Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1557 results about "Conduction band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
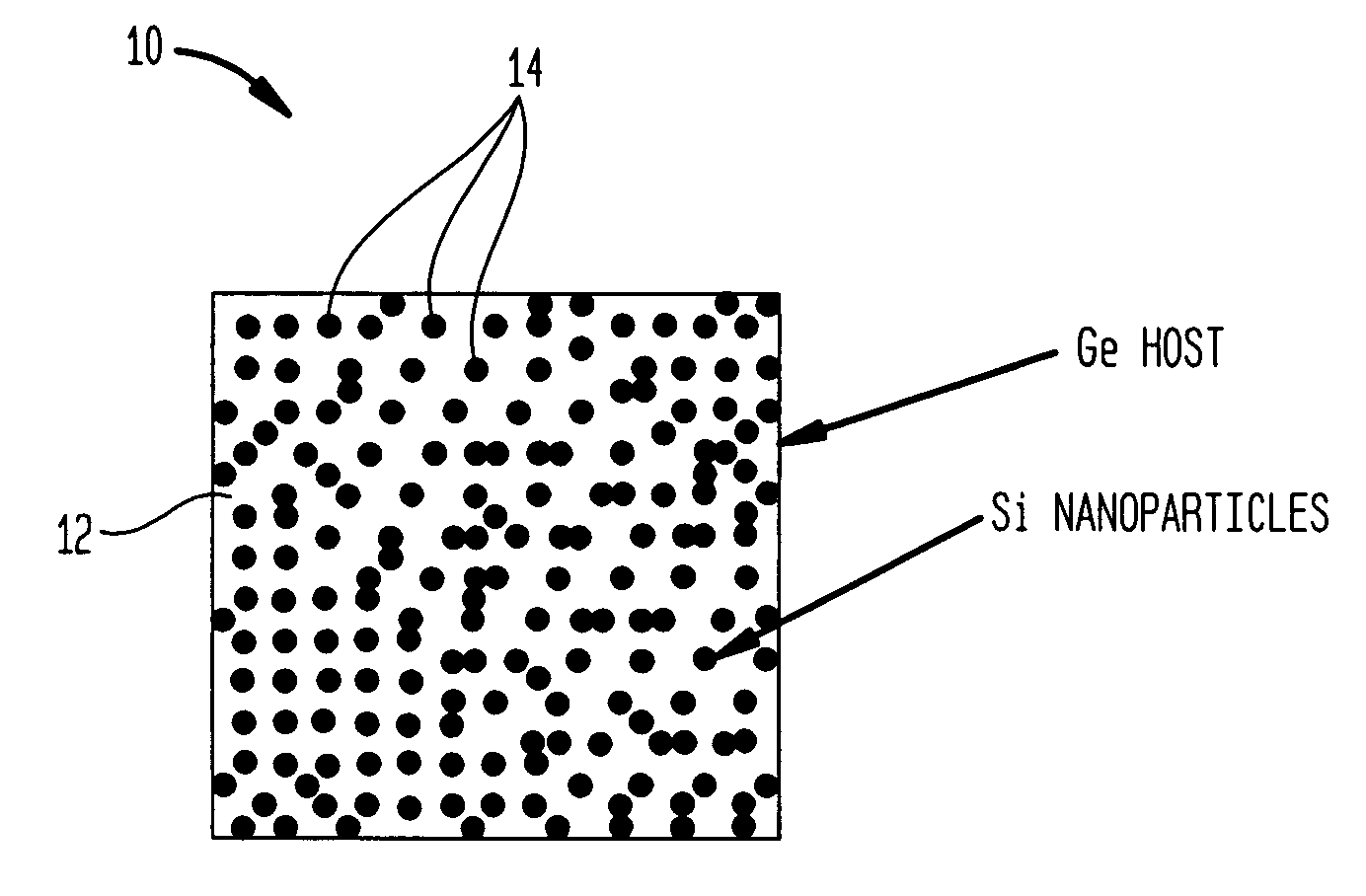
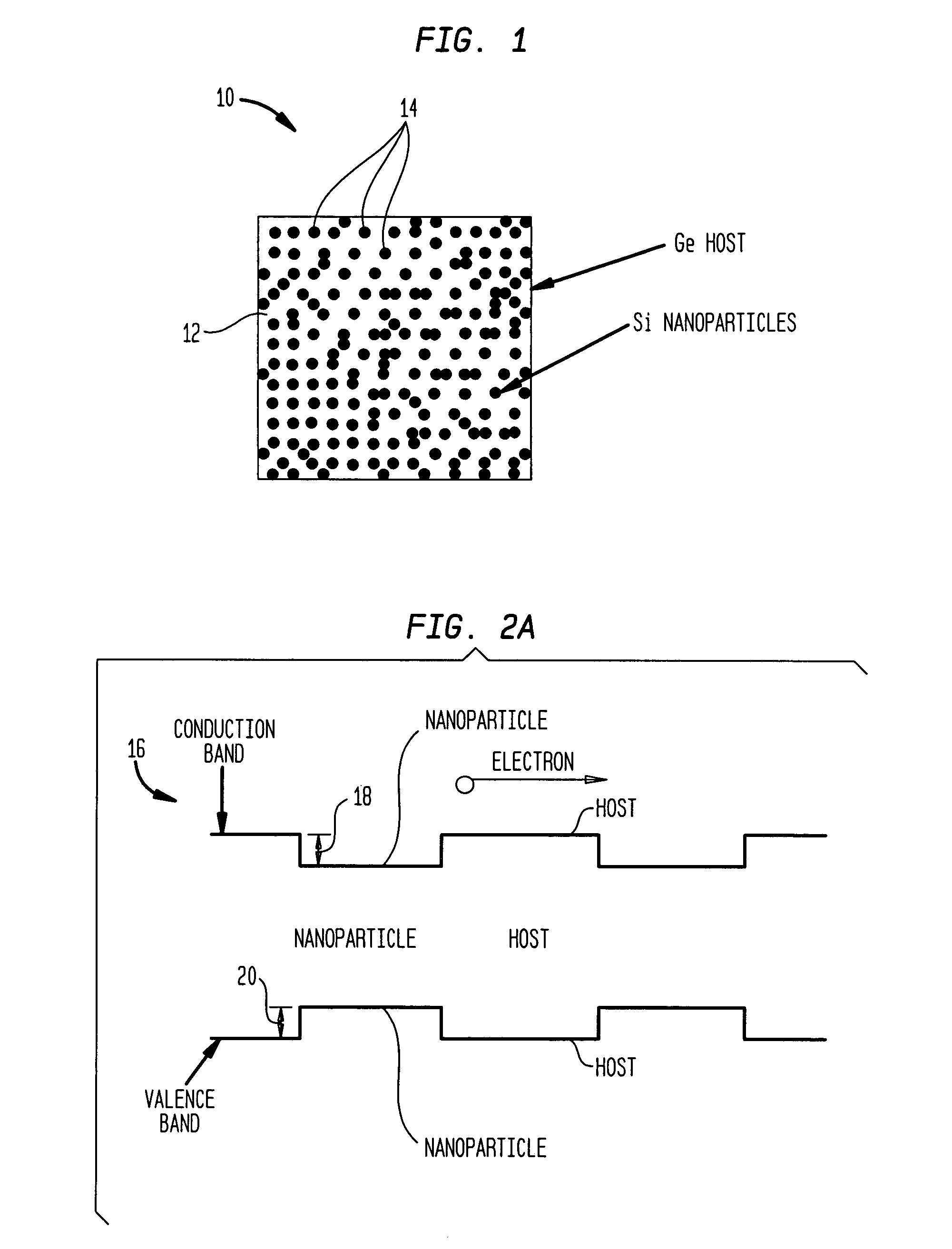
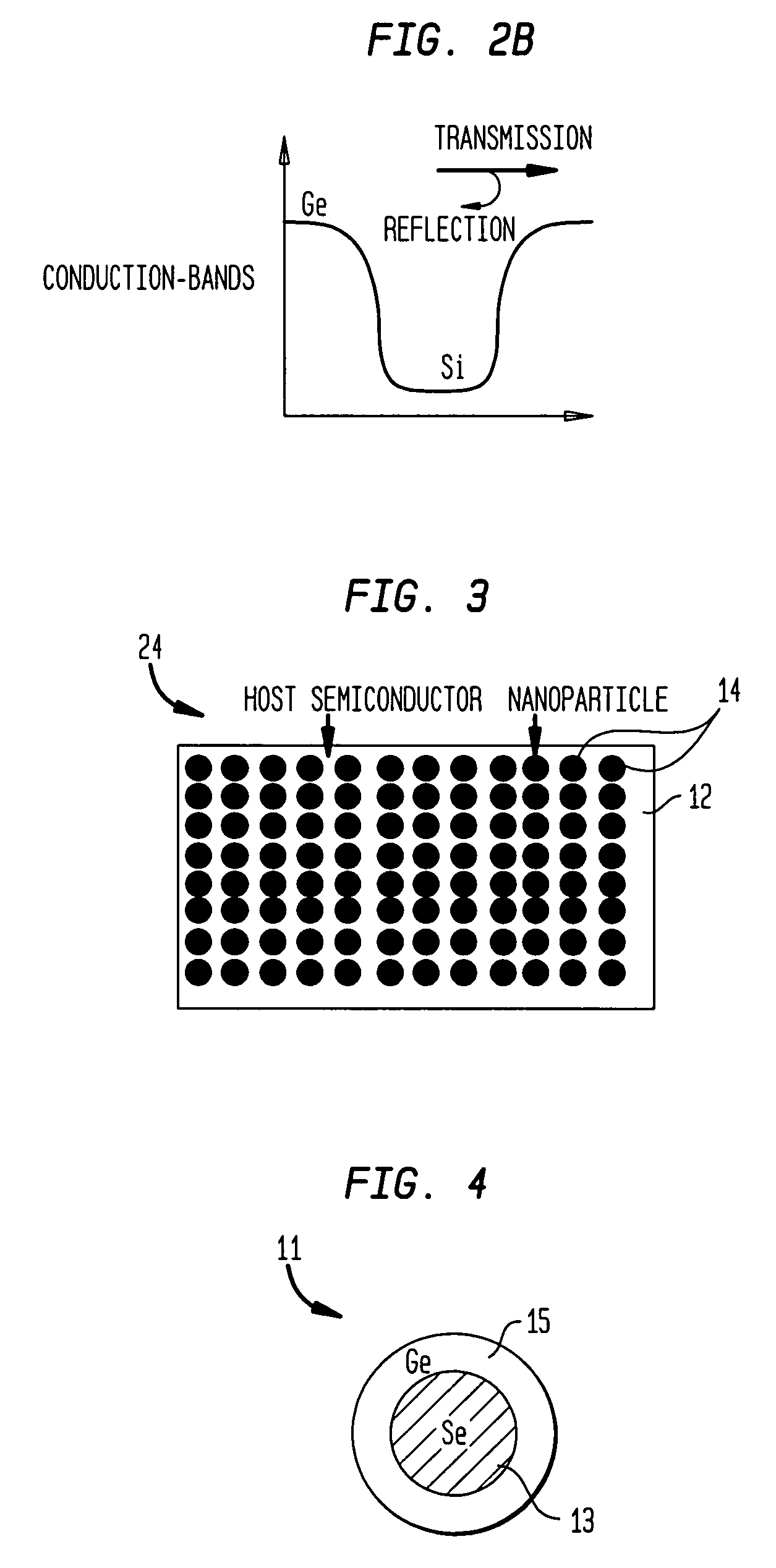
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In non-metals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature, while the conduction band is the lowest range of vacant electronic states. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the Fermi level, while the conduction band is located above it.
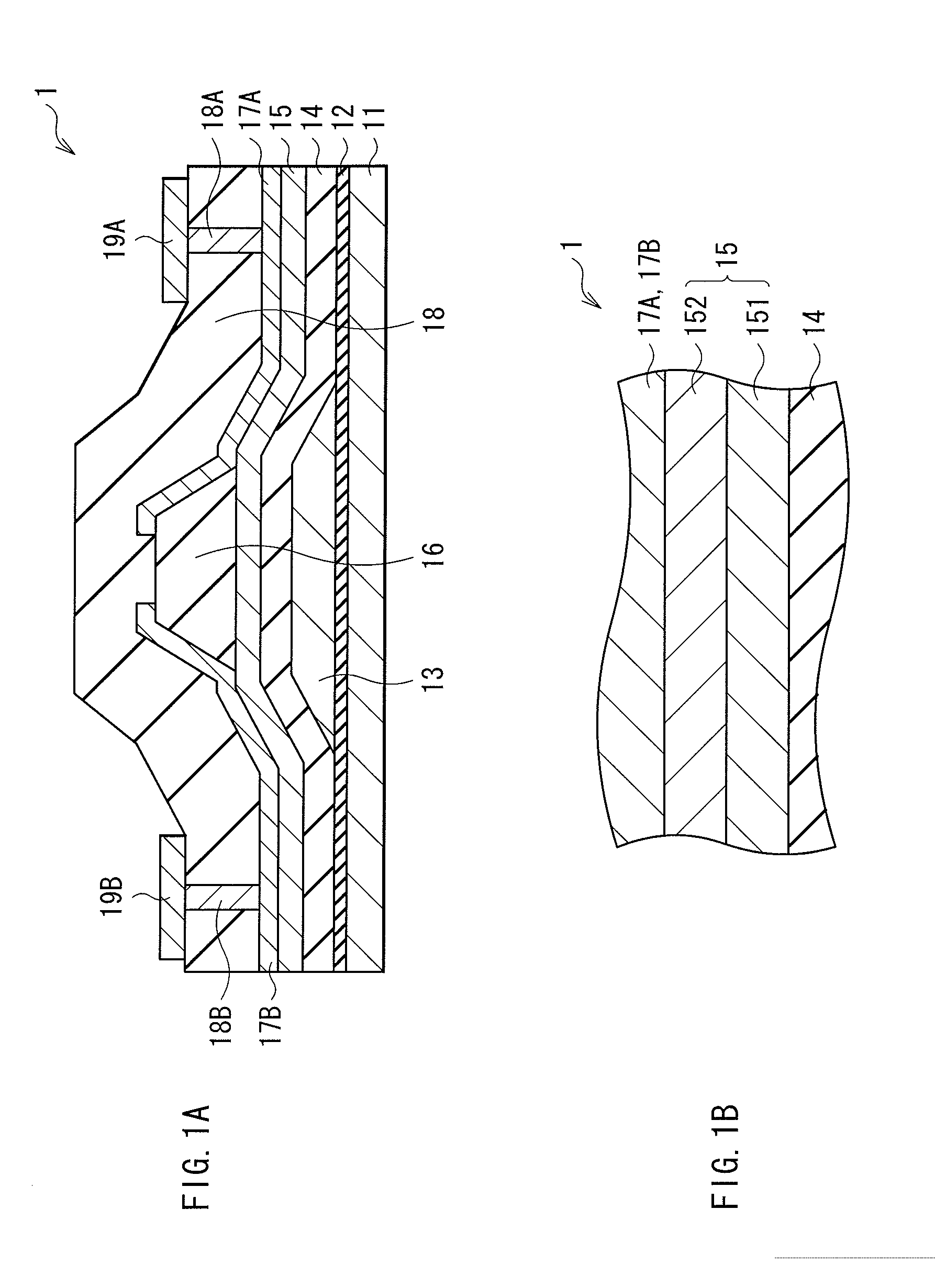
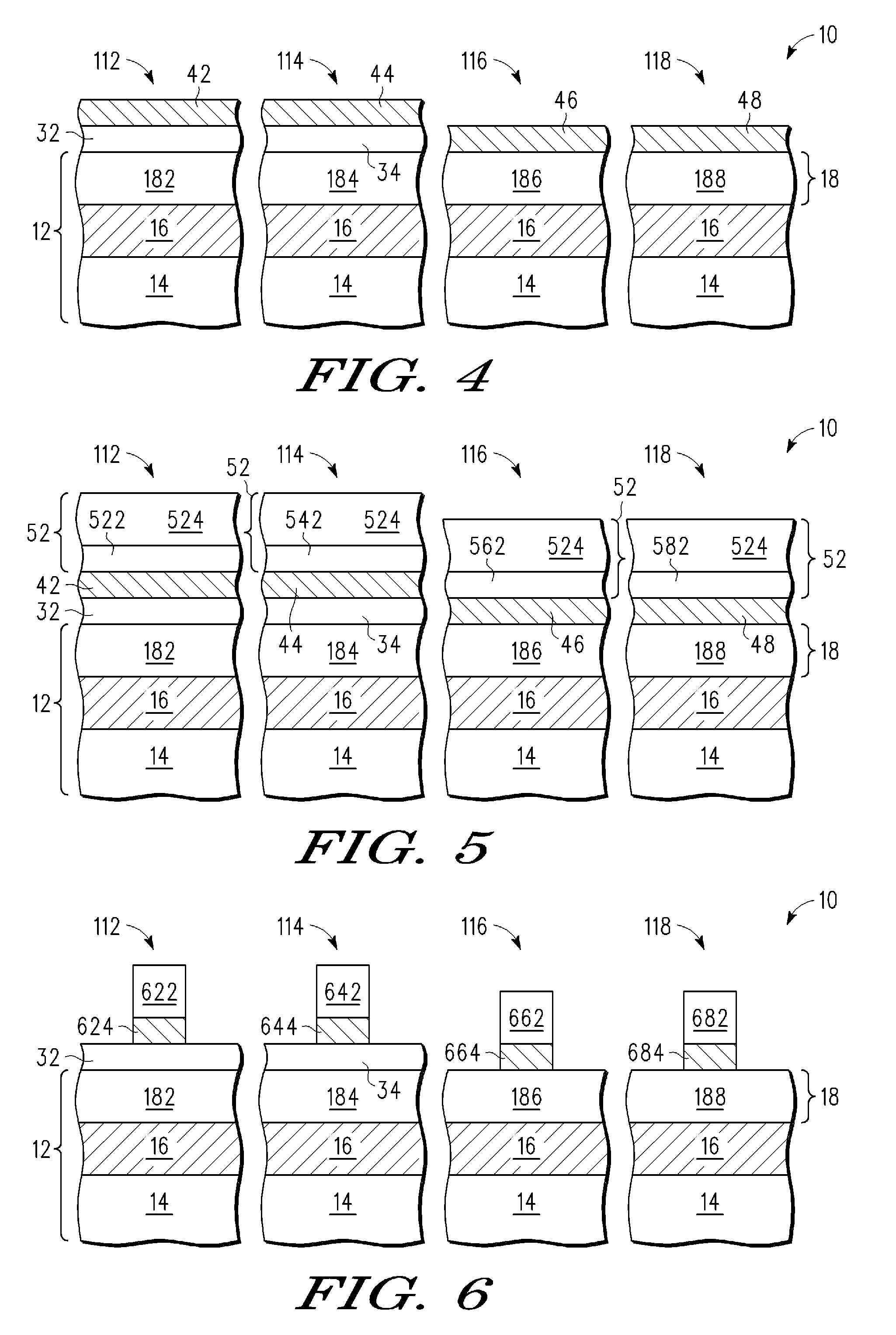
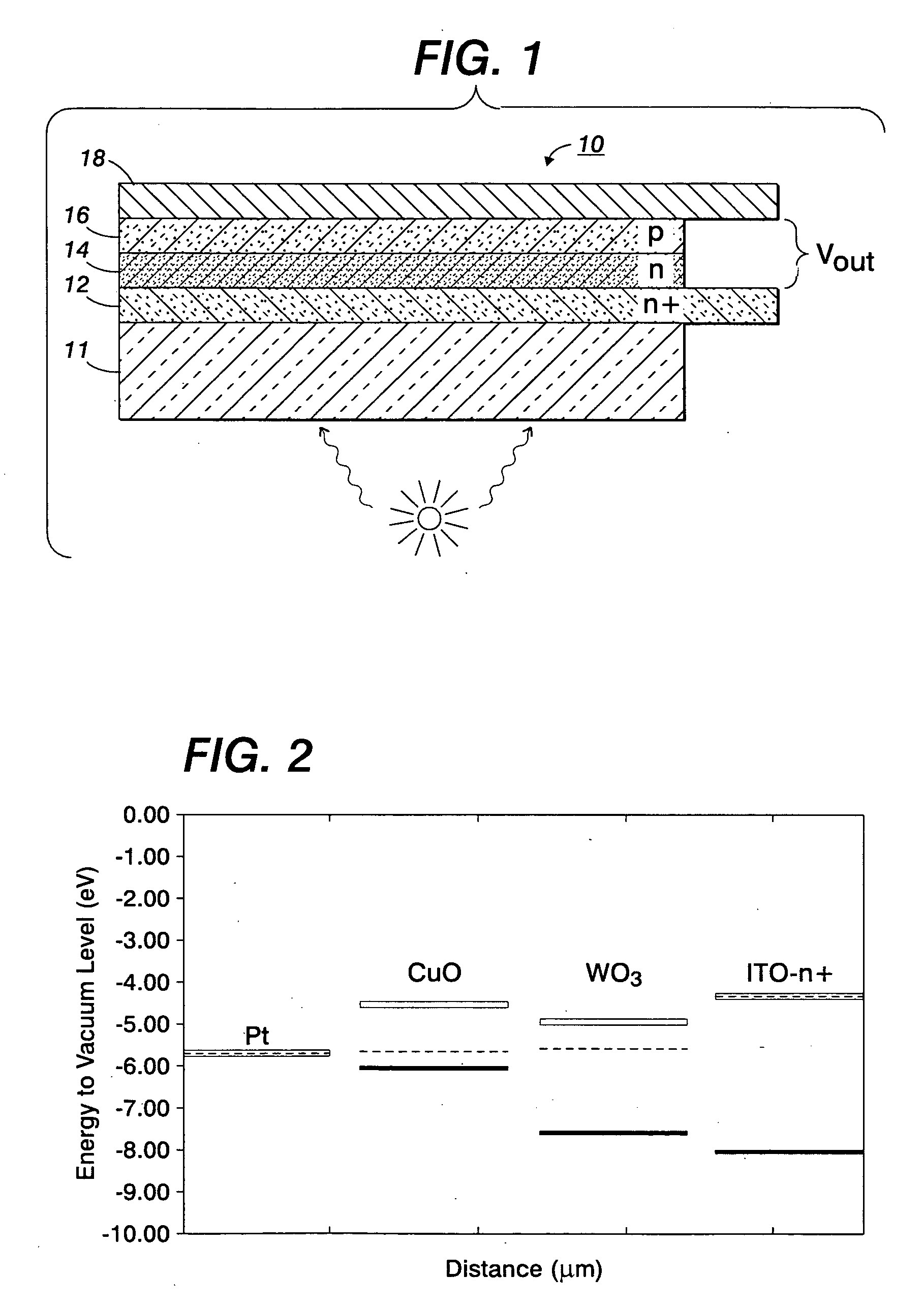
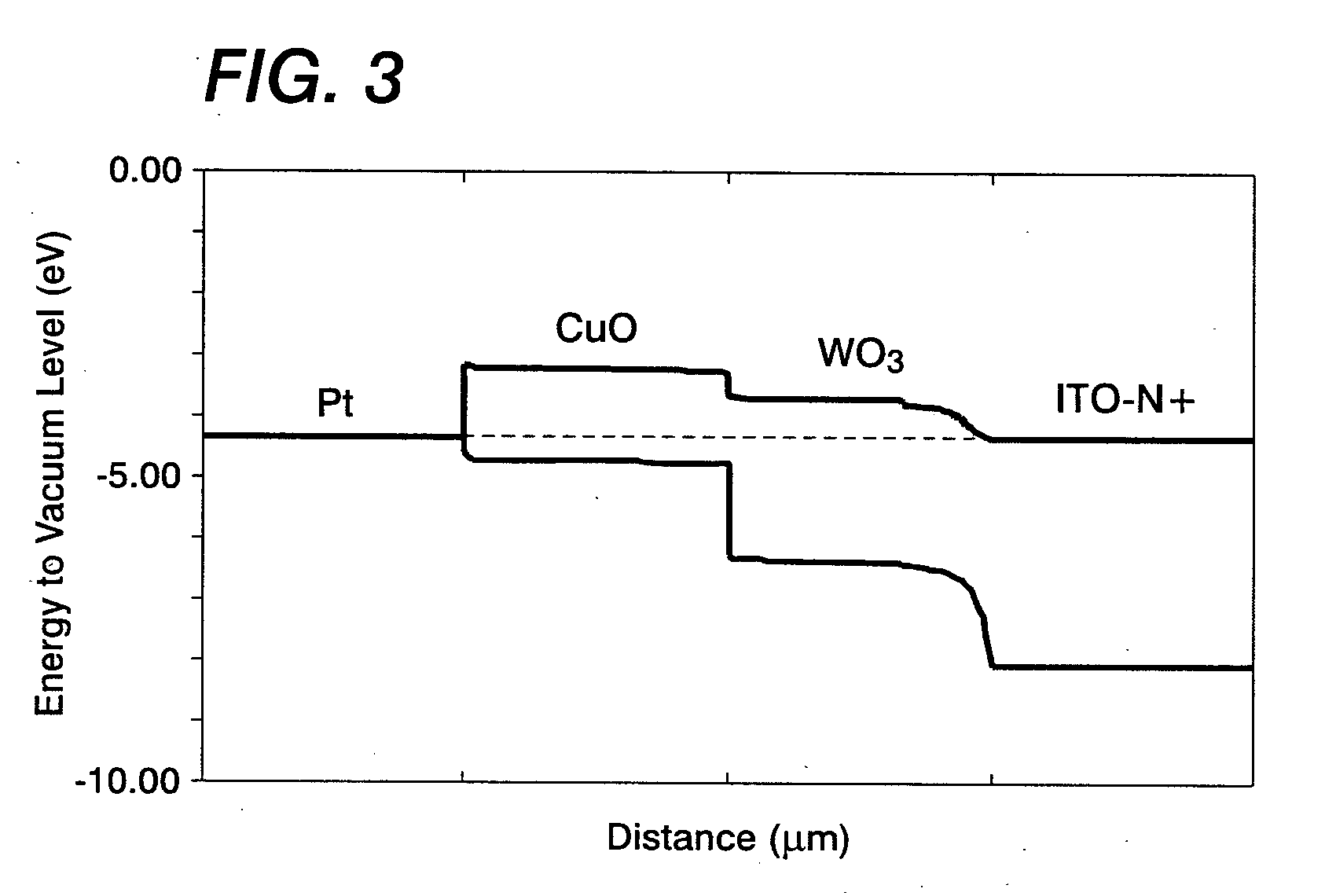
Current-induced magnetic switching device and memory including the same
InactiveUS6256223B1High bulk densitySimpler driving circuitsNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsNanoparticleConduction band
A magnetic switching device, includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a nanoparticle having a magnetic moment and being disposed between the first and second electrodes. At least one of the first electrode and the second electrode includes a magnetic material which has a net spin polarization in its conduction band for injecting, into the nanoparticle, an electrical current including a net spin polarization for overcoming the magnetic moment of the nanoparticle upon selection of a predetermined magnitude for the electrical current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Thin film transistor, display device, and electronic device
ActiveUS20120119205A1Maintain good propertiesLarge carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandMaximum level
A thin film transistor, which is capable of improving carrier mobility, and a display device and an electronic device, each of which uses the thin film transistor, are provided. The thin film transistor includes: a gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor layer including a multilayer film including a carrier travel layer configuring a channel and a carrier supply layer for supplying carriers to the carrier travel layer; a gate insulating film provided between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; and a pair of electrodes as a source and a drain. A conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply source of the carrier supply layer is higher in energy than a conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply destination of the carrier travel layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
Gate oxides
InactiveUS6844203B2Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEquivalent oxide thicknessGadolinium
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset of 2 eV or greater. Gate oxides formed from elements such as yttrium and gadolinium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
InactiveUS20060102224A1Improve thermoelectric performanceLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectValence bandConduction band
The present invention is generally directed to nanocomposite thermoelectric materials that exhibit enhanced thermoelectric properties. The nanocomposite materials include two or more components, with at least one of the components forming nano-sized structures within the composite material. The components are chosen such that thermal conductivity of the composite is decreased without substantially diminishing the composite's electrical conductivity. Suitable component materials exhibit similar electronic band structures. For example, a band-edge gap between at least one of a conduction band or a valence band of one component material and a corresponding band of the other component material at interfaces between the components can be less than about 5 kBT, wherein kB is the Boltzman constant and T is an average temperature of said nanocomposite composition.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
Crystalline or amorphous medium-K gate oxides, Y2O3 and Gd2O3
InactiveUS20050032292A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEquivalent oxide thicknessGadolinium
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset of 2 eV or greater. Gate oxides formed from elements such as yttrium and gadolinium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Highly reliable amorphous high-k gate oxide ZrO2
InactiveUS20050029605A1Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsConduction band
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset in a range of approximately 5.16 eV to 7.8 eV. Gate oxides formed from elements such as zirconium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
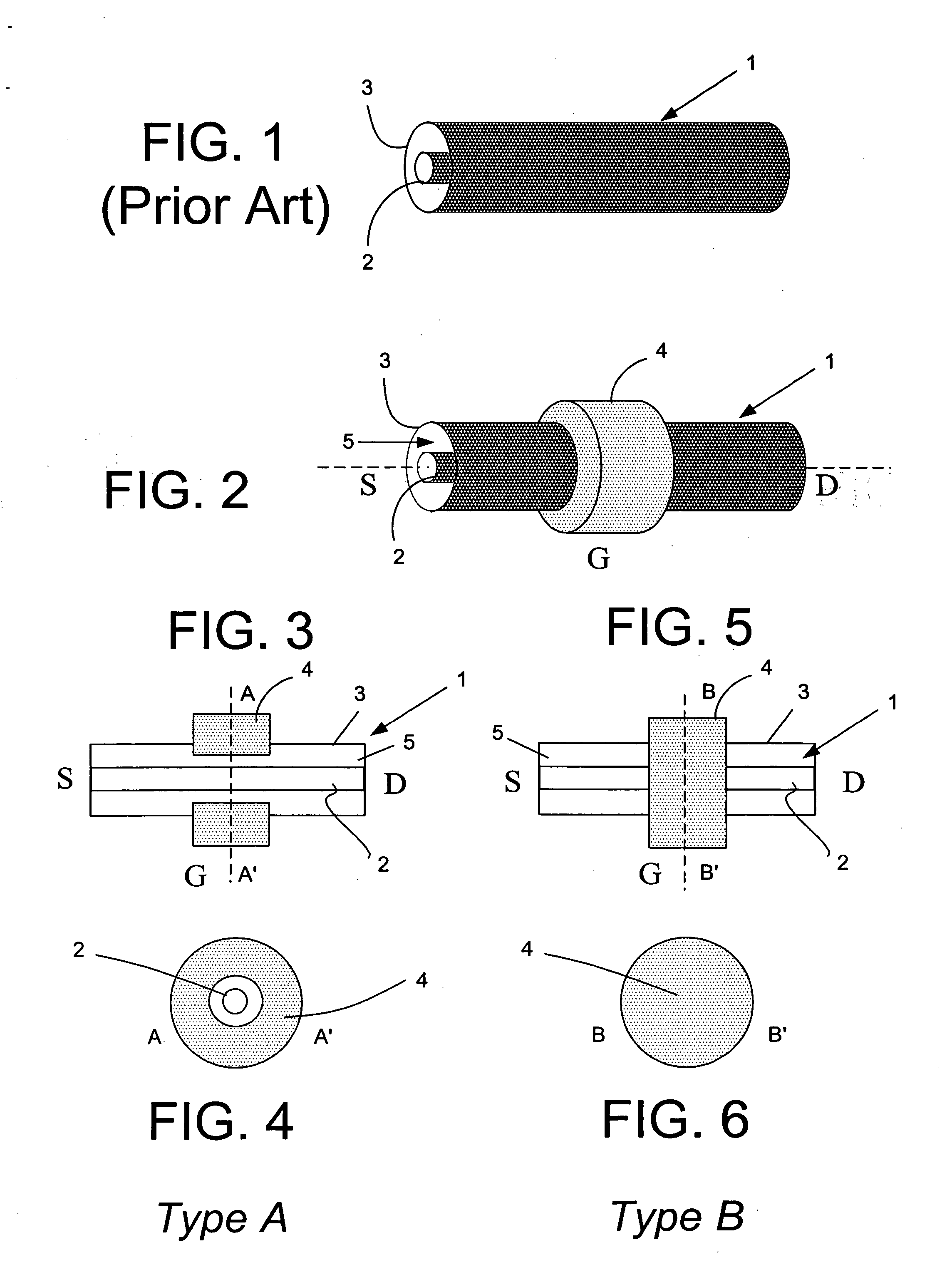
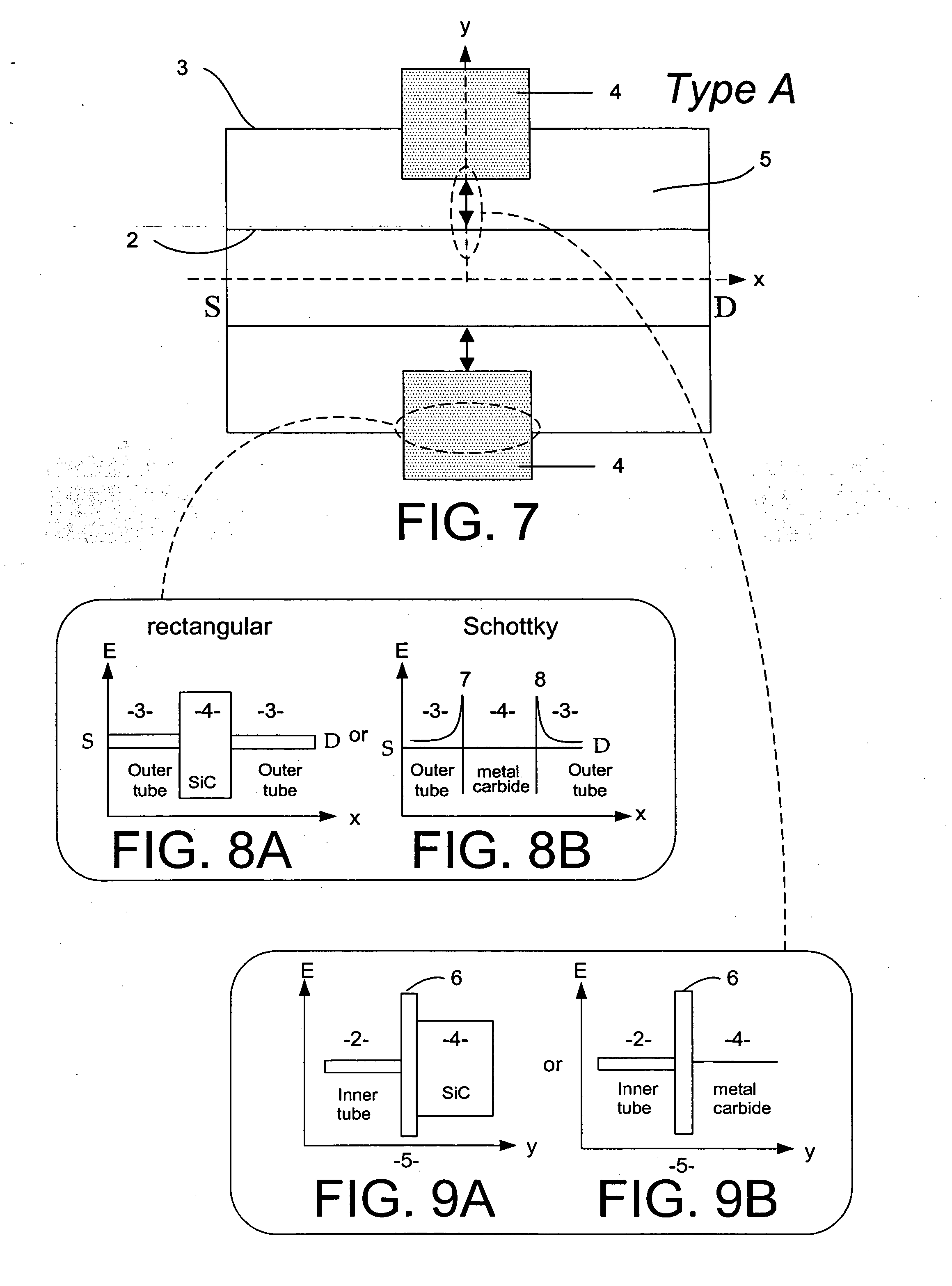
Method concerning a junction barrier Schottky diode, such a diode and use thereof
InactiveUS6524900B2Change resistanceChange the on-state resistance of the diodeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSemiconductor materials
A method for controlling the temperature dependence of a junction barrier Schottky diode of a semiconductor material having an energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band exceeding 2 eV provides for doing this when producing the diode by adjusting the on-state resistance of the grid portion of the diode during the production for obtaining a temperature dependence of the operation of the diode adapted to the intended use thereof.
Owner:CREE INC
Photovoltaic devices fabricated from insulating nanostructured template
Photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. A device may be characterized by an architecture with an inorganic insulating nanostructured template having template elements between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter with a elements density of between about 1012 elements / m2 and about 1016 elements / m2. A first charge-transfer material coats the walls of the template elements leaving behind additional space. A second charge-transfer material fills the additional space such that the first and second charge-transfer materials are volumetrically interdigitated. At least one charge transfer material has an absorbance of greater than about 103 / cm. The first and second charge-transfer materials have complementary charge transfer properties with respect to each other. A lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) or conduction band of the first charge-transfer material is offset from a LUMO or conduction band of the second charge-transfer material by greater than about 0.2 eV. An electrically conductive material may optionally be disposed between the nanostructured template and the first charge-transfer material.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP +1
Semiconductor device with a field stop zone and process of producing the same
ActiveUS20080054369A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantConduction band
Embodiments discussed herein relate to processes of producing a field stop zone within a semiconductor substrate by implanting dopant atoms into the substrate to form a field stop zone between a channel region and a surface of the substrate, at least some of the dopant atoms having energy levels of at least 0.15 eV below the energy level of the conduction band edge of semiconductor substrate; and laser annealing the field stop zone.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Thin film transistor, display device, and electronic device
ActiveUS8384080B2Maintain good propertiesLarge carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandMaximum level
A thin film transistor, which is capable of improving carrier mobility, and a display device and an electronic device, each of which uses the thin film transistor, are provided. The thin film transistor includes: a gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor layer including a multilayer film including a carrier travel layer configuring a channel and a carrier supply layer for supplying carriers to the carrier travel layer; a gate insulating film provided between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; and a pair of electrodes as a source and a drain. A conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply source of the carrier supply layer is higher in energy than a conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply destination of the carrier travel layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
Process for forming an electronic device including a transistor having a metal gate electrode
An electronic device includes an n-channel transistor and a p-channel transistor. The p-channel transistor has a first gate electrode with a first work function and a first channel region including a semiconductor layer immediately adjacent to a semiconductor substrate. In one embodiment, the first work function is less than the valence band of the semiconductor layer. In another embodiment, the n-channel transistor has a second gate electrode with a second work function different from the first work function and closer to a conduction band than a valence band of a second channel region. A process of forming the electronic device includes forming first and second gate electrodes having first and second work functions, respectively. First and second channel regions having a same minority carrier type are associated with the first and second gate electrodes, respectively.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
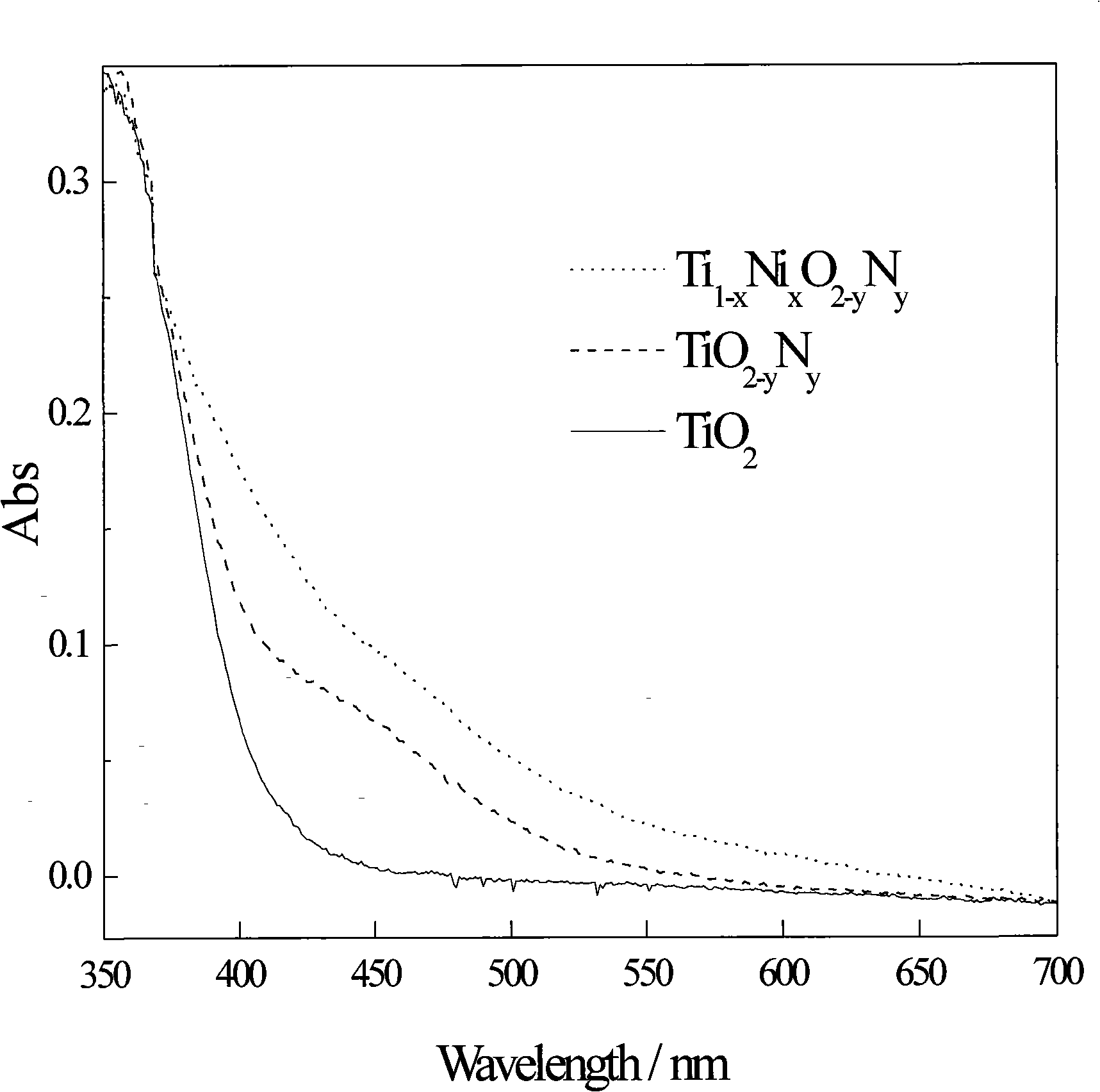
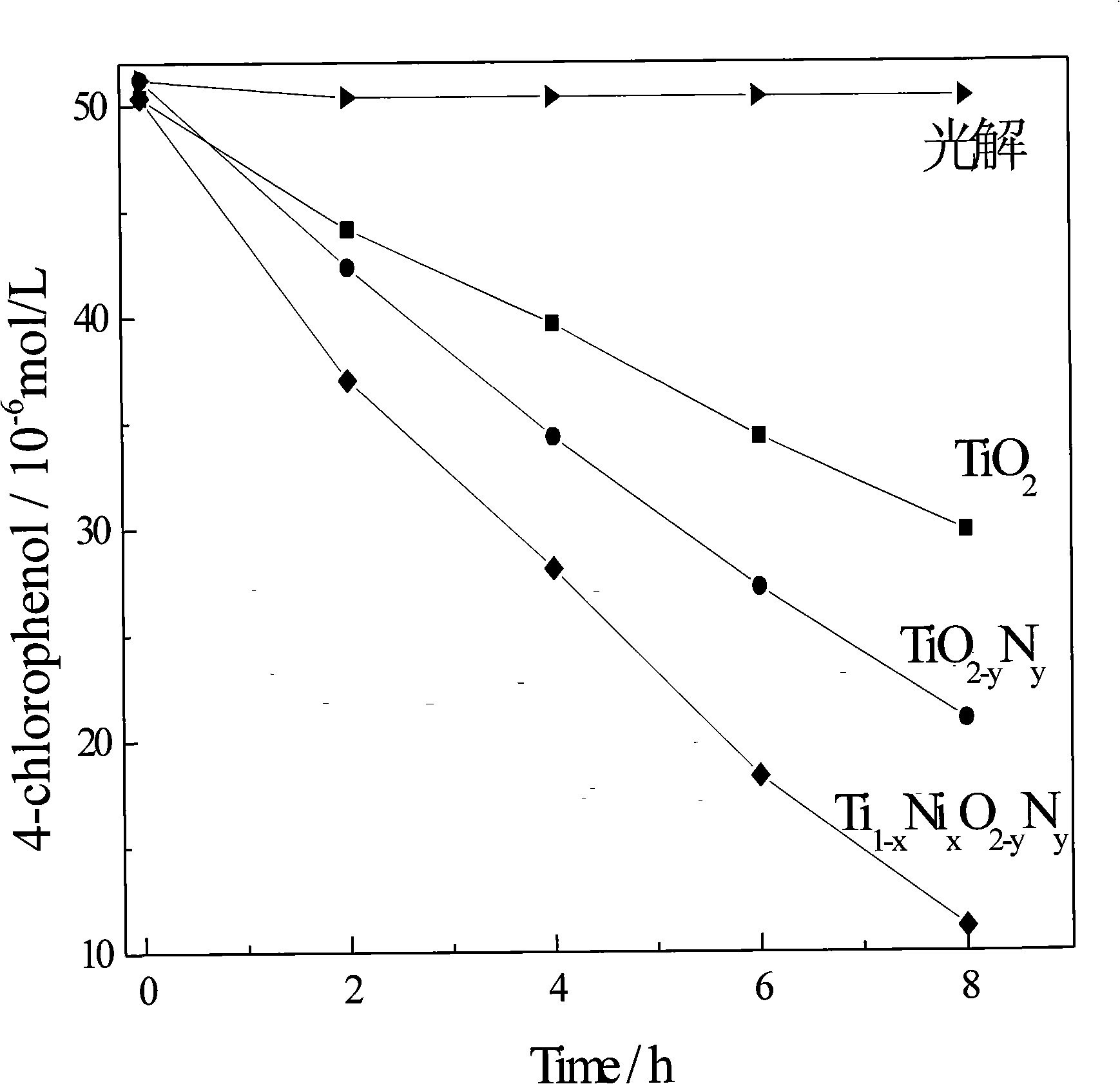
Method for preparing high efficiency metallic, non-metallic ion co-doped nano-TiO2 visible-light responsive photocatalyst
InactiveCN101301619AVisible light catalytic activity is highEnhanced inhibitory effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationPhotocatalytic reactionLight responsive
The invention discloses a process for preparing a high efficiency nanometer Tio2 visible light catalyst codoped with metal and non metallic ion, belonging to the photocatalysis technology field. The invention adopts titanic acid ester as precursor, uses metal salt and non-metallic compound as dopant, in accordance with sol-gel method, prepares the nanometer TiO2-based photocatalyst with codoping, high efficiency and visible light catalytic activity, wherein the catalytic activity is greatly higher than that of single-doped TiO2-based catalyst. The invention is characterized by the following: 1. due to codoping of the metal and non metallic ion, discrete localized doping level is formed respectively on the lower part of the conduction band energy level and the upper part of the valence band energy level of the TiO2-based catalyst, thus increasing the absorption of visible light and greatly improving the catalytic activity; 2. the doping level can inhibit the recombination of photogenerated carrier, promote the probability of the photogenerated carrier entering into the photocatalytic reaction and efficiently degrade pollutant molecules.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
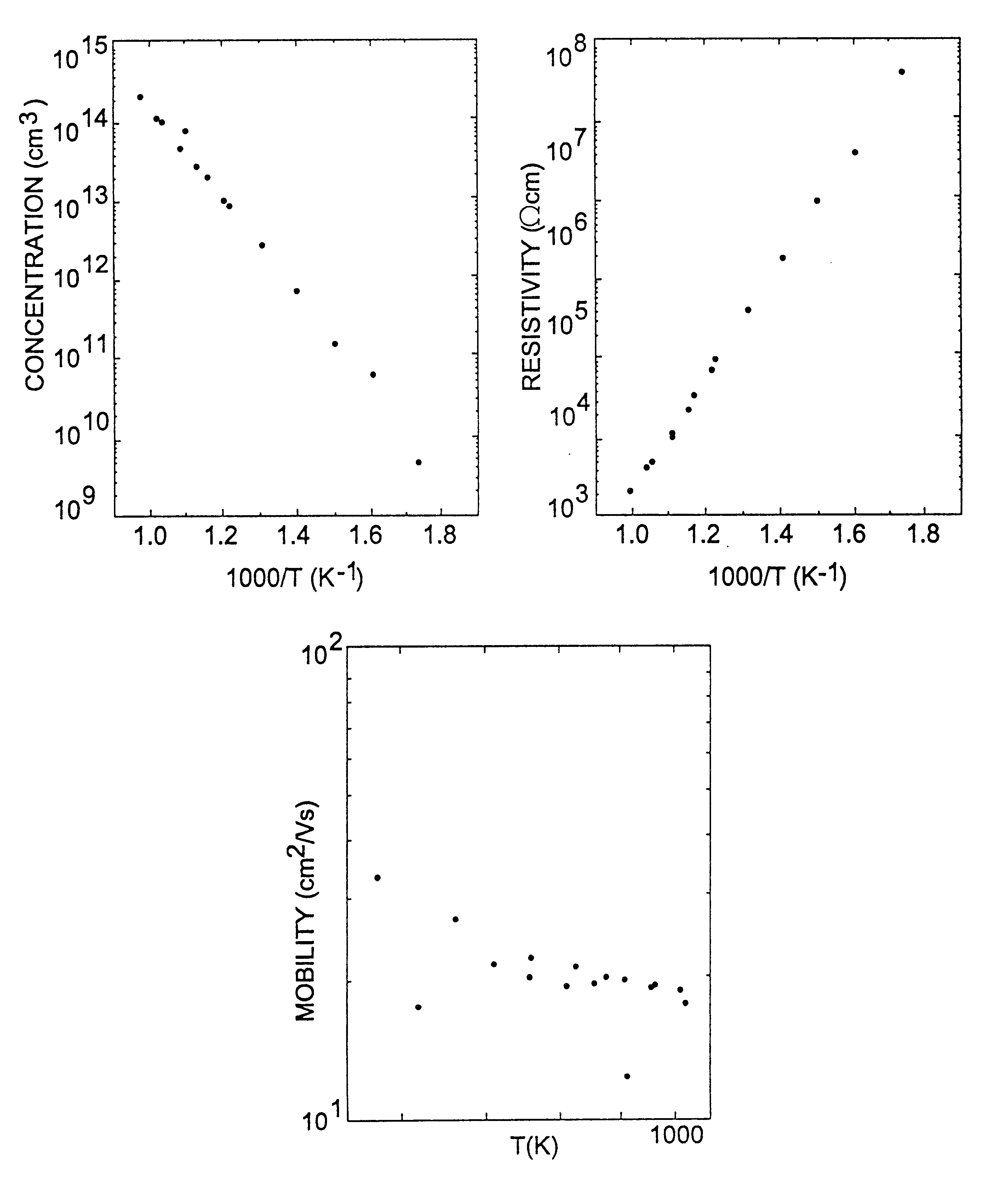
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
InactiveUS6396080B2High-frequency operationReduce complicationsPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formRoom temperature
A semi-insulating bulk single crystal of silicon carbide is disclosed that has a resistivity of at least 5000 OMEGA-cm at room temperature and a concentration of trapping elements that create states at least 700 meV from the valence or conduction band that is below the amounts that will affect the resistivity of the crystal, preferably below detectable levels. A method of forming the crystal is also disclosed, along with some resulting devices that take advantage of the microwave frequency capabilities of devices formed using substrates according to the invention.
Owner:CREE INC
Dielectric passivation for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7332795B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsConduction band
Owner:CREE INC
High-isolation slot antenna array
ActiveCN104124527AImprove isolationReduce radiationPolarised antenna unit combinationsAntenna couplingsMulti inputDielectric substrate
A high-isolation slot antenna array relates to a multi-input multi-output antenna. The antenna is composed of three slot antennas which are arranged together, the radiation polarization directions of every two slot antennas intersect, and each slot antenna is formed by a micro-strip feeder on a dielectric substrate and a metal ground plane. A radiation slit and a plurality of isolation slots are formed in the metal ground plane. The isolation slots are formed in the periphery of the radiation slit, and the isolation slots are parallel to each other. The long side direction of the radiation slit is perpendicular to the long side direction of the isolation slots, and the length of the isolation slots enables the resonance frequency to be lower than the working efficiency of the antennas. An antenna input output port is formed in one end of the micro-strip feeder, a metal short circuit needle is arranged at the tail end of a micro-strip feeder conduction band at the other end of the micro-strip feeder, and the conduction band and the metal ground plane are connected on the edge of the radiation slit through the metal short circuit needle. The antenna can effectively reduce adverse effects of shielding and isolation of the metal ground plane on antenna normal radiation.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN BROADBAND TECH +1
Reduced dark current photodetector
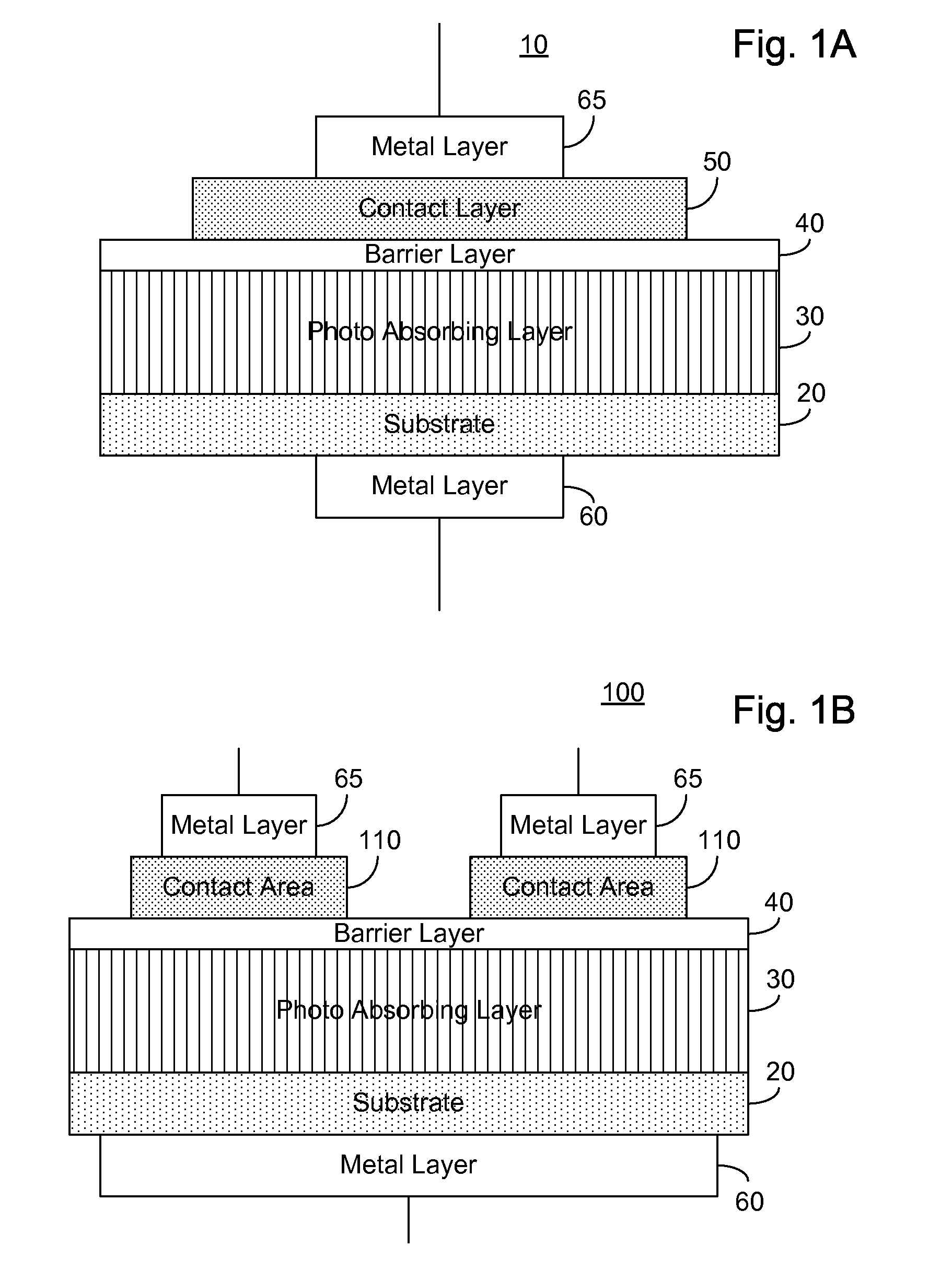
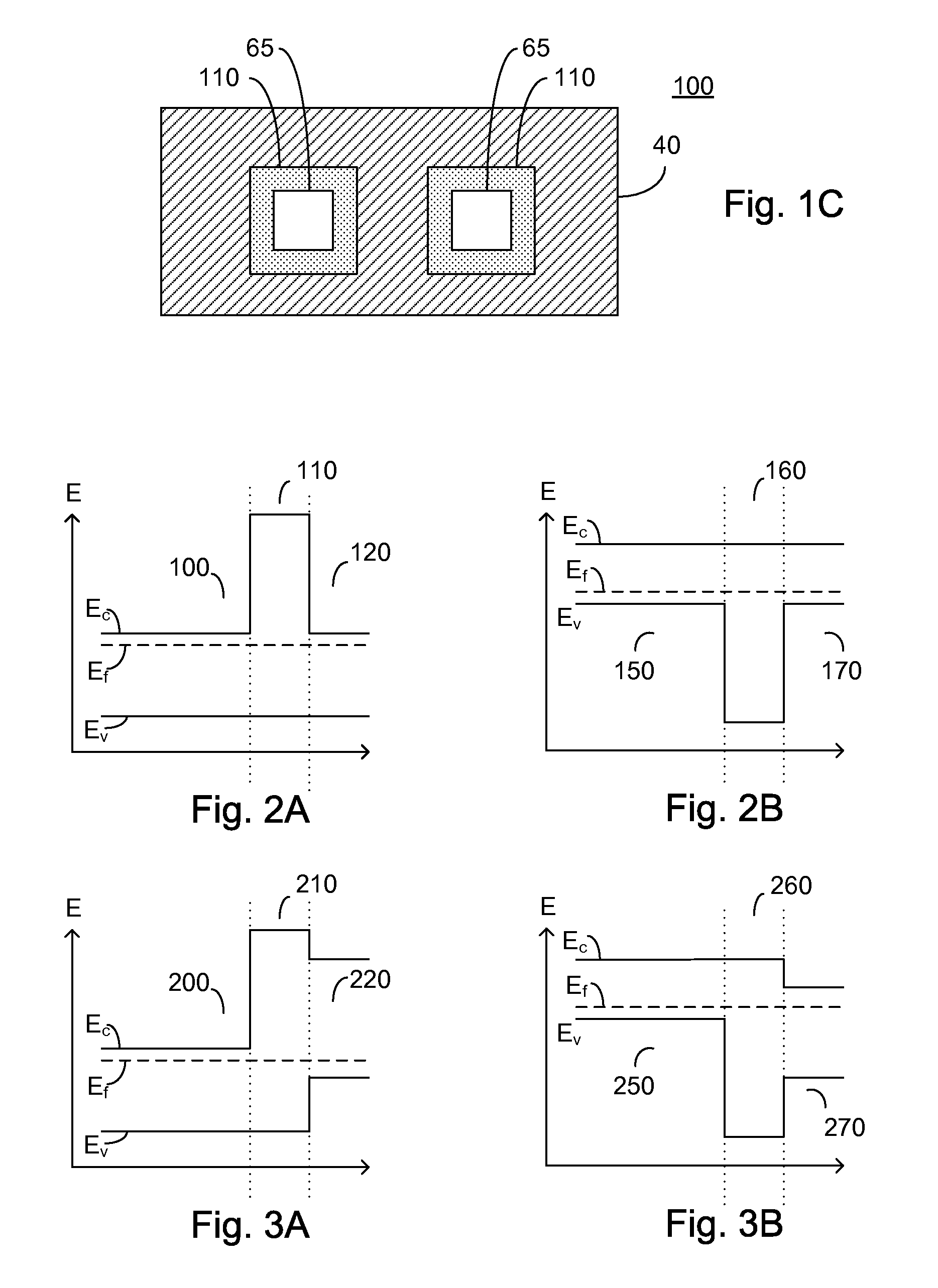
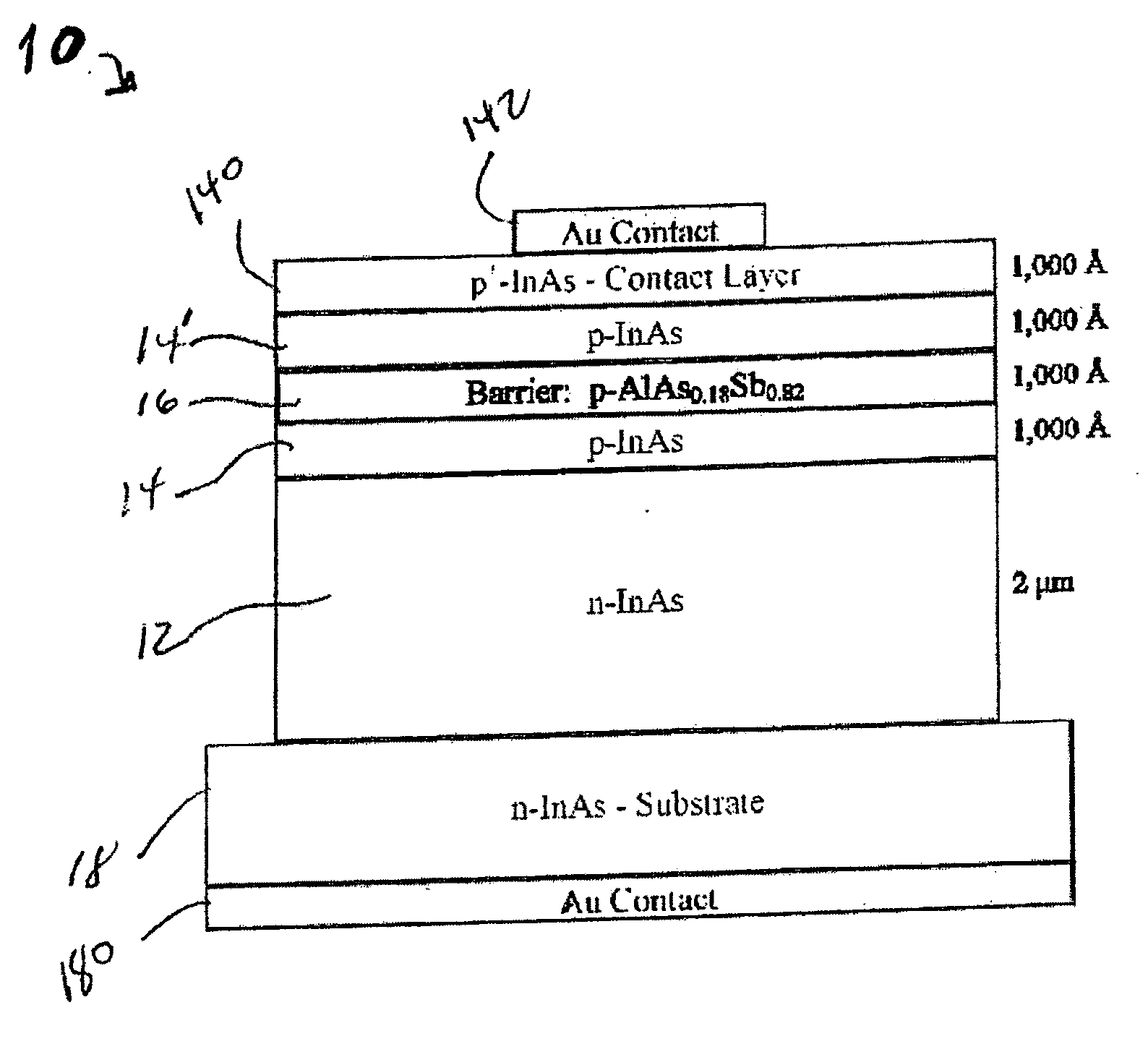
ActiveUS20070215900A1Overcome disadvantagesAvoid tunnelingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandPhotodetector
A photo-detector comprising: a photo absorbing layer comprising an n-doped semiconductor exhibiting a valence band energy level; a barrier layer, a first side of the barrier layer adjacent a first side of the photo absorbing layer, the barrier layer exhibiting a valence band energy level substantially equal to the valence band energy level of the doped semiconductor of the photo absorbing layer; and a contact area comprising a doped semiconductor, the contact area being adjacent a second side of the barrier layer opposing the first side, the barrier layer exhibiting a thickness and a conductance band gap sufficient to prevent tunneling of majority carriers from the photo absorbing layer to the contact area and block the flow of thermalized majority carriers from the photo absorbing layer to the contact area. Alternatively, a p-doped semiconductor is utilized, and conductance band energy levels of the barrier and photo absorbing layers are equalized.
Owner:MAIMON SHIMON
Method for fabricating flash memory device
ActiveUS20050074937A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConduction bandDielectric layer
A method for fabricating a flash memory includes forming a tunnel oxide layer by depositing a material with a conduction band energy level lower than that of SiO2 on a semiconductor substrate; forming a floating gate by depositing polysilicon on the tunnel oxide layer; forming an intergate dielectric layer on the floating gate; forming a control gate on the intergate dielectric layer; forming a gate electrode by patterning the tunnel oxide layer, the floating gate, the intergate dielectric layer and the control gate; and forming a source / drain region by implanting impurities into the substrate using the gate electrode as a mask.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
High dielectric constant materials
ActiveUS20060151823A1Large capacityReduce leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesConduction bandMetal electrodes
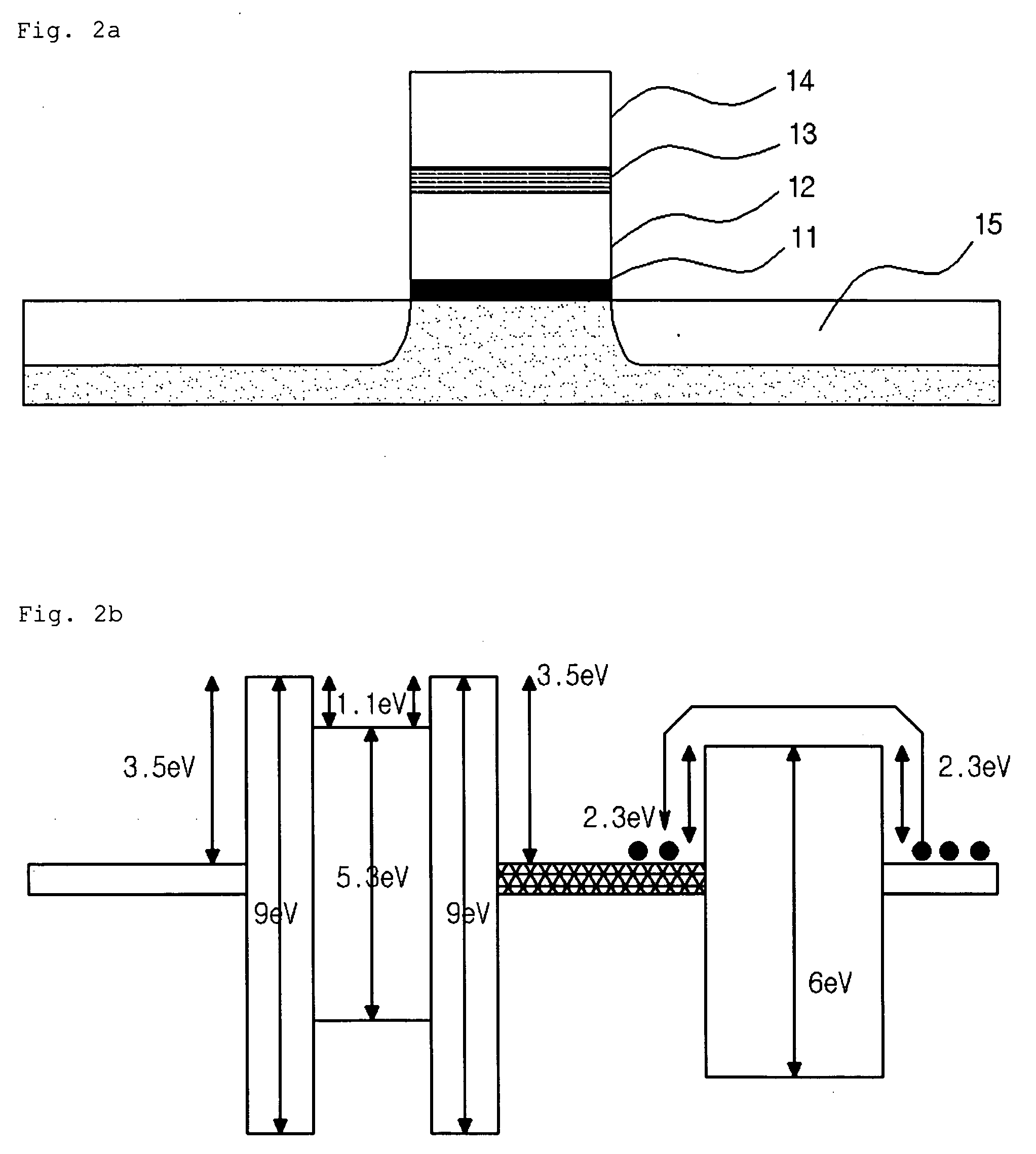
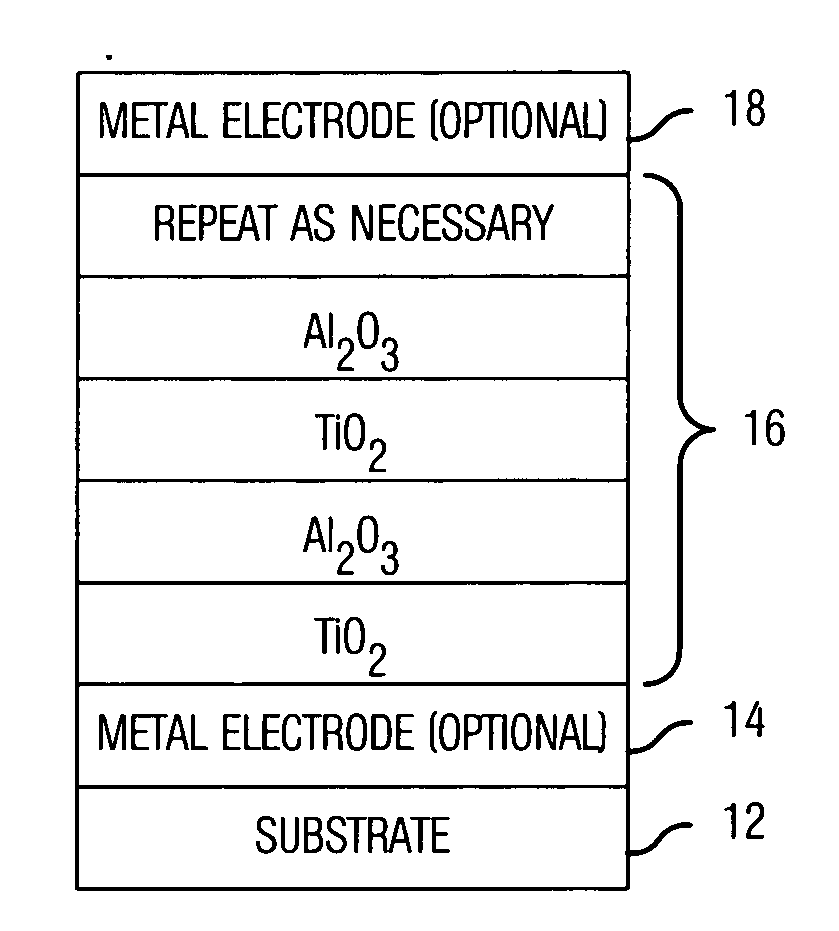
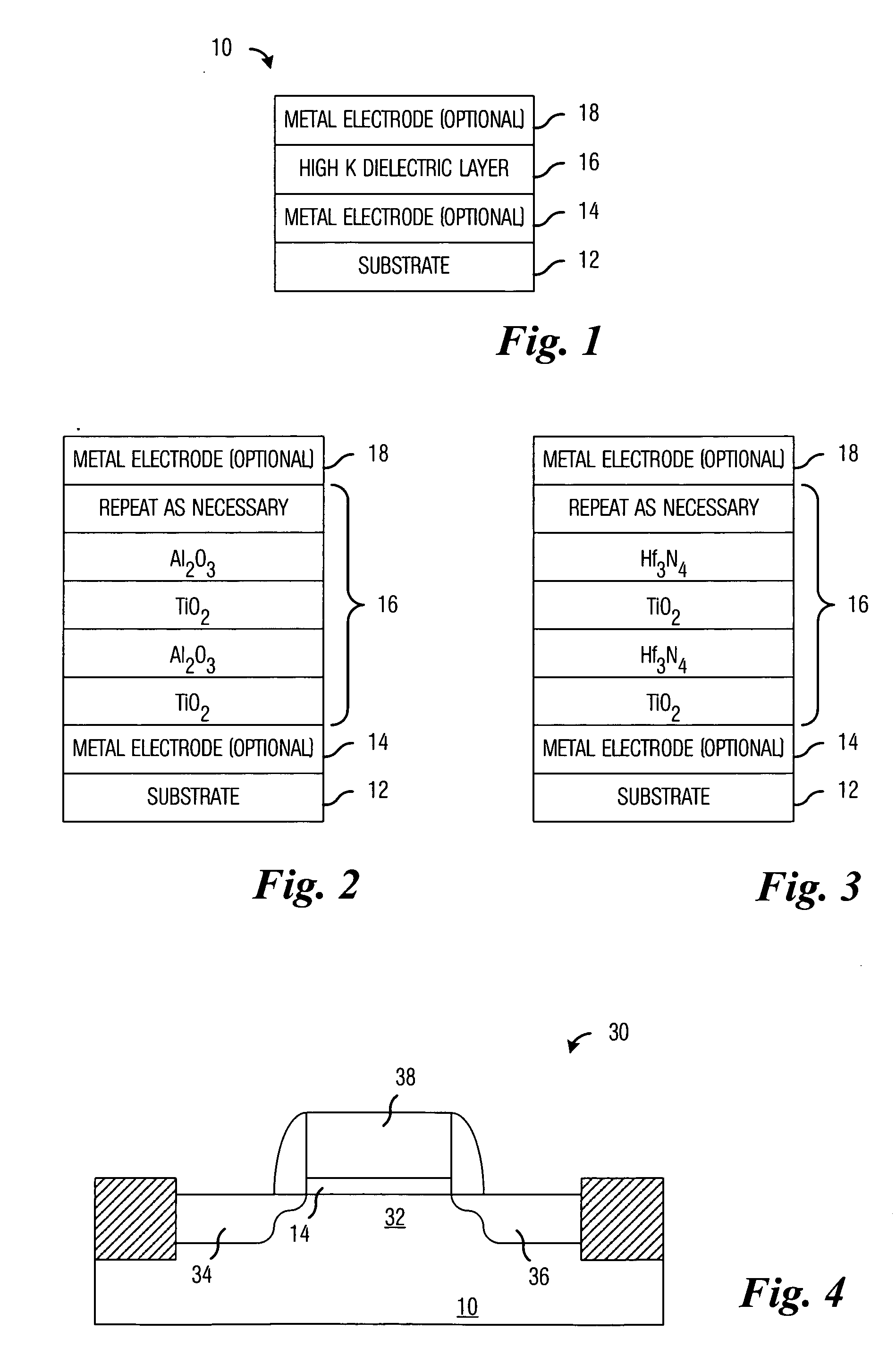
A capacitor (10) includes a substrate (12) and two metal electrodes (14, 18). A dielectric layer (16) is formed between the electrodes. Preferably, the dielectric layer has a dielectric constant greater than 25 and an adequate conduction band offset with silicon. Exemplary embodiments proposed use the following material systems: HfuTivTawOxNy, HfuTivOxNy, TiuSrvOxNy, TiuAlvOxNy and HfuSrvOxNy (where u, v, w, x, and y are the atomic proportions of the elements in the dielectric stack).
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Heterojunction photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20060130890A1Final product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
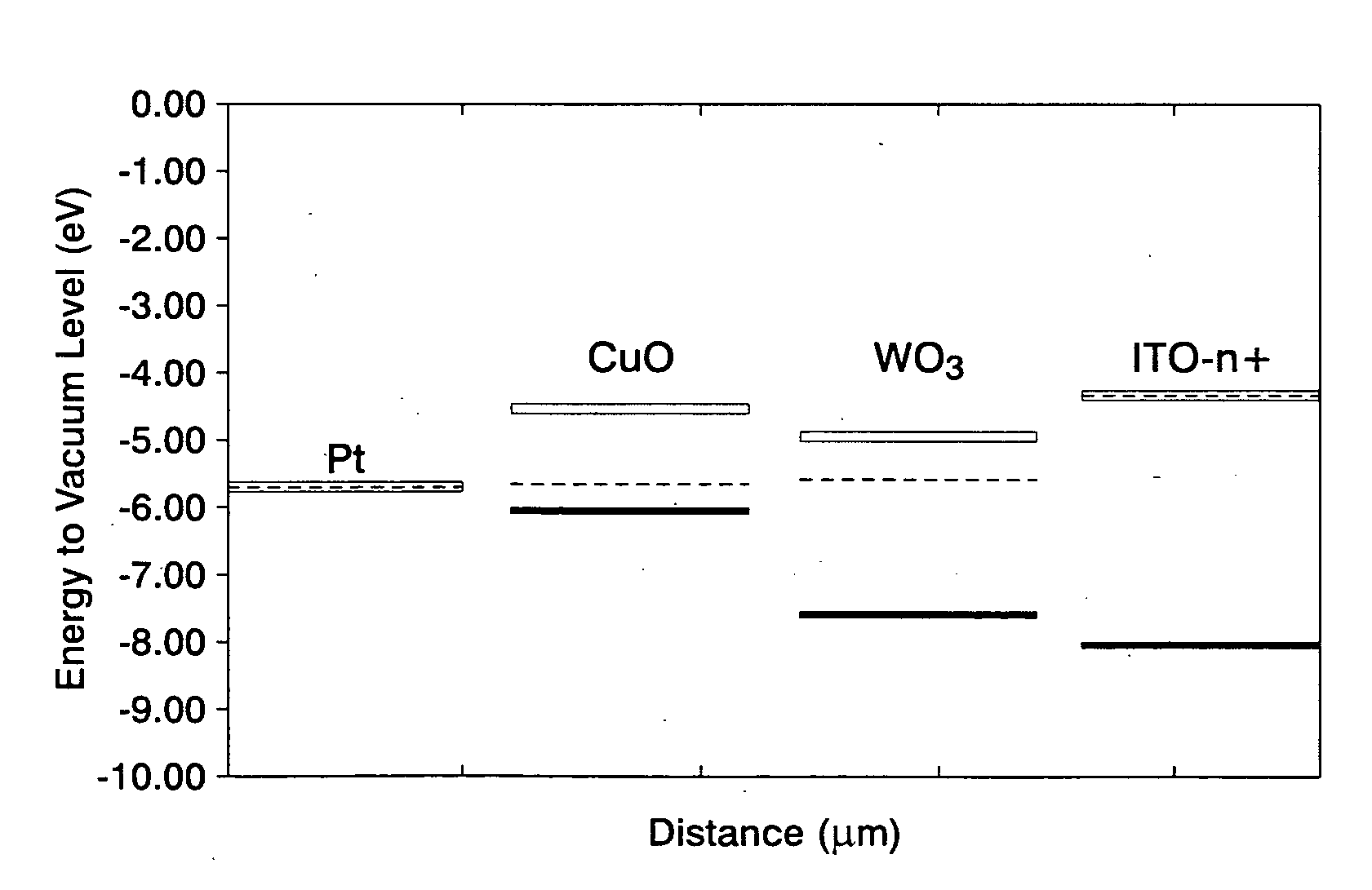
In accordance with one aspect of the present disclosure, a solar photovoltaic device is disclosed. The semiconductor material of the solar photovoltaic device is a heterostructure of two different binary compounds of a pair of immiscible metals. The two different binary compounds have a conduction band edge offset of greater than about 0.4 eV. The binary compound acting as the optical absorbing material of the solar photovoltaic device has a bandgap of about 1.0 eV to about 1.8 eV.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Method for fabricating flash memory device
ActiveUS6977201B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConduction bandDielectric layer
A method for fabricating a flash memory includes forming a tunnel oxide layer by depositing a material with a conduction band energy level lower than that of SiO2 on a semiconductor substrate; forming a floating gate by depositing polysilicon on the tunnel oxide layer; forming an intergate dielectric layer on the floating gate; forming a control gate on the intergate dielectric layer; forming a gate electrode by patterning the tunnel oxide layer, the floating gate, the intergate dielectric layer and the control gate; and forming a source / drain region by implanting impurities into the substrate using the gate electrode as a mask.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
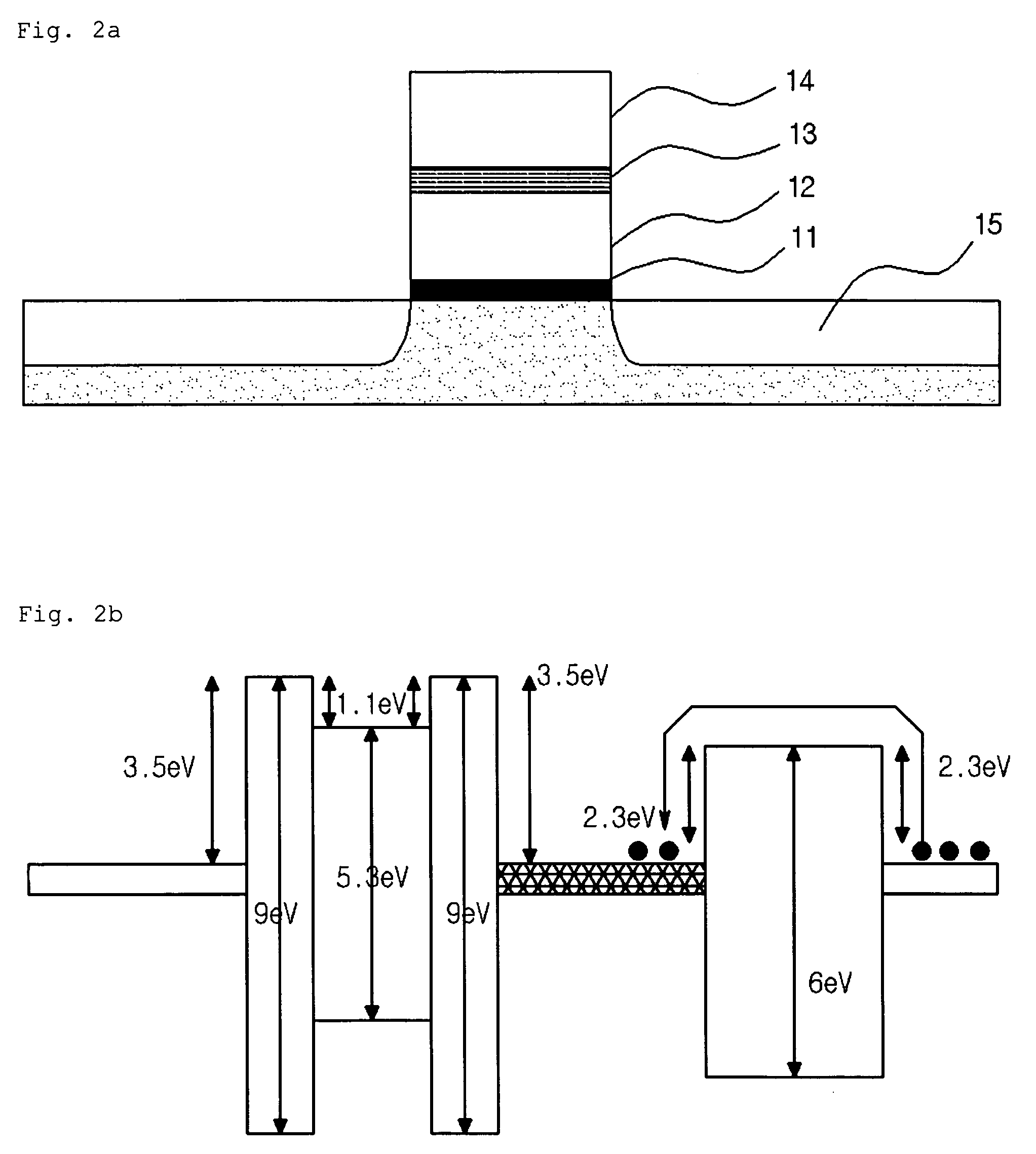
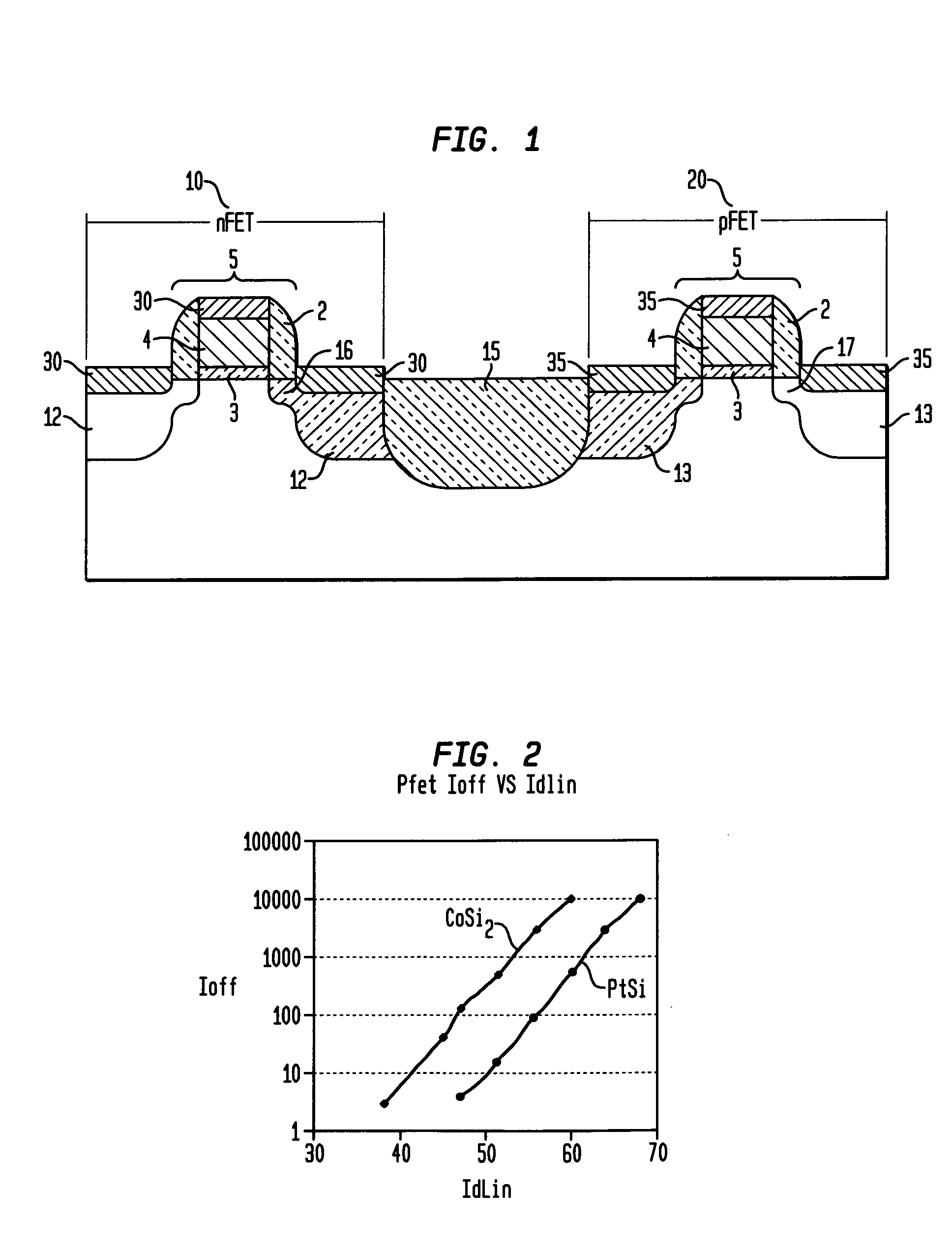
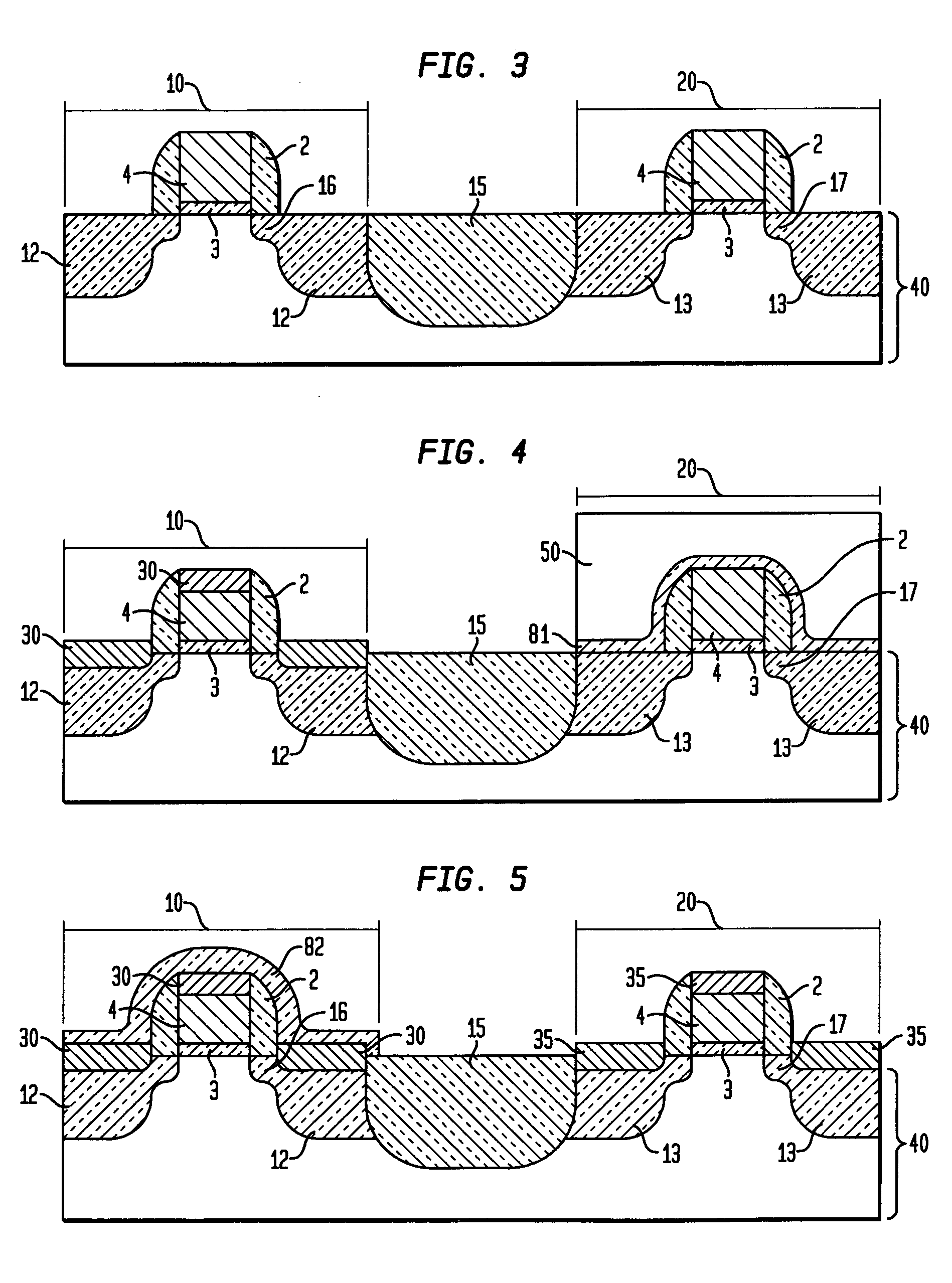
Dual silicide process to improve device performance
InactiveUS20060163670A1Reduced resistivity for contactingReduce contactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSalicide
A semiconducting structure and a method of forming thereof, includes a substrate having a p-type device region and an n-type device region; a first-type suicide contact to the n-type device region; the first-type suicide having a work function that is substantially aligned to the n-type device region conduction band; and a second-type silicide contact to the p-type device region; the second-type silicide having a work function that is substantially aligned to the p-type device region valence band. The present invention also provides a semiconducting structure and a method of forming therefore, in which the silicide contact material and silicide contact processing conditions are selected to provide strain based device improvements in pFET and nFET devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for biopolymer identification during translocation through a nanopore
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for identifying and sequencing a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. The apparatus of the present invention provides a first electrode, a second electrode and a potential means for applying a bias ramping potential across the electrodes to produce resonant tunneling of current carriers between the two electrodes. As the bias potential is ramped across the electrodes the increase in tunneling current occurs as the carrier energy sequentially matches the conduction band energies of the translocating biopolymer. This technique allows for real-time identification and sequencing of a biopolymer as the band energy spectra of the individual portions of the bipolymer are recorded, differentiated and identified. A method for identifying the biopolymer is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140042435A1Stable electrical characteristicsImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationPower semiconductor deviceConduction band
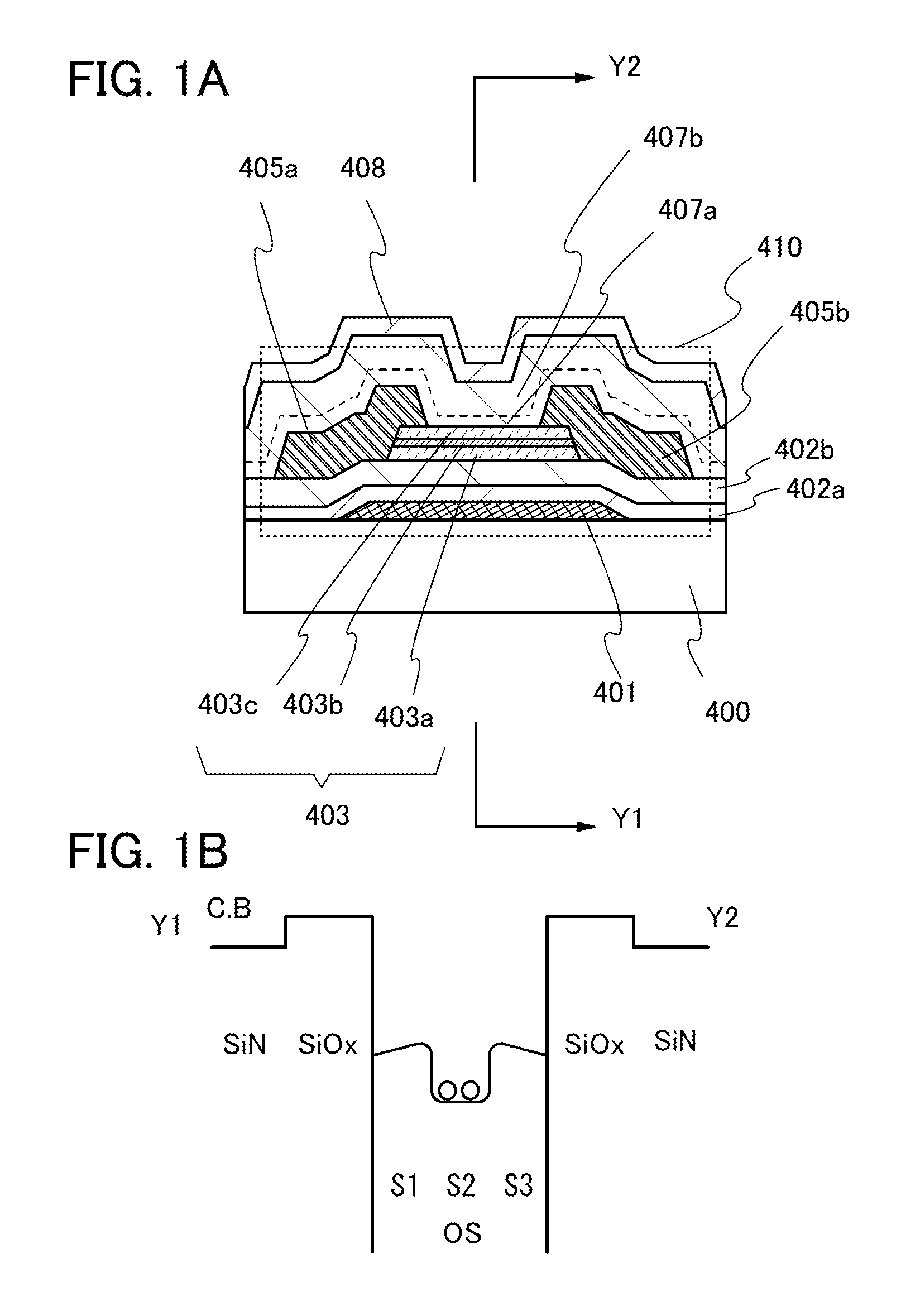
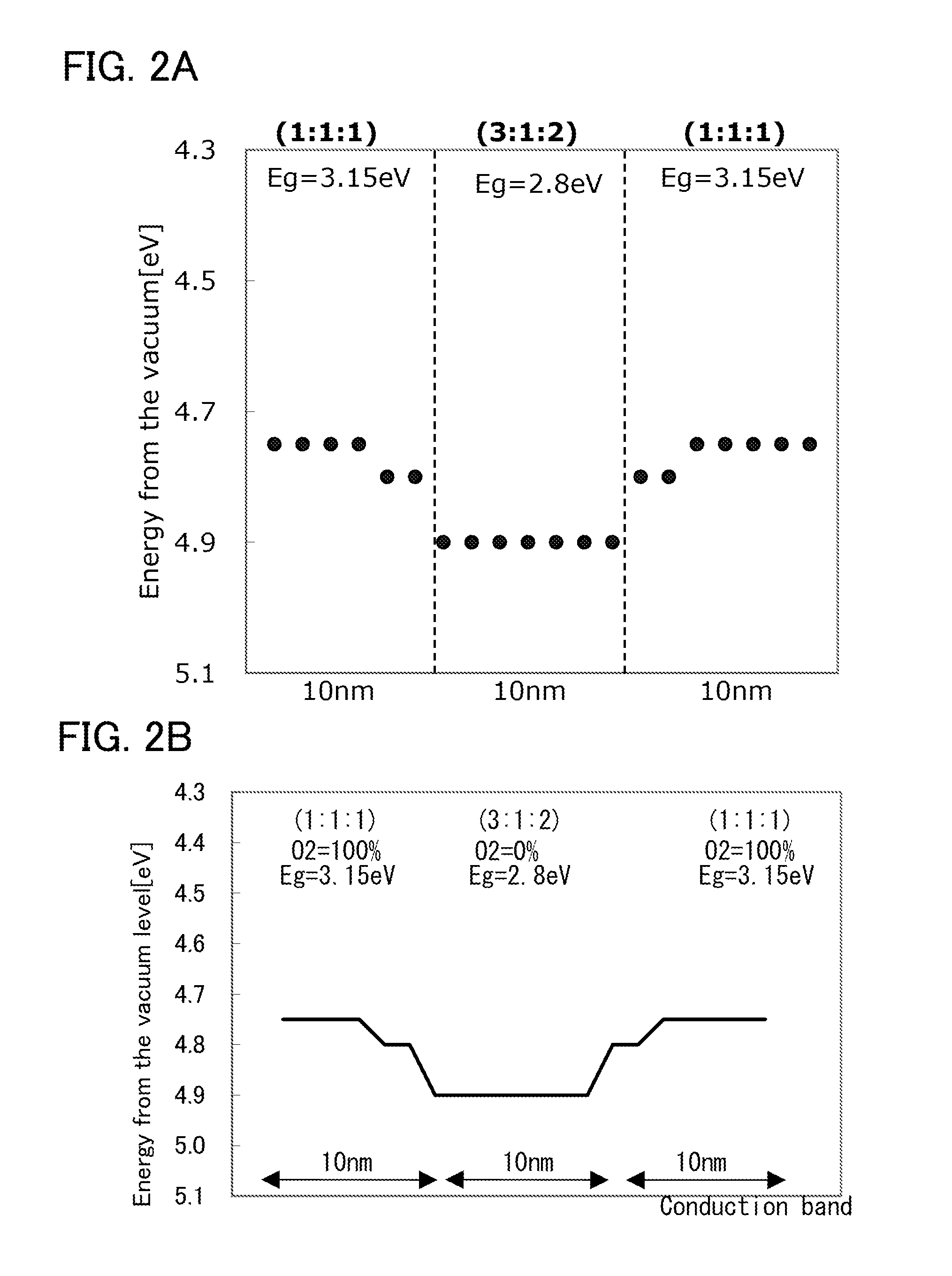
A highly reliable semiconductor device exhibiting stable electrical characteristics is provided. Further, a highly reliable semiconductor device is provided. Oxide semiconductor films are stacked so that the conduction band has a well-shaped structure. A second oxide semiconductor film having a crystalline structure is provided over the first oxide semiconductor film and a third oxide semiconductor film is provided over the second oxide semiconductor film. The bottom of a conduction band in the second oxide semiconductor film is deeper from a vacuum level than the bottom of a conduction band in the first oxide semiconductor film and the bottom of a conduction band in the third oxide semiconductor film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
High-isolation semi-groove slot antenna array
ActiveCN104134871AImprove isolationReduce volumeAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsConduction bandHigh isolation
The invention discloses a high-isolation semi-groove slot antenna array, and relates to a multiple-input-multiple-output antenna. The antenna array consists of three semi-groove slot antennas which are placed together and are pairwise orthogonal in radiating polarization directions, wherein each semi-groove slot antenna consists of a microstrip feeder line on a medium substrate, and a metal ground surface; a radiating semi-groove slot and a plurality of isolation slots are formed in each metal ground surface; the radiating semi-groove slots are rectangular; one end of each radiating semi-groove slot is short-circuit; the other end of each radiating semi-groove slot is open-circuit; the isolation slots around the radiating semi-groove slots are mutually parallel; long side directions of the radiating semi-groove slots are perpendicular to long side directions of the isolation slots; the resonant frequency of the isolation slot is lower than the working frequency of the antennas; one end of each microstrip feeder line is an input-output port of each antenna; and metal short-circuit pins are arranged at the tail ends of microstrip feeder line conduction bands at the other ends of the microstrip feeder lines, and connect the conduction bands and the metal ground surfaces on the edges of the radiating semi-groove slots. The antenna array can effectively reduce adverse effects of the metal ground surfaces on shielding and isolation of normal radiation of the antennas.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN BROADBAND TECH +1
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
Nanotube transistor device
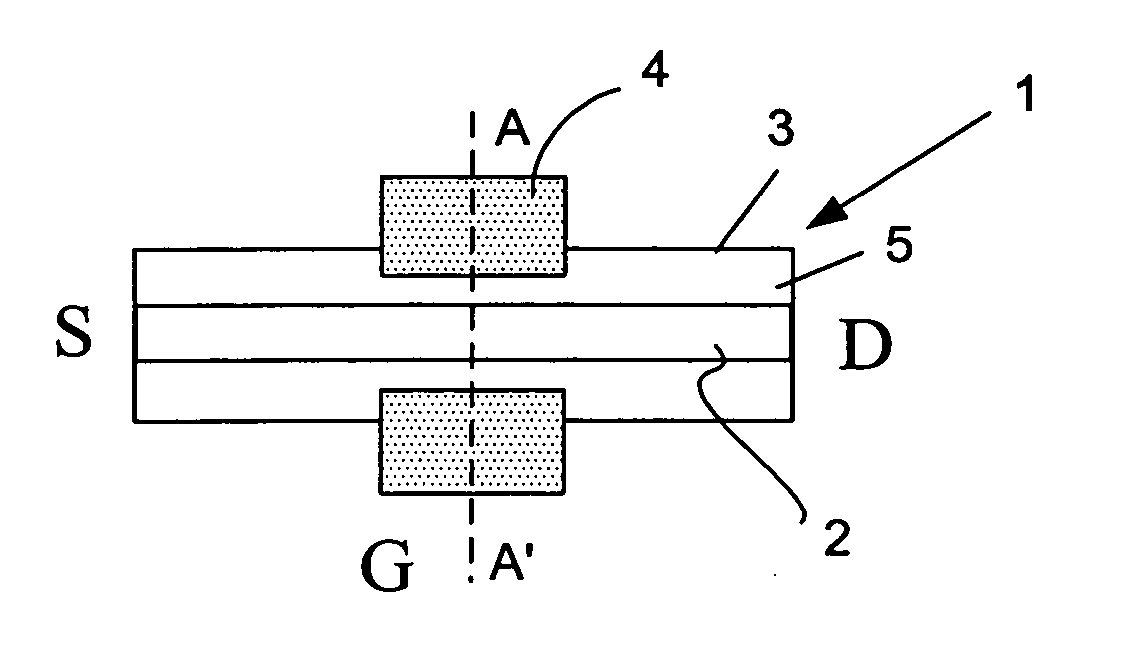
A transistor device comprising source and drain regions (S, D), a nanotube structure (2, 3) providing a path for electrical charge carriers between the source and drain regions, and a gate region (4). The nanotube structure has its conduction band structure locally modified in the gate region, e.g. by doping, for controlling the passage of the charge carriers in the path. The device can be used as a flash memory or as a memory element in a DRAM.
Owner:KIM BYONG MAN +2
Field effect transistor and method for fabricating the same
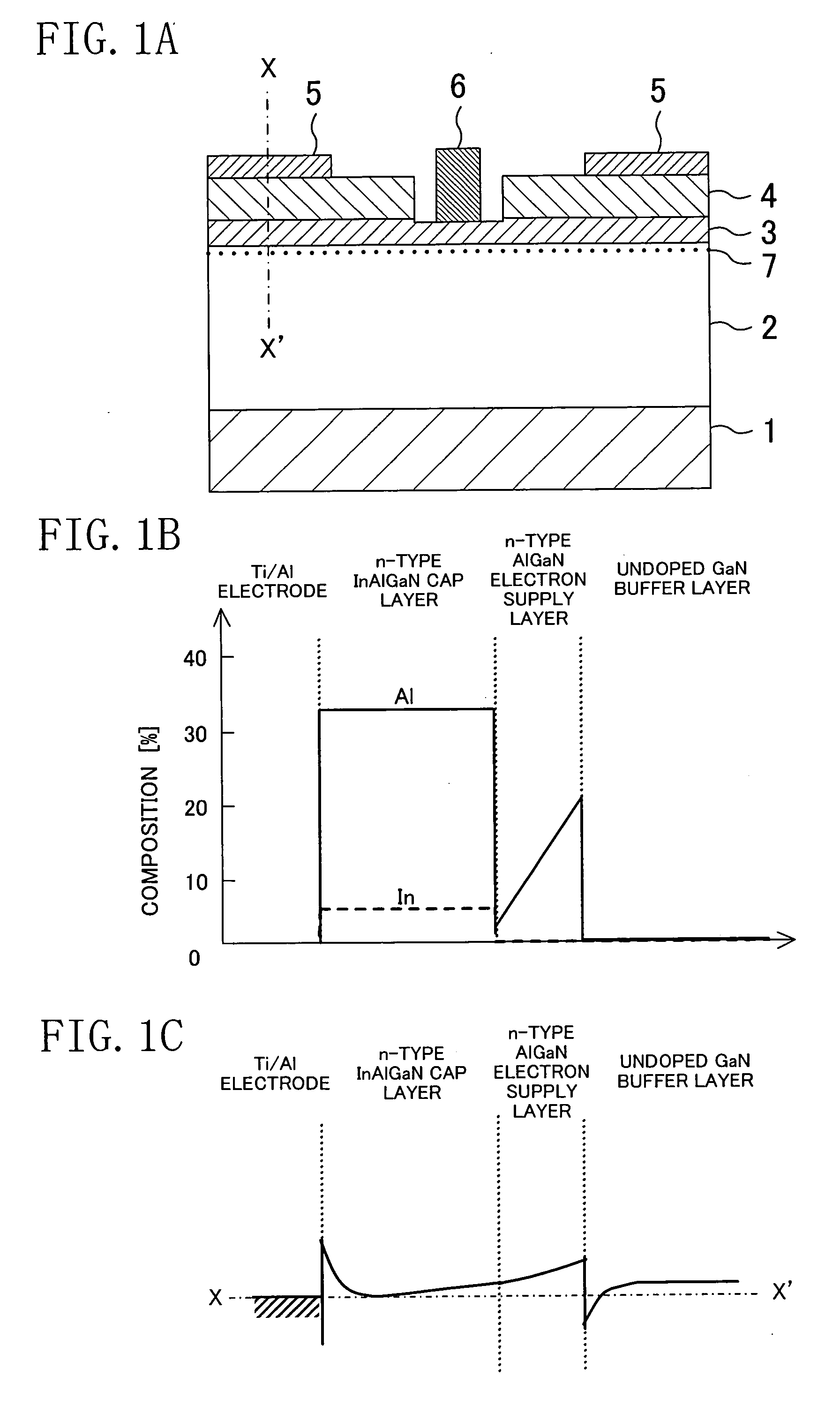
ActiveUS20060180831A1High crystallinityIncrease parasitic resistanceSemiconductor devicesConduction bandField-effect transistor
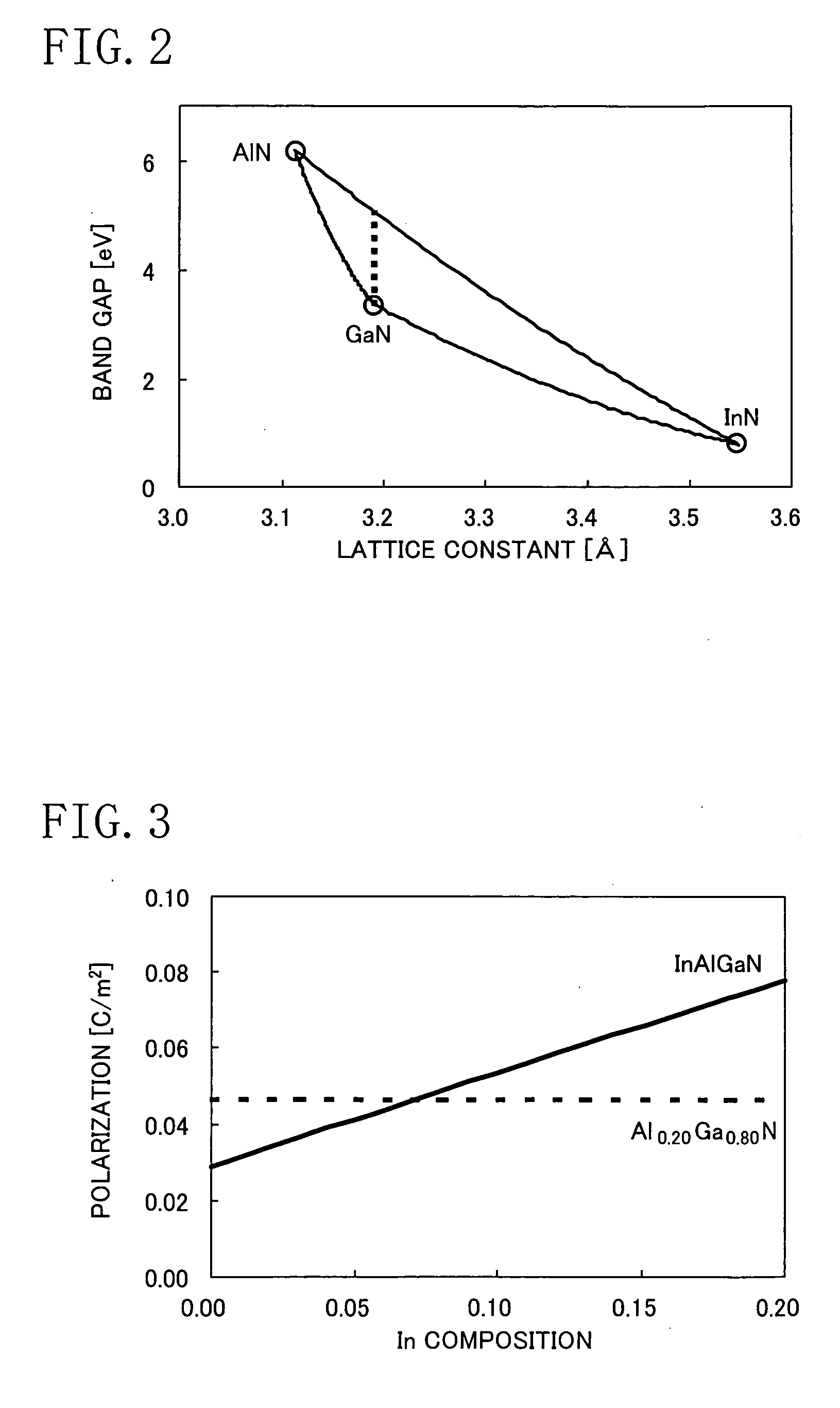
A field effect transistor includes a nitride semiconductor layer; an InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer (wherein 0<x<1, 0<y<1 and 0<x+y<1) formed on the nitride semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed on and in contact with the InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer. The lower ends of the conduction bands of the nitride semiconductor layer and the InxAlyGa1-x-yN layer are substantially continuous on the interface therebetween.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
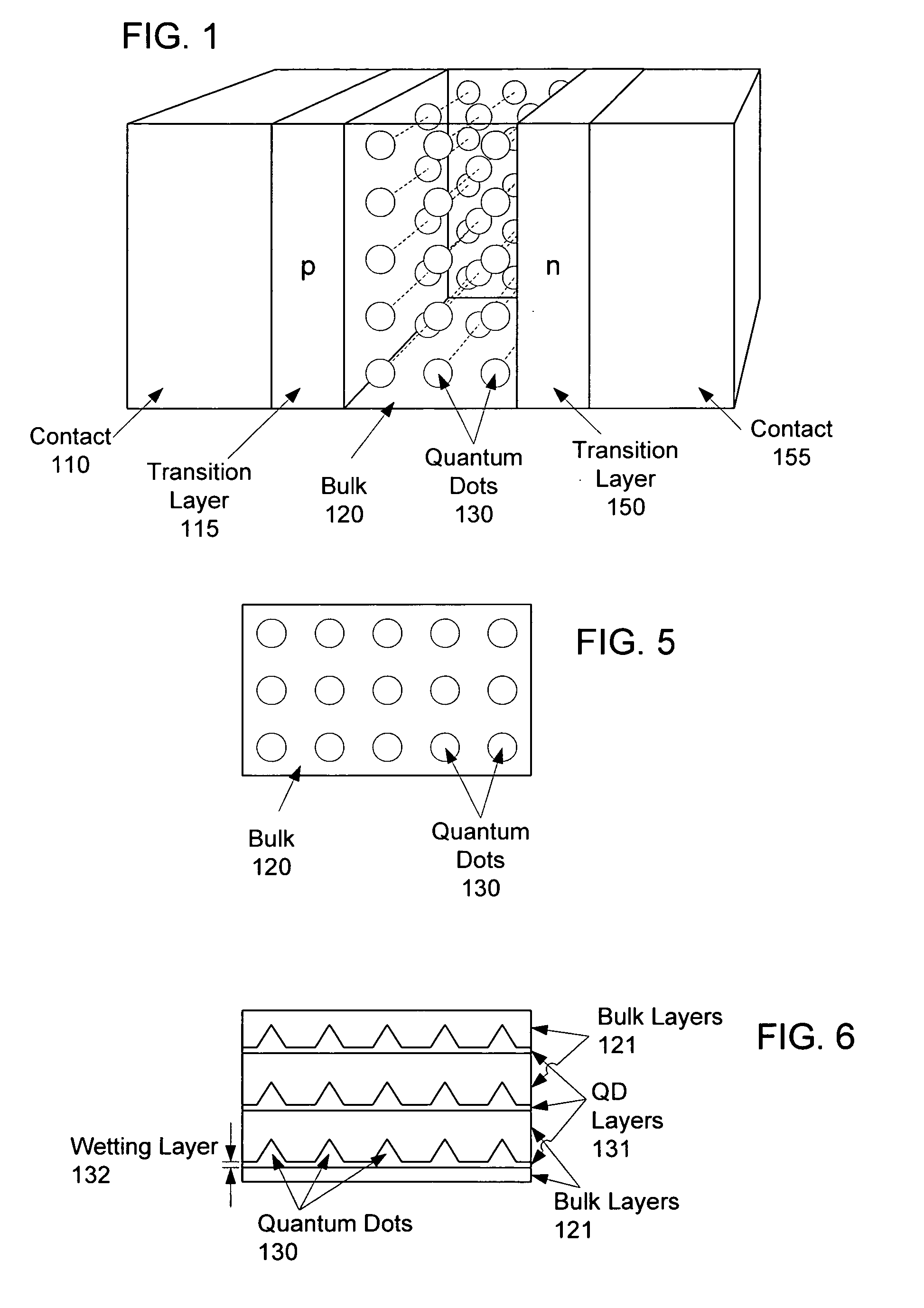
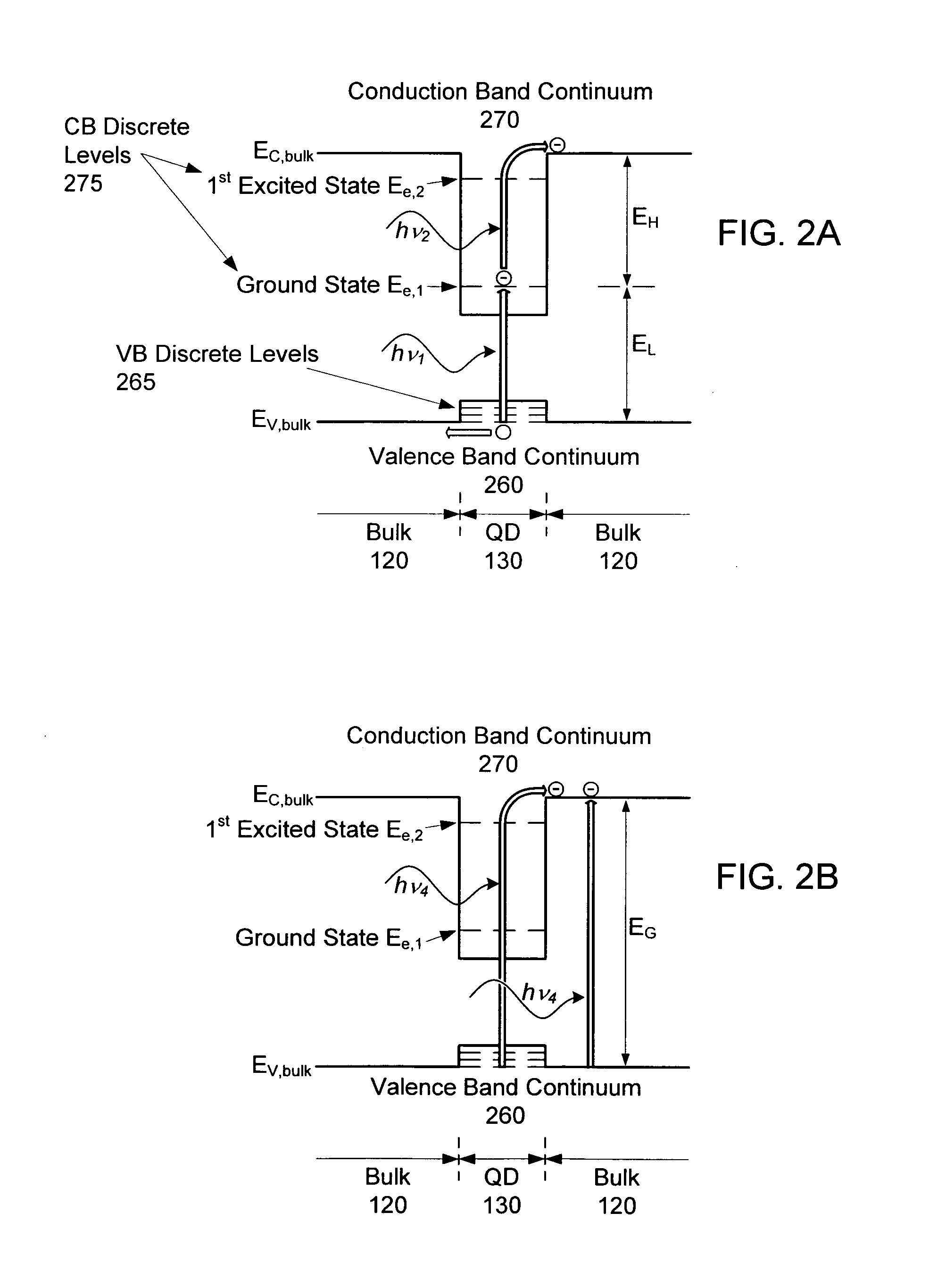
Intermediate-band photosensitive device with quantum dots having tunneling barrier embedded in inorganic matrix
A plurality of quantum dots comprise a first inorganic material, and each quantum dot is coated with a second inorganic material. The coated quantum dots being are in a matrix of a third inorganic material. At least the first and third materials are photoconductive semiconductors. The second material is arranged as a tunneling barrier to require a charge carrier (an electron or a hole) at a base of the tunneling barrier in the third material to perform quantum mechanical tunneling to reach the first material within a respective quantum dot. A first quantum state in each quantum dot is between a conduction band edge and a valence band edge of the third material in which the coated quantum dots are embedded. Wave functions of the first quantum state of the plurality of quantum dots may overlap to form an intermediate band.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
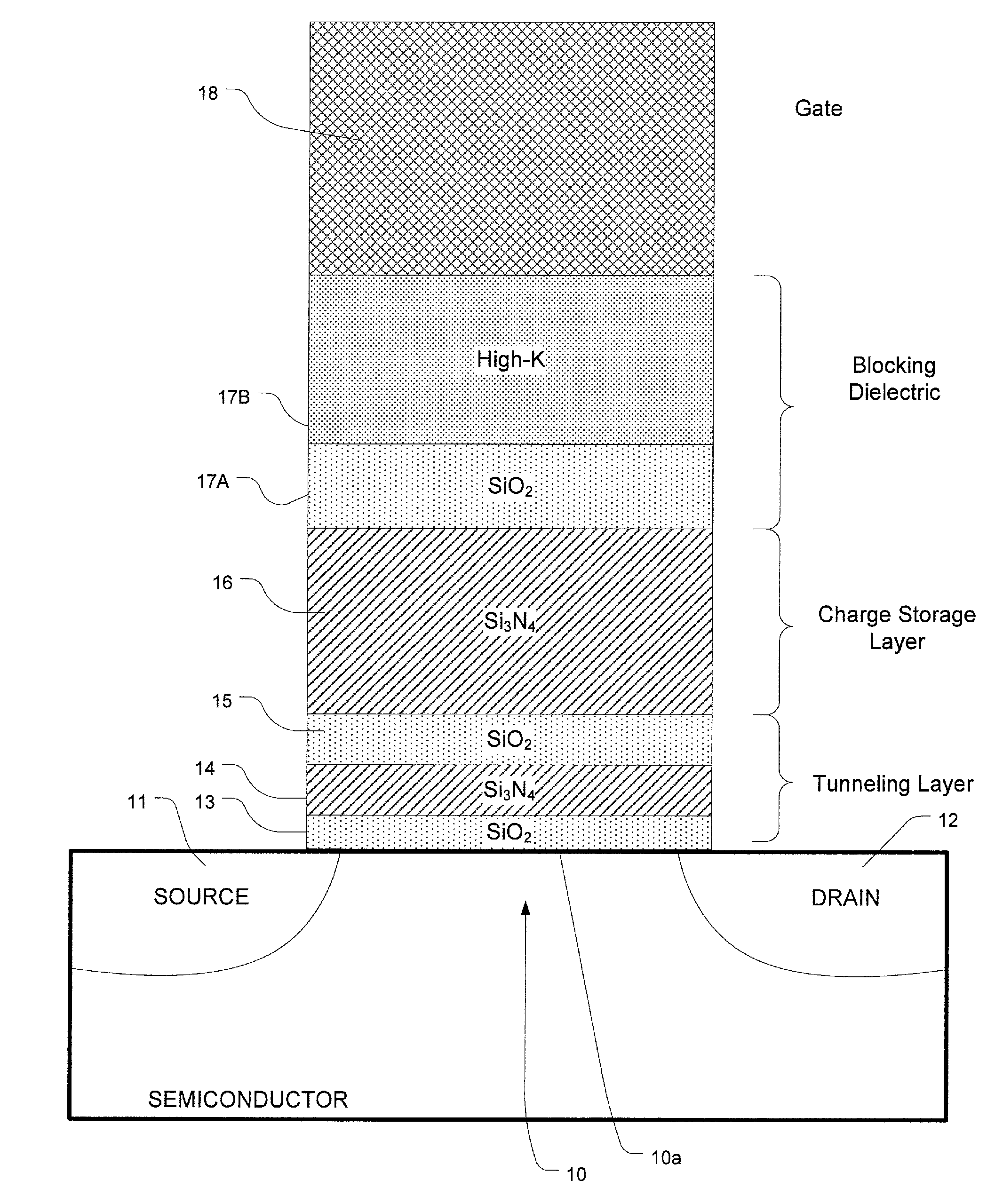
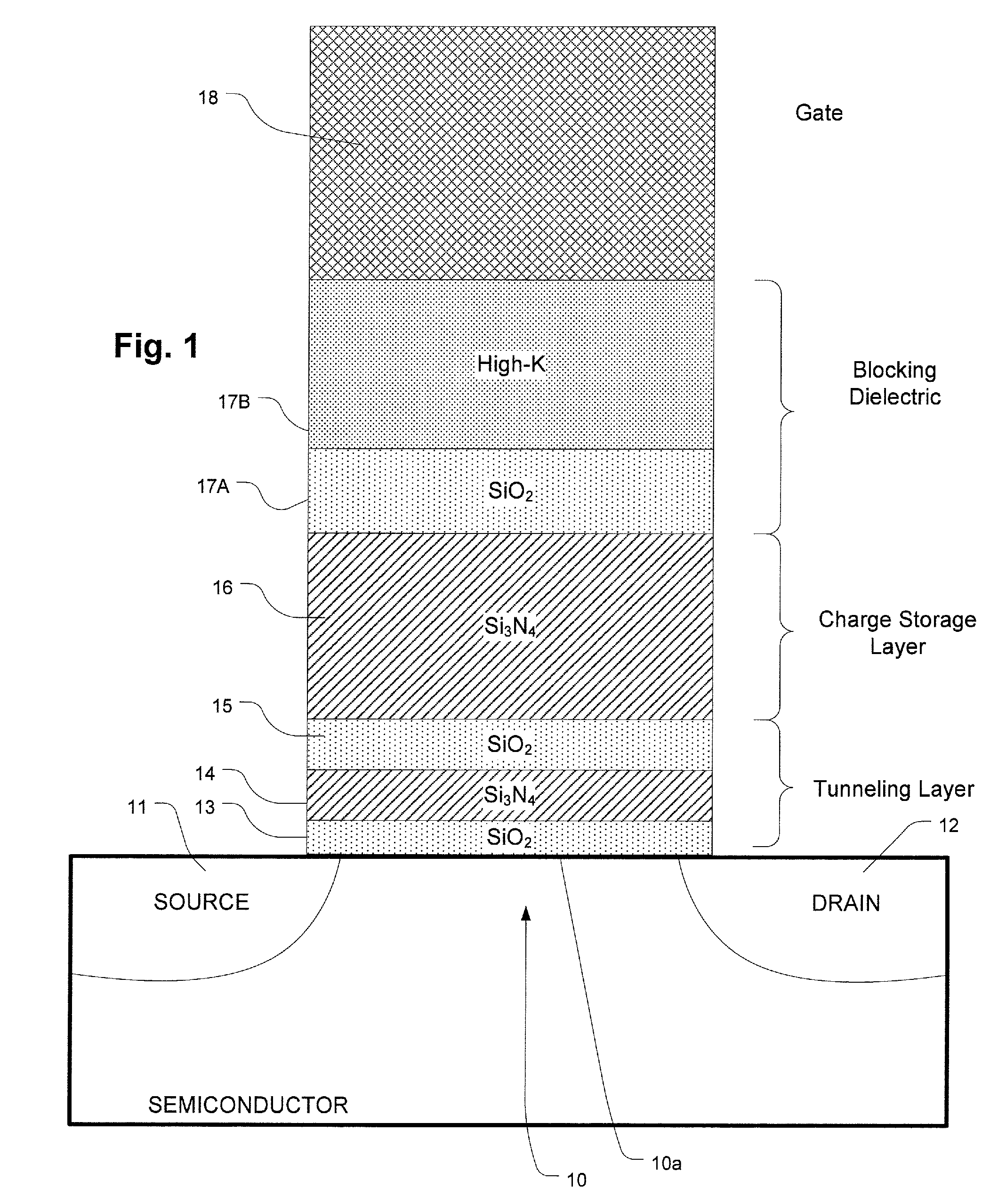
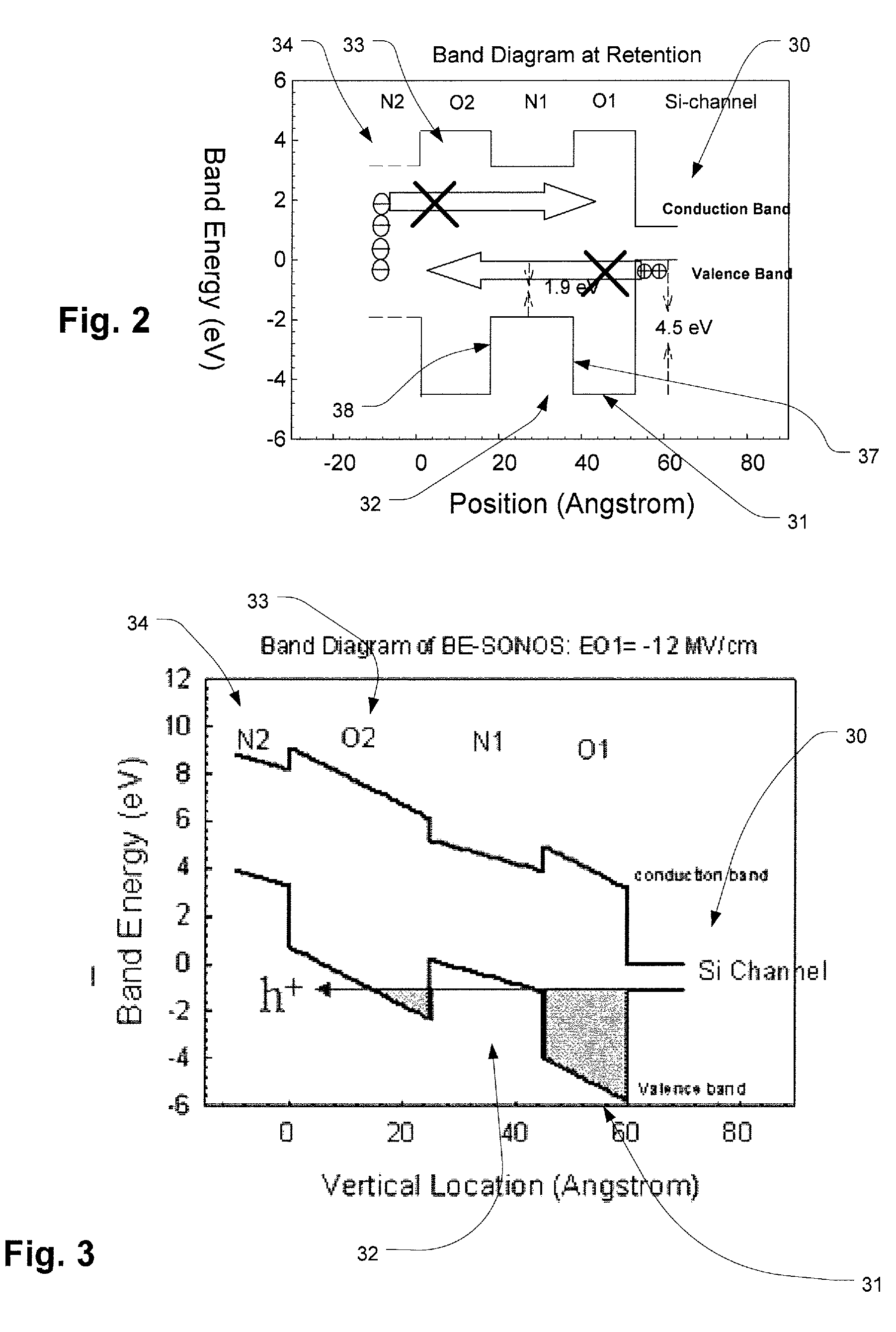
High-κ capped blocking dielectric bandgap engineered SONOS and MONOS
ActiveUS7816727B2Excellent characteristicsImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectricTrapping
A blocking dielectric engineered, charge trapping memory cell includes a charge trapping element that is separated from a gate by a blocking dielectric including a buffer layer in contact with the charge trapping element, such as silicon dioxide which can be made with high-quality, and a second capping layer in contact with said one of the gate and the channel. The capping layer has a dielectric constant that is higher than that of the first layer, and preferably includes a high-κ material. The second layer also has a conduction band offset that is relatively high. A bandgap engineered tunneling layer between the channel and the charge trapping element is provided which, in combination with the multilayer blocking dielectric described herein, provides for high-speed erase operations by hole tunneling. In an alternative, a single layer tunneling layer is used.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method
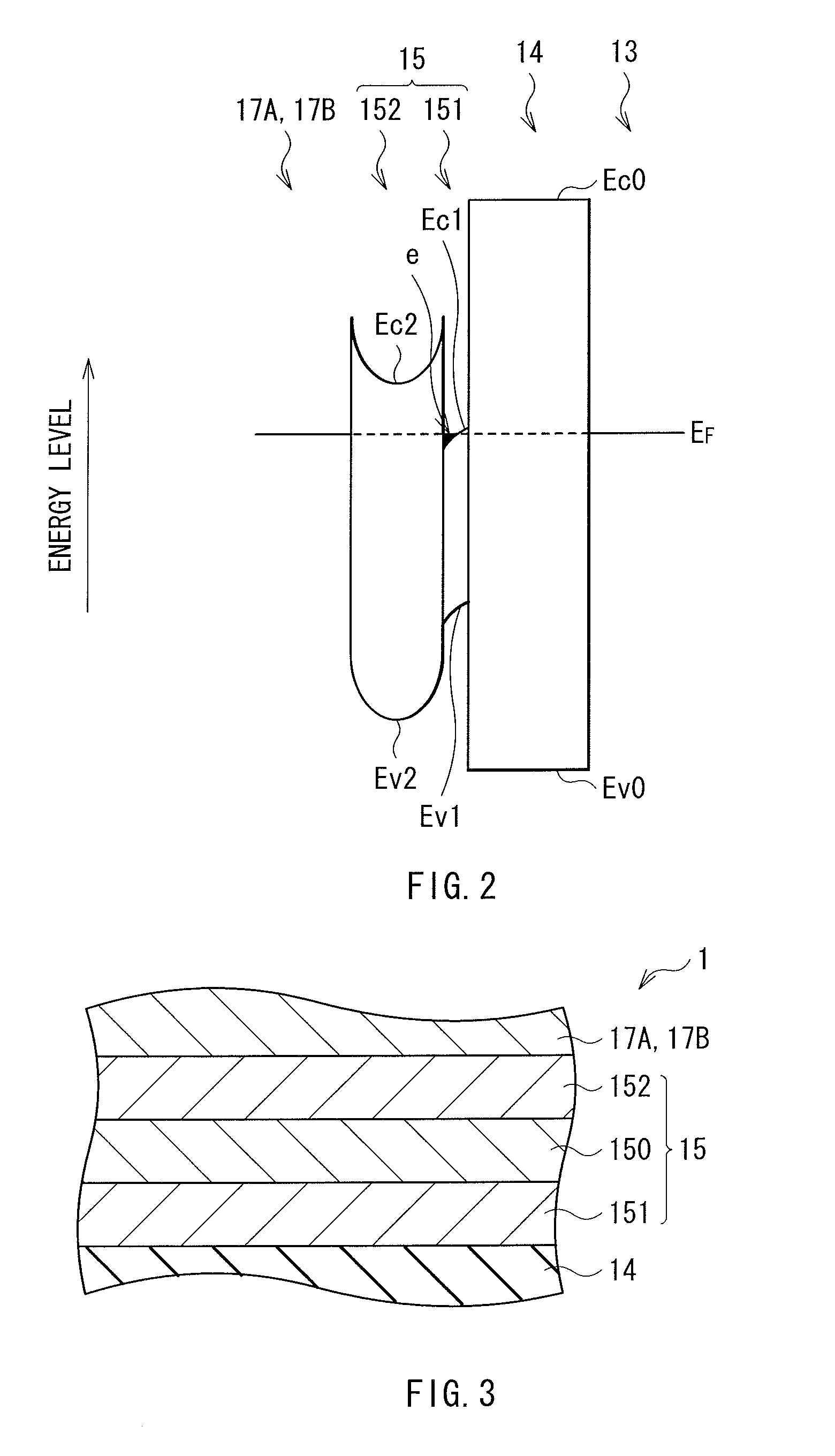
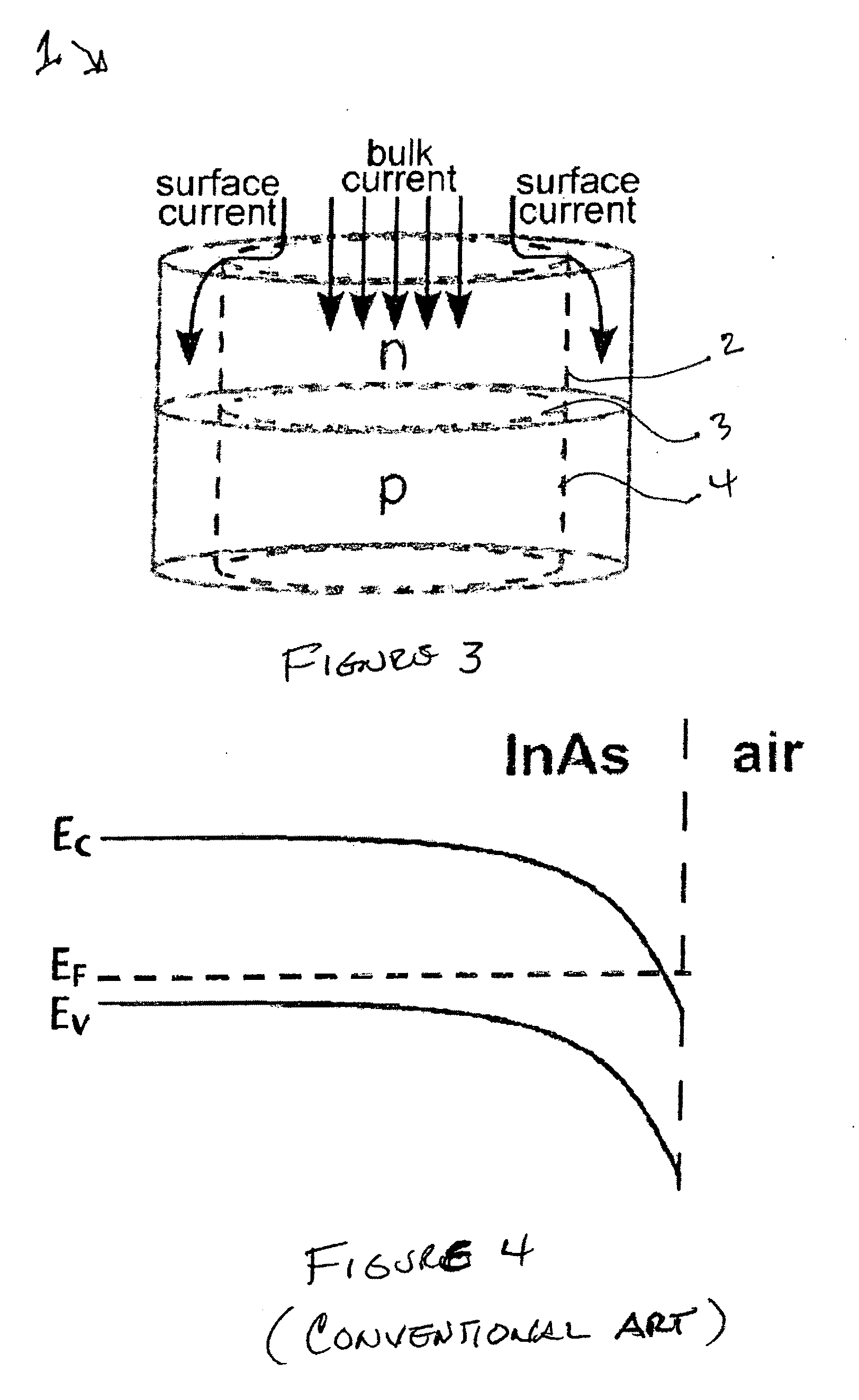
ActiveUS20100230720A1Eliminate surface leakage currentReduce surface currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsValence bandConduction band
The present invention is directed to a semiconductor device that includes at least one p-n junction including a p-type material, an n-type material, and a depletion region. The at least one p-n junction is configured to generate bulk photocurrent in response to incident light. The at least one p-n junction is characterized by a conduction band energy level, a valence band energy level and a surface Fermi energy level. The surface Fermi energy level is pinned either near or above the conduction band energy level or near or below the valence band energy level. A unipolar barrier structure is disposed in a predetermined region within the at least one p-n junction. The unipolar barrier is configured to raise the conduction band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or above the conduction band energy level or lower the valence band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or below the valence band energy level such that the unipolar barrier is configured to propagate the bulk photocurrent and substantially block surface leakage current. The at least one p-n junction and the unipolar barrier are integrally formed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com