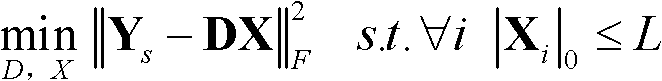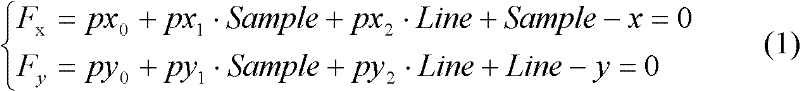Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2830 results about "Synthetic aperture radar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
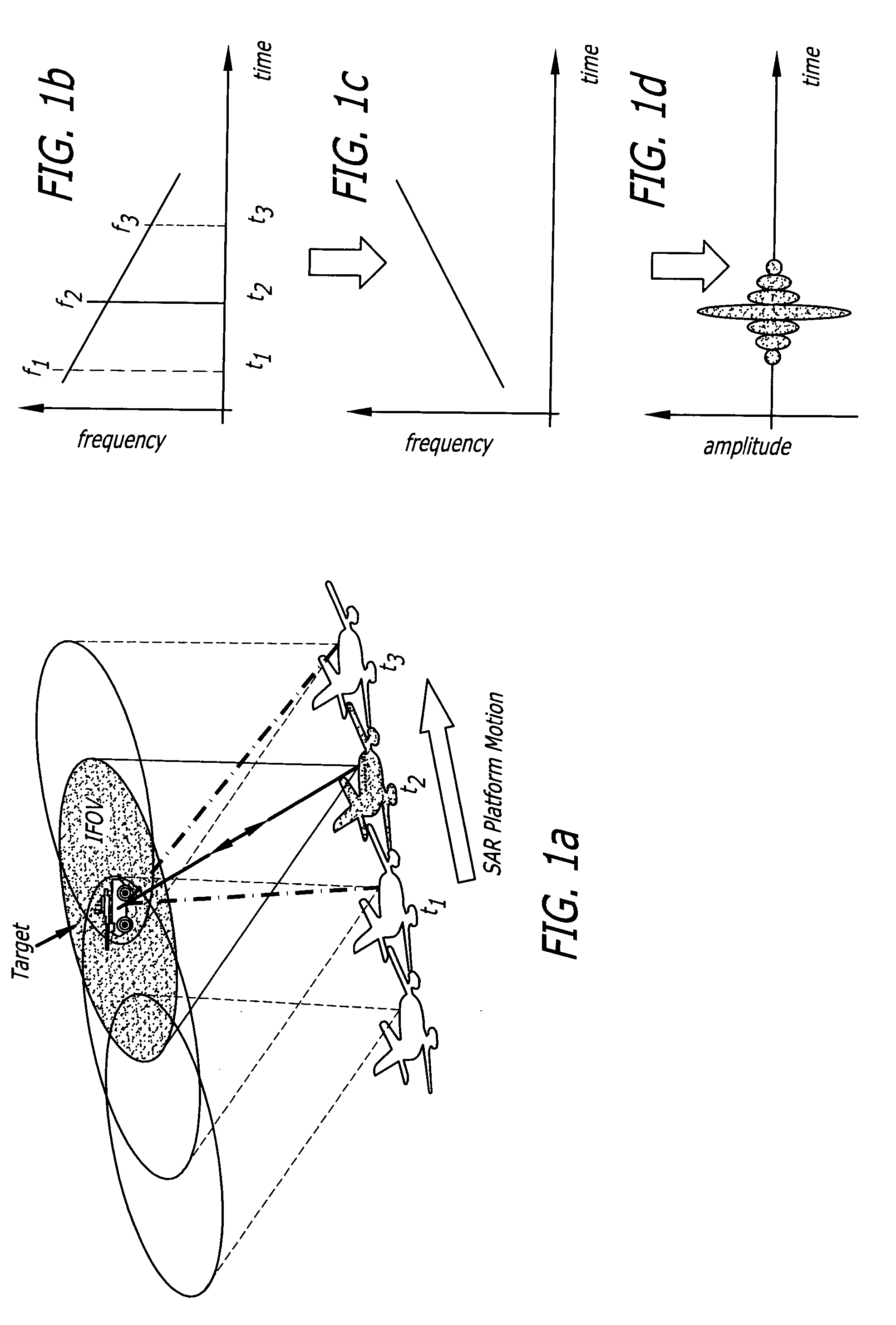
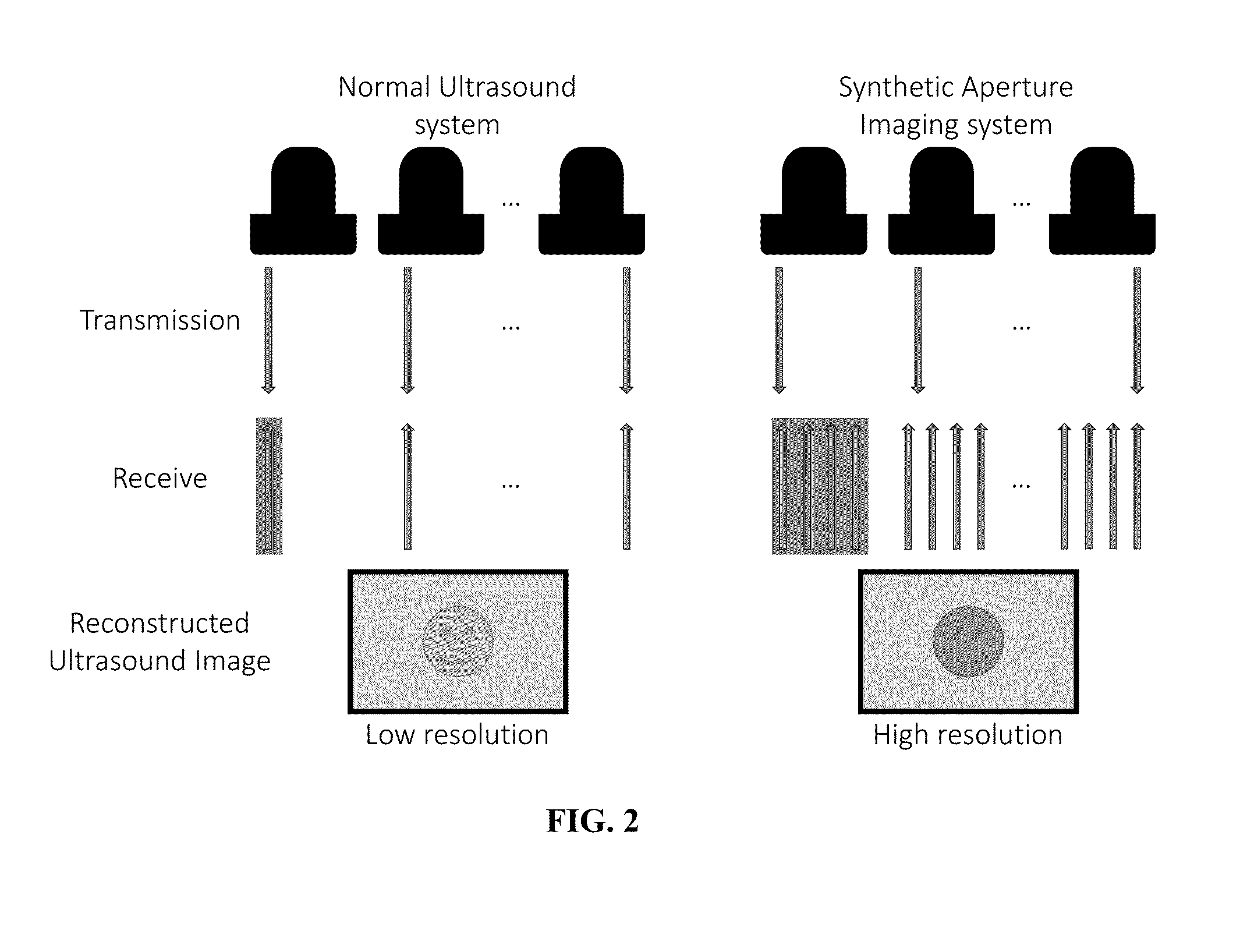
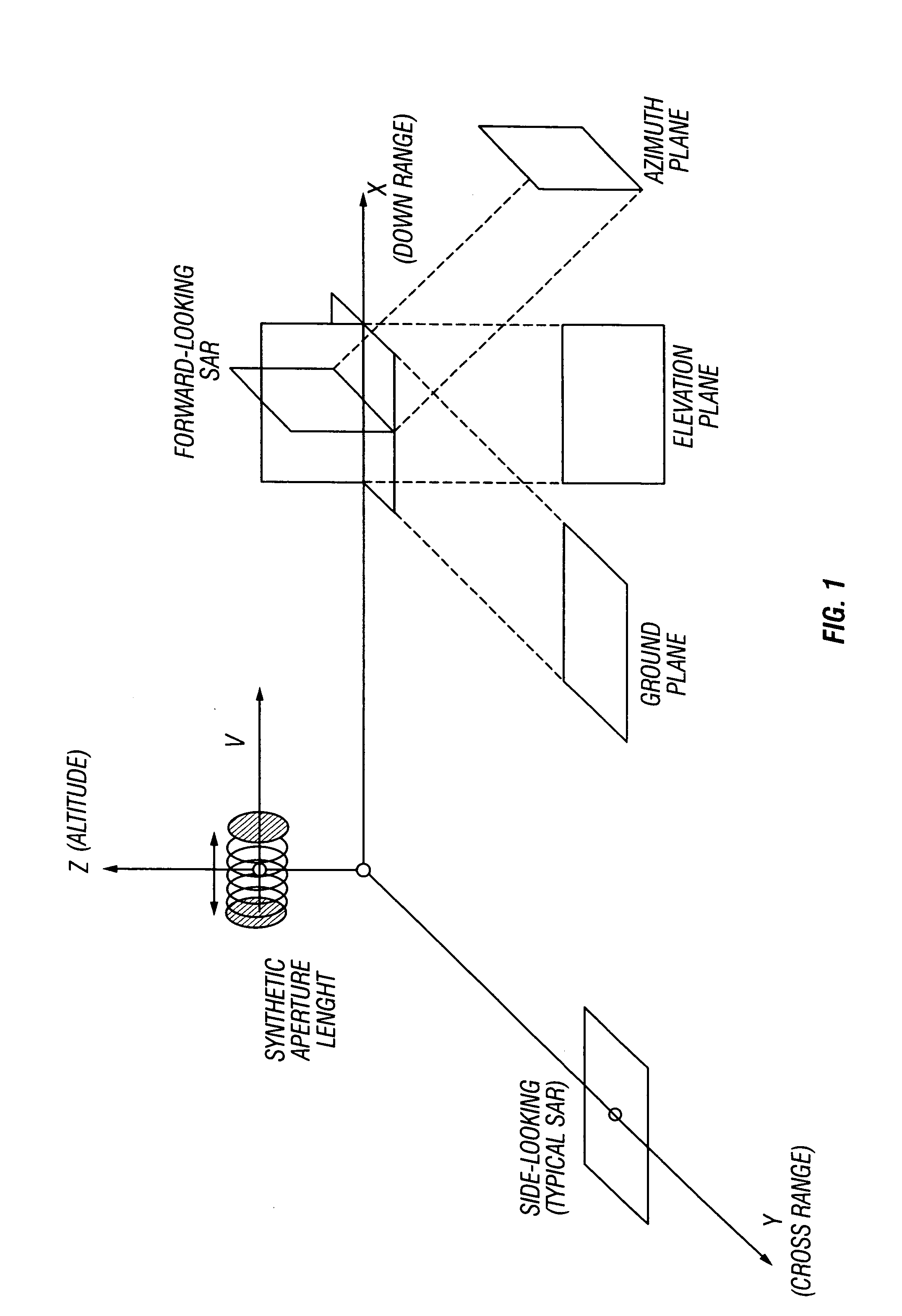
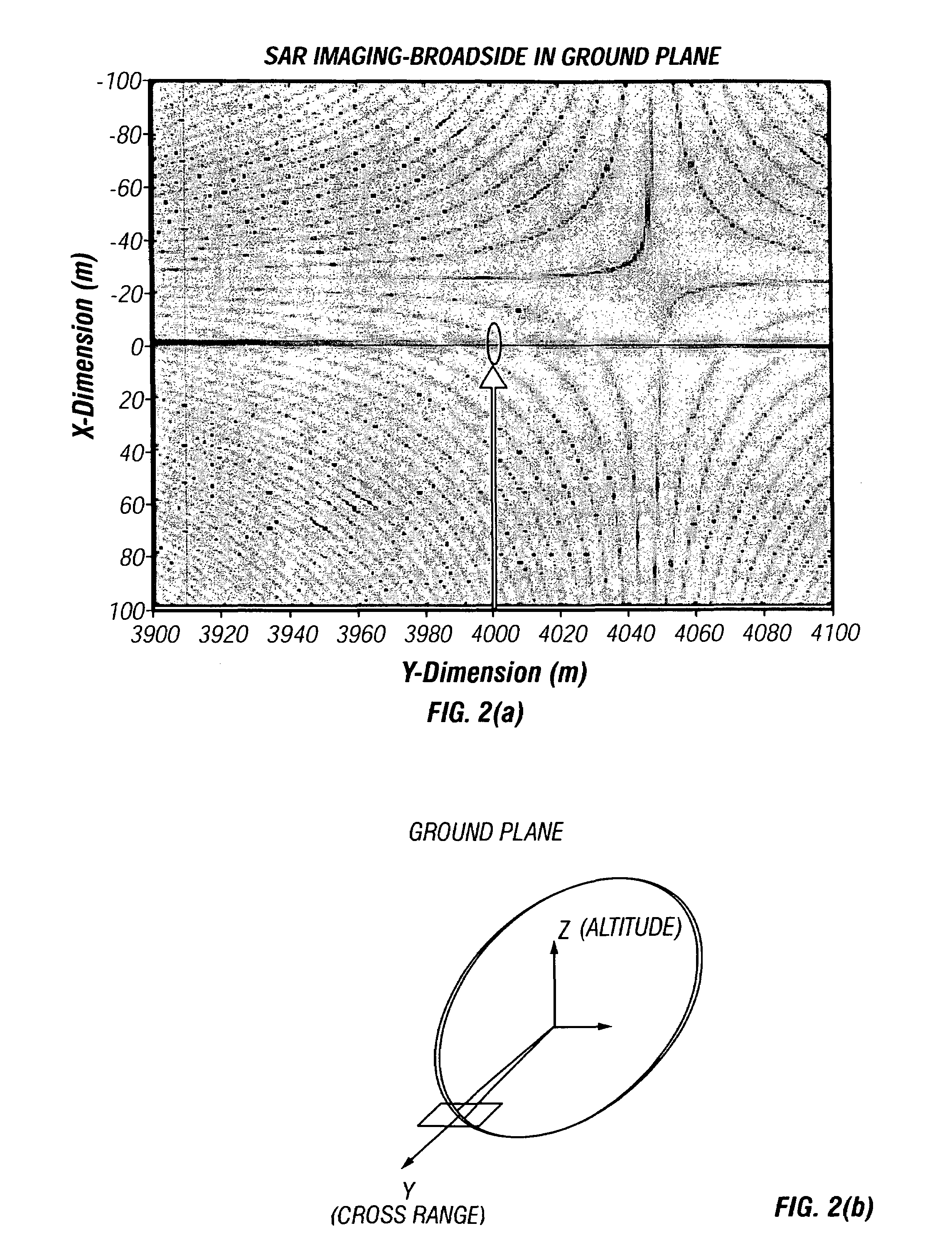
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target in the time taken for the radar pulses to return to the antenna creates the large synthetic antenna aperture (the size of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. Additionally, SAR has the property of having larger apertures for more distant objects, allowing consistent spatial resolution over a range of viewing distances.
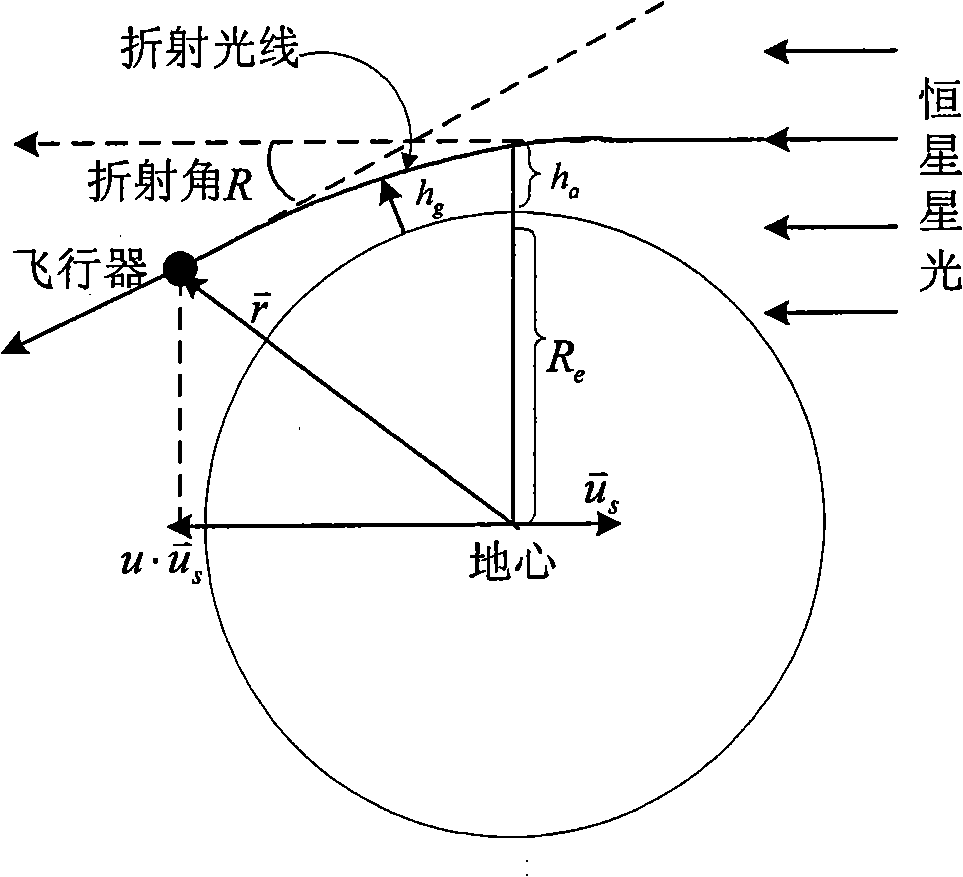
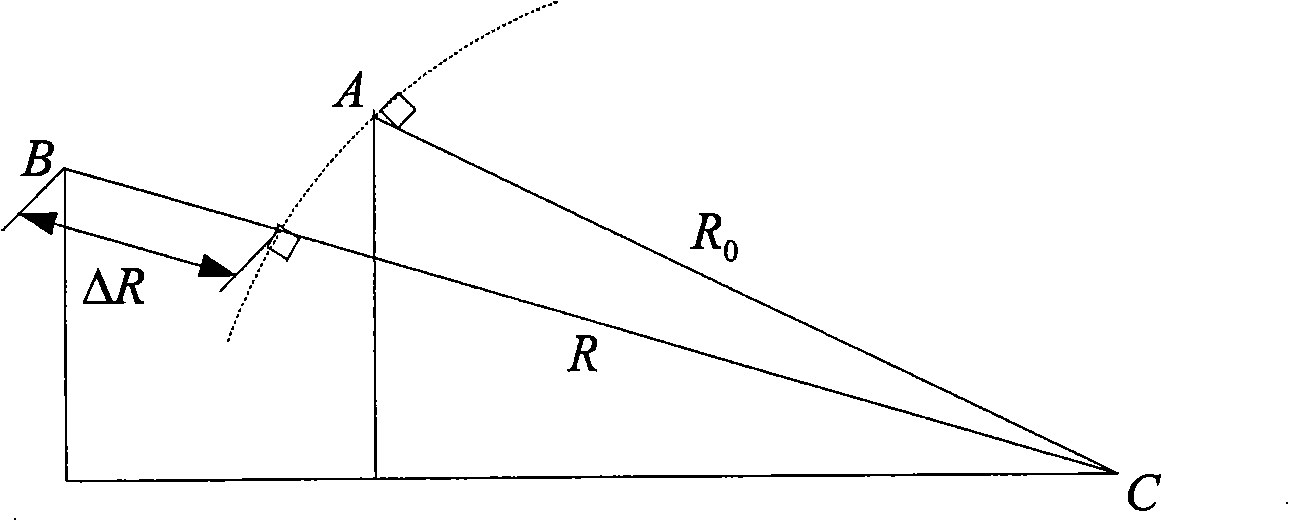
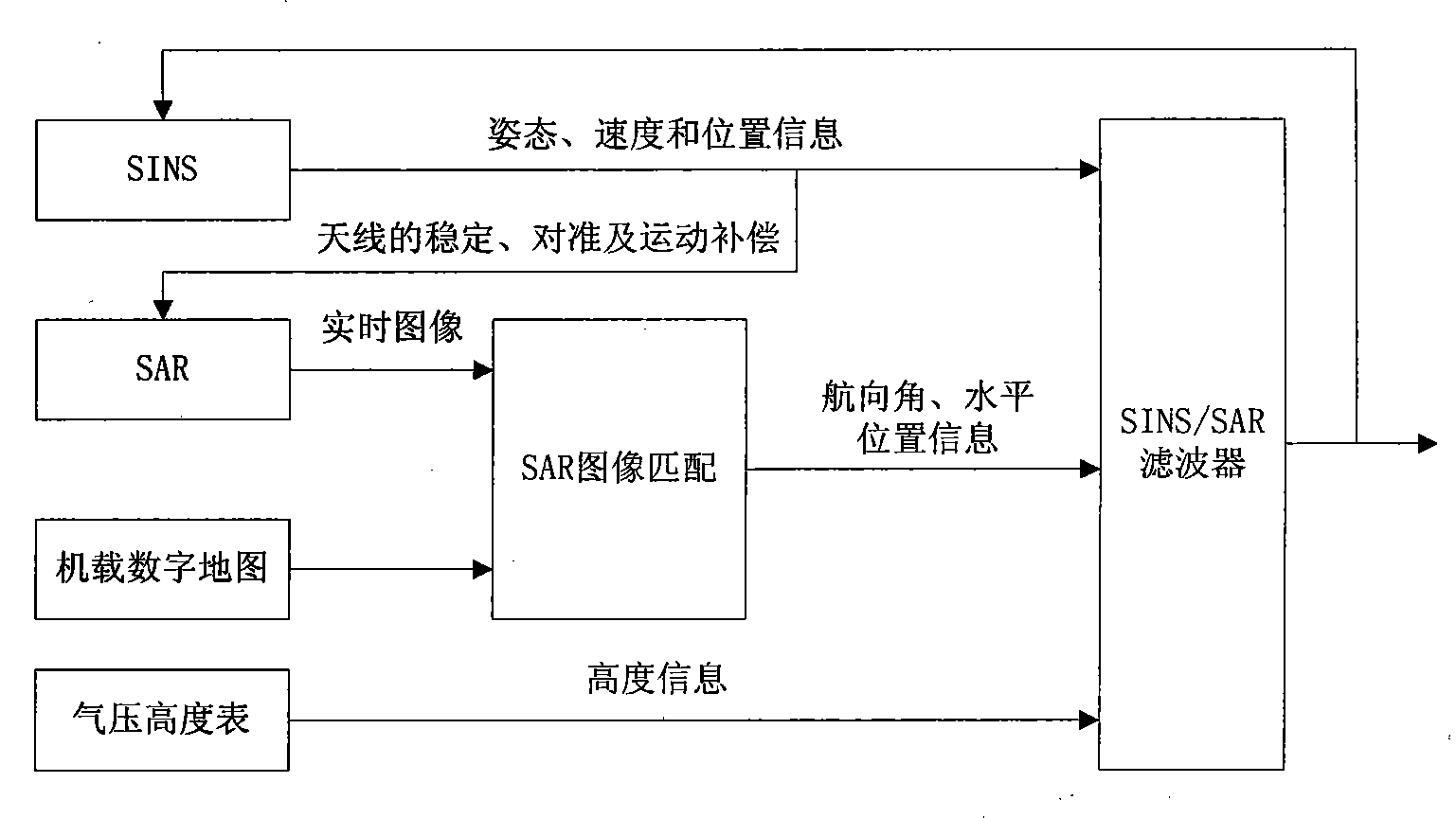
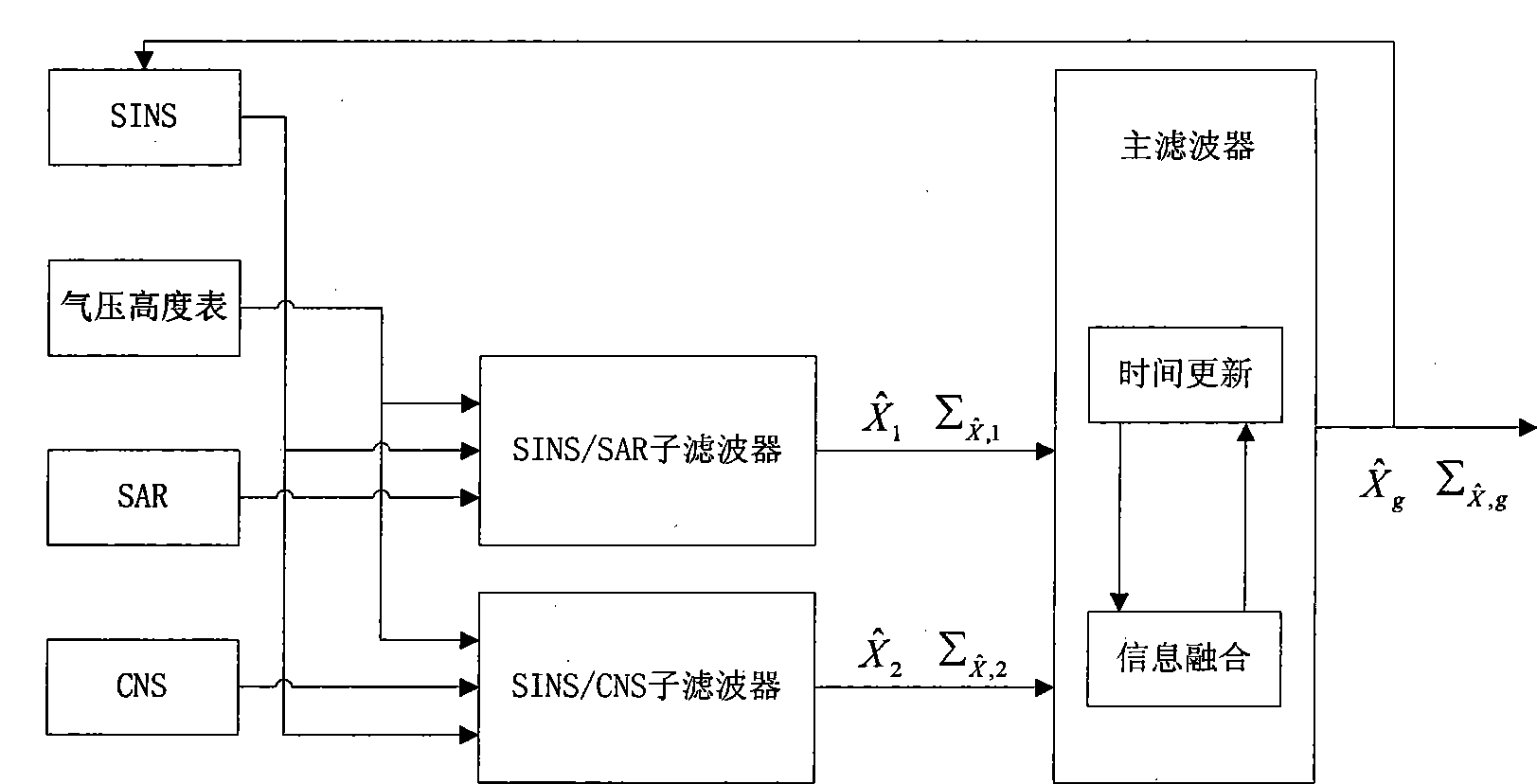
Remote high-precision independent combined navigation locating method
InactiveCN101270993AImprove drop point (hit) accuracyHigh resolutionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSynthetic aperture radarNavigation system
The invention relates to a remote high precision autonomous integrated navigation and positioning method, which is characterized in that a Strapdown Inertial Navigation System (SINS) is used as a main navigation system during the whole flight course of the aircraft, assisted by 3D high precision position and attitude angle information provided by celestial navigation system (CNS) based on the least square differential correction in boost phase (or middle segment). In reentry phase (terminal), using the characteristics of synthetic aperture radar (SAR), such as strong penetration capability, high resolving precision and all-weather, the SINS can be corrected through accurate location information and course information provided by SAR scene matching after motion compensation when the aircraft reentry into atmospheres, so the impact point (hit) accuracy of the aircraft can be increased and the invention has remarkable effects of eliminating or decreasing non-guidance error. The invention has advantages of autonomy and high precision, which can be used for improving remote ballistic missile, remote cruise missile, navigation and positioning accuracy of remote aircraft, such as long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle, etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Systems, apparatus, and methods for data acquisition and imaging
InactiveUS20140368378A1Data augmentationIndoor communication adaptationIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsSynthetic aperture radarData acquisition
A scanning system uses synthetic aperture radar and photography. The system is capable of conjoint use of image data developed by these and other scanning apparatus to form a model of a zone. In some versions, the model includes subsurface image information. Methods for use to scan and for implementation of images and models developed by the scan are also disclosed.
Owner:SADAR 3D
Digital intermediate frequency receiver module for use in airborne SAR applications
ActiveUS6864827B1Increase flexibilityIncrease spacingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
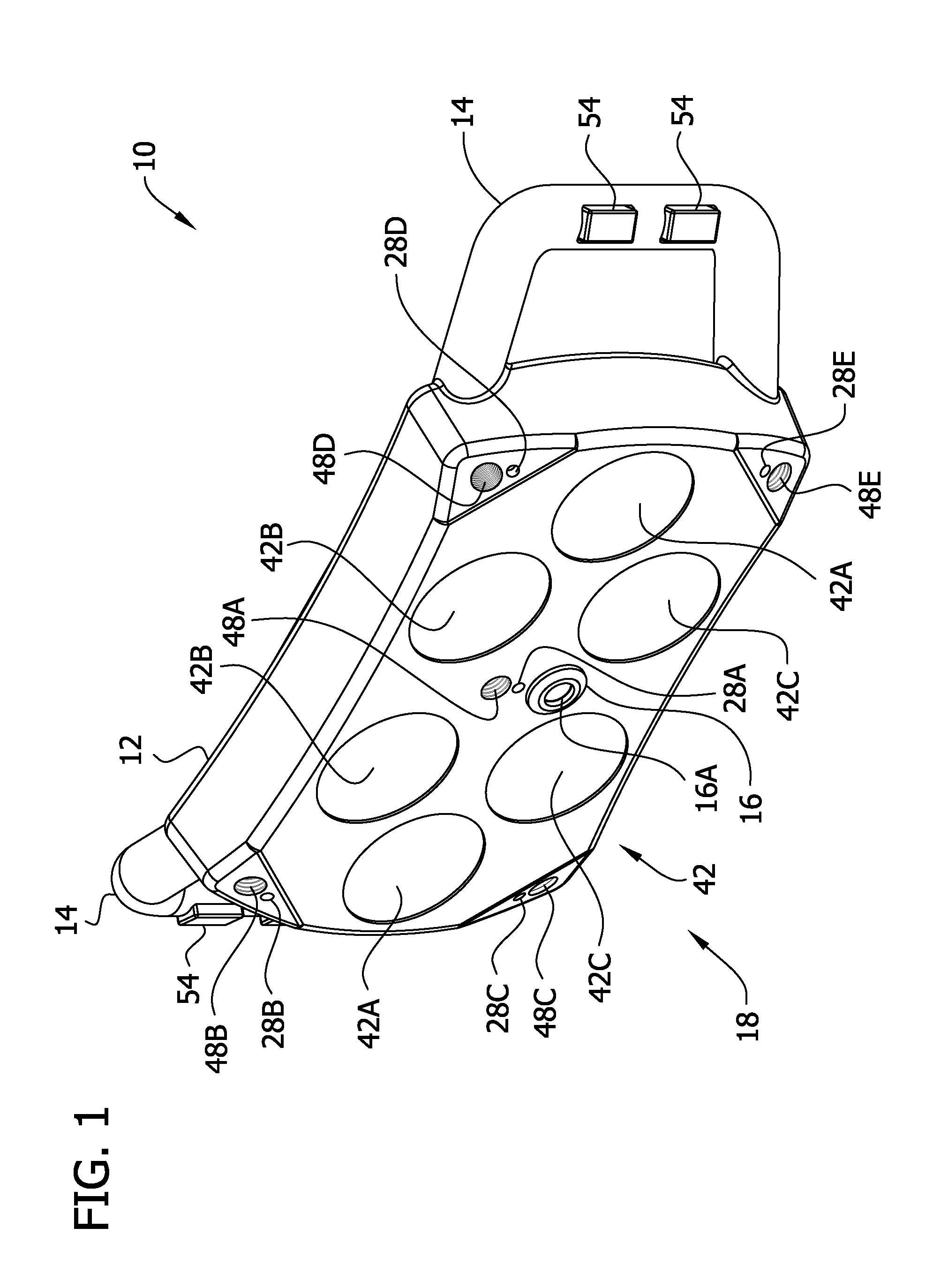
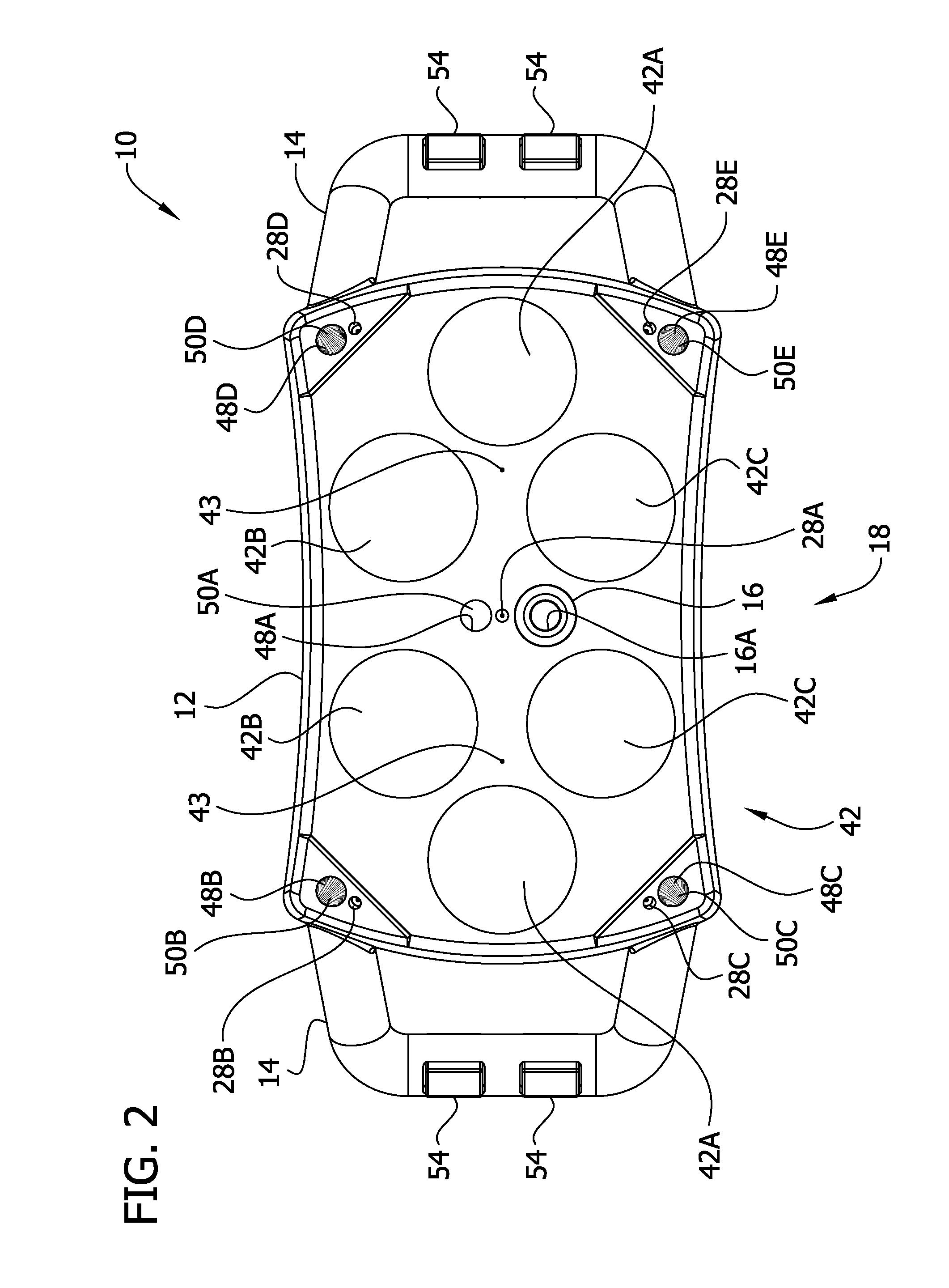
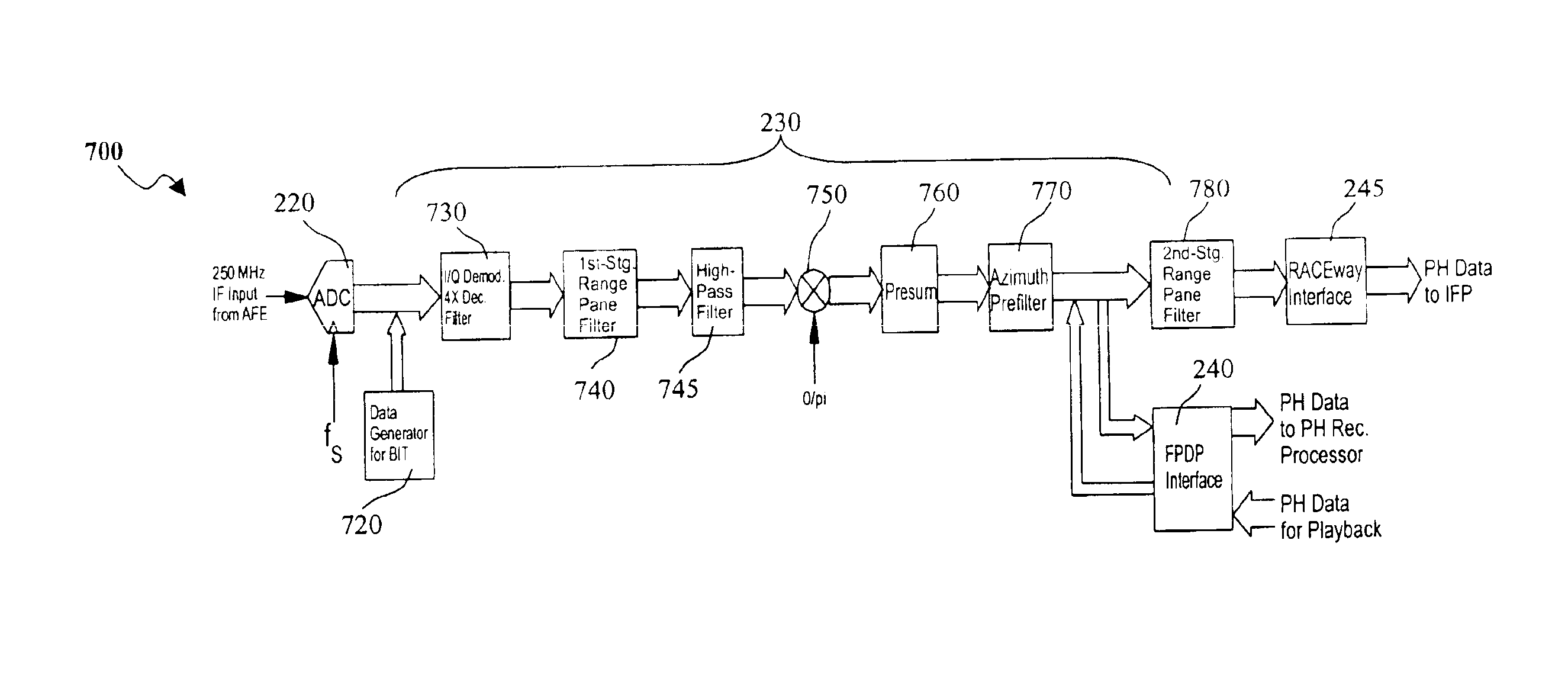
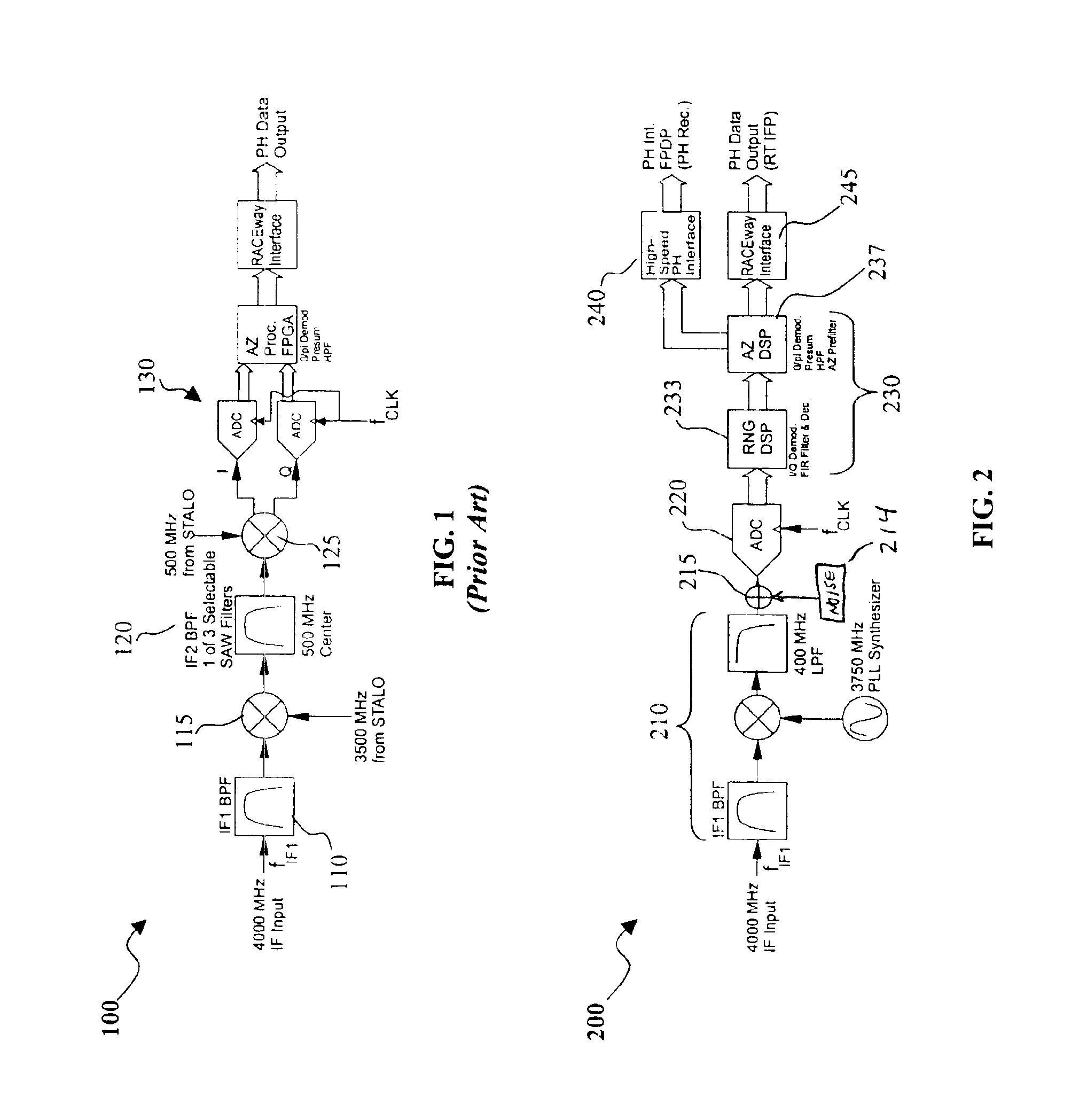
A digital IF receiver (DRX) module directly compatible with advanced radar systems such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems. The DRX can combine a 1 G-Sample / sec 8-bit ADC with high-speed digital signal processor, such as high gate-count FPGA technology or ASICs to realize a wideband IF receiver. DSP operations implemented in the DRX can include quadrature demodulation and multi-rate, variable-bandwidth IF filtering. Pulse-to-pulse (Doppler domain) filtering can also be implemented in the form of a presummer (accumulator) and an azimuth prefilter. An out of band noise source can be employed to provide a dither signal to the ADC, and later be removed by digital signal processing. Both the range and Doppler domain filtering operations can be implemented using a unique pane architecture which allows on-the-fly selection of the filter decimation factor, and hence, the filter bandwidth. The DRX module can include a standard VME-64 interface for control, status, and programming. An interface can provide phase history data to the real-time image formation processors. A third front-panel data port (FPDP) interface can send wide bandwidth, raw phase histories to a real-time phase history recorder for ground processing.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
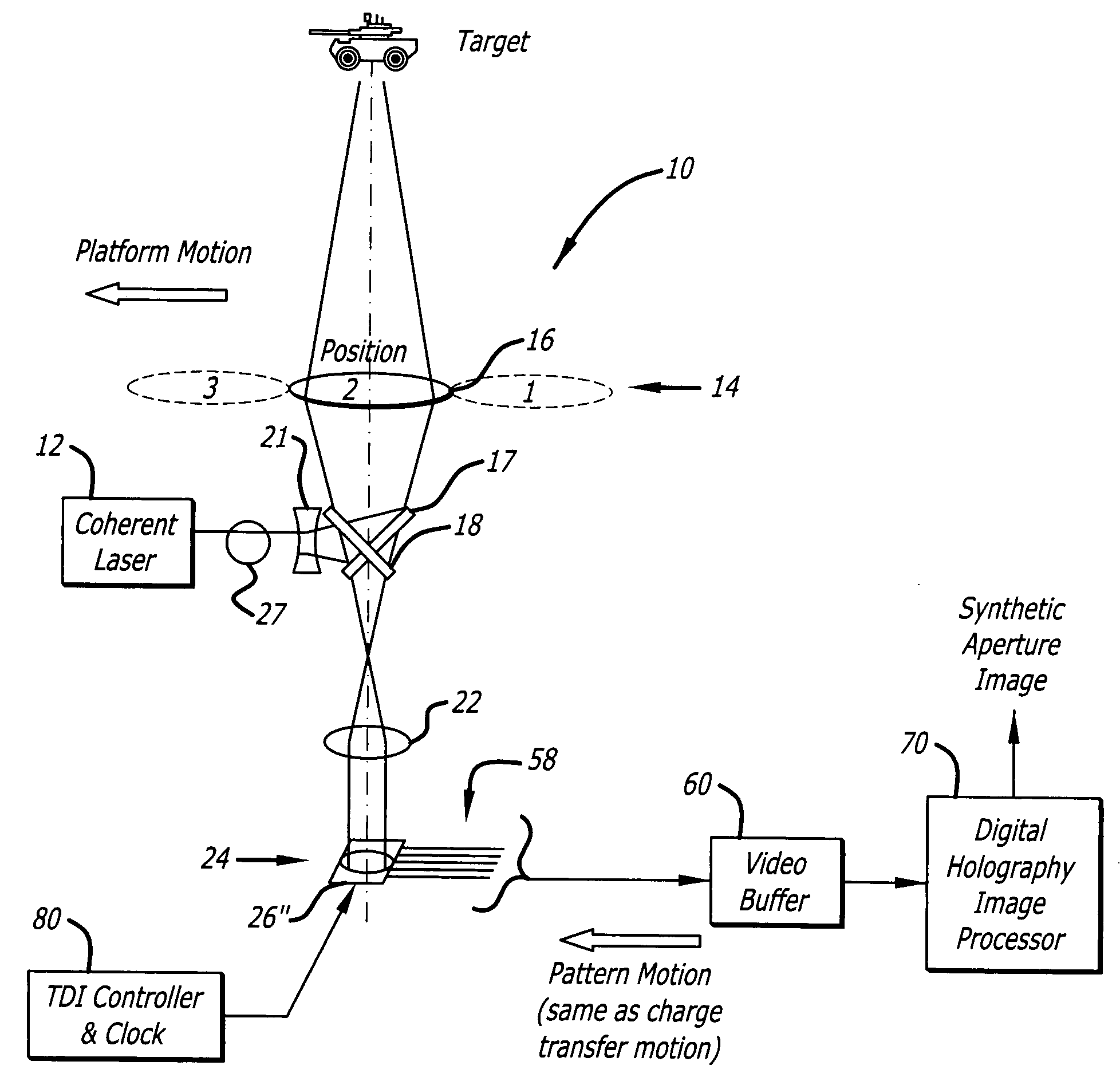
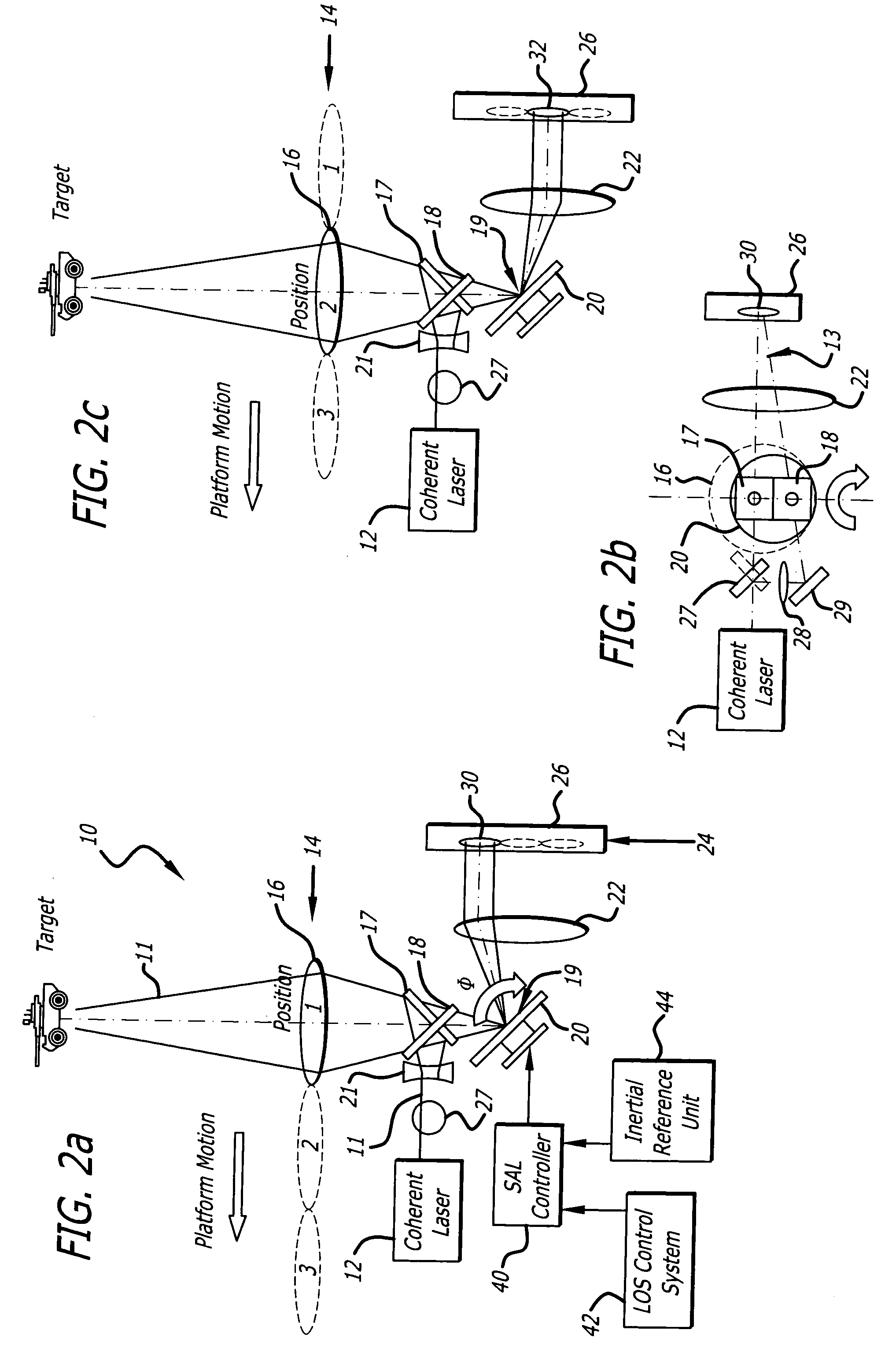
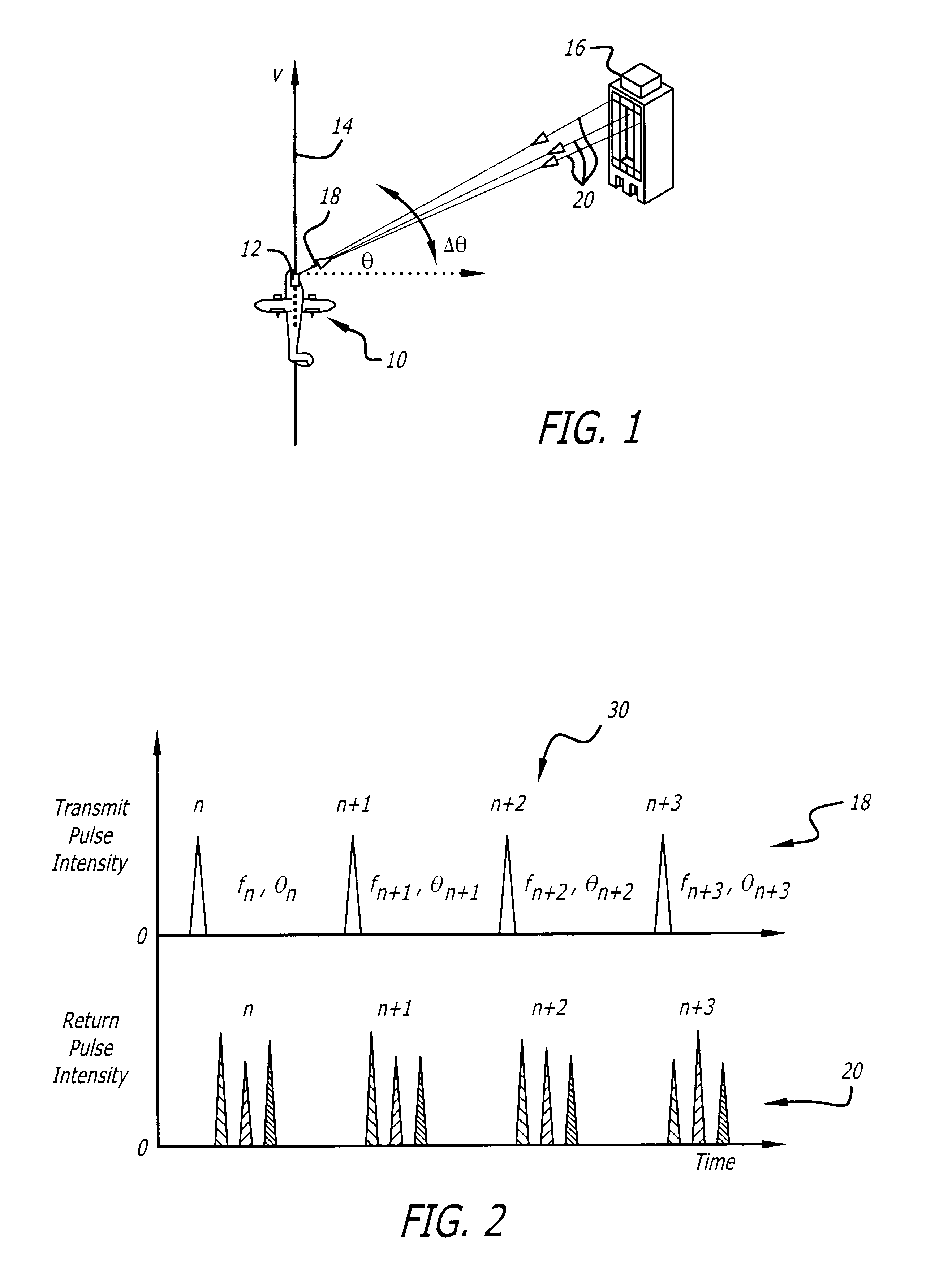
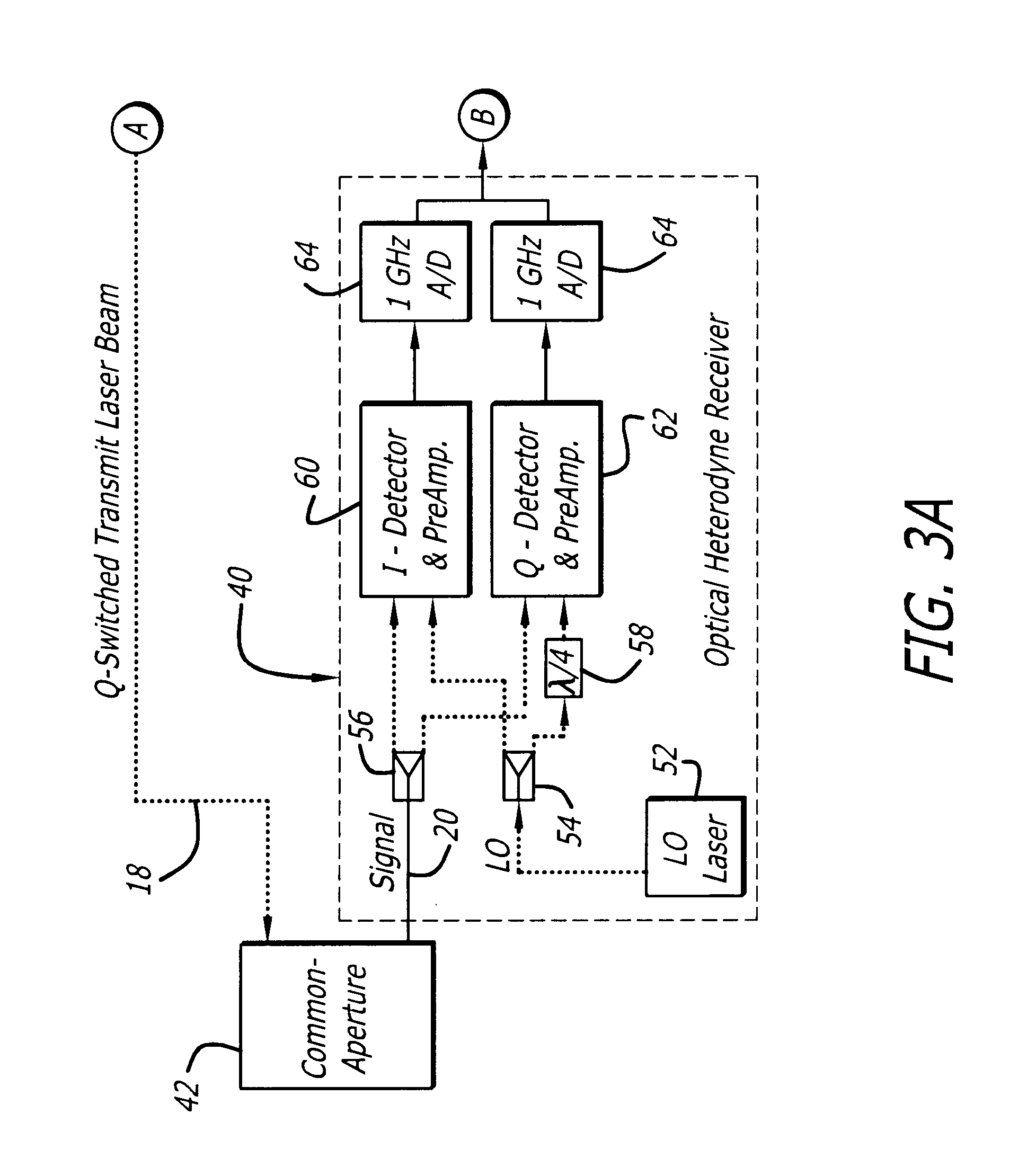
Synthetic aperture ladar system and method using real-time holography
ActiveUS20050057654A1Motion compensationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersSynthetic aperture radarReal time holography
This invention uses a real-time holographic medium to record the amplitude and phase information collected from a moving platform at the aperture plane of a side-looking optical sensor over the collection time. A back-scan mirror is used to compensate platform motion during the synthetic aperture integration time. Phase errors caused by a nonlinear platform motion are compensated by controlling the phase offset between the illumination beam and the reference beam used to write the hologram based on inertial measurements of the flight path and the sensor line-of-sight pointing angles. In the illustrative embodiment, a synthetic aperture ladar (SAL) imaging system is mounted on a mobile platform. The system is adapted to receive a beam of electromagnetic energy; record the intensity and phase pattern carried by the beam; and store the pattern to compensate for motion of the platform relative to an external reference. In the illustrative embodiment, the image is stored as a holographic image. The system includes a back-scan mirror, which compensates the stored holographic pattern for motion of the platform. The medium and back-scan mirror may be replaced with a digital camera and one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays may be used. In a specific embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used with a time delay and integration (TDI) scheme, which compensates for motion of the platform in the storage of the optical signals. In an alternative embodiment, a back-scanning mirror is used to compensate for motion of the platform. Consequently, the interference pattern between a relayed image of the aperture plane and a reference beam is continuously stored. In this embodiment, the instantaneous location of the received beam on the recording medium is controlled to compensate for motion of the platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
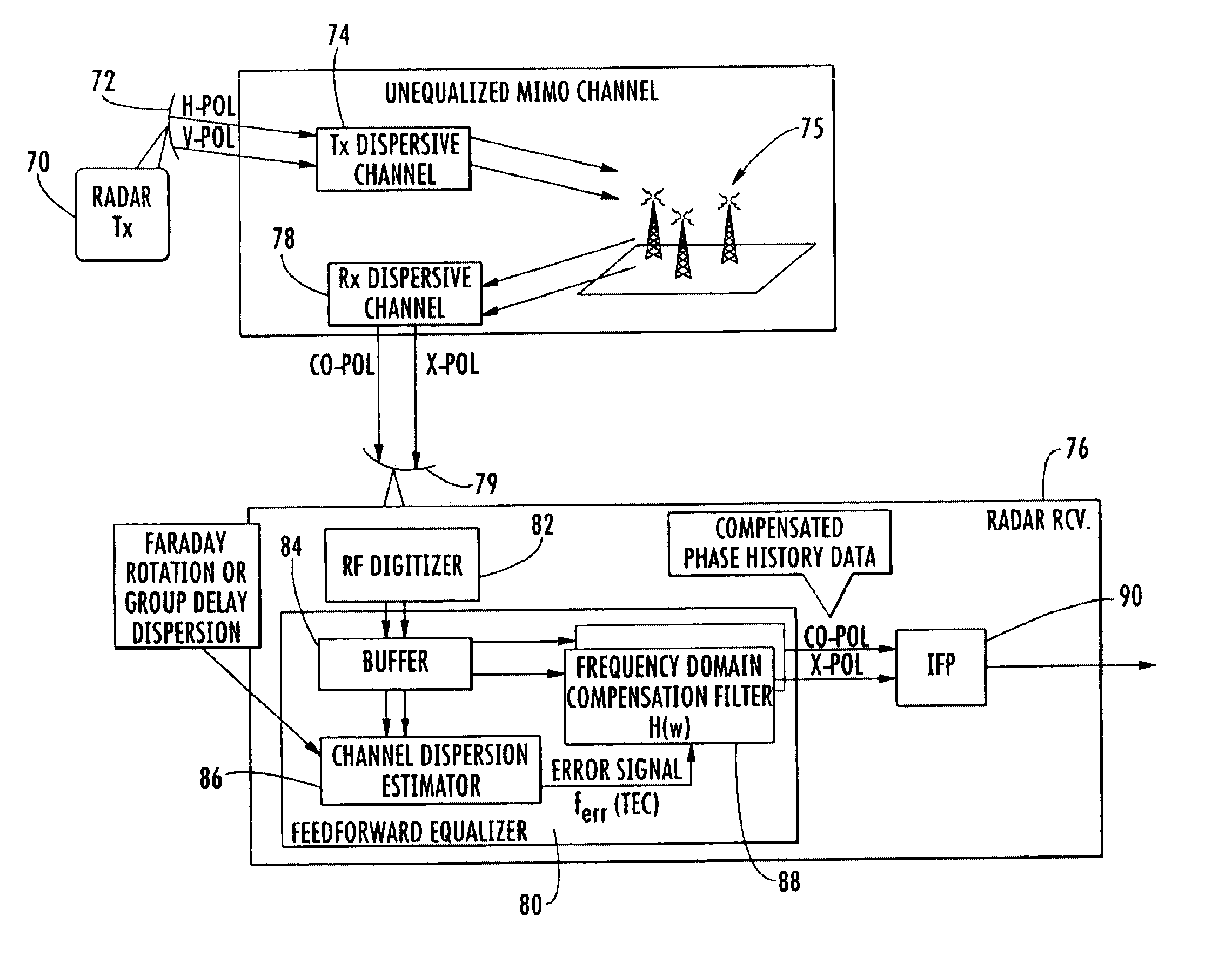
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) compensating for ionospheric distortion based upon measurement of the group delay, and associated methods
InactiveUS6919839B1Reducing ionospheric distortionReduce distortion problemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionMulti inputSynthetic aperture radar
A synthetic aperture radar (SAR) compensates for ionospheric distortions based upon measurement of the group delay, particularly when operating in the VHF / UHF band. The SAR is based upon a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) technique for estimating the effective ionospheric conditions, which is referred to as the group delay approach. The group delay approach is divided into a 1-dimensional (range) approach and a 2-dimensional (range and cross-range) approach. The group delay measures the effective or observed TEC, which is used to reduce the ionospheric distortion.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
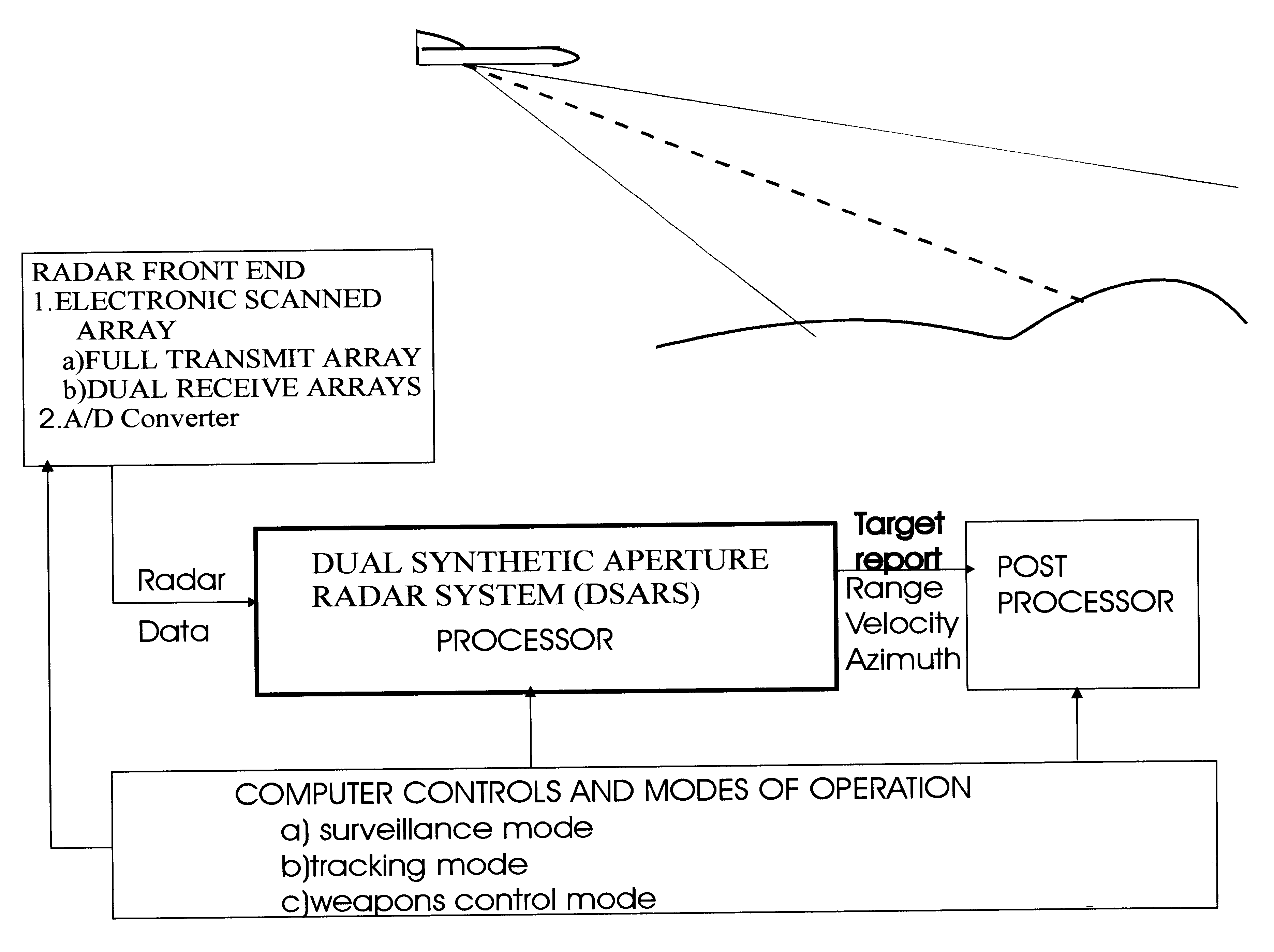
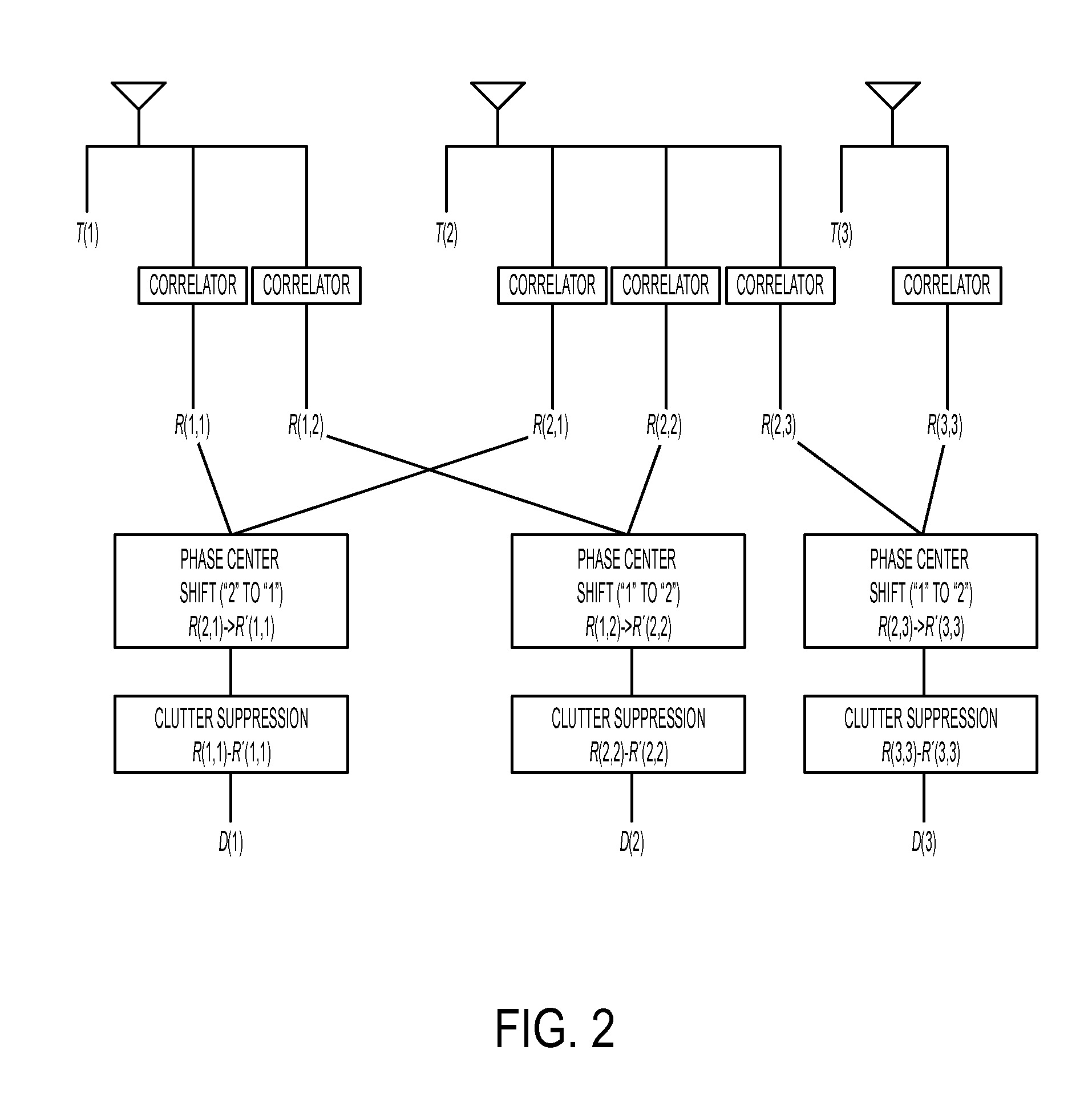
Dual synthetic aperture radar system
InactiveUS6633253B2Accurate angular positionAccurately radial velocityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumControl system
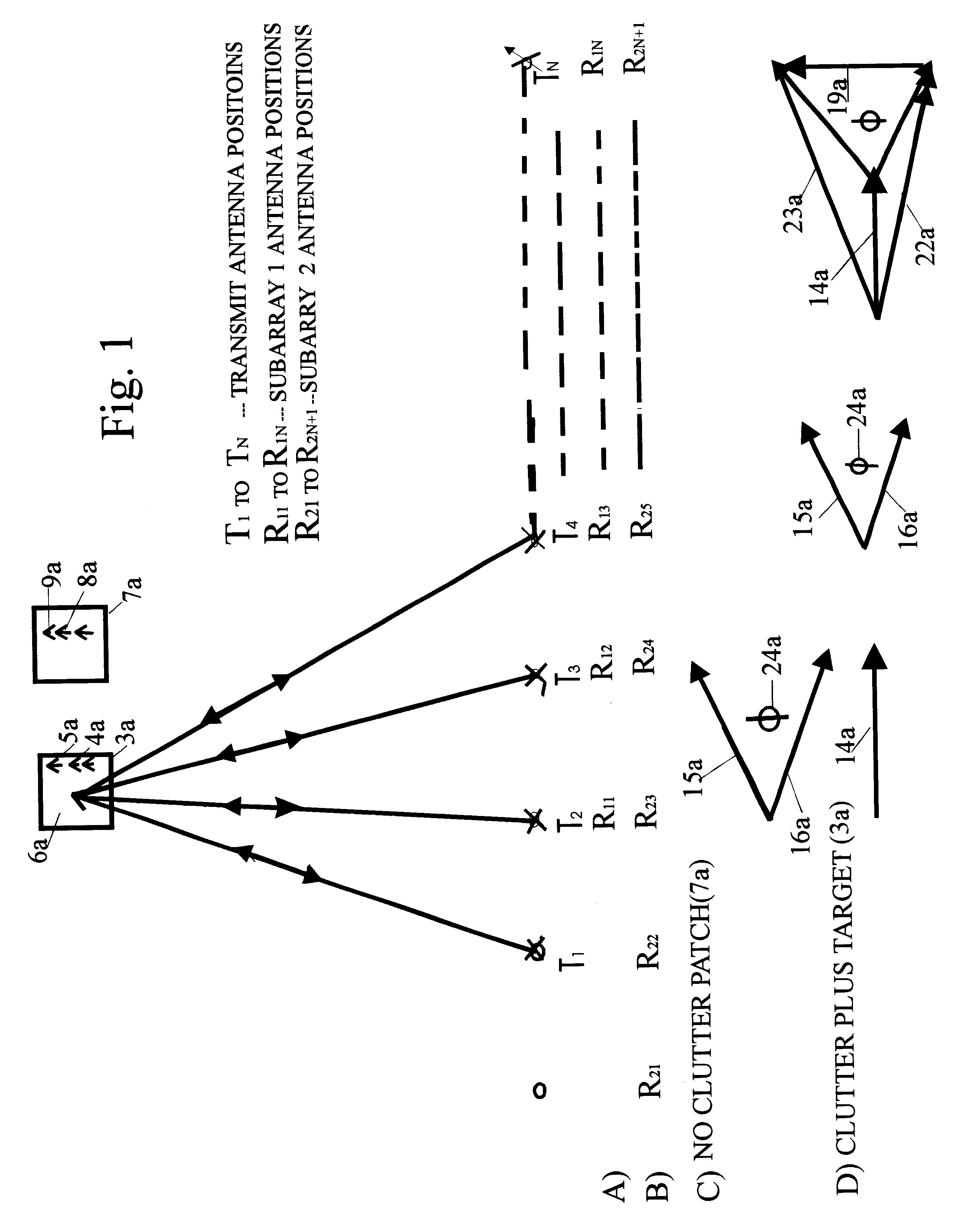
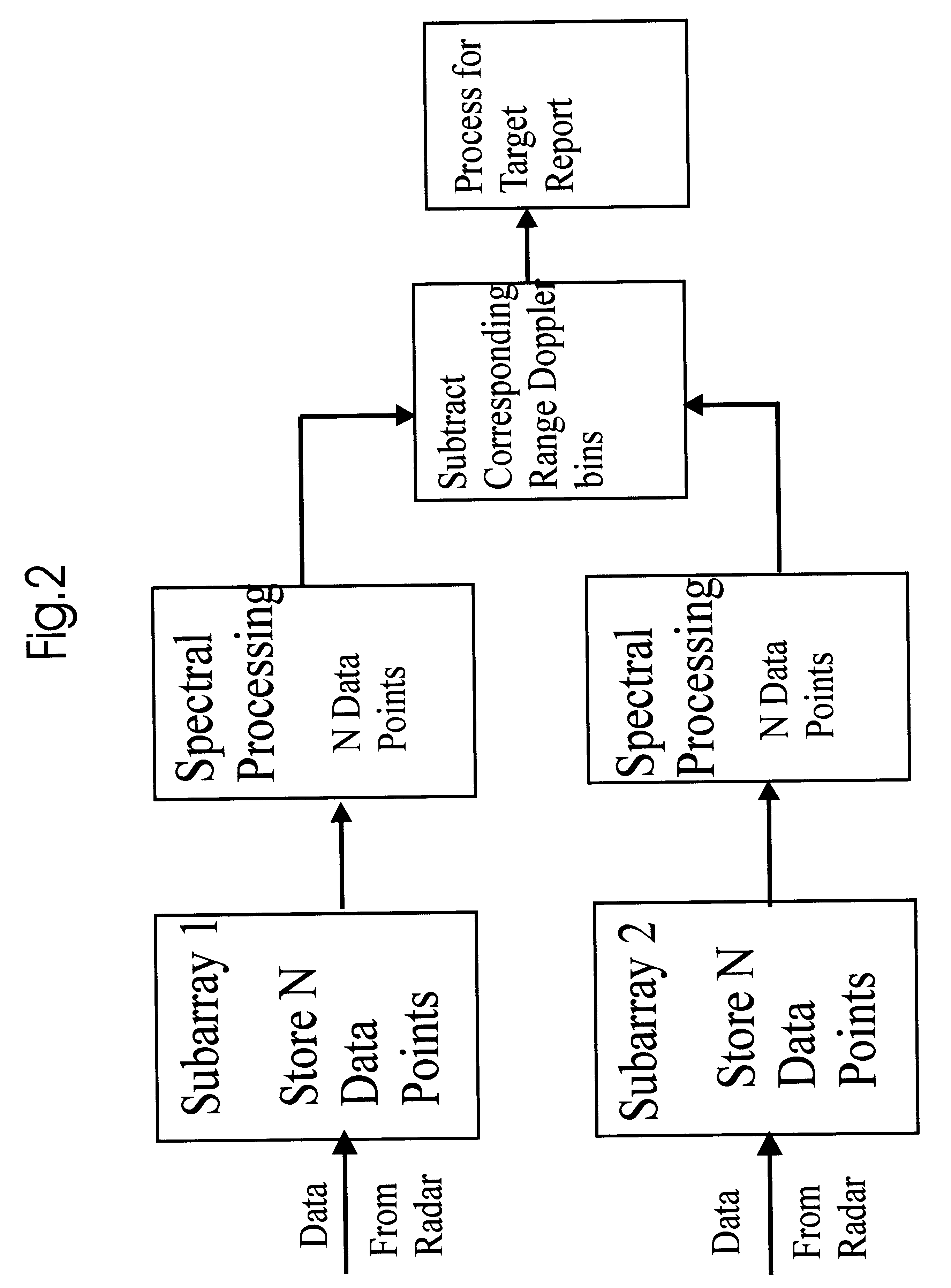
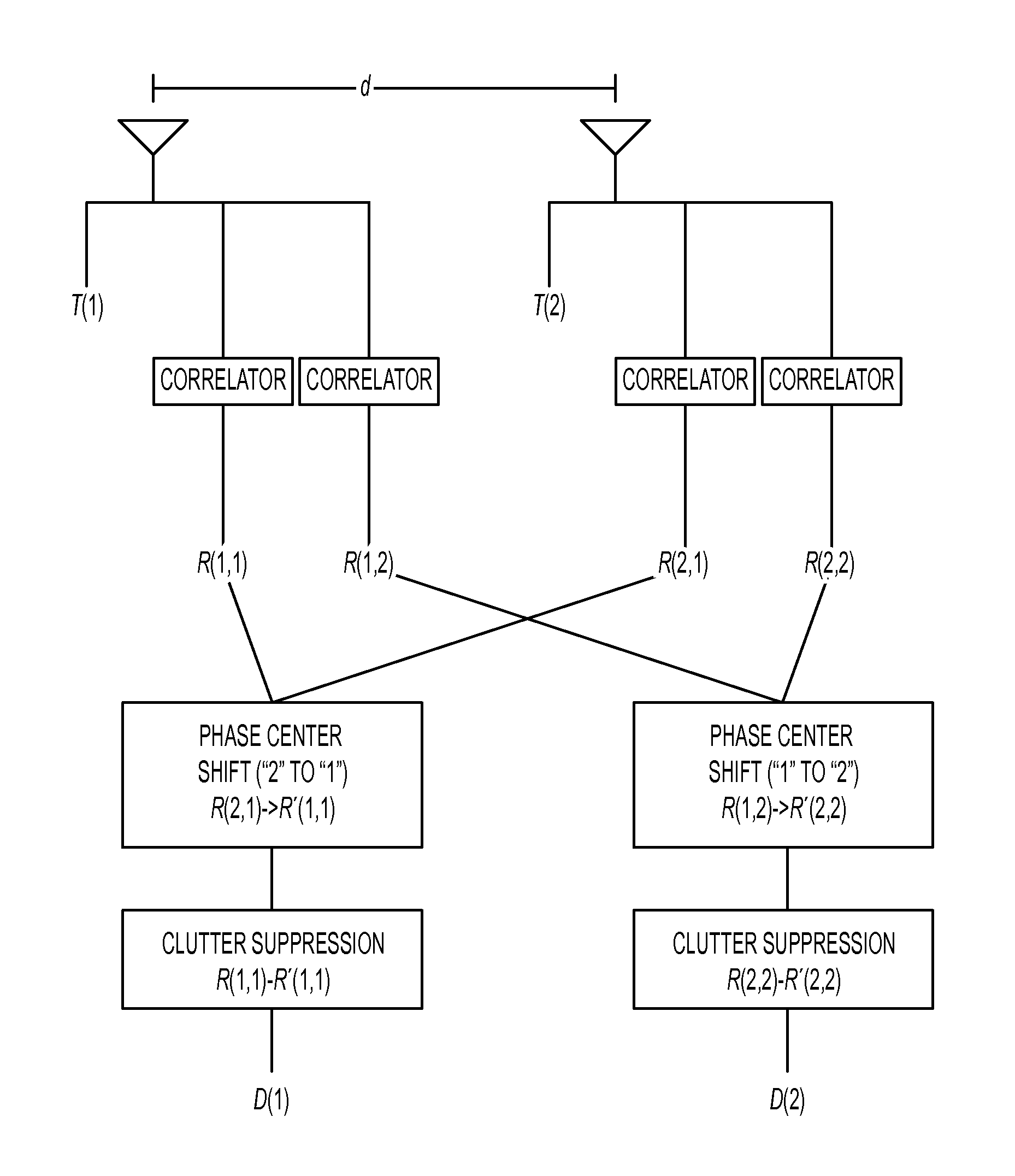
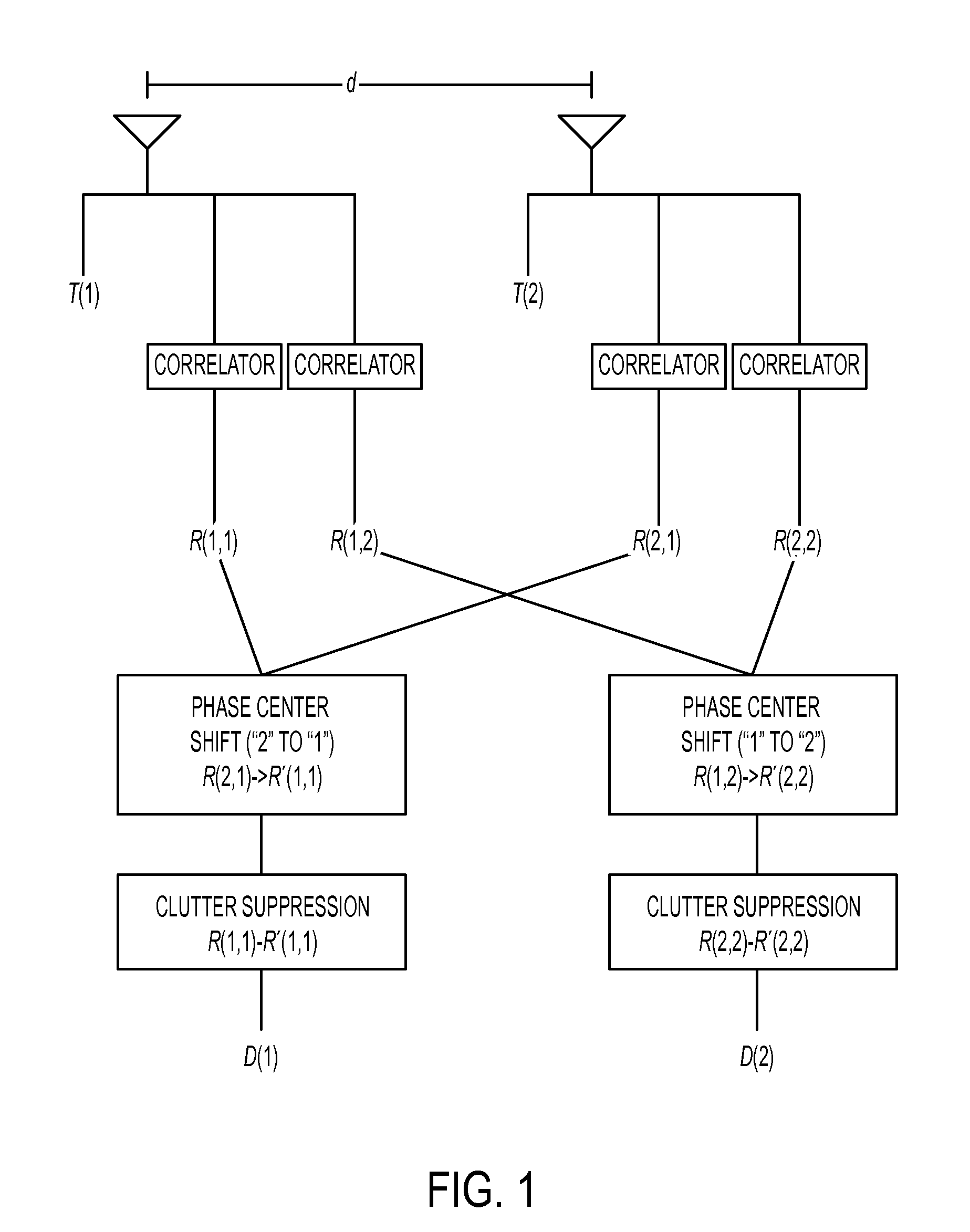
The dual synthetic aperture array system processes returns from the receiving arrays. The two identical receiving arrays employing displaced phase center antenna techniques subtract the corresponding spectrally processed data to cancel clutter. It is further processed that a moving target is detected and its velocity, angular position and range is measured, in or out of the presence of clutter. There are many techniques presented in the disclosure. These techniques are basically independent but are related based on common set of fundamental set of mathematical equations, understanding of radar principles and the implementations involved. These many techniques may be employed singly and / or in combination depending on the application and accuracy required. They are supported by a system that includes, optimization of the number of apertures, pulse repetition frequencies, DPCA techniques to cancel clutter, adaptive techniques to cancel clutter, motion compensation, weighting function for clutter and target, and controlling the system in most optimum fashion to attain the objective of the disclosure.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CATALDO THOMAS J
Methods And Systems For Multiple Input Multiple Output Synthetic Aperture Radar Ground Moving Target Indicator
A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system. The radar system includes spatially offset transmitting antennas simultaneously transmitting at least two distinguishable waveform signals and receiving antennas receiving incoming waveform returns for each of the distinguishable waveform signals. The radar system also includes a displaced phase center antenna (DPCA) processing unit adapted to perform processing on the incoming waveform returns, and a synthetic aperture radar processing unit adapted to produce a plurality of spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. The radar system also generates a plurality of clutter-suppressed signals using the spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. For each of two MIMO transmissions from spatially displaced transmitters, clutter is cancelled simultaneously in at least two spatially displaced receive channels via DPCA processing. This results in at least two spatially displaced but simultaneous clutter cancelled complex SAR images, which are combined in a monopulse processor to enhance target detection and unambiguously determine target angle.
Owner:SRC INC
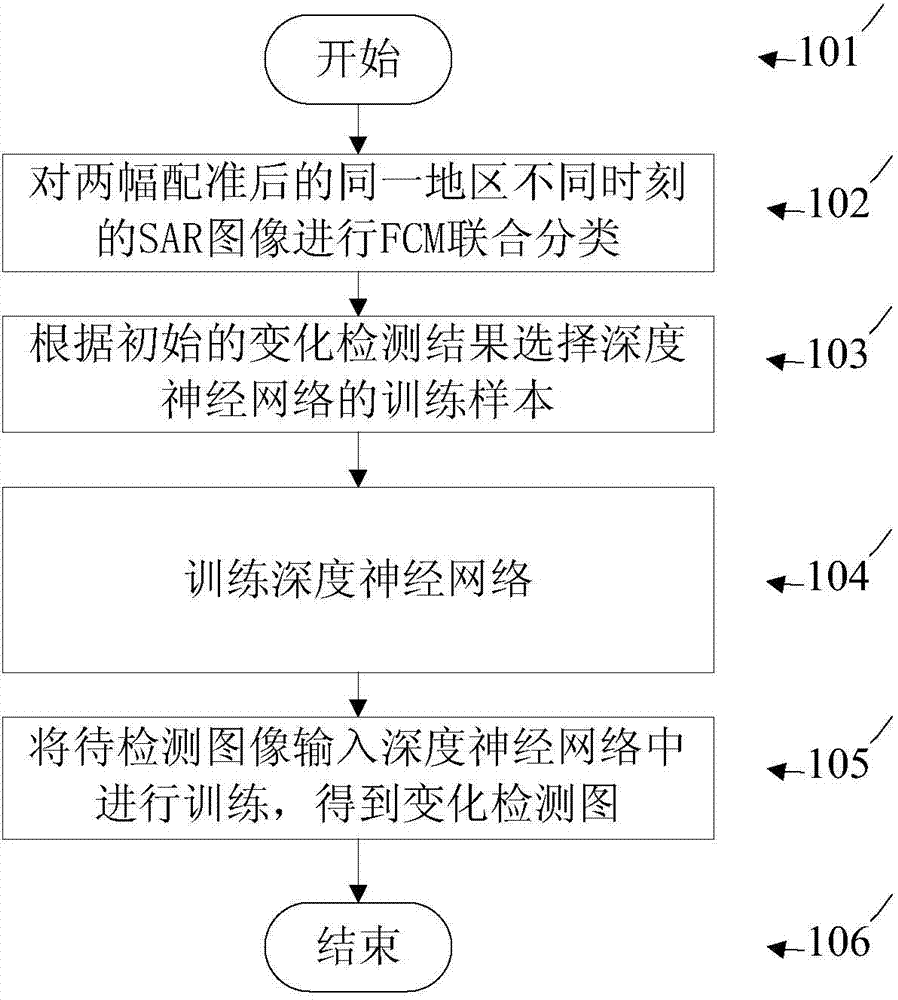
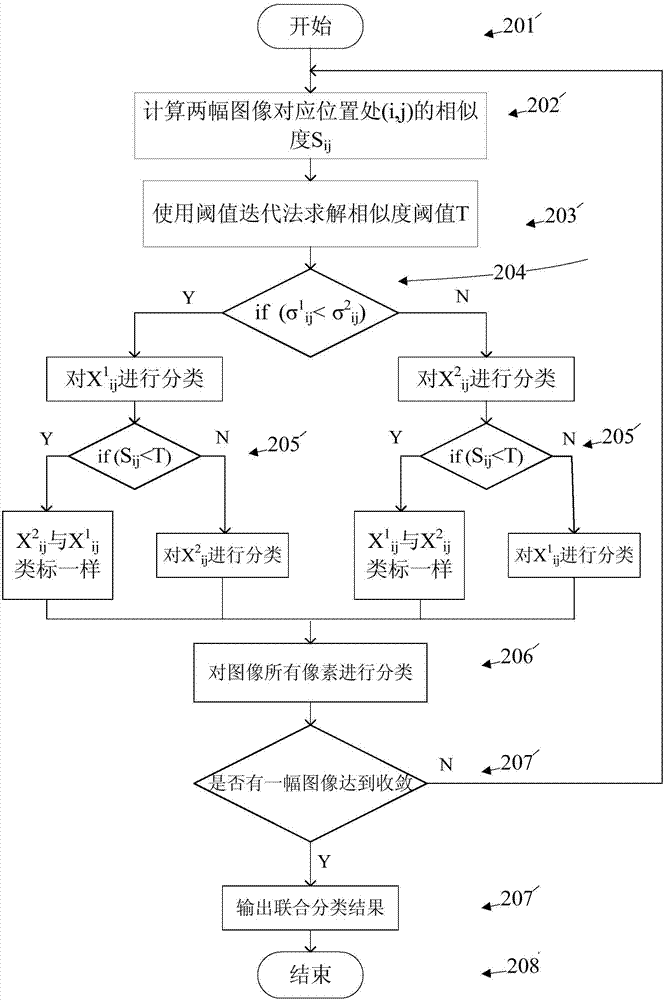
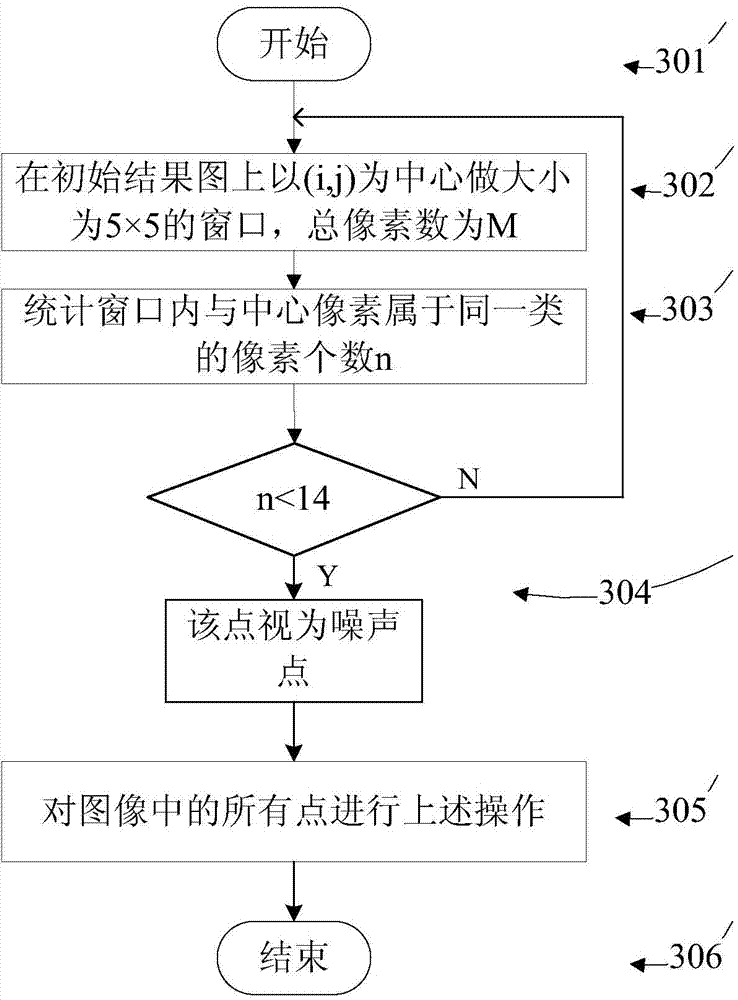
SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image change detection method based on non-supervision depth nerve network
InactiveCN103810699ASimple and clear thinkingTo achieve the purpose of change detectionImage analysisBiological neural network modelsPattern recognitionNerve network
The invention provides an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image change detection algorithm based on non-supervision depth network learning. The algorithm includes the steps: 101 starting an SAR image change detection method based on a non-supervision depth nerve network; 102 performing FCM (fuzzy c-mean) joint classification for two registered SAR images of different time phases in the same area to obtain rough change detection results; 103 selecting noiseless points with large possibility to serve as training samples of the depth network according to initial change detection results; 104 inputting sample points to be trained to the designed depth nerve network to be trained; 105 inputting two images to be detected to the trained depth nerve network to obtain a final change detection result map; 106 finishing the SAR image change detection method based on the non-supervision depth nerve network. Ohm= {ohm1 and ohm2}. Construction links of a difference map are avoided, sensitivity of noise is improved to a certain extent, and detection efficiency and detection accuracy are remarkably improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
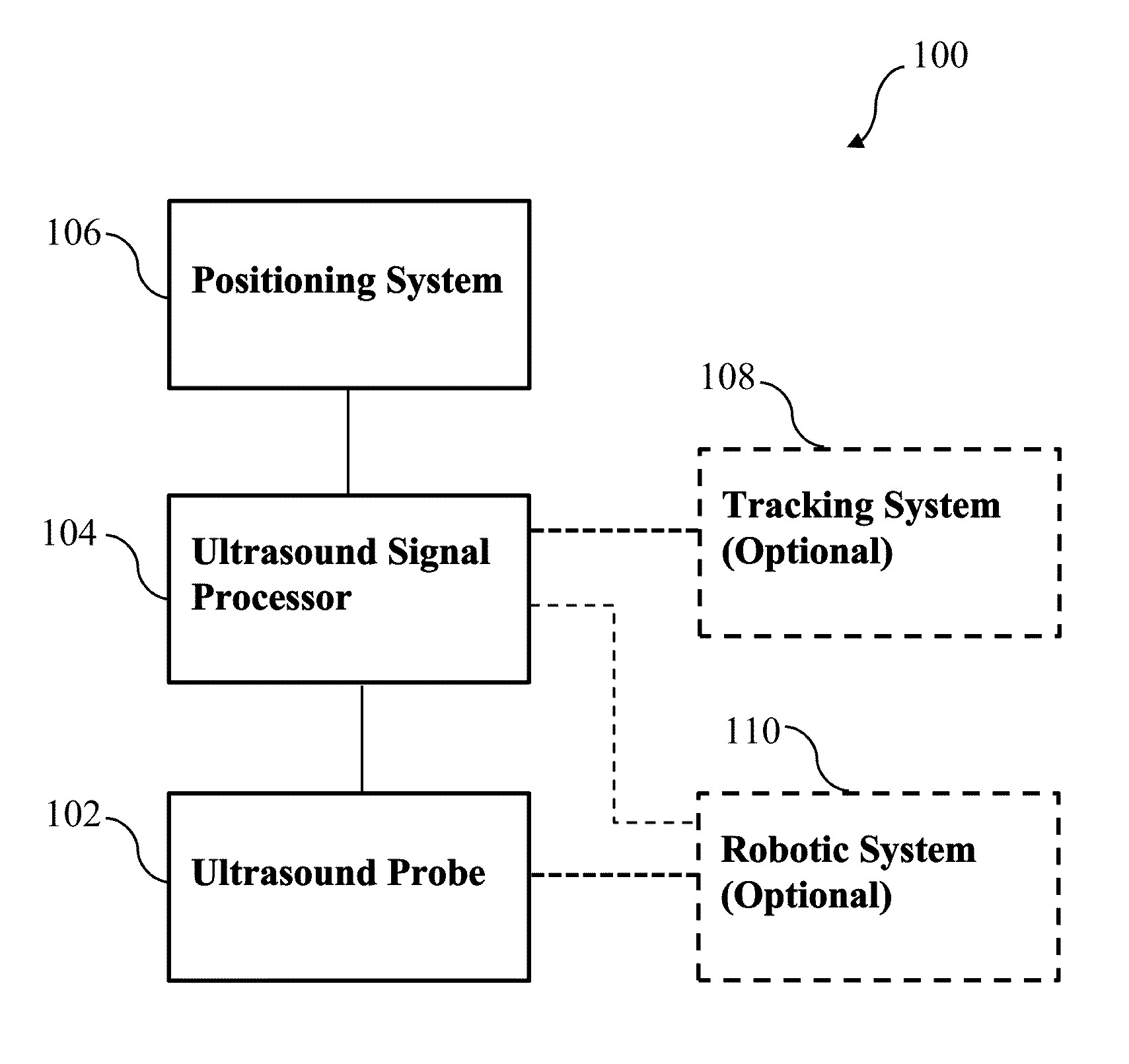
Synthetic aperture ultrasound system
ActiveUS20150359512A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationSynthetic aperture radar
A synthetic aperture ultrasound system includes an ultrasound probe, and an ultrasound signal processor configured to communicate with the ultrasound probe to receive phase and amplitude information from a plurality of ultrasonic echo signals from a corresponding plurality of ultrasound pulses. The synthetic aperture ultrasound system also includes a positioning system configured to communicate with the ultrasound signal processor to provide probe position information. The positioning system is configured to determine a first position and a second position of the ultrasound probe relative to a region of interest. The ultrasound signal processor is further configured to coherently sum, utilizing the probe position information, at least one of the plurality of ultrasonic echo signals from the first position with at least one of the plurality of ultrasonic echo signals from the second position to provide a synthetic aperture that is larger than a physical aperture of the ultrasound probe.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
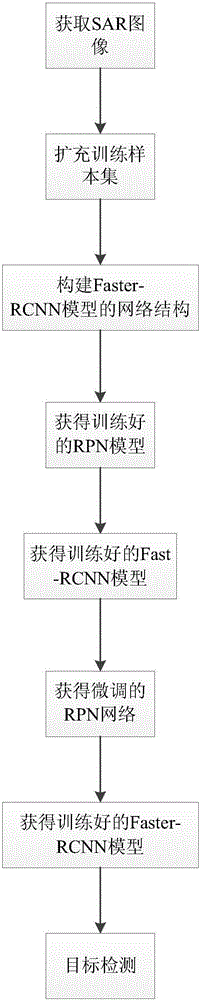
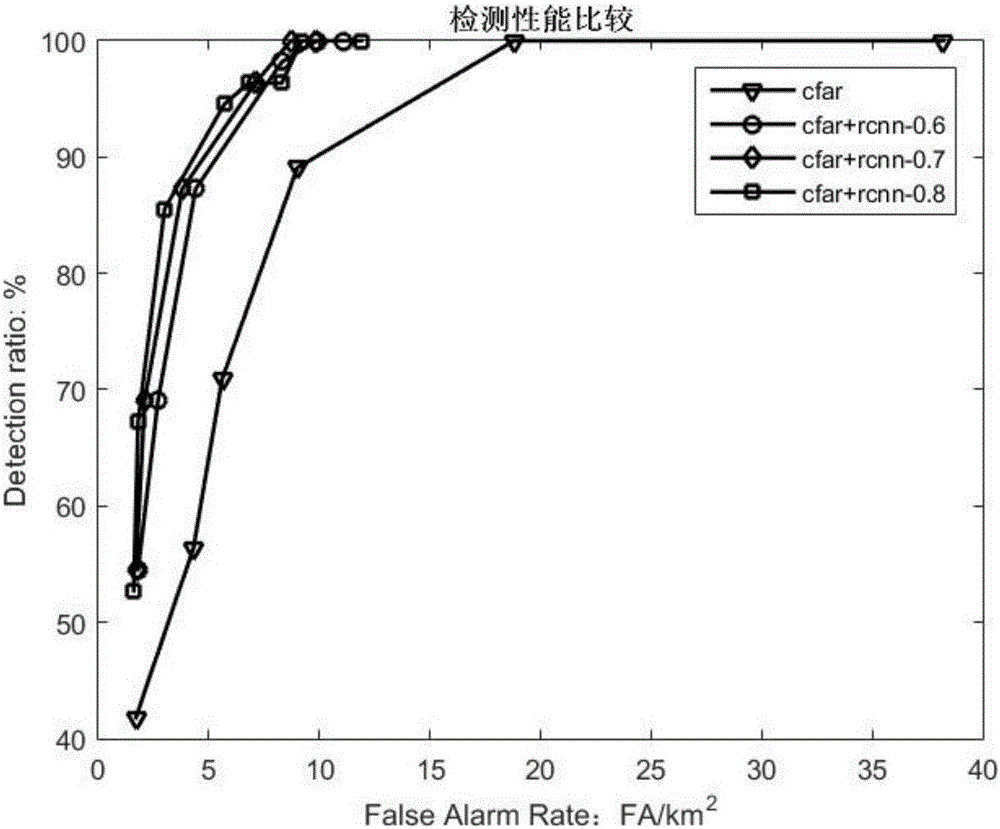
CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection and depth learning-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) target detection method
ActiveCN106156744AEasy to adjustOvercome the problem that end-to-end detection cannot be done and takes a long timeScene recognitionNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionLearning based
The invention discloses a CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection and depth learning-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) target detection method. The method includes the following steps that: (1) SAR images are obtained; (2) a training sample set is expanded; (3) the network structure of a Faster-RCNN model is constructed; (4) a trained RPN model is obtained; (5) a trained Fast-RCNN model is obtained; (6) a finely-adjusted RPN network is obtained; (7) a trained Faster-RCNN model is obtained; and (8) target detection is carried out. With the CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection and depth learning-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) target detection method of the invention adopted, end-to-end image-level detection is realized, and major problems in existing SAR target detection technologies can be solved. The method has good detection performance under complex conditions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Airborne multi-antenna SAR chromatography three dimensional imaging system and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN102221697AControl load3D Imaging RealizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarDimensional modeling
Provided is an airborne multi-antenna SAR chromatography three dimensional imaging system and an imaging method thereof. The invention is directed to the field of electronic signal processing technology and particularly relates to an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) chromatography three dimensional imaging technology. According to the invention, a multi-antenna system structure is used to realize an SAR chromatography three dimensional imaging characterized by low flight risk, high resolution and large range. A multi-antenna working mode of single reception and multiple transmissions is adopted to reduce a loader load; meanwhile the possible imaging height scope is enlarged twice. An imaging method based on signal sparse expression is employed to realize a single flight super-resolution three dimensional imaging of the multi-antenna system. After the multi-antenna system structure is adopted, it requires less flight times to realized the three dimensional imaging. Meanwhile, the design of each flight locus is more flexible. Spaces are expanded for the application of SAR three dimensional imaging technologies in the airborne platform.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Double-threshold constant false alurm motion target detecting method of double base synthetic aperture radar
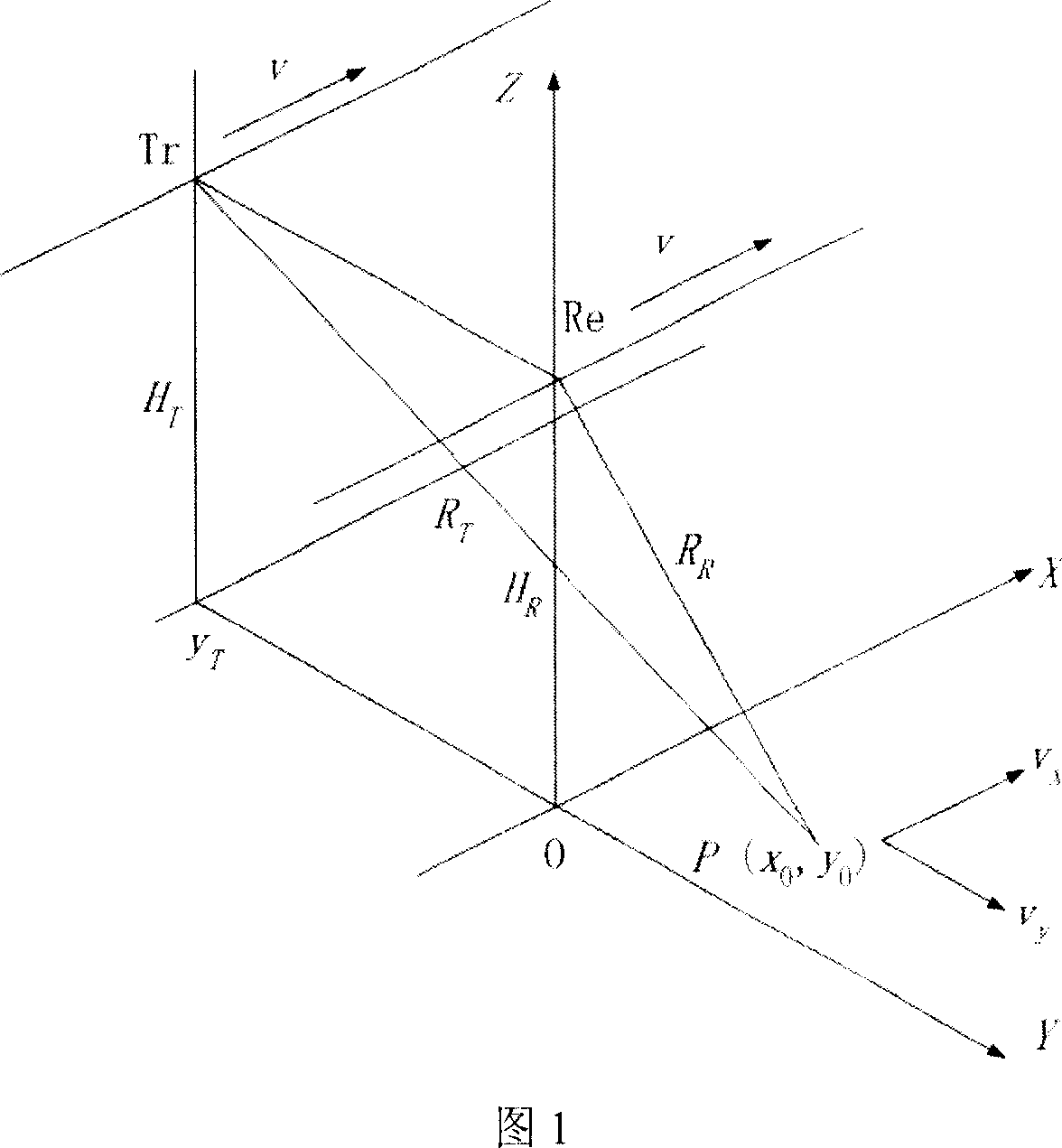
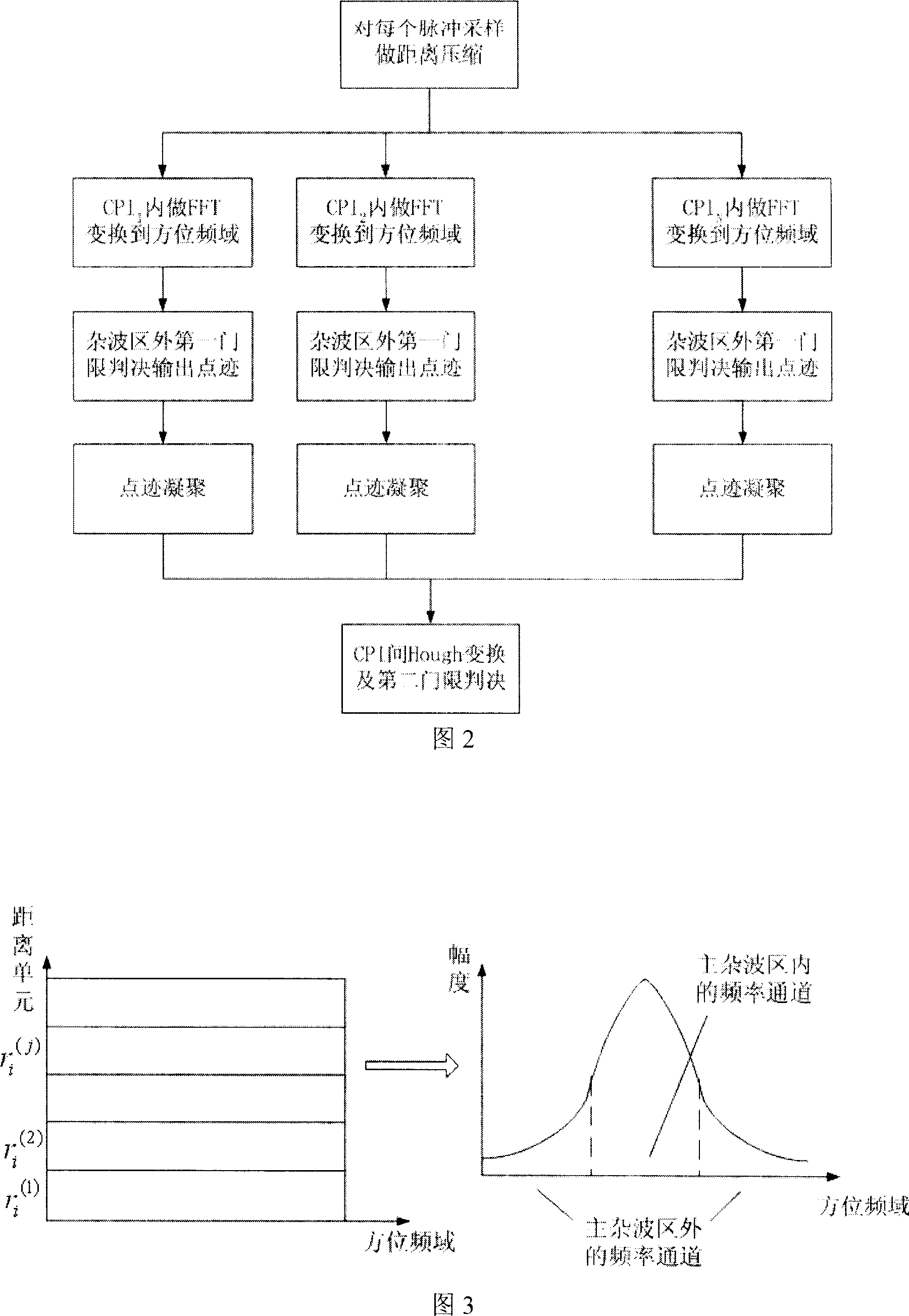
A detection method of double-threshold constant false alarm movement object on double-base synthetic aperture radar includes finalizing distance compression of various pulse-sampling, dividing orientation time to be multiple CPI, carrying out FFT in each CPI to enter orientation frequency domain, comparing data amplitude of frequency channel at external of clutter region with the first threshold and outputting point trace, making coagulation on point trace, making Hough transform in point trace domain and making decision of the second threshold.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Synthetic aperture ladar system using incoherent laser pulses
InactiveUS6559932B1Optical rangefindersDevices using optical meansRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
An incoherent ladar transmitter (12) adapted for use with synthetic aperture processing. The system (12) includes a first mechanism (44, 48, 50) for generating a laser beam (18). A second mechanism (44, 68) records phase information pertaining to the laser beam (18) and subsequently transmits the laser beam (18) from the system in response thereto. A third mechanism (40) receives a reflected version (20) of the laser beam and provides a received signal in response thereto. A fourth mechanism (72) corrects the received signal based on the phase information recorded by the second mechanism (44, 68). In a more specific embodiment, the ladar system (12) includes a synthetic aperture processor (46) for correcting the received signal based on the phase information and providing a corrected laser signal in response thereto. The synthetic aperture processor (46) includes a mechanism (76) for applying, a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) to the corrected laser signal to obtain high frequency resolution and cross-range resolution. A fifth mechanism (48) constructs a range-Doppler image based on the corrected laser signal and the movement of the ladar system (12).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
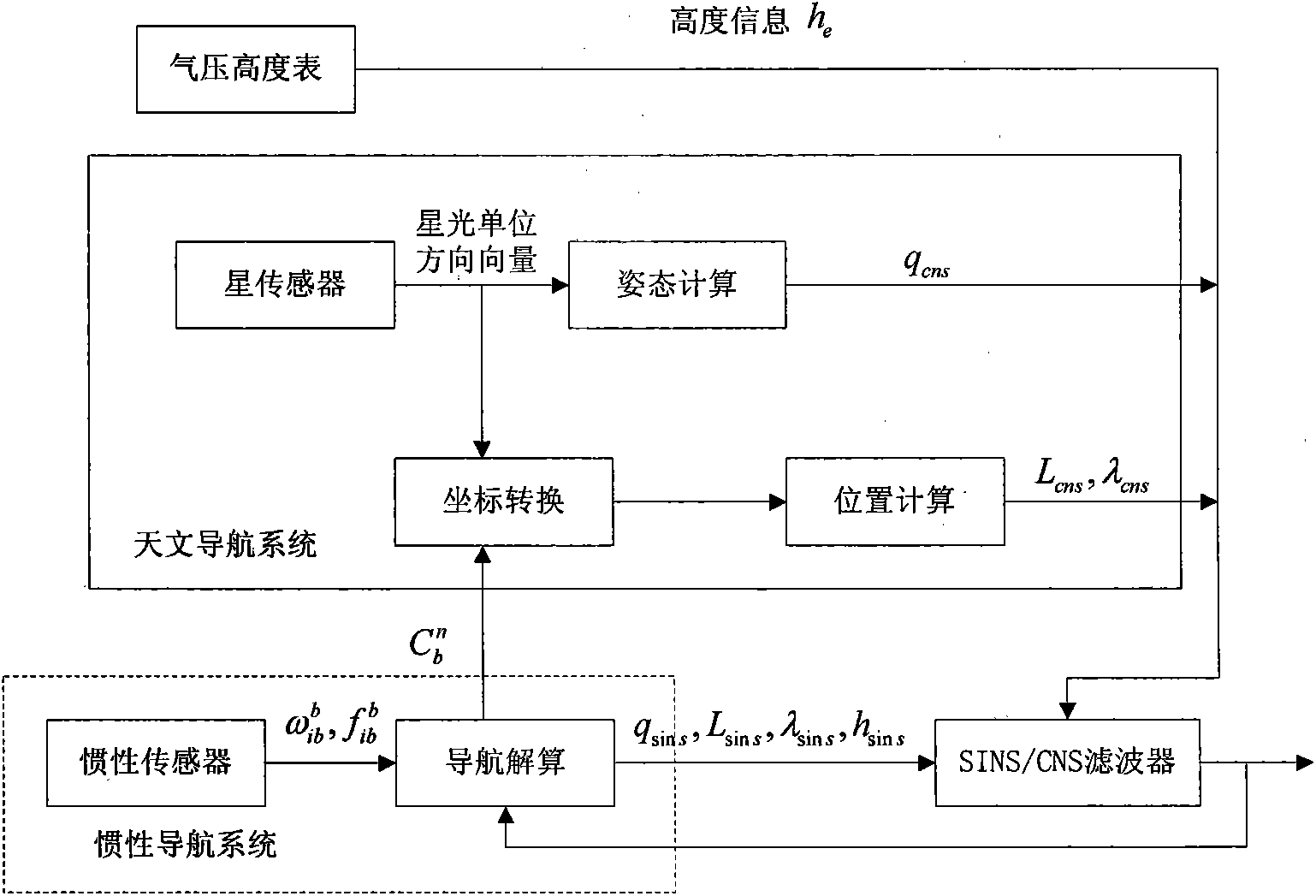
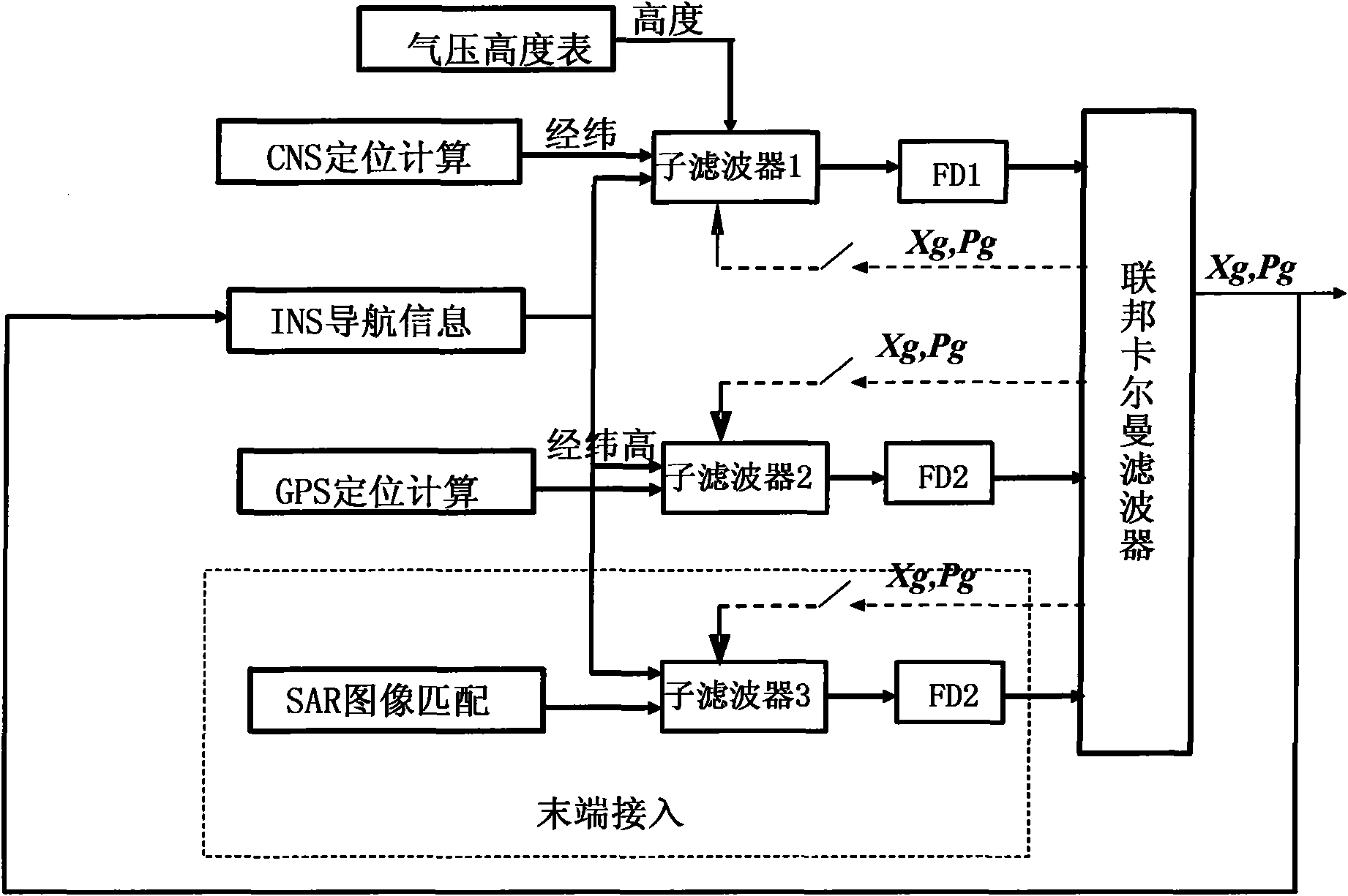
Autonomous integrated navigation system
InactiveCN103528587AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsSynthetic aperture radarCovariance
The invention relates to an autonomous integrated navigation system which belongs to the technical field of navigation systems. The SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) / CNS (Celestial Navigation System) integrated navigation system takes SINS as a main navigation system and SAR and CNS as aided navigation systems and is established by the following steps: firstly, designing SINS / SAR and SINS / CNS navigation sub-filters, calculating to obtain two groups of local optimal estimation values and local optimal error covariance matrixes of the integrated navigation system state, then transmitting the two groups of local optimal estimation values into a main filter by a federal filter technology for fusion to obtain an overall optimal estimation value and an overall optimal error covariance matrix, and finally, performing real-time correction on the error according to the overall optimal estimation value so as to obtain an optimal estimation fusion algorithm of the SINS / SAR / CNS integrated navigation system. The autonomous integrated navigation system, disclosed by the invention, is less in calculation amount and high in reliability, is applicable to aircrafts in near space, aircrafts flying back and forth in the aerospace, aircrafts for carrying ballistic missiles, orbit spacecrafts and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
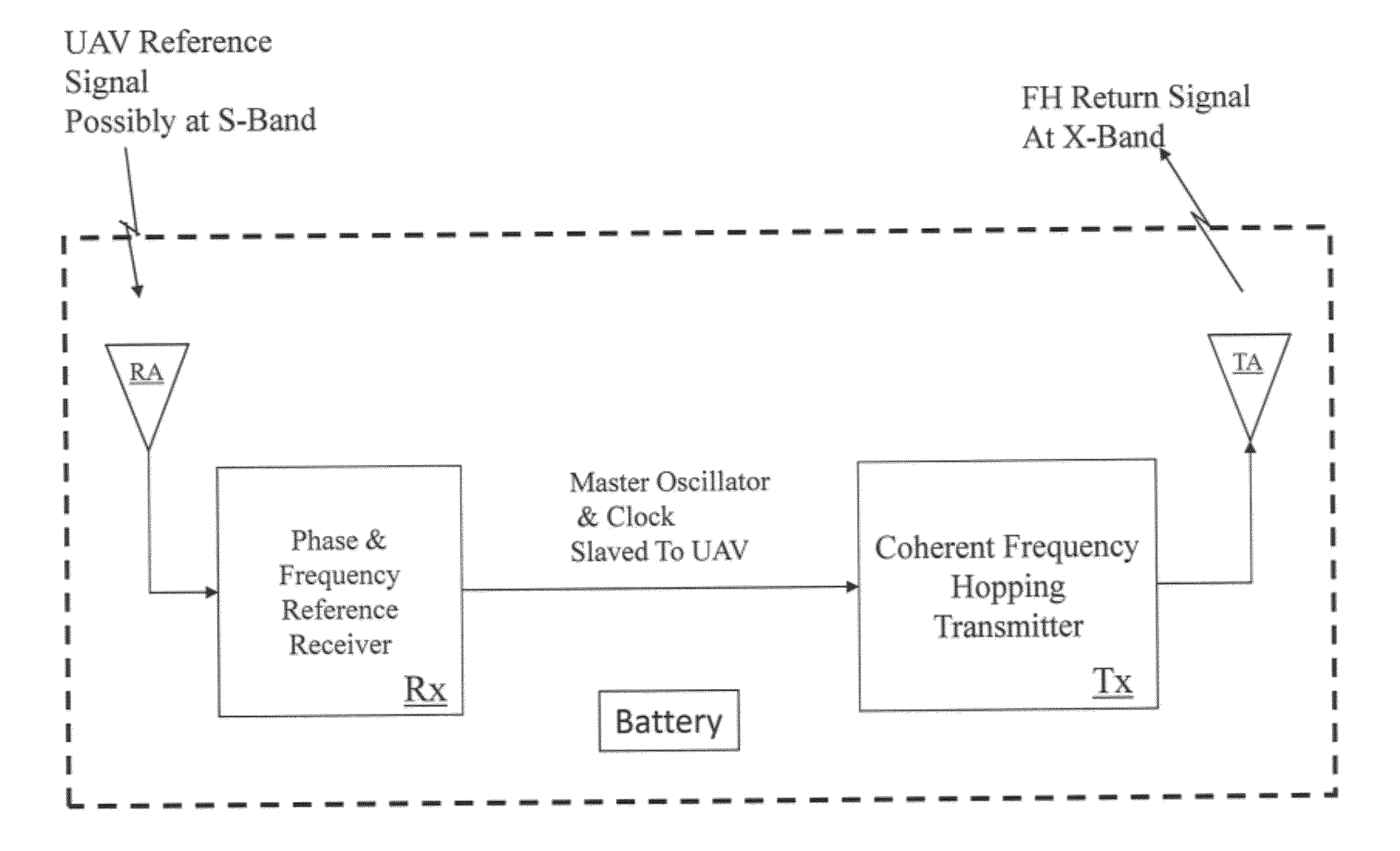
Interrogator and System Employing the Same
ActiveUS20120256730A1Sensing detailsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarElectrical and Electronics engineering
An interrogator and system employing the same. In one embodiment, the interrogator includes a receiver configured to receive a return signal from a tag and a sensing module configured to provide a time associated with the return signal. The interrogator also includes a processor configured to employ synthetic aperture radar processing on the return signal in accordance with the time to locate a position of the tag.
Owner:LONE STAR IP HLDG LP
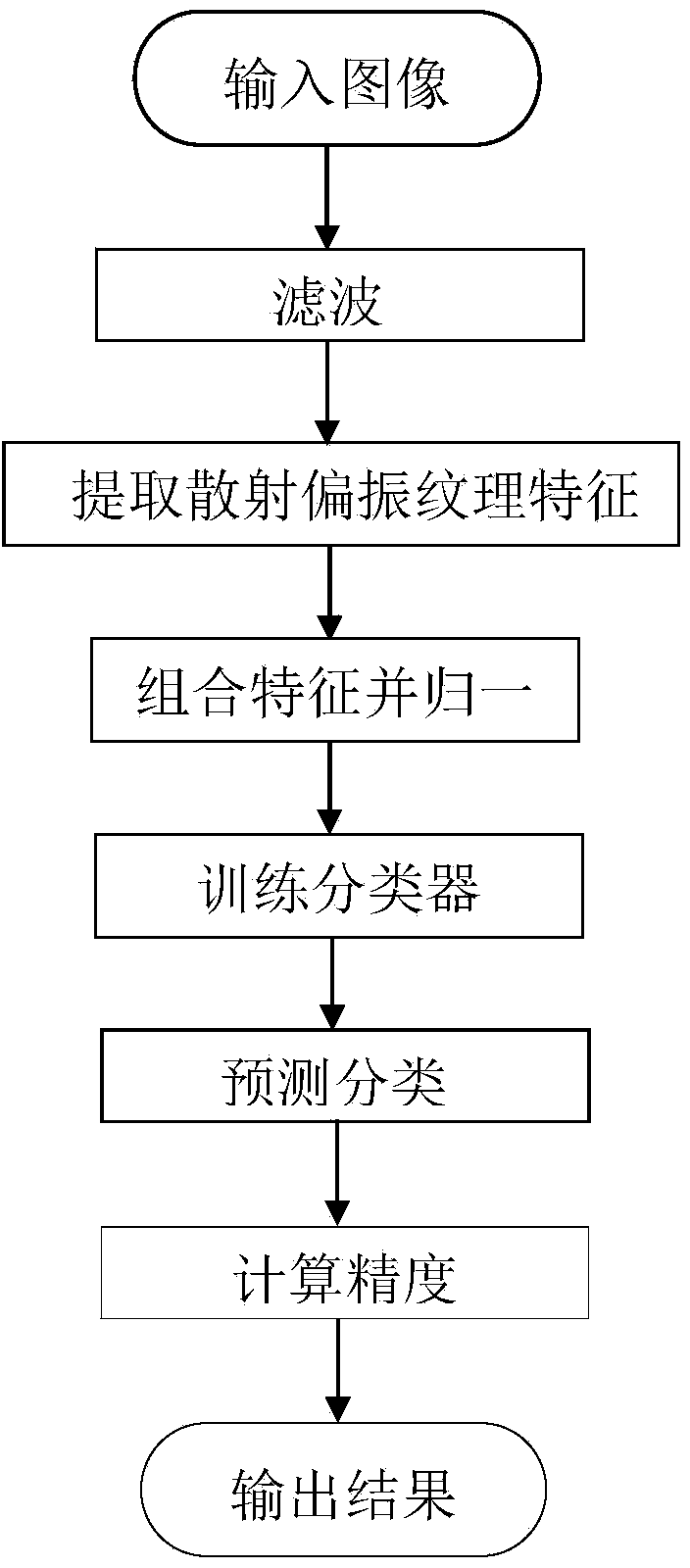
Polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image classification method based on SDIT (Secretome-Derived Isotopic Tag) and SVM (Support Vector Machine)
InactiveCN103824084ALow riskAvoid the curse of dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineImaging quality
The invention discloses a polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image classification method based on an SDIT (Secretome-Derived Isotopic Tag) and an SVM (Support Vector Machine). The method comprises the implementation steps of (1) inputting an image, (2) filtering, (3) extracting scattering and polarization textural features, (4) combining and normalizing the features, (5) training a classifier, (6) predicting classification, (7) calculating precision and (8) outputting a result. Compared with an existing method, the polarimetric SAR image classification method based on the SDIT and the SVM enables the empirical risk and the expected risk to be minimal at the same time, and has the advantages of high generalization capability and low classification complexity and also the advantages of describing the image characteristics comprehensively and meticulously and improving the classification precision, and in the meantime, the polarimetric SAR image classification method has a good denoising effect, and further is capable of enabling the outlines and edges of the polarimetric SAR images to be clear, improving the image quality, and enhancing the polarimetric SAR image classification performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
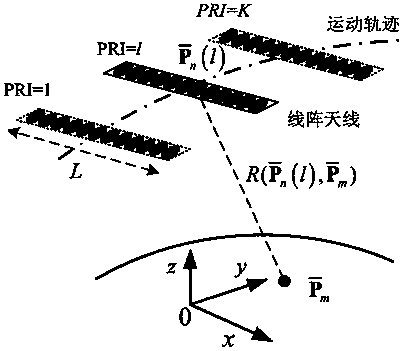
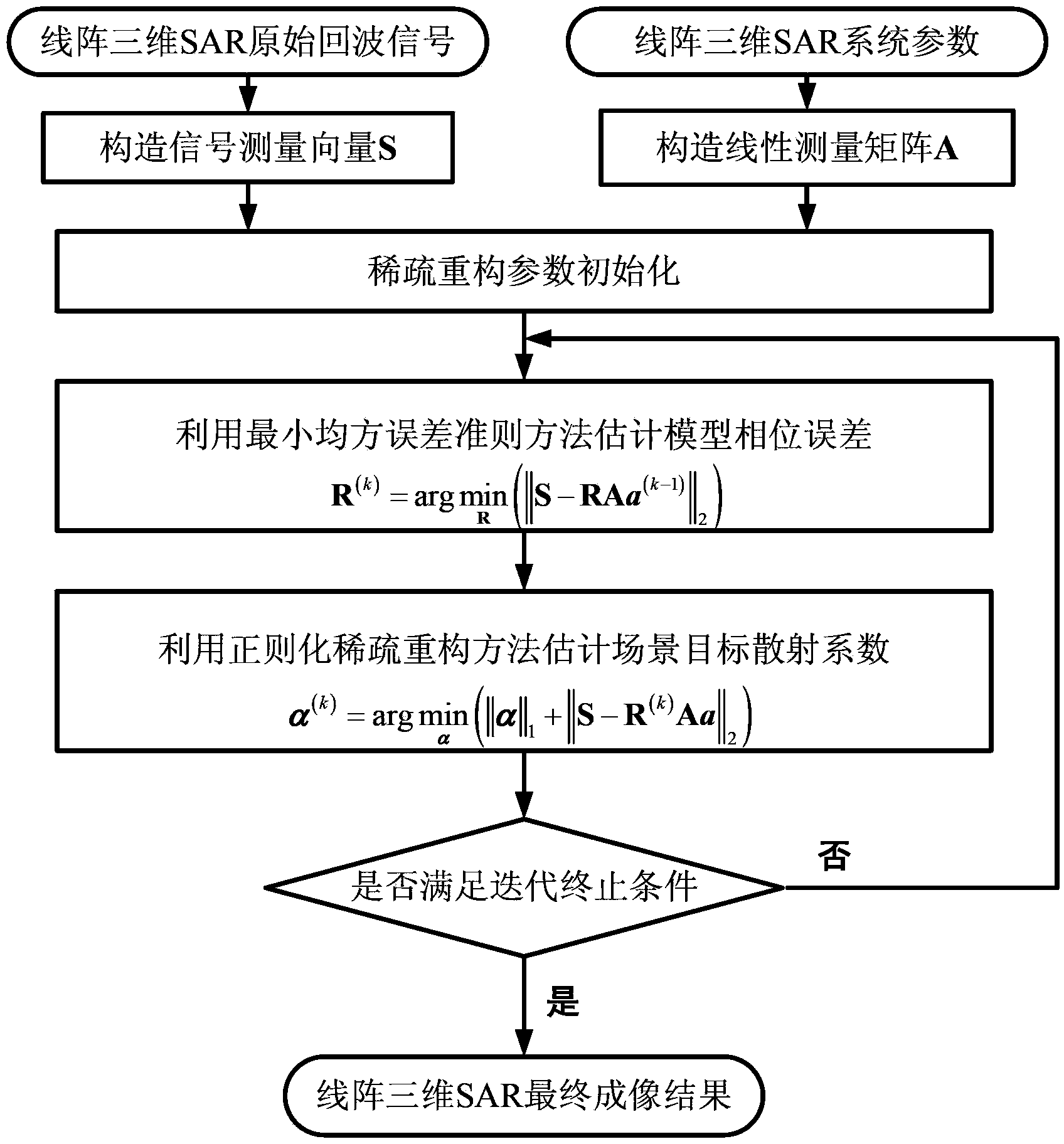
Linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and phase error correction method
ActiveCN103439693ASparse imaging suppressionImproving Sparse Reconstruction Imaging PerformanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarCorrection method
The invention discloses a linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method. According to the characteristic that scattering targets are sparse in an actual linear array three-dimensional SAR imaging scene space, the linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method establishes a linear measurement matrix of linear array SAR original echo signals and scattering coefficients in a scene target space, phase error factors existing in the linear array three-dimensional SAR actual measurement are also taken into account, a scattering phase vector between a phase error matrix and a scene target is estimated through iterative optimization, imaging processing of the sparse targets in a linear array SAR three-dimensional space is realized, the effect on imaging by phase errors is restrained, and the stability of linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and the imaging precision of a linear array SAR are improved. The linear array SAR sparse reconstitution imaging and model phase error correction method can be applied to synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging, earth remote sensing and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Deep learning-based radar echo signal target identification method
ActiveCN108229404AConvenient cross-validationImprove recognition accuracyScene recognitionNeural architecturesSynthetic aperture radarComputer science
The invention discloses a deep learning-based radar echo signal target identification method. The method directly identifies radar echo signals, consequently, information loss in the process of complex two-dimensional matched filtering processing and imaging of an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image is prevented, and the accuracy of identification is effectively improved. In addition, the methodutilizes a convolutional neural network, thus avoiding the complex preprocessing and feature extraction process for echo signals and greatly simplifying the identification processing process. The deeplearning-based radar echo signal target identification method mainly solves the problem that imaging preprocessing is required by a conventional SAR image-based target identification method; applyingthe convolutional neural network method in original radar echo data, the deep learning-based radar echo signal target identification method has the advantages of high identification accuracy and goodanti-noise performance, and moreover, the deep learning-based radar echo signal target identification method has higher effectiveness and practicability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for registering synthetic aperture radar image with change area based on point pair constraint and Delaunay
InactiveCN104867126AImprove discriminationSolve the "many-to-one" situationImage analysisSynthetic aperture radarRadar
The present invention discloses a method for registering synthetic aperture radar image with a change area based on a point pair constraint and Delaunay, and the problem of SAR image registration with a change area without using ground control point data is mainly solved. The method comprises a step of filtering inputted floating image and reference image respectively and then using a SURF algorithm to extract feature points, a step of carrying out similarity measure matching of a normalized descriptor matrix on obtained reference image feature point and floating image feature point and then carrying out distance and wiring direction angle constraint to obtain an initial candidate matching point pair set, a step of using matching feature points in the floating image and the reference image to construct Delaunay, searching a homonymous triangle pairs in the Delaunay of the two images to update the candidate matching point pair set, and taking non-repeated vertices in all homonymous triangle pairs corresponding to a minimum affine error as a final matching point pair set, and calculating an affine change matrix, carrying out affine conversion and bicubic interpolation on the floating image, and obtaining a final registration result image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
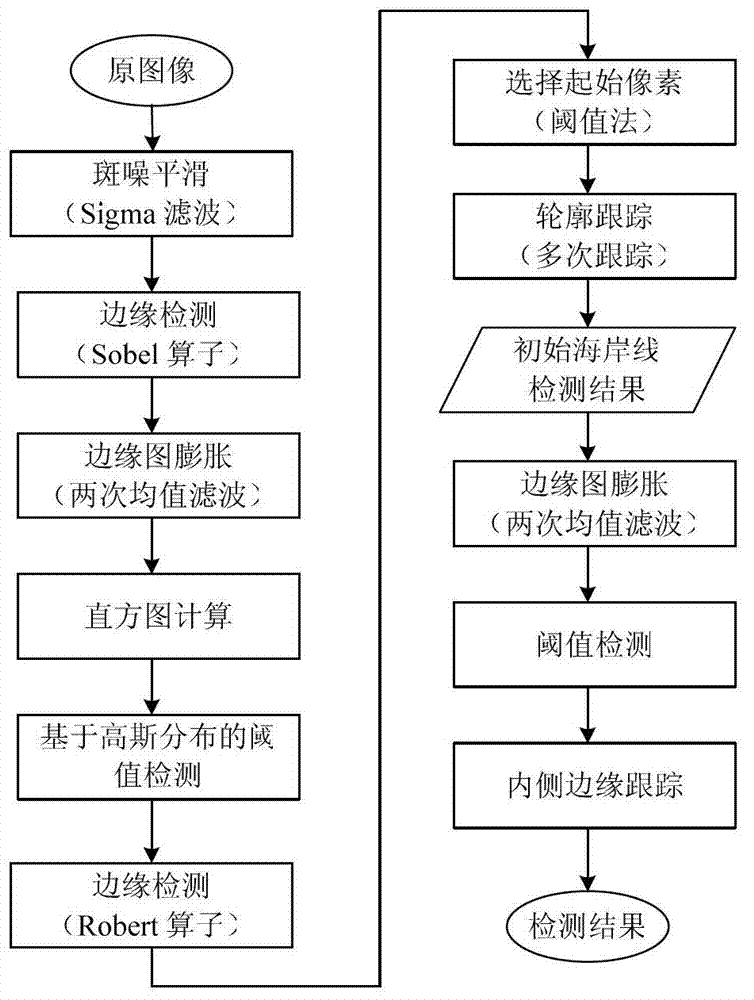
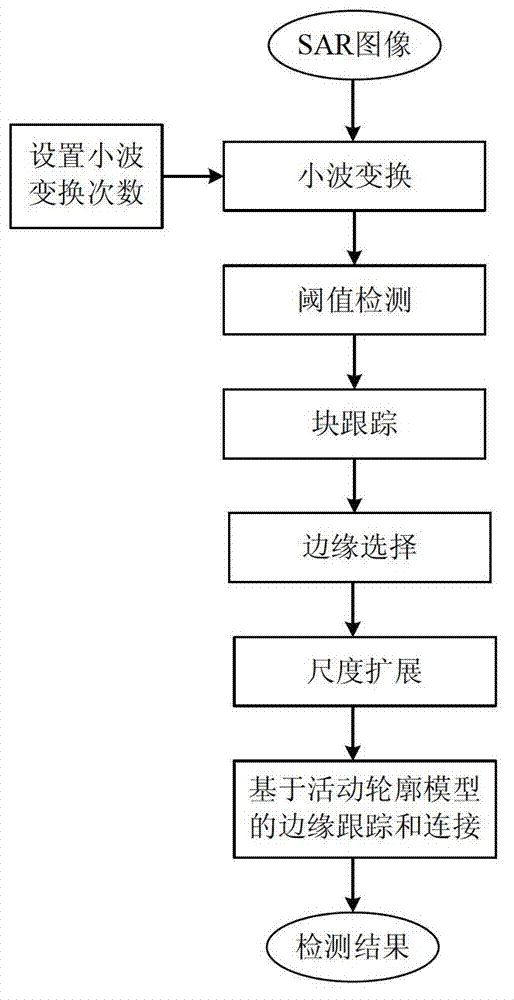
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image sea-land segmentation method based on wavelet transform and OTSU threshold
ActiveCN102968798ASuppression of speckleImprove applicabilityImage analysis2D-image generationPattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image sea-land segmentation method based on a wavelet transform and OTSU threshold. According to the method, speckle noise in an SAR image is suppressed by using the noise smoothing property of wavelet transform; then land areas are roughly segmented by using an unsupervised optimal OTSU threshold method, and the detection results under each scale are merged based on the multiscale analysis property of wavelet transform; and finally the final coastline detection results are obtained through automatic subsequent treatment and edge tracking. Compared with the prior sea-land segmentation methods, the SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image sea-land segmentation method comprehensively utilizes the speckle noise suppressing and multiscale analysis function of wavelet transform and the self-adaptive, unsupervised and high-robustness properties of the OTSU threshold algorithm, and has great improvement in automation degree, universality, simplicity and applicability of high-resolution SAR images.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
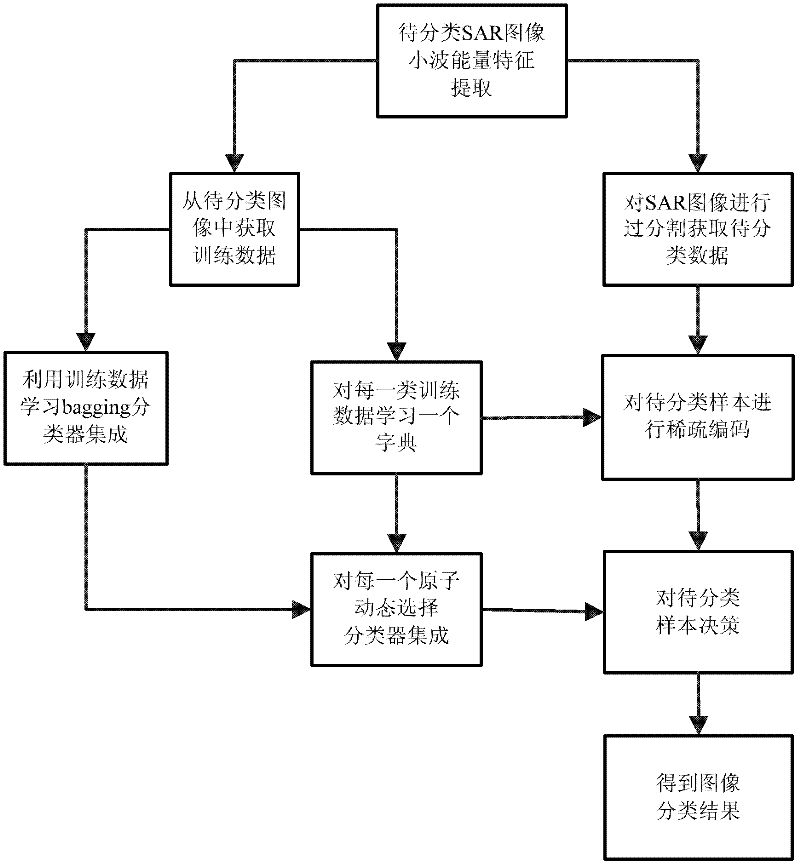
Sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image terrain classification method
ActiveCN102651073AExpress abilityImprove classification effectCharacter and pattern recognitionEnsemble selectionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image terrain classification method, which mainly solves the problem that the speed of the conventional dynamic ensemble selection algorithm and the conventional dynamic classifier selection algorithm for terrain classification in SAR images is low. The implementation process of the sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR image terrain classification method is as follows: (1) a wavelet energy feature is extracted from an SAR image to be classified; (2) training data is acquired from the SAR image to be classified; (3) the SAR image to be classified is regionalized to obtain data to be classified; (4) training samples are utilized to learn ensemble systems; (5) a dictionary is learnt for each class of training data, and a synthetic dictionary is obtained; (6) dynamic ensemble selection is carried out on each atom in the synthetic dictionary; (7) samples to be classified are sparsely coded; (8) the samples to be classified are marked according to a sparse coefficient and classifier ensembles corresponding to the atoms; (9) the marks of the samples to be classified are mapped onto pixels in the SAR image, so that a terrain classification result is obtained. The sparse dynamic ensemble selection-based SAR image terrain classification method has the advantages of high speed and good classification effect, and can be used for SAR image target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
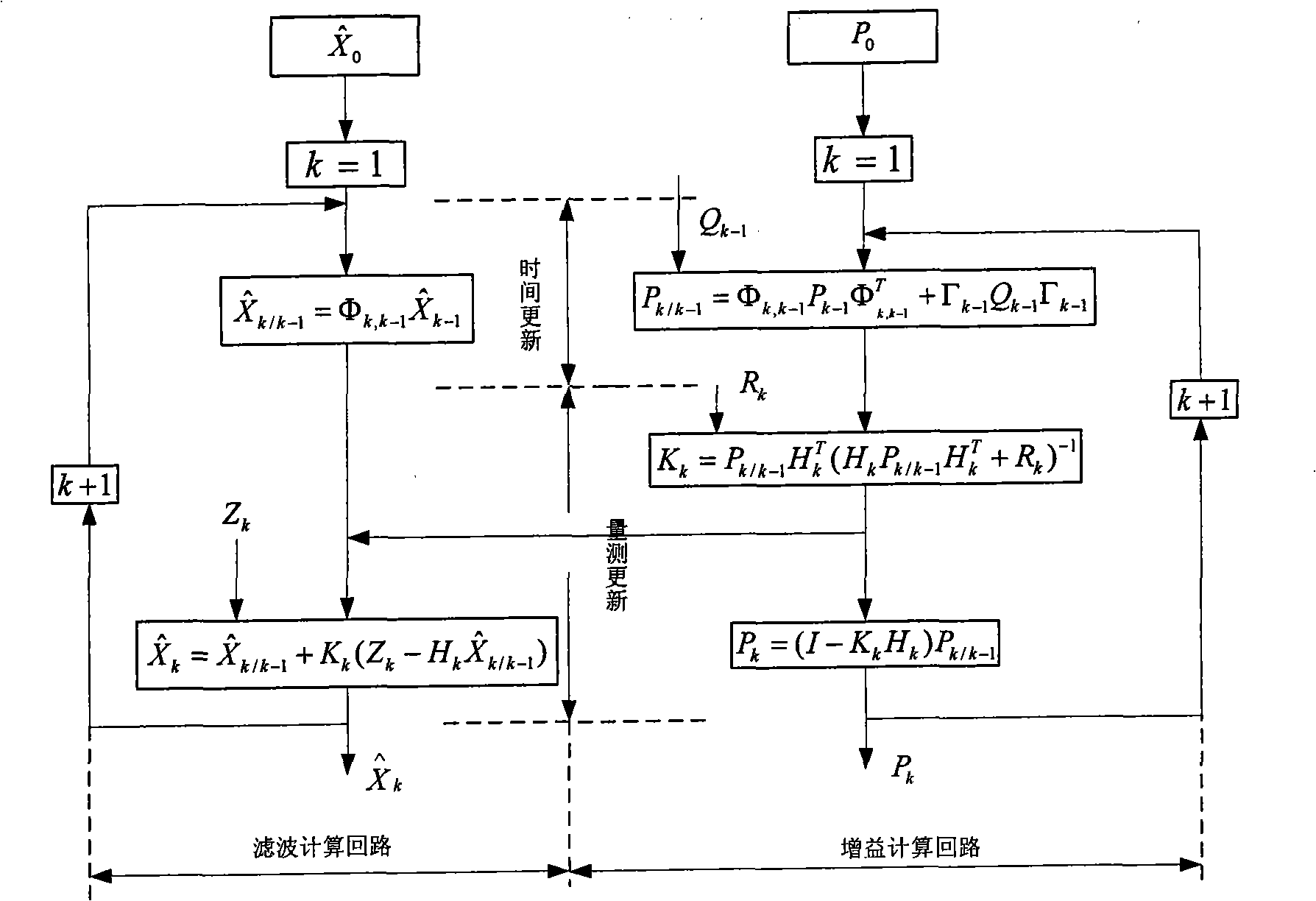
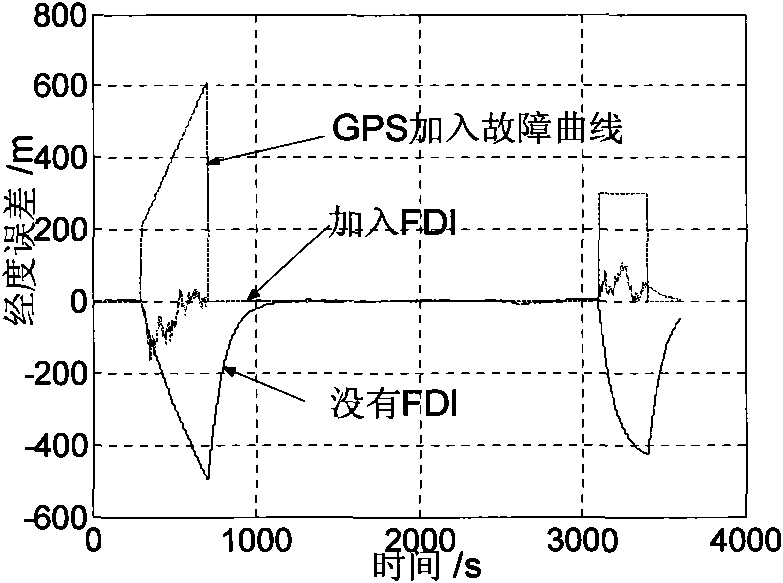
Fault-tolerance autonomous navigation method of multi-sensor of high-altitude long-endurance unmanned plane
InactiveCN101858748AOvercoming the lack of navigation stabilityDoes not affect workInstruments for comonautical navigationFault toleranceFault detection algorithm
The invention discloses a fault-tolerance autonomous navigation method of a multi-sensor of a high-altitude long-endurance unmanned plane. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out theory analysis on work environment and work characteristics of three navigation sensors including GPS (Global Position System), CNS (astronomy) and SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), and establishing an observation linearity measurement equation by combining a geography system based on a position combined observation principle of inertia / GPS, inertia / astronomy and inertia / SAR under an airborne geography system; then analyzing error characteristics of a navigation sensor and simulating the output during the fault of GPS, and establishing a corresponding fault detection algorithm unit to carry out fault detection and isolation on a filter; and finally, designing and completing an inertia / GPS combined navigation system mathematic model based on the assistance of astronomy and SAR, and optimally evaluating the error state of the inertia navigation by means of federated filtering. The invention has high navigation precision, and can fully play the role of evaluating the error state quantity of an airborne inertia navigation system by the combined navigation of the multi-sensor under the geography system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
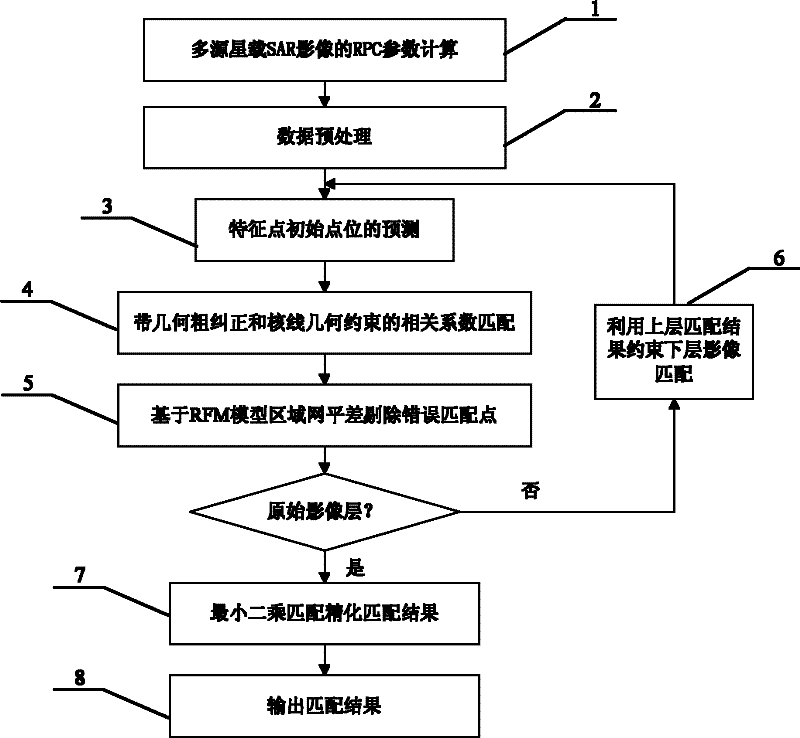
Method for automatically matching multisource space-borne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) images based on RFM (Rational Function Model)
ActiveCN102213762AAutomatic and reliable matchingMeet the requirements for co-locationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarWorkload
The invention discloses a method for automatically matching multisource space-borne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) images based on an RFM (Rational function model). The method comprises the following steps of: calculating respective RPC (Rational Polynominal Coefficient) parameter of images; performing forecast of initial positions of points to be matched, matching of approximate epipolar line geometric establishment constraints and geometric rough correction of matched window images by using the RPC parameters of the images on every pyramid image layer, deleting wrong matching points from the image matching result of every layer of pyramid by adopting regional computer network error compensation based on an RFM model; refining the RPC parameters of the images and calculating the object space coordinates of the matching points; refining the matching result to the original image layer by layer; and refining a matching result by using a least square image matching method to realize automatic and reliable matching of common points of multisource space-borne SAR images. In the method, the RFM model is introduced into automatic matching of the multisource space-borne SAR images, and the regional computer network error compensation of the RFM model is blended into the image matching process of every layer pyramid, so that wrong matching points in the matching process can be effectively deleted, and the workload of manual measurement of common points is effectively lowered.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HIGHWAY CONSULTANTS CO LTD
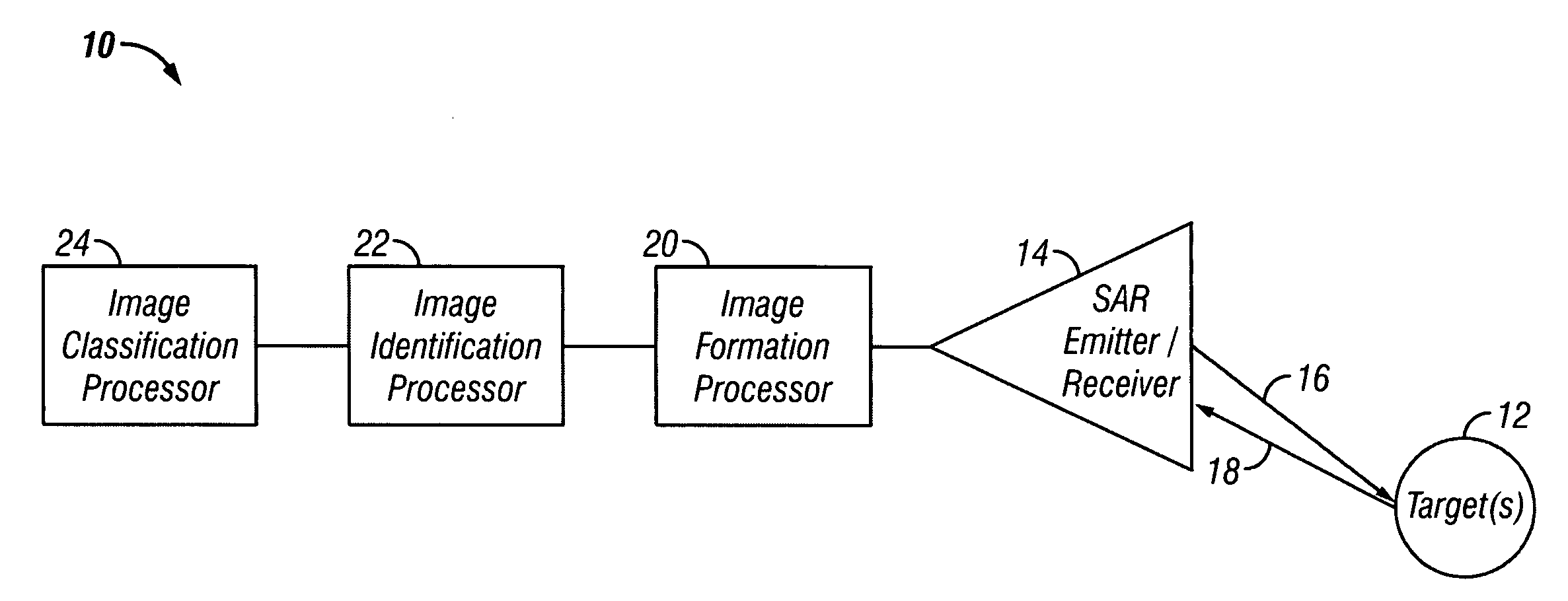
Creating and identifying synthetic aperture radar images having tilt angle diversity
An apparatus for and method of employing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to automatically classify a target comprising emitting and collecting SAR signals at a plurality of squint angles, forming a plurality of SAR images of the target from the collected signals, the plurality of SAR images substantially having tilt angle diversity, automatically classifying the target from each of the plurality of SAR images, and generating a most probable target classification from the classifications of the plurality of SAR images.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
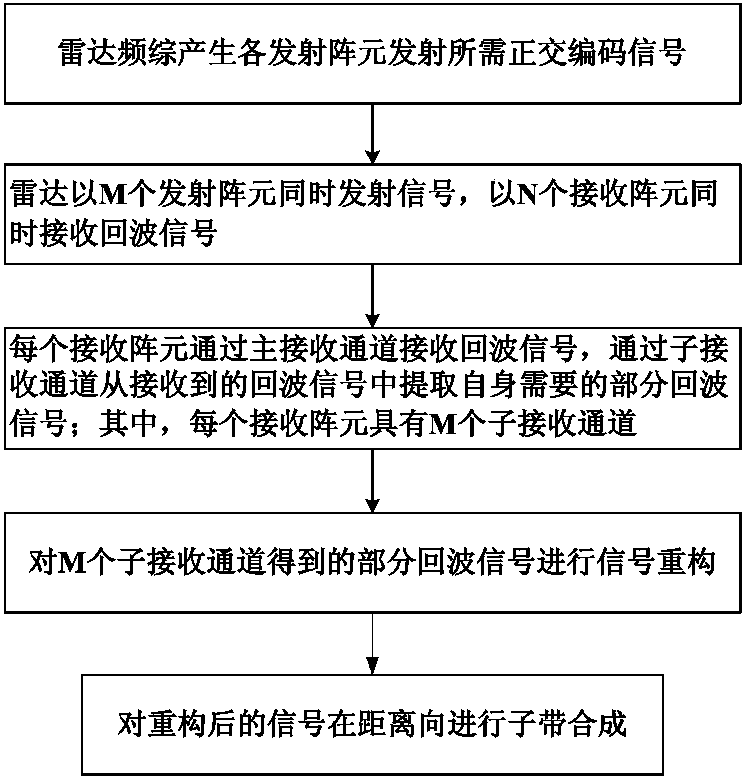
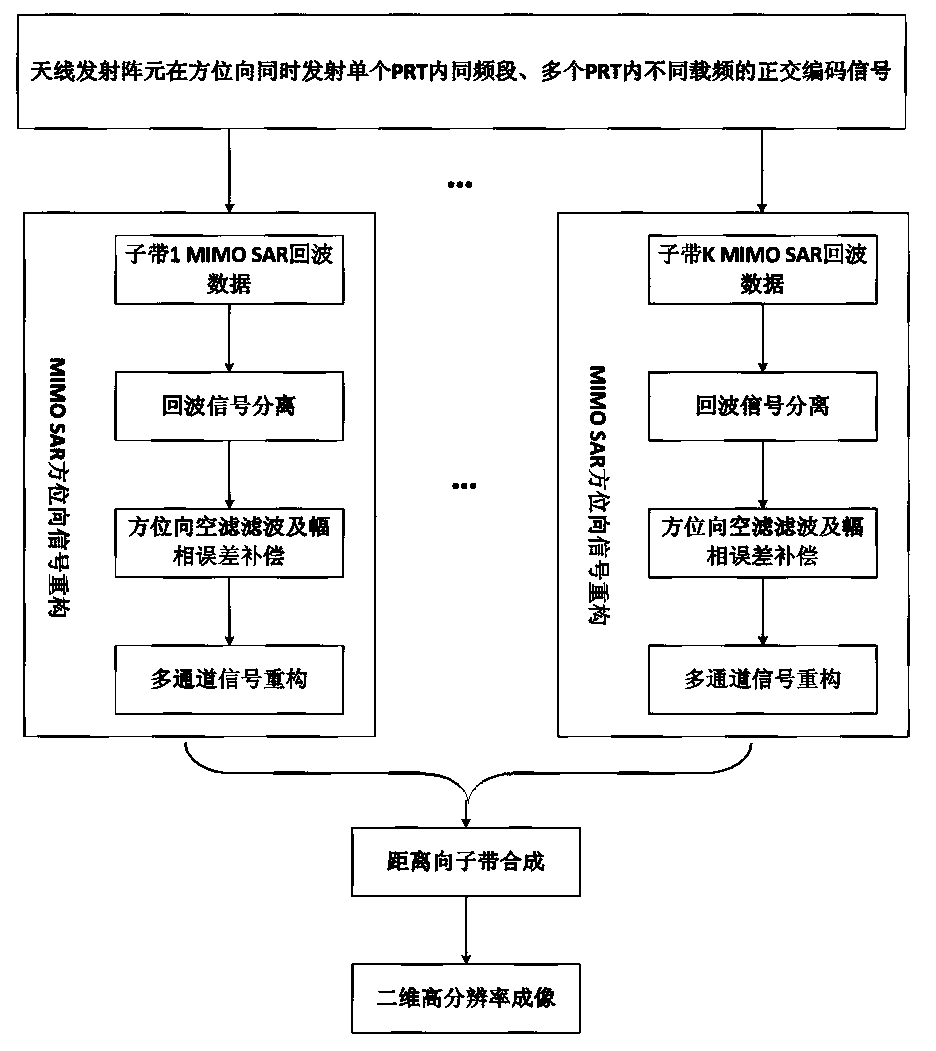
Method for designing multiple-input-multiple-output synthetic aperture radar system on basis of sub-band synthesis
ActiveCN104166141AWork lessWork around limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSystems designRadar waveforms
The invention relates to a method for designing a multiple-input-multiple-output synthetic aperture radar (MIMOSAR) system on the basis of sub-band synthesis. The method includes the steps that a radar waveform generating module generates quadrature encoding signals needed for transmission of various transmitting array elements; according to radar, M transmitting array elements are used for transmitting signals at the same time, and N receiving array elements are used for receiving echo signals simultaneously; each receiving array element receives the echo signals through a main reception channel, extracts a part of the echo signals as required from the echo signals received by the main reception channel through minor reception channels and is provided with the M minor reception channels; signal reconstruction is carried out on the part of the echo signals obtained by the M minor reception channels of each receiving array element; sub-band synthesis is conducted on the reconstructed signals in a distance. The orientation multi-aperture MIMOSAR system based on a sub-pulse linear frequency modulation stepping system namely sub-band synthesis is adopted, the instantaneous operation bandwidth and sampling rate of the MIMOSAR system are reduced manyfold, and remote high-resolution wide-observation-band imaging can be achieved in an SAR mode.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Segmentation combination-based adaptive constant false alarm rate target detection method for SAR image
InactiveCN101975940AEasy to detectSmall amount of calculationImage analysisRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionReference window
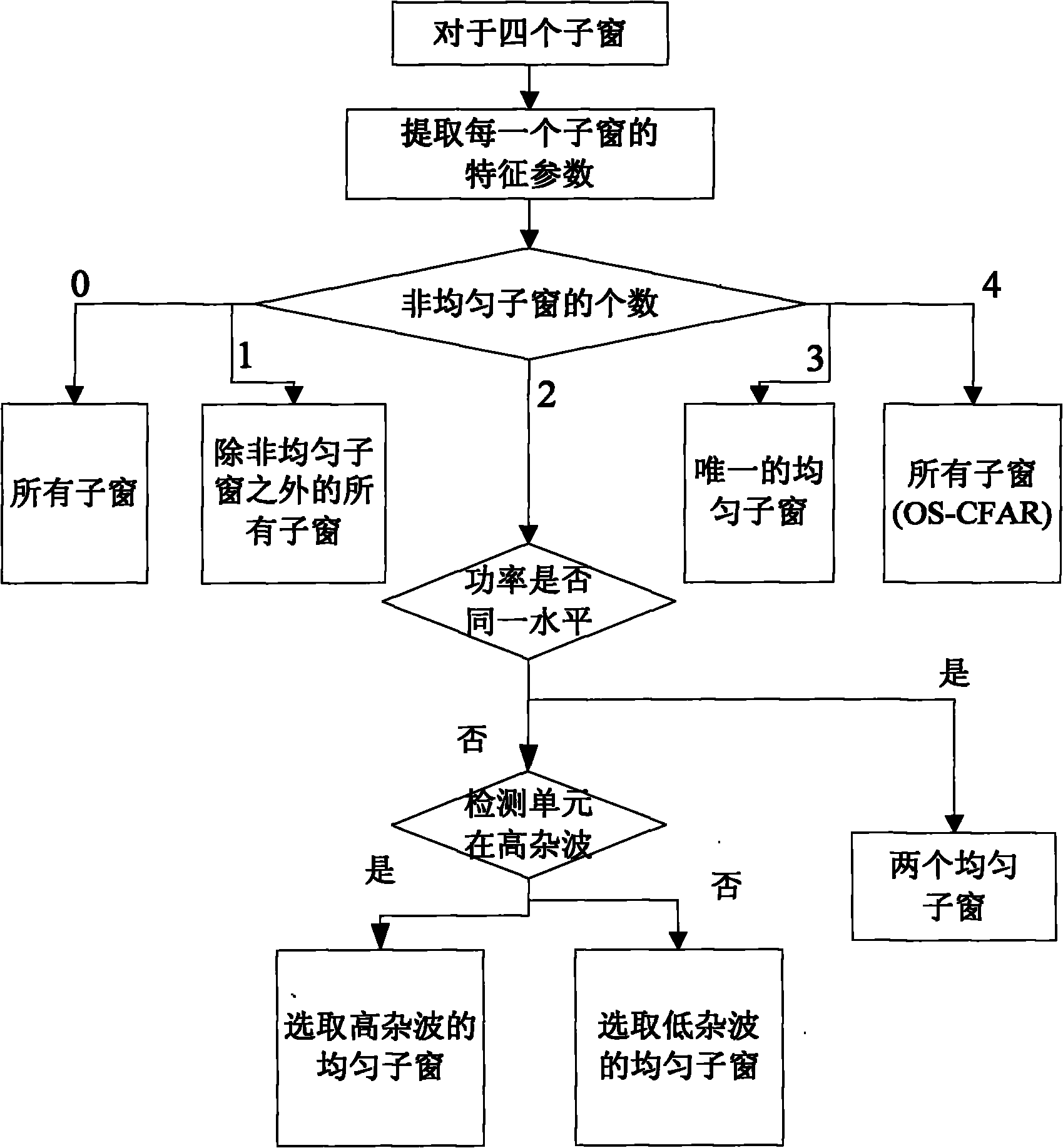
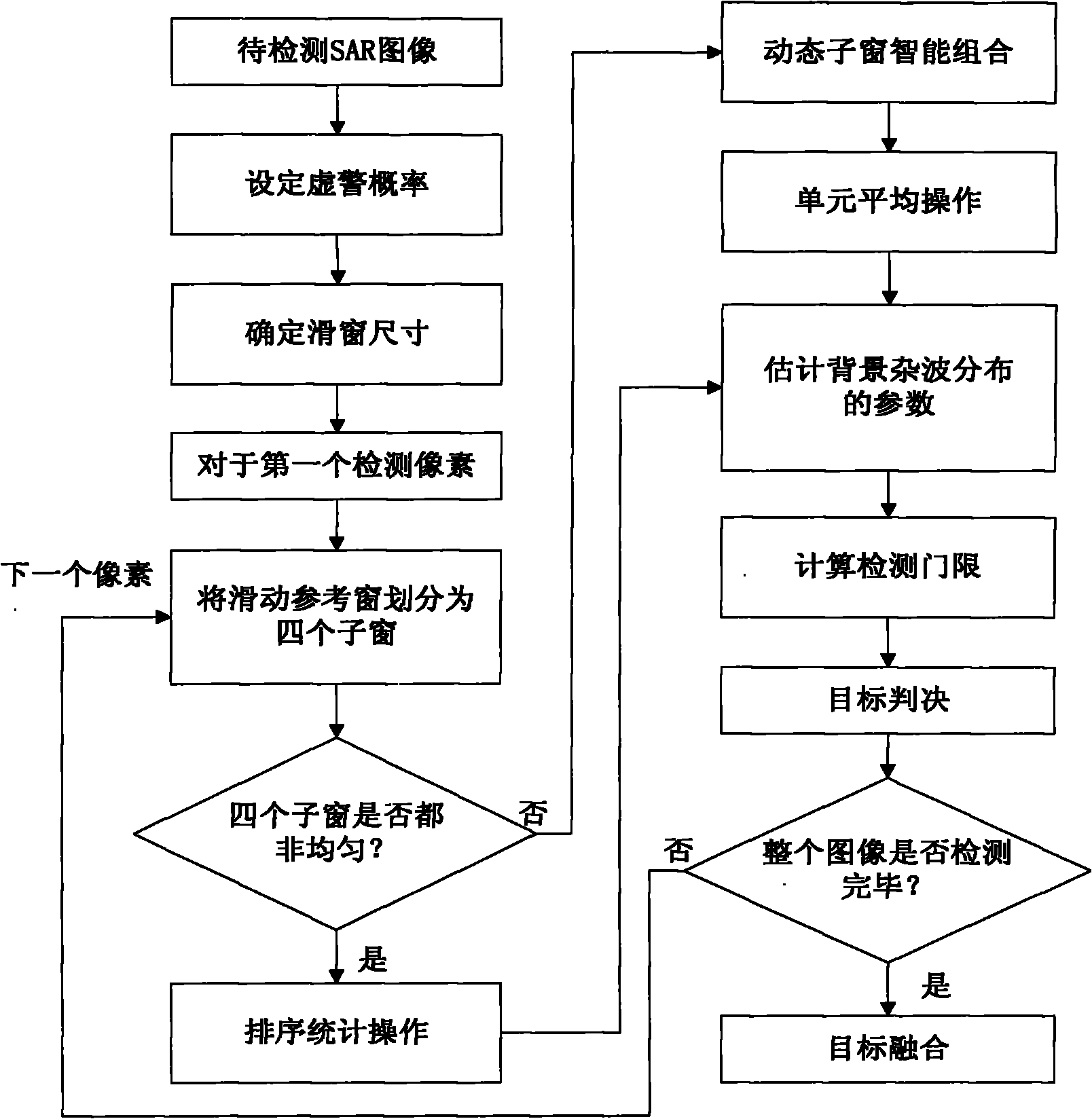
The invention discloses a segmentation combination-based adaptive constant false alarm rate target detection method for an SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image, and belongs to the technical field of synthetic aperture radars. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing a reference window into four sub windows, extracting uniformity statistics of the four sub windows and judging whether the sub windows are uniform; obtaining parameters for estimating background clutter models by adopting corresponding sub window combination strategies according to the non-uniform number, and then obtaining a detection threshold value by using a false alarm probability and a relationship between the clutter models; and comparing the pixel value of a current detection unit with the detection threshold value, judging whether a target exists, detecting the whole SAR image to be detected by adopting a running water form, and performing target fusion operation on the detected SAR image. According to the scheme, the method has low calculation quantity and simple operation, solves the problems of low detection probability, high false alarm rate and the like when the environment is complex and changeable and multiple targets are adjacent under high-resolution large scenes in the prior art, obviously improves the detection effect, and can keep good detection performance under various complex detection environments.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
System and method for data inversion with phase unwrapping
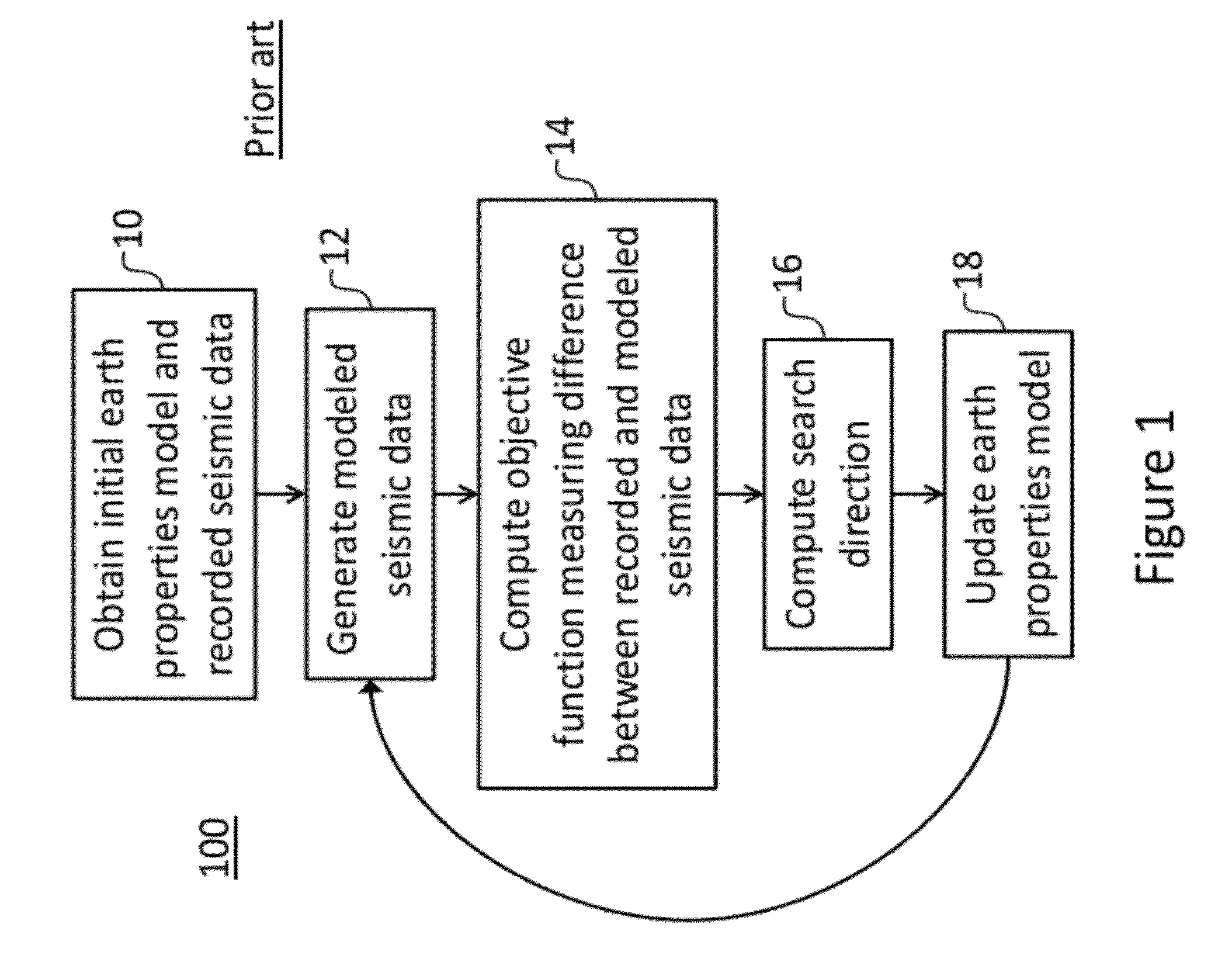
InactiveUS20120316844A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationSynthetic aperture radarData source
A system and computer-implemented method for inverting data from an area of interest to determine physical properties of the area of interest is disclosed. The method includes transforming the data into a Fourier frequency domain to obtain frequency domain data wherein the frequency domain data includes an amplitude portion and a phase portion, performing phase unwrapping of the phase portion of the frequency domain data to generate an unwrapped phase portion, and inverting the unwrapped phase portion to determine the physical properties of the area of interest. The method may also extrapolate the phase. The data inverted may be, for example, seismic data or synthetic aperture radar data. The system includes a data source, a user interface, and a processor configured to execute computer modules designed to execute the method.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Pulse compression radar
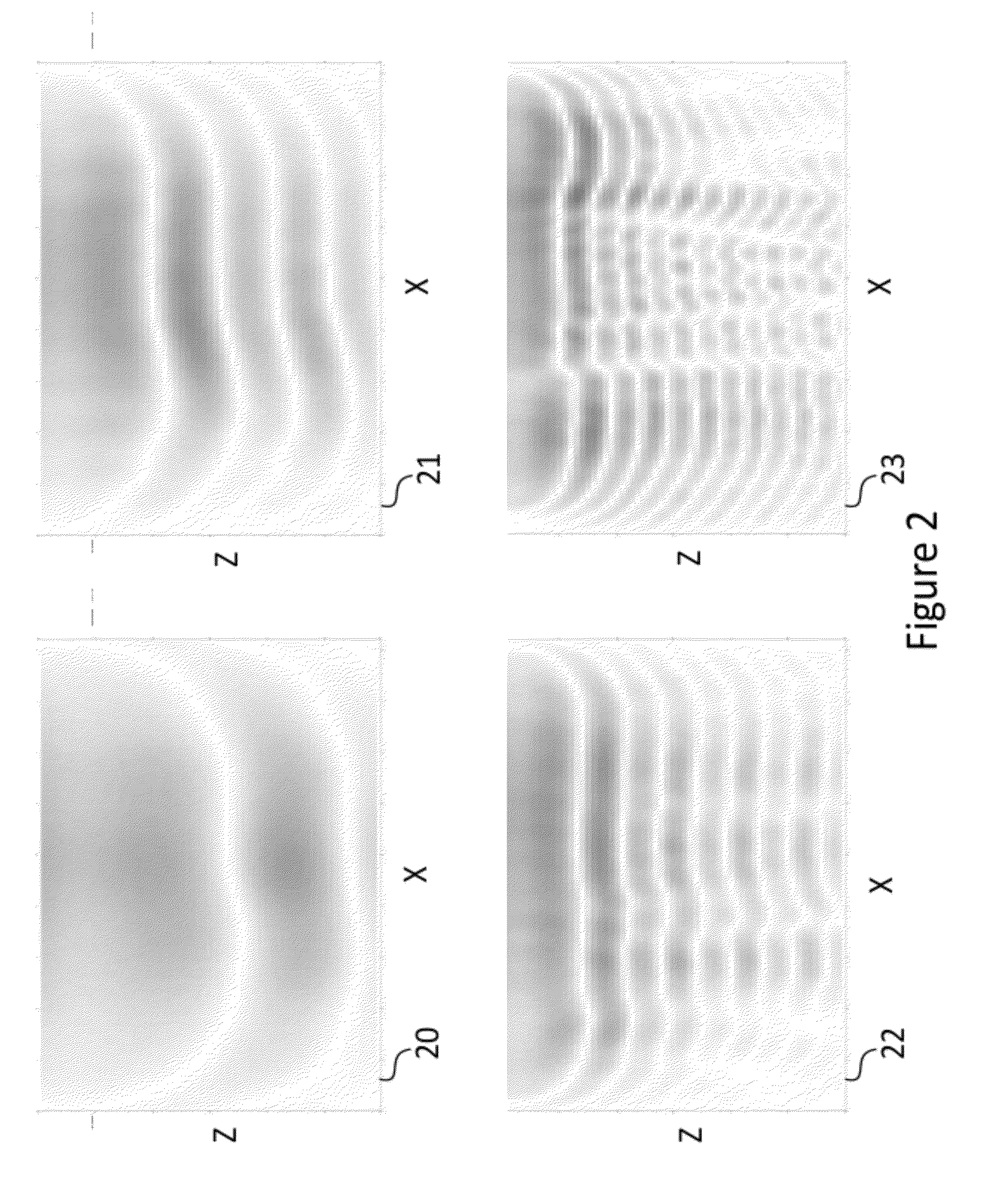
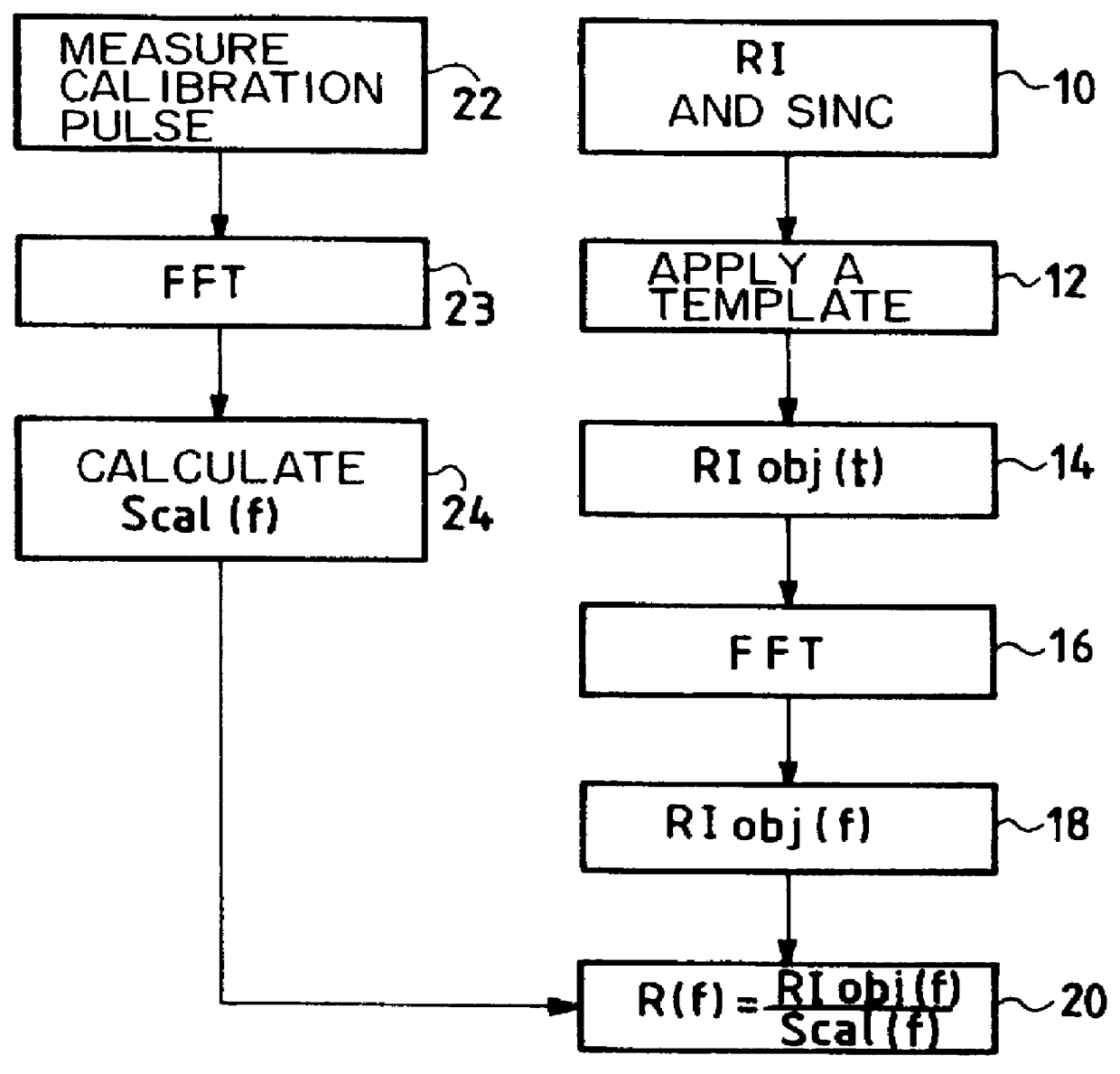
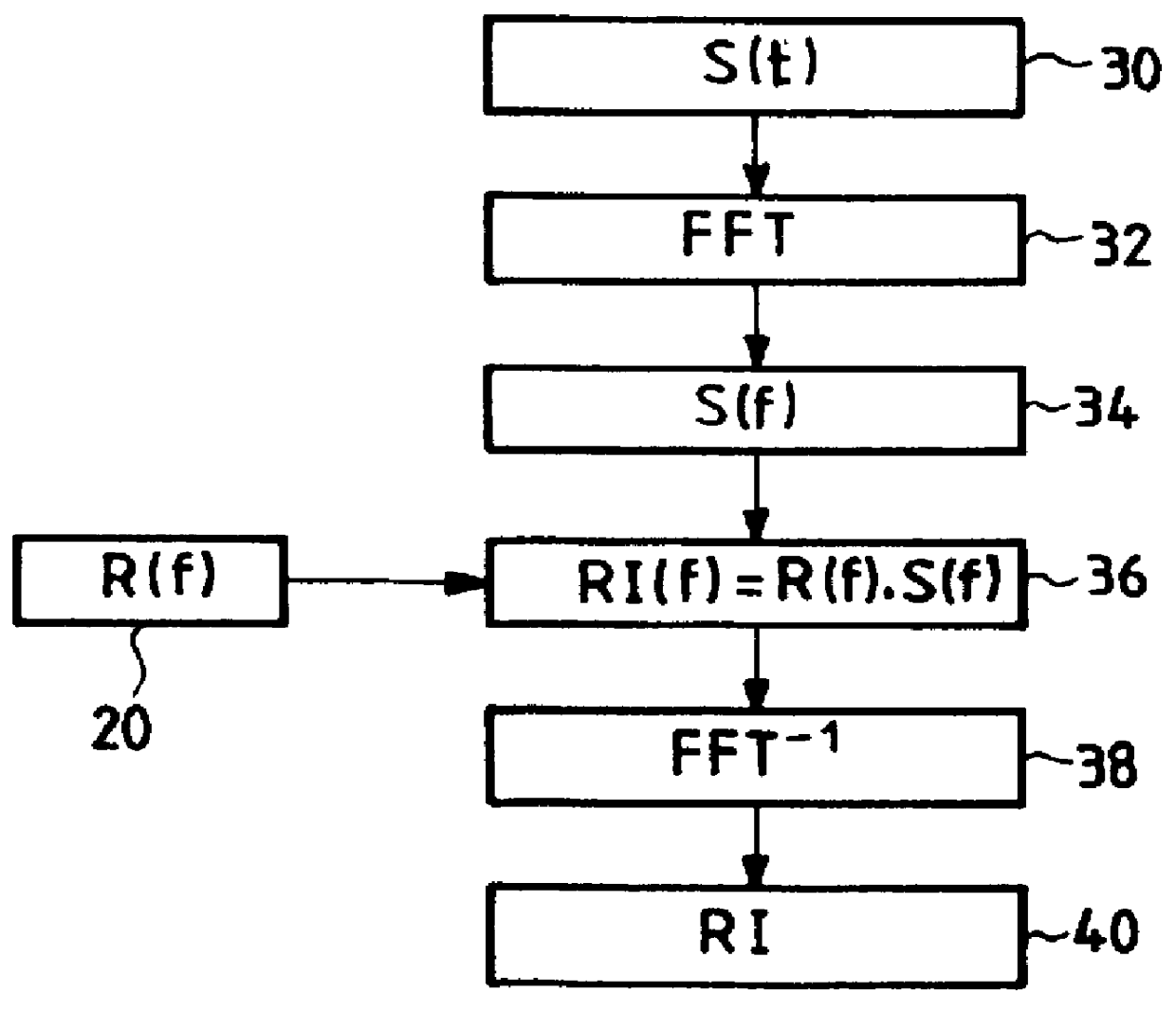
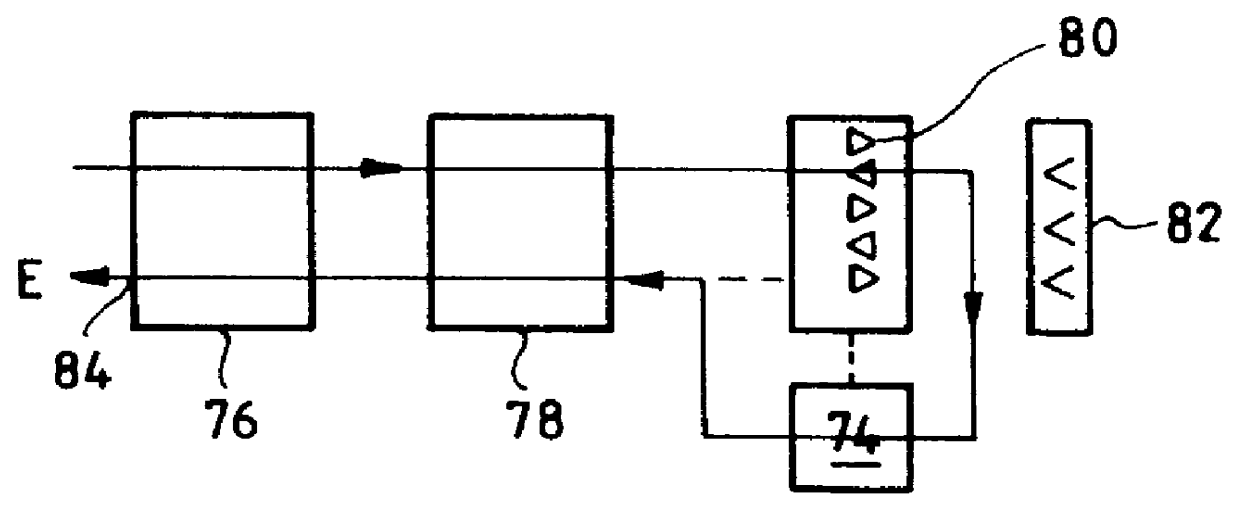
The invention concerns a method of synthesizing a replica used in the compression filter of pulse compression radar. The replica is calculated from the spectrum of a required impulse response. The required impulse response is preferably obtained from an analytical function, such as a sinc function or a weighted sinc function, and a template. It is preferable to use calibration signals of the instrument to calculate the replica. The invention also applies to synthetic aperture radar.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
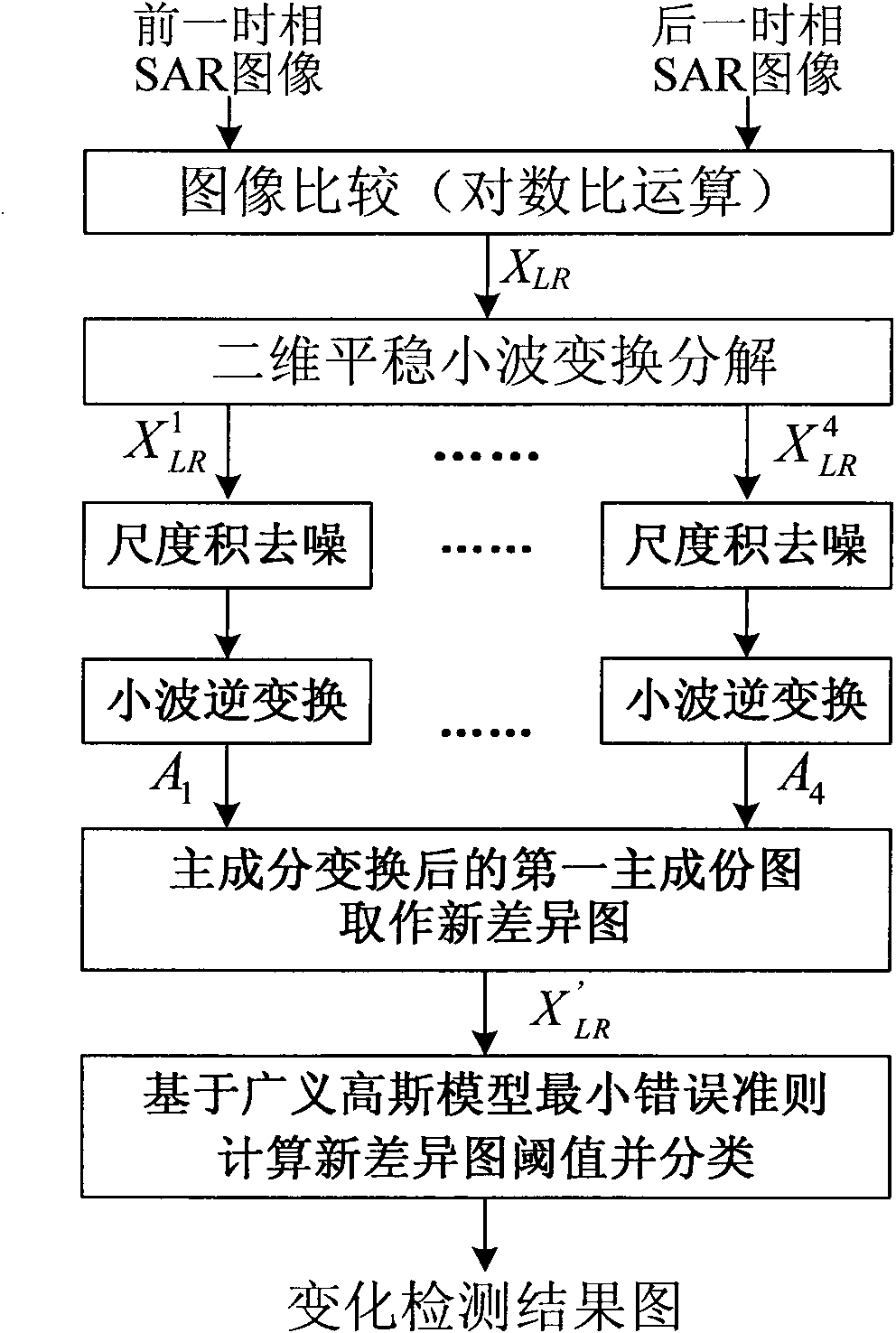
Method for detecting changes of SAR images based on multi-scale product and principal component analysis
InactiveCN101634709AImprove applicabilitySuppress speckle noiseImage enhancementImage analysisApplicability domainPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a method for detecting changes of SAR (synthetic aperture radar) images on the basis of multi-scale product and principal component analysis ( PCA ), mainly solving the problems that the adaptability is poor, the application range is narrow and the change detection results are subject to image misregistration. The method comprises the following specific implementation procedures: firstly, conducting the logarithmic ratio operation on two inputted time phase SAR images to obtain a difference image; carrying out the wavelet transform on the difference image; carrying out the multi-scale product de-noising on the high-frequency information of each decomposition layer; then, combining the de-noised images of each layer and carrying out the PCA transform, wherein, a first PCA image is used as a new difference image; and finally classifying the new difference image by using the minimum error ratio threshold value of the generalized Gaussian model to obtain the final result image of changes. The experiment shows that the invention can enhance the change information, have strong antinoise performance and reduce the influence of image misregistration, thus having high applicability and can be applied to the disaster detection of SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
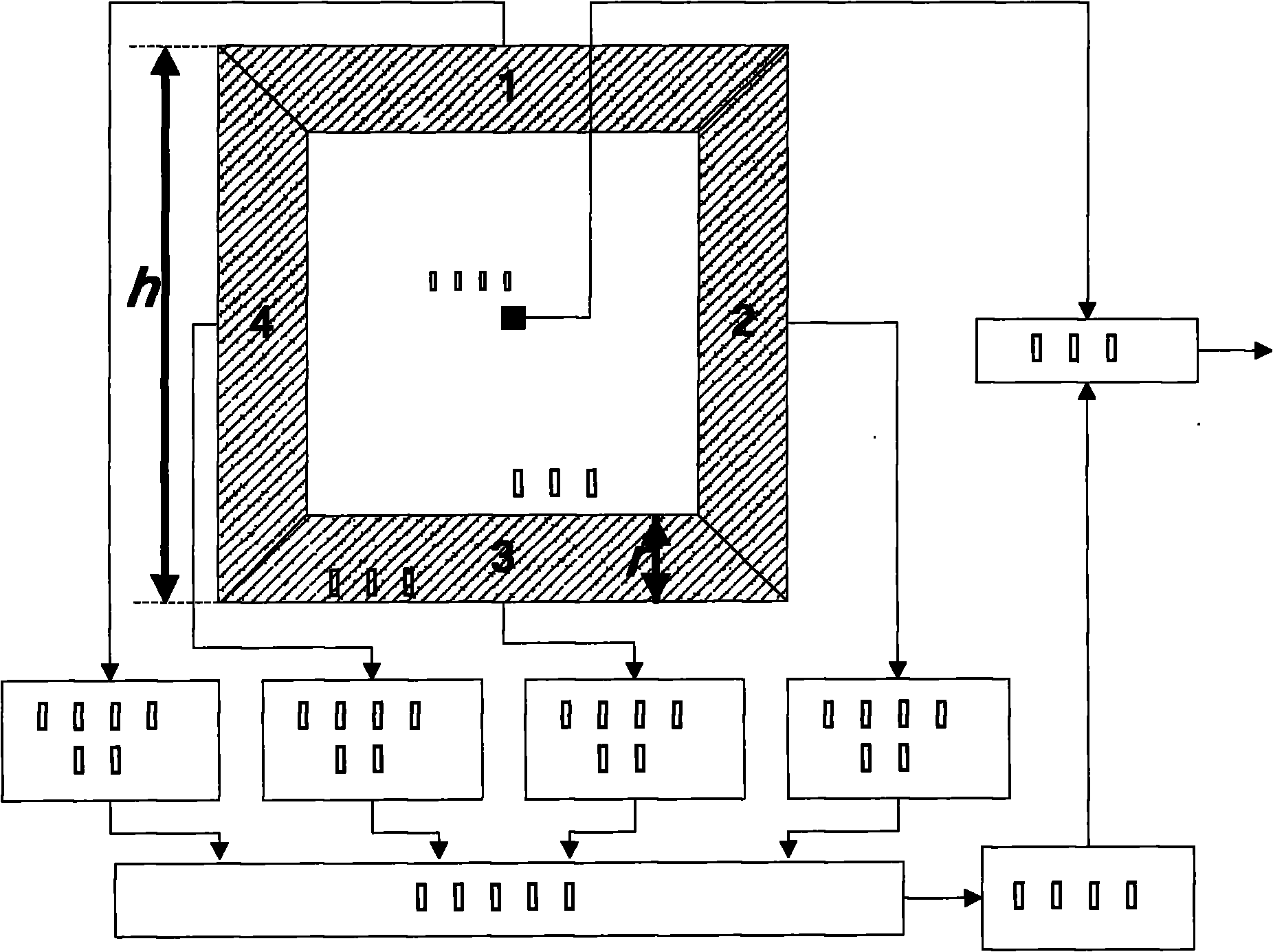
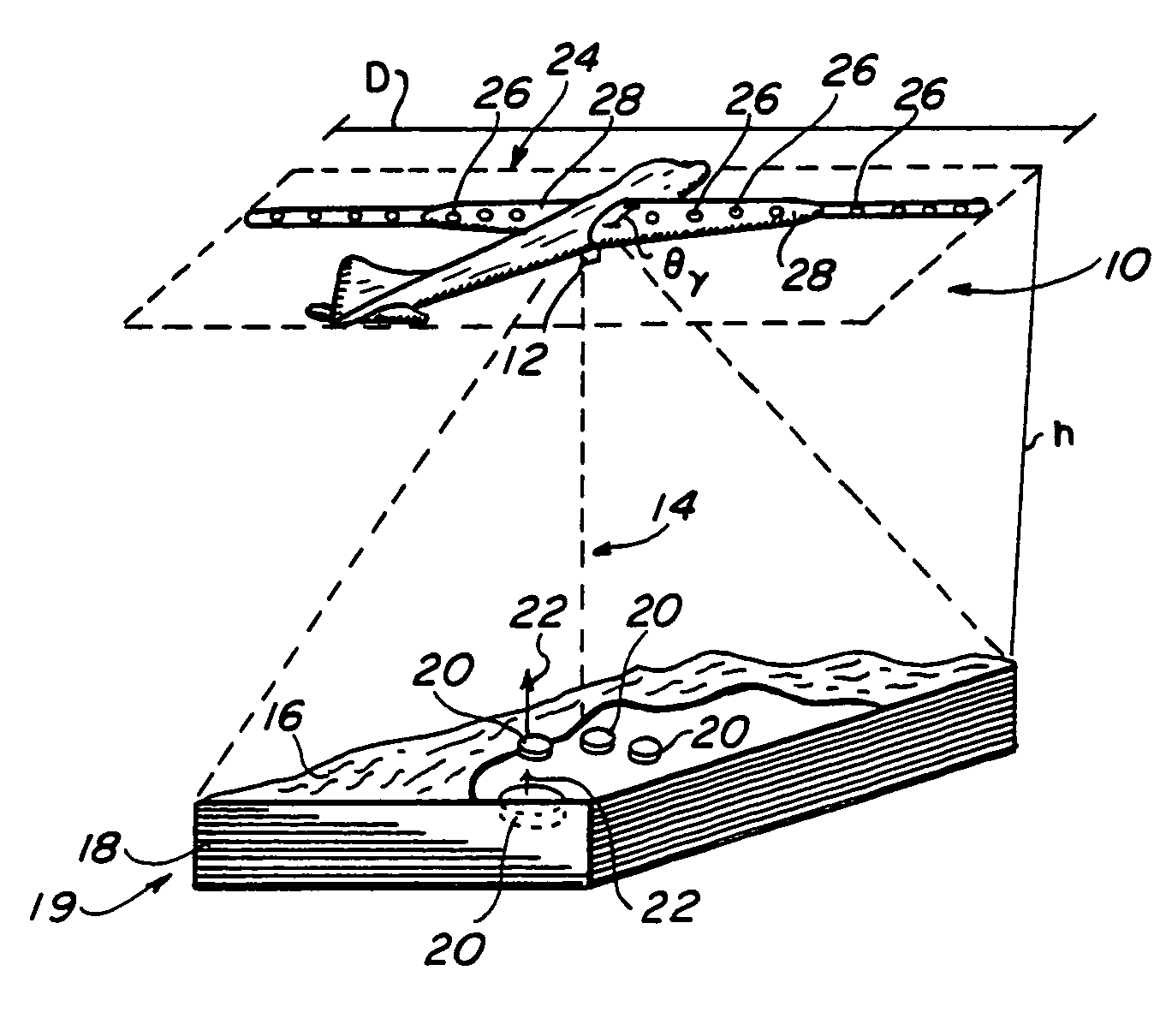
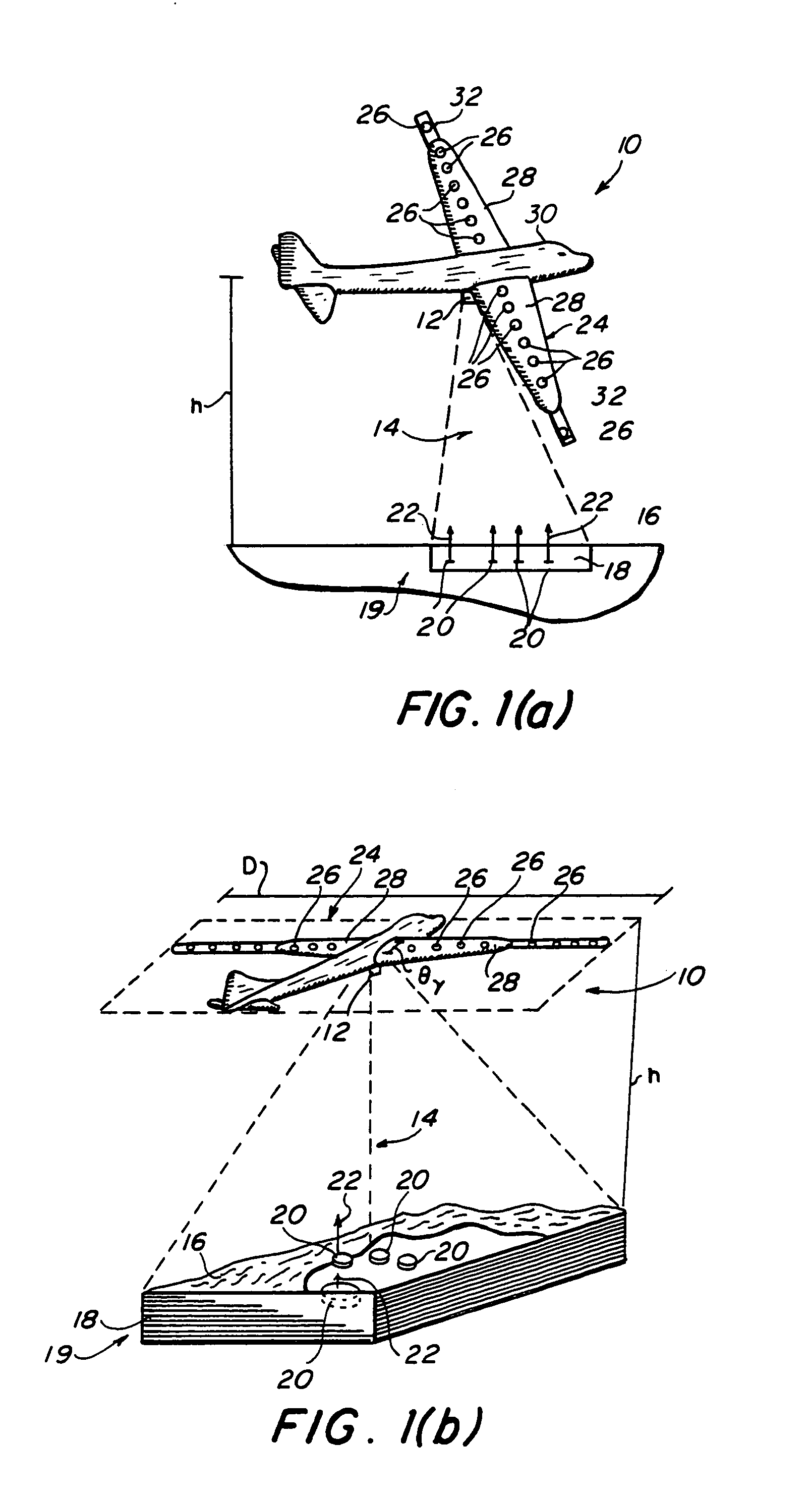
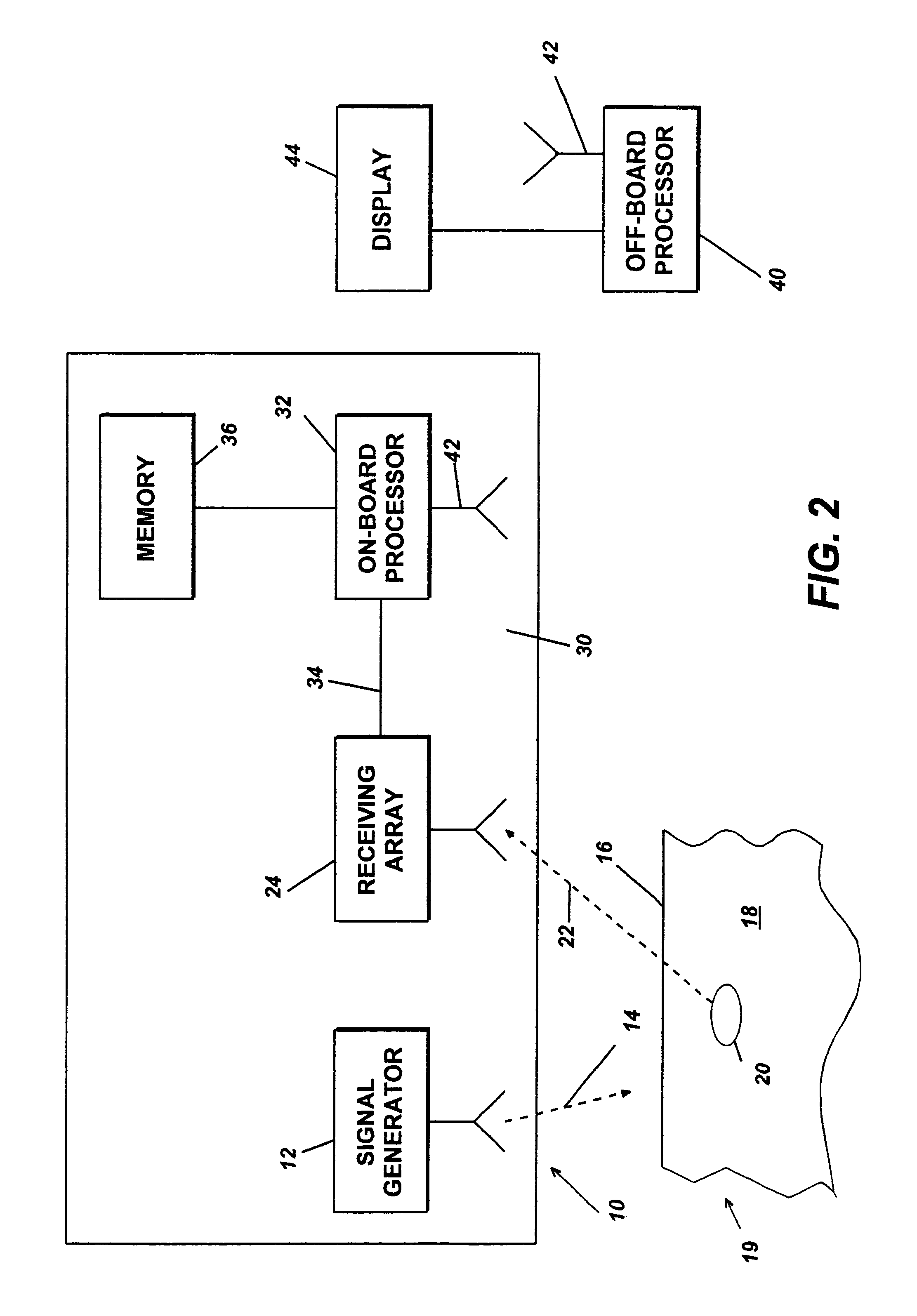
Three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar for mine detection and other uses
InactiveUS6982666B2Improve imaging resolutionDefence devicesTraining ammunitionRadar systemsFlight vehicle
A radar system for generating a three-dimensional image includes a radar transmitter which is operable to produce a radar signal of a frequency of at least three gigahertz. A plurality of radar receiving antennas from an antenna array. The antenna array is aerially translatable. For example, in one embodiment, the antenna array is disposed along the wings of an aircraft which, in operation, flies over the intended target area. A three-dimensional image is generated from a reflected radar signal returned from the surface of an object in response to the transmitted radar signal. The radar system may be incorporated into an aircraft and adapted to detect subsurface objects such as mines buried beneath the surface of the ground as the aircraft traverses over a target area.
Owner:NAVY USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com