Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
901 results about "Water splitting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
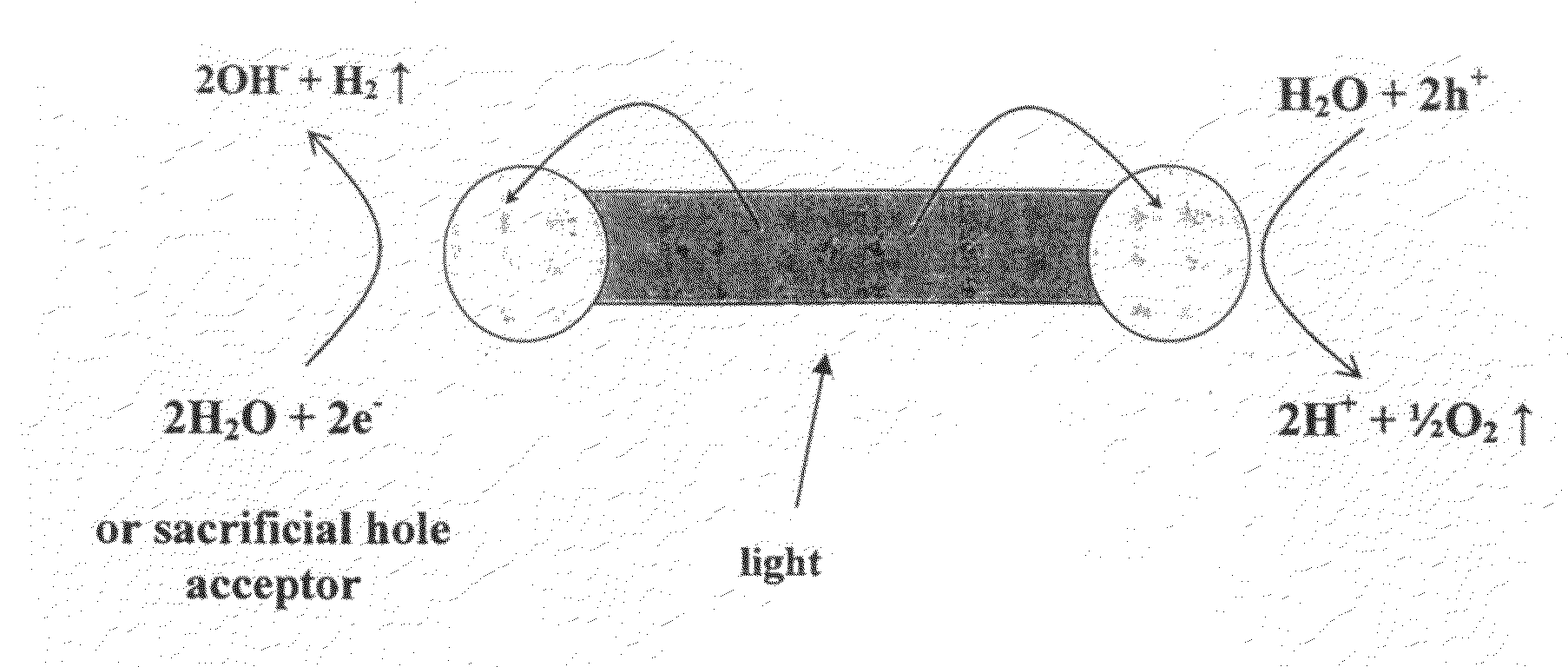
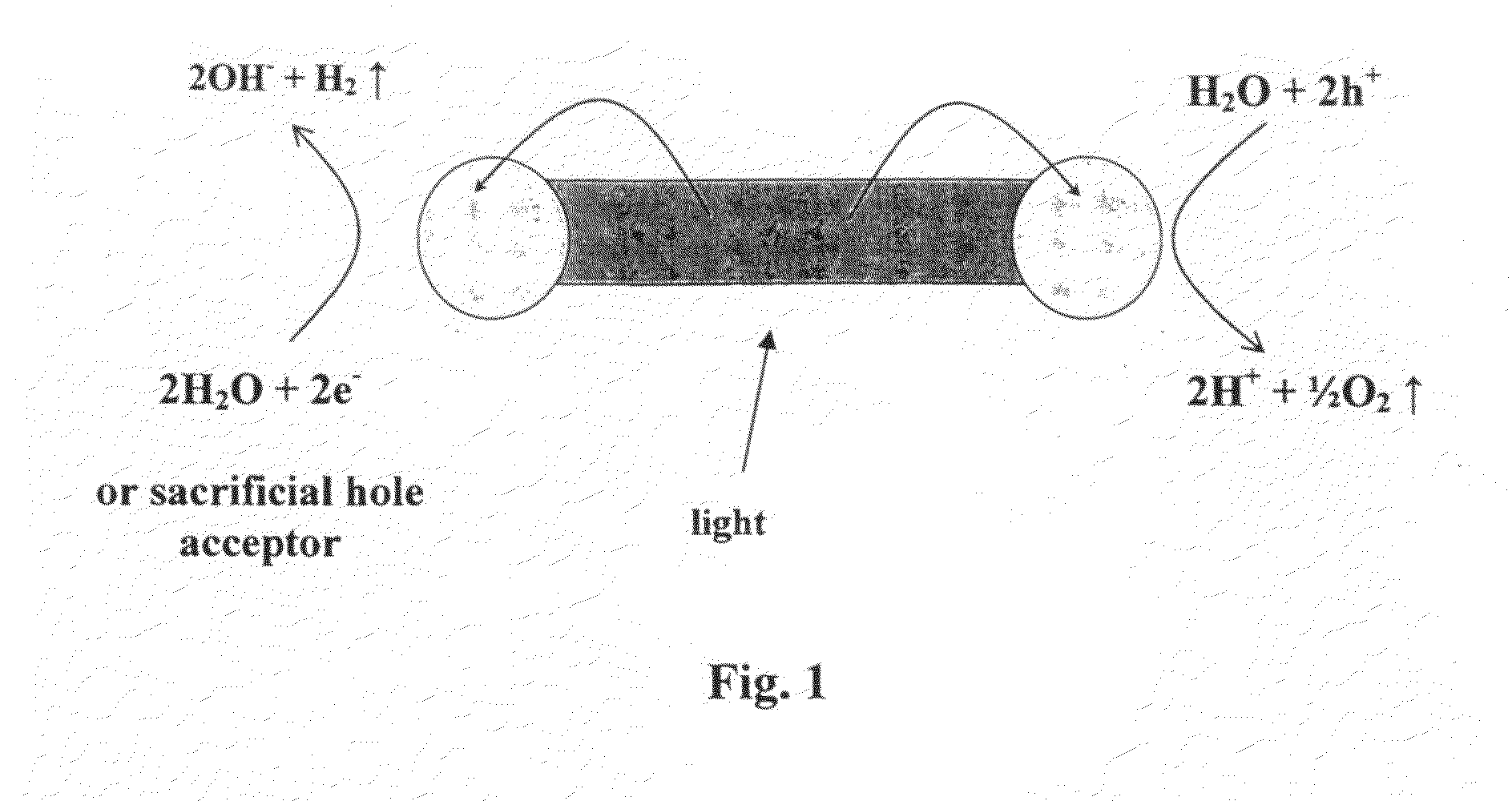
Water splitting is the chemical reaction in which water is broken down into oxygen and hydrogen...
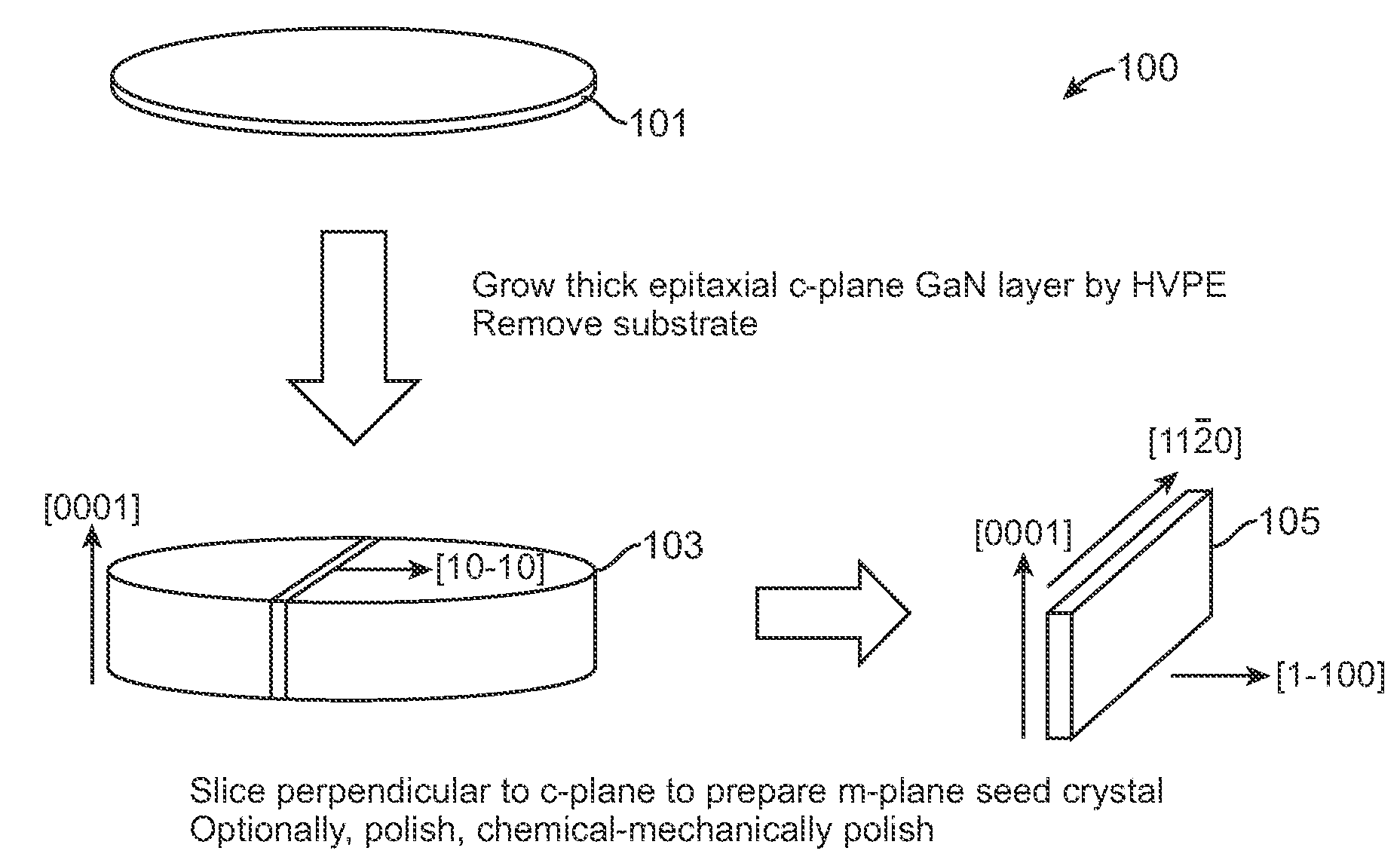
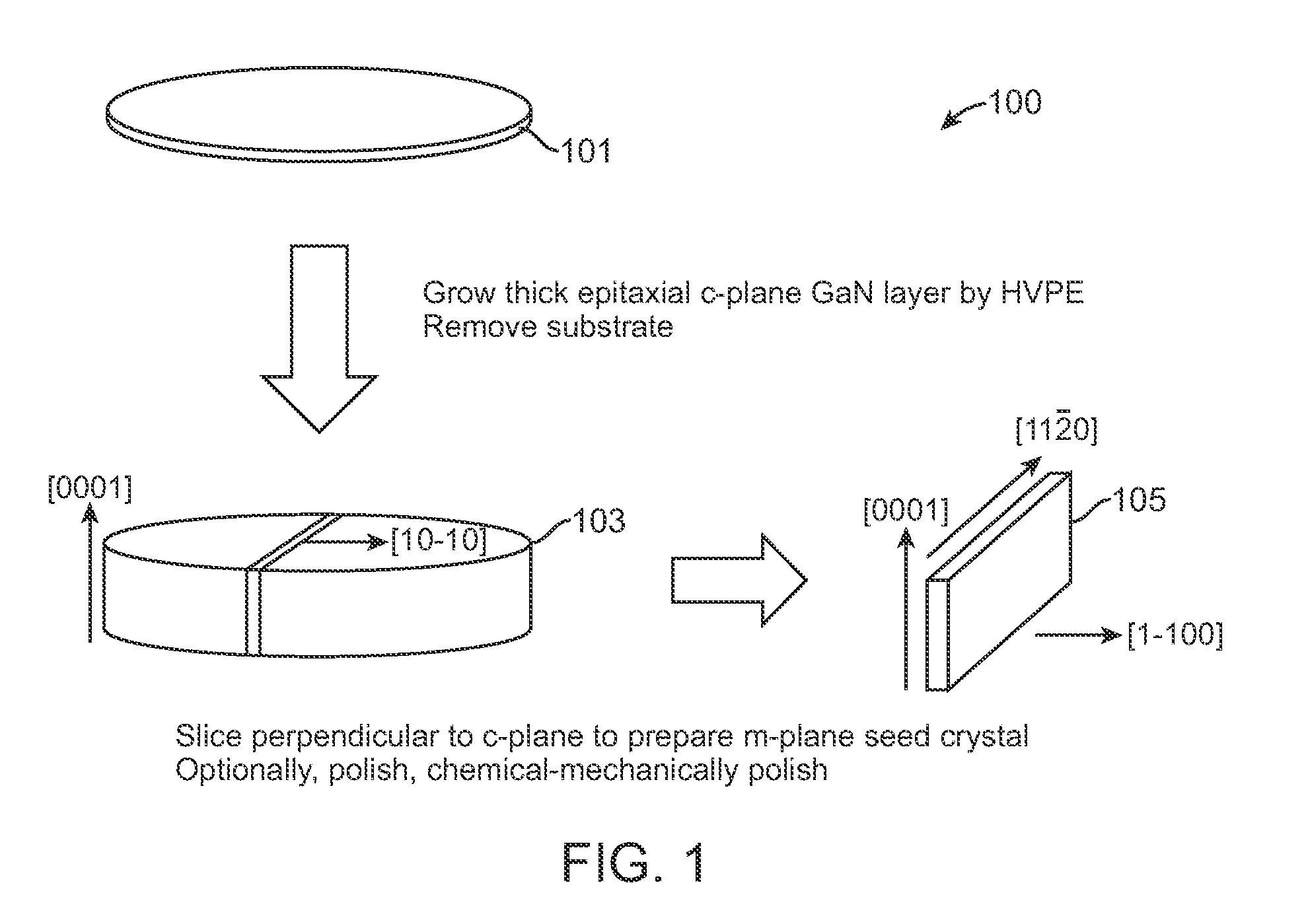
High quality large area bulk non-polar or semipolar gallium based substrates and methods
InactiveUS20100003492A1Great area of substrateCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialPhotodetectorSolar cell
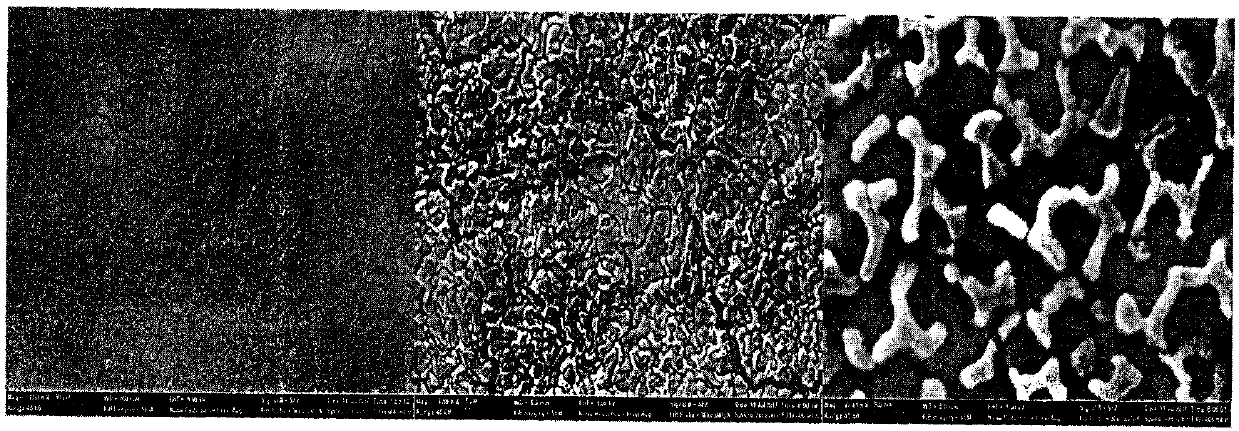
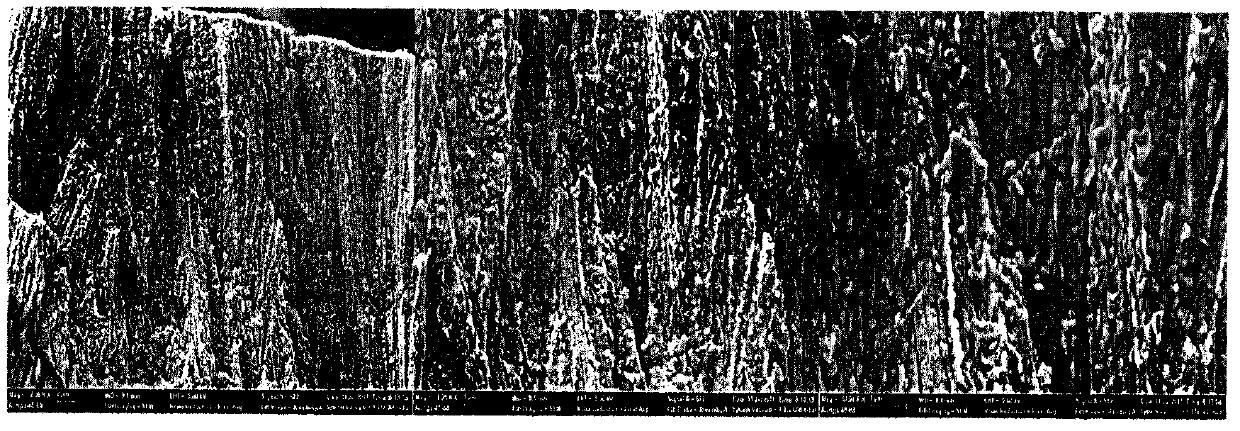
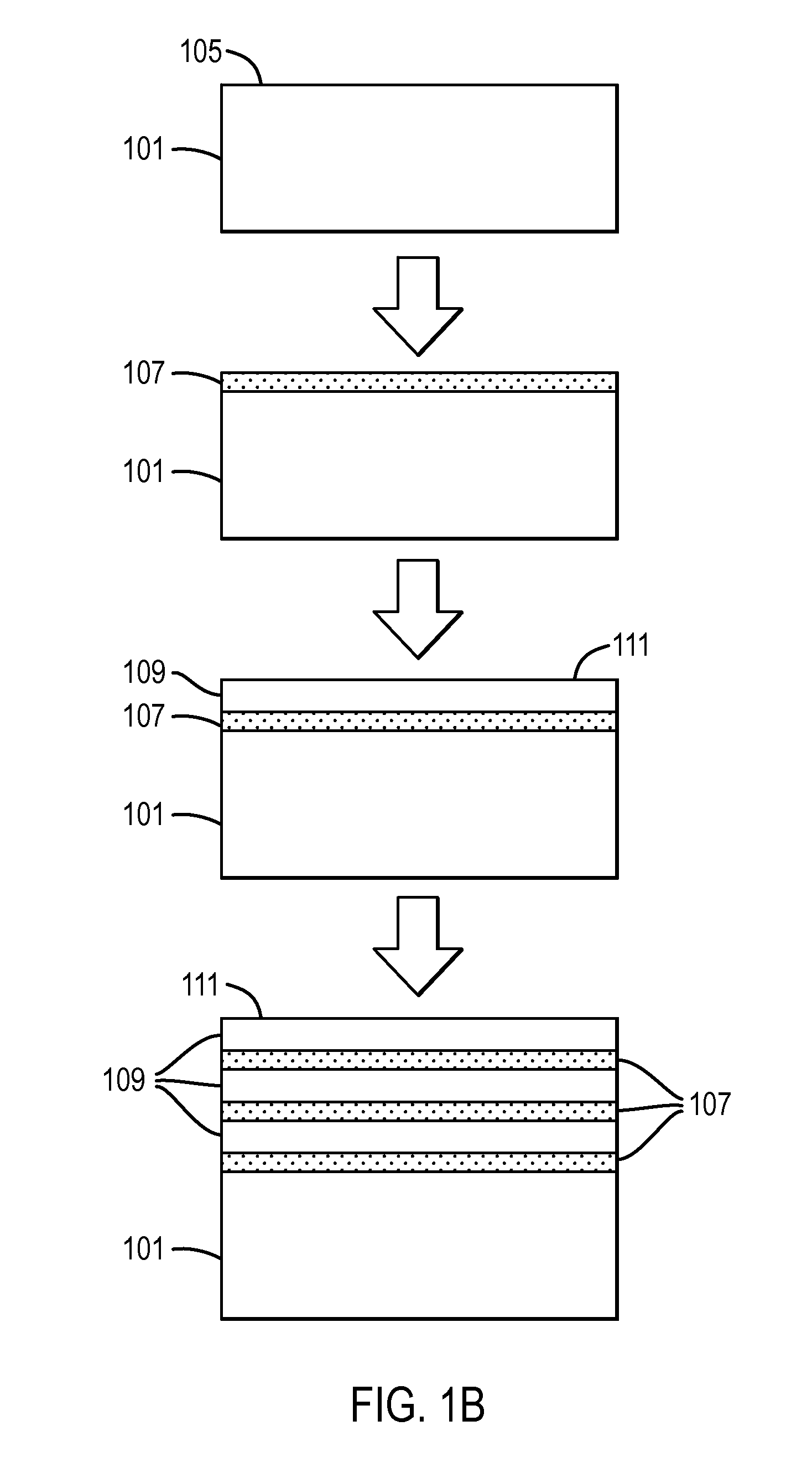
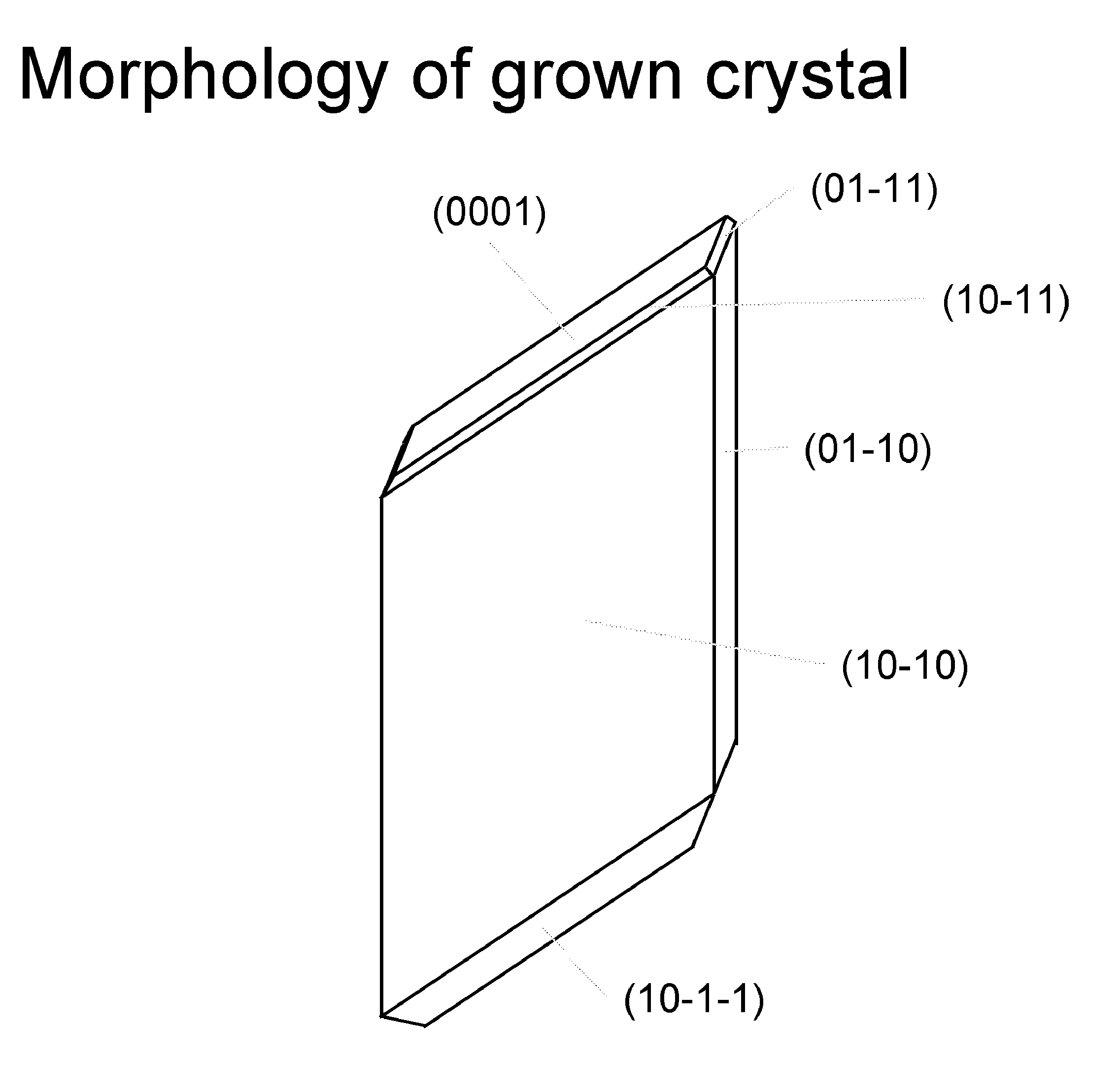
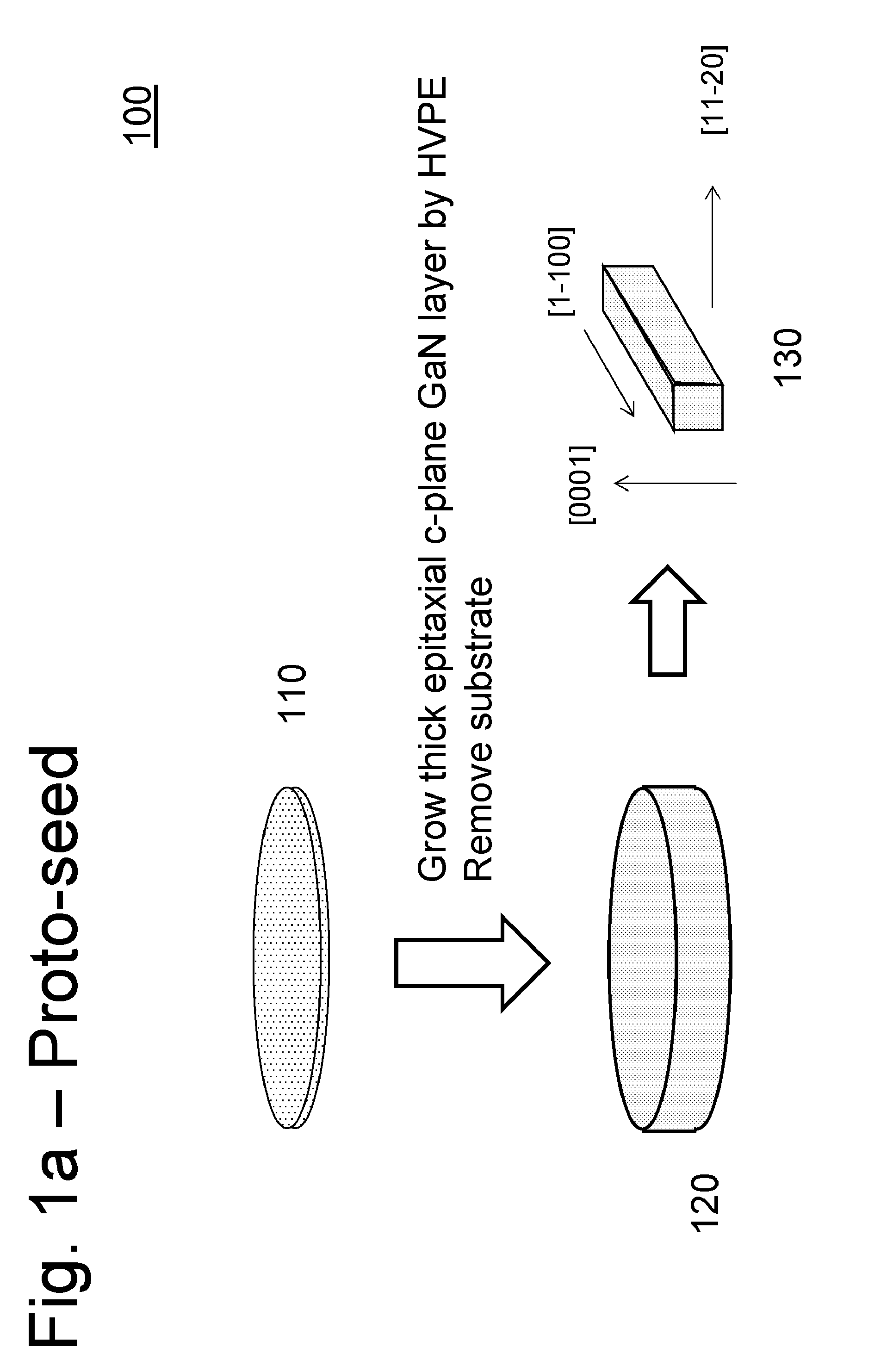
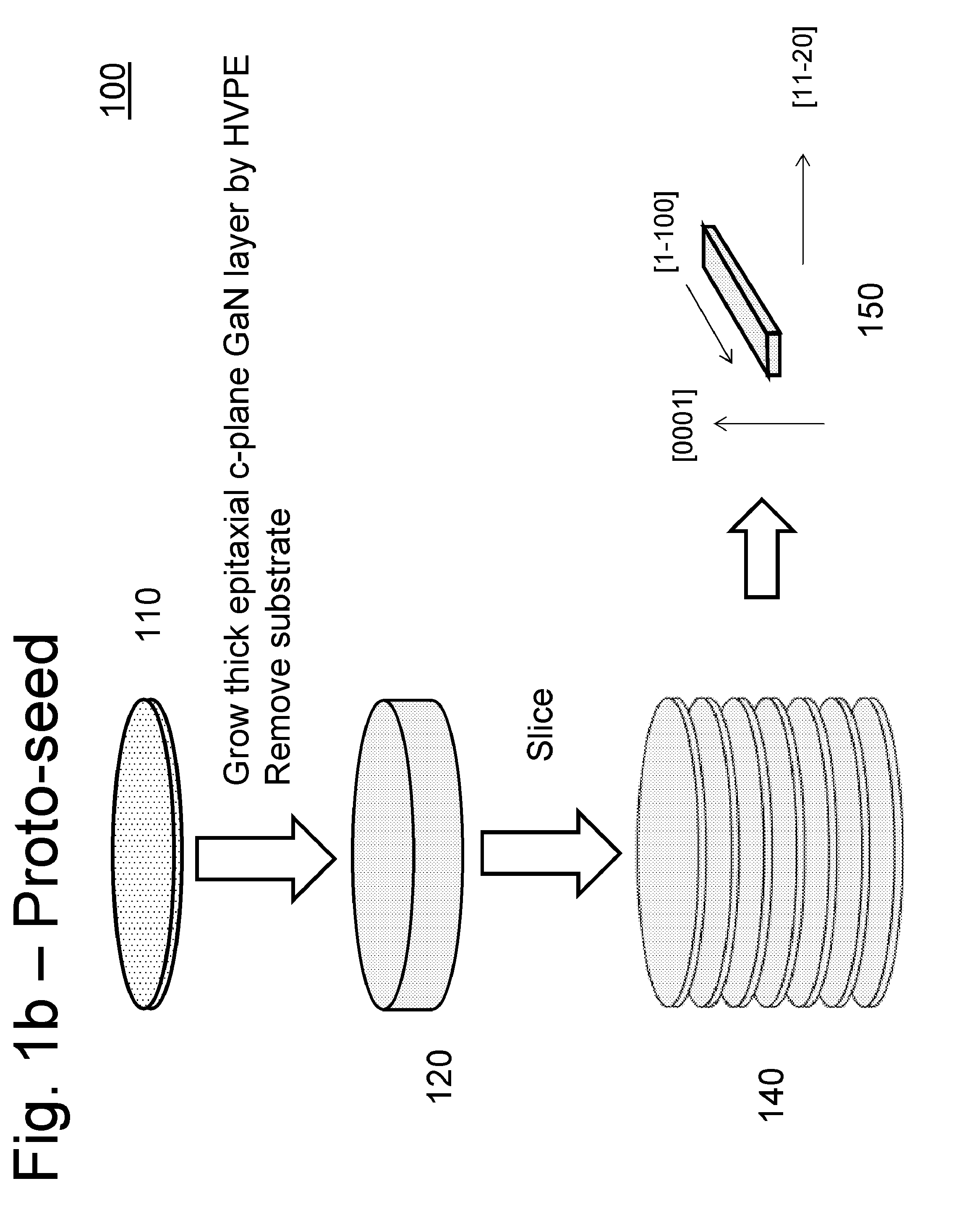
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method for making. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SORAA
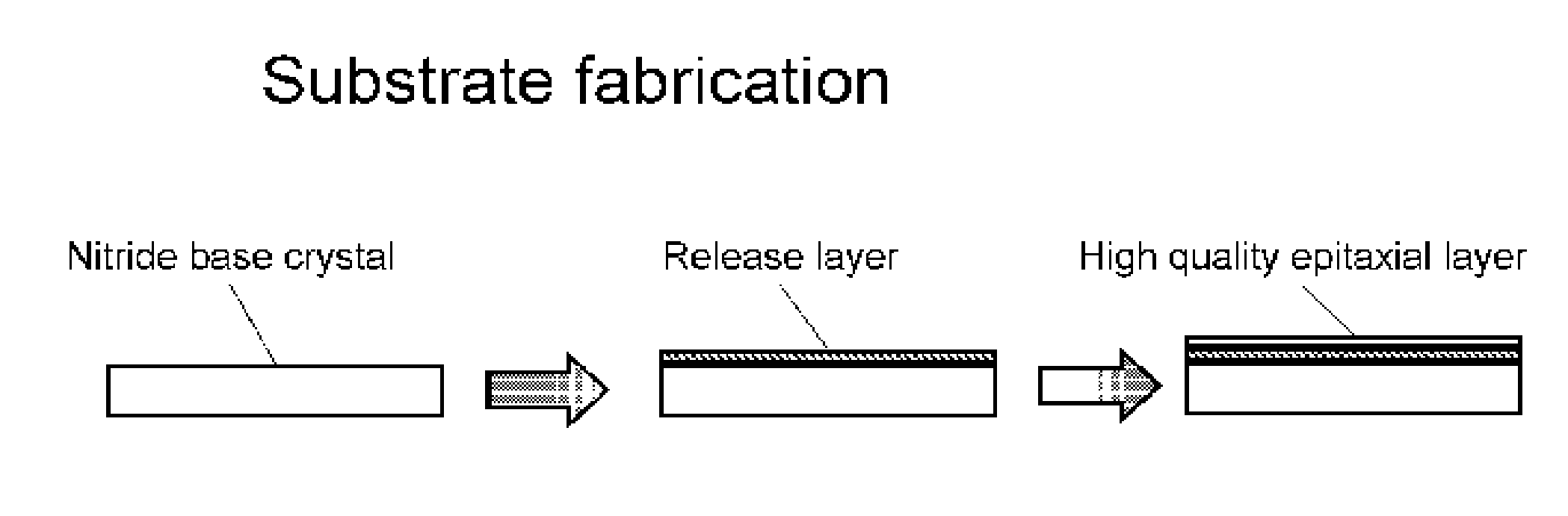
Nitride crystal with removable surface layer and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS8148801B2Quality improvementSimple and cost-effectivePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
Owner:SLT TECH
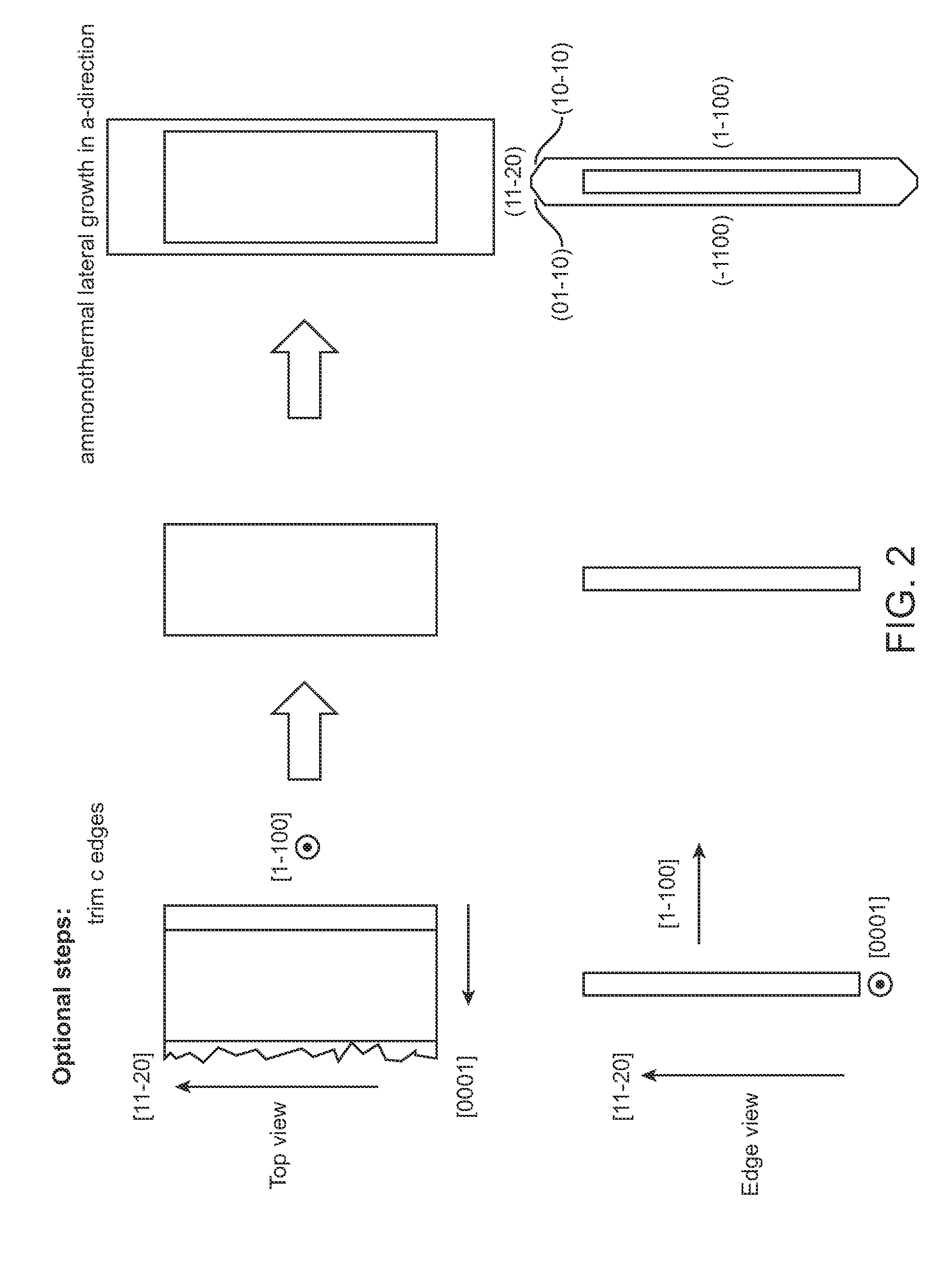
Large area nitride crystal and method for making it
Techniques for processing materials in supercritical fluids including processing in a capsule disposed within a high-pressure apparatus enclosure are disclosed. The disclosed techniques are useful for growing crystals of GaN, AlN, InN, and their alloys, including InGaN, AlGaN, and AlInGaN for the manufacture of bulk or patterned substrates, which in turn can be used to make optoelectronic devices, lasers, light emitting diodes, solar cells, photoelectrochemical water splitting and hydrogen generation devices, photodetectors, integrated circuits, and transistors.
Owner:SLT TECH
Method for Synthesis of High Quality Large Area Bulk Gallium Based Crystals
ActiveUS20110256693A1Improve crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method of manufacture. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SLT TECH
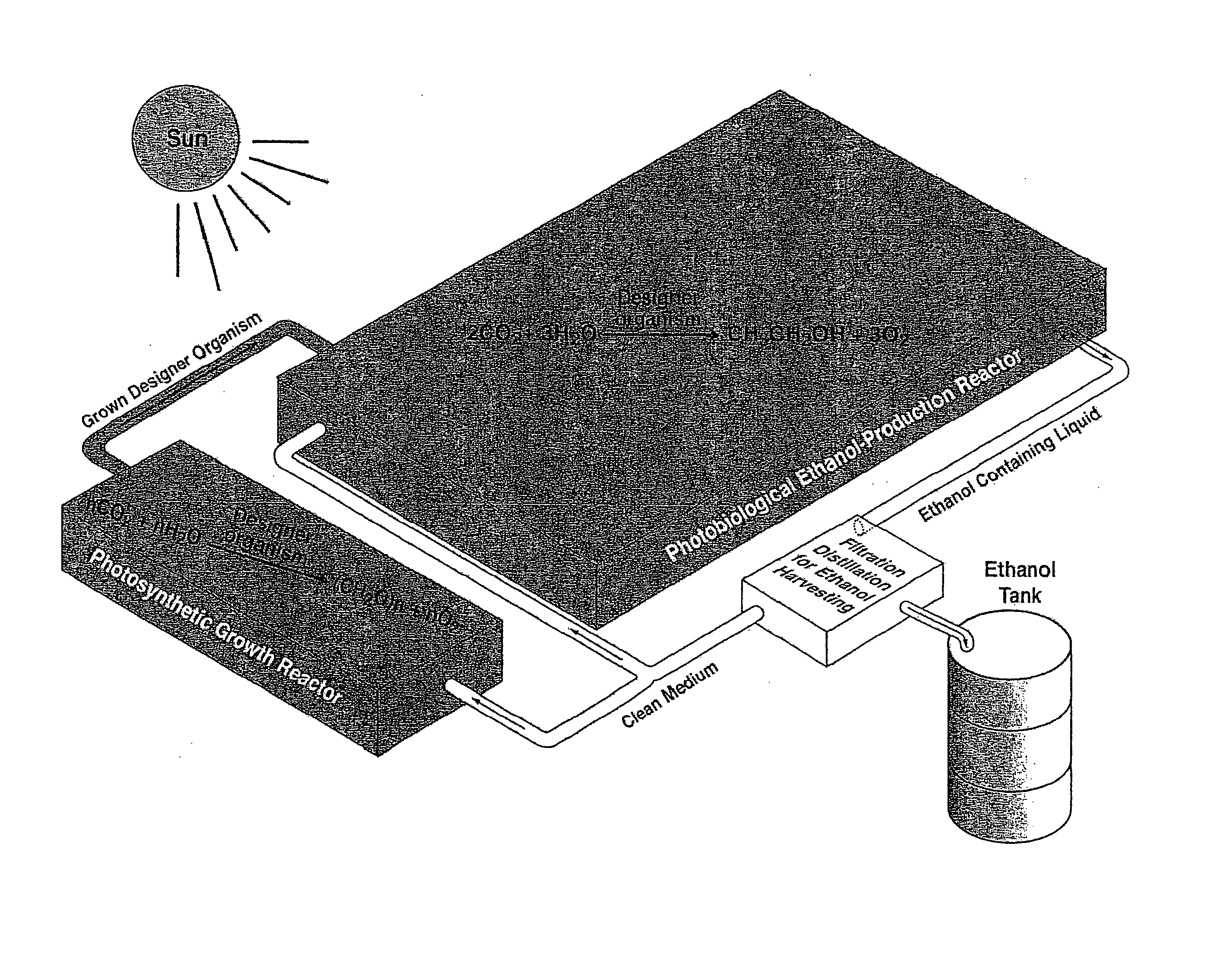
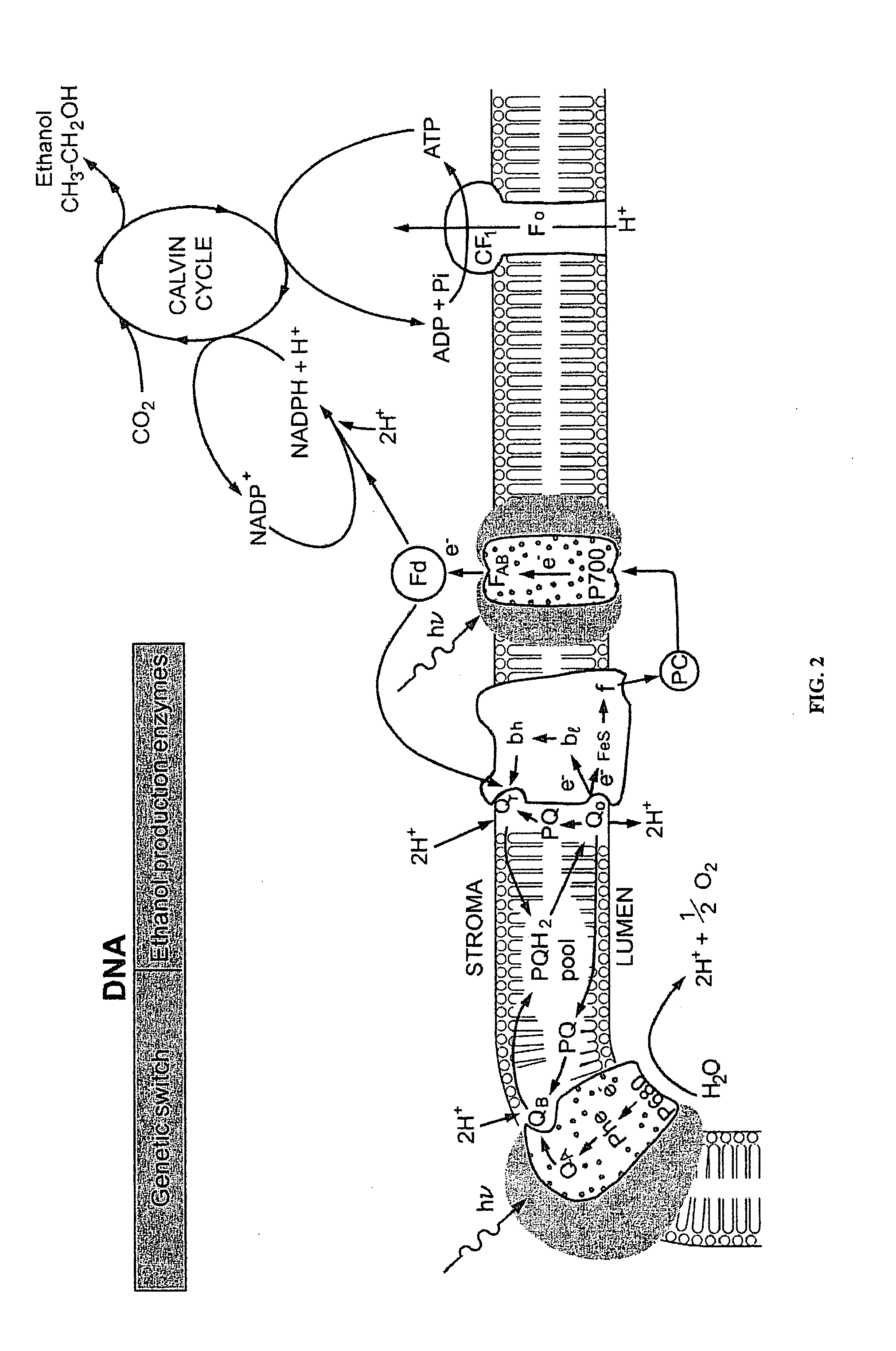
Designer Organisms for photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide and water
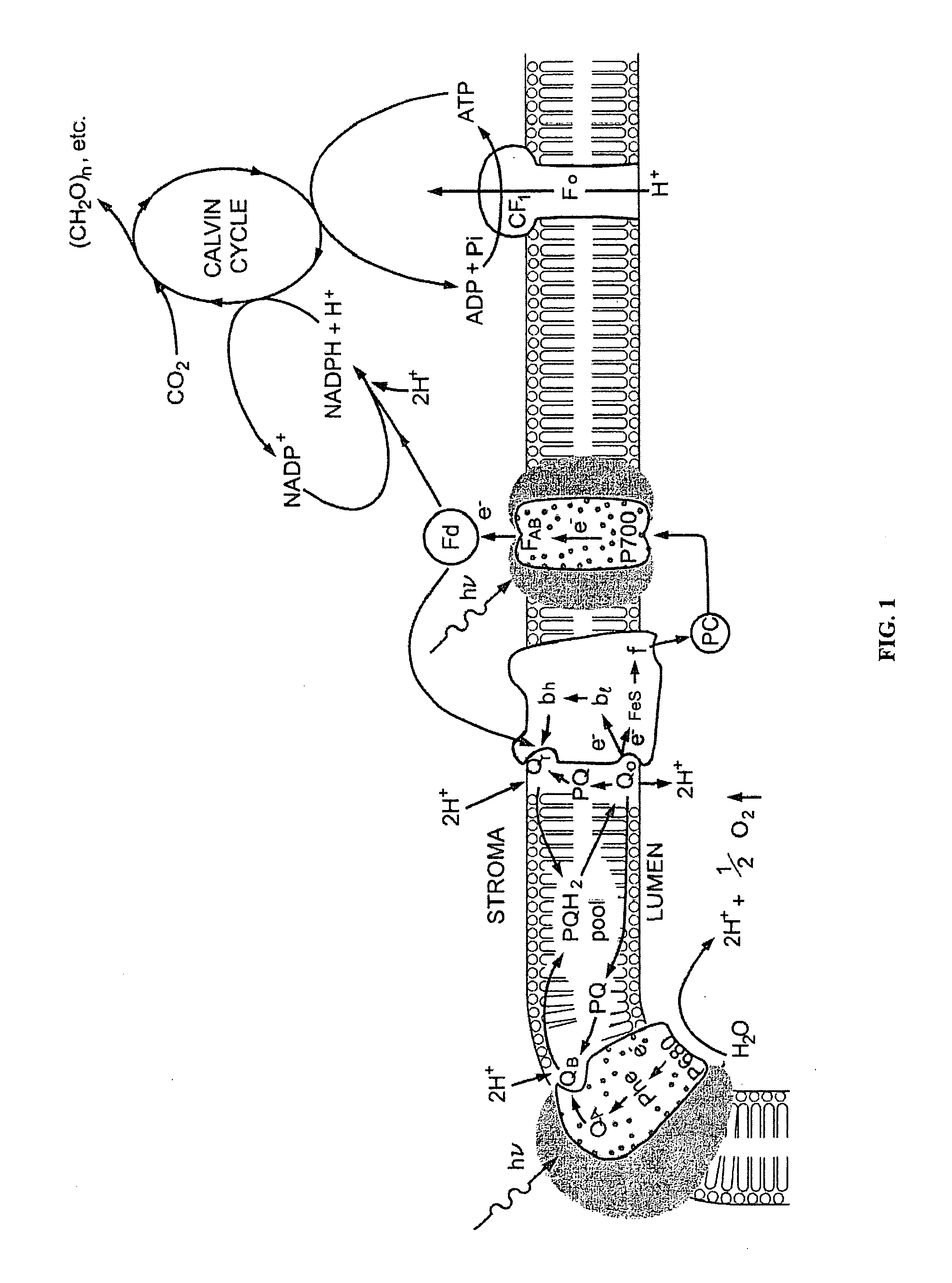
The present invention provides a revolutionary photosynthetic ethanol production technology based on designer transgenic plants, algae, or plant cells. The designer plants, designer algae, and designer plant cells are created such that the endogenous photosynthesis regulation mechanism is tamed, and the reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) acquired from the photosynthetic water splitting and proton gradient-coupled electron transport process are used for immediate synthesis of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) directly from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The ethanol production methods of the present invention completely eliminate the problem of recalcitrant lignocellulosics by bypassing the bottleneck problem of the biomass technology. The photosynthetic ethanol-production technology of the present invention is expected to have a much higher solar-to-ethanol energy-conversion efficiency than the current technology and could also help protect the Earth's environment from the dangerous accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Nitride crystal with removable surface layer and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20100219505A1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
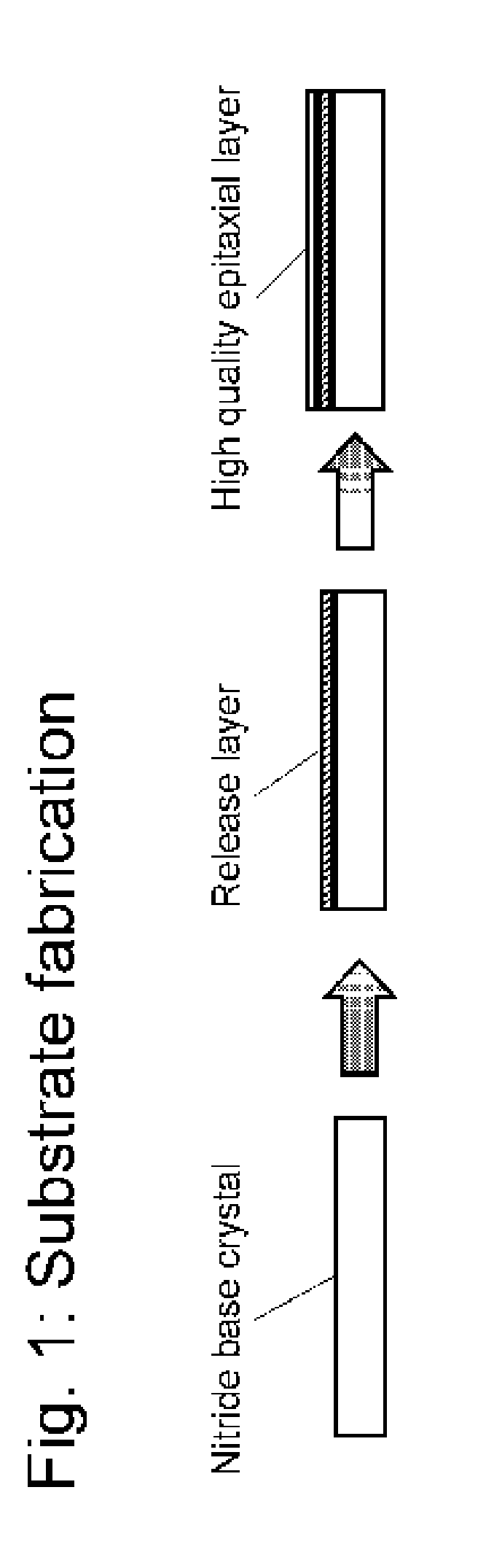
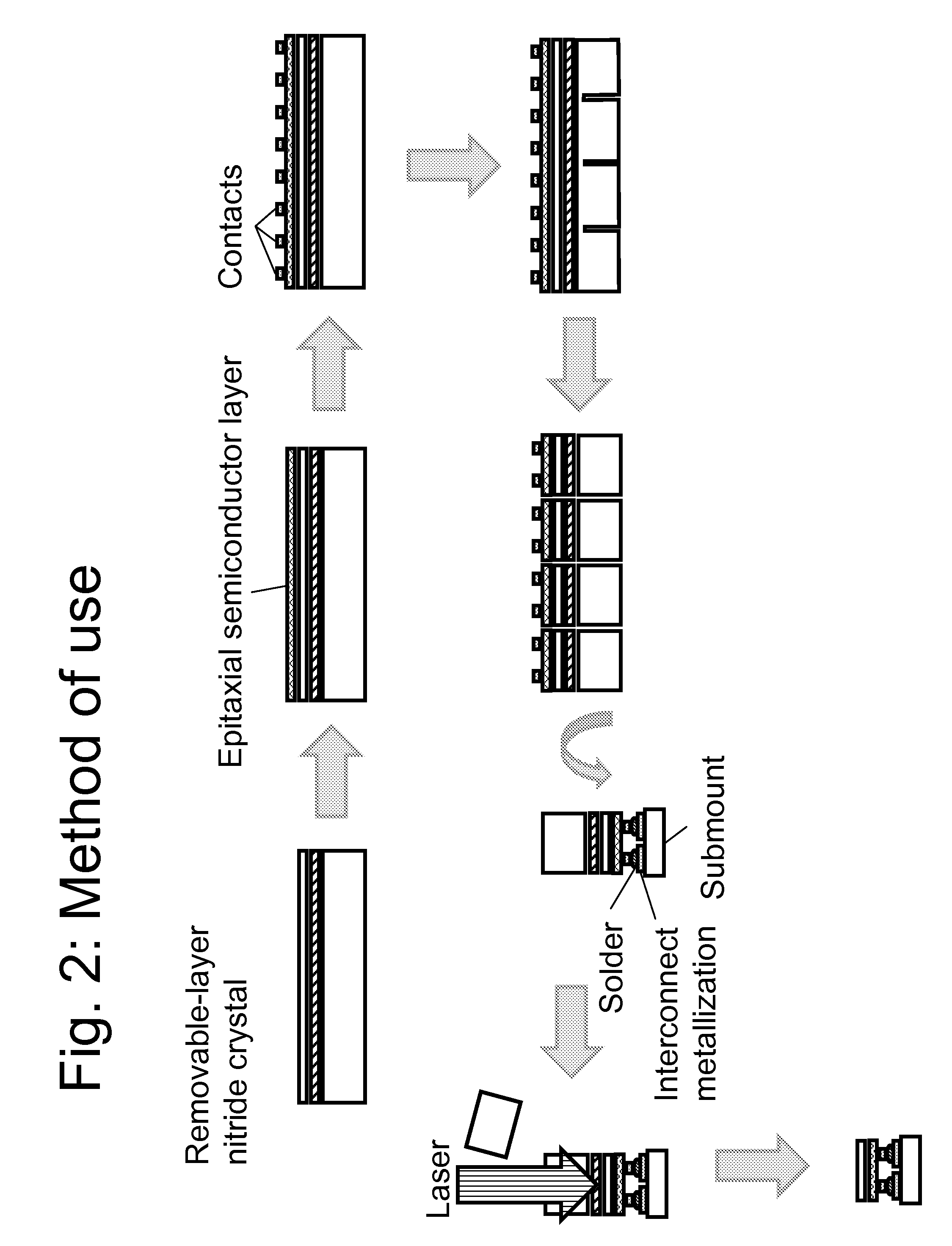
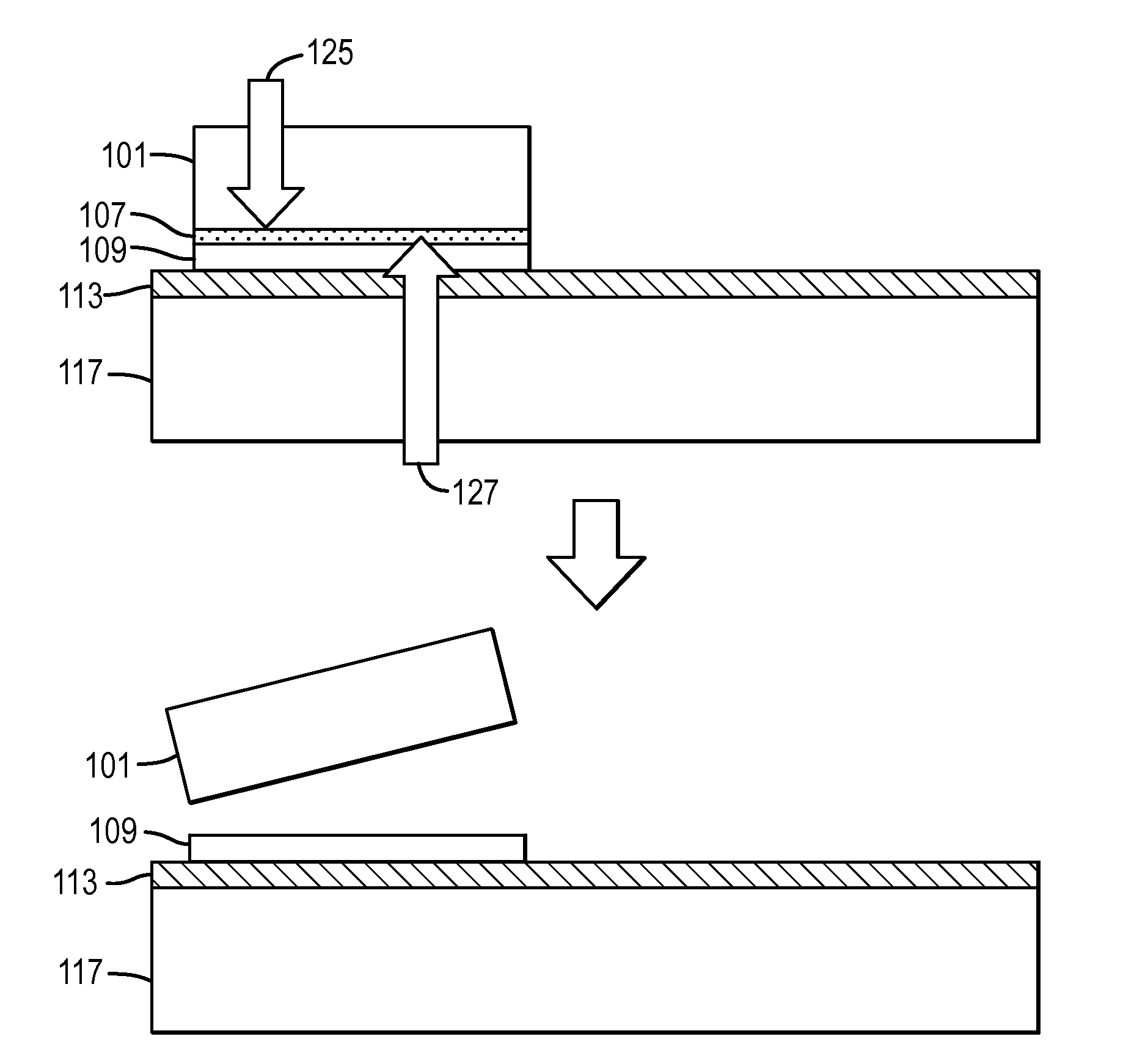
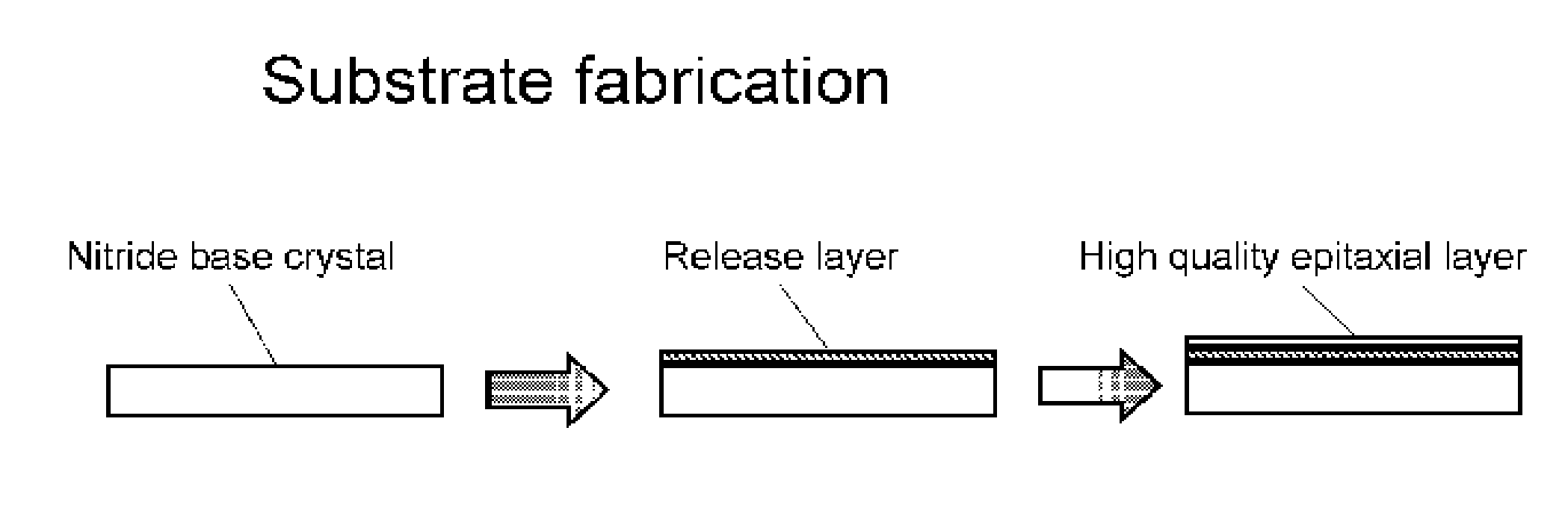
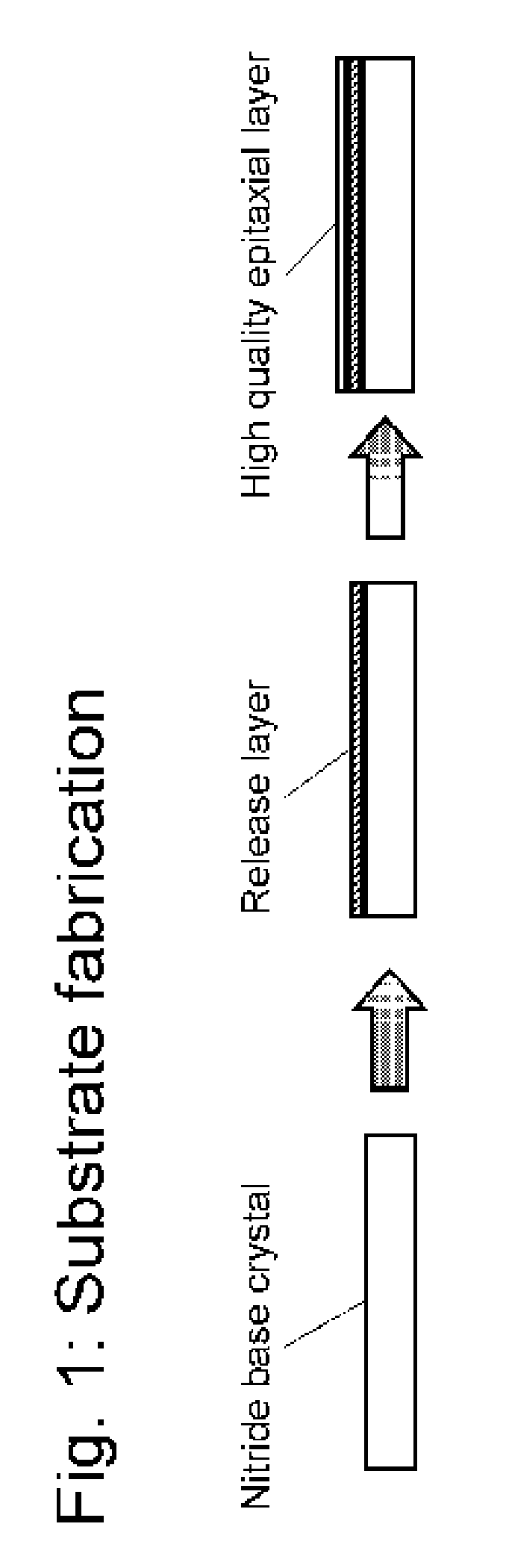
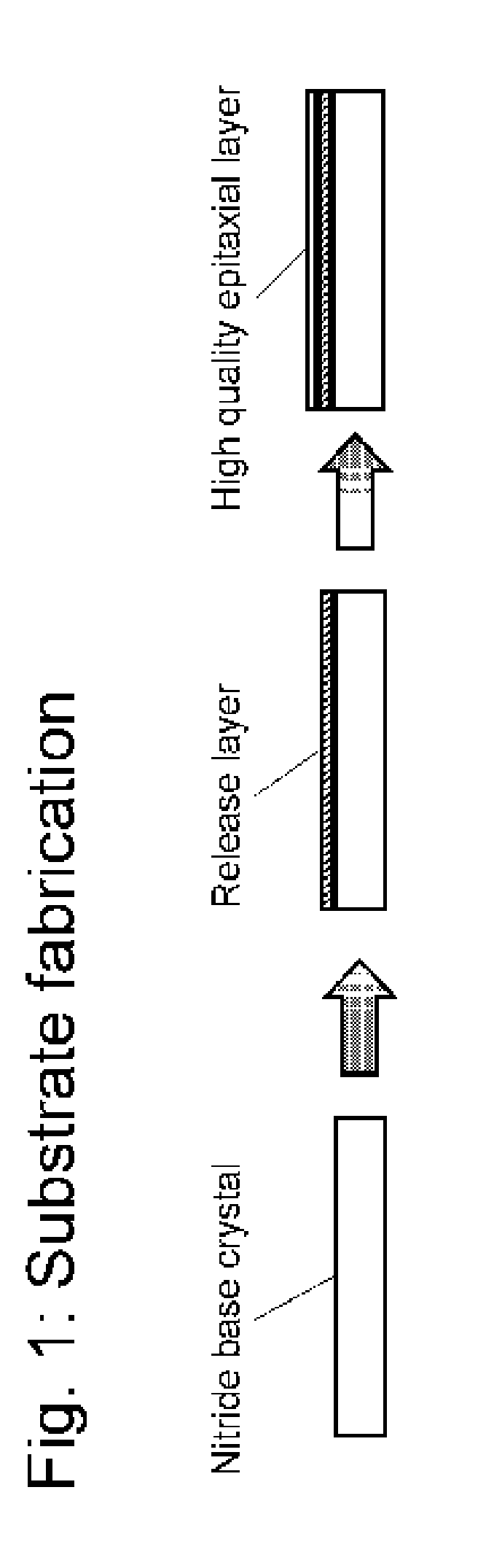
A nitride crystal or wafer with a removable surface layer comprises a high quality nitride base crystal, a release layer, and a high quality epitaxial layer. The release layer has a large optical absorption coefficient at wavelengths where the base crystal is substantially transparent and may be etched under conditions where the nitride base crystal and the high quality epitaxial layer are not. The high quality epitaxial layer may be removed from the nitride base crystal by laser liftoff or by chemical etching after deposition of at least one epitaxial device layer. The nitride crystal with a removable surface layer is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SLT TECH
Hydrogen generation from water split reaction
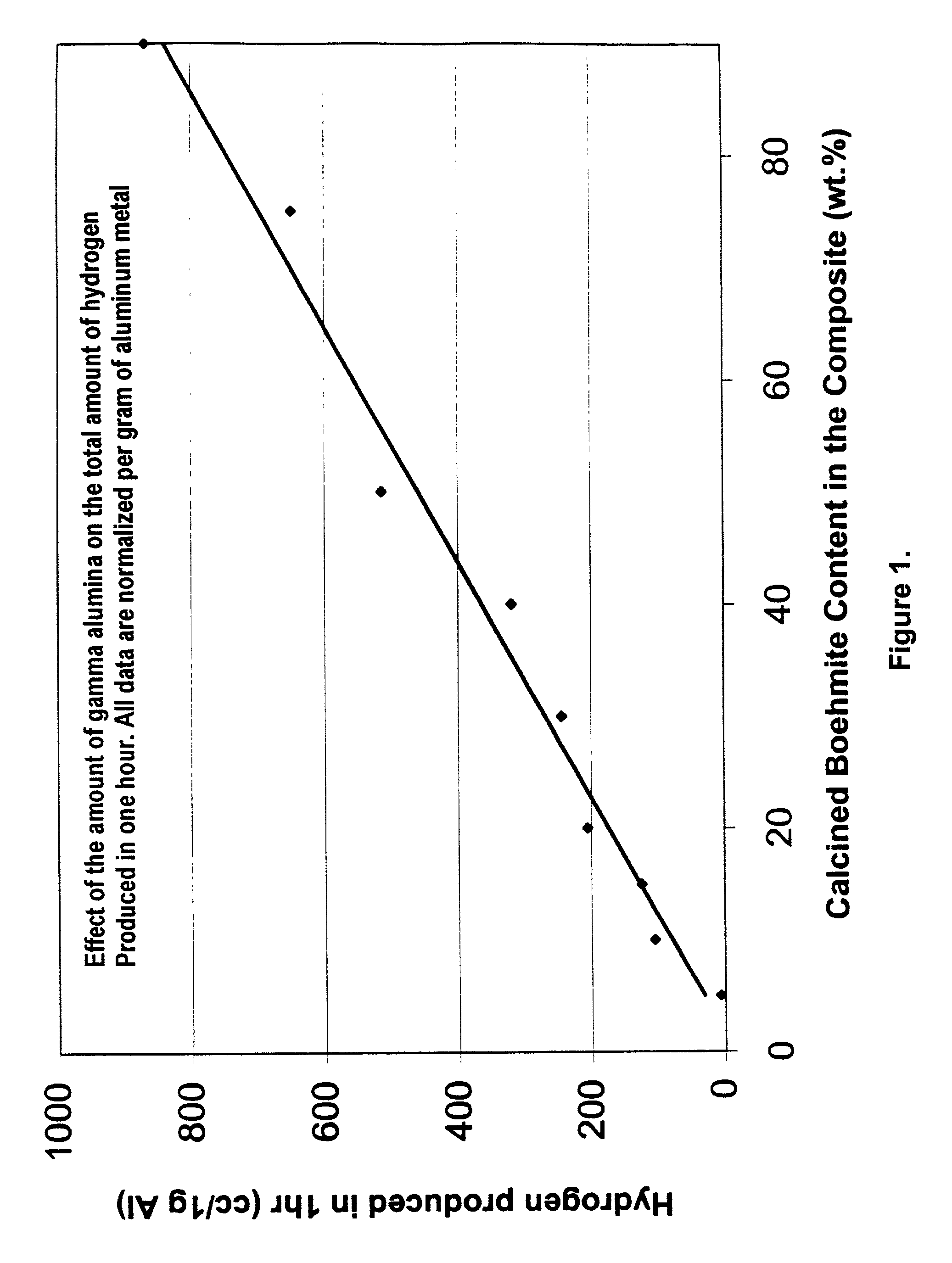
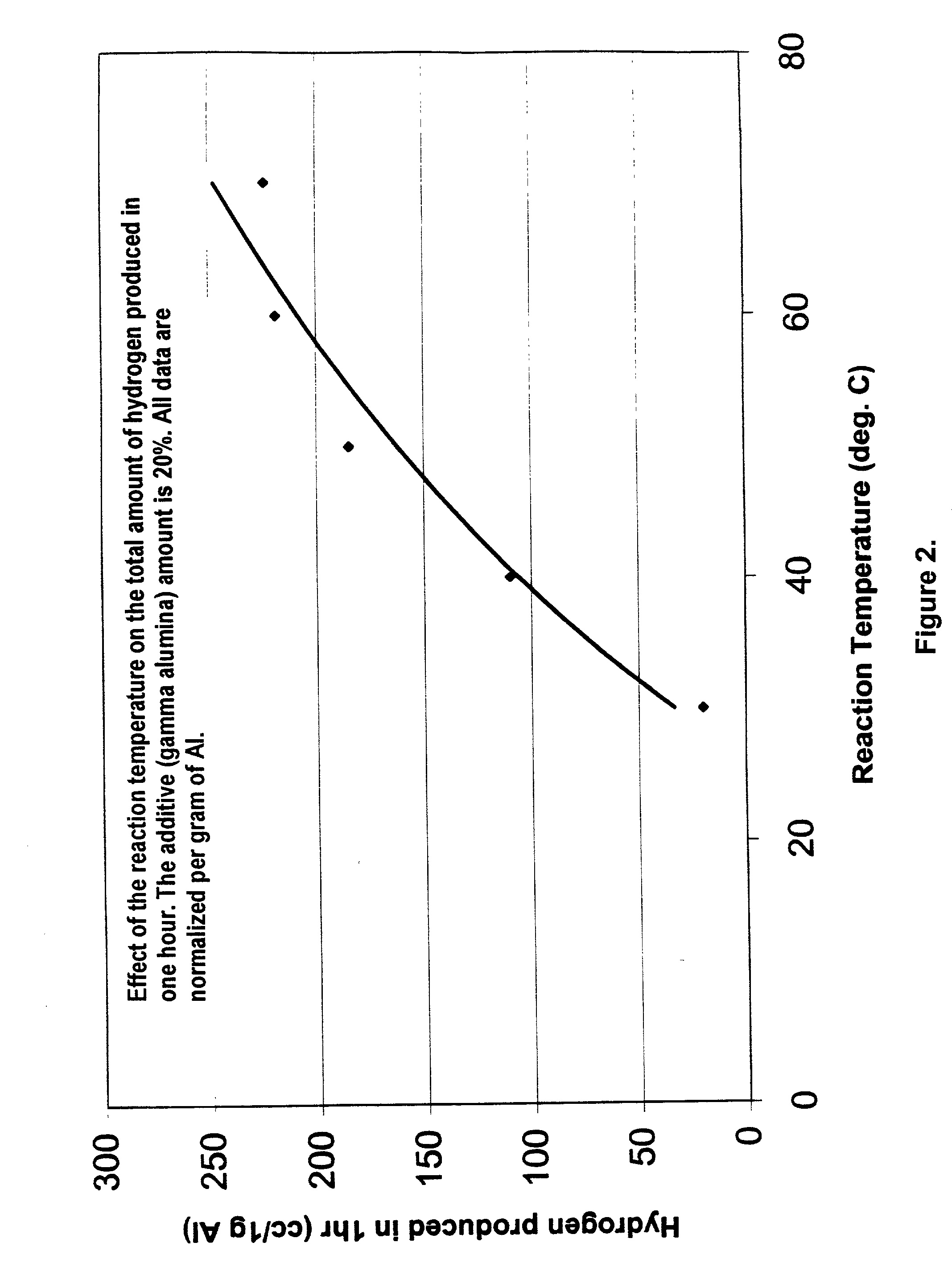
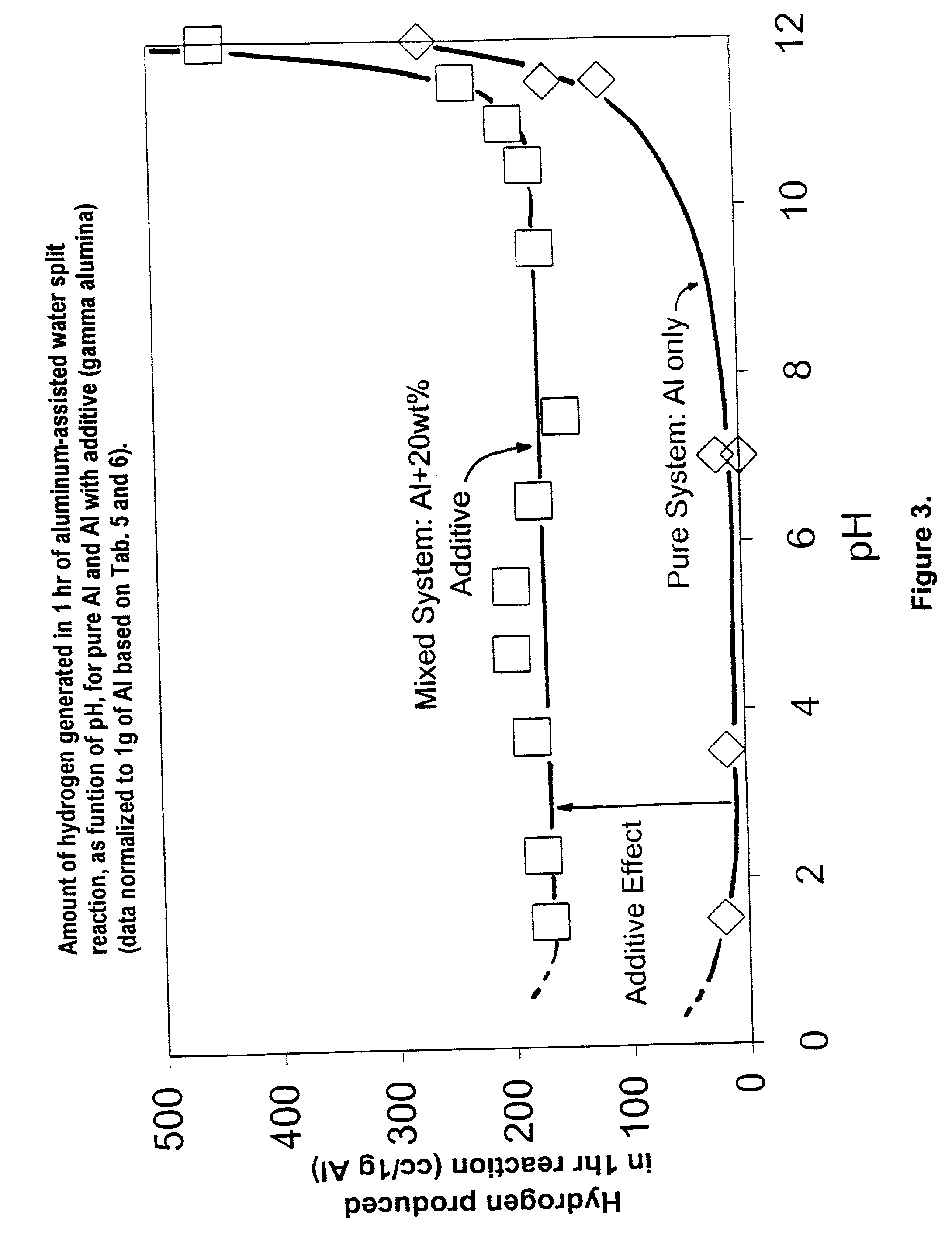
A method of producing Hydrogen by reacting a metal selected from the group consisting of Aluminum (Al), Magnesium (Mg), Silicon (Si) and Zinc (Zn) with water in the presence of an effective amount of a catalyst at a pH of between 4 and 10 to produce Hydrogen. The catalyst or other additive is selected to prevent or slow down deposition of the reaction products on the (impair reactions with the) metal that tend to passivate the metal and thereby facilitates the production of said Hydrogen.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
System and sub-systems for production and use of hydrogen
InactiveUS20060065302A1Most efficientSimple designPhotography auxillary processesPV power plantsHydrogenProton
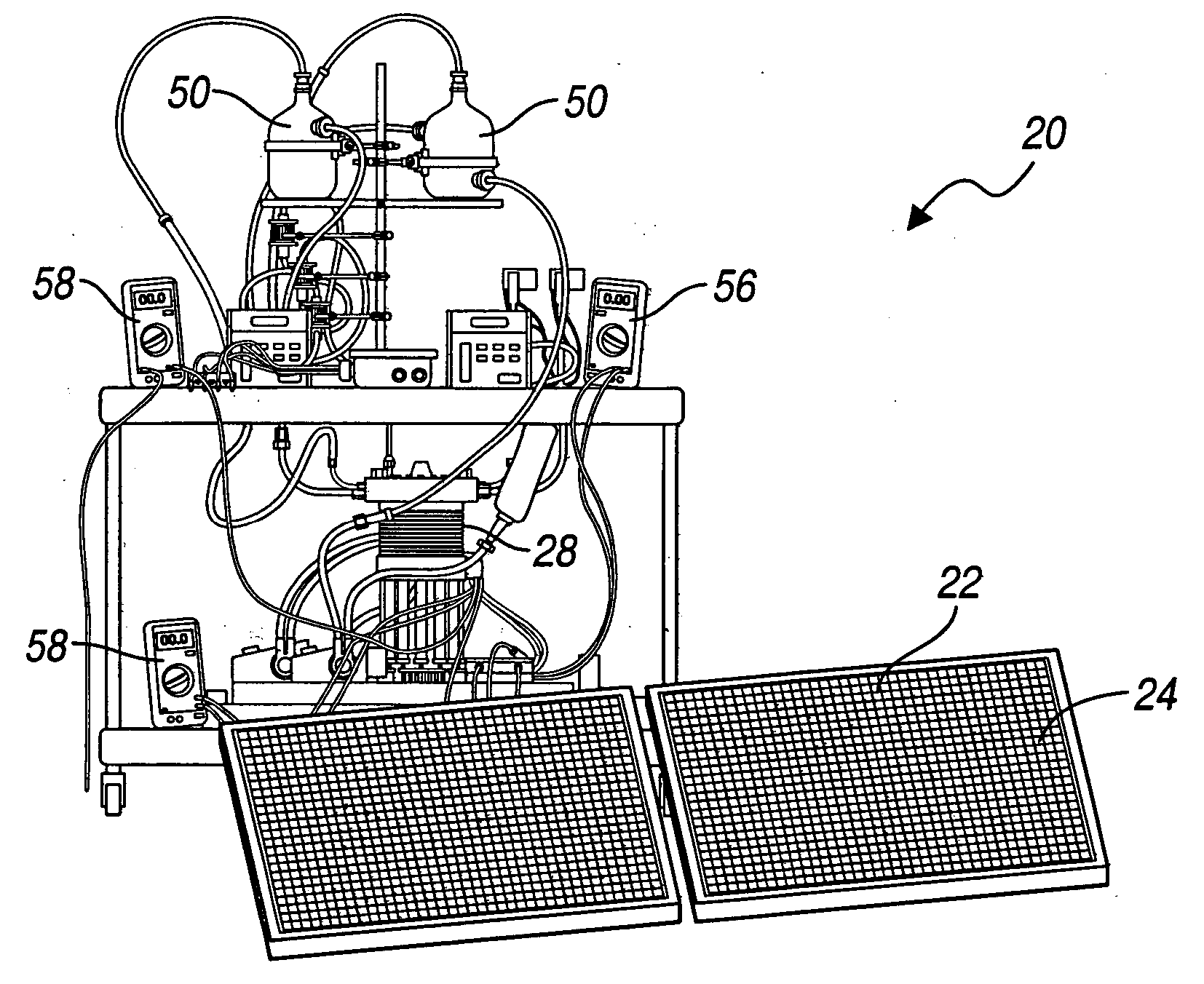
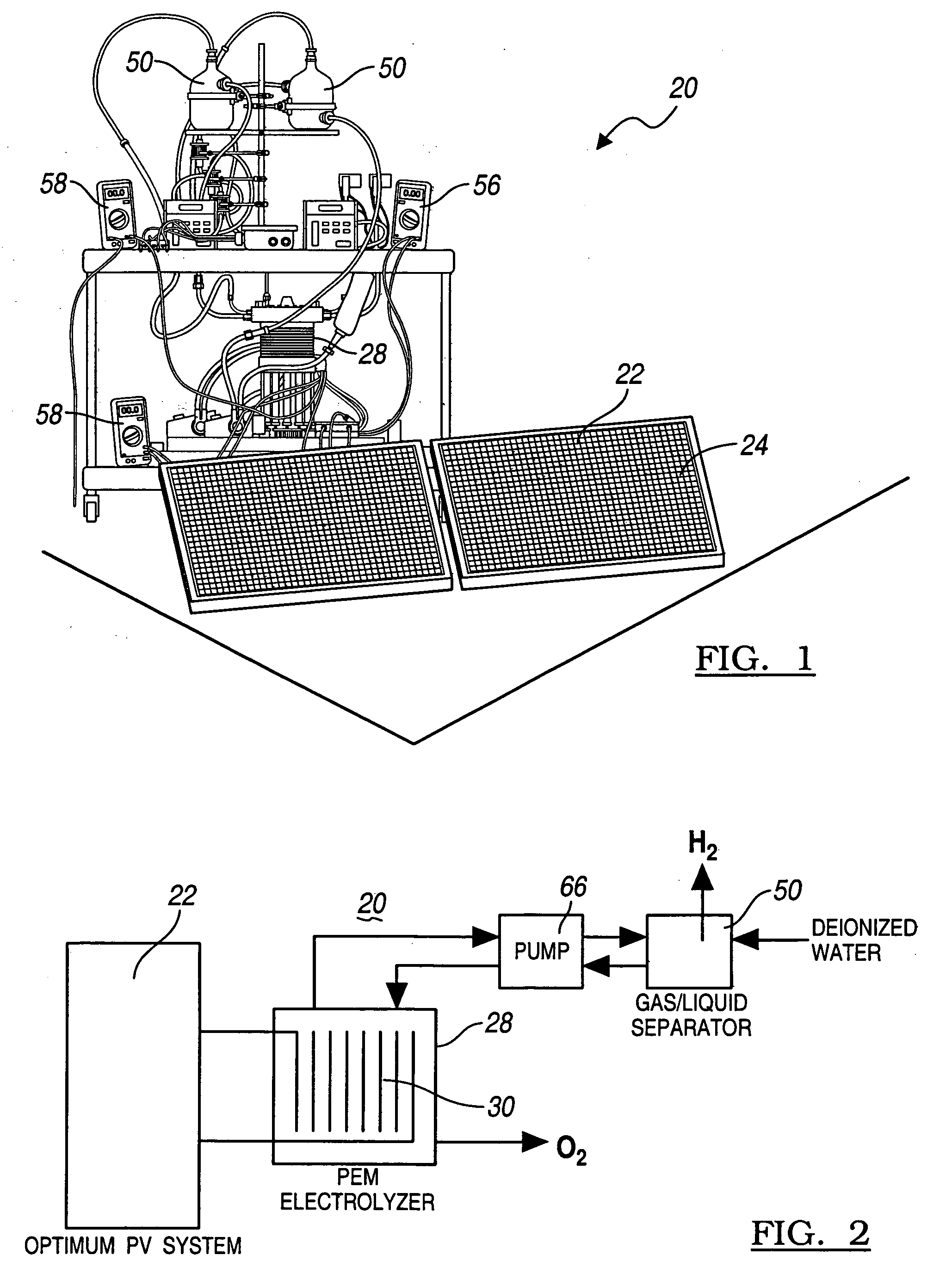
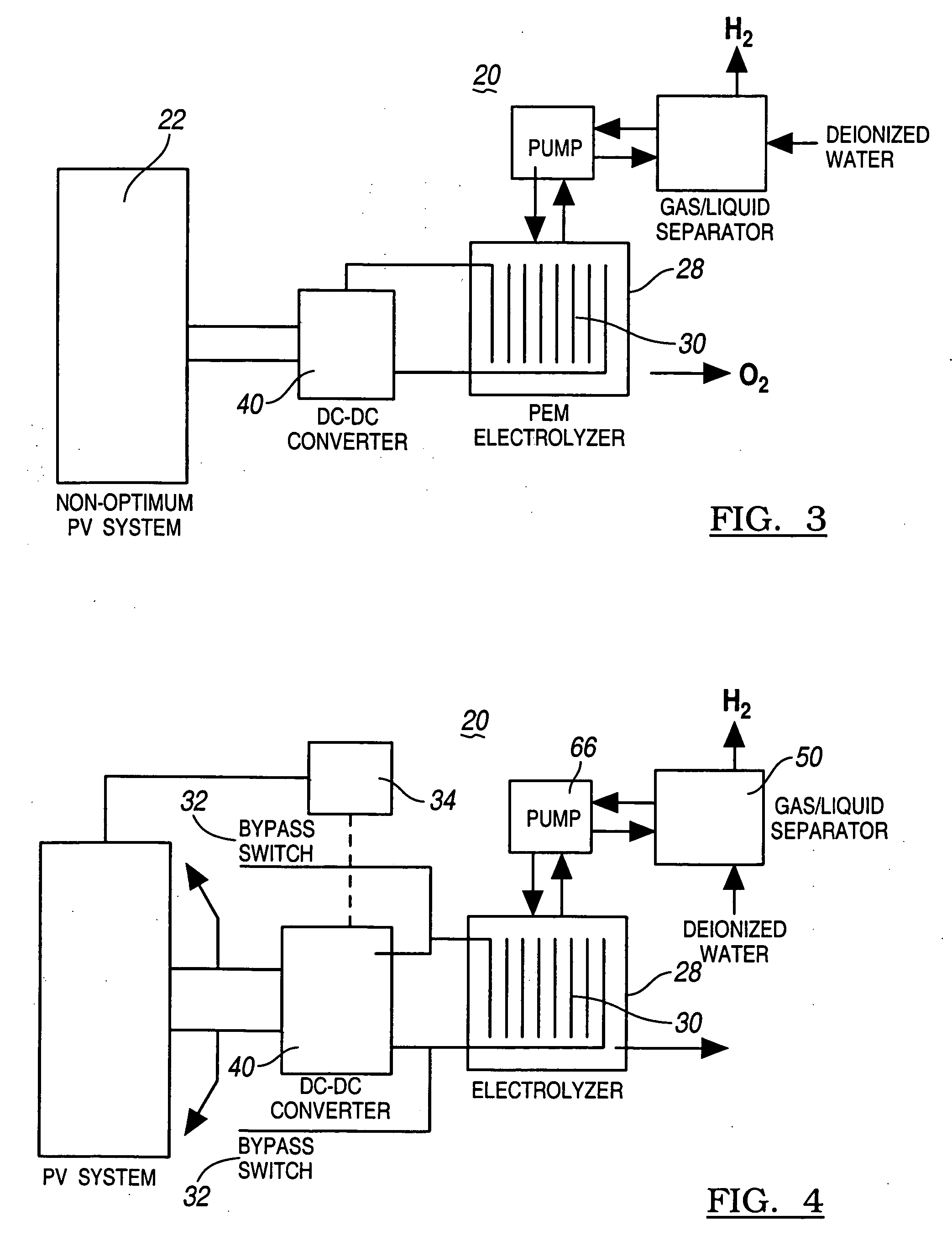
A method for optimizing the efficiency of a solar powered hydrogen generation system is disclosed. The system utilizes photovoltaic modules and a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer to split water into hydrogen and oxygen with an efficiency greater than 12%. This high efficiency for the solar powered electrolysis of water was obtained by matching the voltage generated by photovoltaic modules to the operating voltage of the electrolyzer. Optimizing PV-electrolysis systems makes solar generated hydrogen less expensive and more practical for use as an environmentally clean and renewable fuel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Metal-oxide based process for the generation of hydrogen from water splitting utilizing a high temperature solar aerosol flow reactor
InactiveUS20060188433A1Suppress heterogeneous nucleationReduce recombinationCatalytic gas-gas reactionZinc oxides/hydroxidesHydrogenReactor system
The invention provides methods for reduction of metal oxide particles using a high temperature solar aerosol reactor. The invention also provides metal-oxide based processes for the generation of hydrogen from water splitting using a high temperature solar aerosol reactor. In addition, the invention provides solar thermal reactor systems suitable for use with these processes.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Large Area, Low-Defect Gallium-Containing Nitride Crystals, Method of Making, and Method of Use
ActiveUS20140065360A1Improve crystal qualityFrom normal temperature solutionsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic detectorsHydrogen
An ultralow defect gallium-containing nitride crystal and methods of making ultralow defect gallium-containing nitride crystals are disclosed. The crystals are useful as substrates for light emitting diodes, laser diodes, transistors, photodetectors, solar cells, and photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generators.
Owner:SLT TECH
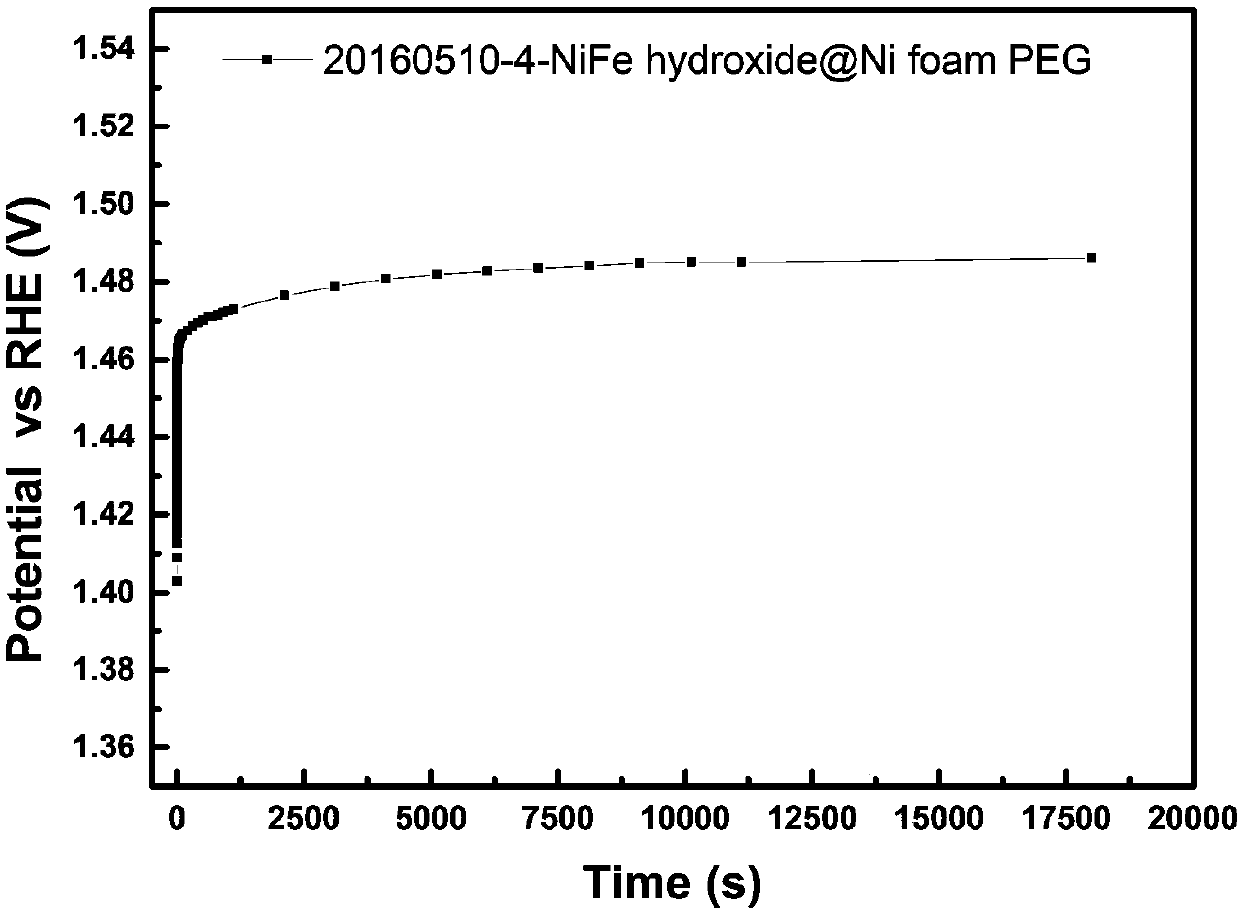
Hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107620087AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesElectrolysisExternal bias
The invention relates to a hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode applicable to alkaline mediums and a preparation method and application thereof. The electrode is applicable to the oxygen evolution reaction in the water-electrolytic hydrogen making process under catalytic alkaline conditions. The hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages as follows: the nickel-iron hydroxide integrated electrode is shape-controlled, the preparation process is simple and under mild conditions, and the electrode can be used for a water electrolytic tank for hydrogen production from water splitting under external bias potentials; the prepared hydroxyloxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode further has a better performance when being used in an alkaline solid polymer electrolyte (AEM) water electrolytic tank; and besides, an extensive utilization value in achieved in regenerative fuel cells (RFC), photoelectro-catalytic devices and electrolytic hydrogen generators.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
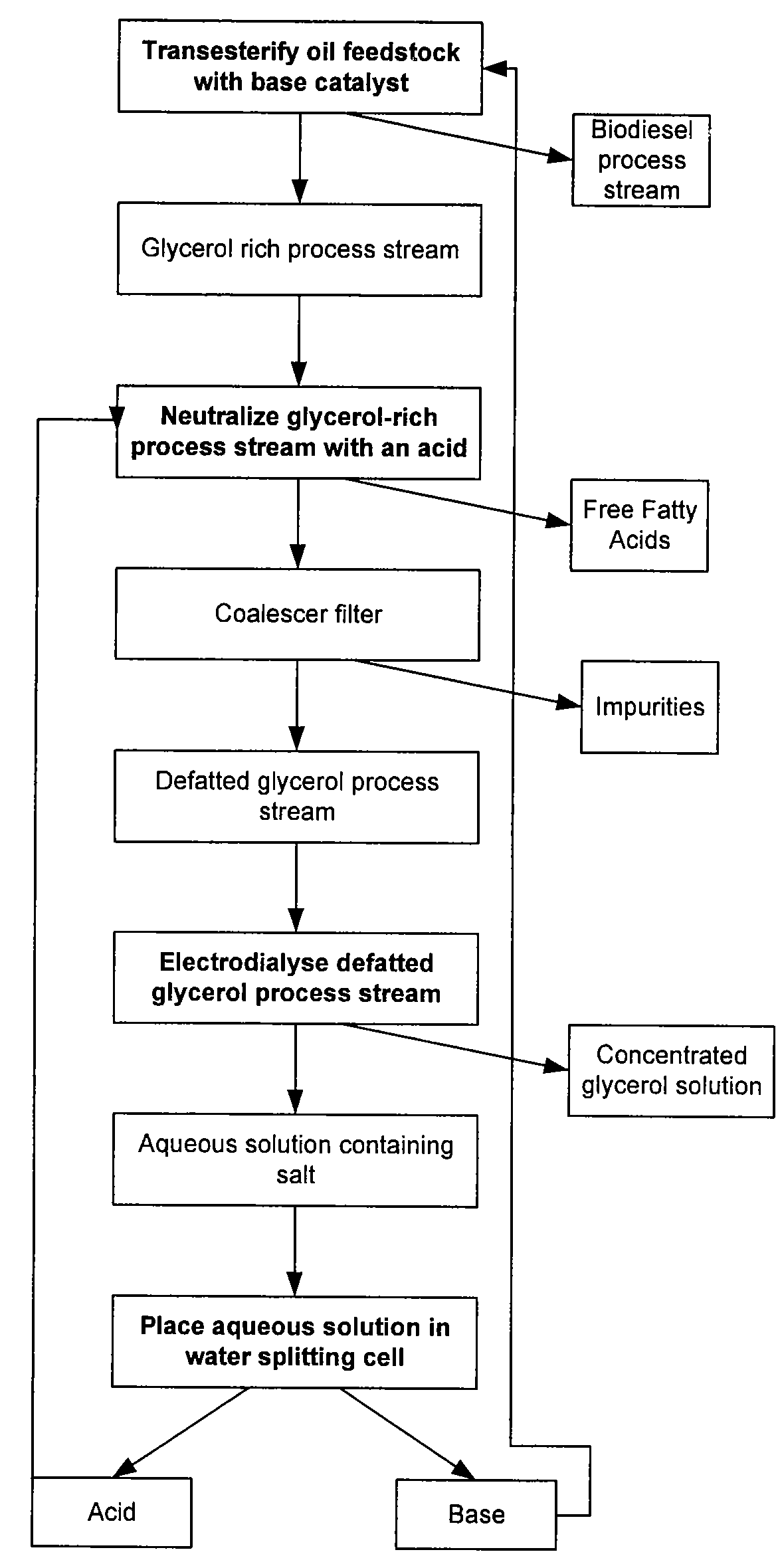
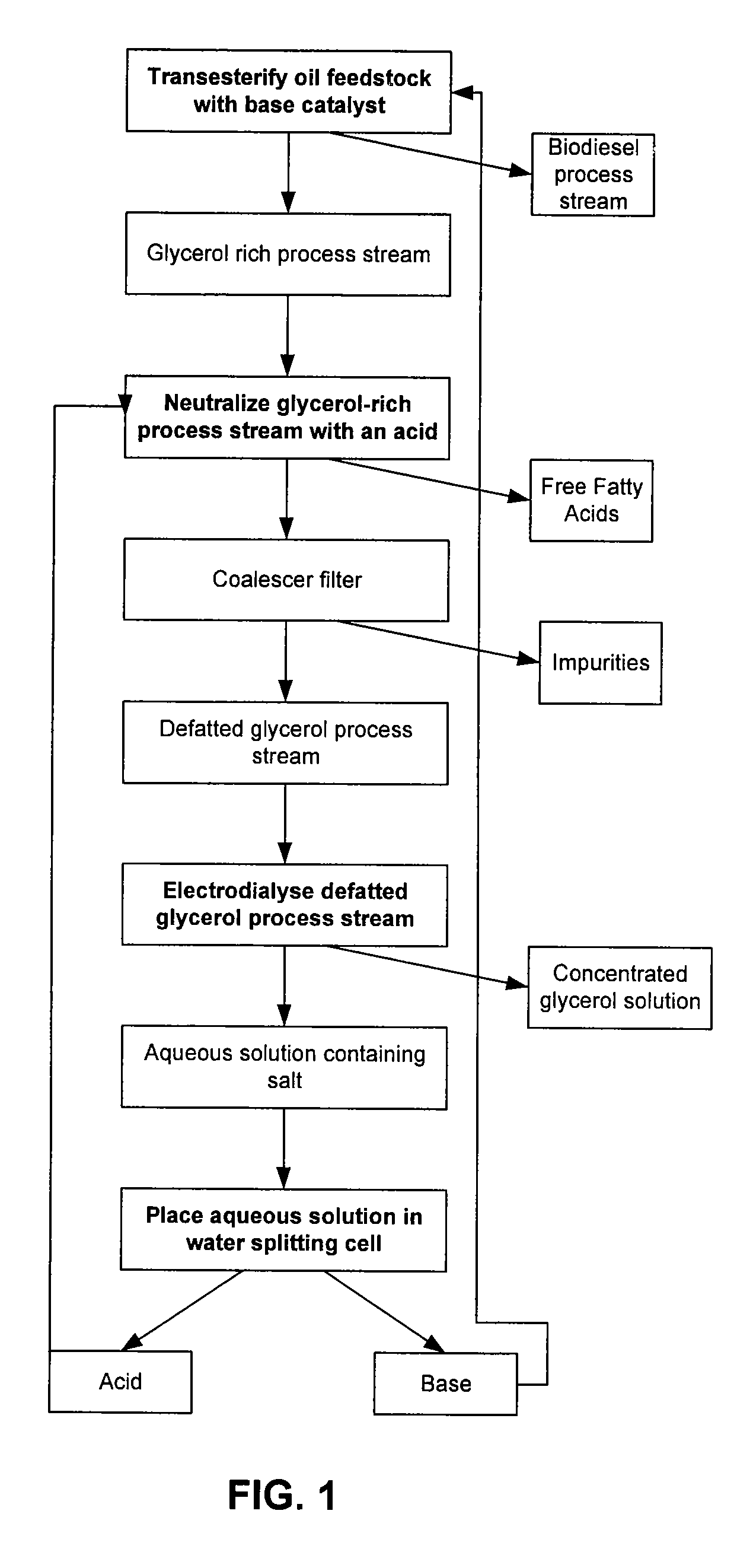
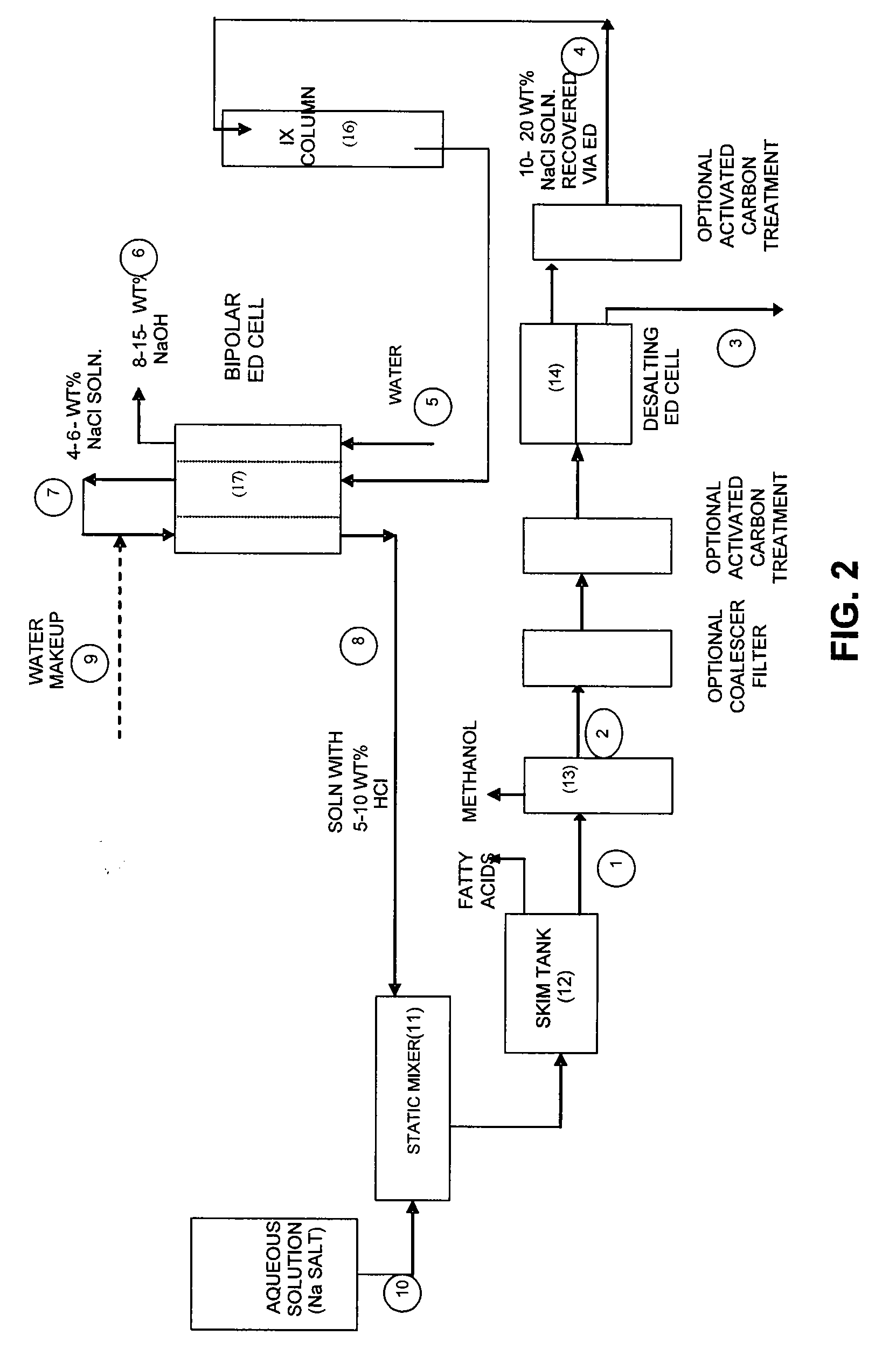
Process for Desalting Glycerol Solutions and Recovery of Chemicals
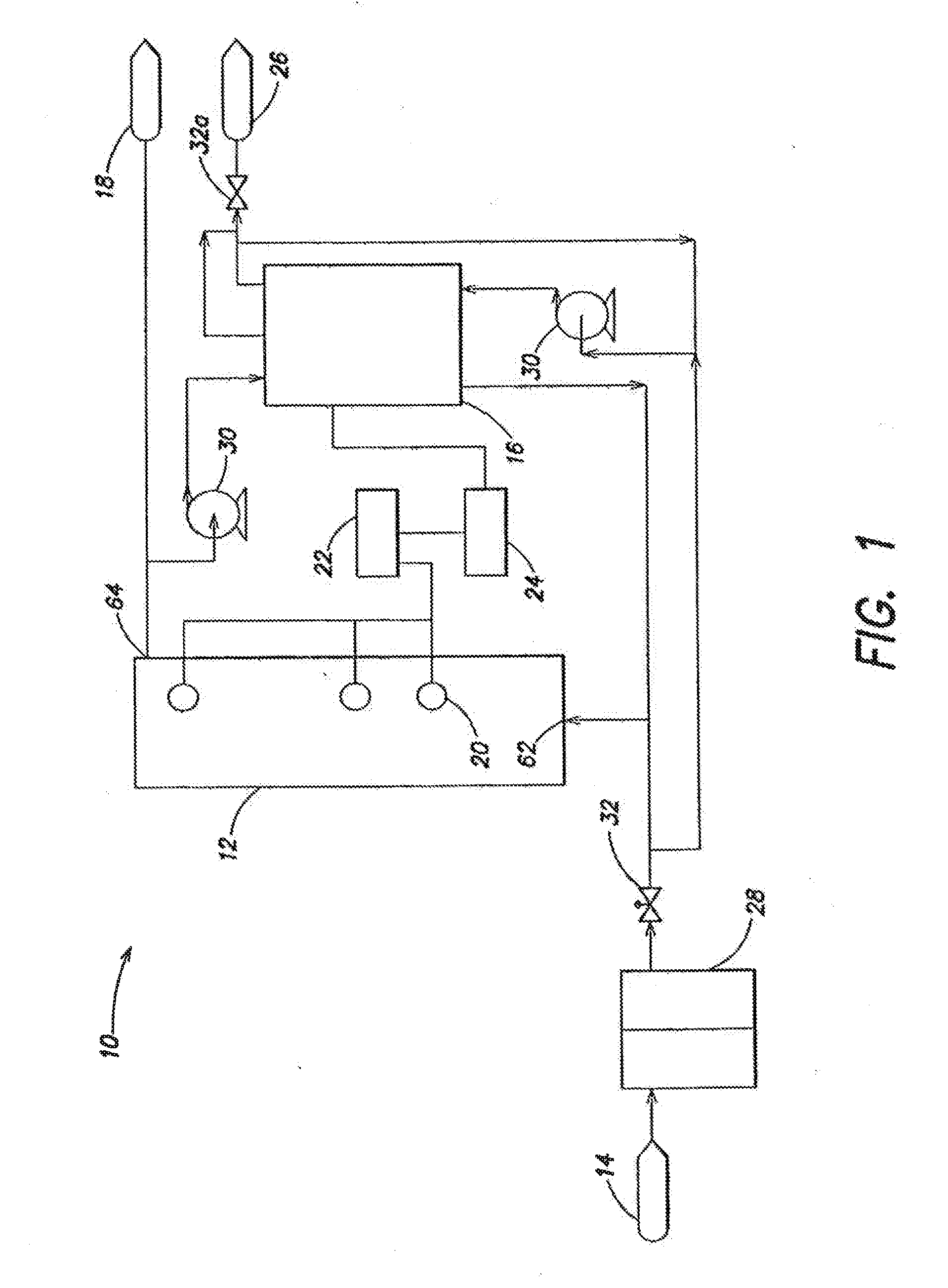
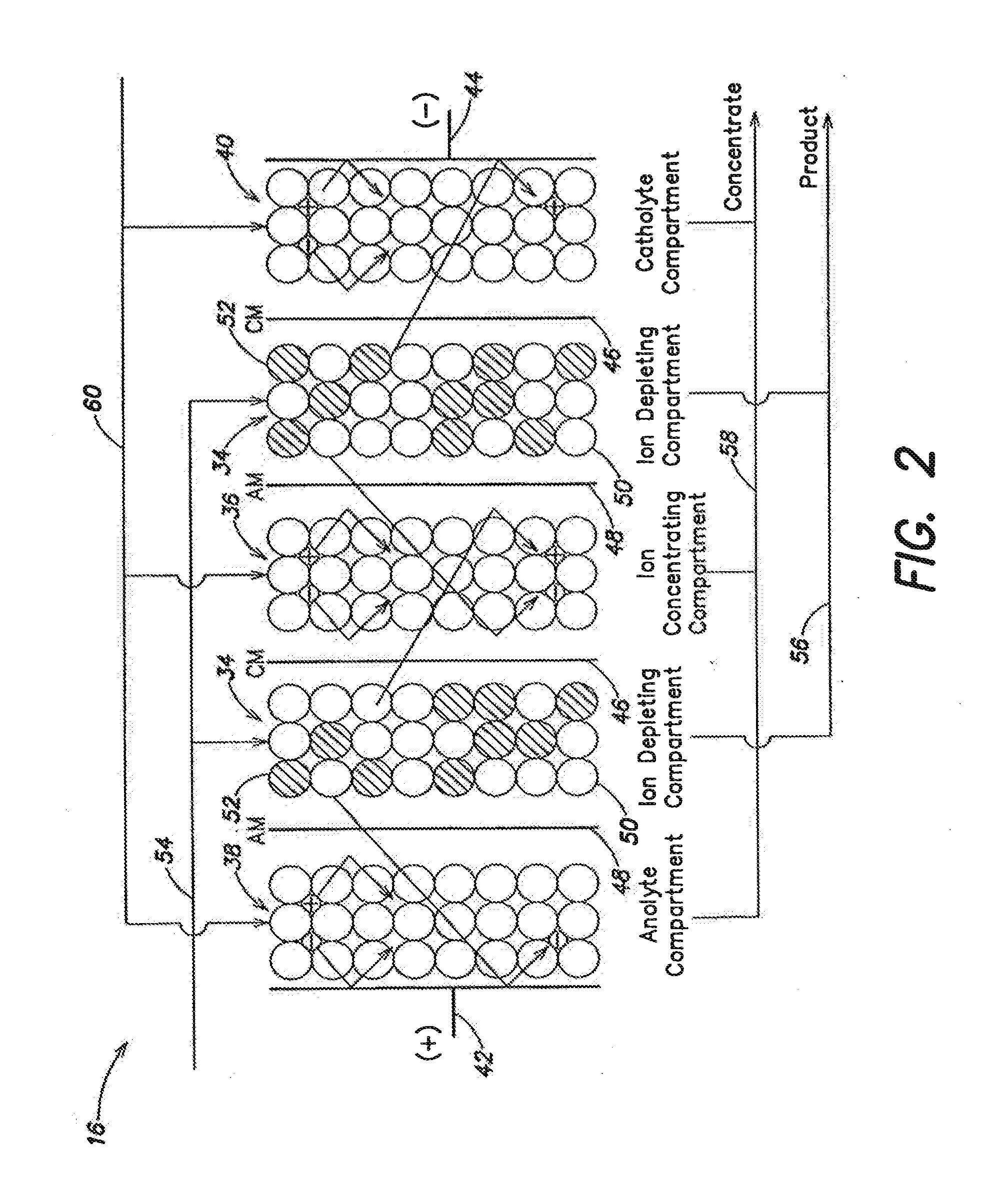
Processes for desalting glycerol-rich solutions or process streams using electrodialysis are provided. The glycerol-rich process streams are typically byproducts from the production of biodiesel. Following electrodialysis, the resulting aqueous salt solution is placed in a water splitting cell to recover the acid and base components of the salt. These acid and base components, in turn, can be reused in other processes, such as biodiesel production.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Reusable nitride wafer, method of making, and use thereof
ActiveUS20160020284A1High secondary electron yieldPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSolar cell
Techniques for processing materials for manufacture of gallium-containing nitride substrates are disclosed. More specifically, techniques for fabricating and reusing large area substrates using a combination of processing techniques are disclosed. The methods can be applied to fabricating substrates of GaN, AlN, InN, InGaN, AlGaN, and AlInGaN, and others. Such substrates can be used for a variety of applications including optoelectronic devices, lasers, light emitting diodes, solar cells, photo electrochemical water splitting and hydrogen generation, photo detectors, integrated circuits, transistors, and others.
Owner:SLT TECH
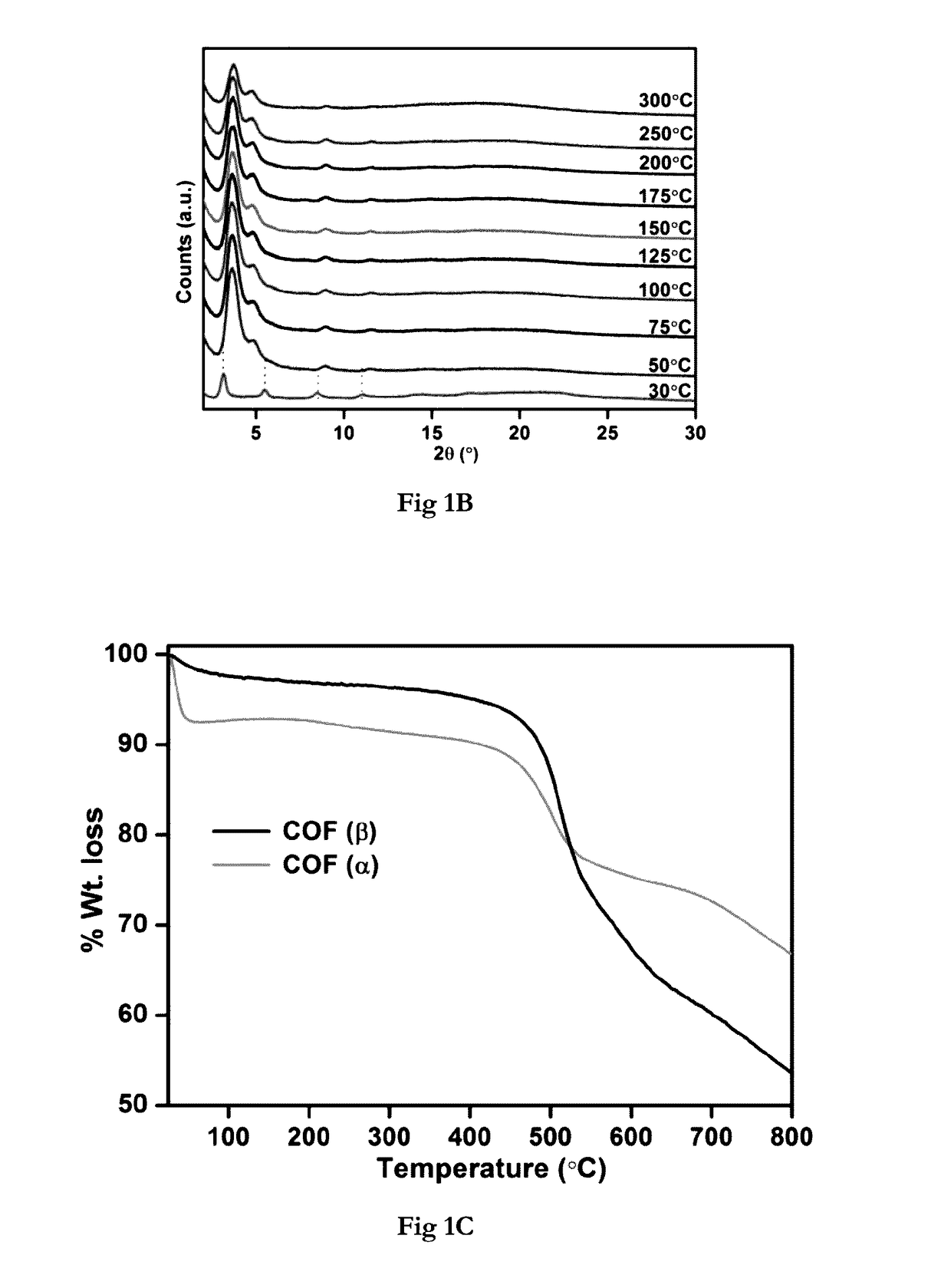
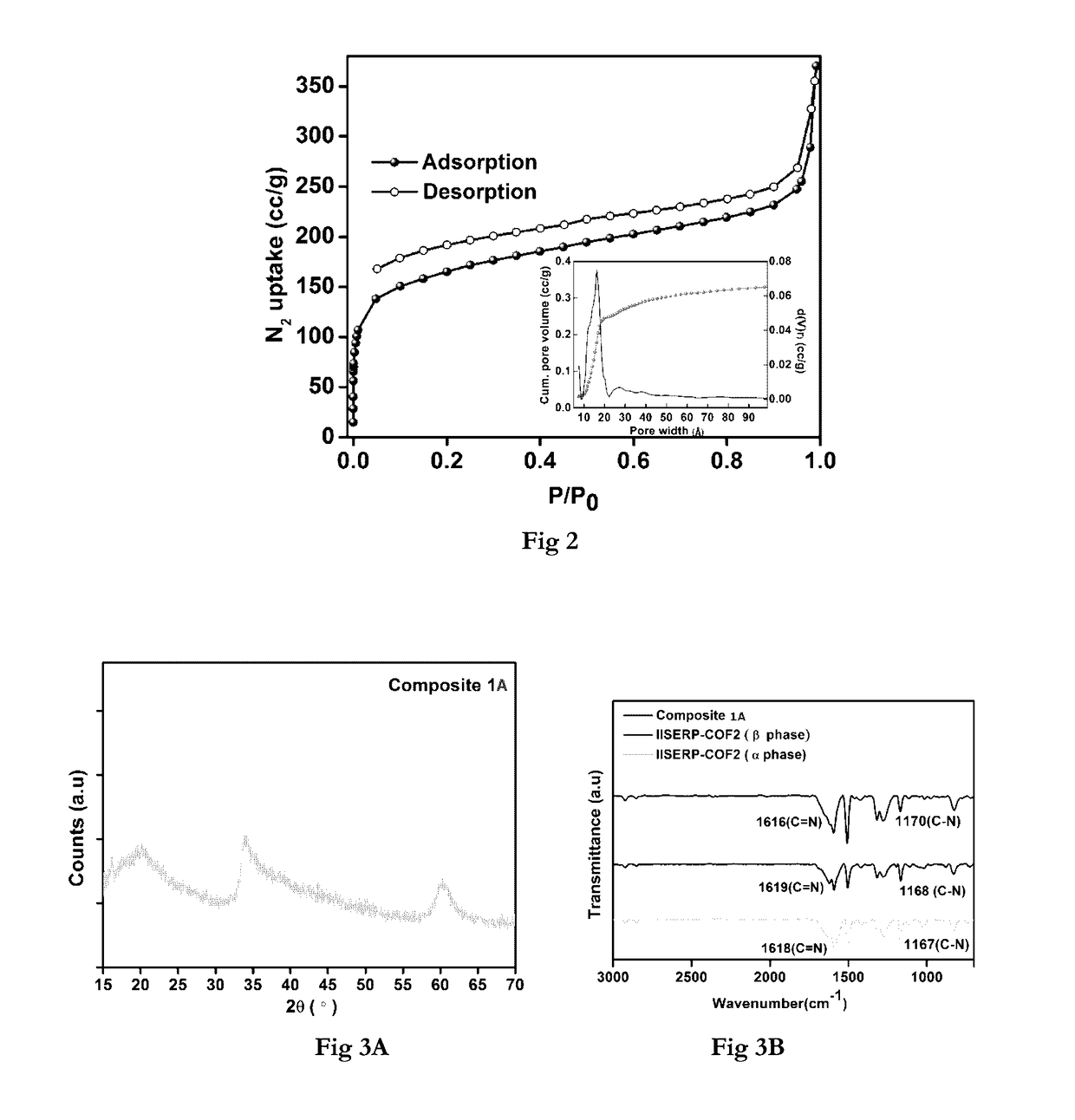
Covalent organic frameworks as porous supports for non-noble metal based water splitting electrocatalysts
ActiveUS20170130349A1Smooth connectionImprove performanceMultiple component coatingsElectrode with substrate and coatingMetal-organic frameworkManganese
The present invention discloses porous covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles which are useful as electrocatalysts for a water splitting system, and to the process for preparation of such electrocatalysts. The covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles have general formula (I):COF_AxBy(M)n (Formula I)wherein COF is selected from a Tris (4-formylphenyl)amine terephthaldehyde polymer or a benzimidazole-phloroglucinol polymer;‘A’ and ‘B’ each independently represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof; or ‘A’ and ‘B’ together represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof;‘M’ represents hydroxide or a nitride ion;‘x’ and ‘y’ represent the weight % of the metal loadings; or a ratio of x:y is between 0:1 and 1:0; and‘n’ is an integer 1 or 2 or 3.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF SCI EUDCATION & RES
A nanometer porous high-entropy alloy electrode, a preparing method thereof and applications of the electrode
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalytic and energy storage applications of high-entropy alloys, and particularly relates to a nanometer porous high-entropy alloy catalytic electrode,a preparing method thereof and applications of the electrode in bi-functional catalytic water splitting to produce hydrogen and oxygen. The electrode includes, by mole, 15-50% of Ni, 5-20% of a transition metal A, 15-50% of Mo, 5-25% of a transition metal B and 5-40% of Mn, wherein the transition metal A is Fe or Cu, and the transition metal B is one of Co, Ti or W. The alloy electrode has a porous structure, pore diameters range from 2 nm to 500 nm, and the specific surface area is 10-80 m<2> / g. The alloy electrode has advantages of 1) capability of being three-dimensional, porous, self-supporting and no need of any support or adhesive; 2) a large specific surface area and good electrical conductivity; 3) a simple material structure of the non-noble-metal porous high-entropy electrode, rich raw material sources, low prices and controllable preparation conditions; and 4) excellent catalytic performance.
Owner:宁波杰士兄弟工具有限公司
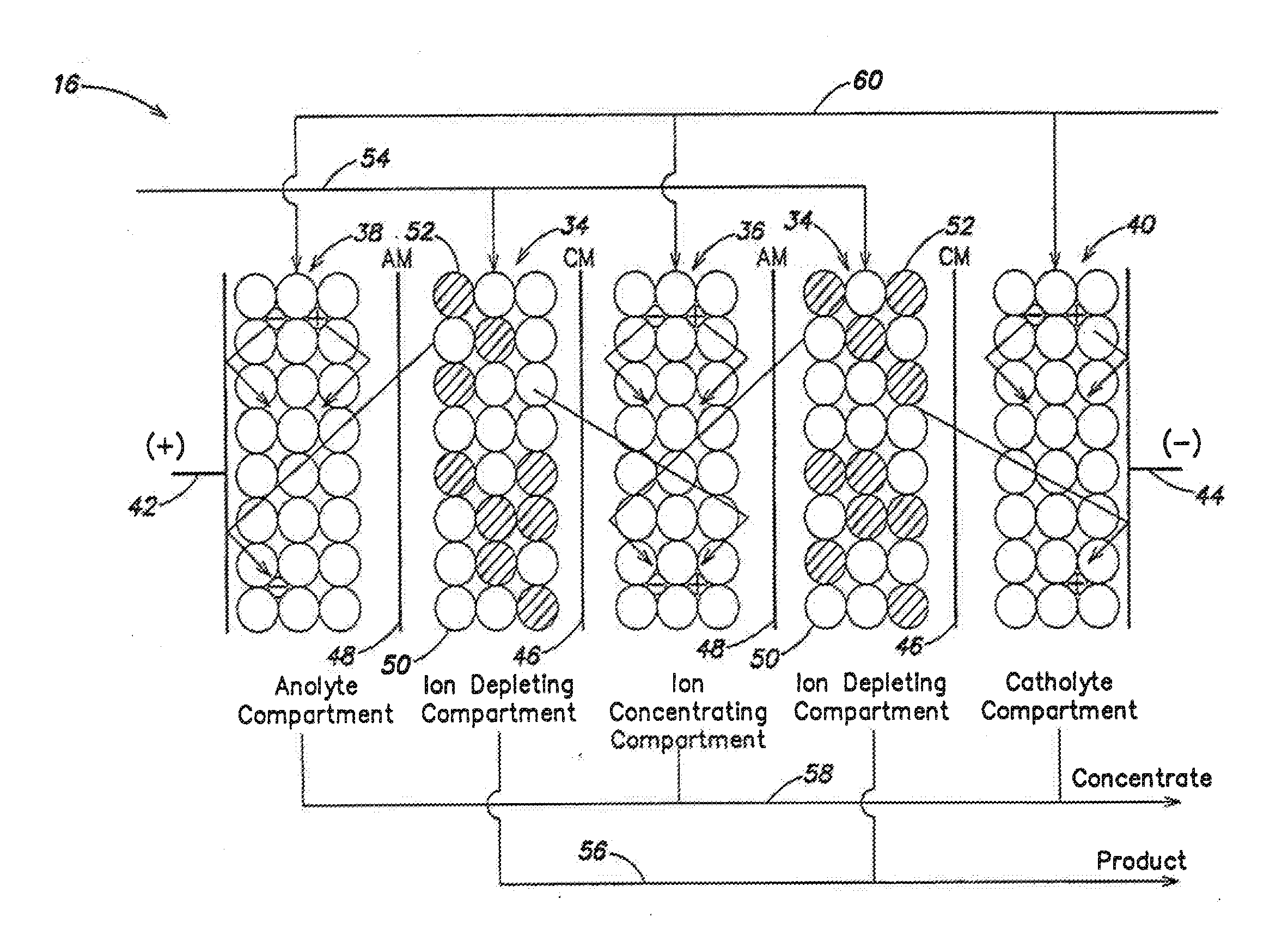
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20110120886A1Reduce likelihood of formationPrevent scalingCellsWater treatment parameter controlElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system. The electrochemical device can be operated at a low current and low flow rate to minimize water splitting or polarization, which minimizes scale formation.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
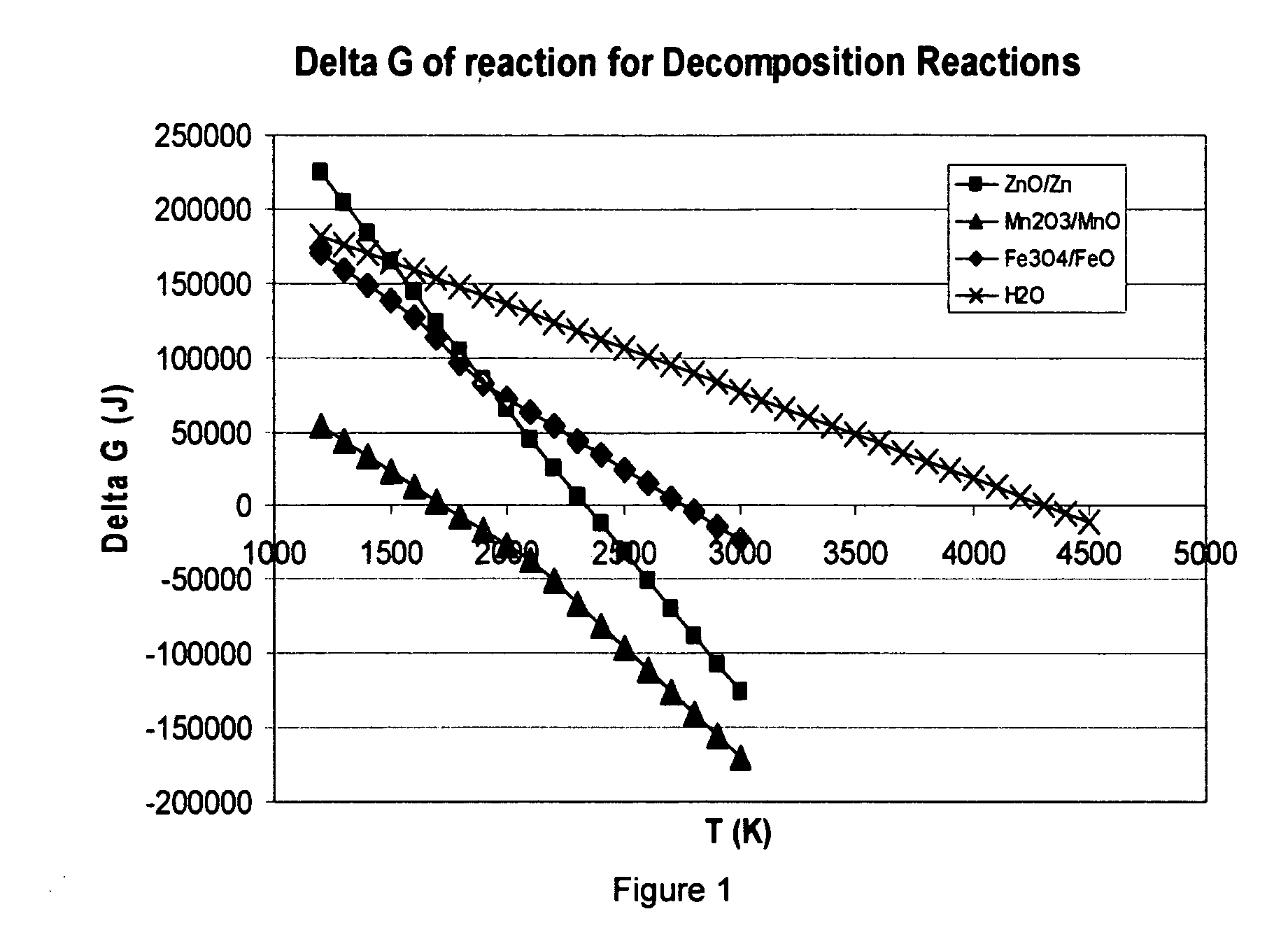
Thermochemical hydrogen produced from a vanadium decomposition cycle
InactiveUS20050013771A1Improve reliabilityHydrogen separation using liquid contactEnergy inputHydrogenDecomposition
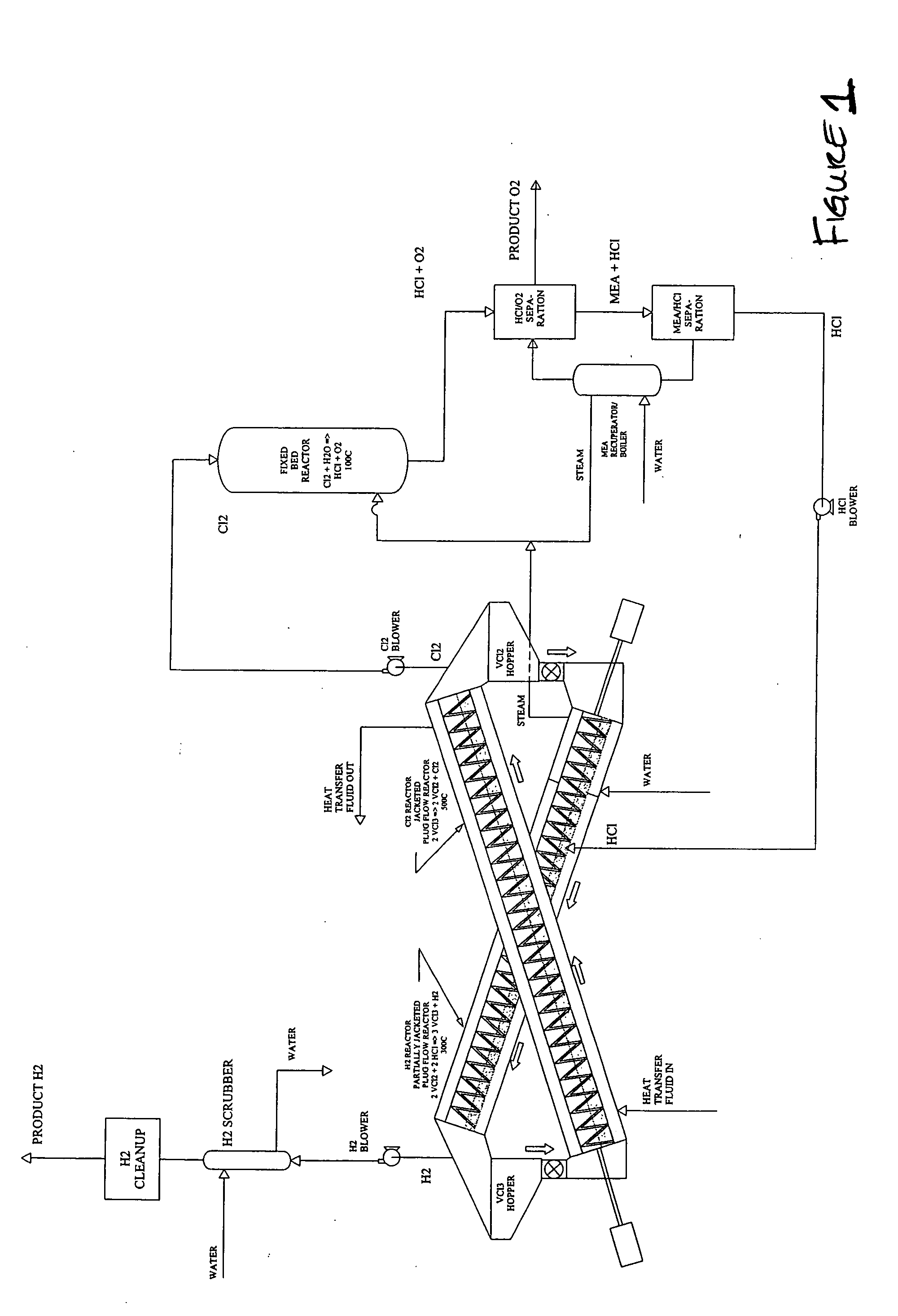
A thermochemical water-splitting process all reactions of which operate at relatively low temperatures and high efficiencies, and in which relatively inexpensive materials and processing methods are made possible. This invention involves the decomposition of a metal halide compound, i.e., one which is capable of being reduced from a higher oxidation state to lower oxidation state, e.g. vanadium chloride III→vanadium dichloride. The process is cyclic and regenerative, and the only net inputs are water and heat; and the only net outputs are hydrogen and oxygen. The process makes it possible to utilize a wide variety of available heat, including solar, sources for the energy input.
Owner:AMENDOLA STEVEN
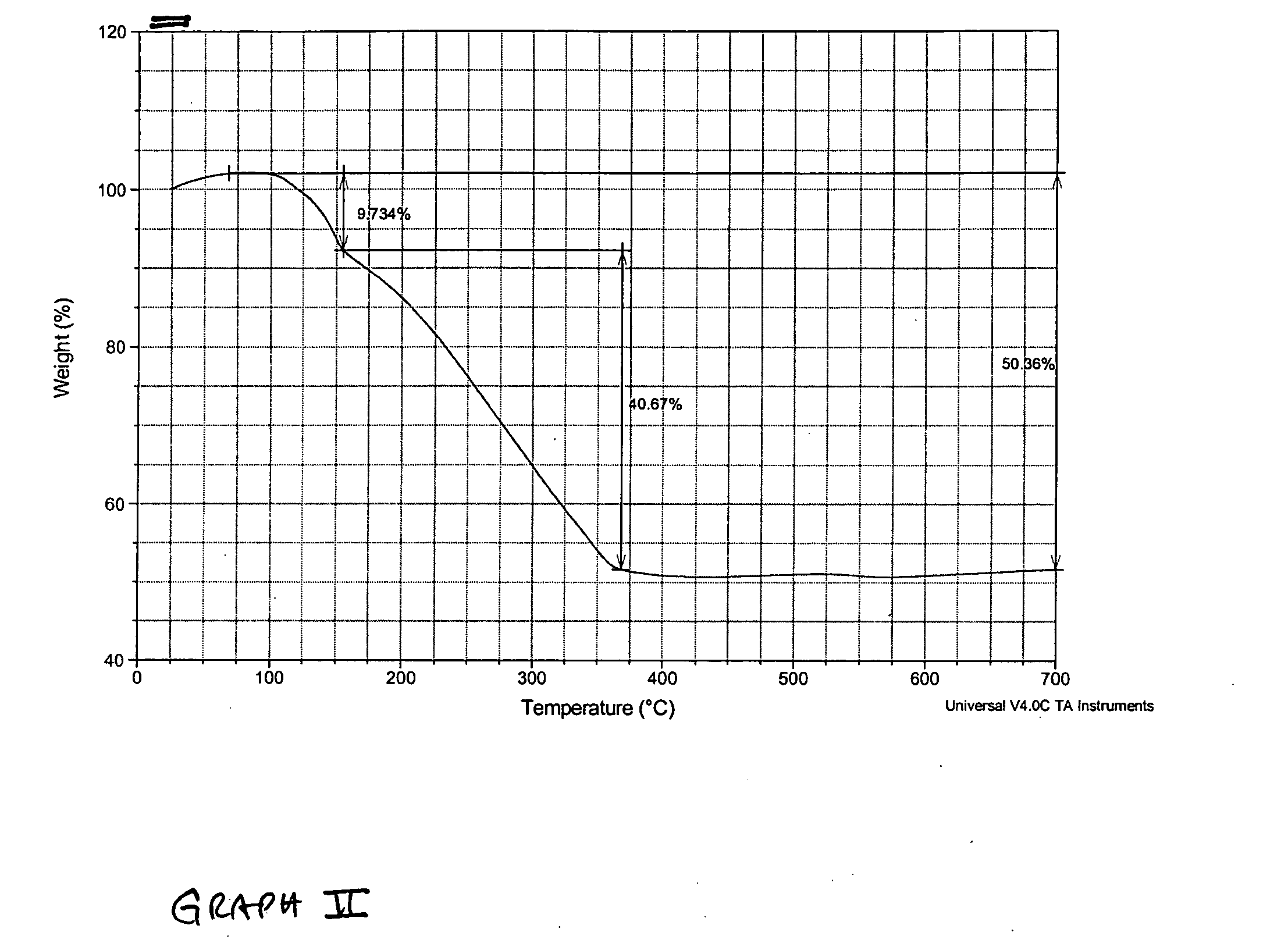
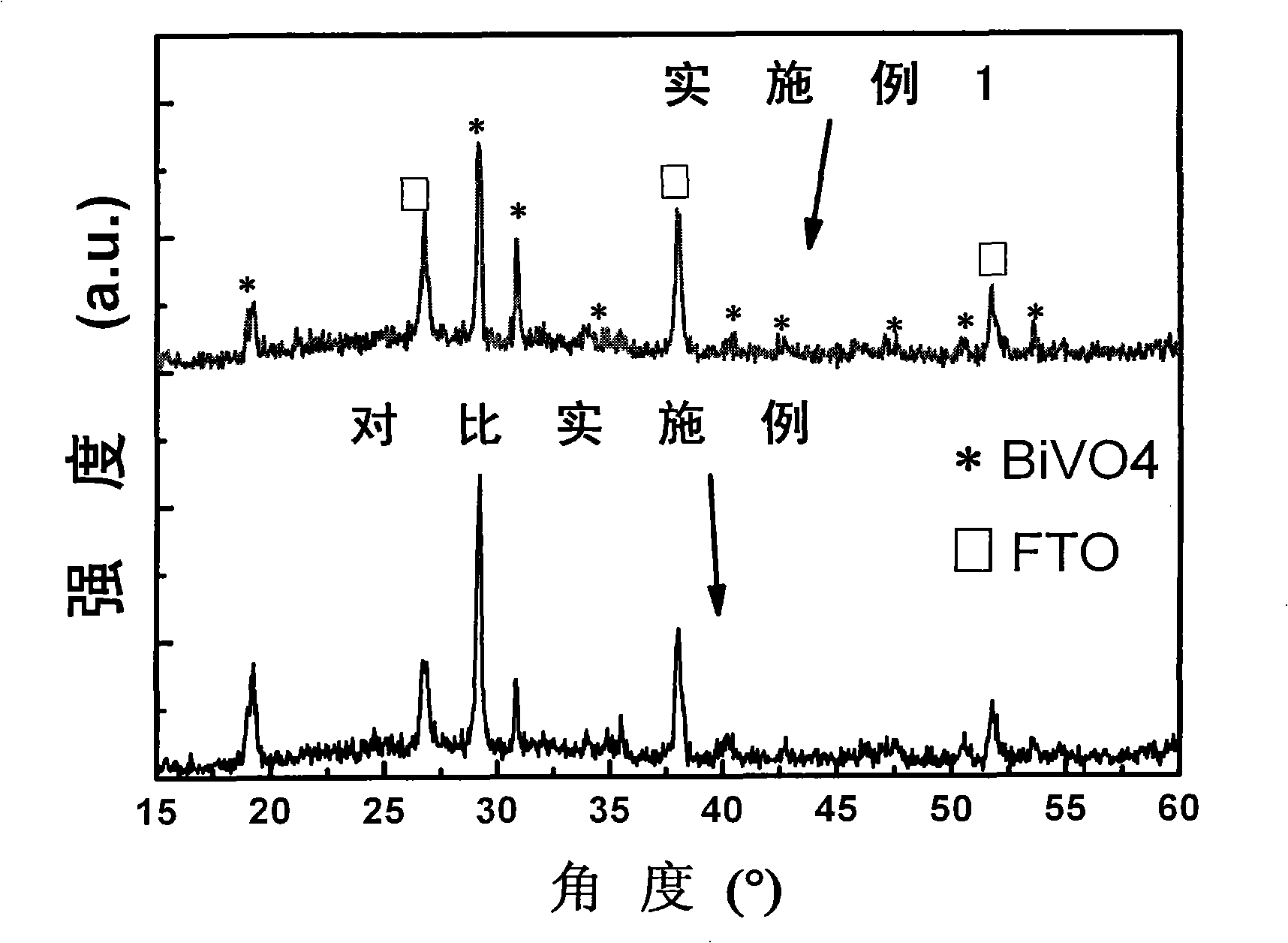
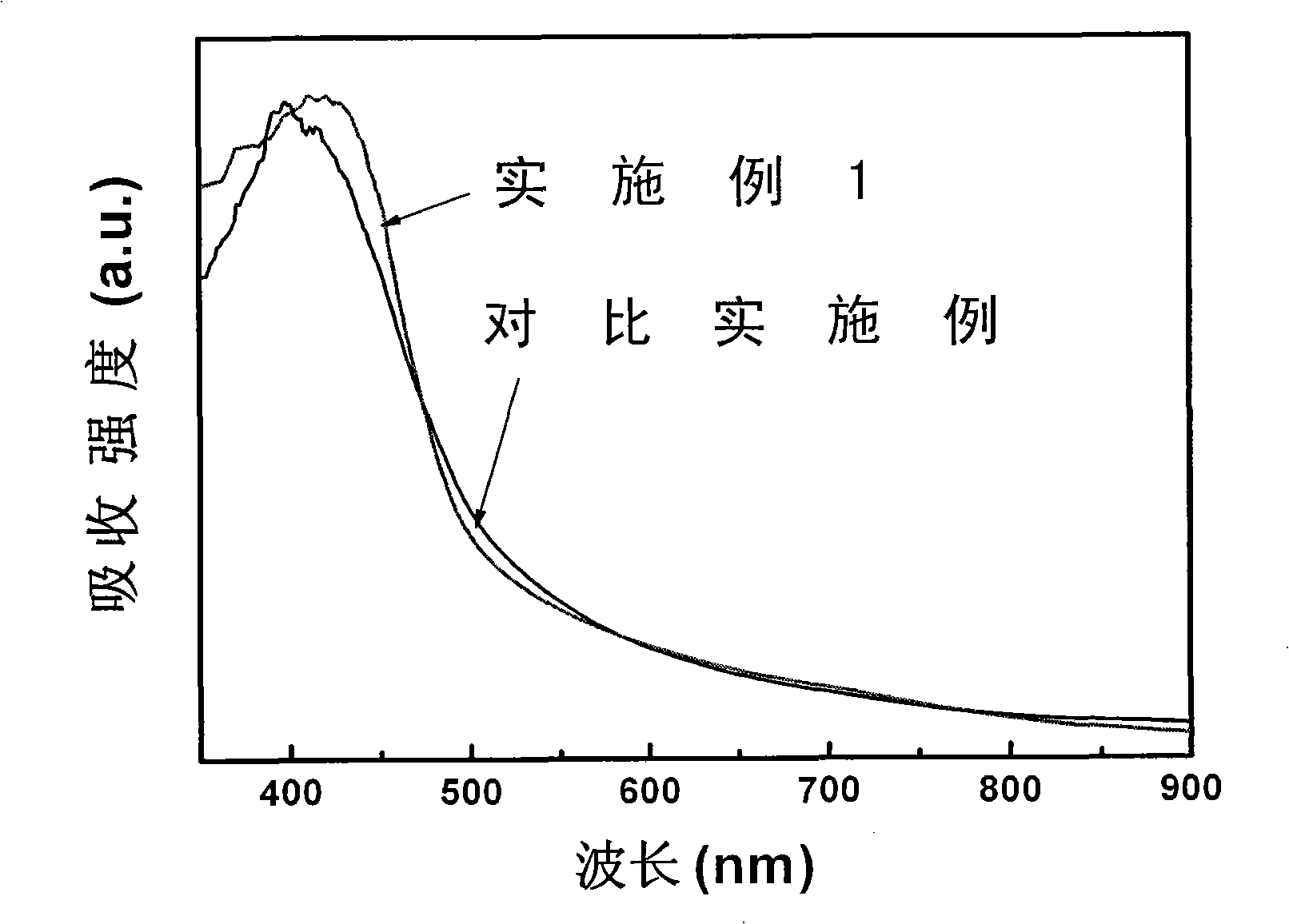
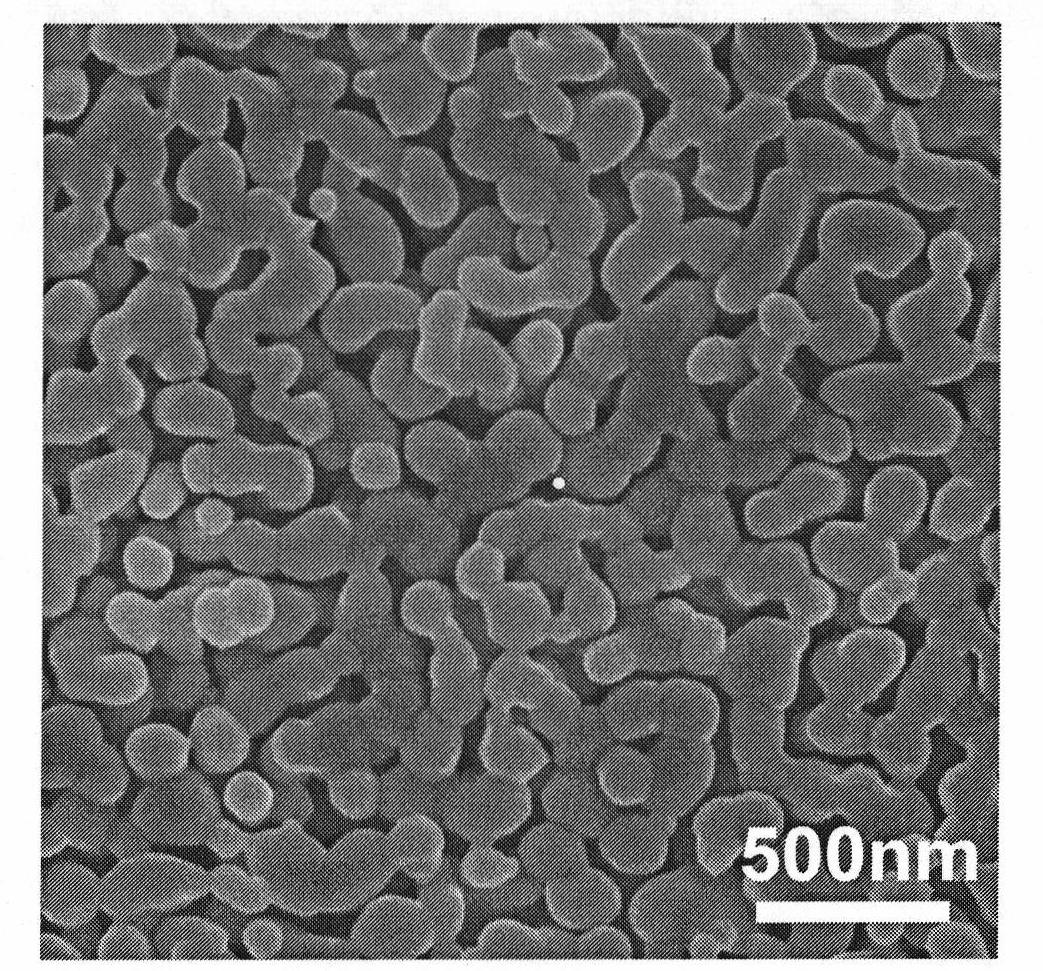
BiVO4 nano photoelectrode and application thereof in hydrogen production from water splitting
InactiveCN101775615AImprove quantum conversion efficiencyBroaden the photoresponse rangeElectrodesPhotocurrentWavelength range
The invention relates to a BiVO4 nano photoelectrode and application thereof in the aspect of hydrogen production from water splitting, which can increase photocurrent and greatly improve the efficiency of quantum conversion. The BiVO4 nano photoelectrode comprises a BiVO4 nano-pore thin film, and BiVO4 is doped with metal cation, wherein the metal cation is one or a mixture with an arbitrary proportion of more than two of Sr<2+>, Ba<2+>, Cr<6+> and W<6+> by arbitrary proportion. As an improvement of the invention, the surface of the BiVO4 nano-pore thin film is also modified with a catalyst, wherein the catalyst is one or a mixture with an arbitrary proportion of more than two of the oxides of the hydroxides of Rh, W, Mo, Co, Fe, Mn and Ni. Compared with a pure BiVO4 electrode, the quantum conversion efficiency of the invention is greatly increased and reaches 70 percent within a wavelength range of 360-450nm, and a photoresponse range is broadened to 510nm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
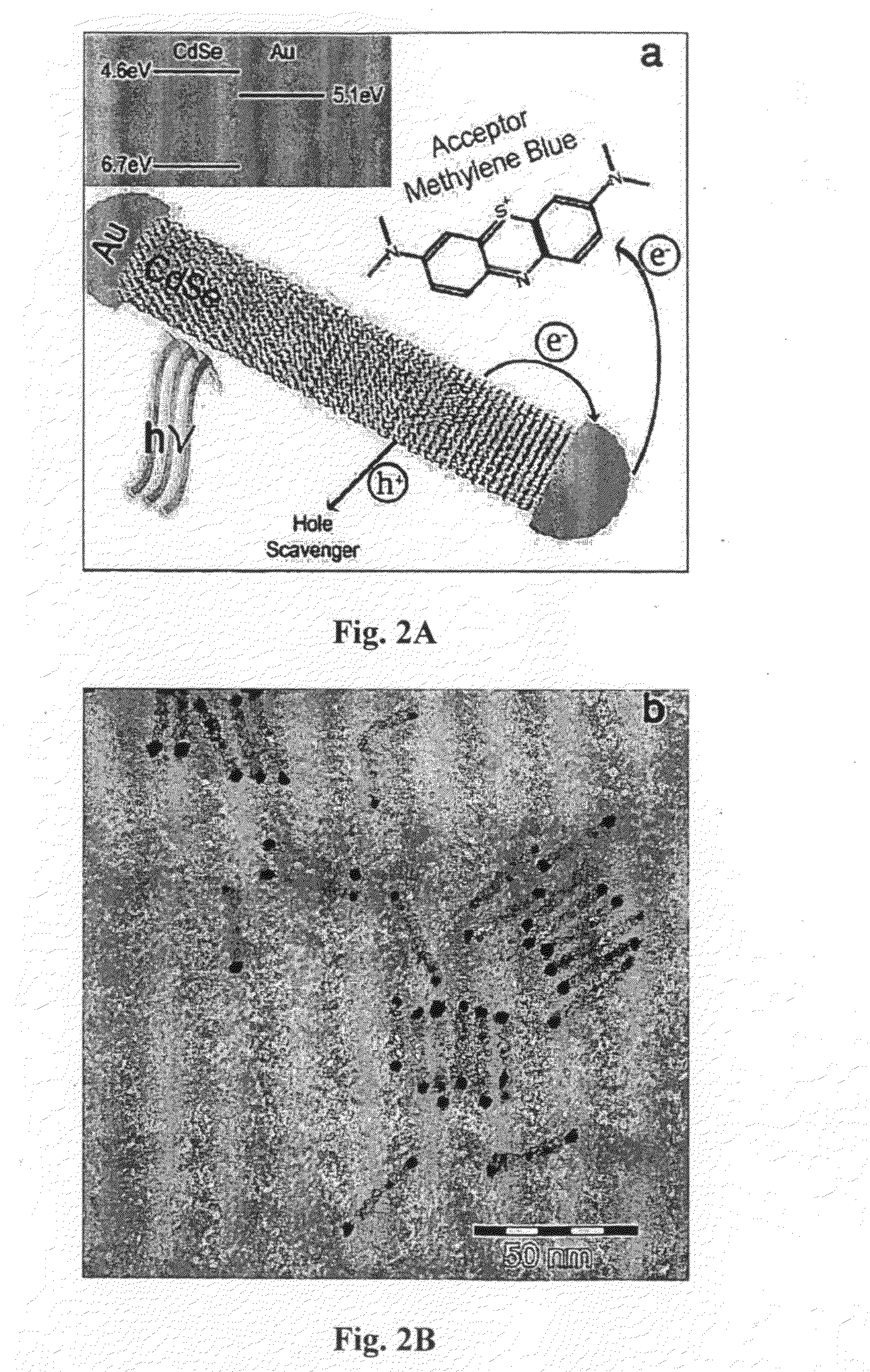
Hybrid metal-semiconductor nanoparticles and methods for photo-inducing charge separation and applications thereof
InactiveUS20100044209A1Easy to controlEfficient use ofMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesChemical reactionOxidation-Reduction Agent
The development and use of hybrid metal-semiconductor nanoparticles for photocatalysis of a variety of chemical reactions such as redox reactions and water-splitting, is provided.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
NiFeP bifunctional transition metal phosphide catalyst as well as preparation and use thereof
ActiveCN107376958AImprove catalytic performanceEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesHydrolysisAmmonium fluoride
The invention provides a NiFeP bifunctional transition metal phosphide catalyst which has a nanosheet structure, wherein the nanosheet has a length of 2-5 m and a thickness of 100-200 nm; the invention also provides a preparation method and use of the NiFeP bifunctional transition metal phosphide catalyst. The NiFeP bifunctional transition metal phosphide catalyst provided by the invention has a microstructure that the nanosheet having a relatively large specific surface area is used as a water-splitting electro-catalyst, so that the catalyst has higher catalytic performance. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: using ferronickel compound, ammonium fluoride and urea as raw materials; growing NiFe-LDH nanosheets on a substrate under heat preservation; and phosphating at a low temperature to obtain NiFeP transition metal phosphide nanosheets. The operation is simple; the production cost is low; and the prepared phosphide catalyst is applied to full hydrolysis in an alkaline environment and has excellent full hydrolysis catalyzing performance.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Single-trap level favorable region optimal selection method under multi-geological factor quantitative constraints
InactiveCN104991274ARich and perfect evaluation methodsSeismic signal processingPorosityWell logging
The invention relates to a single-trap level favorable region optimal selection method under multi-geological factor quantitative constraints. The method includes the following steps that: based on a high-resolution stratigraphic framework, a sedimentary unit-level isochronous sedimentary stratum can be formed through division in a longitudinal direction; five kinds of two-sandstone section oil and water splitting models can be established according to well logging data, mud logging data, well testing data, well logging interpretation oil and water data and seismic data; single-sand body-level oil and water splitting can be realized under the sedimentary unit-level isochronous stratigraphic framework; a single-sand body-level sub-layer roof surface structural graph, a sedimentary microfacies planar graph and an oil and water distribution law can be compiled; oil-containing traps can be determined according to river boundaries, faultage, micro-amplitude structures, and sandstone updip wedge out lines; trap area superimposition and trap thickness accumulation are performed on the oil-containing traps in different single-sand body-level sub-layers; favorable region evaluation indexes of trap type, reservoir porosity, reservoir depth, organic matter type, maturity, hydrocarbon-generating intensity and source-reservoir-cap combination are combined together so as to build an oil reservoir forming element probability and oil reservoir forming matching probability double-factor favorable evaluation model; and favorable regions can be selected optimally.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Power Generation From Solid Aluminum
InactiveUS20080056986A1Control of reactionProduction controlEnergy inputBlast furnace detailsChemistrySource material
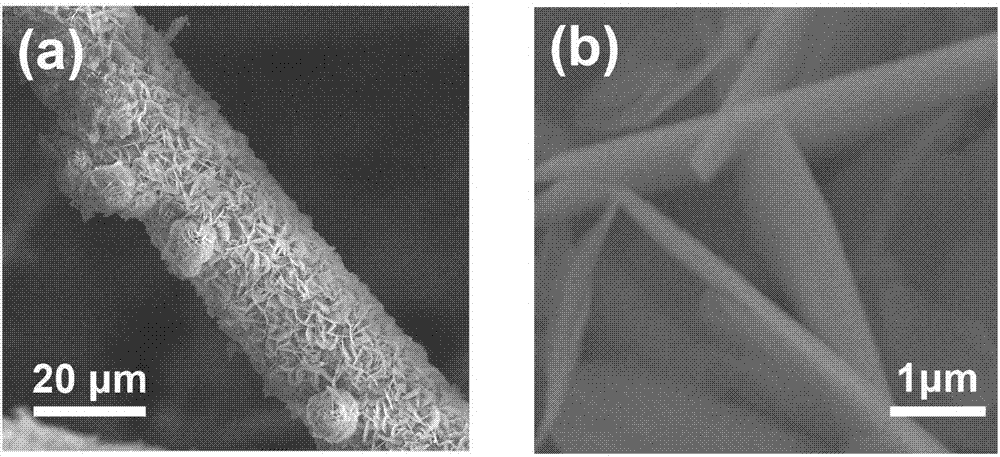
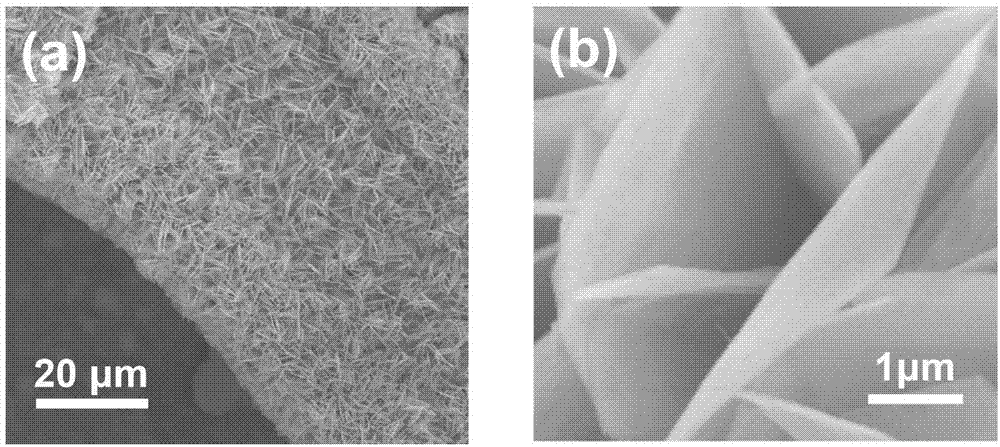
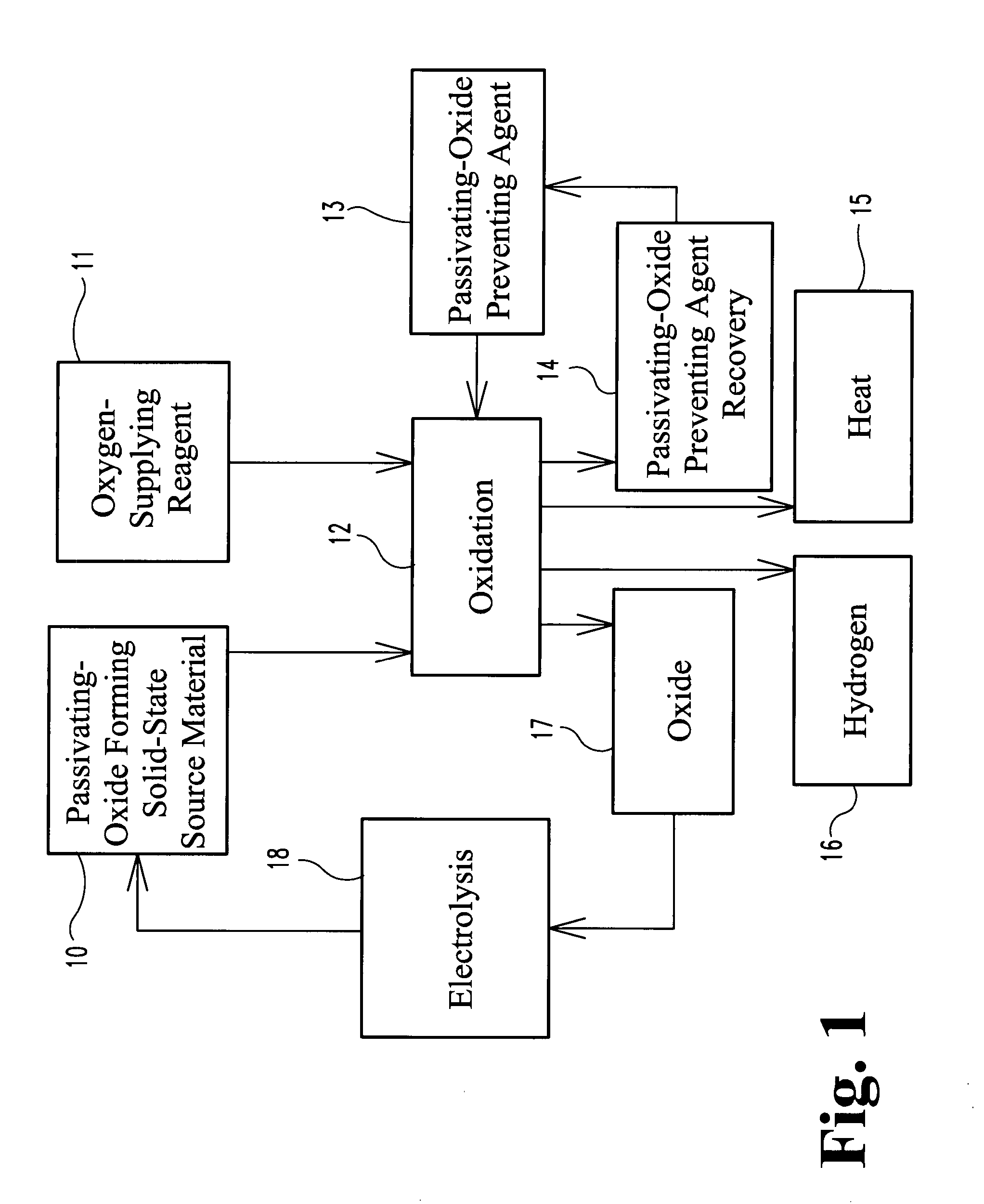
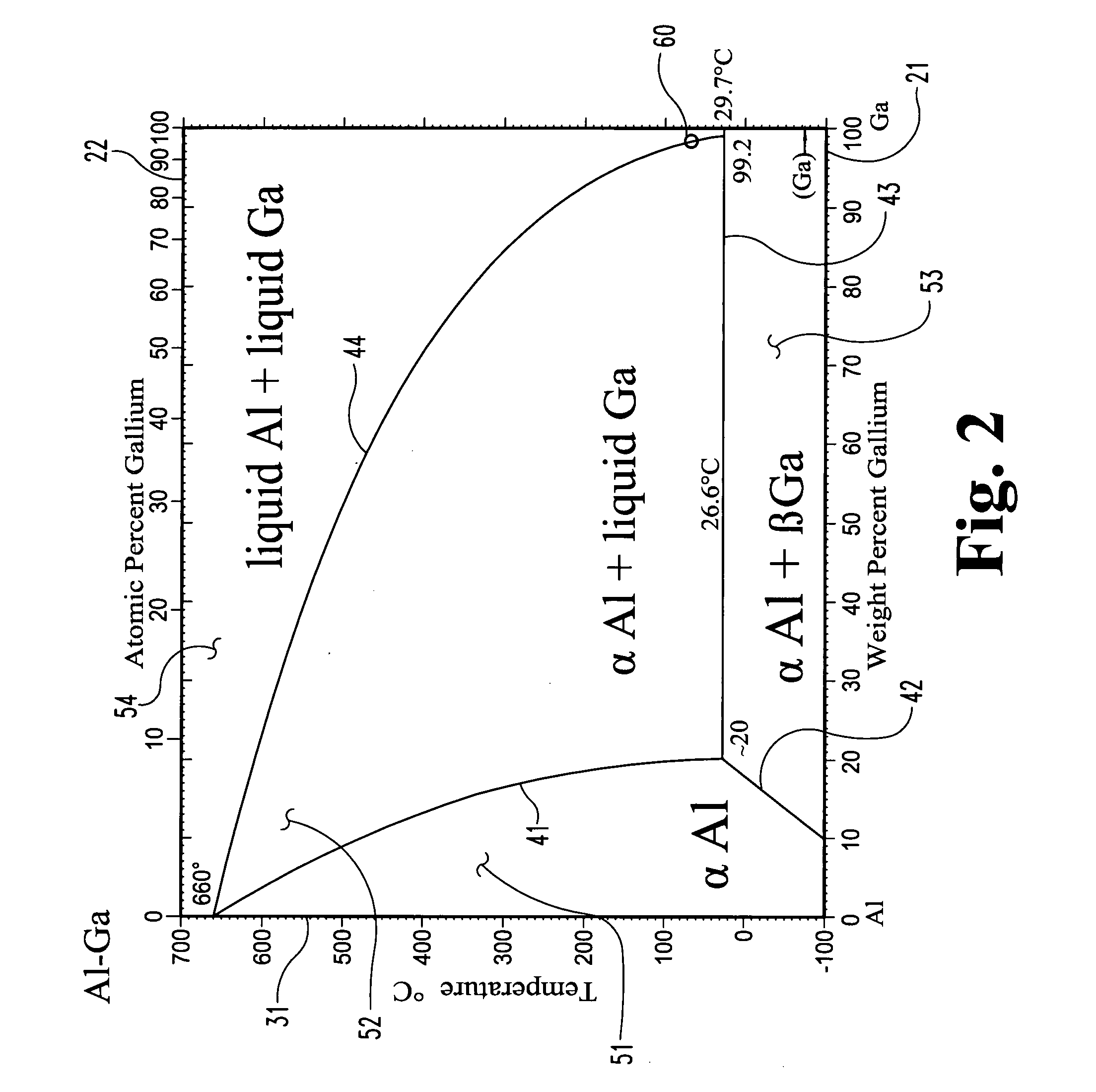
A fuel for splitting water into hydrogen and an oxide component comprises a substantially solid pellet formed from a solid-like mixture of a solid-state source material capable of oxidizing in water to form hydrogen and a passivation surface layer of the oxide component, and a passivation preventing agent that is substantially inert to water in an effective amount to prevent passivation of the solid-state material during oxidation. The pellets may be introduced into water or other suitable oxidizer in a controlled rate to control the rate of reaction of the source material with the oxidizer, and thereby control the rate of formation of hydrogen. Methods are described for producing the solid-like mixture in varying weight percent of source material to passivation preventing agent.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Application of heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material in photocatalysis
ActiveCN108889334AStructure location is clearAdjustable performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMonomerPhotochemistry
The invention belongs to the field of photocatalyst application of organic semiconductors and in particular relates to application of a heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material in photocatalysis. The heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material serves as a photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: introducing heteroatoms through heterocyclic aldehyde group monomers, carrying out a condensation polymerization reaction with binary or poly-element amidino compounds in the presence of a basic catalyst, thereby obtaining theproduct. The material serves as the photocatalyst, and is capable of degrading organic pollutants in water and producing hydrogen under light conditions by virtue of water splitting. According to themethods, the heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material is introduced to serve as the photocatalyst, and is high in catalytic efficiency, high in applicability and suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
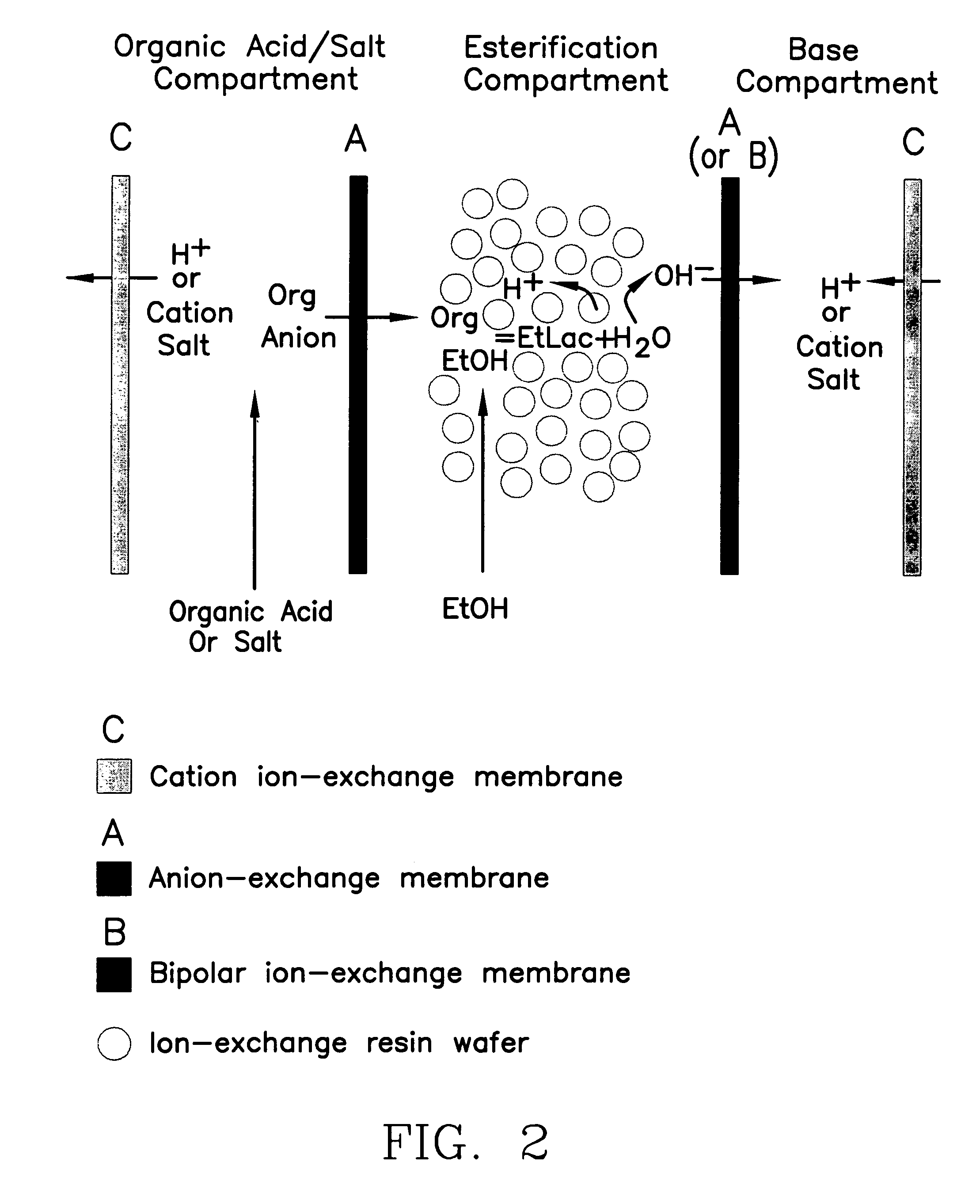
Single-stage separation and esterification of cation salt carboxylates using electrodeionization
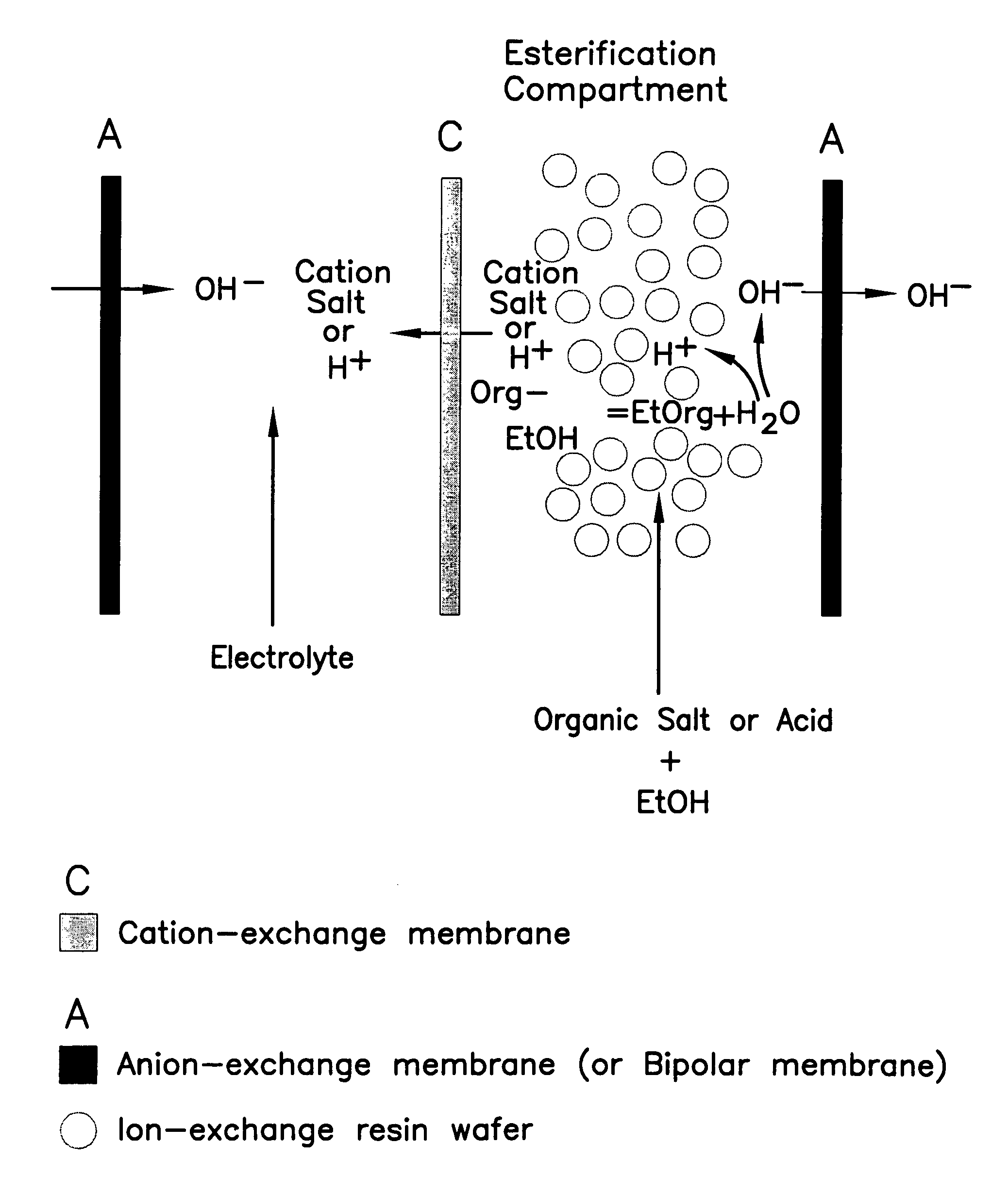
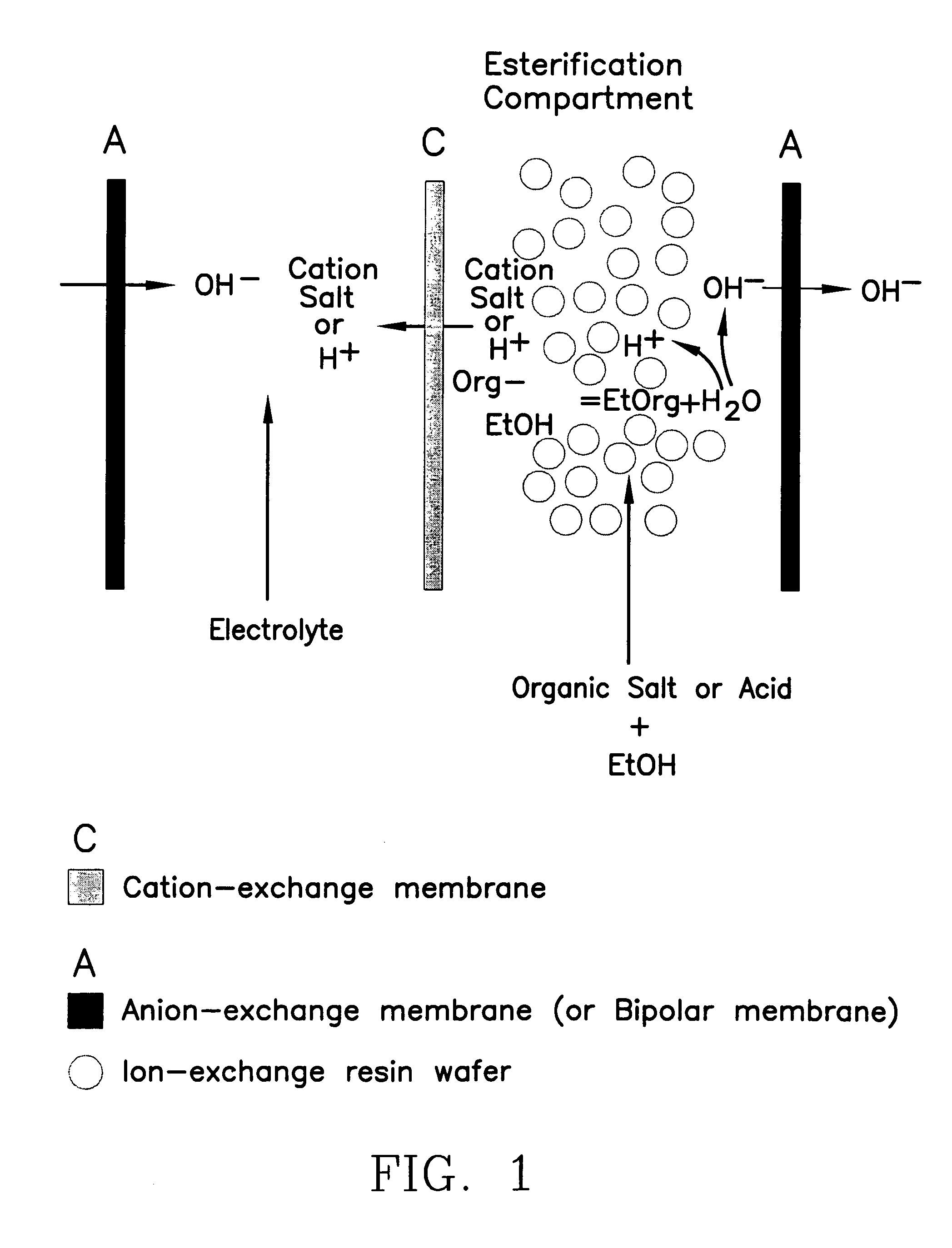
ActiveUS7141154B2Promote migrationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIon-exchange resinBioreactor
A method of and apparatus for continuously making an organic ester from a lower alcohol and an organic acid is disclosed. An organic acid or salt is introduced or produced in an electrode ionization (EDI) stack with a plurality of reaction chambers each formed from a porous solid ion exchange resin wafer interleaved between anion exchange membranes or an anion exchange membrane and a cation exchange membrane or an anion exchange membrane and a bipolar exchange membranes. At least some reaction chambers are esterification chambers and / or bioreactor chambers and / or chambers containing an organic acid or salt. A lower alcohol in the esterification chamber reacts with an anion to form an organic ester and water with at least some of the water splitting with the ions leaving the chamber to drive the reaction.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
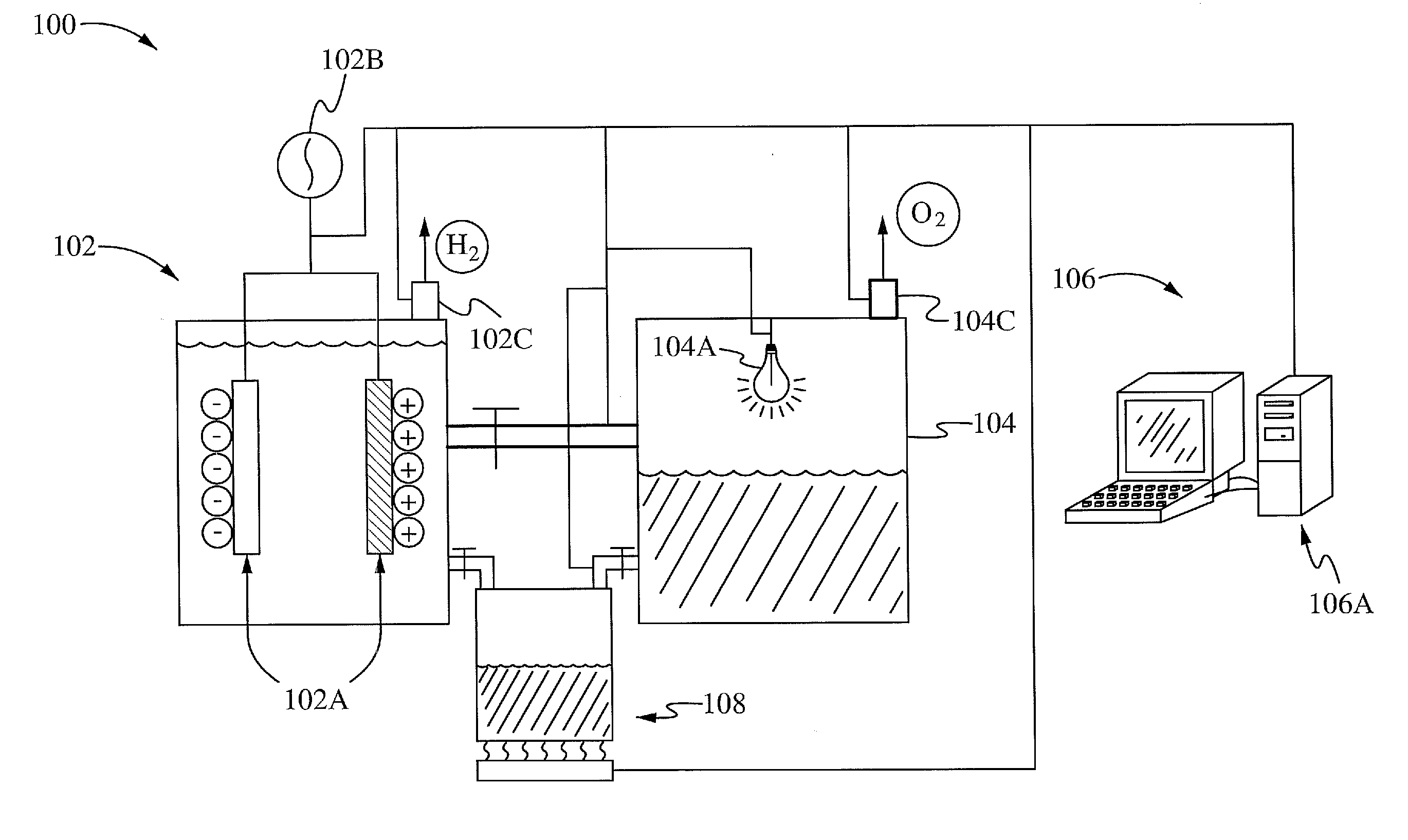
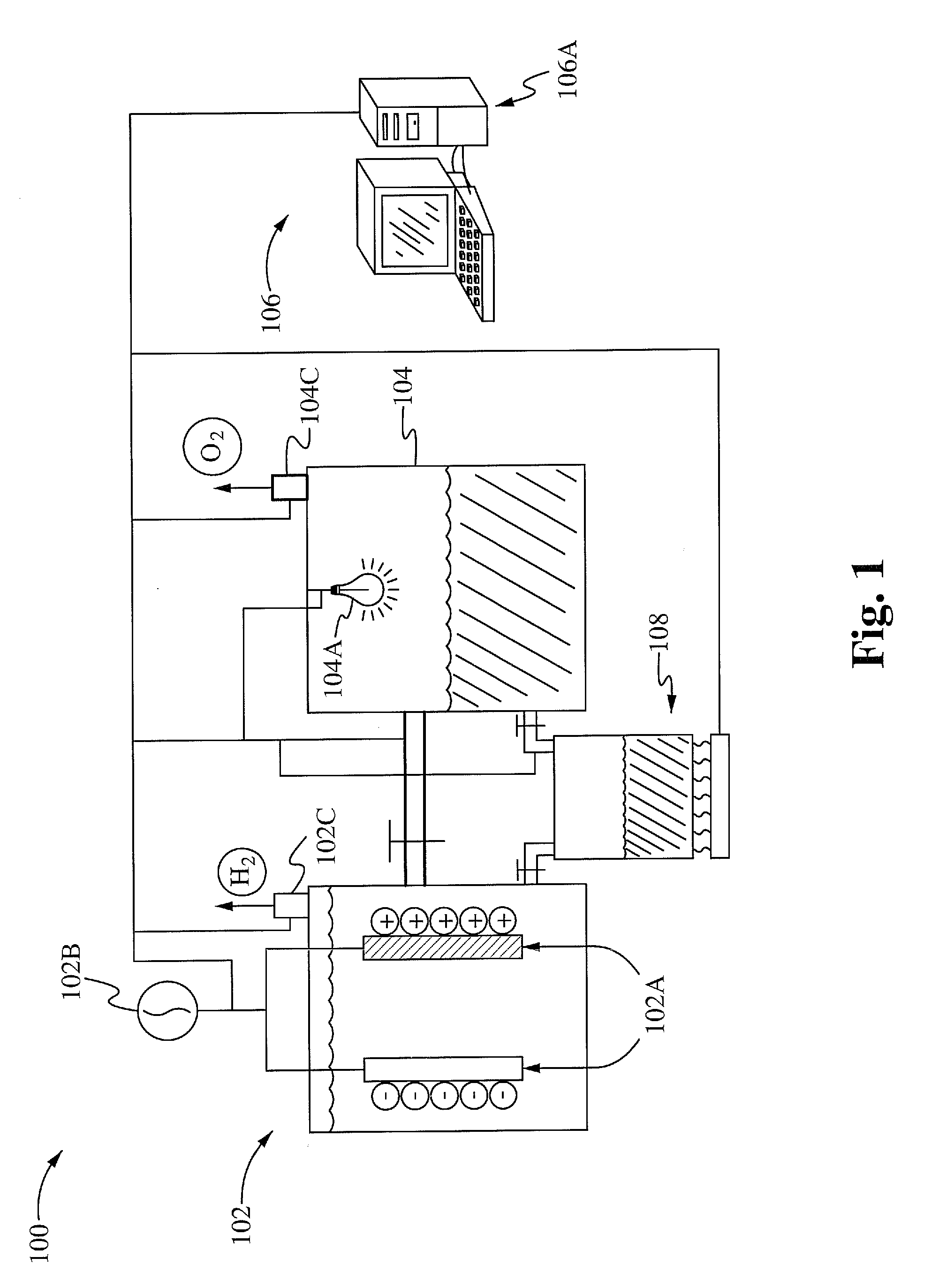
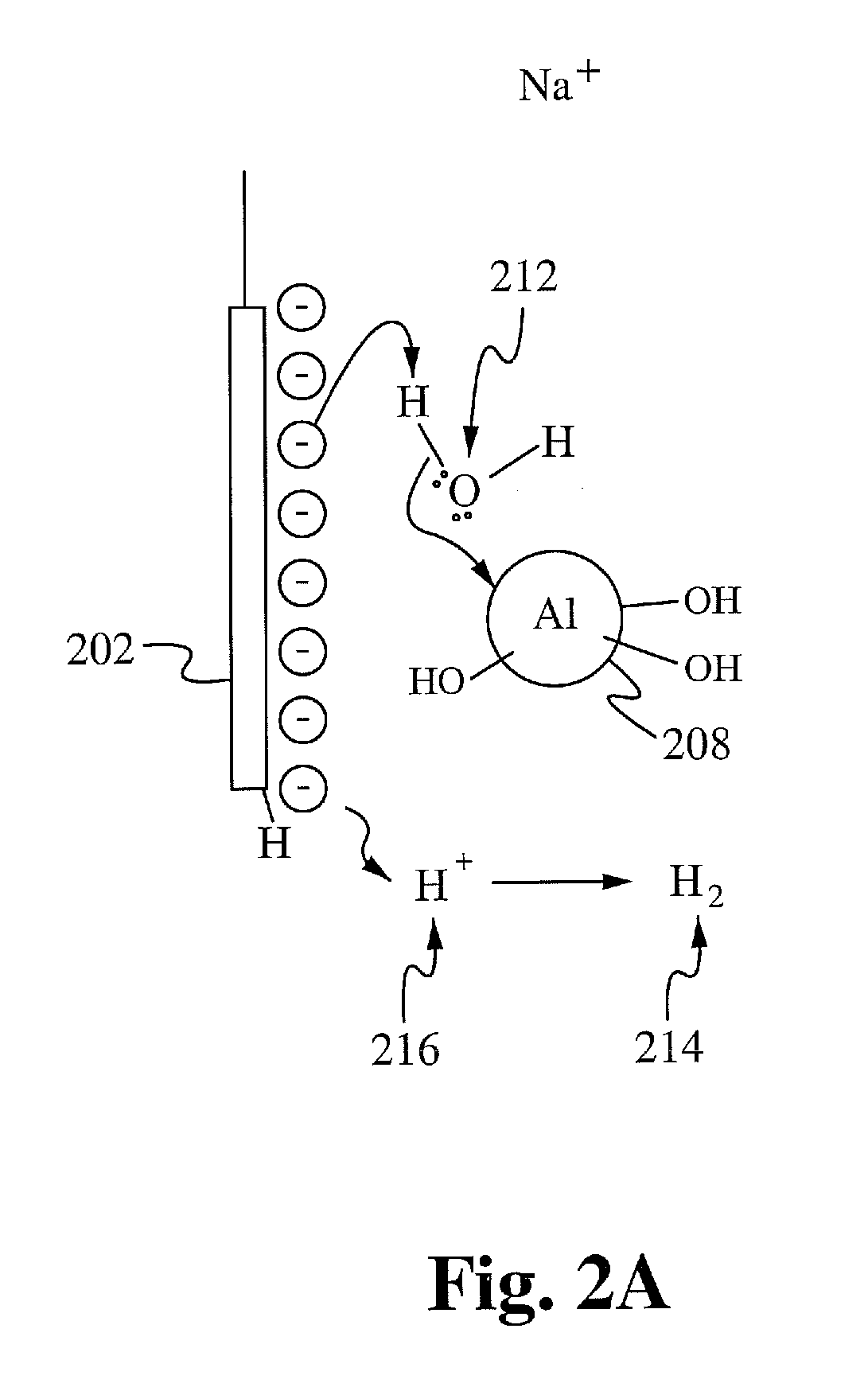
Method and apparatus for efficient on-demand production of h2 and o2 from water using waste heat and environmentally safe metals
InactiveUS20100224502A1Weaken energyPhotography auxillary processesElectrolytic organic productionWater useDecomposition
A method of and apparatus for efficient on-demand production of H2 and O2 from water and heat using environmentally safe metals are disclosed. In one aspect, the apparatus for the hydrogen generation through water decomposition reaction includes a main reactor, an oxidizer reactor, and a computer controlling system. The main reactor contains a hydrogen generating substance, such as aluminium hydroxide. In some embodiments, the main reactor includes hydroxide shuttles, such as Cu ion and Ag ion. In another aspect, the system for hydrogen generation through water decomposition includes the steps of (1) REDOX reaction, (2) pre-generation reaction, (3) generation reaction, (4) regeneration reaction, (5) second hydrogen reaction, and (6) oxygen reaction.
Owner:MARINE POWER PRODS
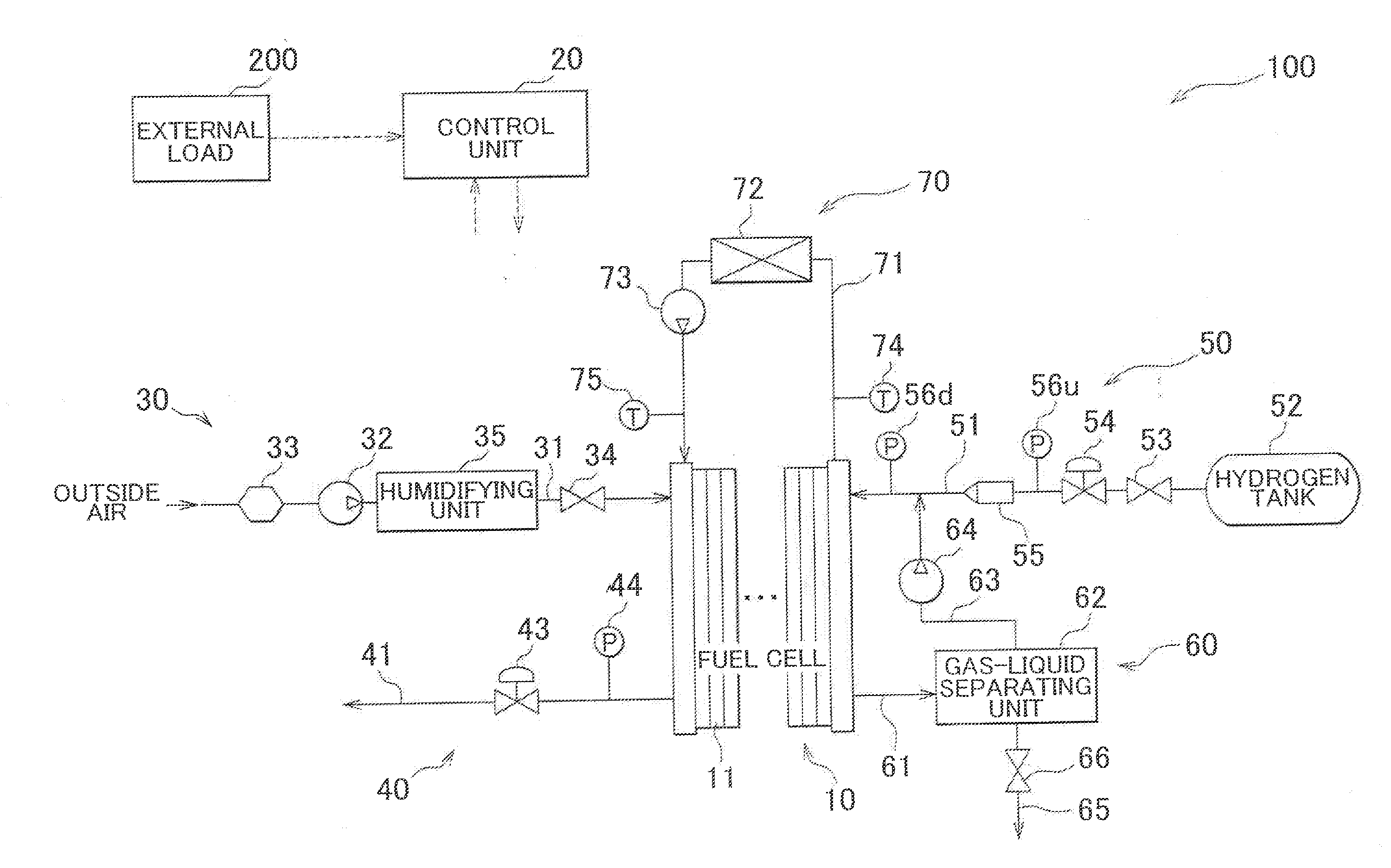
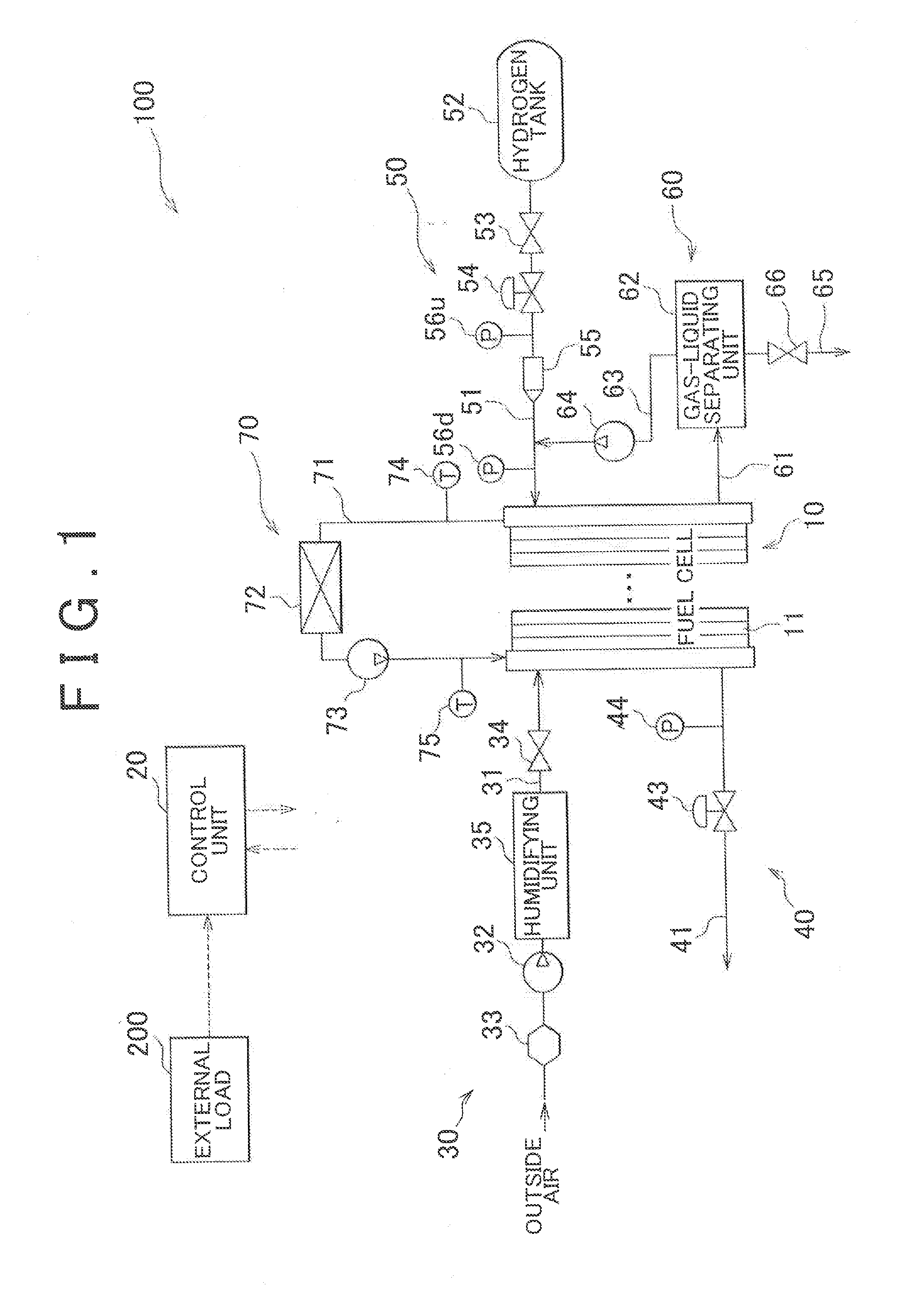
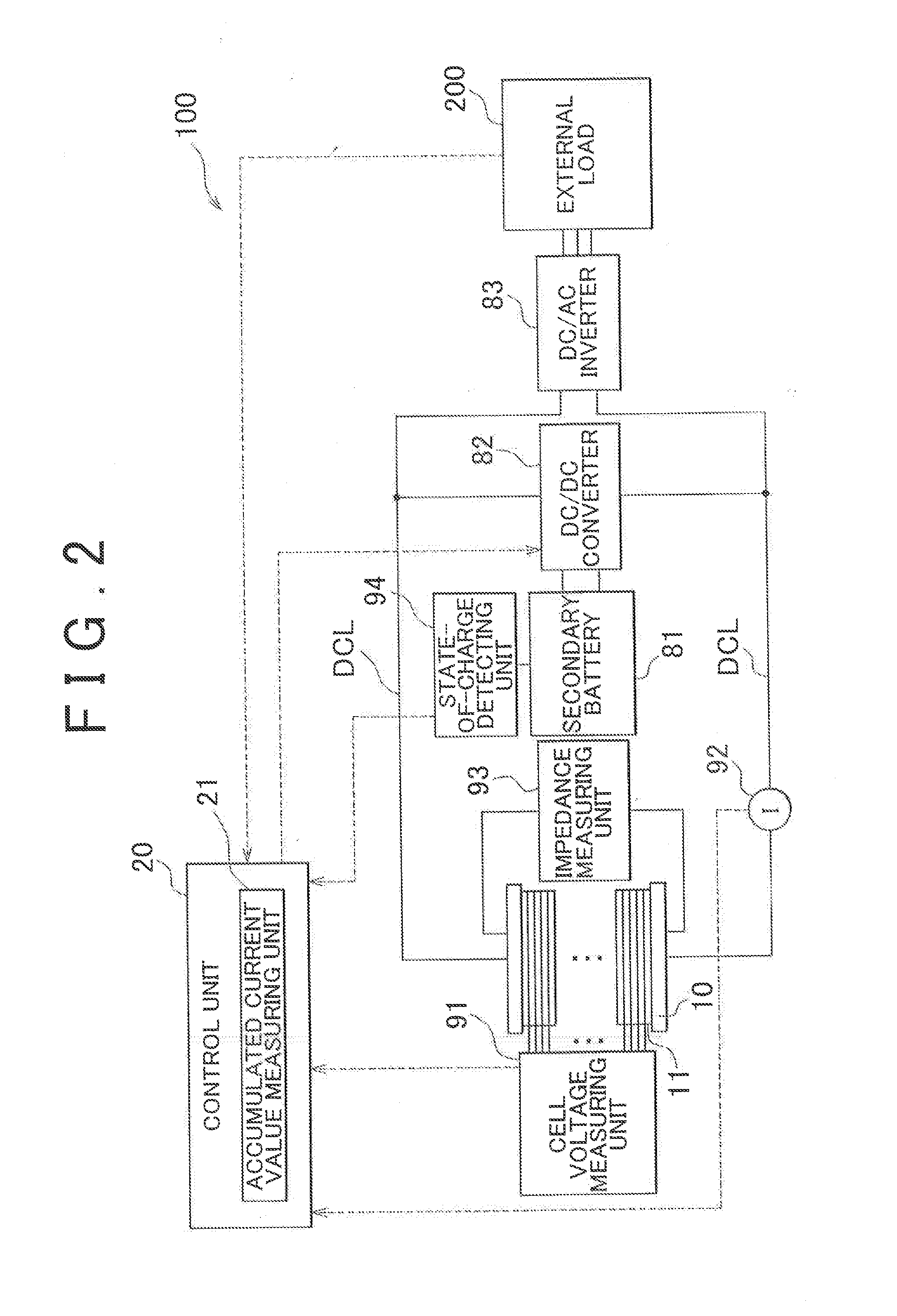
Fuel cell system and control method therefor
ActiveUS20130095405A1Avoid performanceAvoid performance degradationBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsFuel cell auxillariesProduction rateFuel cells
A fuel cell system includes an accumulated current value measuring unit. The accumulated current value measuring unit measures an accumulated current value by time integration of current output from the fuel cell in a period during which oxygen is produced by water-splitting reaction in an anode of a negative voltage cell. A control unit uses a first correlation between the accumulated current value in the oxygen generation period and an oxygen consumption rate in the anode and a second correlation between a current density of the fuel cell in the oxygen generation period and an oxygen production rate in the anode to obtain a current density at or below which the amount of oxygen in the anode may be reduced, and causes the fuel cell to output electric power at a current density lower than the obtained current density.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
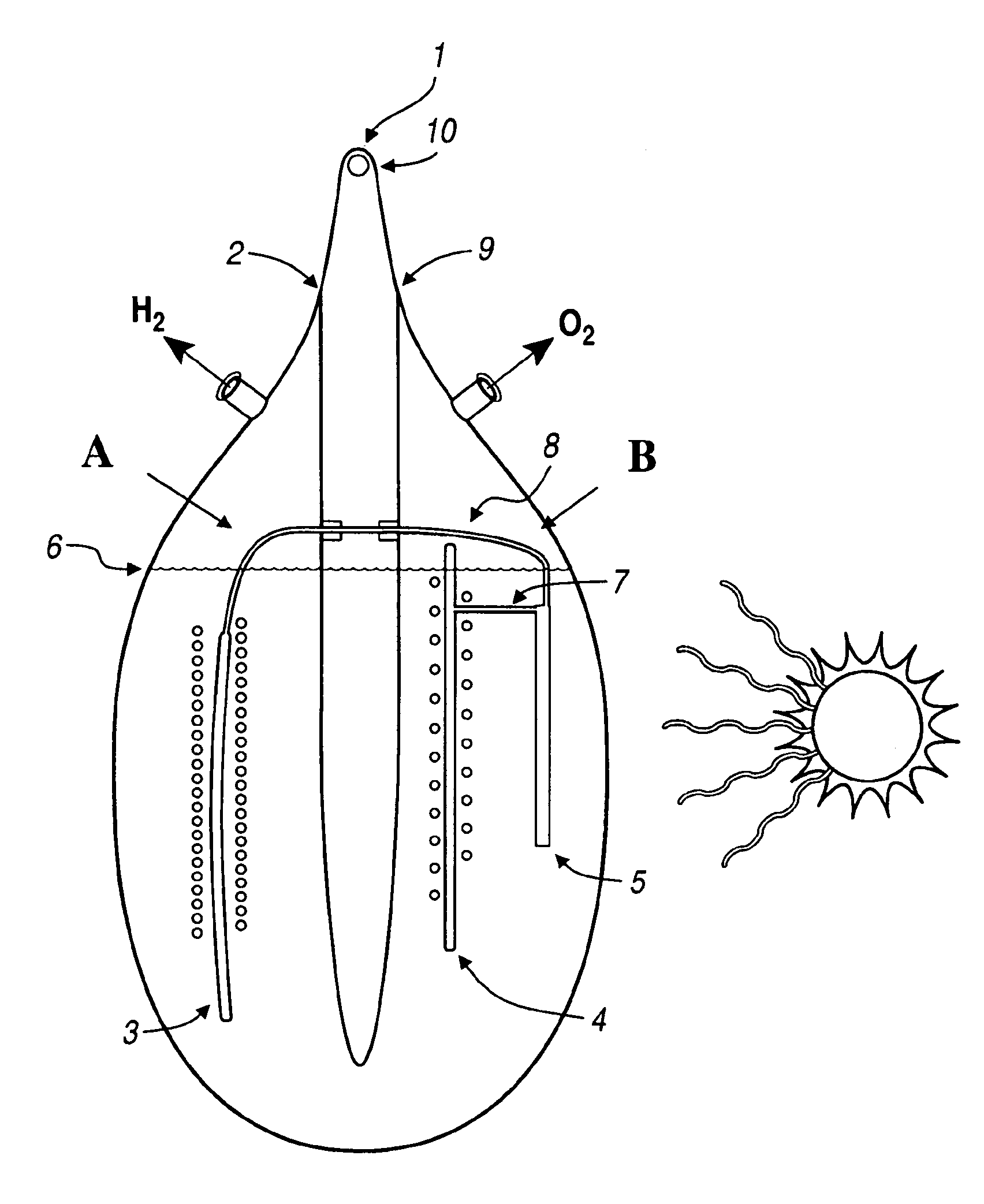
Hydrogen generator photovoltaic electrolysis reactor system
An apparatus for creating hydrogen from the disassociation of water using sunlight (photoelectrolysis) is provided. The system utilizes an aqueous fluid filled container which functions both to hold the water to be disassociated and as a light collecting lens. A photovoltaic module is positioned at a point to most efficiently accept the refracted light from the fluid filled container. A pair of electrodes which are coupled to the photovoltaic module are disposed within the fluid and configured to split the water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Water decomposition photocatalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104857978AImprove stabilityQuantum efficiency decayPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionPhoto catalyticPtru catalyst
The present invention provides a water decomposition photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, wherein the catalyst is a carbon quantum dot-carbon nitride composite catalyst, the carbon quantum dot concentration in the catalyst is 4.8*10<-3>, and carbon quantum dots are respectively performed, the carbon quantum dot solution is further treated through ammonia water, and the obtained material and carbon nitride are subjected to compounding preparation. According to the present invention, the catalyst can have good stability after being subjected to dry reuse 200 times, and the quantum efficiency of the catalyst does not produce significant degeneration after 50 cycles.
Owner:SUZHOU FANGSHENG OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing electrocatalytic water-splitting oxygen production electrode
ActiveCN105369306AHigh activityImprove oxygen production efficiencyFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesN dimethylformamideMetal-organic framework
The invention particularly relates to a method for preparing an electrocatalytic water-splitting oxygen production electrode, with Fe / Ni duplex metal coordinating with trimesic acid, of a metal organic framework material and belongs to the field of electrodeposition / electrocatalysis. The method comprises the steps that (1) Ni(NO3)2.6H2O, Fe(NO3)3.9H2O and the trimesic acid are all dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide, then tributylmethylammonium methyl sulfate is added, and sufficient stirring is conduced till all the components are completely dissolved, so that electrolyte, with the Fe / Ni duplex metal coordinating with the trimesic acid, for the metal organic framework material is obtained; (2) a standard three-electrode system is assembled by using foamed nickel as a working electrode, a silver / silver chloride saturated electrode as a reference electrode, a platinum sheet as a counter electrode and the solution prepared in the step (1) as the electrolyte; and (3) the standard three-electrode system assembled in the step (2) is connected to an electrochemical workstation, and the working electrode is taken out of the electrolyte, cleaned and dried after constant-potential electrodeposition is conducted, so that the electrocatalytic water-splitting oxygen production electrode is obtained.
Owner:理工清科(北京)科技有限公司
Apparatus for removing dissolved metals from wastewater by electrocoagulation
InactiveUS6582592B2Improve treatmentIncrease pressureElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentIndustrial effluentElectrocoagulation
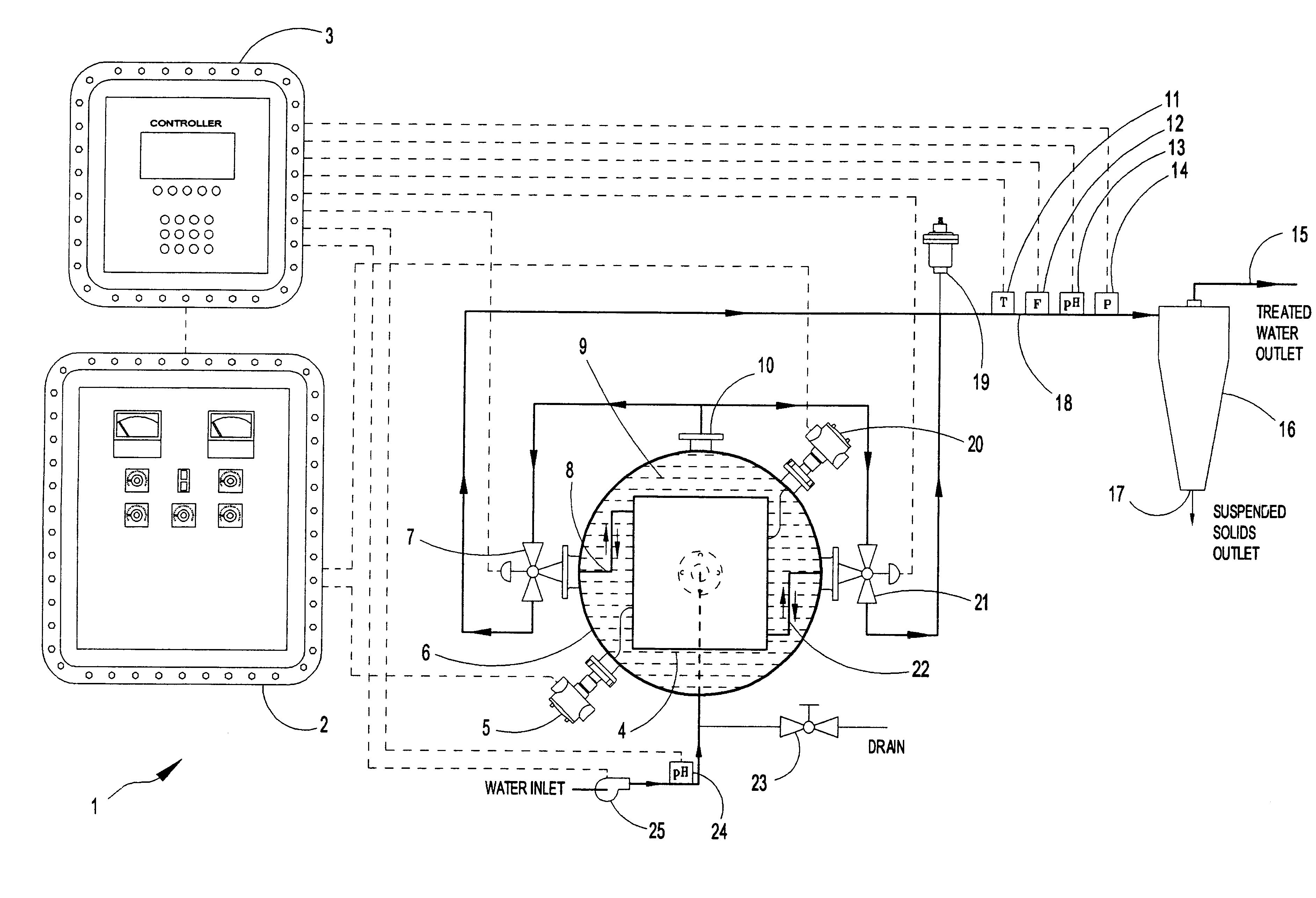
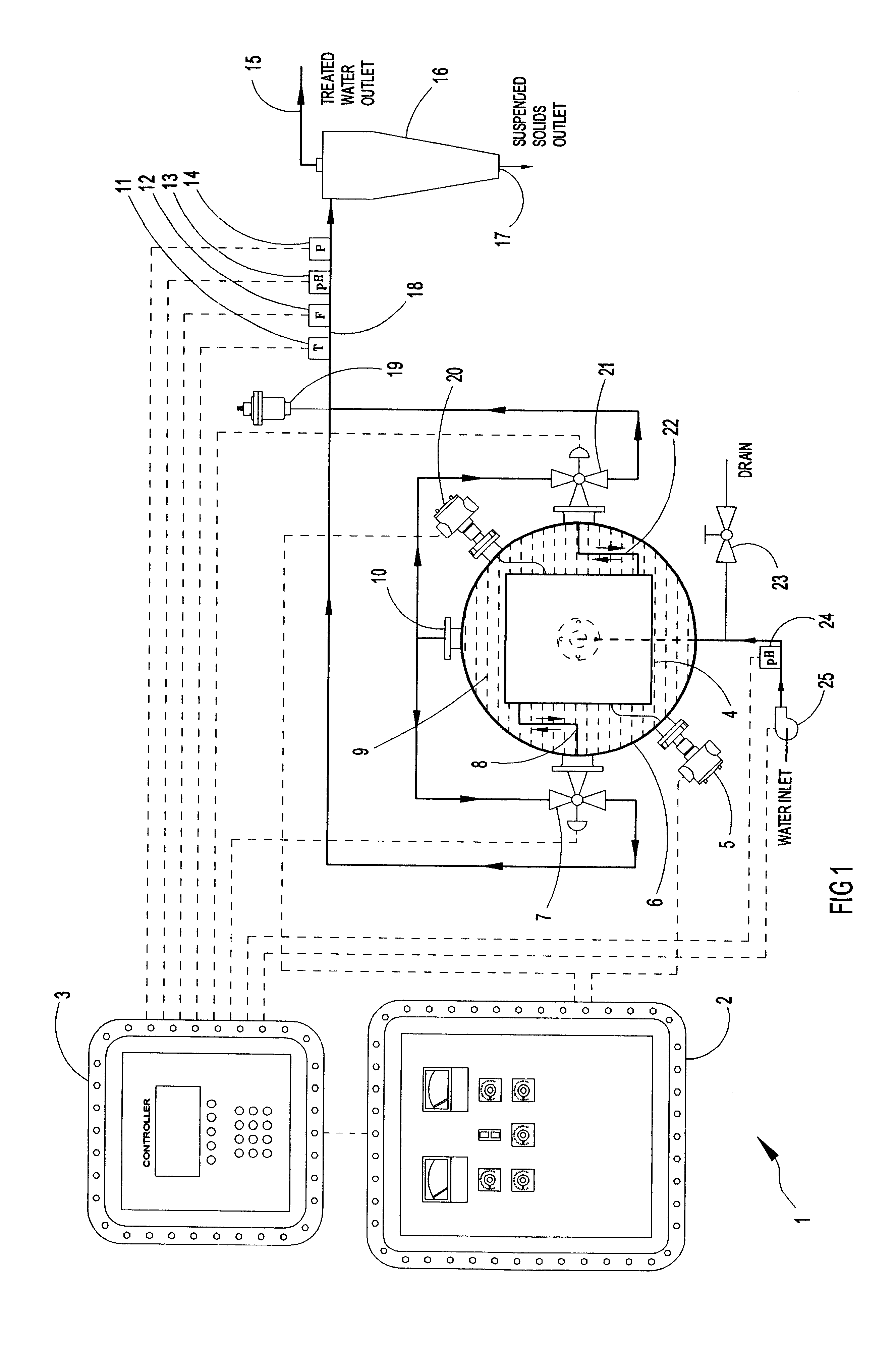
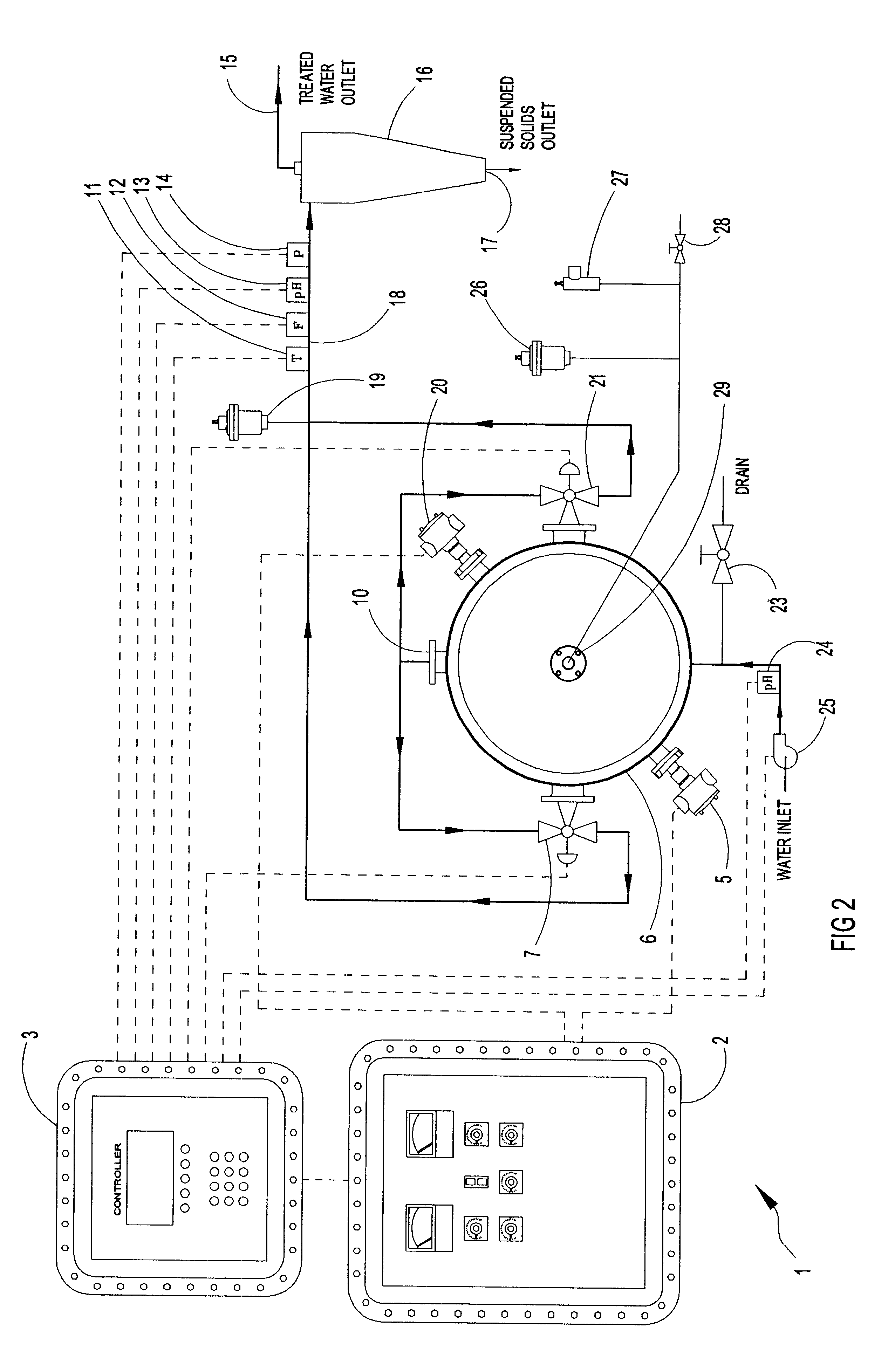
A system is provided for removing dissolved metals from industrial wastewater by electrocoagulation. The system includes an electrocoagulation reactor with a DC power supply having an insulation support enclosure with positive and negative electrode plates disposed thereon. The electrode plates are insulated for each other but remain in direct contact with the wastewater as it flows between the electrodes. The DC power supply induces opposite charges on alternate electrodes thereby generating an electric field between adjacent electrodes to cause the electrodes to ionize and go into solution for interaction with the contaminants in the wastewater as it flows through the reactor. The reactor is housed in a pressure vessel container so the exterior pressure on the reactor is higher than its internal pressure preventing leakage of fluids and oxygen and hydrogen gases produced in the reactor by decomposition of water. The pressure vessel allows higher operating pressures to retain higher concentrations of dissolved oxygen and hydrogen dispersed in the water for reaction with the contaminants. The electrical supply includes explosion proof connection housings for operation in hazardous environments. The system also includes a cyclone filter for separating the precipitated solid particles from the fluid and automatic control of the reactor by monitoring fluid flow, temperature, pH, and pressure.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com