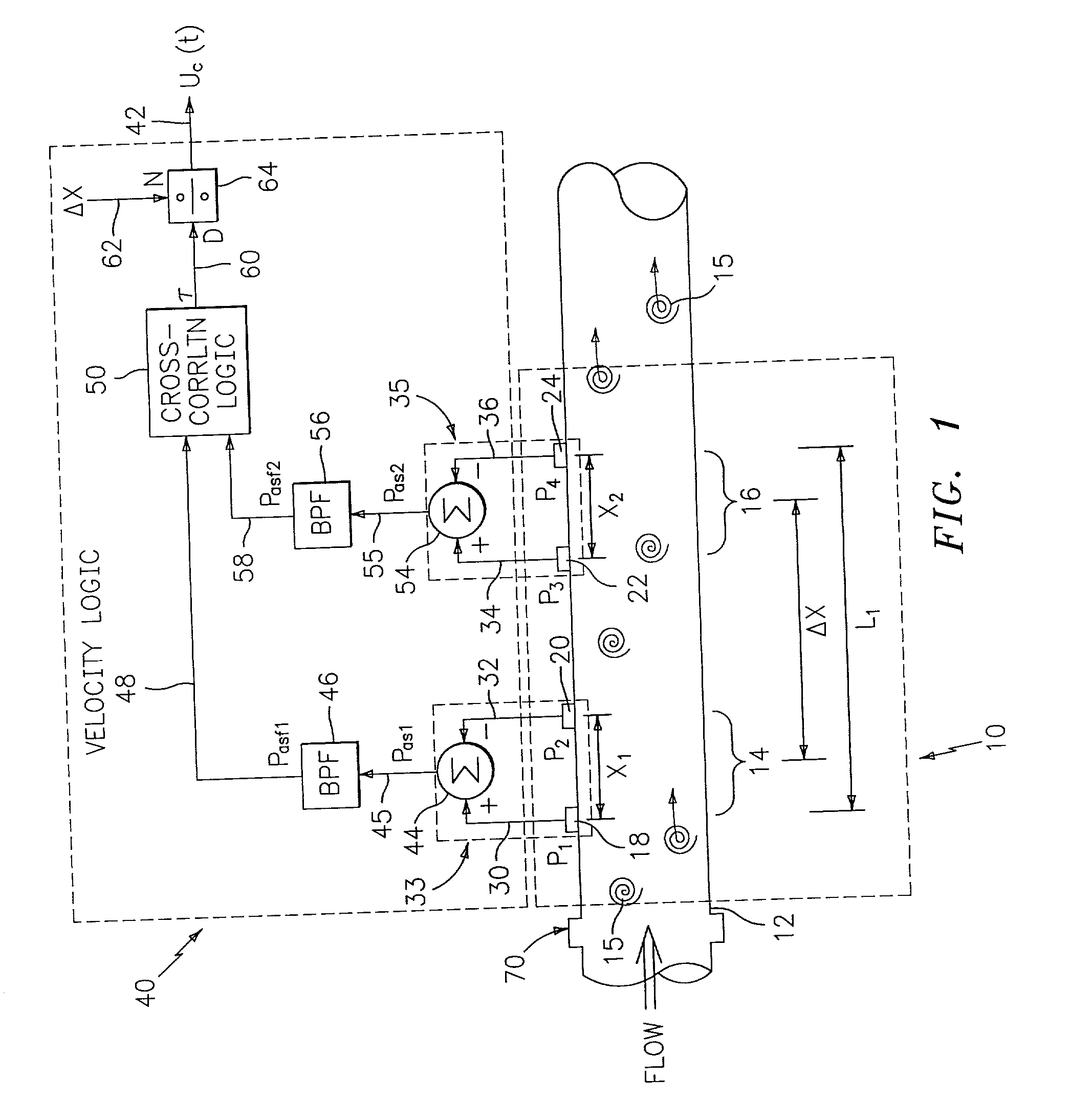Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
343 results about "Wavelength filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
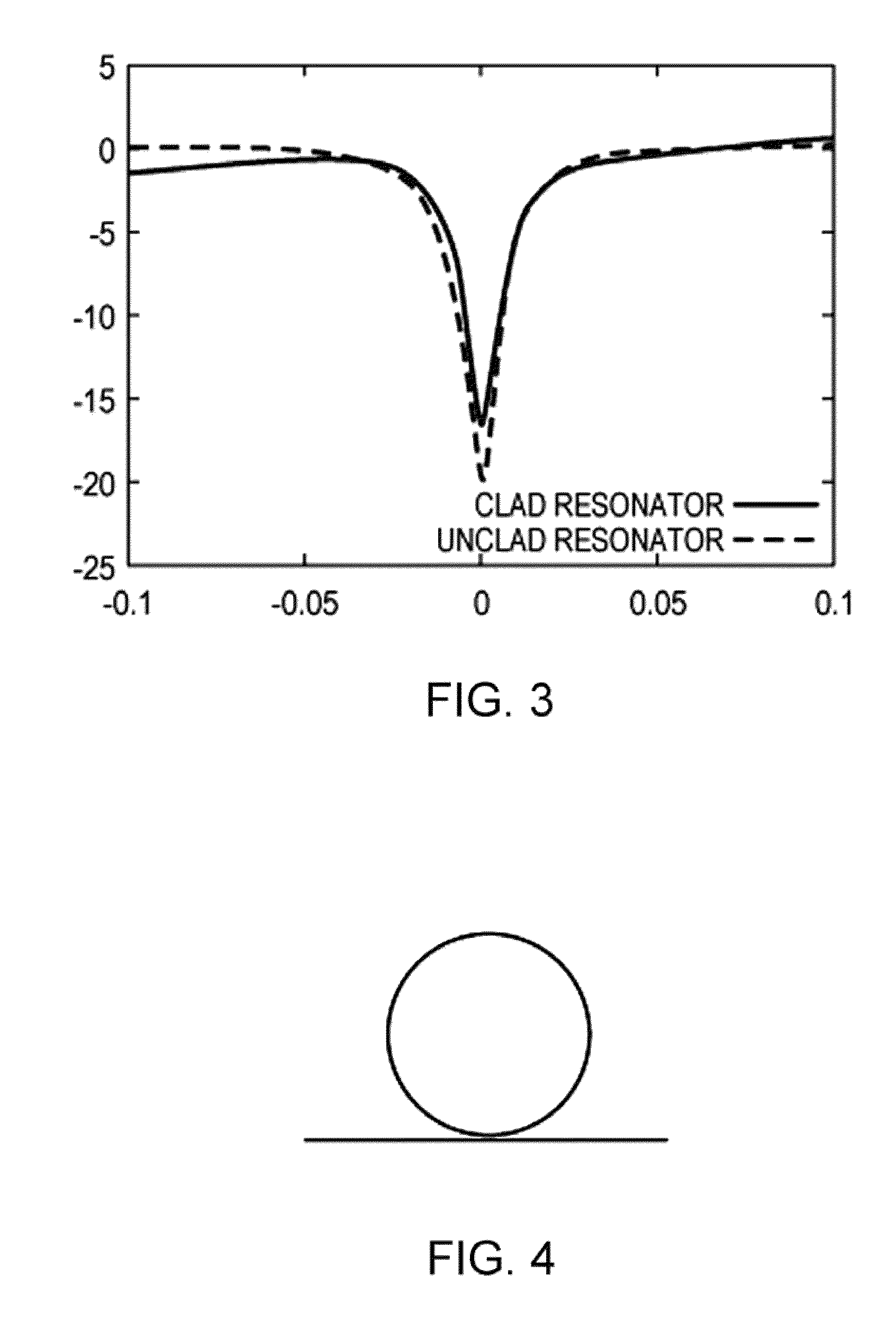
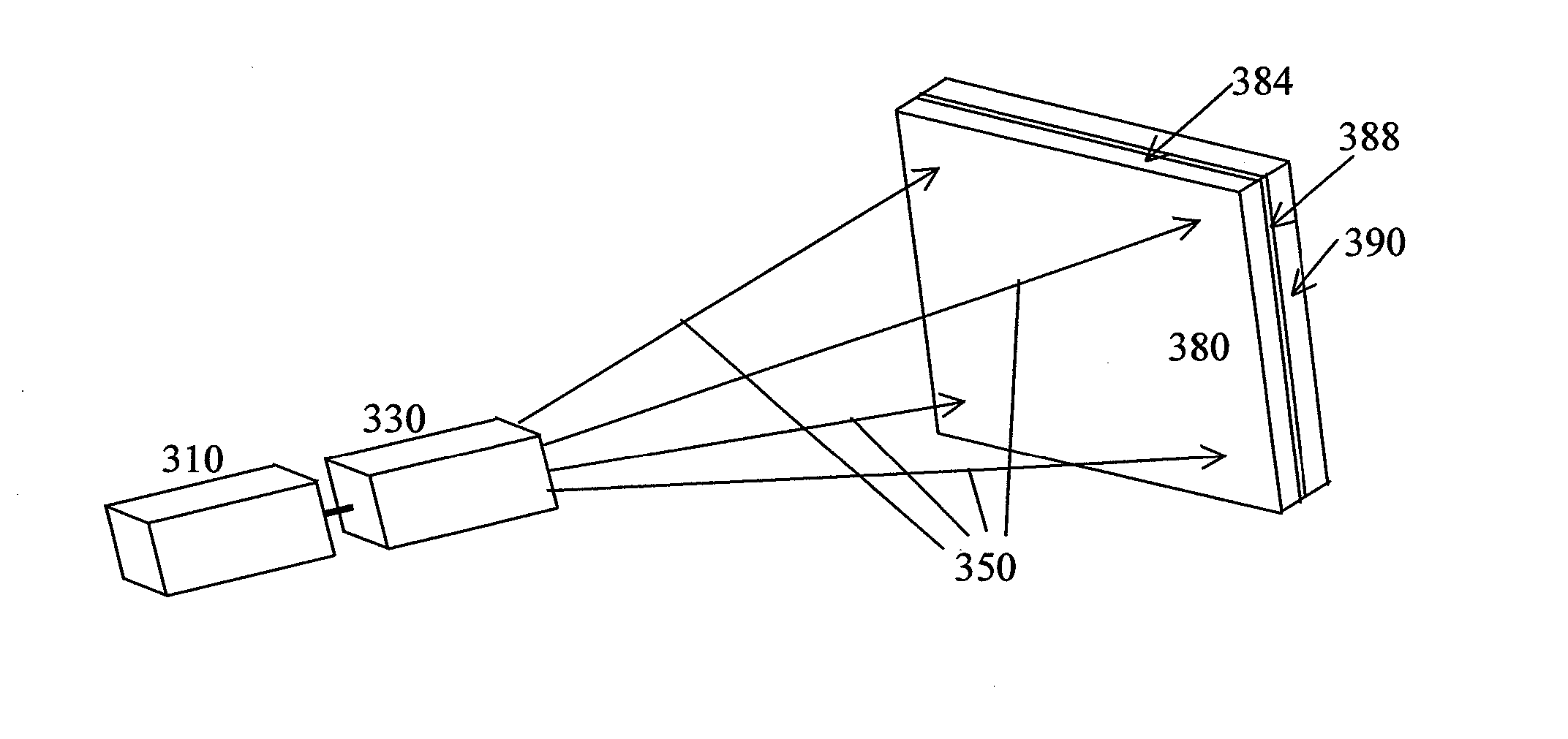
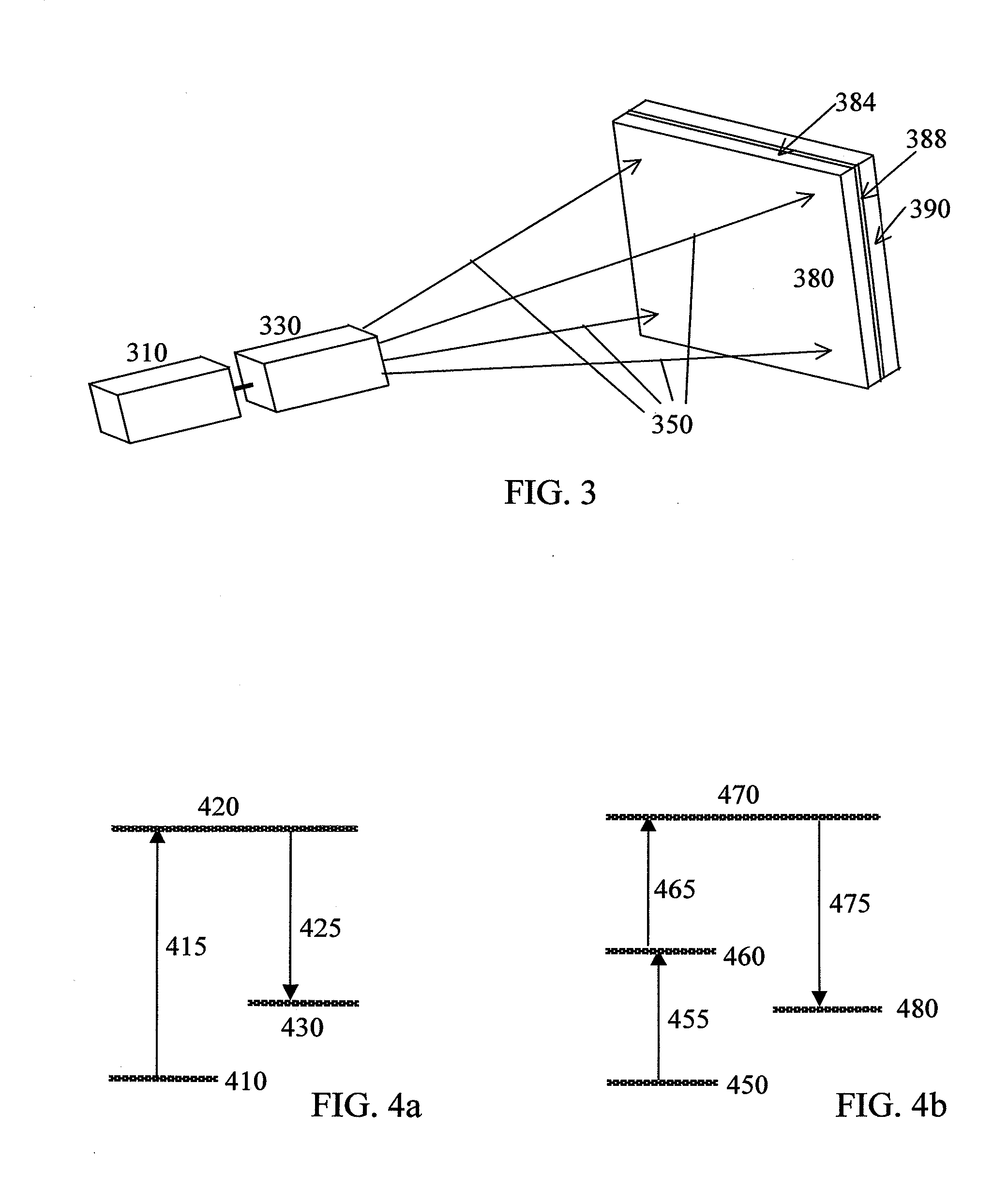
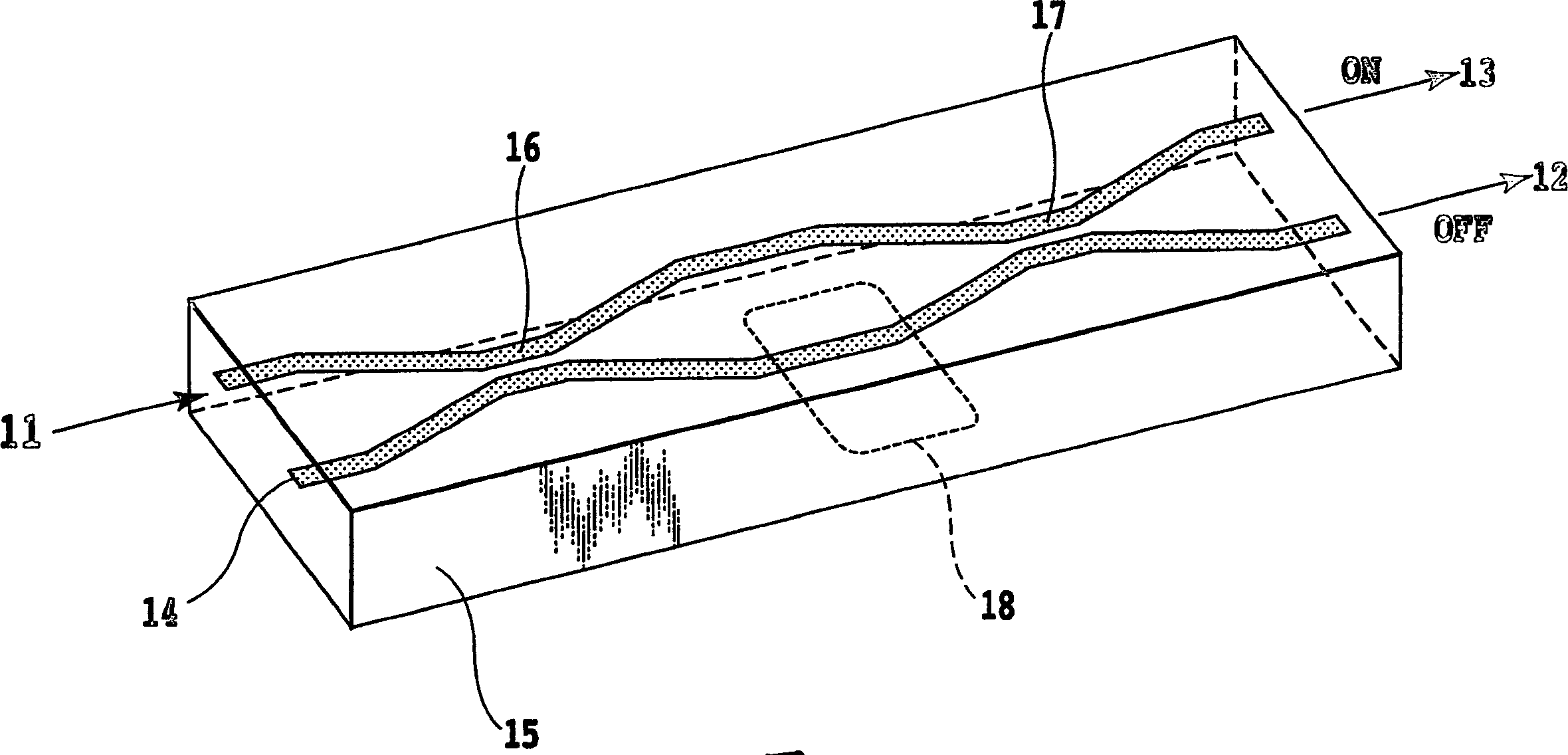
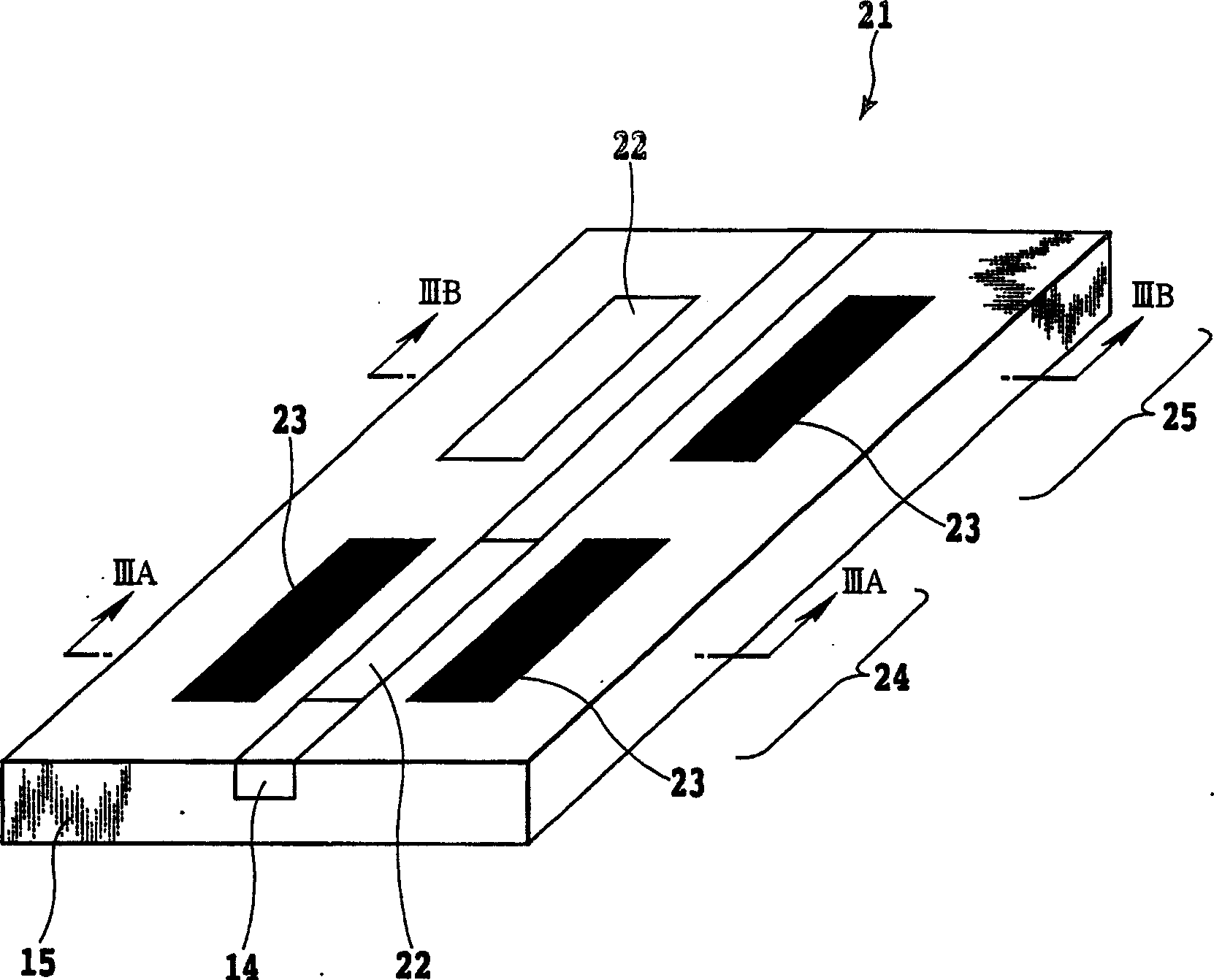
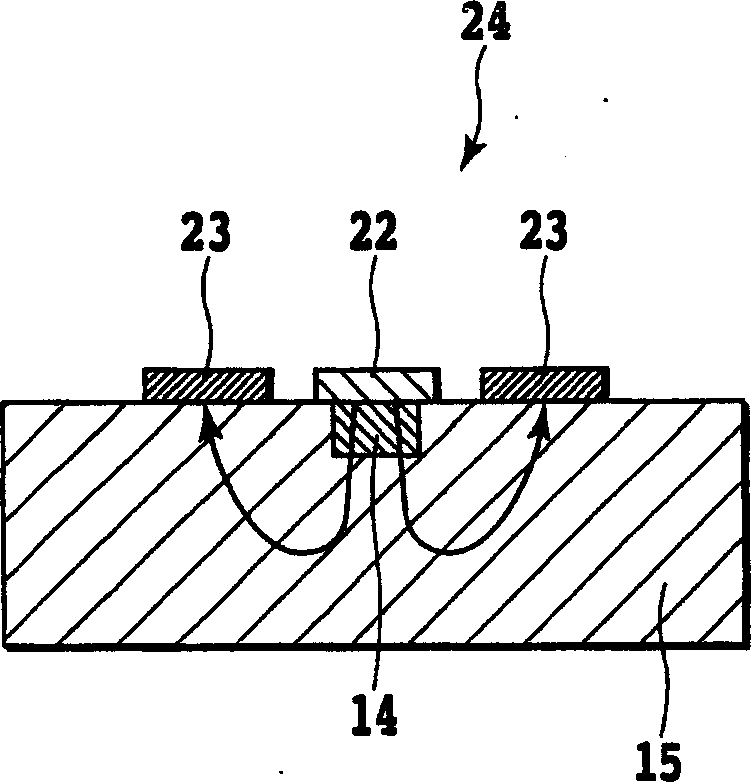
Filters can be made at any given wavelength from near ultraviolet to near infrared. Short pass filters block a select band of longer wavelengths. This example, short pass filters block a select band of longer wavelengths. Short wave pass cutoff filter passes light from 325-450nm and blocks visible light from 500-700nm.
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Integrated Biometric Sensing and Display Device
InactiveUS20120271121A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyBiometric dataWavelength filter
A biometric device configured to be attached to a portion of a body of a user measures biometric data of the user. The device includes an optical emitter, a wavelength filter, an optical sensor and a processor, for sending a light to the body of a user, receiving light received from the user, filtering and processing it to measure biometric data of the user, including for example, heart rate and blood flow rate. In addition, the biometric device may include other sensors, such as a galvanic skin response sensor, an ambient temperature sensor, skin temperature, motion sensor, etc., to enable the biometric device to measure arousal or conductivity changing events, ambient temperature, user temperature and motion associated with the user. Additionally, information from each sensor may be used to further filter noise in one or more signals received by the sensors to provide biometric data to the user.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nano particles and molecules
ActiveUS7090355B2Avoid viewingDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsColor imageWavelength filter
A system and a method of a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion (FC) of nano-particles and molecules are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a color image display system consists of a light source equipped with two-dimensional scanning hardware and a FC display screen board. The FC display screen board consists of a transparent fluorescence display layer, a wavelength filtering coating, and an absorption substrate. In another preferred embodiment, two mechanisms of light excitation are utilized. One of the excitation mechanisms is up-conversion where excitation light wavelength is longer than fluorescence wavelength. The second mechanism is down-conversion where excitation wavelength is shorter than fluorescence wavelength. A host of preferred fluorescence materials for the FC screen are also disclosed. These materials fall into four categories: inorganic nanometer sized phosphors; organic molecules and dyes; semiconductor based nano particles; and organometallic molecules. These molecules or nano-particles are incorporated in the screen in such a way that allows the visible transparency of the screen. Additionally, a preferred fast light scanning system is disclosed. The preferred scanning system consists of dual-axes acousto-optic light deflector, signal processing and control circuits equipped with a close-loop image feedback to maintain position accuracy and pointing stability of the excitation beam.
Owner:SUN INNOVATIONS
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
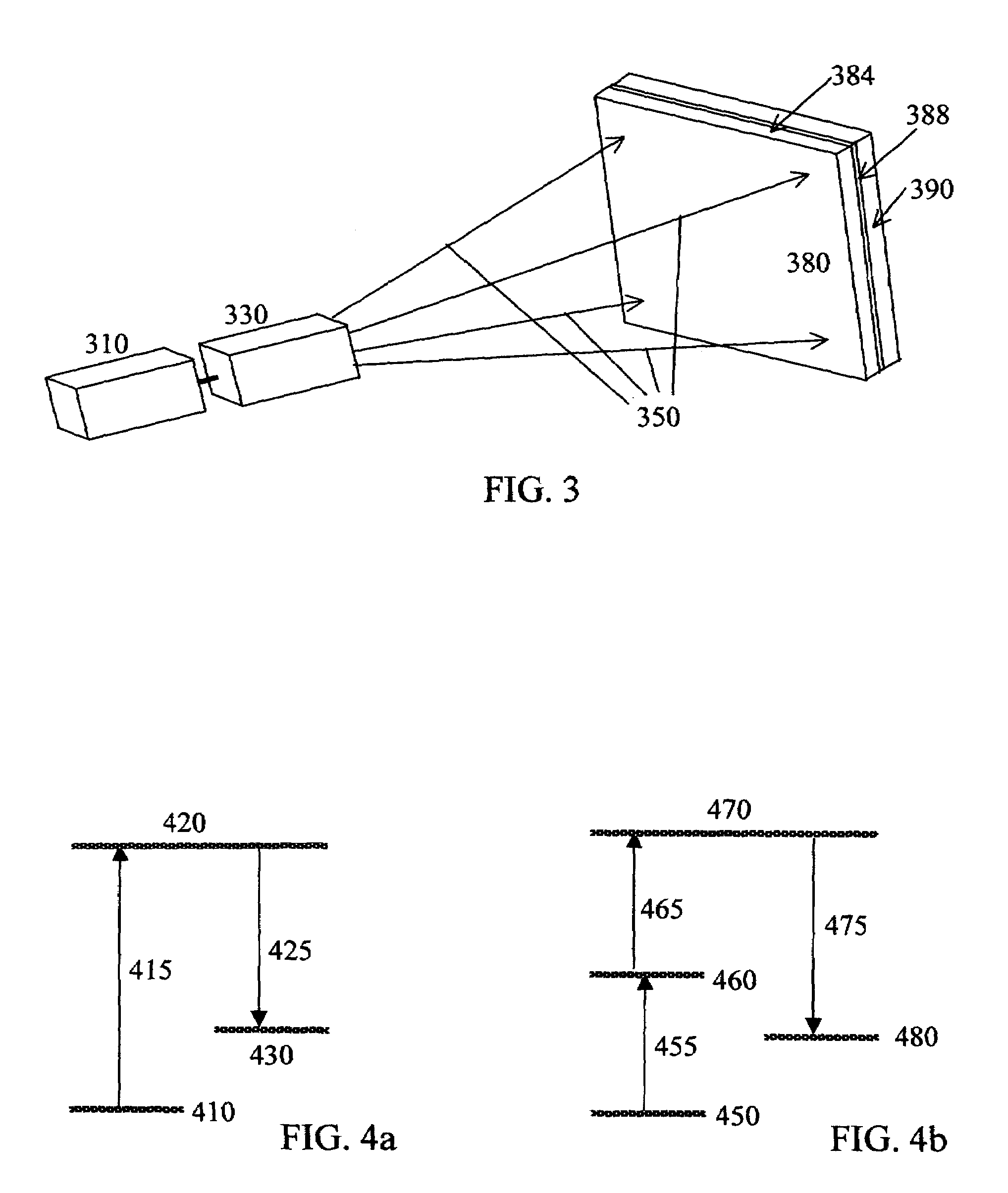
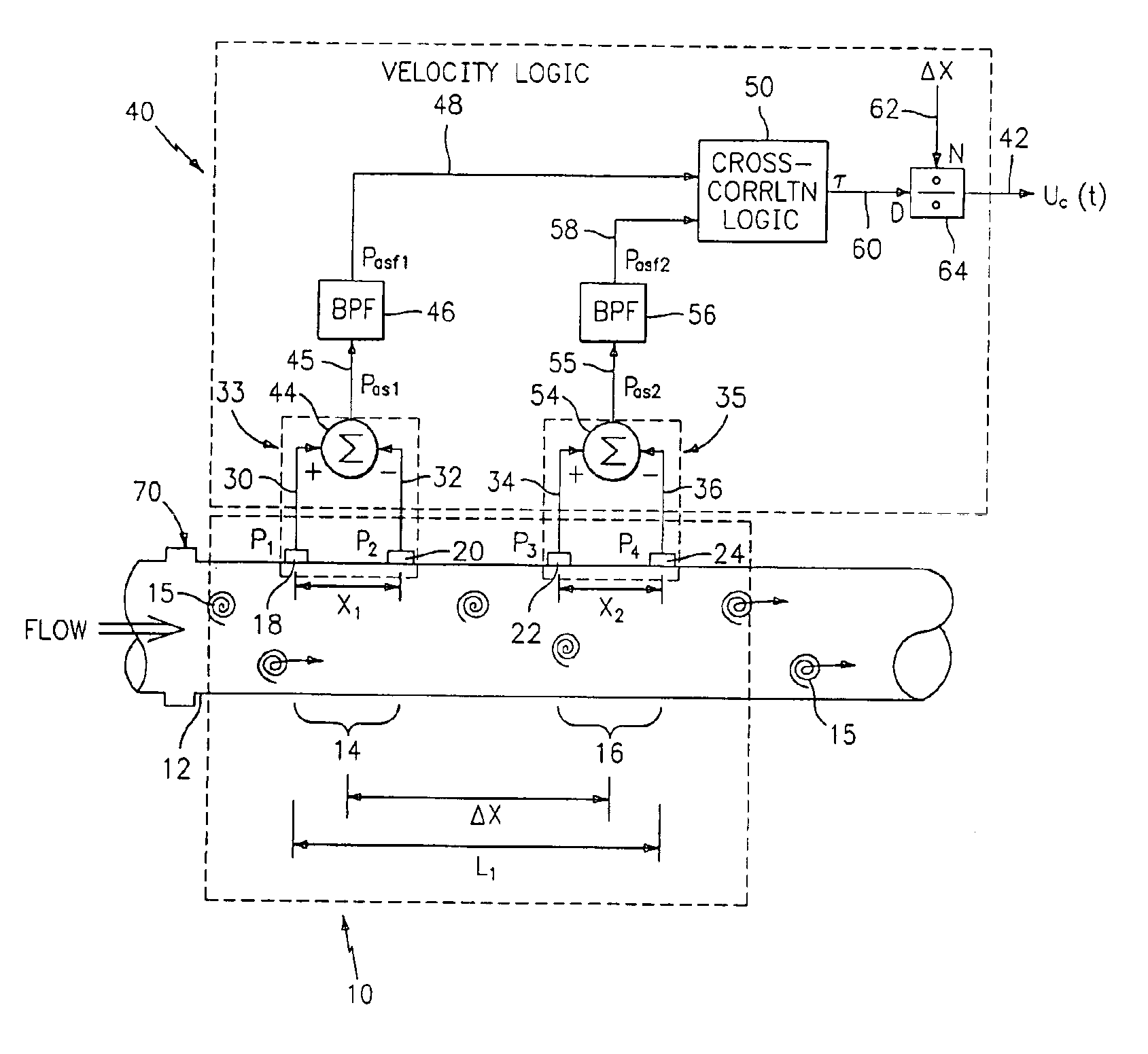
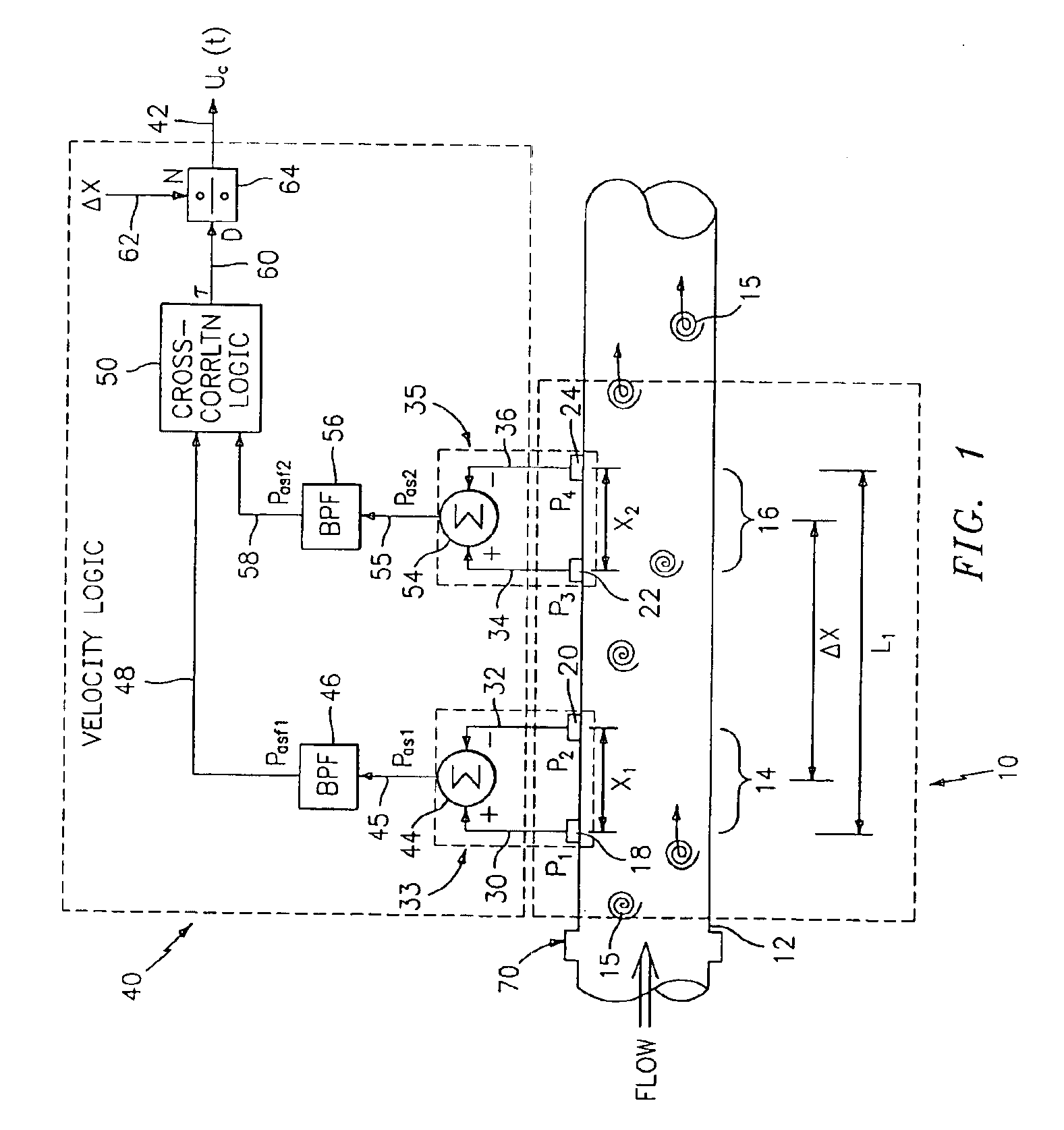
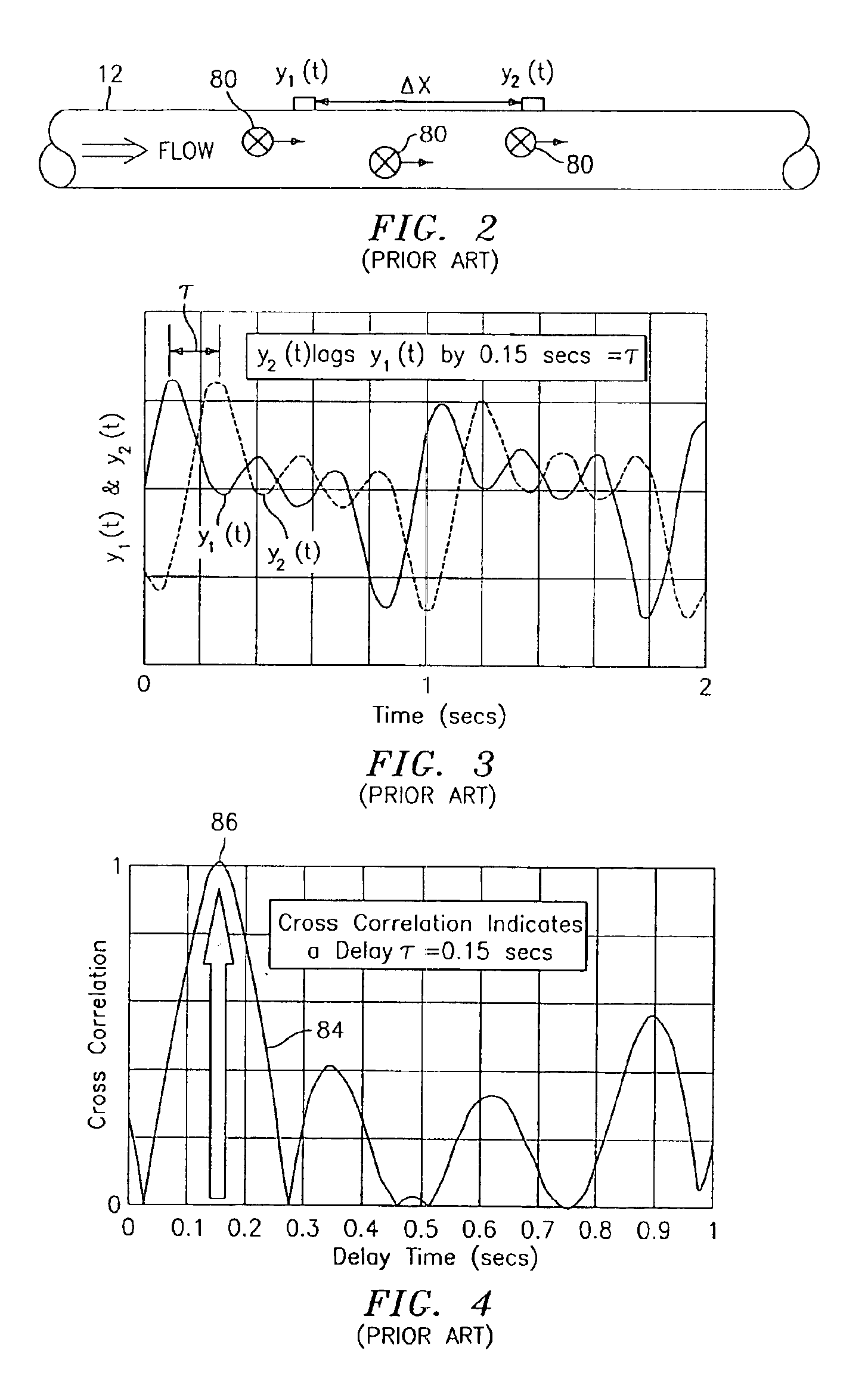
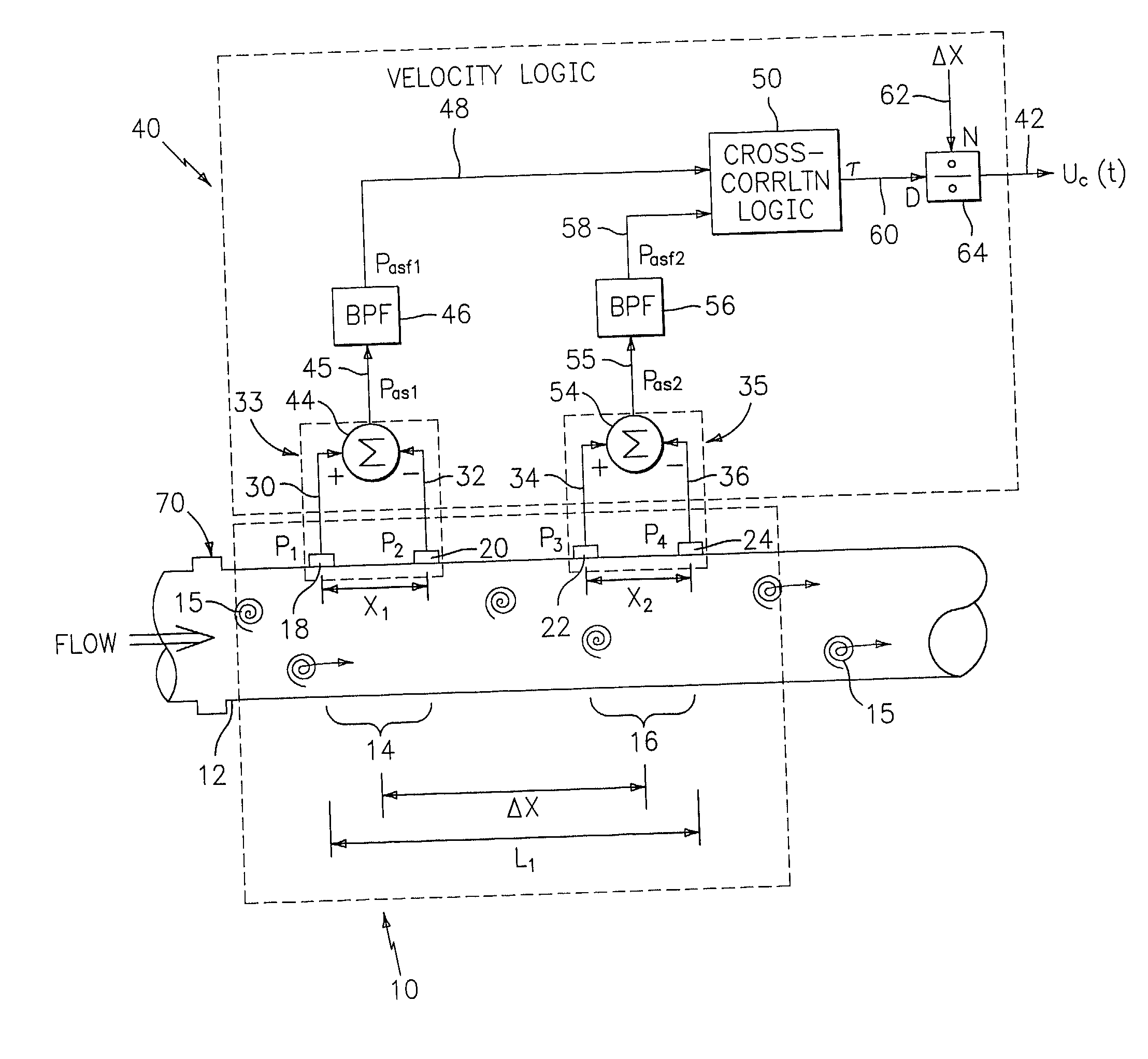
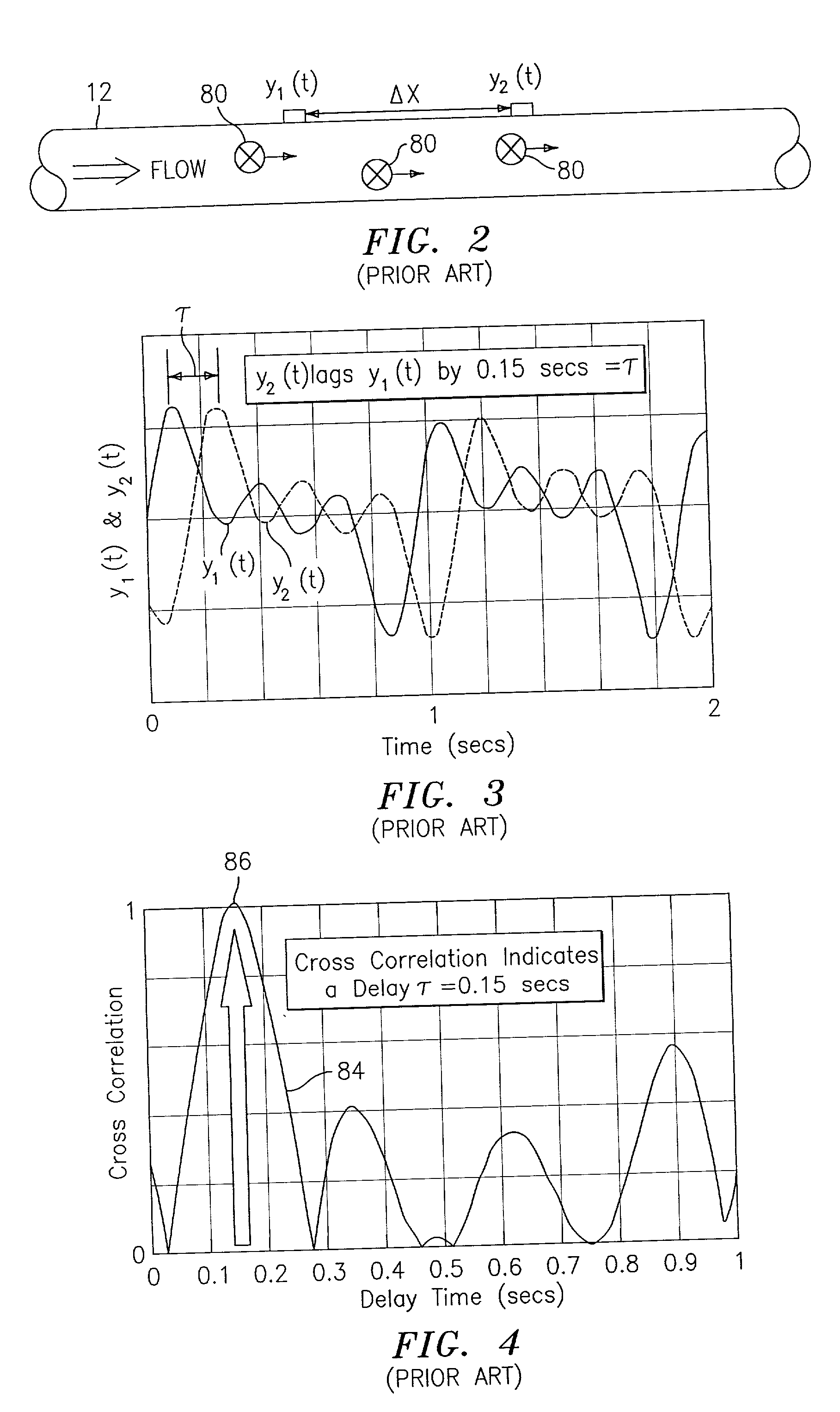
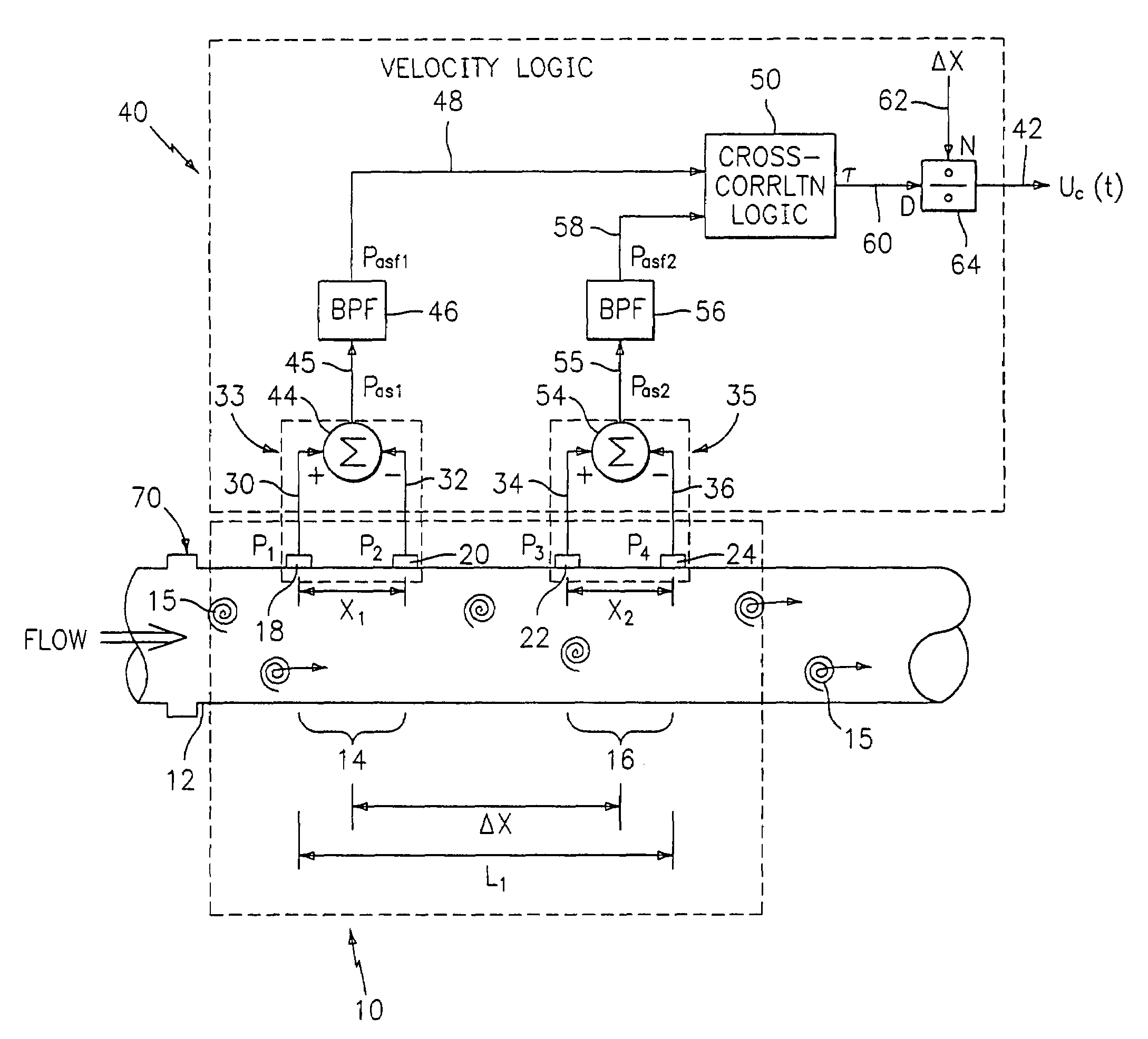
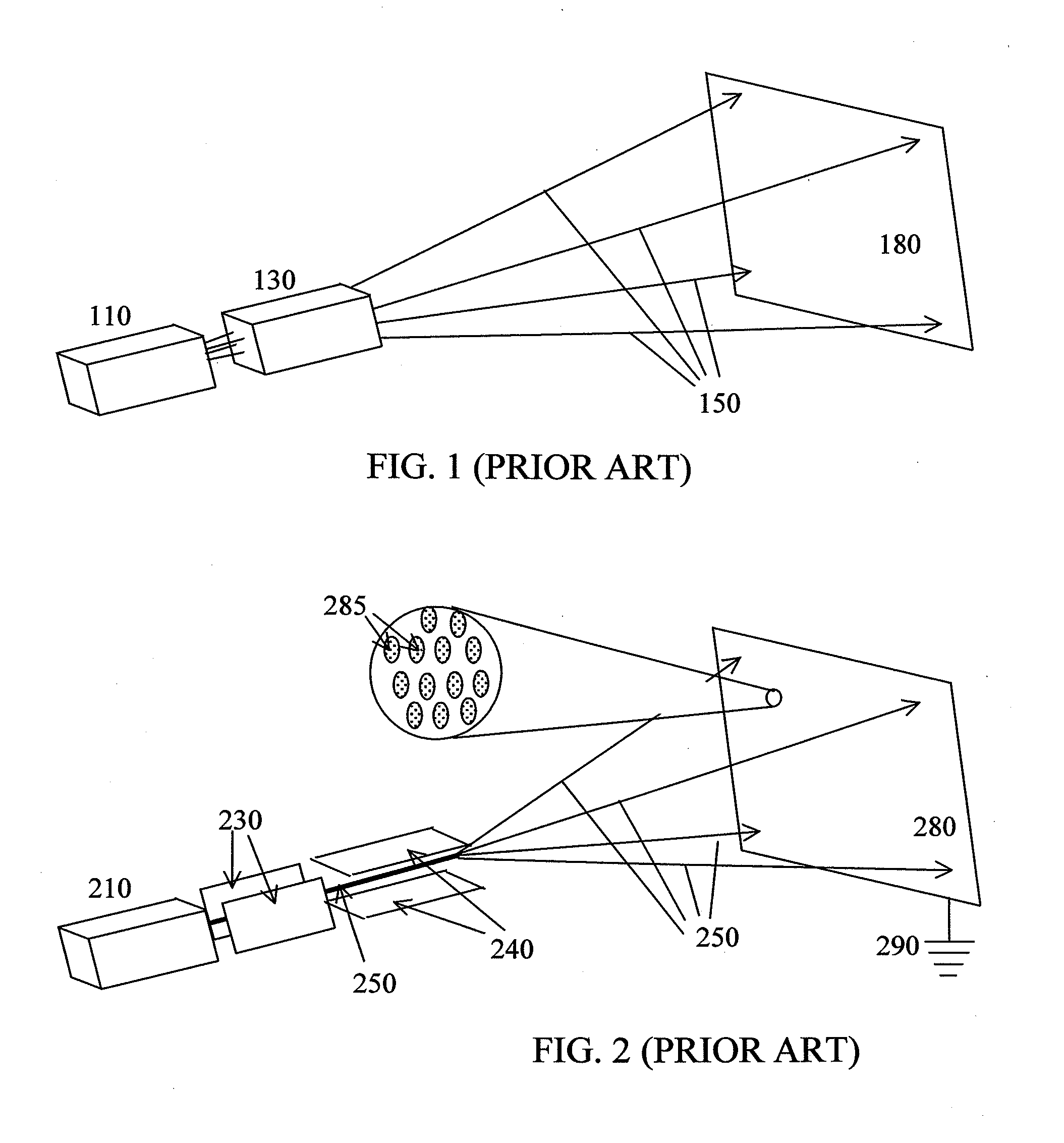
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical -dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
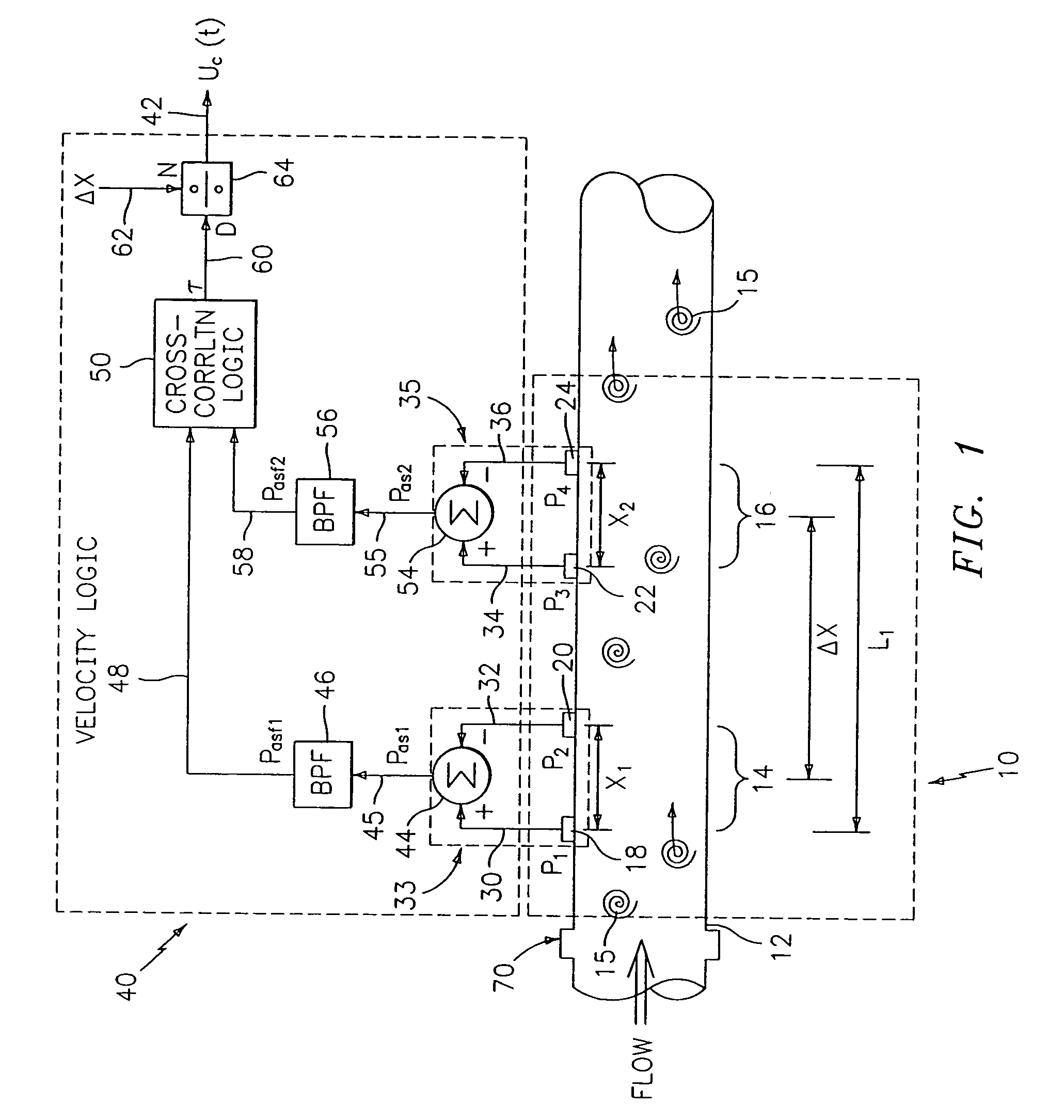
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance .DELTA.X apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X.sub.1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X.sub.2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances P.sub.acoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances P.sub.vortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals P.sub.as1,P.sub.as2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The P.sub.vortical -dominated filtered signals P.sub.asf1,P.sub.asf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay .tau. between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance .DELTA.X to obtain a convection velocity U.sub.c(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
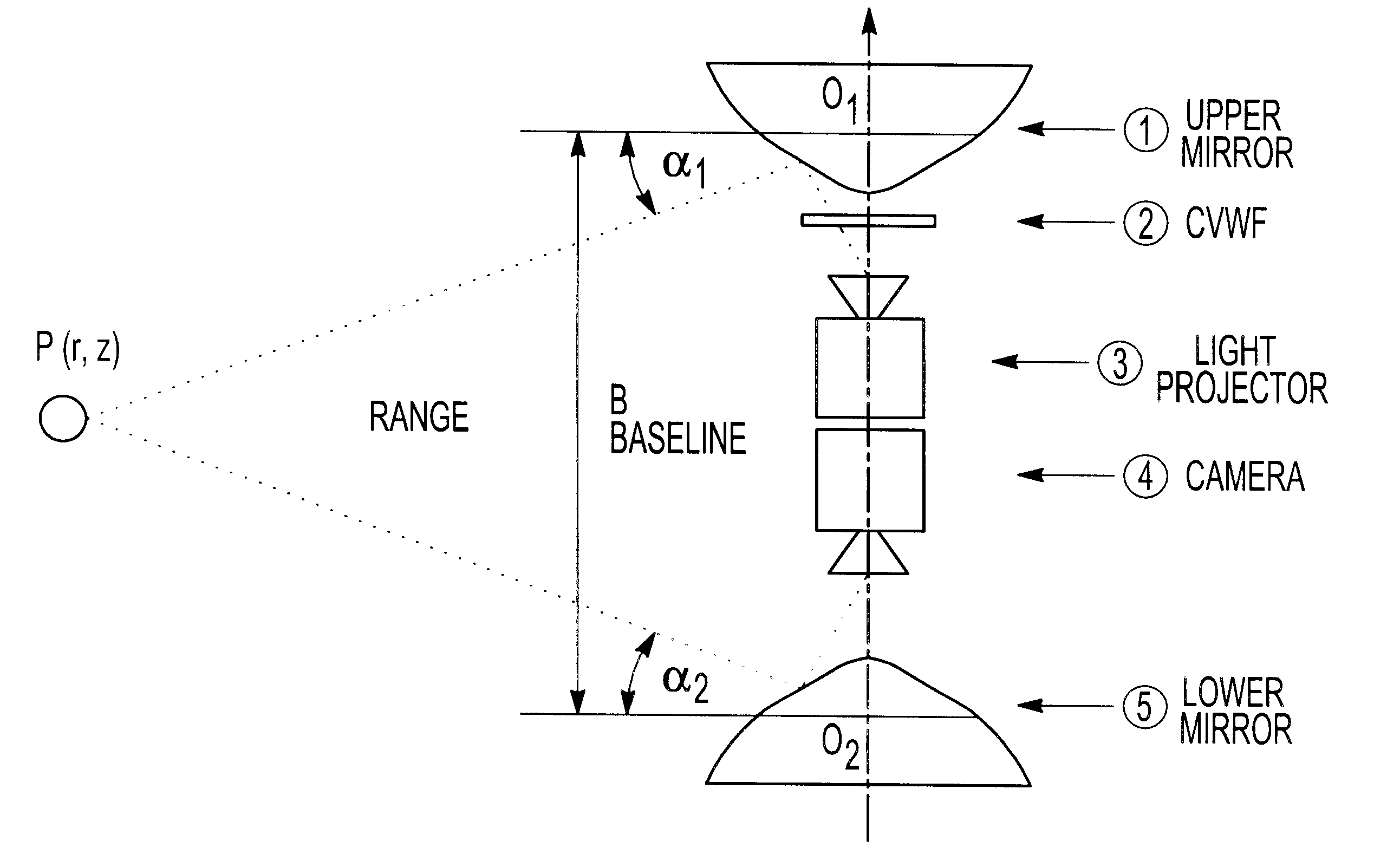
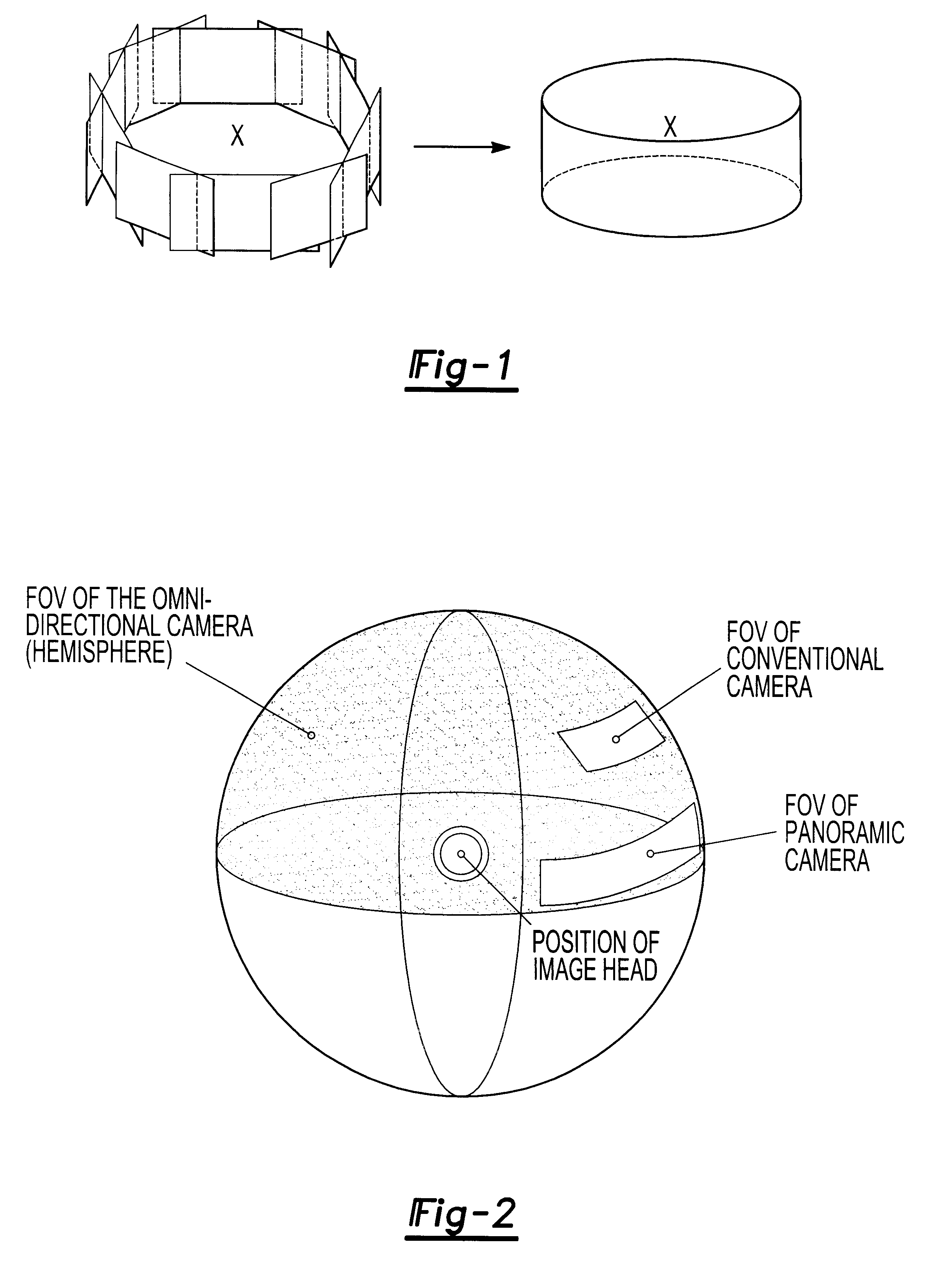
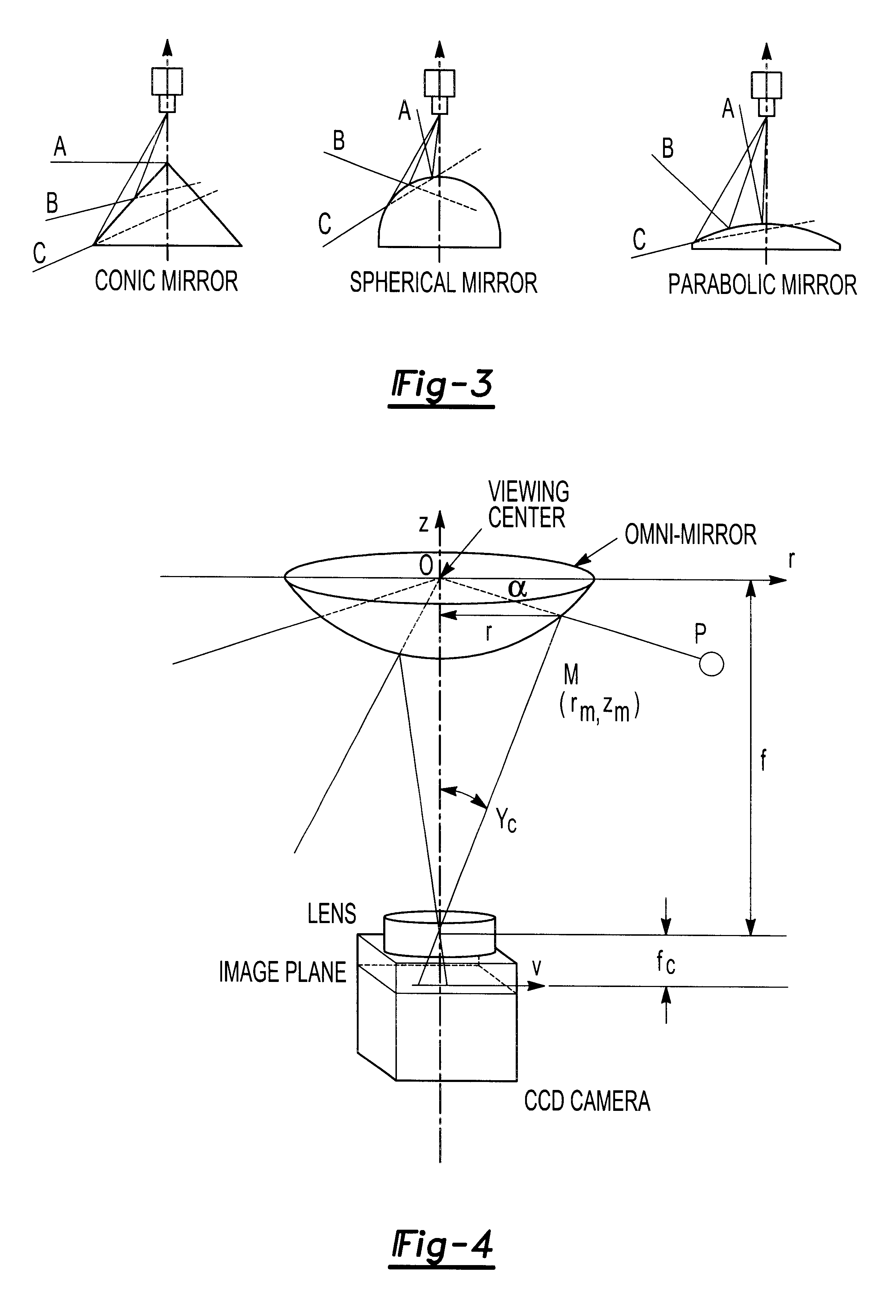
Method and apparatus for omnidirectional imaging
InactiveUS6304285B1Convenient lightingEasy to viewTelevision system detailsImage analysisWavelength filterLight beam
An omnidirectional imaging system comprising a reflective mirror for viewing object within a hemispherical field of view form a single virtual view point at the local center of said reflective mirror, a projector for projecting a light beam toward said reflective mirror, and a variable wavelength filter optically positioned between said projector and said reflective mirror for generating a pattern having a spatially distributed wavelength spectrum of said reflective mirror, where a generator responsive to the hemispherical image data for generating three-dimensional image.
Owner:TECHNEST HLDG
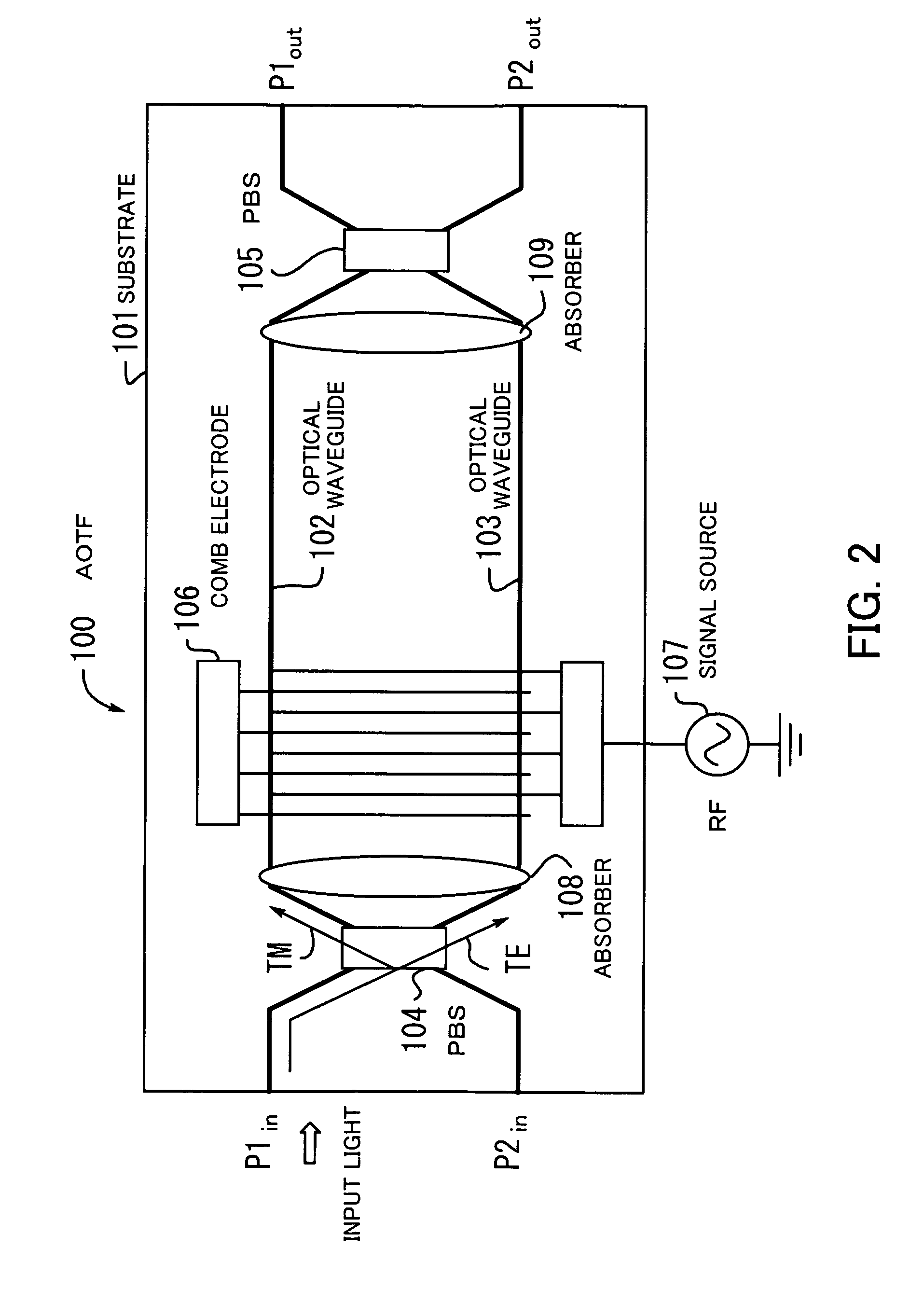
Variable-wavelength filter and variable-wavelength laser
InactiveUS20090122817A1Laser output is improvedReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersWavelength filterLength wave
Only the light at an overlapping wavelength of the transmission characteristics of at least two wavelength selecting filters is looped, and at least one of the wavelength selecting filters varies a selected wavelength. Since a loss due to the optical filters is small and there is not a loss caused by a highly reflecting film, the output of an external-resonator variable-wavelength laser can be increased. Optical circuit component (8) divides light input from external device (1) into at least two ports. Loop waveguide (11) interconnects at least ports (9, 10) divided by optical circuit component (8) in the form of a loop. At least two first wavelength selecting filters (12, 13) are inserted in series in a path of loop waveguide (11), and have periodic transmission characteristics on a frequency axis which are different from each other. At least one of first wavelength selecting filters (12, 13) varies the selected wavelength.
Owner:NEC CORP
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
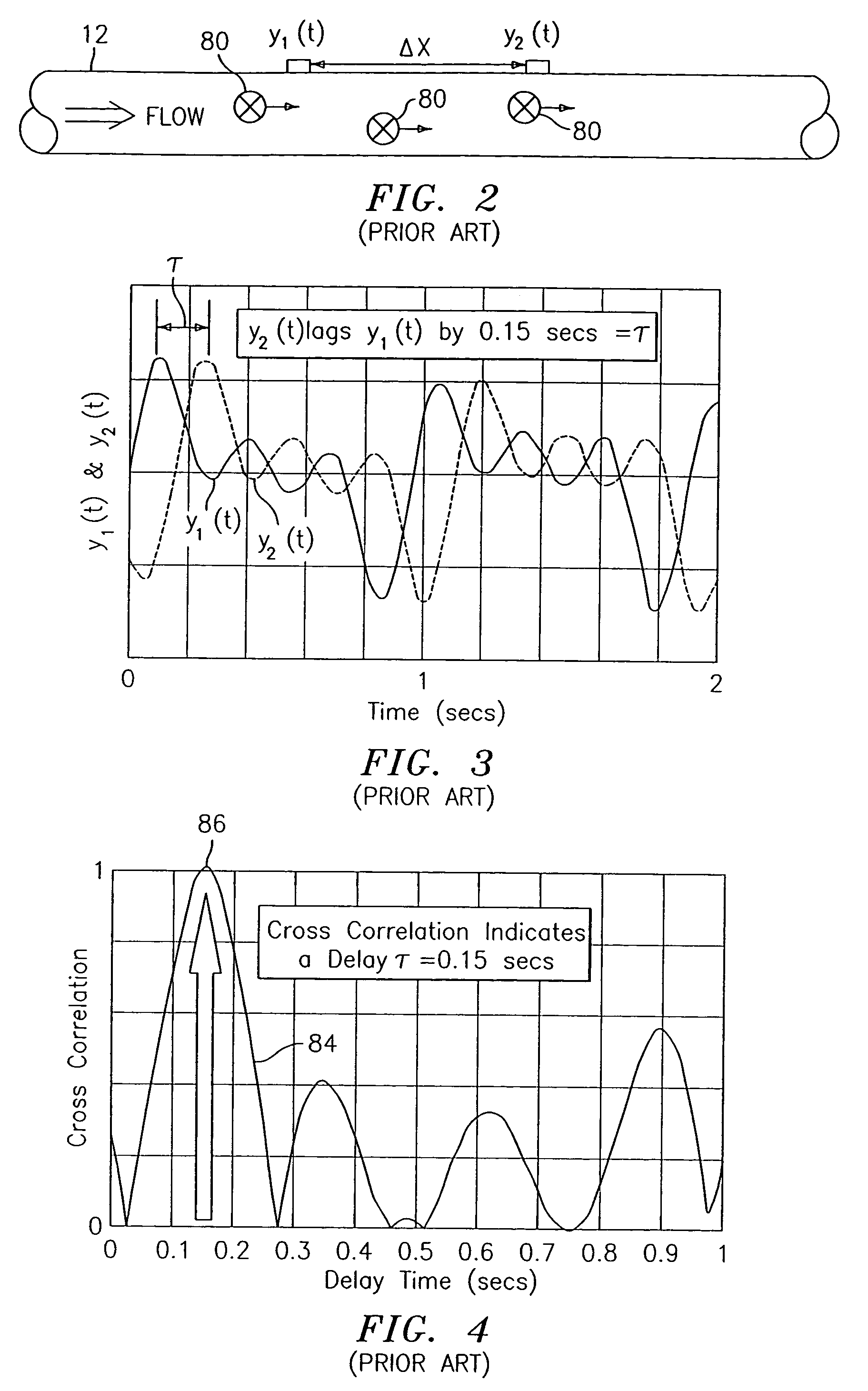
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical-dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Optical cross connect unit, optical add-drop multiplexer, light source unit, and adding unit
InactiveUS6285479B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingCross connection
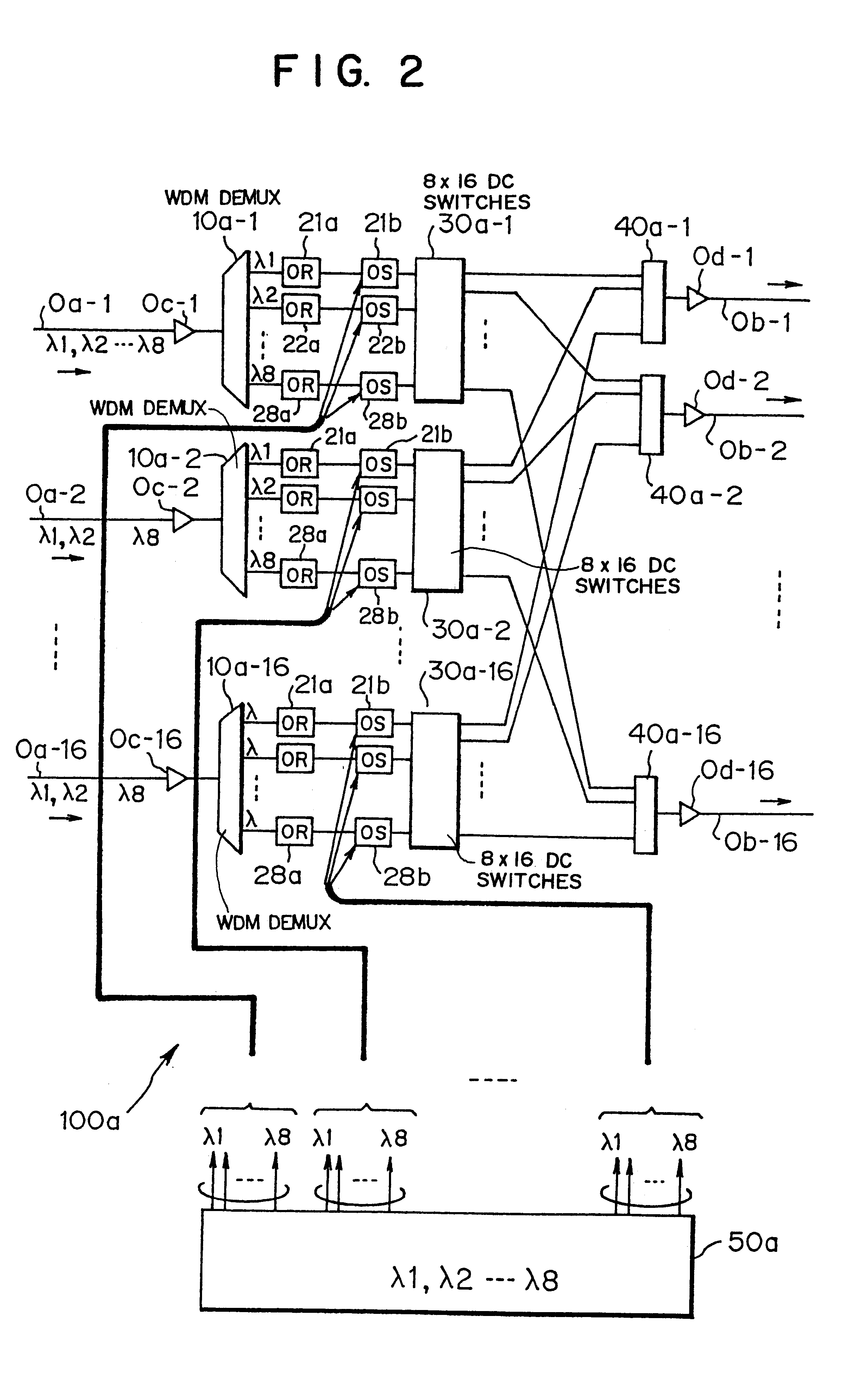
The present invention relates to an optical cross connect unit comprising M wavelength separating sections for receiving multiplexed optical signals each having N kinds of wavelengths different from each other through M optical fibers, respectively, and for wavelength-separating each of the multiplexed optical signals into N optical signals, M optical reproduction relay sections each for conducting an optical reproduction and relay in a manner of making a conversion of each of the N optical signals, wavelength-separated in each of the wavelength separating sections, into an electric signal and then modulating it with a desired optical wavelength, a refill section for mutually refilling M sets of optical signals optically reproduced and relayed in the optical reproduction relay sections, a focusing section for focusing the M sets of optical signals refilled in the refill section, and a light source unit for supplying input lights having desired wavelengths to be modulated in the M optical reproduction relay sections. The light source unit includes N light sources for outputting lights having the N kinds of optical wavelengths, a multiplexing and branching section for multiplexing the lights from the N light sources to produce a multiplexed light having N kinds of optical wavelength components and further for branching the multiplexed light into MxN lights to output them as multiplexed and distributed lights, M wavelength filter sections for distributively receiving N multiplexed and distributed lights of the MxN multiplexed and distributed lights branched in the multiplexing and branching section to output N lights due to the passage of only arbitrary wavelengths of the N kinds of optical wavelengths, and a wavelength setting control section for setting optical wavelengths, which pass through the wavelength filter sections, so that they differ from each other. The N lights from each of the M wavelength filter sections are supplied as the input lights. In the case that many light sources are necessary for the modulation processing by modulators or the like, this optical cross connect unit is also suitable because of using given wavelengths from a small number of light sources for a lot of modulation processing.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
InactiveUS20120075577A1Improved contrast sensitivityHigh sensitivitySpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensWavelength filterLength wave
The present invention relates to ophthalmic systems and coatings comprising a selective light wavelength filter, wherein said selective filter provides improved contrast sensitivity.
Owner:ISHAK ANDREW W +7
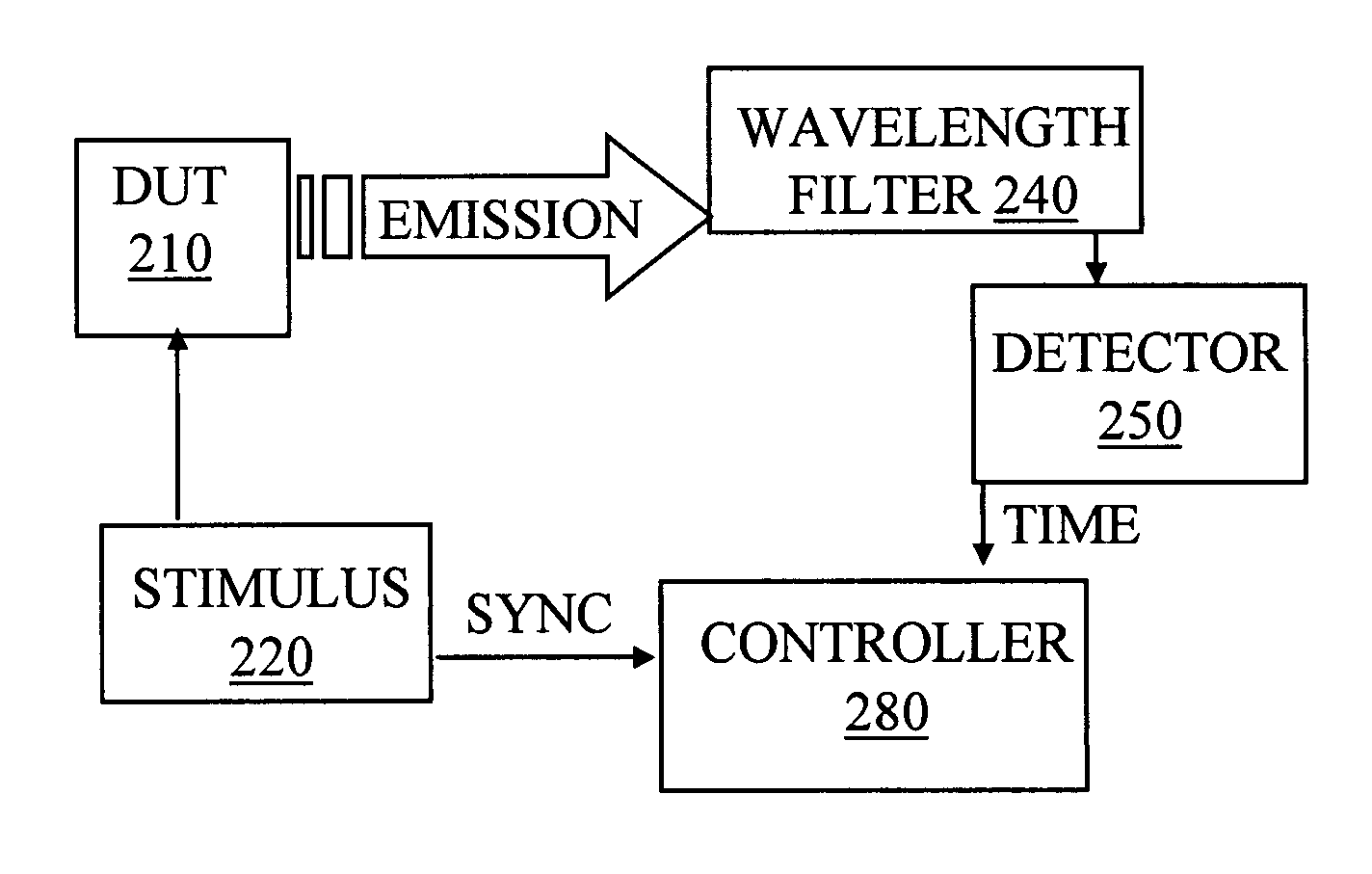
Time resolved emission spectral analysis system
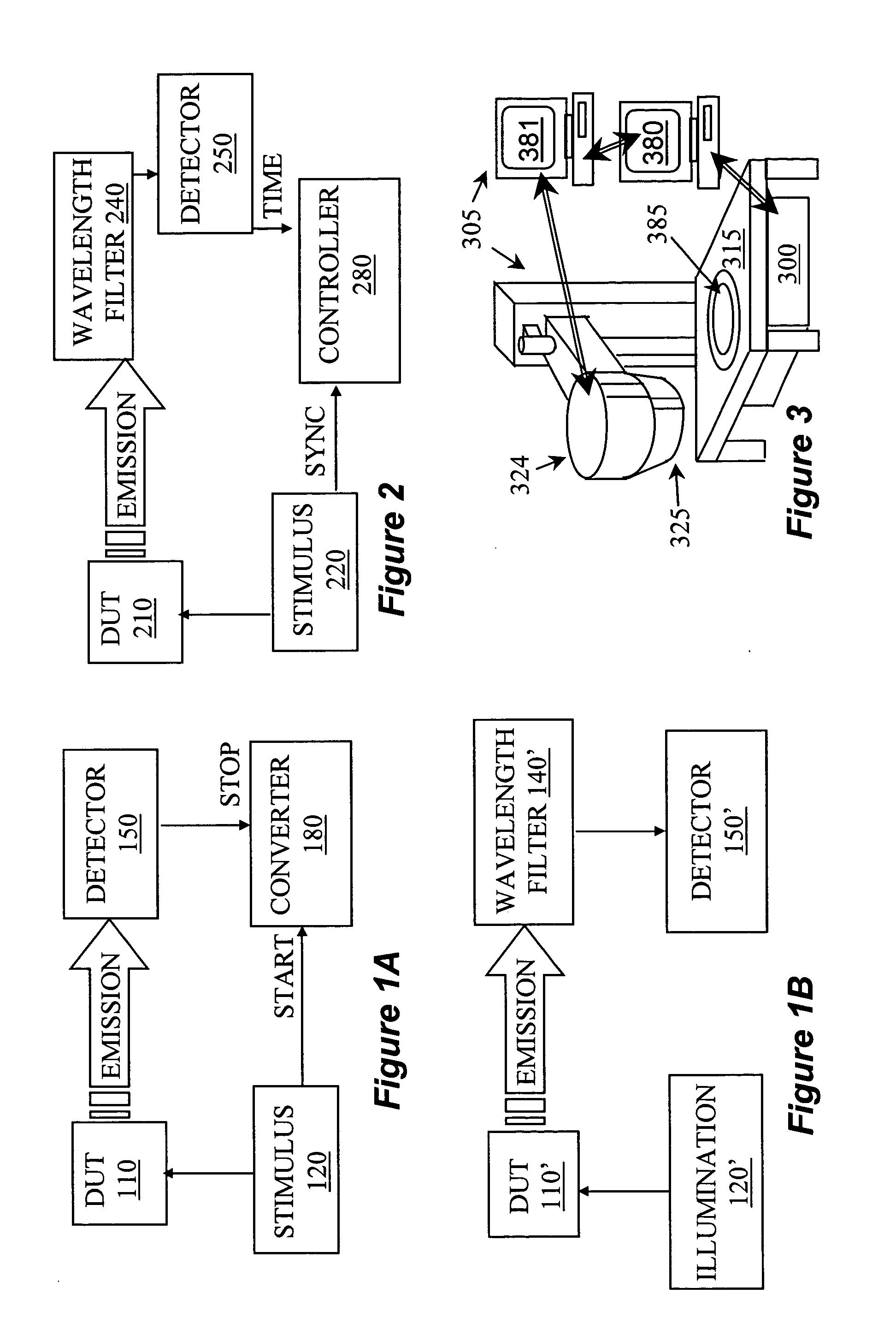
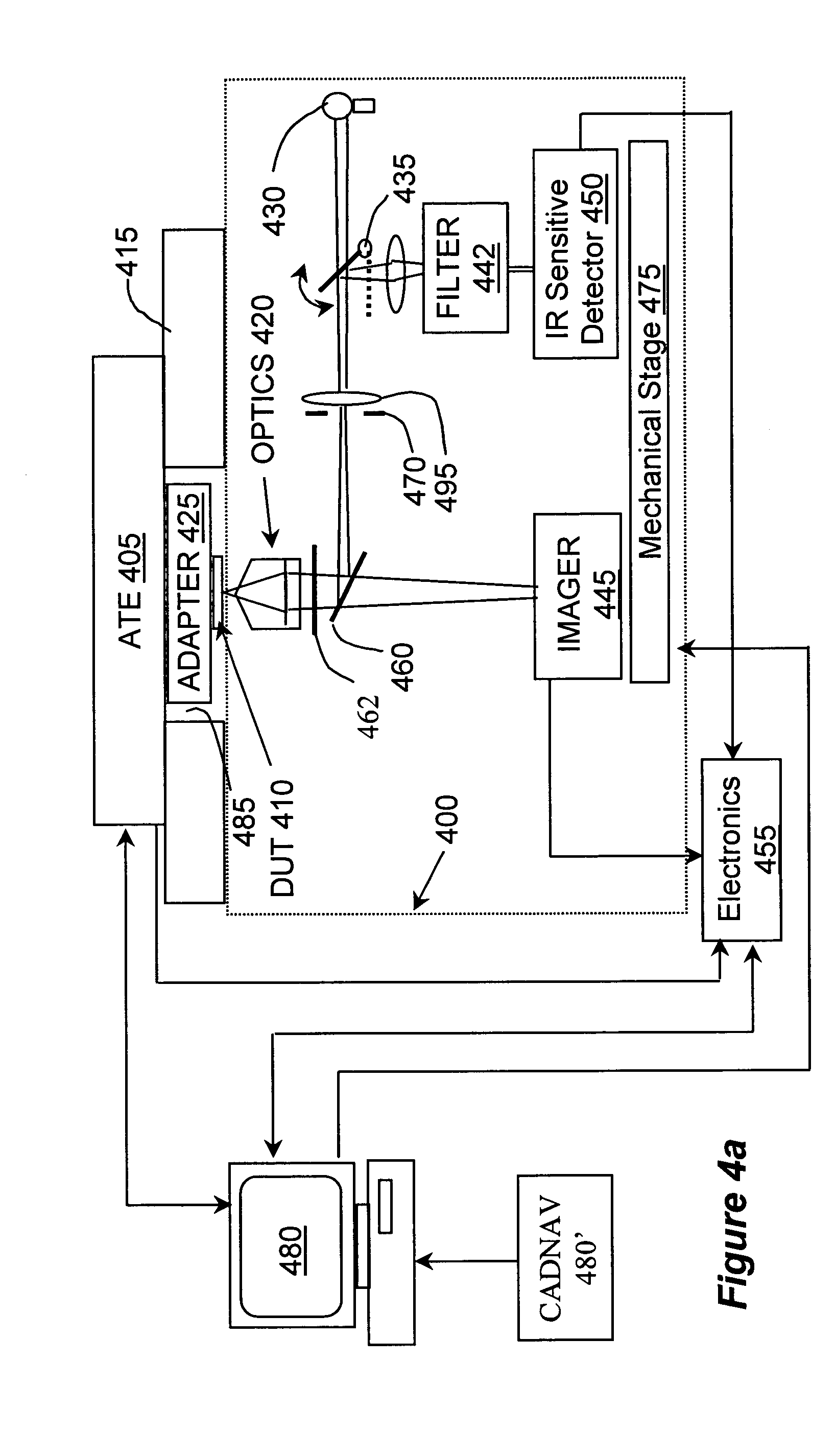
InactiveUS20050002028A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce noiseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhoton emissionWavelength filter
A system for temporal and spectral resolved detection of photon emission from an integrated circuit is disclosed. A DUT is stimulated by a conventional ATE, so that its active devices emit light. The signal from the ATE is also sent to the system's computer as a synchronization signal. The light emitted from the switching devices is passed through a wavelength filter. Selected bands of wavelengths are then passed to respective detector(s) and the detector(s) response with respect to the time correlated ATE stimulus is studied.
Owner:ONTONICS
Method of performing hyperspectral imaging with photonic integrated circuits
ActiveUS8203115B2Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsWavelength filterElectromagnetic radiation
According to the invention, an integrated hyperspectral imager includes a planar photonic substrate. A plurality of imaging pixel photonic circuits is disposed in a M×N array on the planar photonic substrate. Each imaging pixel photonic circuit includes an input coupler configured to receive a broadband input electromagnetic radiation. A waveguide is optically coupled to the input coupler. A plurality of wavelength filters is optically coupled to the waveguide. Each wavelength filter has a wavelength filter input and a wavelength filter output. Each detector has a detector input optically coupled respectively to each of the wavelength filter outputs. Each detector has a respective detector output. The integrated hyperspectral imager is configured to provide electrical signals that are representative of a hyperspectral image of the received broadband input electromagnetic radiation. A method for recording an image based on a received electromagnetic radiation is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Target for surveying instrument
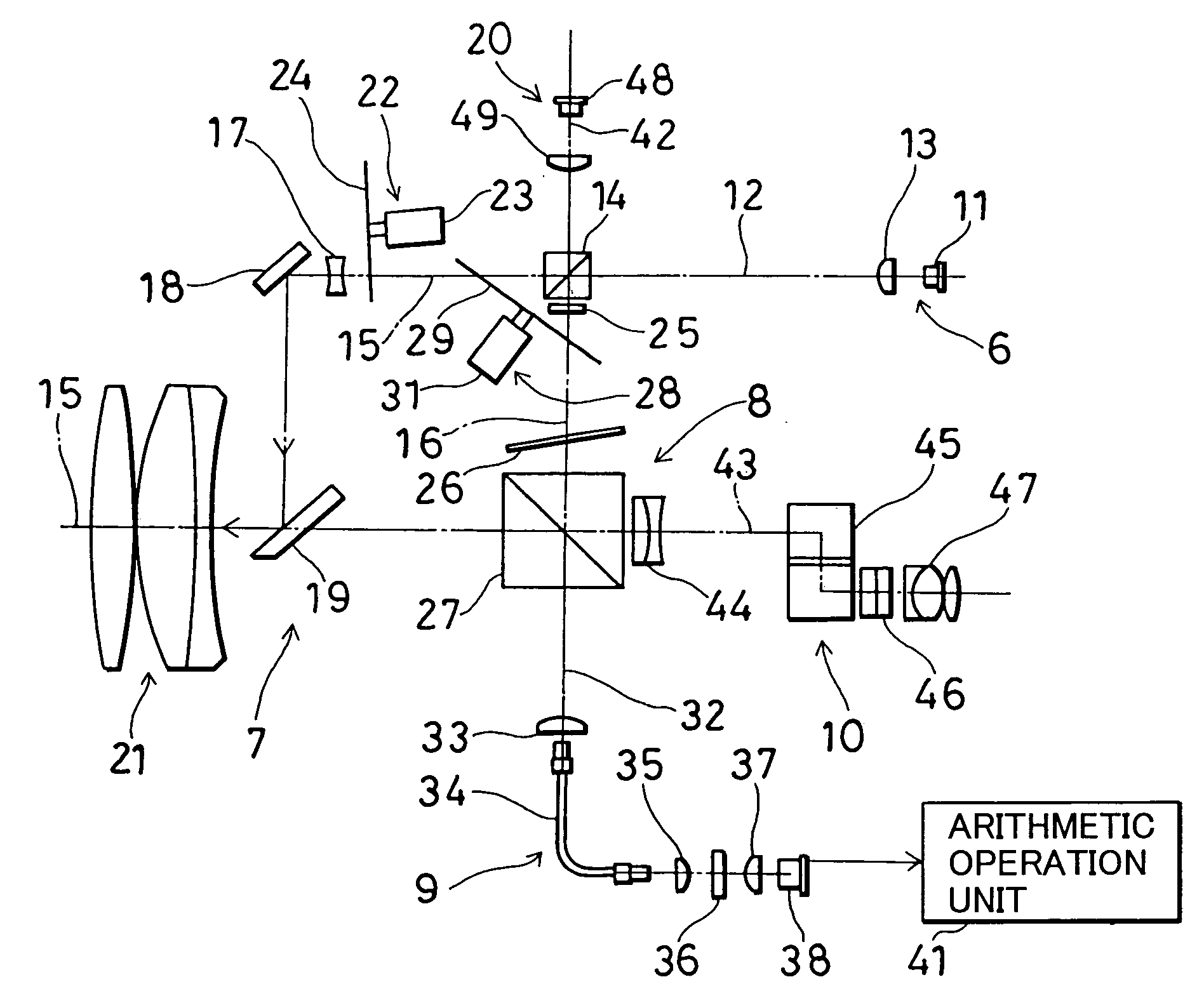
ActiveUS7130035B2Efficiently confirmed visuallyLong distanceAngle measurementOptical rangefindersPoint lightWavelength filter
A target for a surveying instrument, which receives from the surveying instrument a laser point light indicating a position and a distance measuring light to measure a distance, comprising a reflection diffusion layer for reflecting and diffusing the distance measuring light, a wavelength filter layer for selectively transmitting the laser point light passing through the reflection diffusion layer, and a transmission diffusion layer for spreading in a given direction and for transmitting the laser point light passing through the wavelength filter layer, wherein a projecting position of the laser point light can be confirmed.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Method of performing hyperspectral imaging with photonic integrated circuits
ActiveUS20100187402A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsWavelength filterBroadband
According to the invention, an integrated hyperspectral imager includes a planar photonic substrate. A plurality of imaging pixel photonic circuits is disposed in a M×N array on the planar photonic substrate. Each imaging pixel photonic circuit includes an input coupler configured to receive a broadband input electromagnetic radiation. A waveguide is optically coupled to the input coupler. A plurality of wavelength filters is optically coupled to the waveguide. Each wavelength filter has a wavelength filter input and a wavelength filter output. Each detector has a detector input optically coupled respectively to each of the wavelength filter outputs. Each detector has a respective detector output. The integrated hyperspectral imager is configured to provide electrical signals that are representative of a hyperspectral image of the received broadband input electromagnetic radiation. A method for recording an image based on a received electromagnetic radiation is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Gas component detection device
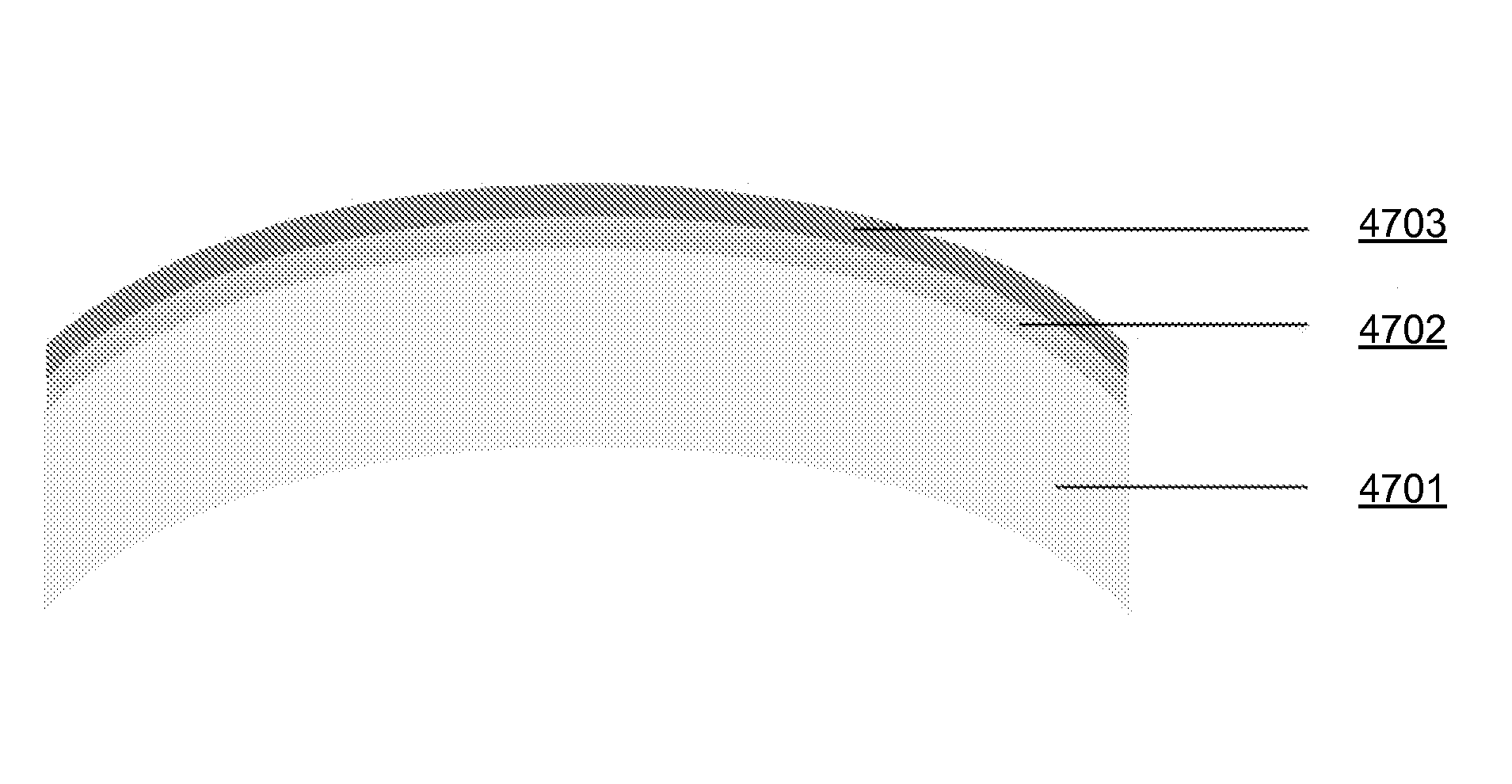
ActiveUS20140070101A1Suppressing decrease amountSuppression amountSolid-state devicesColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredAngle dependence
An optical path of infrared rays (see the broken lines in FIG. 1) is modified to a substantially U-like shape by a first reflecting mirror and a second reflecting mirror. An incidence angle of the infrared rays incident on the wavelength filter (an angle between the infrared rays incident on the surface of the wavelength filter and the line perpendicular to the surface of the wavelength filter) is nearly zero. For this reason, as compared with a conventional example, the influence of the incidence angle dependence of the wavelength filter can be reduced. As a result, the amount of the infrared rays reaching the light receiving unit through the wavelength filter is increased, thereby suppressing a decline in the detection accuracy of the gas component.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Light-emitting device with precisely tuned and narrowed spectral width of optical output and an optical signal source providing the same
InactiveUS20090046748A1Narrow widthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionWavelength filterSpectral width
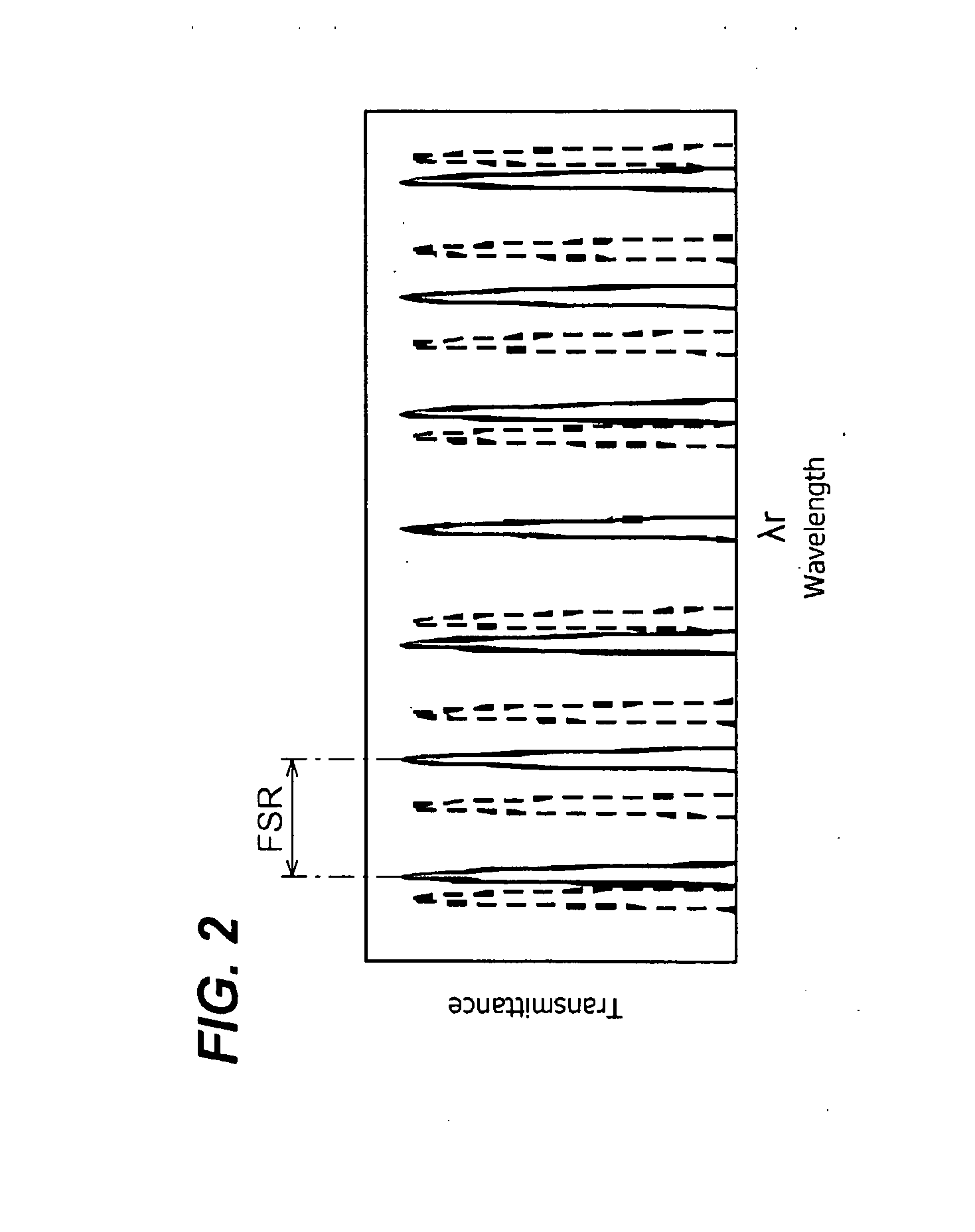
A light-emitting device whose output wavelength is easily variable is disclosed. The device provides a light-generating portion that emits light by the carrier injection and a variable wavelength filter that sets a specific wavelength λr. The variable wavelength filter includes two ring waveguide optical coupled with each other and having optical paths different from each other and at least an electrode to apply an electrical signal to the corresponding ring waveguide. By tuning the specific wavelength λr to the wavelength emitted from the light-generating portion, the output wavelength from the light-emitting device may be narrowed.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20070110453A1Low costSmall sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionWavelength filterPeak value
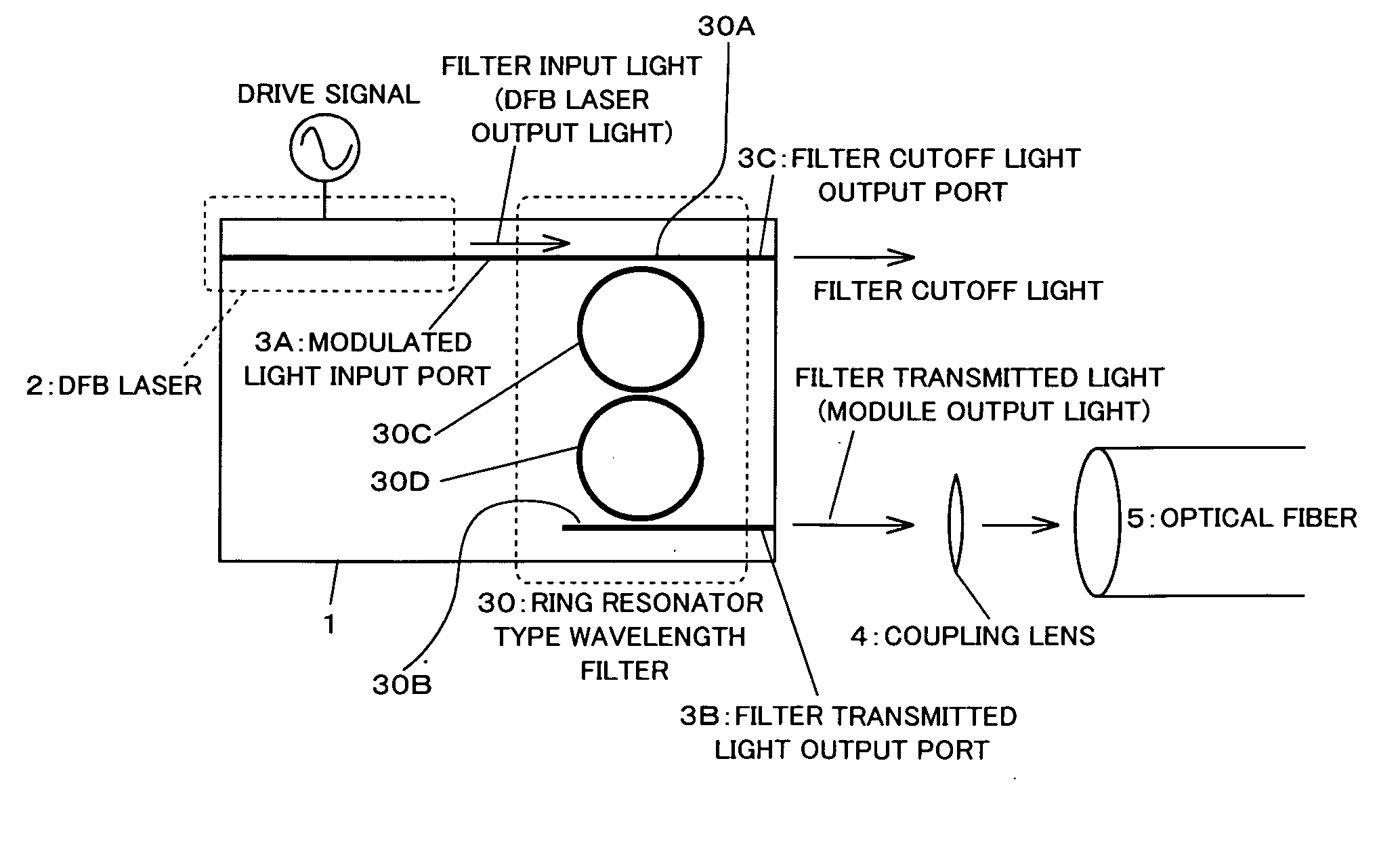
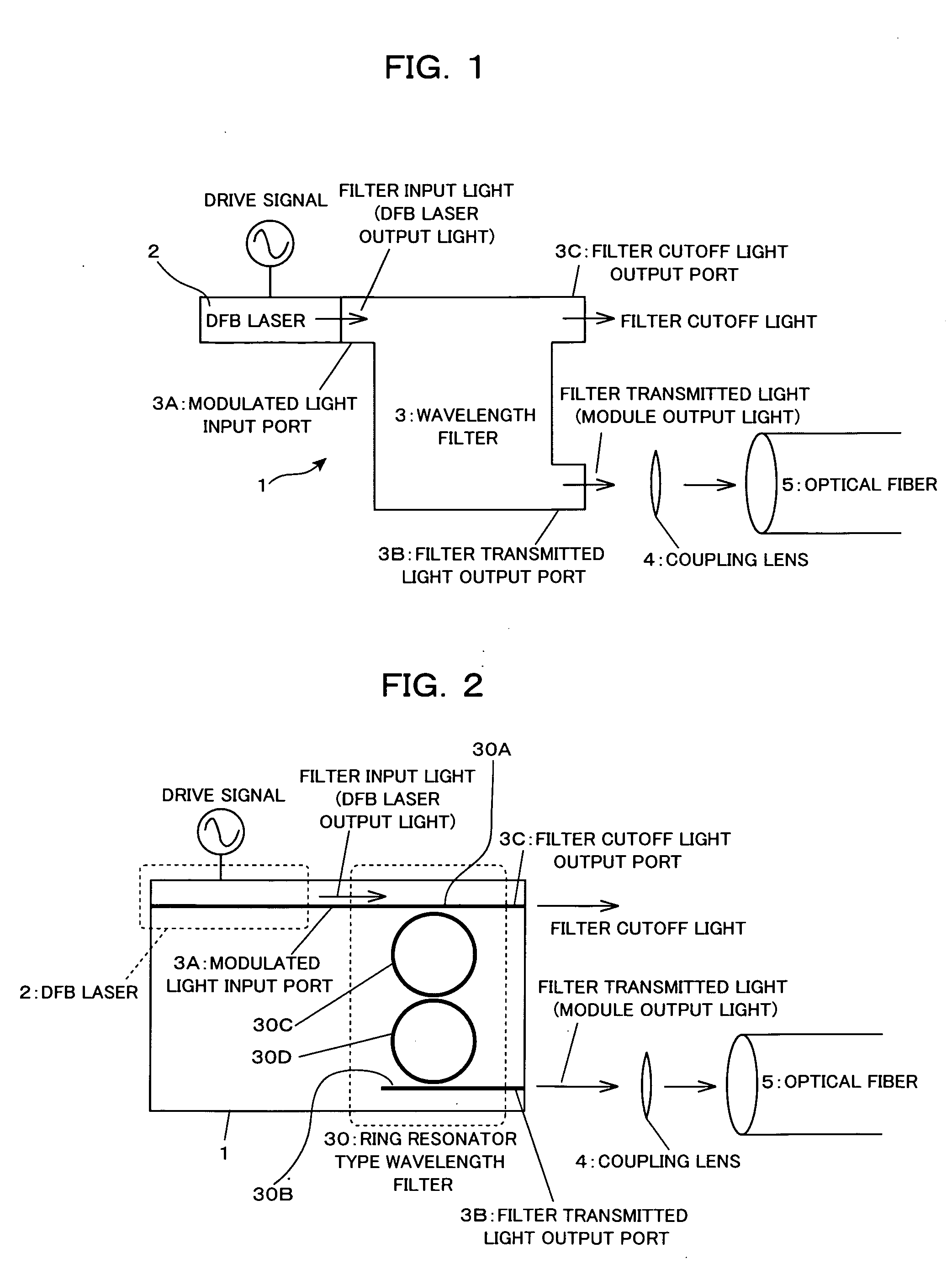
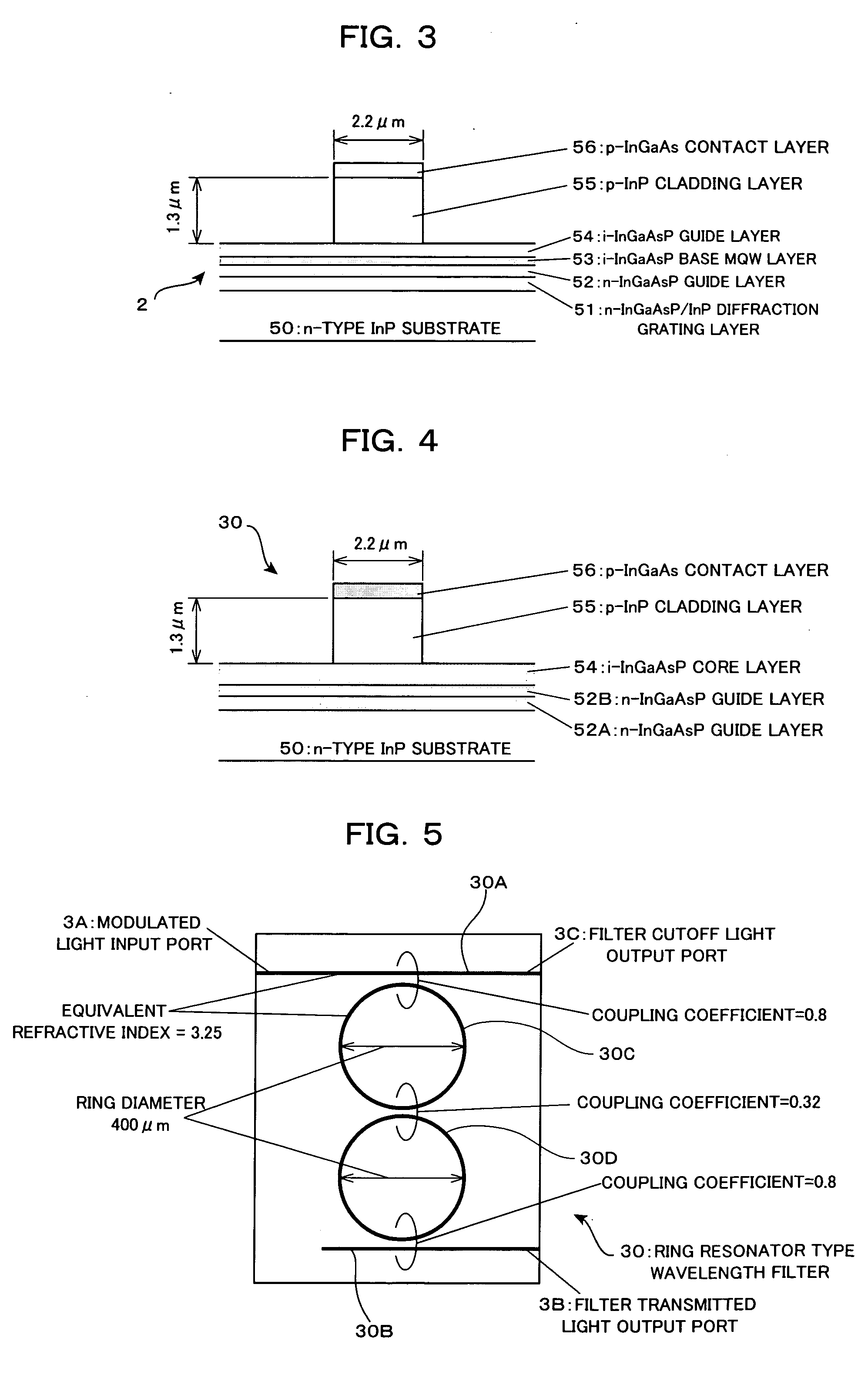
In an optical transmitter comprising a directly modulated laser and a wavelength filter provided on a post-stage of the directly modulated laser, the wavelength filter has a modulated light input port for inputting modulated light output from the directly modulated laser, a filter transmitted light output port for outputting light having a wavelength included in a filter transmission band among the modulated light as filter transmitted light, and a filter cutoff light output port provided separately from the modulated light input port and the filter transmitted light output port and outputting light having a wavelength included in a filter cutoff band among the modulated light as filter cutoff light, and the peak of the filter transmission band is set on a shorter-wave side from the peak of the spectrum of modulated light output from the directly modulated laser.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nanoparticles and molecules
InactiveUS20060290898A1ProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesColor imageWavelength filter
Owner:SUPERIMAGING
VIS-SNIR multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
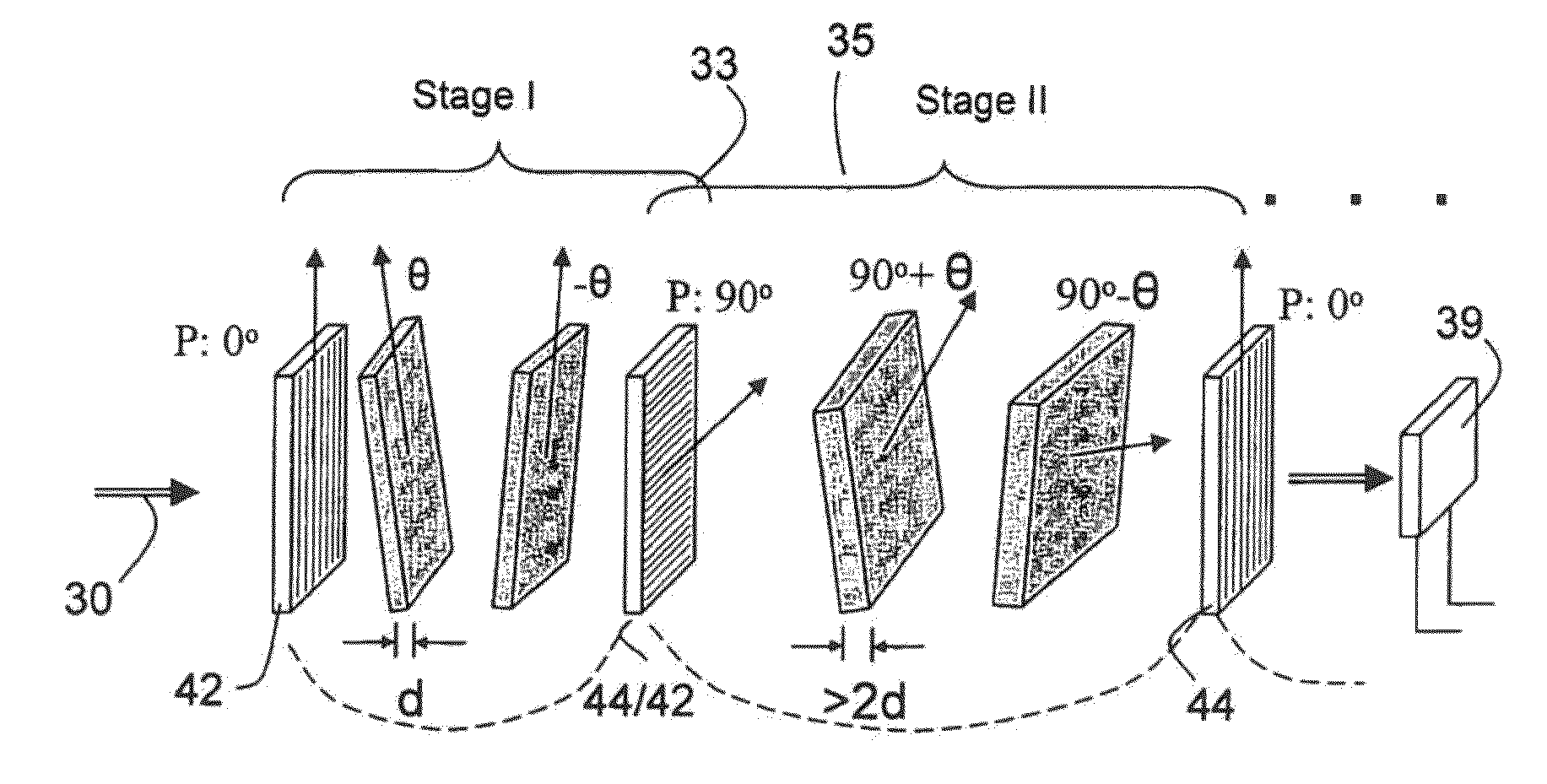
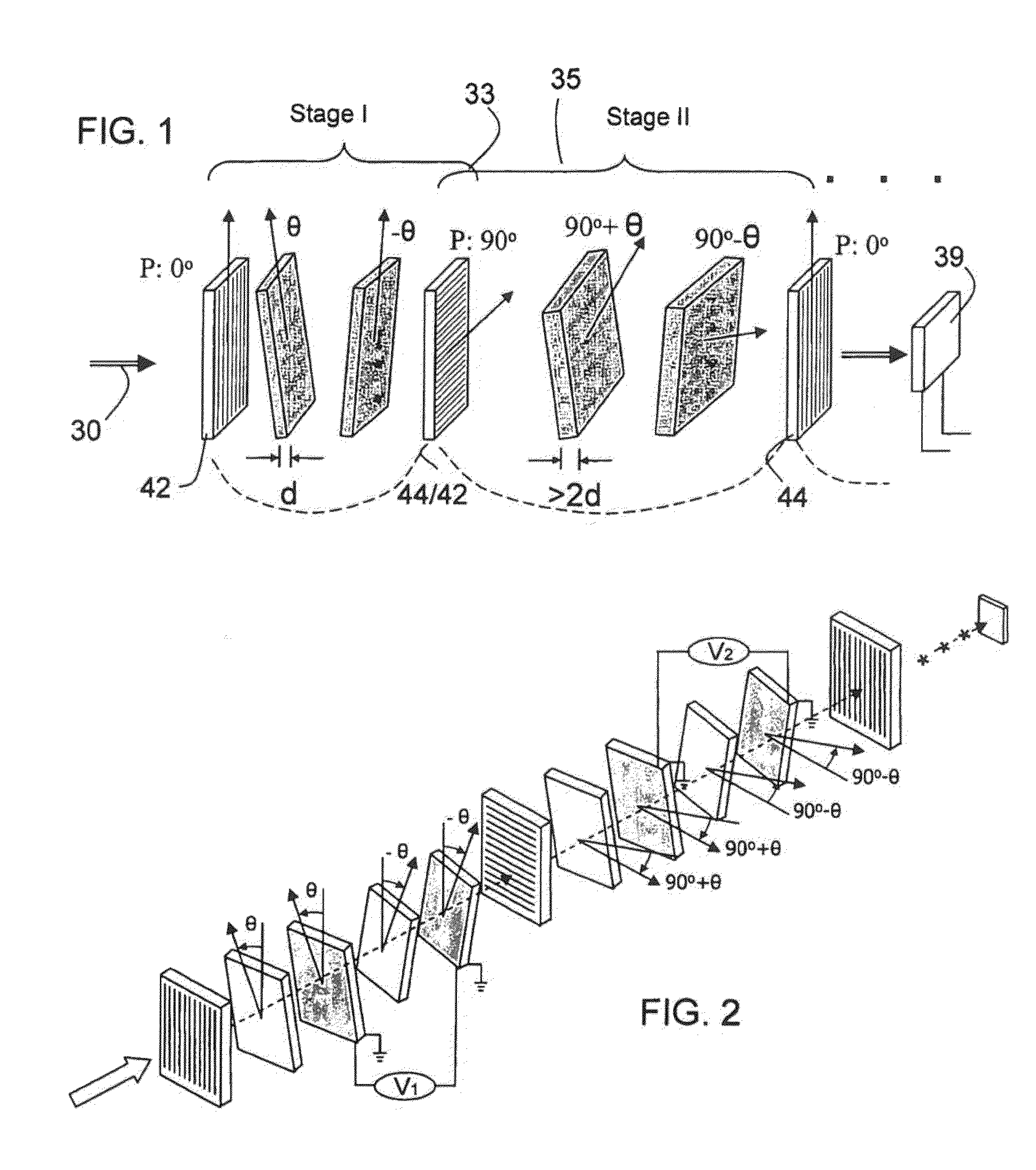
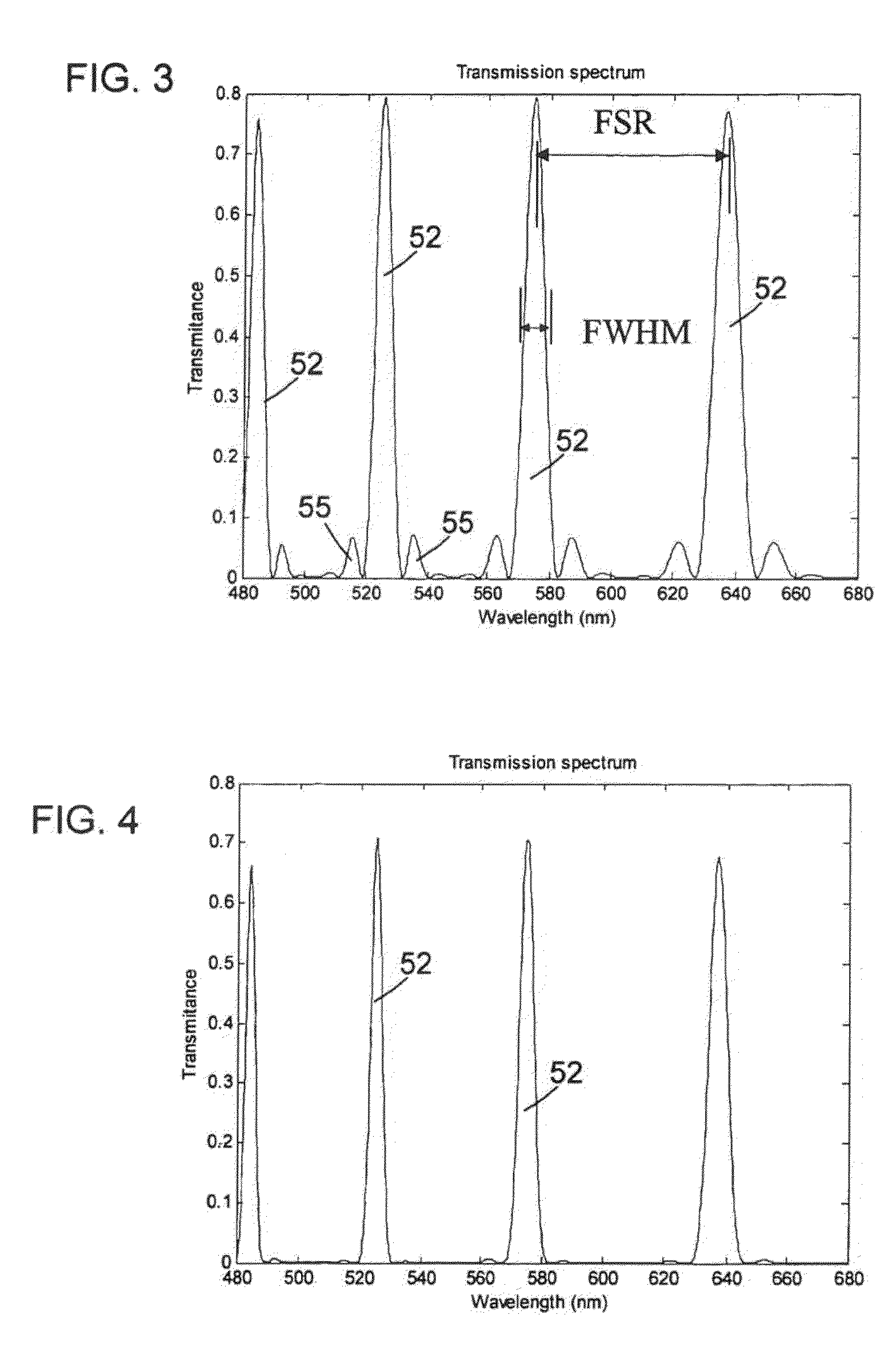
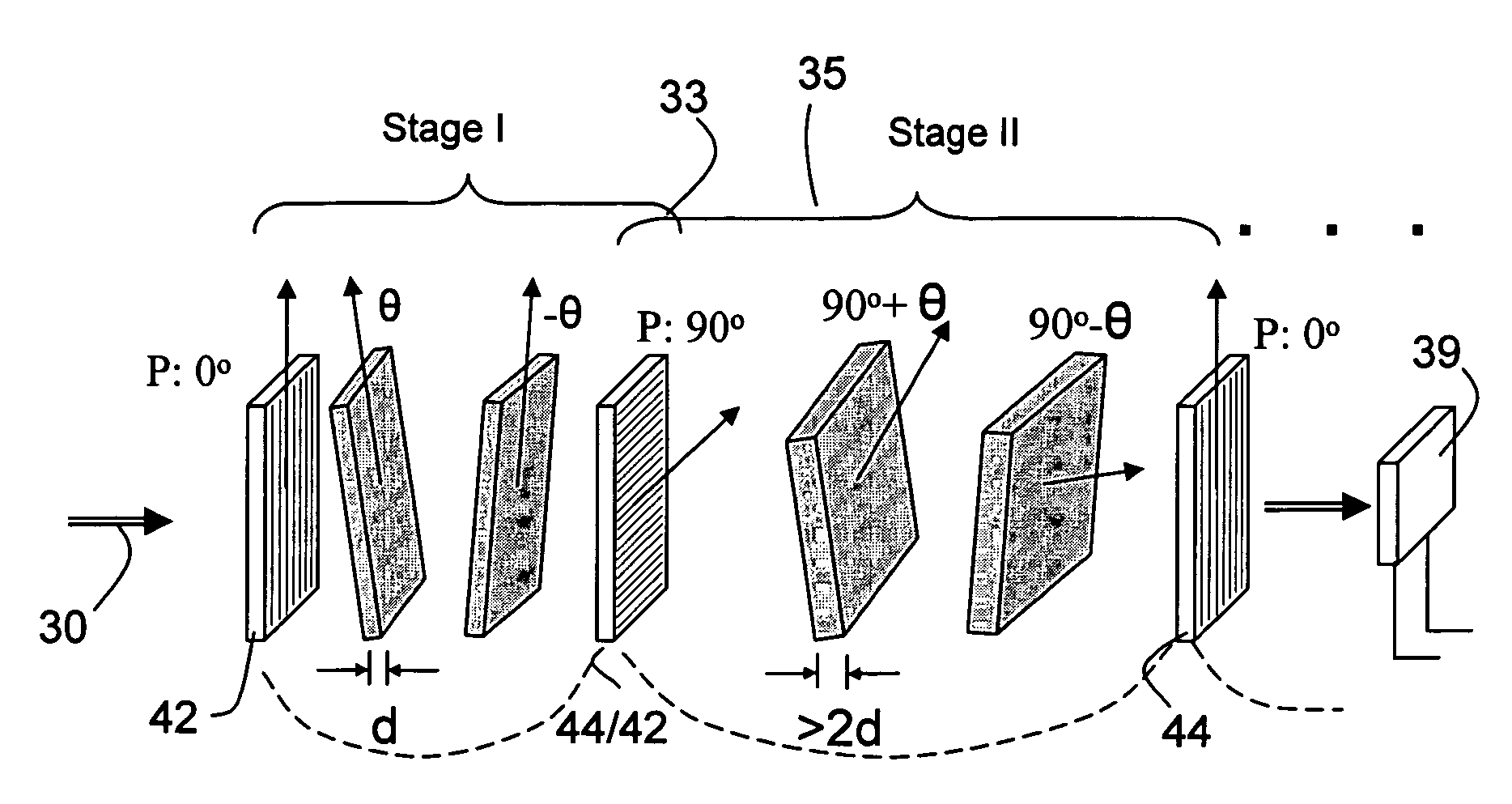
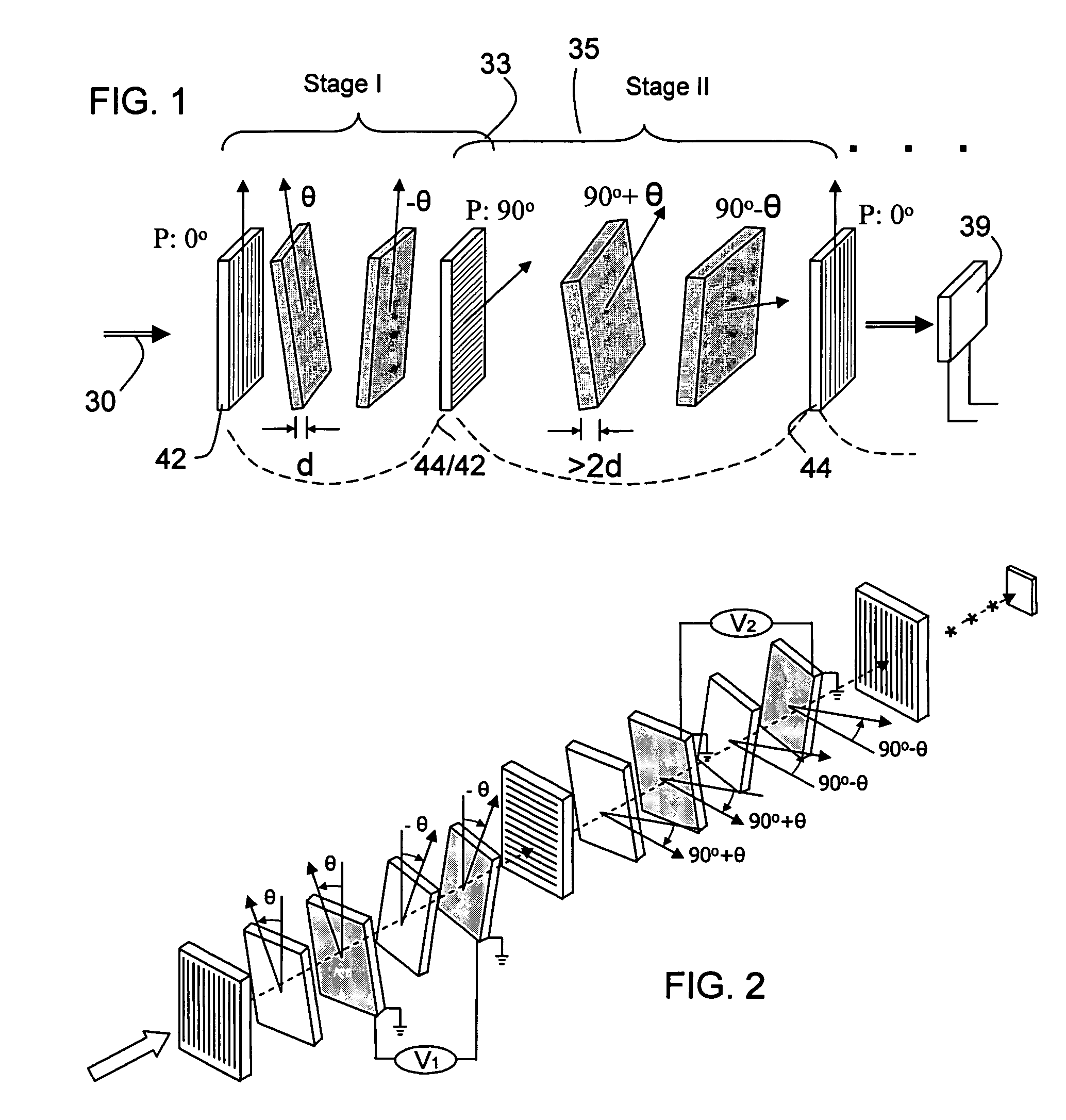
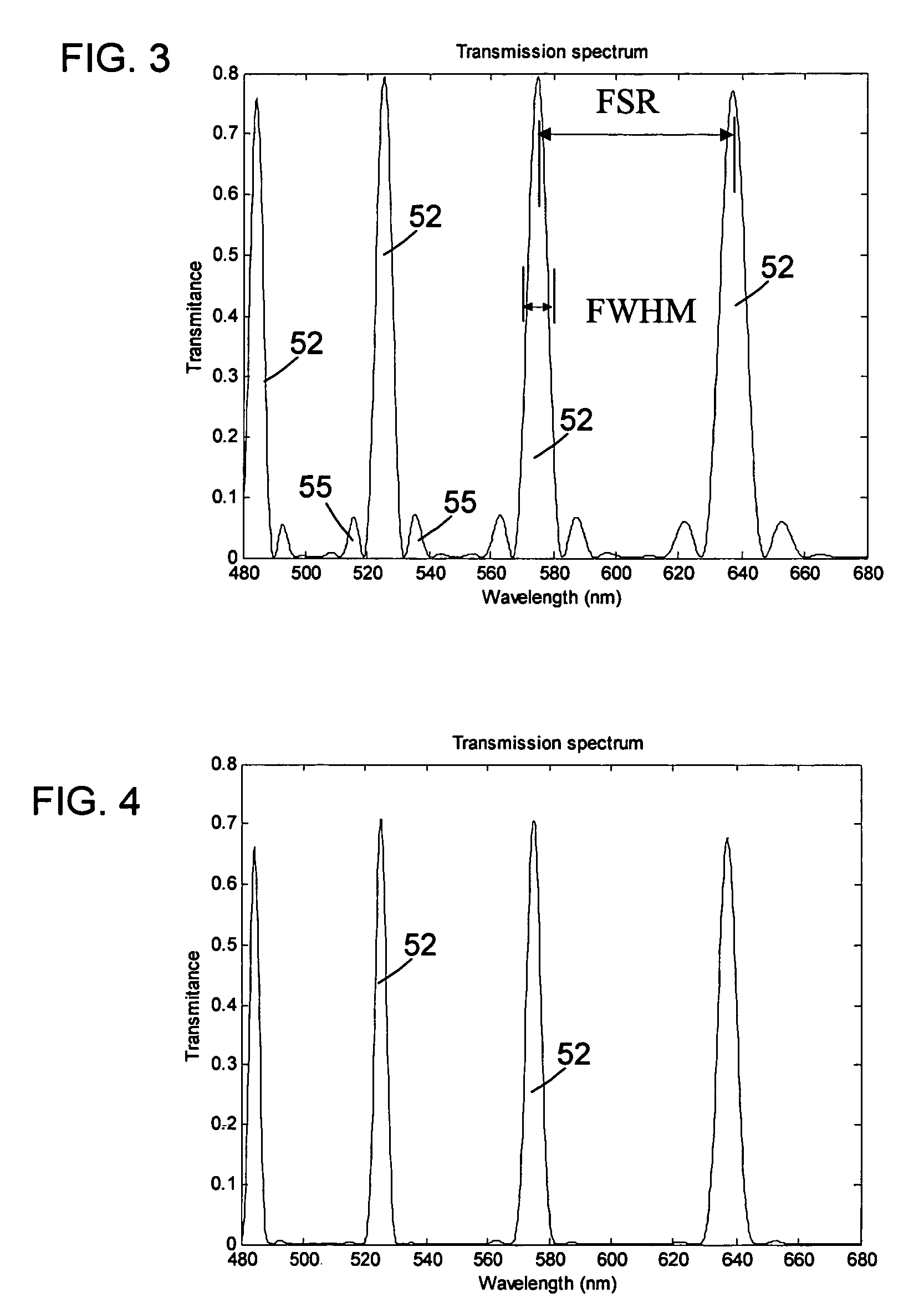
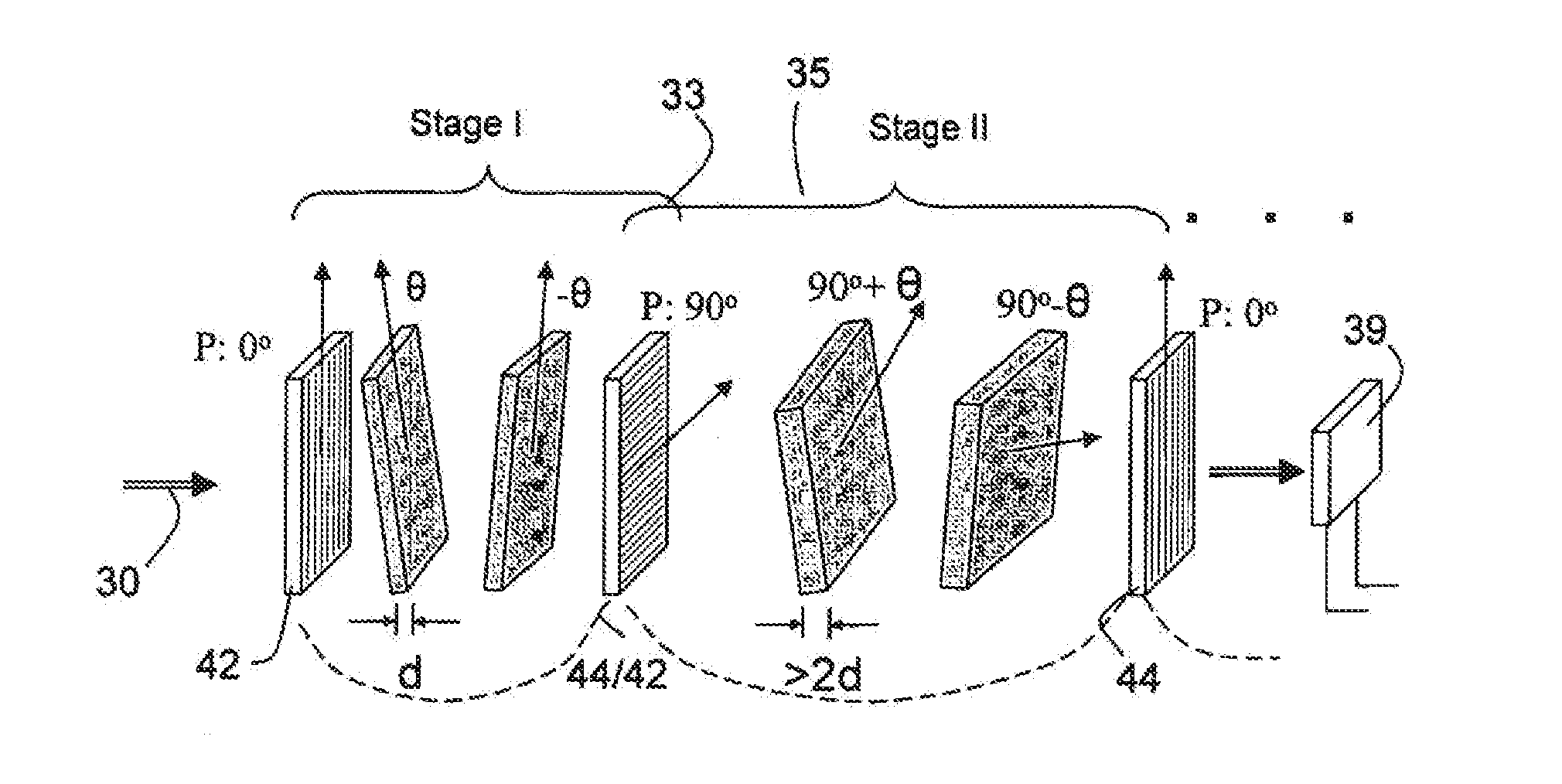
ActiveUS20120300143A1Improve transmittanceExcellent out-of-band rejection ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers. The retarders can include active retarders such as tunable liquid crystal birefringent elements, passive retarders such as fixed retarders, and / or combinations thereof. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging. The filter may be configured to provide faster switching speed and increased angle of acceptance and may operate in the rage of approximately 400-1100 nm.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Multi-conjugate liquid crystal tunable filter
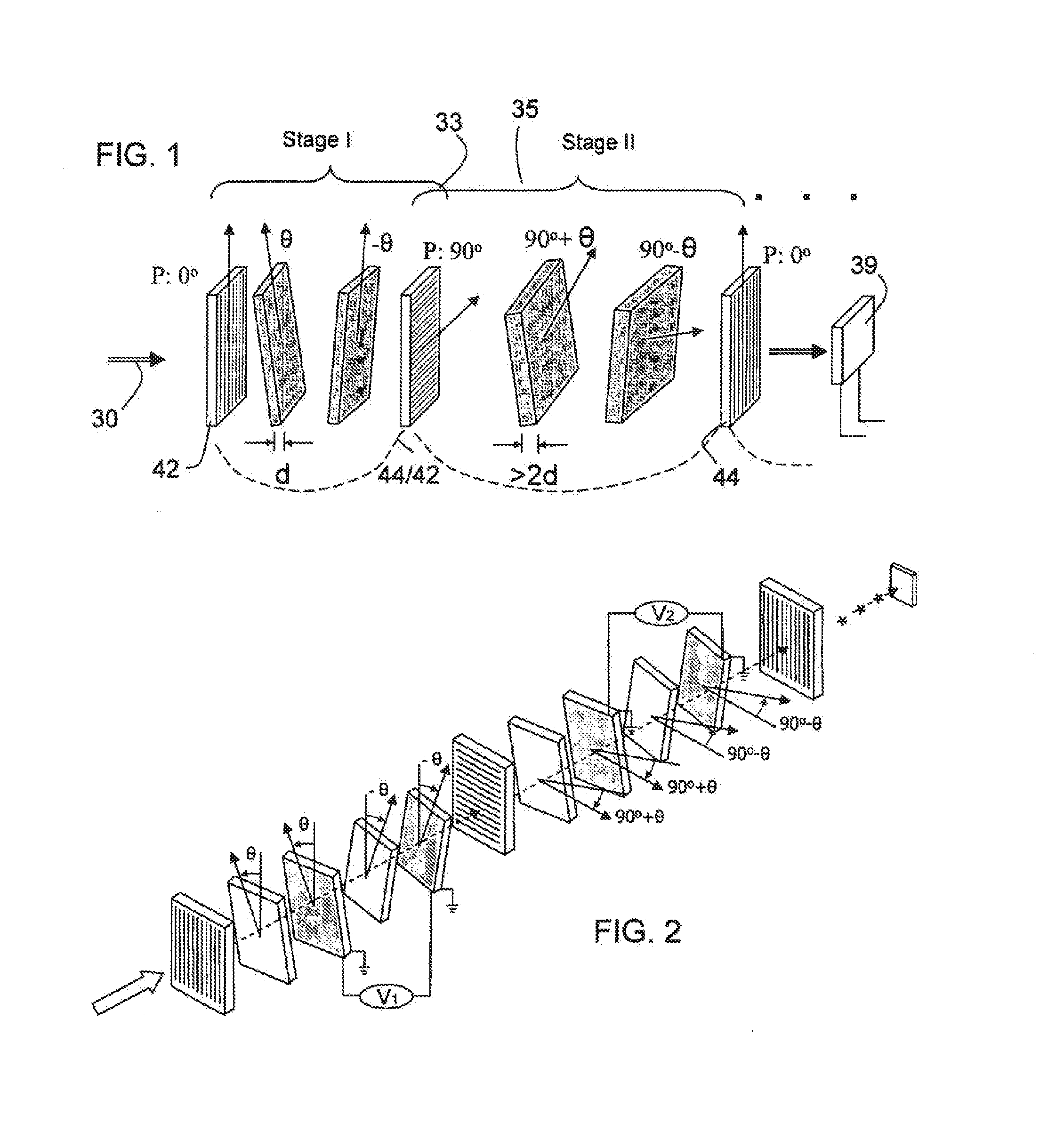
ActiveUS7362489B2High finesse spectral filtersIncrease gear ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A hyper-spectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers forming interference filters. The retarders can include tunable birefringent elements such as liquid crystals controlled in unison, fixed retarders and / or combined tunable and fixed birefringences. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Short-Wavelength Infrared (SWIR) Multi-Conjugate Liquid Crystal Tunable Filter
ActiveUS20140098309A1Fast tuningImprove transmittanceOptical filtersNon-linear opticsWavelength filterPolarizer
A SWIR hyperspectral imaging filter has serial stages along an optical signal path with angularly distributed birefringent retarders and polarizers. The retarders can include active retarders such as tunable liquid crystal birefringent elements, passive retarders such as fixed retarders, and / or combinations thereof. Distinctly different periodic transmission spectra are provided by different filter stages, each having multiple retarders, in particular with some stages having broad bandpass peaks at wide spectral spacing and other stages have very narrow closely spaced peaks. The respective spectra include at least one tunably selectable band at which the transmission spectra of the filter stages coincide, whereby the salutary narrow bandpass and wide spectral spacing ranges of different stages apply together, resulting in a high finesse wavelength filter suitable for spectral imaging. The filter may be configured to provide faster switching speed and increased angle of acceptance and may operate in the rage of approximately 850-1700 nm.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Waveguide optically pre-amplified detector with passband wavelength filtering
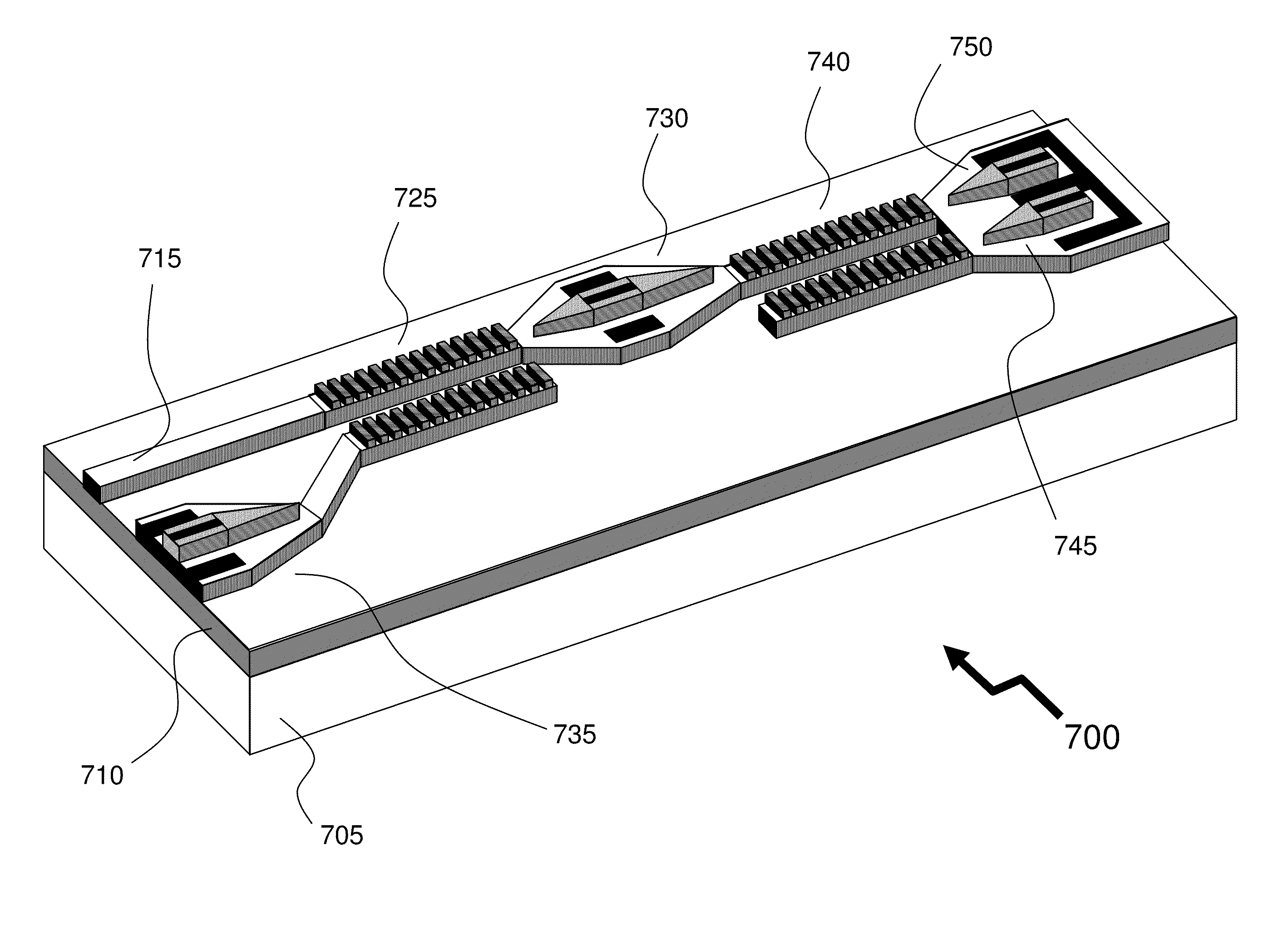
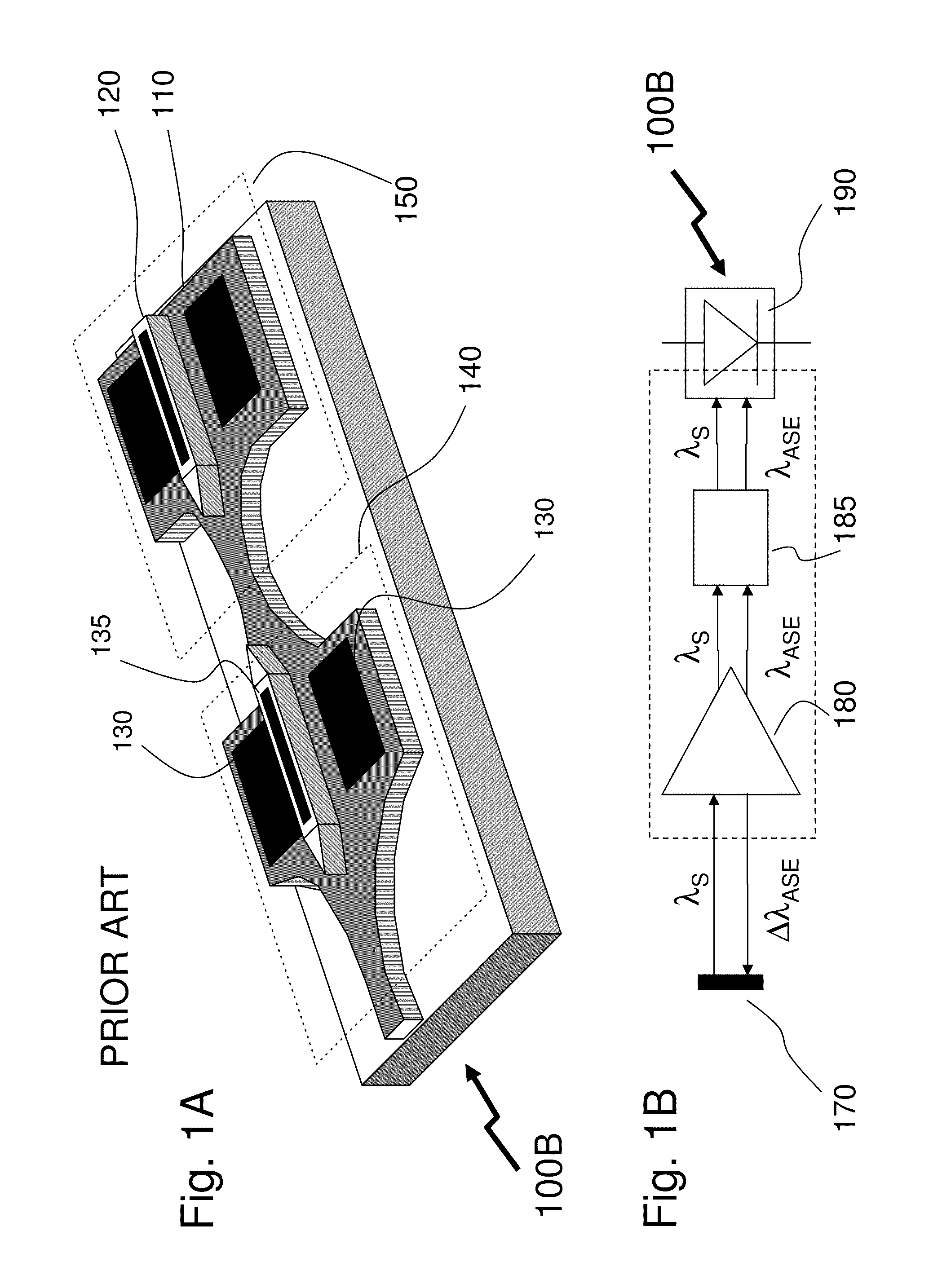
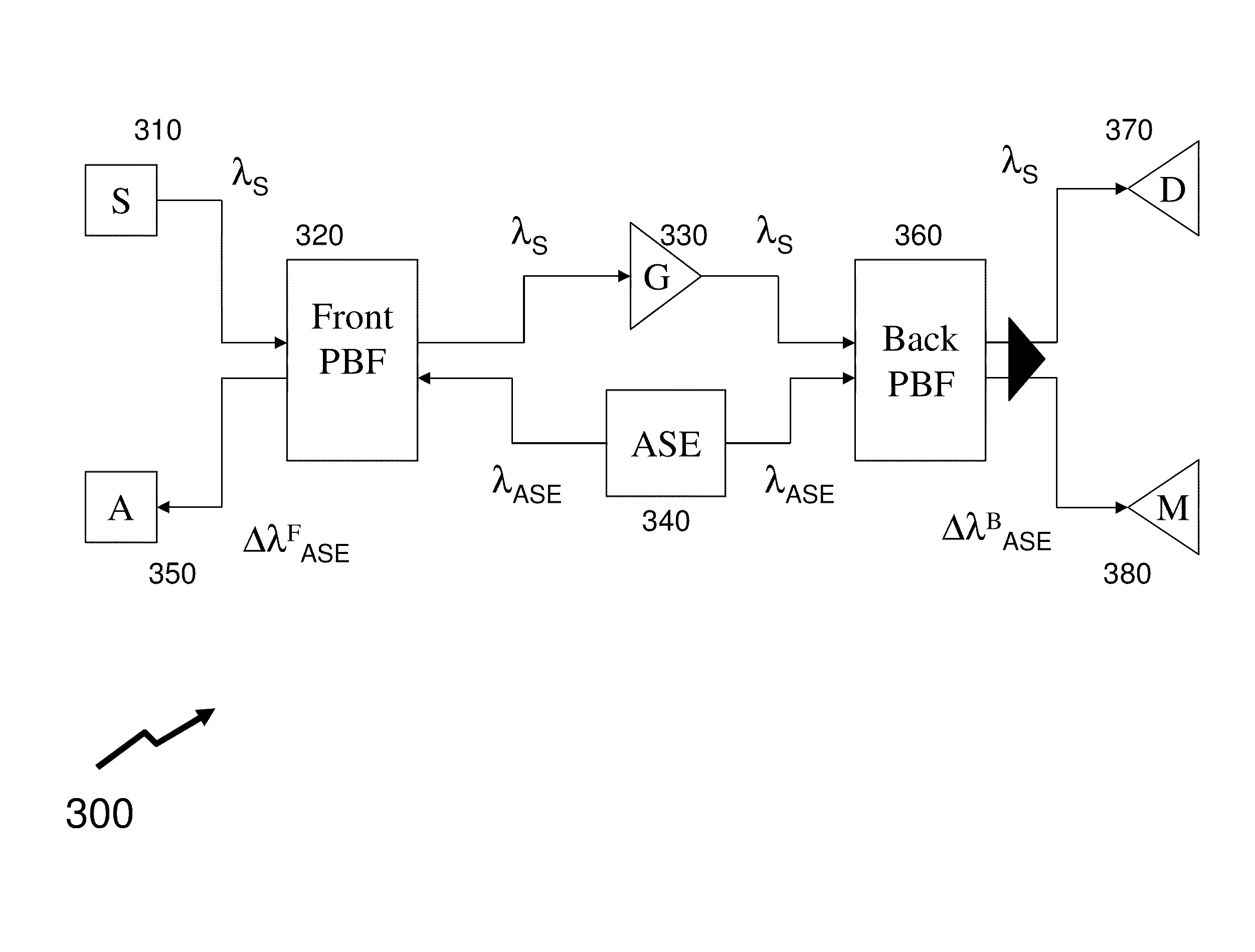
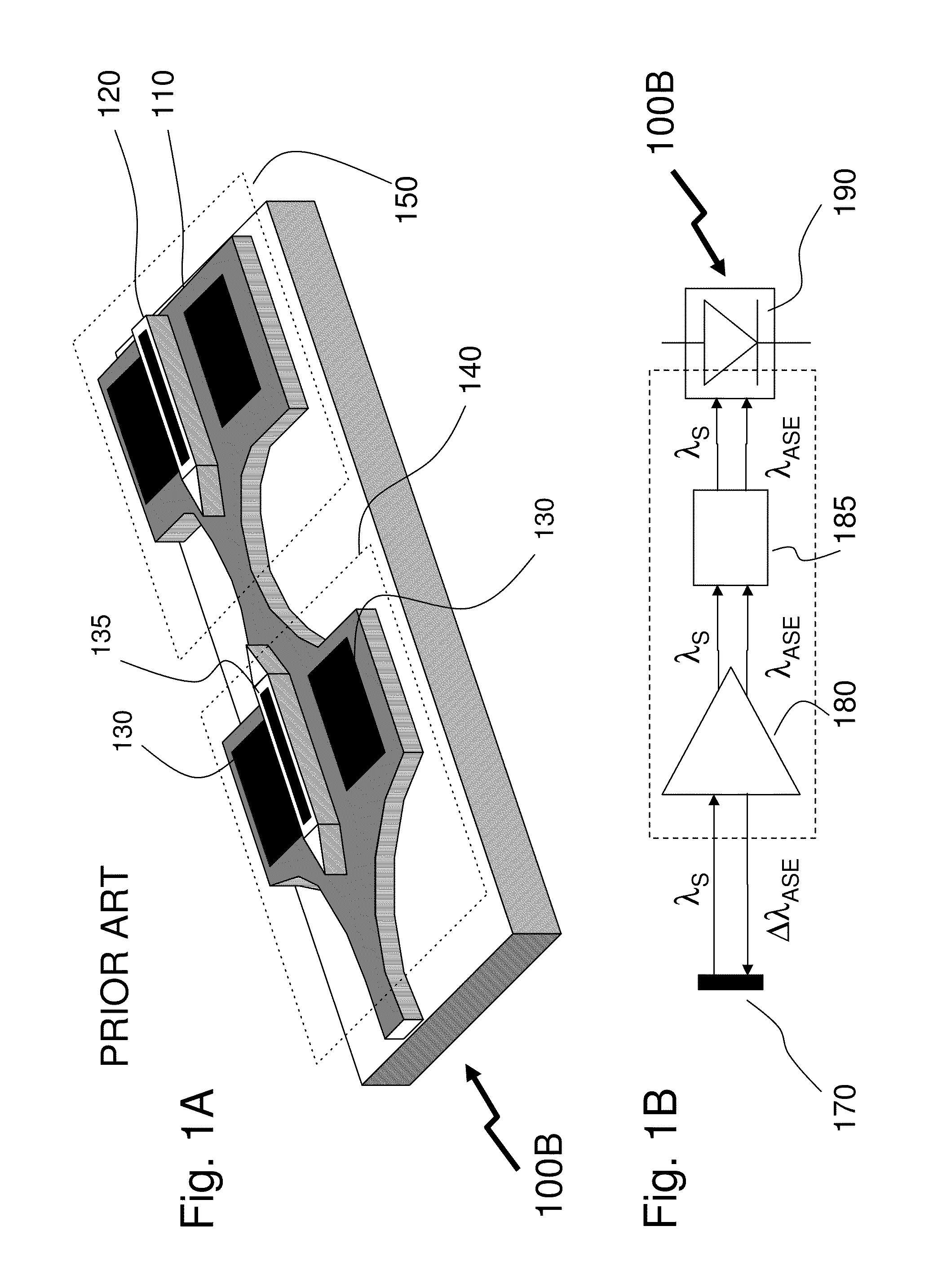
ActiveUS8098969B2Reduce impactImprove device performanceSemiconductor lasersOptical waveguide light guideWavelength filterMultimode interference
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration (MGVI) structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, allowing for the integration of semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) and PIN photodetector (PIN) structures within a common wavelength-designated waveguide of the plurality of the vertically integrated wavelength-designated waveguides forming the MGVI structure. The integration includes a wavelength filter integrated between the SOA and PIN to reduce noise within the PIN arising from ASE generated by the SOA. In exemplary embodiments of the invention, the wavelength filter is integrated into MGVI structure either within a common wavelength designated waveguide or within the wavelength-designated waveguide. Further in other embodiments the wavelength filter is provided by a thin-film filter abutting a facet of the integrated-photonics arrangement wherein optical signals are coupled by optical waveguides and / or additional optical elements such as a multimode interference device.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Optical transmission device
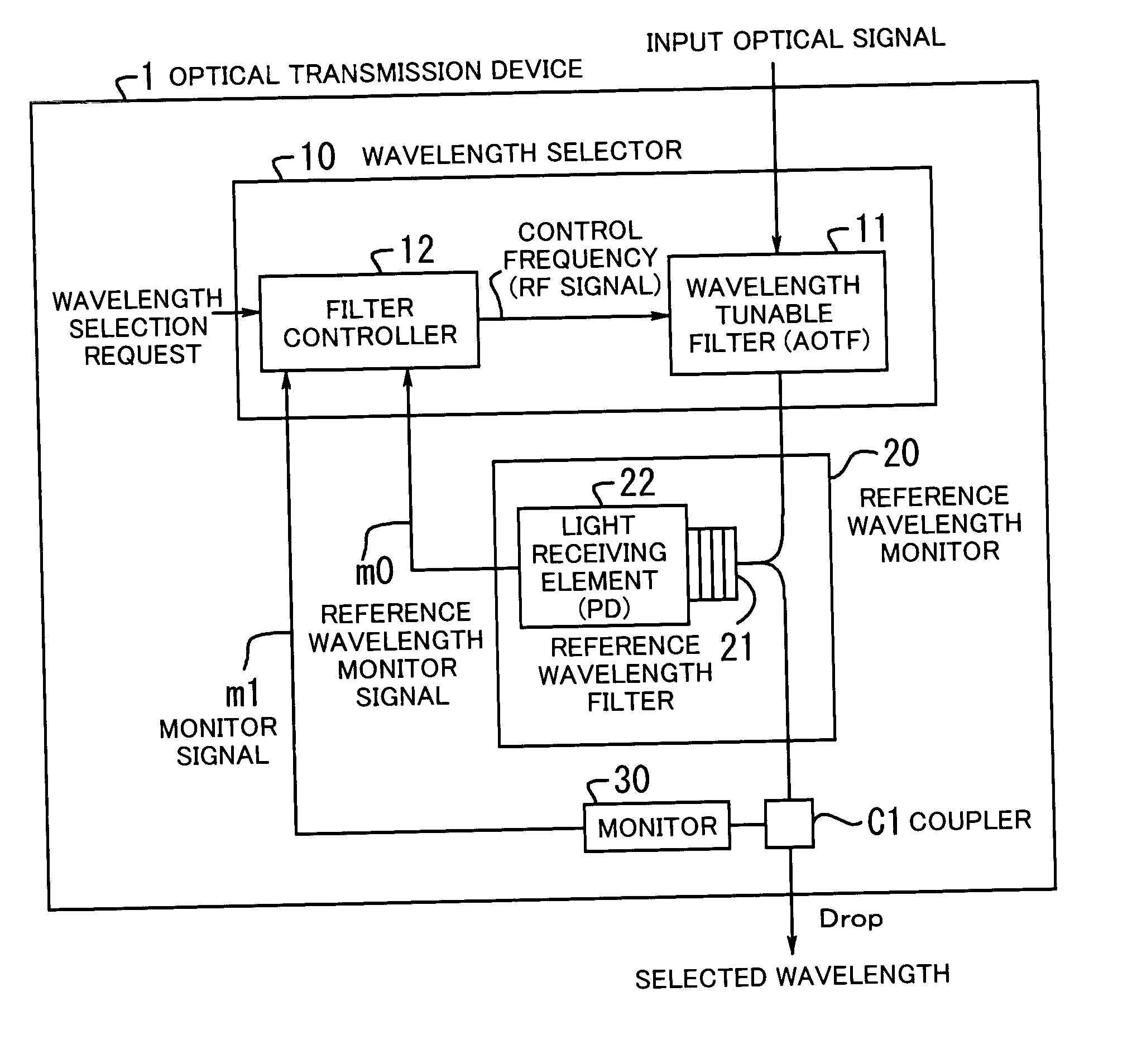
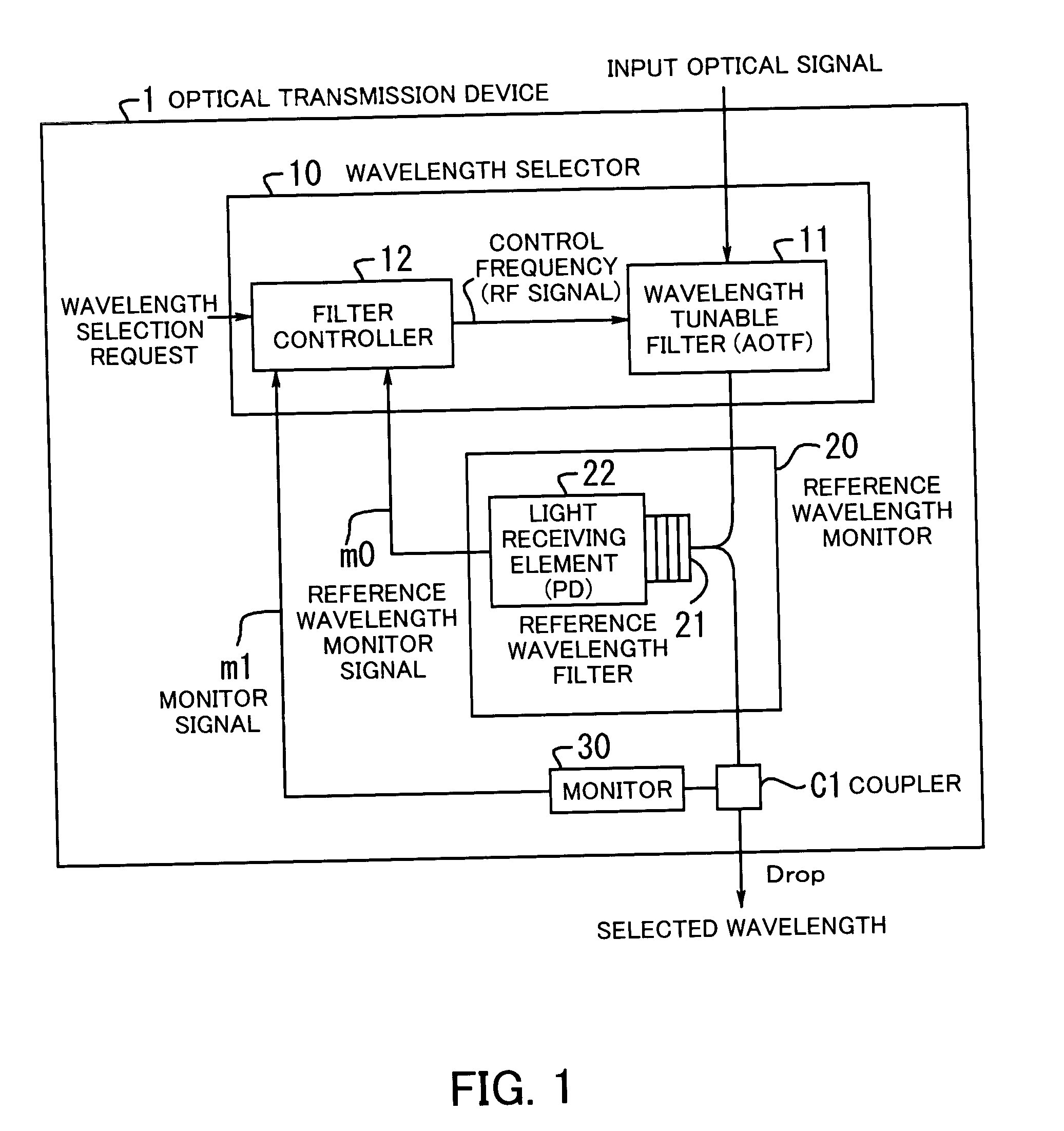
InactiveUS20050169633A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsWavelength filterTarget control
An optical transmission device improved in quality and reliability of OADM function and permitting configuration of highly-flexible, economical OADM networks. A wavelength tunable filter variably selects a wavelength according to a control frequency. A filter controller applies the control frequency to the filter while scanning wavelength over an entire signal bandwidth, to detect, from a reference wavelength monitor signal supplied thereto, a reference control frequency which permits the filter to select a reference wavelength and according to which wavelength is matched. On receiving a wavelength selection request, the controller obtains a target control frequency from the reference control frequency and the position of a target wavelength relative to the reference wavelength, and applies the obtained frequency to the filter. A reference wavelength filter transmits the reference wavelength therethrough. A light-receiving element monitors the transmitted reference wavelength to generate the monitor signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
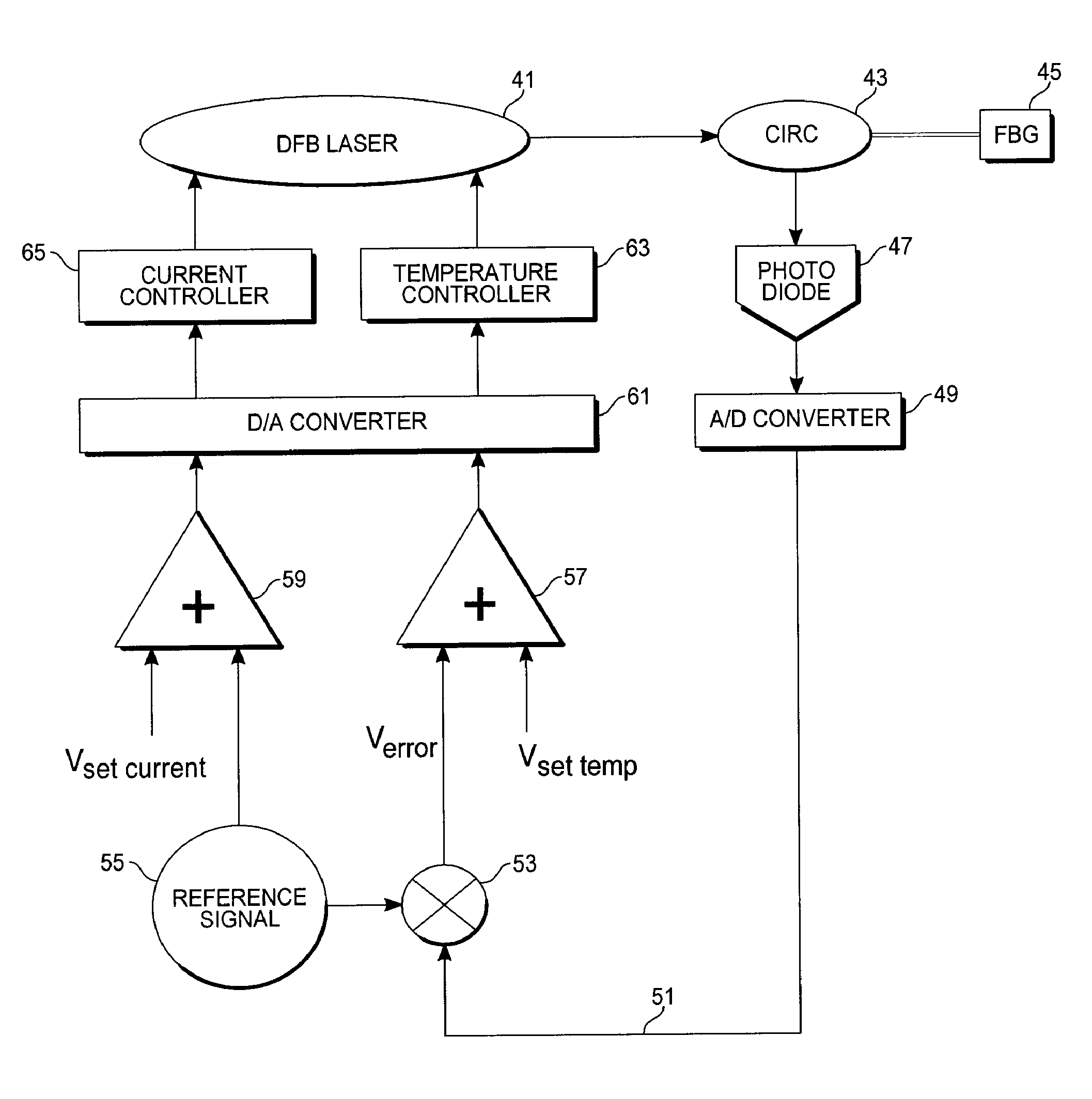
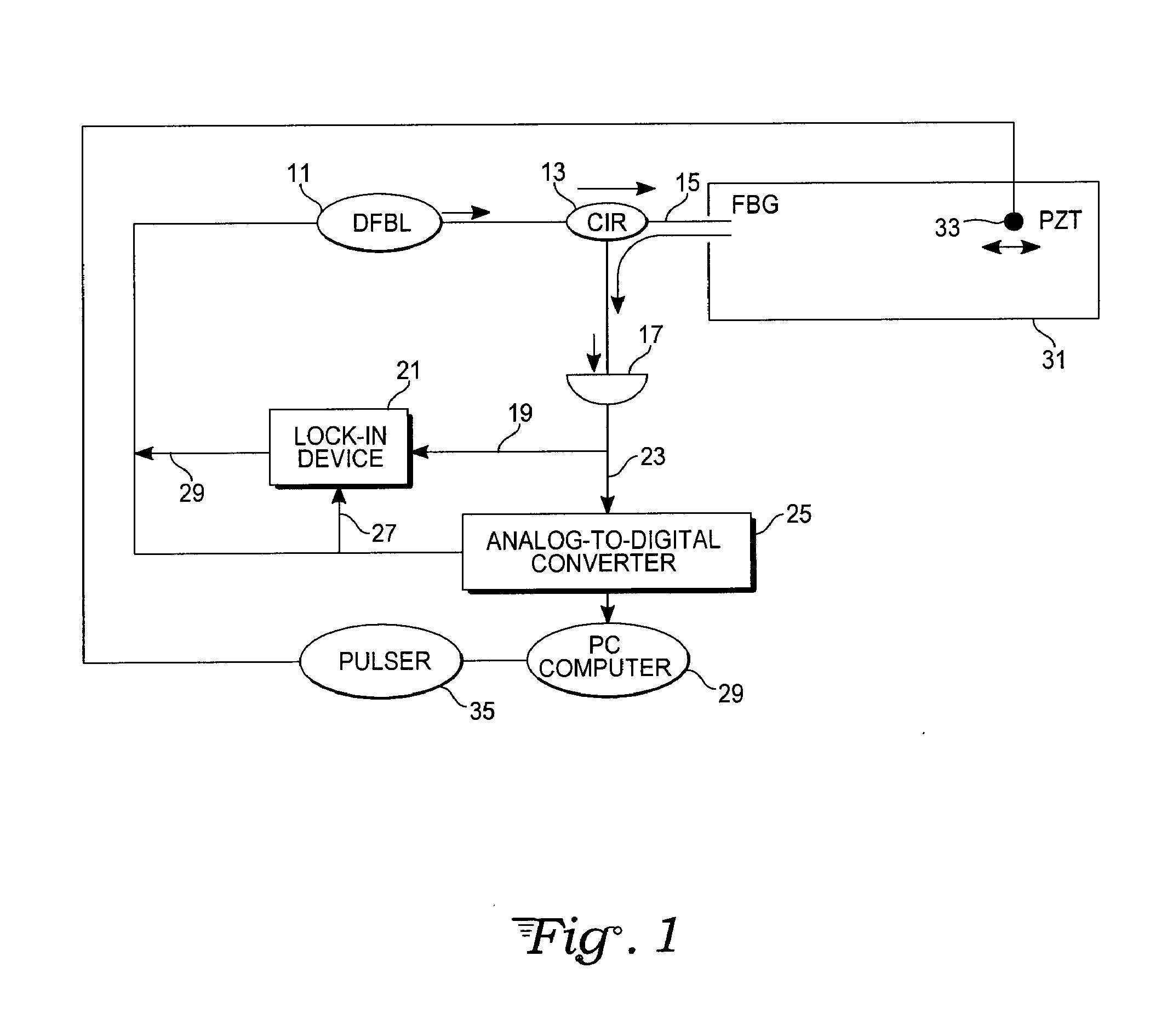
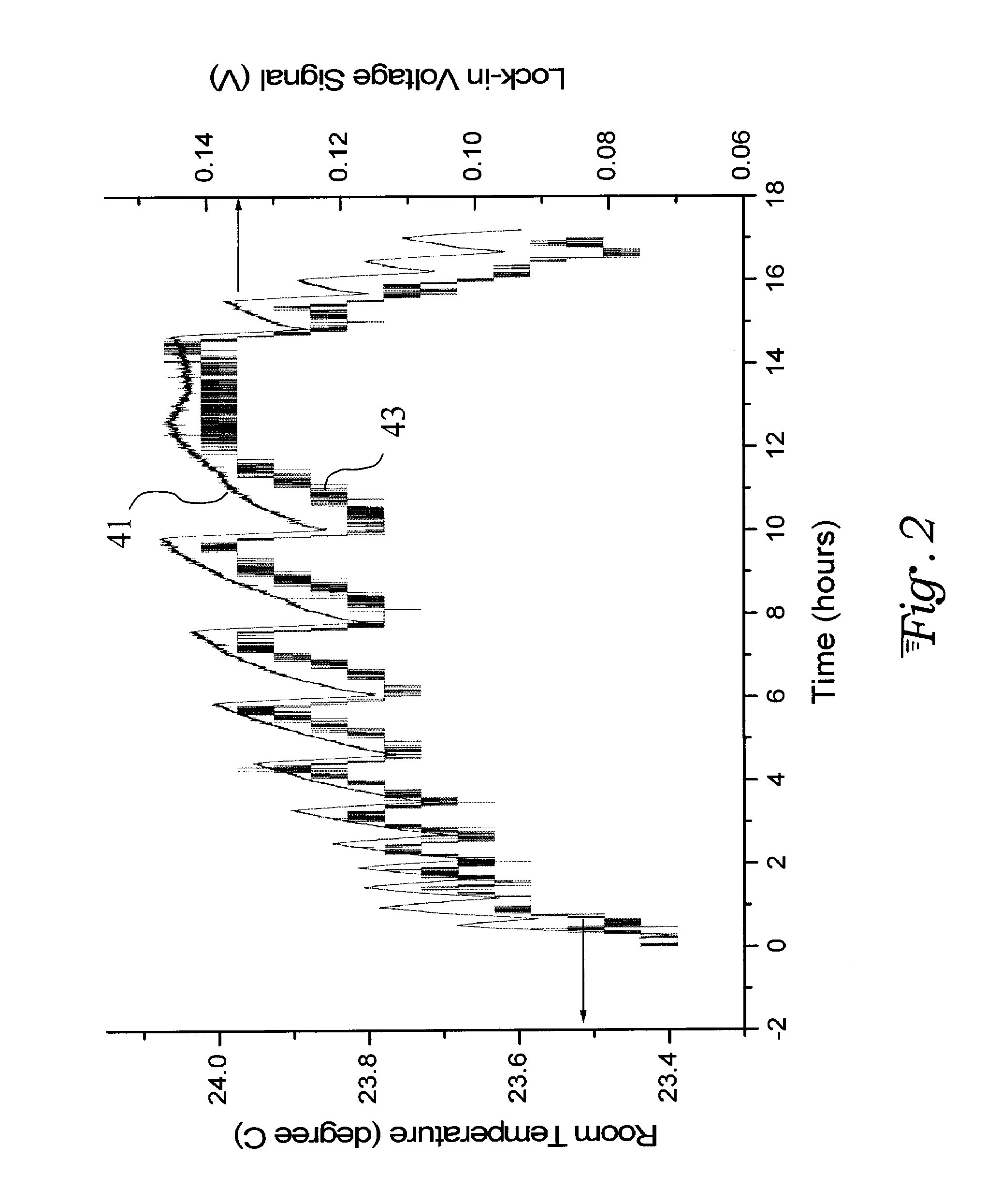
Lock-in demodulation technique for optical interrogation of a grating sensor
InactiveUS20090059209A1Increase resistanceAchieve accuracyForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingWavelength filter
A grating sensor and method for optical interrogation of that sensor uses a lock-in technique to achieve simultaneous measurements of strain (and related temperature) and ultrasonic stress wave signals, as well as other environmental conditions that affect a reflection spectrum of the grating sensor. It achieves this by using a lock-in amplifier or a software demodulator to detect slight shifts in the grating reflection spectrum with high sensitivity and accuracy. A dynamic feedback loop based on the lock-in error signal output retunes the light wavelength of the light source (e.g., a tunable laser) or of a wavelength filter in the reflection path to maintain it relative to a specified reflection point of the grating reflector. The lock-in error signal serves as a measure of temperature / strain changes and of ultrasonic vibrations.
Owner:LOS GATOS RES
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
The present invention relates to ophthalmic systems comprising a selective light wavelength filter, wherein said selective filter provides improved contrast sensitivity.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
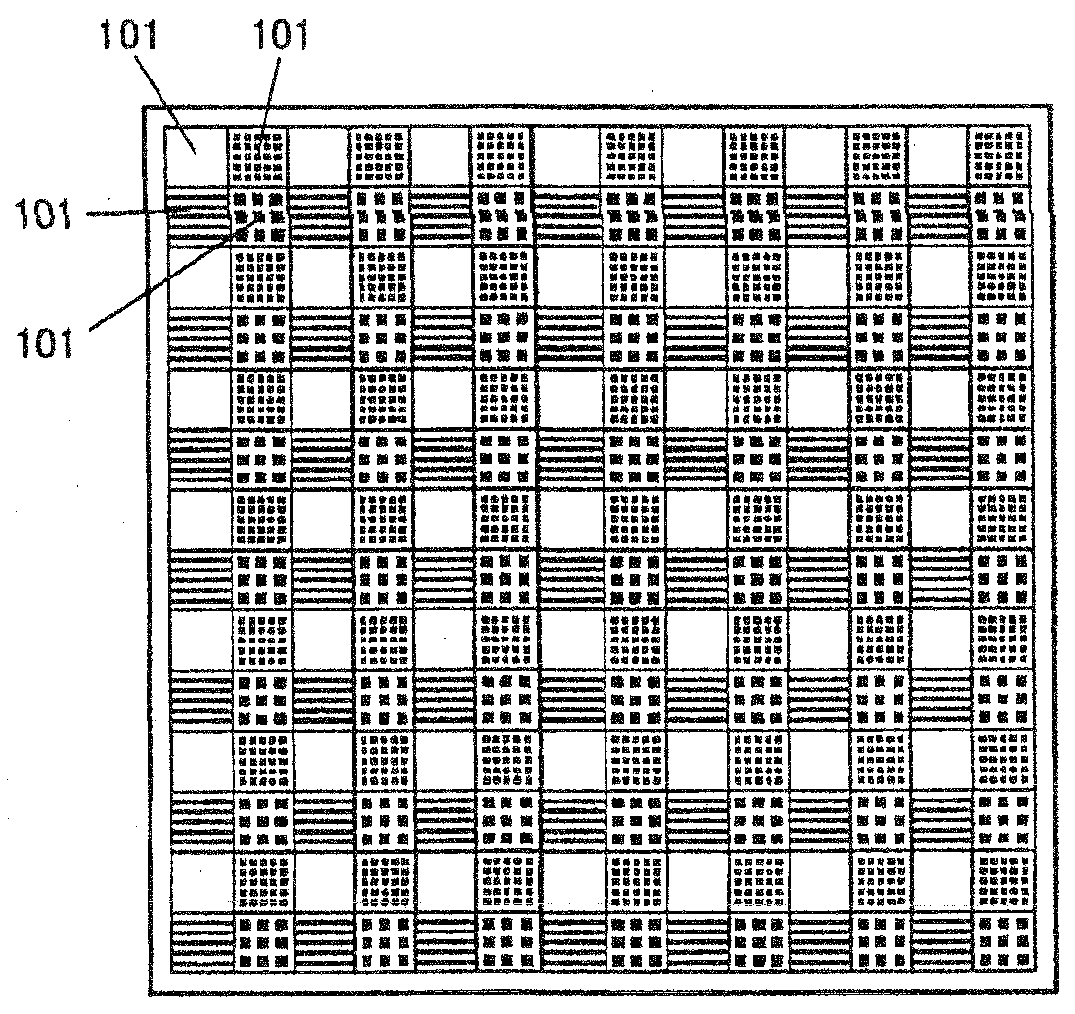
Wavelength division image measuring device
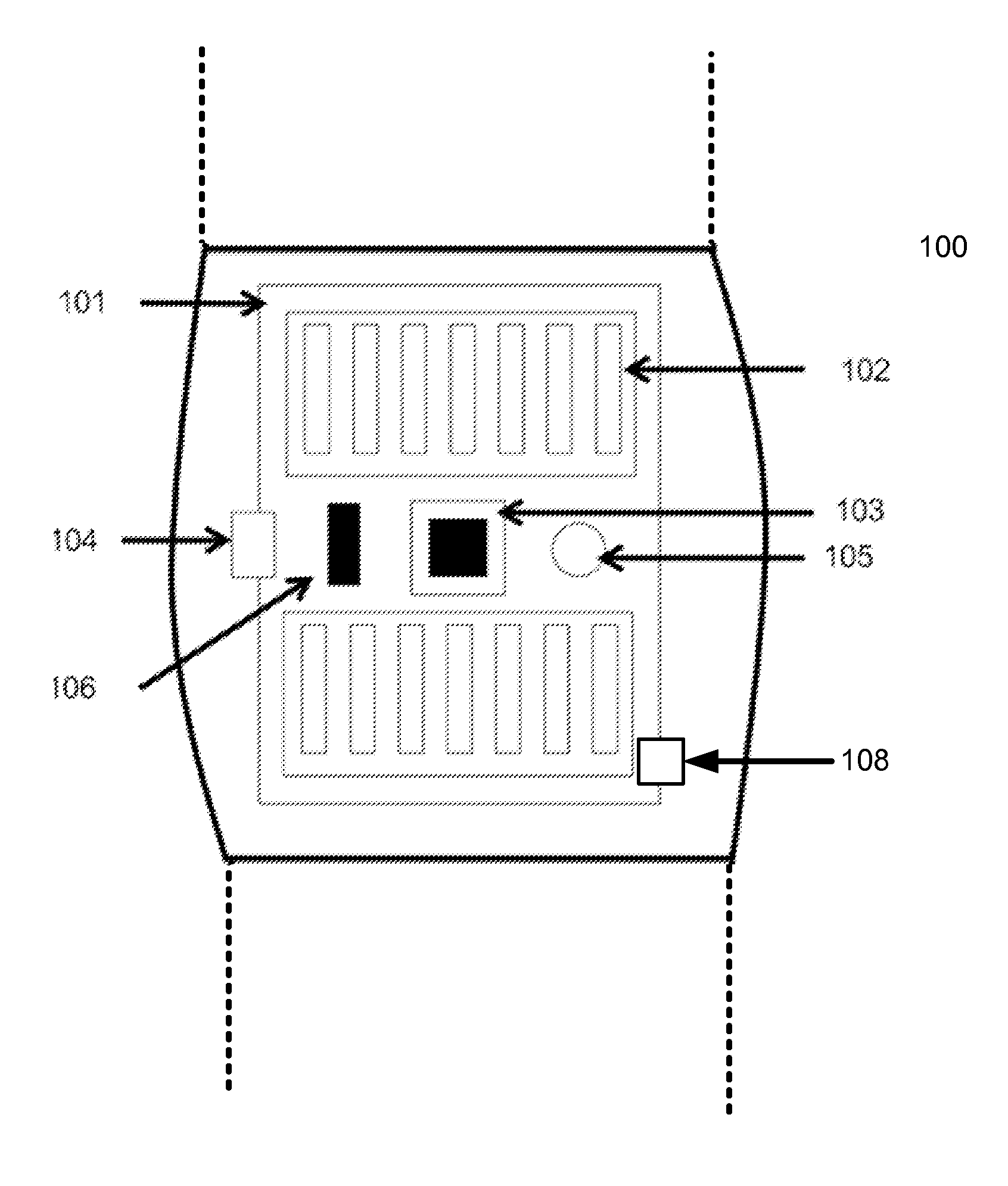
InactiveUS20090116029A1Sharp selectivityEasy to integrateRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryWavelength filterRefractive index
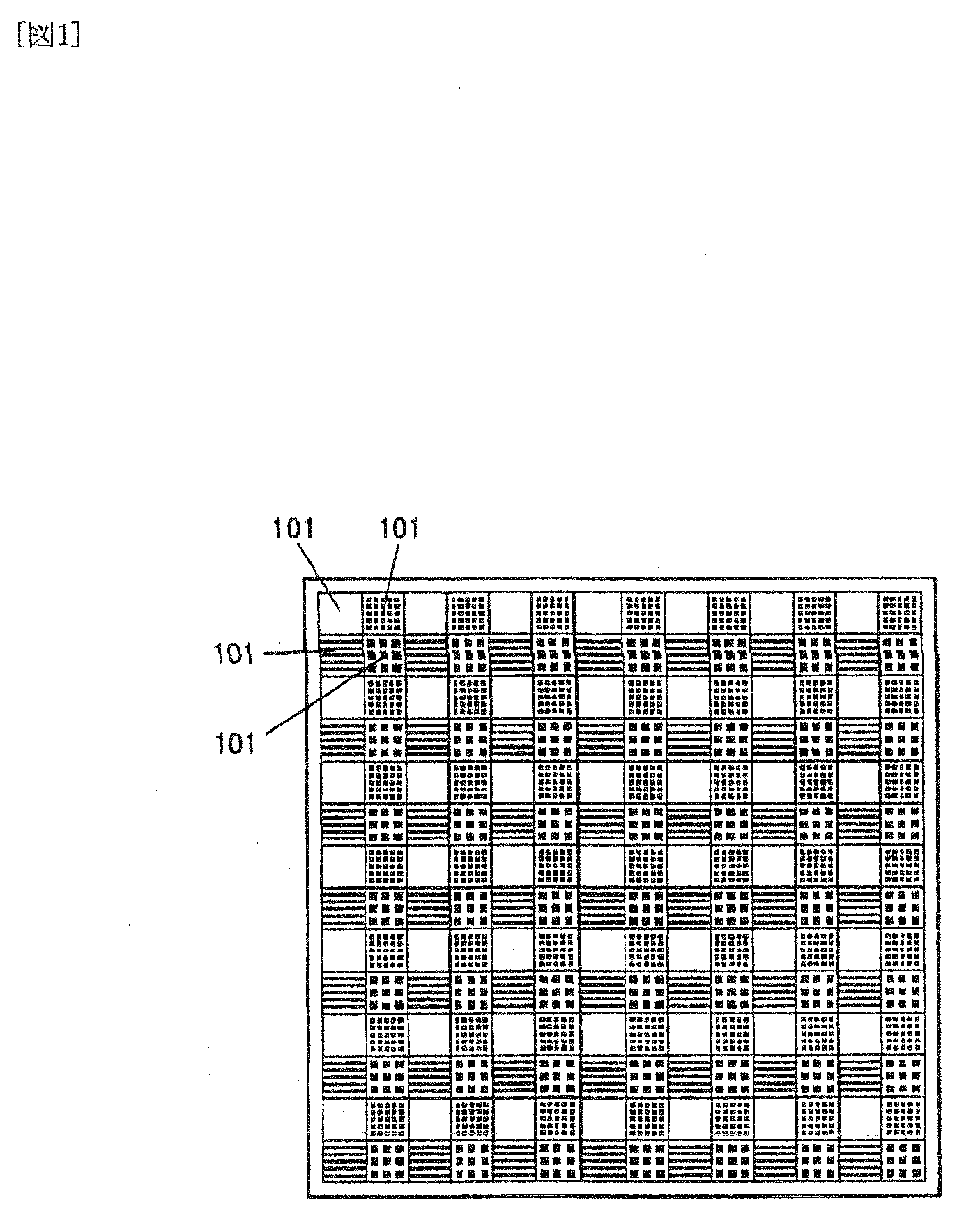
A wavelength division image measuring device that can divide a wideband incident light from a measurement object into a plurality of wavelengths with high selectivity to thereby measure these images simultaneously and collectively. Micro periodic irregular lattices are formed on a substrate 302. At this time, a plurality of microscopic element areas 101 with different lattice shapes and lattice periods are repeatedly arranged within a plane of the substrate 302. Next, a high refractive index material and a low refractive index material are alternately laid thereon so as to form a multilayer using a bias spatter method to thereby form a wavelength filter 301 with a photonic crystal structure. Thus, an array of the photonic crystal wavelength filters 031 with a sharp selectivity and different wavelength transmission characteristics can be obtained.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD +1
Refractometer
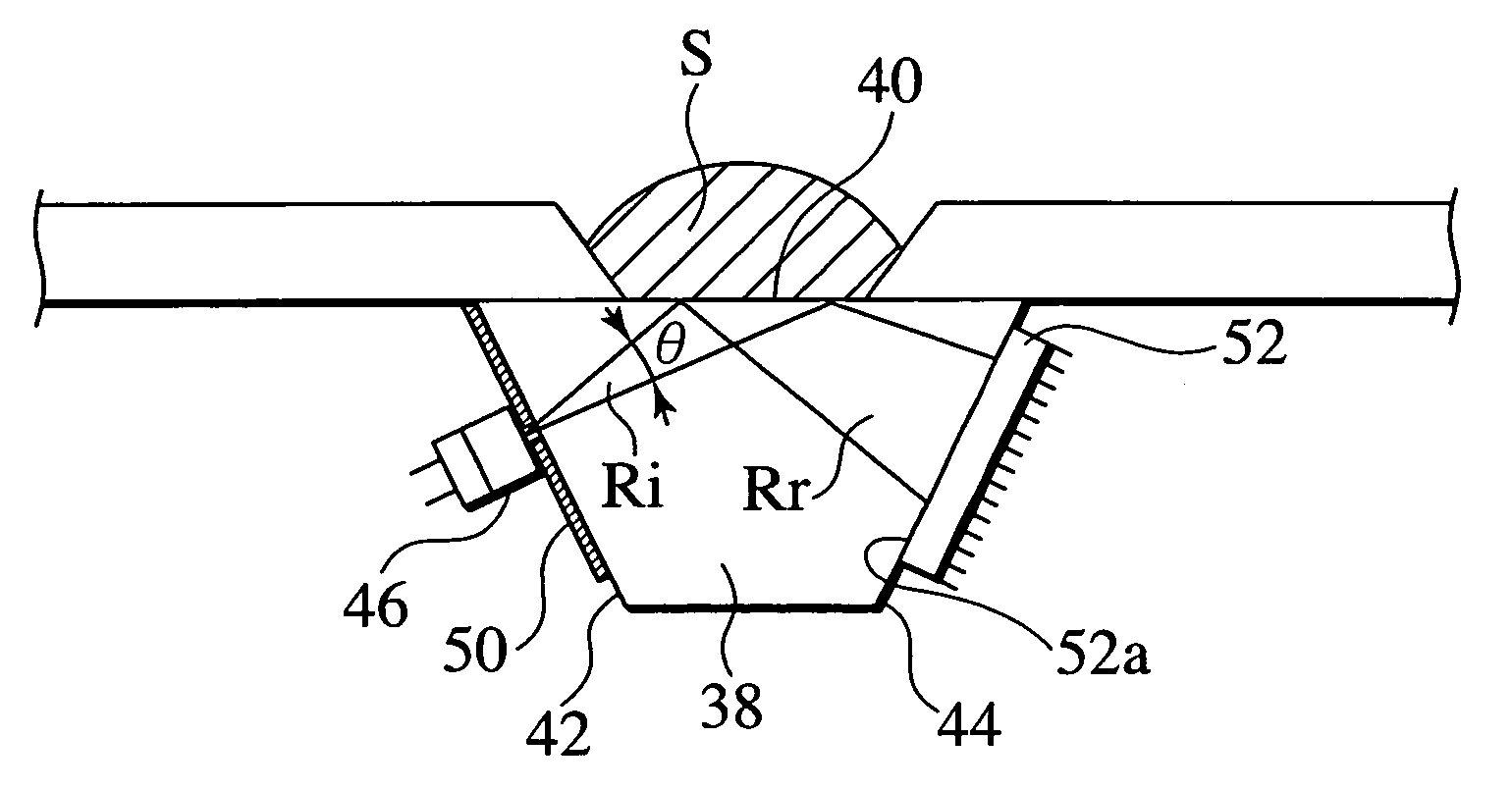
InactiveUS7492447B2Low production costEfficient measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsWavelength filterPrism
A refractometer for measuring refractive index of a sample comprising a prism having an interface contacting the sample, a light source that radiates light towards the interface from an entrance face of the prism, and a photoelectric sensor for receiving light reflected at the interface and directed outward from an exit face of the prism. The light source and the photoelectric sensor are secured to the prism. The refractometer comprises a sample stage arranged surrounding the interface surface. This sample stage provides a non-adhesive coating formed on the surface thereof. The refractometer comprises filter means arranged between the interface surface and the photoelectric sensor. This filter means includes a wavelength filter that selectively allows transmission of light having a wavelength within a prescribed region, including a wavelength of light of the light source.
Owner:ATAGO
Optical switch, optical modulator and variable wavelength filter
A high-speed optical switch simple in structure, low in drive voltage and polarization-independent, an optical modulator, and a variable wavelength filter. The optical switch comprises a 3dB coupler (16) provided on the input side thereof, a 3dB coupler (17) provided on the output side, and two optical waveguides that connect the input-side 3dB coupler with the output-side 3dB coupler. In addition, a phase modulator (18) for applying an electric field to one or both of the two optical waveguides in provided. At least two optical waveguides consist of a crystal material having a composition consisting of KTa1-xNbxO3 (0 G02F 1 / 313 G02F 1 / 035 46 50 10 2004 / 3 / 18 1705908 2005 / 12 / 7 100410796 2008 / 8 / 13 2008 / 8 / 13 2008 / 8 / 13 Nippon Telegraph & Telephone Japan Enbutsu Koji Fujiura Kazuo Fushimi Hiroshi Imai Tadayuki Kurihara Takashi Matsuura Touru Sasaura Masahiro Shimokozono Makoto Tate Akiyuki Toyota Seiji li zheng yang xiaoguang 11247 Japan 2003 / 3 / 19 075105 / 2003 Japan 2003 / 3 / 20 077142 / 2003 Japan 2003 / 7 / 16 275521 / 2003 Japan 2003 / 8 / 28 305023 / 2003 Japan 2003 / 12 / 8 409658 / 2003 Japan 2003 / 12 / 11 412951 / 2003 2005 / 5 / 27 PCT / JP2004 / 003665 2004 / 3 / 18 WO2004 / 083953 2004 / 9 / 30 Japanese
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
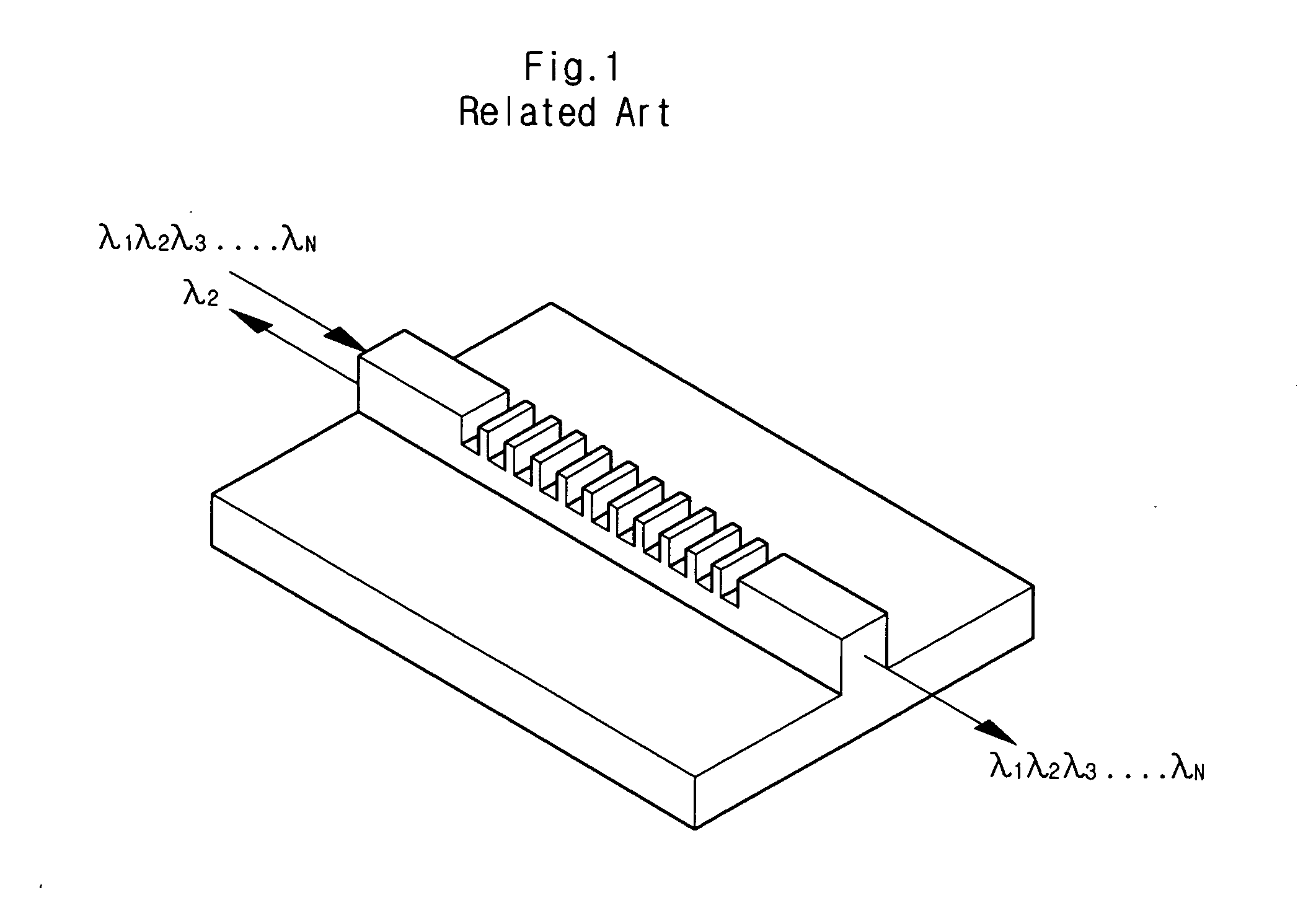
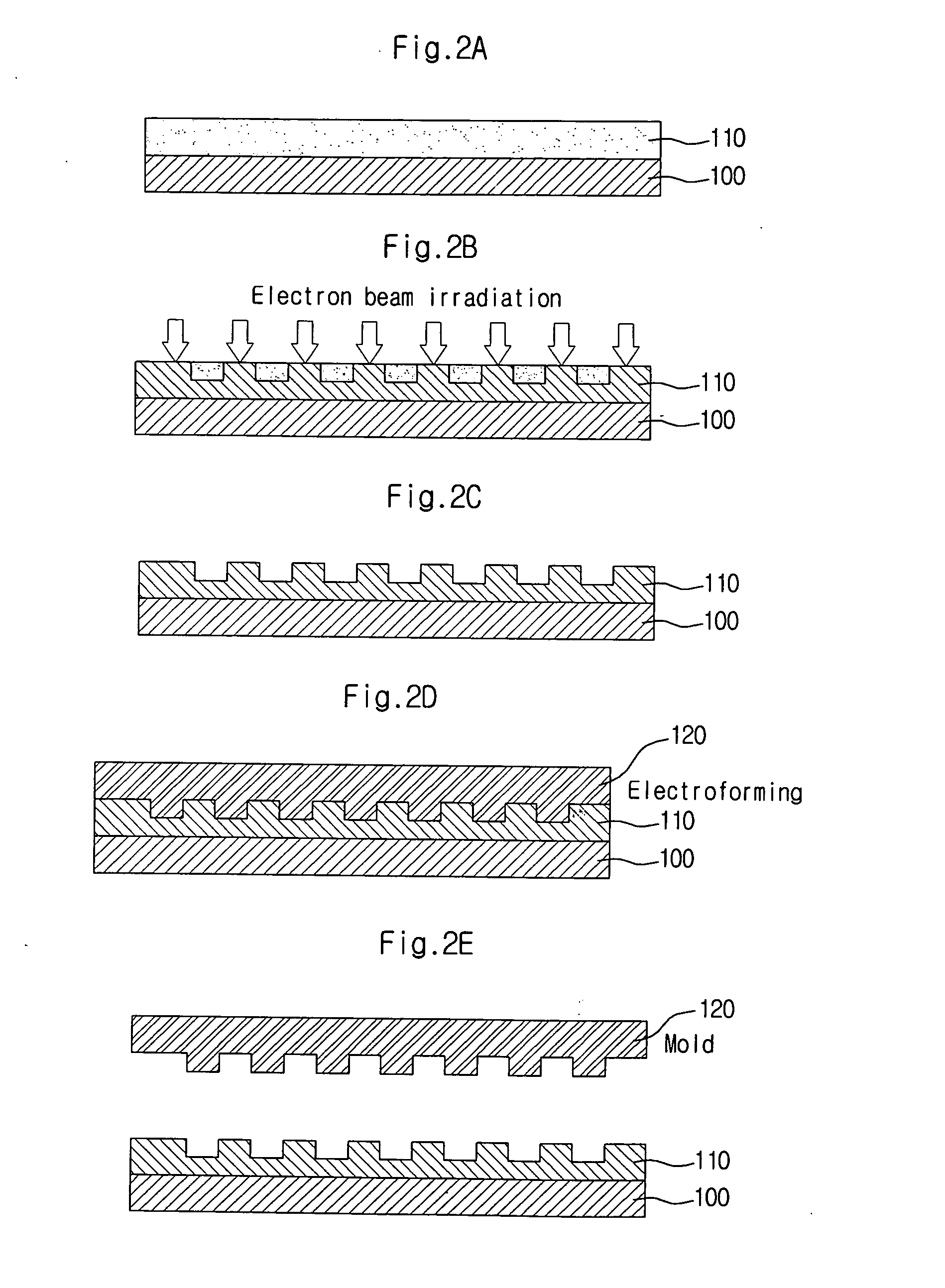
Manufacturing method of wavelength filter
InactiveUS20050008286A1Well formedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWavelength filterPolymer
A manufacturing method of a wavelength filter includes the steps of: depositing on a substrate a lower clad layer and a core layer, each made from a polymer material; compressing the core layer with a mold to lithograph a pattern of the mold onto the core layer; stabilizing the lower clad layer and the core layer; separating the core layer from the mold; forming an upper clad layer on the core layer; and forming an electrode on the upper clad layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Waveguide Optically Pre-Amplified Detector with Passband Wavelength Filtering
ActiveUS20110135314A1Reduce impactImprove device performanceElectromagnetic transmissionSemiconductor lasersWavelength filterMultimode interference
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration (MGVI) structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, allowing for the integration of semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) and PIN photodetector (PIN) structures within a common wavelength-designated waveguide of the plurality of the vertically integrated wavelength-designated waveguides forming the MGVI structure. The integration includes a wavelength filter integrated between the SOA and PIN to reduce noise within the PIN arising from ASE generated by the SOA. In exemplary embodiments of the invention, the wavelength filter is integrated into MGVI structure either within a common wavelength designated waveguide or within the wavelength-designated waveguide. Further in other embodiments the wavelength filter is provided by a thin-film filter abutting a facet of the integrated-photonics arrangement wherein optical signals are coupled by optical waveguides and / or additional optical elements such as a multimode interference device.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com