Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
187results about How to "Available bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
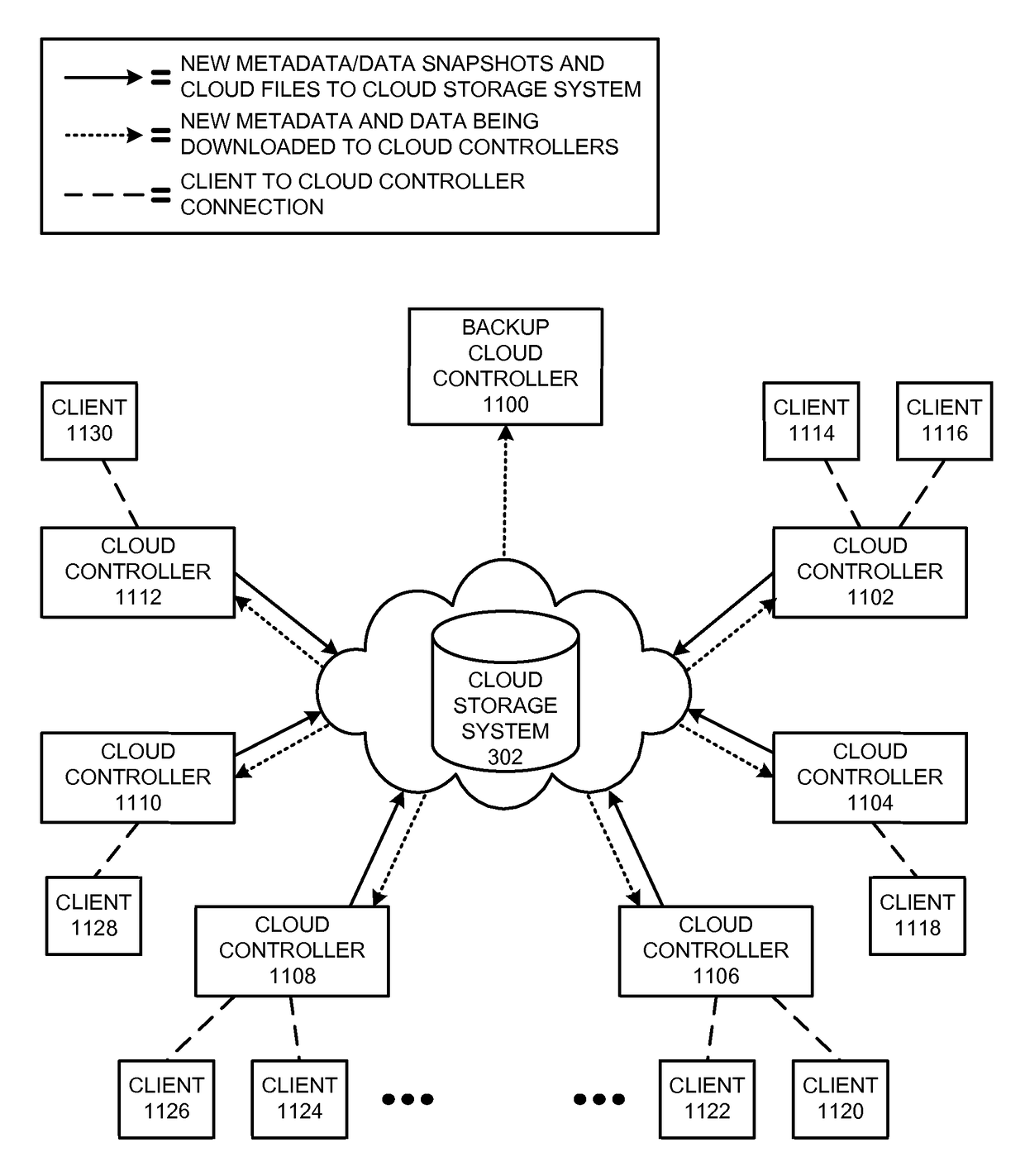
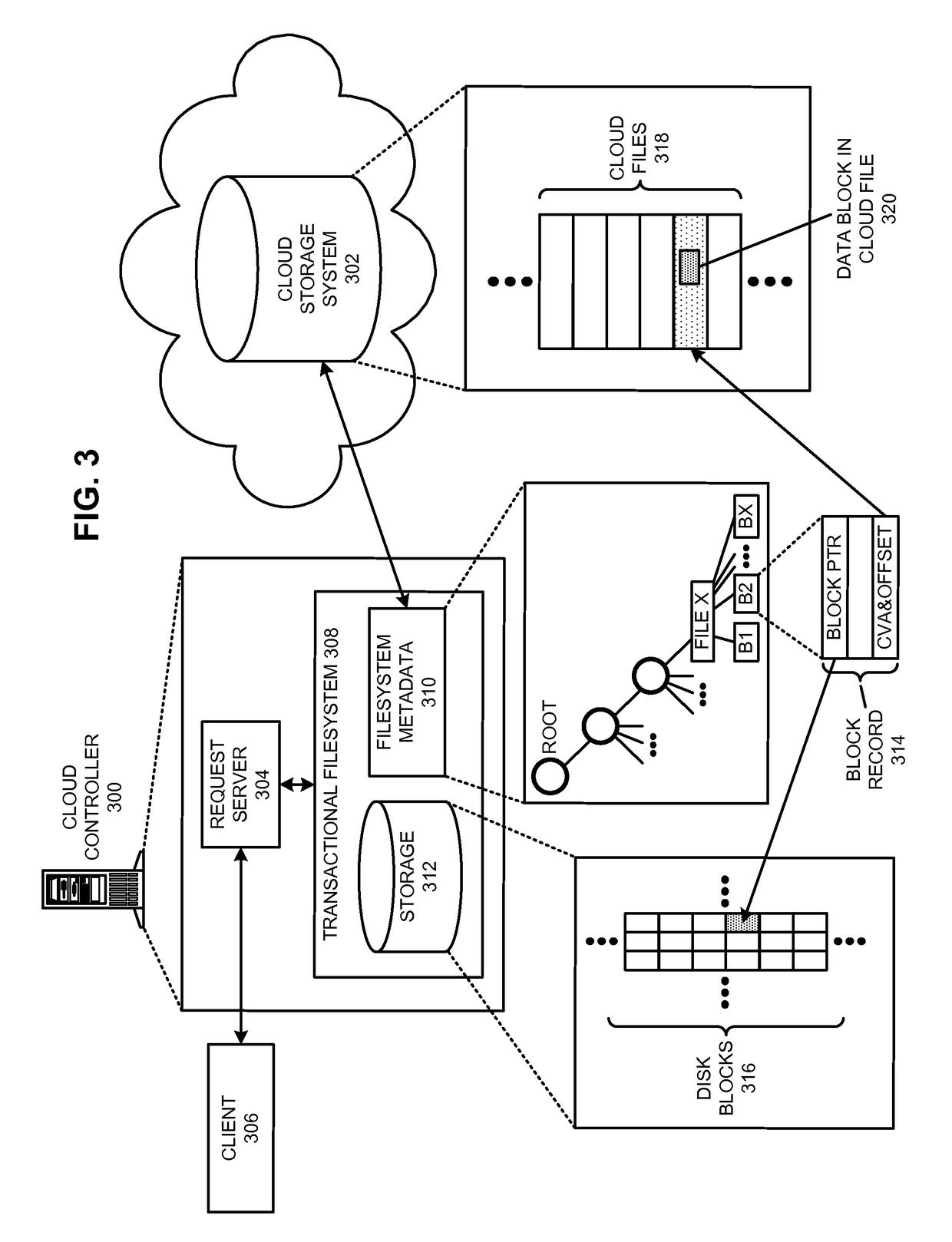
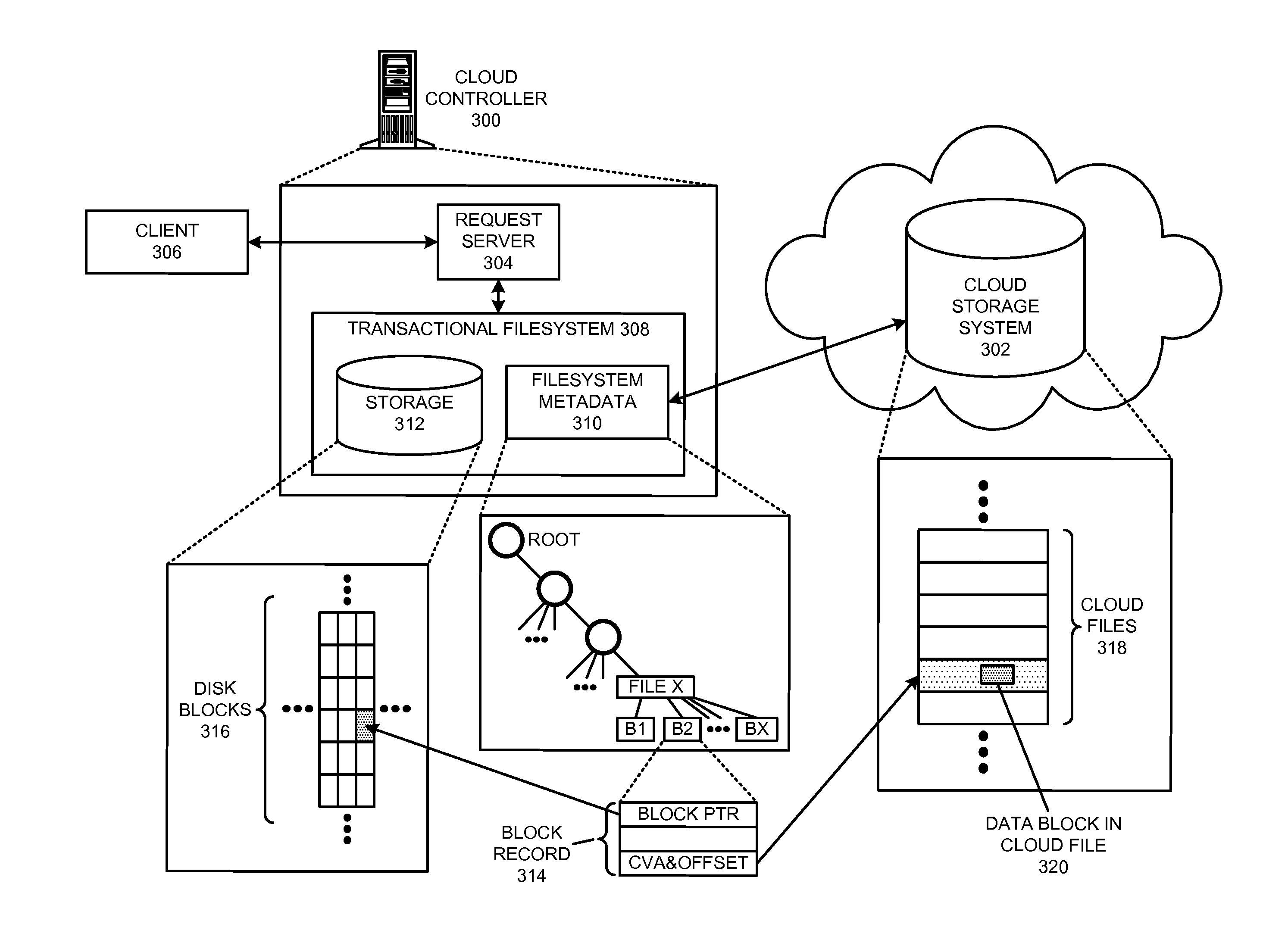
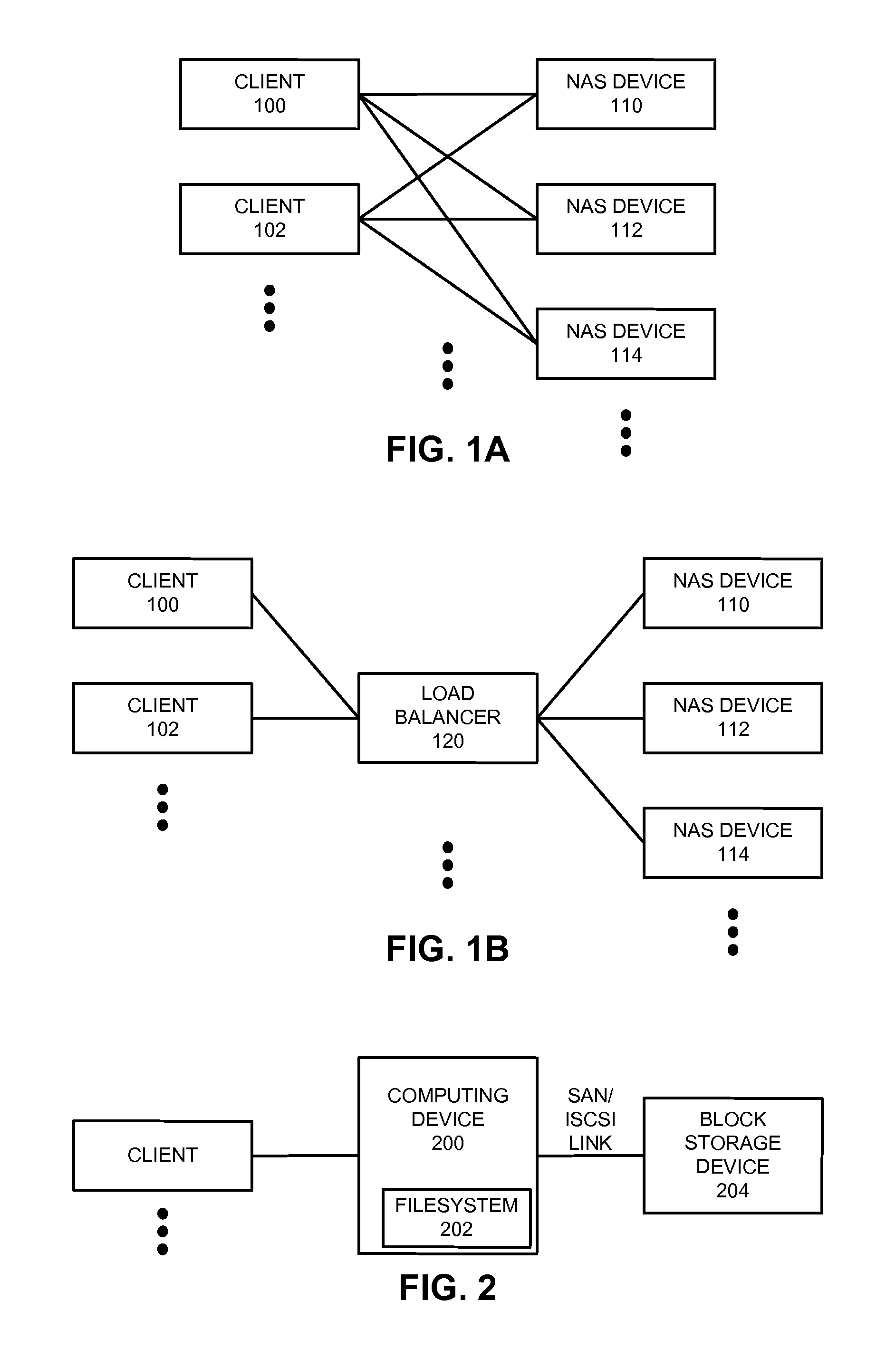
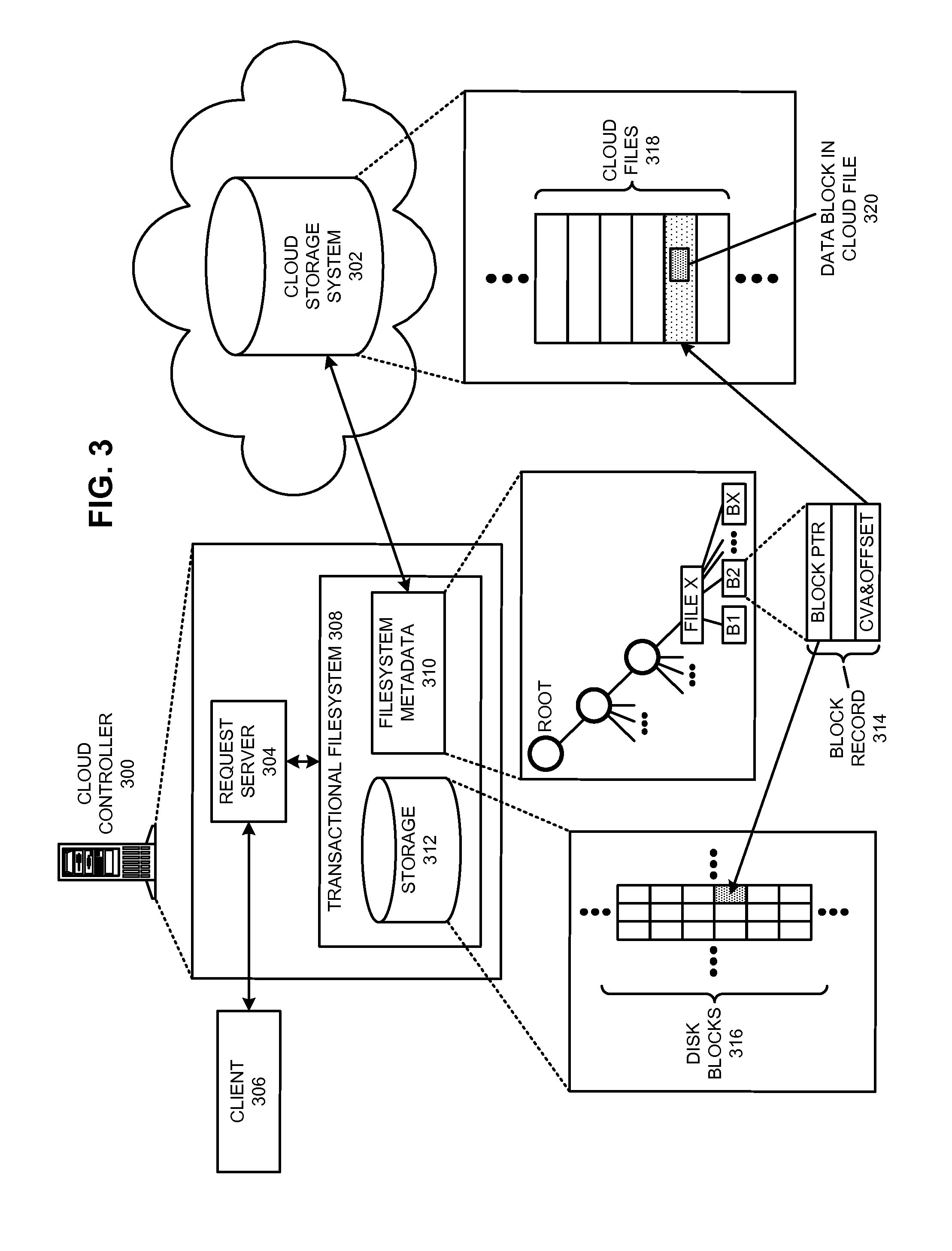
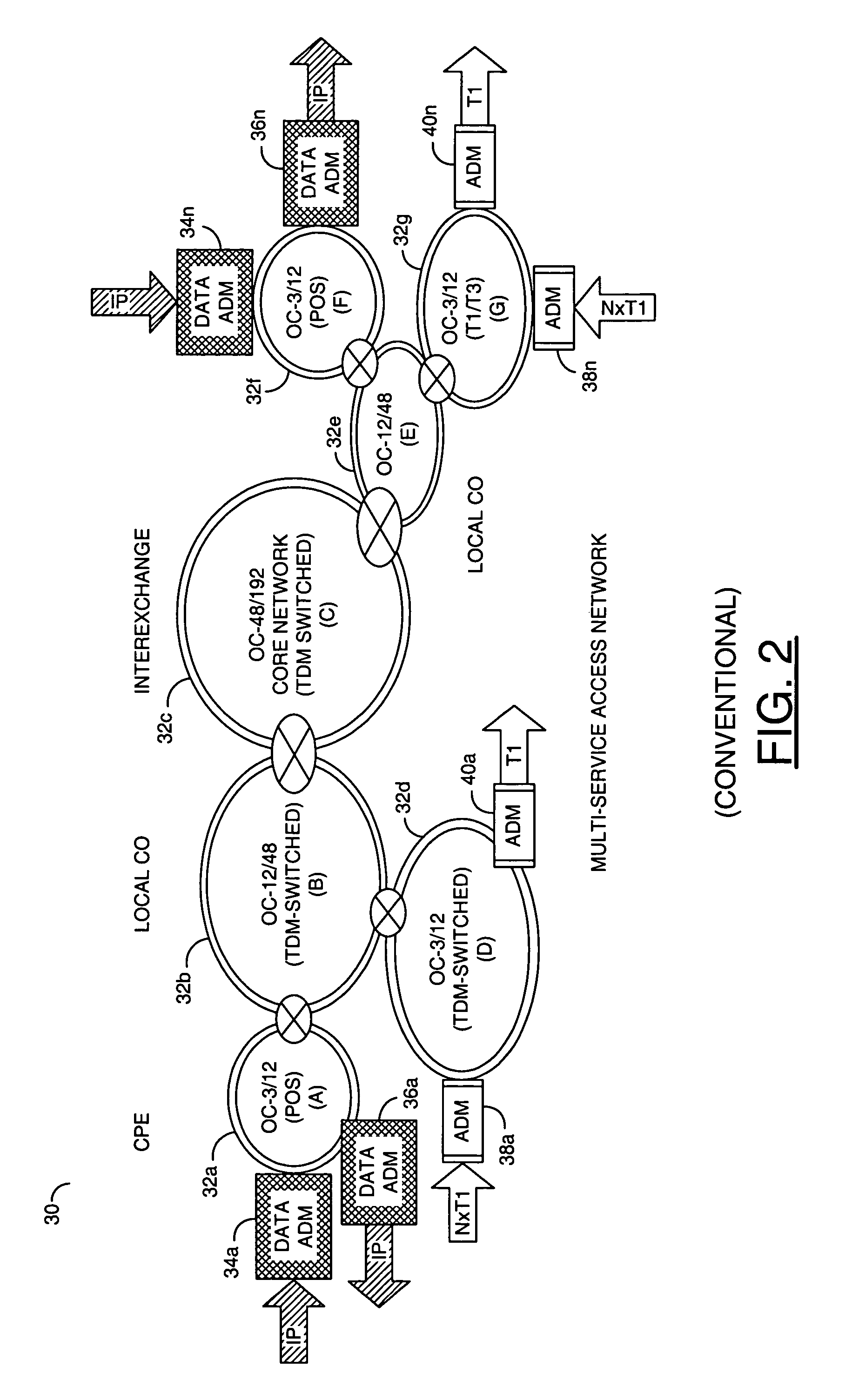
Restoring an archived file in a distributed filesystem
ActiveUS9804928B2Raise priorityIncreased restore budgetDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersDistributed File SystemFile system
The disclosed embodiments disclose techniques for restoring an archived file in a distributed filesystem. Two or more cloud controllers collectively manage distributed filesystem data that is stored in one or more cloud storage systems; the cloud controllers ensure data consistency for the stored data, and each cloud controller caches portions of the distributed filesystem. Furthermore, cloud controllers may archive infrequently-accessed files in an archival cloud storage system. During operation, a cloud controller receives a request from a client system to access an archived file, and restores this archived file from the archival cloud storage system.
Owner:PANZURA LLC
Restoring an archived file in a distributed filesystem
ActiveUS20140006357A1Raise priorityIncreased restore budgetDigital data processing detailsRedundant operation error correctionDistributed File SystemFile system
The disclosed embodiments disclose techniques for restoring an archived file in a distributed filesystem. Two or more cloud controllers collectively manage distributed filesystem data that is stored in one or more cloud storage systems; the cloud controllers ensure data consistency for the stored data, and each cloud controller caches portions of the distributed filesystem. Furthermore, cloud controllers may archive infrequently-accessed files in an archival cloud storage system. During operation, a cloud controller receives a request from a client system to access an archived file, and restores this archived file from the archival cloud storage system.
Owner:PANZURA LLC
Asynchronous replication correctness validation
ActiveUS20140181016A1Easily recoverGreat level of data protectionInput/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalClient-sideClient data
Owner:ZETTA LLC
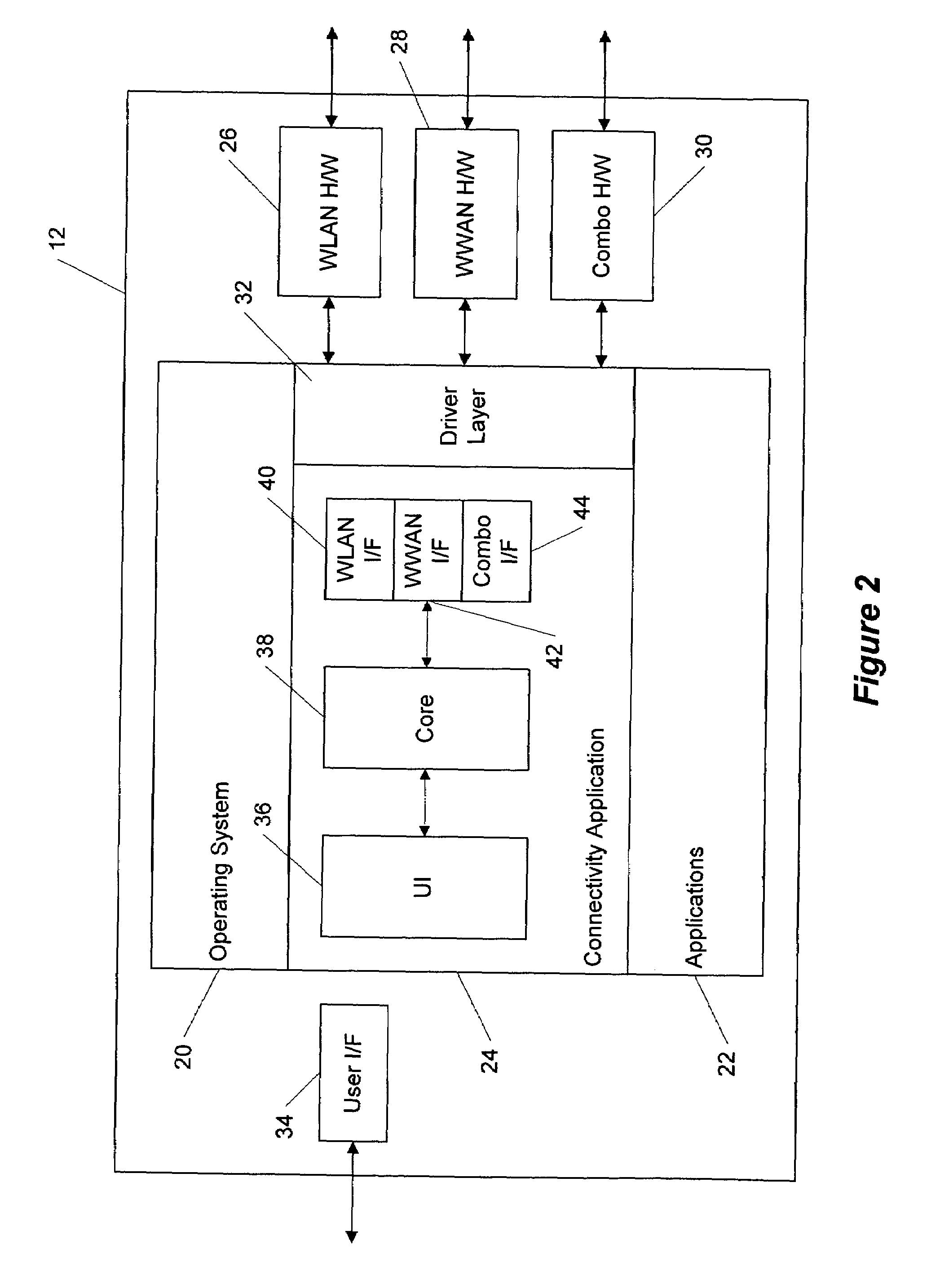
Method and system for a communication node with a plurality of network interfaces
ActiveUS20070195765A1Easy to useRobust and secure data transmissionError preventionTransmission systemsIp addressNetwork interface
The invention relates to a method for a communication node with a plurality of network interfaces. Configured on the communication node is a virtual interface, which is accessible from the applications able to be executed on the communication node. A configuration module generates an identifier assigned to the communication node. The identifier is stored in an identifier table. The configuration module checks the communication node for available network interfaces and sets up a network interface table with the available network interfaces. At least one IP address of an available network interface is stored in the identifier table in a way assigned to the identifier, and a connection module connects at least one of the available network interfaces to the virtual interface.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
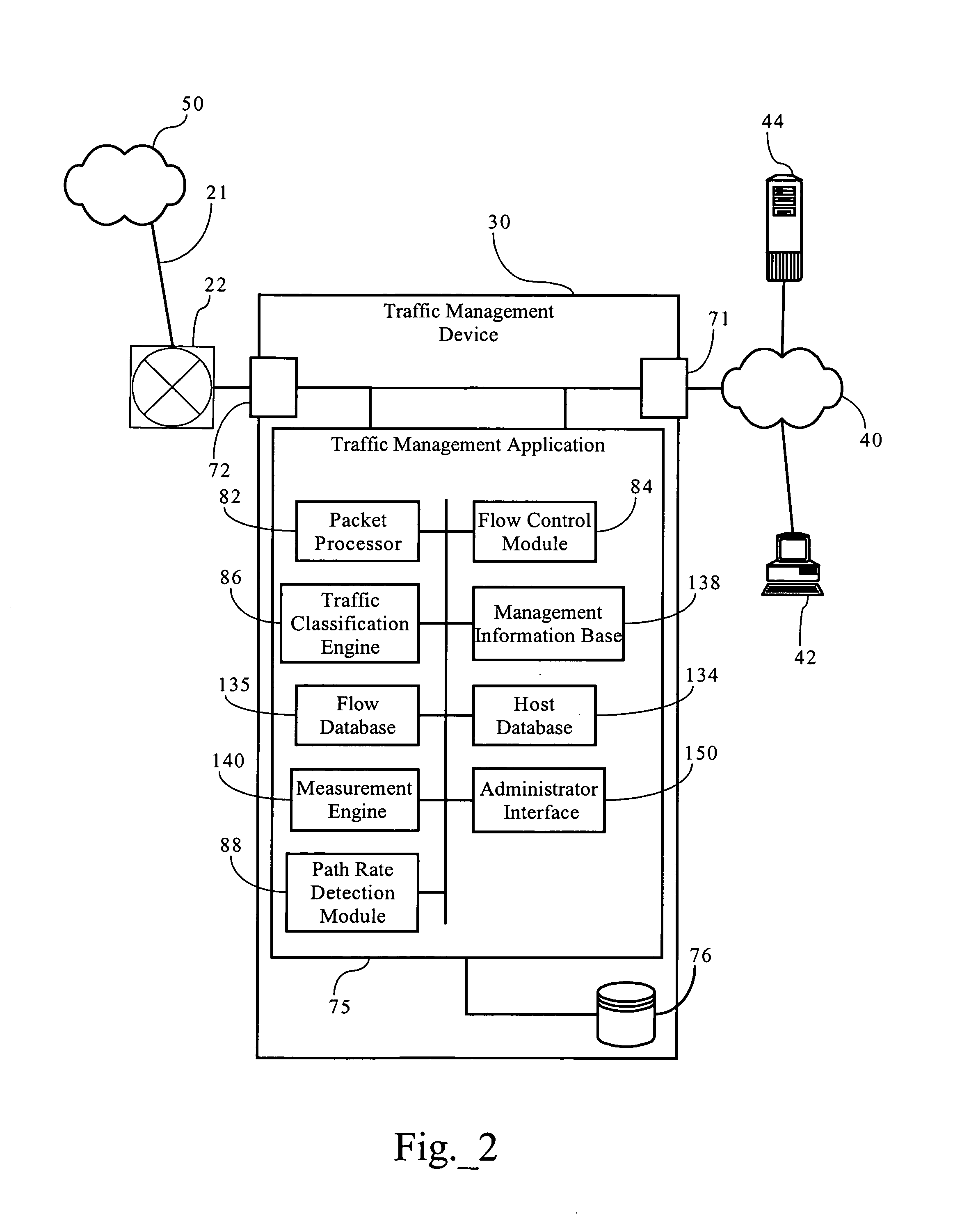
Slow-start adaptive mechanisms to improve efficiency of bandwidth allocation
ActiveUS7426181B1Improve efficiencyReducing over-allocationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationSlow-start
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to improving the efficiency of bandwidth allocation schemes by adapting to slow-start mechanisms associated with network communications protocols, such as the TCP / IP protocol suite. In one implementation, the present invention scales down the initial target rate assigned to a data flow to a fraction of an initial estimate of the effective rate capacity of the communications path between two hosts. As packets are received, the target rate is gradually increased, eventually up to the detected rate capacity of the communications path. Implementations of the present invention improve the efficiency of bandwidth allocation by reducing the over-allocation of bandwidth to data flows during the slow-start phase, leaving more bandwidth available to other data flows.
Owner:CA TECH INC
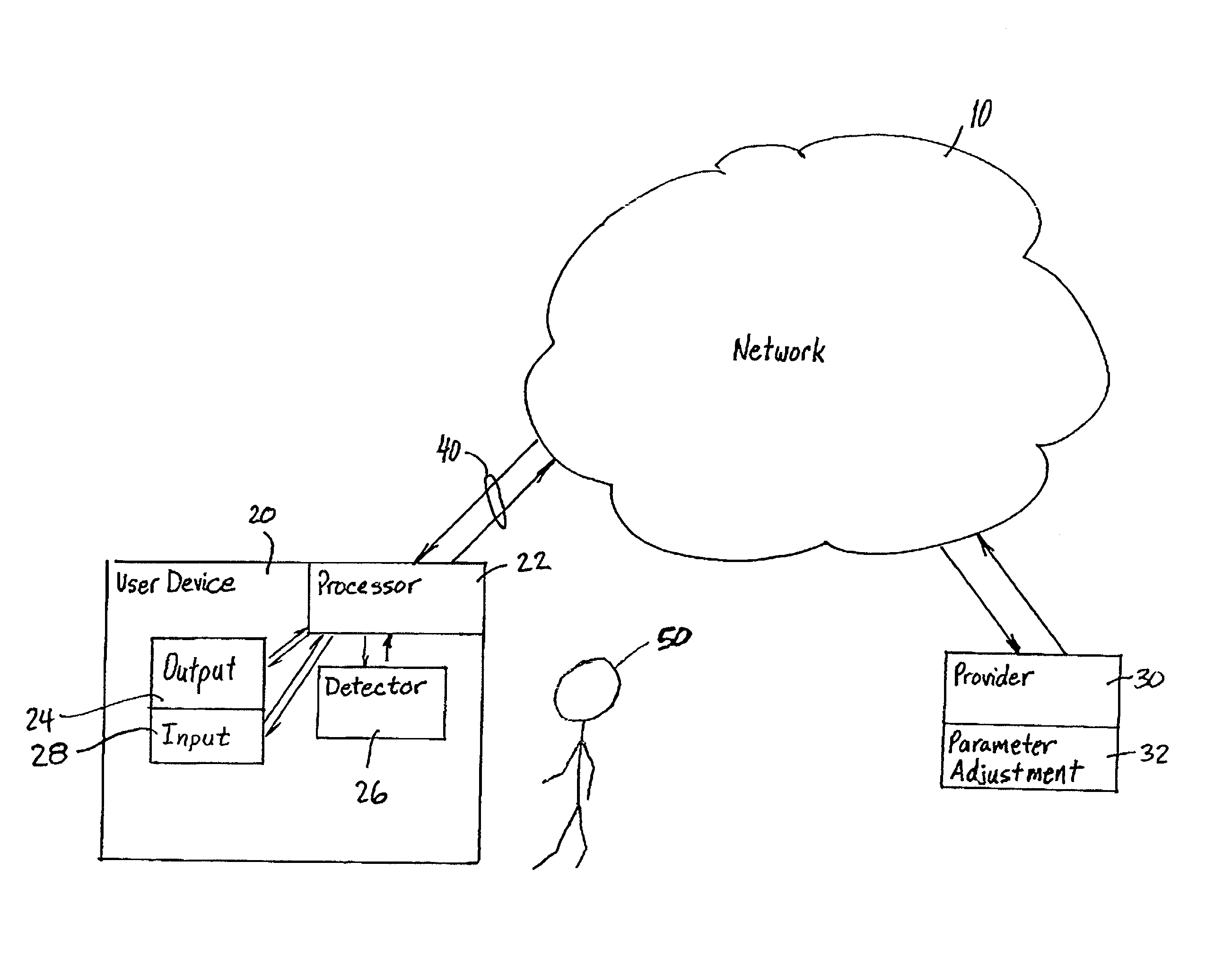
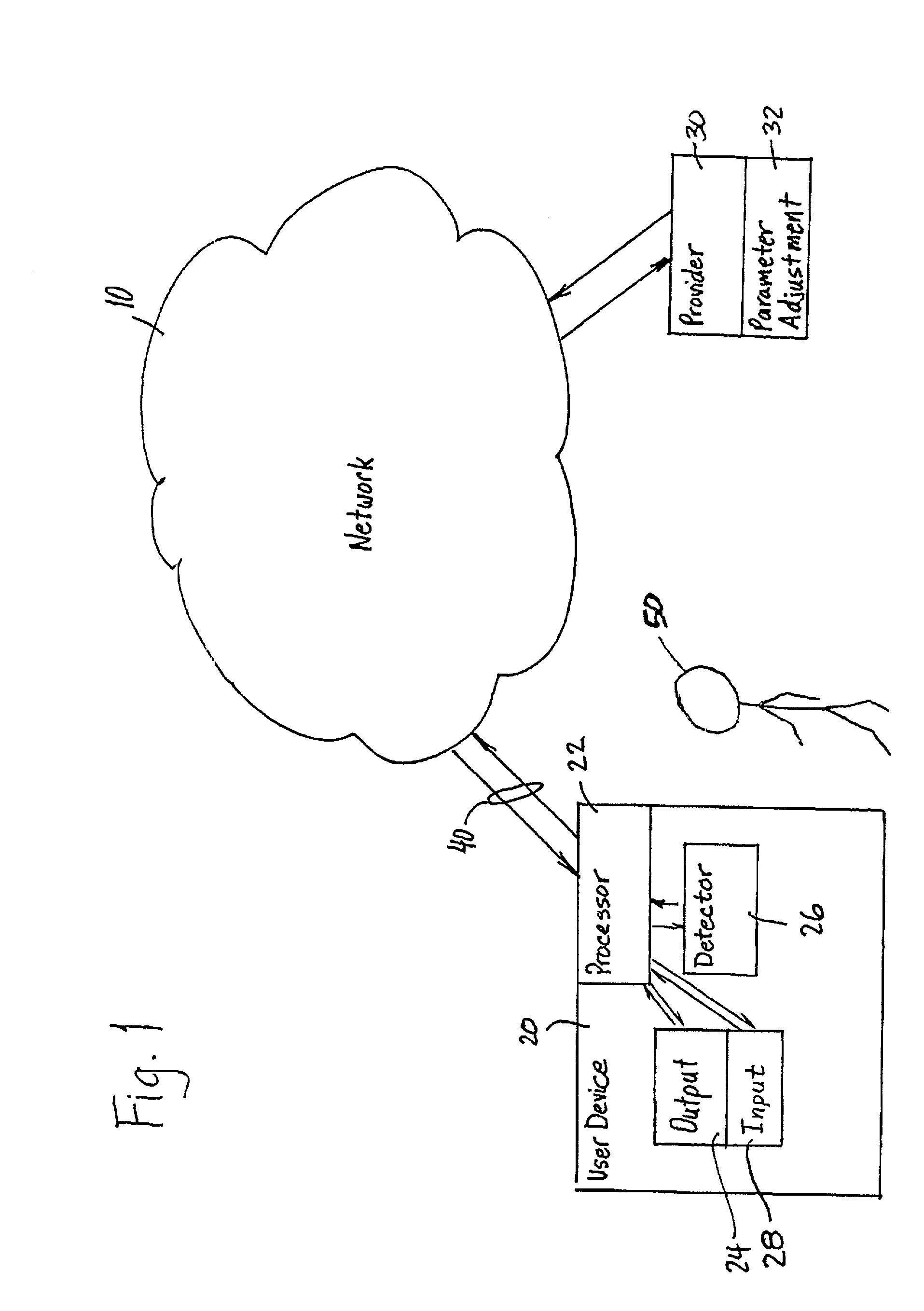
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
InactiveUS20030052911A1Reduce data transfer rateMoreData processing applicationsImage analysisUser deviceQuality level
A method for transmitting a stream of multi-media content from provider server to a user device includes transmitting multi-media content from the provider server to the user device via a communication network and outputting the multi-media content from the user device to a user via an output on the user device such that the multi-media content is delivered from the provider server to the user in real-time. A degree of attention that the user directs to the output of the user device is continuously determined during the transmission and a parameter adjusting module at the provider server adjusts a parameter of the multi-media content in response to the degree of attention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
VOIP endpoint call admission
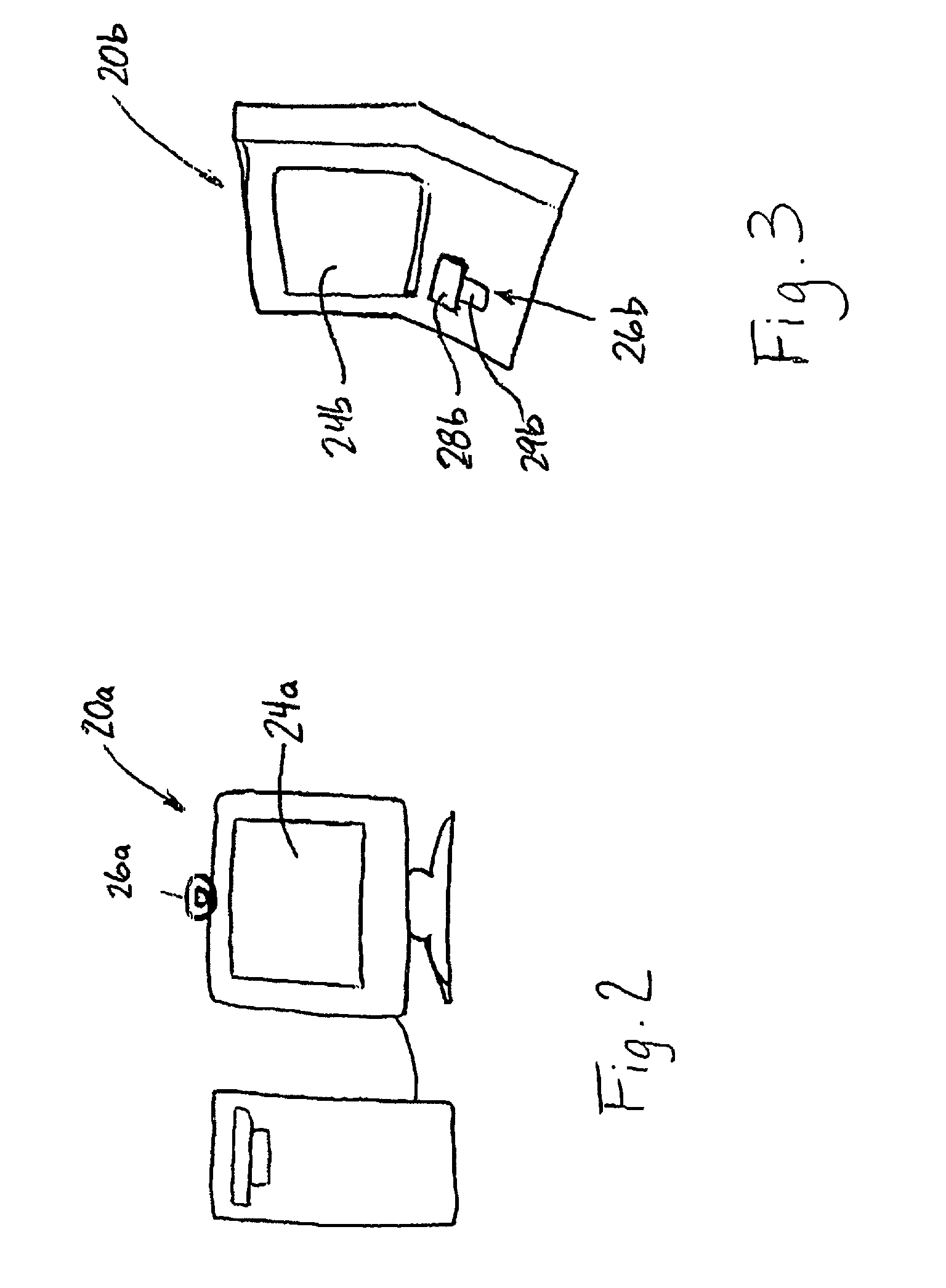
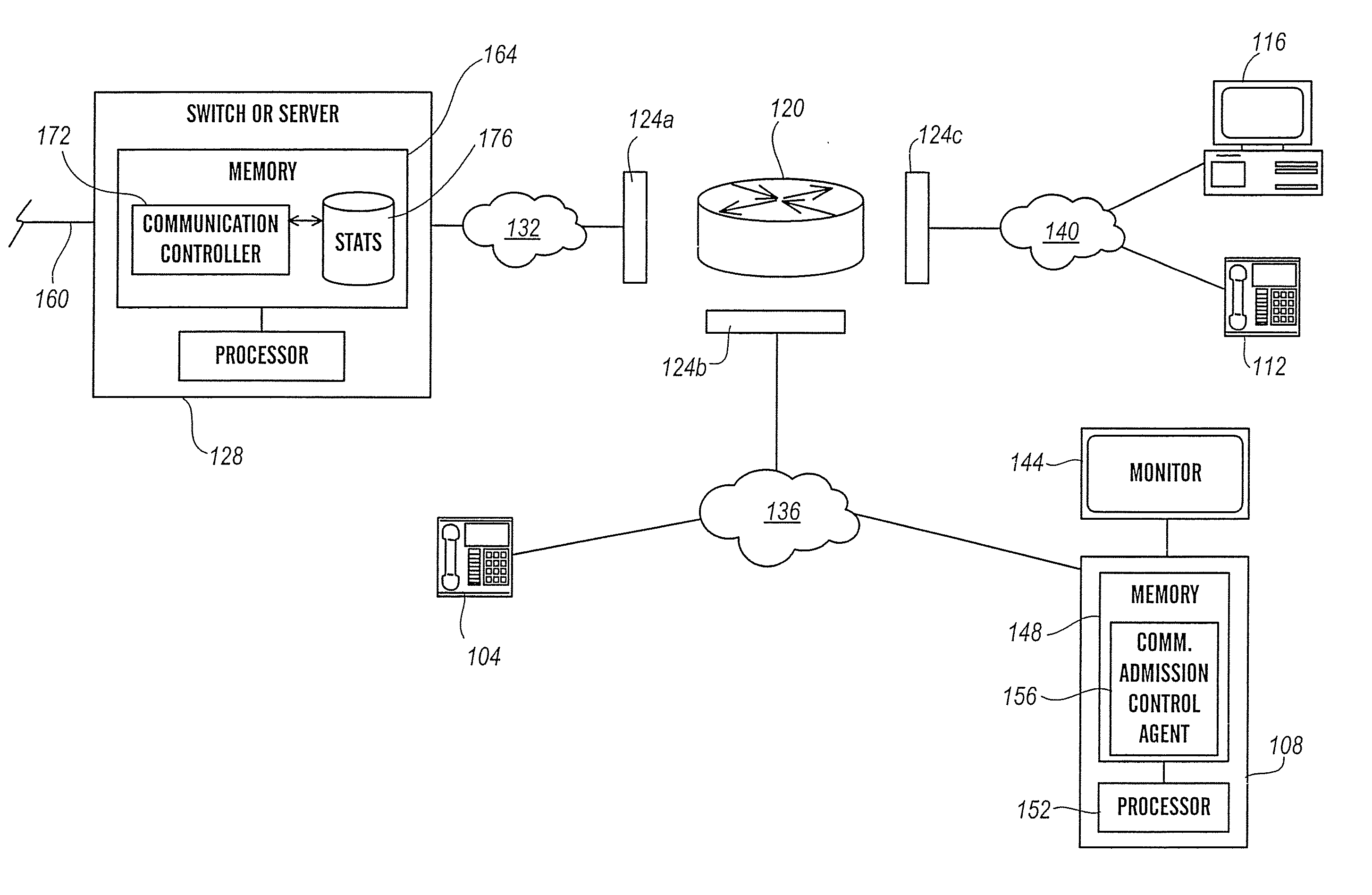
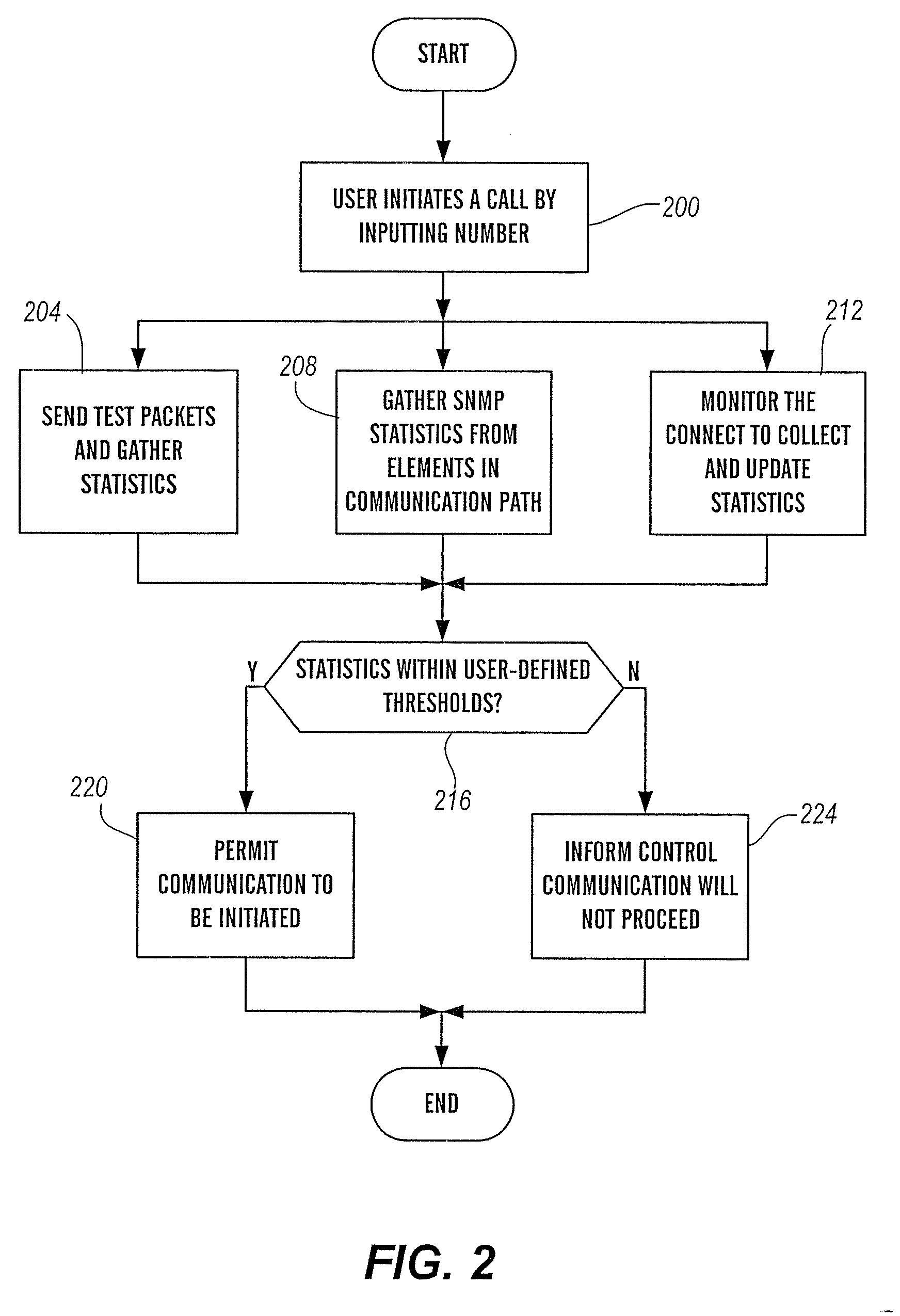
InactiveUS20070133403A1High likelihood of failureAvailable bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsRelevant information
The present invention is directed generally to an intelligent endpoint or communication device that can collect available bandwidth-related information metrics and / or perform call admission control functions. The present invention is further directed to an architecture comprising a switch or media server in communication with a plurality of subscriber communication devices in which the subscriber communication devices act as network nodes to collect available bandwidth-related information.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Wireless local area network (wlan) as a public land mobile network for wlan/telecommunications system interworking
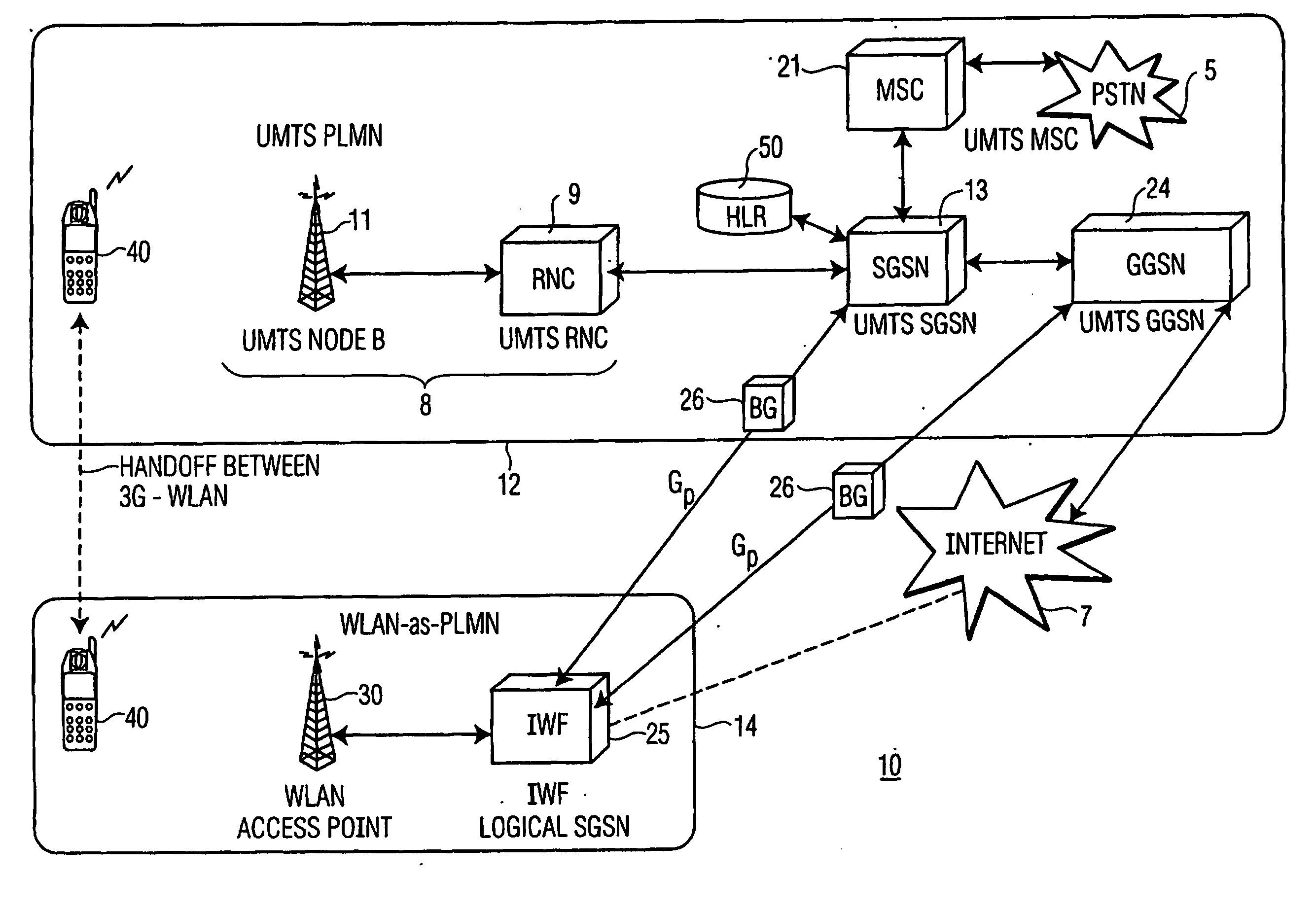
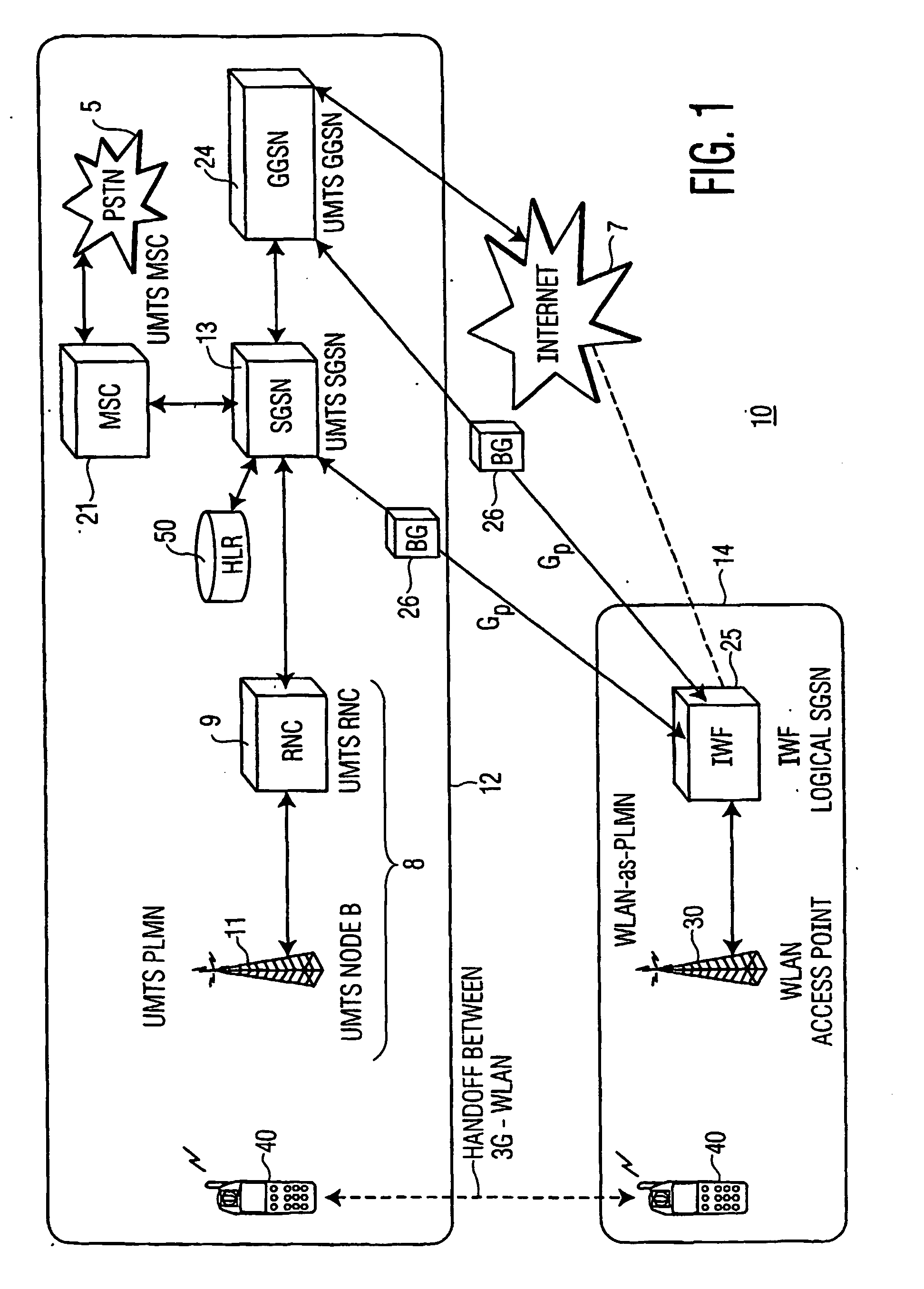
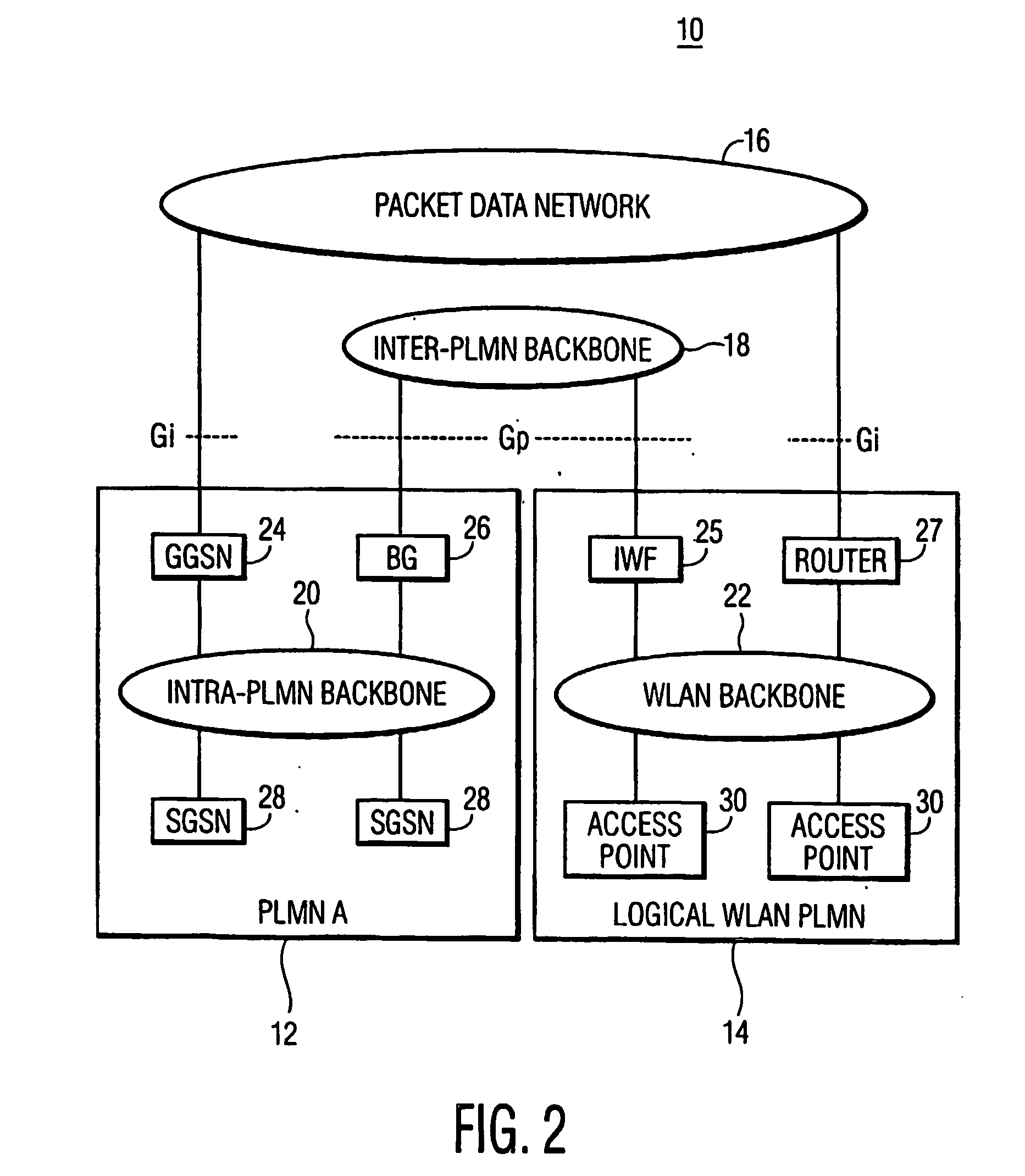
InactiveUS20050254469A1Increase bandwidthAvailable bandwidthNetwork topologiesTelephonic communicationTelecommunicationsMobile Web
A telecommunications system includes a Public Land Mobile Network for providing wireless service to users and a wireless local area network functioning outside the said PLMN as a separate PLMN. An inter-PLMN backbone interfaces the WLAN to the PLMN, and an interworking function is coupled to the WLAN to provide seamless interactions between the PLMN and the WLAN to increase available service bandwidth provided for users of the PLMN.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
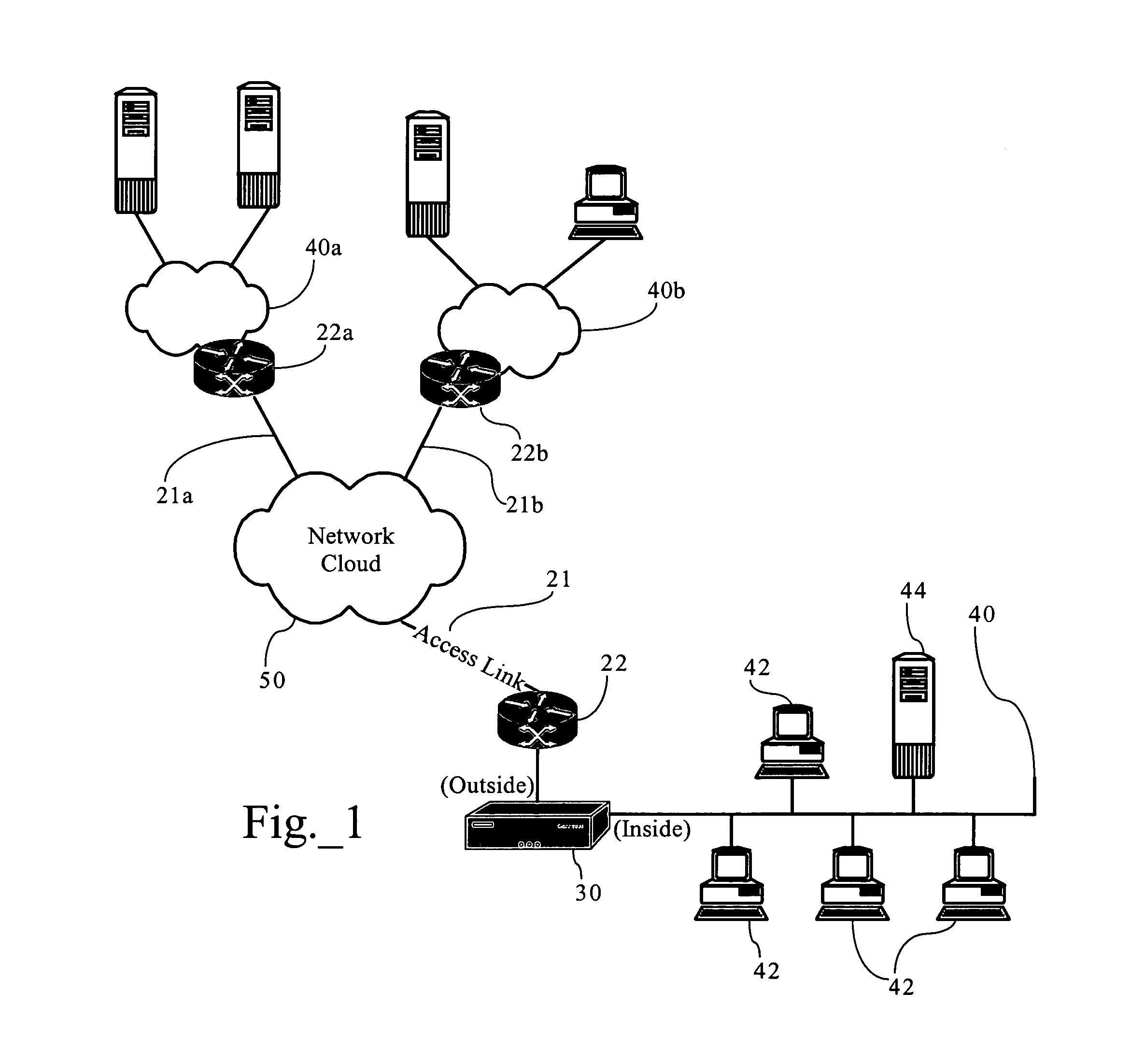
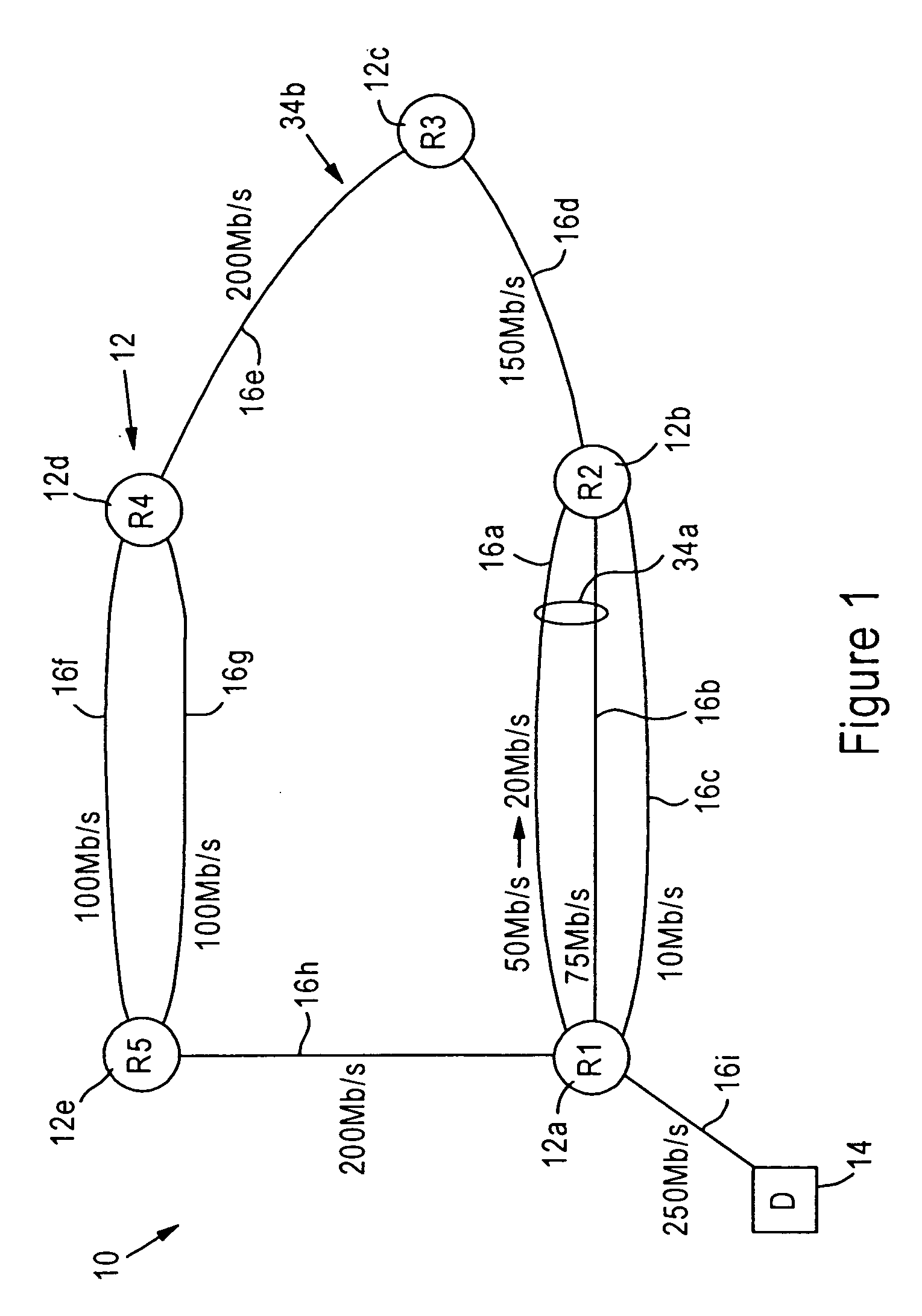
Router configured for outputting update messages specifying a detected attribute change of a connected active path according to a prescribed routing protocol
ActiveUS20050195835A1Easy to routeEfficient sharingEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationData streamComputer science
A first router is configured for monitoring prescribed attributes of an active path connected to the first router, and supplying an update message to a second router, according to a prescribed routing protocol such as Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), that specifies a detected change by the first router in at least one of the prescribed attributes of the connected active path. Hence, the second router, in response to receiving the update message, can update an internal topology table based on the detected change in the active path connected to the first router, and selectively adjust an internal routing table based on the detected change relative to queuing policies for prescribed data flows.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
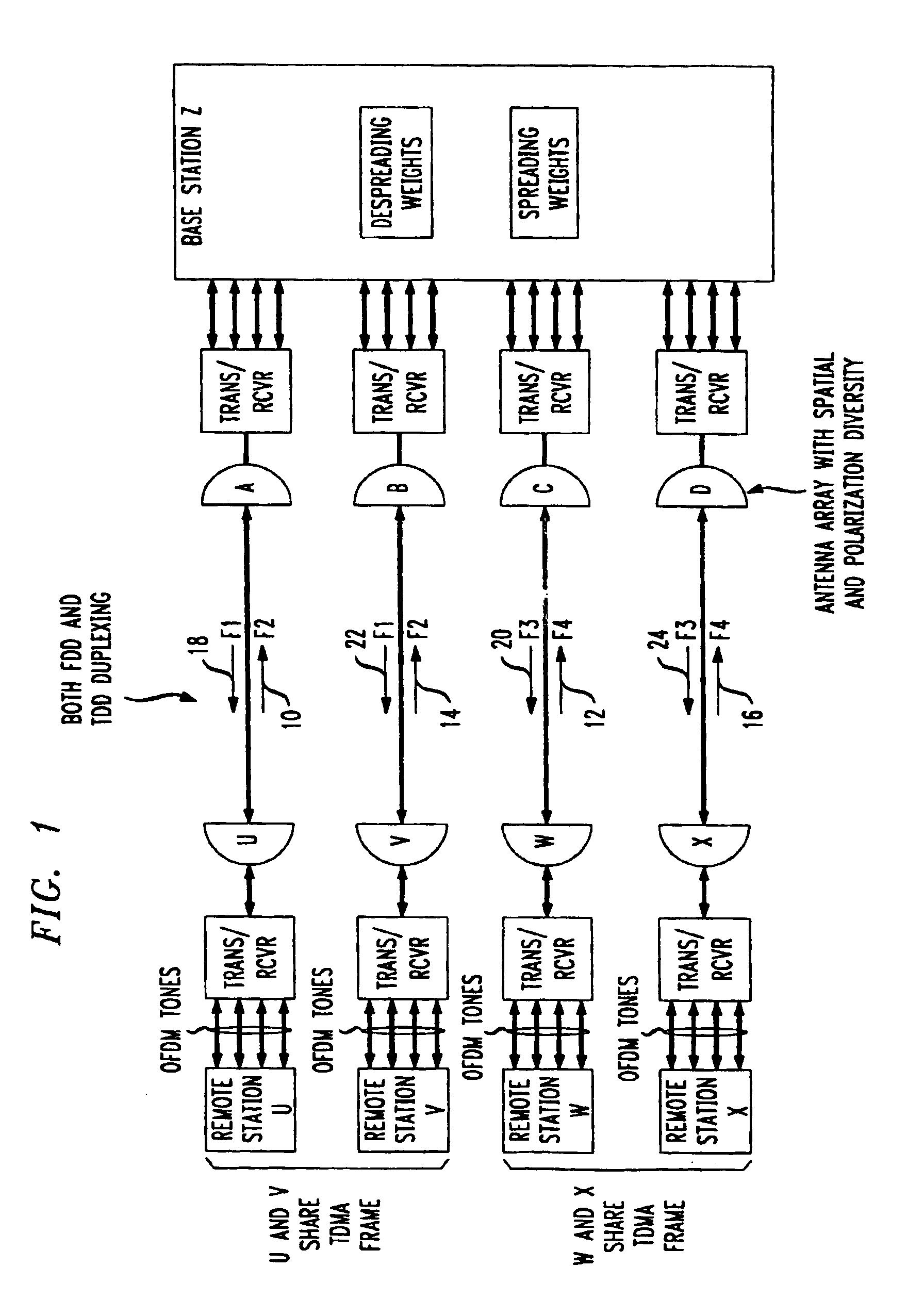
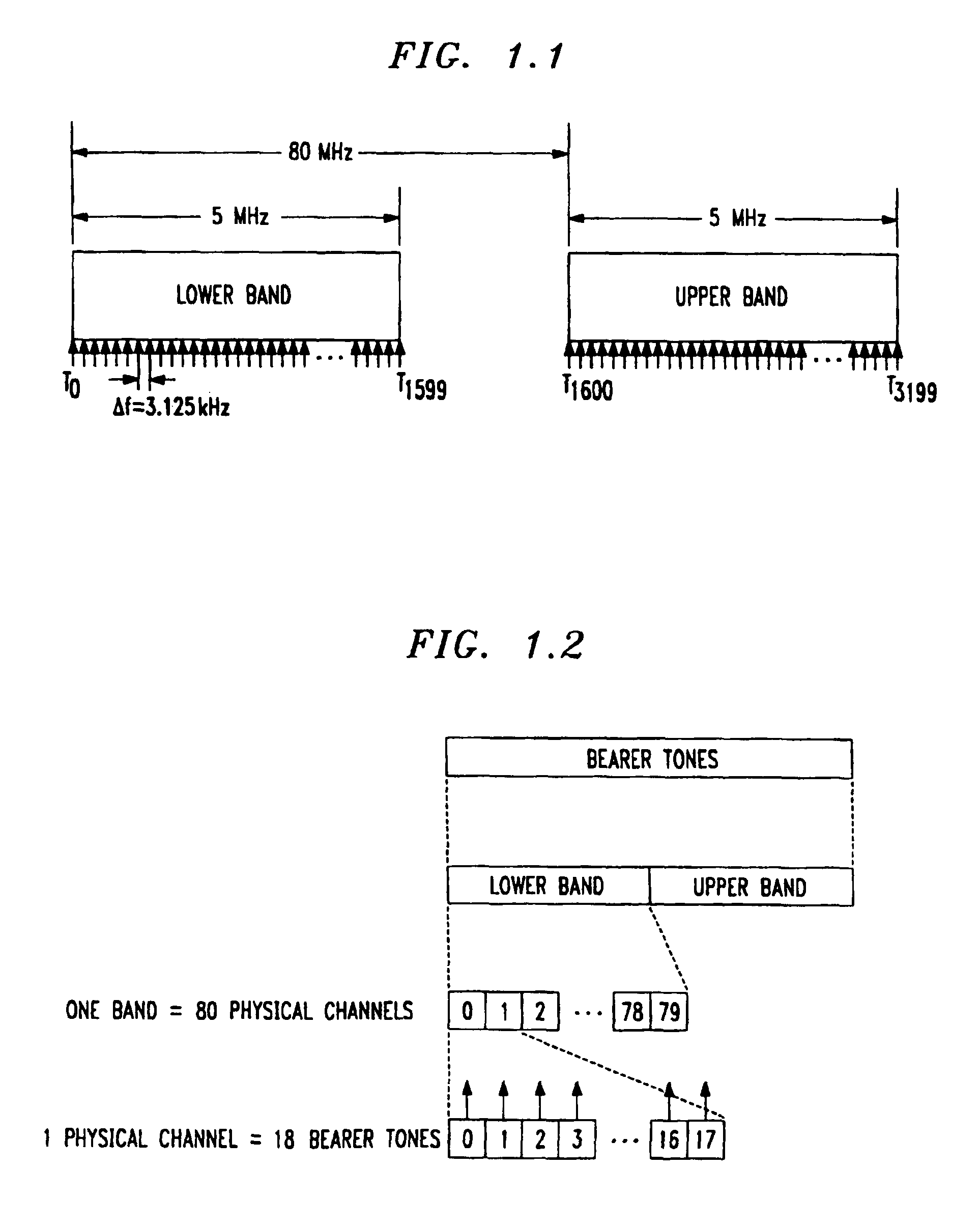
Method for frequency division duplex communications
InactiveUS6853629B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsPolarization diversity
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
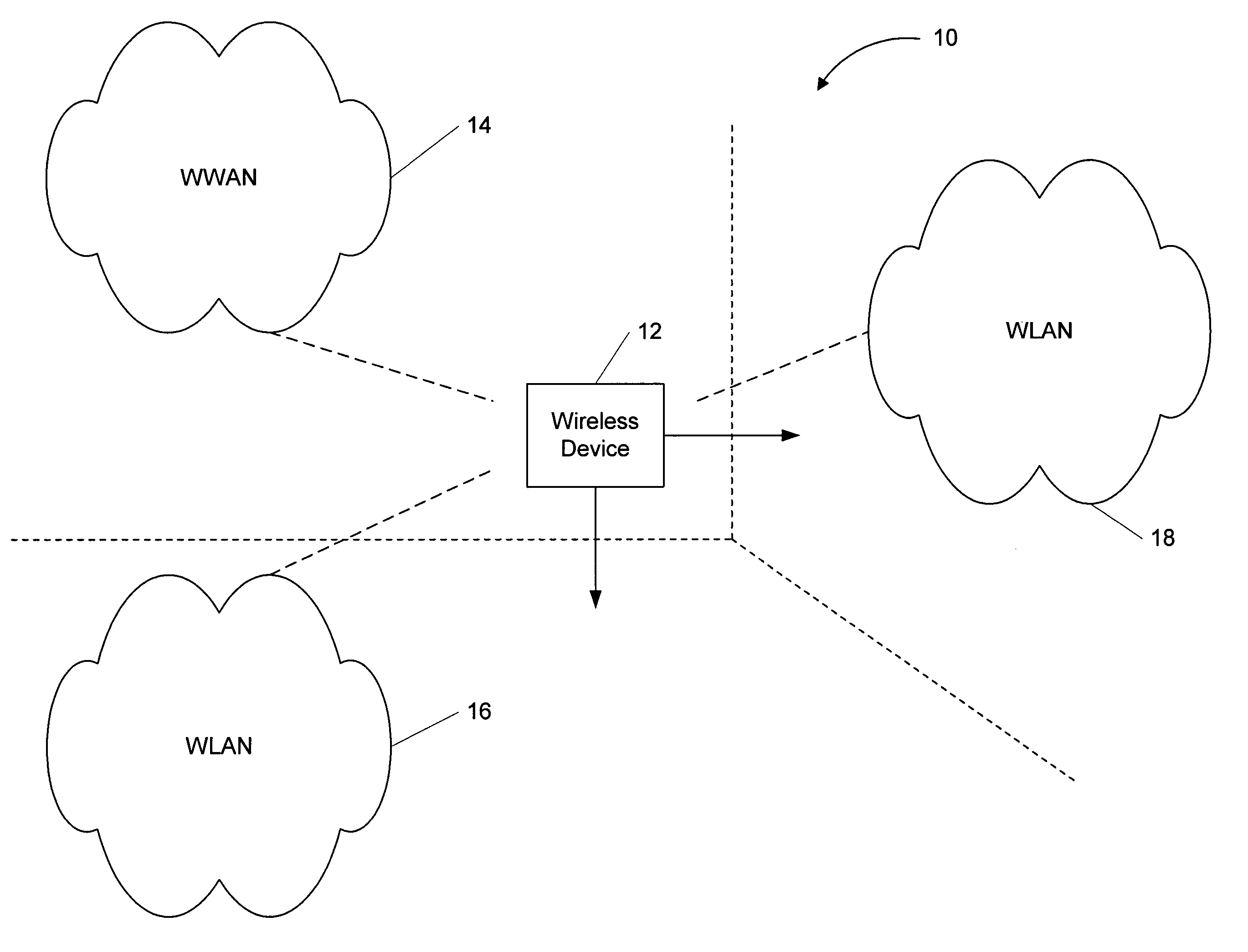
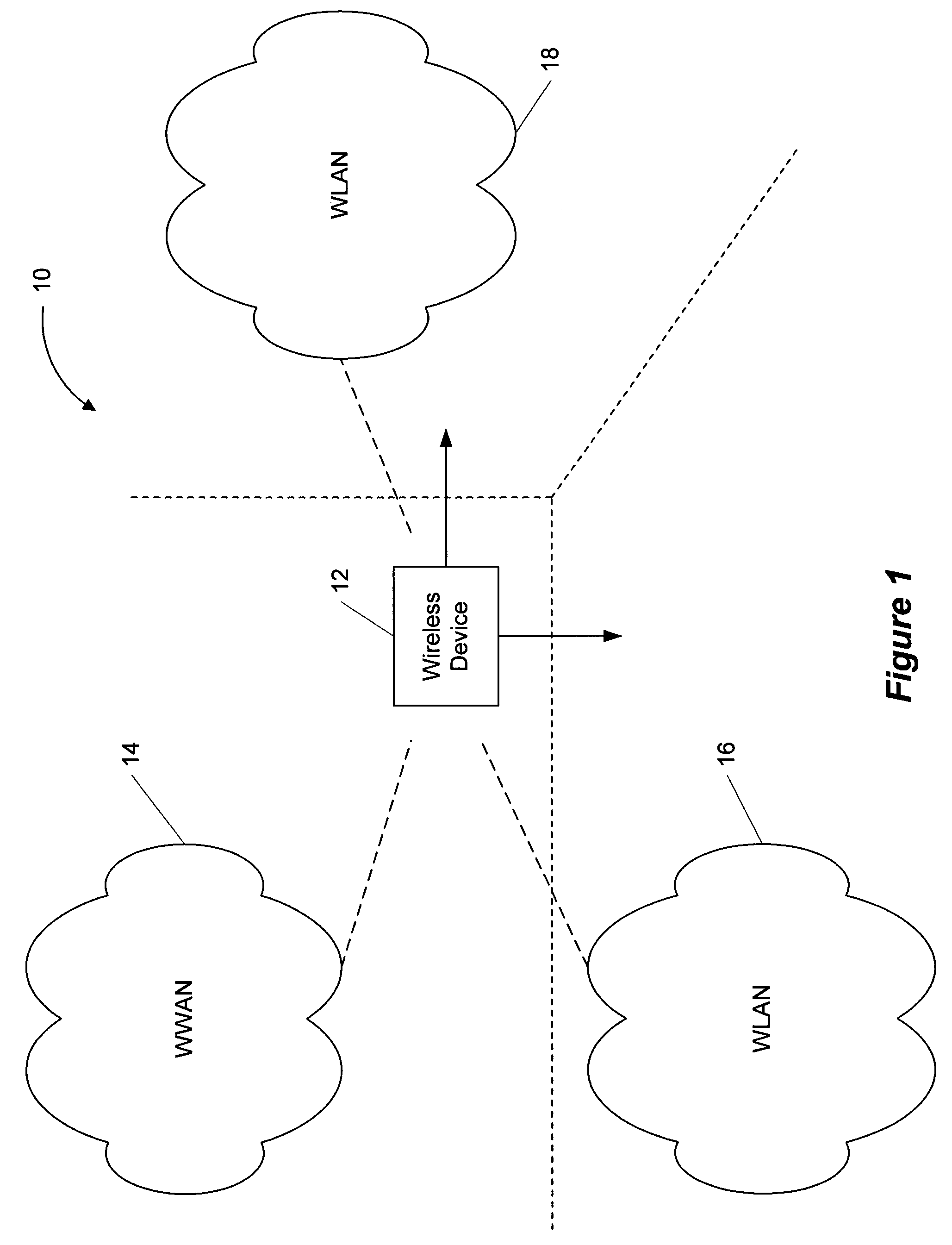
Systems and methods for seamless roaming between wireless networks
ActiveUS7133669B2Available bandwidthNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWide areaWireless mesh network
A method for the seamless switching of a wireless device between wireless wide area networks (WWANs) and wireless local area networks (WLANs) includes automatically detecting the available WWANs and WLANs, selecting one of the available networks for use by the wireless device, and connecting the wireless device to the selected network. The method also includes maintaining the network connection by monitoring the connection and, upon determining that the connection has been lost, selecting a another available network for use and connecting the wireless device the other network. Additionally, the method communicates information about the availability networks and connection status to a user of the wireless device, which allows the user to manually switch the wireless device connection from the automatically selected available network to another available network. Further, a wireless device implements the above described method.
Owner:SMITH MICRO SOFTWARE INC
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
InactiveUS7284201B2Reduce data transfer rateMoreImage analysisData processing applicationsUser deviceEngineering
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
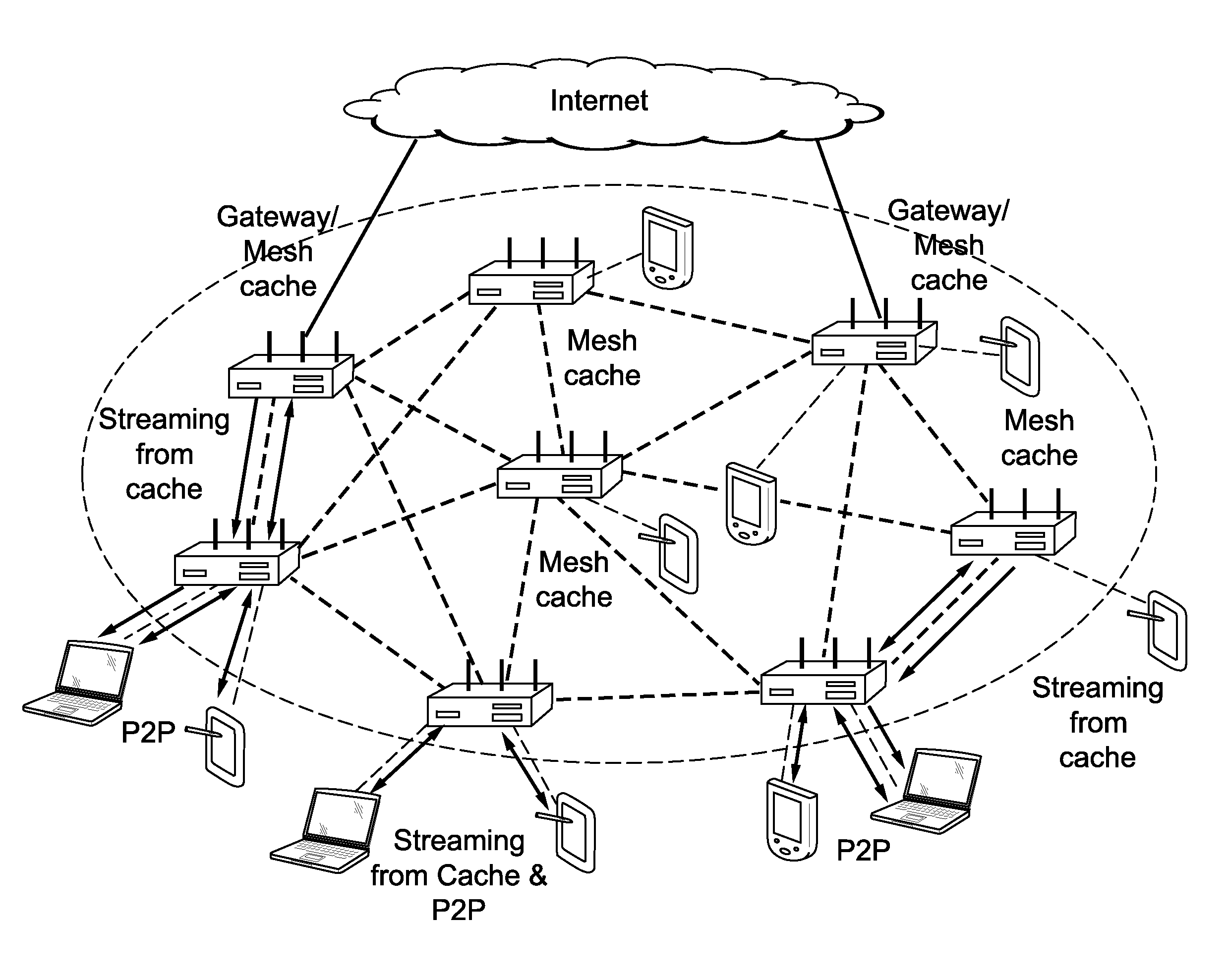
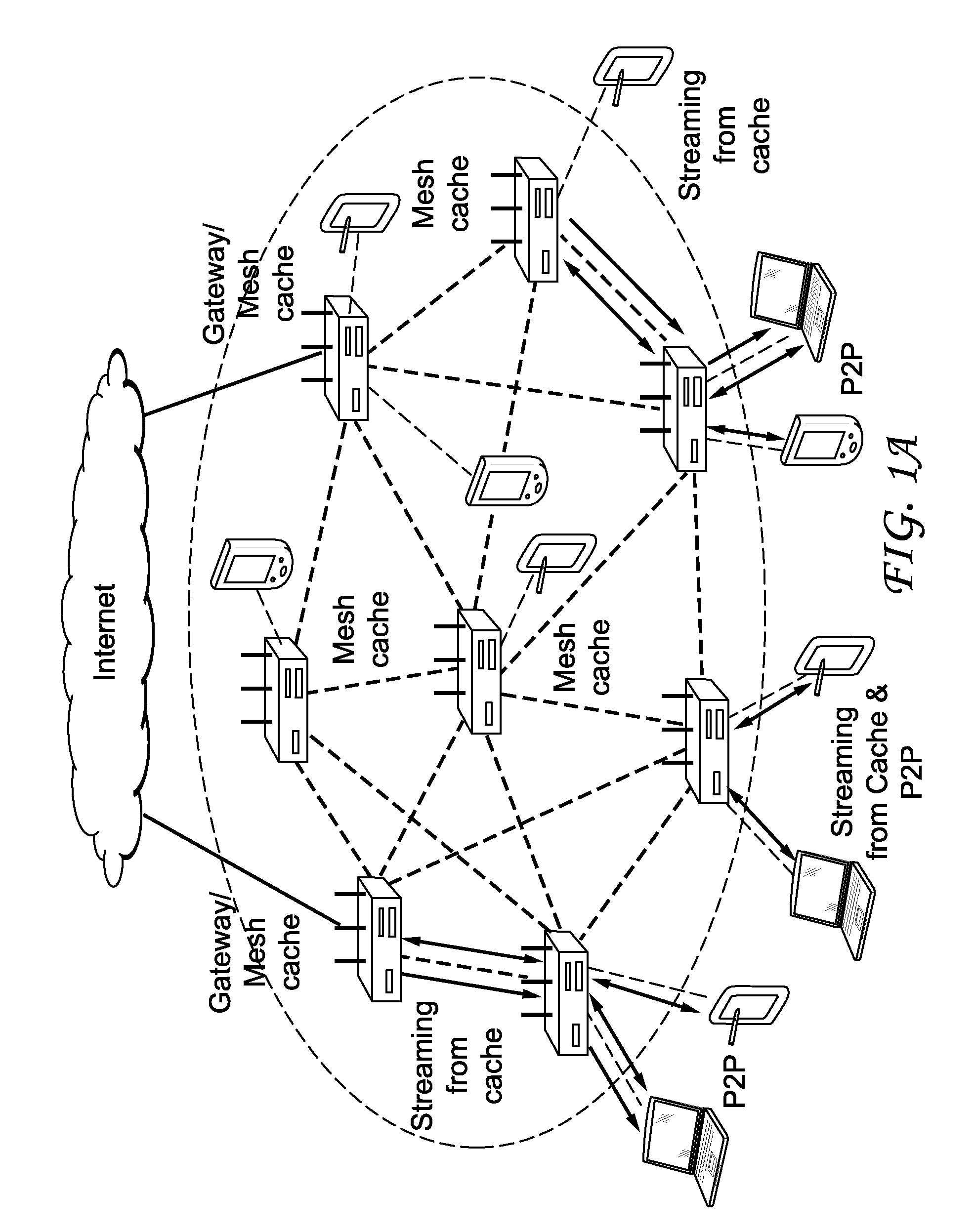
Unified cache and peer-to-peer method and apparatus for streaming media in wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20110225311A1Reduce throughputQuality improvementBroadcast transmission systemsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceRouting table
A method and apparatus are described including receiving a route request message to establish a streaming route, determining a cost of a reverse route and traffic load introduced by the requested streaming route, discarding the route request message if one of wireless interference constraints for the requested streaming route cannot be satisfied and quality of service requirements for the requested streaming route cannot be satisfied, pre-admitting the route request message if wireless interference constraints for the requested streaming route can be satisfied and if quality of service requirements for the requested streaming route can be satisfied, adding a routing table entry responsive to the pre-admission, admitting the requested streaming route, updating the routing table and transmitting a route reply message to an originator if requested content is cached, updating the route request message and forwarding the updated route request message if the requested content is not cached, receiving a route reply message and deleting the pre-admitted routing table entry if a time has expired.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
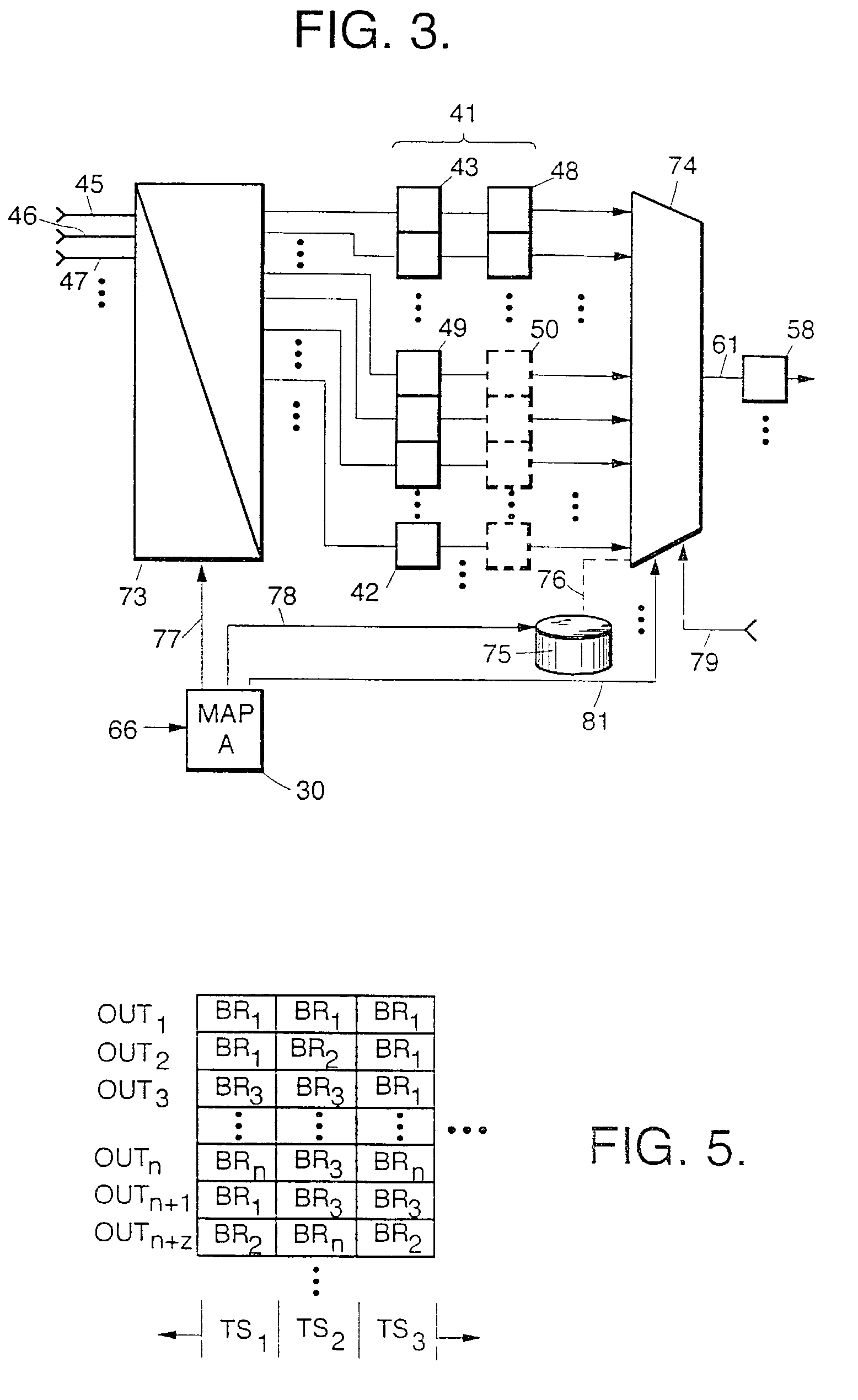
Dynamic mapping of broadcast resources
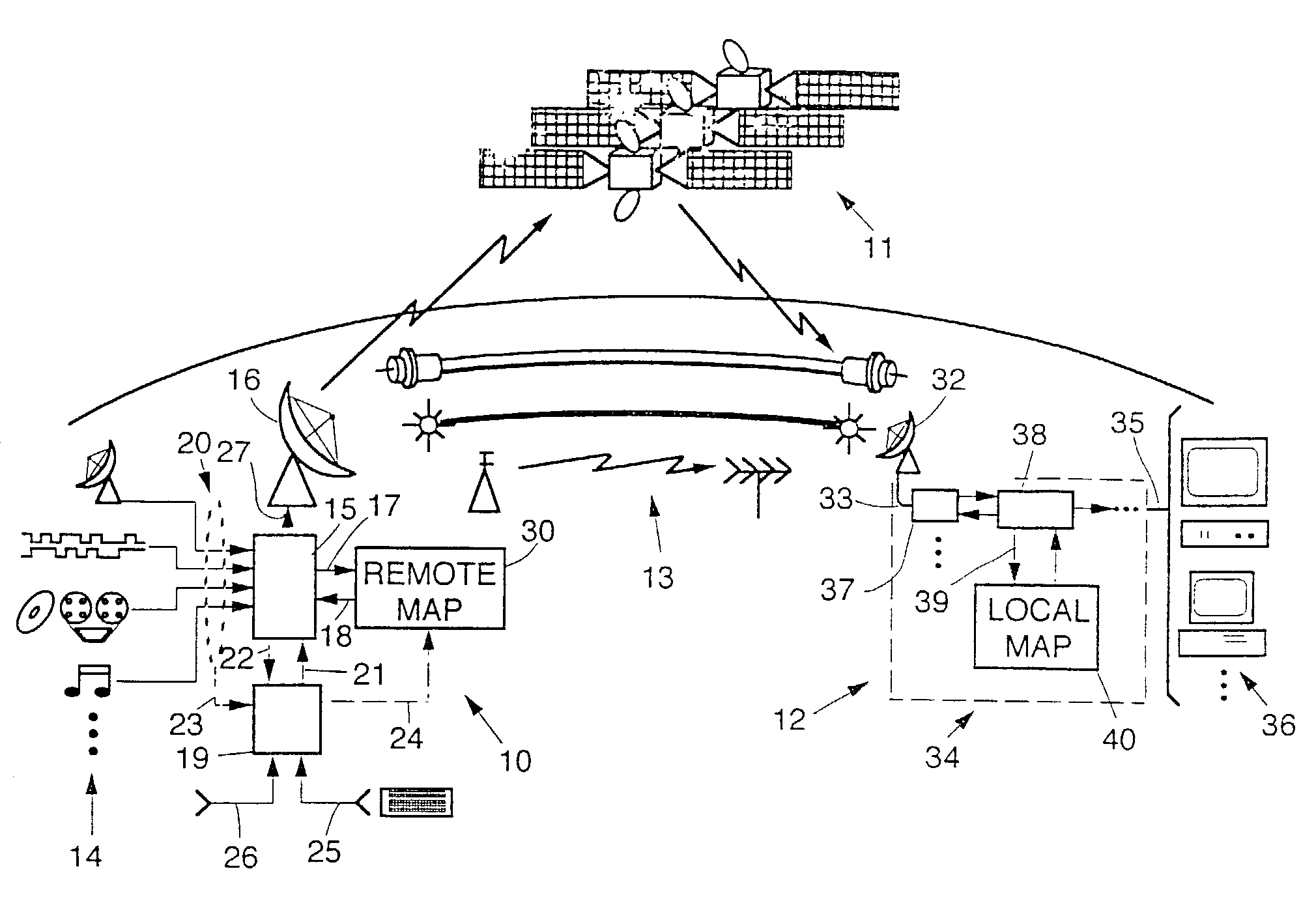
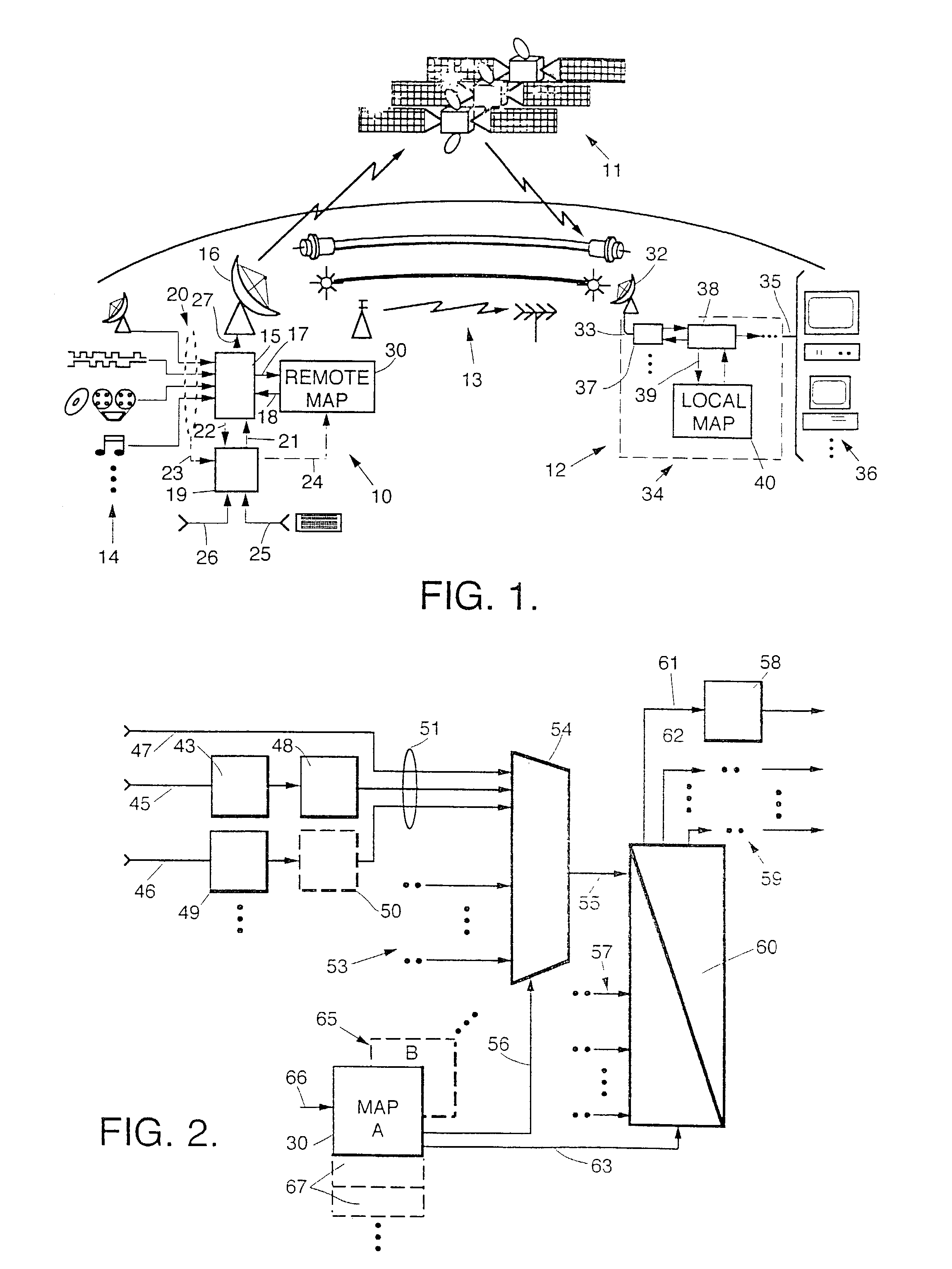
InactiveUS7075945B2Significant utilityAvailable bandwidthResource management arrangementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCommunications systemData stream
In a data communication system such as a high capacity DBS system, dynamic mapping of broadcast resources is provided to exploit occasional redundancy in the program content of two or more input data streams, freeing at least one broadcast resource to carry alternate bitstreams, such as additional programs or existing programs at higher quality. Transmission maps defining the correspondence between input data streams and broadcast resources, and reception maps defining the correspondence between broadcast resources and output data streams, are updated as needed to dynamically modify broadcast resource mapping to increase effective utilization of available bandwidth. Beneficial n:n−y:m mapping in a high capacity consumer DBS entertainment system is provided. Apparatus and methods for efficiently generating, maintaining and updating allocation maps with reduced overhead requirements, are disclosed.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
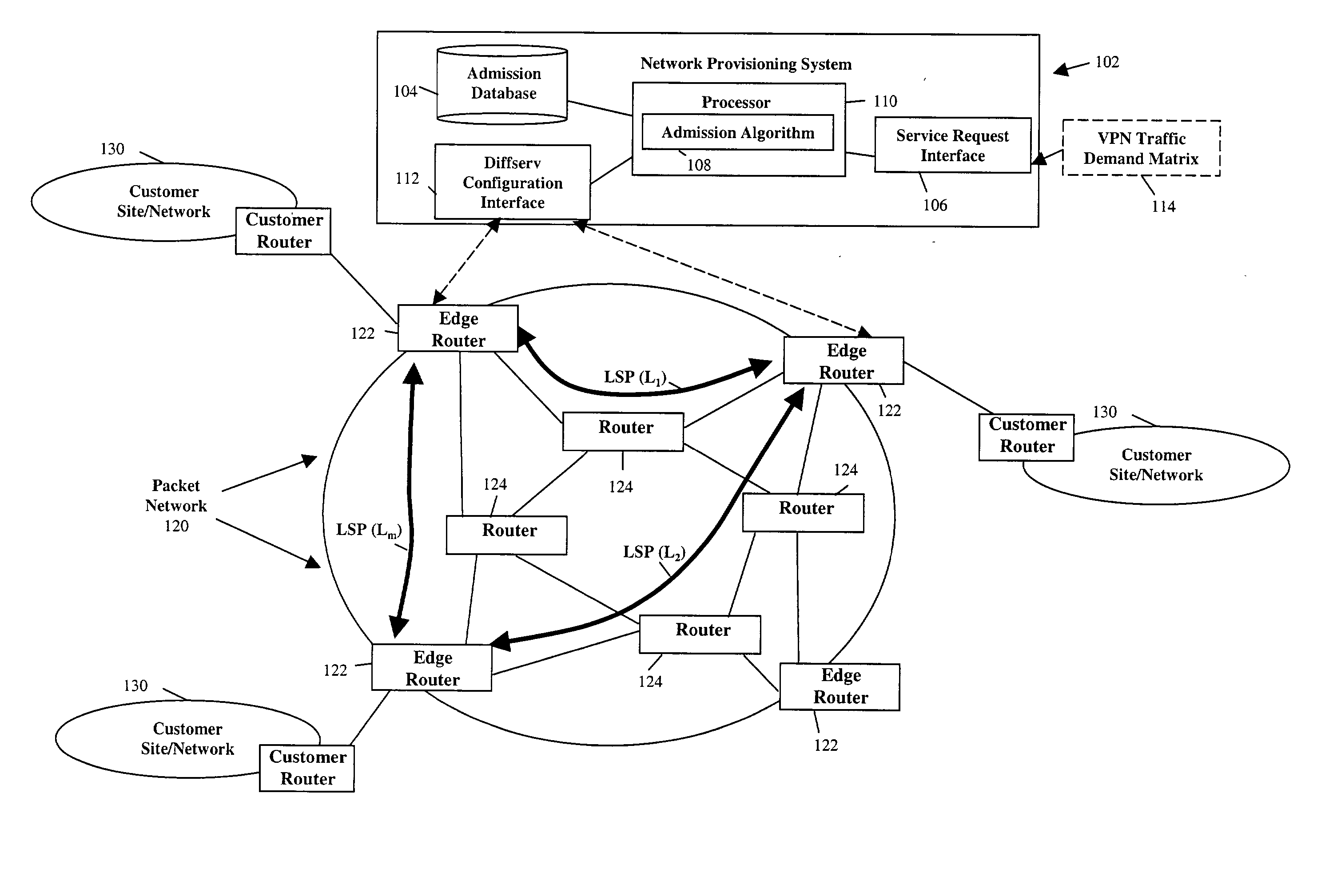
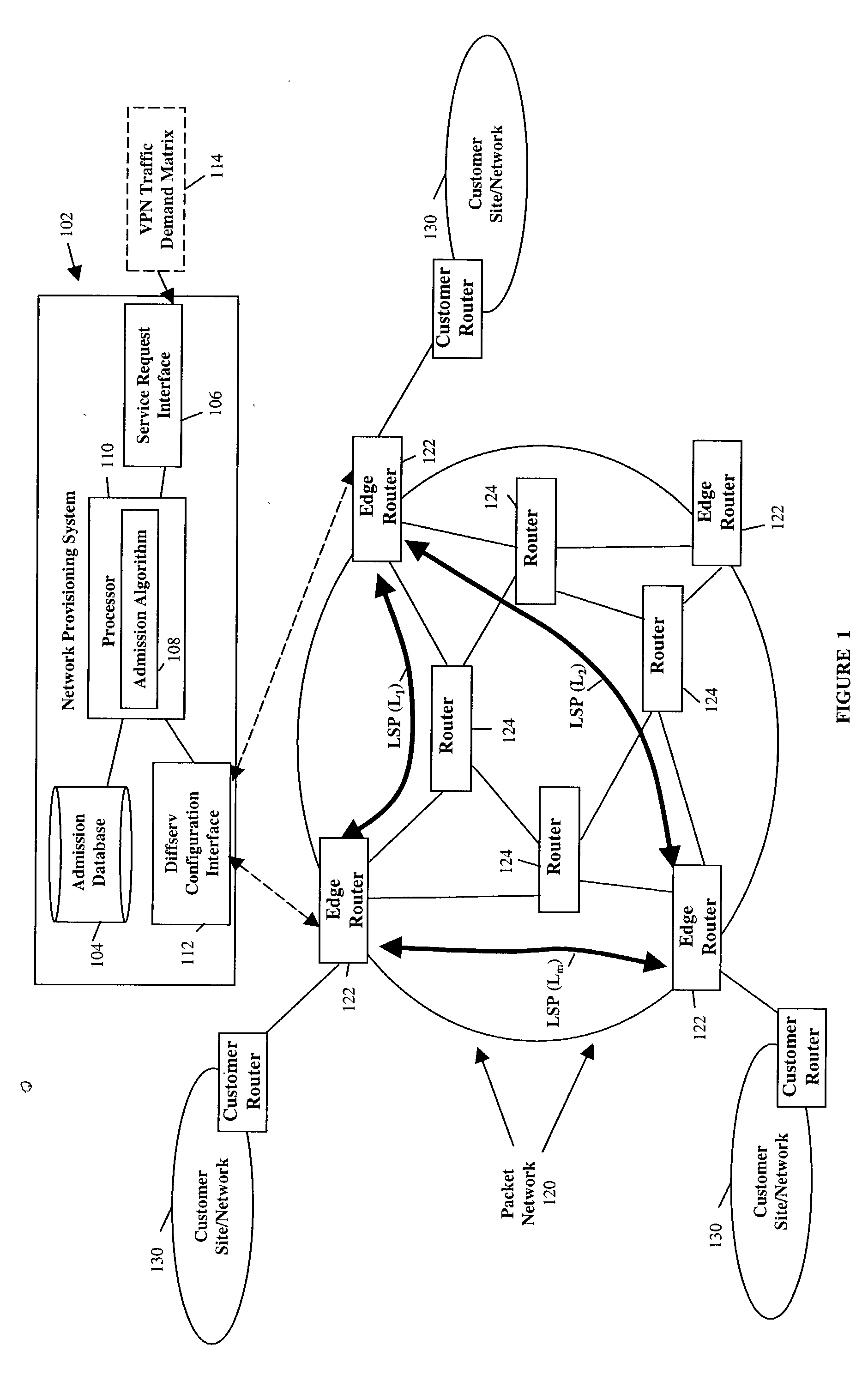
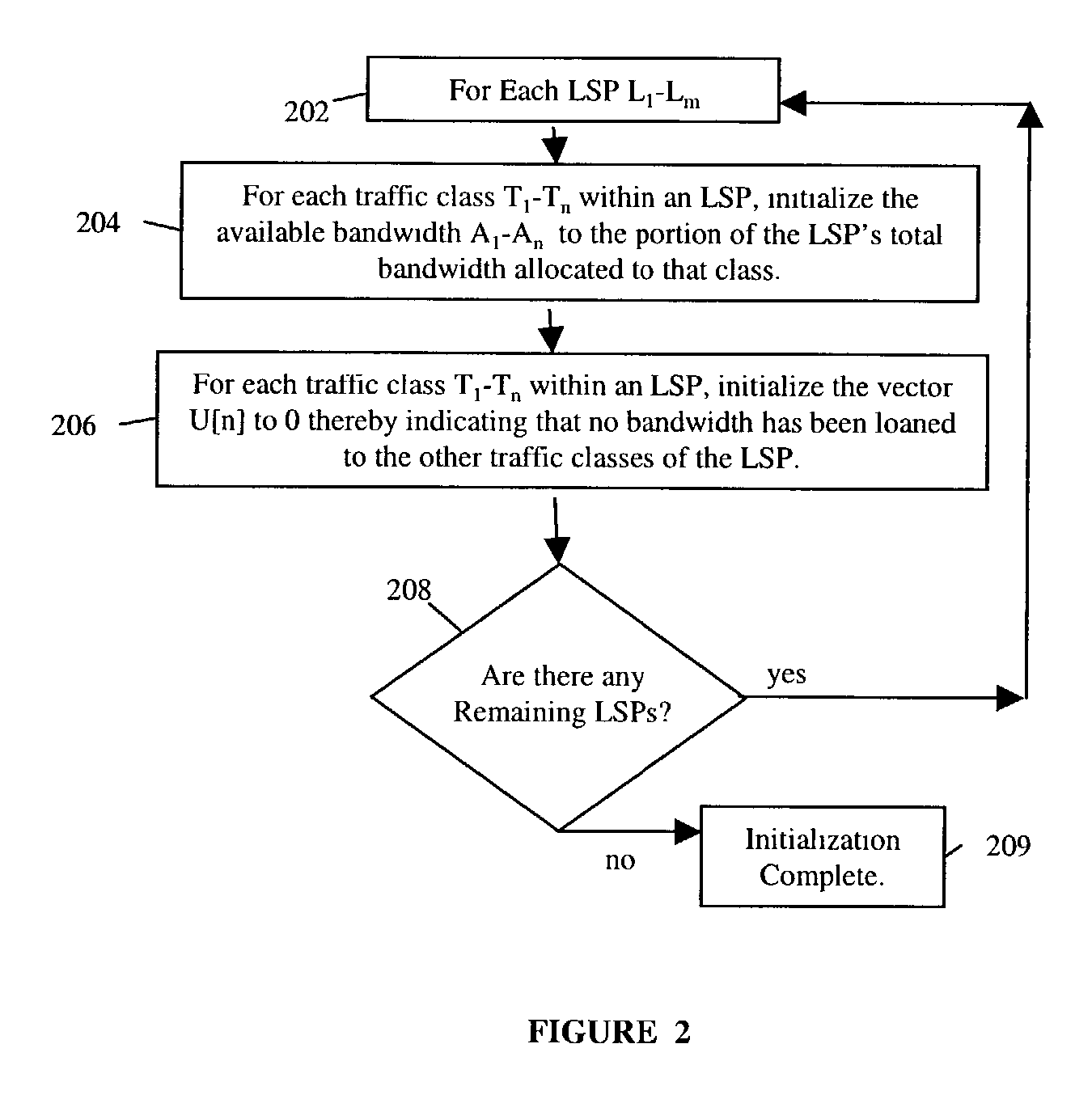
Dynamic bandwidth reallocation
ActiveUS20040028054A1Available bandwidthLess bandwidthTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionDynamic bandwidth allocationSystem maintenance
Bandwidth allocated between the traffic classes of a network path is dynamically reallocated when one or more traffic classes have insufficient available bandwidth to support a service request for the traffic classes, wherein the reallocation occurs without modifying the traffic class bandwidth allocations enforced by router mechanisms. A provisioning system maintains an available bandwidth indication for each traffic class, which indications are decremented as a service request is admitted to the path. If a requested traffic class has insufficient available bandwidth to support a request, one or more other traffic classes can loan bandwidth to the requested traffic class by decrementing the available bandwidth indicators for the one or more other traffic classes in the amount of the insufficiency, thereby indicating that less bandwidth is available in these classes for future requests. The provisioning system also maintains an indication of the amount of bandwidth each traffic class loans to the other traffic classes.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
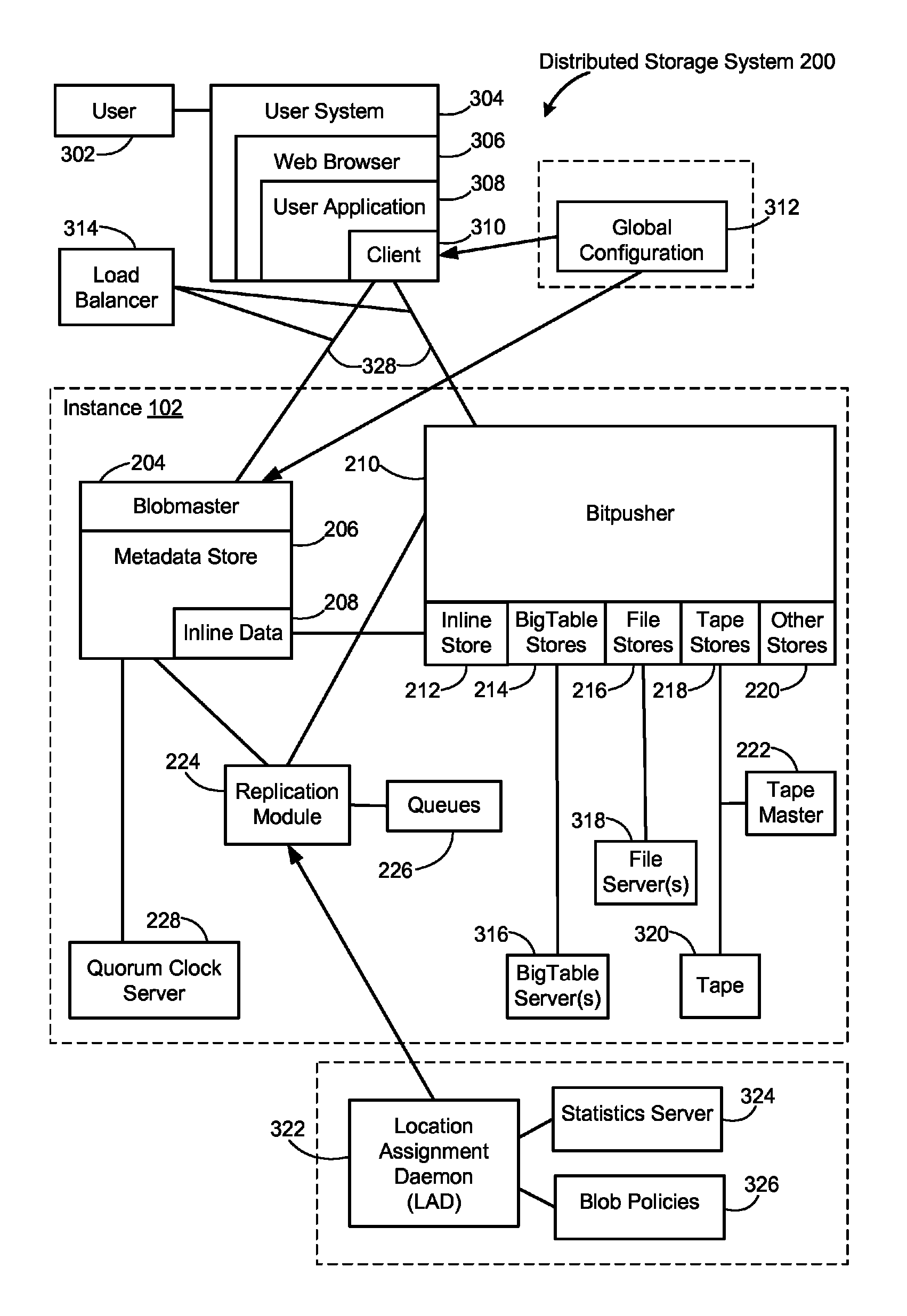
Method and system for dynamically replicating data within a distributed storage system
ActiveUS8341118B2Easy to useFaster replicationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSystem identificationDatabase
A server computer at a first storage sub-system of a distributed storage system receives from a client a first client request for an object. If the object is not present in the first storage sub-system, the server computer identifies a second storage sub-system of the distributed storage system as having a replica of the requested object, the requested object including content and metadata. The server computer submits an object replication request for the requested object to the second storage sub-system and independently receives the content and metadata of the requested object from the second storage sub-system. The server computer generates a new replica of the object at the first storage sub-system using the received metadata and content and returns the metadata of the new replica of the object to the client.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Hybrid data transport scheme over optical networks
InactiveUS6999479B1Available bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexData transmissionHybrid data
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
System and Method for Performing Error Correction at a Memory Device Level that is Transparent to a Memory Channel
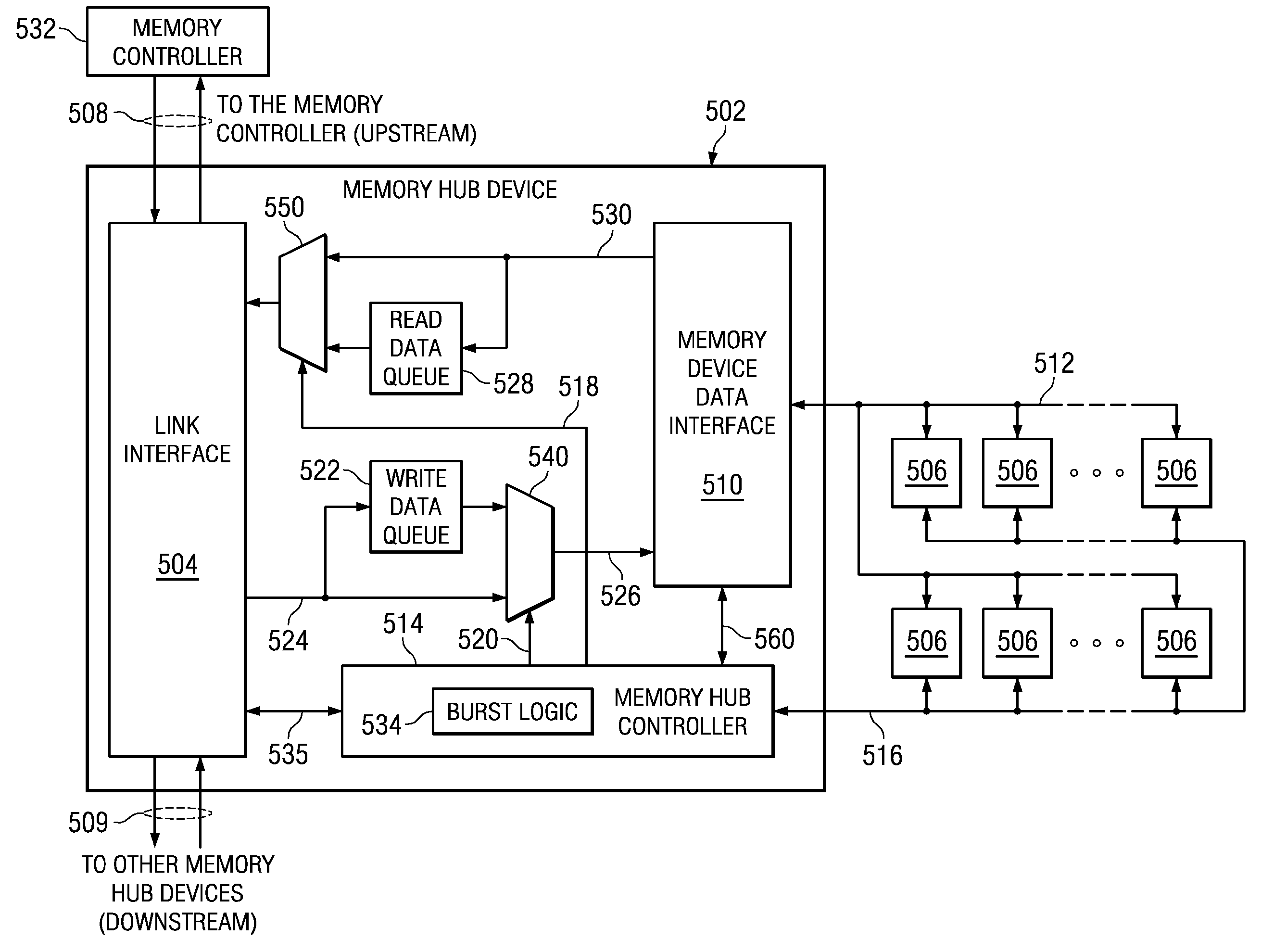
InactiveUS20090063923A1Increased memory bandwidthReduce the amount requiredError preventionTransmission systemsExternal storageMemory controller
A memory system is provided that performs error correction at a memory device level that is transparent to a memory channel. The memory system comprises a memory hub device integrated in the memory module and a set of memory devices coupled to the memory hub device. The memory hub device comprises first error correction logic provided in write logic integrated in the memory hub device. The memory hub device comprises second error correction logic provided in read logic integrated in the memory hub device. The first error correction logic and the second error correction logic performs error correction operations on data transferred between a link interface and the set of memory devices. The memory hub device transmits and receives data via a memory channel between the external memory controller and the link interface without any error correction code.
Owner:IBM CORP
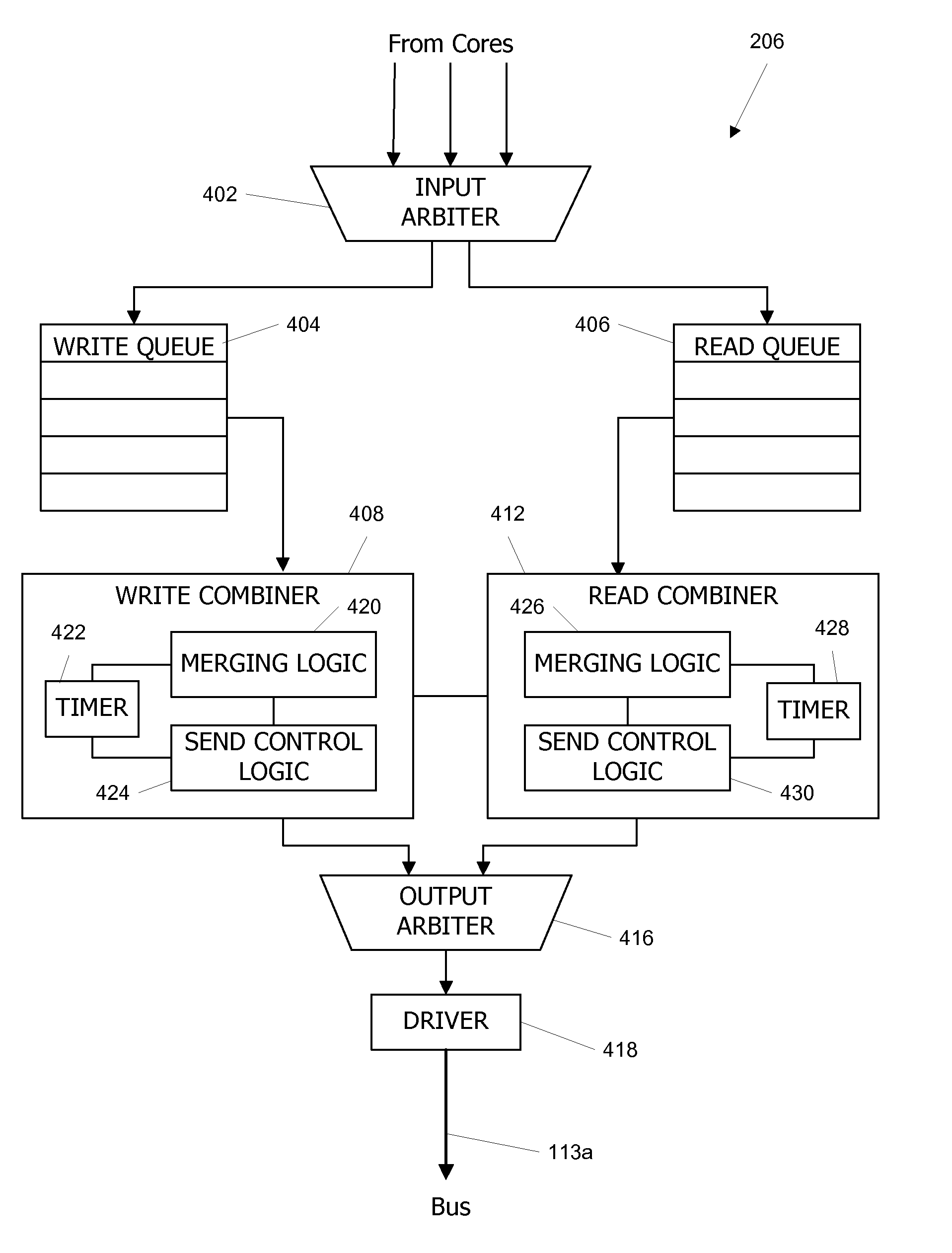
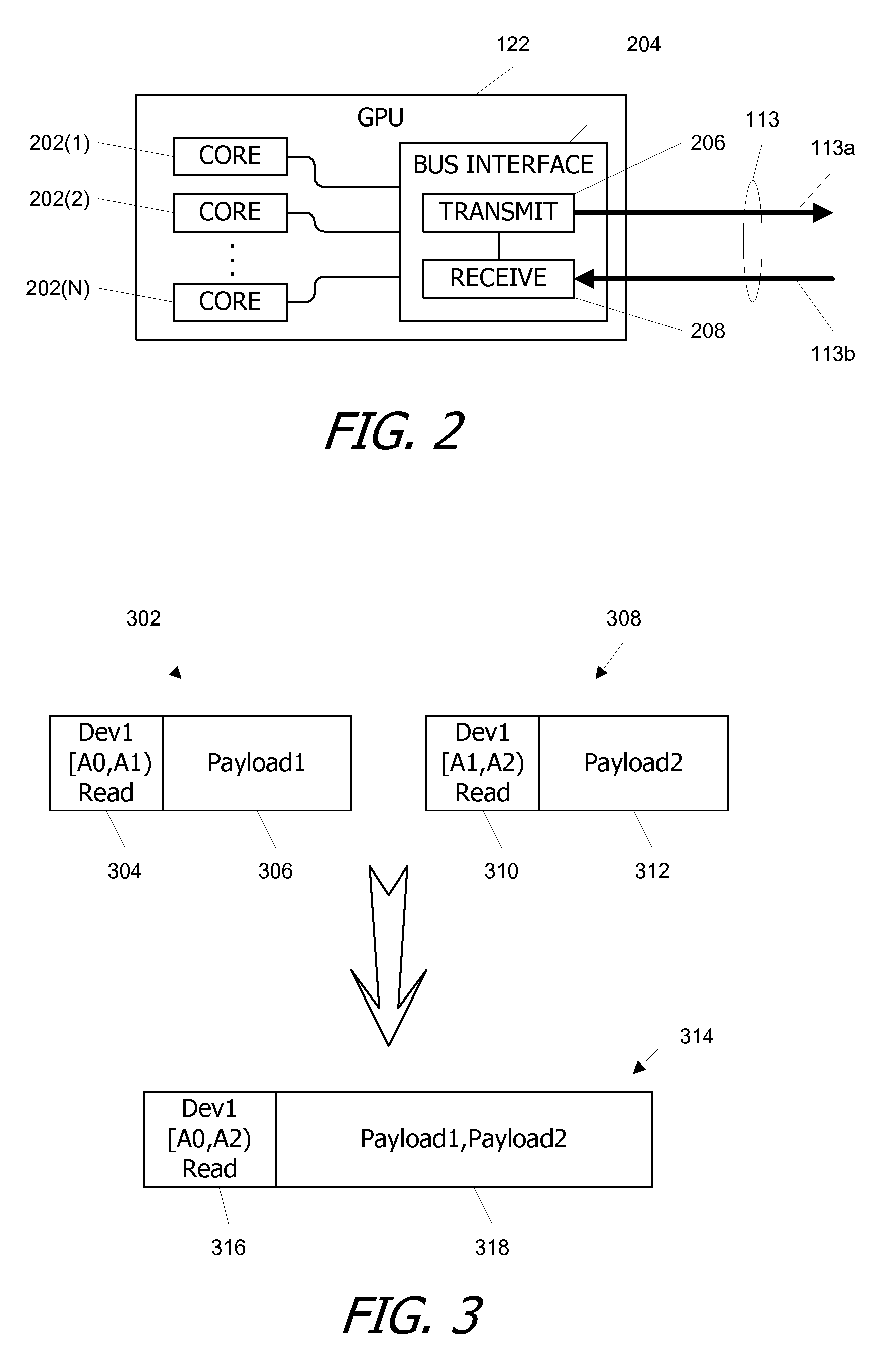
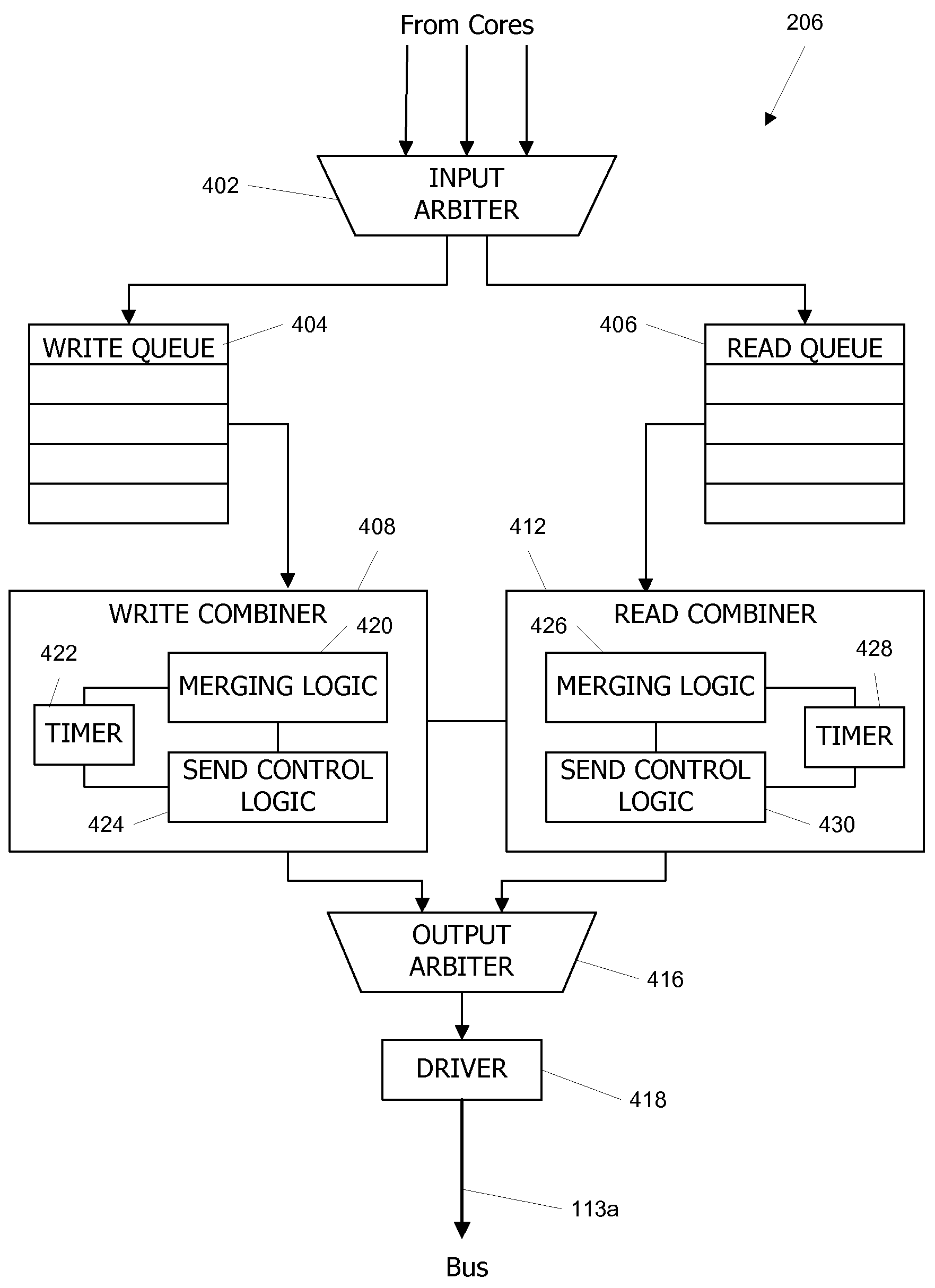
Packet Combiner for a Packetized Bus with Dynamic Holdoff time
ActiveUS20070079044A1Reduce traffic problemsLower performance requirementsEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexData packPCI Express
Multiple data transfer requests can be merged and transmitted as a single packet on a packetized bus such as a PCI Express (PCI-E) bus. In one embodiment, requests are combined if they are directed to contiguous address ranges in the same target device. An opportunistic merging procedure is advantageously used that merges a first request with a later request if the first request and the later request are mergeable and are received within a holdoff period that is dynamically determined based on a level of bus activity; otherwise, requests can be transmitted without merging.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
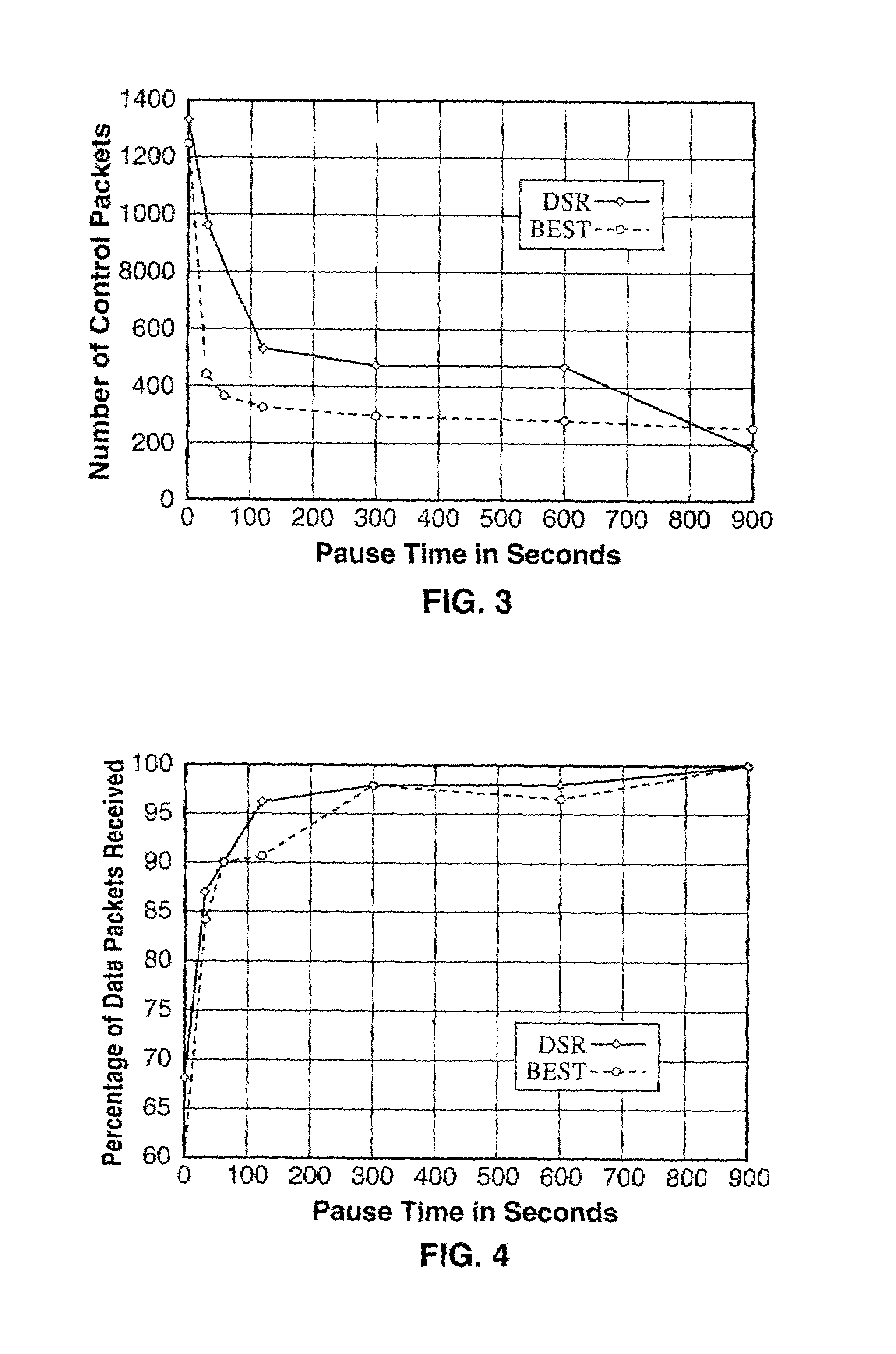
Bandwidth efficient source tracing (BEST) routing protocol for wireless networks
ActiveUS7002949B2Reduce control overheadIncrease available bandwidthPower managementNetwork topologiesPathPingDistance-vector routing protocol
A bandwidth efficient routing protocol for wireless ad-hoc networks. This protocol can be used in ad-hoc networks because it considerably reduces control overhead, thus increasing available bandwidth and conserving power at mobile stations. It also gives very good results in terms of the throughput seen by the user. The protocol is a table-driven distance-vector routing protocol that uses the same constraints used in on-demand routing protocols, i.e., paths are used as long as they are valid and updates are only sent when a path becomes invalid. The paths used by neighbors are maintained and this allows the design of a distance-vector protocol with non-optimum routing and event-driven updates, resulting in reduced control overhead.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System for Performing Error Correction Operations in a Memory Hub Device of a Memory Module
InactiveUS20090063922A1Increased memory bandwidthReduce the amount requiredError preventionTransmission systemsExternal storageMemory controller
A memory system is provided for performing error correction operations in a memory module. The memory system comprises a memory hub device integrated in the memory module and a set of memory devices coupled to the memory hub device. The memory hub device comprises a link interface integrated into the memory hub device that provides a communication pathway between an external memory controller and the set of memory devices. The memory hub device also comprises error correction logic integrated in the memory hub device and coupled to the link interface. The error correction logic performs error correction operations on data transferred between the link interface and the set of memory devices. The memory hub device transmits and receives data via a memory channel between the external memory controller and the link interface without any error correction code.
Owner:IBM CORP
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
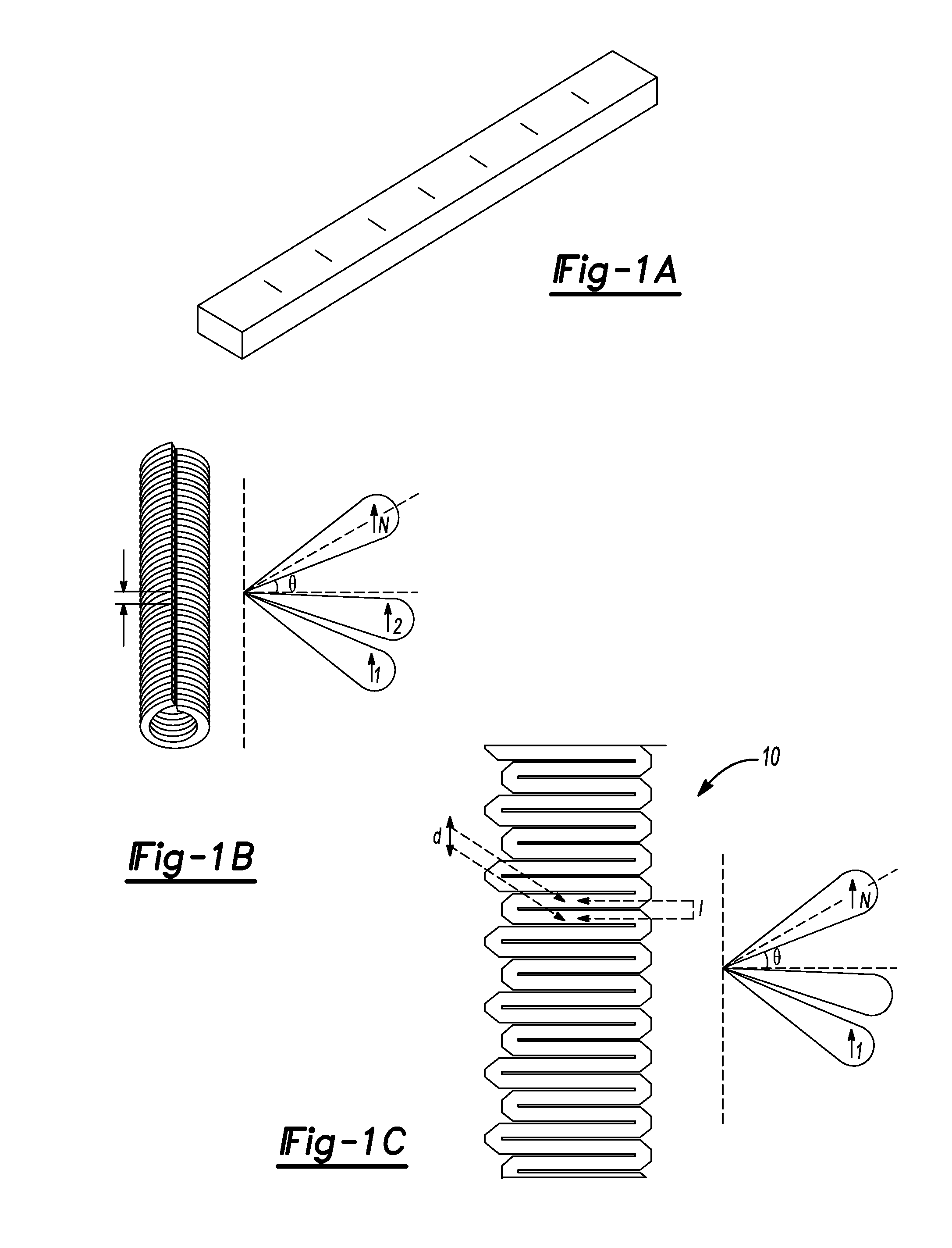
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Dynamic wireless network
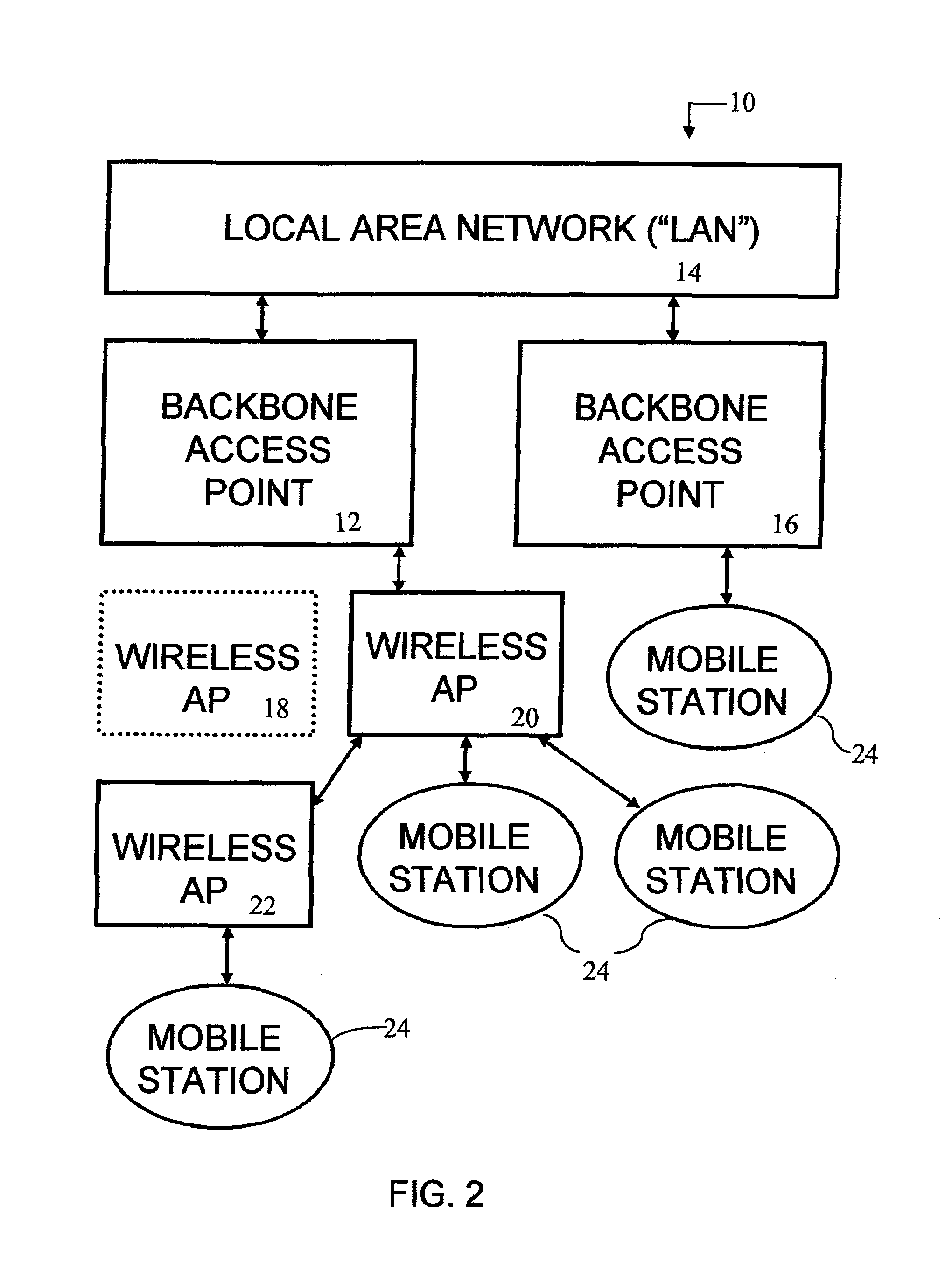
ActiveUS7269174B2Maximize signal strengthOptimize bandwidthNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationMedia access controlIp address
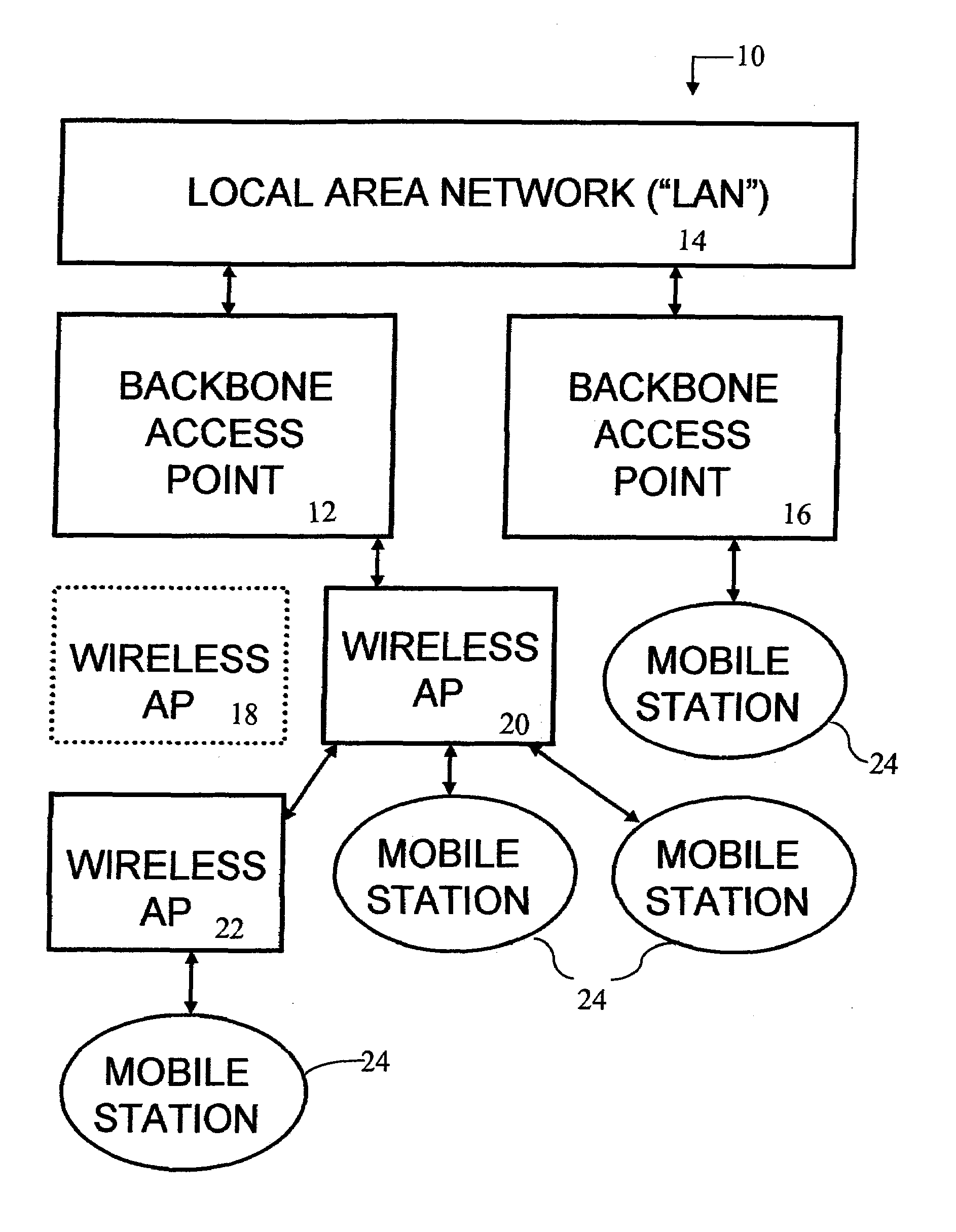
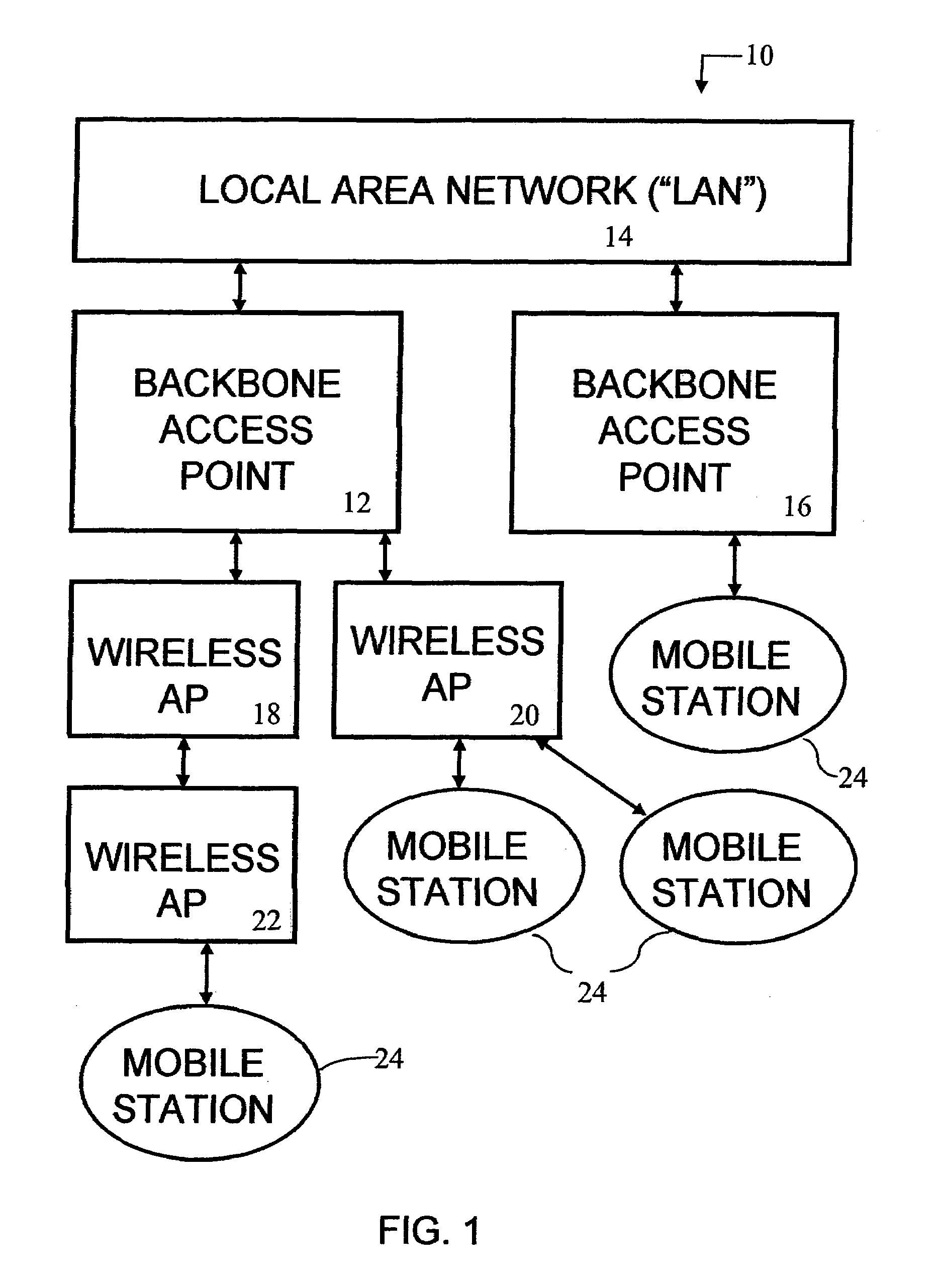
A Dynamically Reconfigurable Dynamic Wireless Network for connecting a local area network (“LAN”) to wireless Mobile Stations. Backbone Access Points (“Backbone APs”) are physically connected to the LAN. Levels of Wireless Access Points (“Wireless APs”) are daisy-chained together and connected to the Backbone AP, providing an extended area of network coverage. Mobile stations are connected to either Backbone APs or Wireless APs. Dynamic Reconfiguration prevents single point failures. Each AP contains a router, Address Resolution Protocol (“ARP”) cache, and Distributed Routing Table (“DR Table”). The DR Table maintains the Media Access Control (“MAC”) address and the Internet Protocol (“IP”) address of each AP below it in the Distributed Routing Tree. Additionally, each DR Table also maintains the IP address for the device each AP is connected. The Distributed Routing Tree is dynamically reconfigured to minimize transmission hops or to maximize signal strength between Mobile Stations and the LAN.
Owner:MODULAR MINING SYSTEMS
Systems and methods for state consistent replication
ActiveUS20140181027A1Easily recoverGreat level of data protectionDigital data processing detailsTransmissionClient-sideClient data
Owner:ZETTA LLC
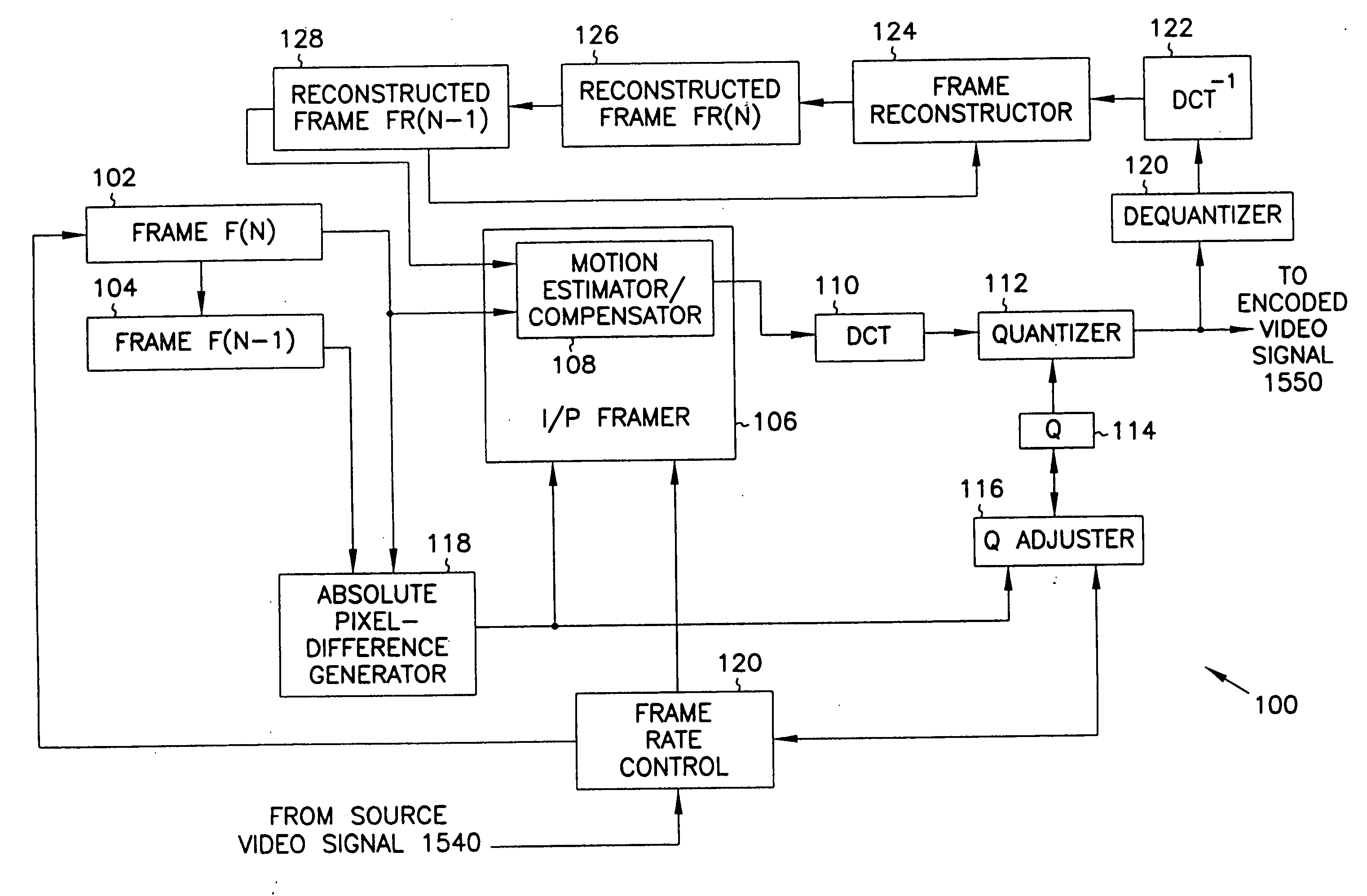
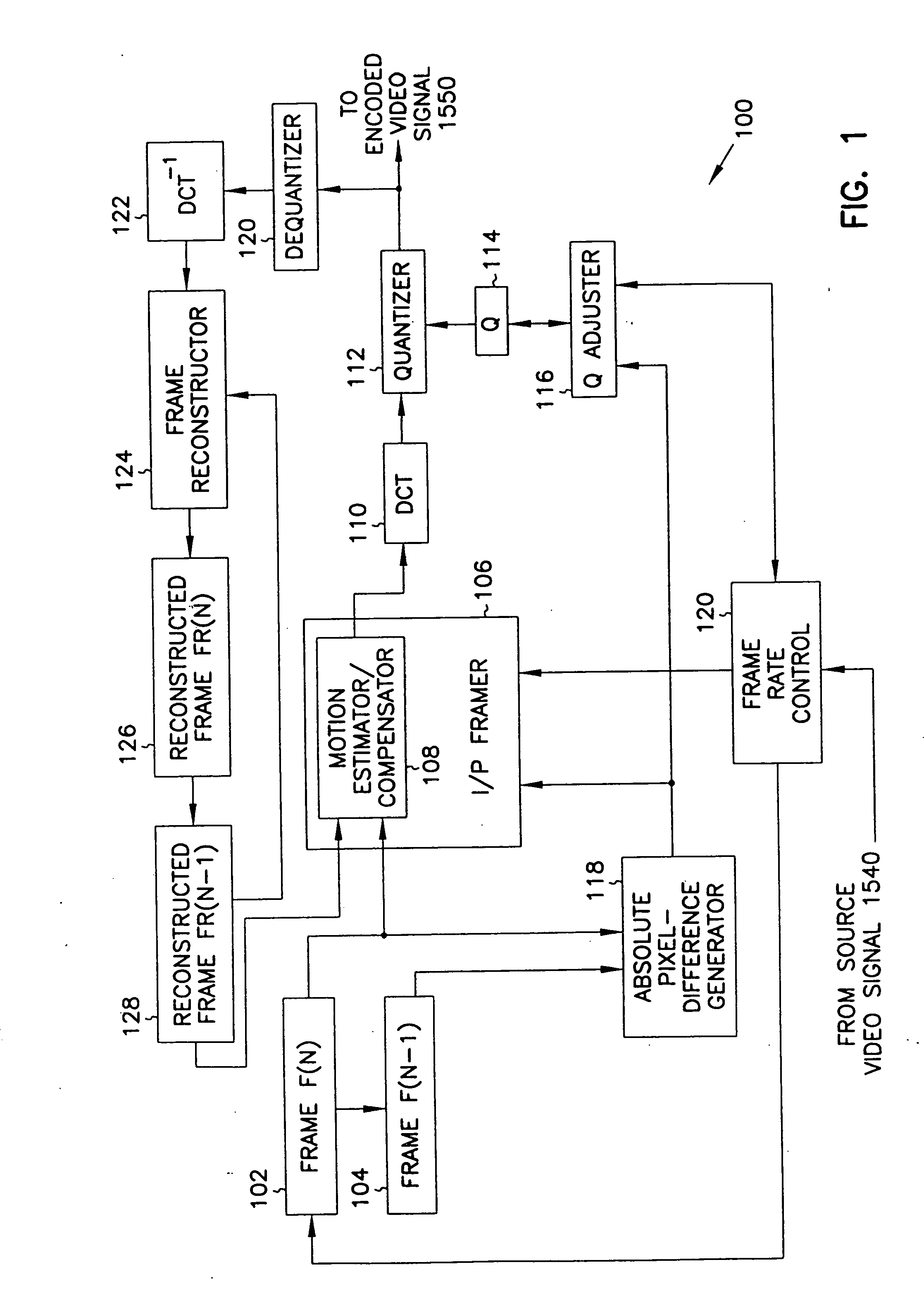
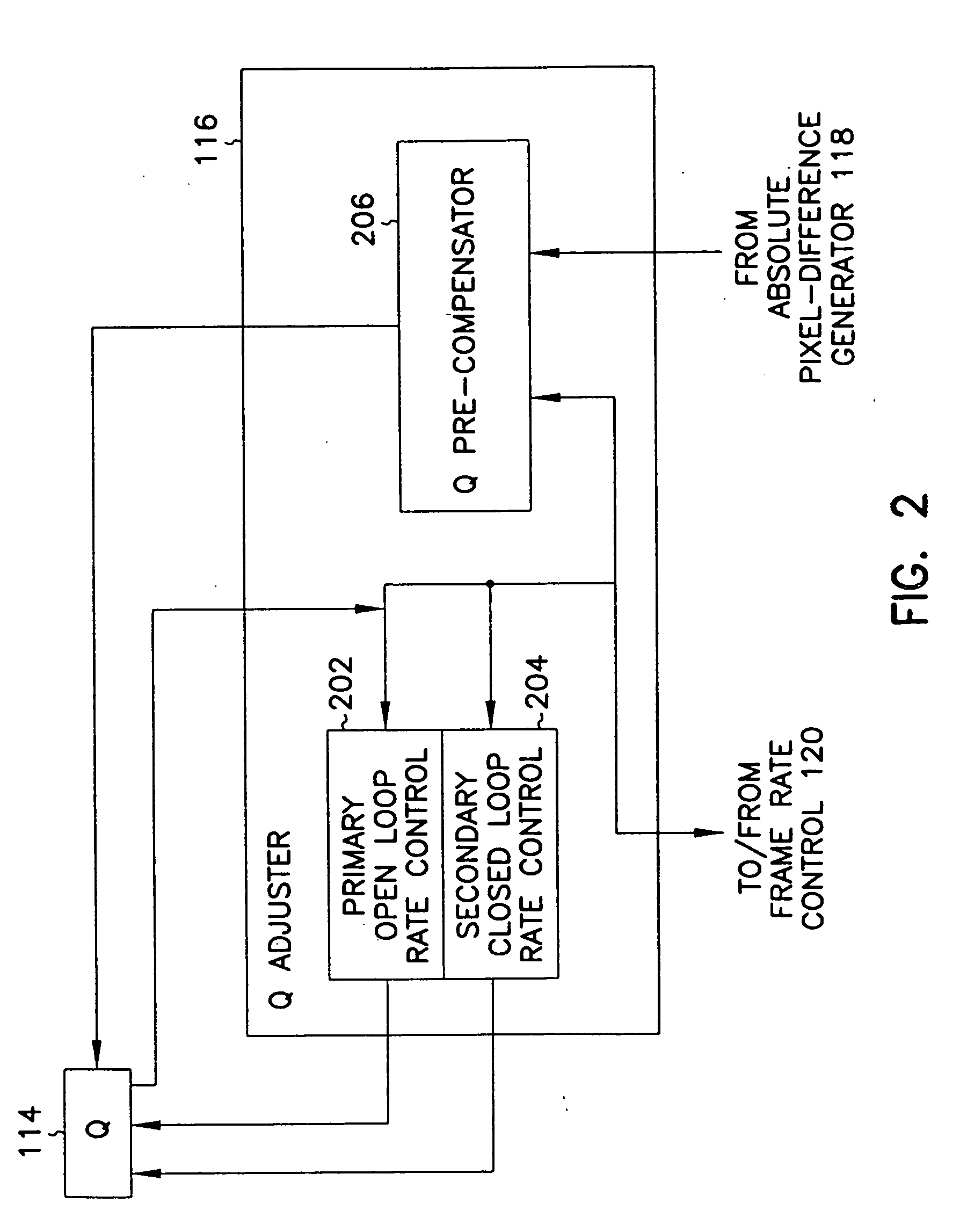
Digital video signal encoder and encoding method
InactiveUS20050220188A1Less bandwidthImprove image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDigital video
A motion video signal encoder maximizes image quality without exceeding transmission bandwidth available to carry the encoded motion video signal by comparing encoded frames of the motion video signal to a desired size of frame. If the size of encoded frames differ from the desired size, quantization is adjusted to produce encoded frames closer in size to the desired size. In addition, a cumulative bandwidth balance records an accumulated amount of available bandwidth. The cumulative bandwidth balance is adjusted as time elapses to add to the available bandwidth and as each frame is encoded to thereby consume bandwidth. If the cumulative bandwidth balance deviates from a predetermined range, quantization is adjusted as needed to either improve image quality to more completely consume available bandwidth or to reduce image quality to thereby consume less bandwidth. Rapid changes in the amount of change or motion in the motion video signal are detected by comparing the amount of change between two consecutive frames and the amount of change between the next two consecutive frames. Quantization is precompensated according to the measured rapid change. Conditional replenishment is improved by dividing macroblocks into quadrants and measuring differences between corresponding quadrants of macroblocks. As a result, sensitivity to changes along edges and corners of macroblocks is increased. In addition, sensitivity to changes in a particular macroblock is increased when an adjacent macroblock contains sufficient change to be encoded and therefore not a candidate for conditional replenishment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
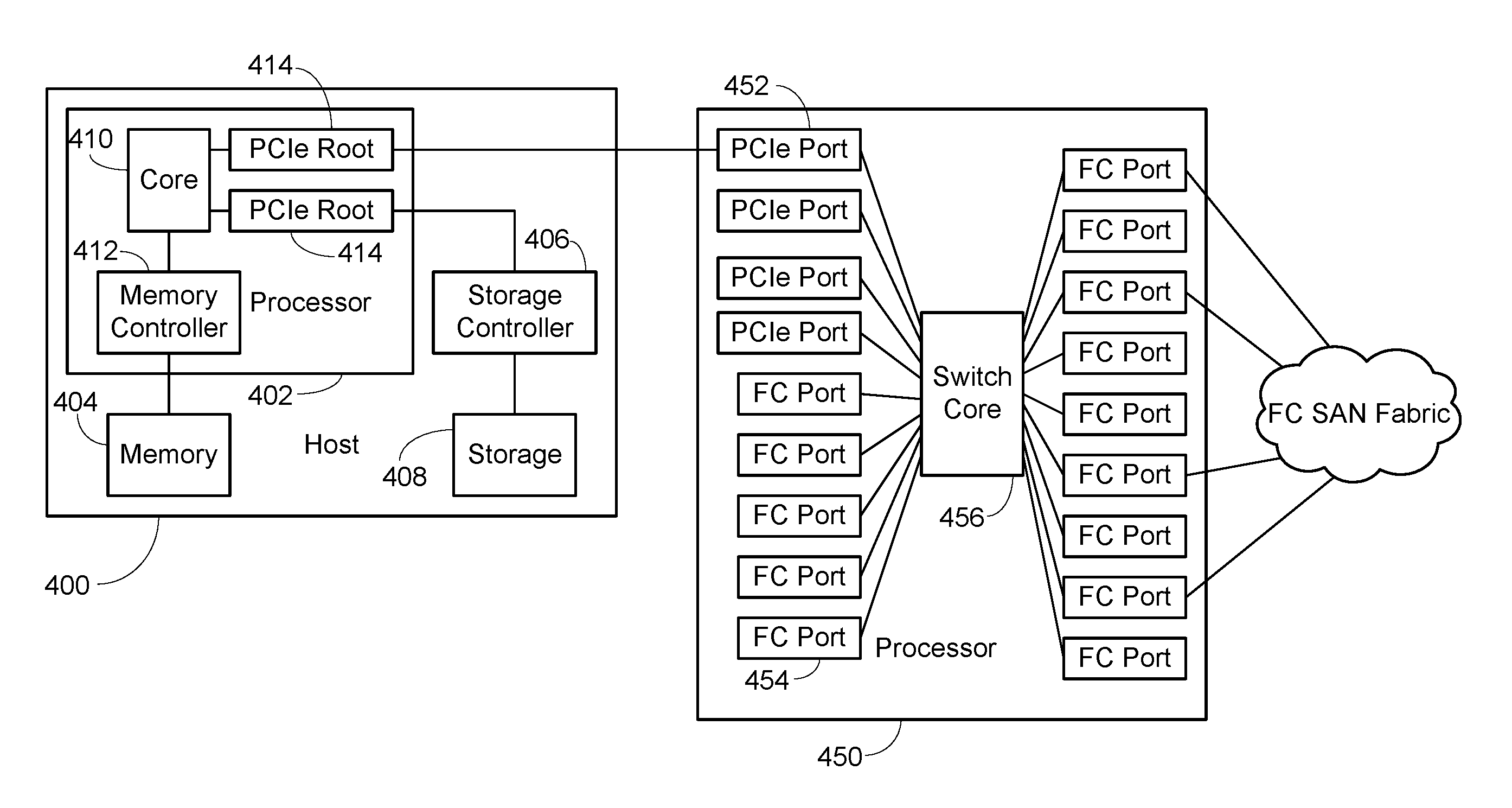
PCI Express Connected Network Switch
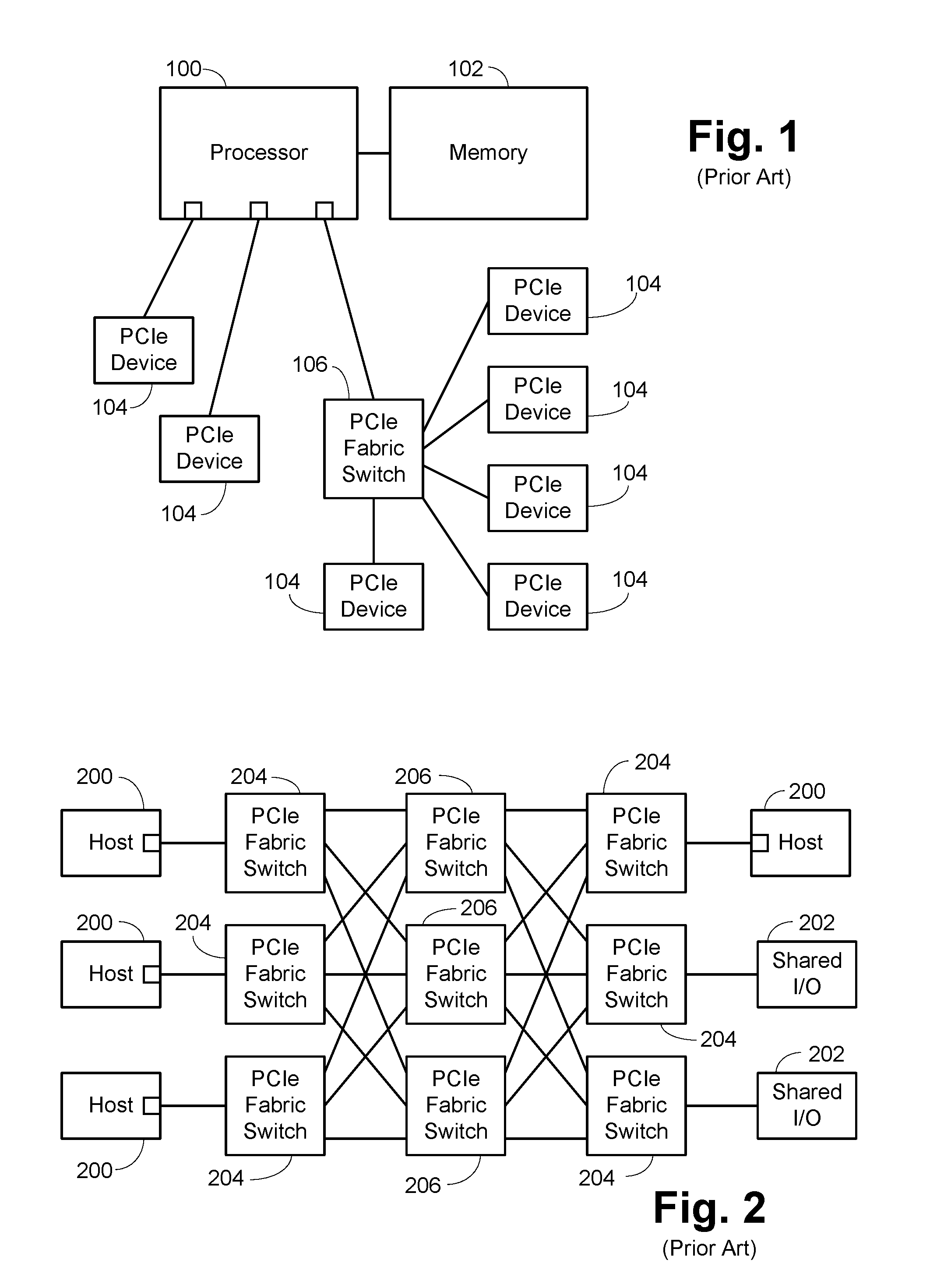
ActiveUS20170052916A1Low costSave spaceElectric digital data processingNetworking protocolNetwork packet
A host connected to a switch using a PCI Express (PCIe) link. At the switch, the packets are received and routed as appropriate and provided to a conventional switch network port for egress. The conventional networking hardware on the host is substantially moved to the port at the switch, with various software portions retained as a driver on the host. This saves cost and space and reduces latency significantly. As networking protocols have multiple threads or flows, these flows can correlate to PCIe queues, easing QoS handling. The data provided over the PCIe link is essentially just the payload of the packet, so sending the packet from the switch as a different protocol just requires doing the protocol specific wrapping. In some embodiments, this use of different protocols can be done dynamically, allowing the bandwidth of the PCIe link to be shared between various protocols.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System for Supporting Partial Cache Line Write Operations to a Memory Module to Reduce Write Data Traffic on a Memory Channel
InactiveUS20090063730A1Increased memory bandwidthReduce the amount requiredMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData trafficMemory systems
A memory system is provided that supports partial cache line write operations to a memory module to reduce write data traffic on a memory channel. The memory system comprises a memory hub device integrated in the memory module and a set of memory devices coupled to the memory hub device. The memory hub device comprises burst logic integrated in the memory hub device. The burst logic determines an amount of write data to be transmitted to the set of memory devices and generates a burst length field corresponding to the amount of write data. The memory hub also comprises a memory hub controller integrated in the memory hub device. The memory hub controller controls the amount of write data that is transmitted using the burst length field. The memory hub device transmits the amount of write data that is equal to or less than a conventional data burst amount.
Owner:IBM CORP
Gateway with improved QoS awareness
ActiveUS8184550B2Available bandwidthImprove quality experienceError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkClassification rule
A device and method for exchanging data frames are disclosed. In one aspect, the device exchanges data between a WAN and one or more LAN segments in an optimized way leading to a better quality of experience for the user. The device comprises an interface exchanging data frames over an access network, at least a first and second subnet interface exchanging data frames and arranged for being coupled to a network, a memory storing classification rules, a classification agent extracting information from an incoming data frame and applying the rules to the extracted information to determine the interface via which the incoming data frame is to be forwarded, and a Quality of Service monitoring agent for retrieving Quality of Service information from the subnet interfaces and dynamically updating the classification rules according to the QoS information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
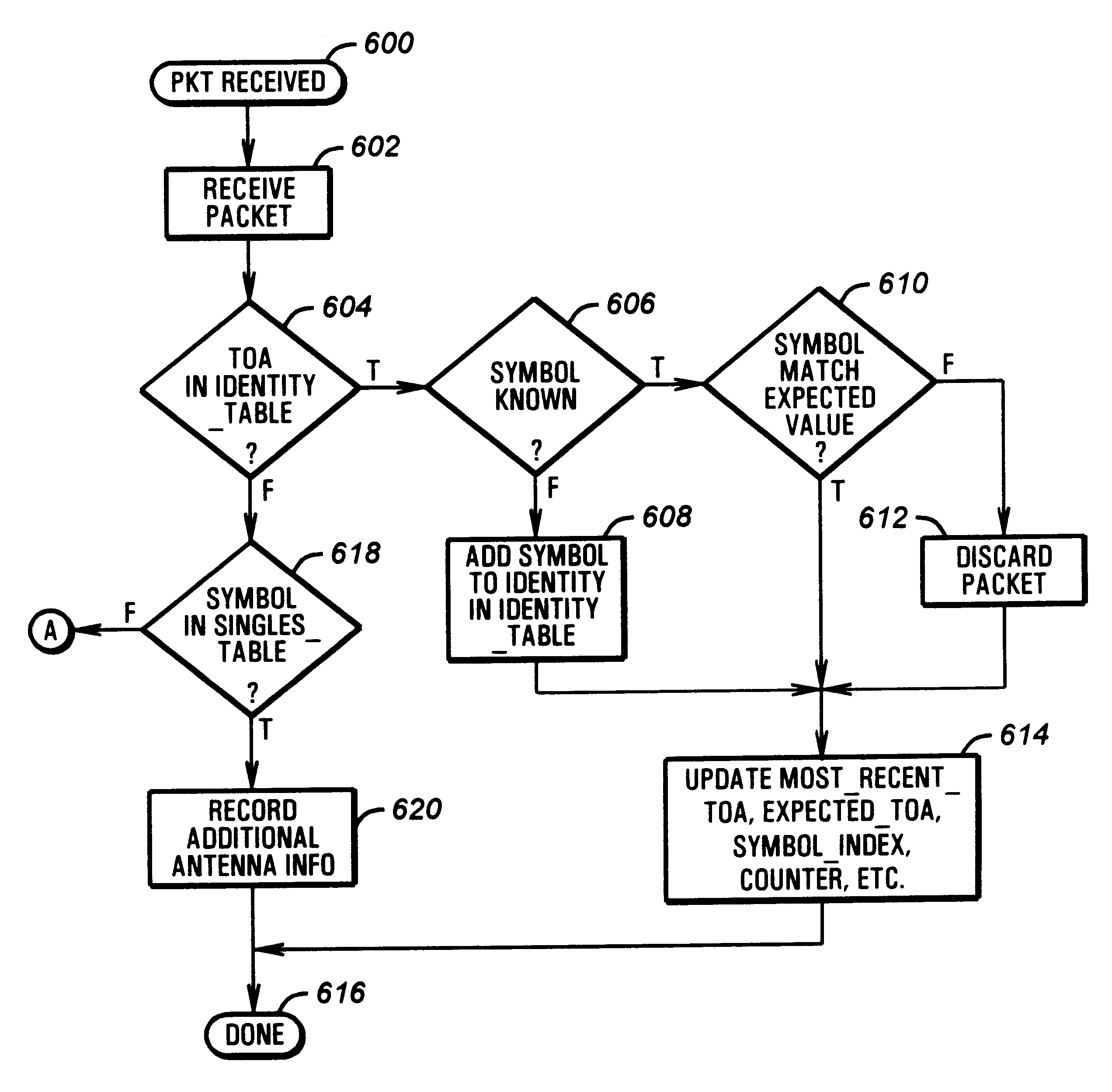
Location, identification and telemetry system using strobed signals at predetermined intervals
InactiveUS6222440B1Save powerAvailable bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsDirection finders using radio wavesEngineeringWireless transmitter
A tracking system is implemented according to the invention in which the identification data of a wireless transmitter is divided into multiple bursts. Instead of transmitting the entire identification in a single burst, the identification is split among bursts, so that it takes a period of time to uniquely identify a particular transmitter. However, the time between bursts falls under tight tolerance, so once a transmitter is identified, it can be further identified based on when it transmits as opposed to what it transmits. In this way, high tractability can be maintained without repeatedly transmitting the entire identification code of the transmitter.
Owner:FRESHLOC TECH
Packet combiner for a packetized bus with dynamic holdoff time
ActiveUS7526593B2Reduce traffic problemsLower performance requirementsEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexPCI ExpressData transmission
Multiple data transfer requests can be merged and transmitted as a single packet on a packetized bus such as a PCI Express (PCI-E) bus. In one embodiment, requests are combined if they are directed to contiguous address ranges in the same target device. An opportunistic merging procedure is advantageously used that merges a first request with a later request if the first request and the later request are mergeable and are received within a holdoff period that is dynamically determined based on a level of bus activity; otherwise, requests can be transmitted without merging.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com