Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Optical absorption coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
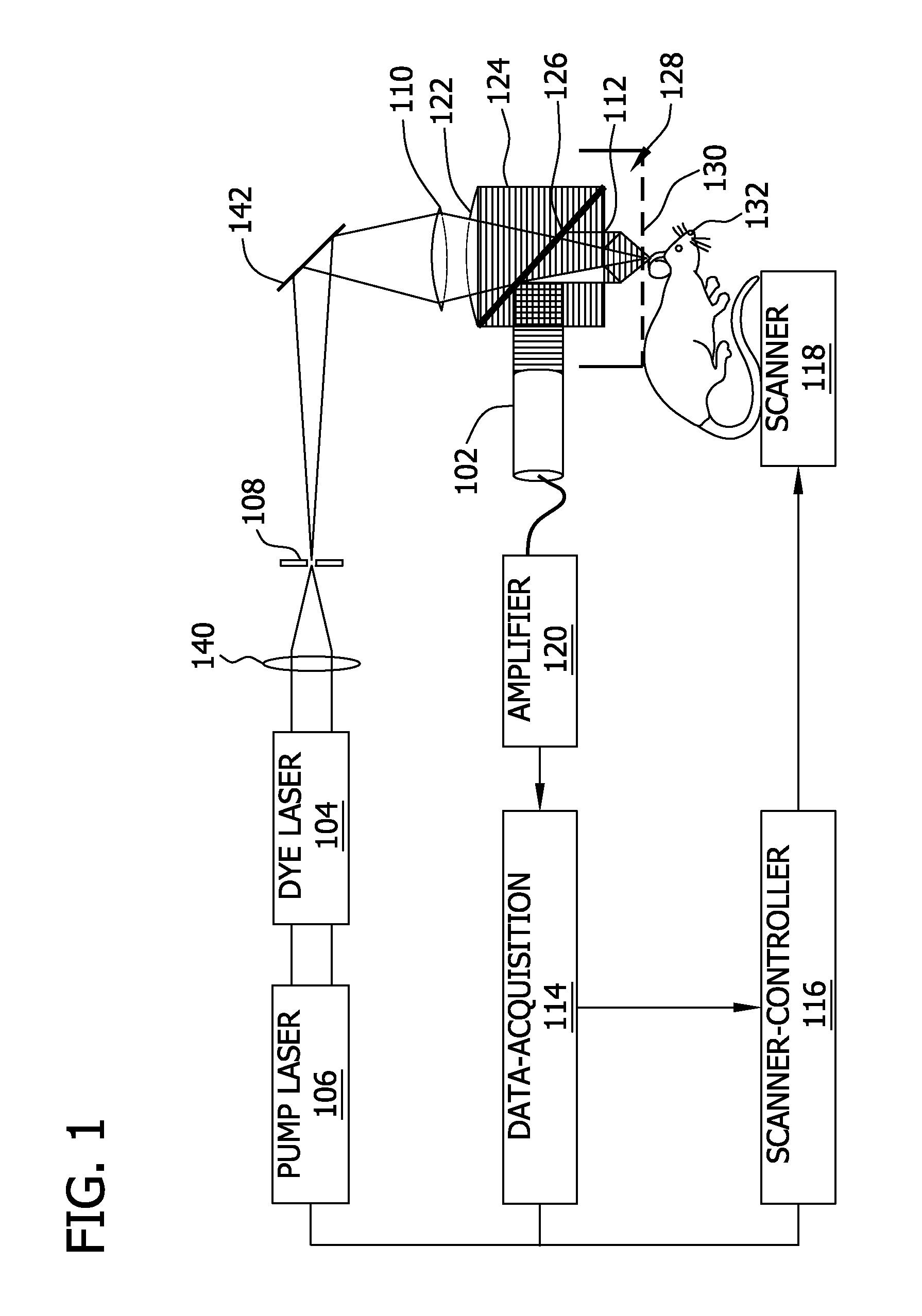
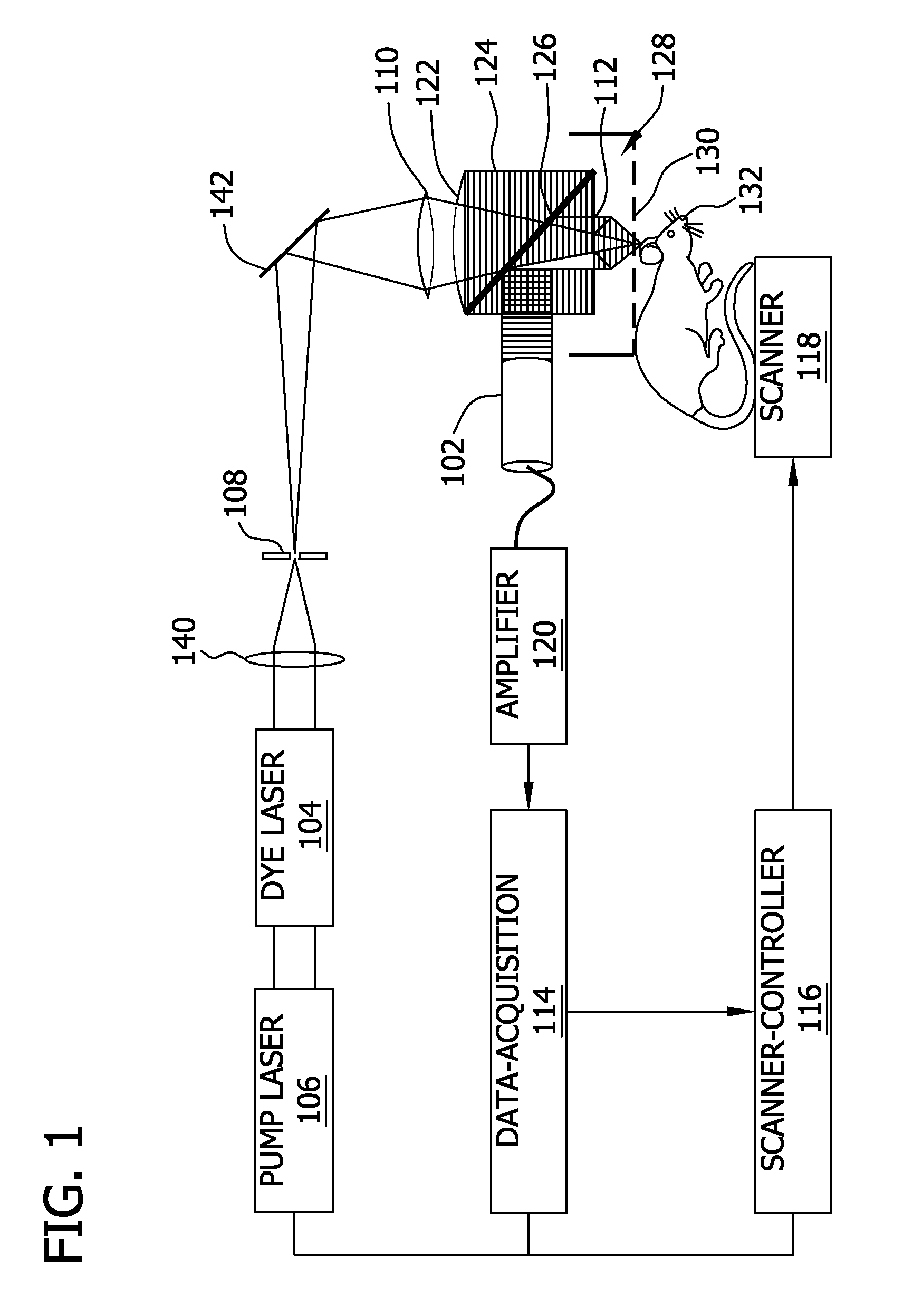
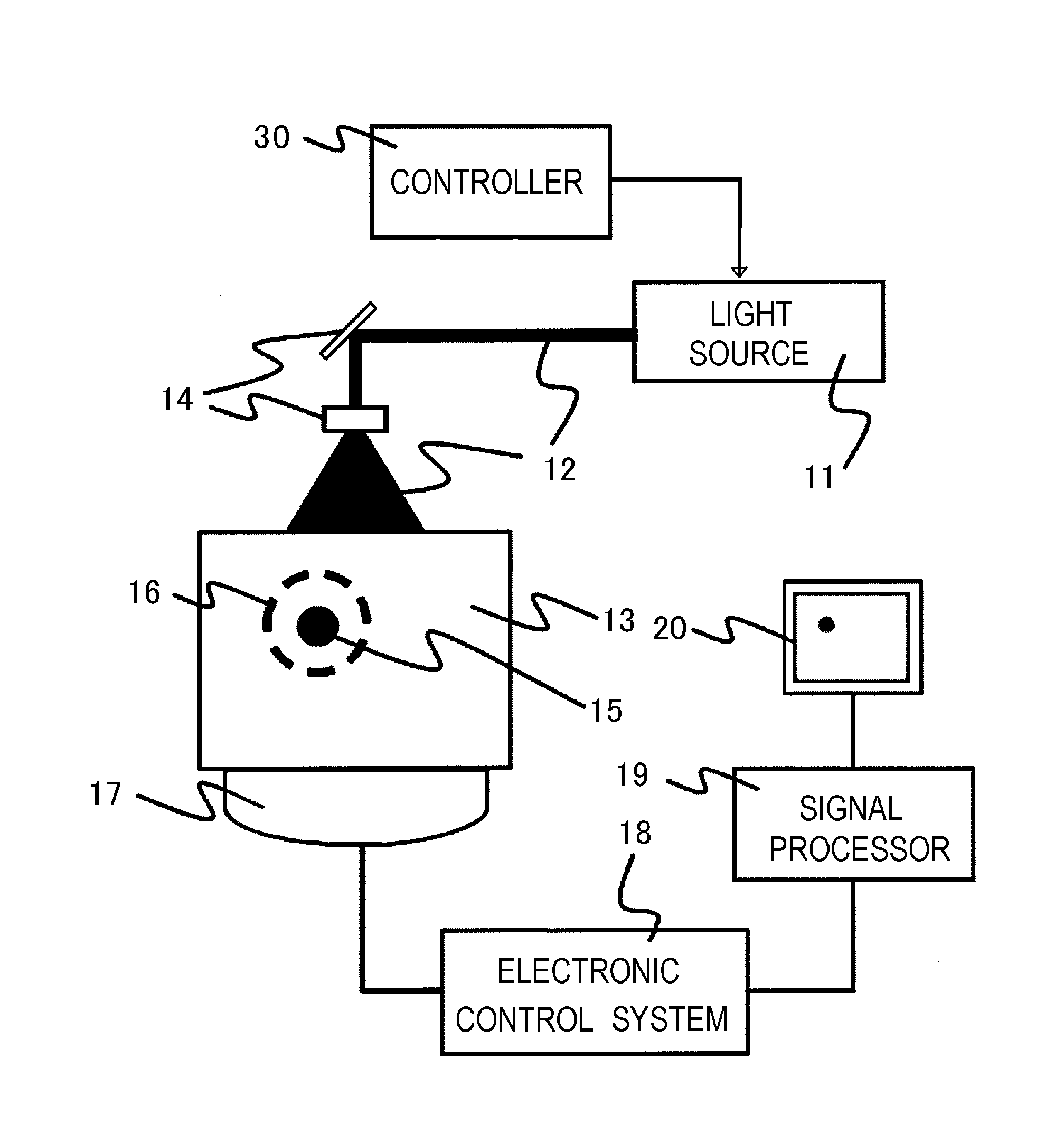
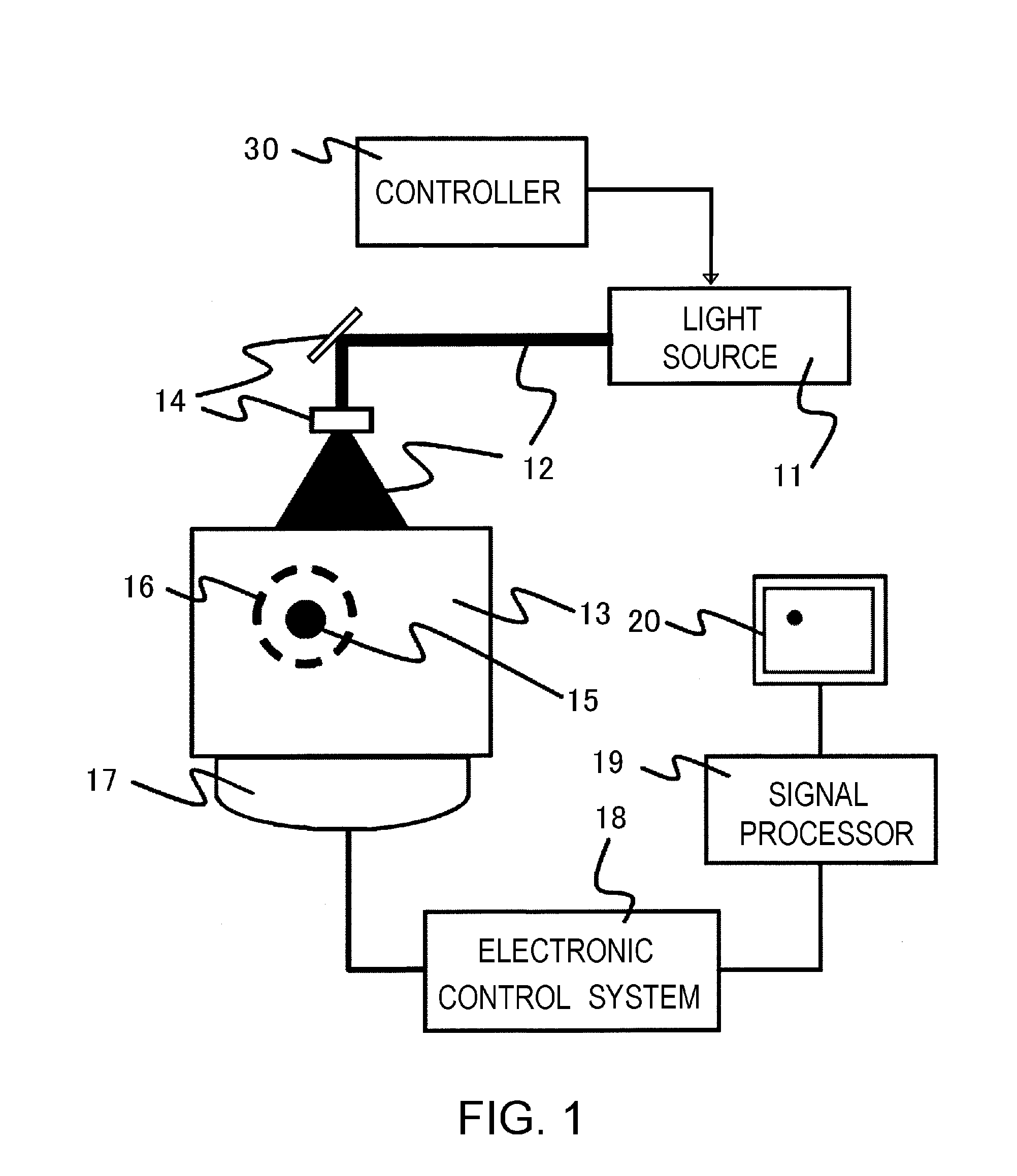
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
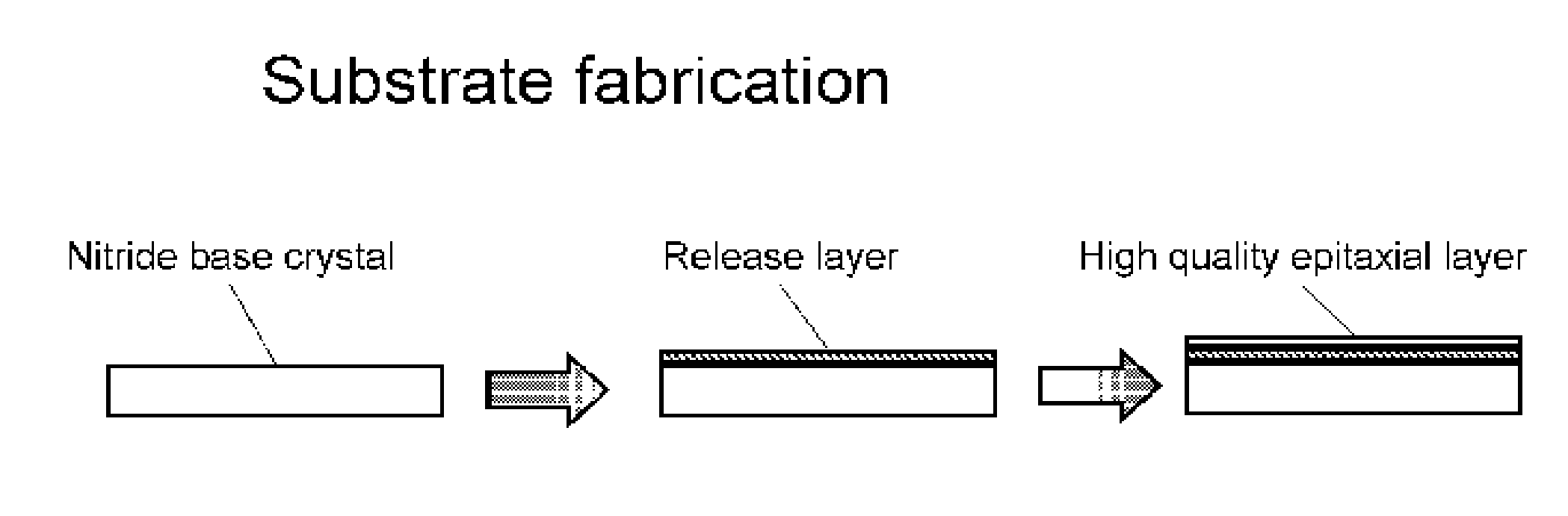
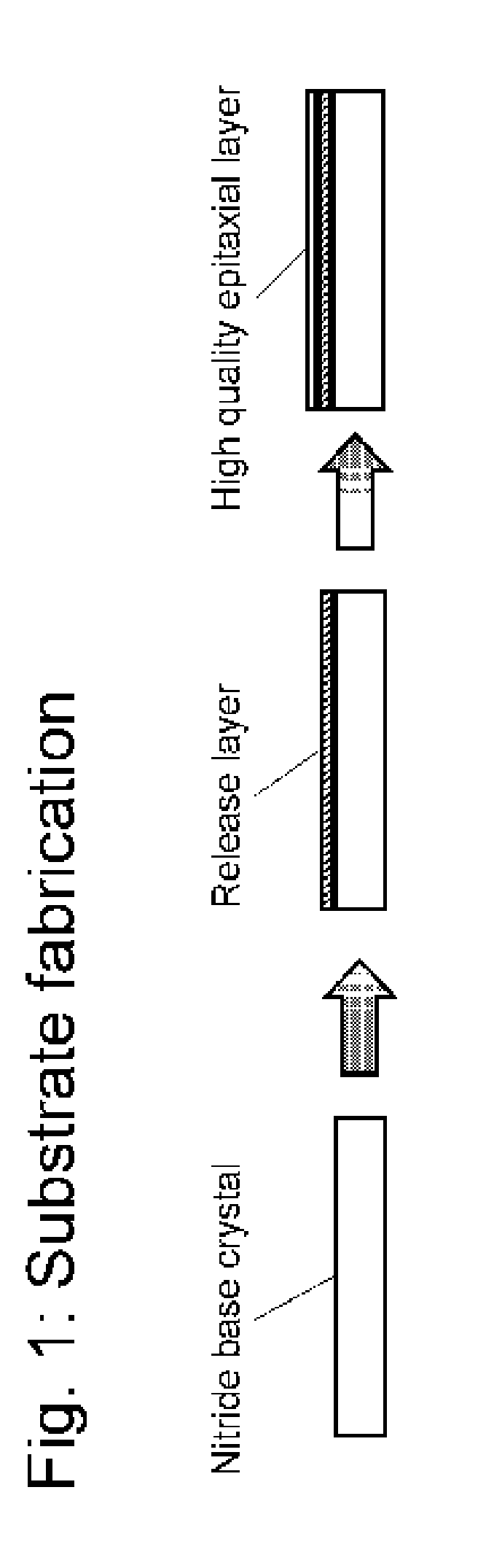
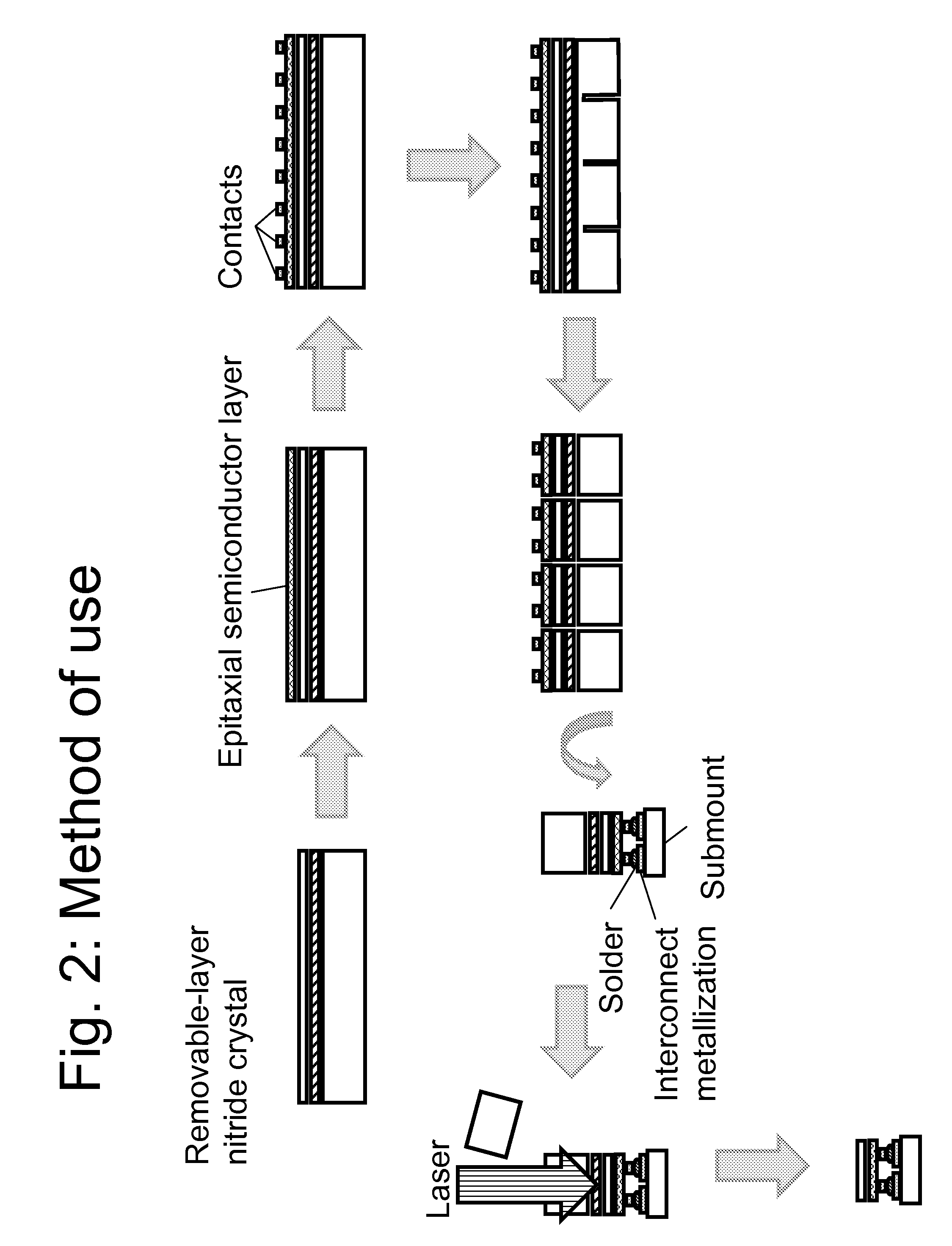
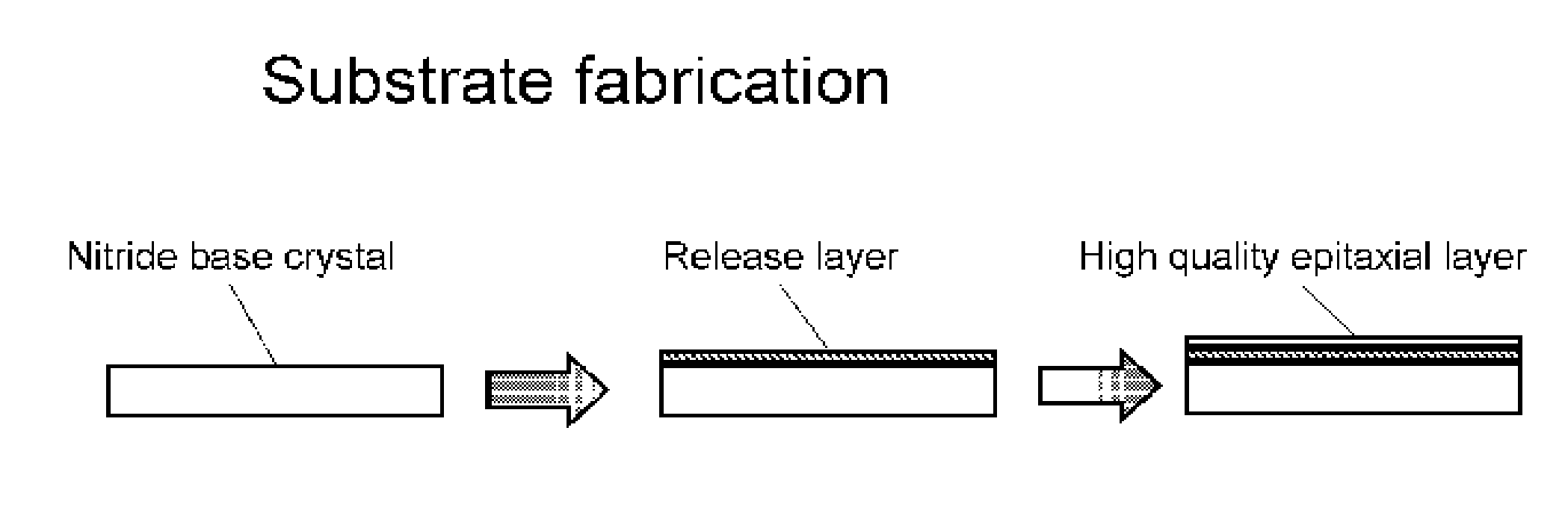
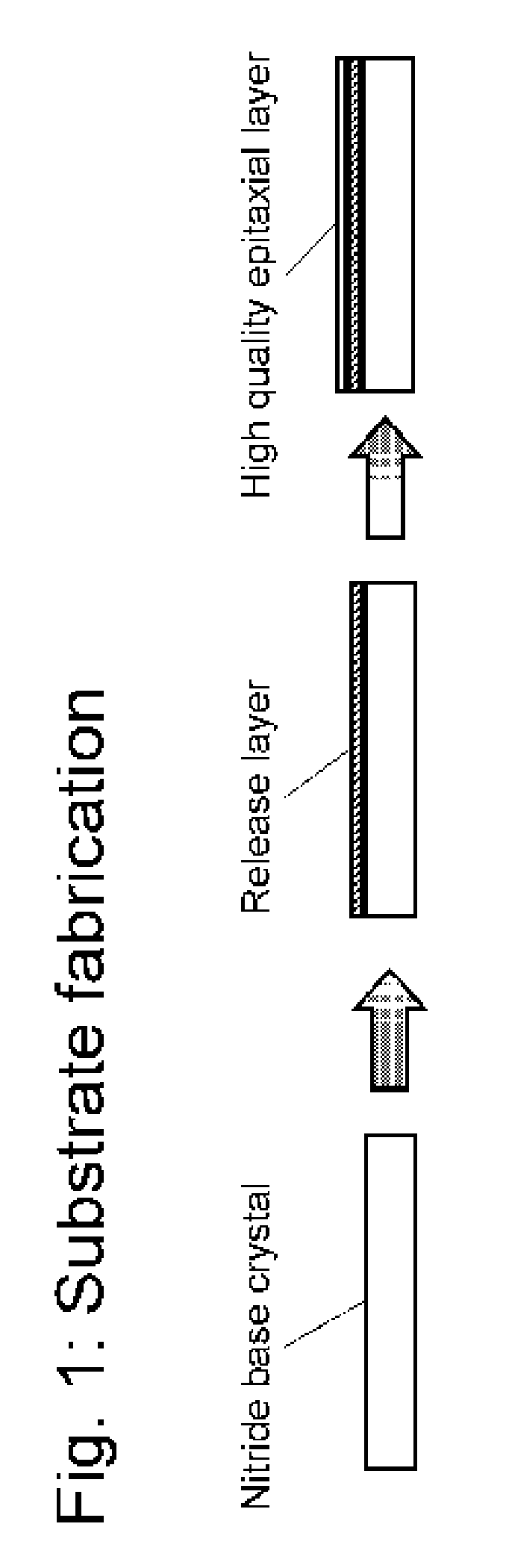
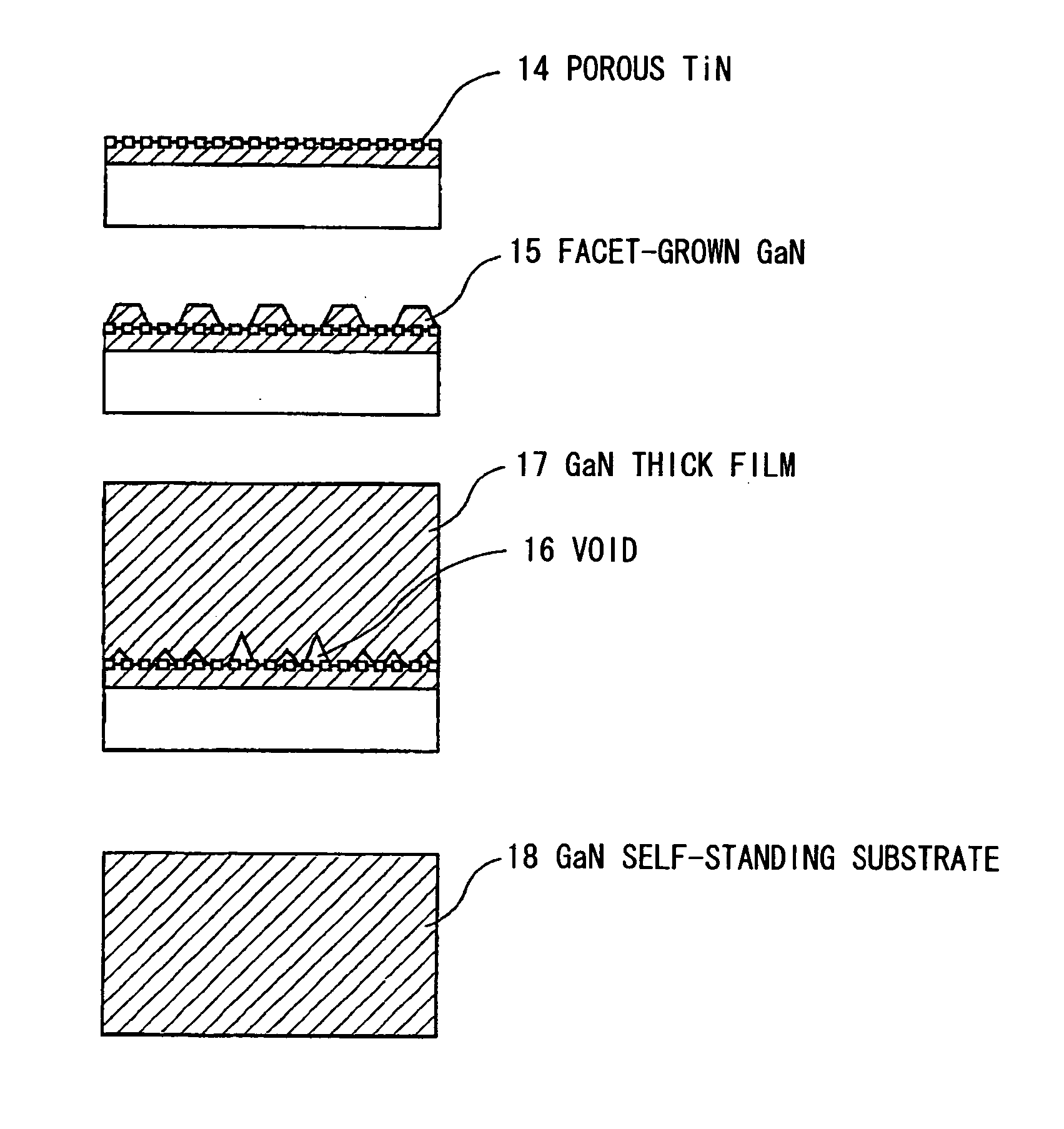
Nitride crystal with removable surface layer and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS8148801B2Quality improvementSimple and cost-effectivePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
Owner:SLT TECH
Nitride crystal with removable surface layer and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20100219505A1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotodetectorSolar cell
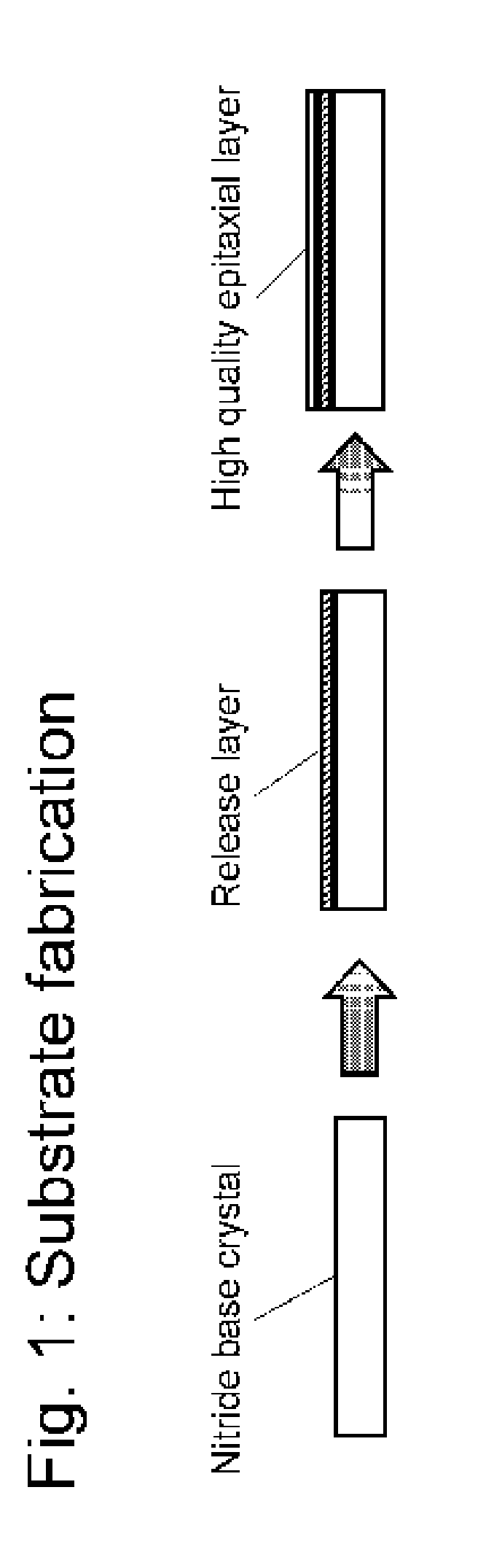
A nitride crystal or wafer with a removable surface layer comprises a high quality nitride base crystal, a release layer, and a high quality epitaxial layer. The release layer has a large optical absorption coefficient at wavelengths where the base crystal is substantially transparent and may be etched under conditions where the nitride base crystal and the high quality epitaxial layer are not. The high quality epitaxial layer may be removed from the nitride base crystal by laser liftoff or by chemical etching after deposition of at least one epitaxial device layer. The nitride crystal with a removable surface layer is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SLT TECH
Optically reliable nanoparticle based nanocomposite HRI encapsulant, photonic waveguiding material and high electric breakdown field strength insulator/encapsulant
InactiveUS20070221939A1Good physical propertiesImprove photodegradation resistanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor devicesEpoxyLight equipment
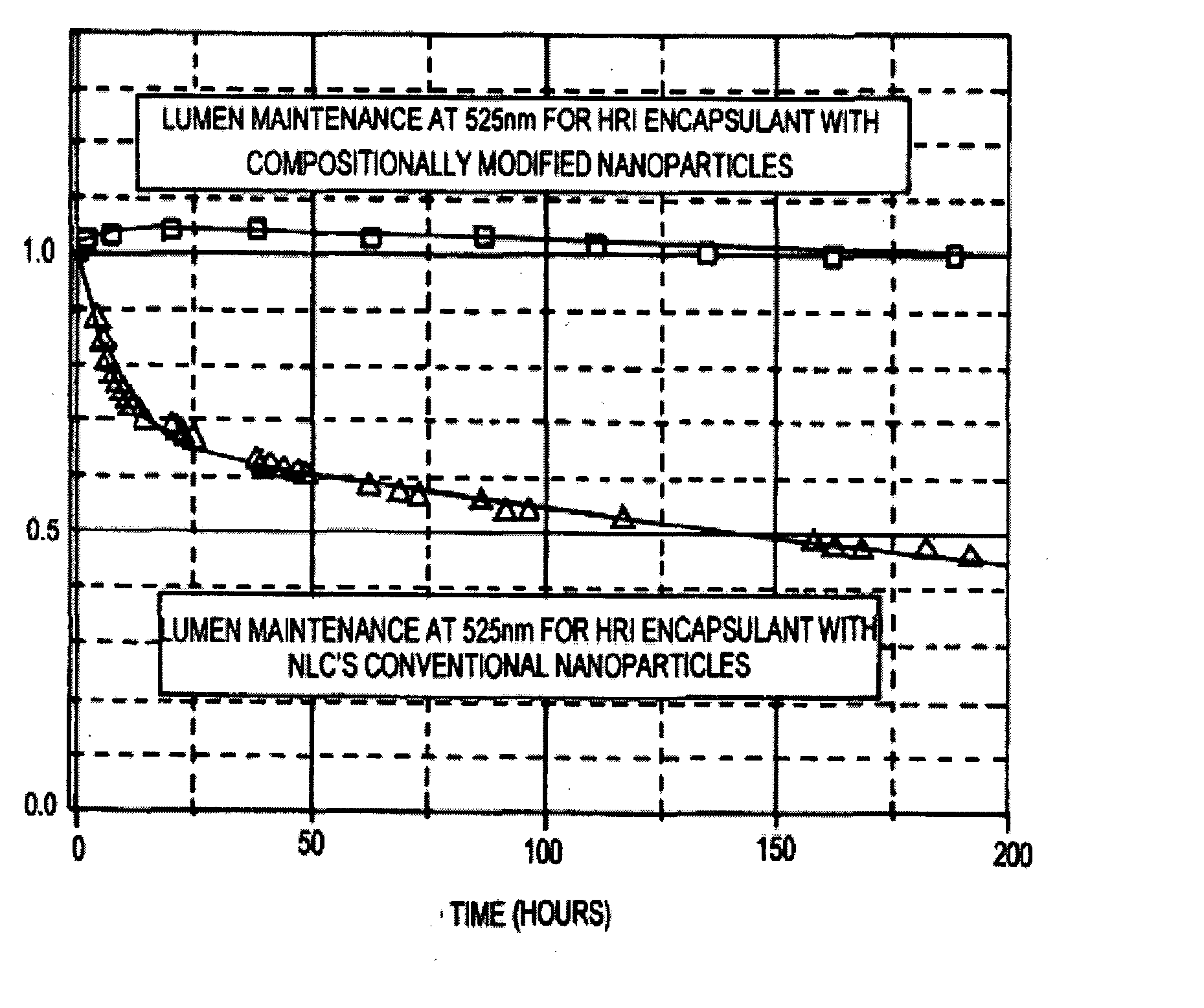
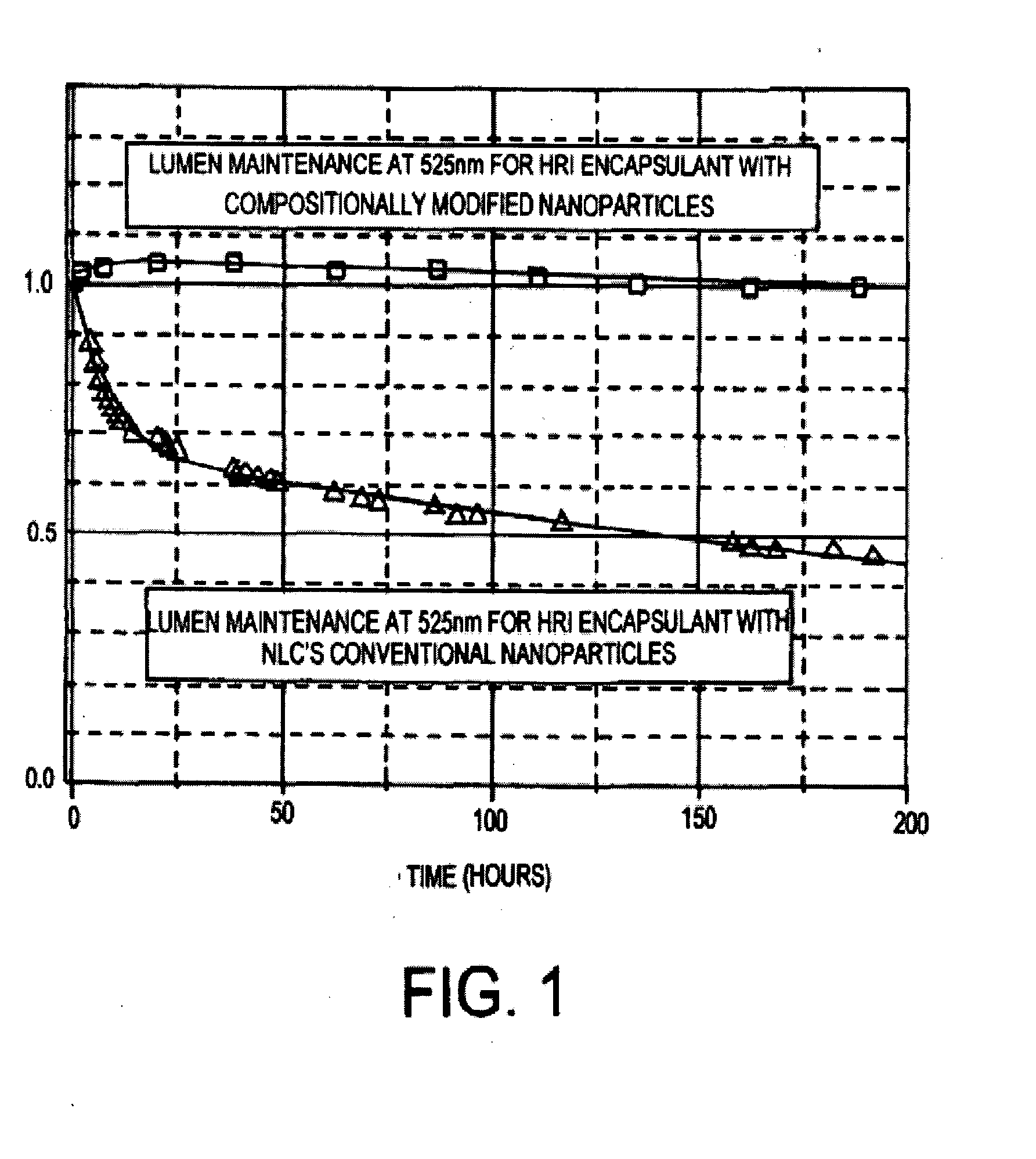
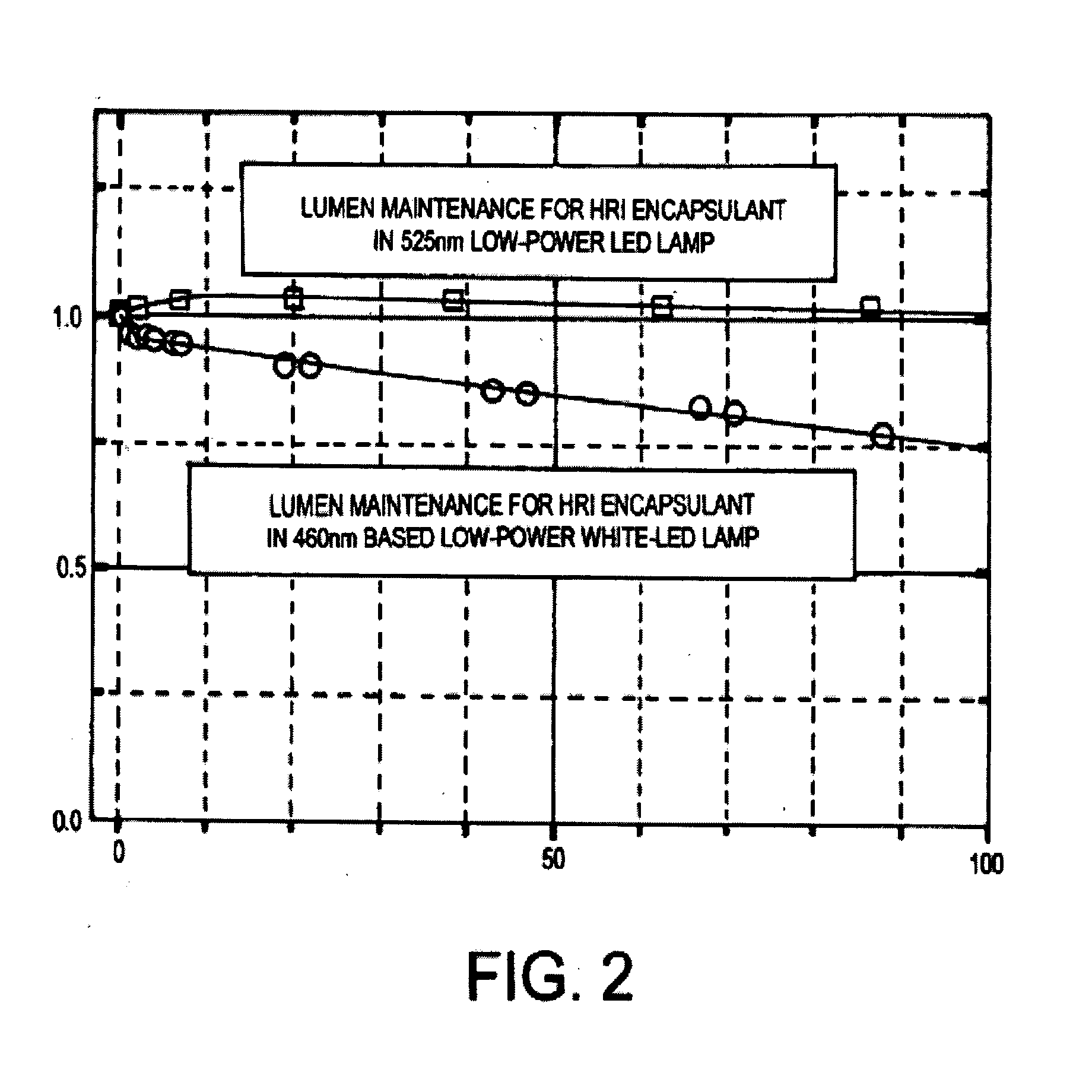
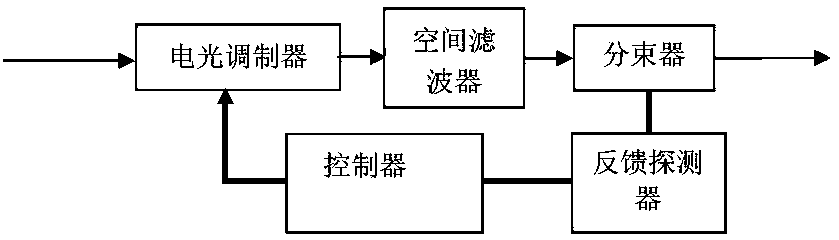
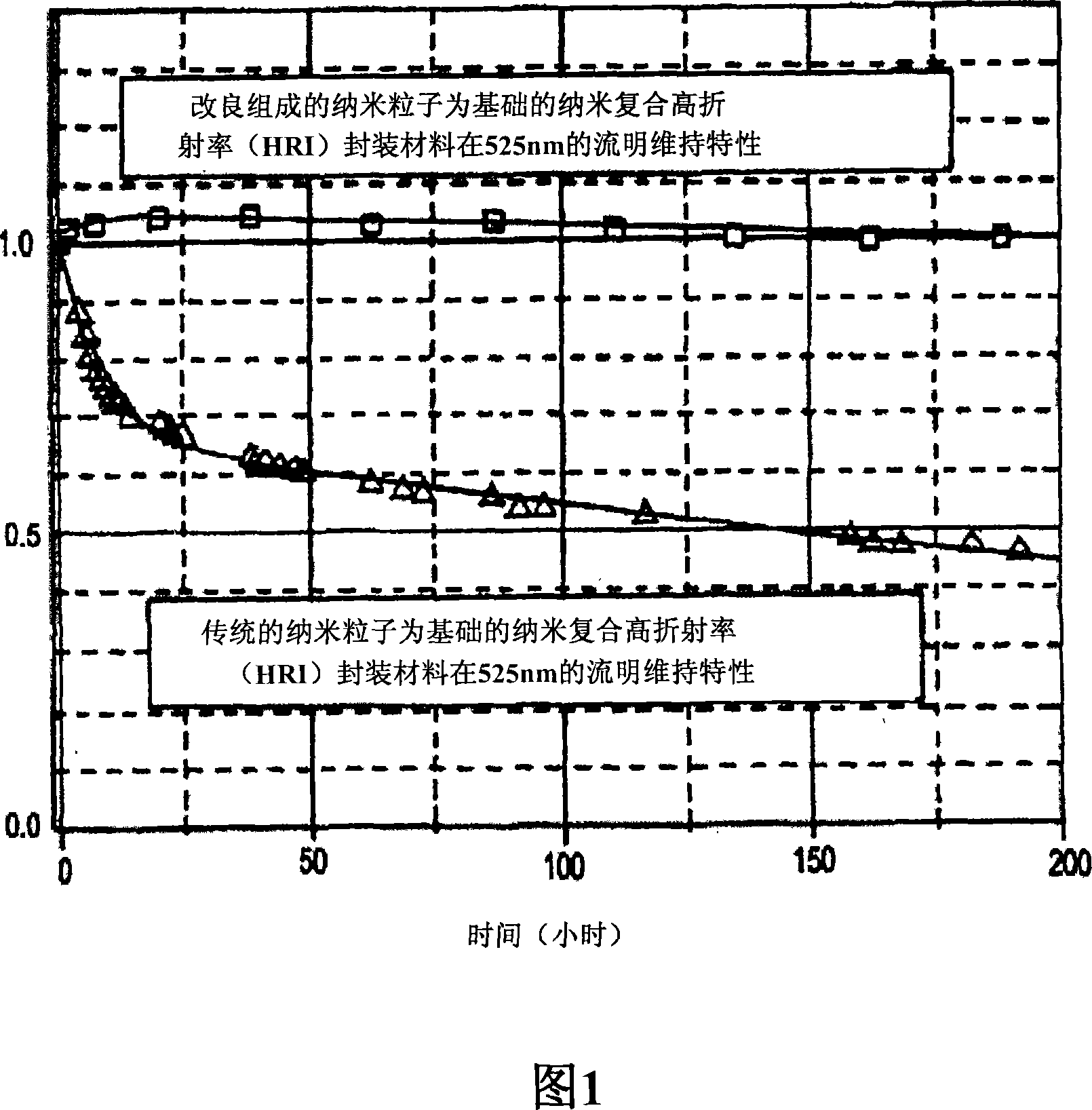
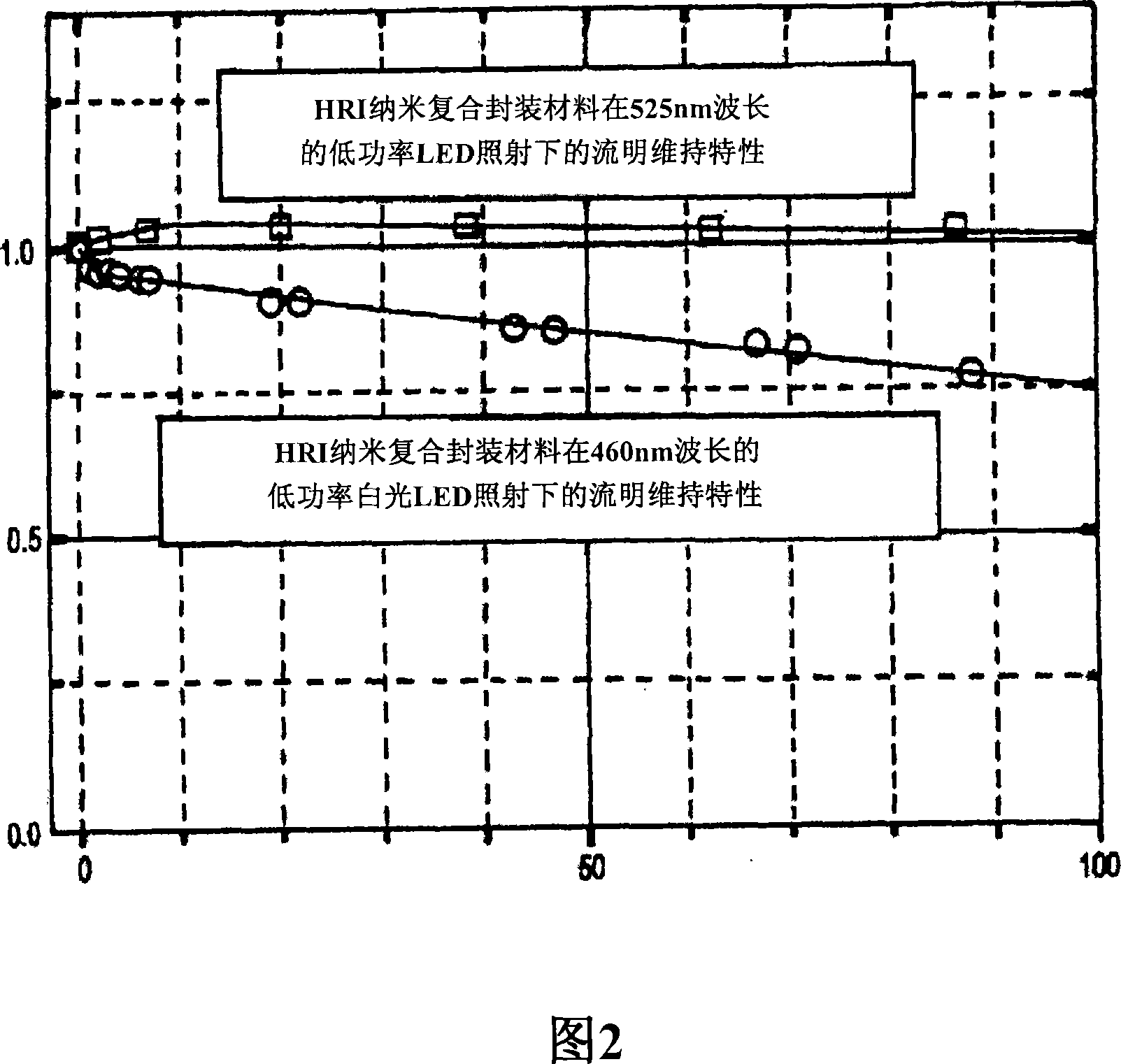
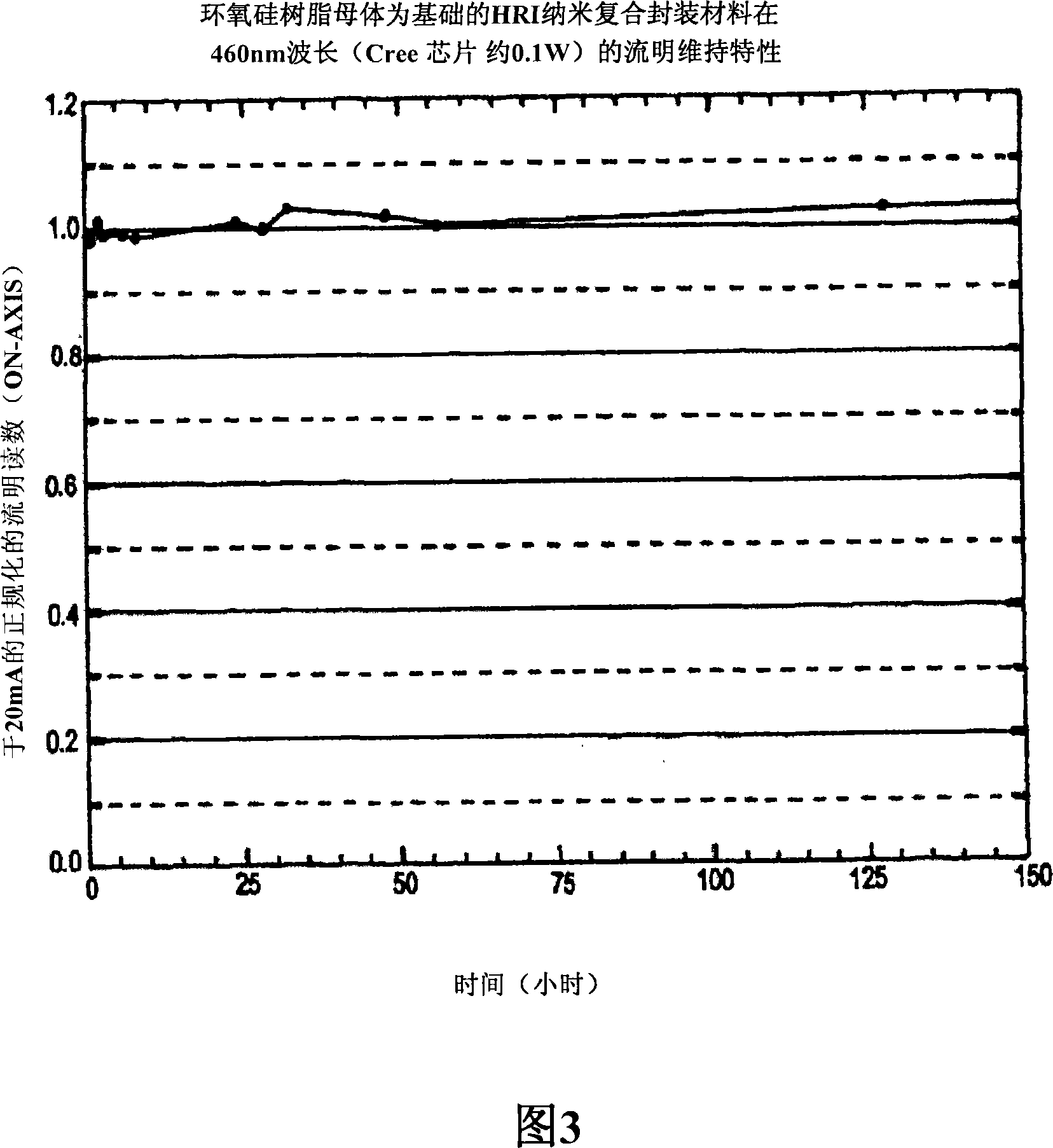
An optically reliable high refractive index (HRI) encapsulant for use with Light Emitting Diodes (LED's) and lighting devices based thereon. This material may be used for optically reliable HRI lightguiding core material for polymer-based photonic waveguides for use in photonic-communication and optical-interconnect applications. The encapsulant includes treated nanoparticles coated with an organic functional group that are dispersed in an Epoxy resin or Silicone polymer, exhibiting RI˜1.7 or greater with a low value of optical absorption coefficient α<0.5 cm−1 at 525 nm. The encapsulant makes use of compositionally modified TiO2 nanoparticles which impart a greater photodegradation resistance to the HRI encapsulant.
Owner:NANOCRYSTALS TECH
Method and structure for thin film photovoltaic materials using bulk semiconductor materials
InactiveUS8017860B2NanoinformaticsPhotovoltaic energy generationElectron holeSemiconductor materials
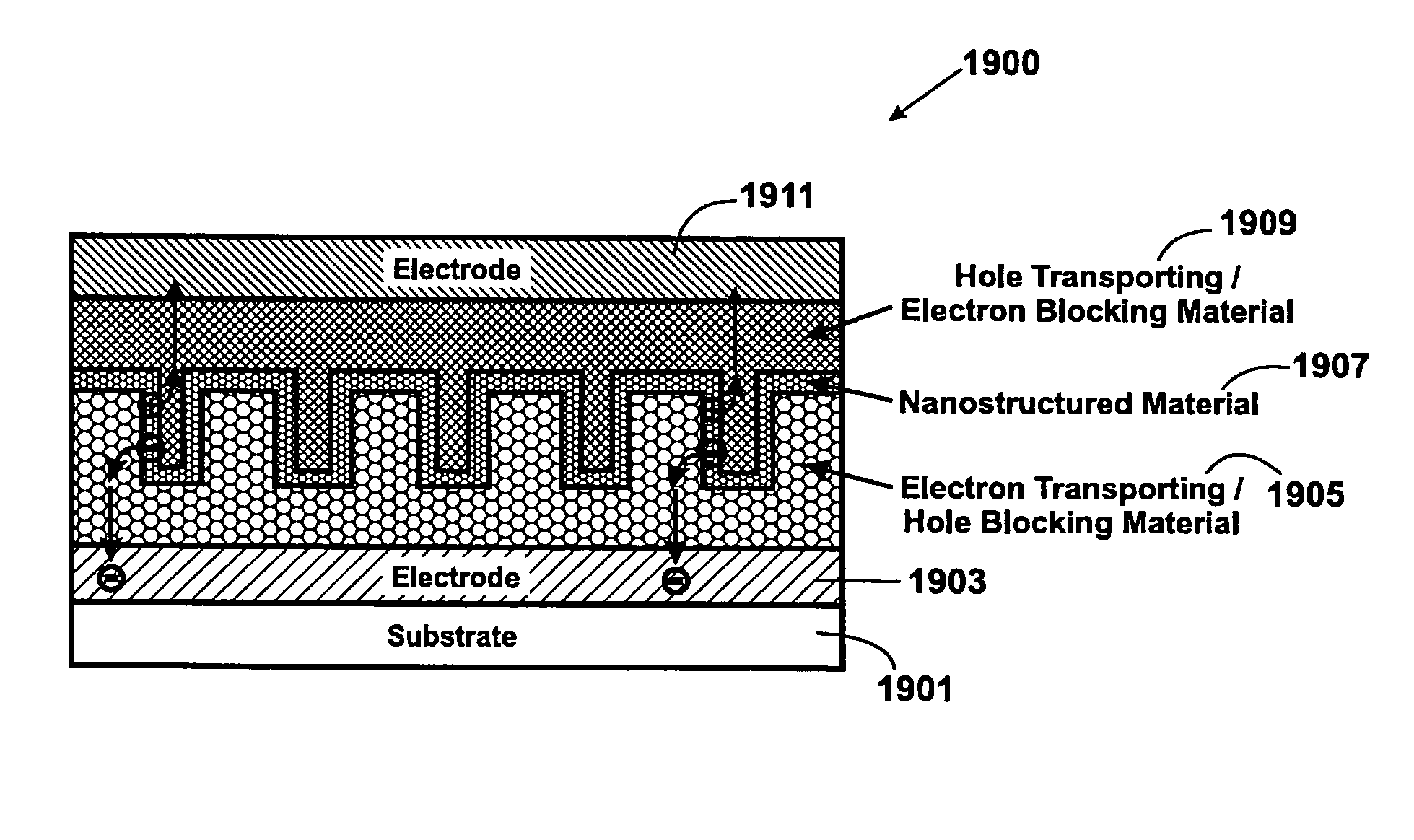
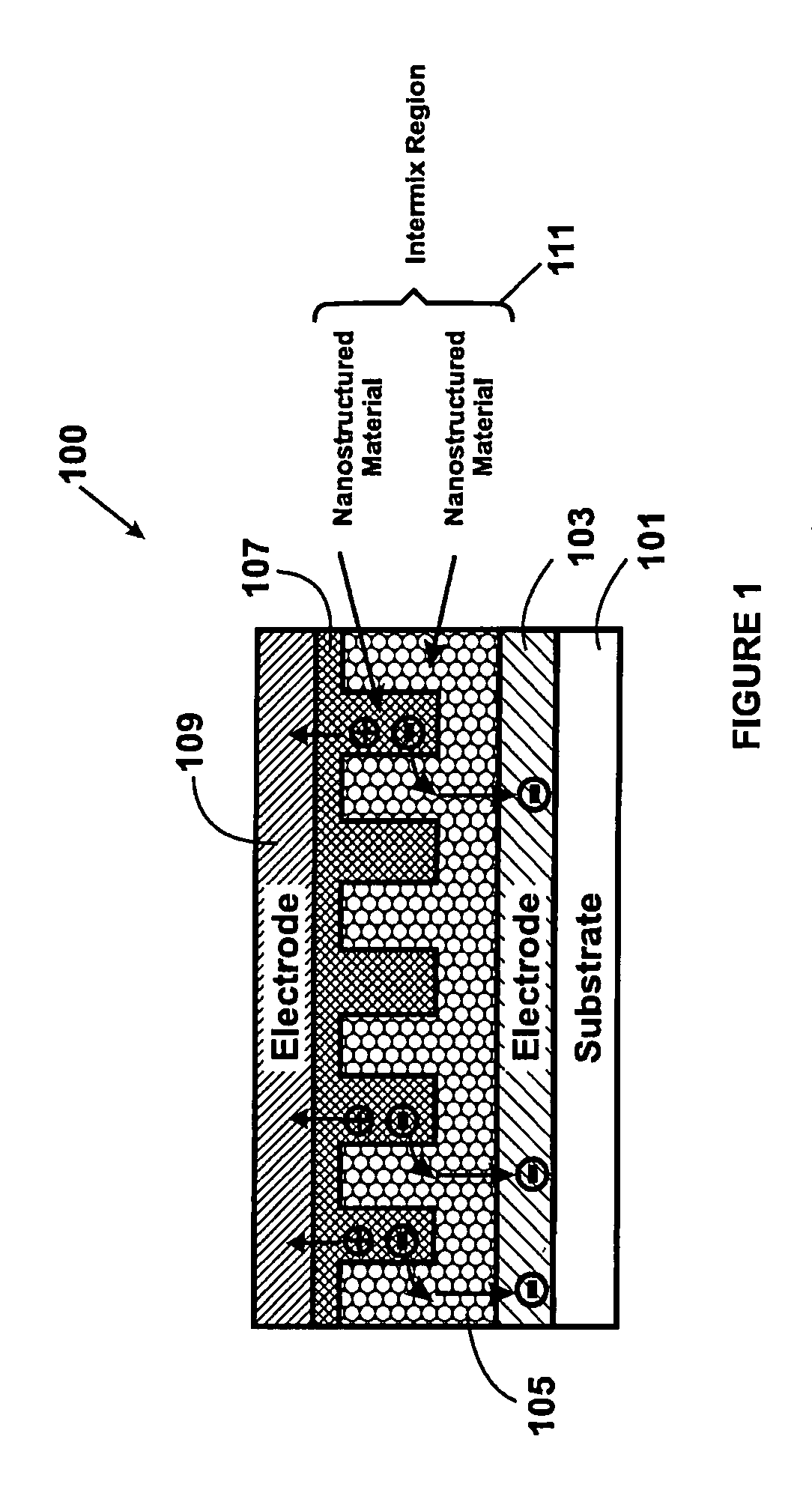
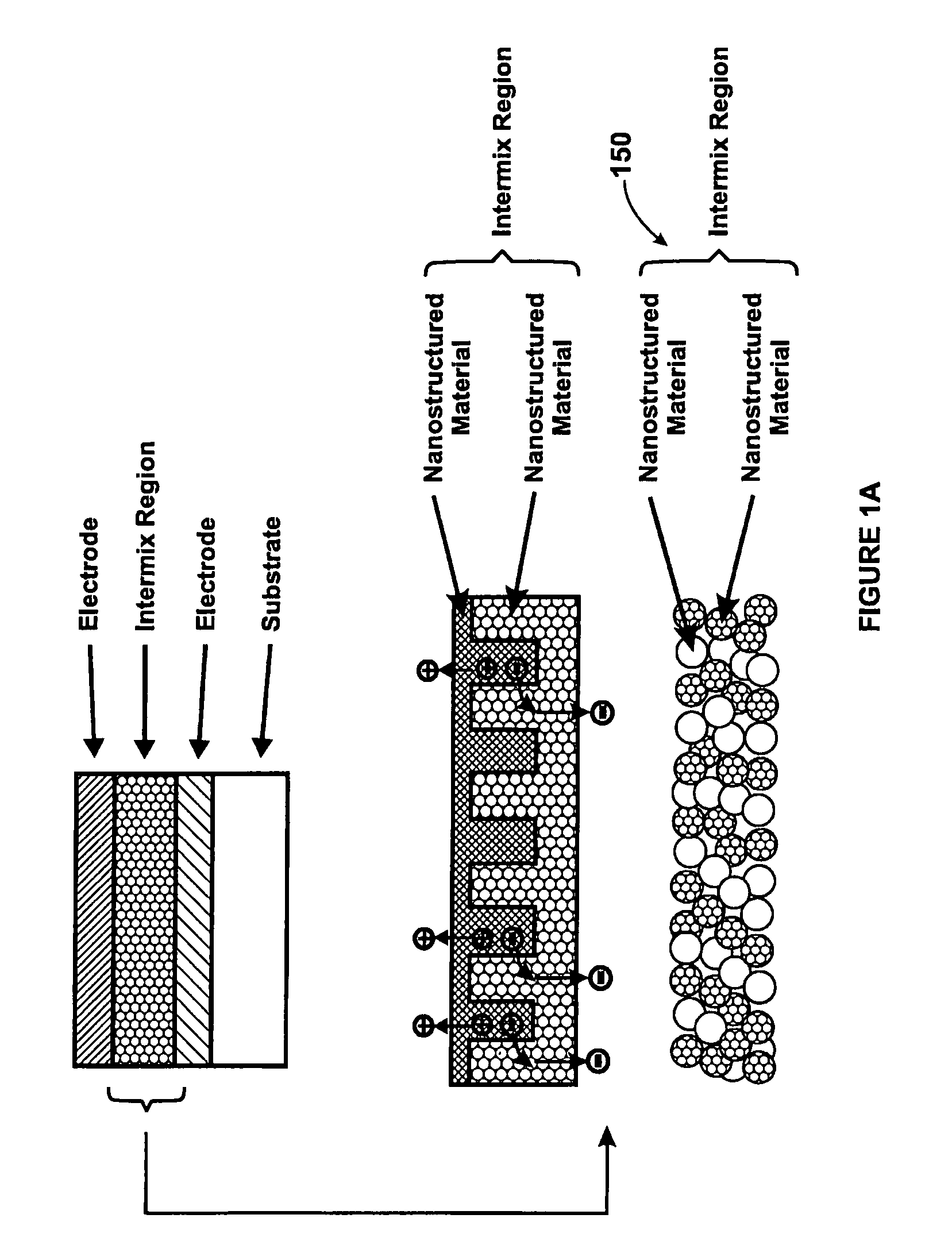
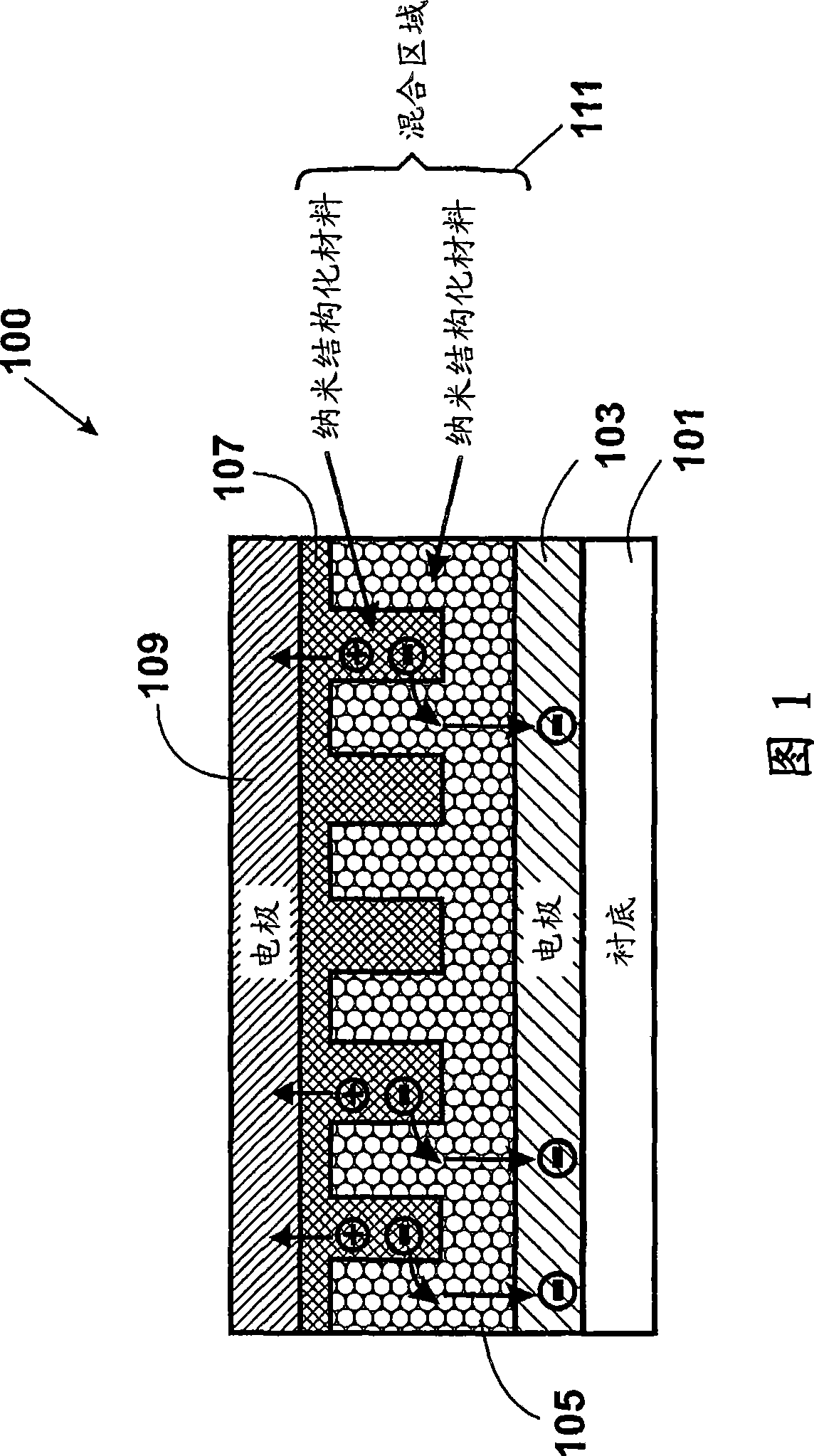
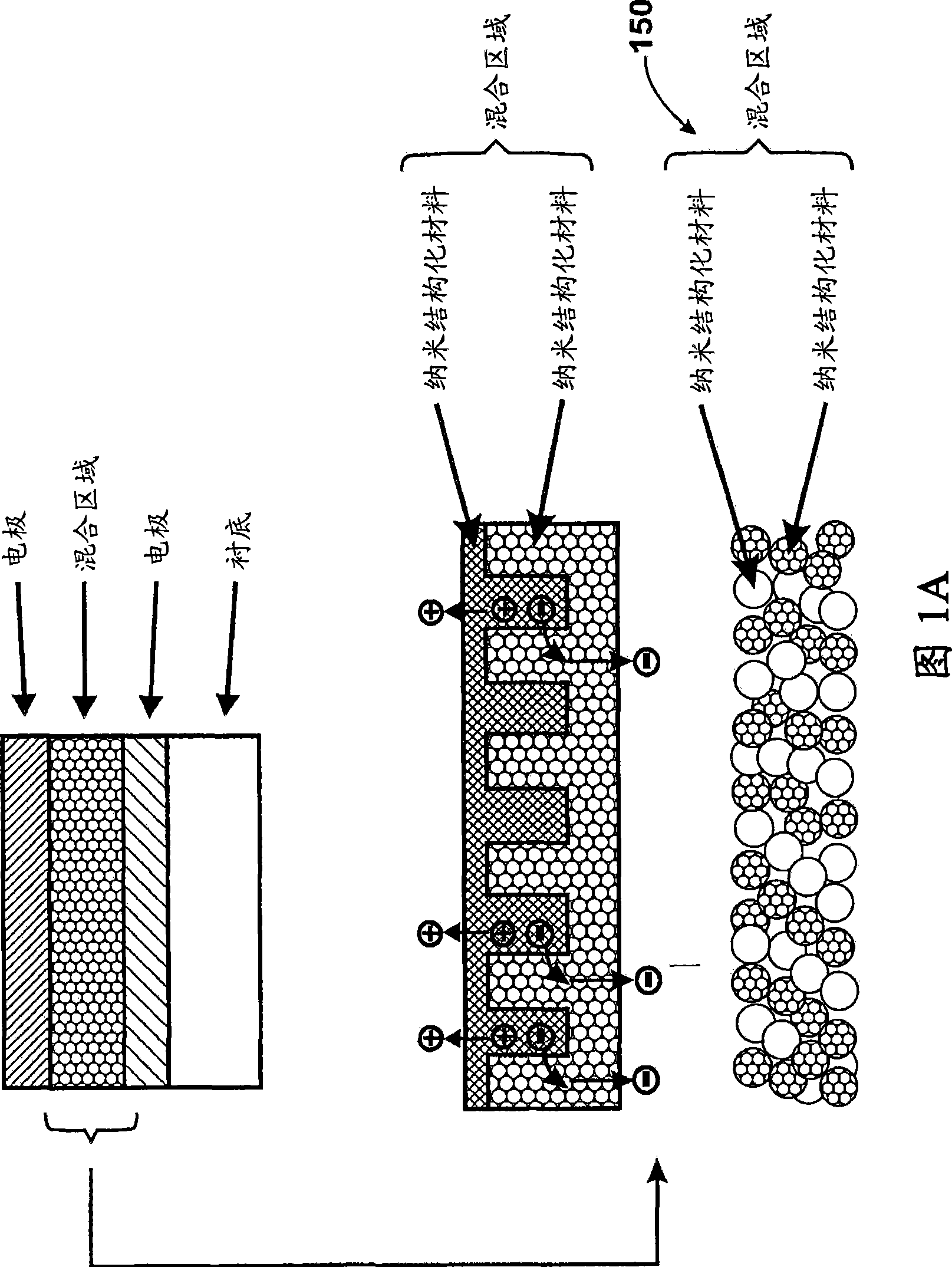
A photovoltaic device and related methods. The device has a structured material positioned between an electron collecting electrode and a hole collecting electrode. An electron transporting / hole blocking material is positioned between the electron collecting electrode and the structured material. In a specific embodiment, negatively charged carriers generated by optical absorption by the structured material are preferentially separated into the electron transporting / hole blocking material. In a specific embodiment, the structured material has an optical absorption coefficient of at least 103 cm−1 for light comprised of wavelengths within the range of about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
Owner:CM MFG
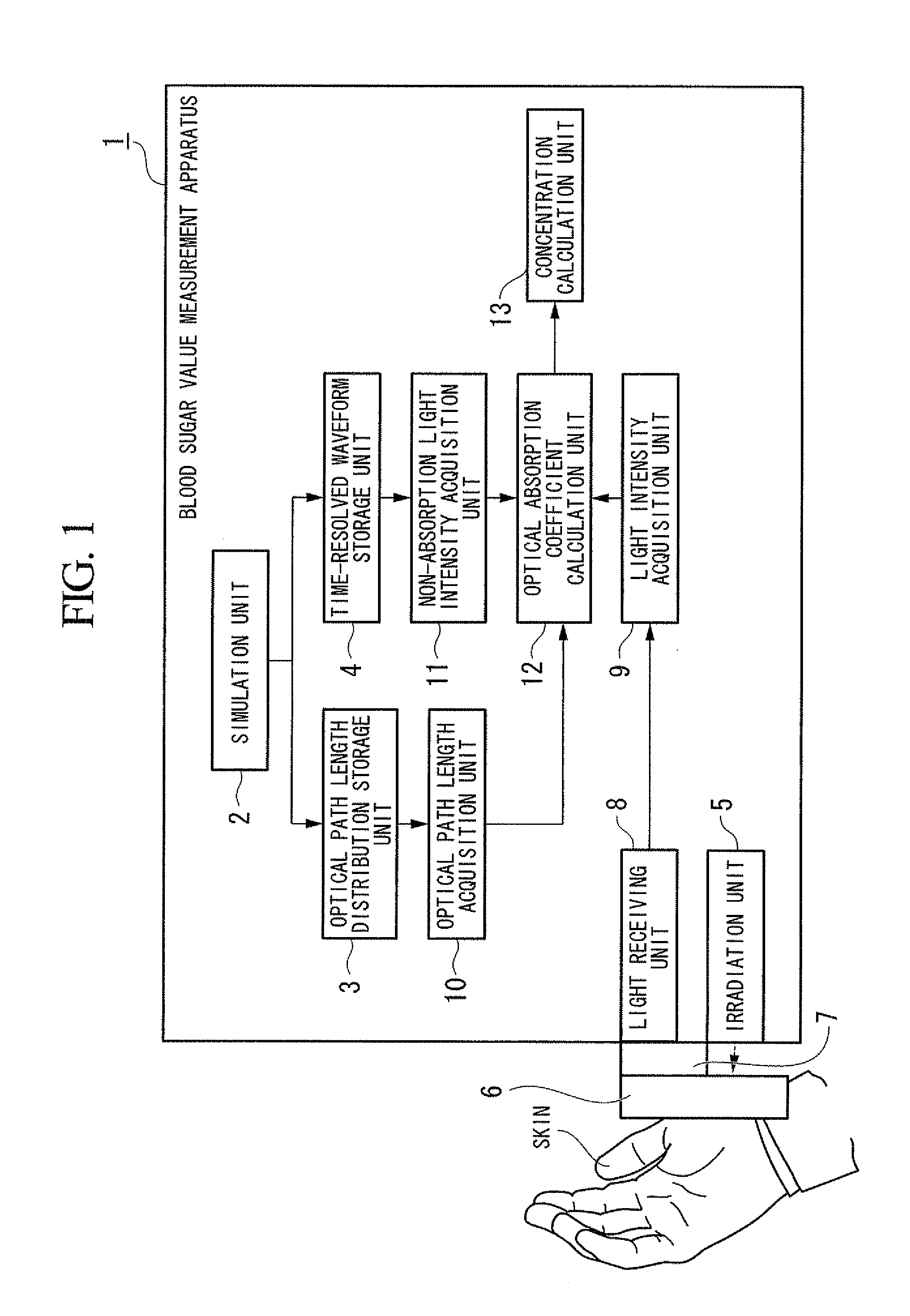
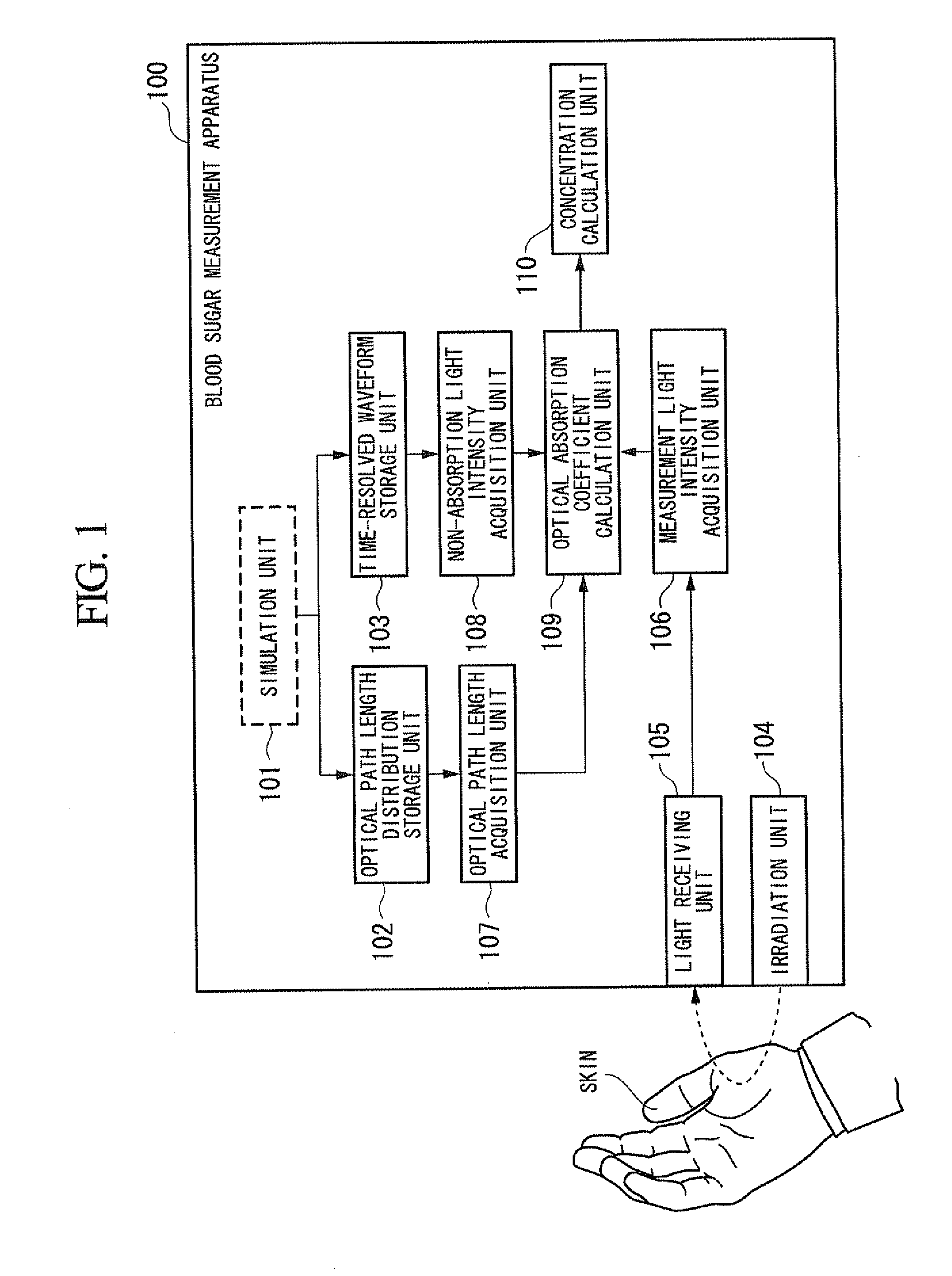
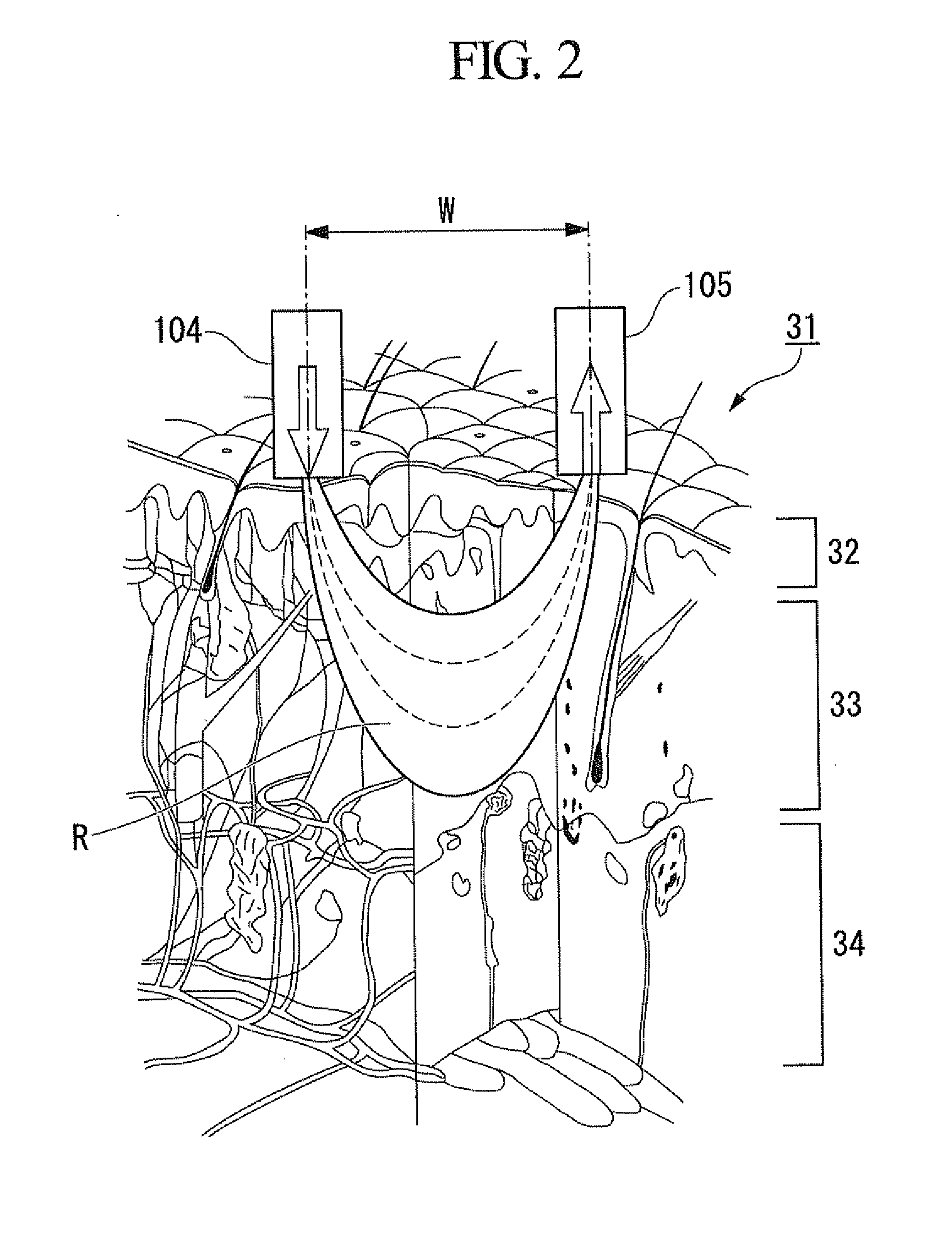
Concentration determination apparatus, probe, concentration determination method, and program
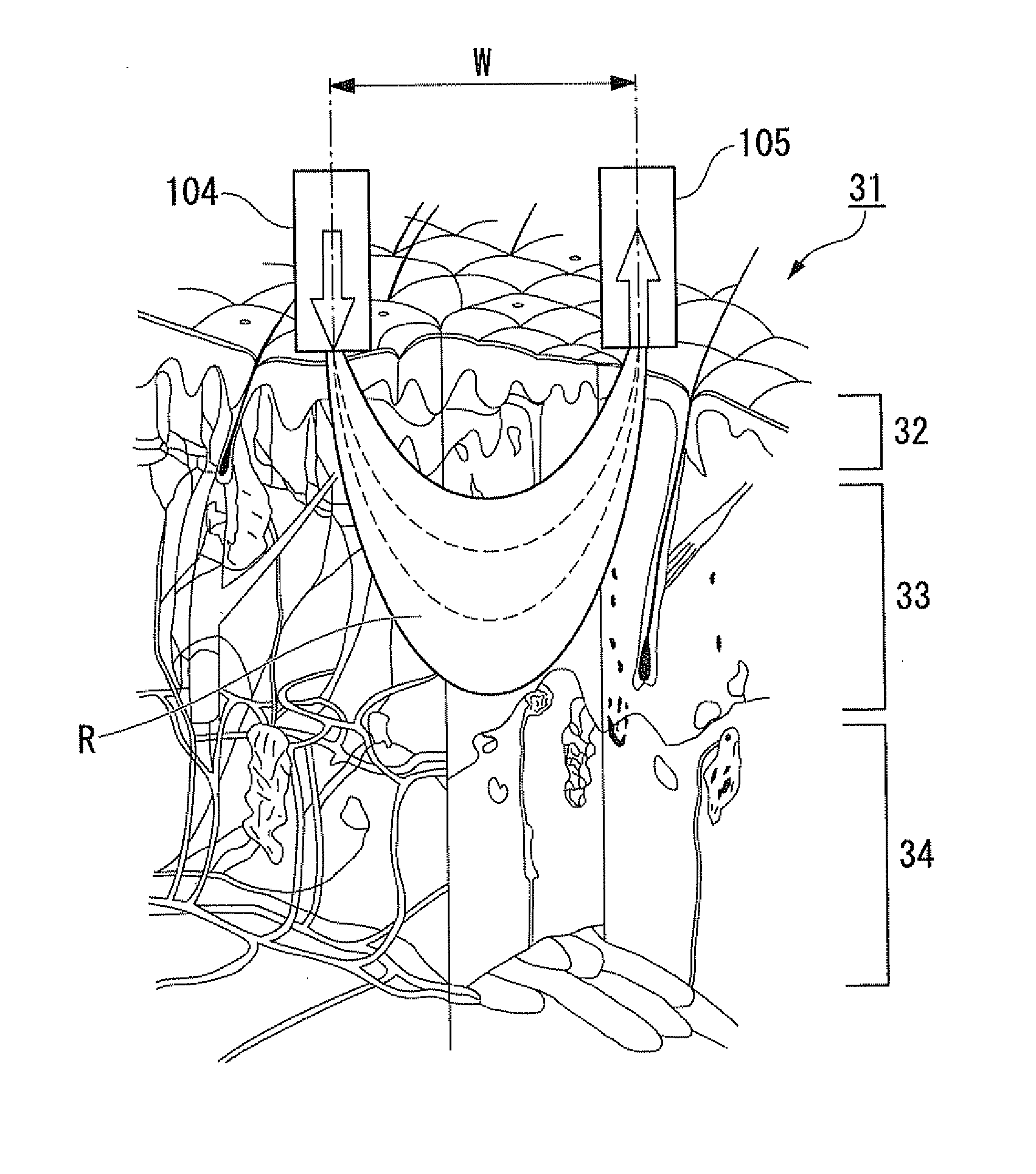
InactiveUS20120010477A1Accurate detectionAccurate measurementElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using spectroscopyIrradiationMedia layer
A concentration determination apparatus may determine a concentration of a target component in an arbitrary layer of an observed object including a plurality of light scattering medium layers. The concentration determination apparatus may include an irradiation unit, light scattering medium layer selection unit, a light receiving unit, a light intensity acquisition unit, an optical absorption coefficient calculation unit, and a concentration calculation unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Column structure thin film material using metal oxide bearing semiconductor material for solar cell devices
InactiveUS20110277836A1Improve efficiencyLow costPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsThin membrane
Owner:CM MFG
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS20130199299A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
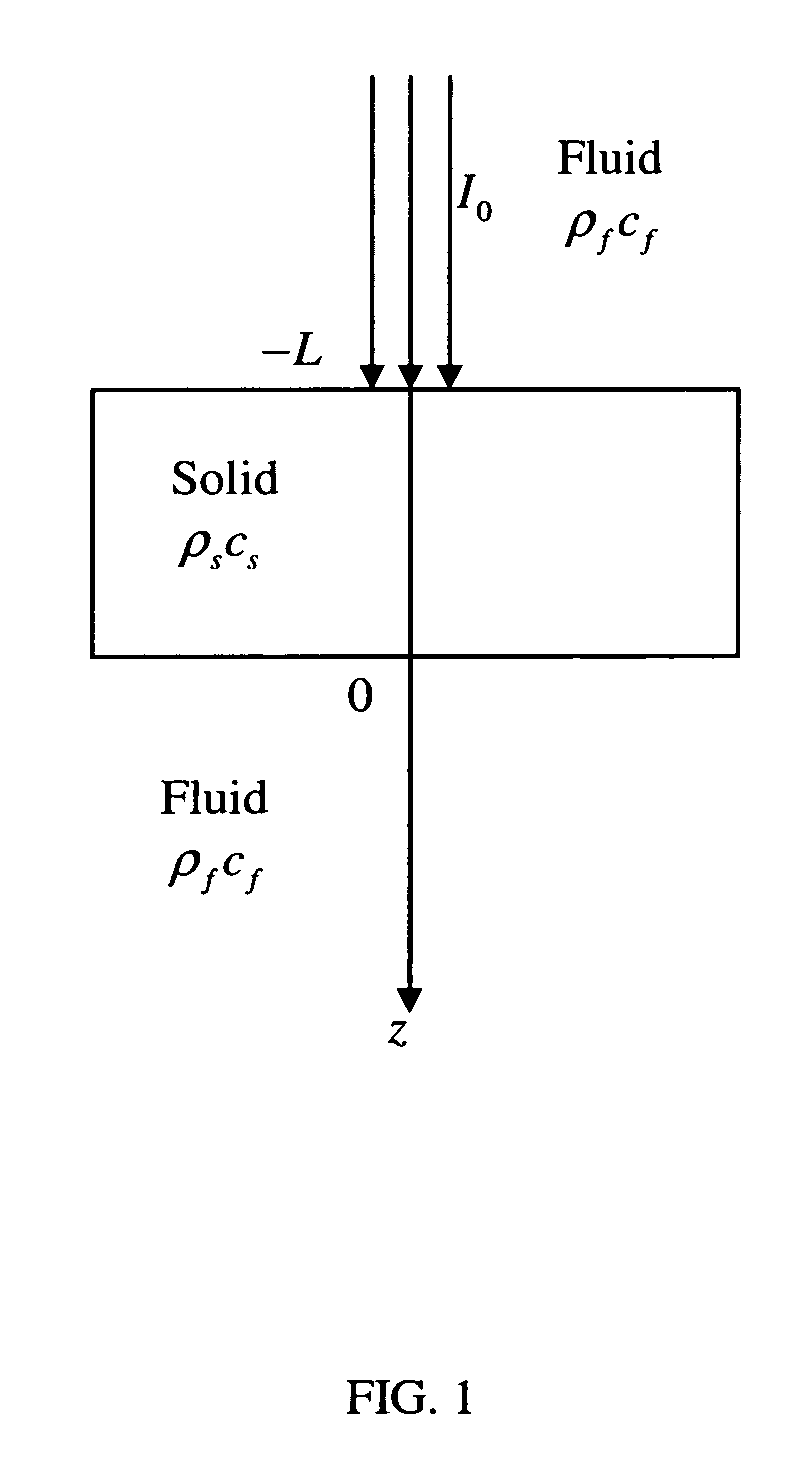
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
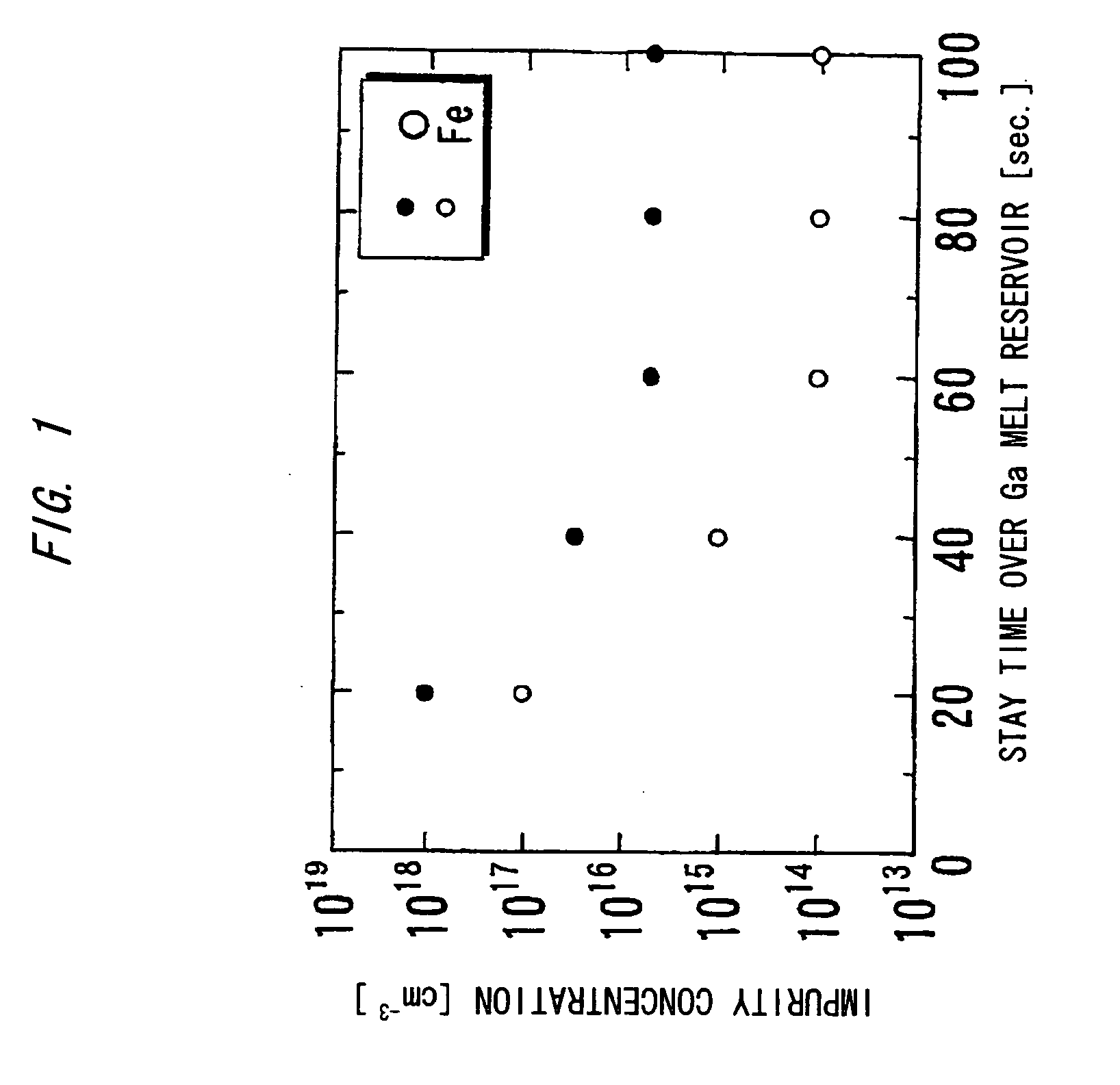
Nitride-based semiconductor substrate and method of making the same
ActiveUS20070096147A1High transparencyImprove conductivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrometerLength wave
A nitride-based semiconductor substrate having a diameter of 25 mm or more, a thickness of 250 micrometers or more, and an optical absorption coefficient of less than 7 cm−1 to light with a wavelength of 380 nm or more. The nitride-based semiconductor substrate is made by the HVPE method that uses gallium chloride obtained by reacting a Ga melt with a hydrogen chloride gas. The Ga melt is contacted with the hydrogen chloride gas for one minute or more to produce the gallium chloride.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
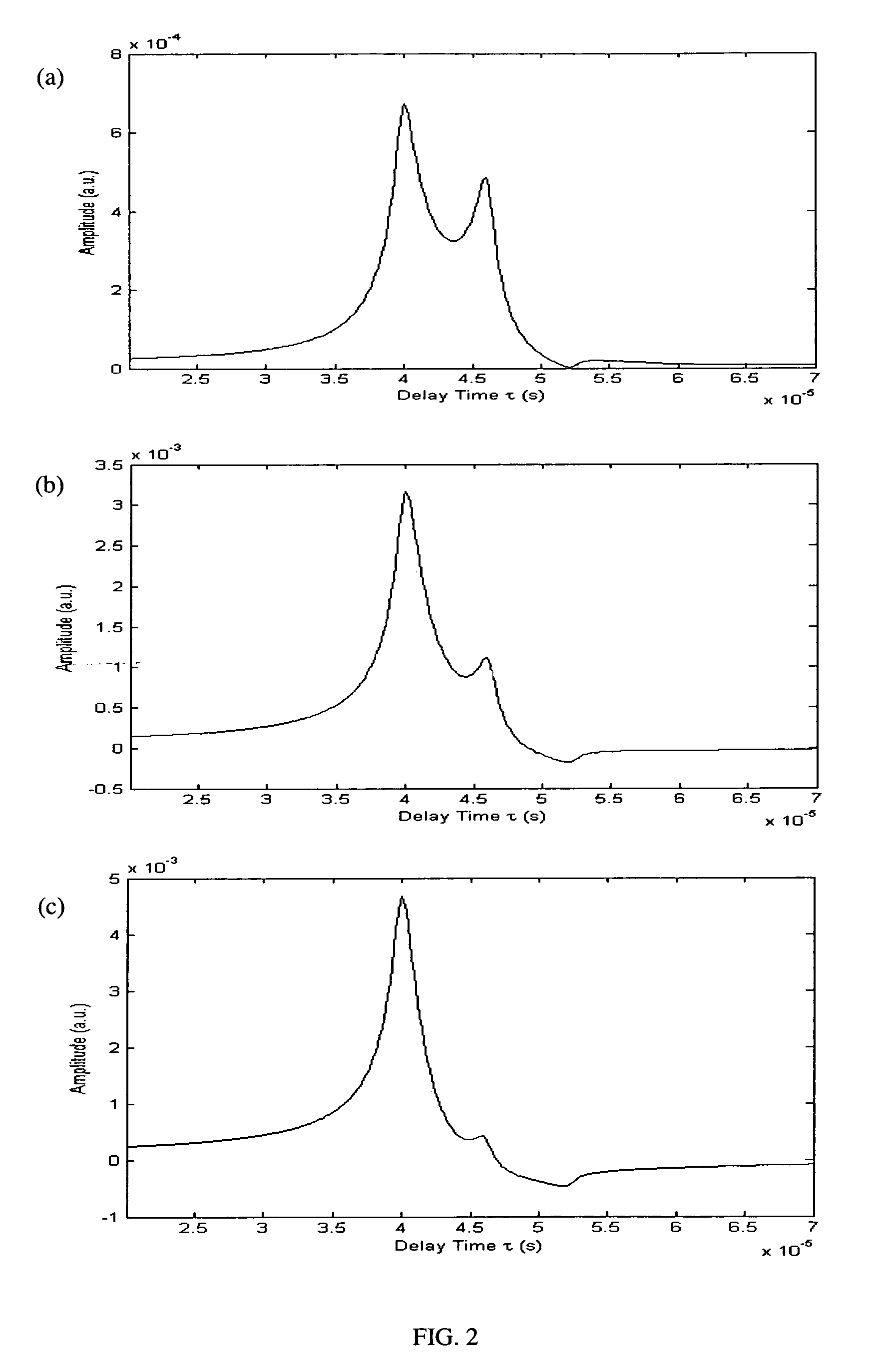
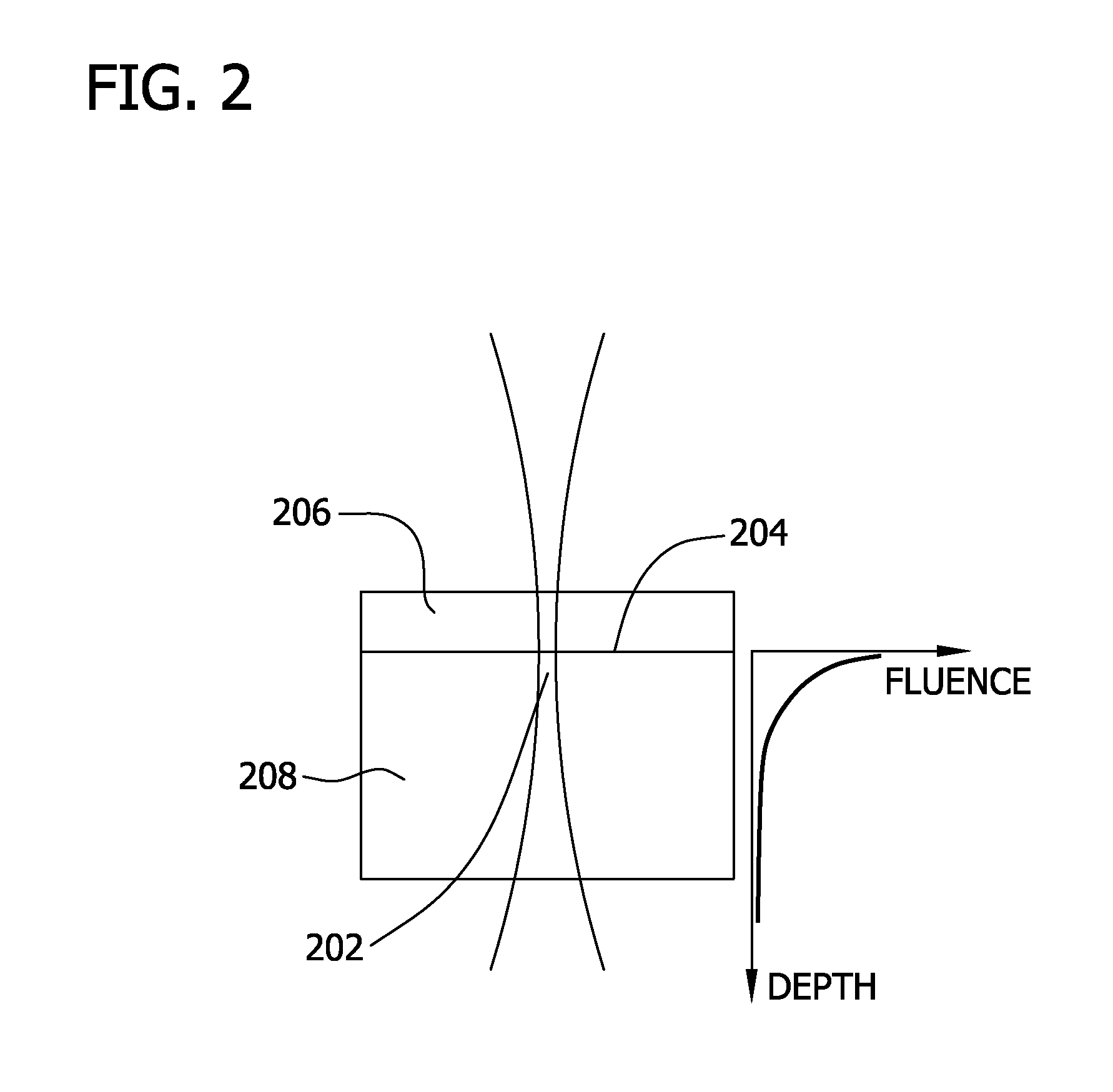
Laser photo-thermo-acoustic (PTA) frequency swept heterodyned lock-in depth profilometry imaging system
InactiveUS20050234319A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSubsurface imagingOptical absorption coefficient
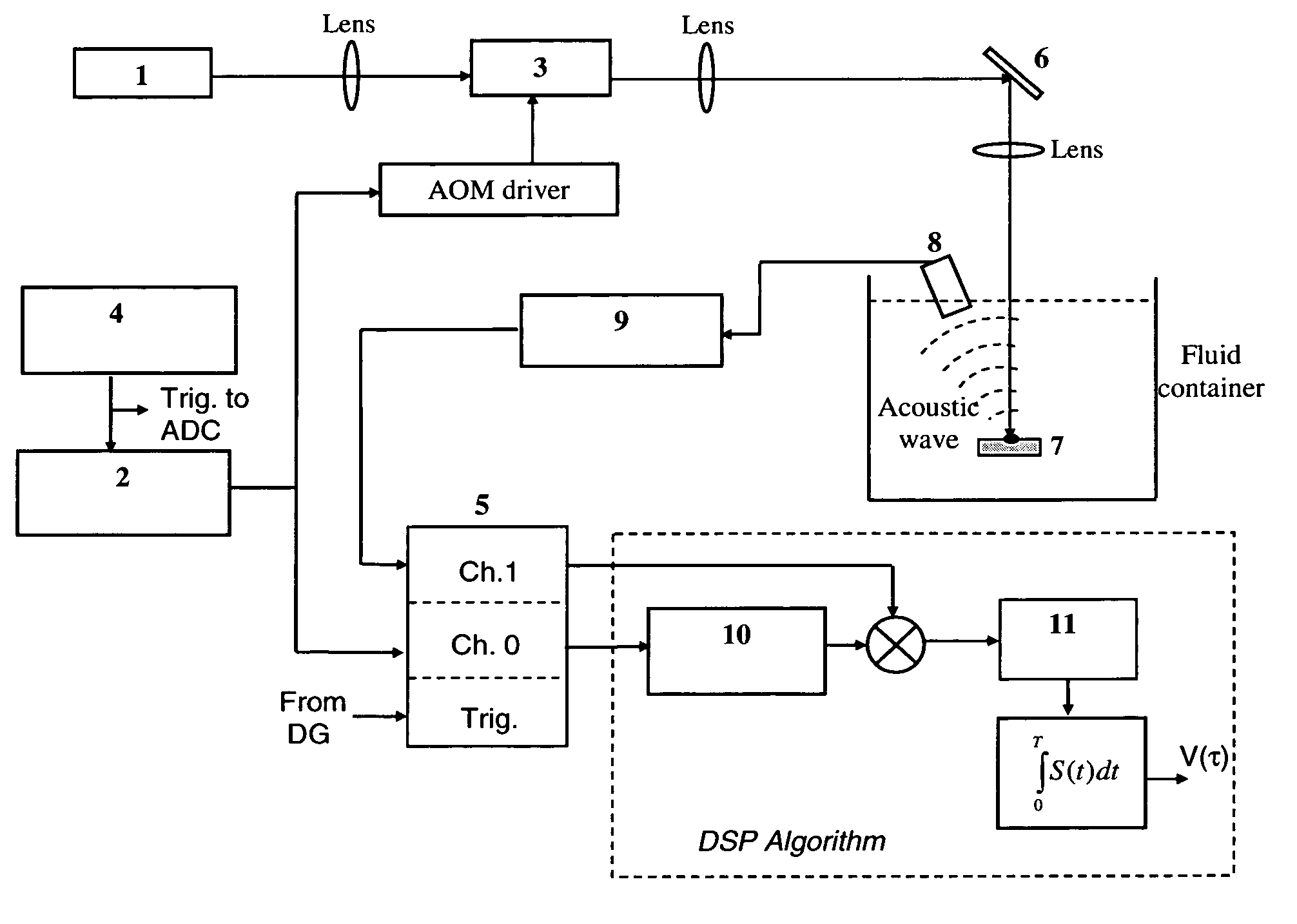
A method and apparatus for biomedical subsurface imaging and measurement of thickness, elastic and optical properties of industrial and biomedical materials based on laser Photo-Thermo-Acoustic (PTA) frequency-swept heterodyne depth profilometry, In particular, the invention relates to biomedical imaging and measure of tissue and tumour thickness, L, speed of sound, cs, acoustic attenuation coefficient, γ, optical absorption coefficient, μa, and optical scattering coefficient, μs. The method and apparatus involves providing for a sample of the material to be characterized; irradiating the material for a selected period of time with an excitation waveform from a modulated optical excitation source wherein a photo-thermo-acoustic emission is responsively emitted from said solid; detecting said emitted photo-thermo-acoustic emission; processing the electronic signal to convert the frequency-domain signal into time-domain and perform depth profilometric imaging and determining thermoelastic and optical properties of the material sample;
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +3
Thin film metal oxide bearing semiconductor material for single junction solar cell devices
InactiveUS20090250105A1Improve conversion efficiencyLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsHigh resistivity
A structure for a single junction solar cell. The structure includes a substrate member having a surface region. The structure includes a first electrode structure overlying the surface region of the substrate member. A P absorber layer is formed overlying the first electrode structure. In a specific embodiment, the P absorber layer has a P− type impurity characteristics and a first optical absorption coefficient greater than 104 cm−1 in a wavelength range comprising 400 nm to 800 nm. An N+ layer is provided overlying the P absorber layer and an interface region formed within a vicinity of the P layer and the N+ layer. The structure also includes a high resistivity buffer layer overlying the N+ layer and a second electrode structure overlying the buffer layer.
Owner:CM MFG
Solid-state image capturing apparatus, method for manufacturing the same, and electronic information device
InactiveUS20100177231A1Highly integratedReduce yieldTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectronic informationOptical absorption coefficient
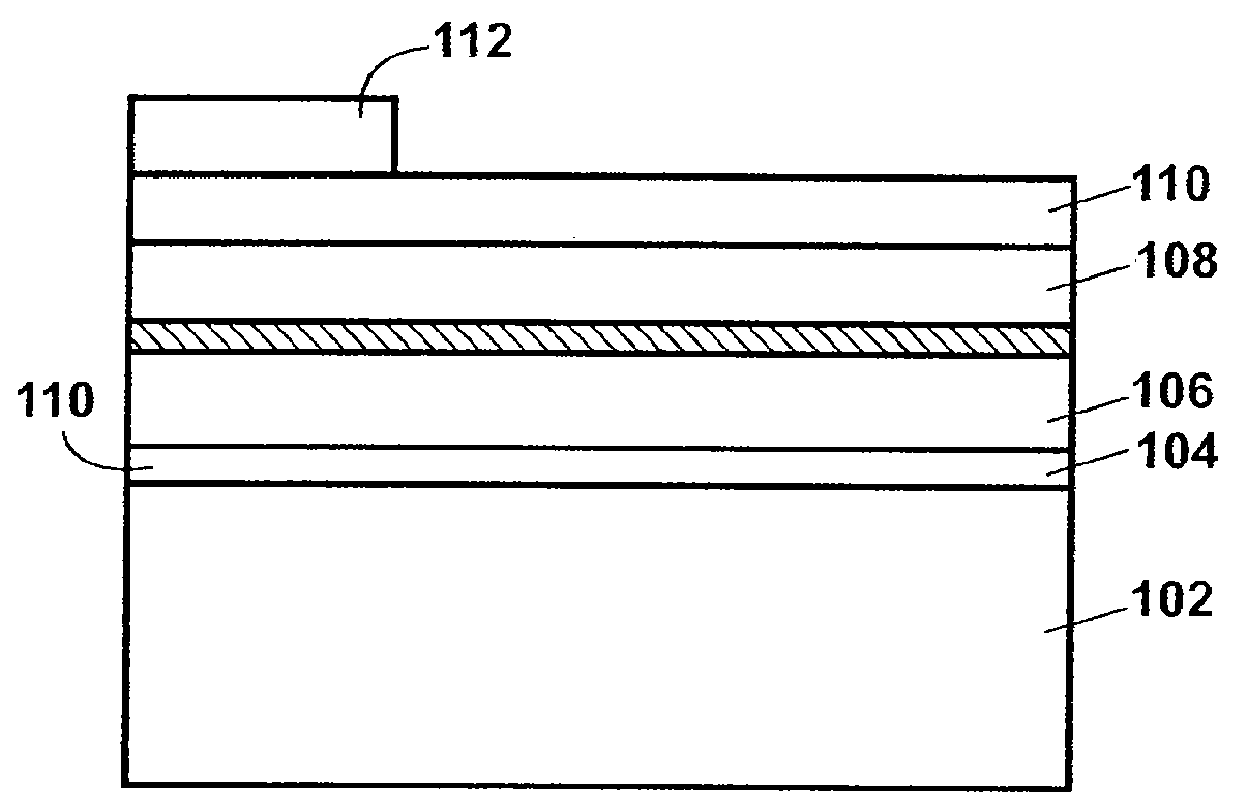
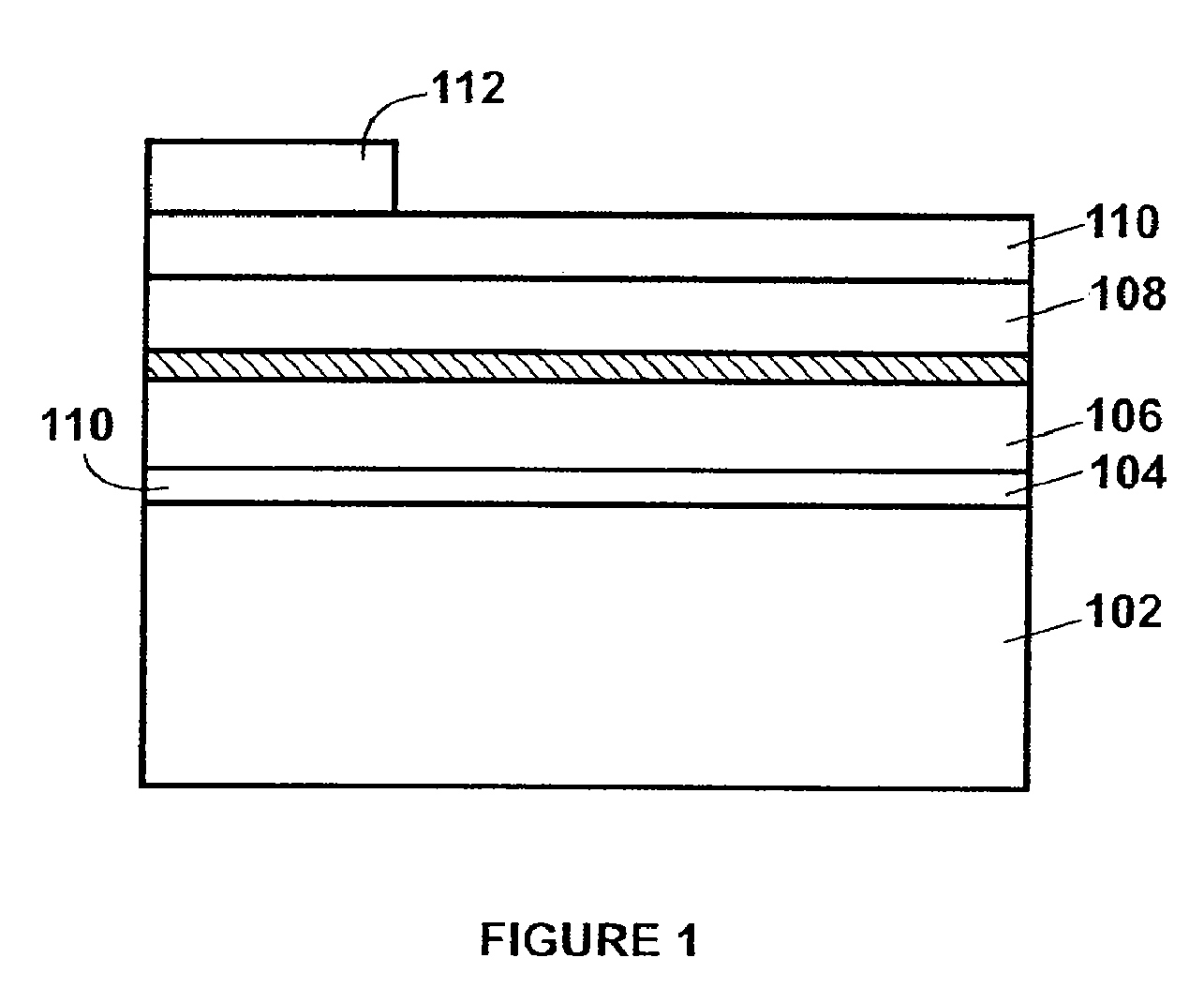
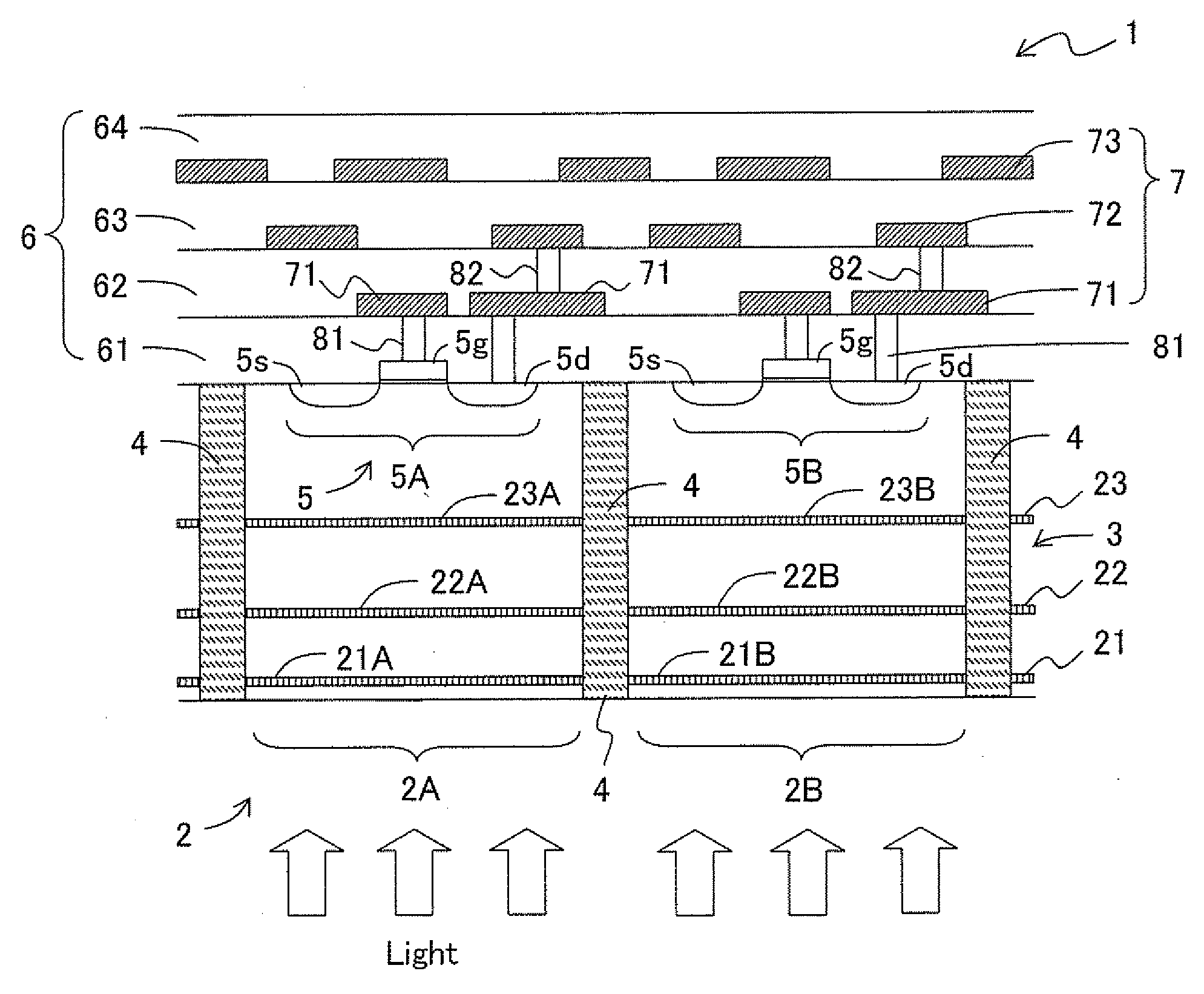
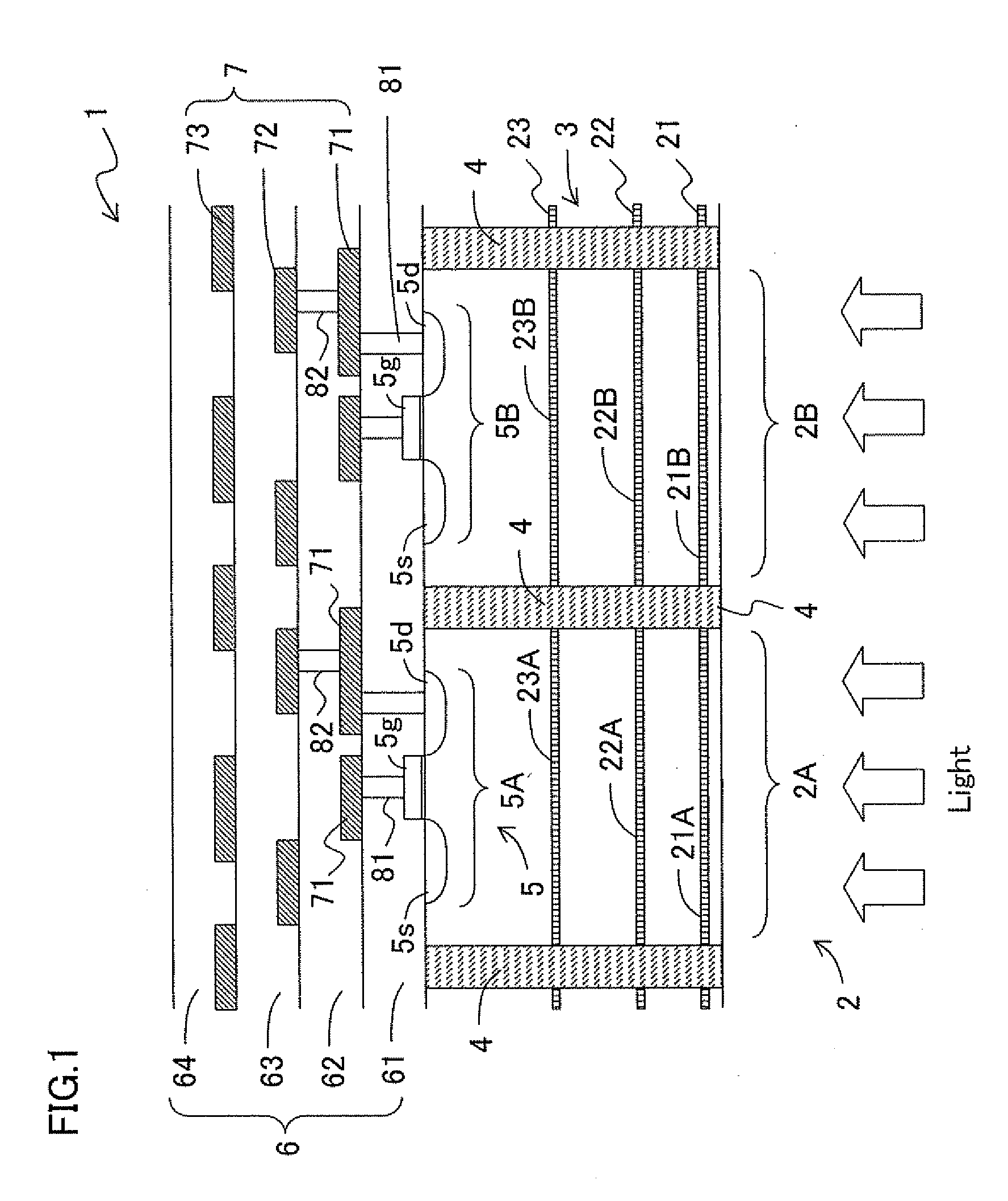
A solid-state image capturing apparatus is manufactured, which has a high sensitivity and high resolution with no color filter or no on-chip microlens required and with no shading generated or no variance in performance between pixel sections. In a solid-state image capturing apparatus 1, a plurality of pixel sections 2 (solid-state image capturing devices), each having light receiving sections 21 to 23 laminated in a depth direction of a semiconductor substrate 3, is repeatedly arranged according to a sequence in a direction along a plane of the semiconductor substrate 3. For incident light, electromagnetic waves having wavelength bands corresponding to the depths of the respective light receiving sections 21 to 23 are detected at the light receiving sections 21 to 23 in accordance with the wavelength dependency of optical absorption coefficient of semiconductor substrate material, and signal charges are generated. The pixel sections 2 are electrically separated from each other by pixel separation section diffusion layers 4. Wiring layers 71 to 73, which forms transfer paths for transferring signal charges from the light receiving sections 21 to 23, and the required number of transistors 5 are provided on the surface of the semiconductor substrate 3, which is the opposite side of the electromagnetic wave incidence side.
Owner:SHARP KK
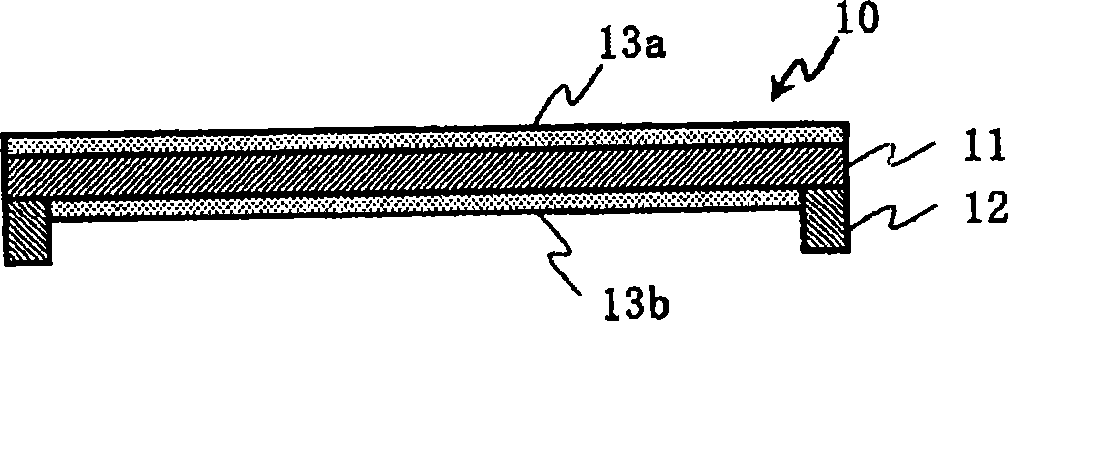
Pellicle and method for manufacturing the same
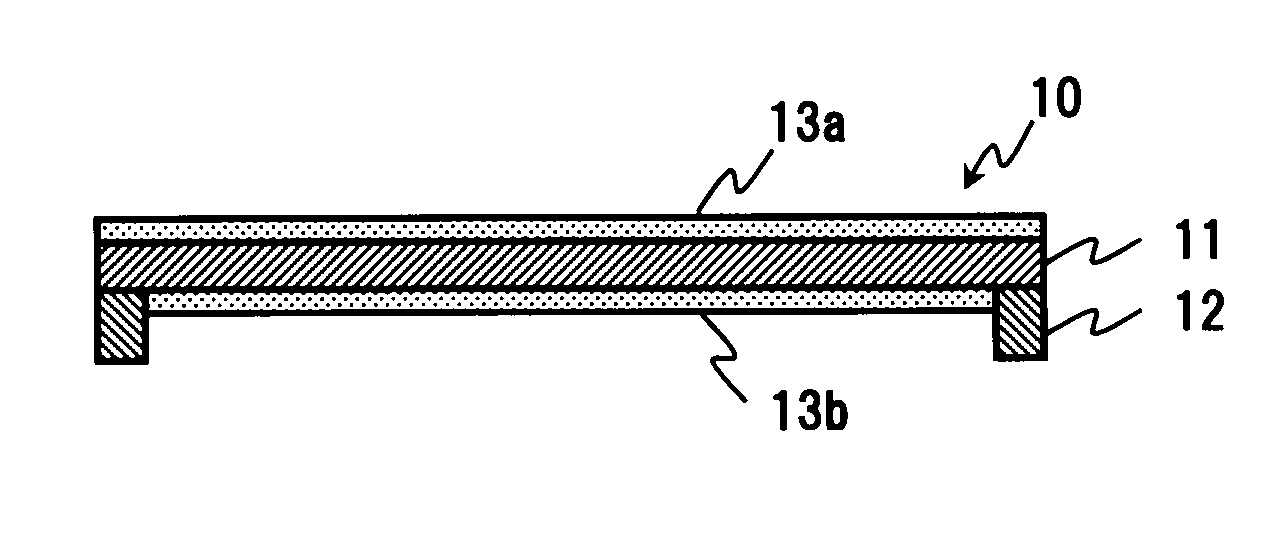
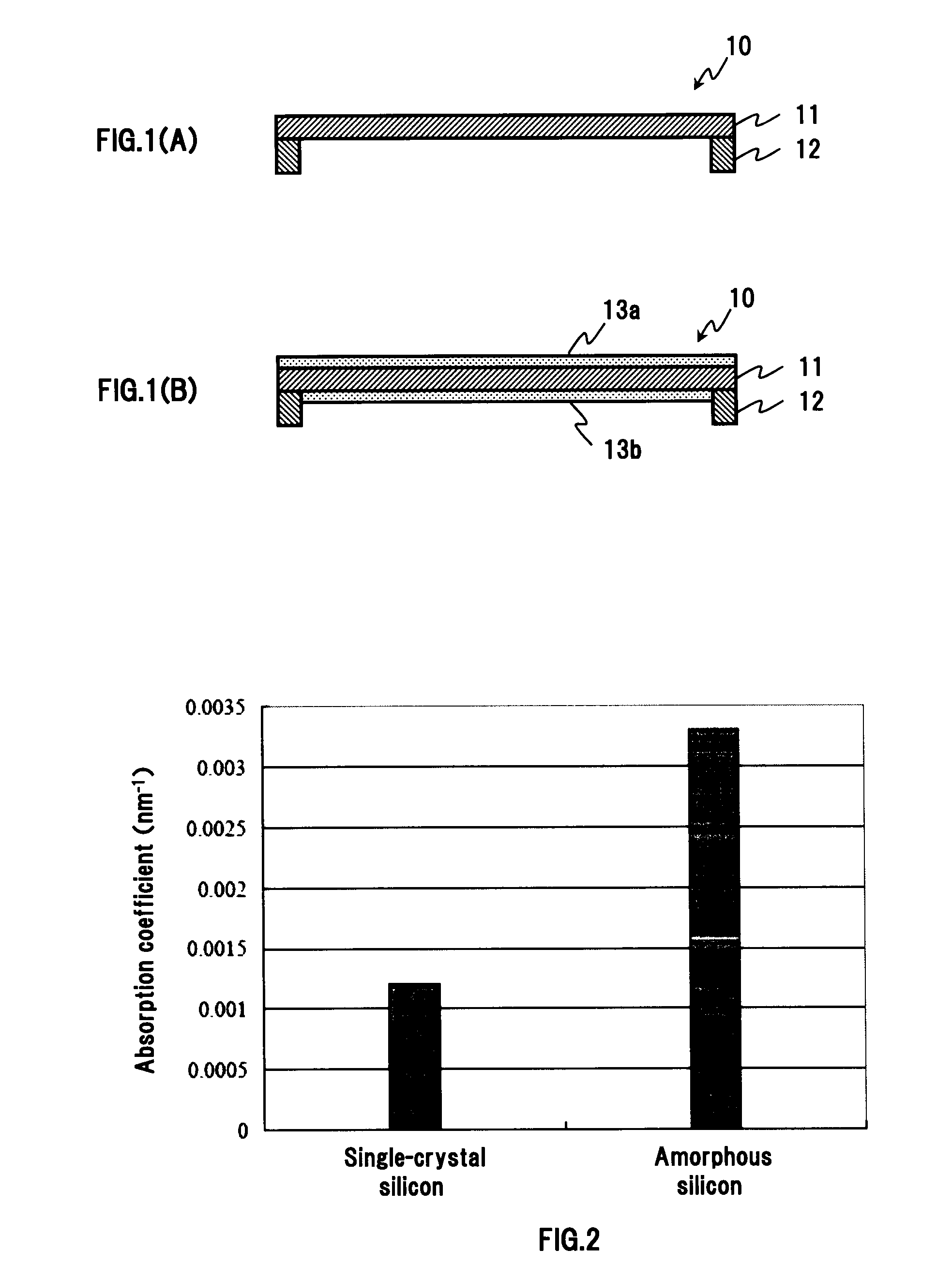
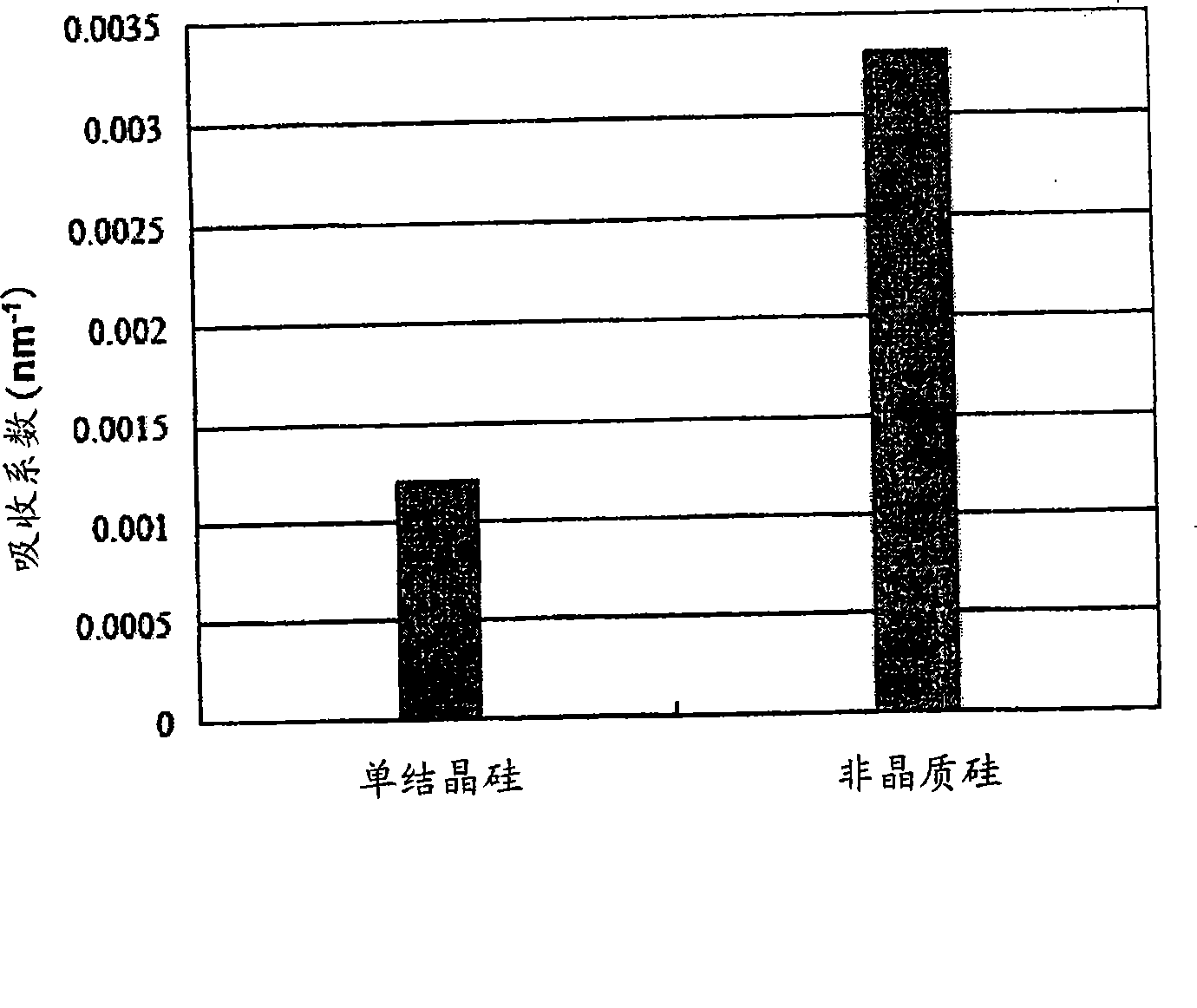
ActiveUS20090104544A1Good chemical stabilityImprove transmittancePicture framesNanoinformaticsTransmittanceAmorphous silicon
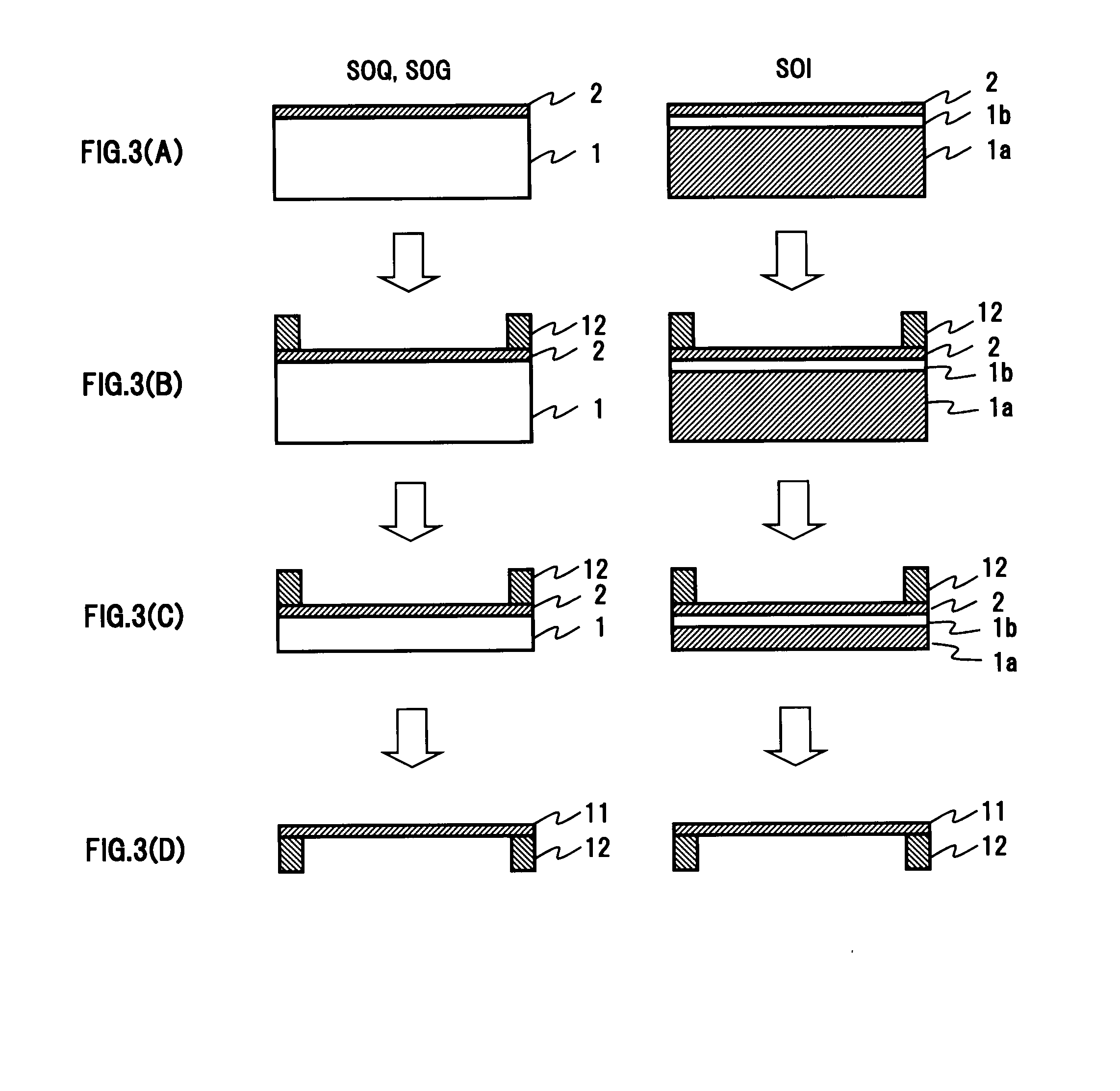
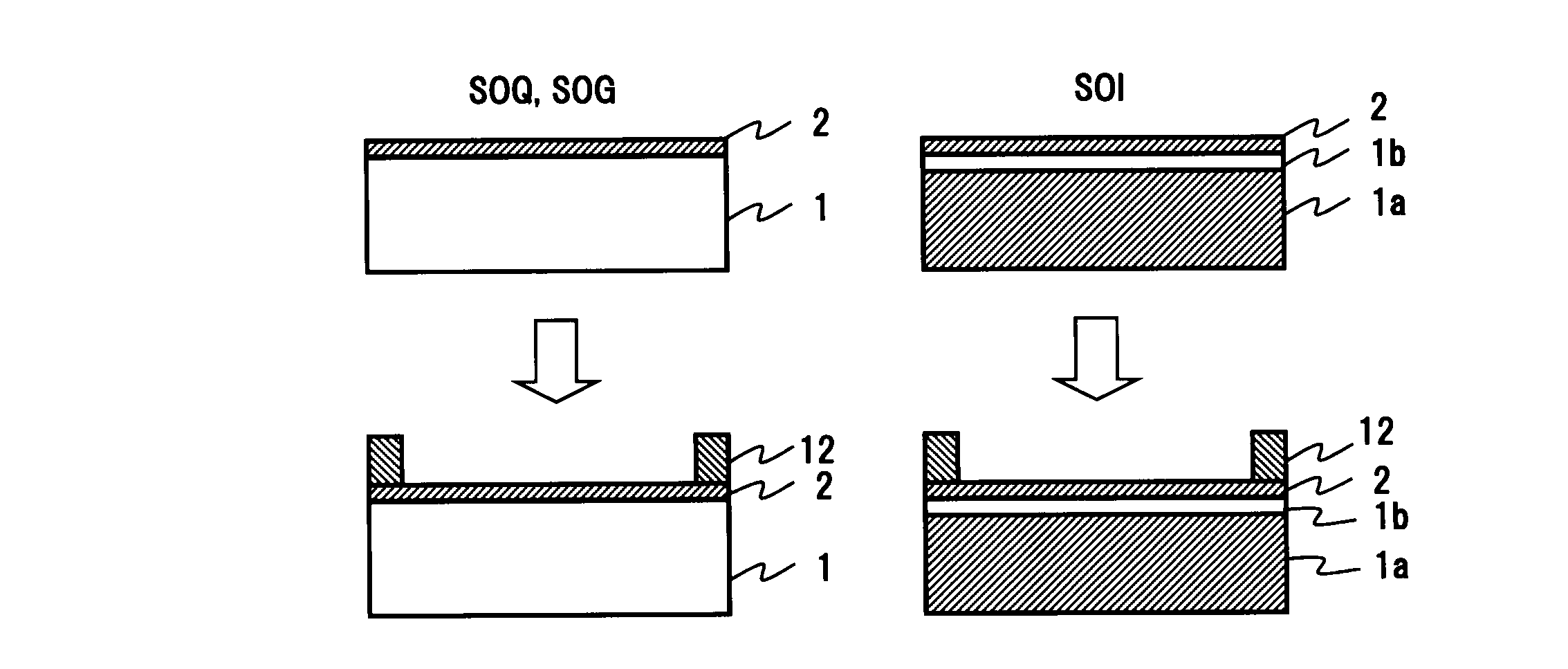
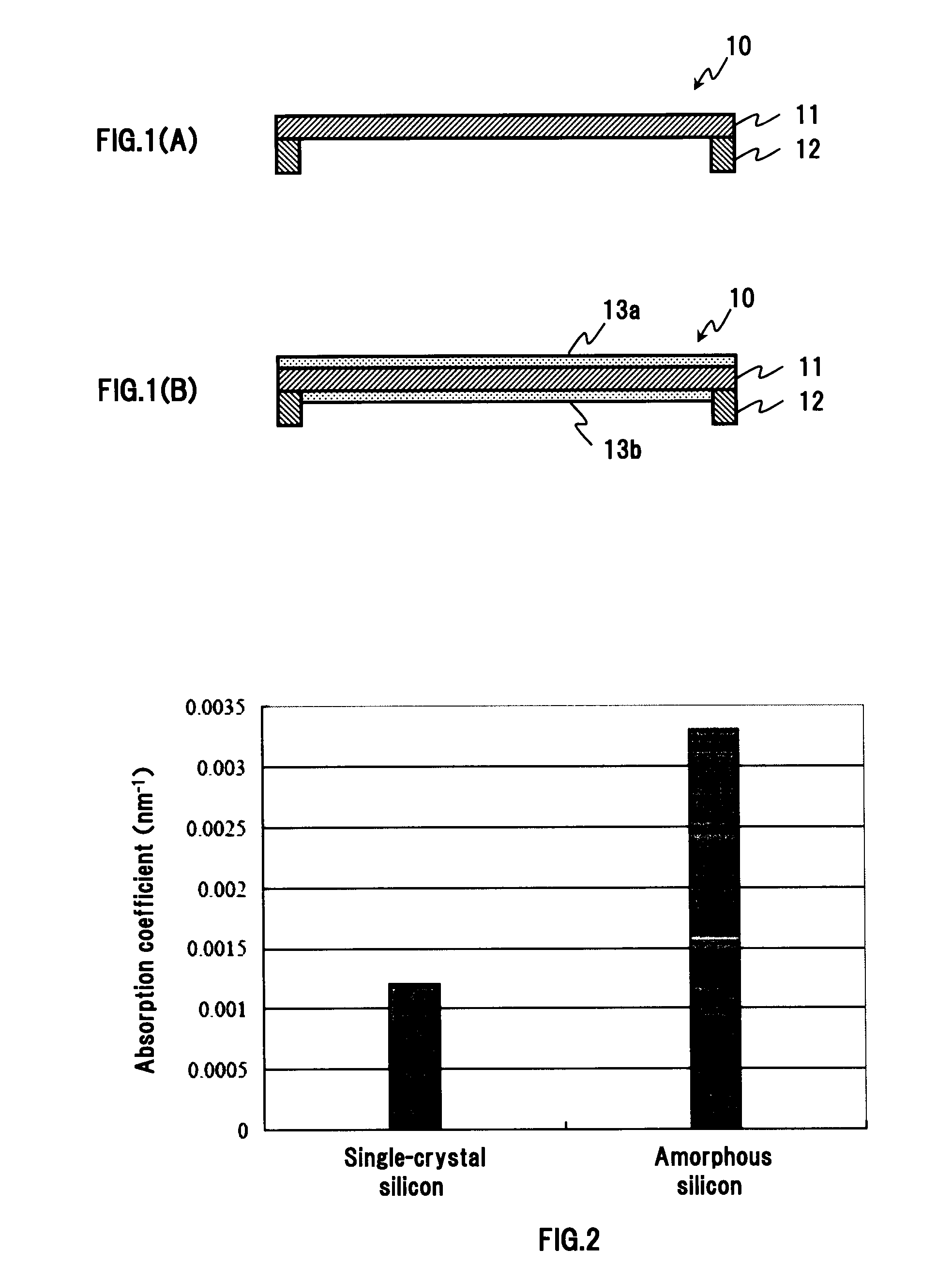
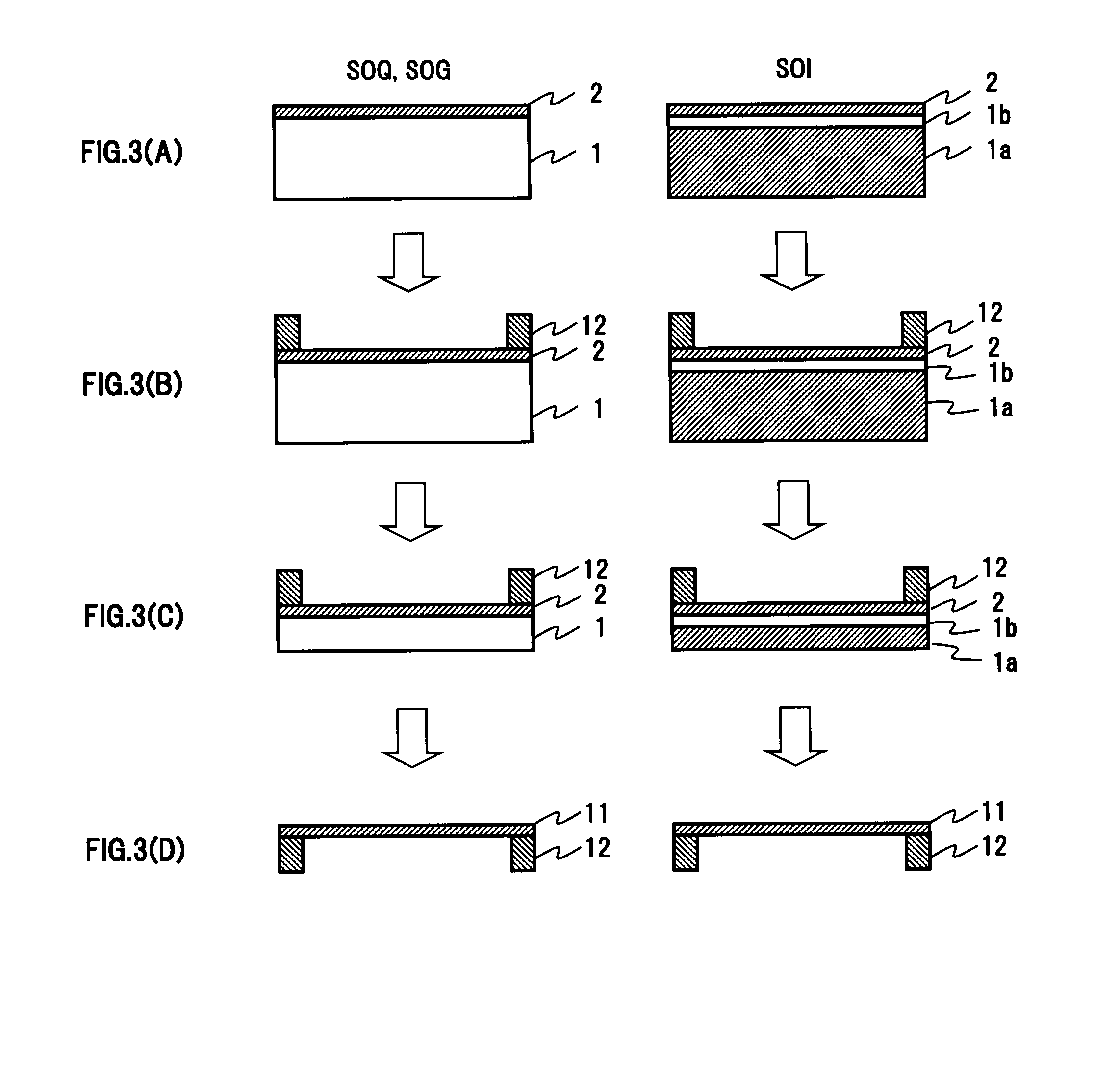
A pellicle of the present invention is provided with a silicon crystal film, the absorption coefficient of which is 0.005 / nm or lower with respect to light having a wavelength of 13.5 nm, as a pellicle film. The silicon crystal film is an indirect transition type semiconductor film and, therefore, the optical absorption coefficient thereof is relatively low. In particular, a single-crystal silicon film has a lower absorption coefficient than an amorphous silicon film and a polysilicon film. Thus, it is easy to obtain desired transmissivity required of a pellicle film for EUV from the single-crystal silicon film. Such a pellicle film as described above can be fabricated from an SOI film obtained by thin-filming an SOI substrate (including an SOQ substrate and an SOG substrate).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Optically driven carbon nanotube actuators
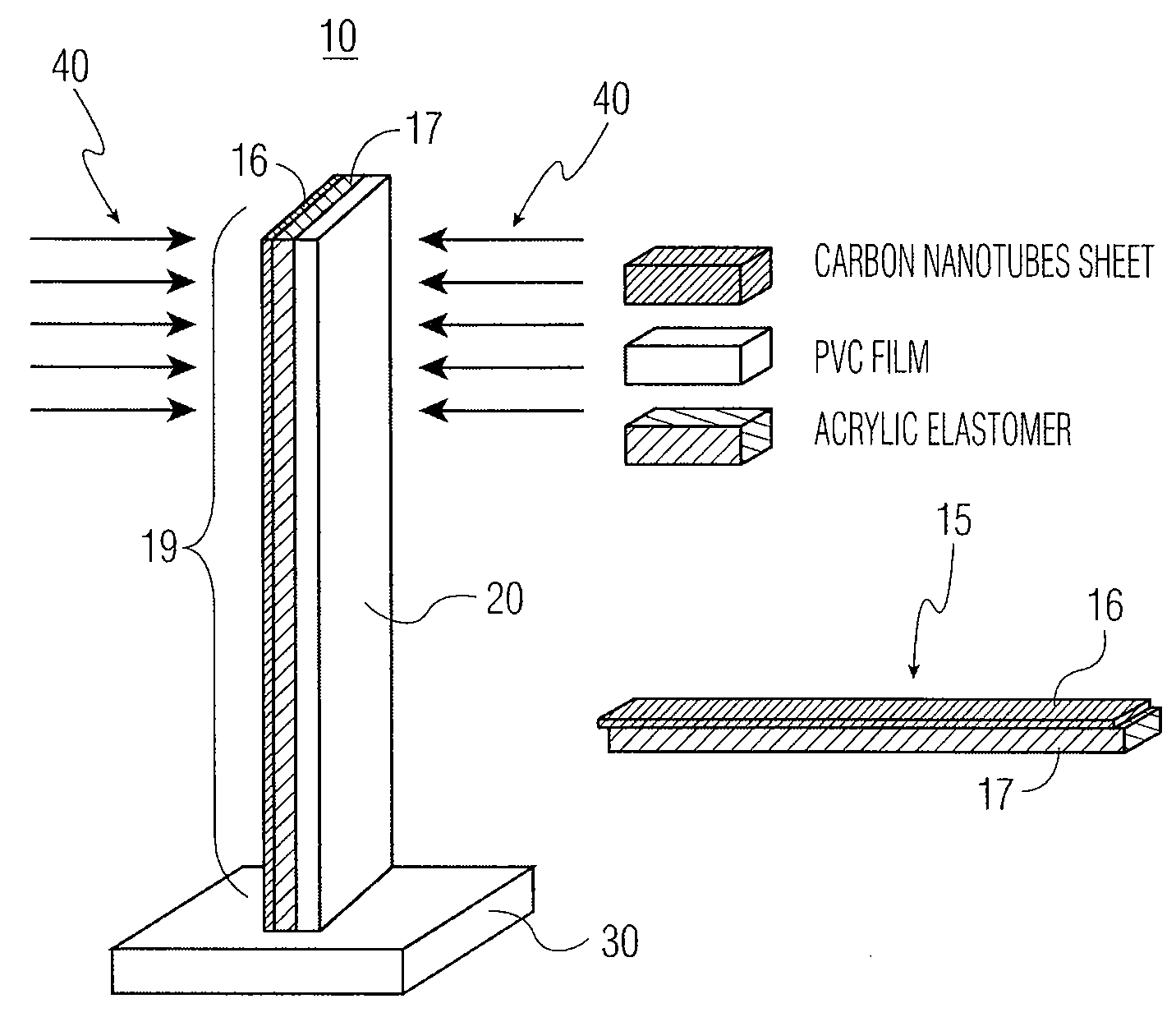
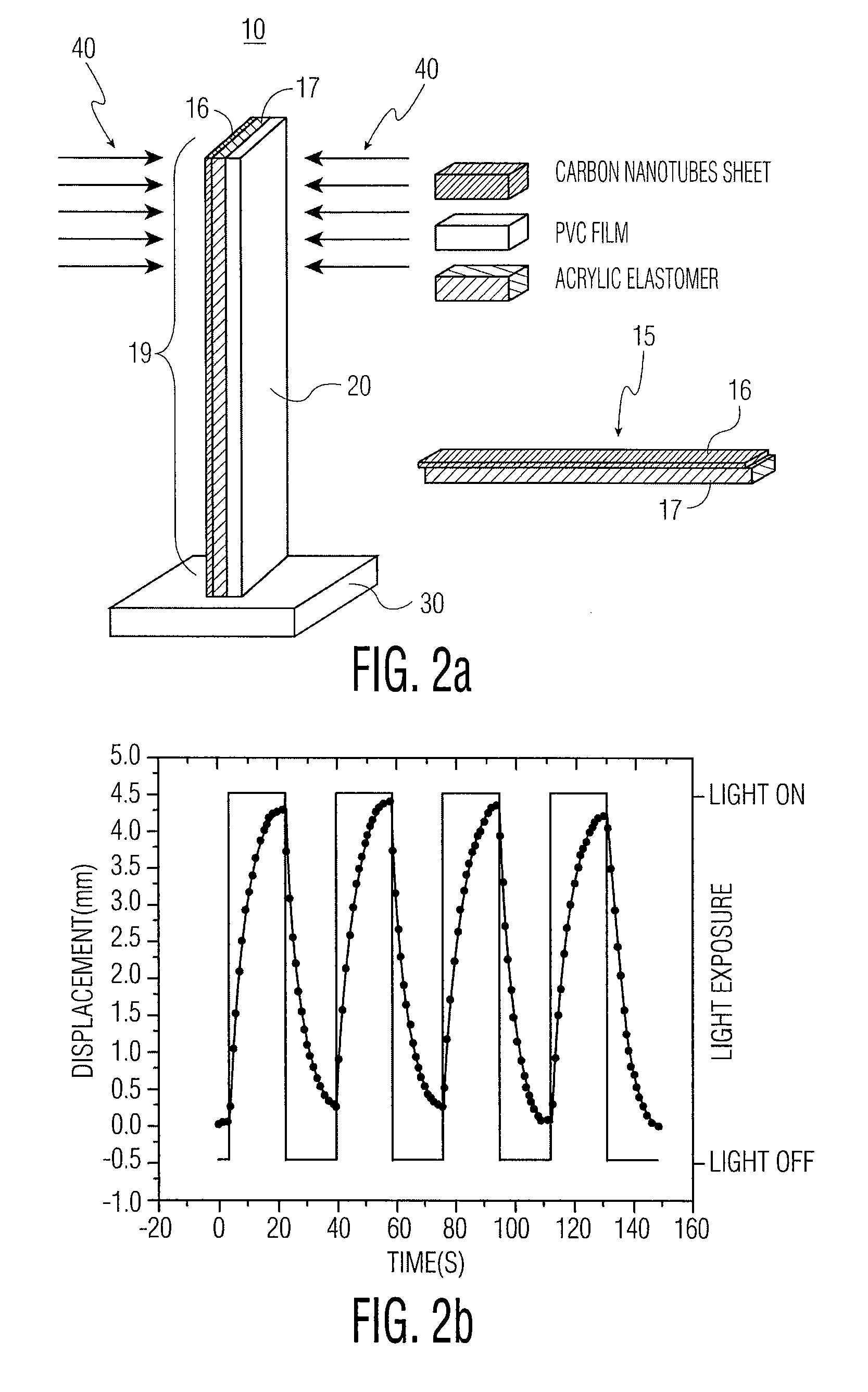
InactiveUS20080185936A1High feature resolutionFast etchMaterial nanotechnologyOptical articlesMechanical energyCarbon nanotube
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Method and structure for thin film photovoltaic materials using semiconductor materials
A photovoltaic device and related methods. The device has a nanostructured material positioned between an electron collecting electrode and a hole collecting electrode. An electron transporting / hole blocking material is positioned between the electron collecting electrode and the nanostructured material. In a specific embodiment, negatively charged carriers generated by optical absorption by the nanostructured material are preferentially separated into the electron transporting / hole blocking material. In a specific embodiment, the nanostructured material has an optical absorption coefficient of at least 10<3 >cm<-1 >for light comprised of wavelengths within the range of about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
Owner:CM MFG
Laser photo-thermo-acoustic (PTA) frequency swept heterodyned lock-in depth profilometry imaging system
InactiveUS7525661B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSubsurface imagingOptical absorption coefficient
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +3
Method of producing single-polarized lithium tantalate crystal and single-polarized lithium tantalate crystal
InactiveUS20050066879A1Fast decayImprove conductivityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCurie temperatureReducing atmosphere
A method of producing a lithium-tantalate crystal comprising, at least subjecting a single-polarized lithium-tantalate crystal wherein an optical absorption coefficient at a wave number of 3480 cm−1 is 0.3 cm−1 or less to a heat treatment under a reducing atmosphere at a temperature of not lower than 250° C. and not higher than Curie temperature and a single-polarized lithium-tantalate crystal wherein an optical absorption coefficient at a wave number of 3480 cm−1 is 0.3 cm−1 or less and an electric conductivity is 1×10−12 Ω−1·cm−1 or more. There can be provided a method of producing a single-polarized lithium-tantalate crystal in a short time efficiently wherein the surface charge generated due to a pyroelectric property can be decayed quickly by improving the electric conductivity and a single-polarized lithium-tantalate crystal.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Dicyclohexyl ethylene group substituted diphenylacetylene liquid crystal compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103805208ALow melting pointLow viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsHydrocarbonsCrystallographyLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a dicyclohexyl ethylene group substituted diphenylacetylene liquid crystal compound and a preparation method thereof. The structural general formula of the dicyclohexyl ethylene group substituted diphenylacetylene liquid crystal compound is shown in the specification, wherein (F)m, (F)n and (F)x respectively represent fluorine atom substitution, m, n and x represent substitution number of the fluorine atoms and the value of m, n and x is 0 or 1, and the cyclohexyl is trans-cyclohexyl; both R and R' represent C1-C15 alkyl, C1-C15 alkenyl, C1-C15 alkoxy, C1-C15 alkenyloxy, fluoro-substituted C1-C15 alkyl or fluoro-substituted C1-C15 alkenyl. The dicyclohexyl ethylene group substituted diphenylacetylene liquid crystal compound not only has high clearing point, wide nematic phase section, large birefringence, and low optical absorption coefficient, but also has low melting point, low viscosity and good intermiscibility, and can be used in liquid crystal optical elements; the dicyclohexyl ethylene group substituted diphenylacetylene liquid crystal compound with side fluorine can also be used in a double frequency liquid crystal display mode.
Owner:XIAN CAIJING OPTO ELECTRICAL SCI & TECH
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS9086365B2Vibration measurement in solidsMedical imagingFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Pellicle and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101414118AGood light transmission performanceGood chemical stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentRoom temperatureAmorphous silicon
The present invention relates to a pellicle. It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a pellicle provided with a practical pellicle film for EUV superior in transmittance and chemical stability. A pellicle of the present invention is provided with a silicon crystal film, the absorption coefficient of which is 0.005 / nm or lower with respect to light having a wavelength of 13.5 nm, as a pellicle film. The silicon crystal film is an indirect transition type semiconductor film and, therefore, the optical absorption coefficient thereof is relatively low. In particular, a single-crystal silicon film has a lower absorption coefficient than an amorphous silicon film and a polysilicon film. Thus, it is easy to obtain desired transmissivity required of a pellicle film for EUV from the single-crystal silicon film. Such a pellicle film as described above can be fabricated from an SOI film obtained by thin-filming an SOI substrate (including an SOQ substrate and an SOG substrate). If a pellicle film of the silicon crystal film is made from the SOI film, no excessive stress is subjected in the pellicle film formation process, and the pellicle film is formed under room temperature without causing strains.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Acoustic wave measuring apparatus, acoustic wave imaging apparatus and method for controlling acoustic wave measuring apparatus
InactiveUS8991261B2Increase signal strengthReduce equipment costsVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic waveLength wave
Owner:CANON KK
Biological information imaging apparatus
InactiveCN102149314AObtaining the Optical Absorption CoefficientDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionElectricityAttenuation coefficient
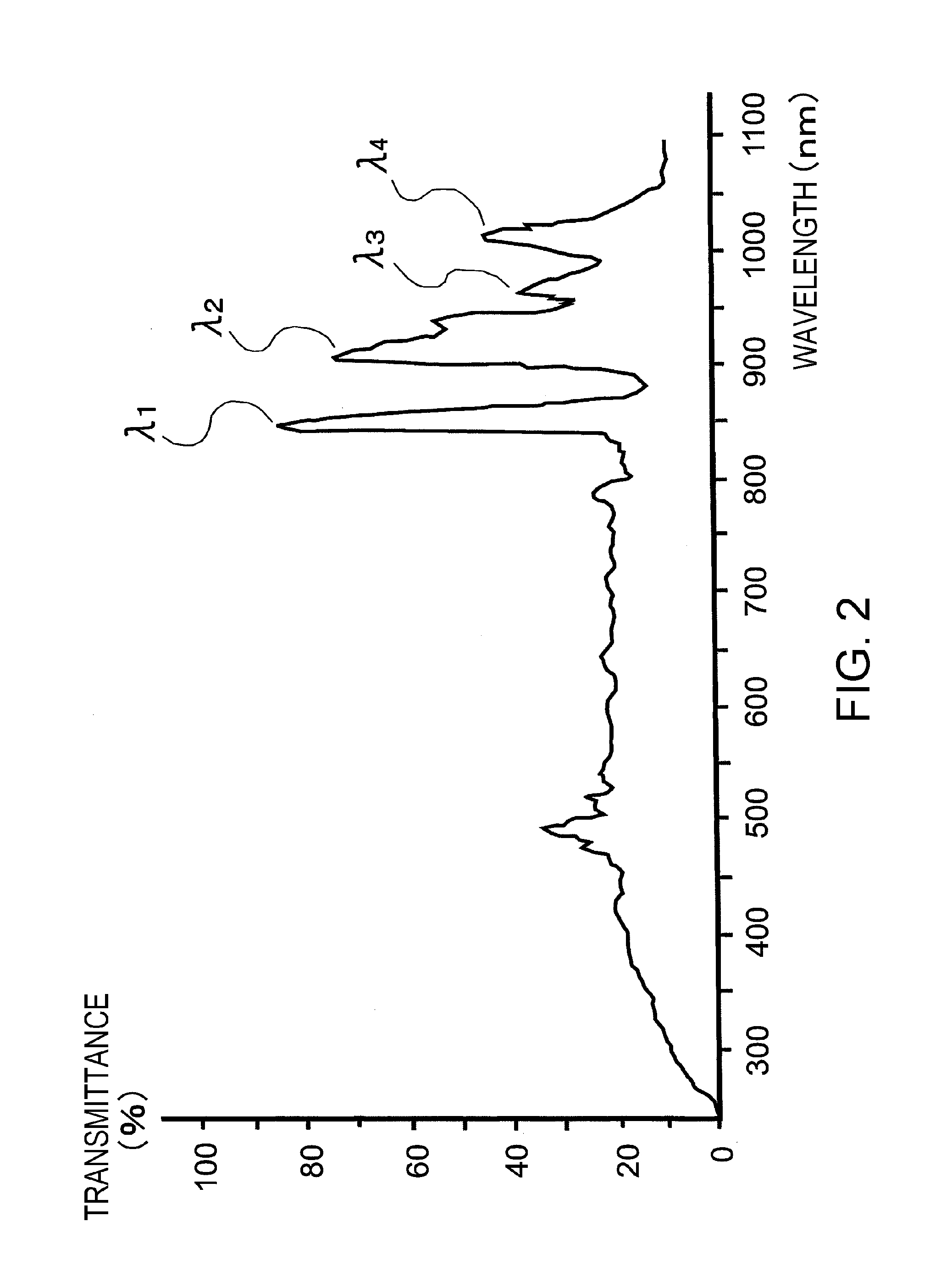
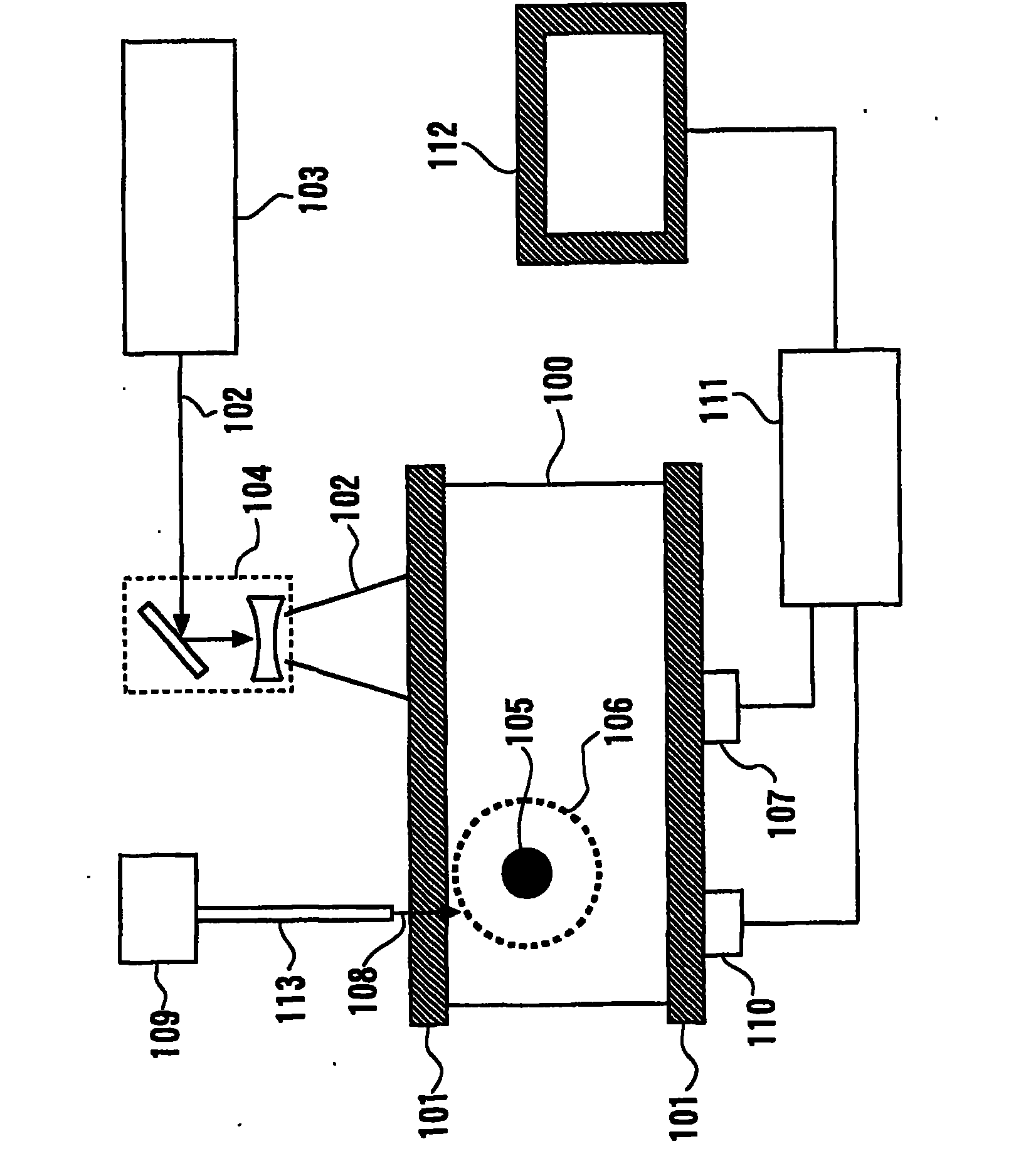
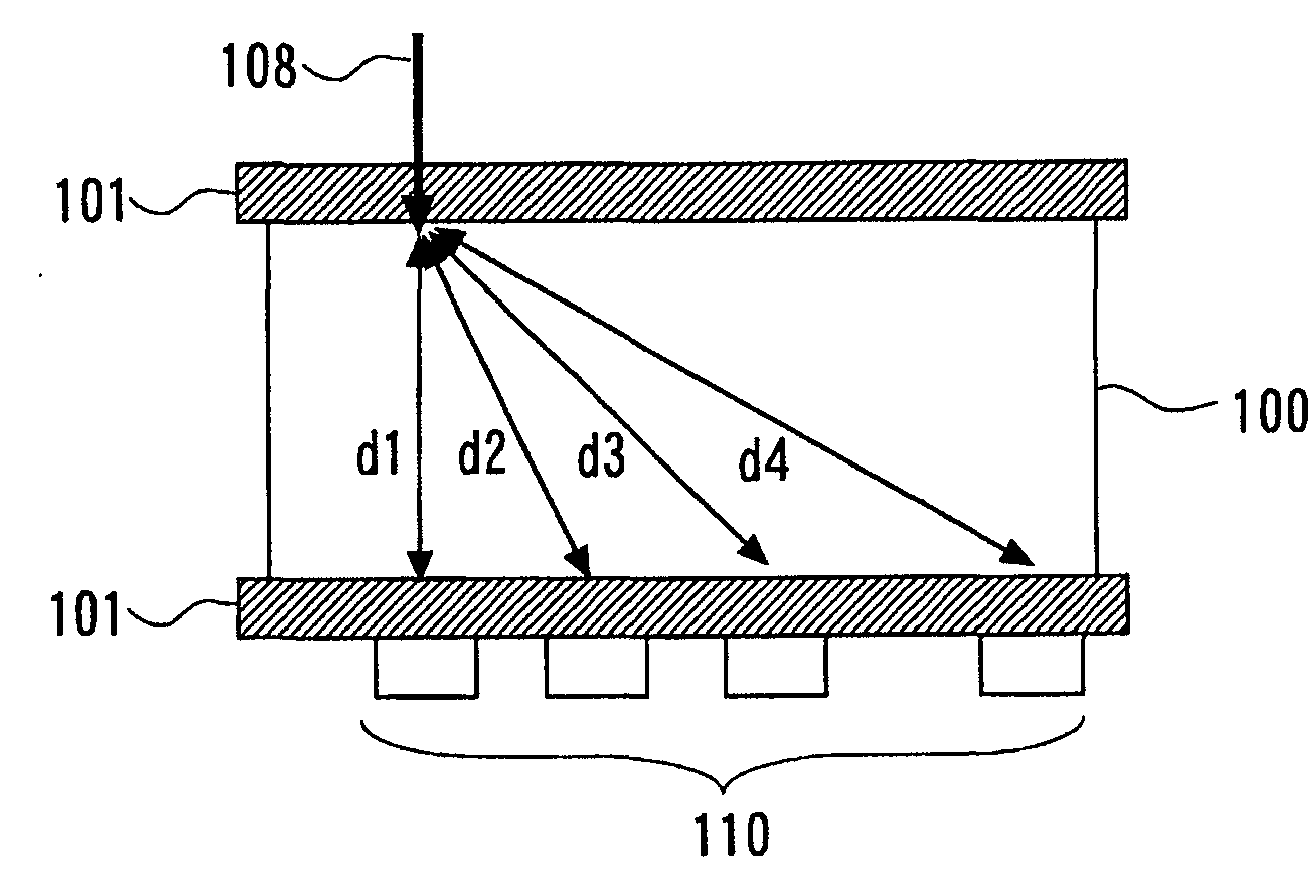
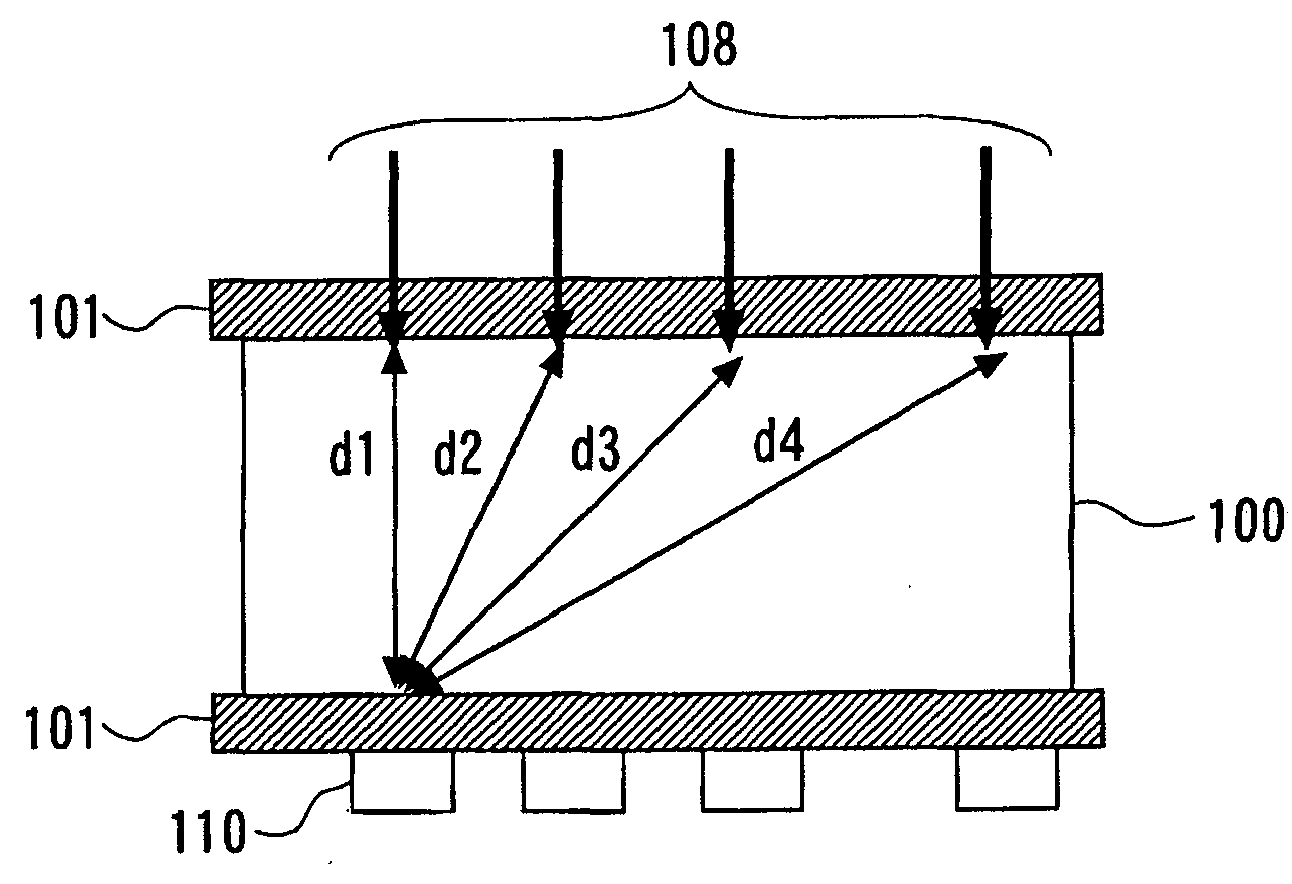
The biological information imaging apparatus includes an acoustic wave detector 107 that detects an acoustic wave that is generated from a light absorber 105 and converts it to a first electrical signal; a photo-detector 110 that detects intensities of the light corresponding to a plurality of propagation distances of the light which propagates through the specimen 110 and converts it to a second electrical signal; a signal processing apparatus 111 that derives an average effective attenuation coefficient [mu]eff of the specimen 110 based on the second electrical signal and derives an optical absorption coefficient [mu]a of the specimen 110 based on the first electrical signal and the average effective attenuation coefficient [mu]eff; and an image constructing apparatus 111 that constructs an image of the distribution of the optical absorption coefficient [mu]a based on the distribution of the optical absorption coefficient [mu]a.
Owner:CANON KK
Pellicle and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7901846B2Improve stabilityImprove transmittancePicture framesNanoinformaticsAmorphous siliconTransmittance
A pellicle of the present invention is provided with a silicon crystal film, the absorption coefficient of which is 0.005 / nm or lower with respect to light having a wavelength of 13.5 nm, as a pellicle film. The silicon crystal film is an indirect transition type semiconductor film and, therefore, the optical absorption coefficient thereof is relatively low. In particular, a single-crystal silicon film has a lower absorption coefficient than an amorphous silicon film and a polysilicon film. Thus, it is easy to obtain desired transmissivity required of a pellicle film for EUV from the single-crystal silicon film. Such a pellicle film as described above can be fabricated from an SOI film obtained by thin-filming an SOI substrate (including an SOQ substrate and an SOG substrate).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Lead-Free Bismuth Glass
InactiveUS20090042715A1Avoid distractionHigh precisionPhotosensitive materialsGas discharge electrodesLight irradiationLength wave
An object of the present invention is to provide a lead-free bismuth glass wherein decrease of the degree of accuracy of the patterning is prevented. Specifically, the present invention provides a lead-free bismuth glass characterized in that said lead-free bismuth glass is used for an optical patterning glass material which is patterned by light irradiation and the optical-absorption coefficient to light with a wavelength of 365 nm is 300 to 3000 cm−1.
Owner:NIHON YAMAMURA GLASS CO LTD +1
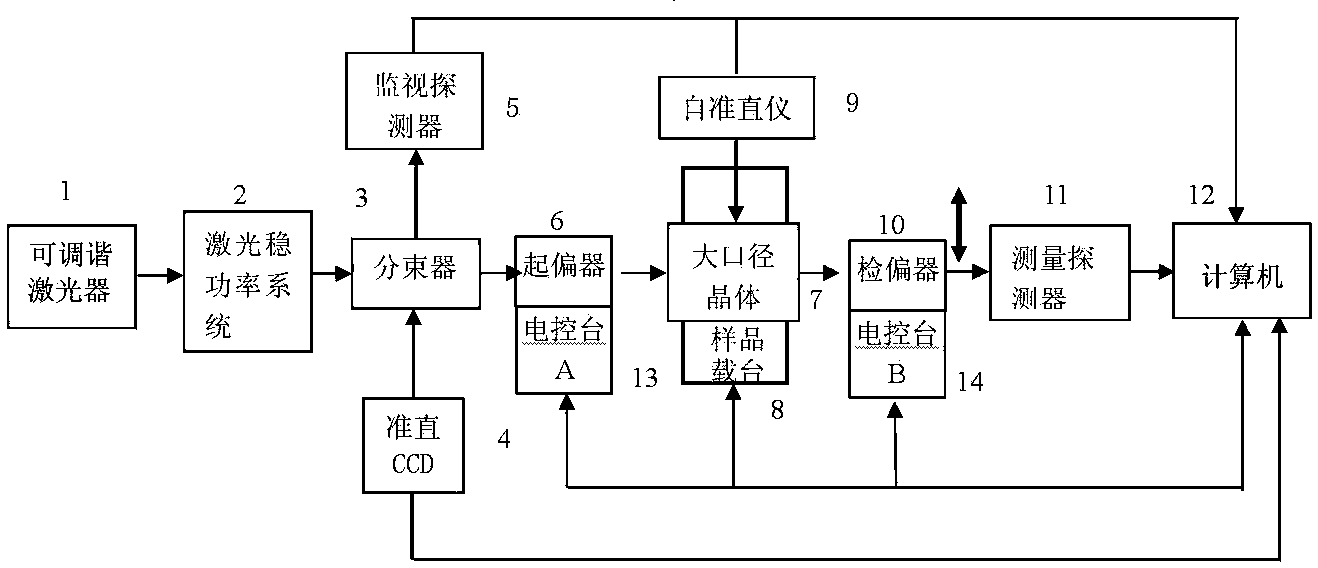
Device for measuring optical absorption coefficient of large-caliber crystalline material
InactiveCN103900963AEasy to operateImprove measurement repeatabilityPolarisation-affecting propertiesMeasurement devicePolarizer
The invention provides a device for measuring an optical absorption coefficient of a large-caliber crystalline material. According to the measurement device, stable collimated laser beams are formed by utilizing a tunable laser light source and a stable laser power system, the stable laser beams irradiate a measured large-caliber crystal, the perpendicularity between incident laser and the surface of the large-caliber crystal and the perpendicularity between the o-axis or e-axis of the large-caliber crystal and the table board are monitored by utilizing an optical autocollimating method, the laser polarization direction is adjusted and output to be parallel to the o-axis or e-axis of the large-caliber crystal by utilizing a polarizer and an analyzer, a transmission ratio of the o-light or e-light of the large-caliber crystal in a specific polarization state is measured, and a single-point absorption coefficient formula of the crystalline material on o-light or e-light is deduced by utilizing a Beer-Lambert law, so that the absorption coefficient of the large-caliber crystal can be measured, and finally, the large-caliber crystalline material is subjected to scanning and splicing measurement through a high-precision scanning sample platform deck mechanism, and precision measurement of the large-caliber crystalline material on the optical absorption coefficient of the o-light or e-light is realized.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Optically reliable nanoparticle based nanocomposite hri encapsulant, photonic waveguiding material and high electric breakdown field strength insulator/encapsulant
InactiveCN101084112AEnhanced light and heat decay resistanceThermal attenuation suppressionMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsEpoxyRefractive index
Owner:NANOCRYSTAL LIGHTING
Concentration determination apparatus, concentration determination method, and program
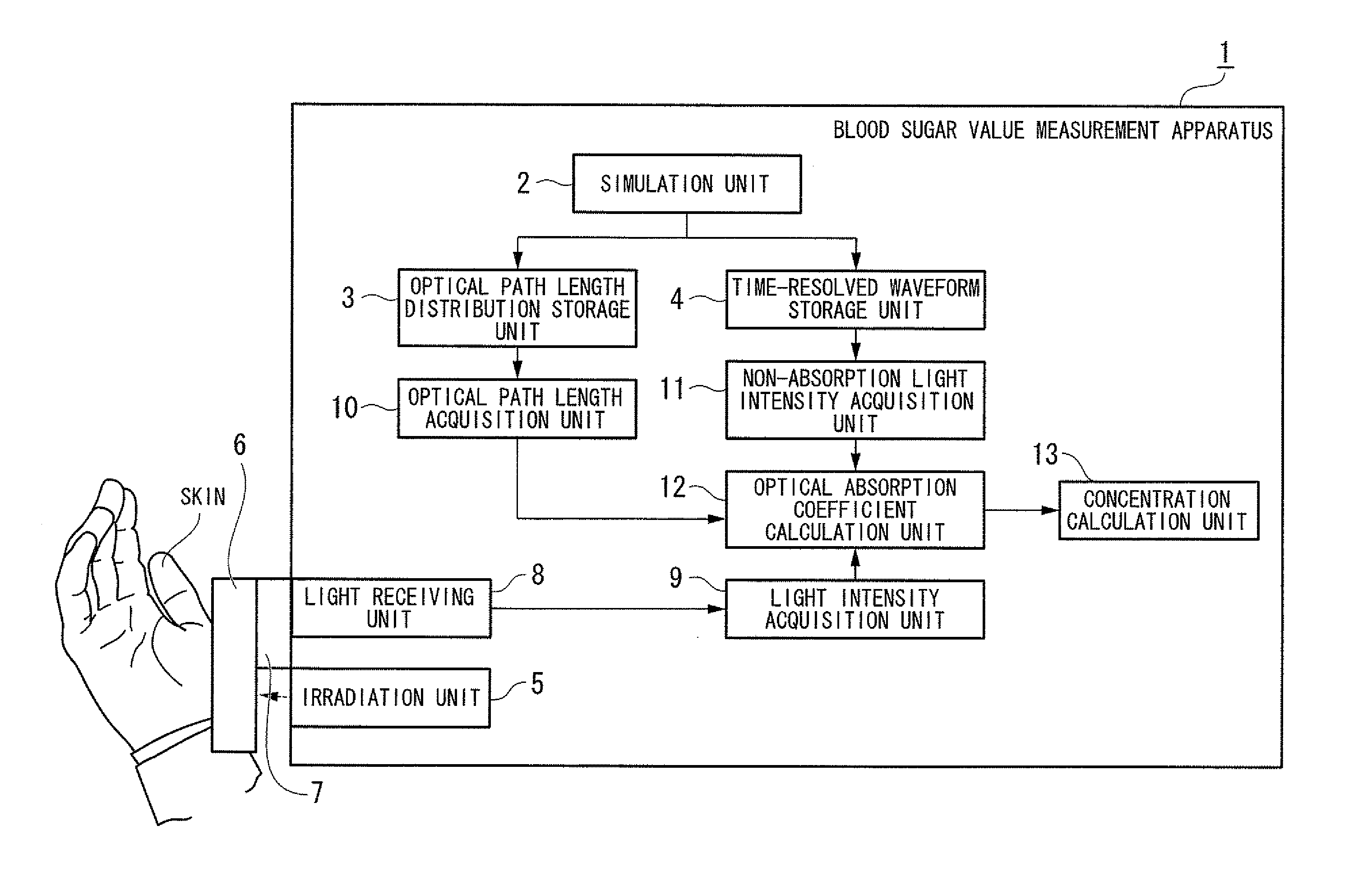
InactiveUS20120101347A1Accurate measurementAccurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringColor/spectral properties measurementsTime rangeOptical path length
A concentration determination apparatus may include: an irradiation unit that irradiates short-pulsed light to an observed object; a light receiving unit that receives light backscattered from the observed object; a light intensity acquisition unit that acquires an intensity distribution of the light; an optical path length distribution storage unit that stores a model of an optical path length distribution in each layer of the plurality of layers of the short-pulsed light; an optical path length acquisition unit that acquires the optical path length distribution of each layer; a time-resolved waveform storage unit that stores a model of a time-resolved waveform; a light intensity model acquisition unit that acquires a light intensity model; an integral interval calculation unit that calculates a time range of an area; an optical absorption coefficient calculation and acquisition unit that calculates and acquires an optical absorption coefficient; and a concentration calculation unit that calculates the concentration.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Making method for iron-doped lithium tantalum crystal
InactiveCN106192007AReduce reflectionReduce transgranular cleavage crackingPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsIridiumNon doped
The invention discloses a making method for an iron-doped lithium tantalum crystal. High-purity Ta2O5 and Li2CO3 are doped with 0.1-0.15 wt% Fe2O3, the raw materials are subjected to procedures of baking dehumidification, premixing, briquetting, high-temperature sintering and the like, then, the raw materials are put into an iridium crucible of a crystal growth furnace, and under the protective atmosphere, by means of czochralski method for crystal growing, the large size (3-6 inches) lithium tantalum crystal grows. According to the lithium tantalum crystal, by means of doping of Fe3+, polycrystalline producing in the crystal growing shoulder expanding process and isometrical later period is reduced, the quality of the crystal is effectively improved, the photorefraction performance, impact toughness and an optical absorption coefficient are improved, the crystal is more applicable to make a surface acoustic wave (SAW) filter and can completely replace a non-doped lithium tantalum crystal, and in application to the SAW filter, the iron-doped lithium tantalum crystal has important production improvement significance and market prospects.
Owner:TDG HLDG CO LTD
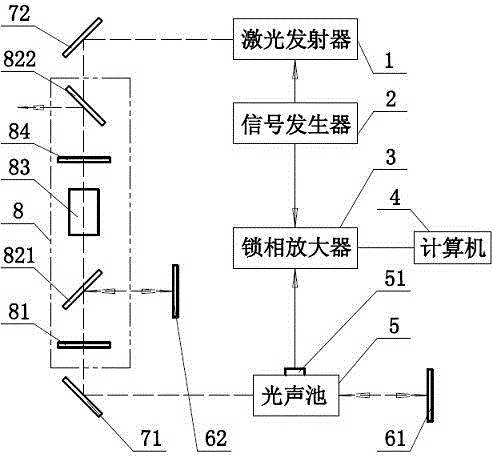
Laser multiple reflection photoacoustic spectroscopy technology-based aerosol optical absorption coefficient detection apparatus
ActiveCN104792703AIncrease laser powerIncrease amplitudeMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsorption factorOptical isolator
The invention provides a laser multiple reflection photoacoustic spectroscopy technology-based aerosol optical absorption coefficient detection apparatus. Laser passes through an optical isolator and an optoacoustic cell and is reflected by a first reflector, reflected laser passes through the optoacoustic cell and the optical isolator and is reflected by a second reflector, newly obtained reflected laser passes through the optical isolator and the optoacoustic cell and is reflected by the first reflector, the reflected laser passes through the optoacoustic cell and the optical isolator and then is output, a lock-in amplifier is connected with a microphone and a signal generator, and an optoacoustic signal is extracted from noises and is counted by a computer to obtain the absorption coefficient of aerosol. A technical problem that the influences of insufficient utilization of laser power on the detection precision of photoacoustic spectroscopy technology-based aerosol optical absorption coefficient detection apparatuses in the prior art is solved in the invention. Multiple reflection of the laser is carried out in the optoacoustic cell, so the laser power in the optoacoustic cell is improved without improving the laser output power; and the sensitivity of the amplitude enhancement detection apparatus of the optoacoustic signal is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEASUREMENT SCI RES INST
Photoelectric transistor based on GeSn materials and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106024922AOvercome rangeOvercome absorbencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSPhotodetector
The invention discloses a photoelectric transistor based on GeSn materials and a manufacturing method thereof, aiming to solve the problem that present III-V infrared photodetectors are difficult to perform silicon-based integration and IV silicon and germanium detectors have a narrow detection range. The collector region, light absorption region, base region, and emitter region of the photoelectric transistor all employ IV GeSn alloys. A substrate, the collector region, the light absorption region, the base region, and the emitter region are successively vertically distributed, and a protective layer covers the periphery of the collector region, the light absorption region, the base region, and the emitter region. The photoelectric transistor is prepared by employing the standard CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technique, utilizes GeSn materials having gaps and a high optical absorption coefficient, and has a wider infrared detection range compared with a Ge detector, and higher luminous sensitivity and photoelectric current.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com