Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12202results about "Stone-like material working tools" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
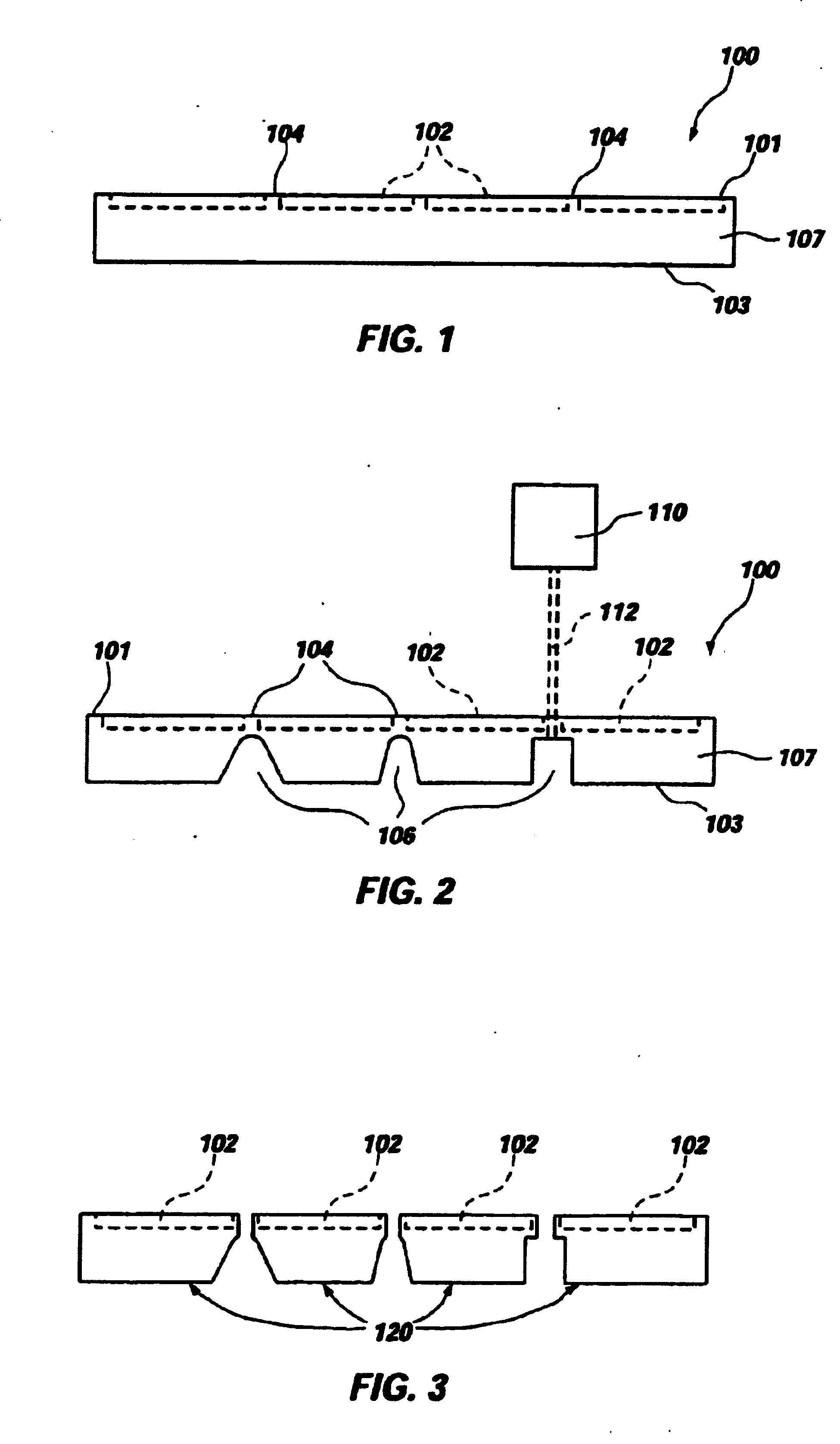
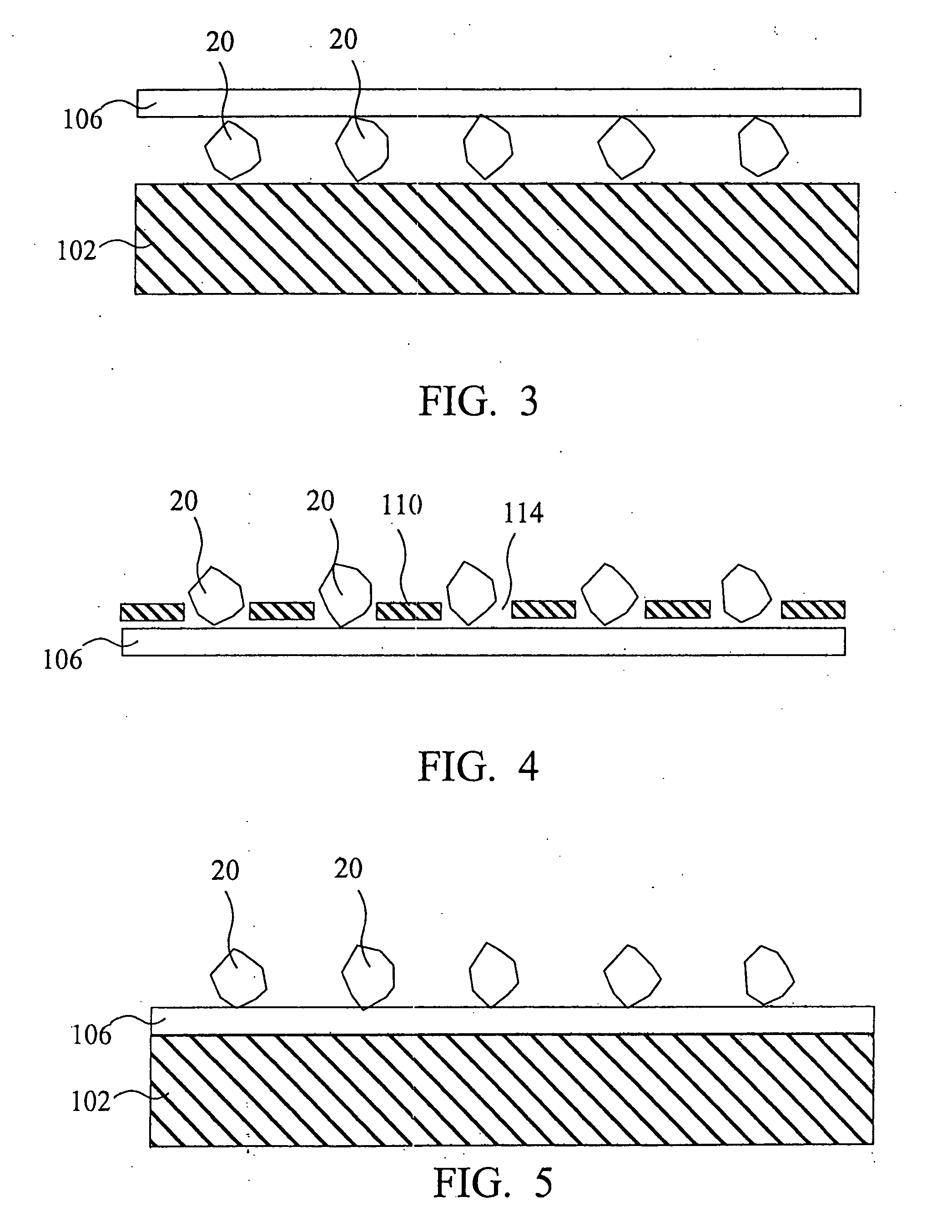
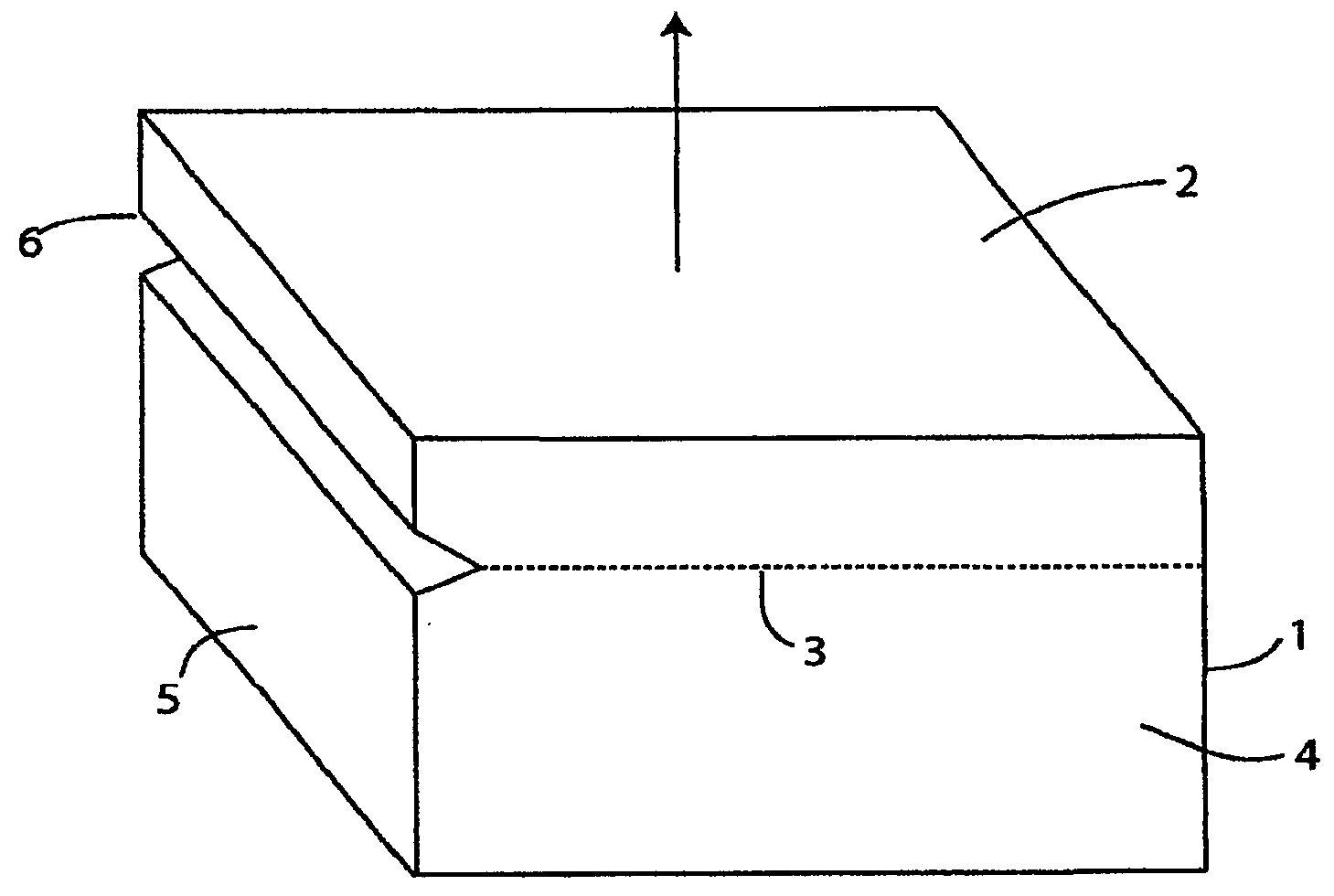
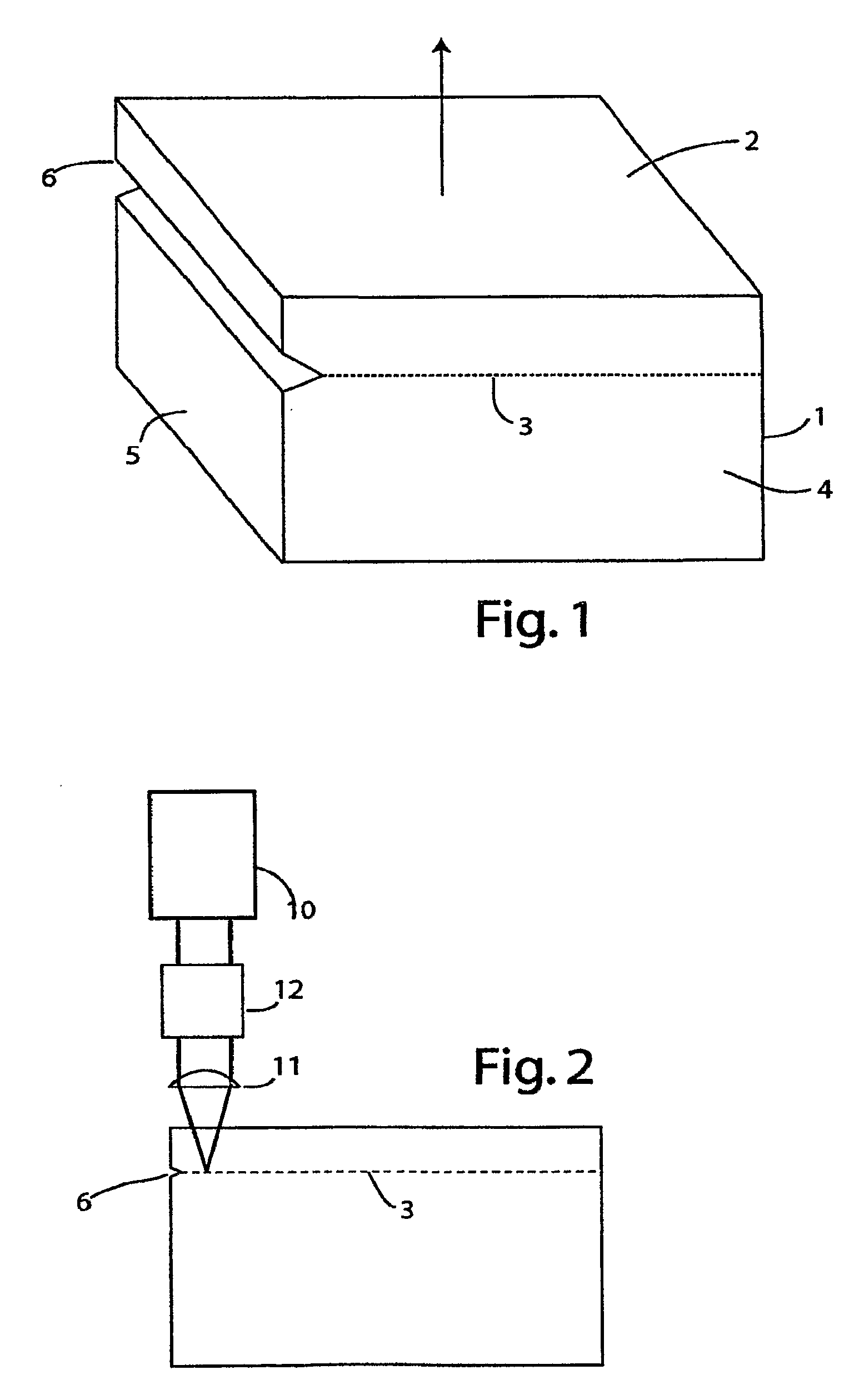
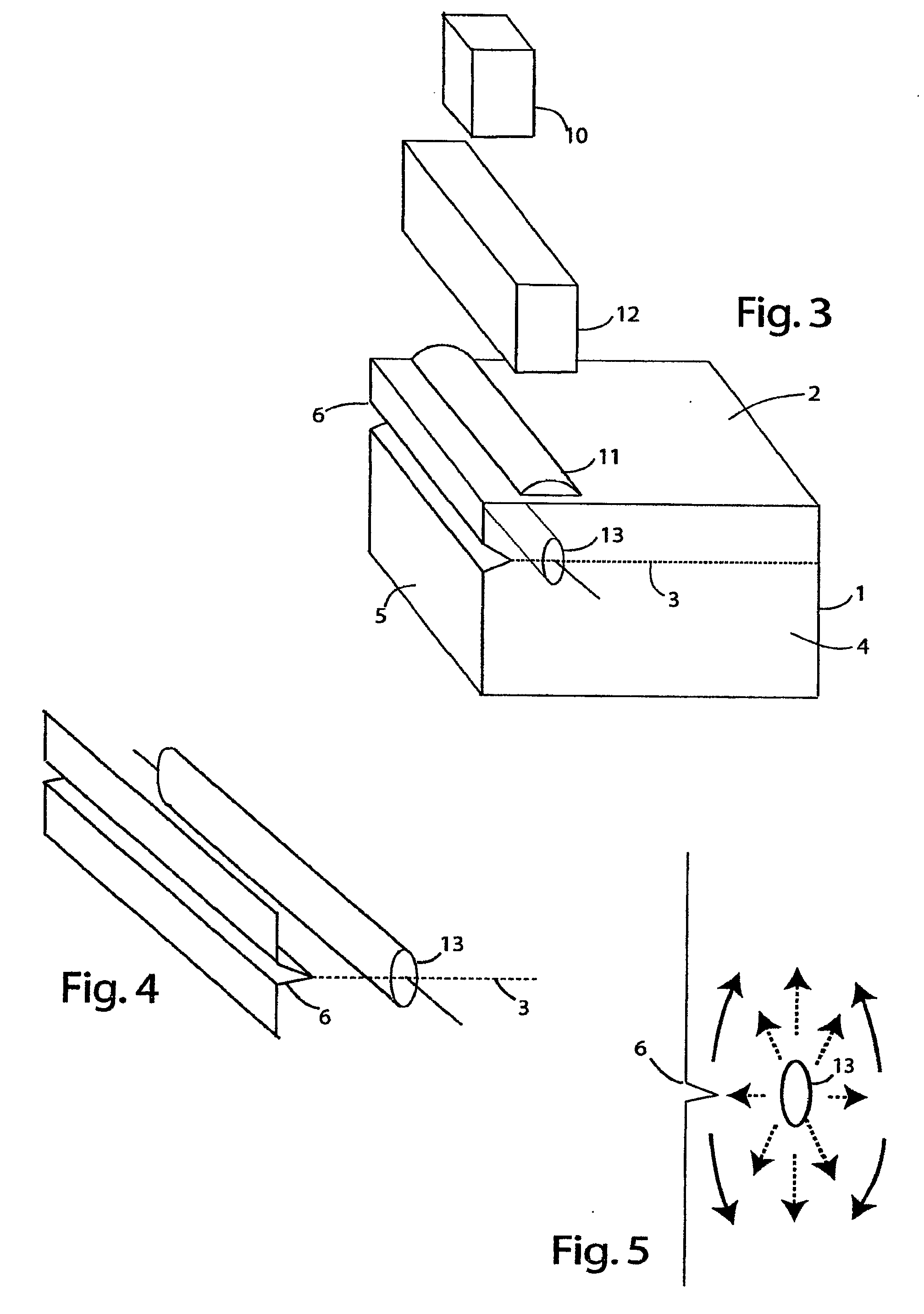
Process for the production of thin semiconductor material films
InactiveUSRE39484E1Uniform and controlled thicknessHigh implantationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesIon bombardmentMicrobubbles
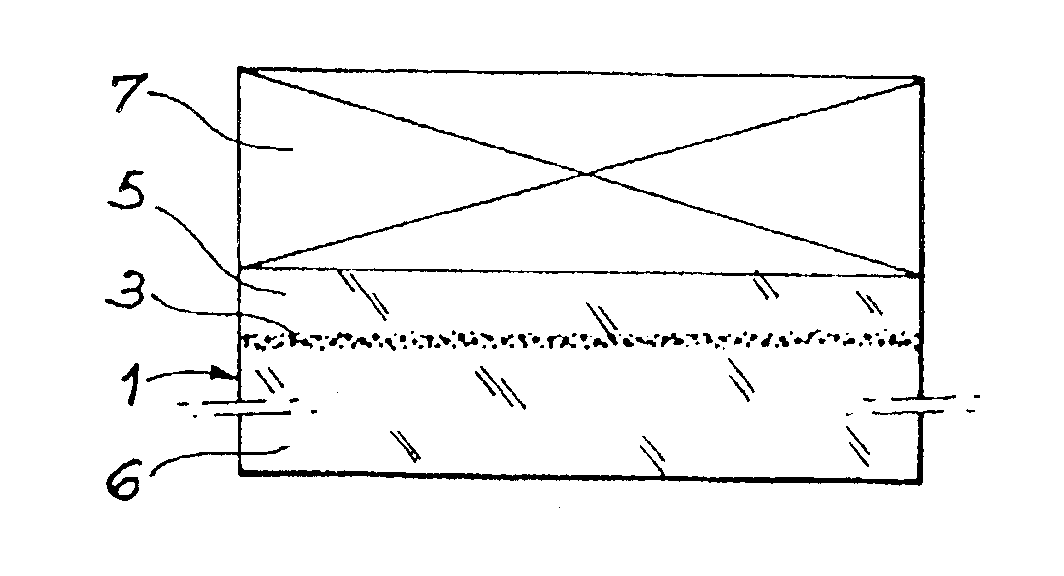
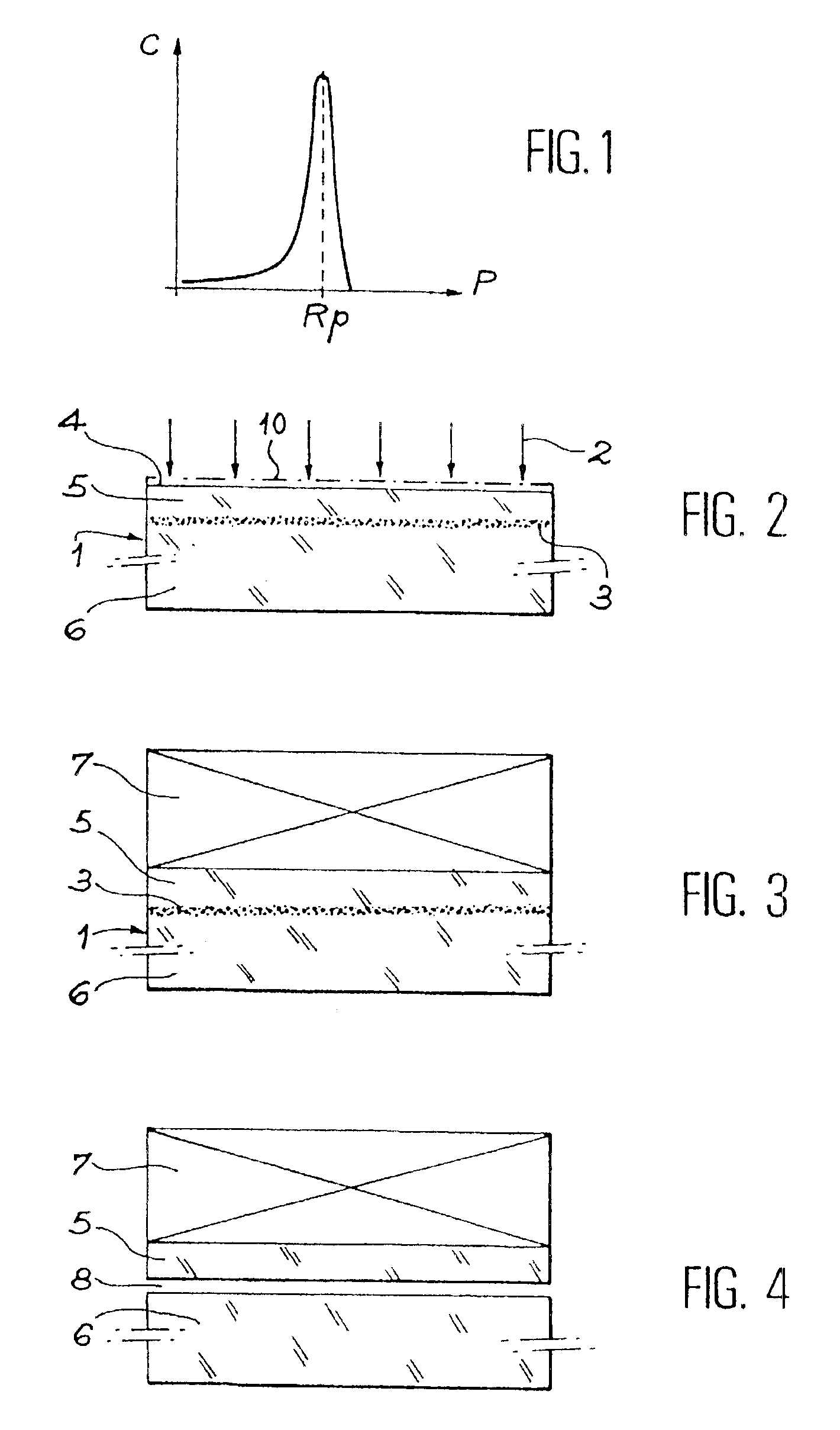
Process for the preparation of thin monocrystalline or polycrystalline semiconductor material films, characterized in that it comprises subjecting a semiconductor material wafer having a planar face to the three following stages: a first stage of implantation by bombardment (2) of the face (4) of the said wafer (1) by means of ions creating in the volume of said wafer a layer (3) of gaseous microbubbles defining in the volume of said wafer a lower region (6) constituting the mass of the substrate and an upper region (5) constituting the thin film, a second stage of intimately contacting the planar face (4) of said wafer with a stiffener (7) constituted by at least one rigid material layer, a third stage of heat treating the assembly of said wafer (1) and said stiffener (7) at a temperature above that at which the ion bombardment (2) was carried out and sufficient to create by a crystalline rearrangement effect in said wafer (1) and a pressure effect in the said microbubbles, a separation between the thin film (5) and the mass of the substrate (6).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
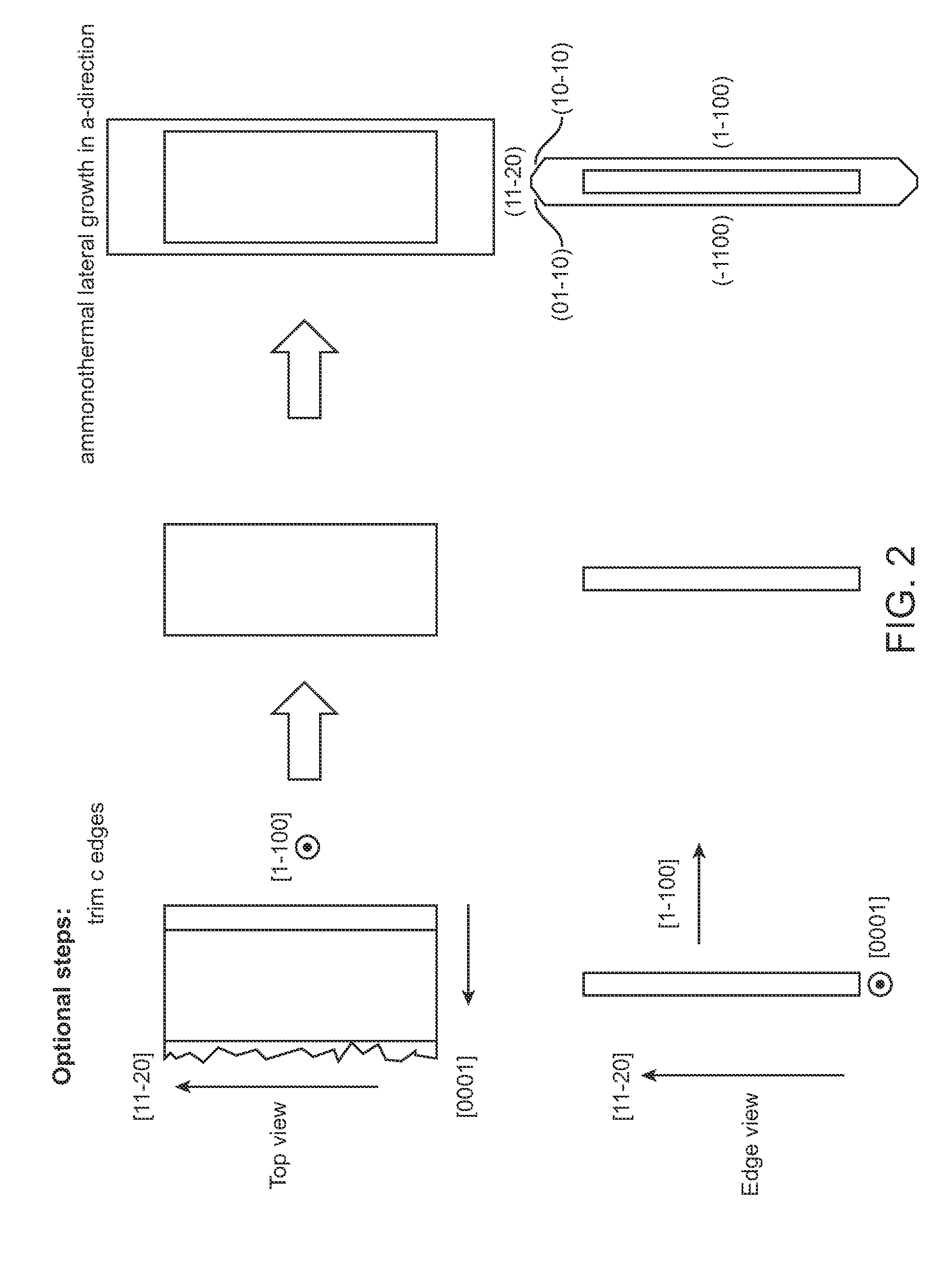
High quality large area bulk non-polar or semipolar gallium based substrates and methods
InactiveUS20100003492A1Great area of substrateCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialPhotodetectorSolar cell
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method for making. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SORAA
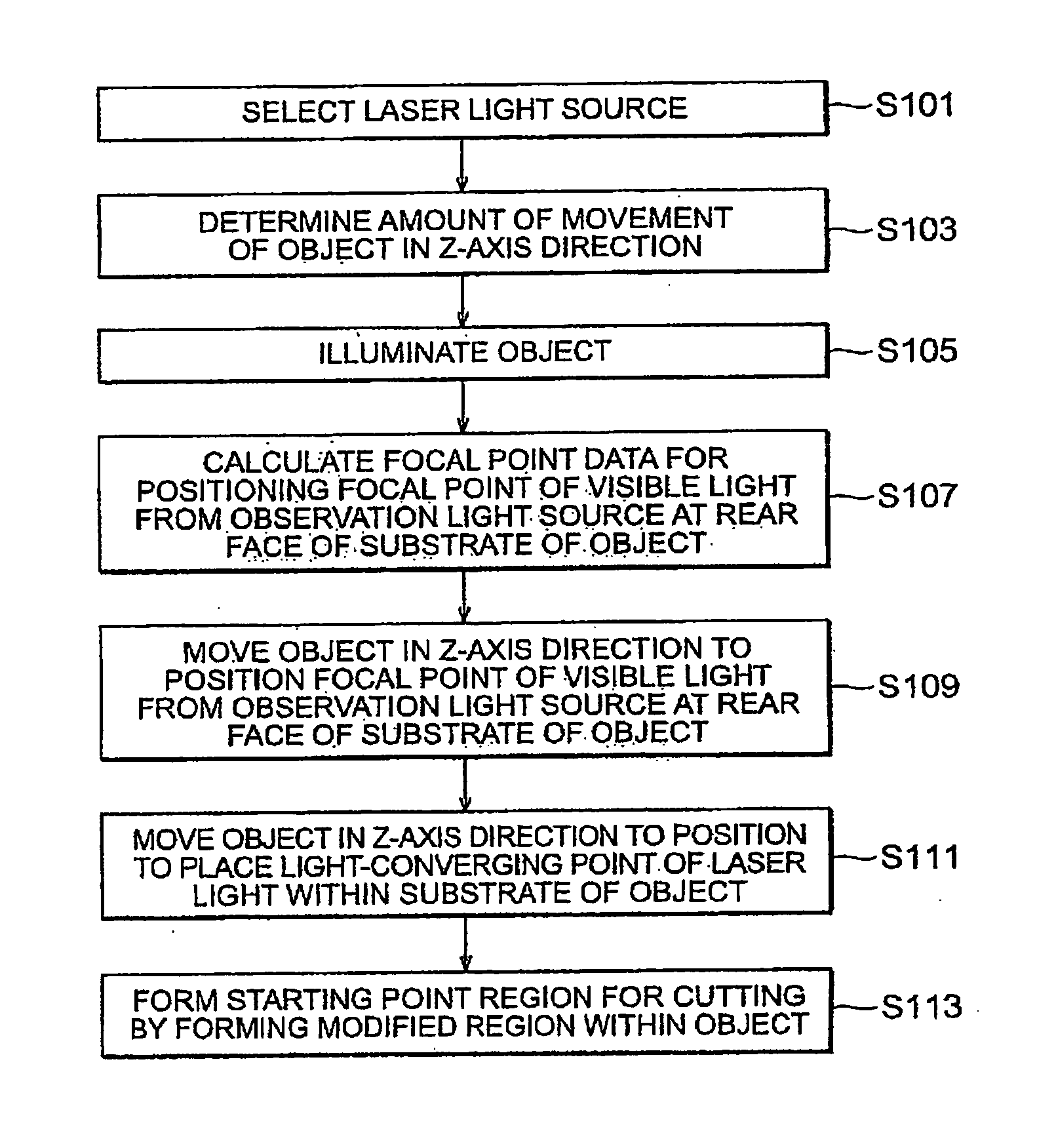
Laser processing method
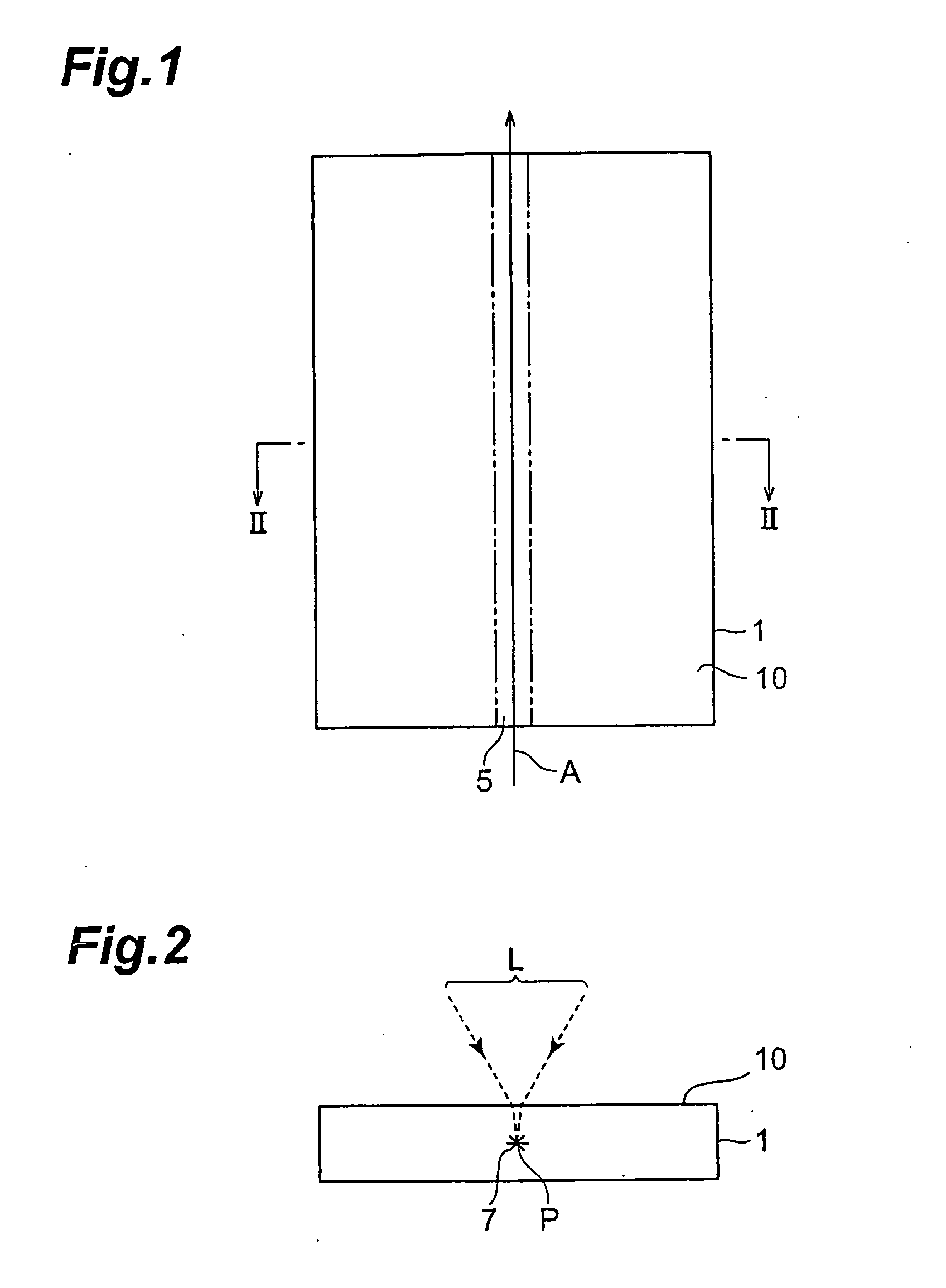
ActiveUS20050202596A1Force is smallImprove accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser processingLaser light
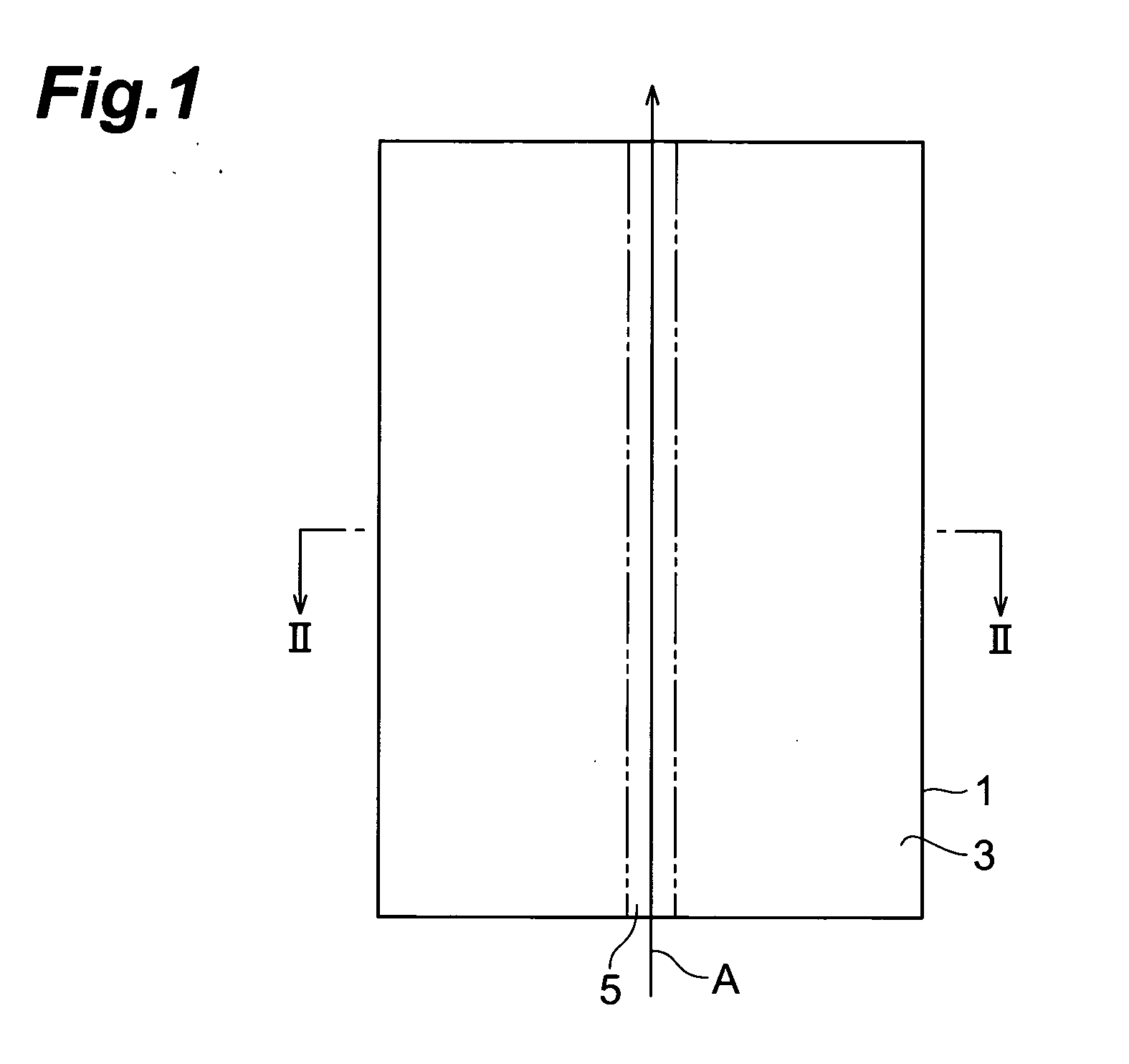
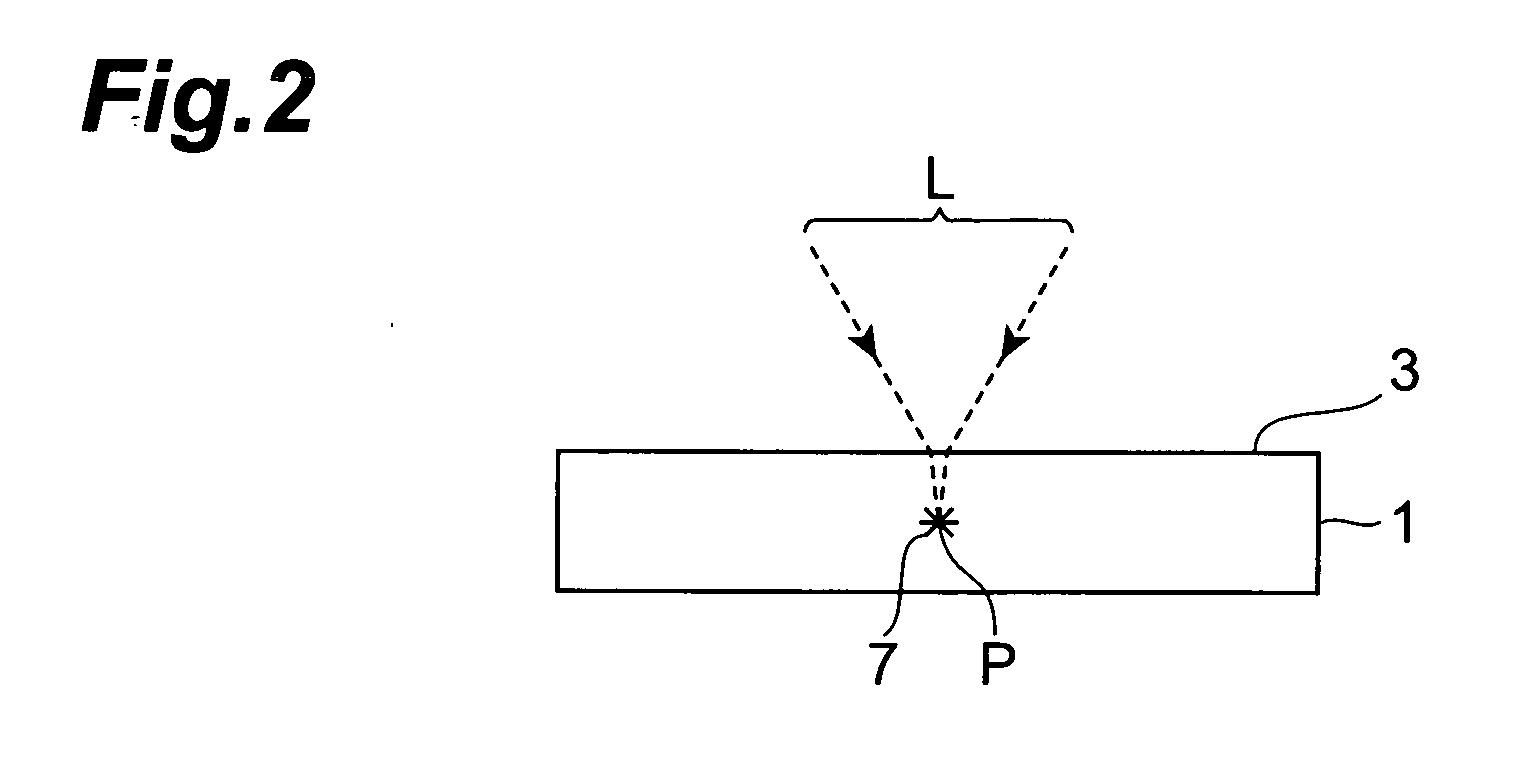
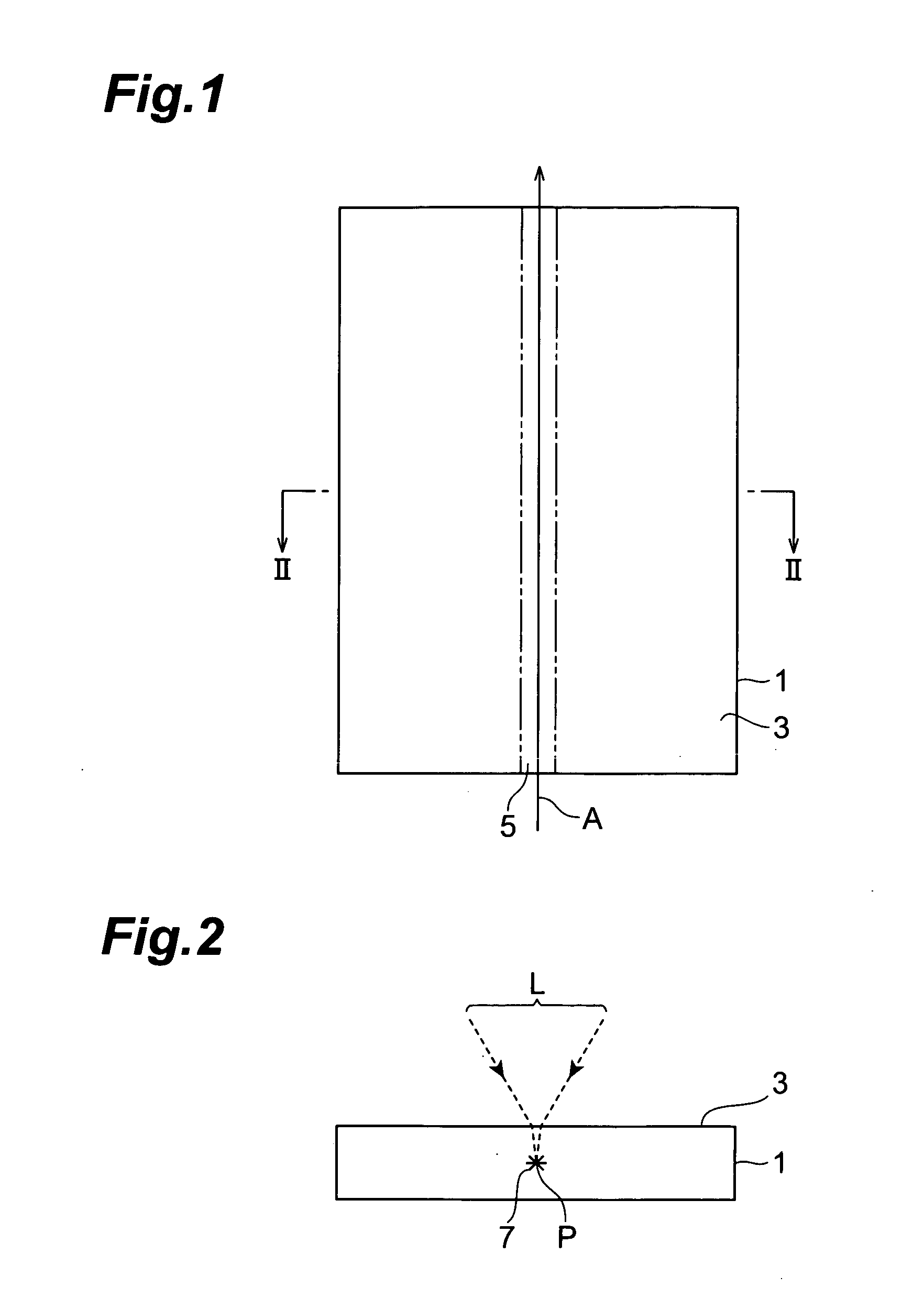
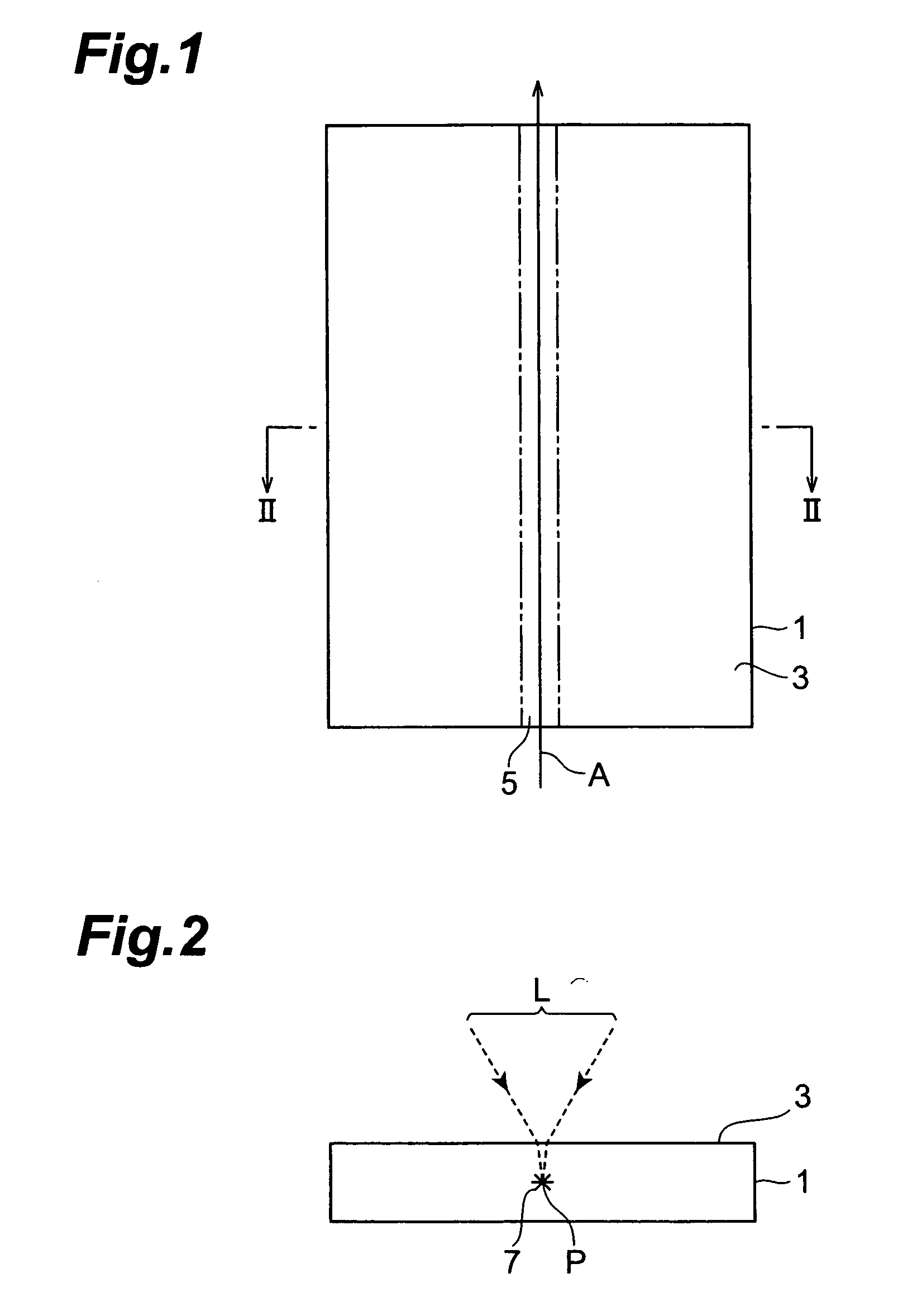
A laser processing method which can highly accurately cut objects to be processed having various laminate structures is provided. An object to be processed comprising a substrate and a laminate part disposed on the front face of the substrate is irradiated with laser light L while a light-converging point P is positioned at least within the substrate, so as to form a modified region due to multiphoton absorption at least within the substrate, and cause the modified region to form a starting point region for cutting. When the object is cut along the starting point region for cutting, the object 1 can be cut with a high accuracy.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Strengthened glass substrate sheets and methods for fabricating glass panels from glass substrate sheets
Owner:CORNING INC
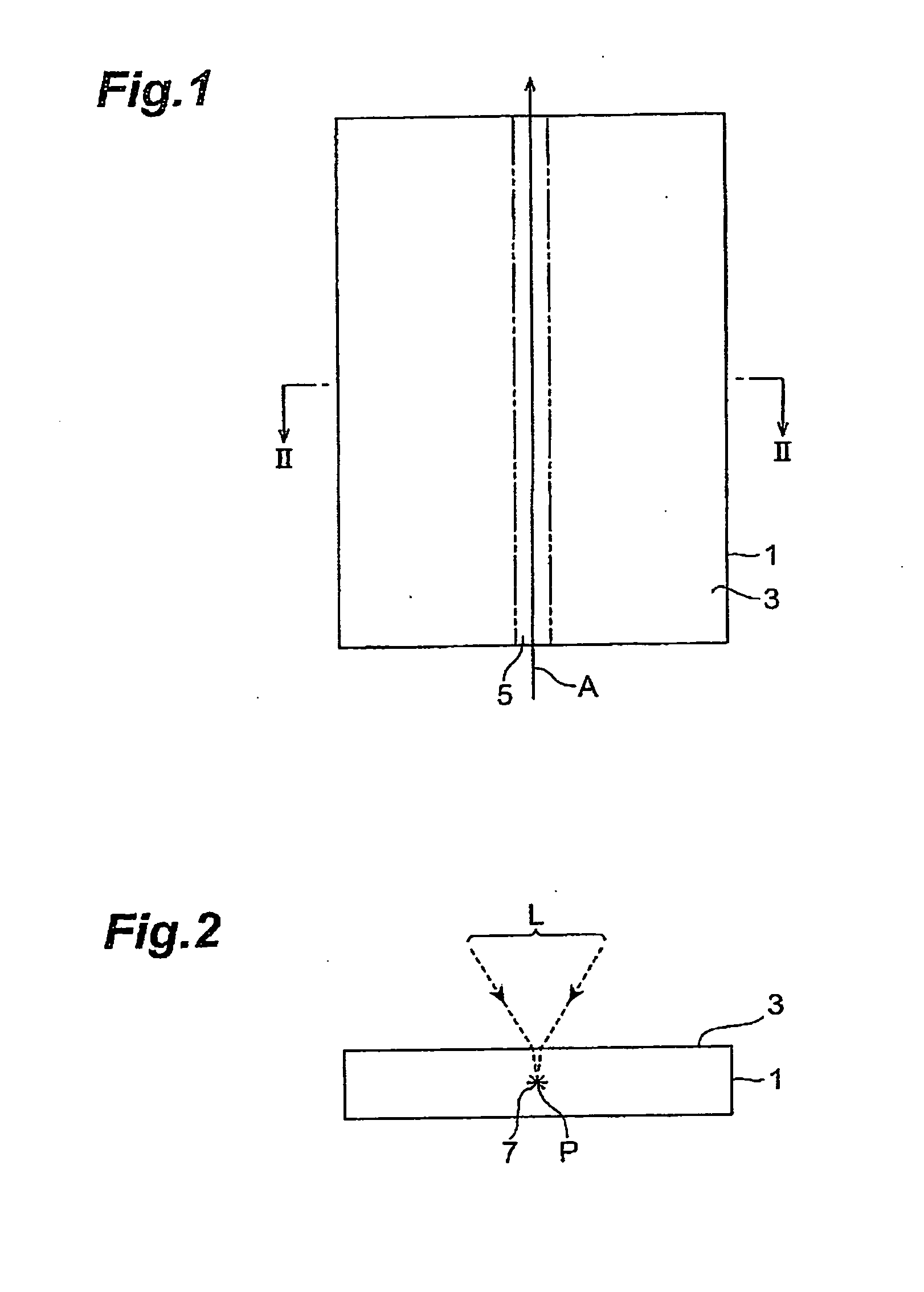
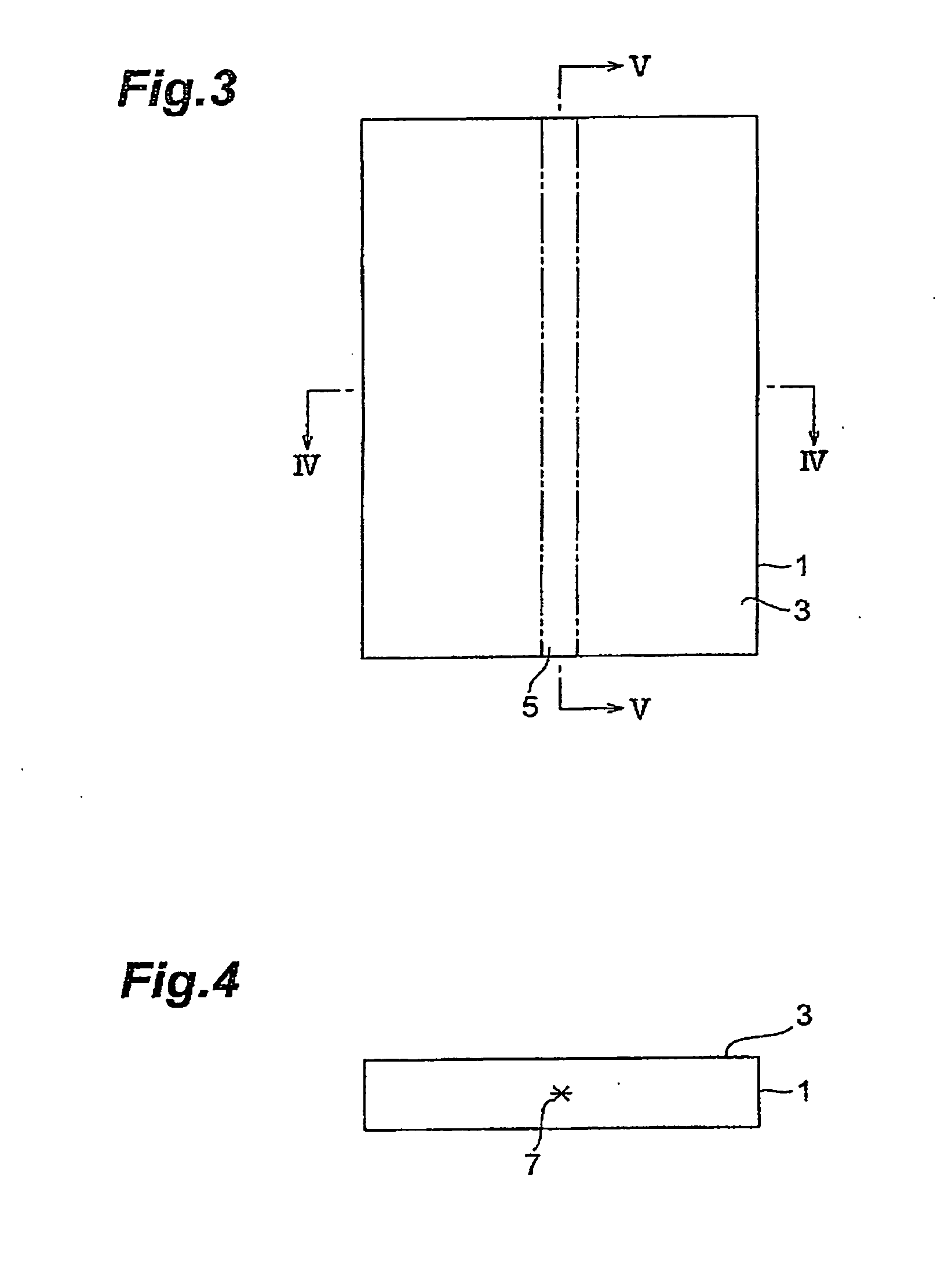
Method of cutting processed object
InactiveUS20060011593A1Precise cuttingPrevent unnecessary fracturesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingClassical mechanicsLaser light
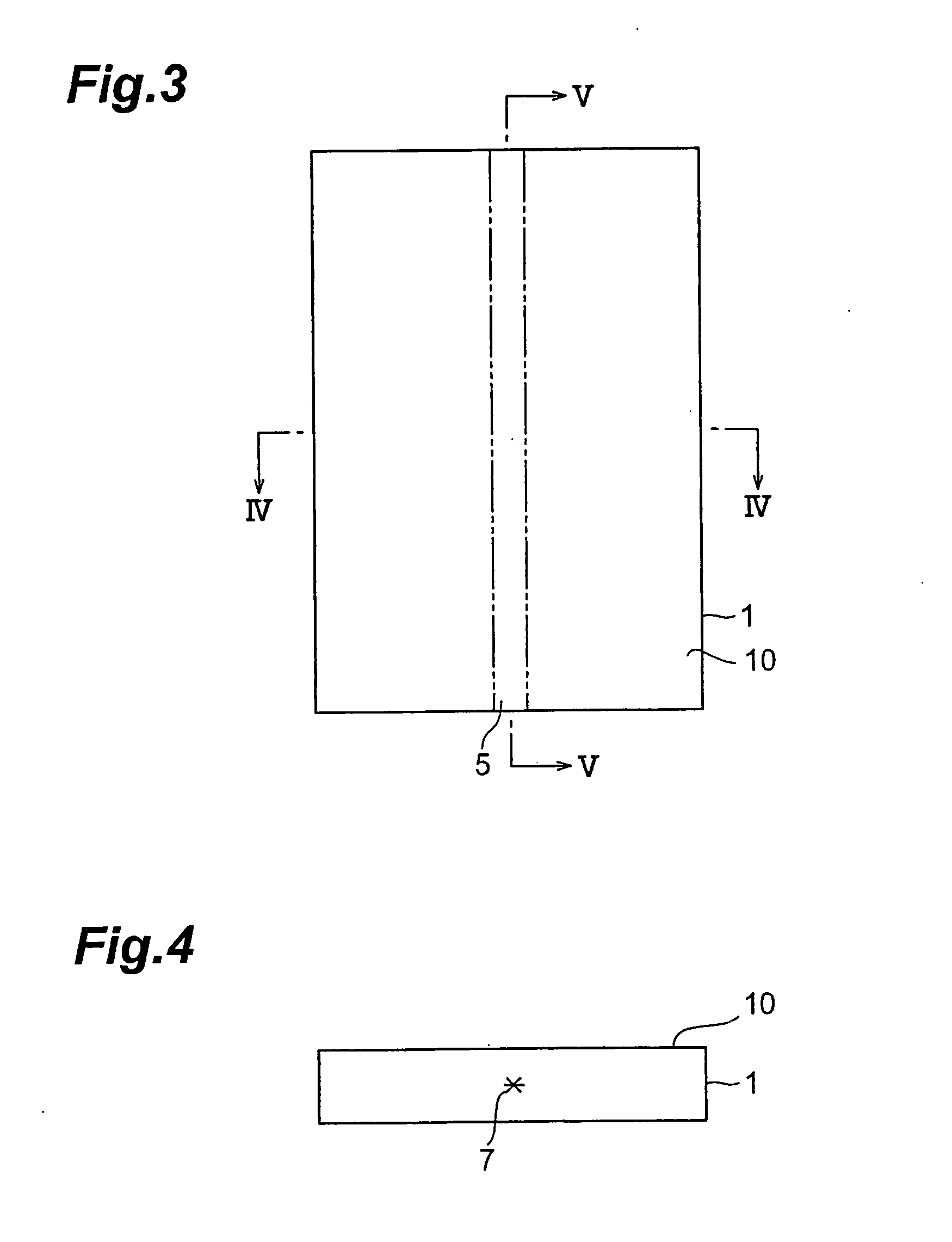
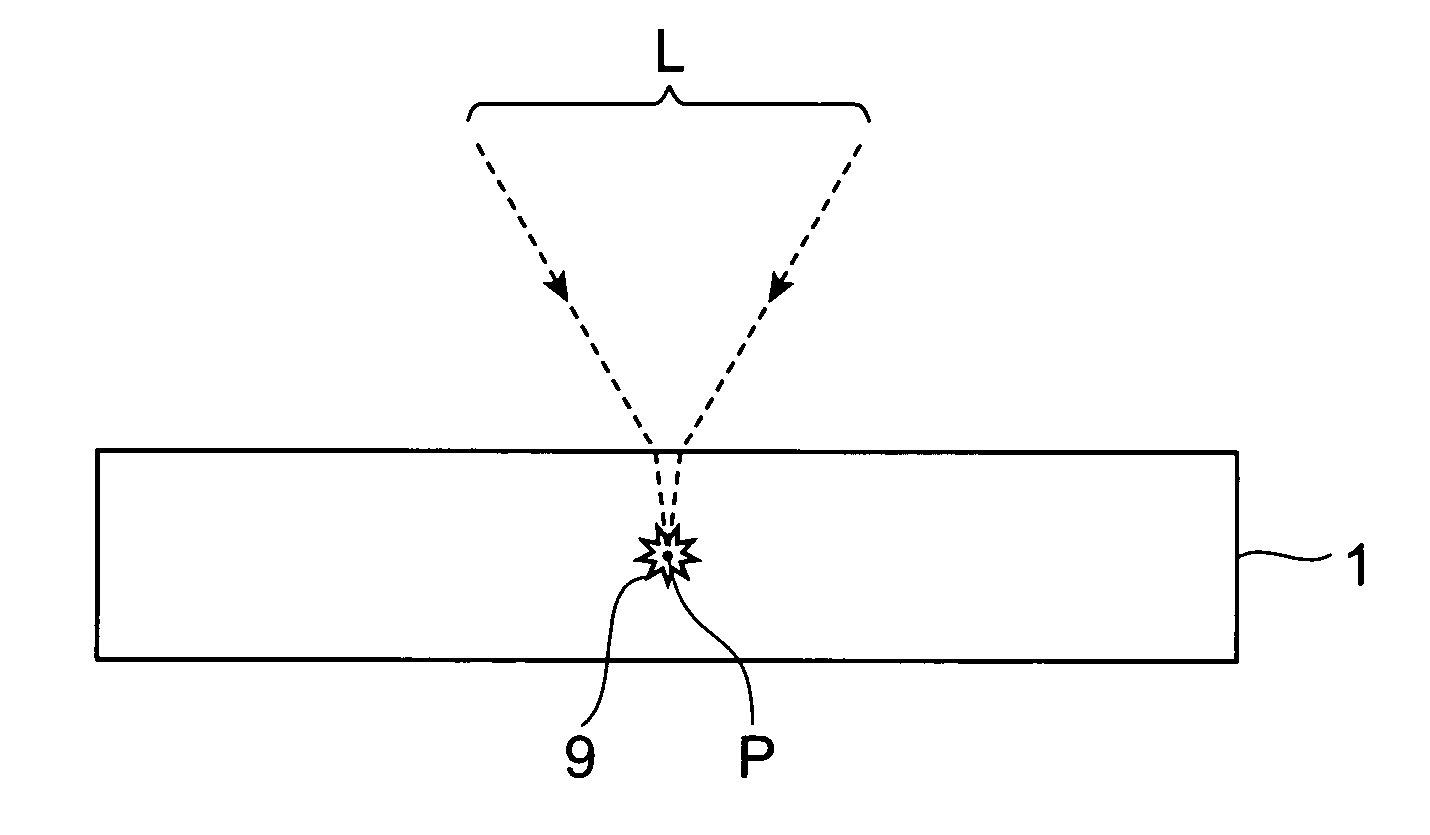
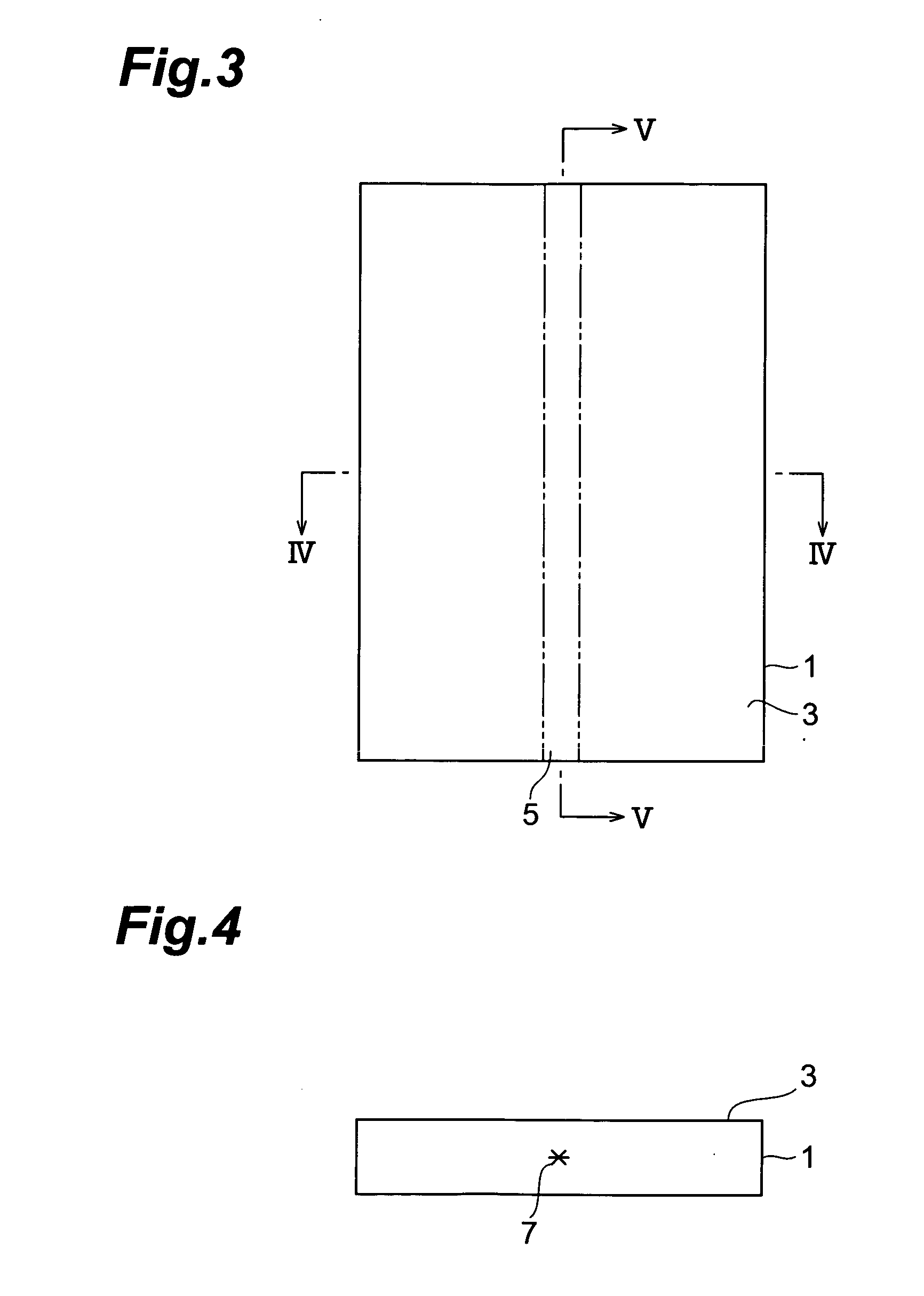
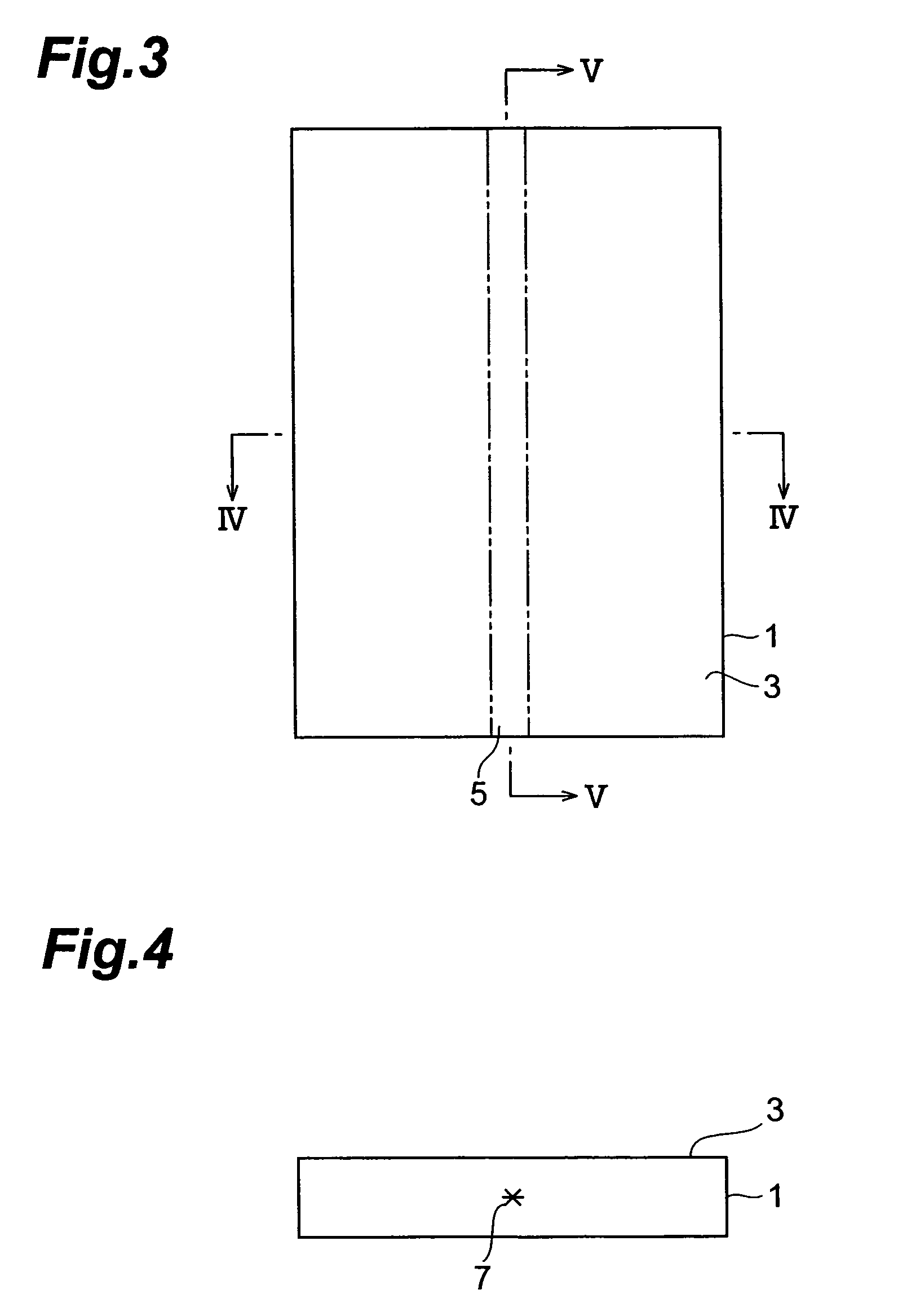
A method of cutting an object which can accurately cut the object is provided. An object to be processed 1 such as a silicon wafer is irradiated with laser light L while a light-converging point P is positioned therewithin, so as to form a modified region 7 due to multiphoton absorption within the object 1, and cause the modified region 7 to form a starting point region for cutting 8 shifted from the center line CL of the thickness of the object 1 toward the front face 3 of the object 1 along a line along which the object should be cut. Subsequently, the object 1 is pressed from the rear face 21 side thereof. This can generate a fracture from the starting point region for cutting 8 acting as a start point, thereby accurately cutting the object 1 along the line along which the object should be cut.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine
InactiveUS6199956B1Sufficient supportLess stressPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesMaximum diameterEngineering
A round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine or the like, having a bit head and a bit shank, wherein the bit head has a bit tip, maintained by a base element in a receptacle of the bit head. Starting at the base element, the bit tip tapers in a direction toward the free end of the bit tip, wherein the base element forms a maximum diameter of the bit tip, and wherein the bit tip has recesses on its outer contour. In order to assure good rotational behavior over the entire length of the operating time, the base element has the recesses on an outer circumference forming the maximum diameter.
Owner:BETEK BERGBAU UND HARTMETALLTECHN KARL HEINZ SIMON
Cutting tool with hardened tip having a tapered base
InactiveUS6739327B2Improved cutting tipReduce harmSlitting machinesFine working devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cutting tool has a centrally located tungsten carbide insert brazed into a seat at the forward end of the tool. The seat has a circular mouth and rearward of the mouth is a frustoconical inner wall. At the bottom of the seat is a transverse surface. A tungsten carbide insert is brazed into the seat and the base of the insert is complementary in shape to the seat. A second annular insert may also be brazed into a complementary shaped annular seat that surrounds the centrally located seat.
Owner:THE SOLLAMI COMPANY
Laser processing method
ActiveUS20070158314A1Reduce manufacturing stepsImprove accuracyFine working devicesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingProcess region
The present invention provides a laser processing method comprising the steps of attaching a protective tape 25 to a front face 3 of a wafer 1a, irradiating a substrate 15 with laser light L while employing a rear face of the wafer 1a as a laser light entrance surface and locating a light-converging point P within the substrate 15 so as to form a molten processed region 13 due to multiphoton absorption, causing the molten processed region 13 to form a cutting start region 8 inside by a predetermined distance from the laser light entrance surface along a line 5 along which the object is intended to be cut in the wafer 1a, attaching an expandable tape 23 to the rear face 21 of the wafer 1a, and expanding the expandable tape 23 so as to separate a plurality of chip parts 24 produced upon cutting the wafer 1a from the cutting start region 8 acting as a start point from each other.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
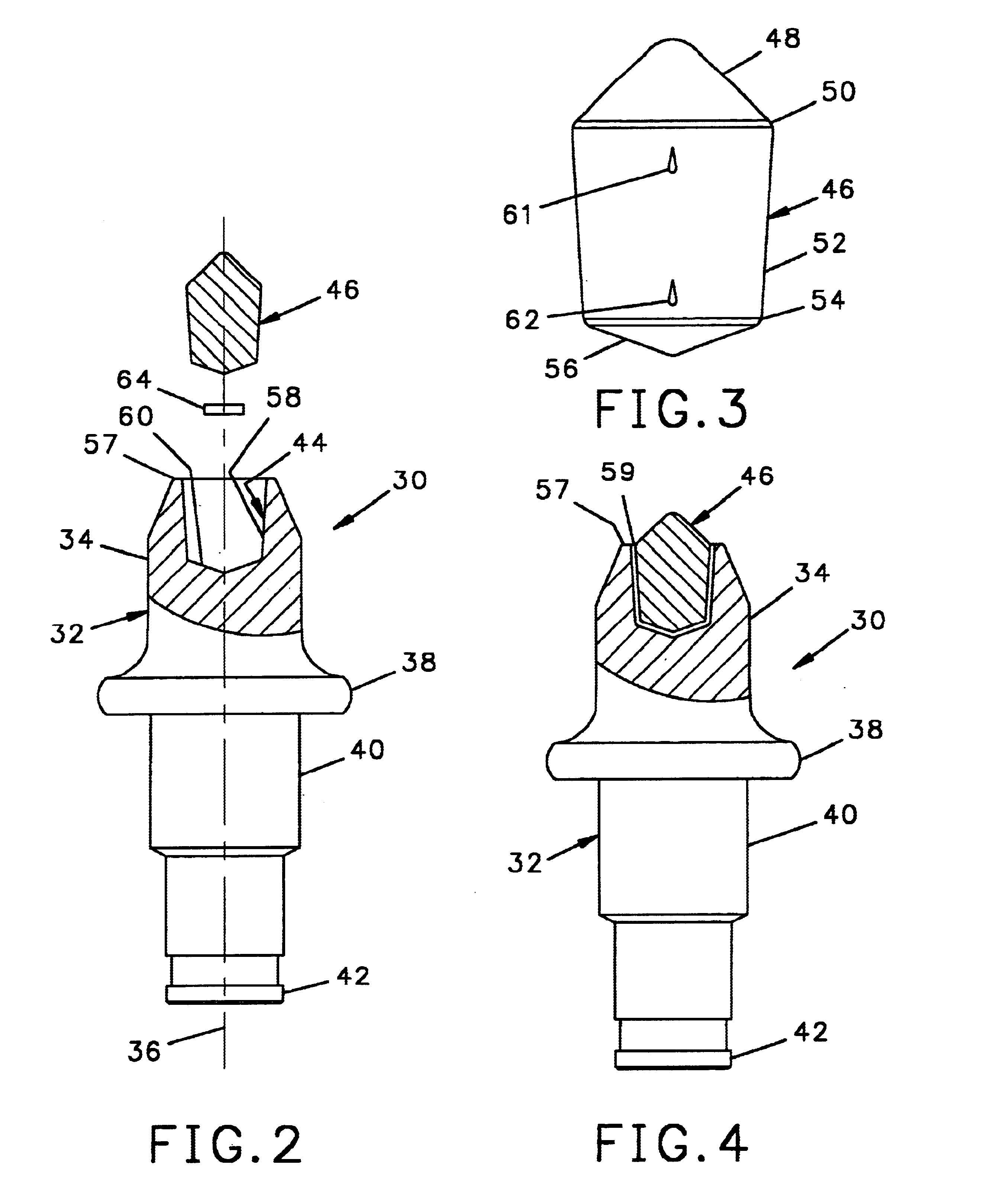
Rotary cutting bit with material-deflecting ledge
InactiveUS7204560B2Prolong lifeEasy to manufactureSlitting machinesRoads maintainenceBiomedical engineeringDrill bit
A cutting bit includes a body having a front surface and a side surface, the side surface including a shoulder below the front surface and extending substantially perpendicular to a central axis of the body, and a ring that is harder than the body attached to the body at a front surface of the shoulder. Wear life of the cutting bit is enhanced by maintaining particular dimensional relationships regarding the position of the ring on the body, and the diameter of portions of the body.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
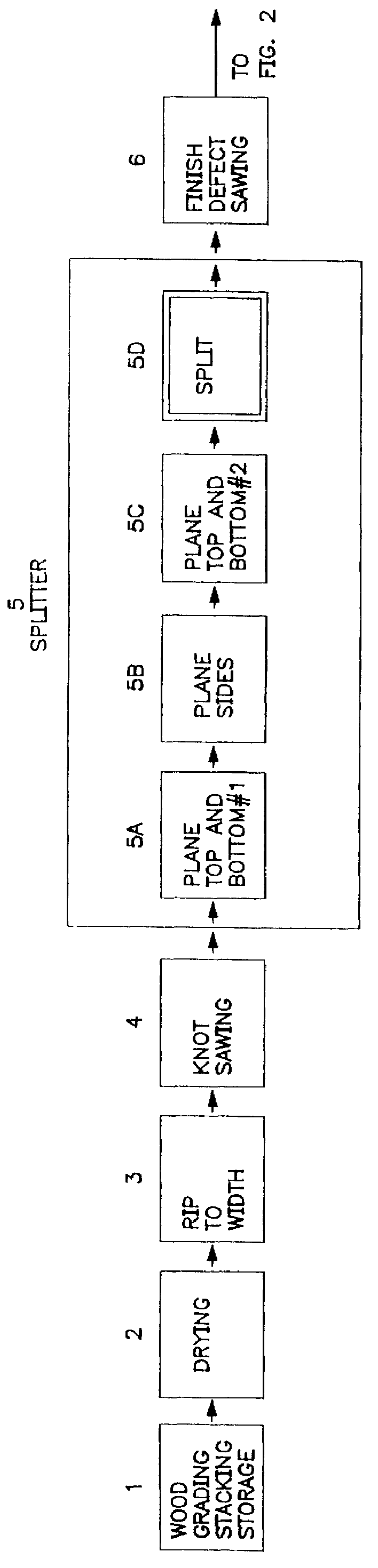
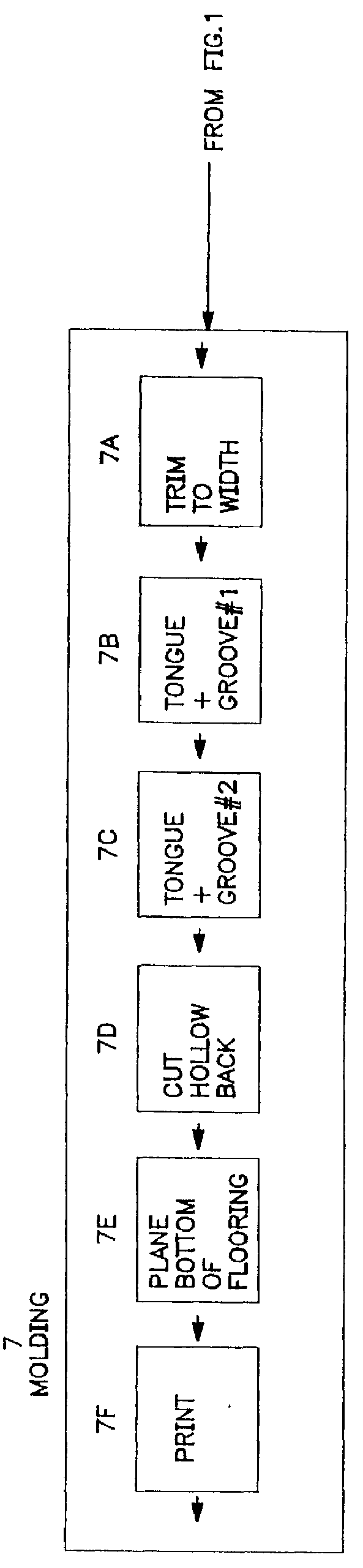
Low profile hardwood flooring strip and method of manufacture
InactiveUS6148884AConsiderable quantityImprove rigidityDovetailed workMulti-purpose machinesCircular sawTongue and groove
A method of producing a hardwood flooring product, including the steps of processing a strip of raw wood into a blank having a predetermined thickness and width, and top and bottom surfaces defining parallel planes relative to each other, and splitting the blank along the width of the blank from one side to the other to form two low profile flooring strips having the same width as the blank and a thickness less than one-half the thickness of the blank. The splitting step includes the steps of providing first and second circular saw blades mounted on spaced-apart vertical axes for rotation in a single plane intermediate and parallel to the planes of the top and bottom surfaces of the blank and positioning the blank on conveying means upstream from the saw blades with the plane of rotation of the saw blades intermediate and parallel to the planes of the top and bottom surfaces of the blank for movement of the blank from an upstream position to a downstream position relative to the saw blades. The blank is moved downstream into the plane of rotation of the saw blades during rotation of the saw blades thereby horizontally splitting the blank to form first and second low-profile flooring strips. Interlocking members, such as molded, mating tongue and groove members, are molded into first and second longitudinally-extending side edges of the flooring strips for securing together the flooring strips when placed side-to-side to form a floor.
Owner:ARMSTRONG HARDWOOD FLOORING CO +2
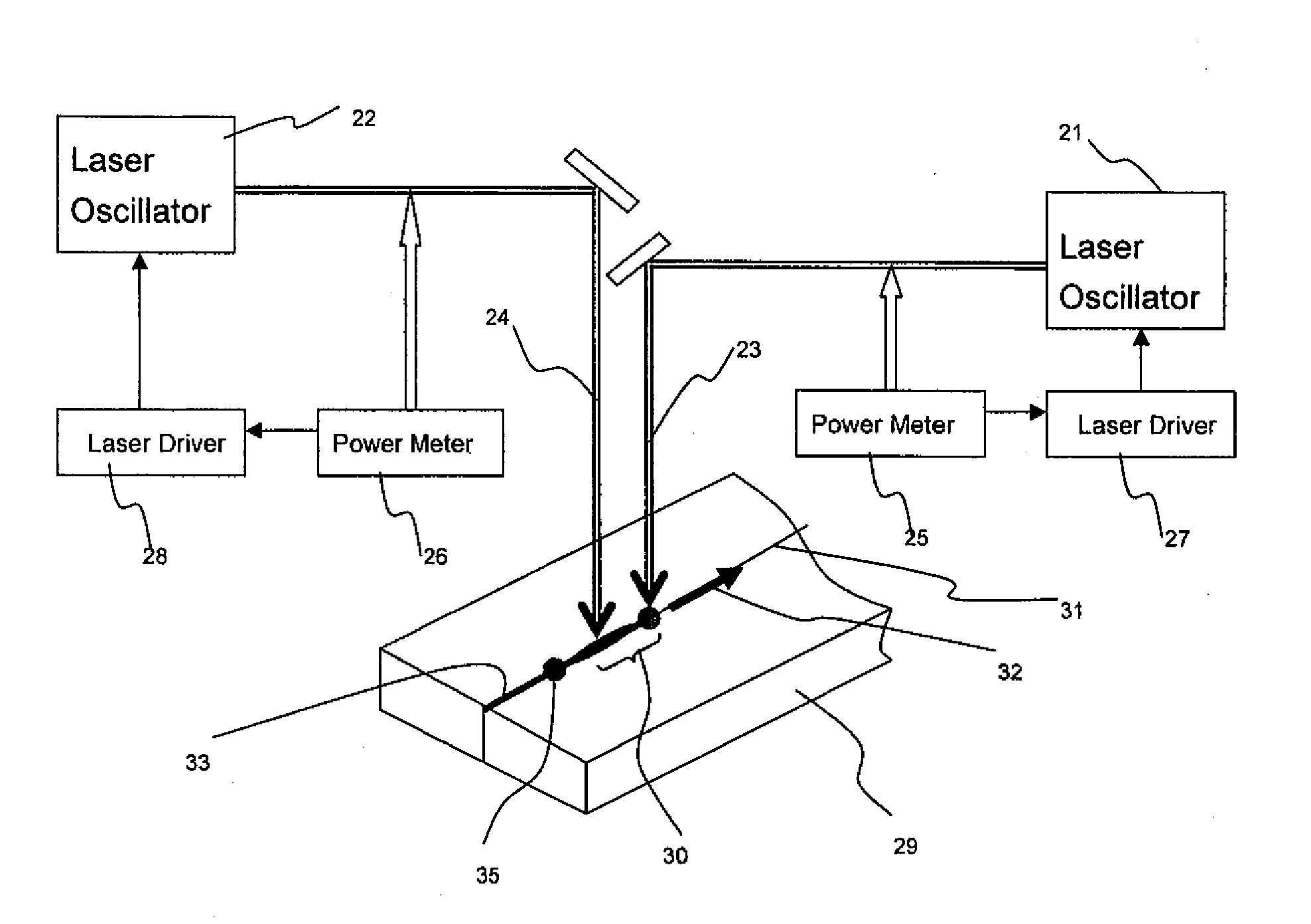
Device and method for laser processing
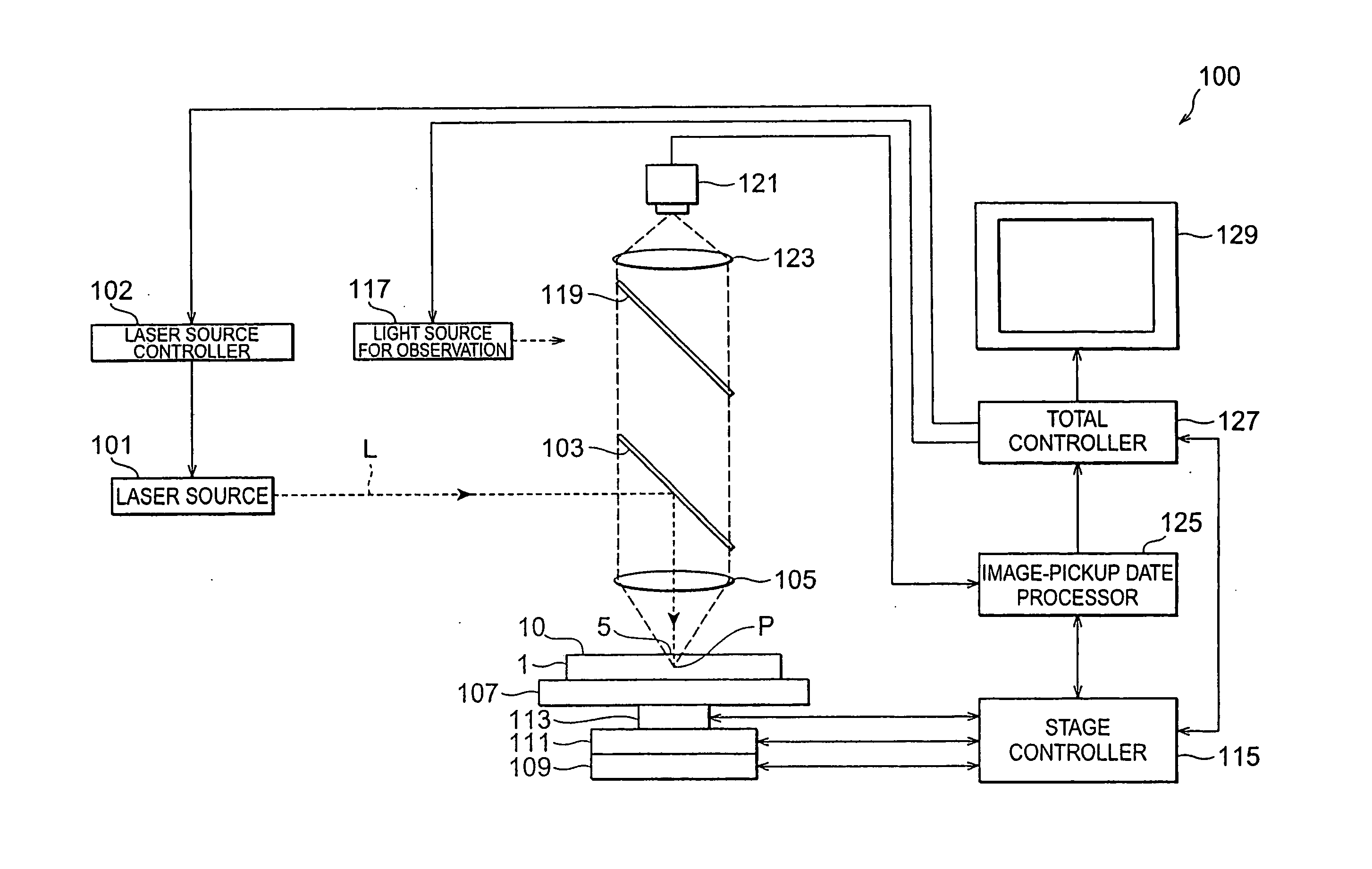
InactiveUS20060144828A1Prevent movementImprove accuracyLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser processingLaser light
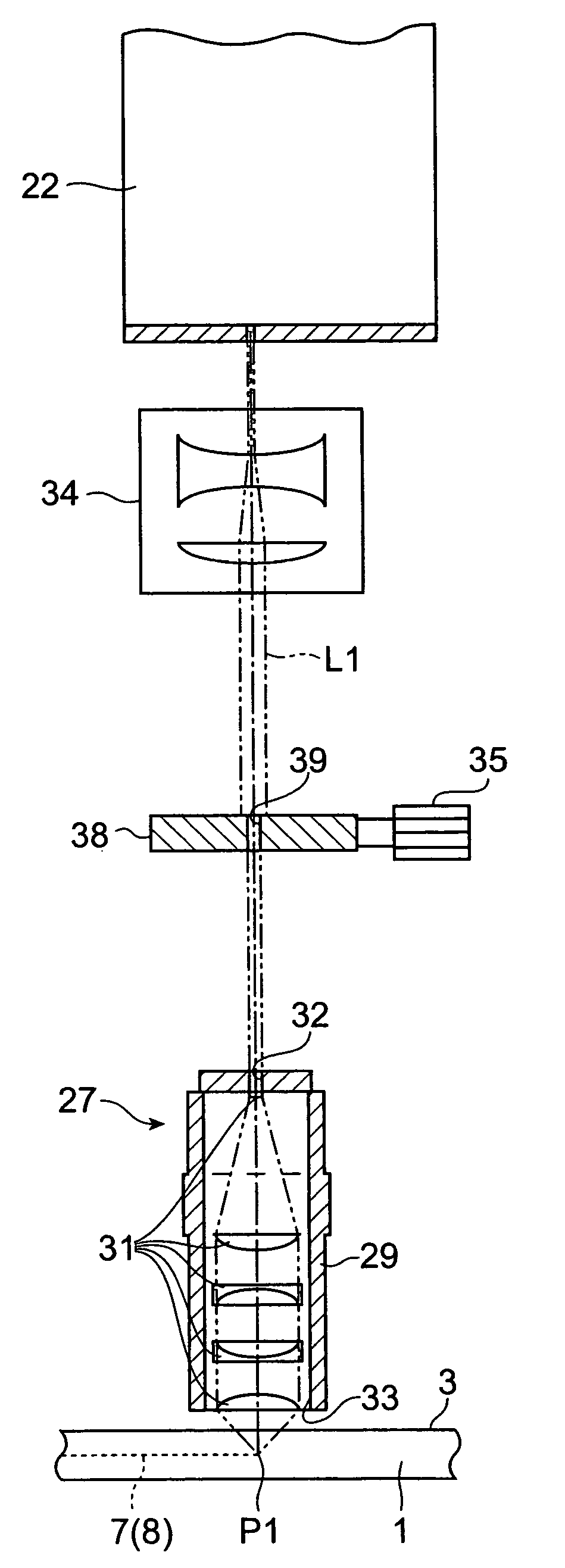
A laser processing apparatus and a laser processing method which can accurately converge processing laser light at a predetermined position are provided. In the laser processing apparatus, a condenser lens 31 converges processing laser light L1 and rangefinding laser light L2 onto an object to be processed 1 on the same axis. Here, light-converging point position control means40 detects reflected light L3 of the rangefinding laser light reflected by the front face 3 of the object 1, and places a light-converging point P1 of the processing laser light L1 at a predetermined position. Since the processing by the processing laser light L1 and the measurement of displacement of the front face 3 by the rangefinding laser light L2 are carried out on the same axis as such, the light-converging point P1 of processing laser light L1 can be prevented from shifting from the predetermined position because of vibrations of the stage 21 and the like. Therefore, the processing laser light L1 can accurately be converged at the predetermined position.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Laser beam processing machine
ActiveUS6998571B2Welding/cutting auxillary devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTectorial membraneLaser beam machining
A laser beam processing machine comprising a chuck table for holding a workpiece and a laser beam application means for applying a laser beam to the workpiece held on the chuck table, wherein the machine further comprises a protective film forming means for forming a protective film on the to-be-processed surface of the workpiece before laser beam processing.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Methods and apparatus relating to singulating semiconductor wafers and wafer scale assemblies
ActiveUS20050202651A1Increase distanceAvoid excessive widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Methods relating to the singulation of dice from semiconductor wafers. Trenches or channels are formed in the bottom surface of a semiconductor wafer, corresponding in location to the wafer streets. The trenches may be formed by etching or through an initial laser cut. The wafer is then singulated along the streets with a laser preferably having a beam narrower than the trenches. Multiple, laterally spaced lasers may be used in combination during a single pass to perform simultaneous singulating cuts. Additional edge protection for integrated circuitry on the active surface of the semiconductor dice may be provided by forming trenches or channels along the streets in the active surface instead of the bottom surface, disposing protective material along the streets and within the trenches prior to singulation and cutting through the wafer, leaving protective material on the sidewalls of the channels.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Laser cutting apparatus and method
The present invention disclose a laser cutter for cutting an object being cut such as a two glasses-attached panel for LCD using a laser beam. The laser cutter includes a laser unit for irradiating a laser beam with a specific wavelength along a marked cutting line of the object, a pre-scriber for forming a pre-cut groove at starting edge of the marked cutting line, and a cooling unit for cooling the cutting line which said laser beam has been irradiated.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Brazed diamond tools and methods for making the same
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Laser processing device
ActiveUS7489454B2Suppress positional fluctuationReduce lightLaser detailsFine working devicesBeam expanderLaser processing
A laser processing apparatus which can suppress the positional fluctuation in light-converging point of laser light during laser processing is provided. On an optical path of laser light L1 connecting a beam expander 34 and a first light-transmitting hole 32 of a lens holder 29 to each other in a laser processing apparatus 20, a stop member 38 including a second light-transmitting hole 39 having the same diameter as that of the first light-transmitting hole 32 is disposed. Hence, the amount of laser light L1 cut by the surrounding part of the first light-transmitting hole 32 can substantially be eliminated, whereby the lens holder 29 can be prevented from being heated upon irradiation with the laser light L1. Also, even when the stop member 38 is heated by the laser light L1 cut by the surrounding part of the second light-transmitting hole 39, heat is prevented from being transmitted from the stop member 38 to the lens holder 29, since the stop member 38 is separated from the lens holder 29. Therefore, the positional fluctuation in light-converging point P1 of the laser light L1 during laser processing can be suppressed to a low level.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
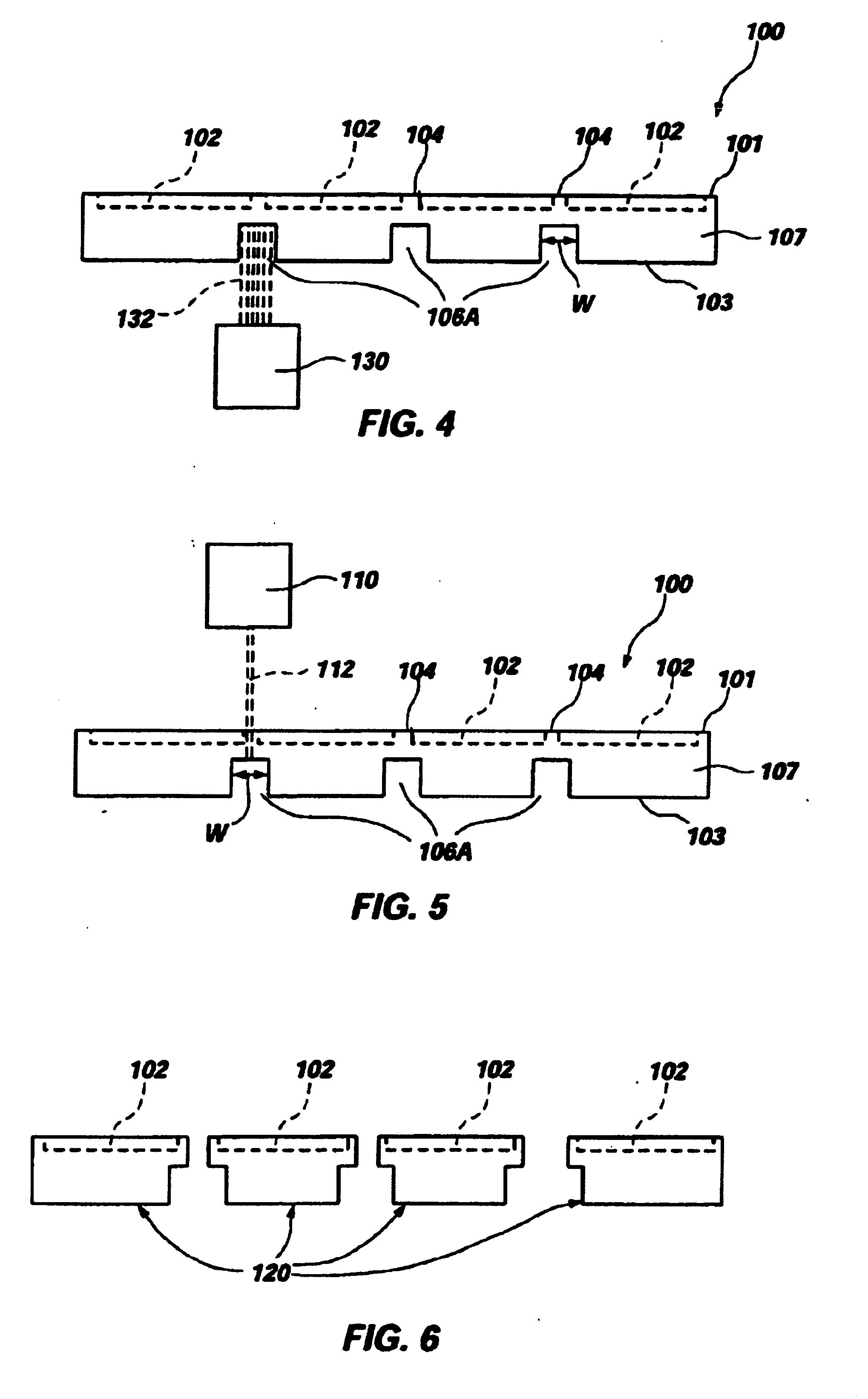
Solar Cell (Sliver) Sub-Module Formation
InactiveUS20080223429A1Provide mechanical stabilityAvoid damageLine/current collector detailsPV power plantsWaferingElectrical battery
A solar cell sub-module (100) for a photovoltaic device, including a plurality of elongate solar cells (slivers) (101) mounted in a structure that maintains the elongate solar cells in a longitudinally parallel and generally coplanar configuration, the structure providing one or more conductive pathways (201) electrically interconnecting the elongate solar cells (101). Also claimed are inventions related to releasing elongate substrate from a wafer frame; providing a plurality of mutually spaced elongate storage bins with a particular spacing; dispensing elongate solar cells into an alignment jig and attaching the cells to a substrate; engaging a length of electrical interconnect with an engagement tool having spaced engagement sections and applying a cutting tool; forming an electrical connection in a photovoltaic module with a conductor defining an indirect path between locations to compensate for thermal expansion; maintaining the solar cell orientation of sliver solar cells when releasing them from a wafer frame; engaging only opposing faces of elongate substrates, interconnected by a wafer frame, when releasing them; storing elongate substrate in a stacked configuration with a translation mechanism.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
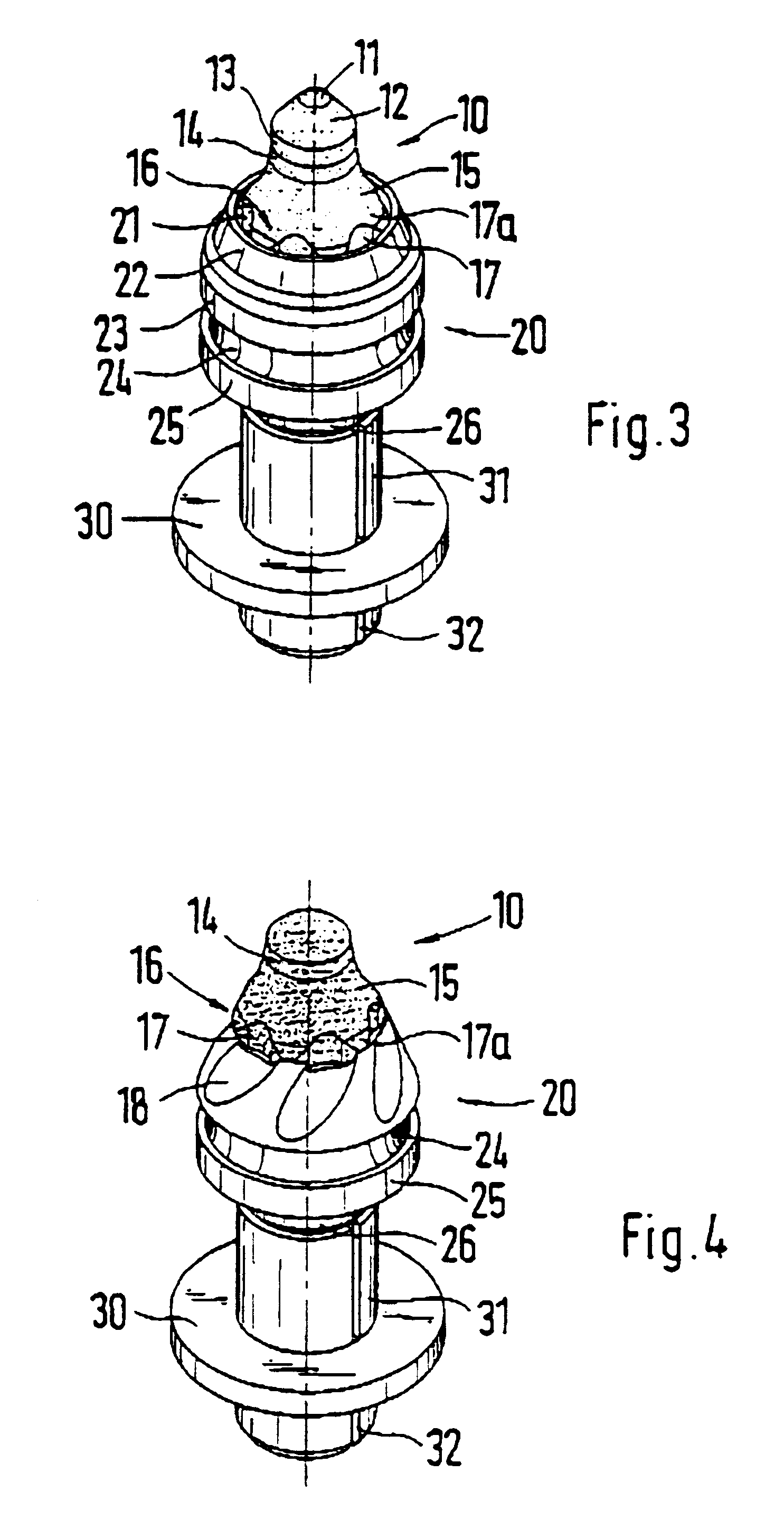
Fixture for a round shank chisel having a wearing protection disk
A fixture for attaching a round shank chisel to a road milling machine or the like. The round shank chisel has a chisel head and a chisel shank. With a bearing surface the chisel head rests upon a wearing protection disk which in turn rests on and is supported by a chisel holder. The chisel shank is accommodated by a location bore of the chisel holder. This invention prevents dirt from penetrating the area of the location bore of such a fixture and at the same time ensures that the free movability of the round shank chisel is not impaired. Thus, the chisel holder has a circumferential projection or a circumferential depression which extends along the location bore. Also, the wearing protection disk has a circumferential receiving groove or a circumferential shoulder and the projection or the depression of the chisel holder engages with the receiving groove or the depression of the wearing protection disk when the round shank chisel is assembled.
Owner:BETEK BERGBAU UND HARTMETALLTECHN KARL HEINZ SIMON
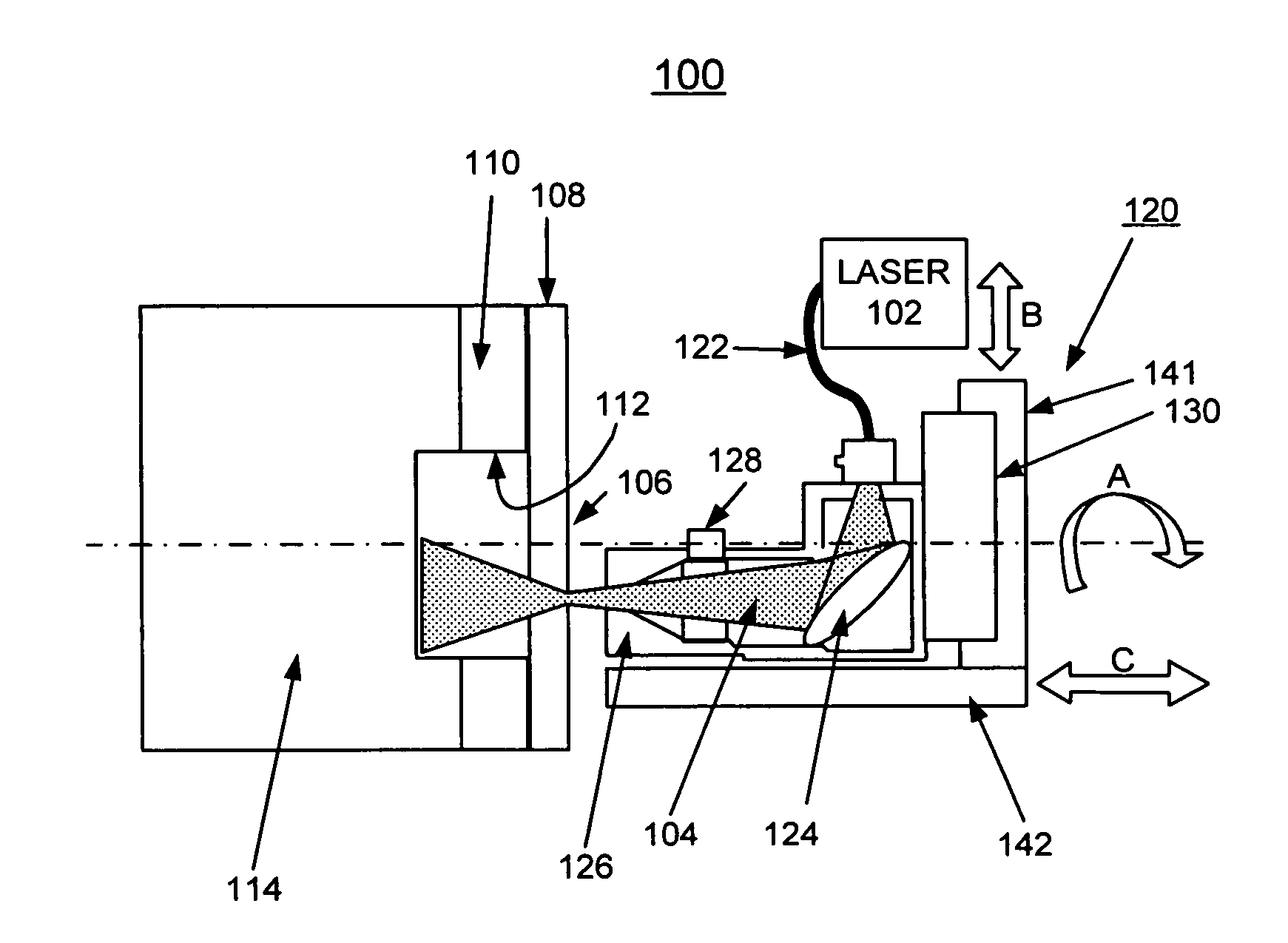
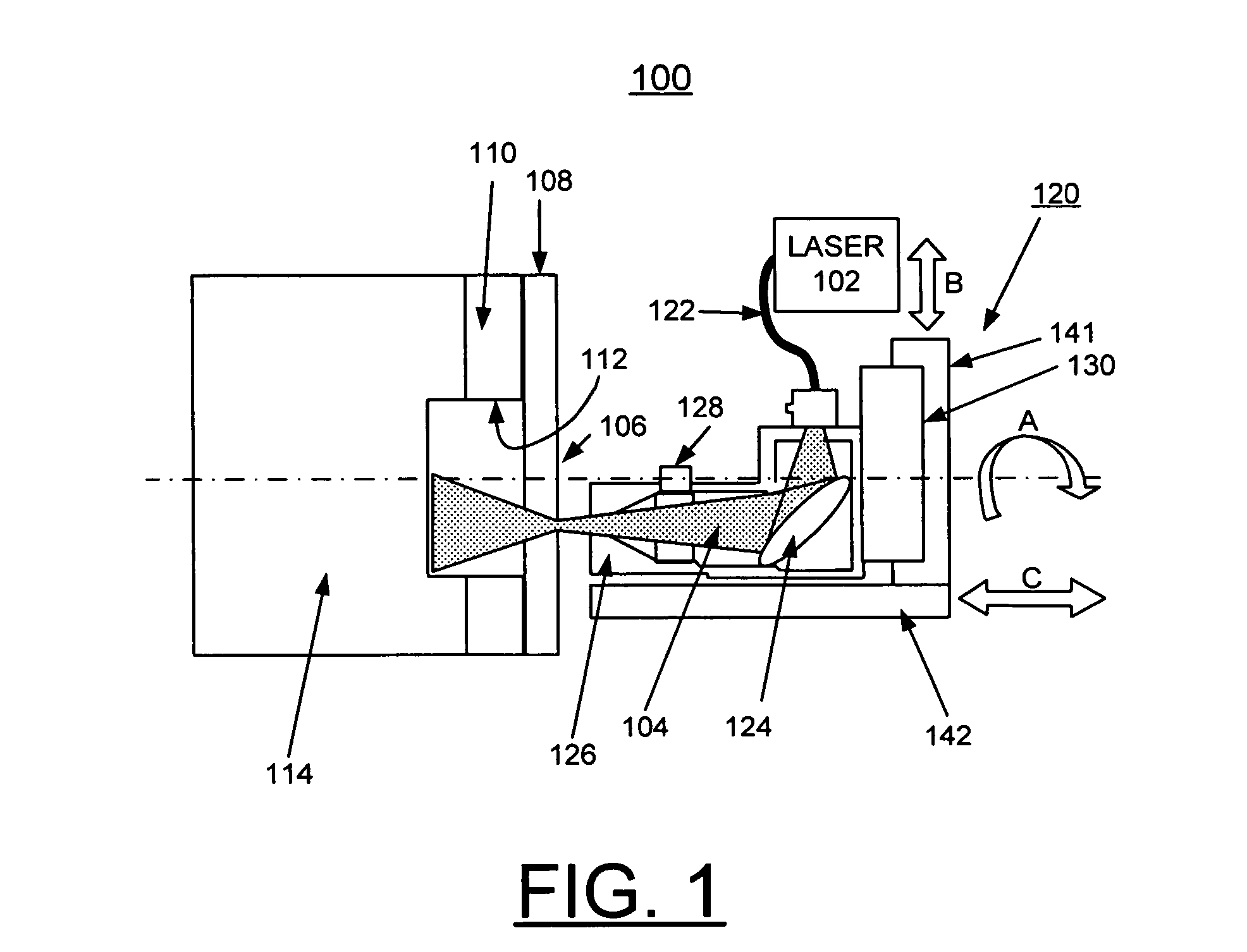
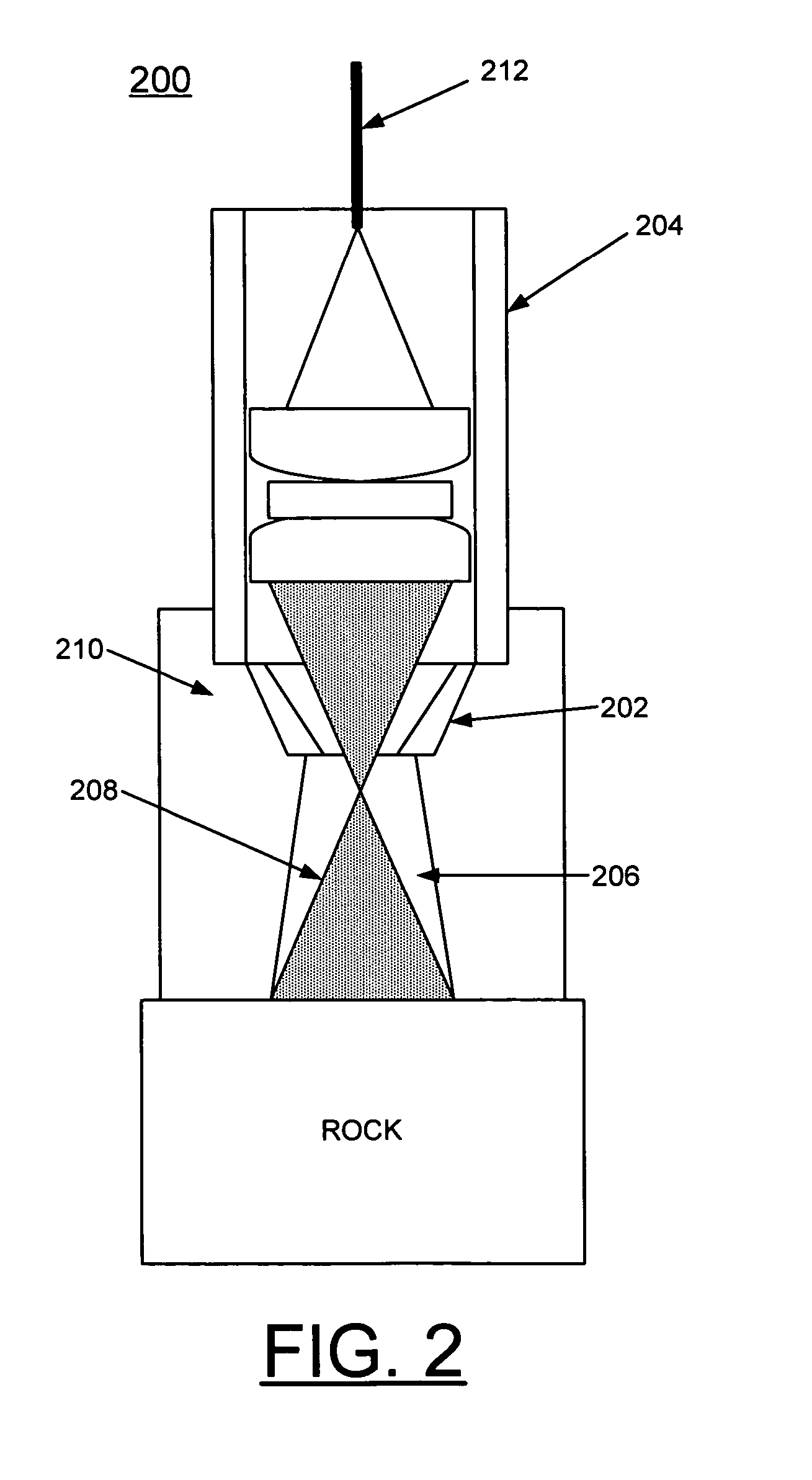
Methods of using a laser to perforate composite structures of steel casing, cement and rocks
ActiveUS20060231257A1Improve breathabilityReduce hole taperingDisloding machinesThermal drillingHigh power lasersSmall fragment
Apparatus and methods of using lasers are provided for the perforation of oil and gas well casings and rock formations. A rock removal process called laser spallation is provided that utilizes a combination of laser-induced thermal stress and laser induced superheated steam explosions just below the surface of the laser / rock interaction to spall or fracture the rock into small fragments that can then be easily removed from the rock formation. The use of high power laser beams of kilowatt level is provided to rapidly cut the steel casings and perforate into the formation. Techniques of the invention increase permeability and reduce hole tapering while perforating a deep hole in reservoir rock formations.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Superabrasive wire saw and associated methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6915796B2Improving particle retentionHigh material removal ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesWire rodAlloy
A superabrasive wire saw having a plurality of individual coated superabrasive particles attached to a wire with an organic binder is disclosed and described. The superabrasive particle can be coated with a solidified coating of a molten braze alloy that is chemically bonded to the superabrasive particle. The organic binder can optionally contain filler materials and / or an organometallic coupling agent to improve the retention of coated superabrasive particles. The resulting superabrasive wire saws can be produced having diameters of less than 0.5 mm which significantly reduce kerf loss. Various methods for making and using such a superabrasive wire saw are additionally disclosed and described.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Laser cutting apparatus and method
The present invention disclose a laser cutter for cutting an object being cut such as a two glasses-attached panel for LCD using a laser beam. The laser cutter includes a laser unit for irradiating a laser beam with a specific wavelength along a marked cutting line of the object, a pre-scriber for forming a pre-cut groove at starting edge of the marked cutting line, and a cooling unit for cooling the cutting line which said laser beam has been irradiated.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Reciprocating wire saw for cutting hard materials
InactiveUS7089925B1Low costIncrease valueBelt grinding machinesMetal sawing toolsEngineeringWire saw
The present invention features a reciprocating wire saw particularly adapted or configured for cutting hard materials. In one aspect, the reciprocating wire saw comprises (a) a flexible wire; (b) a plurality of cutting segments fittable onto the flexible wire, wherein each of the cutting segments comprises an outer surface; and a (c) plurality of superabrasive particles braze bonded onto the outer surface of the cutting segments to form a cutting wire. In another aspect, the reciprocating wire saw comprises a plurality of superabrasive particles braze bonded directly to the wire itself to form a cutting wire. The cutting wire is unique in that it comprises a pre-determined superabrasive particle concentration and is configured to cut various materials, such as granite, in a reciprocating manner.
Owner:KINIK
Cutting machine with built-in miter cutting feature
A miter cutting arrangement for a cutting machine is provided to accommodate cutting work at an angle or a bevel for precisely cutting on a work piece. It includes a platform support arm longitudinally mounting to a cutting head support bracket, a platform pivot arm transversely extended from the platform support arm, a head platform pivotally connected with the platform pivot arm to support a motor, a miter supporting unit, and a locker device for selectively locking the cutting head at the normal position and the slanted position. The miter supporting unit includes a miter support provided at an outer side of the head platform and a miter stopper provided at an outer end of the platform pivot arm to block the miter support when the head platform is rotated at the slanted position.
Owner:LEE WY PERON
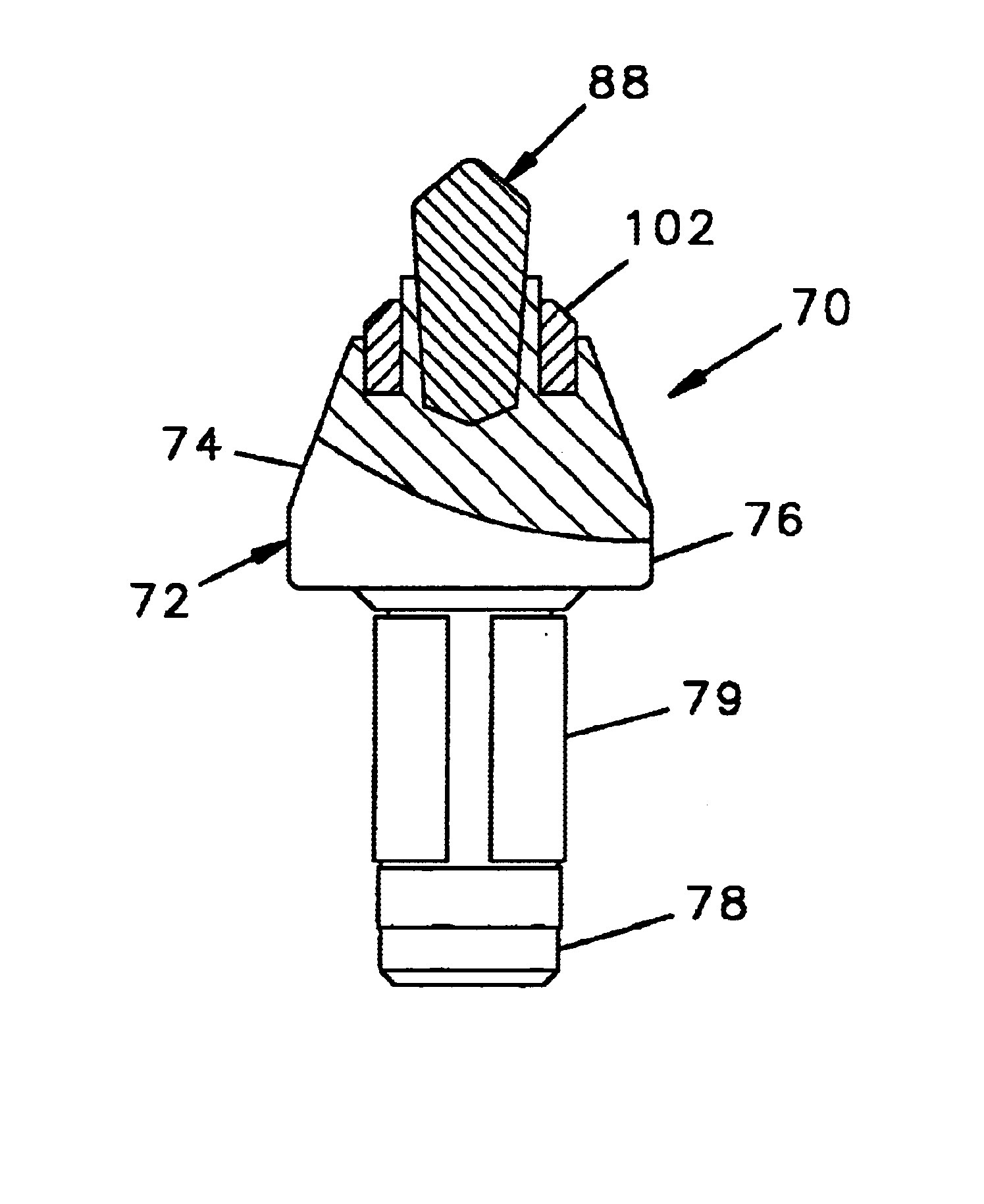
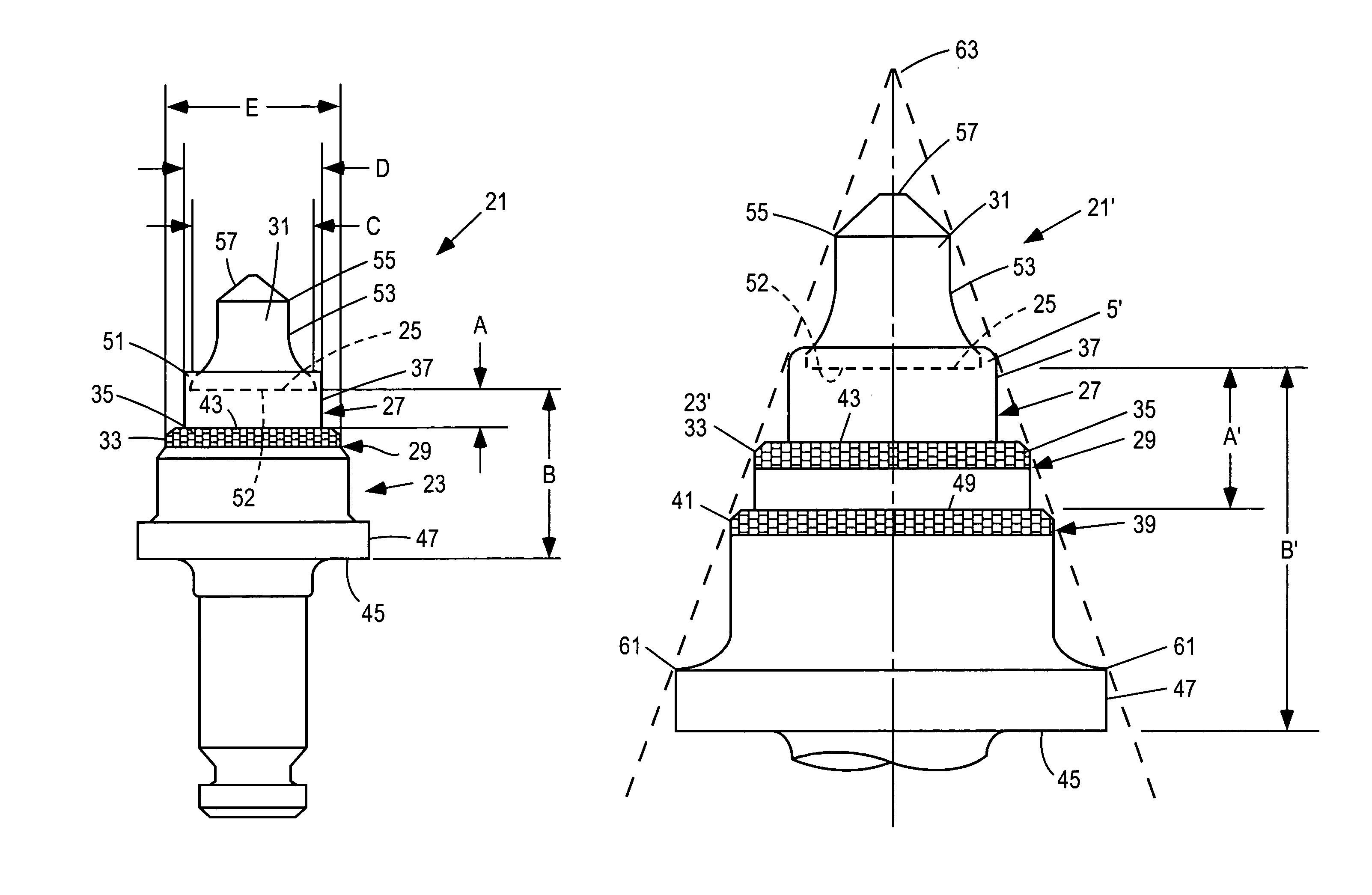
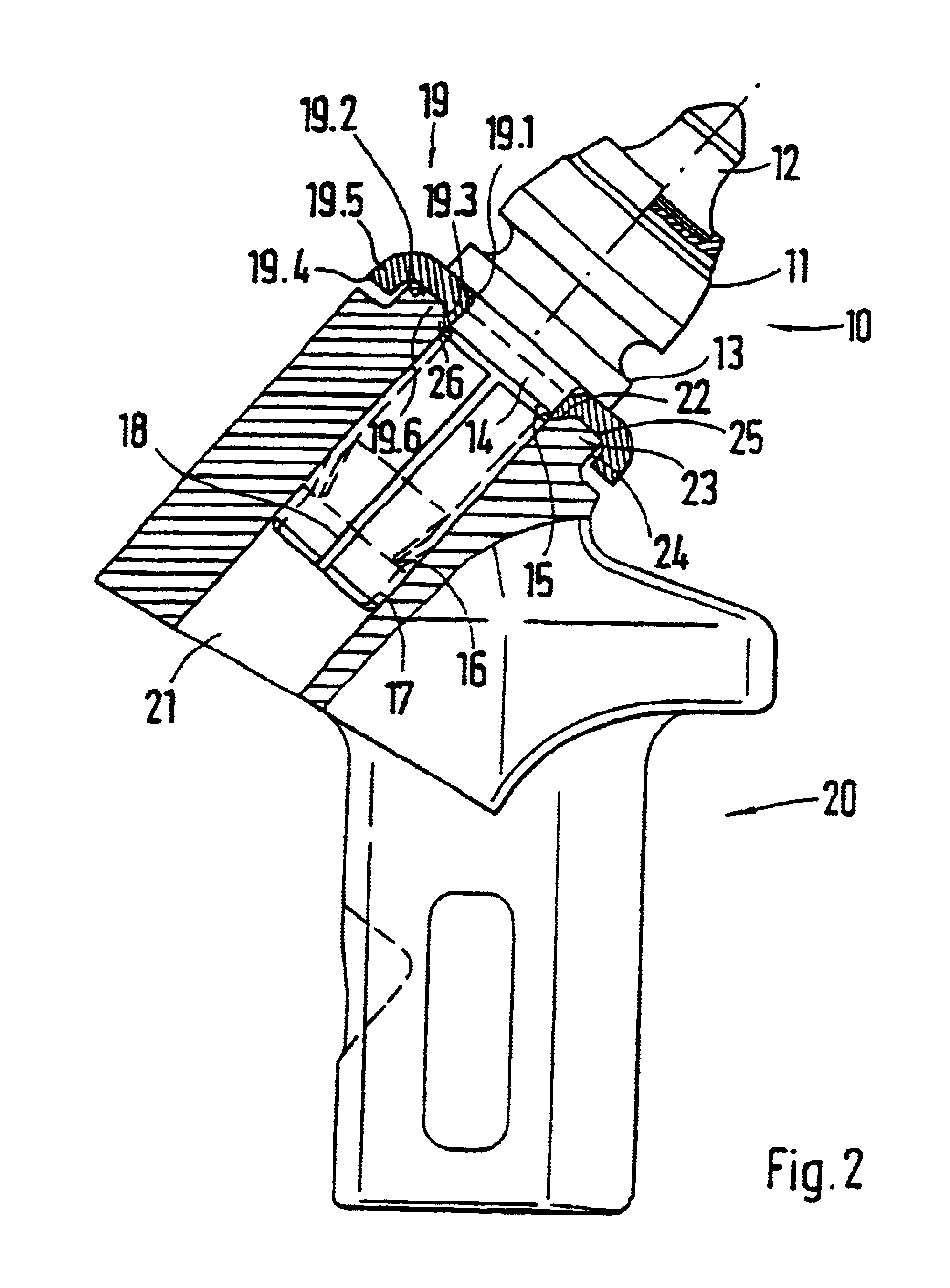
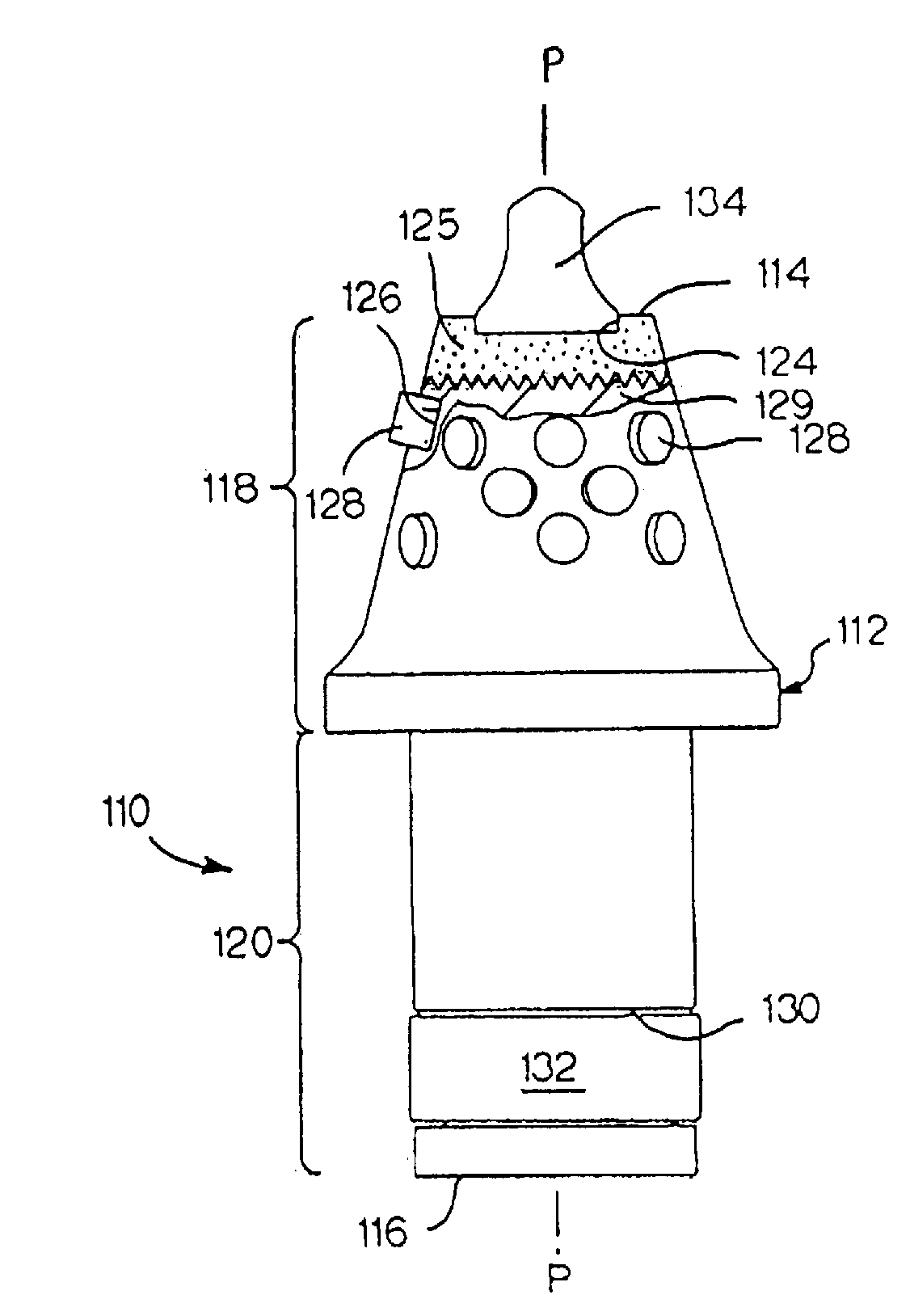
Reverse taper cutting tip with a collar
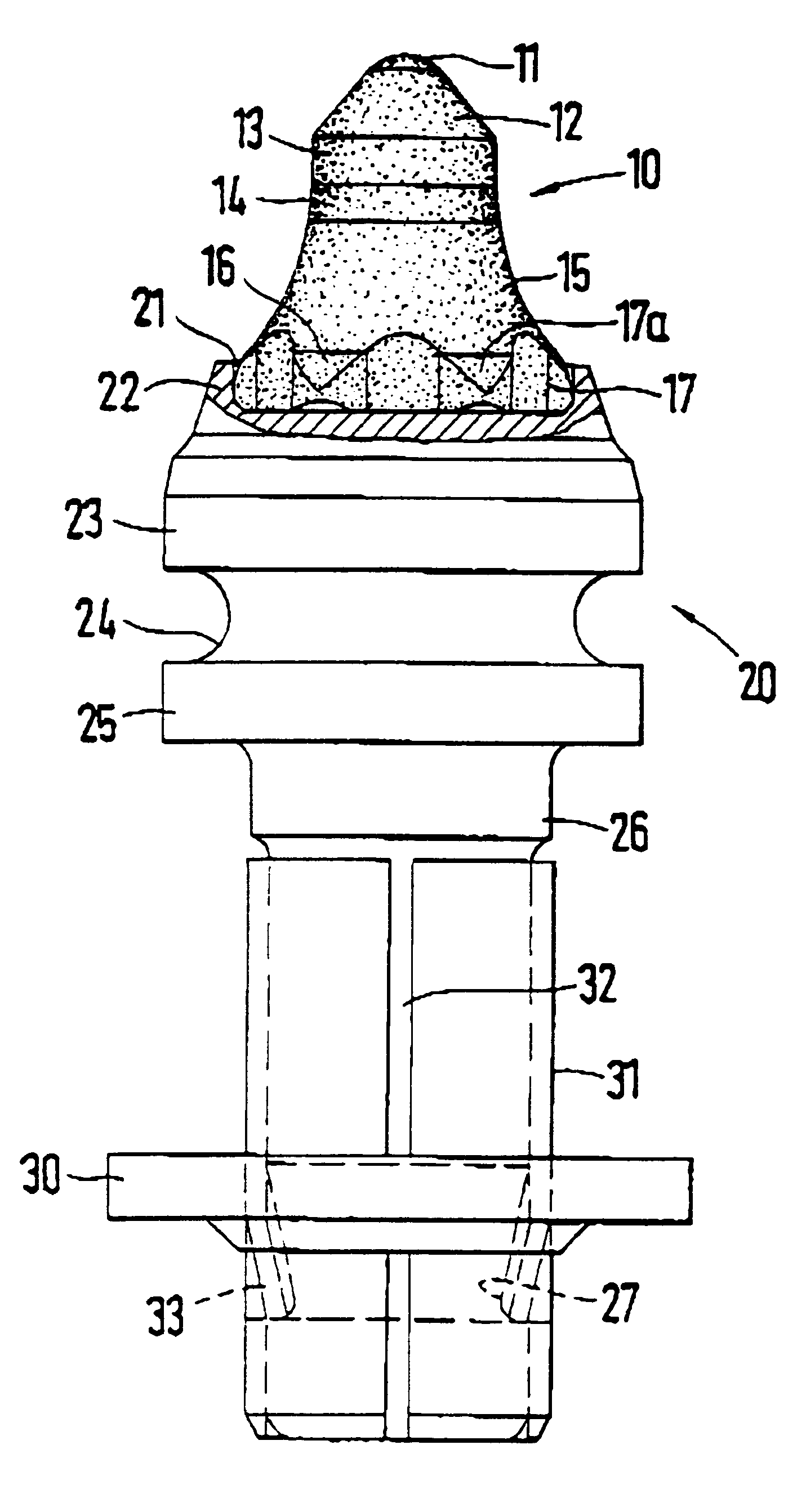
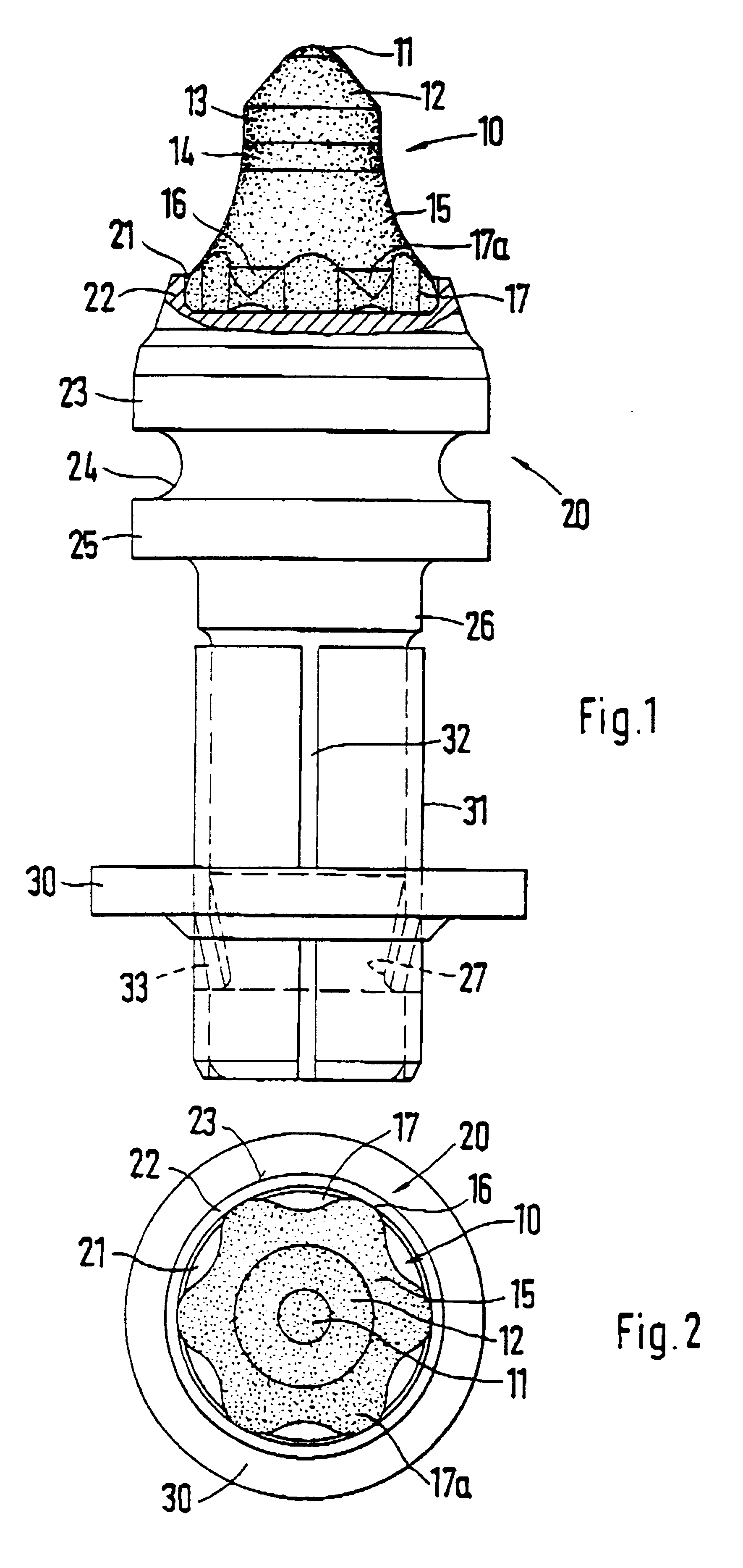
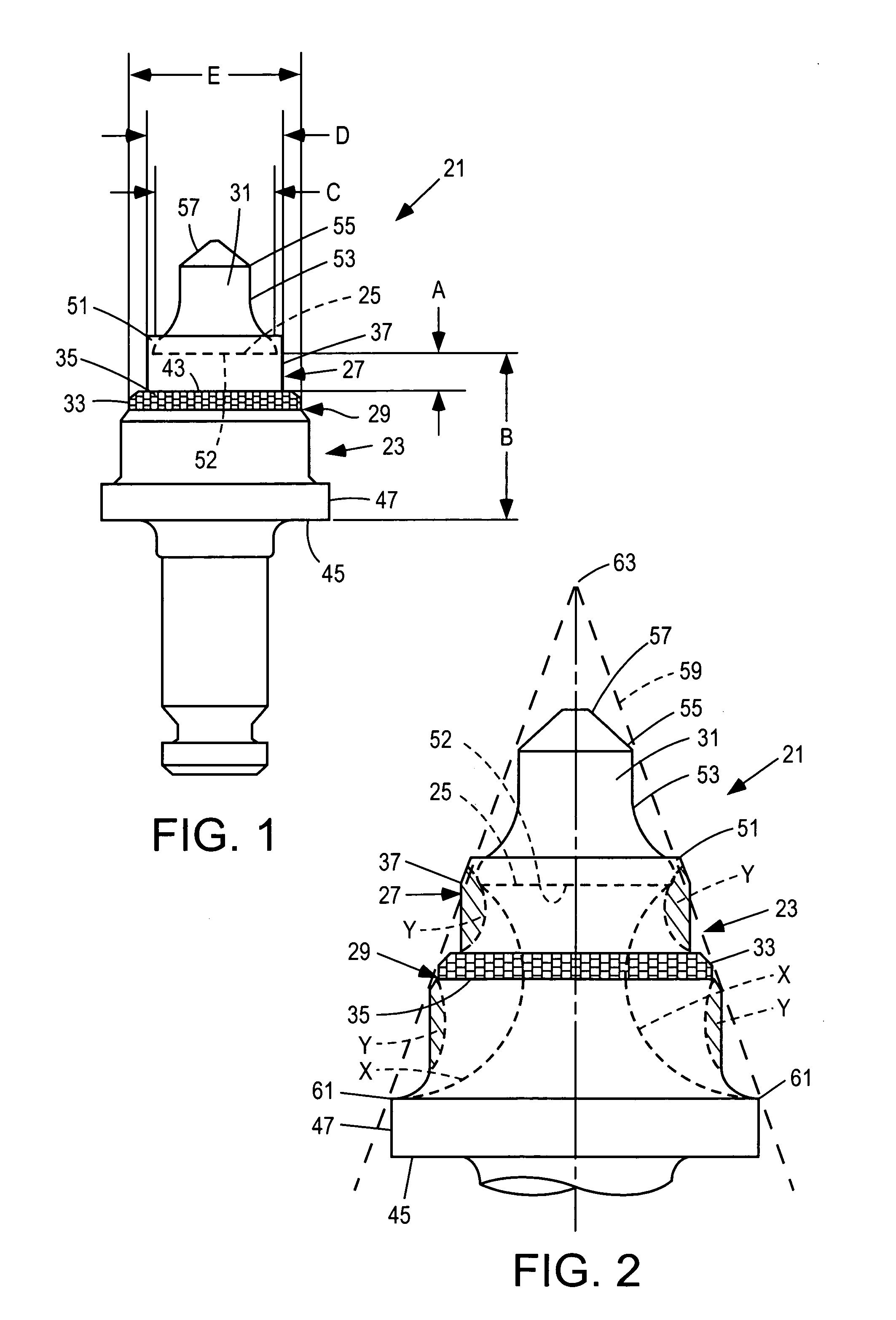
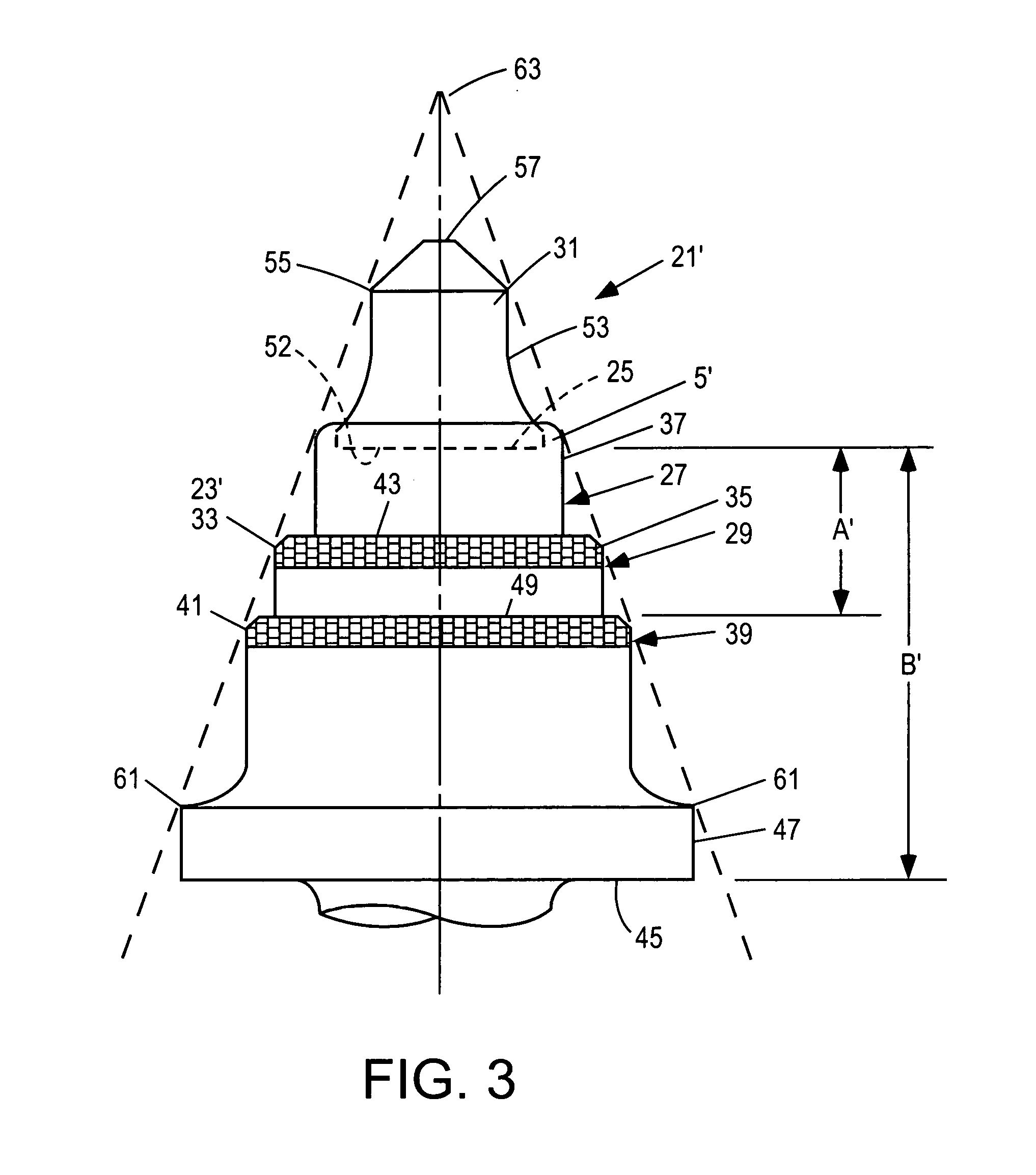
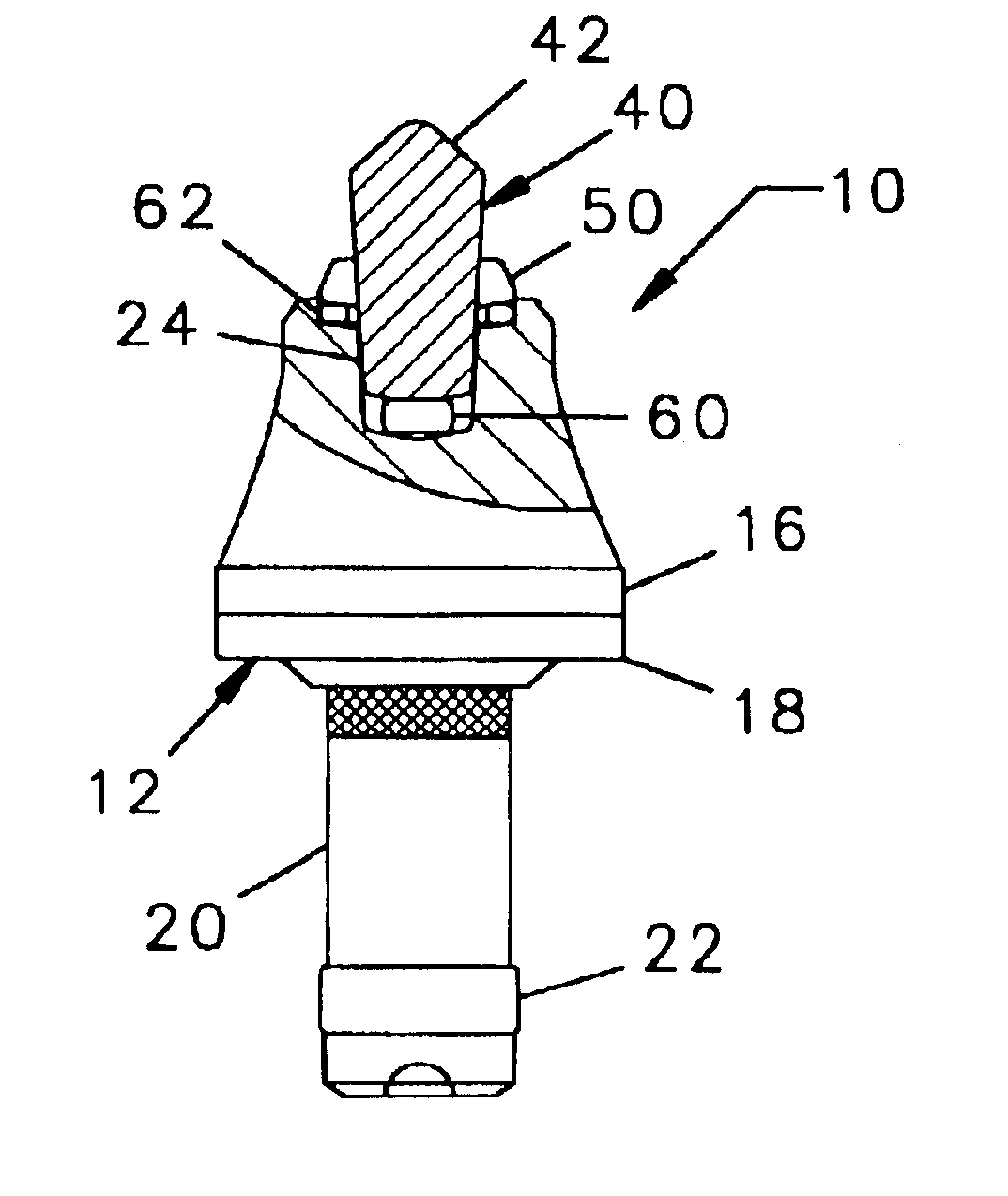
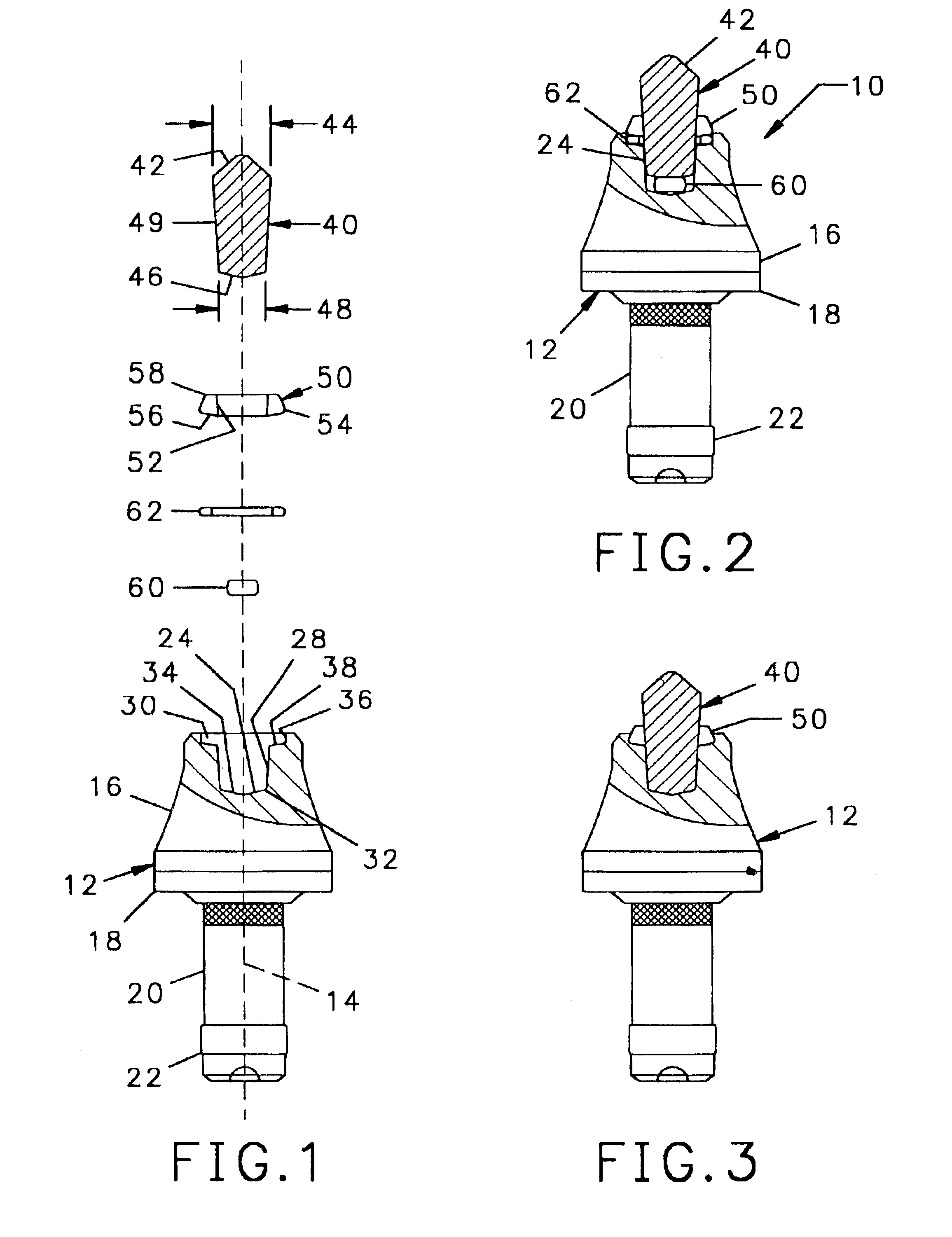
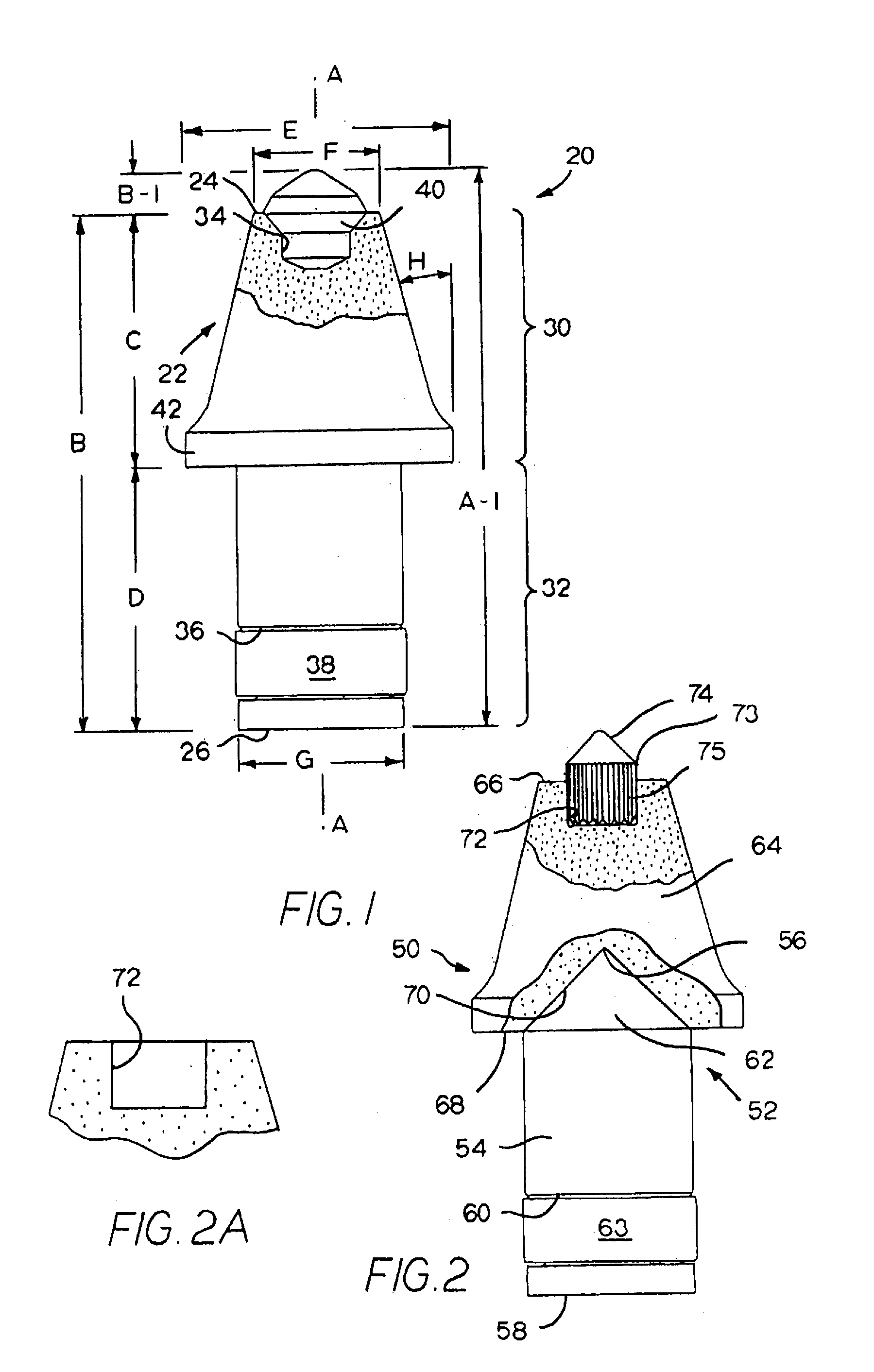
InactiveUS6846045B2Reduce breakageExtended service lifeSlitting machinesStone-like material working toolsMechanical engineering
A cutting tool has tool body with a seat at a forward end thereof. A hard cutting insert is bonded into the seat. The insert is made of a hard material and Ahas an elongate central portion having a maximum upper diameter and a maximum lower diameter that is less than the maximum upper diameter. A collar, also made of a hard material, surrounds the base of the elongate central portion of the insert.
Owner:THE SOLLAMI COMPANY
Brazed diamond tools and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20040112359A1Avoid large movementsImprove cutting efficiencyDrill bitsConstructionsChemical LinkageBraze alloy
Superabrasive tools and methods for the making thereof are disclosed and described. In one aspect, superabrasive particles are chemically bonded to a matrix support material according to a predetermined pattern by a braze alloy. The brazing alloy may be provided as a powder, thin sheet, or sheet of amorphous alloy. A template having a plurality of apertures arranged in a predetermined pattern may be used to place the superabrasive particles on a given substrate or matrix support material.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
High speed laser scribing method of fragile material
InactiveUS20100089882A1Accelerate thermal stress scribingAvoid disadvantagesFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
In a method for scribing fragile material, a laser beam is irradiated onto a work plate of the fragile material. The work plate is heated by absorption of the irradiated laser beam and generating thermal stress by the heating. The laser beam is formed by a plurality of laser beam groups arranged along a beam scanning direction on a same line, and the plurality of laser beam groups are divided into two groups. One takes charge of initial heating and rising up temperature of the work plate, and another takes charge of temperature holding of the work plate. The laser beam intensity corresponding to each of the laser beam groups is adjusted so as to obtain optimum values.By the method, it is possible to remarkably increase scribing speed of the work plate of the fragile materials without increasing heating temperature.
Owner:GLOBALY TECH CO LTD
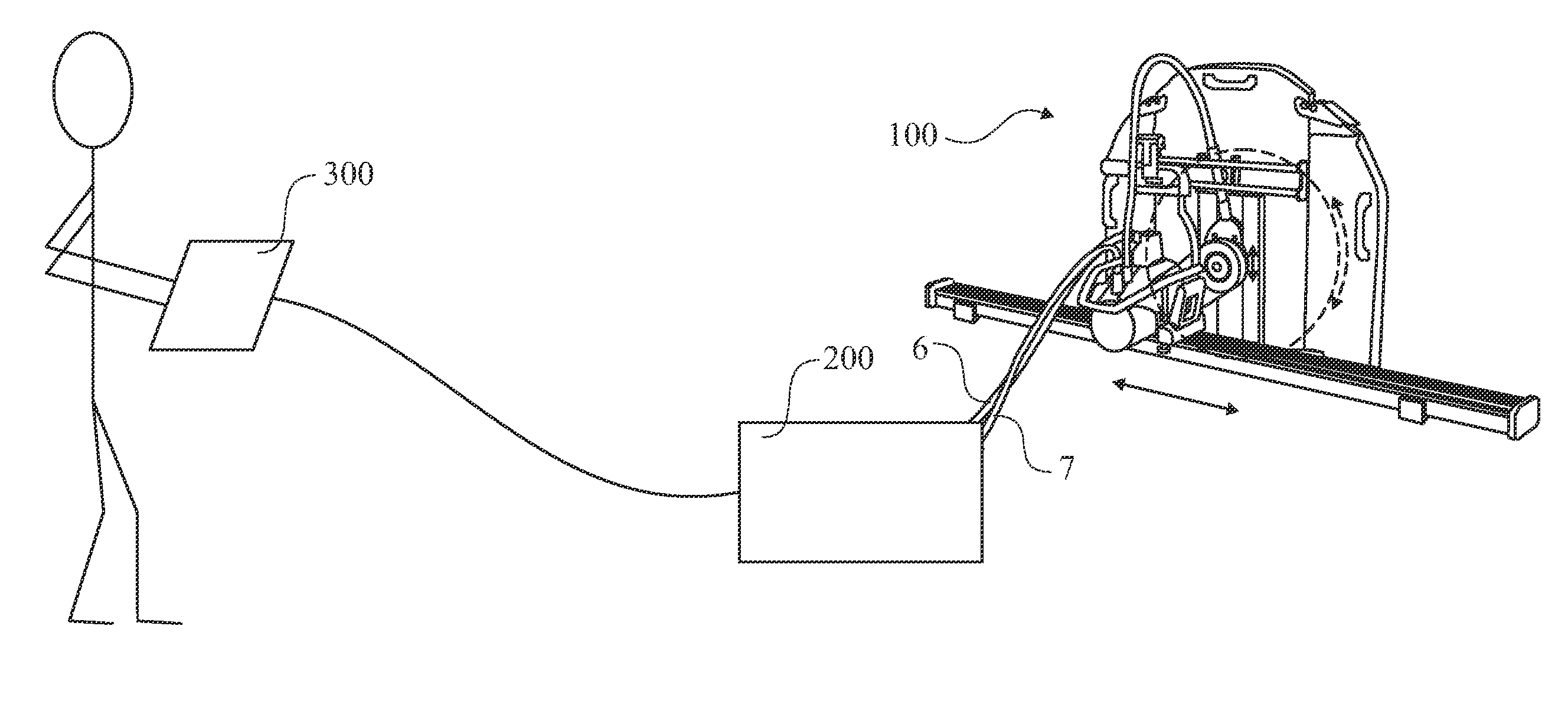
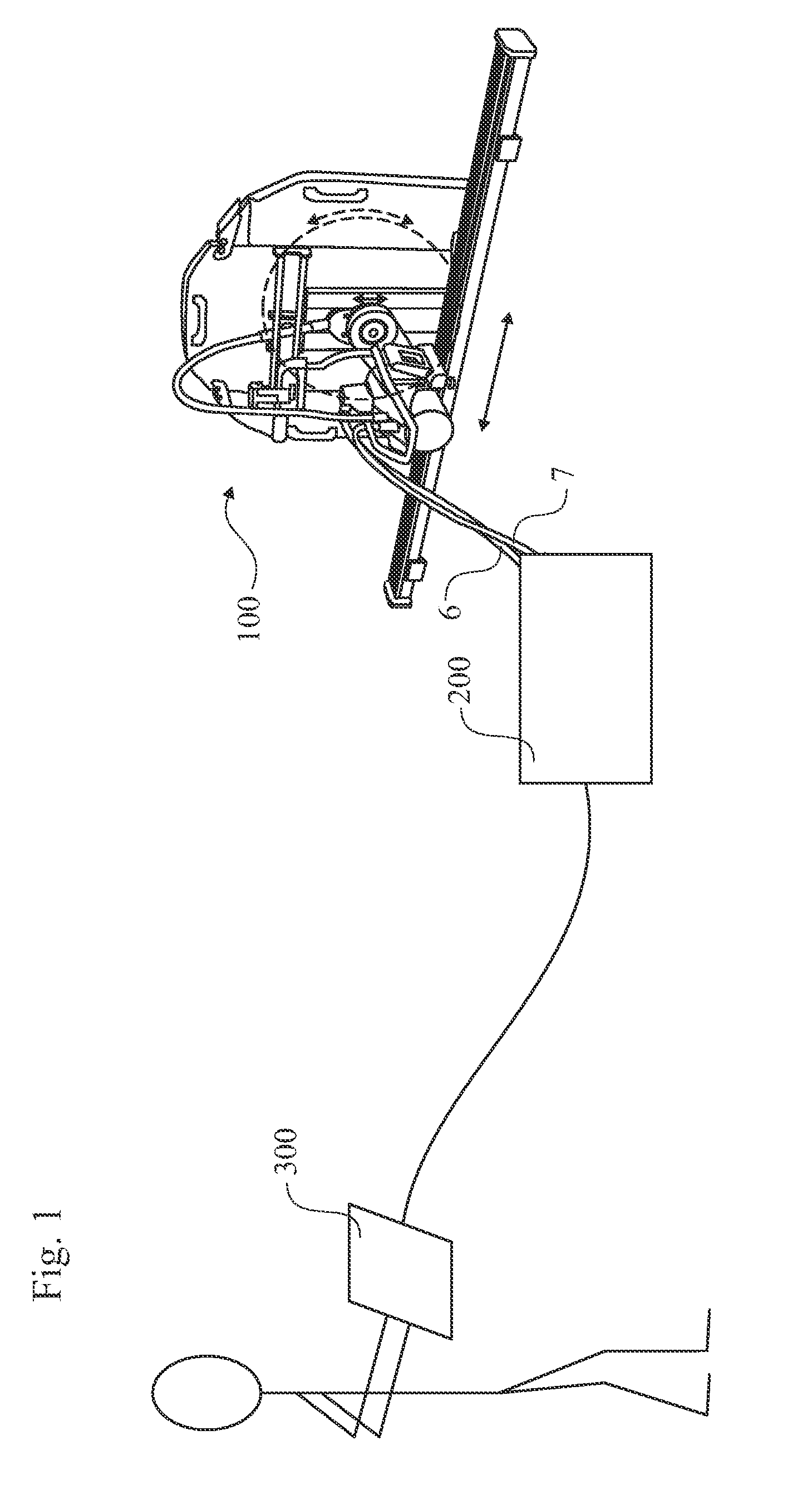
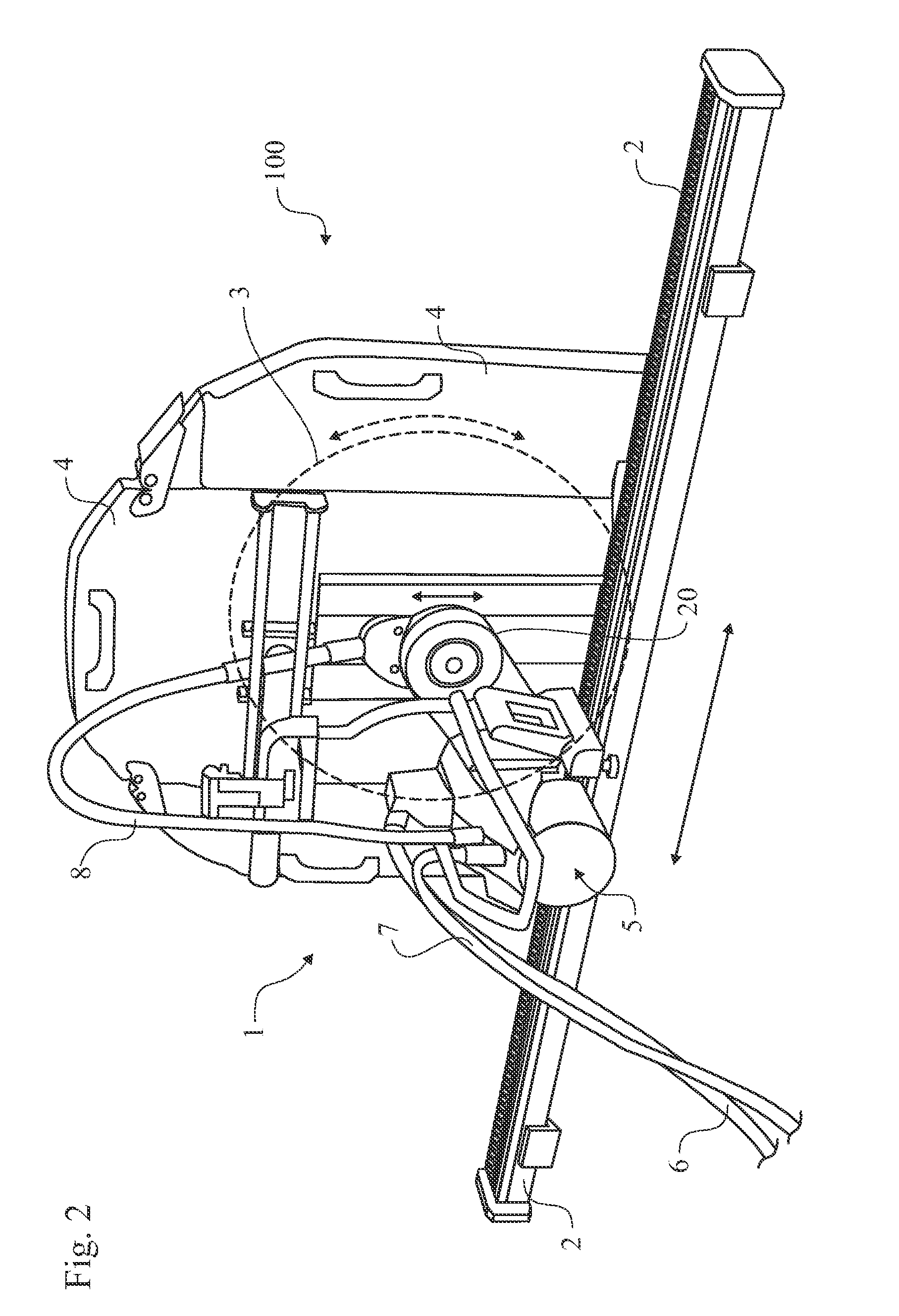
Electric saw communication
ActiveUS20110056716A1Easy to handleEasy to adjust the positionSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMulticore cablePermanent magnet motor
The present invention relates to an electric saw (1) being powered by an external power supply (200) through a multicore cable (6). The multicore cable (6) includes electrical wires (24, 25, 27) for supplying power to the motors (5, 12, 13) of the electric saw (1) and communication wires (26) for data communication between the electric saw (1) and the power supply (200). Two motors (12, 13) of the electric saw are three phase permanent magnet motors (12, 13), with an outer rotor (31) and an inner stator (30). Each of the two motors (12, 13) has three Hall Effect sensors (H1, H2, H3) located around the outer rotor (31).
Owner:HUSQVARNA AB
Cutting bit useful for impingement of earth strata
A cutting bit for impinging earth strata wherein the cutting bit includes a highly wear-resistant elongate cutting bit body, which has an axial forward end and an axial rearward end, an enlarged dimension head portion at the axial forward end and a reduced dimension shank portion at the axial rearward end. The highly wear-resistant elongate cutting bit body has a maximum transverse dimension and a longitudinal axial length. The cutting bit includes a superhard insert, which is affixed to the head portion at the axial forward end of the cutting bit body. The cutting bit has a slimness ratio, which comprises the ratio of the maximum transverse dimension to the longitudinal axial length wherein the cutting bit exhibits a slimness ratio ranging between about 0.15 and about 0.60.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Attack tool
In one aspect of the invention, an attack tool is disclosed which comprises a wear-resistant base suitable for attachment to a driving mechanism. The wear-resistant base has a shank and a metal segment. A cemented metal carbide segment is bonded to the metal segment and the shank has a wear-resistant surface. The wear-resistant surface has a hardness greater than 60 HRc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
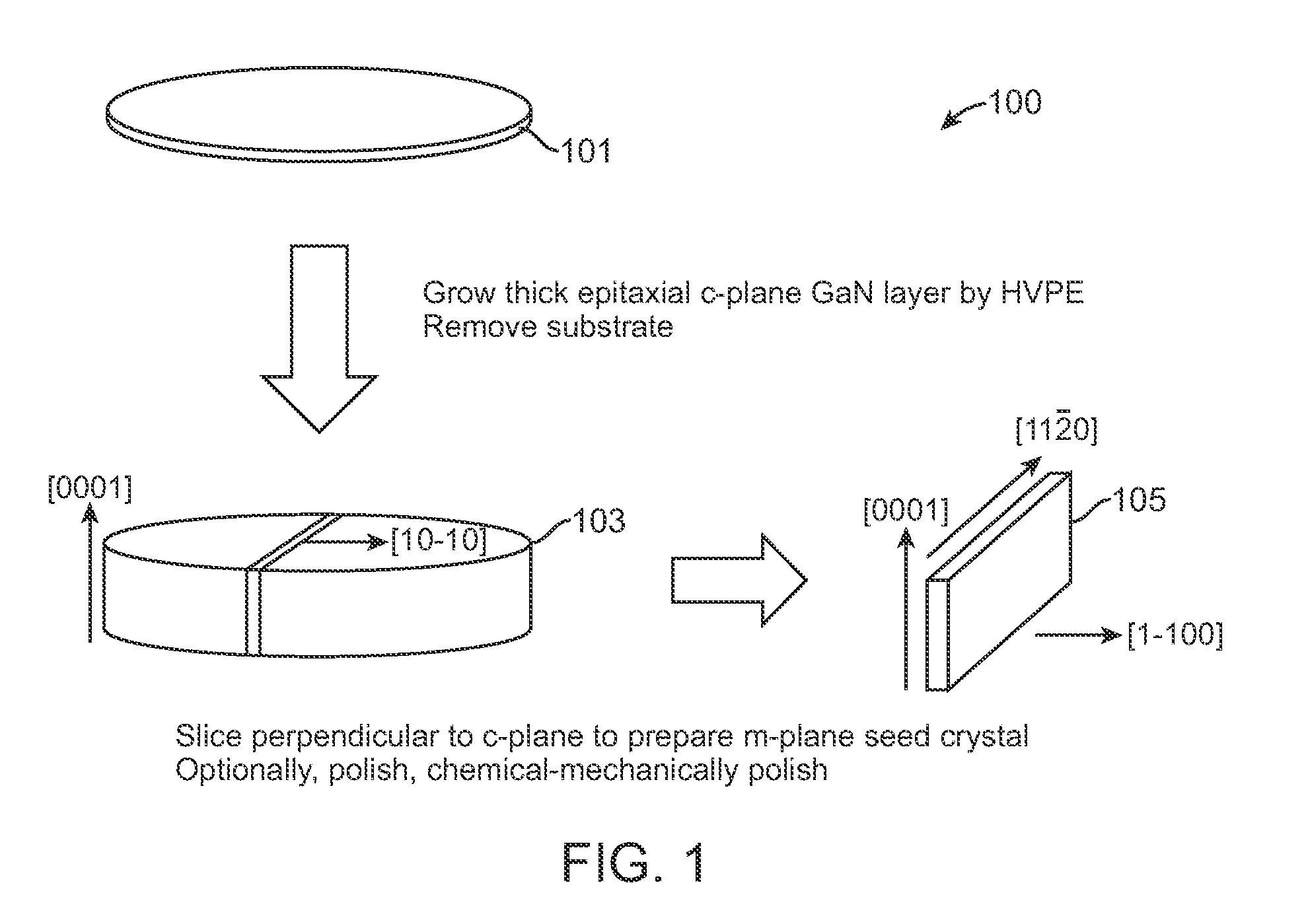
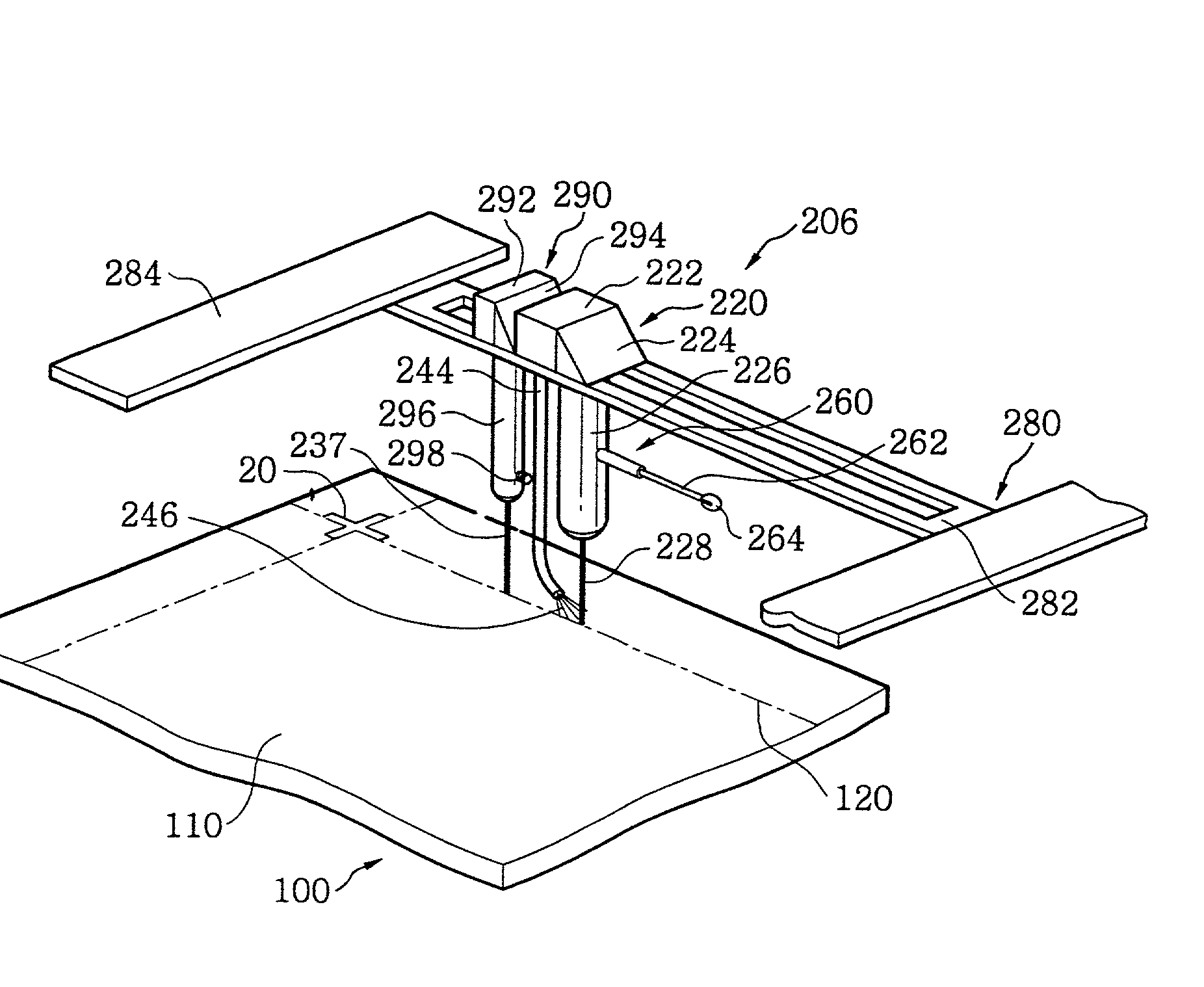
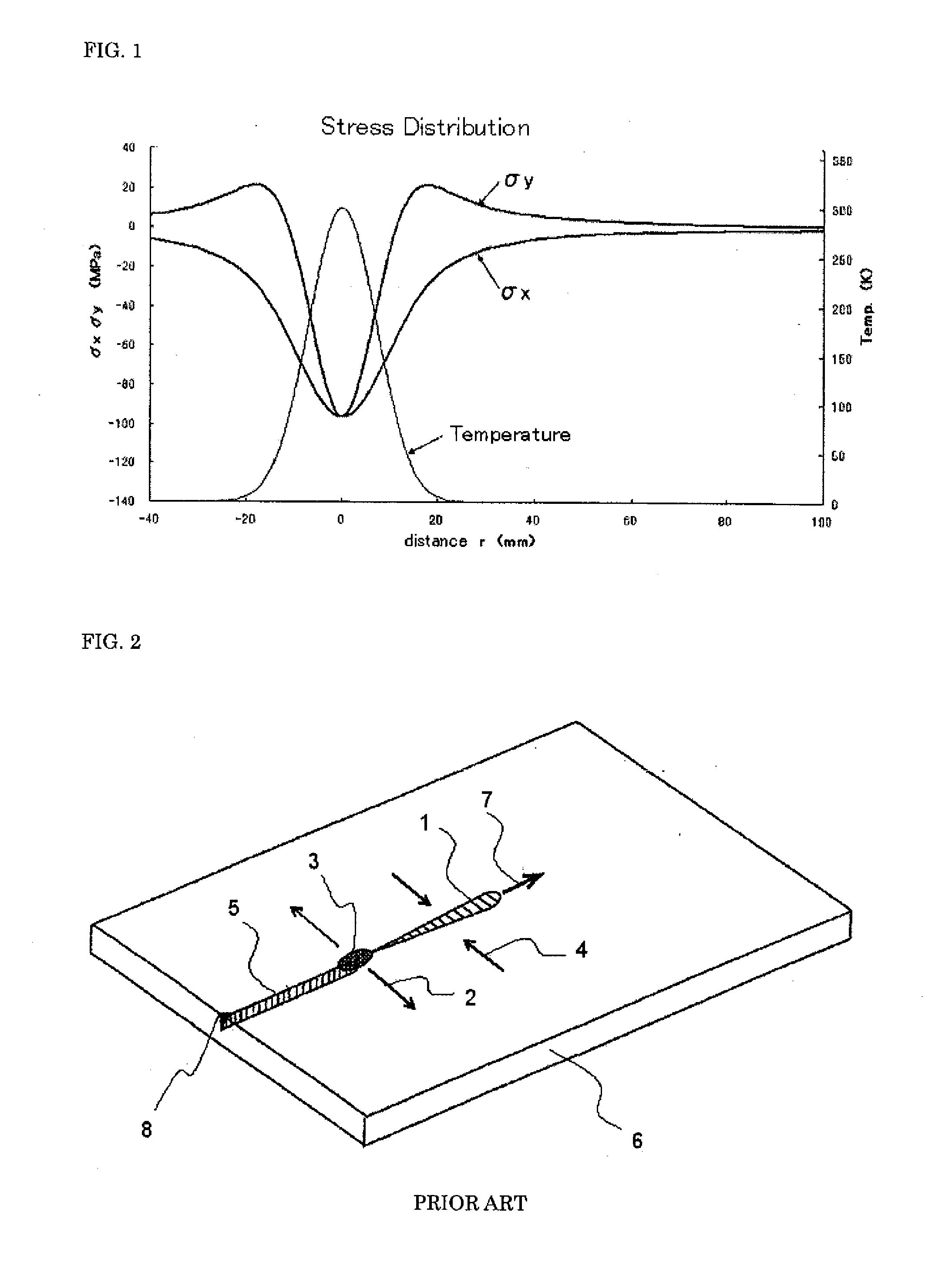
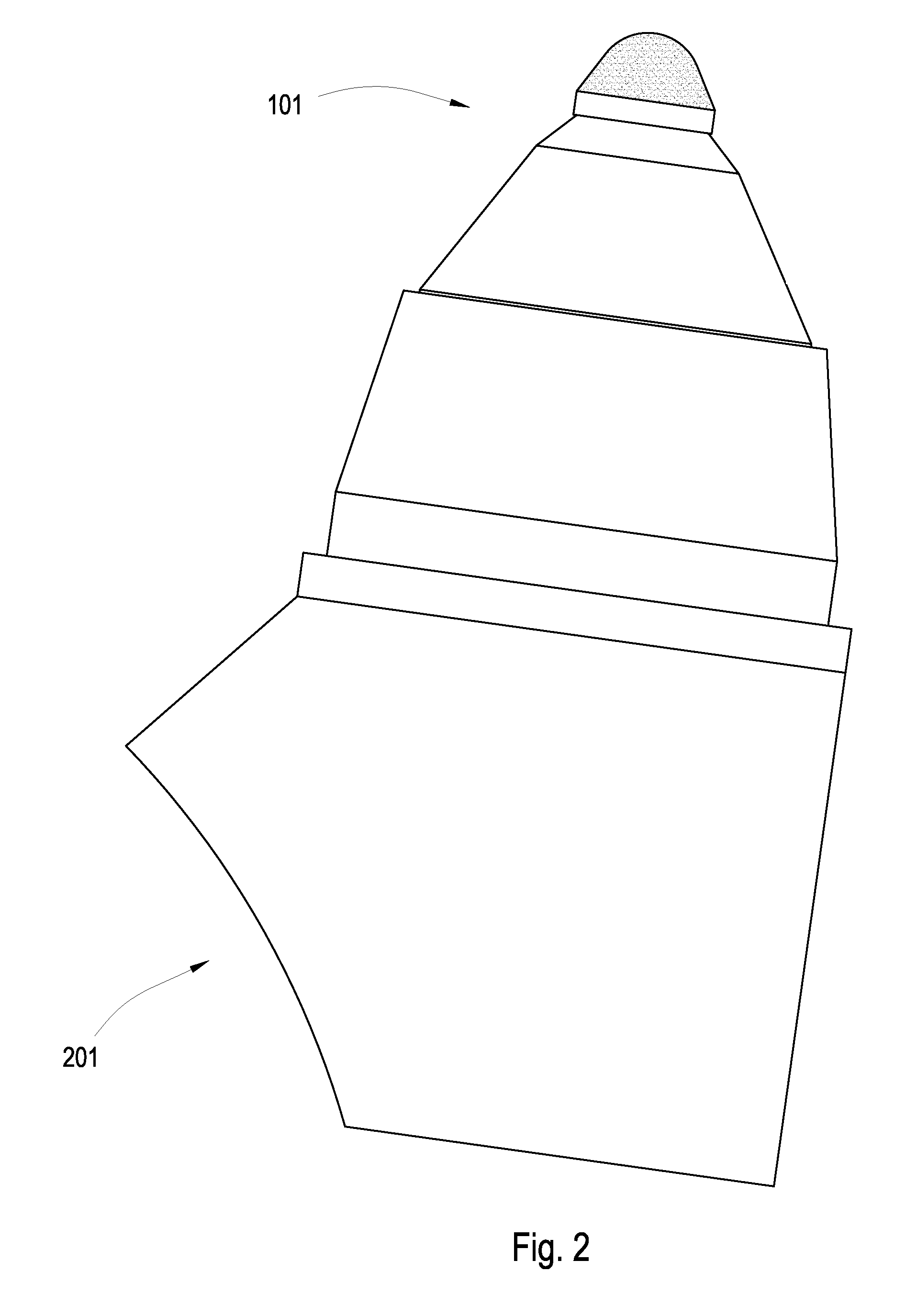
Cleaving Wafers from Silicon Crystals
ActiveUS20090056513A1Effective absorptionIncrease the areaAutomatic control devicesPolycrystalline material growthShortest distanceIngot
A method of creating thin wafers of single crystal silicon wherein an ingot of single-crystal silicon with a (111) axis is flattened and polished at one end normal to the axis, and a notch with a vertex in the (111) plane is produced on a side or edge of the ingot, such that the distance between this vertex and said end is the desired thickness of a wafer to be cleaved from the ingot and such this vertex is in the desired plane of cleavage. Light of a wavelength able to penetrate into the silicon crystal without significant absorption, when the intensity of the beam is low, but is efficiently absorbed and converted to heat when the intensity of the beam is high, is focused to an elongated volume with an axis of elongation in the desired cleavage plane, parallel to and a short distance from said notch edge. Heating and the resulting transient local expansion of the silicon in this illuminated volume causes tensile stress at the vertex of said notch, substantially normal to the desired cleavage plane, thereby causing fracture of the crystal in the chosen cleavage plane. Movement of the illuminated volume relative to the ingot allows the fracture to propagate across the desired cleavage plane, thereby completely severing the wafer from the rest of the ingot.
Owner:BAER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com