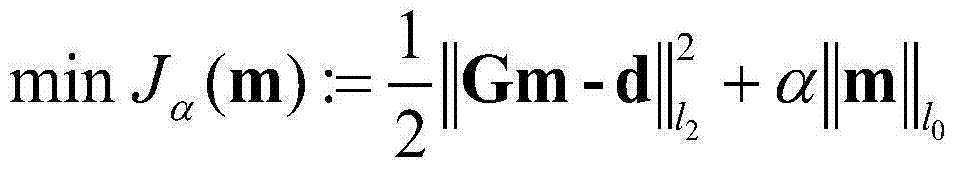Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Subsurface imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
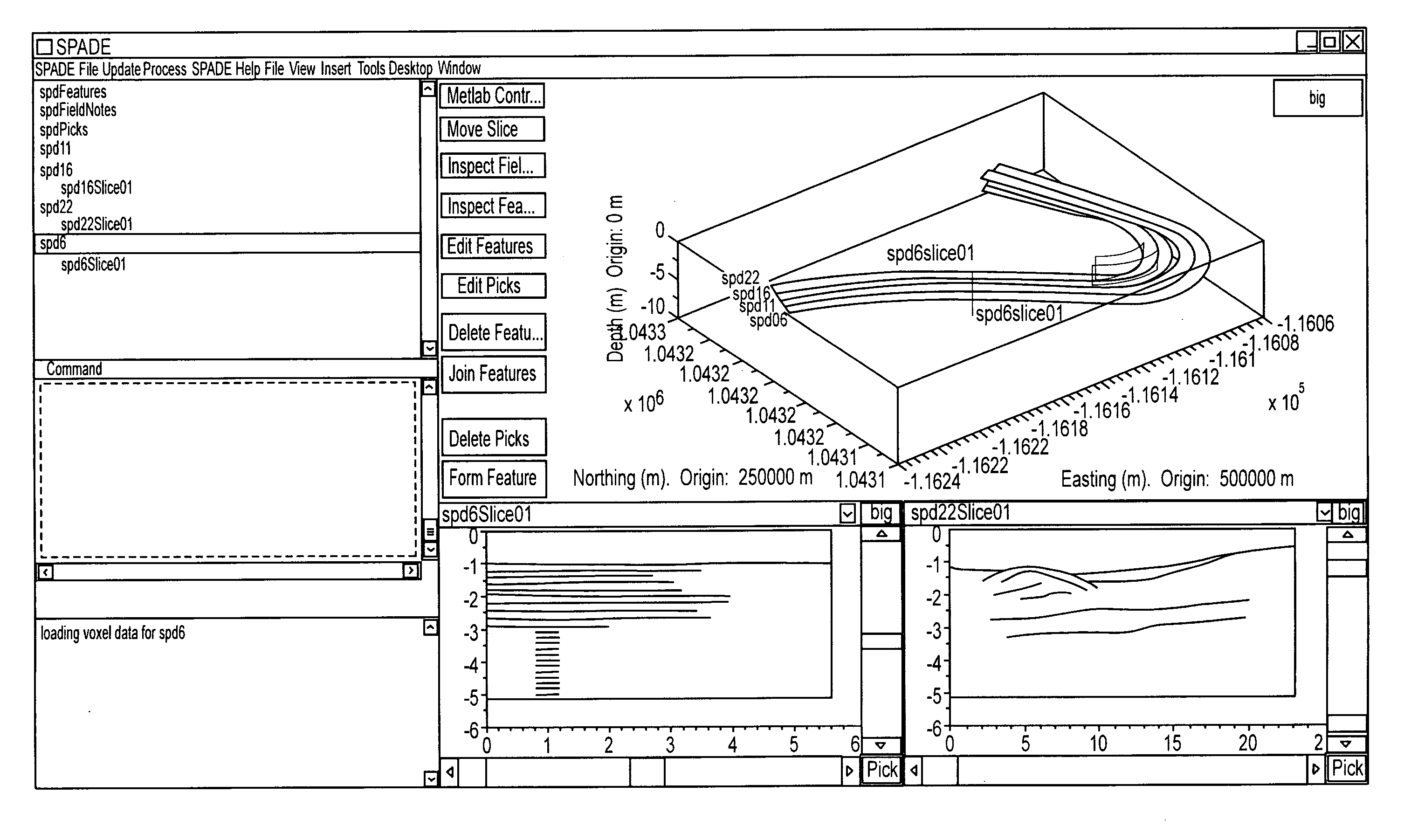
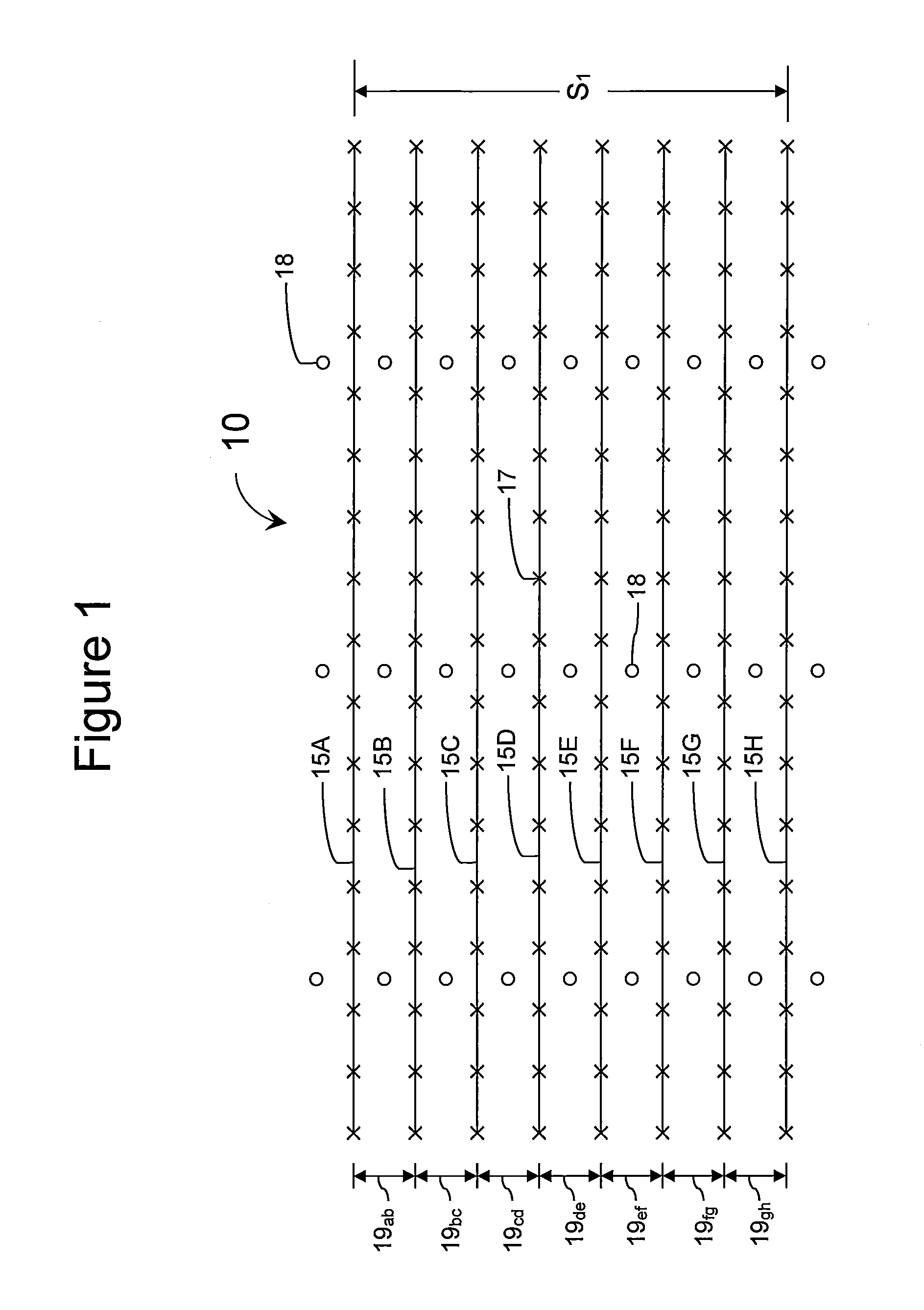
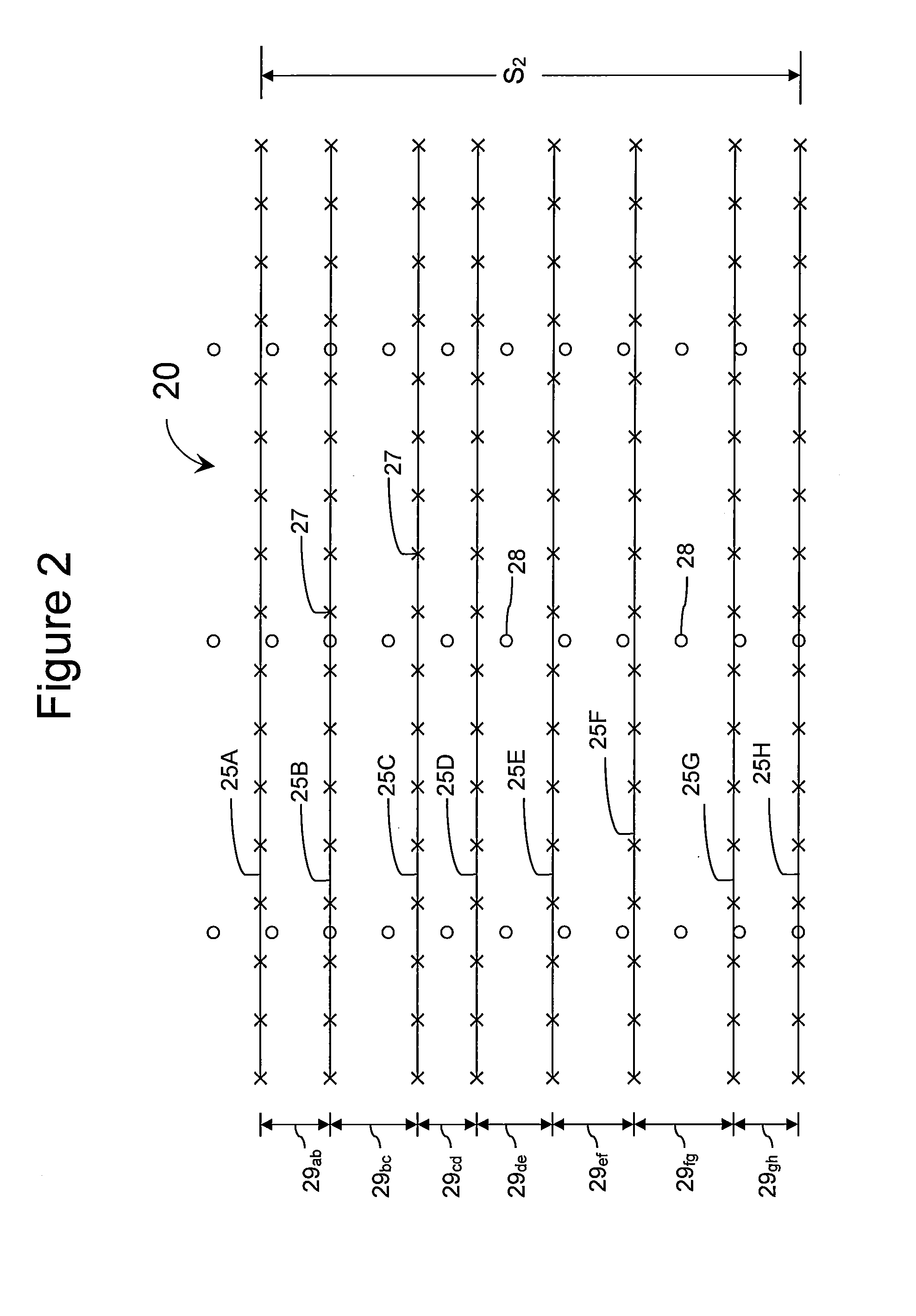
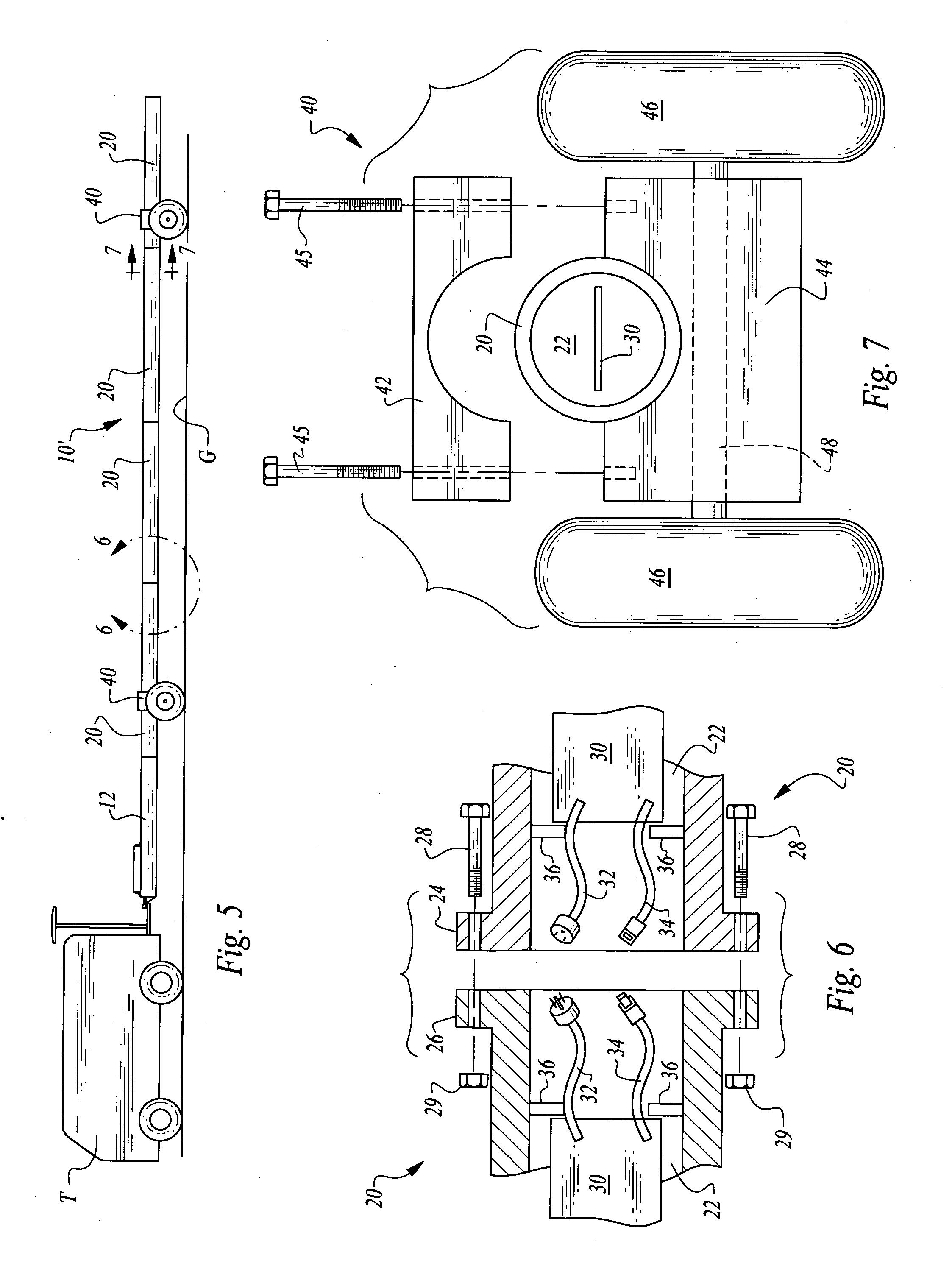
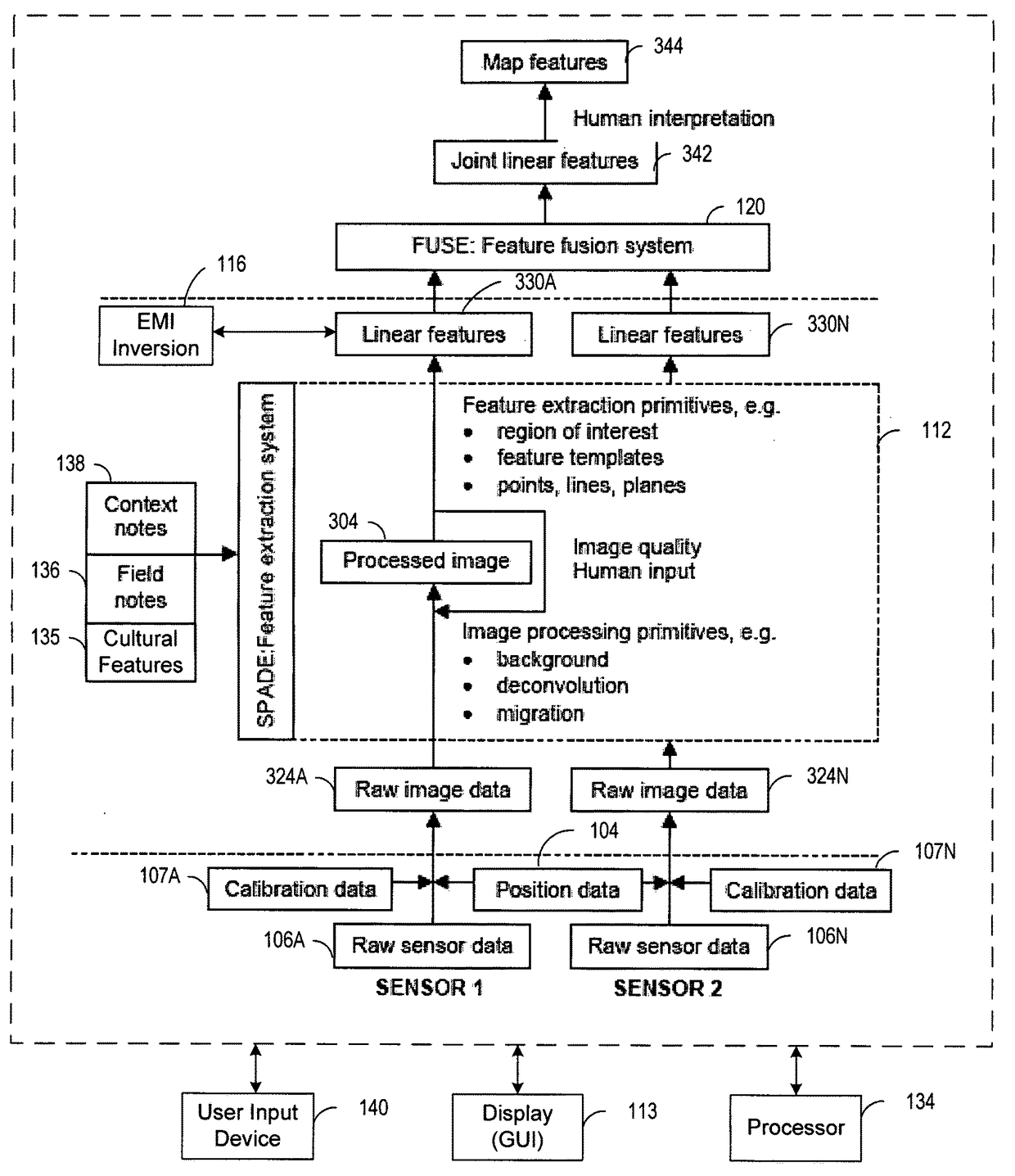
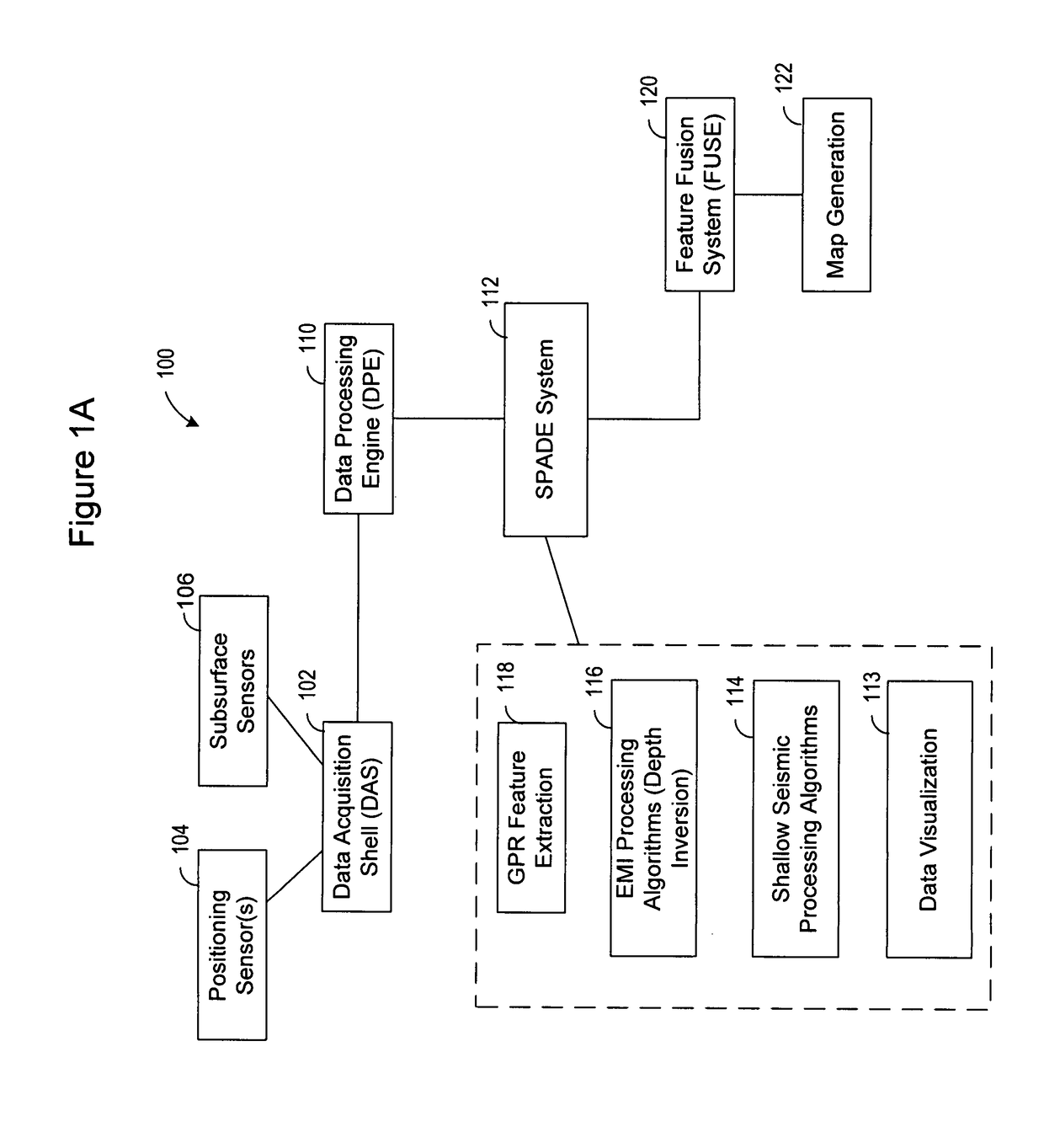
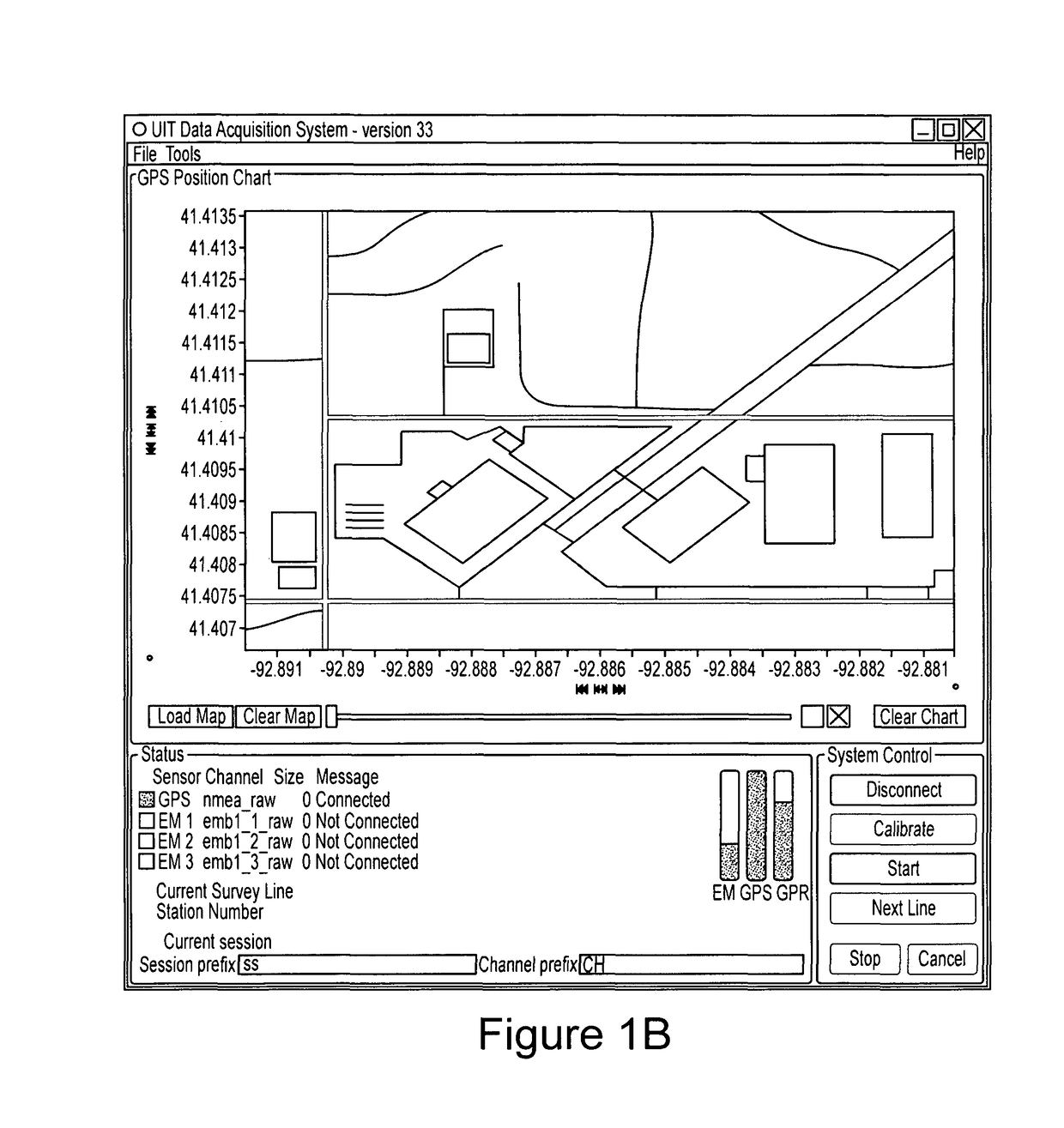
System and method for visualizing multiple-sensor subsurface imaging data
A user interface includes a display for displaying of a plurality of sensor data sets representative of signals associated with a plurality of sensors configured for sensing of a subsurface. At least some of the sensors are configured for subsurface sensing in a manner differing from other sensors of the plurality of sensors. Each of the sensor data sets comprises sensor data samples each associated with geographic position data. The sensor data sets are shown overlaid within a volume depicted on the display. The graphical representations of the sensor data sets are individually viewable within the volume and displayed in geographical alignment relative to one another within the volume in accordance with the geographic position data of the sensor data samples of each of the sensor data sets.
Owner:UNDERGROUND IMAGING TECH
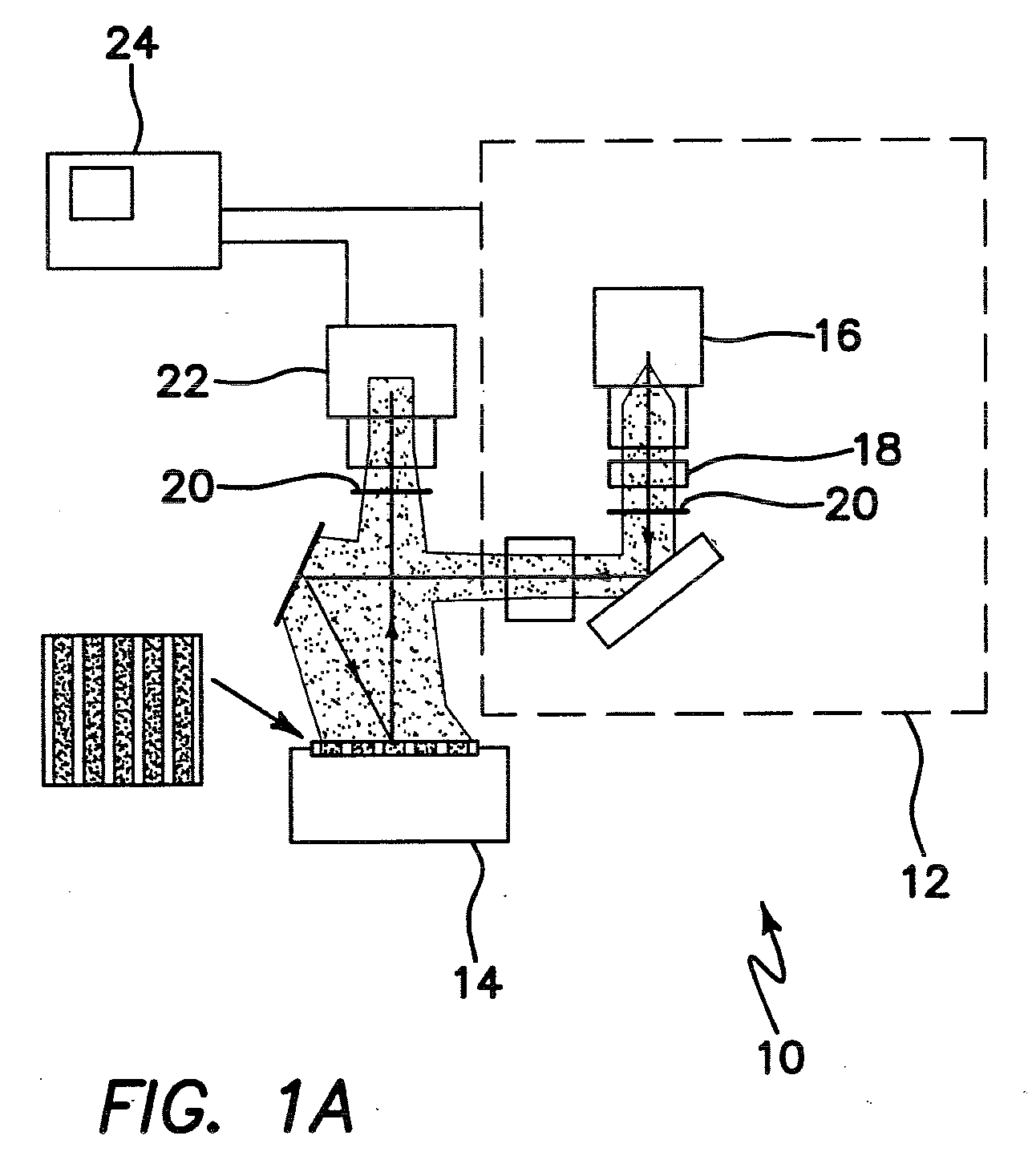
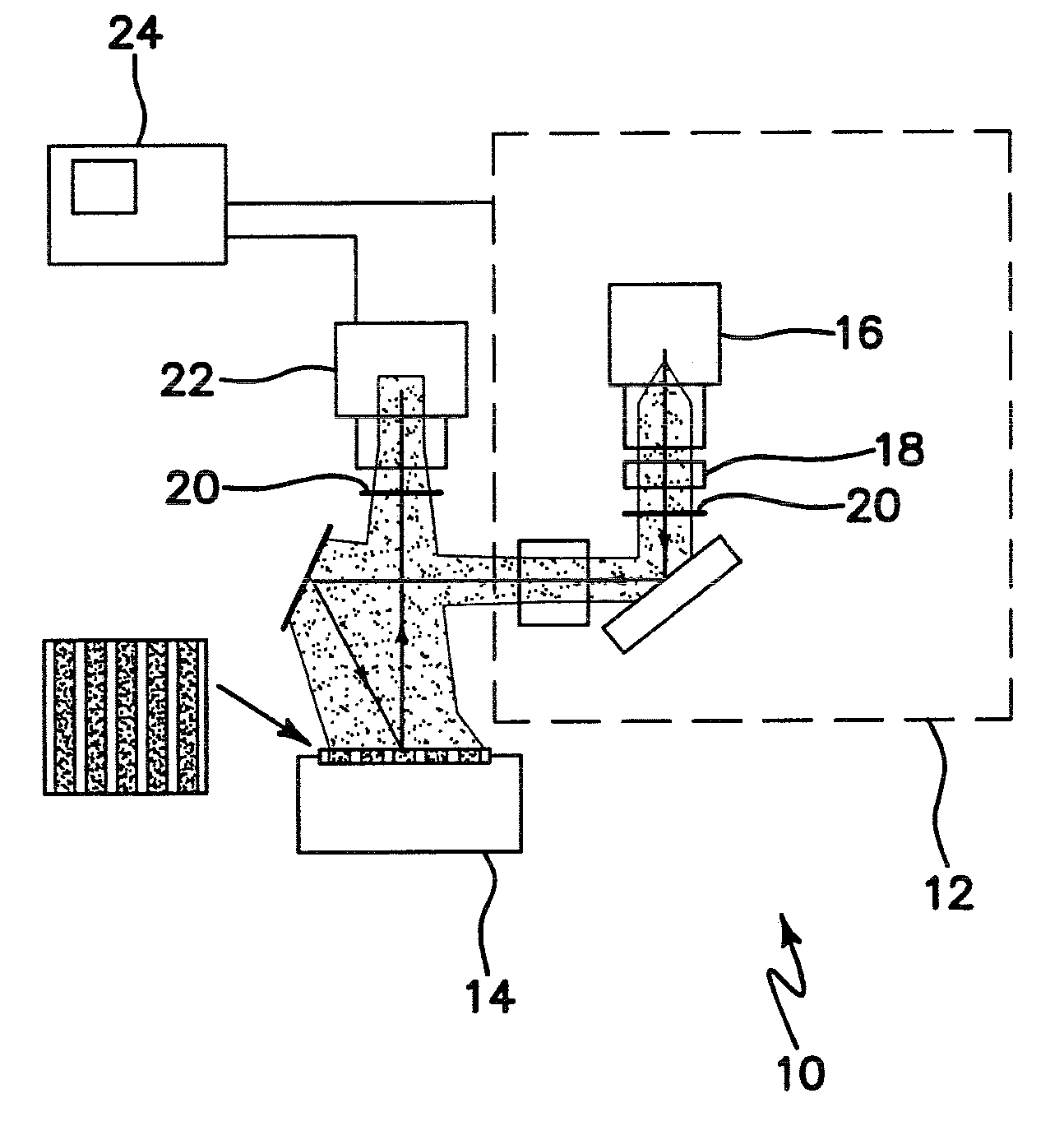
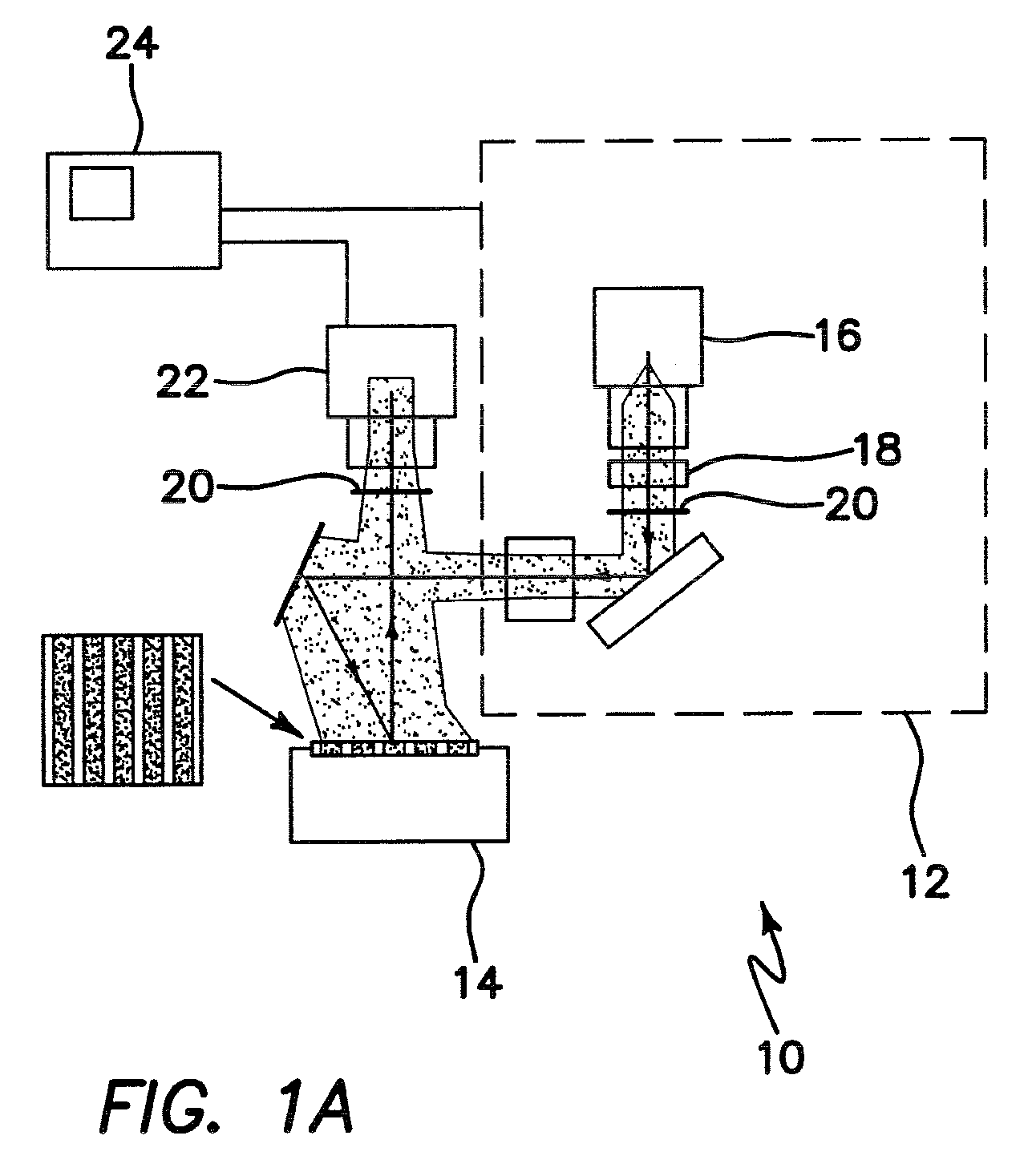
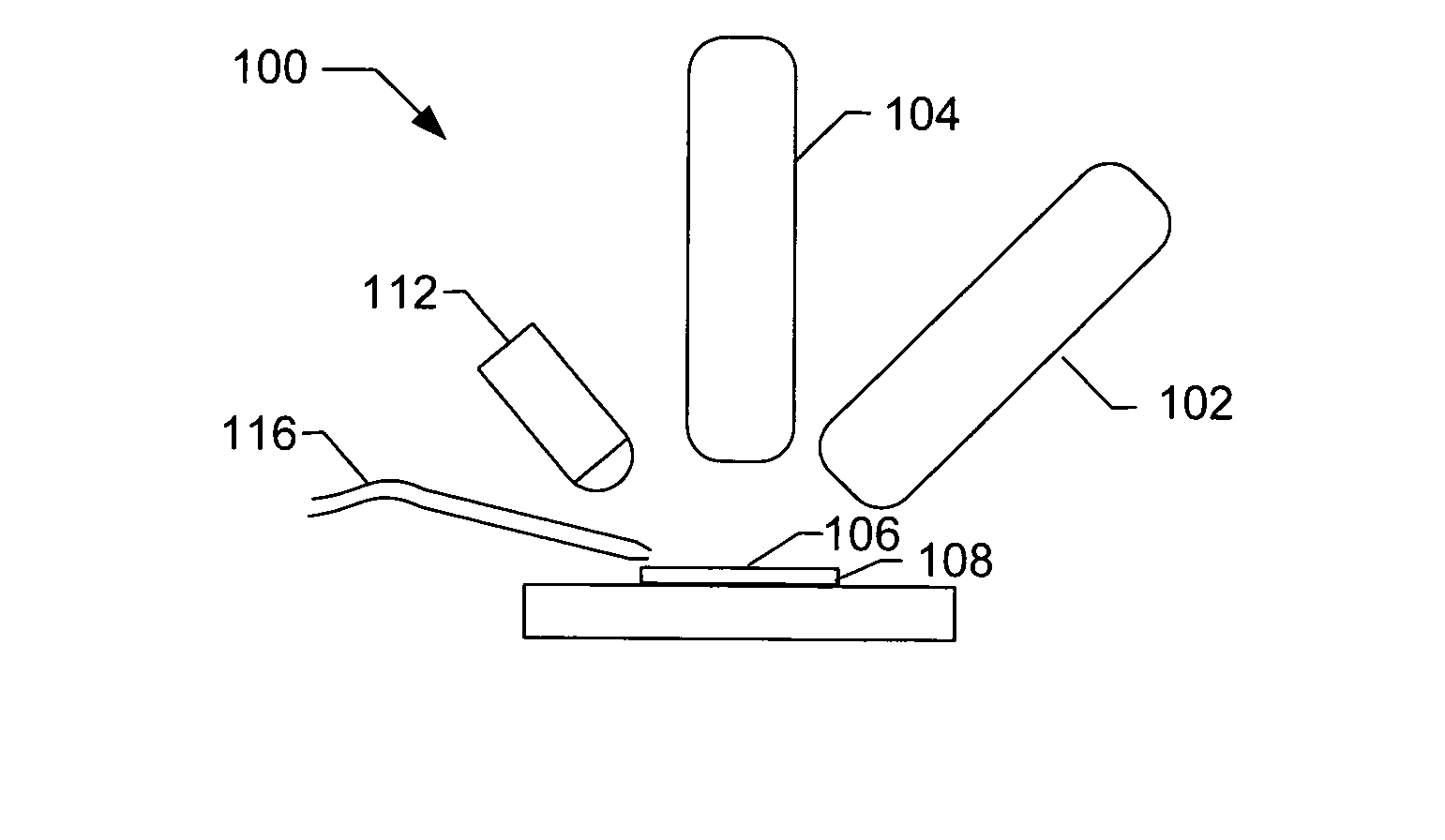
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR WIDEFIELD FUNCTIONAL IMAGING (WiFI) USING INTEGRATED STRUCTURED ILLUMINATION AND LASER SPECKLE IMAGING
ActiveUS20090118622A1Minimal artifactHigh degree of fidelity and spatial localizationMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterWide fieldFunctional imaging
An apparatus for wide-field functional imaging (WIFI) of tissue includes a spatially modulated reflectance / fluorescence imaging (SI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales, and a laser speckle imaging (LSI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales using integrated with the (SI) device. The SI device and LSI device are capable of independently providing quantitative measurement of tissue functional status.
Owner:MODULATED IMAGING
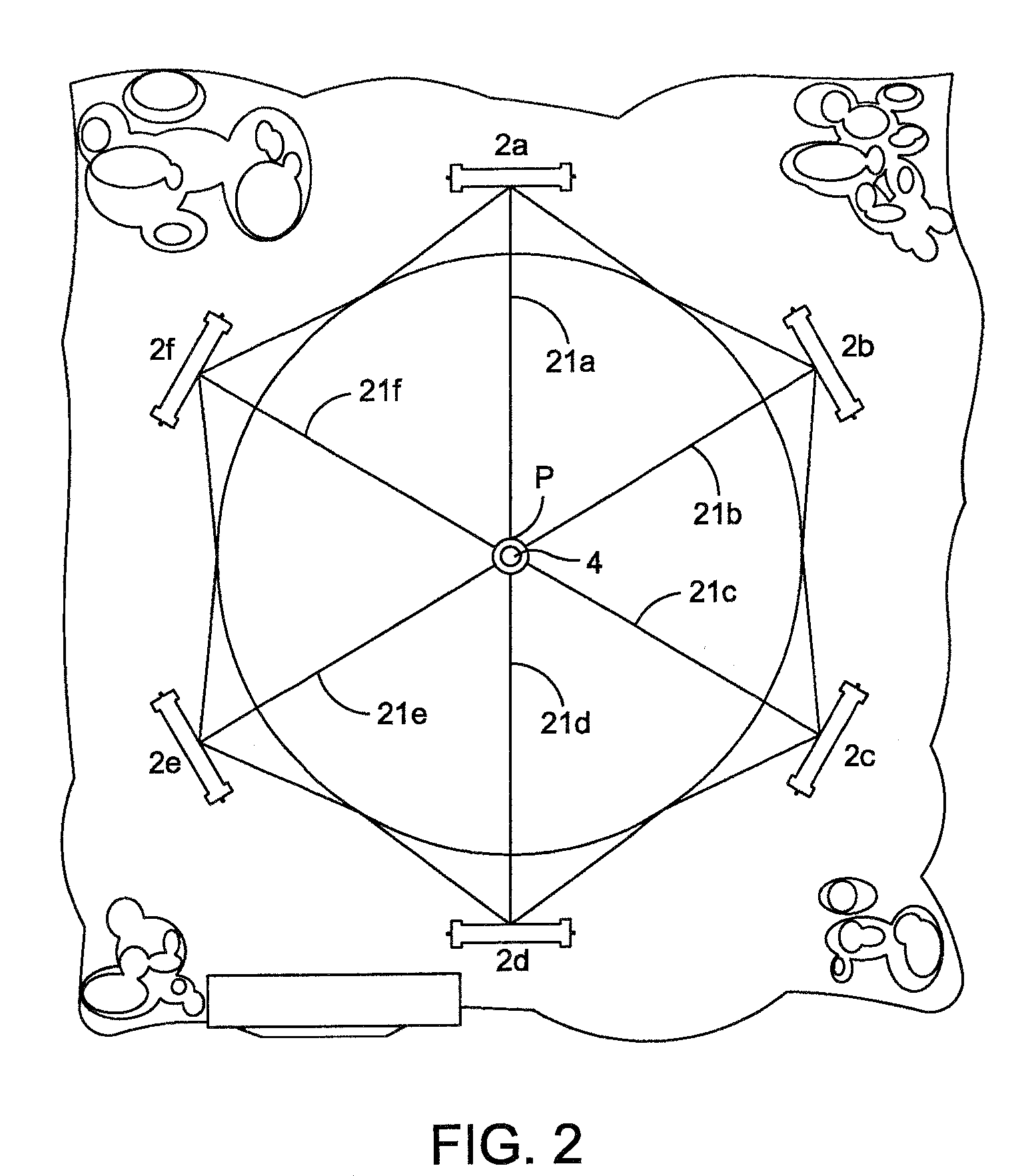
High precision subsurface imaging and location mapping with time of flight measurement systems
A system for tracking a ground imaging apparatus includes a plurality of fixed devices and at least one tracked device. The fixed devices are positioned at fixed locations and the tracked device is affixable to the ground imaging apparatus. The fixed devices and the tracked device are configured to transmit and / or receive signals used for time of flight measurements. A processor is configured to determine one or more positions of the tracked device relative to one or more of the fixed devices based upon one or more time of flight measurements between the tracked device and one or more of the fixed devices.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
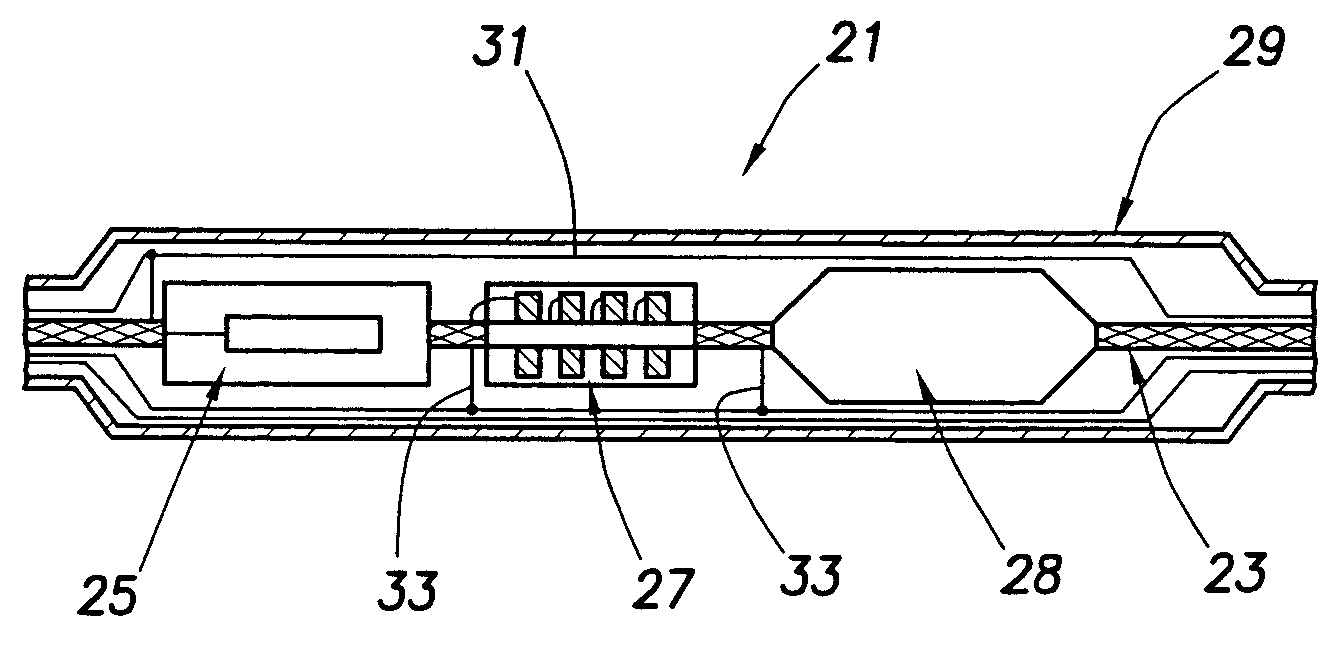
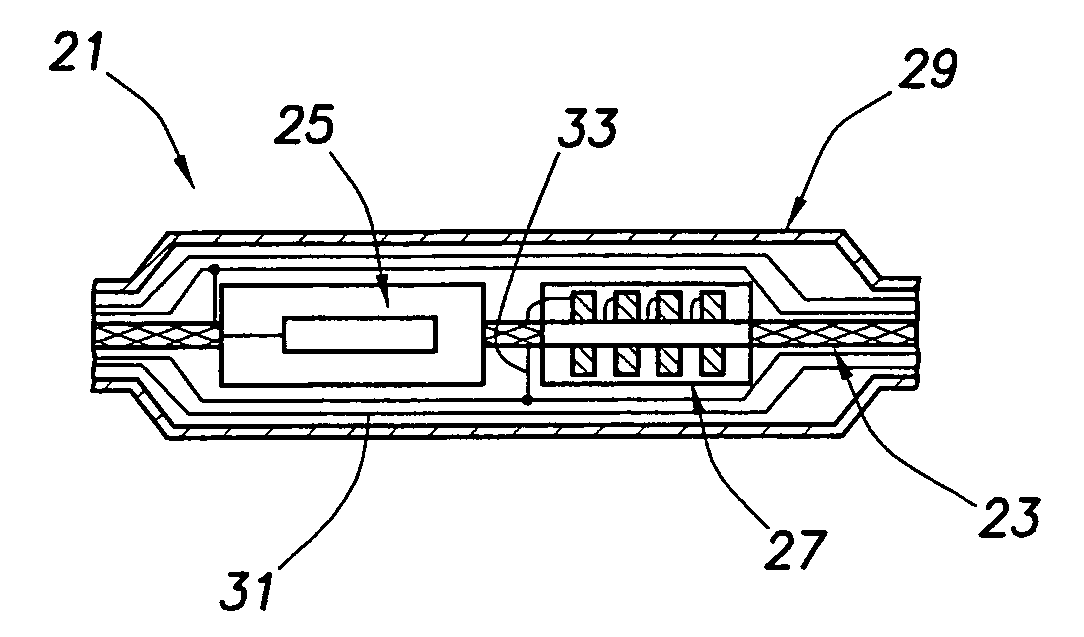
Subsurface conductivity imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS7023213B2Detection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic sourceElectricity
A subsurface imaging cable includes a plurality of sensor modules, wherein the plurality of the sensor modules are flexible and each of the plurality of the sensor modules is spaced apart on the subsurface imaging cable at a selected distance; and a flexible medium connecting the plurality of the sensor modules, wherein the subsurface imaging cable is flexible and adapted to be wound on a reel. A method for subsurface images includes acquiring direct-current measurements at a plurality of sites in a survey area; acquiring a first set of electric and magnetic measurements from natural electromagnetic fields at the plurality of sites; acquiring a second set of electric and magnetic measurements using controlled electric and magnetic sources at the plurality of sites; and determining a subsurface conductivity distribution from the direct-current measurements and the first set and the second set of electric and magnetic measurements.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for widefield functional imaging (WiFI) using integrated structured illumination and laser speckle imaging
ActiveUS8509879B2High degree of fidelity and spatial localizationSufficient spatiotemporal resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterWide fieldFluorescence
An apparatus for wide-field functional imaging (WiFI) of tissue includes a spatially modulated reflectance / fluorescence imaging (SI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales, and a laser speckle imaging (LSI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales using integrated with the (SI) device. The SI device and LSI device are capable of independently providing quantitative measurement of tissue functional status.
Owner:MODULATED IMAGING
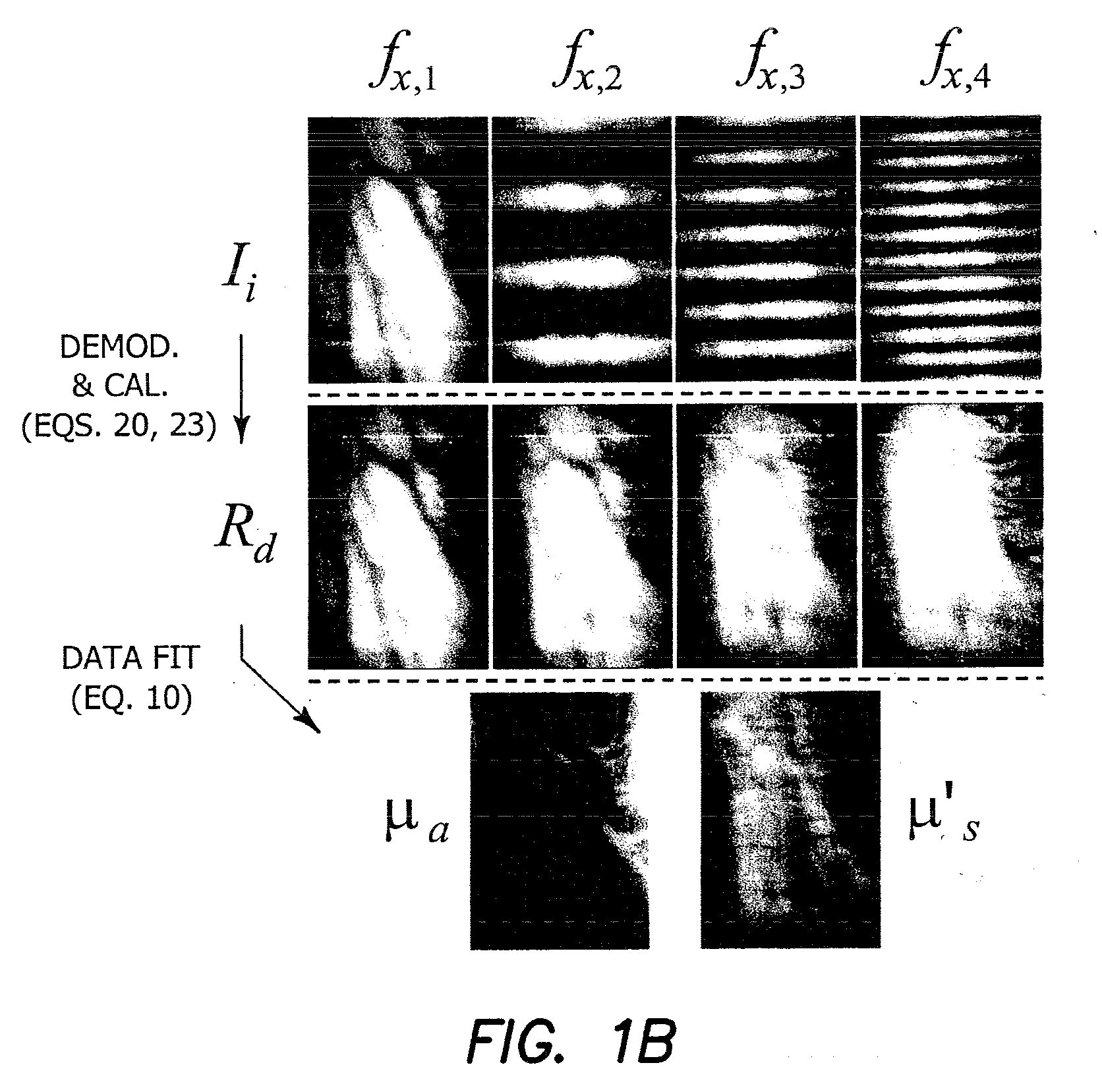
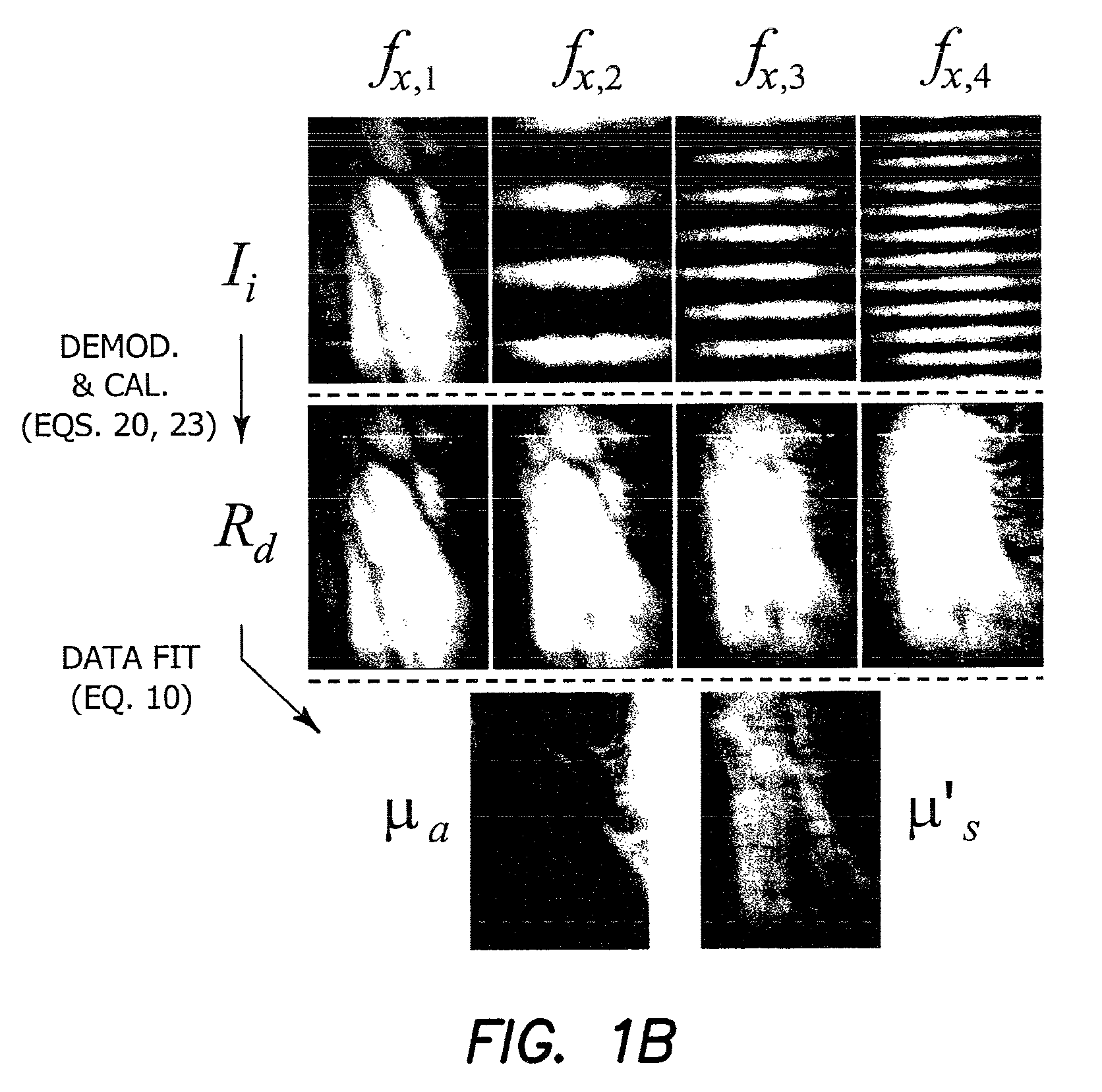
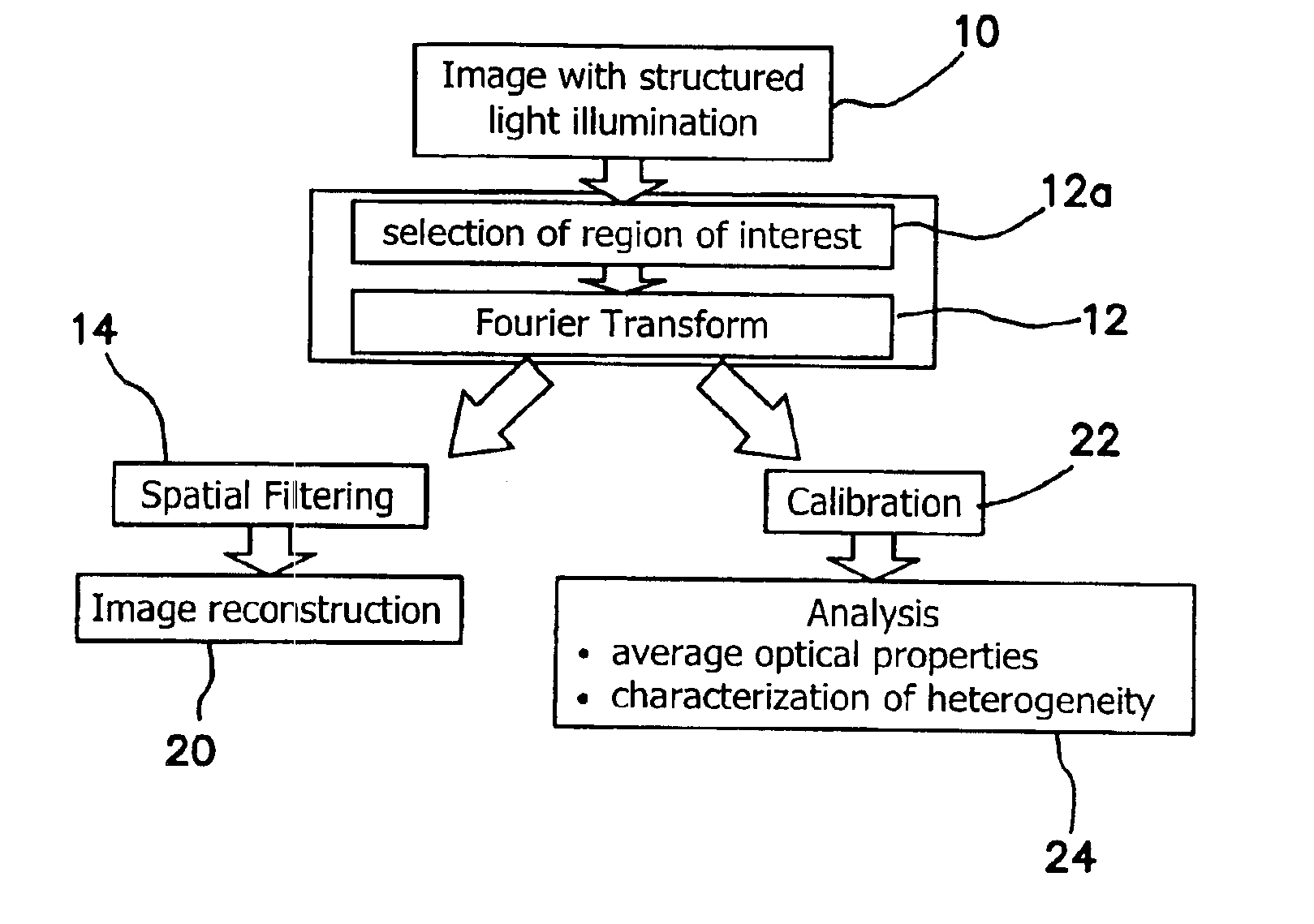
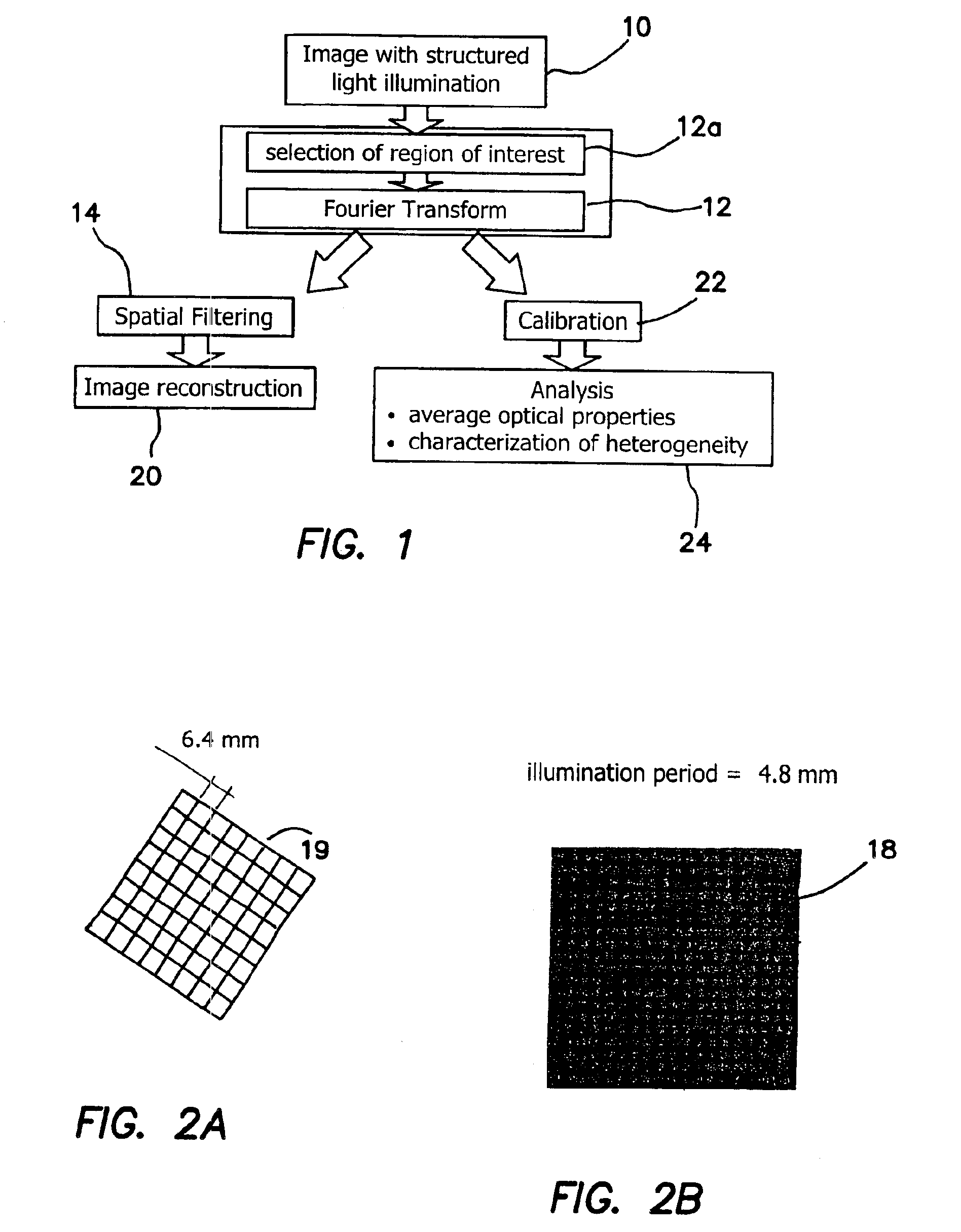
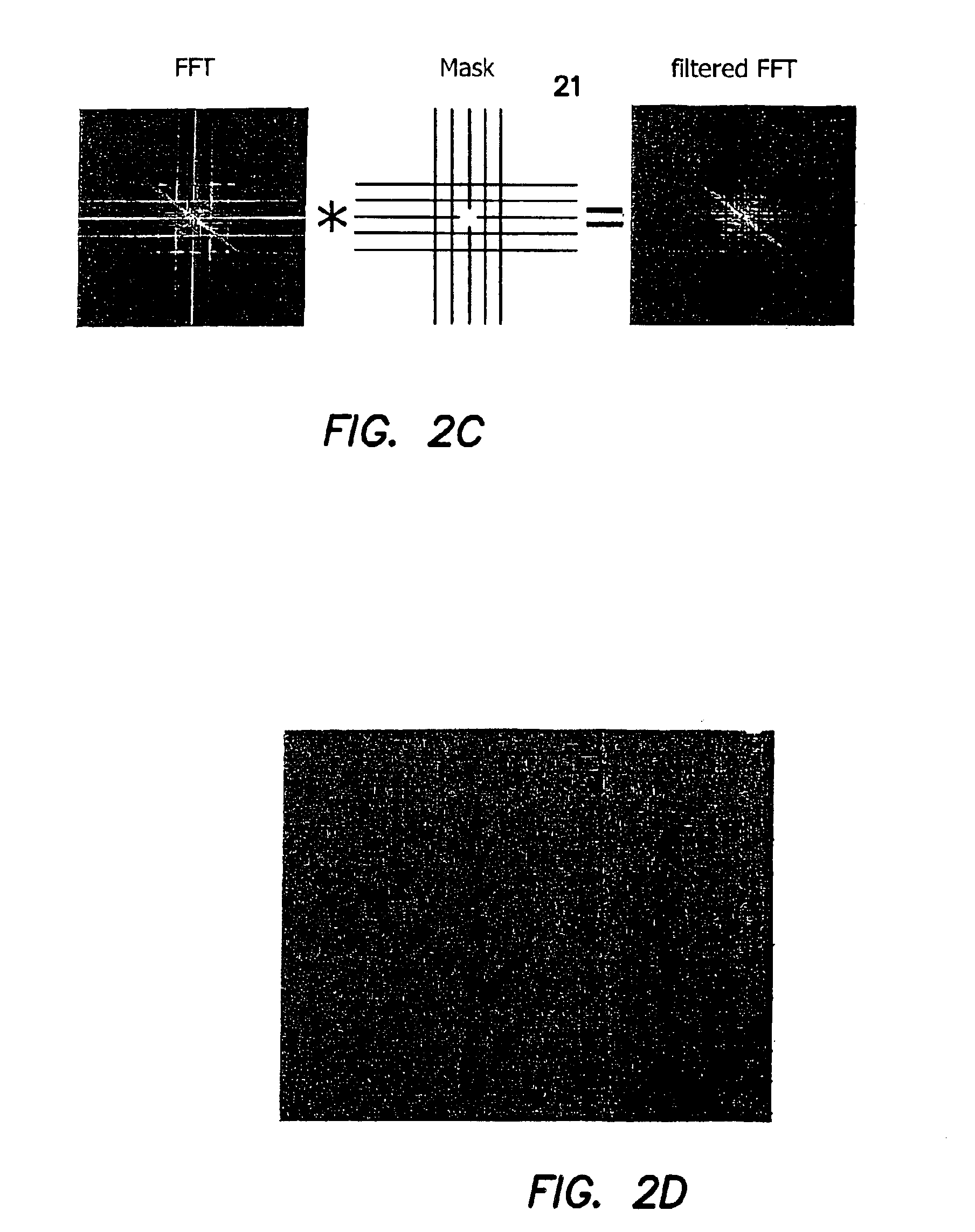
Method and apparatus for performing quantitative analysis and imaging surfaces and subsurfaces of turbid media using spatially structured illumination
ActiveUS6958815B2Recover optical propertyScattering properties measurementsOptical propertySpatial structure
Illumination with a pattern of light allows for subsurface imaging of a turbid medium or tissue, and for the determination of the optical properties over a large area. Both the average and the spatial variation of the optical properties can be noninvasively determined. Contact with the sample or scanning is not required but may be desired. Subsurface imaging is performed by filtering the spectrum of the illumination in the Fourier domain but other filtering approaches, such as wavelet transform, principle component filter, etc may be viable as well. The depth sensitivity is optimized by changing the spatial frequency of illumination. A quantitative analysis of the average optical properties and the spatial variation of the optical properties is obtained. The optical properties, i.e. reduced scattering and absorption coefficients are determined from the modulated transfer function, MTF.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
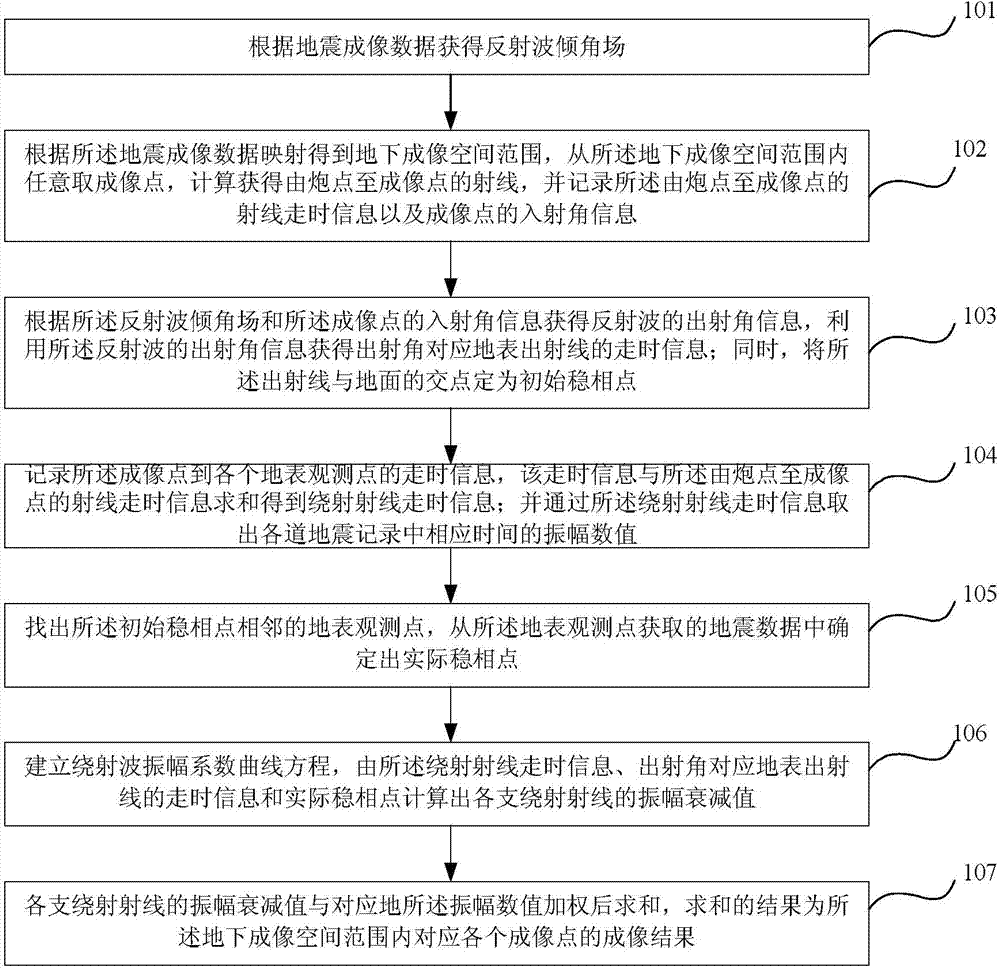
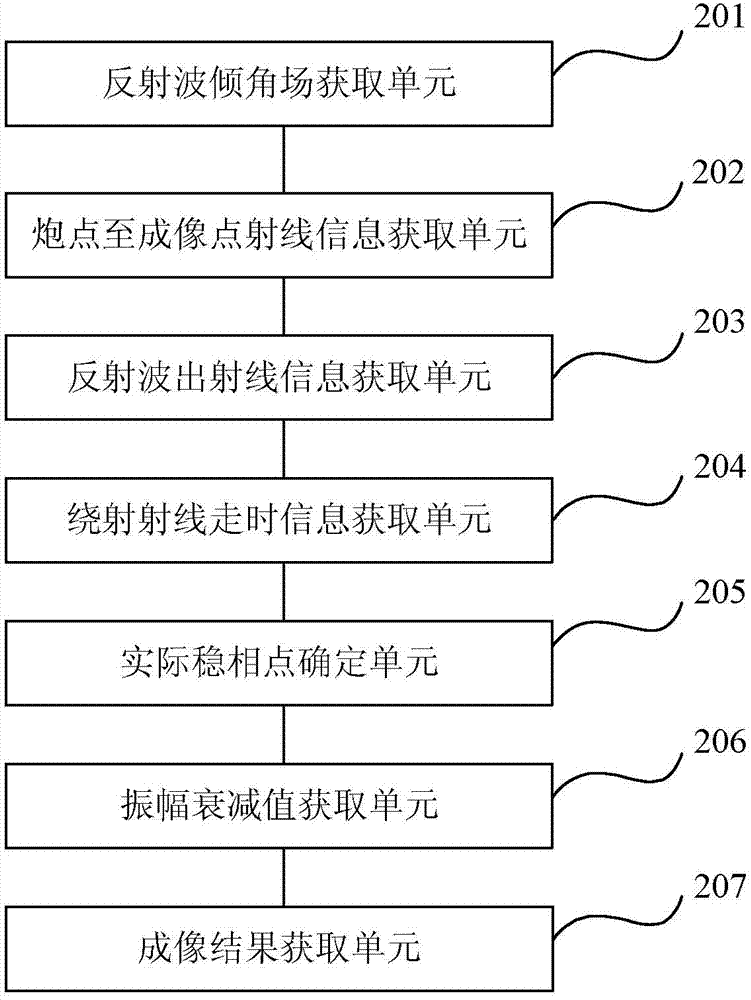
Diffracted wave imaging method and diffracted wave imaging device based on dynamical features
The invention relates to a diffracted wave imaging method and a diffracted wave imaging device based on dynamical features. The diffracted wave imaging method comprises the following steps of acquiring a reflected wave inclination field according to earthquake imaging data; optionally taking an imaging point and recording travel time information of a ray from a shot point to the imaging point and the information of incident angle of the imaging point; acquiring travel time information of a ground surface emergent ray corresponding to an emergent angle; setting an intersection point of the emergent ray and the ground as an initial stationary phase point; recording travel time information from the imaging point to various ground surface observation points; summing the travel time information and the travel time information of the ray from the shot point to the imaging point so as to obtain travel information of a diffraction ray; taking out an amplitude numerical value of corresponding time in various earthquake records and determining an actual stationary phase point; establishing a diffracted wave amplitude coefficient curvilinear equation; acquiring an amplitude attenuation value of a diffraction ray according to the travel time information of the diffraction ray, the travel time information of the emergent angle corresponding to the ground surface emergent ray and the actual stationary phase point; and performing summing after weighting the amplitude attenuation value of the diffraction ray and a corresponding ground amplitude numerical value so as to obtain imaging results of various corresponding imaging points in an underground imaging space range.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Subsurface imaging using an electron beam
ActiveUS20060219953A1Sufficient energyAccurate locationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLight beamSubsurface imaging
A method of navigating or endpointing a microscopic structure by subsurface imaging using a beam of electrons having sufficient energy to penetrate the surface and produce a subsurface image. For endpointing, when the subsurface image become relatively clear at a known electron energy, a user knows that he is approaching the buried feature. For navigating, a subsurface image can be formed of fiducials or other features to determine the position of the beam on the device.
Owner:FEI CO
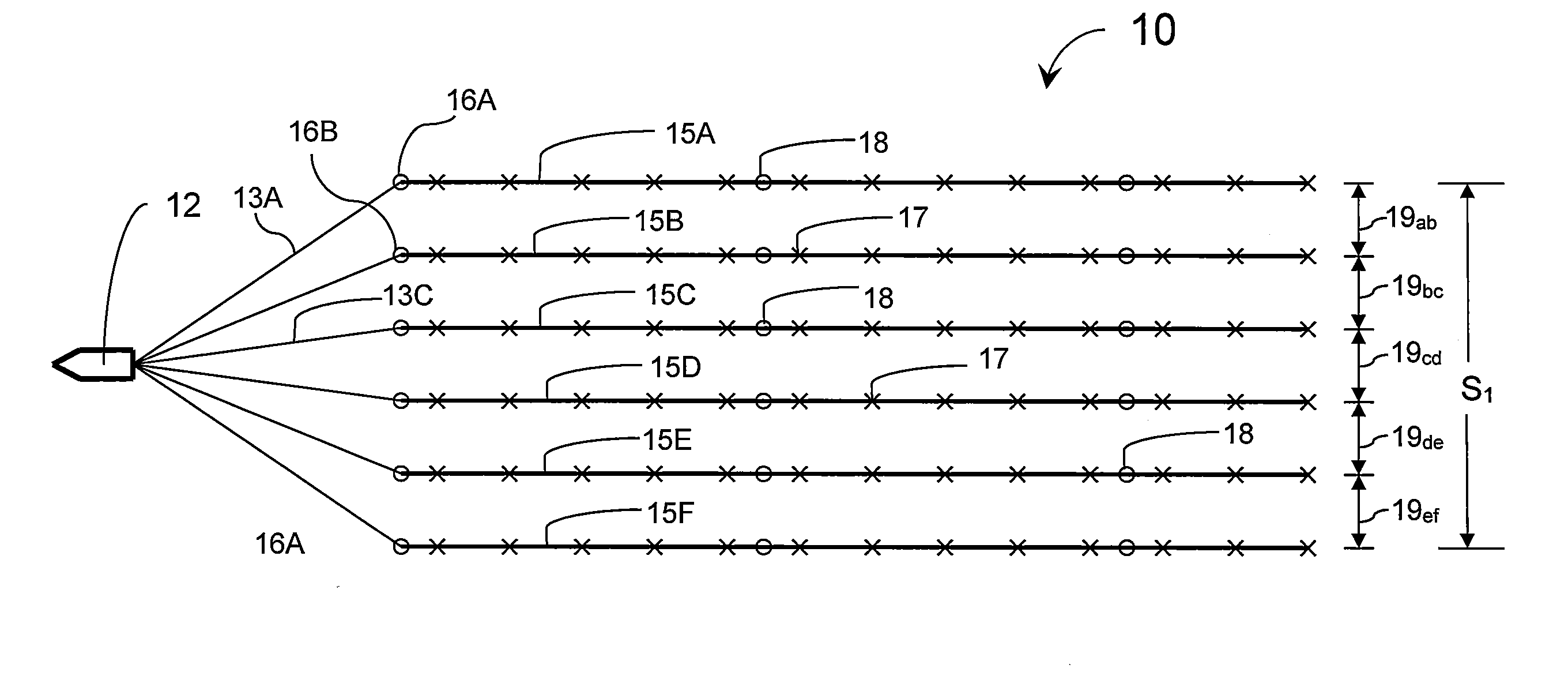
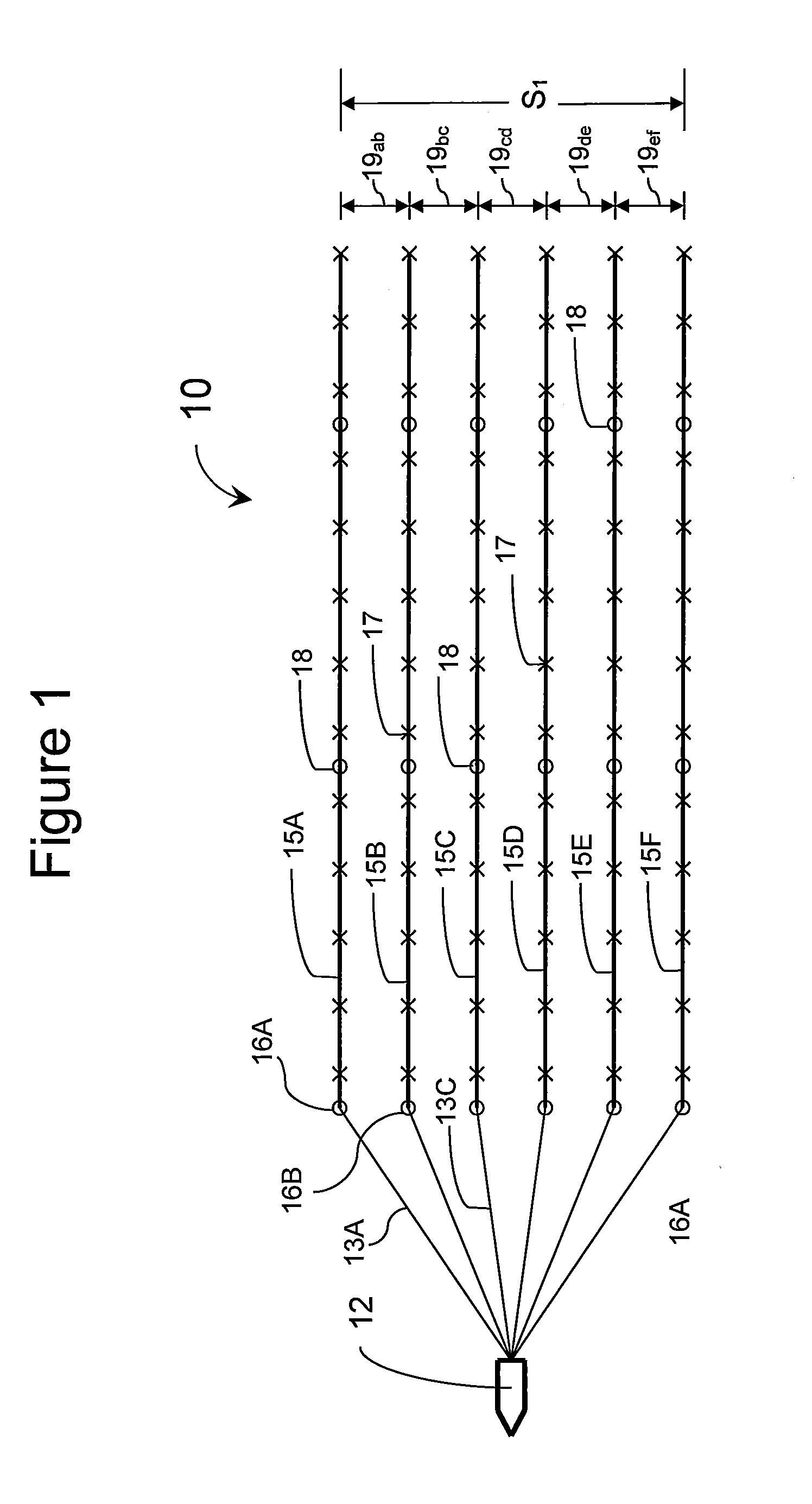
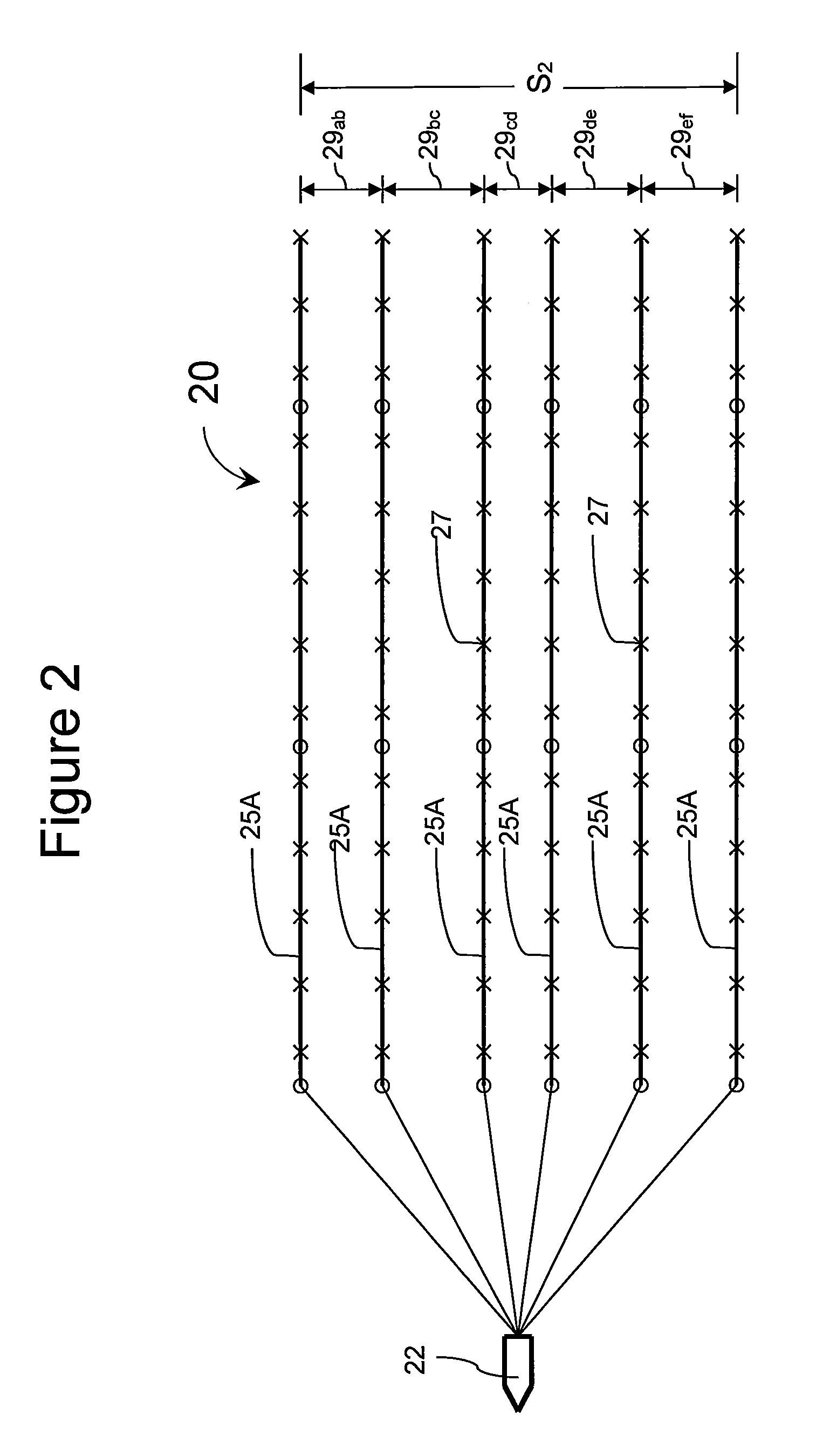
Marine seismic data acquisition using designed non-uniform streamer spacing
ActiveUS20110305106A1Seismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasData acquisitionWave field
The invention relates to an arrangement for seismic streamers used in the acquisition of seismic data in a marine environment where the spacing between each adjacent pair of streamers is not all the same. Some streamer spacings and / or receiver spacings are larger and some are smaller to provide a higher quality wavefield reconstruction when covering a larger total area or for a similar total area of seismic data acquisition while providing a wavefield that is optimally sampled by the receivers so that the wavefield reconstruction is suitable for subsurface imaging needs.
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
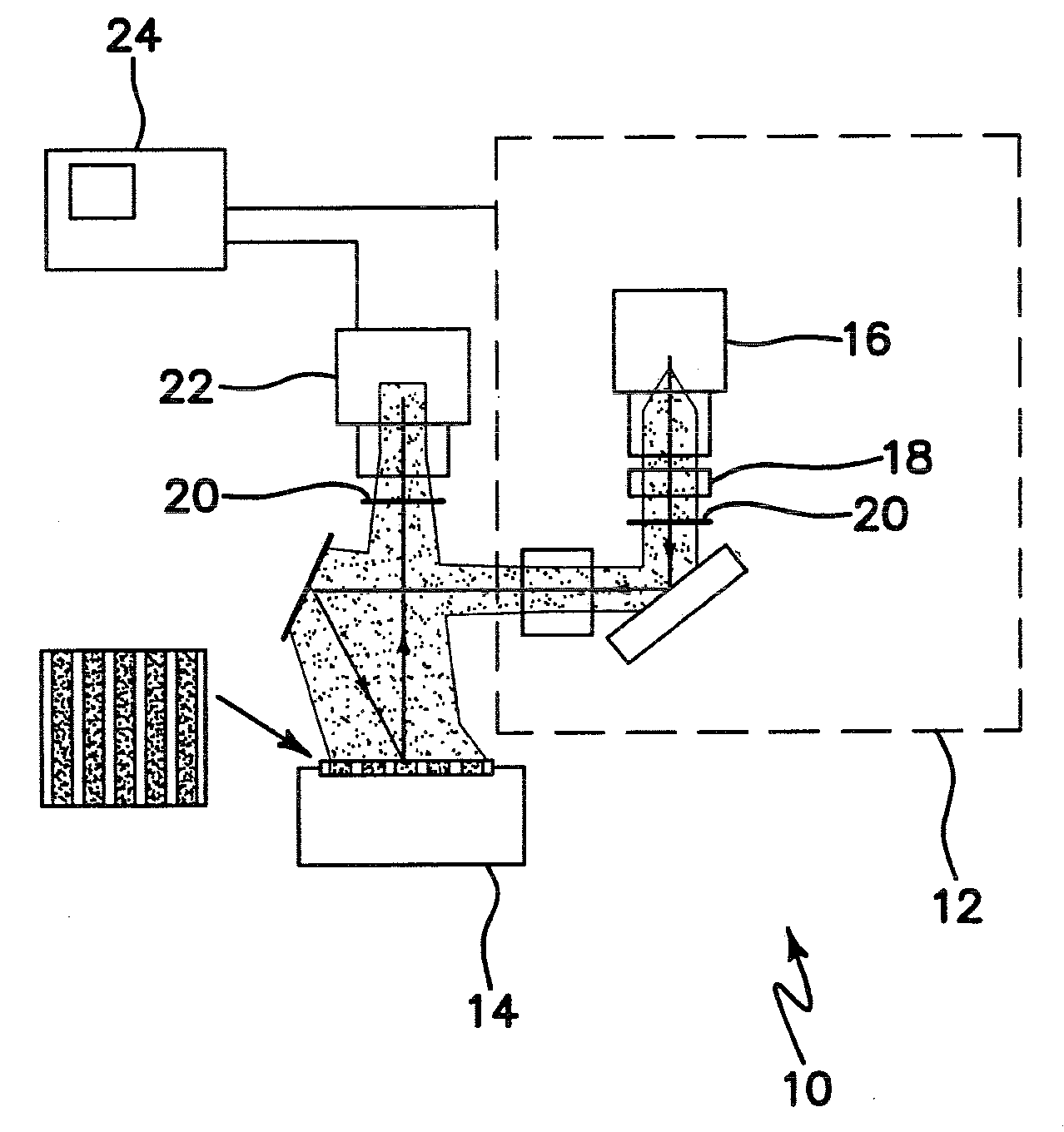
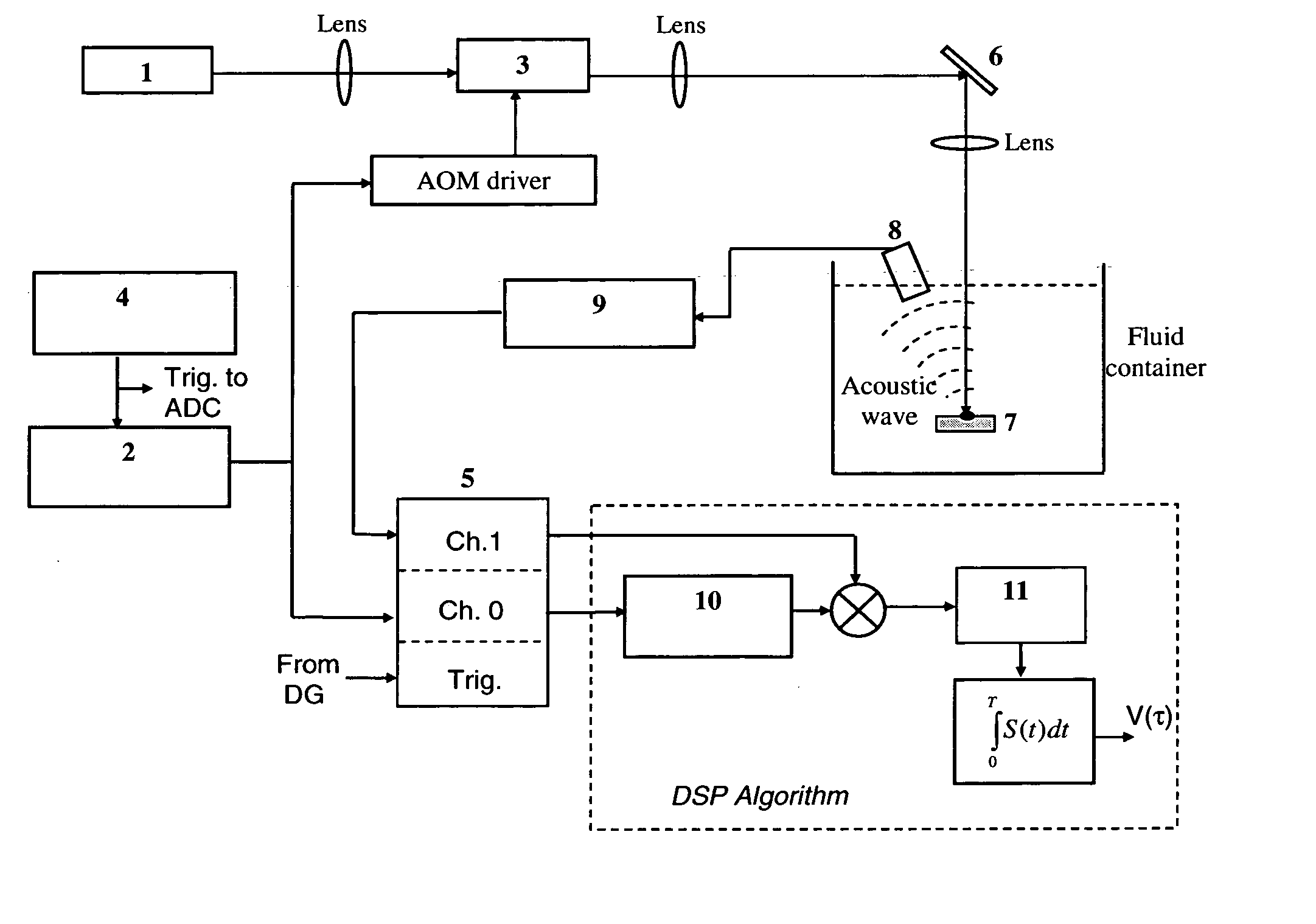
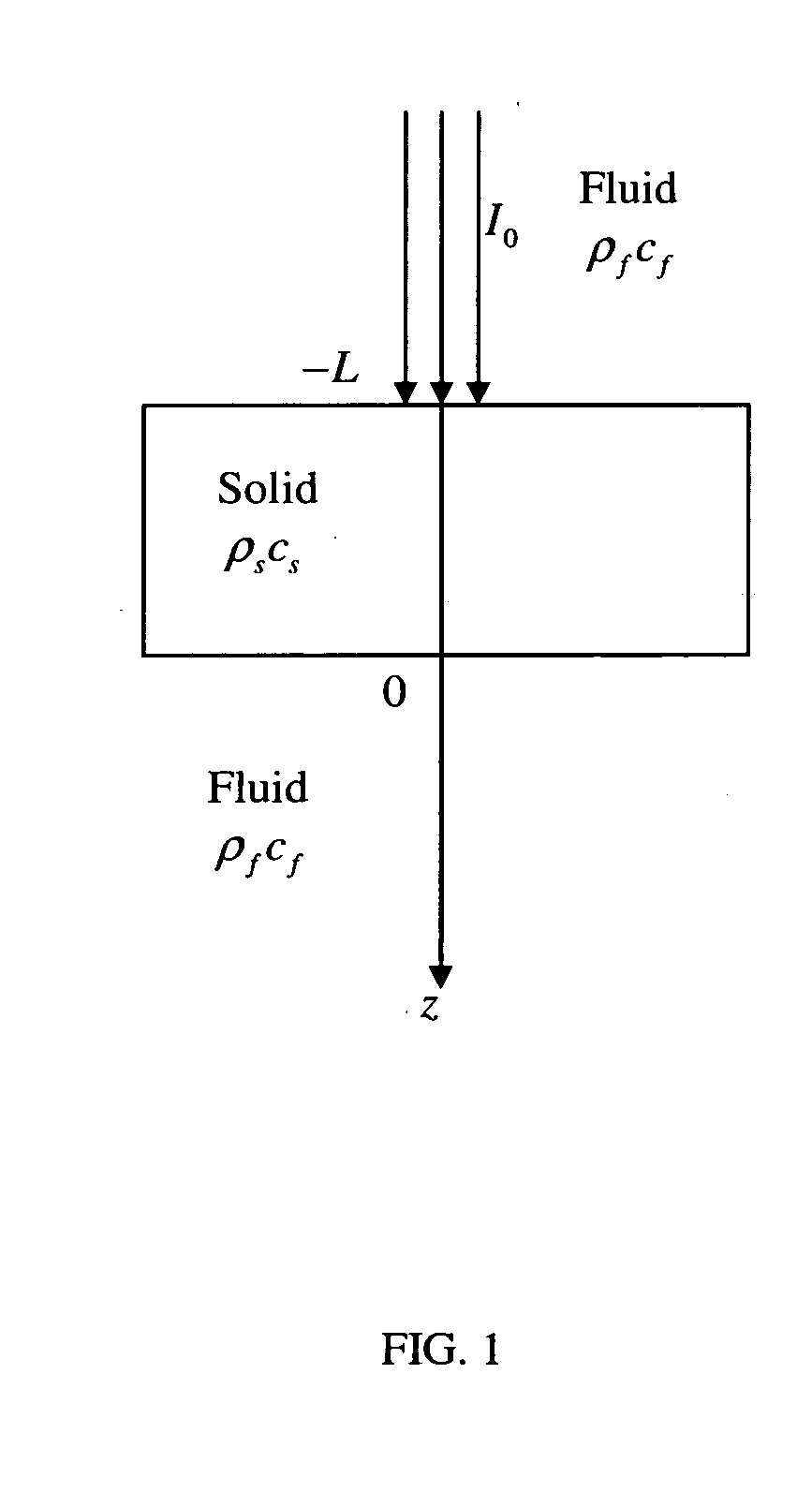
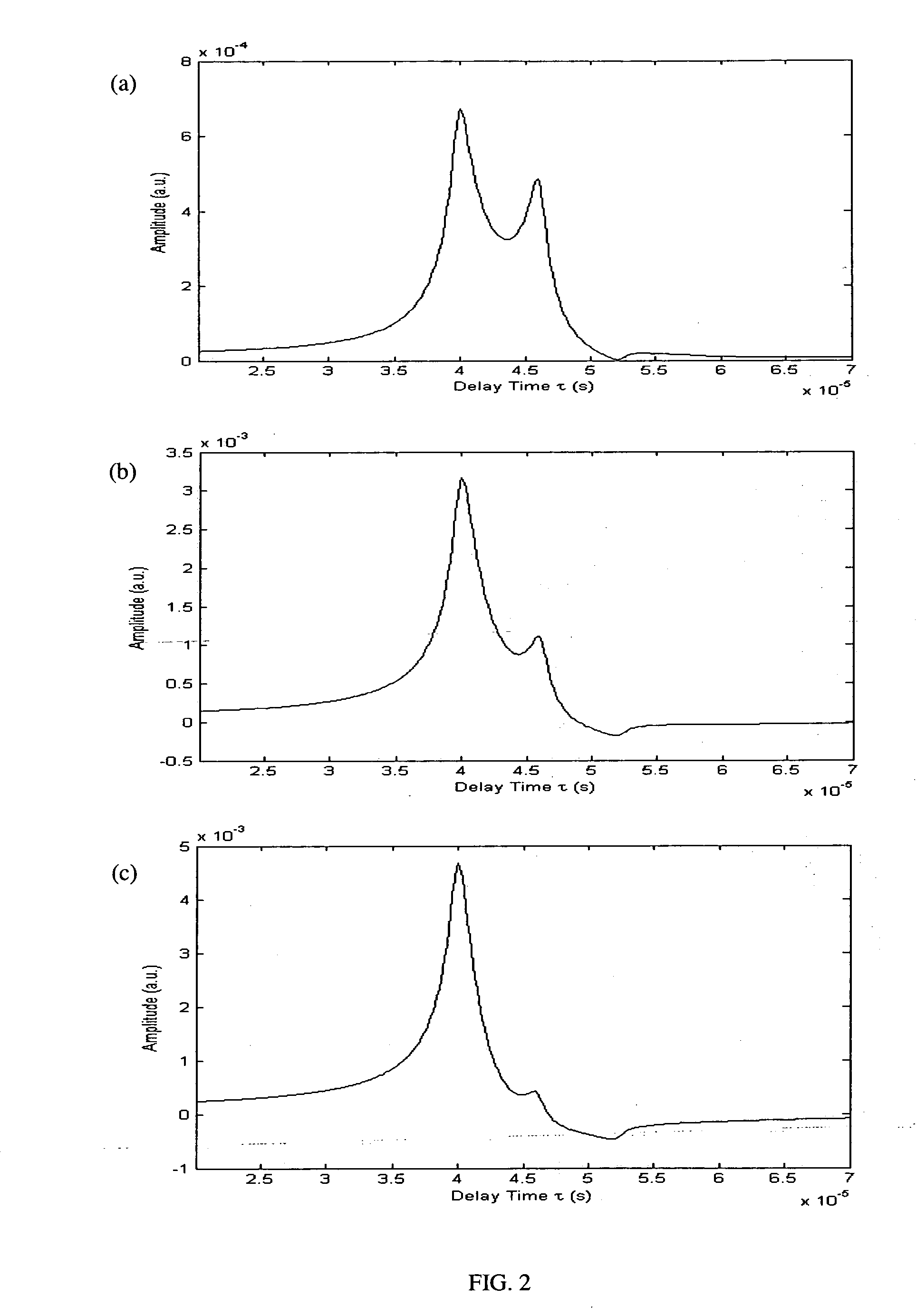
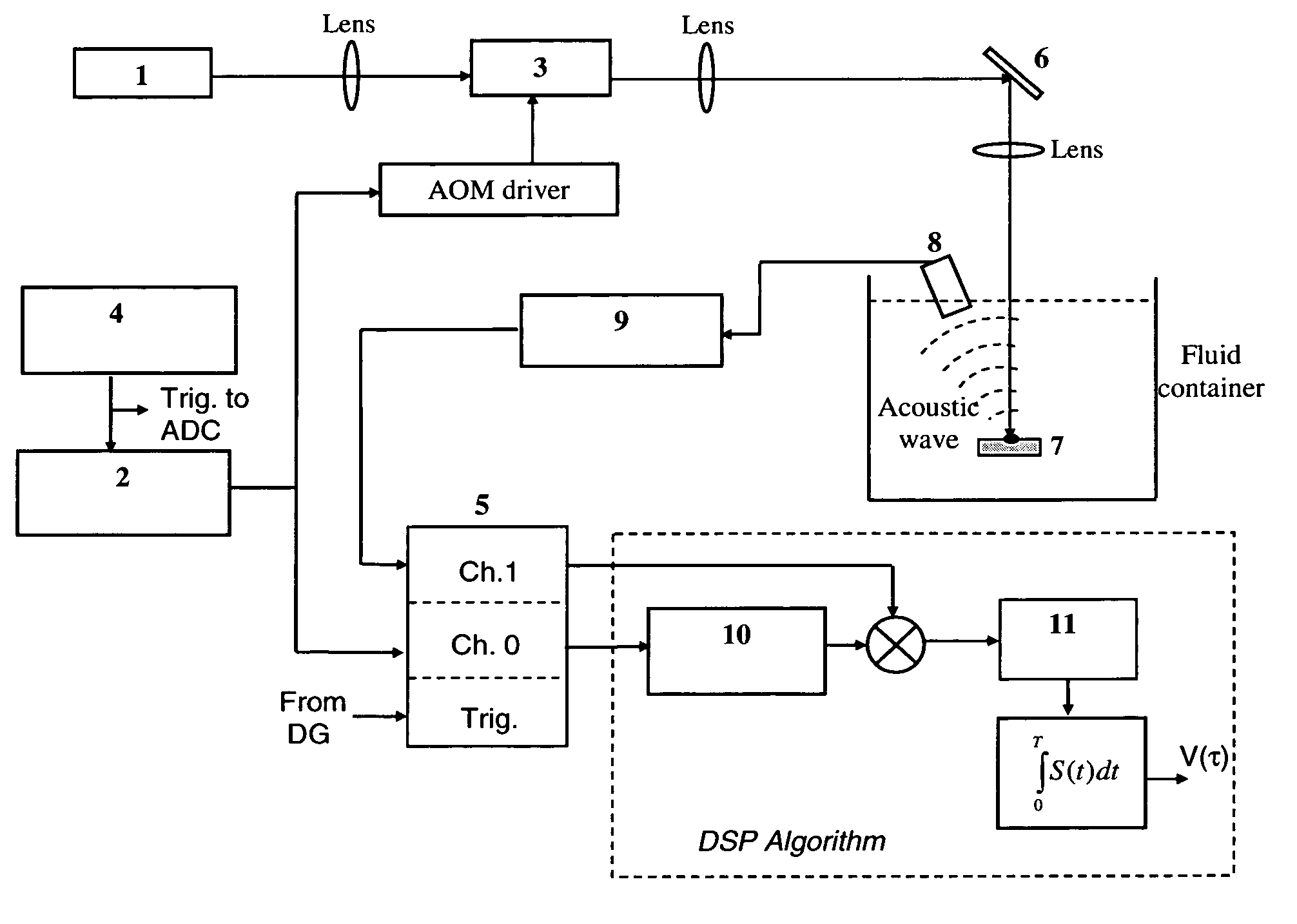
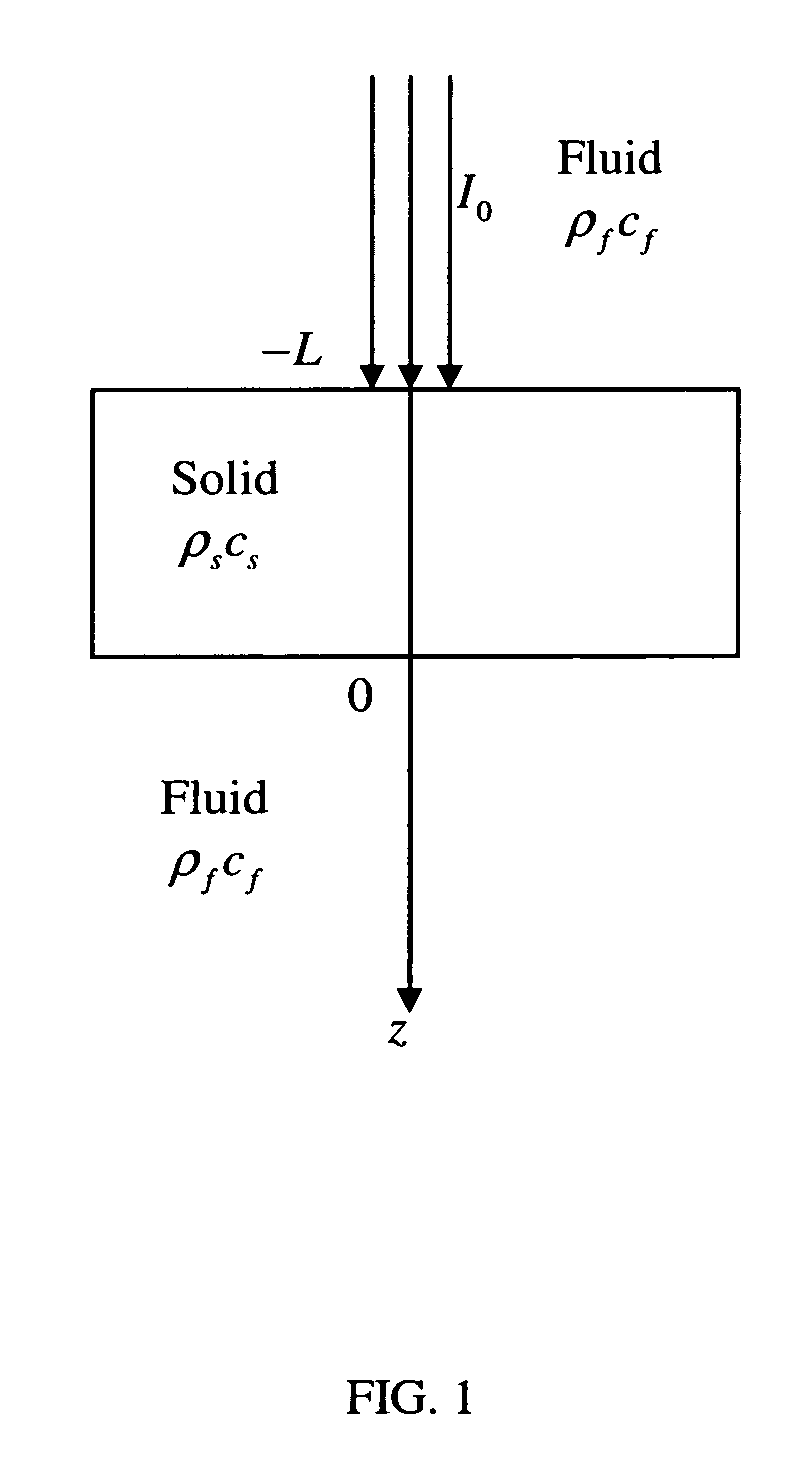
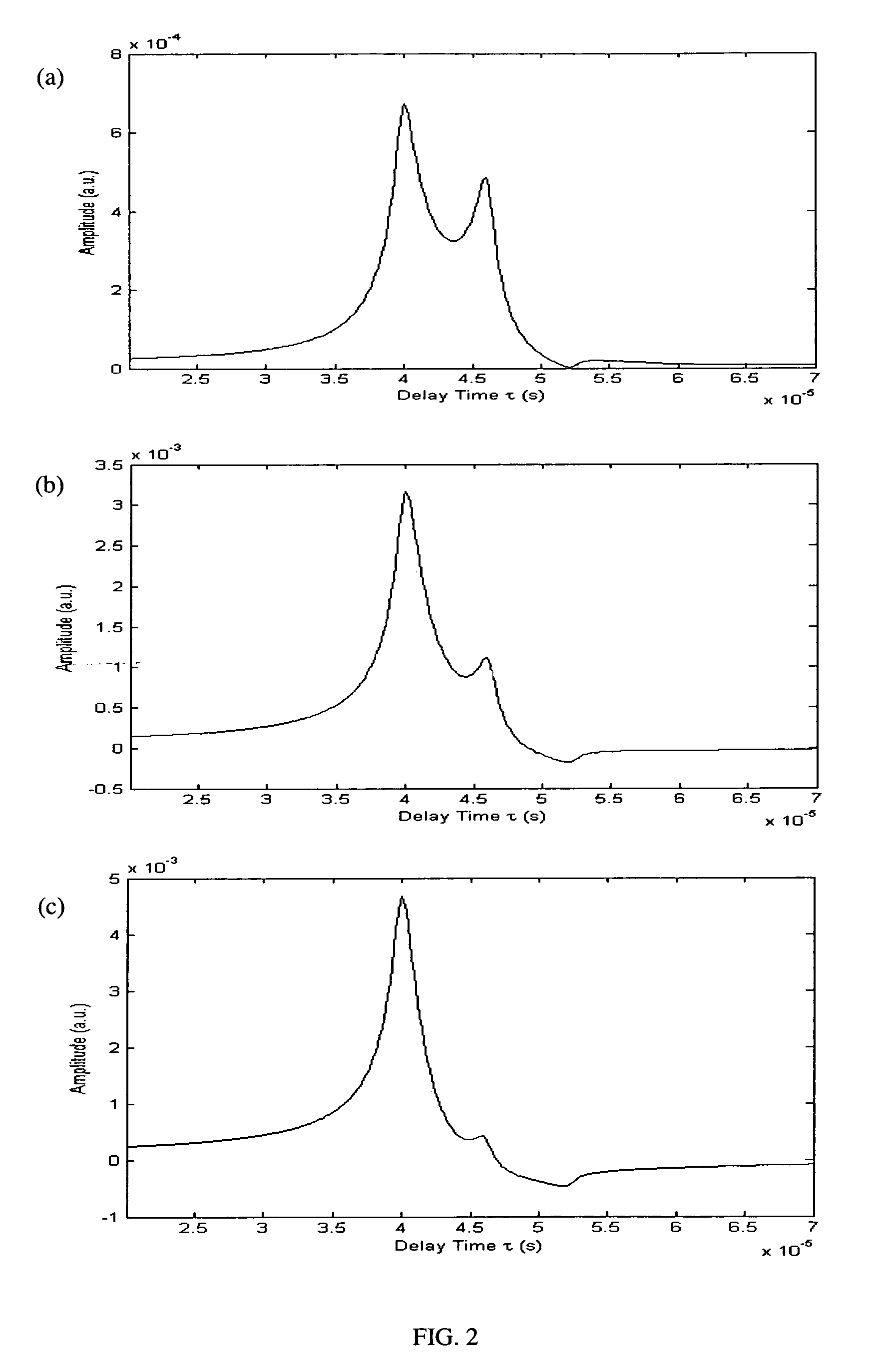
Laser photo-thermo-acoustic (PTA) frequency swept heterodyned lock-in depth profilometry imaging system
InactiveUS20050234319A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSubsurface imagingOptical absorption coefficient
A method and apparatus for biomedical subsurface imaging and measurement of thickness, elastic and optical properties of industrial and biomedical materials based on laser Photo-Thermo-Acoustic (PTA) frequency-swept heterodyne depth profilometry, In particular, the invention relates to biomedical imaging and measure of tissue and tumour thickness, L, speed of sound, cs, acoustic attenuation coefficient, γ, optical absorption coefficient, μa, and optical scattering coefficient, μs. The method and apparatus involves providing for a sample of the material to be characterized; irradiating the material for a selected period of time with an excitation waveform from a modulated optical excitation source wherein a photo-thermo-acoustic emission is responsively emitted from said solid; detecting said emitted photo-thermo-acoustic emission; processing the electronic signal to convert the frequency-domain signal into time-domain and perform depth profilometric imaging and determining thermoelastic and optical properties of the material sample;
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +3
Subsurface conductivity imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20050134278A1Detection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic sourceElectricity
A subsurface imaging cable includes a plurality of sensor modules, wherein the plurality of the sensor modules are flexible and each of the plurality of the sensor modules is spaced apart on the subsurface imaging cable at a selected distance; and a flexible medium connecting the plurality of the sensor modules, wherein the subsurface imaging cable is flexible and adapted to be wound on a reel. A method for subsurface images includes acquiring direct-current measurements at a plurality of sites in a survey area; acquiring a first set of electric and magnetic measurements from natural electromagnetic fields at the plurality of sites; acquiring a second set of electric and magnetic measurements using controlled electric and magnetic sources at the plurality of sites; and determining a subsurface conductivity distribution from the direct-current measurements and the first set and the second set of electric and magnetic measurements.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
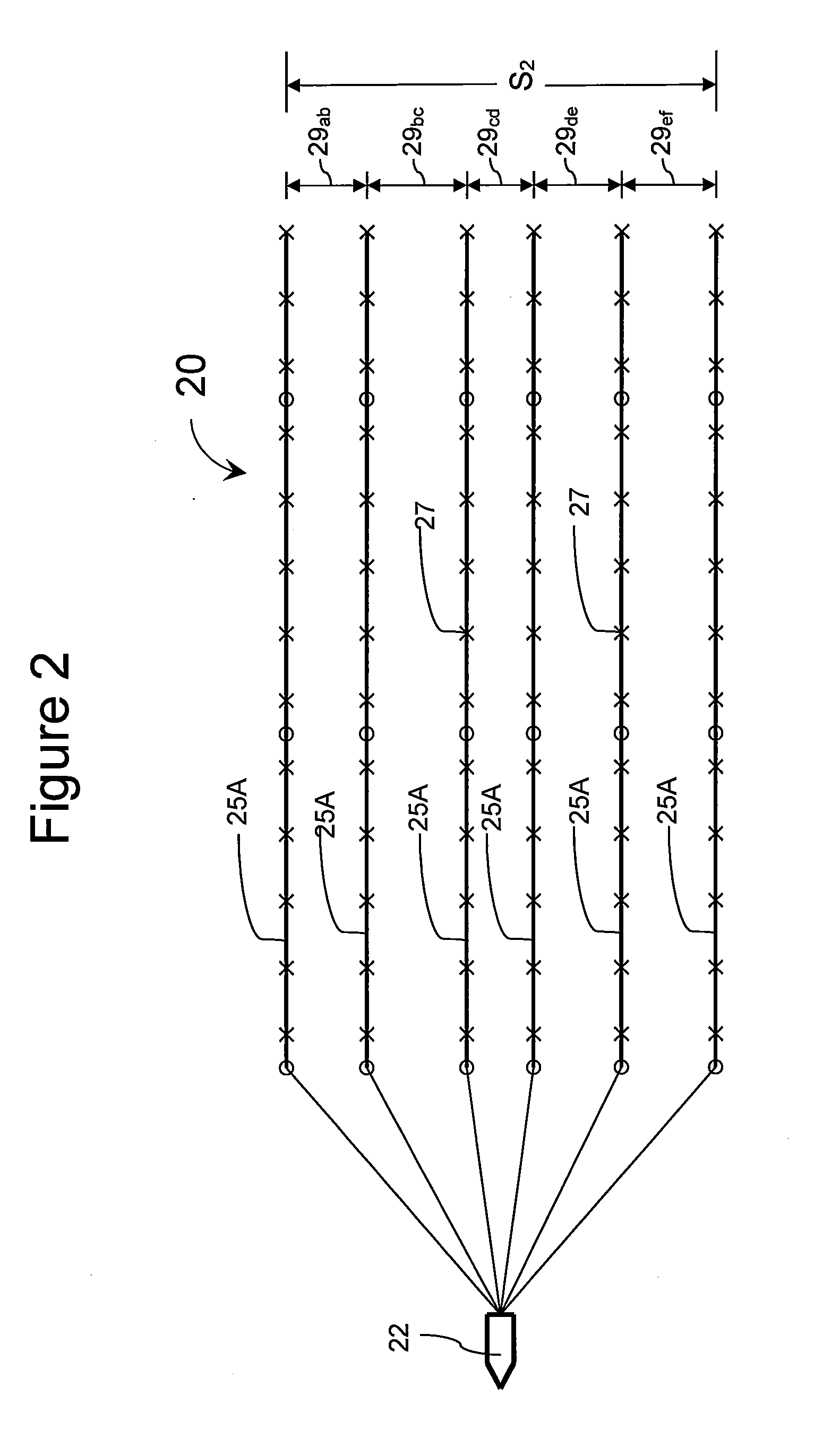
Marine seismic data acquisition using designed non-uniform streamer spacing
ActiveUS8897094B2Seismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasWave fieldData acquisition
The invention relates to an arrangement for seismic streamers used in the acquisition of seismic data in a marine environment where the spacing between each adjacent pair of streamers is not all the same. Some streamer spacings and / or receiver spacings are larger and some are smaller to provide a higher quality wavefield reconstruction when covering a larger total area or for a similar total area of seismic data acquisition while providing a wavefield that is optimally sampled by the receivers so that the wavefield reconstruction is suitable for subsurface imaging needs.
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
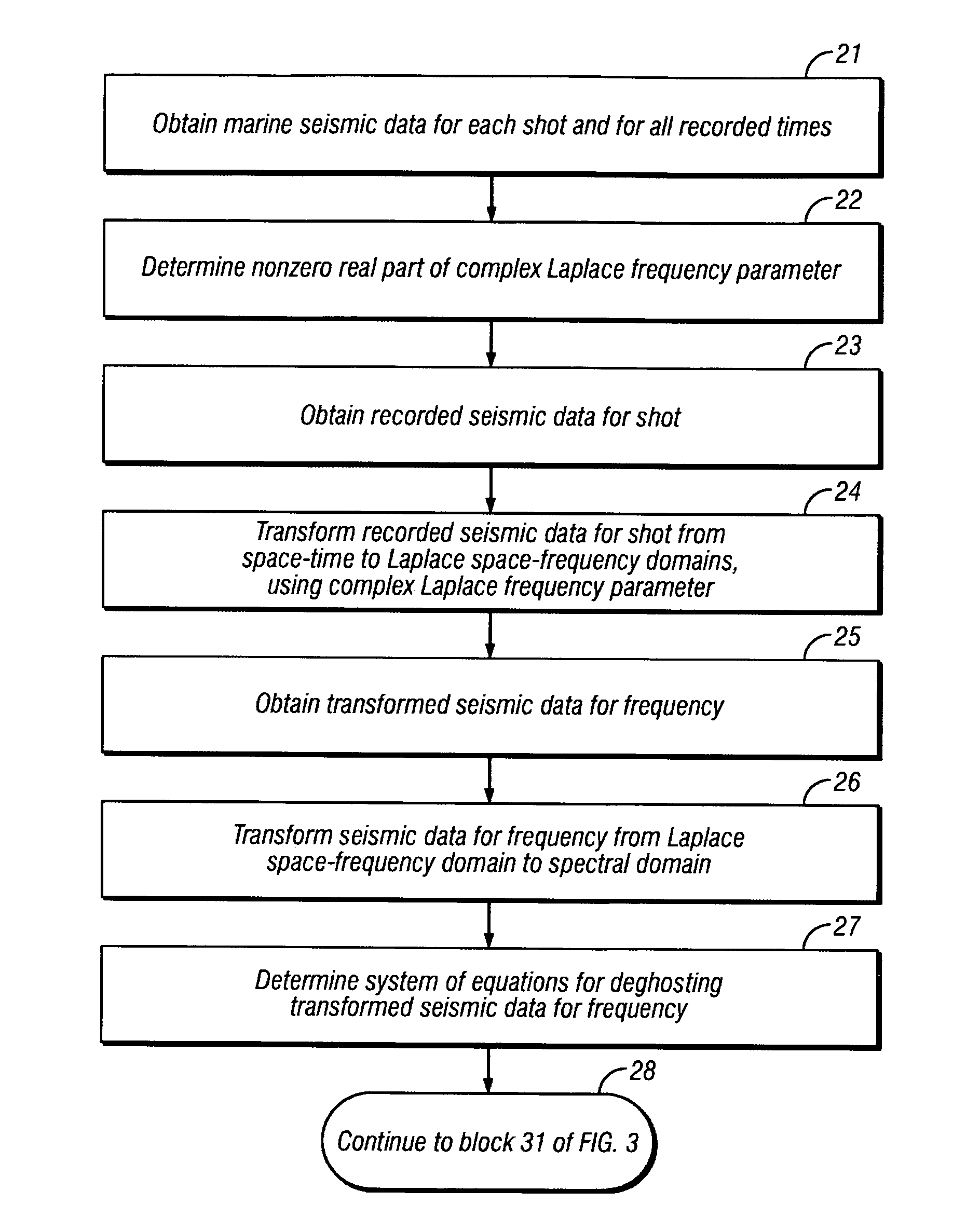
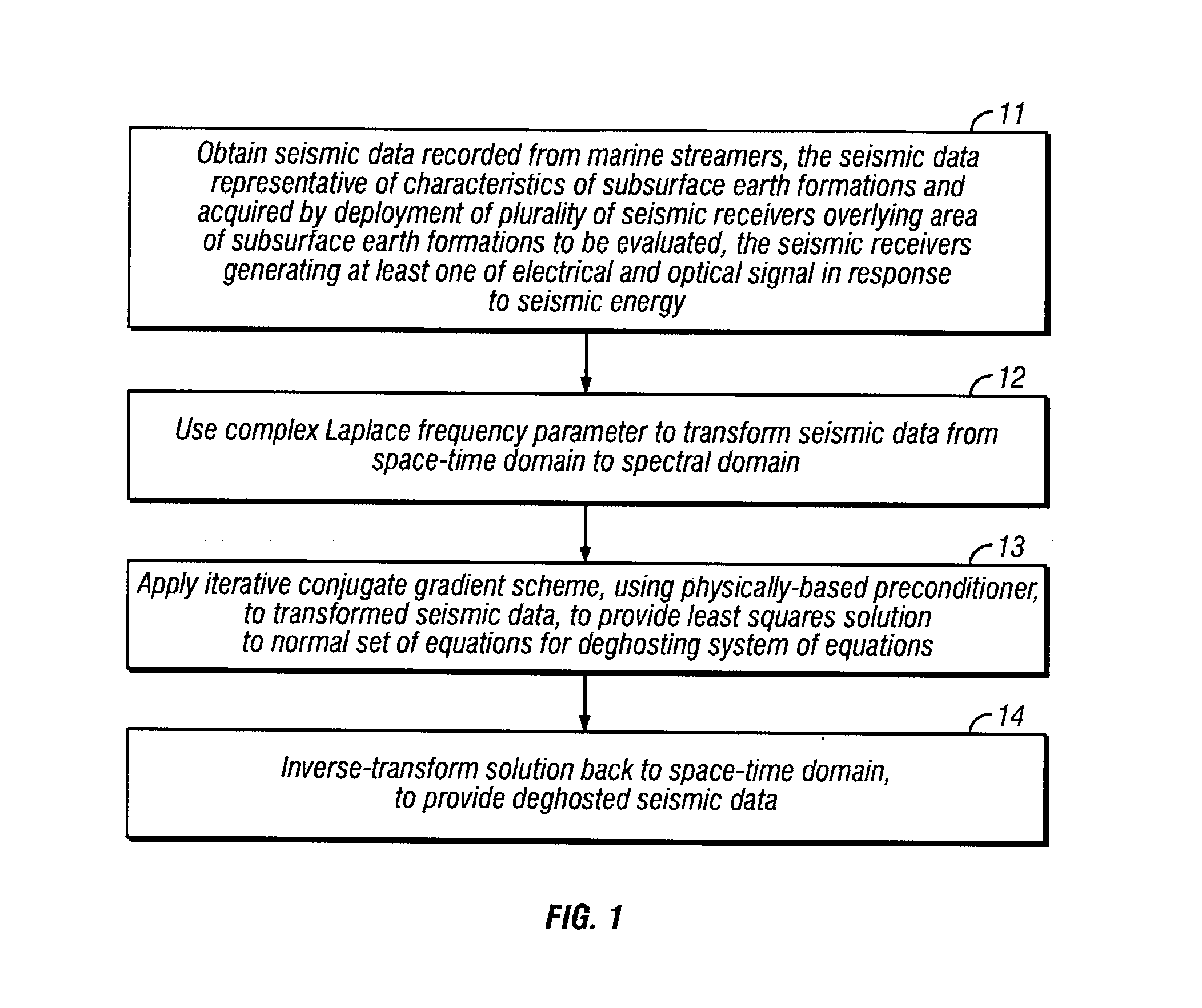
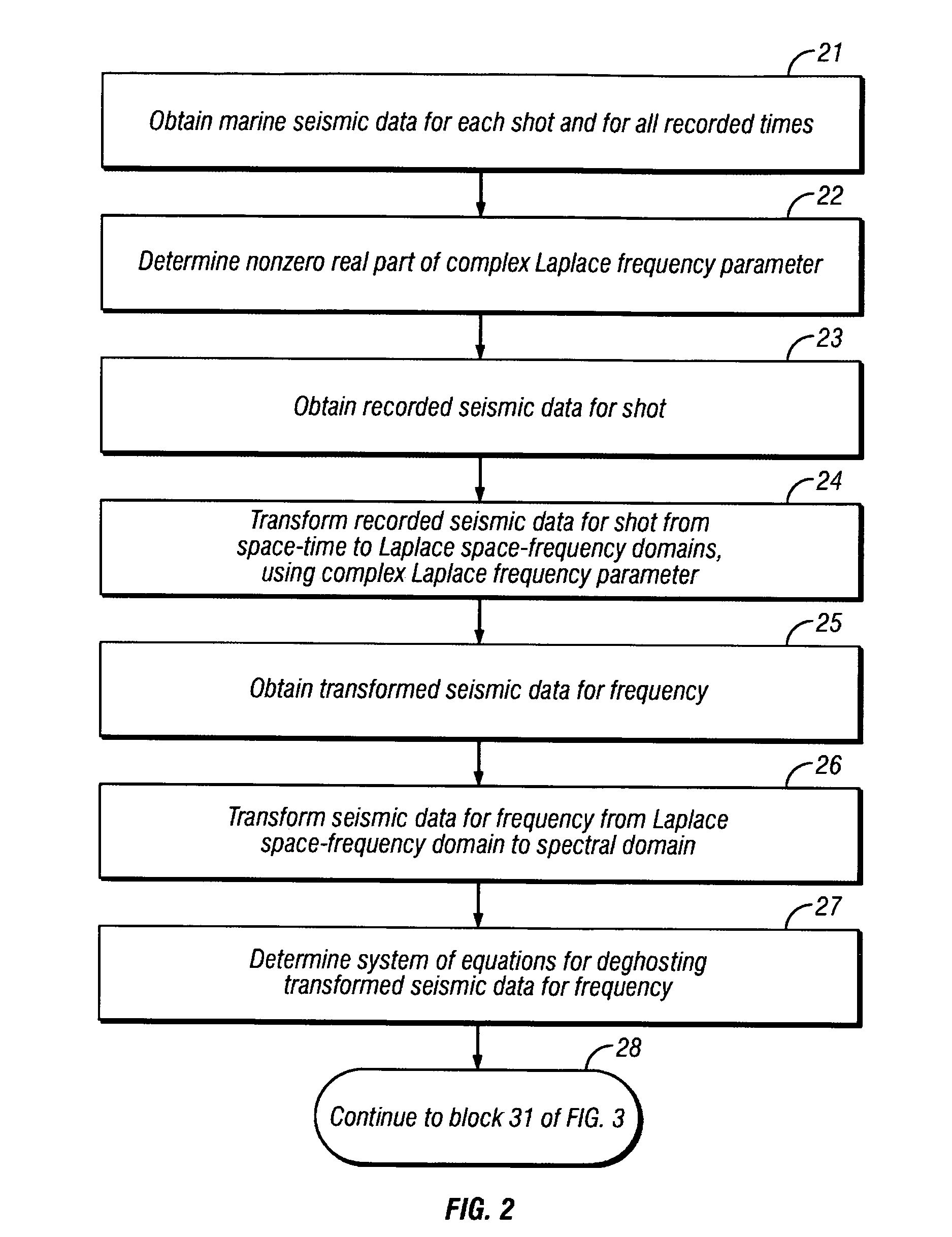
Method for full-bandwidth deghosting of marine seismic streamer data
Seismic data recorded in a marine streamer are obtained, with the seismic data being representative of characteristics of subsurface earth formations and acquired by deployment of a plurality of seismic receivers overlying an area of the subsurface earth formations to be evaluated, the seismic receivers generating at least one of an electrical and optical signal in response to seismic energy. A complex Laplace frequency parameter is used to transform the seismic data from a space-time domain to a spectral domain. An iterative conjugate gradient scheme, using a physically-based preconditioner, is applied to the transformed seismic data, to provide a least squares solution to a normal set of equations for a deghosting system of equations. The solution is inverse-transformed back to a space-time domain to provide deghosted seismic data, which is useful for imaging the earth's subsurface.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Laser photo-thermo-acoustic (PTA) frequency swept heterodyned lock-in depth profilometry imaging system
InactiveUS7525661B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSubsurface imagingOptical absorption coefficient
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +3
System and Method Using Near and Far Field ULF and ELF Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar for Subsurface Imaging
ActiveUS20150123835A1Promote resultsReduce and eliminate phase unwrapping errorDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarSubsurface imaging
This invention relates to devices and processes for geophysical prospecting, subsurface fluid monitoring and, more particular, to the use of interferometric techniques using Control Source Electromagnetic (“CSEM”) and Magnetoturelic (“MT”) signals to create images of sub-surface structures and fluids.
Owner:DEEP IMAGING TECH
Seismic data acquisition using designed non-uniform receiver spacing
The invention relates to an arrangement for seismic acquisition the spacing between each adjacent pairs of receiver and sources lines is not all the same. Some receiver and / or source lines and / or receiver and / or source spacings are larger and some are smaller to provide a higher quality wavefield reconstruction when covering a larger total area or for a similar total area of seismic data acquisition while providing a wavefield that is optimally sampled by the receivers and sources so that the wavefield reconstruction is suitable for subsurface imaging needs.
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
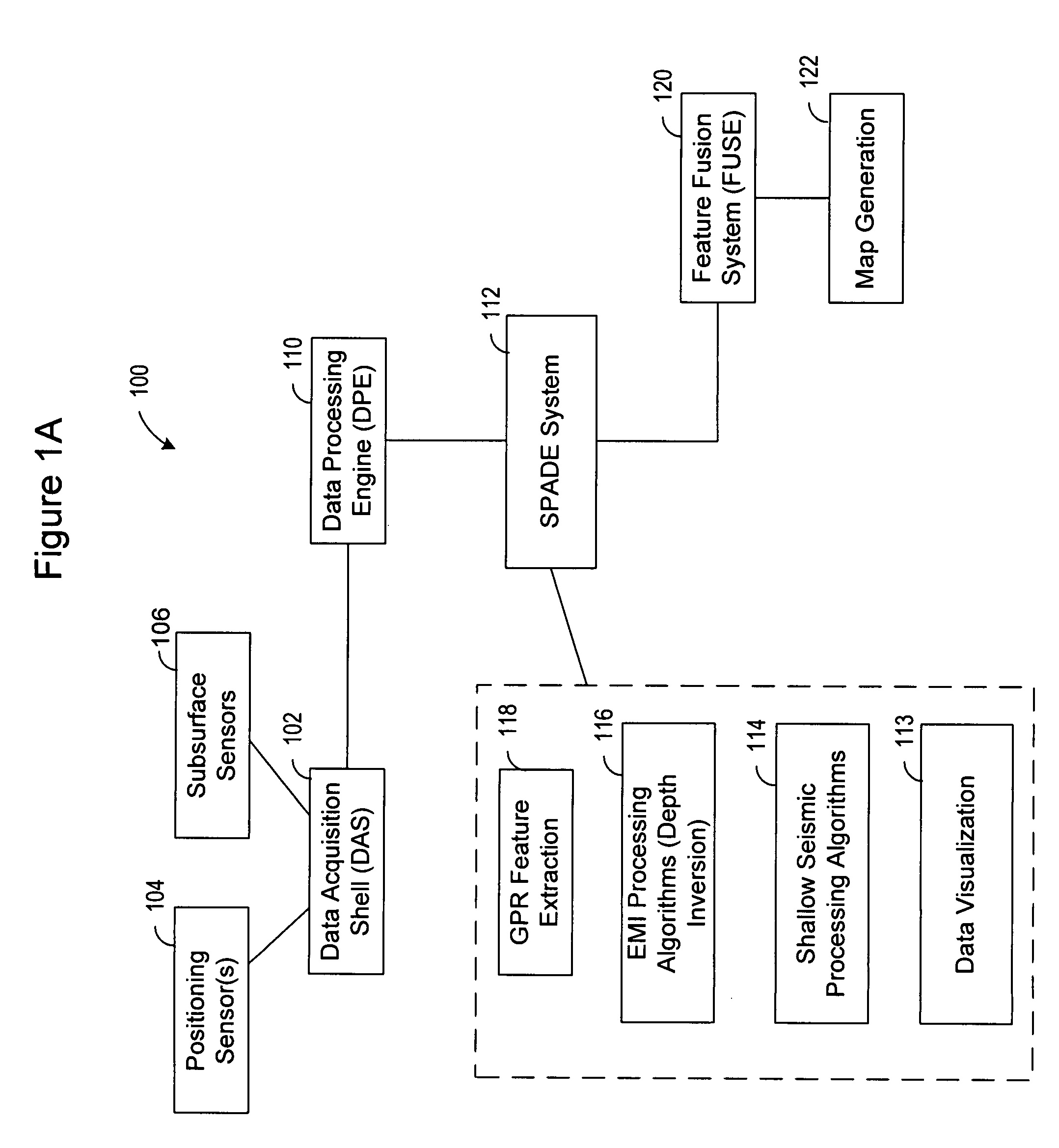
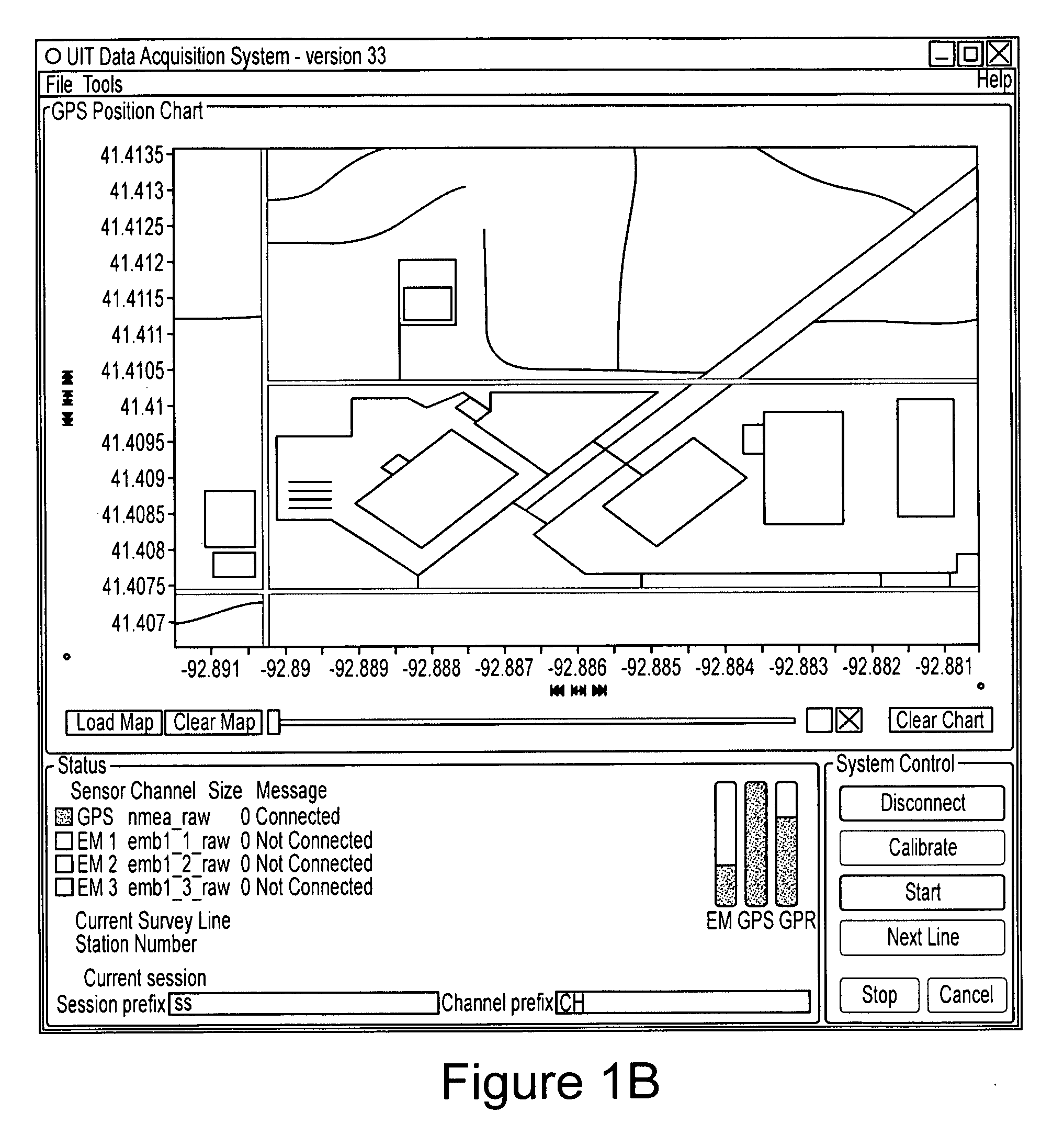
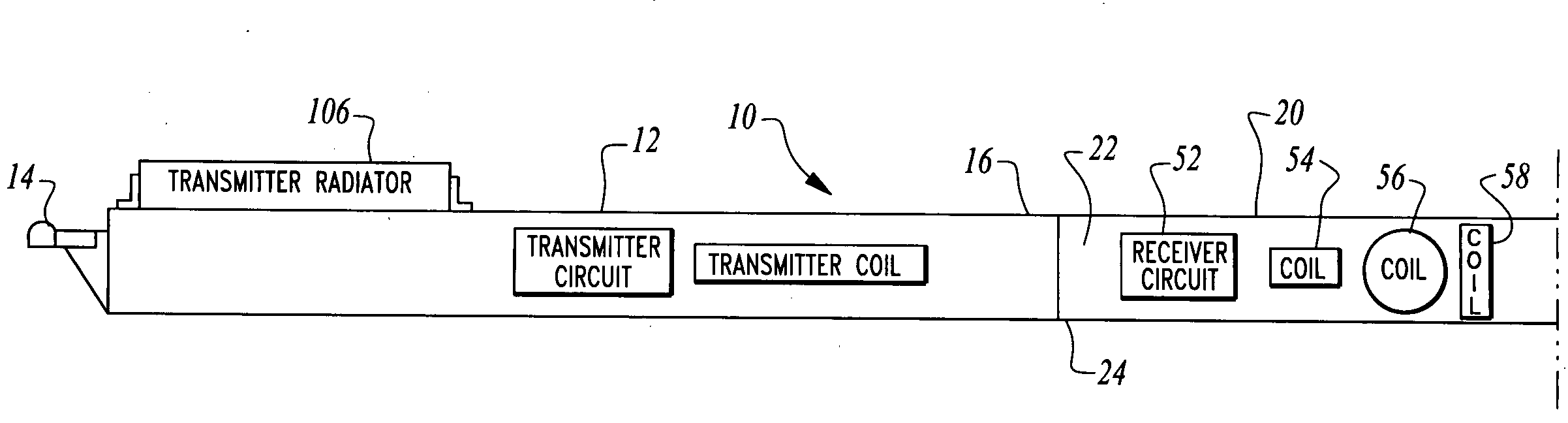
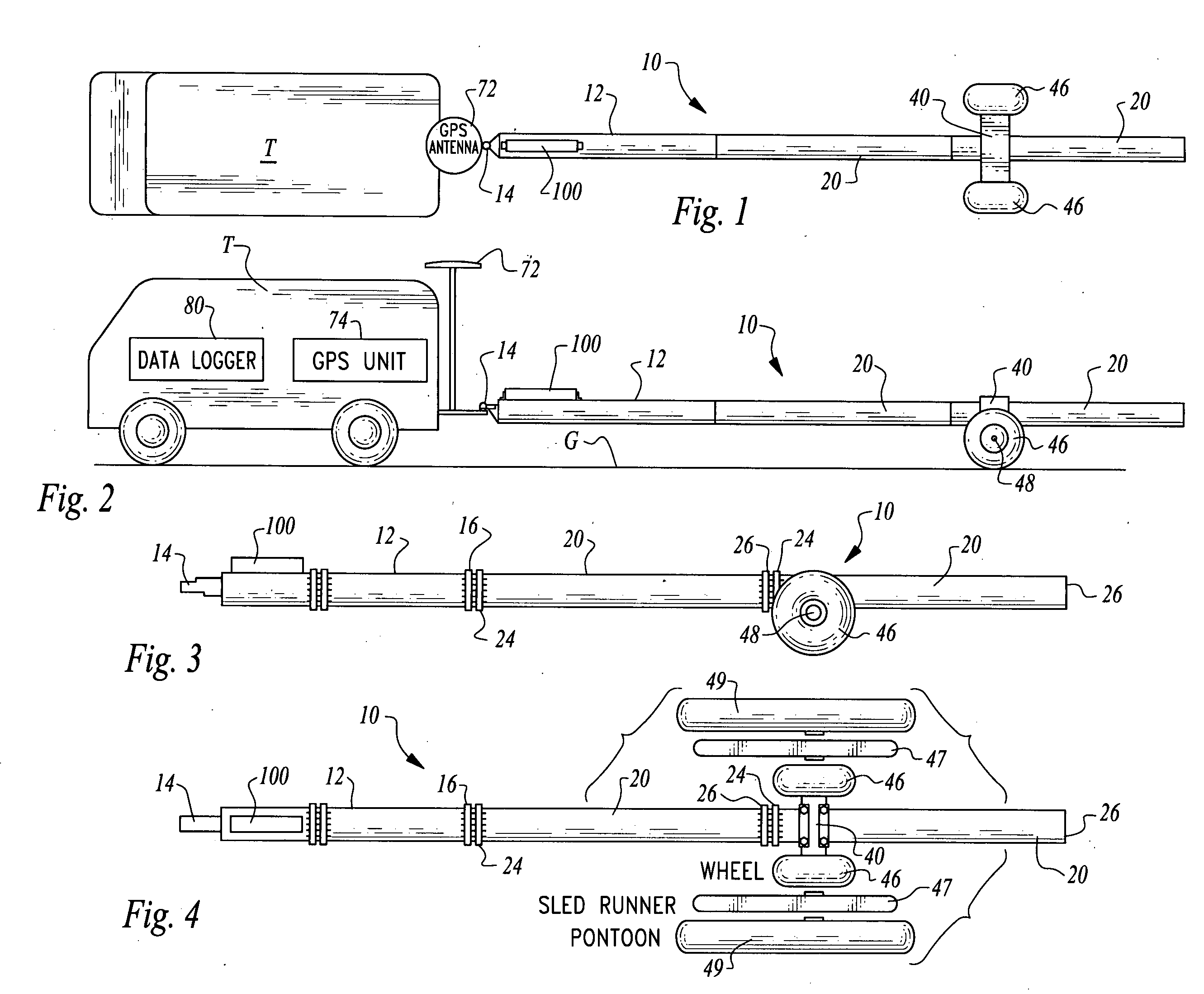
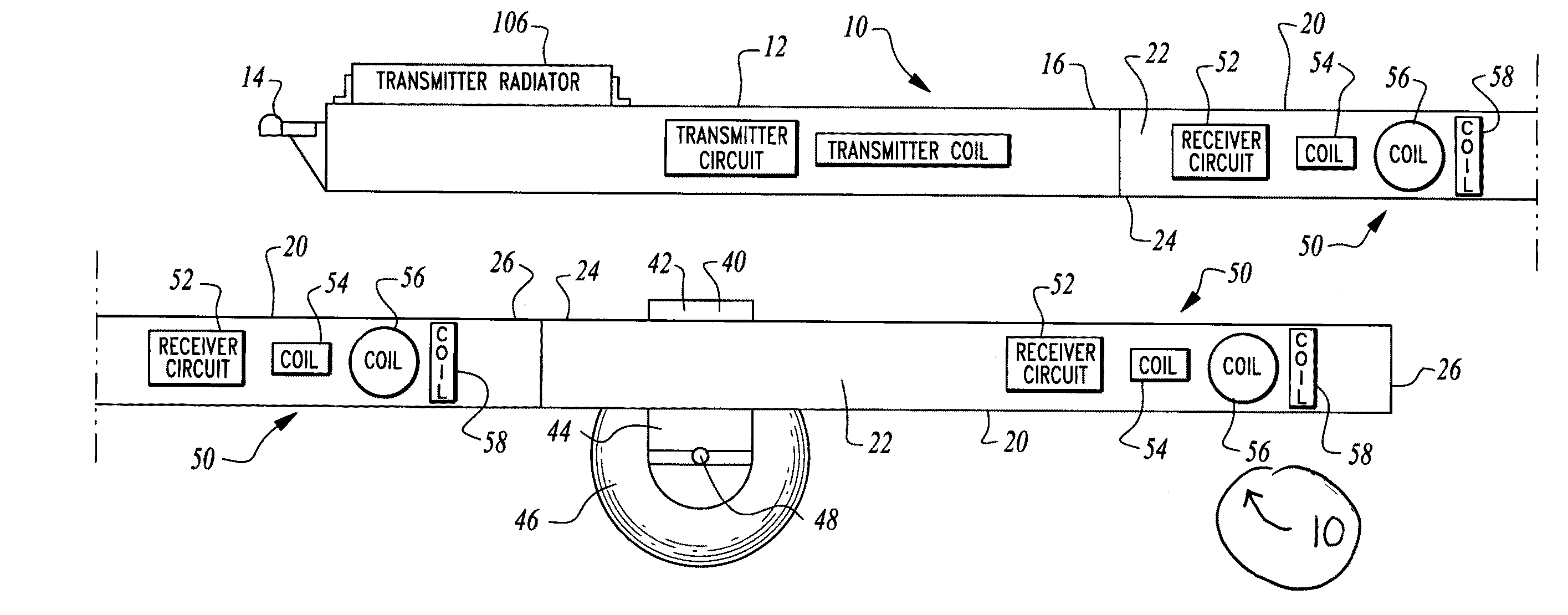
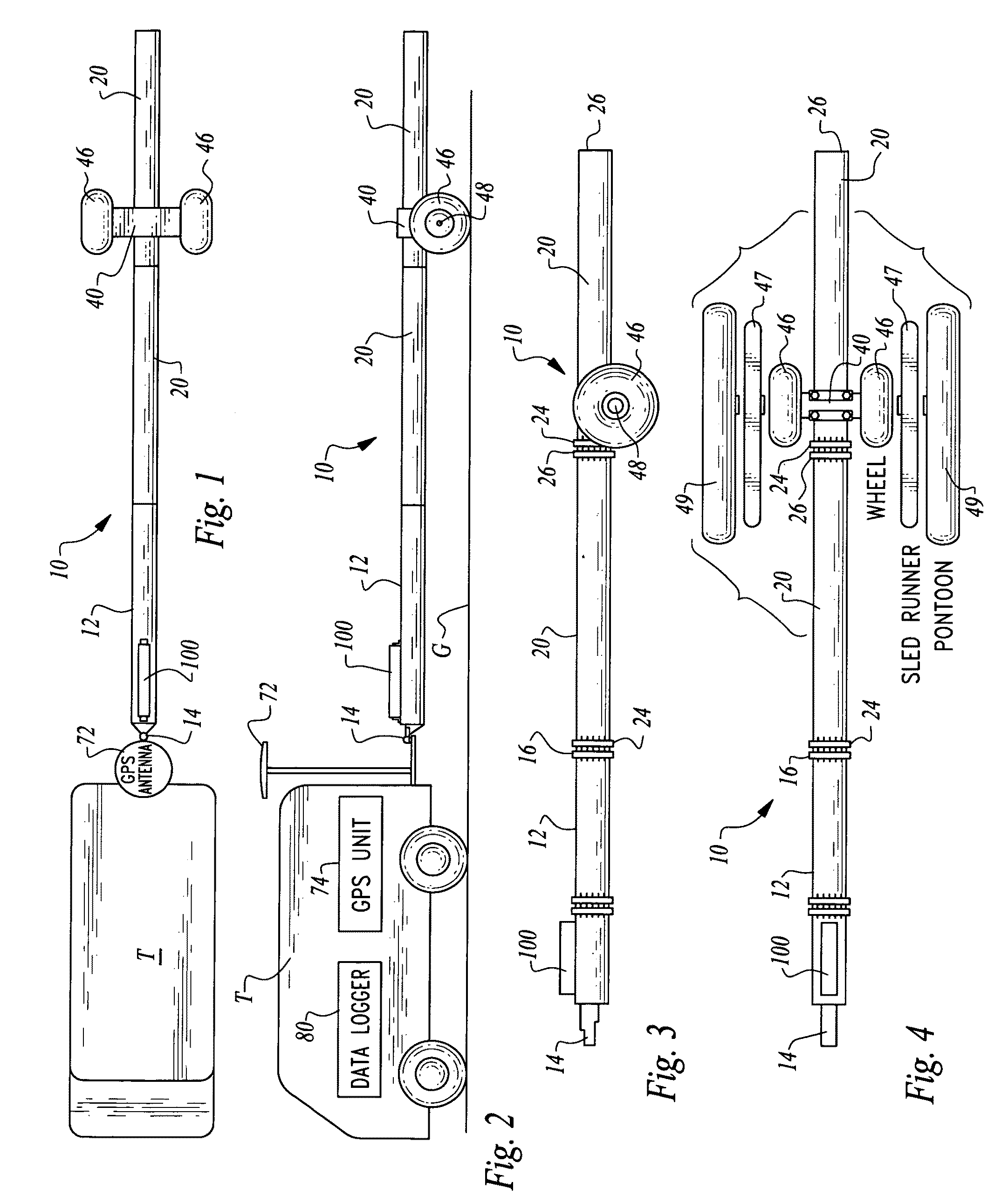
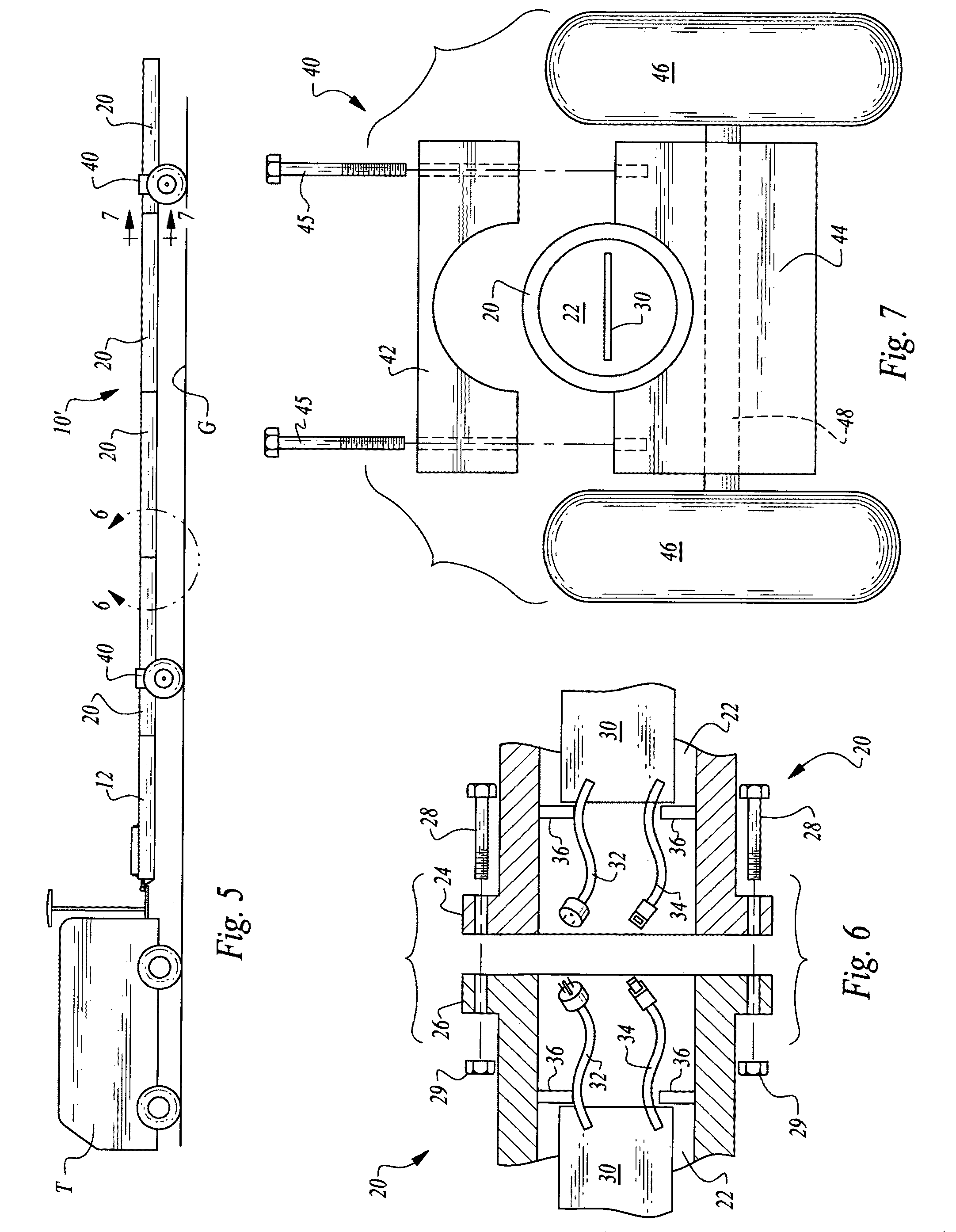
Electromagnetic subterranean imaging instrument
ActiveUS20090302850A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove scalabilityAcoustic wave reradiationElectric/magnetic detection for transportModularitySubsurface imaging
The instrument utilizes at least one electromagnetic signal transmitter and at least one electromagnetic signal receiver with the receiver detecting a receiver signal responsive to the transmitter signal and indicative of subterranean details adjacent to the instrument. The instrument is attachable to a tow vehicle for transport and includes a GPS antenna and tags data gathered by the instrument with GPS position information. The instrument is formed- in modular sections which can be removably attached for collapsing into a smaller space and to allow for flexible configuration of the instrument in various different ways. A wheeled carriage is provided to carry the instrument over the ground. Antennas for the transmitter and receiver, as well as circuitry and cooling systems are all provided to supply the instrument with high resolution and a clear signal indicative of the position and characteristics of subterranean details of interest.
Owner:LOPEZ JOHN A +4
Subsurface imaging using an electron beam
ActiveUS7388218B2Sufficient energyAccurate locationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesLight beamSubsurface imaging
A method of navigating or endpointing a microscopic structure by subsurface imaging using a beam of electrons having sufficient energy to penetrate the surface and produce a subsurface image. For endpointing, when the subsurface image become relatively clear at a known electron energy, a user knows that he is approaching the buried feature. For navigating, a subsurface image can be formed of fiducials or other features to determine the position of the beam on the device.
Owner:FEI CO
Passive reflective imaging for visualizing subsurface structures in earth and water
A system and method is provided that uses signals from a plurality of seismic sensors to define an acoustic lens for subsurface imaging. More specifically signals provided by an array of sensors / geophones may be utilized to form an acoustic lens that can be focused on a subterranean point by properly adjusting the signals recorded at each sensor prior to summation of those signals. To form such an acoustic lens, each of the seismic sensors is moved onto a hypothetical acoustic lens surface (e.g., spherical surface) having a focal point located on the subterranean point of interest in order to calculate a time delay for each signal. Once the signals for each sensor is time-delayed, information in the time-delayed signals, which is received from the point of interest, may be temporally aligned. Accordingly, the time delayed signals may be combined to generate reflection information for the point of interest.
Owner:SIMON WAYNE
Method and Apparatus for Separating Seismic Diffracted Wave
InactiveUS20180292553A1Improve amplitude integrityImprove waveform consistencySeismic signal processingImage resolutionWave field
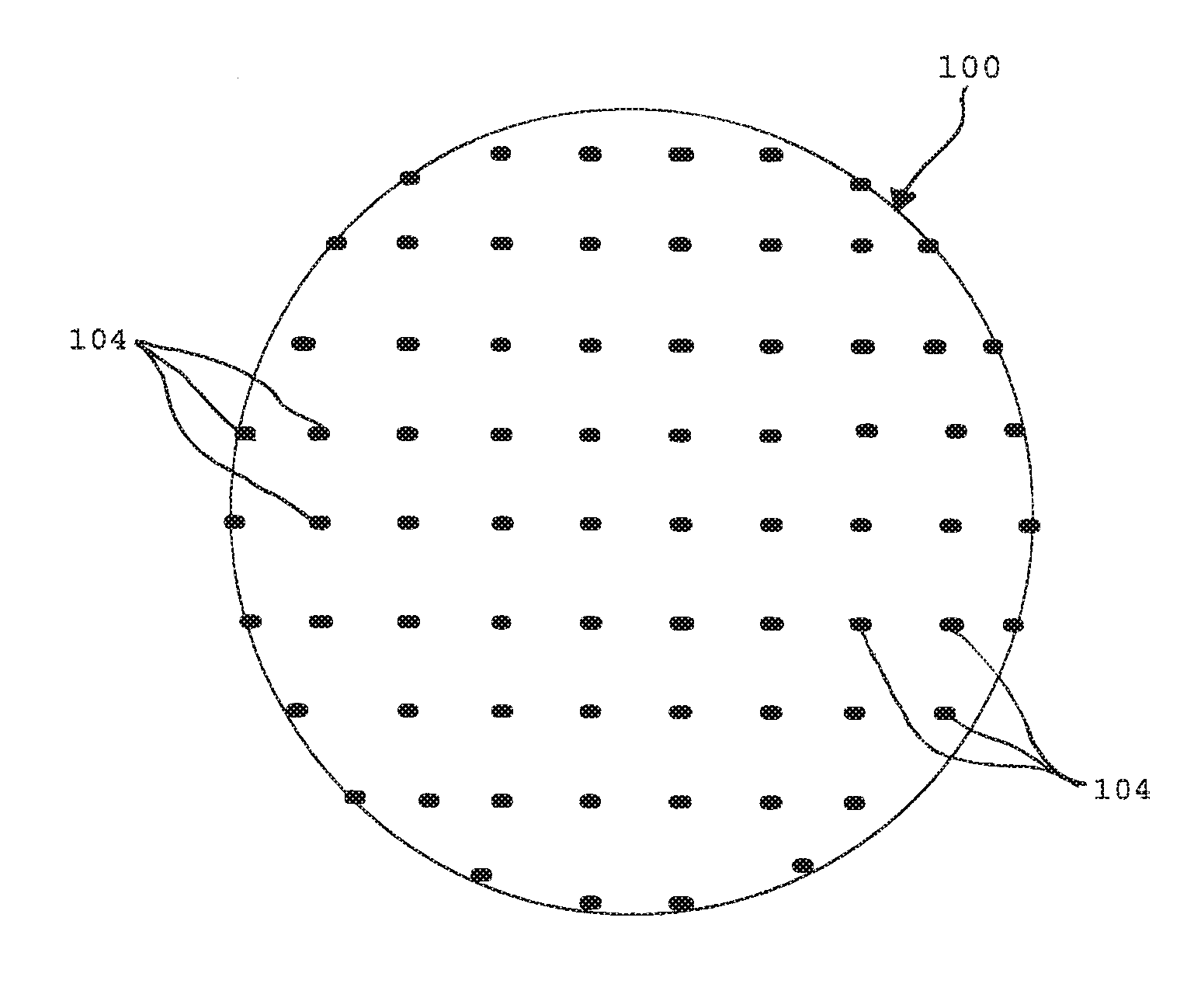
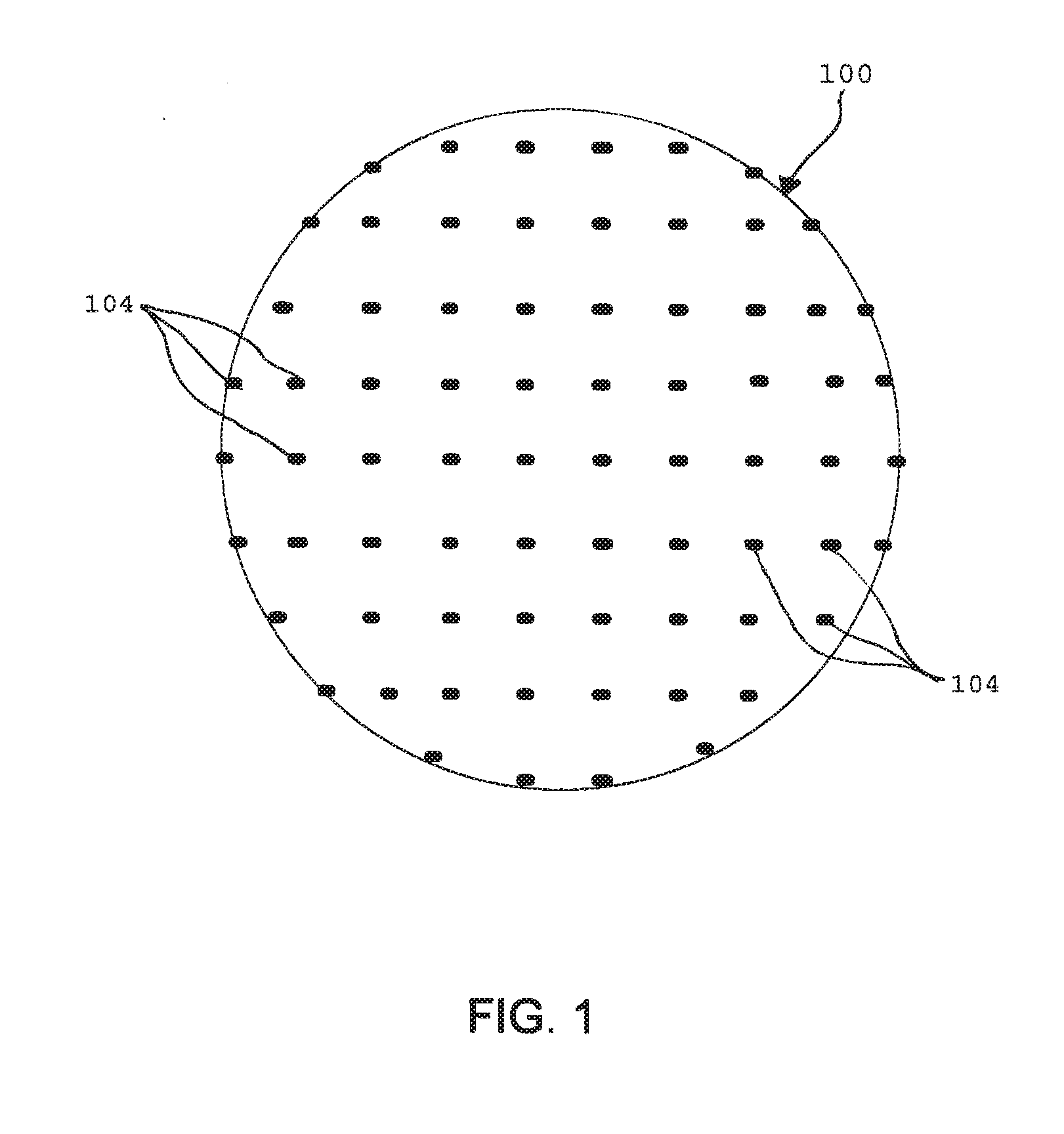
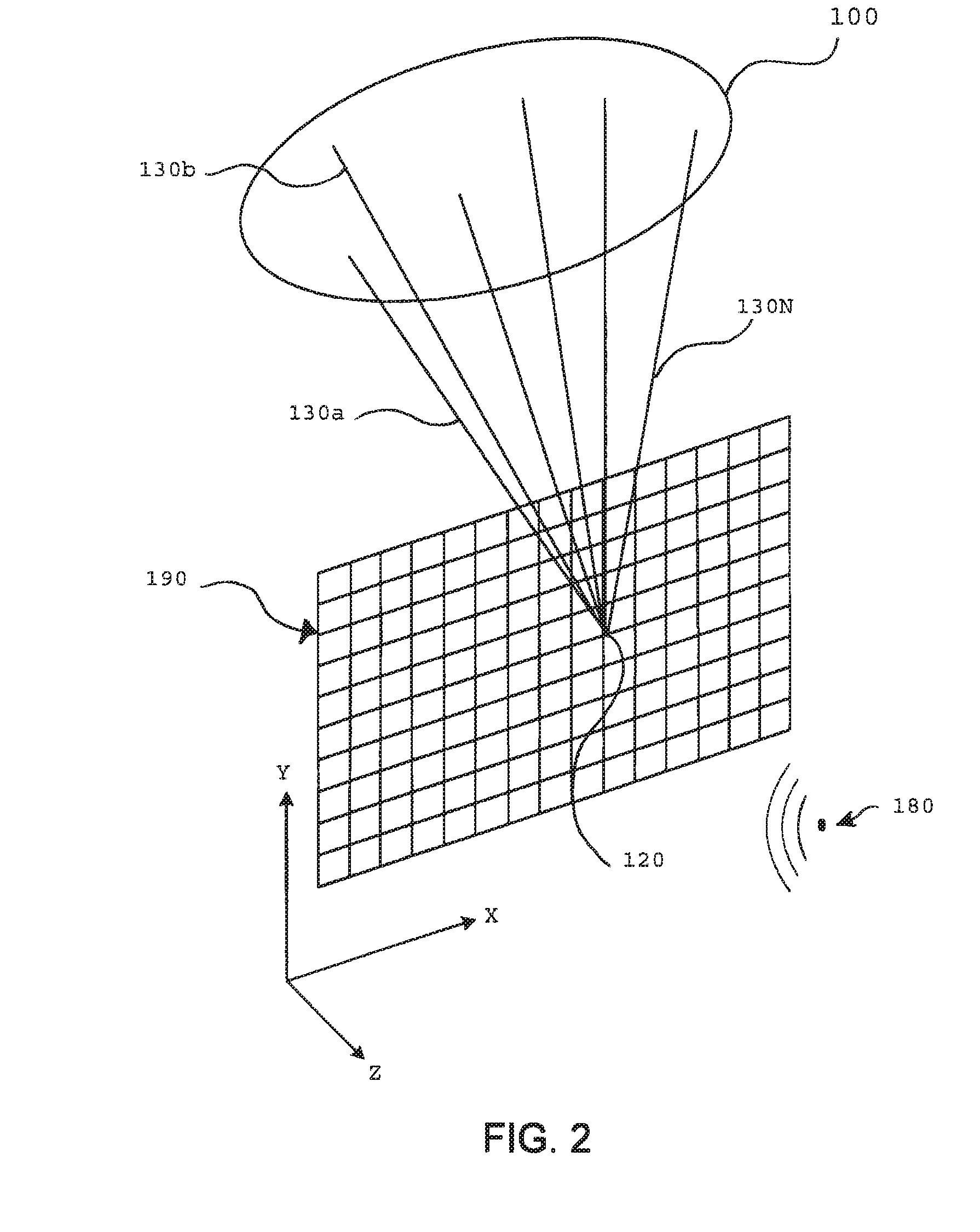
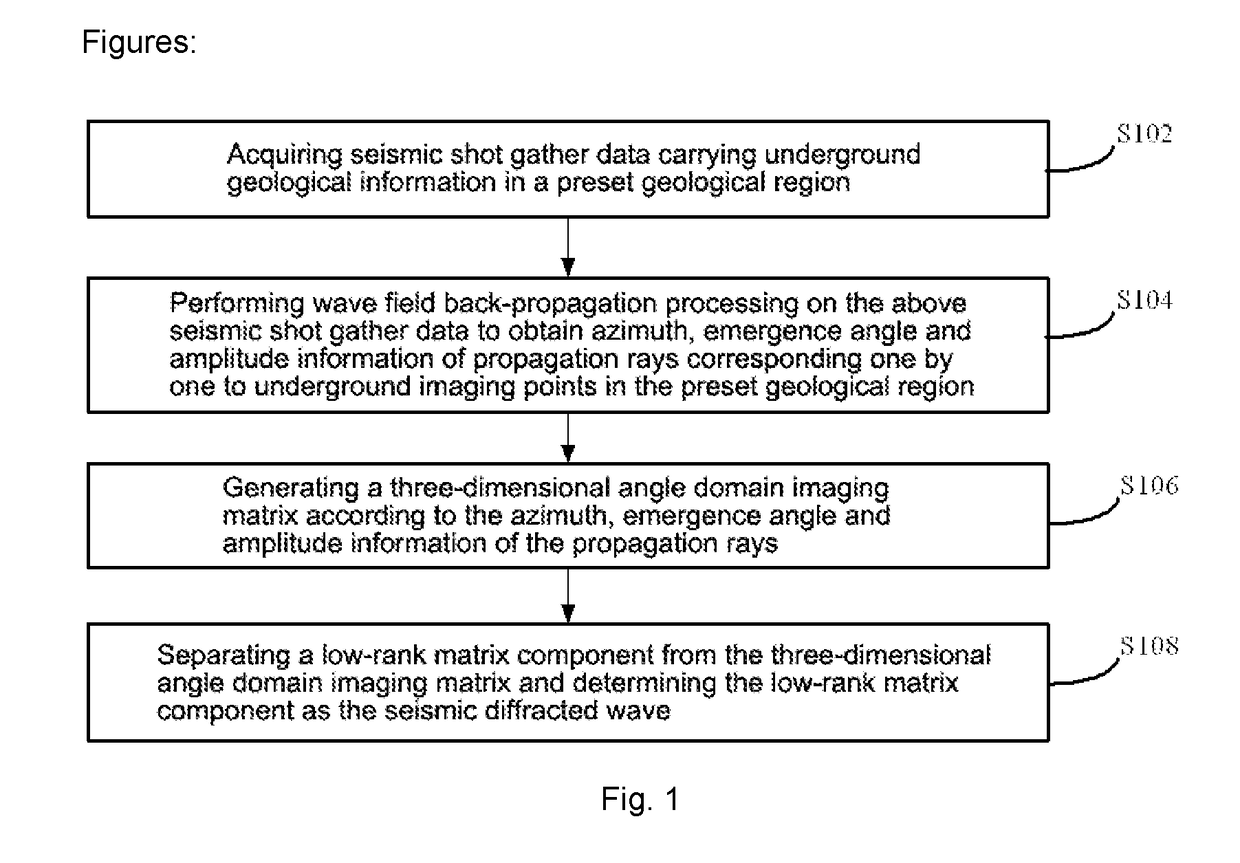
Method and apparatus for separating seismic diffracted waves, in seismic exploration field. The method comprises acquiring seismic shot gather data carrying underground geological information in preset geological region; inputting preprocessed single-shot data obtained by preprocessing seismic shot gather data and a preset migration velocity model to three-dimensional single-shot angle domain imaging formula and performing wave field back-propagation processing on the seismic shot gather data to obtain information of azimuth, emergence angle and amplitude of propagation rays, according to which three-dimensional angle domain imaging matrix is generated, the obtained information corresponding one by one to underground imaging points in the preset geological region; separating low-rank matrix component from the three-dimensional angle domain imaging matrix and determining the low-rank matrix component as the seismic diffracted wave through a preset three-dimensional diffracted wave separating model, improving amplitude integrity and waveform consistency of separated diffracted waves and imaging resolution of geological structures.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Diffracted wave imaging method and device based on L0 semi-norm
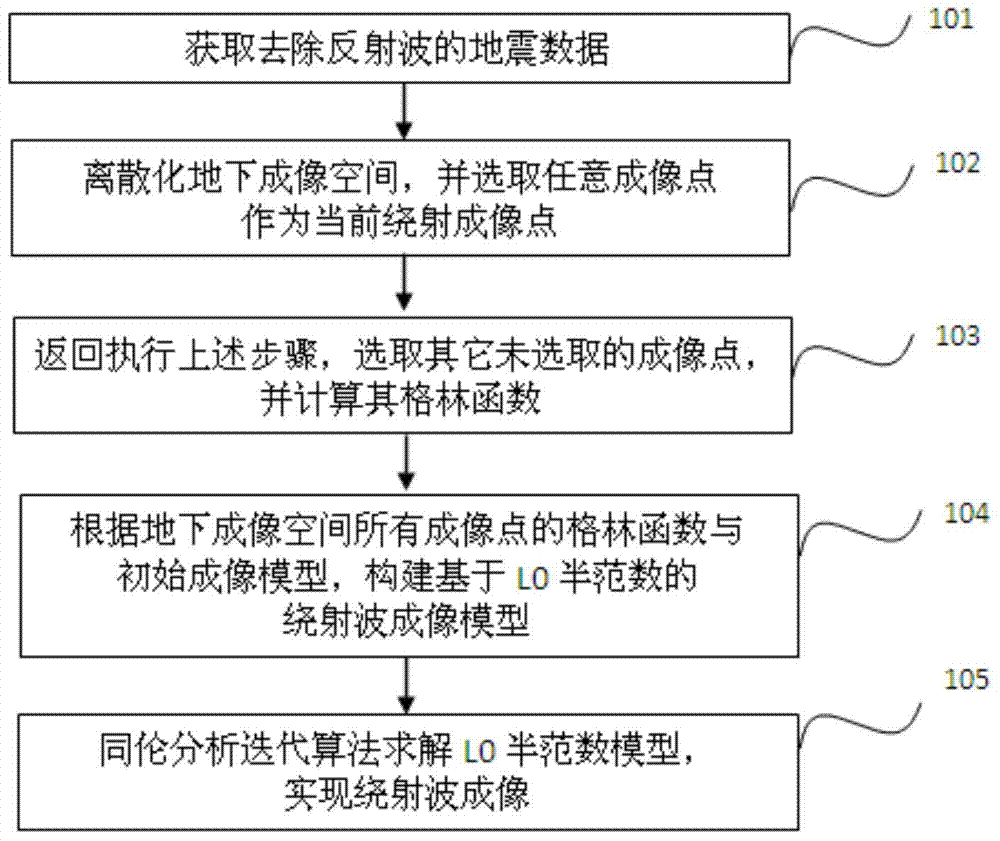
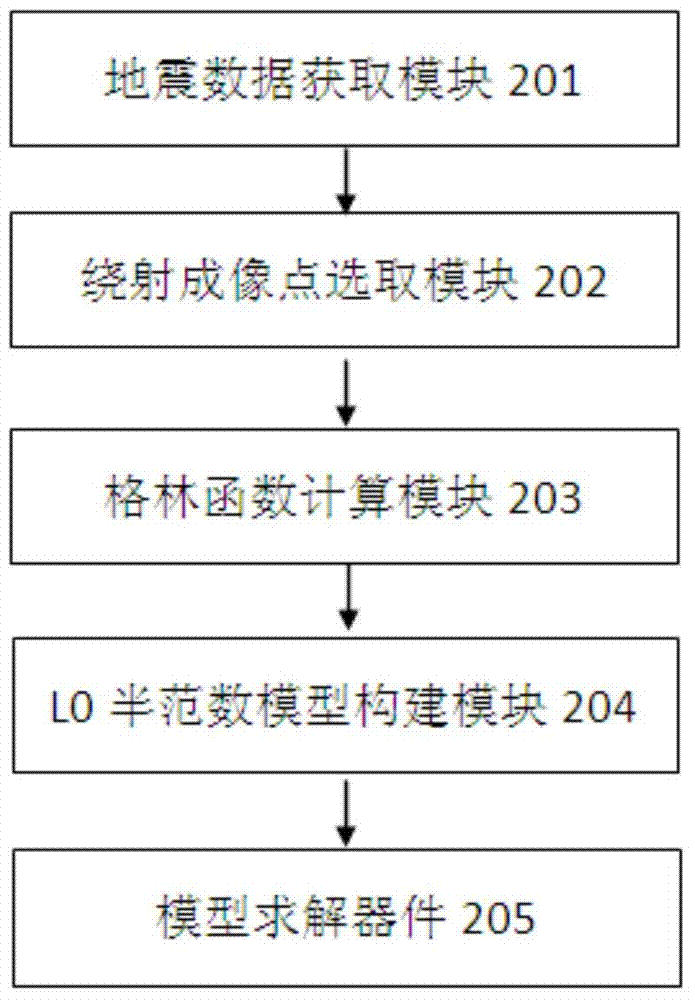
ActiveCN104730572ABounded sparsityImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image resolution
The invention discloses a diffracted wave imaging method based on the L0 semi-norm. The method comprises the steps that seismic data with no reflected waves are obtained to be used as input data; discretization is carried out on underground imaging space, any imaging point is selected as the current diffracted imaging point, and a green function of any diffracted imaging point is calculated according to a given speed model and the relation between short points and wave detection points in the input seismic data; other imaging points which are not selected are executed in a loop mode, and other corresponding green functions are calculated until the green functions of all the imaging points in the underground imaging space are obtained; a diffracted wave imaging model based on the L0 semi-norm is built; the homotopy analysis iterative algorithm is used for solving the model, and a diffracted wave imaging result is obtained. The invention further discloses a diffracted wave imaging device based on the L0 semi-norm. By means of the diffracted wave imaging method and device based on the L0 semi-norm, the seismic data imaging resolution ratio can be improved, the diffracted wave imaging signal to noise ratio is increased, and therefore a small-scale geological unit related to reservoir space connectivity can be recognized more easily.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
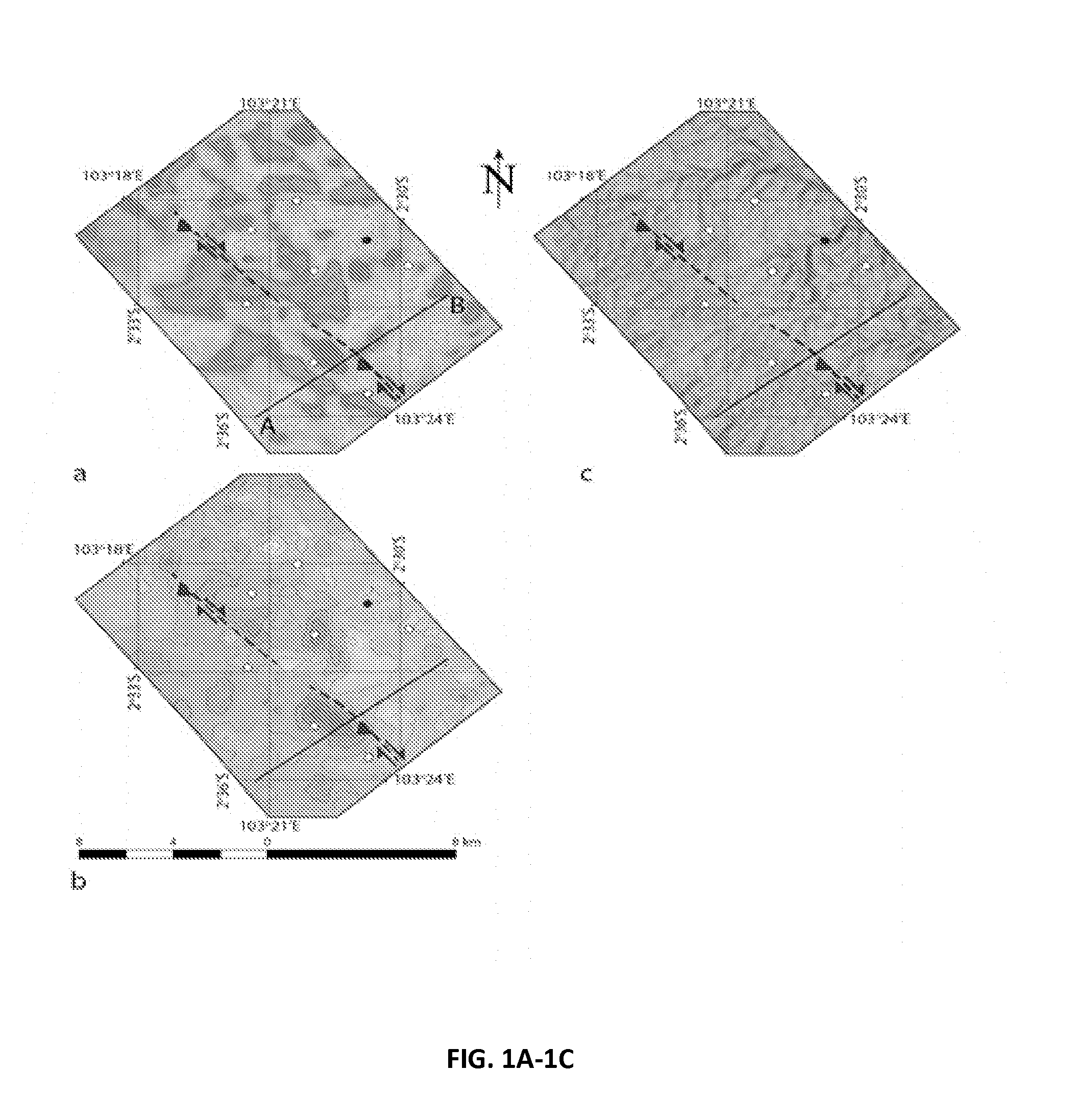
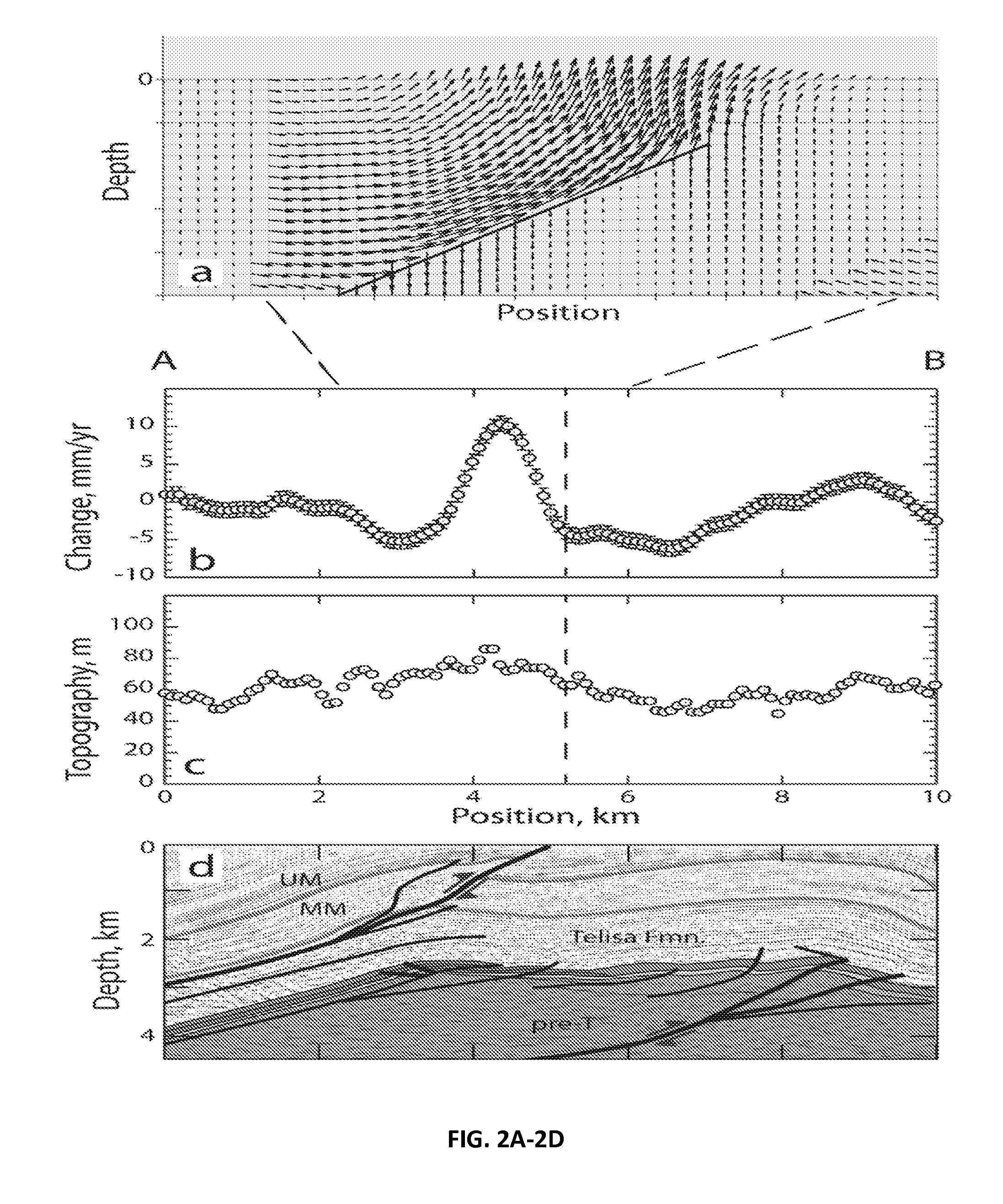
Satellite geodesy and reservoir performance
Satellite geodesy can identify fault-related surface deformation above onshore oil and gas fields through the use of radar interferometry (InSAR). The method provides an independent and cost-effective approach to identifying faults and damage zones that can be associated with increased reservoir performance beyond traditional tools of subsurface imaging and reservoir evaluation.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Sub-surface imaging using antenna array for determing optimal oil drilling site
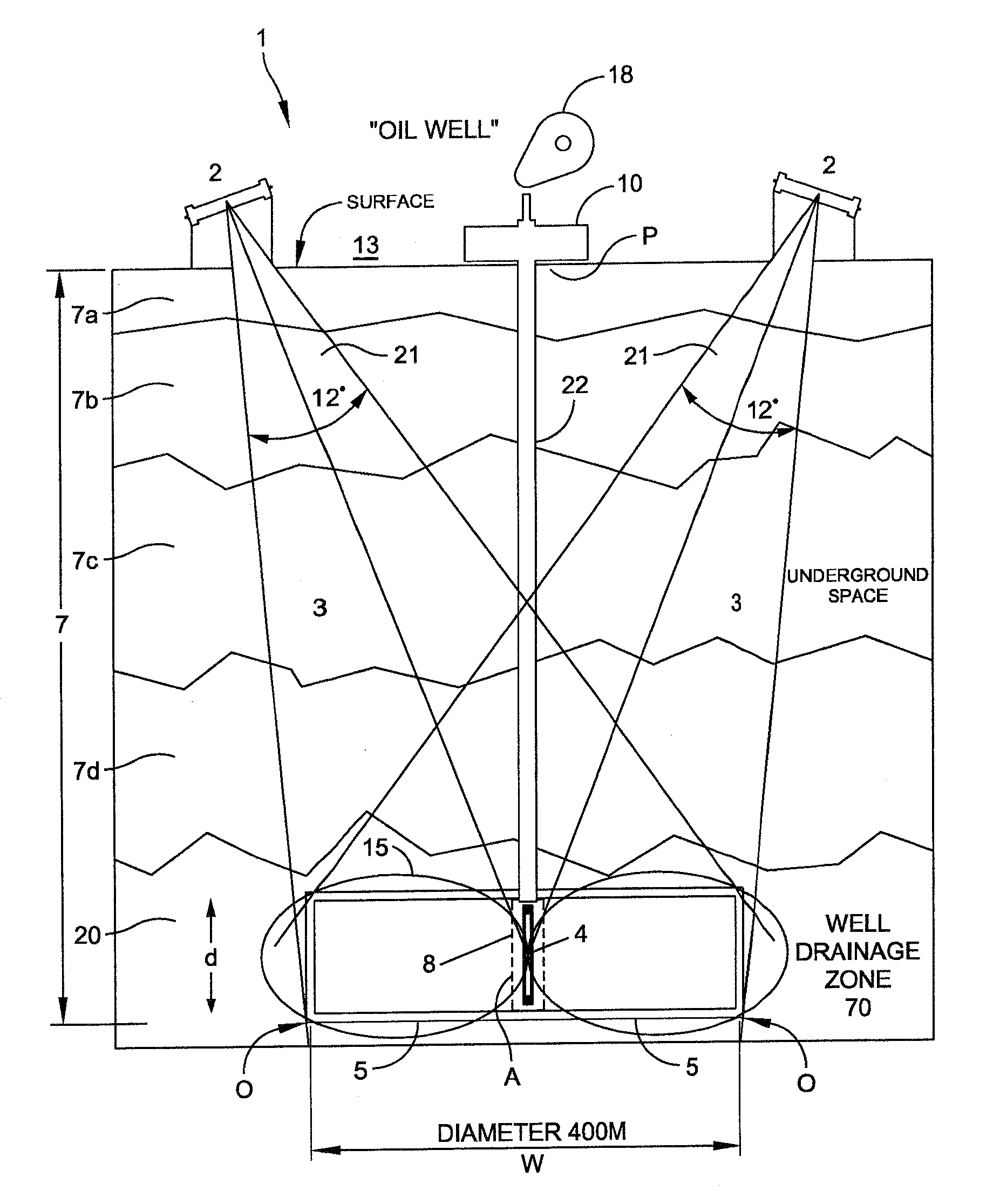
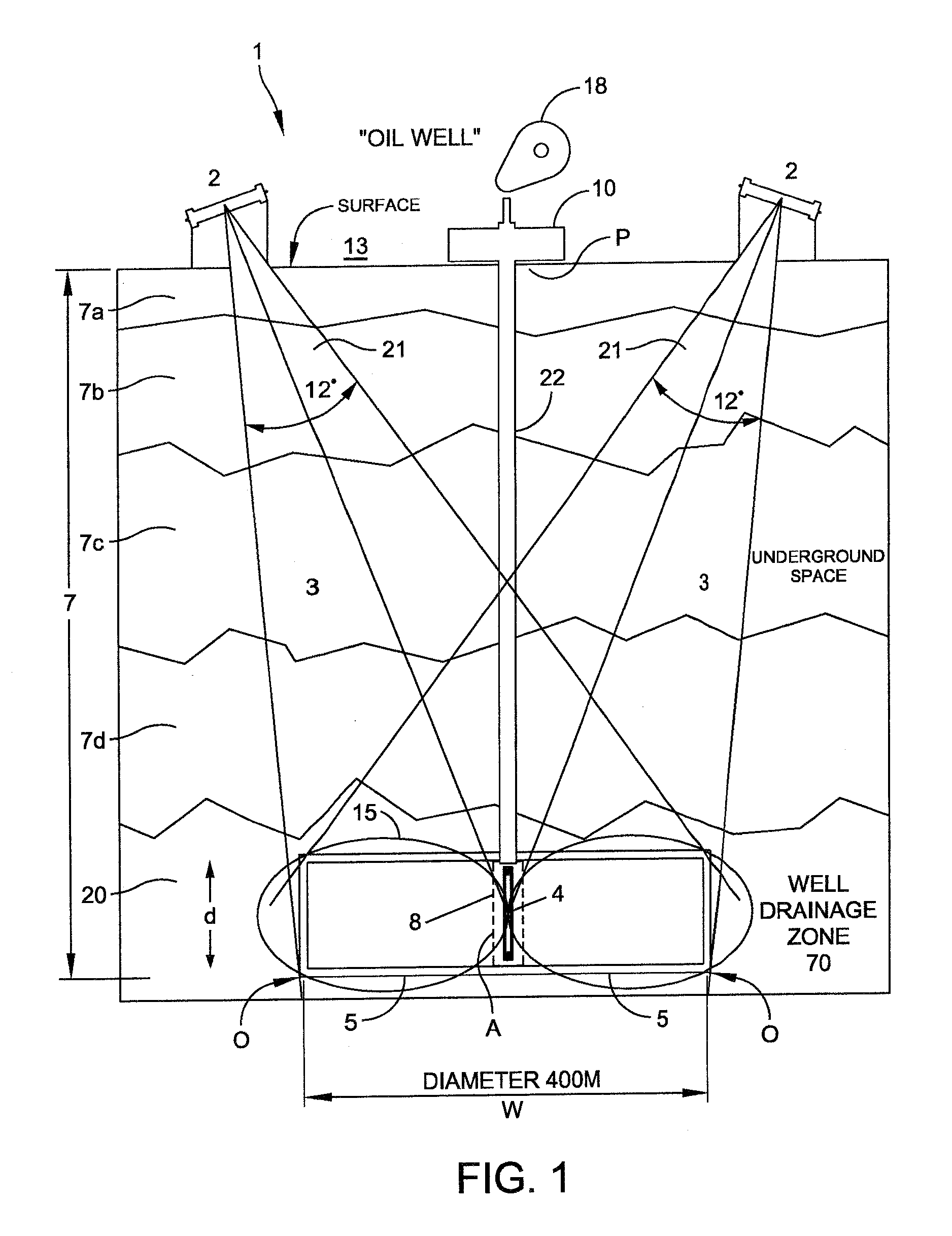
InactiveUS20100071955A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElectromagnetic launchPhase shifted
The invention provides for systems and methods of enhancing crude oil recovery providing an array of electromagnetic receiver antennae arranged and operated in conjunction with an array of far field electromagnetic transmitter antennae for mapping subsurface features of a reservoir. Mapping is performed according to the relative intensities, frequencies, phase shifts, and / or other reflected signal parameters of the reflections received by the receiver antennae (relative to the transmit signals) associated with a given location or target area within a reservoir. Such mapping aids in determining an optimal location of a production well or the location of an auxiliary well relative to the production well.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Electromagnetic subterranean imaging instrument
ActiveUS8098070B2Improve scalabilityAcoustic wave reradiationElectric/magnetic detection for transportModularityEngineering
The instrument utilizes at least one electromagnetic signal transmitter and at least one electromagnetic signal receiver with the receiver detecting a receiver signal responsive to the transmitter signal and indicative of subterranean details adjacent to the instrument. The instrument is attachable to a tow vehicle for transport and includes a GPS antenna and tags data gathered by the instrument with GPS position information. The instrument is formed in modular sections which can be removably attached for collapsing into a smaller space and to allow for flexible configuration of the instrument in various different ways. A wheeled carriage is provided to carry the instrument over the ground. Antennas for the transmitter and receiver, as well as circuitry and cooling systems are all provided to supply the instrument with high resolution and a clear signal indicative of the position and characteristics of subterranean details of interest.
Owner:LOPEZ JOHN A +4
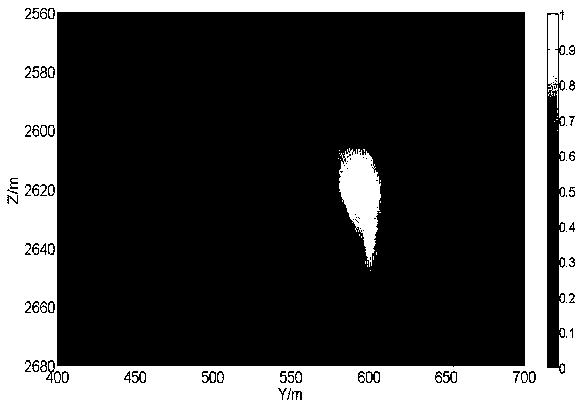
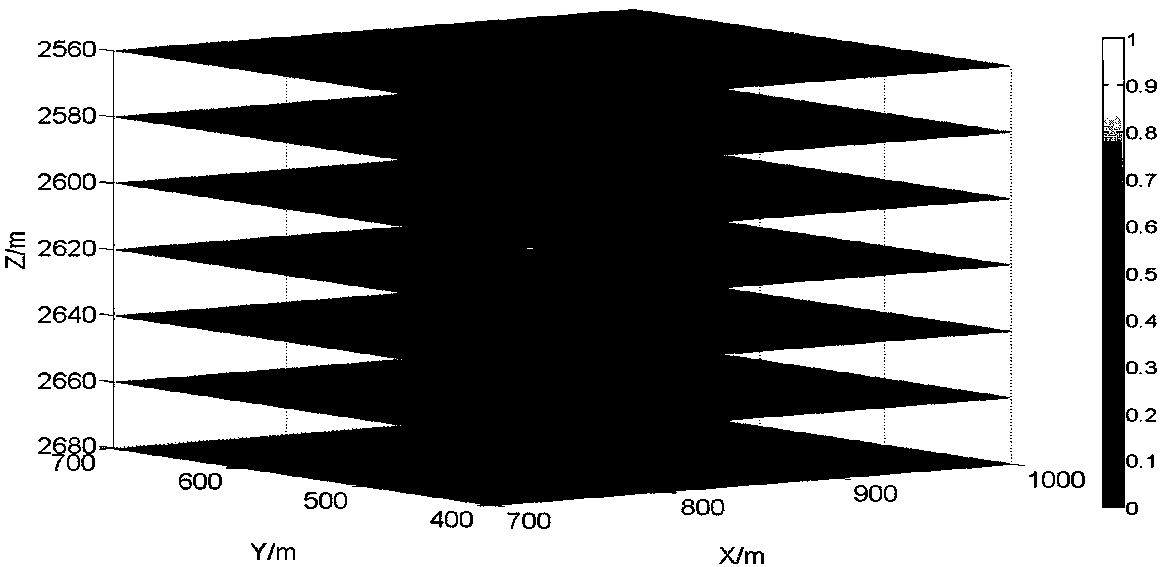
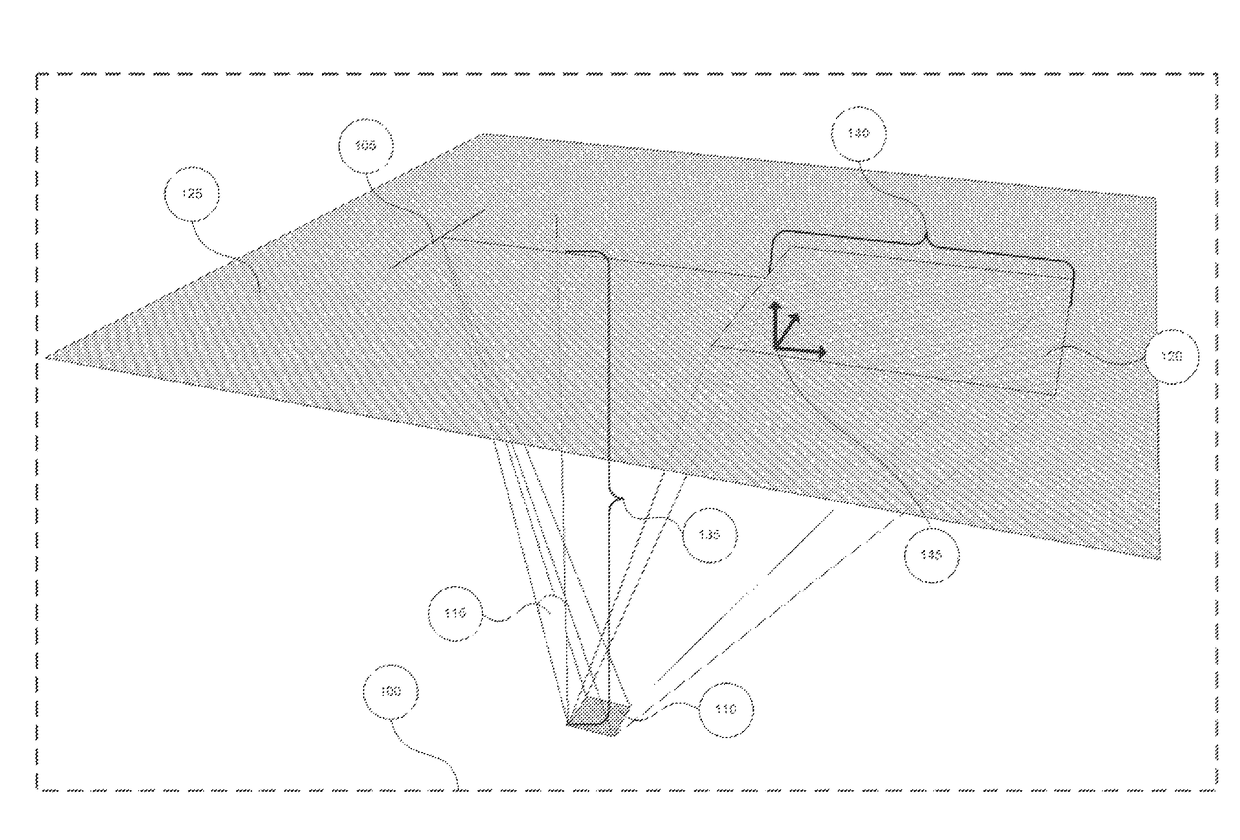
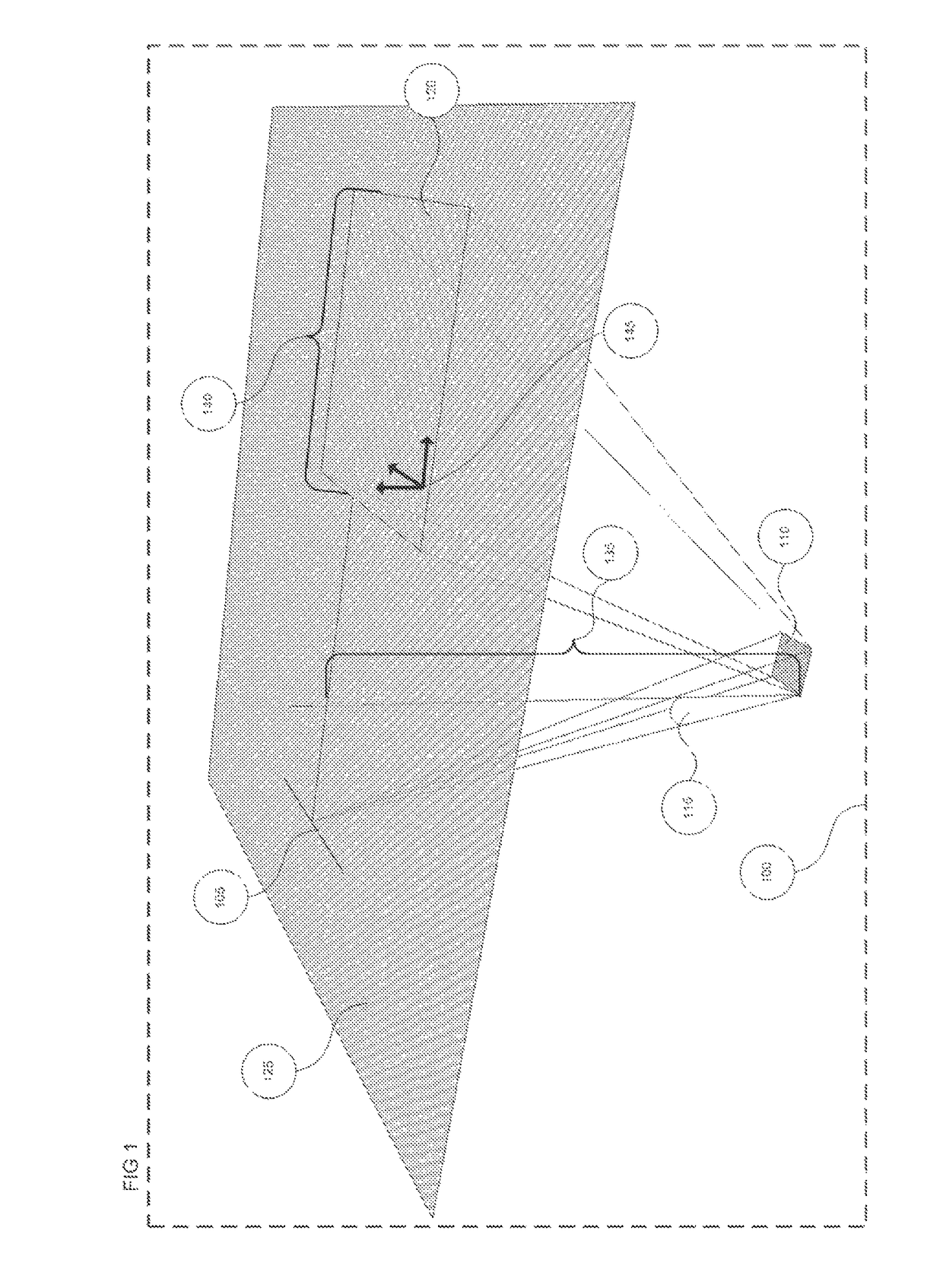
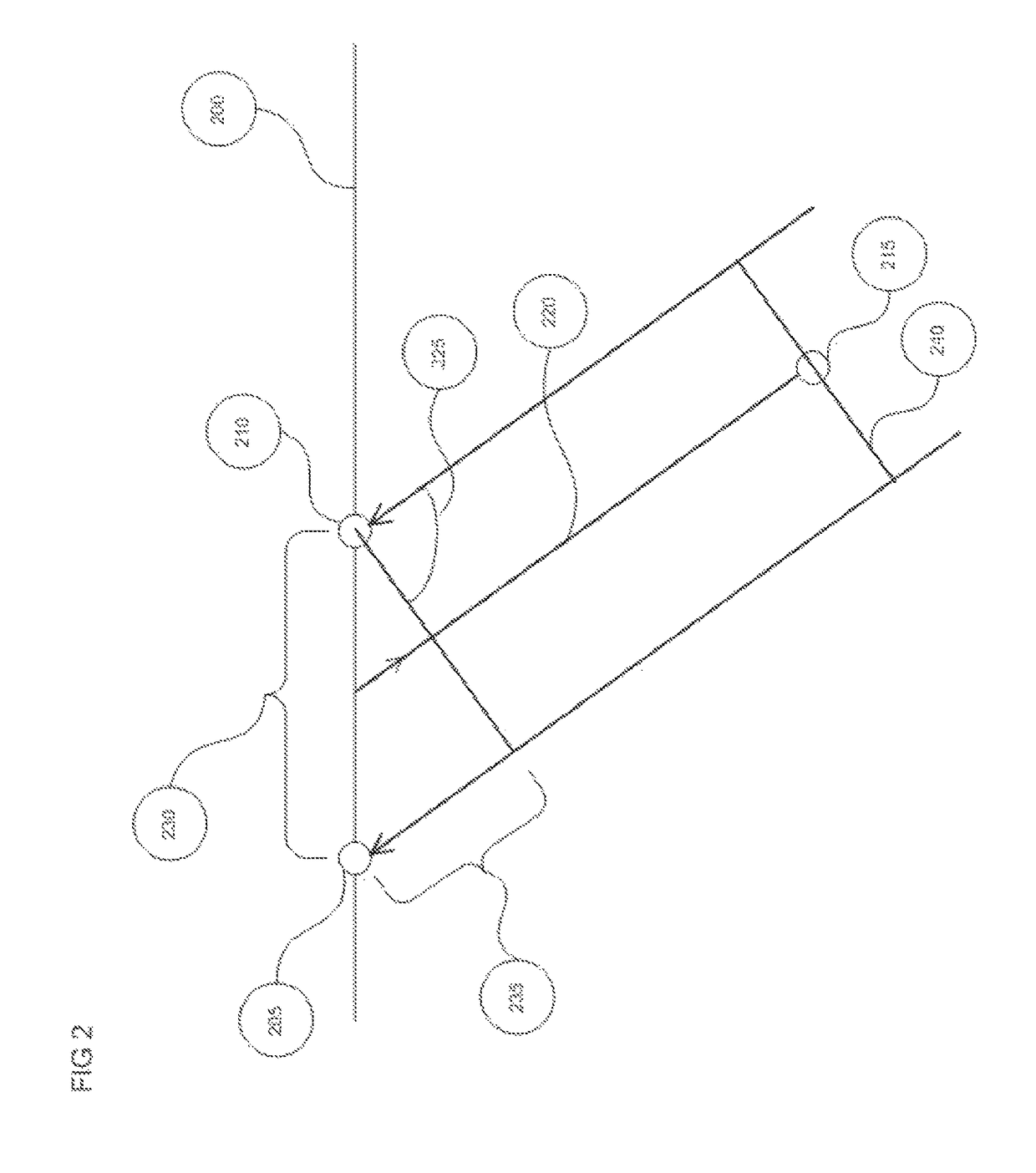
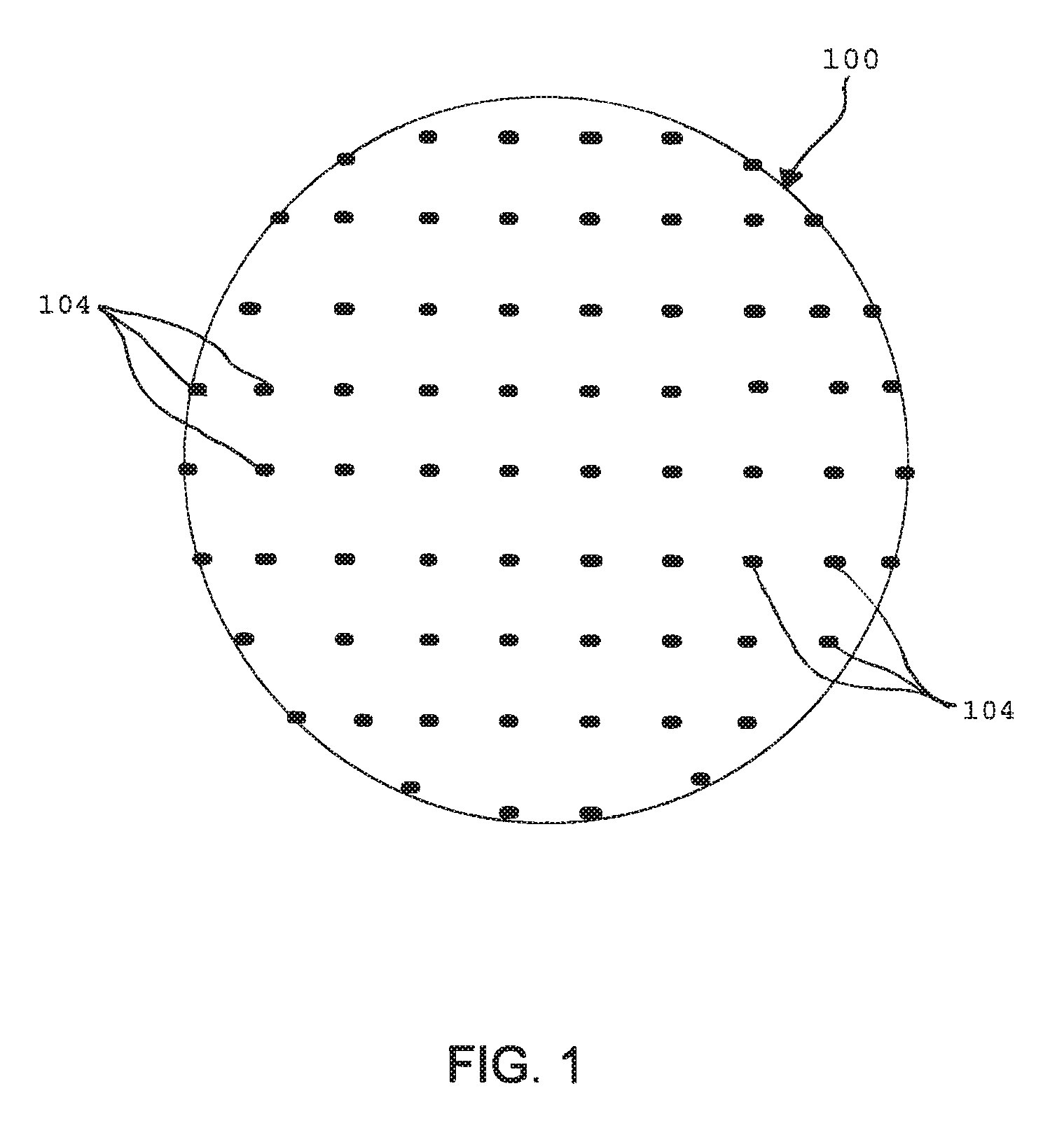
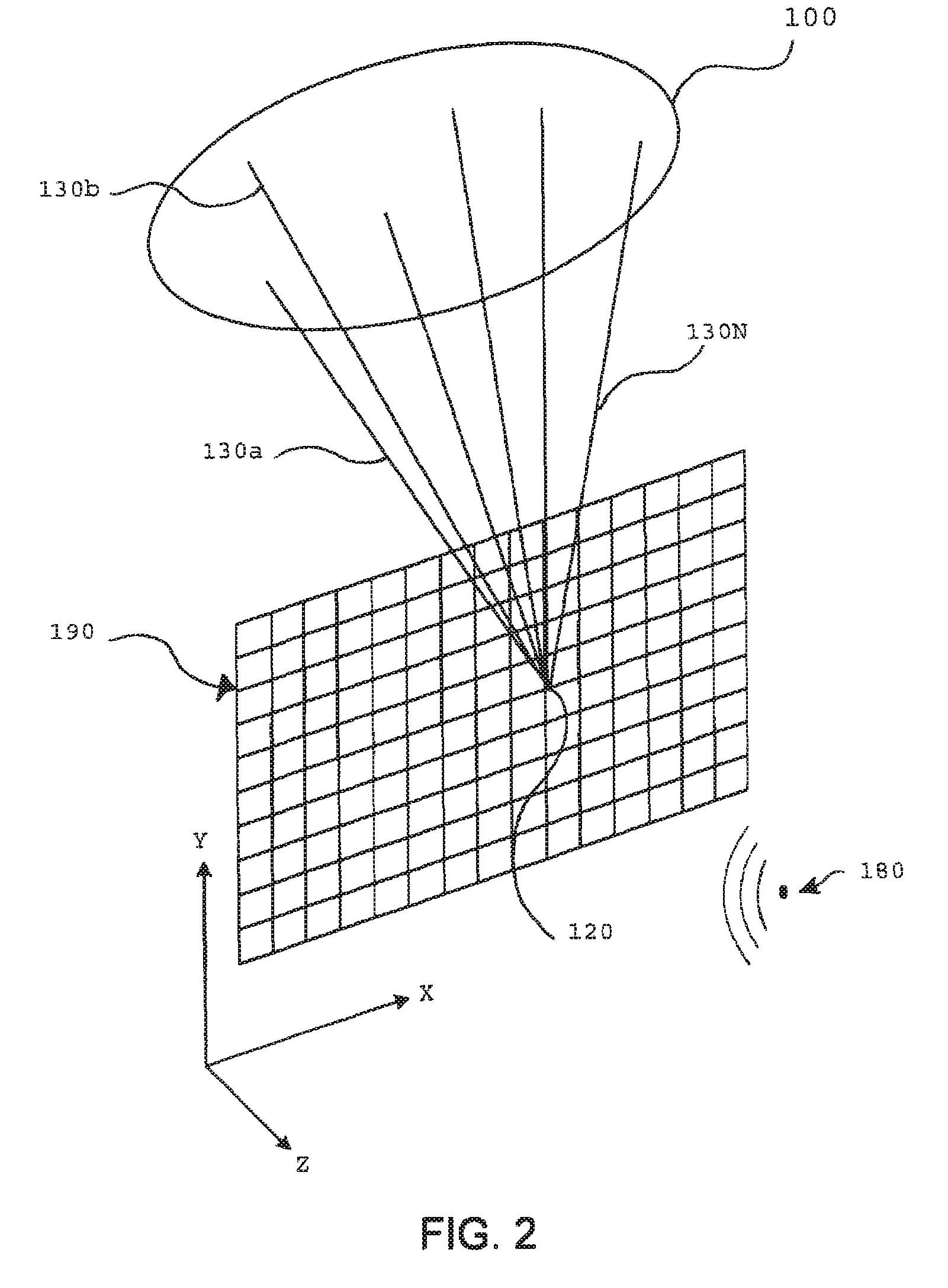
System and method for visualizing multiple-sensor subsurface imaging data
A user interface includes a display for displaying of a plurality of sensor data sets representative of signals associated with a plurality of sensors configured for sensing of a subsurface. At least some of the sensors are configured for subsurface sensing in a manner differing from other sensors of the plurality of sensors. Each of the sensor data sets comprises sensor data samples each associated with geographic position data. The sensor data sets are shown overlaid within a volume depicted on the display. The graphical representations of the sensor data sets are individually viewable within the volume and displayed in geographical alignment relative to one another within the volume in accordance with the geographic position data of the sensor data samples of each of the sensor data sets.
Owner:UNDERGROUND IMAGING TECH
Micro-seismic migration imaging positioning method based on multiplication of waveform cross correlation coefficients
InactiveCN110389377AAchieve double suppressionAvoid inversionSeismic signal processingSeismic migrationDual effect
The invention relates to a micro-seismic migration imaging positioning method based on multiplication of waveform cross correlation coefficients, and belongs to the technical field of oil-gas reservoir fracture micro-seismic monitoring. The method includes the following steps of: preprocessing actual micro-seismic data; performing subsurface imaging point division, and calculating the travel timeof all imaging points to each receiving point on the ground; for a certain imaging point, eliminating the arrival time difference of the imaging point to different receiving points, calculating the cross-correlation coefficient of a micro-seismic record after the time difference correction; calculating the cross-correlation energy value E of the imaging point; repeating the third and fourth stepsto obtain the energy values E of all underground imaging points; and setting an energy threshold E0, obtaining the imaging point position of an energy maximum value greater than the energy threshold as the occurrence position of a micro-seismic source. The method realizes the dual-effect suppression of the noise by using the form of multiplication of the waveform cross-correlation coefficients soas to greatly improve an anti-noise capability, avoids the interference of the first arrival polarity on the positioning imaging results, has high calculation efficiency and satisfies the real-time monitoring of the micro-seism.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method using near and far field ULF and ELF interferometry synthetic aperture radar for subsurface imaging
ActiveUS9638826B2Detection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarSubsurface imaging
This invention relates to devices and processes for geophysical prospecting, subsurface fluid monitoring and, more particular, to the use of interferometric techniques using Control Source Electromagnetic (“CSEM”) and Magnetoturelic (“MT”) signals to create images of sub-surface structures and fluids.
Owner:DEEP IMAGING TECH INC
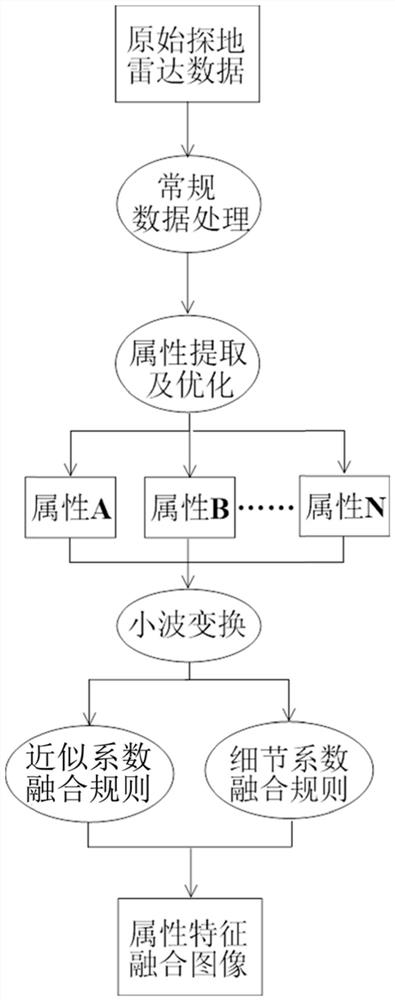
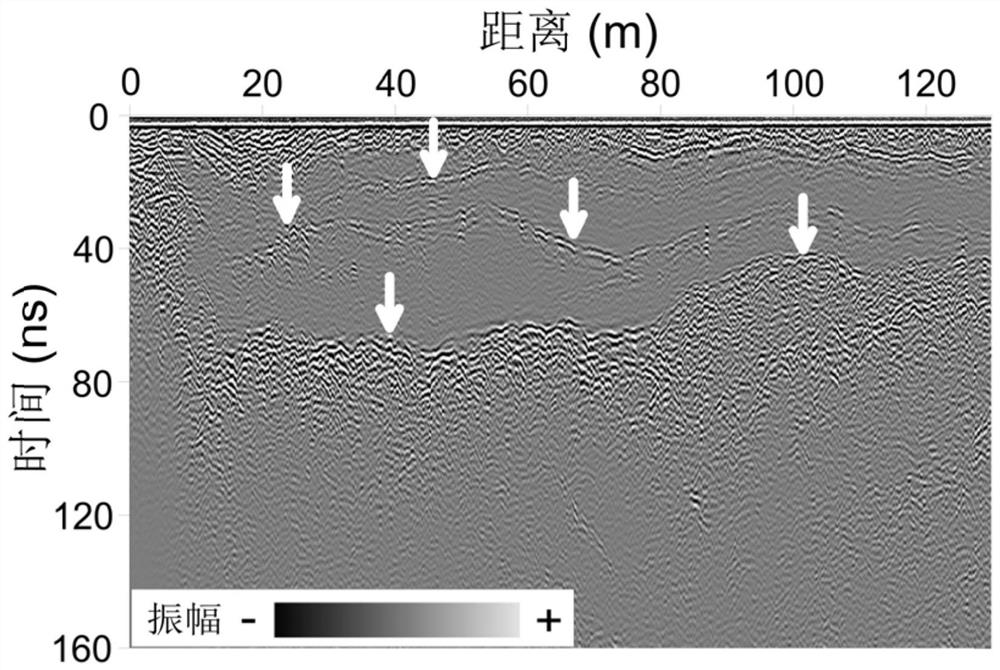
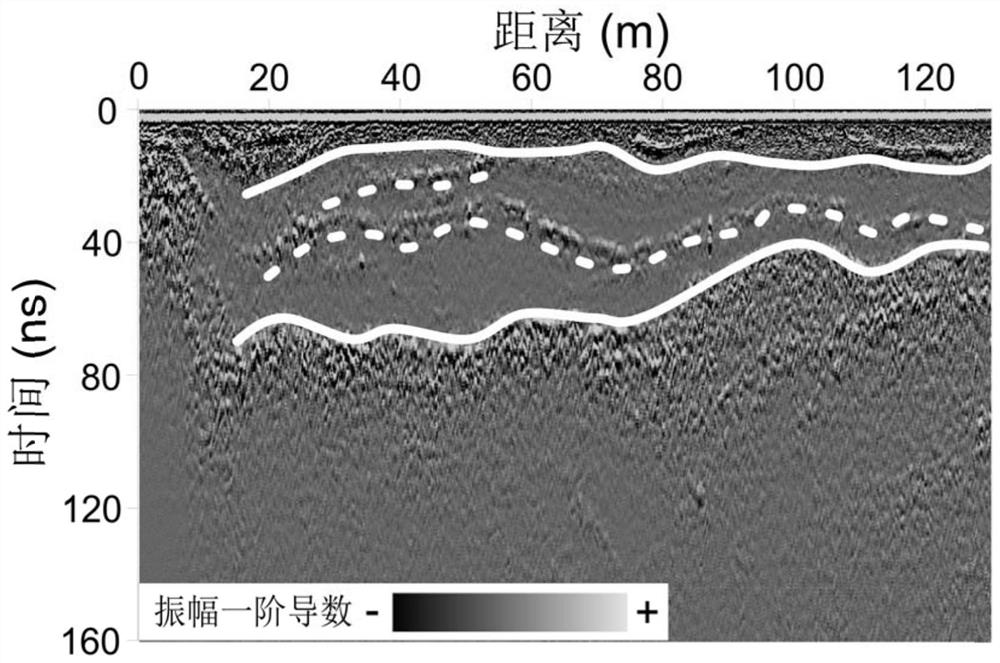
Method for fusing attribute features of ground penetrating radar by wavelet transform
PendingCN111627035AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for fusing attribute features of a ground penetrating radar by wavelet transform, and belongs to the technical field of near-surface geophysics. According to the method, extraction and optimization selection of multiple attribute characteristics are carried out on physical and geometric properties of an underground potential target body, and the different attributeprofiles are synthesized into a composite output display, so that underground imaging is improved by utilizing information such as amplitude, coherence, reflection characteristics, phase and spectralcontent at the same time. According to the method, different attributes from the same ground penetrating radar data are fused through wavelet transform, extraction of effective information is optimized, people are helped to better describe features and locate potential targets, and an automatic or computer-aided interpretation road is further opened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
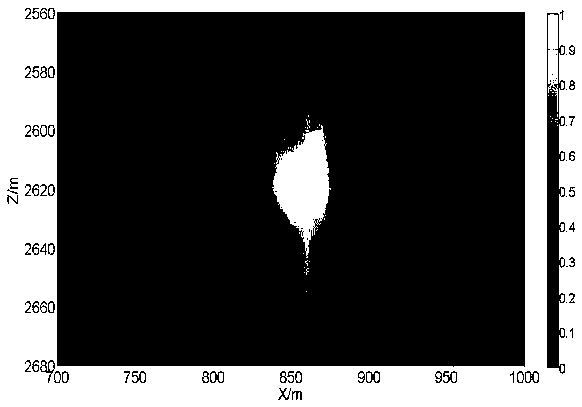
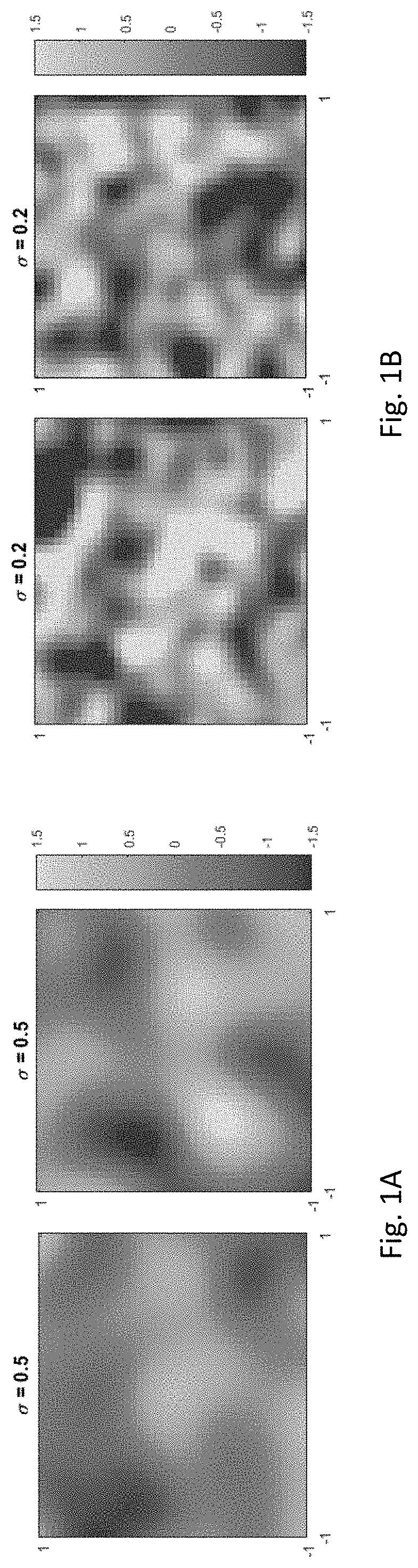
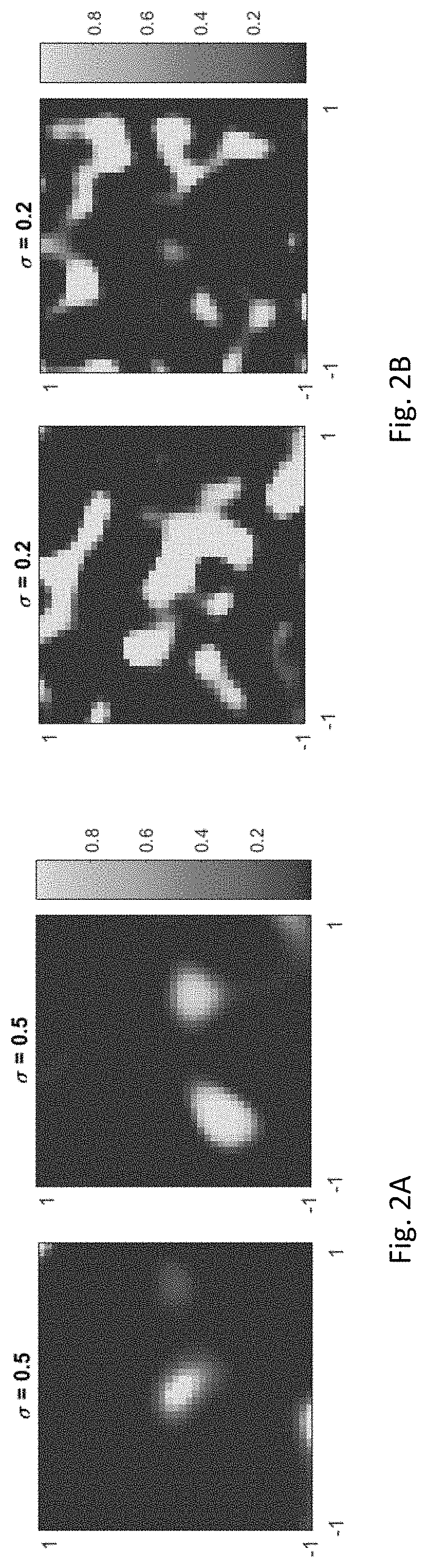
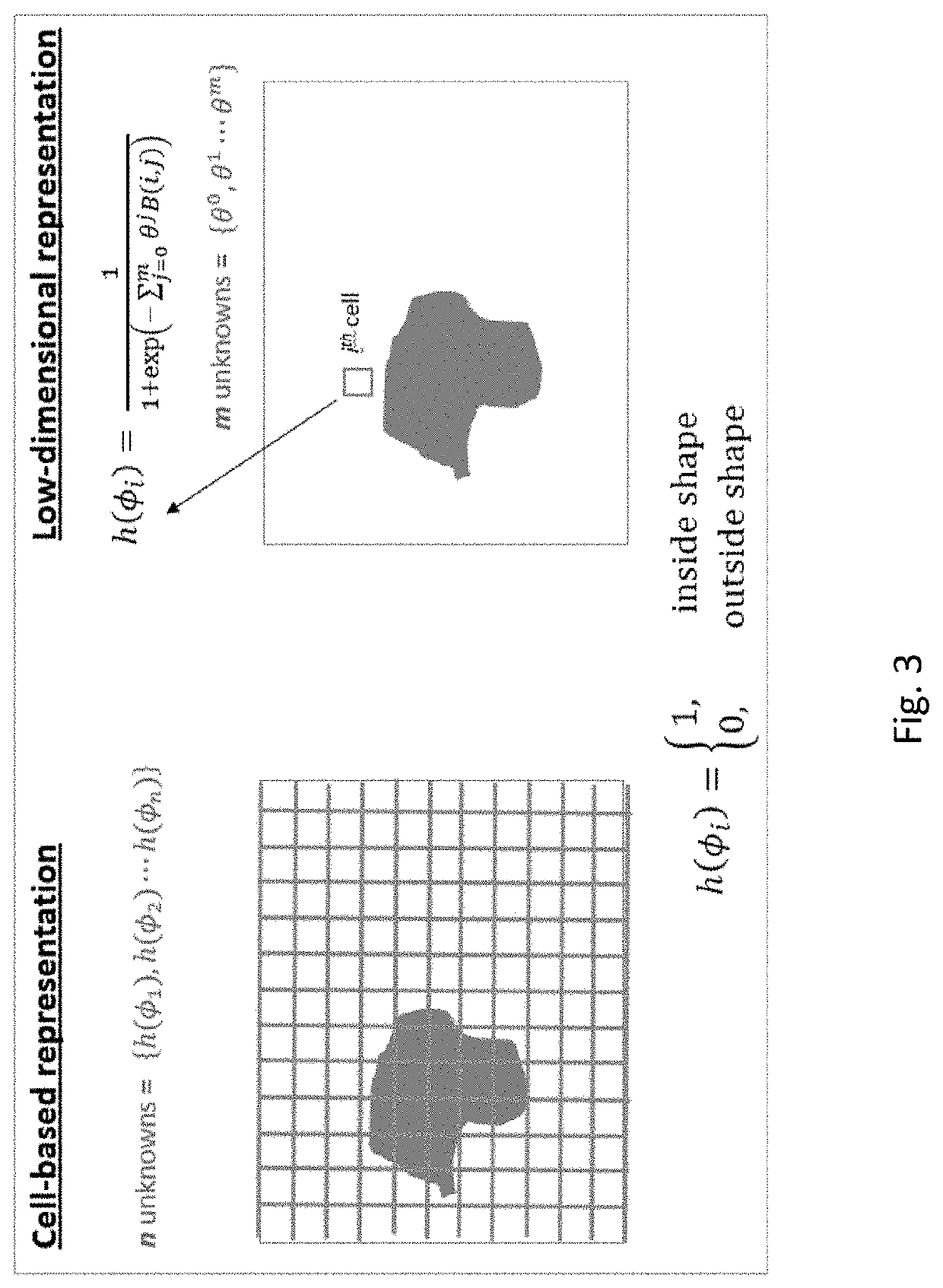
Inversion of large, nearly-homogeneous geobodies via ultra low-dimensional shape representation using orthogonal basis functions
ActiveUS20200066035A1Minimizing misfitSeismologyDesign optimisation/simulationData setSubsurface imaging
A two-stage method for iteratively inverting geophysical data for the purpose of subsurface imaging, including: obtaining at least one geophysical dataset and an initial subsurface model; representing subsurface such that a geometry of a geobody is defined using a set of basis functions, and a number of such basis functions is significantly smaller than the number of cells used in cell-based geobody representations, wherein an order of magnitude reduction is two or more for 2-D domains and 3 or more for 3-D domains; in a first stage, successively updating the initial subsurface model, only for the geobody, by performing iterative low-dimensional geophysical inversion based on minimizing a misfit between simulated geophysical data and the geophysical dataset, wherein the simulated geophysical data is generated from a current subsurface model at each iteration; generating a subsurface image from a final updated subsurface model obtained via the low-dimensional geophysical inversion, wherein the subsurface image includes an inverted geobody; in a second stage, successively updating the subsurface model with the inverted geobody by performing iterative cell-based geophysical inversion based on minimizing a misfit between simulated geophysical data and the geophysical dataset, wherein the simulated geophysical data is generated from a current subsurface model at each iteration.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Passive reflective imaging for visualizing subsurface structures in earth and water
A system and method is provided that uses signals from a plurality of seismic sensors to define an acoustic lens for subsurface imaging. More specifically signals provided by an array of sensors / geophones may be utilized to form an acoustic lens that can be focused on a subterranean point by properly adjusting the signals recorded at each sensor prior to summation of those signals. To form such an acoustic lens, each of the seismic sensors is moved onto a hypothetical acoustic lens surface (e.g., spherical surface) having a focal point located on the subterranean point of interest in order to calculate a time delay for each signal. Once the signals for each sensor is time-delayed, information in the time-delayed signals, which is received from the point of interest, may be temporally aligned. Accordingly, the time delayed signals may be combined to generate reflection information for the point of interest.
Owner:SIMON WAYNE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com