Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
271 results about "External bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lateral diffusion field effect transistor with a trench field plate
InactiveUS20090140343A1High conductanceImprove the immunityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricElectrical conductor
A dielectric material layer is formed on a bottom surface and sidewalls of a trench in a semiconductor substrate. The silicon oxide layer forms a drift region dielectric on which a field plate is formed. Shallow trench isolation may be formed prior to formation of the drift region dielectric, or may be formed utilizing the same processing steps as the formation of the drift region dielectric. A gate dielectric layer is formed on exposed semiconductor surfaces and a gate conductor layer is formed on the gate dielectric layer and the drift region dielectric. The field plate may be electrically tied to the gate electrode, may be an independent electrode having an external bias, or may be a floating electrode. The field plate biases the drift region to enhance performance and extend allowable operating voltage of a lateral diffusion field effect transistor during operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
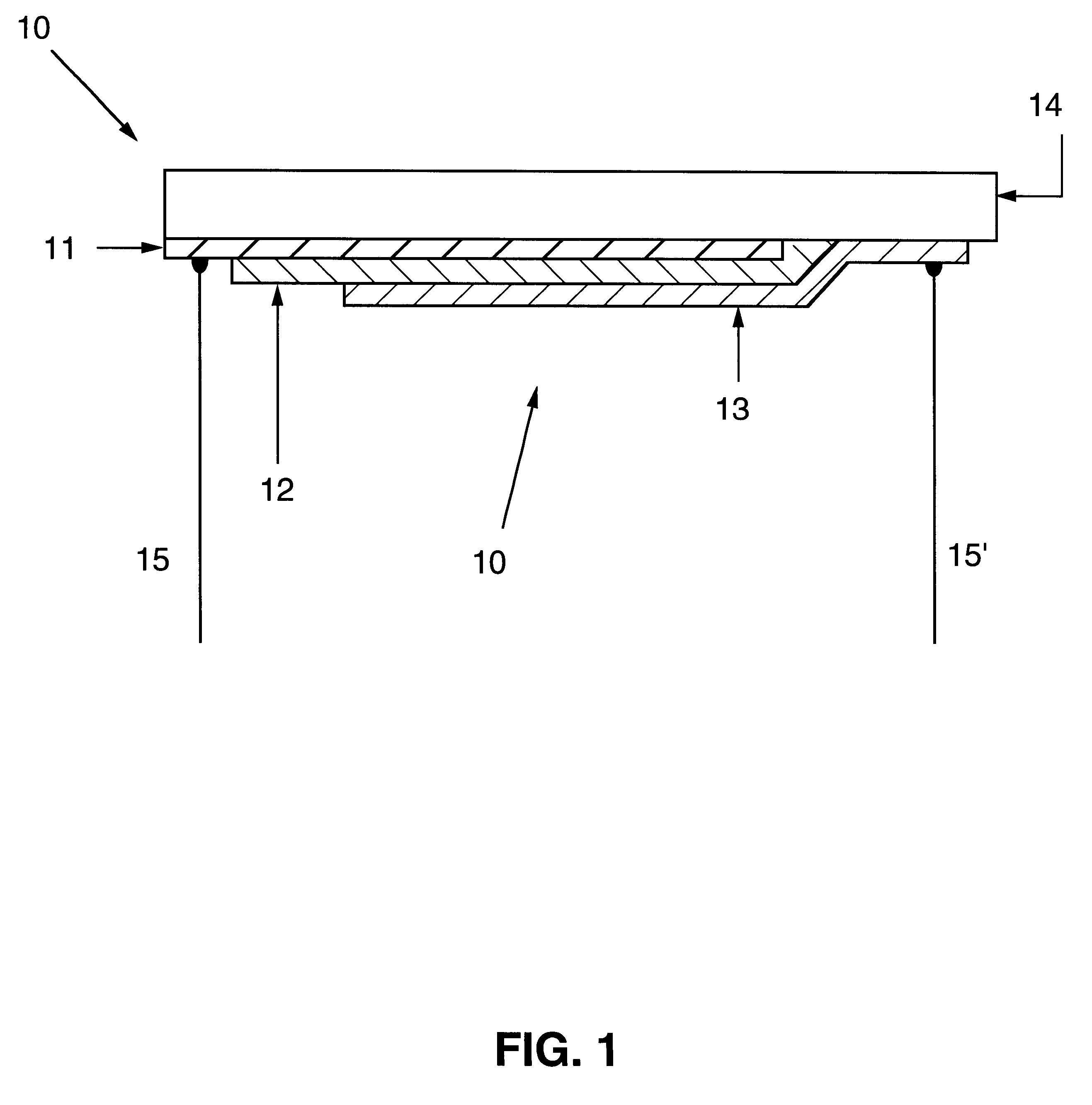
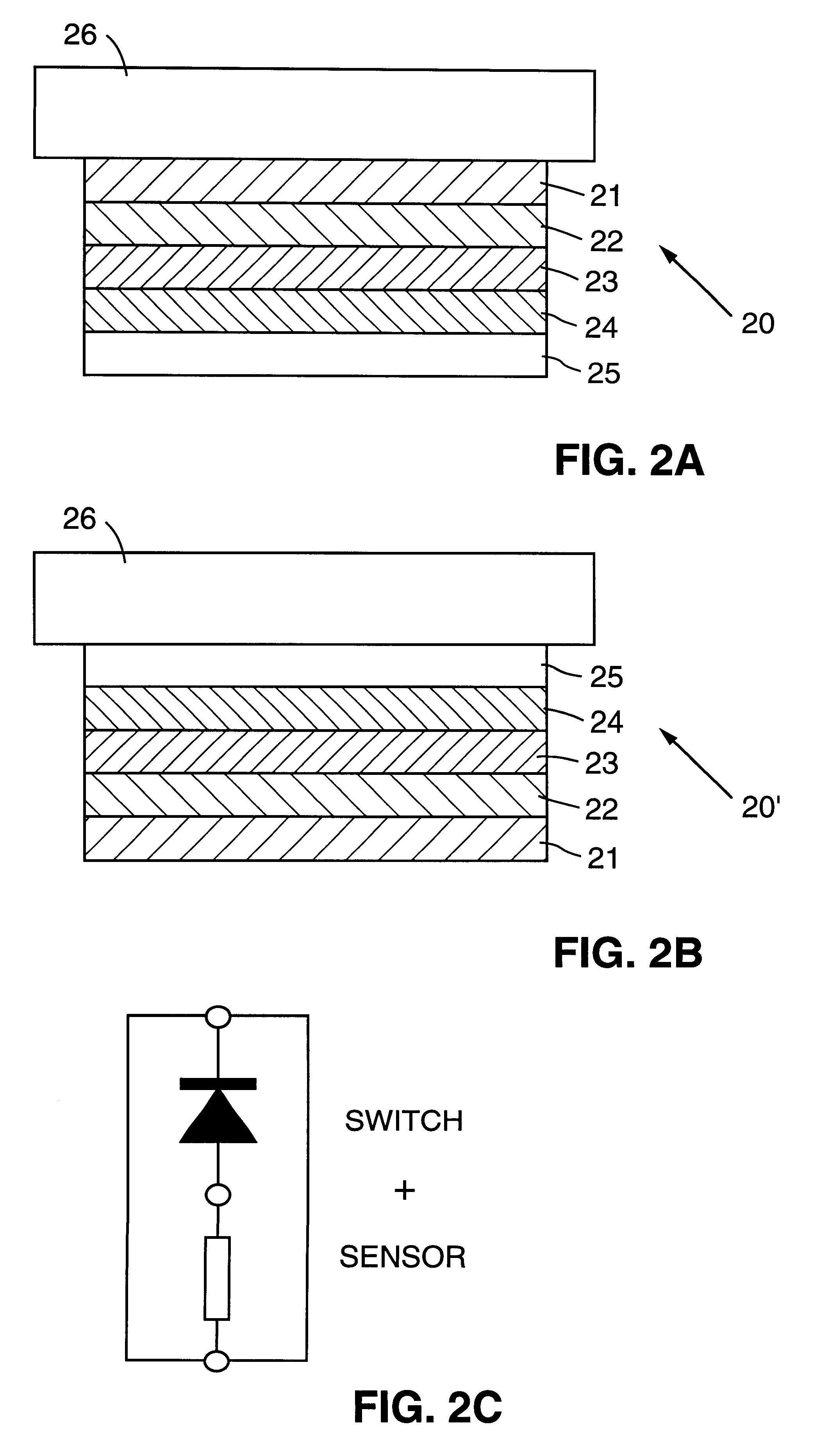
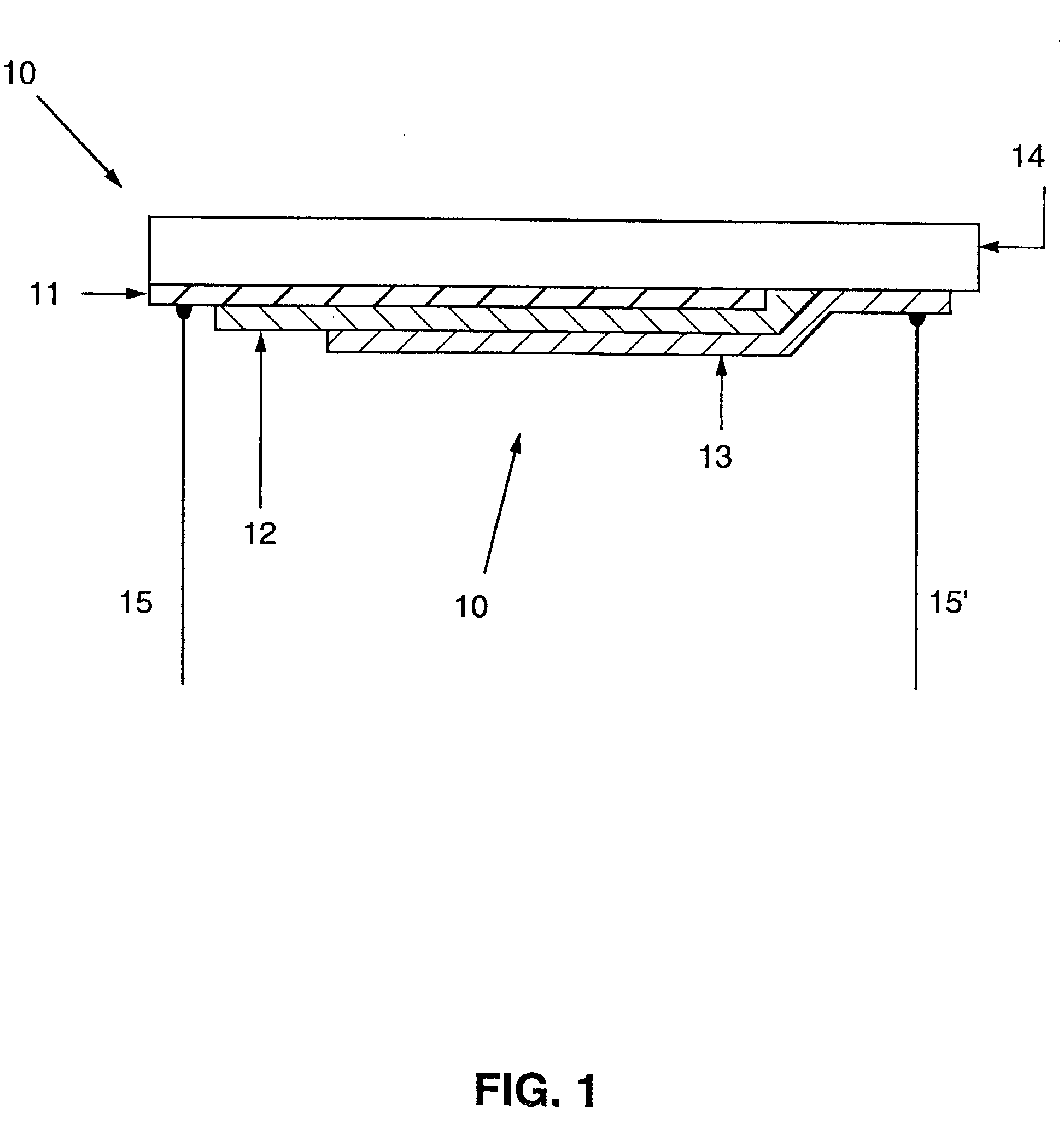
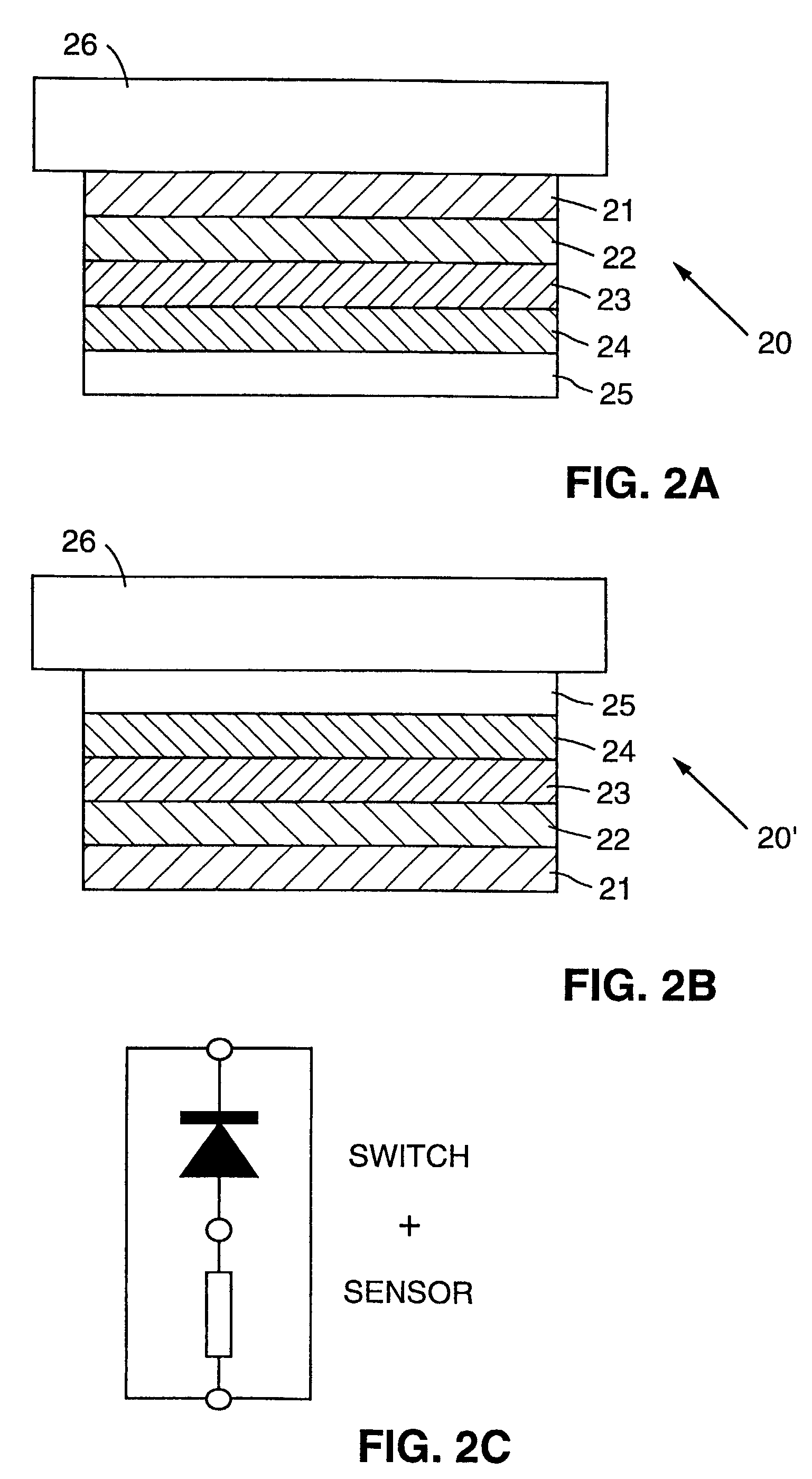
Column-row addressable electric microswitch arrays and sensor matrices employing them
The present invention relates generally to fabricating two-terminal electric microswitches comprising thin semiconductor films and using these microswitches to construct column-row (x-y) addressable microswitch matrices. These microswitches are two terminal devices through which electric current and electric potential (or their derivatives or integrals) can be switched on and off by the magnitude or the polarity of the external bias. The microswitches are made from semiconducting thin films in a electrode / semiconductor / electrode, thin film configuration. Column-row addressable electric microswitch matrices can be made in large areas, with high pixel density. Such matrices can be integrated with a sensor layer with electronic properties which vary in response to external physical conditions (such as photon radiation, temperature, pressure, magnetic field and so on), thereby forming a variety of detector matrices.
Owner:DUPONT DISPLAY +1
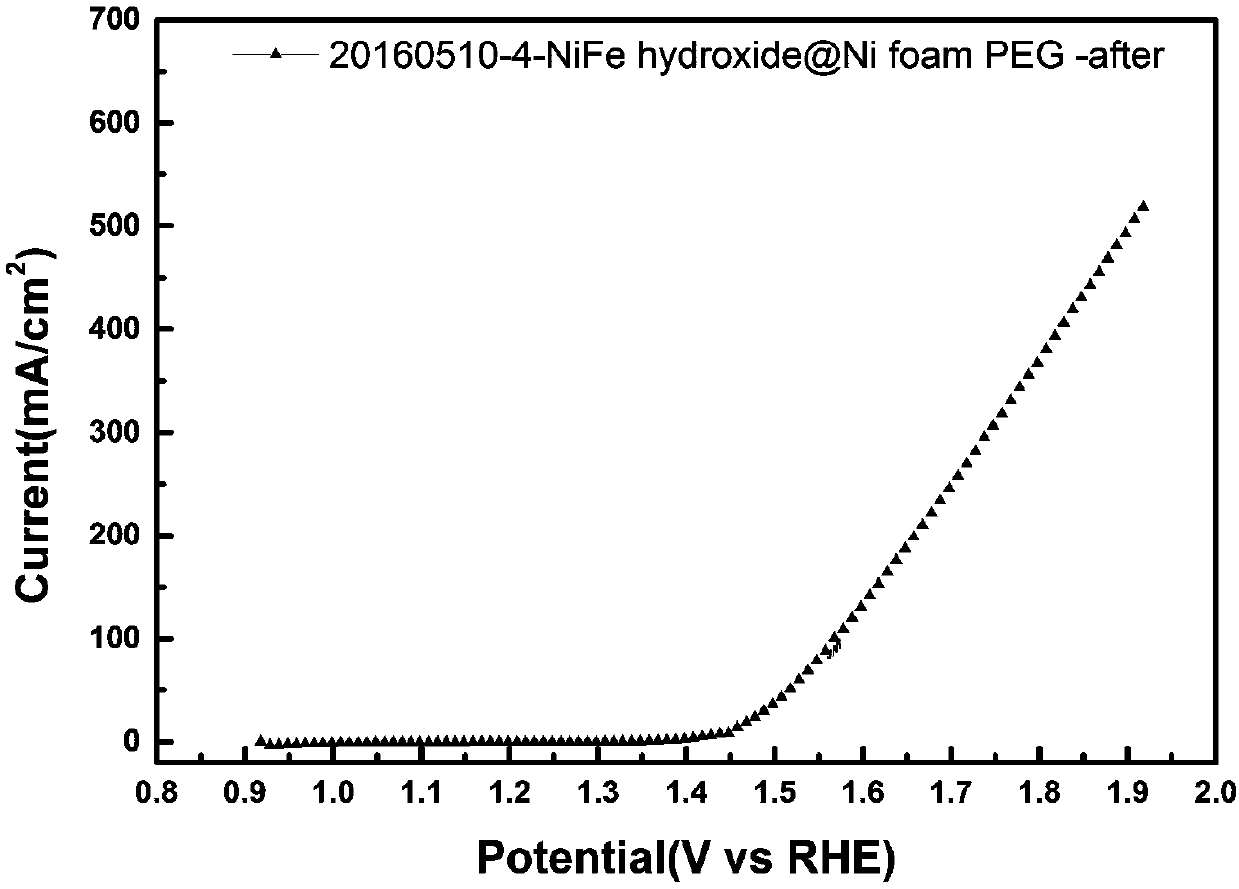
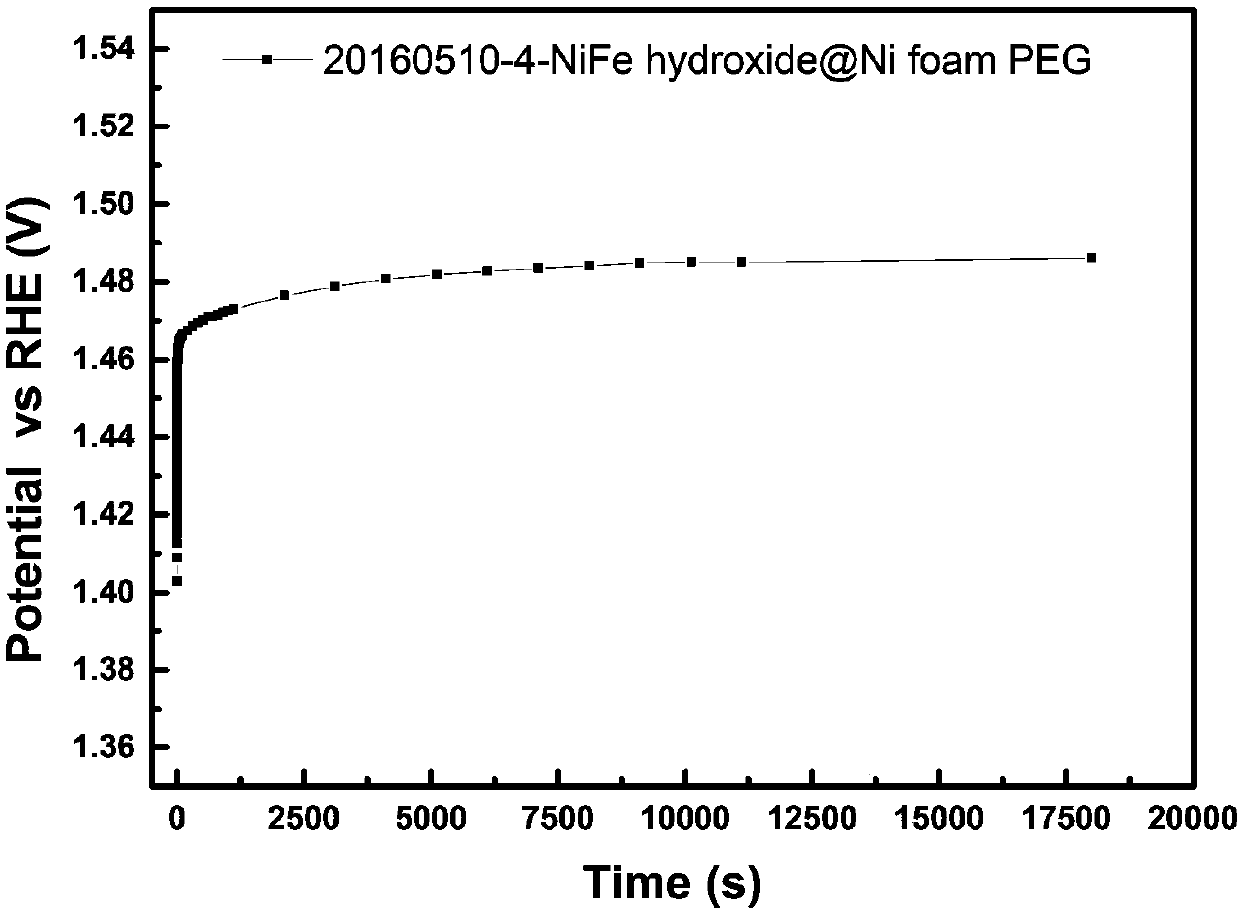
Hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107620087AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesElectrolysisExternal bias
The invention relates to a hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode applicable to alkaline mediums and a preparation method and application thereof. The electrode is applicable to the oxygen evolution reaction in the water-electrolytic hydrogen making process under catalytic alkaline conditions. The hydroxyl oxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages as follows: the nickel-iron hydroxide integrated electrode is shape-controlled, the preparation process is simple and under mild conditions, and the electrode can be used for a water electrolytic tank for hydrogen production from water splitting under external bias potentials; the prepared hydroxyloxidize iron-nickel-iron hydrotalcite integrated oxygen evolution electrode further has a better performance when being used in an alkaline solid polymer electrolyte (AEM) water electrolytic tank; and besides, an extensive utilization value in achieved in regenerative fuel cells (RFC), photoelectro-catalytic devices and electrolytic hydrogen generators.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
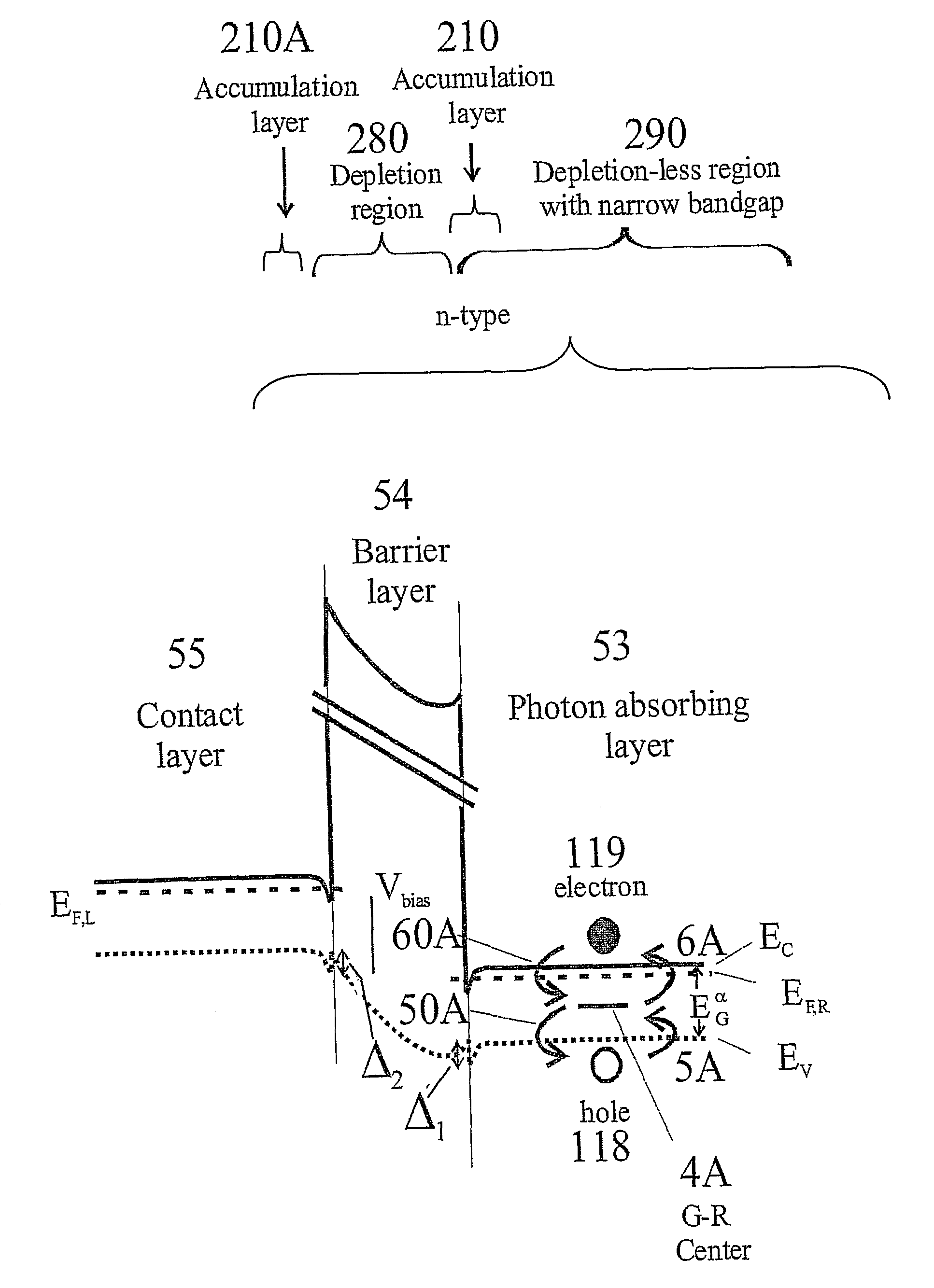
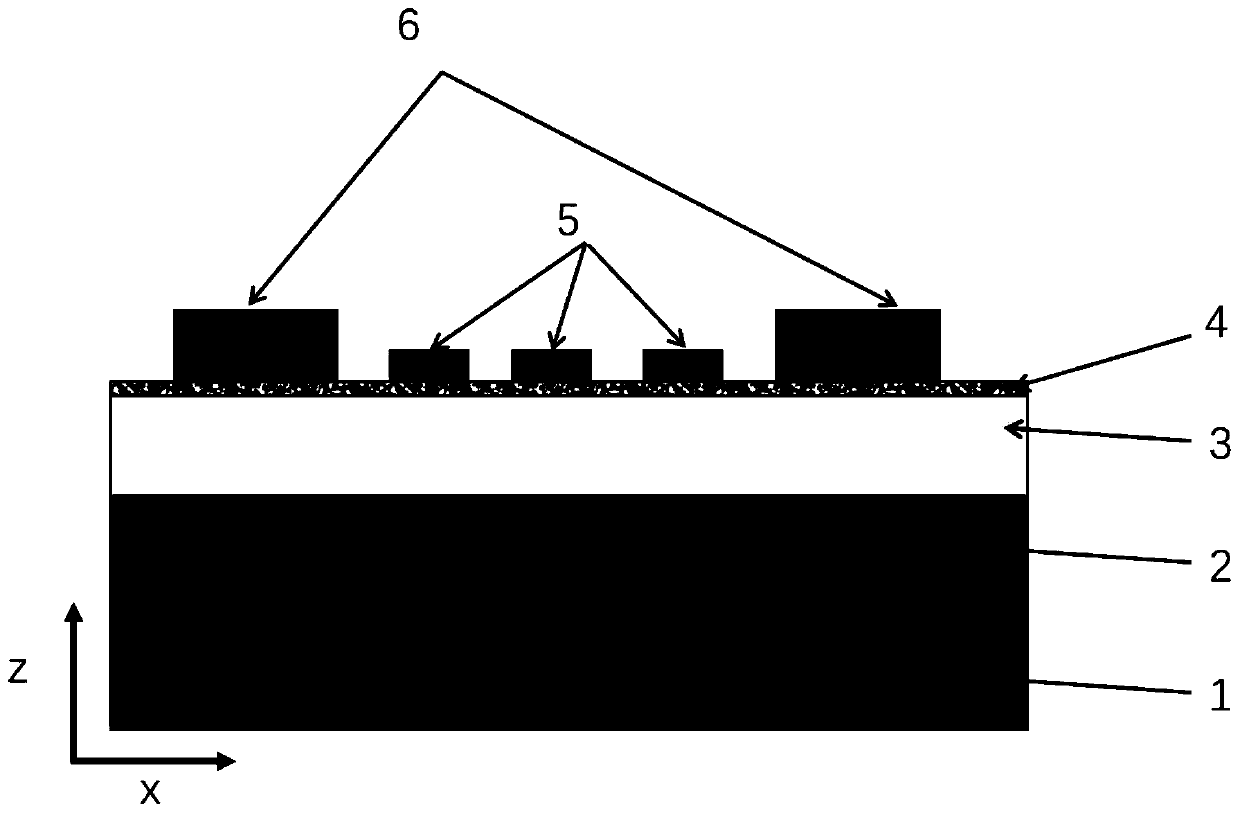
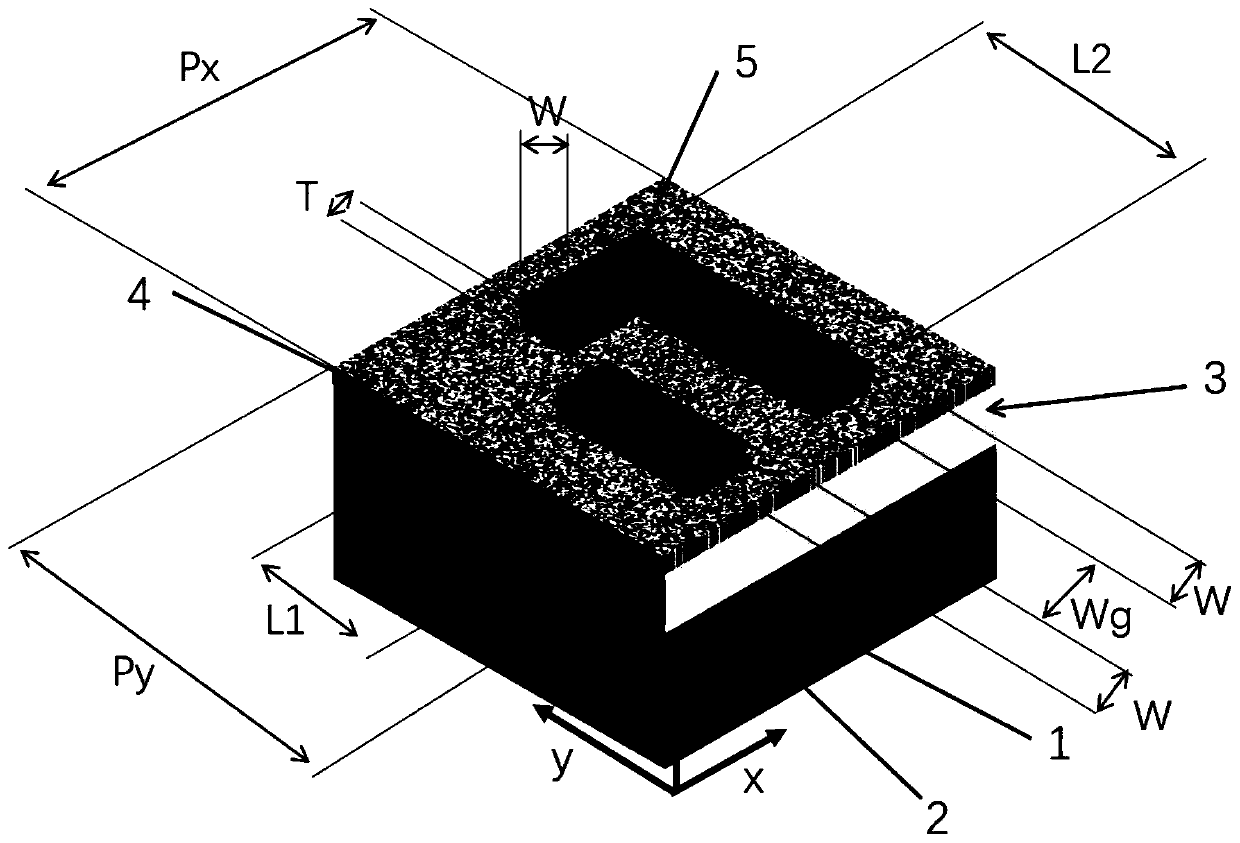
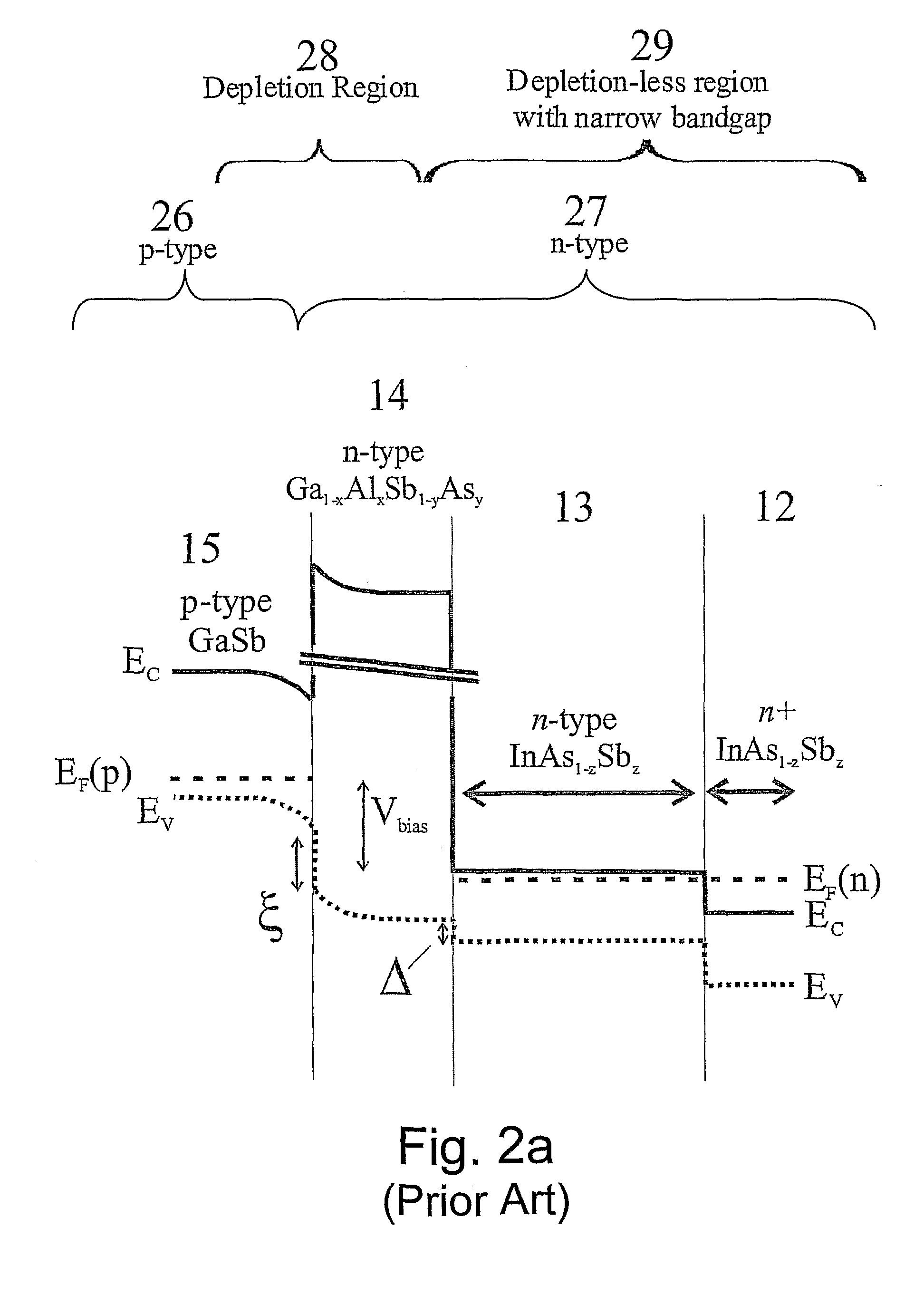
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090256231A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal biasPhotodetector
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Array substrate, display device and shutdown ghost improving circuit for display device
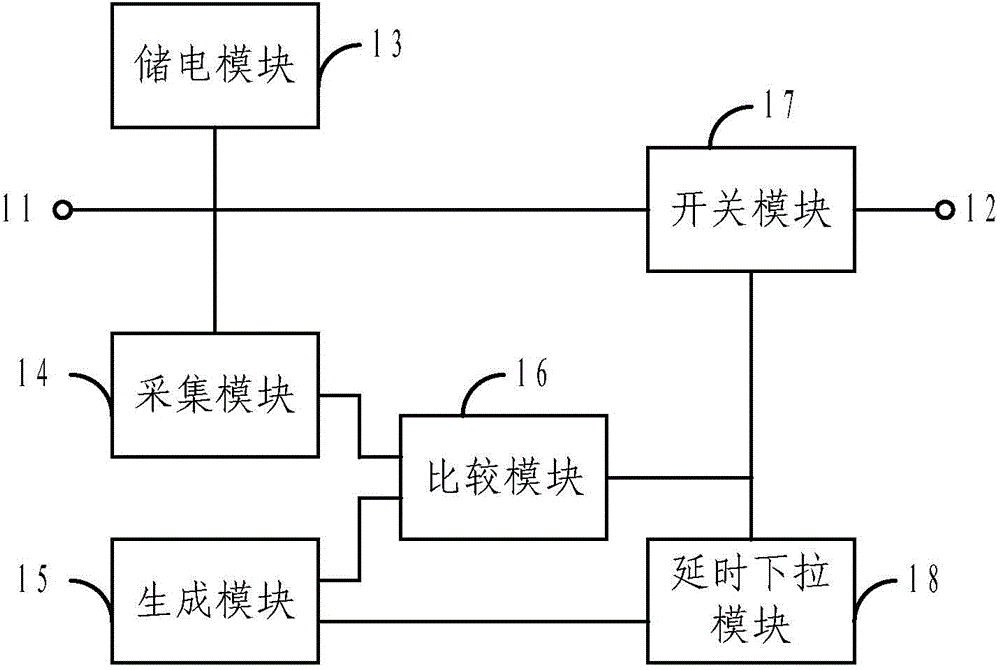
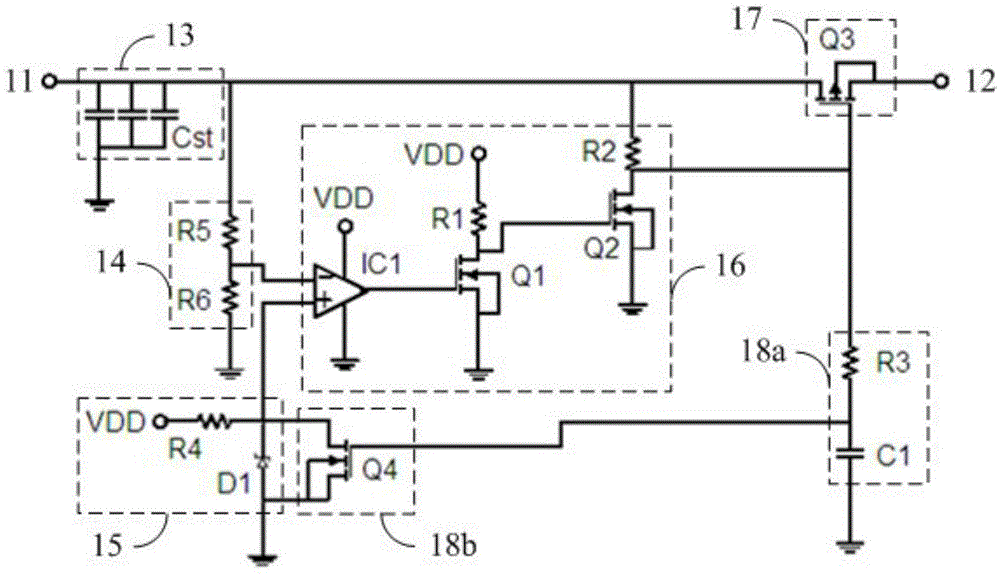
ActiveCN104795040AOpen fullySolve the problem of residual chargeStatic indicating devicesElectricityExternal bias
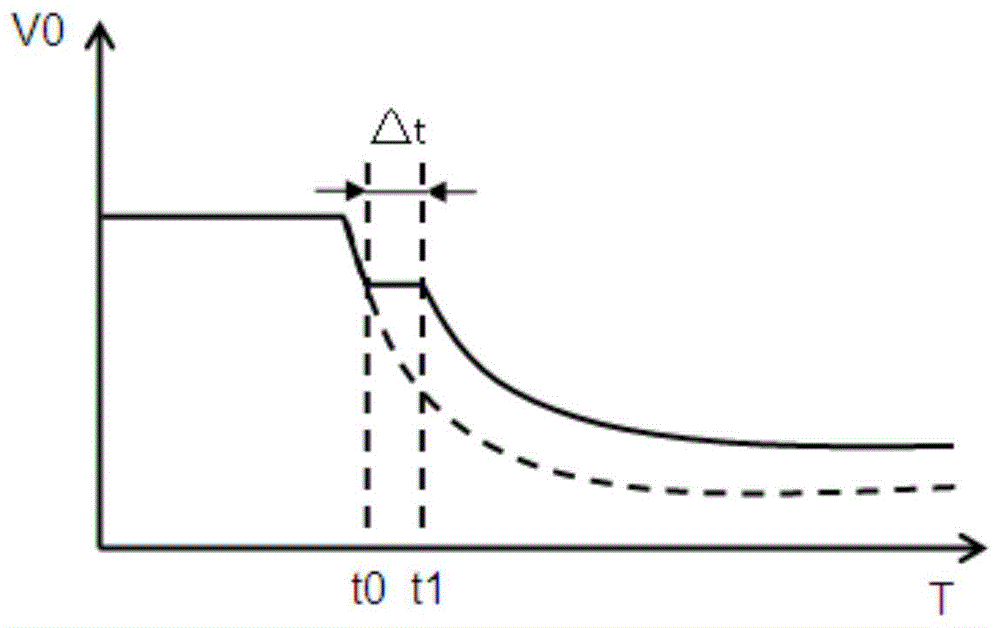
The invention provides an array substrate, a display device and a shutdown ghost improving circuit for the display device. The shutdown ghost improving circuit comprises a first connecting end, a second connecting end, an accumulation module, an acquisition module, a generation module, a comparison module, a switching module and a delay pull-down module; the first connecting end is used for being connected with external bias voltage; the second connecting end is used for being connected with a scanning driving circuit in the display device; the accumulation module is used for storing charge so as to keep potential at the first connecting end; the acquisition module is used for acquiring external bias voltage; the generation module is used for generating reference voltage with a preset initial value; the comparison module is used for generating a first control signal when sampled voltage is lower than the reference voltage; the switching module is used for cutting off electrical connection between the first connecting end and the second connecting end when receiving the first control signal; the delay pull-down module is used for pulling down the reference voltage to preset potential at preset time after the first control signal is received. The problem of charge residue in pixels due to rapid decrease of high-level external bias voltage after shutdown in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Organic electroluminescent device and method for producing the same
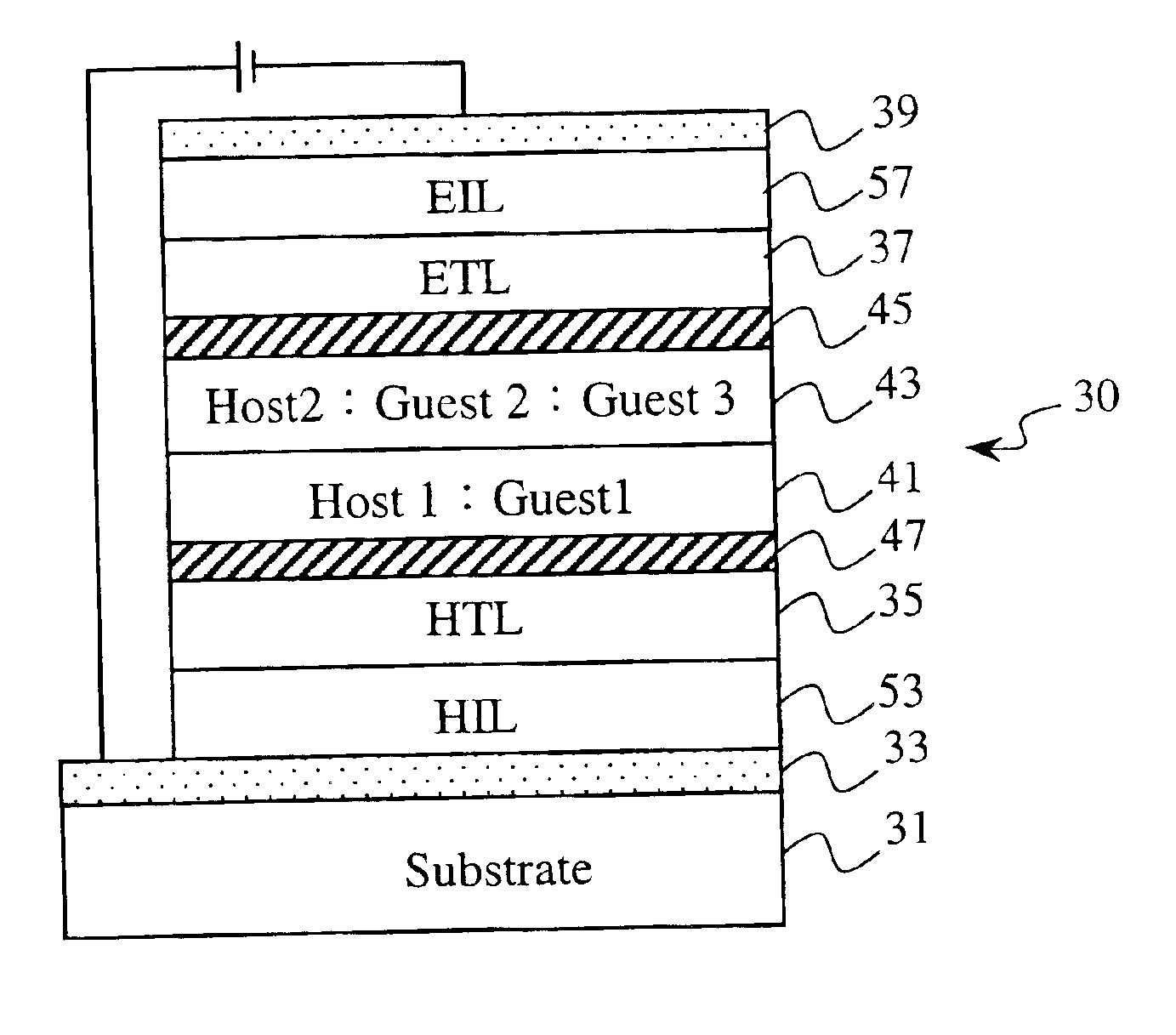
InactiveUS6933522B2Improve distributionThe implementation process is simpleDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesExternal biasHole transport layer
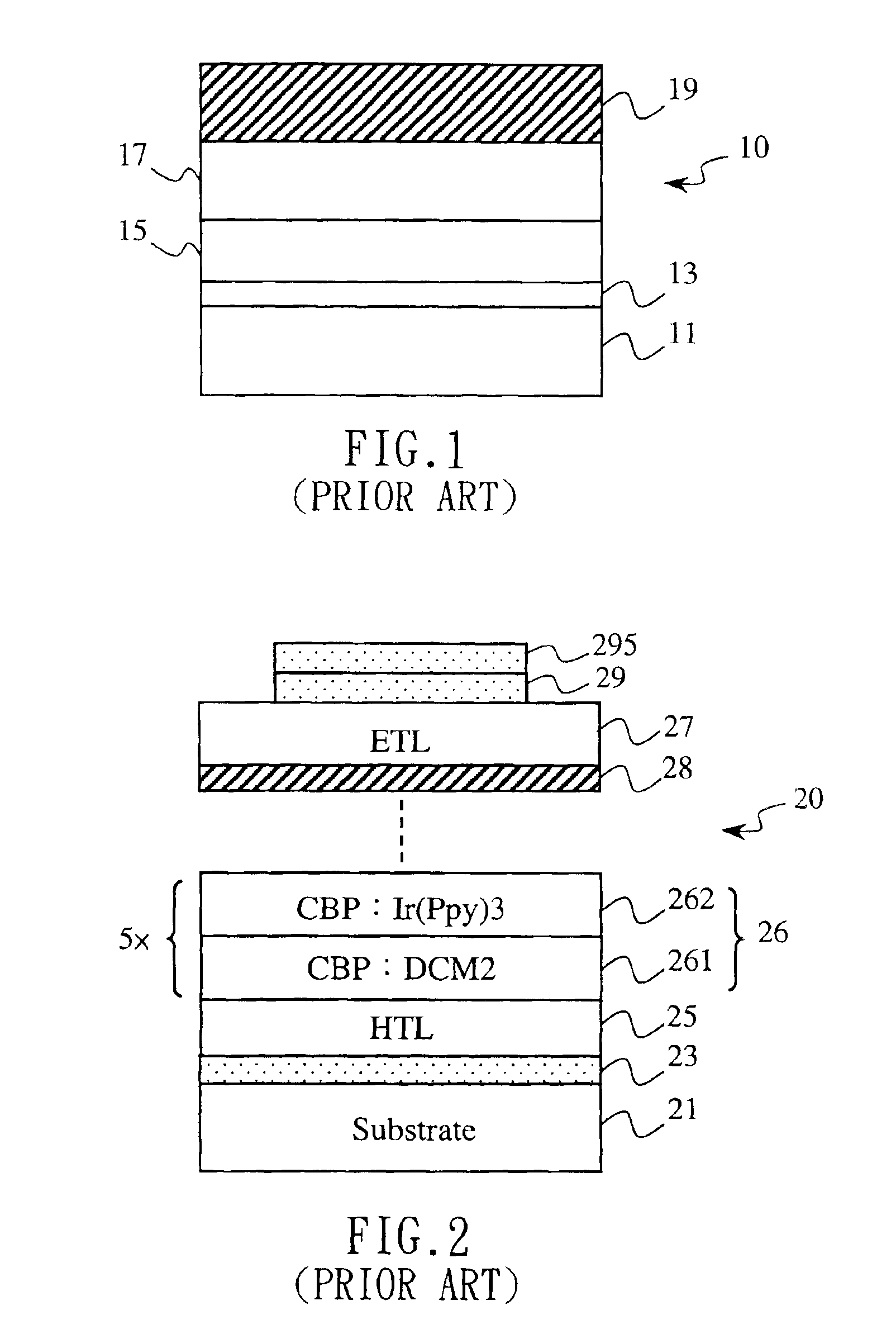
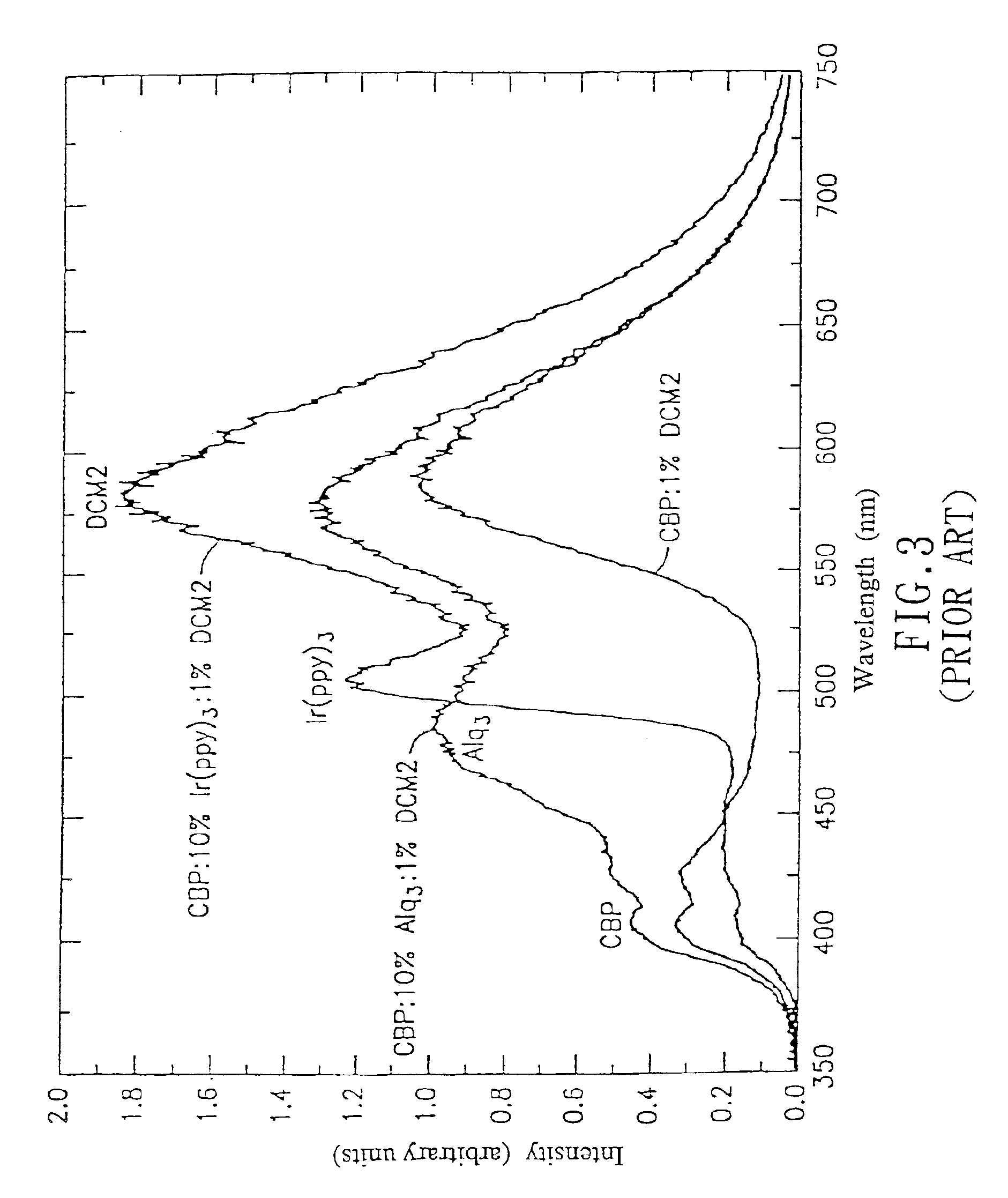
An organic electroluminescent device with the feature of three-wavelength luminescence is provided. The device includes a hole transporting layer, an electron blocking layer, a first host material layer, a second host material layer, a hole blocking layer, and an electron transporting layer placed between an anode and a cathode in turn. In which, the first host material layer has a first guest luminous substance mixed therein for projecting a first color light source (B), while the second host material layer correspondingly has a second guest luminous substance and a third guest luminous substance mixed therein for projecting a second color light source (G) and a third color light source (R), respectively, under the effect of an external bias voltage, wherein said second guest luminous substance or said third guest luminous substance may be a phosphorescence substance. Thus, not only a continuously full-band, full-colored light source featuring three-wavelength may be acquired directly by means of the combination of RGB colors, but also an effective utilization of phosphorescence substance and thus significantly raised luminescence efficiency may be obtained.
Owner:OPTO TECH
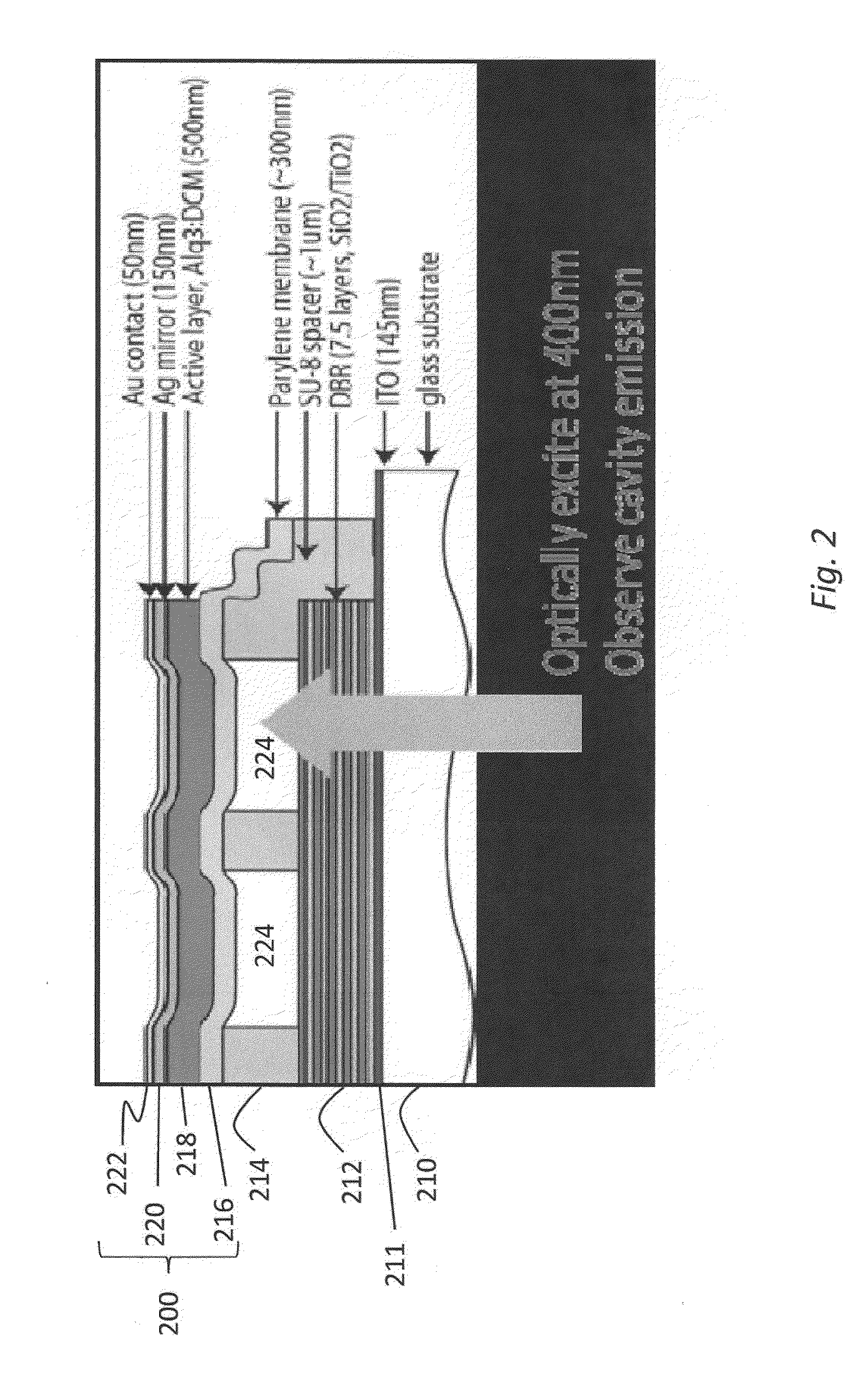
Method and applications of thin-film membrane transfer
ActiveUS20150311664A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMicrocontact printingExternal bias
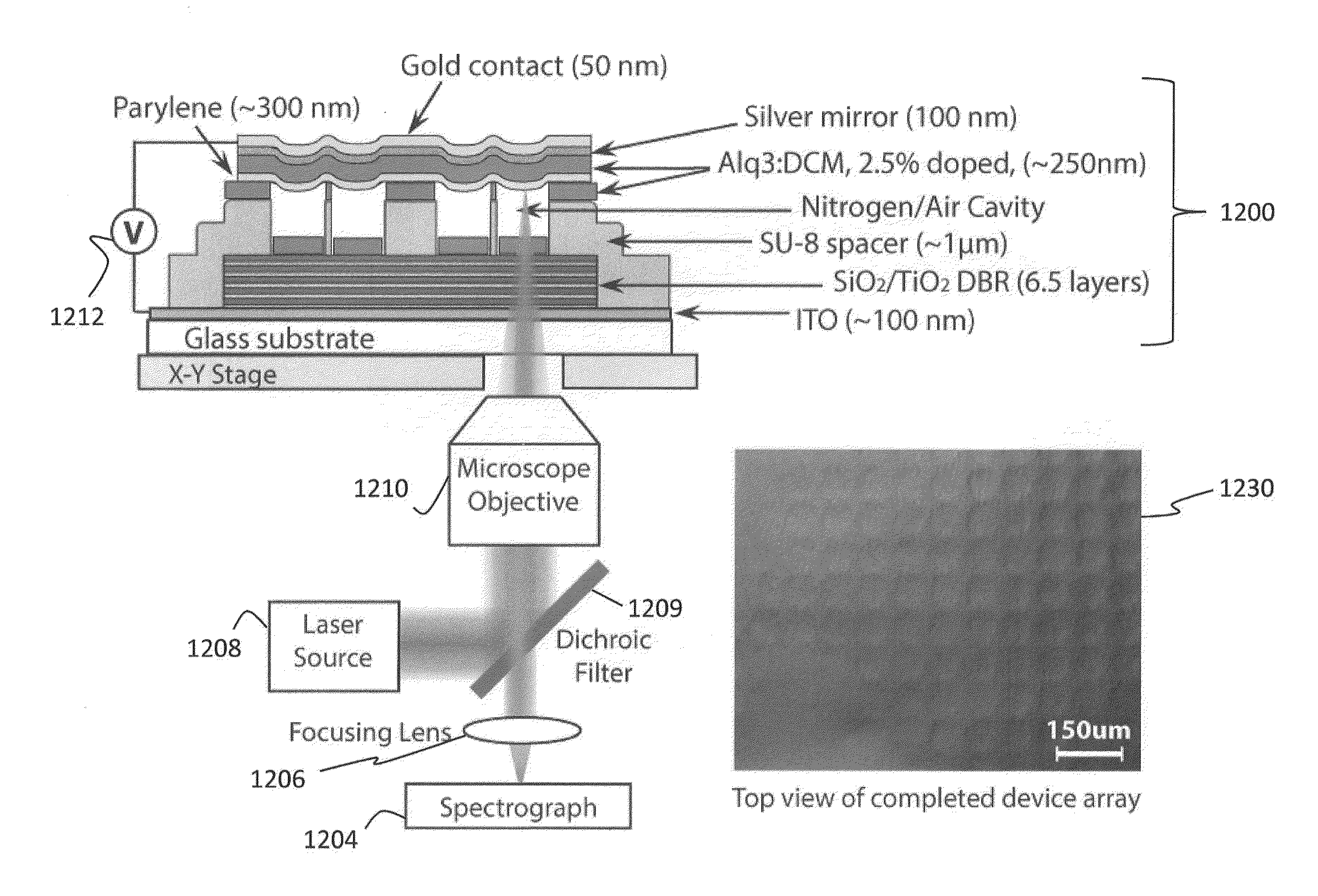
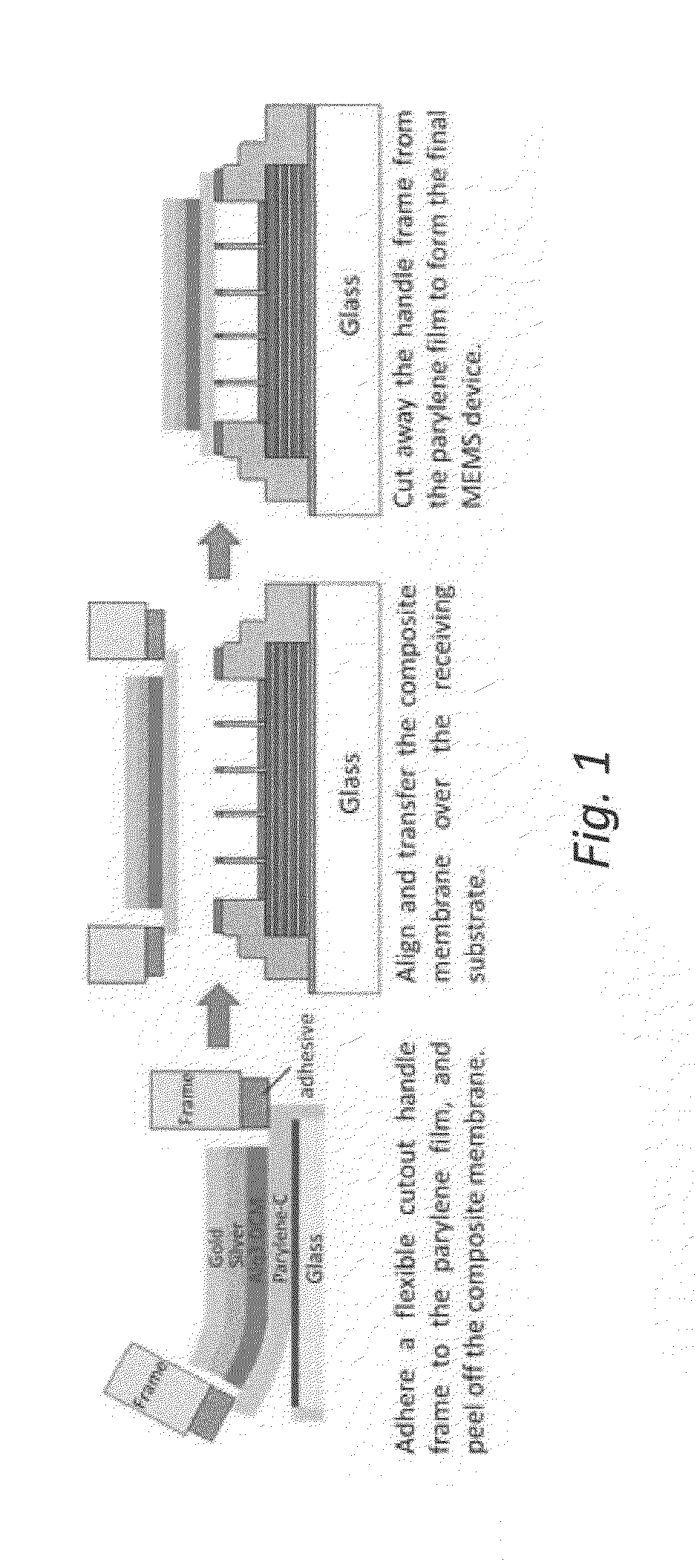
The disclosure relates to method and apparatus for micro-contact printing of micro-electromechanical systems (“MEMS”) in a solvent-free environment. The disclosed embodiments enable forming a composite membrane over a parylene layer and transferring the composite structure to a receiving structure to form one or more microcavities covered by the composite membrane. The parylene film may have a thickness in the range of about 100 nm-2 microns; 100 nm-1 micron, 200-300 nm, 300-500 nm, 500 nm to 1 micron and 1-30 microns. Next, one or more secondary layers are formed over the parylene to create a composite membrane. The composite membrane may have a thickness of about 100 nm to 700 nm to several microns. The composite membrane's deflection in response to external forces can be measured to provide a contact-less detector. Conversely, the composite membrane may be actuated using an external bias to cause deflection commensurate with the applied bias. Applications of the disclosed embodiments include tunable lasers, microphones, microspeakers, remotely-activated contact-less pressure sensors and the like.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Conversion apparatus, radiation detecting apparatus, and radiation detecting system
InactiveUS7629564B2Prevent leakageSuppress noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansExternal biasEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
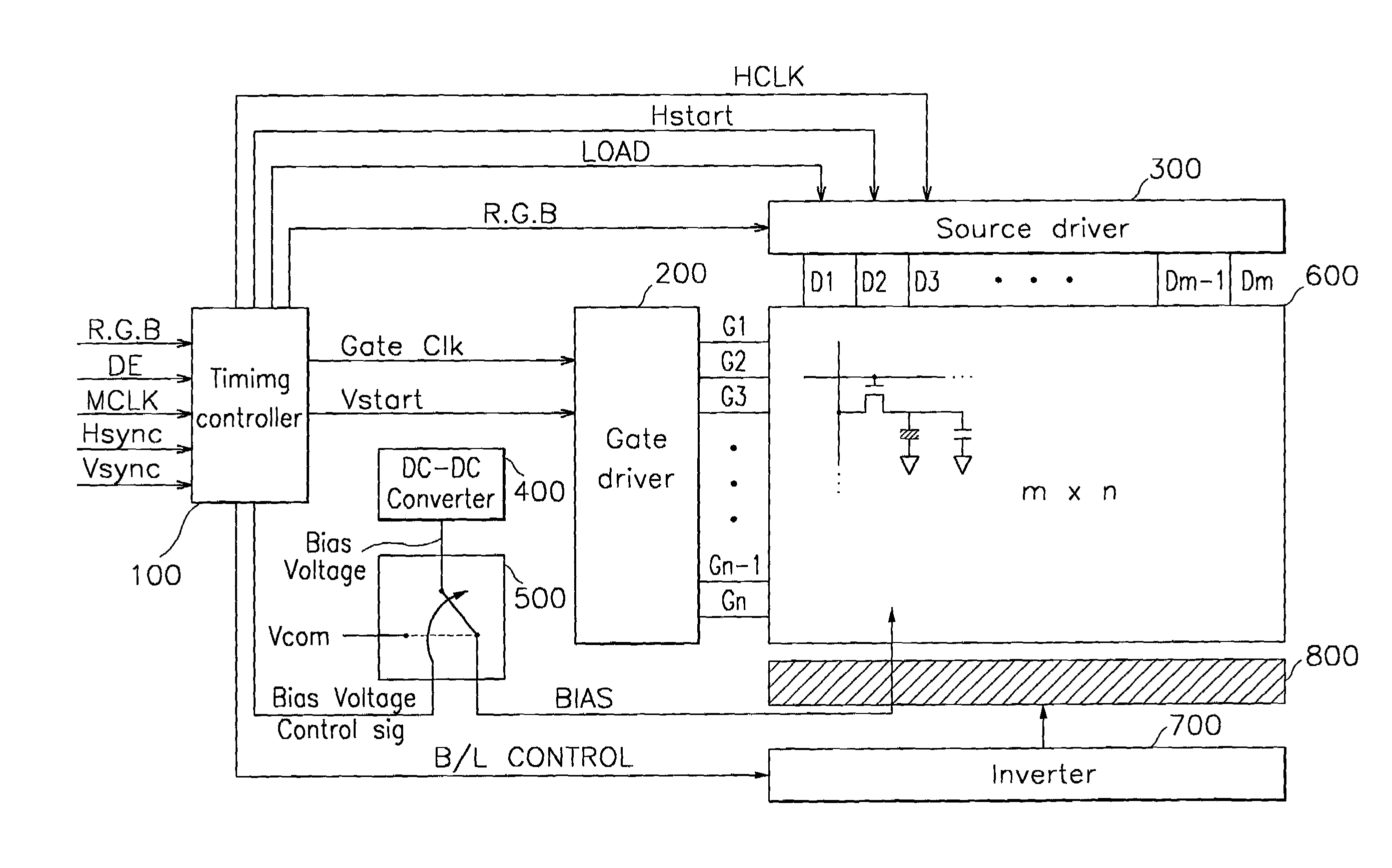
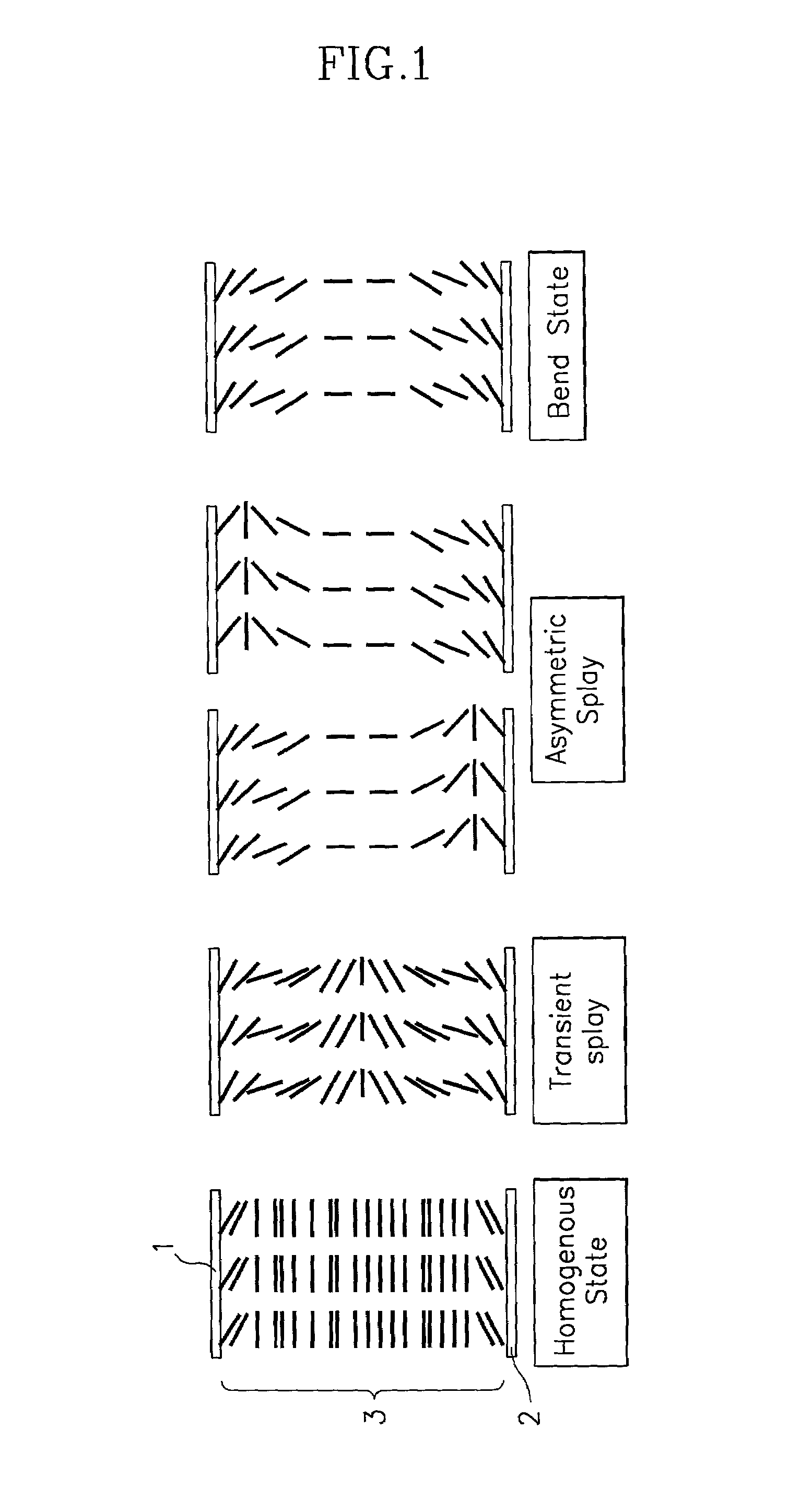
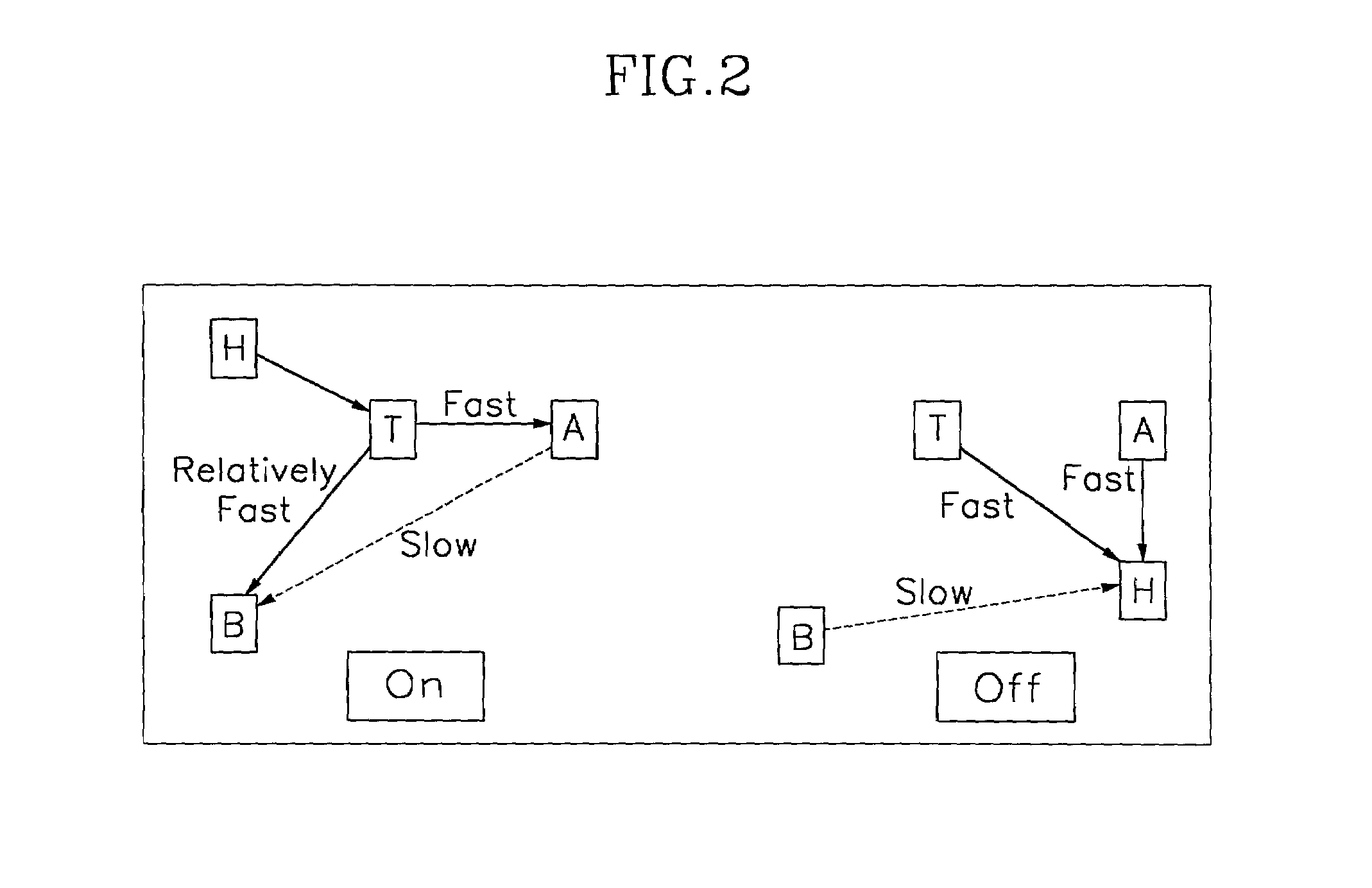
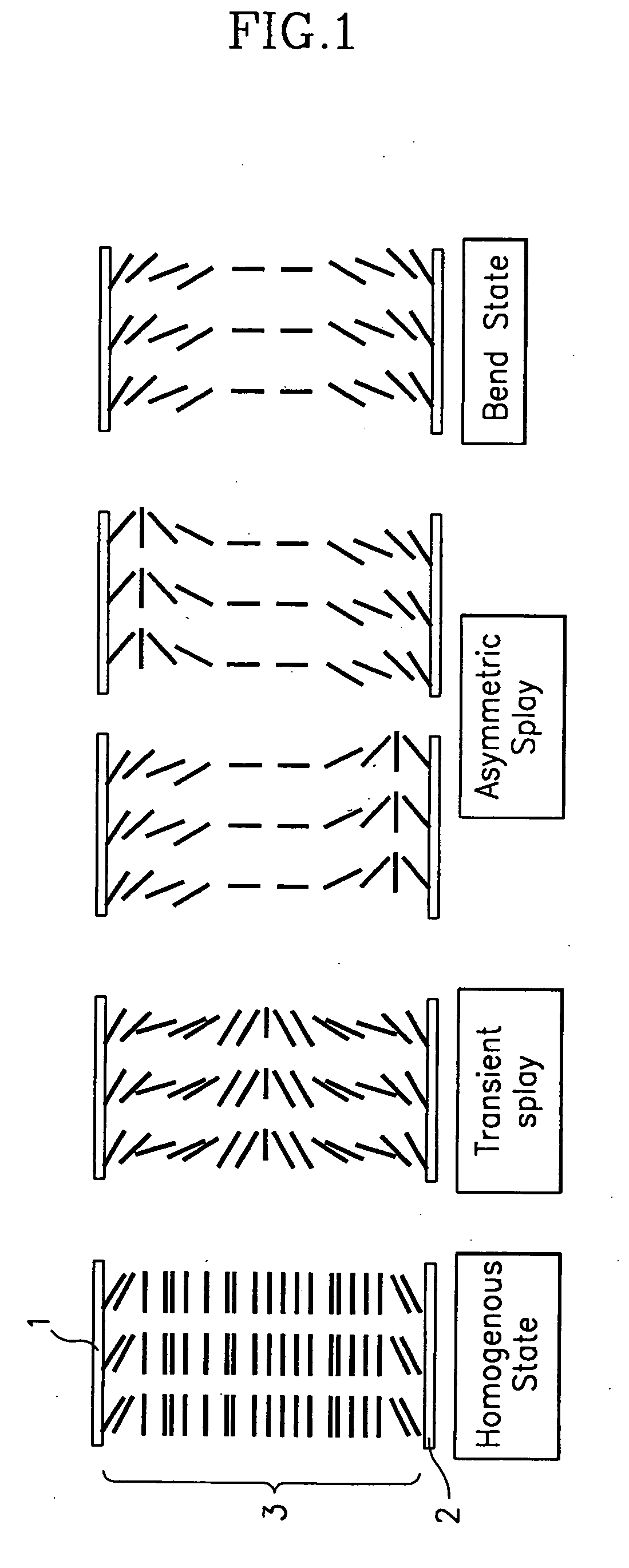
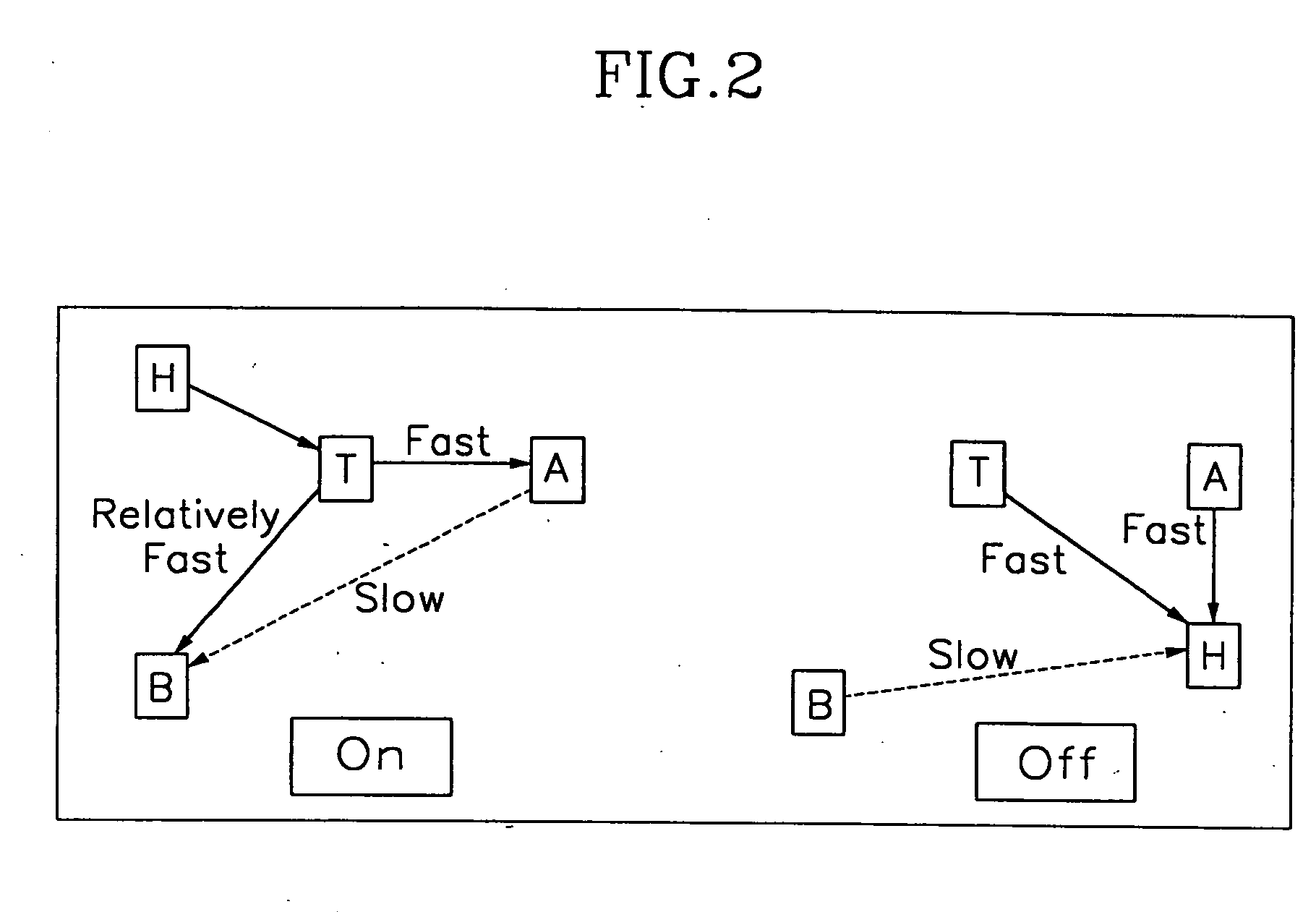
LCD for speeding initial bend state, driver and method thereof
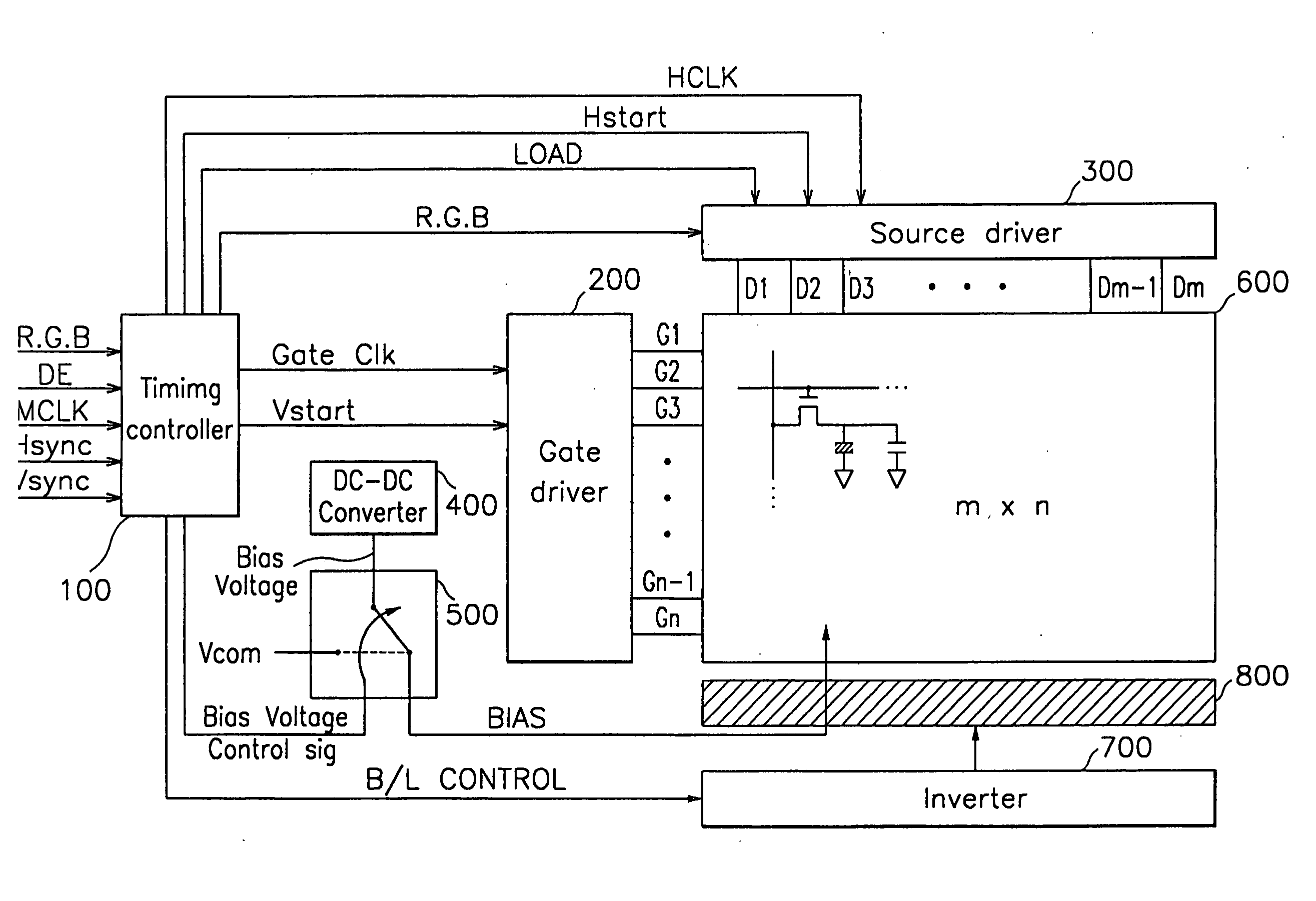
ActiveUS7019728B2Quick transitionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsExternal biasDisplay device
The present invention is directed to a liquid crystal display device and a method for driving the same for a fast transition into a bend state at initial operation such as immediately after power is inputted in a liquid display device with an OCB mode. According to one feature of the present invention, as power is inputted, a timing controller controls to output at least one of a gate voltage for a scan signal, a data voltage for a picture signal, and a driving voltage for a backlight by outputting a first switching signal to a switching unit, and controls to output one of an external bias voltage and a common electrode voltage by outputting a second switching signal to the switching unit so that fast transition into bend state of liquid crystal arranged in a LCD panel is accomplished. As a result, by applying a voltage of less level than that of the typical common electrode voltage to the LCD panel, as DC voltage of at least 10 volt to 20 volt is applicable to a common electrode, time for transition into bend state can be reduced at initial operation of the liquid crystal display device using the LCD panel with OCB mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Column-row addressable electric microswitch arrays and sensor matrices employing them
The present invention relates generally to fabricating two-terminal electric microswitches comprising thin semiconductor films and using these microswitches to construct column-row (x-y) addressable microswitch matrices. These microswitches are two terminal devices through which electric current and electric potential (or their derivatives or integrals) can be switched on and off by the magnitude or the polarity of the external bias. The microswitches are made from semiconducting thin films in a electrode / semiconductor / electrode, thin film configuration. Column-row addressable electric microswitch matrices can be made in large areas, with high pixel density. Such matrices can be integrated with a sensor layer with electronic properties which vary in response to external physical conditions (such as photon radiation, temperature, pressure, magnetic field and so on), thereby forming a variety of detector matrices.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Self-driven photodetector based on ZnO nanorod/CH3NH3PbI3/MoO3 structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105304747ANovel structureLow costMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureWater bathsHeterojunction
The invention provides a self-driven photodetector based on an FTO / ZnO nanorod / CH3NH3PbI3 / MoO3 / Au structure and a preparation method thereof. The specific structure comprises an FTO layer and a ZnO nanorod which is an electron transporting layer and a hole blocking layer. CH3NH3PbI3 is a perovskite light absorbing layer. Semiconductor oxide MoO3 is a hole transporting layer and an electron blocking layer. A metal electrode is made of an Au film. The self-driven photodetector is synthesized through spin coating and water bath and is prepared through evaporation and the like. According to the invention, an organic-inorganic hybrid heterojunction structure formed by the ZnO nanorod / CH3NH3PbI3 is used; the semiconductor oxide MoO3 is the hole transporting layer; the self-driven photodetector has the advantages of high response degree and sensitivity; the response rate and the detection rate are respectively up to 24.3A / W and 3.56*1014cmHz1 / 2 / W; the self-driven photodetector has a certain degree of self-driven capacity and does not need the drive of external bias, which is conducive to energy conservation; the performances are far more than the performances of a currently reported Si-based detector; near-ultraviolet and visible infrared detection can be realized; and the self-driven photodetector has the advantages of simple operation steps, low experiment cost and good application prospect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Single-electron transistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS6894352B2Reduce spacingIncrease operating temperature to room temperatureTransistorNanoinformaticsEtchingExternal bias
A method for fabricating a single-electron transistor (SET). A one dimensional channel is formed between source and drain on a silicon-on-insulator substrate, and the separated polysilicon sidewall spacer gates are formed by electron-beam lithographically etching process in a self-aligned manner. Operation of the single-electron transistor with self-aligned polysilicon sidewall spacer gates is achieved by applying external bias to the self-aligned polysilicon sidewall spacer gates to form two potential barriers and a quantum dot capable of storage charges between the two potential barriers. A metal upper gate is finally formed and biased to induce a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) and control the energy level of the quantum well. Accordingly, the method of the invention comprises a combination of electron beam (E-beam) lithography with multilayer-aligned direct writing technology, oxidation, and wet etching to form a nanoscale one-dimensional channel between source and drain on a silicon-on-insulator substrate.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
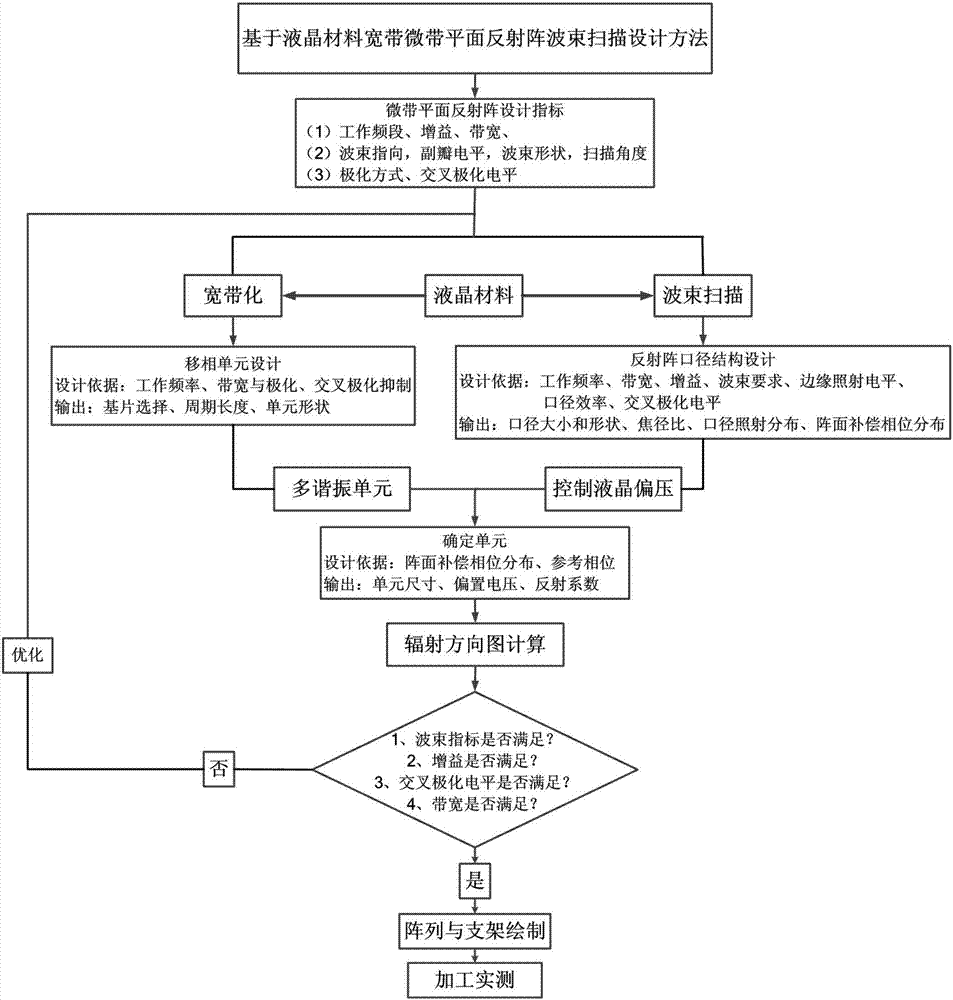
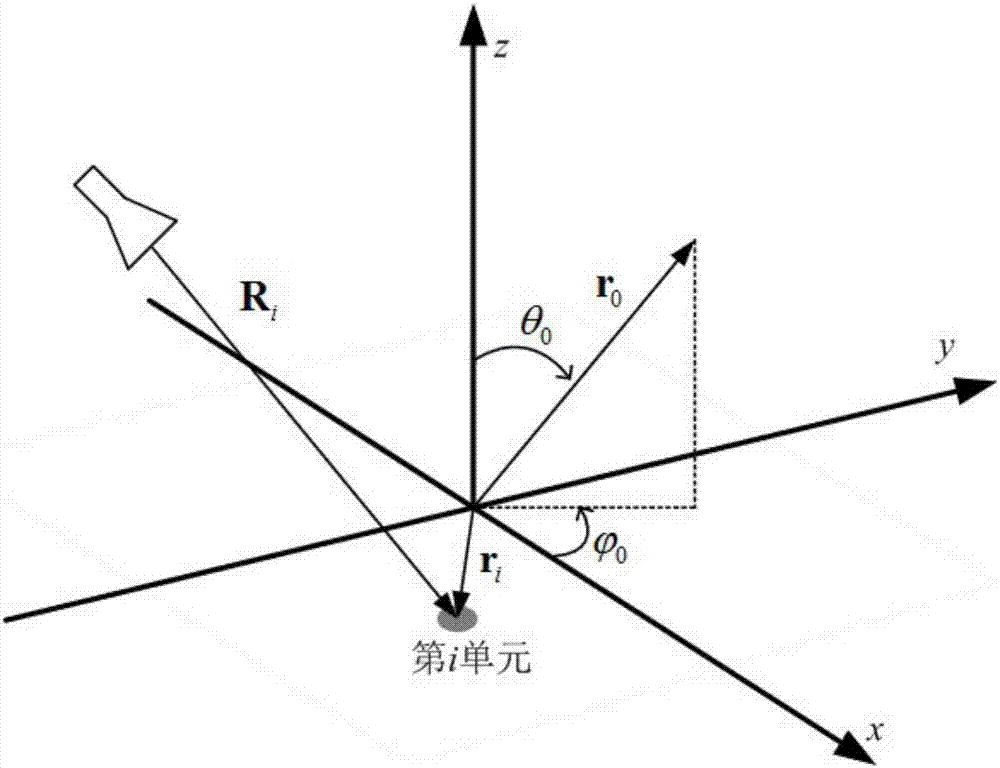
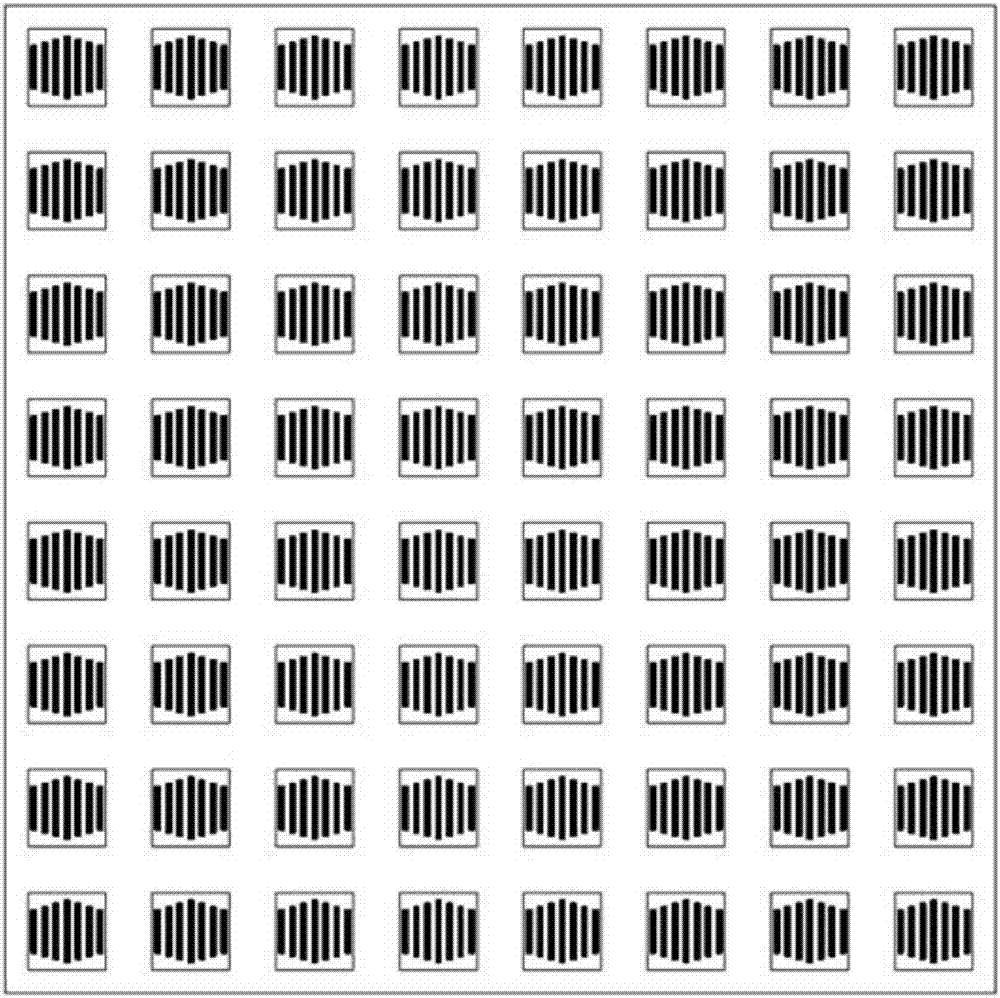
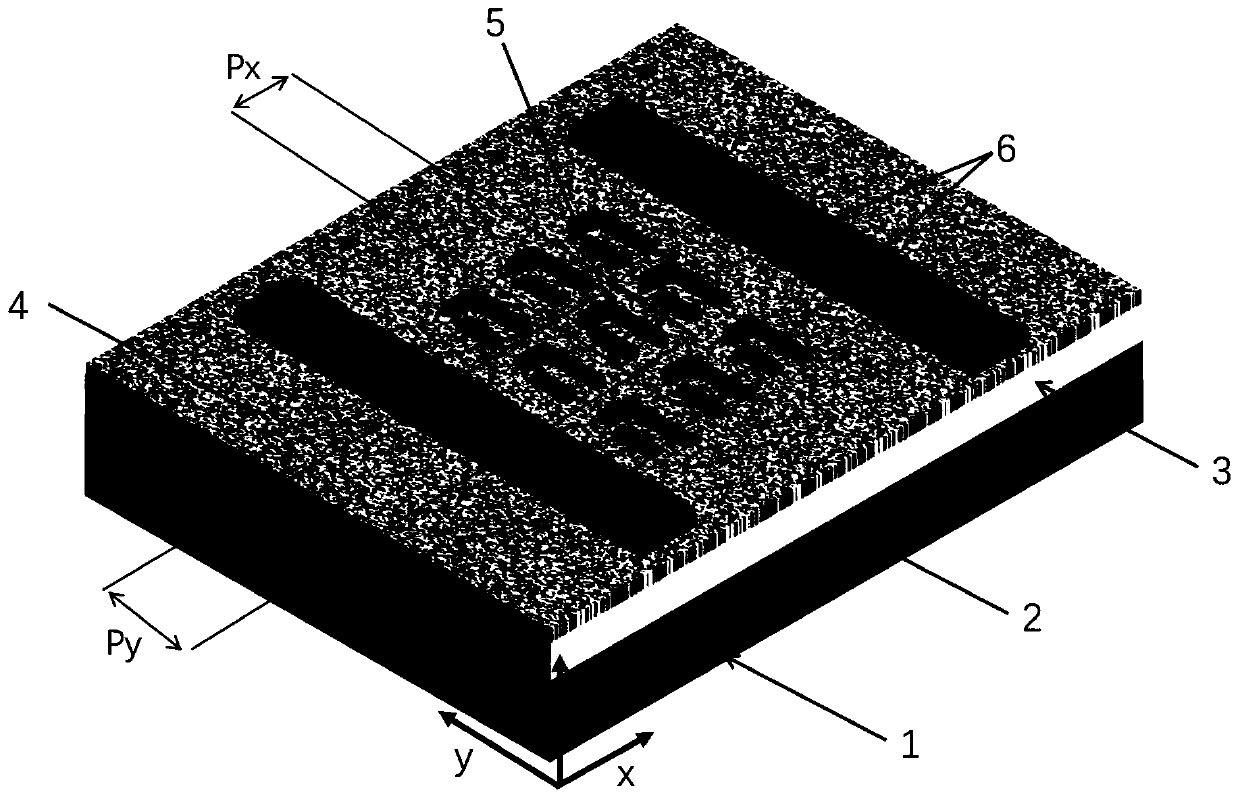
Beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna based on microcrystal material and fabrication method of beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna
InactiveCN107046176AIncrease working frequencyLarge power capacityAntenna arrays manufactureRadar systemsExternal bias
The invention relates to a beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna based on a microcrystal material and a fabrication method of the beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna, which are mainly used for solving the technical problems of low power capacity and low working frequency band in the prior art. The beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna comprises phase shift units, beam scanning devices and a feeding source, wherein the phase shift units are arranged right below a microstrip reflection array and are in contact with the microstrip reflection array, the beam scanning device are correspondingly connected with the phase shift units, the feeding source is connected with the beam scanning device and is arranged right below the microstrip reflection array, the phase shift units are liquid crystal units and are used for connecting an input / output end of the antenna, and the beam scanning devices are used for providing external bias for the phase shift units. By the technical scheme, the problem is solved very well, and the beam scanning microstrip planar reflection array antenna can be used for a communication and radar system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Circularly polarized light detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111029416ARealize photodetectionQuick responseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesExternal biasPhotocurrent
The invention discloses a circularly polarized light detector and a preparation method thereof. The circularly polarized light detector comprises a substrate, a metal reflection layer, a dielectric layer, a single-layer transition metal chalcogenide, a chiral surface plasmon metasurface and an electrode, wherein the chiral surface plasmon metasurface integrated on the single-layer transition metalchalcogenide can generate selective absorption enhancement on incident circularly polarized light, therefore, the number of photon-generated carriers generated by the single-layer transition metal chalcogenide under the incident condition of circularly polarized light is modulated, measurable photocurrents of different sizes can be generated corresponding to different circularly polarized light under the action of external bias voltage, and photoelectric detection and distinguishing of different circularly polarized light are achieved. The circularly polarized light detector is an integratedphotoelectric detector for realizing a circularly polarized light detection function in a single planar device for the first time, works in a visible light waveband, and has the characteristics of ultra-thin thickness, high response speed and convenience in integration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
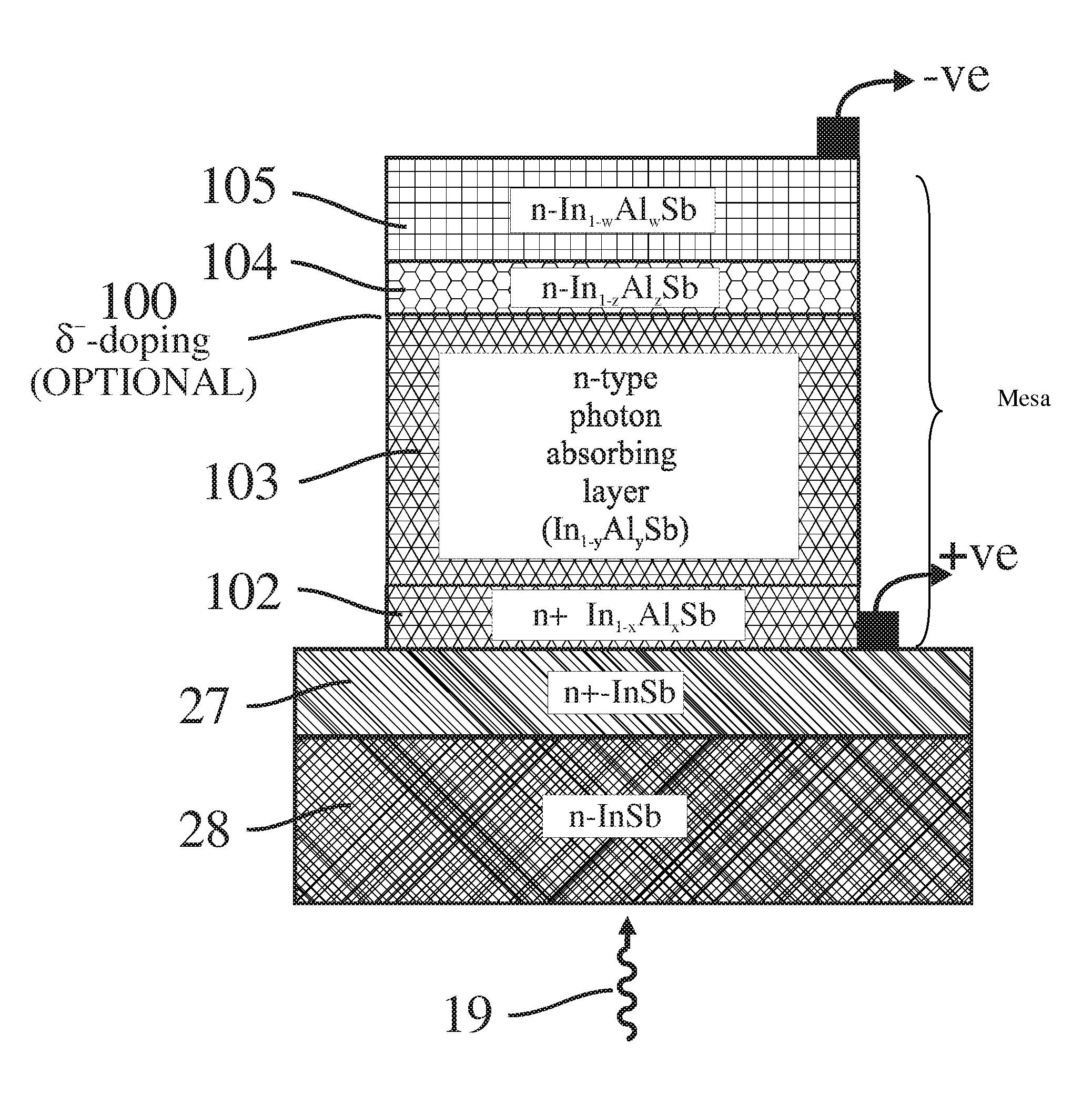
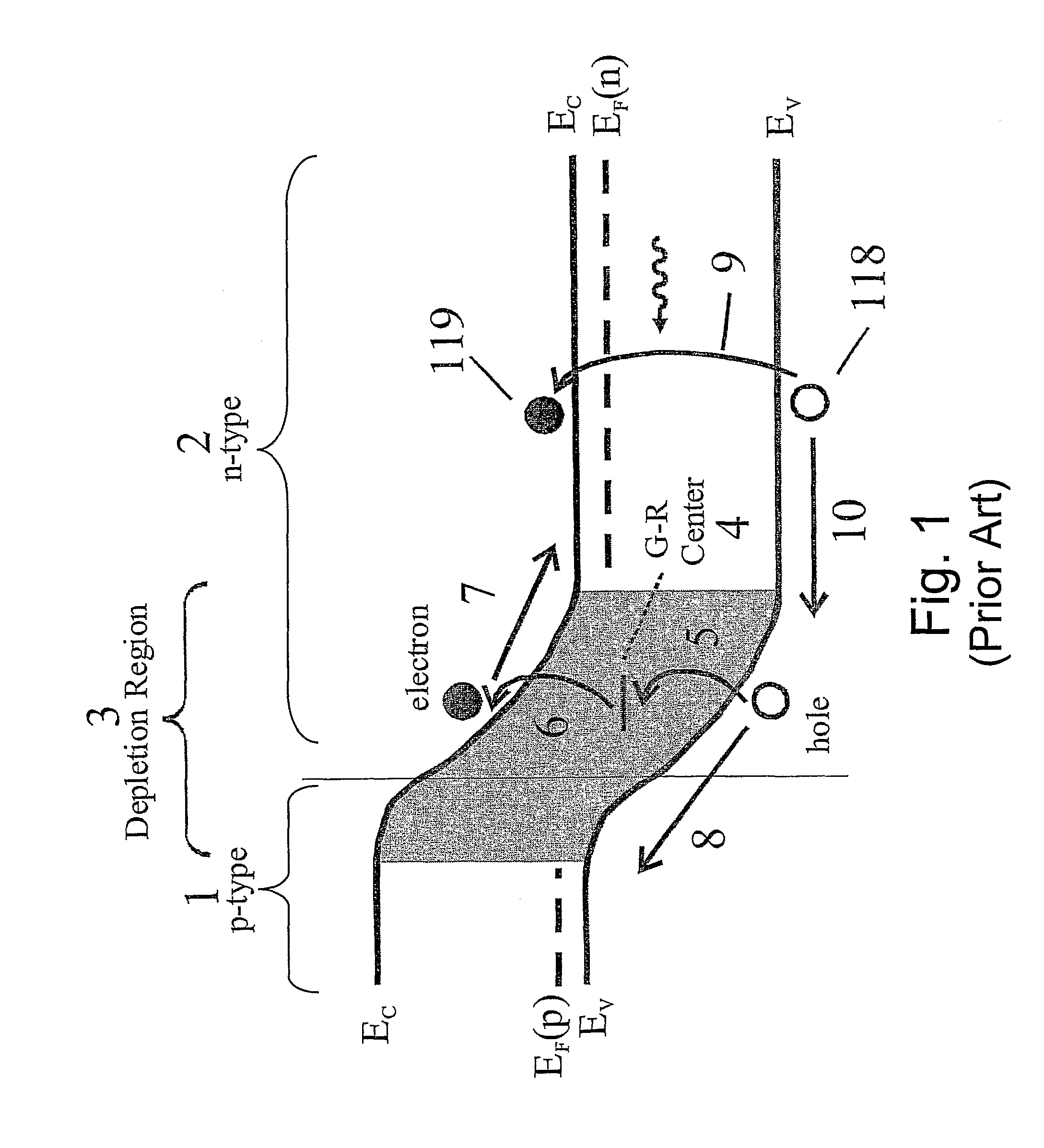
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8004012B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesValence bandExternal bias
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Terahertz graphene microstructure modulator
The invention provides a terahertz modulator with a graphene complementary microstructure as an active area. The modulator comprises a substrate, a doped semiconductor layer growing on the substrate, an insulating layer and an active area layer which are sequentially stacked, and an electrode growing on the topmost active area layer, wherein the insulating layer at the bottommost grows on the doped semiconductor layer, the active area layer is arranged on the top, and the active area layer is a graphene layer with the complementary microstructure. The invention further provides a manufacturing method of the terahertz modulator. The Fermi level of graphene is changed through external bias, and accordingly deep modulation of incident THz waves is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for realizing continuous terahertz spectrum detection
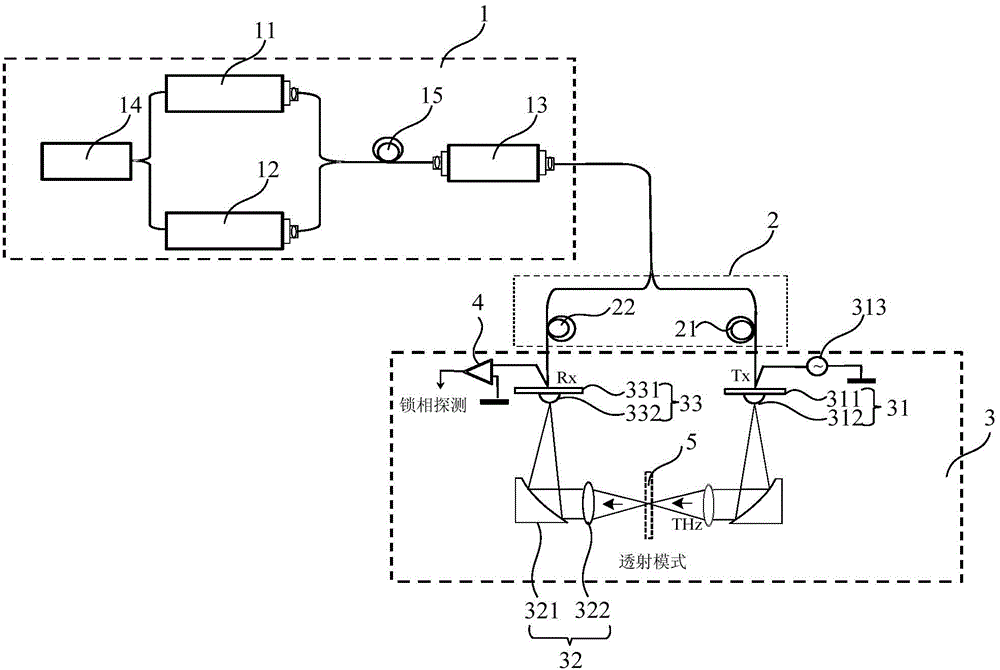
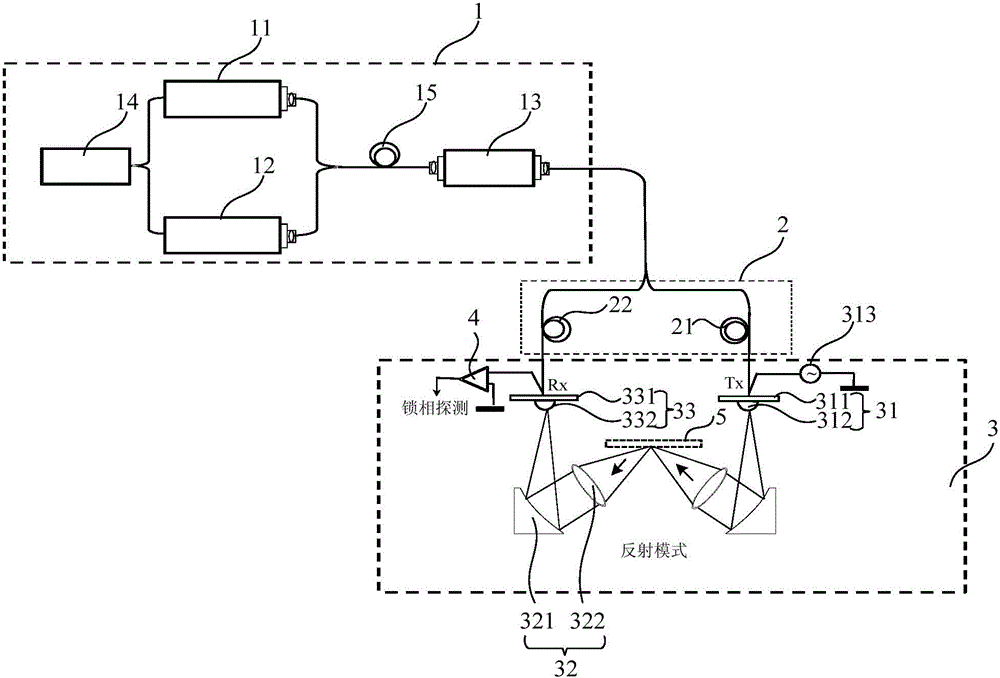
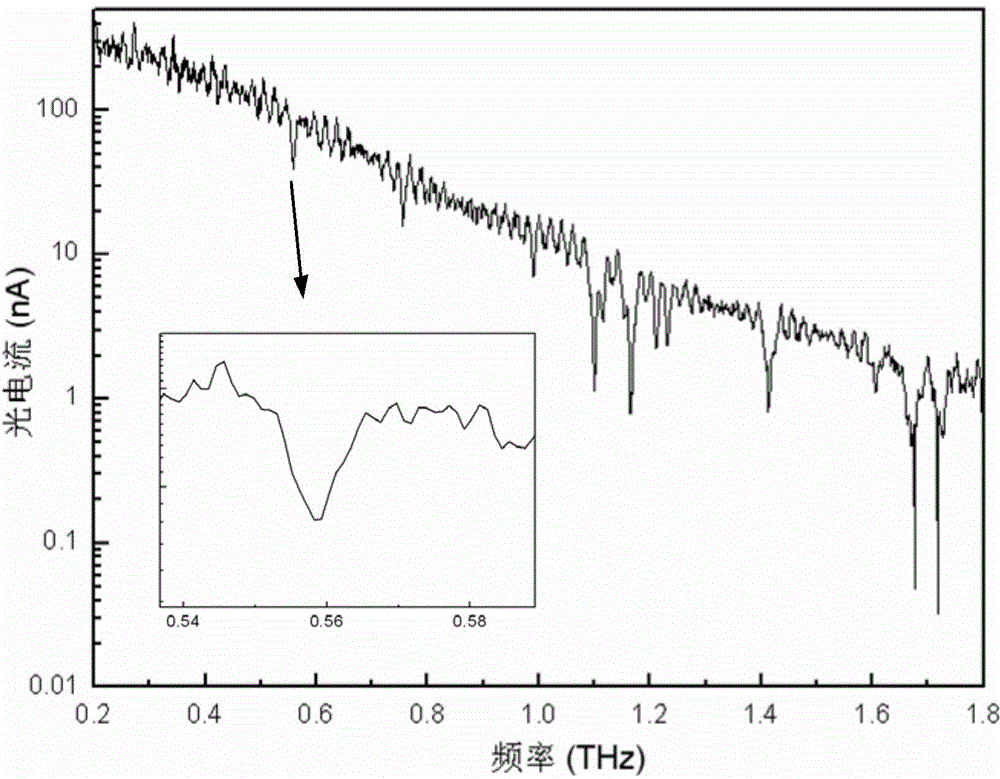
InactiveCN104458645AAchieving Phase ModulationAverage signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansExternal biasTerahertz radiation
The invention provides a method and a system for realizing continuous terahertz spectrum detection. A pair of high-stability single longitudinal mode near-infrared lasers serve as seed light sources, a laser signal is modulated by utilizing optical fibers, and continuous terahertz waves are radiated outwards under external bias potential by virtue of an optical mixer; and the terahertz waves are subjected to coherent detection at a signal receiving end by adopting a photoconductive switch and an antenna. The temperature modulation is performed on the lasers, and wide bandwidth difference frequency continuous terahertz radiation output is realized. Compared with a common terahertz time-domain impulse spectral system, the system has the advantages that the spectral resolution acquired by the technology is greatly improved, and the system has an excellent effect of promoting the development of terahertz spectroscopy and related fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bias circuit of electroabsorption modulated laser
ActiveCN102571003AImprove work performanceLow costLaser constructional detailsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceElectro-absorption modulator
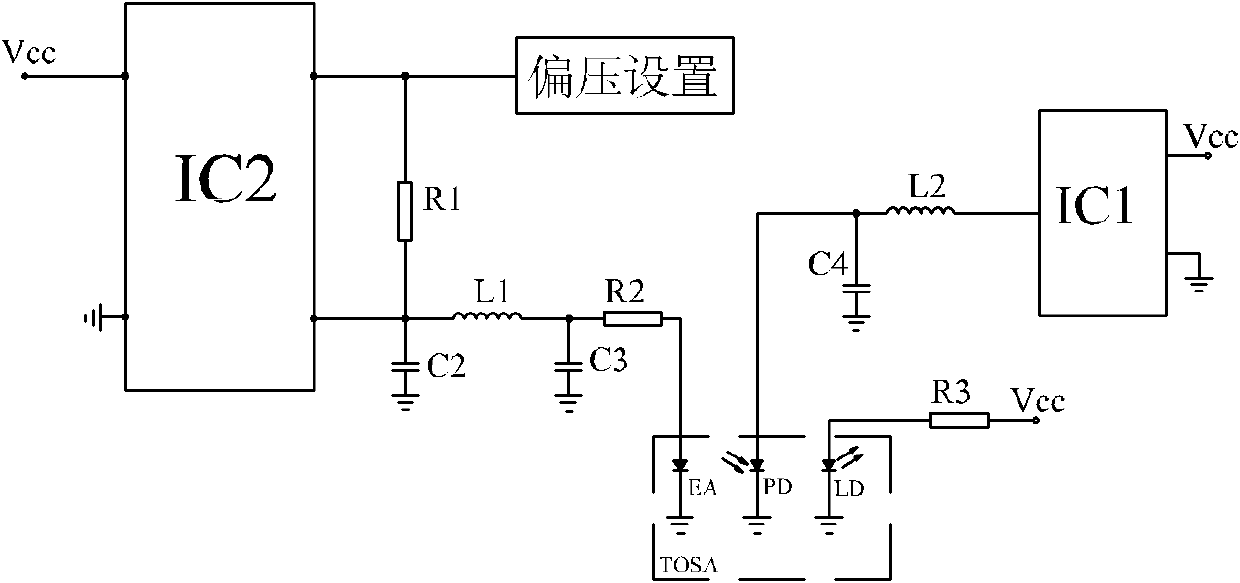
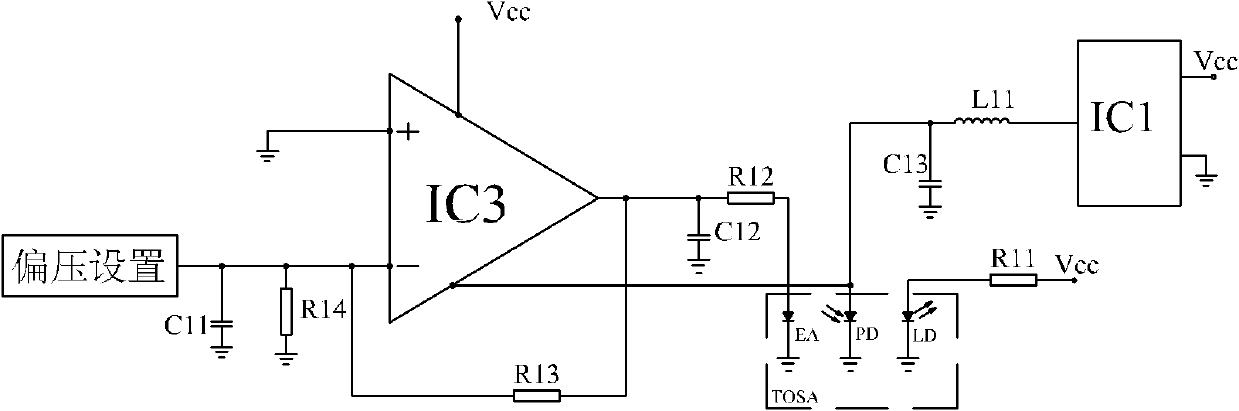
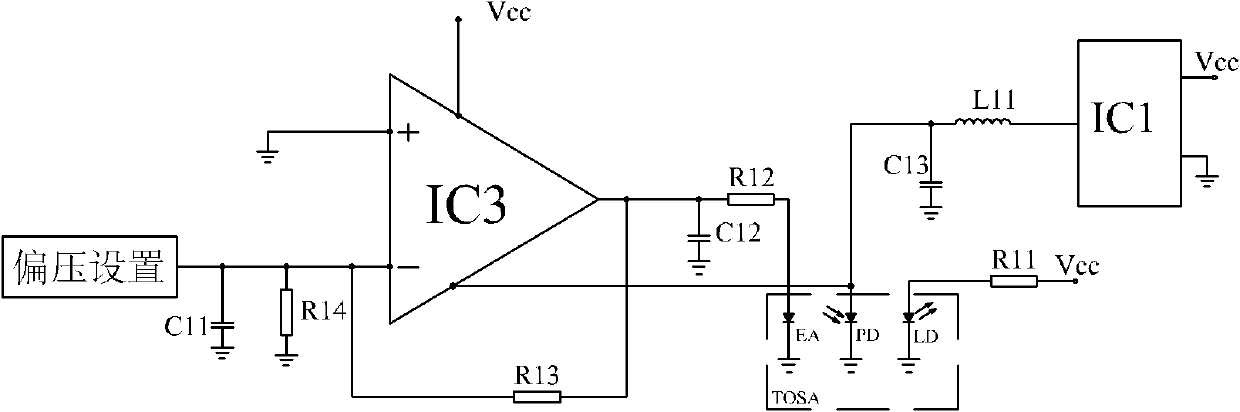
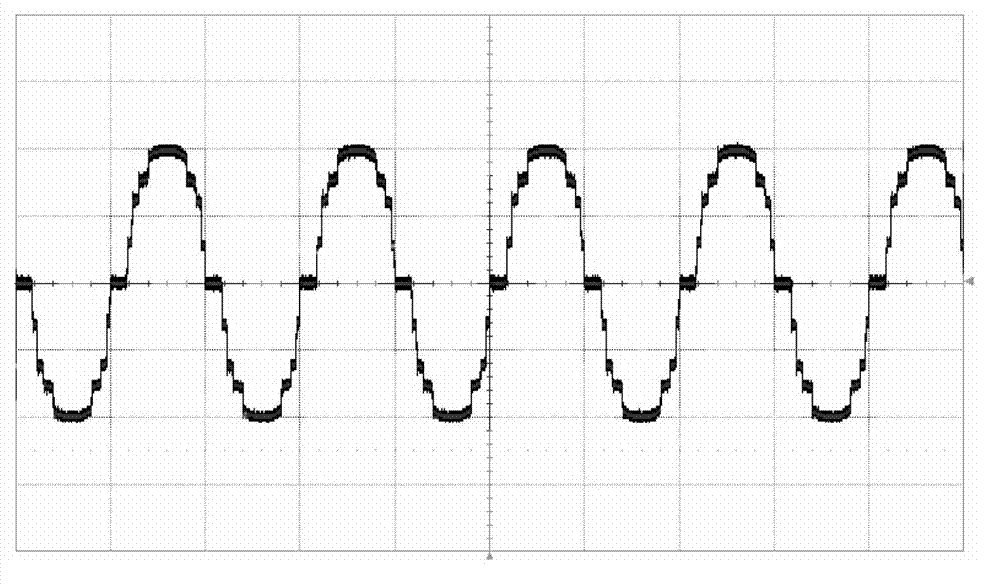
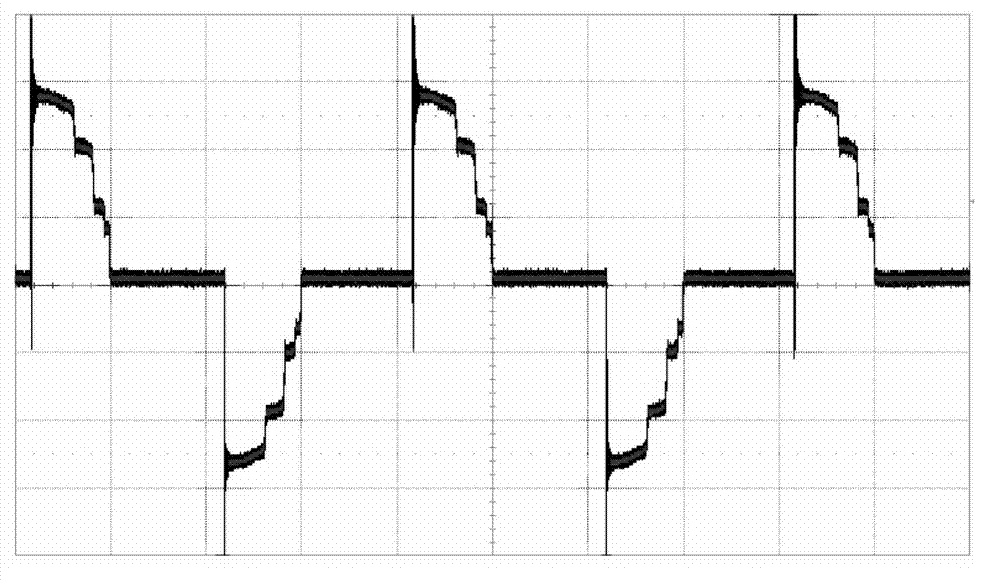
The invention provides a bias circuit of an electroabsorption modulated circuit. The bias circuit comprises a light emitting assembly TOSA (Transmitter Optical Sub Assembly), a conversion charge pump with nonadjustable output voltage or a switch tube chip, an operation amplifier, and a feedback resistor, wherein the light emitting assembly TOSA is composed of an electroabsorption modulator EA, a semiconductor laser LD and a monitor diode PD, which have a common grounded cathode; the anode of the semiconductor laser LD is connected with a power supply Vcc through a first current limiting resistor; the conversion charge pump or the switch tube chip has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a grounded negative power pin, and an output pin connected with one end of a first inductor; the other end of the inductor is connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD and with one end of a third filter capacitor; the other end of the capacitor is grounded; the operation amplifier has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a negative power pin connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD, a grounded positive input pin, a negative input pin connected with an external bias unit through a loop resistor, and an output pin connected with the anode of the electroabsorption modulator EA; and the feedback resistor is connected between the negative input pin and the output pin of the operation amplifier.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEOPHOTONICS TECH
Strobe-free alternating current drive LED light source dimming system and method thereof
ActiveCN103118466ASolve the stroboscopic problem of varying degreesNo need to change sizeElectric light circuit arrangementExternal biasControl signal
The invention provides a strobe-free alternating current drive LED light source dimming system and a method thereof. The system comprises a rectifying module, an LED array, a switch module, a sampling module, a drive power supply chip and a voltage-controlled current source module. The rectifying module is used for rectifying received alternating current and outputting work voltage. The LED array comprises multi-stage lamp groups divided according to progressive increasing number of serially-connected LEDs. The switch module comprises a plurality of switches correspondingly connected to an output end of each stage of lamp groups, and the switches are used for communicating and cutting off a power supply circuit of each stage of lamp groups. The sampling module comprises multi-stage sampling resistor strings according to progressive decreasing number of serially-connected resistors. The drive power supply chip is used for providing a standard level for the power supply circuit of each stage of lamp groups. The voltage-controlled current source module is used for generating a direct current level in a preset range according a lighting control signal output by a light control center, and the direct current lever generates bias current to modulate amplitude and dim an LED light source. LED current can be changed by changing external bias current according to the control signal, and strobe-free deep dimming can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI YAMING LIGHTING
MEMS-based actuator devices using electrets
Electrets are used in a variety of MEMS-based actuator devices. The electret is able to store electrical charge for a long time with negligible charge leakage. Therefore, when an electret is incorporated into a MEMS device that requires actuation, the device can be initially biased to any desired actuation state for a long period of time without the use of external bias voltages. Such a MEMS-based device may include a MEMS-based actuator having at least a first deflectable member and at least a second member. The first deflectable member and the second member are provided with a floating electrode and a second electrode. A charge on the first floating electrode is selected so as to position the first deflectable member at a desired separation distance from the second member. The device may be used to align an optical component or to change the electrical characteristics of an electrical element.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Plasma generating apparatus
InactiveUS20080168945A1Evenly distributedLower impedanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal biasEngineering
Provided is a plasma generating apparatus. The plasma generating apparatus includes a vacuum chamber, an ElectroStatic Chuck (ESC), an antenna unit, and an antenna cover. The vacuum chamber has a hollow interior and is sealed at a top. The ESC disposed at an internal center of the vacuum chamber receives an external bias Radio Frequency (RF). The antenna unit covers and seals the through-hole of an insulating vacuum plate. The antenna cover covers a top of the antenna unit and has a gas injection port.
Owner:JEHARA CORP
Autotracking switch type charge pump for phase lock loop
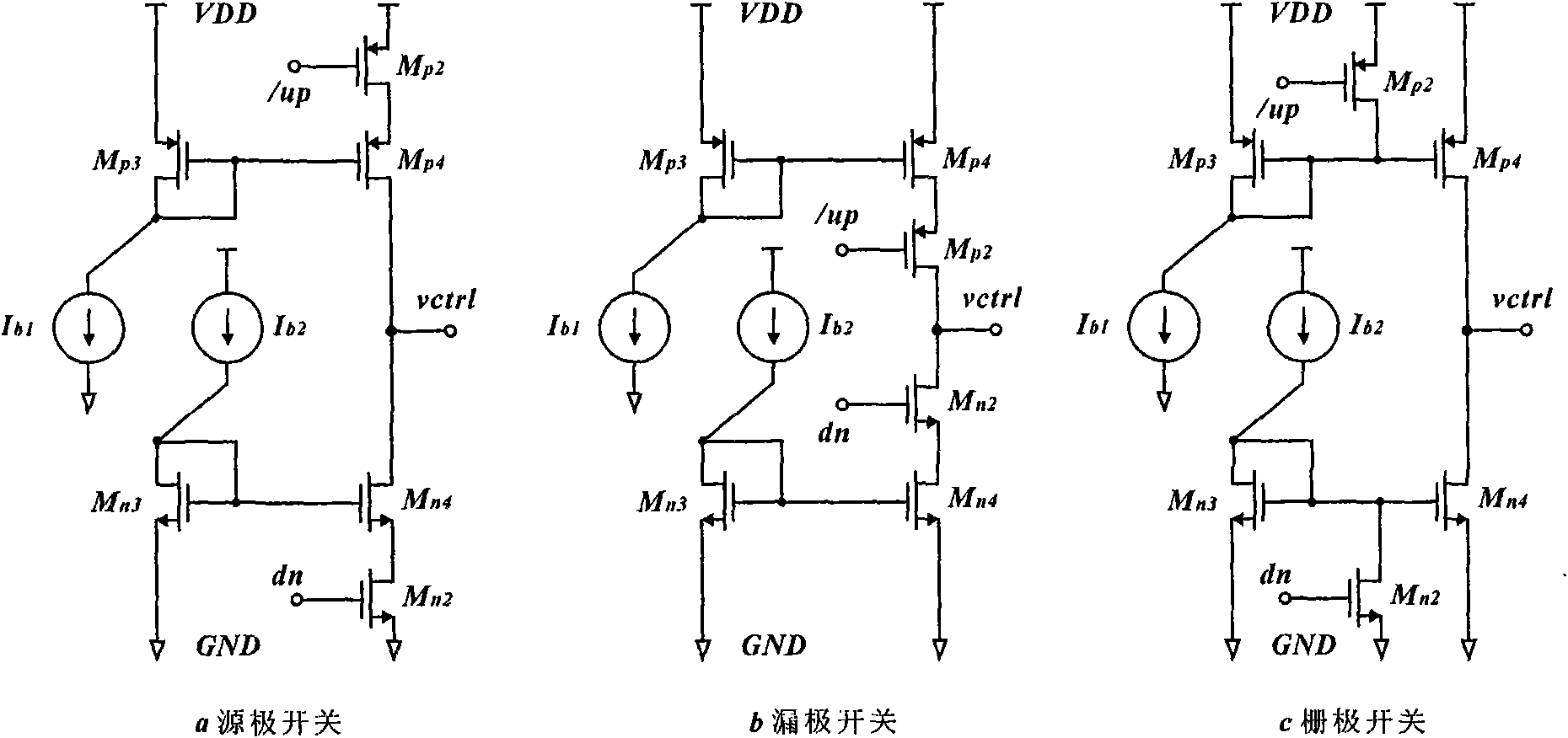
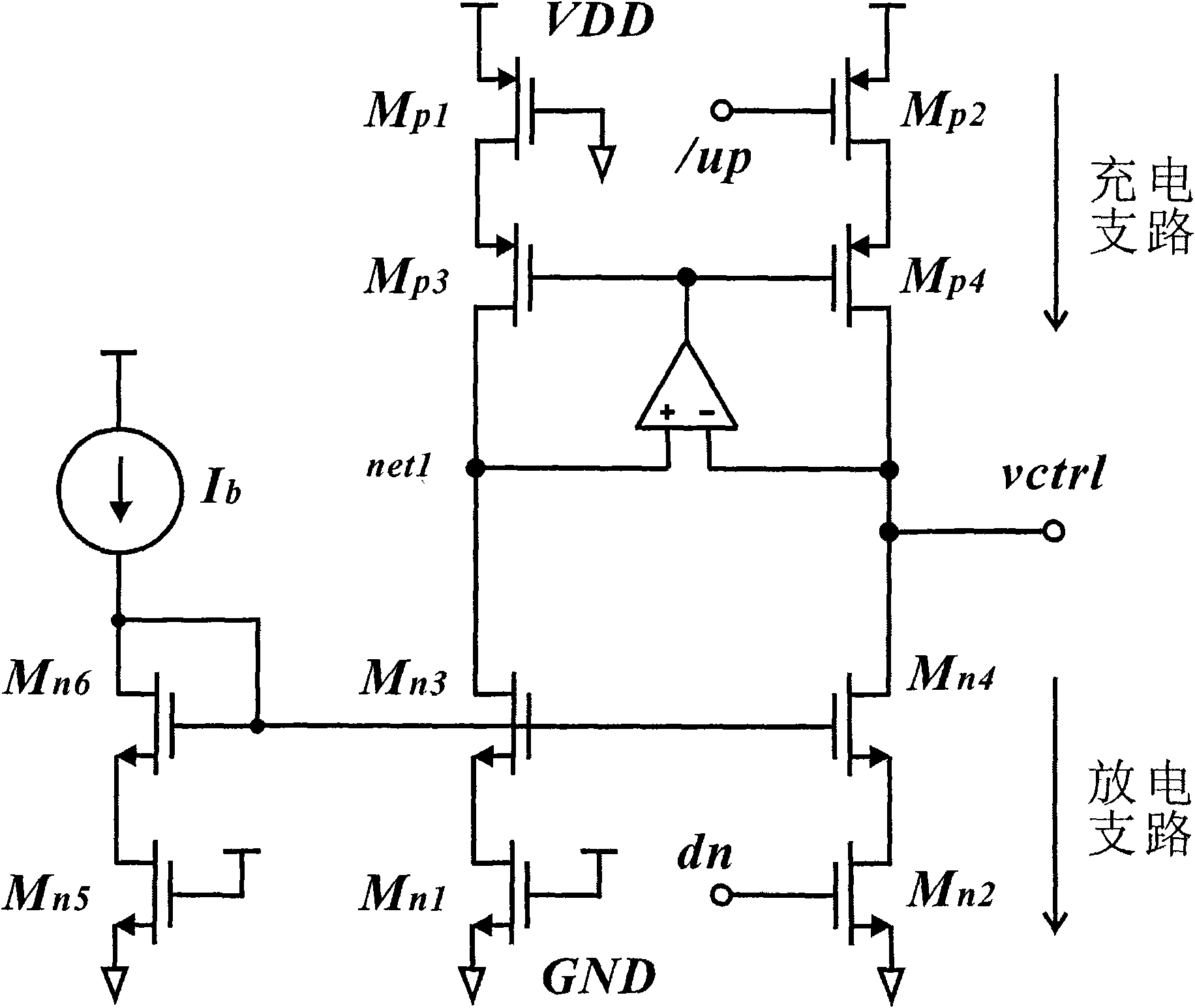
ActiveCN102006063ARealize non-constant currentReduce complexityPulse automatic controlApparatus without intermediate ac conversionExternal biasEngineering
The invention discloses an autotracking switch type charge pump for a phase lock loop, comprising a pull-up circuit, a pull-down circuit and a feedback control circuit, wherein the pull-up circuit comprise a pull-up switch transistor and a pull-up current mirror; the pull-down circuit comprises a pull-down switch transistor and a pull-down current mirror; the feedback control circuit comprises a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor and a NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor and is used for controlling the magnitude of the charging / discharging current dynamically; and the switch transistors are connected to the source end, the drain end and the grid end of the current mirror and respectively correspond to three type of charge pumps of an autotracking source switch type, an autotracking drain switch type and an autotracking grid switch type. The autotracking switch type charge pump provided in the invention realizes non-constant current and ensures the charging current to be in dynamic tracking matching with the discharging current. Compared with the structure of the traditional charge pump, the charge pump in the invention has no need of a feedbackamplifier and an external bias current, uses the least number of transistors, has simple structure, and is easy to realize.
Owner:中科芯未来微电子科技成都有限公司
ZnO-perovskite structure based ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector and preparation method thereof
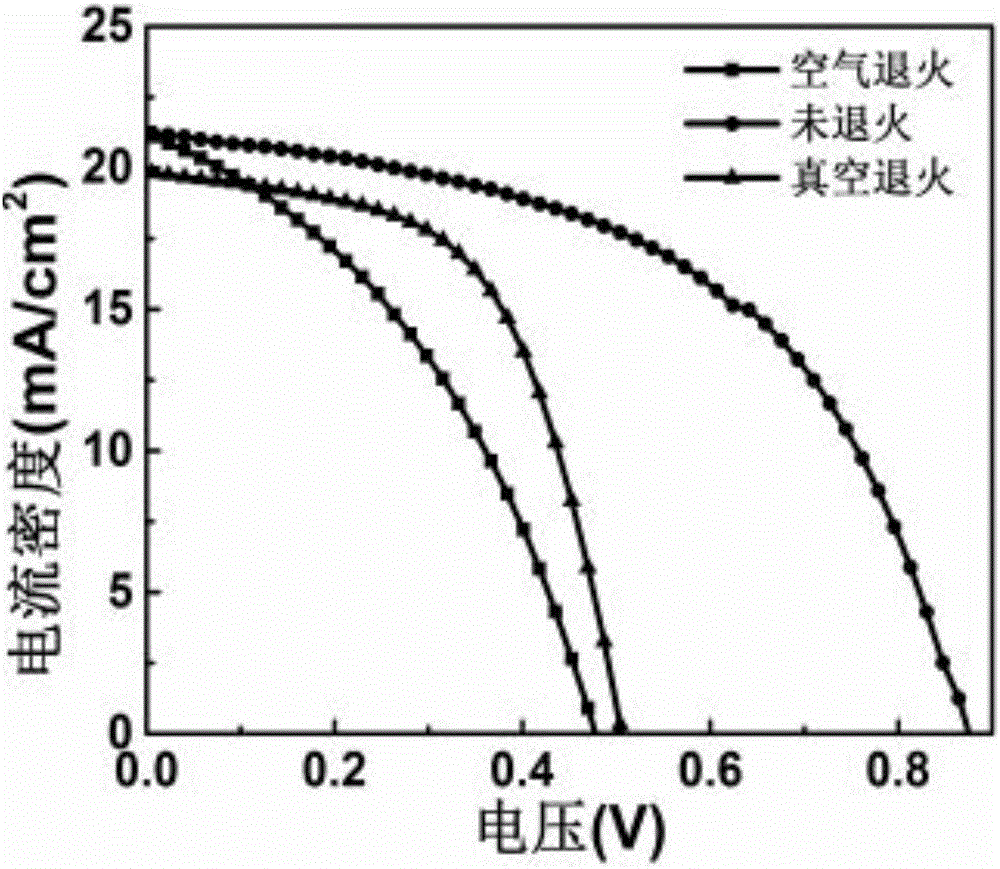
ActiveCN106571425ASimple preparation processLow costOrganic semiconductor materialsSolid-state devicesExternal biasUltraviolet lights
The invention provides a ZnO-perovskite structure based ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof. The ZnO-perovskite structure based ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector is in the structure of FTO / ZnO nanorod / CH3NH3PbI3 / Spiro-OMe TAD / Au, wherein the FTO layer is an anode, the ZnO nanorod is an electron transport layer, the CH3NH3PbI3 is a perovskite light absorption layer, the Spiro-OMe TAD is a hole transport layer, and the Au is a metal electrode. The ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector shows 9.56% of the photoelectric conversion efficiency under an unannealed condition. Meanwhile, the ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector shows the highest photoelectric response degree which reaches up to 7.8A / W in value under the bias voltage of 0. The detection degree of the ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector reaches the highest after vacuum annealing and reaches the responsivity of 10<14>, and the photoelectric detection performance of the ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector is ultraviolet light; and the photoelectric detection performance of the ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector is visible light after air annealing. In addition, the ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector has certain self-driving capability, and is not required to be driven by external bias voltage, thereby being conducive to energy conservation. The ultraviolet-visible tunable photoelectric detector is simple in operating step and low in experiment cost, and the manufactured detector has high responsivity and high detection sensitivity.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
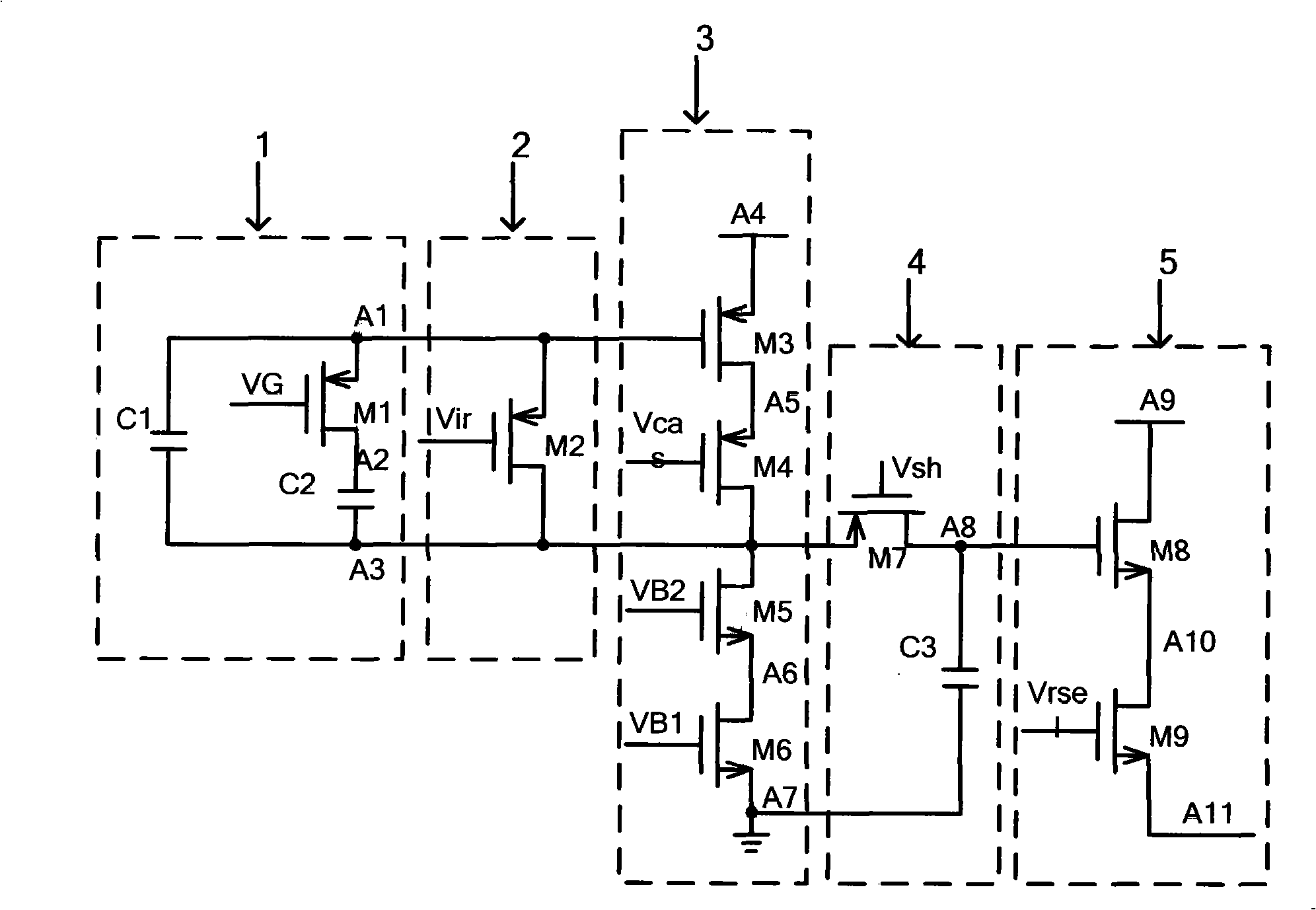
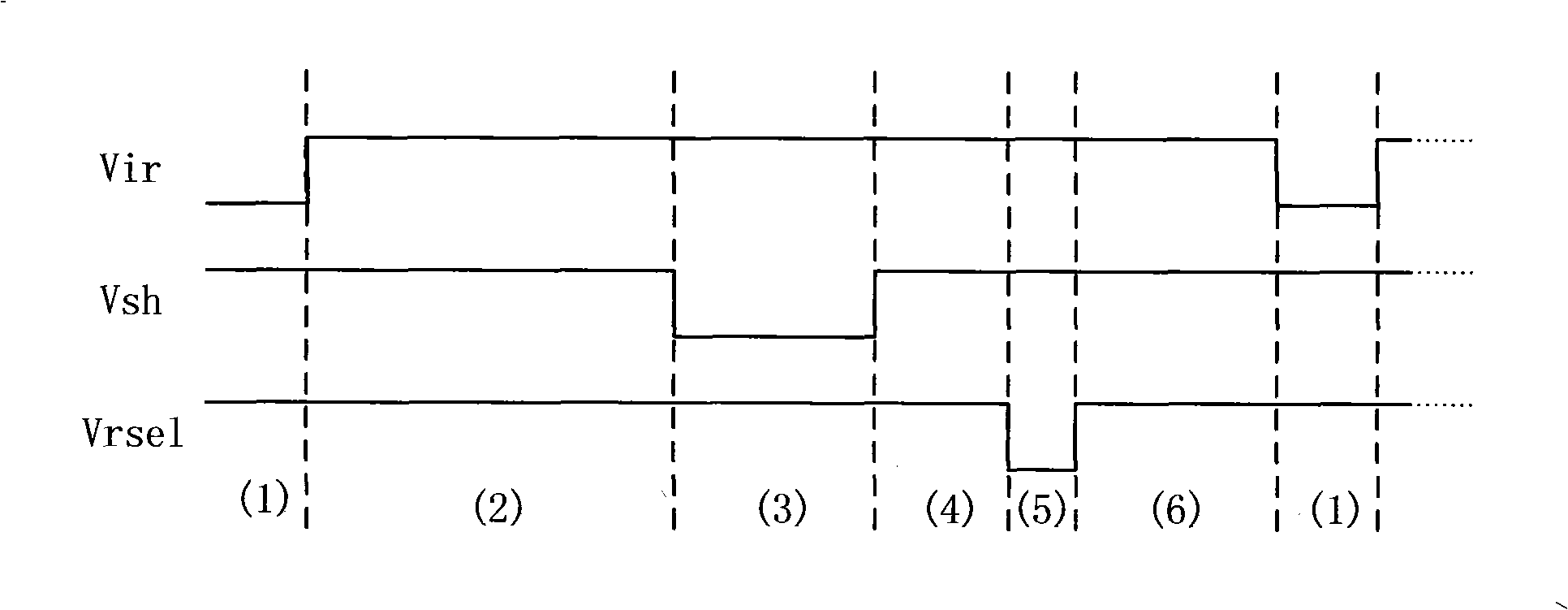
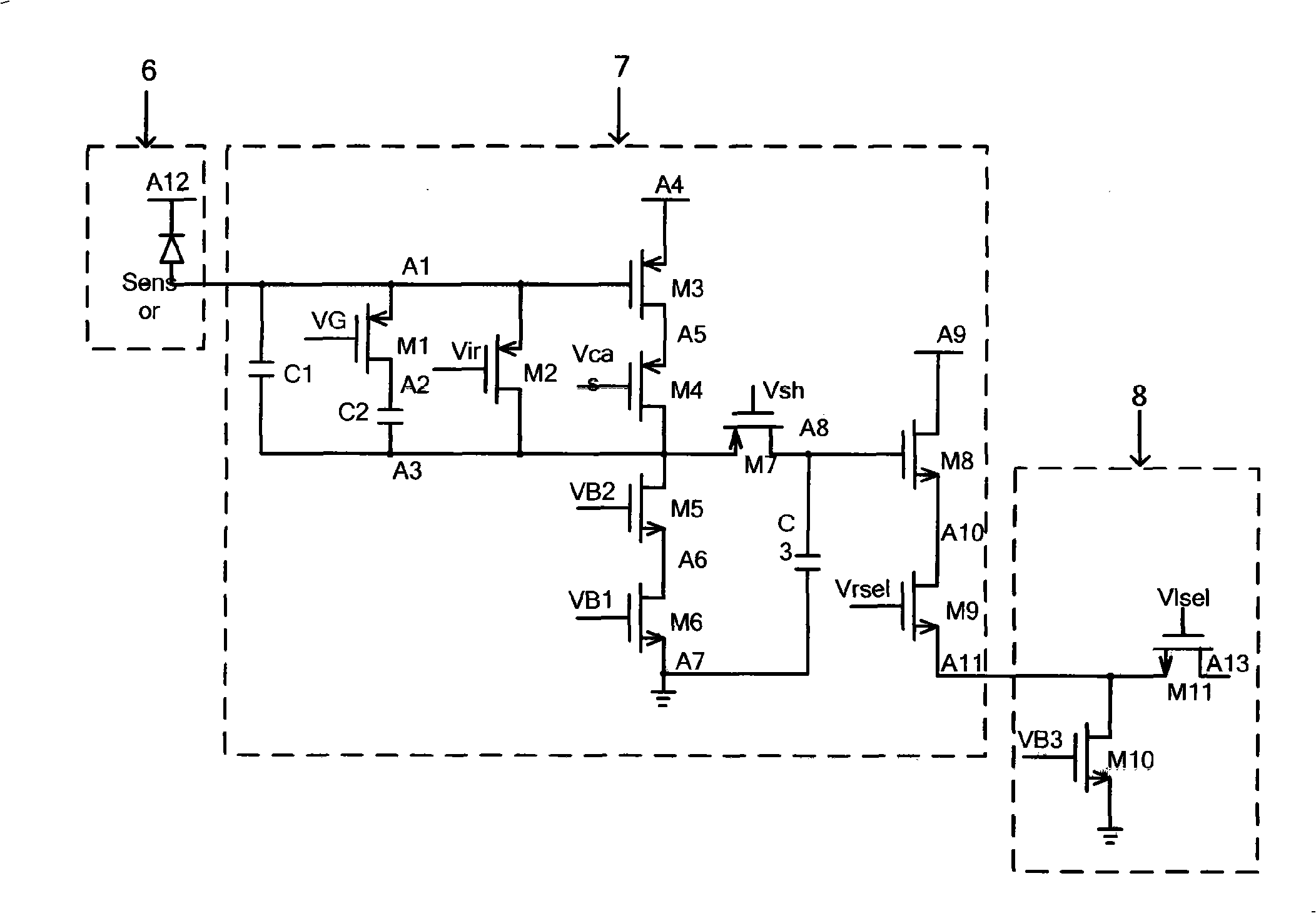
Infrared focal plane read-out circuit unit circuit
InactiveCN101261160ANo external bias requiredReduce noisePyrometry using electric radation detectorsCapacitanceExternal bias
The invention discloses a unit circuit of an infrared focal plane reading-out circuit, which is characterized in that the unit circuit comprises an integral capacitor selection unit, an integral / reset control unit, an input amplifier, a sampling keeping unit and a source following unit. The unit circuit utilizes the reset of the integral / reset control unit to provide constant infrared detector bias voltage inside the unit circuit, without requirement of external bias voltage; most transistors adopt P-typed MOS pipes, thus effectively reducing the noise of the unit circuit; a differential amplifier is replaced by a single-step amplifier, the power loss of the unit circuit is reduced, and the unit area is saved; two capacitor values are designed to be selected, thus meeting the requirement of different background conditions; the integral time can be suitably selected according to the current of different detectors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Conversion apparatus, radiation detecting apparatus, and radiation detecting system
InactiveUS20090127435A1Prevent leakageSuppress noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansExternal biasEngineering
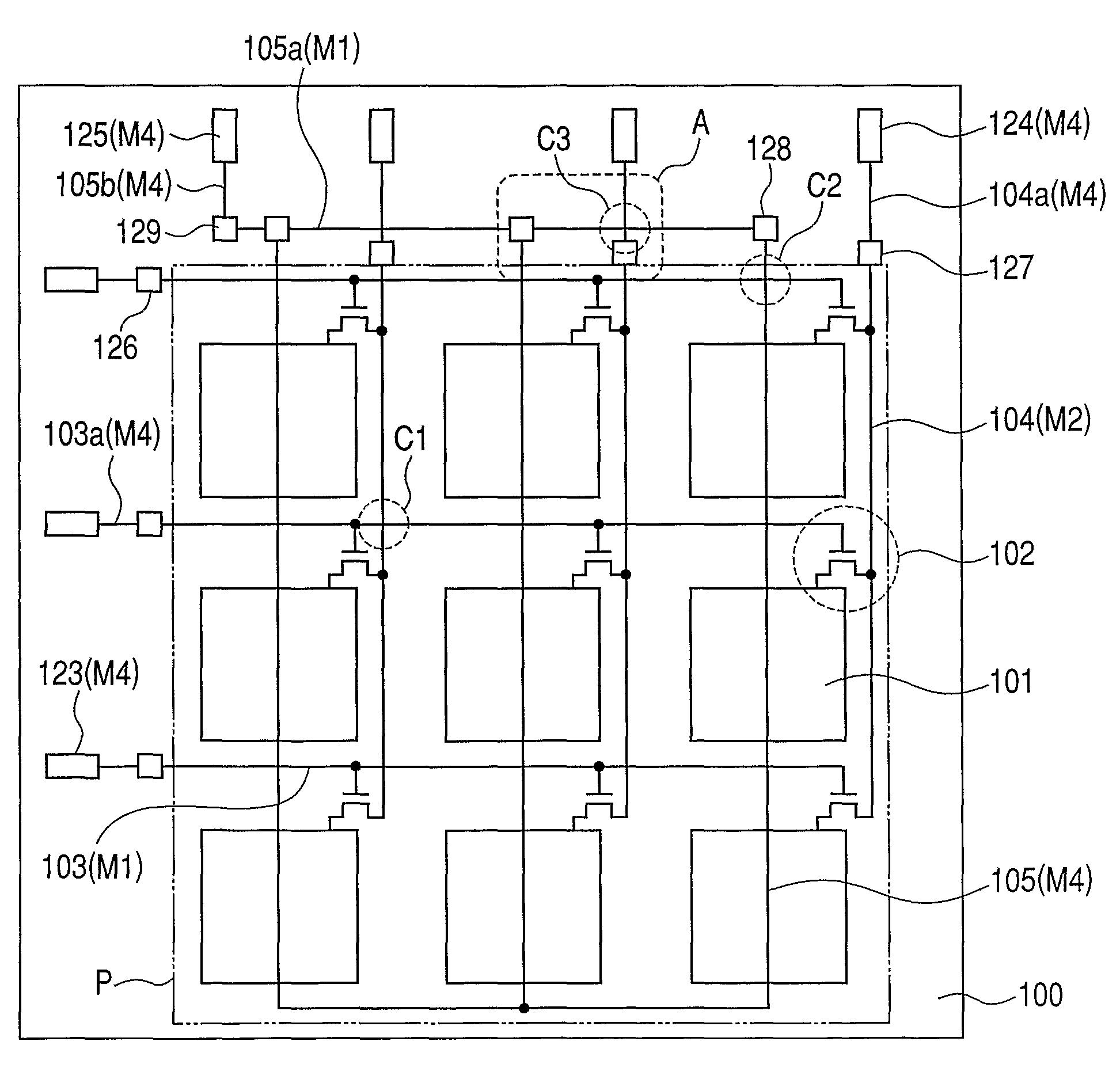
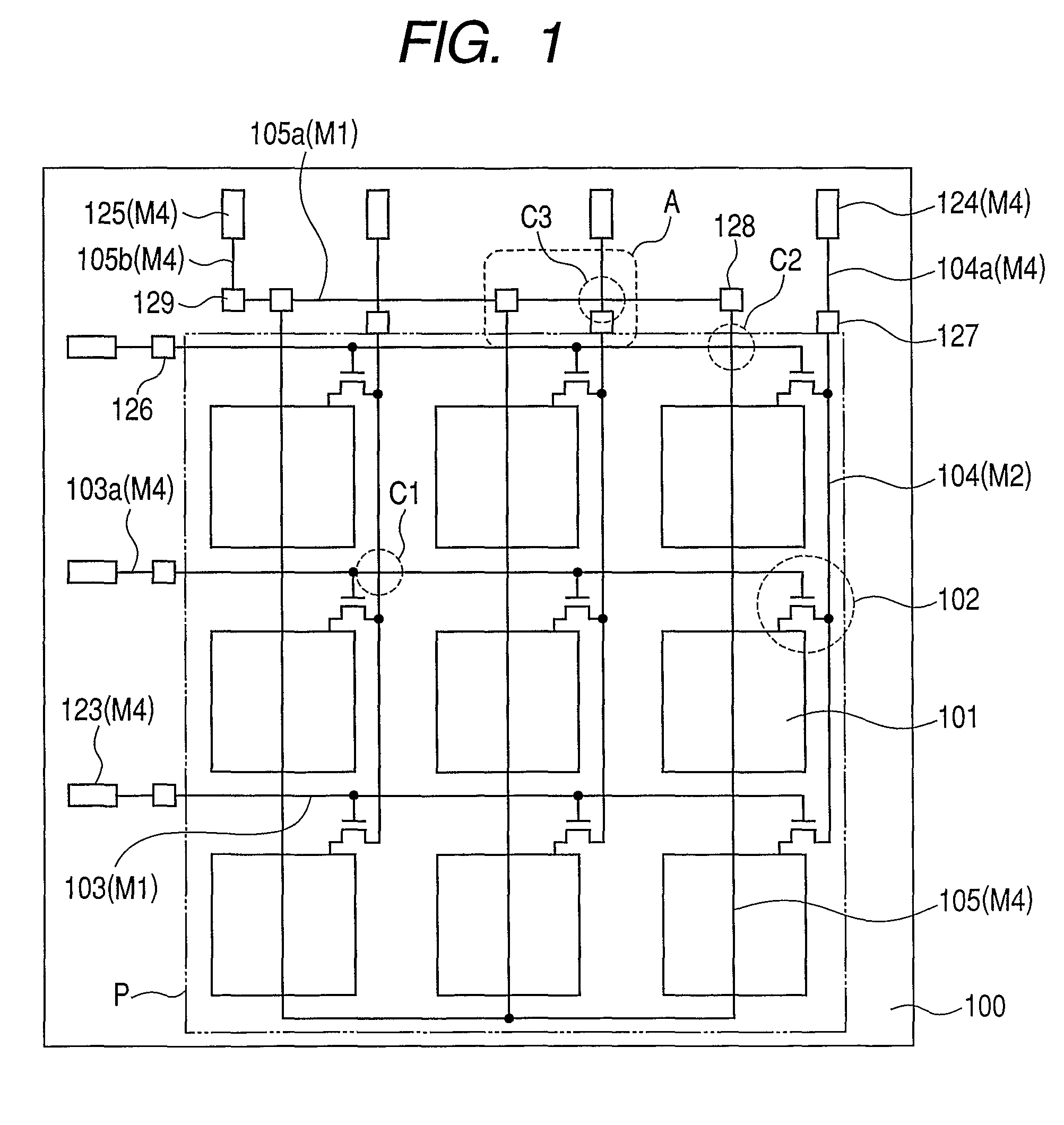
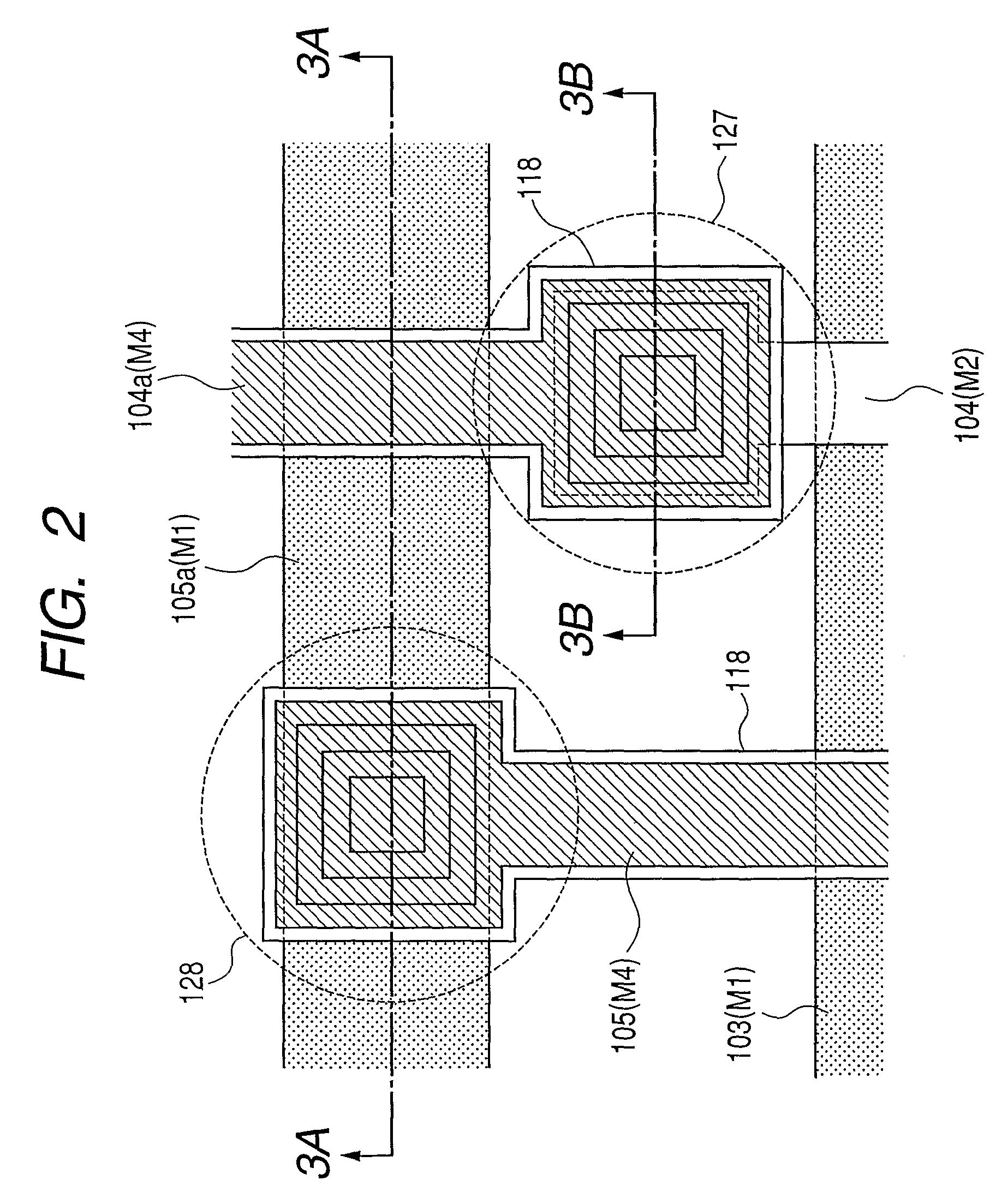
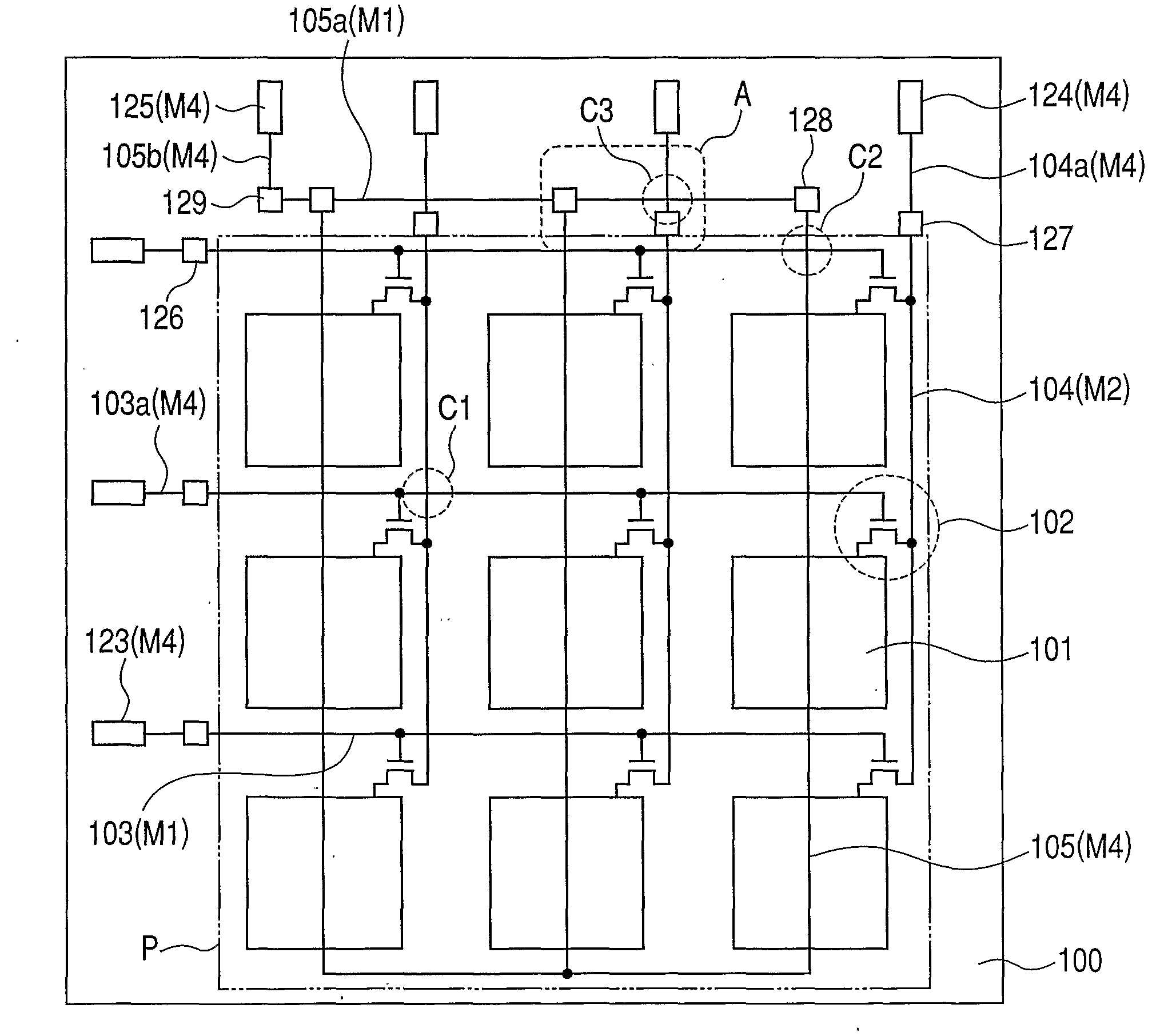
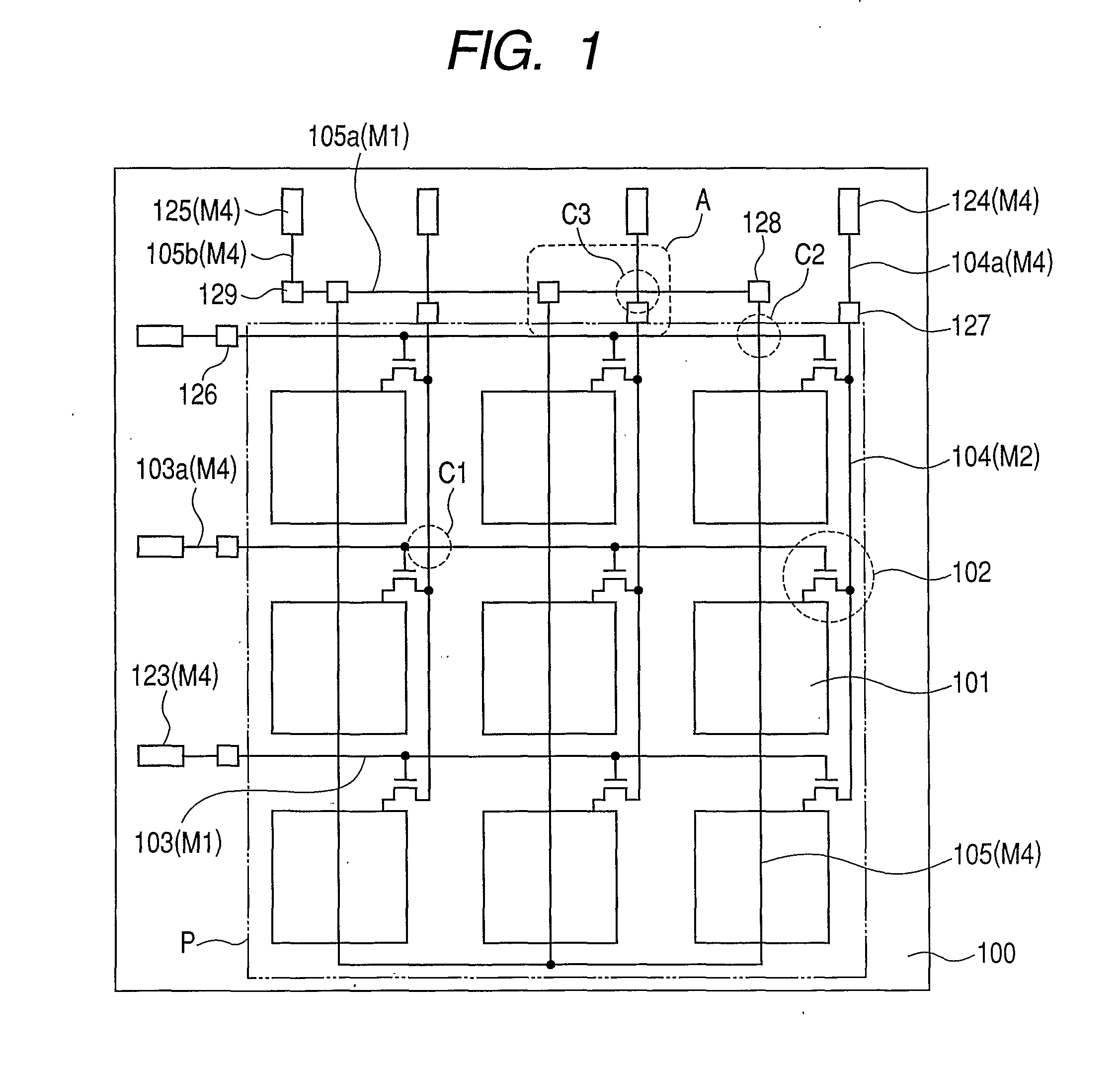
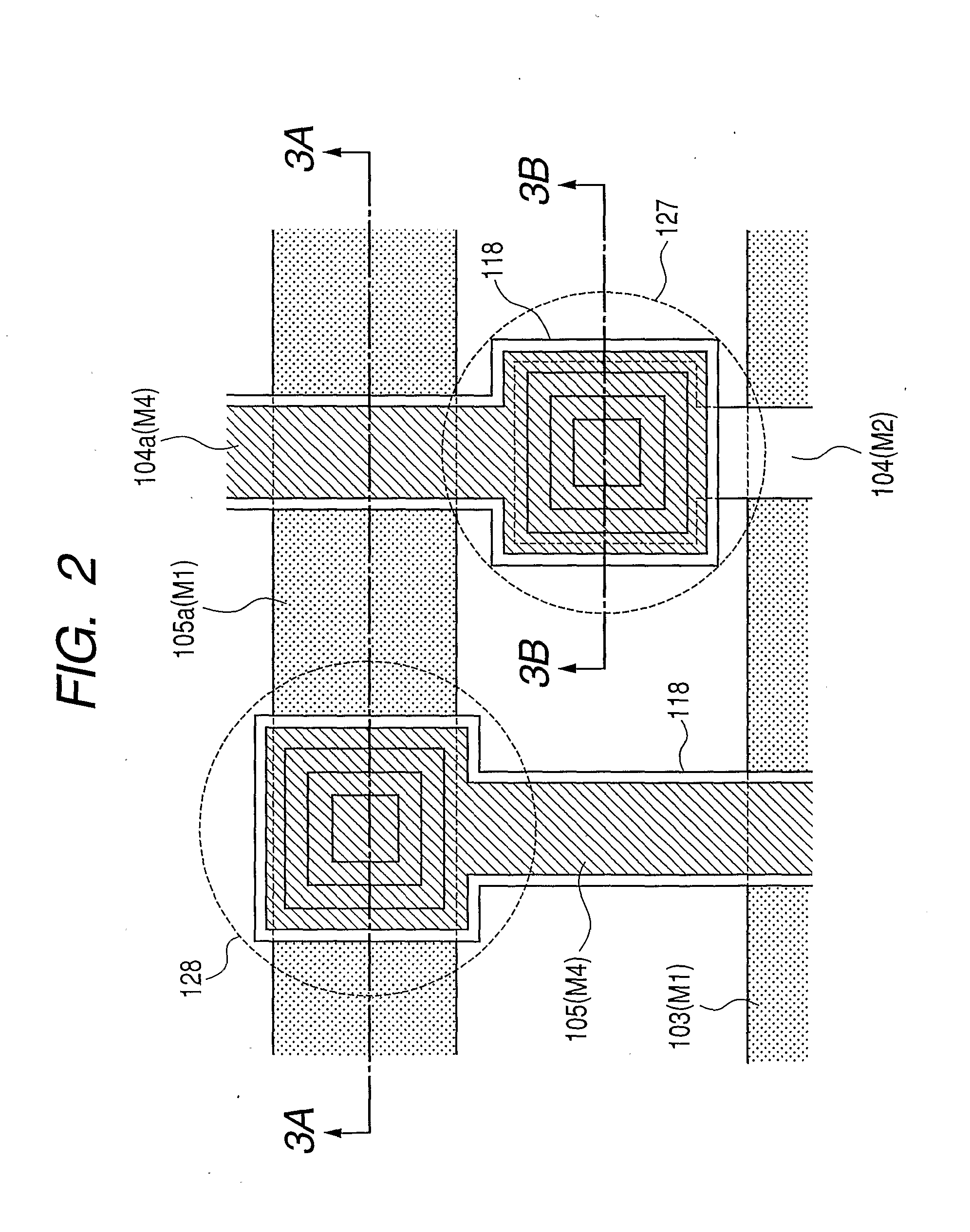
A conversion apparatus of the present invention includes a plurality of pixels including switching elements and conversion elements. The pixels are arranged in a pixel region including a switching element region in which switching elements are arranged in row and column directions and a conversion element region in which conversion elements are arranged in row and column directions. A plurality of wirings are including a second metal layer are connected to the plurality of switching elements of the column direction. Plural bias wirings of a fourth metal layer are connected to plural conversion elements. An external signal wiring of the fourth metal layer outside the pixel region is connected to the signal wirings. An external bias wiring of a first metal layer outside the pixel region is connected to the plurality of bias wirings. The external signal wiring and the external bias wiring intersect each other.
Owner:CANON KK
LCD for speeding initial bend state, driver and method thereof
InactiveUS20060114215A1Quick transitionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsExternal biasDisplay device
Owner:LEE CHANG HUN +4
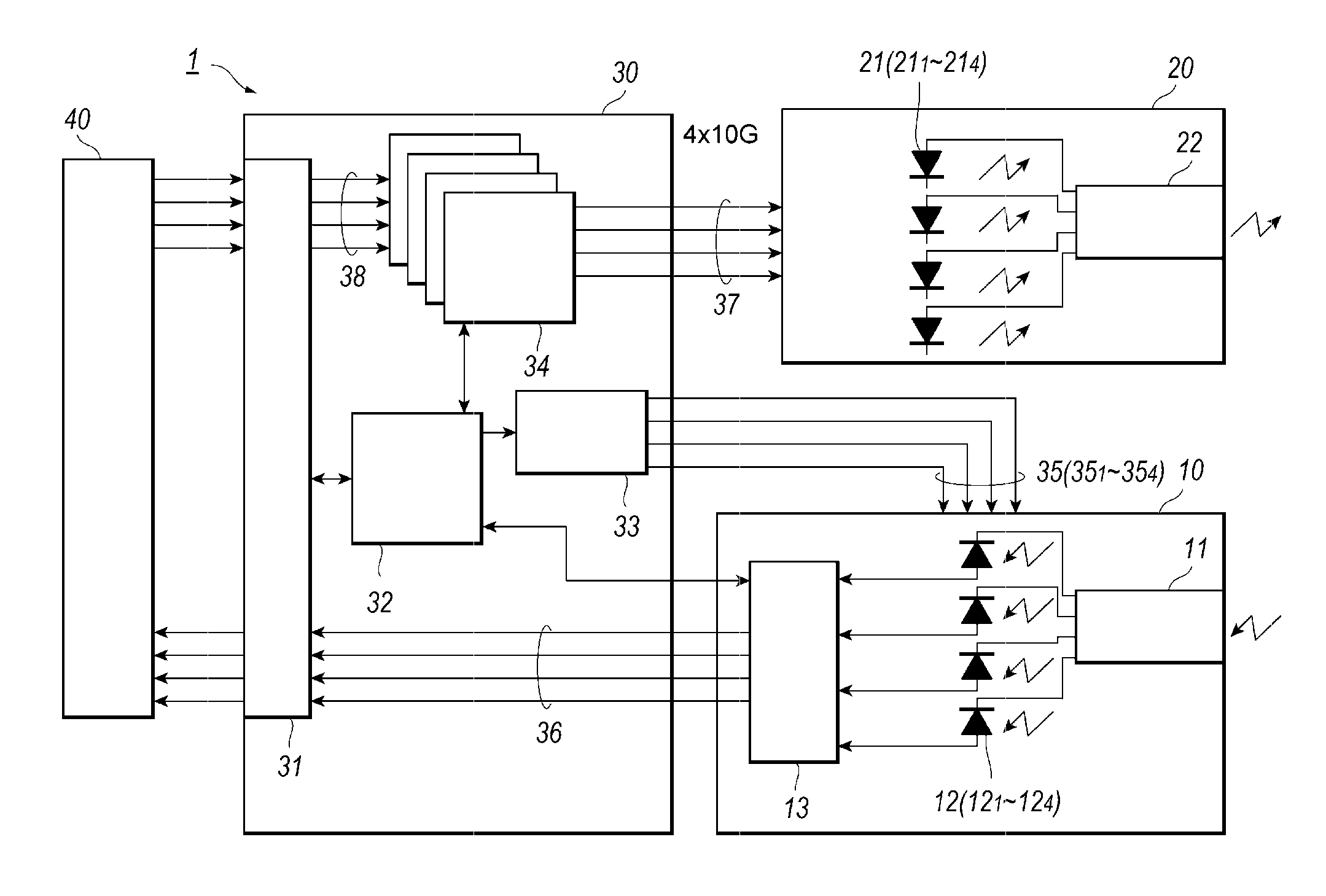
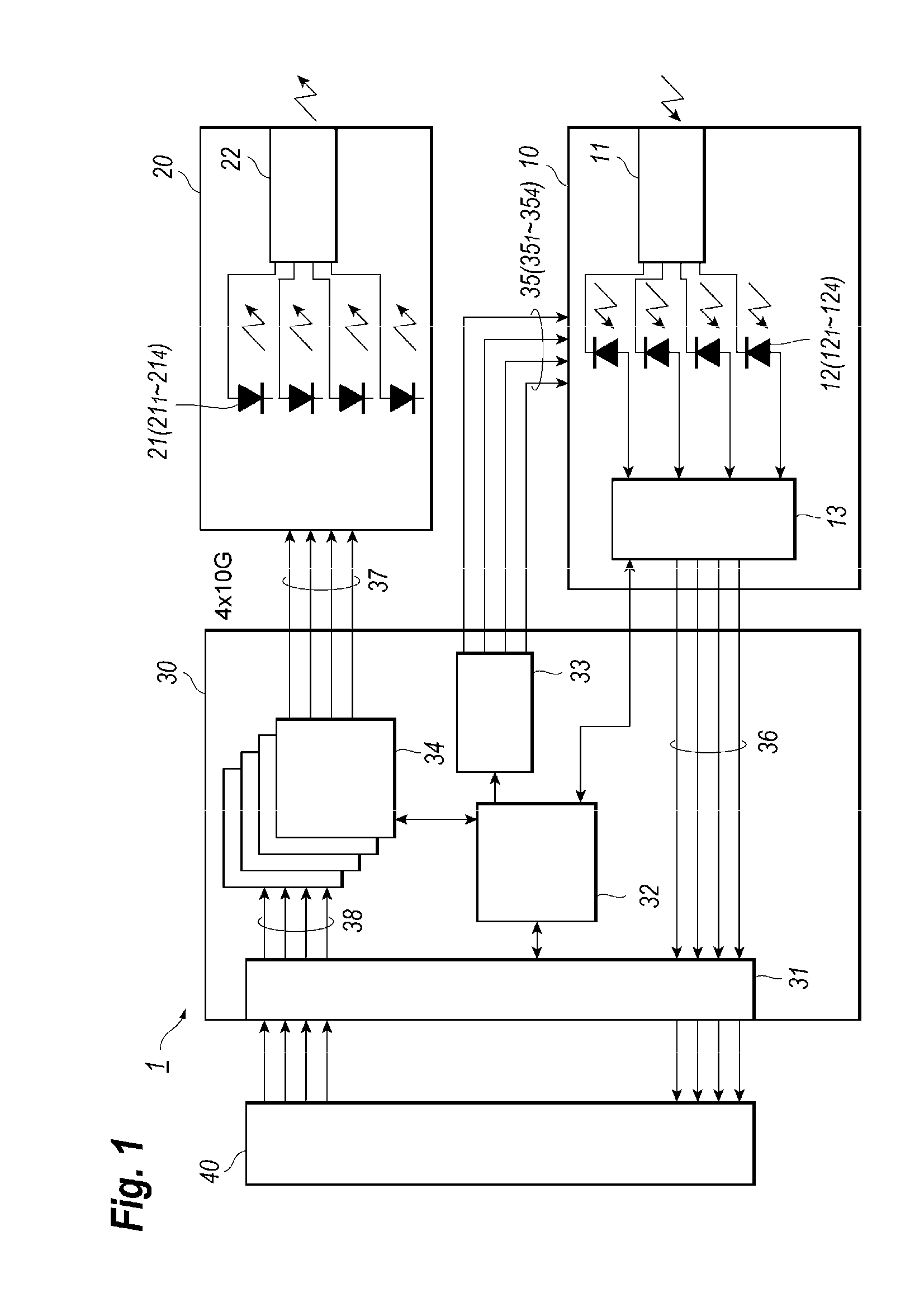
Optical transceiver outputting wavelength multiplexed signal and receiving another wavelength multiplexed signal
ActiveUS20160149643A1Multiple-port networksCross-talk/noise/interference reductionTransceiverExternal bias
An optical transceiver that provides a receiver optical module including a plurality photodiodes (PDs) each biased through internal bias lines, signal lines carrying driving signals to an optical transmitter module, and external bias lines each connected to the internal bias lines. One of the internal bias lines connected to one of the external bias lines arranged closest to the signal lines has a length shorter than lengths of the other internal bias lines so as not to affect EMI noises induced from the signal lines to the other internal bias lines.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Electrodynamic transducer and use thereof in loudspeakers and geophones
An electrodynamic transducer includes a frame and contains at least one electric coil which is placed in a static magnetic field and which can move about a rest position in a vertical free space. The coil(s) is wound around and fixed to a mandrel and a return member is used to return the coil-bearing mandrel to the rest position in the absence of an external bias, the straight cylinder defining an inner volume and an outer volume. The magnetic field is produced by outer and inner magnetic structures which each comprise at least one fixed permanent magnet in the form of a ring. The motor does not contain any ferromagnetic or magnetic part between the outer volume and the inner volume. At least the part of the frame that is used to fix the magnets is made from a non-ferromagnetic and non-magnetic material.
Owner:GILLES MILOT +1
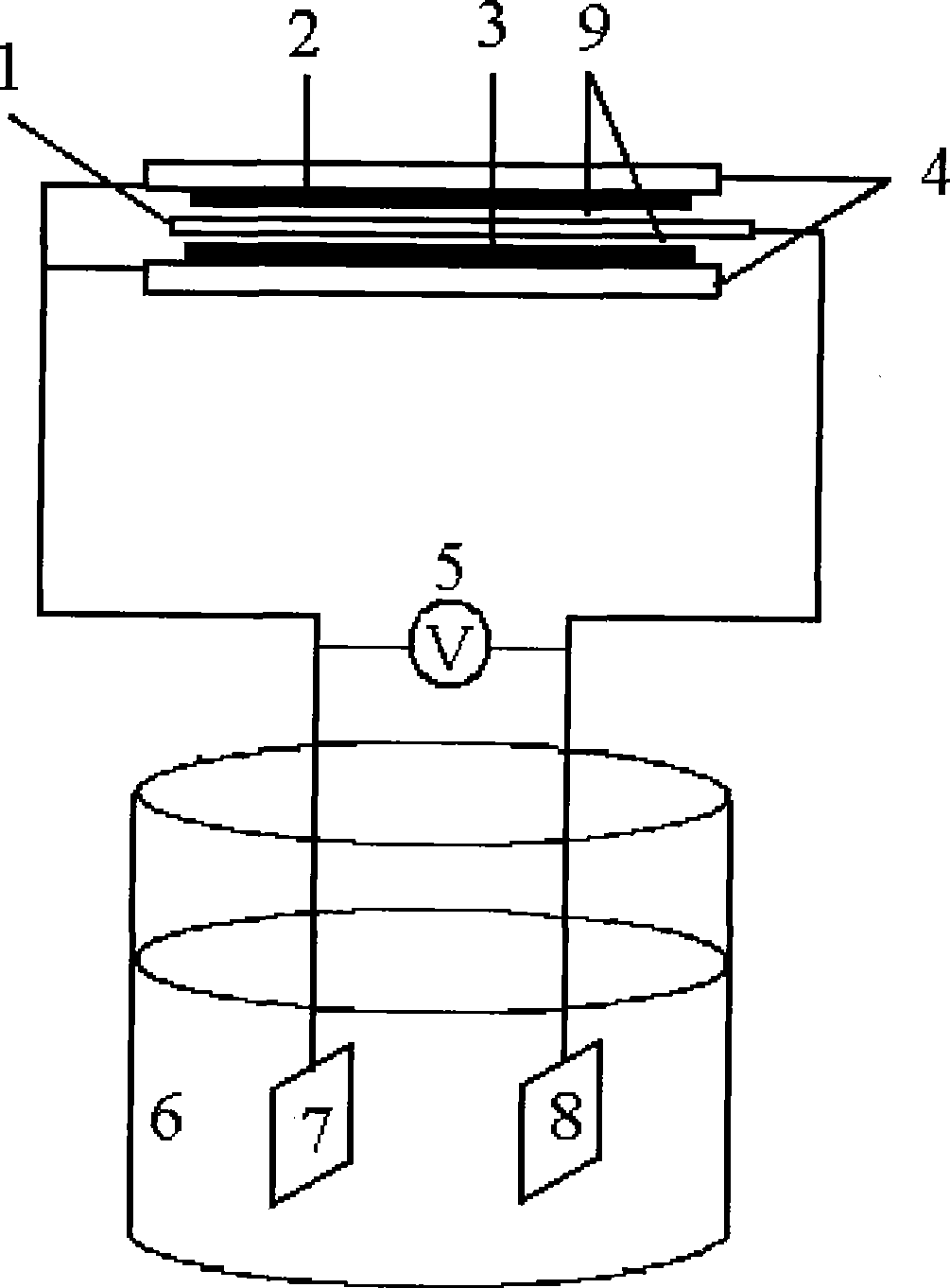
Photoelectrochemistry composite or coupled hydrogen making and oxygen making apparatus and method
InactiveCN101376987APromote absorptionImprove hydrogen production efficiencyCellsEnergy inputOrganic solar cellExternal bias
The invention relates to a device for producing hydrogen and oxygen through photoelectrochemistry composite or coupling, and a method thereof, which belongs to the technical field of green renewable energy. The device is characterized by comprising a solar battery at the upper part and a photoelectrochemistry pool at the lower part; the solar battery at the upper part comprises an electrode base plate, a photo-anode, electrolyte and a counter electrode; the solar battery at the upper part is a silicon solar battery, a dye-sensitized solar battery, an organic solar battery, a chemical compound semi-conductor solar battery or a polymer solar battery and the like; the photoelectrochemistry pool at the lower part comprises a photo-anode, electrolyte and a counter electrode. During use, under the irradiation of sunlight or simulated sunlight, the solar battery at the upper part discharges and generates external bias voltage, and the photo-anode of the photoelectrochemistry pool generates potential or energy. The external bias voltage and the potential or energy generated by the photo-anode of the photoelectrochemistry pool reach the schizolysis energy of water in the photoelectrochemistry pool, and the electrodes respectively generate hydrogen and oxygen. The device is characterized by high conversion efficiency of solar energy and hydrogen energy, low cost, simple process, and easy mass production of hydrogen.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
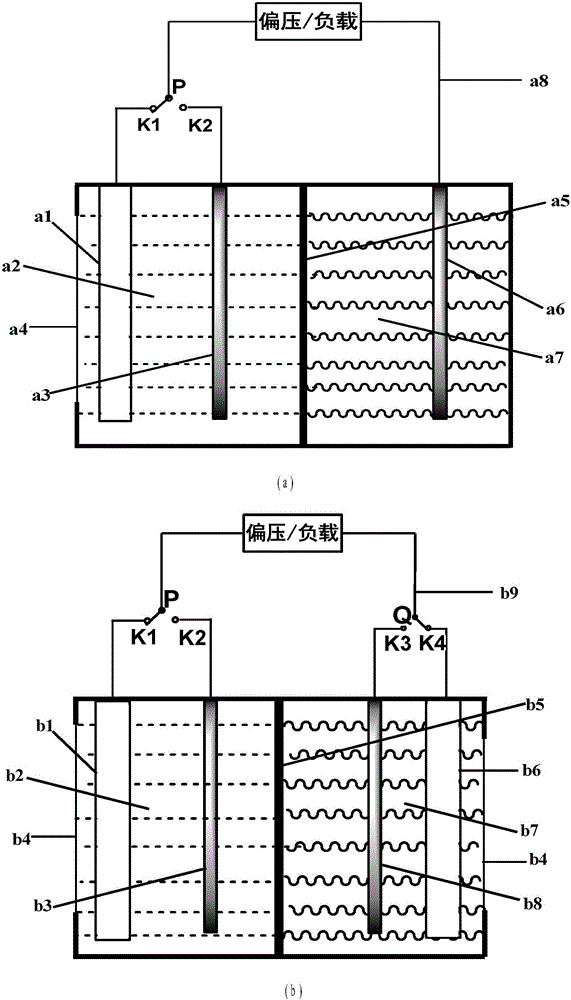
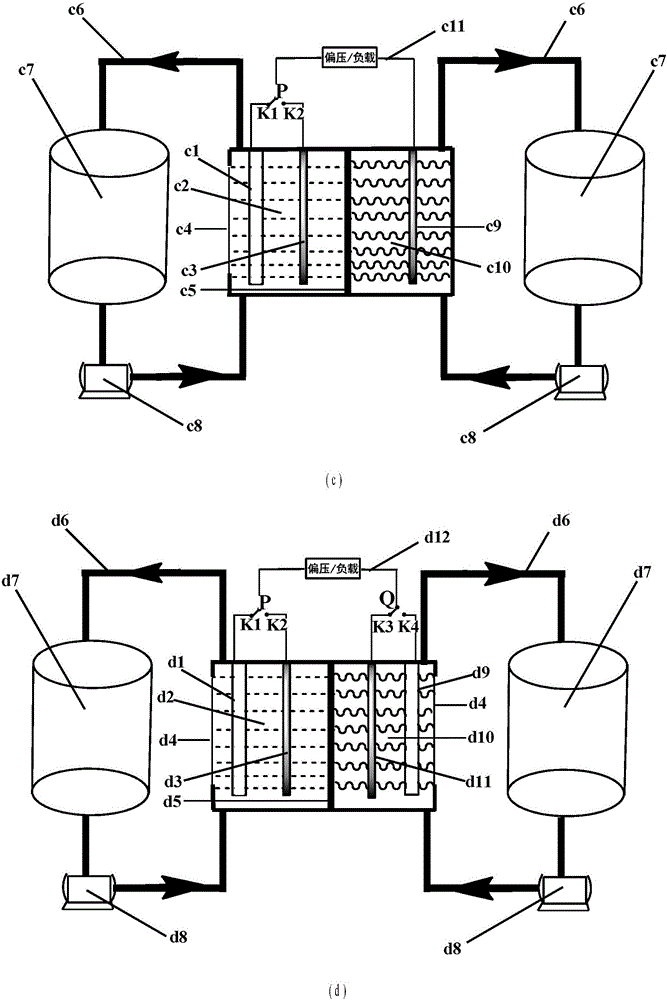
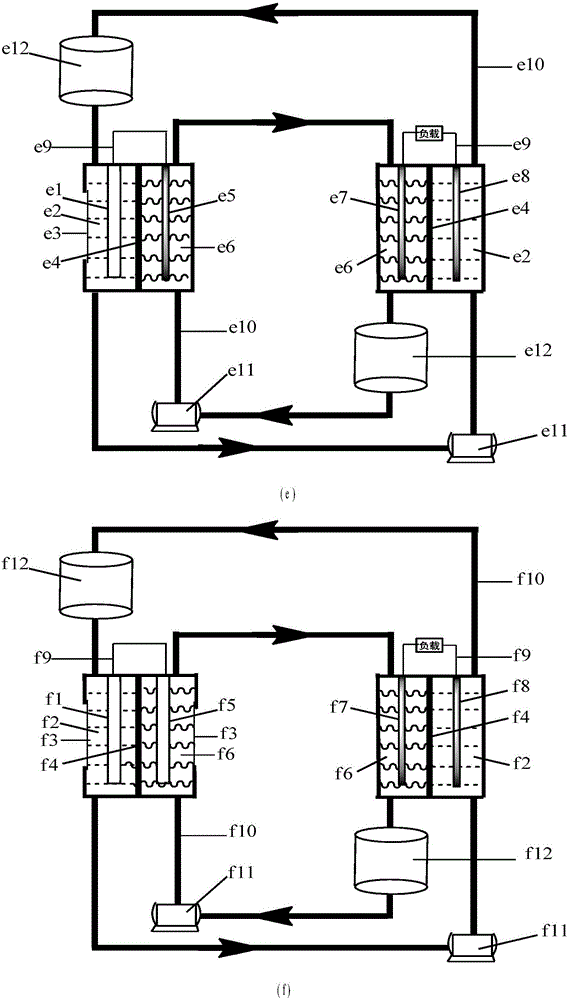
Water-soluble fast reaction kinetics couple-based photoelectrochemical energy storage battery
ActiveCN106329033AEasy in situ transformationAdjustable capacityPhotoelectrochemical storage cellsElectrochemical responseExternal bias
The invention provides a water-soluble fast reaction kinetics couple-based photoelectrochemical energy storage battery. When the battery is charged, in-situ transformation of light energy into chemical energy is achieved by using photoelectrochemical reaction driven by self-bias of narrow band gap photoelectrodes and the chemical energy is stored into an active material of a battery electrolyte; and when the battery is discharged, electrochemical reaction is carried out, thereby achieving transformation of the chemical energy into electric energy. The photoelectrochemical energy storage battery integrates a photoelectrochemical battery and a flow battery; the disadvantage that a solar cell cannot achieve electric energy storage is overcome; meanwhile, a single charging mode of the energy storage battery is also expanded; and solar energy in-situ transformation, storage and controllable utilization without assistance of external bias are achieved. Water-soluble fast reaction kinetics redox couples are adopted as the active material; the utilization rate of photo-induced carriers on the surfaces of photoelectrodes is close to 100%; meanwhile, the discharge power density of the battery can reach 0.5W / cm<2>; large-scale amplification can be achieved; and the photoelectrochemical energy storage battery is suitable for different scales of solar energy-energy storage-power generation processes.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com