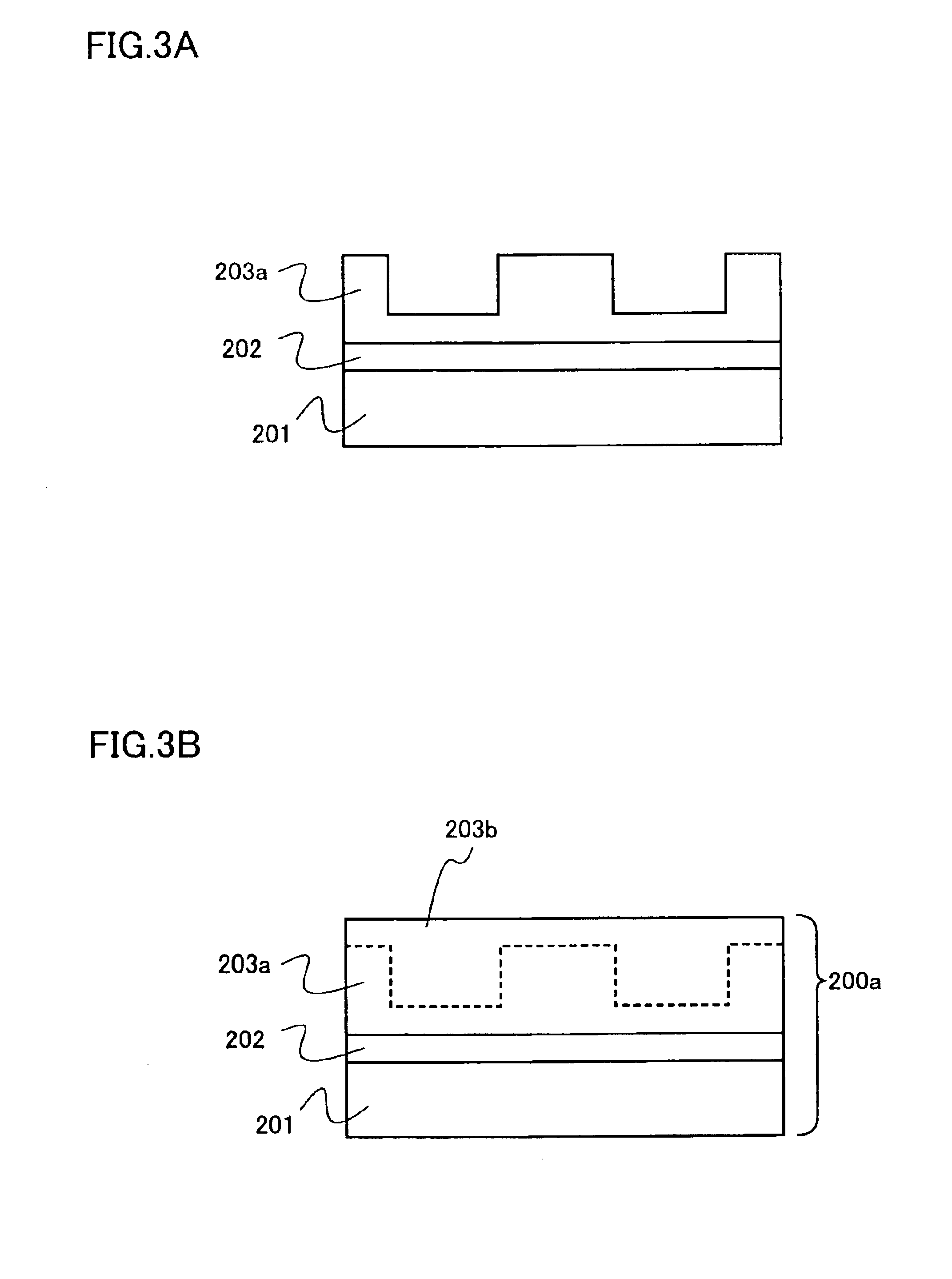
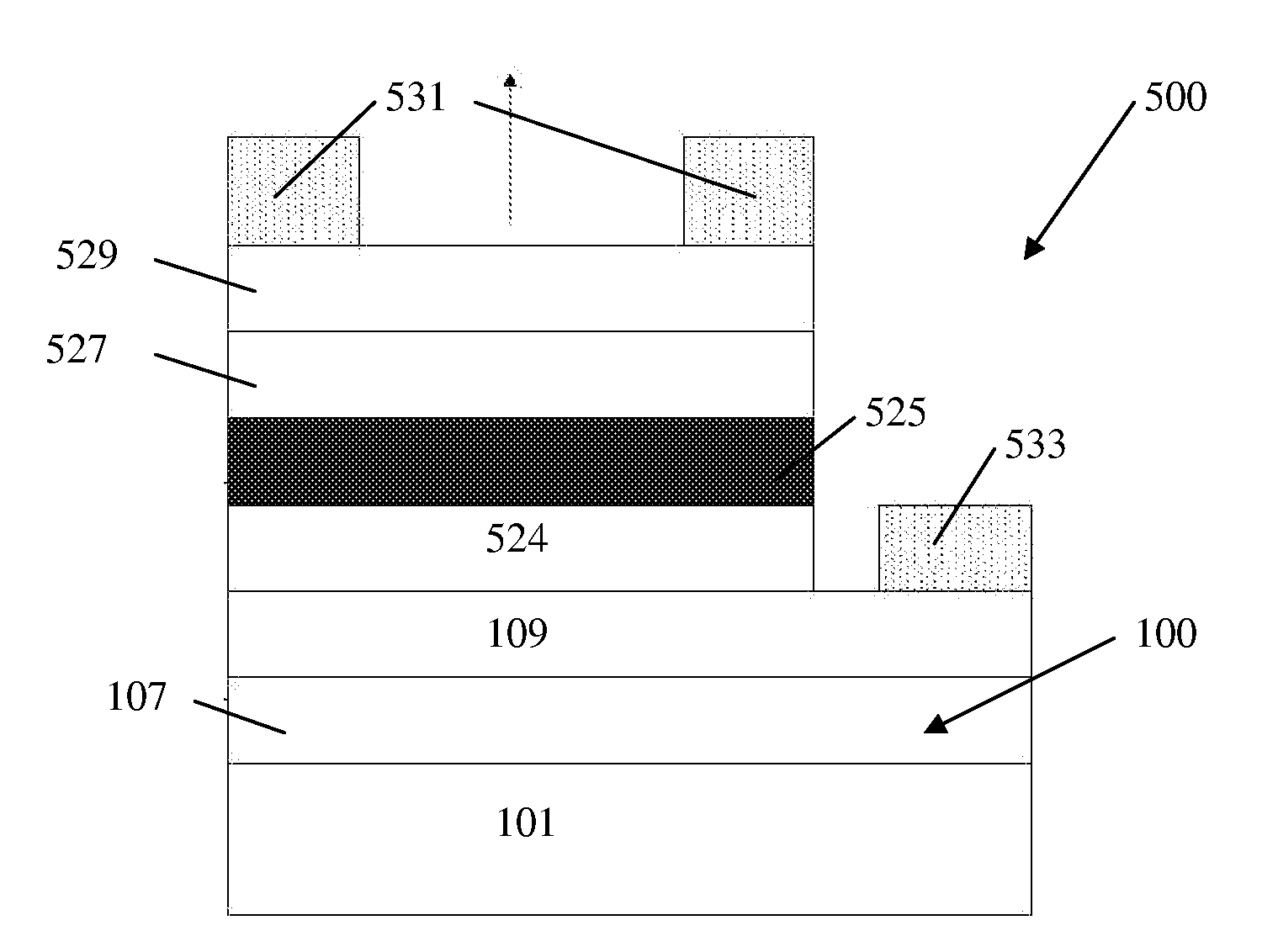
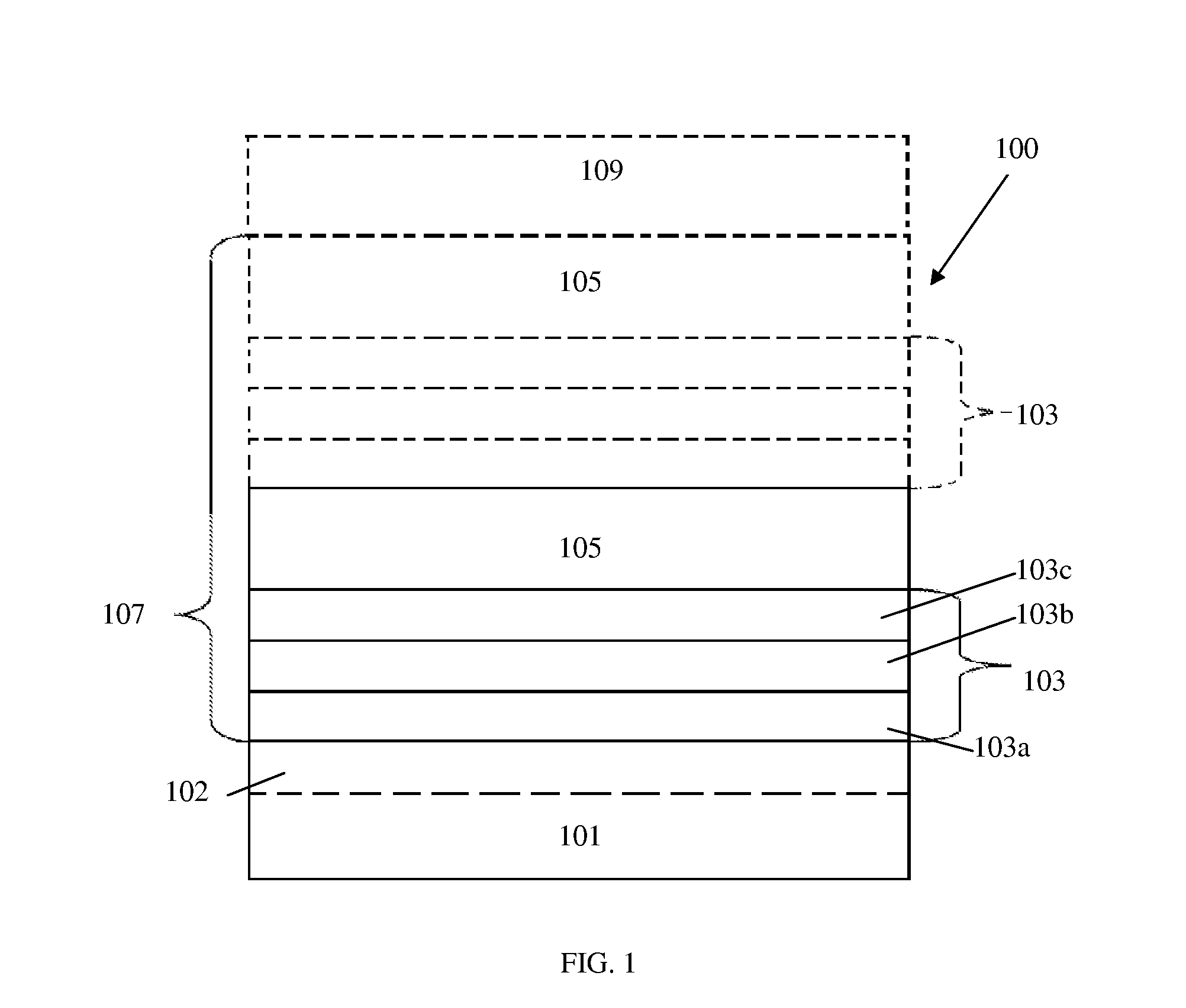
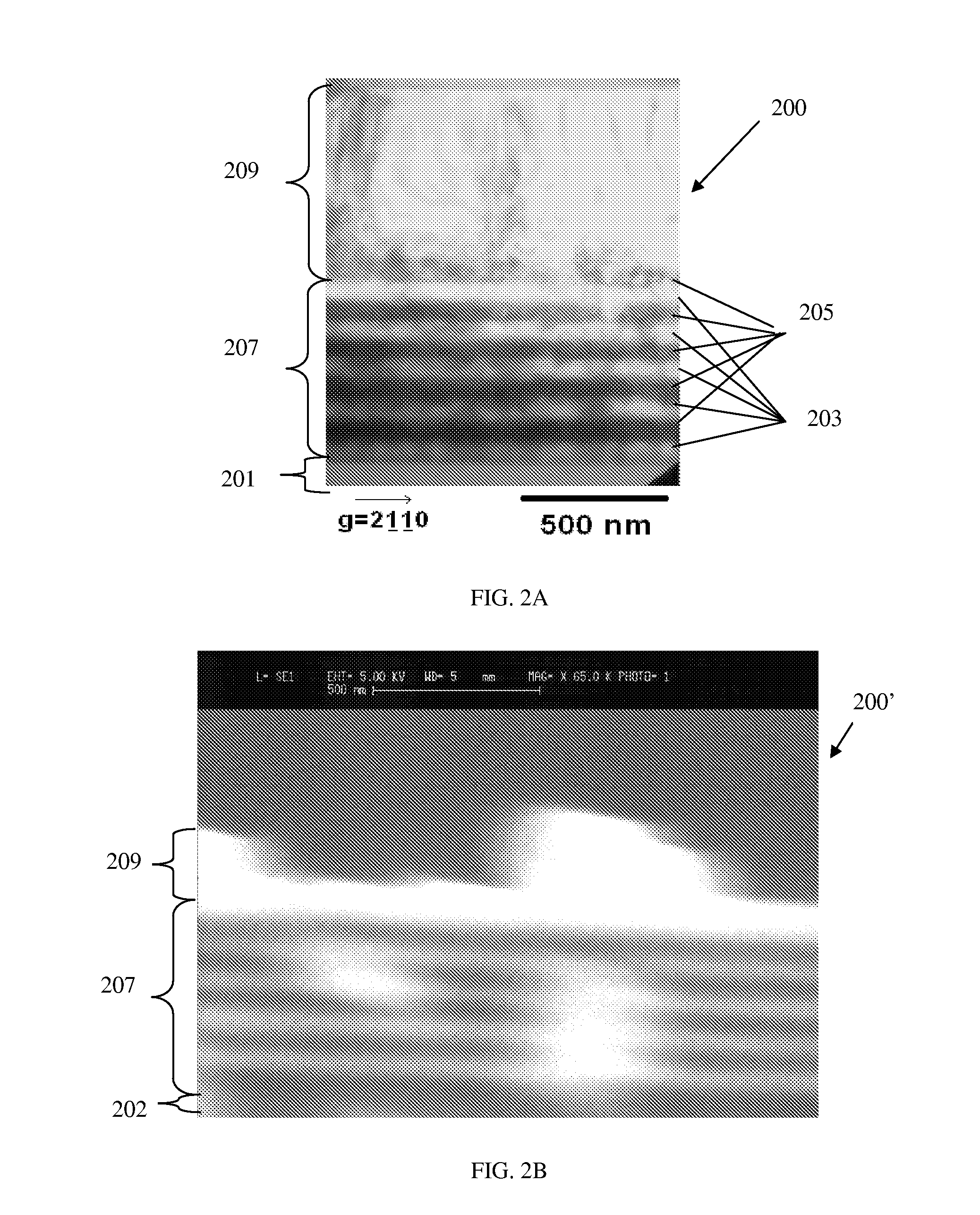
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13576results about "Semiconductor lasers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
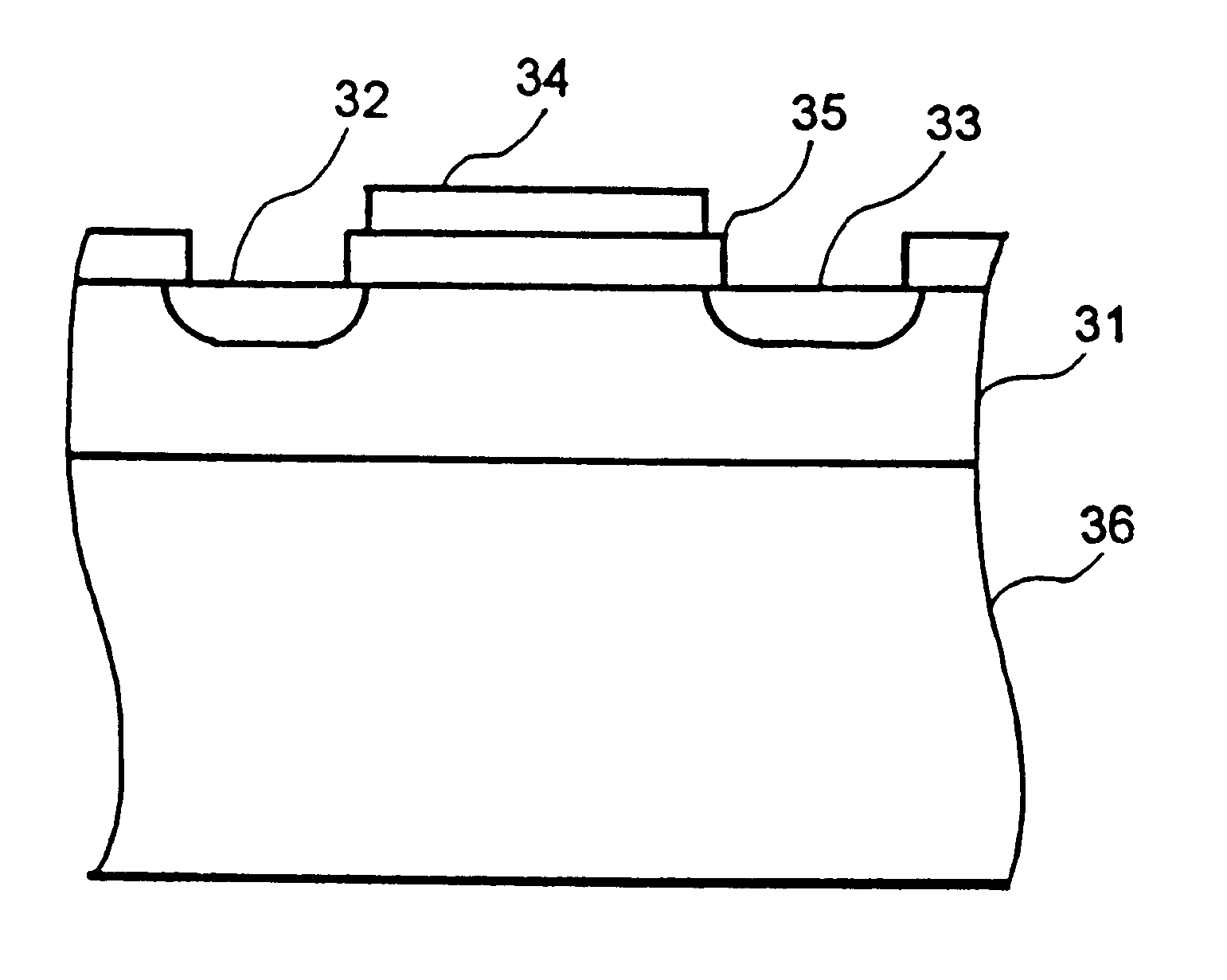
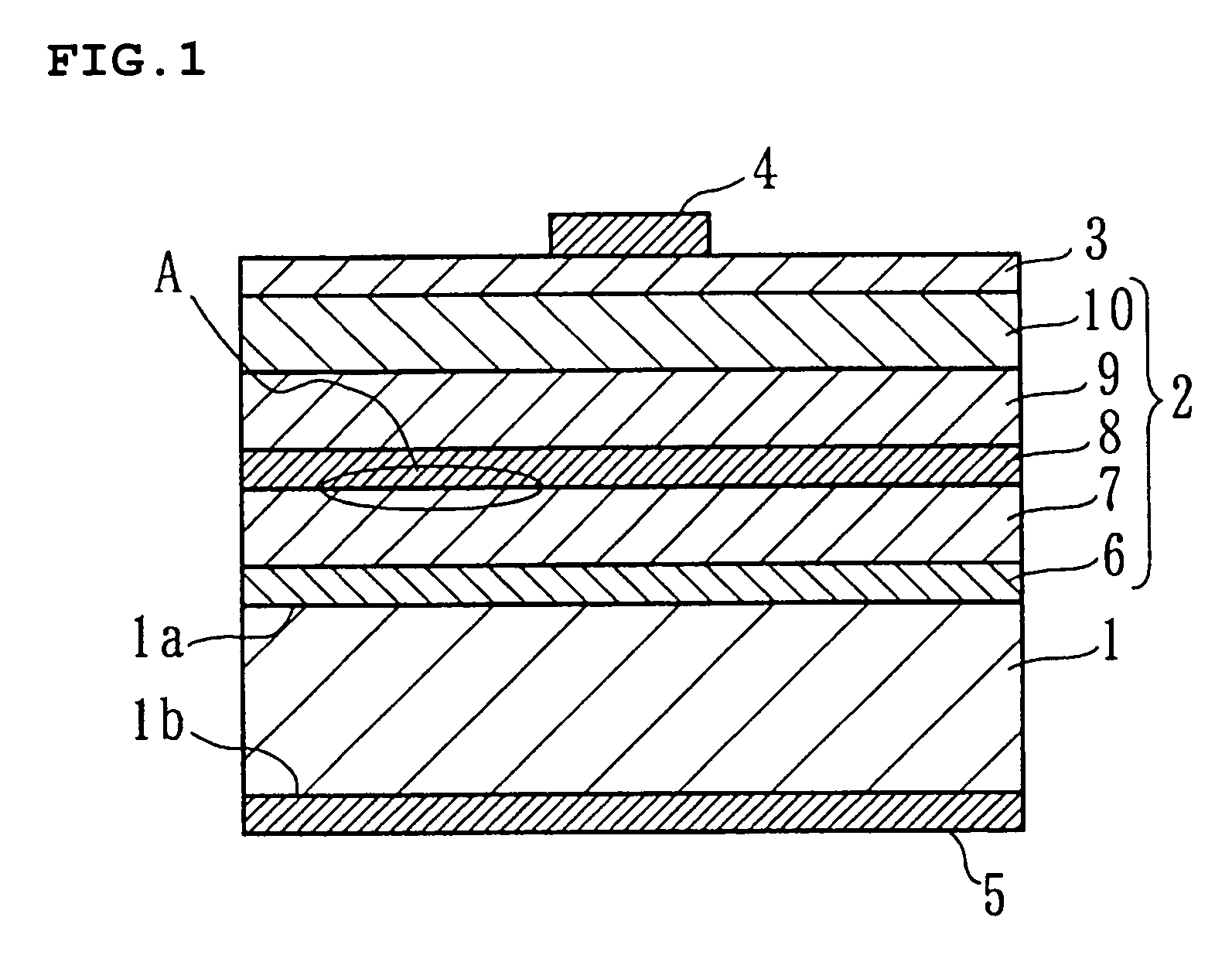
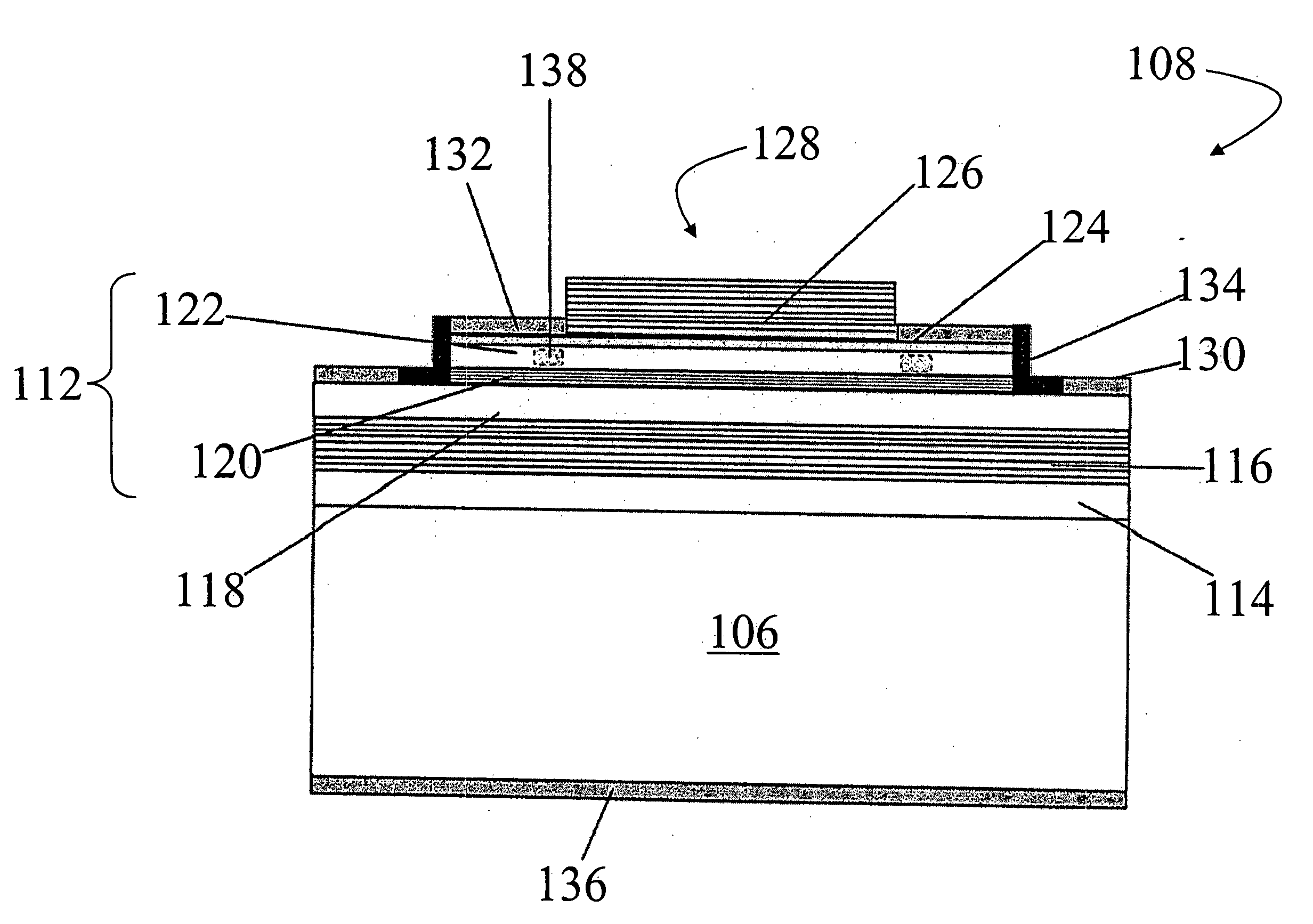
Transistor and semiconductor device
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
High definition lidar system
ActiveUS7969558B2More compactMore ruggedAngle measurementOptical rangefindersHigh definition tvPower coupling
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Optical systems fabricated by printing-based assembly
ActiveUS7972875B2Low costImprove performanceFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsLight sensingSingle crystal
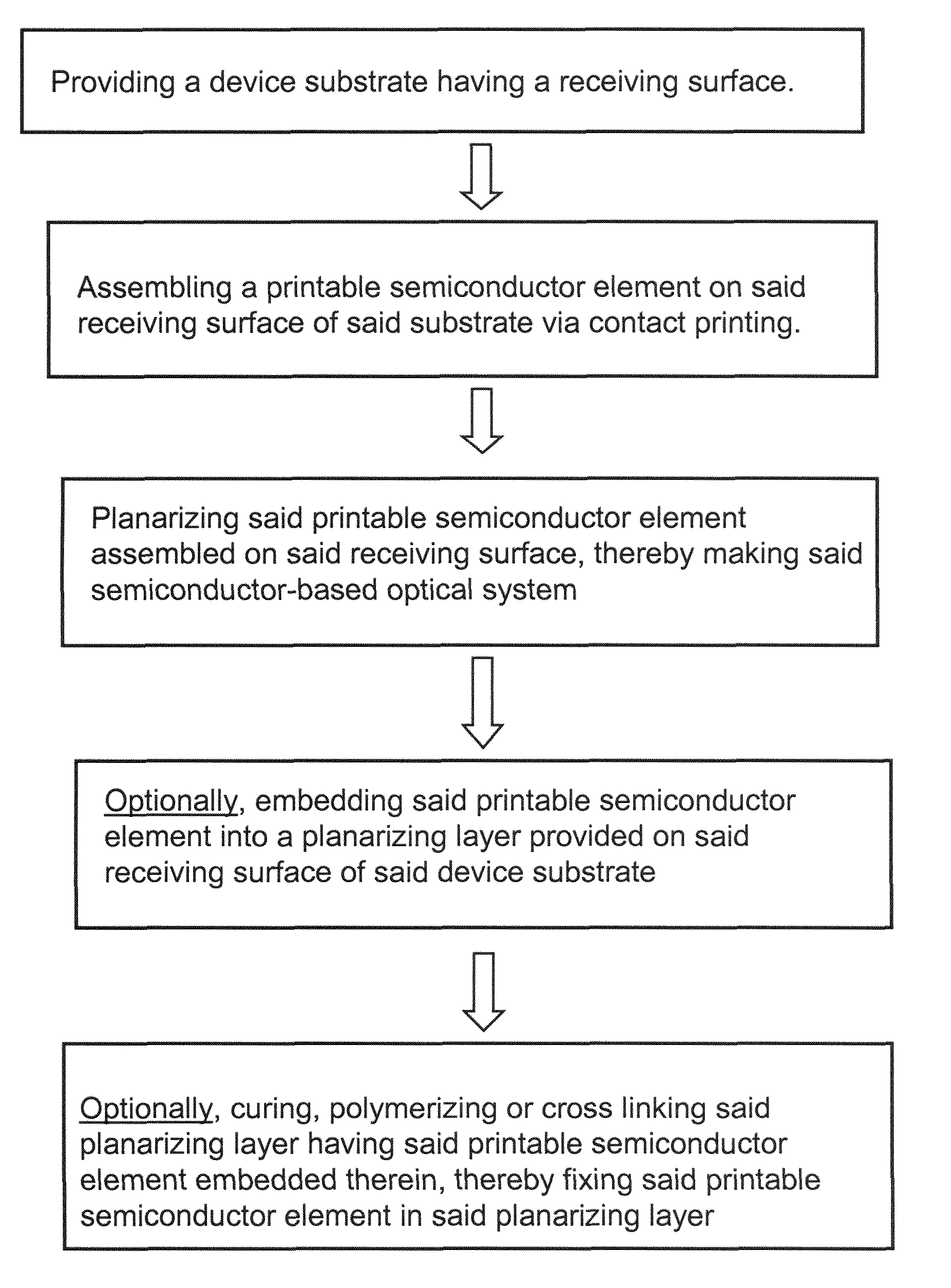
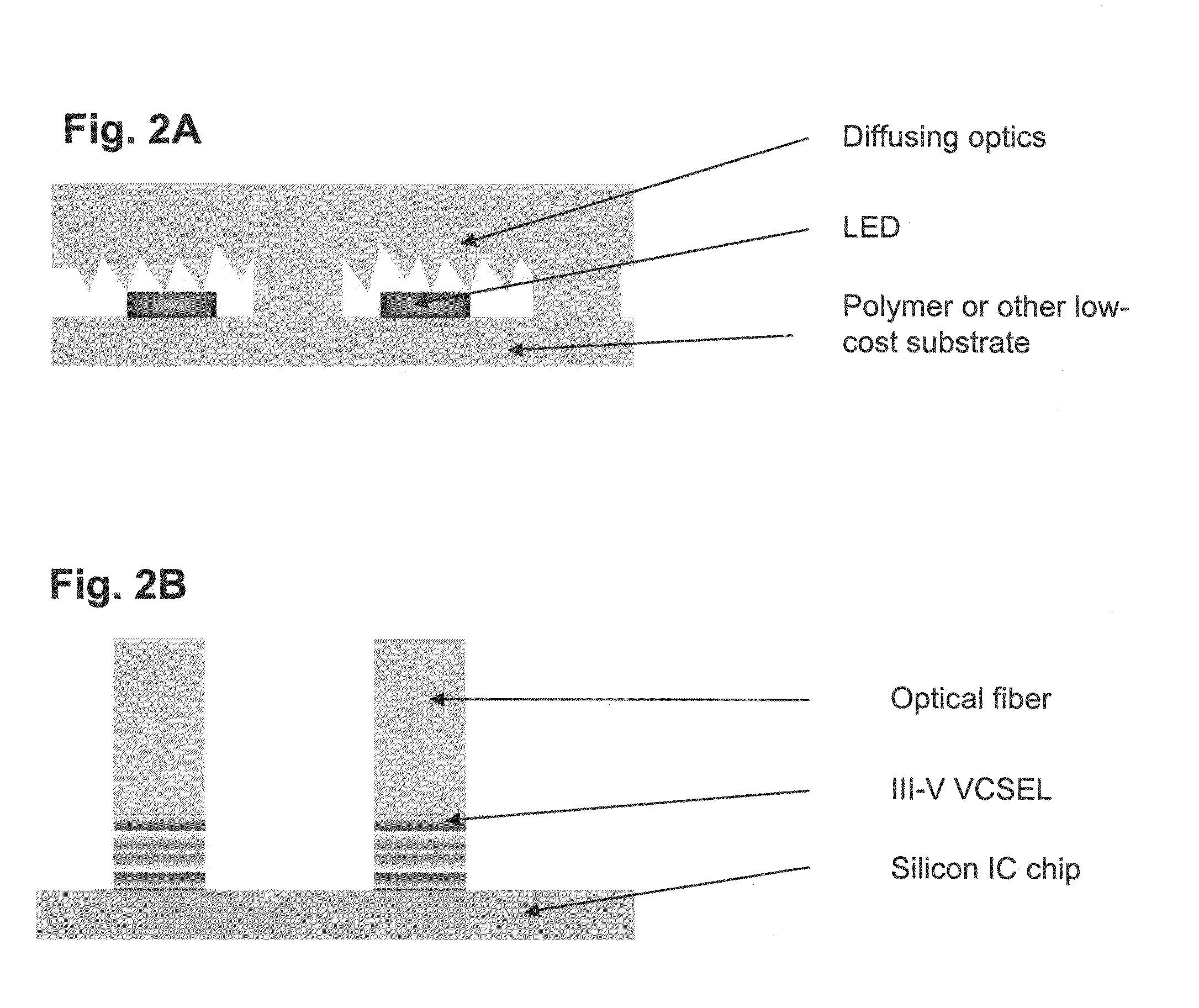
Provided are optical devices and systems fabricated, at least in part, via printing-based assembly and integration of device components. In specific embodiments the present invention provides light emitting systems, light collecting systems, light sensing systems and photovoltaic systems comprising printable semiconductor elements, including large area, high performance macroelectronic devices. Optical systems of the present invention comprise semiconductor elements assembled, organized and / or integrated with other device components via printing techniques that exhibit performance characteristics and functionality comparable to single crystalline semiconductor based devices fabricated using conventional high temperature processing methods. Optical systems of the present invention have device geometries and configurations, such as form factors, component densities, and component positions, accessed by printing that provide a range of useful device functionalities. Optical systems of the present invention include devices and device arrays exhibiting a range of useful physical and mechanical properties including flexibility, shapeability, conformability and stretchablity.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
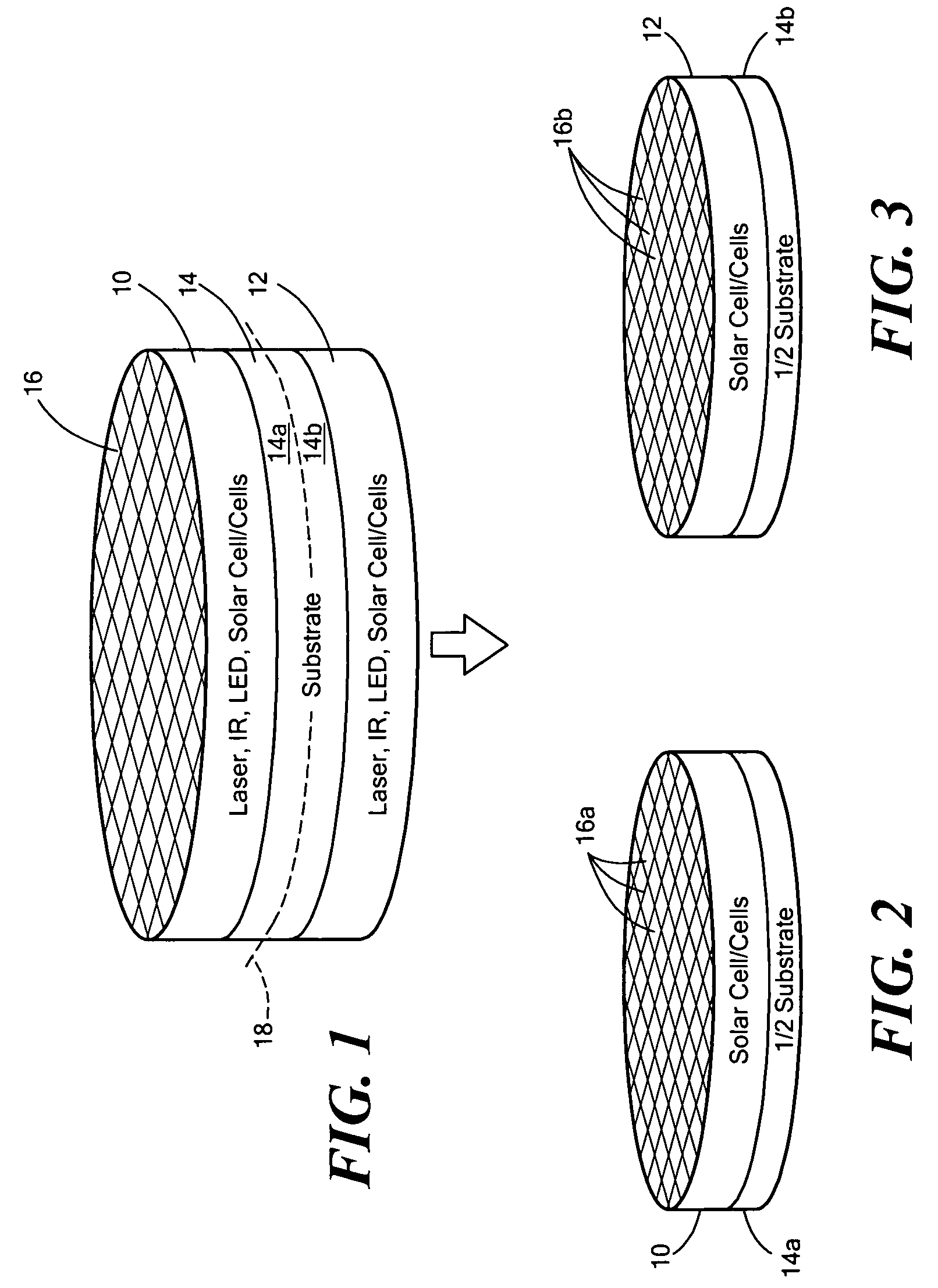
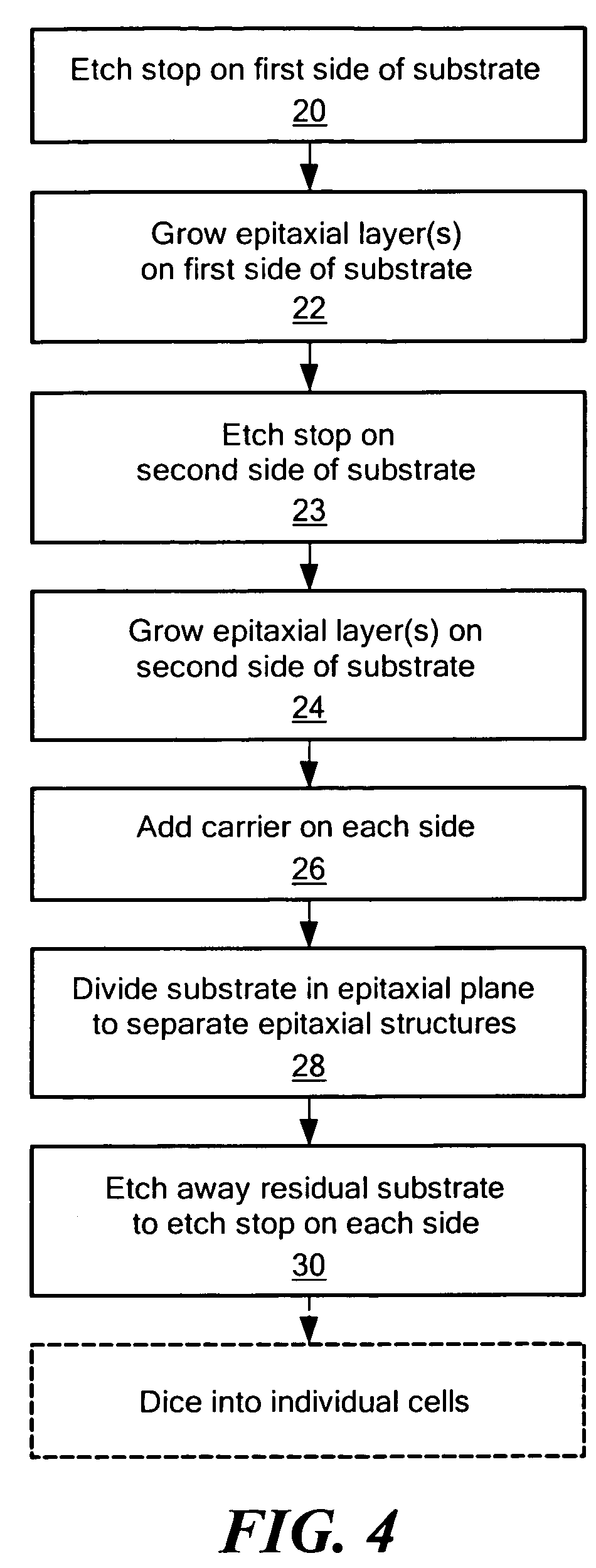
Method of fabricating epitaxial structures
ActiveUS8455290B2Reduce in quantitySimple and direct removalFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsPhysics
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA +1
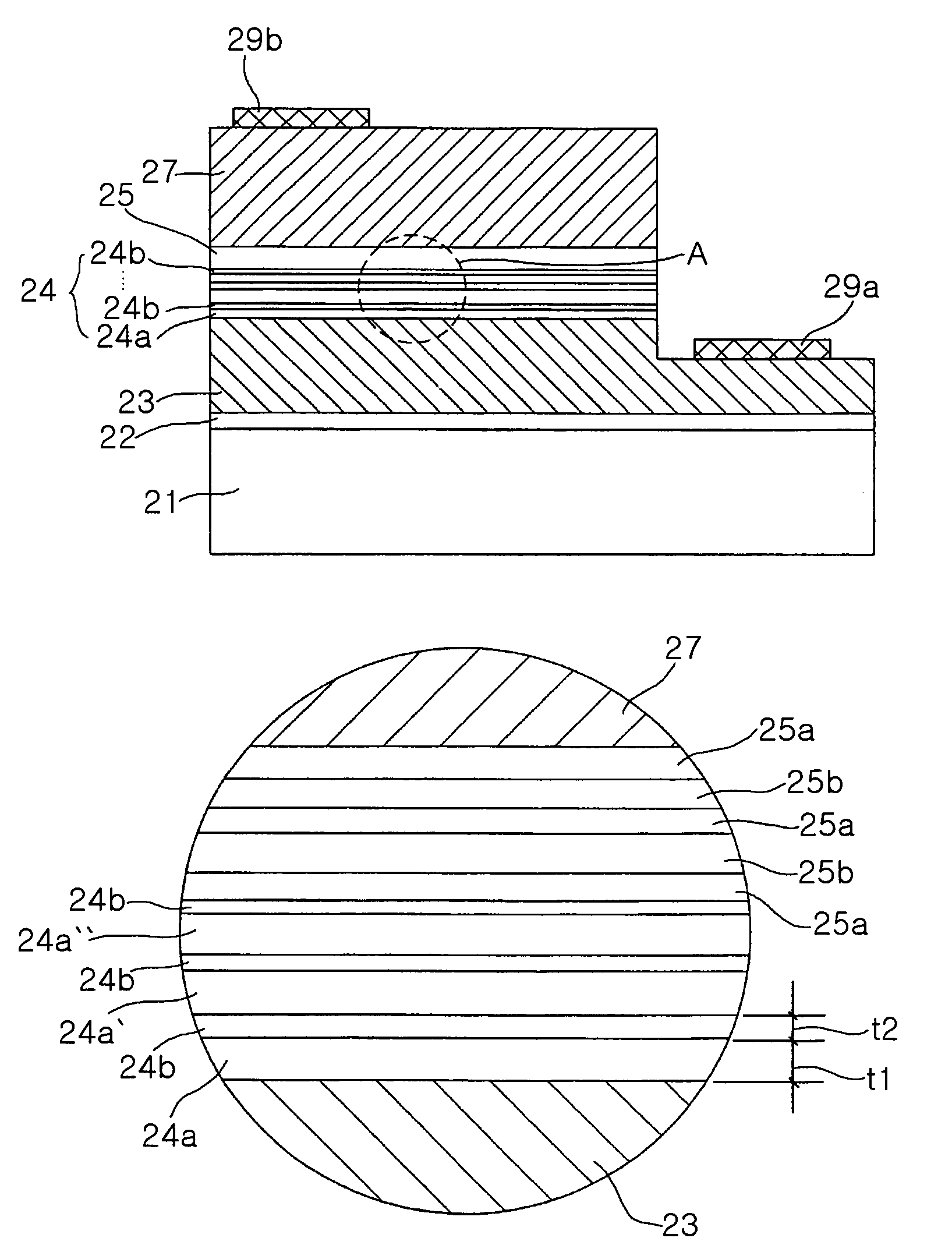
Nitride based semiconductor device
ActiveUS7084420B2Improve efficiencyEliminate the effects ofNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersDevice materialQuantum well
The present invention provides a nitride based semiconductor device comprising an active layer having a quantum well layer and a quantum barrier layer, wherein the device includes an electron emitting layer formed of at least two repeats of a first nitride semiconductor layer and a second nitride semiconductor layer having different compositions between a n-type nitride semiconductor layer and the active layer, the first nitride semiconductor layer has an energy band gap greater than that of the quantum well layer, smaller than that of the quantum barrier layer, and decreasing closer to the active layer, and the second nitride semiconductor layer has an energy band gap at least higher than that of the adjacent first nitride semiconductor layer(s) and has a thickness capable of tunneling electrons.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
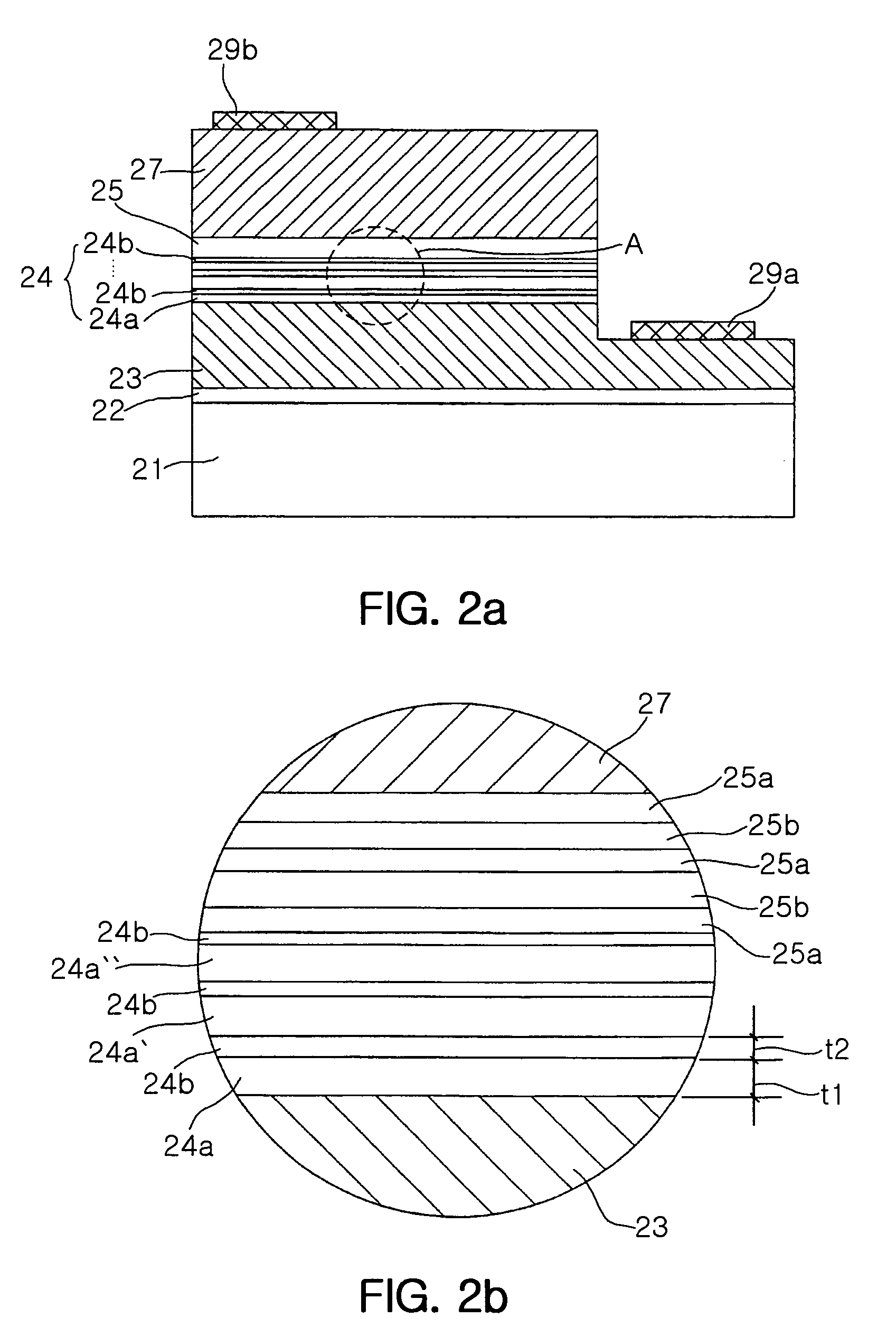
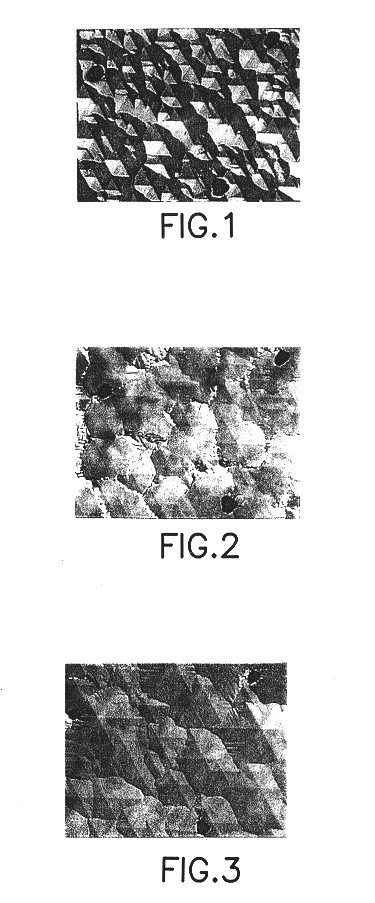
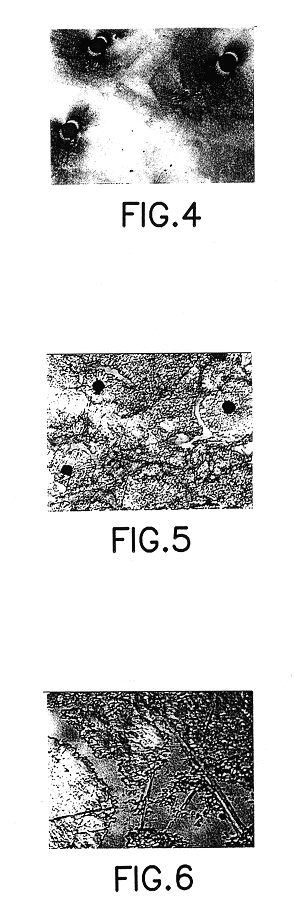
Method for achieving improved epitaxy quality (surface texture and defect density) on free-standing (aluminum, indium, gallium) nitride ((al,in,ga)n) substrates for opto-electronic and electronic devices
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 105, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 103 torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 500 microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
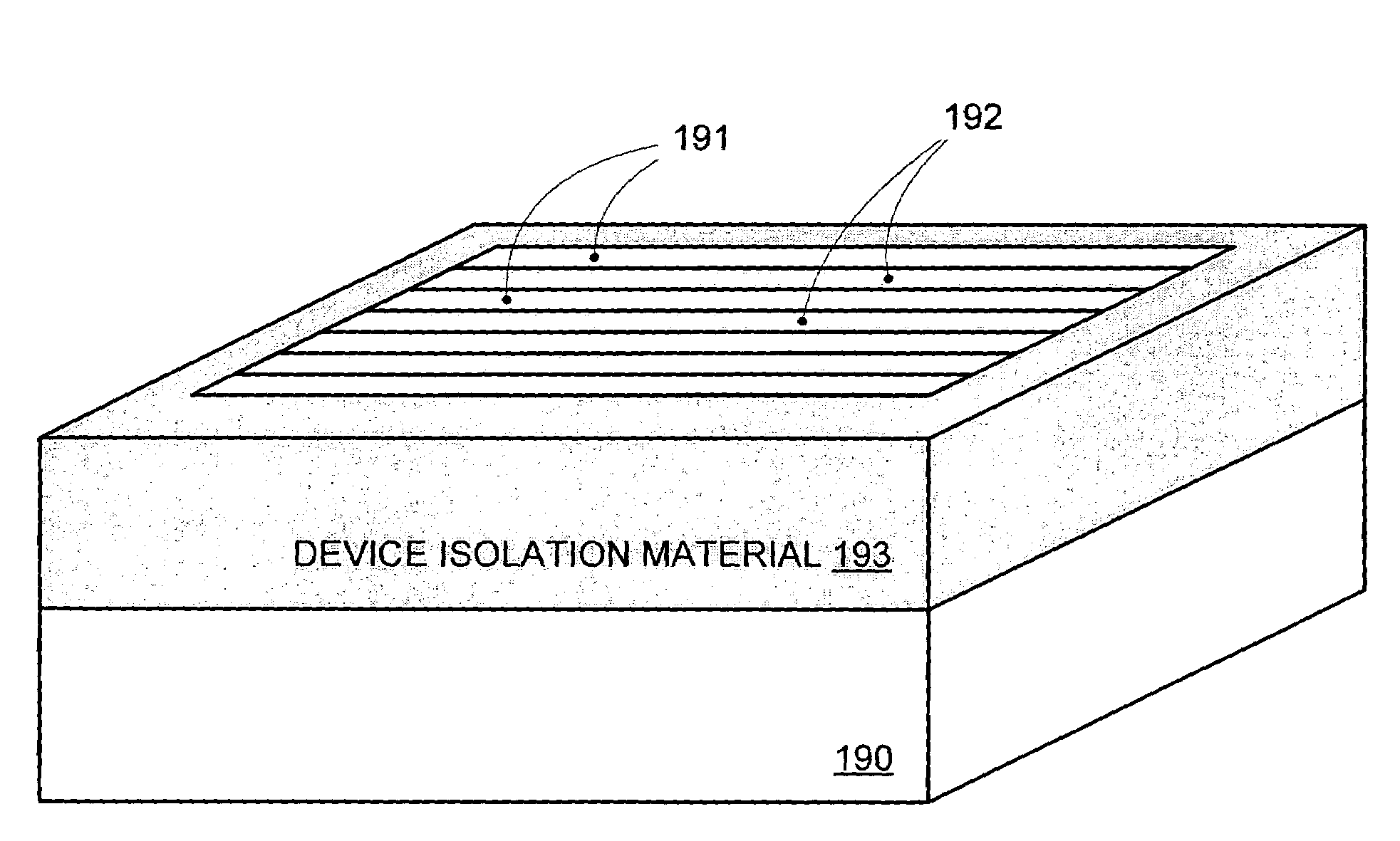
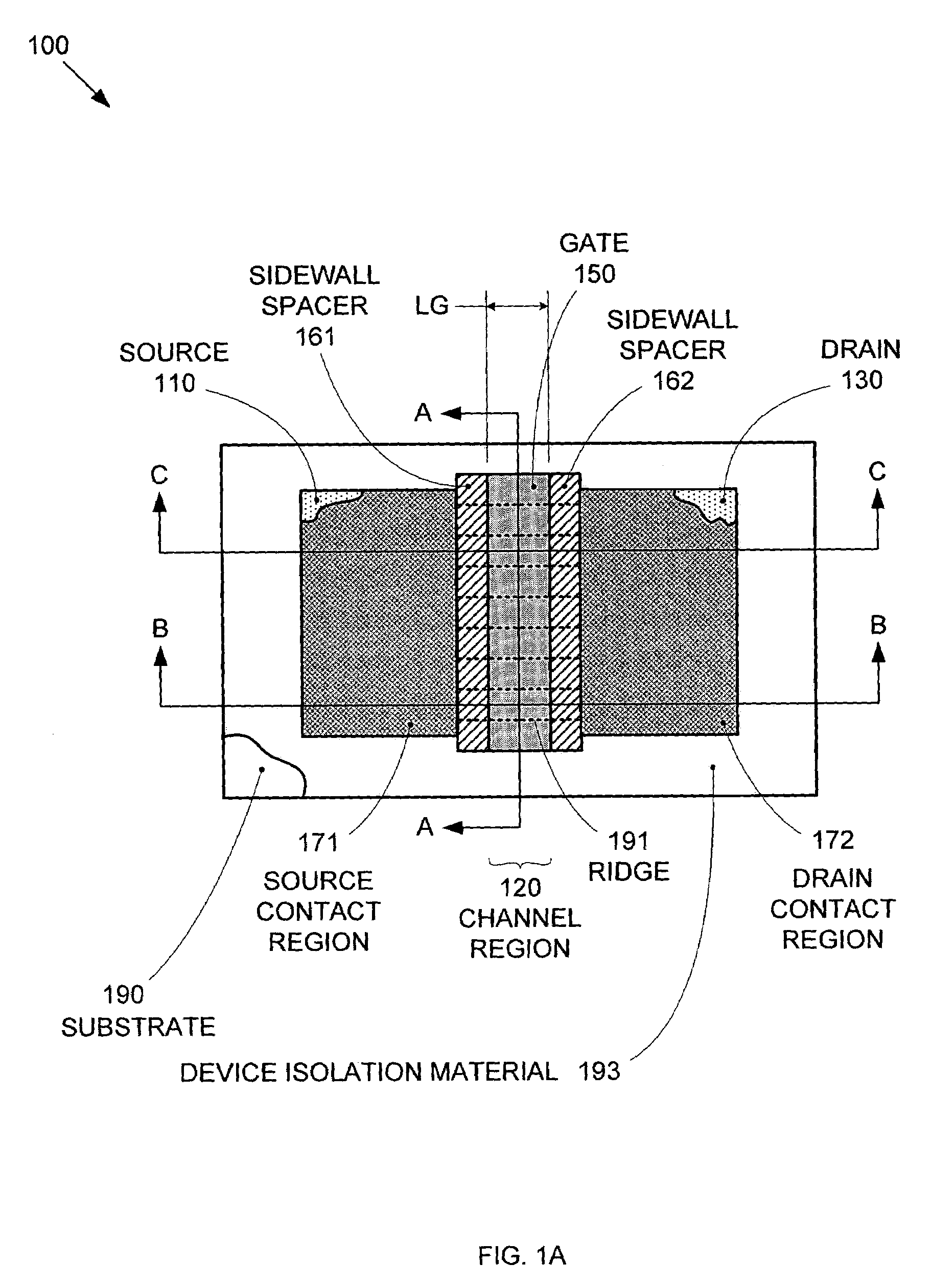
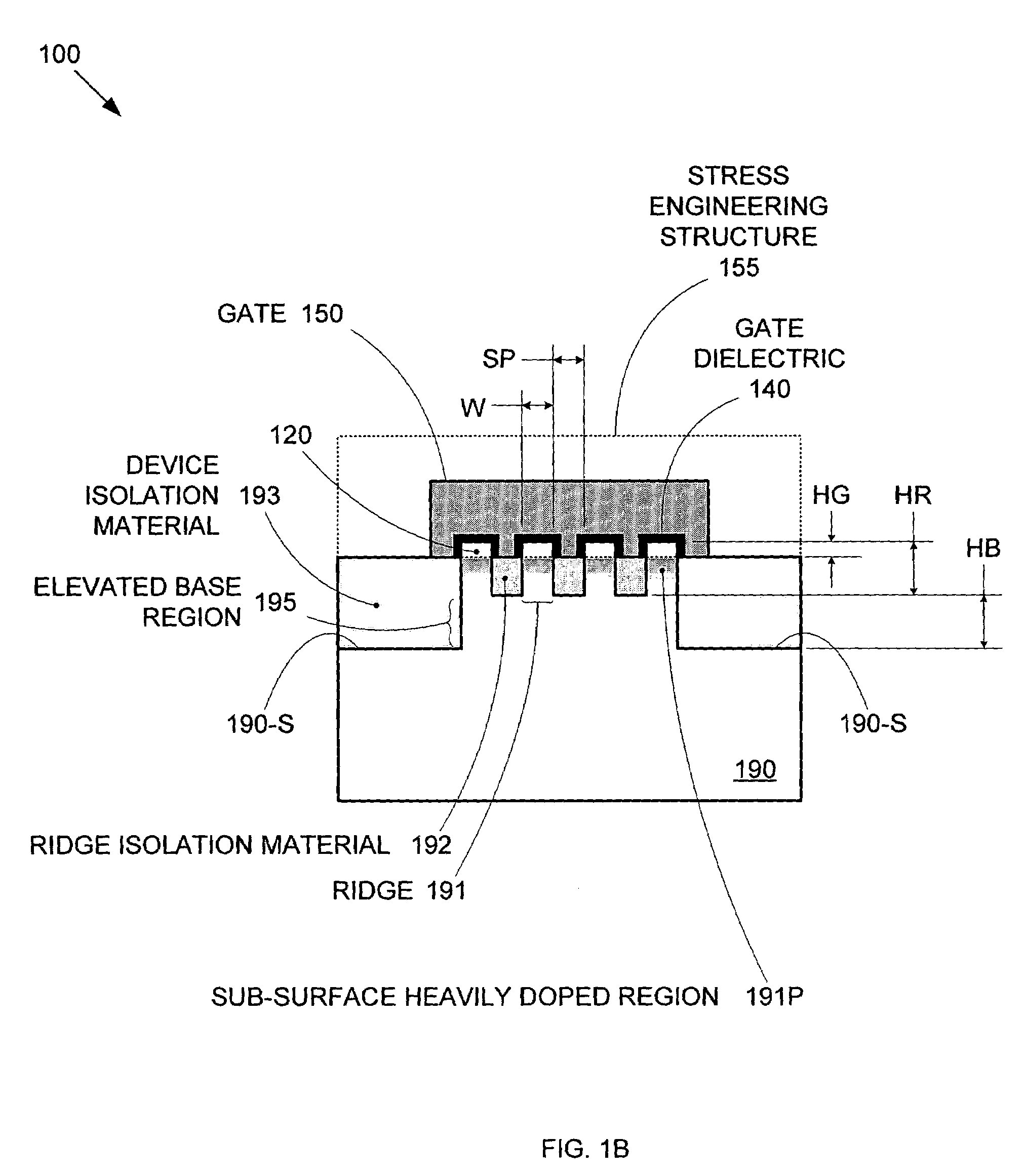
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7265008B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
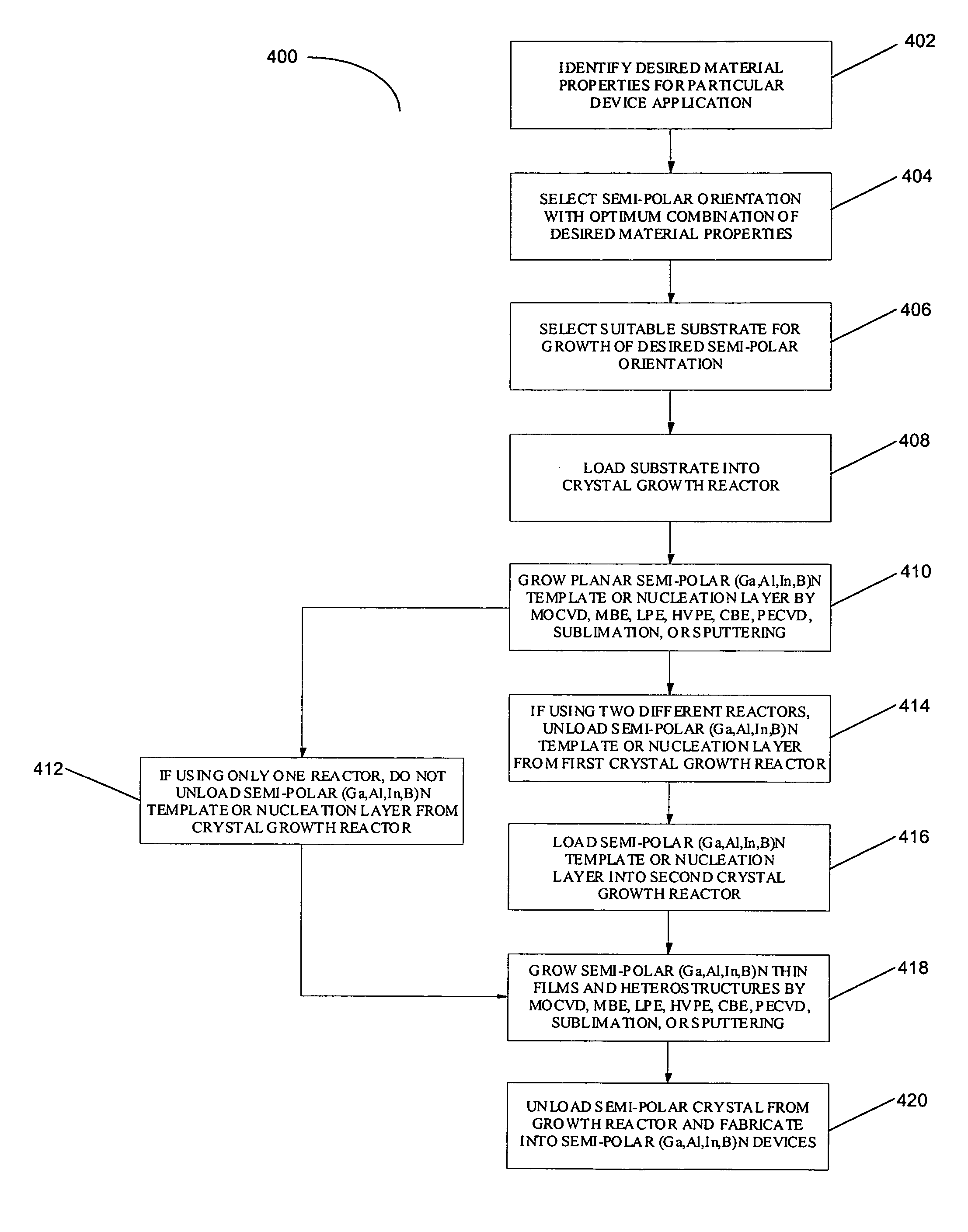
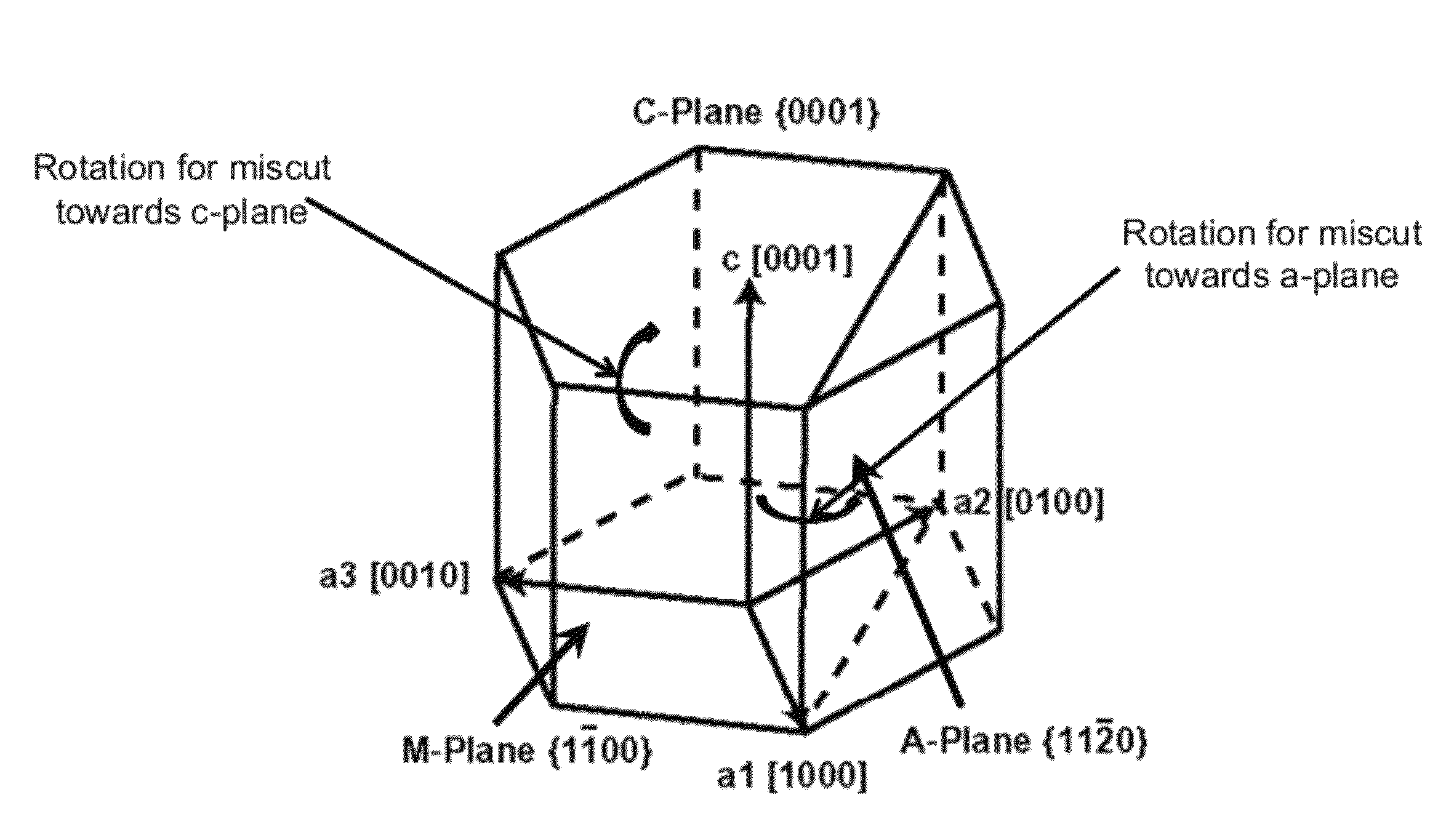
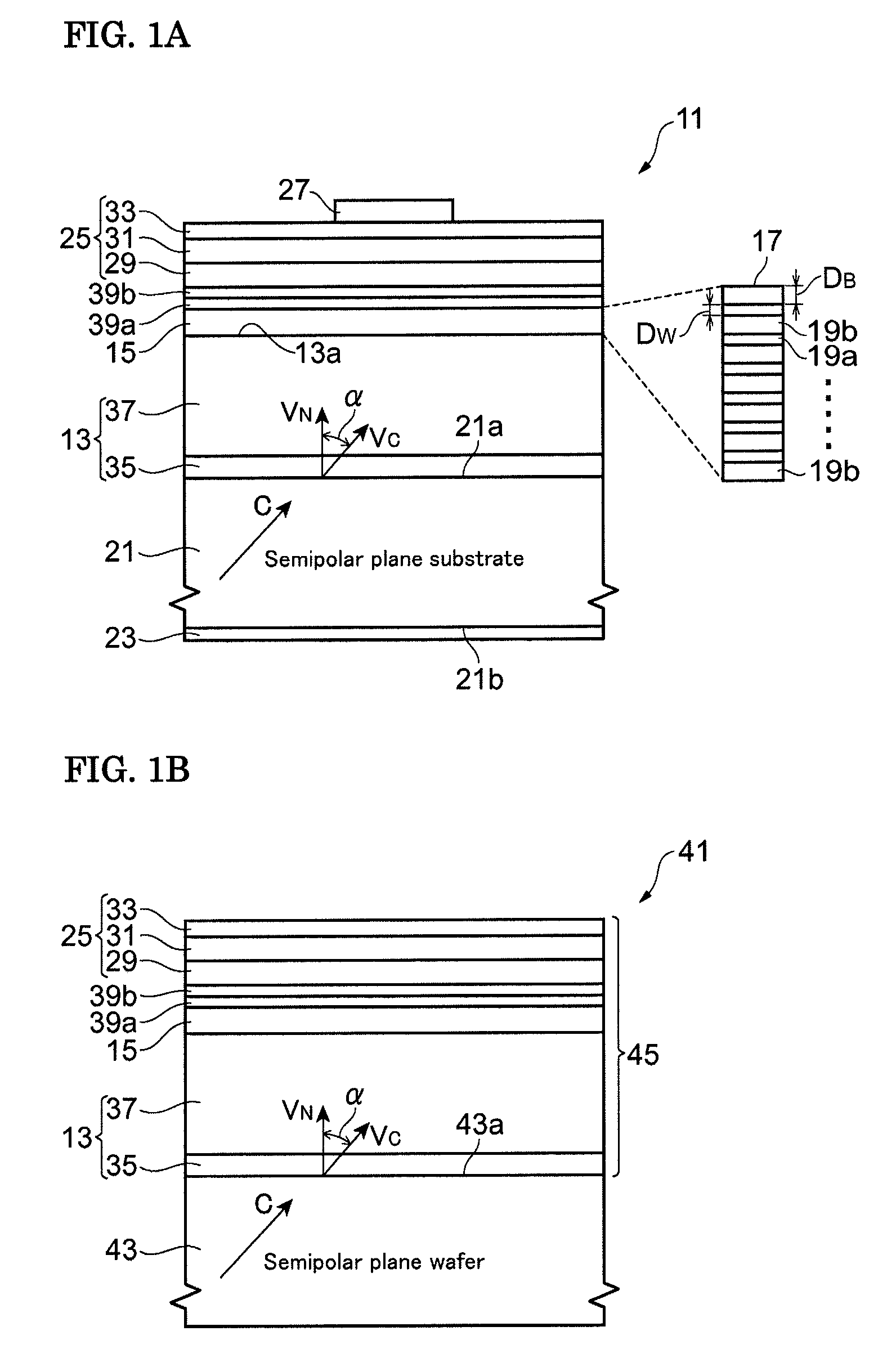
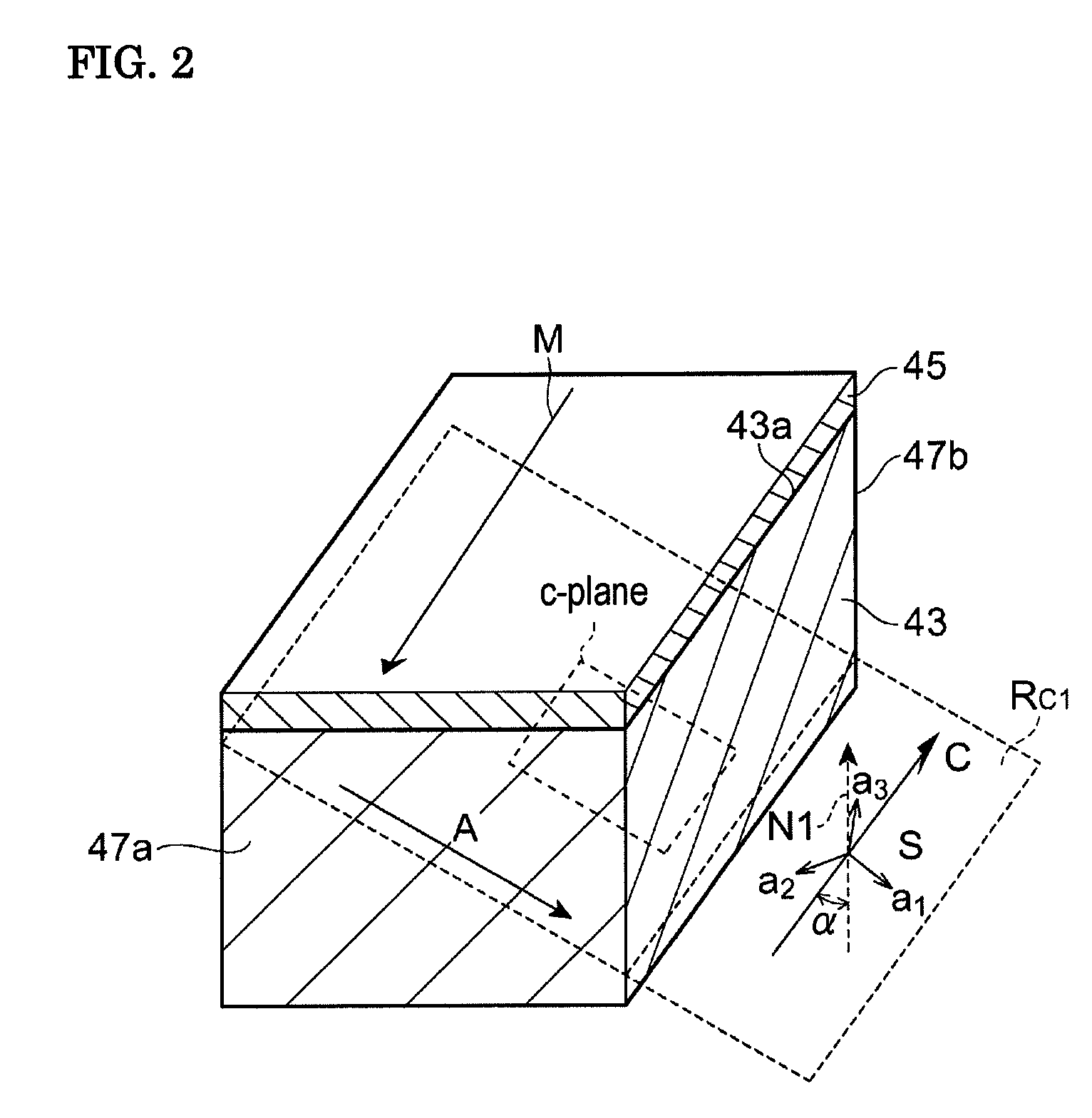
Technique for the growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga,A1,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices
ActiveUS20070093073A1Improve device performanceLarge parameter spacePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNucleationBiology
A method for growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices, comprising identifying desired material properties for a particular device application, selecting a semipolar growth orientation based on the desired material properties, selecting a suitable substrate for growth of the selected semipolar growth orientation, growing a planar semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N template or nucleation layer on the substrate, and growing the semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures or devices on the planar semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N template or nucleation layer. The method results in a large area of the semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices being parallel to the substrate surface.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
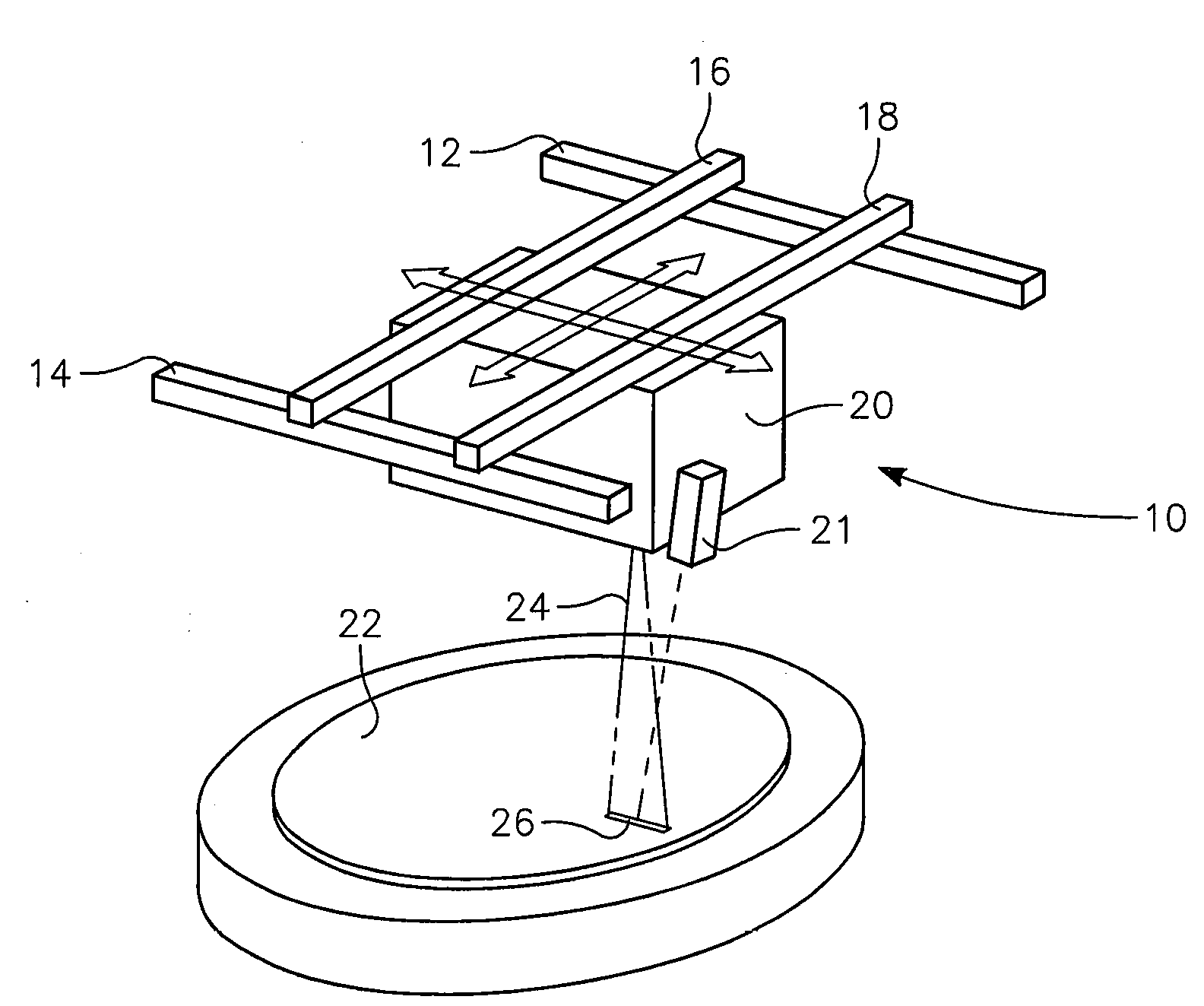
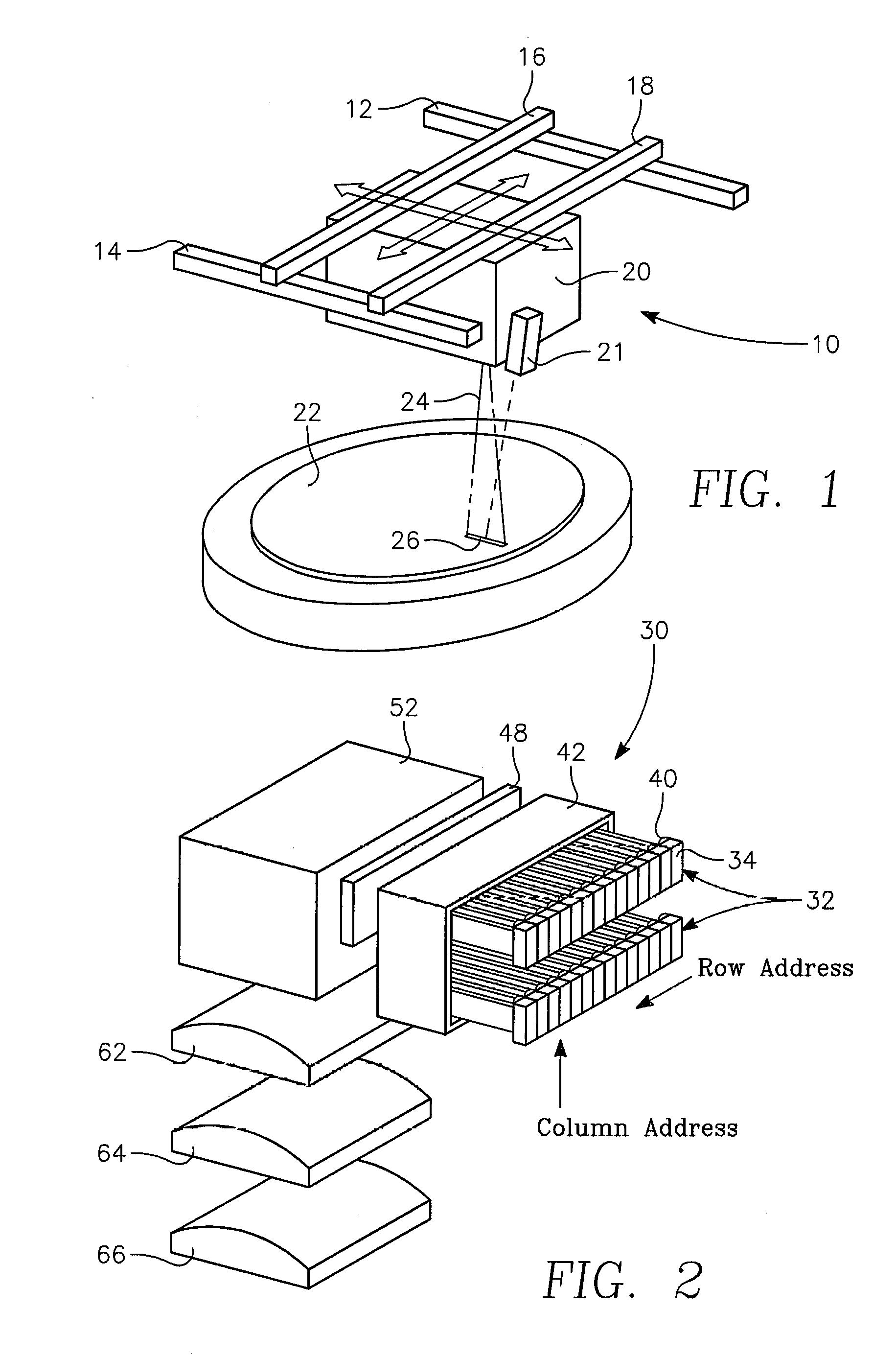
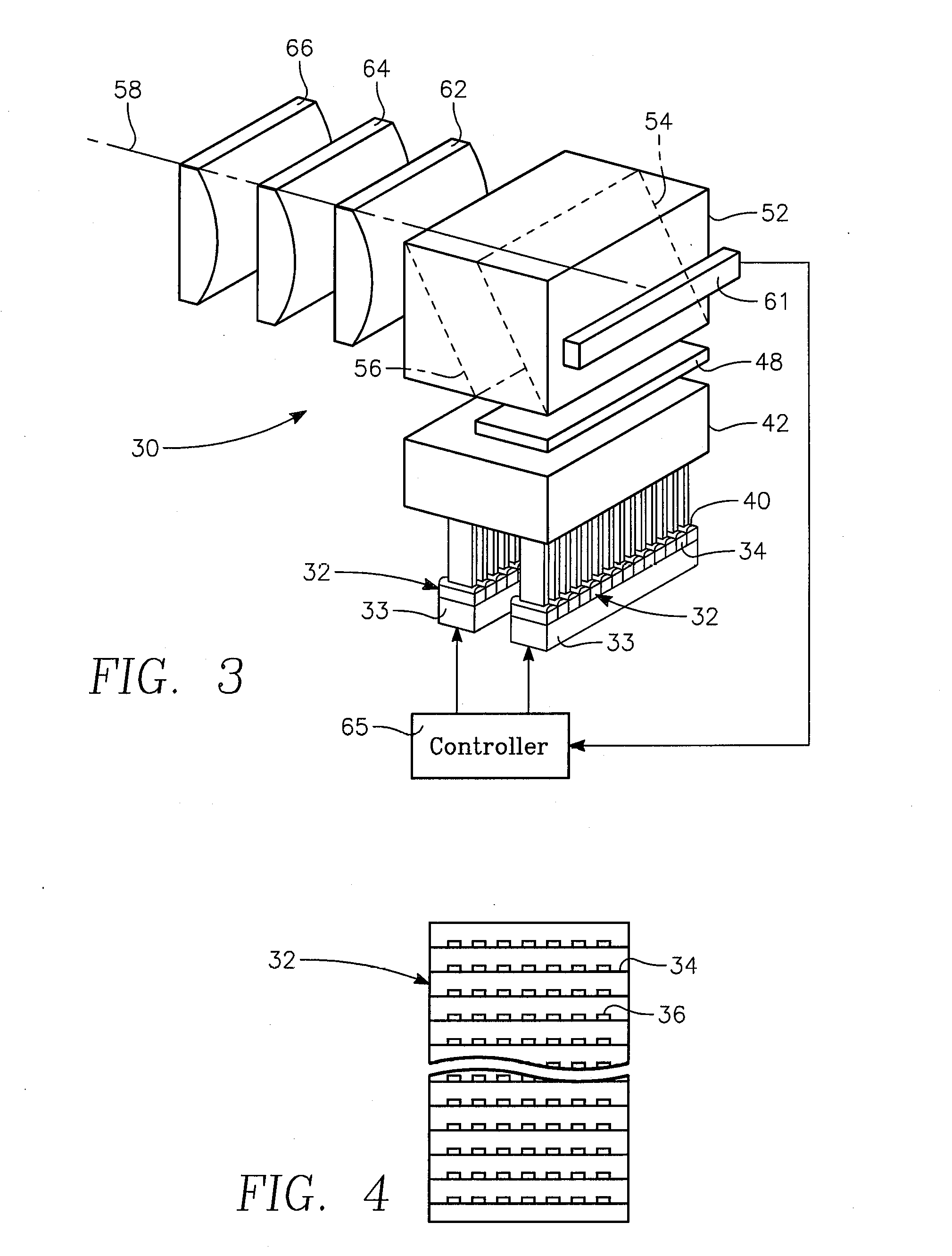
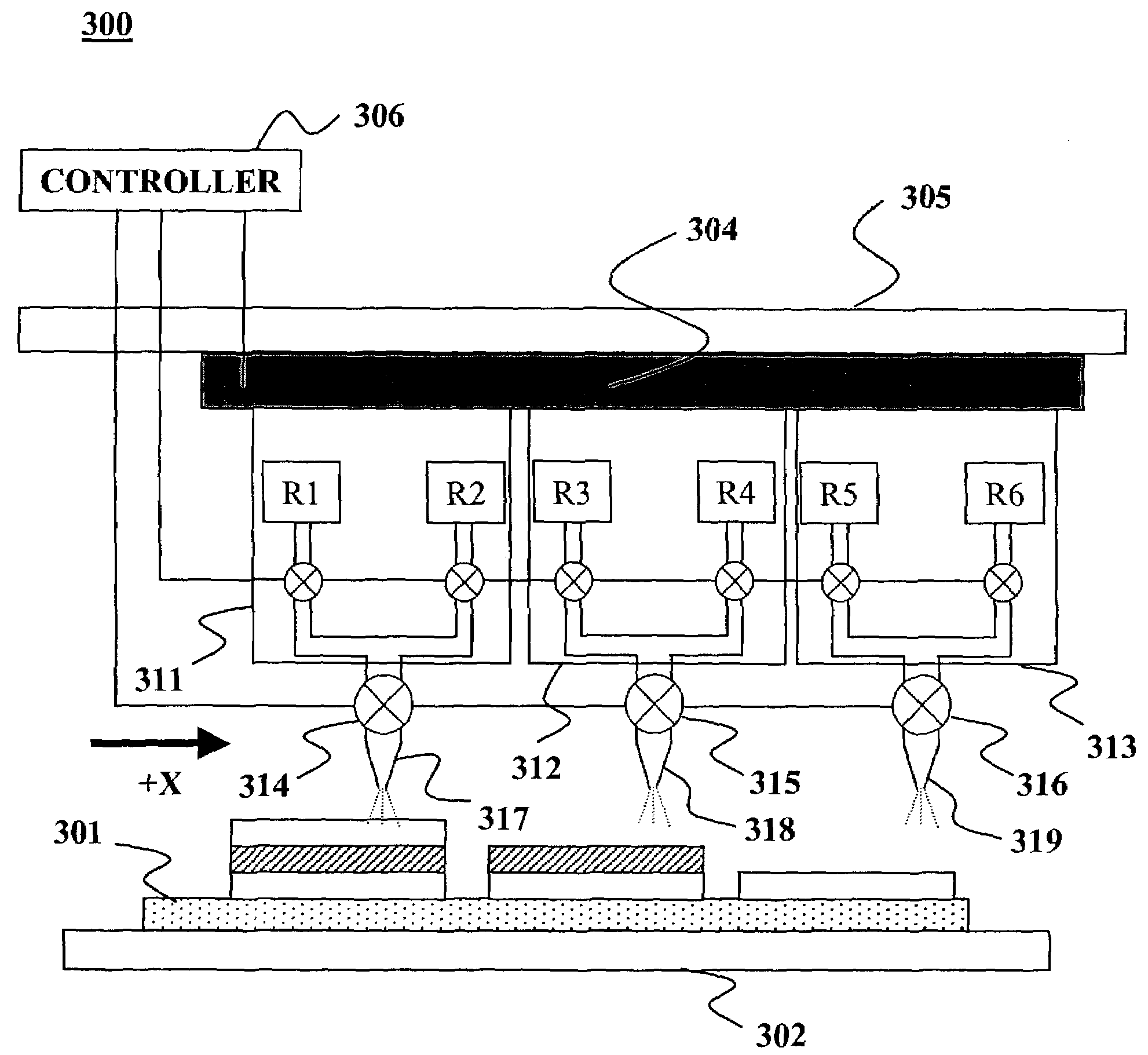
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
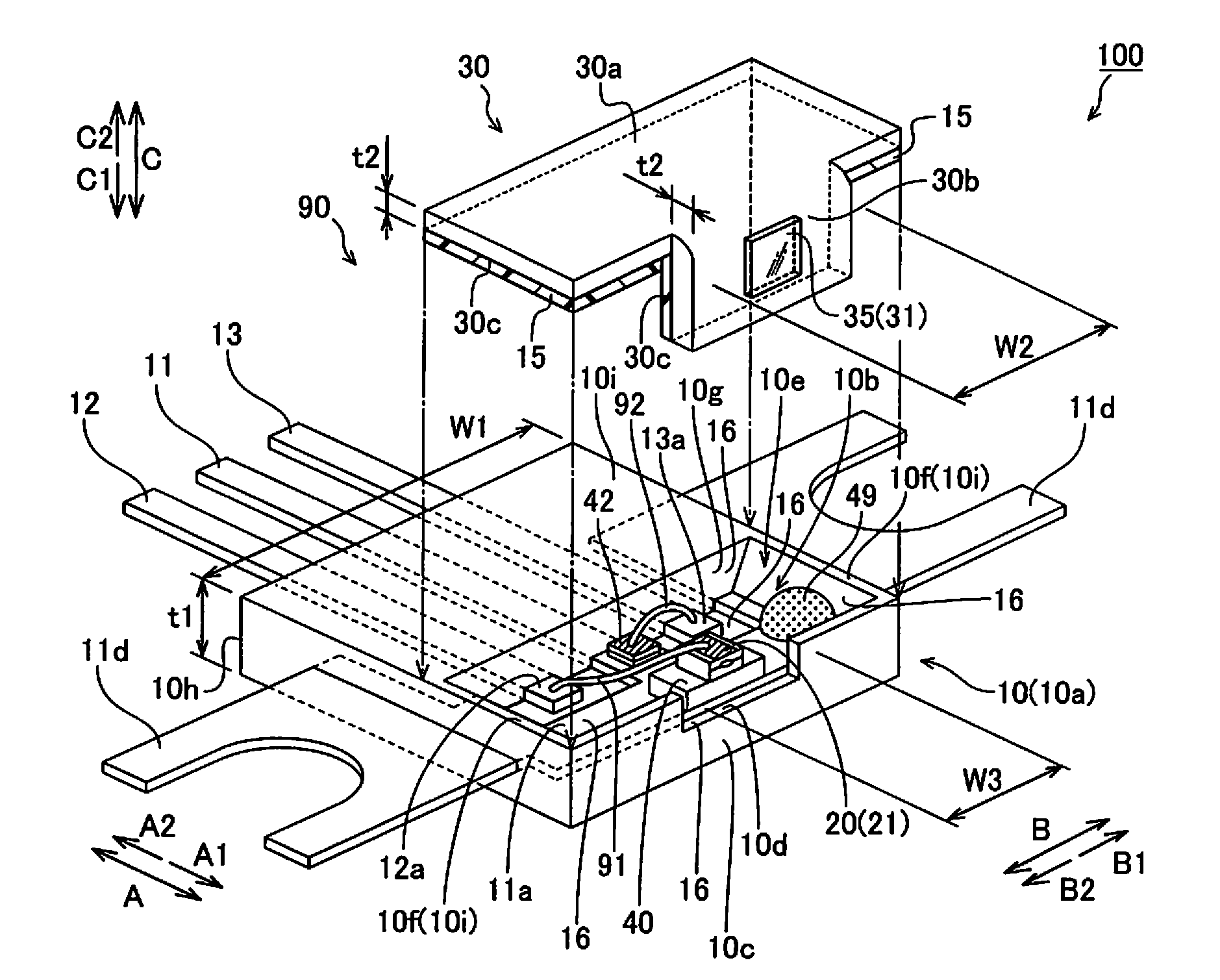
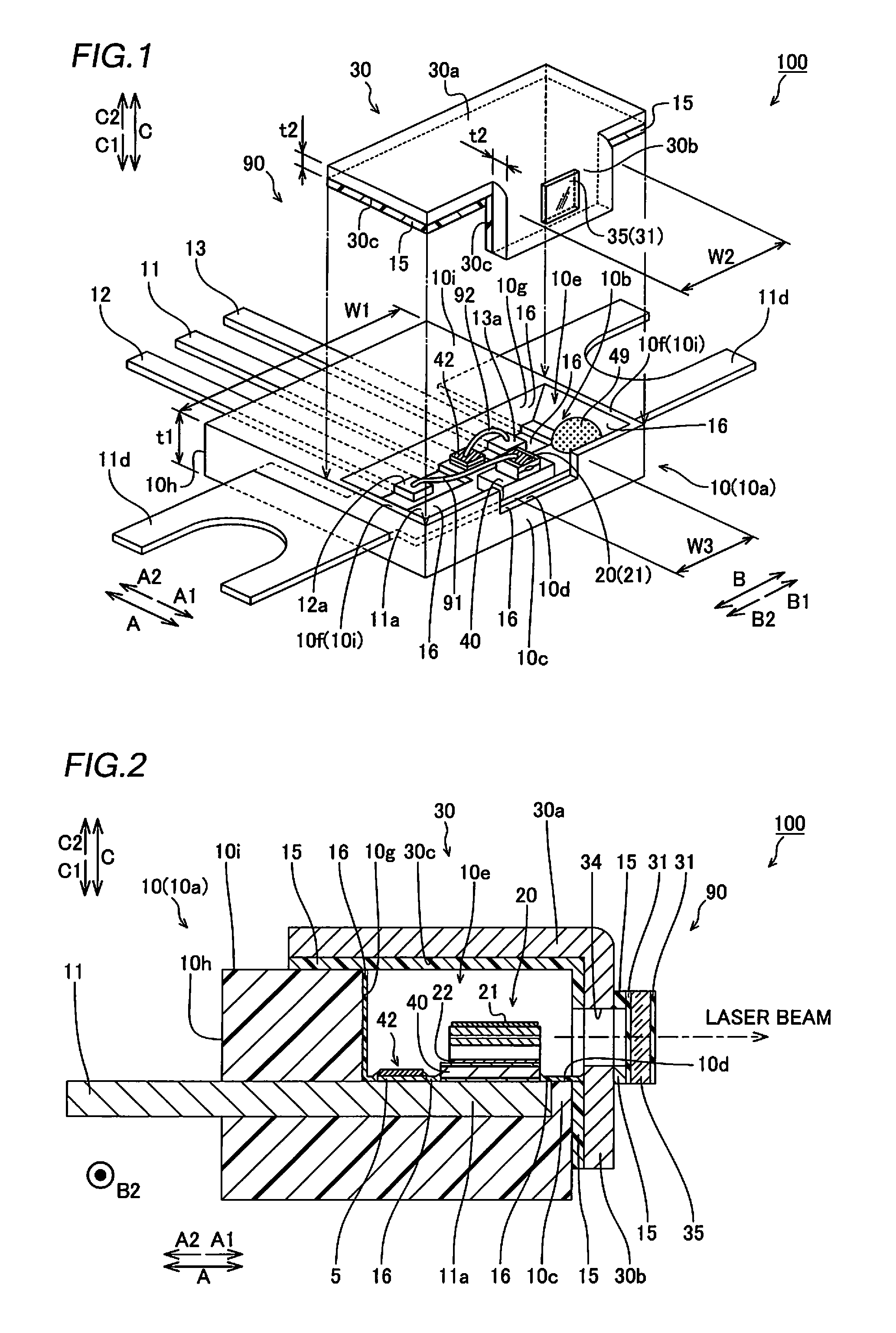
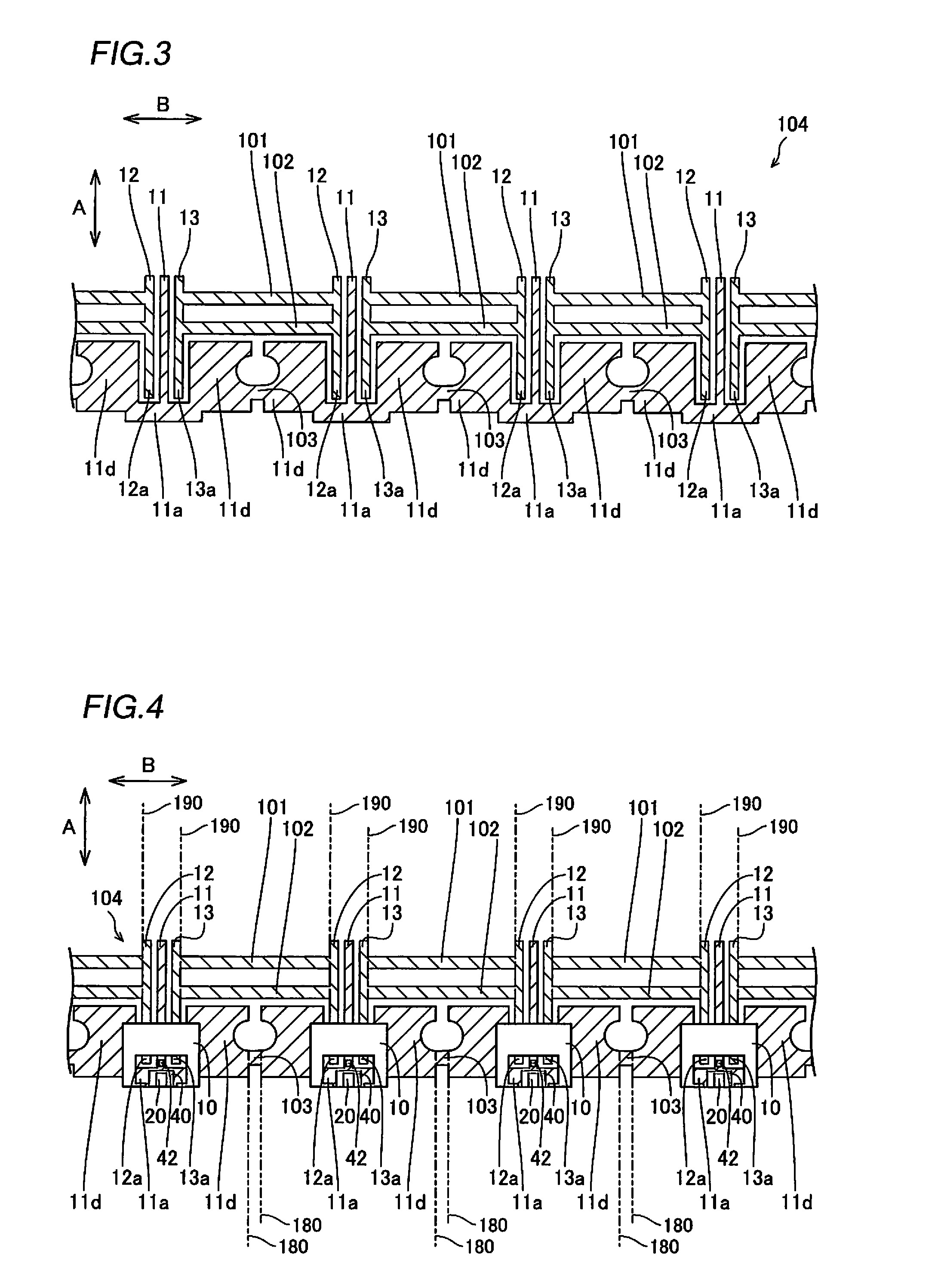
Semiconductor laser apparatus and optical apparatus
InactiveUS20120033695A1Improve sealingPromote absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersPolyvinyl alcoholSemiconductor chip
This semiconductor laser apparatus includes a package constituted by a plurality of members, having sealed space inside and a semiconductor laser chip arranged in the sealed space, while surfaces of the members located in the sealed space are covered with a covering agent made of an ethylene-polyvinyl alcohol copolymer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Resonant cavity light emitting devices and associated method
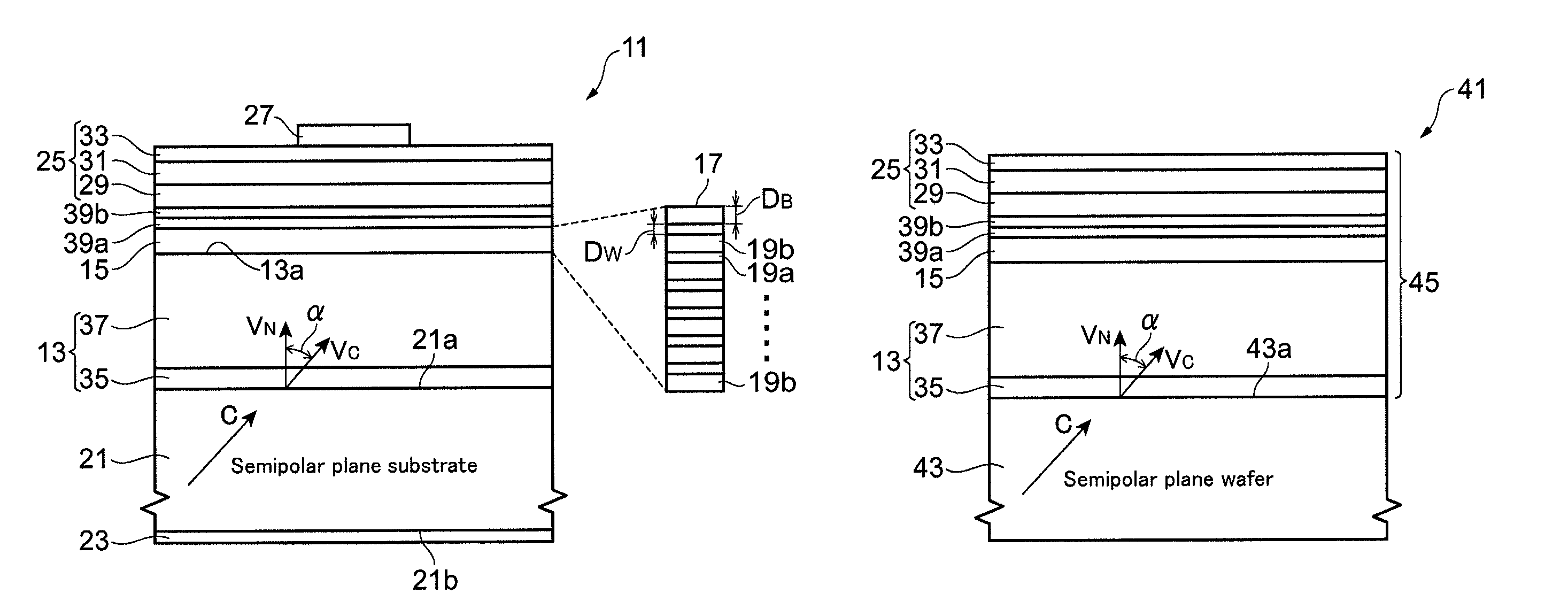
InactiveUS20060118799A1Increase probabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonant cavitySource material
A method may produce a resonant cavity light emitting device. A seed gallium nitride crystal and a source material in a nitrogen-containing superheated fluid may provide a medium for mass transport of gallium nitride precursors therebetween. A seed crystal surface may be prepared by applying a first thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material. Gallium nitride material may be grown on the prepared surface of the seed gallium nitride crystal by applying a second thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material while the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material are in the nitrogen-containing superheated fluid. A stack of group III-nitride layers may be deposited on the single-crystal gallium nitride substrate. The stack may include a first mirror sub-stack and an active region adaptable for fabrication into one or more resonant cavity light emitting devices.
Owner:SORAA
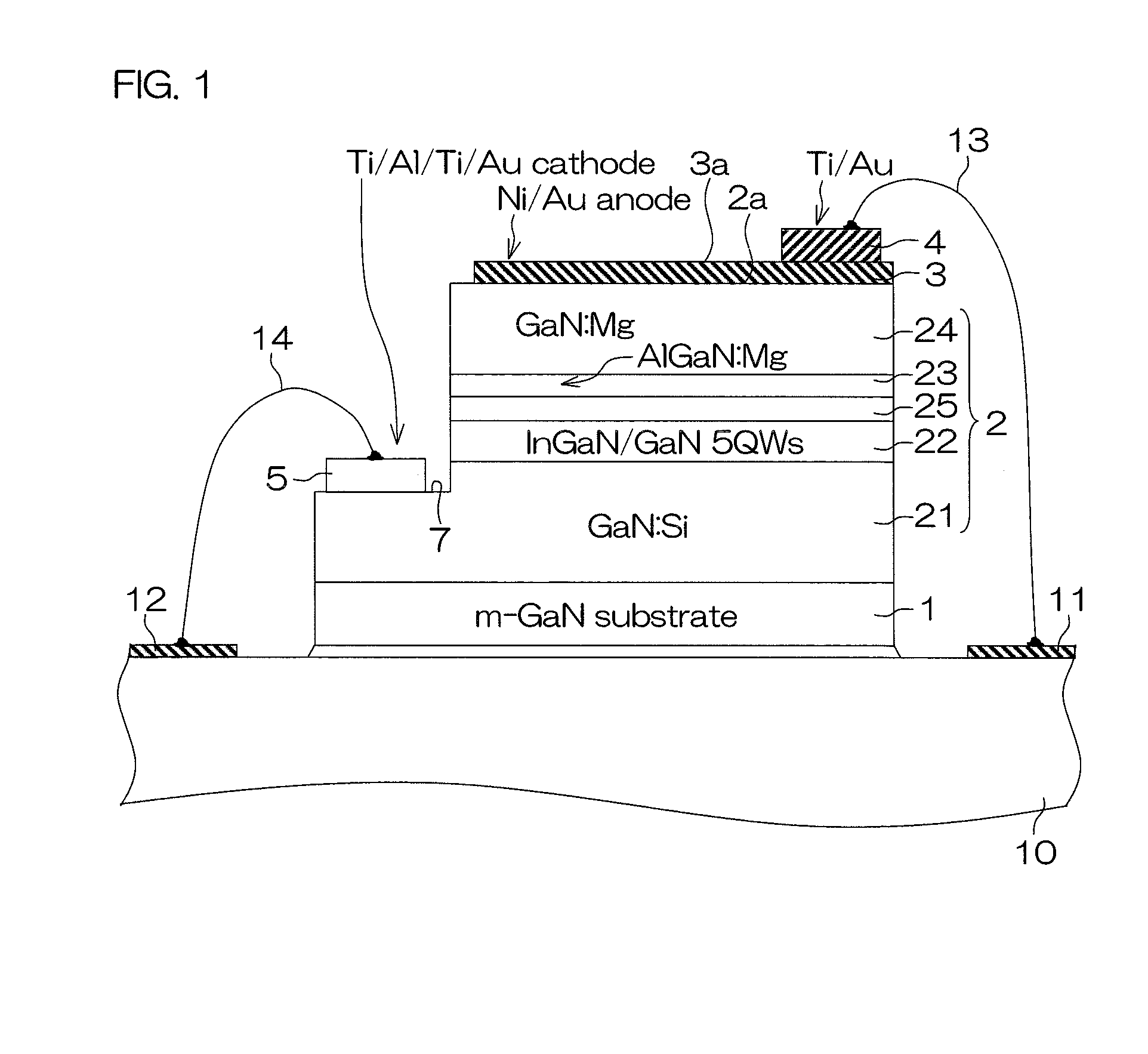
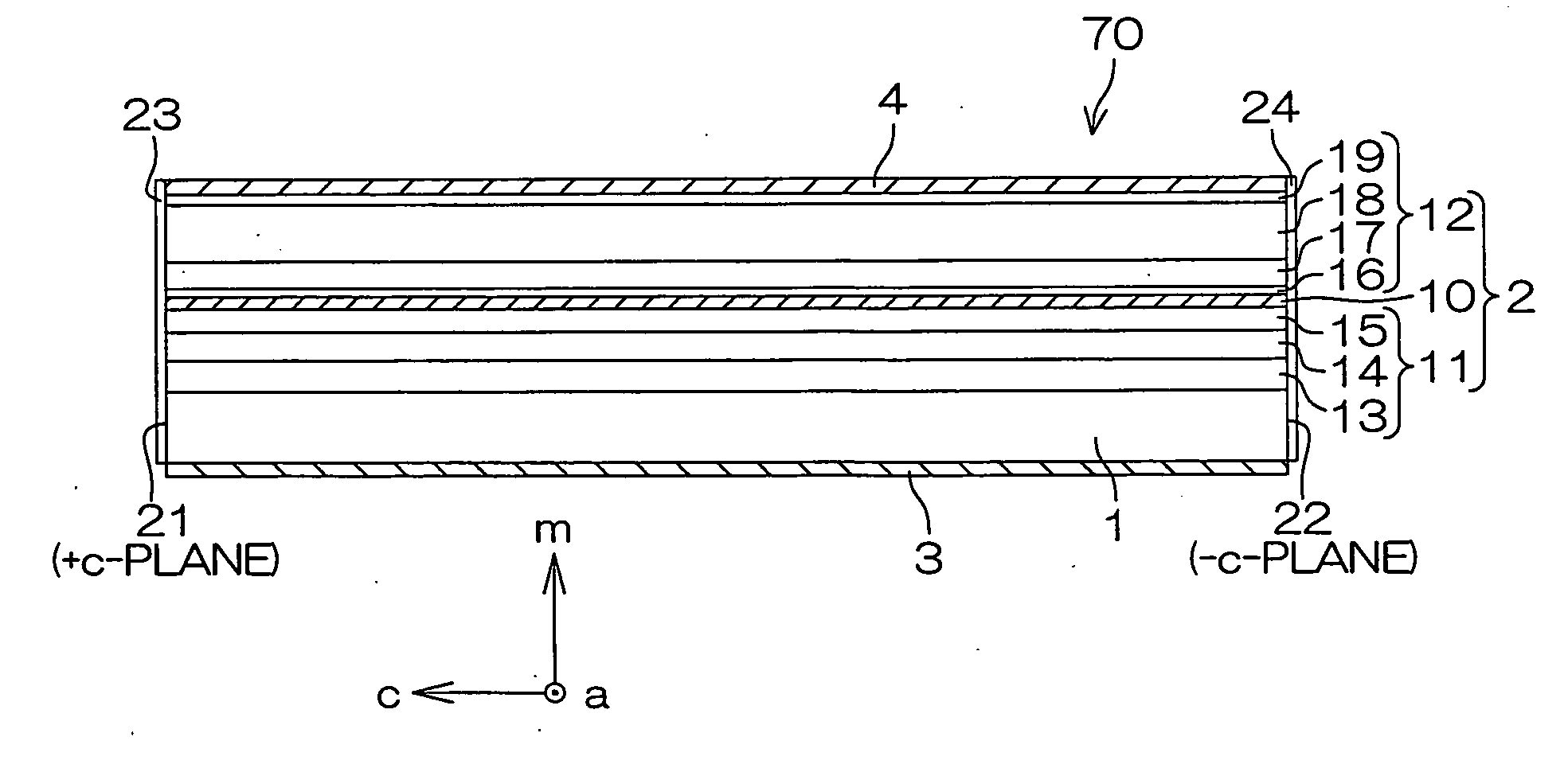
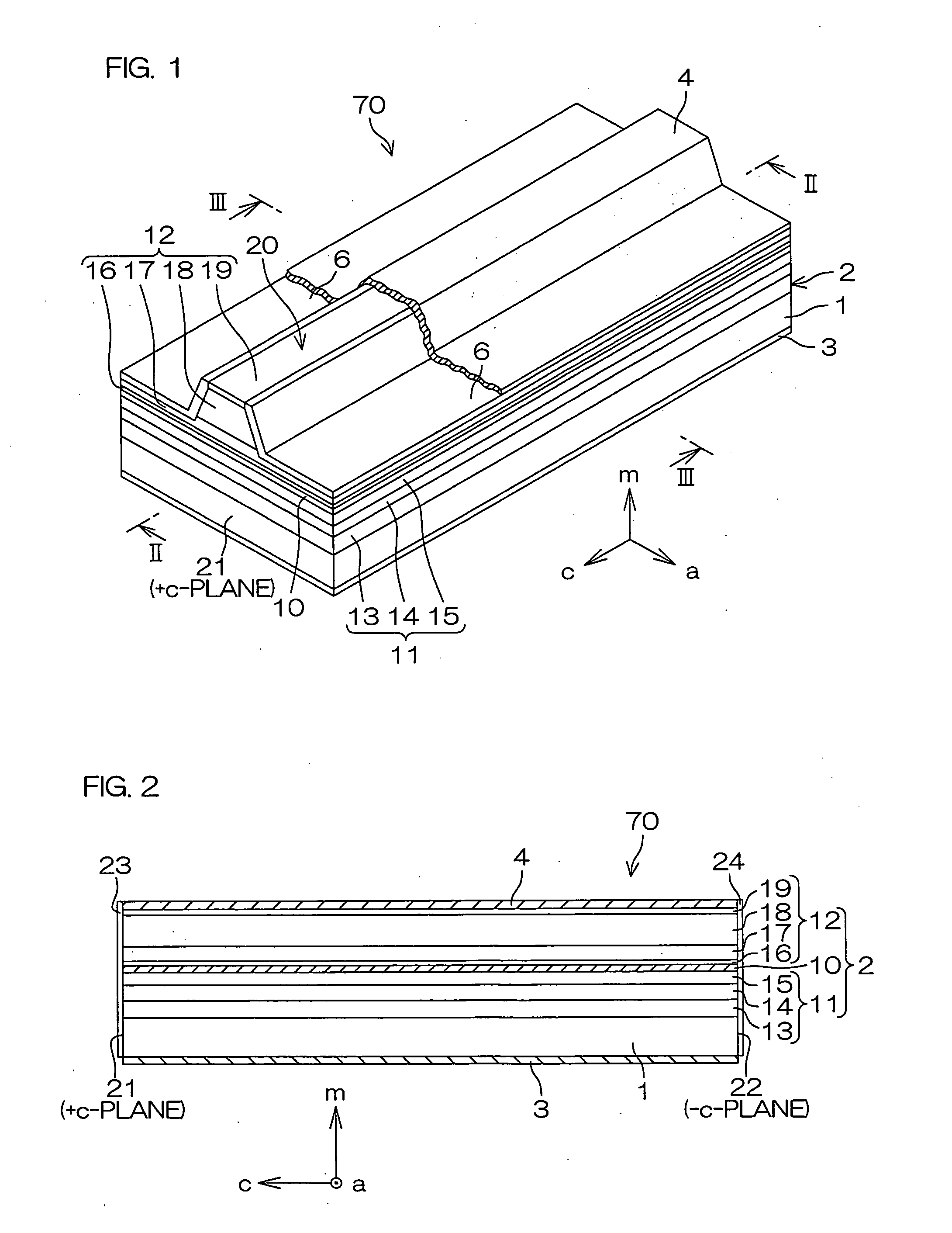
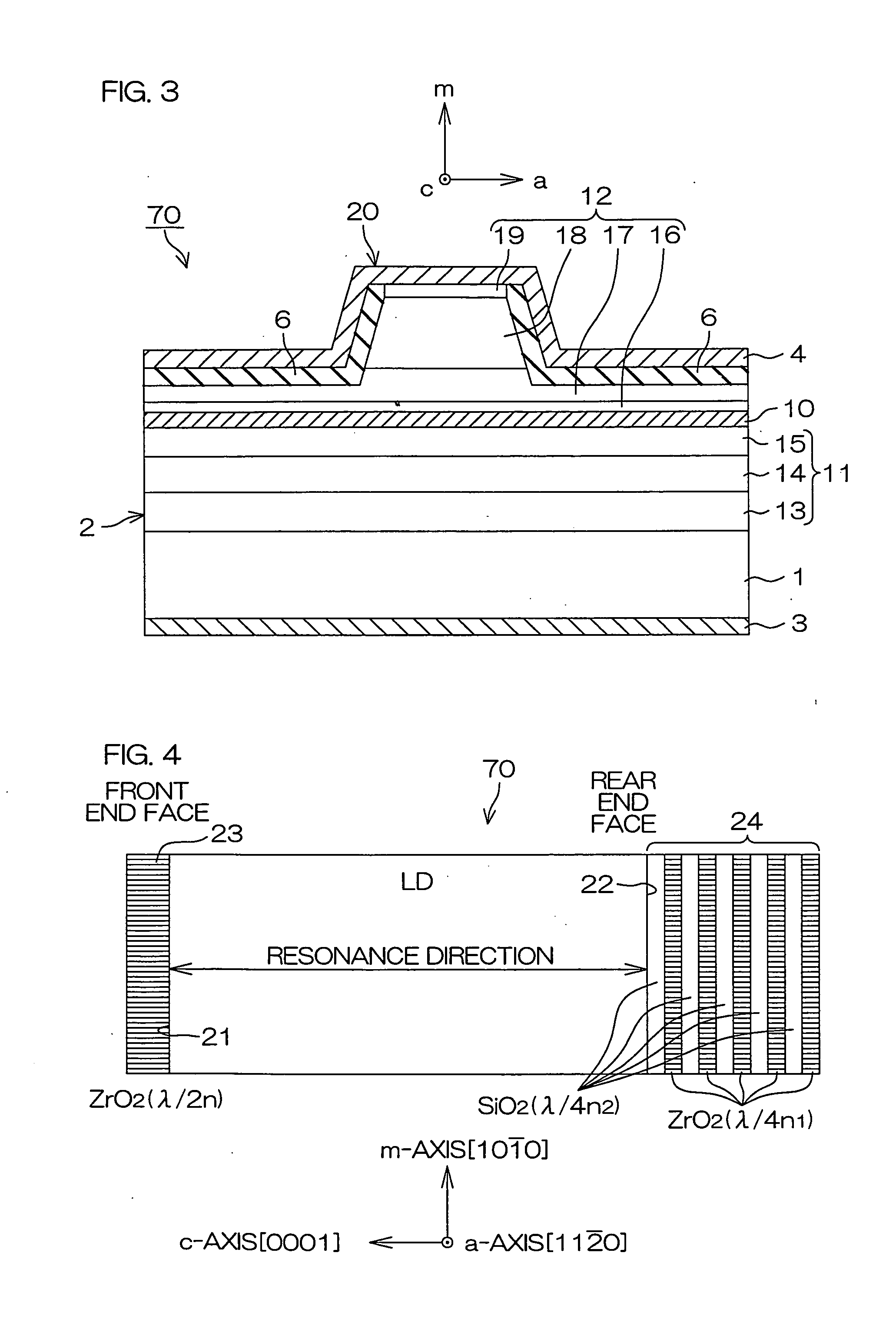
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS20100096615A1Generate efficientlyEfficient use ofSolid-state devicesNanoopticsLight emitting deviceNitride semiconductors
A light-emitting device includes a group III nitride semiconductor layer of a multilayer structure consisting of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane or a semipolar plane and having at least an n-type layer and a p-type layer. A surface of the group III nitride semiconductor layer on a light extraction side is a mirror surface. The light-emitting device may further include a transparent electrode in contact with the surface of the group III nitride semiconductor layer on the light extraction side. In this case, a surface of the transparent electrode on the light extraction side is preferably a mirror surface.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
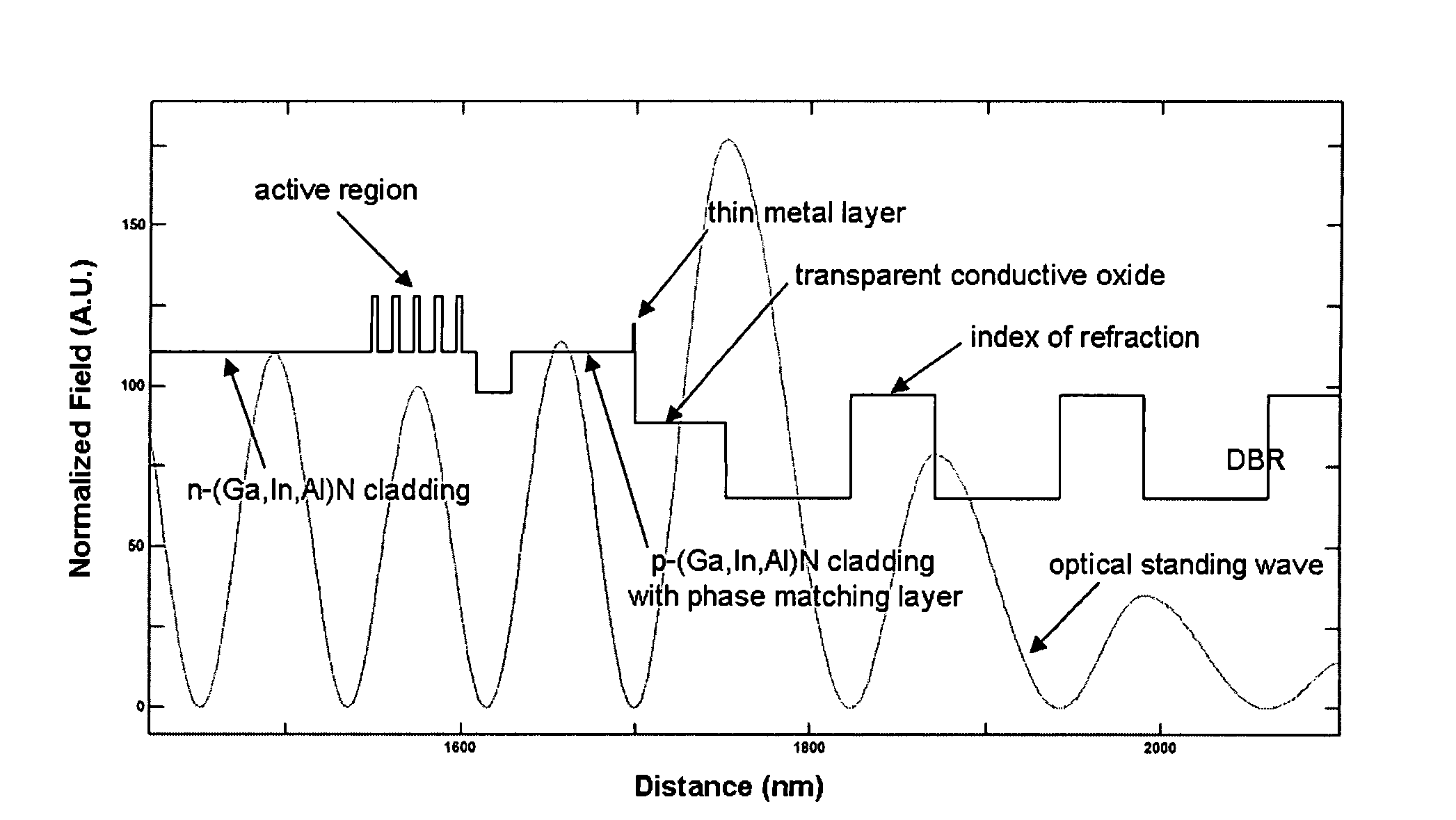
Electrically-pumped (Ga,In,Al)N vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS20070280320A1Good ohmic contactOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersThin metalVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
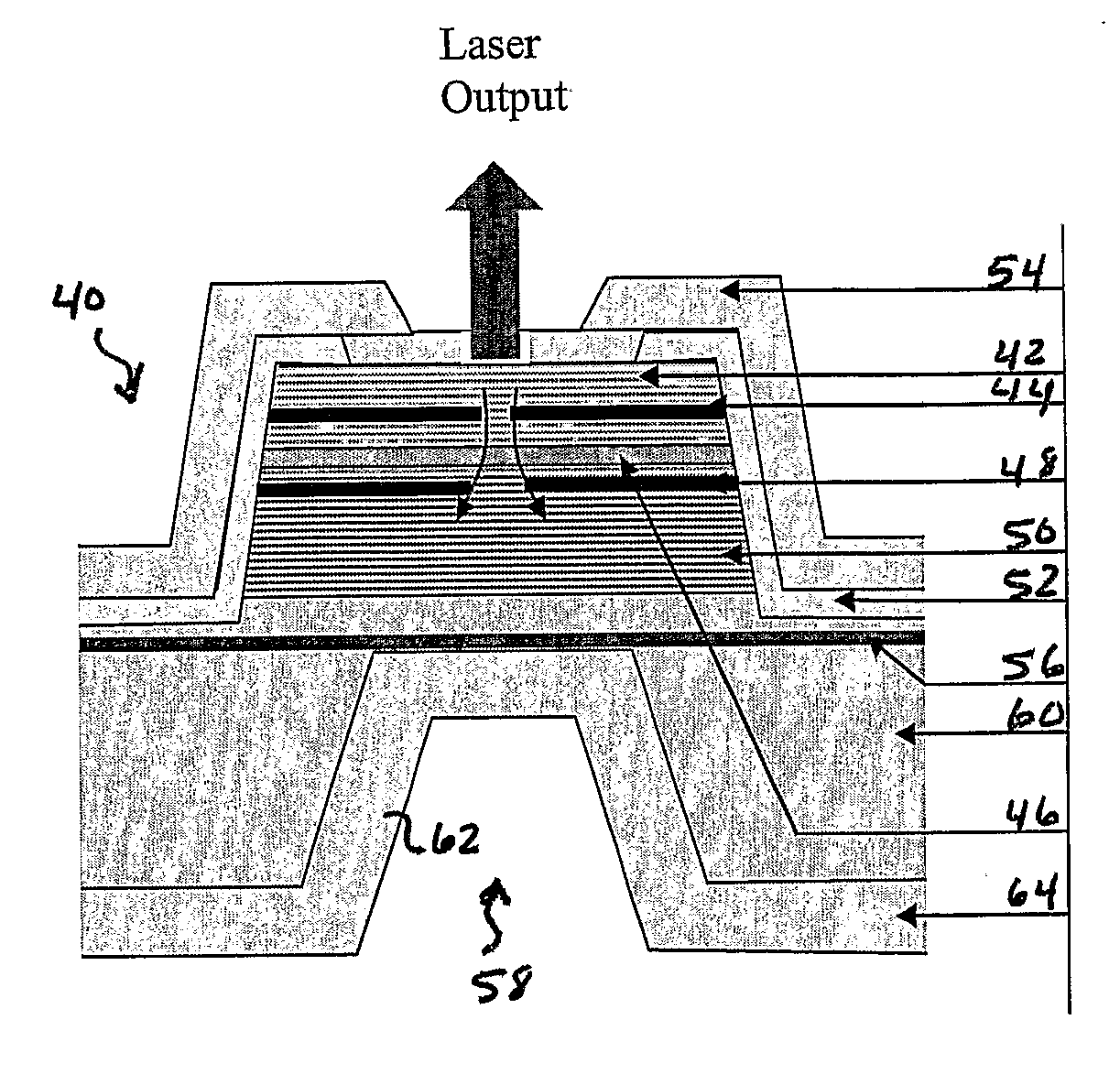
A vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) comprising a low-loss thin metal contact and current spreading layer within the optical cavity that provides for improved ohmic contact and lateral current distribution, a substrate including a plano-concave optical cavity, a (Ga,In,Al)N multiple quantum well (MQW) active region contained within the optical cavity that generates light when injected by an electrical current, and an integrated micromirror fabricated onto the substrate that provides for optical mode control of the light generated by the active region. A relatively simple process is used to fabricate the VCSEL.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
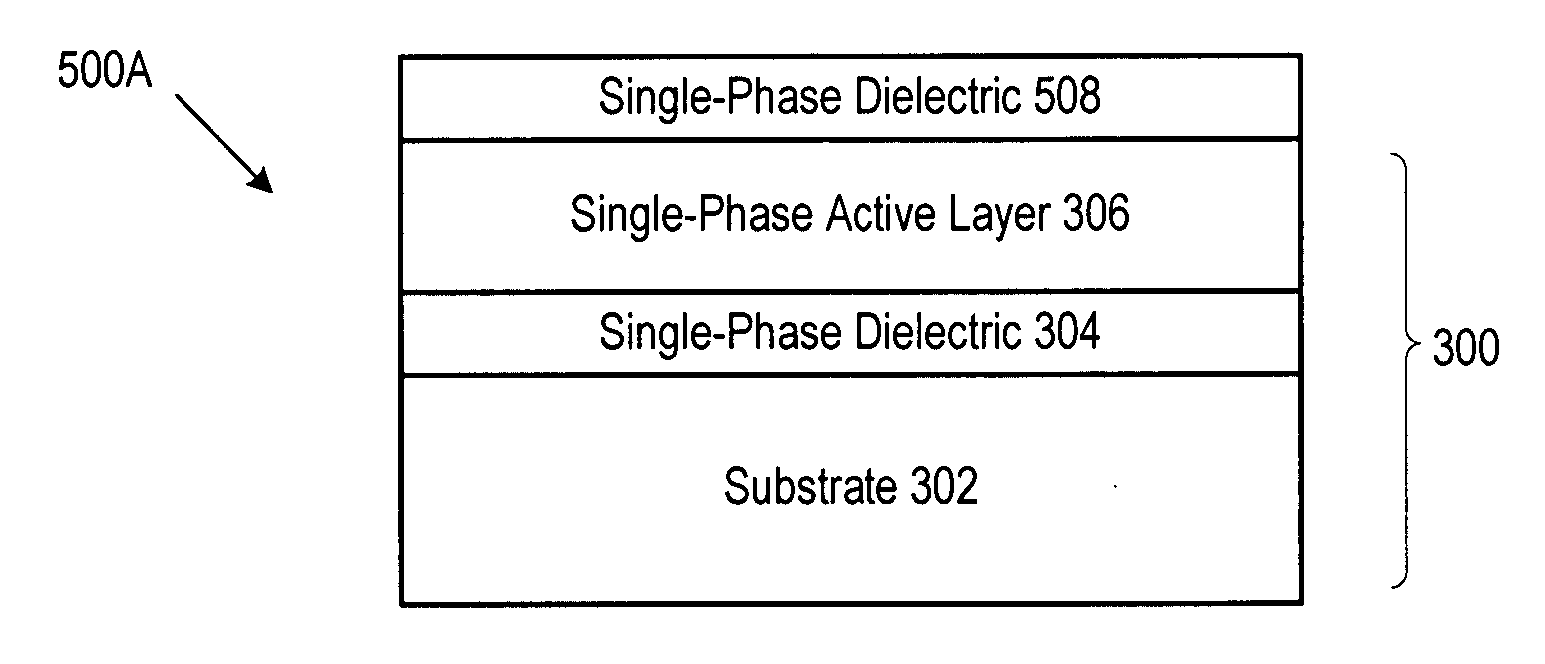
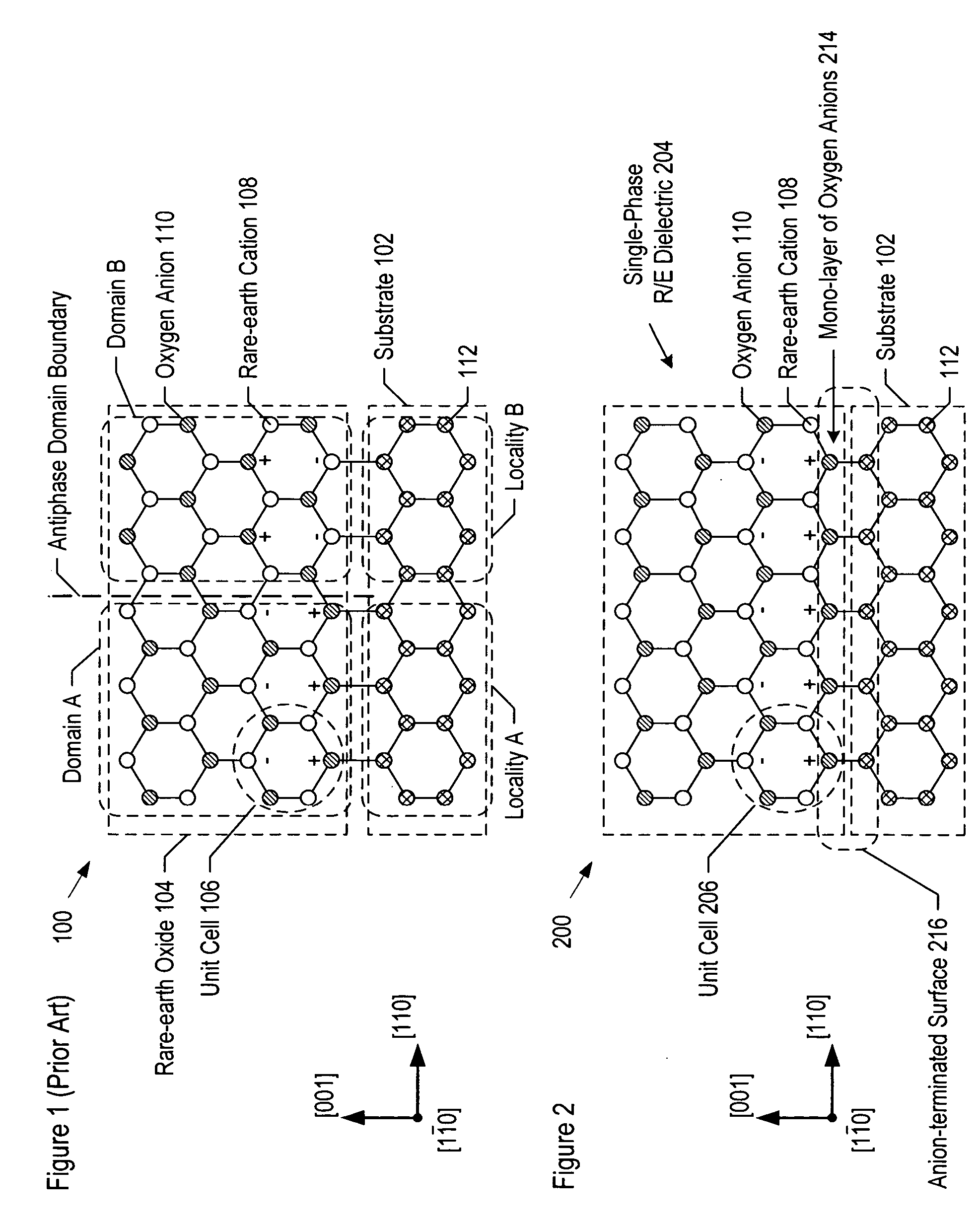
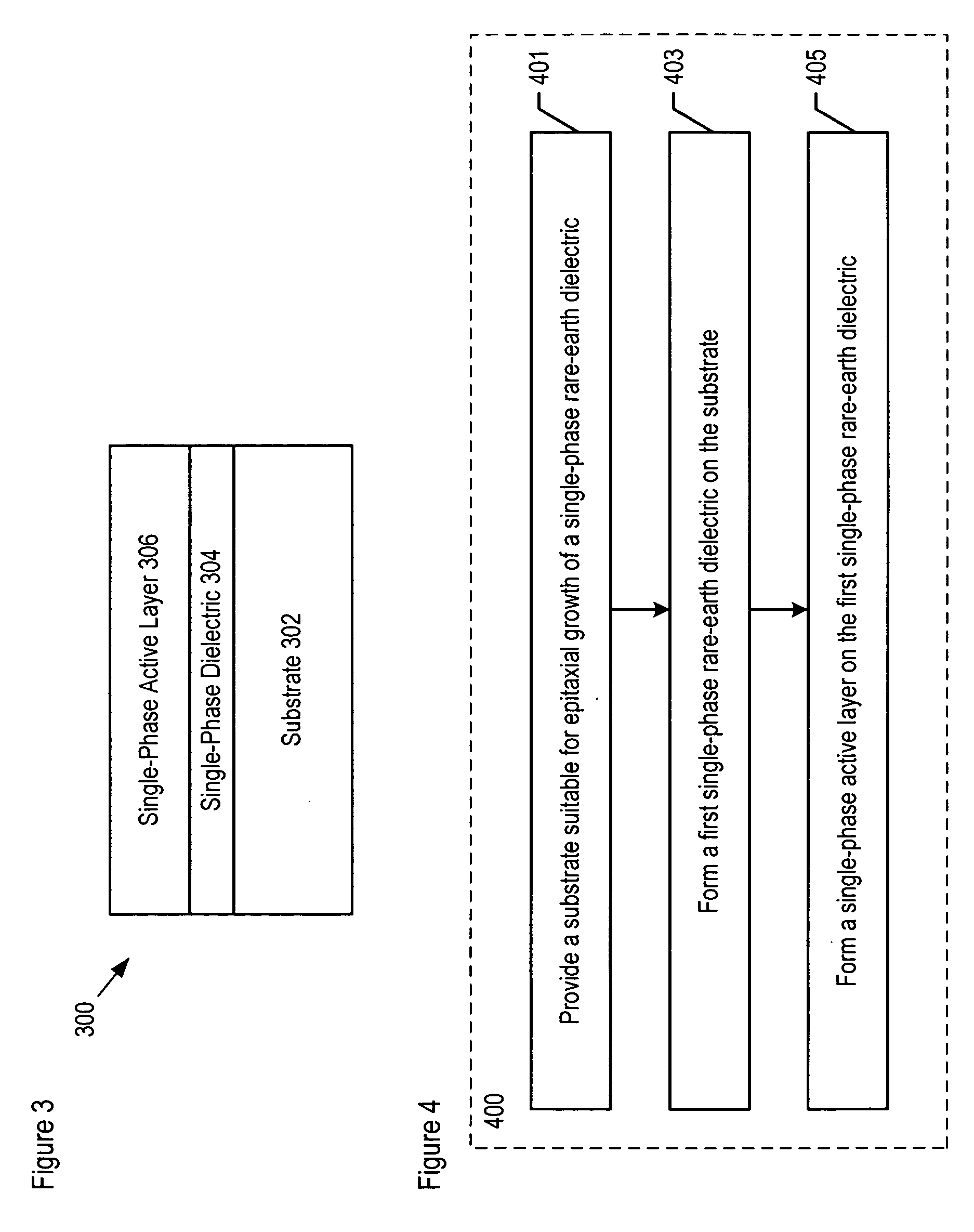
Method of forming a rare-earth dielectric layer
ActiveUS20060060131A1Quality improvementPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsSemiconductor structureRare earth
Methods for forming compositions comprising a single-phase rare-earth dielectric disposed on a substrate are disclosed. In some embodiments, the method forms a semiconductor-on-insulator structure. Compositions and structures that are formed via the method provide the basis for forming high-performance devices and circuits.
Owner:IQE
Semiconductor optoelectronic device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20080095492A1Reducing internal lossImprove internal quantum efficiencyNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellOpto electronic
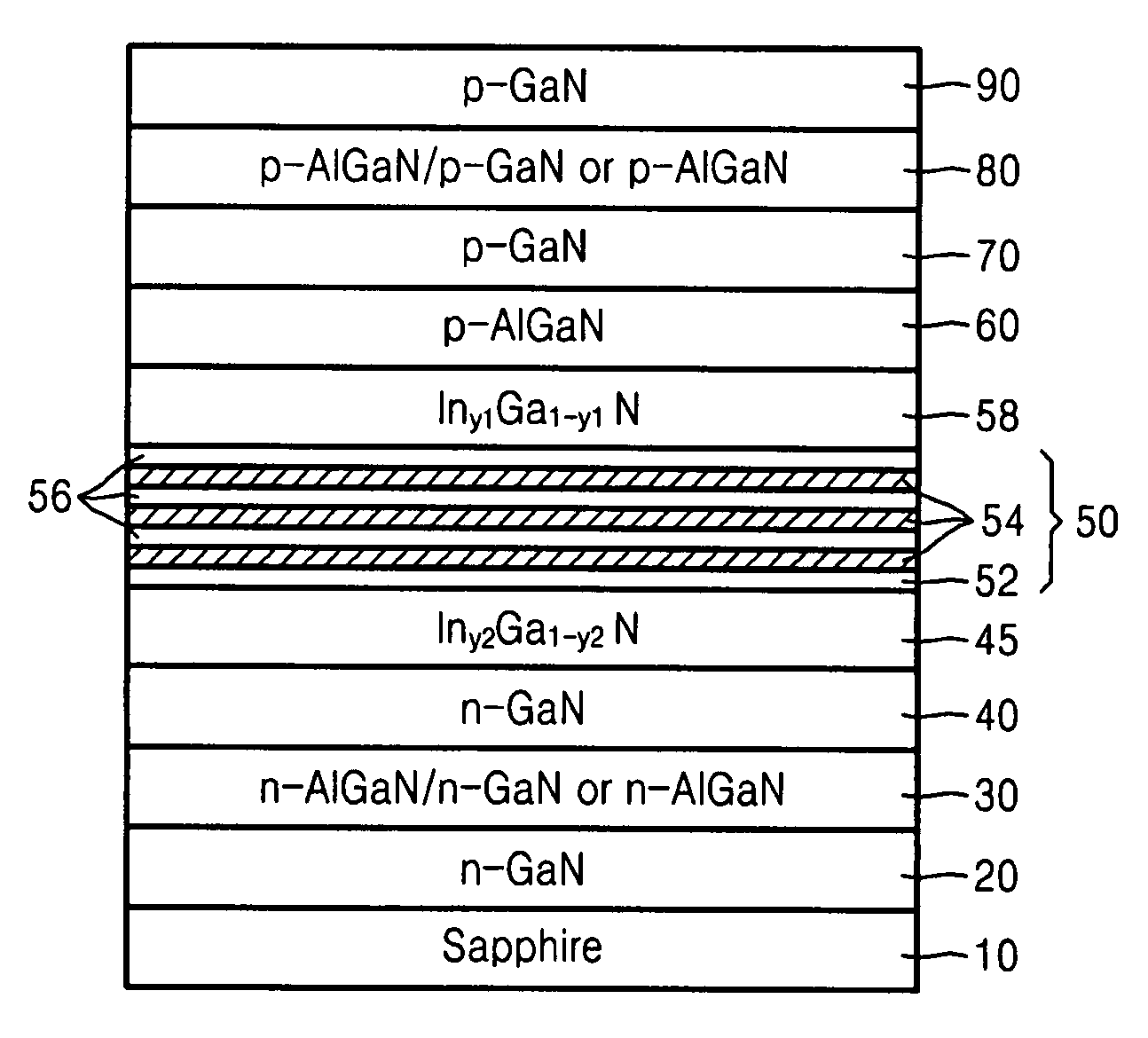
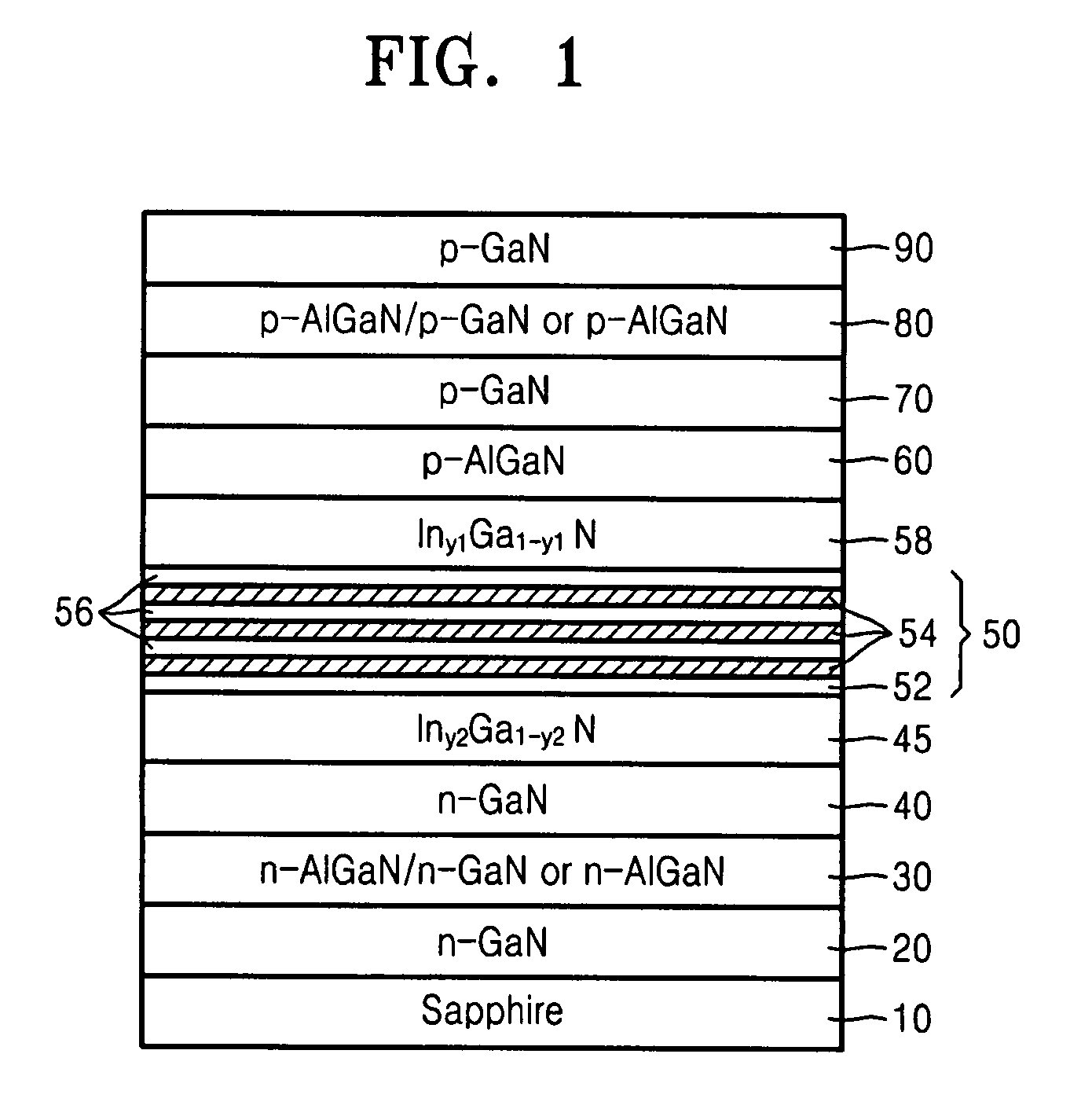
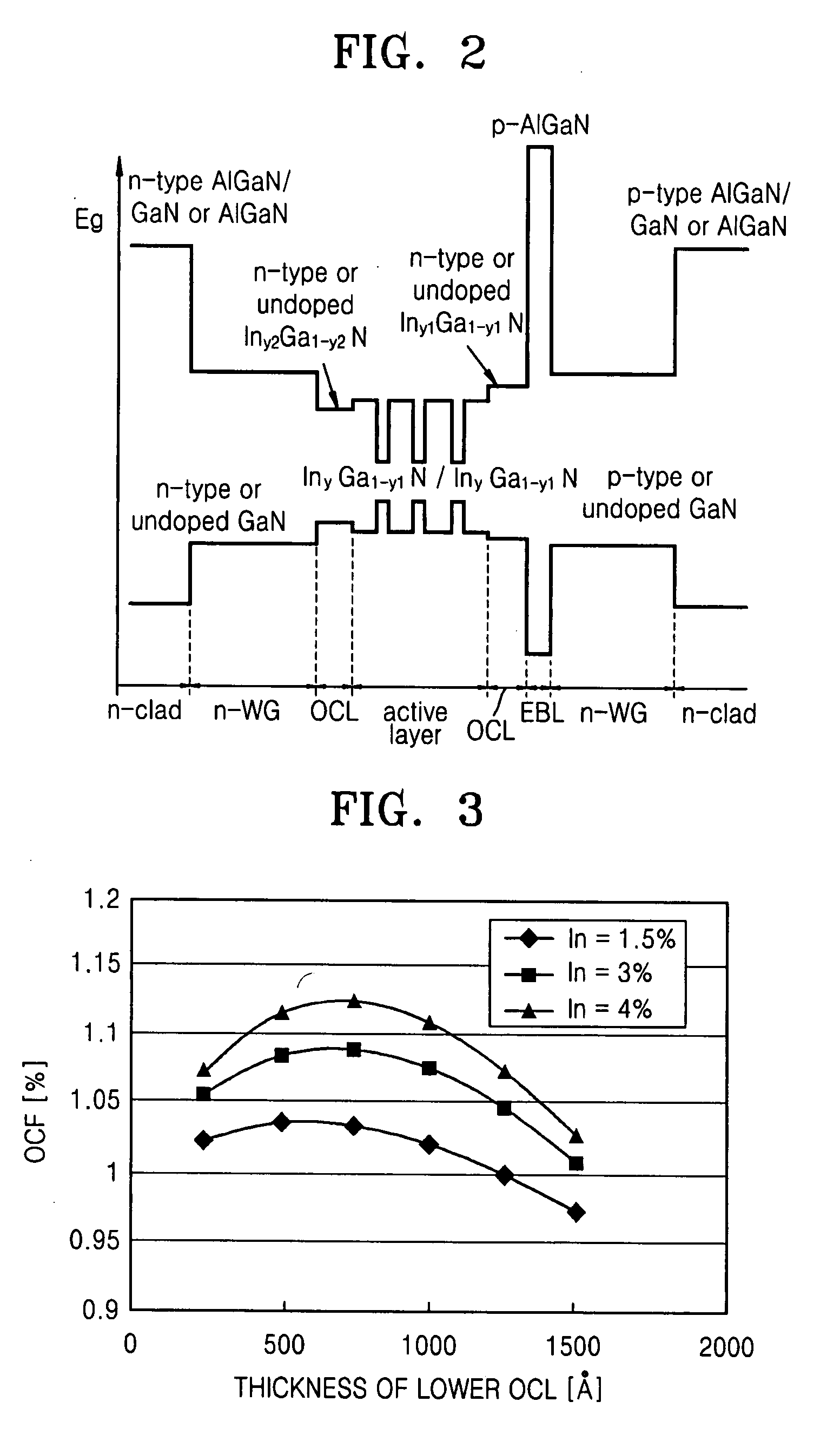
Provided is a semiconductor opto-electronic device that may comprise an active layer including a quantum well and a barrier layer on a substrate, upper and lower waveguide layers on and underneath the active layer, respectively, and upper and lower clad layers on and underneath the upper and lower waveguide layers, respectively. The semiconductor opto-electronic device may further comprise an upper optical confinement layer (OCL) between the active layer and the upper waveguide layer and having an energy gap smaller than the energy gap of the upper waveguide layer and equal to or larger than the energy gap of the barrier layer, and a lower OCL between the active layer and the lower waveguide layer and having an energy gap smaller than the energy gap of the lower waveguide layer and equal to or smaller than the energy gap of the barrier layer. Also provided is a method of fabricating the semiconductor opto-electronic device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
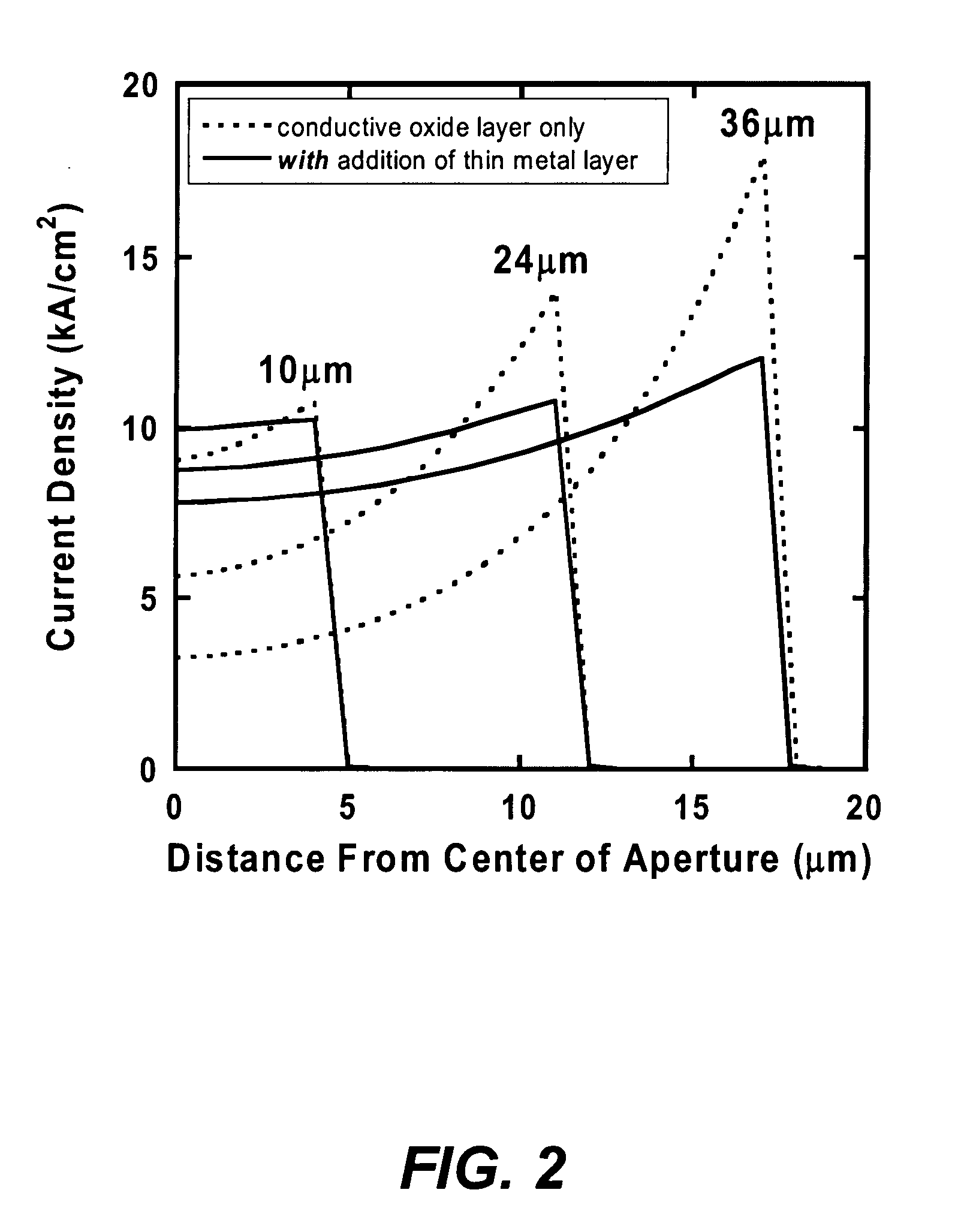
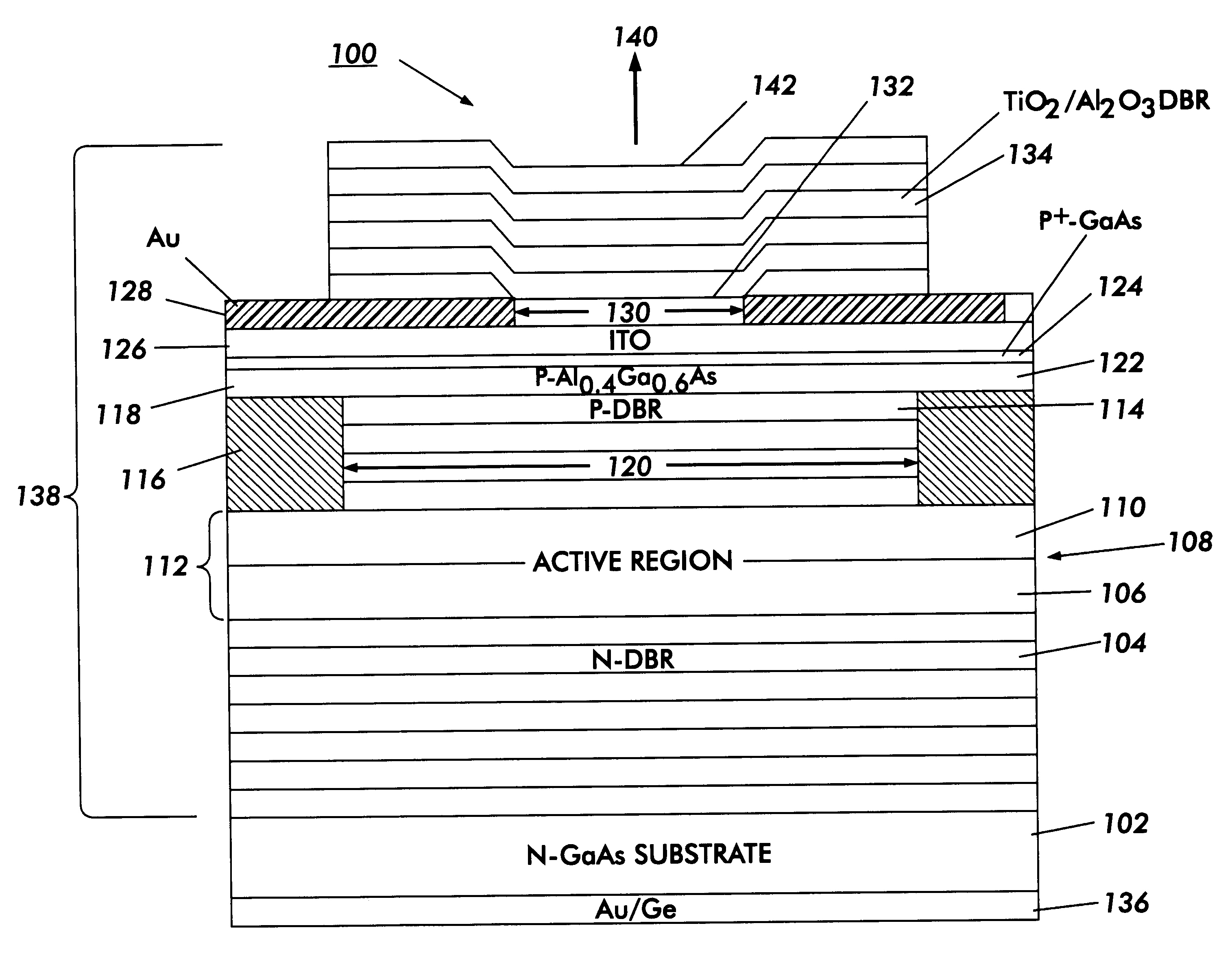
Metal spatial filter to enhance model reflectivity in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser
InactiveUS6185241B1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
An annular metal layer is provided between a conductive oxide layer and a dielectric mirror in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The annular metal layer defines the output window for the laser cavity which matches the TEM.sub.00 fundamental mode of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL. The metal layer outside the output window provides modal reflectivity discrimination against high order transverse modes of the light beam emitted by the active region of the VCSEL.
Owner:XEROX CORP
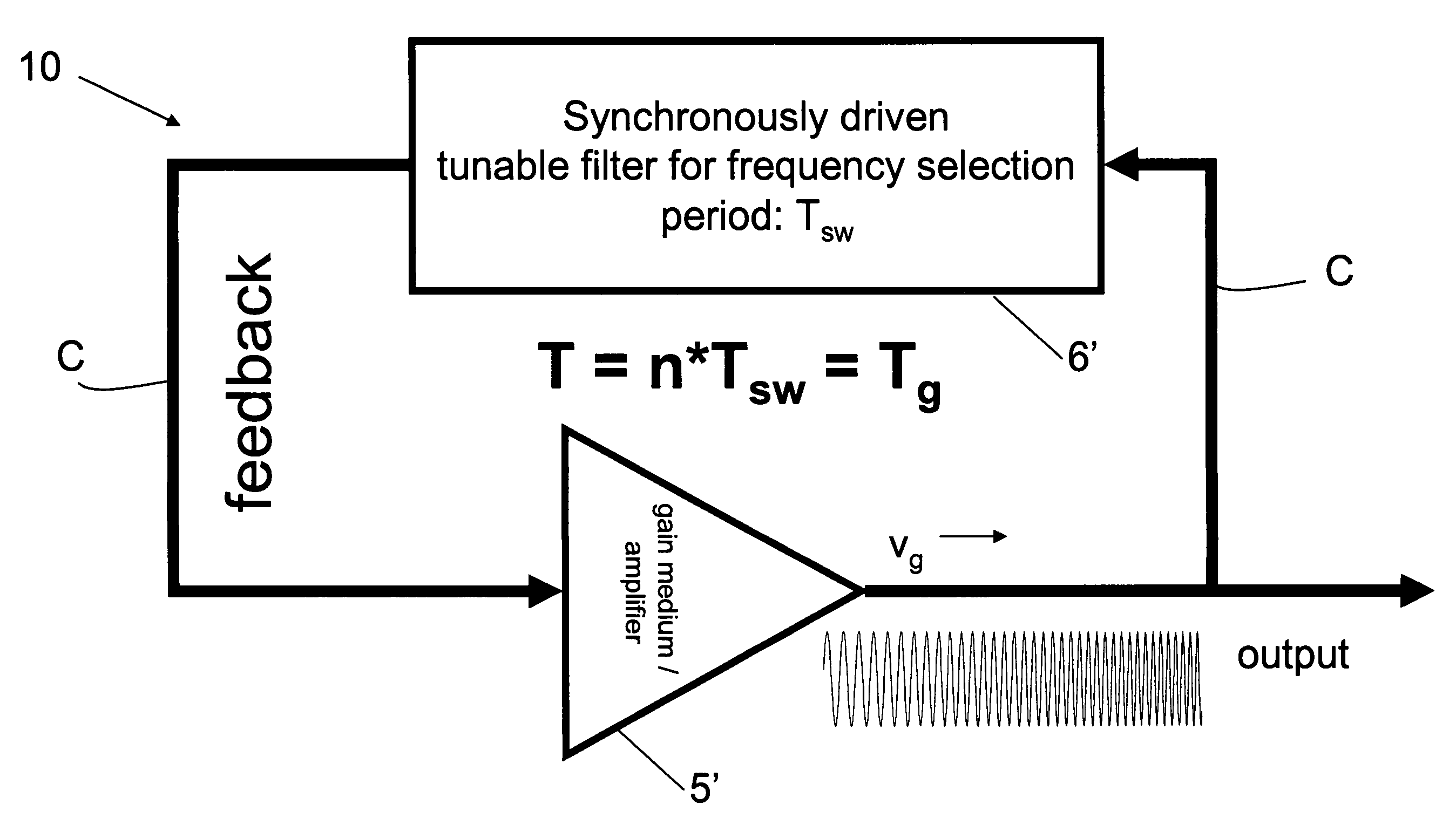
Mode locking methods and apparatus
In one aspect the invention relates to a frequency varying wave generator. The generator includes a gain element adapted to amplify a wave having a wavelength; a time varying tunable wavelength selective filter element in communication with the gain element, the tunable filter element adapted to selectively filter waves during a period T; and a feedback element in communication with the tunable filter element and the gain element, wherein the tunable wavelength selective filter element, the gain element and the feedback element define a circuit such that the roundtrip time for the wave to propagate through the circuit is substantially equal to a non-zero integer multiple of the period T.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
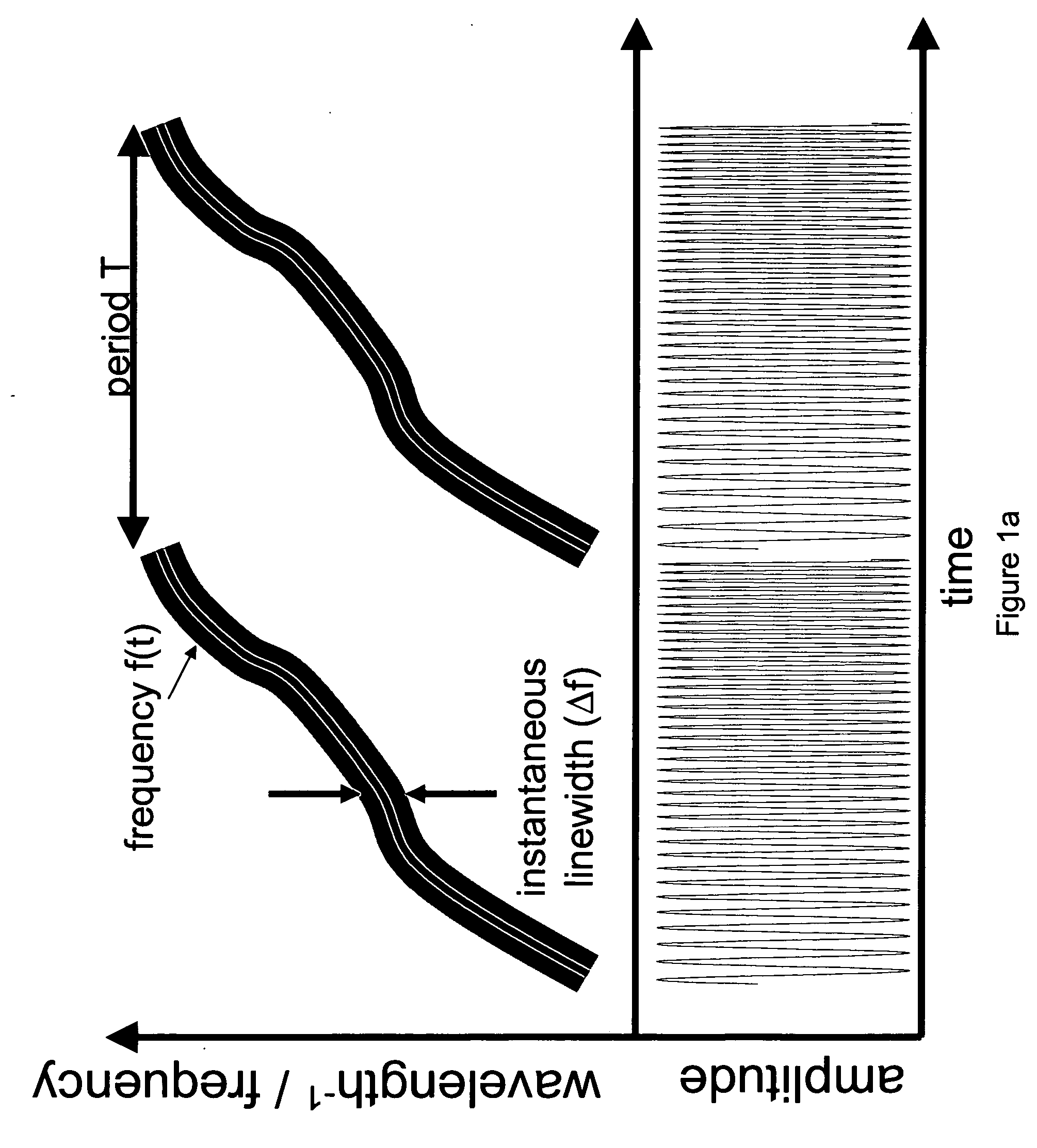
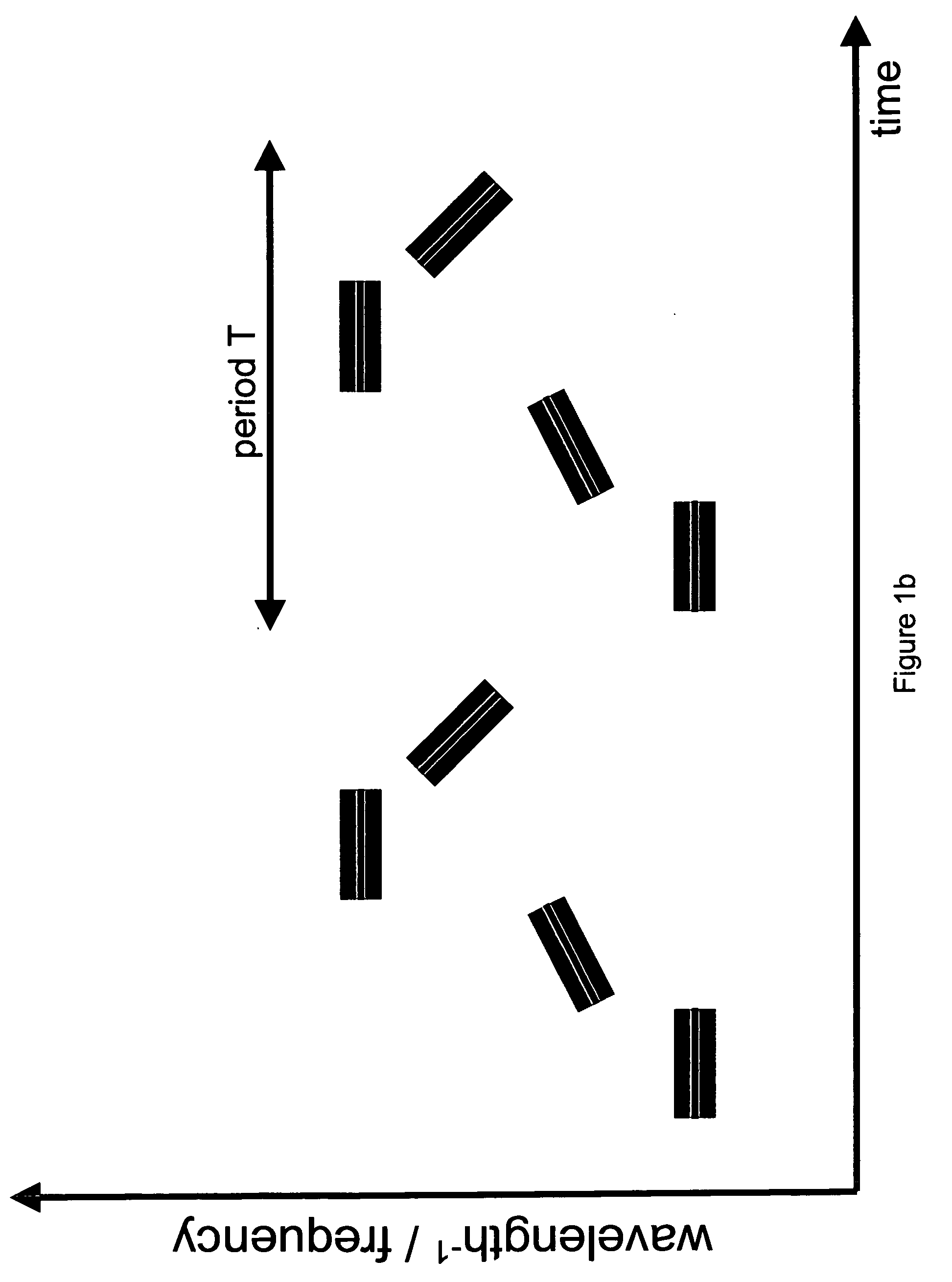
Process and apparatus for a wavelength tuning source
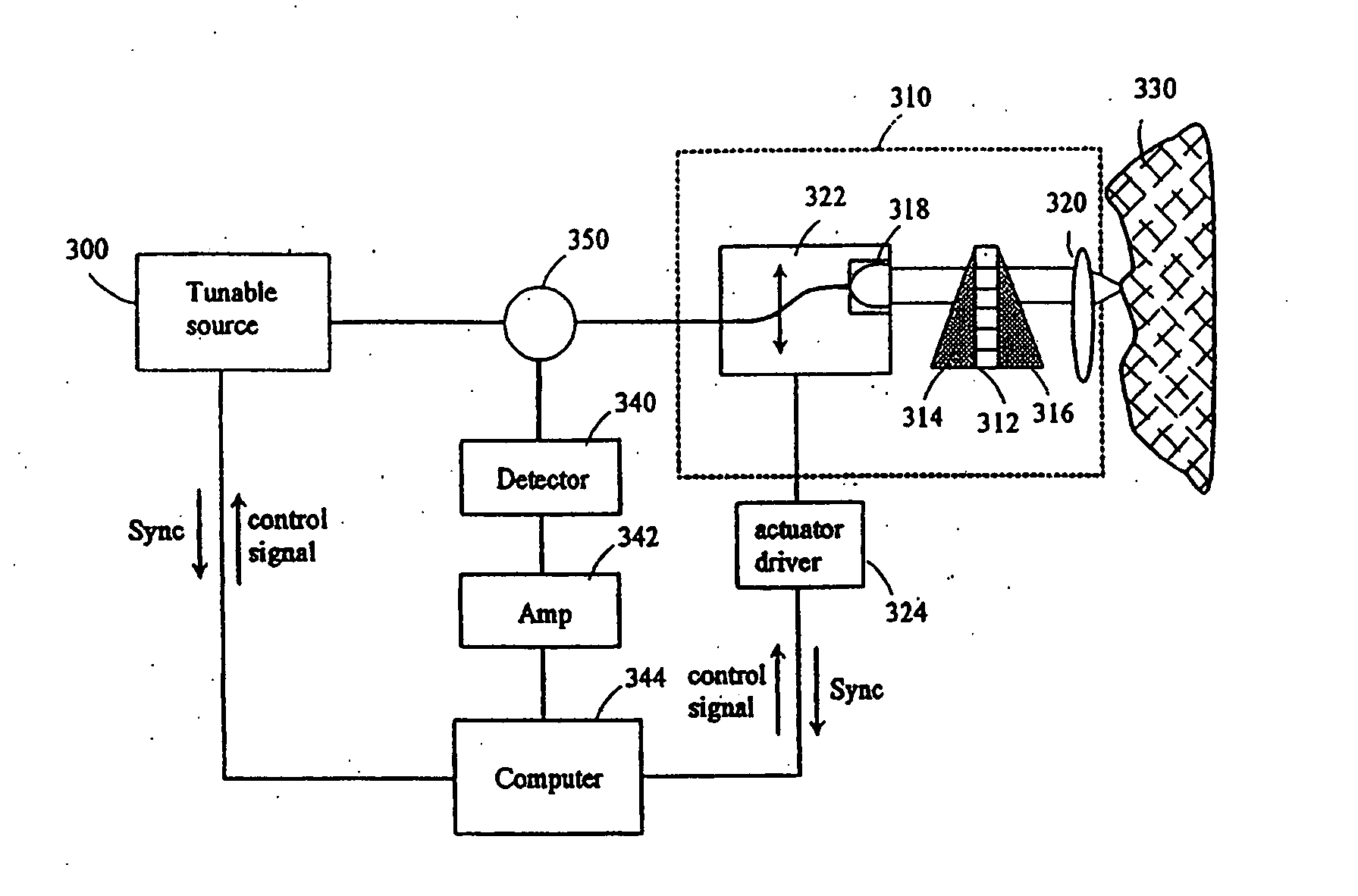
ActiveUS20050035295A1Low spontaneous-emission backgroundTuning rateOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryLight beamLength wave
An apparatus and source arrangement for filtering an electromagnetic radiation can be provided which may include at least one spectral separating arrangement configured to physically separate one or more components of the electromagnetic radiation based on a frequency of the electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus and source arrangement may also have at least one continuously rotating optical arrangement which is configured to receive at least one signal that is associated with the one or more components. Further, the apparatus and source arrangement can include at least one beam selecting arrangement configured to receive the signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Manufacturable vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser arrays
InactiveUS20070153866A1Reduce component countReduce in quantityProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayOptoelectronics
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
LED luminaire
InactiveUS7102172B2Point-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectrical junctionModularity
A modular light emitting diode (LED) mounting configuration is provided including a light source module having a plurality of pre-packaged LEDs arranged in a serial array. The module is connected to a heat dissipating plate configured to mount to an electrical junction box. Thus, heat from the LEDs is conducted to the heat dissipating plate and to the junction box. A sensor is configured to detect environmental parameters and a driver is configured to illuminate the LEDs in response to the environmental parameters, thereby selectively configuring the LEDs to function in a wide variety of useful applications.
Owner:DIAMOND CREEK CAPITAL LLC
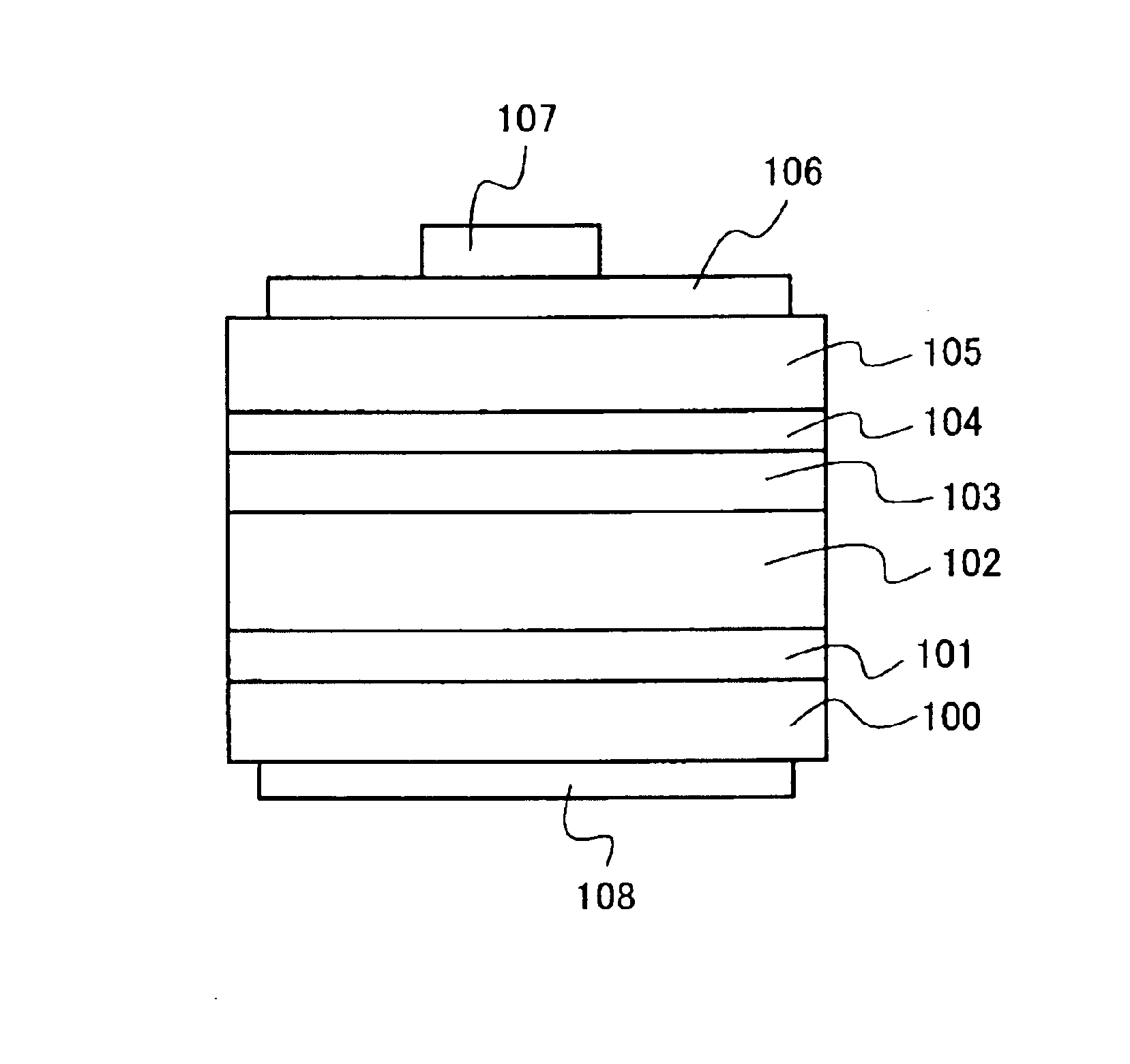
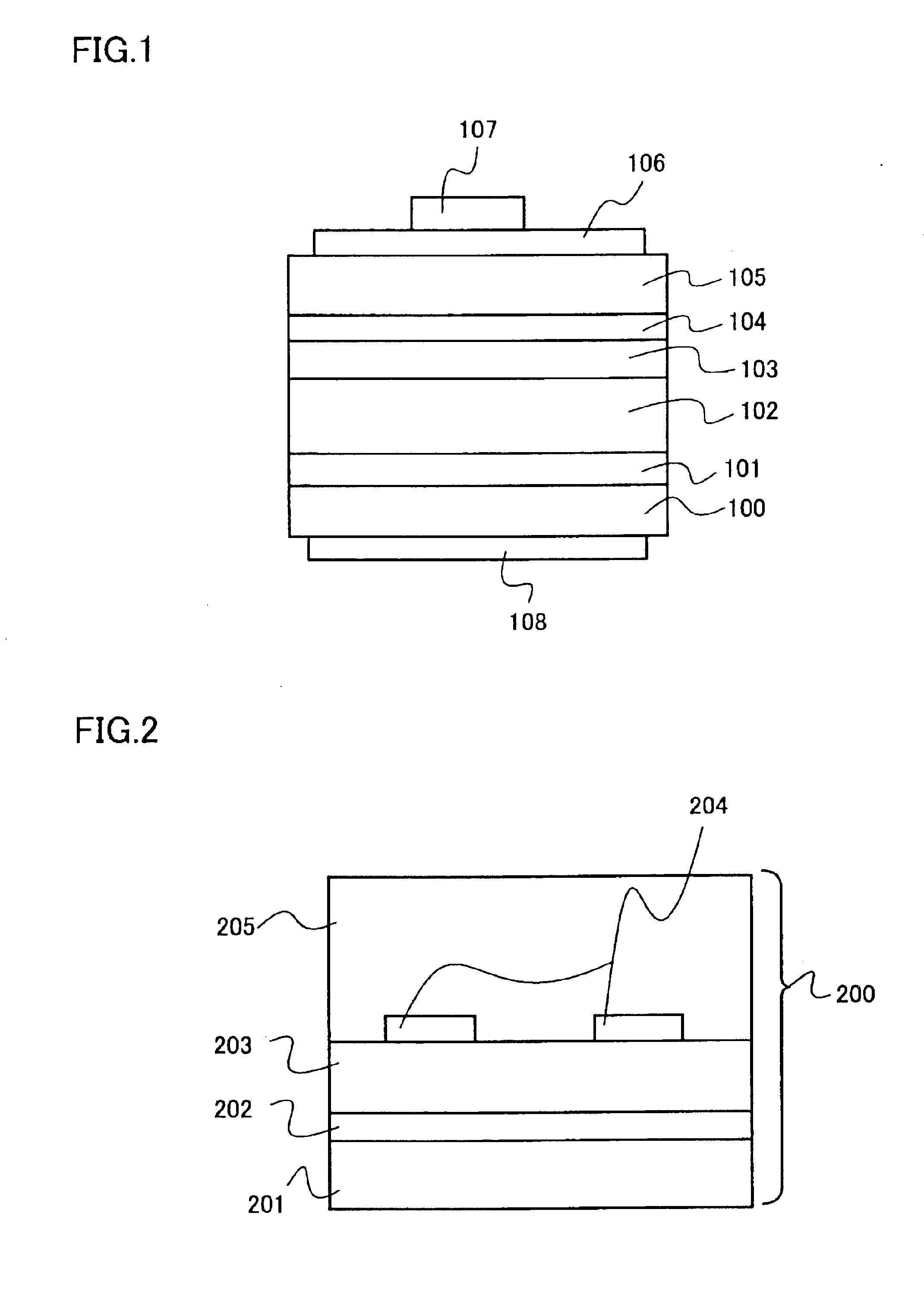
Semiconductor light-emitting element and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100295054A1Improve luminous efficiencyLow thresholdLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveActive layer
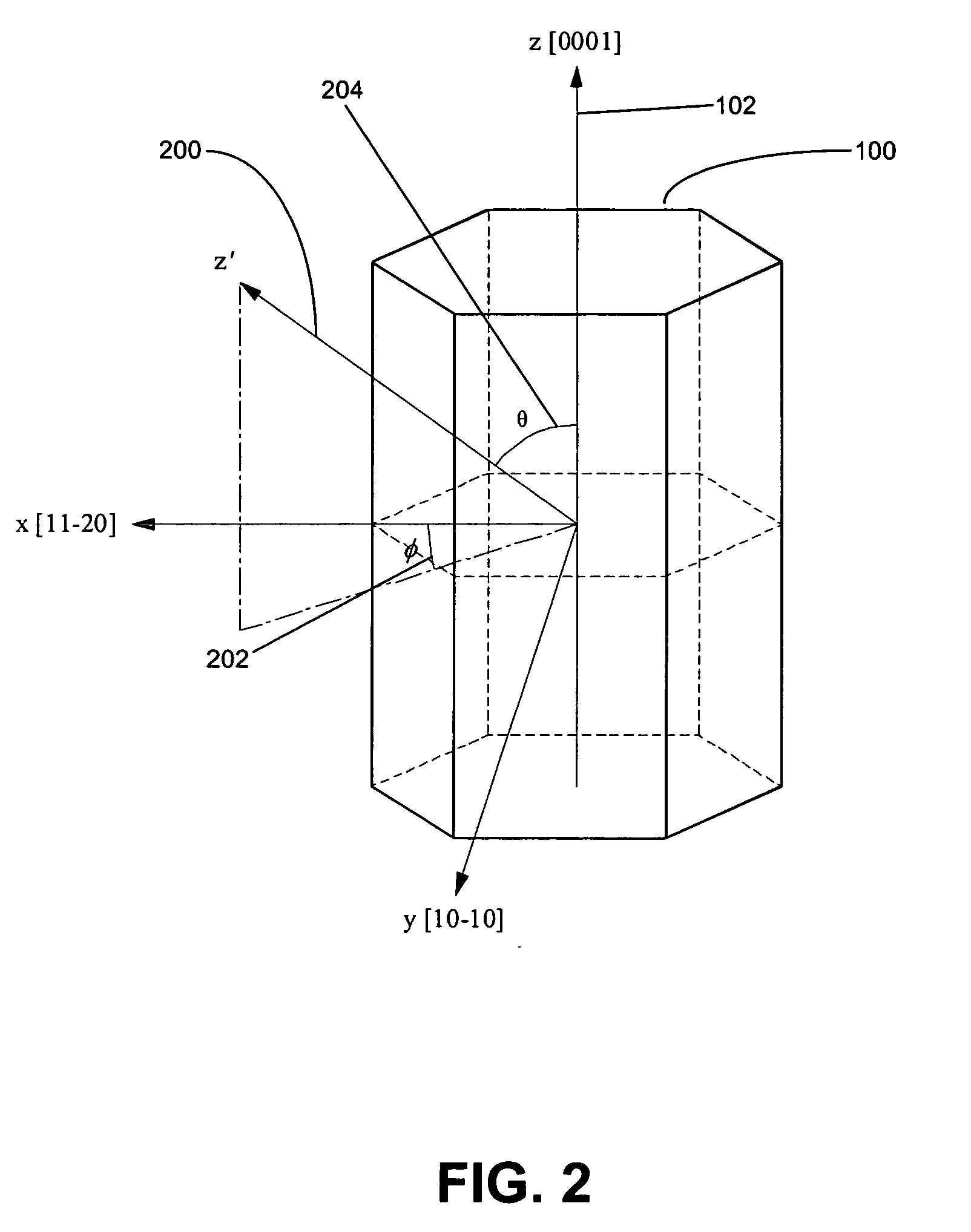
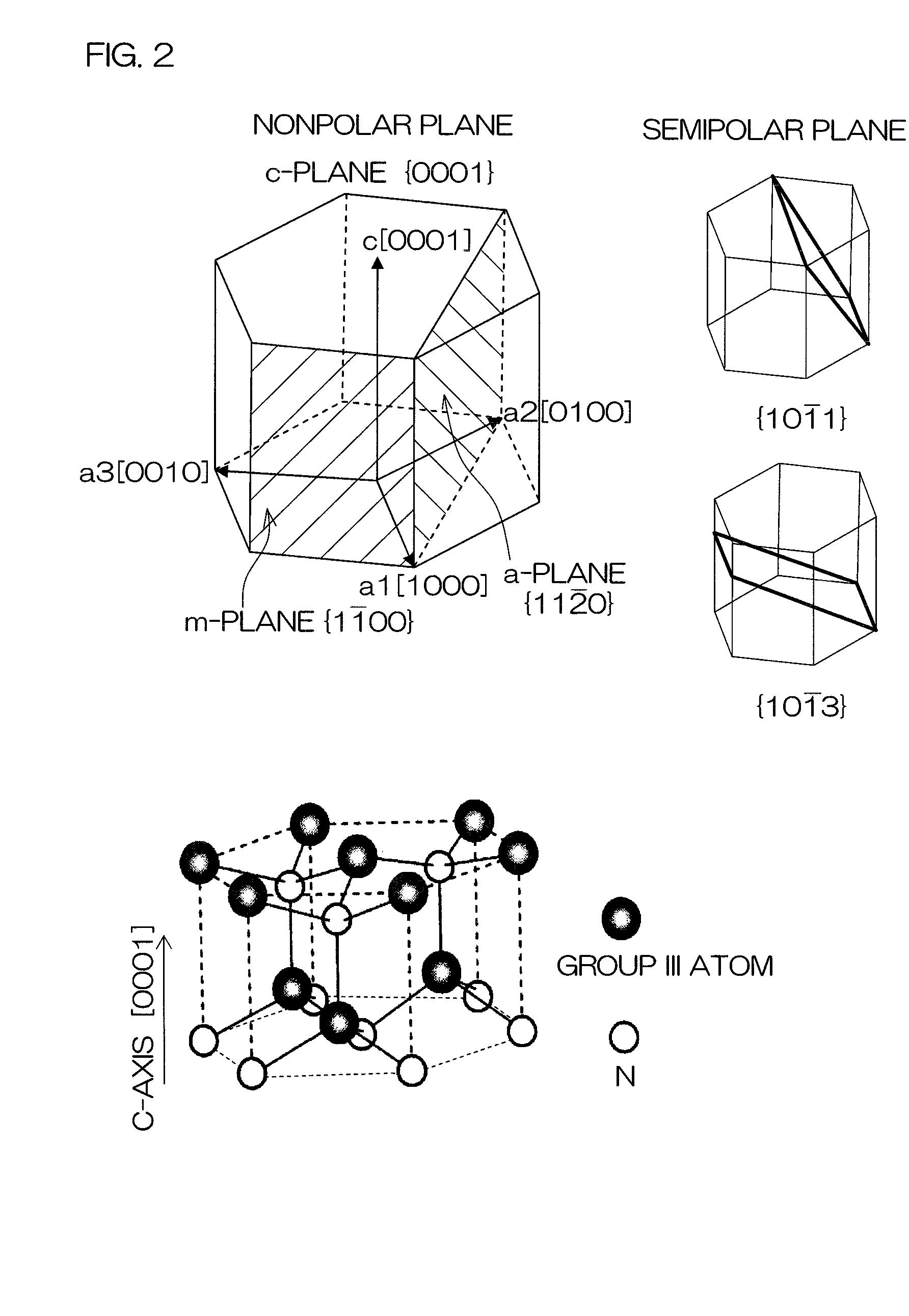
The semiconductor light-emitting element includes a group III nitride semiconductor multilayer structure having an active layer containing In as well as a p-type layer and an n-type layer stacked to hold the active layer therebetween. The group III nitride semiconductor multilayer structure is made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane whose offset angle in a c-axis direction is negative. A remarkable effect is attained when the emission wavelength of the active layer is not less than 450 nm. In the group III nitride semiconductor constituting the group III nitride semiconductor multilayer structure, the offset angle θ in the c-axis direction preferably satisfies −1°<θ<0°.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
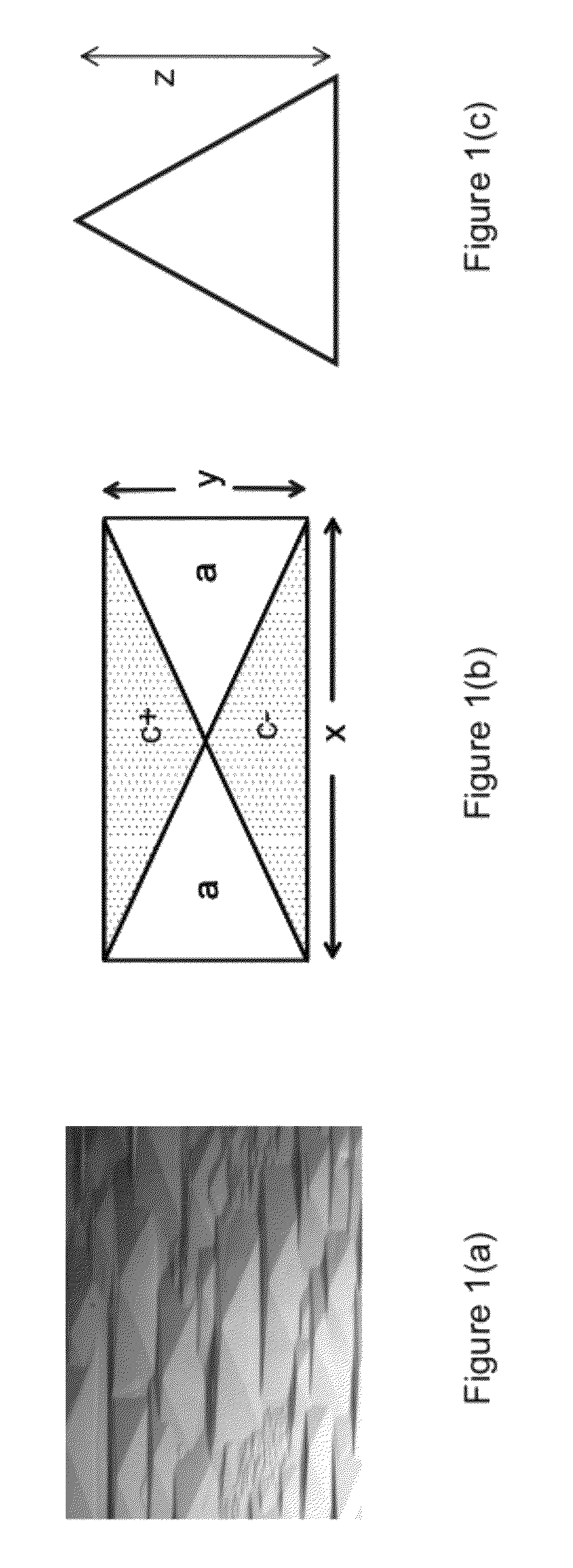
Method and surface morphology of non-polar gallium nitride containing substrates
ActiveUS8247887B1Improve device performanceCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesGallium nitrideLaser
An optical device, e.g., LED, laser. The device includes a non-polar gallium nitride substrate member having a slightly off-axis non-polar oriented crystalline surface plane. In a specific embodiment, the slightly off-axis non-polar oriented crystalline surface plane is up to about −0.6 degrees in a c-plane direction, but can be others. In a specific embodiment, the present invention provides a gallium nitride containing epitaxial layer formed overlying the slightly off-axis non-polar oriented crystalline surface plane. In a specific embodiment, the device includes a surface region overlying the gallium nitride epitaxial layer that is substantially free of hillocks.
Owner:SLT TECH
Group-III nitride light-emitting device
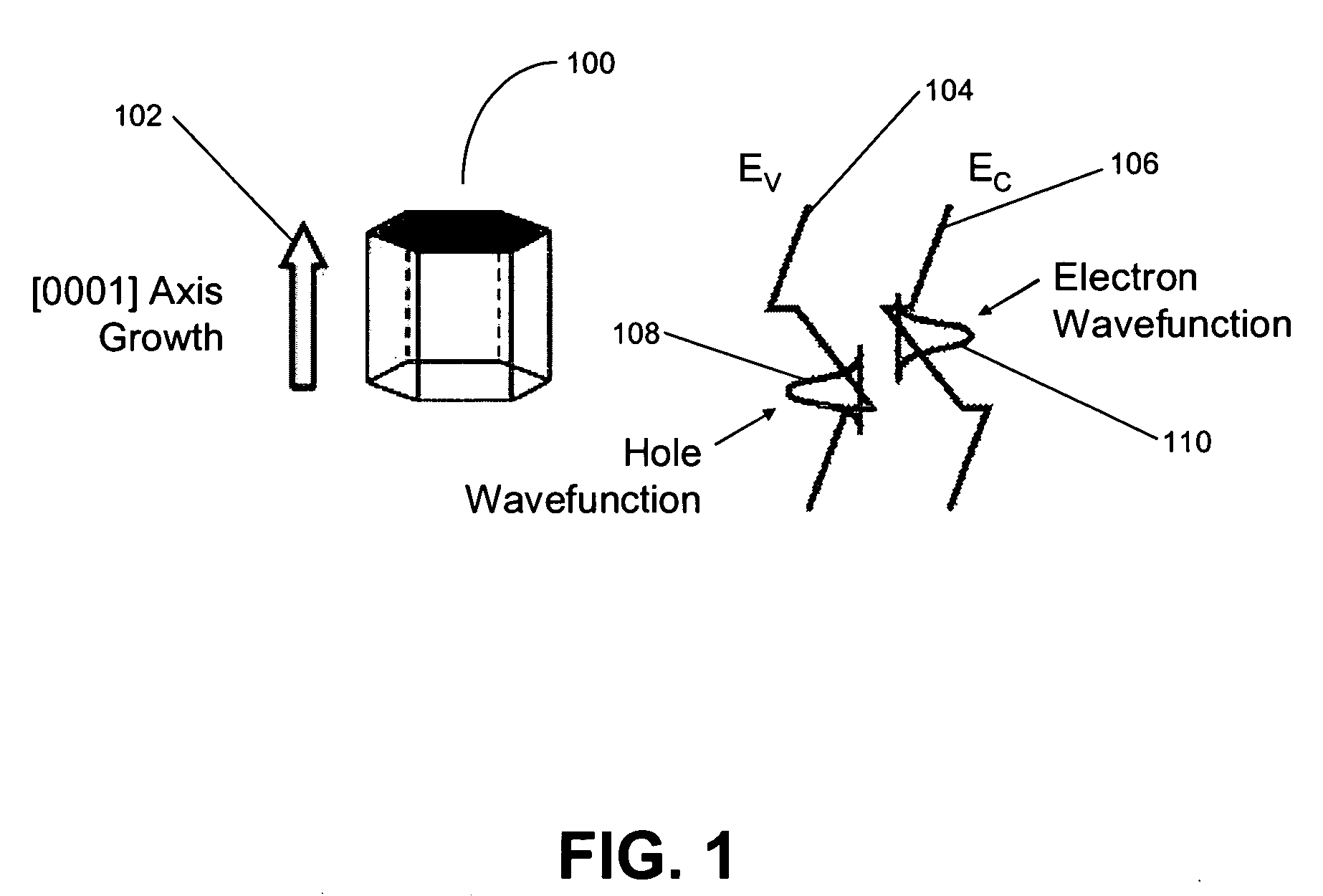
ActiveUS7968864B2Piezoelectric field is reducedLow efficiencyThyristorSolid-state devicesQuantum wellLength wave
A group-III nitride light-emitting device is provided. An active layer having a quantum well structure is grown on a basal plane of a gallium nitride based semiconductor region. The quantum well structure is formed in such a way as to have an emission peak wavelength of 410 nm or more. The thickness of a well layer is 4 nm or more, and 10 nm or less. The well layer is composed of InXGa1-XN (0.15≦X<1, where X is a strained composition). The basal plane of the gallium nitride based semiconductor region is inclined at an inclination angle within the range of 15 degrees or more, and 85 degrees or less with reference to a {0001} plane or a {000-1} plane of a hexagonal system group III nitride. The basal plane in this range is a semipolar plane.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Nitride semiconductor light-emitting device and optical device including the same
InactiveUS6858882B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellLight emitting device
A nitride semiconductor light-emitting device includes an emission layer (103) formed on a substrate (100), and the emission layer includes a quantum well layer of GaN1-x−y−zAsxPySbz (0<x+y+z≦0.3) containing Al.
Owner:SHARP KK
Group iii-nitride growth on silicon or silicon germanium substrates and method and devices therefor
InactiveUS20080128745A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A structure including a Si1-xGex substrate and a distributed Bragg reflector layer disposed directly onto the substrate. The distributed Bragg reflector layer includes a repeating pattern that includes at least one aluminum nitride layer and a second layer having the general formula AlyGa1-yN. Another aspect of the present invention is various devices including this structure. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a method of forming such a structure comprising providing a Si1-xGex substrate and depositing a distributed Bragg reflector layer directly onto the substrate. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a photodetector or photovoltaic cell device, including a Si1-xGex substrate device, a group III-nitride device and contacts to provide a conductive path for a current generated across at least one of the Si1-xGex substrate device and the group III-nitride device upon incident light.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Method for producing a gallium nitride epitaxial layer
InactiveUS6325850B1GaN crystal qualityImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsEtchingGallium nitride
The invention concerns a method for producing a gallium nitride (GaN) epitaxial layer characterised in that it consists in depositing on a substrate a dielectric layer acting as a mask and depositing on the masked gallium nitride, by epitaxial deposit, so as to induce the deposit of gallium nitride patterns and the anisotropic lateral growth of said patterns, the lateral growth being pursued until the different patterns coalesce. The deposit of the gallium nitride patterns can be carried out ex-situ by dielectric etching or in-situ by treating the substrate for coating it with a dielectric film whereof the thickness is of the order of one angstrom. The invention also concerns the gallium nitride layers obtained by said method.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CRISTAUX & DETECTEURS
High Power Vcsels With Transverse Mode Control
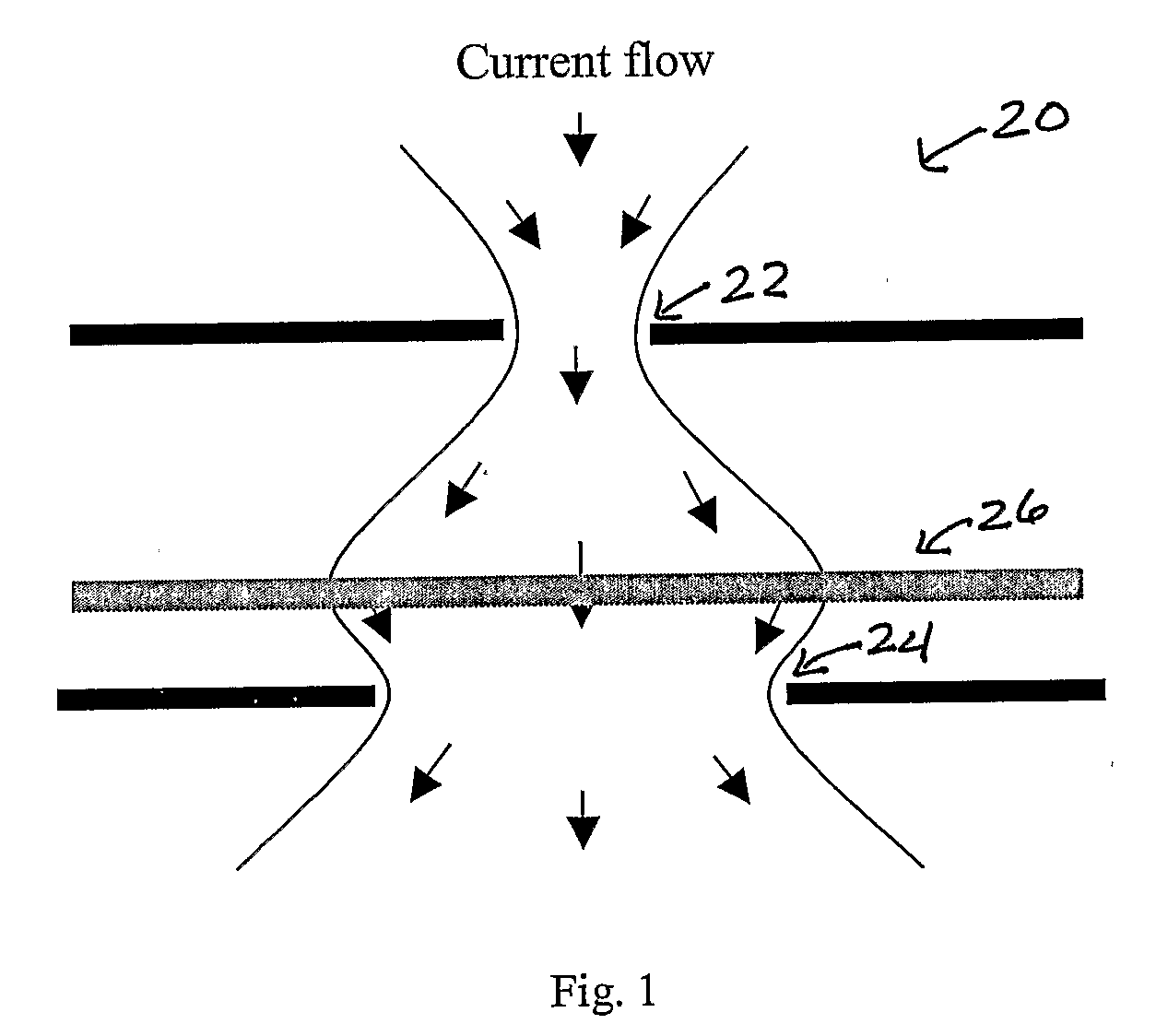
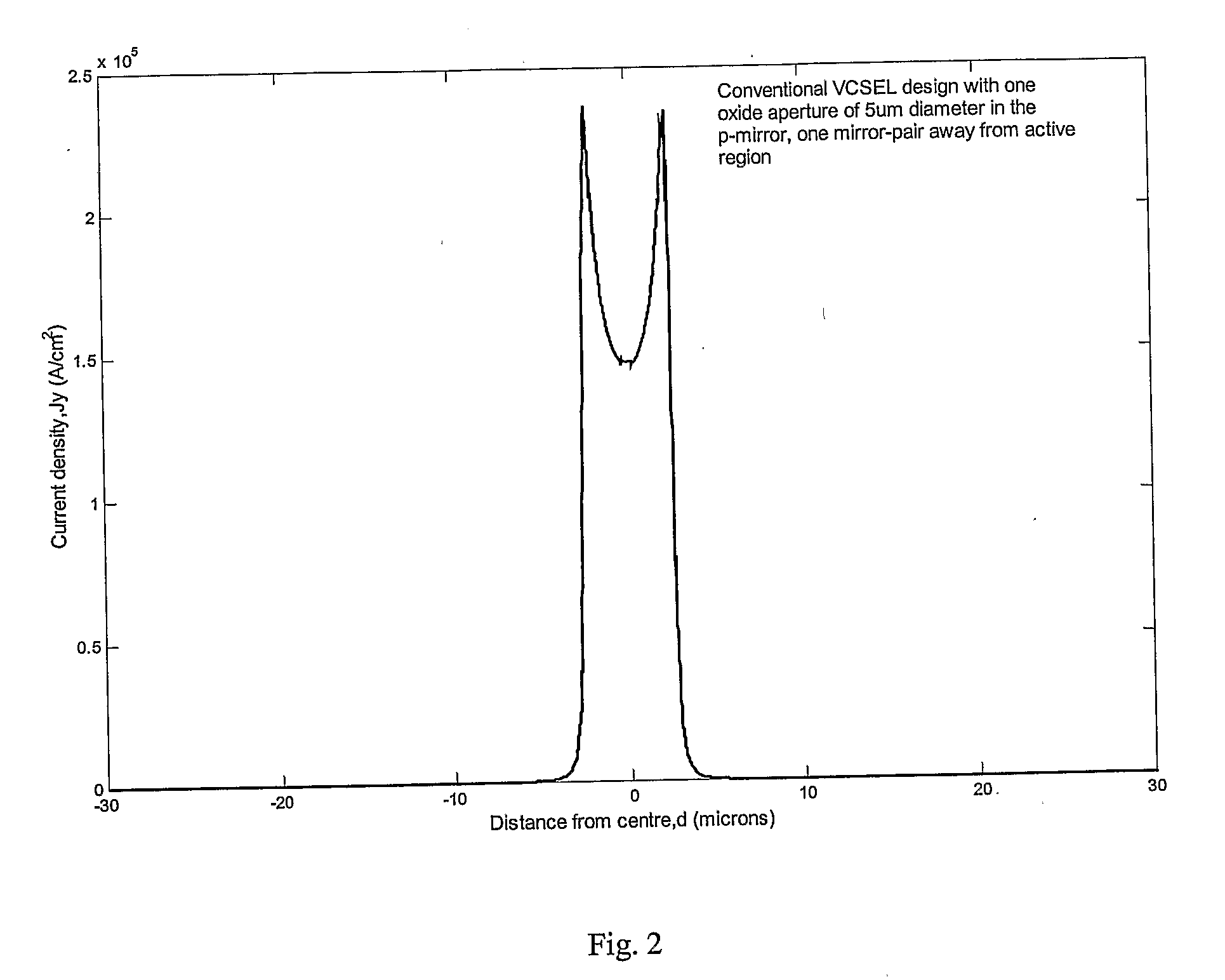
InactiveUS20070242716A1High yieldSimple designLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersHigh power lasersMode control
A single mode high power laser device such as a VCSEL is formed with two oxide apertures, one on each side of the active region or cavity. The sizes of the apertures and the distances from the apertures to the cavity center are chosen or optimum, near-Gaussian current density distribution. The high power of a VCSEL thus formed is improved still more by good heat removal by either formation of a via through the substrate and gold plating on top and bottom of the VCSEL (including the via) or by lifting the VCSEL structure from the substrate and locating it on a heat sink.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
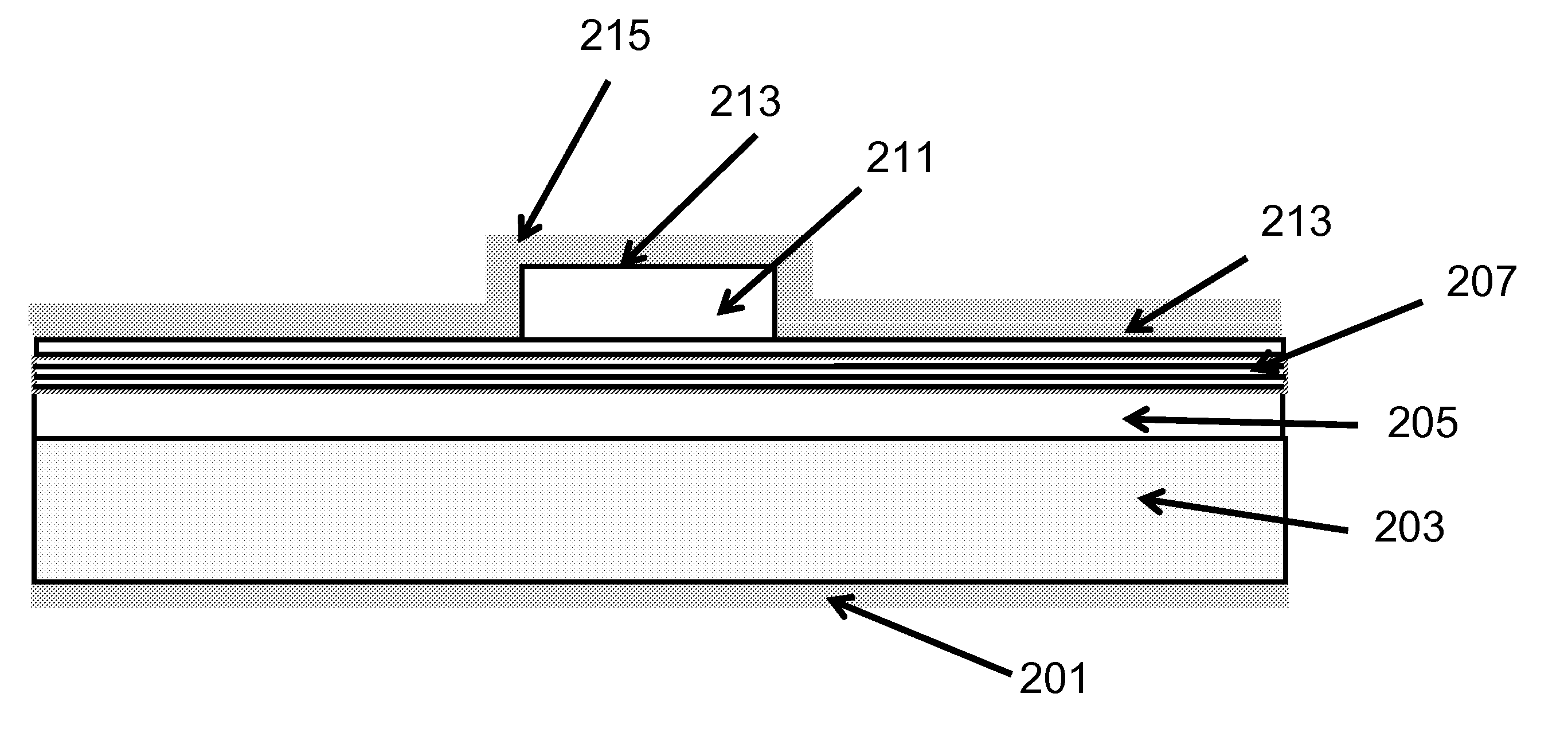
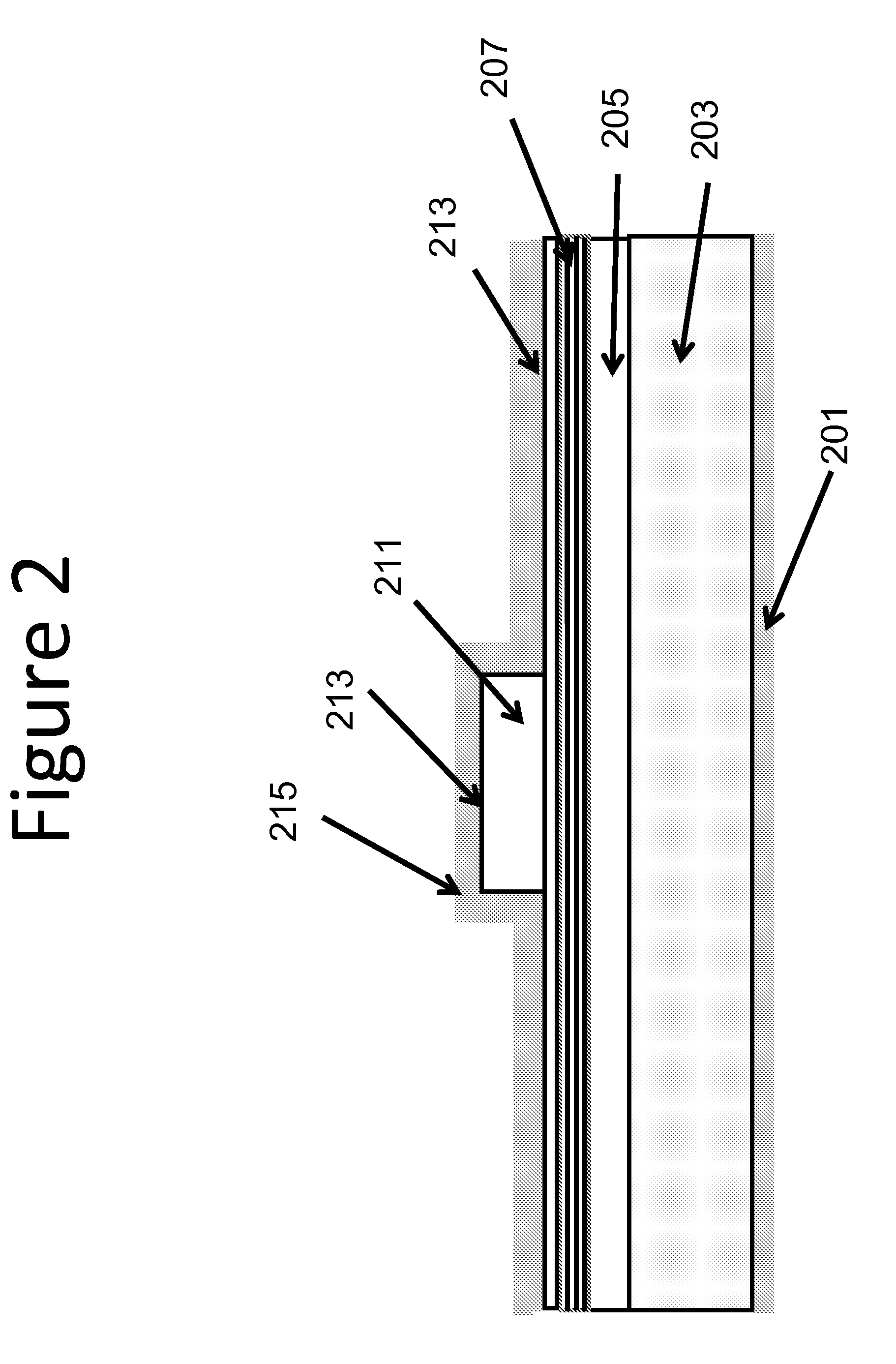
Growth structures and method for forming laser diodes on {30-31} or off cut gallium and nitrogen containing substrates
ActiveUS8351478B2Improved cleavesCost-effectiveLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenGallium
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
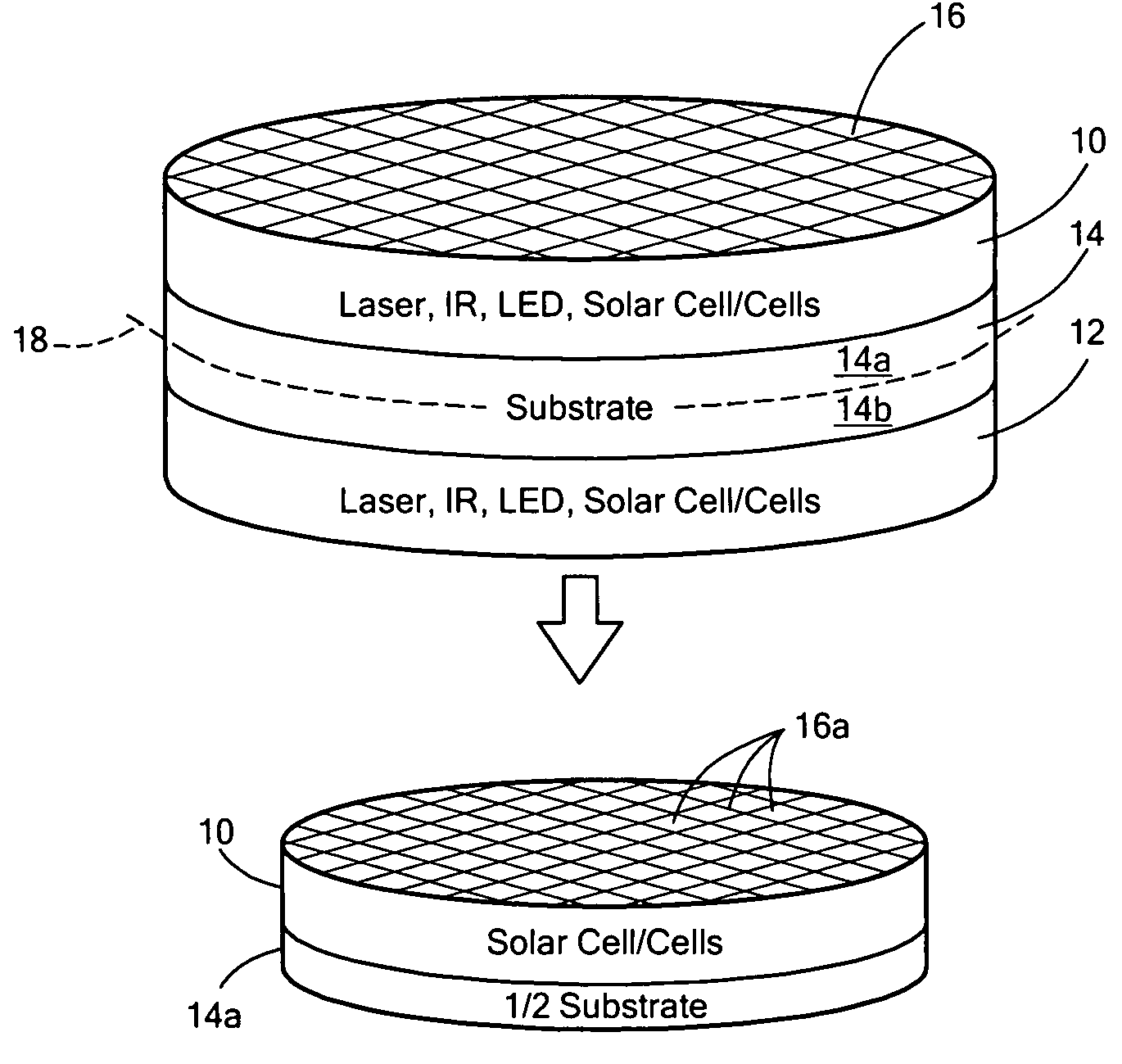
Combinatorial fabrication and high-throughput screening of optoelectronic devices
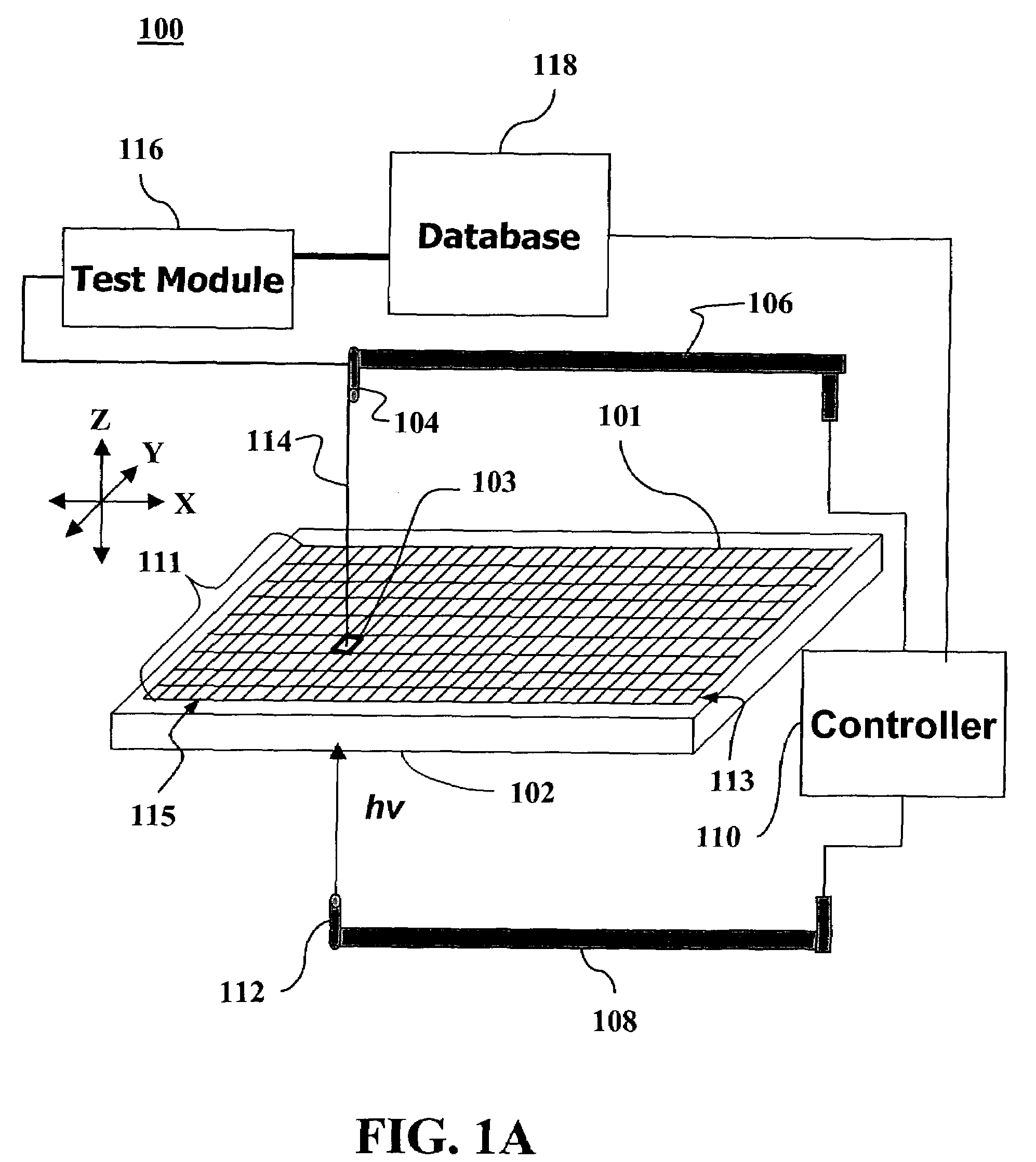
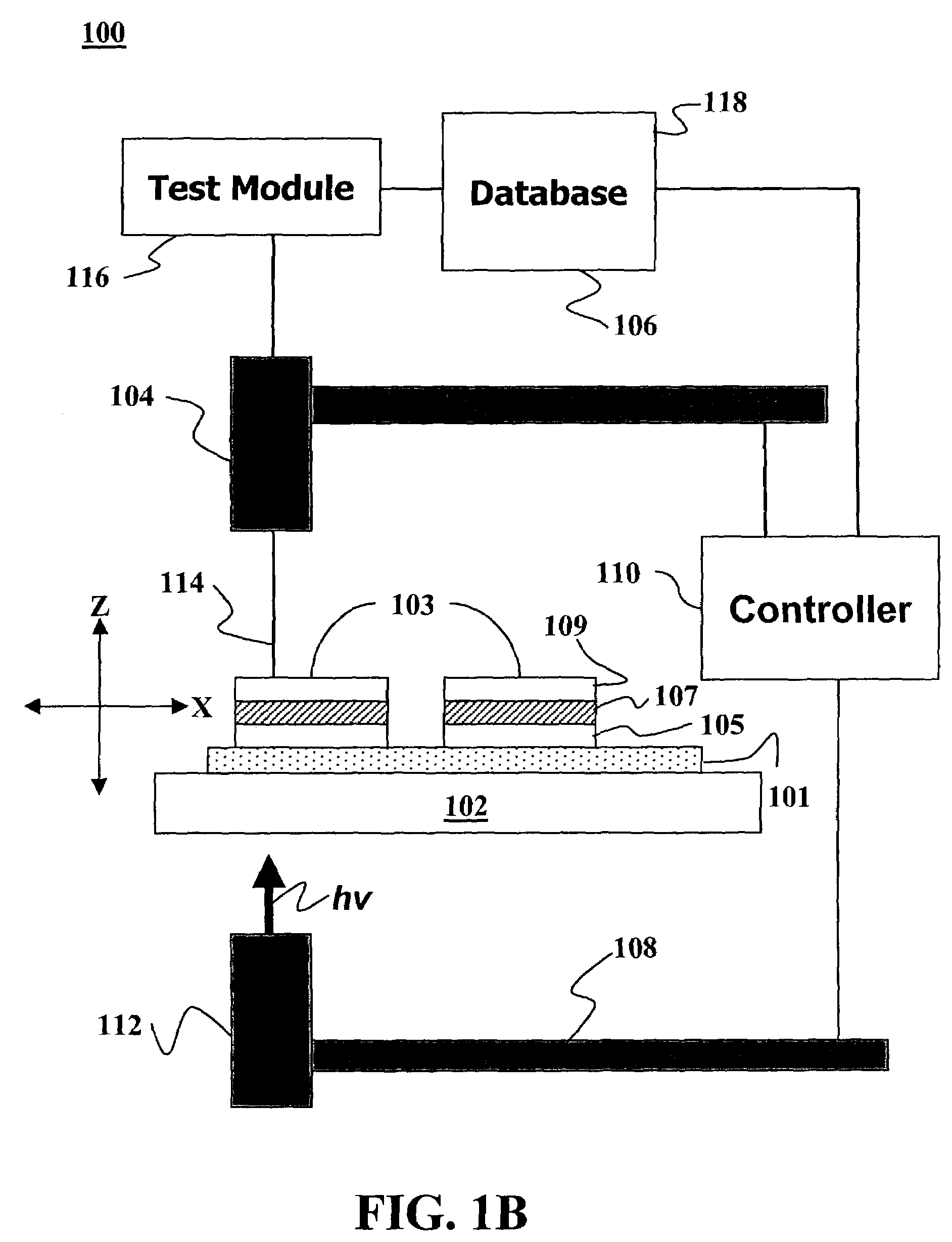
InactiveUS7247346B1Solid-state devicesSpecial surfacesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsComputer science
Methods and apparatus for the rapid and parallel synthesis of optoelectronic cell devices and for the high-throughput screening of such devices for useful properties are disclosed. The methods comprise the parallel synthesis of arrays of optoelectronic devices fabricated within an addressable sample-holding matrix. Each optoelectronic device is created and tested within an addressable sample-holder in the fabrication device.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com