Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
152 results about "Aperture plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
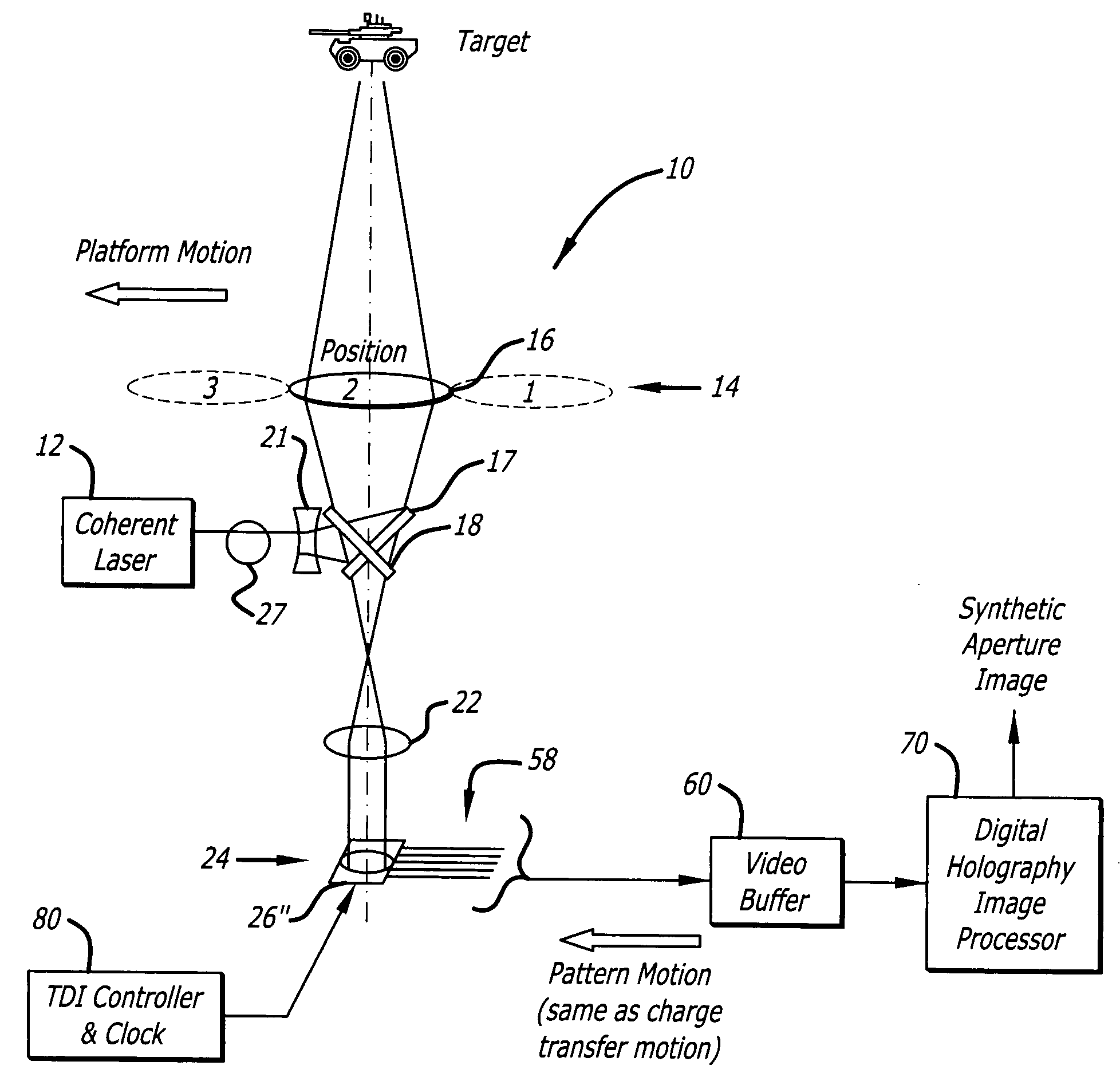
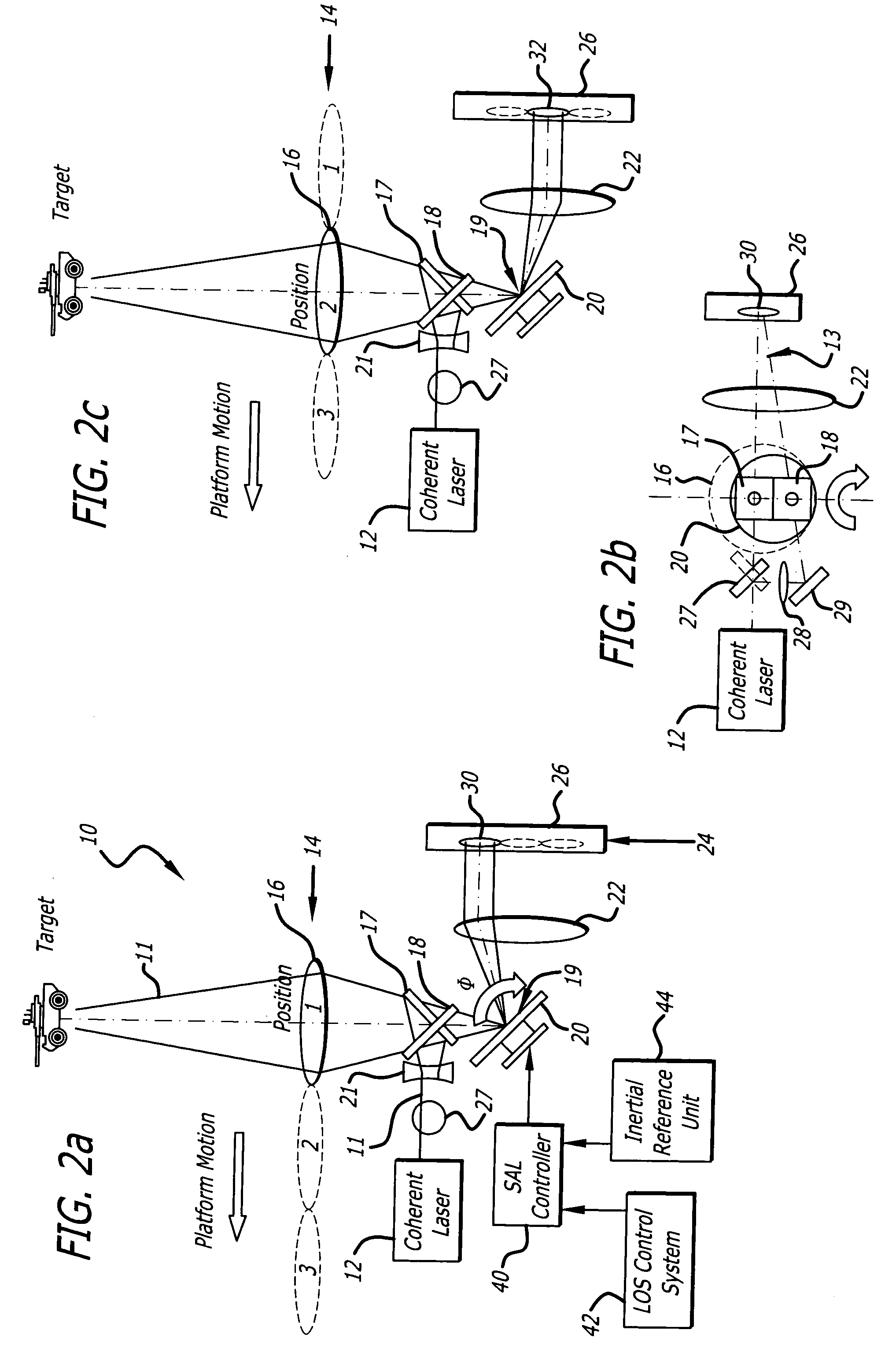
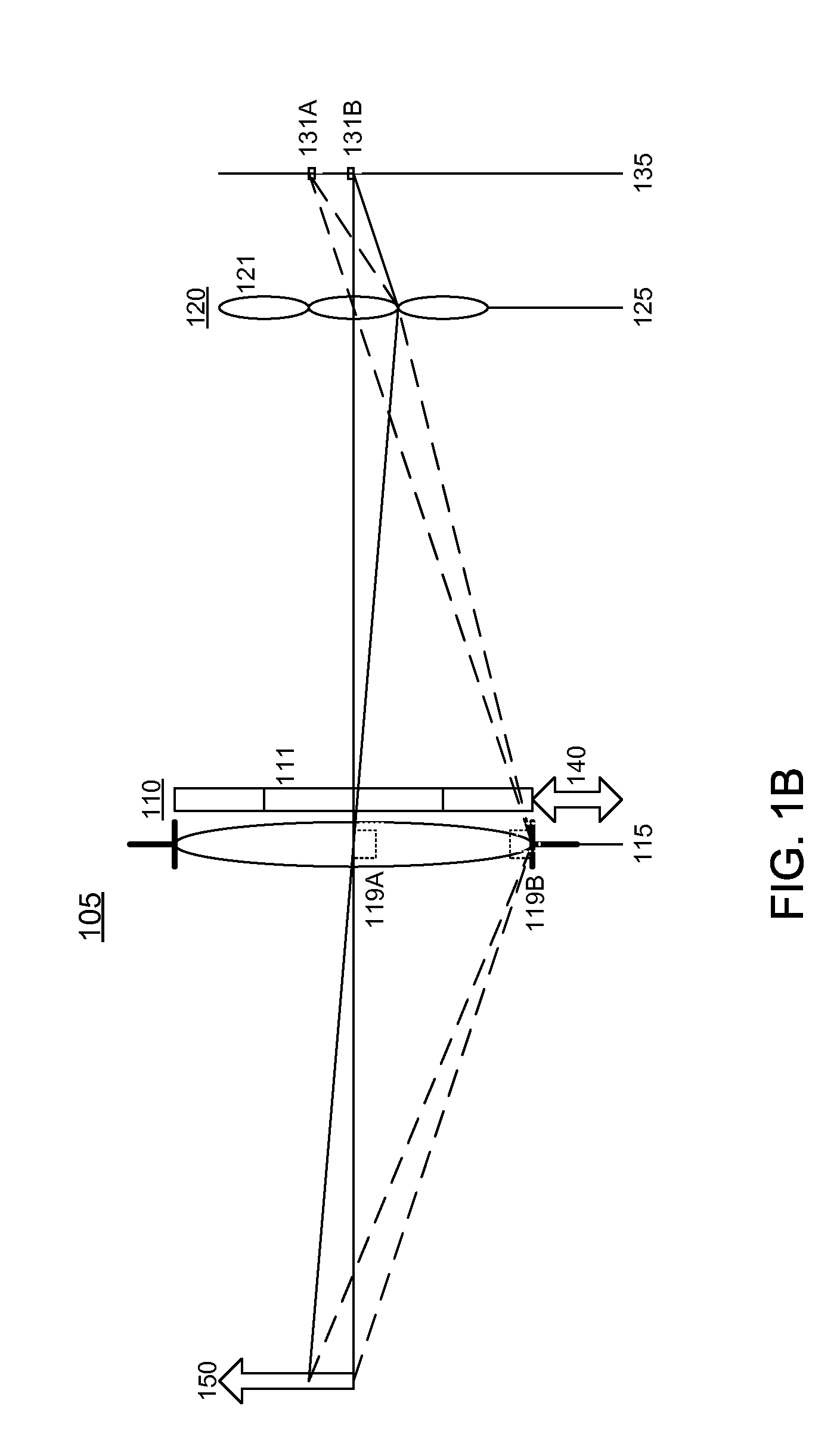
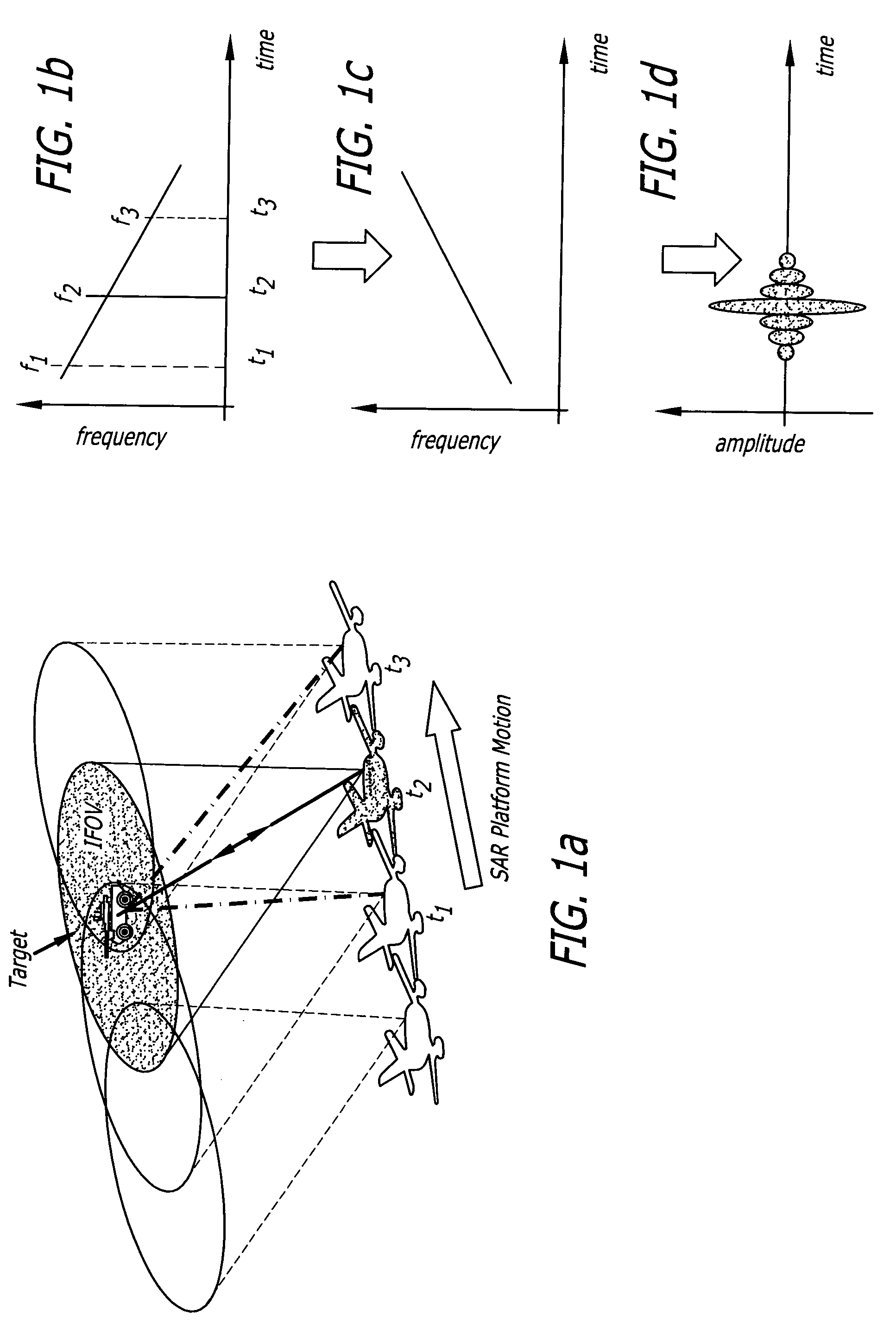
Synthetic aperture ladar system and method using real-time holography
ActiveUS20050057654A1Motion compensationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersSynthetic aperture radarReal time holography
This invention uses a real-time holographic medium to record the amplitude and phase information collected from a moving platform at the aperture plane of a side-looking optical sensor over the collection time. A back-scan mirror is used to compensate platform motion during the synthetic aperture integration time. Phase errors caused by a nonlinear platform motion are compensated by controlling the phase offset between the illumination beam and the reference beam used to write the hologram based on inertial measurements of the flight path and the sensor line-of-sight pointing angles. In the illustrative embodiment, a synthetic aperture ladar (SAL) imaging system is mounted on a mobile platform. The system is adapted to receive a beam of electromagnetic energy; record the intensity and phase pattern carried by the beam; and store the pattern to compensate for motion of the platform relative to an external reference. In the illustrative embodiment, the image is stored as a holographic image. The system includes a back-scan mirror, which compensates the stored holographic pattern for motion of the platform. The medium and back-scan mirror may be replaced with a digital camera and one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays may be used. In a specific embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used with a time delay and integration (TDI) scheme, which compensates for motion of the platform in the storage of the optical signals. In an alternative embodiment, a back-scanning mirror is used to compensate for motion of the platform. Consequently, the interference pattern between a relayed image of the aperture plane and a reference beam is continuously stored. In this embodiment, the instantaneous location of the received beam on the recording medium is controlled to compensate for motion of the platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Cameras with Varying Spatio-Angular-Temporal Resolutions
A camera includes a lens and a sensor. A dynamic mask is arranged at an aperture plane between the lens and the sensor, and a static mask is arranged immediately adjacent to the sensor. Angular, temporal or spatial variations in light rays acquired of a scene by the sensor are mapped to individual pixels of the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Partitioned aperture wavefront imaging method and system
InactiveUS20140267674A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh quality optical lensOptical measurementsColor television detailsIntermediate imageWavefront
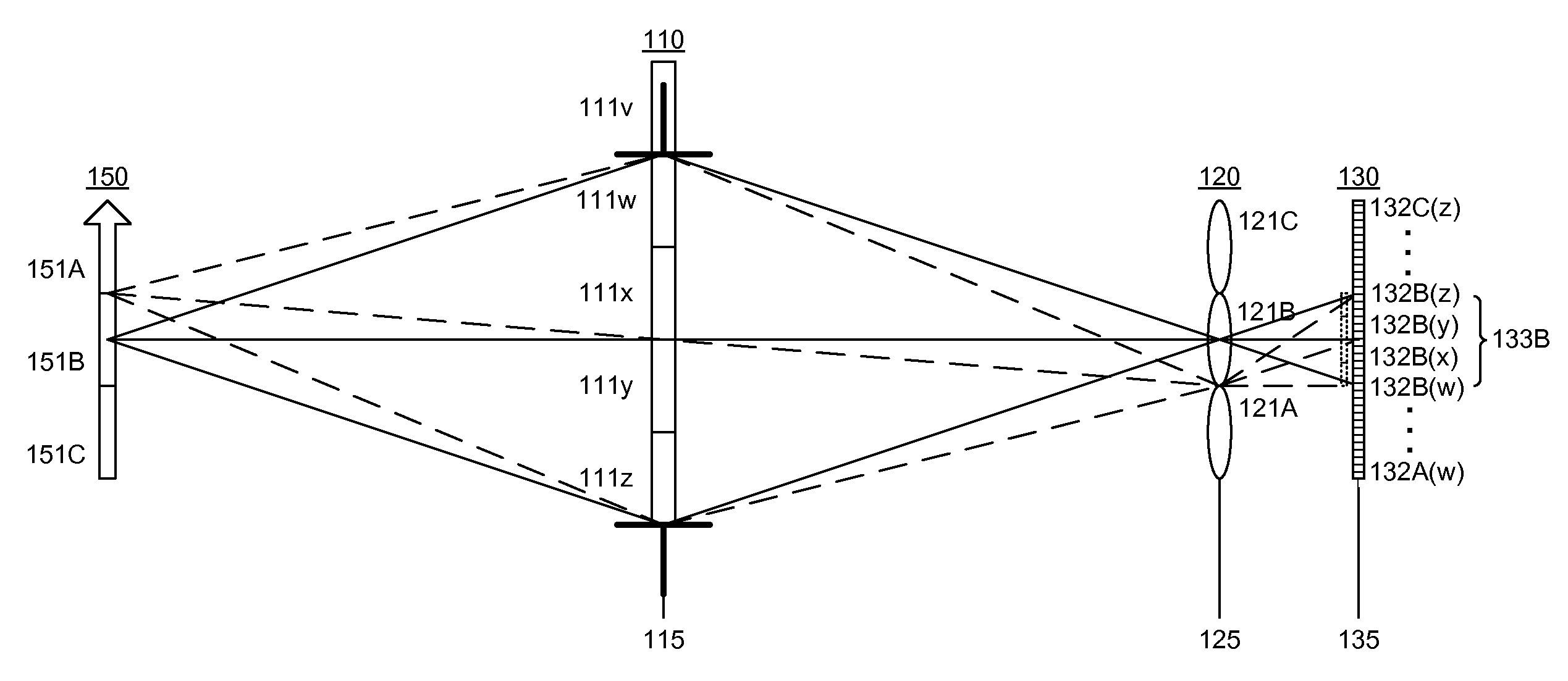
A partitioned aperture wavefront imaging system includes an imaging system comprising a partitioned aperture lens array positioned at the aperture plane or Fourier plane between the entrance plane and camera plane of an imaging system. The partitioned aperture lens array can include 2 or more off-axis lenses symmetrically distributed about an optical axis, and adapted to produce simultaneously at the camera plane at least two images of an object, or intermediate image of an object, presented at the entrance plane. Preferably, the partitioned aperture lens array includes from 3 to 5 off-axis lenses and produces 3 to 5 images at the camera plane from which phase and amplitude information about the light field can be determined. The partitioned aperture wavefront imaging system provides enough information about the light field presented at the entrance plane to enable reconstruction of the light field at other planes relative to the entrance plane.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Adjustable Multimode Lightfield Imaging System
InactiveUS20110073752A1Overcome limitationsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationEngineeringImage system
An adjustable multimode lightfield imaging system. A non-homogeneous filter module is positioned at the aperture plane of the lightfield imaging system and provides the multimode capability. The filter module can be moved relative to the imaging system, thus allowing adjustment of the multimode capability.
Owner:RICOH KK
Projection lens and microlithographic projection exposure apparatus
A projection exposure apparatus for microlithography has a light source, an illumination system, a mask-positioning system and a projection lens. The latter has a system aperture plane and an image plane and contains at least one lens that is made of a material which has a birefringence dependent on the transmission angle. The exposure apparatus further has an optical element, which has a position-dependent polarization-rotating effect or a position-dependent birefringence. This element, which is provided close to a pupil plane of the projection exposure apparatus, compensates at least partially for the birefringent effects produced in the image plane by the at least one lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
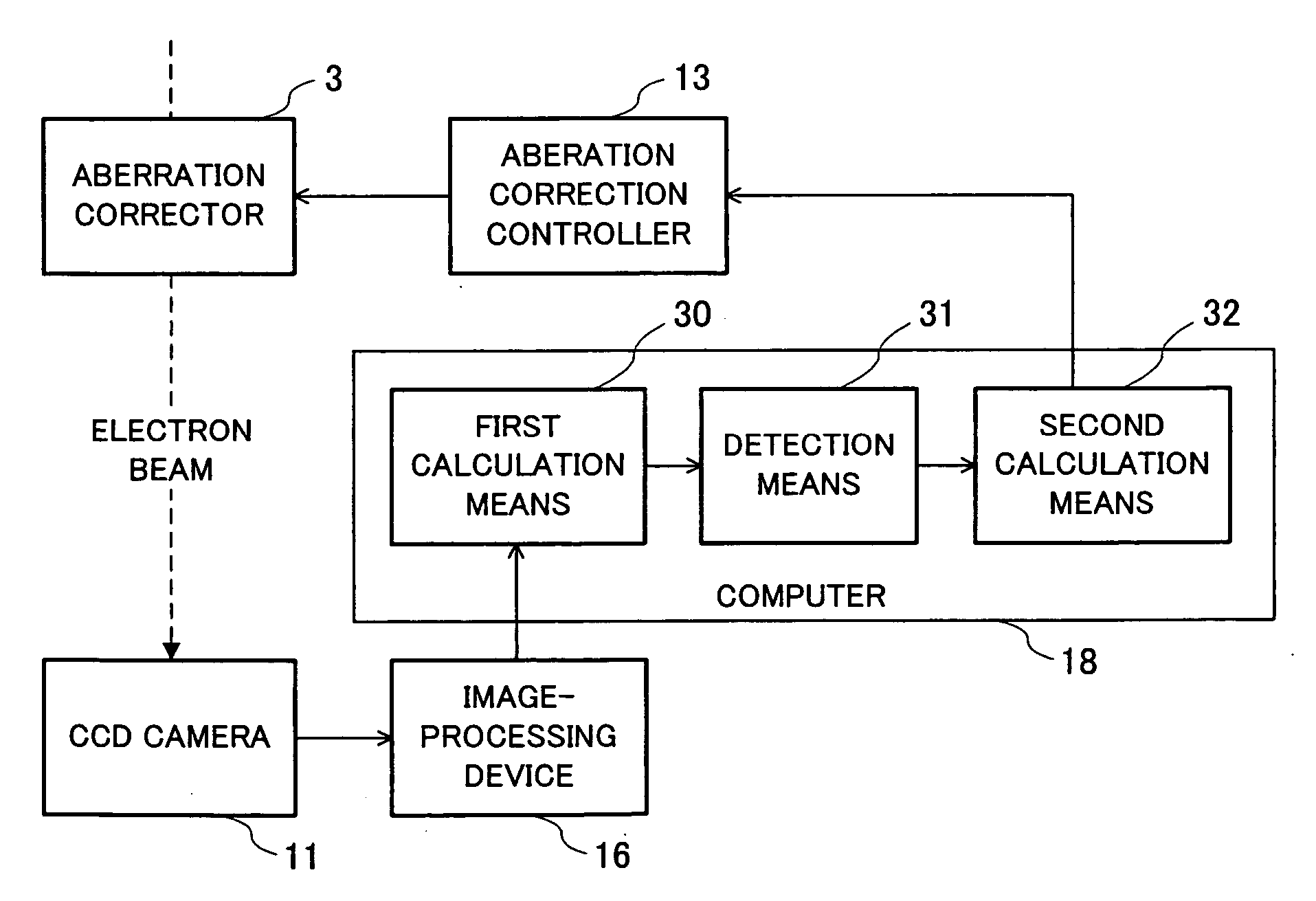
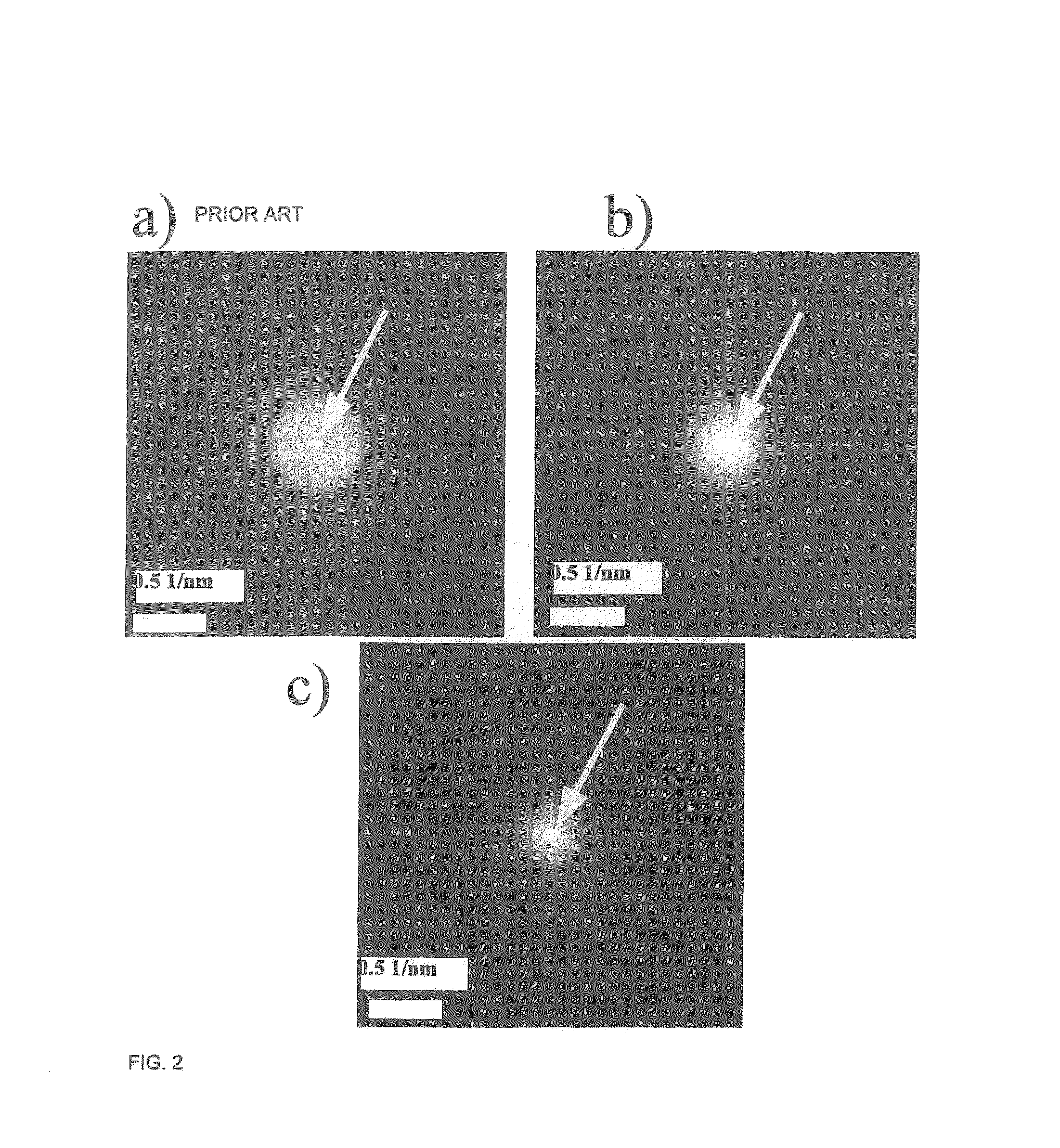
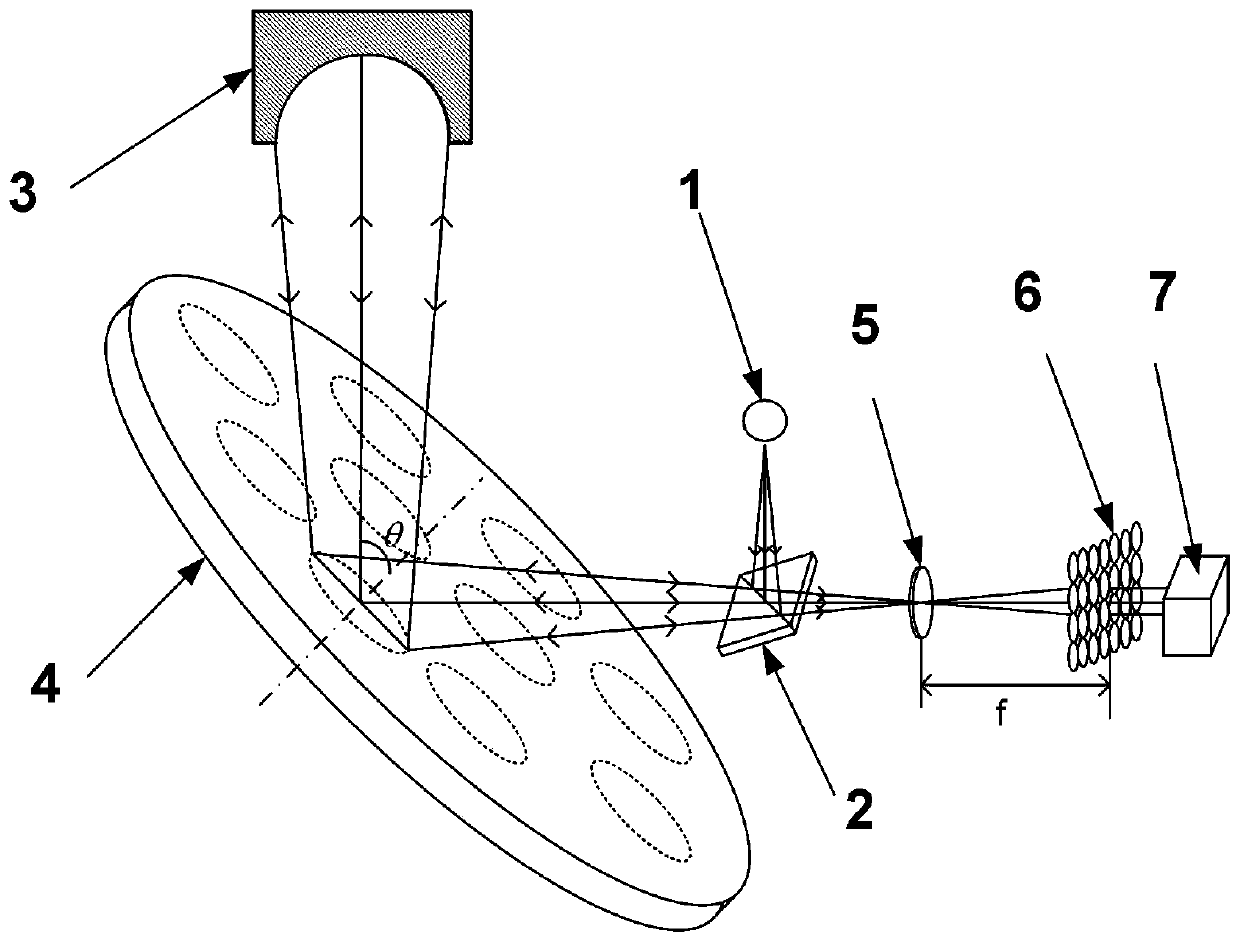
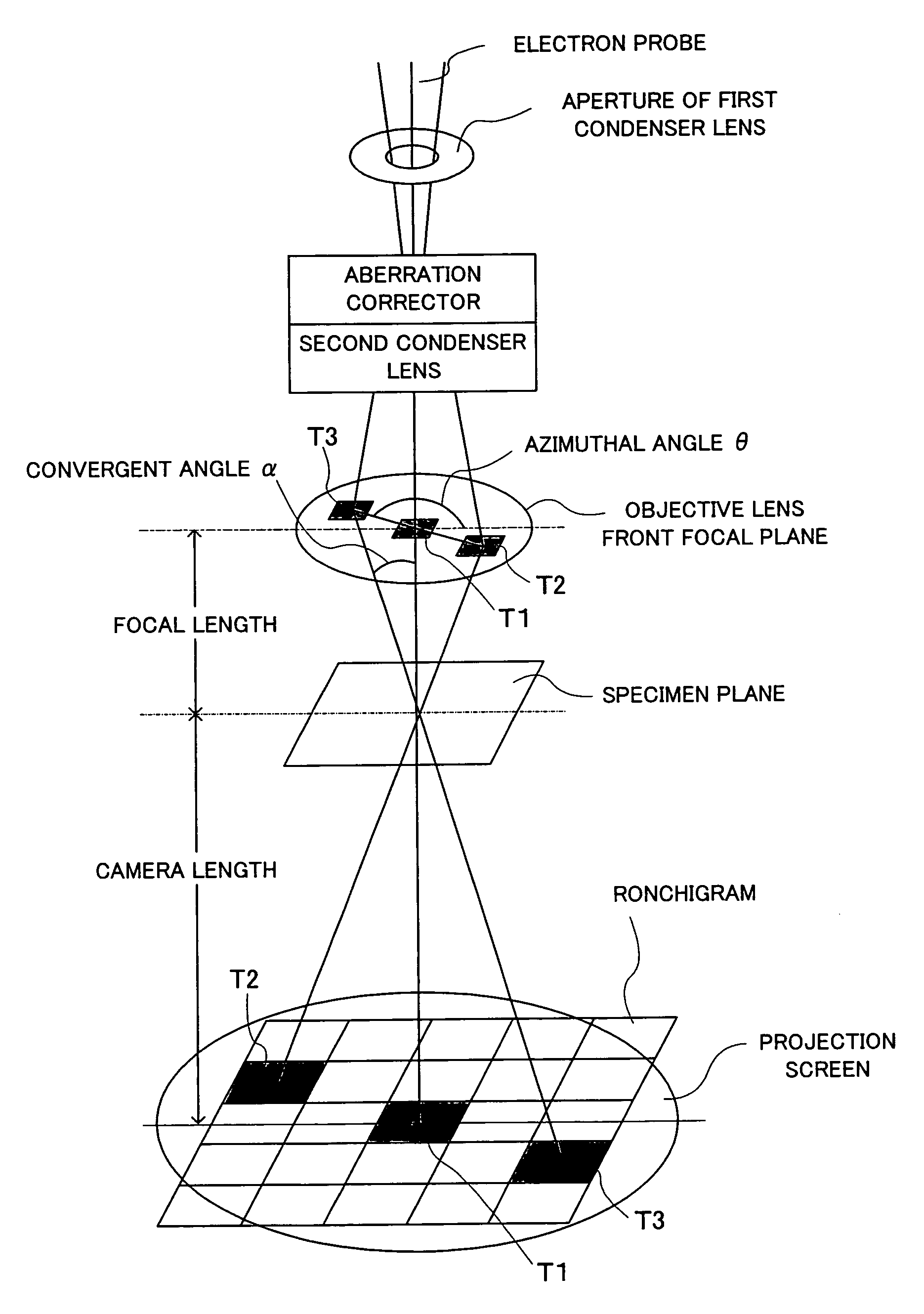
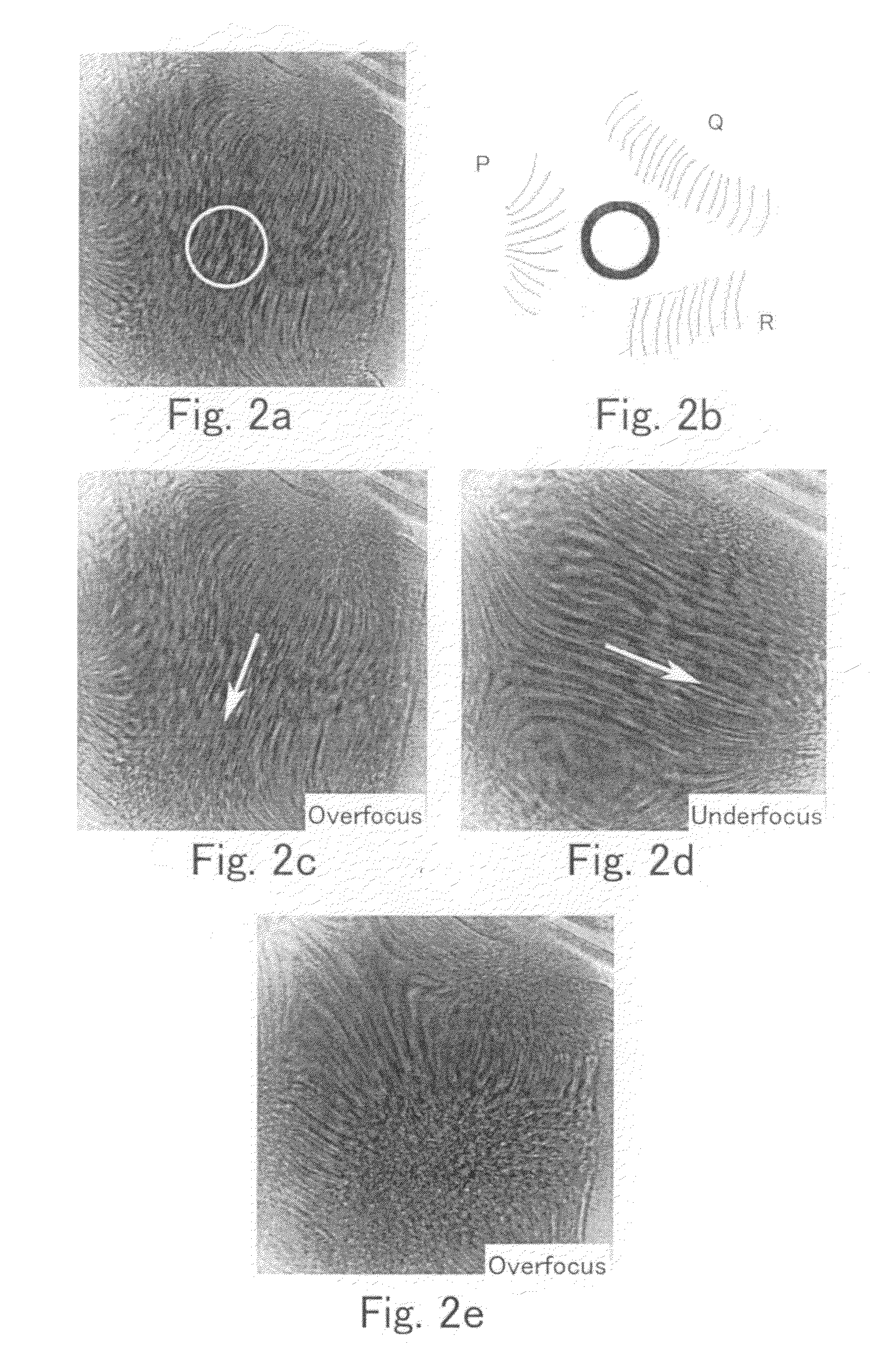
Method of measuring aberrations and correcting aberrations using ronchigram and electron microscope
ActiveUS20070120055A1Accurate analysisElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationLight beamComputational physics
A method and apparatus for correcting aberrations using a Ronchigram. A STEM apparatus has first calculation means for taking autocorrelation of minute regions on a Ronchigram of an amorphous specimen, detection device for detecting aberrations in the beam formed from local angular regions on an aperture plane from the autocorrelation or from Fourier analysis of the autocorrelation, second calculation device for calculating the aberrations based on the results of the detection, and control device for controlling operation for correcting the aberrations based on results of calculations performed by the second calculation device.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Phase contrast imaging and preparing a tem therefor
ActiveUS20110174971A1Simplified phase plate positioningEasy to placeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesOptical propertyX-Ray Phase-Contrast Imaging
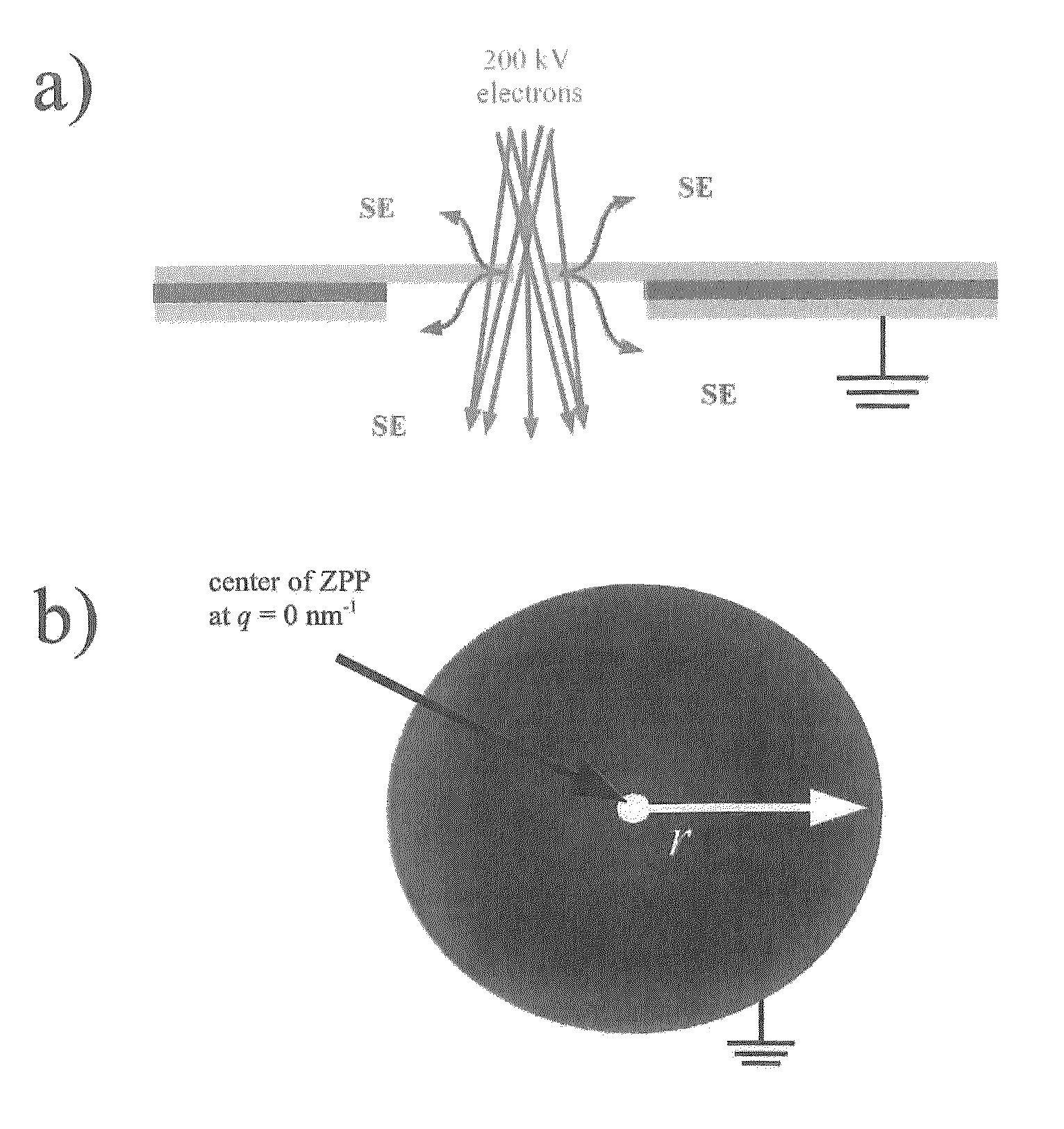
New methods for phase contrast imaging in transmission electron microscopy use the imaging electron beam itself to prepare a hole-free thin film for use as an effective phase plate, in some cases eliminating the need for ex-situ fabrication of a hole and reducing requirements for the precision of the ZPP hardware. The electron optical properties of the ZPP hardware are modified primarily in two ways: by boring a hole using the electron beam; and / or by modifying the electro-optical properties by charging induced by the primary beam. Furthermore a method where the sample is focused by a lens downstream from the ZPP hardware is disclosed. A method for transferring a back focal plane of the objective lens to a selected area aperture plane and any plane conjugated with the back focal plane of the objective lens is also provided.
Owner:JEOL LTD
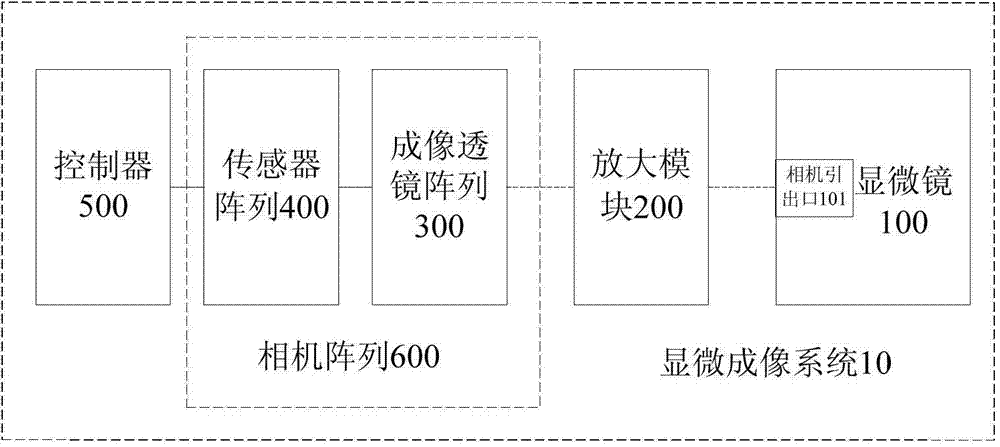
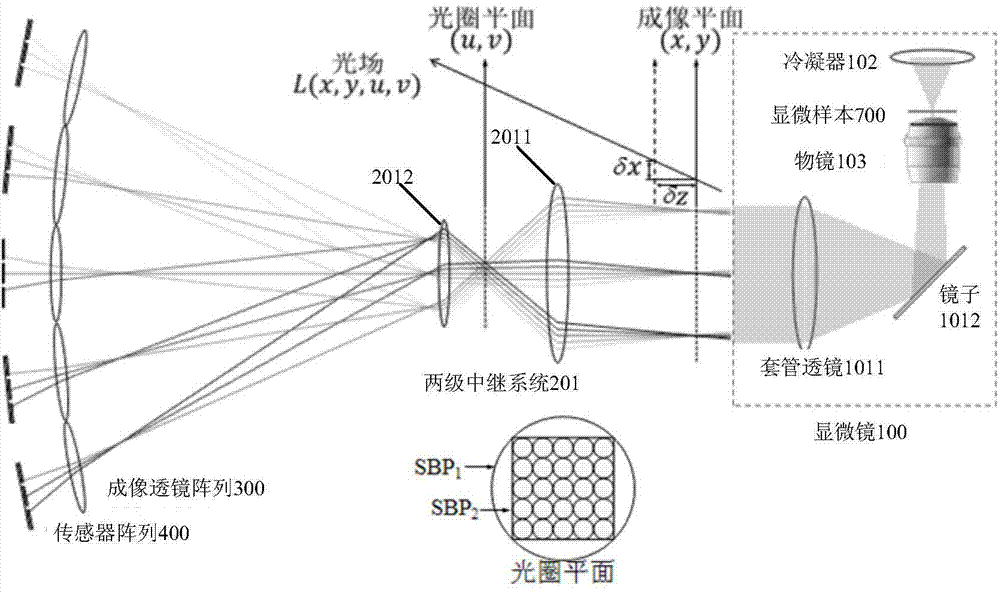
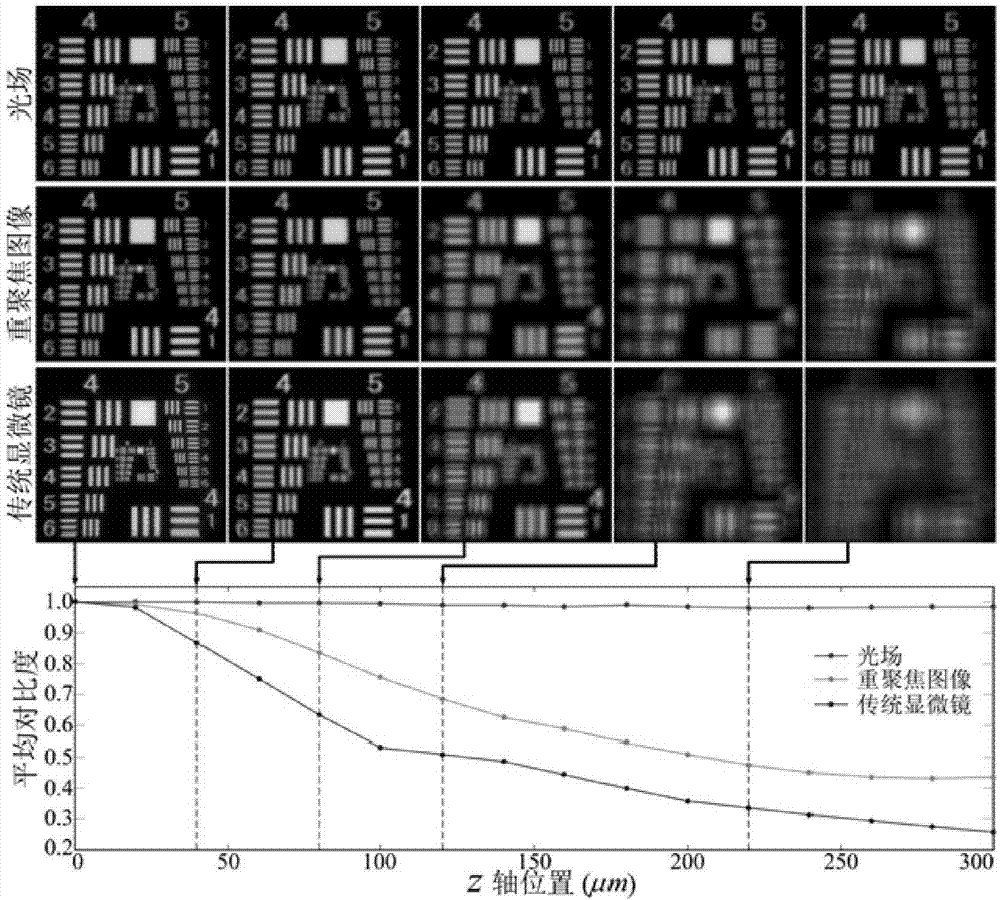
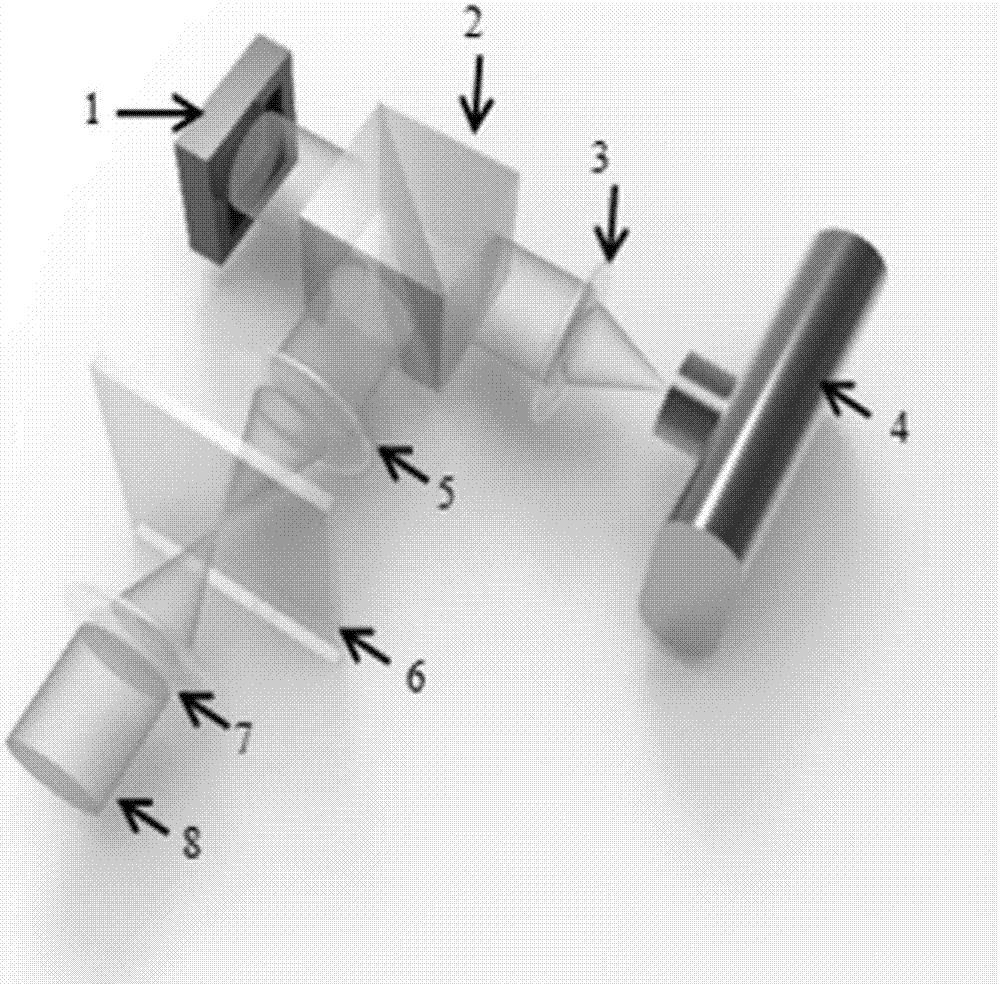
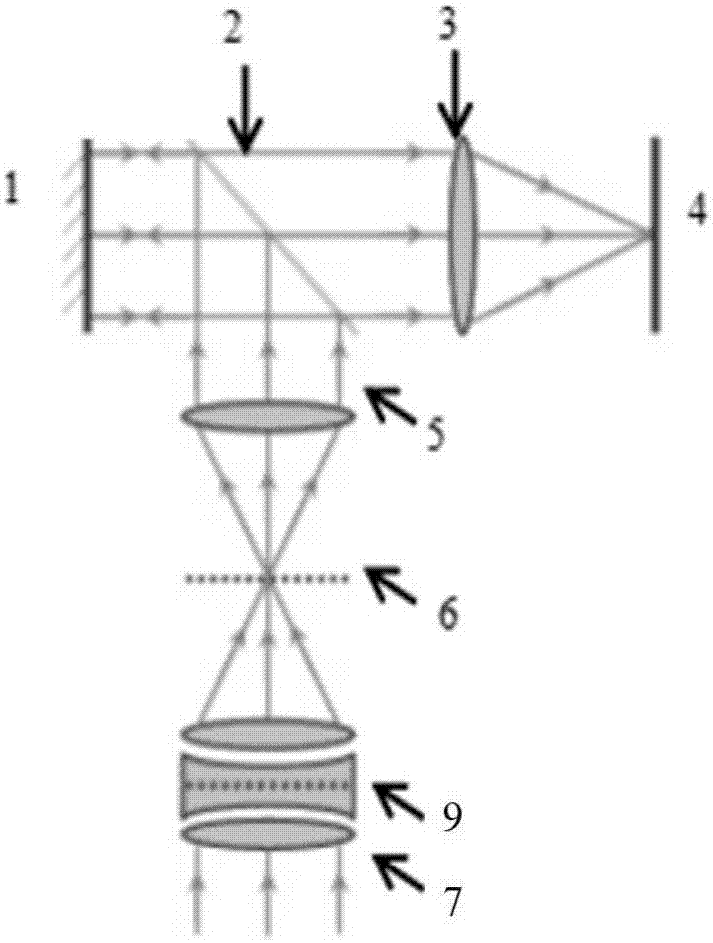
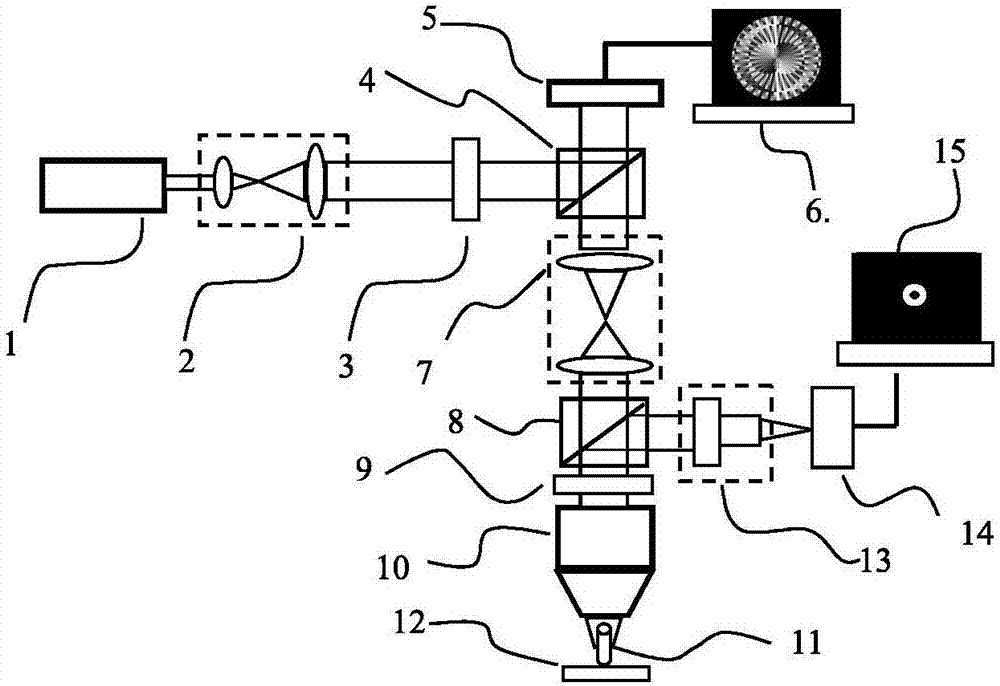
Camera array-based light field microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN104849852AImprove user experienceHigh resolutionMicroscopesSensor arrayHigh spatial resolution
The present invention discloses a camera array-based light field microscopic imaging system and method. The system includes a microscope which enlarges a microscopic sample to an image plane through a cameral lead-out opening, an enlargement module which can generate an aperture plane, an imaging lens array which obtains sample images of the microscopic sample under different angles of view, a sensor array wherein each sensor correspondingly records a sample image obtained by an imaging lens corresponding to the sensor, and a controller which acquires and calibrates the sample images synchronously so as to obtain the light field and / or light field video of the microscopic sample. According to the camera array-based light field microscopic imaging system and method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the sample images of the microscopic sample under different angles of view are obtained and calibrated, so that the light field and / or light field video of the microscopic scene can be obtained, and therefore, high-performance microscopic imaging and application can be realized, and spatial resolution can be improved, and use experience of users can be also improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Slot Antenna
InactiveUS20090121952A1Simple structureLinear waveguide fed arraysCoupling devicesImpedance matchingWaveguide
Impedance matching is achieved in a waveguide of a slot antenna, which is provided with an input waveguide that is fed power via an aperture plane; a stairway structure is provided in the input waveguide; the structure creates a step going upward toward a surface provided with a slot; the step difference and height of the step going upward are adjusted so that the impedance at a plane above the step and the impedance at the aperture plane match.
Owner:JAPAN RADIO CO LTD
Adjustable multimode lightfield imaging system having an actuator for changing position of a non-homogeneous filter module relative to an image-forming optical module
InactiveUS8143565B2Overcome limitationsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical ModuleComputer module
An adjustable multimode lightfield imaging system. A non-homogeneous filter module is positioned at the aperture plane of the lightfield imaging system and provides the multimode capability. The filter module can be moved relative to the imaging system, thus allowing adjustment of the multimode capability.
Owner:RICOH KK
Composite phase mask plate
The invention discloses a composite phase mask, the phase distribution function of which contains two different functions, namely, a sinusoidal type function and a third power type function. The function expression of the phase distribution function Theta(x, y) is as follows: Theta(x, y) is equal to Alpha question mark (x plus y) plus Beta question mark (sin(Omega question mark x) plus sin(Omega question mark y)), and in the expression, Beta question mark (sin(Omega question mark x) plus sin(Omega question mark y)) is a sinusoidal type function, and Alpha question mark (x plus y) is a third power type function; wherein Alpha is the amplitude of the third power type function, Beta is the amplitude of the sinusoidal type function, Omega expresses the angular frequency of the sinusoidal type function, and x, y is space coordinate with normalized aperture plane. The invention also discloses an imaging system which adopts the composite phase mask compounded by the sinusoidal type function and the third power type function and has smaller numerical value of the Fisher information, and the phase mask is not sensitive to defocusing, thus having better expansion capability of depth of focus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Annular focusing light spot realization method and realization device thereof
ActiveCN106950705APrecise position controlPrecise size controlOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorLight spot
The invention discloses an annular focusing light spot realization method. The method includes that a laser beam is expanded and collimated and then the expanded and collimated laser beam is converted into a linearly polarized laser beam; the laser beam phase modulation is carried out on the linearly polarized laser beam after the collimation and expansion by means of a reflective pure phase spatial light modulator; the linearly polarized light is imaged after the phase modulation to the rear aperture plane of a focusing object lens via a 4F imaging system; the object lens is used to focus the phase-modulated incident linearly polarized laser beam, a plurality of focal points are generated on the circumference in the focal plane area, and the azimuthal spacing between the focal points equal is equal; an annular light spot is generated when the circumference radius is reduced to a wavelength lambda, and the size of the annular light spot is continuously decreased when the circumference radius r changes until a solid light spot is formed; and when a plurality of phase modulation graphs are calculated, the change in the corresponding position movement of each graph is small, and the phase map of the spatial light modulator is updated so that the annular light spot moves continuously. The annular focusing light spot realization method realizes the non-vortex plane linearly polarized light focusing to generate the dynamic annular light spot which is accurate in position and size control.
Owner:唐山斯腾光电科技有限公司
Engineered Point Spread Function for Simultaneous Extended Depth of Field and 3D Ranging
InactiveUS20140192166A1Reduce impactRestore fine detailImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spreadWavefront
Optical systems utilize waveplates to simultaneously encode information for increasing image depth of field and for providing a depth map of the imaged object or sample. These waveplates are configured to result in a focus-invariant point spread function in one focal region, and to result in point spread functions that vary as a function of range within the imaged object in a different focal region. For example, a basic compound microscope might have a specially shaped waveplate inserted at the back aperture plane of the microscope objective to manipulate the phase of the wavefront. An image formed on one side of the plane of best focus is focus invariant, and is brought into focus by a restoring algorithm. An image formed on the other side of the plane of best focus captures point spread functions comprising rings that vary with depth within the imaged object.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Insulating panel
ActiveUS7748169B2Improve insulation effectReduce conductionShutters/ movable grillesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringMembrane structure
An insulating panel attachable to a building, the building defining a building aperture, the building aperture defining an aperture plane extending substantially thereacross. The insulating panel includes a membrane structure defining a first external wall and a substantially opposed second external wall; a peripheral wall extending between the first and second external walls, the first external wall, second external wall and peripheral wall together defining an enclosure; and an internal wall system located between the first and second external walls, the internal wall system being configured so as to divide the enclosure into a first cell located substantially adjacent to the first external wall and a second cell located substantially adjacent to the second external wall, the first and second cells being substantially spaced apart respectively from the second and first external walls by the internal wall system. A frame is attachable to the building, the frame being operatively coupled to the membrane structure for maintaining the first external wall substantially parallel to the aperture plane and substantially in register with at least a portion of the building aperture when the frame is attached to the building.
Owner:SECCO INT
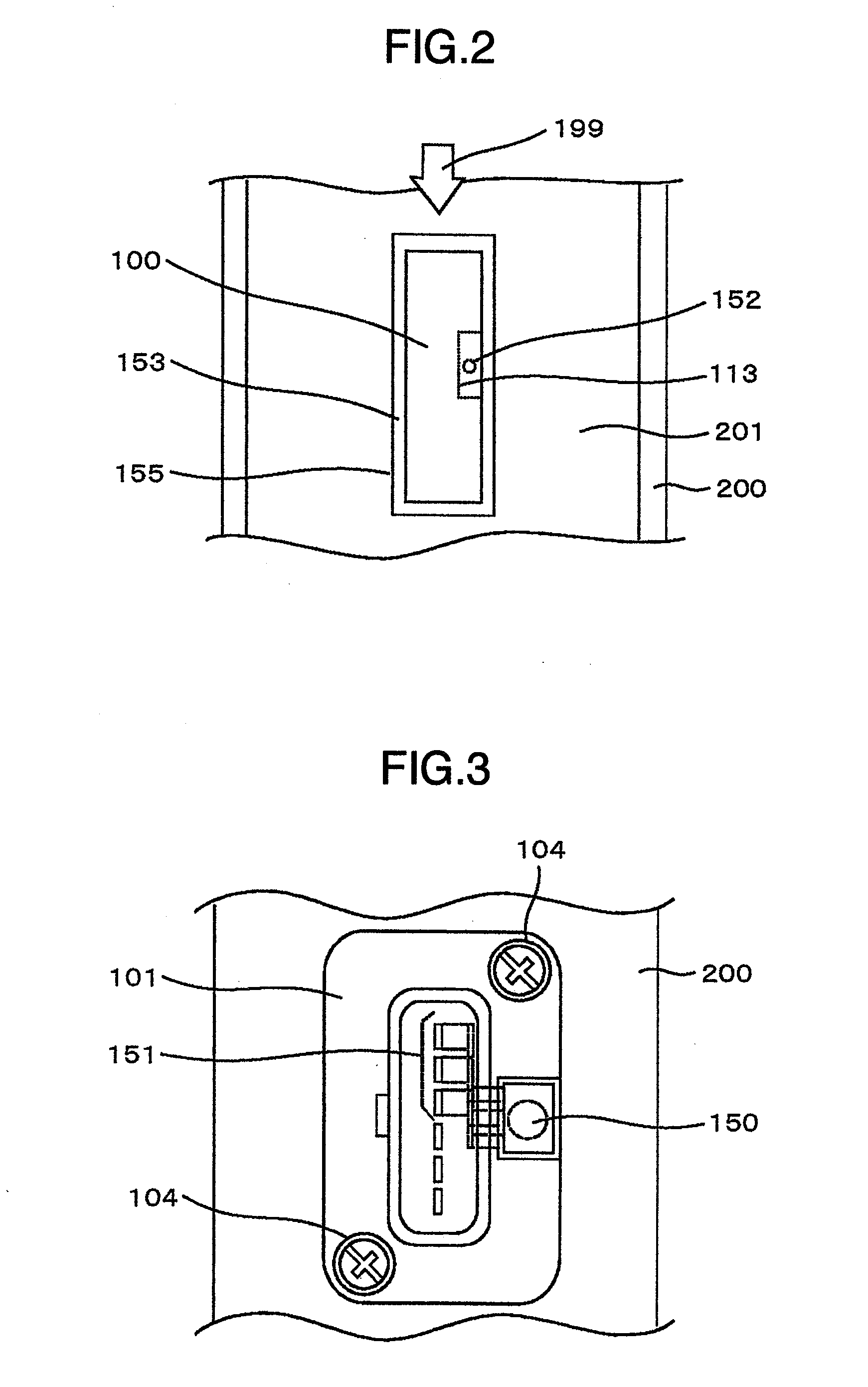
Intake air mass flow measurement device
ActiveUS20080302173A1Save natural resourcesReduce the amount requiredEngine testingVolume flow proportion measurementMeasurement devicePressure sense
In an intake air mass flow measurement device, for preventing clogging in a pressure intake tube due to water or the like entering the pressure intake tube in a device measuring a pressure in the intake air tube, the intake air mass flow measurement device includes a mass air flow measurement device for measuring an intake air mass flow in an intake air tube; and a pressure sensing device for sensing pressure in the intake air tube, the pressure sensing device being integrated with the mass air flow measurement device, and an aperture plane opened to the inside of a main air flow passage for detection of the pressure takes in pressure by using a gap generated between a main air flow passage constituting member and an insertion part of the mass air flow measurement device when a measurement part of the mass air flow measurement device is inserted into the main air flow passage. With this construction, it is possible to provide a structure in which water or the like can hardly clog the pressure intake port.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
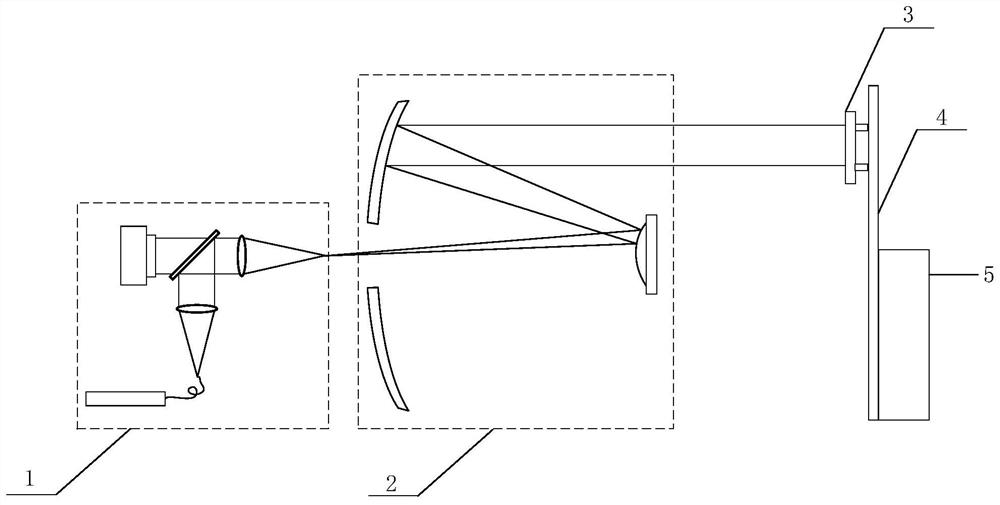
Large-aperture optical system MTF measuring device and method
InactiveCN111912607AReduce testing costsReduce usageTesting optical propertiesWavefront sensorWave aberration
The invention provides a large-aperture optical system MTF measuring device and method in order to solve the technical problems that in a traditional large-aperture optical system MTF detecting mode,the testing precision is easily affected by the surface shape of an optical element in a large-aperture collimator, the disturbance resisting capacity is poor, and the testing cost is high. Accordingto the invention, a small-aperture plane mirror is used as a reference plane mirror, an active Hartmann wavefront sensor is used as wavefront measurement equipment, the small-aperture plane mirror ismoved to each sub-aperture position of a large-aperture optical system, and the active Hartmann wavefront sensor is used to acquire the wave aberration of each sub-aperture. When the full aperture iscompletely covered, sub-aperture wave aberration data are spliced by adopting a sub-aperture splicing algorithm to obtain full aperture wave aberration, and the full aperture wave aberration can be converted into an MTF value of an optical system after numerical calculation. According to the invention, the use of an interferometer and a large-aperture plane mirror is avoided, the anti-disturbancecapability of the whole system is improved, and the test cost is reduced.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
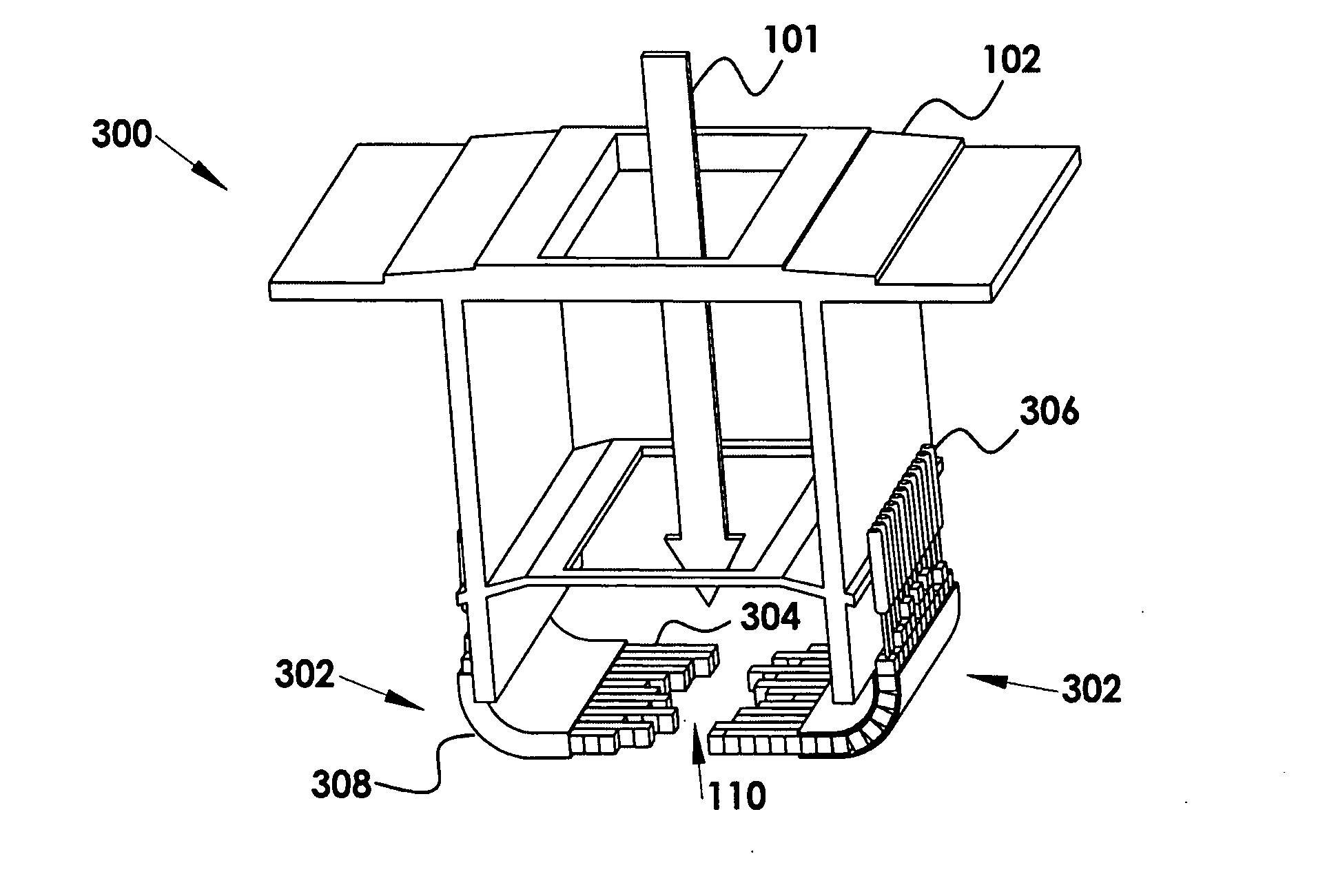
Multileaf collimator for electron radiotherapy
InactiveUS20090001295A1Easy accessFaster patient treatmentElectrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A flexible multi-leaf collimator for electron radiotherapy is provided, where the leaves are not a single rigid component, but are configured in a manner that curves away from the patient to provide greater clearance. The invention includes a plurality of flexible assemblies, at least one guide supporting the assemblies, and a plurality of assembly drivers. The driver engages the assembly and moves the assembly along the guide. The assembly has an extended state and a retracted state relative to the guide, such that when in the extended state the assembly is held in the aperture plane and when in the retracted state the assembly conforms along the guide. When in the extended state the assemblies are disposed as a treatment aperture.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Metal foil for secondary battery and secondary battery
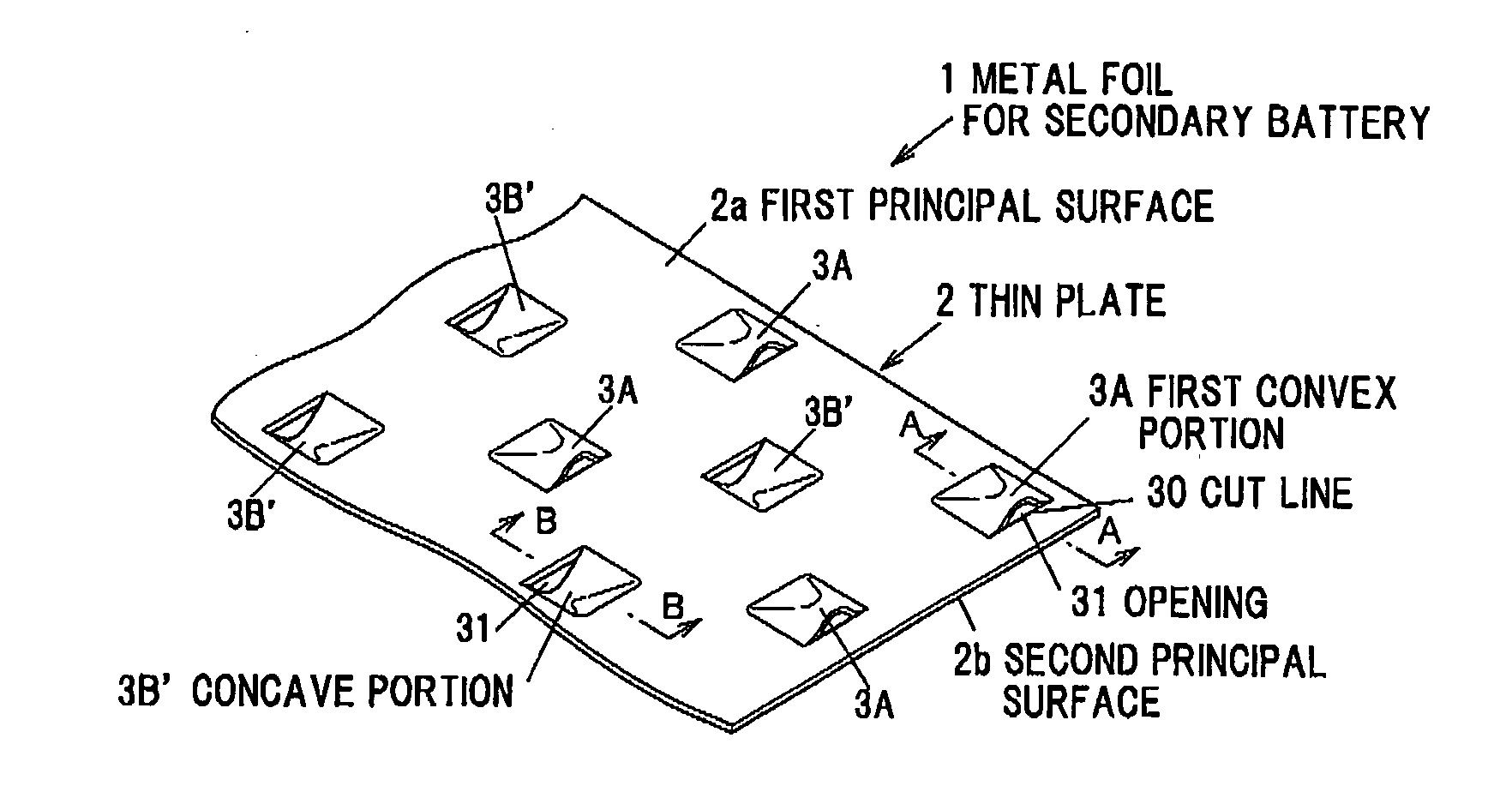
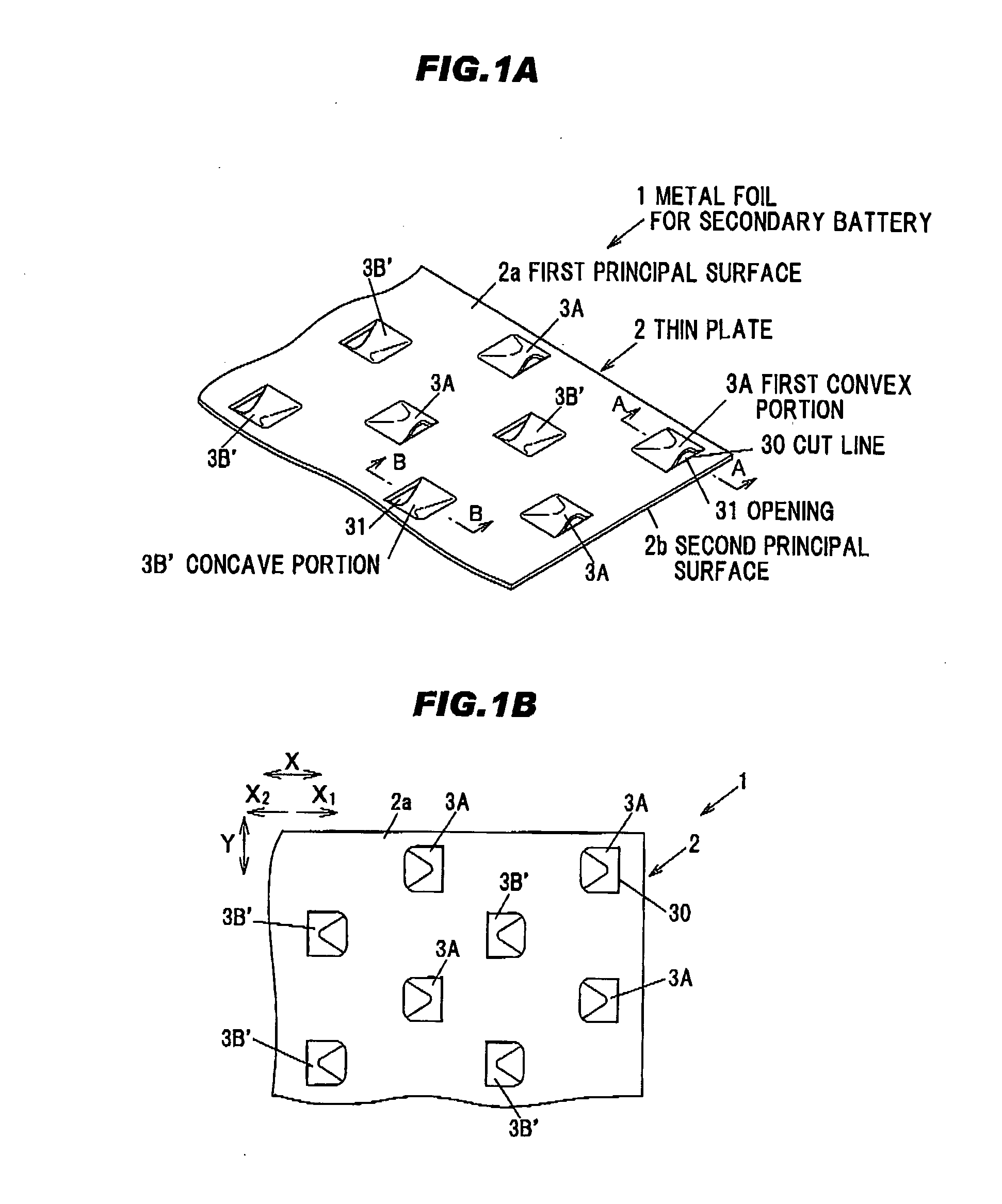
InactiveUS20110311877A1Less cutting chipsIncrease opening ratioLayered productsElectrode carriers/collectorsMetal foilEngineering
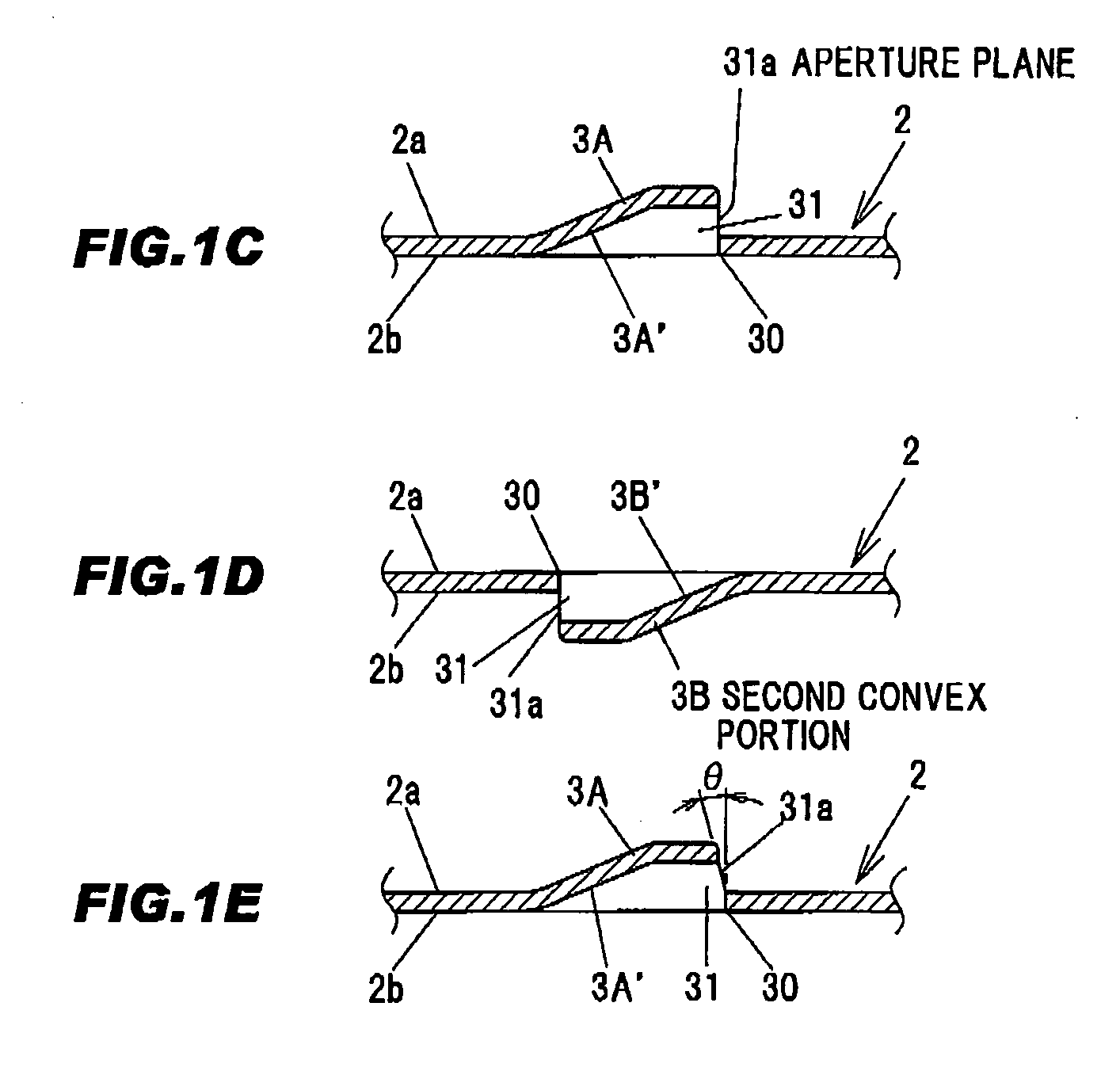
A metal foil for secondary battery generating less cutting chips at the time of forming an opening and allowed to have a higher aperture ratio without reducing strength and a secondary battery in which short circuit caused by generation of electrode debris can be suppressed are provided. A metal foil 1 for secondary battery is provided with a metal thin plate 2, plural first convex portions 3A formed on a first principal surface 2a of the thin plate 2 by plastic forming and plural second convex portions 3B formed on a second principal surface 2b opposite to the first principal surface 2a by the plastic forming, wherein the convex portions 3A and 3B each have an opening 31 of which aperture plane 31a is orthogonal or substantially orthogonal to the principal surfaces 2a and the 2b.
Owner:FINECS
Method, lens assembly and camera for reducing stray light
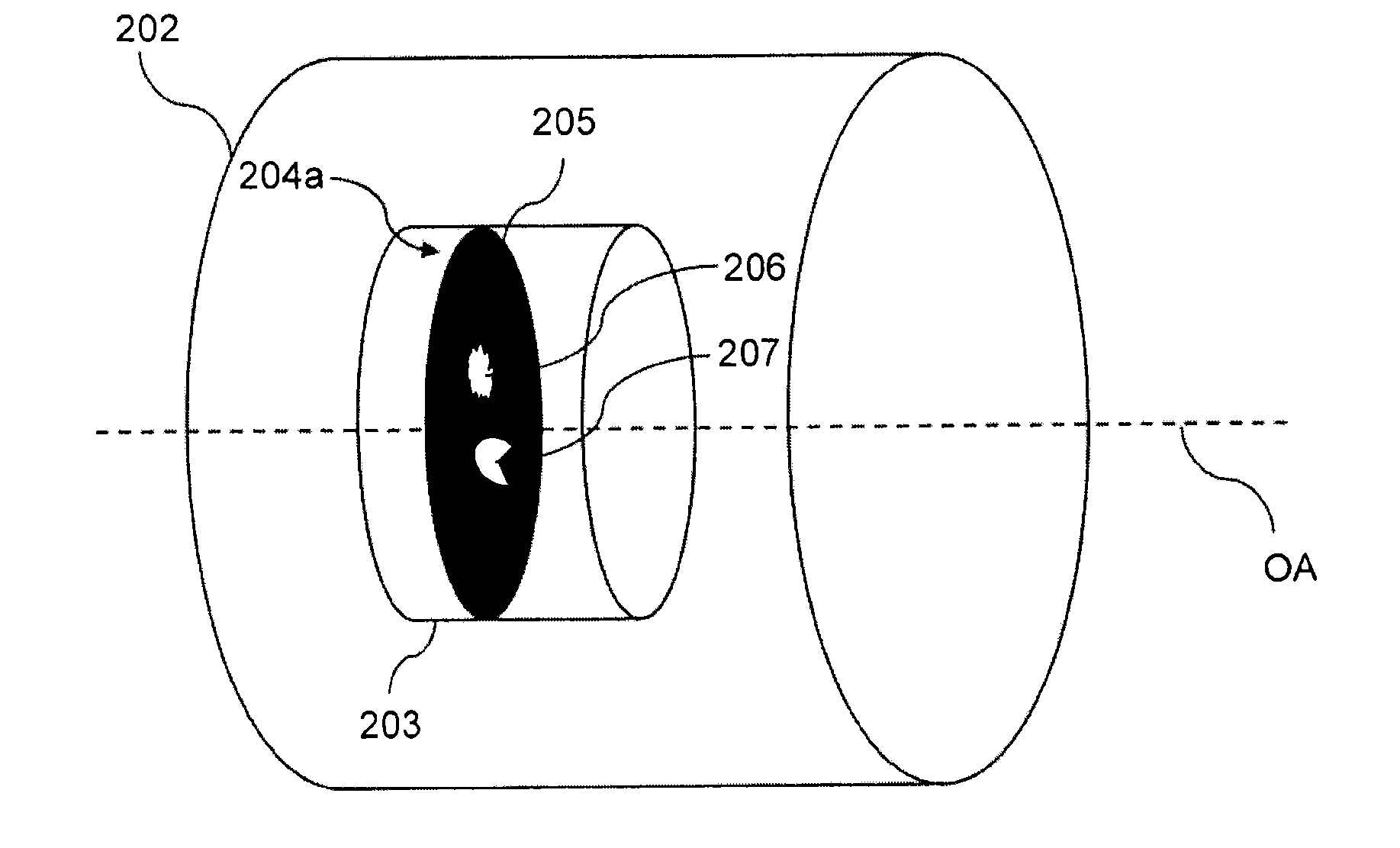
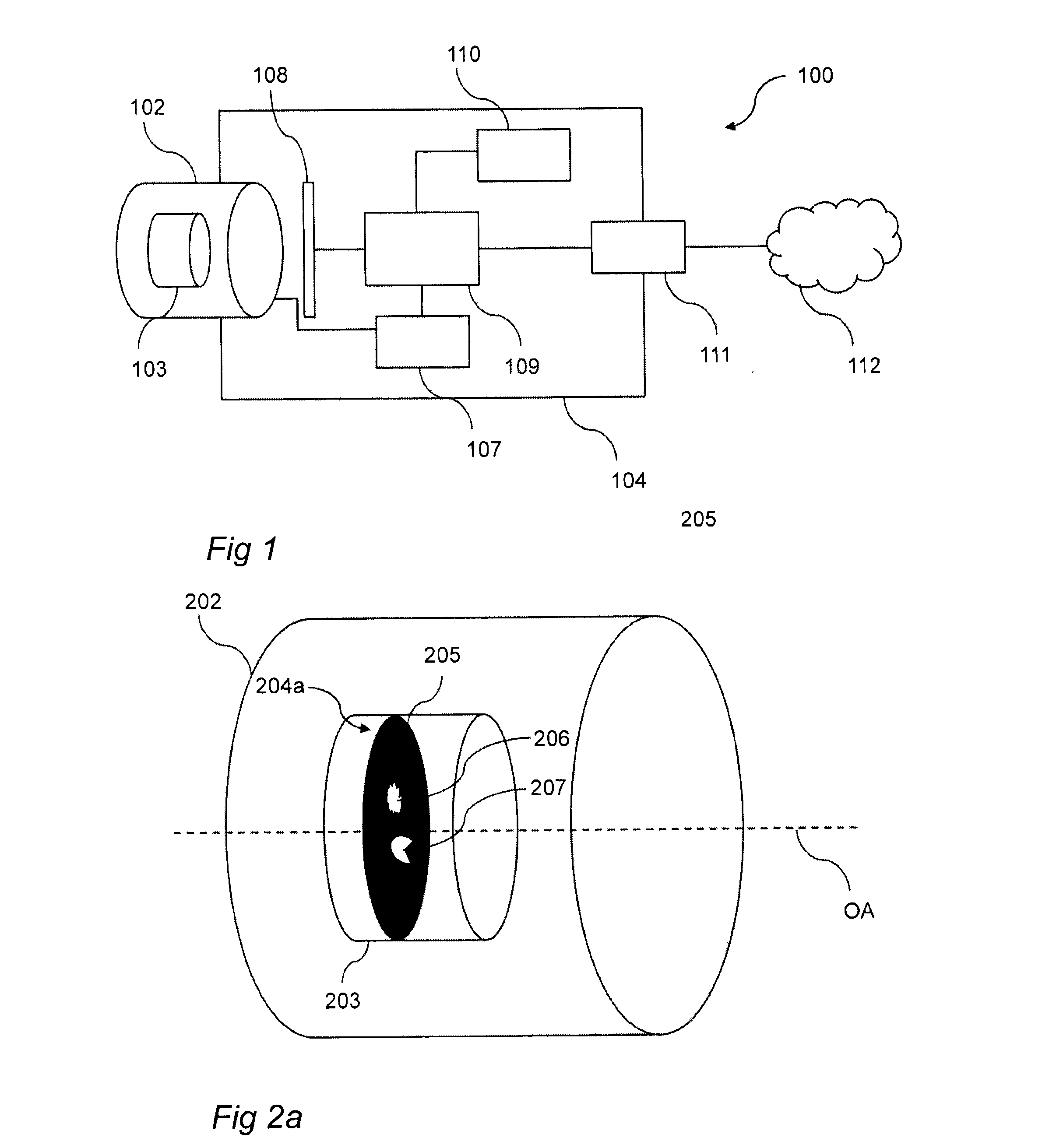
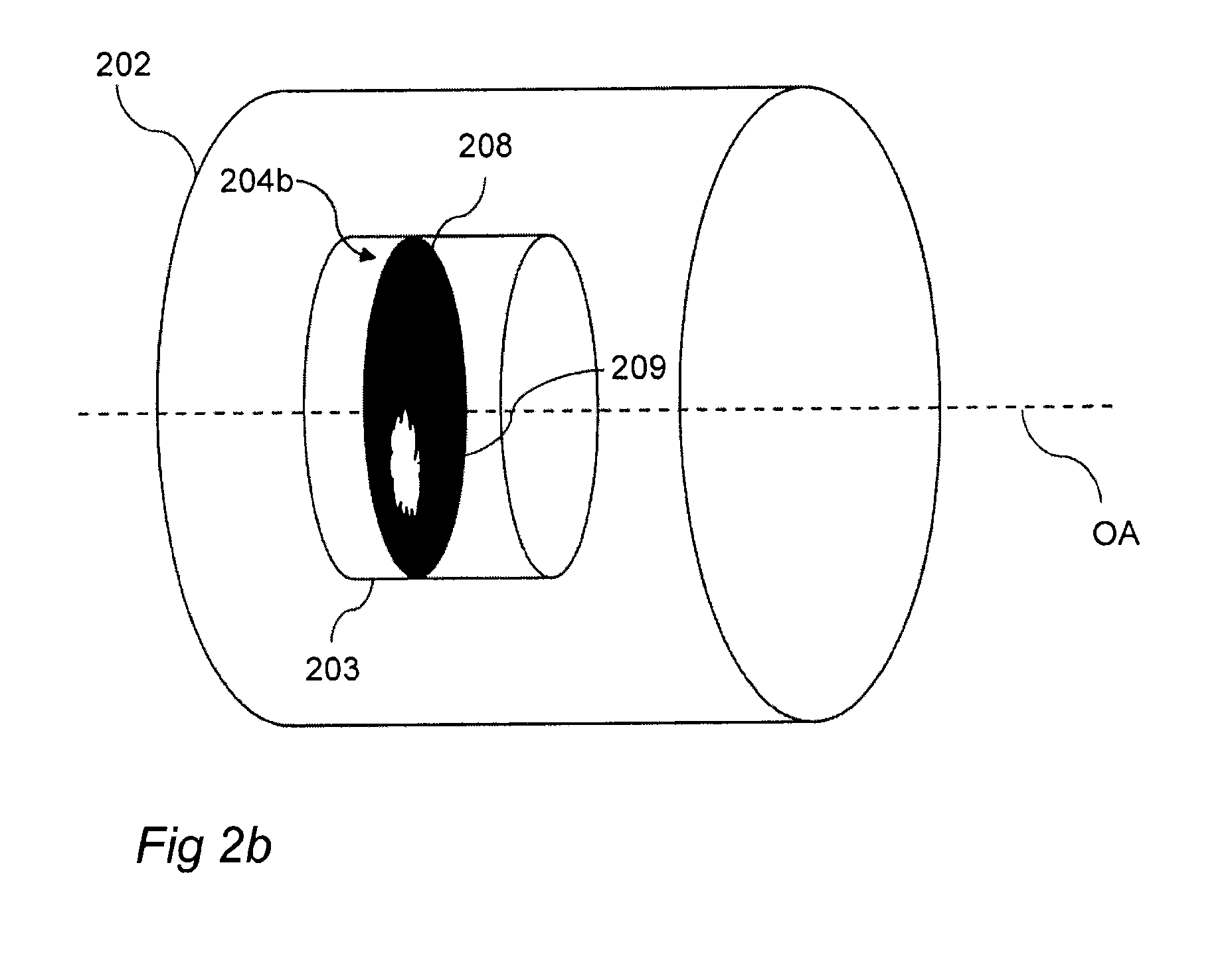
ActiveUS20140320686A1Size of aperture easilyEasy positioningTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical axis
The present invention relates to a method (300) for reducing stray light in an output image of a scene, said method comprising; providing (301) a camera (100) comprising a lens assembly (102, 202), providing (302) an aperture unit (103, 203) having an aperture gate (204a, 204b) in an aperture plane being orthogonal to an optical axis (OA) of said lens assembly (102, 202), said aperture gate (204a, 204b) being adjustable in said aperture plane, acquiring (303), by means of said camera (100), a plurality of images of said scene, wherein each image of said plurality of images is acquired using an unique aperture gate setting, wherein each of said unique aperture gate settings correspond to a unique combination of a position and a shape of said aperture gate (204a, 204b) in said aperture plane, analyzing (305) said plurality of images for generating data pertaining to a difference in stray light content with respect to said plurality of images, and producing (306) said output image based on said data pertaining to said difference in stray light content.
Owner:AXIS
Space segment payload architecture for mobile satellite services (MSS) systems
ActiveUS8354956B2Not adversely impactedReduce complexityRadio transmissionAntennasAudio power amplifierLight beam
A antenna system for generating and distributing power among a plurality of non-focused beams is provided The system comprises a reflector having a focal plane and a non-parabolic curvature configured to form the defocused beams. The curvature is configured to create a symmetrical quadratic phase-front in an aperture plane of the reflector. The system further comprises a plurality of feed antennas disposed in the focal plane of the reflector and configured to illuminate the reflector. Each feed antenna is configured to contribute power toward each of the defocused beams. The system further comprises a plurality of fixed-amplitude amplifiers, at least one of which corresponds to each feed antenna.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Charging of a hole-free thin film phase plate
ActiveUS8785850B2Precise positioningEasy to placeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesOptical propertyLight beam
New methods for phase contrast imaging in transmission electron microscopy use the imaging electron beam itself to prepare a hole-free thin film for use as an effective phase plate, in some cases eliminating the need for ex-situ fabrication of a hole and reducing requirements for the precision of the ZPP hardware. The electron optical properties of the ZPP hardware are modified primarily in two ways: by boring a hole using the electron beam; and / or by modifying the electro-optical properties by charging induced by the primary beam. Furthermore a method where the sample is focused by a lens downstream from the ZPP hardware is disclosed. A method for transferring a back focal plane of the objective lens to a selected area aperture plane and any plane conjugated with the back focal plane of the objective lens is also provided.
Owner:JEOL LTD
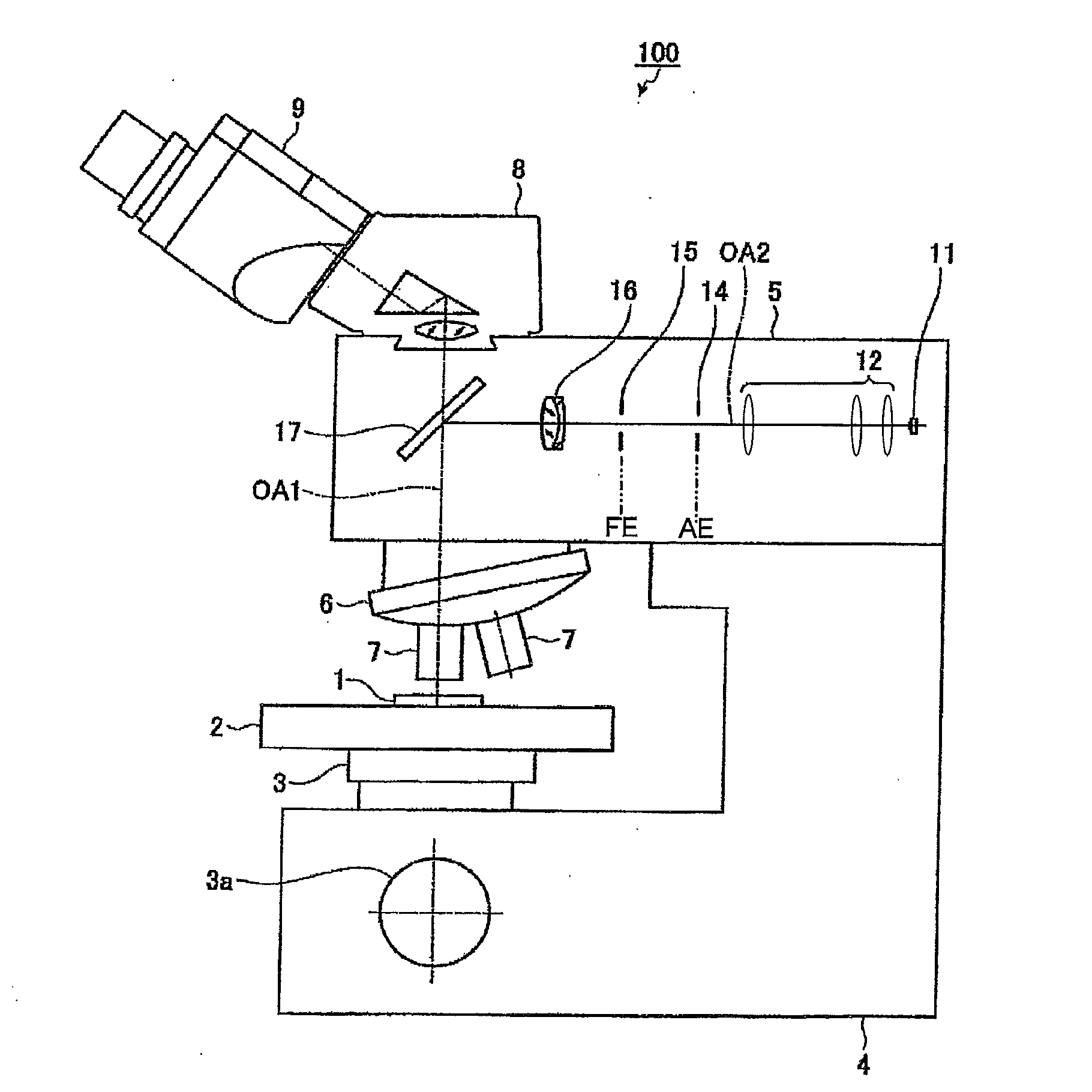
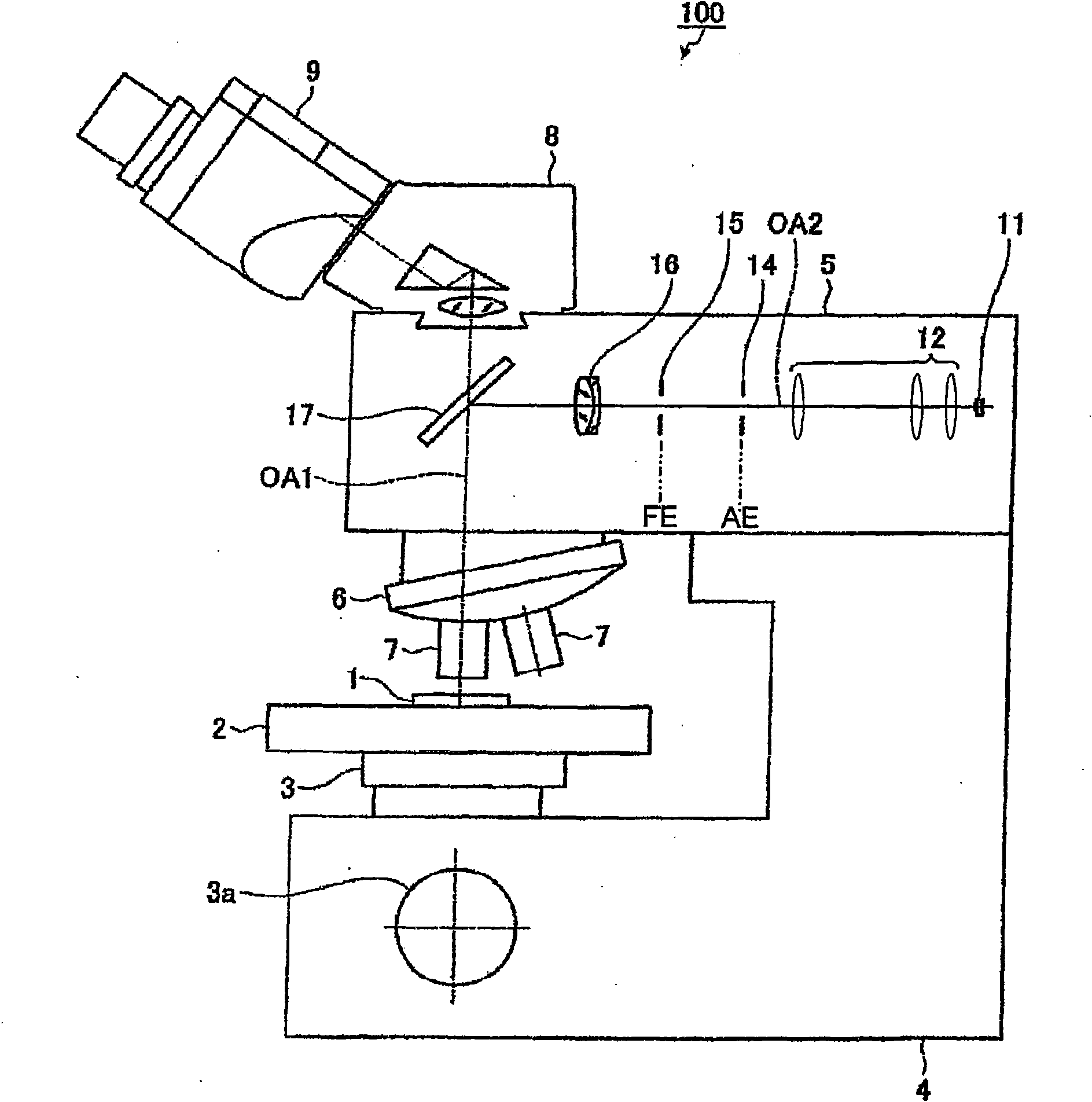
Incident illumination device for a microscope
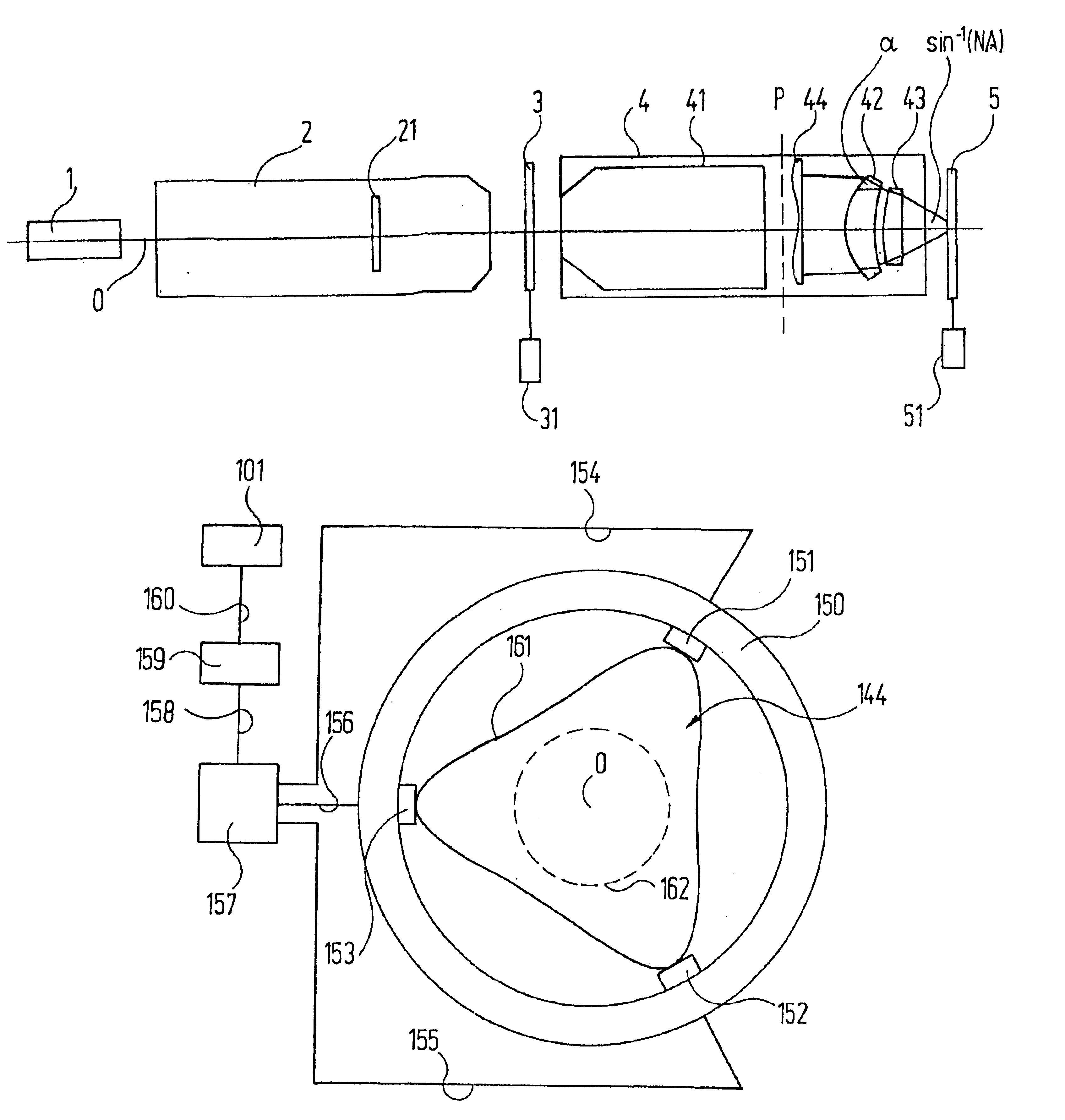
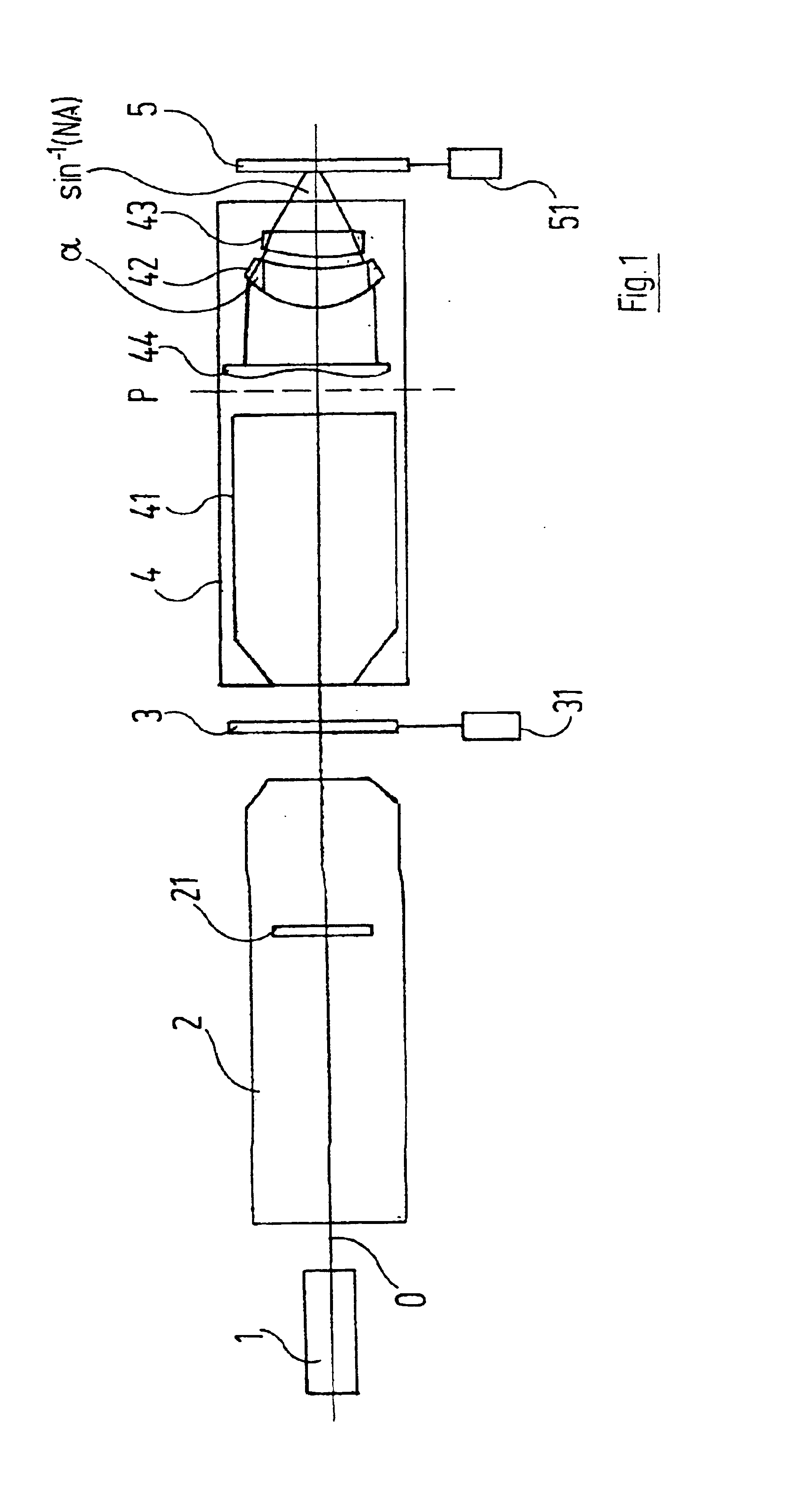
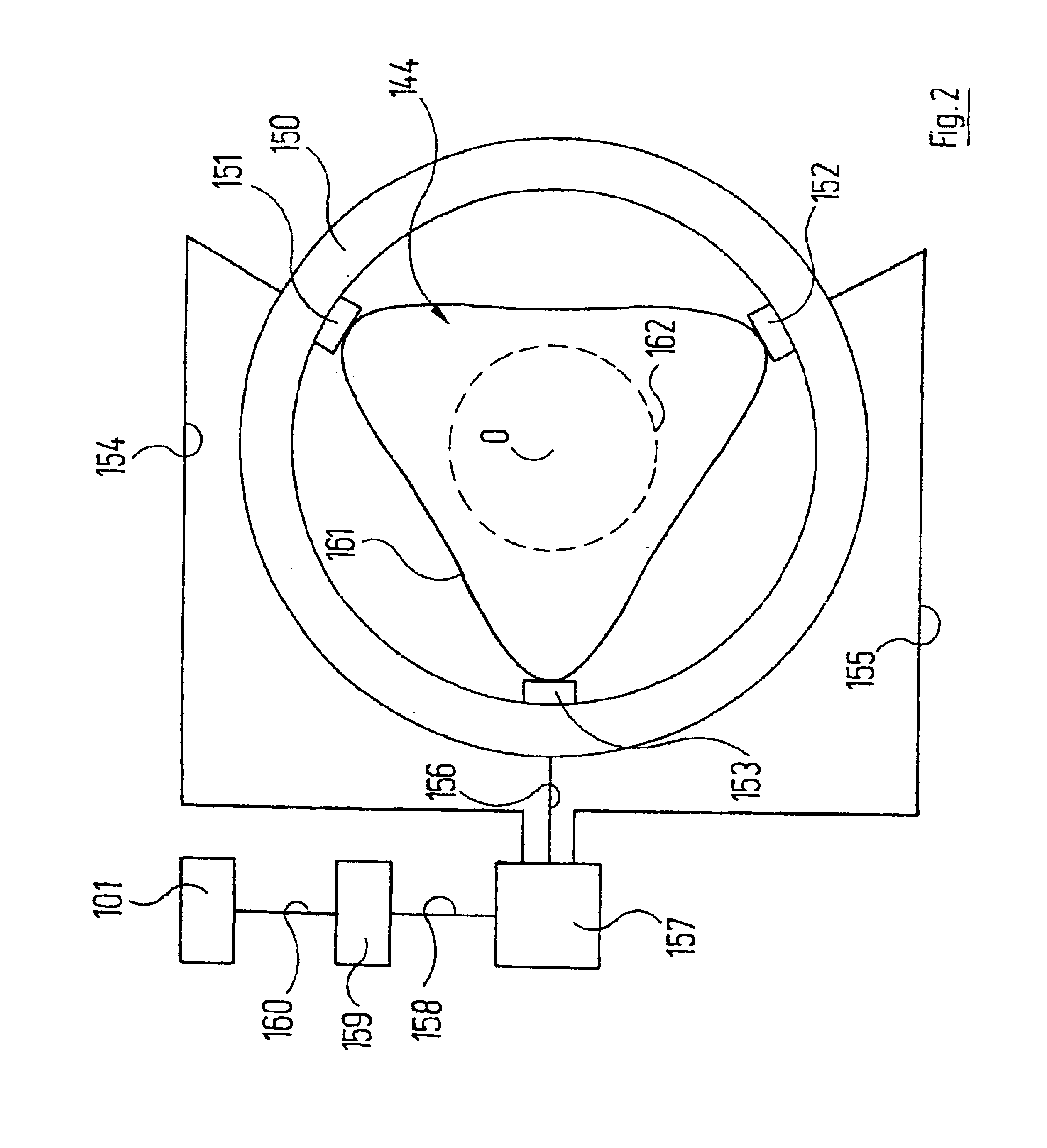
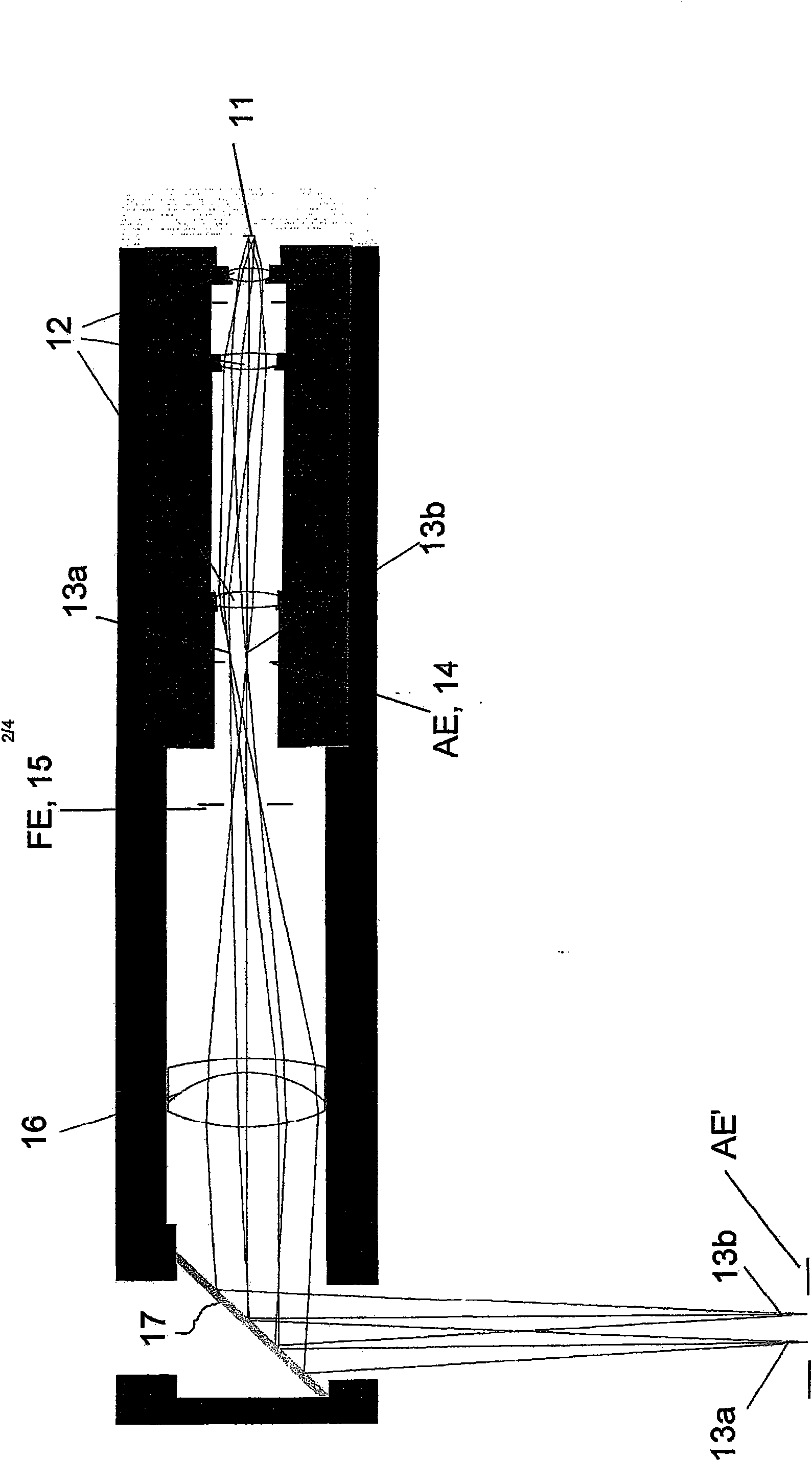
An incident illumination device for a microscope for providing oblique or straight incident illumination is described. The illumination device comprises a light source that includes at least two 2-dimensional, surface light-emitting segments and is imaged into an aperture plane of the incident illumination device. At least one of the at least two light-emitting segments of the light source is designed to be activated individually. Further, a microscope comprising this incident illumination device is described, and methods of using this microscope both for oblique and straight illumination are described. In addition to conventional incident bright-field illumination, the described microscope and methods of use thereof allow also to select between angular or oblique incident illumination.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
Incident illumination device for a microscope
The present invention relates to an incident illumination device(5) for a microscope (100), comprising a light source (11) that includes at least two light-emitting segments and is imaged into an aperture plane (AE) of the incident illumination device (5). At least one of the at least two light-emitting segments of the light source (11) is designed to be activated individually. The described microscope and methods of use thereof allow also to select between angular or oblique incident illumination.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
Medium-order and low-order surface shape detection device and system for large-aperture plane mirror and storage medium
The invention discloses a low-order surface shape detection device of a large-aperture plane mirror, a medium-order surface shape detection device of the large-aperture plane mirror, a medium-low-order surface shape detection system and device of the large-aperture plane mirror, and a computer readable storage medium. The low-order surface shape detection device and the medium-order surface shapedetection device both use the same Rayleigh-Coanda optical path architecture; a detection part similar to an HASO wavefront sensor is formed by a micro lens array and a camera to detect low-order surface shape data; therefore, the low-order surface shape of the large-aperture plane mirror is obtained, the difficulty and the cost of low-order surface shape detection are simplified, the camera and the aperture baffle plate are matched with the medium surface shape data, the medium surface shape data of the large-aperture plane mirror are further obtained, the influence of environmental vibrationon medium surface shape detection is avoided, and the detection cost is reduced. The medium-order surface shape detection device and the low-order surface shape detection device are combined to realize medium-low surface shape detection of the large-aperture plane mirror.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of measuring aberrations and correcting aberrations using Ronchigram and electron microscope
ActiveUS7619220B2Accurate analysisElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationLight beamComputational physics
A method and apparatus for correcting aberrations using a Ronchigram. A STEM apparatus has first calculation means for taking autocorrelation of minute regions on a Ronchigram of an amorphous specimen, detection device for detecting aberrations in the beam formed from local angular regions on an aperture plane from the autocorrelation or from Fourier analysis of the autocorrelation, second calculation device for calculating the aberrations based on the results of the detection, and control device for controlling operation for correcting the aberrations based on results of calculations performed by the second calculation device.
Owner:JEOL LTD
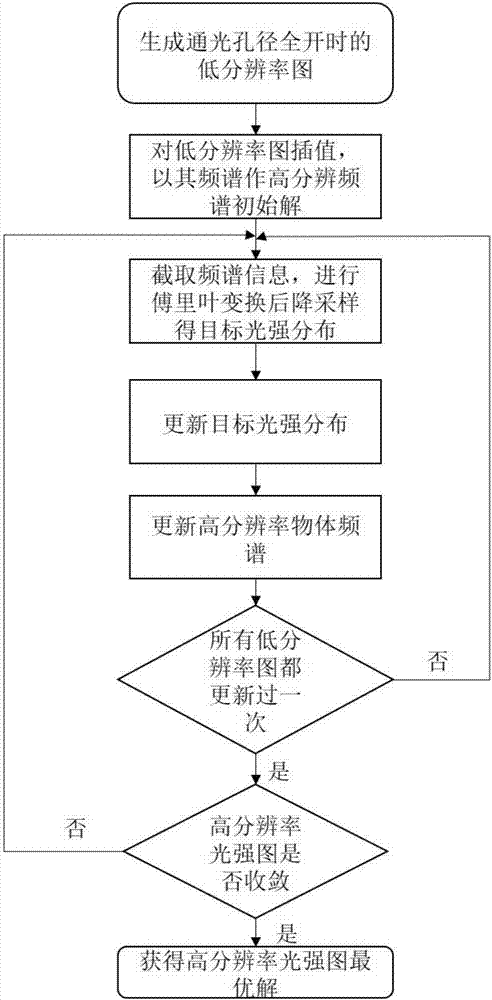
Programmable aperture imaging system based on LCOS spatial light modulator and super-resolution reconstruction method using the same
ActiveCN107395933AAvoid diffraction effectsSimple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDiffraction effectSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a programmable aperture imaging system based on an LCOS spatial light modulator and a super-resolution reconstruction method using the same. The programmable aperture imaging system is composed of a spatial light modulator, a beam splitter, a lens II, a camera, a lens I, and an imaging main lens group. The lens II, the beam splitter and the lens I form a 4f system reflective optical path structure; included angles between the beam splitter and the lens II and between the beam splitter and the lens I are 45 degrees; and the distances between the lens II and the beam splitter and between the lens I and the beam splitter and are equal. The aperture plane of the imaging main lens group is imaged on the spatial light modulator; and the spatial light modulator is arranged on a rear focal plane of the lens I and is also arranged on a front focal plane of the lens II. The camera is arranged at the rear focal plane of the 4f system lens II. According to the invention, no mechanical scanning device is needed. Moreover, the programmable aperture imaging system has advantages of simple structure, rapid measurement, and simple operation. And with the LCOS spatial light modulator, the optical grating diffraction effect is avoided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
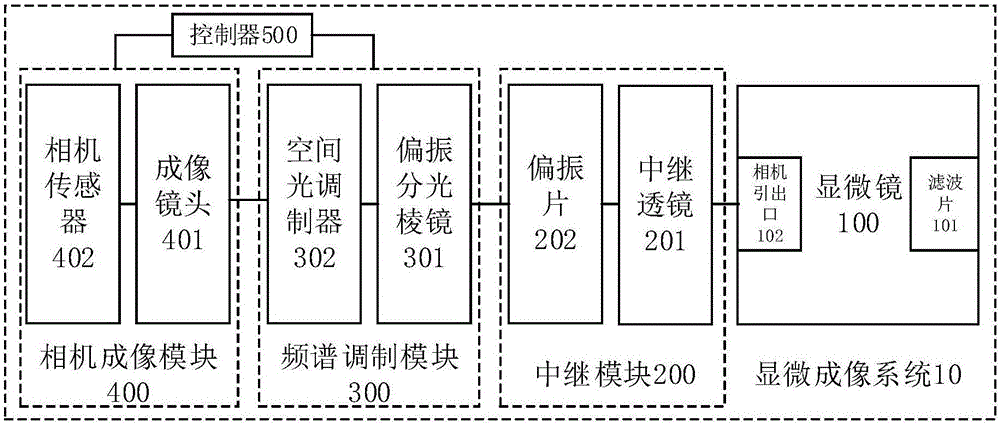
Collection end frequency domain pasting microscopic system based on spatial light modulator
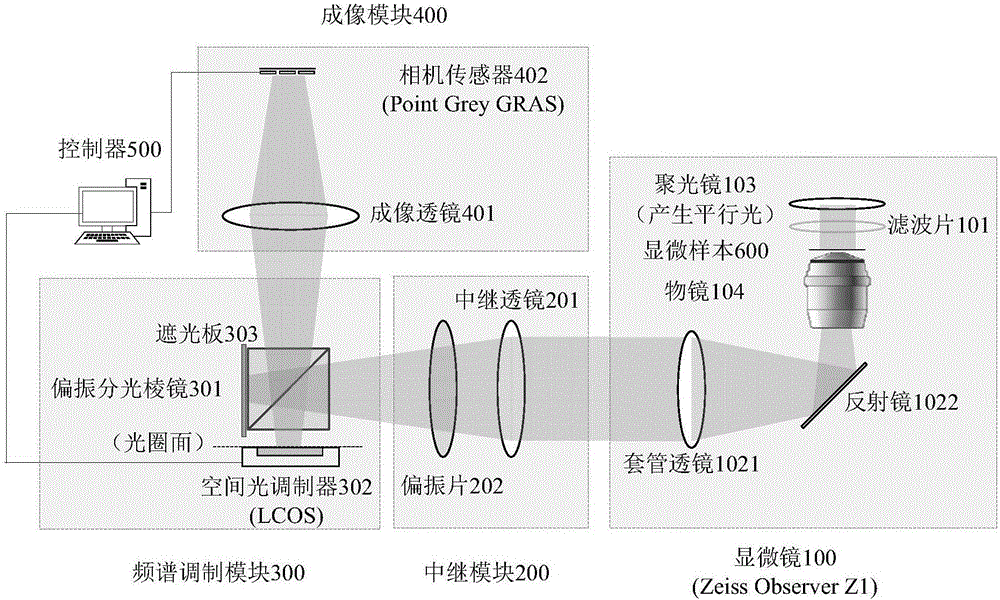
ActiveCN106707492AImprove spatial resolutionRealize acquisitionMicroscopesFrequency spectrumSpatial light modulator
The present invention provides a collection end frequency domain pasting microscopic system based on a spatial light modulator. The system comprises: a microscope configured to amplify a microscopic sample into an image plane; a relay module configured to reduce the aperture plane of imaging of the sample; a frequency spectrum modulation module consisting of a polarization splitting prism and a spatial light modulator; a camera imaging module consisting of an imaging lens and a camera sensor and configured to receive optical signals through frequency spectrum modulation through the spatial light modulator and then through the emission through the slope of the polarization splitting prism and collect the corresponding sample image; a controller configured to perform synchronous control of frequency spectrum modulation and image collection and rapidly collect a plurality of low-resolution images in different spatial frequency spectrums to obtain an original image data required by the single-frame high-resolution images or the multi-frame high-resolution video. On the premise of ensuring the field of view with a certain width, the spatial resolution collected by the camera sensor is improved, the high-resolution reconstruction with a certain thickness sample is realized, the collection of the dynamic samples is realized to some extent, and the collection end frequency domain pasting microscopic system based on the spatial light modulator is simple and easy to realize.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nanometer scale uniform optical tunnel generating method and device
The invention discloses a nanometer scale uniform optical tunnel generating method and device. The method comprises the steps that a laser beam is enlarged, collimated and converted into a linearly polarized laser beam; a reflection-type pure phase spatial light modulator is used to carry out quadratic special fan-shaped partition phase modulation on the collimated and enlarged linearly polarized laser beam to acquire a phase-modulated linearly polarized vortex beam; the phase-modulated linearly polarized vortex beam is converted into a phase-modulated radially polarized vortex beam by a radially polarized light converter; a 4F imaging system is used to image the phase-modulated radially polarized vortex beam to the rear aperture plane of a focusing objective lens; the objective lens focuses the phase-modulated radially polarized vortex beam to acquire a nanometer scale uniform optical tunnel in a focal area. The uniform optical tunnel is formed by optimizing and splicing four same optical tunnels produced by quadratic special fan-shaped partition phase modulation. The longitudinal intensity uniformity of the optical tunnel is within 10 wavelengths, and the intensity fluctuation error is less than three percent.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Synthetic aperture ladar system and method using real-time holography
ActiveUS7474332B2Motion compensationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSynthetic aperture sonarInverse synthetic aperture radar
This invention uses a real-time holographic medium to record the amplitude and phase information collected from a moving platform at the aperture plane of a side-looking optical sensor over the collection time. A back-scan mirror is used to compensate platform motion during the synthetic aperture integration time. Phase errors caused by a nonlinear platform motion are compensated by controlling the phase offset between the illumination beam and the reference beam used to write the hologram based on inertial measurements of the flight path and the sensor line-of-sight pointing angles. In the illustrative embodiment, a synthetic aperture ladar (SAL) imaging system is mounted on a mobile platform. The system is adapted to receive a beam of electromagnetic energy; record the intensity and phase pattern carried by the beam; and store the pattern to compensate for motion of the platform relative to an external reference. In the illustrative embodiment, the image is stored as a holographic image. The system includes a back-scan mirror, which compensates the stored holographic pattern for motion of the platform. The medium and back-scan mirror may be replaced with a digital camera and one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays may be used. In a specific embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used with a time delay and integration (TDI) scheme, which compensates for motion of the platform in the storage of the optical signals. In an alternative embodiment, a back-scanning mirror is used to compensate for motion of the platform. Consequently, the interference pattern between a relayed image of the aperture plane and a reference beam is continuously stored. In this embodiment, the instantaneous location of the received beam on the recording medium is controlled to compensate for motion of the platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
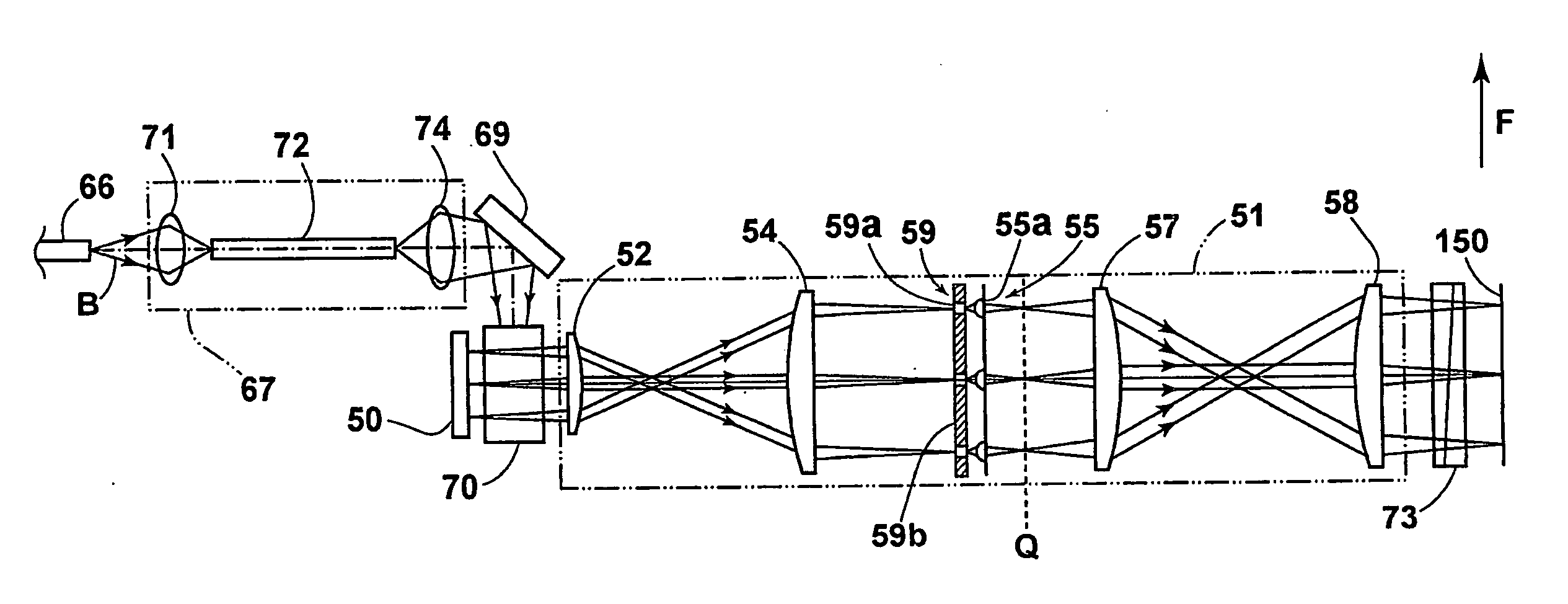
Image exposing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100044596A1Degradation in resolutionHigh resolution imageElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusImage resolutionMicro lens array
An image exposing apparatus capable of avoiding degradation in the resolution of an exposed image due to fluctuations in the traveling direction of light that focuses pixel images of the pixel sections of a spatial optical modulation device. The apparatus includes the spatial optical modulation device, such as a DMD having multitudes of pixel sections disposed two-dimensionally; a light source; and image focusing optical systems. It further includes an aperture array disposed at the image location focused by the image focusing optical systems such that each of the pixel images of the pixel sections is positioned at the plane of each of the apertures. The pixel images positioned at the aperture planes of the aperture array are focused into an image by a microlens array, which is then projected onto a photosensitive material by optical systems.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com