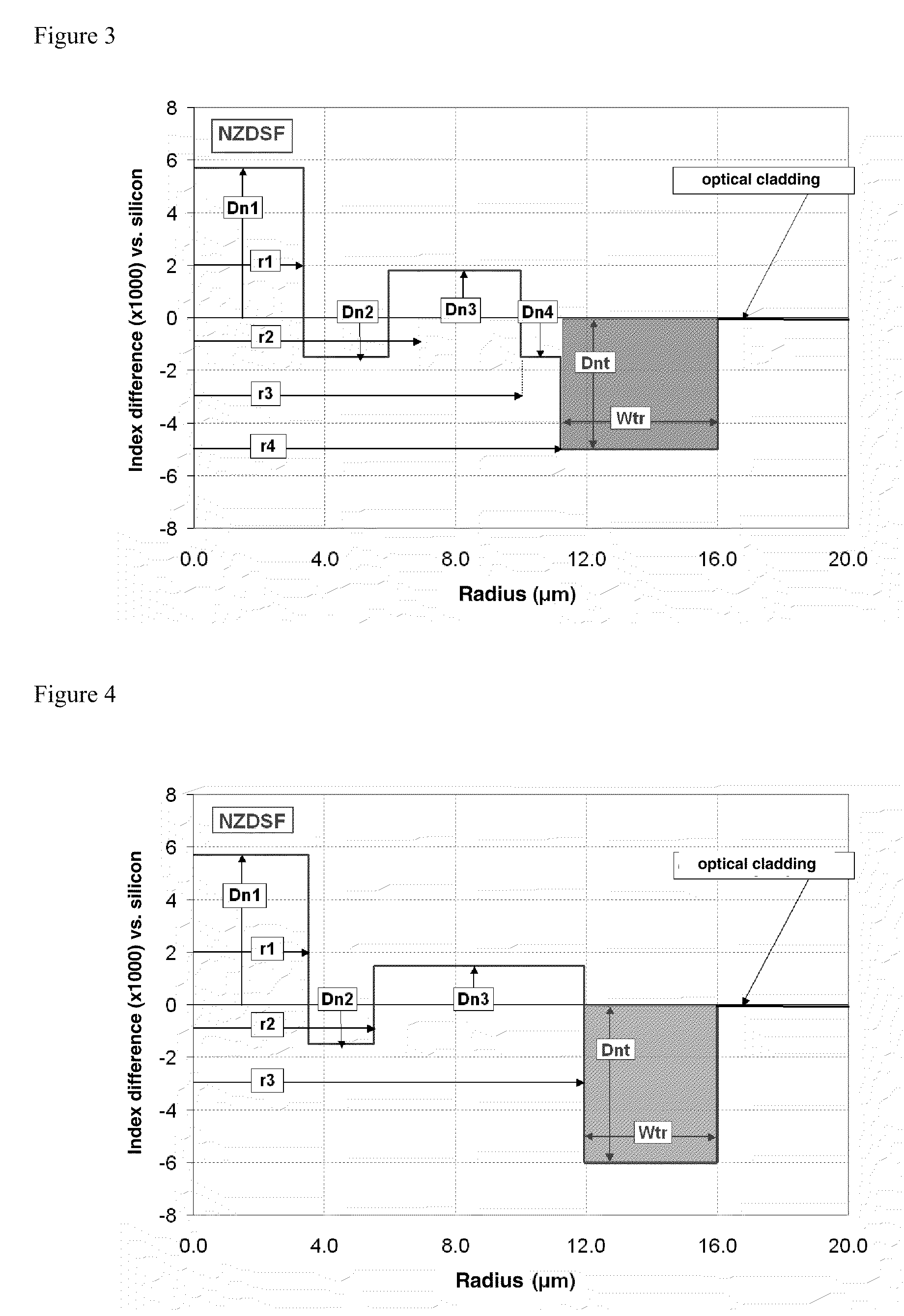
A dispersion-shifted optical fiber (NZDSF) includes a central core (r1, Dn1), an inner cladding having at least three zones with a first intermediate cladding zone (r2, Dn2), a second ring zone (r3, Dn3) and a third buried trench zone (Wtr, Dnt). The buried trench zone has an index difference (Dnt) with the optical cladding between −5·10−3 and −15·10−3 and has a width (Wtr) between 2.5 μm and 5.5 μm. The present optical fiber, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, has reduced Rayleigh scattering losses of less than 0.164 dB / km, with limited bending losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Distributed optical fibre measurements
InactiveUS7284903B2Not distort measurementHigh measurement accuracyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
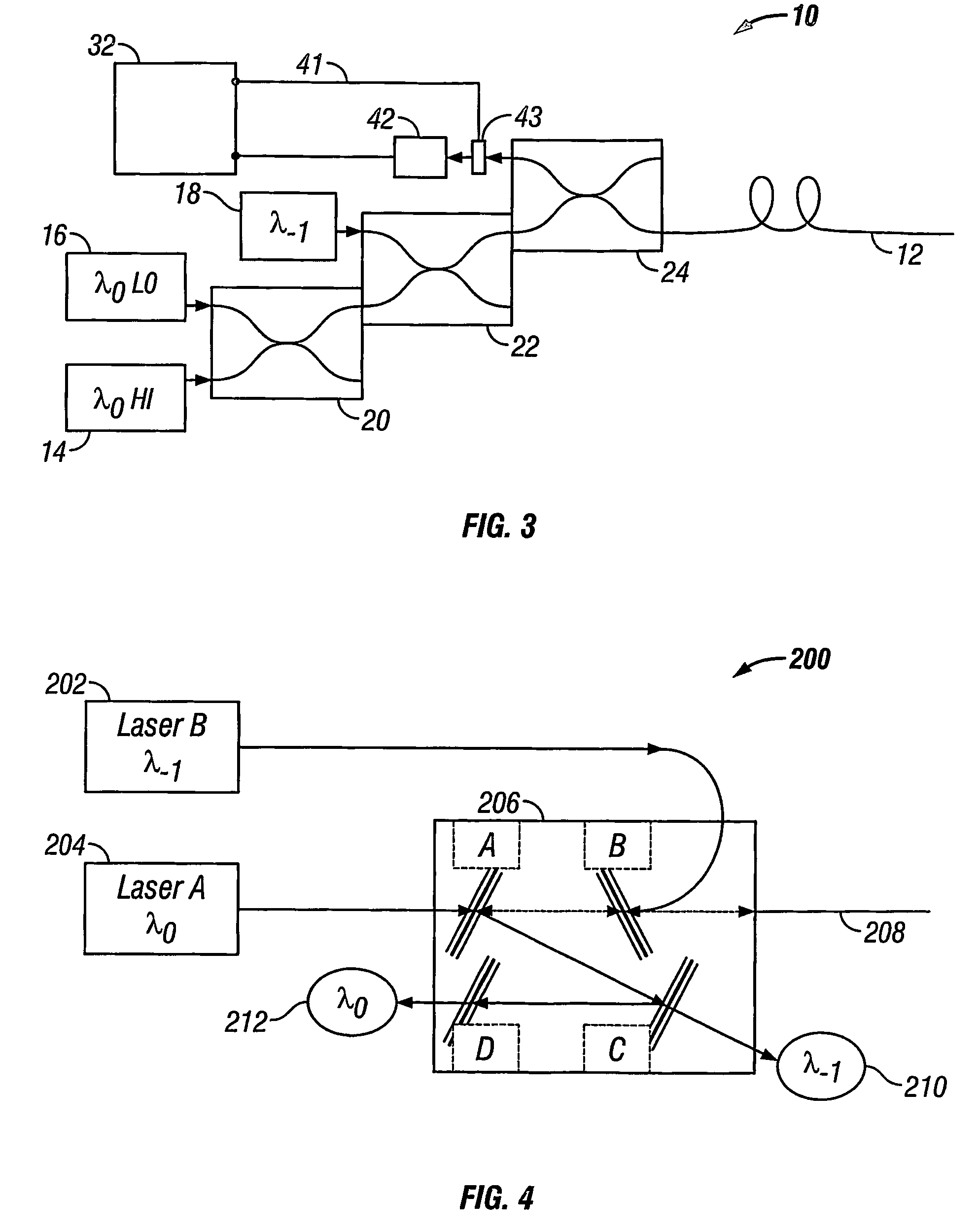
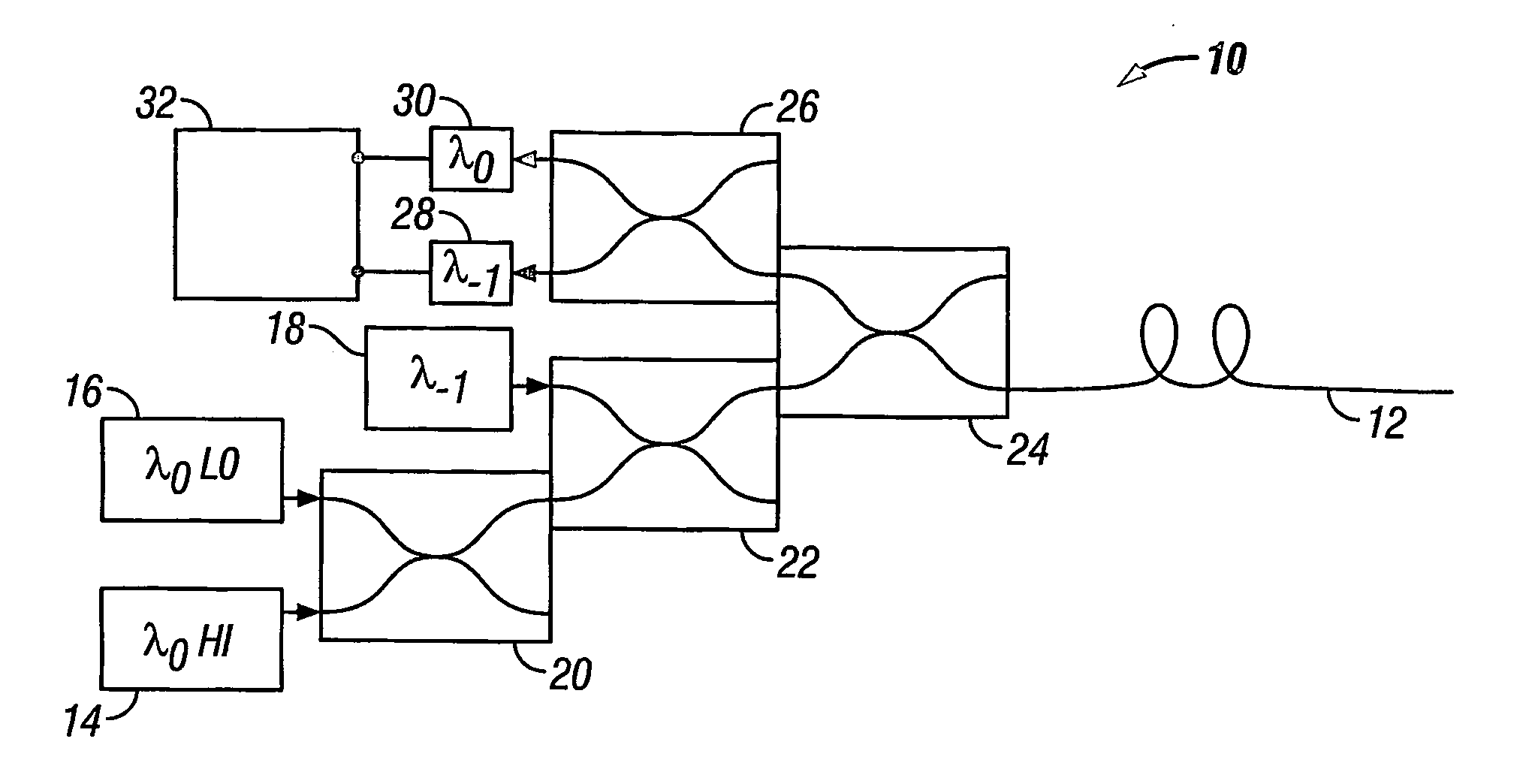
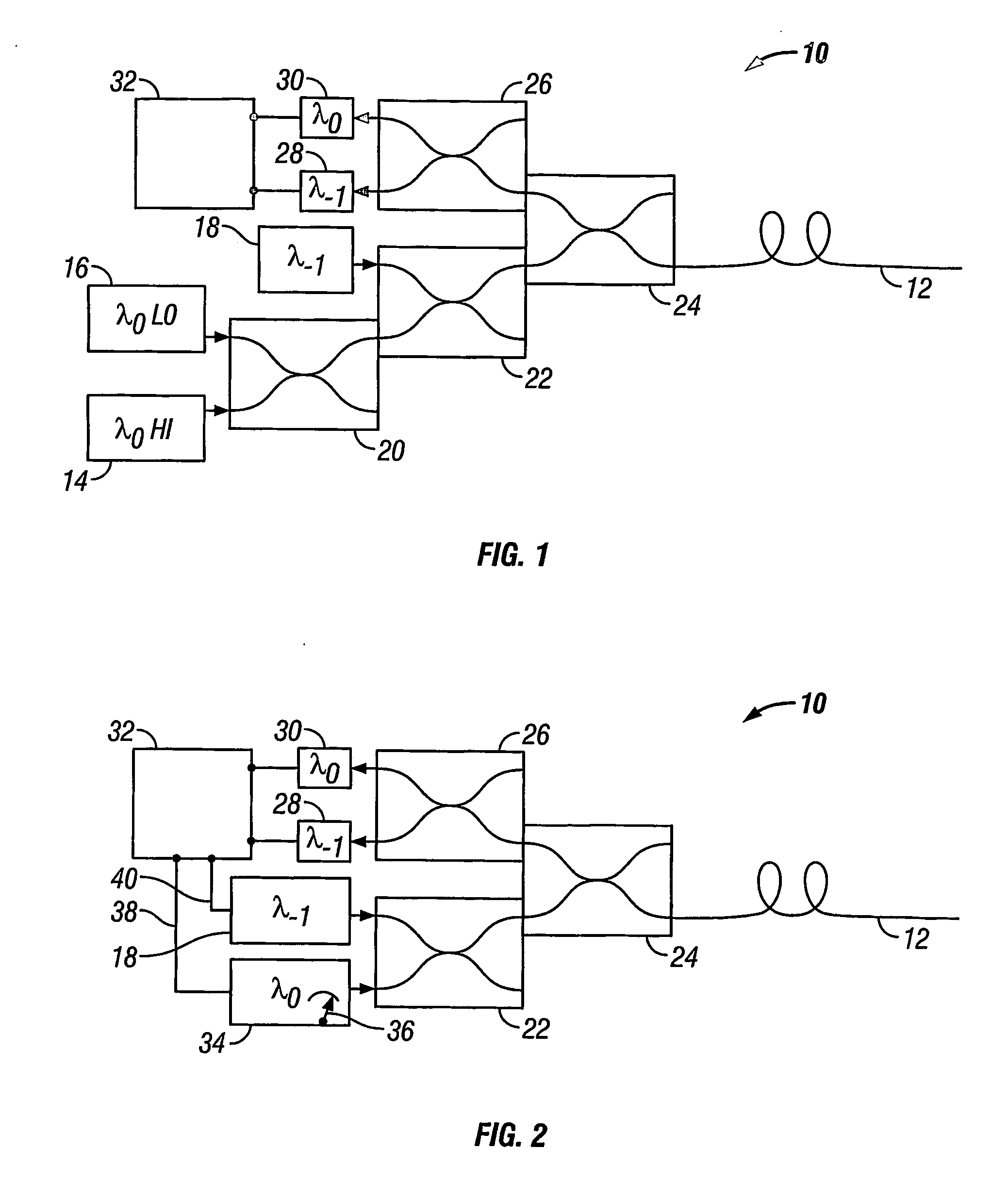
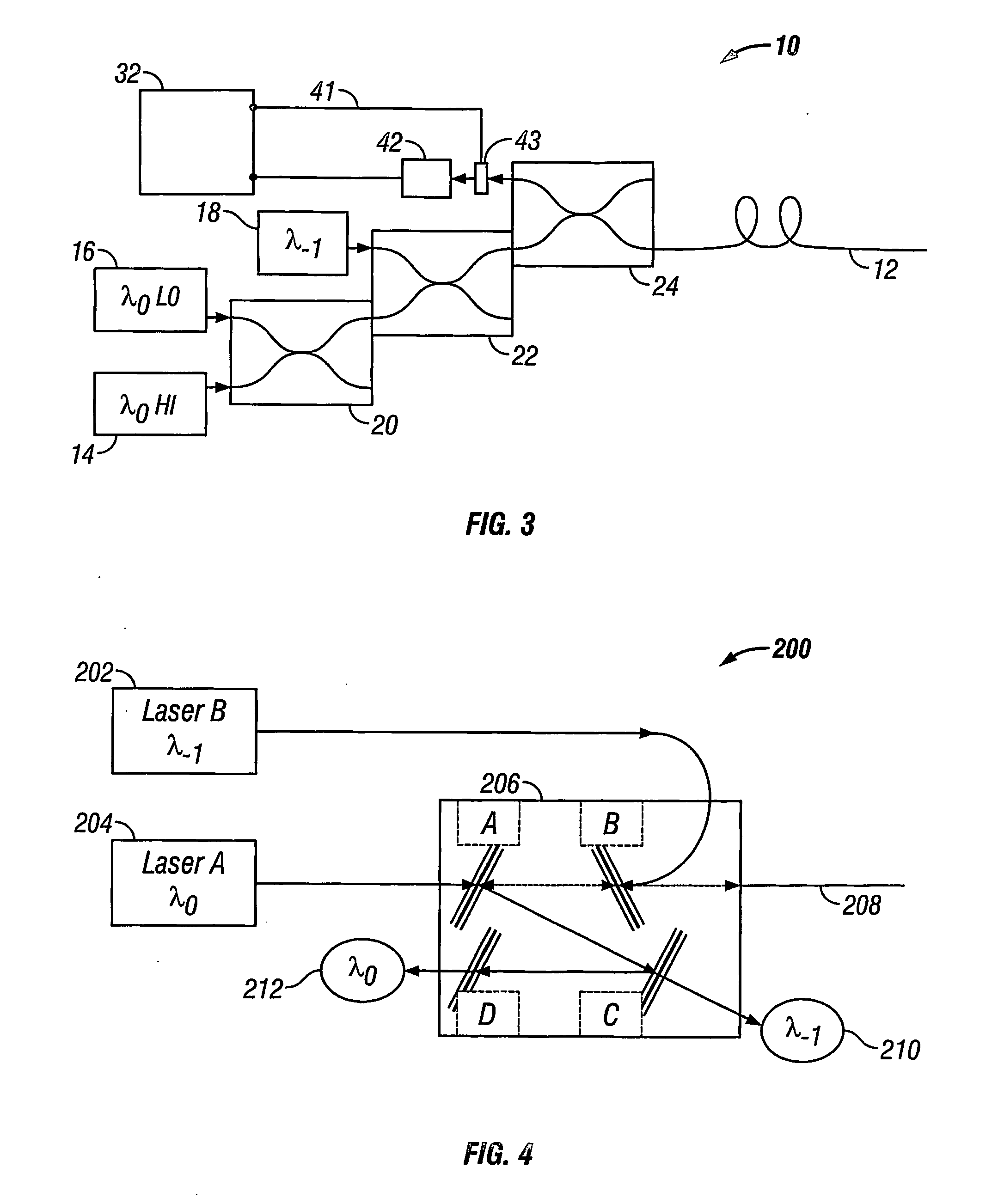
A method of obtaining a distributed measurement comprises deploying an optical fibre in a measurement region of interest, and launching into it a first optical signal at a first wavelength λ0 and a high power level, a second optical signal at a second wavelength λ−1, and a third optical signal at the first wavelength λ0 and a low power level. These optical signals generate backscattered light at the second wavelength λ−1 arising from Raman scattering of the first optical signal which is indicative of a parameter to be measured, at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the first optical signal, at the second wavelength λ—1 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the second optical signal, and at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the third optical signal. The backscattered light is detected to generate four output signals, and a final output signal is derived by normalising the Raman scattering signal to a function derived from the three Rayleigh scattering signals, which removes the effects of wavelength-dependent and nonlinear loss.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Distributed optical fiber sensor
ActiveUS20110228255A1Improve spatial resolutionPolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
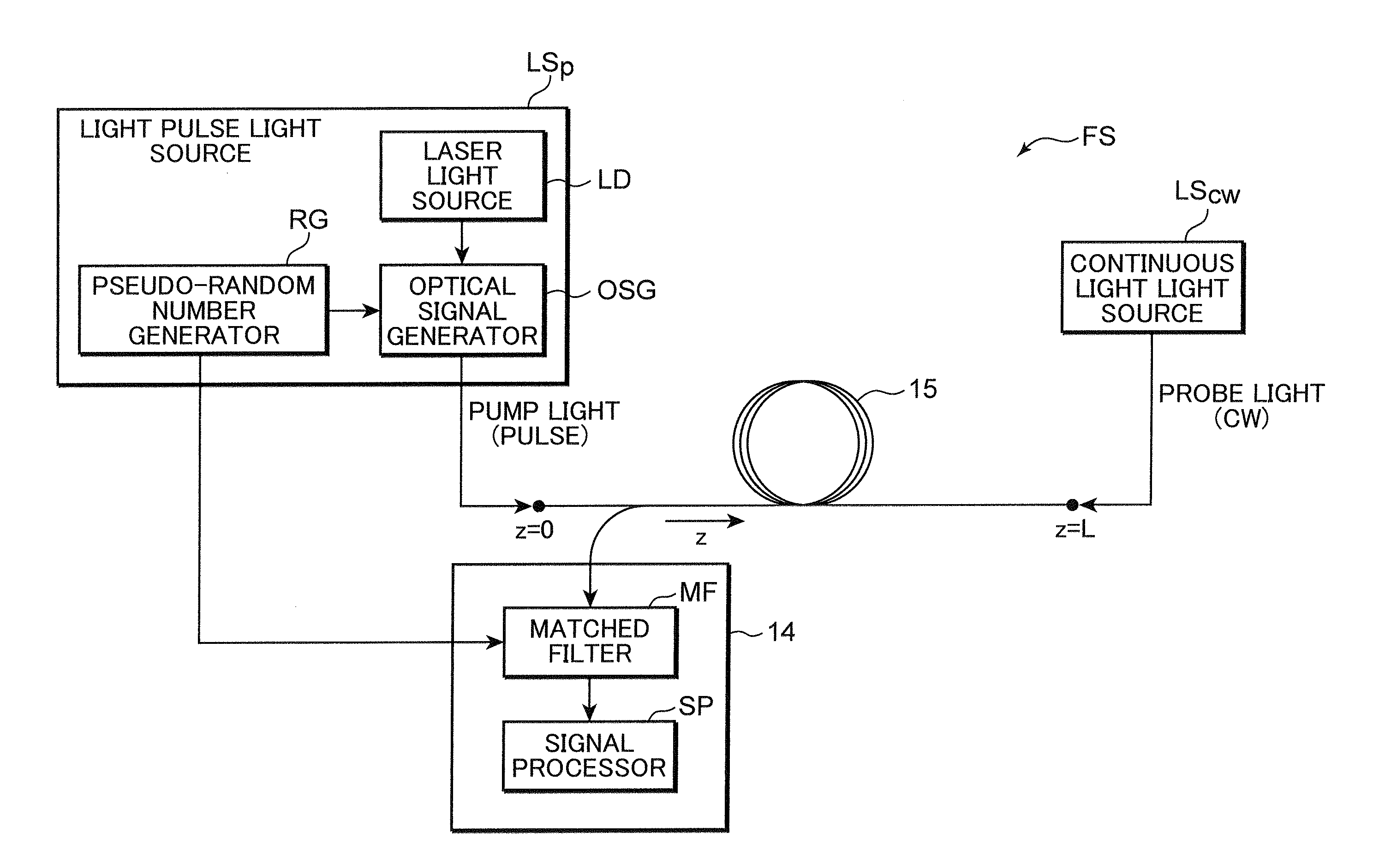
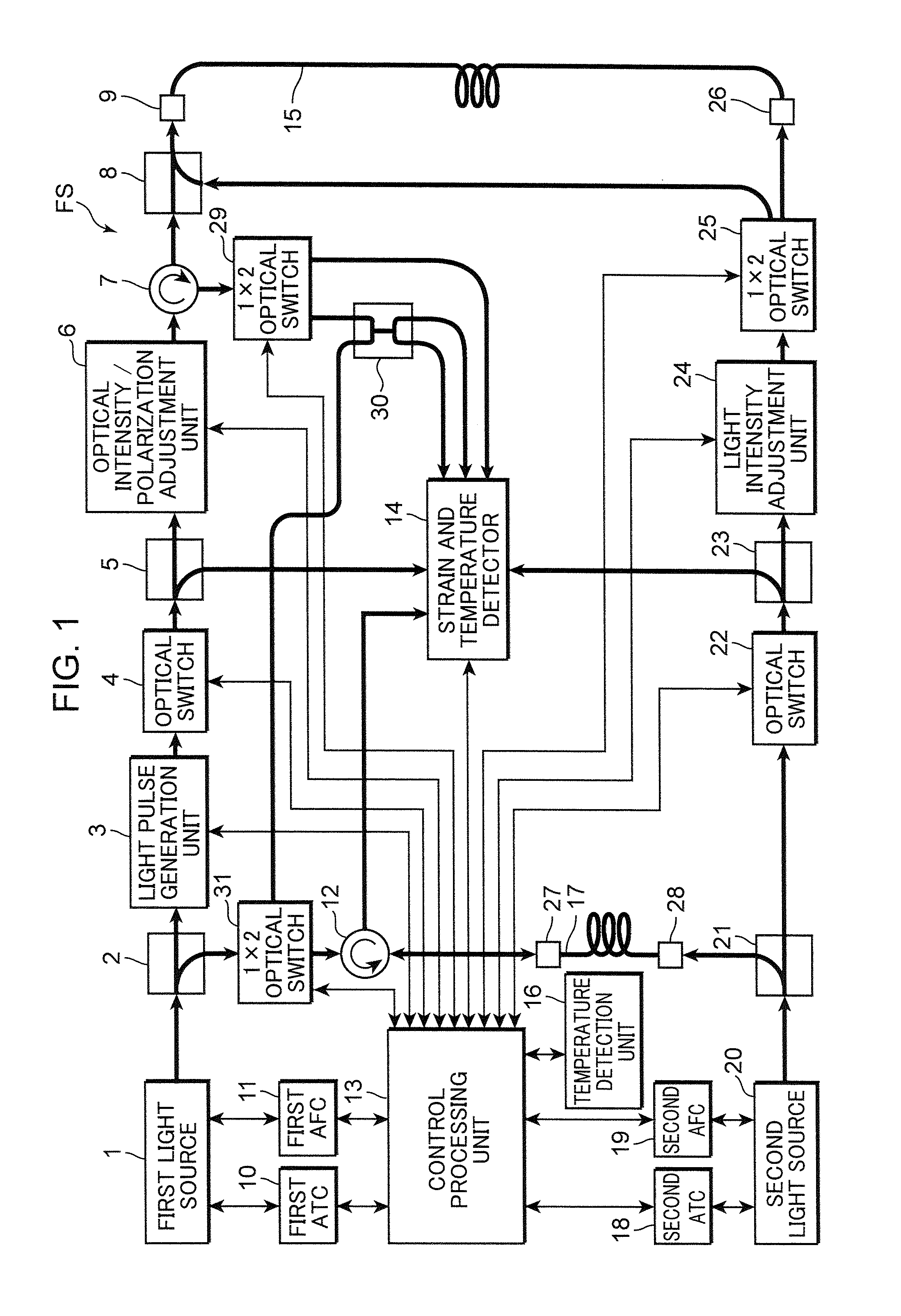
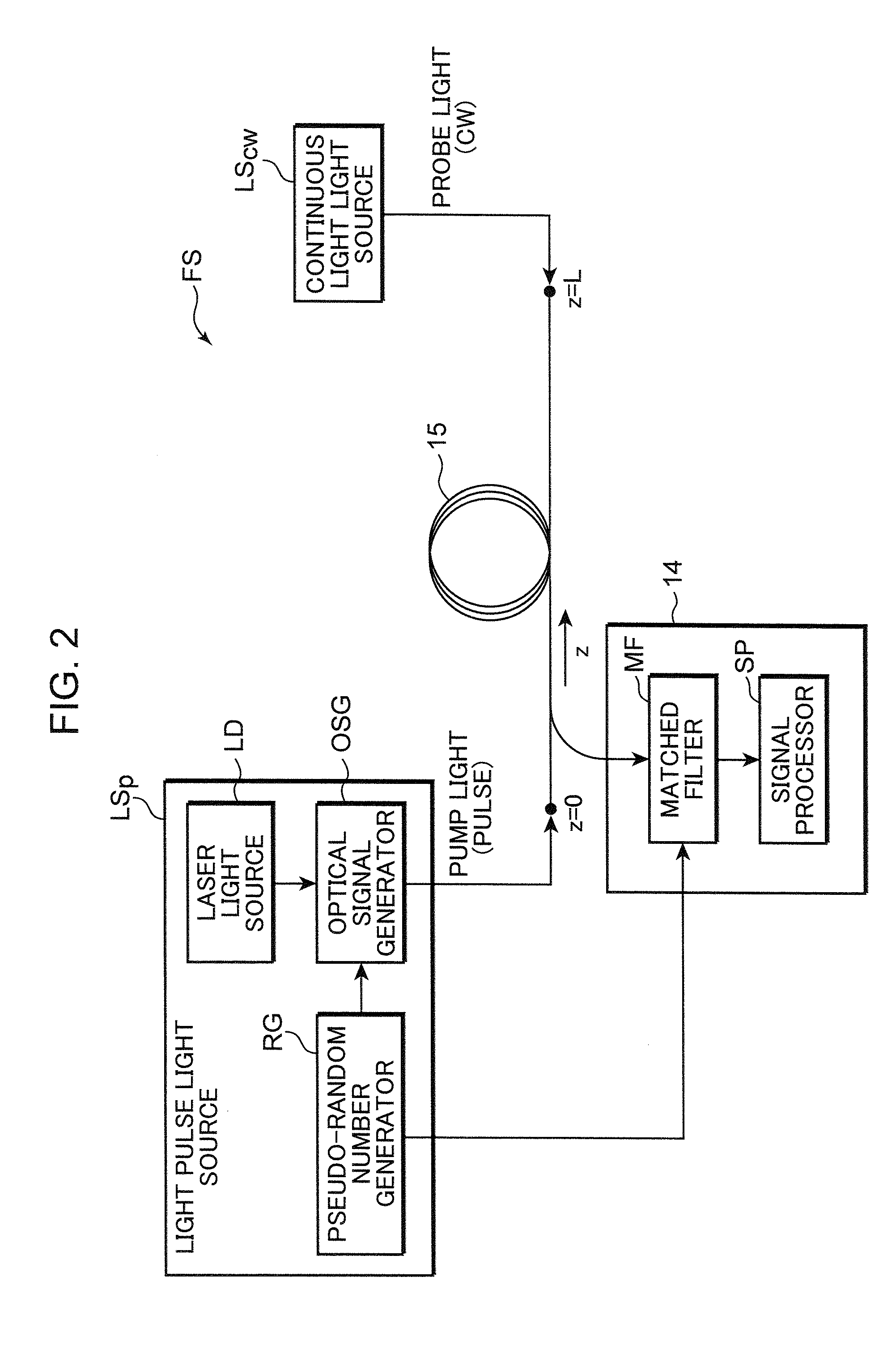
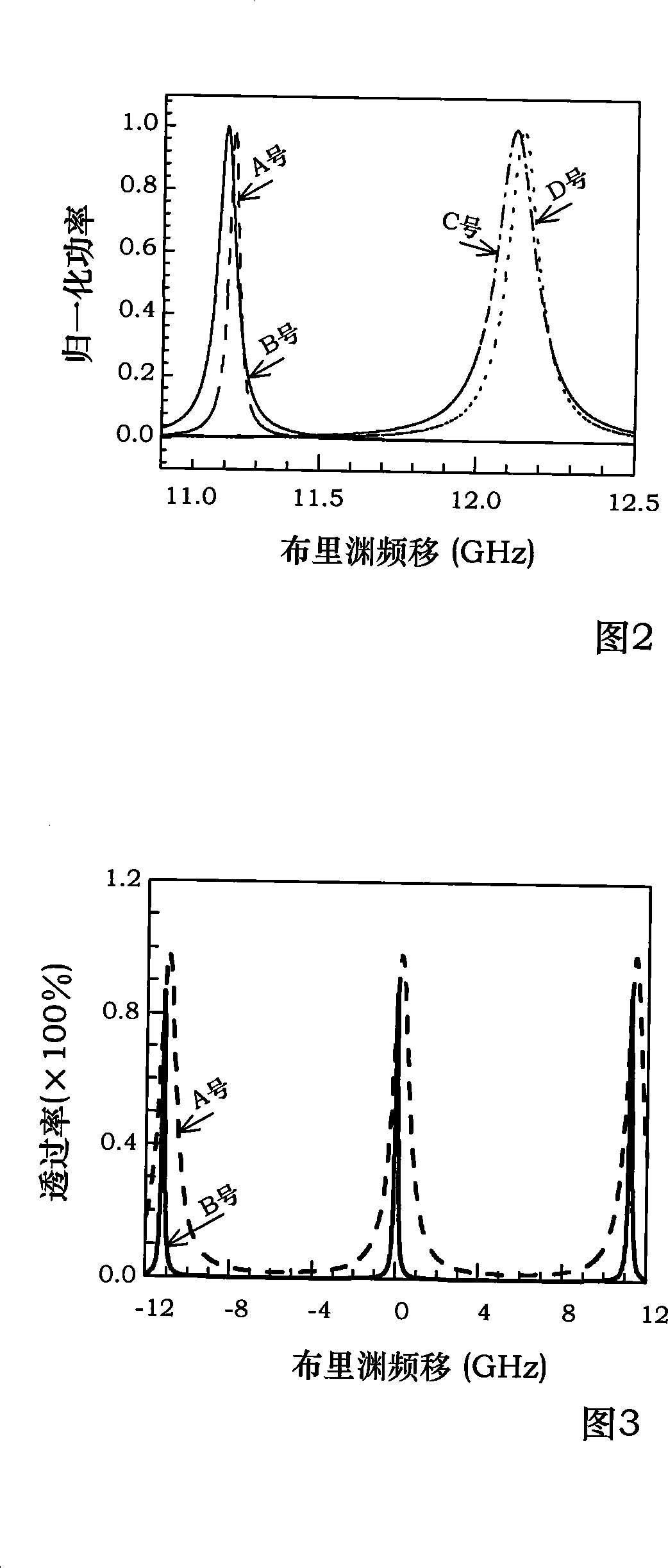
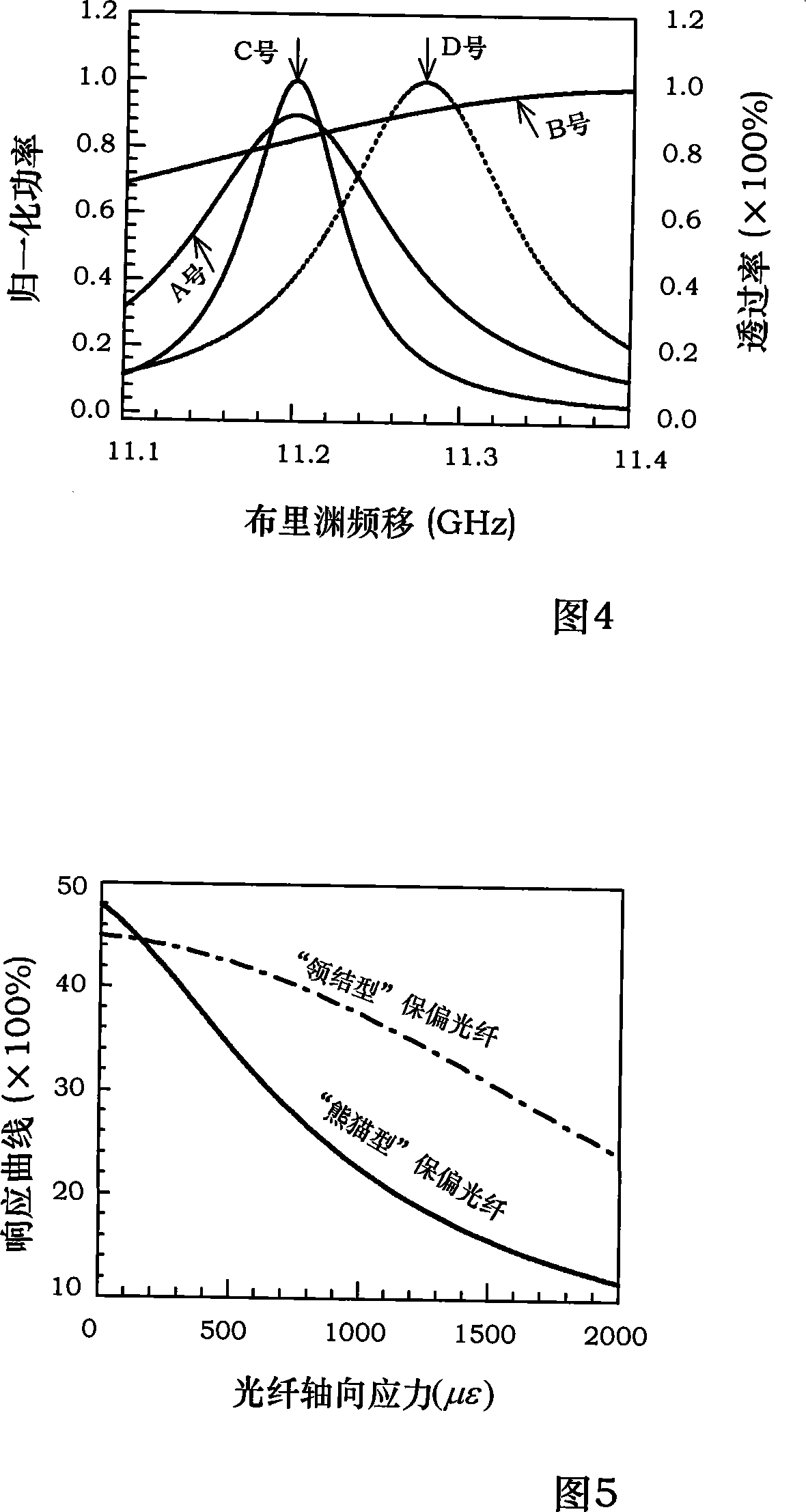
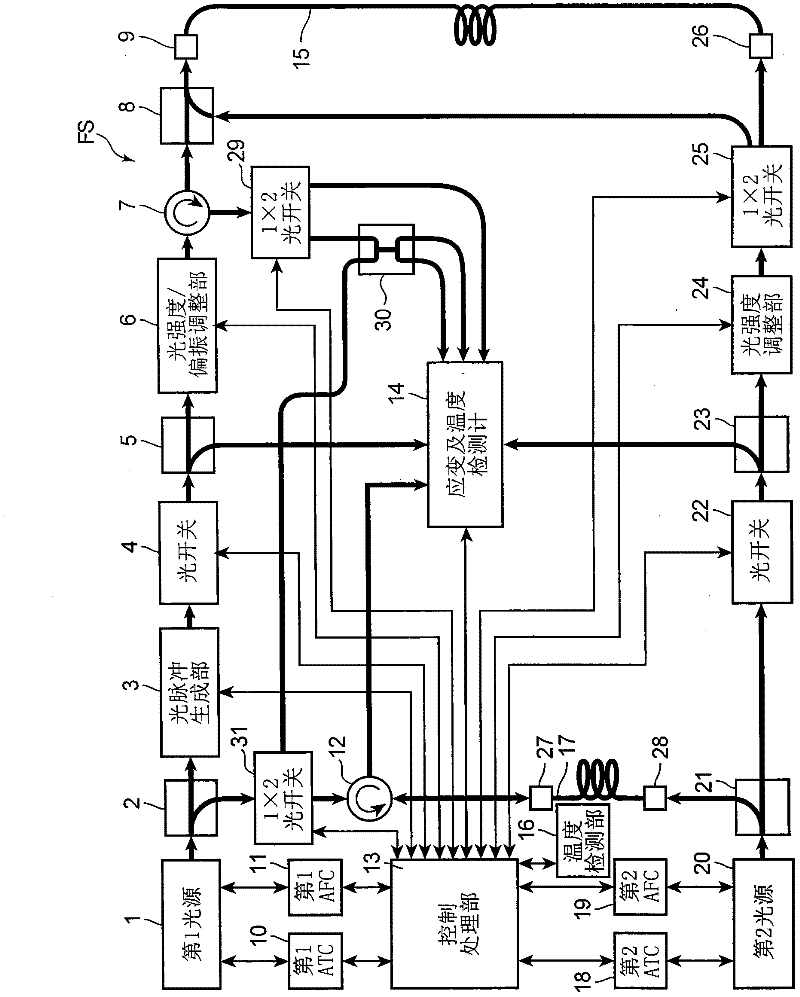
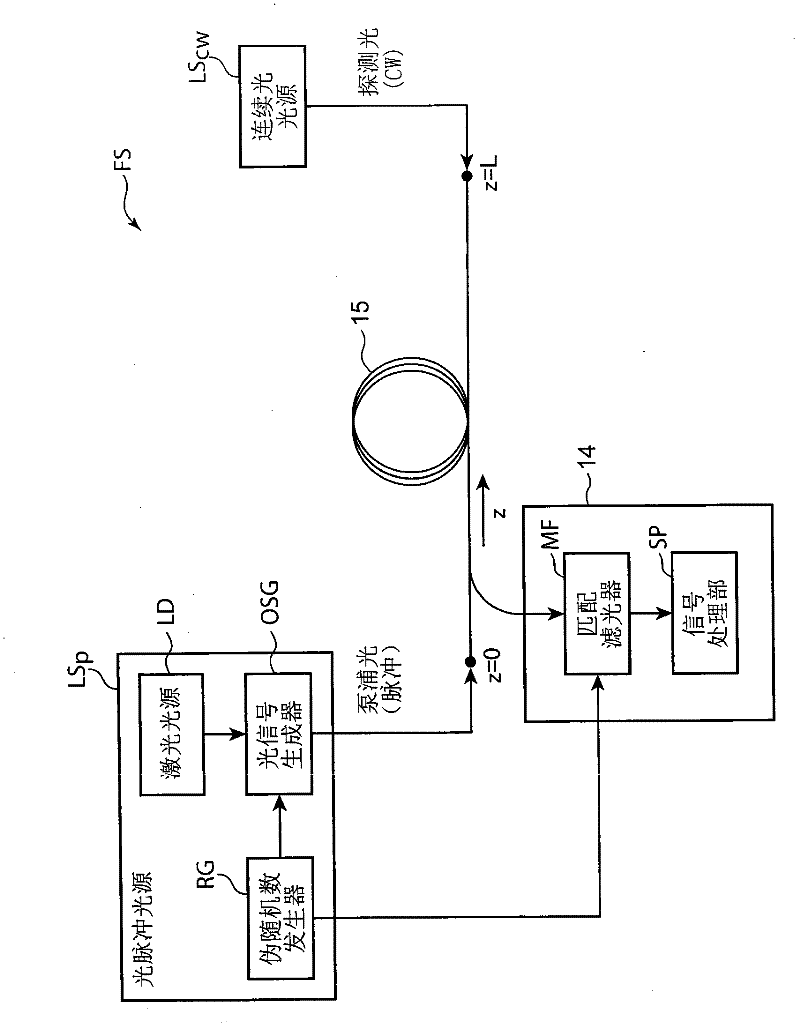
The present invention provides a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor FS is a distributed optical fiber sensor which uses an optical fiber 15 as a sensor, and a strain and temperature detector 14 measures a Brillouin frequency shift amount caused by a strain and a temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures a Rayleigh frequency shift amount caused by the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 from the measured Brillouin frequency shift amount and Rayleigh frequency shift amount.
Owner:NEUBREX
Calculation of birefringence in a waveguide based on Rayleigh scatter
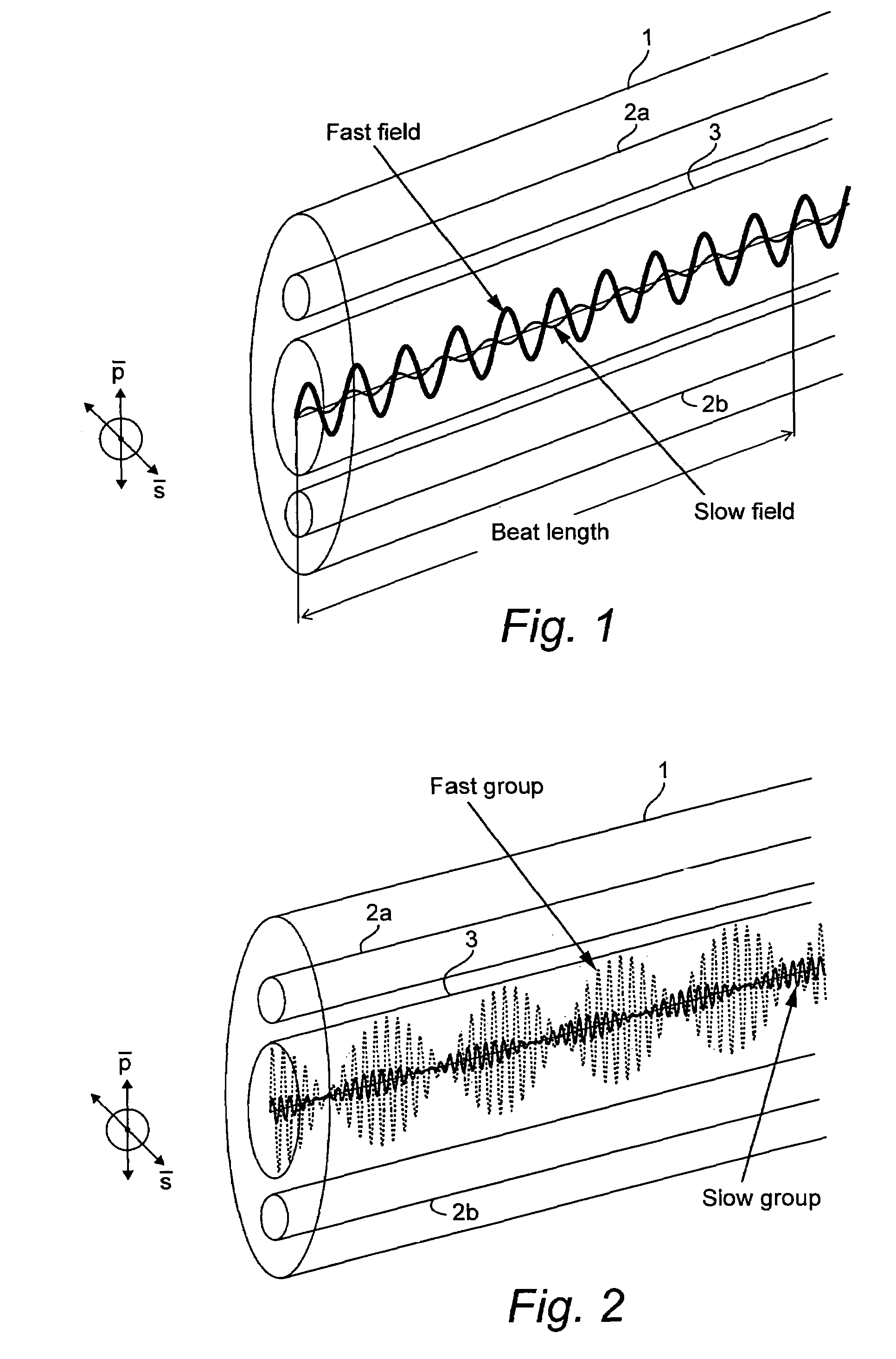
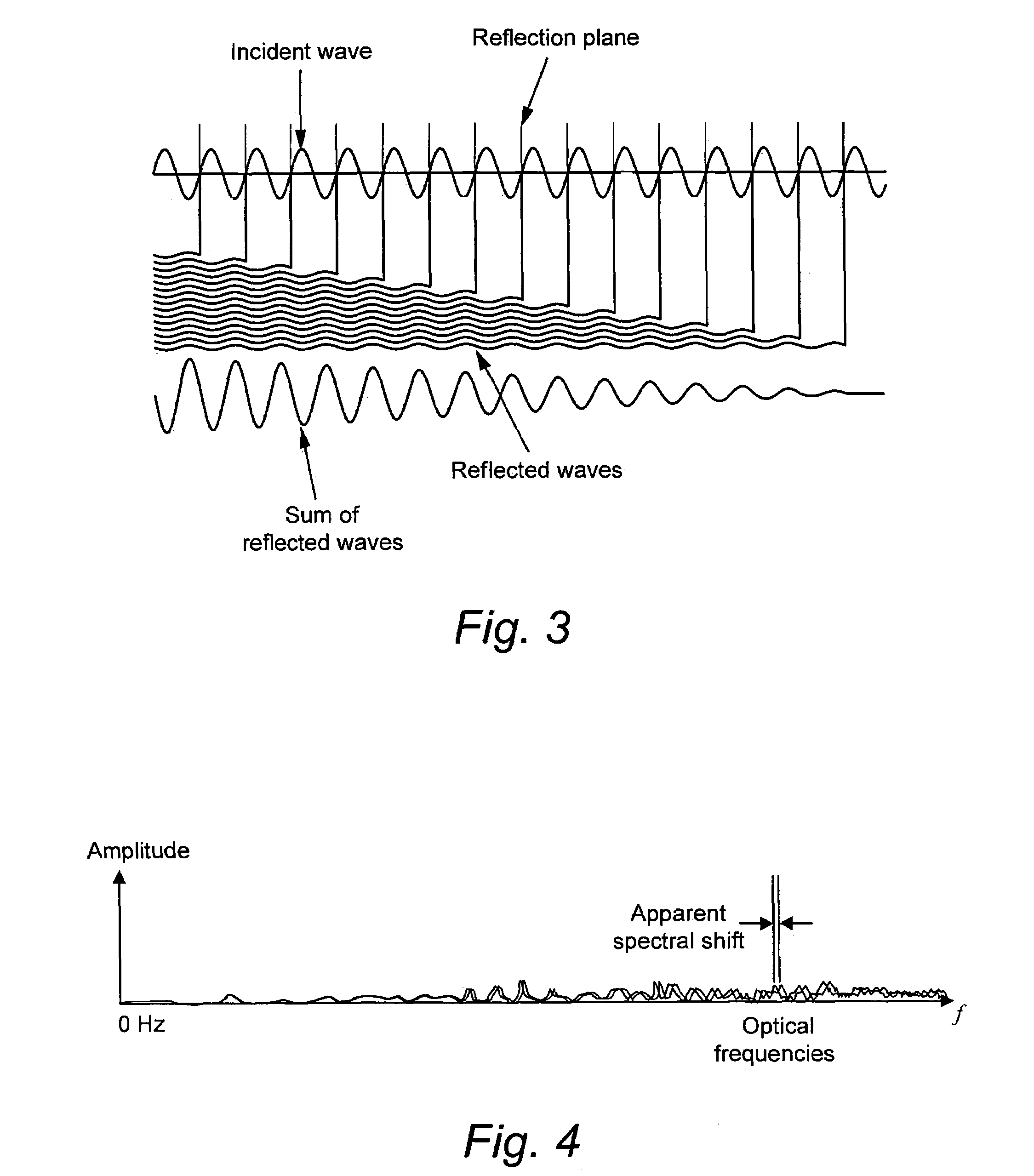
ActiveUS7330245B2Reflectometers dealing with polarizationCladded optical fibreRayleigh scatteringSpectral response
Light is coupled into two polarization modes of a waveguide, e.g., an optical fiber. The spectral response of Rayleigh backscatter in the waveguide segment for the two polarization modes is measured, e.g., using OFDR, OTDR, OLCR, etc. The autocorrelation of the spectral response is calculated. The spectral (wavelength) shift from a main autocorrelation peak to a side autocorrelation peak, corresponding to one of the two polarization modes of the waveguide segment, is determined. The spectral shift, corresponding to a beat length of the waveguide segment, is multiplied by an average index of refraction to determine a birefringence of the waveguide segment.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
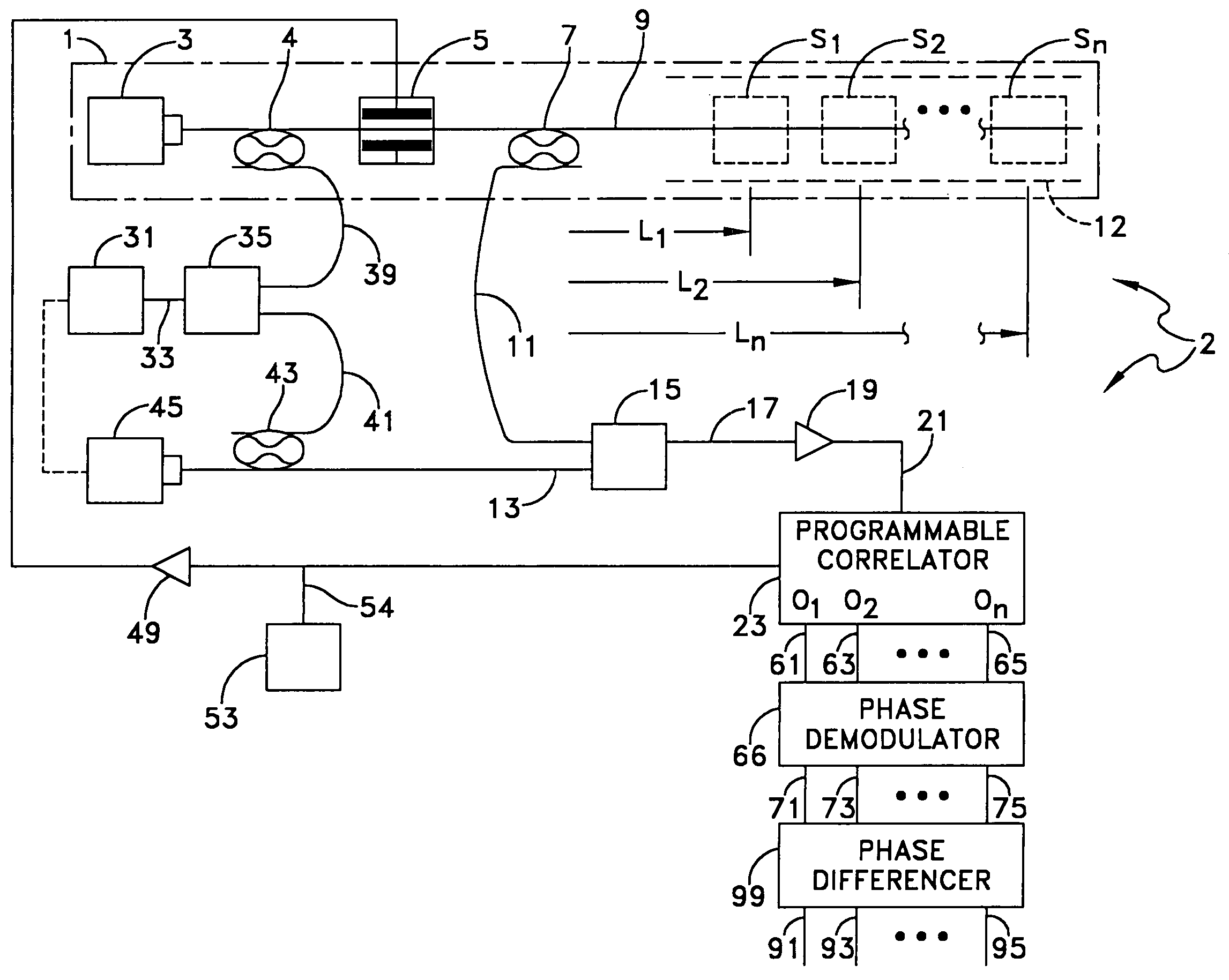
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Power monitor for optical fiber using background scattering
InactiveUS20140313513A1Scattering properties measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
An optical power monitoring device includes a photodetector disposed in close proximity to the cladding of an optical fiber for measuring Rayleigh scattered light from the core of the optical fiber. To ensure only Rayleigh scattered light is measured, a cladding stripper is provided to remove any cladding light prior taking a reading with the photodetector.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
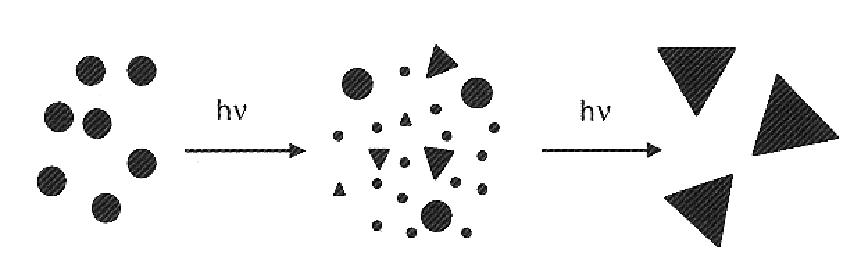
Nanoprisms and method of making them
InactiveUS7135054B2Stable maintenanceAvoid contactMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingOptical propertyRayleigh Light Scattering
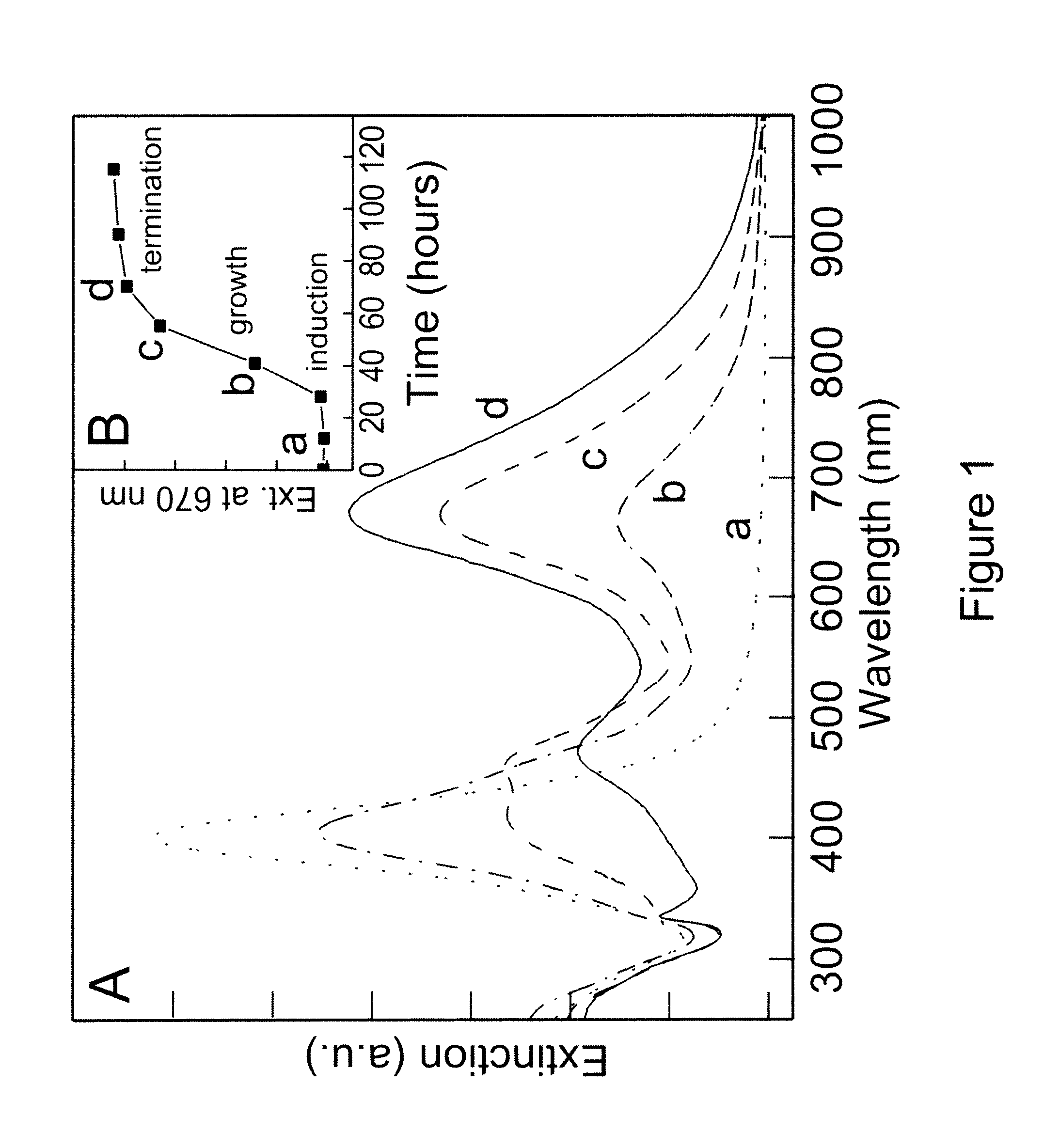
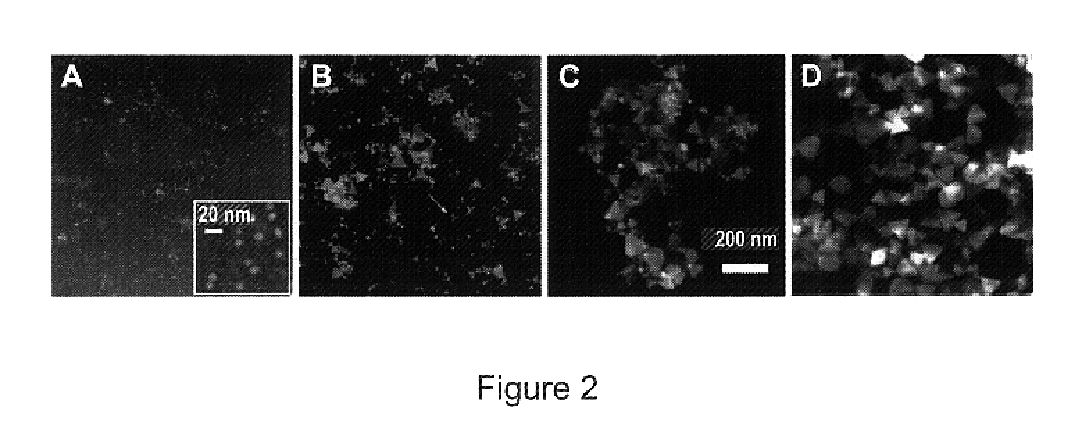
The invention is a novel photo-induced method for converting large quantities of silver nanospheres into nanoprisms, the nanoprisms formed by this method and applications in which the nanoprisms are useful. Significantly, this light driven process results in a colloid with a unique set of optical properties that directly relate to the nanoprism shape of the particles. Theoretical calculations coupled with experimental observations allow for the assignment of the nanoprism plasmon bands and the first identification of two distinct quadrupole plasmon resonances for a nanoparticle. Finally, unlike the spherical particles from which they derive and which Rayleigh light scatter in the blue, these nanoprisms exhibit scattering in the red, permitting multicolor diagnostic labels based not only on nanoparticle composition and size but also on shape.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Time correlation system and method
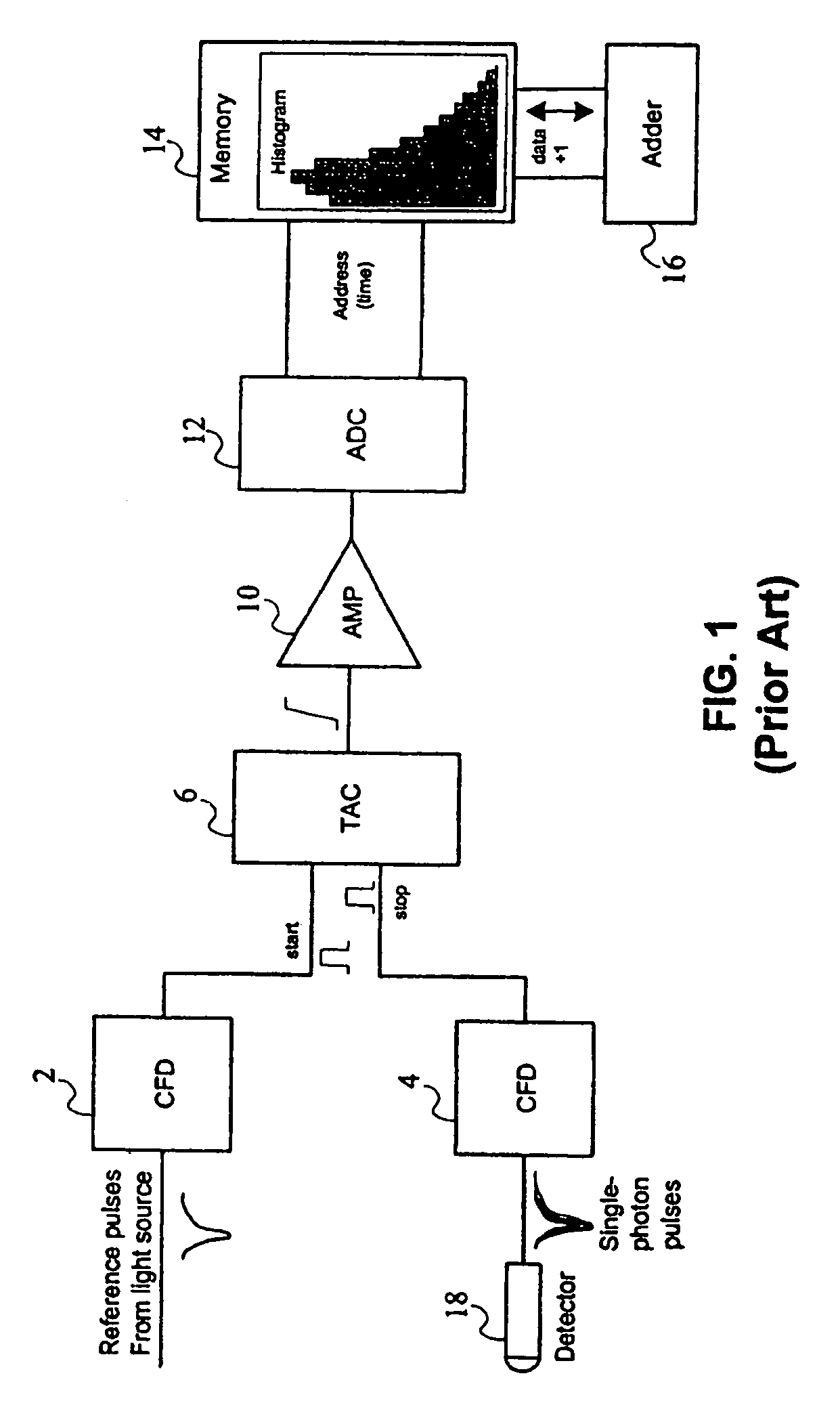
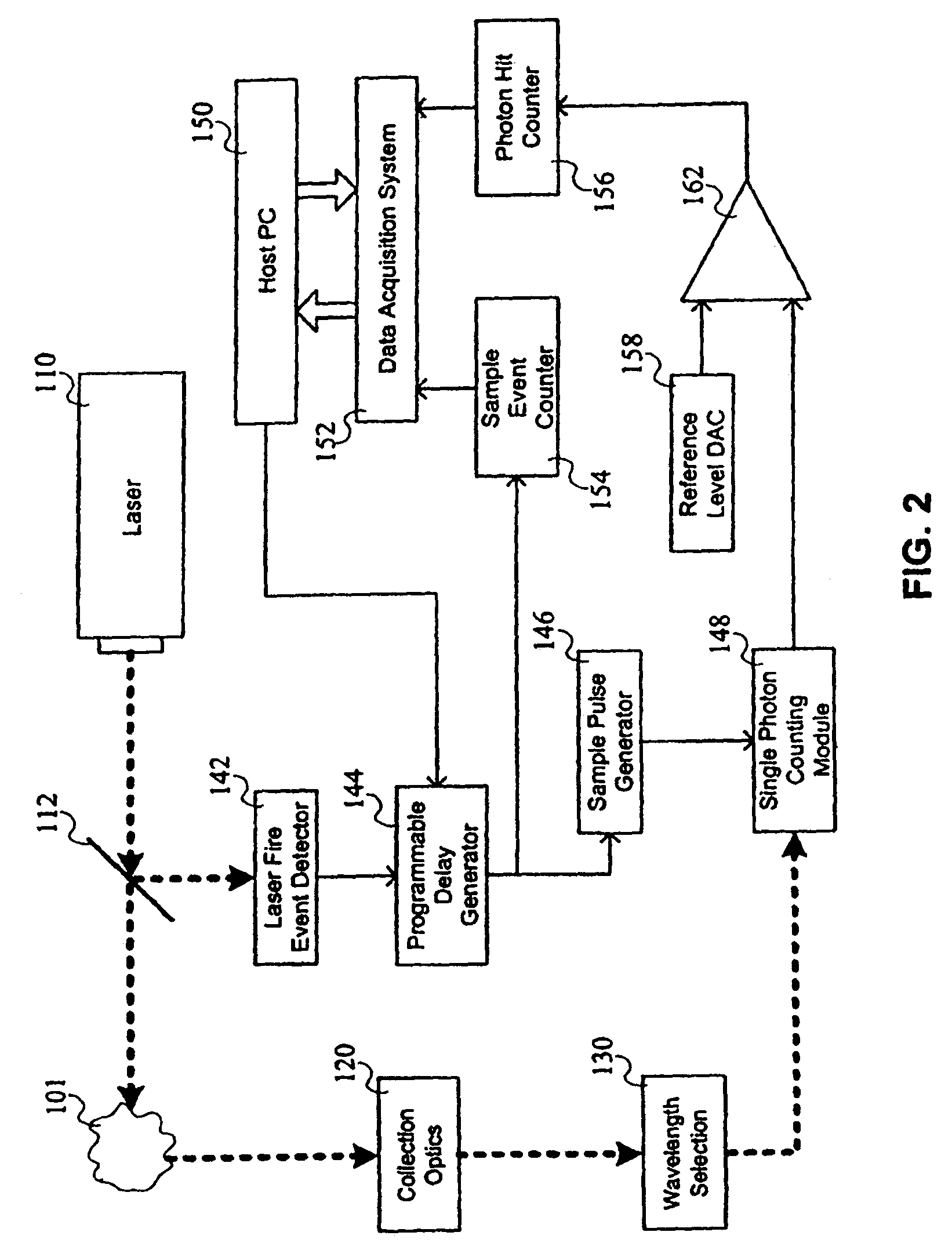
A time correlated single photon counting system having a programmable delay generator triggered by a laser fire event detector. The system may be used for chemical agent detection based on Rayleigh scattering using optical time domain reflectometry techniques. The system may also be used for Raman detection using frequency to time transformations.
Owner:OPTECH VENTURES
Optical fiber and method of making the same
InactiveUS20020044753A1Reduce transmission lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusRayleigh scatteringFiber
An optical fiber preform 2 having a viscosity ratio Reta=eta0 / etat of 2.5 or less between the core average viscosity eta0 and the total average viscosity etat is prepared, and is drawn by a drawing furnace 11 so as to yield an optical fiber 3, which is then heated to a temperature within a predetermined range so as to be annealed by a heating furnace 21 disposed downstream the drawing furnace 11. Here, upon annealing in the heating furnace 21, the fictive temperature Tf within the optical fiber lowers, thereby reducing the Rayleigh scattering loss. At the same time, the viscosity ratio condition of Reta<=2.5 restrains the stress from being concentrated into the core, thereby lowering the occurrence of structural asymmetry loss and the like. Hence, anoptical fiber which can reduce the transmission loss caused by the Rayleigh scattering loss and the like as a whole, and a method of making the same can be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Distributed optical fiber sensing system for measuring temperature, strain and vibration simultaneously
ActiveCN107917738ADemodulation frequencyReduce intensityConverting sensor output opticallyMultiplexingRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber sensing system for measuring temperature, strain and vibration simultaneously. Based on an Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (ODTR) multiplexing technology, optical time-division multiplexing unequal-width dipulse serves as detection light, coherent detection technologies of Brillouin scattering signals and Rayleigh scattering signals are merged,and a set of distributed optical fiber sensing system which can conduct single-ended measuring on the temperature, strain and vibration is achieved; meanwhile, the measuring range of the vibration frequency can reach the MHz level, and the problems are solved that a traditional ODTR system can only measure the temperature strain or the static strain while cannot timely respond to the dynamic change, or it is hard to measure the temperature strain and the static strain simultaneously, or the measurable range of the vibration frequency is limited by the length of sensing optical fiber. The distributed optical fiber sensing system can conduct single-ended measuring, and is simple in structure, easy to implement, and good in application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSTIY SUZHOU HIGH TECH INST
Spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device
ActiveCN103439254AImproving the Detection Capability of Micro-area Raman SpectroscopyHigh detection sensitivityRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging, and relates to a spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device, wherein a confocal microscopic technology and a Raman spectrum detecting technology are combined. A spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by using rayleigh scattering light discarded in confocal Raman spectrum detection, high-resolution imaging and detection of a three-dimensional geometric position of a sample are realized; and a spectrum detection system is controlled by using an extreme point of the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system to be capable of accurately capturing Raman spectrum information excited by a focusing point of an objective lens, and further spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum high-space-resolution imaging and detection of image and spectrum integration are realized. The spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device provide a new technical approach for high-space-resolution detection of the three-dimensional geometrical position and spectrum in a microcell, can be widely applied to the fields such as physics, chemistry, biomedicine, material science, environmental sciences, petrochemical engineering, geology, medicines, foods, criminal investigation and jewelry verification, and are capable of carrying out nondestructive identification and deep spectrum analysis of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
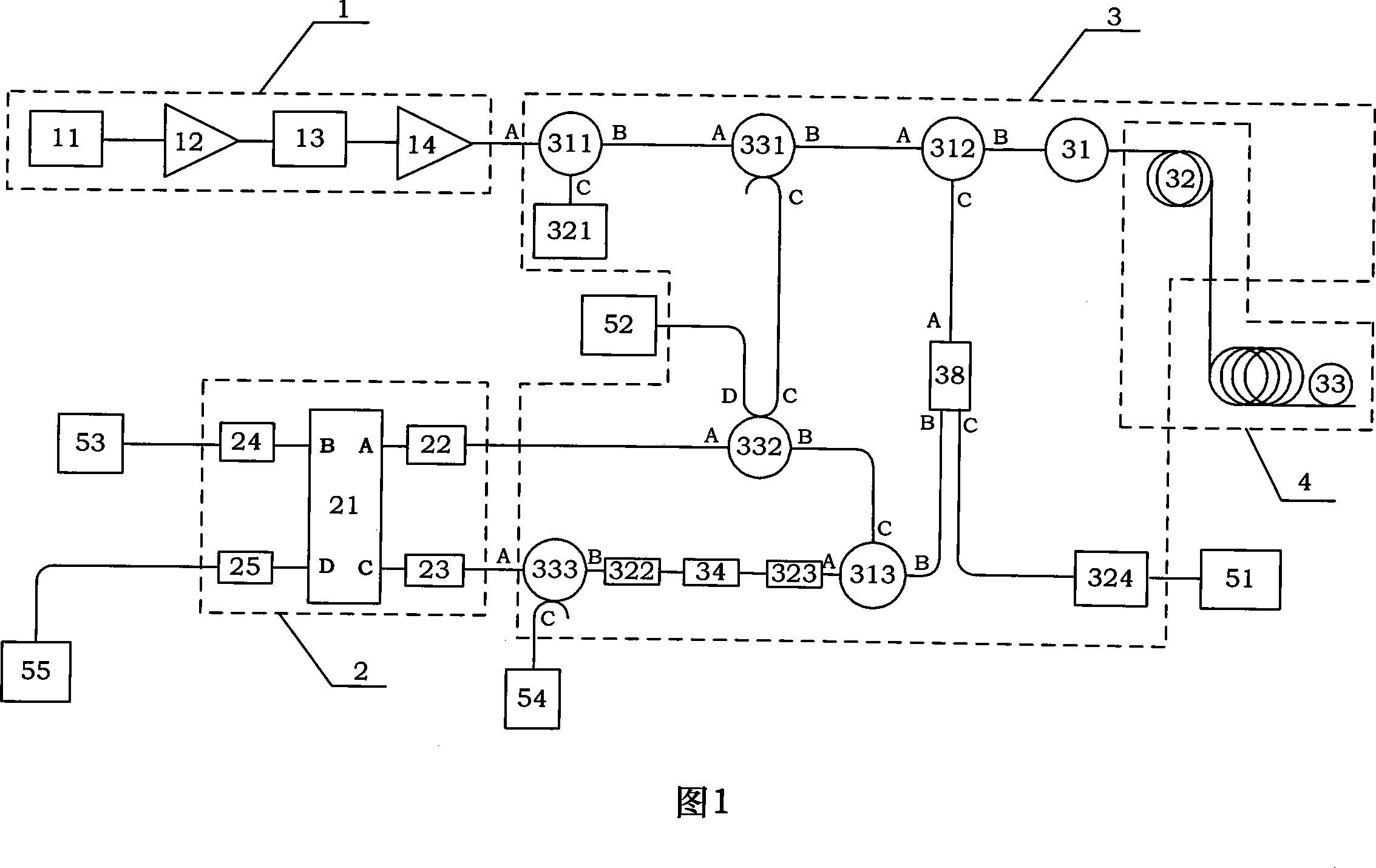
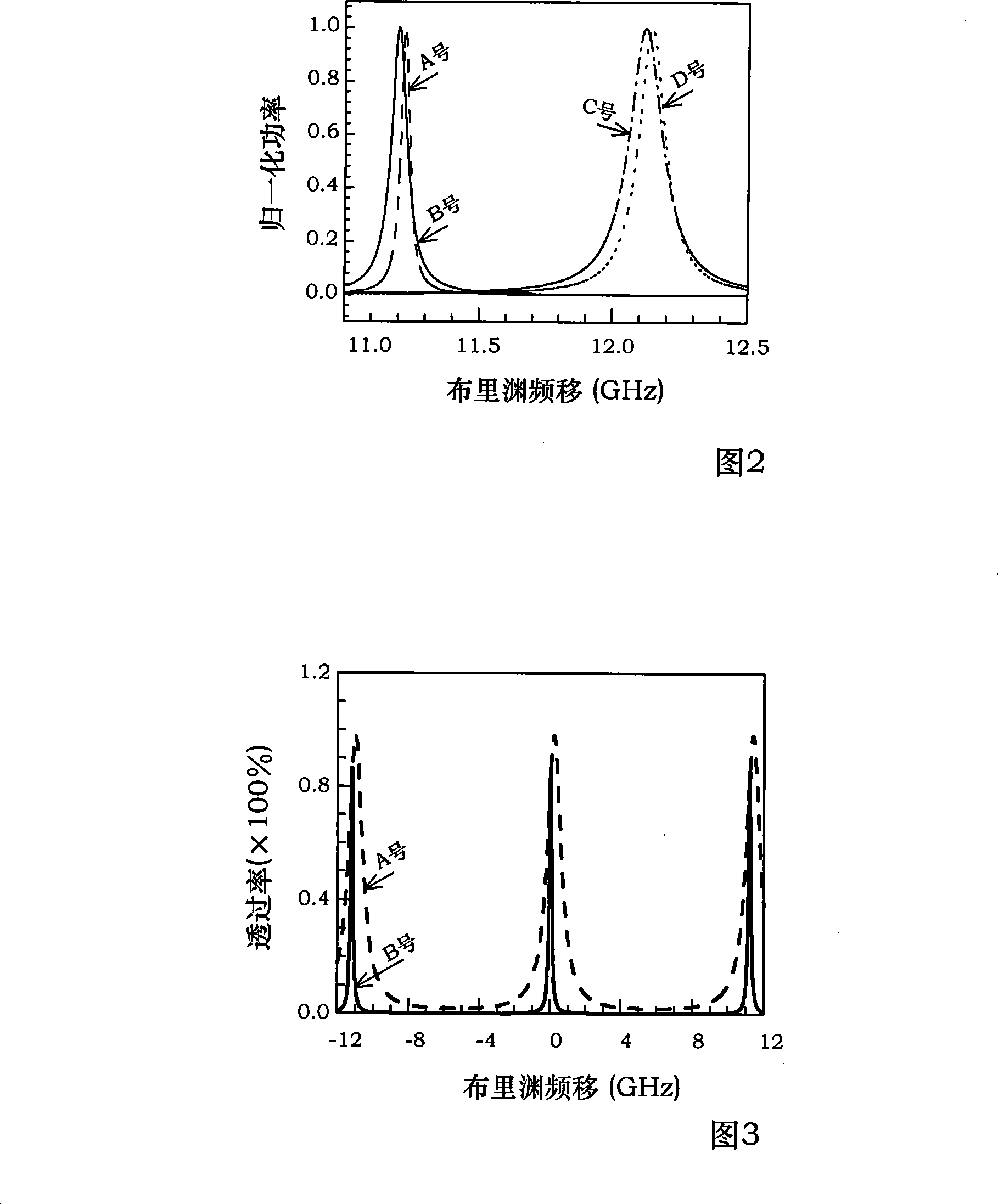
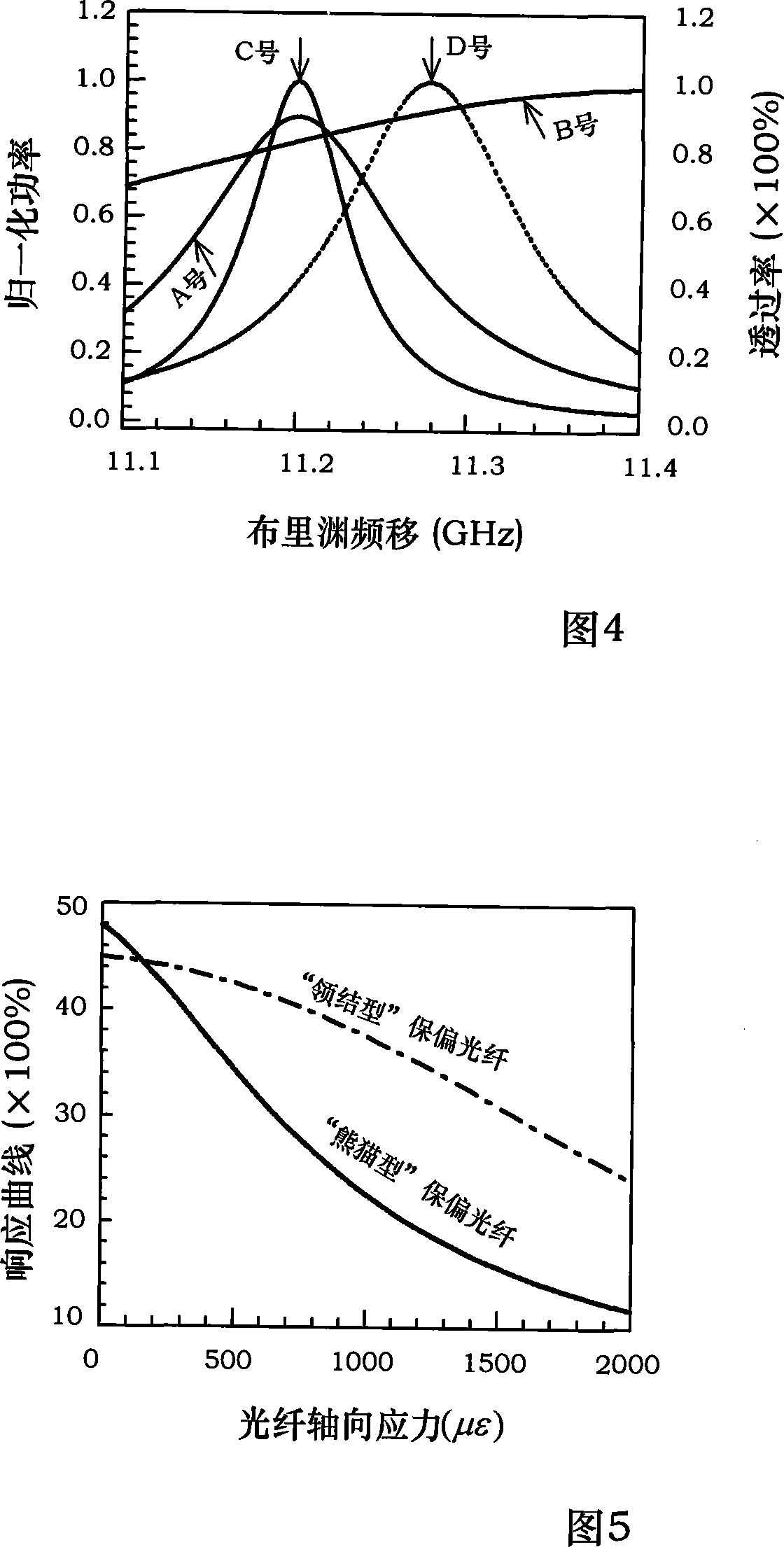
Optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
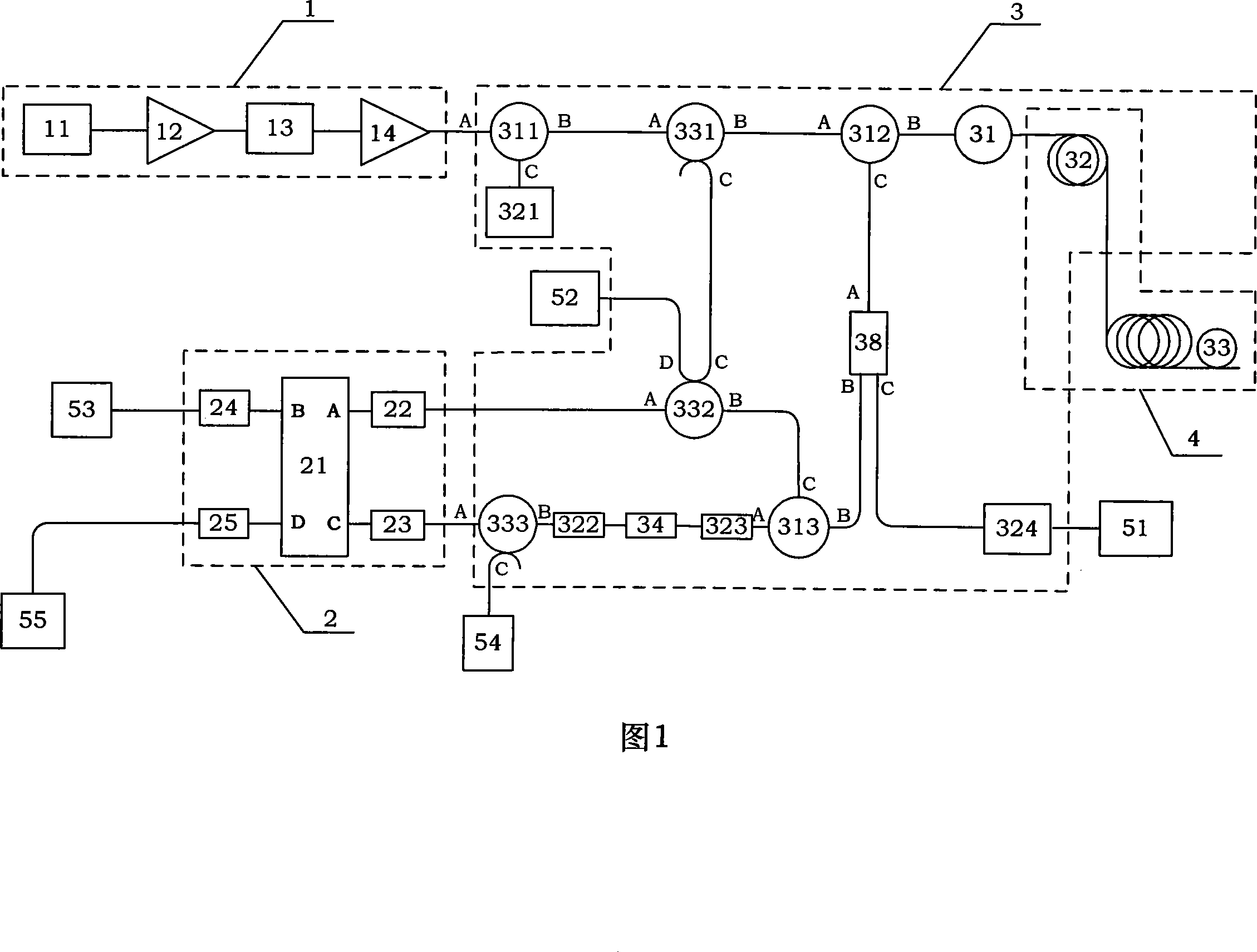
InactiveCN101158592AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolving Measurement Range IssuesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesObservational errorDiscriminator
The invention discloses a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress and mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to a frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of the frequency discrimination is not sensitive to frequency drift of the light source and fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Signal profiling for medical imaging systems
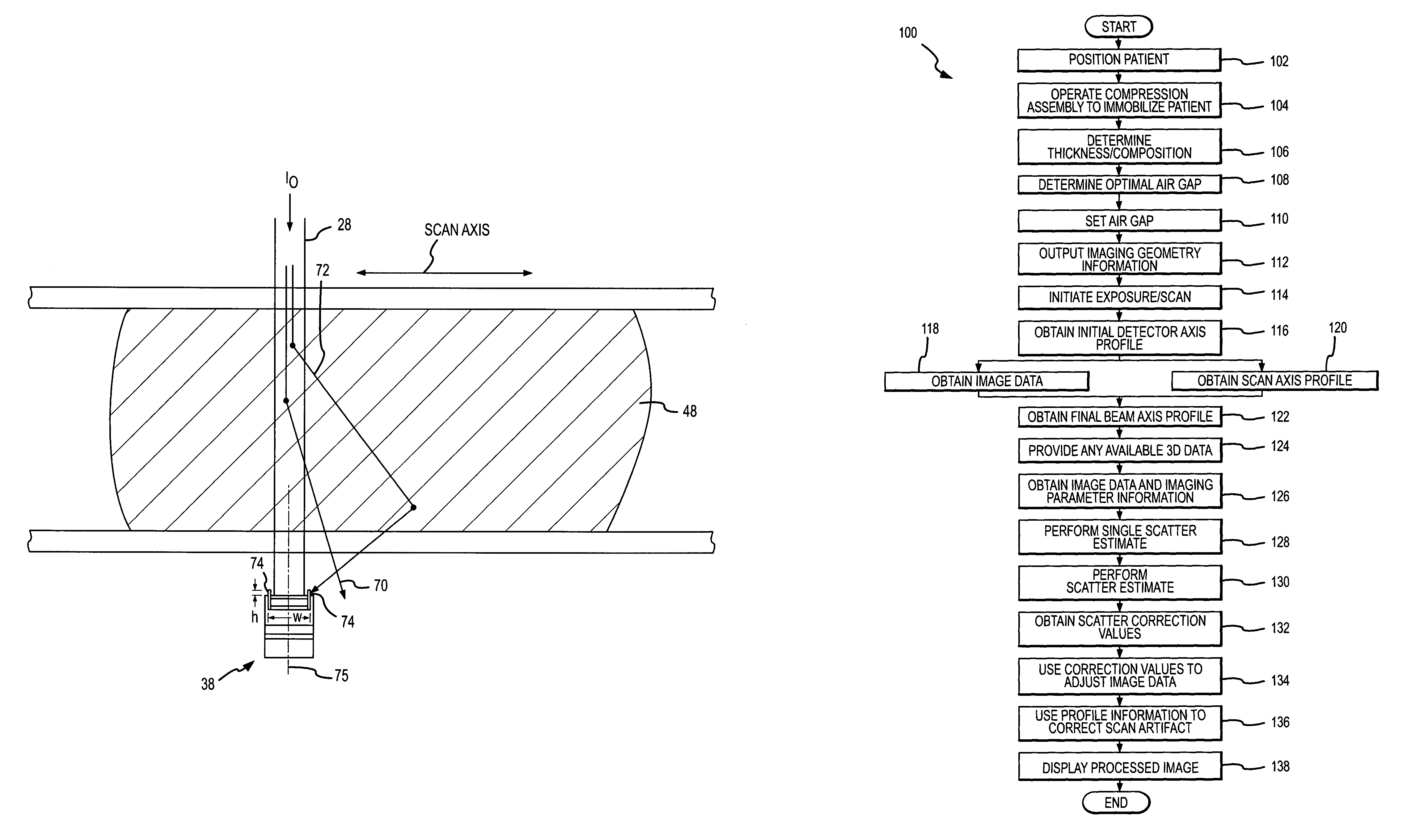
InactiveUS7092482B2Improved scatter compensationReduced scatter composite imaging informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsRayleigh scatteringScattering effect
Scatter effects are reduced in a radiographic imaging device, such as a digital slot scan mammographic imaging device, by reducing detected scatter and processing detector information to compensate for scatter effects. Spatial intensity profile information together with other imaging signal and patient dependent parameters can be used in image processing to estimate and compensate for various scatter effects including single and multiple scatters and Compton and Rayleigh scatter.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
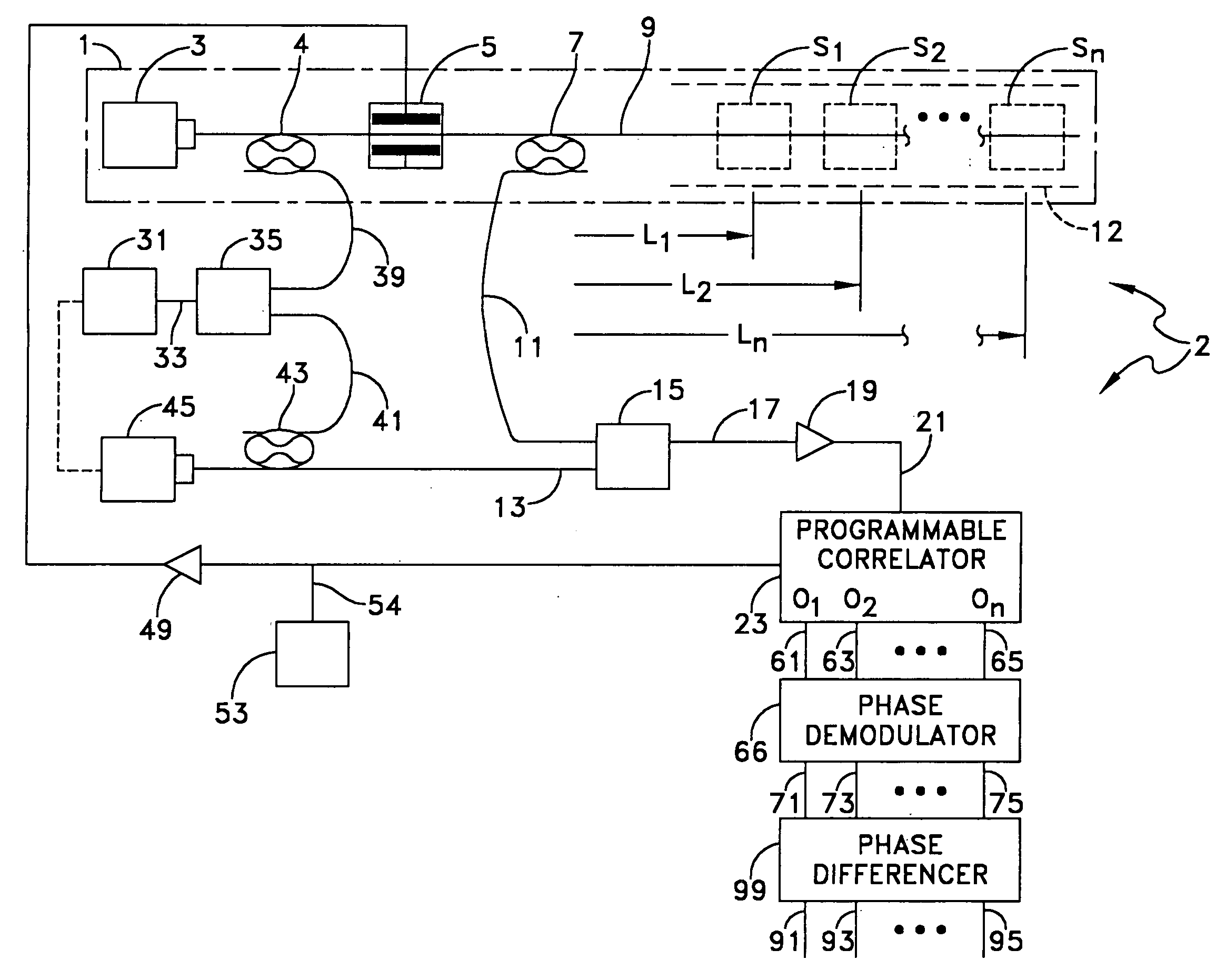
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual signal sensing array capability
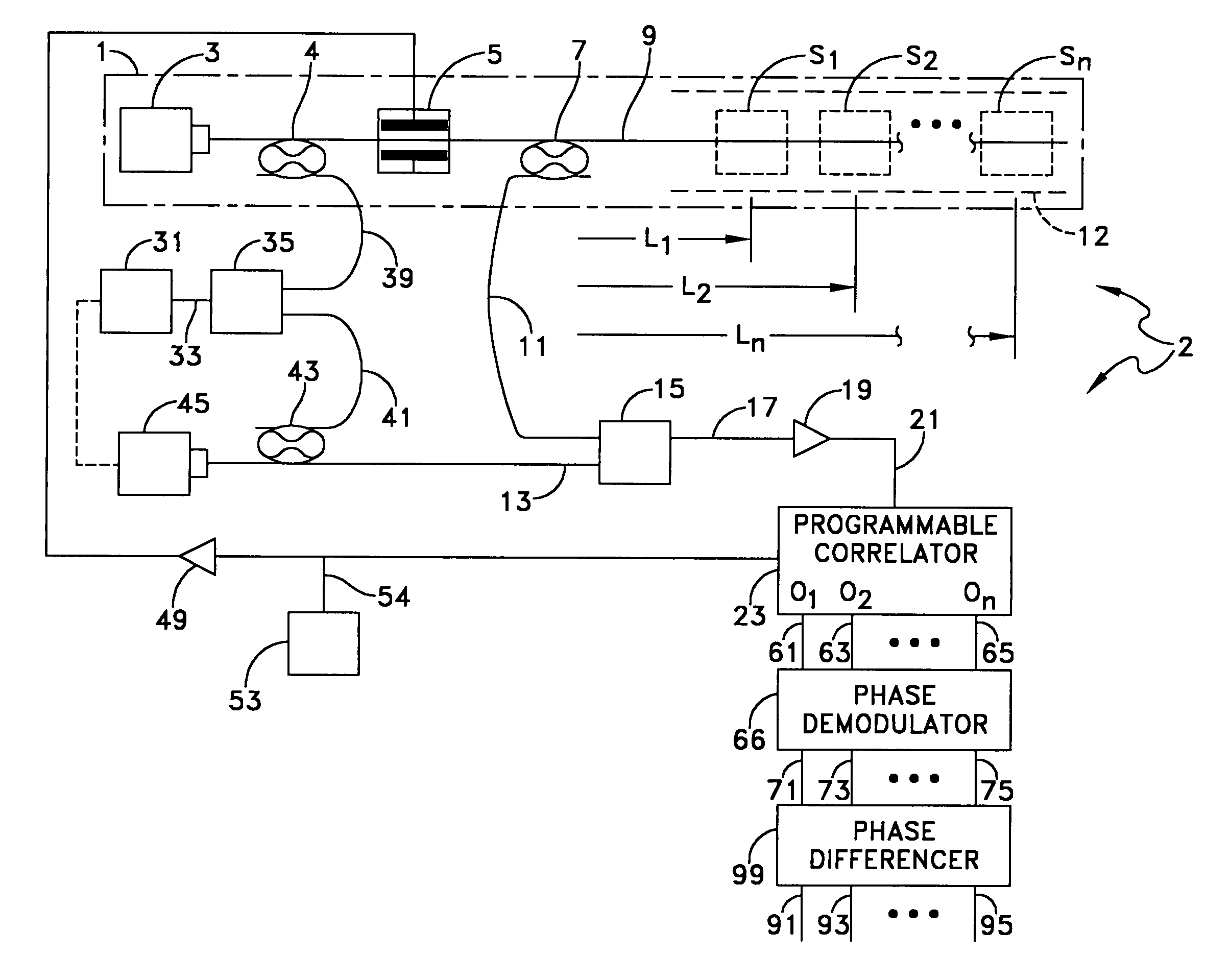
ActiveUS7030971B1To offer comfortLow costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringTime delays
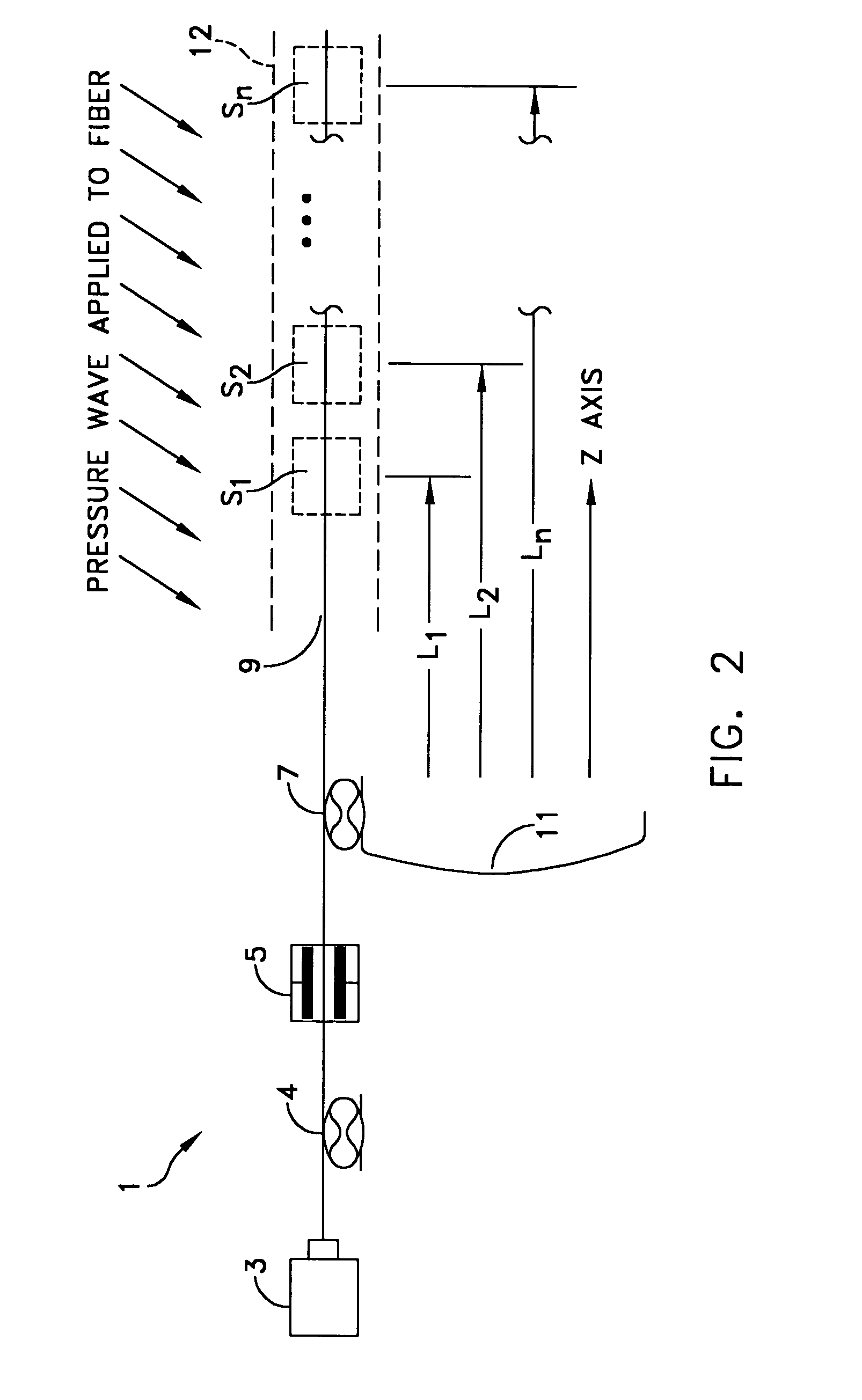
A CW lightwave modulated by a continuously reiterated binary pseudorandom code sequence is launched into an end of a span of ordinary optical fiber cable. Portions of the launched lightwave back propagate to the launch end from a continuum of locations along the span because of innate fiber properties including Rayleigh scattering. This is picked off the launch end and heterodyned to produce a r.f. beat signal. The r.f. beat signal is processed by a plurality (which can be thousands) of correlator type binary pseudonoise code sequence demodulators respectively operated in different delay time relationships to the timing base of the reiterated modulation sequences. The outputs of the demodulators provide r.f. time-domain reflectometry outputs representative of signals (e.g., acoustic pressure waves) incident to virtual sensors along the fiber at positions corresponding to the various time delay relationships.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE OFFICE OF NAVAL RES
Distributed optical fibre measurements
InactiveUS20060245468A1Different spectrumHigh measurement accuracyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
A method of obtaining a distributed measurement comprises deploying an optical fibre in a measurement region of interest, and launching into it a first optical signal at a first wavelength λ0 and a high power level, a second optical signal at a second wavelength λ−1, and a third optical signal at the first wavelength λ0 and a low power level. These optical signals generate backscattered light at the second wavelength λ−1 arising from Raman scattering of the first optical signal which is indicative of a parameter to be measured, at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the first optical signal, at the second wavelength λ−1 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the second optical signal, and at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the third optical signal. The backscattered light is detected to generate four output signals, and a final output signal is derived by normalising the Raman scattering signal to a function derived from the three Rayleigh scattering signals, which removes the effects of wavelength-dependent and nonlinear loss.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for simultaneously measuring distributed type temperatures and strain
ActiveCN103674084AReduce complexityReduce manufacturing costThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansTime-domain reflectometerRayleigh scattering
The invention provides a method for simultaneously measuring distributed type temperatures and strain. A brillouin optical time domain reflectometer and a coherent light time domain reflectometer share the same optical path system and the same circuit system and serve as a sensing measurement system. The sensing measurement system works in a BOTDR mode and a COTDR mode in an alternate mode to measure a brillouin scattering spectrum and a Rayleigh scattering spectrum which are distributed along a single single-mode sensing optical fiber and detect the frequency shift of the brillouin scattering spectrum and the frequency shift of the Rayleigh scattering spectrum, a linear equation set in two unknowns about the temperature and the strain is set up according to the characteristic that the frequency shift of the two scattering spectra is in the linear relationship with the temperature and the strain, and the temperature and the strain of each position of the sensing optical fiber can be obtained by solving the equation set, and then the temperatures and the strain distributed along the whole sensing optical fiber can be obtained. According to the method, the complexity and the manufacturing cost of the system are greatly reduced, no special requirement for the brillouin frequency shift coefficient of the optical fiber exists, and the application range of the measurement system is enlarged.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Detecting method suitable for optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
InactiveCN101158591AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolve the problem of measuring range of large temperature 0~400℃Force measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesDiscriminatorRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a detection method suitable for a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress. The sensing device of the optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The detection method of the invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring the relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to the frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, and outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of frequency discrimination is not sensitive to the frequency drift of the light source and the fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Distributed optical fiber sensor
ActiveCN102227615APolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Provided is a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor (FS) uses an optical fiber (15) as a sensor, wherein a distortion and temperature detector (14) measures the amount of Brillouin frequency shift due to the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures the amount of Rayleigh frequency shift due to the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) from the measured amount of Brillouin frequency shift and amount of Rayleigh frequency shift.
Owner:NEUBREX
Fiber air turn for low attenuation fiber
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber in a treatment zone wherein the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Methods for producing optical fibers along nonlinear paths incorporating fluid bearings are also provided thereby allowing for increased vertical space for the fiber treatment zone.
Owner:CORNING INC
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual differential signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS7274441B2To offer comfortReduce noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Long-distance distributed optical fiber vibration sensing system and method thereof
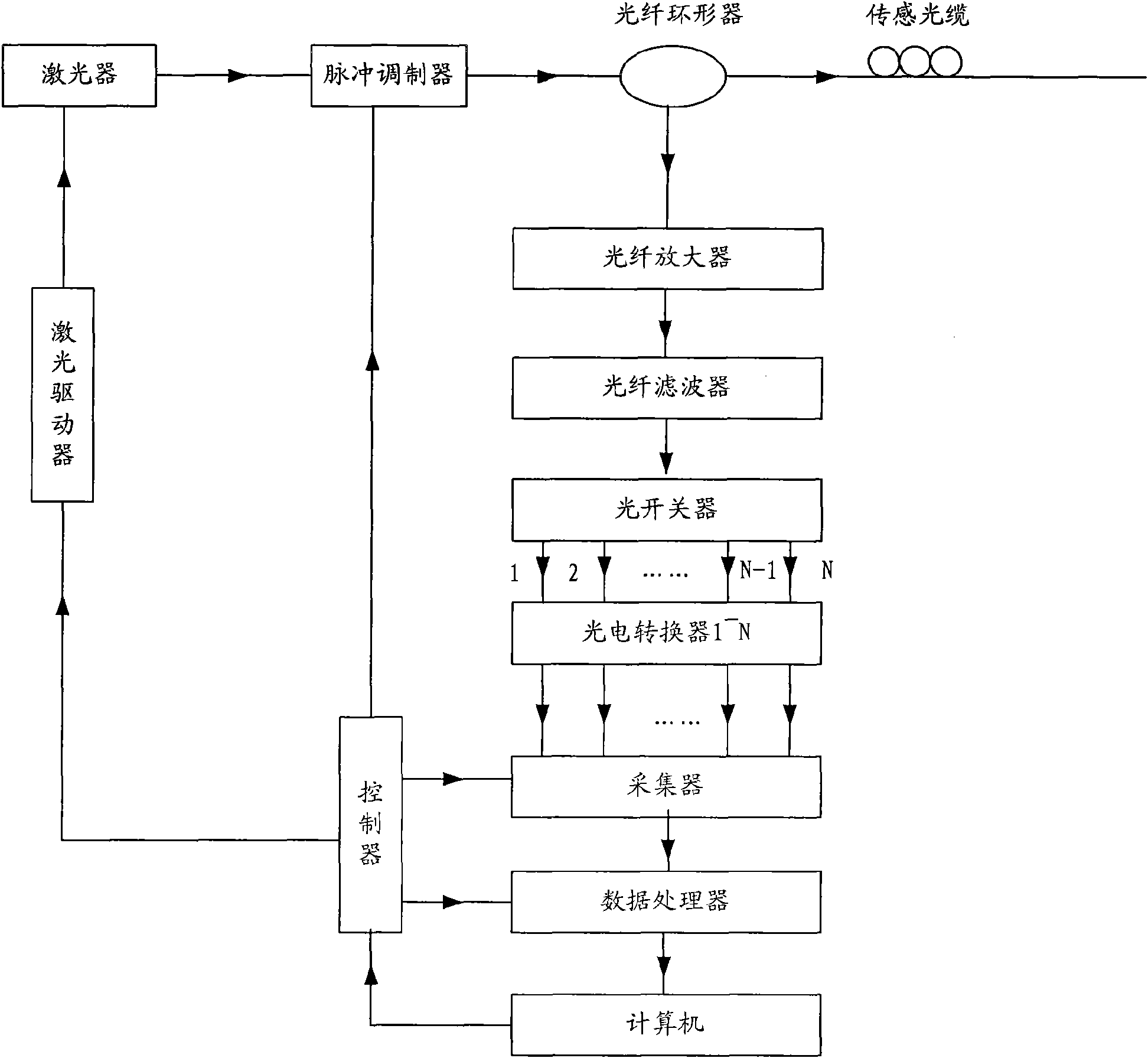
InactiveCN101603856ALarge dynamic rangeHigh detection sensitivitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansRayleigh scatteringPulse modulator
The invention discloses a long-distance distributed optical fiber vibration sensing system and a method thereof. The system comprises an induction system for inducting outside vibration events and a detecting and controlling system for detecting and controlling vibration signals; the induction system is connected with the detecting and controlling system. The induction system comprises a light source, a pulse modulator, an optical fiber circulator, a first optical fiber amplifier, and a light switch of a first optical fiber filter. The detecting and controlling system comprises a plurality of optical-electrical converters and a system control unit; the system control unit collects output light of the converters, analyzing the collected signals and judges whether the alarm is needed according to the analysis result. The invention adopts the optical switch technology to adopt time-division processing on backward Rayleigh scattering light which is reflected back, the dynamic range of the system is large, and the sensible distance can be tens of kilometers as high as possible, even hundreds of kilometers; and the invention adopts phase detecting technology and optical time domain reflection technology and can greatly improve detecting sensibility of the system and positioning precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH +1
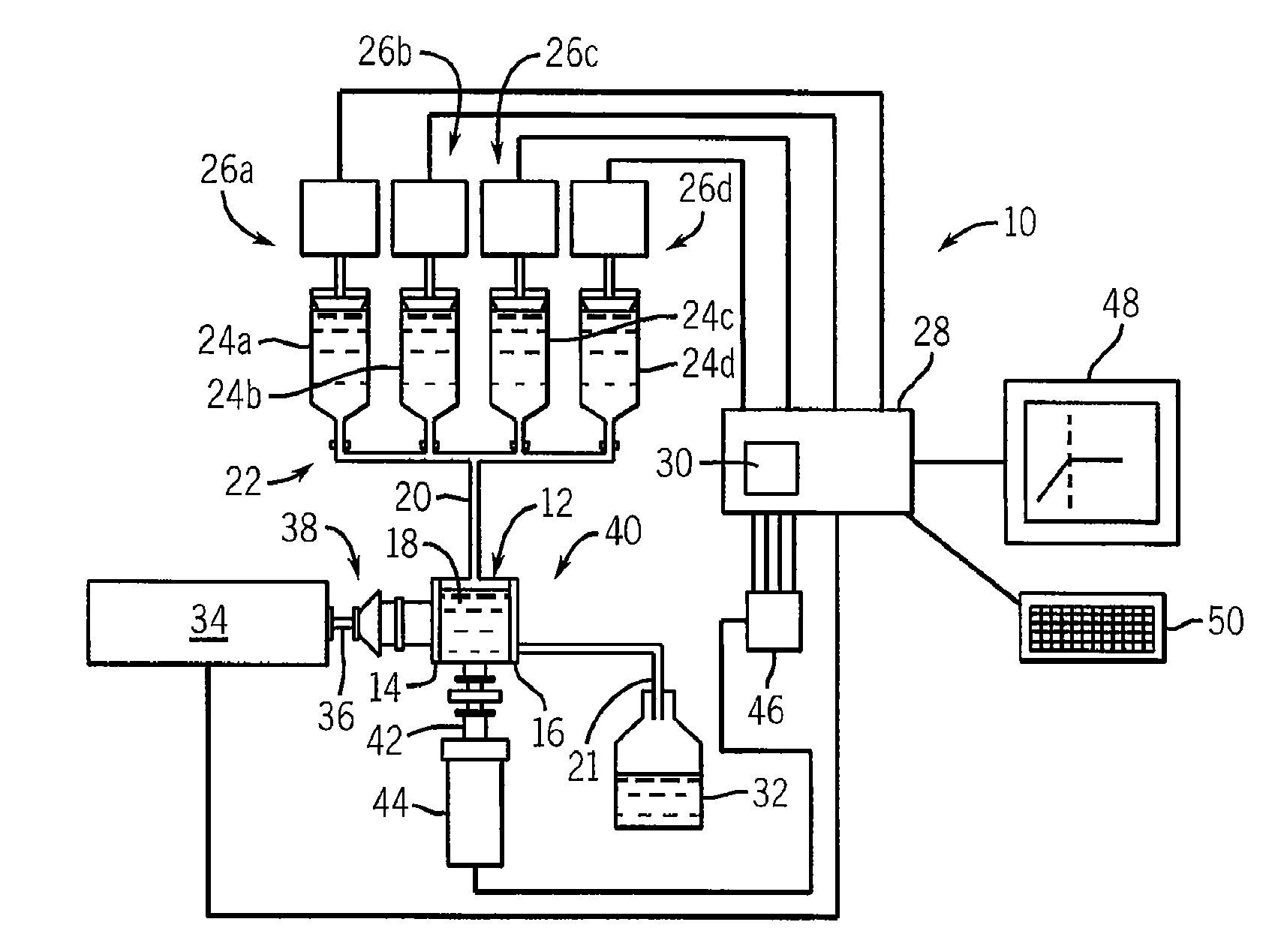
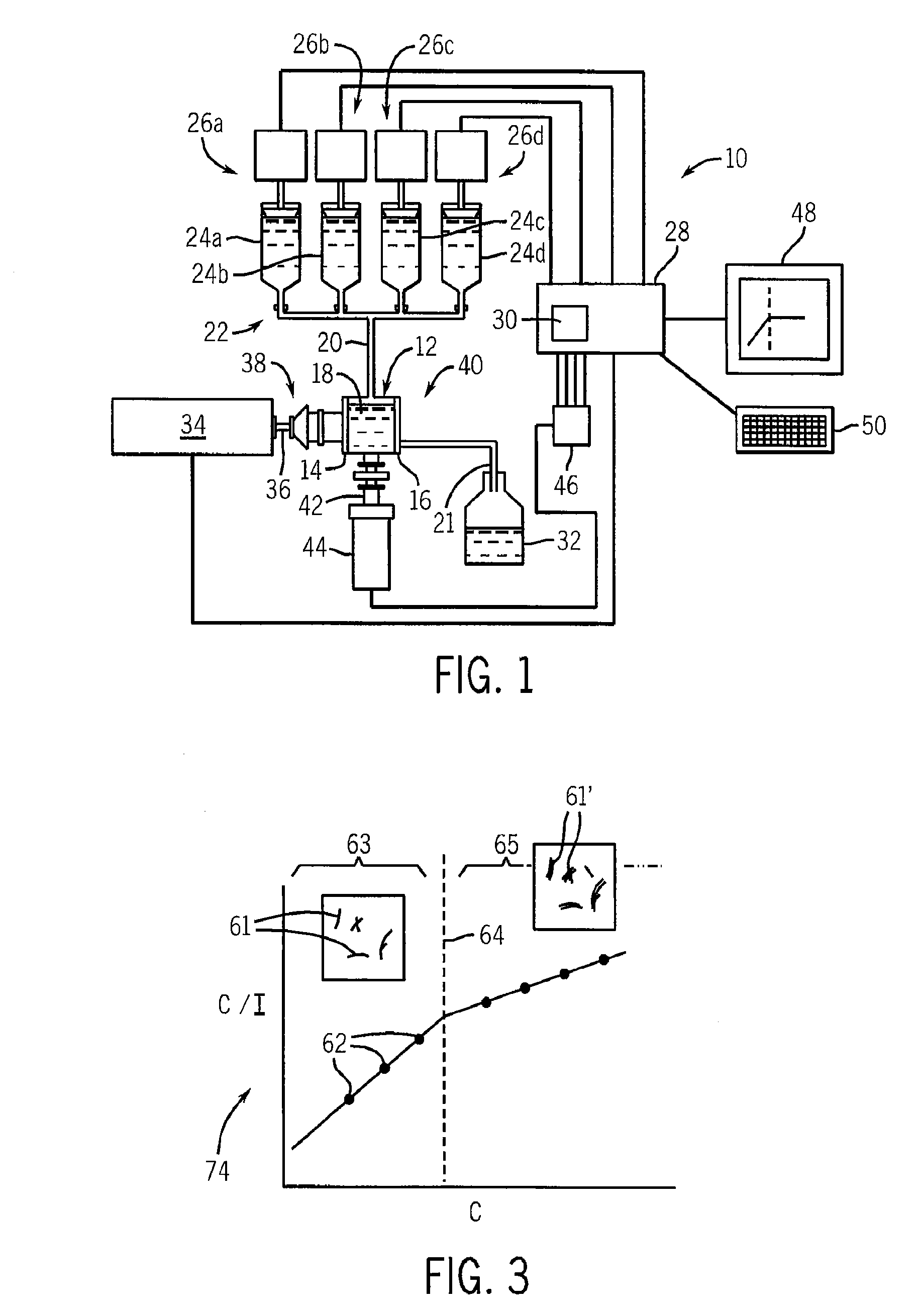
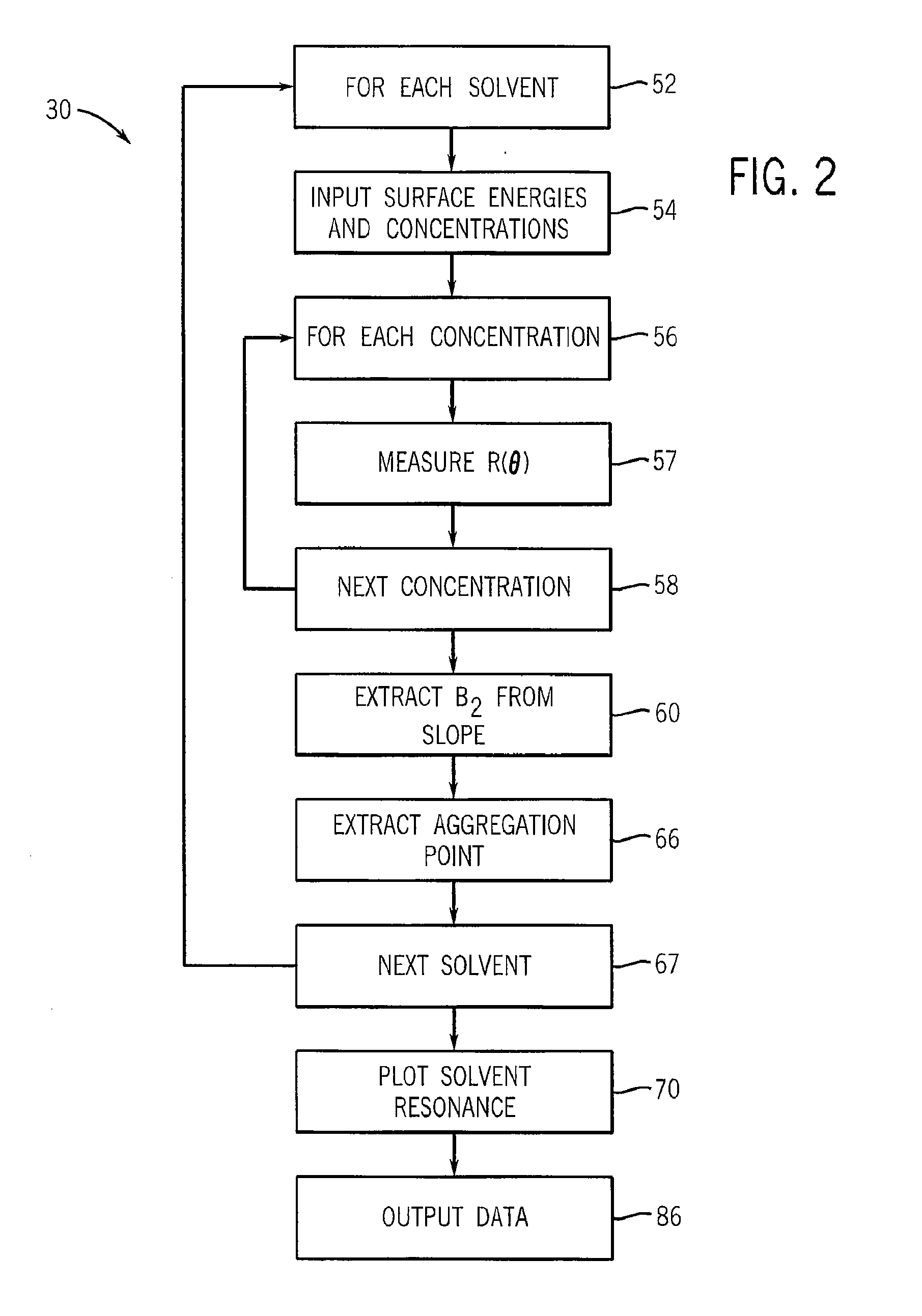
Method And Apparatus For Identifying And Characterizing Material Solvents And Composited Matrices And Methods Of Using Same
ActiveUS20110117361A1High composite strengthMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Solvents for macromolecules generally believed to be insoluble in their pristine form are identified by generation of a ‘solvent resonance’ in the relationship between solvent quality (deduced by Rayleigh scattering) and an intrinsic property of solvents. A local extreme of the solvent resonance identifies the ideal intrinsic property of an ideal solvent which may then be used to select a particular solvent or solvent combination. A solvent for graphene is used in the production of transparent conductive electrodes.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
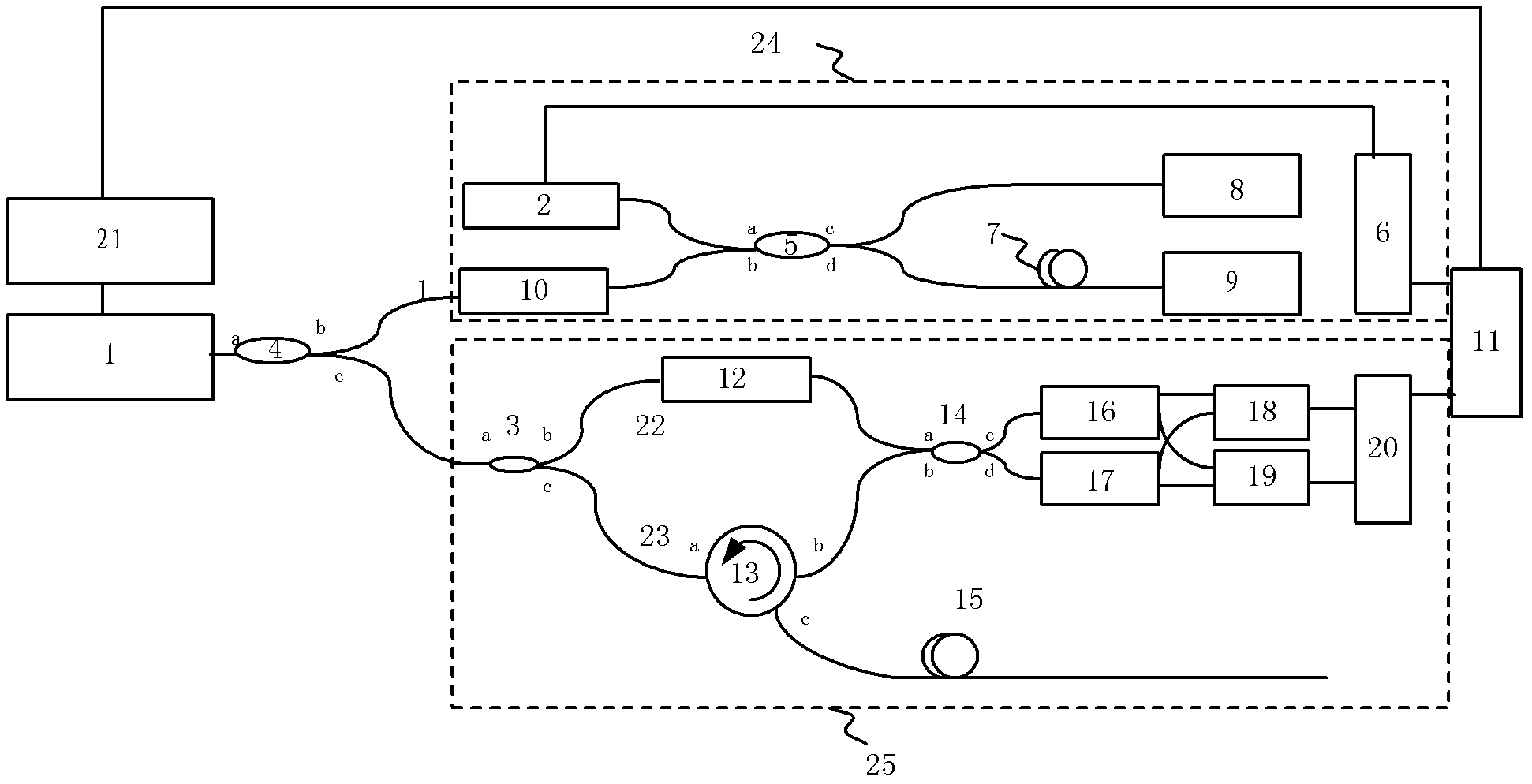
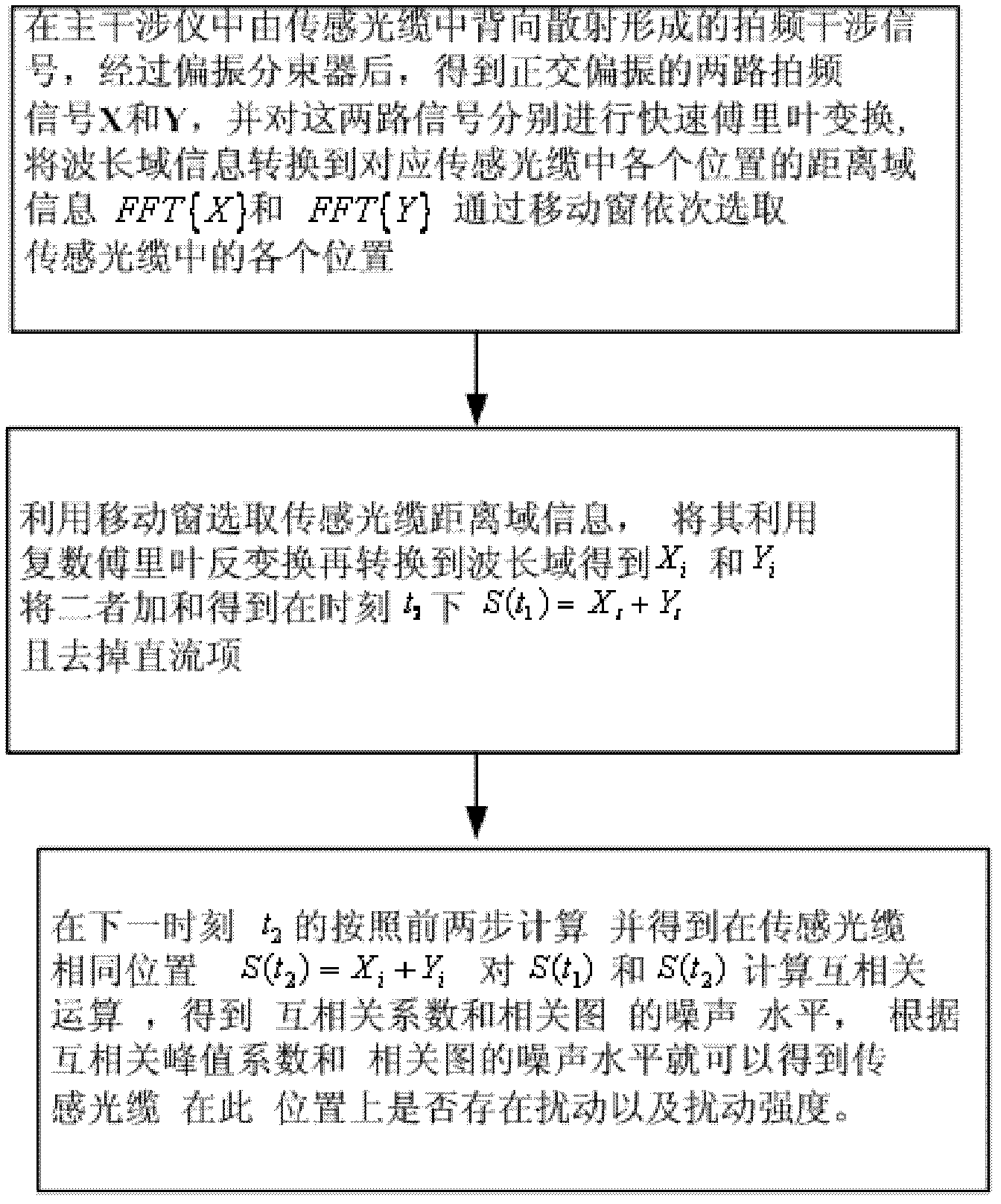
Distributed disturbance sensor on basis of Rayleigh scattering spectrum related coefficient and demodulating method thereof
ActiveCN102636196APrecise positioningConverting sensor output opticallyRayleigh scatteringFast Fourier transform
The invention relates to a demodulating method of a distributed disturbance sensor based on a Rayleigh scattering spectrum related coefficient. The distributed disturbance sensor adopts a technical method of optical frequency zone reflection and beat frequency interference of a laser source of a linear tuning ultra-narrow line width echo wall mold self-injecting locked mode. The distributed disturbance sensor comprises a main interferometer used for obtaining sensing signals and an auxiliary interferometer used for providing clock triggering signals for a collecting device. The demodulating method comprises the following steps: obtaining different beat frequency signals through a linear tuning light source and converting information of a wavelength zone to the information of distance zones of positions of corresponding cables by utilizing fast Fourier transform. Signals of the sensing optical cables are selected in the distance zones by a movable window, and then, are converted to the wavelength zone through plural fast Fourier inversion to form the Rayleigh scattering spectrums. The Rayleigh scattering spectrums disturbed by the outside world at different moments are compared, i.e., the disturbed Rayleigh scattering spectrums at the different moments are compared. The demodulating method is characterized in that information of whether the sensing optical cables is disturbed or not and the information of the disturbance intensity are obtained through related coefficients.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
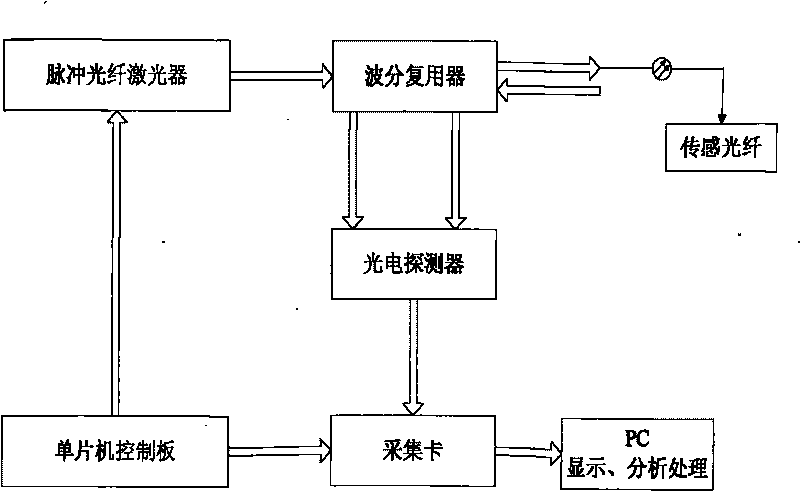
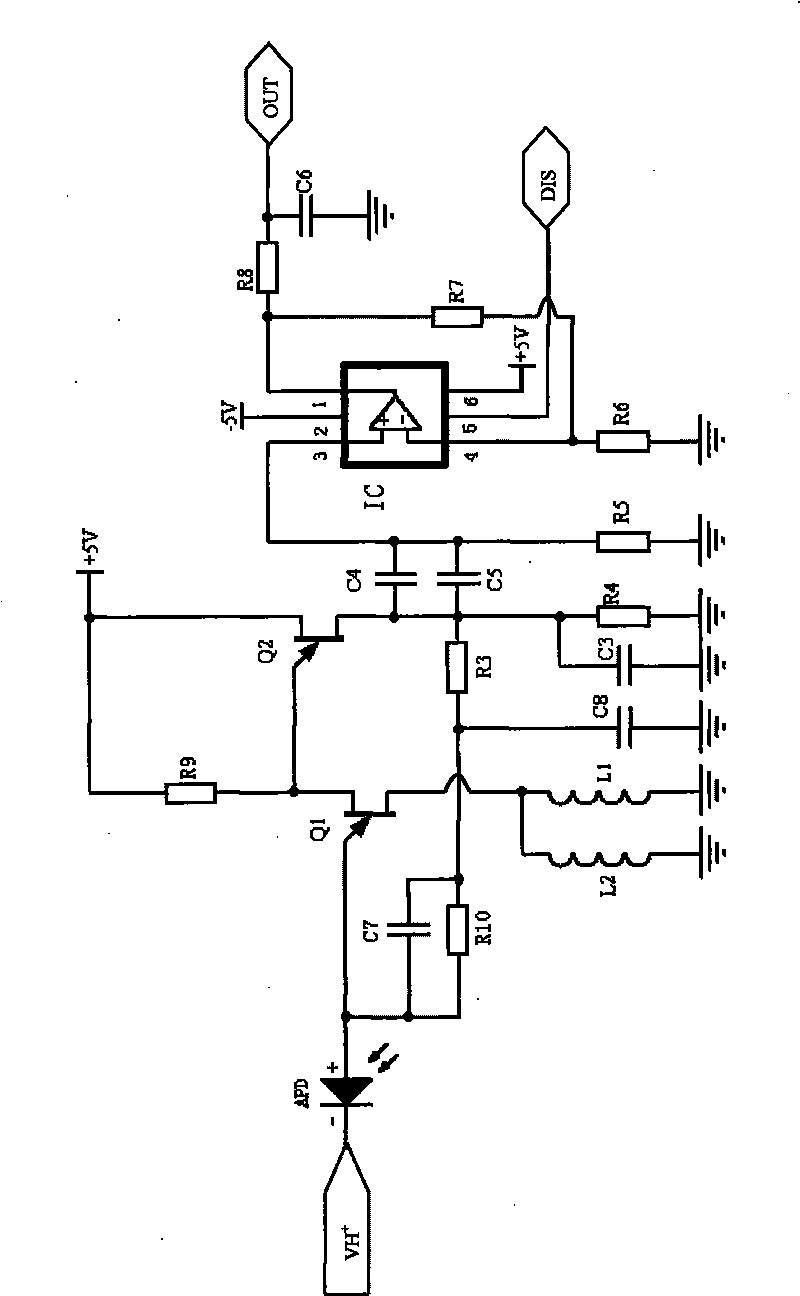
Temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers
InactiveCN101713689AContinuous Temperature MonitoringIncreased monitoring distance lengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesEquipment temperatureRayleigh scattering
The invention relates to a temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers, aiming at the continuous monitoring of temperature parameters of underground electromechanical transport equipment. The temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers comprises a singlechip control board, a fiber temperature field information acquisition module, a photoelectric detector and a circuit signal post-processing module, wherein the fiber temperature field information acquisition module comprises a pulse fiber laser and a wavelength division multiplexer; the circuit signal post-processing module comprises an acquisition card and a personal computer (PC); the singlechip control board is connected with the pulse fiber laser and the acquisition card by leads; the wavelength division multiplexer is connected with the pulse fiber laser and the photoelectric detector by fibers; incident light emitted by the pulse fiber laser is output to the sensing fiber by the wavelength division multiplexer; the sensing fiber feeds backward scattered light with temperature variance information of mine equipment back to the wavelength division multiplexer; and the wavelength division multiplexer extracts two scattered light beams of anti-Stokes and Stokes from the backward scattered light to restrain Rayleigh scattered light and other non-linear scattered light; and the photoelectric detector is connected with the acquisition card by a lead.
Owner:太原市电子研究设计院
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060066839A1Low costTo offer comfortForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringEngineering
A CW lightwave modulated by a continuously reiterated binary pseudorandom code sequence is launched into an end of a span of ordinary optical fiber cable. Portions of the launched lightwave back propagate to the launch end from a continuum of locations along the span because of innate fiber properties including Rayleigh scattering. This is picked off the launch end and heterodyned to produce a r.f. beat signal. The r.f. beat signal is processed by a plurality (which can be thousands) of correlator type binary pseudonoise code sequence demodulators respectively operated in different delay time relationships to the timing base of the reiterated modulation sequences. The outputs of the demodulators provide r.f. time-domain reflectometry outputs representative of signals (e.g., acoustic pressure waves) incident to virtual sensors along the fiber at positions corresponding to the various time delay relationships.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE OFFICE OF NAVAL RES
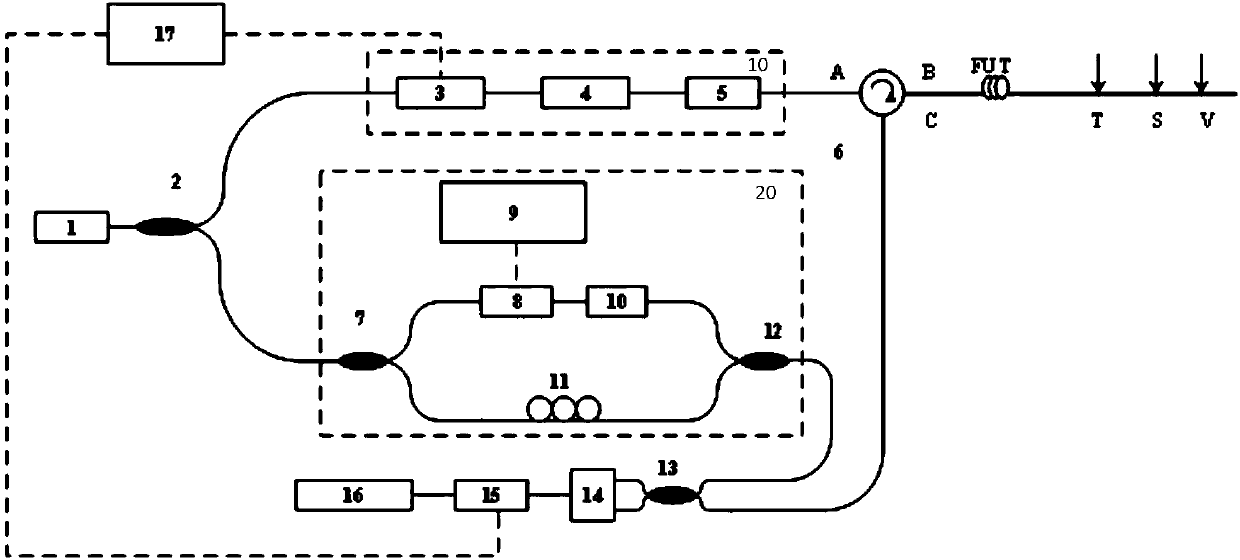
Optical fiber disturbance detection method and apparatus
ActiveCN101488805AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementRayleigh scatteringTime domain
The invention relates to an optical fiber sensor. The invention discloses an optical fiber destabilization detecting method combining based on a phase sensitivity light time domain reflection and a polarization sensitivity light time domain reflection method and distributed optical fiber sensing system thereof to improve the detecting accuracy and reliability of the optical fiber destabilization. The method comprises: a. injecting an optical signal with determined polarization state into the optical fiber; b. receiving the back rayleigh scattering light in the optical fiber; c. diving the rayleigh scattering light into two bundles to perform the Phi-OTDR data acquisition and the POTDR data acquisition; d. determining the destabilization and position thereof based on the distortion points of the Phi-OTDR data and the POTDR data. The invention also discloses an optical fiber destabilization detecting device. The technical scheme of the invention is used for monitoring and protecting the optical cable lines, thereby greatly improving the precision and the sensitivity of the monitoring system and reducing the erroneous judgment rate and the missing report rate.
Owner:OPTICAL SCI & TECH (CHENGDU) LTD
Methods and apparatus for forming heat treated optical fiber
InactiveUS20070022786A1Trend downDecreases micro-density variationGlass fibre drawing apparatusGlass productionFiberRayleigh scattering
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber within a treatment temperature range for a treatment time. Preferably also, the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Apparatus are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
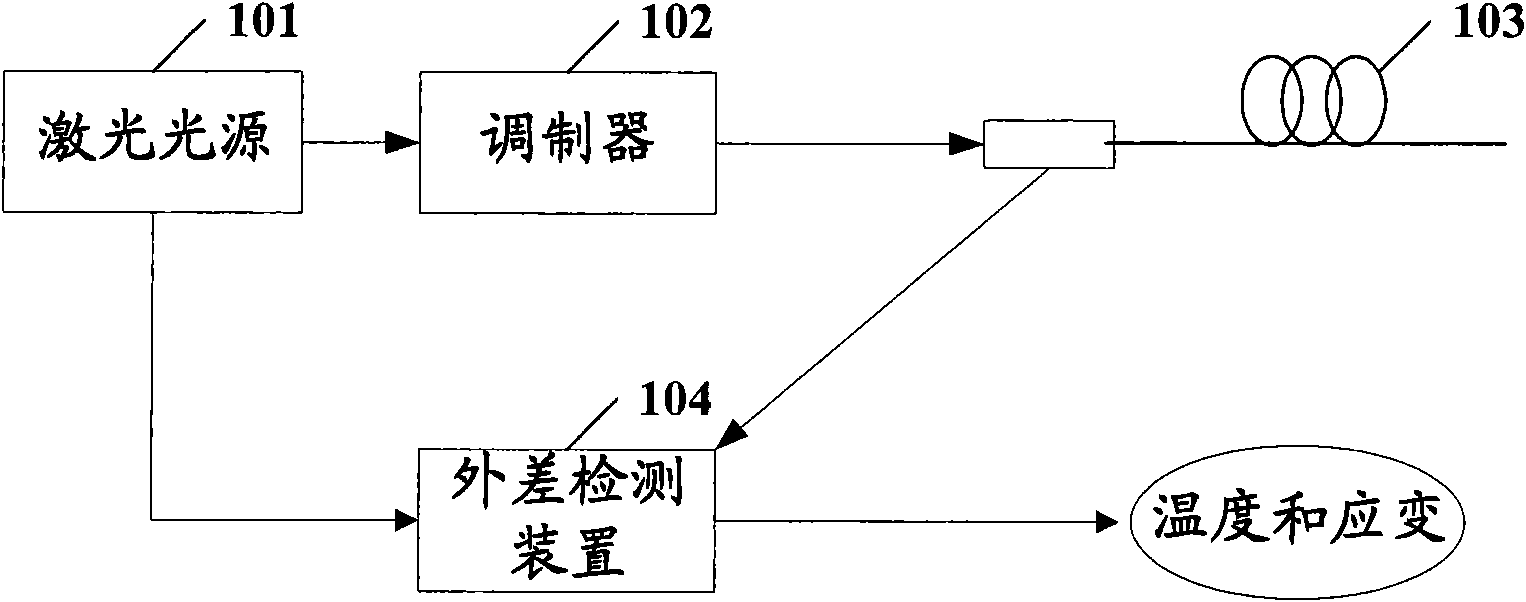
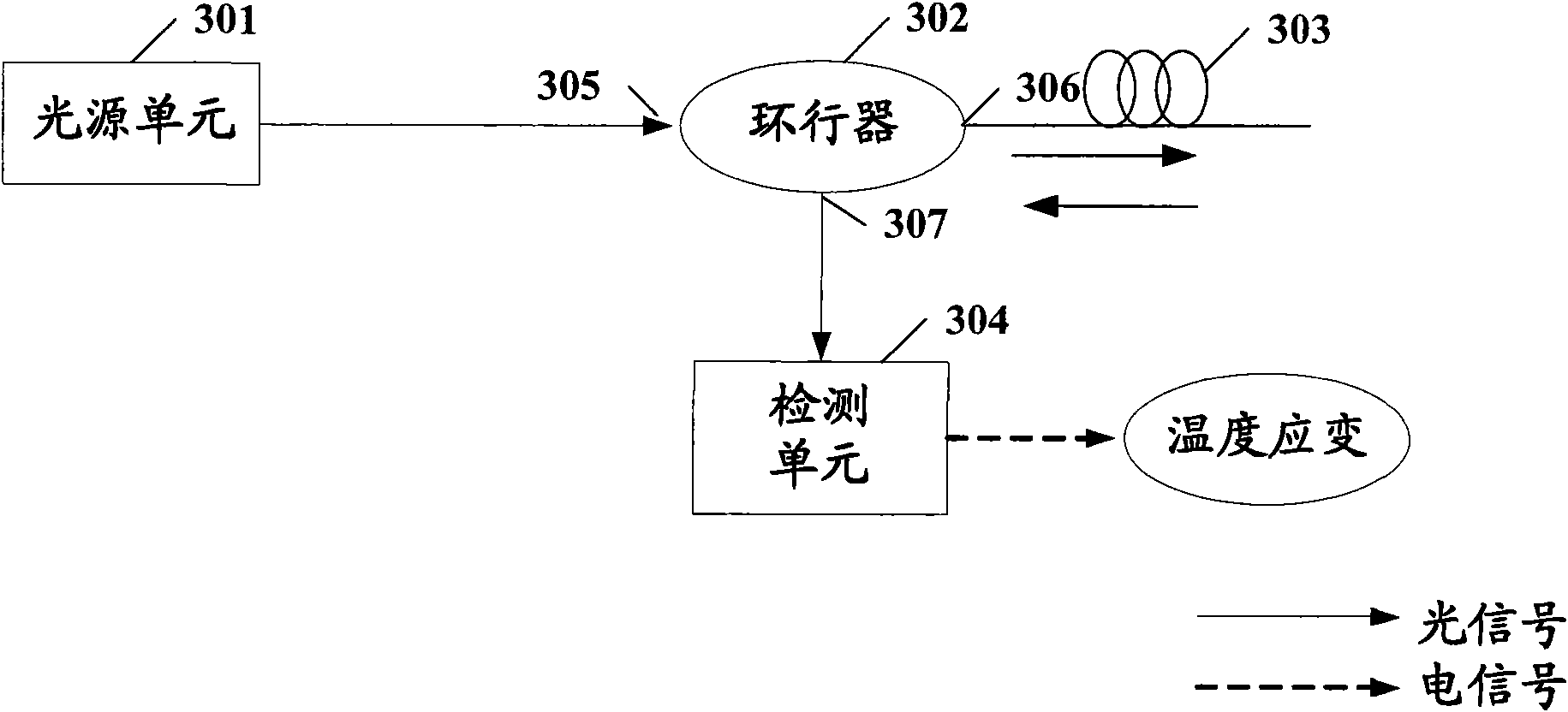
Distributed optical fiber sensing system and detection method utilizing same
InactiveCN101629855AReduce usageEasy to installThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber sensing system and a detection method utilizing the same. The optical fiber sensing system comprises a light source unit, an optical circulator, and a detection unit, wherein the light source unit emits light which is suitable for detecting and processing; the optical circulator receives the light which comes from the light source unit, and transmits the received light into a sensing optical fiber used for the detection; and the detection unit receives backscattered light caused by the light which enters the sensing optical fiber from the optical circulator, interference light formed by Rayleigh scattering light and scattered light of one component of Brillouin in the backscattered light through heterodyne interference is obtained in the detection unit and is converted into an electrical signal, and the detection unit also detects the electrical signal to obtain the change of the temperature and strain in the sensing optical fiber.
Owner:派克森公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com