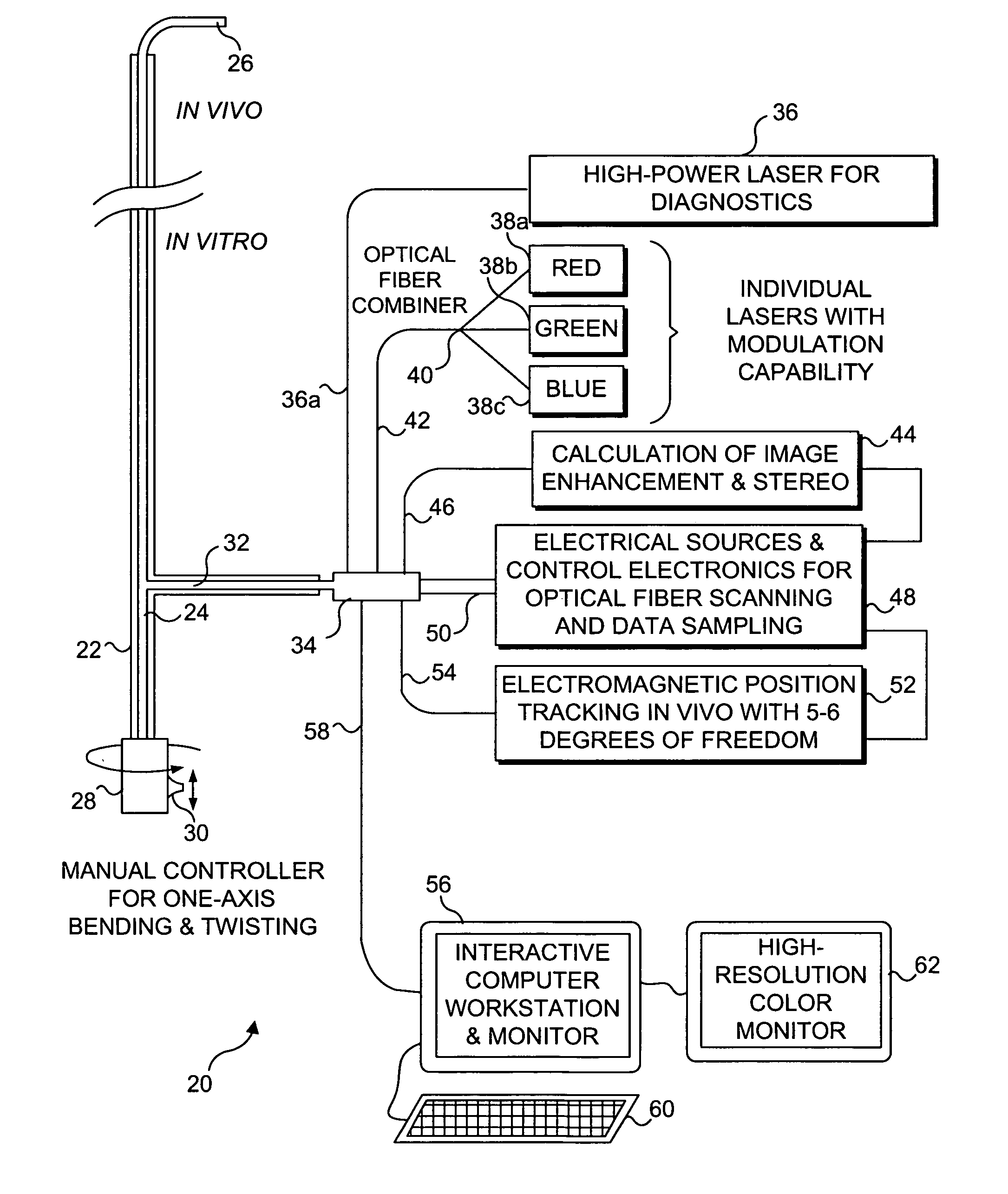
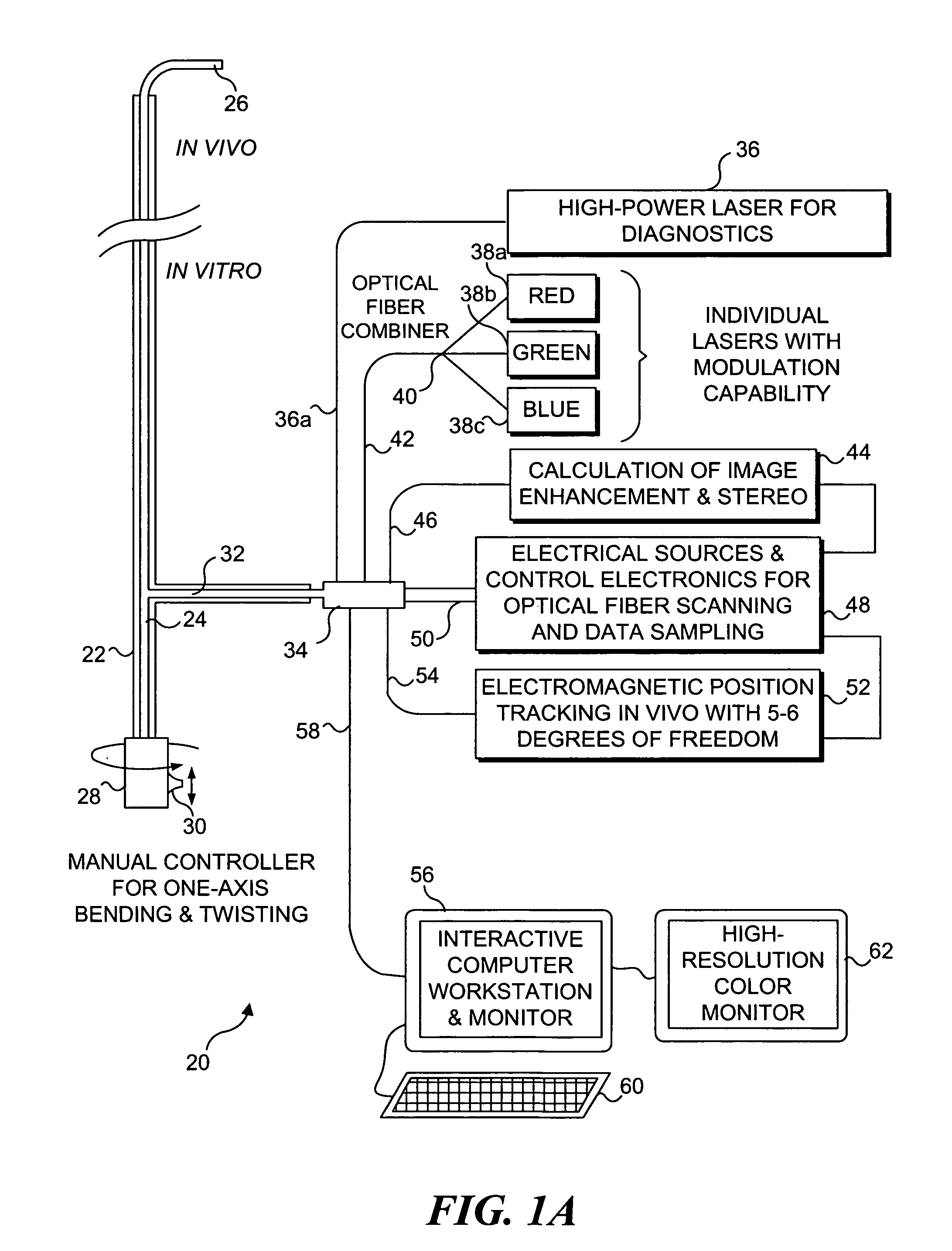
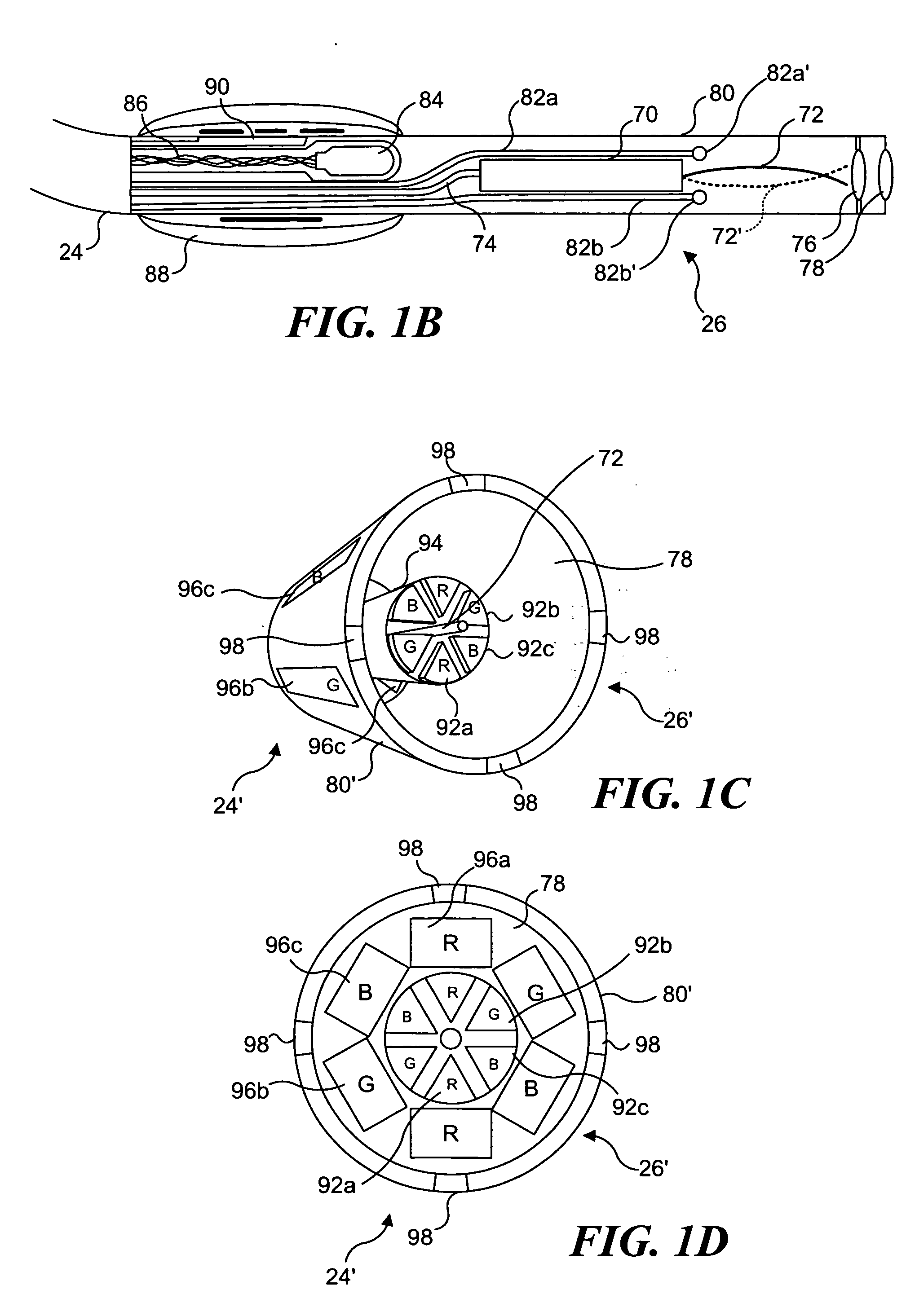
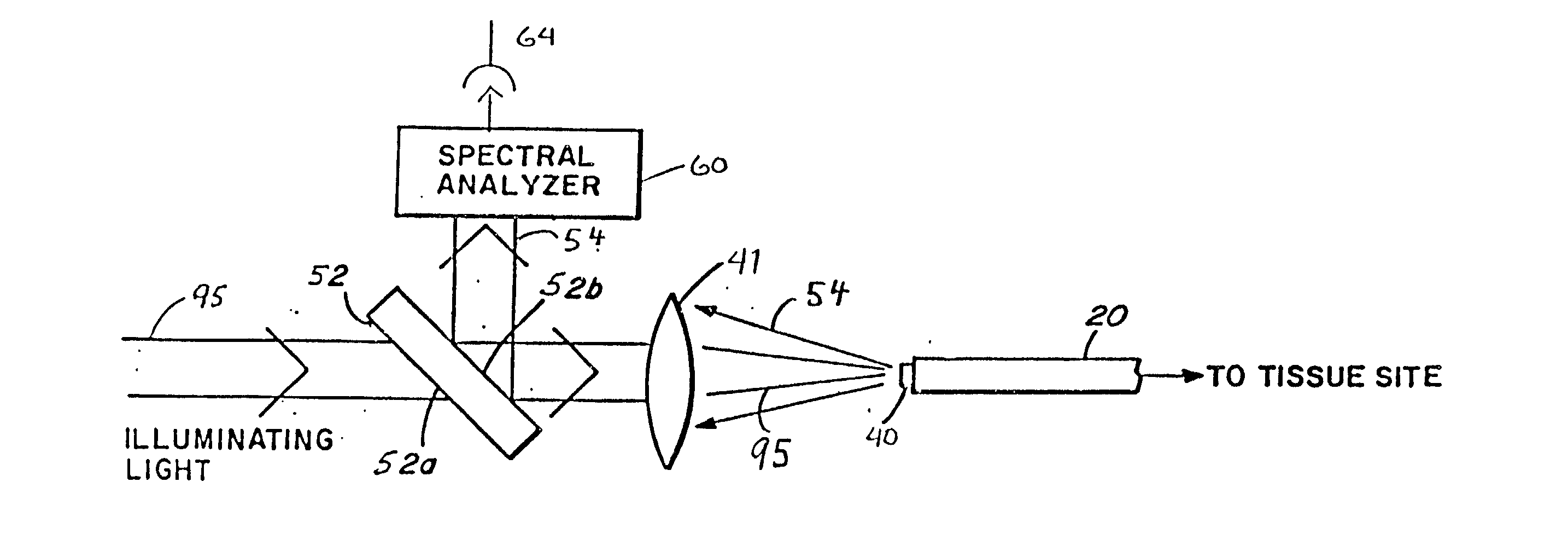
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2806results about "Bundled fibre light guide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
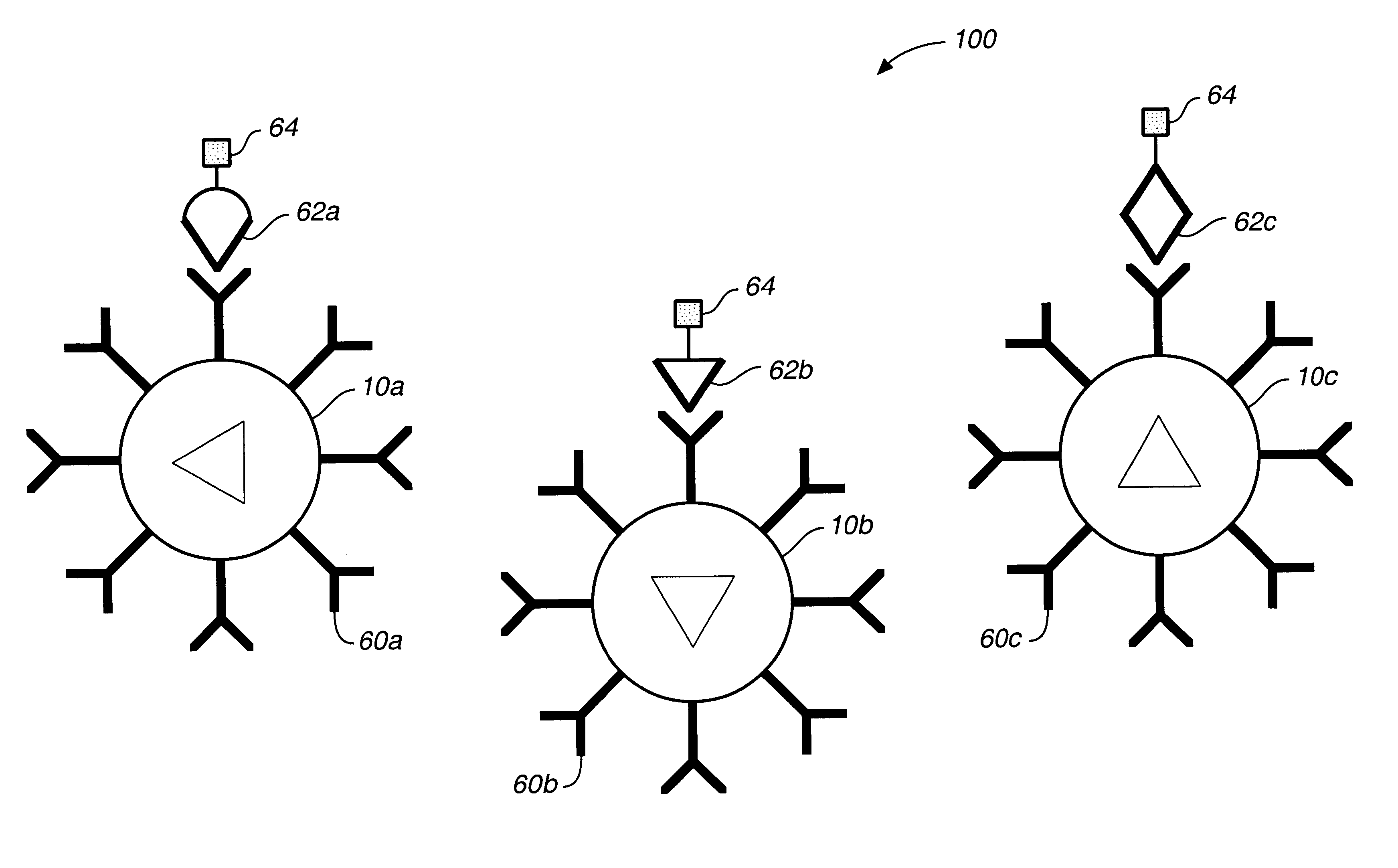
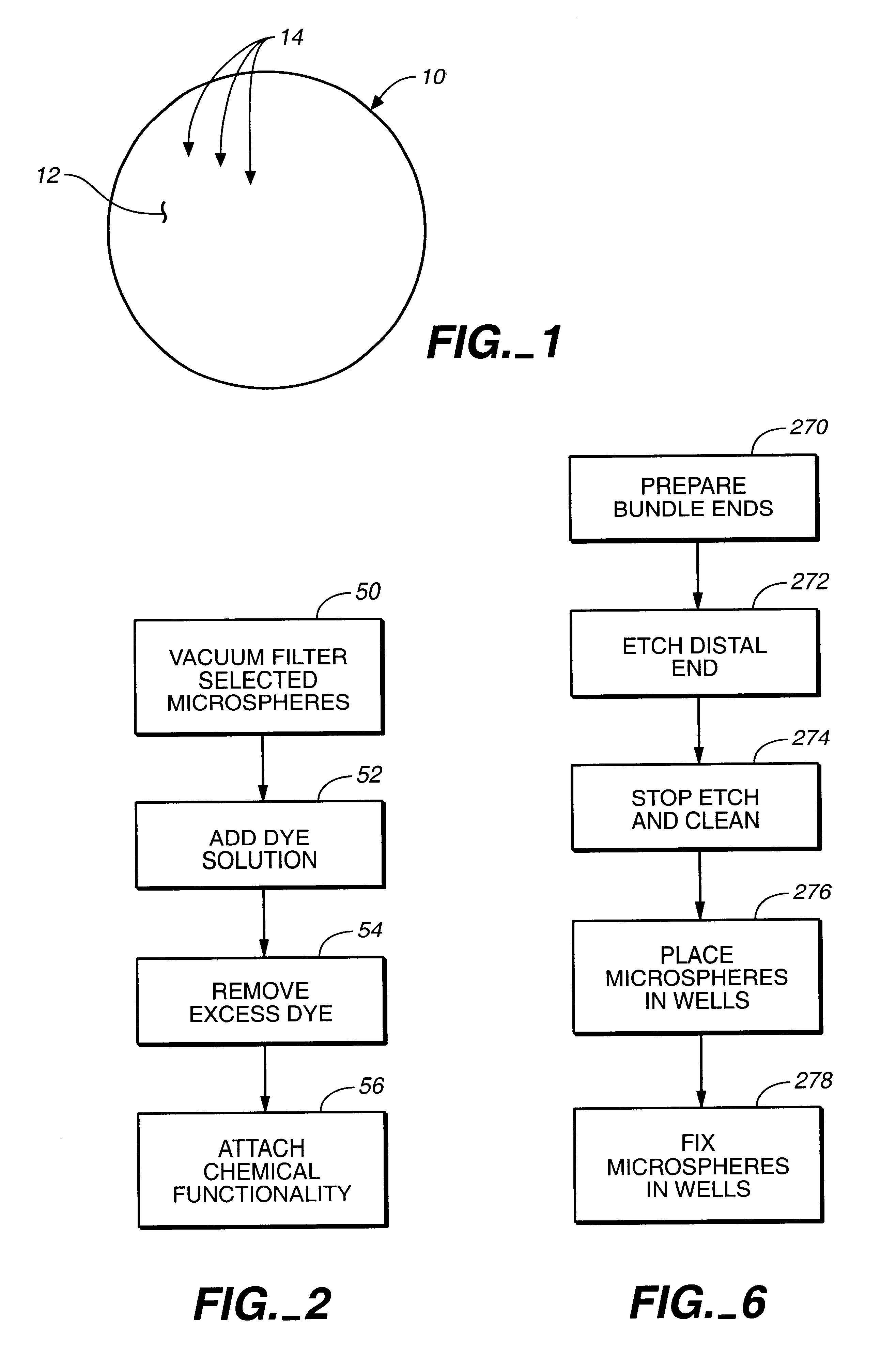
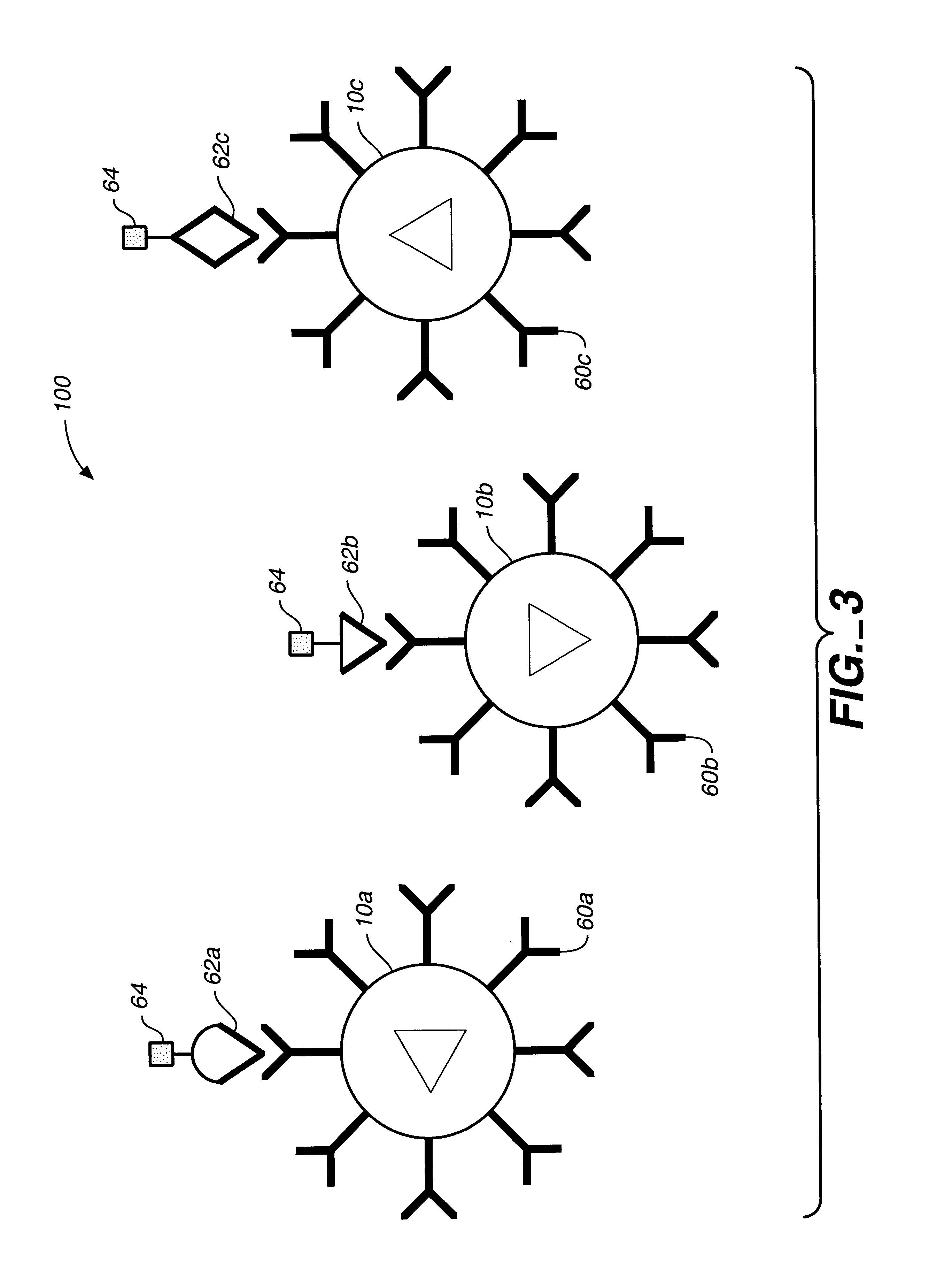
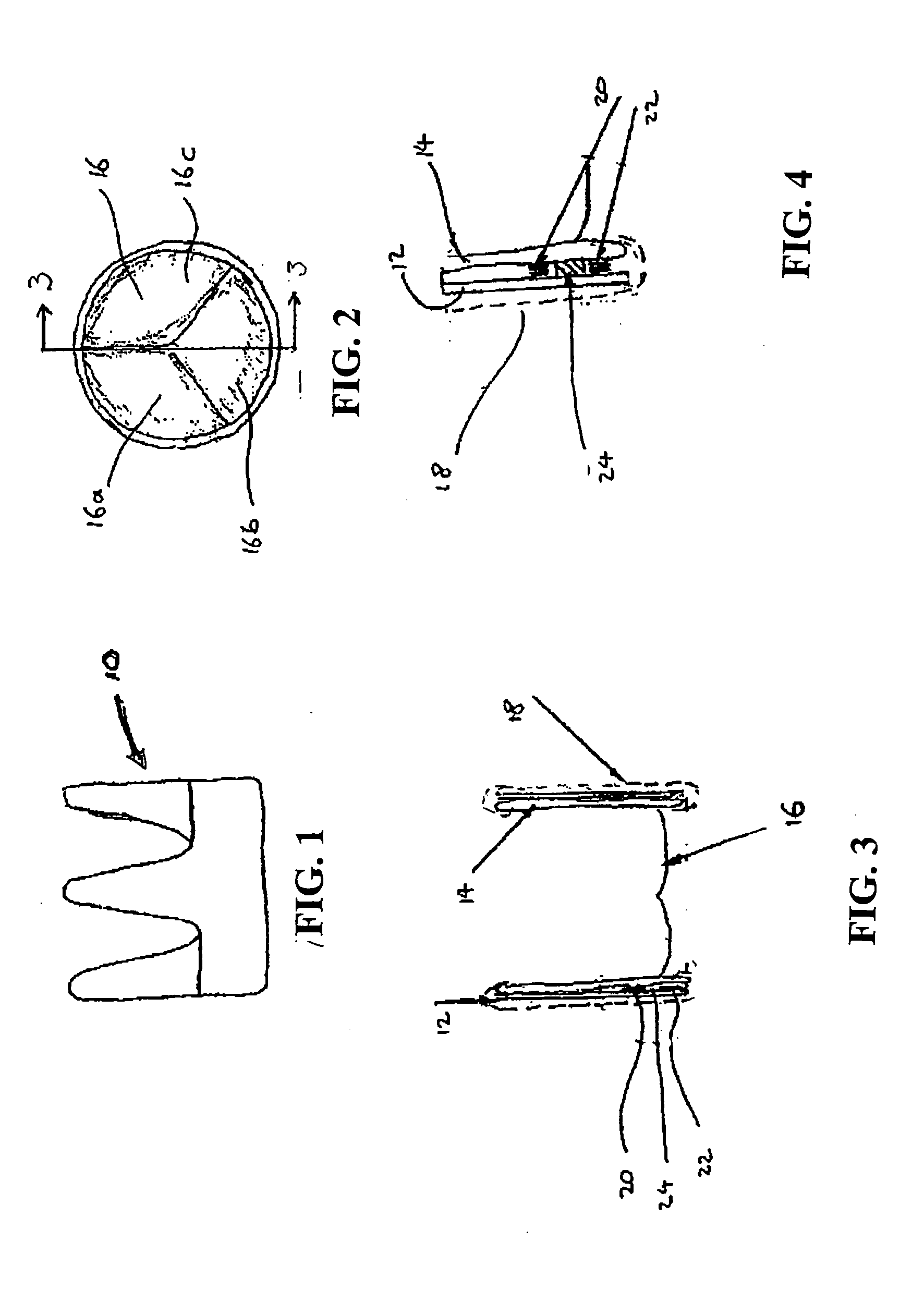
Target analyte sensors utilizing microspheres
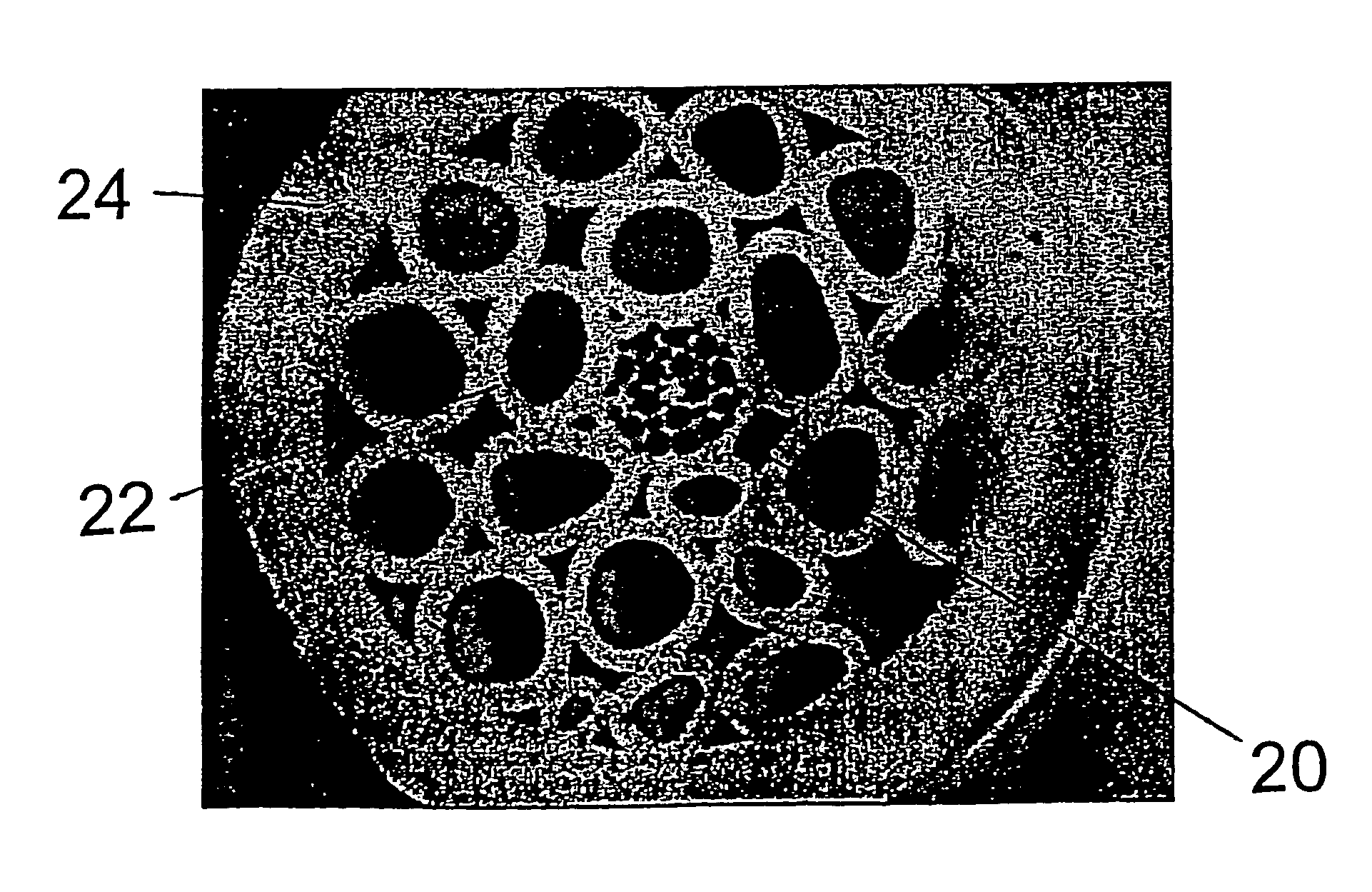
A microsphere-based analytic chemistry system and method for making the same is disclosed in which microspheres or particles carrying bioactive agents may be combined randomly or in ordered fashion and dispersed on a substrate to form an array while maintaining the ability to identify the location of bioactive agents and particles within the array using an optically interrogatable, optical signature encoding scheme. A wide variety of modified substrates may be employed which provide either discrete or non-discrete sites for accommodating the microspheres in either random or patterned distributions. The substrates may be constructed from a variety of materials to form either two-dimensional or three-dimensional configurations. In a preferred embodiment, a modified fiber optic bundle or array is employed as a substrate to produce a high density array. The disclosed system and method have utility for detecting target analytes and screening large libraries of bioactive agents.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
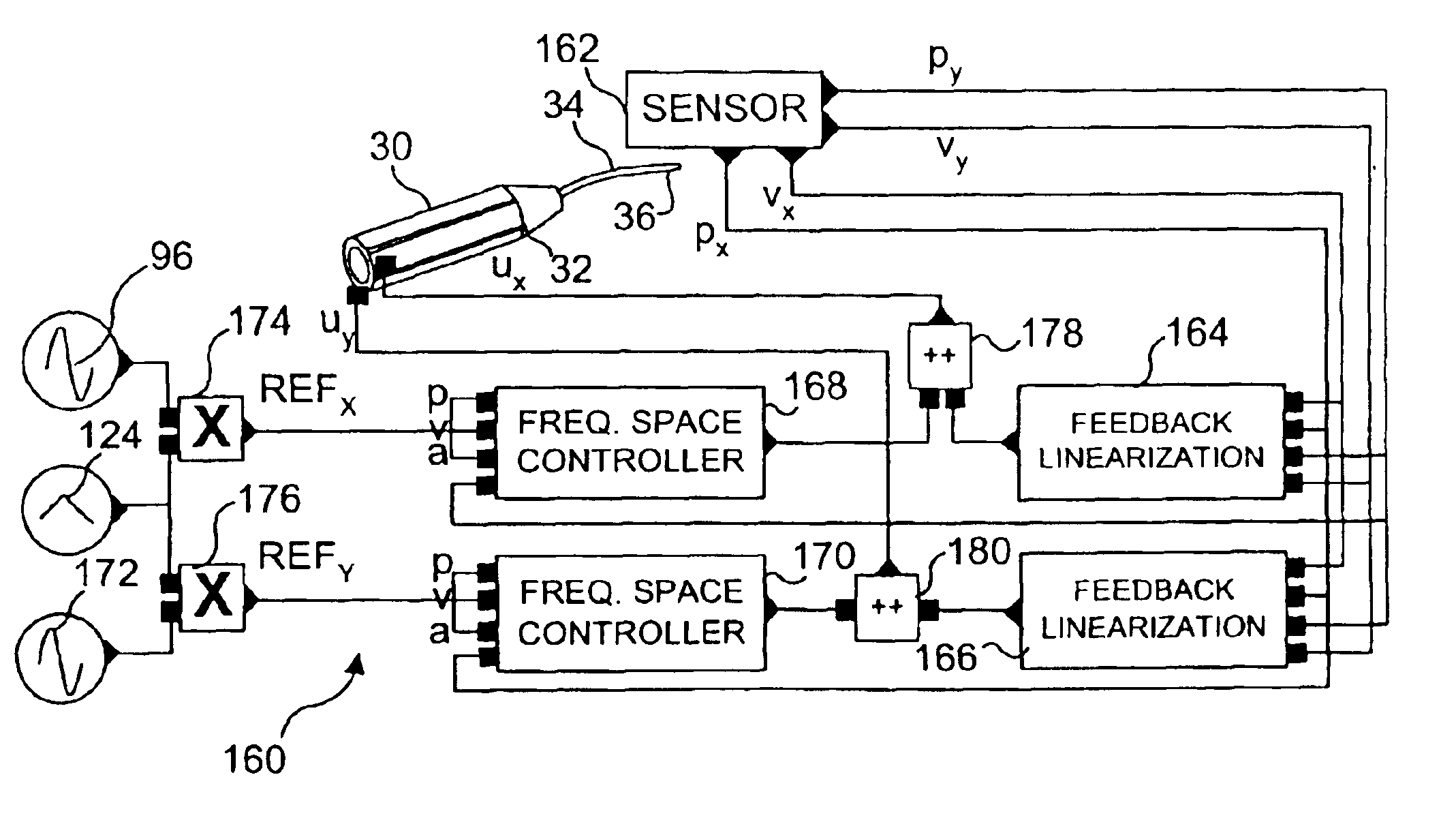
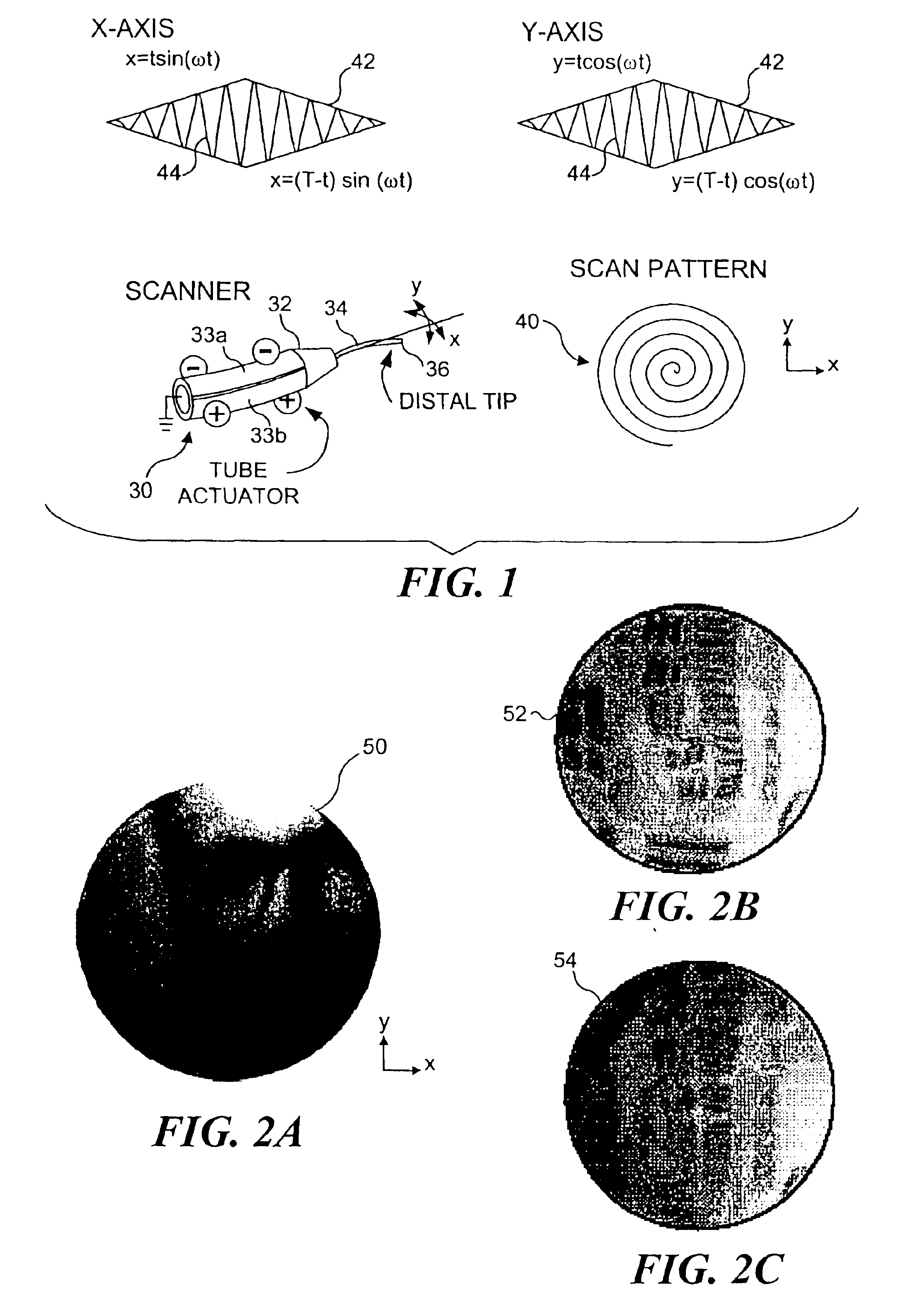
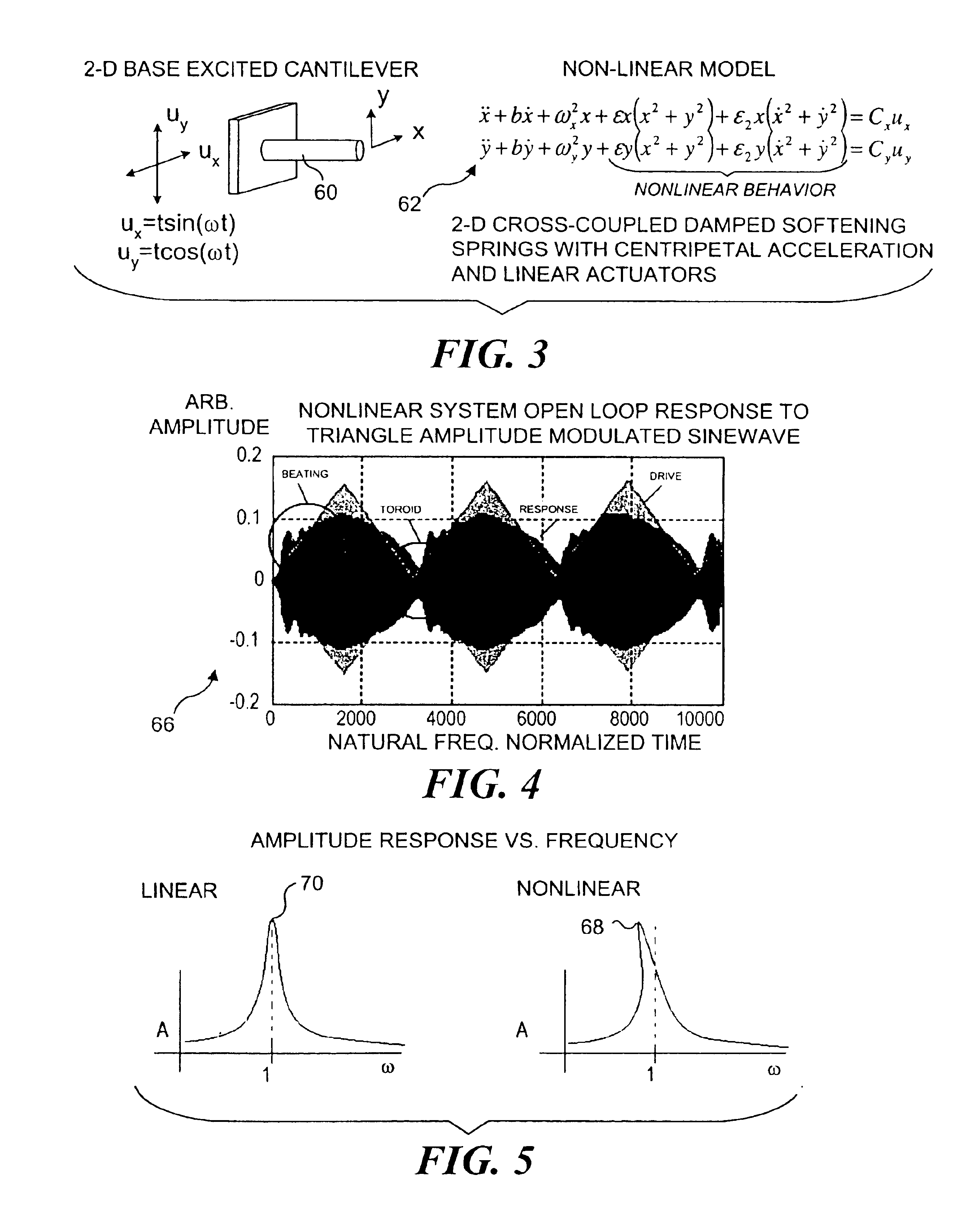
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Multicore optical fibre
InactiveUS6301420B1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
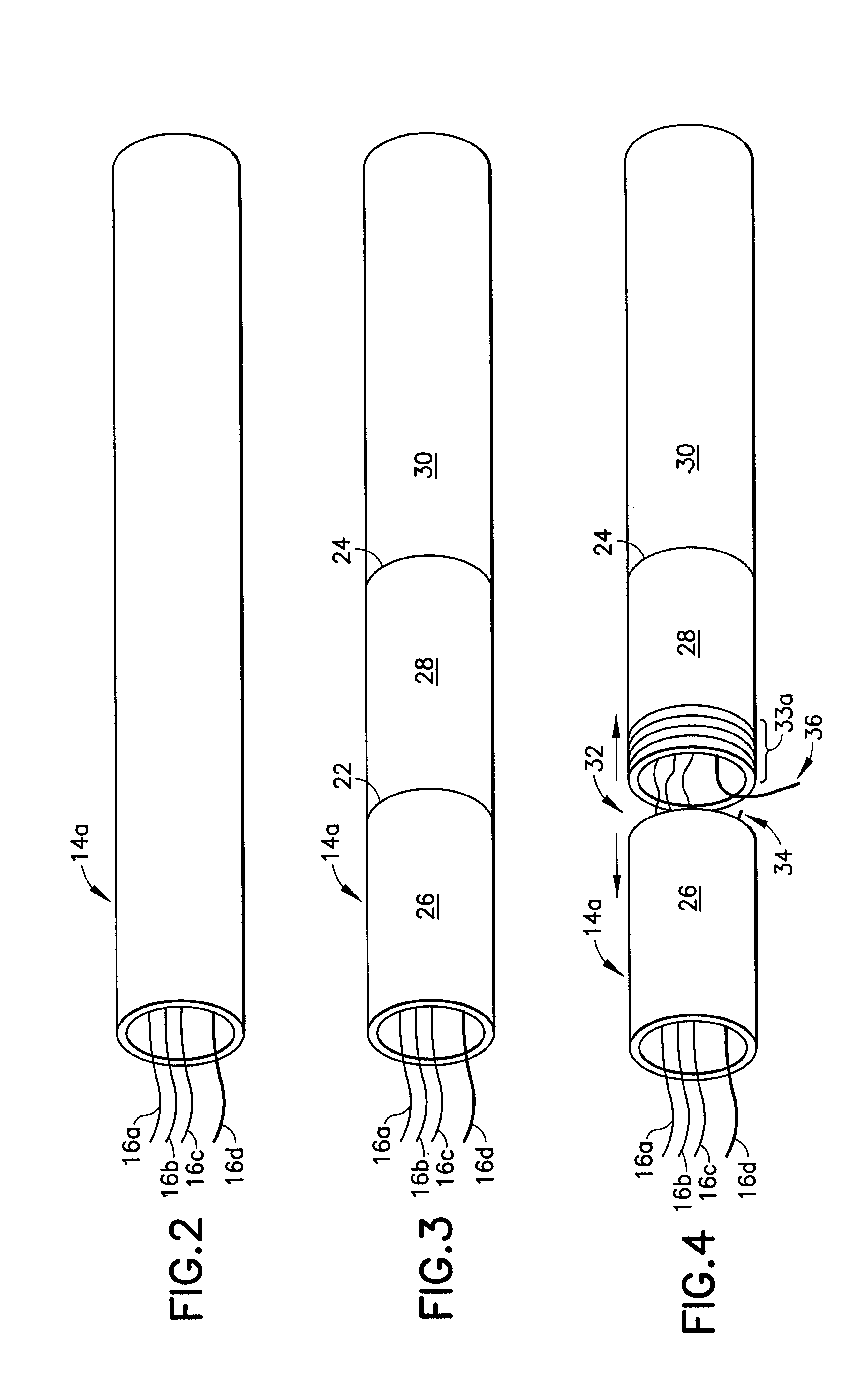
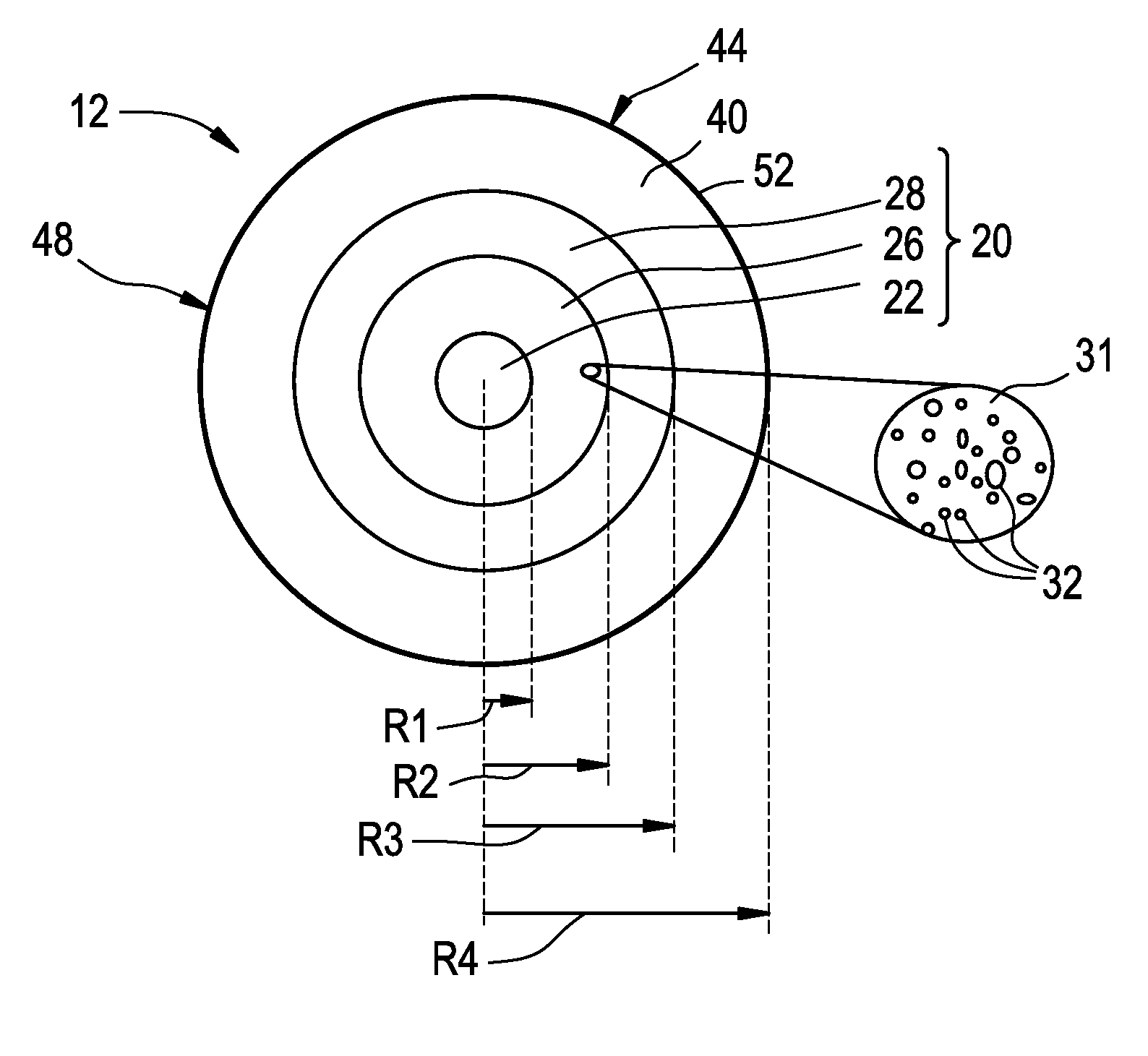
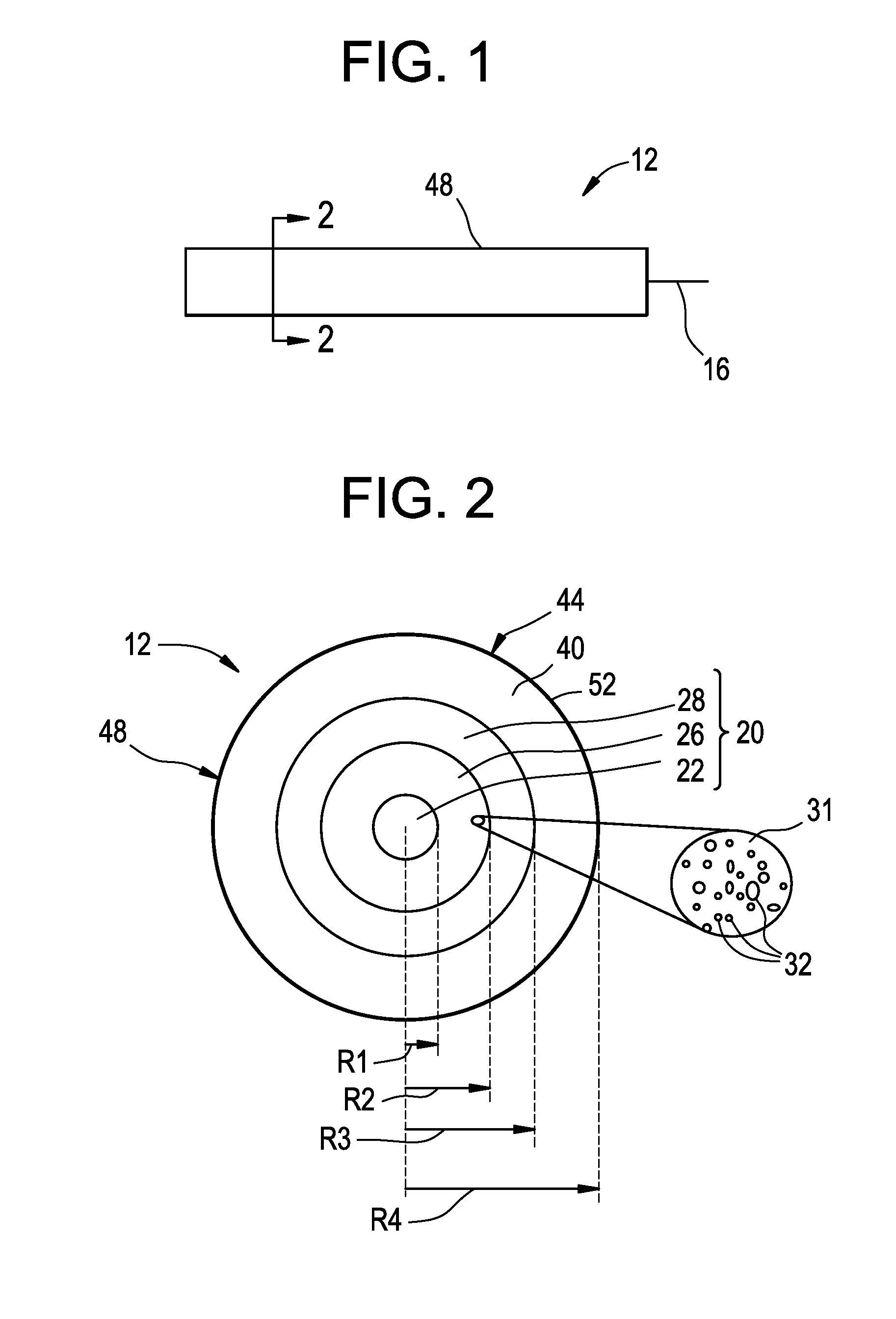
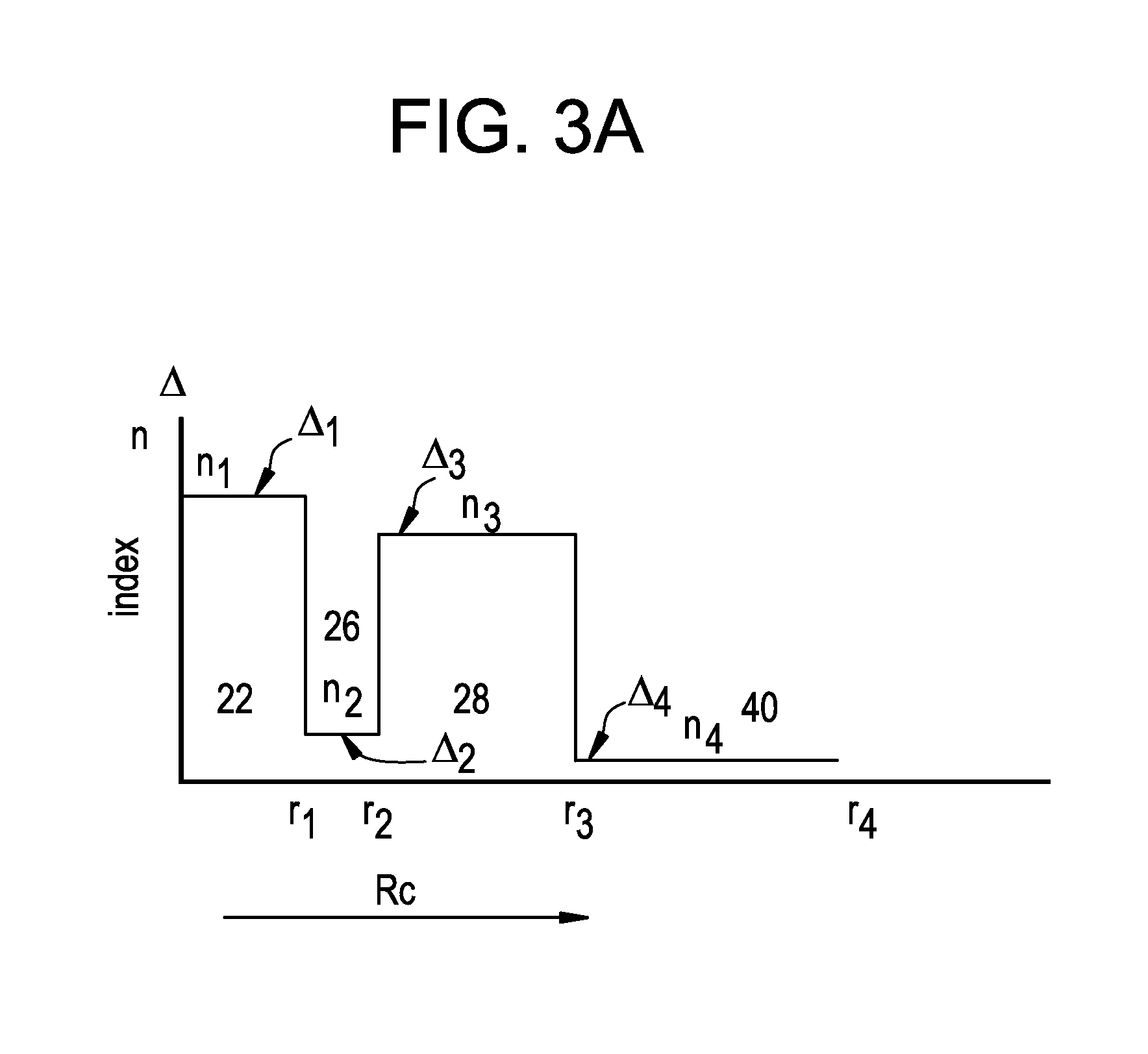
An optical fiber for transmitting radiation comprising two or more core regions, two or more core regions, each core region comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core refractive index, a core length, and a core diameter, wherein said core regions are arranged within a cladding region, said cladding region comprising a length of first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, wherein said first substantially transparent cladding material has an array of lengths of a second cladding material embedded along its length, wherein the second cladding material has a second refractive index which is less than said first refractive index, such that radiation input to said fiber propagates along at least one of said core regions. The cladding region and the core regions may be arranged such that radiation input to said optical fiber propagates along one or more said lengths of said core regions in a single mode of propagation. The optical fiber may be used as a bend sensor, a spectral filter or a directional coupler. The invention also relates to a method of manufacturing a multicore optical fiber.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
Catheterscope 3D guidance and interface system
ActiveUS20060149134A1Effective steeringReduce errorsBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesHigh-resolution computed tomographyGraphics
Visual-assisted guidance of an ultra-thin flexible endoscope to a predetermined region of interest within a lung during a bronchoscopy procedure. The region may be an opacity-identified by non-invasive imaging methods, such as high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) or as a malignant lung mass that was diagnosed in a previous examination. An embedded position sensor on the flexible endoscope indicates the position of the distal tip of the probe in a Cartesian coordinate system during the procedure. A visual display is continually updated, showing the present position and orientation of the marker in a 3-D graphical airway model generated from image reconstruction. The visual display also includes windows depicting a virtual fly-through perspective and real-time video images acquired at the head of the endoscope, which can be stored as data, with an audio or textual account.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Laser ablation process and apparatus
InactiveUS20020045811A1Reduce Fresnel reflectionMaximize transmitted lightControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostics using spectroscopyFiberLaser light
A laser catheter is disclosed wherein optical fibers carrying laser light are mounted in a catheter for insertion into an artery to provide controlled delivery of a laser beam for percutaneous intravascular laser treatment of atherosclerotic disease. A transparent protective shield is provided at the distal end of the catheter for mechanically diplacing intravascular blood and protecting the fibers from the intravascular contents, as well as protecting the patient in the event of failure of the fiber optics. Multiple optical fibers allow the selection of tissue that is to be removed. A computer controlled system automatically aligns fibers with the laser and controls exposure time. Spectroscopic diagnostics determine what tissue is to be removed.
Owner:KITTRELL CARTER +2
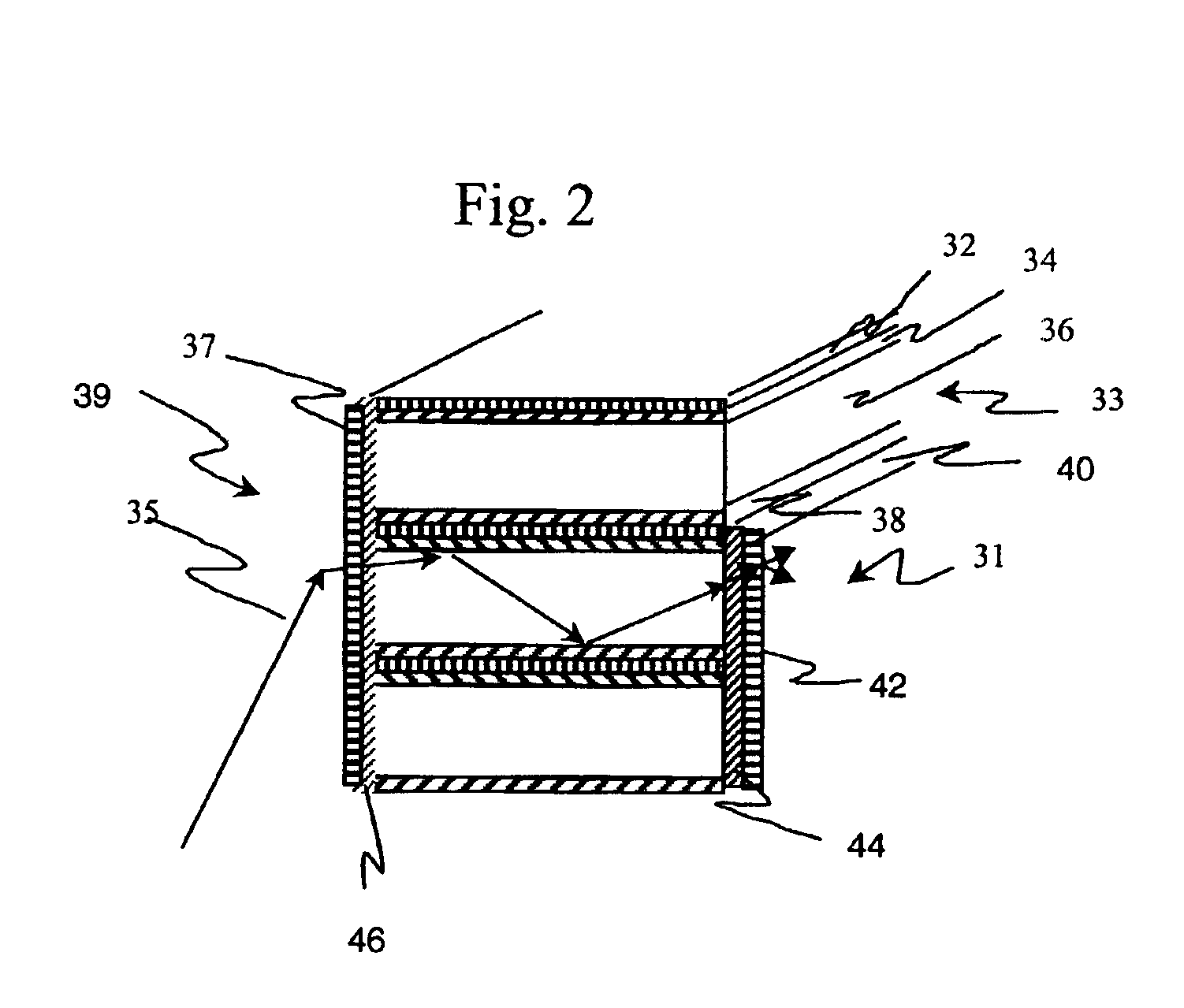
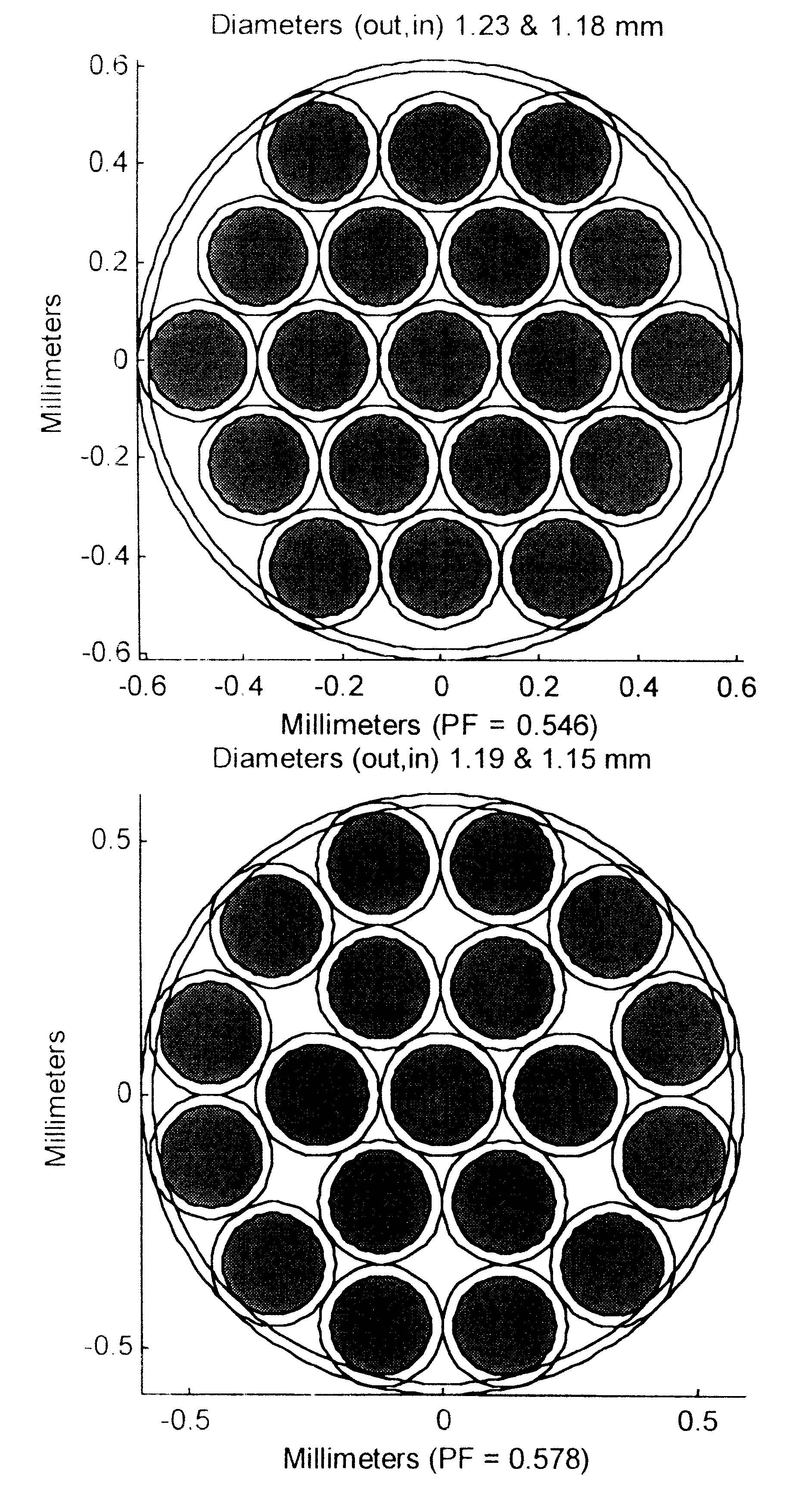
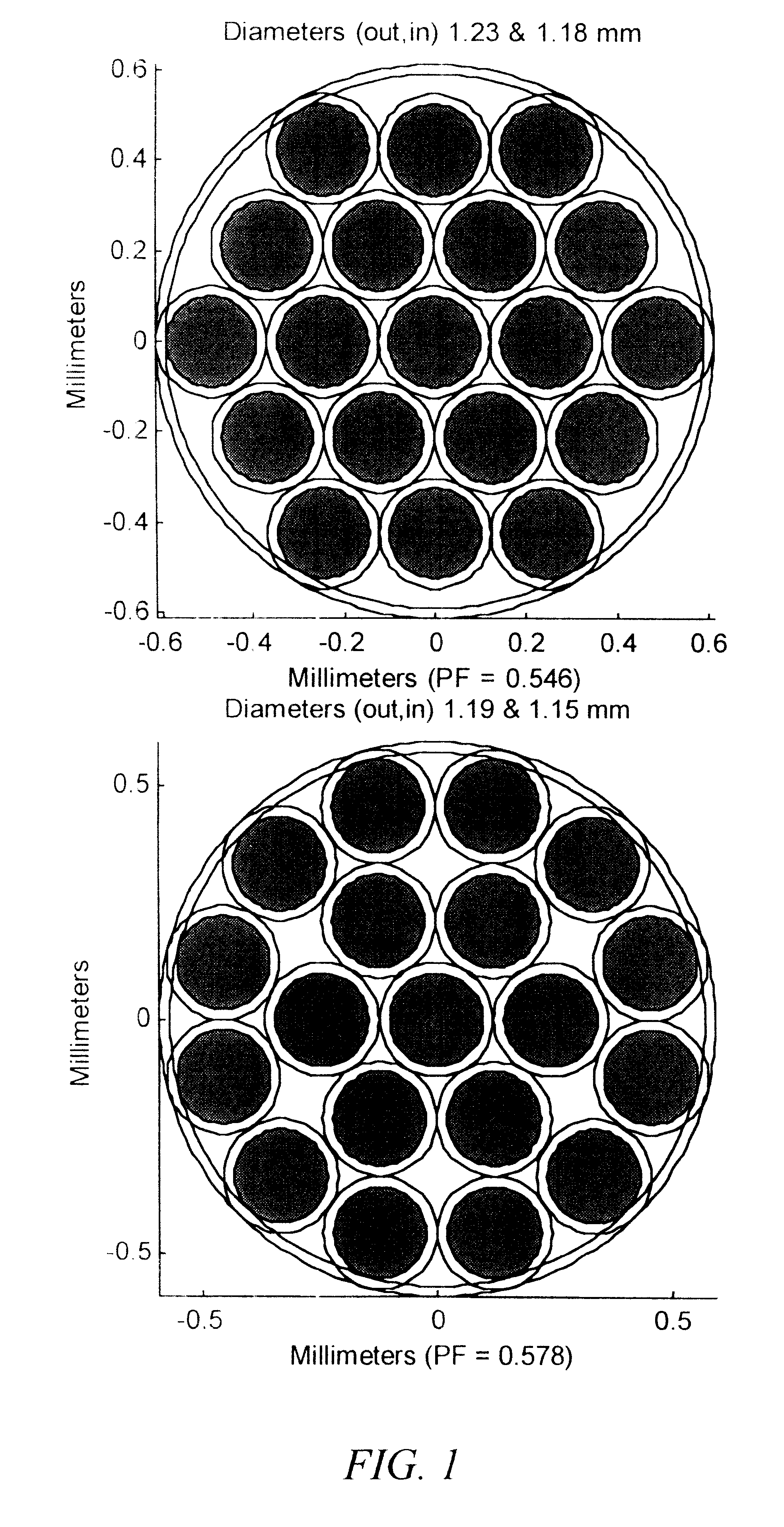
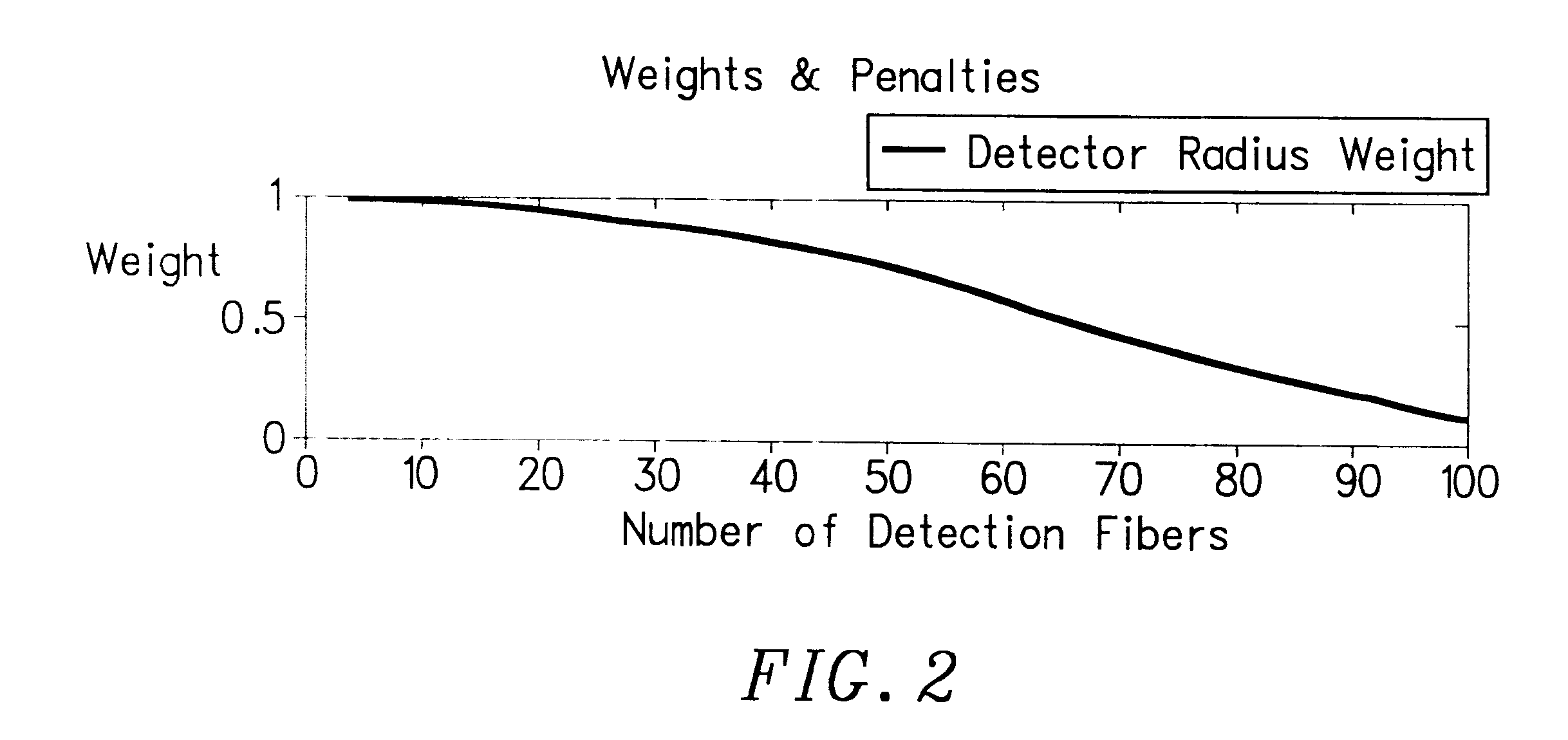
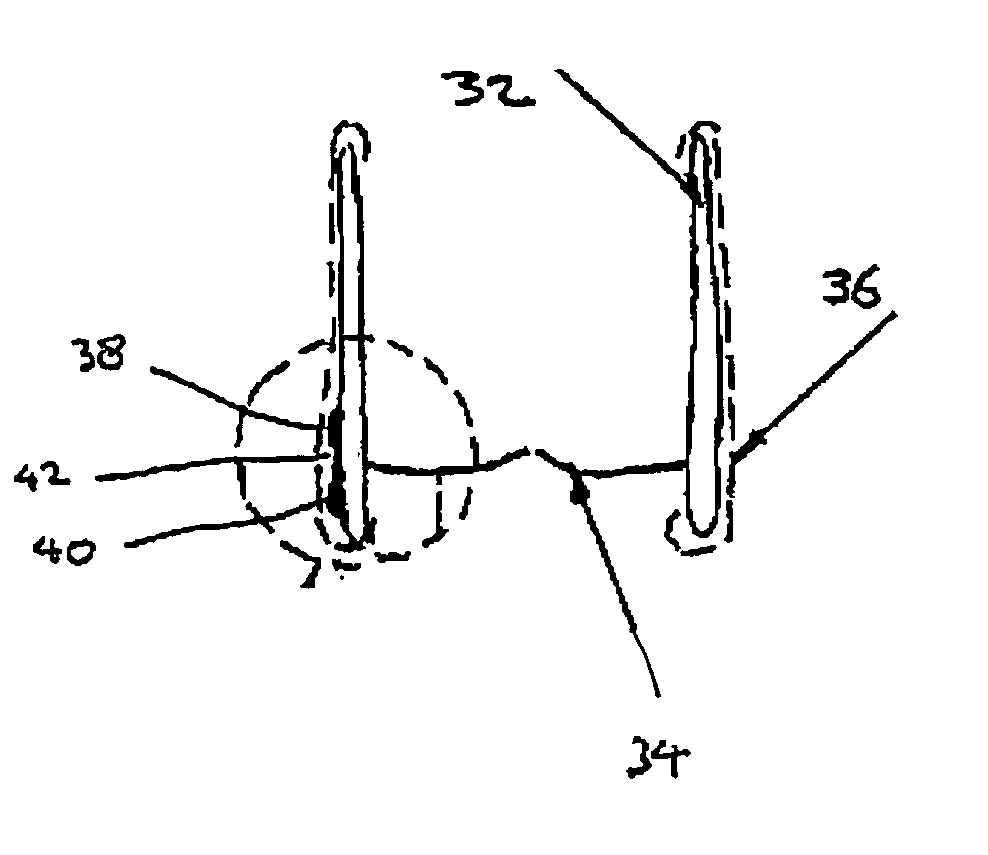
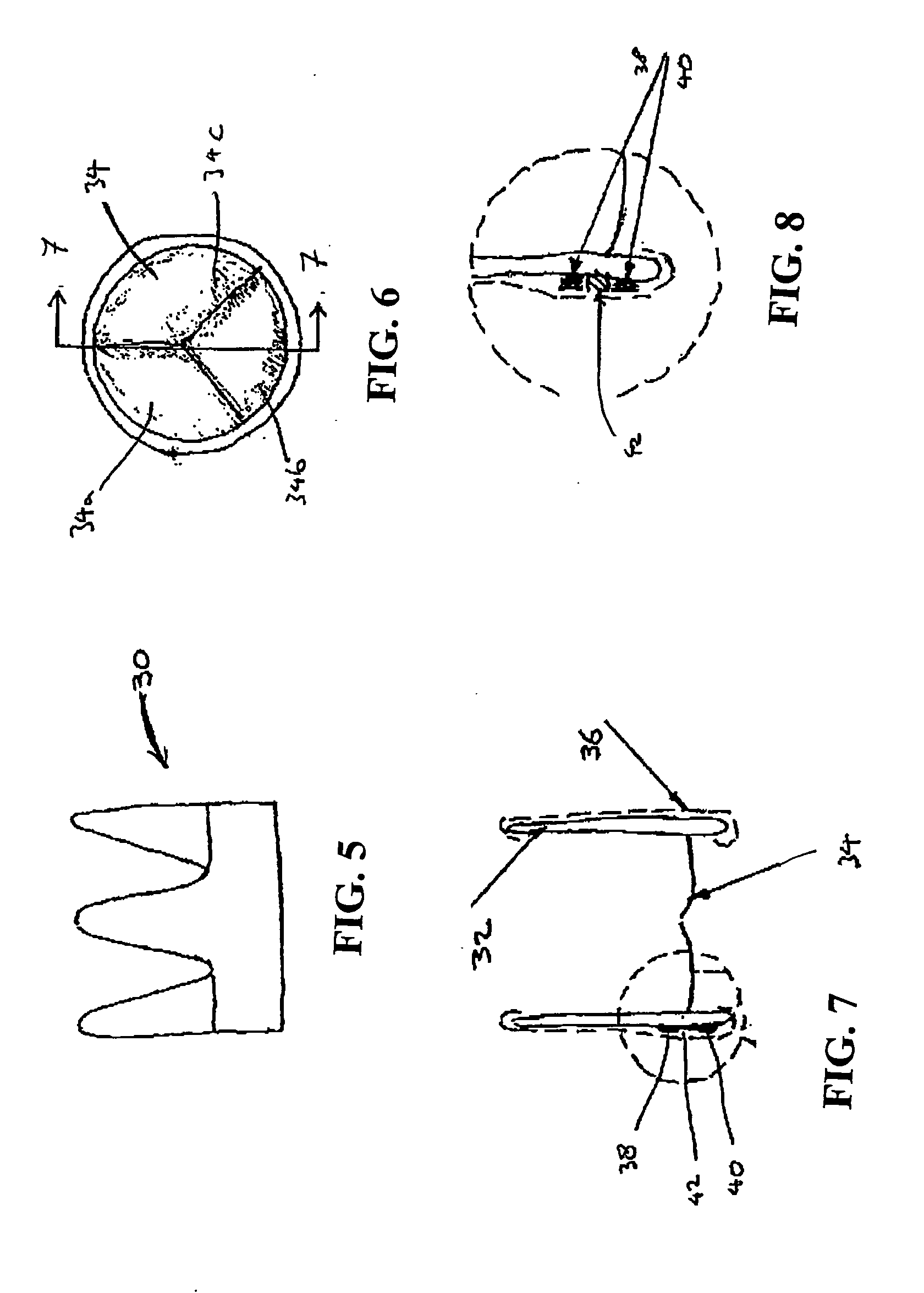
Fiber optic illumination and detection patterns, shapes, and locations for use in spectroscopic analysis
InactiveUS6411373B1Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberMonochromator
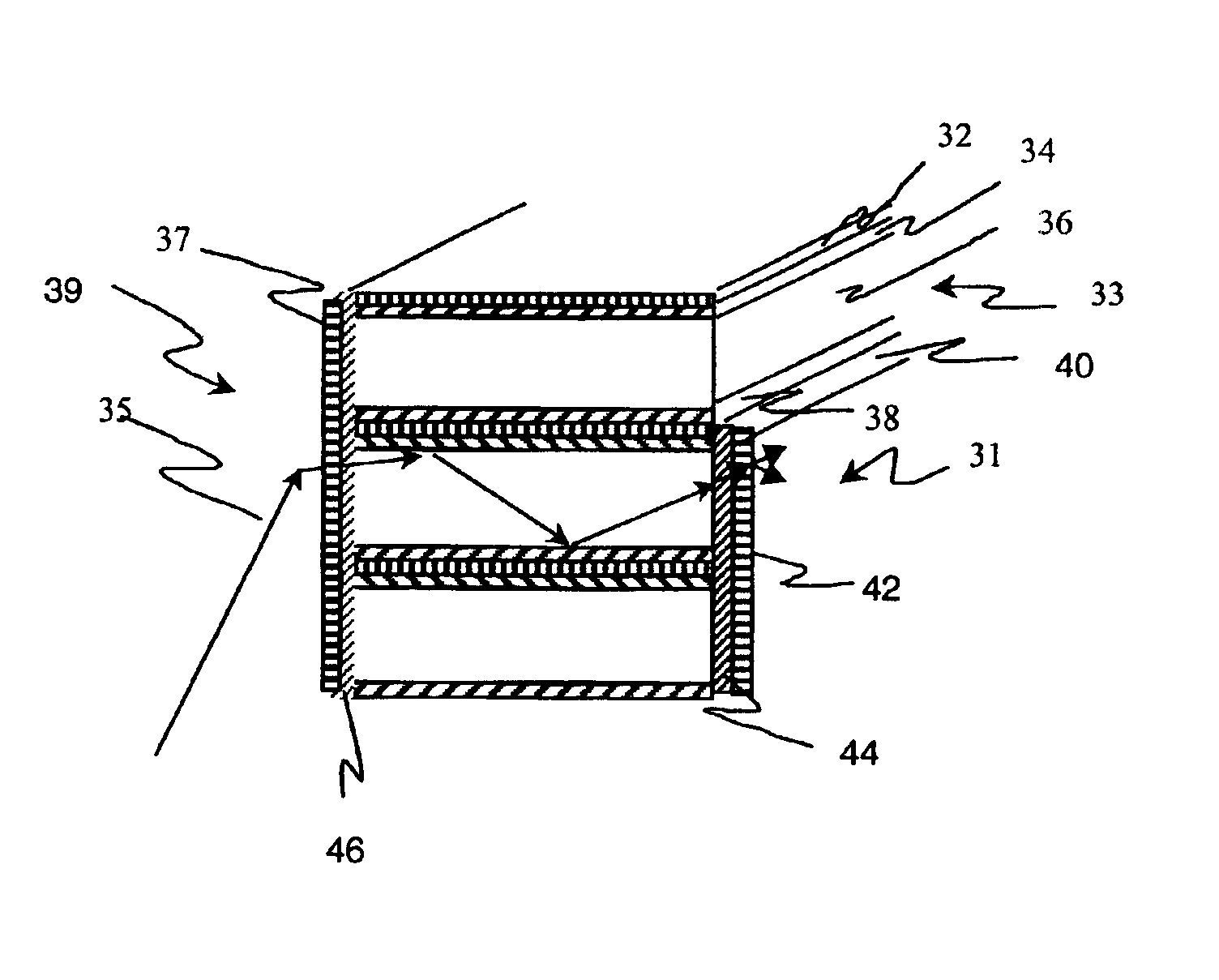
The invention provides a design process that is used in the determination of the pattern of detector and illumination optical fibers at the sampling area of a subject. Information about the system, specifically a monochromator (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at an output slit) and the bundle termination at a detector optics stack (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at the bundle termination), is of critical importance to this design. It is those numbers that determine the ratio and number of illumination to detection fibers, significantly limiting and constraining the solution space. Additional information about the estimated signal and noise in the skin is necessary to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the wavelength range of interest. Constraining the fibers to a hexagonal perimeter and prescribing a hex-packed pattern, such that alternating columns contain illumination and detection fibers, yields optimal results. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, two detectors share the totality of the detection fibers at the sampling interface. A third group of detection fibers is used for classification purposes.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Methods and devices for facilitating visualization in a surgical environment
ActiveUS7559925B2Avoid insufficient lengthSufficient lightingMedical devicesEndoscopesMedicineLight emitting device
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20050243570A1Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of LED outputs into a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. The optical manifolds can be used to combine multiple LEDs of the same color and provide a high intensity output aperture with very high uniformity and sharp borders, or they can be used to generate a multiwavelength output, such as red, green, and blue LEDs that are combined to generate white light. Embodiments are also disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. The optical manifolds are designed to alleviate substantial luminance inhomogeneities inherent to LEDs. The optical manifold utilizes principles of non-imaging optics to transform light and provide directed, substantially uniform light sources.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Far-field display
A flat-panel projection display comprises a transparent slab and integral area grating, a transparent rod with rectangular cross-section and integral linear grating, arranged along the edge of the slab, and a small video projector. The projector is arranged to direct a virtual image into the end of the rod, directly or via mirrors, the light travelling along the rod via total internal reflection. The linear grating diverts the light into the plane of the slab, and the area grating projects it out of the slab towards a viewer, so that the viewer sees an image at infinity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS7286296B2Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of LED outputs into a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. The optical manifolds can be used to combine multiple LEDs of the same color and provide a high intensity output aperture with very high uniformity and sharp borders, or they can be used to generate a multiwavelength output, such as red, green, and blue LEDs that are combined to generate white light. Embodiments are also disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. The optical manifolds are designed to alleviate substantial luminance inhomogeneities inherent to LEDs. The optical manifold utilizes principles of non-imaging optics to transform light and provide directed, substantially uniform light sources.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Holey optical fibres
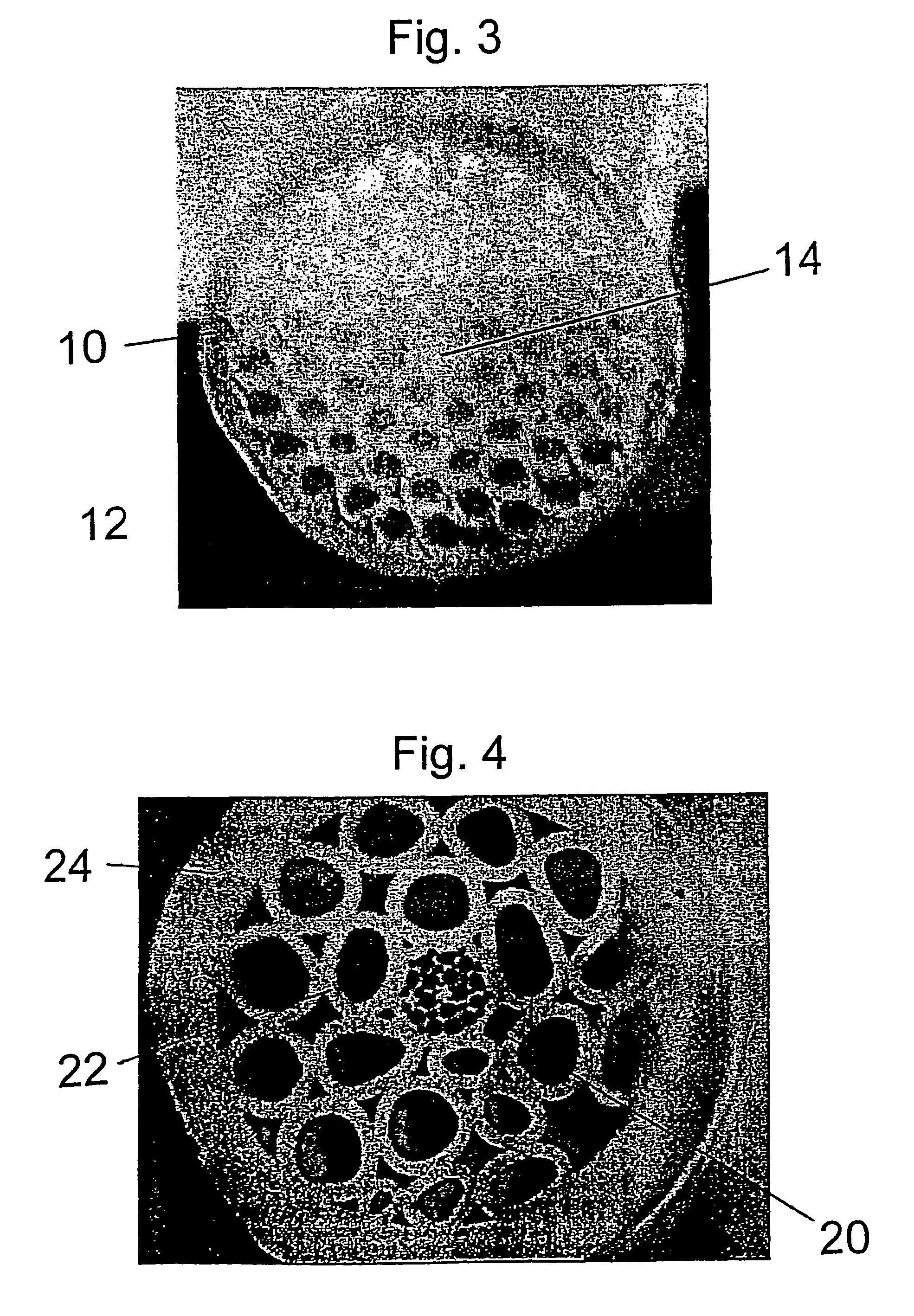
An optical fiber structure having a holey fiber arranged in a holey outer support structure made up of holey tubes encased in a thin walled outer jacket. The holey fiber may have a solid core surrounded by a holey cladding having a plurality of rings of holes. With the invention it is possible to produce robust, coated and jacketed fibers with microstructured core features of micrometer size relatively easily using existing fiber fabrication technology. This improvement is a result of the outer holey structure which reduces the thermal mass of the supporting structure and makes it possible to reliably and controllably retain small hole features during the fiber fabrication process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
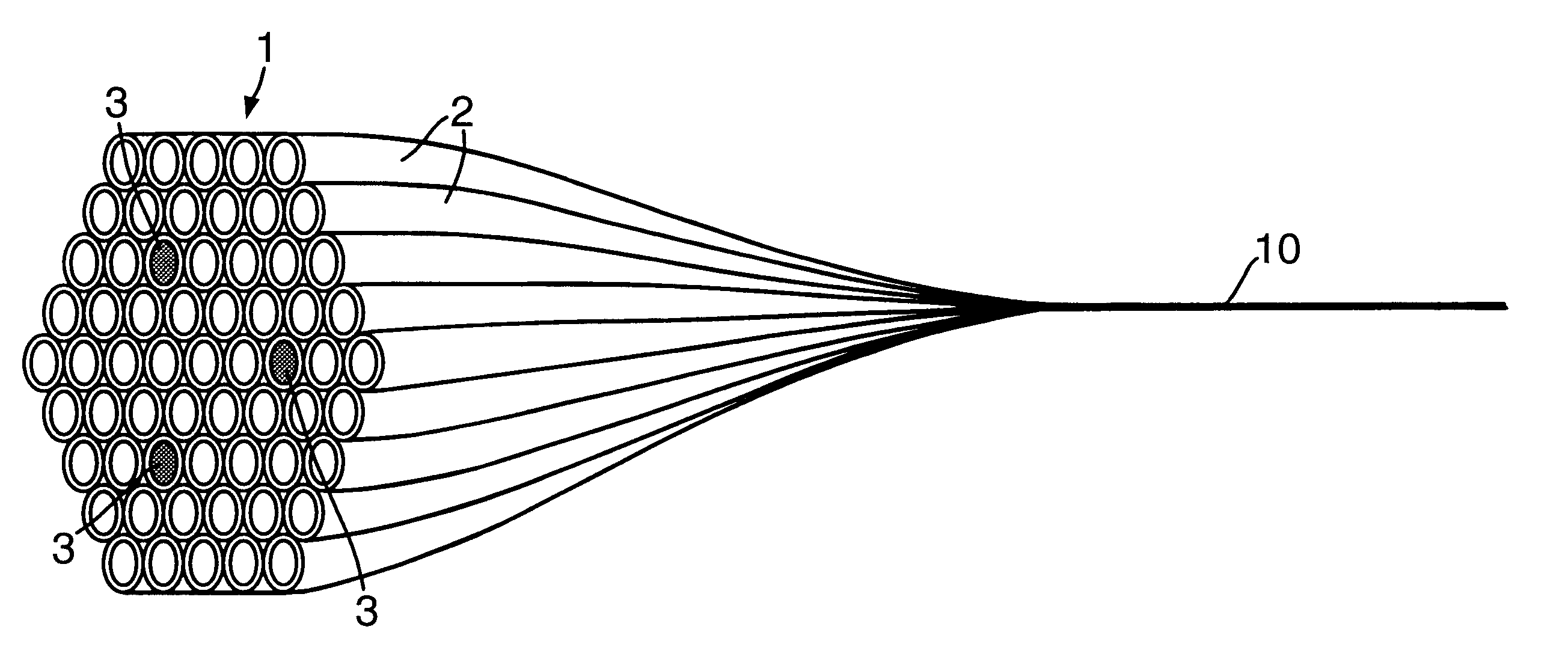
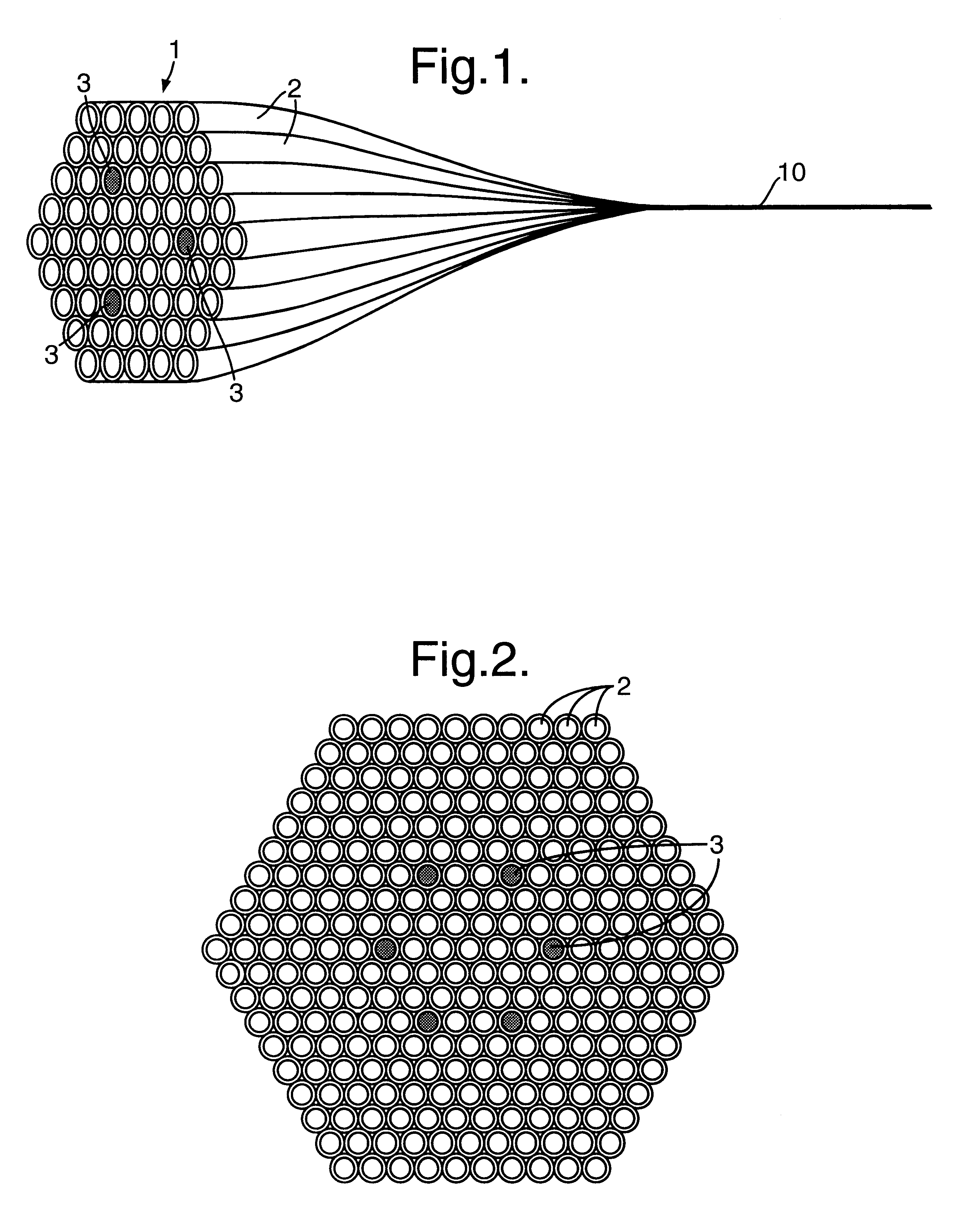
Optical fiber structure and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS7509009B2Easily branchedPromote divisionGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
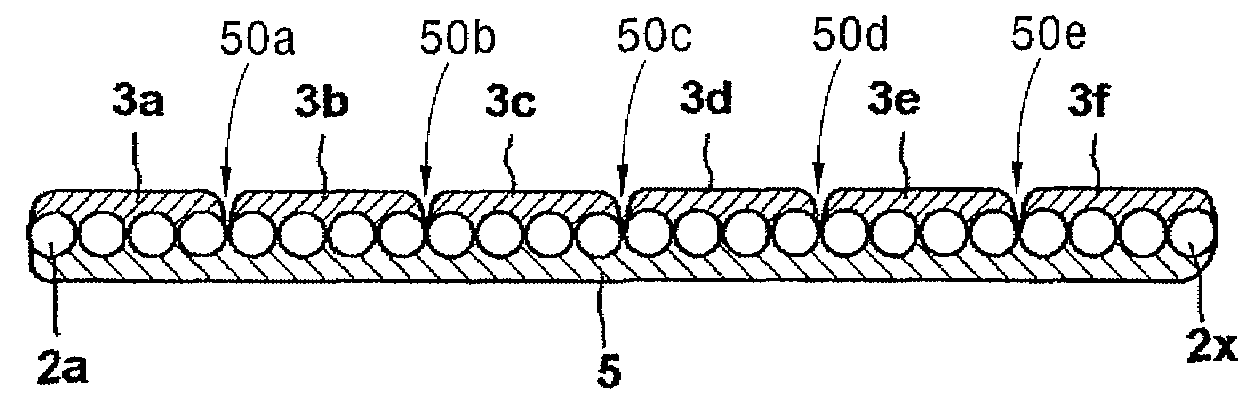
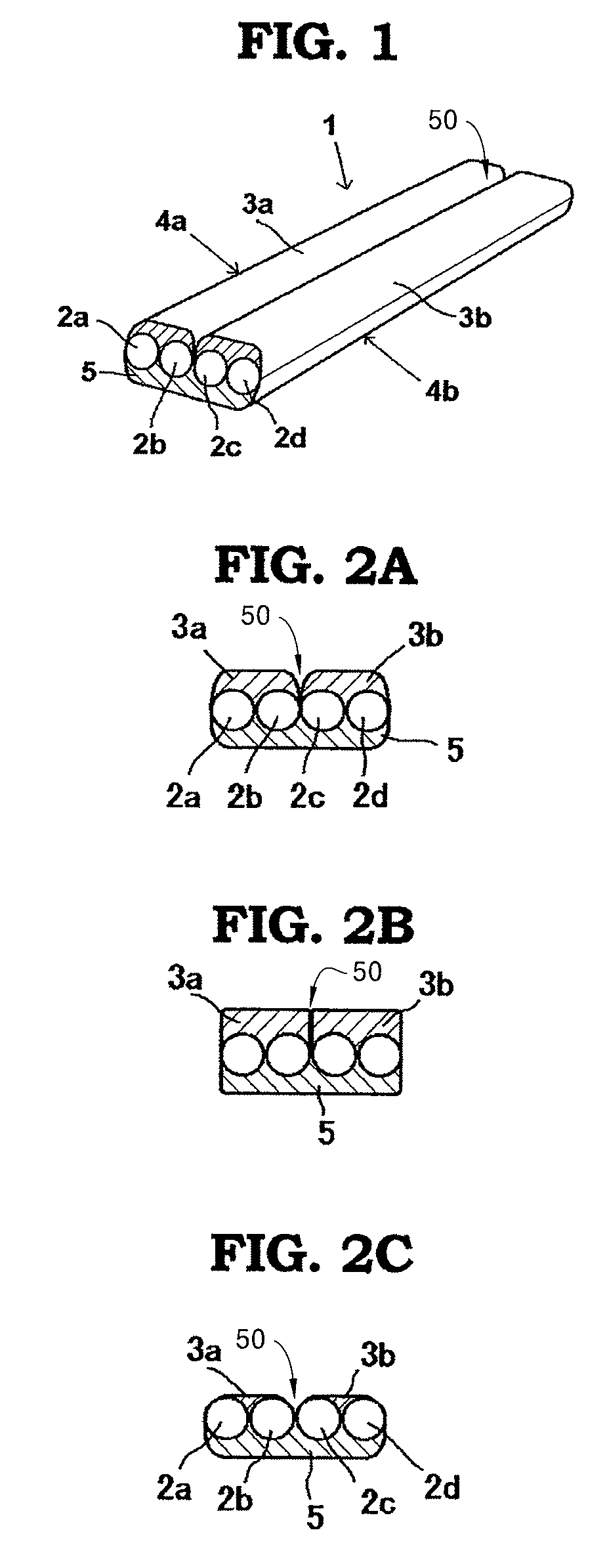
The present invention provides an optical fiber structure that allows for reliable and easy branching of optical fibers, as well as a method of manufacturing such optical fiber structure. The optical fiber structure proposed by the present invention is characterized by a structure wherein multiple optical fiber units, each comprising multiple optical fibers that are aligned two-dimensionally in such a way that one side is covered by a first covering body, are aligned so that the covered surfaces face the same direction, and the covered or uncovered surfaces of the multiple optical fiber units are integrally covered by a second covering body. The second covering body should preferably be made of silicone rubber having a tearing strength of 29 kgf / cm or below.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for filtering an optical fiber
InactiveUS6222970B1Improve responseReduce sensitivityCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh energyPhotonics
Filtering of optical fibers and other related devices. High-energy methods for depositing thin films directly onto the ends of optical fibers can be used to produce high-quality, high-performance filters in quantity at a reasonable cost. These high-quality filters provide the high performance needed for many demanding applications and often eliminate the need for filters applied to wafers or expanded-beam filtering techniques. Having high-quality filters applied directly to optical fiber and faces permits production of high-performance, micro-sized devices that incorporate optical filters. Devices in which these filters may be used include spectroscopic applications including those using fiber optic probes, wavelength division multiplexing, telecommunications, general fiber optic sensor usage, photonic computing, photonic amplifiers, pump blocking and a variety of laser devices.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
Imaging catheter with integrated reference reflector
In part, the invention relates to a lens assembly. The lens assembly includes a micro-lens; a beam director in optical communication with the micro-lens; and a substantially transparent film. The substantially transparent film is capable of bi-directionally transmitting light, and generating a controlled amount of backscatter. In addition, the film surrounds a portion of the beam director.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Multi-core fiber
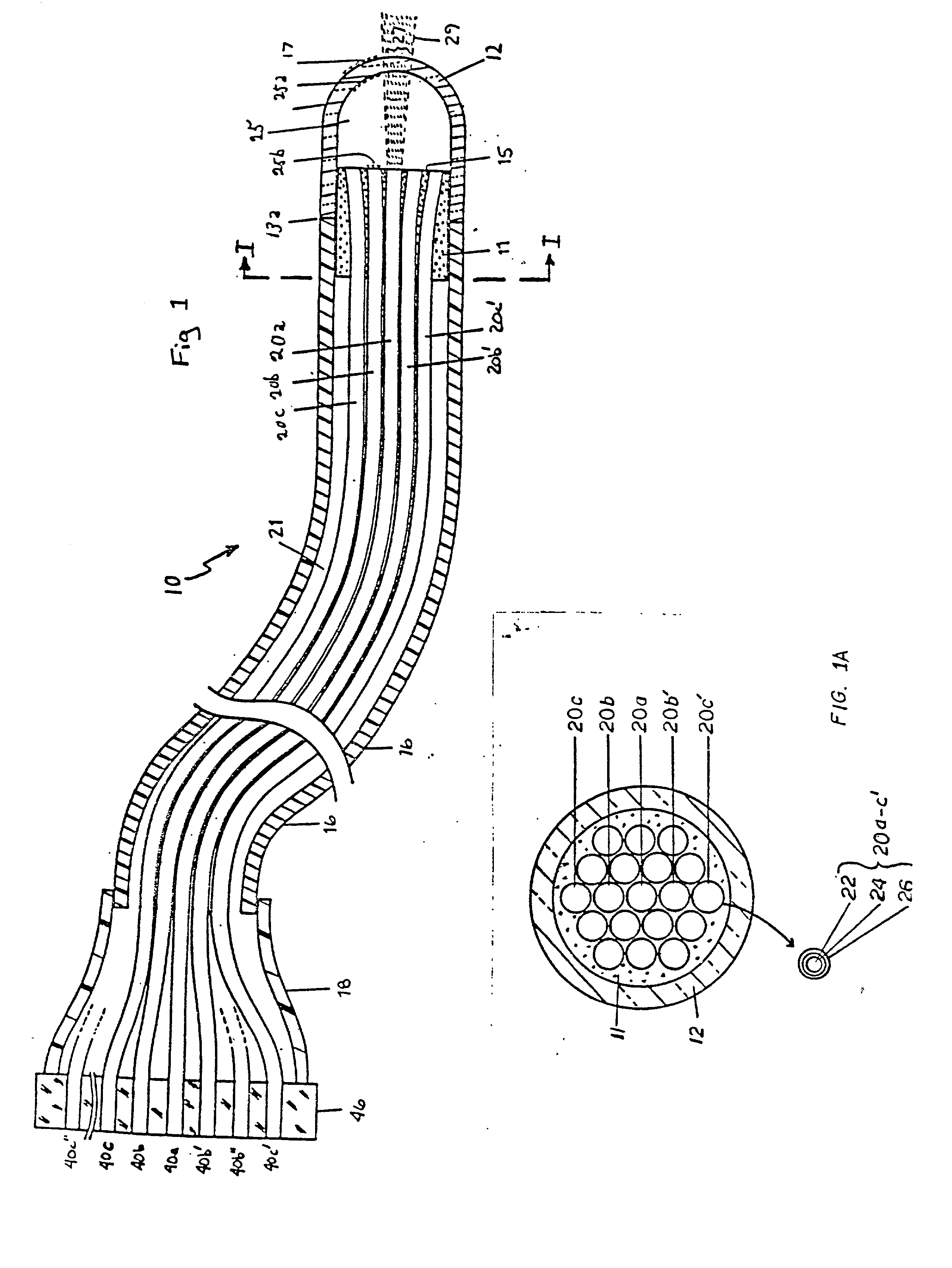
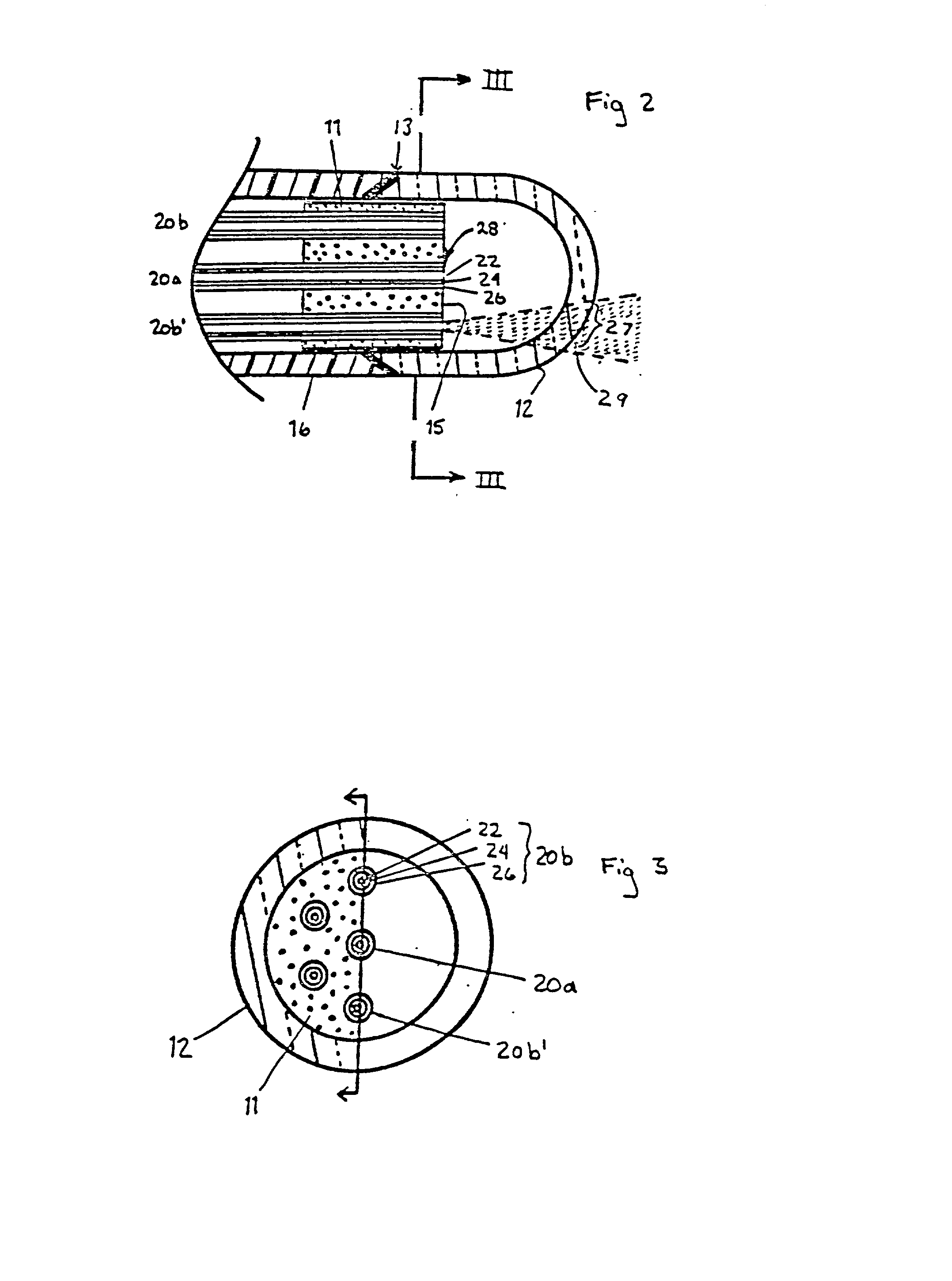
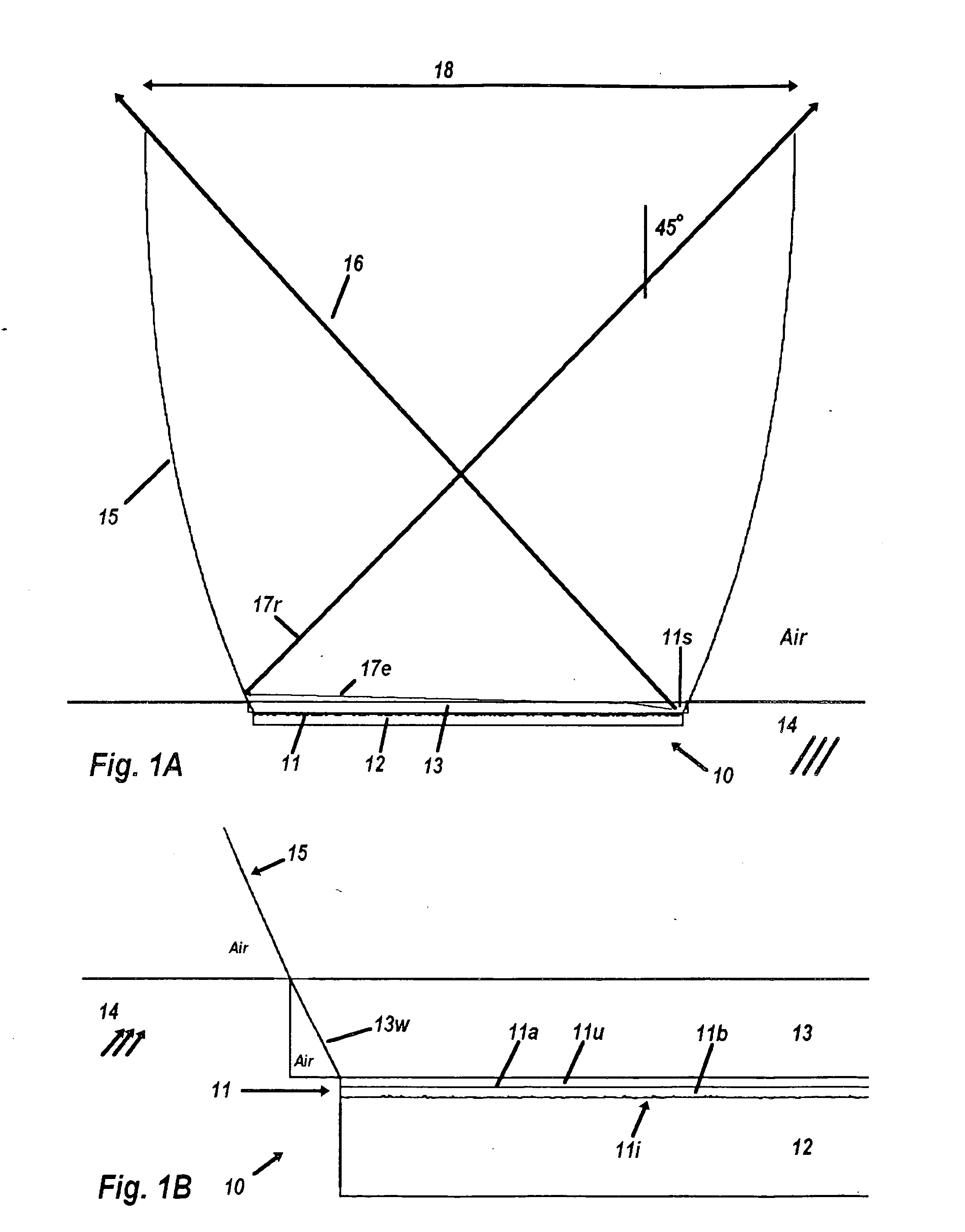
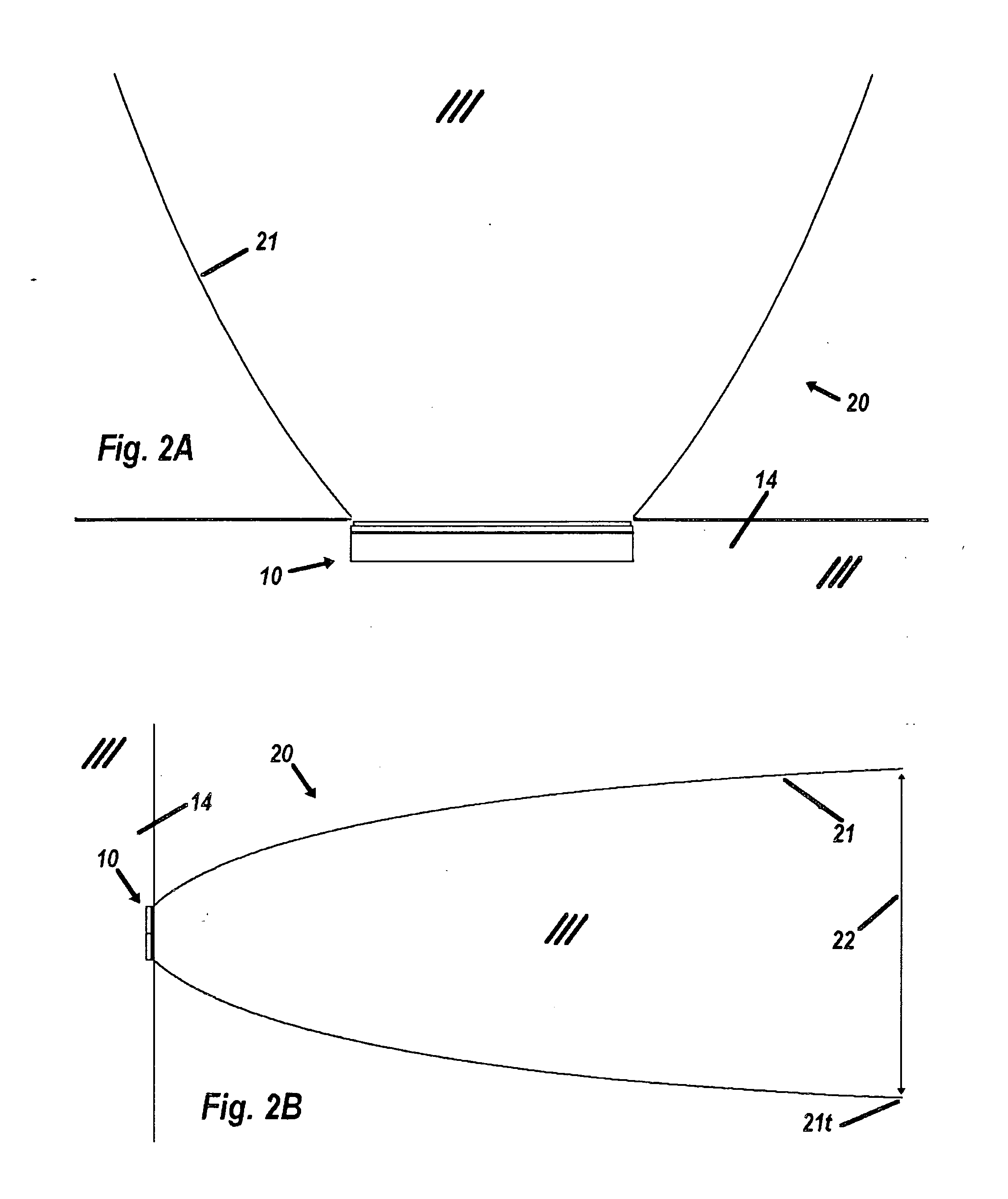
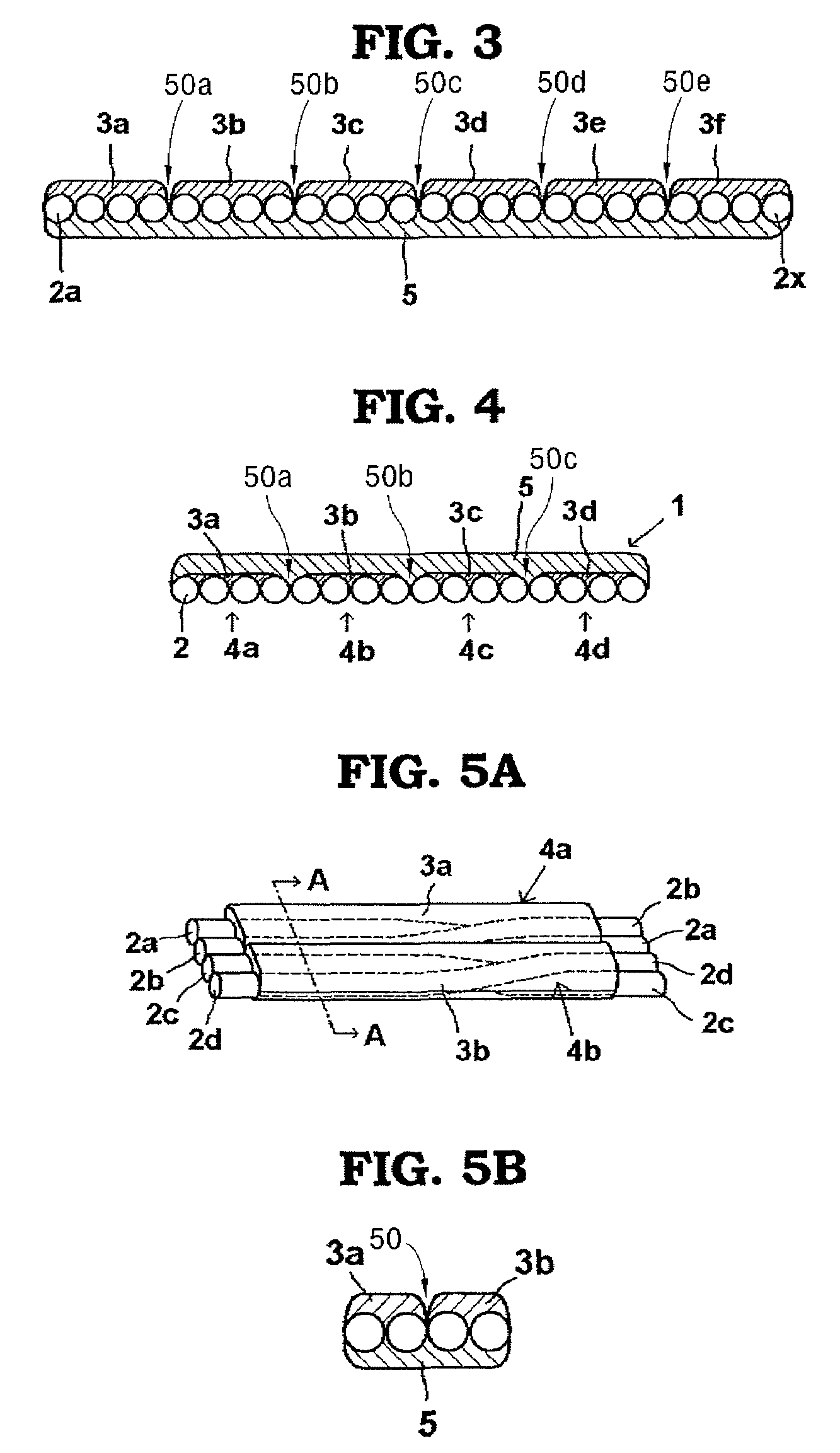
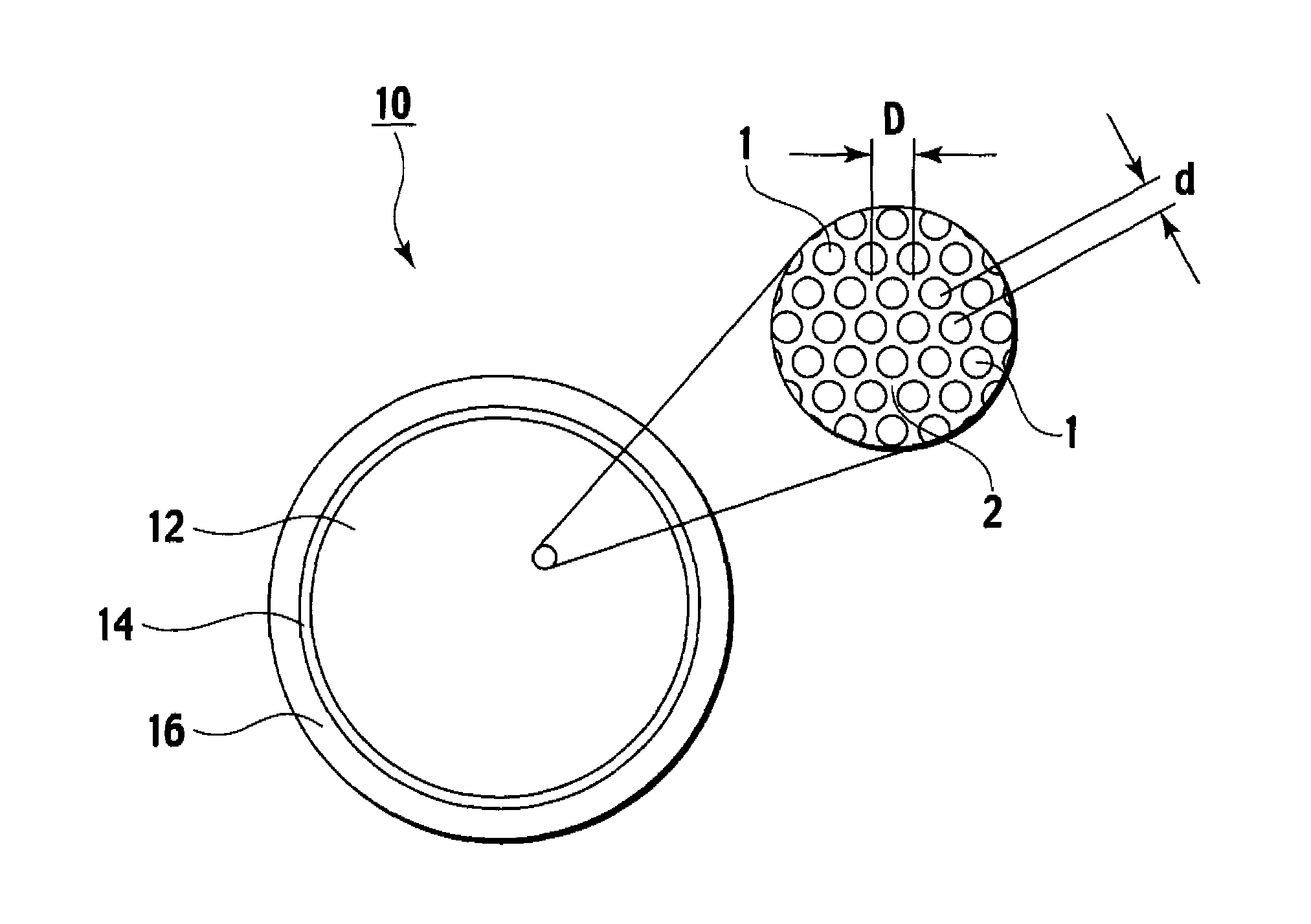
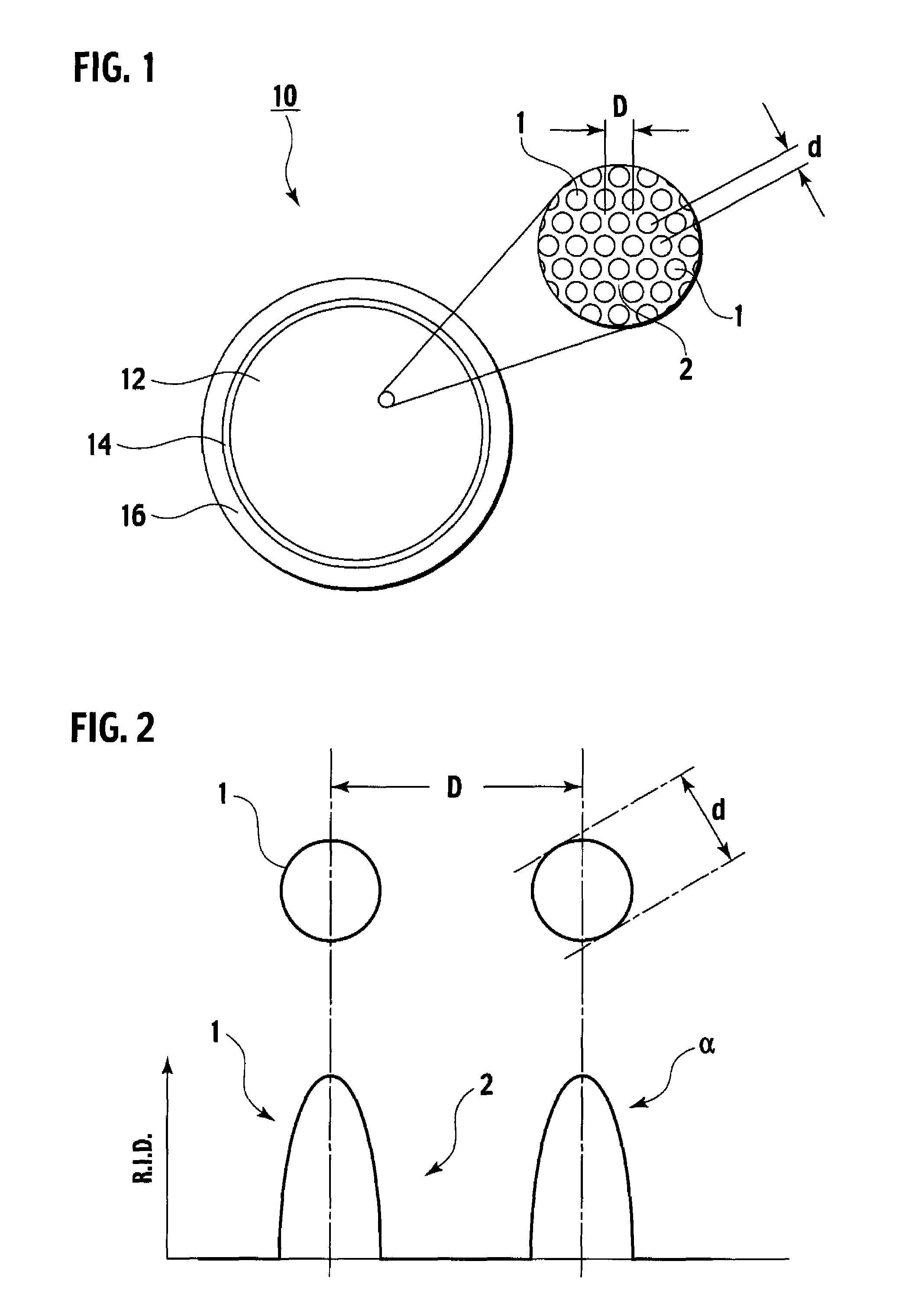
ActiveUS7418178B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBundled fibre light guideQuartzNumerical aperture
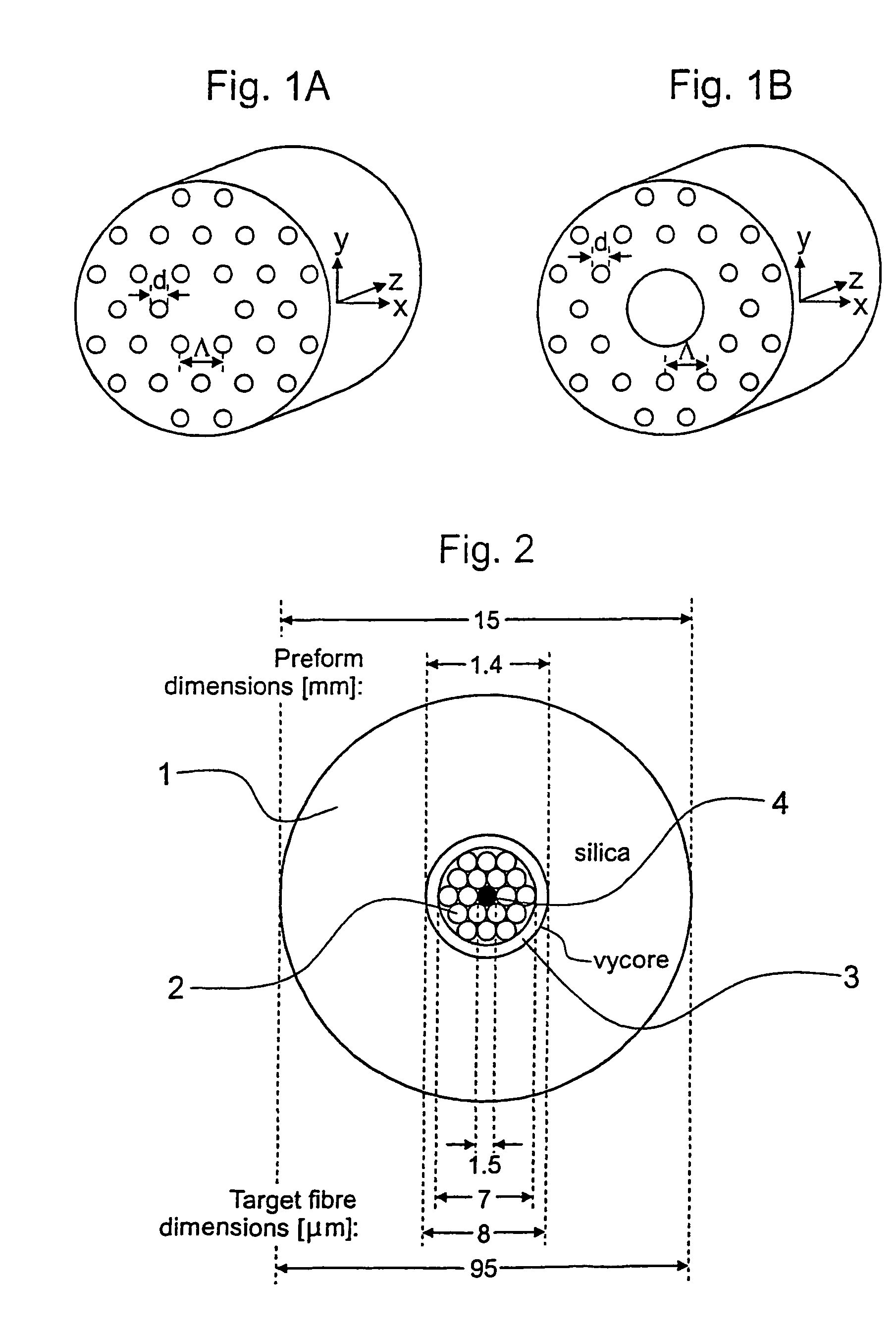
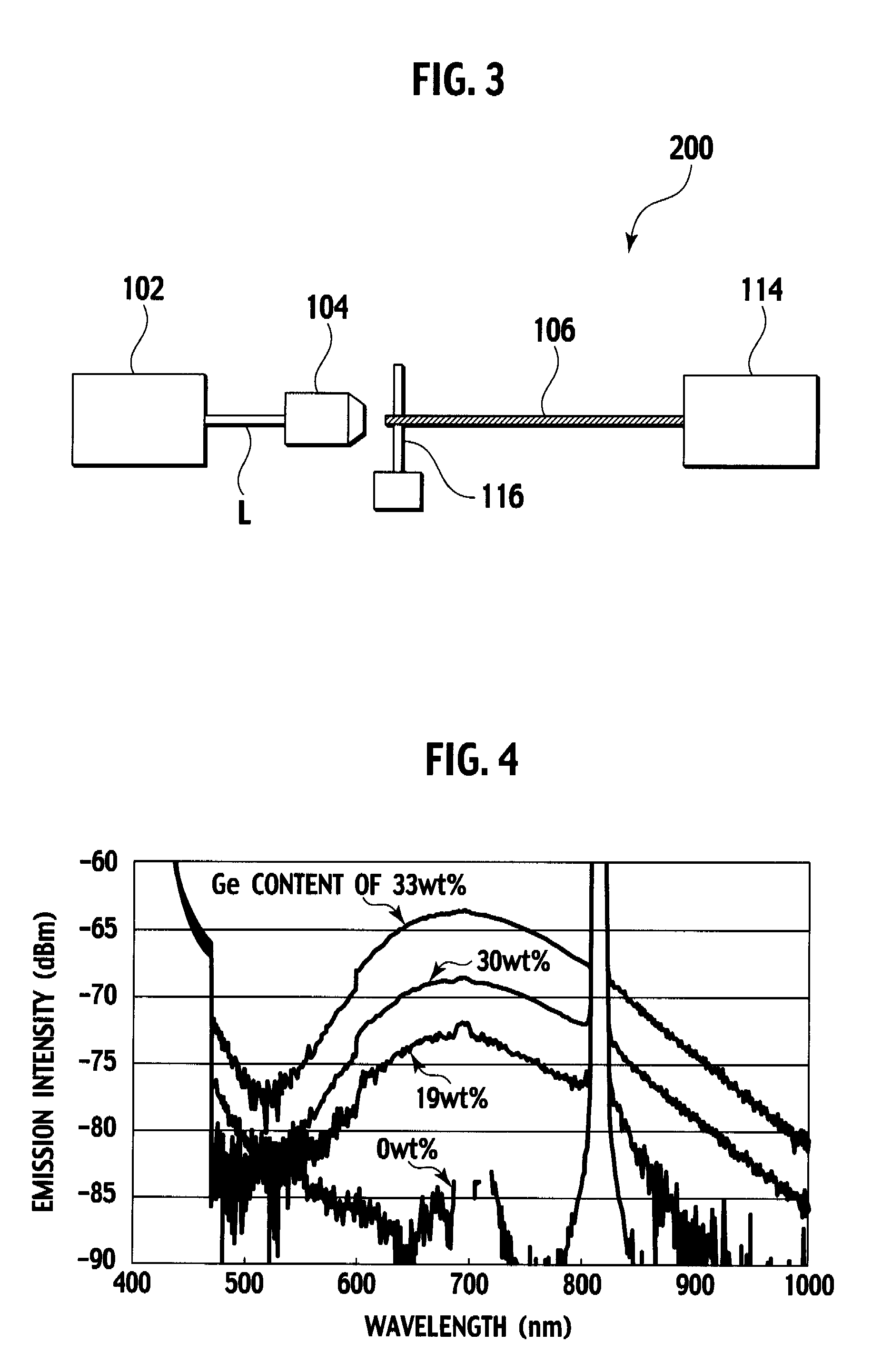
A multi-core optical fiber apparatus is disclosed. The multi-core optical fiber apparatus includes a cladding comprising quartz and a plurality of cores embedded in the cladding. Each of the cores has a diameter (D) ranging from 1.3 μm to 2.0 μm, a numerical aperture (NA) from 0.35 to 0.45 and a refractive index profile factor (α) from 2.0 to 4.0. A center of each of the cores has a germanium content of 20 wt % to 30 wt %. An interval between adjacent cores is 3.0 μm or more.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Battery-powered light source arrangement for endoscope
InactiveUS6260994B1Less overall consumptionLittle electrical powerMechanical apparatusPrintersElectrical batteryLight guide
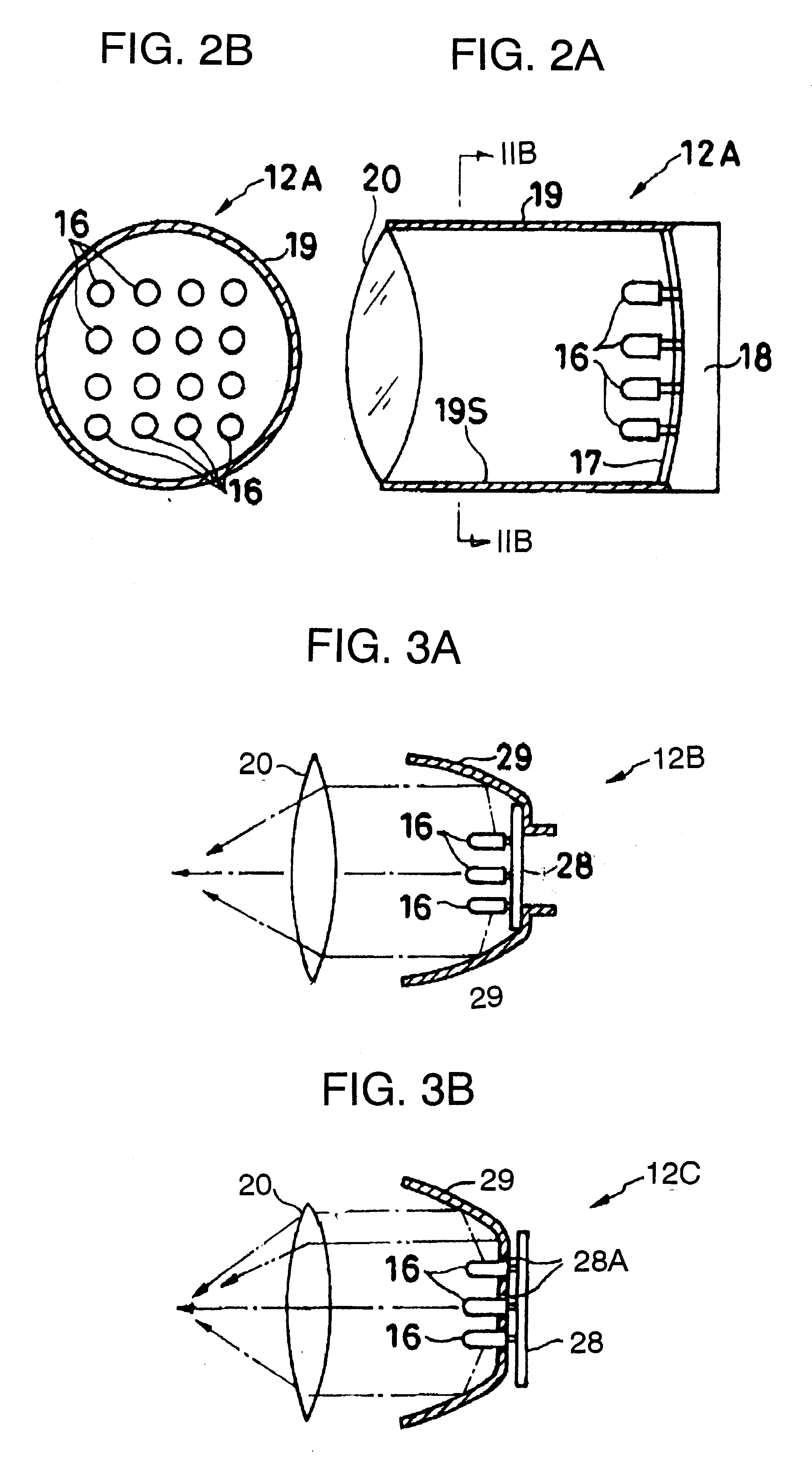
A light source arrangement for a battery-powered light source unit of an endoscope comprises a cylindrical housing, a base disposed at one end of the housing, a plurality of LEDs connected to a flexible circuit board supported on the base and a focusing lens. A light guide for directing light emanating from the LEDs. The light guide comprises a reflective surface formed on an inner wall of the housing, a reflector having a concave reflective surface which is disposed at one end of the housing so as to surround the LEDs or a micro-lens array disposed in front of the LEDs with each micro lens aligned with the LED.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Head-mounted optical apparatus using an OLED display
A see-through head-mounted optical apparatus for a viewer has at least one display module, each display module having a display energizable to form an image and a positive field lens optically coupled to the surface of the display and disposed to direct imaged light from the display toward a first surface of a prism. A curved reflector element is in the path of the imaged light through the prism and disposed at a second surface of the prism, opposite the first surface. The curved reflector element has a refractive surface and a curved reflective surface disposed to collimate imaged light received from the display and direct this light toward a beam splitter that is disposed within the prism and that is at an oblique angle to the collimated reflected light. The beam splitter redirects the incident collimated reflected light through the prism to form an entrance pupil for the viewer.
Owner:NVIS
Flat-panel display using tapered waveguide
InactiveUS7410286B2Reduce blurIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusFlat panel displayWaveguide
A video display for two or three dimensions has a flat liquid-crystal screen which ejects light from the plane at a selectable line. One or, in the case of a 3-D display, several video projectors project a linear image into the plane from an edge. A complete image is written on the screen by addressing the line with appropriate images as it is scanned down the screen. To screen a three-dimensional image, the video projectors, each projecting an image as seen at a slightly different angle, combine to constitute a three-dimensional display which produces a three-dimensional image that is one line high.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Light source device, imaging apparatus and endoscope apparatus
A light source device includes a first light source, a second light source having an emission wavelength that is different from the first light source, and a phosphor that is disposed to be distant from the first light source and the second light source and absorbs light in a predetermined excitation wavelength band to emit fluorescence. The phosphor is disposed on an emission light optical path that is shared by the first light source and the second light source. The emission wavelength of the first light source is in the predetermined excitation wavelength band. The emission wavelength of the second light source is outside of the predetermined excitation wavelength band.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging system and related techniques
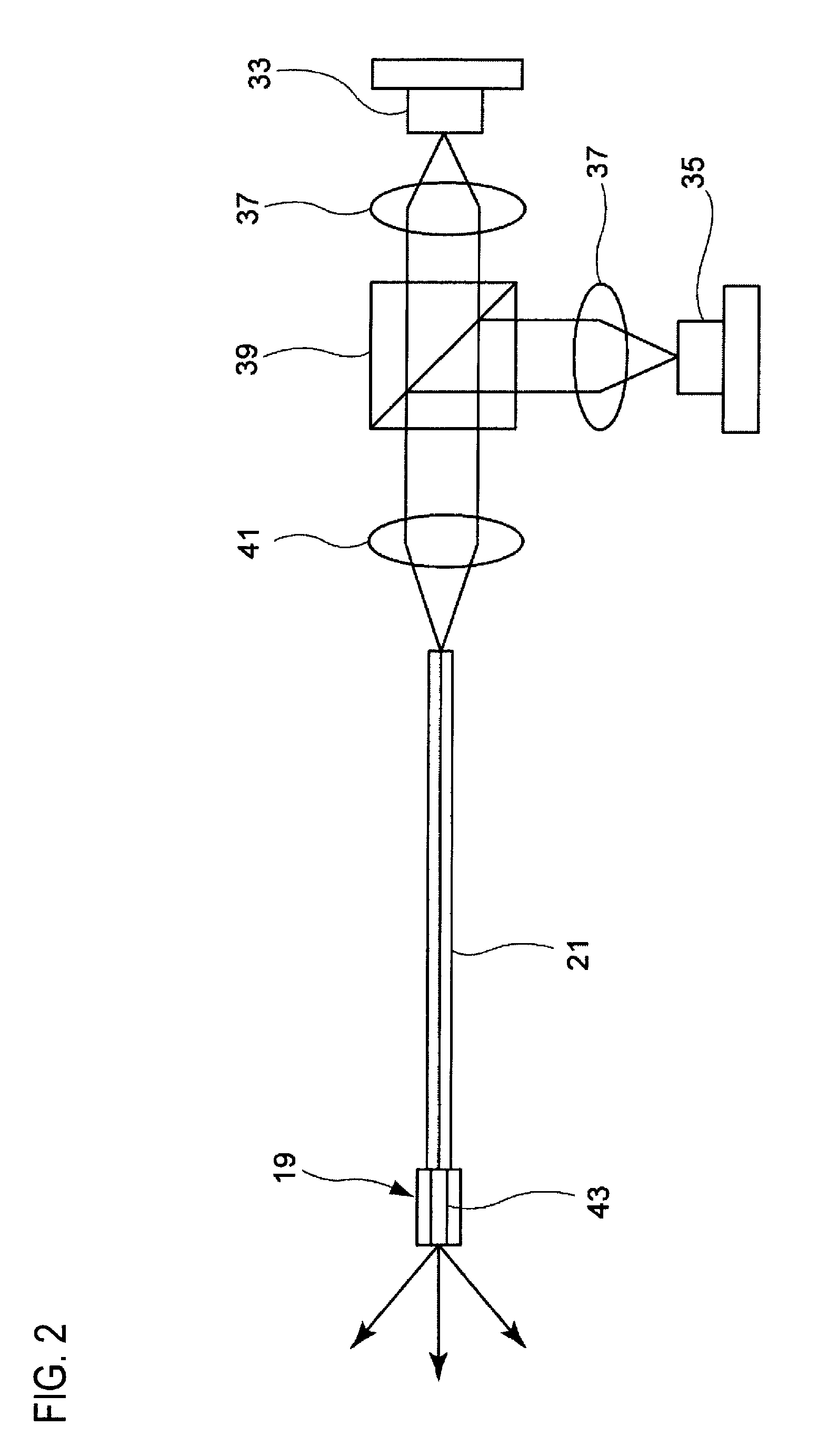
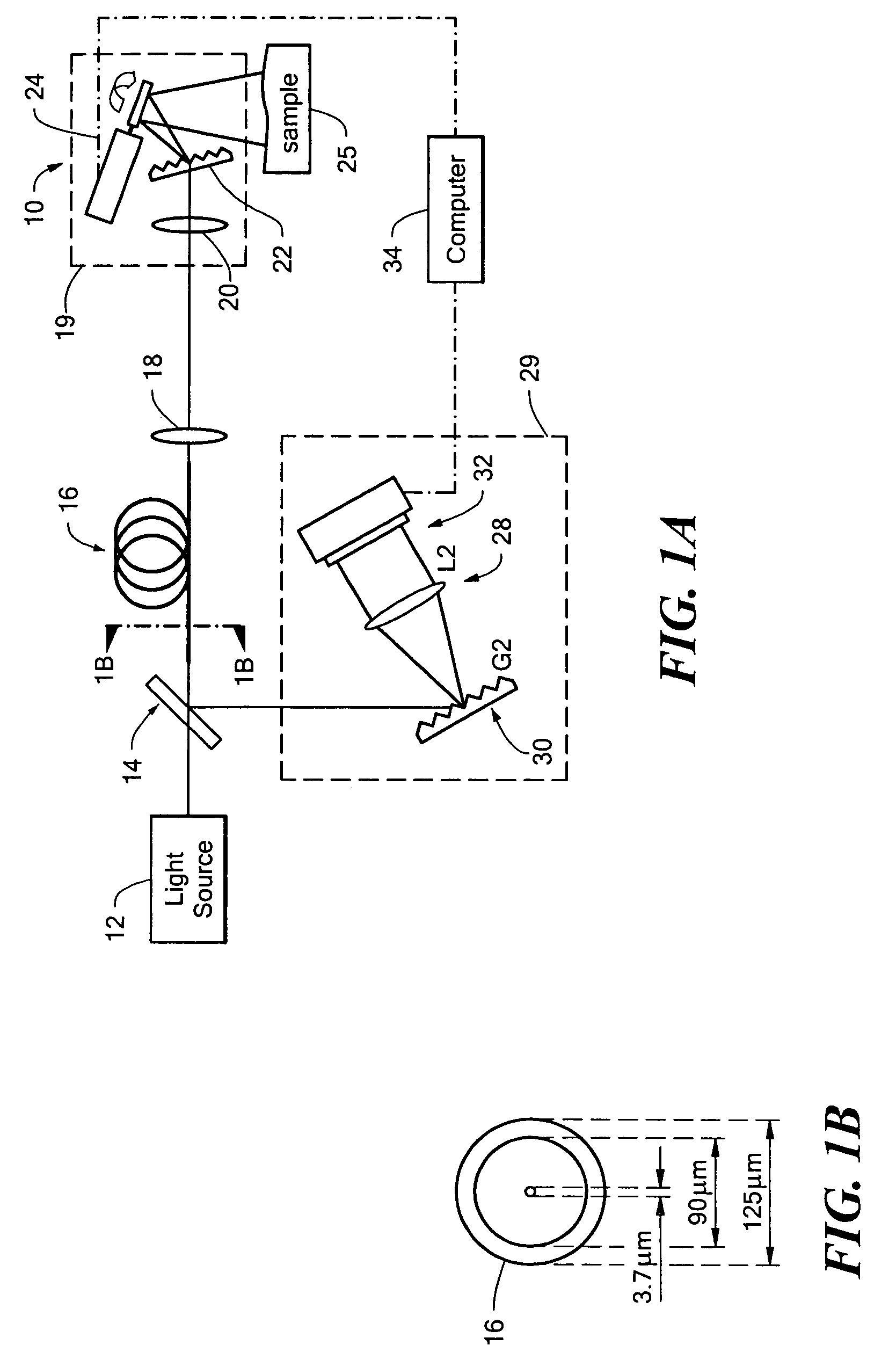
ActiveUS7447408B2Reduces image speckleAdd depthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDouble-clad fiberComputer science
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Medical devices
InactiveUS20050165317A1Easy to getLittle and no inconvenienceStentsHeart valvesMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
There is disclosed a medical device for implantation in a body comprising: one or more sensors for sensing a physiologically or clinically relevant parameter; and telemetric communications means for telemetrically transmitting data related to a parameter sensed by the one or more sensors to a remote device.
Owner:L P100
Solid state light device
A photon emitting device comprises a plurality of solid state radiation sources to generate radiation. The solid state radiation sources can be disposed in an array pattern. Optical concentrators, arranged in a corresponding array pattern, receive radiation from corresponding solid state radiation sources. The concentrated radiation is received by a plurality of optical waveguides, also arranged in a corresponding array pattern. Each optical waveguide includes a first end to receive the radiation and a second end to output the radiation. A support structure is provided to stabilize the plurality of optical waveguides between the first and second ends. The photon emitting device can provide a replacement for a discharge lamp device in various applications including road illumination, spot lighting, back lighting, image projection and radiation activated curing.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
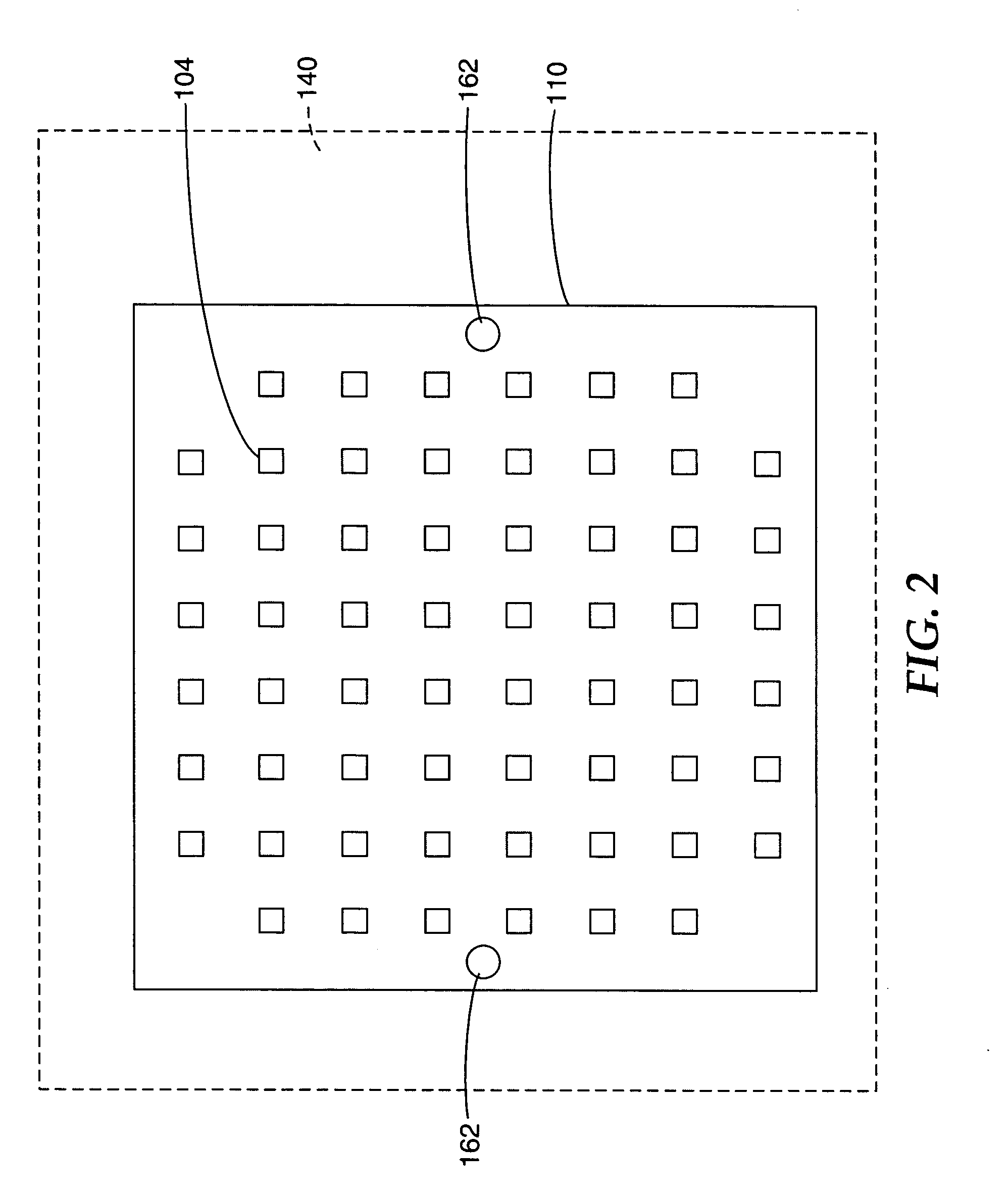
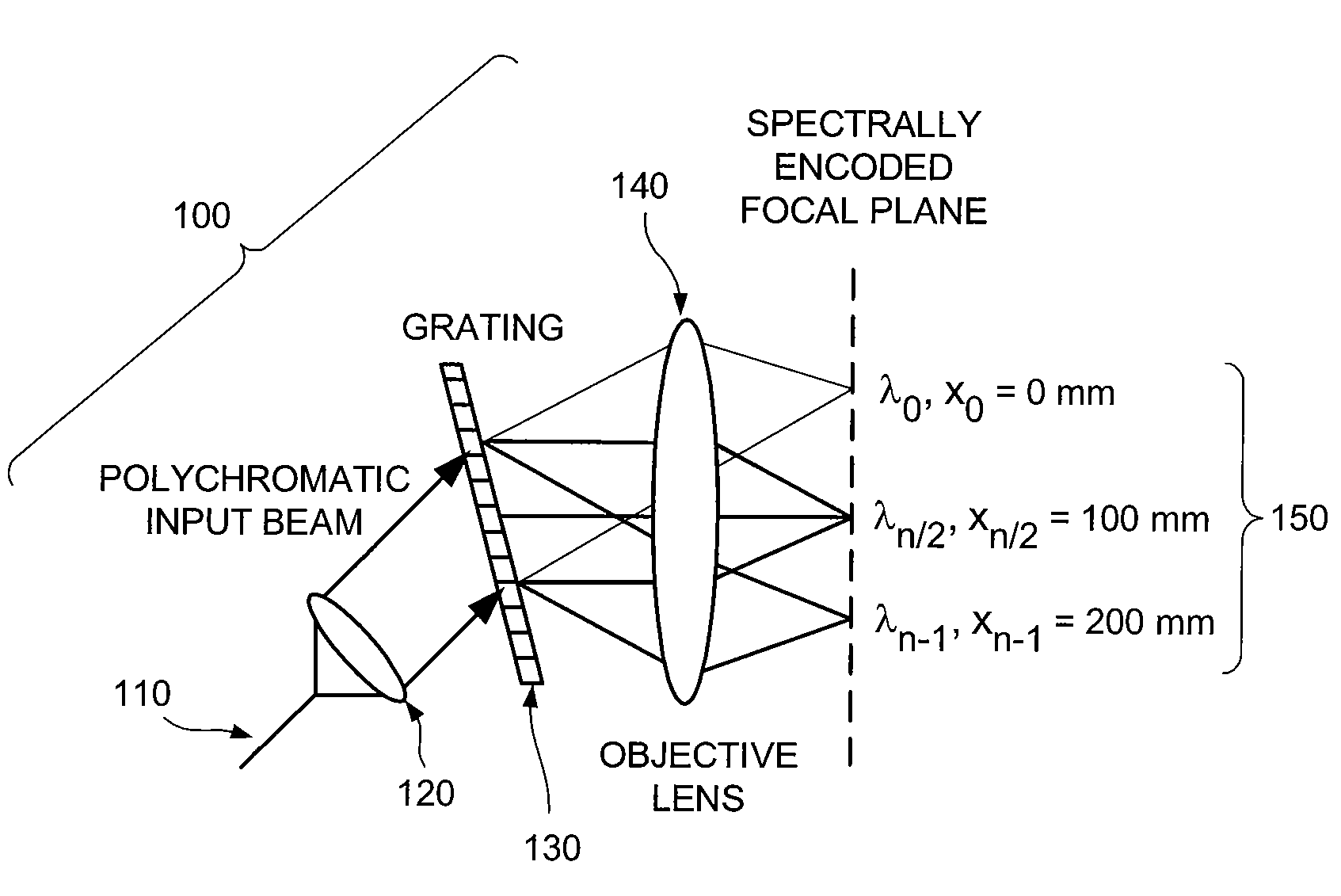
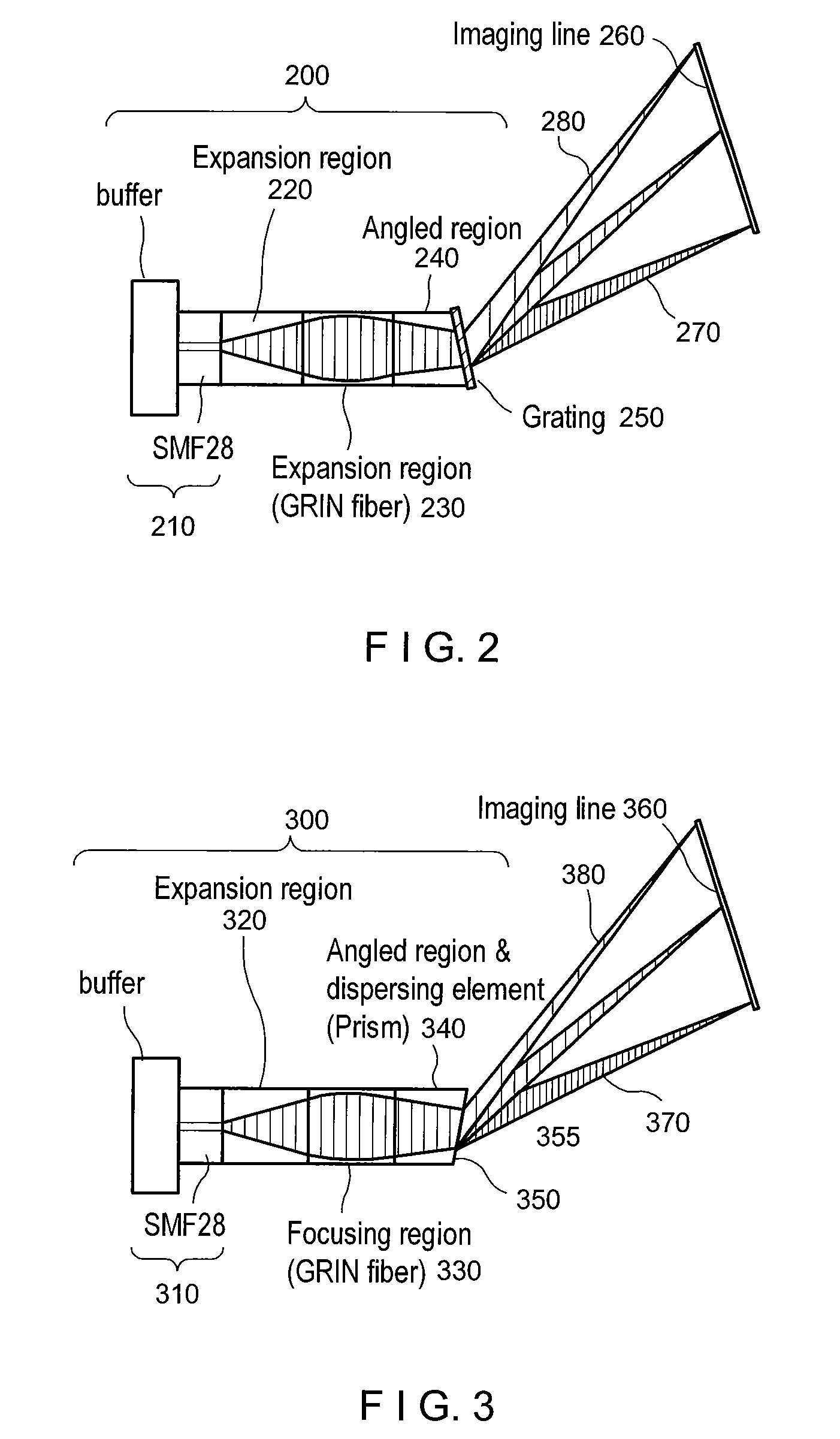
Apparatus for obtaining information for a structure using spectrally-encoded endoscopy teachniques and methods for producing one or more optical arrangements
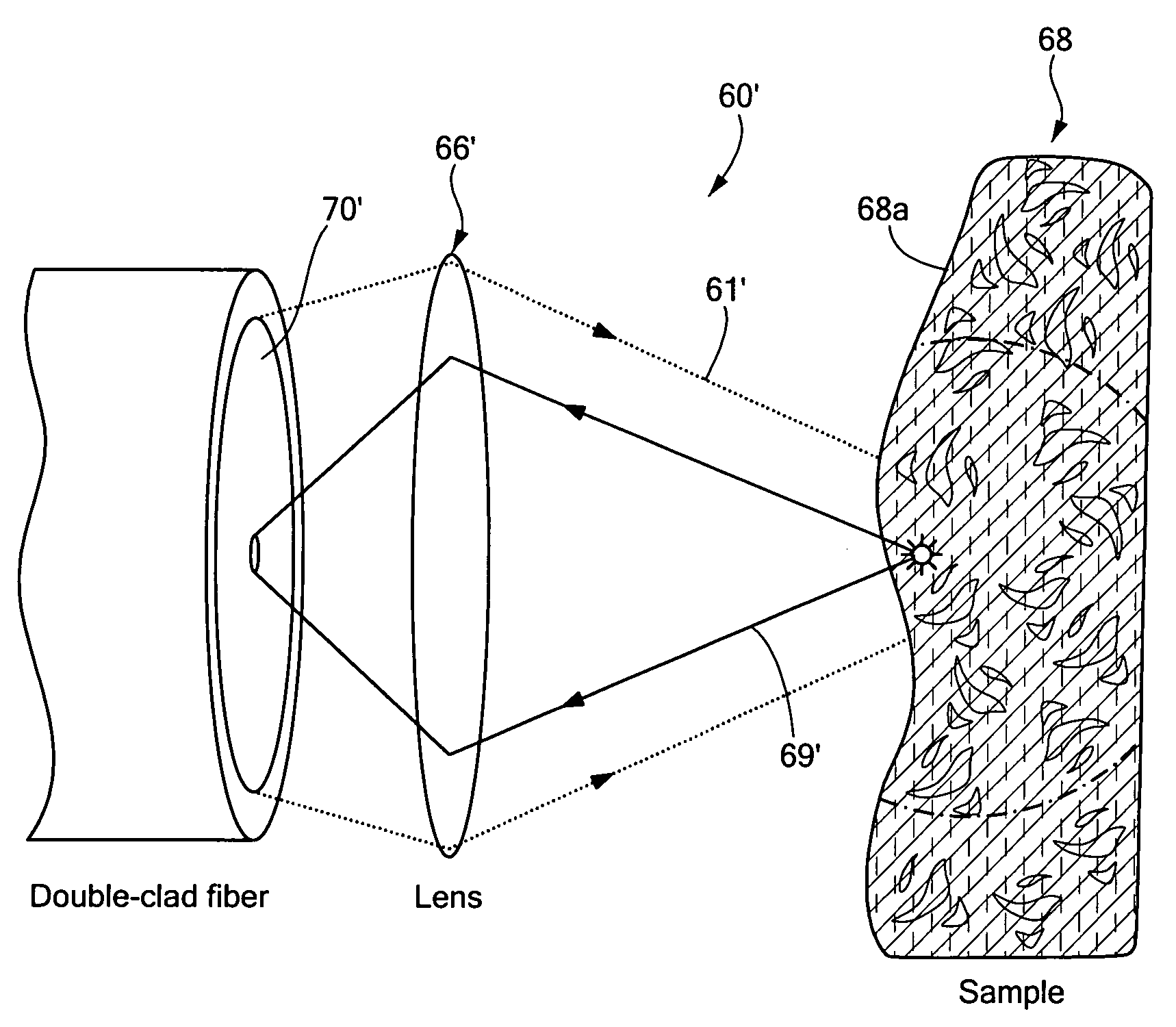
ActiveUS20070188855A1Improve collection efficiencyMinimizing speckleEdge grinding machinesSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFiberEngineering
Exemplary apparatus for obtaining information for a structure can be provided. For example, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one first optical fiber arrangement which is configured to transceive at least one first electromagnetic radiation, and can include at least one fiber. The exemplary apparatus can also include at least one second focusing arrangement in optical communication with the optical fiber arrangement. The second arrangement can be configured to focus and provide there through the first electromagnetic radiation. Further, the exemplary apparatus can include at least one third dispersive arrangement which is configured to receive a particular radiation which is the first electromagnetic radiation and / or the focused electromagnetic radiation, and forward a dispersed radiation thereof to at least one section of the structure. At least one end of the fiber can be directly connected to the second focusing arrangement and / or the third dispersive arrangement. In addition, an exemplary embodiment of a method for producing an optical arrangement can be provided. For example, a first set of optical elements having a first size in a first configuration and a second set of optical elements in cooperation with the second set and having a second size in a second configuration can be provided. The first and second sets can be clamped into a third set of optical elements. The third set can be polished, and a further set of optical elements may be deposited on the polished set.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
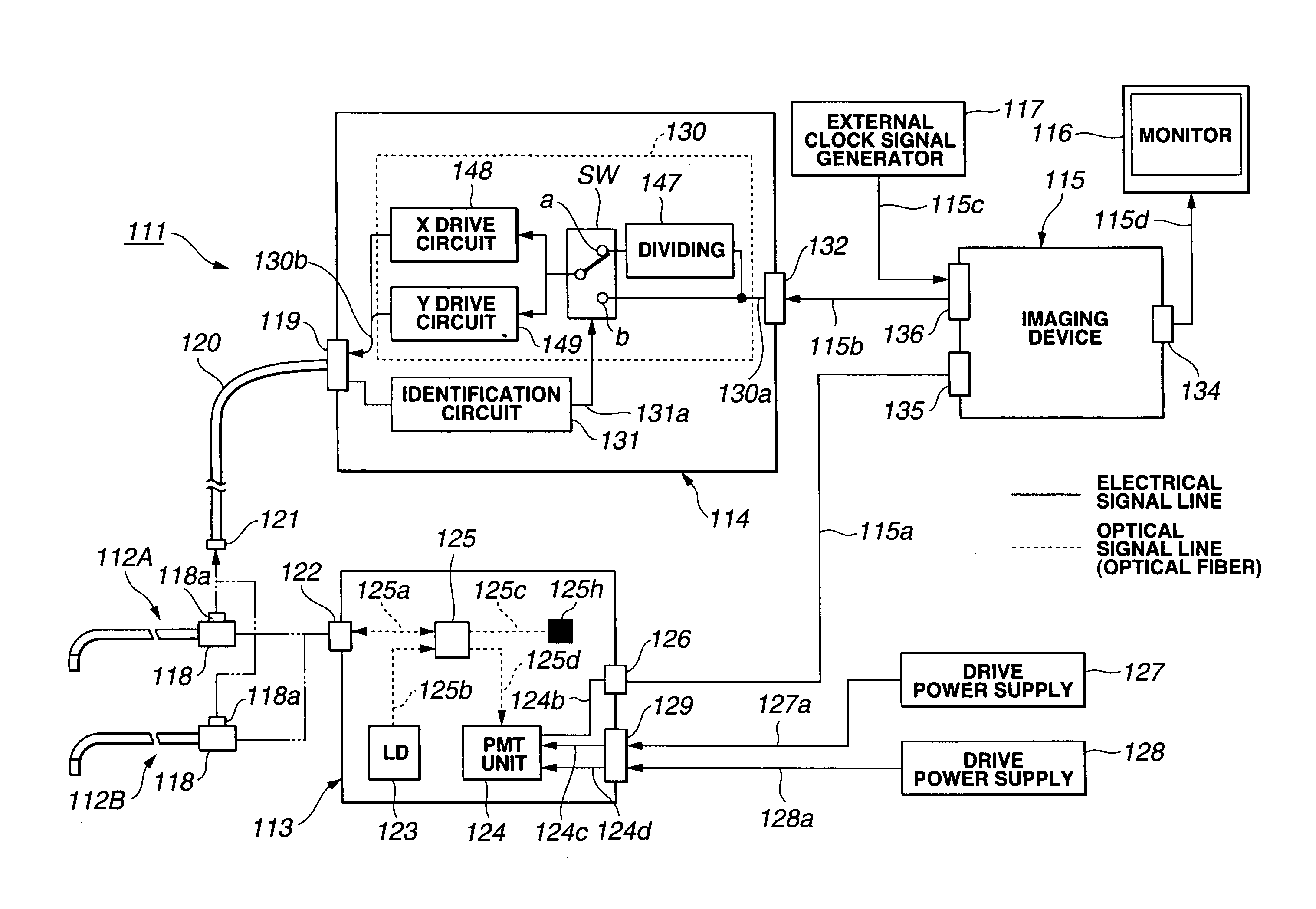
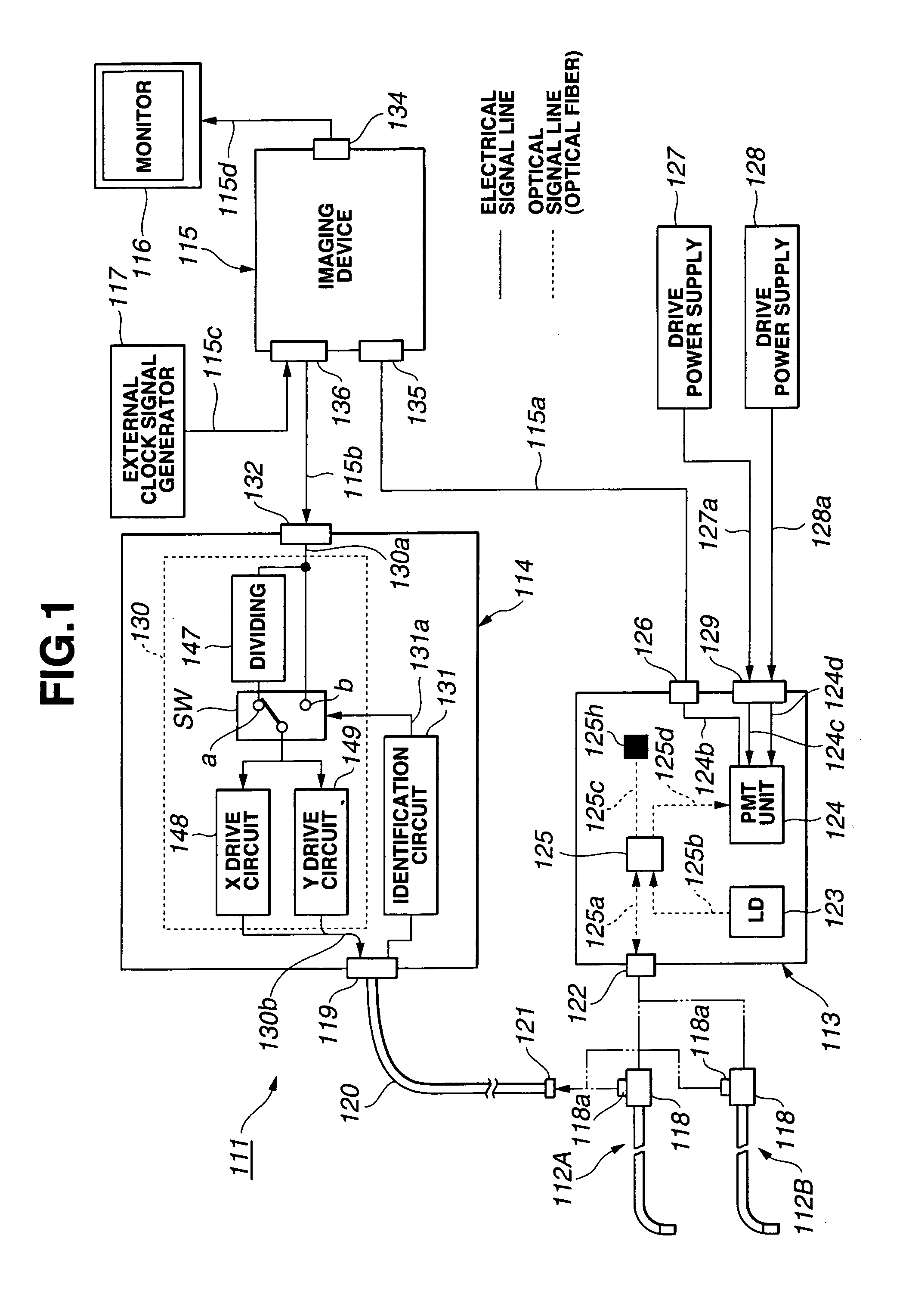
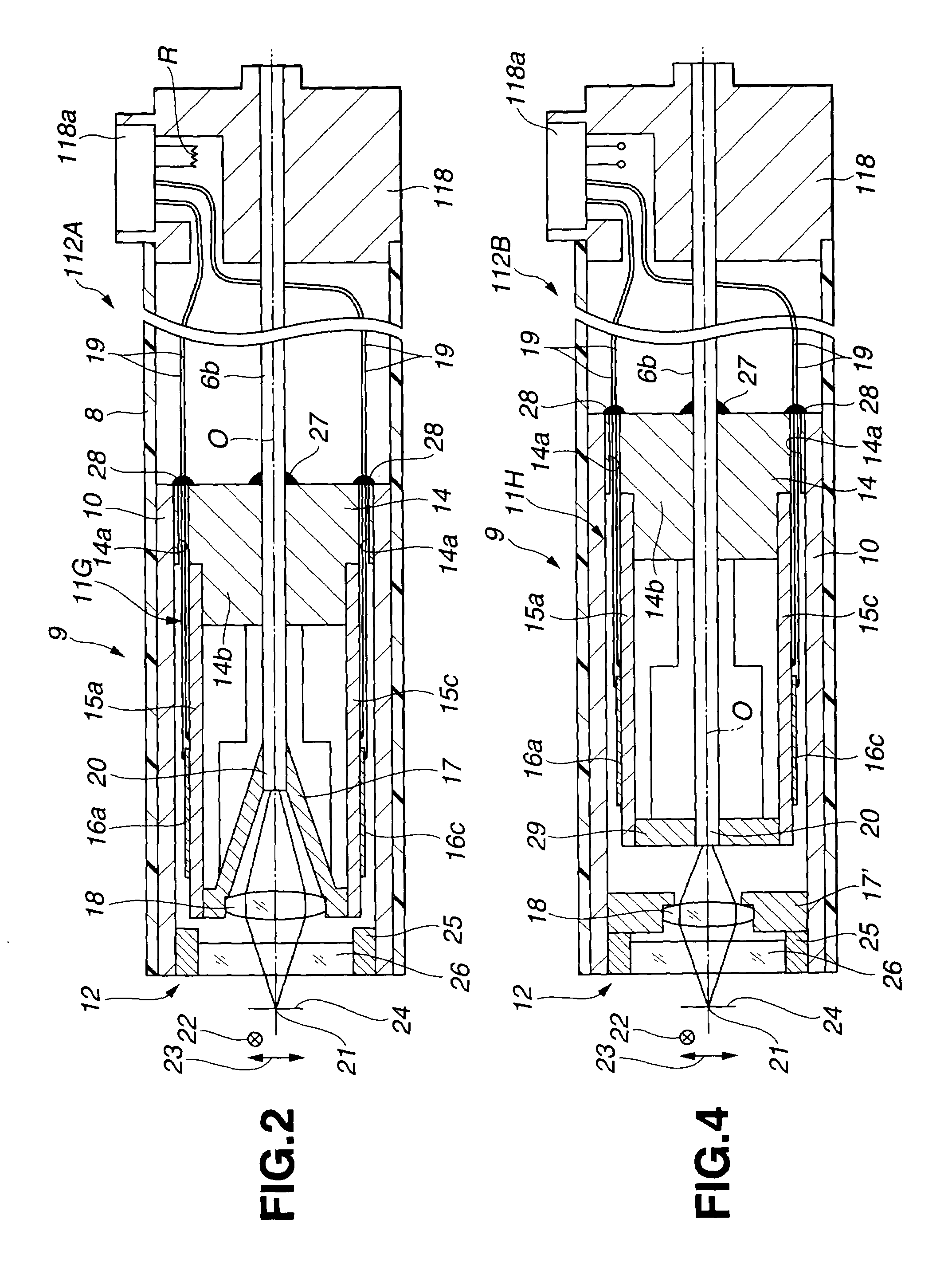
Optical scanning probe system
InactiveUS7129472B1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansDisplay deviceControl circuit
An identification circuit (131) recognizes optical probes (112A, 112B) of different scanning types that are connected to a light source unit (113) and a control device (114), the frequency of the drive signal of a control circuit (130) for driving a scanner inside the optical probe is varied by this recognition signal, corresponding drive signals are applied to the optical probes connected, the scanner of each probe is scanned, and two-dimensional optical information is imaged by an imaging device (115) and displayed on a monitor (116).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
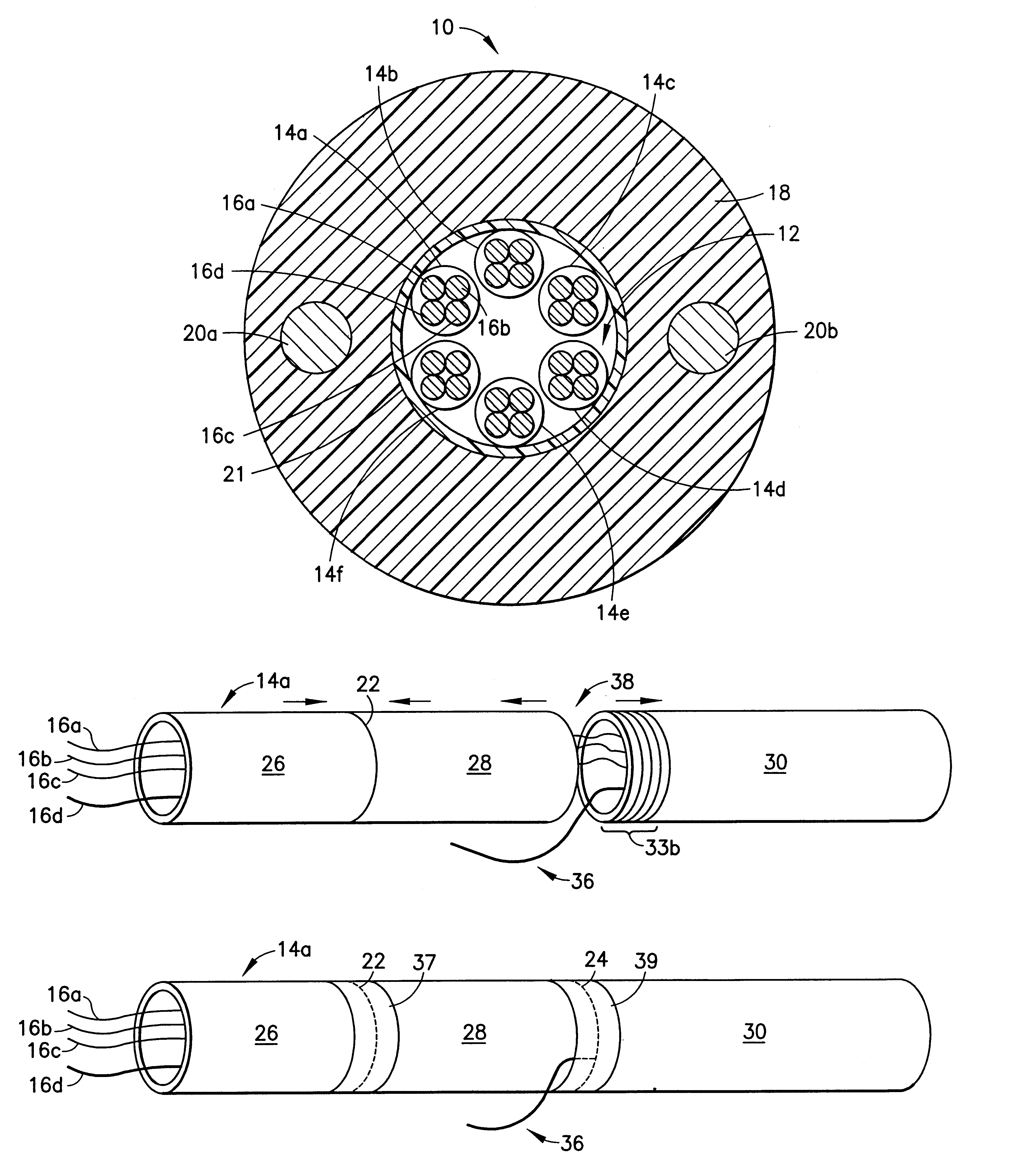
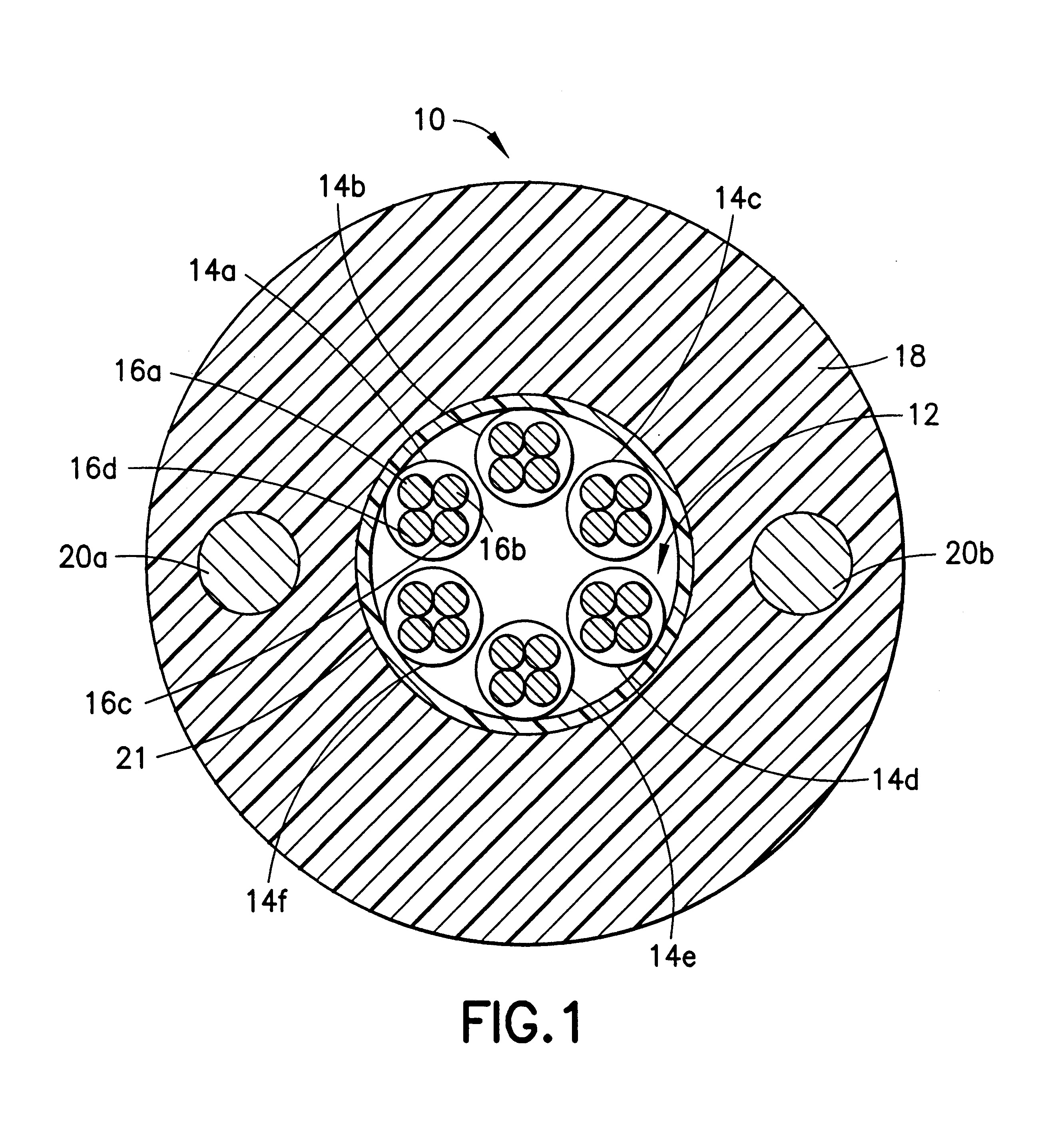
Method for accessing optical fibers contained in a sheath
The present invention provides a method for accessing a fiber from a bundle of fibers disposed in a sheath. The method comprises several steps which include cutting the sheath circumferentially at a leading position as well as circumferentially at a trailing position to divide the sheath into a leading section, a mid-section and a trailing section. The sheath is spread along the axis of the sheath between the leading section and the mid-section to create a first access opening. A fiber to be accessed is cut at the first access opening. The leading section and mid-section are pushed together to close the first access opening. The sheath is spread along the axis of the sheath between the mid-section and the trailing section to create a second access opening wherein the fiber is pulled from the mid-section of the sheath so that it extends out of the second access opening. The mid-section and trailing section of the sheath are pushed together to close the second access opening while the fiber is permitted to extend out of the trailing cut. Tape may be placed around the cuts to physically join the sections of the sheath and to seal out contaminants.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Optical Fiber Illumination Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20110122646A1Efficient deliveryReduce dependenceGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberUltrasound attenuation
An illumination system generating light having at least one wavelength within 200 nm a plurality of nano-sized structures (e.g., voids). The optical fiber coupled to the light source. The light diffusing optical fiber has a core and a cladding. The plurality of nano-sized structures is situated either within said core or at a core-cladding boundary. The optical fiber also includes an outer surface. The optical fiber is configured to scatter guided light via the nano-sized structures away from the core and through the outer surface, to form a light-source fiber portion having a length that emits substantially uniform radiation over its length, said fiber having a scattering-induced attenuation greater than 50 dB / km for the wavelength(s) within 200 nm to 2000 nm range.
Owner:CORNING INC
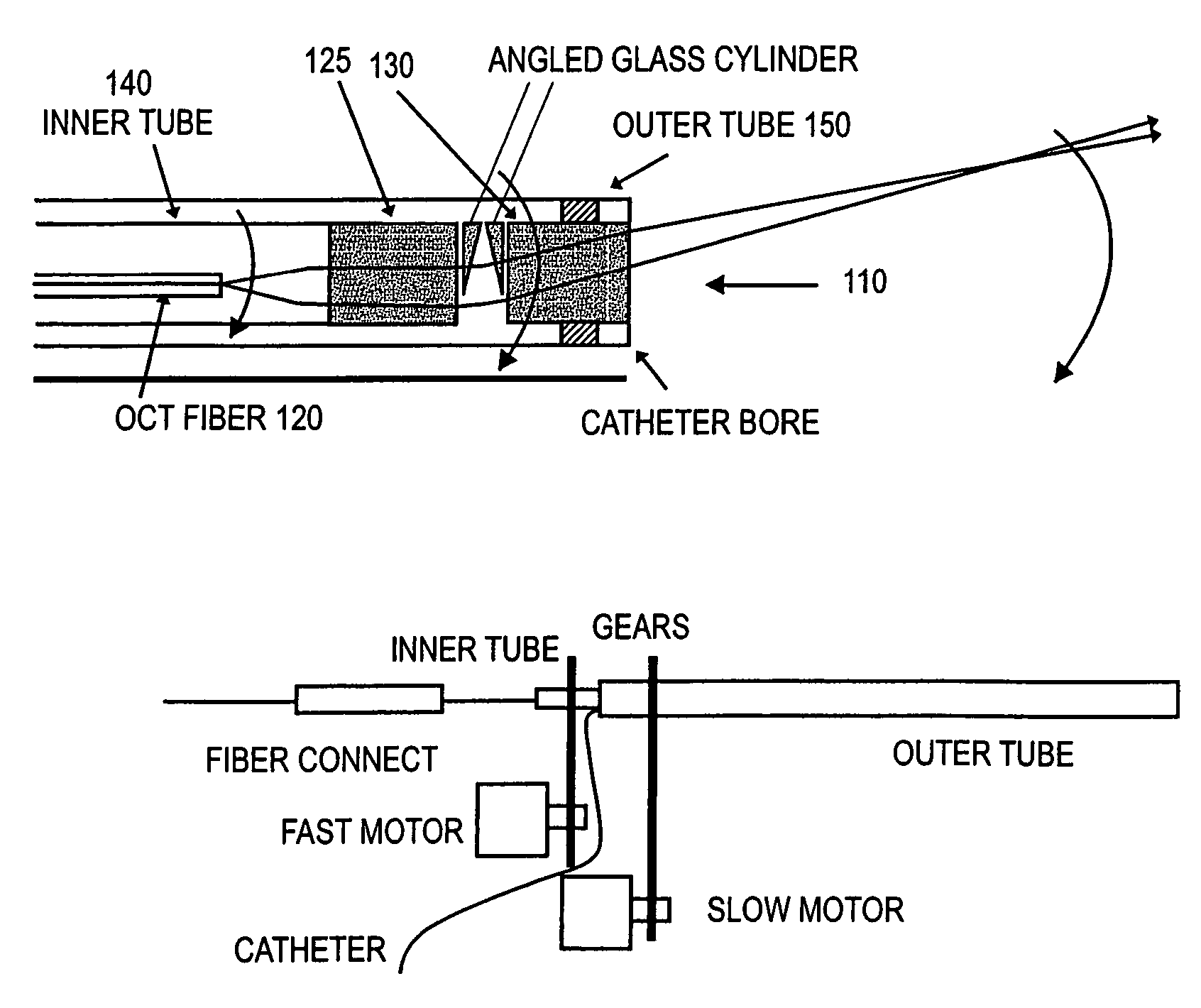
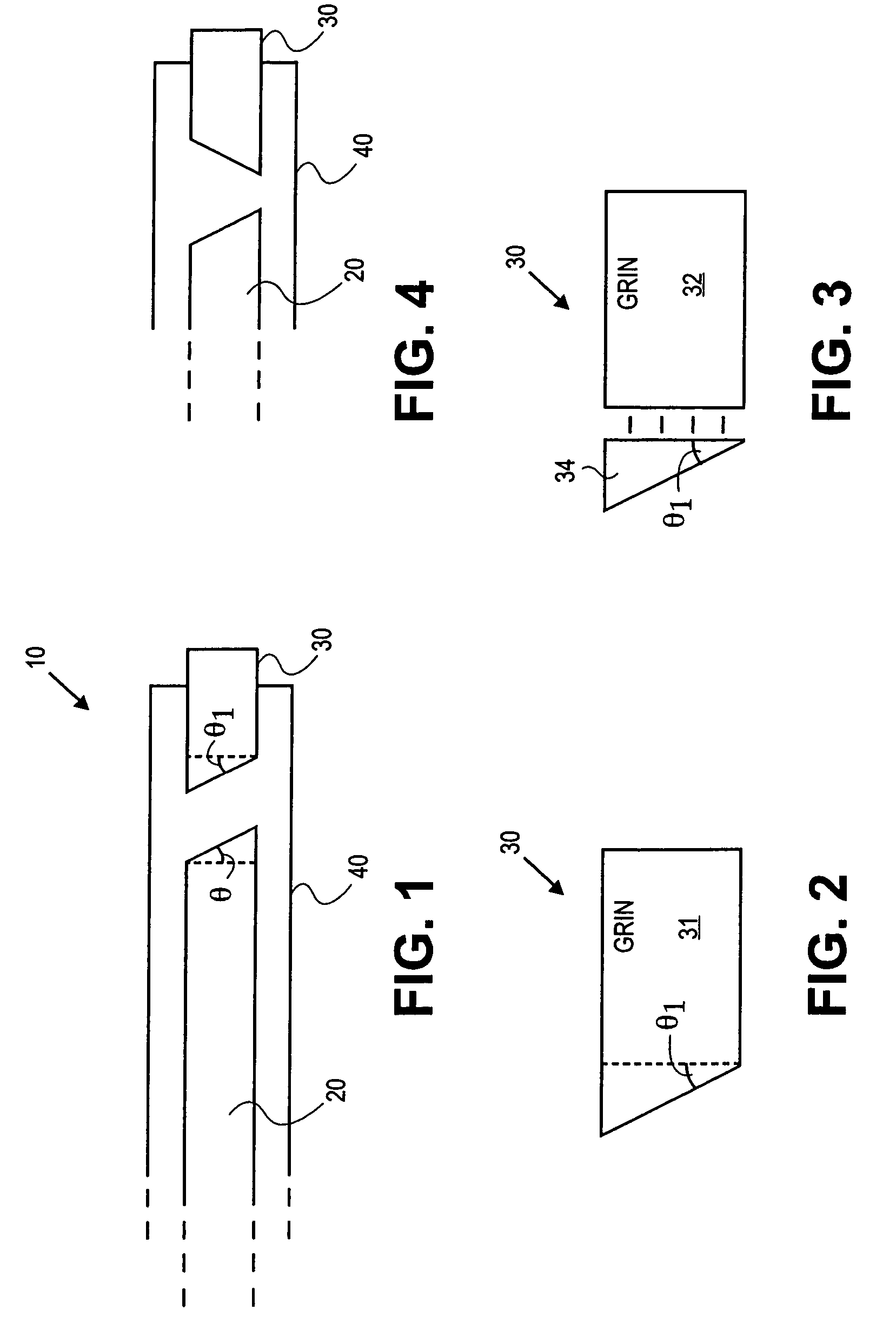
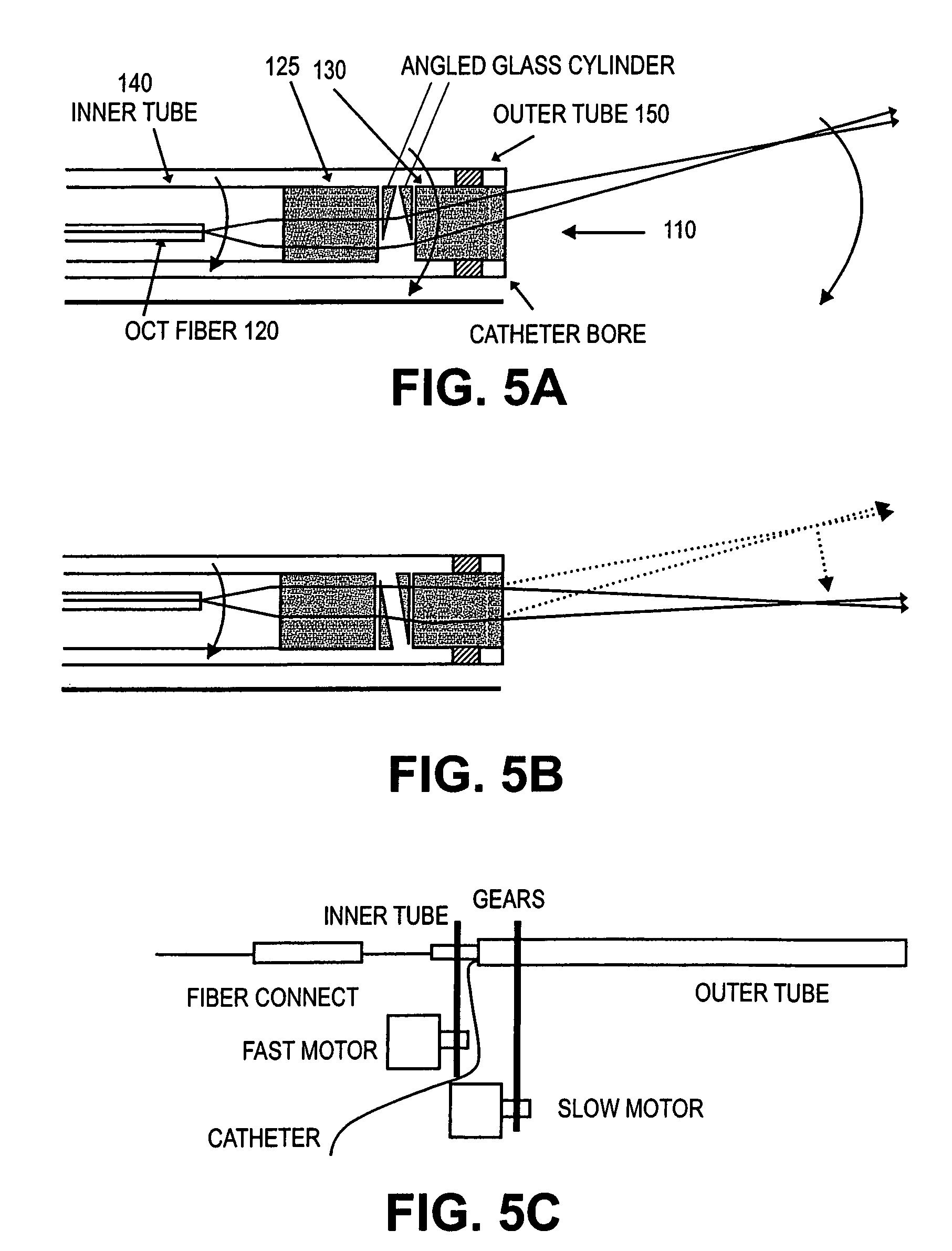
Forward scanning imaging optical fiber probe
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Medical diagnostic instrument having portable illuminator
ActiveUS20090287192A1Great degreeExcellent ease of useBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A portable medical diagnostic instrument includes an instrument head and a handle portion having an open-ended receiving cavity. A compact illuminator defined by a housing retaining a miniature light source and a power supply is releasably fitted within the open-ended receiving cavity of the handle portion wherein the light source of the illuminator is optically coupled with the instrument on assembly therewith. The handle portion can be integral with the instrument or releasably attached. The handle portion according to at least one version is made from a plastic or other suitable material, permitting disposability and / or single patient use. In one version, the handle portion is flexibly deformable, at least partially, to facilitate release of the portable illuminator.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Fluidic Adaptive Lens
InactiveUS20070211207A1Adaptive optical propertyOptical property can be variedBundled fibre light guideNon-optical partsOptical property
A fluidic adaptive lens, a multi-lens apparatus employing the fluidic adaptive lens, and a method of fabricating a fluidic adaptive lens are disclosed. The lens includes a first partition that is flexible and optically transparent, and a second partition that is coupled to the first partition, where at least a portion of the second partition is optically transparent, and where a first cavity is formed in between the first partition and the second partition. The lens further includes a first fluidic medium positioned within the cavity, the fluidic medium also being optically transparent; and a first device capable of controlling a parameter of the fluidic medium, where when the parameter of the fluidic medium changes, the first partition flexes and an optical property of the lens is varied.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com