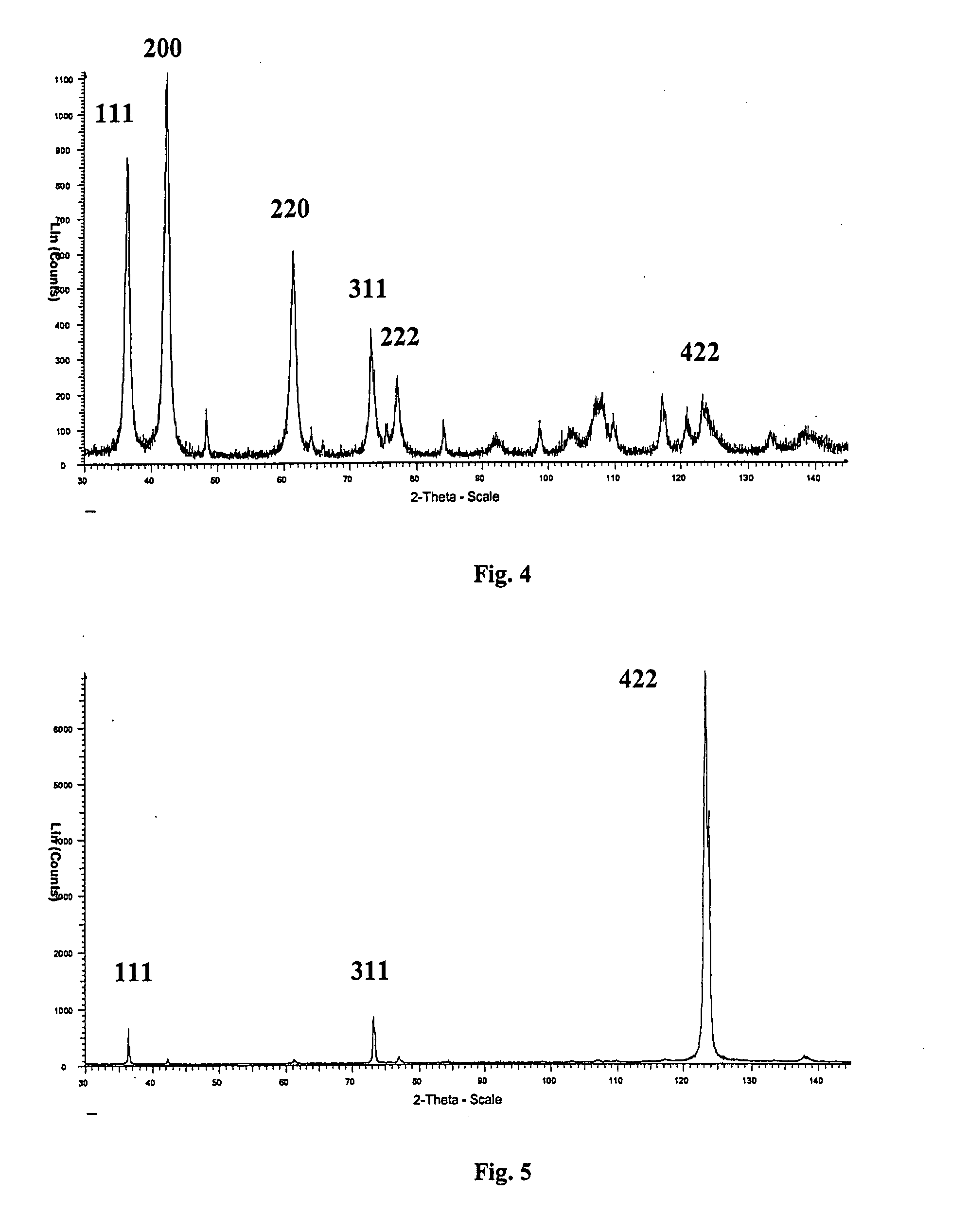
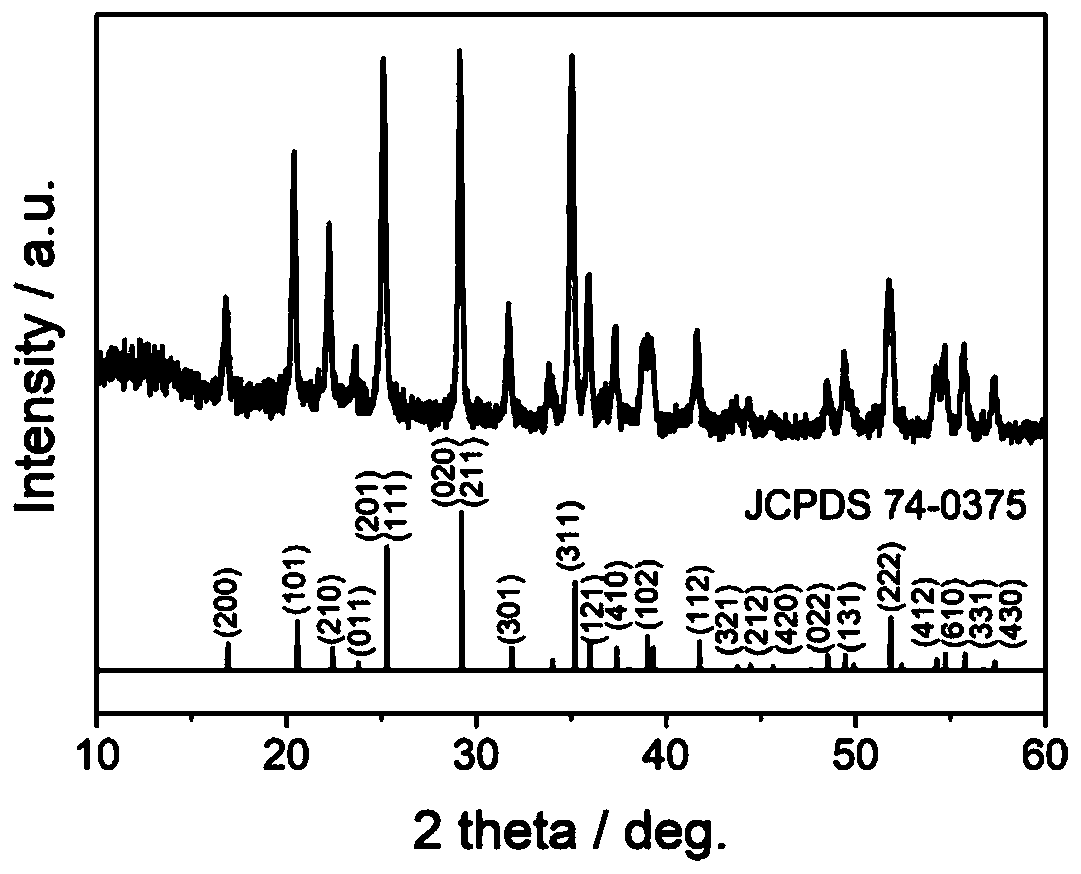
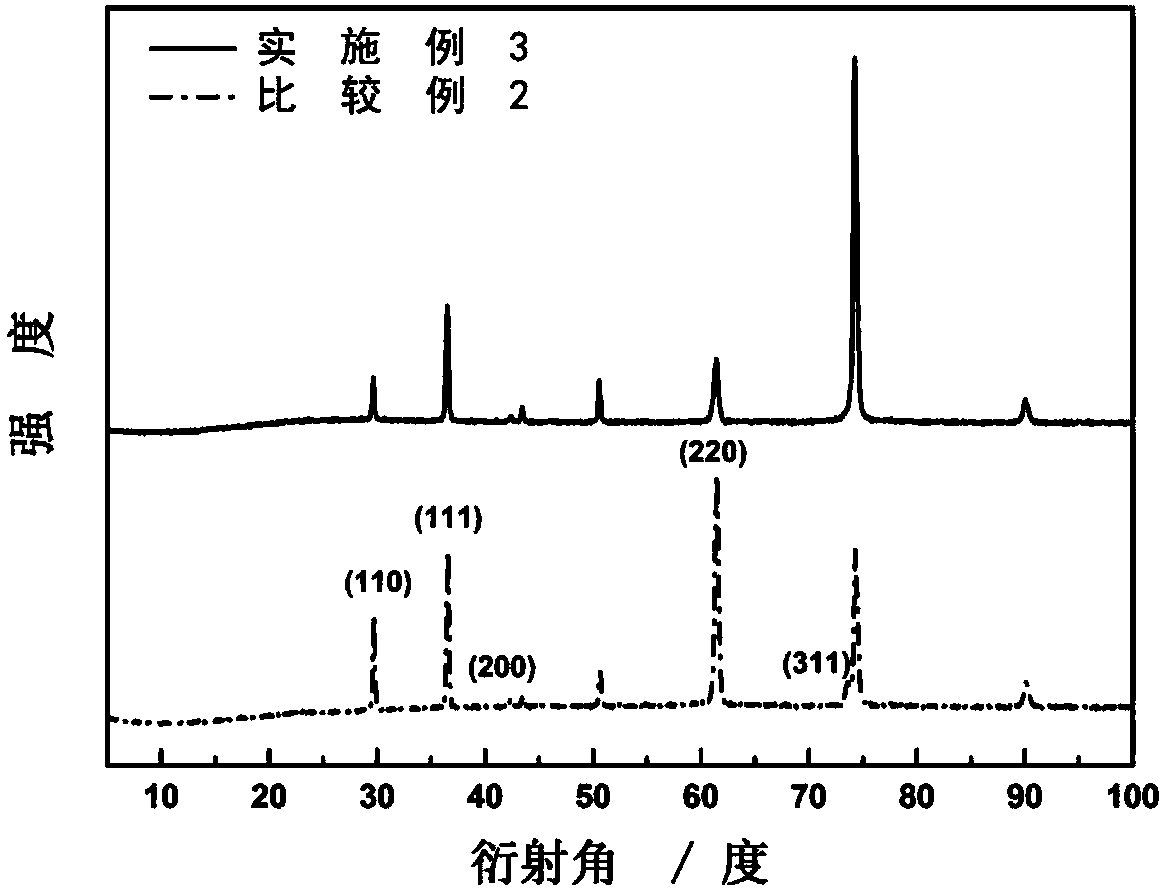
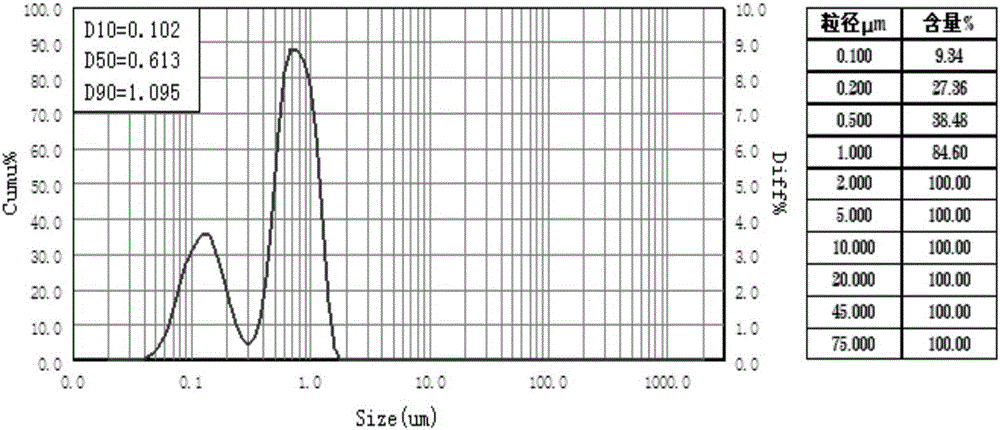
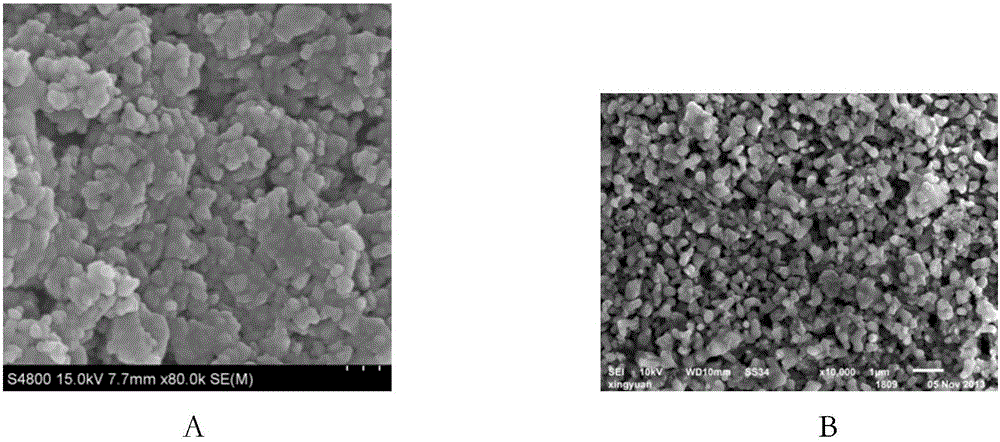
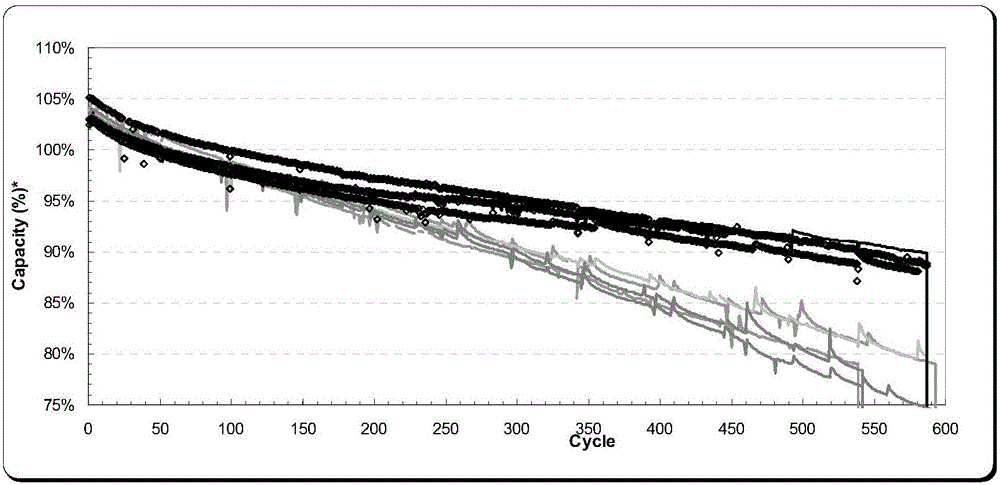
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Growth orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
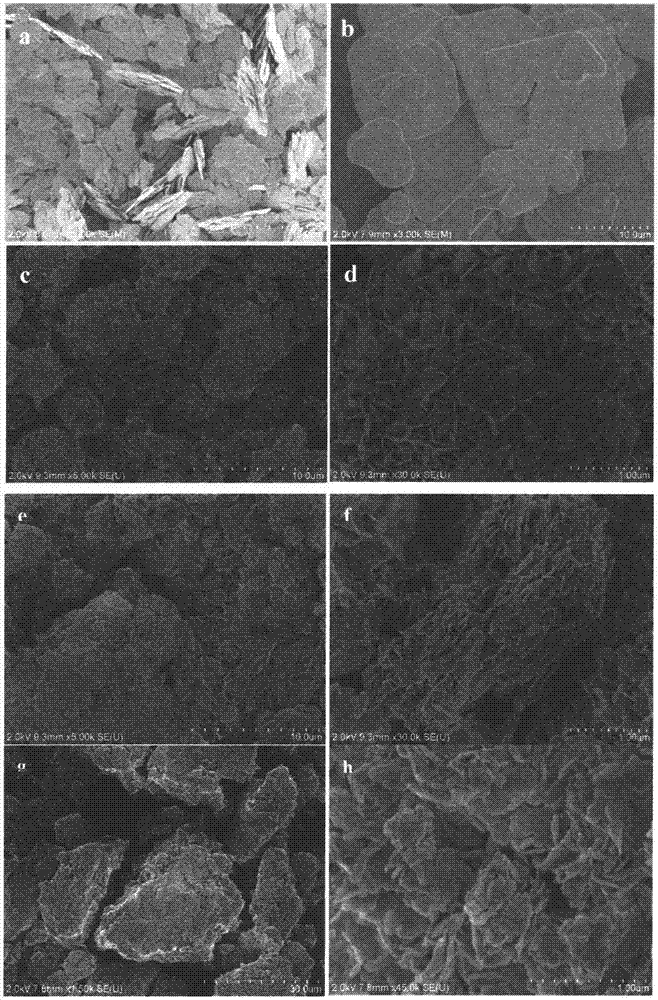
Technique for the growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga,A1,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices
ActiveUS20070093073A1Improve device performanceLarge parameter spacePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNucleationBiology
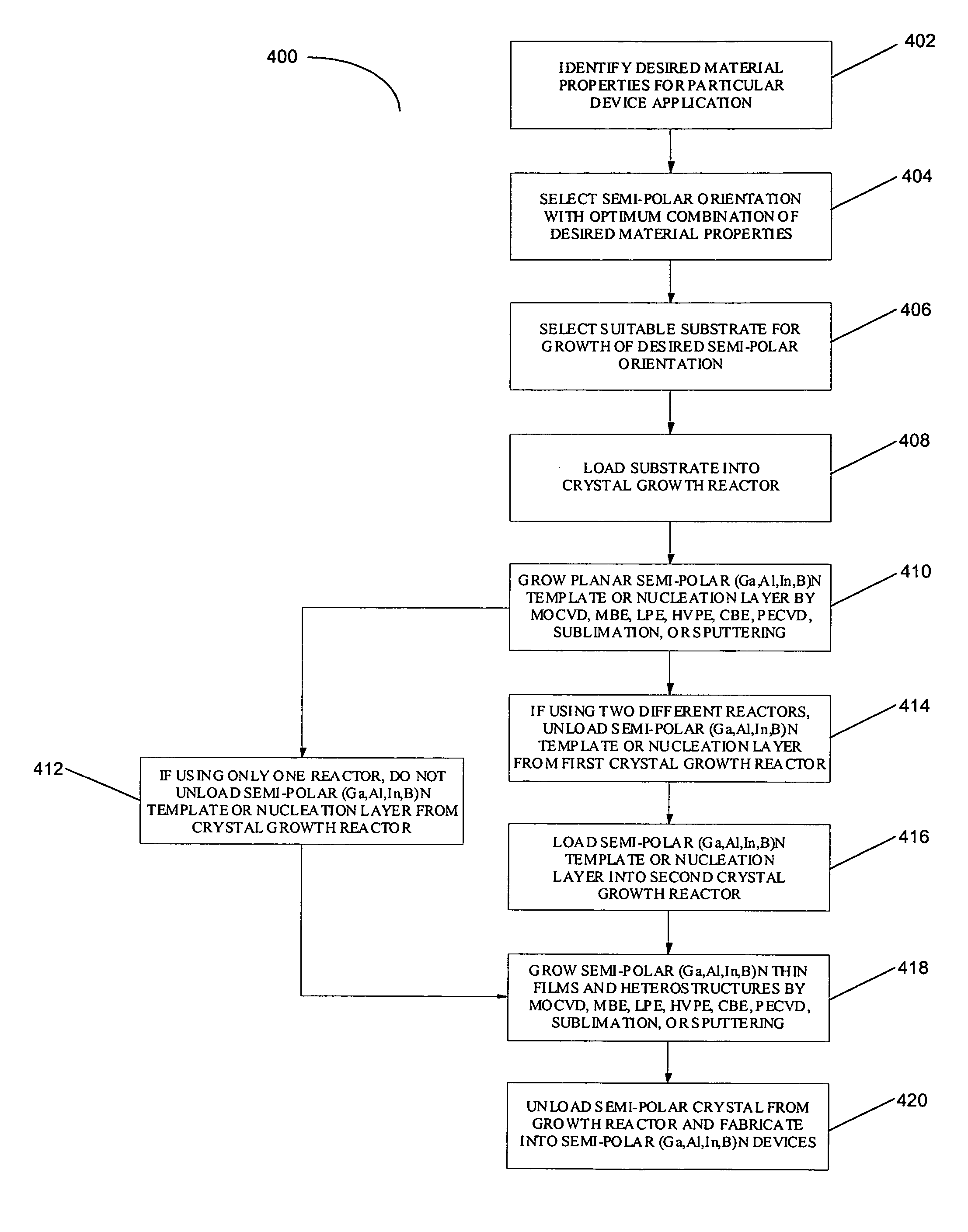
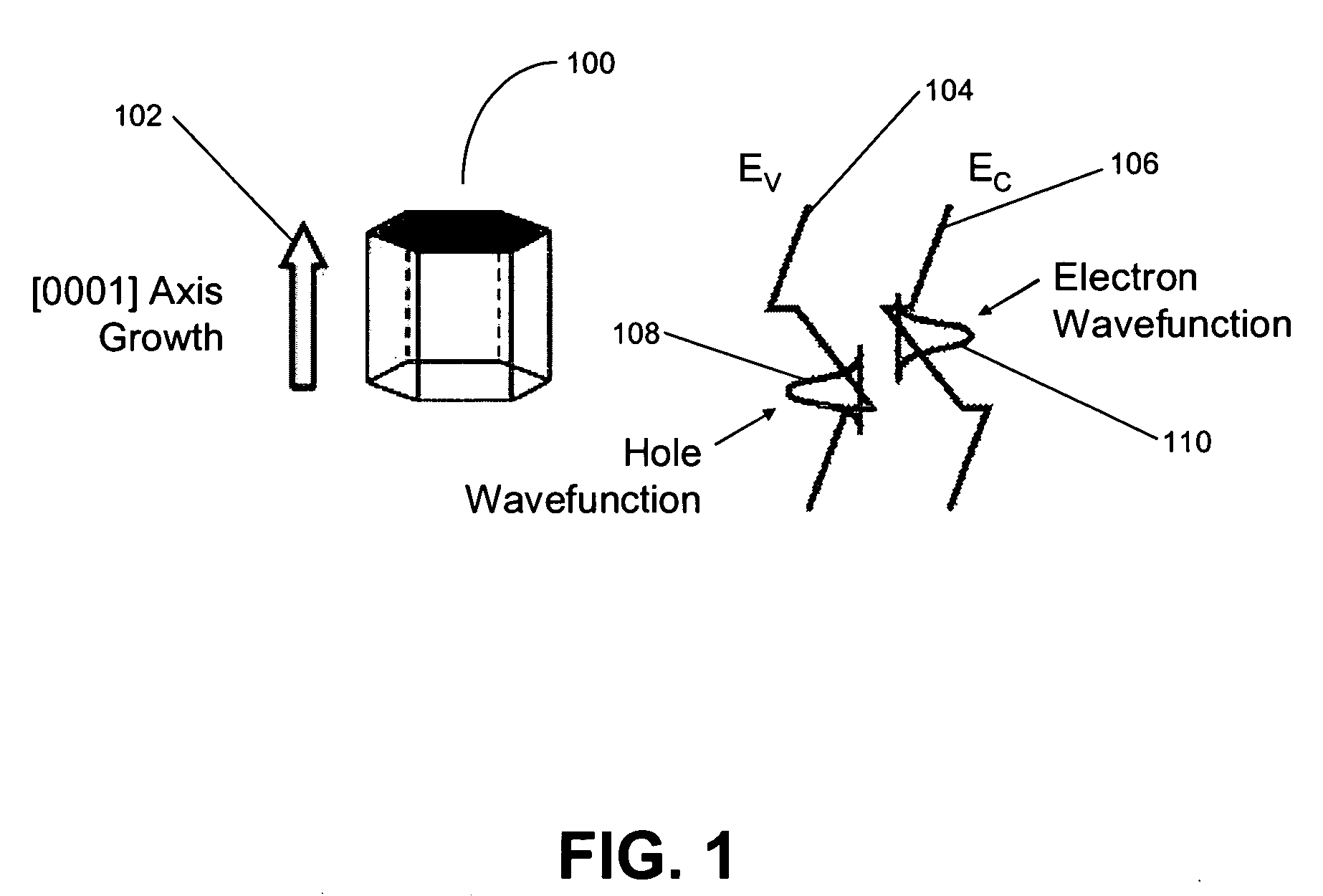
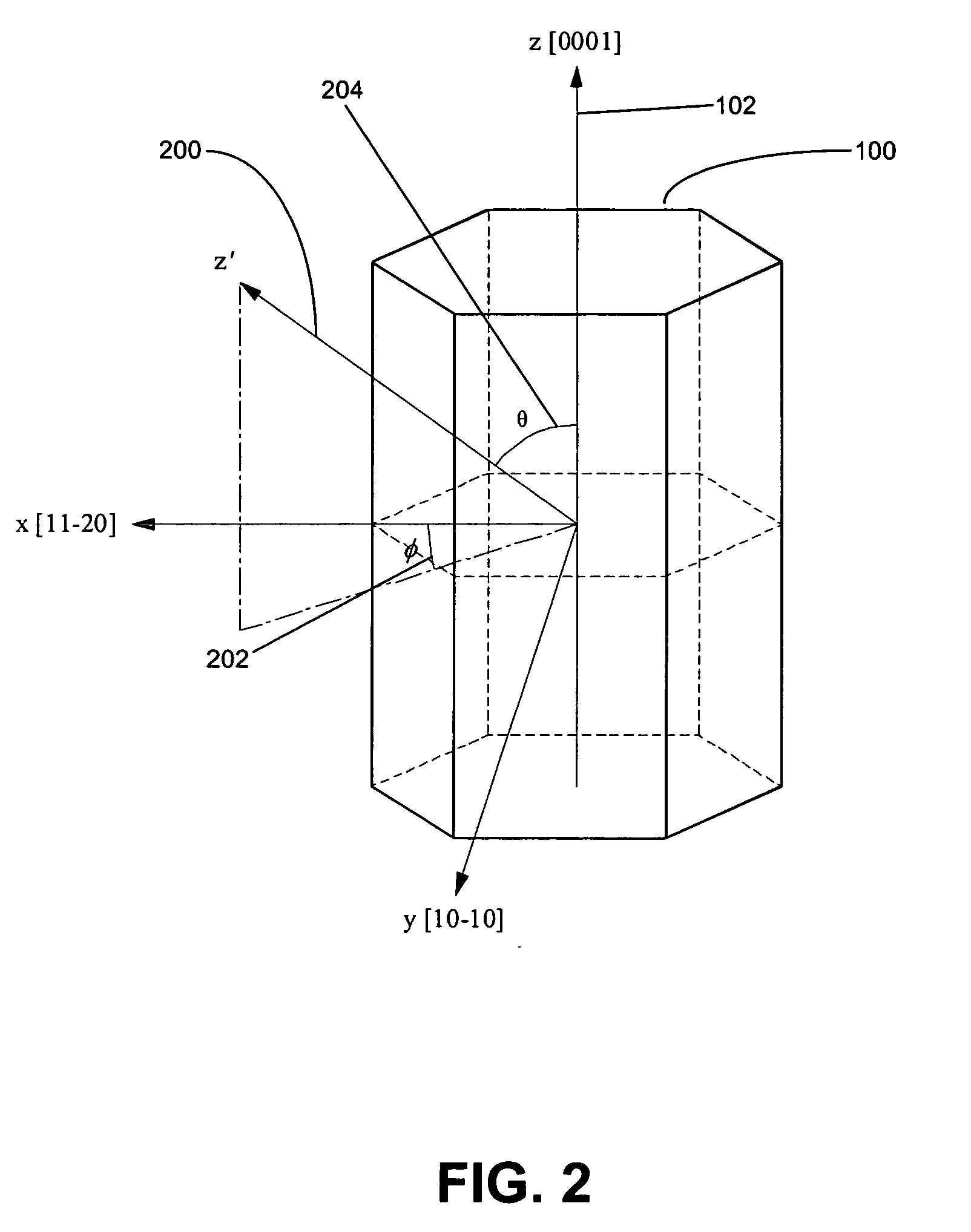
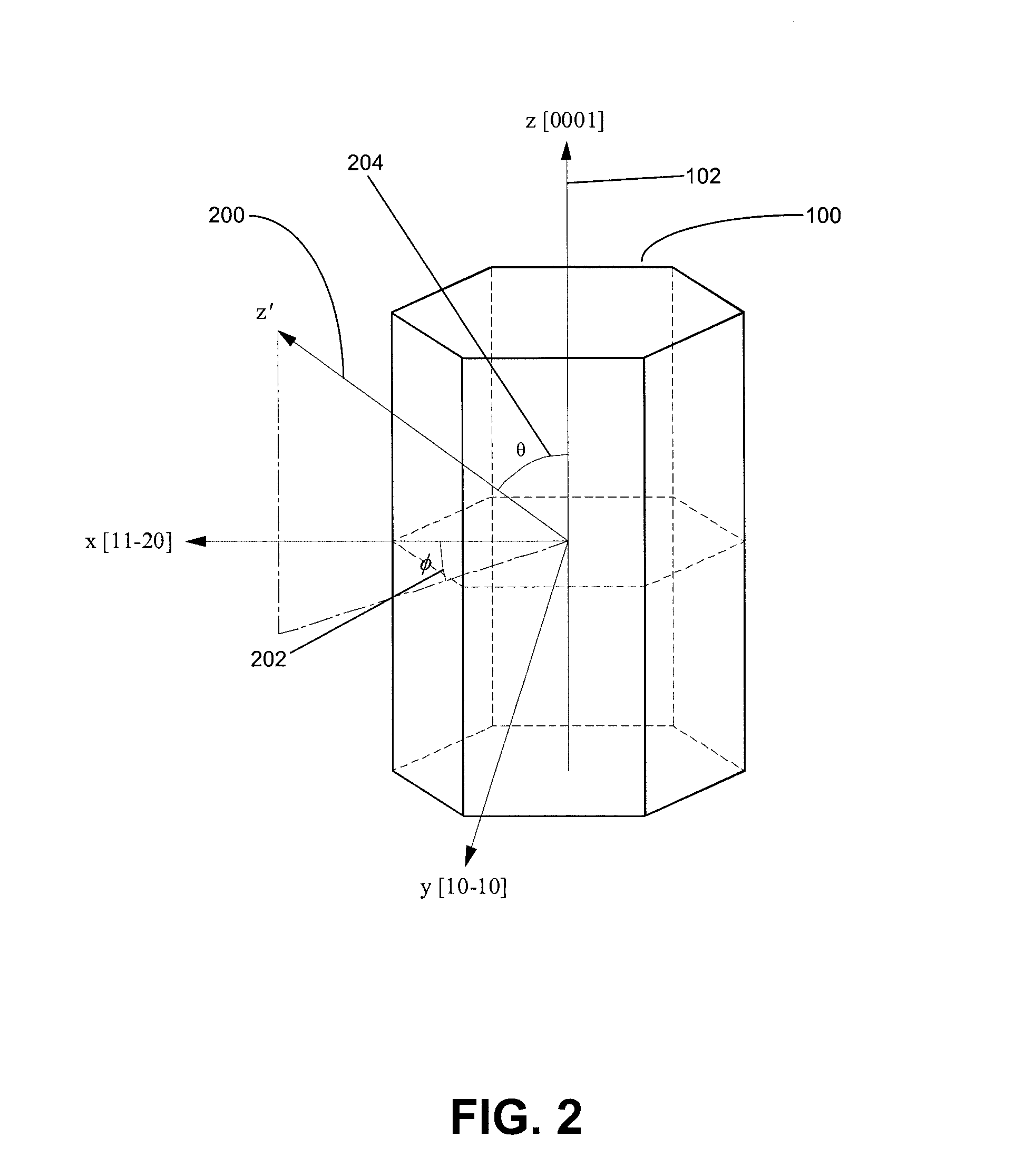
A method for growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices, comprising identifying desired material properties for a particular device application, selecting a semipolar growth orientation based on the desired material properties, selecting a suitable substrate for growth of the selected semipolar growth orientation, growing a planar semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N template or nucleation layer on the substrate, and growing the semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures or devices on the planar semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N template or nucleation layer. The method results in a large area of the semipolar (Ga, Al, In, B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices being parallel to the substrate surface.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Technique for the growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga,A1,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices
ActiveUS7846757B2Easy to separateImprove device performancePolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyNucleation
A method for growth and fabrication of semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices, comprising identifying desired material properties for a particular device application, selecting a semipolar growth orientation based on the desired material properties, selecting a suitable substrate for growth of the selected semipolar growth orientation, growing a planar semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N template or nucleation layer on the substrate, and growing the semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures or devices on the planar semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N template or nucleation layer. The method results in a large area of the semipolar (Ga,Al,In,B)N thin films, heterostructures, and devices being parallel to the substrate surface.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for conforming a micro-electronic array to arbitrary shapes
ActiveUS7292381B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectThree dimensional shape
Described is a method for conforming electronics to arbitrary shapes. The method comprises acts of forming a device structure to have a growth substrate, an etch stop layer affixed with the growth substrate, and a micro-electronic array. The micro-electronic array comprises a plurality of components atop the etch stop layer. The micro-electronic array is thereafter embedded into a shrinkable layer. The shrinkable layer is then mounted onto a handle wafer that includes a layer of adhering film with the shrinkable layer being pressed into the layer of adhering film. The growth substrate and the etch stop layer are thereafter removed. The adhering film is then dissolved to demount the micro-electronic array and shrinkable layer. Finally, the shrinkable layer is shrunk to conform the micro-electronic array to a three-dimensional shape, with the growth orientation flipped such that metal interconnects may be made to both the top and bottom of the chip.
Owner:HRL LAB
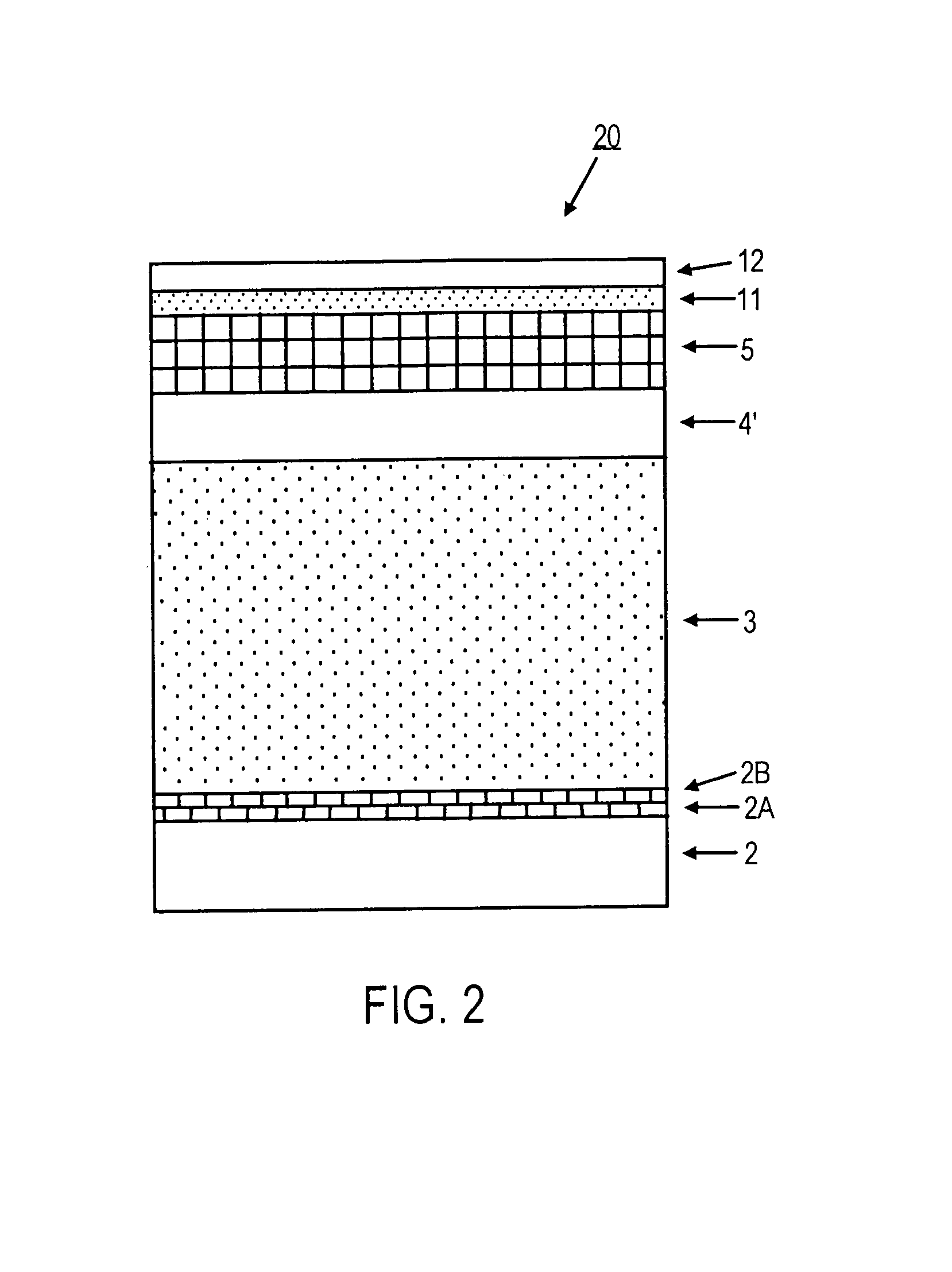
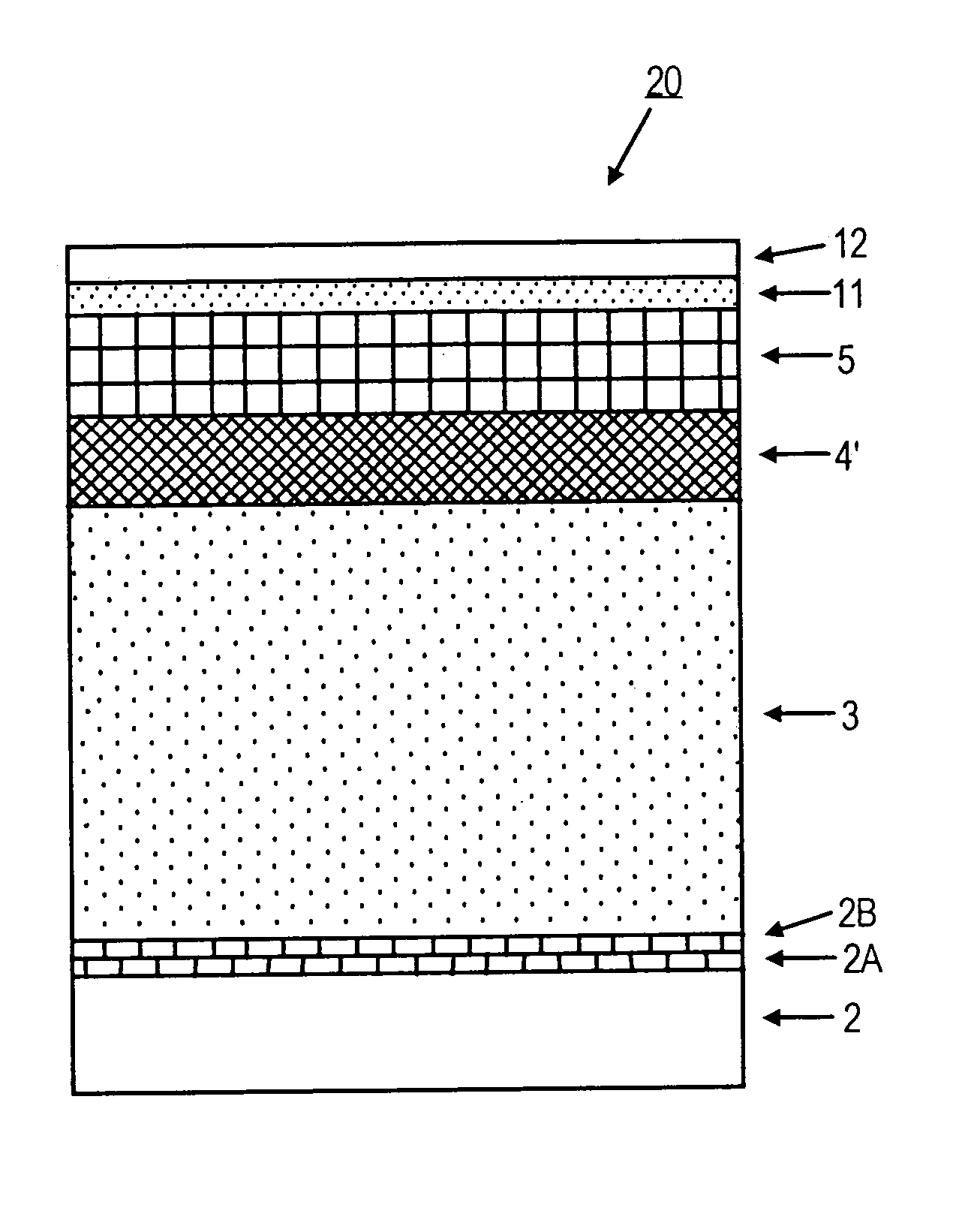
Thin film structures providing strong basal plane growth orientation and magnetic recording media comprising same
InactiveUS7211340B2Multiple layer structureImprove scalabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageOut of planeMultiple layer
A multiple layer structure comprising a pair of spaced-apart crystalline layers of different materials with an intermediate crystalline layer between and in contact with each of the pair of crystalline layers, the intermediate crystalline layer providing one of the crystalline layers of the pair with a stronger out-of-plane preferred growth orientation than if each of the pair of crystalline layers are in overlying contact. Disclosed and preferred embodiments include perpendicular magnetic recording media comprising the multiple layer structure as an intermediate layer structure beneath a perpendicular magnetic recording layer for strengthening a preferred out-of-plane growth orientation of the latter.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Molybdenum disulfide nano tube and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101704552ASimple and easy to control hollow structureTypical hollow structureNanostructure manufactureMolybdenum sulfidesSemiconductor materialsHydrodesulfurization
The invention discloses a molybdenum disulfide nano tube and a preparation method thereof. The invention takes ammonium thiomolybdate ((NH4)2MoS4) as raw material, uses AAO (anodic aluminum oxide) as a template, uses hydrogen (H2) as a reducer, uses nitrogen (N2) as protective gas and controls the growth direction of products by restrictive effect of upper holes of the template, thus synthetizing a molybdenum disulfide nano tube array with high isotonicity in size and growth orientation by large amount under the relative low temperature condition and solving the problem of the size and size distribution of the molybdenum disulfide nano tube. The method has simple technique and low cost; and the prepared molybdenum disulfide nano tube can be widely used as a solid lubricating agent, a hydrodesulfurization catalyst, a semiconductor material, an intercalation material and an anhydrous lithium battery material and the like, and is applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:无锡润鹏复合新材料有限公司
Alterant of iron-rich phase in secondary aluminum and alteration method
The invention relates to an alterant of an iron-rich phase in secondary aluminum and an alteration method. The alterant is composed of a [Mn] agent and a [B] agent. The alteration method includes the steps that part of secondary aluminum is heated to form a melt, then the [Mn] agent is added, the remaining secondary aluminum is added after the [Mn] agent melts, the [B] agent is added, refining is carried out after the [B] agent melts, pouring is carried out after standing is carried out for a period of time, and the secondary aluminum obtained after alteration treatment is obtained. According to the alterant and the alteration method, the Fe element in the iron-rich phase can be replaced through the [Mn] agent, the advantage growth orientation of the iron-rich phase is changed, and therefore a needle-like beta-Fe phase is eliminated; meanwhile, the forming temperature of the iron-rich phase can be reduced through B in the [B] agent, the growth time of a primary iron-rich phase is shortened, the growth space of the primary iron-rich phase is reduced, the B can also serve as a surface-active element, and is absorbed to the surface of the iron-rich phase in the initial phase of formation of the iron-rich phase, and growth of the iron-rich phase is restrained, so that through the combined action of the [Mn] agent and the [B] agent, existence of the needle-like iron-rich phase and the primary iron-rich phase can be completely eliminated, the uniform Chinese character type iron-rich phase is obtained; and in addition, the adding amount of the Mn can be greatly reduced, and the mechanical performance and the machining performance of the secondary aluminum can be greatly improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF NEW MATERIALS
Method for preparing rare earth barium copper oxide superconducting block material
InactiveCN101717256AGuaranteed efficient growthHigh success rate of preparationRare earthHigh temperature superconducting
A method for preparing rare earth barium copper oxide superconducting block material comprises the steps of executing calcining and grinding processes in turn after mixing the RE123 and RE211 in the mole ratio of 100: (20-35); pressing the ground powder into precursor bottom piece and precursor top piece respectively; putting the precursor top piece on top of the precursor bottom piece; putting seed crystal on the precursor top piece, then putting the precursor bottom piece on a zirconium oxide bead substrate; rising temperature for heating in a sealing container, and then cooling to prepare the rare earth barium copper oxide superconducting block material. The method can prepare the high temperature superconducting block material with high performance, large single domain structure and good growth orientation under the conditions that no impurity exists and crystal lattices match completely, thereby solving the key problems of the growth and application of the superconducting block material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
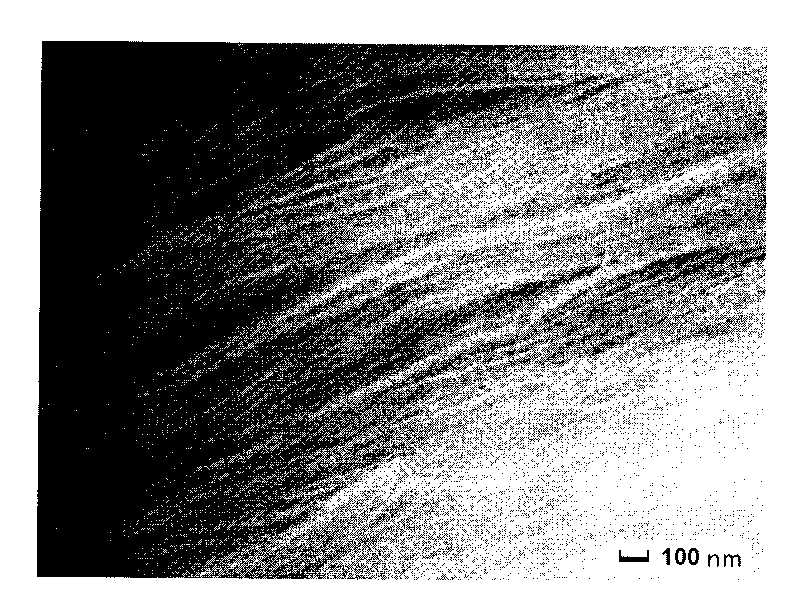
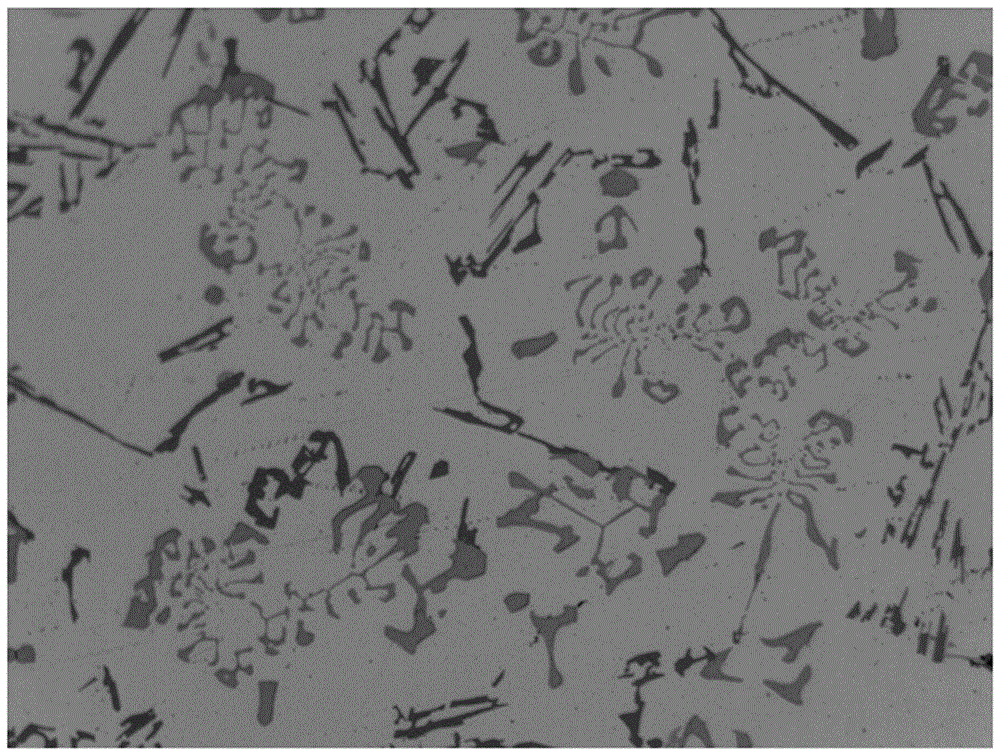
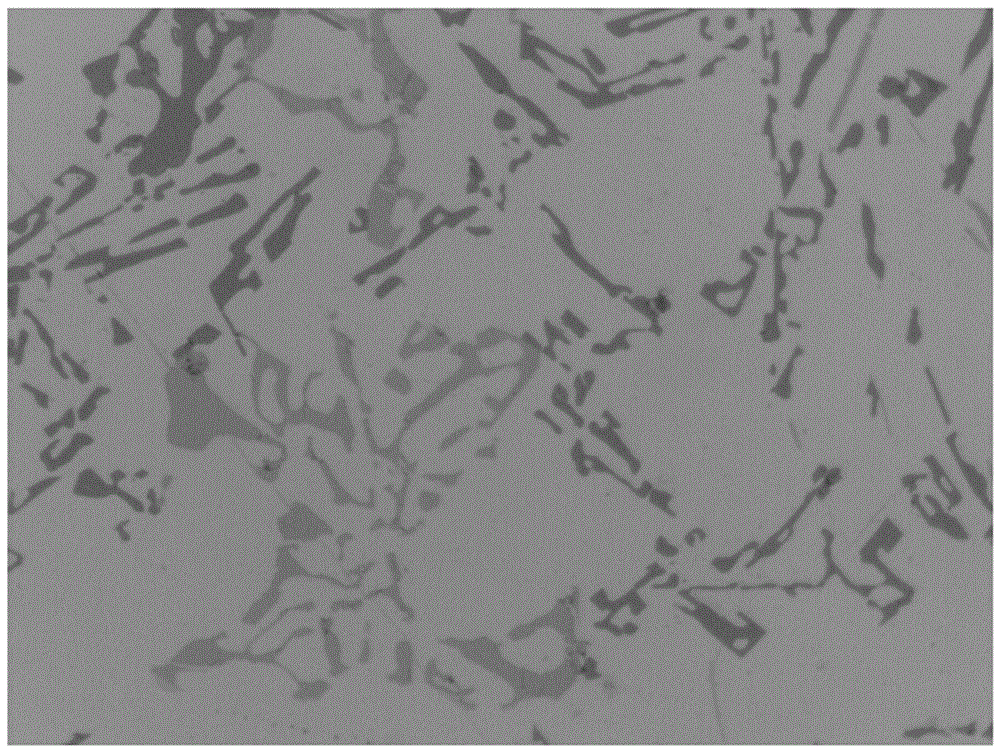
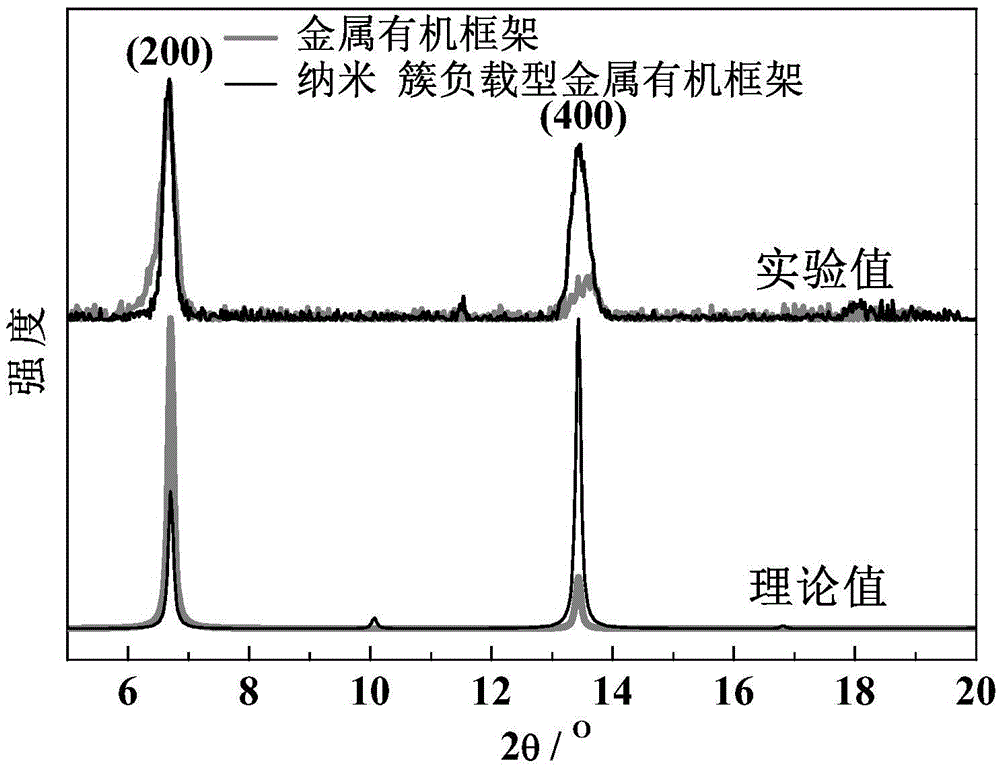
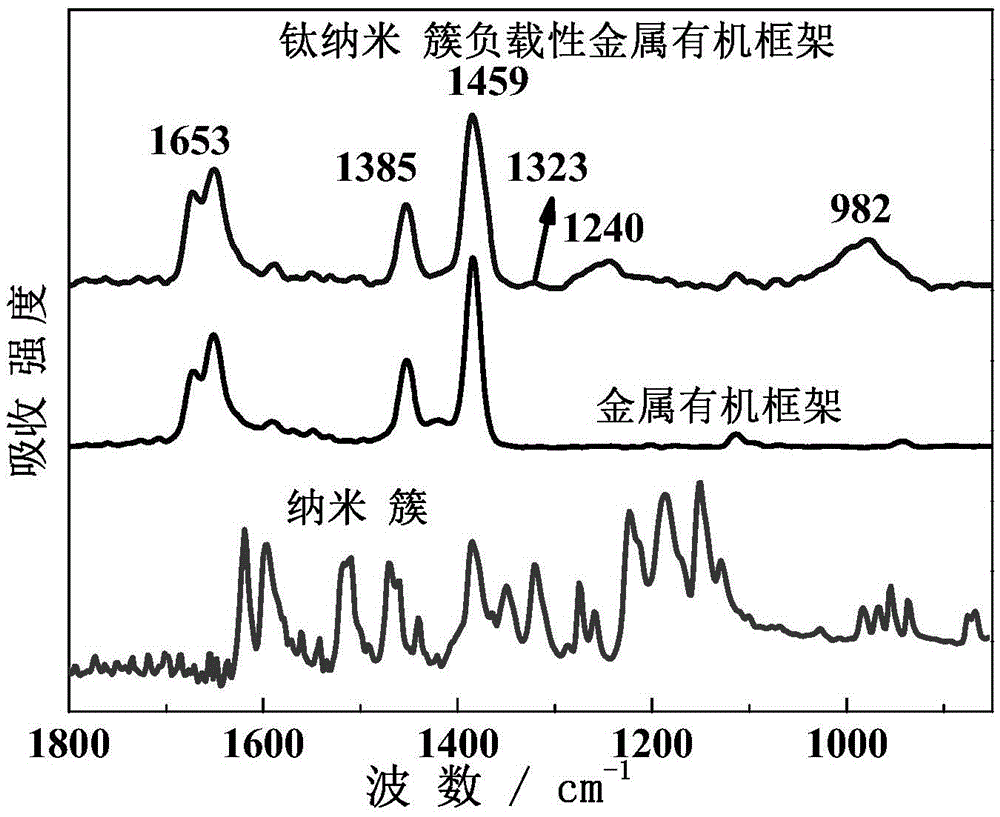
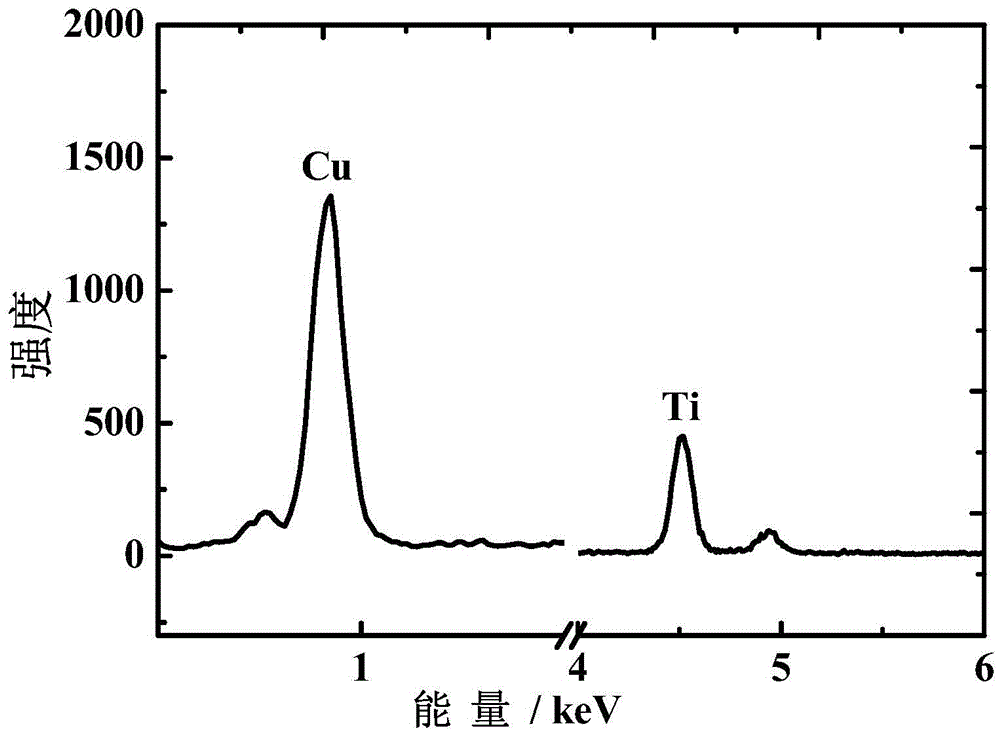
Nanocluster loaded type metal organic framework thin film and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105597833AEfficientGrowth does not affectOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal-organic frameworkControllability
The invention discloses a nanocluster loaded type metal organic framework thin film and a preparation method and an application thereof. Nanoclusters are loaded on a metal organic framework thin film by a liquid phase epitaxial growth method. The method can accurately control the thickness and area of the thin film in the preparation process, ensures growth orientation and thin film thickness uniformity, and makes the formed nanocluster loading have high efficiency, high orientation and uniformity. Because the loaded nanoclusters of each layer can fall inside pore channels of the metal organic framework, the nanoclusters are loaded in each layer while the growth of the metal organic framework is not affected, and thus the nanocluster loaded type metal organic framework thin film is effectively synthesized. The method has the advantages of fast synthesis speed, high efficiency of nanocluster loading, controllability of the thin film thickness, flexible selection of a growth substrate according to the need and the like, and provides a convenient method for large-scale preparation in sensors, devices and other thin-film products.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
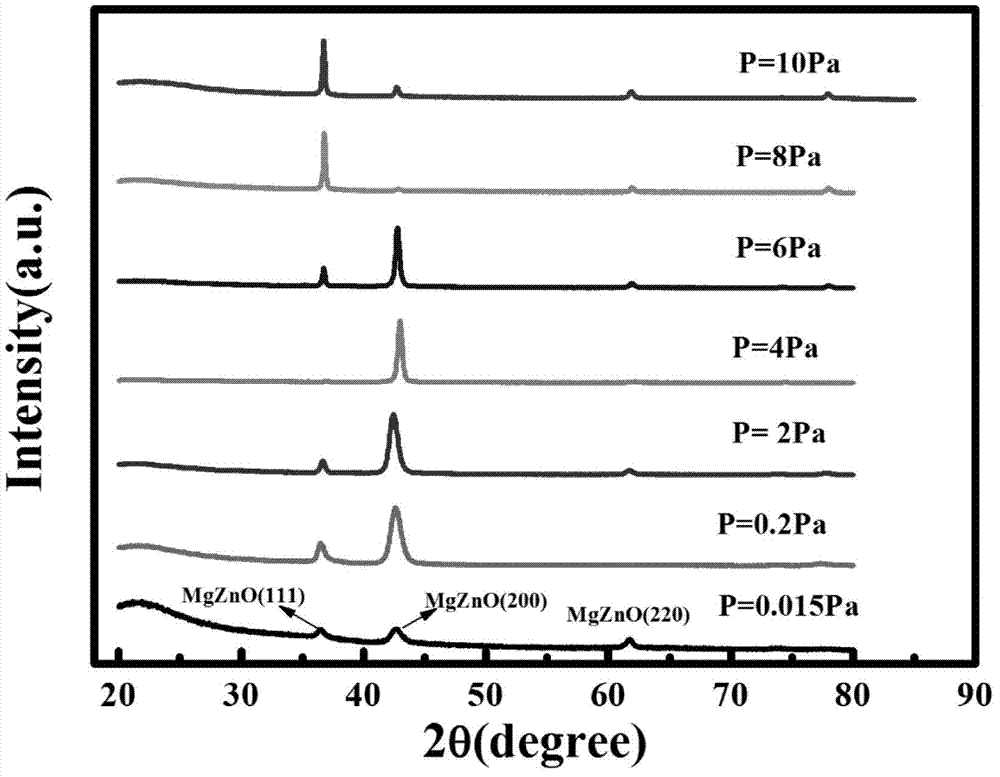
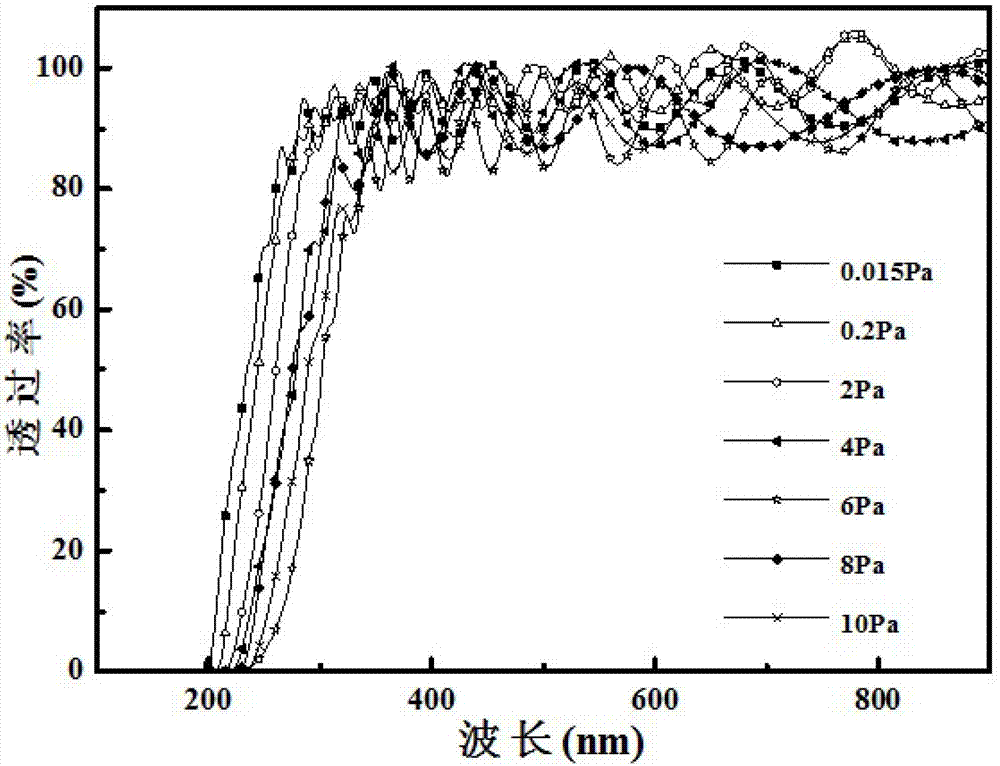
Production method of cubic MgZnO film
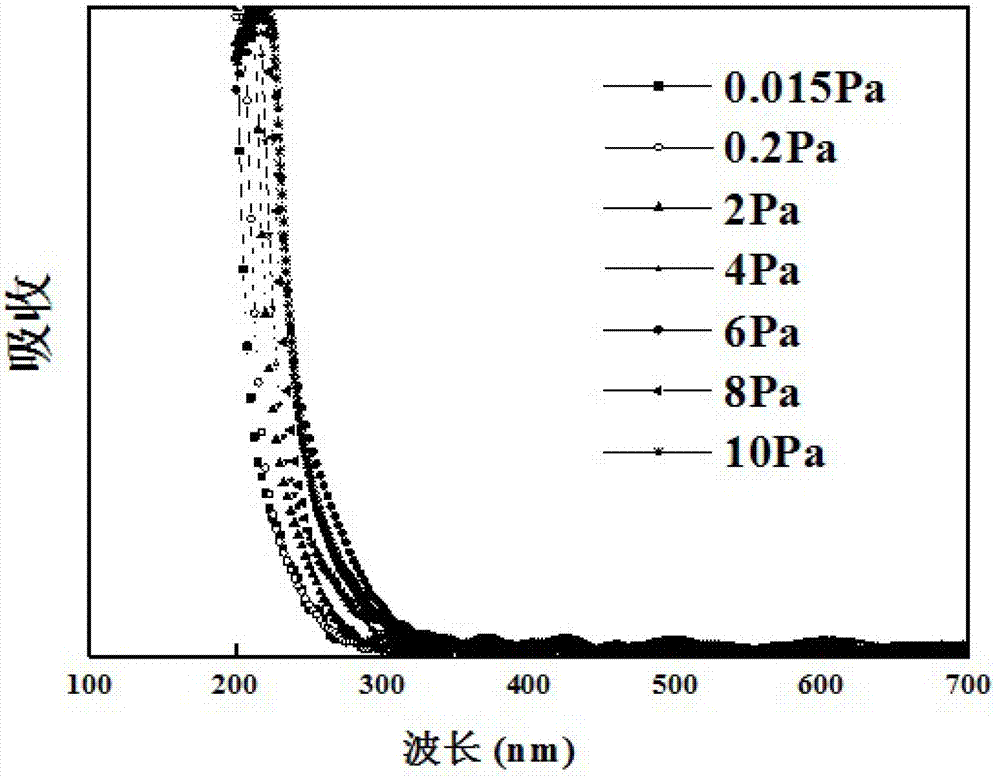
ActiveCN103205706AGrowth orientationAchieving quality controlVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSemiconductor materialsAlloy
The invention relates to the field of production of semiconductor materials and provides a production method of a cubic MgZnO film. The production method includes the steps of, preparing a Mg0.5Zn0.5O target; placing a substrate in a cavity, heating the substrate to 400 DEG C-500 DEG C, introducing 10sccm-70scm oxygen to keep the pressure intensity of the cavity at 4-8Pa, and subjecting the Mg0.5Zn0.5O target to pulse deposition on the substrate so as to obtain the cubic MgZnO film. Growth orientation of the cubic MgZnO film can be effectively controlled according to different migration energies of deposition atoms under different growth conditions, and the convenient and effective means for producing different-orientation high-quality cubic MgZnO multicomponent alloy films is provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for detecting profile phenotype of arabidopsis
InactiveCN103471523ADoes not affect normal growthRealize non-destructive testingUsing optical meansImage calibrationRgb image
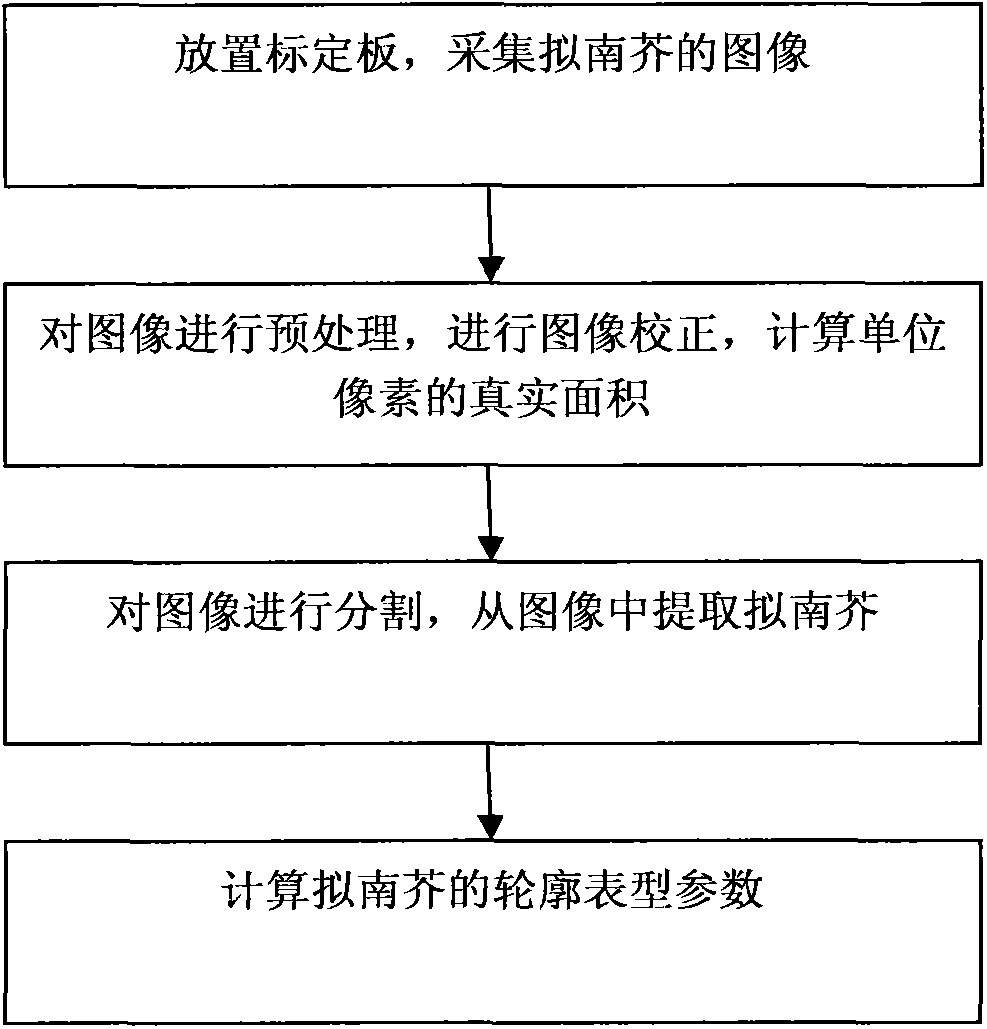
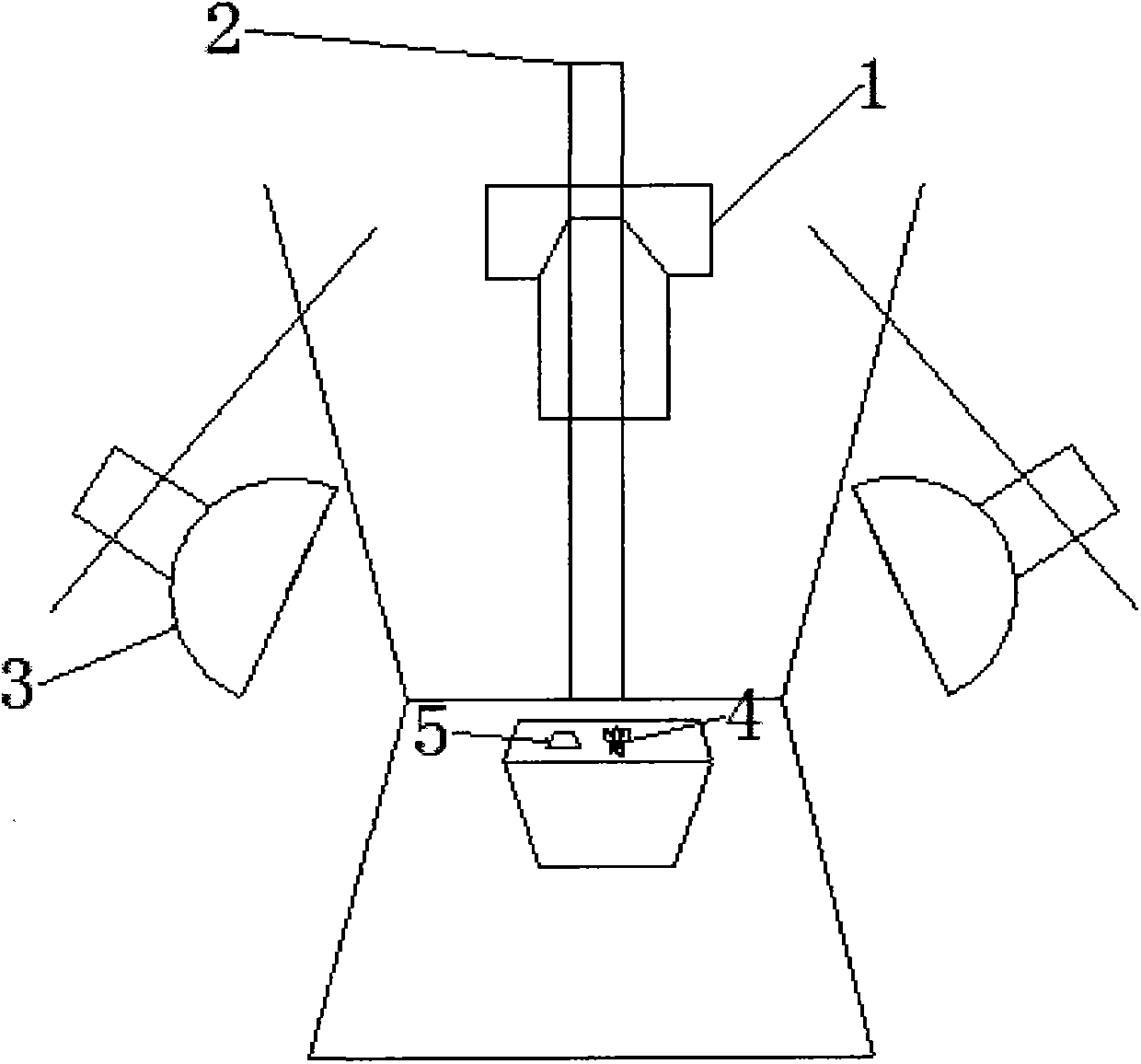
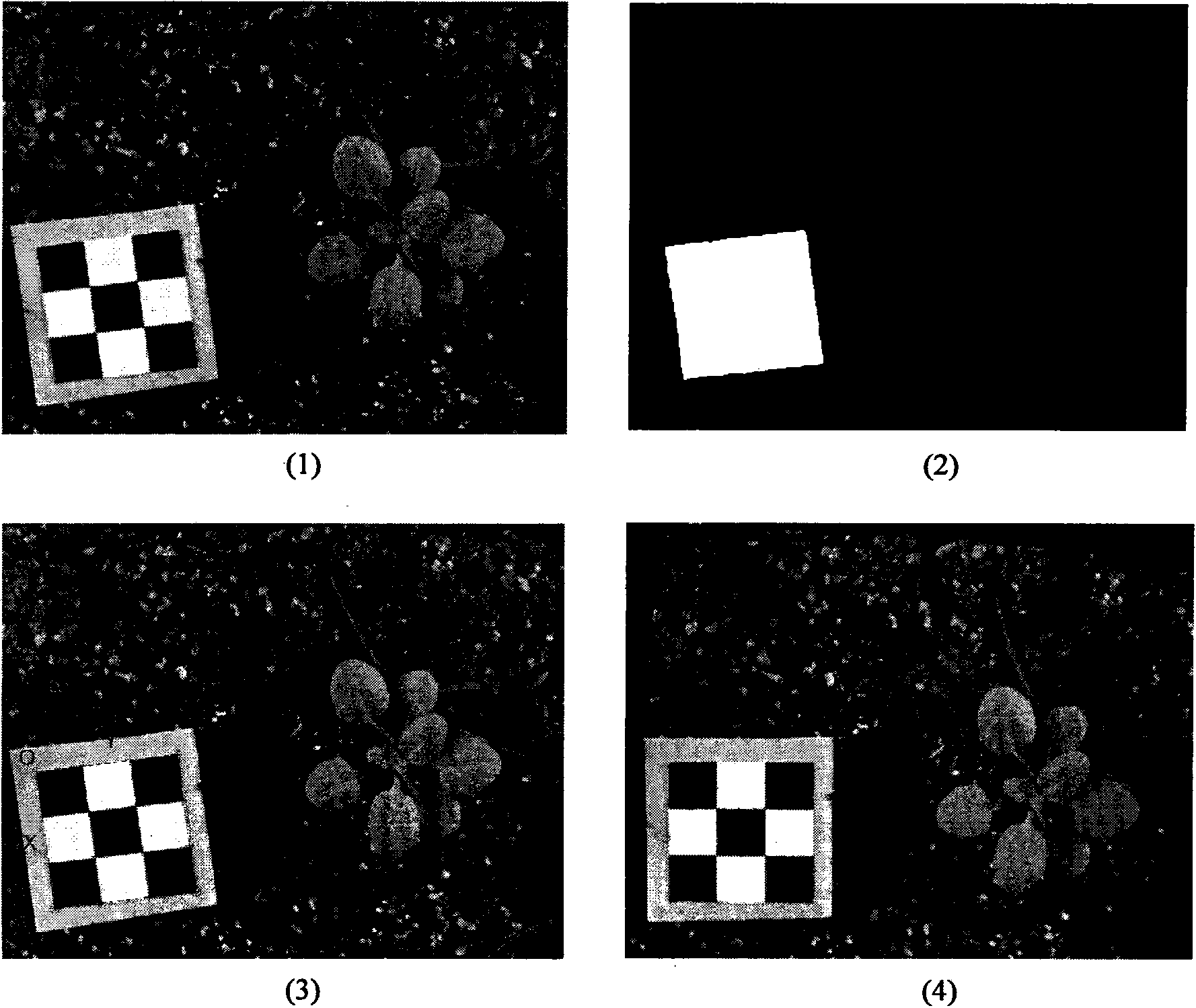
Provided is a method for detecting a profile phenotype of arabidopsis. The method includes the steps that a calibration board is placed in a planting pot of the arabidopsis, an RGB image of the arabidopsis is collected through a camera, the collecting image is preprocessed, automatic correction and calibration of the image are achieved, image correction is used for correcting deformation of the image, image calibration is used for obtaining a real size of a unit pixel, the preprocessed image is divided, the arabidopsis is separated from the background and extracted from the image, after the arabidopsis image is separated, a profile phenotype parameter of the arabidopsis is extracted, and an overall profile of the arabidosis is quantitatively described through an oval Fourier descriptor. The differences of the overall profile and growth orientation of the arabidopsis with different genes can be described through analysis of the profile phenotype parameters, and accordingly the function of different genes and influences of the different genes on the arabidopsis can be concluded.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
One-dimensional cadmium sulfide nanorod catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106044848AConform to structural featuresPiezoelectricMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsSolvent moleculeSound energy
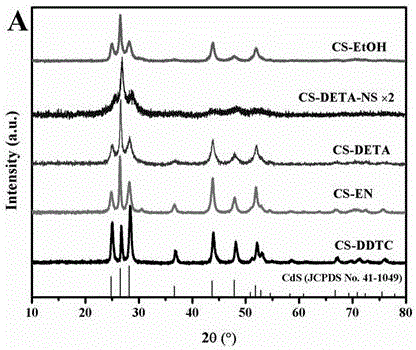
The invention discloses a one-dimensional cadmium sulfide nanorod catalyst, and a preparation method thereof and an application thereof in producing hydrogen through acoustic catalytic cracking of water. The catalyst has a wurtzite crystal structure, and is non-centrosymmetric crystal. The catalyst satisfy the structural condition of piezoelectric crystal. The specially oriented nanorod shape of the catalyst can enrich environmental soundwave energy through piezoelectric effect, such that negative charge is produced on the surface of the nanorods. Therefore, pure water cracking is catalyzed, and hydrogen gas is produced. The preparation method mainly relates to a one-step solvothermal method. Cadmium sulfide growth orientation is regulated with the coordination or chelation effect of crystal seeds and diethylenetriamine solvent molecules, and the one-dimensional nanorod morphology is obtained under appropriate reaction temperature and reaction time conditions. The activity of the obtained cadmium sulfide nanorods for cracking pure water to produce hydrogen under sound driving is substantially higher than those of nano-flake wurtzite-type cadmium sulfide sample, micro-spherical wurtzite-type cadmium sulfide sample, and nanorod wurtzite-type cadmium sulfide samples obtained with a traditional two-step synthesis method. The cadmium sulfide nanorod catalyst provided by the invention has a good application prospect in the field of sound energy-hydrogen energy conversion. The preparation method is simple to operate, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for forming deposited film
InactiveCN101932748AEase of mass productionIncrease production capacityElectrode manufacturing processesVacuum evaporation coatingLithiumCrucible
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
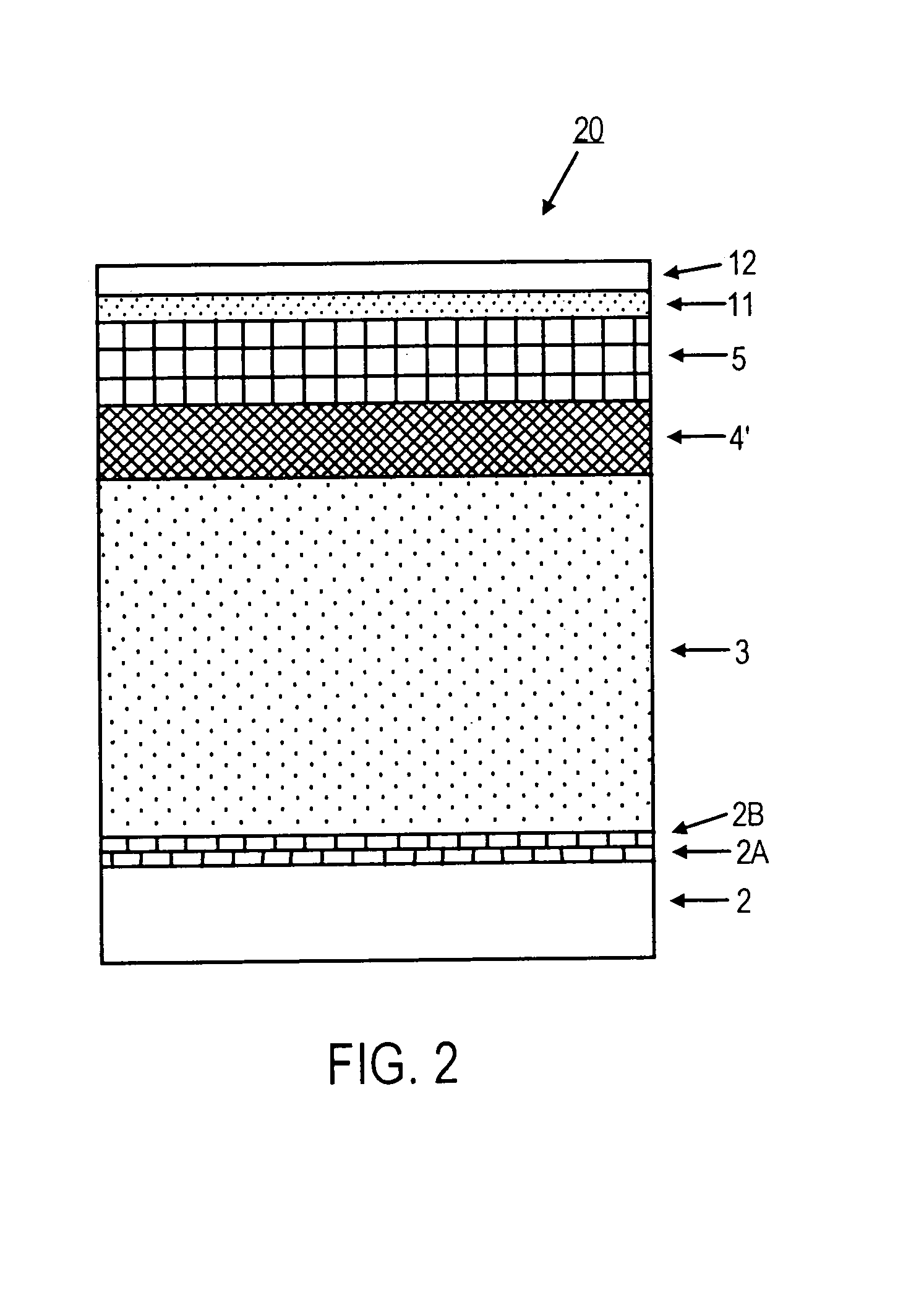
Coating with controlled grain size and morphology for enhanced wear resistance and toughness
InactiveUS20040265541A1Reduce grain sizeImprove toughnessPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesGranularityWear resistance
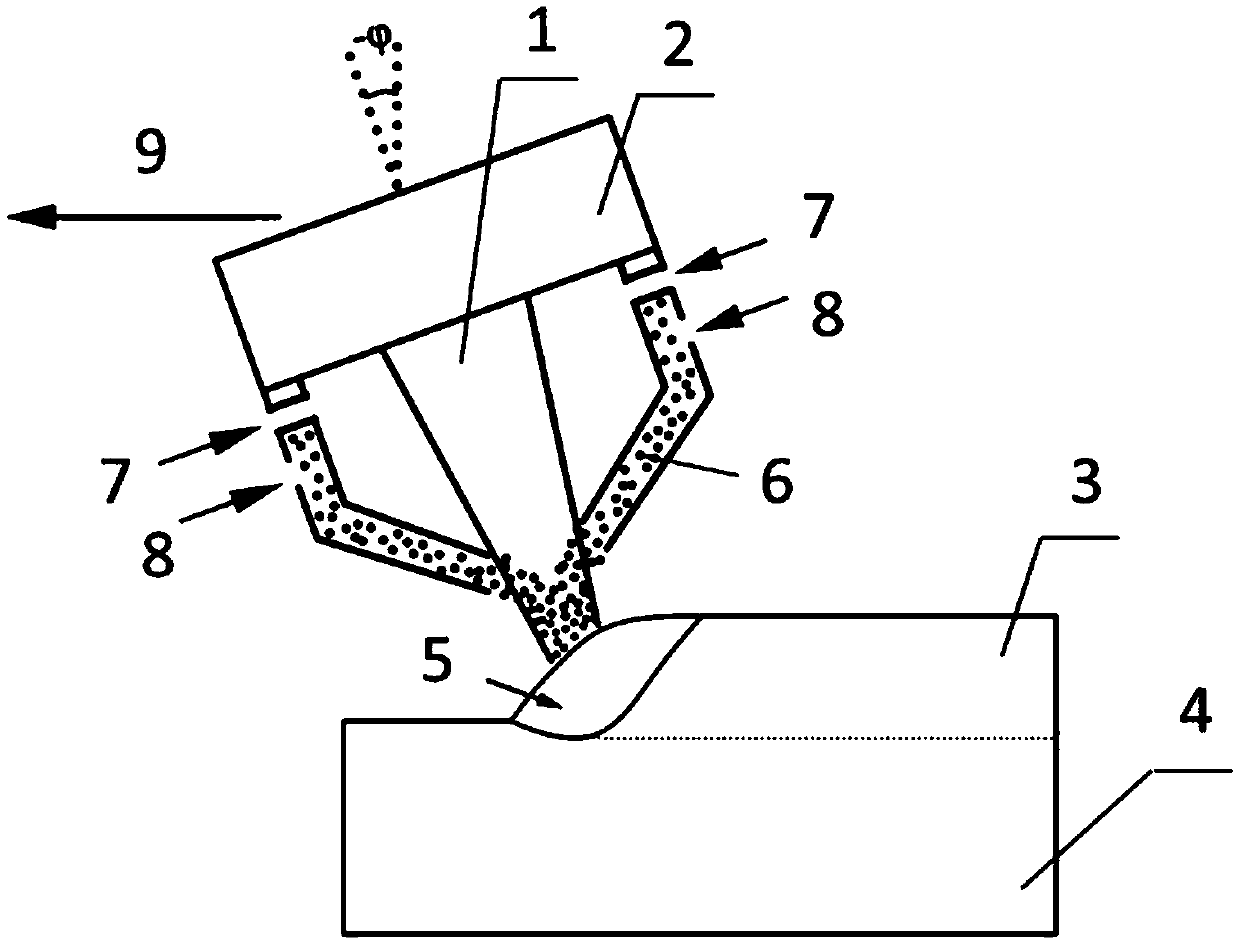
Wear resistance of the prior-art Ti(C,N) layers can be considerably enhanced by optimising the grain size and microstructure. This invention describes a method to obtain controlled, fine, equiaxed grain morphology in Ti(C,N) layers produced using moderate temperature CVD (MTCVD). The control of the grain size and shape can be obtained by doping using CO, CO2, ZrCl4 and AlCl3 or combinations of these. Doping has to be controlled carefully in order to avoid nanograined structures and oxidisation. This kind of coatings shows new enhanced wear properties. The fine grain size together with equiaxed grain morphology enhances the toughness of the coating with at least maintained wear resistance, which can be seen especially in sticky steels like stainless steels. The optimum grain size is from about 50 to about 300 nm, preferably from about 50 to about 150. The coatings according to this invention are characterised by the lack of any strong preferred growth orientation, the length-to-width ratio (L / W) around 1 and only with a slight to moderate XRD line broadening.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
High-nickel positive electrode material with primary particles being directionally arranged, and preparation method for high-nickel positive electrode material
ActiveCN109713297AGood dispersionFacilitated releaseCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumThermal insulation
The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a high-nickel positive electrode material precursor, a lithium source and a dopant capable of reducing the surface energy of a crystalsurface 003 of a layered structure of the high-nickel positive electrode material into a mixing kettle, and performing stirring and uniform mixing to obtain a mixture; (2) putting the mixture obtainedat the step (1) into a muffle furnace for sintering, performing thermal insulation, cooling and screening to obtain the high-nickel positive electrode material with primary particles being directionally arranged, wherein the molecular formula of the high-nickel positive electrode material with primary particles being directionally arranged is LiNixMyO2, x is greater than or equal to 0.5 and lessthan 1, y is greater than or equal to 0 and less than 0.5, x + y is equal to 1, and M is one or more than one metal element. According to the invention, the growth orientation and shape of primary particle crystals are controlled by selecting a dopant capable of reducing the surface energy of a specific crystal face of the crystal, so that the high-nickel positive electrode material secondary particles with long circulation and high safety are obtained, wherein the primary particles in the high-nickel positive electrode material secondary particles are arranged in a radial manner and grow directionally.
Owner:NINGBO RONBAY LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
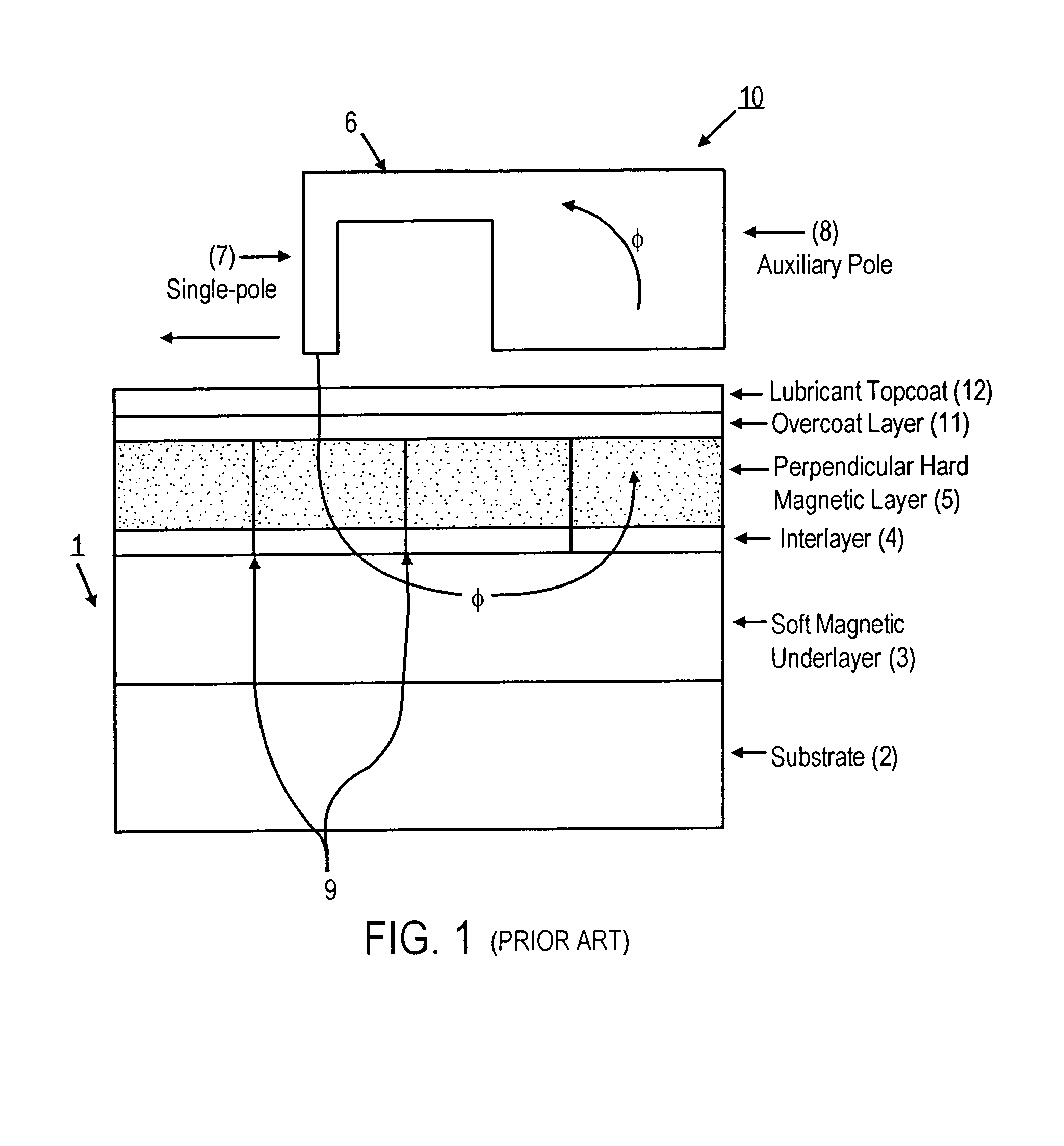
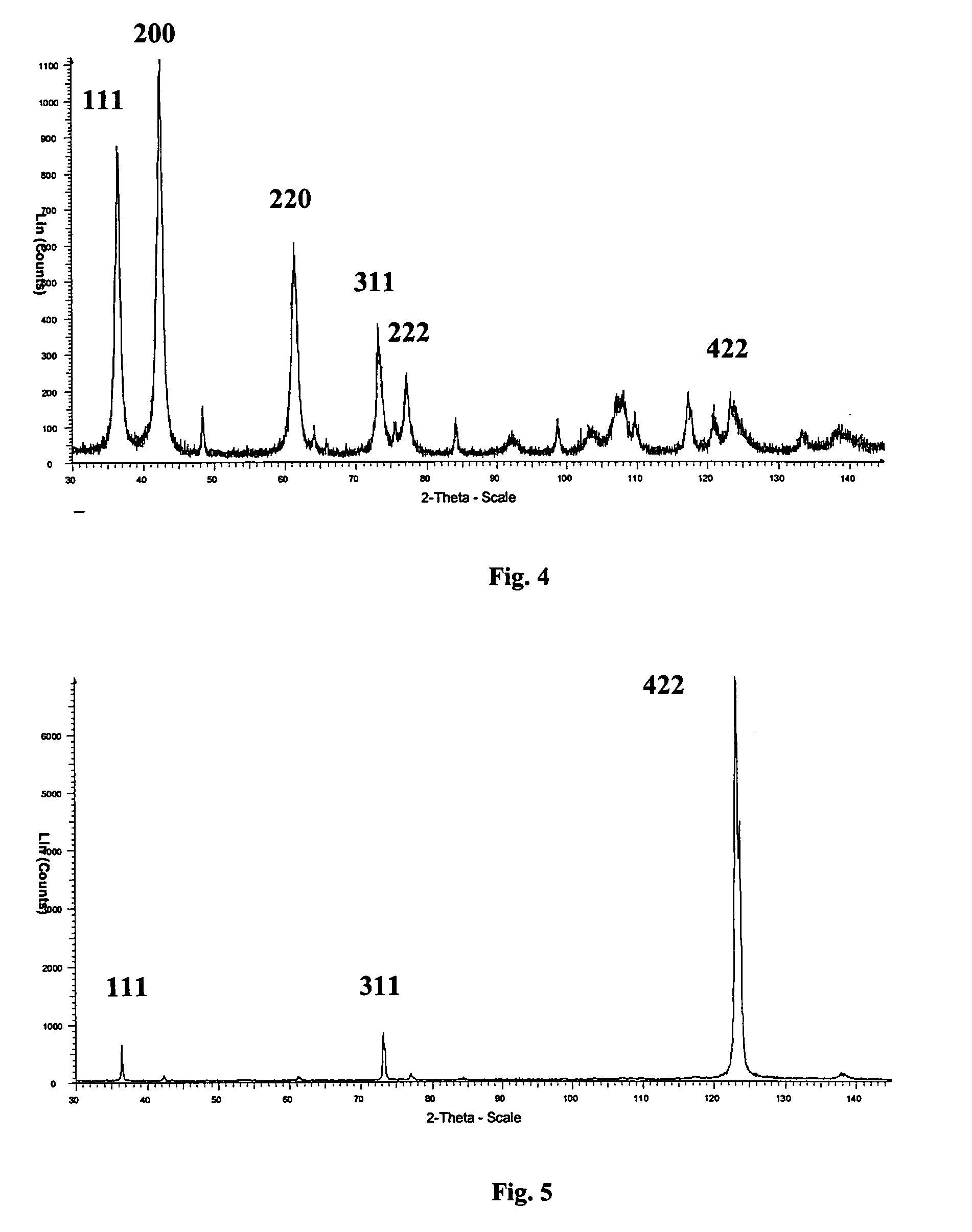
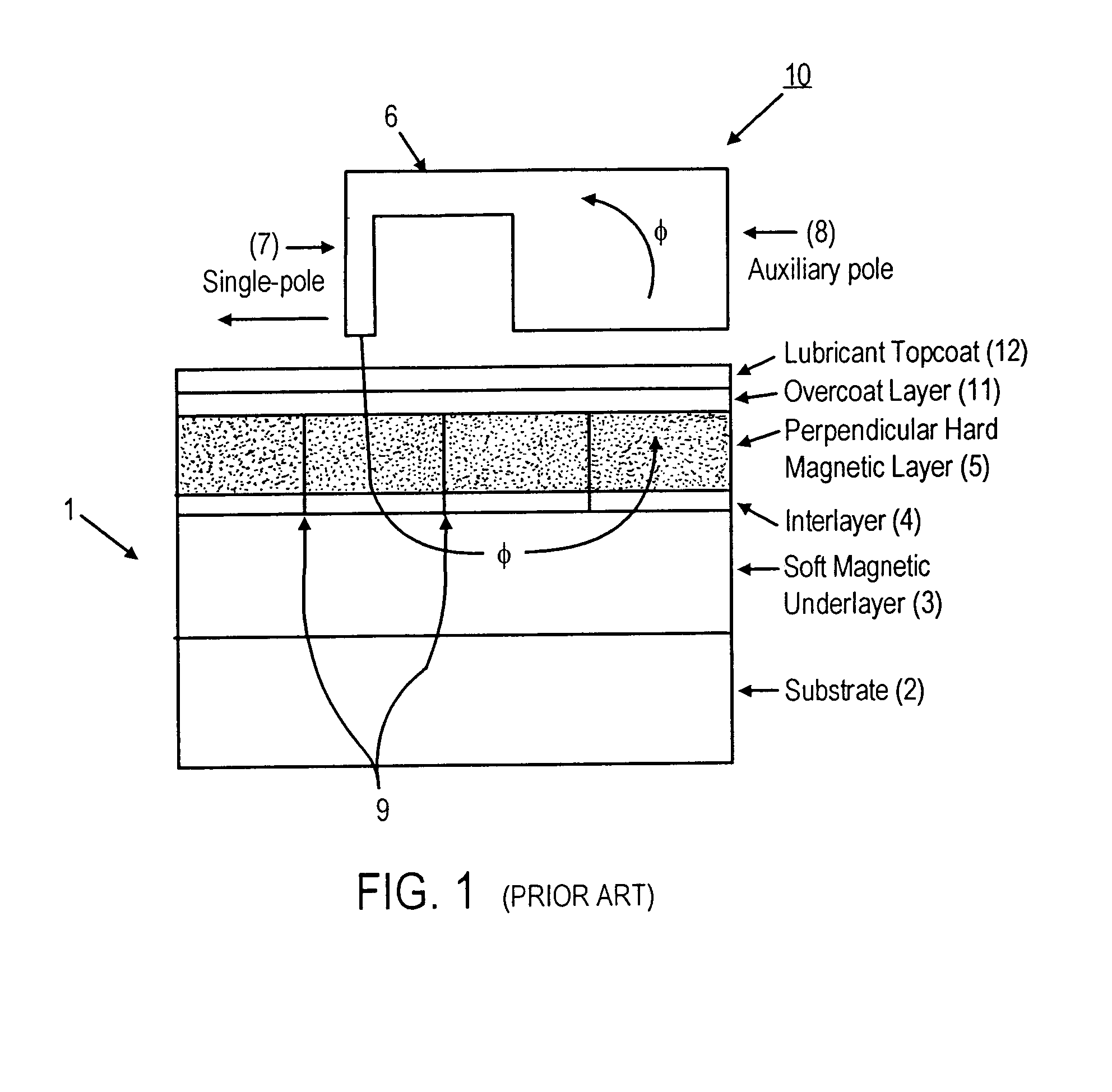
Highly oriented perpendicular magnetic recording media
InactiveUS7247396B2Enhanced structure of layerStrong growthBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageHigh surfaceGrowth orientation
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium including an interlayer structure for crystallographically orienting a layer of a hexagonal close-packed (hcp) perpendicular magnetic recording material formed thereon, comprising in overlying sequence from a surface of a magnetically soft underlayer:(1) a first crystalline layer of a material having a first lattice parameter and a strong preferred growth orientation;(2) a second crystalline layer of a material having a second lattice parameter and the same strong preferred growth orientation as the first crystalline layer; and(3) a third crystalline layer of an hcp material, having a [0002] lattice parameter similar to or different from that of the second lattice parameter of the second crystalline layer and a strong <0002> preferred growth orientation, wherein:the second crystalline layer has a lower interfacial energy with the first crystalline layer and a higher interfacial energy with the third crystalline layer, owing to a lower surface energy of the first crystalline layer and a higher surface energy of the second crystalline layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method for planting leaf-used lycium barbarum
ActiveCN103190274APromote growth and developmentImprove disease resistanceFertilising methodsHorticultureDiseaseNutrient solution
The invention discloses a method for planting leaf-used lycium barbarum, relates to a method for planting leaf-used plants and belongs to the field of agricultural planting. The method is characterized by comprising steps of preparing nutrient solution A, nutrient solution B and nutrient solution C; and spraying the nutrient solution A on lycium barbarum leaves when leaf primordia of the lycium barbarum leaves are formed, spraying the nutrient solution B on the lycium barbarum leaves in a middle growth period of the leaves, and spraying the nutrient solution C on the lycium barbarum leaves in a vigorous growth period of the leaves. The method has the advantages that nutrients required by the leaves in different growth periods are different, so that the growth orientation of the lycium barbarum can be changed by applying different fertilizers, leaf fertilizers are emphasized instead of fruit fertilizers, and the purpose of increasing the quantity of the lycium barbarum leaves is achieved; each nutrient solution contains various components such as growth promoters, induction-resistant chemical substances and nutrient substances, and is scientifically proportioned, the disease resistance and the like of the leaves can be effectively improved while the growth and the development of the lycium barbarum leaves are promoted, and diseases are suppressed; and the method plays an important role in aspects of reducing the application amount of chemical pesticides to the leaves and residue of the chemical pesticides.
Owner:曾小虎
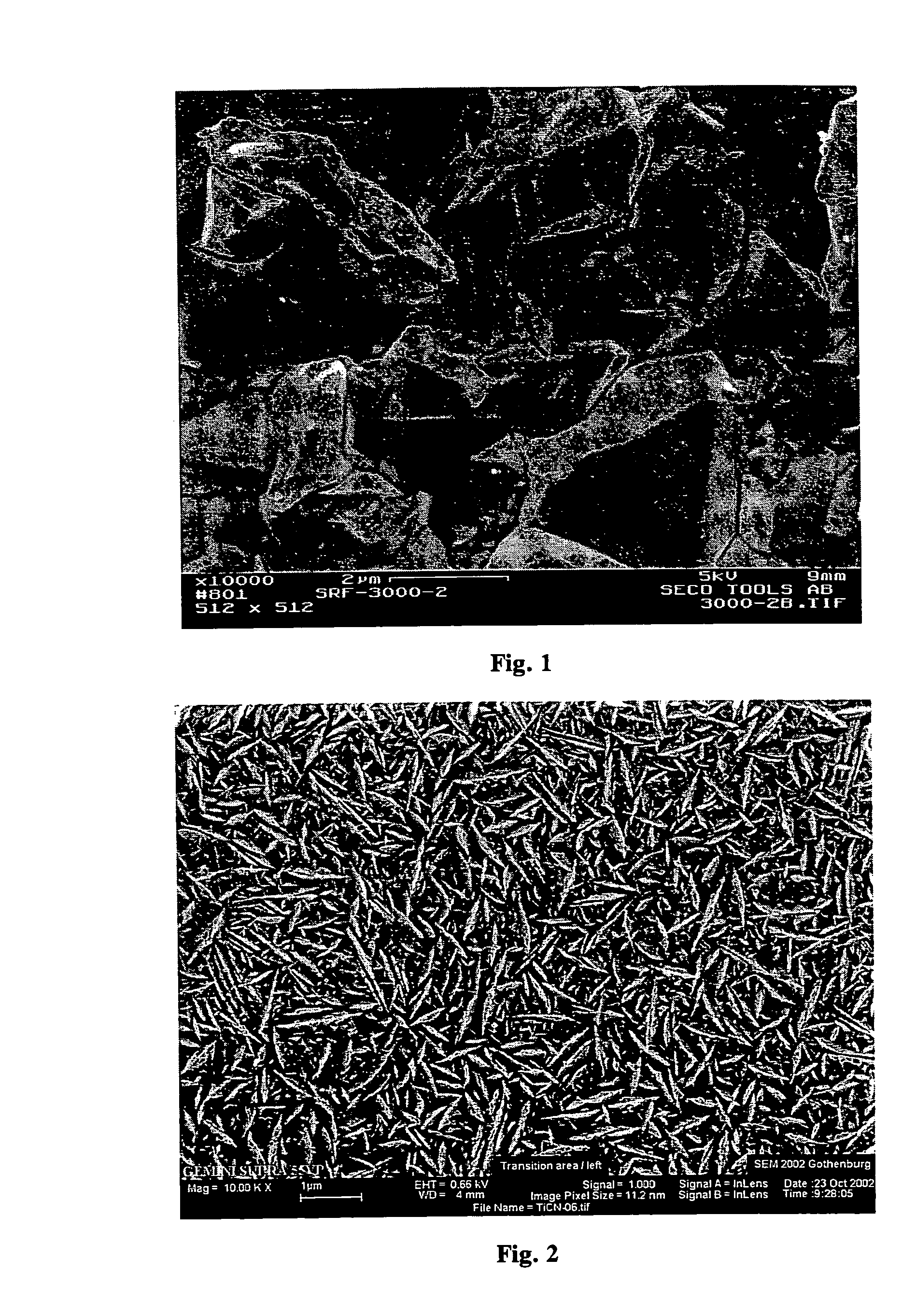
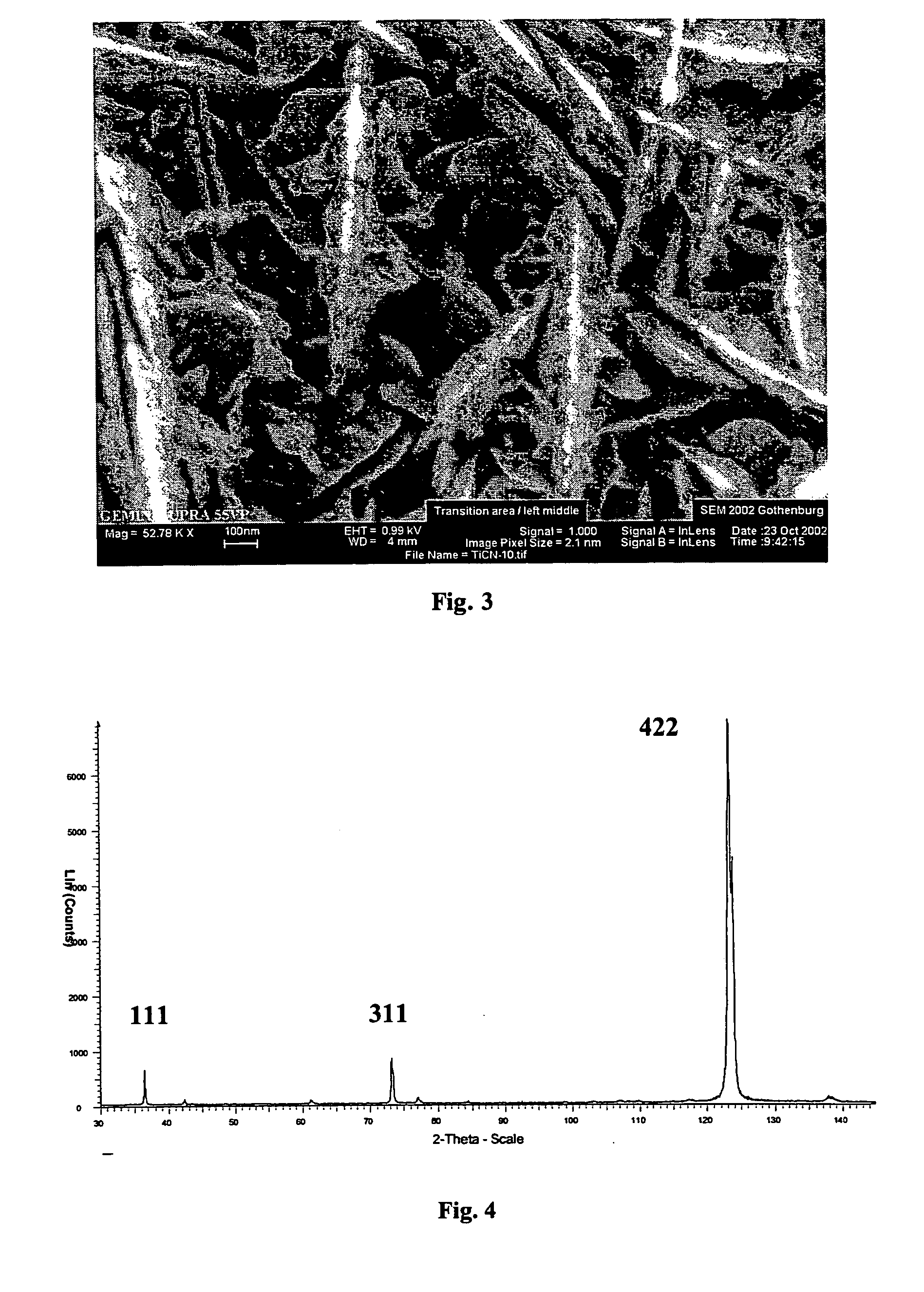
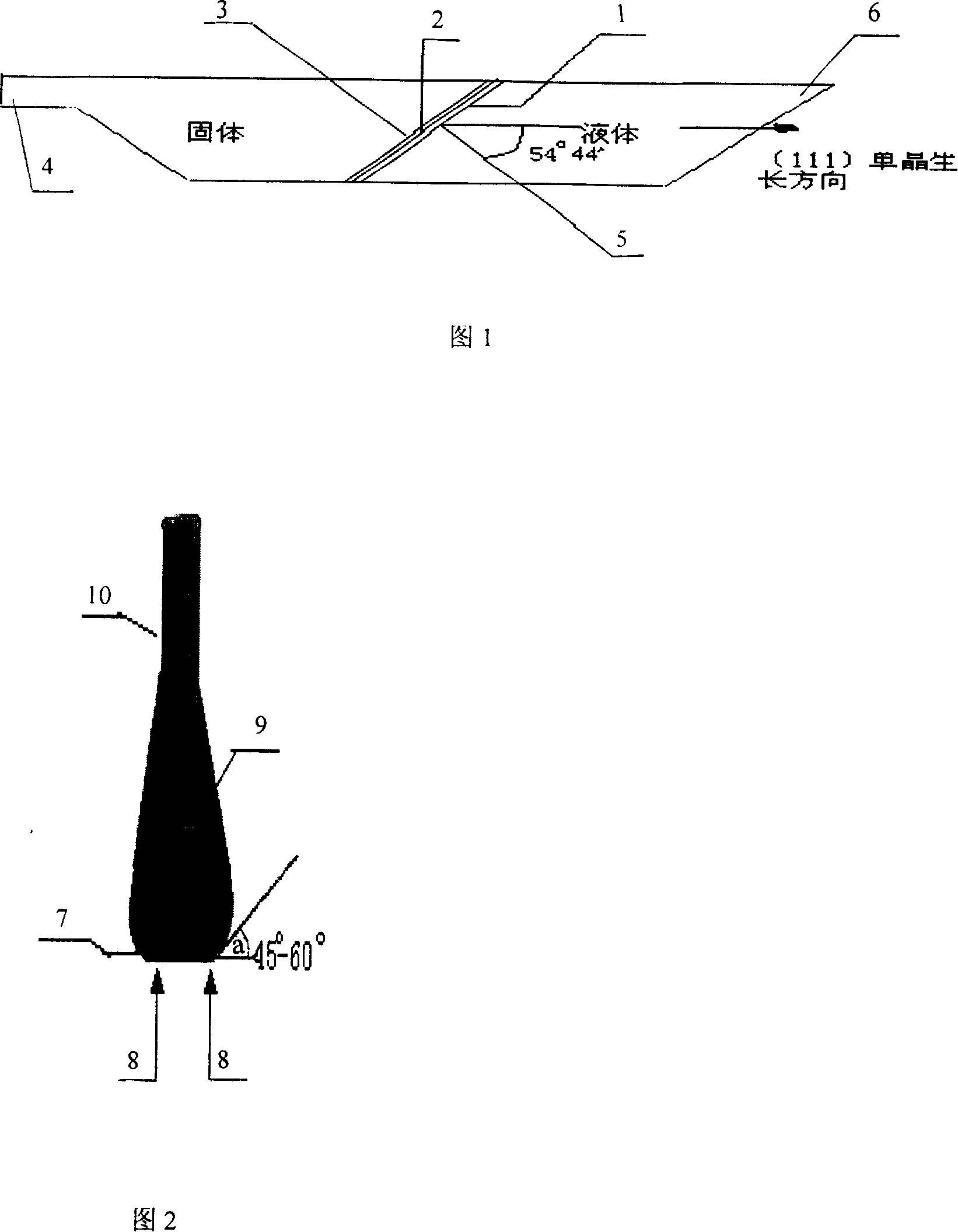
Layer with controlled grain size and morphology for enhanced wear resistance
ActiveUS20050013995A1Reduce grain sizeMaintain structurePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesWear resistanceCarbon steel
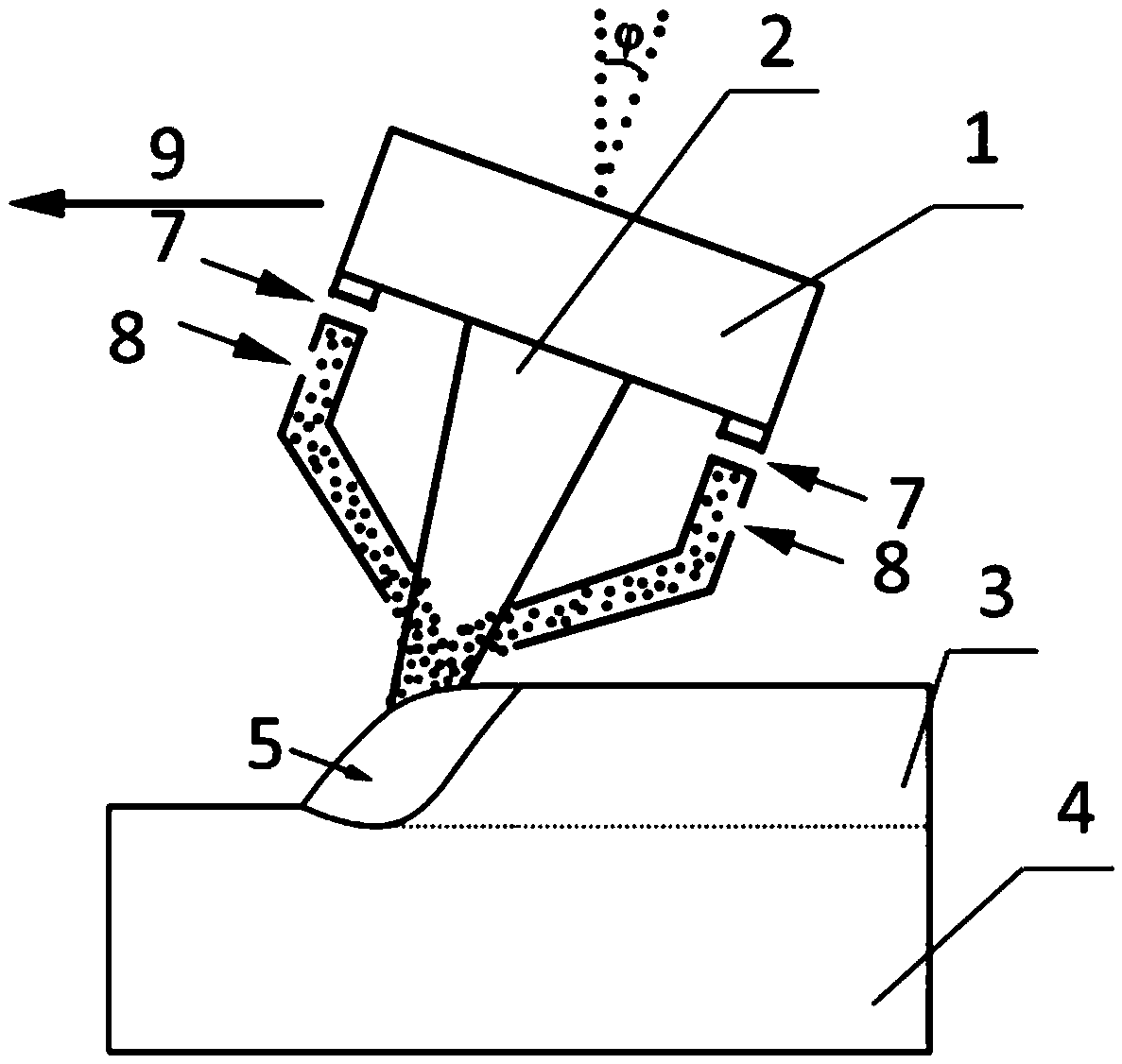
Wear resistance of the prior-art Ti(C,N) layers can be considerably enhanced by optimising the grain size and microstructure. Considerably better wear resistance in, for example in many carbon steels, can be obtained by modifying the grain size and morphology of prior art MTCVD Ti(C,N) coatings. The improved coating is composed of small columnar crystals. Doping by using CO, CO2, ZrCl4, HfCl4 and AlCl3 or combinations of these can ensure the control of the grain size and shape. Doping has to be controlled carefully in order maintain the columnar structure and also in order to avoid nanograined structures and oxidisation. The preferred grain size should be in the sub-micron region with the grain width of from about 30 to about 300 nm. The length to width ratio should be more than 5, preferably more than 10 and the coating should exhibit a strong preferred growth orientation along 422 or 331. The XRD line broadening should be weak.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Technique for cutting horizontal gallium arsenide single-crystal wafer with inside diameter slicer
InactiveCN101130265ALess bendingControl deformationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStone-like material working toolsWaferingHigh volume manufacturing
The invention relates to a process that inside diameter slicing machine is used to cut level gallium arsenide single-crystal wafer, which comprises following procedures. (1) edge cutting treatment is carried out for level gallium arsenide single-crystal ingot with the length of 50-500mm. (2) the single-crystal ingot is bonded with the surface of graphite strip and the surface of graphite support. (3) bonded single-crystal ingot is fixed on the ingot-pushing device of inside diameter slicing machine. (4) cutting blade is installed; switch is on and the machine runs. (5) working table is lift and a piece of wafer is cut to confirm crystal orientation; after confirmation calibrating thickness of single-wafer cutting is set; said cutting orientations are parts of (100) to the nearest [100] and [011]; the angle between the crystal orientation and the growth orientation of gallium arsenide single crystal is 54degree 44'. (6) cutting speed is set to cut wafers in multiple piece automatically and continuously. (7) after the whole single-crystal ingot is cut cutting blade is washed and machine is off. Level gallium arsenide single-crystal wafer with the diameter of Phi50. 8mm-Phi76mm and the thickness of 280um-470um can be cut in the process and average production yield can be more than 95%. Production stability and repeatability are good and mass production can be realized.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG +1
Method for preparing briented growth dielectric-constant adjustable strontium lead titanate film
InactiveCN101070617ABroaden the preparation routeAvoid dependencyPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesStrontium titanateSingle crystal
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method capable of controlling oriented growth of bismuth oxybromide photocatalysts
ActiveCN104258877ASimple processEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsBismuth compoundsAcetic acidControl oriented
The invention discloses a preparation method capable of controlling oriented growth of bismuth oxybromide photocatalysts and belongs to the field of photocatalysis. The preparation method is mainly characterized in that bismuth salt, bromide, glacial acetic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) are taken as raw materials, the added amounts of glacial acetic acid and PVP are controlled, the bismuth oxybromide photocatalysts with different growth orientations are obtained by virtue of a simple hydrothermal method, and photocatalytic performance of the bismuth oxide bromide photocatalysts are compared. The preparation method is simple in technology and low in cost, and the prepared bismuth oxybromide photocatalysts with different growth orientations have different visible light catalytic activities.
Owner:浙江三行电气科技有限公司
Component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts
ActiveCN110245449AAccurate calculationPredicting Macrosegregation FormationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCellular automationEnergy conservation
The invention discloses a component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts, and relates to a component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that macrosegregation formation of the magnesium alloy casting parts cannot be accurately predicted by an existing method. The component nonuniformity numerical prediction method comprises the following steps: 1, simulating the growth of alpha-Mg dendrites with different growth orientations by adopting a cellular automaton method to obtain a curve that the specific surface area of the dendrites changes along with the solid phase fraction; 2, performing mesh generation on the casting system; 3, calculating an energy, component and momentum conservation equation for all grids with subscript char = 0, and obtaining distribution of temperature, average component and speed in the casting parts; 4, calculating an energy conservation equation for all grids of which the subscript chars are not 0 to obtain temperature distribution; and 5, repeating the step 2, the step 3 and the step 4 until solidification is finished, and outputting an average component field in the casting parts. The component nonuniformity numerical prediction method is applied to the field of magnesium alloy casting part component prediction.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for quantitatively analyzing EBSD measured body-centered cubic alloy solidification structure grain sizes
InactiveCN103902841AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpecial data processing applicationsDistribution characteristicGrain structure
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively analyzing measured body-centered cubic alloy solidification structure grain sizes, in particular to a method for quantitatively analyzing EBSD measured body-centered cubic alloy solidification structure grain sizes. The purpose is to solve the technical problem that because dendritic structures, not grain structures, are currently measured through EBSD, the grain sizes can not be evaluated. The method includes the steps that step1, EBSD data are obtained; step2, a two-dimensional array is established; step3, a rotation matrix and a growth orientation matrix are established; step4, primary-precipitated phase elements are endowed with attributes; step5, the dendritic structures are evolved as the grain structures; step6, the equivalent diameters of grains are calculated; step7, the average equivalent diameter of the grains in the gravity direction is calculated. The method not only can analyze the grain structures, but also can analyze the dendritic structures, the sizes and distribution characteristics of the grains can be evaluated, and mechanical performance is evaluated with the help of a grain size grade standard. The method is applied to the EBSD measured body-centered cubic alloy solidification structure grain sizes.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
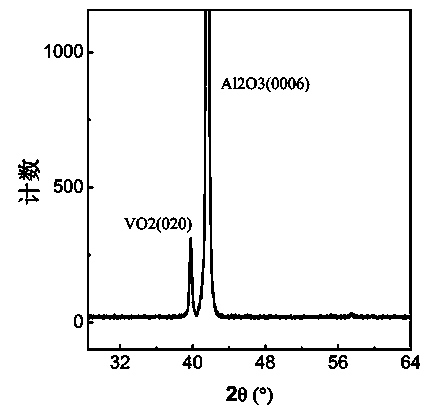
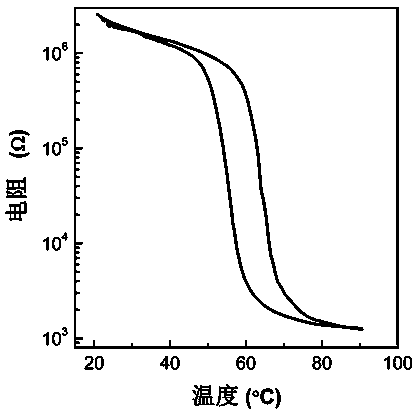
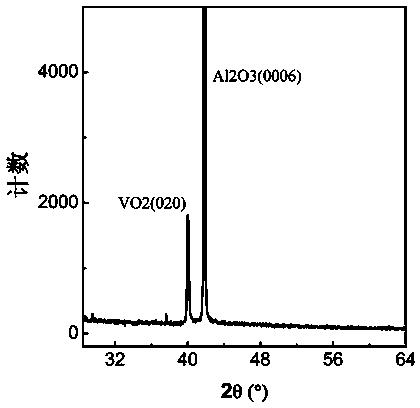
Liquid-phase preparation method of high-oriented vanadium dioxide film
ActiveCN104060241AAct as a reducing agentRestore evenlyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingVanadium dioxidePhase change
The invention discloses a liquid-phase preparation method of a high-oriented vanadium dioxide film, belonging to the field of chemical function materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing precursor liquid by taking triisopropoxyvanadium oxide as solute, coating a sapphire substrate with the obtained precursor liquid to prepare a precursor film, and finally sintering the precursor film in a vacuum environment. According to the preparation method, the vanadium dioxide film is prepared by controlling vacuum sintering conditions on the basis of a liquid-phase method, the obtained film is good in growth orientation, the phase change temperature of the film is about 60 DEG C, and the change of electrical resistivity before and after the phase change is more than three orders of magnitude; in addition, the preparation process is simple and suitable for large-range popularization.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
Method for controlling microstructure and hot crack sensibility of laser cladding coating
ActiveCN105506615AEasy to operateGood effectMetallic material coating processesOptoelectronicsGrowth orientation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the microstructure and the hot crack sensibility of a laser cladding coating, comprising the following steps: changing the incident angle of laser during laser cladding so as to change the microstructure and the growth orientation of the cladding coating, and further change the hot crack initiation resistance of the cladding coating, and achieve the purpose of controlling forming of the cladding hot cracks. The method for controlling microstructure and hot crack sensibility of laser cladding coating can effectively control the microstructure and the hot crack sensibility of the cladding coating by changing the incident angle of the laser, is simple in operation, strong in operability and good in effect, is suitable for the preparation process of various laser cladding coatings, and is particularly applicable to laser cladding of nickel-base superalloy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Coating with controlled grain size and morphology for enhanced wear resistance and toughness
InactiveUS20070190250A1Reduce grain sizeImprove toughnessSpecial buildingChemical vapor deposition coatingAluminium chlorideWear resistance
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
LiMnPO4 hollow microsphere with controllable structure and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110518240AHigh crystallinityPrecise regulation of structureSecondary cellsPositive electrodesMicrospherePhosphate
The invention discloses a LiMnPO4 hollow microsphere with a controllable structure and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of positive electrode materialsfor lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the steps: S1, sodium hydroxide, lithium salt and phosphate are added into the mixed solvent of diethylene glycol and deionized water to fully react, and the reaction product is sequentially subjected to solid-liquid separation, washing and drying so as to obtain Li3PO4 hollow microspheres; and S2, the obtained Li3PO4 hollow microspheres, manganese salt and ammonium salt are added into a mixed solvent of ethylene glycol and deionized water and fully stirred, the stirred suspension is sealed in a reaction kettle, kept warm for a certain period oftime and then cooled to room temperature and the target product LiMnPO4 hollow microspheres are obtained after solid-liquid separation, washing and drying. The invention also discloses the applicationof the hollow microspheres in high-performance lithium ion battery positive electrode materials. The auxiliary additive ammonium salt can adjust the growth orientation of the assemble crystal grainsand adjust the assemble structure of the microspheres, and the obtained hollow microspheres have good crystallinity, accurate structure adjustment and control and excellent magnification performance.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107140975AImprove stabilityRaise the saturation polarization valueFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic shaping apparatusBreakdown strengthSodium bismuth titanate
The invention relates to a sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. A general chemical formula of the sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic is (1-x)[0.9(0.94Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-0.06BaTiO3)-0.1NaNbO3]-xZn, wherein x in the formula is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.01. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing all raw material components according to the stoichiometric ratio, then uniformly mixing all the raw material components and carrying out pre-sintering and grinding in sequence to obtain a ground powder body; secondly, carrying out granulating to obtain a granulated powder body; thirdly, carrying out dry pressing and cold isostatic pressing to obtain a densified ceramic green body, carrying out adhesive removal on the densified ceramic green body, and then sintering to obtain the sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, by doping zinc in the sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic, the breakdown strength and a saturation polarization value of the sodium bismuth titanate-based ferroelectric ceramic are improved, the energy storage density and the stability are improved, leakage current is reduced, growth orientation of crystals is benefited as well as development and application of high-power and high-capacity storage capacitors are facilitated.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation of electrode for electrochemical reduction of CO2 and electrode and application thereof
ActiveCN109652820AEasy to prepareStrong controllabilityElectrolytic organic productionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPhysical chemistryElectrochemistry
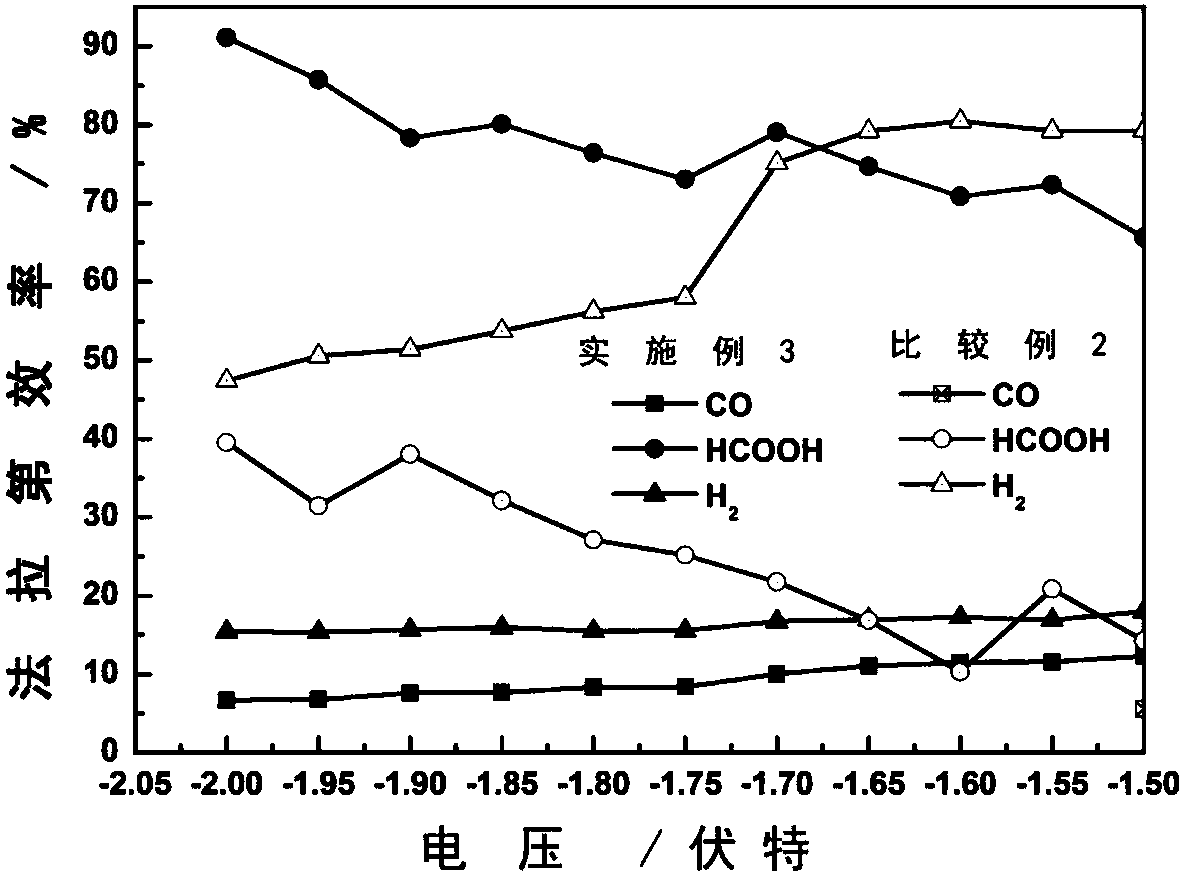
The invention provides preparation of an electrode for electrochemical reduction of CO2, and an electrode and application thereof. The technology of combining hydrothermal reaction and electrochemicalreduction has advantages of simple operation and strong reproducibility, and is characterized in that a surfactant is introduced during the hydrothermal reaction. Through the surfactant for orientedadsorption of the base metal surface, growth orientation of the metallic oxide can be regulated and controlled to obtain a dominant crystal face having high selectivity to HCOOH. The prepared surfaceoxide layer is thin and dense, and can effectively hinder the participation of the base metal in an ERC reaction so as to control the efficient conversion of the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to atarget product.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing resistive random access memory
ActiveCN109920911AEasy to makeComplicated to makeElectrical apparatusStatic random-access memoryLow mobility
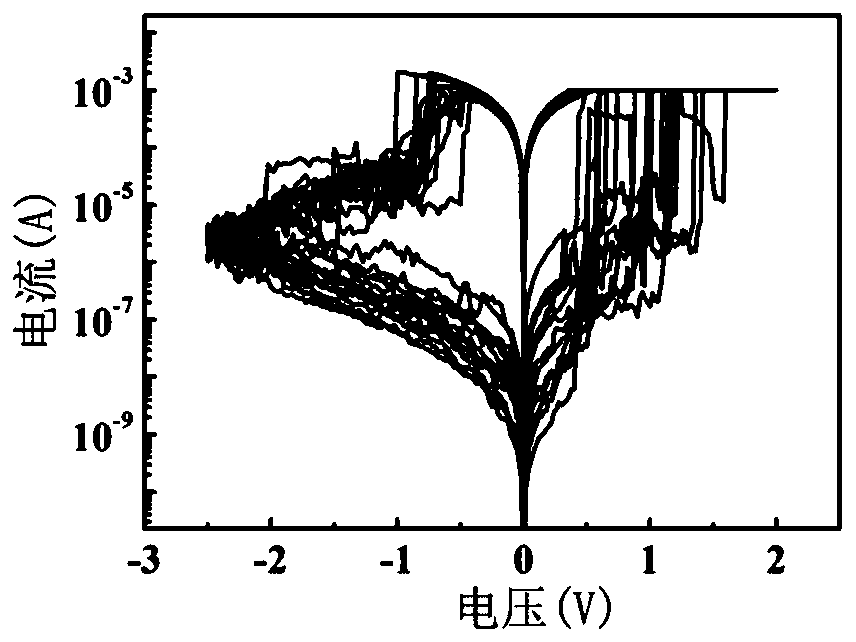
The invention discloses a method for preparing a resistive random access memory. The method comprises the following steps of providing a substrate; depositing a first metal layer on the upper surfaceof the substrate; depositing a resistive functional layer on the upper surface of the first metal layer; depositing a material layer having a low mobility on the upper surface of the resistive functional layer; preparing one or more via holes on the material layer having the low mobility; and depositing a second metal layer on the upper surface of the material layer having the low mobility. According to the method for preparing a resistive random access memory provided by the invention, the resistive random access memory prepared can control the size of conductive filaments. Since the growth orientation, number and size of the conductive filaments can be controlled, the randomness of the growth of the conductive filaments can be reduced and the current fluctuation of the resistive random access memory can be reduced, thereby reducing the parameter fluctuation of the resistive random access memory and improving the reliability of the resistive random access memory.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and products of organic metal complex and aluminum oxide compound
ActiveCN105753459AChange in growth orientationImprove atomic structure compositionDecompositionCoordination complex
The invention provides organic metal complex.The organic metal complex is prepared by mixing bis(2-methyl-8-oxyquinoline-N1, O8)-(1, 1'-biphenyl-4-hydroxyl)aluminum and 8-oxychinolin aluminum, wherein the weight ratio of the bis(2-methyl-8-oxyquinoline-N1, O8)-(1, 1'-biphenyl-4-hydroxyl)aluminum and 8-oxychinolin aluminum to the 8-oxychinolin aluminum is 2-5:5-8.Atmosphere generated during high-temperature decomposition can have embedding and co-growth of certain degree, so that the growth orientation of crystals can be changed, the atomic structure on the surface of microcosmic particles can be improved, and functional material crystal structure design is achieved.When aluminum oxide compound obtained from the organic metal complex is prepared into a coating membrane, the coating membrane is outstanding in water absorption performance, and the self-discharge performance, voltage drop performance and normal-temperature circulation performance of the coating membrane are evidently better than those of a common aluminum oxide coating membrane.The preparation method of the organic metal complex is simple, practical, evident in effect, and capable of satisfying the requirements of large-scale industrial production.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGTIANLI NEW MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com