Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1438results about How to "Expand field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
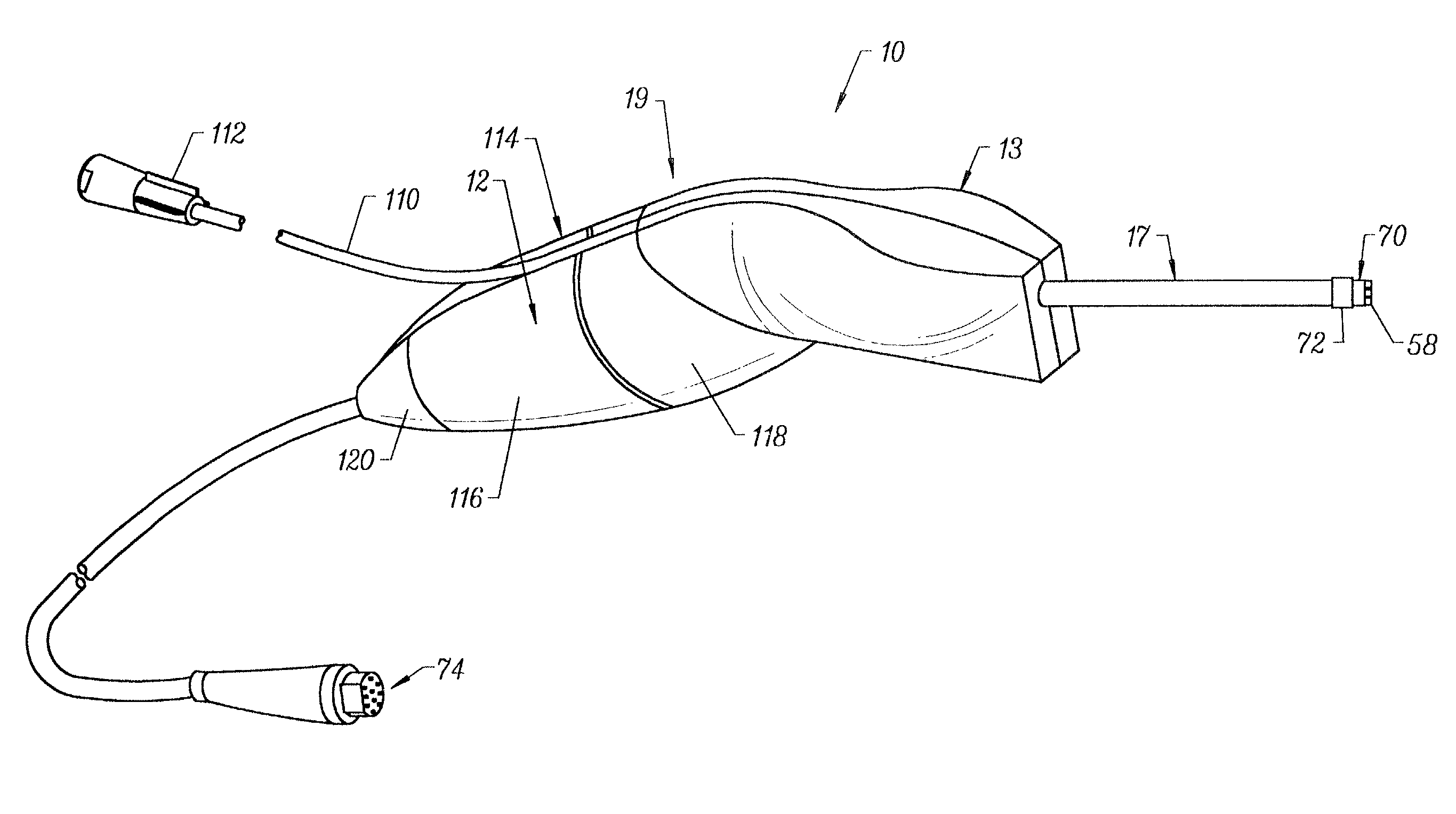
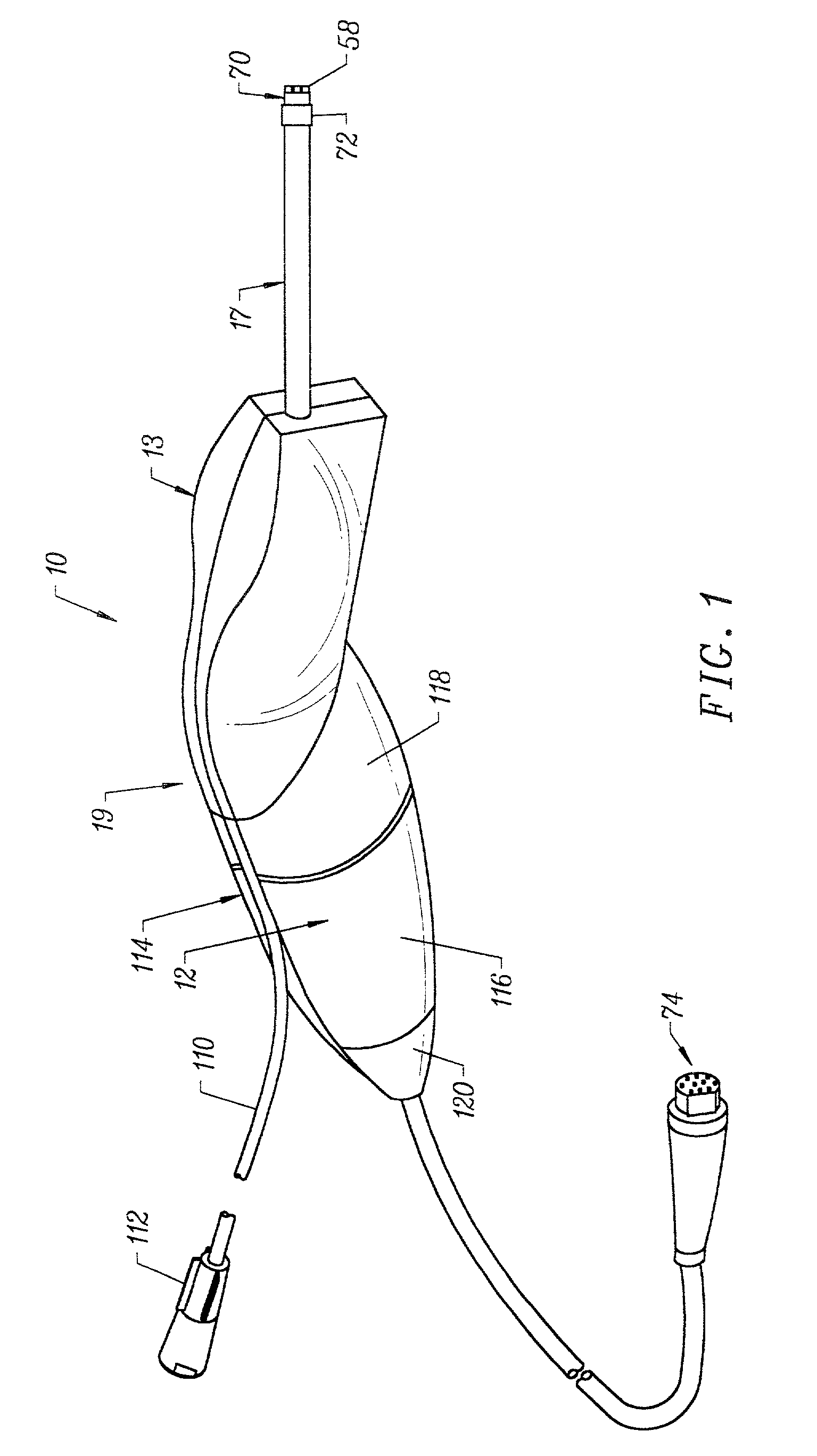
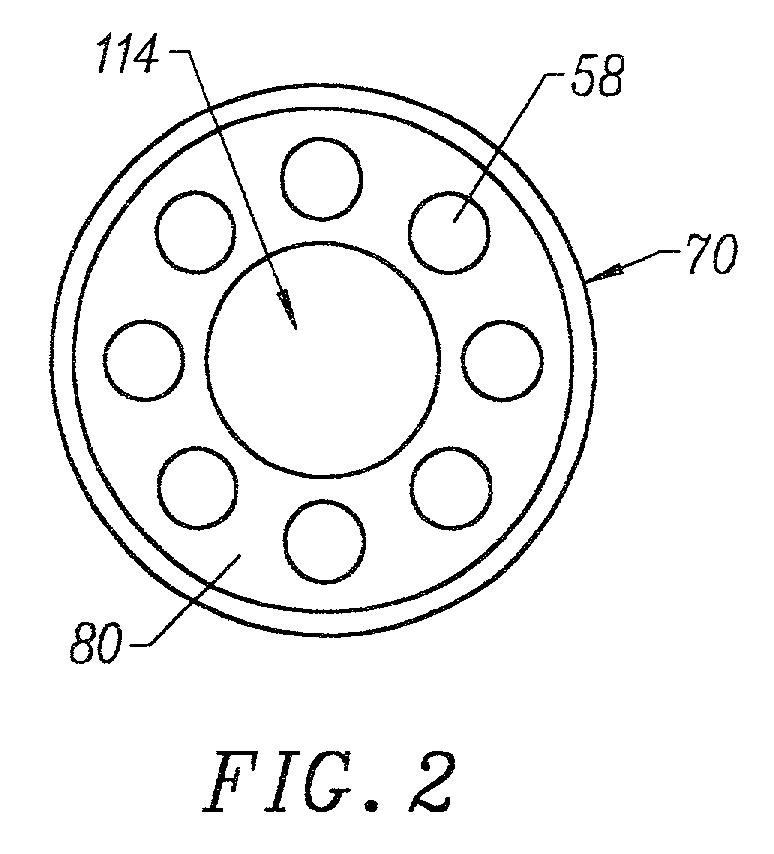
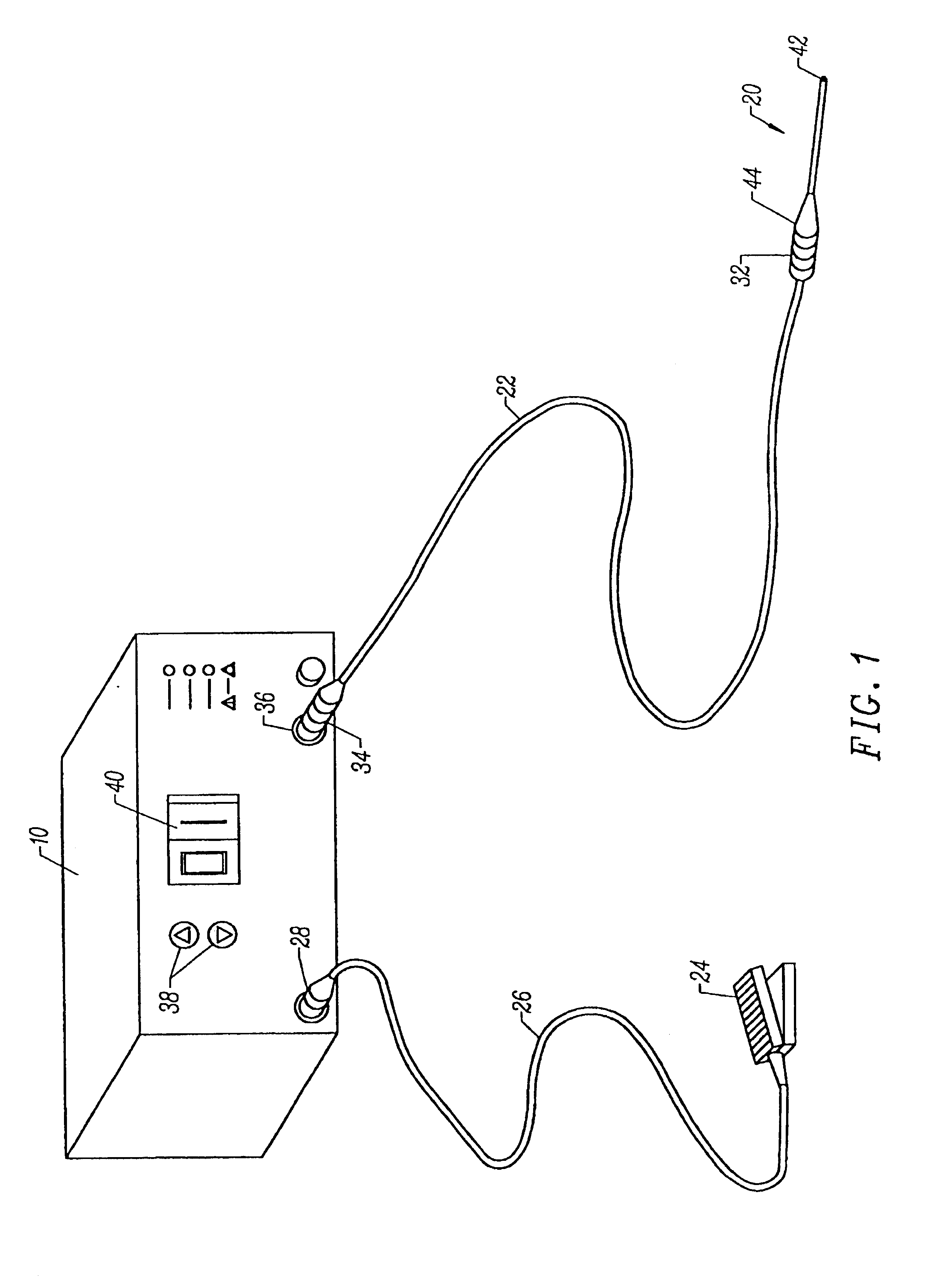
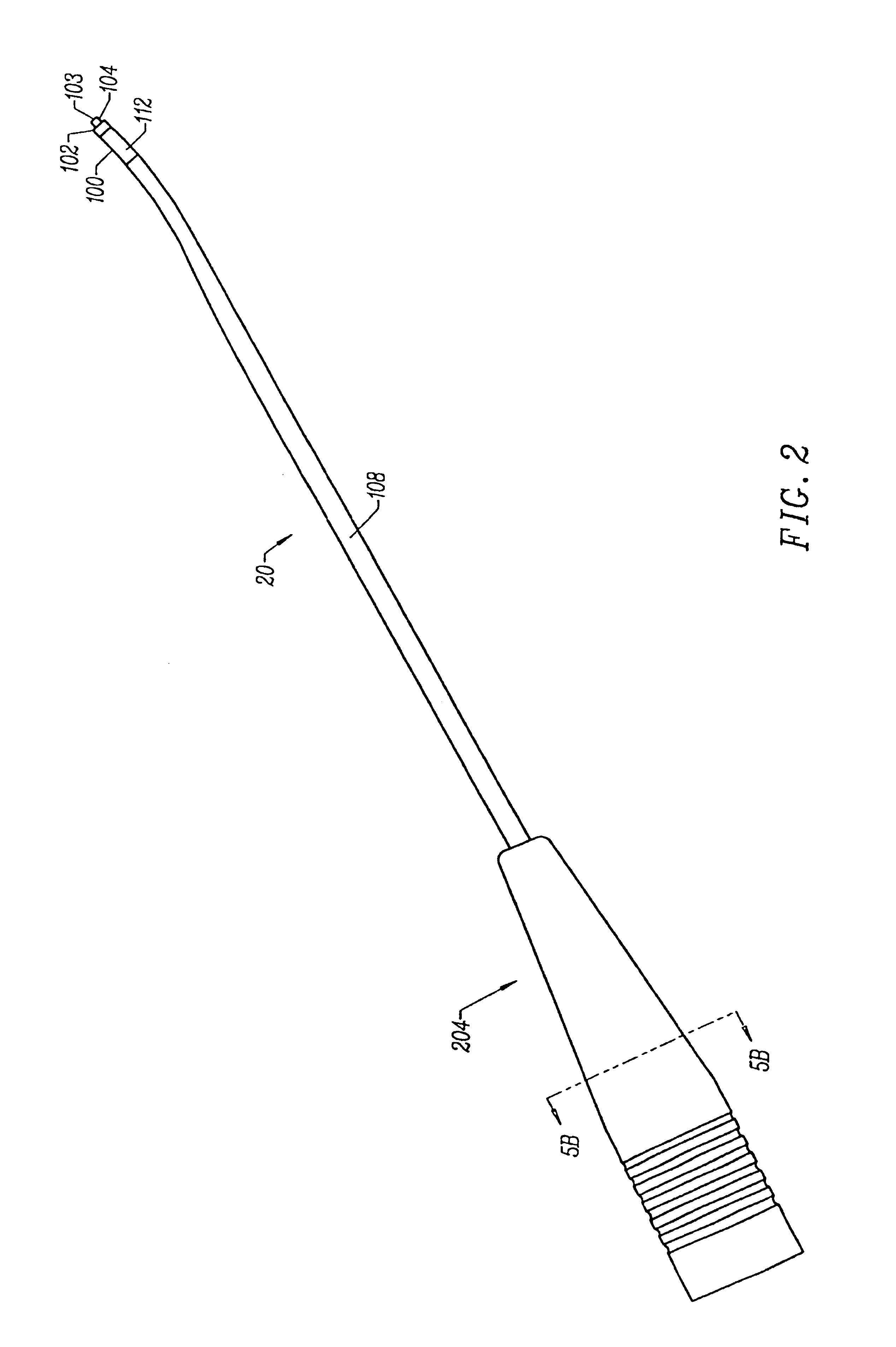
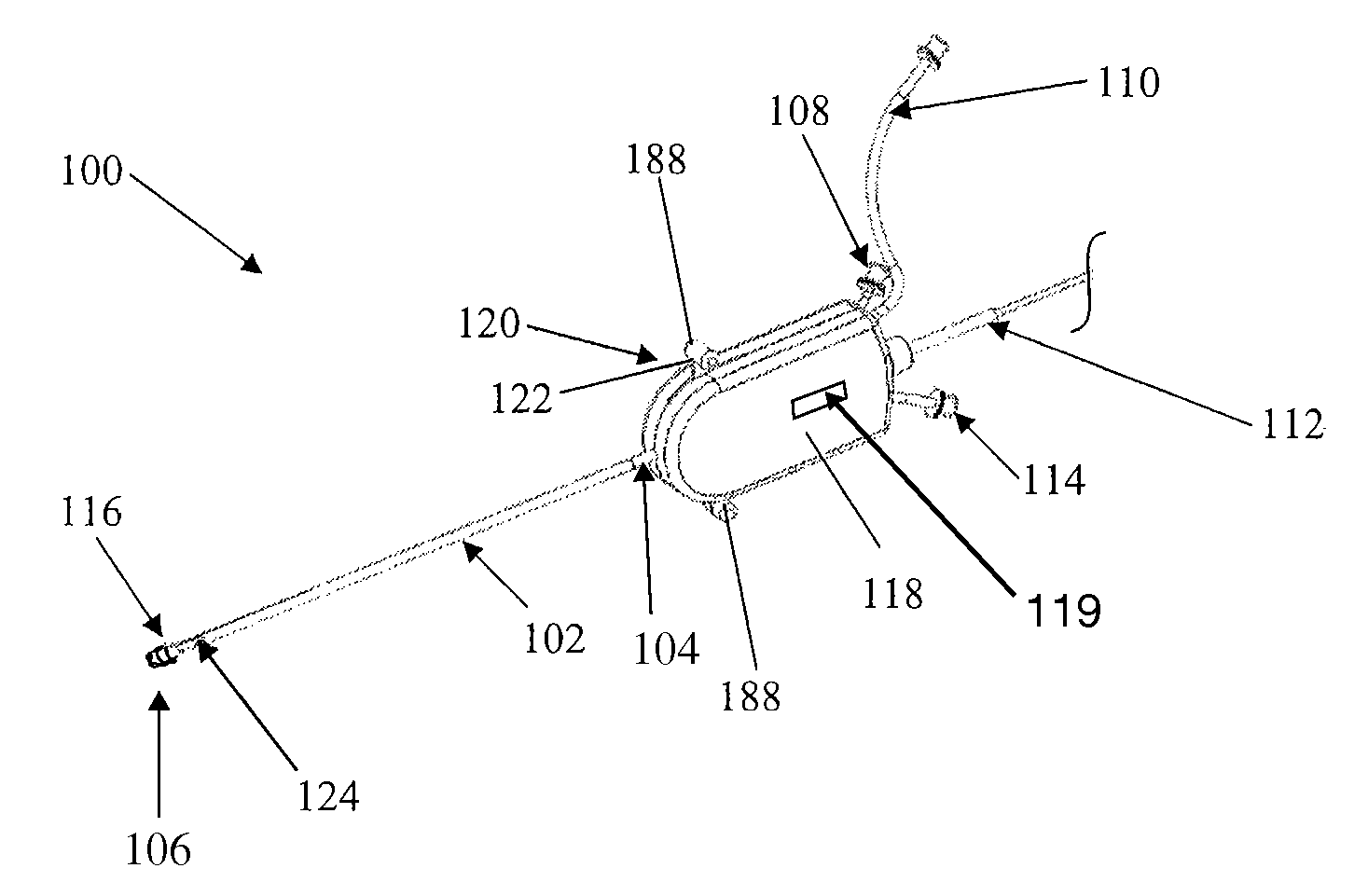
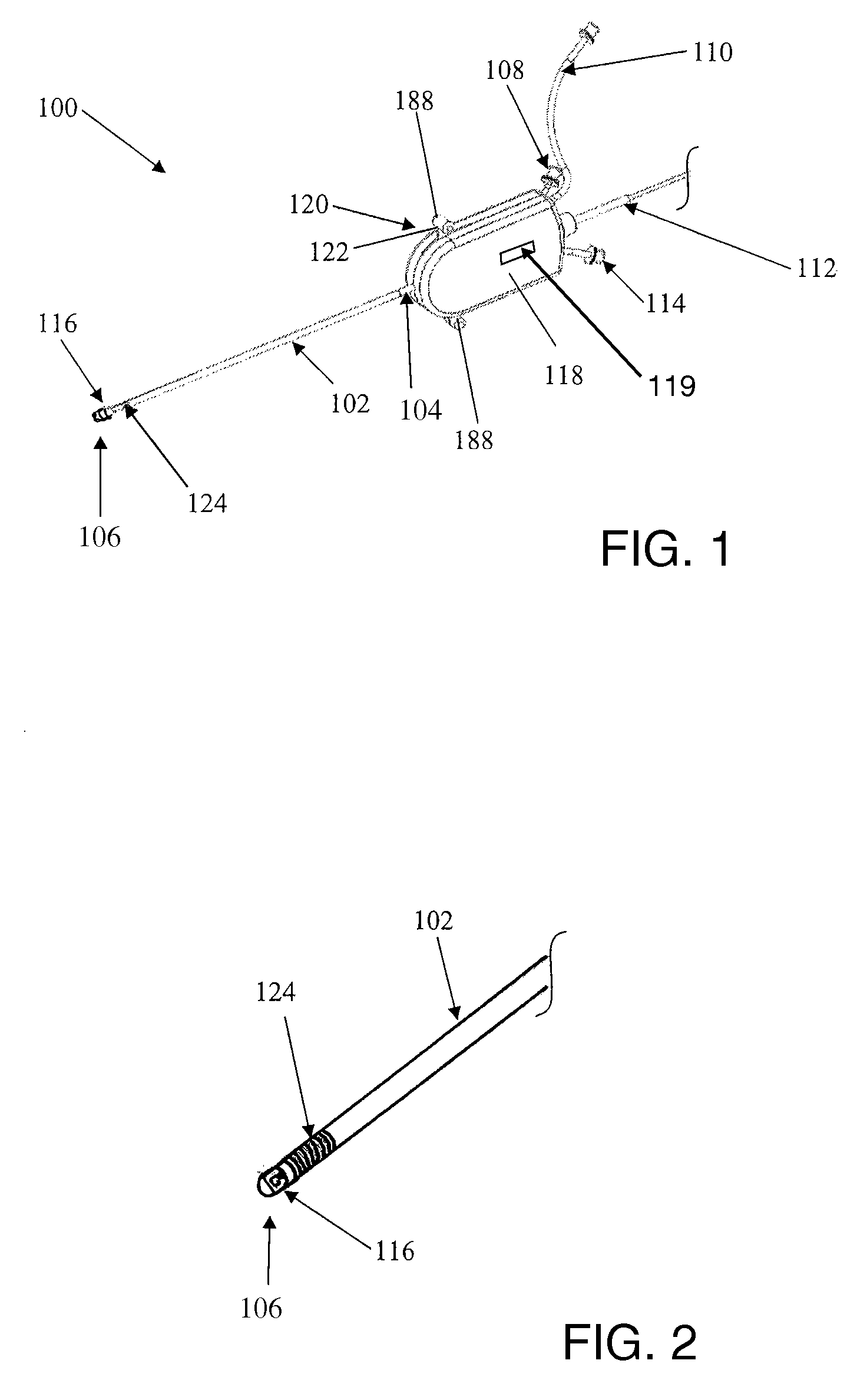
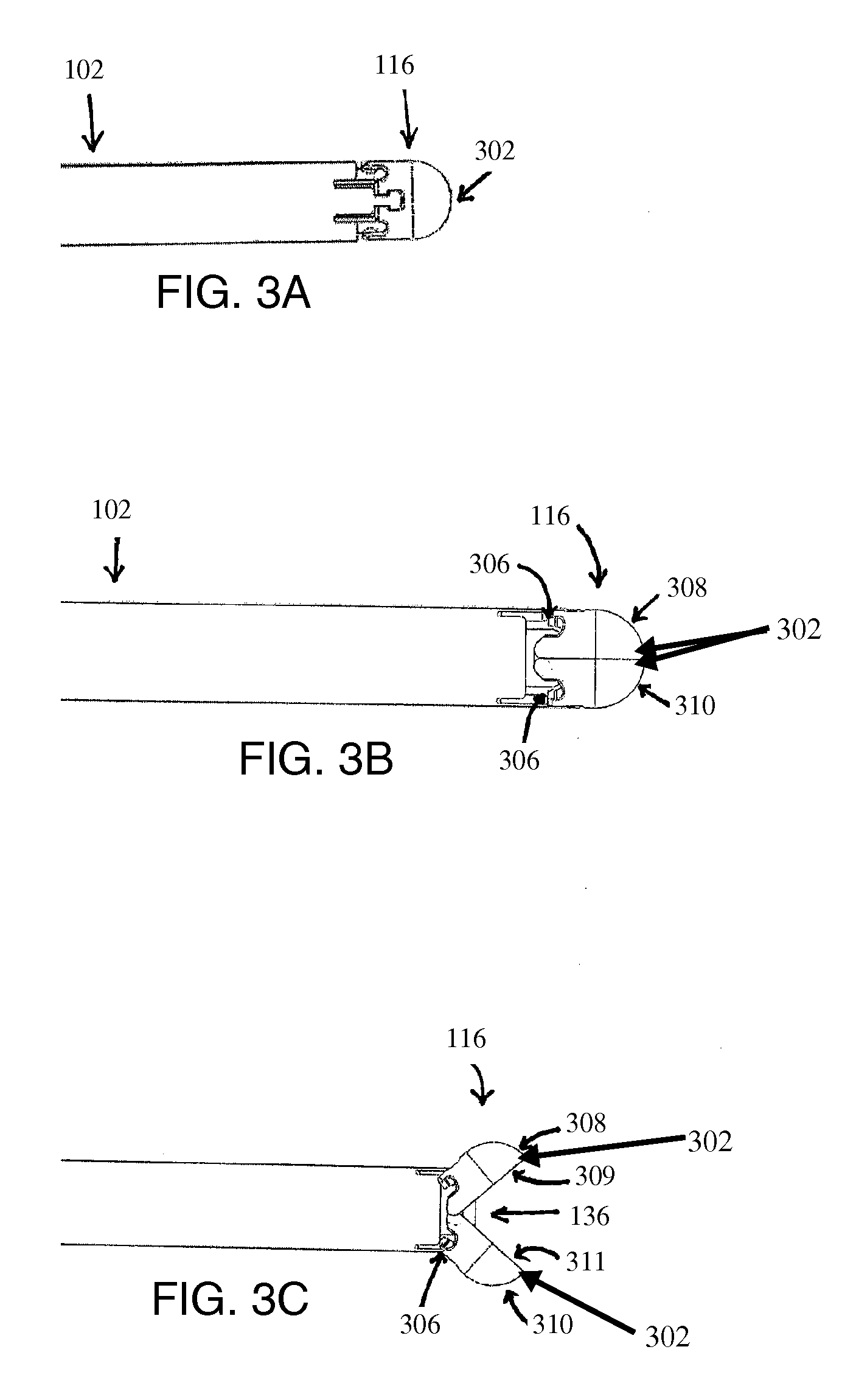
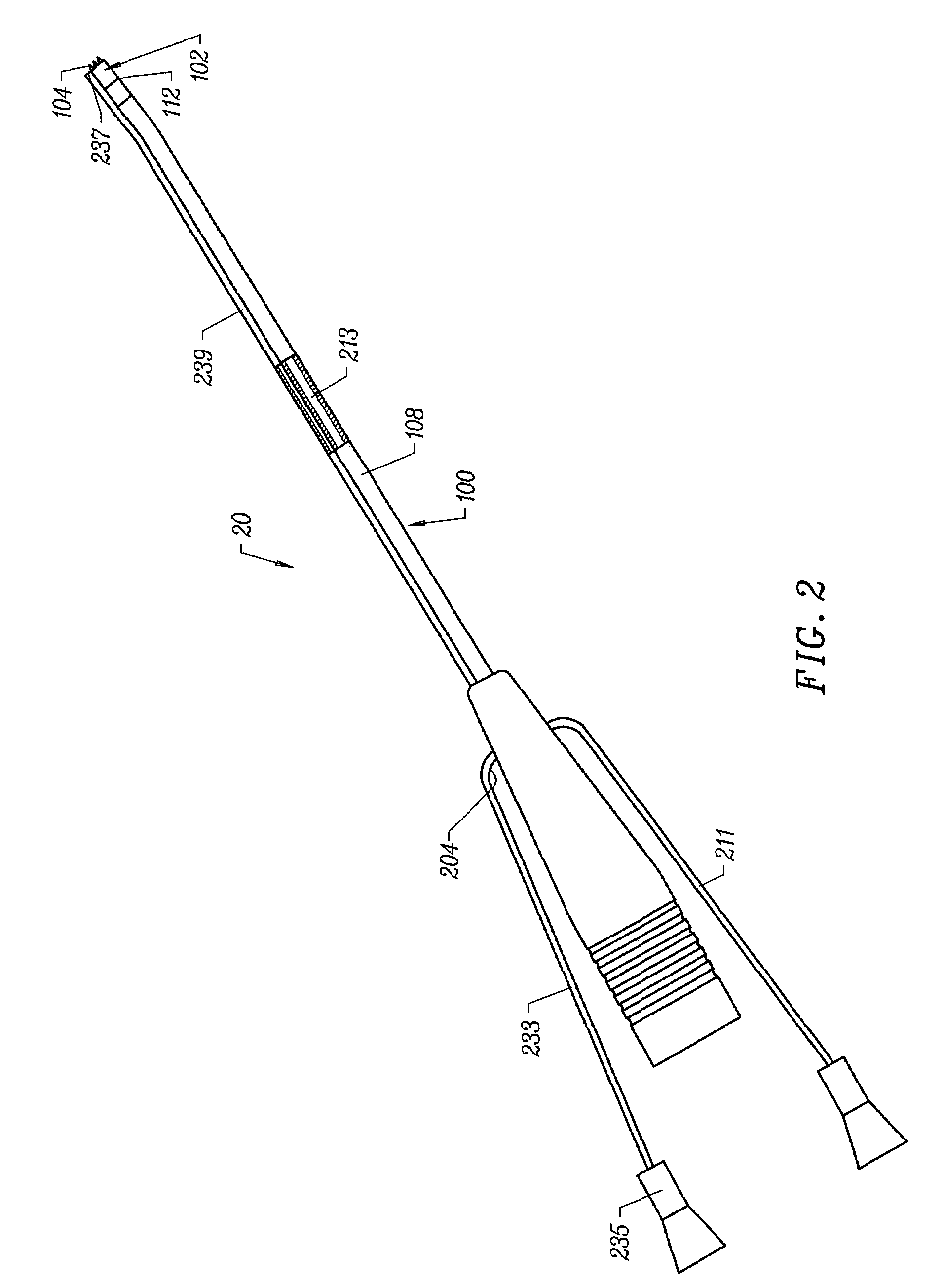
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of turbinates
InactiveUS7442191B2Minimize thermal damageLower the volumeCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsVoltageCartilage
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within the head and neck of a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the ear, nose and throat. In one aspect, a method is provided for reducing the volume of enlarge swollen tissue in the patient's nose, such as swollen nasal tissue, mucus membranes, turbinates, polyps, neoplasms, cartilage (e.g., the nasal septum) or the like. In particular, the turbinates are treated by positioning one or more electrode terminal(s) adjacent to the turbinates, and delivering electrically conductive fluid, such as isotonic saline, to the nasal cavity to substantially surround the electrode terminal(s) with the fluid. High frequency voltage is applied between the electrode terminal(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to remove a small tissue segment, channel or hole from the region near or in the turbinates to shrink the turbinates and prevent swelling, due to the formation of scar tissue as the wound heals. The high frequency voltage may be selected to effect a small amount of thermal damage to the walls of the channel or hole to facilitate the formation of scar tissue without extending this thermal damage beyond the immediate region of the target site.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Electrosurgical apparatus having digestion electrode and methods related thereto
InactiveUS6896674B1High trafficAvoid and minimize current shortingHeart valvesEndoscopesHigh frequency powerDigestion
Methods and apparatus for resecting and ablating tissue at a target site of a patient, the apparatus including a probe having an elongate shaft. The shaft includes a shaft distal end portion and a shaft proximal end portion, and a resection unit located at the shaft distal end portion. The resection unit includes a resection electrode support and at least one resection electrode arranged on the resection electrode support. The at least one resection electrode includes a resection electrode head. The probe and resection electrode head are adapted for concurrent electrical ablation and mechanical resection of target tissue. The shaft may include at least one digestion electrode capable of aggressively ablating resected tissue fragments. At least one fluid delivery port on the shaft distal end portion may provide an electrically conductive fluid to the resection unit or to the target site. The shaft may include at least one aspiration port, located proximal to the resection unit, for aspirating excess or unwanted fluids and resected tissue fragments from the target site. The at least one aspiration port is coupled to an aspiration lumen. The at least one digestion electrode may be arranged within the aspiration lumen for ablation of tissue fragments therein. In use, the digestion and resection electrodes of the probe are coupled to a high frequency power supply. A surgical kit comprising the probe is also disclosed, together with a method of making the probe.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
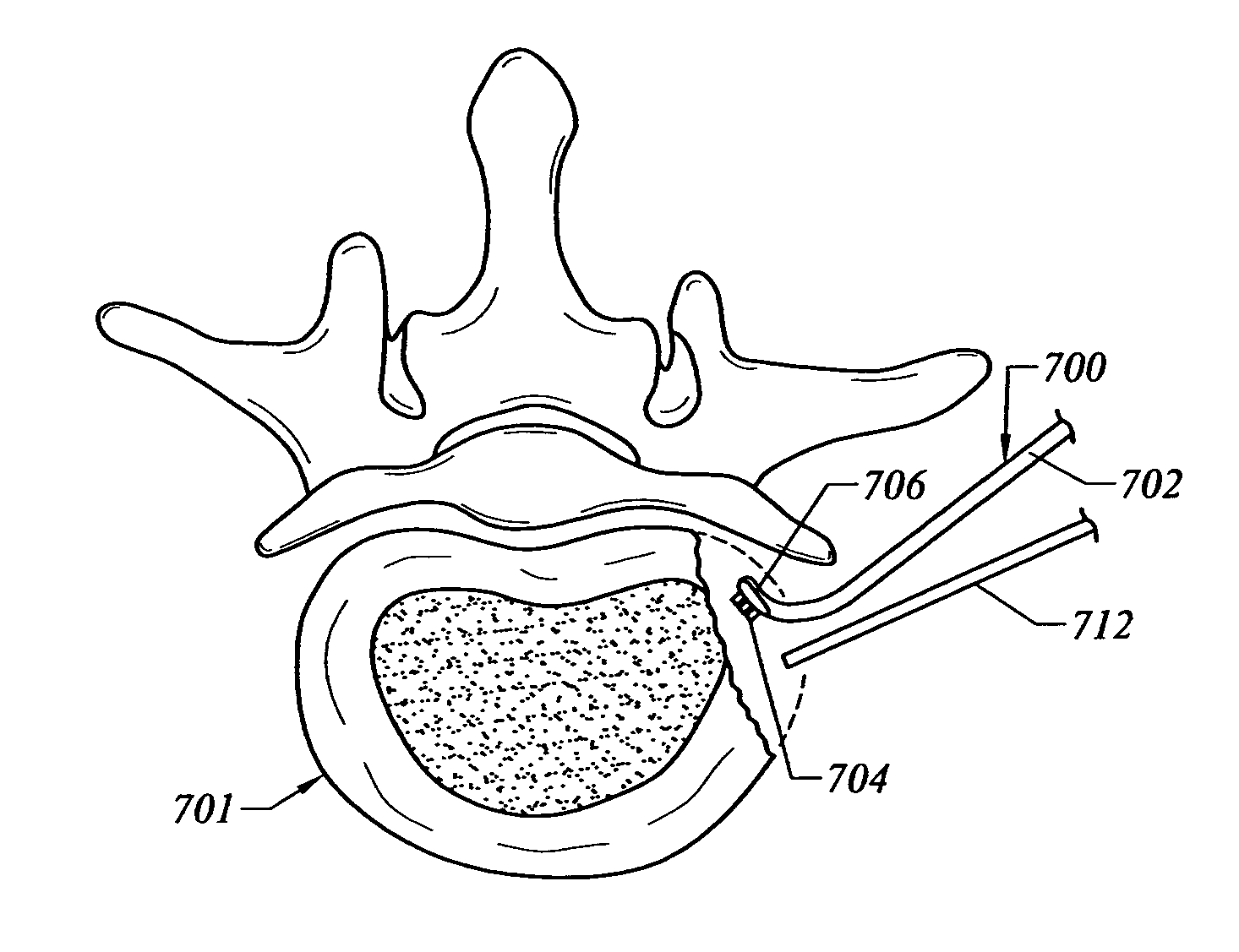
Intervertebral disc replacement method
InactiveUS7104986B2Minimize damageMinimize necrosisCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsFiberIntervertebral disc arthroplasty
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. The present invention applies high frequency (RF) electrical energy to one or more electrode terminals in the presence of electrically conductive fluid to contract collagen fibers within the tissue structures. In one aspect of the invention, a system and method is provided for removing a vertebral disc in preparation for implanting a prosthetic disc or removing a portion of the vertebral disc such as the nucleus pulposus in preparation for placing a prosthetic nucleus within the annulus of the disc. The present invention also teaches shrinking residual tissue in preparation for placing the implants.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
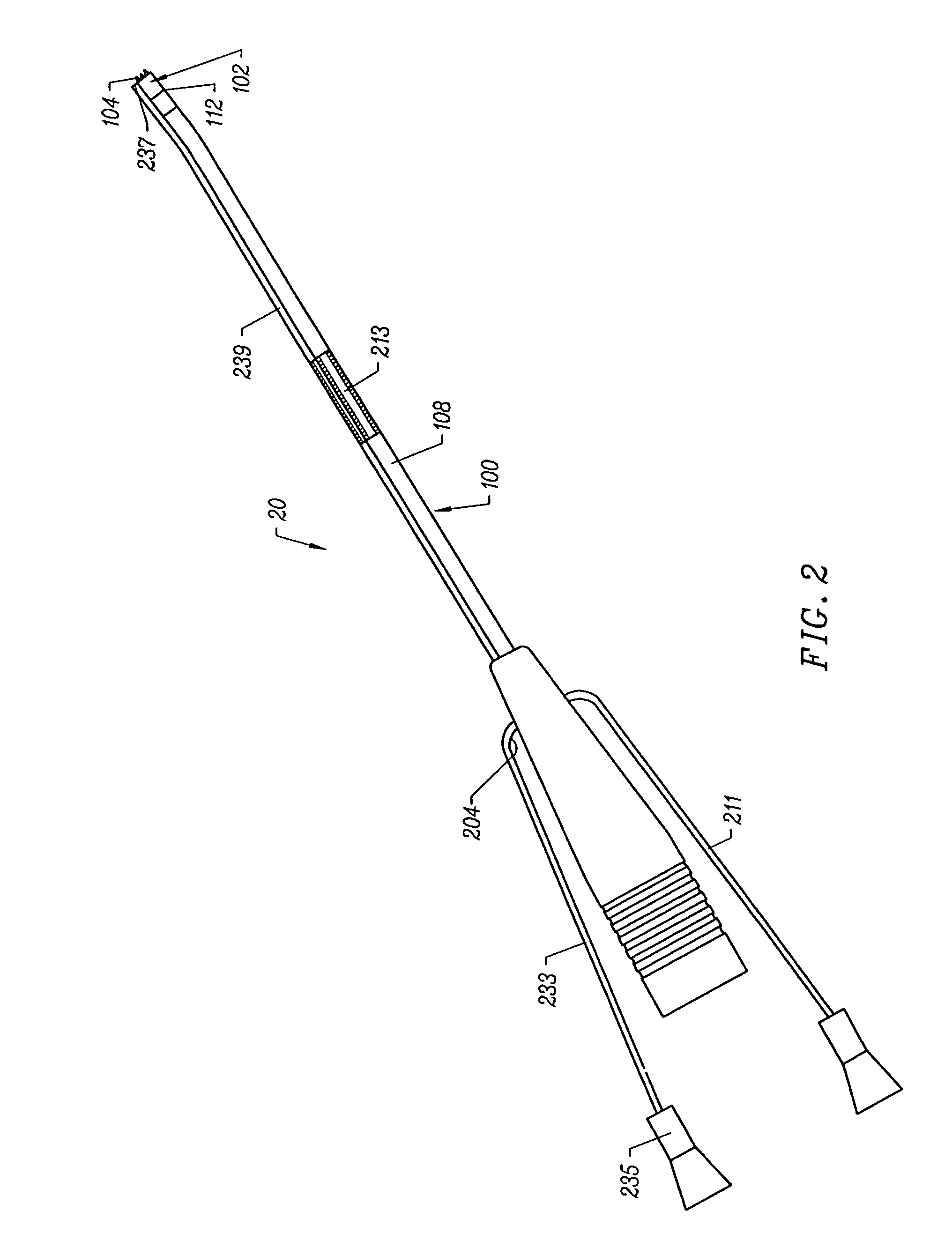
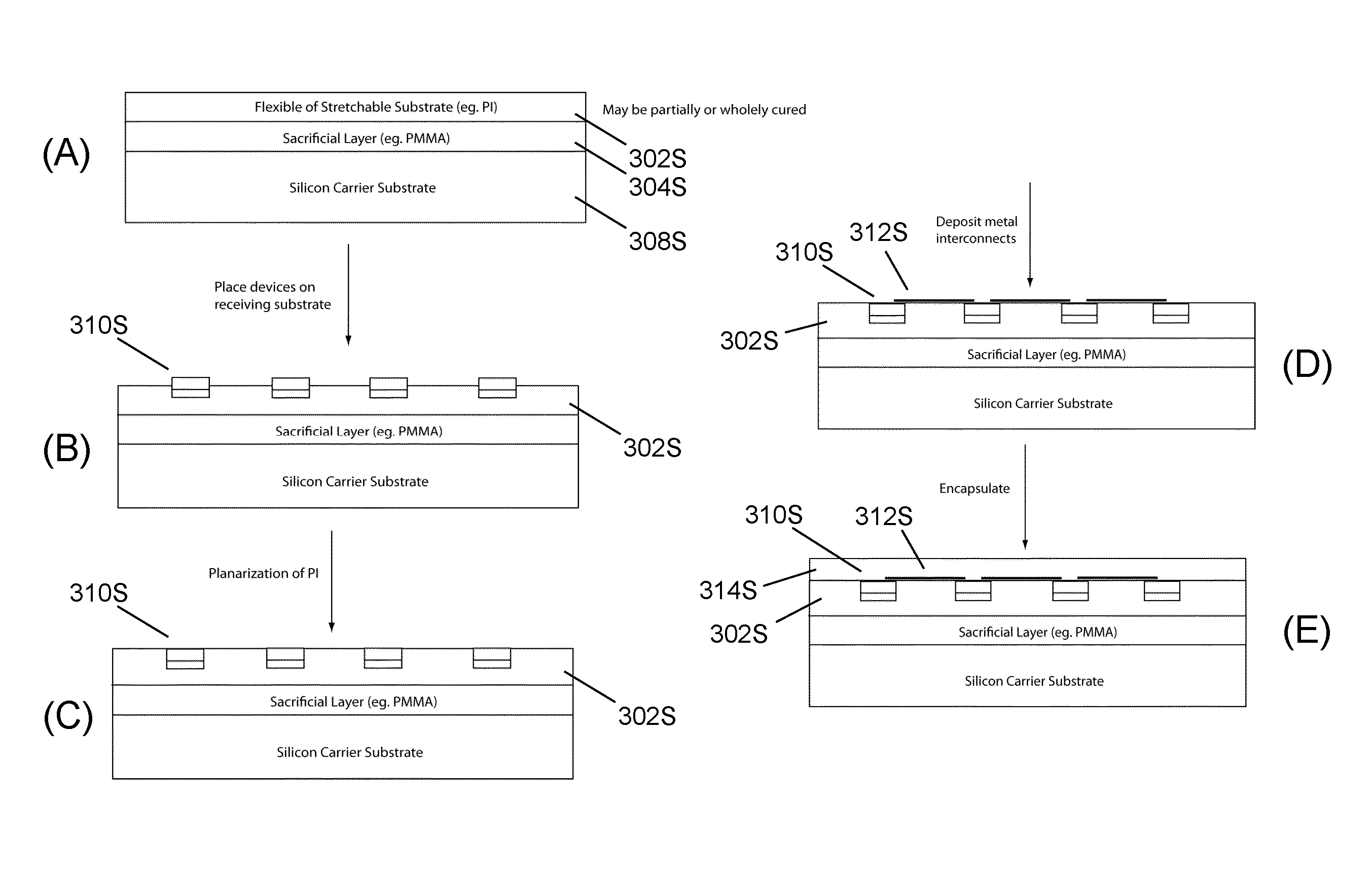
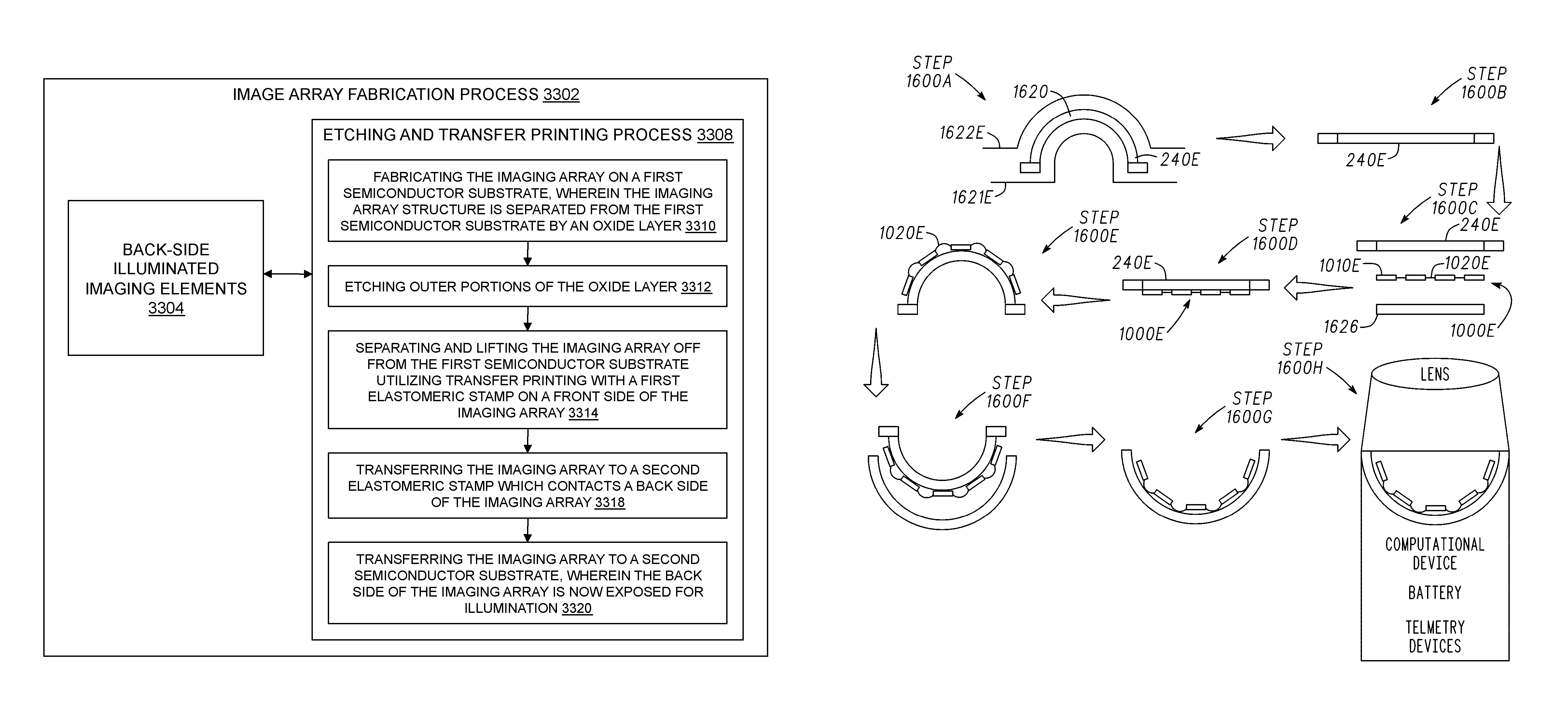
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS20100178722A1Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionEngineering
System, devices and methods are presented that provide an imaging array fabrication process method, comprising fabricating an array of semiconductor imaging elements, interconnecting the elements with stretchable interconnections, and transfer printing the array with a pre-strained elastomeric stamp to a secondary non-planar surface.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
Optical devices particularly for remote viewing applications
ActiveUS7021777B2Facilitates structure fabricationEasy to mergeMirrorsDiffraction gratingsField of viewLight wave
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Repeating titanium clamp pincers
InactiveCN101617950AAvoid the risk of sheddingIncrease the speed of surgerySuture equipmentsSurgical staplesWide fieldTitanium
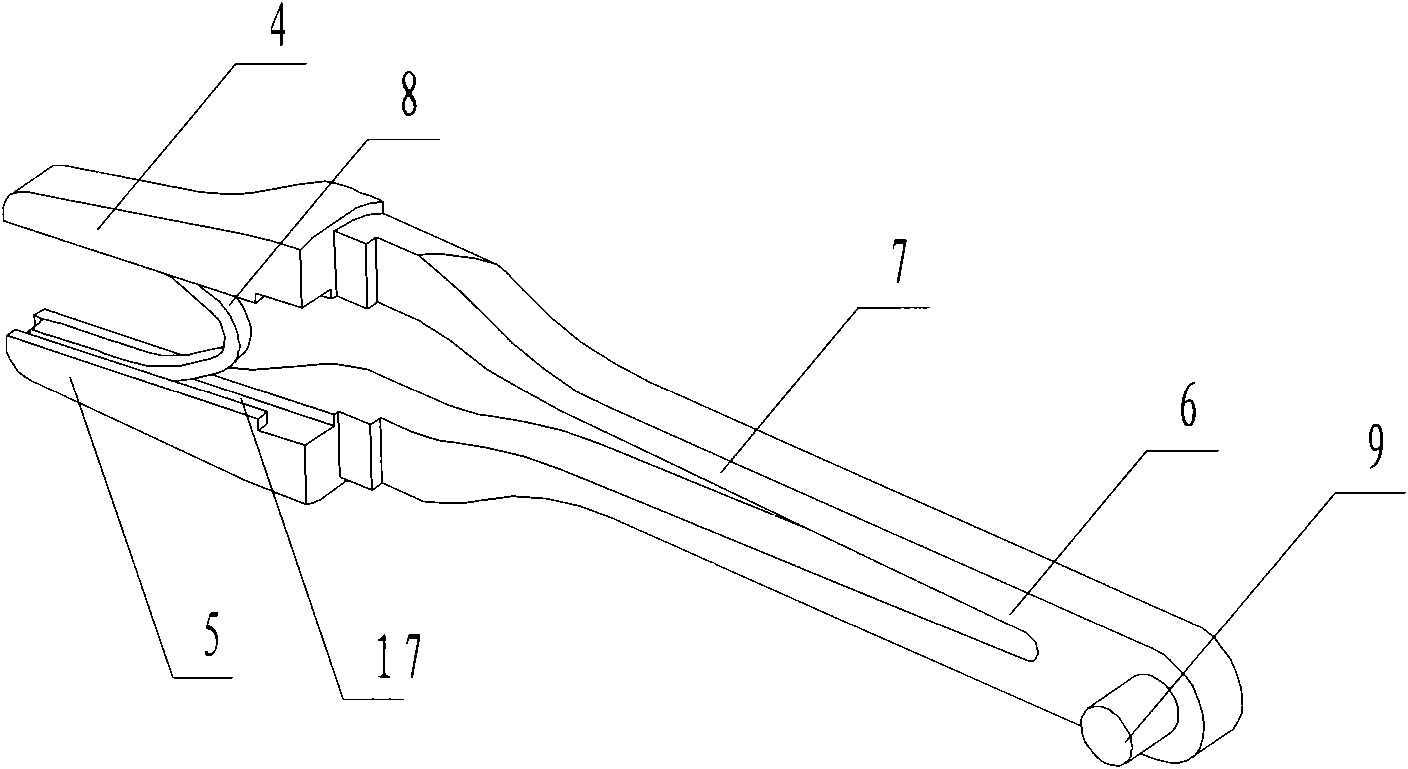
The invention discloses repeating titanium clamp pincers, which comprise a pincer body and a nail storage for filling a titanium clamp. When in use, the clip storage is inserted into the pincer body, and a handle is pinched to realize the clamp-closure of the titanium clamp and is released to finish the automatic filling of the next titanium clamp. The repeating titanium clamp pincers can effectively improve the operative speed, shorten the length of operation and reduce the probability of falling off of the titanium clamp when apparatuses are passed; in addition, only the titanium clamp and the nail storage are disposable apparatuses, while the pincer body can be sterilized and repeatedly used, thus the cost on use of the repeating titanium clamp pincers is low and economical burdens of patients can be relieved; besides, bended pincer heads can provide wider field of view and internal-mounted structural parts are beneficially for being prevented from contaminating by the operation.
Owner:王爱娣
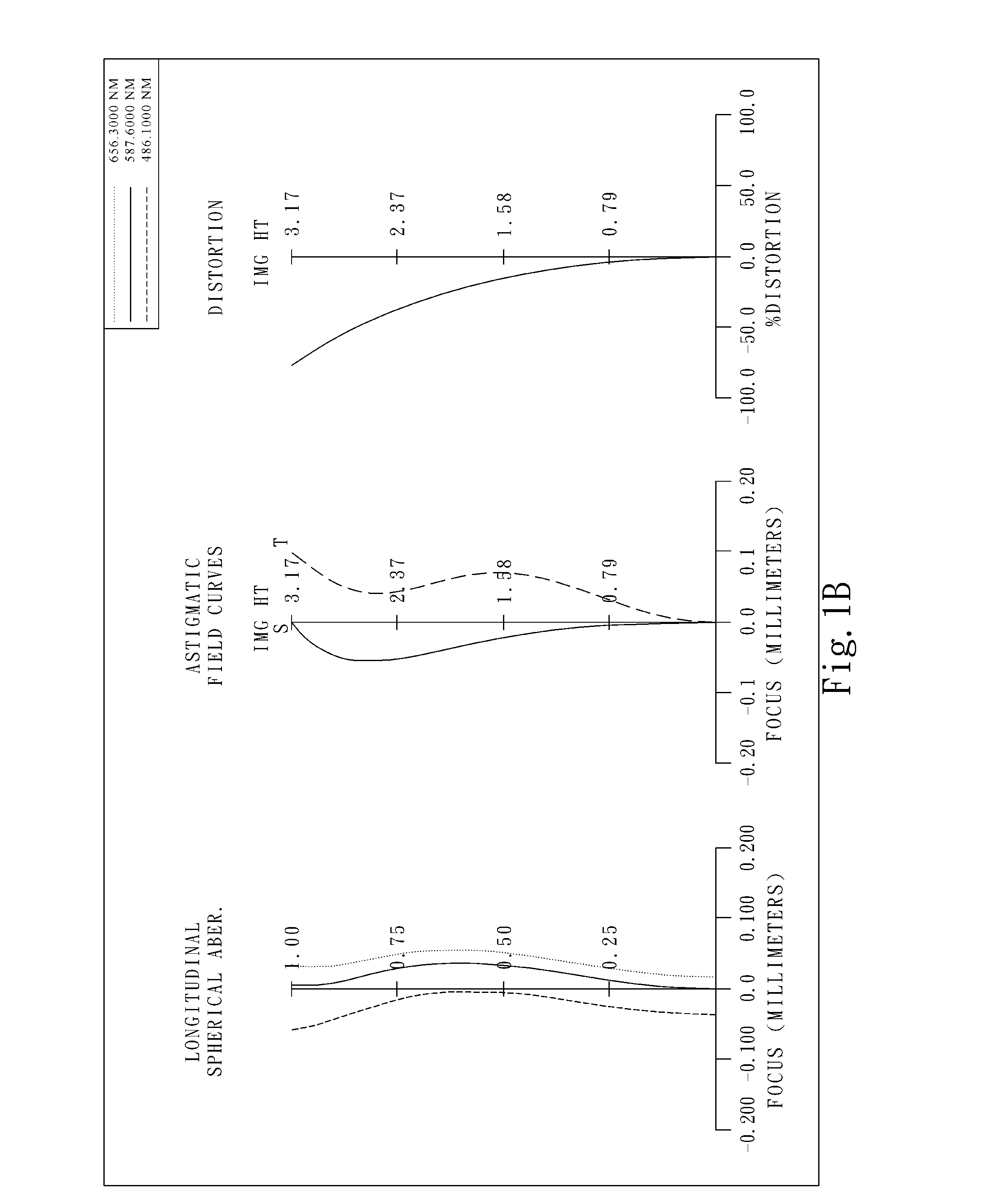
Image capturing optical lens assembly
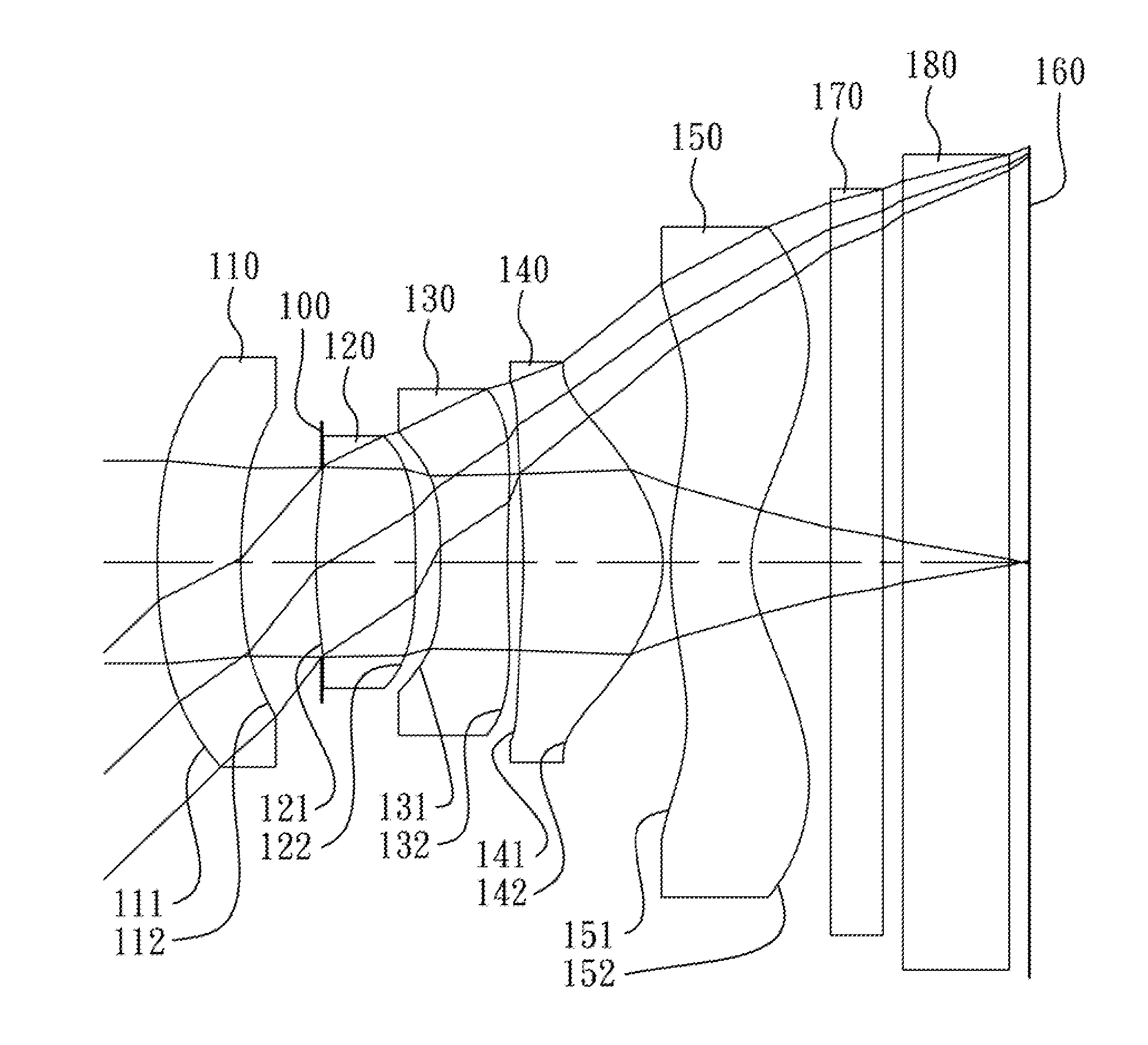
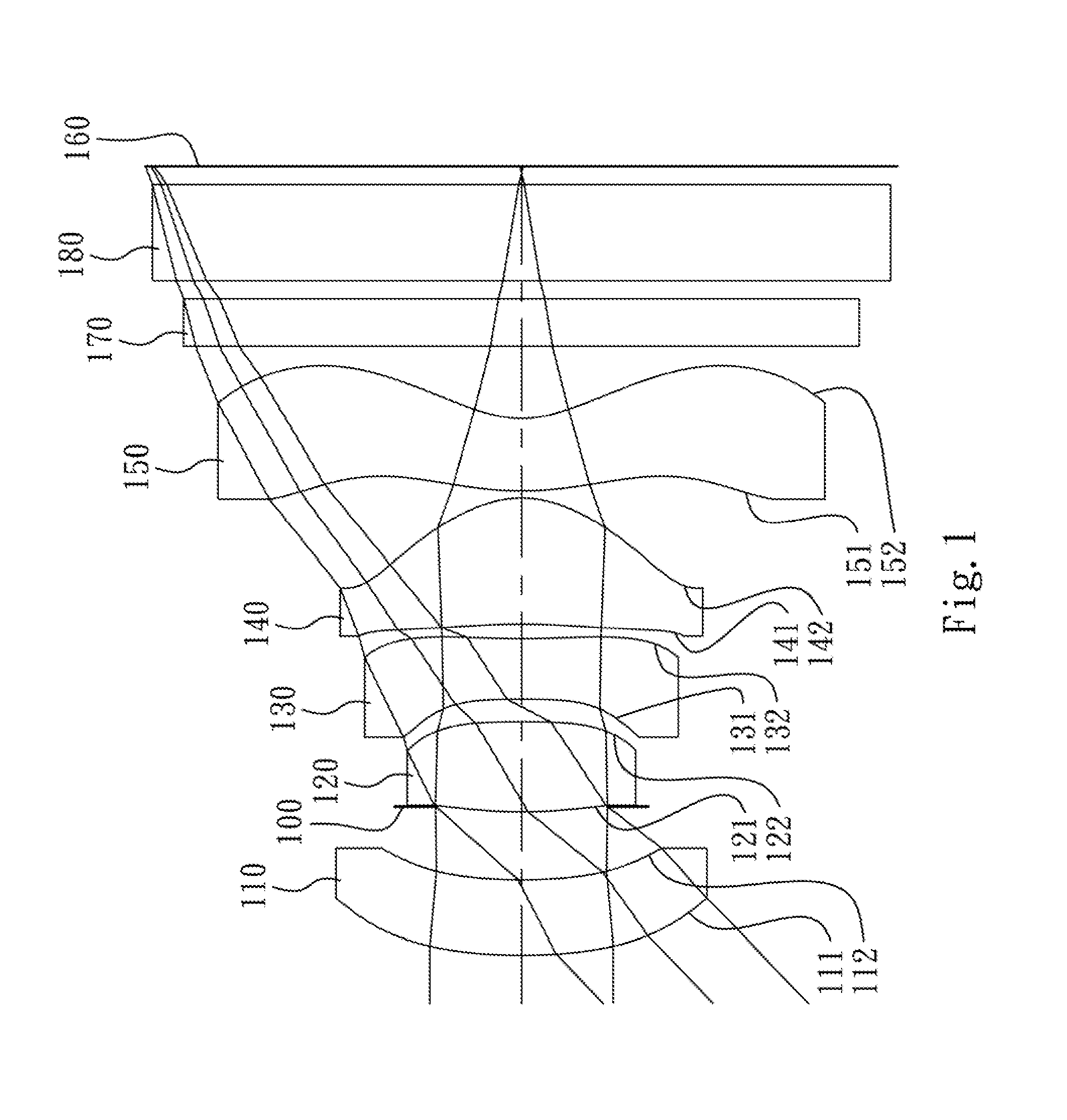
An image capturing optical lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element and a fifth lens element. The first lens element has positive refractive power. The second lens element has positive refractive power. The third lens element has negative refractive power. The fourth lens element has positive refractive power. The fifth lens element with negative refractive power is made of plastic material, and has an image-side surface being concave at a paraxial region and being convex at a peripheral region, wherein at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface of the fifth lens element is aspheric.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging system and methodology
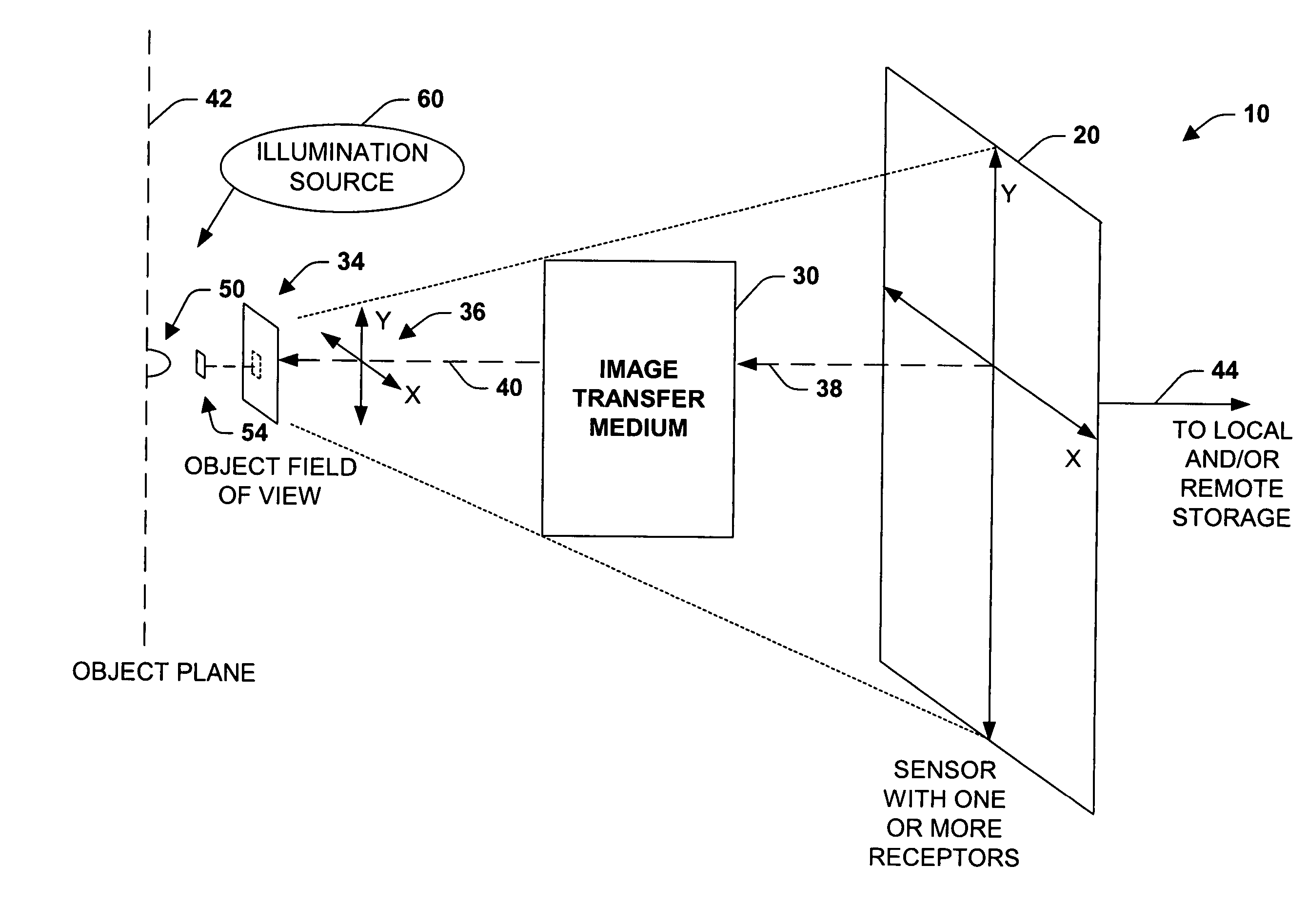
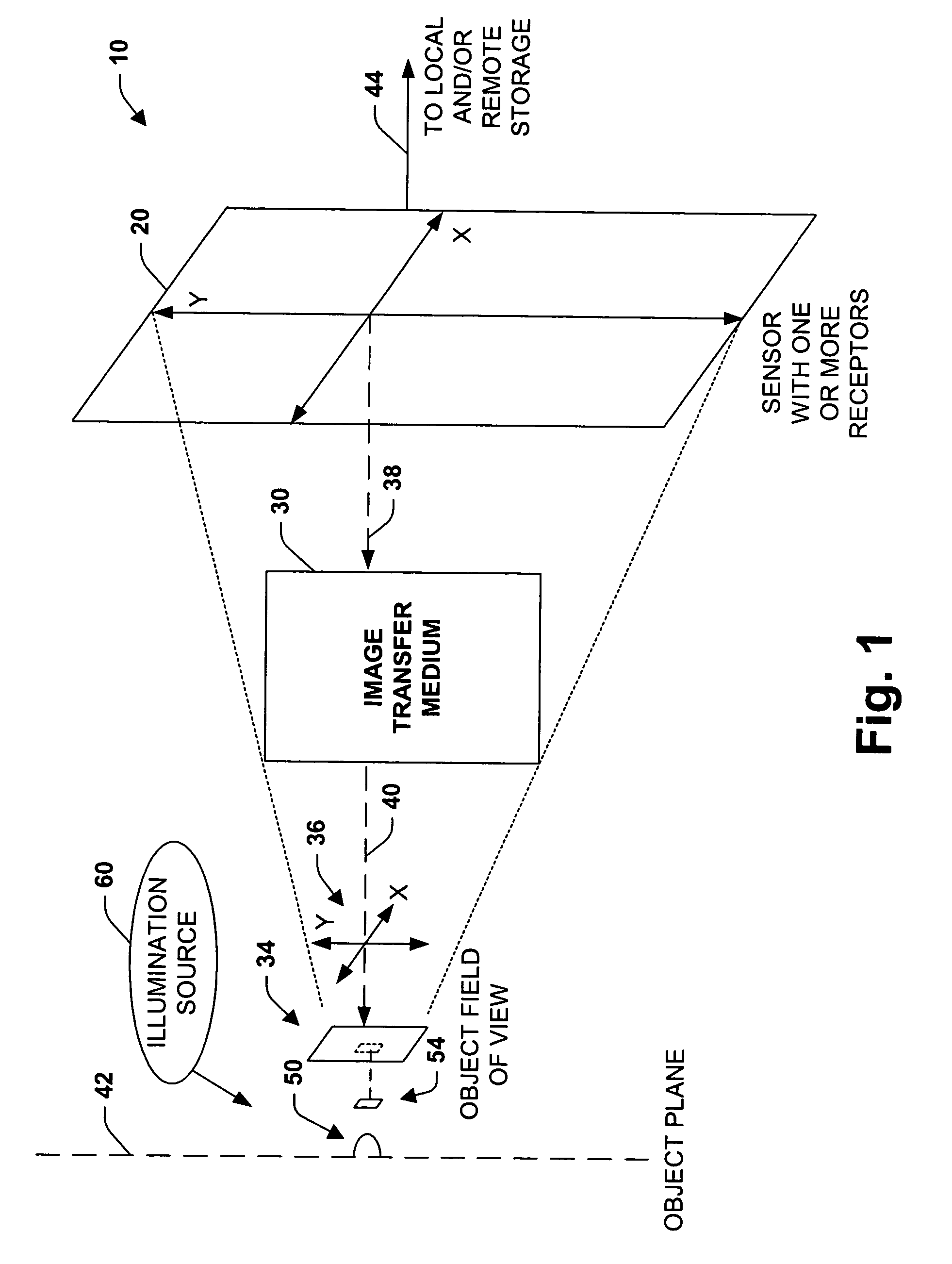
InactiveUS7151246B2Improve performanceEffectively scaledTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage transferDisplay device
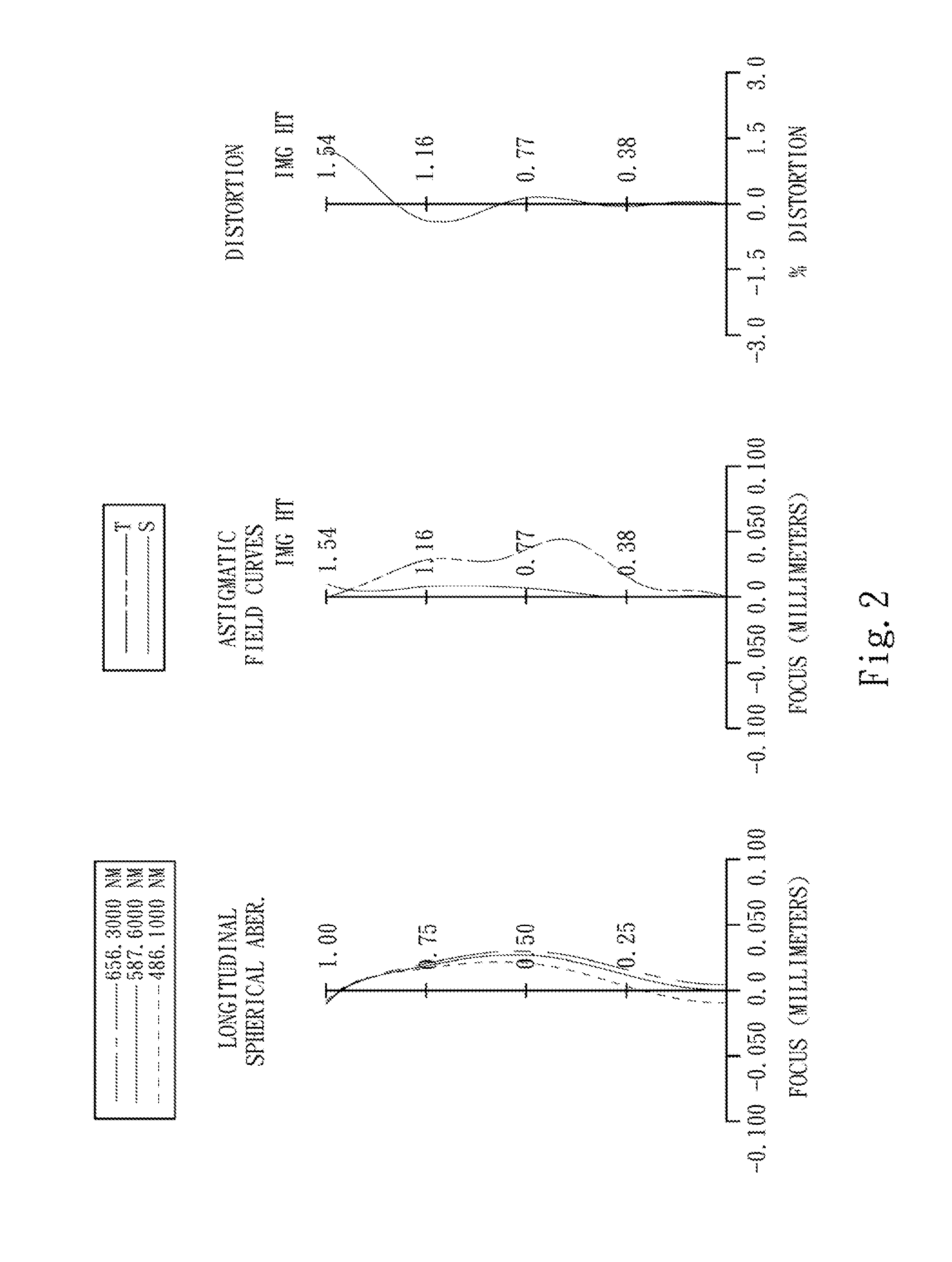
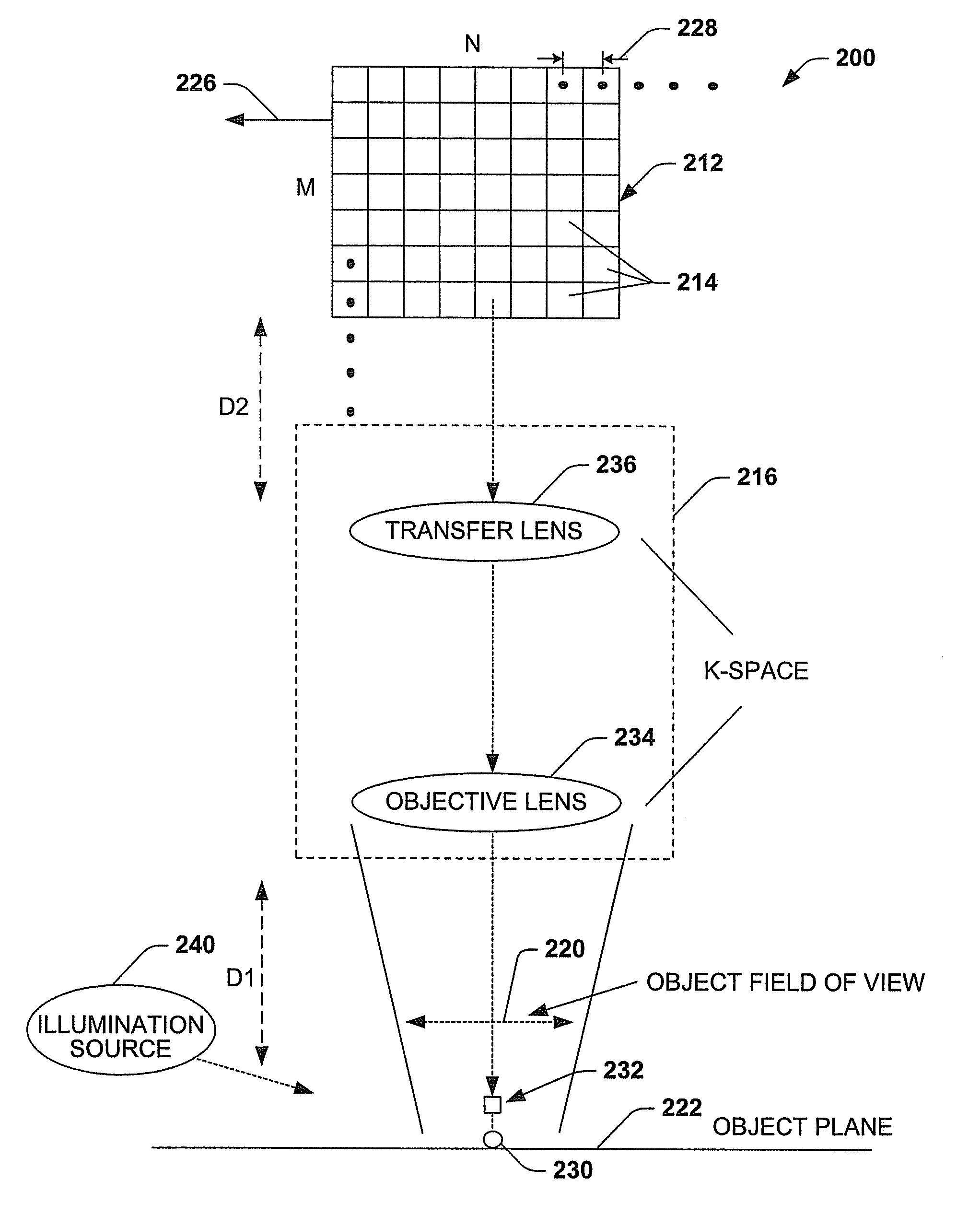
An imaging system, methodology, and various applications are provided to facilitate optical imaging performance. The system contains a sensor having one or more receptors and an image transfer medium to scale the sensor and receptors in accordance with resolvable characteristics of the medium, and as defined with certain ratios. A computer, memory, and / or display associated with the sensor provides storage and / or display of information relating to output from the receptors to produce and / or process an image, wherein a plurality of illumination sources can also be utilized in conjunction with the image transfer medium. The image transfer medium can be configured as a k-space filter that correlates projected receptor size to a diffraction-limited spot associated with the image transfer medium, wherein the projected receptor size can be unit-mapped within a certain ratio to the size of the diffraction-limited spot, both in the object plane.
Owner:HIMANSHU S AMIN +3
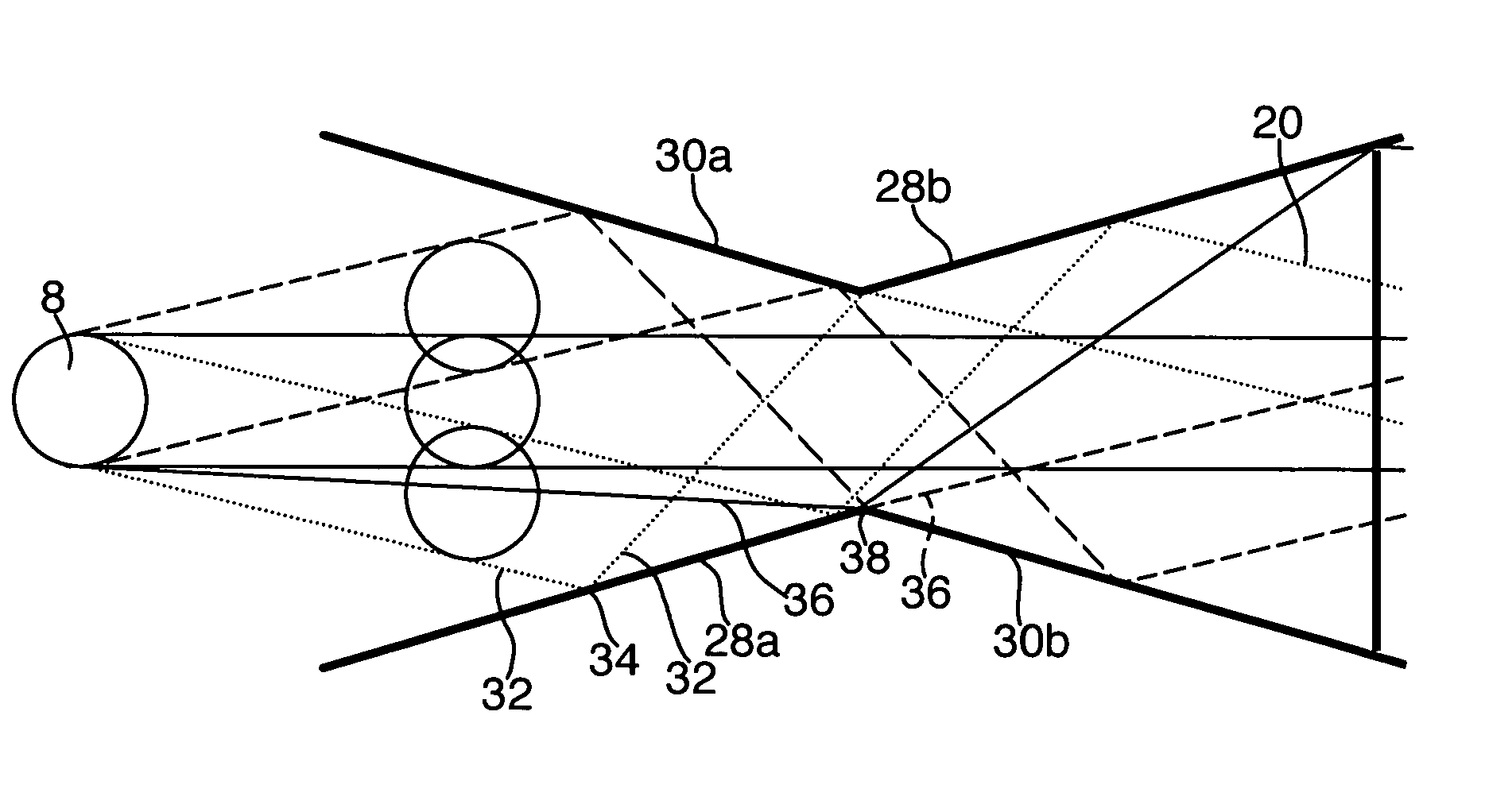
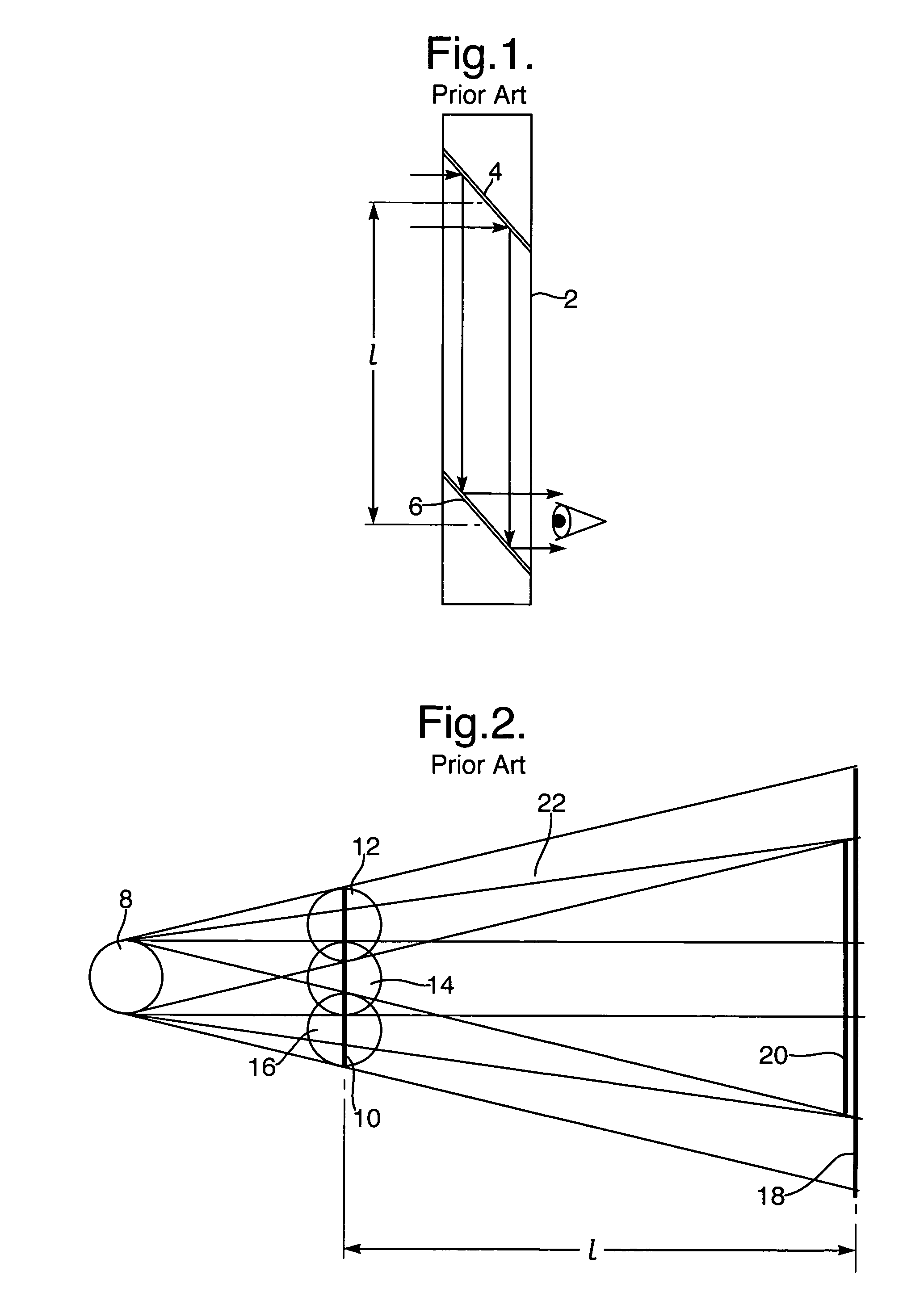
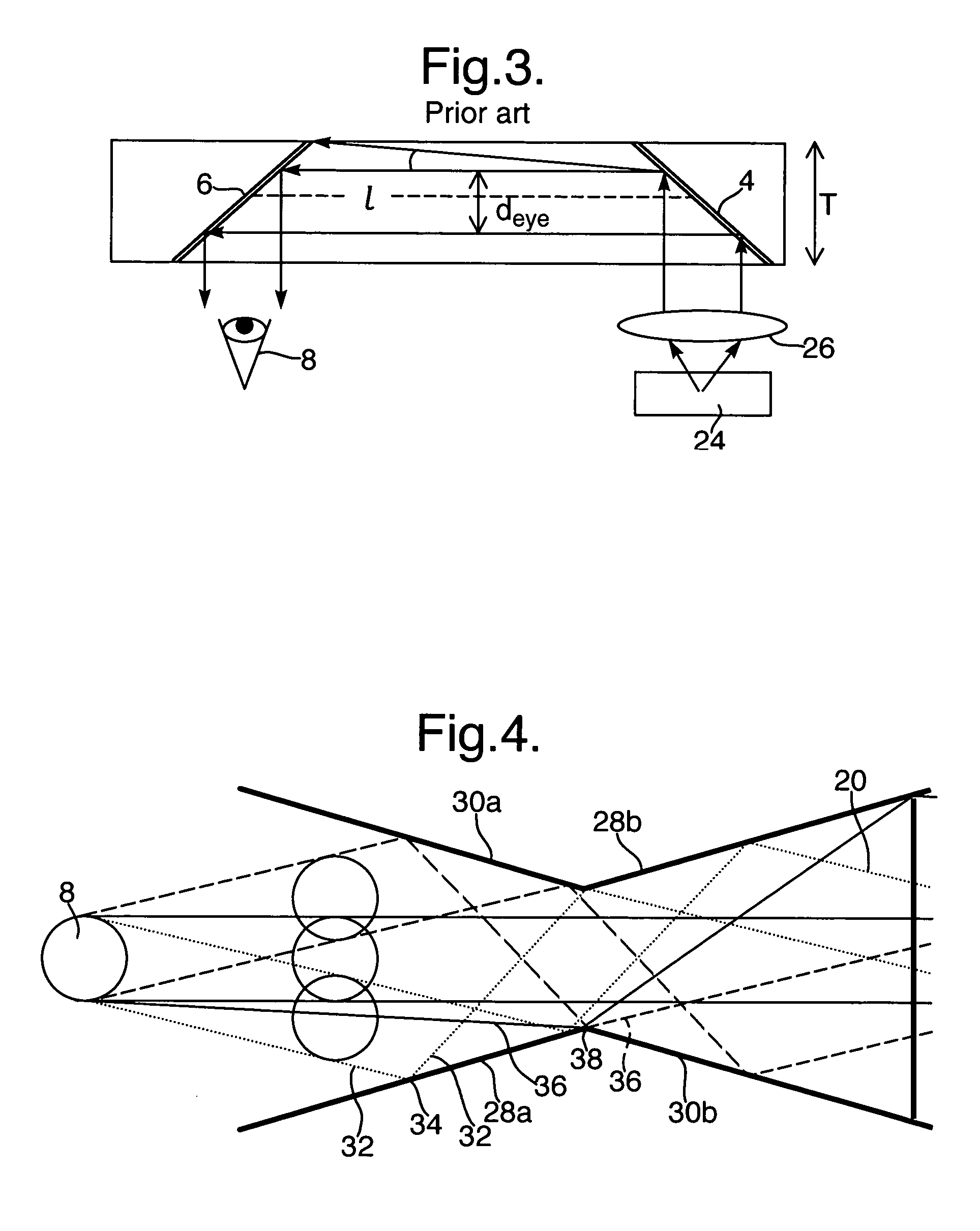
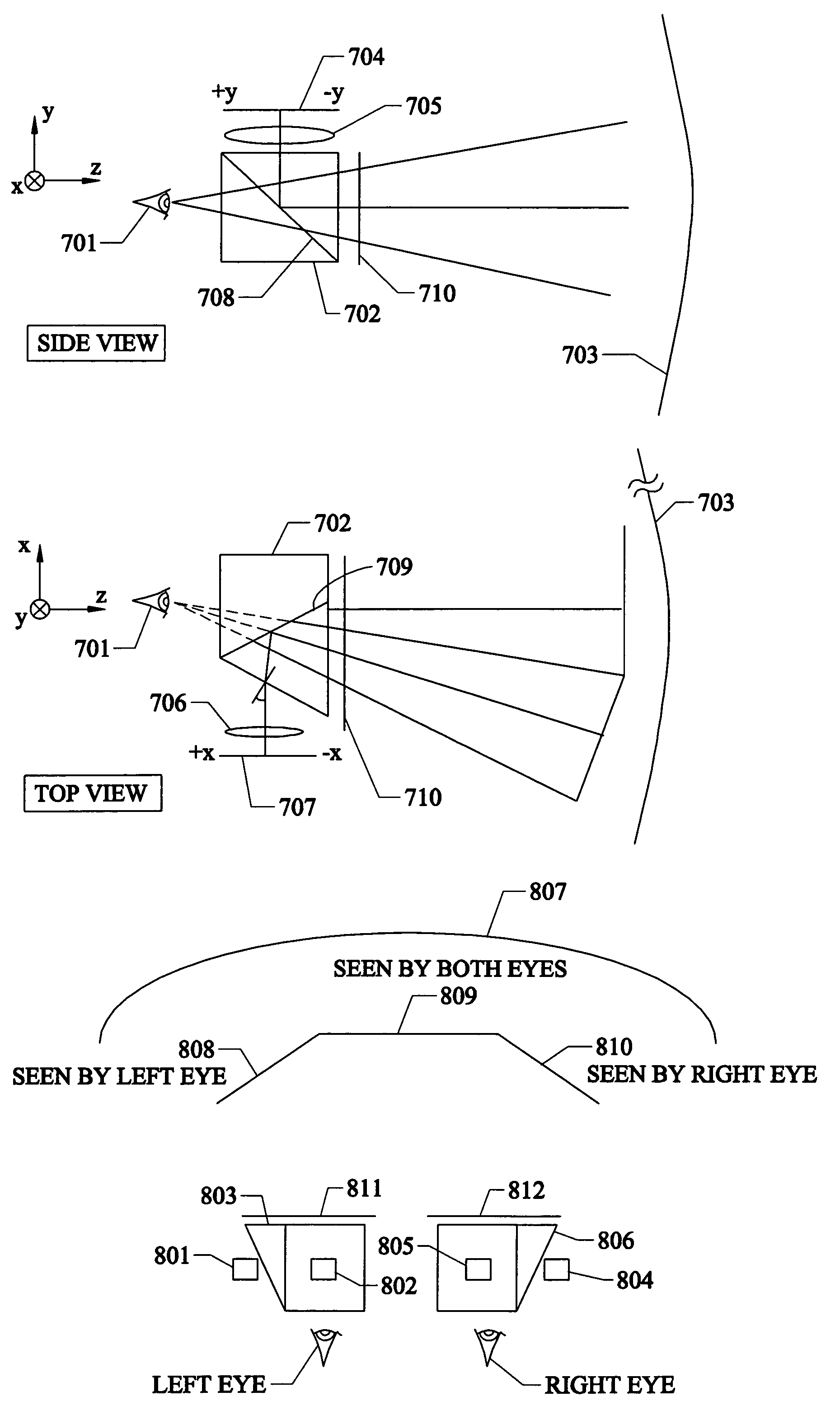
Head mounted projection display with a wide field of view
ActiveUS7119965B1Enhance fieldExpand field of viewCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsHead worn displayImage resolution
A ultra-wide field of view head mounted display has been realized by integrating an ARC display component having a greater than about 70 degrees field of retro-reflection with an optical tiling display which provides a greater than about 80 degrees horizontal field of view by about 50 degrees vertical field of view whereby an overall binocular horizontal field of view greater than about 120 degrees is realized with a greater resolution than about 2 arc minutes. There is also taught a method of providing a wide field of view head mounted display by the steps of: combining an ARC display component and an optical tiling display; and, integrating said component and said tiling display whereby an overall field of view greater than about 120 degrees is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
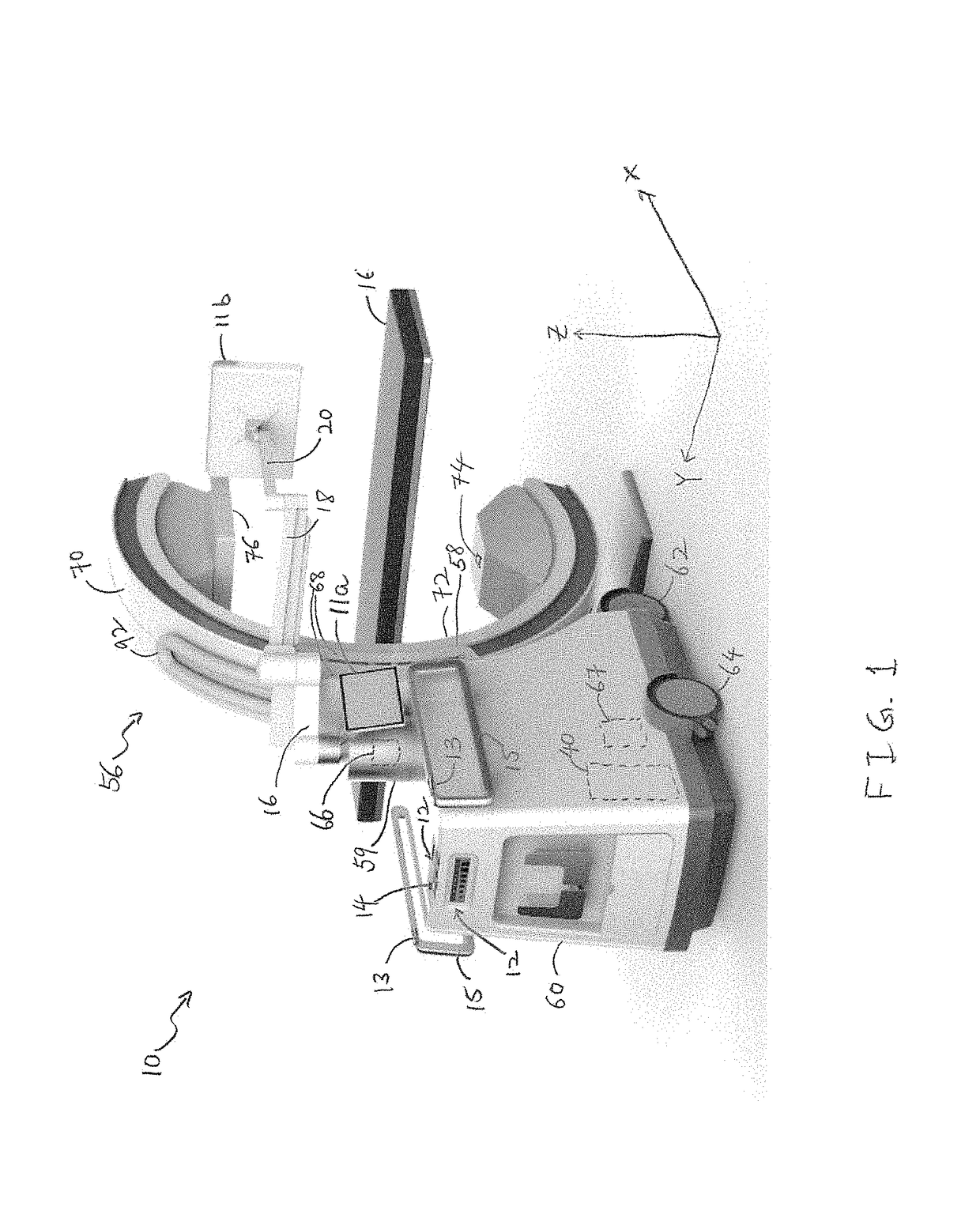
Portable medical imaging system
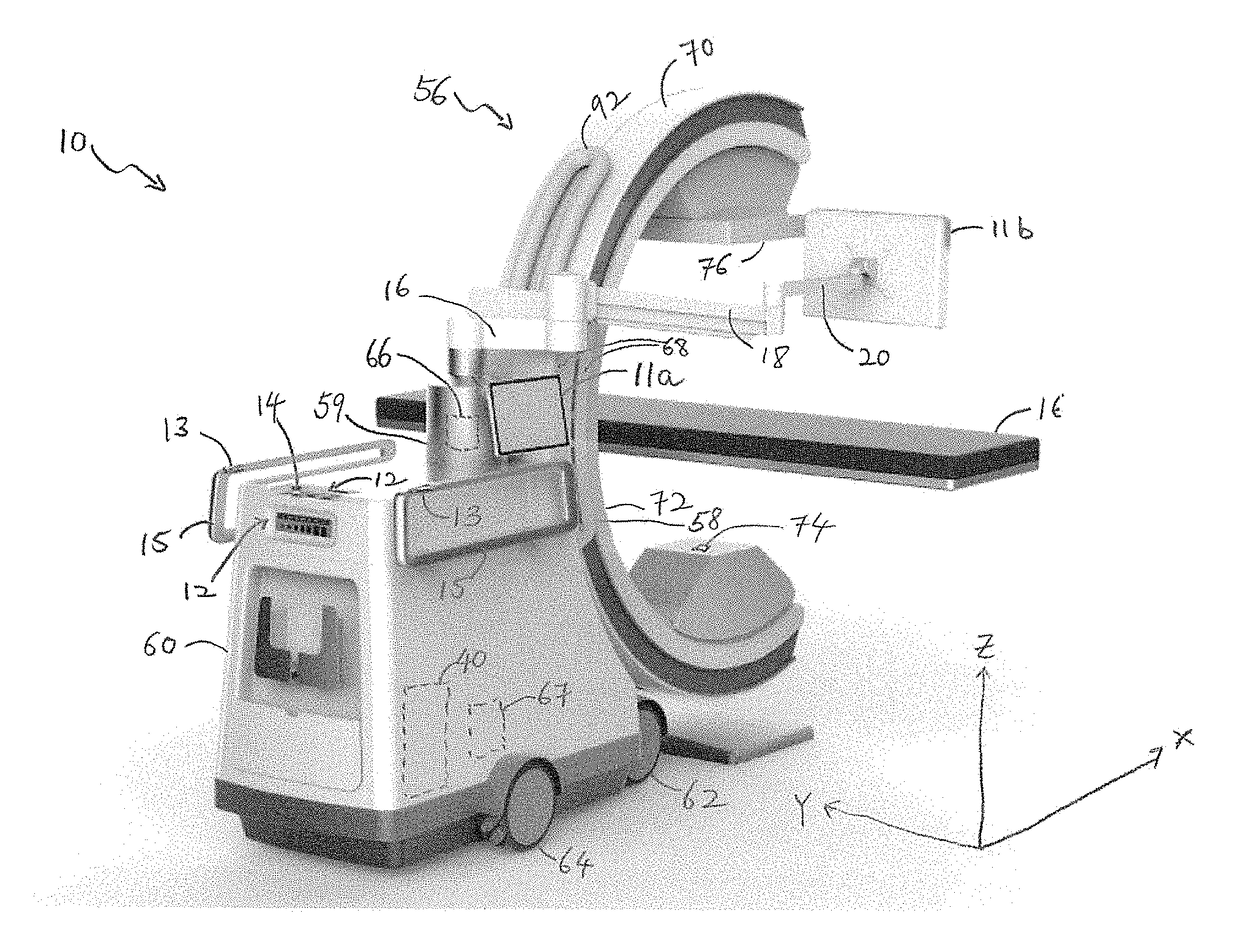
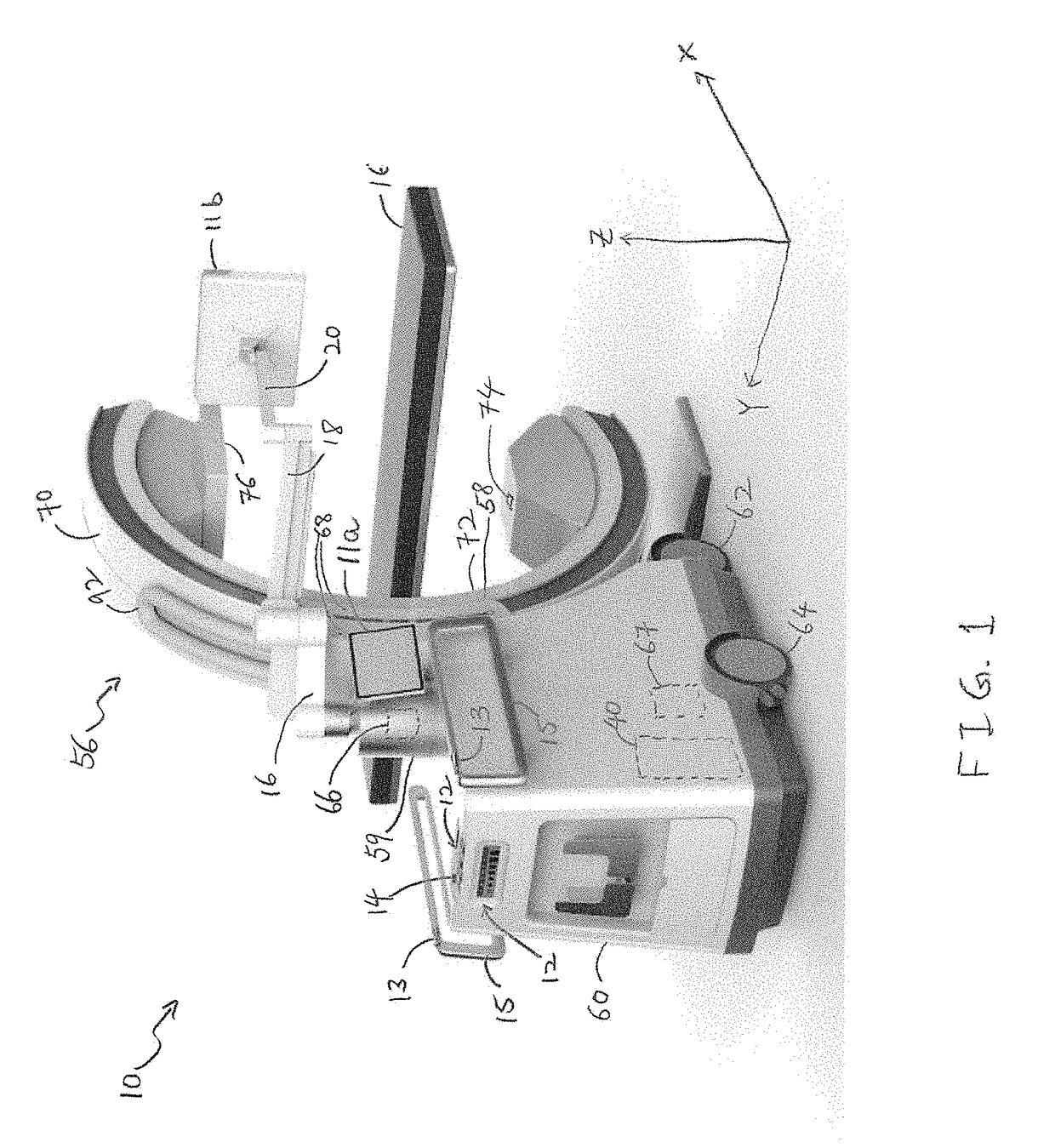
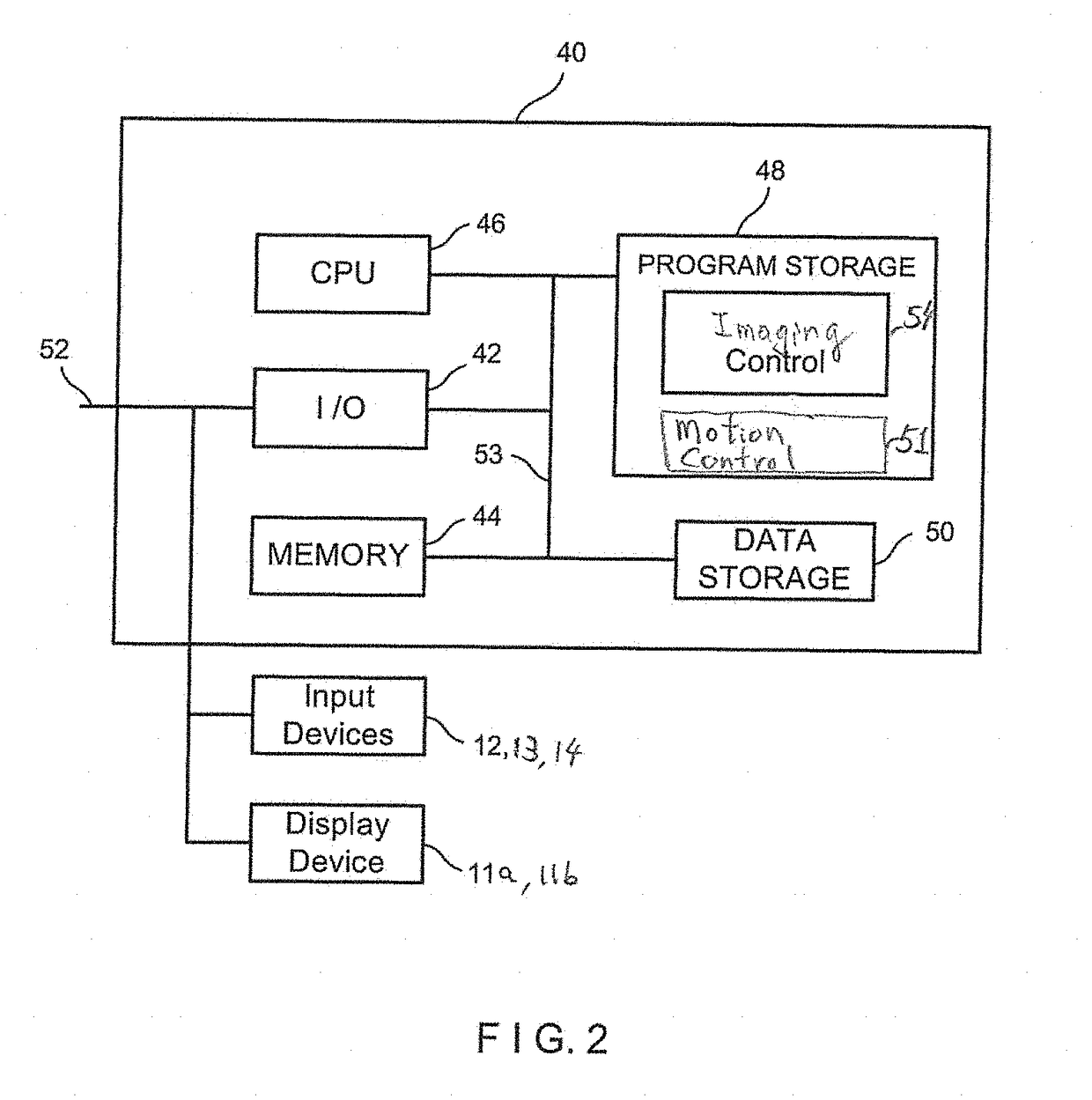
ActiveUS20170215826A1Expand field of viewRadiation diagnosis data transmissionComputerised tomographsControl systemMedical imaging
Medical imaging devices, systems, and methods thereof. The medical imaging system may include a movable station and a gantry. The movable station includes a gantry mount rotatably attached to the gantry. The gantry includes an outer C-arm slidably mounted to and operable to slide relative to the gantry mount, an inner C-arm slidably coupled to the outer C-arm and, an imaging signal transmitter and sensor attached to the C-arms. The two C-arms work together to provide a full 360 degree rotation of the imaging signal transmitter. The movable station may include a motion control system and an imaging control system. In embodiments, the motion control system includes omni-directional wheels for precision controlled-movement of the movable station.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical prevention of disc herniations
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. The present invention applies high frequency (RF) electrical energy to one or more electrode terminals in the presence of electrically conductive fluid or saline-rich tissue to contract collagen fibers within the tissue structures. In one aspect of the invention, a system and method is provided for contracting a portion of the nucleus pulposus of a vertebral disc by applying a high frequency voltage between an active electrode and a return electrode within the portion of the nucleus pulposus, where contraction of the portion of nucleus pulposus inhibits migration of the portion nucleus pulposus through the fissure.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Portable medical imaging system
ActiveUS20170215827A1Expand field of viewComputerised tomographsTomographyMedical imagingEngineering
Medical imaging devices, systems, and methods thereof. The medical imaging system may include a movable station and a gantry. The movable station includes a gantry mount rotatably attached to the gantry. The gantry includes an outer C-arm slidably mounted to and operable to slide relative to the gantry mount, an inner C-arm slidably coupled to the outer C-arm and, an imaging signal transmitter and sensor attached to the C-arms. The two C-arms work together to provide a full 360 degree rotation of the imaging signal transmitter. In embodiment, the imaging signal transmitter and imaging sensor are offset from a center axis of the medical imaging system such that the portable medical imaging system is operable to capture an enlarged field of view.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Dilator with direct visualization
InactiveUS20110098531A1Improve visualizationExpand field of viewCannulasSurgical needlesEpidural spaceSurgical instrument
Dilators with a threaded distal portion and direct visualization capability may be used for penetrating and dilating stiff tissues and bones. The threaded portion of a dilator engages the tissue between the insertion site and the target site, and may be rotated for advancing through the target tissue in a more controlled fashion. The direct visualization capability may be used to visualize the ligament as the threaded distal portion passes through the ligamentum flavum. The devices and methods described may be used in procedures, for example, where ligaments surrounding the epidural space need to be dilated in order to deliver one or more surgical instruments into the epidural space.
Owner:EXPANDING INNOVATIONS INC
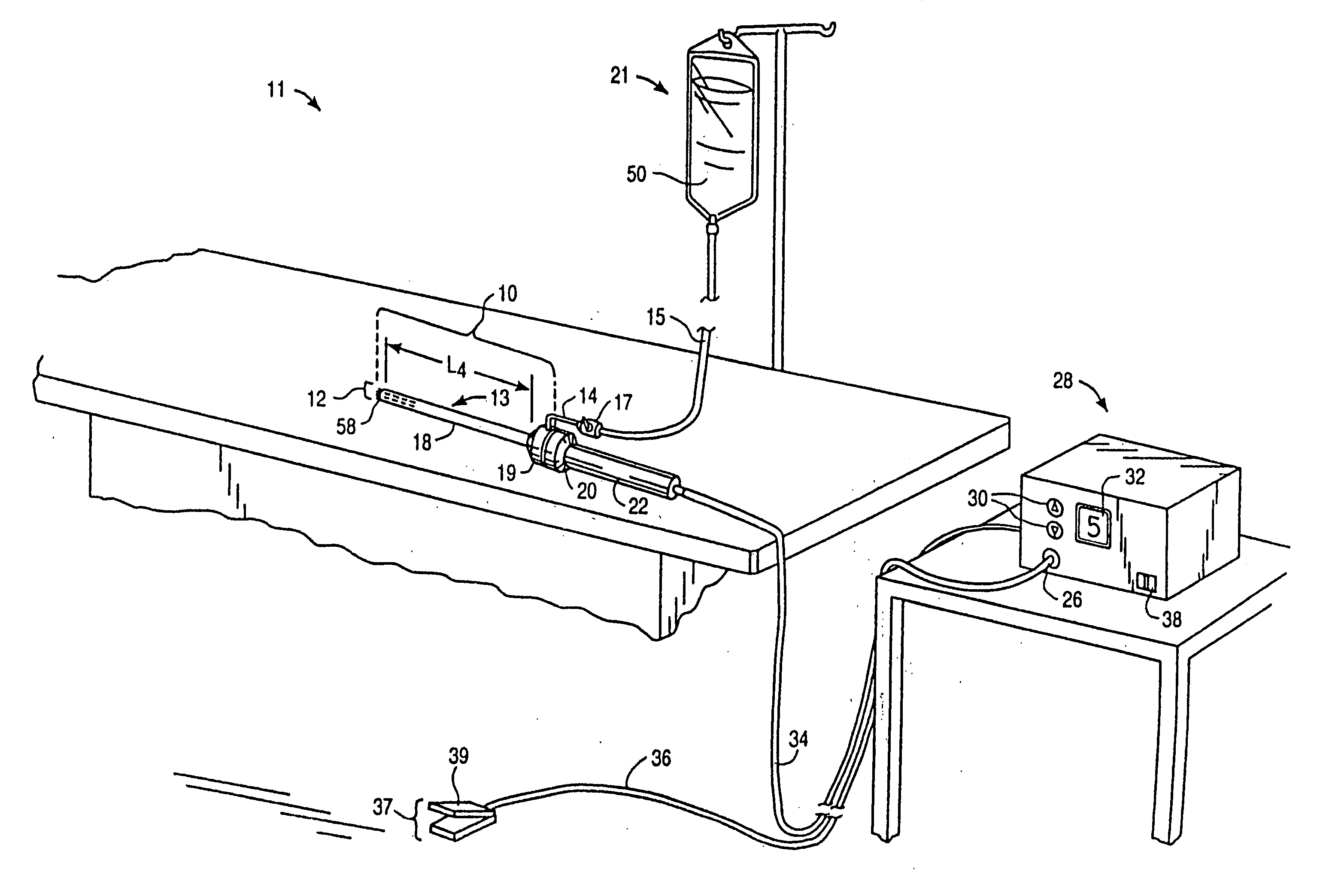
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of fasciitis
InactiveUS20060189971A1Minimize and completely eliminate and damageExpand field of viewStentsHeart valvesFasciitisDamages tissue
Systems, apparatus, and methods are provided for promoting blood flow to a target tissue. In one aspect, the invention involves canalizing or boring channels, divots, trenches or holes through an avascular connective tissue, or through a tissue having sparse vascularity, such as a tendon or a meniscus, in order to increase blood flow within the tissue. In one method, an active electrode is positioned in close proximity to a target site on a tendon, and a high frequency voltage difference is applied between the active electrode and a return electrode to selectively ablate tendon tissue at the target site, thereby forming a channel or void in the tendon. The active electrode(s) may be moved relative to the tendon during, or after, the application of electrical energy to damage or sculpt a void within the tendon, such as a hole, channel, crater, or the like. In another aspect of the invention, an electrosurgical probe is used to elicit a wound healing response in a target tissue, such as an injured tendon, in order to stimulate vascularization of the target tissue. The present invention may also be used for vascularization of a torn or damaged tissue in conjunction with a surgical repair procedure.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
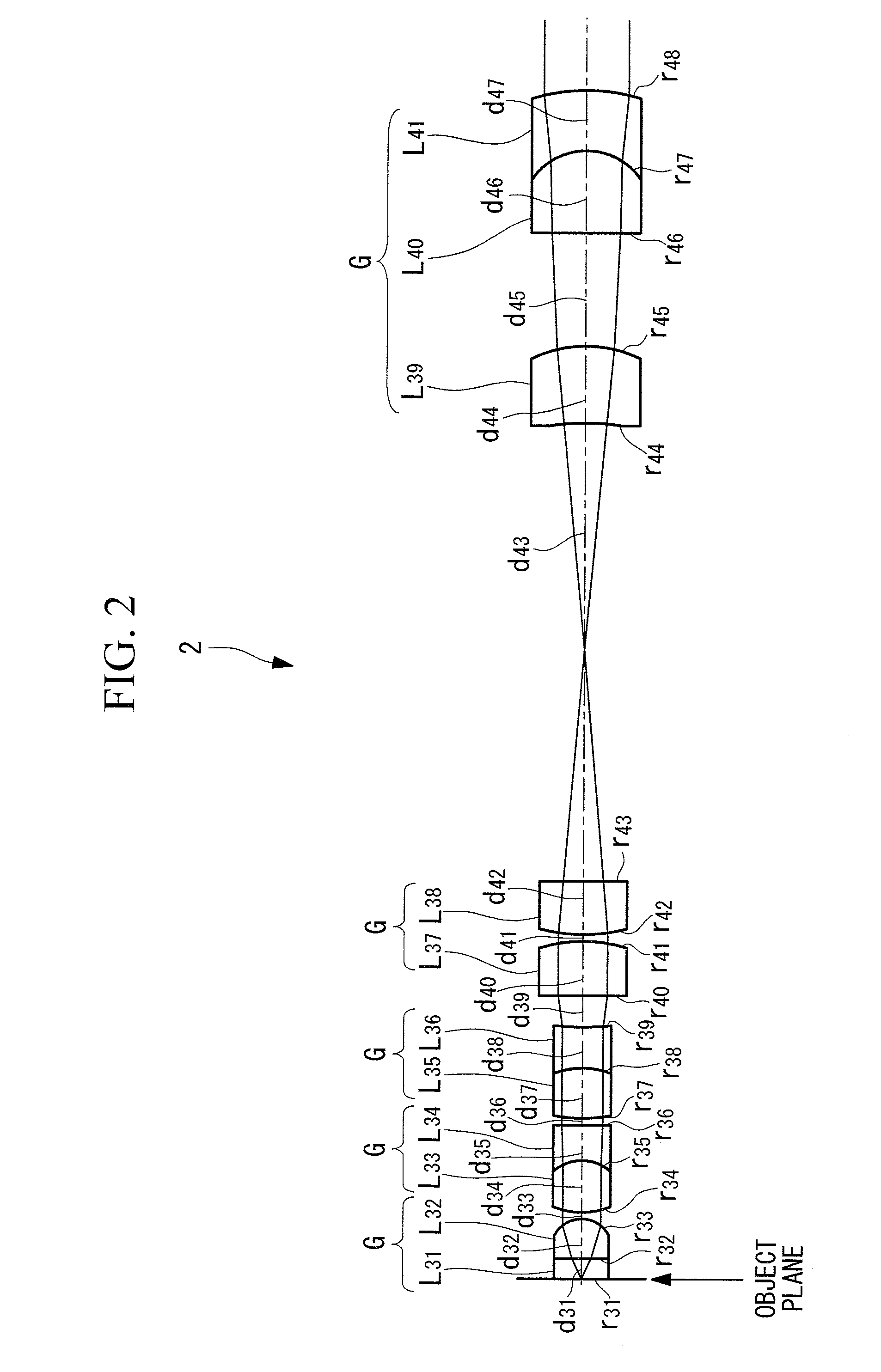
Wide-viewing-angle imaging lens assembly
ActiveUS20110316969A1Expand field of viewReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging lensField of view
The present invention provides a wide-viewing-angle imaging lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a front lens group, a stop, and a rear lens group. The front lens group comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface and a second lens element. The rear lens group comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a third lens element with positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, and a fifth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively enlarge the field of view of the wide-viewing-angle imaging lens assembly, reduce the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain good image quality.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Display device and vehicle
InactiveUS7176790B2Expand field of viewTransistorStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for electrosurgical incisions on external skin surfaces
InactiveUS6896672B1Accurate cutMinimal painSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsCuticleCuldoplasty
Systems and methods are provided for removing fatty tissue underlying a patient's epidermis (e.g., blepharoplasty, brow lifts, eyelid shortening procedures, and the like). These methods include positioning one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) in close proximity to a target site on an external body surface of the patient. A high frequency voltage difference is applied between the active and return electrode(s), and the active electrode(s) are translated across the external body surface to create an incision therein. The bipolar configuration controls the flow of current to within and around the distal end of the probe, which minimizes tissue necrosis and the conduction of current through unwanted paths in the patient. The residual heat from the electrical energy also provides simultaneous hemostasis of severed blood vessels, which increases visualization and improves recovery time for the patient.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
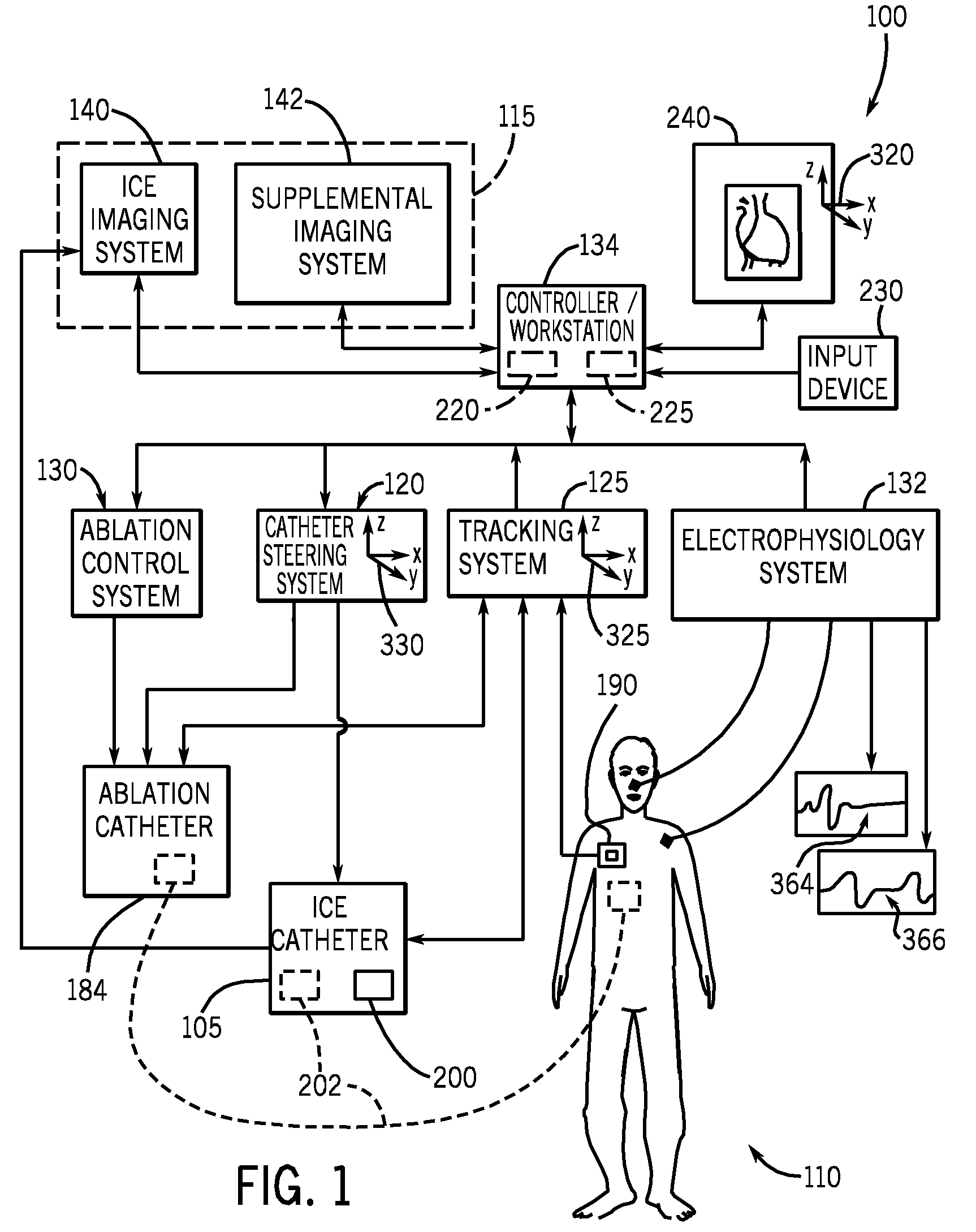
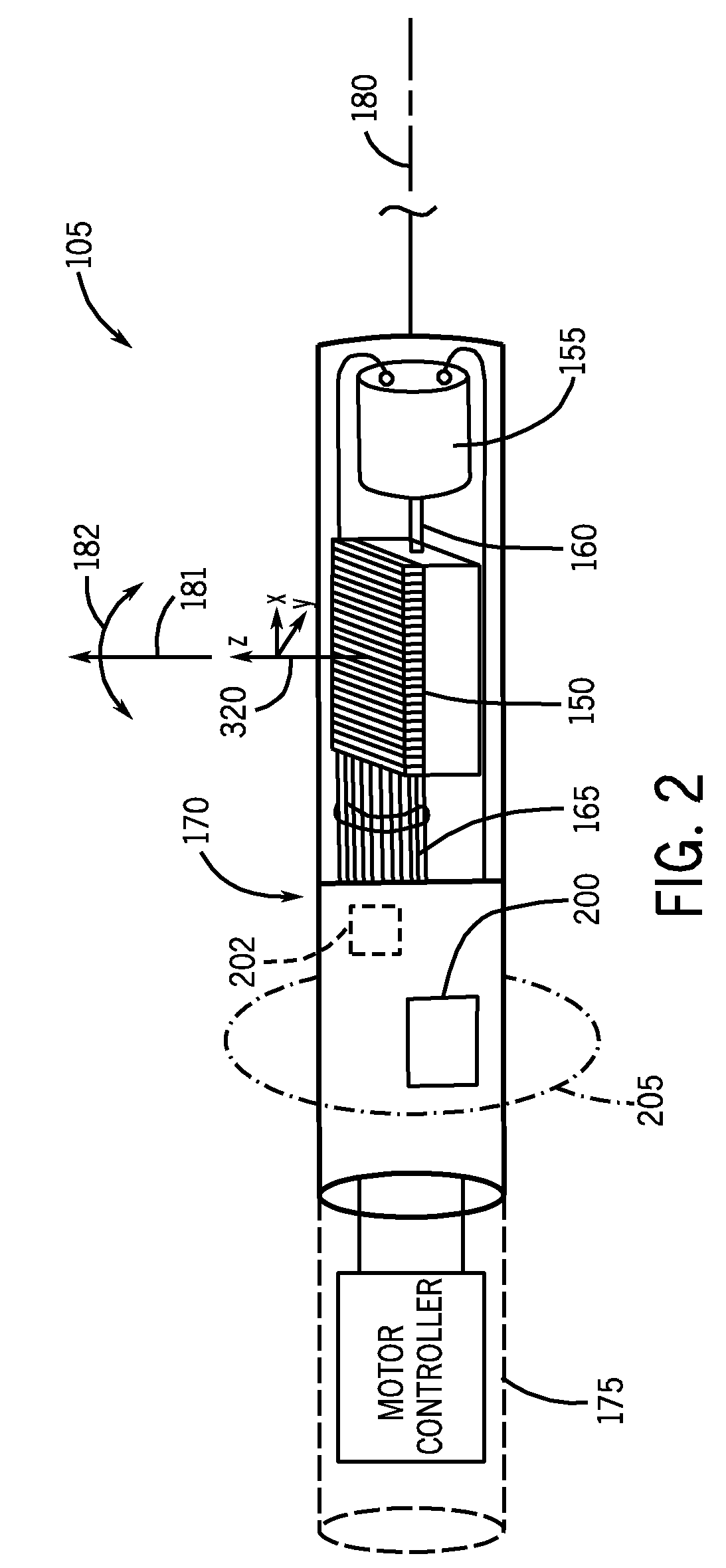
Intracardiac echocardiography image reconstruction in combination with position tracking system
ActiveUS20080287803A1Reduce health risksExpand field of viewUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSonification3d image
A system and method to display a four-dimensional (4D) model of an imaged anatomy is provided. The system comprises a controller, and an imaging system including an imaging probe in communication with the controller. The imaging probe can acquire generally real-time, 3D image data relative to a direction of image acquisition along an imaging plane. The system also includes a tracking system in communication with the controller. The tracking system includes at least one tracking element integrated with the imaging probe. The system is operable to process the generally real-time, 3D image data acquired by the imaging probe relative to generally real-time tracking information acquired by the tracking system so as to display the 4D model of the imaged anatomy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
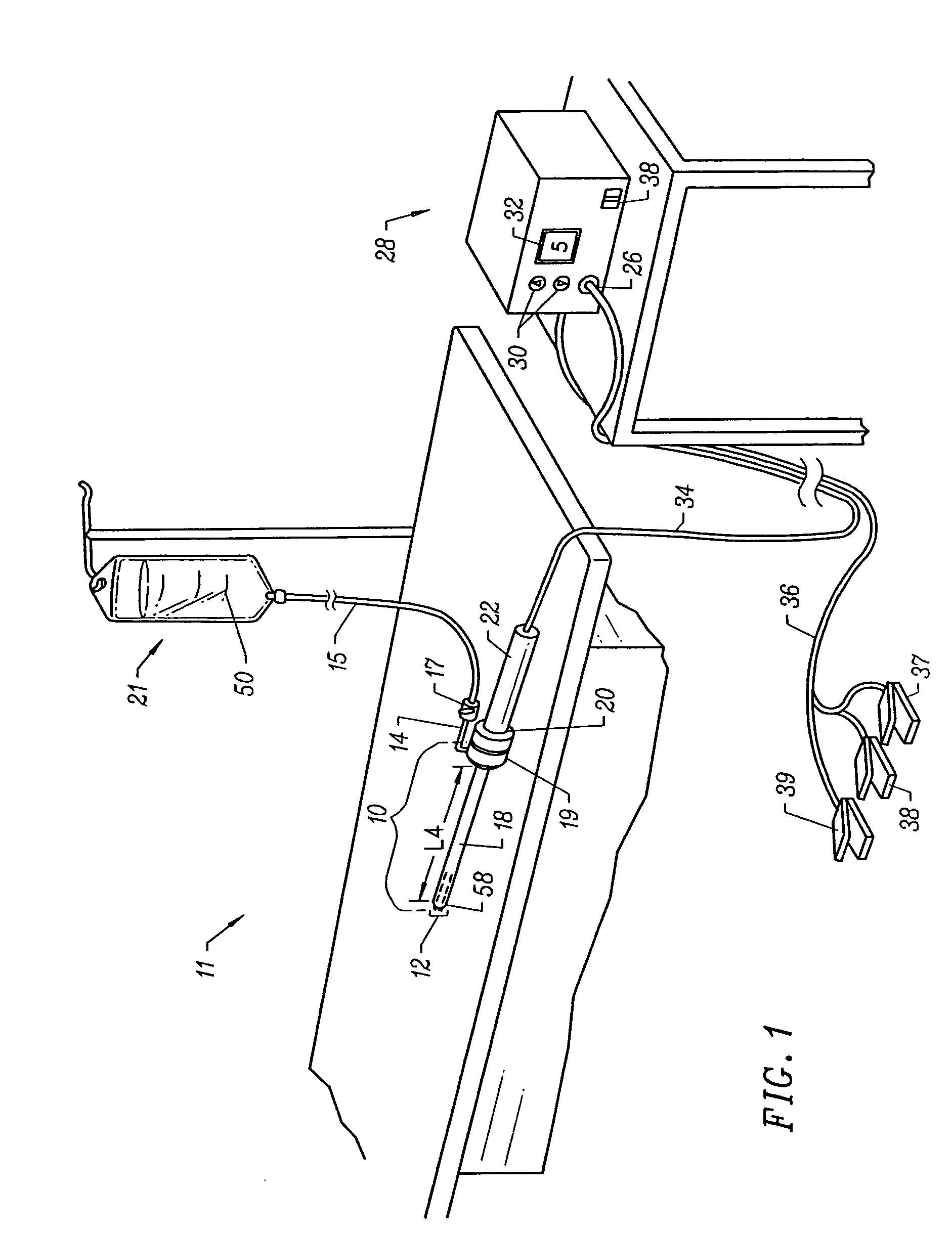
Systems and methods for electrosurgical spine surgery
InactiveUS7462178B2Lower the volumeUse performanceSurgical needlesEndoscopesSpinal cordSurgical department
Methods and apparatus for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. In a method of the invention high frequency (RF) electrical energy is applied to one or more active electrodes on an electrosurgical probe in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to remove, contract or otherwise modify the structure of tissue targeted for treatment. In one aspect, a dura mater and spinal cord are insulated from the electrical energy by an insulator positioned on a non-active side of the probe. In another aspect, a plasma is aggressively formed in the electrically conductive fluid by delivering a conductive fluid to a distal end portion of the probe and aspirating the fluid from a location proximal of the return electrode. In another aspect, a distal end of an electrosurgical probe having at least one electrode on a biased, curved, bent, or steerable shaft is guided or steered to a target site within an intervertebral disc having a disc defect for treatment of tissue to be treated at the target site by the selective application of electrical energy thereto.
Owner:AOL LLC A DELAWARE LLC +1
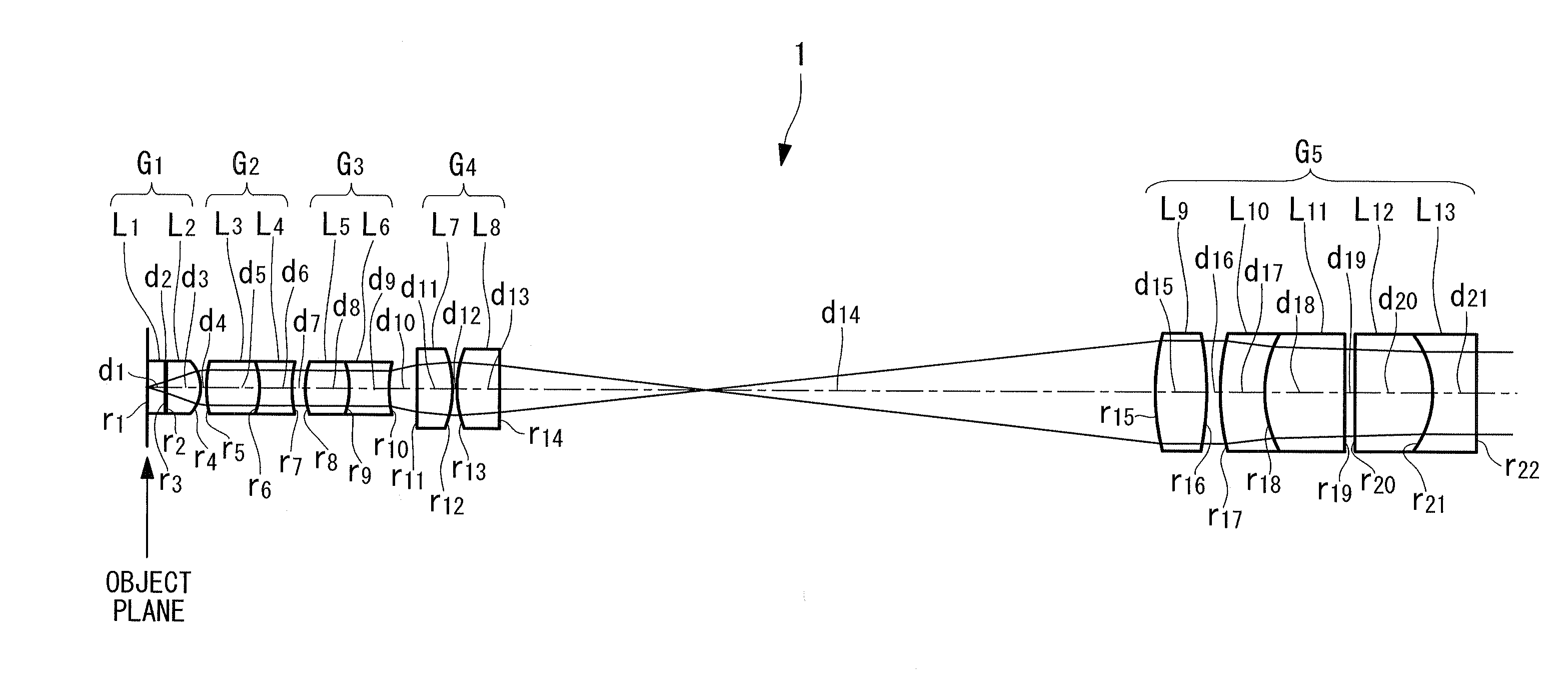
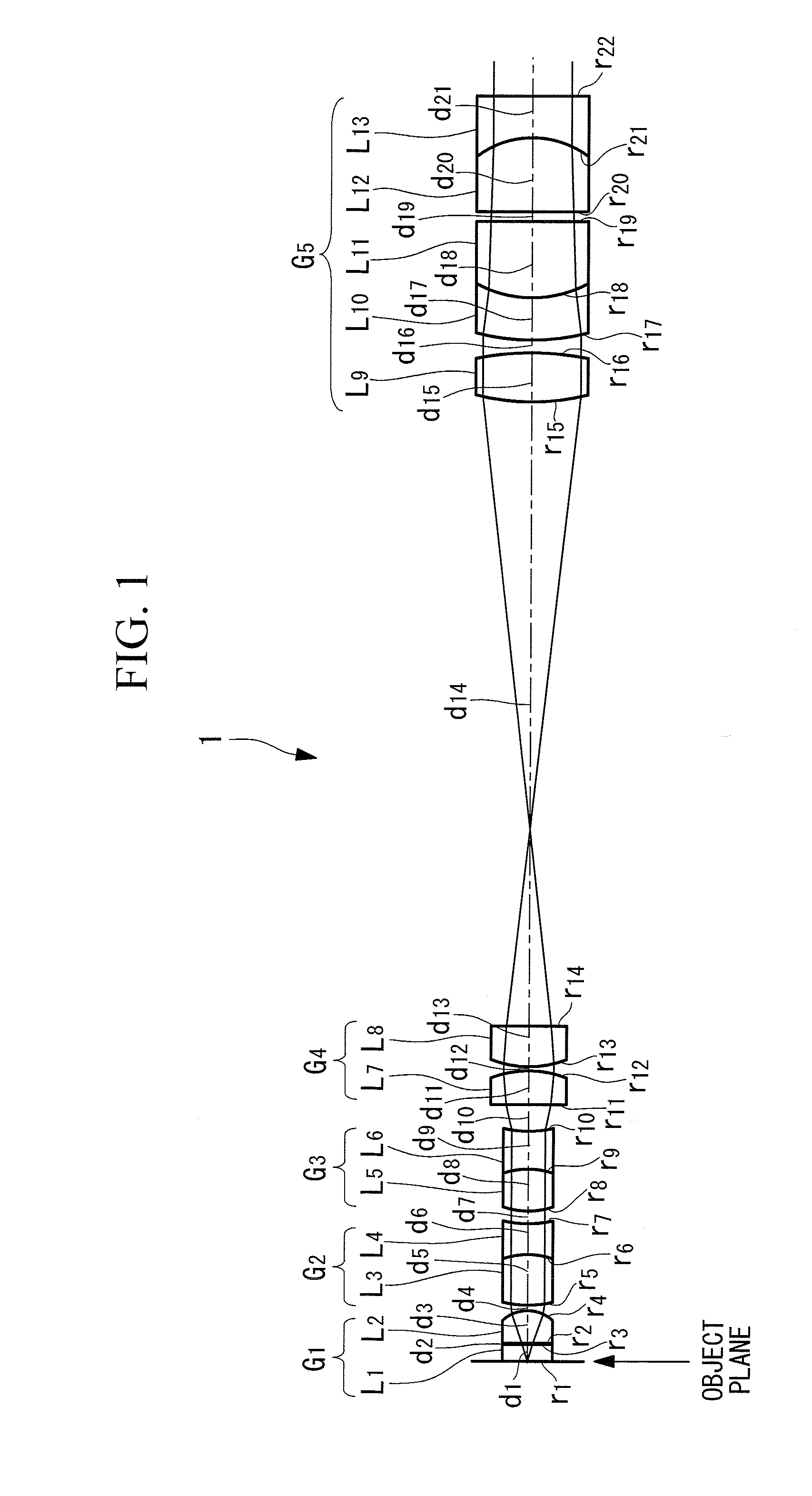
Objective optical system
ActiveUS20100123950A1Minimally invasiveReduce the overall diameterEndoscopesLaproscopesPhysicsConcave surface
An objective optical system includes a first group having positive refractive power and a piano-convex lens with the convex surface facing the image side; a second group having positive refractive power and a lens whose extreme-object-side lens surface is a convex surface facing the object side; a third group having negative refractive power and a lens whose extreme-image-side lens surface is a concave surface facing the image side; a fourth group having positive refractive power and a lens disposed on the extreme object side, whose image-side lens surface is a convex surface facing the image side and a lens disposed on the extreme image side, whose object-side lens surface is a convex surface facing the object side; and a fifth group having positive refractive power and a combined lens formed by joining a convex lens and a concave lens, the joined surface having negative refractive power.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS8372726B2Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionEngineering
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
Automobile exterior sideview mirror system
InactiveUS7167294B2Expand field of viewAdjustable viewing angleMirrorsStands/trestlesEngineeringMagnification
An automobile exterior sideview mirror system includes an exterior sideview mirror assembly, which includes a reflective element assembly. The reflective element assembly includes a first reflective element having a unit magnification and a second reflective element having a curvature. The first reflective element and the second reflective element are supported at a support element. The mirror system preferably further includes an actuator, which is operable to adjust the orientation of the reflective element assembly. The second reflective element is disposed adjacent to and separate from the first reflective element when it is included in the exterior sideview mirror assembly. Further, a demarcation element is provided between the first reflective element and the second reflective element. A portion of the second reflective element adjacent the demarcation element has a front surface that is generally coplanar with the front surface of the first reflective element.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Vision catheter
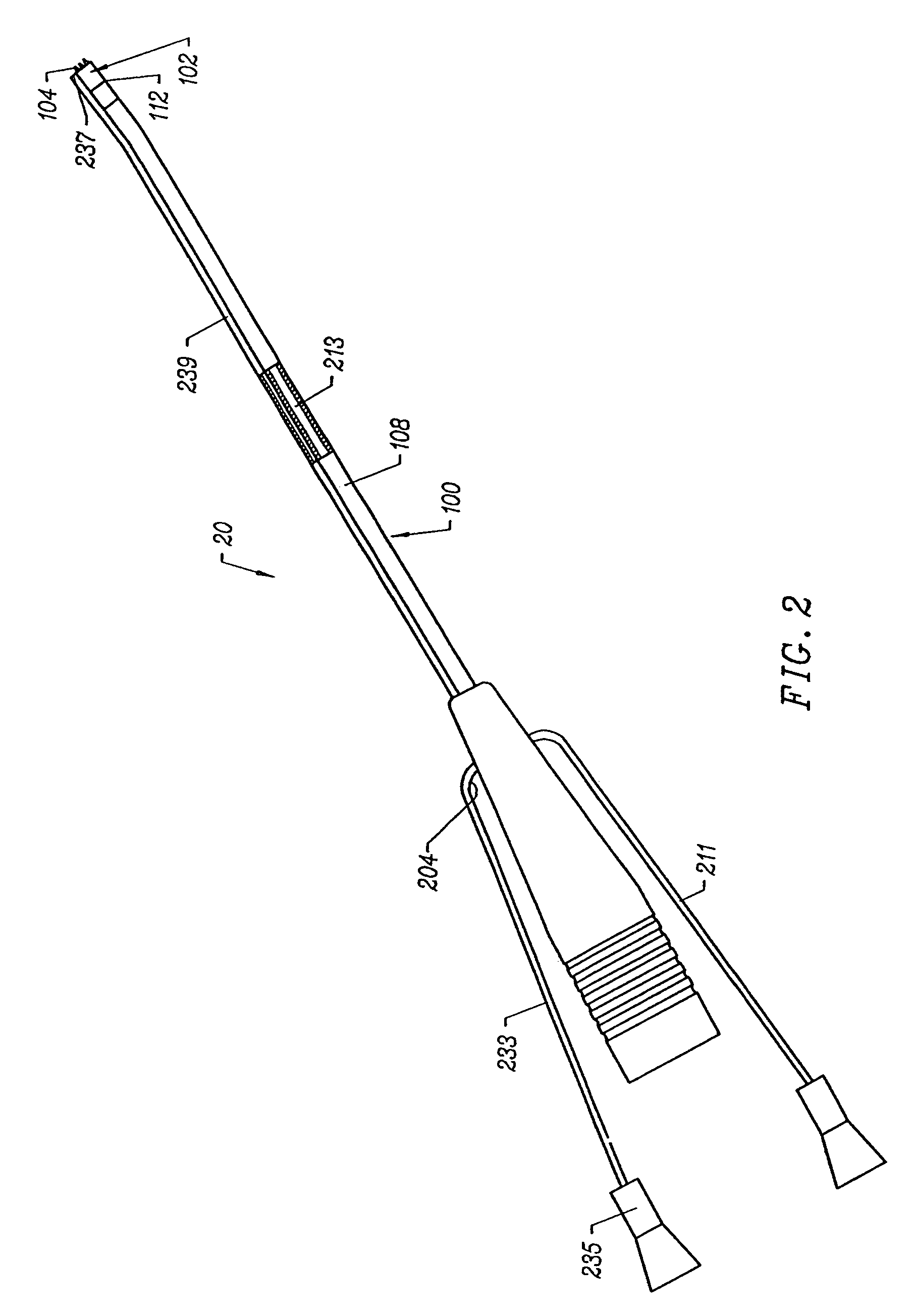
A catheter with a small optical fiber or bundle of fibers includes a scanning mechanism constructed with the use of any vibration capable component. Magnetic, piezoelectric or other mechanisms are used to vibrate the end of the fiber and thus create a scanning effect which extends the field of view. One or more lenses may be utilized, including a lens attached to the distal tip of the image fiber, or a lens attached to the distal tip of the catheter for creating an image plane which can be scanned by the fiber. In one embodiment, multiple light sources may be connected to the fiber for enabling the use of field sequential color techniques for real-time imaging, as well as real-time fluorescent imaging for disease detection. A photodetector assembly connected to the proximal end may contain both filtered and unfiltered detectors for use with both standard imaging and fluorescent imaging. The resulting vision catheter is relatively inexpensive and disposable.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
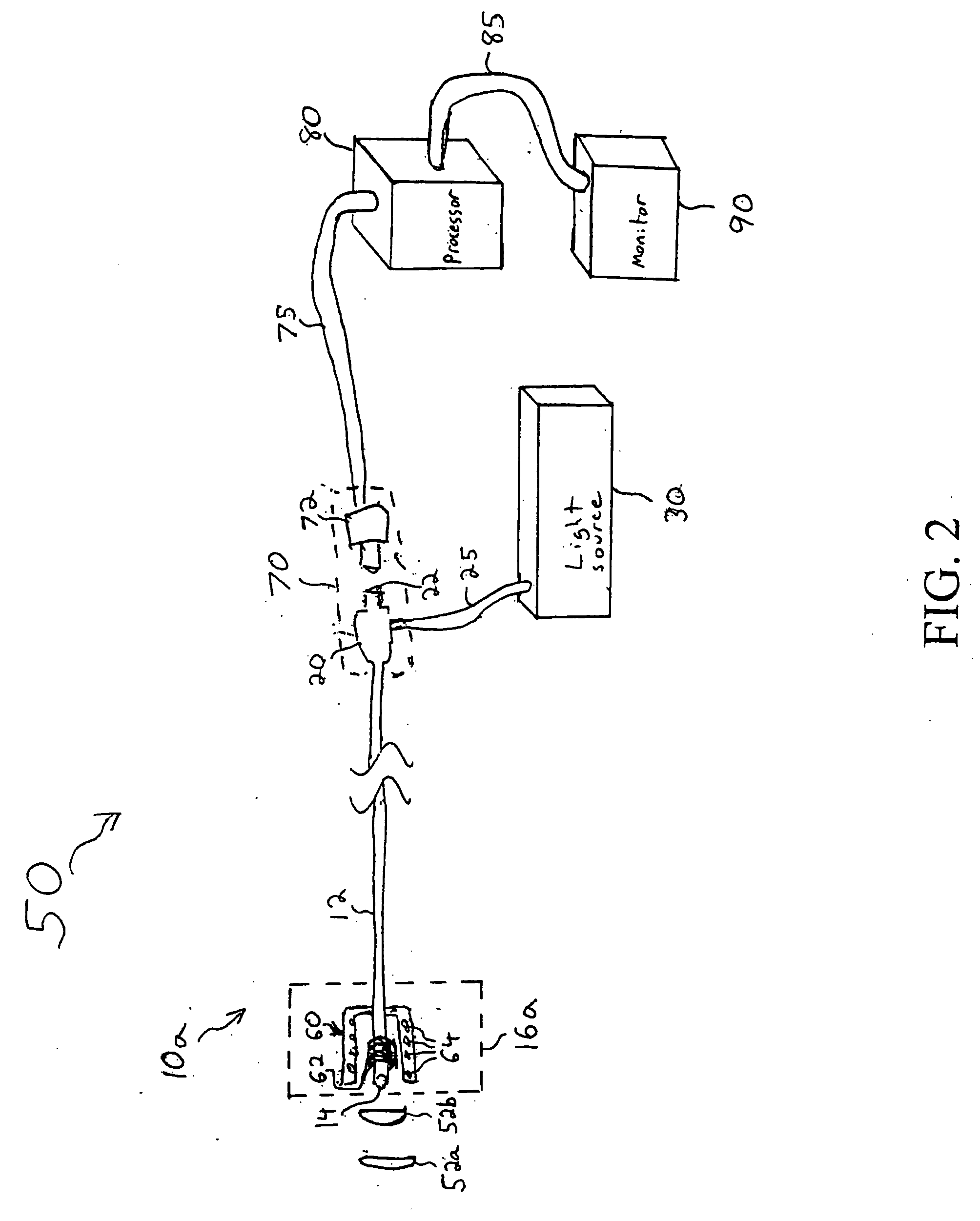
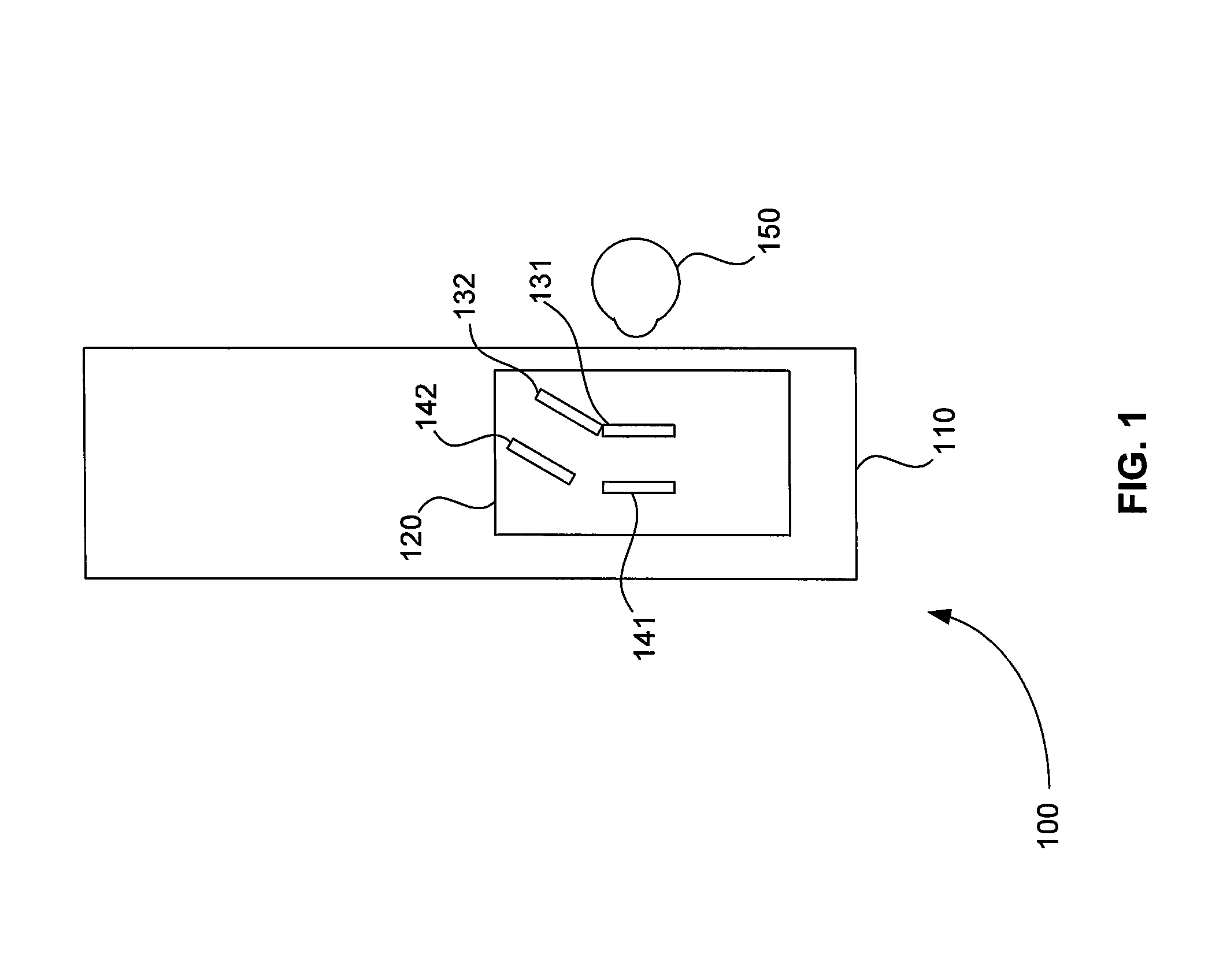
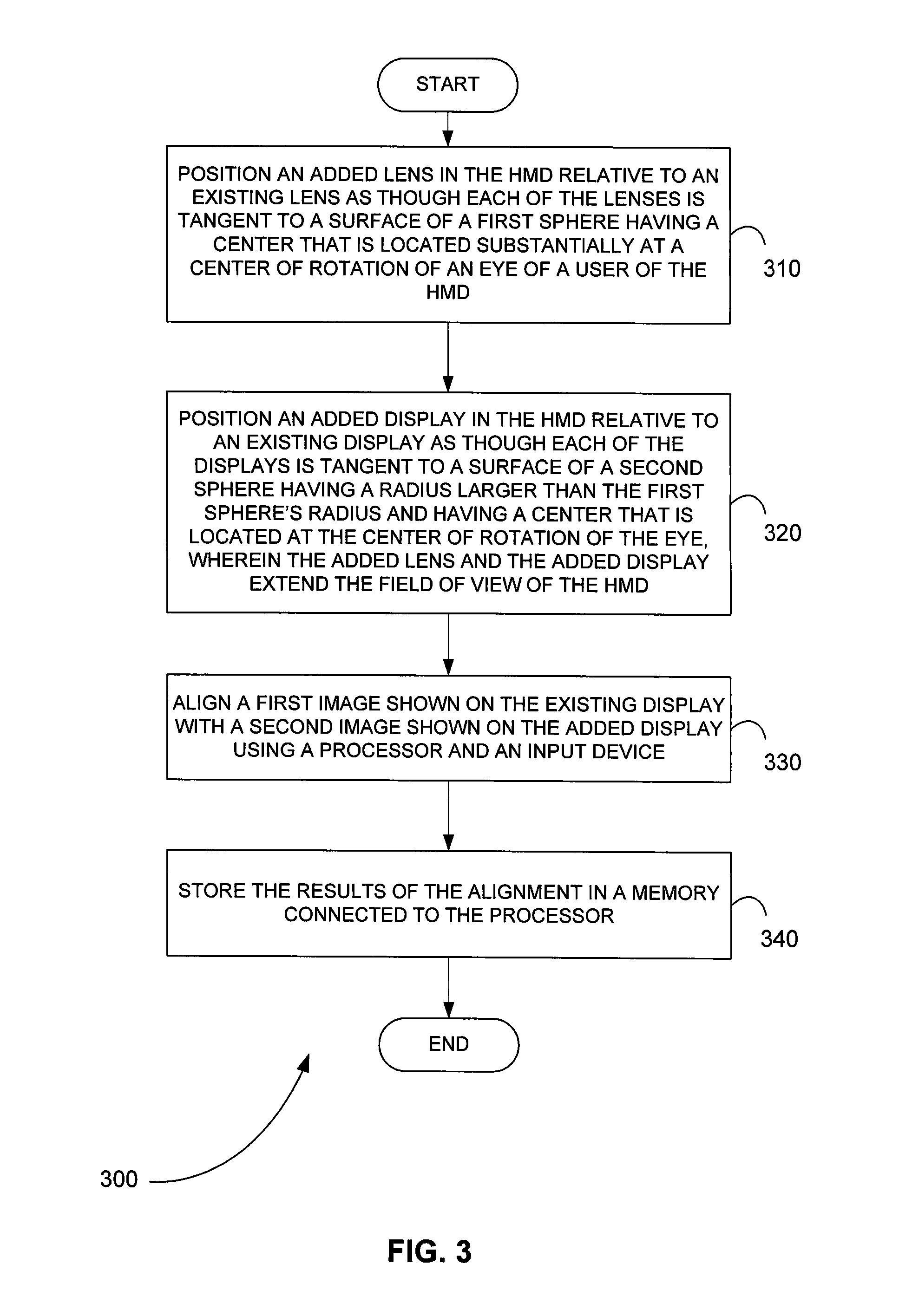
Systems and methods for a head-mounted display
InactiveUS20080106489A1Expand field of viewCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceLens plate
A head-mounted display with an upgradeable field of view includes for at least one eye an existing lens, an existing display, an added lens, and added display. The existing lens and the added lens are positioned relative to one another as though each of the lenses is tangent to the surface of a first sphere having a center that is located substantially at a center of rotation of the eye. The existing display and the added display are positioned relative to one another as though each of the displays is tangent to a surface of a second sphere having a radius larger than the first sphere's radius and having a center that is located at the center of rotation of the eye. A head mount for the head-mounted display includes two parallel rails, one or more brow pads, one or more top pads, and one or more back pads.
Owner:RAZER ASIA PACIFIC
Imaging system and methodology
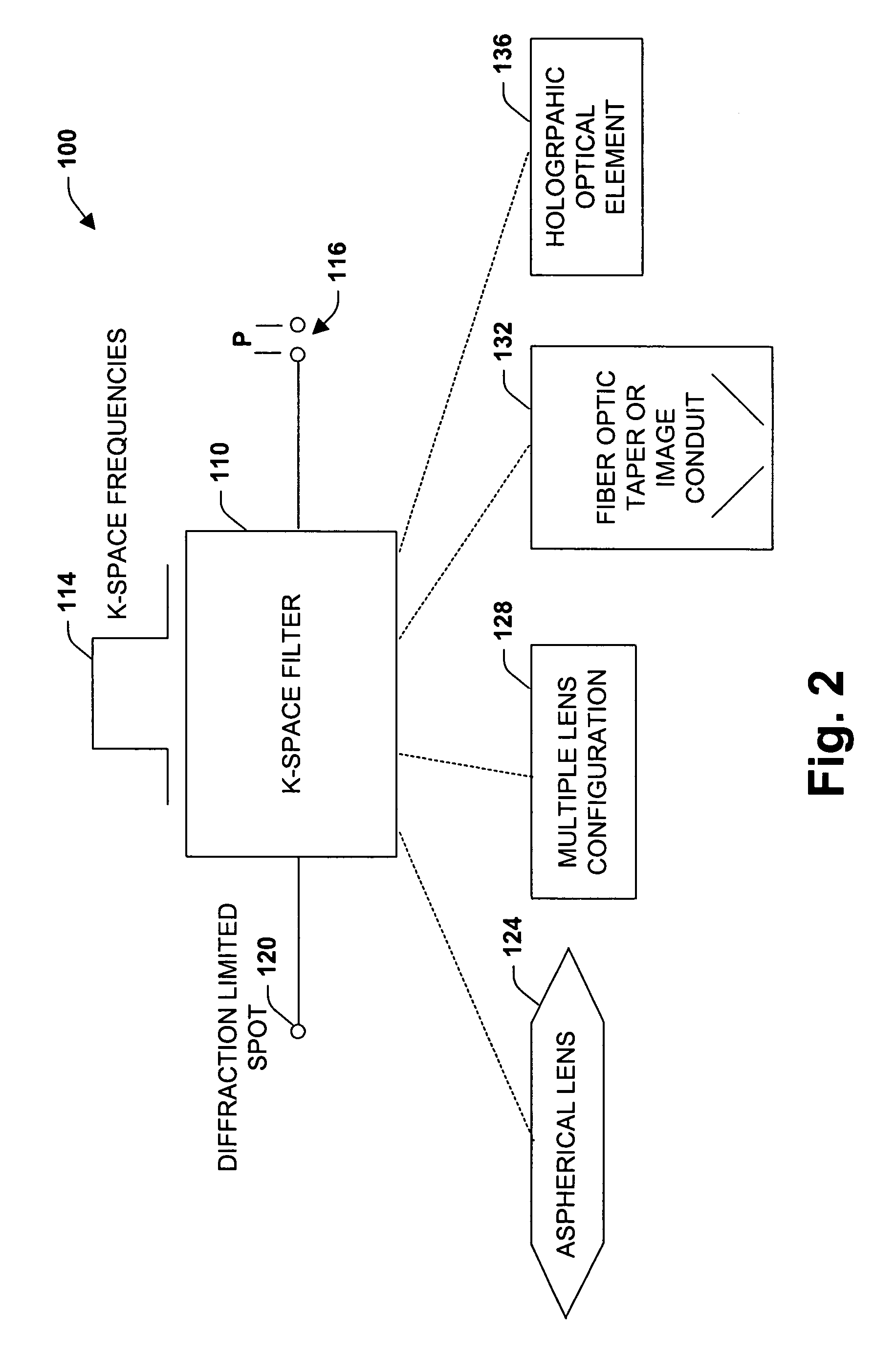
InactiveUS20070139541A1Improve performanceEffectively scaledTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferDisplay device
An imaging system, methodology, and various applications are provided to facilitate optical imaging performance. The system contains a sensor having one or more receptors and an image transfer medium to scale the sensor and receptors in accordance with resolvable characteristics of the medium, and as defined with certain ratios. A computer, memory, and / or display associated with the sensor provides storage and / or display of information relating to output from the receptors to produce and / or process an image, wherein a plurality of illumination sources can also be utilized in conjunction with the image transfer medium. The image transfer medium can be configured as a k-space filter that correlates projected receptor size to a diffraction-limited spot associated with the image transfer medium, wherein the projected receptor size can be unit-mapped within a certain ratio to the size of the diffraction-limited spot, both in the object plane.
Owner:PIXEL MATCHED HLDG
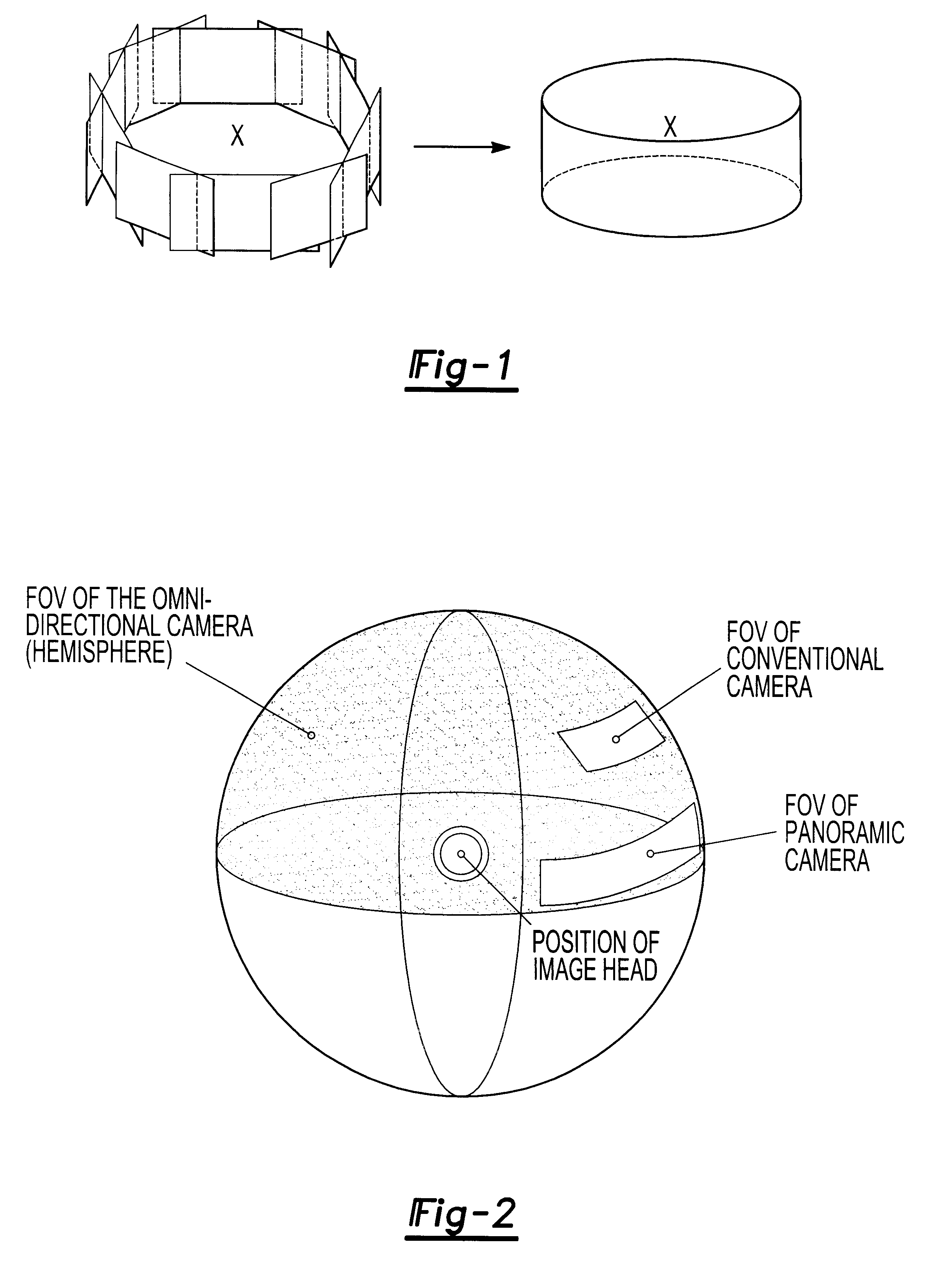
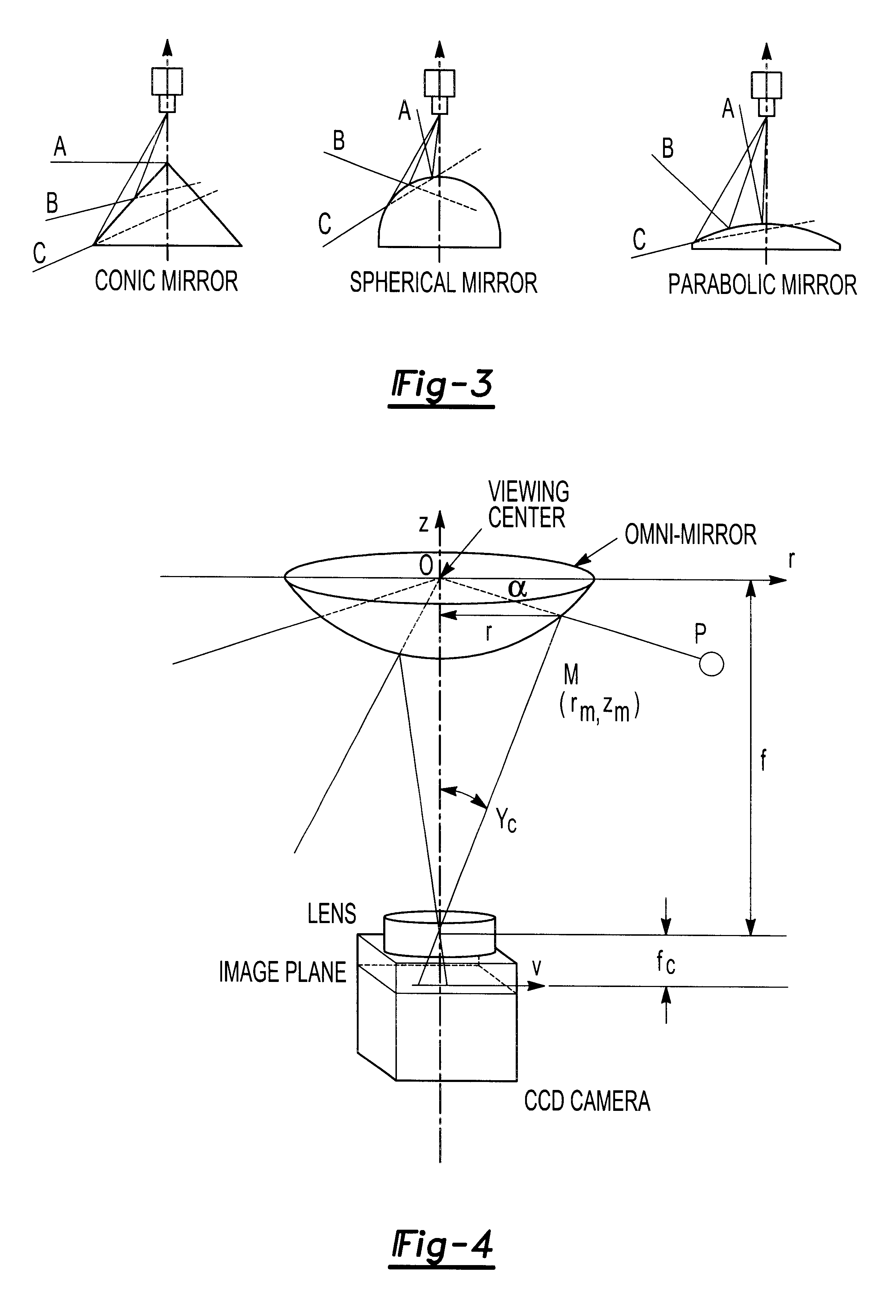
Method and apparatus for omnidirectional imaging
InactiveUS6304285B1Convenient lightingEasy to viewTelevision system detailsImage analysisWavelength filterLight beam
An omnidirectional imaging system comprising a reflective mirror for viewing object within a hemispherical field of view form a single virtual view point at the local center of said reflective mirror, a projector for projecting a light beam toward said reflective mirror, and a variable wavelength filter optically positioned between said projector and said reflective mirror for generating a pattern having a spatially distributed wavelength spectrum of said reflective mirror, where a generator responsive to the hemispherical image data for generating three-dimensional image.
Owner:TECHNEST HLDG
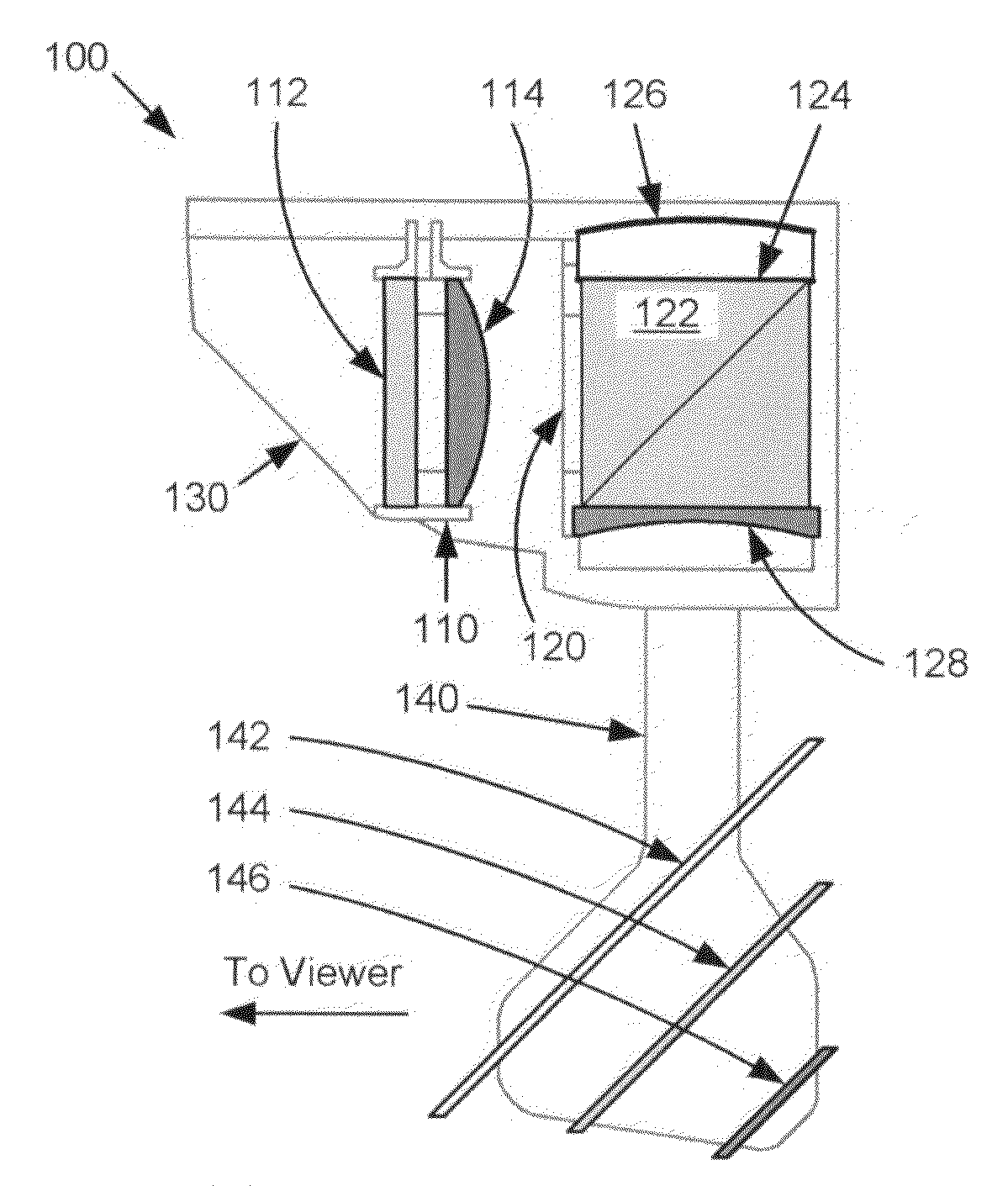
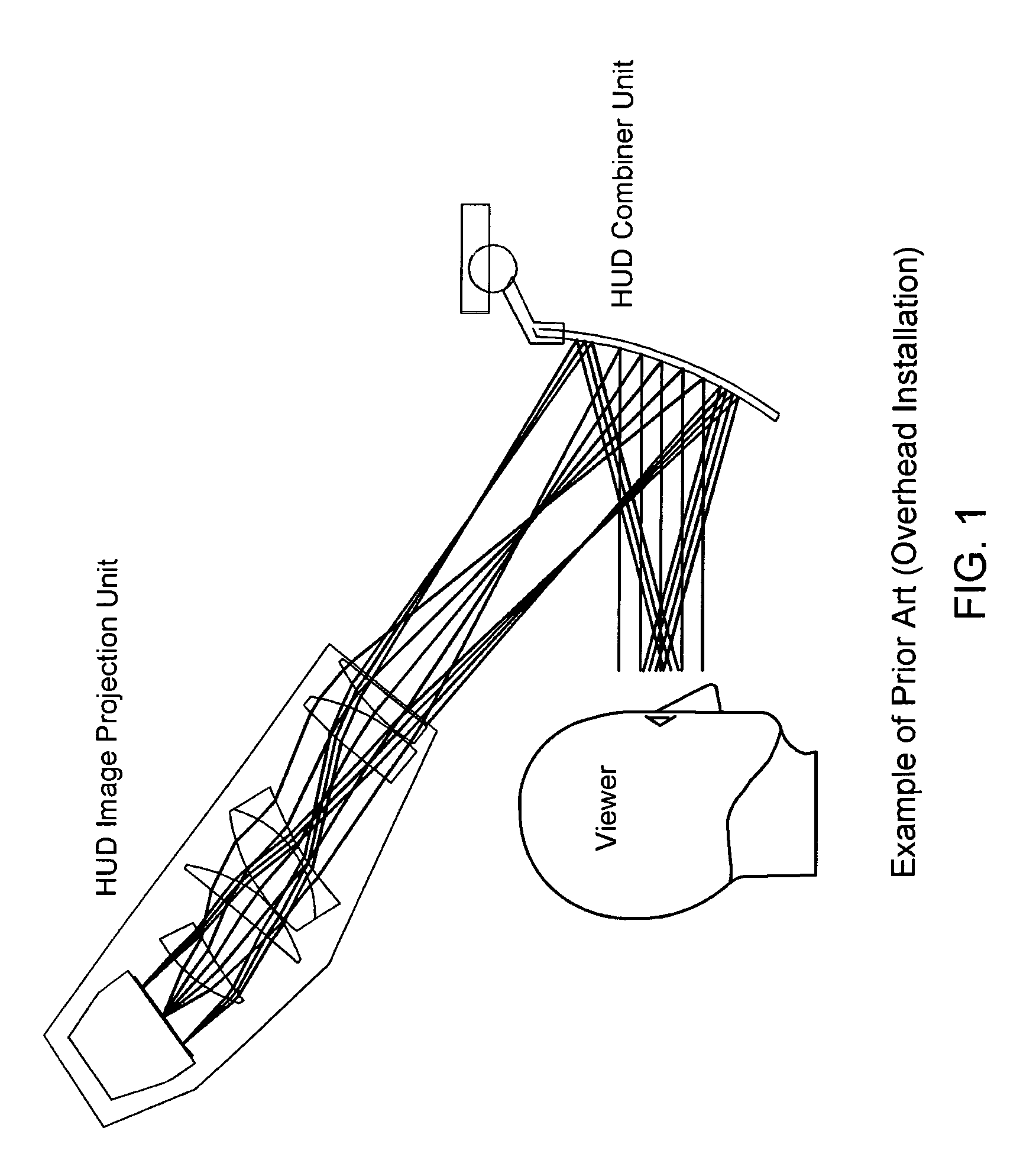
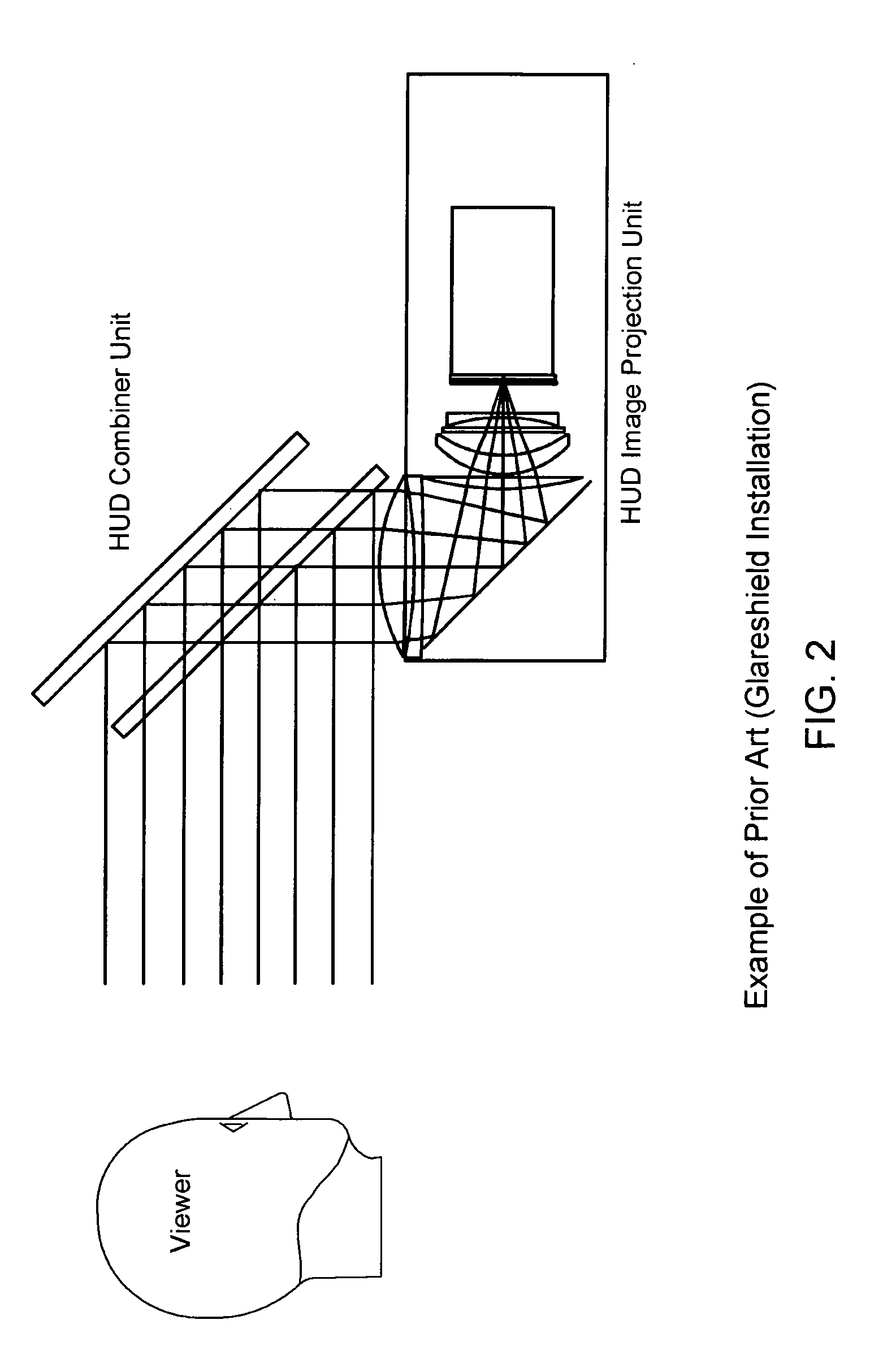
Catadioptric system, apparatus, and method for producing images on a universal, head-up display
A present novel and non-trivial system, apparatus, and method for employing a catadioptric optical system in a Head-Up Display (“HUD”) system are disclosed. A catadioptric optical module is configured to produce a large image size within a small space envelope by folding the optical path back through module and separating the paths by use of a beam splitter. Such module comprised of a beam splitter, collimating mirror, and correcting lens produces collimated beams of light from an image source providing either polarized or non-polarized beams of light. If polarized beams are provided, the module includes a quarter-wave retarder, and the configuration of the module permits the image source to provide either s-polarized or p-polarized beams. A combiner arm assembly comprising of at least one combiner receives the collimated beams, where the employment of a plurality of combiners extends the relatively small instantaneous field of view.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
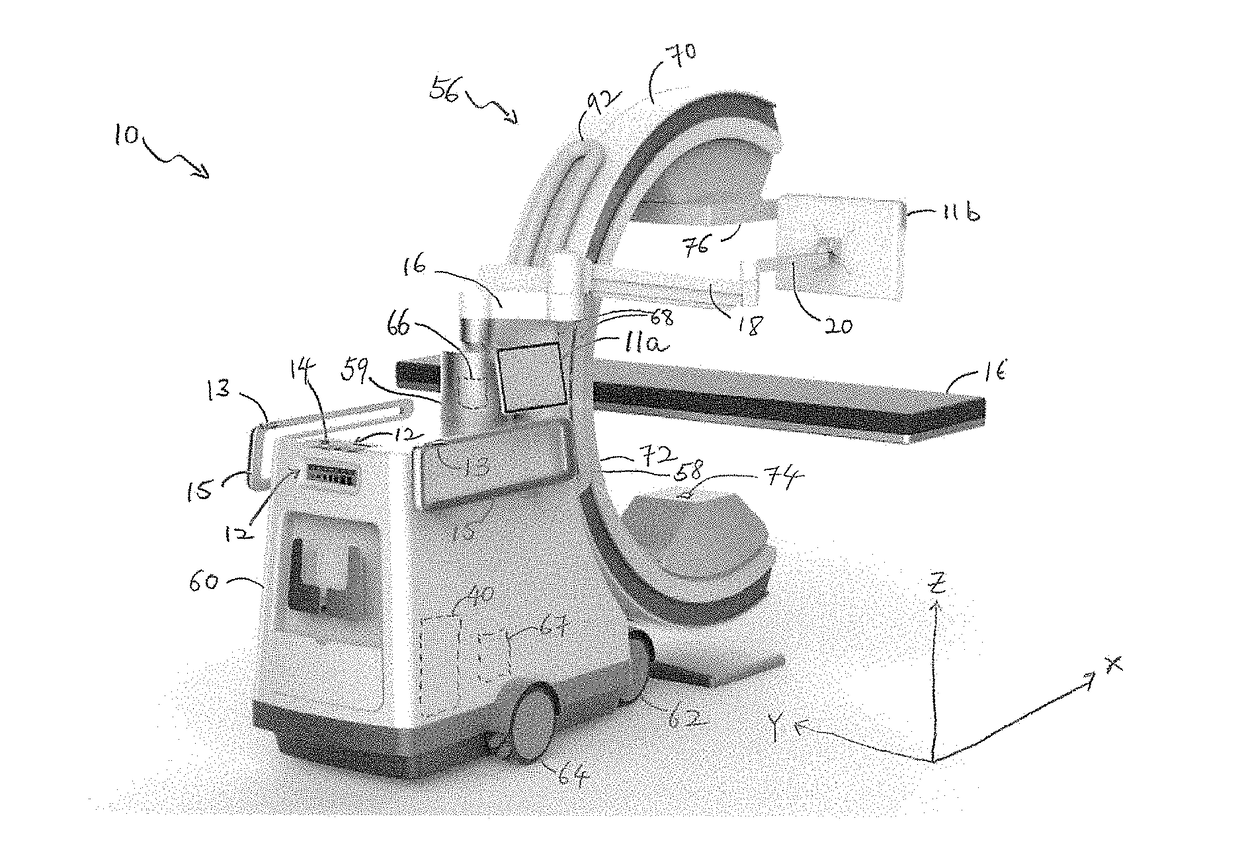
Gantry positioning apparatus for X-ray imaging
InactiveUS7338207B2Expand field of viewMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
A robotically controlled five degree-of-freedom x-ray gantry positioning apparatus, which is connected to a mobile cart, ceiling, floor, wall, or patient table, is being disclosed. The positioning system can be attached to a cantilevered o-shaped or c-shaped gantry. The positioning system can precisely translate the attached gantry in the three orthogonal axes X-Y-Z and orient the gantry about the X-axis and Y-axis while keeping the center of the gantry fixed, (see FIG. 1). The positioning apparatus provides both iso-centric and non iso-centric “Tilt” and “Wag” rotations of the gantry around the X-axis and Y-axis respectively. The iso-centric “Wag” rotation is a multi-axis combination of two translations and one rotation. Additionally, a field of view larger than that provided by the detector is provided in pure AP (anterior / posterior) and lateral detector positions through additional combinations of multi-axis coordinated motion. Each axis can be manually controlled or motorized with position feedback to allow storage of gantry transformations. Motorized axes enable the gantry to quickly and accurately return to preset gantry positions and orientations.A system and method for enlarging the field of view of the object being imaged combines a rotation of the x-ray source and detector with a multi-axis translation of the gantry.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
In-vivo sensing system
ActiveUS20060004255A1Easy to changeReduce frictionSurgeryPerson identificationSurgical siteEngineering
An in-vivo sensing system incorporating a sensing device movably disposed within a housing such that the orientation of the sensing device may be moved or changed in response to substantially small forces. The in-vivo sensing device may bc ingested and may naturally traverse a lumen such as the GI tract or may be anchored at a surgical site. In a preferred embodiment, the in vivo sensing system is an imaging system (100) incorporating a sensing device such as an imaging device (112) suspended in a liquid (114) encapsulated in an covering or housing (110).
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
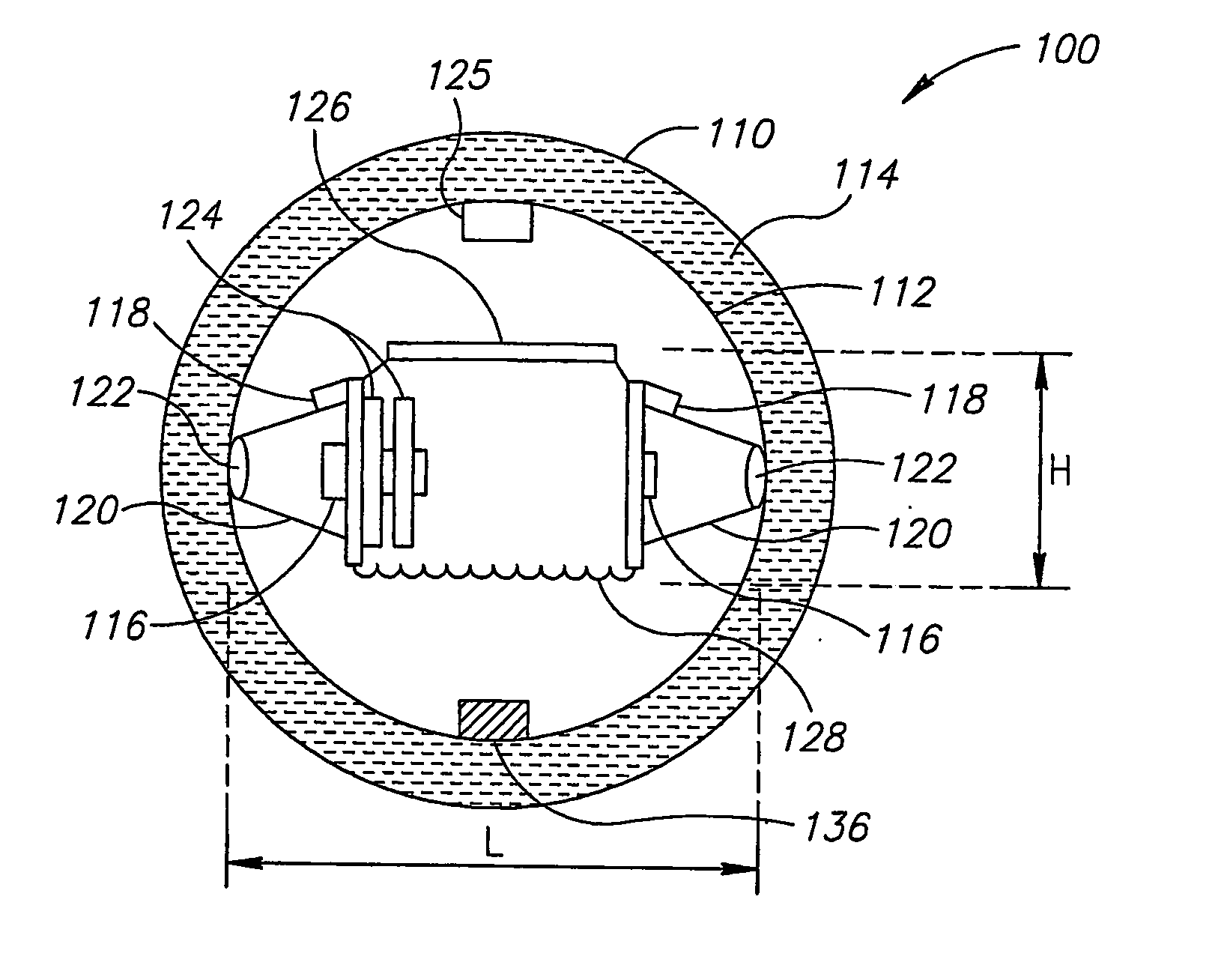
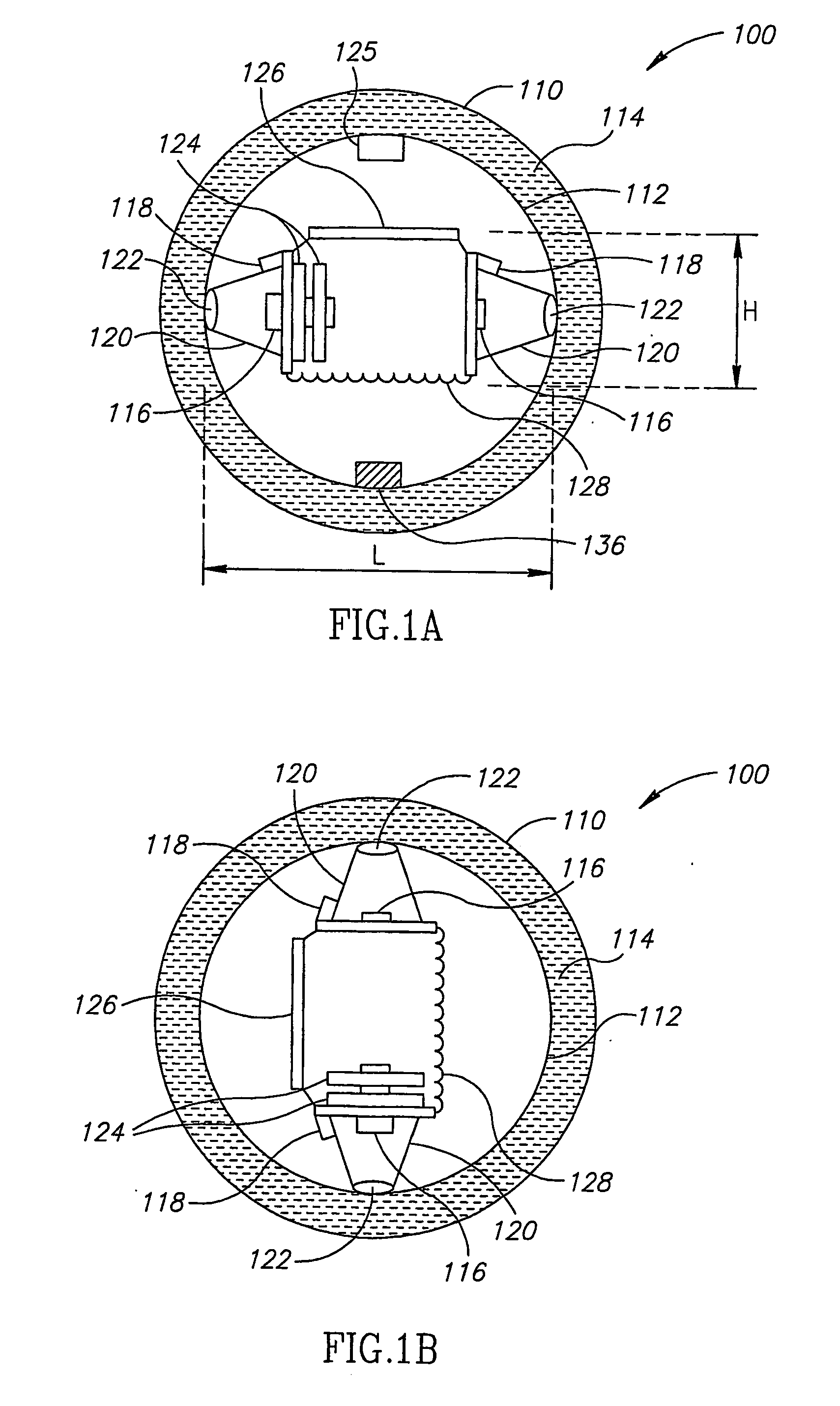
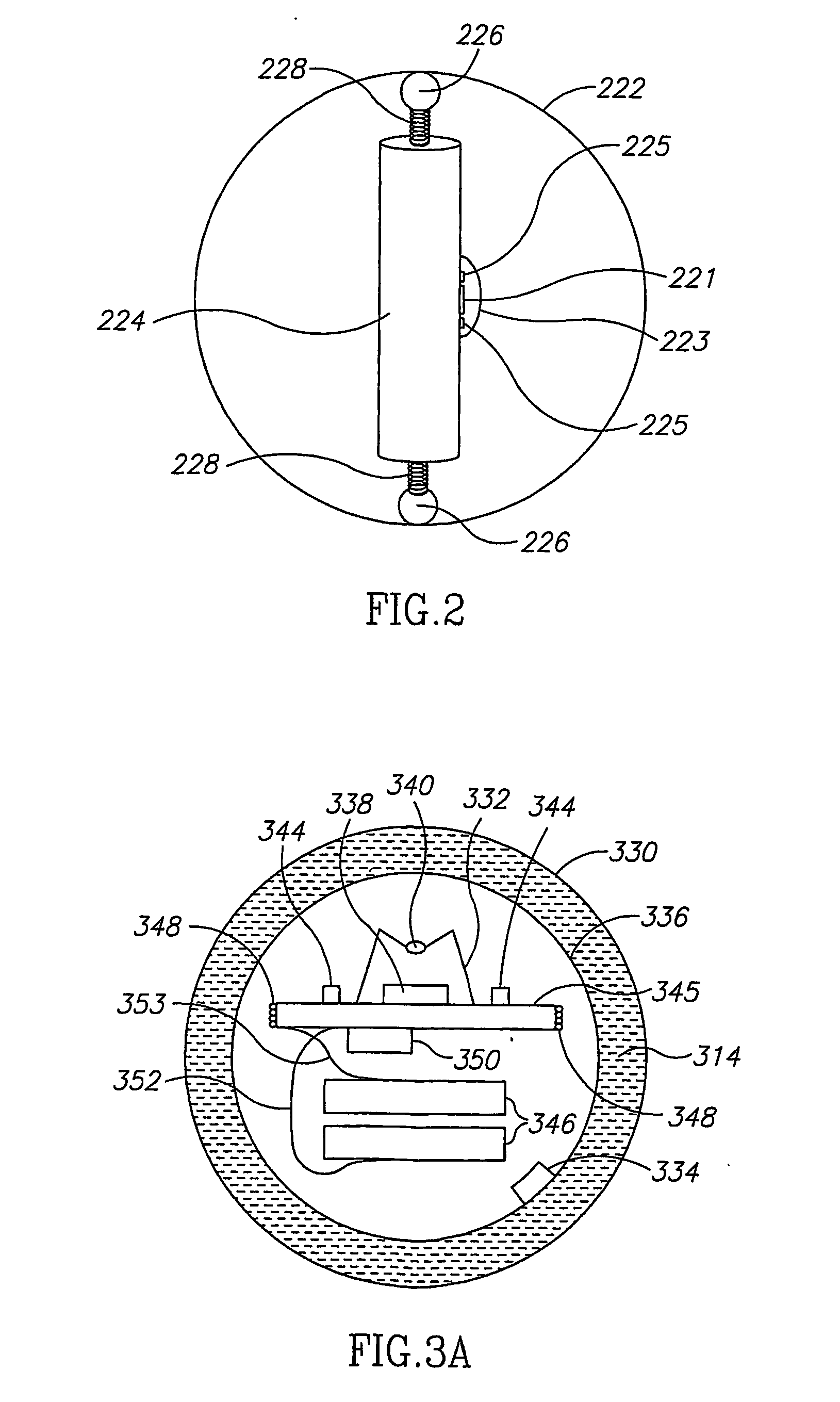
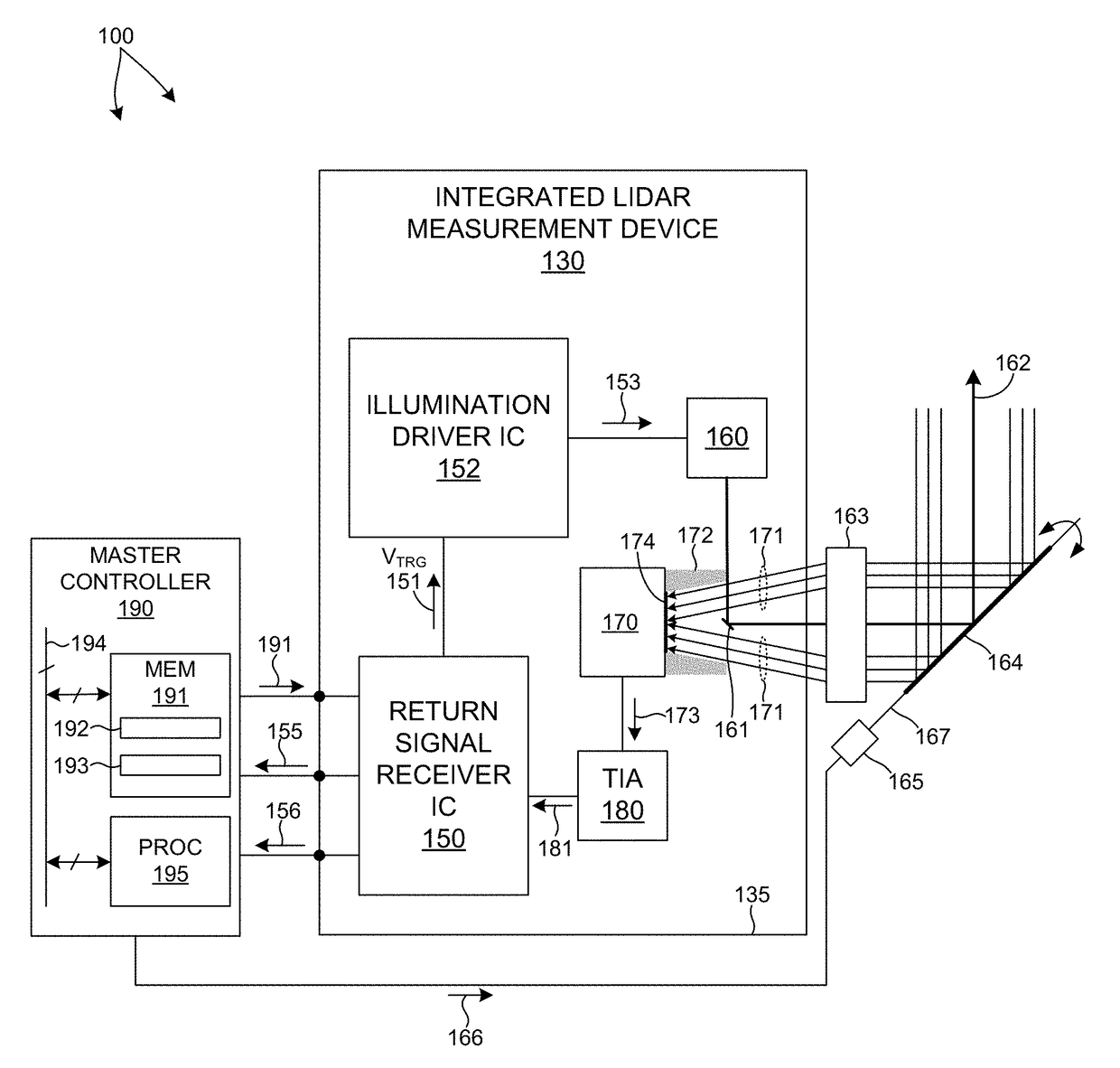
Multiple Pixel Scanning LIDAR
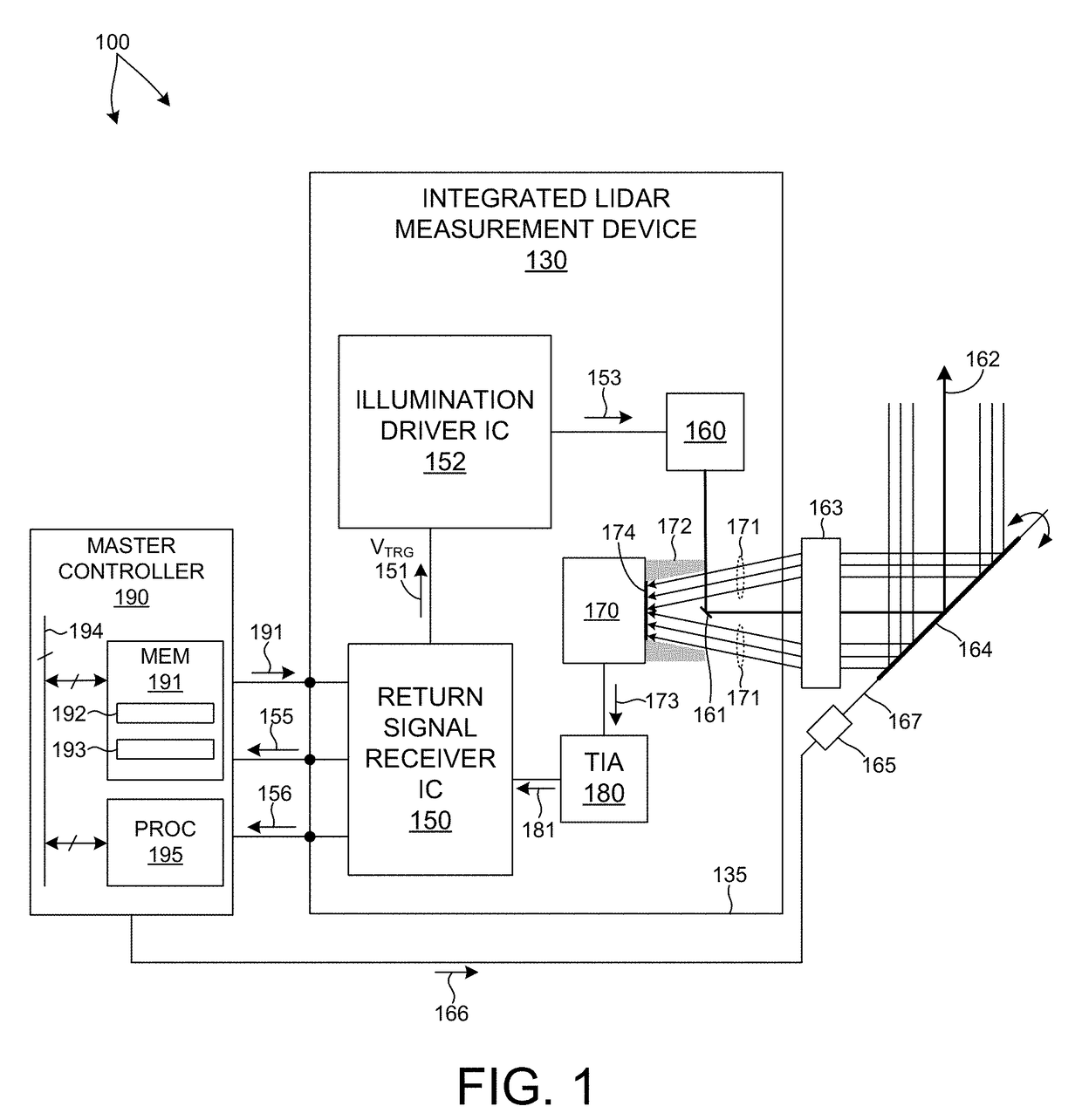
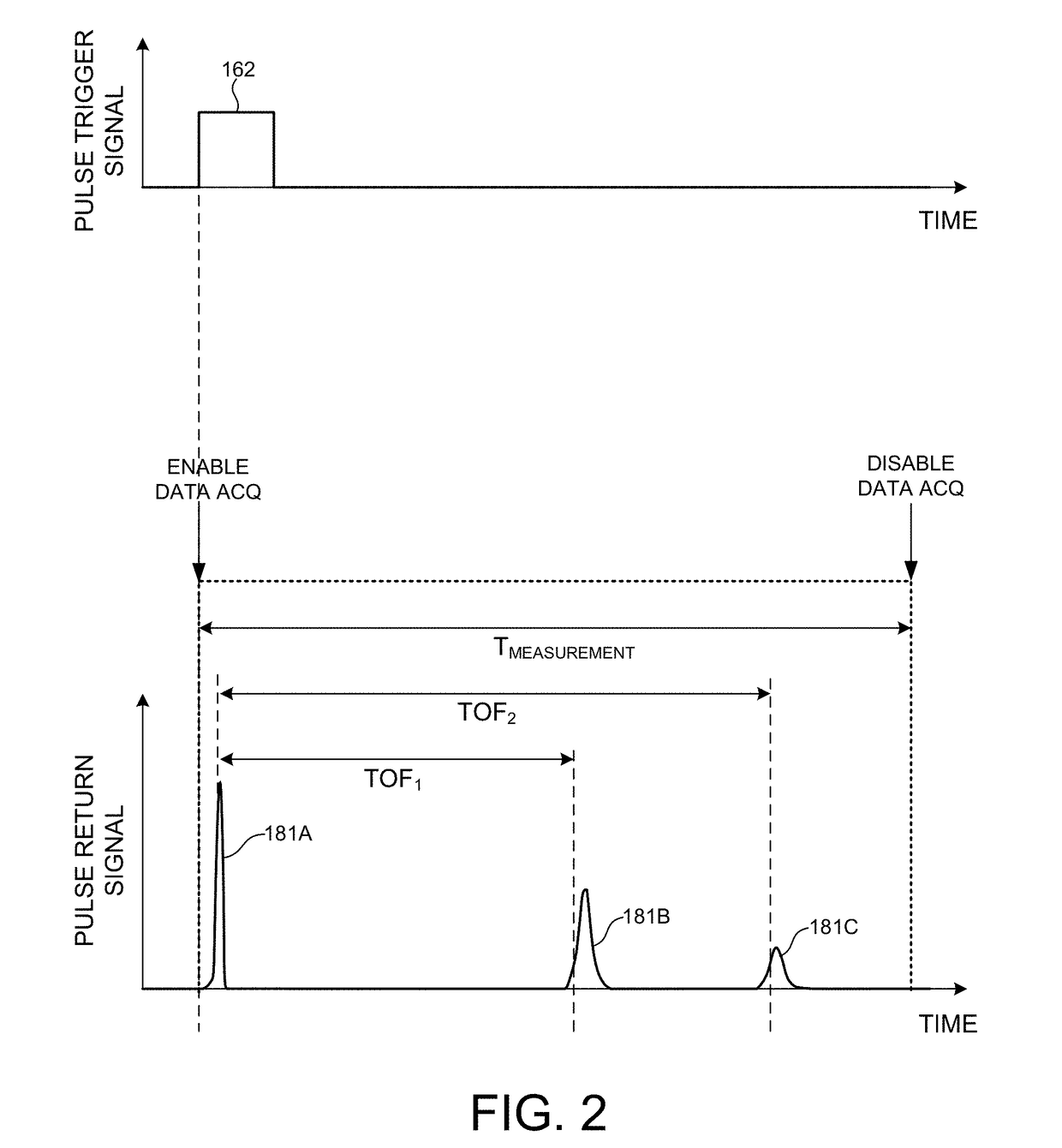
ActiveUS20170350983A1Expand field of viewIncrease sampling densityOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorBeam scanning
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with multiple illumination beams scanned over a three dimensional environment are described herein. In one aspect, illumination light from each LIDAR measurement channel is emitted to the surrounding environment in a different direction by a beam scanning device. The beam scanning device also directs each amount of return measurement light onto a corresponding photodetector. In some embodiments, a beam scanning device includes a scanning mirror rotated in an oscillatory manner about an axis of rotation by an actuator in accordance with command signals generated by a master controller. In some embodiments, the light source and photodetector associated with each LIDAR measurement channel are moved in two dimensions relative to beam shaping optics employed to collimate light emitted from the light source. The relative motion causes the illumination beams to sweep over a range of the three dimensional environment under measurement.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com