Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1747 results about "Geodesy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɪsi/) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space and gravitational field. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivalent measurements for other planets (known as planetary geodesy). Geodynamical phenomena include crustal motion, tides and polar motion, which can be studied by designing global and national control networks, applying space and terrestrial techniques and relying on datums and coordinate systems.
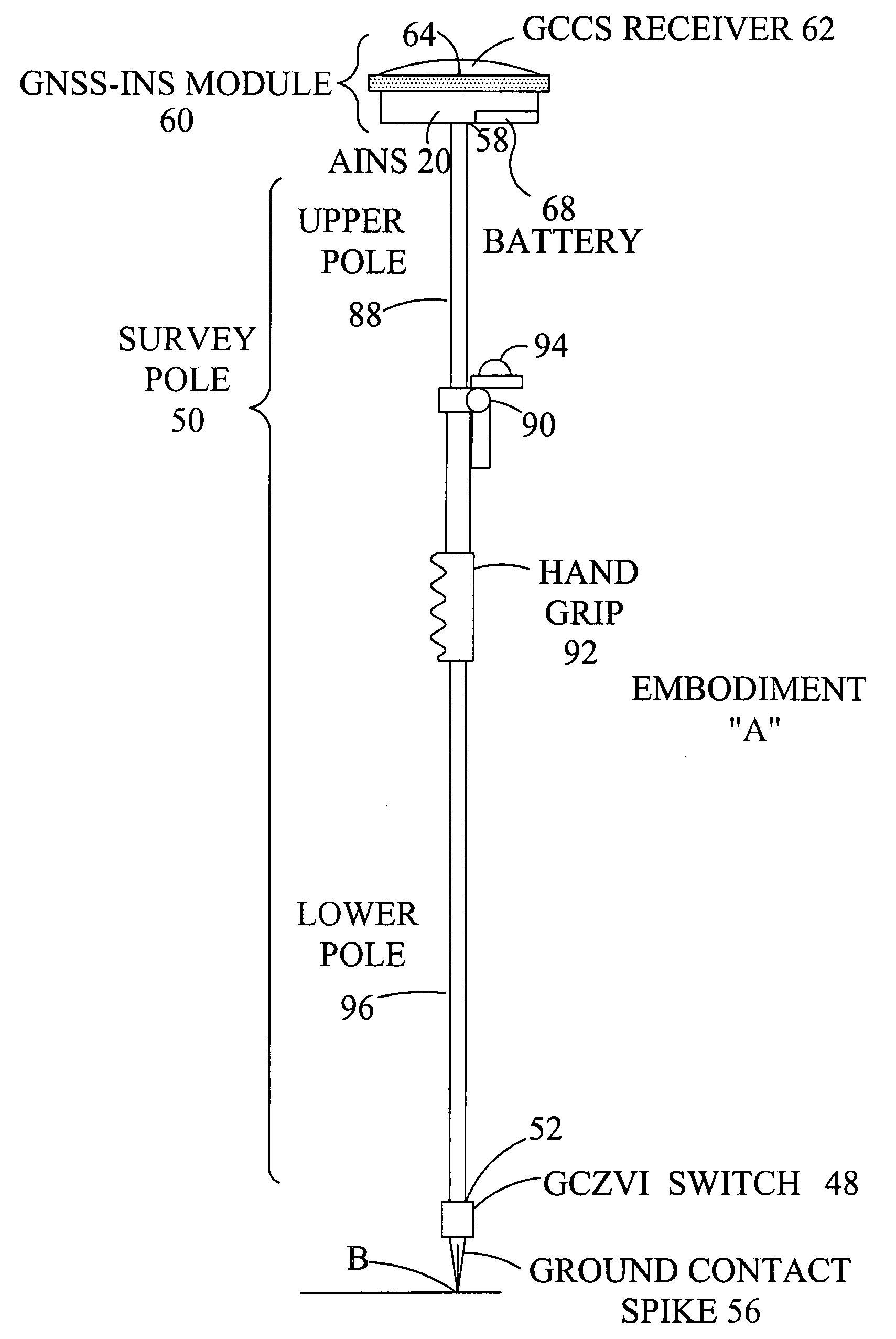
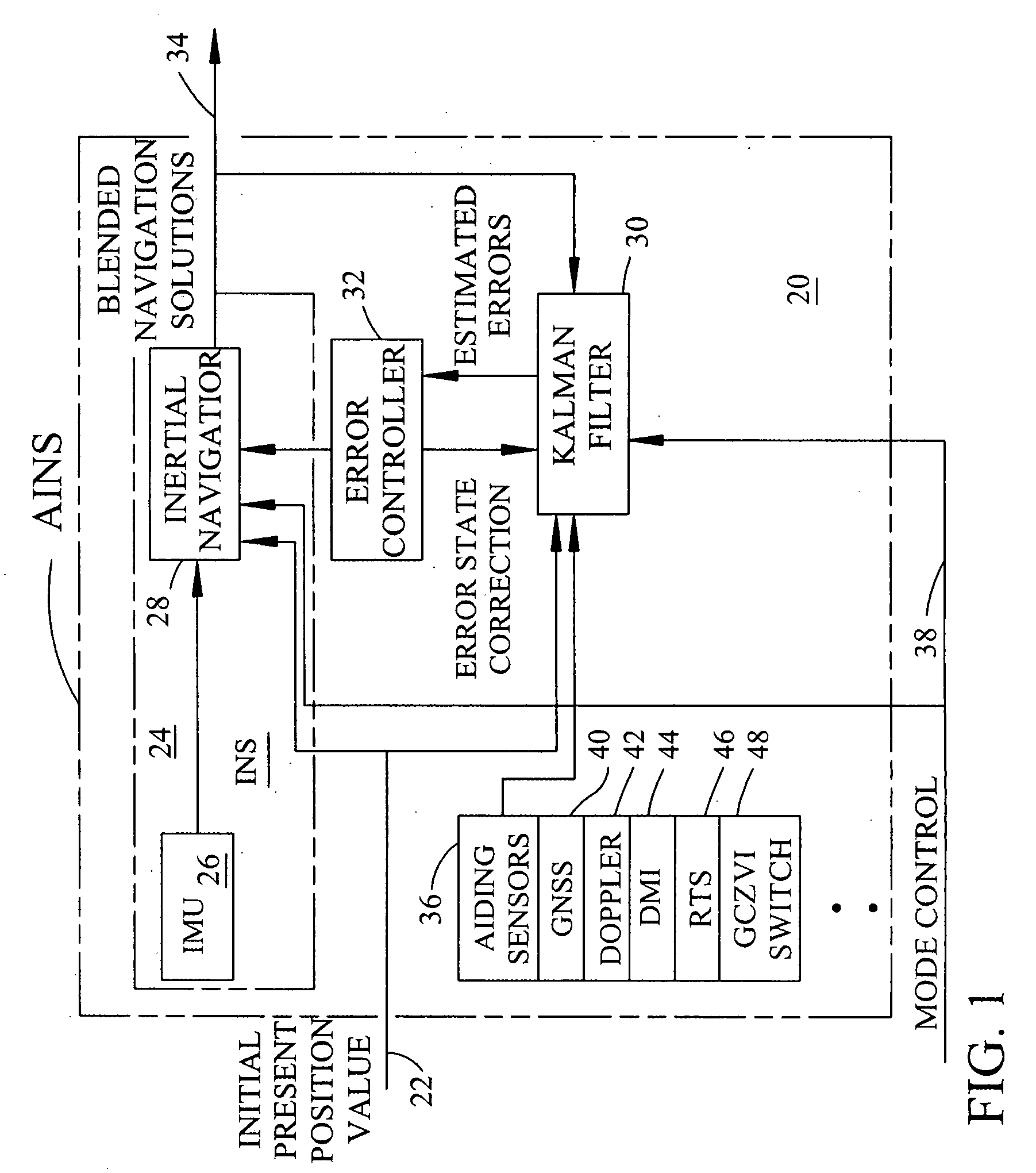
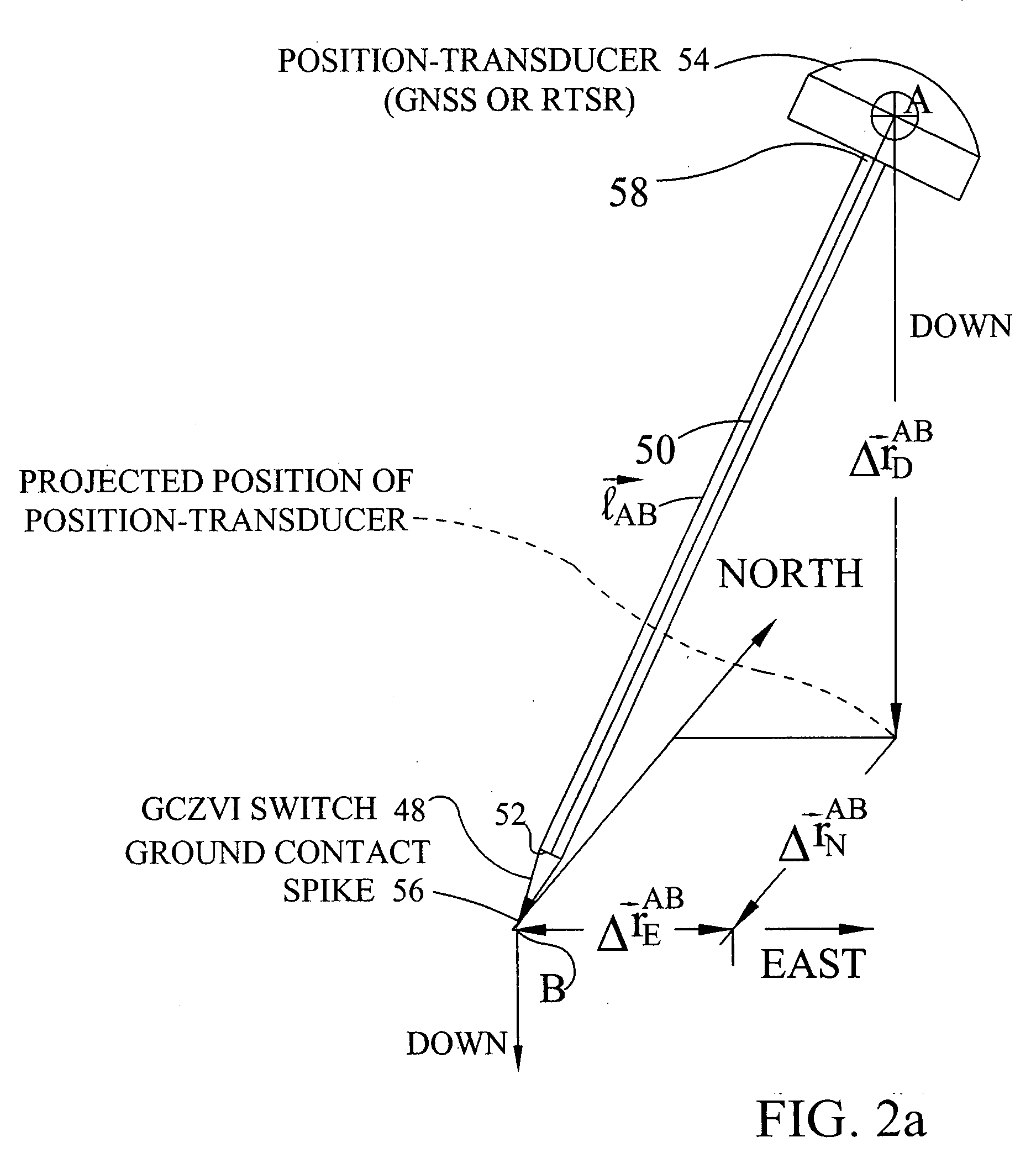
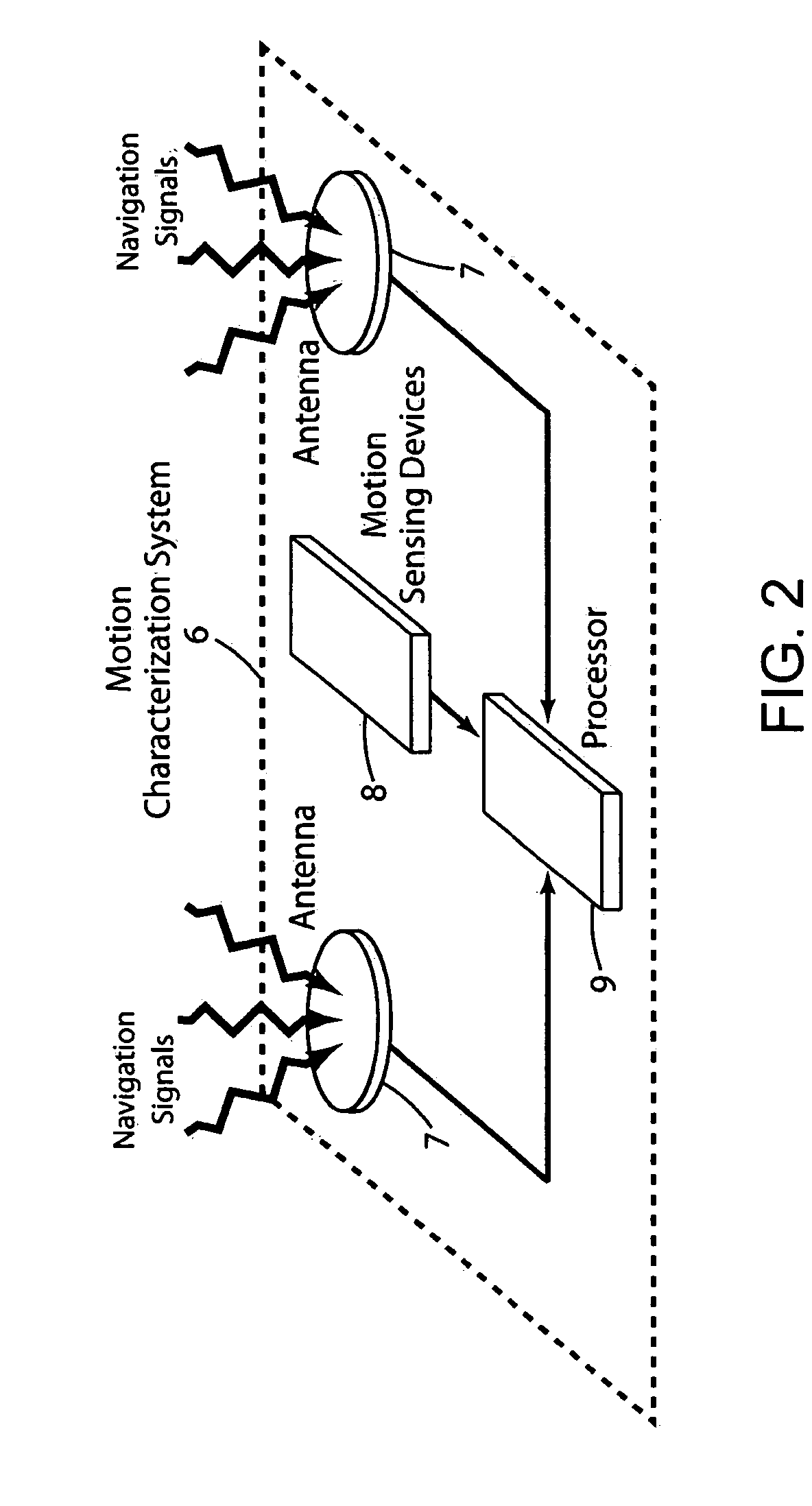
AINS enhanced survey instrument
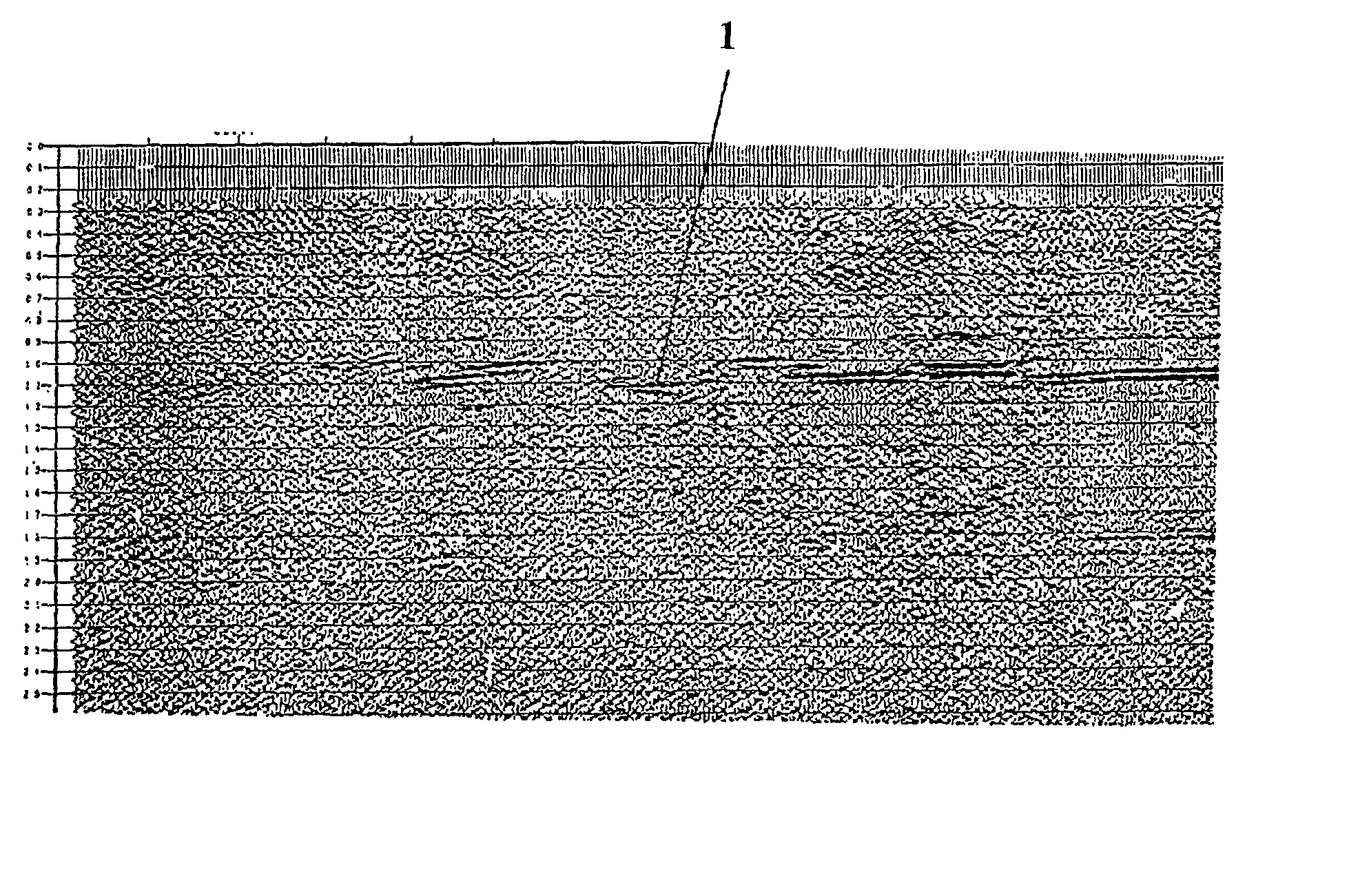
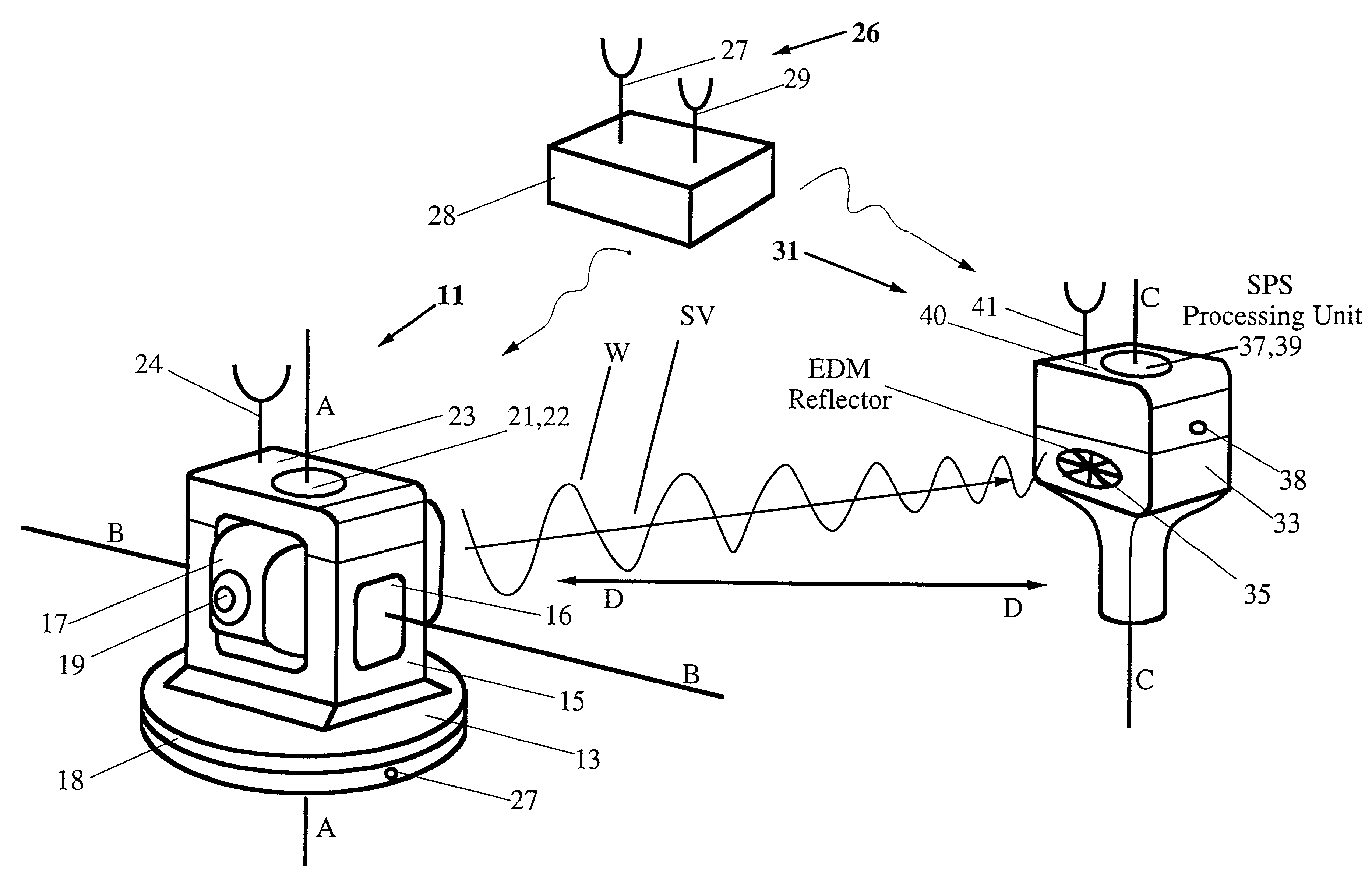
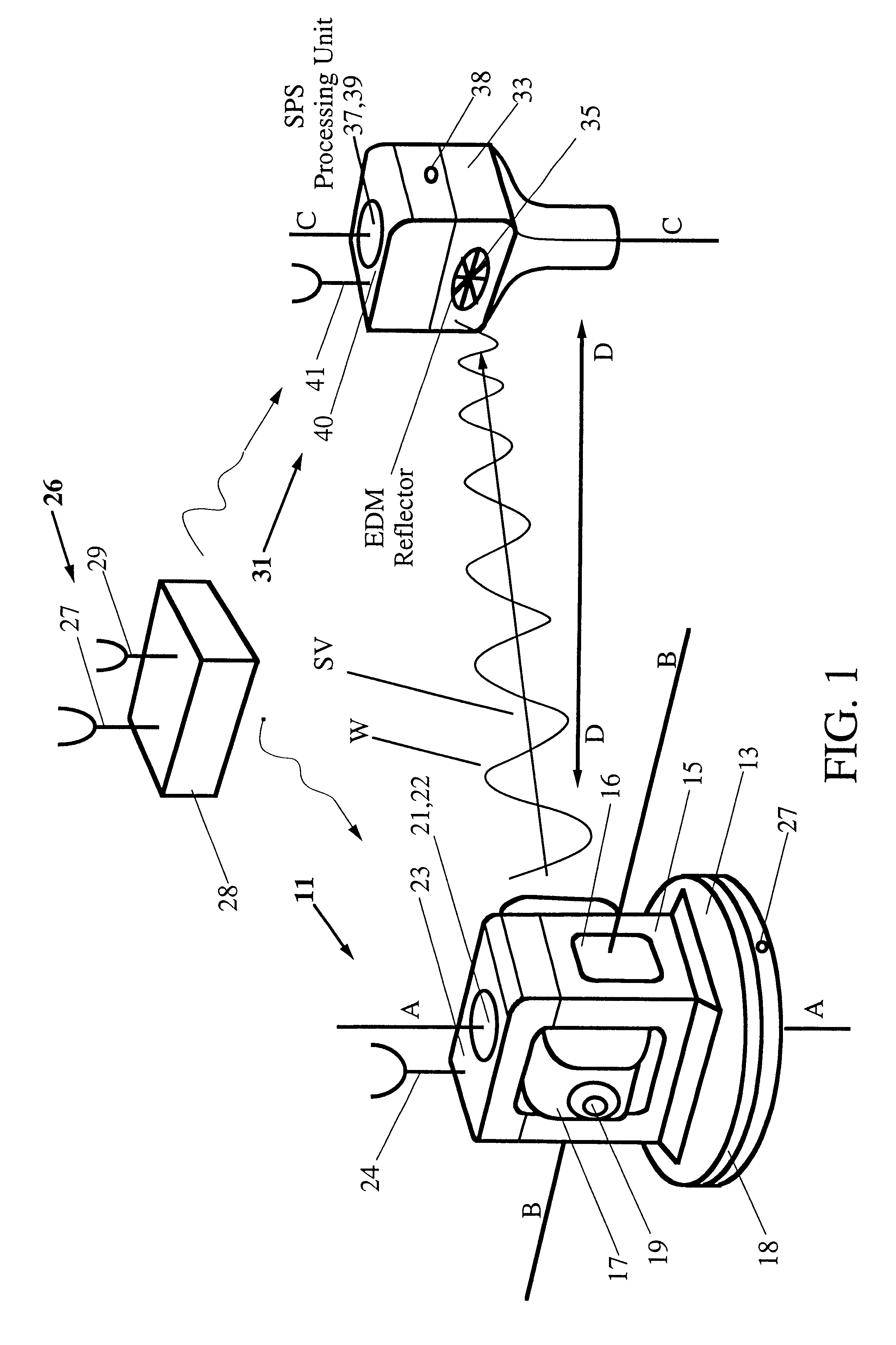
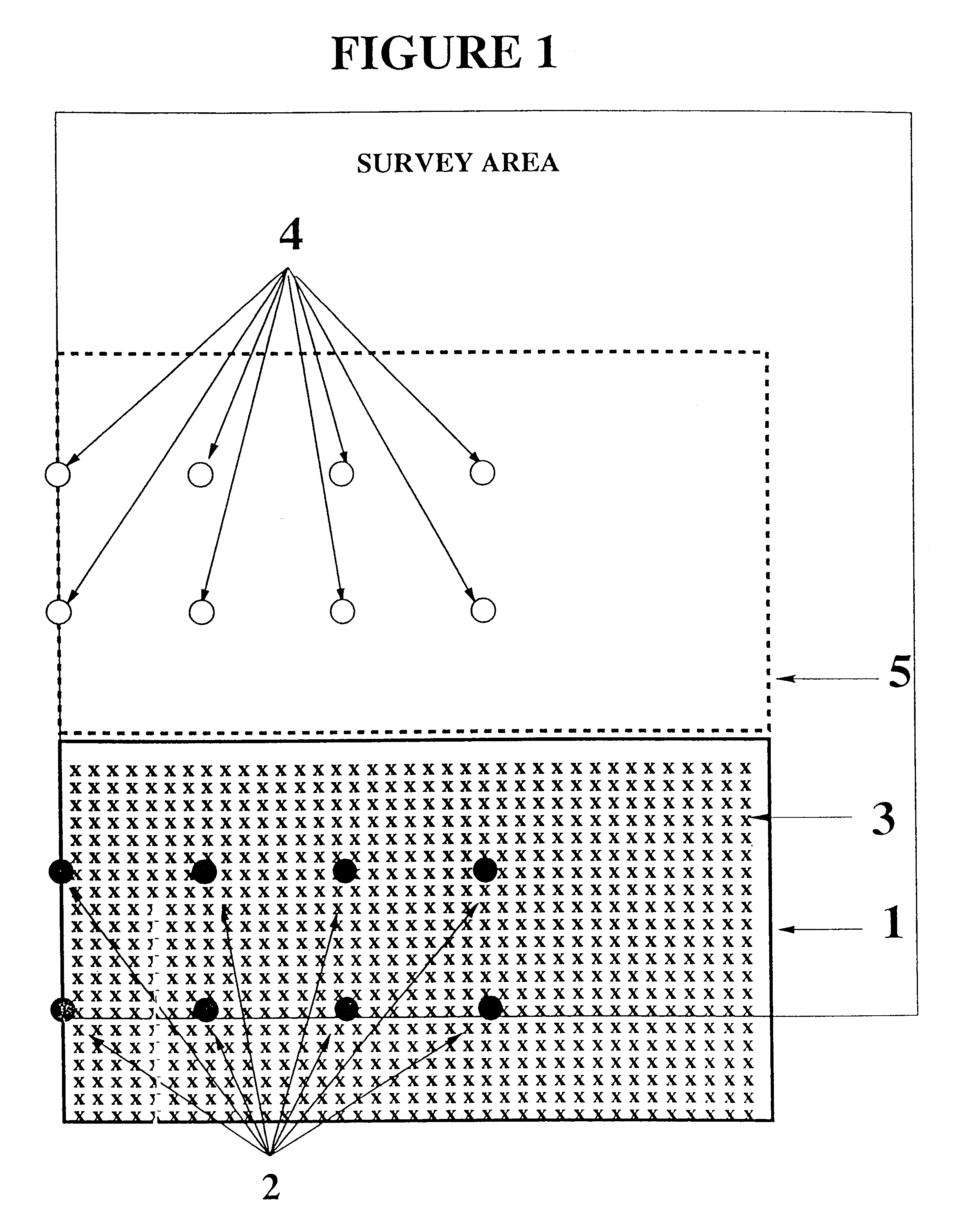
The invention comprises a survey pole having a survey pole bottom end, with a position-transducer coupled to a survey pole top end. A ground contact spike is on the bottom end. The survey pole uses an AINS as a combined tilt and heading sensor. The AINS provides heading and Euler angle outputs characterizing the tilt of the survey pole. The heading and Euler angle outputs are used by a computer and program to perform position transfers from a position-transducer at the pole top end to the GCZVI switch or spike on the ground using a set of position offset or transfer equations. The position-transducer is either a GNSS or an RTS serving as a position-transducer. The transfer of the position data from the position of the position-transducer provides the earth referenced or grid referenced position of the spike at the survey pole survey bottom end.
Owner:APPLANIX
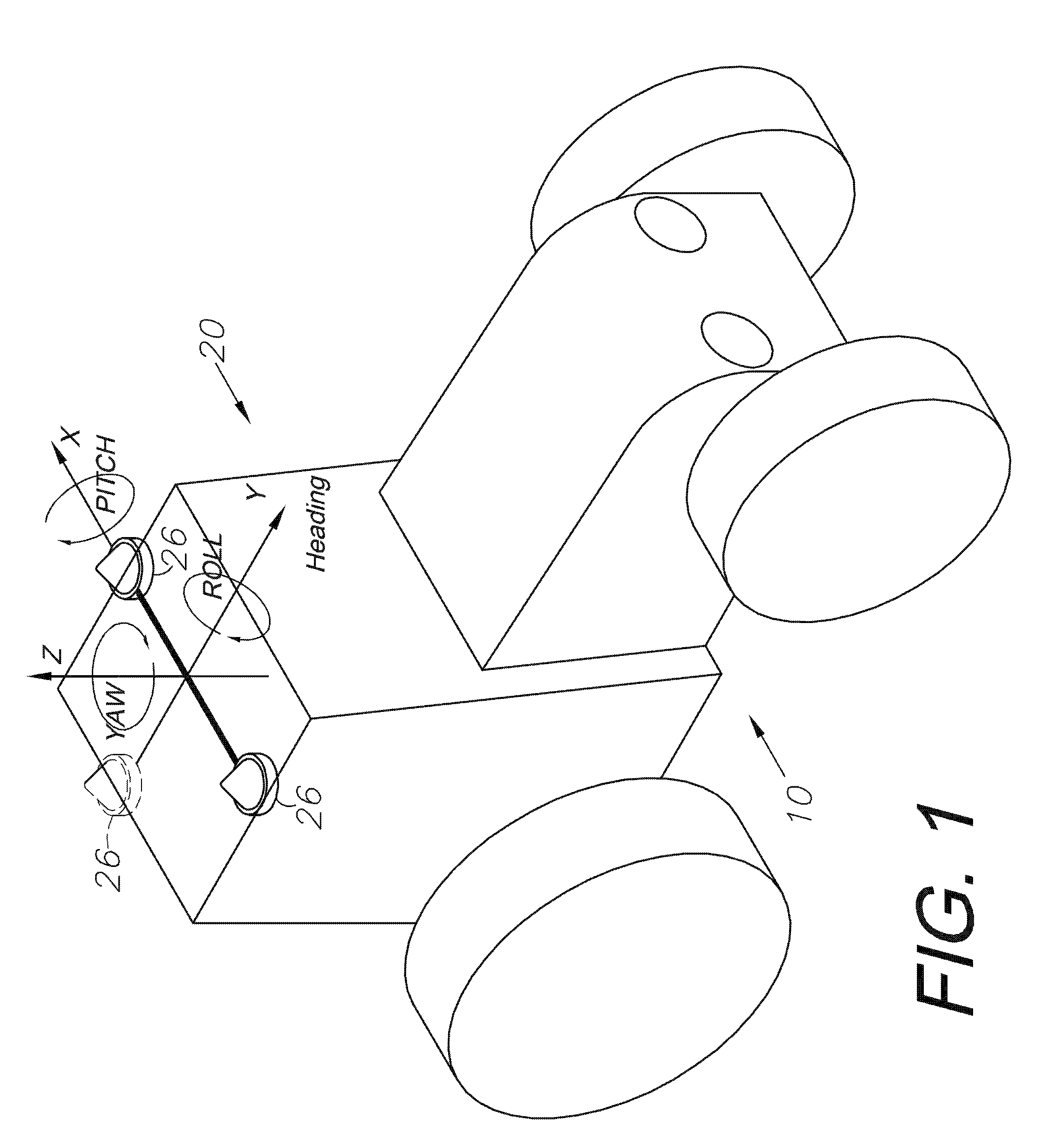
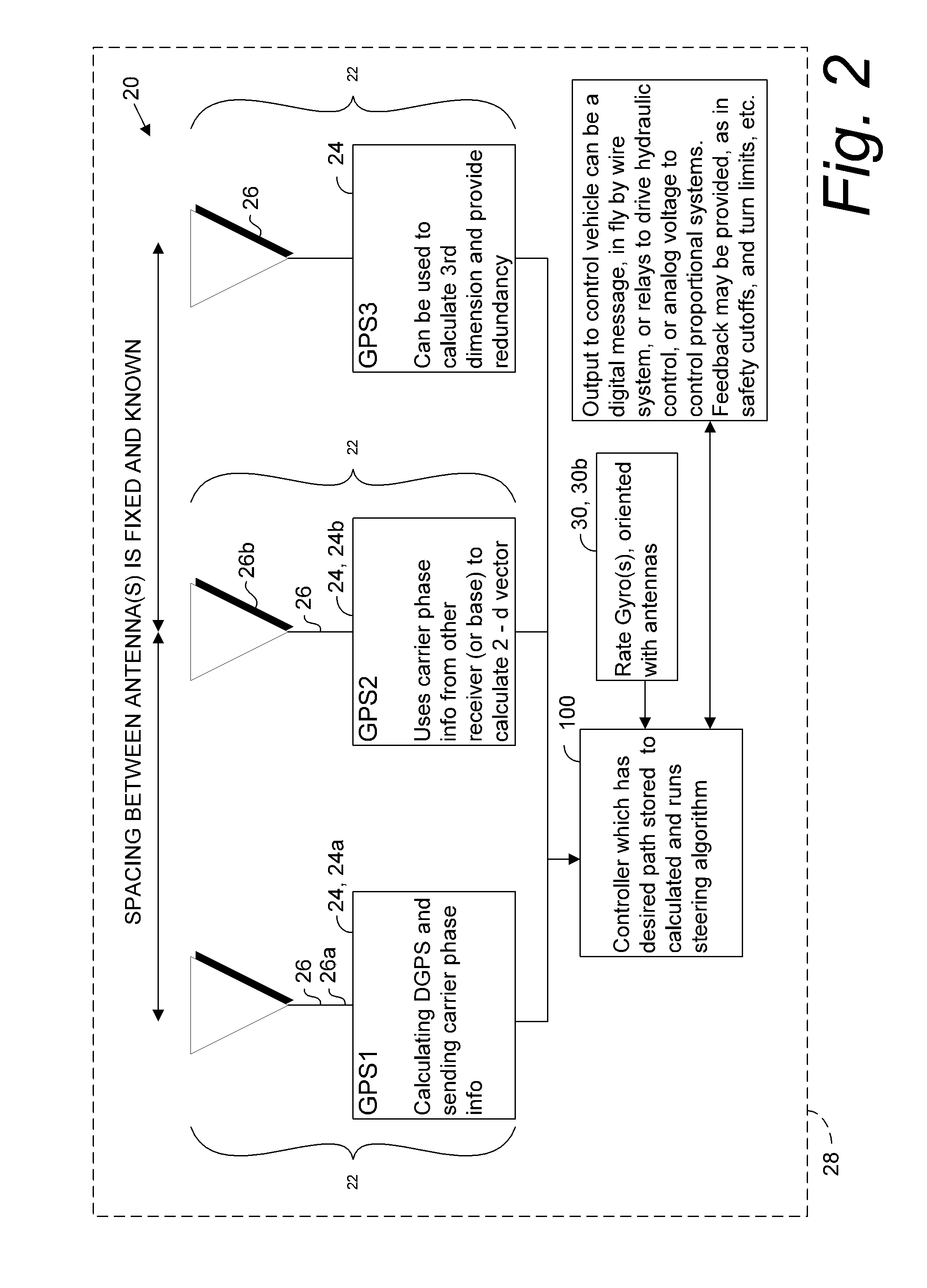
GNSS guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20120174445A1Accurate fillingEasy to correctNavigation instrumentsGuiding agricultural machinesGyroscopeMachine control
A global navigation satellite sensor system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The roll angle facilitates correction of the lateral motion induced position errors resultant from motion of the antennae as the vehicle moves based on an offset to ground and the roll angle. Alternative aspects include multiple-antenna GNSS guidance methods for high-dynamic roll compensation, real-time kinematic (RTK) using single-frequency (L1) receivers, fixed and moving baselines between antennas, multi-position GNSS tail guidance (“breadcrumb following”) for crosstrack error correction, guiding multiple vehicles and pieces of equipment relative to each other, and snow grooming equipment and method applications.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
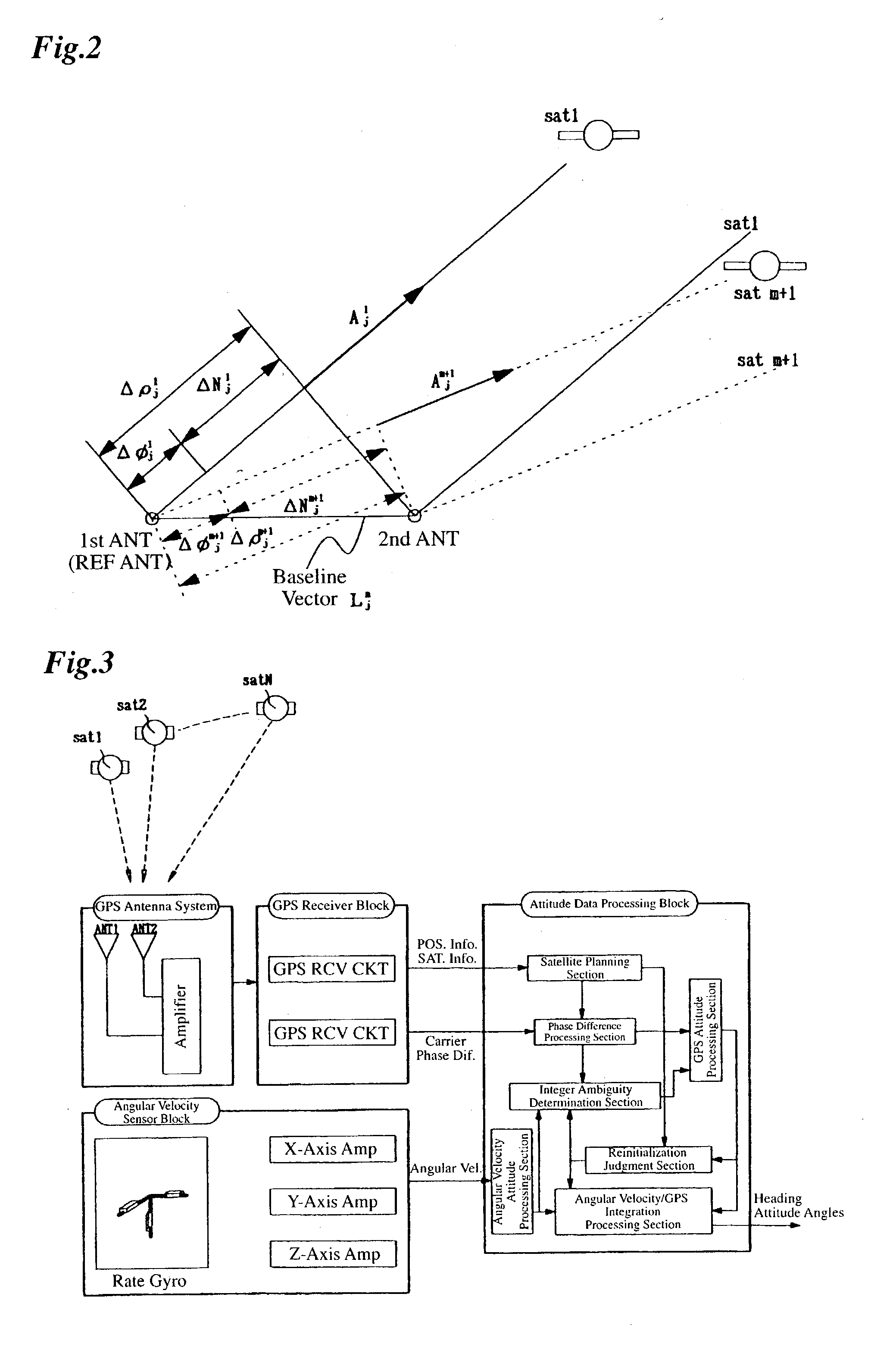
Attitude measurement using a single GPS receiver with two closely-spaced antennas
InactiveUS20050004748A1Simple packagingLess space involvementInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationAccelerometerAmbiguity
A system determines three-dimensional attitude of a moving platform using signals from two closely spaced Global Positioning System (GPS) antennas. The system includes three rate gyroscopes and three accelerometers rigidly mounted in a fixed relationship to the platform to aid in determining the attitude. The system applies signals from one of the two GPS antennas to sufficient channels of a GPS receiver to support navigation. The system applies signals from a second of the two GPS antennas to the additional receive channels to support interferometry. The system resolves the ambiguity normally associated with the interferometric heading solution by having closely spaced GPS antennas, and uses interferometry to refine a coarse heading estimate from a GPS plus Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) transfer alignment solution. The system achieves sub-meter spacing of the two GPS antennas by merging many temporal interferometric measurements and the attitude memory provided by the IMU time-history solution.
Owner:ENPOINT
Airborne vector magnetic surveys
InactiveUS20050116717A1Reduce noiseImprove performanceStray field compensationAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic tension forceMagnetic effect
An aircraft equipped for airborne vector magnetic exploration surveys comprising three magnetometers orthogonally mounted to measure the components of the earth's vector magnetic field; two rotation sensors mounted to measure the angular orientation of the aircraft; and a recording system to record the measurements of the magnetometers, and rotation sensors. The measured angular orientation is used to orientate the measured components of the earth's vector magnetic field to derive true vector acro-magnetic (VAM) data from airborne surveys. Also disclosed is a method for processing magnetic data by removing the permanent, induced, and eddy-current magnetic effects of the aircraft from the magnetic data.
Owner:FUGRO FINANCE
Method and apparatus for seismic signal processing and exploration
InactiveUSRE38229E1Quickly seeSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSeismic trace
A method, a map and an article of manufacture for the exploration of hydrocarbons. In one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises the steps of: accessing 3D seismic data; dividing the data into an array of relatively small three-dimensional cells; determining in each cell the semblance / similarity, the dip and dip azimuth of the seismic traces contained therein; and displaying dip, dip azimuth and the semblance / similarity of each cell in the form a two-dimensional map. In one embodiment, semblance / similarity is a function of time, the number of seismic traces within the cell, and the apparent dip and apparent dip azimuth of the traces within the cell; the semblance / similarity of a cell is determined by making a plurality of measurements of the semblance / similarity of the traces within the cell and selecting the largest of the measurements. In addition, the apparent dip and apparent dip azimuth, corresponding to the largest measurement of semblance / similarity in the cell, are deemed to be estimates of the true dip and true dip azimuth of the traces therein. A color map, characterized by hue, saturation and lightness, is used to depict semblance / similarity, true dip azimuth and true dip of each cell; true dip azimuth is mapped onto the hue scale, true dip is mapped onto the saturation scale, and the largest measurement of semblance / similarity is mapped onto the lightness scale of the color map.
Owner:CORE LAB GLOBAL
Survey system for locating geophysical anomalies
InactiveUS20110066379A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectrical measurementsElectrical field strengthEngineering
A survey system is described for locating and classifying geophysical anomalies. It includes a moving platform equipped with a recording unit for recording the position of the platform. The system also comprises three first measuring units or sensors, adapted to record a varying electric field strength and a varying magnetic field strength at chosen intervals and thus positions, said first measuring units being adapted to measure said field strengths in three independent and mutually orthogonal directions at frequencies in a chosen range. The system includes a calculation unit for combining the measurements from each of said first sensors and calculating and recording as well as comparing the field strength vectors of the varying measured fields at each position, to find anomalies.
Owner:NORWEGIAN EM TECH
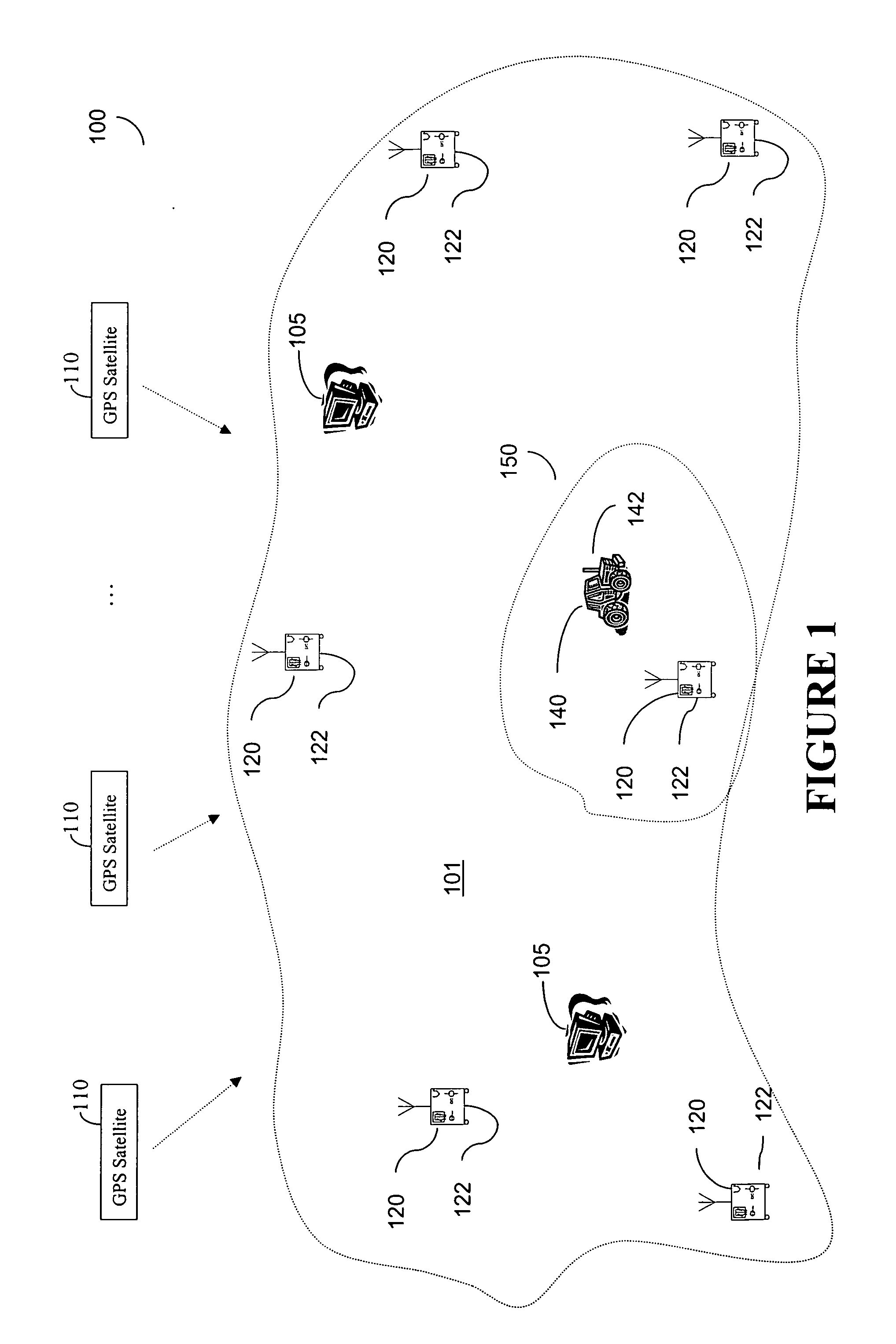
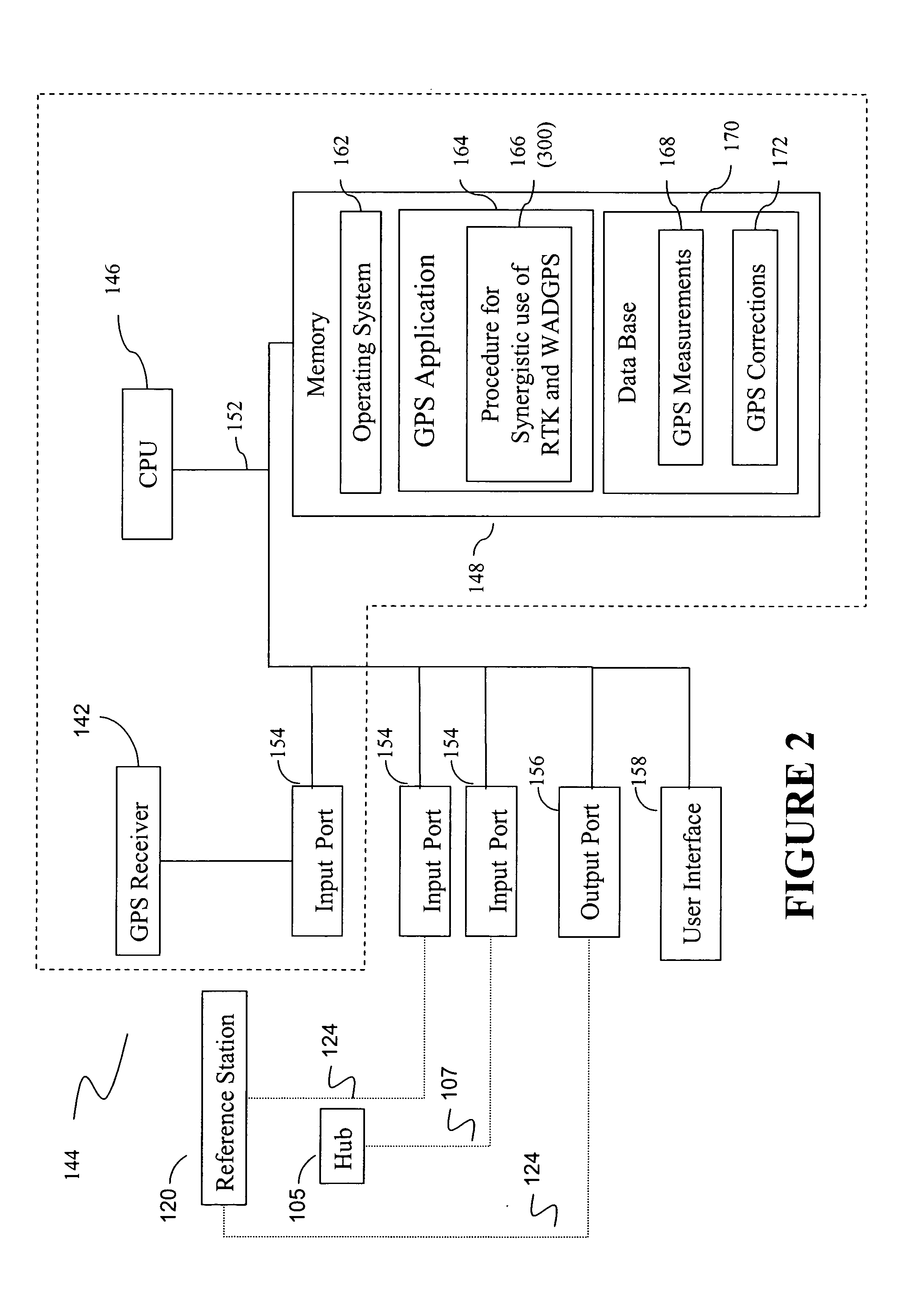
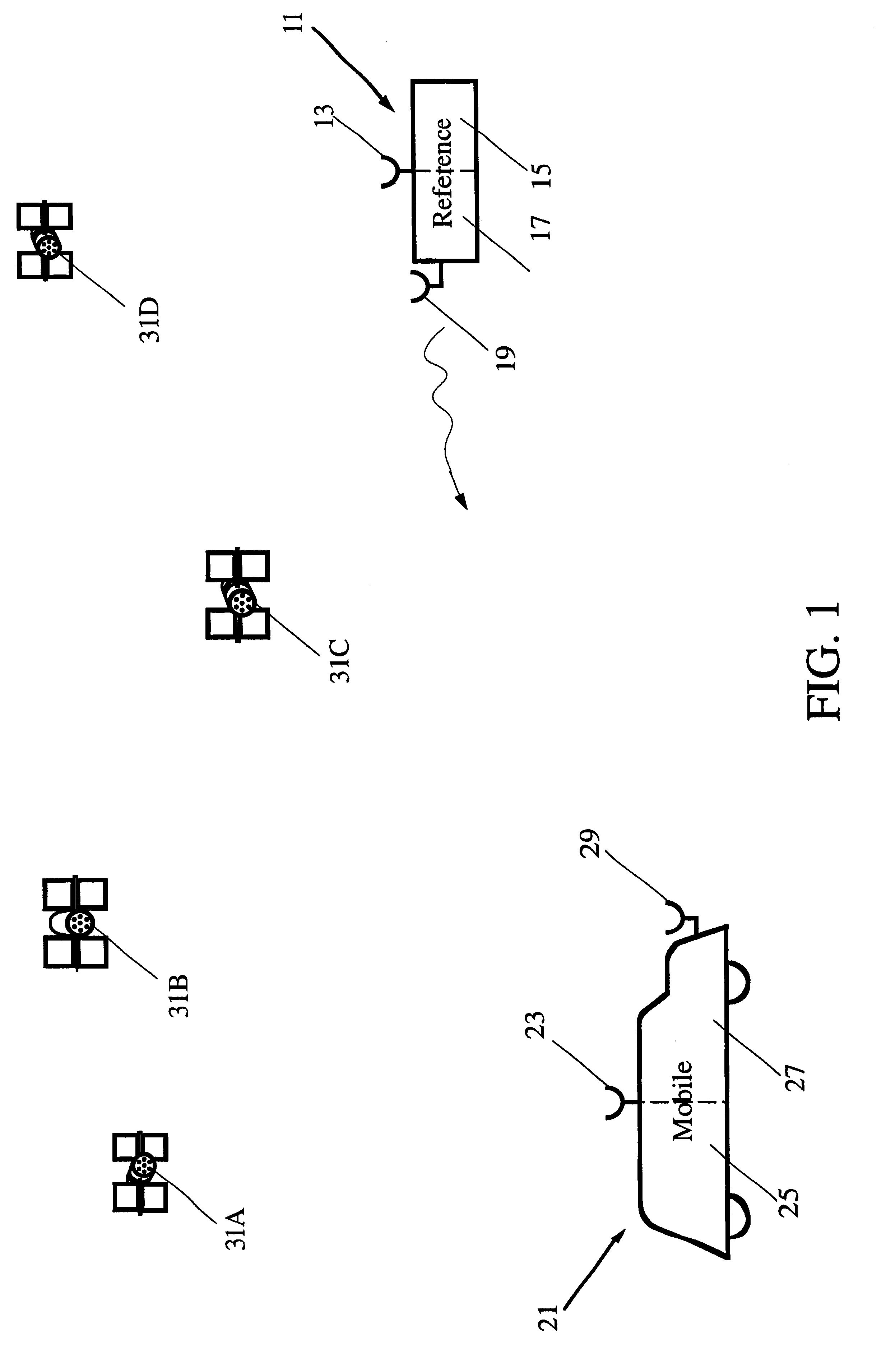
Integrated SATPS total survey station
Apparatus for measuring surveying parameters, such as distances and angular displacements between an instrument survey station and a mobile survey station, with improved accuracy. The invention combines a differential satellite positioning system (DSATPS), available with positioning systems such as GPS and GLONASS, with electromagnetic measurements of distances and optically encoded angles by a conventional electro-optical survey instrument to provide survey measurements that can be accurate to within a few millimeters in favorable situations. The DSATPS relies upon pseudorange measurements or upon carrier phase measurements, after removal of certain phase integer ambiguities associated with carrier phase SATPS signals. The SATPS may be retrofitted within the housing of the conventional electro-optical instrument. In a first approach, a remote station provides DSATPS corrections for the mobile station and / or for the instrument station. In a second approach, the mobile station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the instrument station. In a third approach, the instrument station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the mobile station.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
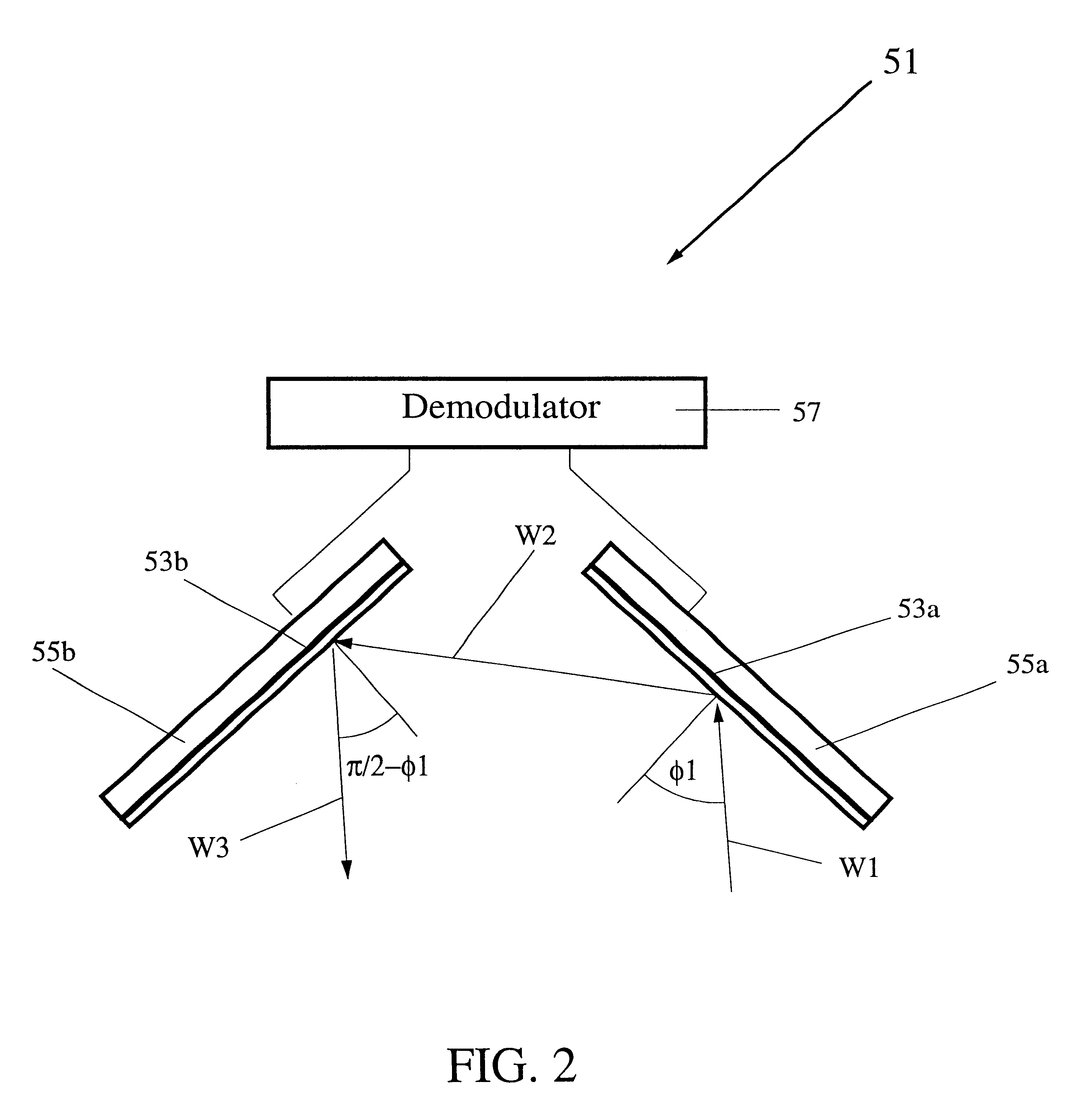
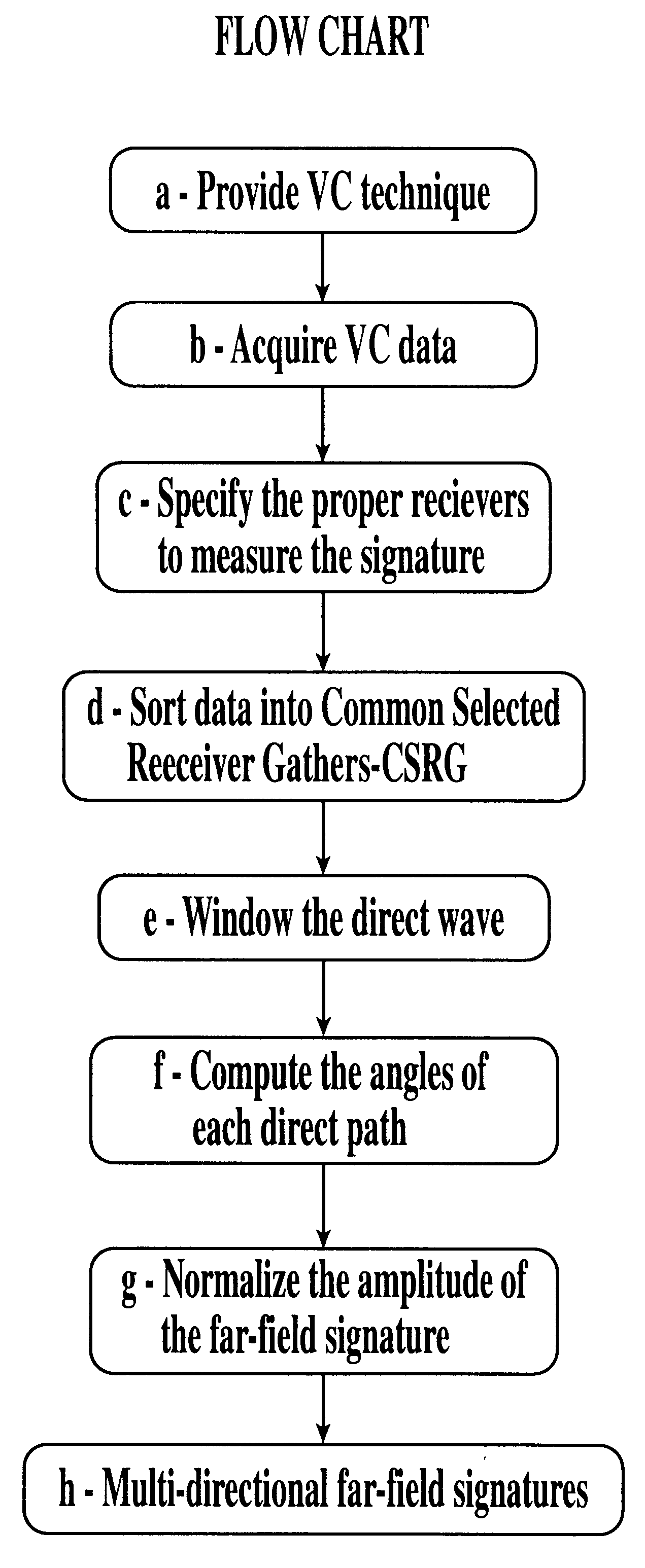
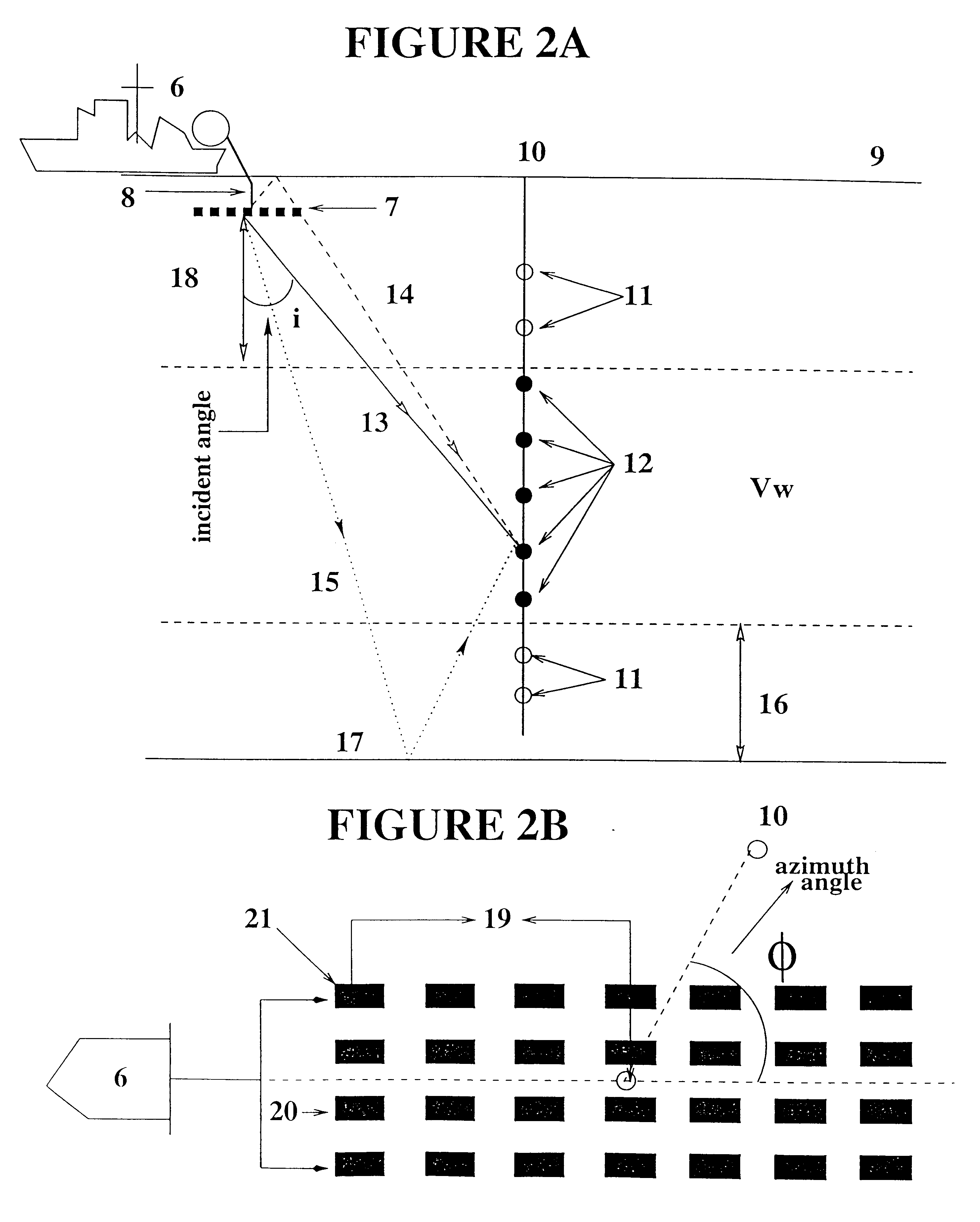
Method for the measurement of multidirectional far-field source signatures from seismic surveys
InactiveUS6256589B1High resolutionImprove accuracySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyAcquisition technique
A method is described for the measurement of multidirectional far-field source signatures from seismic surveys whereby a vertical cable acquisition technique is provided, vertical cable data are acquired, the proper receivers are specified to measure the signature, data are sorted into common selected receiver gathers CSRG, the direct wave within common receiver gather is properly windowed, the angles of each direct path are computed and the amplitude of the signatures is normalized, so as to obtain the multidirectional far-field signatures of the seismic source array having the same characteristics as those that generated the seismic reflections.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
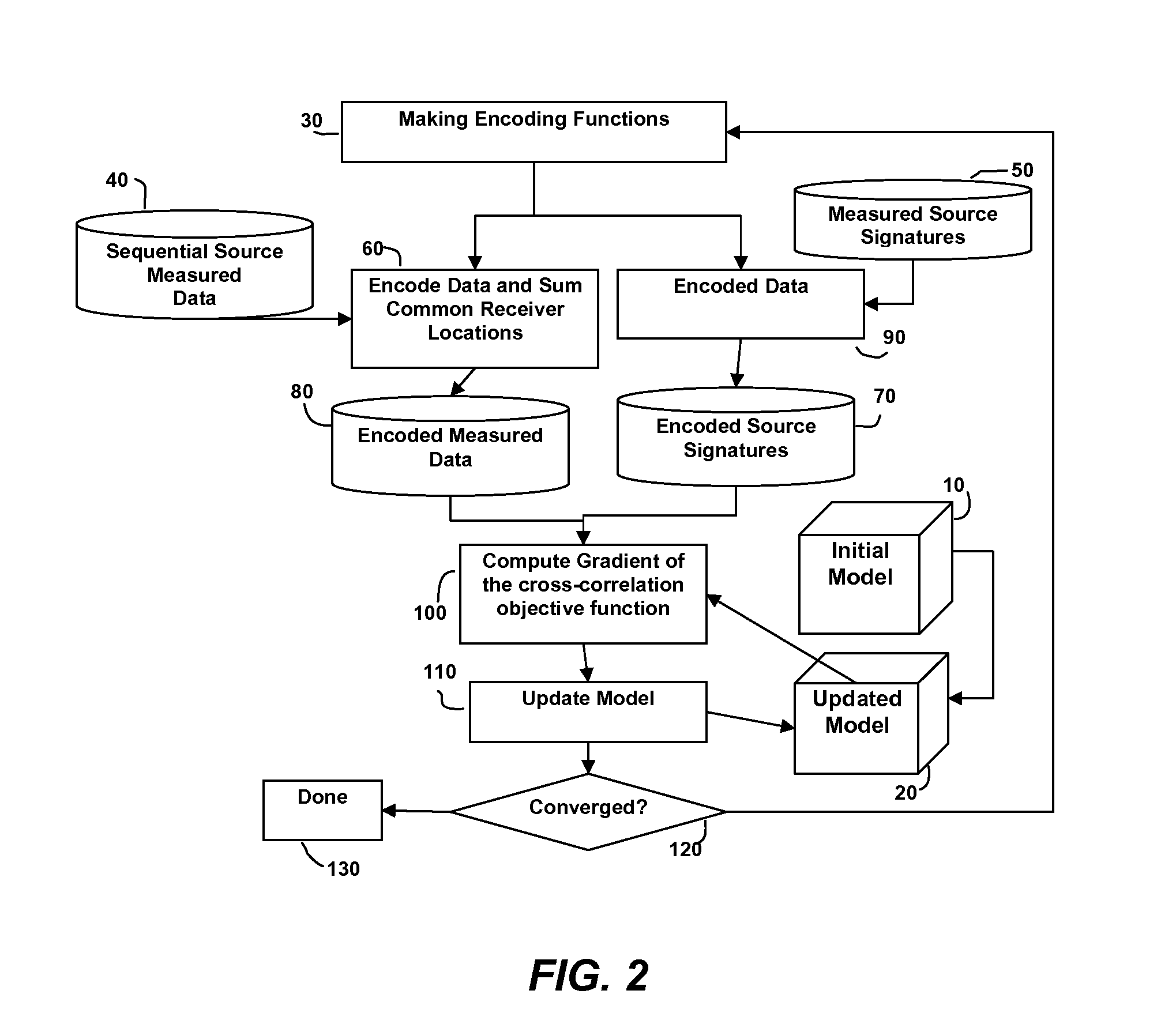
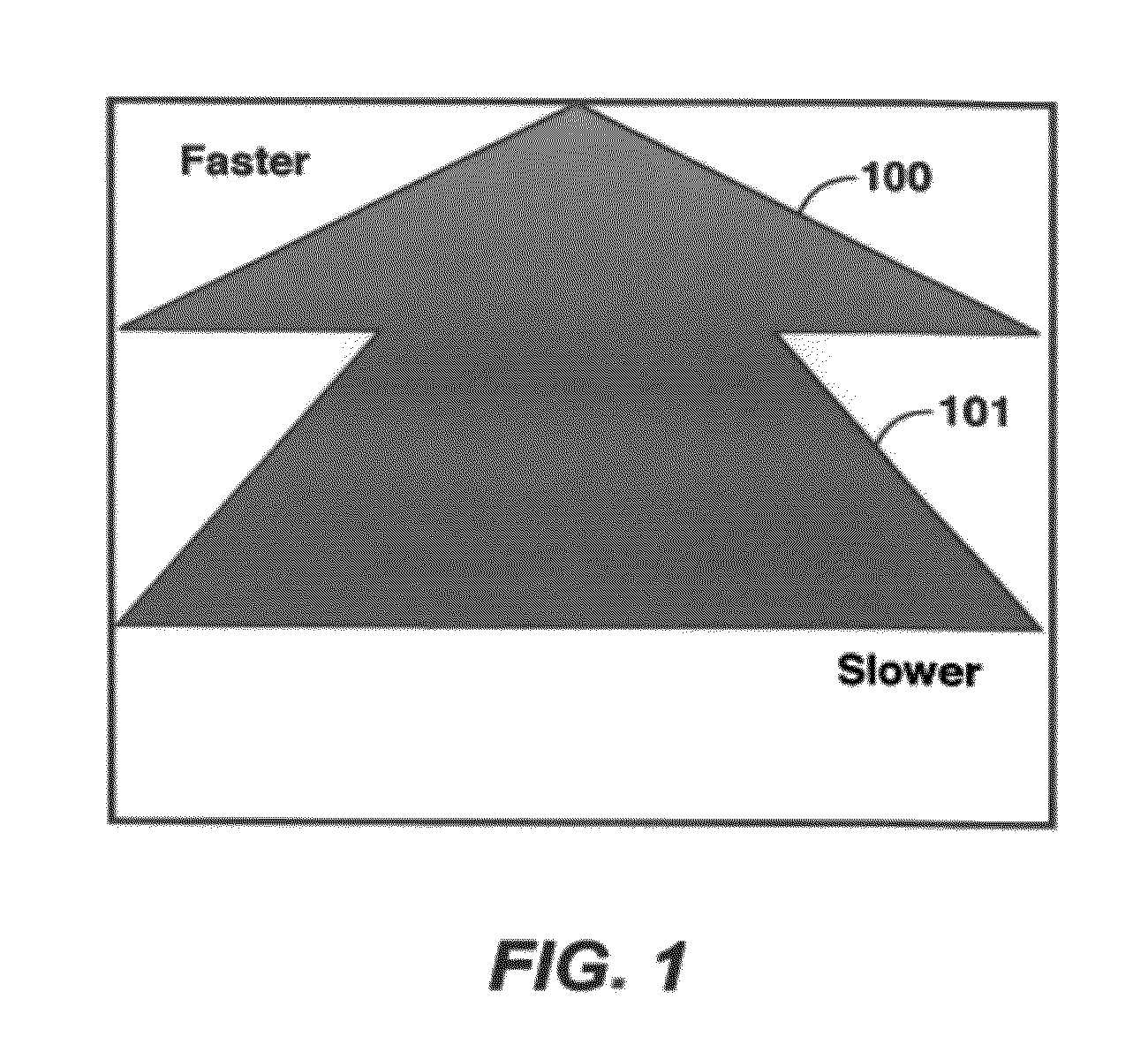
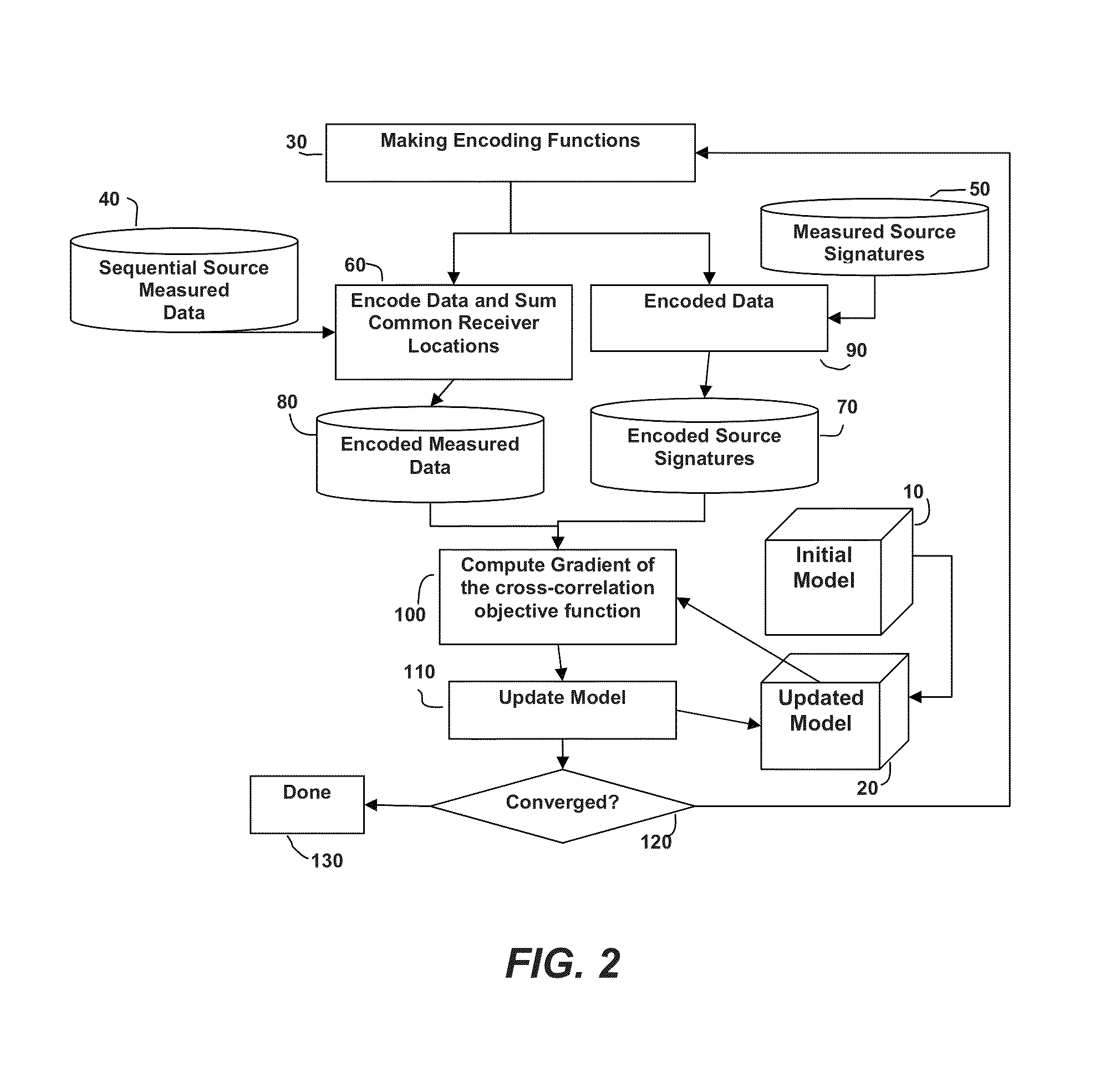
Simultaneous Source Inversion for Marine Streamer Data With Cross-Correlation Objective Function
ActiveUS20120143506A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasData acquisitionPhysical property
Method for simultaneous full-wavefield inversion of gathers of source (or receiver) encoded (30) geophysical data (80) to determine a physical properties model (20) for a subsurface region, especially suitable for surveys where fixed-receiver geometry conditions were not satisfied in the data acquisition (40). The inversion involves optimization of a cross-correlation objective function (100).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Integrity of differential GPS corrections in navigation devices using military type GPS receivers
A method and apparatus for calculating corrections to a navigation solution based on differential GPS data includes receiving GPS ephemeris from at least three GPS satellites. A PVT solution is resolved from the GPS ephemeris. The PVT solution includes a Circular Error Probable (CEP). Differential GPS data for calculating the corrections to the PVT solution is received. A corrected PVT solution is then based upon the differential GPS data. The corrected PVT solution is compared to an area defined by the CEP. Where the corrected PVT solution is not within the area, the corrected PVT solution is rejected in favor of the PVT solution for determining an accurate navigational solution.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
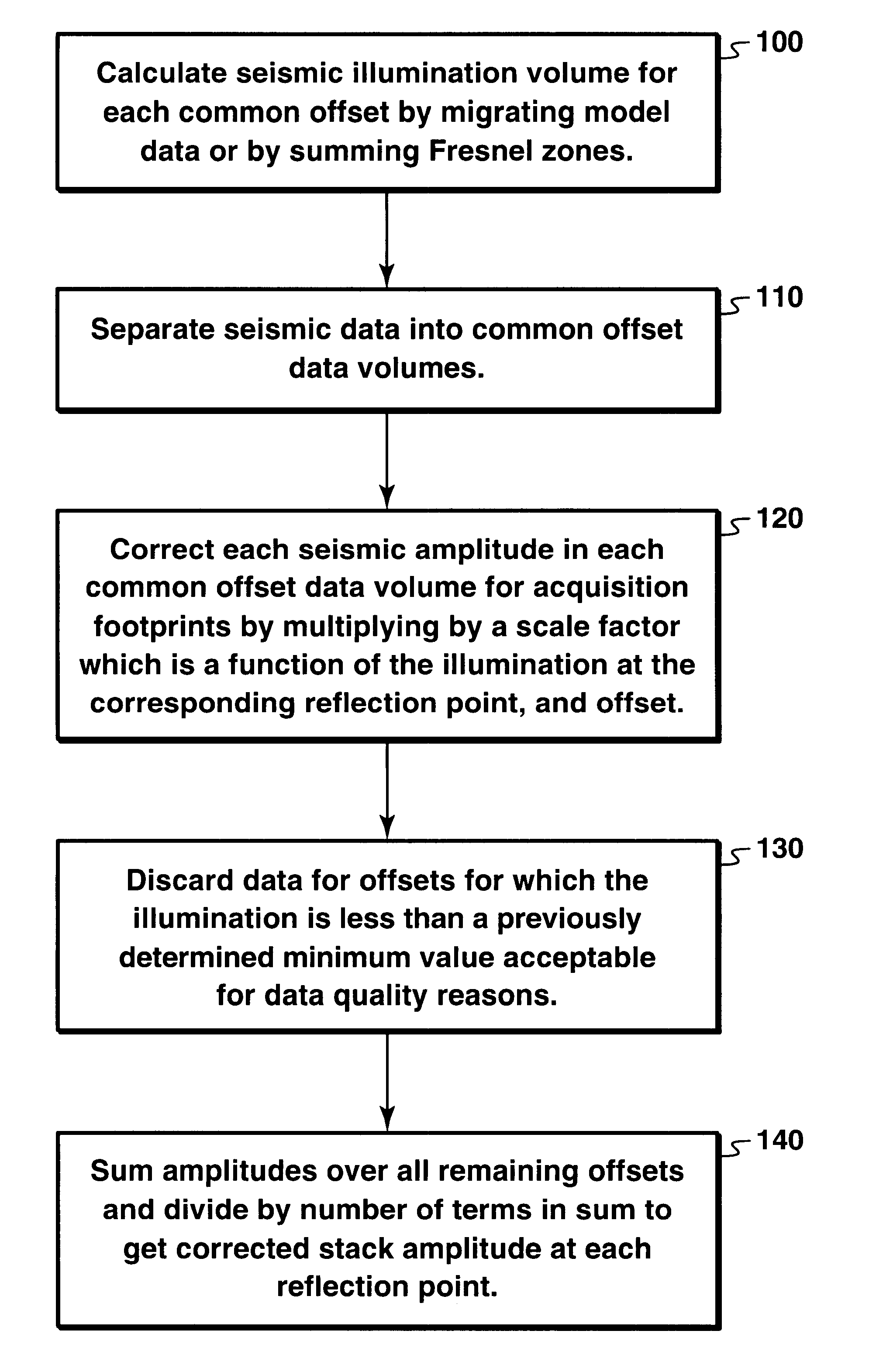
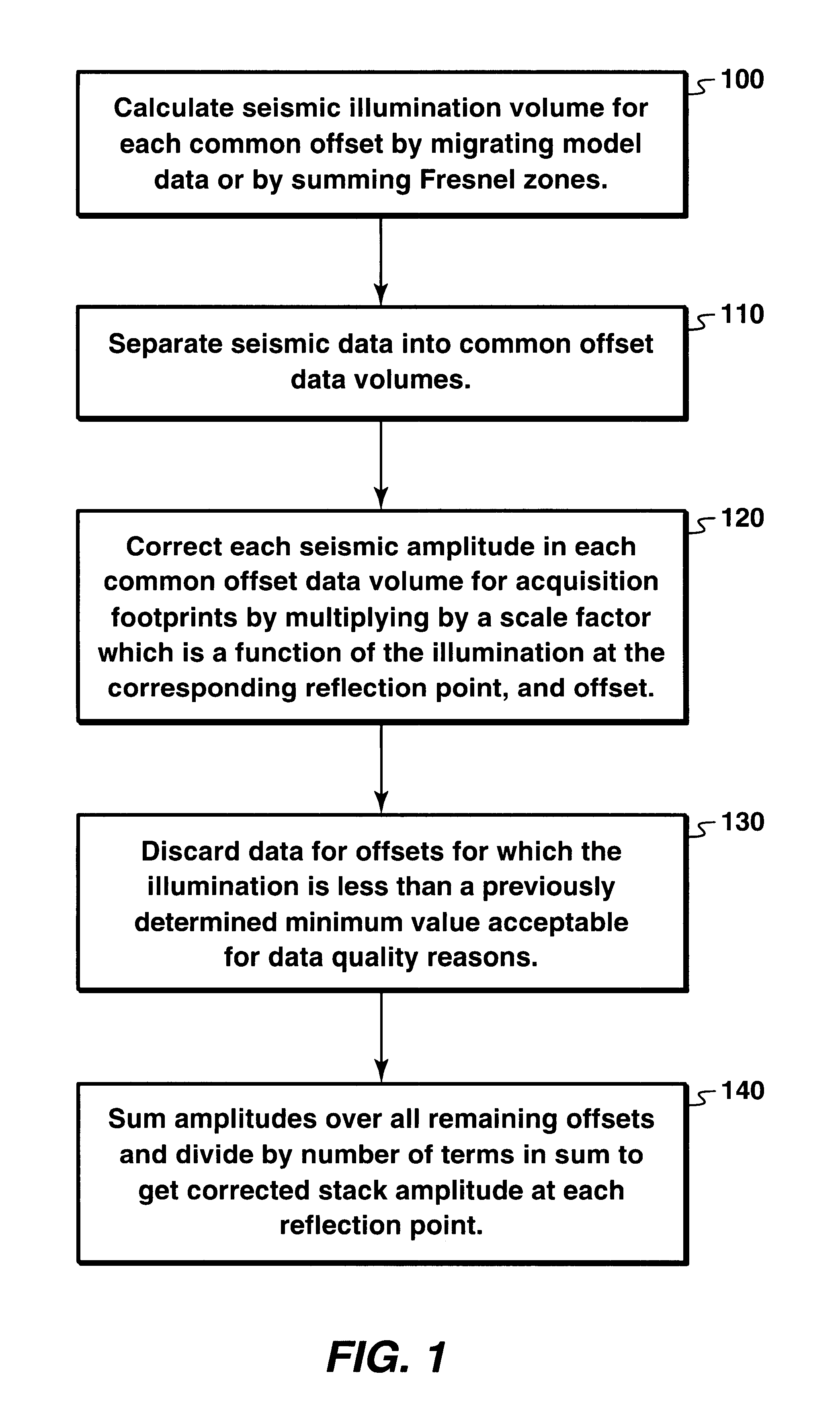
Illumination corrections to reduce geometrical artifacts in seismic data
InactiveUS6343256B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsIlluminanceAmplitude scaling
A method for correcting seismic amplitudes for geometrical artifacts resulting in non-uniform illumination of reflector surfaces. The illumination is calculated for each offset as a function of spatial position. The amplitudes are scaled by a scale factor which may be the reciprocal of the illumination. Data considered to be poor quality due to low illumination may be discarded, and the amplitudes scaled further to compensate for the discarded data.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
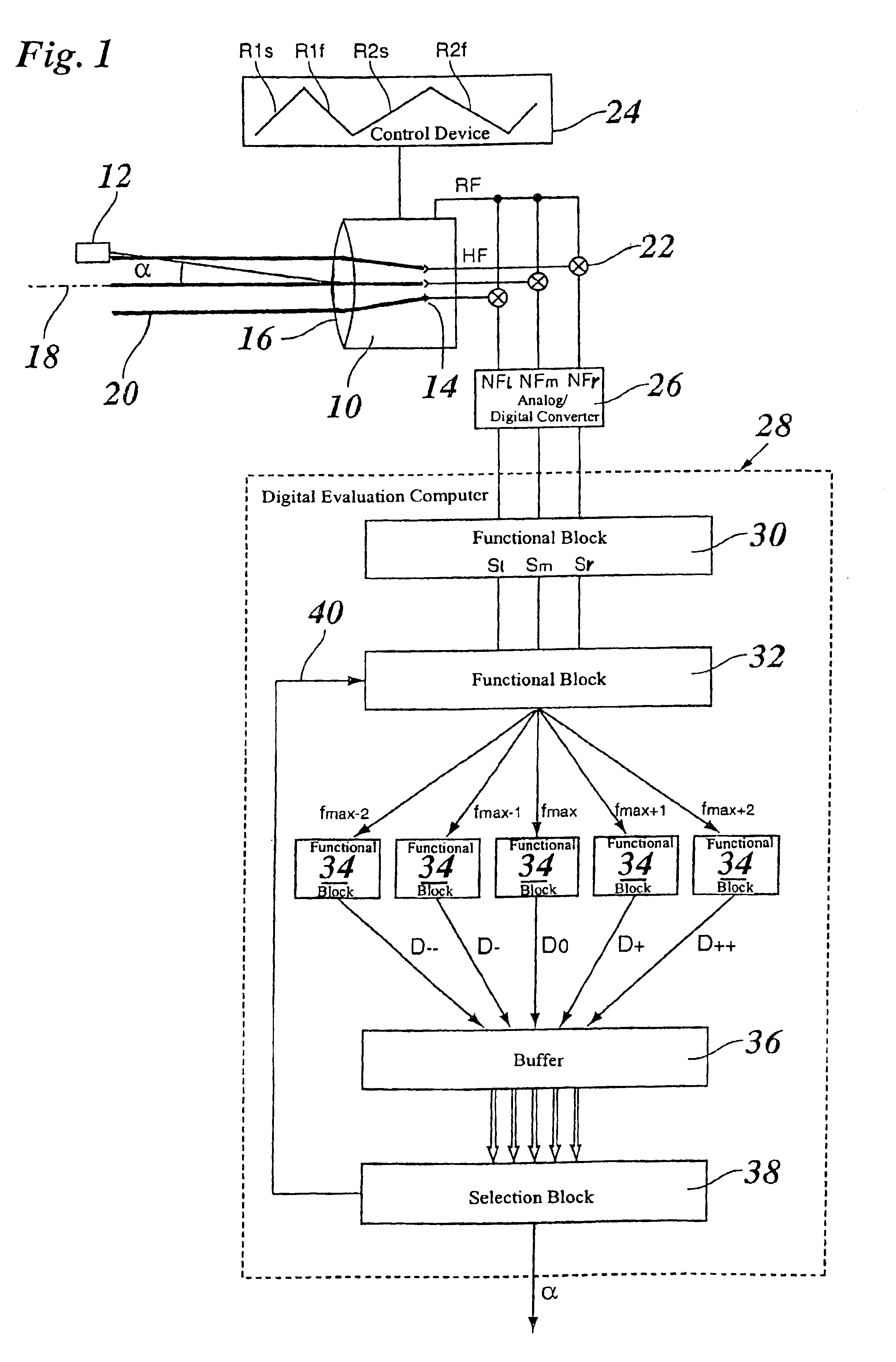
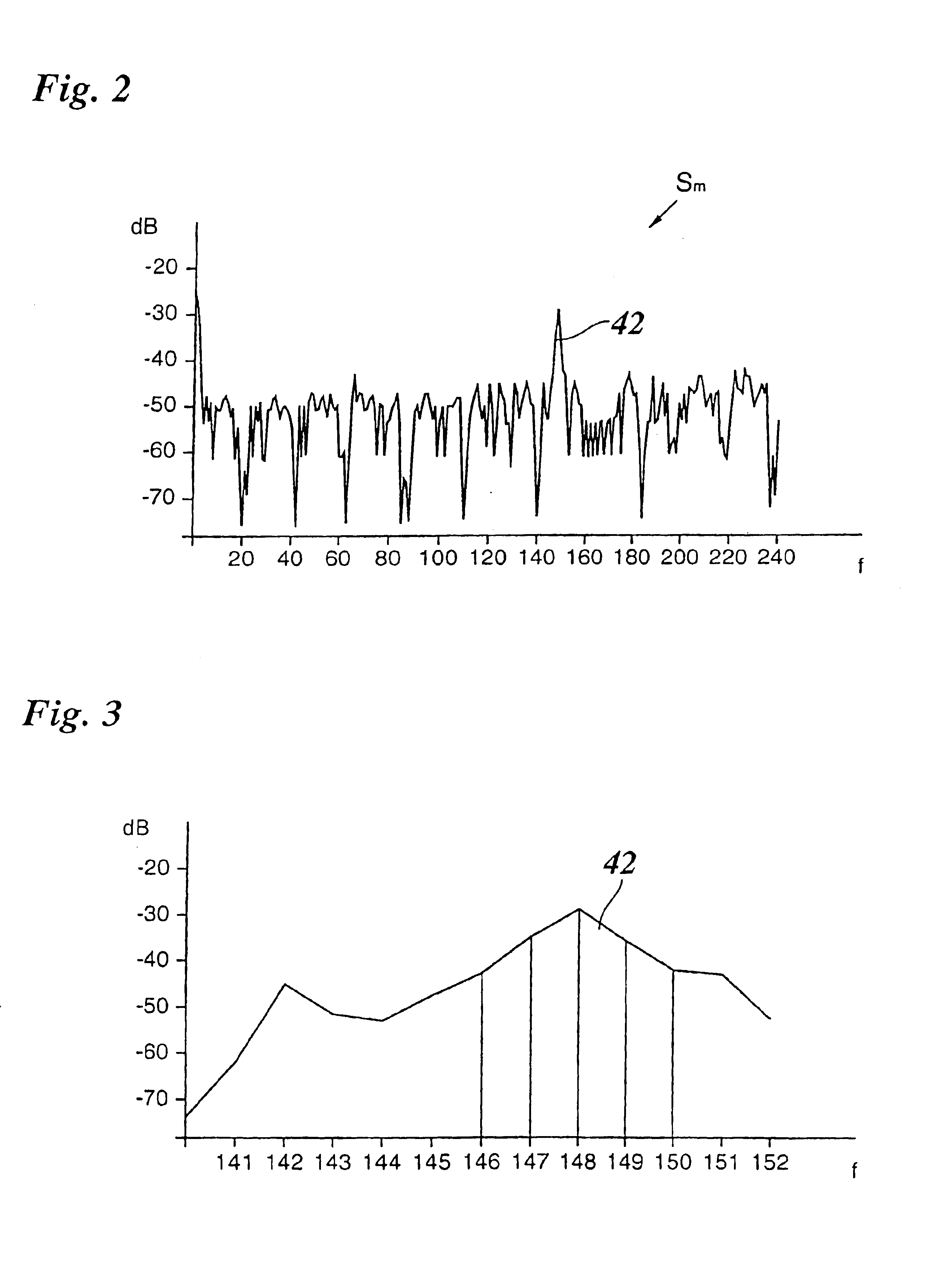
Method and radar system for determining the directional angle of radar objects
InactiveUS6856280B1More reliableReduce riskRadio wave reradiation/reflectionReference patternsRadar systems
A method for determining the directional angle of radar objects using a multibeam radar, including the steps of:(a) recording the frequency spectra of the radar echoes for a plurality of beams;(b) seeking a measuring frequency near a frequency maximum assigned to the radar object; and(c) comparing the phases and / or amplitudes of the radar echoes at the measuring frequency with reference patterns known for various directional angles,steps (b) and (c) being executed repeatedly, each time for different measuring frequencies, and the directional angles obtained for the various measuring frequencies being checked for consistency.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
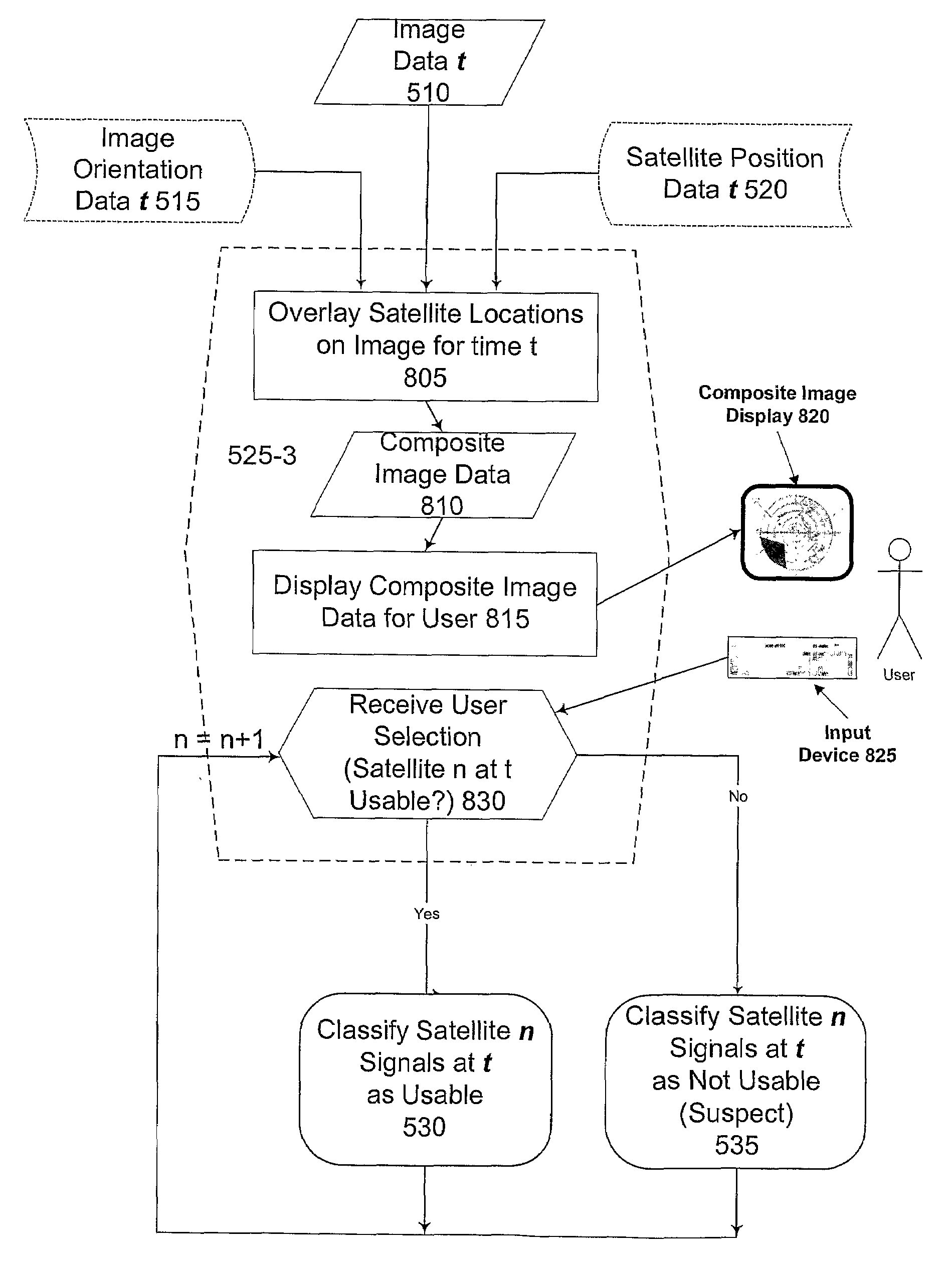
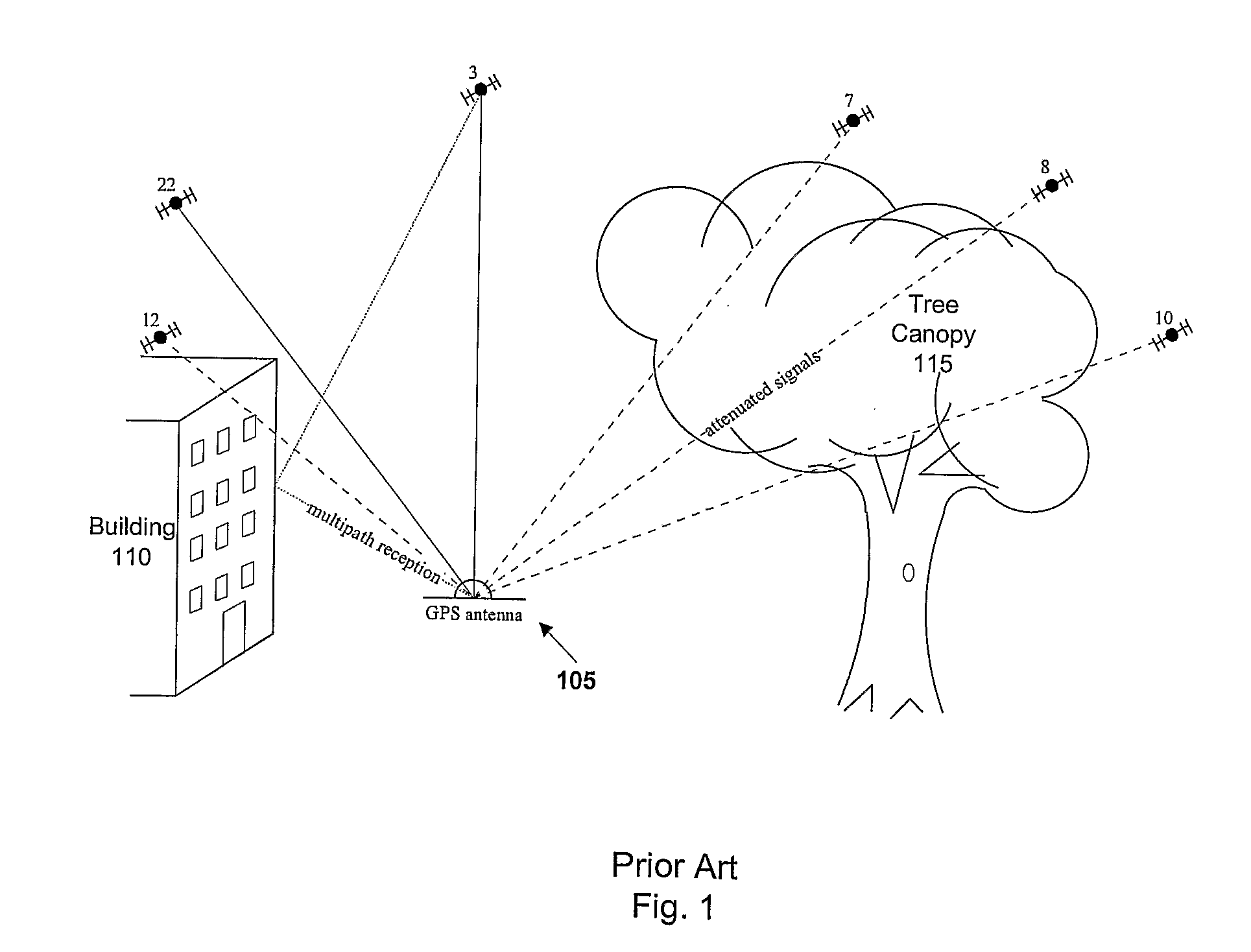
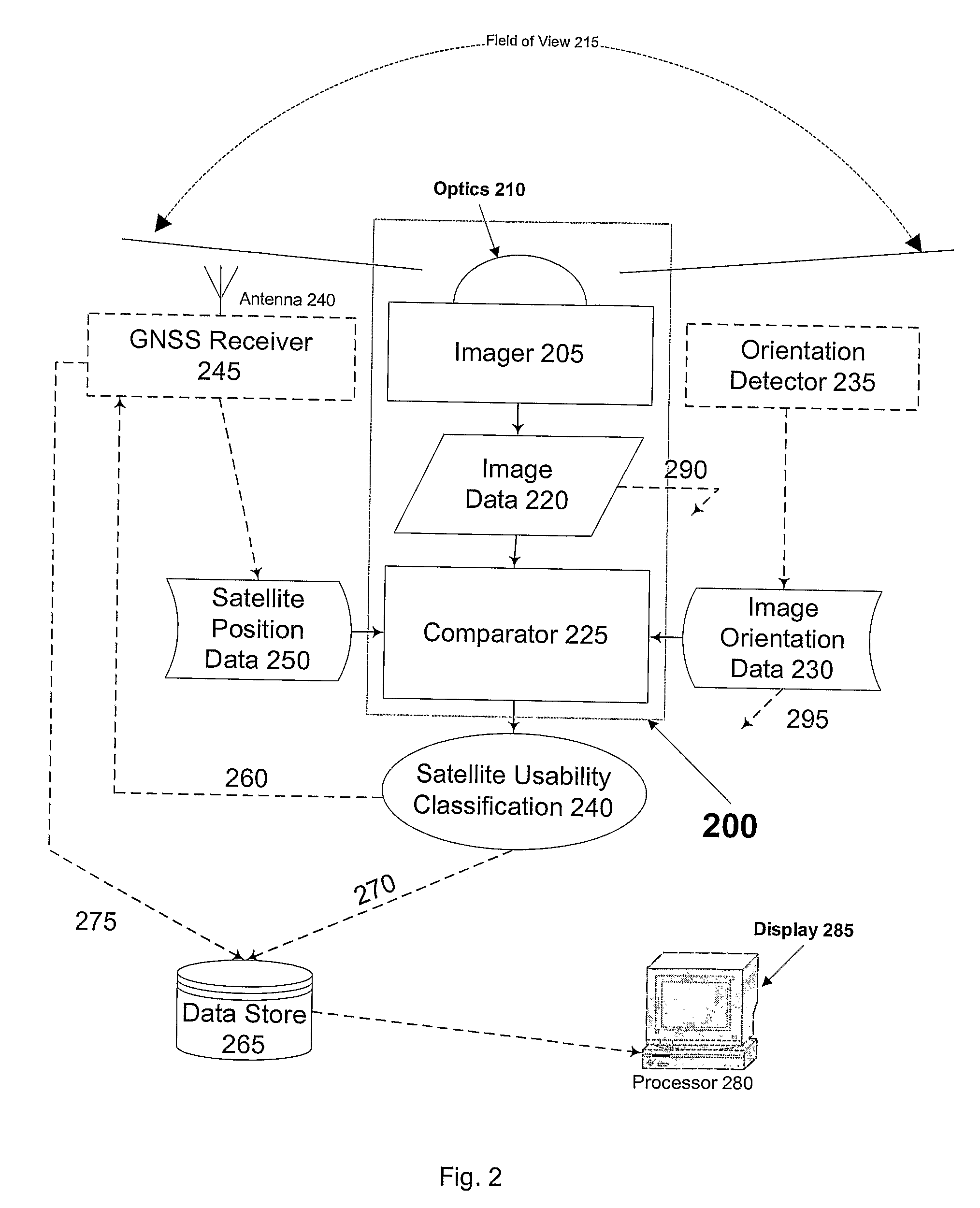
Enhanced Gnss Signal Processing
In accordance with embodiments of the invention, a skyward-looking sensor enables classification of points in its hemispherical field of view as either sky, partial sky or not sky, which in turn enables determination from data supplied by the GNSS receiver of whether each satellite in the GNSS antenna's field of view is in a region of sky, partial sky or not sky. Pseudrange and phase data from GNSS satellites determined to be in a region of sky can be considered reliable and used with confidence in a positioning solution. Pseudrange and phase data from GNSS satellites determined to be in a region of partial sky can be considered suspect and can therefore only contribute to a position solution with limited confidence and decreased accuracy. Pseudorange and phase data from GNSS satellites determined to be in a region of no sky can be considered unreliable and excluded from use in a positioning solution.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
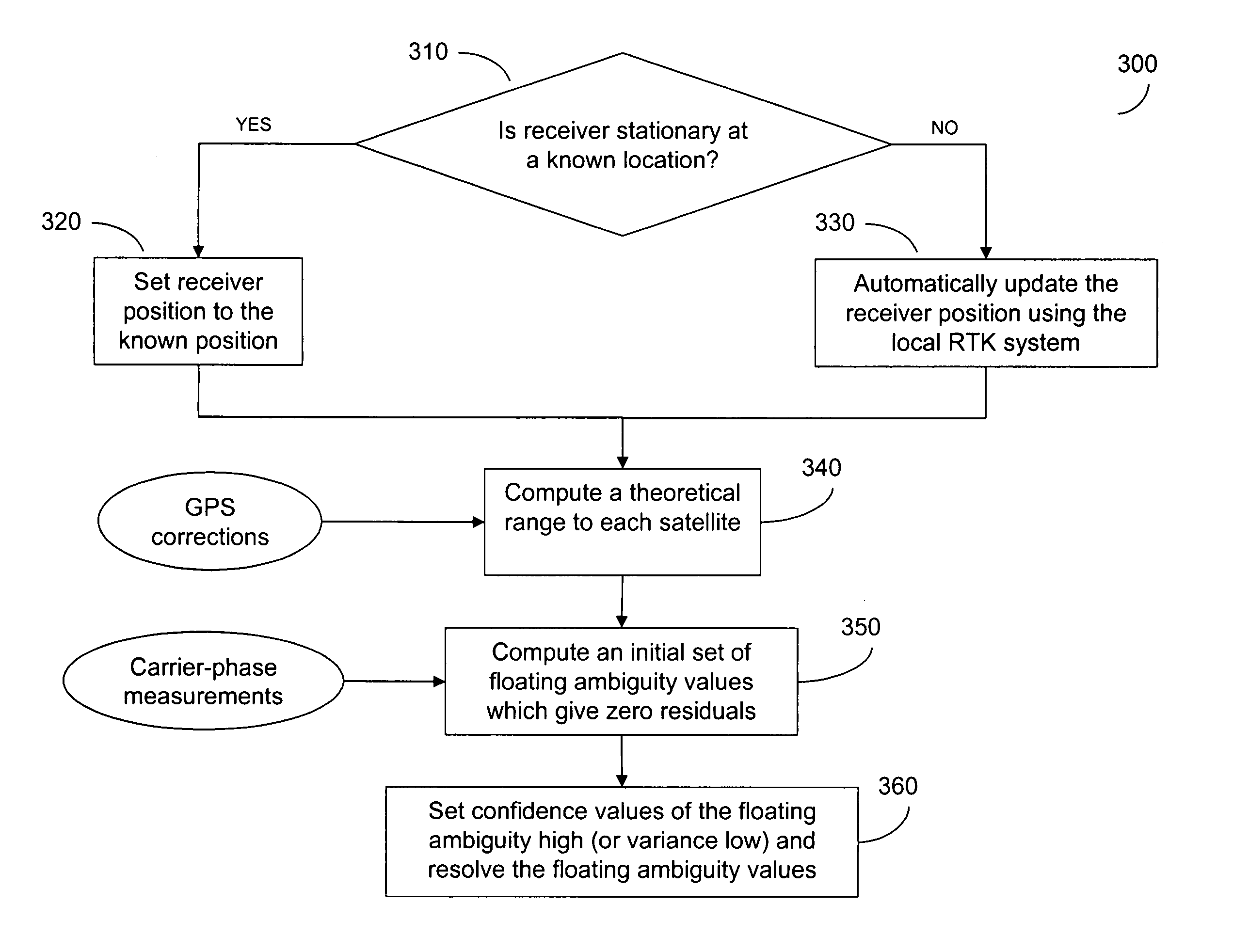
Method for combined use of a local rtk system and a regional, wide-area, or global carrier-phase positioning system
The present invention includes a method for a combined use of a local RTK system and a regional, wide-area, or global differential carrier-phase positioning system (WADGPS) in which disadvantages associated with the RTK and the WADGPS navigation techniques when used separately are avoided. The method includes using a known position of a user receiver that has been stationary or using an RTK system to initialize the floating ambiguity values in the WADGPS system when the user receiver is moving. Thereafter, the refraction-corrected carrier-phase measurements obtained at the user GPS receiver are adjusted by including the corresponding initial floating ambiguity values and the floating ambiguity values are treated as well known (small variance) in subsequent processes to position the user receiver in the WADGPS system.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method for the suppression of multiple reflections from marine seismic data
InactiveUS6507787B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive filterGeophysics
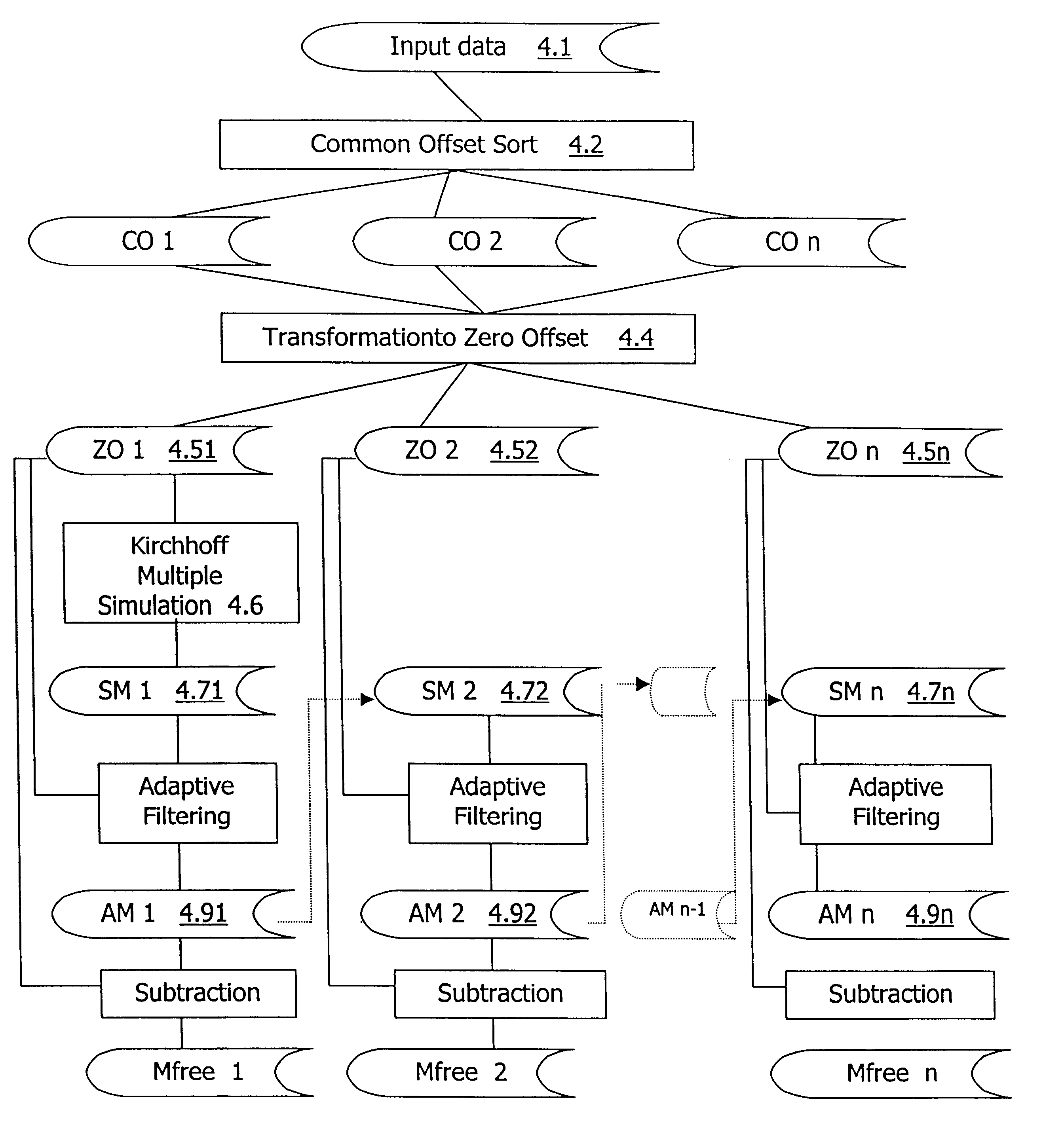
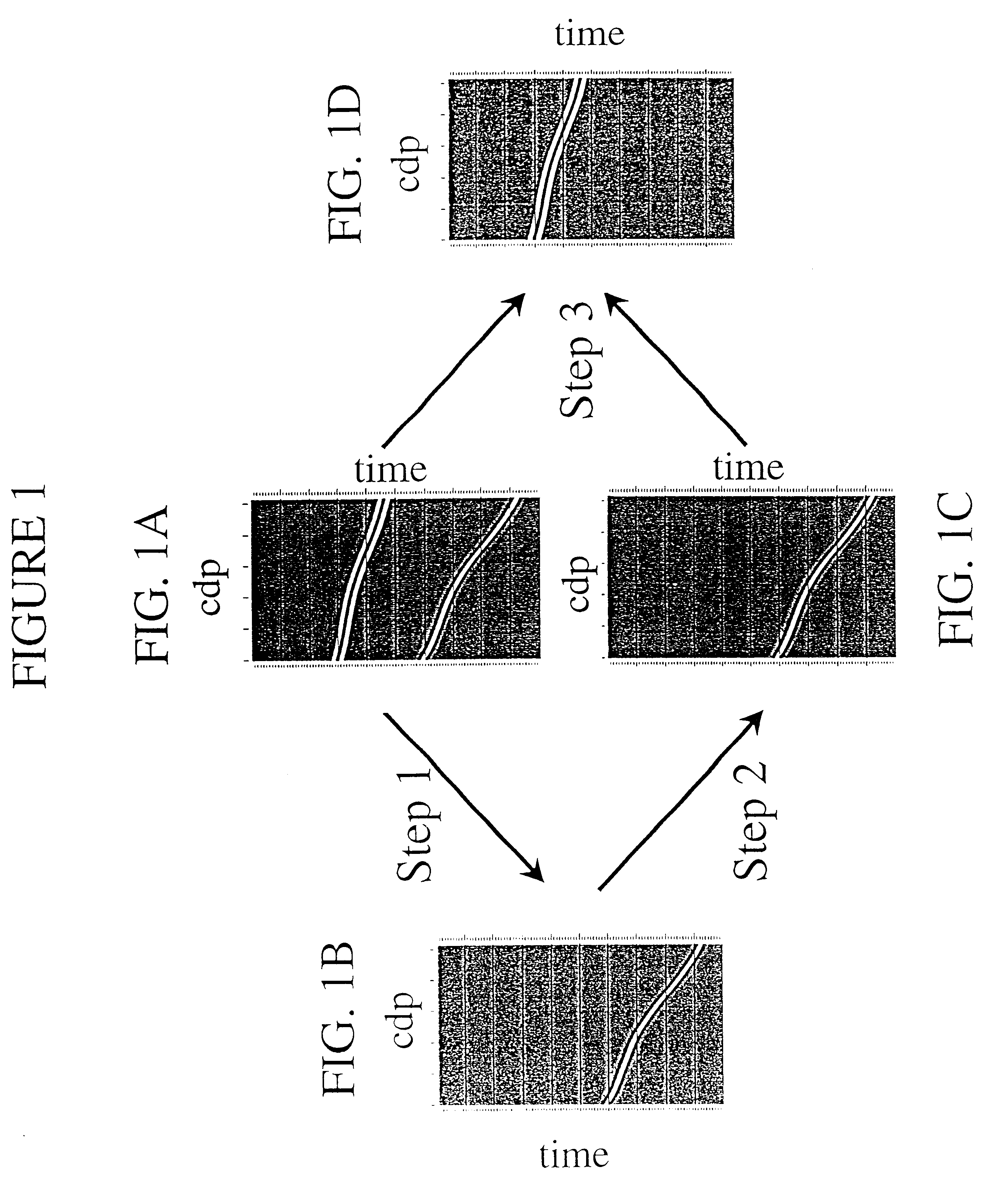
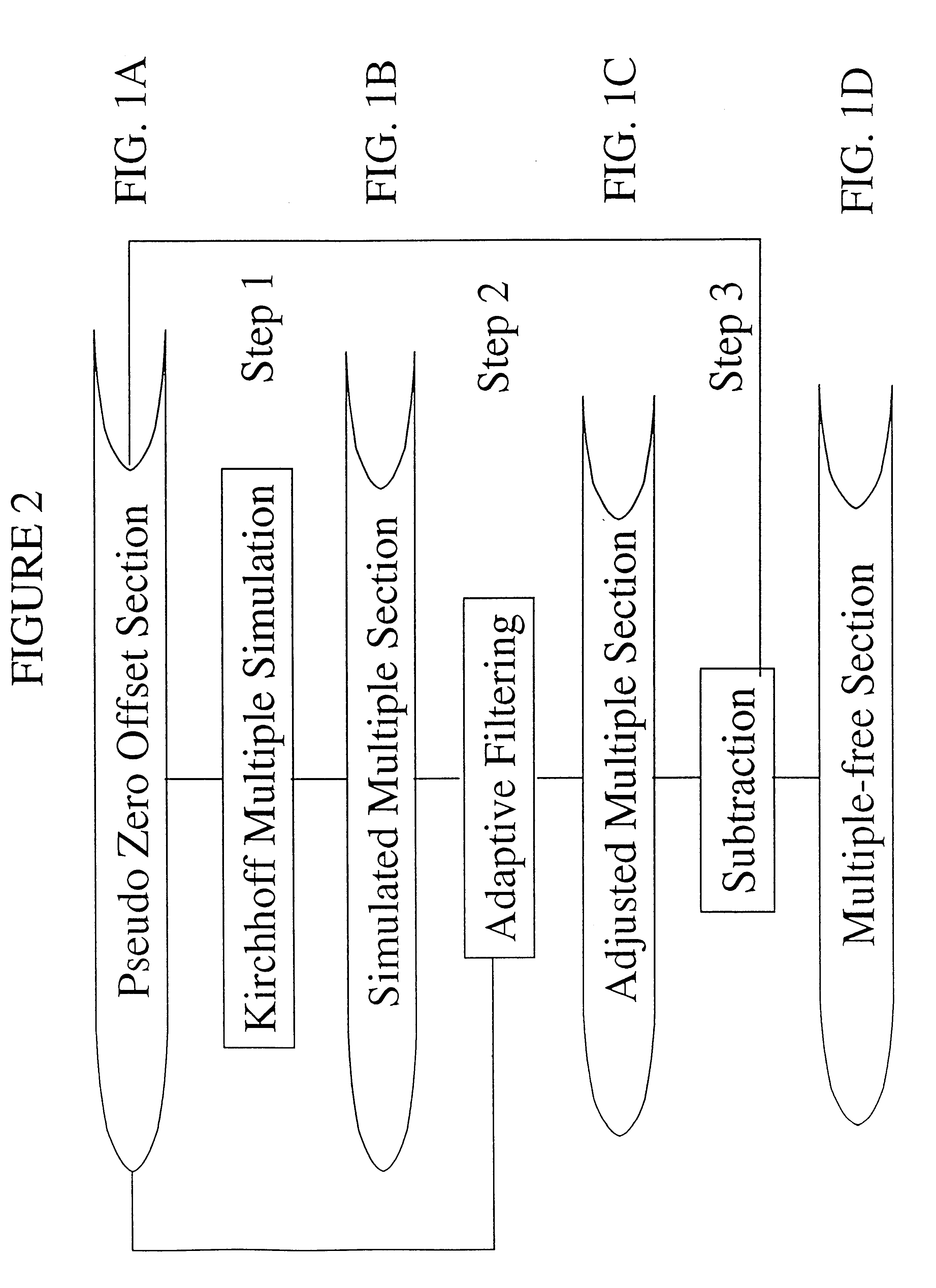
A method for the suppression of multiple reflections using a Kirchhoff algorithm Multiple reflections are simulated by means of a Kirchhoff-type summation applied to a pseudo zero-offset section. An adaptive filter is applied to adjust the simulated multiple. The adjusted simulated multiple is subtracted from the input data.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
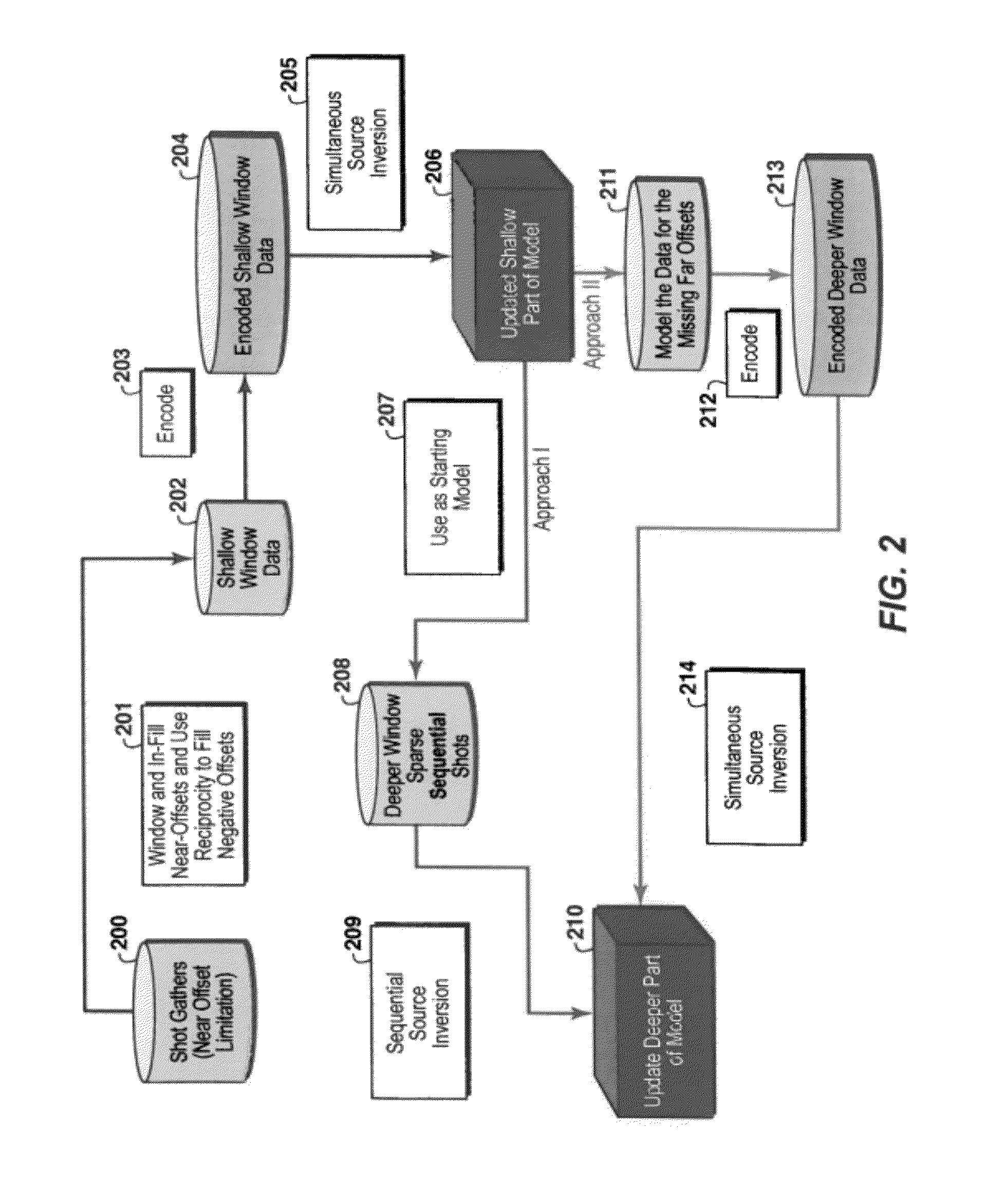
Hybrid method for full waveform inversion using simultaneous and sequential source method
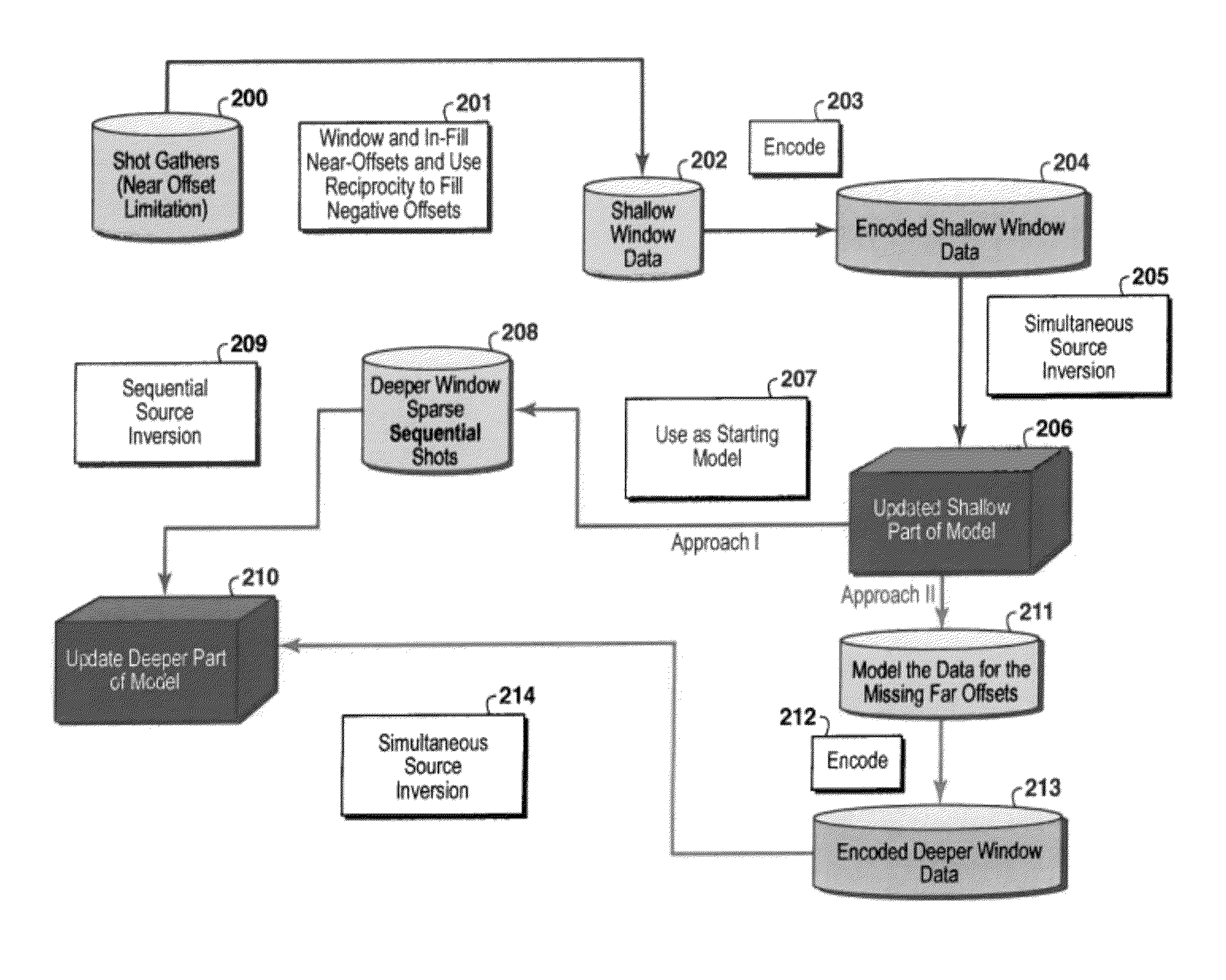
Method for simultaneous full-wavefield inversion of gathers of source (or receiver) encoded geophysical data to determine a physical properties model for a subsurface region, especially suitable for surveys where fixed receiver geometry conditions were not satisfied in the data acquisition. First, a shallow time window of the data (202) where the fixed receiver condition is satisfied is inverted by simultaneous encoded (203) source inversion (205). Then, the deeper time window of the data (208) is inverted by sparse sequential source inversion (209), using the physical properties model from the shallow time window (206) as a starting model (207). Alternatively, the shallow time window model is used to simulate missing far offset data (211) producing a data set satisfying the stationary receiver assumption, after which this data set is source encoded (212) and inverted by simultaneous source inversion (214).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
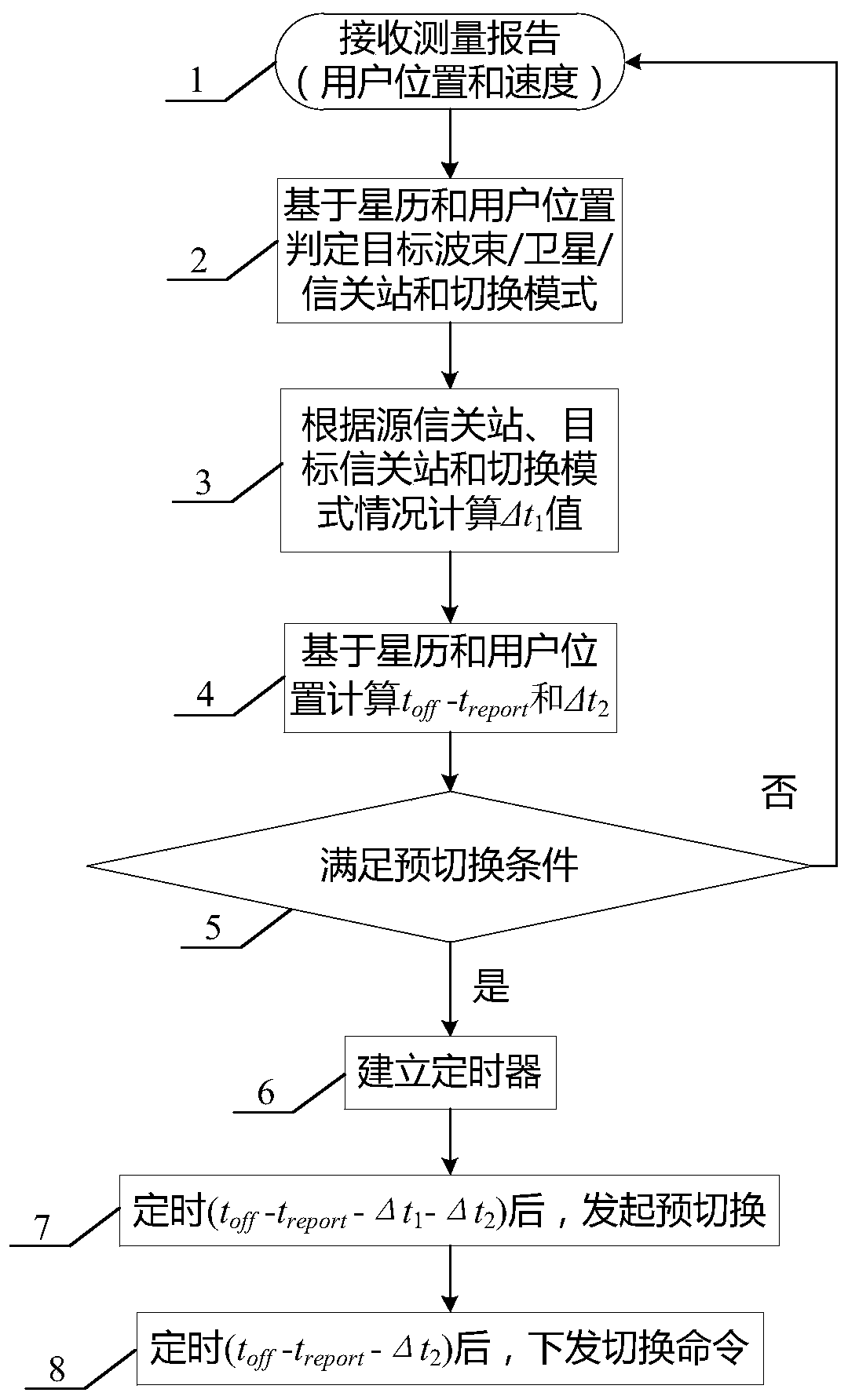
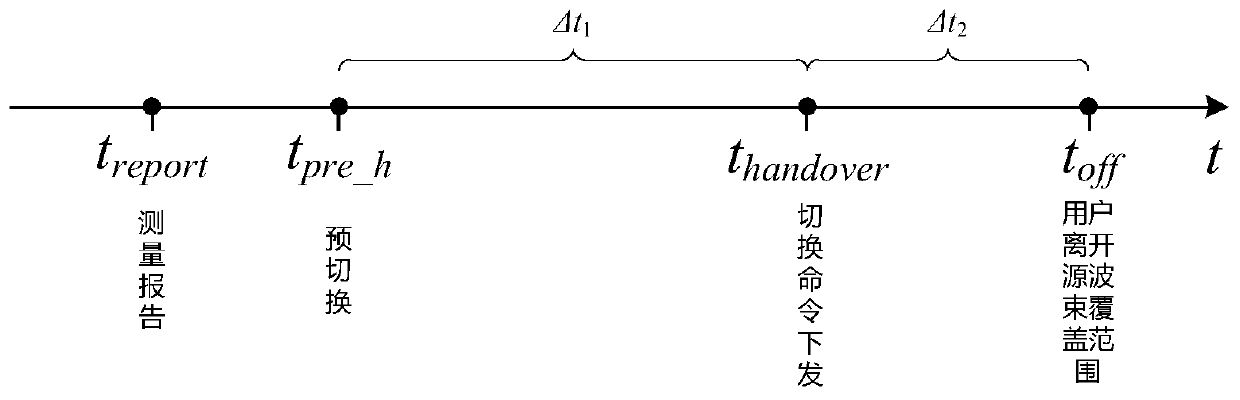
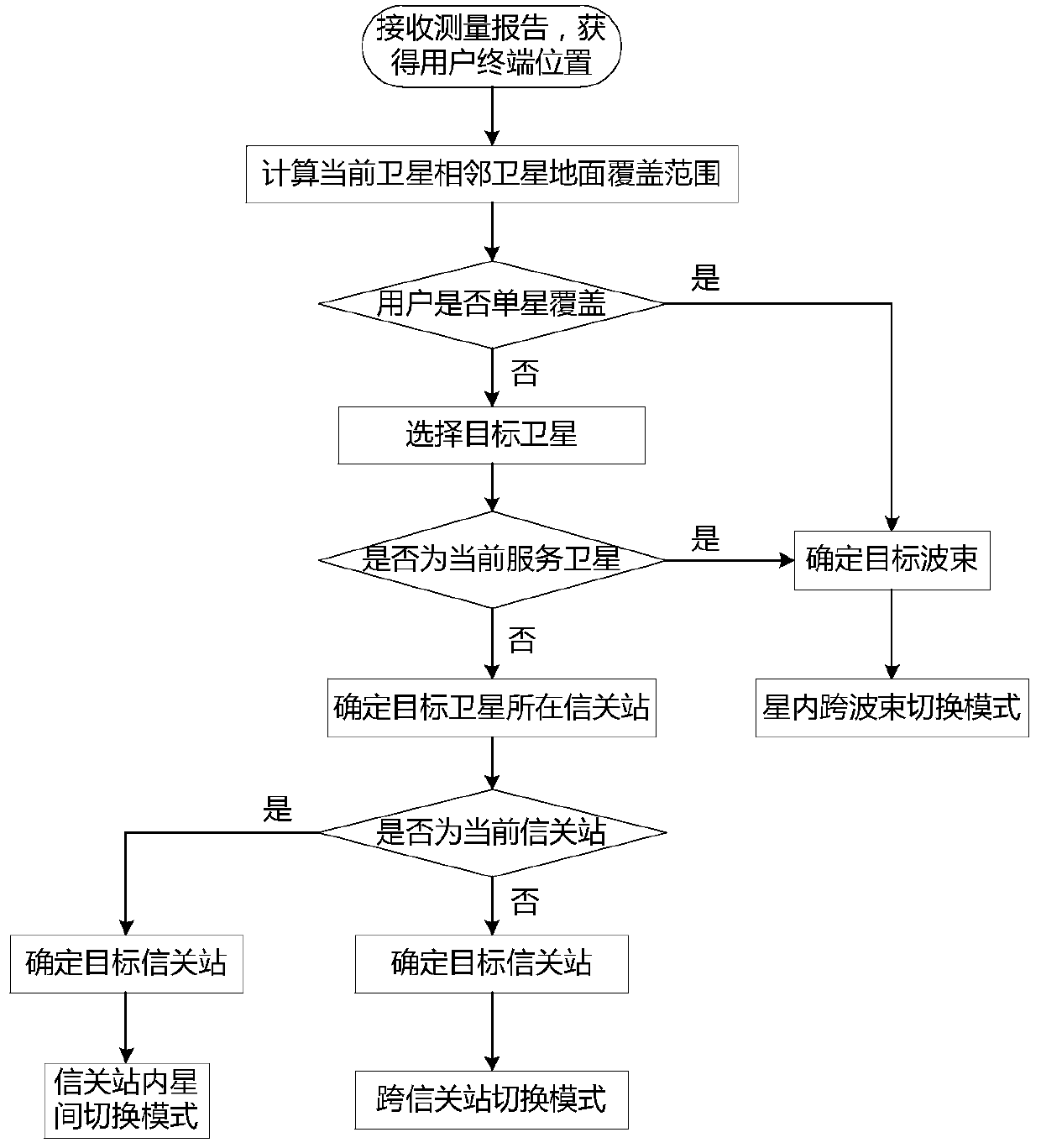
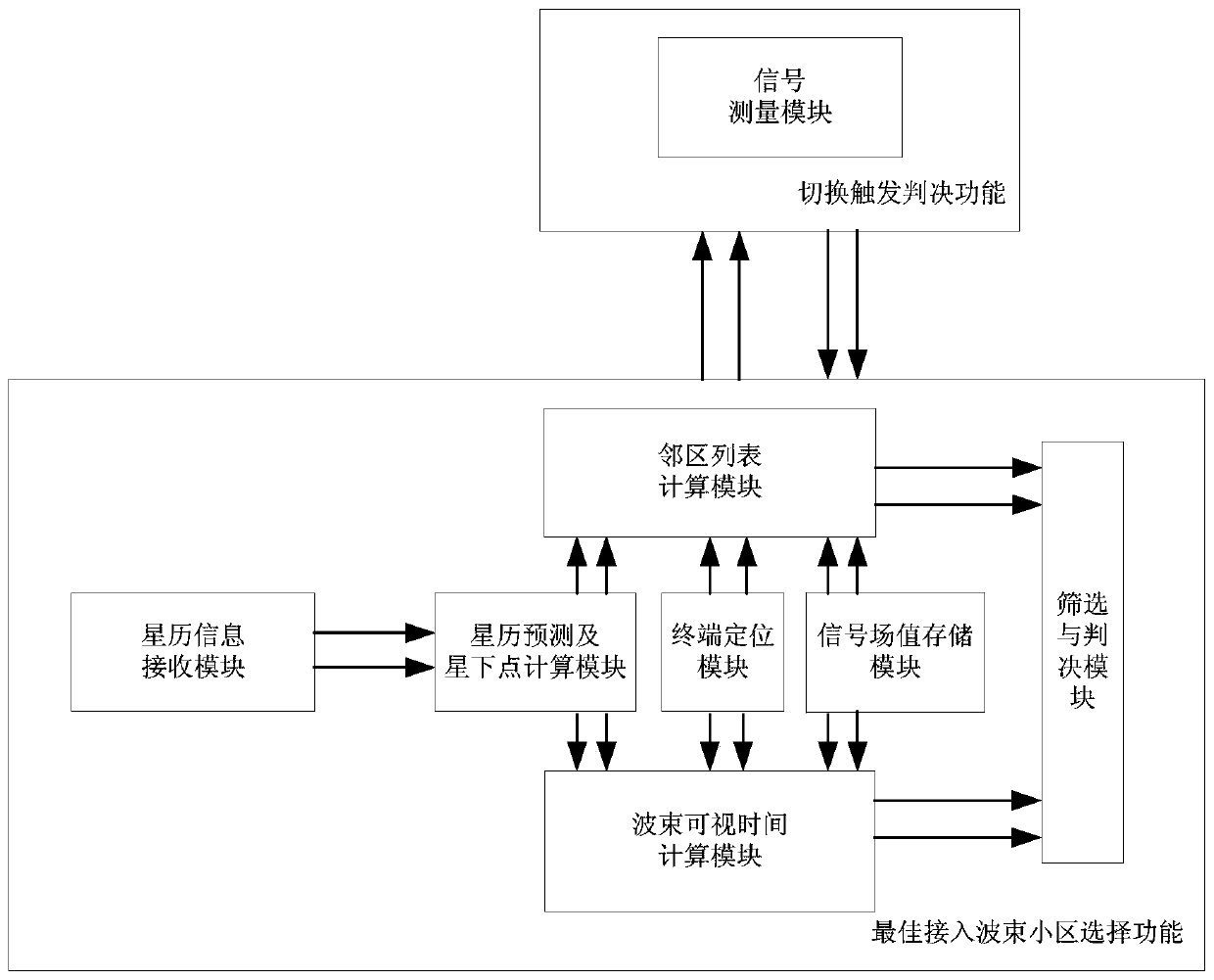
Timing trigger switching method based on ephemeris and user position calculation
ActiveCN110582094AFix switching issuesReduce interaction processRadio transmissionHigh level techniquesTelecommunicationsFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a timing trigger switching method based on ephemeris and user position calculation, and belongs to the field of low-orbit satellite communication. The working principle is as follows: (1) a gateway station receives a position and speed measurement report periodically sent by a user, (2) the gateway station calculates and judges a target wave beam / satellite / gateway station and a switching mode according to the ephemeris; (3) a delta t1 value is calculated according to the conditions of the source gateway station, the target gateway station and the switching mode, (4) a toff-treport value and a delta t2 value are calculated based on the ephemeris and the user position; (5) pre-switching judgment is carried out according to the calculated value; (6) if a pre-switchingcondition is met, a timer is established; (7), pre-switching is initiated by the gateway station according to the timing of the timer; and (8), a switching command is issued to a user by the gateway station after the timing of the timer (toff-treport-delta t1-delta t2). By means of the method, the low-orbit satellite system switching preparation stage depends on gateway station calculation, the terminal does not need to conduct neighbor cell / wave beam pilot frequency measurement, the switching problem of a small wave beam overlapping area is effectively solved, and meanwhile the method is widely applied to various scenes of the low-orbit satellite system.
Owner:成都天奥集团有限公司
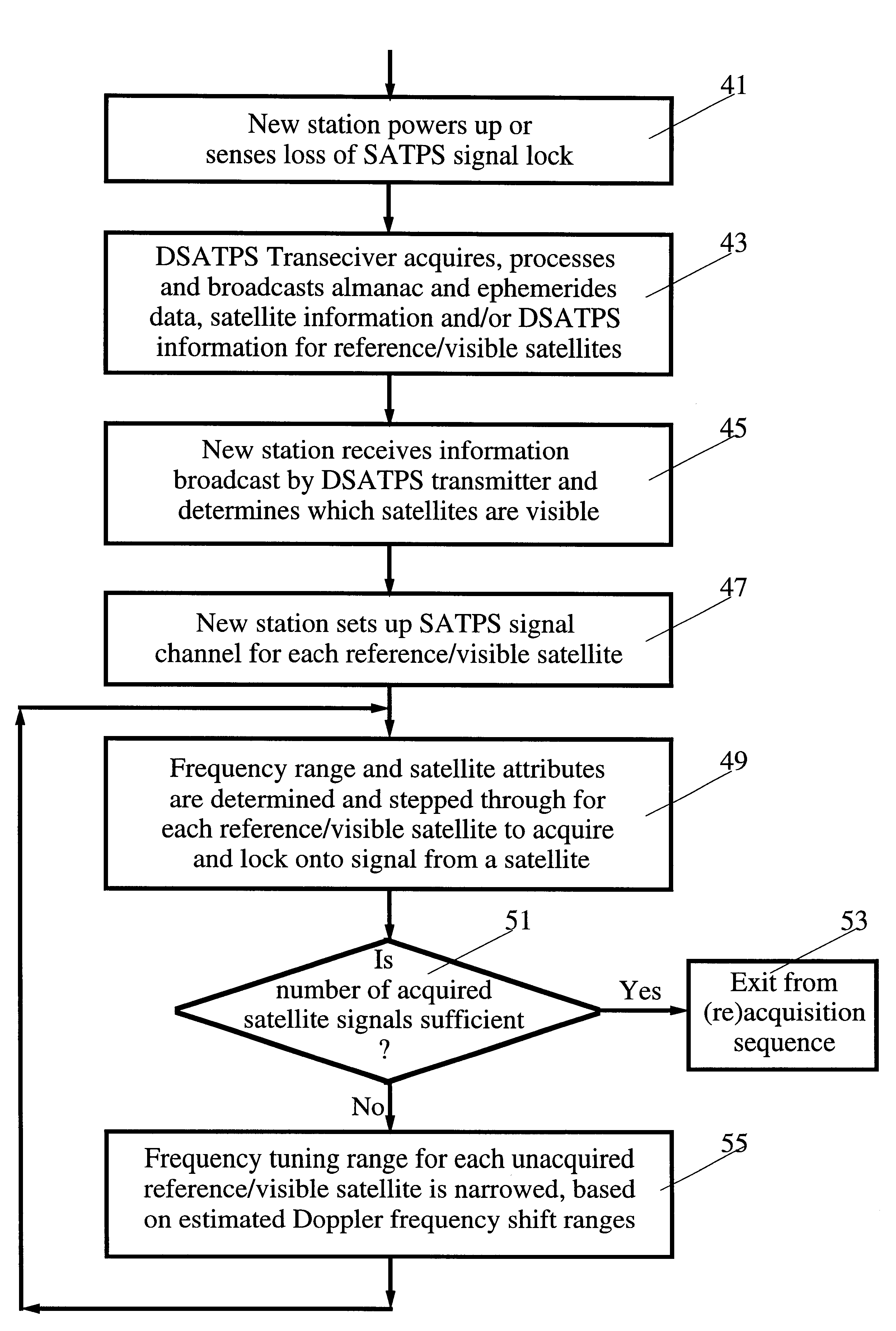
Reduction of time to first fix in an SATPS receiver
InactiveUSRE37408E1Narrow frequency rangeShorten the timePosition fixationBeacon systemsEphemerisTime to first fix
A method for fast acquisition, in as little as 6-15 seconds, of signals from a satellite in a Satellite Positioning System (SATPS), such as GPS or GLONASS, that does not require permanent storage of satellite ephemeris information at an SATPS ground station. This SATPS signal acquisition method can be used whenever the "new" station initially powers up or has lost lock on one or more SATPS signals that must be (re)acquired. A reference SATPS station provides the new SATPS station with an estimated reference station location and ephemeris information for one or more identified SATPS satellites visible from the reference station. The new station receives and uses this information to establish carrier frequency ranges to search for the identified SATPS satellite, by limiting the search to a reduced frequency range based upon estimated Doppler shift of SATPS signals received from this satellite. The actual frequency shift may differ from the estimated Doppler shift, due in part to errors in a frequency source used by the new station. When a first SATPS satellite signal is acquired and locked onto by the new station, the error in the new station frequency source is estimated, and the frequency range for searching for an SATPS signal from another satellite is reduced. Acquisition of additional SATPS satellite signals occurs more quickly. This system also allows the use of less accurate timing sources for the new stations. A new station need not store ephemeris information for the SATPS satellites but may call upon and use the ephemeris information available at the reference station.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
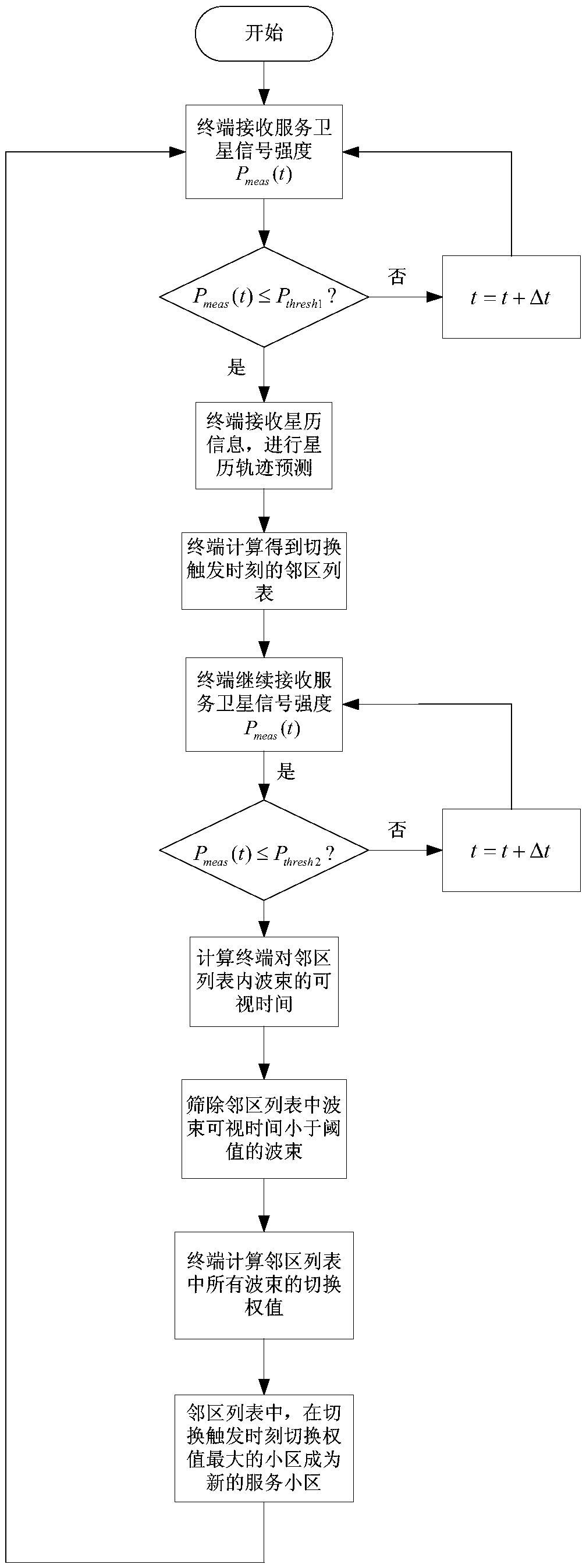
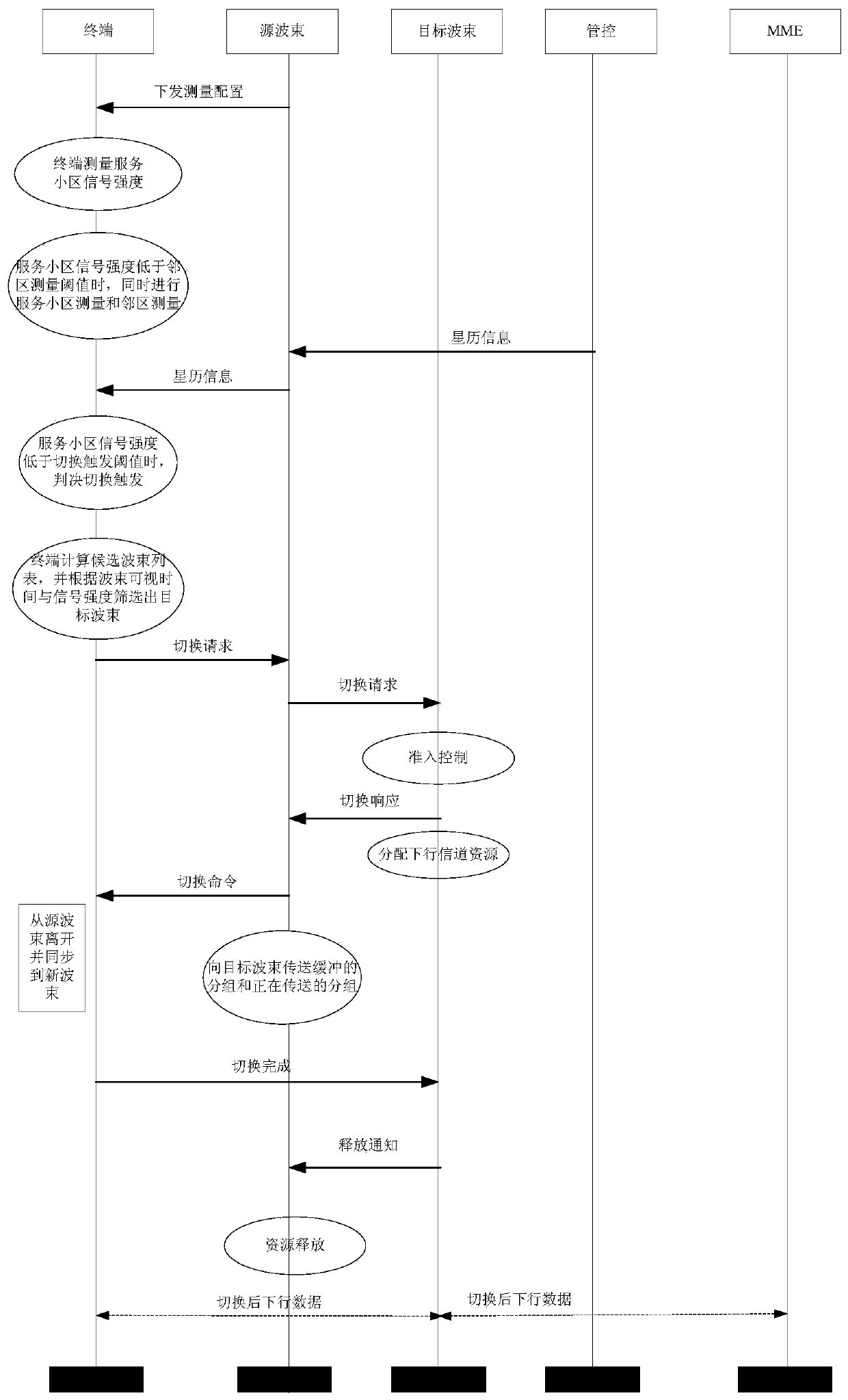
Low-orbit satellite constellation system cell switching method and device based on ephemeris information
ActiveCN111182594AReduce switching frequencyEasy to operateRadio transmissionWireless communicationEphemerisSatellite constellation
The invention discloses a low-orbit satellite constellation system cell switching method and device based on ephemeris information. The method comprises the steps of enabling a mobile terminal to receive the signal intensity of a service satellite; judging a switching triggering moment, then predicting a subsatellite point position of a low-orbit satellite according to a received satellite ephemeris parameter; calculating a coverage satellite set of the switching triggering moment according to the predicted subsatellite point position; and comparing a mobile terminal with a beam feature pointset of all beams of each satellite in the coverage satellite set to obtain an adjacent cell list. The mobile terminal calculates the visual time of each beam in the neighbor cell list, screens out thebeams of which the visual time is less than a beam visual time threshold, selects the beam with the maximum switching weight in the screened neighbor cell list as a target beam, and finally sends a request of switching to the target beam to a source beam. The method has the characteristics that the beam cell switching reliability is improved; the ping-pong switching probability is reduced; the number of system control signaling is reduced; and the network efficiency is improved.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Static correction method for exploration seismic data using first arrivals of seismic waves
InactiveUS20020075759A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic surveyCurve fitting
A shorter spatial wavelength static correction method for exploration seismic data using first arrivals according to the invention includes the steps of: based on a quadratic curve fitting to the first arrivals, which are picked up from seismic wave records of receiver gathers after the field statics, obtaining the difference DELTAi,j between the observed first arrival time tij of the receiver point j with respect to the shot point i and the corresponding time value of the fitted quadratic curve; and forming the original matrix DELTA having mxn elements DELTAi,j, where n is the total number of shot points and m is the total number of receiver points of the line; substituting the elements of each row by the difference between the value of each element and the row average; and substituting the elements of each column by the difference between the value of each element and the column average; repeating the iteration until less than a predetermined error; the sum of the averages of the ith row for all iterations and the sum of the averages of the ith column for all iterations are the static correction value at the ith shot point and the static at the jth receiver point respectively. Said method is applicable to 3-D seismic survey by mean of using a formula of rij={square root}{square root over (DELTAxij2+DELTAyij2)} to transform 3-D seismic data into 2-D data, so that the 3-D seismic data processing is as simple as that of 2-D data.
Owner:ZHOU XIXIANG +1
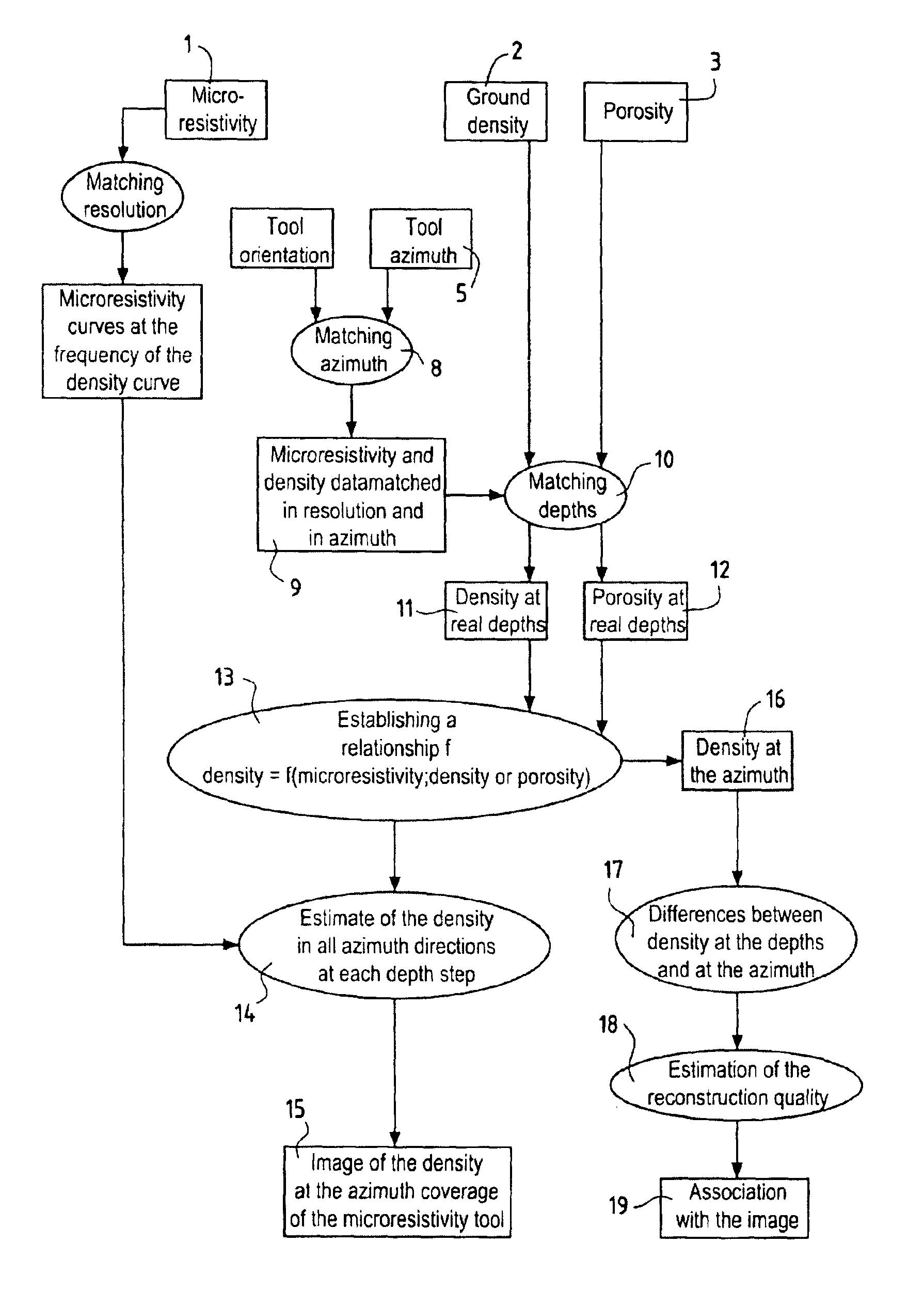
Methods of producing images of underground formations surrounding a borehole
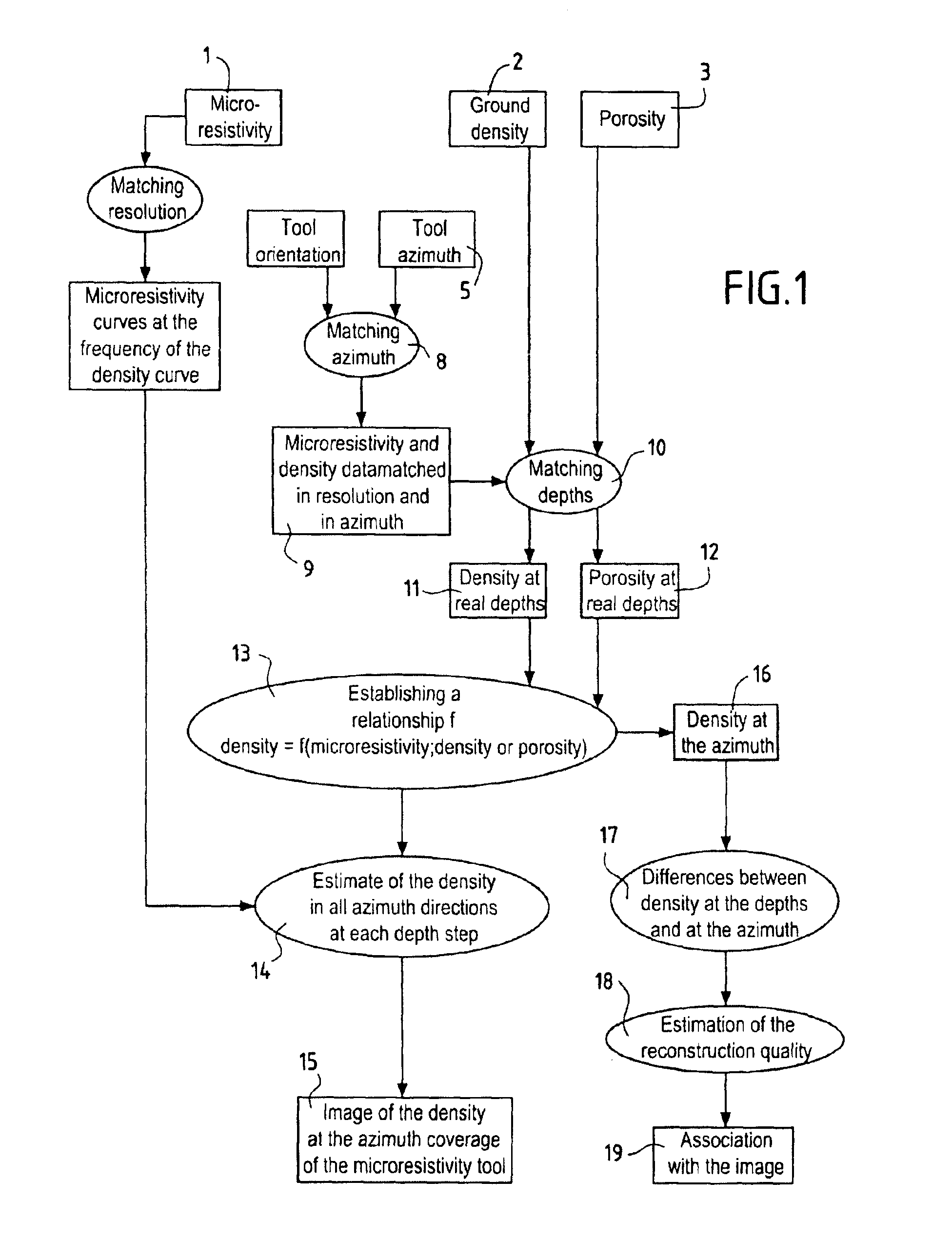
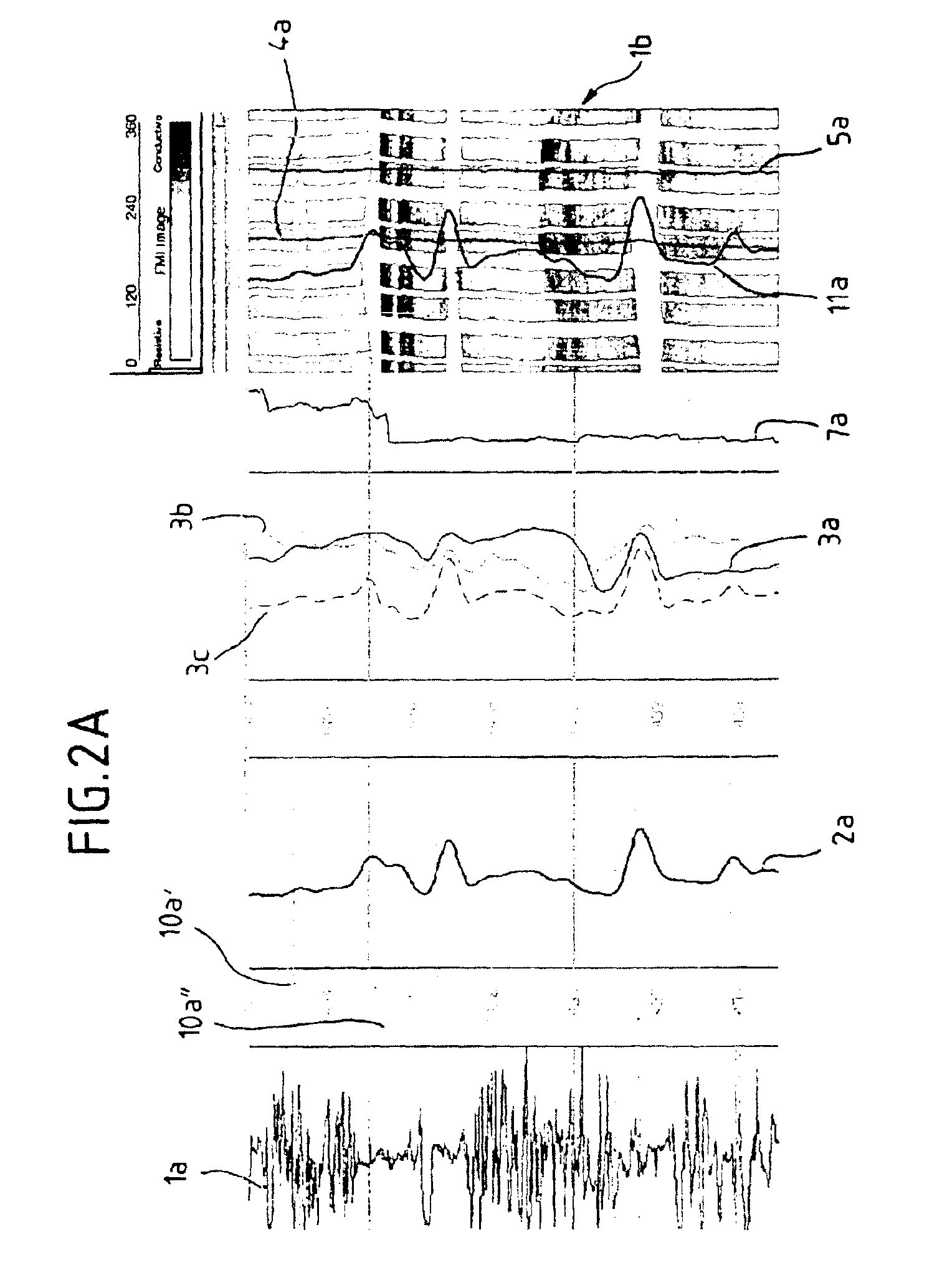
InactiveUS7062072B2High resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyArray data structureImage resolution
A method of producing images of formations surrounding a borehole, comprises: obtaining values of a first parameter in the borehole as a function of depth and azimuth at a first resolution; obtaining values of a second parameter in the borehole as a function of depth only at a second resolution; establishing a relationship between the first and second parameters at a matched resolution; using the relationship to derive values of the second parameter as a function of depth and azimuth; and producing an image of the second parameter as a function of depth and azimuth using the derived values of the second parameter. A method of producing three dimensional images comprises obtaining values of a first parameter in the borehole as a function of depth and azimuth at a first resolution; obtaining values of a second parameter in the borehole as a function of depth only at a second resolution; establishing a relationship between the first and second parameters at a matched resolution; using the relationship to derive values of the second parameter in a three dimensional array; and producing an image of the second parameter in three dimensions using the derived values of the second parameter.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for accurate determination of ocean bottom seismometer positioning and timing
ActiveUS20110273958A1Extension of timeImprove accuracySeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottom seismometerClock drift
There is provided herein a system and method of seismic exploration that produces improved locations and timings for ocean bottom seismometers. The instant method utilizes linearized inversion in conjunction with a conventionally accurate clock to provide both time and positioning for each OBS unit with high accuracy as compared with the prior art approach. Inversion is one mathematical tool that effectively performs the requisite triangulation. Furthermore, the clock drift can be accounted for in the inversion scheme. The inversion not only determines the OBS position and shot timing errors, but also estimates the accuracy of the position and timing determination.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC +1
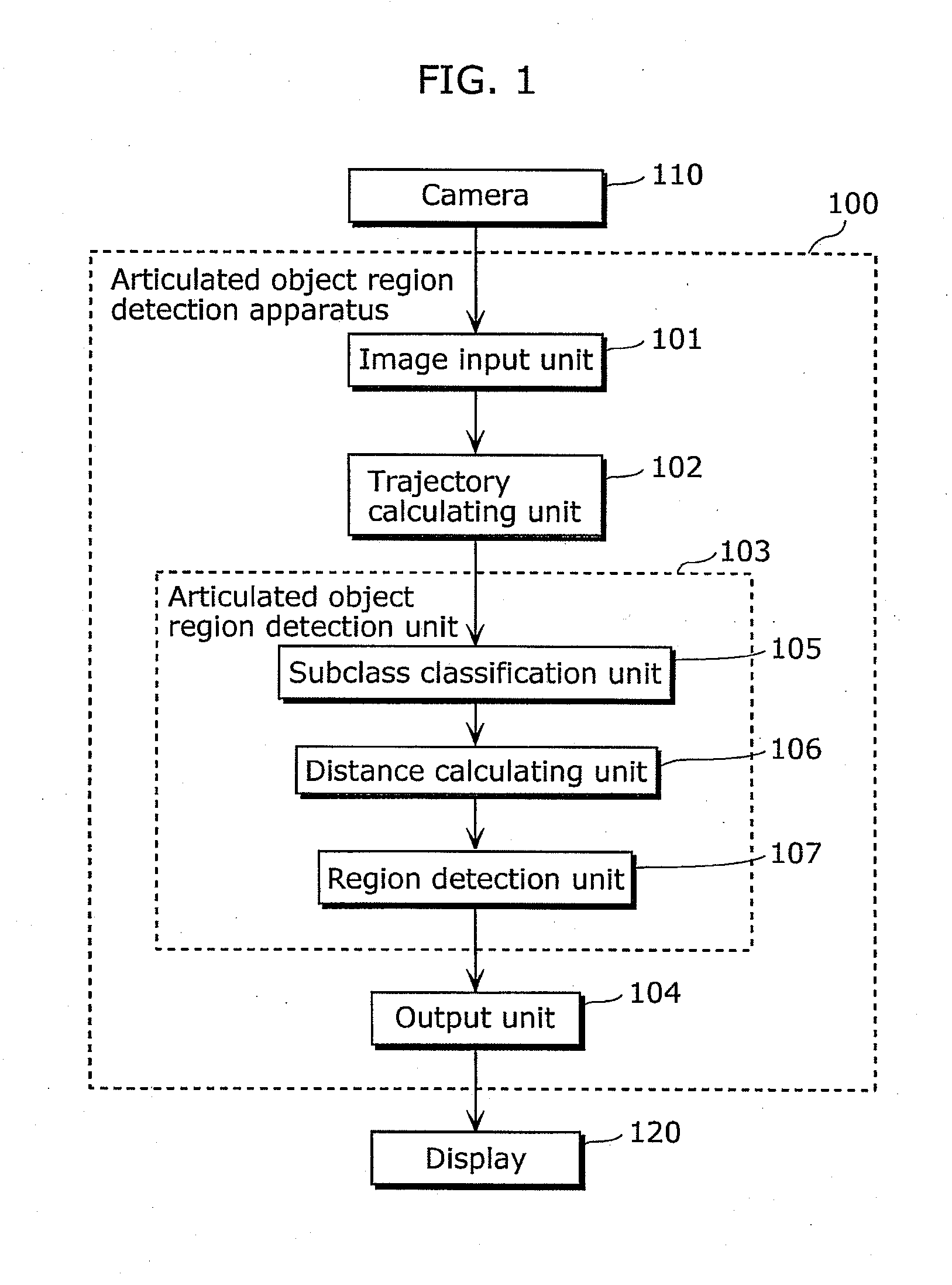
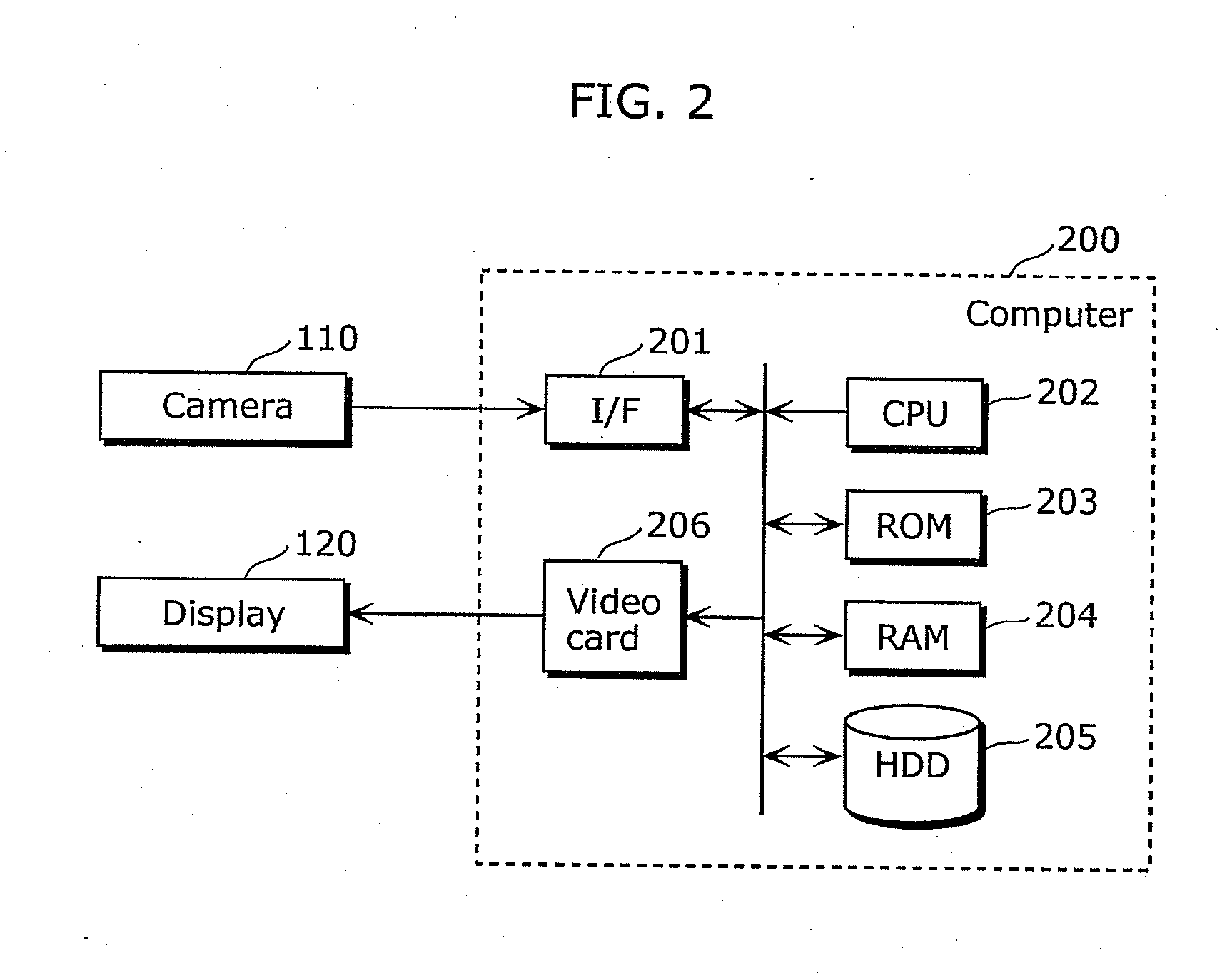
Articulated object regionarticulated object region detection apparatus and method of the same
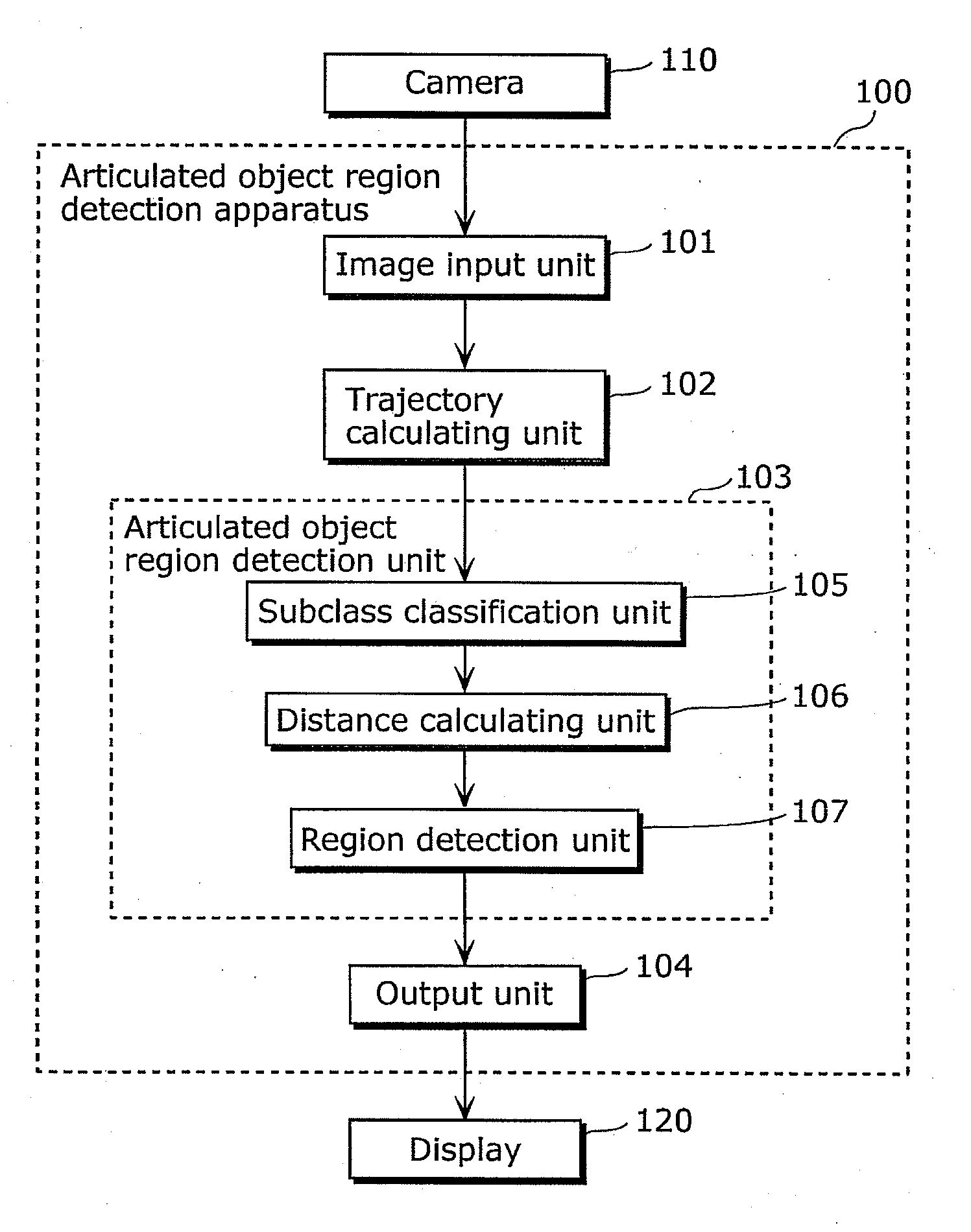
ActiveUS20110255748A1Accurate detectionAccurate extractionImage enhancementImage analysisTemporal changeRegion detection
An articulated object region detection apparatus includes: a subclass classification unit which classifies trajectories into subclasses; a distance calculating unit which calculates, for each of the subclasses, a point-to-point distance and a geodetic distance between the subclass and another subclass; and a region detection unit which detects, as a region having an articulated motion, two subclasses to which trajectories corresponding to two regions connected via the same articulation and indicating the articulated motion belong, based on a temporal change in the point-to-point distance and a temporal change in the geodetic distance between two given subclasses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
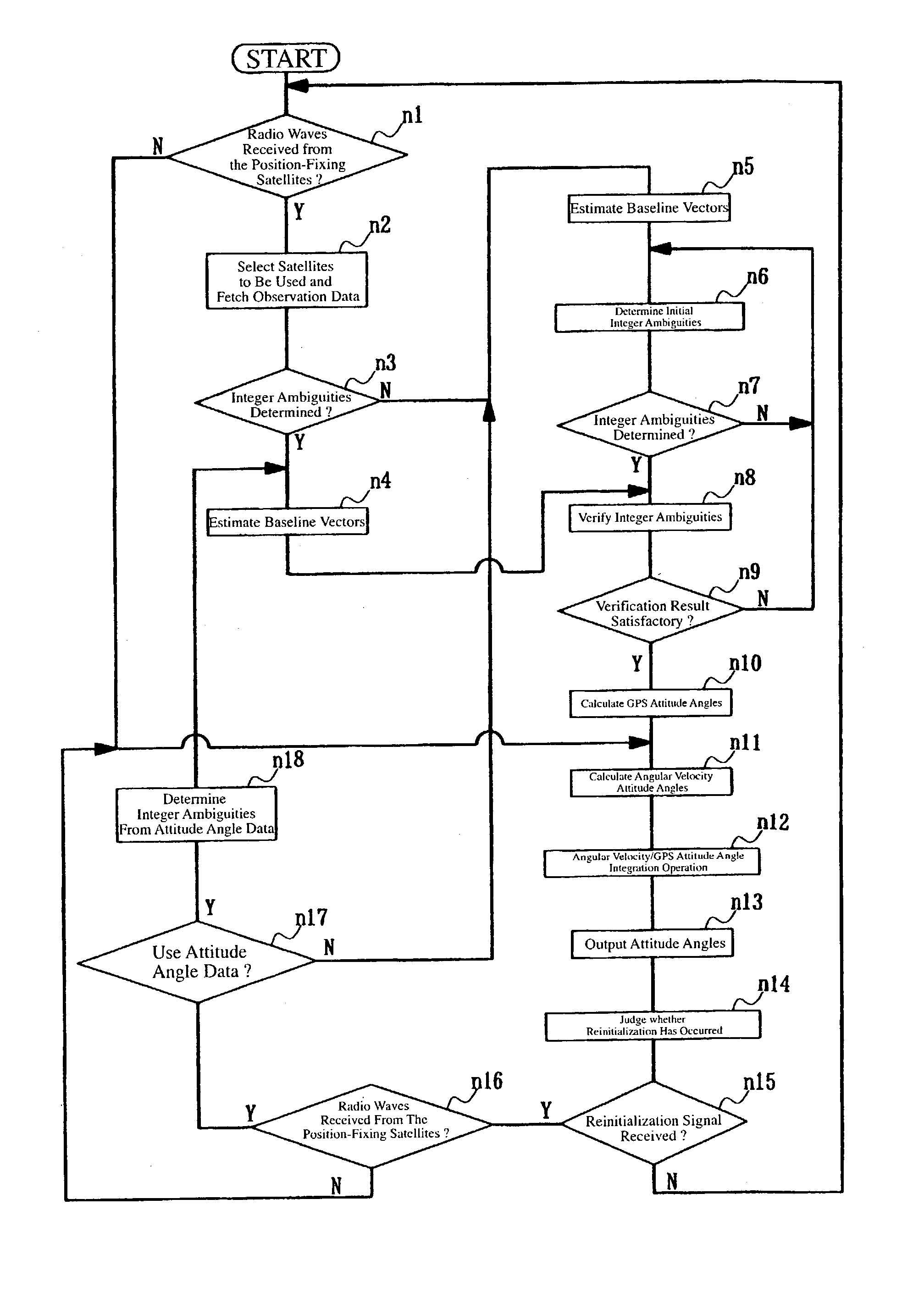
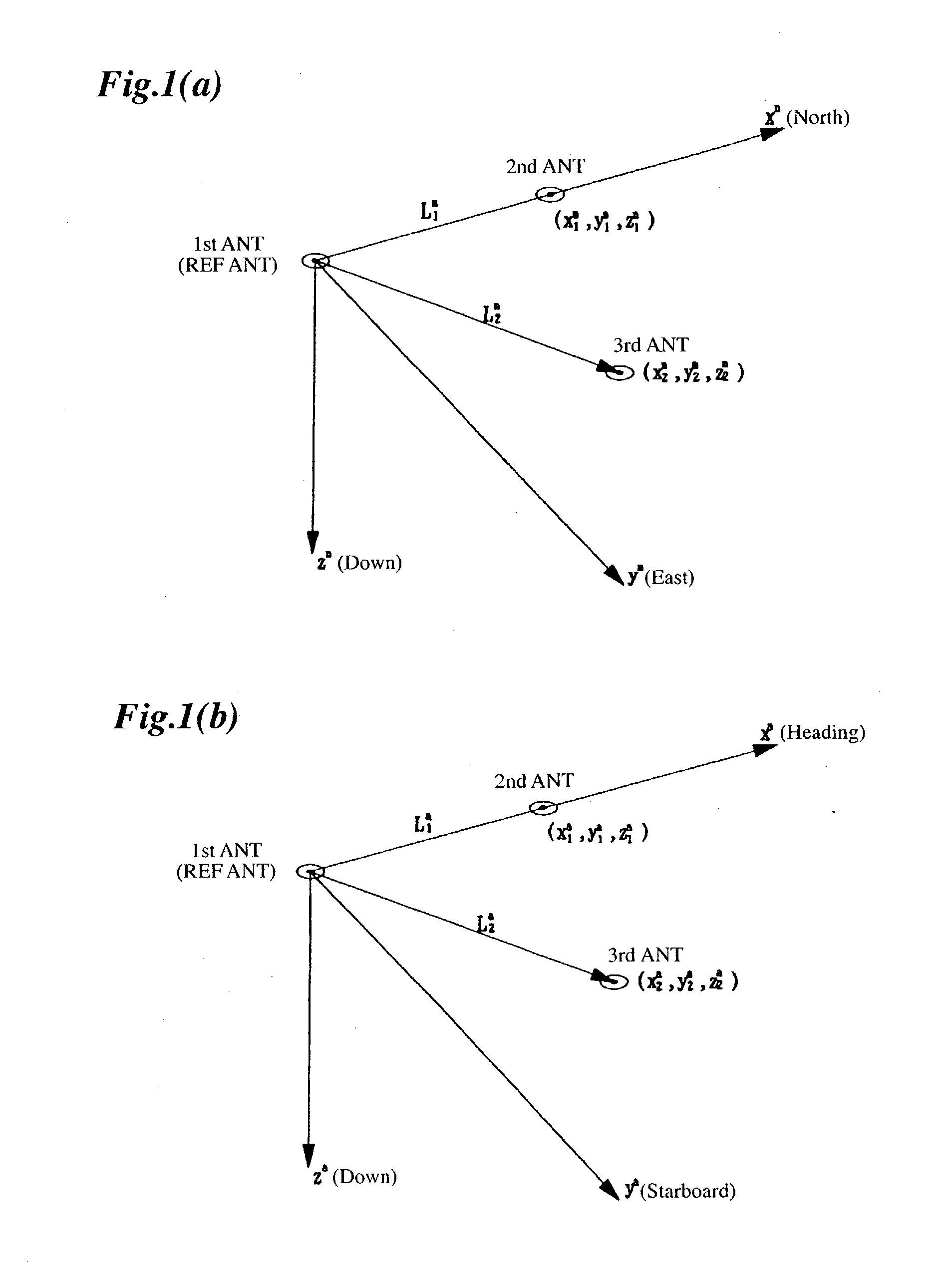
Attitude angle detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20030154049A1Measuring relative positionRedetermine the integer ambiguity quickly and accuratelyDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAmbiguityInteger ambiguity
An attitude angle detecting apparatus receives radio waves transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with multiple antennas located at specific positions of a mobile unit, determines relative positions of the antennas and detects the heading and attitude of the mobile unit by determining carrier phase ambiguities quickly and accurately. When it is needed to redetermine integer ambiguities after recovery from an interruption of the radio waves from the position-fixing satellites or as a result of a change in combination of the position-fixing satellites, for example, the attitude angle detecting apparatus redetermines the integer ambiguities by using attitude angles and an attitude angle error covariance obtained from previous observation. This enables the attitude angle detecting apparatus to uninterruptedly obtain information on the heading and attitude of the mobile unit.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
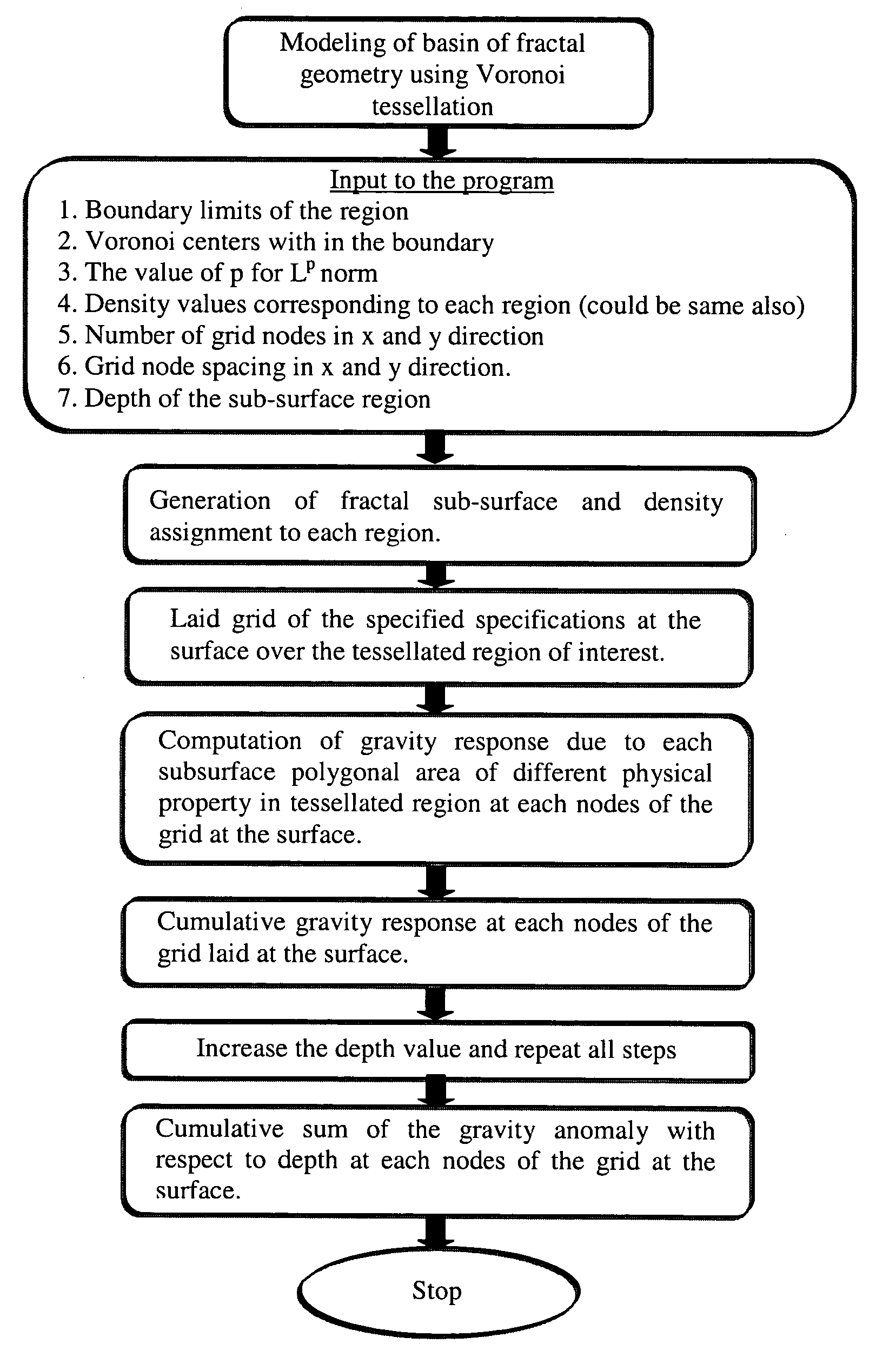
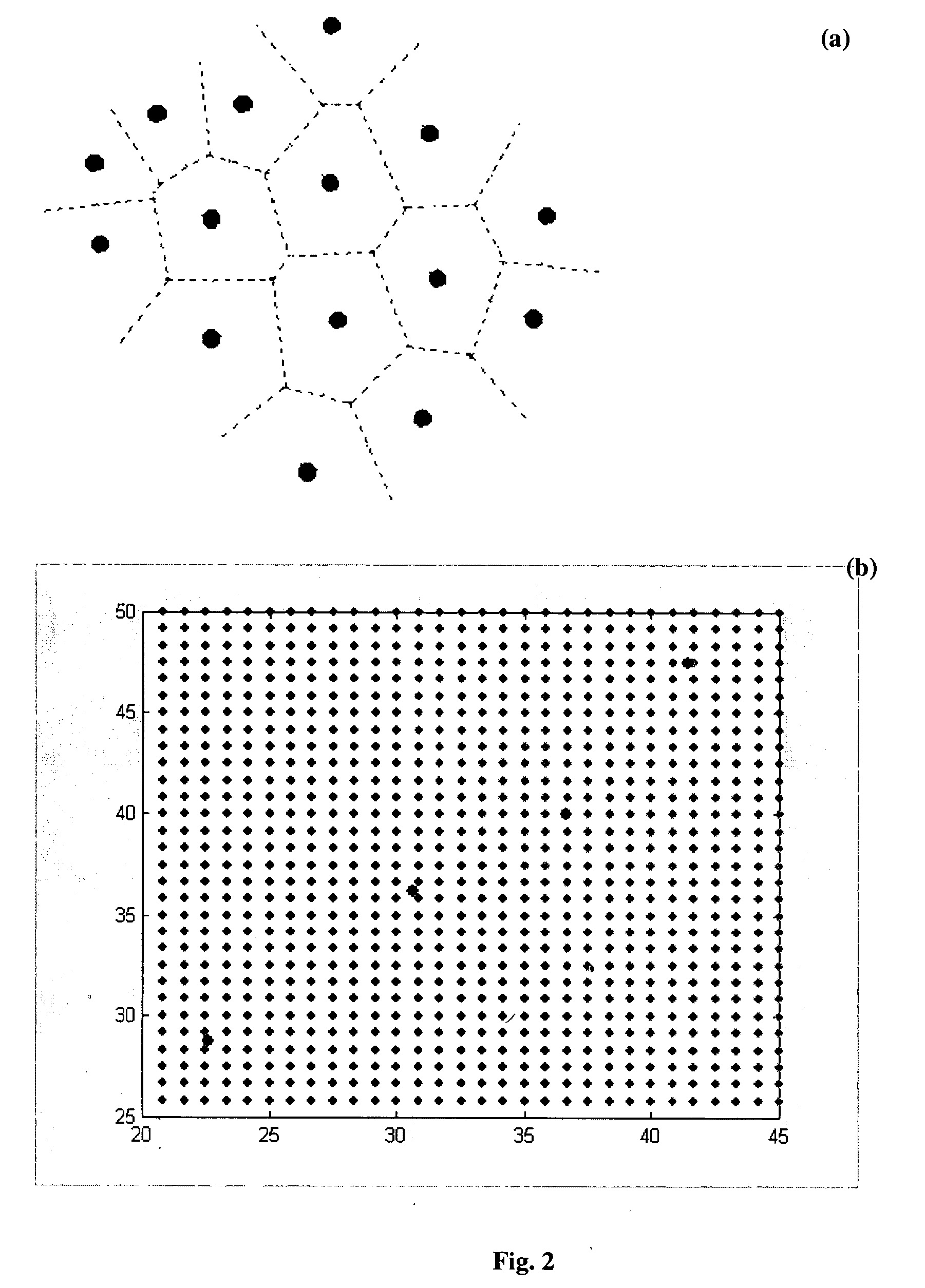
Generation of three dimensional fractal subsurface structure by Voronoi Tessellation and computation of gravity response of such fractal structure
ActiveUS20040201585A1Generate efficientlyImprove variationGravitational wave measurement3D-image renderingTriacontagonPetroleum exploration
The invention is an entirely new application of domain characterization generated by Voronoi tessellation, which is very close to realistic geology and computation of gravity response of such domain, which has three dimensional fractal basin structure, and is favorable for oil exploration. In this work the interfaces or tessellating domains are represented by a set of parameters, which are referred as Voronoi centers. These parameters can be perturbed by any amount without getting into representational problems as faced by the conventional techniques. To accomplish such representation Voronoi tessellation is used, which in two dimensional space consists of enclosing every Voronoi center by a Voronoi polygon such that the common edge of adjacent polygons is perpendicular bisector to the line joining the Voronoi centers on both the sides of that edge. In this invention instead of using conventional Euclidian distances, the notion of Voronoi tessellation is generalized by using Ldistances, where p can hold any real value so that Voronoi domains are not necessarily polygonal. Desired fractal subsurface is generated using this approach that is quite close to the natural settings than the conventional planer or polygonal representation. Next, the gravity response due to this fractal subsurface structure has been computed. The new invention has a significant advantage over the conventional methods especially in geophysical inversion where initial model parameters are updated in each iteration, which can be done more easily and efficiently by Voronoi tessellation merely by changing Voronoi centers.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Three-dimensional focus imaging method of side-looking chromatography synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101581780AReduced requirements for the form of the transmitted signalEfficient use ofRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumMicrowave
The invention relates to a three-dimensional focus imaging method for a side-looking chromatography synthetic aperture radar, which comprises the steps: converting collected original echoed data of the side-looking chromatography synthetic aperture radar to a slope distance wave-number domain and an azimuth wave-number domain, performing elevation frequency spectrum aliasing-free recovery on converted signals and converting the signals to a slope distance three-dimensional wave-number domain, an azimuth three-dimensional wave-number domain and an elevation three-dimensional wave-number domain; converting the signals in the three-dimensional wave-number domains to a rectangular coordinate system by coordinate mapping; and reconstructing a three-dimensional microwave image containing slope distance, azimuth and elevation spatial location information of imaging areas and magnitude-phase information by inverse Fourier transform and image space selection. The method can precisely reconstruct three-dimensional microwave images in the imaging areas without geometry correction on the condition that elevation hits are less, the distribution of elevation synthetic aperture centers is arbitrary or the size of the imaging areas are arbitrary. The method can be also used for the reconstruction of three-dimensional microwave images in imaging observation geometries such as downward-looking, downward side-looking chromatography SARs, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for anisotropic vector plane wave decomposition for 3D vertical seismic profile data
InactiveUS20030195705A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingEigen analysisVertical seismic profile
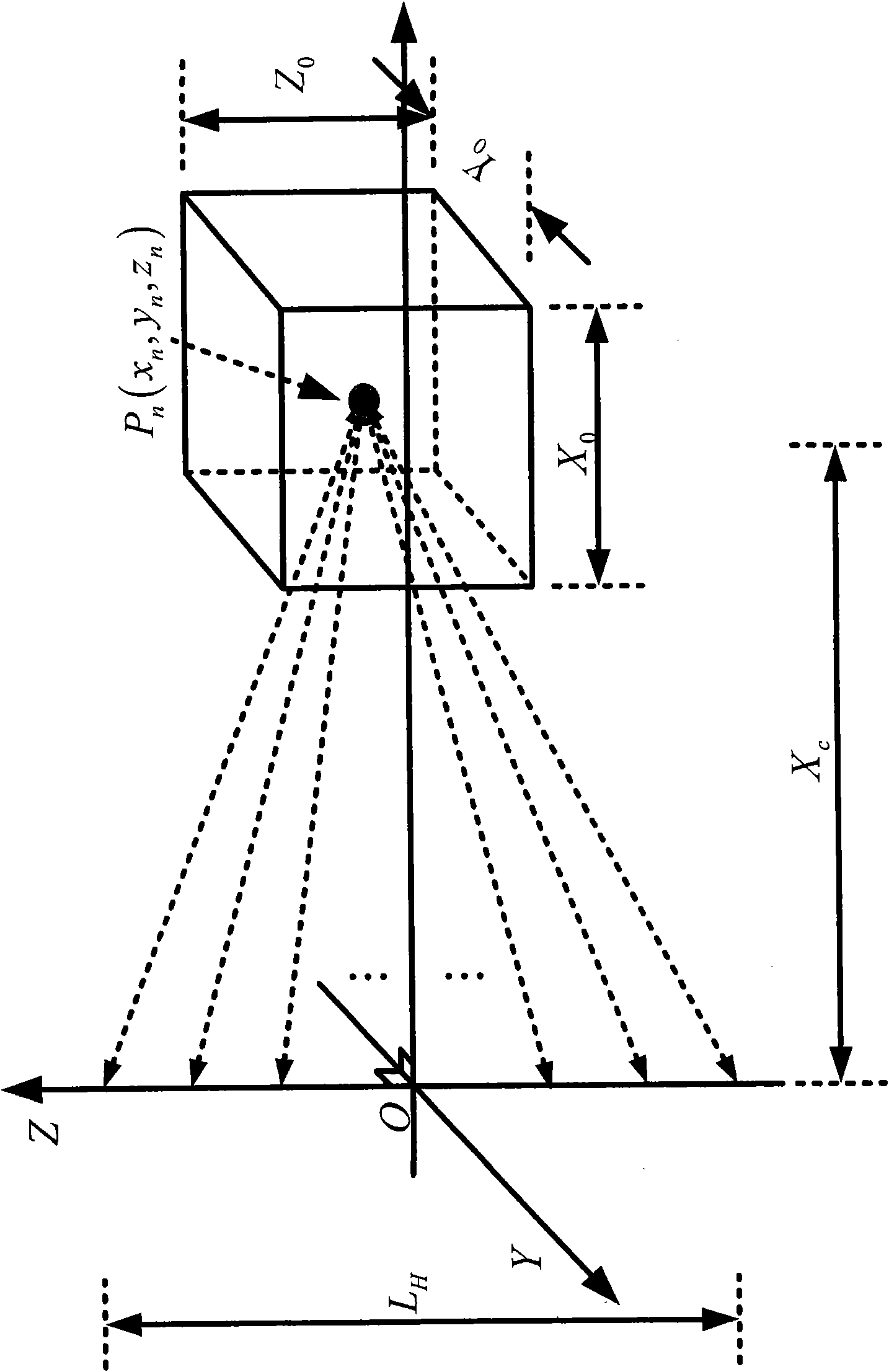
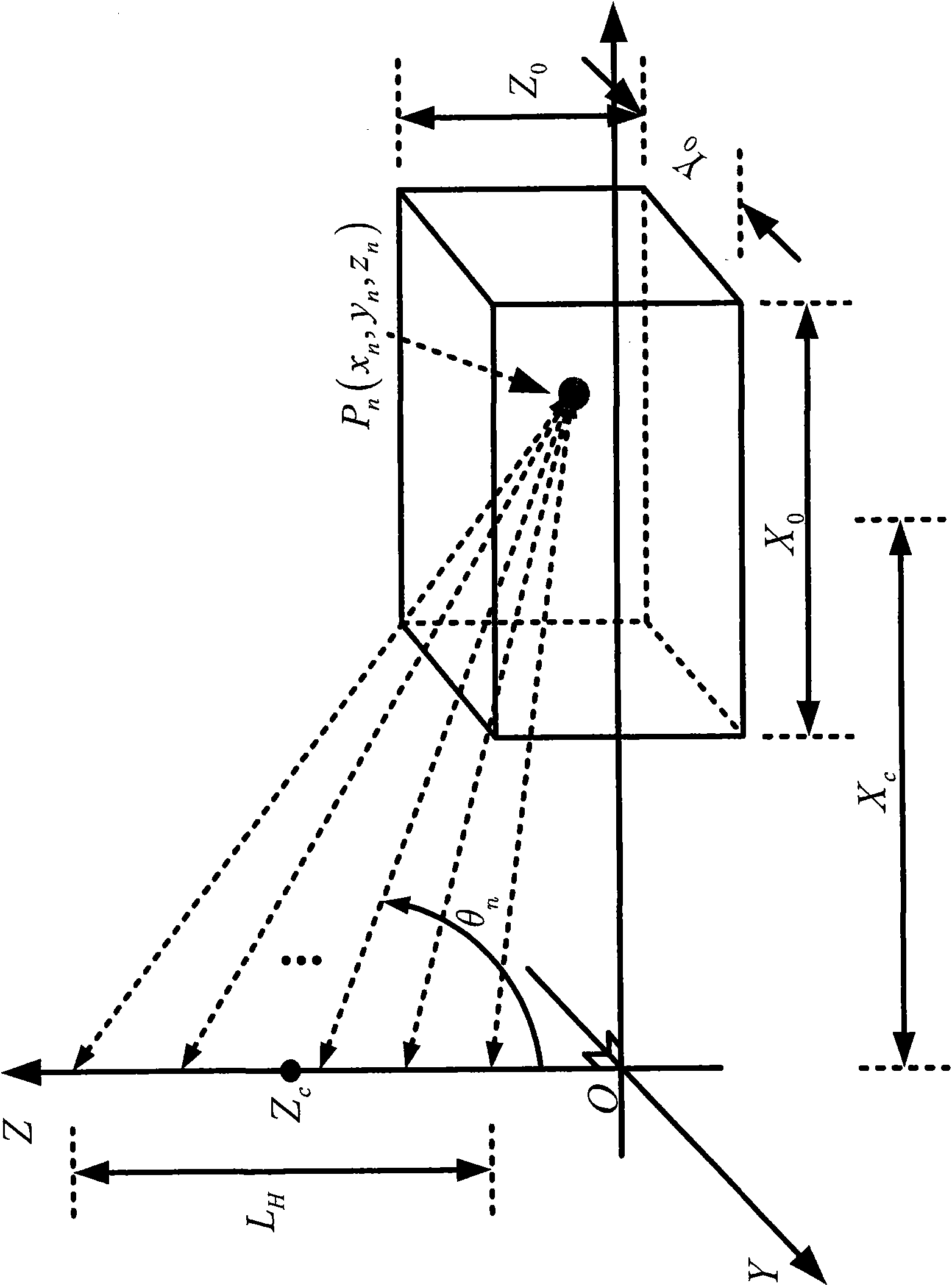
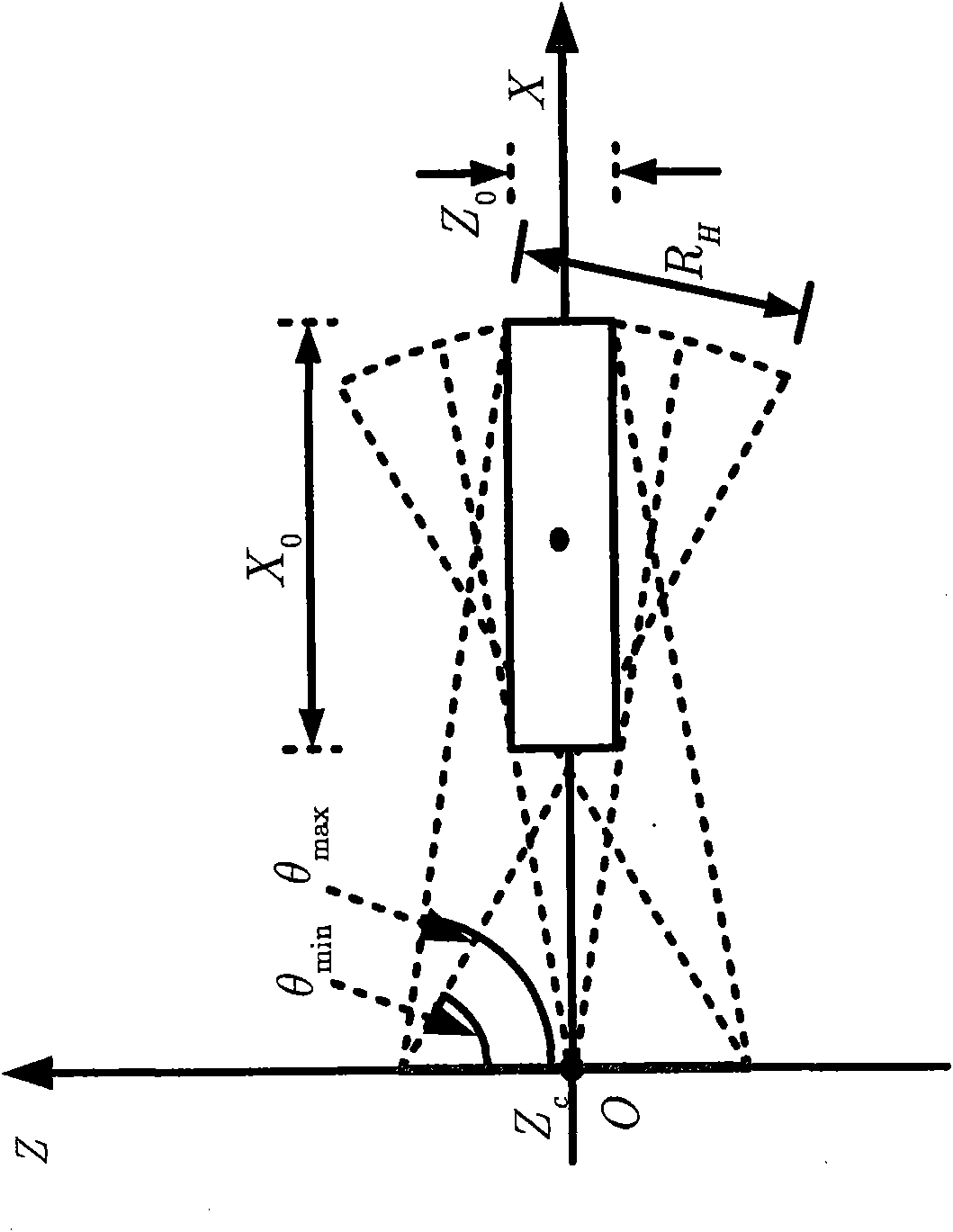
A wavefield separation method and apparatus for 3D VSP data, which handles arbitrary 3D source and receiver geometries, and common shot 3C data oriented to North, East and Vertical geographical coordinates and makes use of anisotropic medium properties at the downhole receivers. When given a range of propagation angles, slowness and polarization vectors are computed for each plane wave and a linear system is solved at each frequency to yield the scalar plane-wave amplitudes. A novel regularization scheme is used that obviates the need for eigen analysis of the steering matrix. Sums within subsets of these scalar plane waves are constructed to provide up and down qP (P), qS (Sv) and Sh wavefields. Vector residuals can be computed for parameter testing, quality control and imaging purposes.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
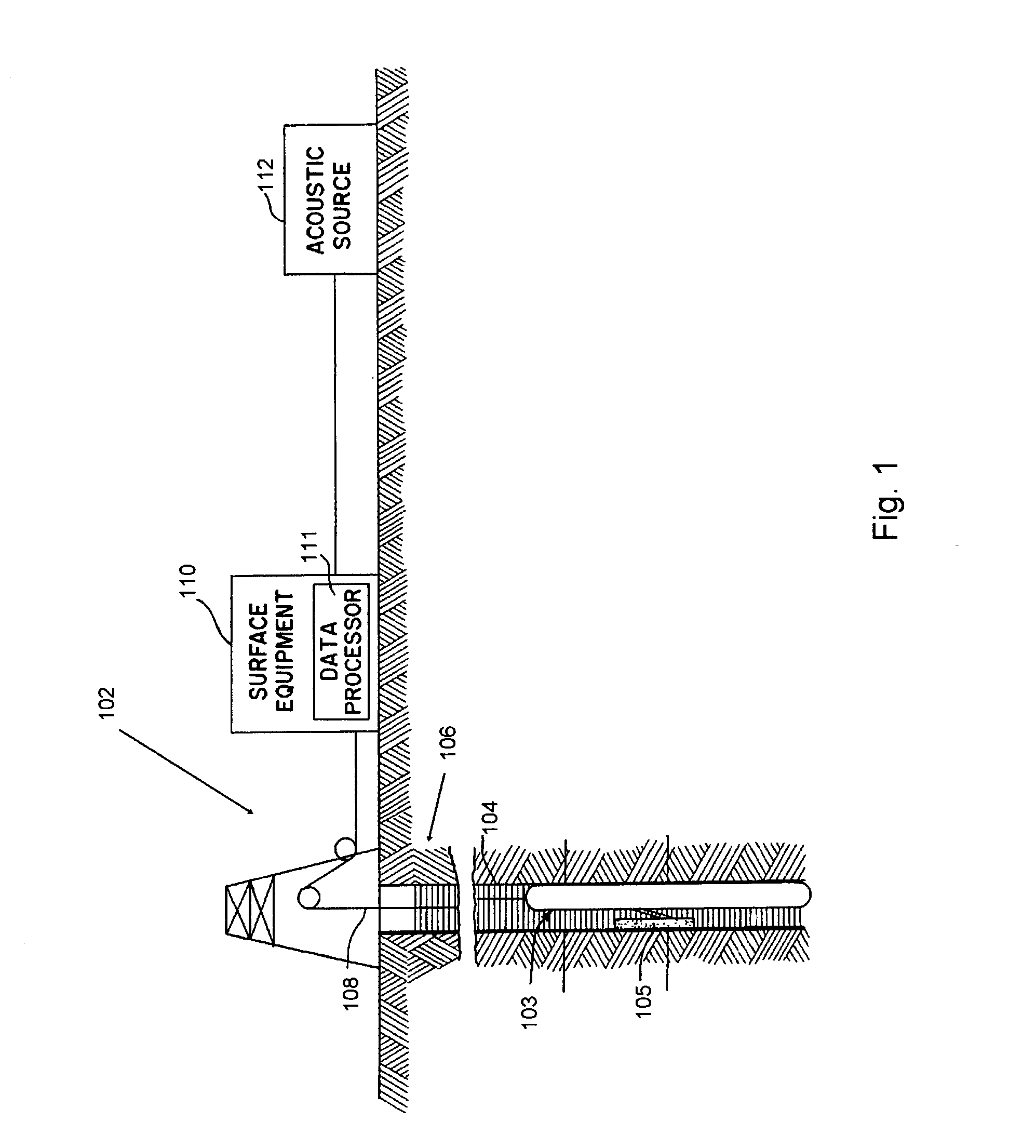
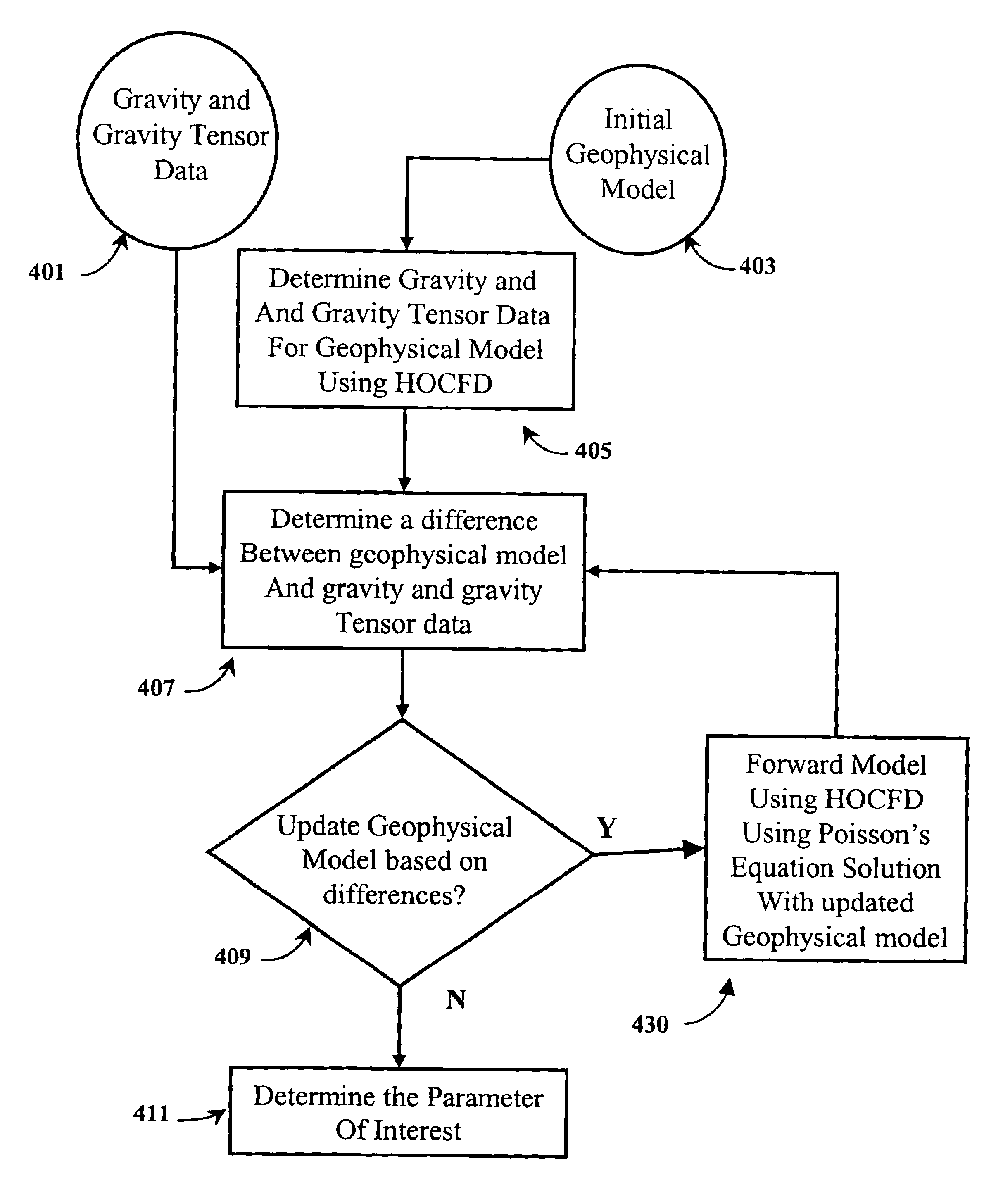
Modeling gravity and tensor gravity data using poisson's equation for airborne, surface and borehole applications
InactiveUS6993433B2Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowPotential fieldPoisson's equation
The present invention is a method for determining a parameter of interest of a region of interest of the earth. At least one component of potential fields data is measured at a plurality of locations over a region of interest including a subterranean formation of interest. The potential fields data are selected from magnetic data and gravity data. An initial geophysical model is determined for the region including the subterranean formation of interest. For the model, geophysical tensor data is updated using a forward model at a plurality of locations using a High Order Compact Finite Difference method. A difference between the estimated model value and the measured value of the potential field measurements are determined, and the geophysical model is updated. The model is iteratively updated and compared to the measured data until the differences reach an acceptable level and the parameter of interest has been determined.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
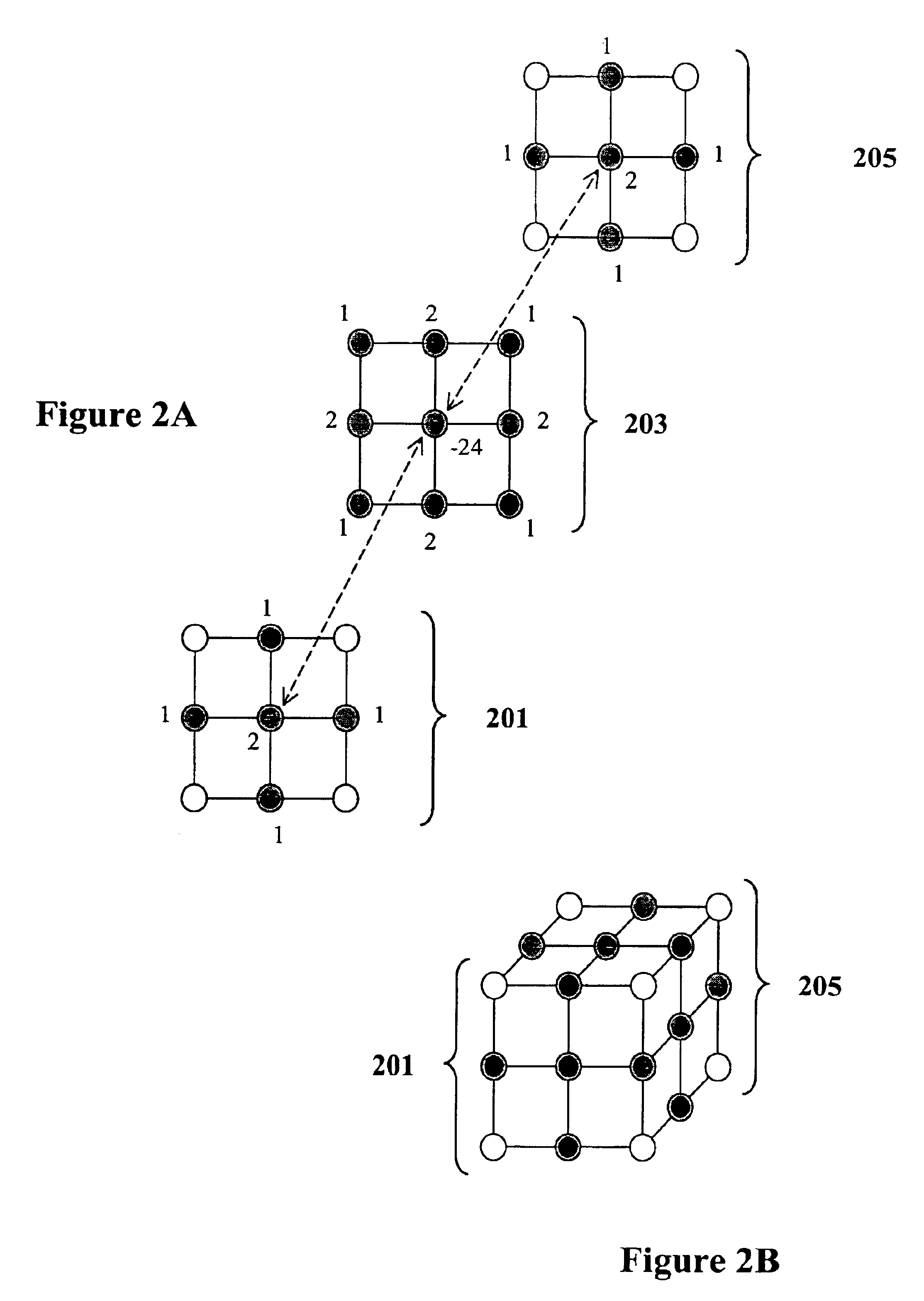
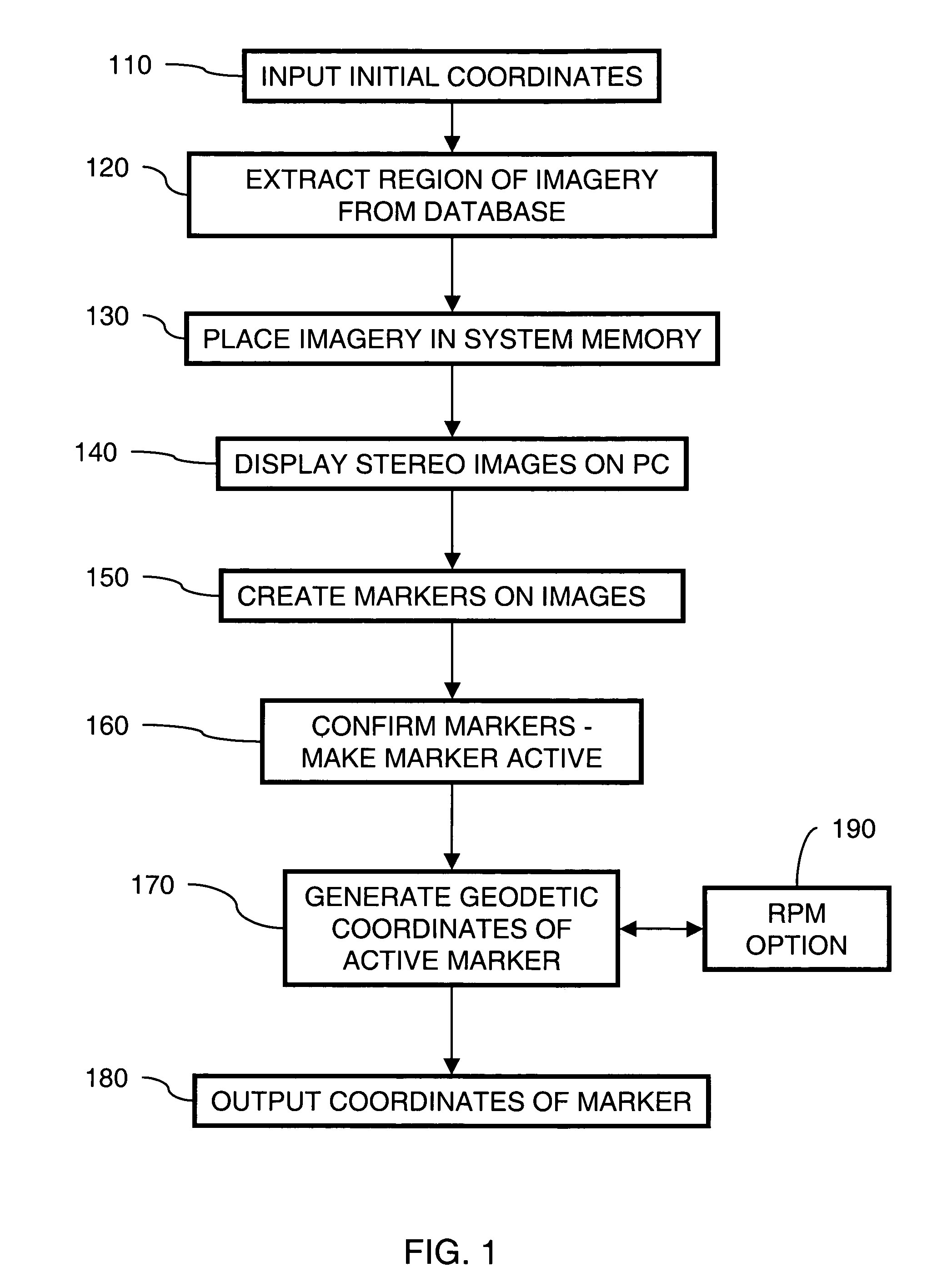
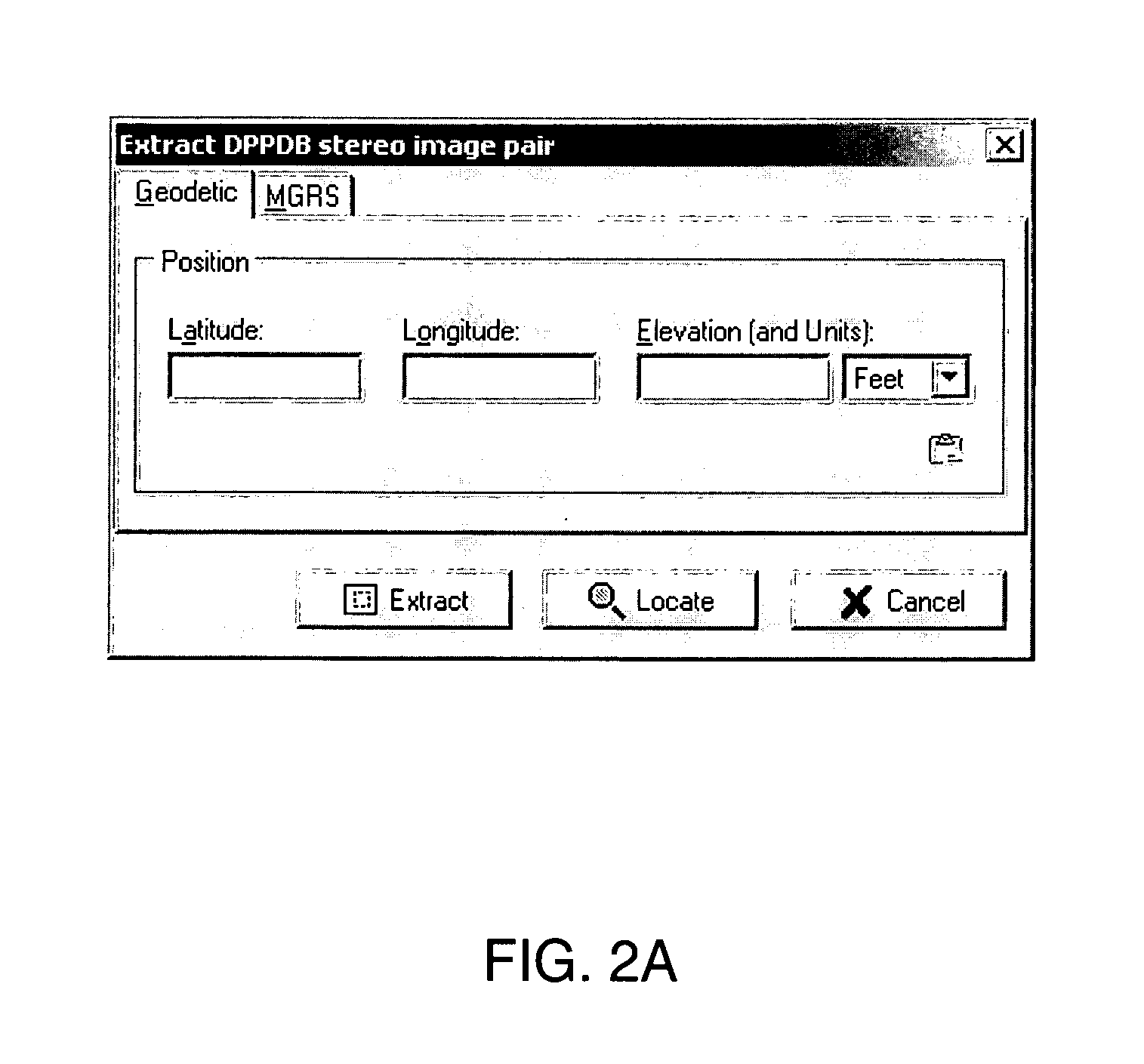
Apparatus and method for providing true geodetic coordinates
InactiveUS6988049B1Navigational calculation instrumentsDigital computer detailsMobile deviceRemote sensing
An embodiment of the present invention utilizes the Reference Point Method (RPM). RPM generates a local magnetic declination variance that is exact for the location of the OP, utilizing an optical stereo imagery database. RPM functions to determine true geodetic coordinates of a target position not available to be displayed in an image database, such as, for example, movable equipment.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Simultaneous source inversion for marine streamer data with cross-correlation objective function
ActiveUS8688381B2Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasData acquisitionPhysical property
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com