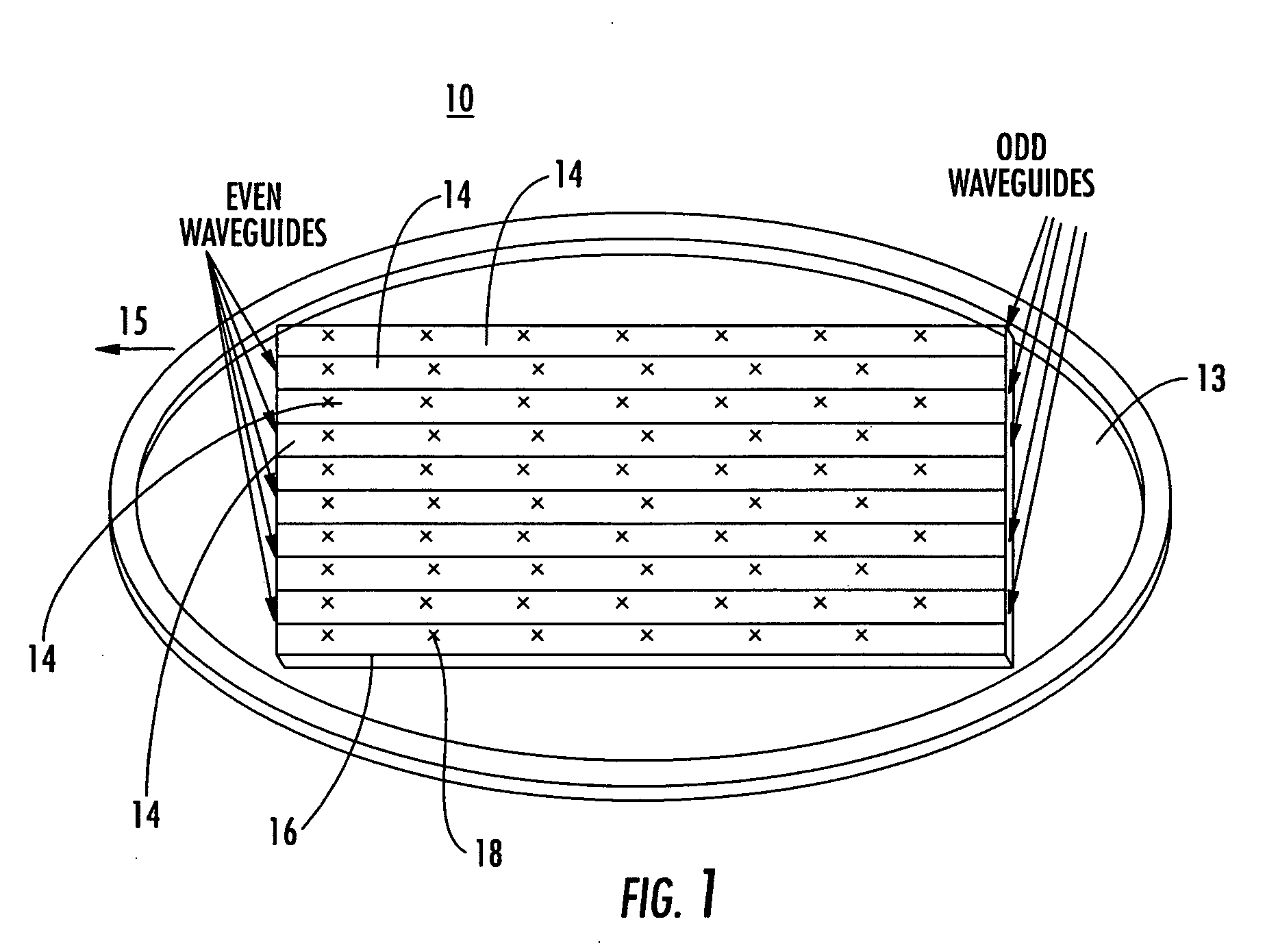
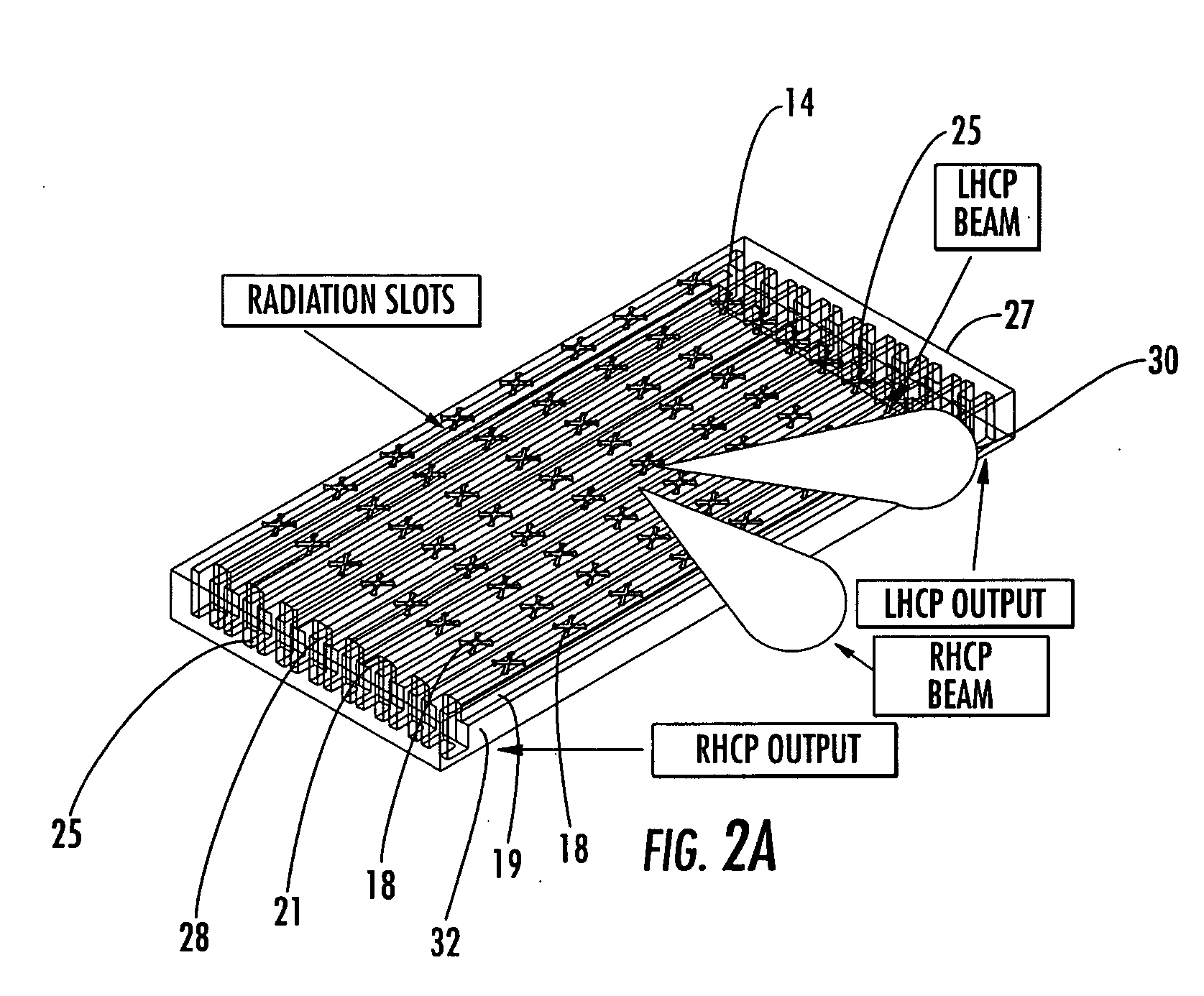
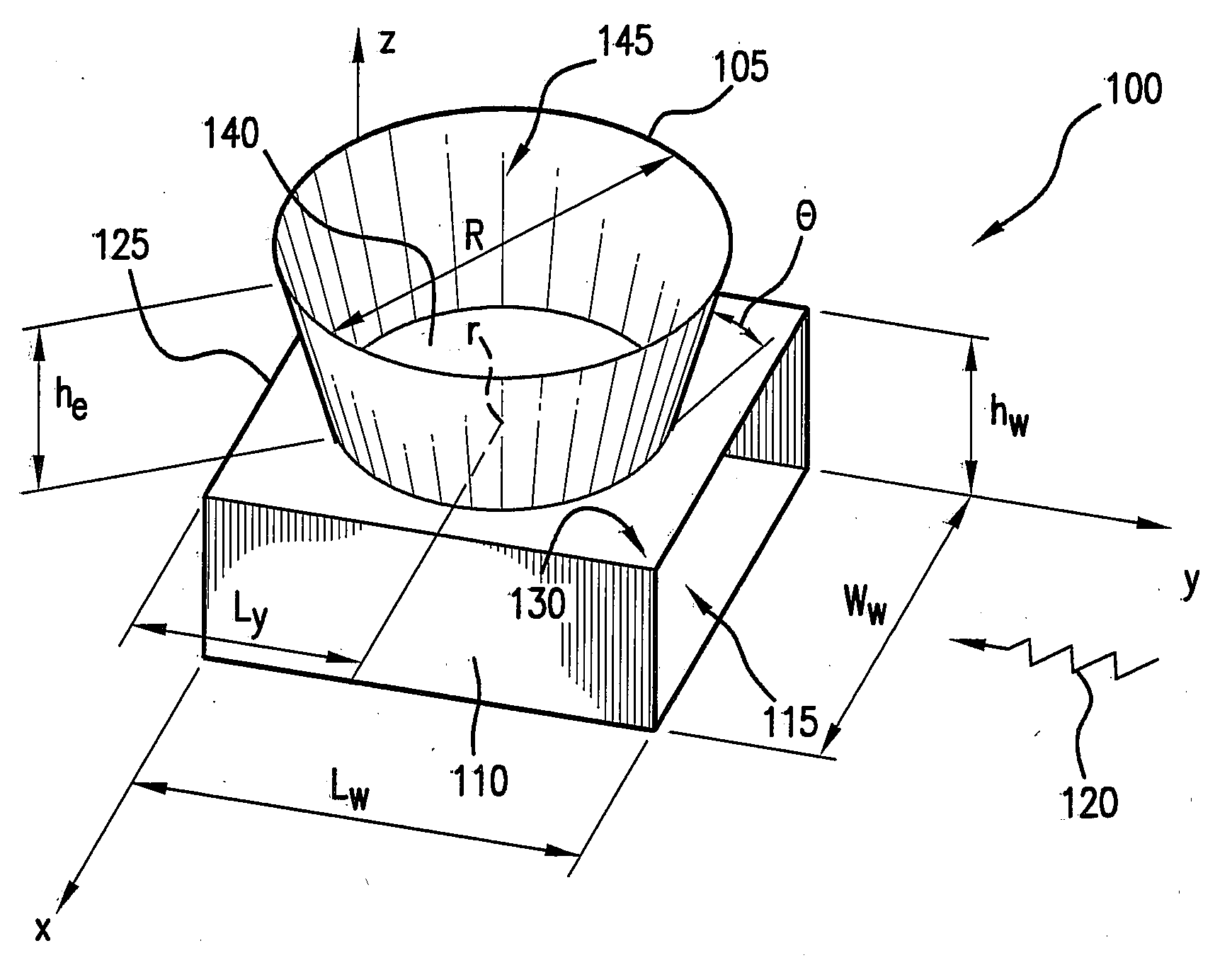
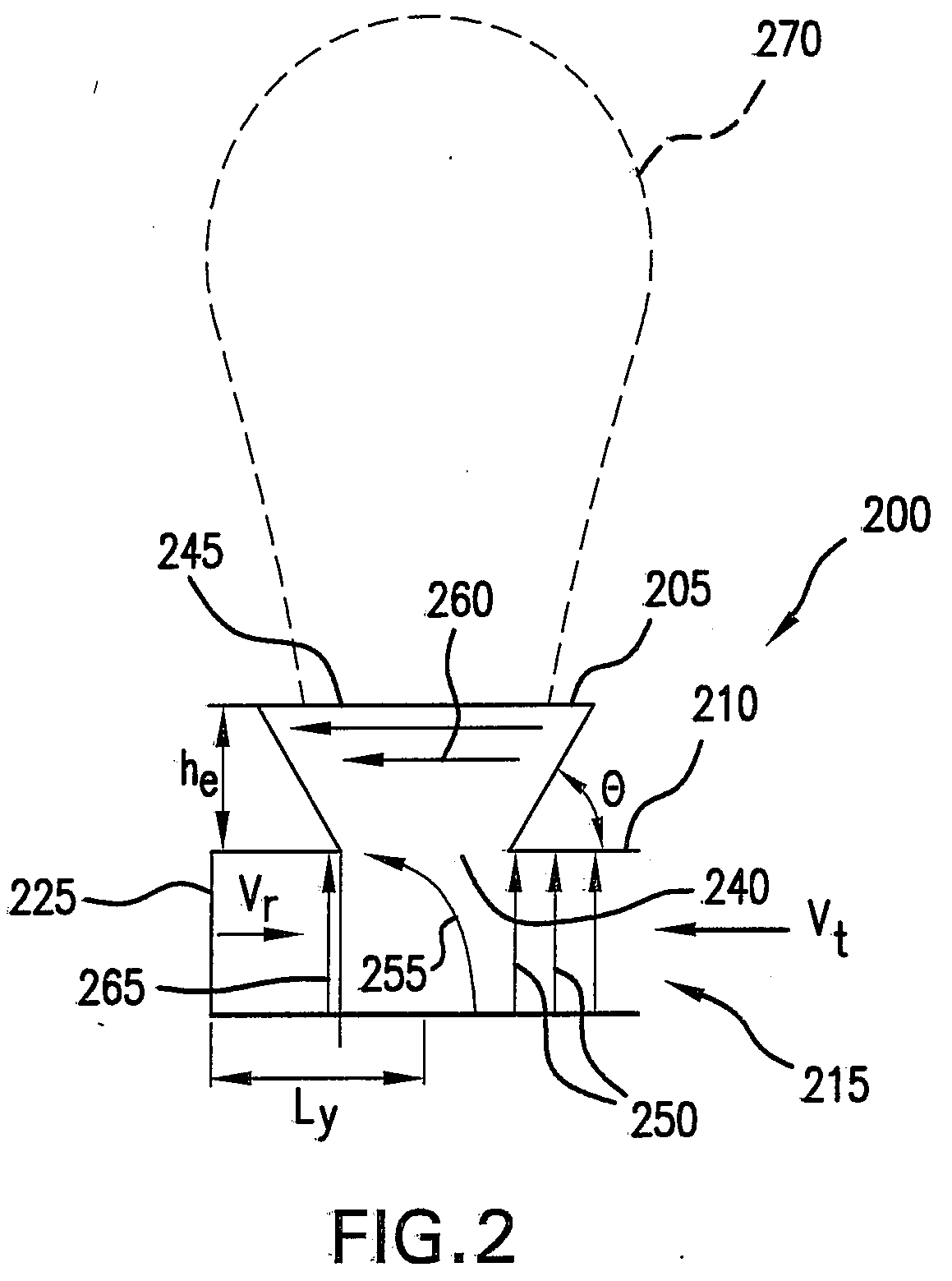
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
490results about "Linear waveguide fed arrays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
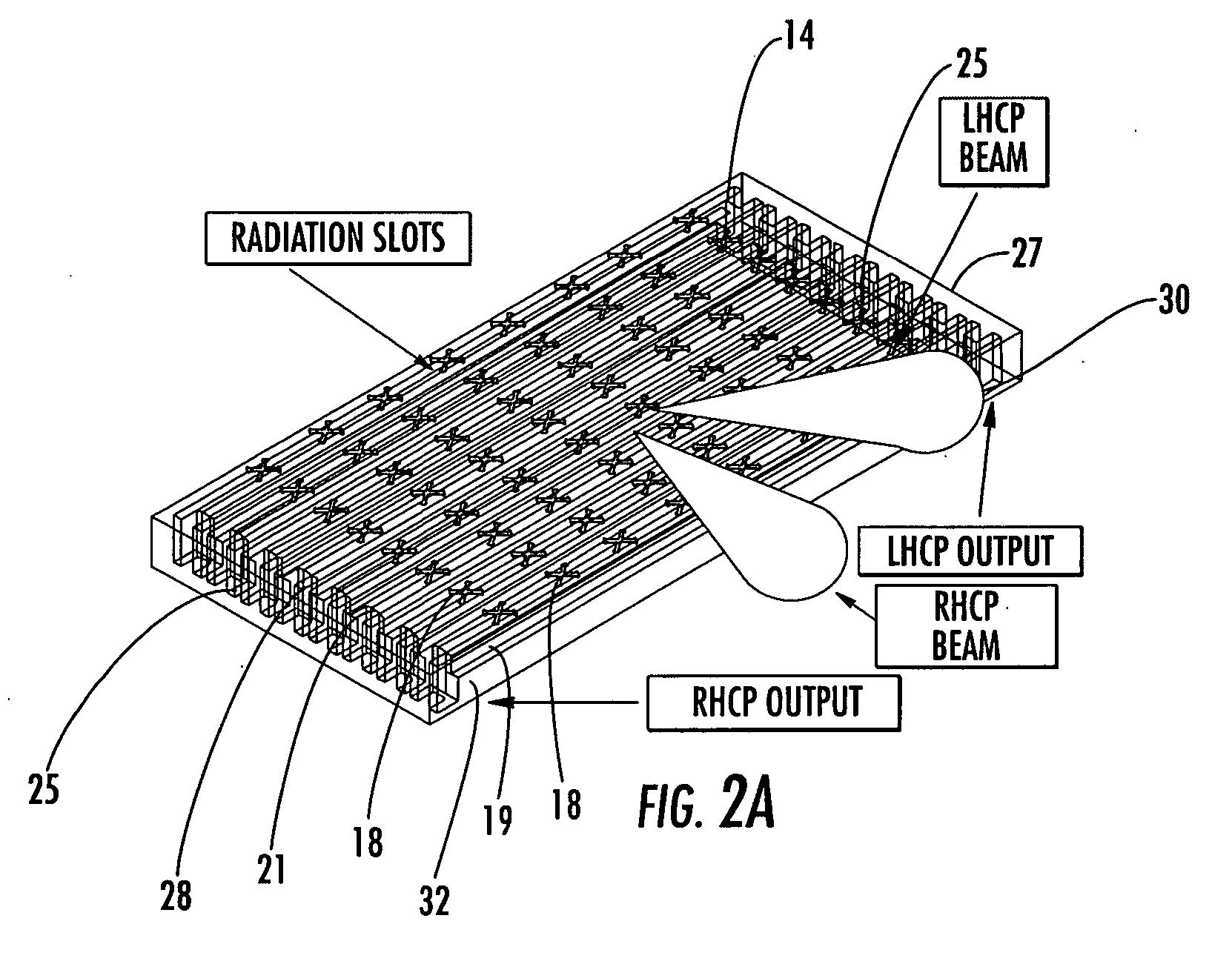
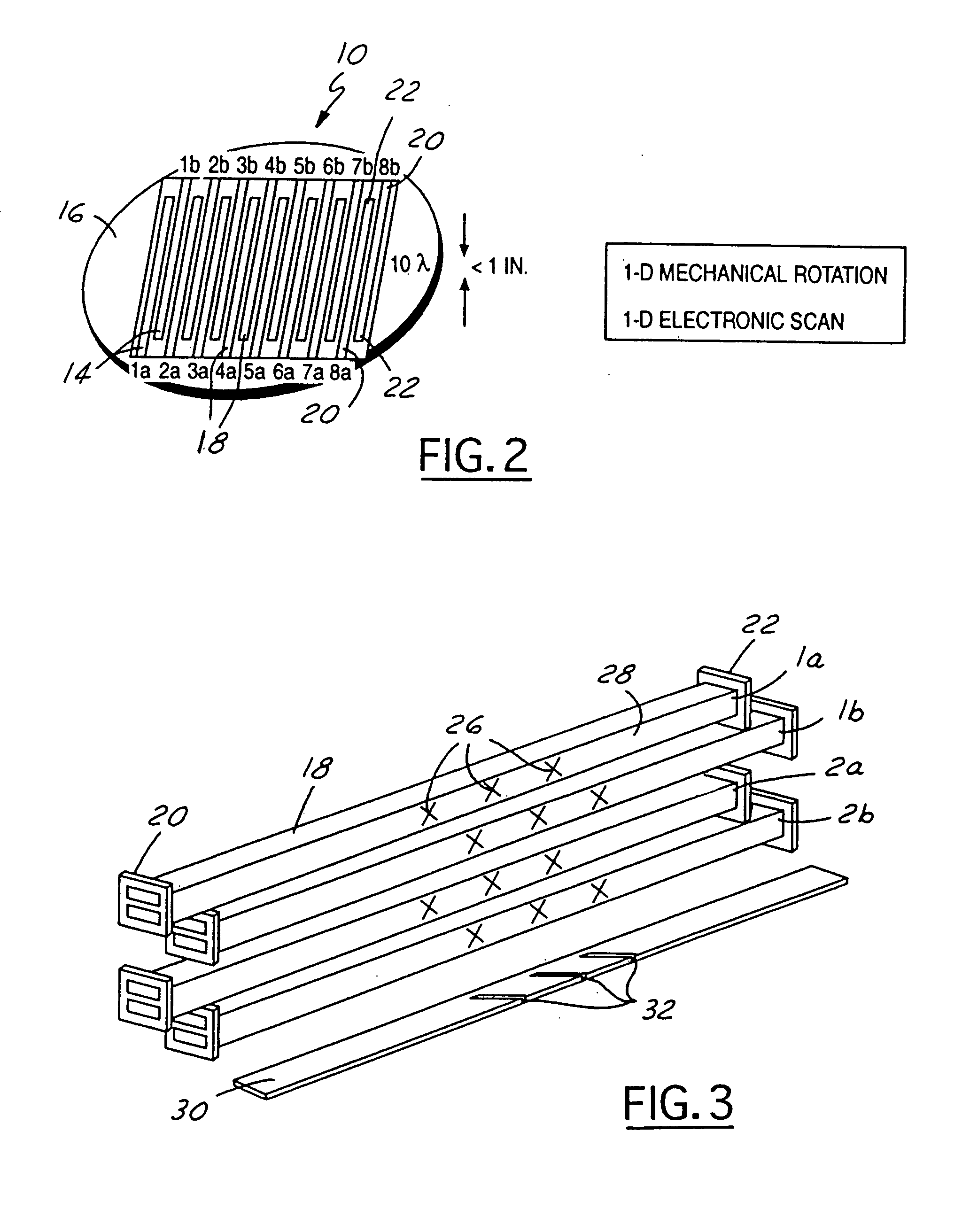
MMW electronically scanned antenna
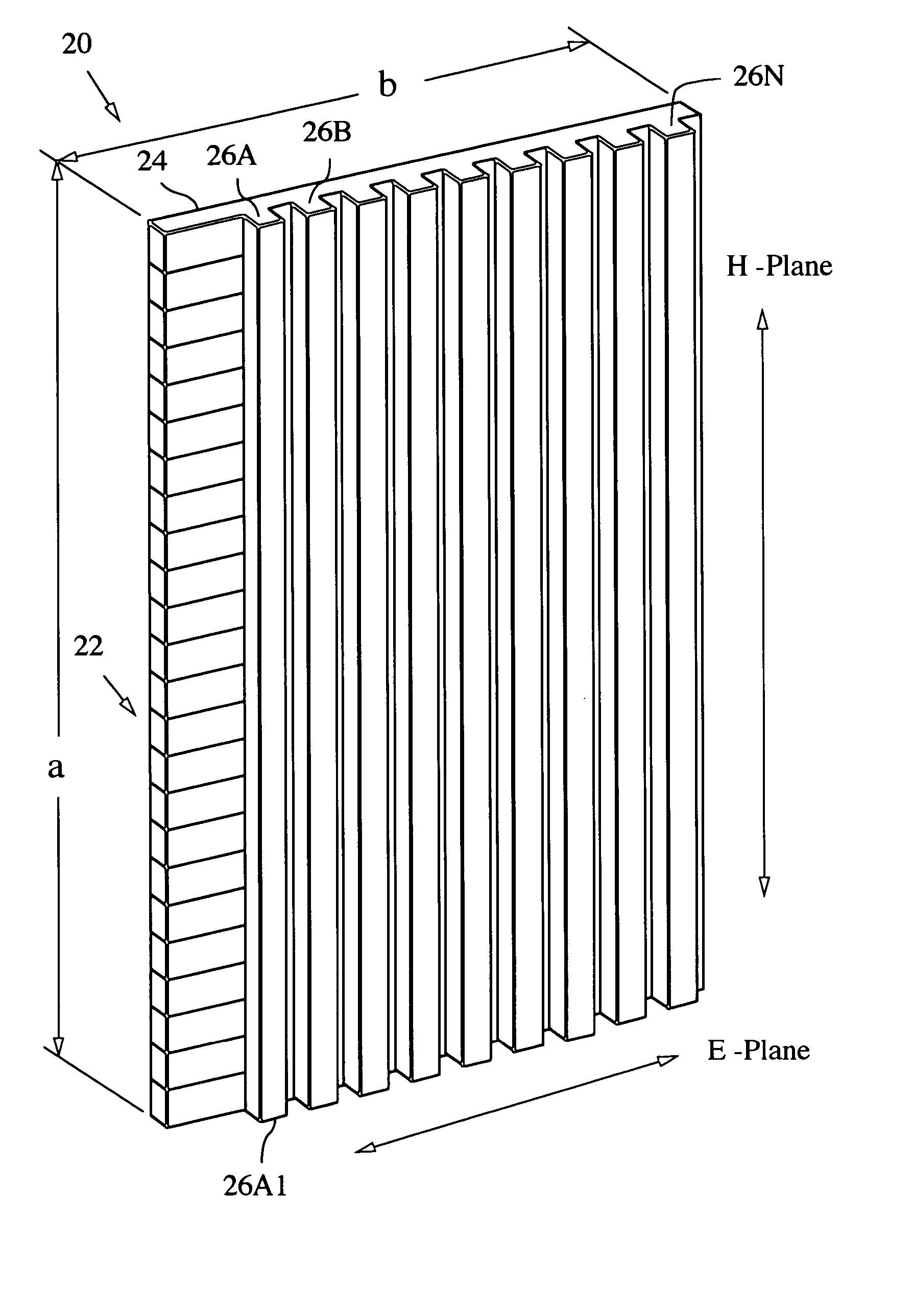
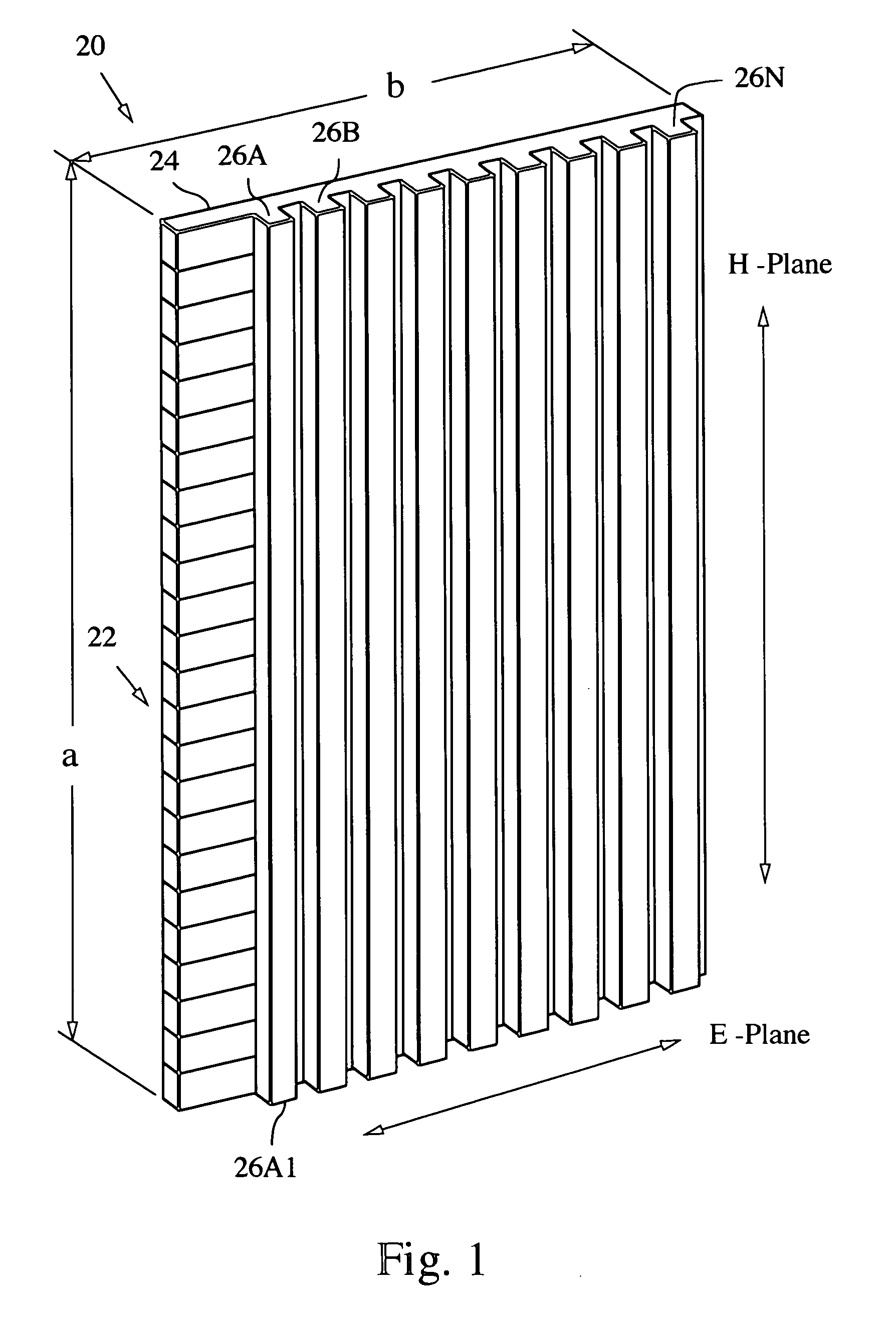
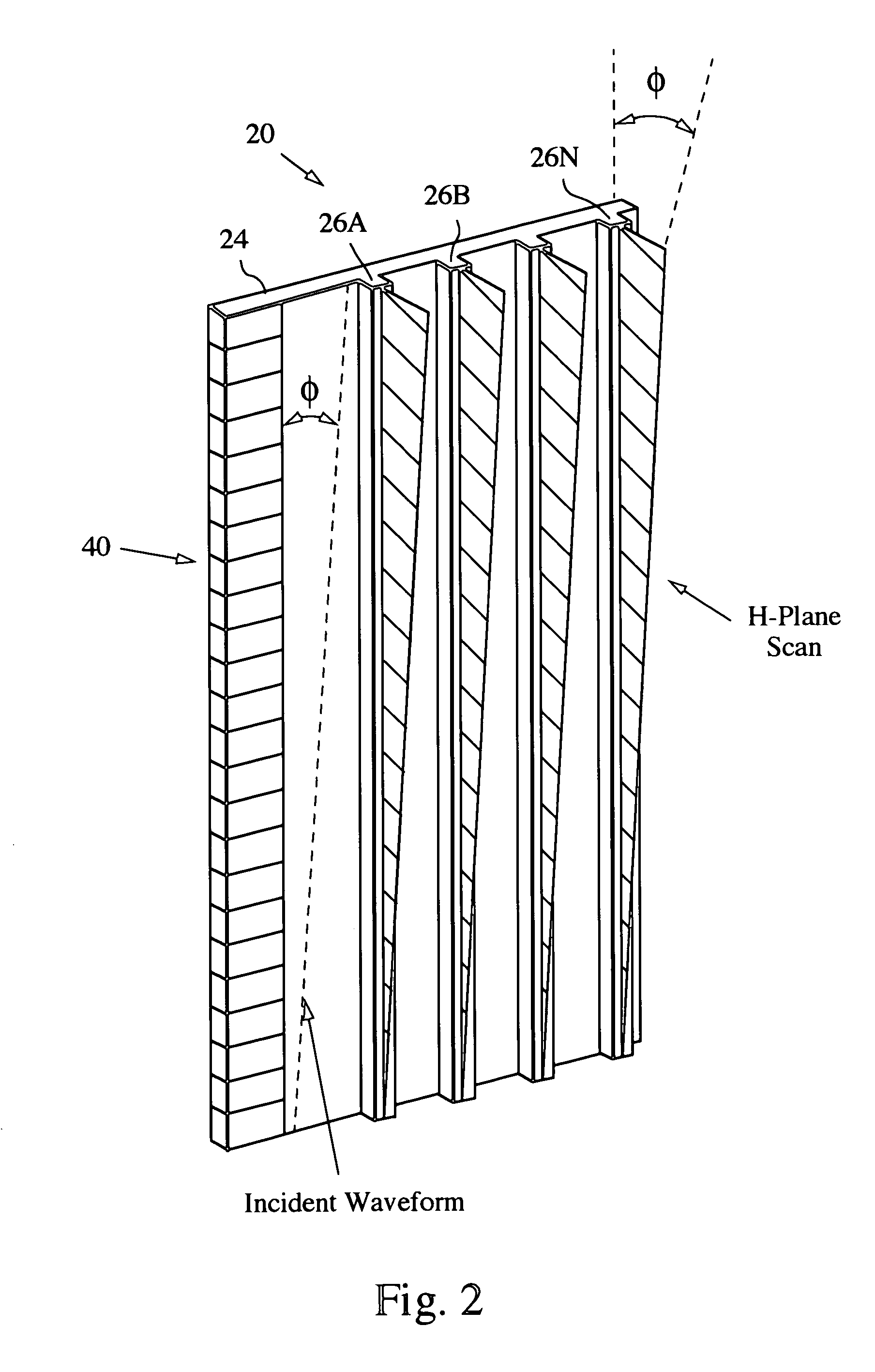
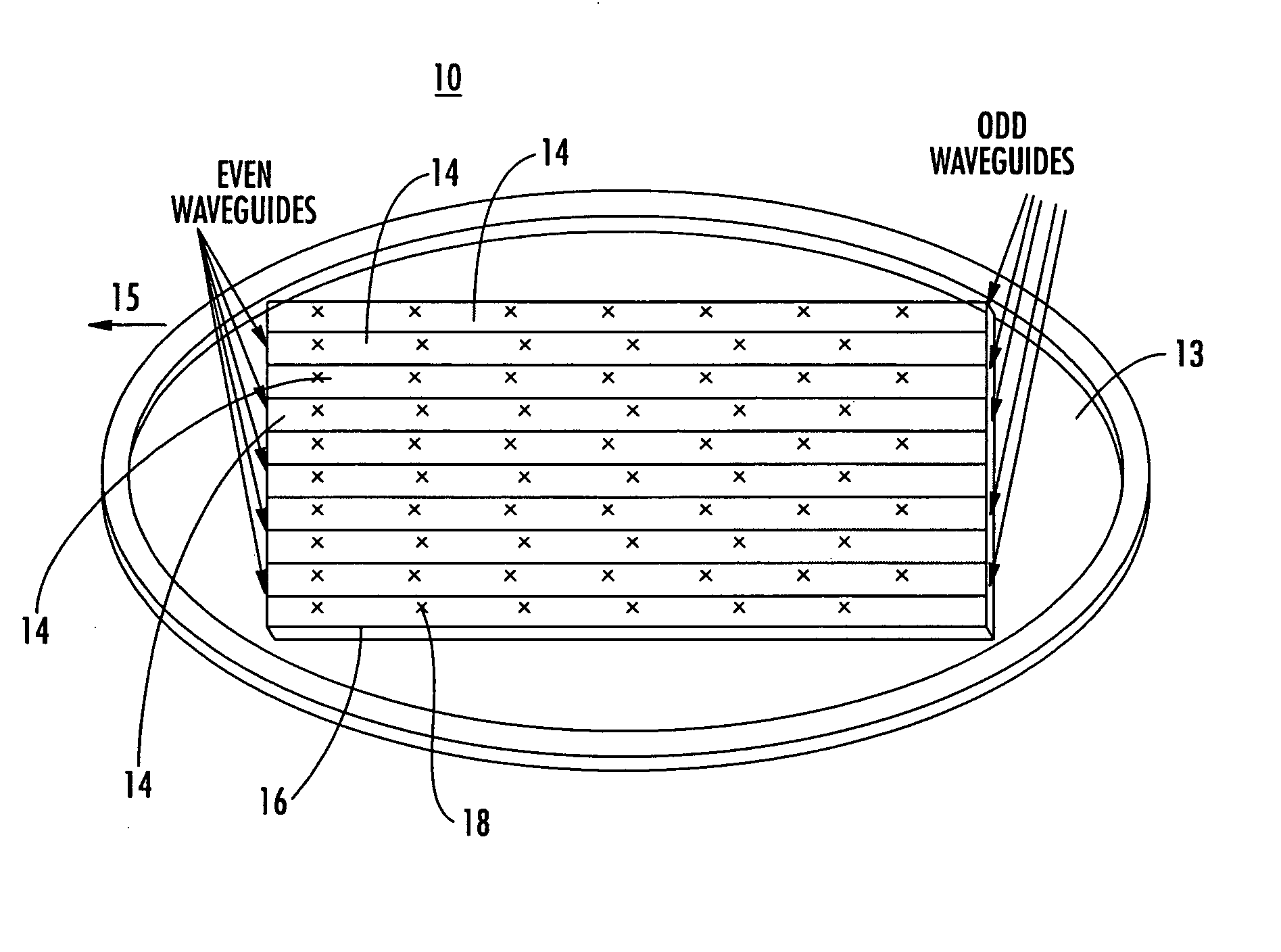
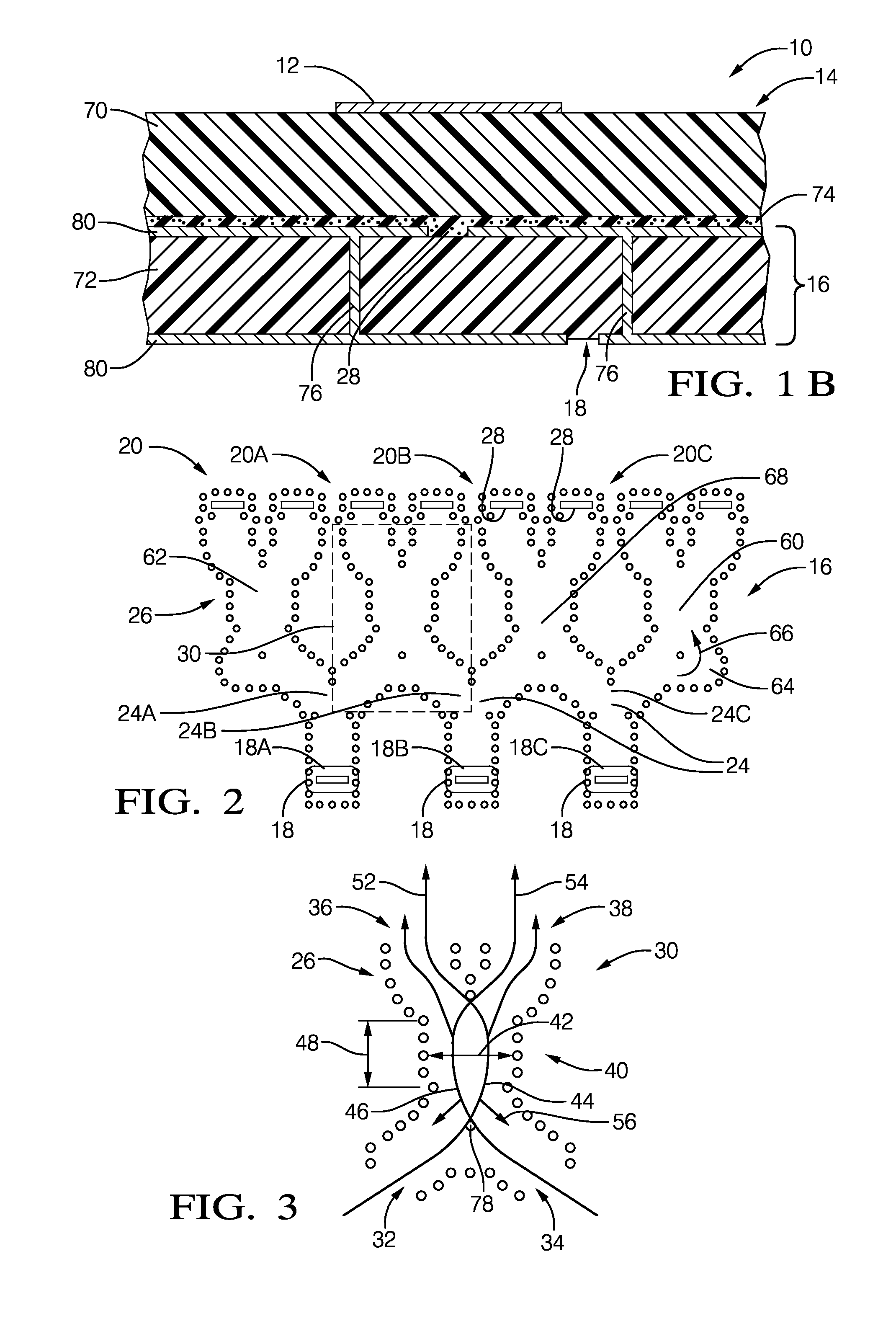
A millimeter wave (MMW) antenna array includes a continuous transverse stub (CTS) radiating aperture comprising a set of spaced continuous transverse stubs, each having a longitudinal extent. A series feed system is coupled to an excitation source for exciting the stubs with MMW electromagnetic energy having a linear phase progression along the longitudinal extent of the stubs to produce an array beam which can be scanned over a beam scan range by changing the excitation frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO +1
Low profile wideband antenna array
InactiveUS6864851B2Low profileWide bandwidthAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysCoaxial cableEngineering
A phased array antenna having a low profile (approximately ⅛ wavelength) wide bandwidth (approximately 50%). The invention teaches making such an antenna using open channel resonators and monopole wave launchers. The wave launchers may conveniently be made on circuit card assemblies with strip lines that mimic coaxial cable monopole wave launchers. The channel resonators may be made in sections that are soldered to the circuit card assemblies. The circuit card assemblies have plated through holes that trace the edges of the resonator sections to provide electrical continuity.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Dynamic polarization and coupling control from a steerable cylindrically fed holographic antenna
ActiveUS20150236412A1Improve performanceNon-resonant long antennasParallel-plate/lens fed arraysAntenna feedPhysics
An apparatus is disclosed herein for a cylindrically fed antenna and method for using the same. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave and a tunable slotted array coupled to the antenna feed.
Owner:KYMETA
Waveguide horn antenna array and radar device
InactiveUS7423604B2Wide range of adjustmentSimple structureLinear waveguide fed arraysElectrical conductorCoupling
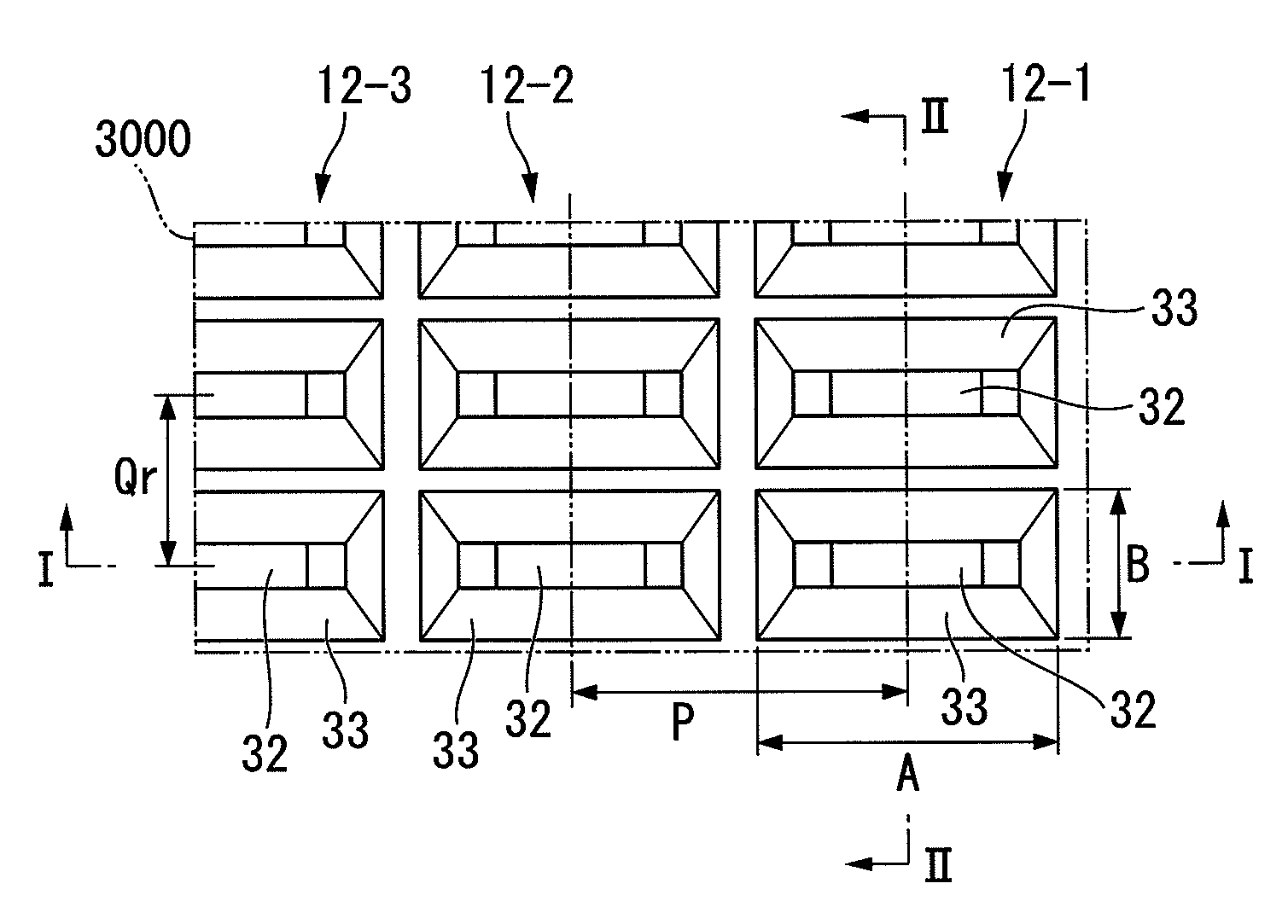
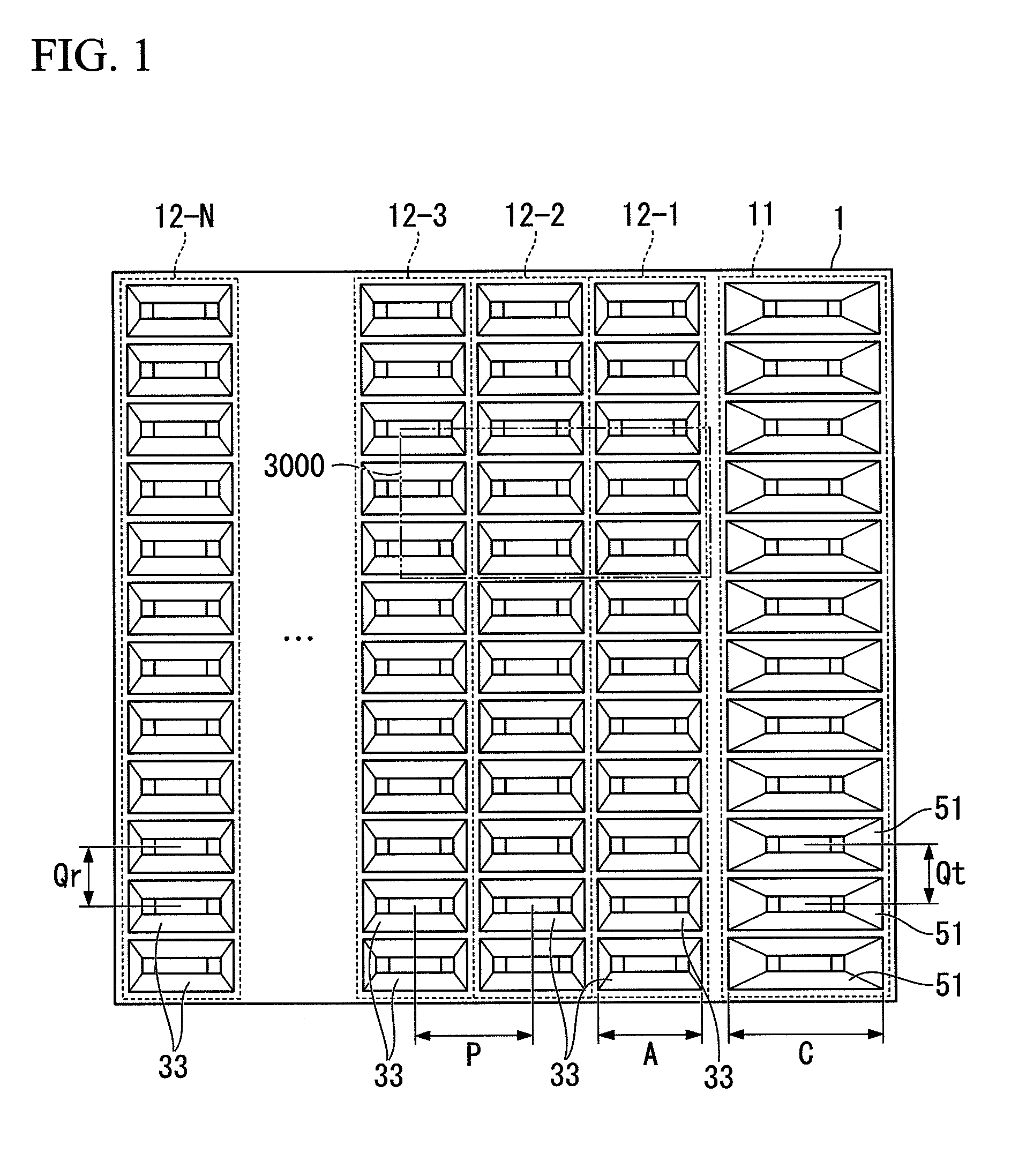
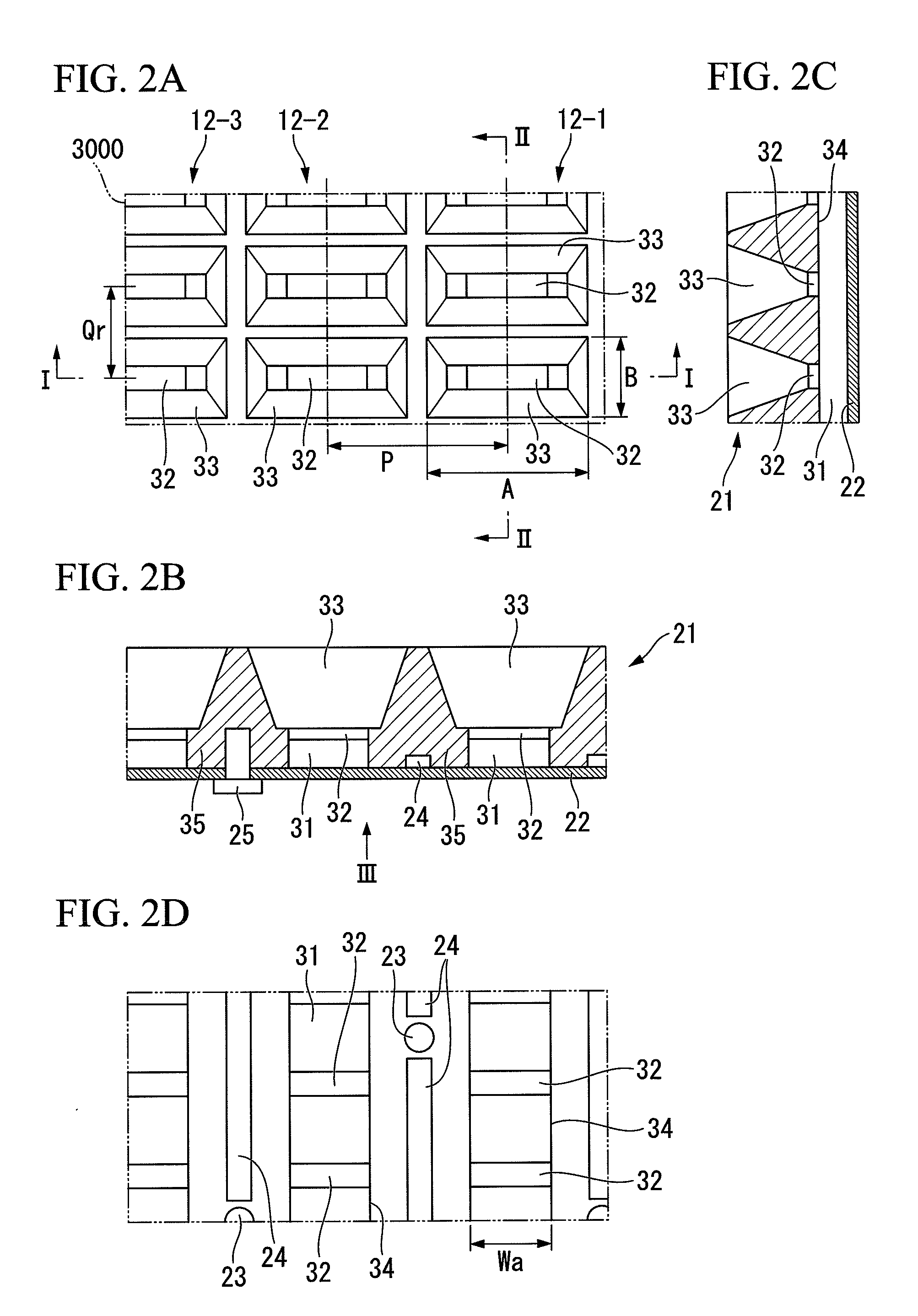
A conductor member contains a linear feed waveguide extending in a fixed direction and a plurality of horn antennas coupled to the feed waveguide and set at an interval of about one half of a wavelength in the extending direction of the feed waveguide. The horn antennas are formed by horns and coupling waveguides, and the coupling waveguides are set so as to partially enter the feed waveguide. When the size of the spatial coupling portion formed by the entrance is changed, the degree of coupling between the feed waveguide and each of the coupling waveguides changes.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Substrate Integrated Waveguide Antenna Array
InactiveUS20090066597A1Reduce the overall heightMeet cutting requirementsLinear waveguide fed arraysWaveguidesMobile antennasDielectric substrate
A substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) slot full-array antenna fabricated employing printed circuit board technology. The SIW slot full-array antenna using either single or multi-layer structures greatly reduces the overall height and physical steering requirements of a mobile antenna when compared to a conventional metallic waveguide slot array antenna. The SIW slot full-array antenna is fabricated using a low-loss dielectric substrate with top and bottom metal plating. An array of radiating cross-slots is etched in to the top plating to produce circular polarization at a selected tilt-angle. Lines of spaced-apart, metal-lined vias form the sidewalls of the waveguides and feeding network. In multi-layer structures, the adjoining layers are coupled by transverse slots at the interface of the two layers.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Array antenna device and radio communication device
InactiveUS20160072191A1Reduce lossEasy to makeAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysEngineeringWaveguide
An array antenna device includes a plurality of slot array antennas which are arranged and each of which includes a plurality of slot antennas and a radiation surface, which is formed to be conformal, and a plurality of waveguides each of which supplies respective power to each of the slot array antennas. After bodies of the waveguides are formed by a resin molding method, surface treatment is performed with respect to inner surfaces of the waveguides with plating.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
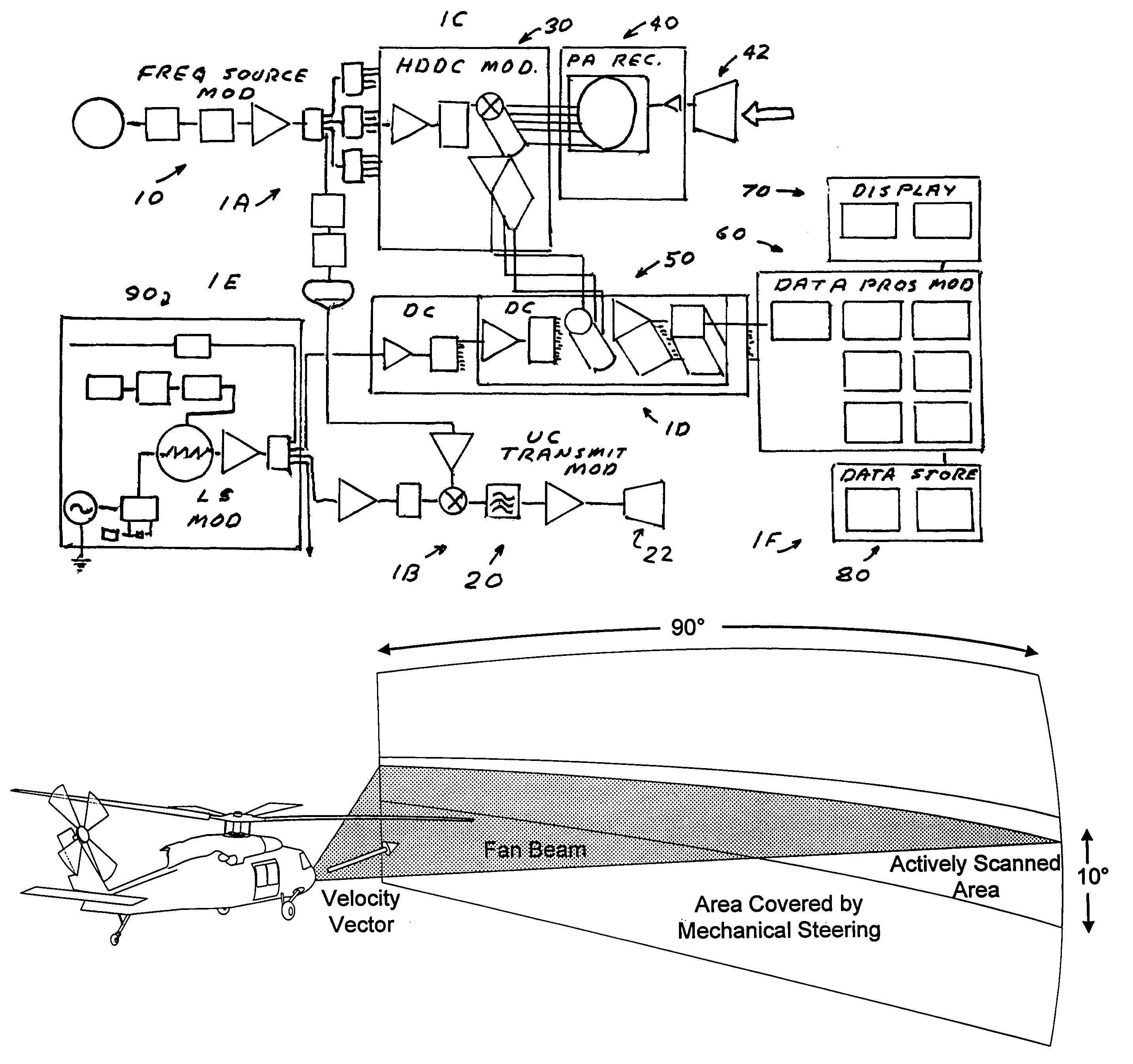
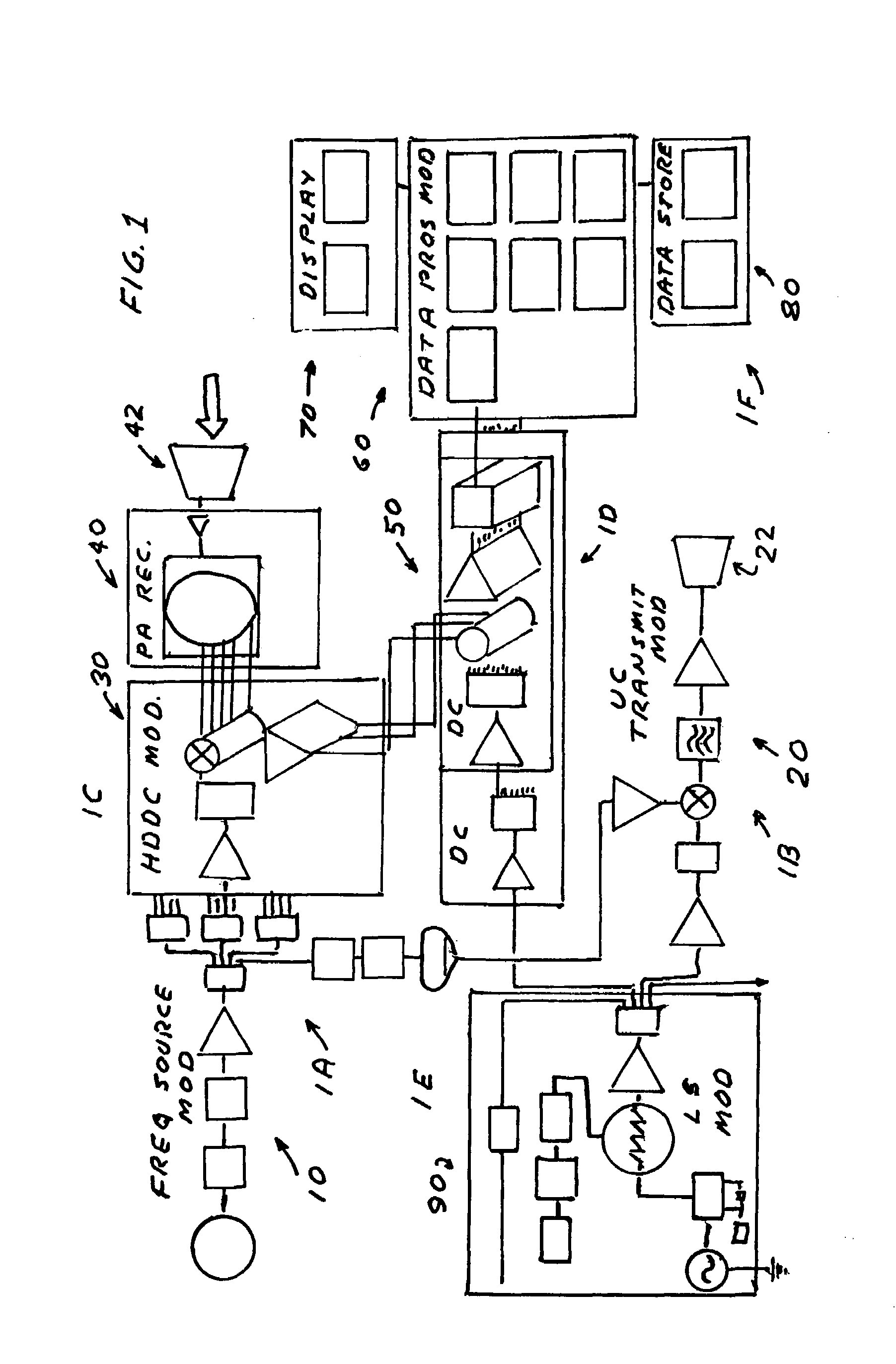
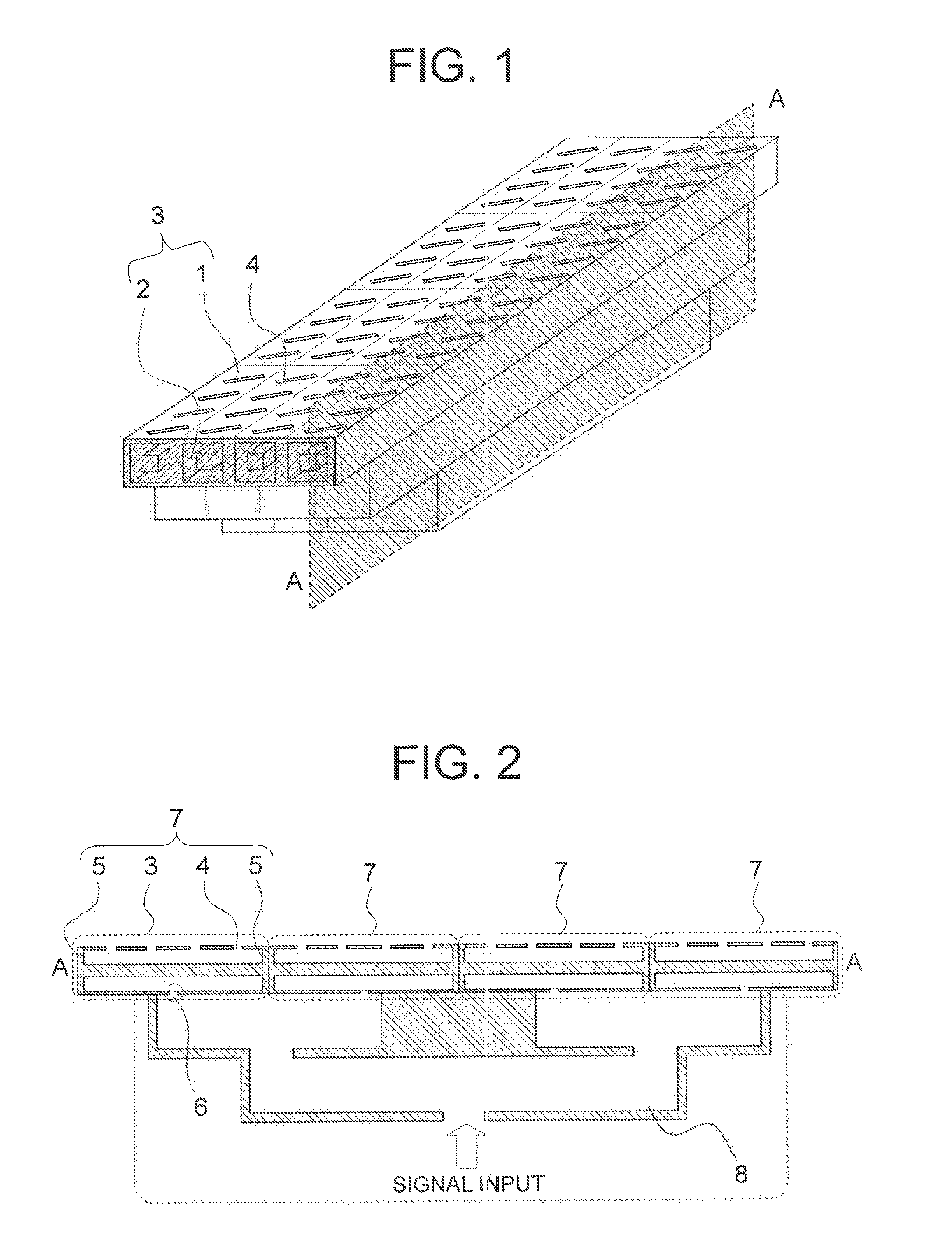
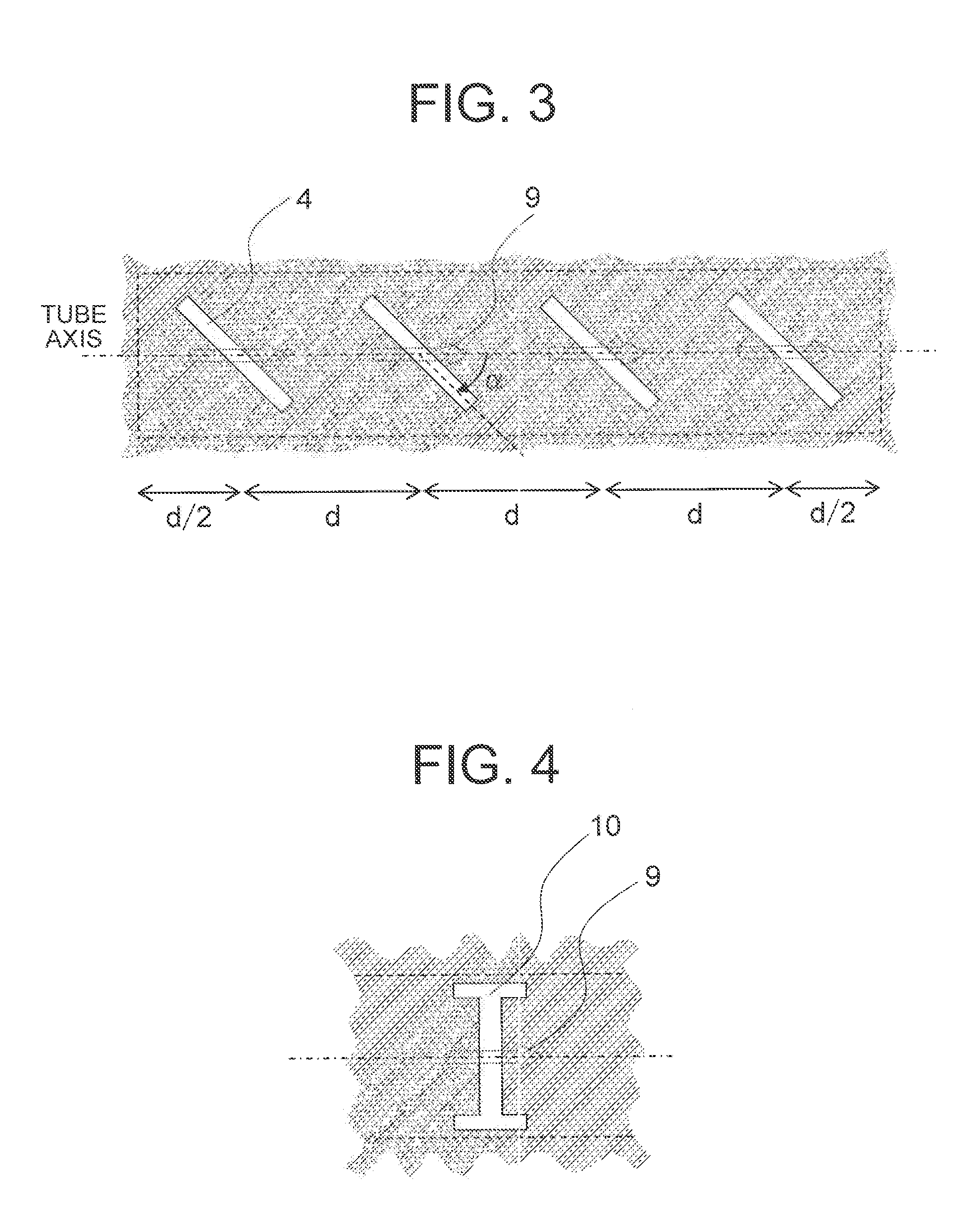
Imaging millimeter wave radar system
InactiveUS7019682B1Linear waveguide fed arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An imaging millimeter wave radar system. The system includes a millimeter wave transmitter transmitting a frequency scanned millimeter beam that is narrow in the scanned direction and wide in a direction perpendicular to the scanned direction. The system includes a receive antenna and a Rotman type lens for forming a one-dimensional image in the perpendicular direction of targets in the antennas field of view based on millimeter wave radiation reflected from the targets. A computer creates a two dimensional image based on the scanning direction of the transmit beam of the transmit antenna and the one dimensional image from the receive antenna. Distance to the target is determined based on difference in frequency of the transmit signal and the receive signal. Thus, a three dimensional view of the systems field of view is determined by the system. This view can be displayed on a monitor using color to represent target distance. In a preferred embodiment the scanned direction is the vertical direction and the receive antenna forms a horizontal image from signals reflected from targets in the field of view. In this preferred embodiment the transmit antenna is a variable frequency millimeter wave single channel wave guide antenna operating in the 78 GHz to 81 Ghz spectral range to produce a scanning range of 10 degrees and a scanning rate of 60 Hz. The receive antenna is a multi-channel (176 channels) strip-line antenna also operating in the 78 GHz to 81 GHz spectral range, which with the Rotman lens, provides 192 horizontal pixel resolution.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Substrate integrated waveguide antenna array
InactiveUS7808439B2Reduce the overall heightMeet cutting requirementsLinear waveguide fed arraysWaveguidesMobile antennasDielectric substrate
A substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) slot full-array antenna fabricated employing printed circuit board technology. The SIW slot full-array antenna using either single or multi-layer structures greatly reduces the overall height and physical steering requirements of a mobile antenna when compared to a conventional metallic waveguide slot array antenna. The SIW slot full-array antenna is fabricated using a low-loss dielectric substrate with top and bottom metal plating. An array of radiating cross-slots is etched in to the top plating to produce circular polarization at a selected tilt-angle. Lines of spaced-apart, metal-lined vias form the sidewalls of the waveguides and feeding network. In multi-layer structures, the adjoining layers are coupled by transverse slots at the interface of the two layers.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
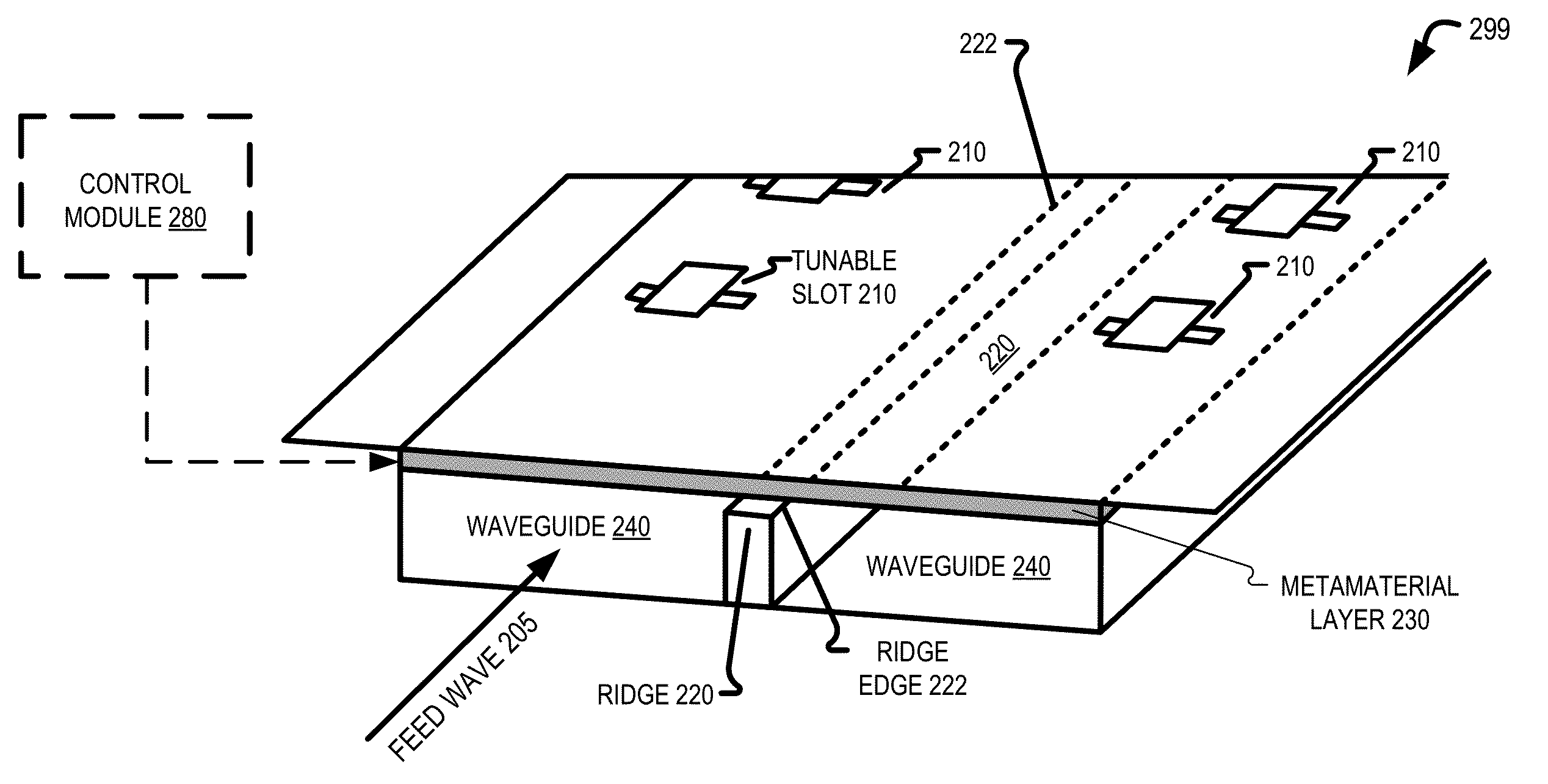
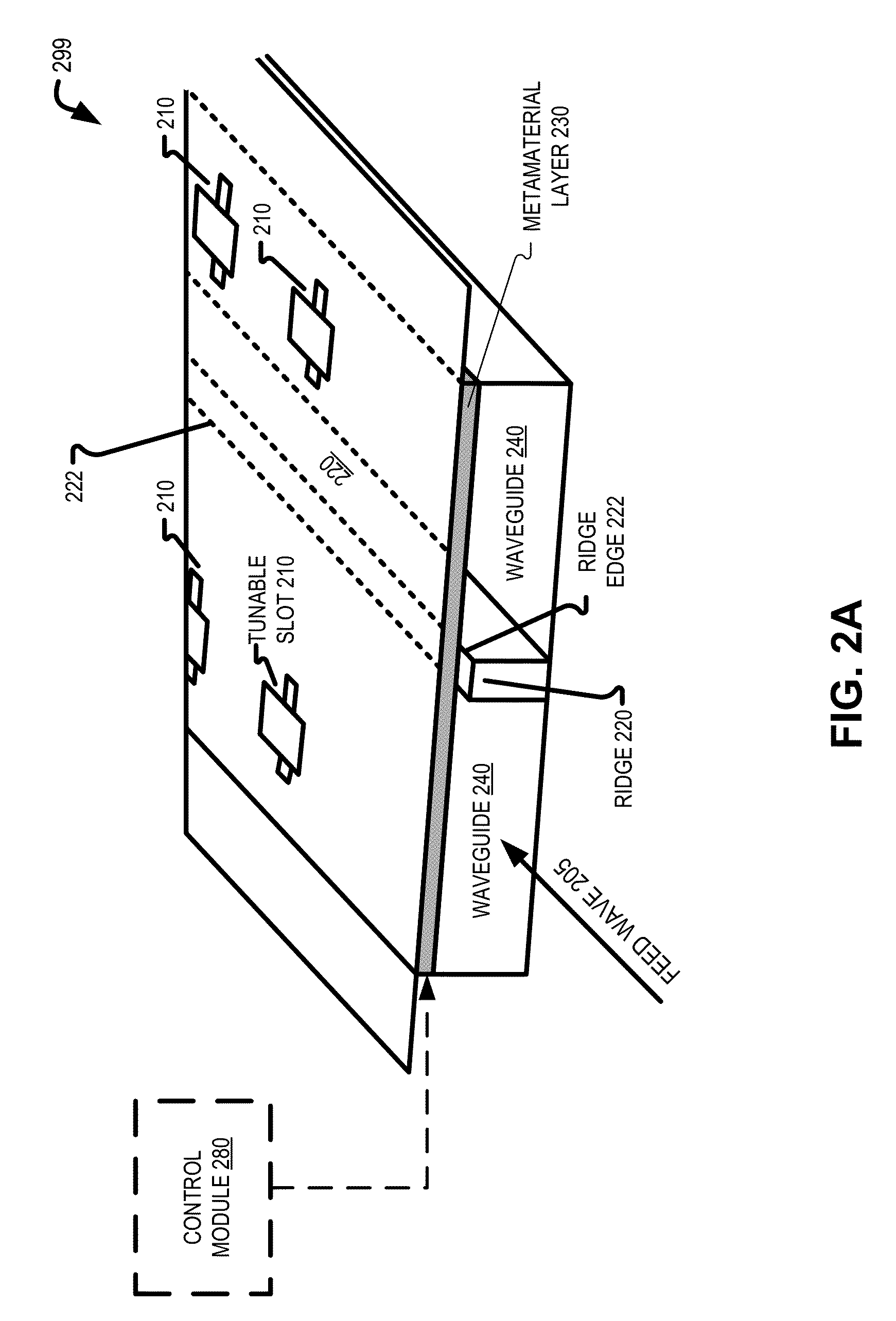
Ridged waveguide feed structures for reconfigurable antenna
A reconfigurable holographic antenna includes a metamaterial layer and a waveguide with at least one ridge. The metamaterial layer includes an array of tunable slots configurable to form holographic diffraction patterns. A reactance of each tunable slot in the array of tunable slots is individually tunable. The at least one ridge influences coupling between tunable slots in the array of tunable slots. The holographic diffraction patterns formed by the array of tunable slots generate a desired antenna wave in response to a received feed wave.
Owner:KYMETA
Tunable substrate integrated waveguide components
A method and an apparatus are provided for providing a tunable substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) for which a parameter of at least some element or portion thereof may be altered or varied to alter the propagation of a signal propagating through the SIW thereby achieving a tunable SIW. In some embodiments a plurality of capacitively variably loaded transverse slots achieve the tunability for the SIW.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
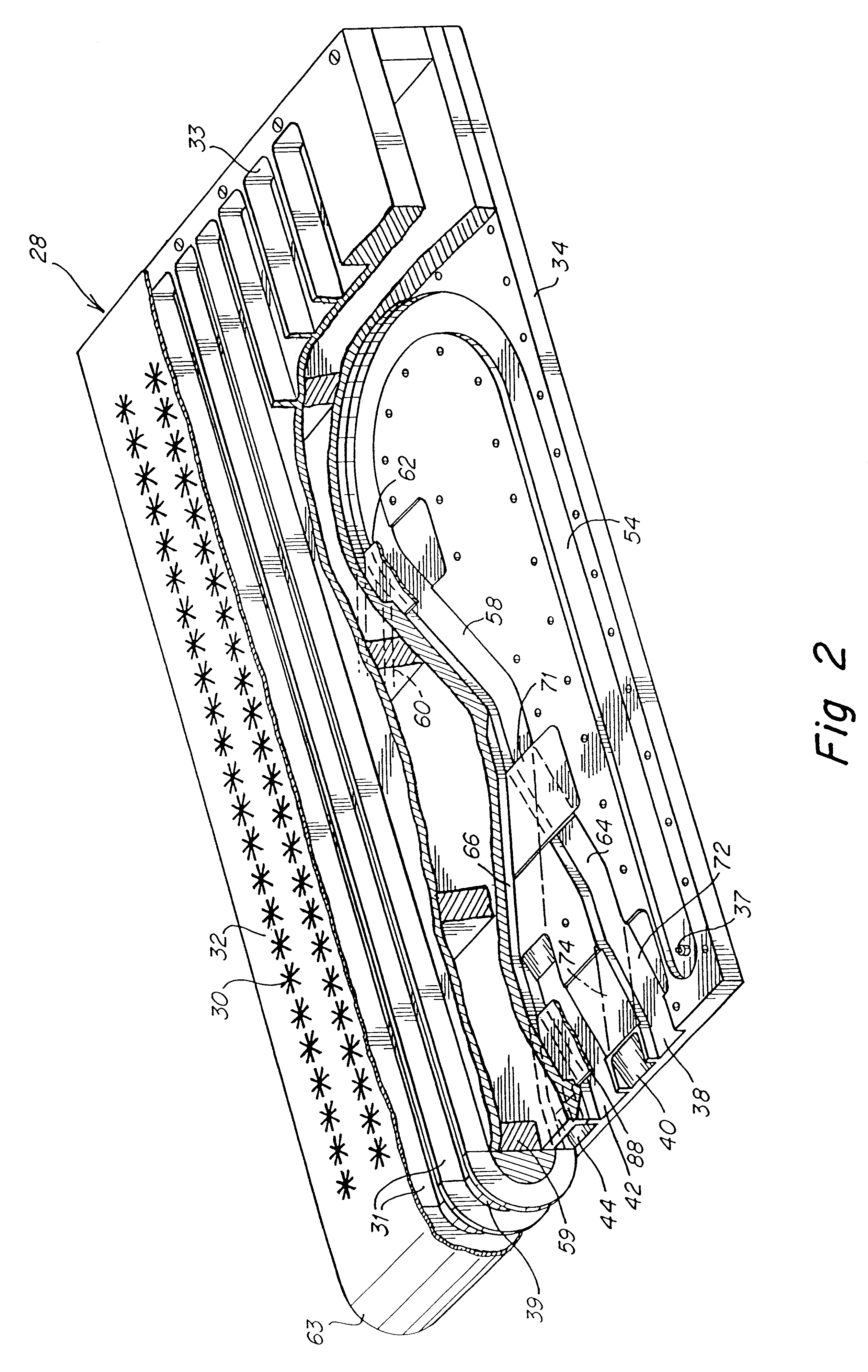
Dual polarized slotted array antenna
InactiveUS6127985AEfficiently signaledPass efficientlyIndividually energised antenna arraysLinear waveguide fed arraysLength waveWaveguide
A waveguide-implemented antenna comprising a planar array of waveguide slot radiators for communicating electromagnetic signals exhibiting simultaneous dual polarization states. The antenna can consist of parallel ridged waveguides having rectangular or "T"-shaped ridged cross sections. The ridged walls of each parallel ridged waveguide contain a linear array of input slots for receiving (transmitting) electromagnetic signals having a first polarization state from (to) the parallel ridged waveguides and for transmitting (receiving) those signals into (from) a corresponding array of cavity sections. The cavity sections comprise a short section of uniform waveguide with a thickness of much less than a wavelength in the propagation direction. The cavity sections feed to output slots which are rotated relative to the input slots; such that the output slots exhibit a second polarization state, which they radiate (receive) to (from) free space. By interlacing parallel ridged waveguides with alternating +45 degree and -45 degree rotations of the output slots, two independent antennas are formed exhibiting simultaneous dual polarizations. Because the input slots are located in the ridge wall of the parallel ridged waveguides, the parallel ridged waveguides can be fed from their broad wall side. Feeding the parallel ridged waveguides from their broad wall side eliminates a need for a complex feed network.
Owner:EMS TECHNOLOGIES
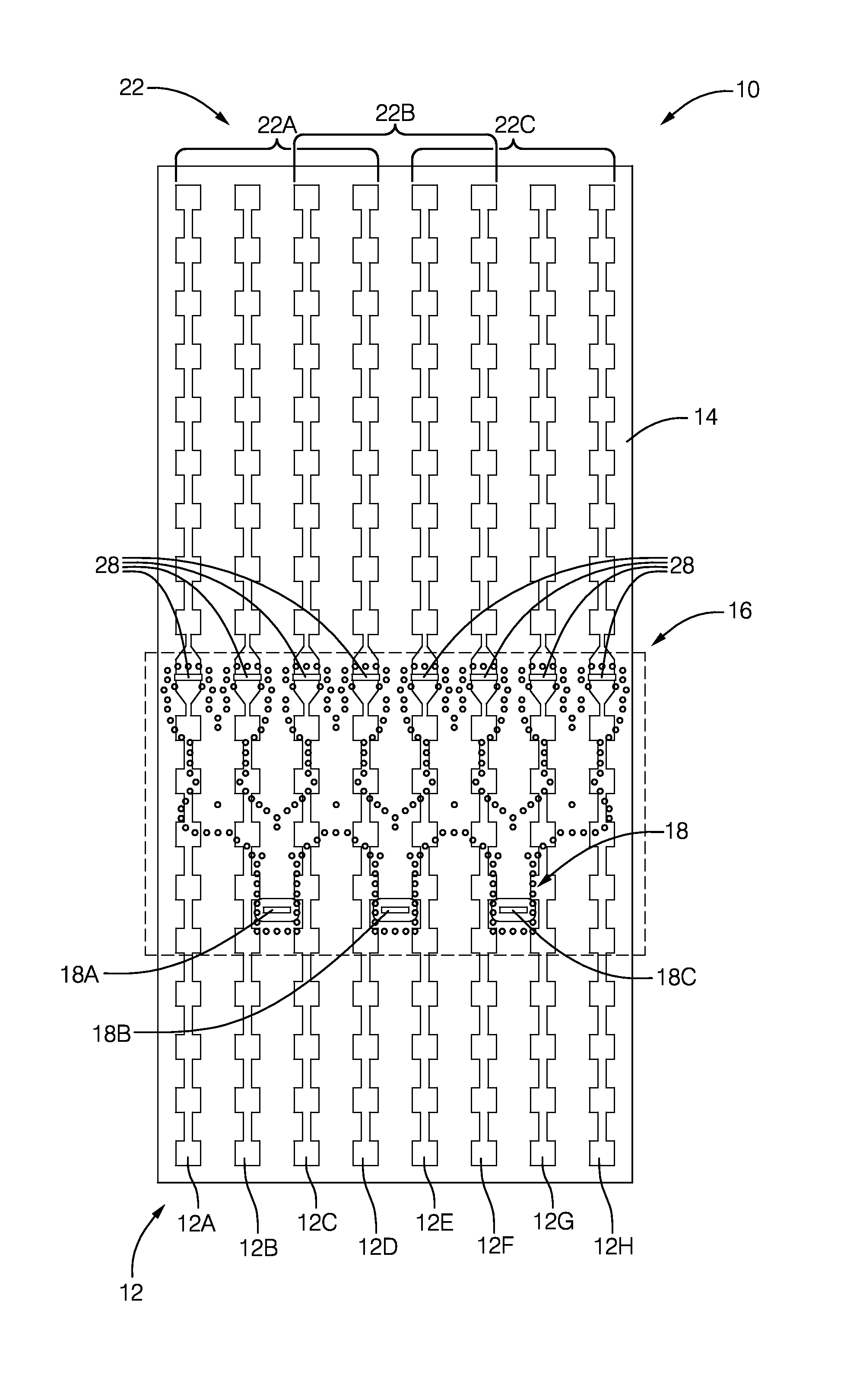
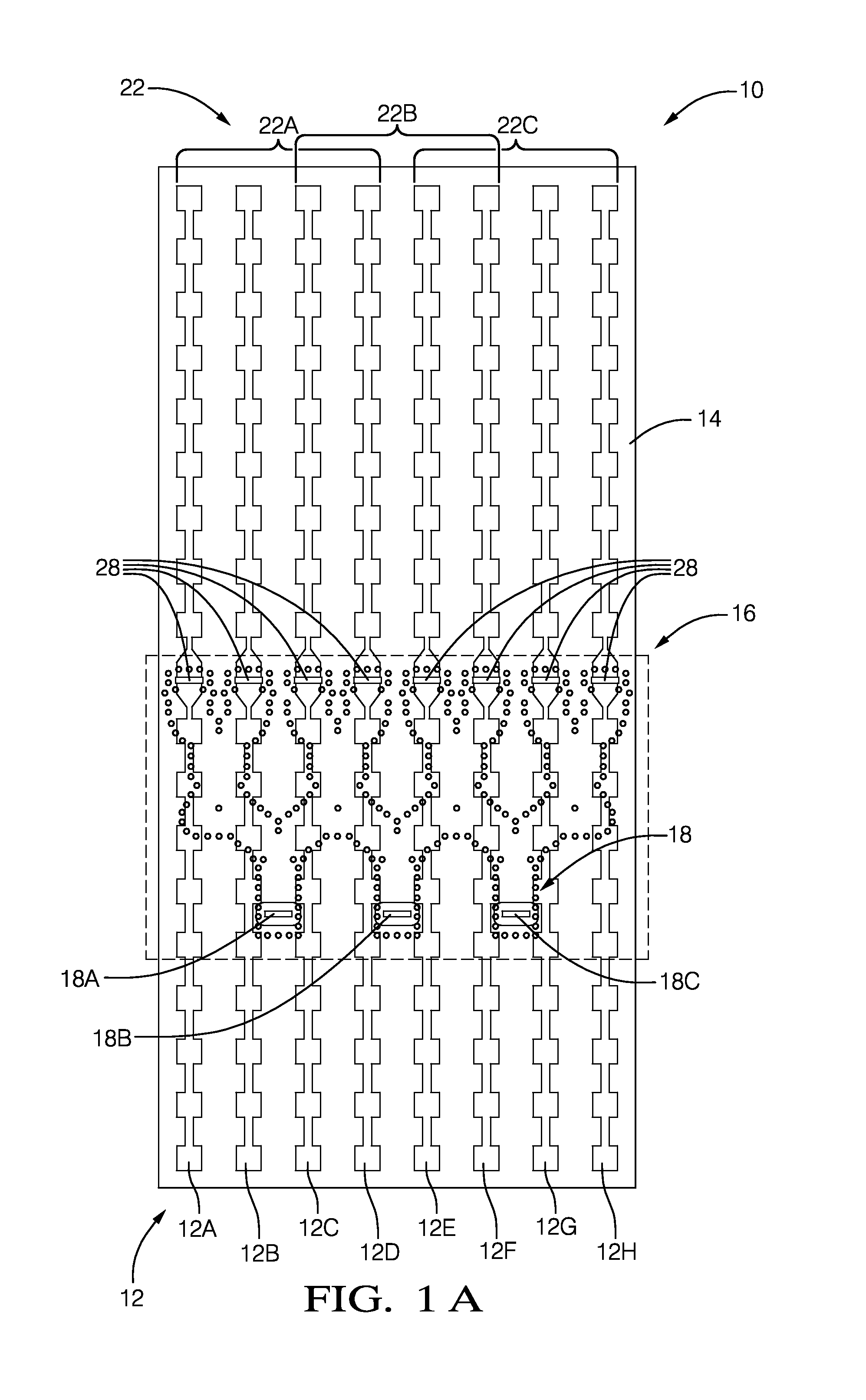
Modular Feed Network
ActiveUS20130120206A1Simple requirementsReduce couplingAntenna arrays manufactureModular arraysModularityEngineering
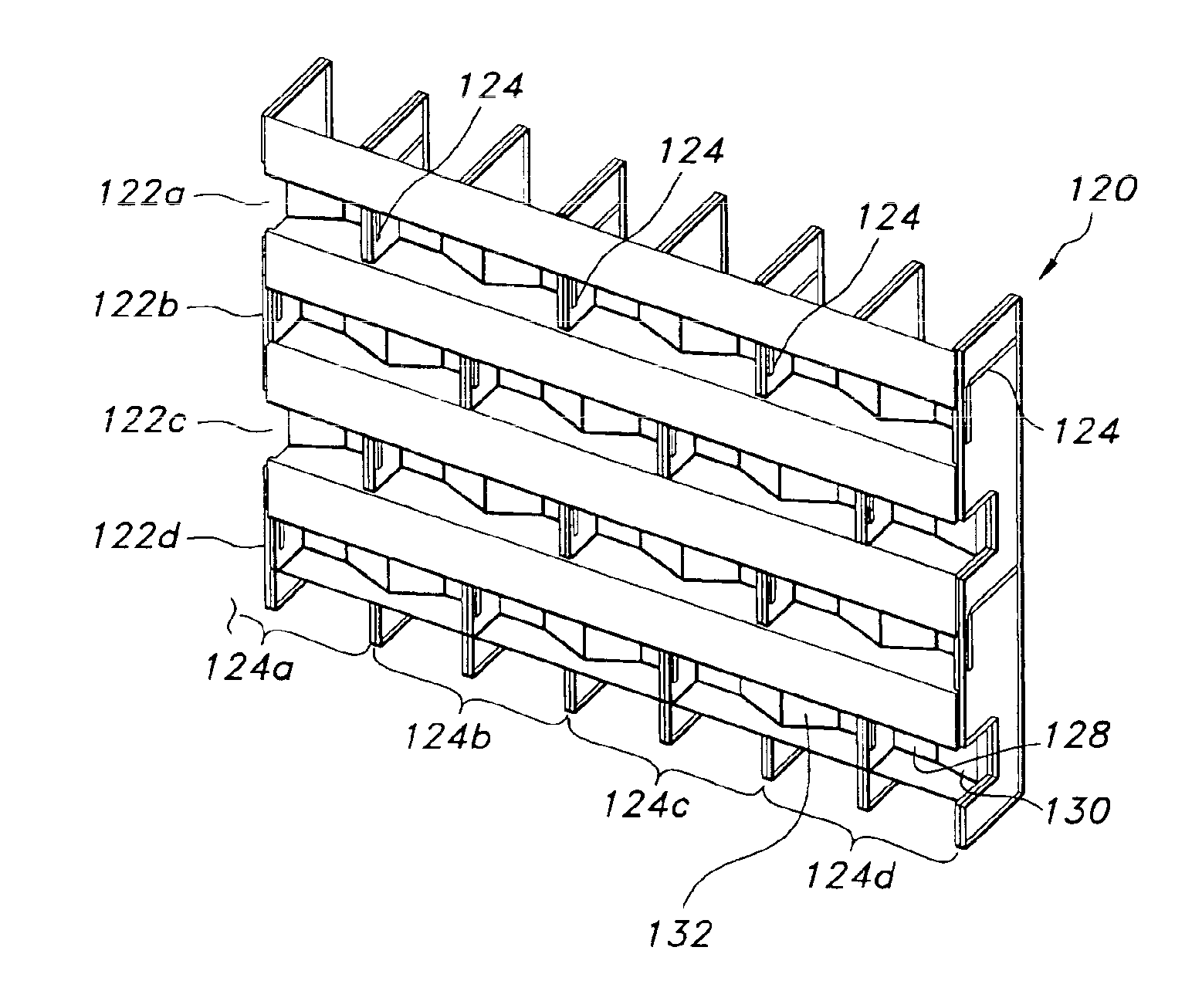
A modular feed network is provided with a segment base provided with a feed aperture, a corner cavity at each corner and a tap cavity at a mid-section of each of two opposite sides. A segment top is provided with a plurality of output ports. The segment top is dimensioned to seat upon the segment base to form a segment pair. the segment base provided with a plurality of waveguides between cavities of the segment base. The modular feed network is configurable via a range of feed, bypass and / or power divider taps seated in the apertures and / or cavities to form a waveguide network of varied numbers of output ports by routing across one or more of the segment tops. For example, the modular feed network may comprise 1, 4 or 16 of the segment bases retained side to side.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Waveguide
InactiveUS20050128028A1Minimize impactAvoid energy leakageLinear waveguide fed arraysDelay linesSlot-waveguideSlotted waveguide
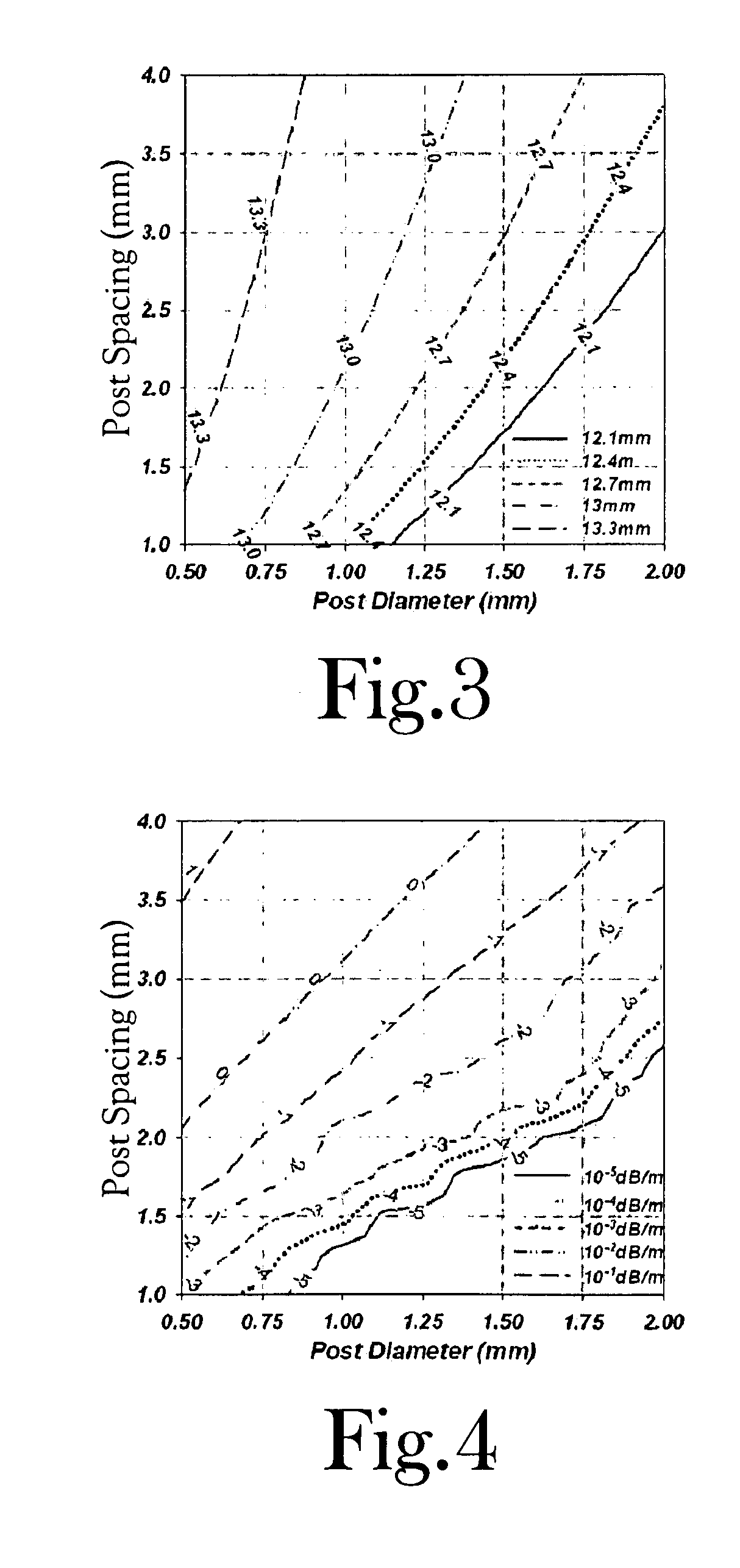
A waveguide structure including two parallels electrically conducting ground planes (1,2), each of which includes at least one row of spaced apart electrically conducting posts (3). The rows of posts are arranged substantially parallel to one another and the space bounded by the plates and posts defines a guided wave region (4) along which electromagnetic radiation may propagate. The posts are connected to only one of the planes so that there is no physical connection between the two ground planes (1,2). Actuating means may be connected to one or both of the ground planes to cause relative movement there between to thereby alter the electrical response of the waveguide. The direction of the relative movement may such that the distance between the rows of posts (3) is changed and / or the distance between the ground planes (1,2) is changed. Various device may utilize the described waveguide construction, including reconfigurable waveguide filters and antenna structures e.g. slotted waveguide arrays.
Owner:ERA PATENTS
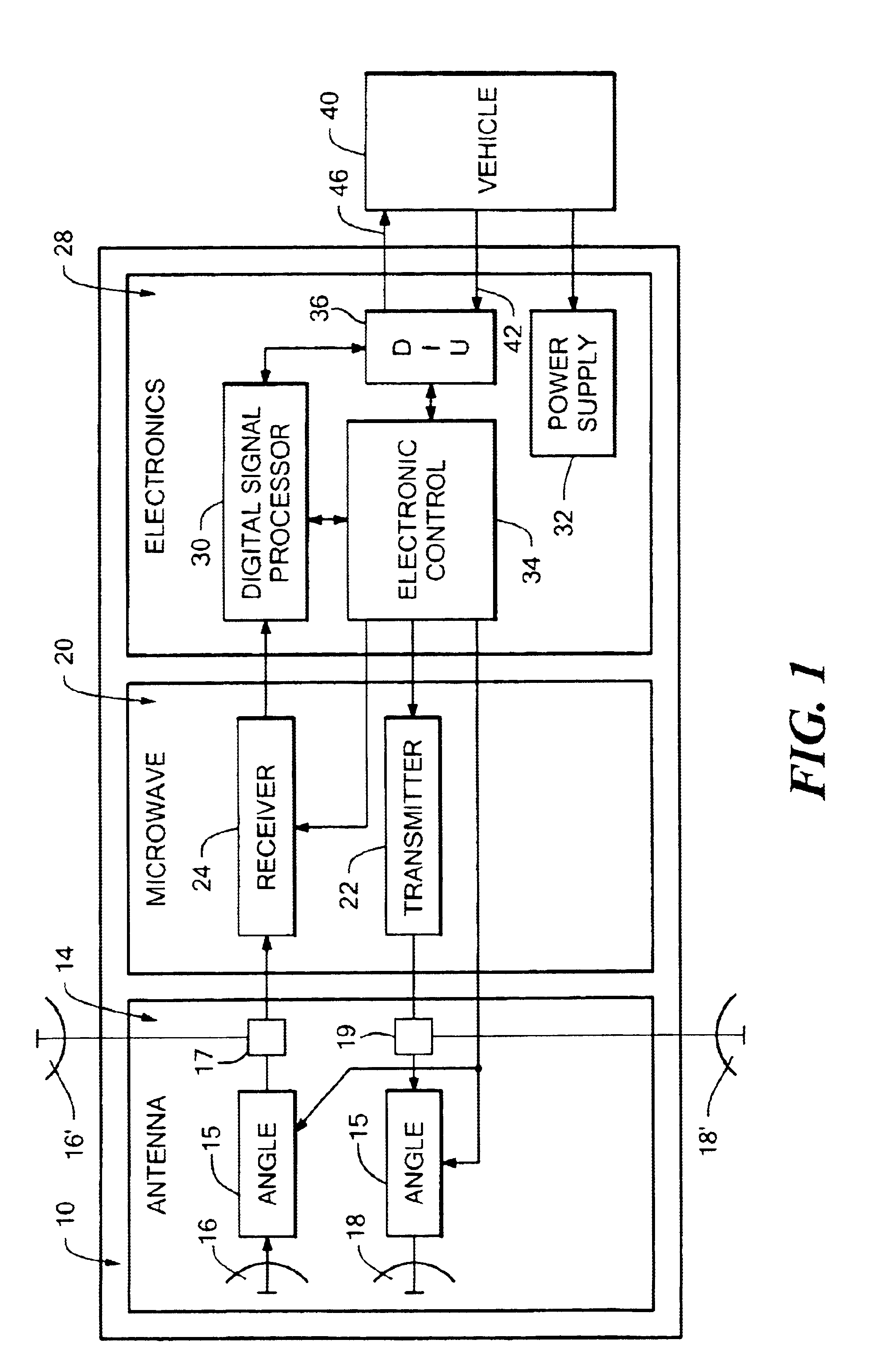
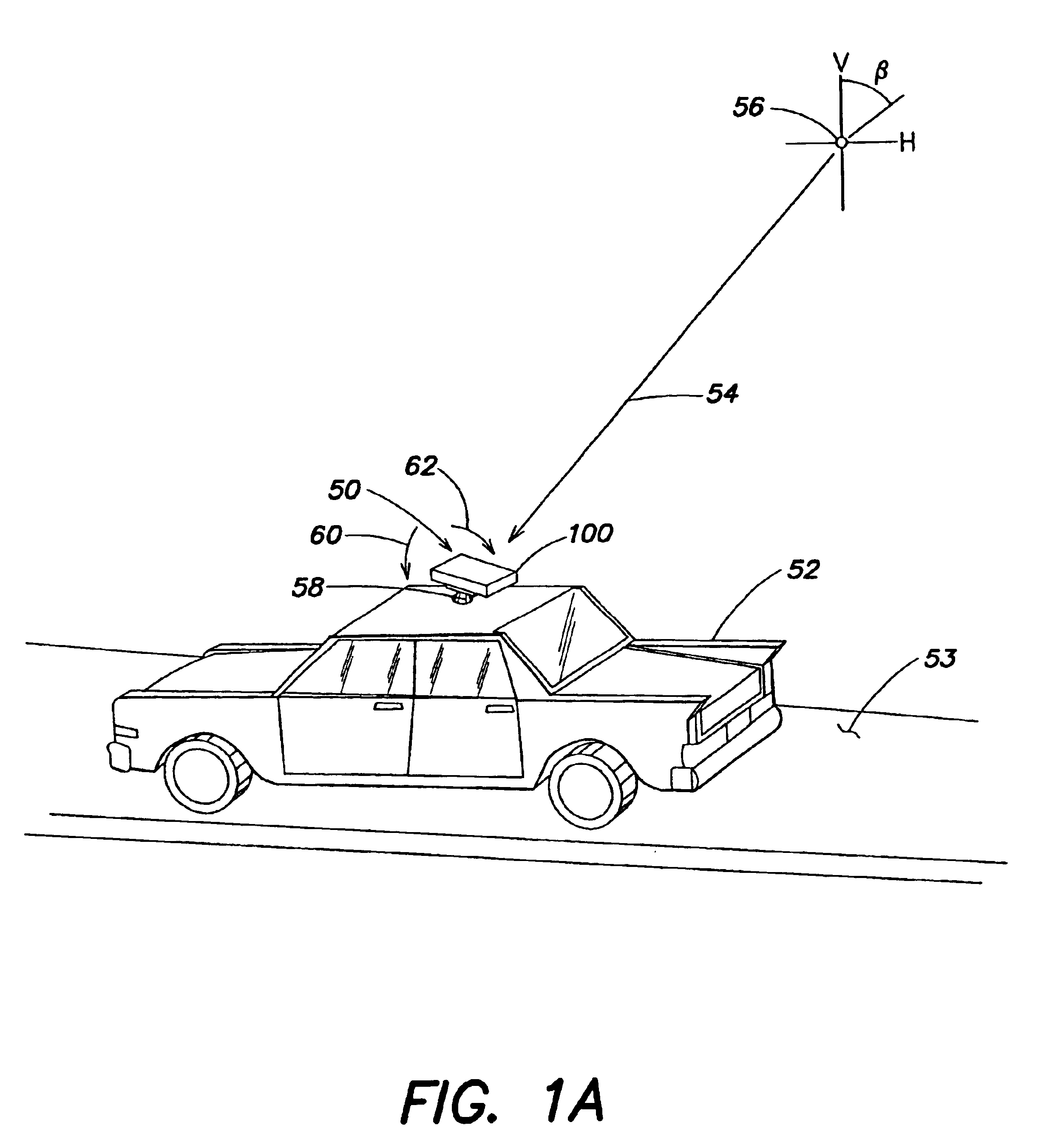
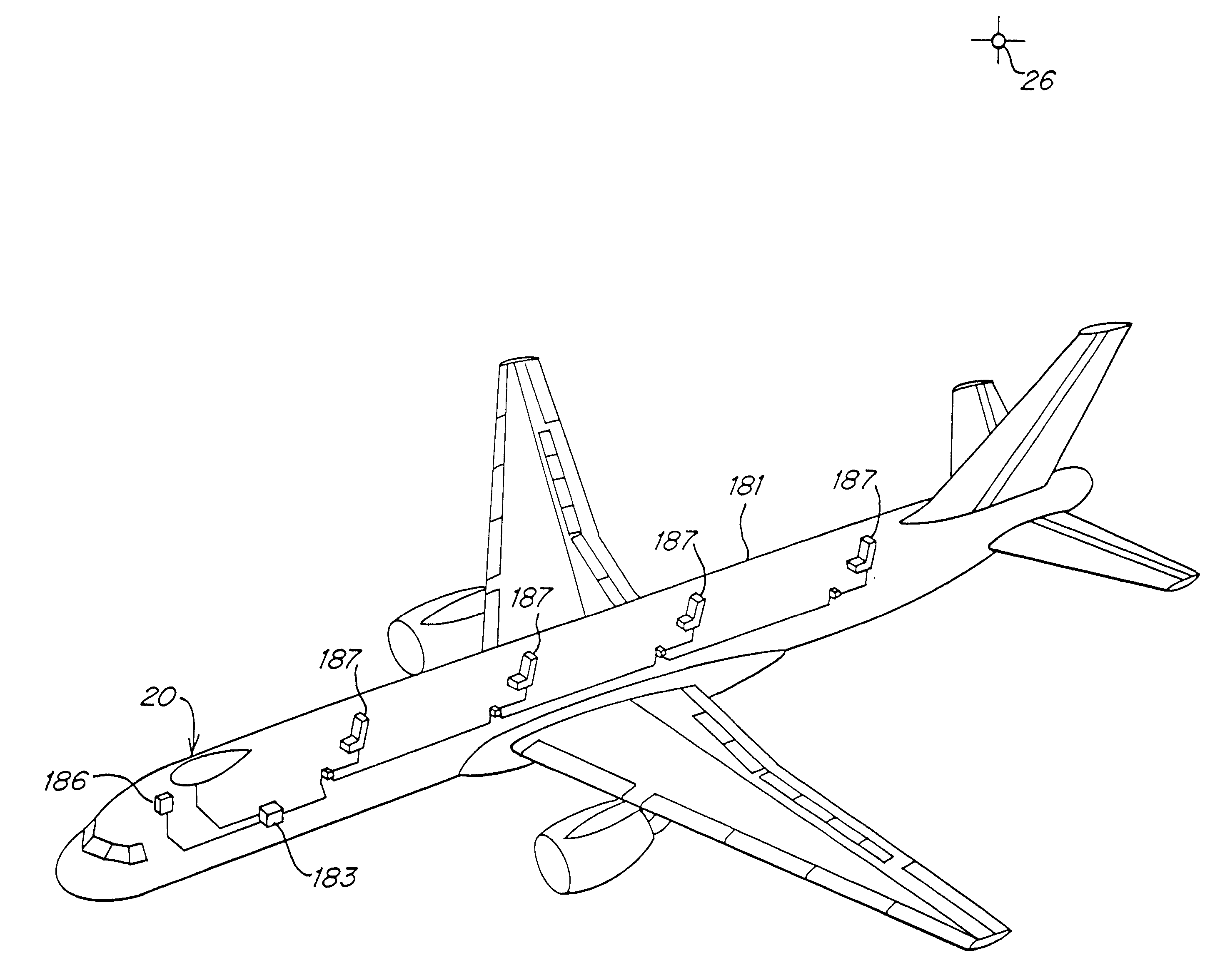
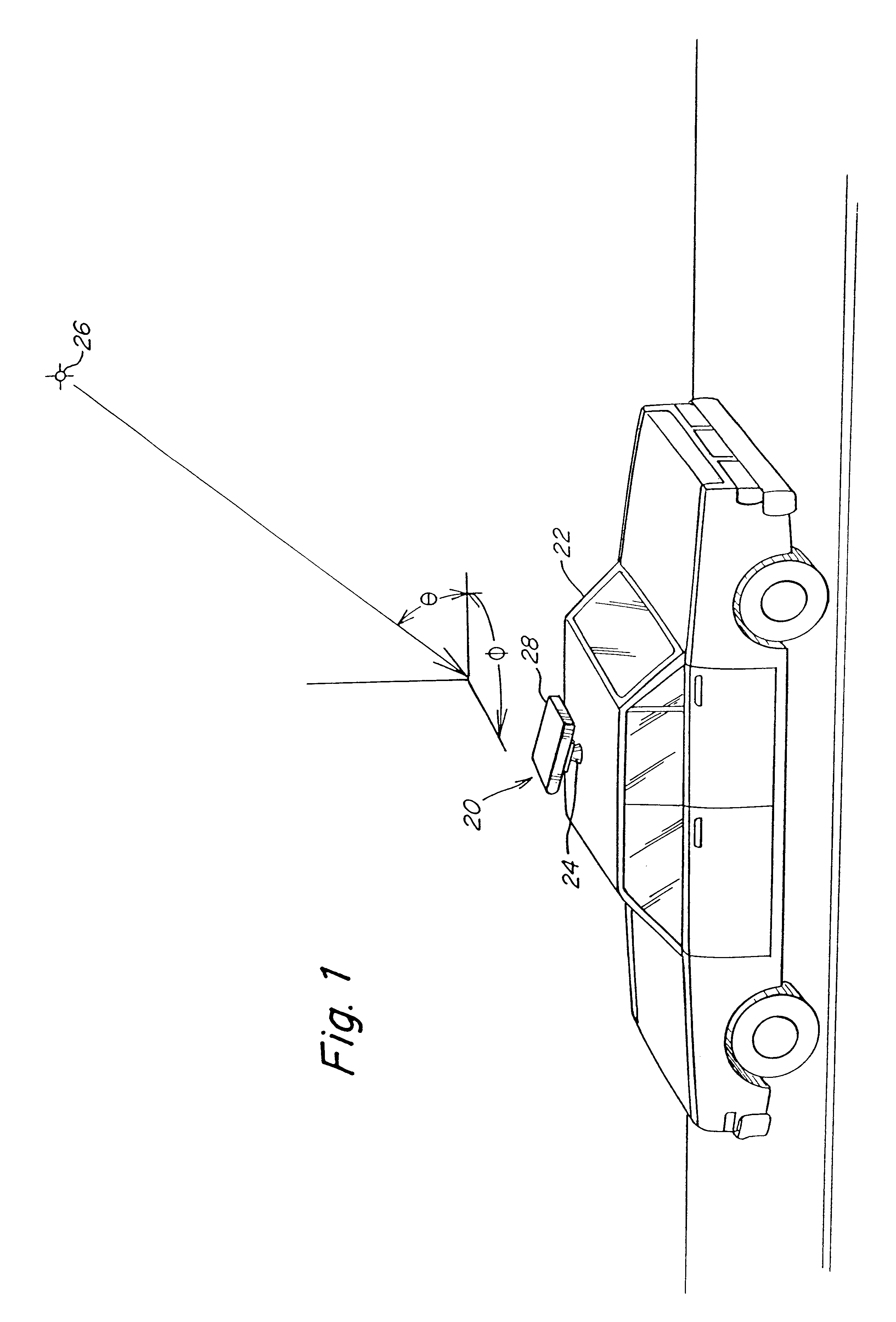
Back-up aid indicator using FMCW chirp signal or a time domain pulse signal
InactiveUS6873250B2Reduce leakageHigh energyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAnti-collision systemsTime domainContinuous wave
A back-up aid indication system includes a sensor for providing detection coverage in a predetermined coverage zone behind a vehicle. The sensor includes a transmit antenna adapted for transmitting an RF signal having a quasi-collimated antenna pattern in a near field. The system further includes a waveform generator which selectively provides one of a frequency modulated continuous wave FMCW Chirp signal and a pulse waveform signal as the transmitted RF signal.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
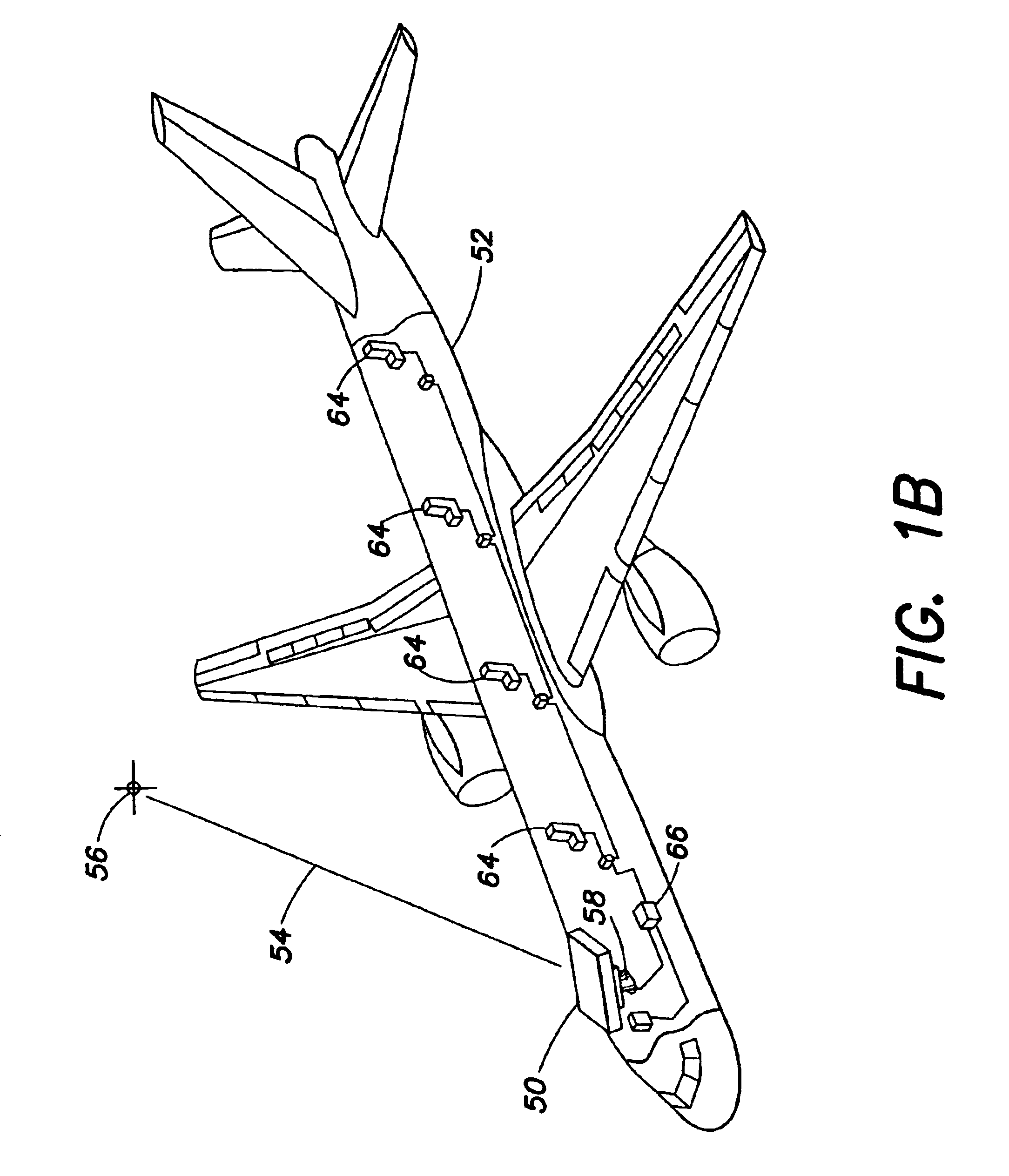
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with ridged waveguide
ActiveUS20060132374A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioRidge waveguides
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a ridged waveguide instead of a conventional rectangular waveguide to alleviate the effects of grating lobes. The ridge waveguide provides a ridged section longitudinally between walls forming the waveguide. A plurality of radiating elements are formed in a radiating surface of the ridged waveguide.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
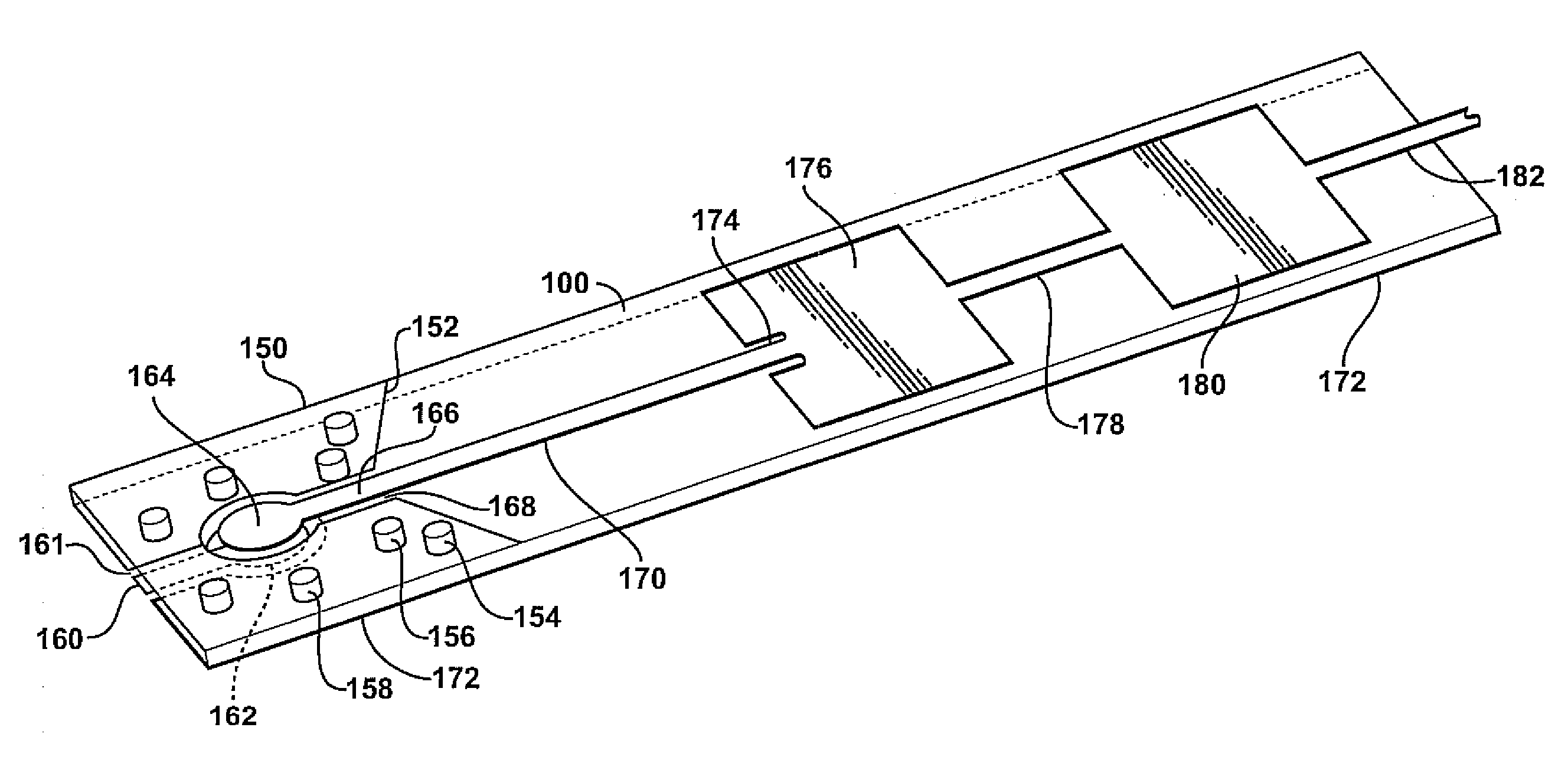
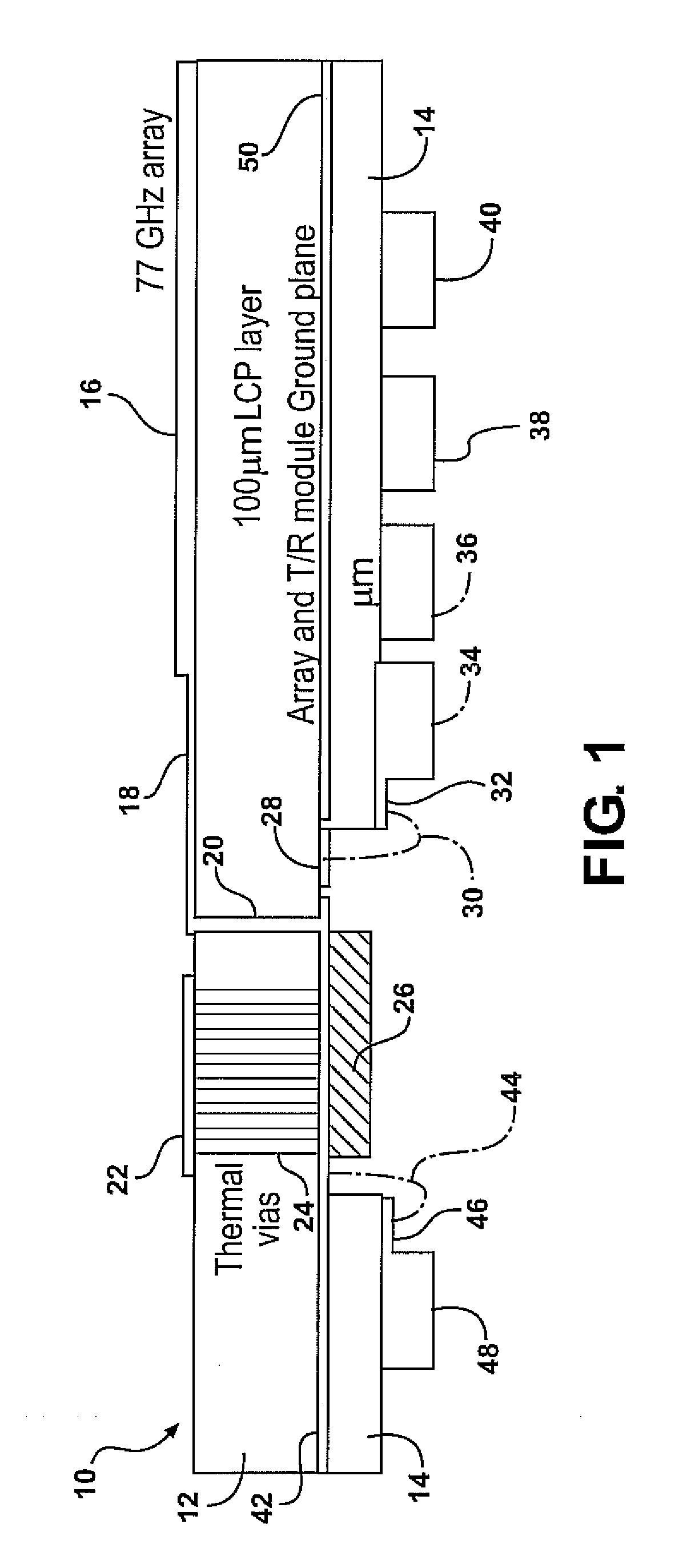
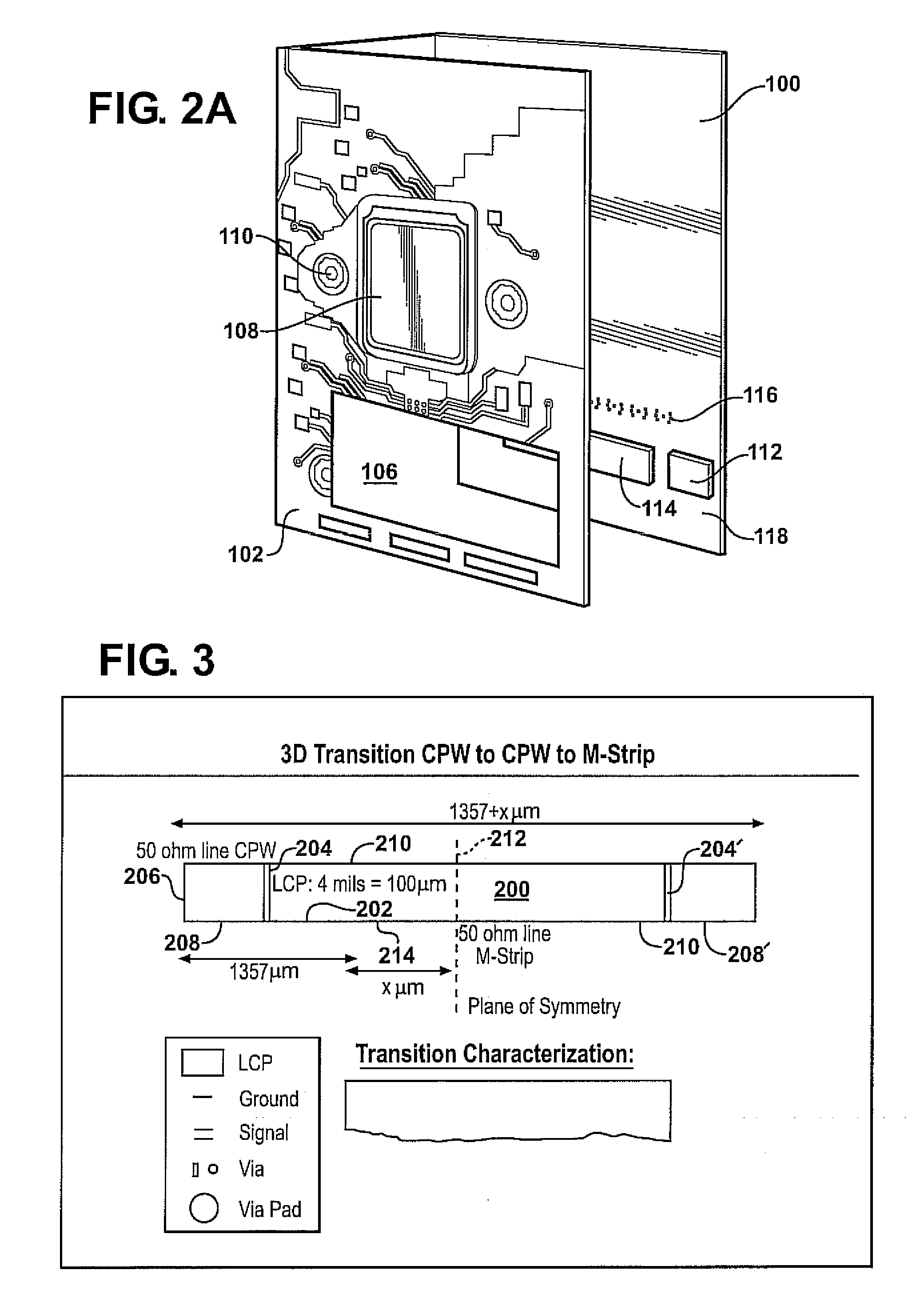
Wideband RF 3D transitions
InactiveUS20100134376A1Reduce return lossReduce lossesSimultaneous aerial operationsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical connection
Apparatus and methods according to examples of the present invention include providing an electrical interconnection between an RF circuit and an antenna, the electrical interconnection including a transition via through an antenna substrate. The electrical connection can be configured so as to provide low losses.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA
Waveguide device, and antenna device including the waveguide device
InactiveUS20180351261A1Radiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysMicrowaveHollow waveguide
A waveguide device includes: a circuit board having a microstrip line thereon; a microwave IC connected to one end of the microstrip line; a first waffle-iron ridge waveguide; a second waffle-iron ridge waveguide; a first hollow waveguide which is at one end connected to another end of the microstrip line, and at another end connected to a first site of the first waffle-iron ridge waveguide; and a second hollow waveguide which is at one end connected to a second site of the first waffle-iron ridge waveguide, and at another end connected to a first site of the second waffle-iron ridge waveguide.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP +1
Phased array antenna
InactiveUS20160141754A1Increase flexibilityLinear waveguide fed arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasRadiating elementPhase array antenna
Embodiments provide a phased array antenna including a feed structure adapted to guide an electromagnetic wave, a plurality of controllable elements coupled to the feed structure and a plurality of radiating elements, wherein each of the radiating elements is coupled to at least two of the plurality of controllable elements.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS20050146479A1Space is requiredPrevent RF leakageRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
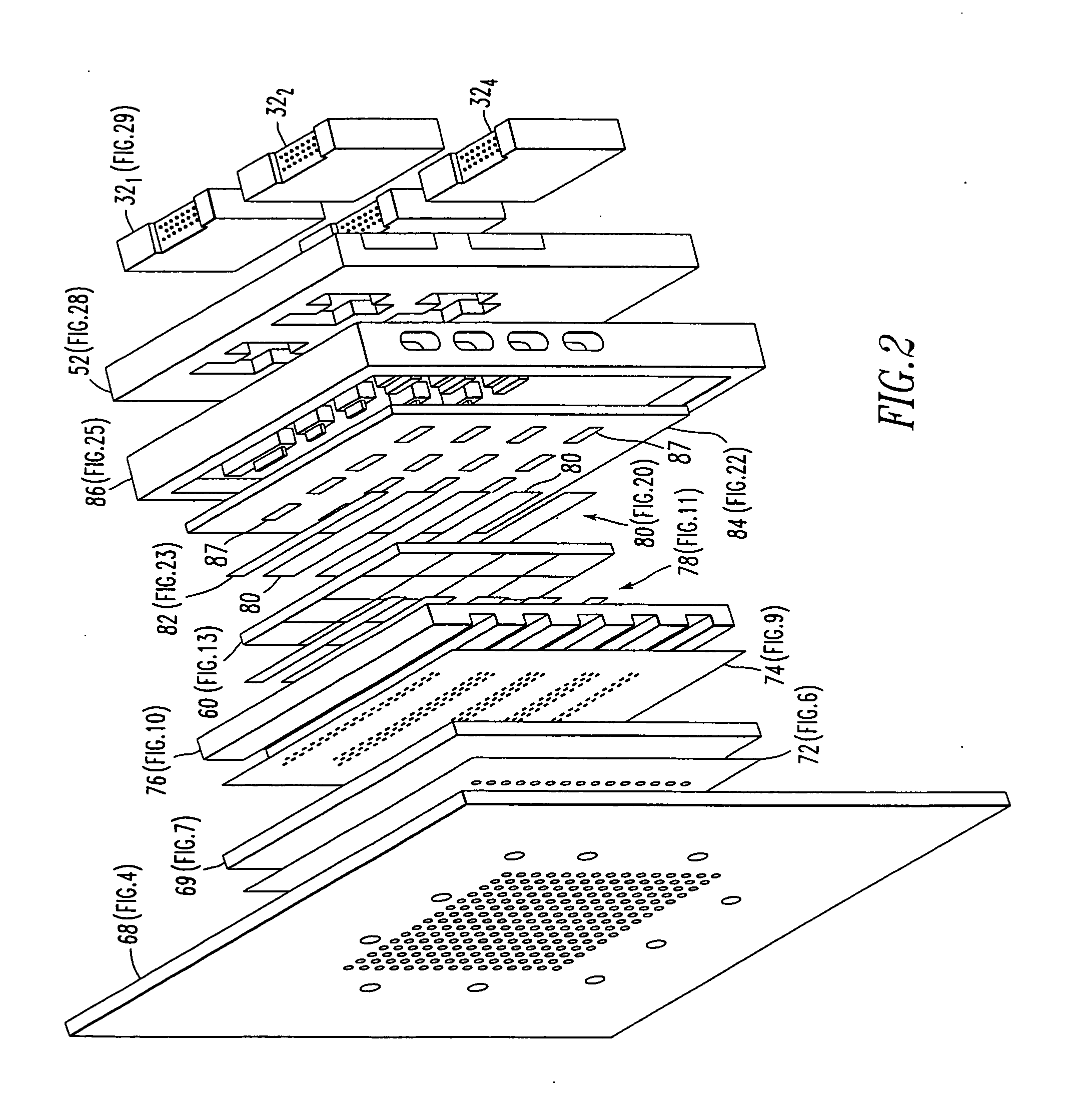
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
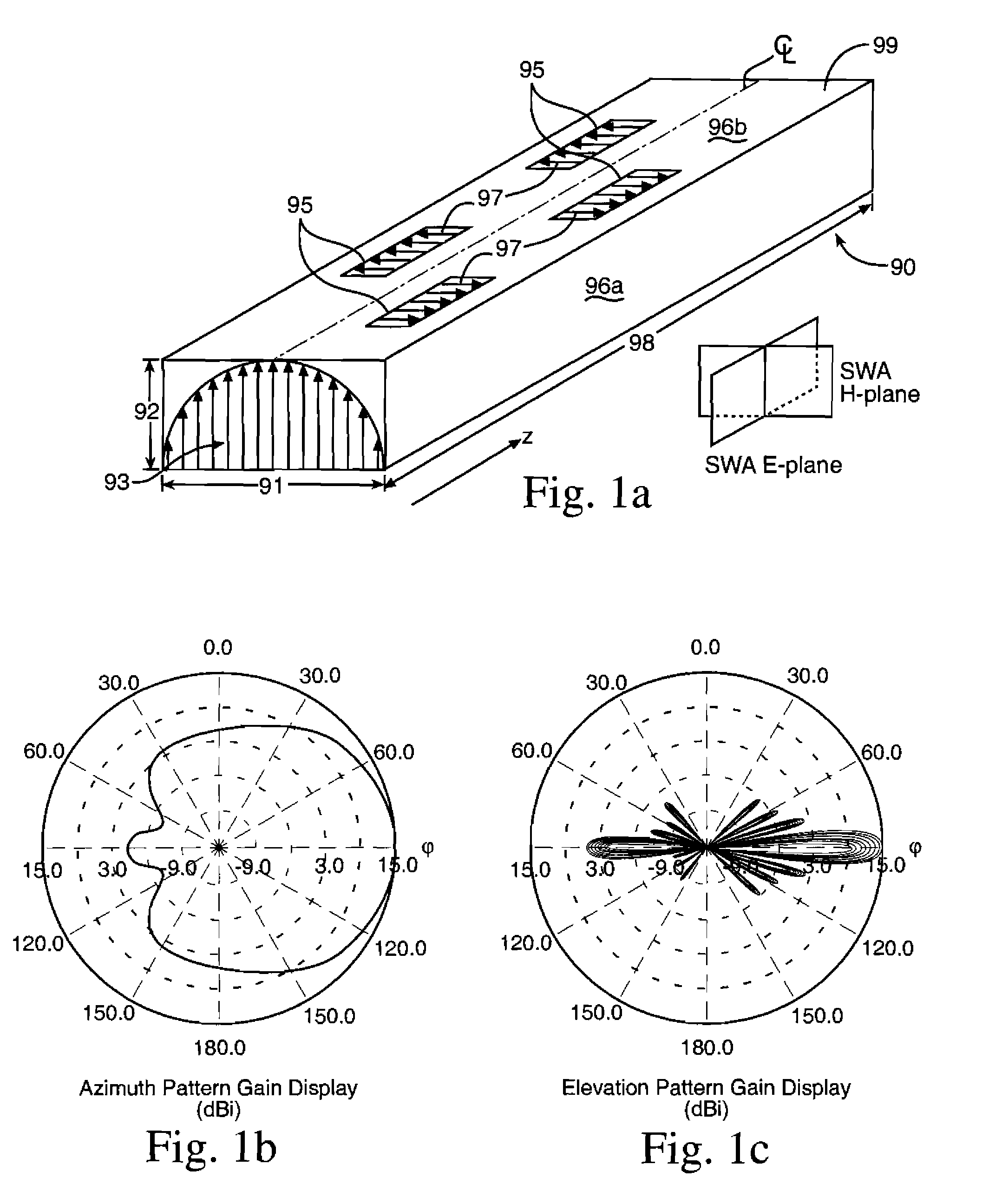
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Multilayer pillbox type parallel-plate waveguide antenna and corresponding antenna system
ActiveUS20120092224A1Good yieldReduce resonance effectLinear waveguide fed arraysSlot antennasParallel plateSlot coupling
A multilayer antenna is provided, which includes a power supply portion generating a wave, a radiating portion, and a guide portion that makes it possible to guide the wave from the power supply portion to the radiating portion. The guide portion includes: at least two stacked guide layers having parallel planes and, for each pair of adjacent layers, a transition between the adjacent layers, including a reflector engaging with a slot-coupling. For at least one pair of adjacent layers, for which the guide portion includes a non-planar reflector, the slot-coupling includes a plurality of slots. Each slot includes a main body that is elongate along at least one axis. The slots are placed on at least one row and together form a pattern that extends along the reflector and has a shape that is dependent on the shape of the reflector.
Owner:UNIV DE RENNES I +1
Antenna device
ActiveUS20130033404A1Prevent leakageLower performance requirementsWaveguide hornsLinear waveguide fed arraysAntenna elementOperating frequency
An antenna device includes antennas, each of which includes antenna elements arranged in a longitudinal direction, arranged side by side in a transverse direction intersecting the longitudinal direction, wherein an interval between the antennas arranged side by side in the transverse direction is approximately 2λ. where λ is a free space wavelength corresponding to an operating frequency, and each of the antenna elements includes a horn formed therein.
Owner:HONDA ELESYS CO LTD
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna embedded within moonroof or sunroof
InactiveUS20050146478A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolarised antenna unit combinationsAxial ratioIn vehicle
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Integrated waveguide antenna and array
ActiveUS20070273599A1Improve conversion efficiencySimple and inexpensive to manufactureLinear waveguide fed arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasBeam steeringWaveguide
An antenna is provided. The antenna may include at least one open-ended structure extending from a surface of a waveguide. The open-ended structure may have a cross section of many different shapes. The walls of the structure may be movable. The antenna structure may be rotated. The antenna may incorporate a number of different wave feeds. The antenna may provide two-dimensional beam steering.
Owner:ORR PARTNERS I
Communication system with broadband antenna
ActiveUS6950073B2Waveguide hornsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPhase correctionCommunications system
A communication system including an antenna array with feed network coupled to communication electronics. In one example, a communication subsystem comprises a plurality of antennas each adapted to receive an information signal and a plurality of orthomode transducers coupled to corresponding ones of the plurality of antennas, each OMT is adapted to provide at a first component signal having a first polarization and a second component signal having a second polarization. The communication subsystem also comprises a feed network that receives the first component signal and the second component signal from each orthomode transducer and provides a first summed component signal at a first feed port and a second summed component signal at a second feed port, and a phase correction device coupled to the first and second feed ports and adapted to phase match the first summed component signal with the second summed component signal.
Owner:ASTRONICS AEROSAT CORP
Antenna with fifty percent overlapped subarrays
ActiveUS20140375525A1Individually energised antenna arraysLinear waveguide fed arraysElectricityRadar systems
An antenna suitable for use as a phased array antenna of a radar system. The antenna includes a plurality of radiating elements, and a substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) configured to form a feed network to couple energy from a plurality of inputs to the radiating elements. The feed network includes over-moded waveguide couplers configured so energy propagates through an over-moded section in multiple modes, TE10 and TE20 modes for example. The feed network also defines sub-arrays configured such that half of the radiators of a sub-group are shared with an adjacent sub-group of an adjacent sub-array, i.e. the sub-arrays are configured to have 50% overlap. Preferably, the feed-network is formed about a single layer of substrate material.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Coaxial line slot array antenna and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100001916A1Reduce lossLow profileIndividually energised antenna arraysLinear waveguide fed arraysElectrical conductorResonance
A planar antenna including slot arrays configured to set a narrow interval between elements so as to perform beam scanning in a wide angle range while keeping low loss and low profile. The planar antenna includes: a coaxial line including an inner conductor, an outer conductor provided so as to surround a circumference of the inner conductor, and both ends short-circuited; a feeding mechanism for exciting the coaxial line; and a plurality of slots formed on the outer conductor with a certain angle with respect to a tube direction of the coaxial line and having approximately a resonance length.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
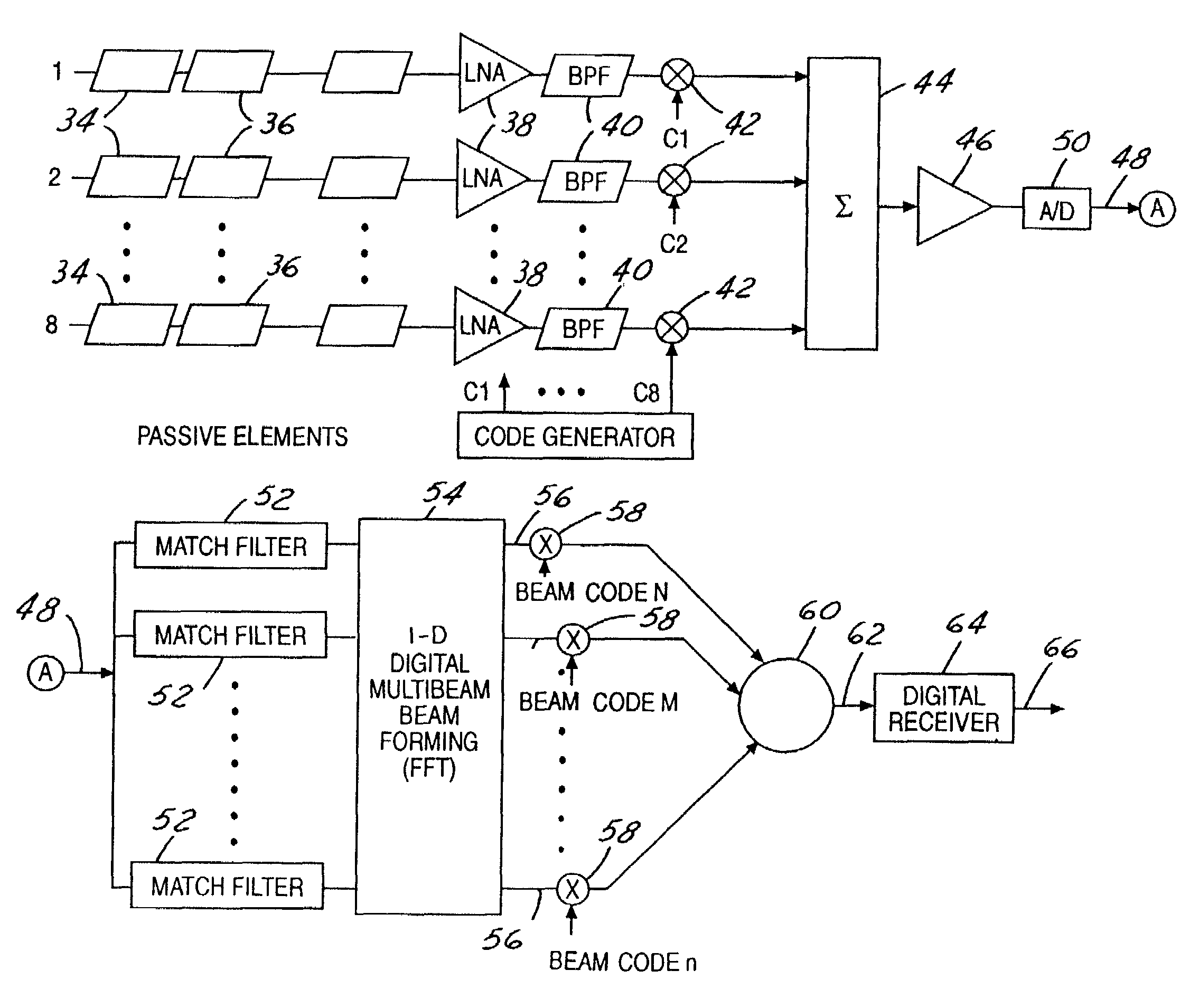
Phased array terminal for equatorial satellite constellations
InactiveUS7339520B2Improve performanceLow profileAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionMultiplexingAzimuth direction
A low cost and low profile antenna for commercial use, either in a fixed or mobile condition is disclosed. The antenna has a generally flat circular plate that rotates to seam the azimuth direction. A plurality of radiation elements are positioned on the surface of the circular plate. The received signals are multiplexed, digitally converted, digitally beamformed, and then transferred to a digital receiver.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Low-height, low-cost, high-gain antenna and system for mobile platforms
InactiveUS6751442B1Reduce height and lengthReduce weightAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesActive radio relay systemsHigh-gain antennaJunction point
A leaky waveguide antenna array that receives and / or transmits electromagnetic signals includes a plurality of radiation waveguides disposed in parallel to each other on a surface plane to form the antenna array. A feed waveguide is located below the surface plane and provides an electromagnetic signal to the plurality of radiation waveguides and / or receives a plurality of electromagnetic signals from the plurality of radiation waveguides and provides a composite electromagnetic signal at an output of the feed waveguide. Each of the plurality of radiation waveguides has a waveguide axis and includes a plurality of apertures arranged in a direction of the waveguide axis. The feed waveguide includes a first section of waveguide having a first end connected to an input / output port. The first section of waveguide has a height substantially the same as the height of each of the plurality of radiation waveguides and the first section of waveguide has a second end coupled to a first junction point. The first junction point transitions from the first section of waveguide to a second section of waveguide and a third section of waveguide that each have a height that is substantially half of the height of the first section of waveguide. The second section of waveguide transitions with an upward sloping ramp to the substantially half height of the first section of waveguide. The third section of waveguide transitions with a downward sloping ramp to the substantially half height of the first section of waveguide.
Owner:ASTRONICS AEROSAT CORP
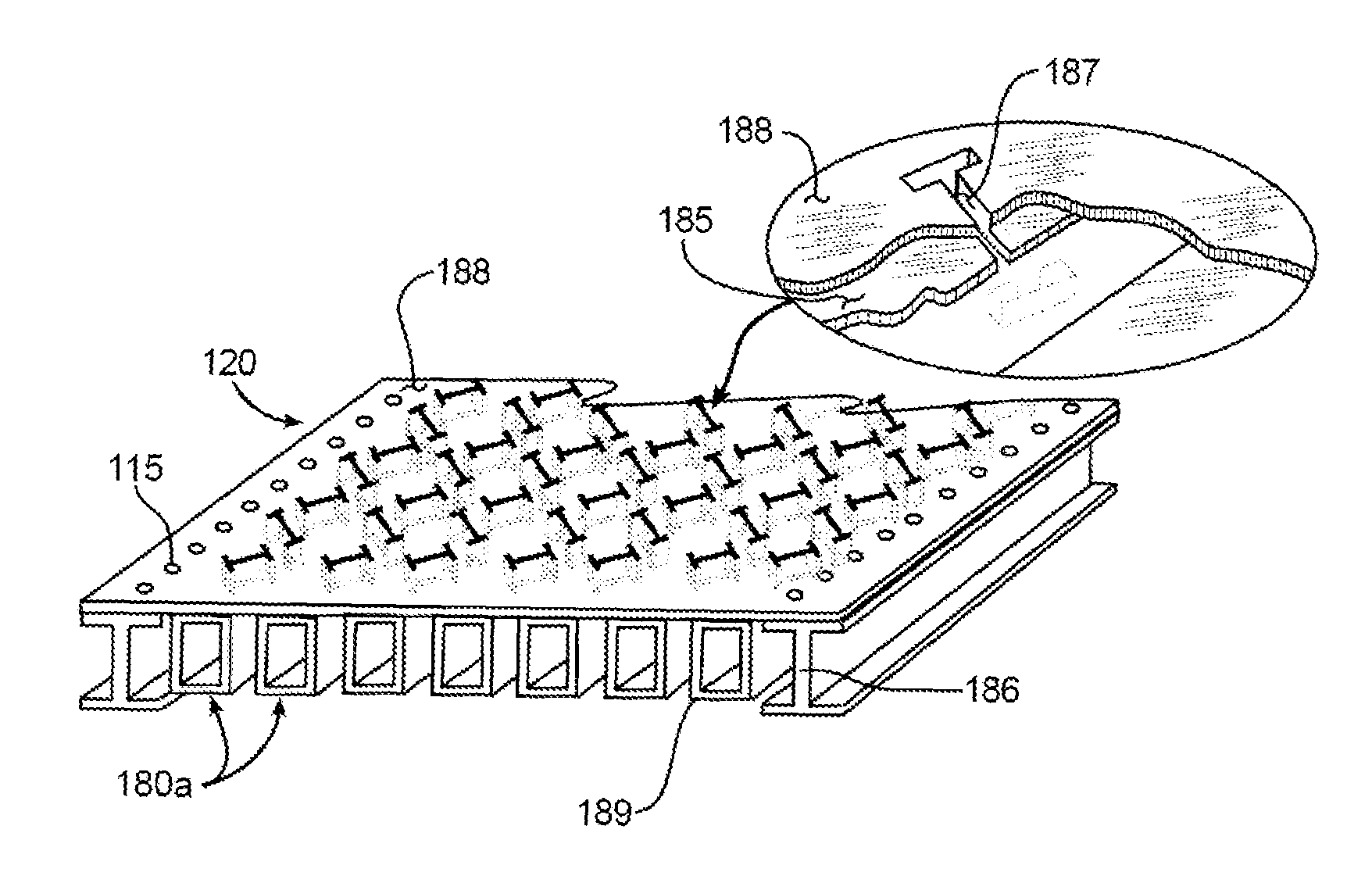
Slotted waveguide antenna stiffened structure
InactiveUS8149177B1Effective radiationReduced vehicle performanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating element housingsSlotted waveguideSealant
A slotted waveguide antenna stiffened structure for an aircraft having an aircraft skin. The slotted waveguide antenna stiffening structure including a structural stiffening element reinforcing the aircraft skin; the structural element connected to a radio frequency feed source, the source providing energy with electromagnetic bandwidth to a slotted waveguide antenna having a plurality of slots. The antenna conformal to the aircraft skin and the structural stiffening element, the structural stiffening elements functioning as waveguides for the electromagnetic bandwidth. The slots may include a slot sealant enclosing the plurality of slots.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com