Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
672results about "Glass fibre drawing apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
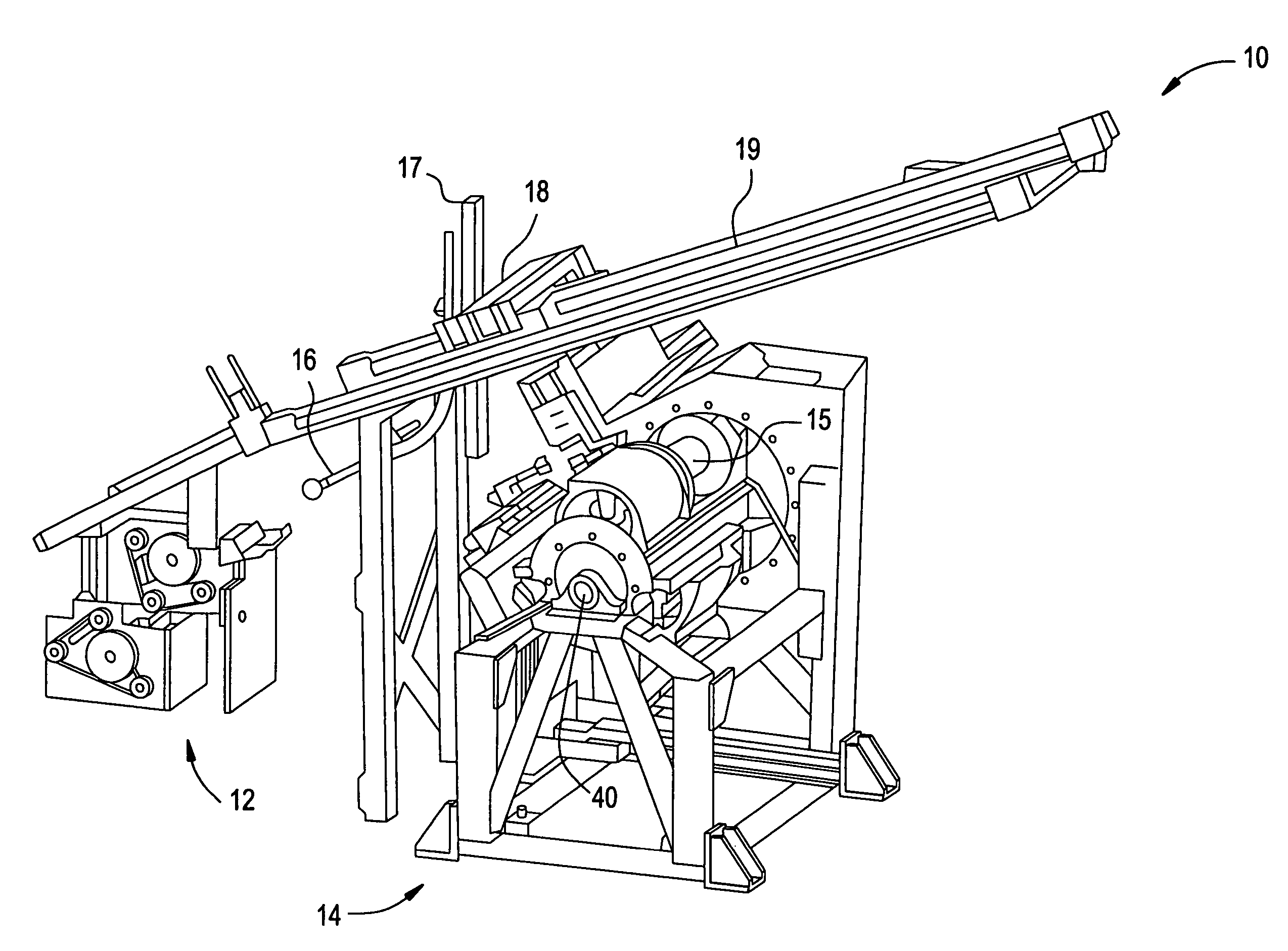
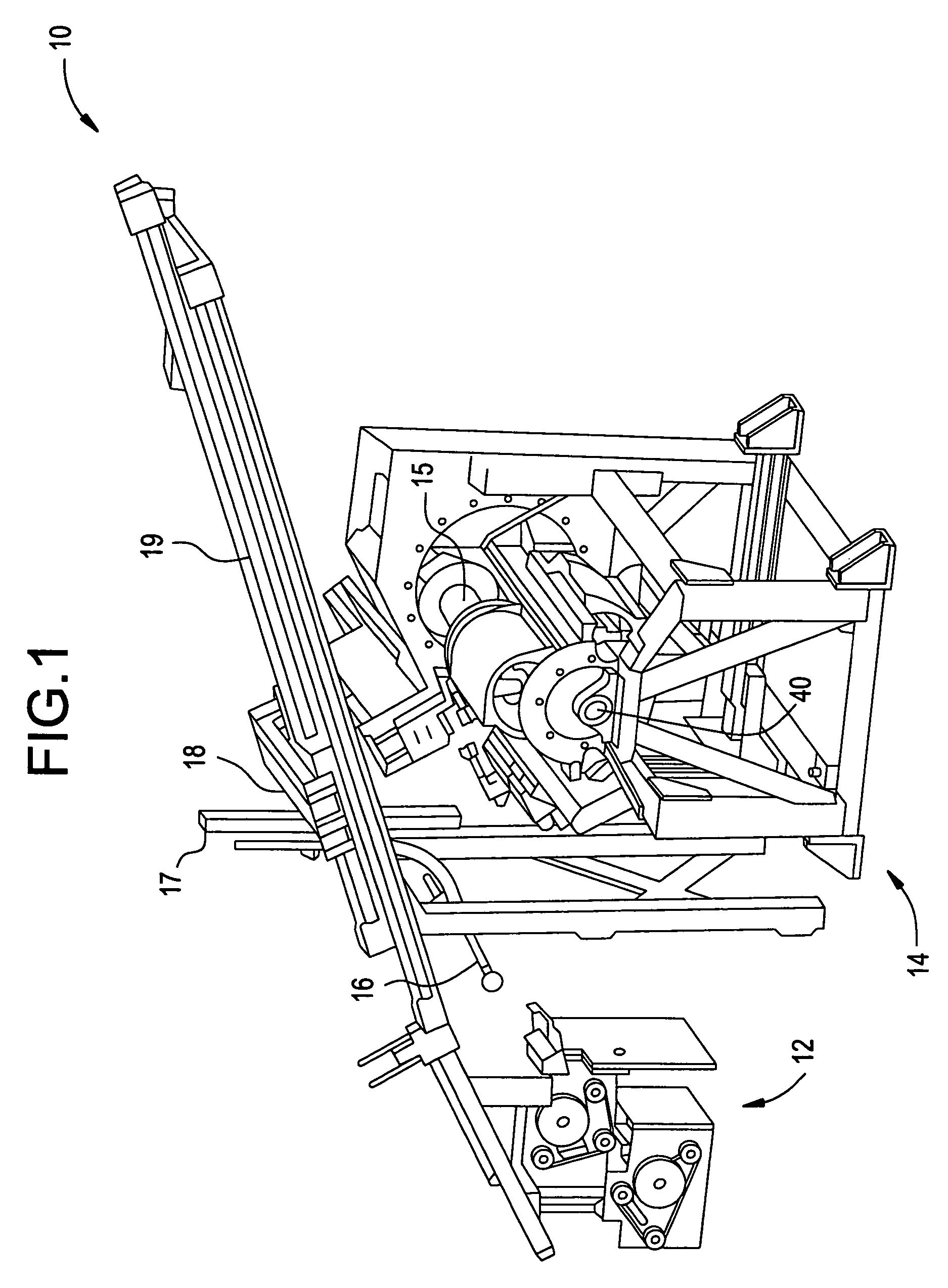
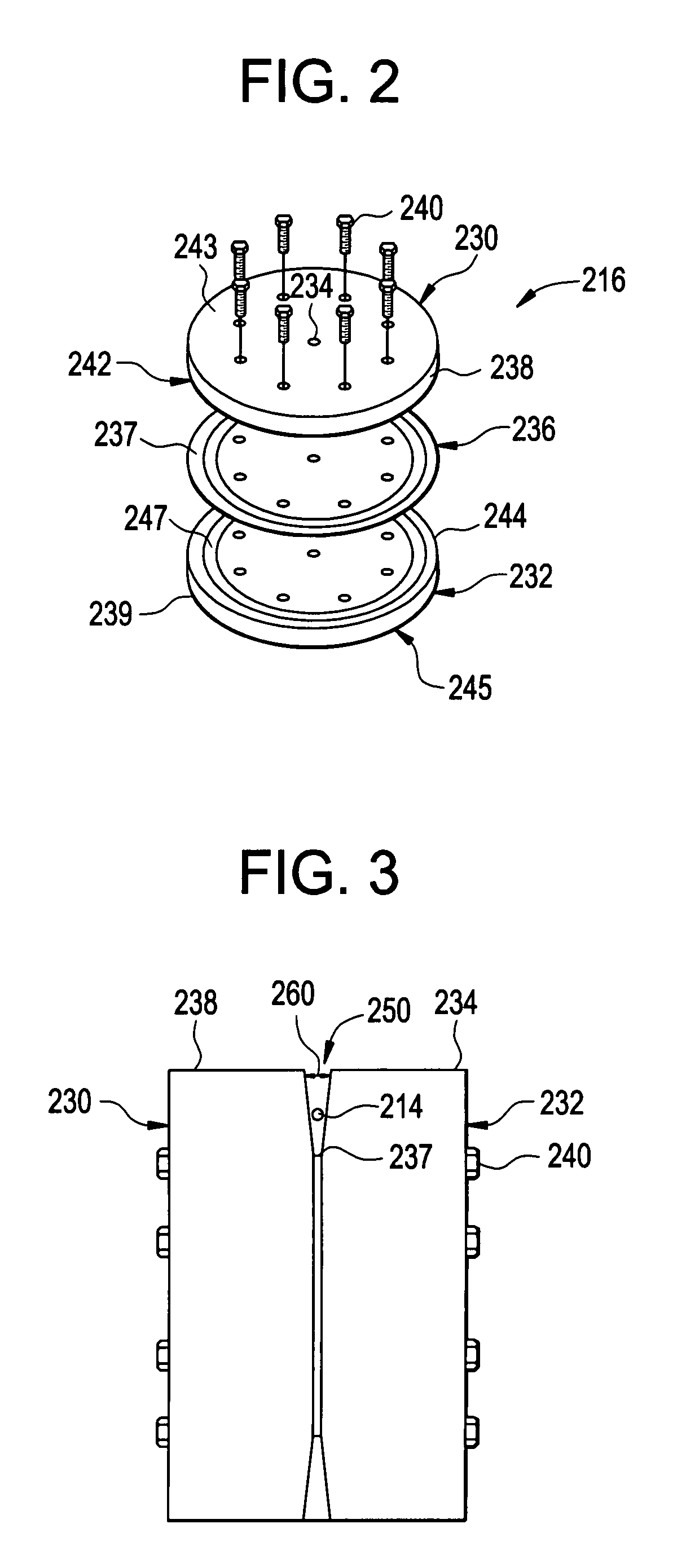
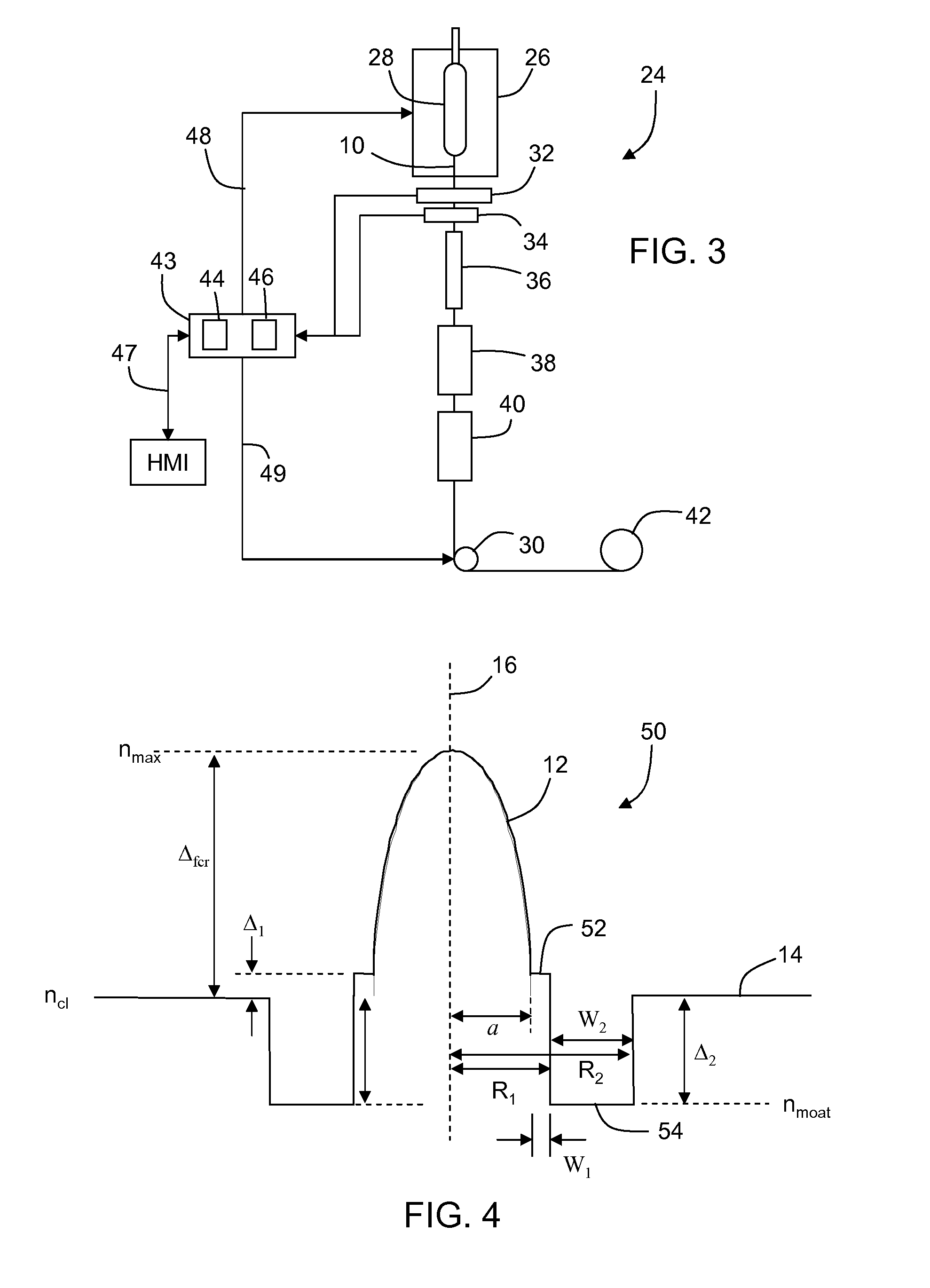
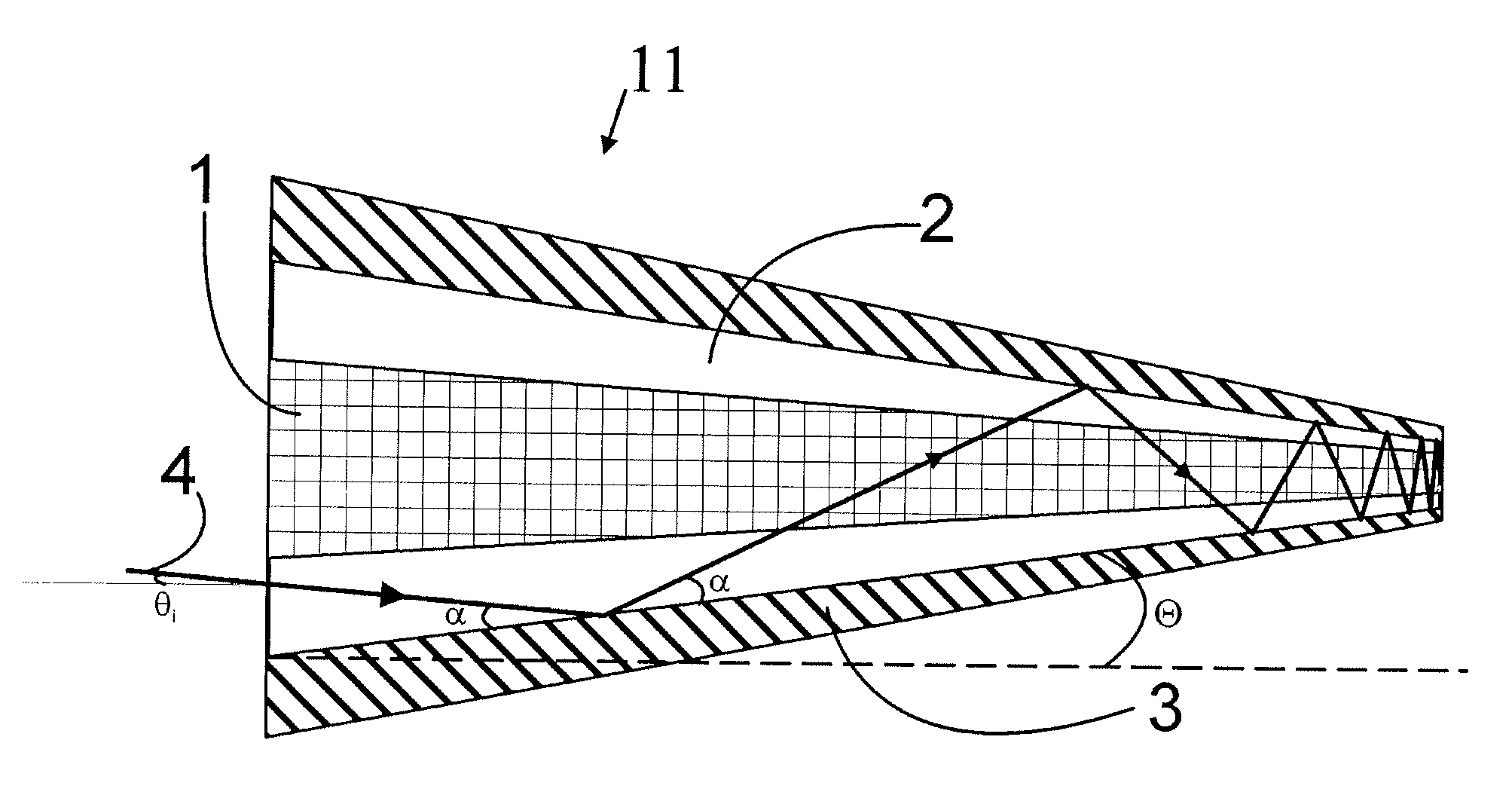
Active optical fiber and method for fabricating an active optical fiber
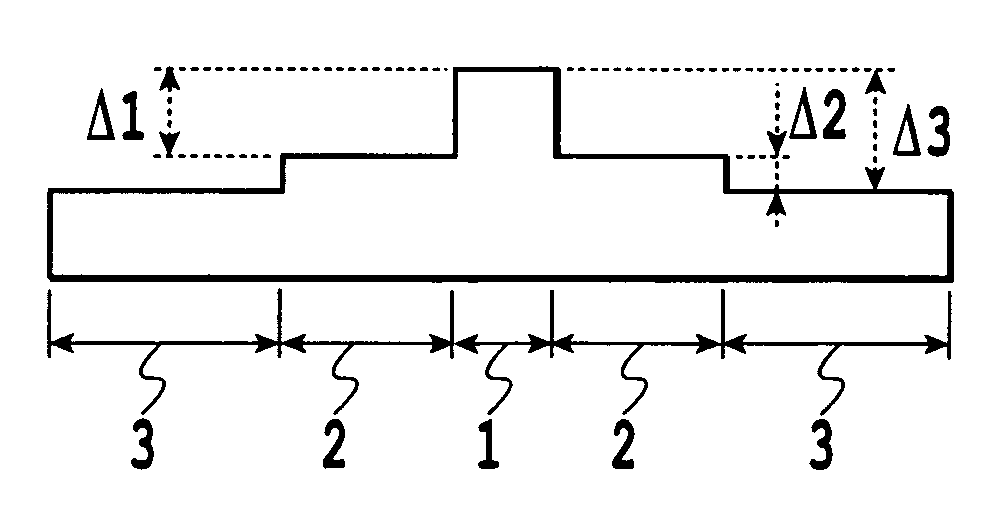
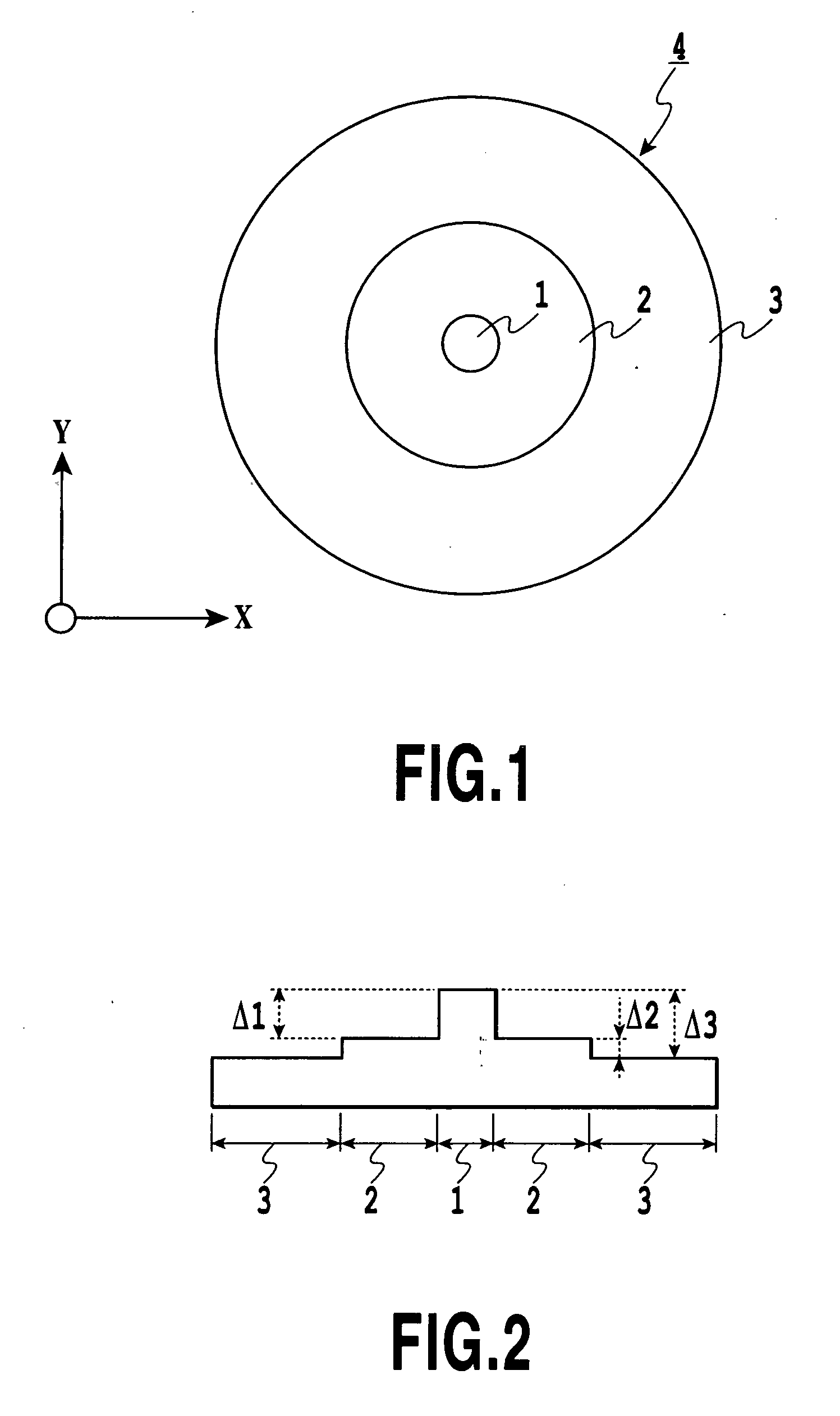
ActiveUS8433168B2Reduce the overall diameterLarge volumeLaser detailsMetal rolling stand detailsFiberActive core
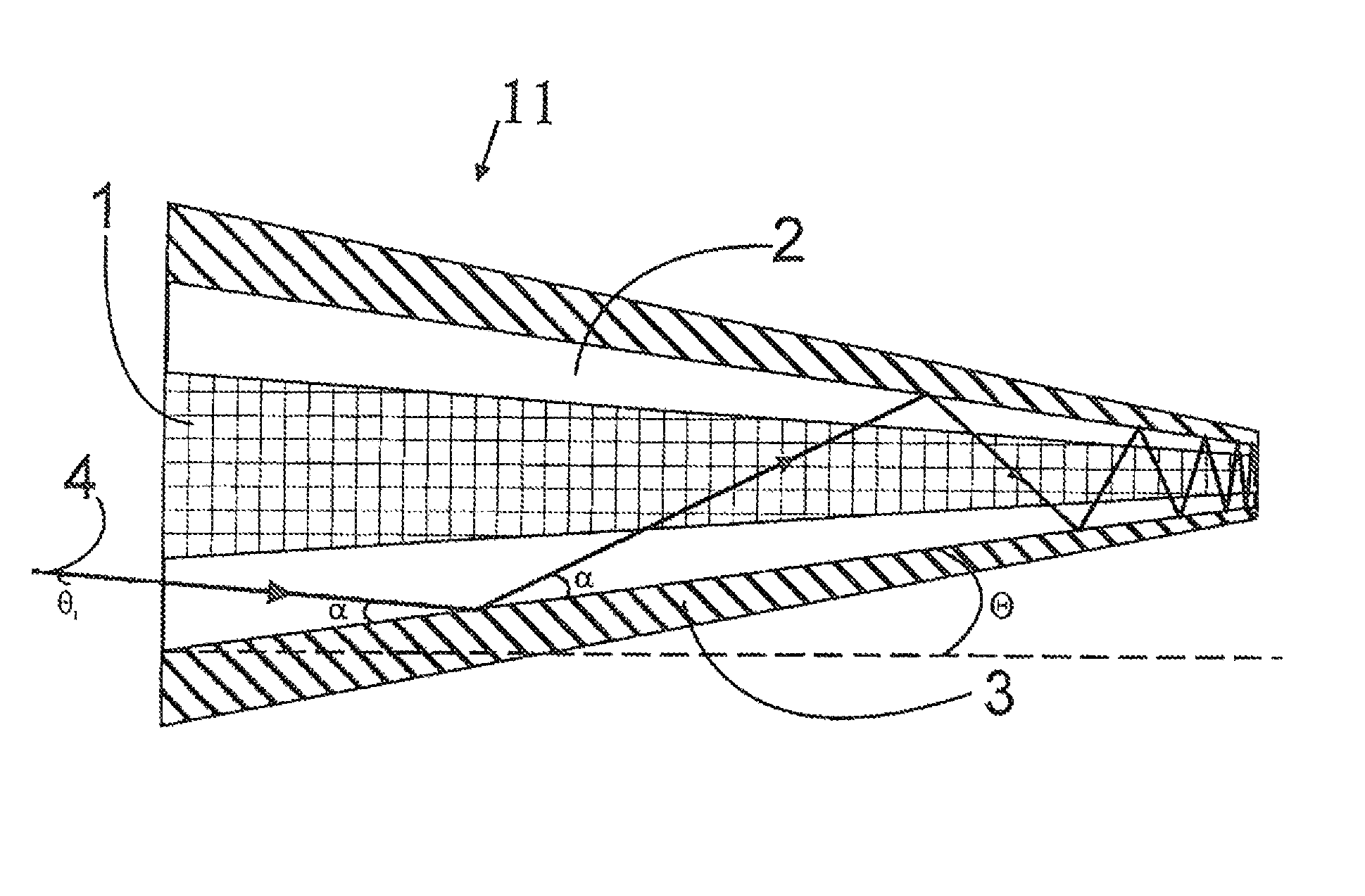
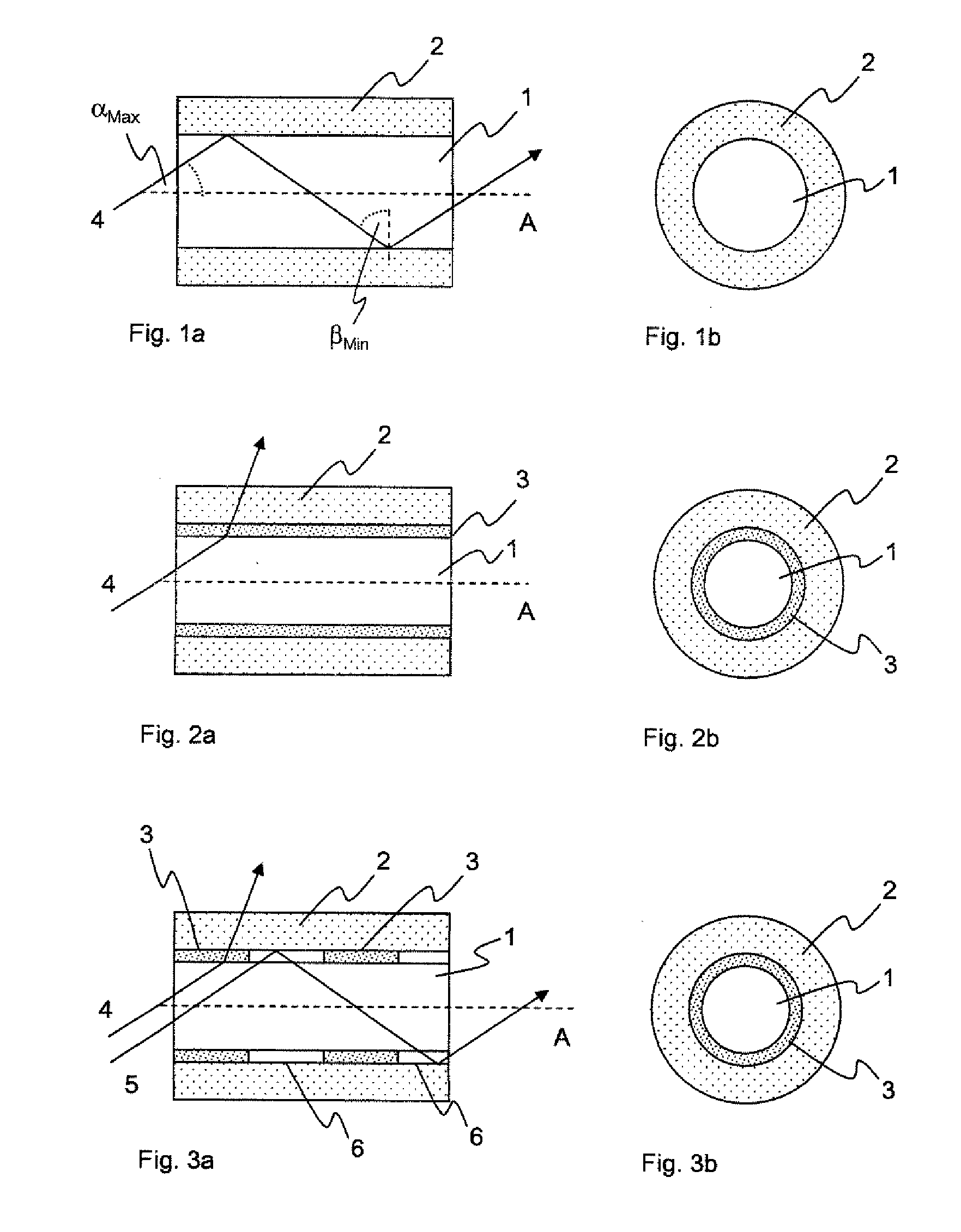
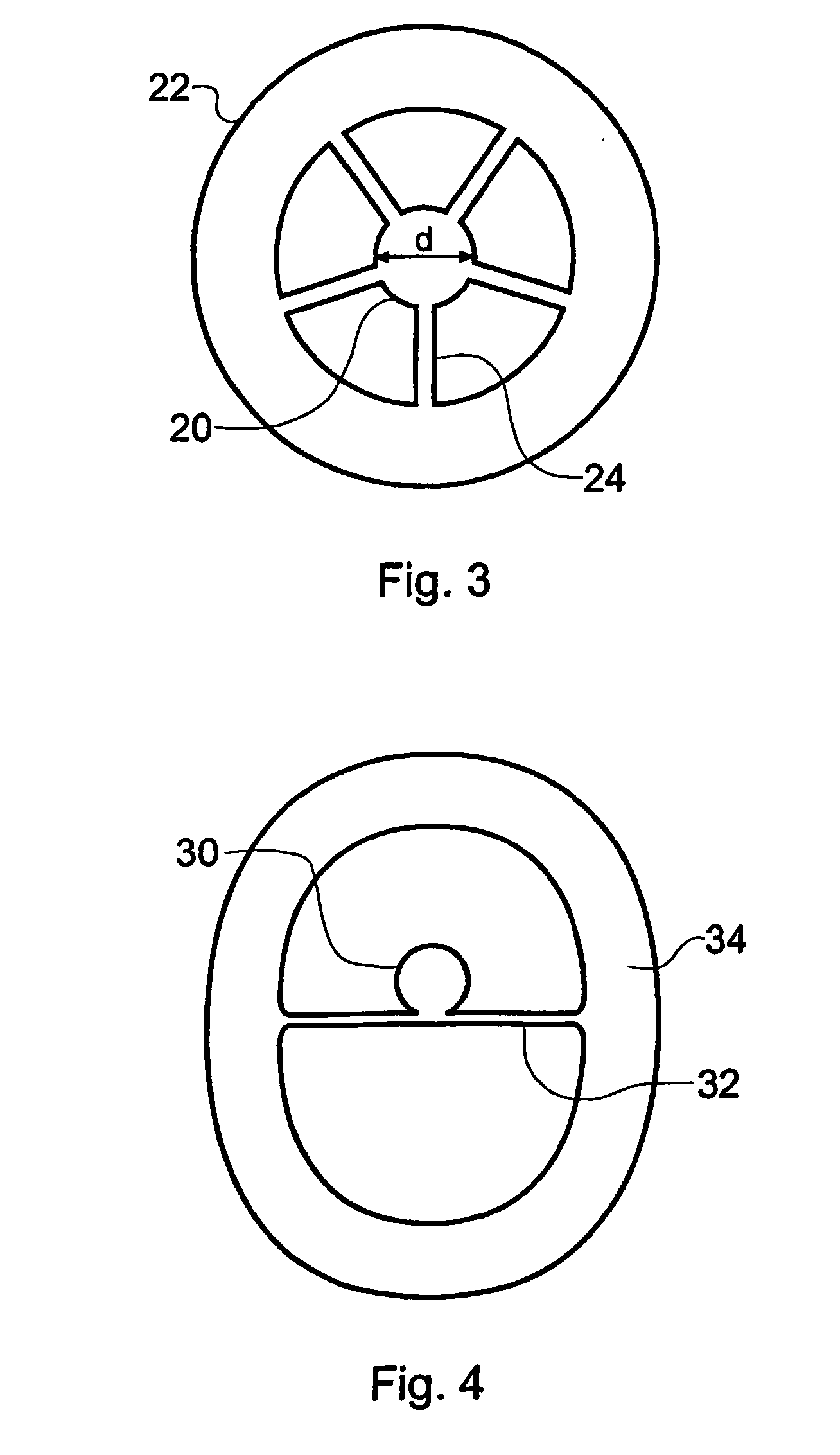
A section of active optical fiber (11) which comprises an active core (1), an inner cladding layer (2) and an outer cladding layer (3). The diameter of said core 1) and the thickness of said inner cladding (2) change gradually along the length of said section of active optical fiber (11). This forms tapered longitudinal profile enabling a continuous mode conversion process along the length of the section of fiber (11). The method for fabricating a section of tapered active optical fiber comprises the steps of fabricating a preform for drawing active optical fiber from said preform, installing said preform into a drawing tower, drawing optical fiber in said drawing tower and altering at least one of the two parameters including the take-off preform speed and the take-up fiber speed during drawing of the optical fiber.
Owner:AMPLICONYX OY
Methods and apparatus for forming heat treated optical fiber
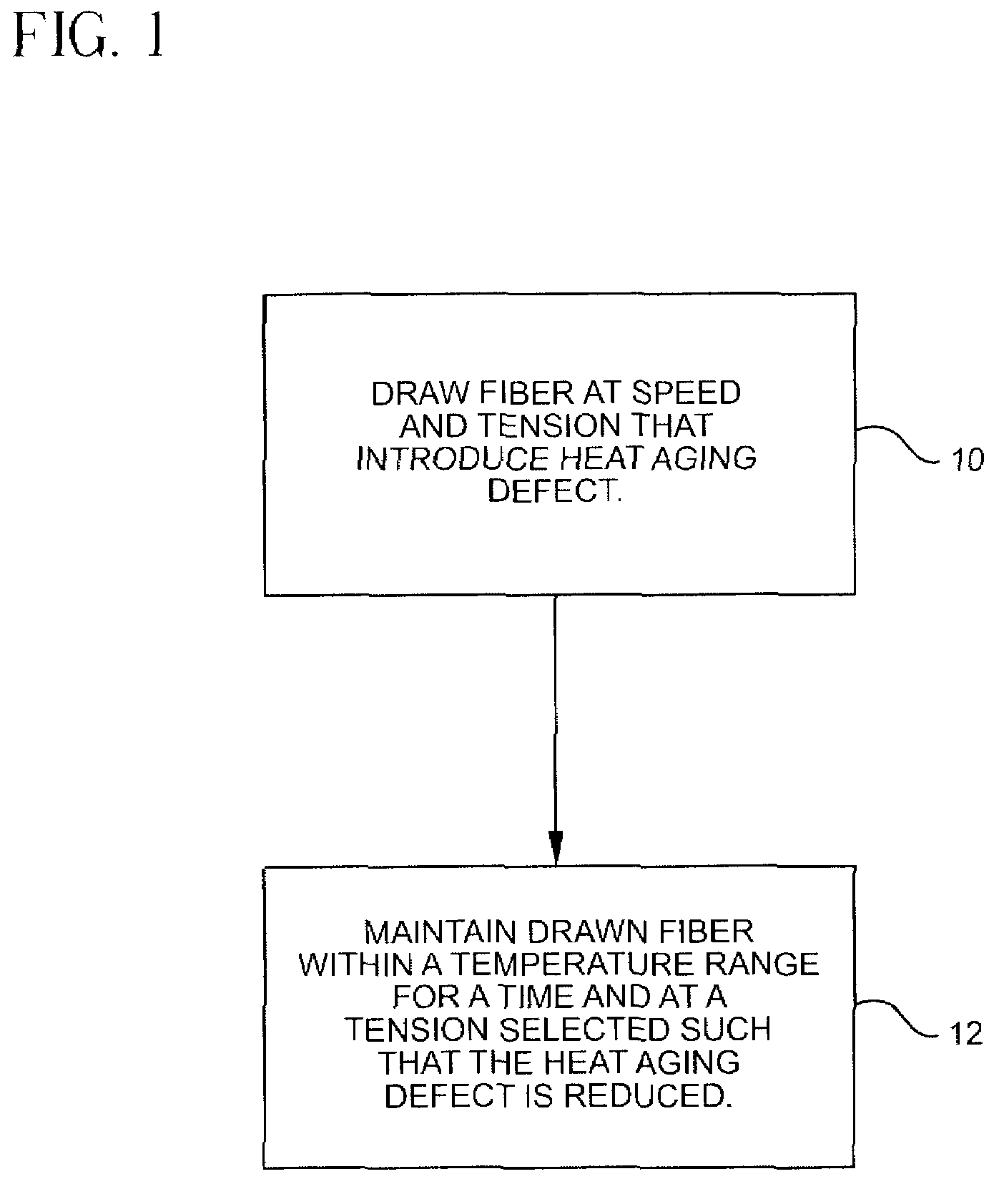
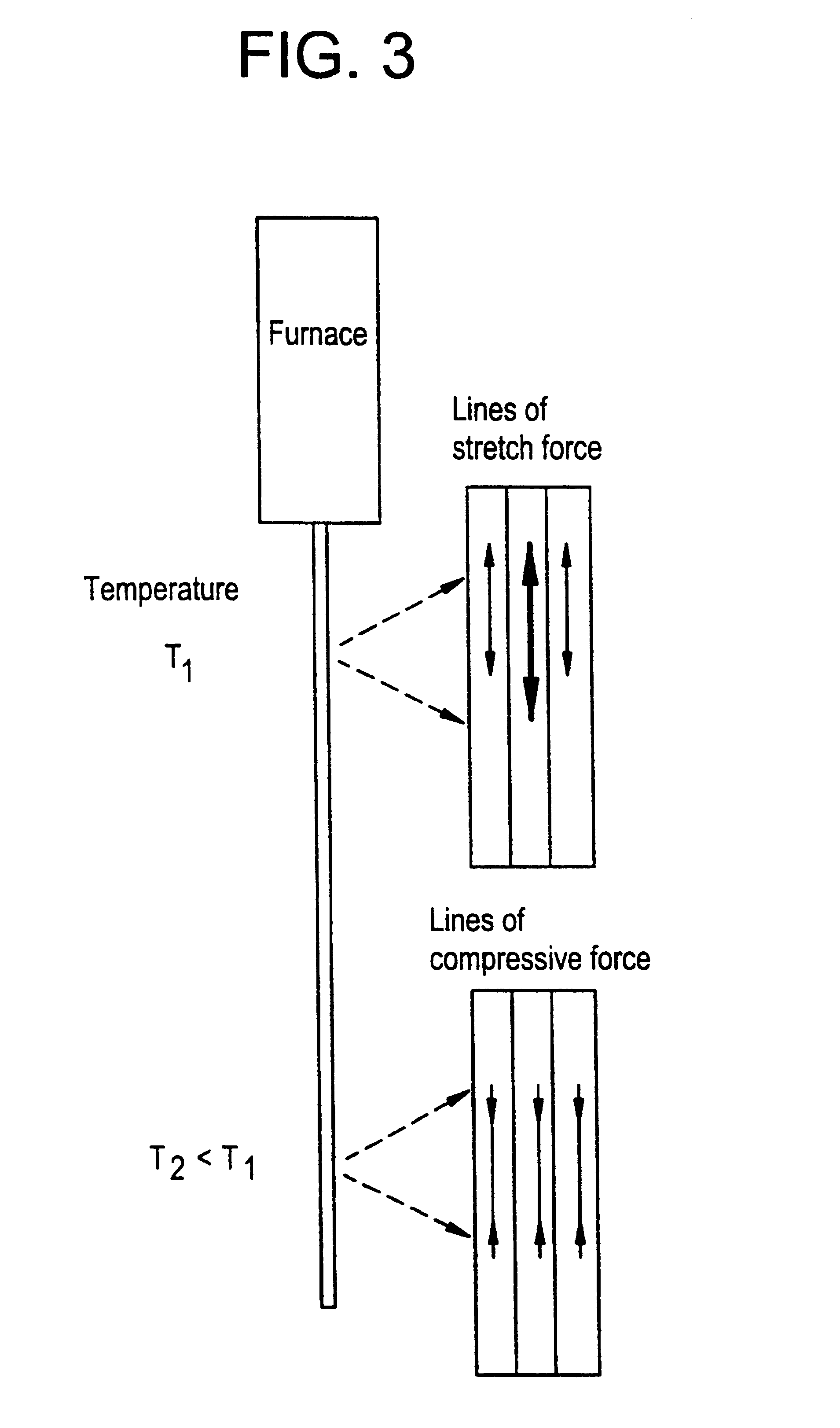
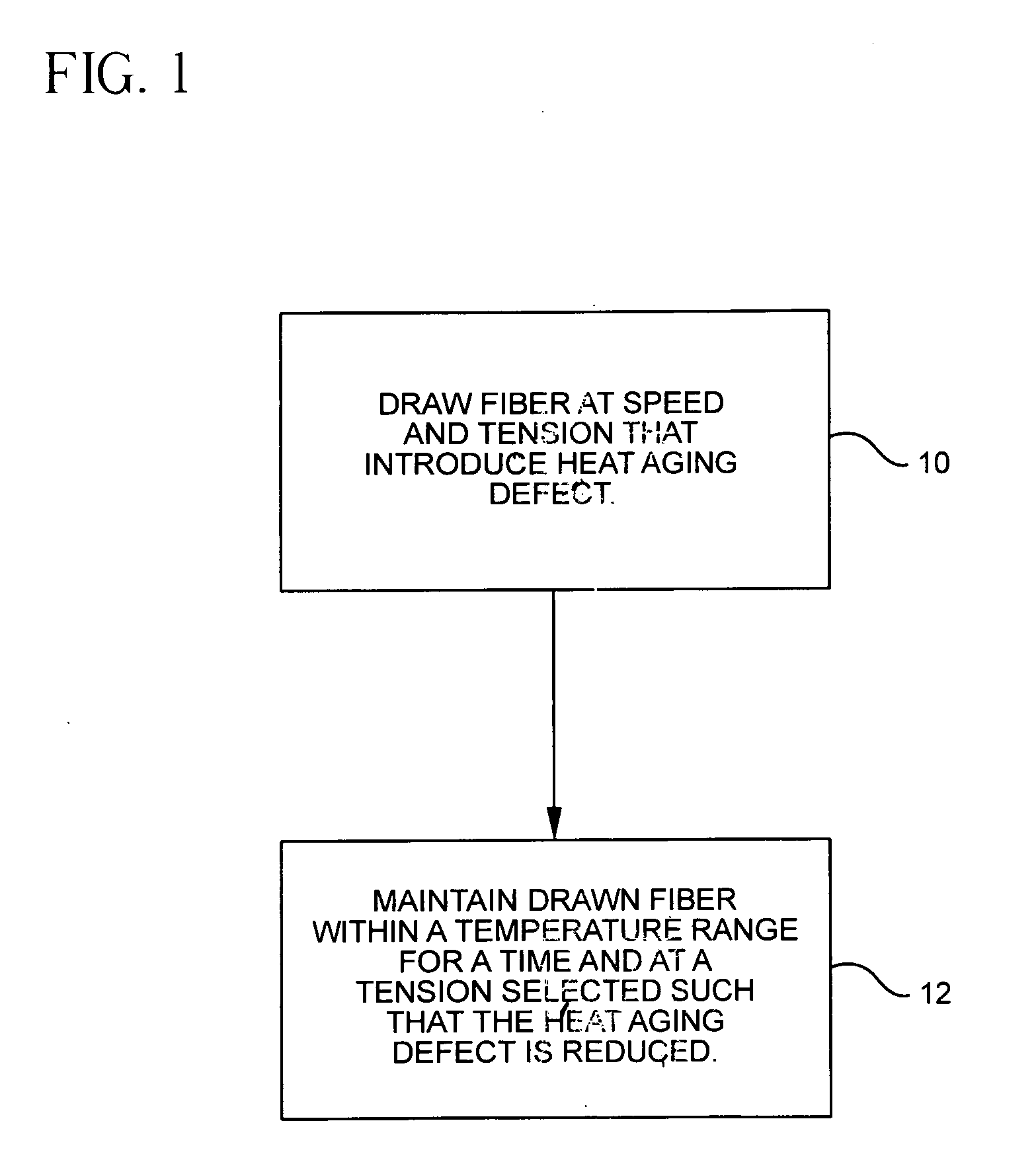
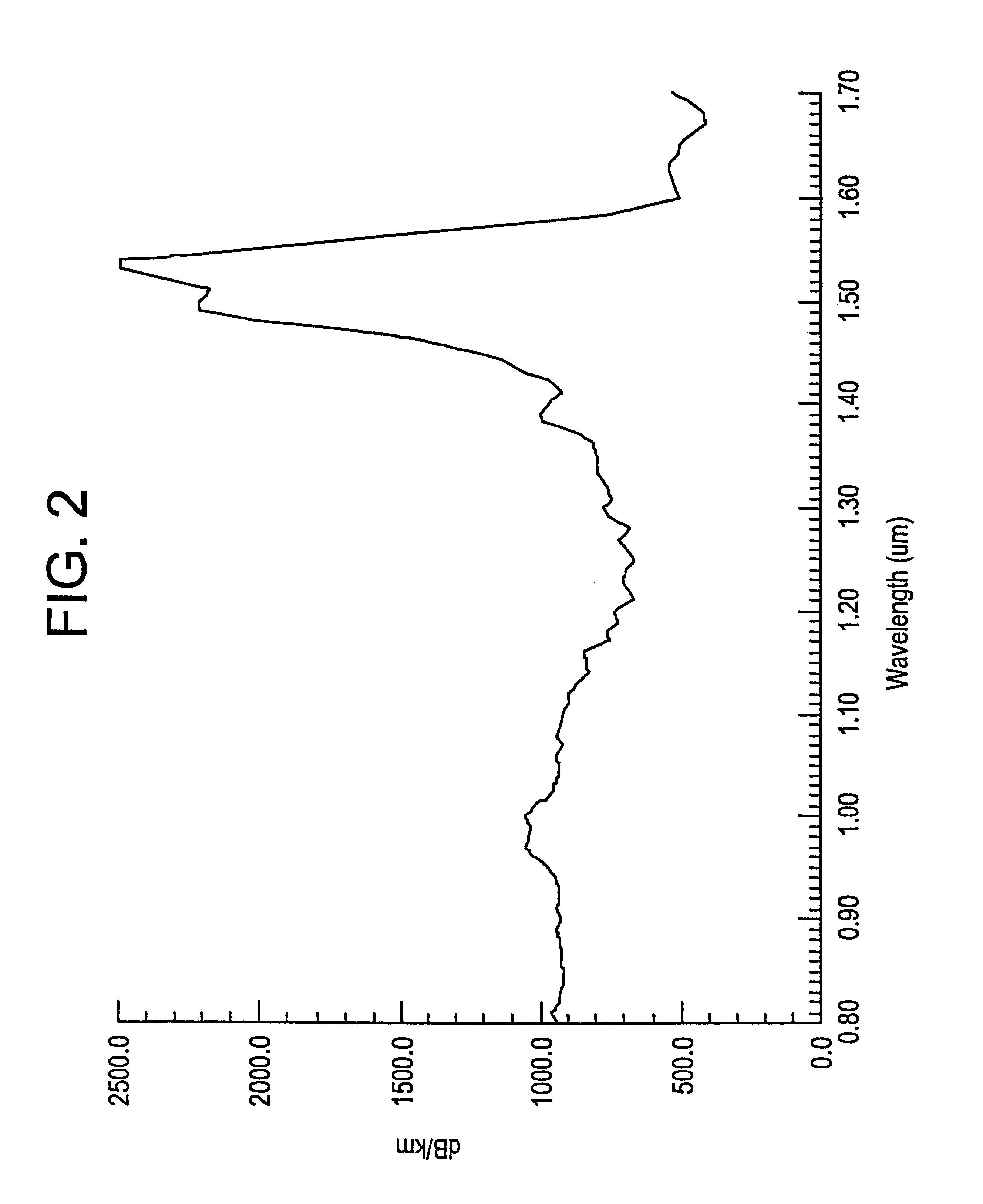
InactiveUS7565820B2Trend downDecreases micro-density variationGlass fibre drawing apparatusNon-linear opticsUltrasound attenuationRayleigh scattering
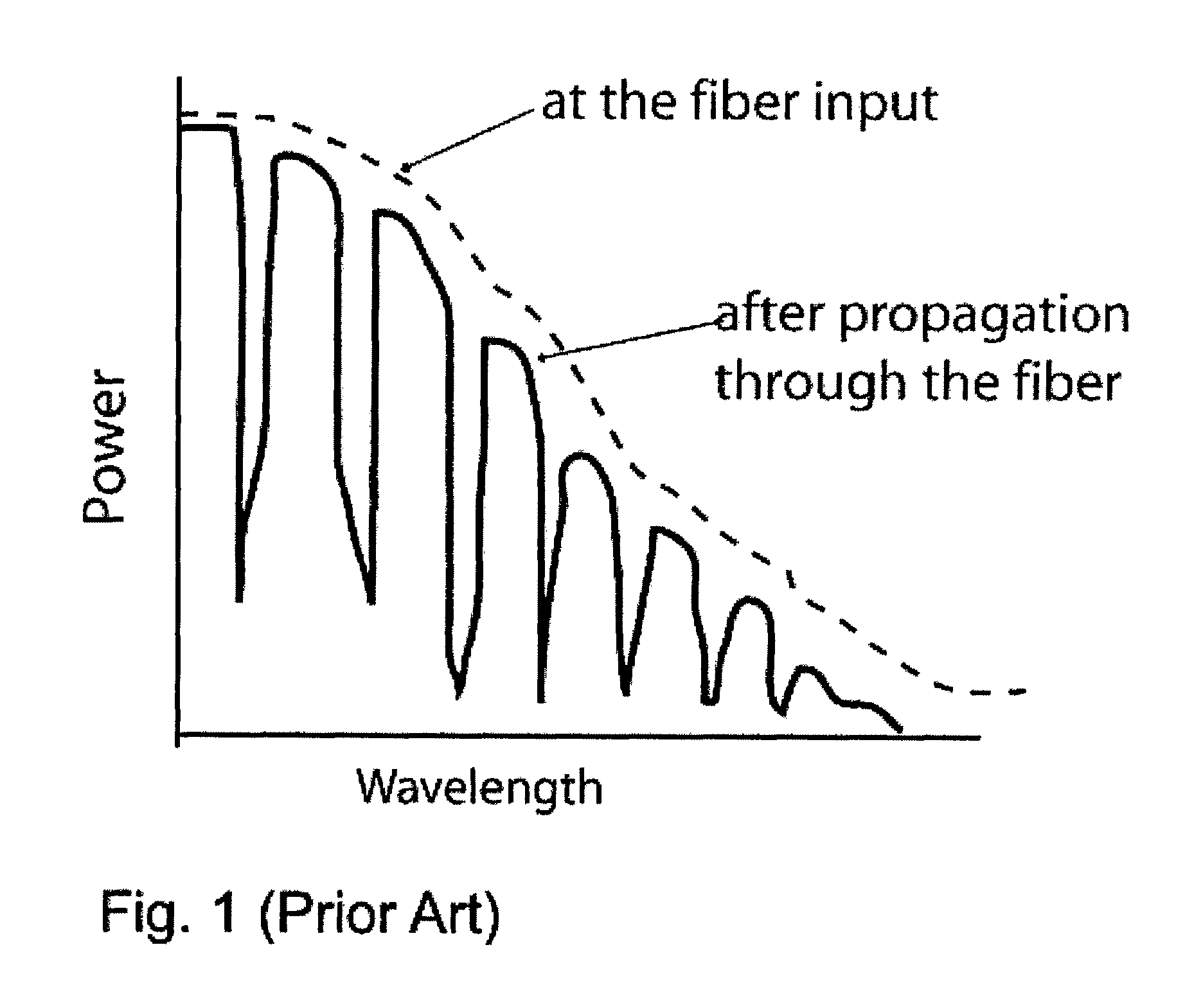
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber within a treatment temperature range for a treatment time. Preferably also, the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Apparatus are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering in optical fiber
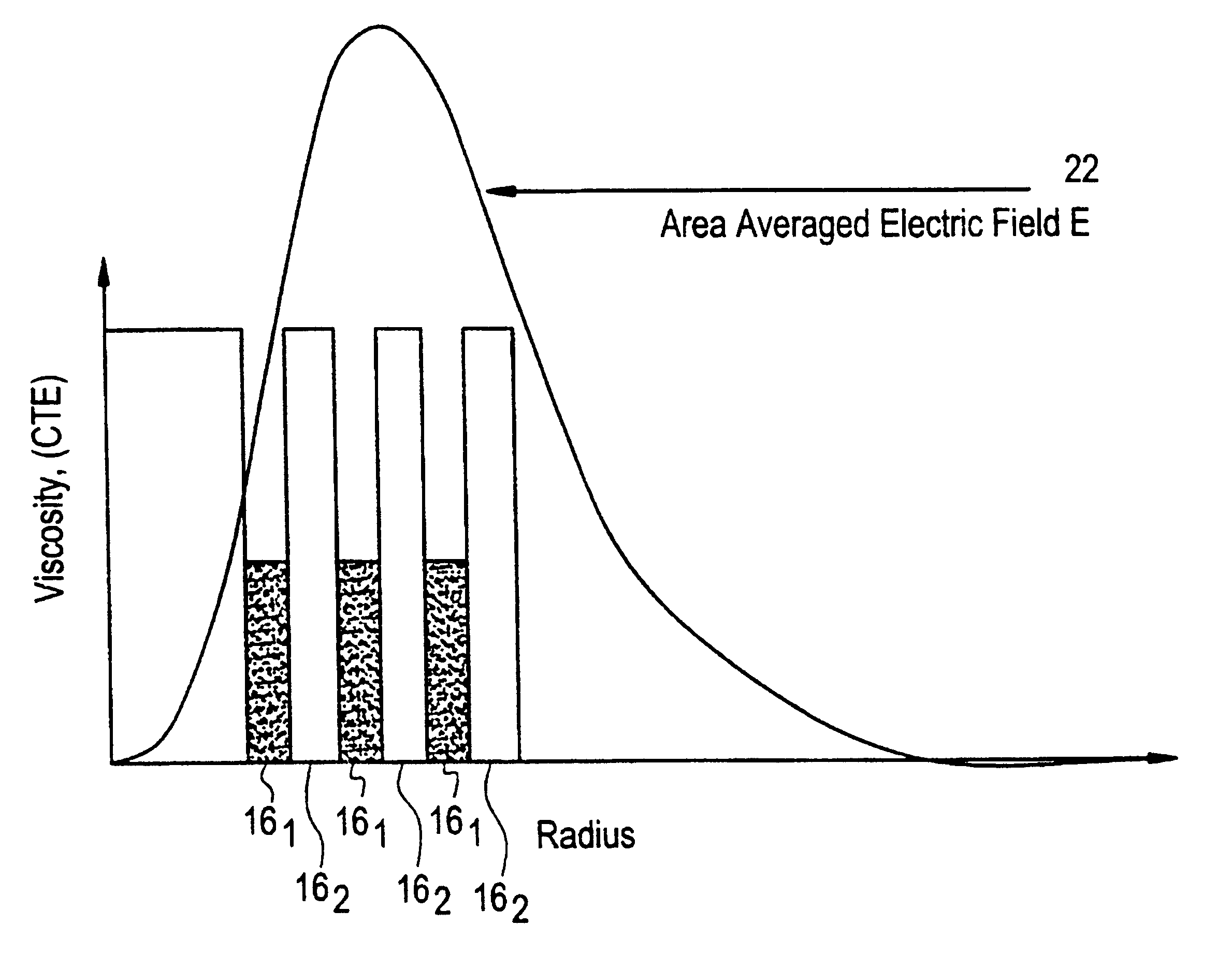
InactiveUS6542683B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberDopant
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) by broadening the energy spectrum of participating SBS photons and / or phonons is achieved in an optical fiber having a core with both radially nonuniform viscosity and CTE profiles provided by alternating layers of glass modifying dopants such as phosphorous and fluorine. The nonuniform thermal expansion and viscosity profiles impart a residual, permanent, nonuniform stress in the fiber. The SBS suppressing effect provided by the nonuniform stress can be controlled and enhanced by applying a uniform or nonuniform tensile force to the fiber as it is being drawn. A preform for the fiber is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
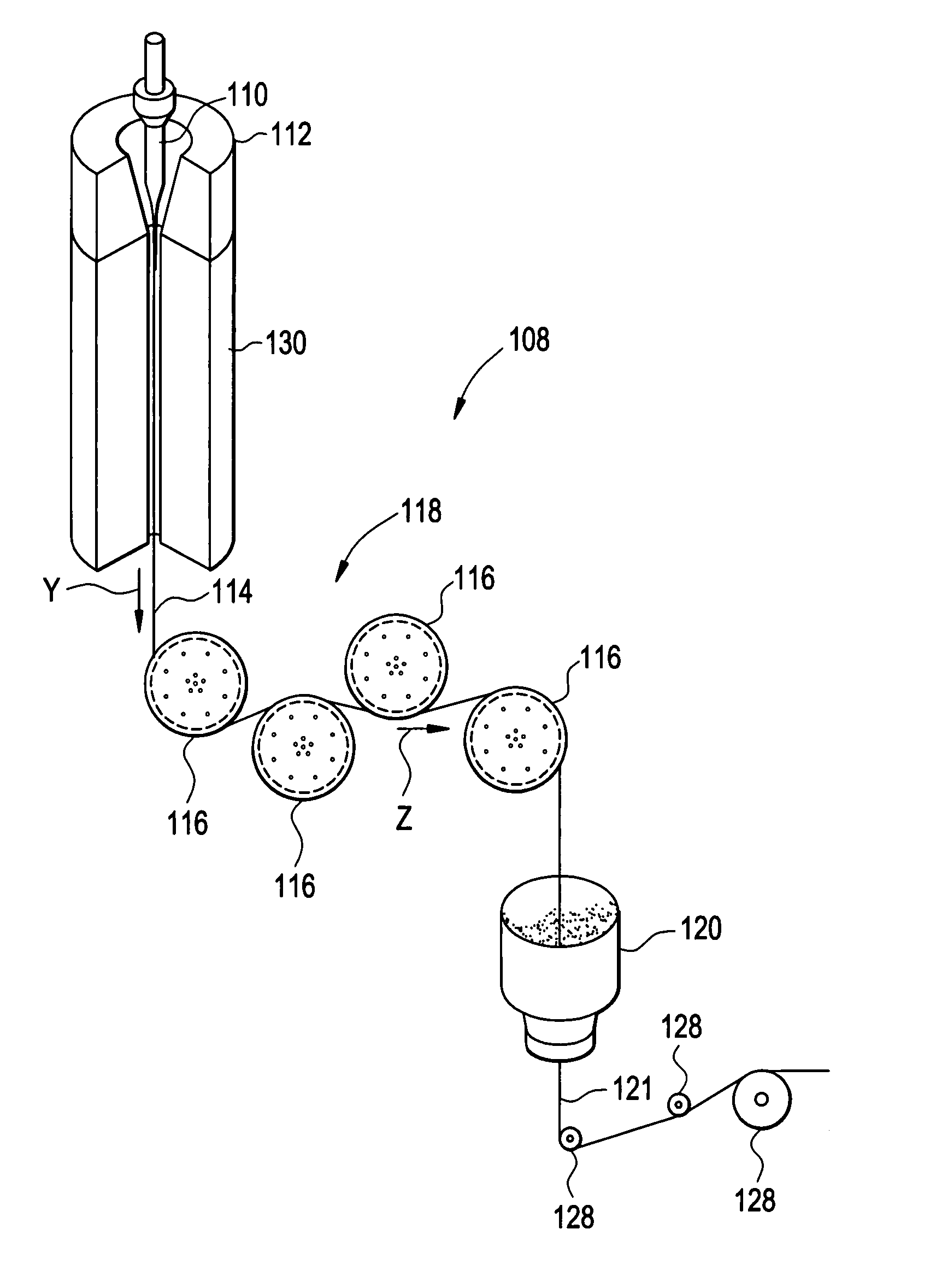
Method and apparatus for tensile testing and rethreading optical fiber during fiber draw
InactiveUS7832675B2Processing speedGlass fibre drawing apparatusFilament handlingFiber drawingTensile testing
A method and apparatus for automatic threading and winding of optical fiber onto various components in a fiber draw system, as well as methods and apparatus for conducting online tensile screening of optical fiber at high speeds. In a preferred embodiment, the fiber is tensile tested during fiber draw and wound directly onto a shipping spool to be shipped to a customer. The tensile stress can be imparted to the fiber during the draw process by feeding the fiber through a screener capstan, which works in conjunction with another capstan to impart the desired tensile stress to the fiber during the draw process. Another aspect is a method and apparatus for threading or rethreading of a moving length of fiber through a fiber draw or fiber testing process, in which fiber is wound onto a spool, comprising activating an aspirator to obtain the fiber at a first location and moving said aspirator in at least two dimensions to thereby move the fiber to a second location and thread the fiber through or onto at least one component in the fiber draw or testing process.
Owner:CORNING INC
Side-emitting step index fiber
ActiveUS20110103757A1Produced economicallyImprove scalabilityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusCouplingRefractive index
Side-emitting step index fibers. Between core and cladding, the side-emitting step index fibers have scattering centers that ensure the coupling out of light from the fiber. The side-emitting step index fibers are produced by preforms that contain inlay rods, in which the scattering centers are embedded and which are applied to the outer region of the fiber core during fiber drawing. Alternatively, at least one inlay tube can be used.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
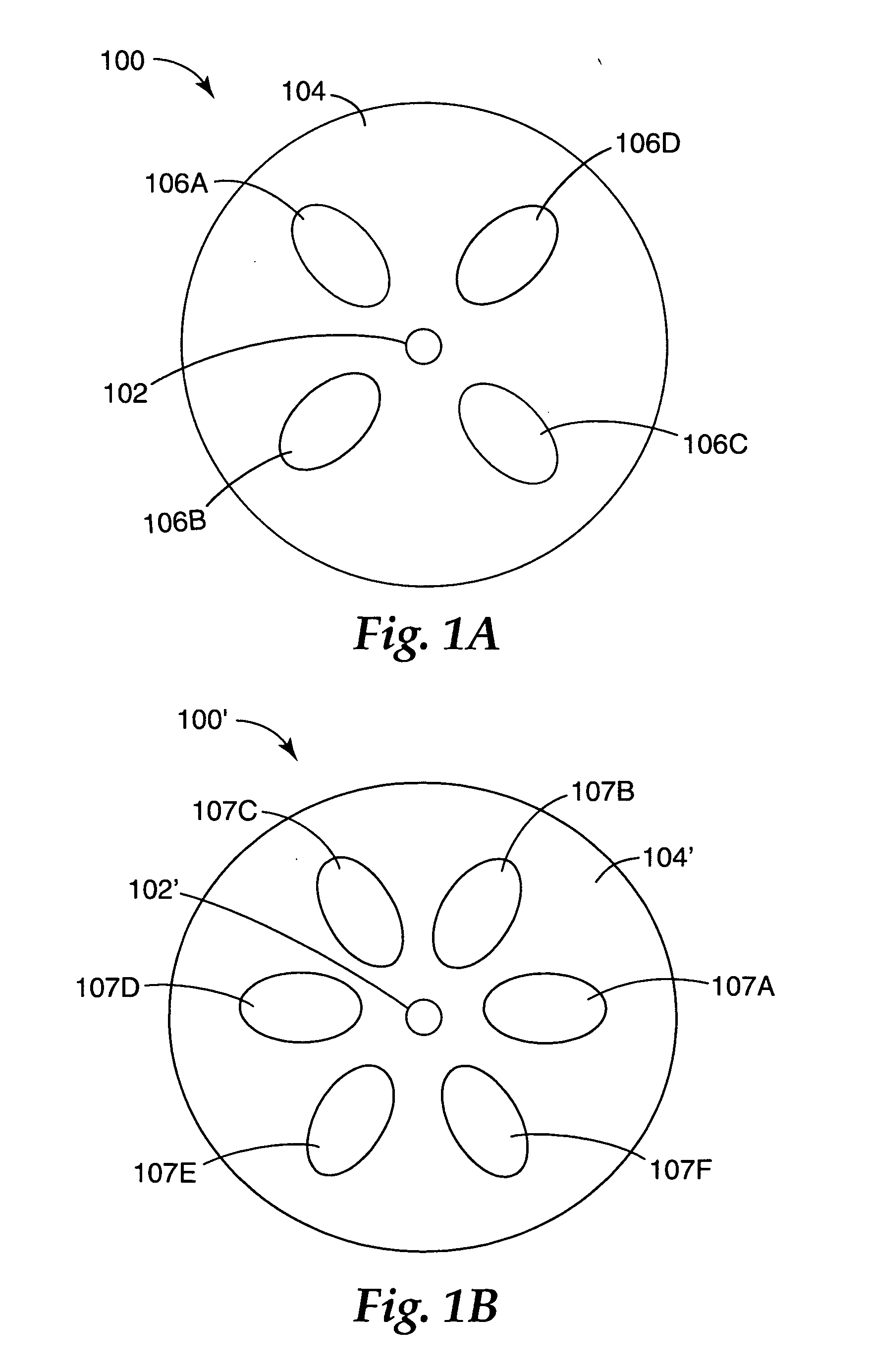
Hole assisted fiber device and fiber preform
A hole-assisted fiber comprises a core region and a cladding region, where the cladding region includes multiple substantially elliptical holes spaced apart from each other to surround the core region. The holes are filled with one of a gas and a liquid to form a low refractive index portion of the cladding region.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
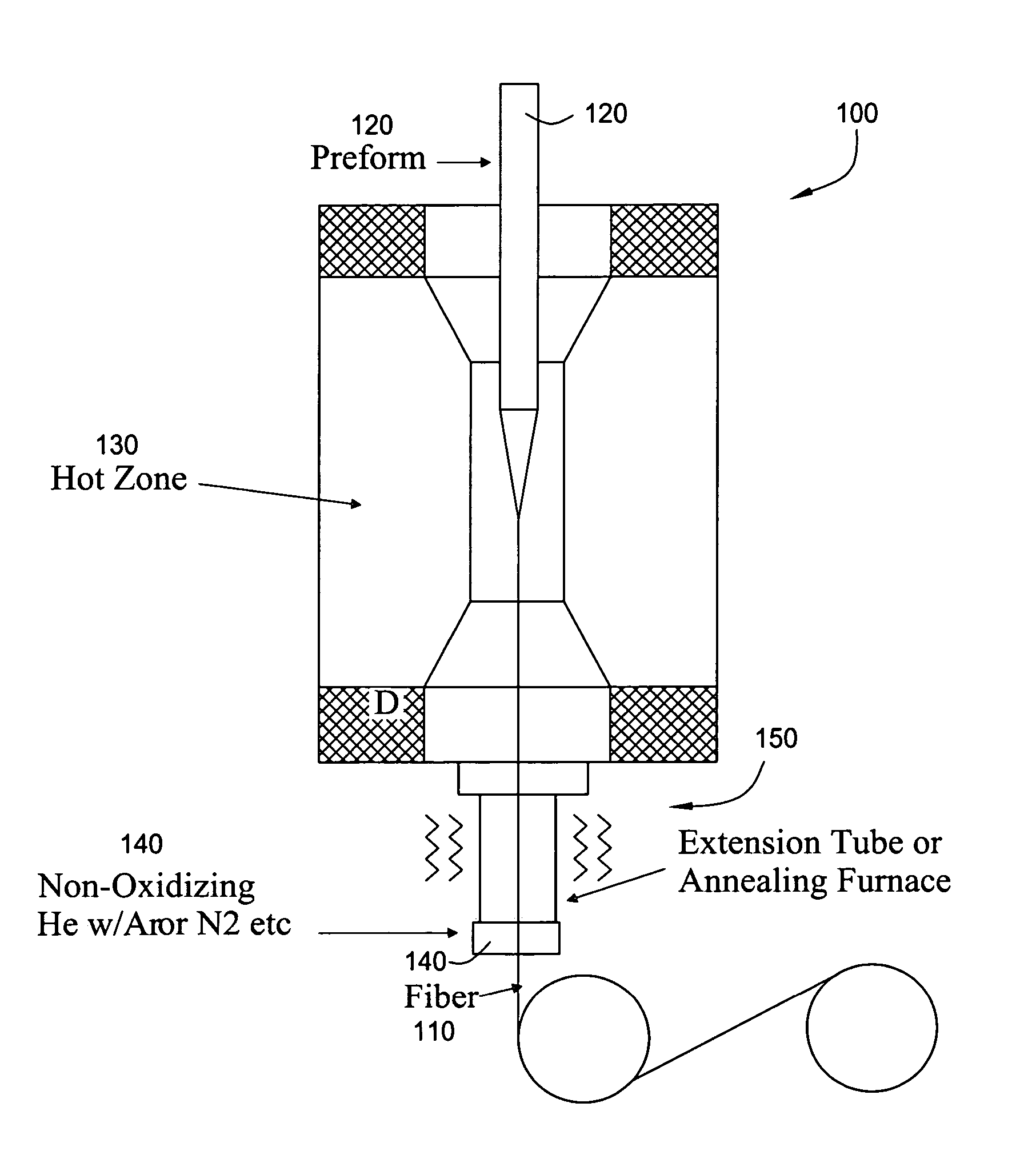
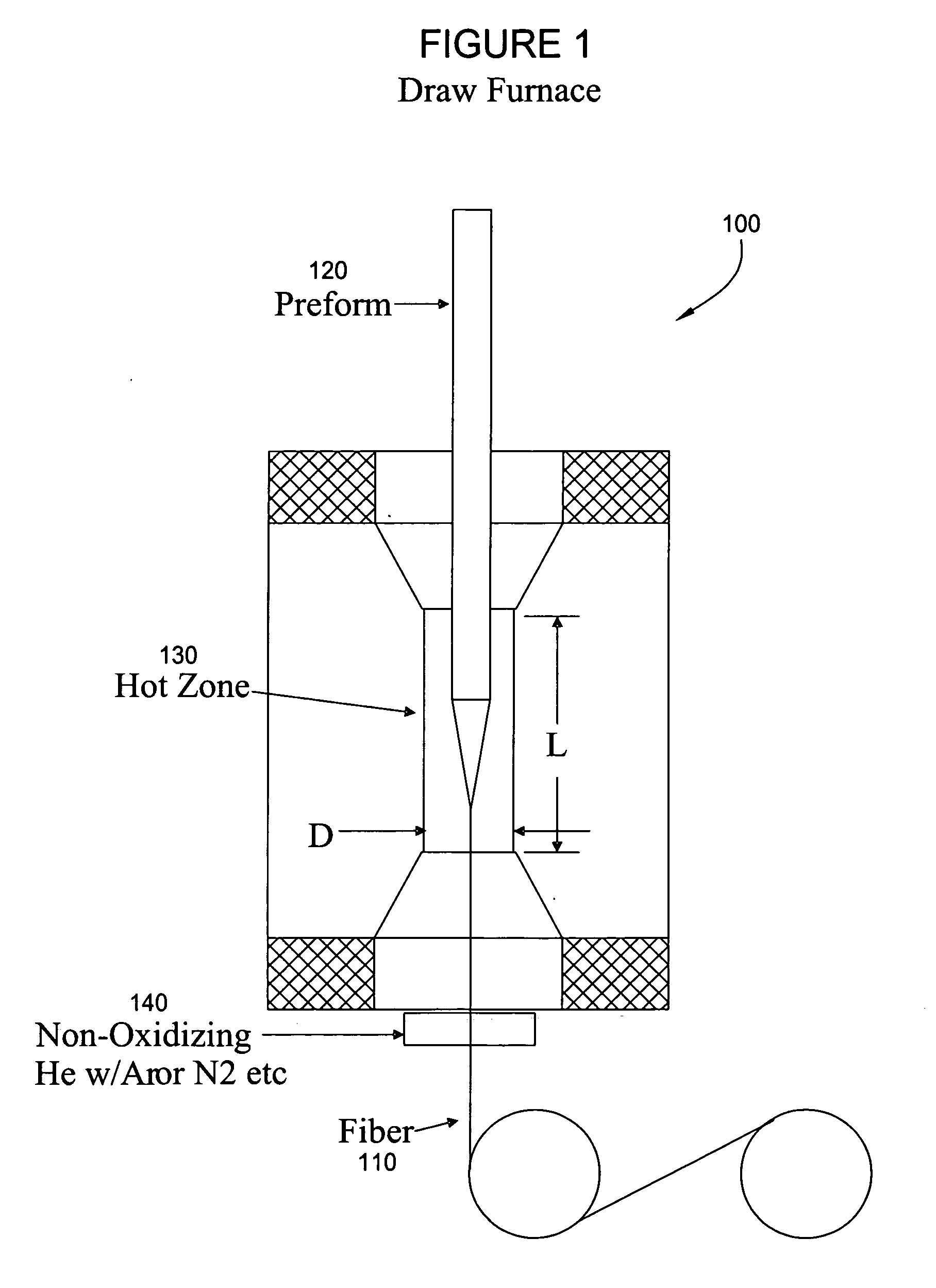
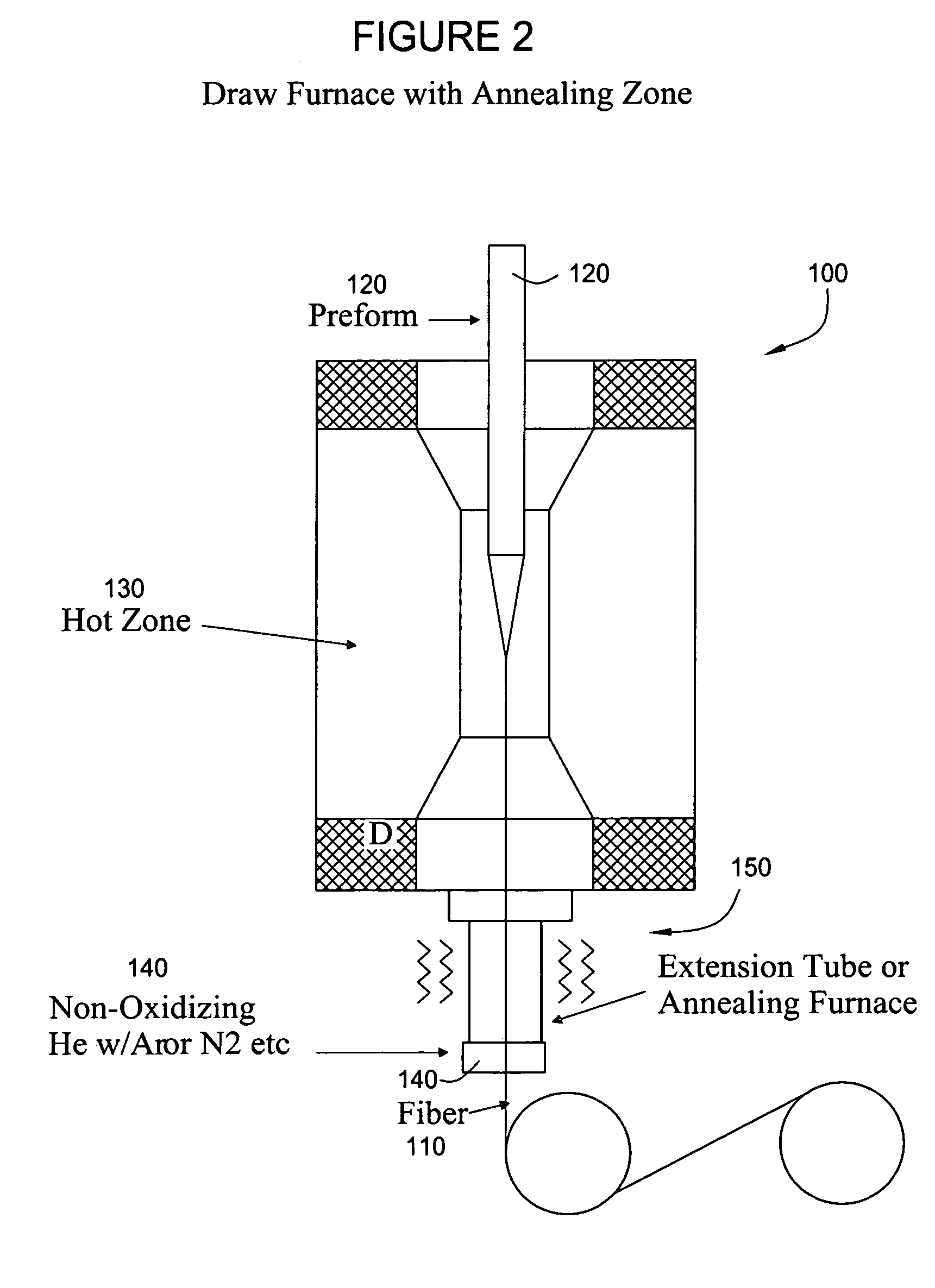
Furnace and process for drawing radiation resistant optical fiber
Apparatus and methods to fabricate a radiation hardened optical fiber from a preform are provided. Various parameters affecting the draw process are controlled to optimize the radiation resistance of the resulting fiber. An annealing zone may be provided to allow a drawn fiber exiting a primary hot zone to undergo an annealing process which may increase radiation resistance.
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB
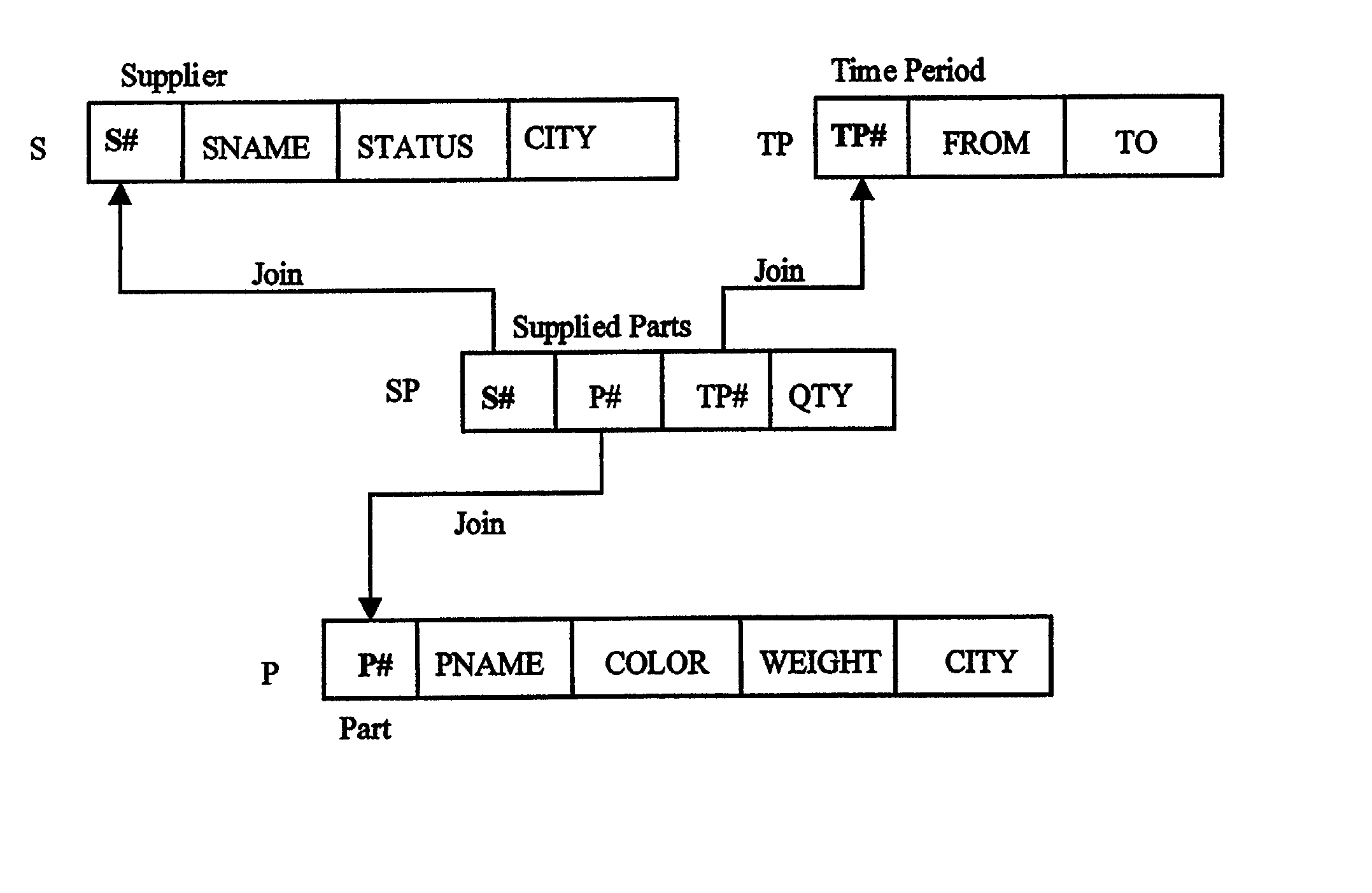
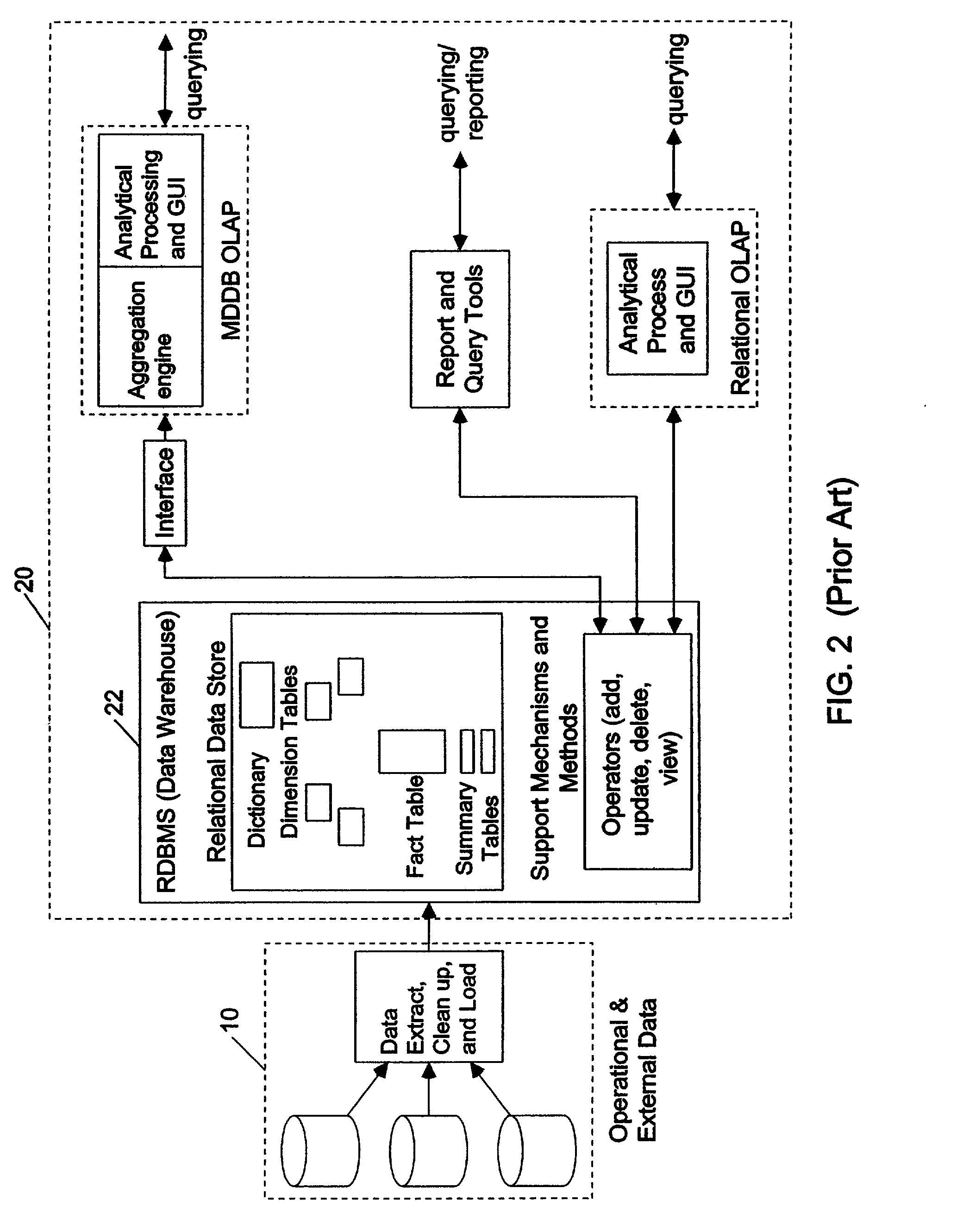
Relational database management system having integrated non-relational multi-dimensional data store of aggregated data elements
InactiveUS20020194167A1Impacting performanceImpacting scalabilityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData warehouseUsability
Improved method of and apparatus for joining and aggregating data elements integrated within a relational database management system (RDBMS) using a non-relational multi-dimensional data structure (MDD). The improved RDBMS system of the present invention can be used to realize achieving a significant increase in system performance (e.g. deceased access / search time), user flexibility and ease of use. The improved RDBMS system of the present invention can be used to realize an improved Data Warehouse for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations or to realize an improved informational database system or the like.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
Fabrication of microstructured optical fibre
InactiveUS20060104582A1Smooth materialImprove optical qualityLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreAudio power amplifierExtinction
Microstructured optical fibre is fabricated using extrusion. The main design of optical fibre has a core suspended in an outer wall by a plurality of struts. A specially designed extruder die is used which comprises a central feed channel, flow diversion channels arranged to divert material radially outwards into a welding chamber formed within the die, a core forming conduit arranged to receive material by direct onward passage from the central feed channel, and a nozzle having an outer part in flow communication with the welding chamber and an inner part in flow communication with the core forming conduit, to respectively define an outer wall and core of the preform. With this design a relatively thick outer wall can be combined with thin struts (to ensure extinction of the optical mode field) and a core of any desired diameter or other thickness dimension in the case of non-circular cores. As well as glass, the extrusion process is suitable for use with polymers. The microstructured optical fibre is considered to have many potential device applications, in particular for non-linear devices, lasers and amplifiers.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Multimode optical fibers with increased bandwidth
InactiveUS7043128B2Glass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingMulti core fiberMulti-mode optical fiber
The specification describes a technique for drawing circular core multimode optical fiber using twist during draw to increase fiber bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Micro-structured optical fiber
InactiveUS6892018B2Reduce coupling lossGood dispersionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusPhotonic bandgapLight guide
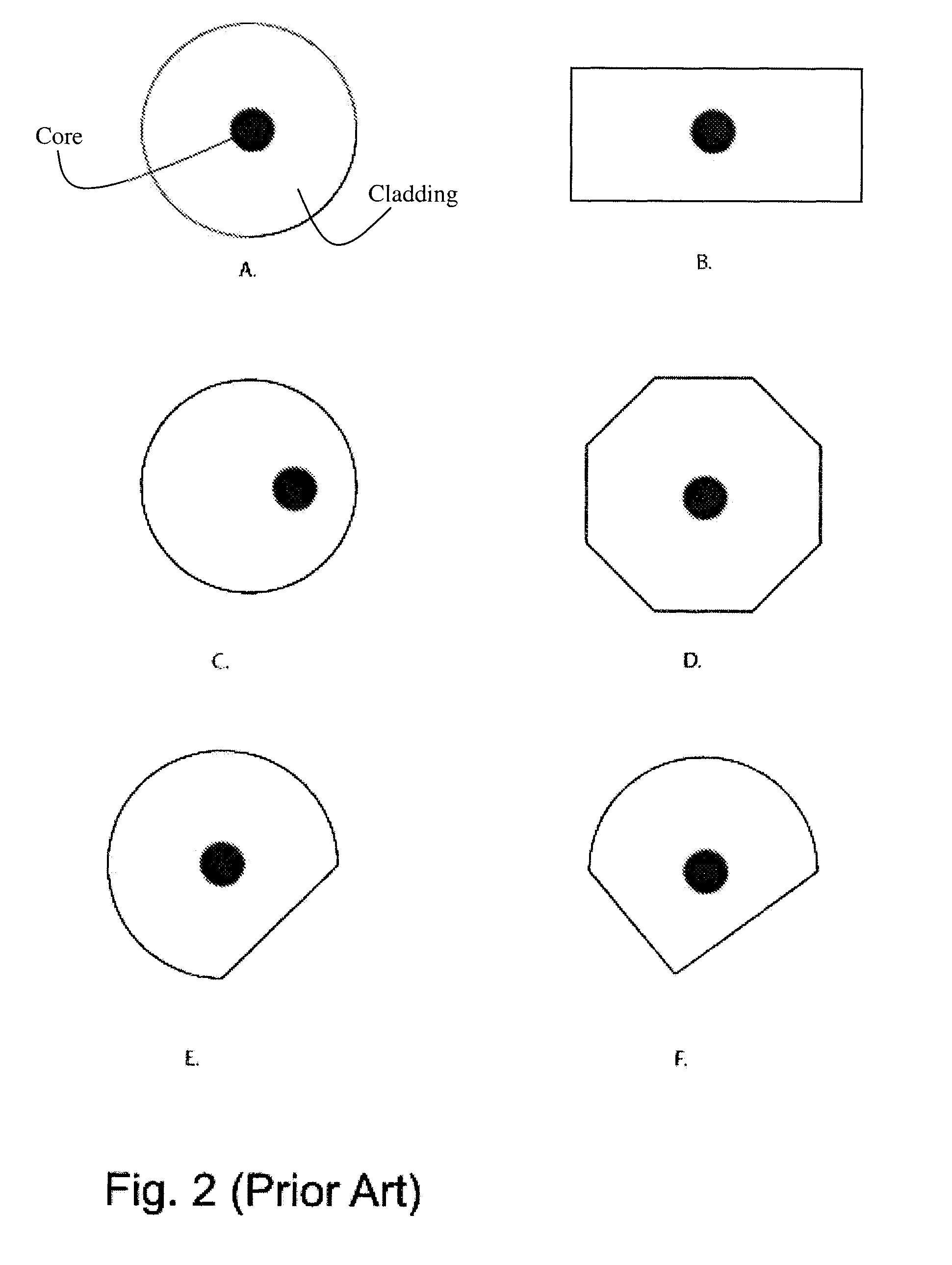
A microstructured fiber having a cladding comprising a number of elongated features that are arranged to provide concentric circular or polygonial regions surrounding the fiber core. The cladding comprises a plurality of concentric cladding regions, at least some of which comprising cladding features. Cladding regions comprising cladding features of a relatively low index type are arranged alternatingly with cladding regions of a relatively high index type. The cladding features are arranged in a non-periodic manner when viewed in a cross section of the fiber. The cladding enables waveguidance by photonic bandgap effects in the fiber core. An optical fiber of this type may be used for light guidance in hollow core fibers for high power transmission. The special cladding structure may also provide strong positive or negative dispersion of light guided through the fiber-making the fiber useful for telecommunication applications.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
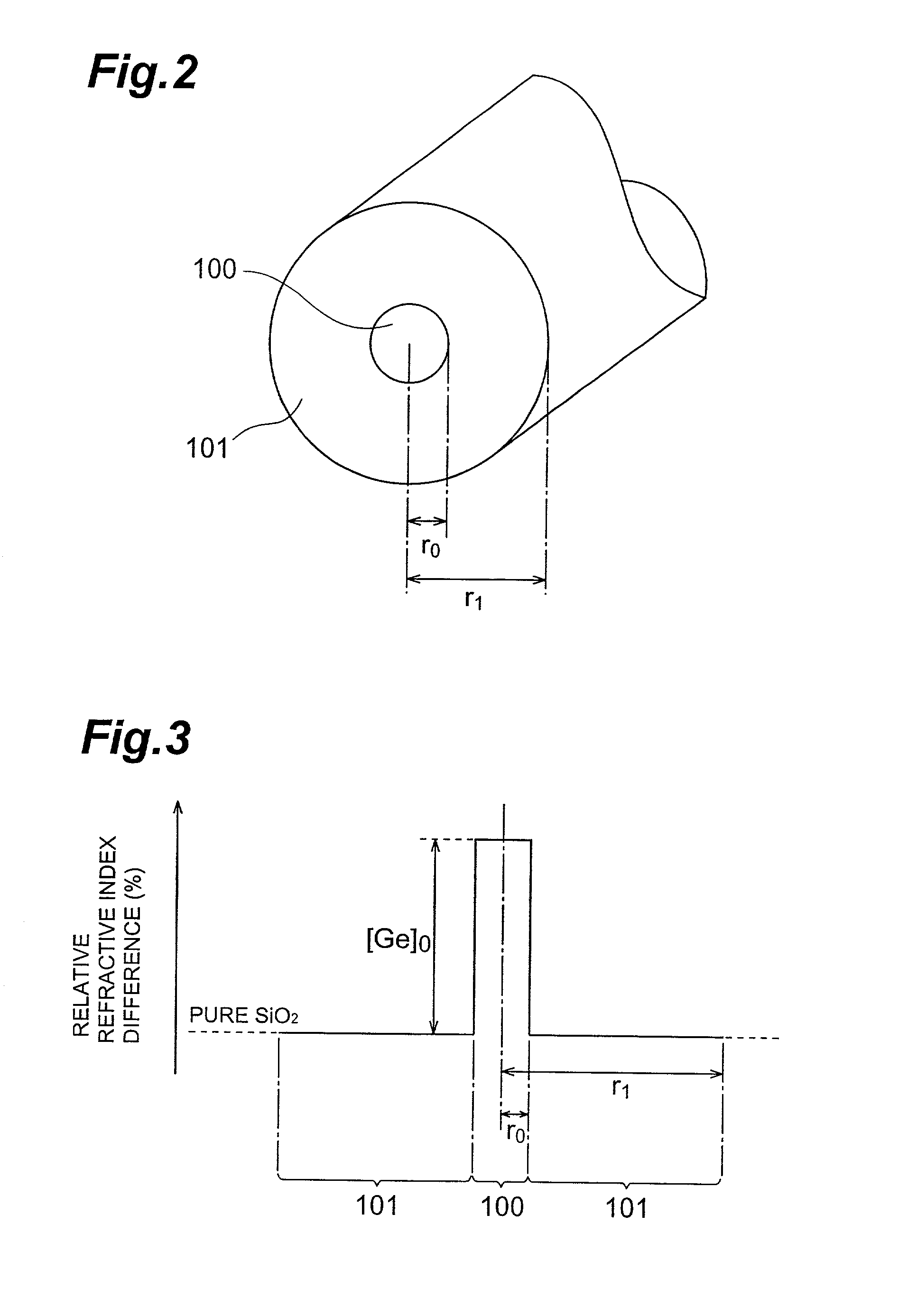
Optical fiber and method of making the same
InactiveUS20020044753A1Reduce transmission lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusRayleigh scatteringFiber
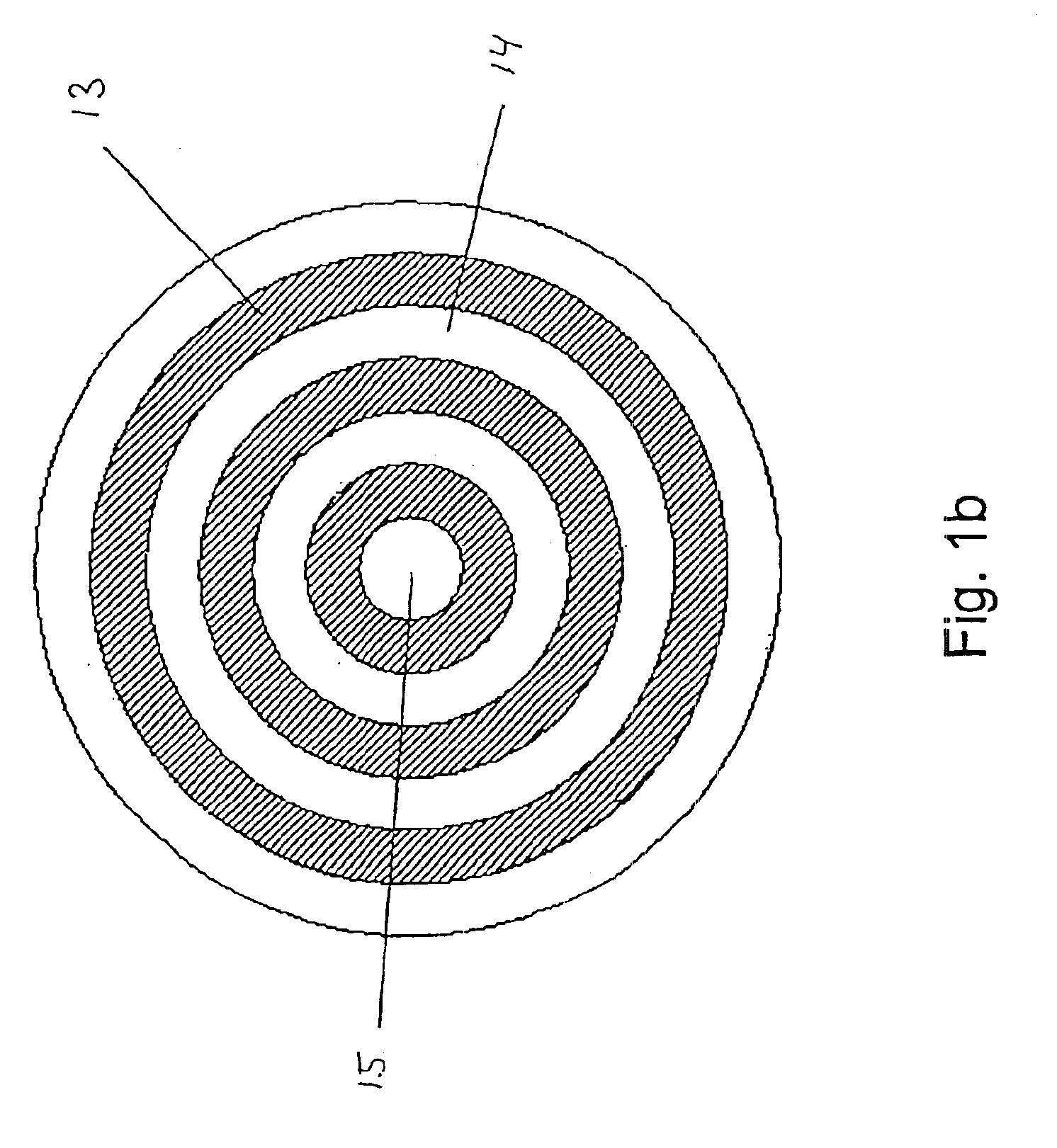
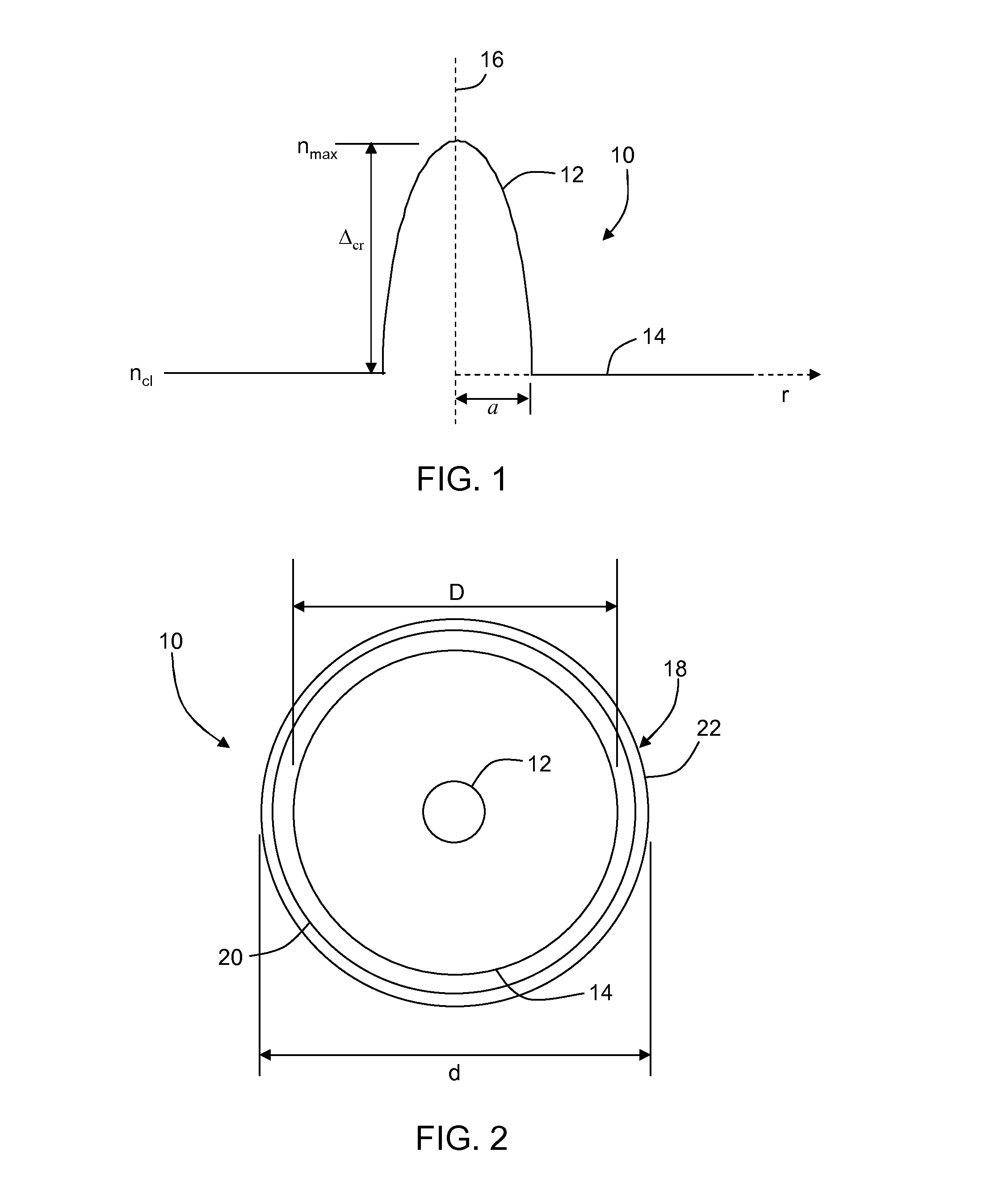
An optical fiber preform 2 having a viscosity ratio Reta=eta0 / etat of 2.5 or less between the core average viscosity eta0 and the total average viscosity etat is prepared, and is drawn by a drawing furnace 11 so as to yield an optical fiber 3, which is then heated to a temperature within a predetermined range so as to be annealed by a heating furnace 21 disposed downstream the drawing furnace 11. Here, upon annealing in the heating furnace 21, the fictive temperature Tf within the optical fiber lowers, thereby reducing the Rayleigh scattering loss. At the same time, the viscosity ratio condition of Reta<=2.5 restrains the stress from being concentrated into the core, thereby lowering the occurrence of structural asymmetry loss and the like. Hence, anoptical fiber which can reduce the transmission loss caused by the Rayleigh scattering loss and the like as a whole, and a method of making the same can be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
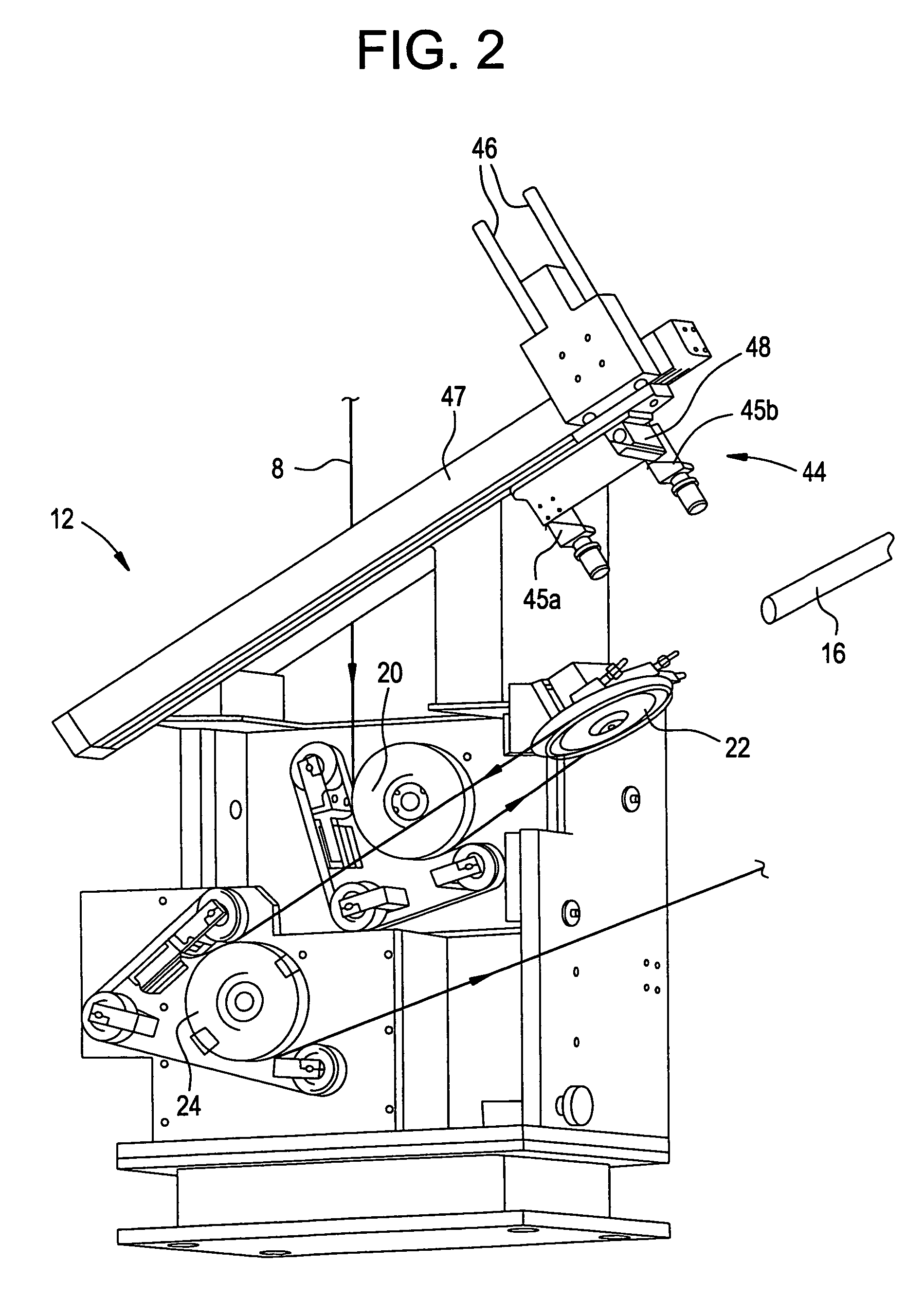
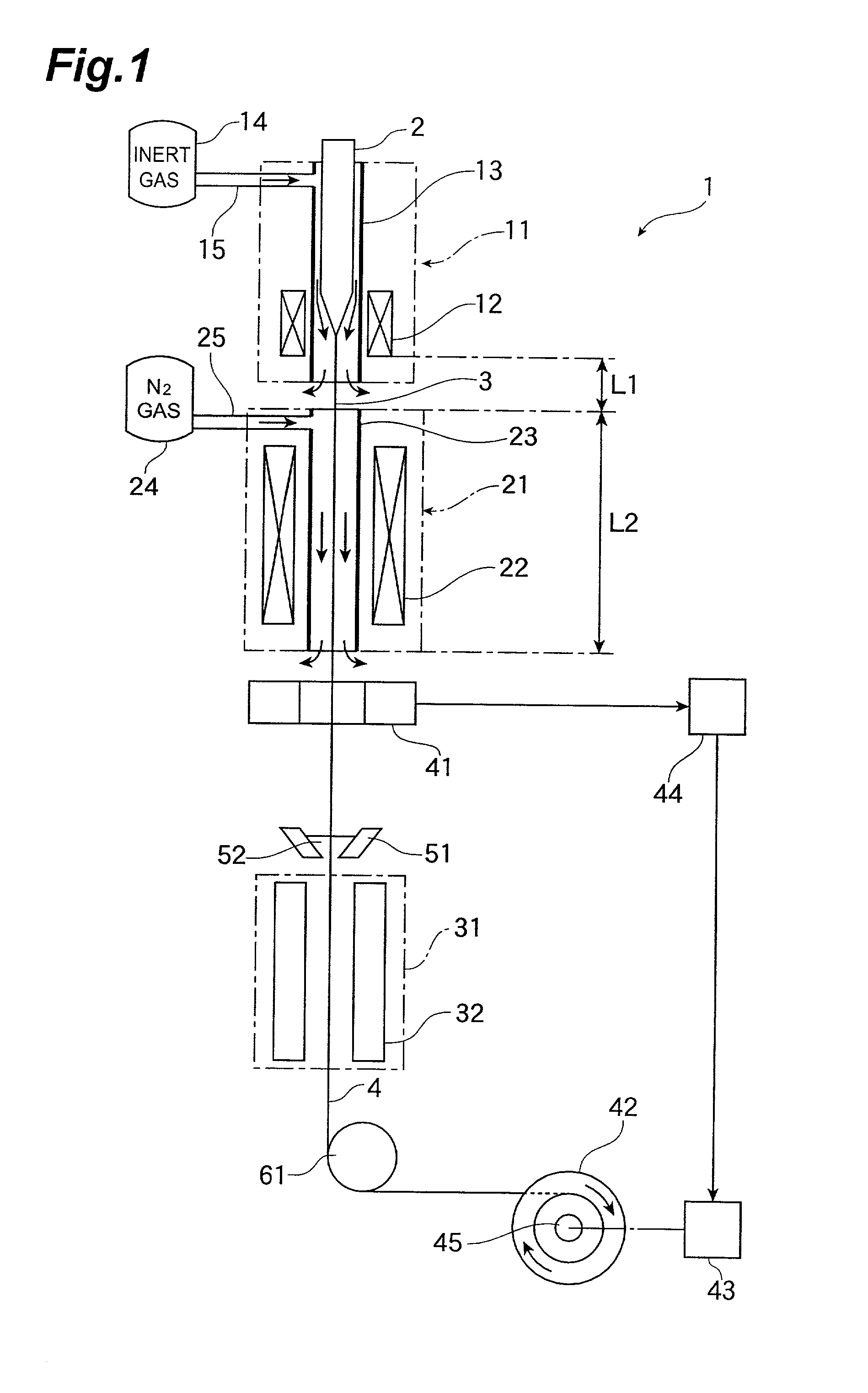
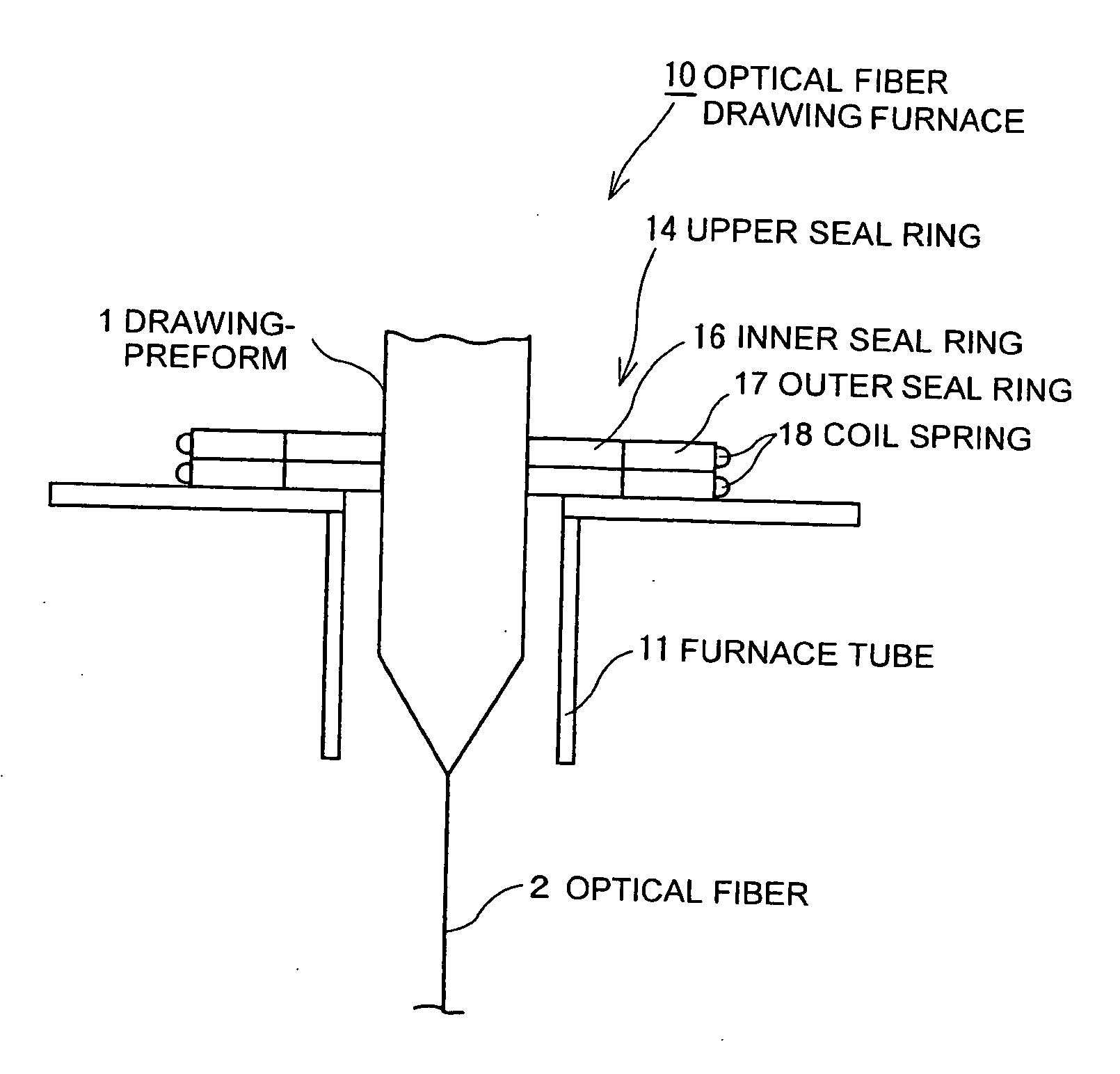
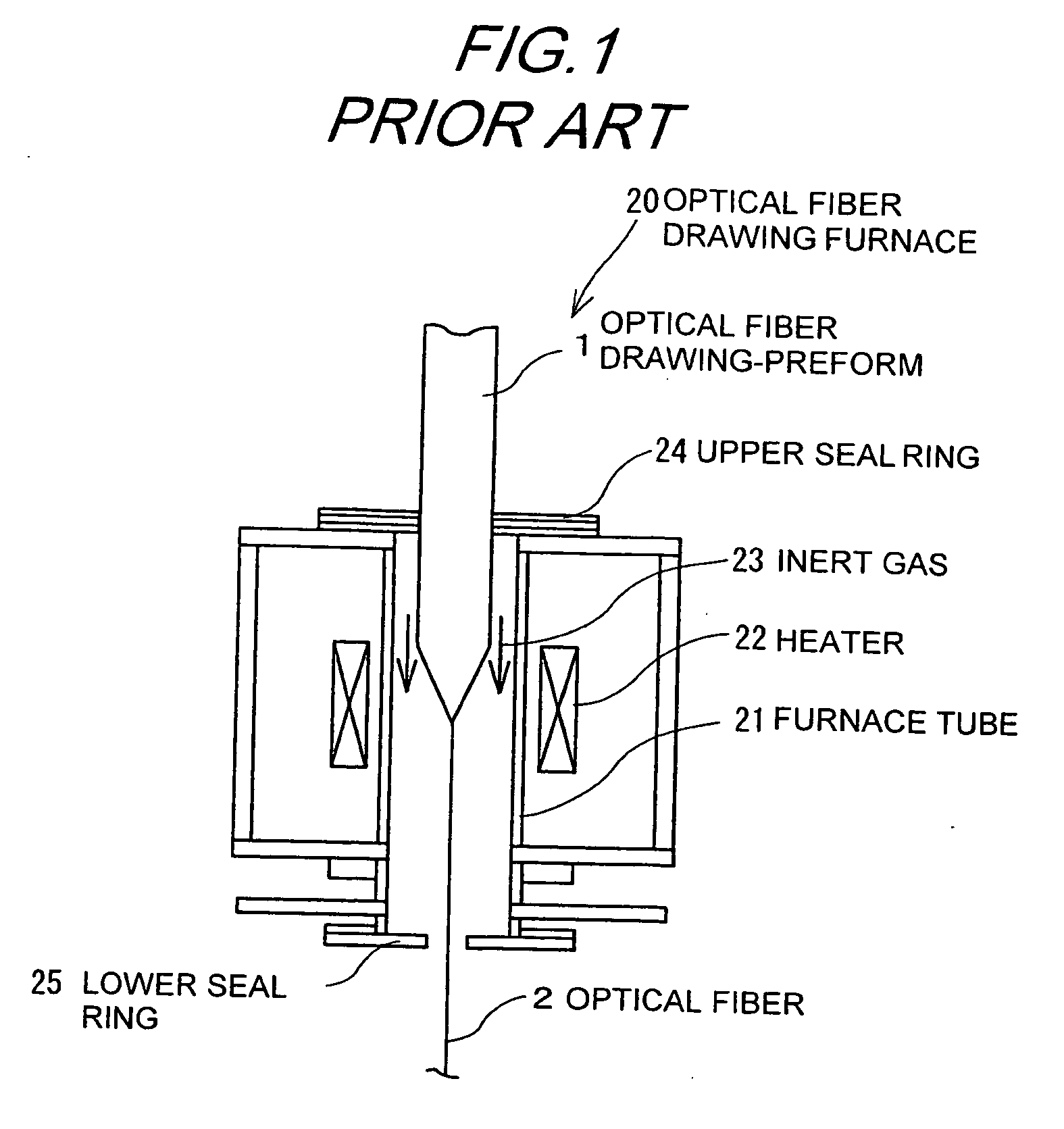
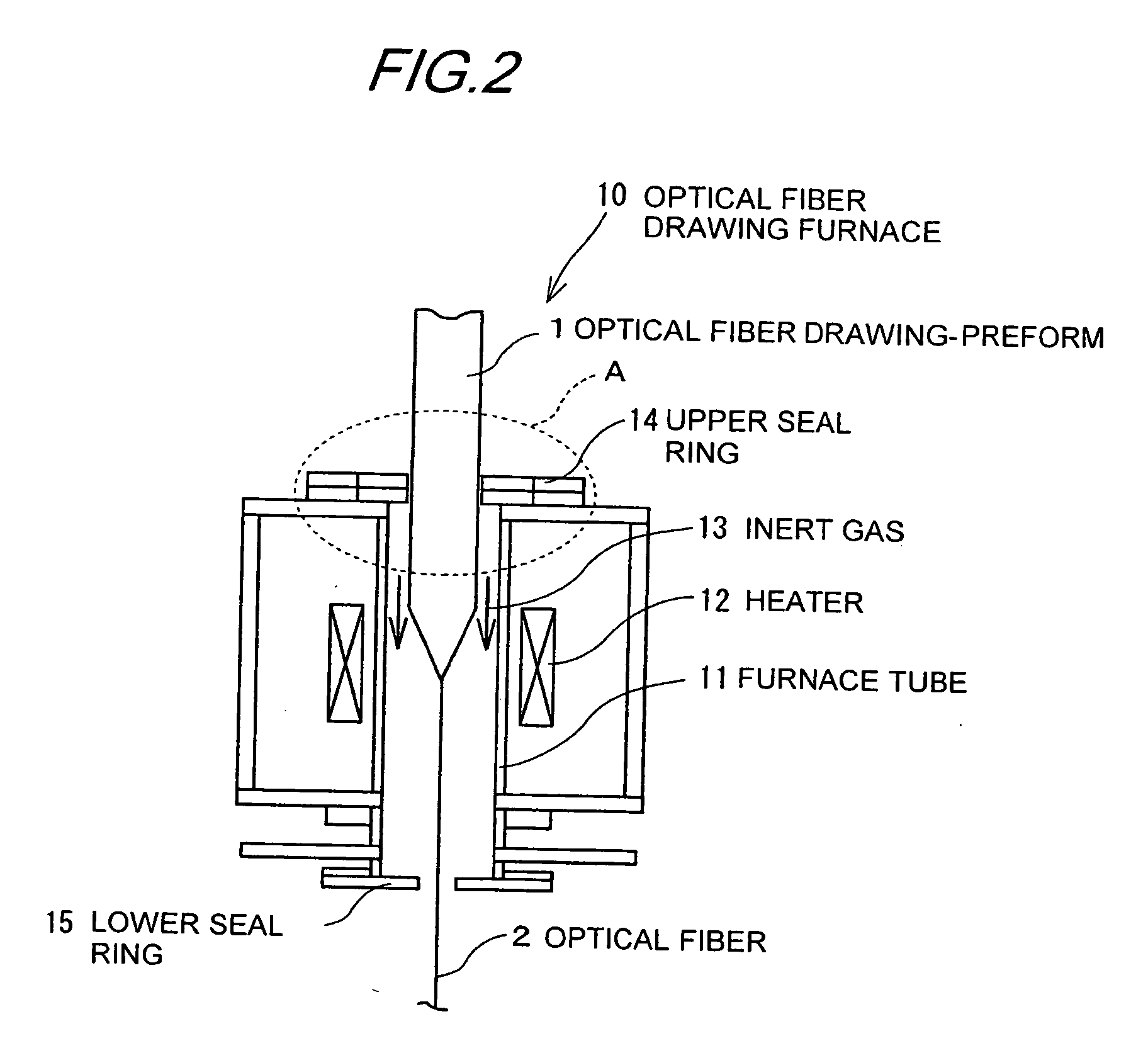
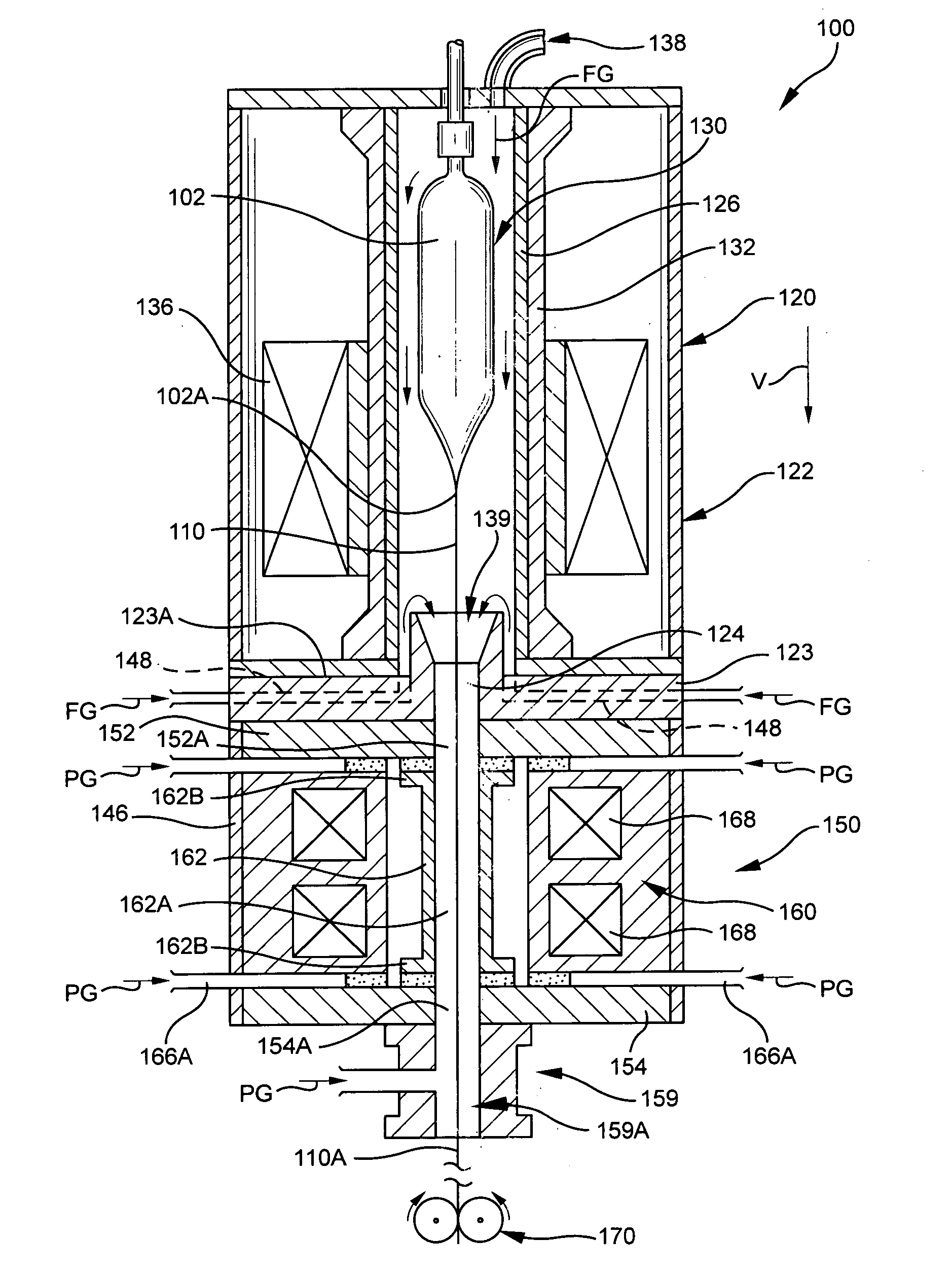
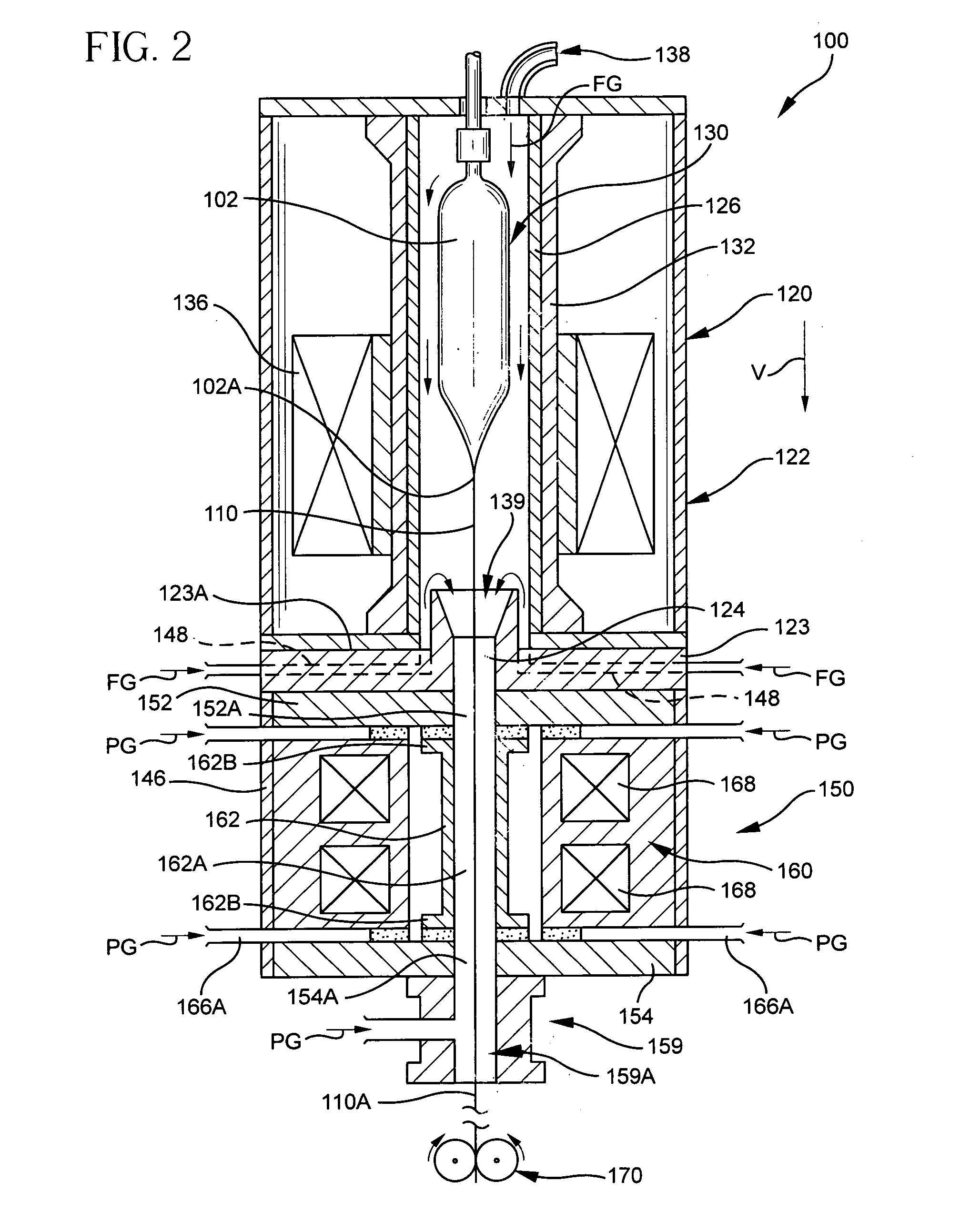
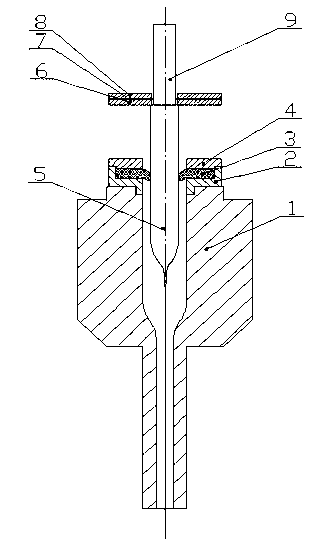
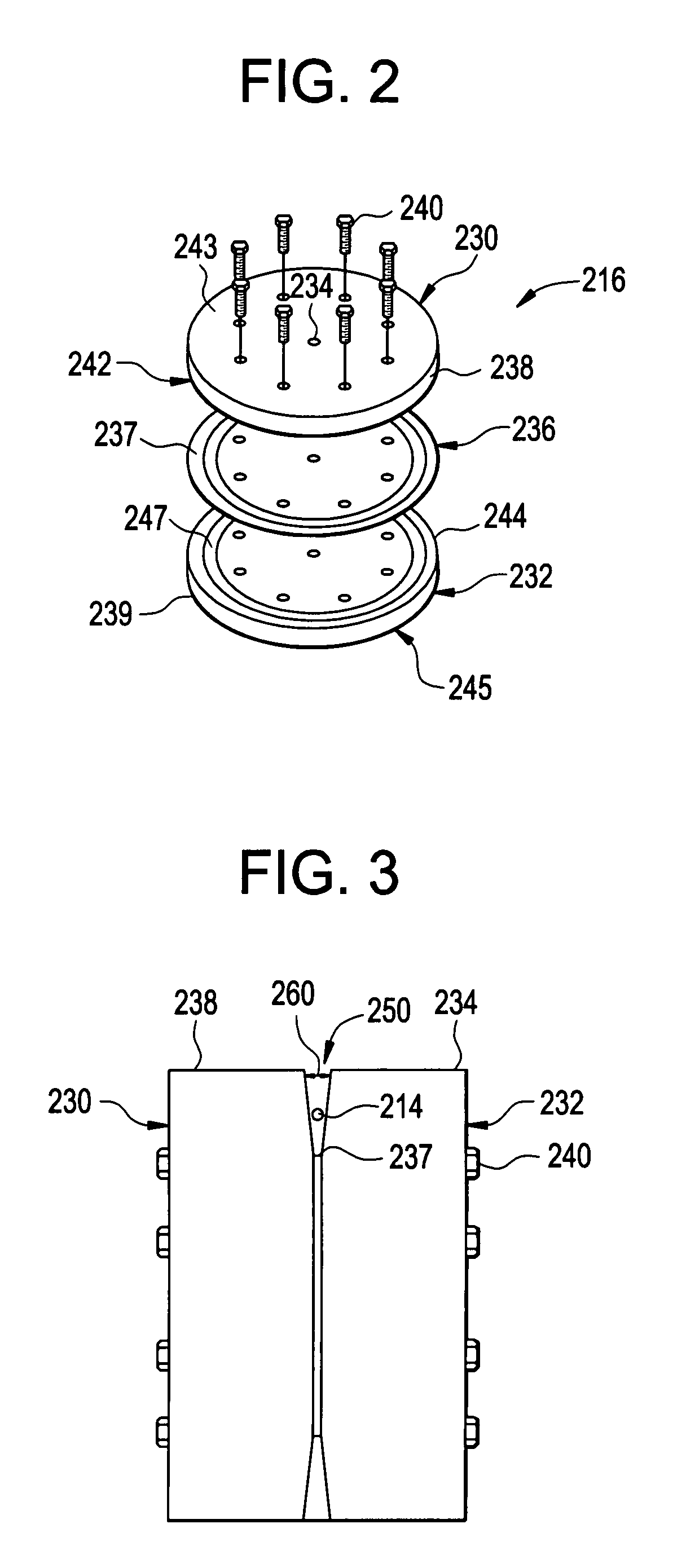
Optical fiber drawing apparatus, sealing mechanism for the same, and method for drawing an optical fiber
InactiveUS20060280578A1Simple structureKeep tightWashersGlass furnace apparatusCoil springEngineering
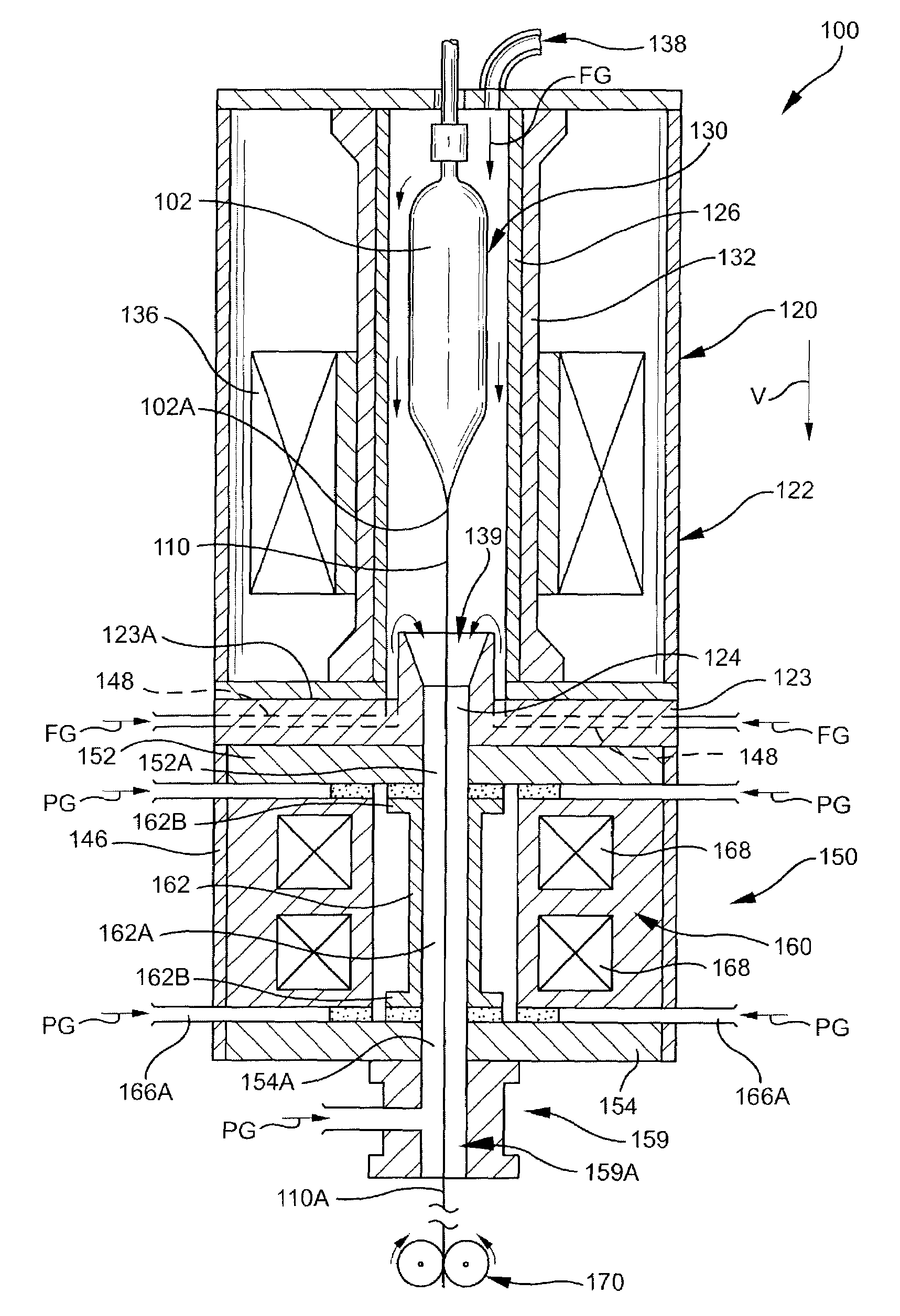
An inner seal ring 16 is composed by connecting a plurality of inner seal ring pieces 16A, an outer seal ring 17 is composed by connecting a plurality of outer seal ring pieces 17A provided at an outer periphery of the inner seal ring 16, and a coil spring 18 is arranged at an outer periphery of the outer seal ring 17. The inner seal ring 16 and the outer seal ring 17 are piled for two or more stages, respectively. A connecting part of the inner seal ring pieces 16A and a connecting part of the outer seal ring pieces 17 are arranged not to overlap each other. An inner diameter of the inner seal ring 16 is variable in accordance with an outer diameter in vertical direction of a drawing-preform 1 by using a coil spring 18.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
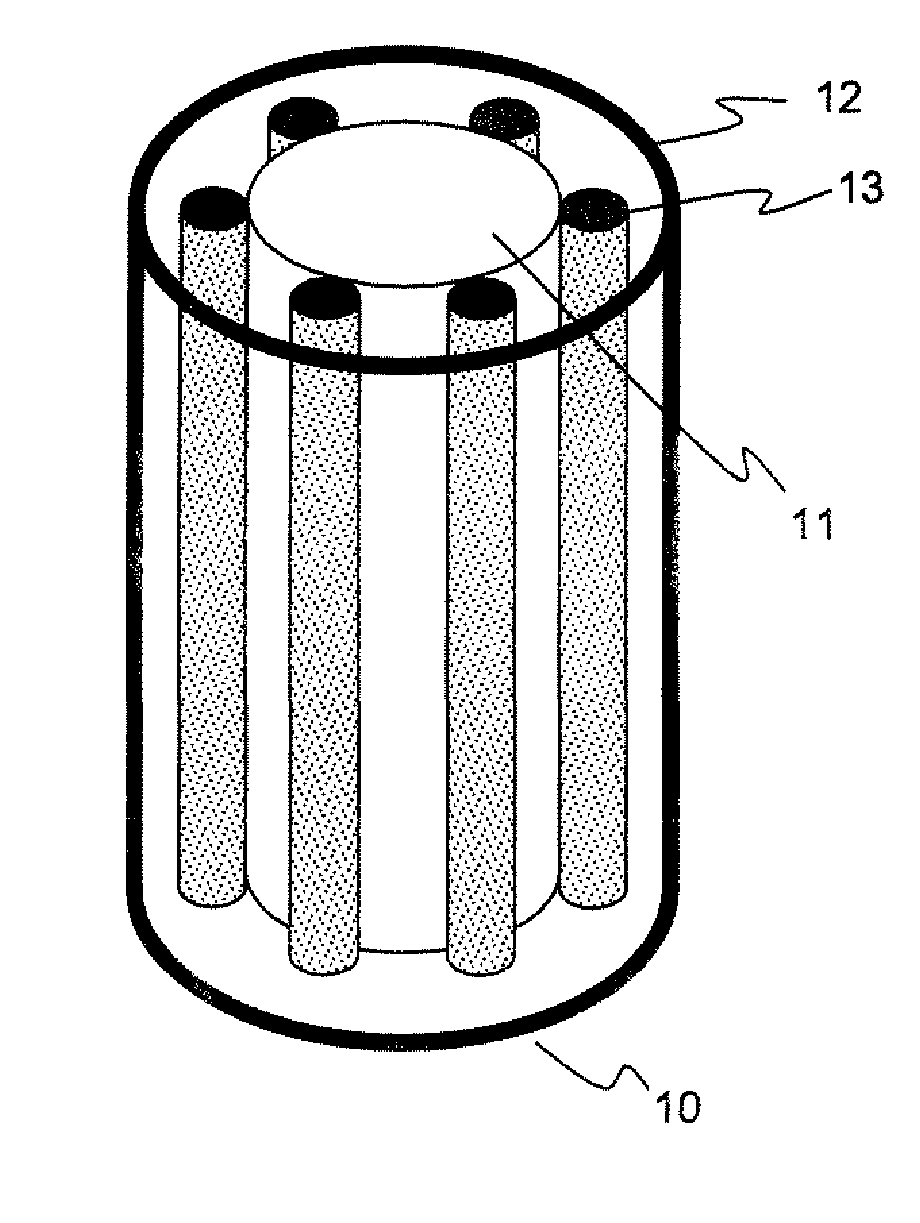
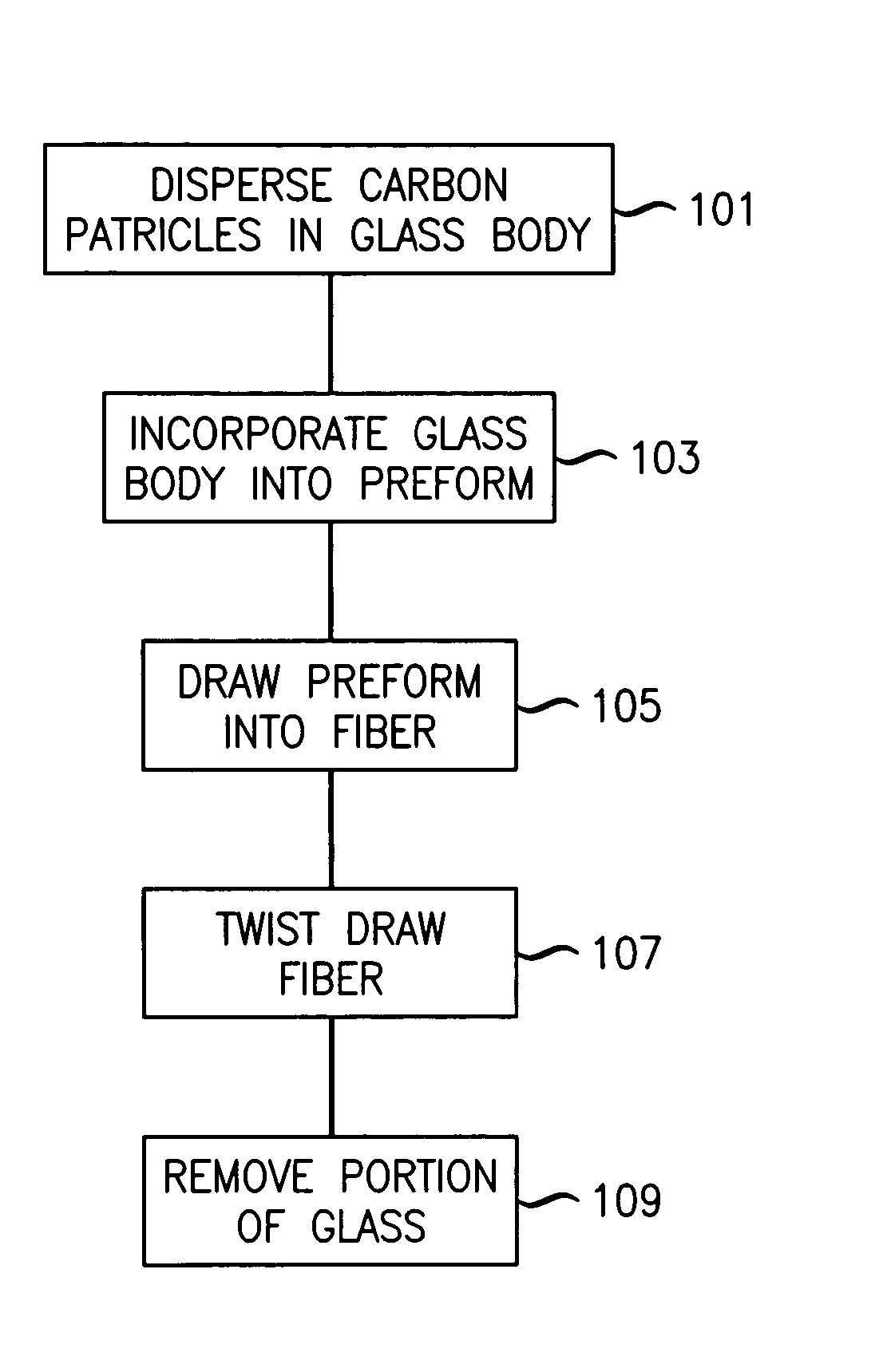
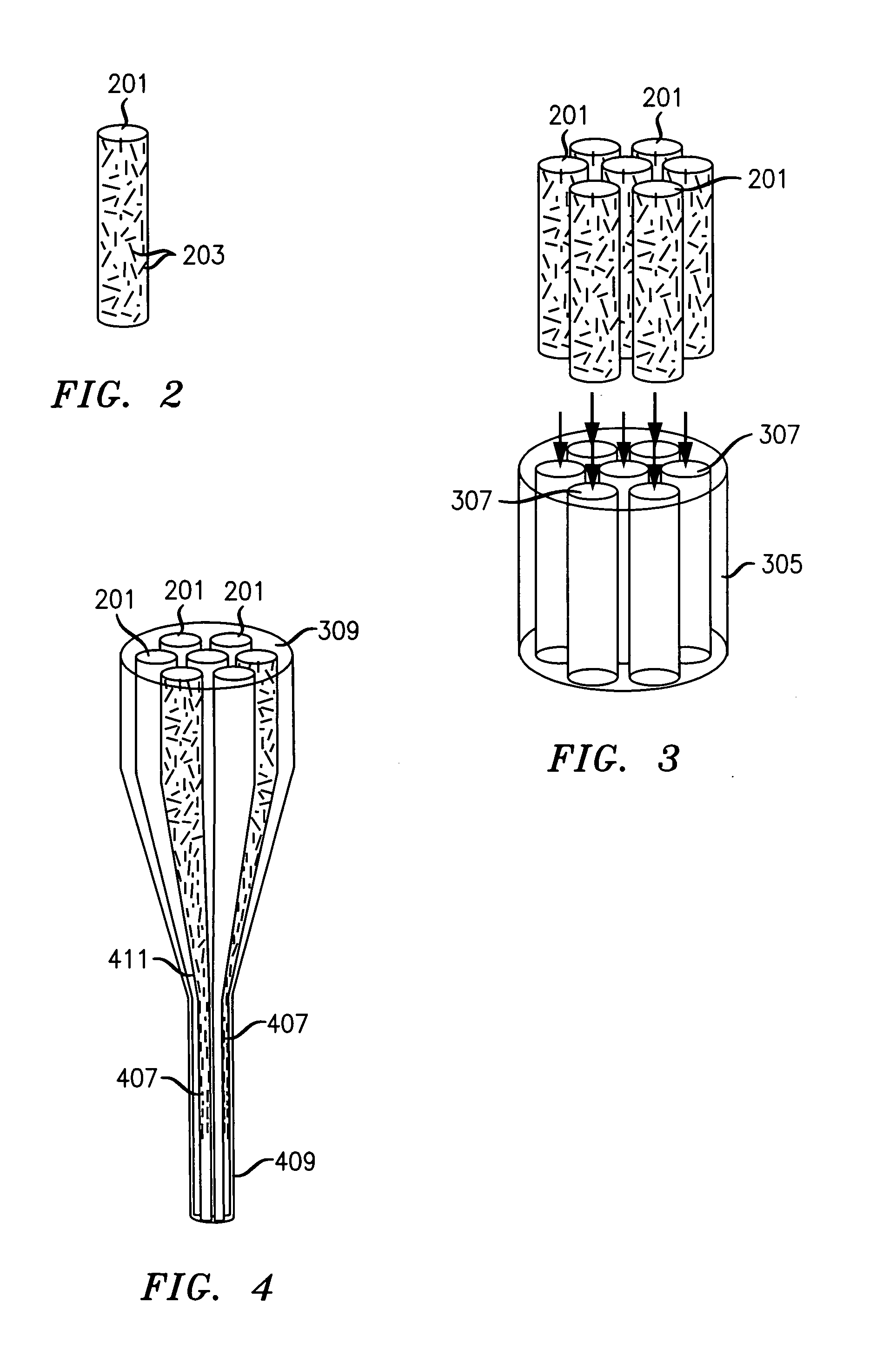
Carbon particle fiber assembly technique
Carbon particles, such as, carbon fibrils and carbon nanotube molecules, are assembled into aligned fibers using processes derived from the processes used to manufacture optical fiber. More particularly, the carbon particles are embedded in glass, which is then drawn to align them. By aligned it is meant the axis along the longest dimension of each of the various particles in a local vicinity are substantially parallel.
Owner:NOKIA OF AMERICA CORP
Optical fiber
InactiveUS20010028775A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusRefractive indexOptical fiber cable
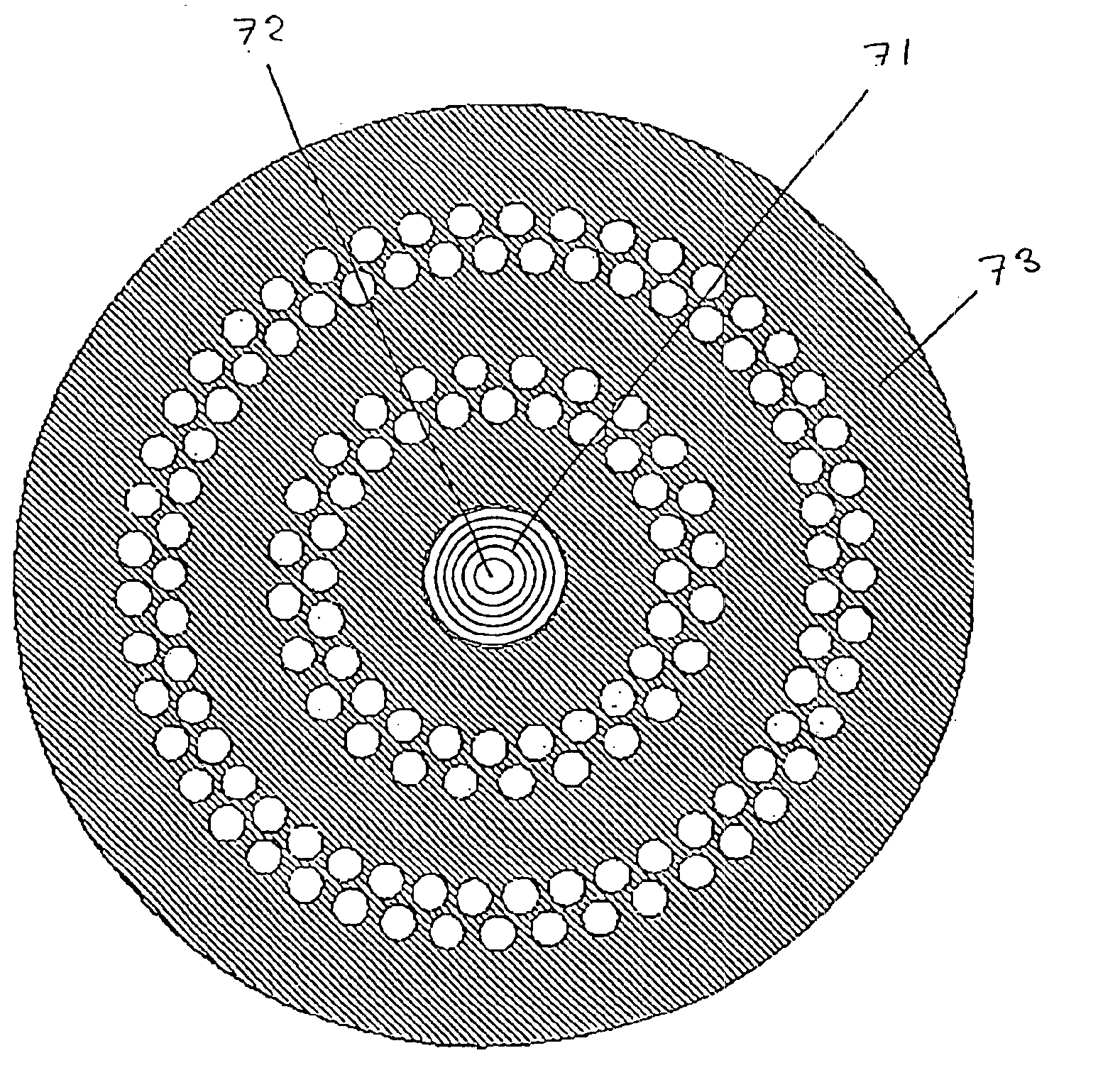
In an optical fiber composed of a core region and a cladding region surrounding the core region and having a plurality of regions made of sub mediums having refractive indices different from a refractive index of a main medium disposed in a main medium constituting this cladding region, these regions made of the sub mediums are arranged in one given or a plurality of a given circular annular regions and the centers of the regions made of the sub mediums in respective circular annular regions are arranged on the same circumference centered at the center of the core.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Large-size optical fiber preform and manufacturing method of optical fiber thereof
ActiveCN101891380AImprove the attenuation effectGuaranteed low water peak performanceGlass optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusAccess networkCore (optical fiber)
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Fiber air turn for low attenuation fiber
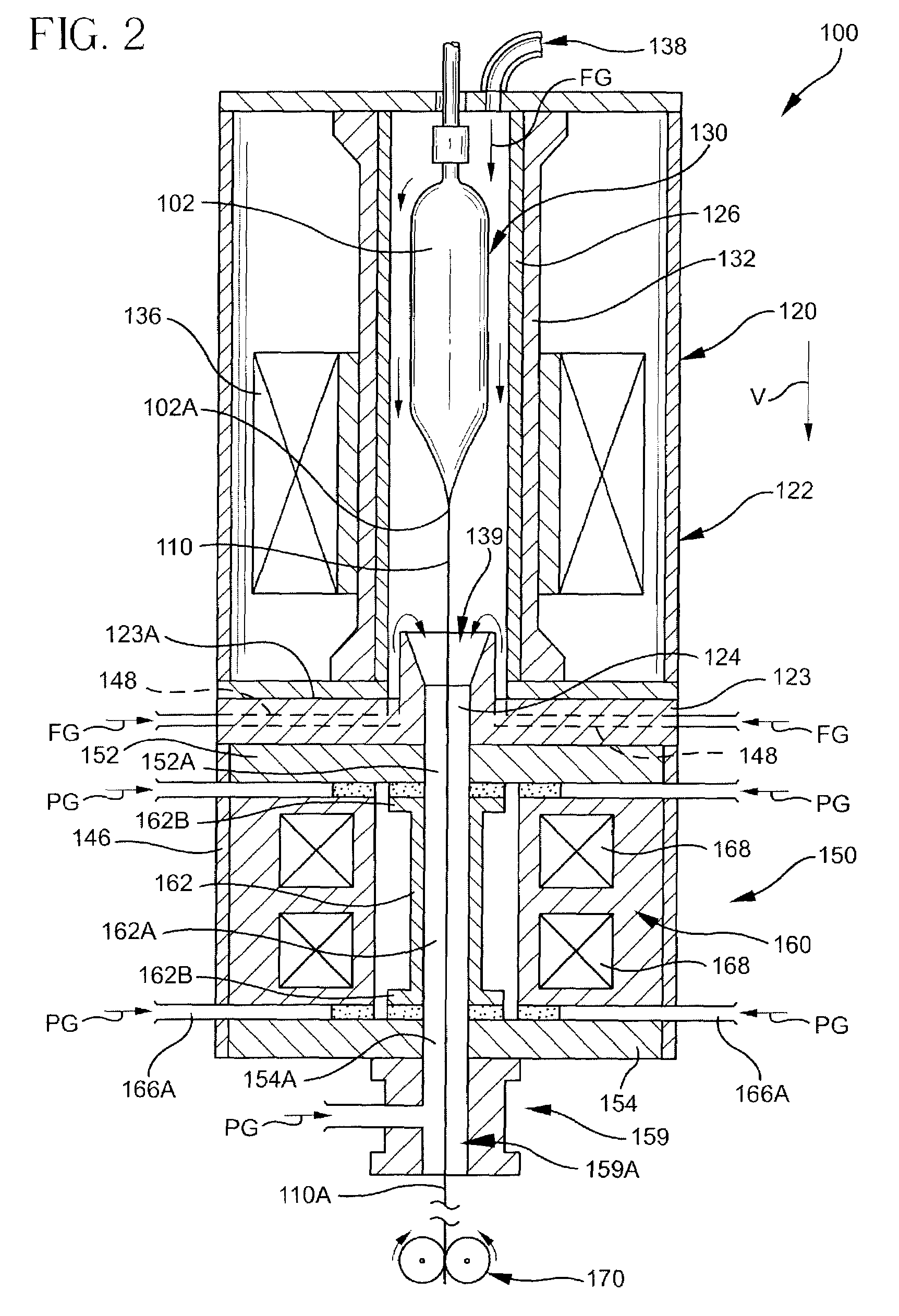
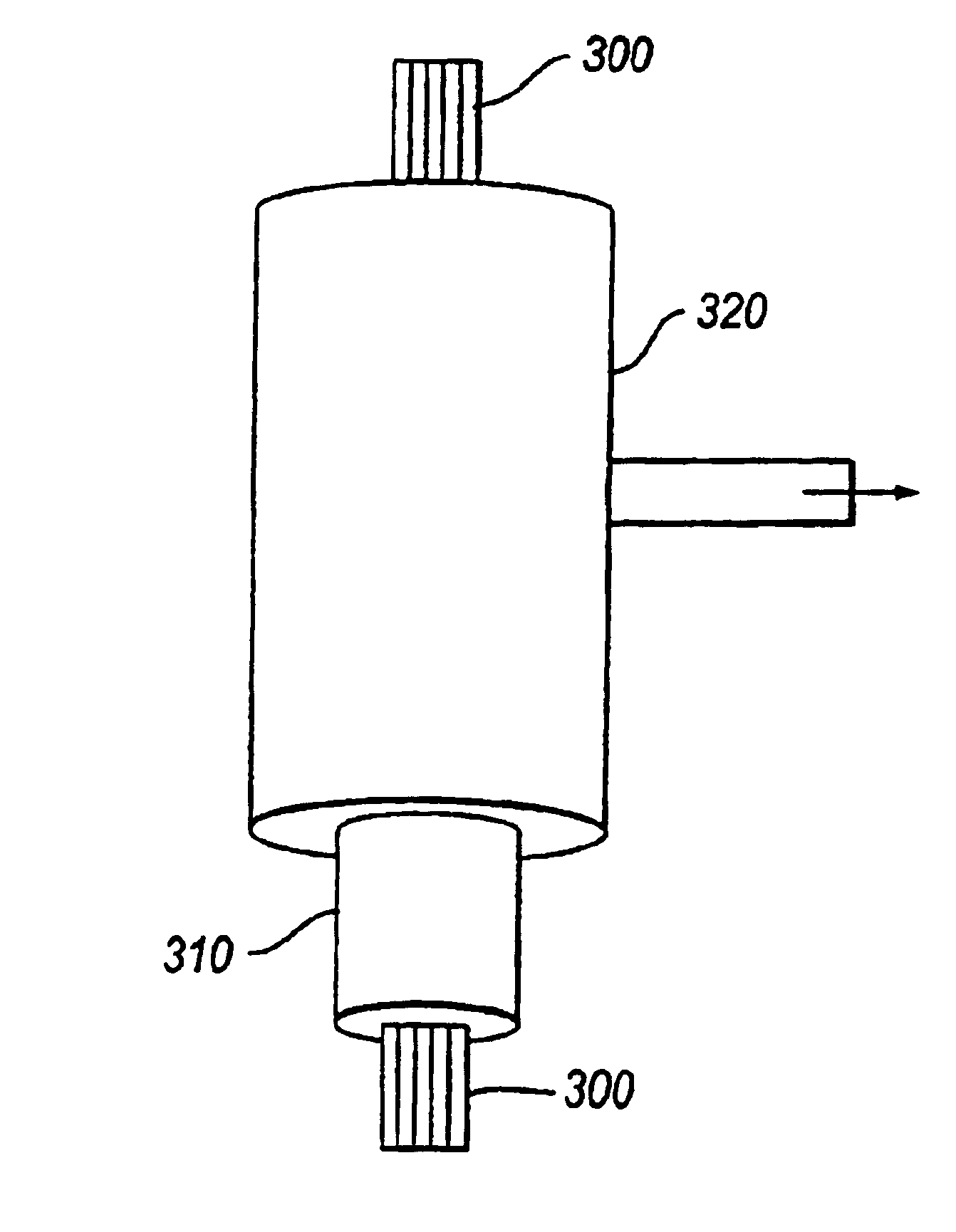
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber in a treatment zone wherein the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Methods for producing optical fibers along nonlinear paths incorporating fluid bearings are also provided thereby allowing for increased vertical space for the fiber treatment zone.
Owner:CORNING INC
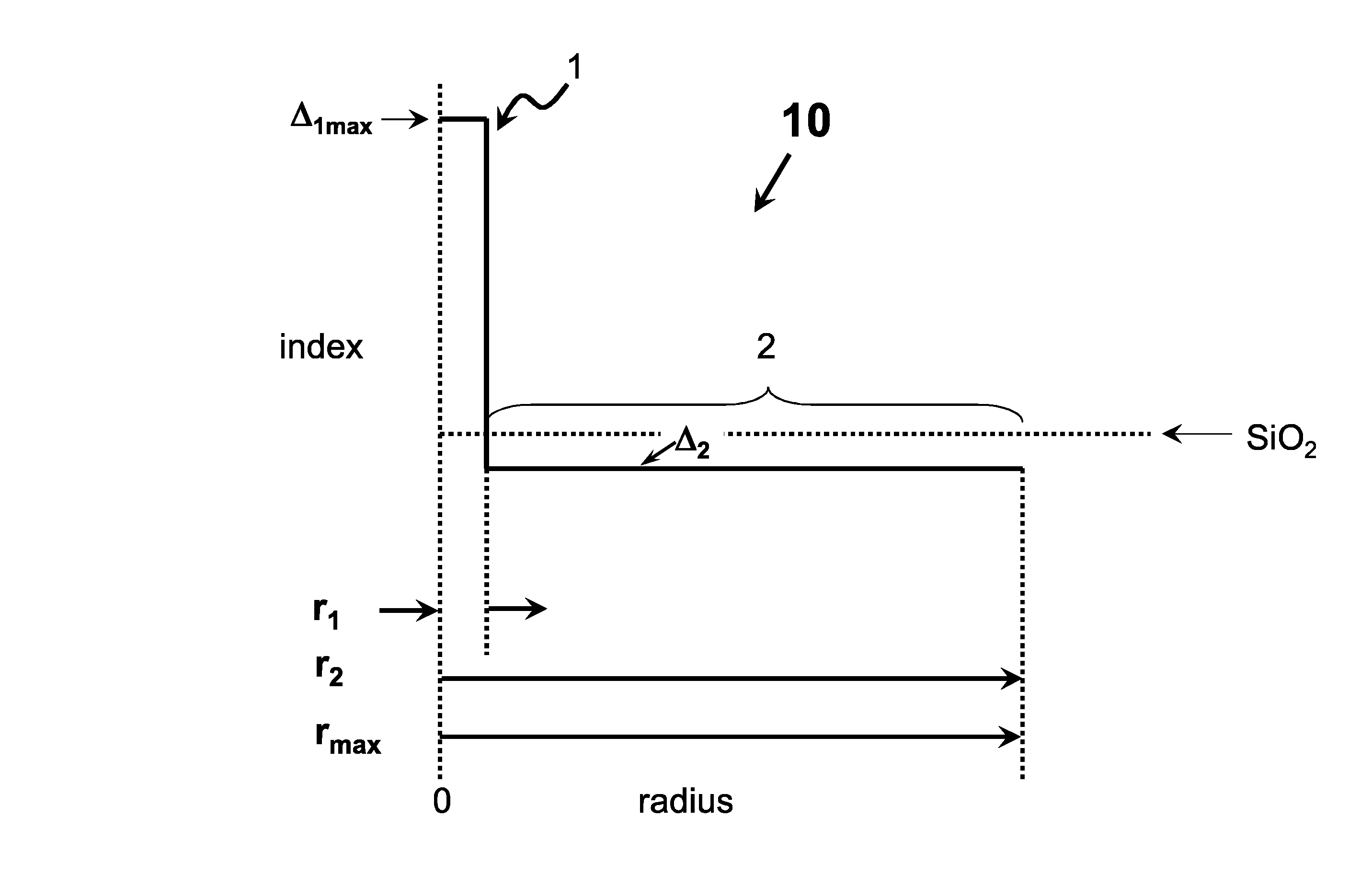
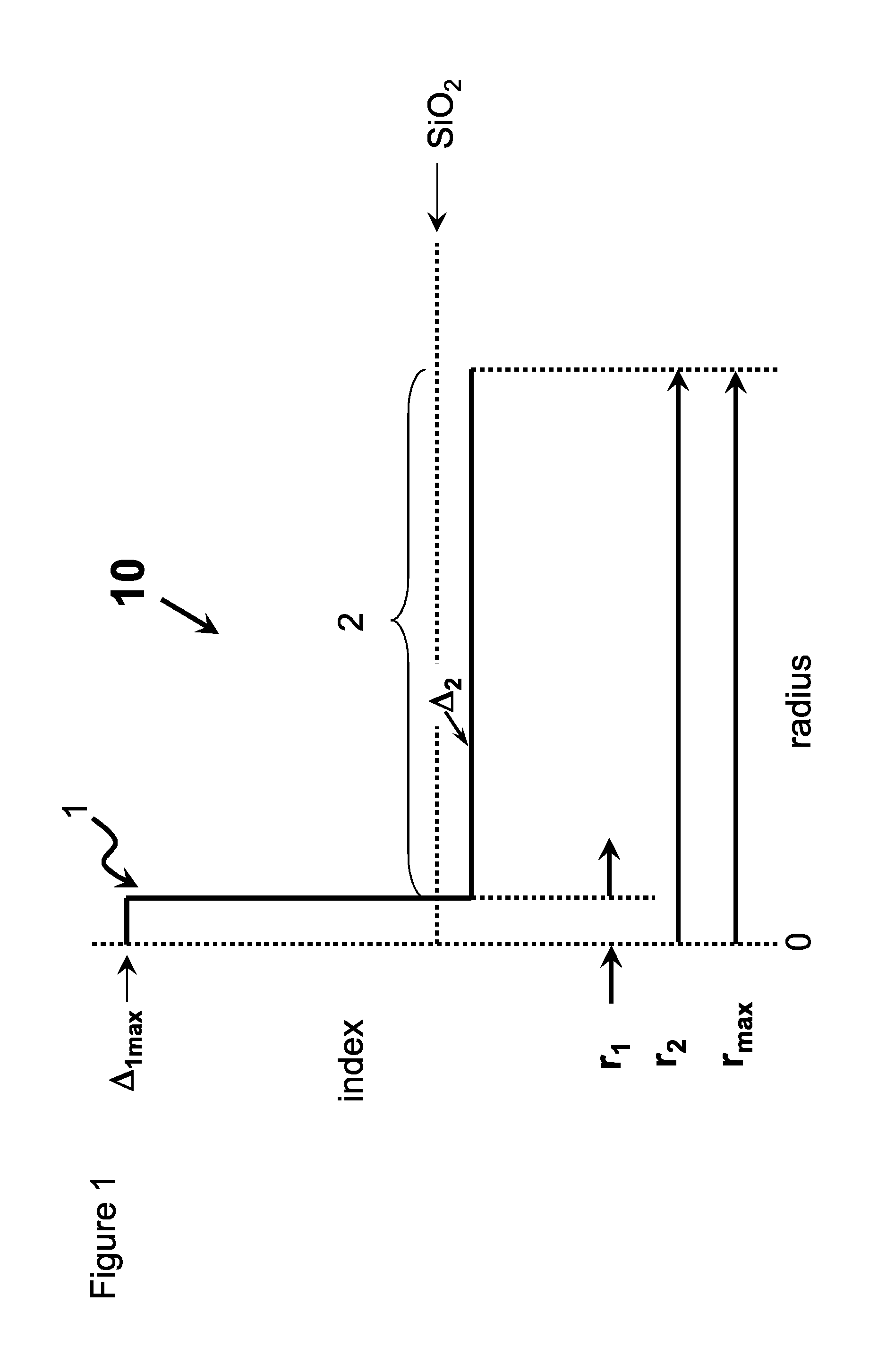
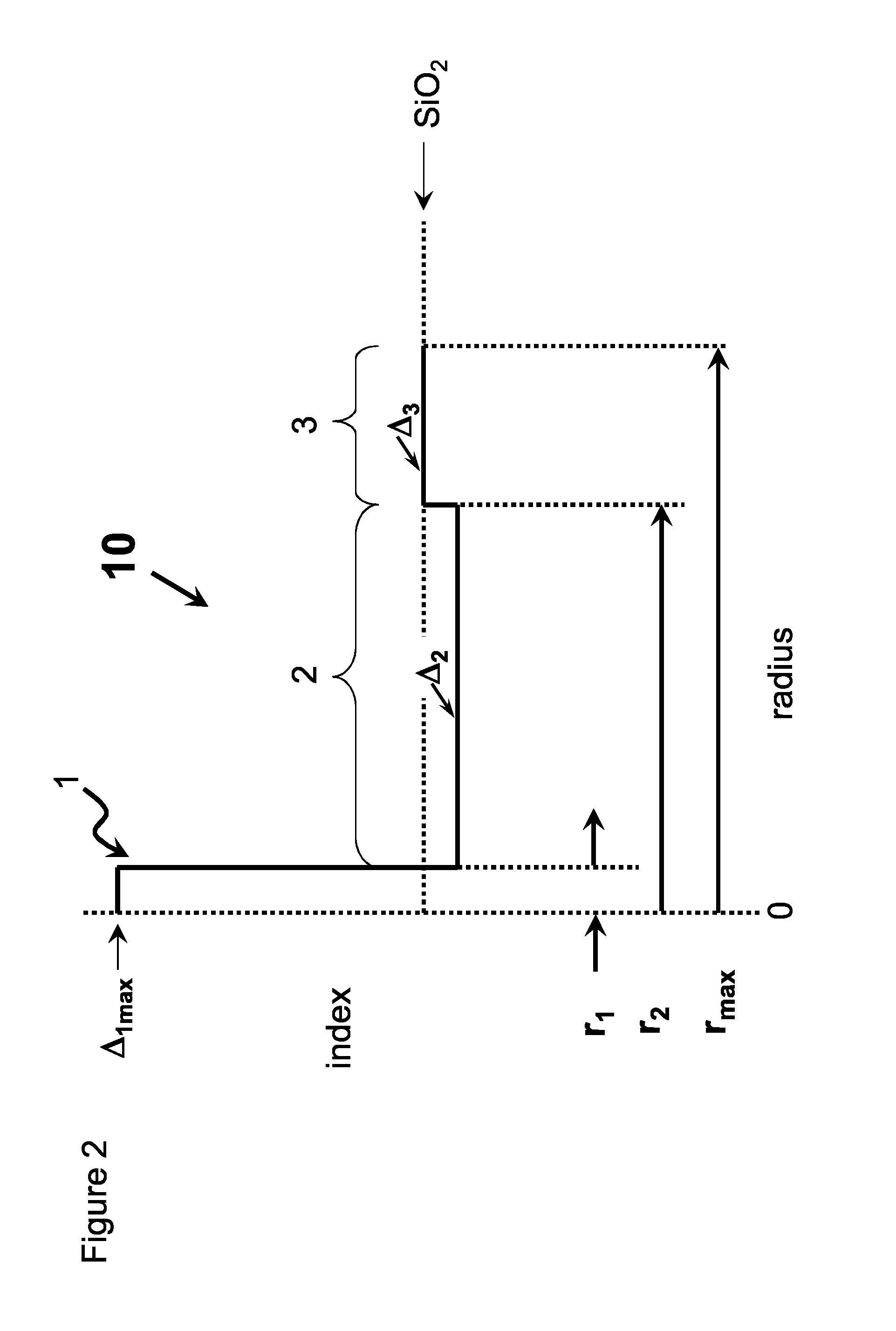
High chlorine content low attenuation optical fiber
ActiveUS20160011365A1Relieve pressureLow viscosityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusRefractive indexMaterials science
An optical fiber having a core comprising silica and greater than 1.5 wt % chlorine and less than 0.5 wt % F, said core having a refractive index Δ1MAX, and a inner cladding region having refractive index Δ2MIN surrounding the core, where Δ1MAX>Δ2MIN.
Owner:CORNING INC
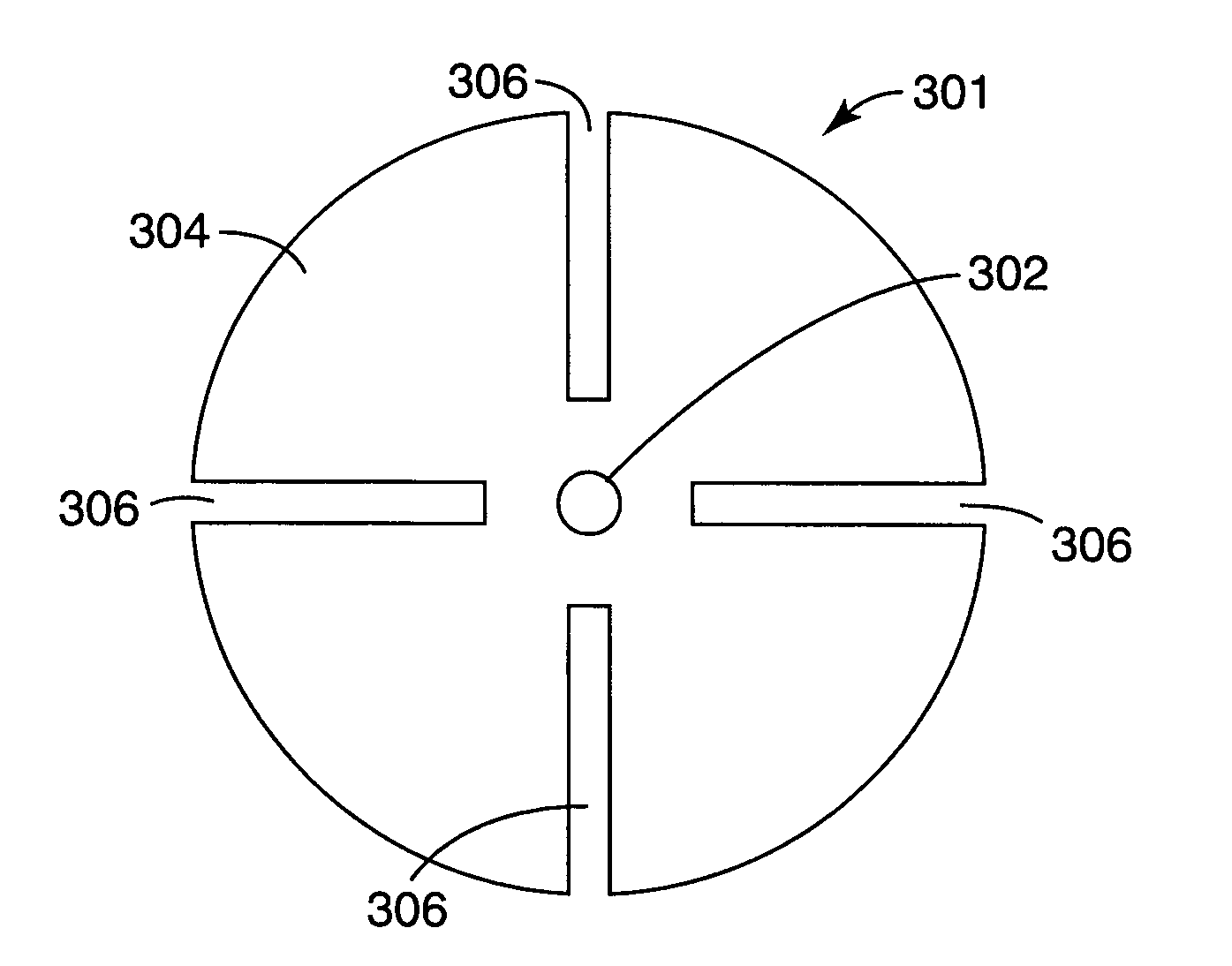
Photonic crystal fibres
InactiveUS6888992B2Reduce problem sizeAltering pattern of stressCladded optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusPhotonic crystalEngineering
In a method of producing a photonic crystal fibre, a preform (300) that includes holes is formed and the preform (300) is drawn into a fibre. The method includes the step of applying a pressure differential to certain of the holes to control changes in the fibre structure during the draw.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Methods and apparatus for forming heat treated optical fiber
InactiveUS20070022786A1Trend downDecreases micro-density variationGlass fibre drawing apparatusGlass productionFiberRayleigh scattering
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber within a treatment temperature range for a treatment time. Preferably also, the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Apparatus are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of making a hole assisted fiber device and fiber preform
InactiveUS20060130528A1Glass fibre drawing apparatusOptical light guidesInternal pressureEngineering
A method of fabricating a hole assisted fiber includes forming one or more slots in the perimeter of the cladding region. A tube is overcollapsed around the perimeter of the cladding region to form one or more channels, where the one or more channels bounded on one side by the overcollapsed tube. A fiber is drawn from the overcollapsed preform. An internal pressure is applied to the one or more channels during the fiber drawing step to form one or more holes of a pre-selected shape within the cladding region.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Holey fiber and method of manufacturing the same
A method of manufacturing a holey fiber includes forming a preform and drawing the preform. The forming includes arranging a core rod at a center of a jacket tube and arranging capillary tubes having hollows around the core rod inside the jacket tube. The drawing includes heat melting the preform in a heating furnace while controlling at least one of a gas pressure to be applied to insides of the hollows of the capillary tubes, a temperature of the heating furnace, and a drawing speed, based on a structure of air holes to be formed in a first layer from the core region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical fiber drawing method for large-diameter optical fiber preform rod
ActiveCN103304135ANot easy to stickControl air flowGlass fibre drawing apparatusShielding gasMaterials science
The invention relates to an optical fiber drawing method for a large-diameter optical fiber preform rod. The method comprises the following steps: continuously moving the large-diameter optical fiber preform rod downwards to enter an optical fiber drawing furnace through a lifter, heating and drawing to form a finished optical fiber, inputting protective gas into the furnace body through an extension pipe at the furnace bottom, allowing the protective gas to flow upwards, allowing the gas to flow out of a gas outlet of a gas guide disc, and allowing the protective gas input by the gas guide disc and a gas sealing cover to flow out of the gas outlet of the gas guide disc. The method has the advantage that the large-diameter optical fiber preform rod can be drawn to form the optical fiber with stable quality.
Owner:JIANGSU FASTEN PHOTONICS
Optical fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20060010921A1Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyCladded optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical fiber, which has a zero-material dispersion wavelength equal to or greater than 2 μm, and a high nonlinear susceptibility χ3 equal to or greater than 1×10−12 esu, and uses tellurite glass having sufficient thermal stability for processing into a low loss fiber, employs a PCF structure or HF structure having strong confinement into a core region. This enables light to propagate at a low loss. The size and geometry of air holes formed in the core region, and the spacing between adjacent air holes make it possible to control the zero dispersion wavelength within an optical telecommunication window (1.2-1.7 μm), and to achieve large nonlinearity with a nonlinear coefficient γ equal to or greater than 500 W−1 km−1.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method of making a multimode optical fiber
ActiveUS20130029038A1Minimize time delayCladded optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusEngineeringBand width
A method of making a multimode optical fiber is disclosed. In one embodiment the method includes calculating a core radius that maximizes the bandwidth of the multimode optical fiber wherein the effect of draw tension is accounted for. The embodiments herein illustrate how core radius can be tuned so the time delay of the outermost guided mode group is reduced. The resultant core radius may be targeted for a value off-nominal from what would be expected for a particular commercial optical fiber type.
Owner:CORNING INC
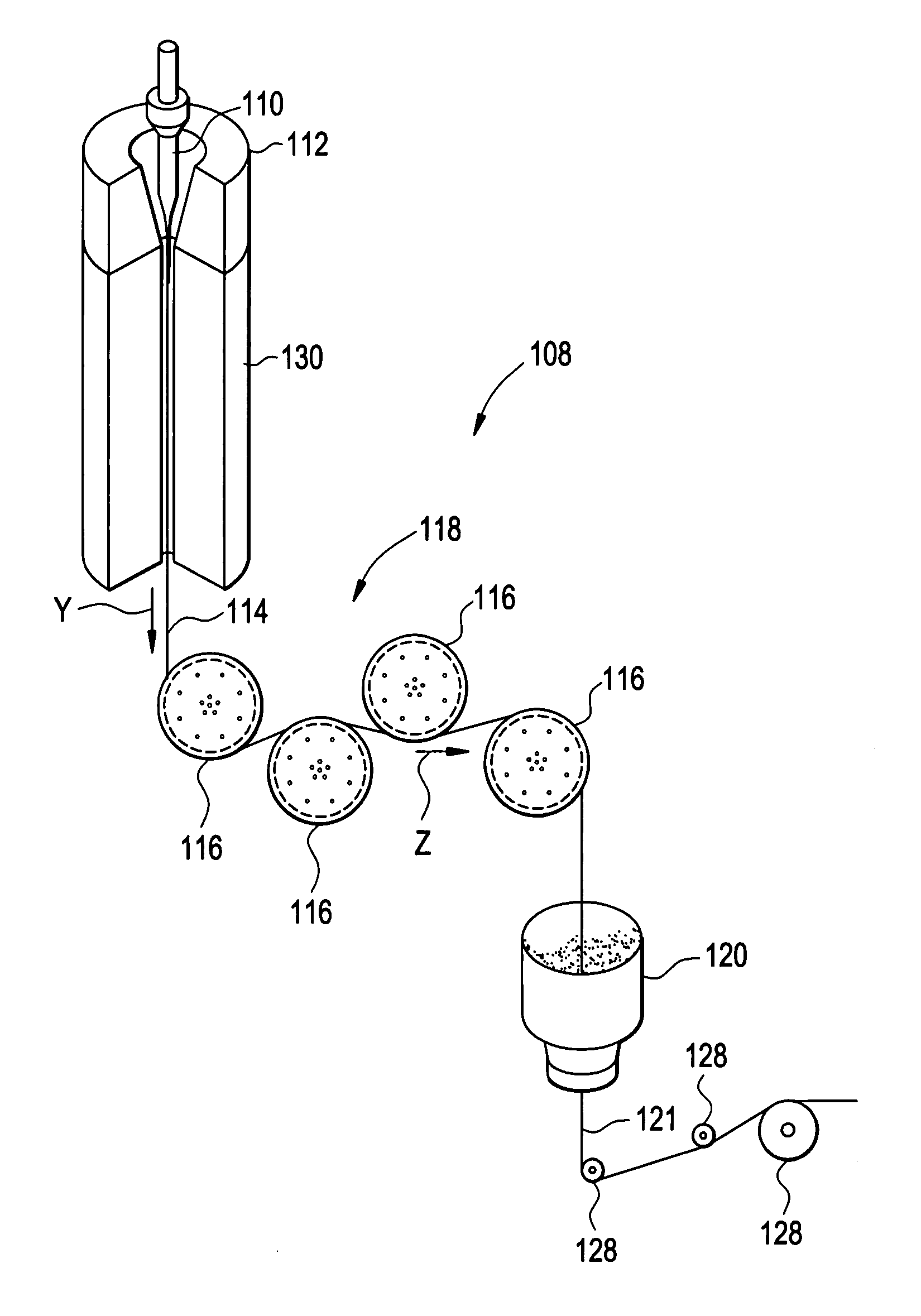
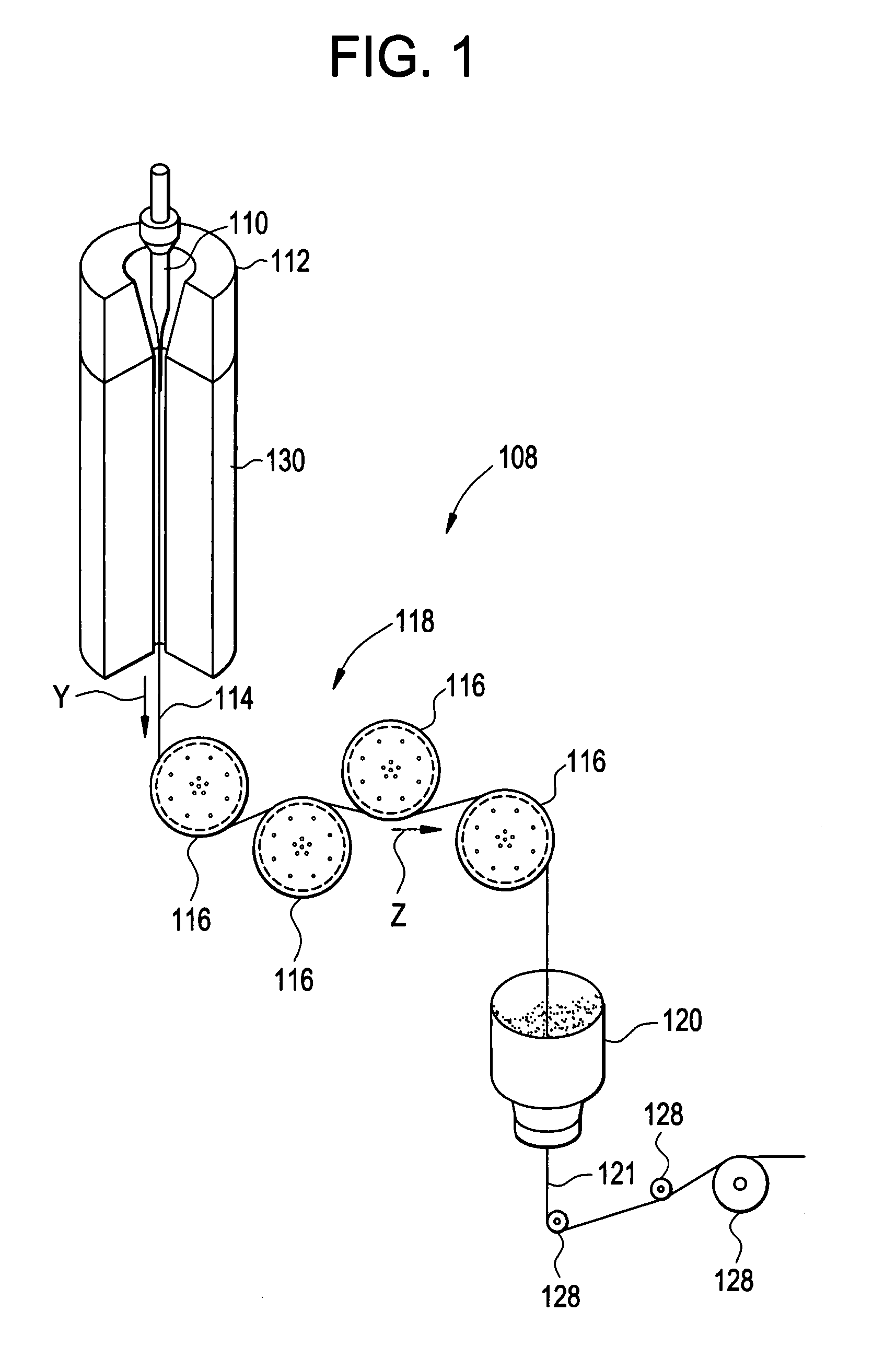
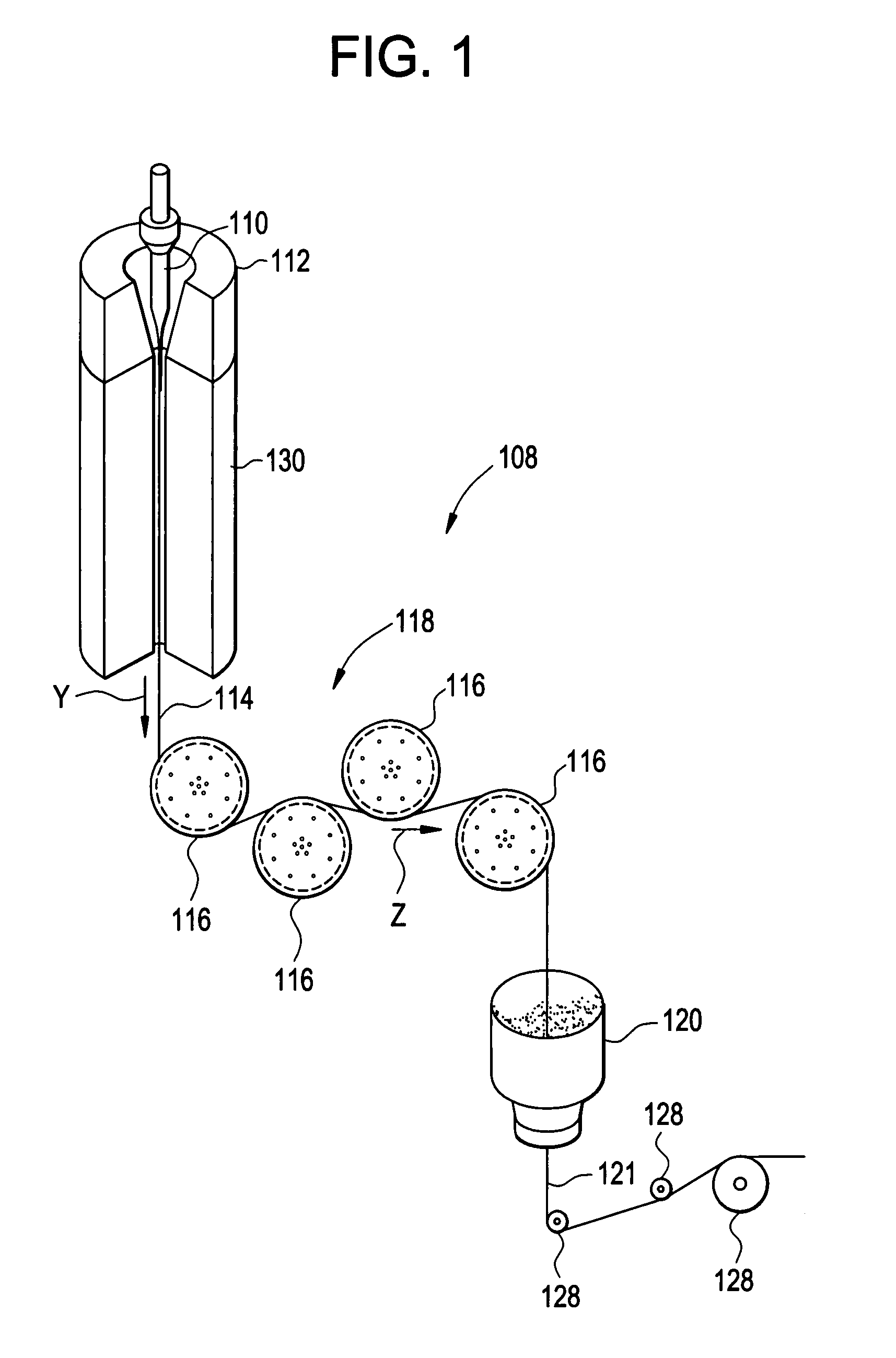
Active optical fiber and method for fabricating an active optical fiber
ActiveUS20100247047A1Stable polarization stateImprove efficiencyLaser detailsMetal rolling stand detailsFiberEngineering
A section of active optical fiber (11) which comprises an active core (1), an inner cladding layer (2) and an outer cladding layer (3). The diameter of said core 91) and the thickness of said inner cladding (2) change gradually along the length of said section of active optical fiber (11). This forms tapered longitudinal profile enabling a continuous mode conversion process along the length of the section of fiber (11). The method for fabricating a section of tapered active optical fiber comprises the steps of fabricating a perform for drawing active optical fiber from said perform, installing said perform into a drawing tower, drawing optical fiber in said drawing tower and altering at least one of the two parameters including the take-off perform speed and the take-up fiber speed during drawing of the optical fiber.
Owner:AMPLICONYX OY
Method of cooling an optical fiber while it is being drawn
InactiveUS6565775B2Improving the cooling of an optical fiberPreserve strengthGlass fibre drawing apparatusOptical articlesFiberSlow cooling
A method of cooling an optical fiber during drawing through contact with at least one cooling fluid in at least one cooling area, wherein fast cooling, i.e. cooling that is faster than cooling in the surrounding air, from an initial temperature of the fiber to a temperature at the end of fast cooling of said fiber, is followed by slow cooling, i.e. cooling slower than cooling in the surrounding air, from a temperature of said fiber at the start of slow cooling to a temperature of said fiber at the end of slow cooling.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Wiredrawing method and wiredrawing device for outer diameter fluctuation optical fiber perform
ActiveCN102838275AStable airflowIncrease the drawing lengthGlass fibre drawing apparatusGlass productionEngineeringLarge size
The invention relates to a wiredrawing method and a wiredrawing device for an outer diameter fluctuation optical fiber perform, particularly a large-size outer diameter fluctuation optical fiber perform. Compared with an existing wiredrawing method, the wiredrawing method has the different points that a radial seal adjustable device is arranged at a furnace mouth at the upper end of a heating cavity of a wiredrawing furnace; and in the wiredrawing process, the optical fiber perform is clung to the radial seal adjustable device, so that a radial gap between the optical fiber perform and the radial seal adjustable device, i.e. the difference between the outer diameter of the optical fiber perform and the seal aperture of the radial seal adjustable device, is kept in the range of 0 to 0.2mm. According to the invention, the radial gap between the large-size perform with nonuniform outer diameter variation and the radial seal adjustable device is always kept in a small allowable gap range or tends to zero in the wiredrawing feeding process, so that the wiredrawing quality is ensured and the technical difficult problem that the large-size outer diameter fluctuation optical fiber perform cannot be directly subjected to wiredrawing processing is solved; and the yield and the processing efficiency of optical fibers are further improved and the stringiness of the single perform is also improved, so that the optical fiber manufacturing cost is further reduced.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Method of making an optical fiber by melting particulate glass in a glass cladding tube
Owner:CORNING INC
Fiber air turn for low attenuation fiber
ActiveUS8074474B2Glass furnace apparatusGlass fibre drawing apparatusRayleigh scatteringUltrasound attenuation
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber in a treatment zone wherein the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Methods for producing optical fibers along nonlinear paths incorporating fluid bearings are also provided thereby allowing for increased vertical space for the fiber treatment zone.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com