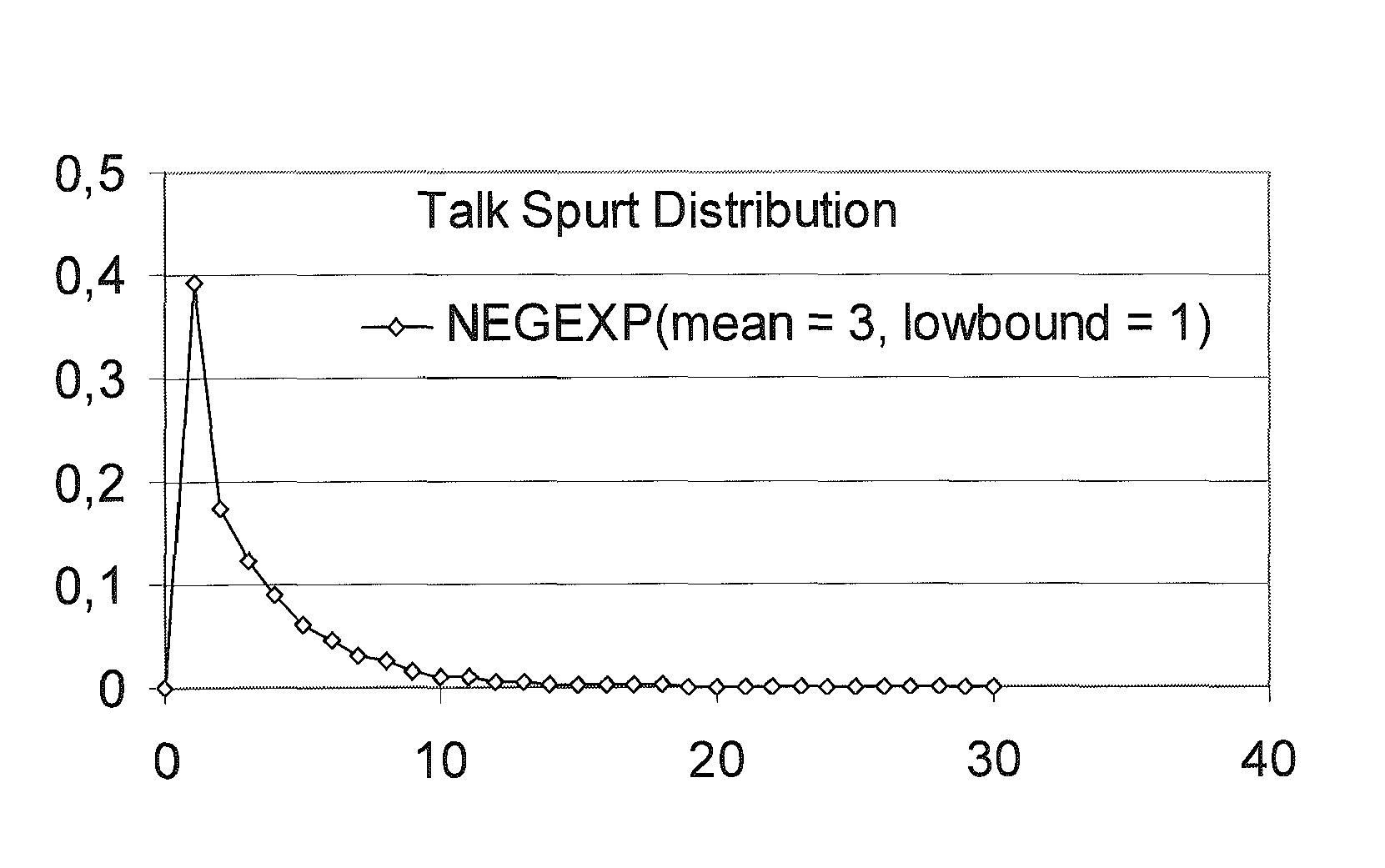
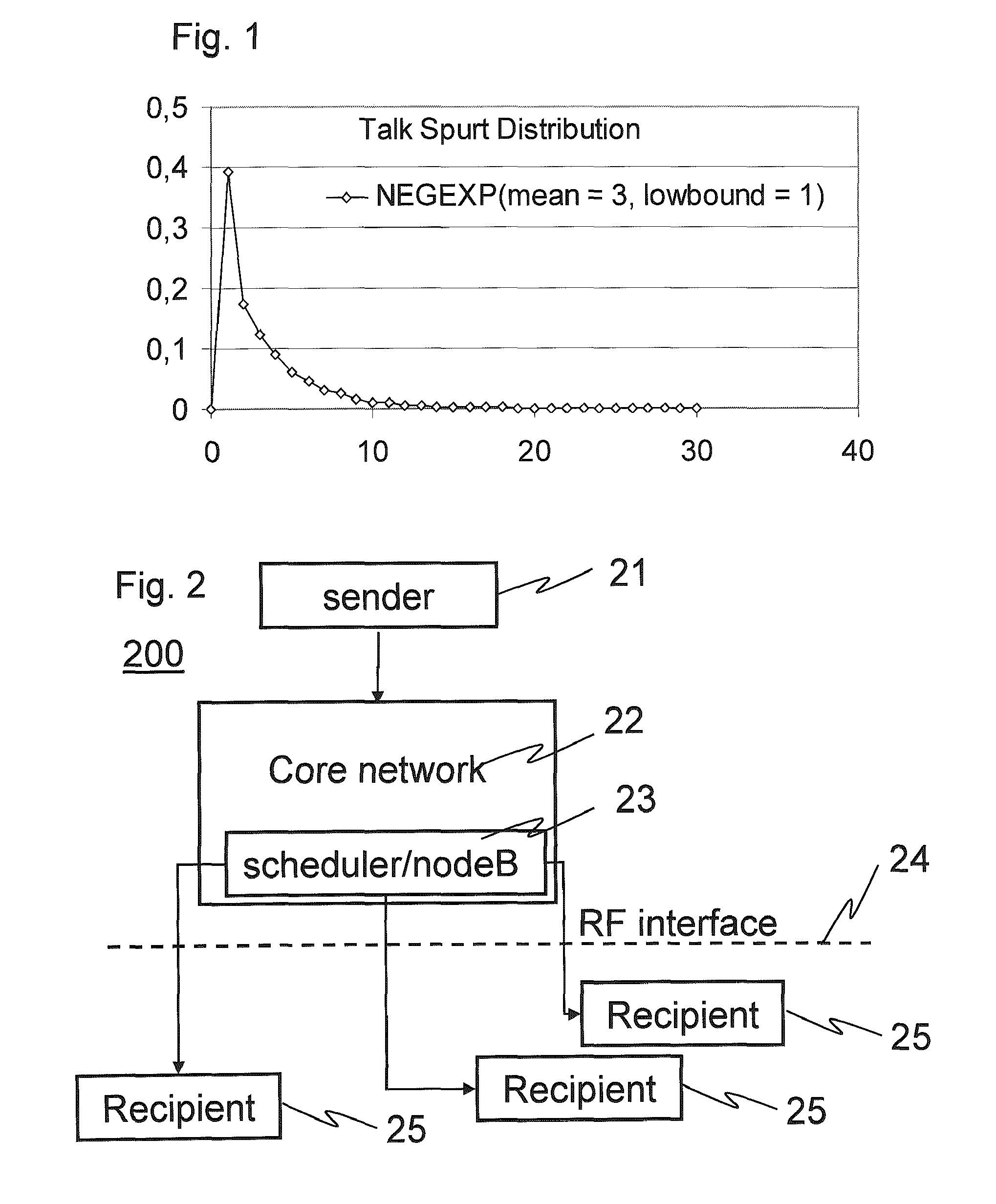
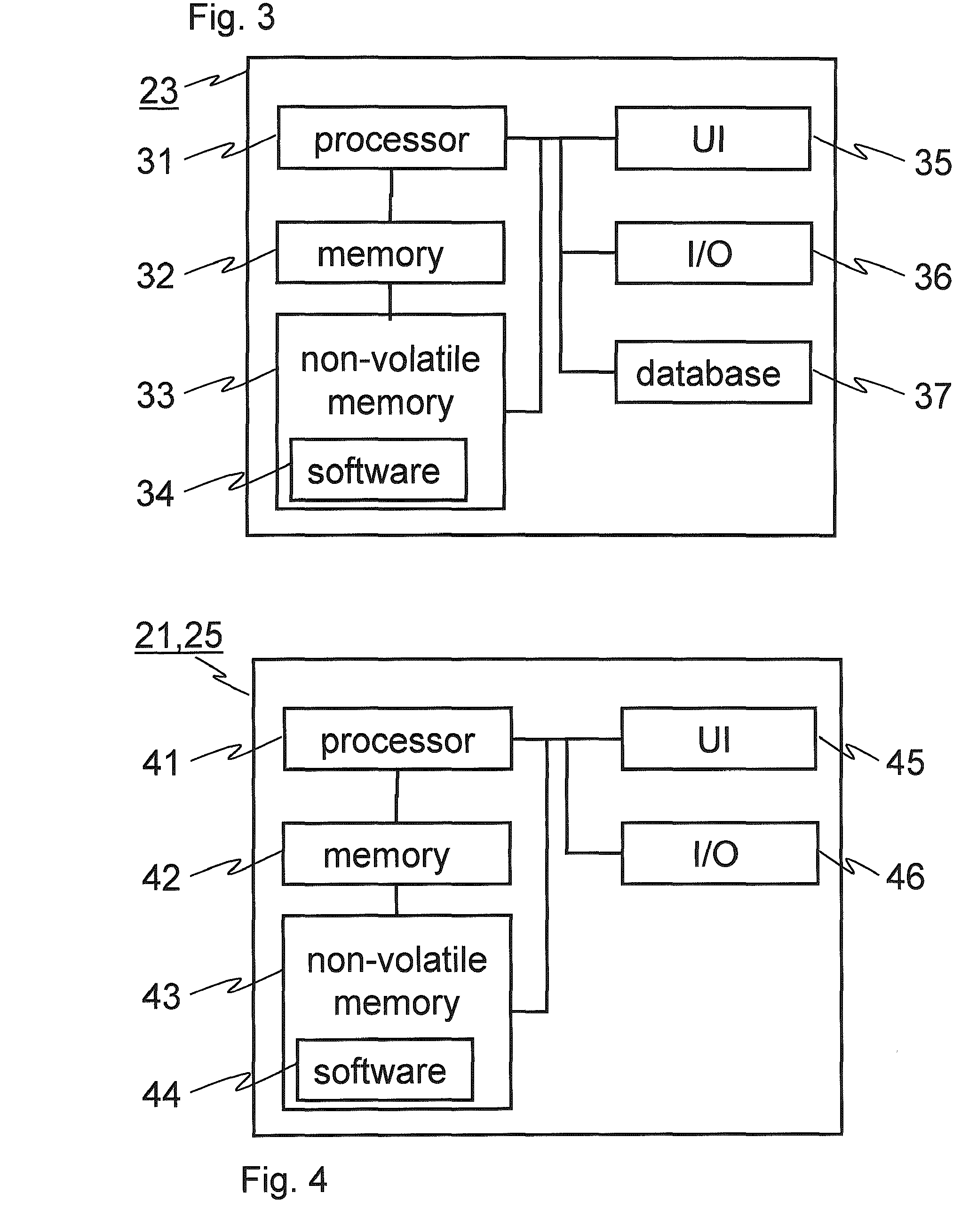
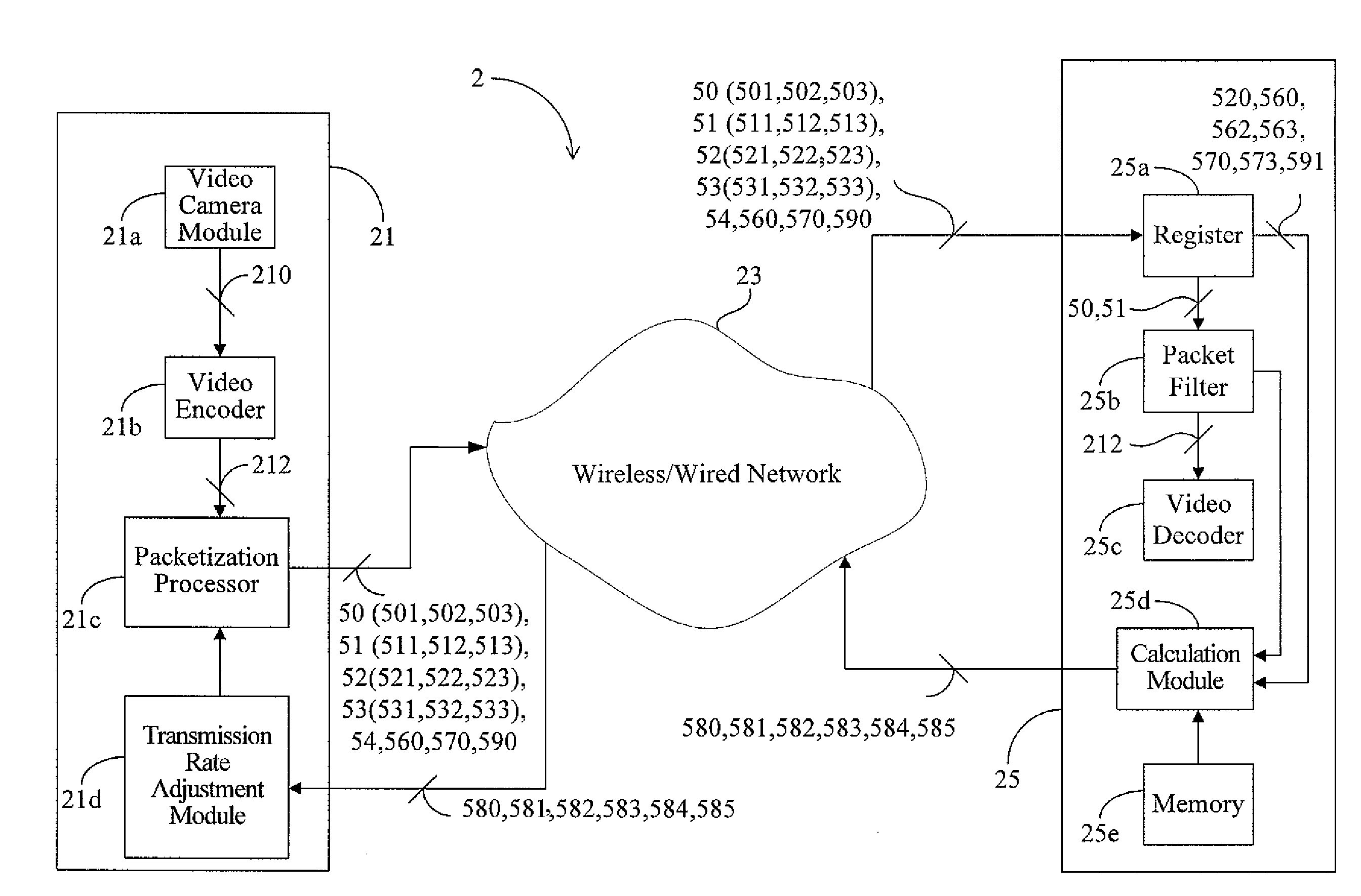
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146results about How to "Reduce data transfer rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
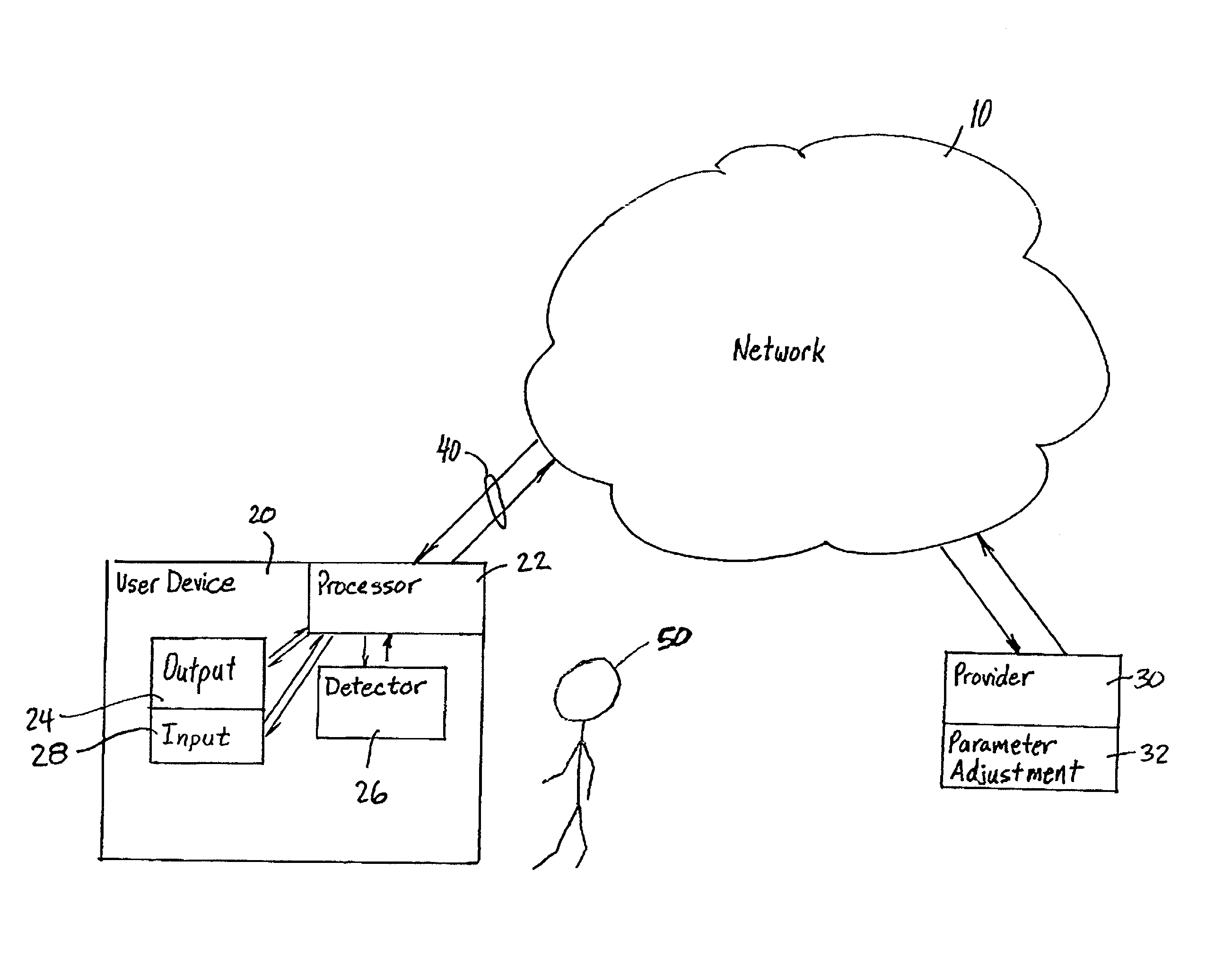
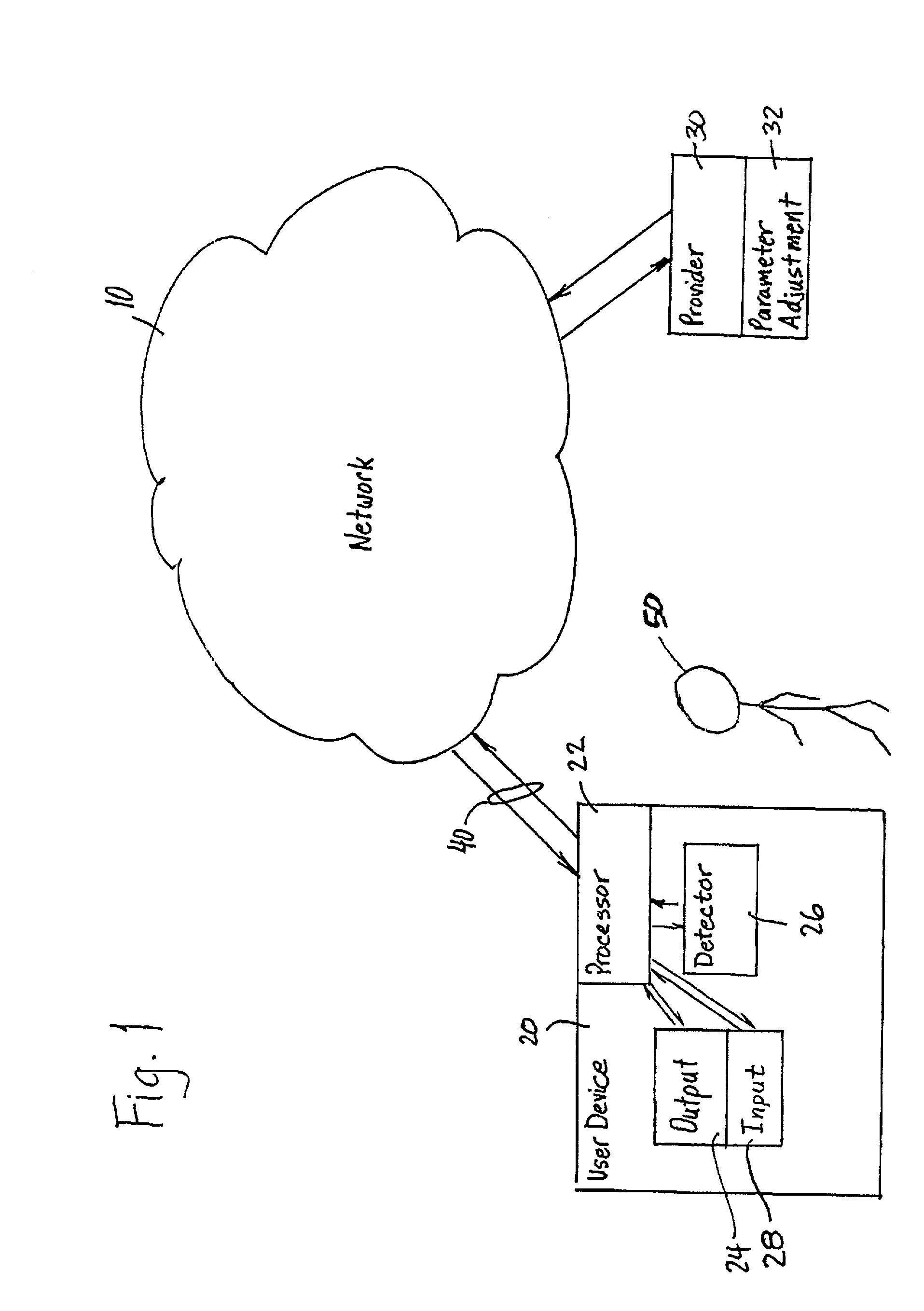
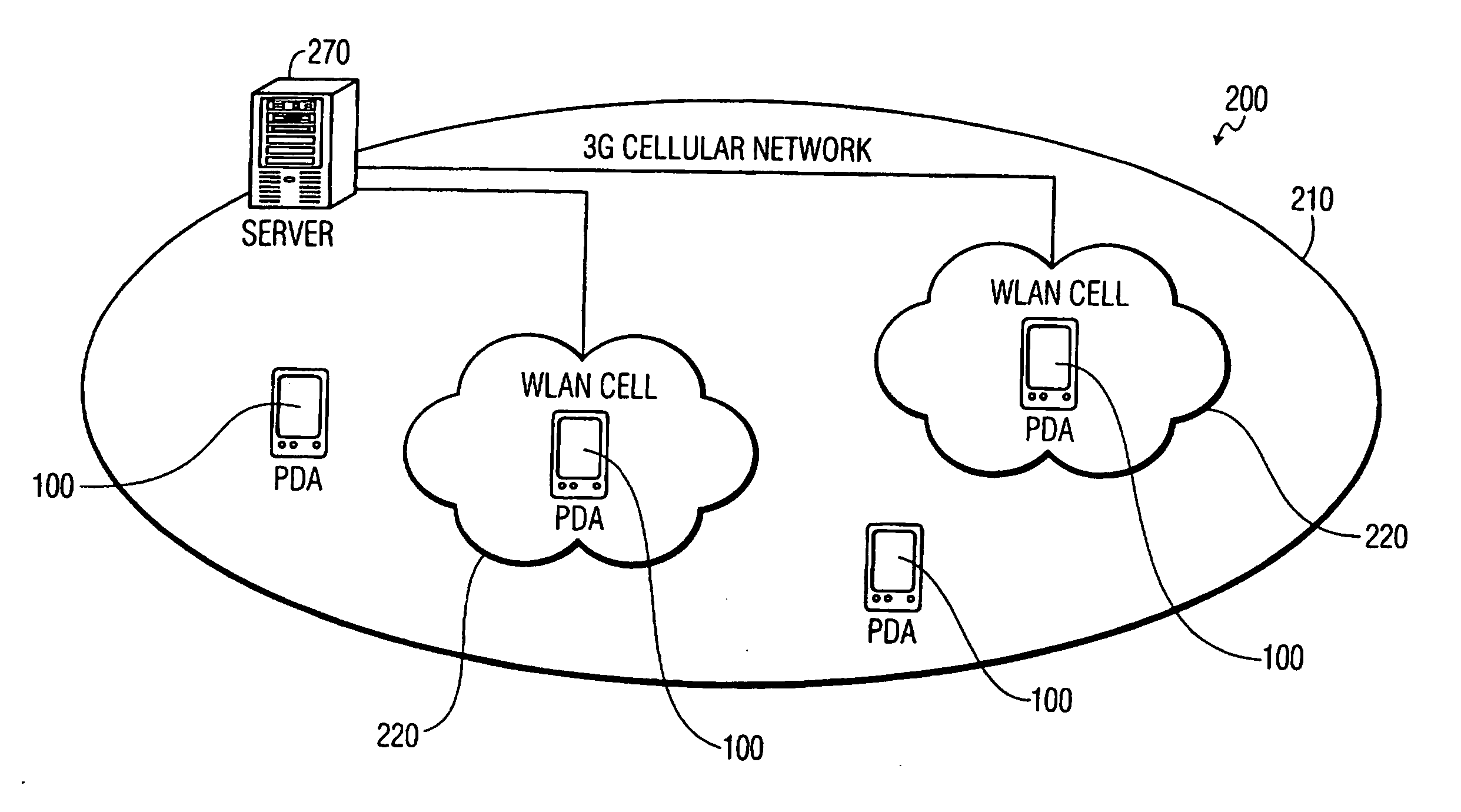
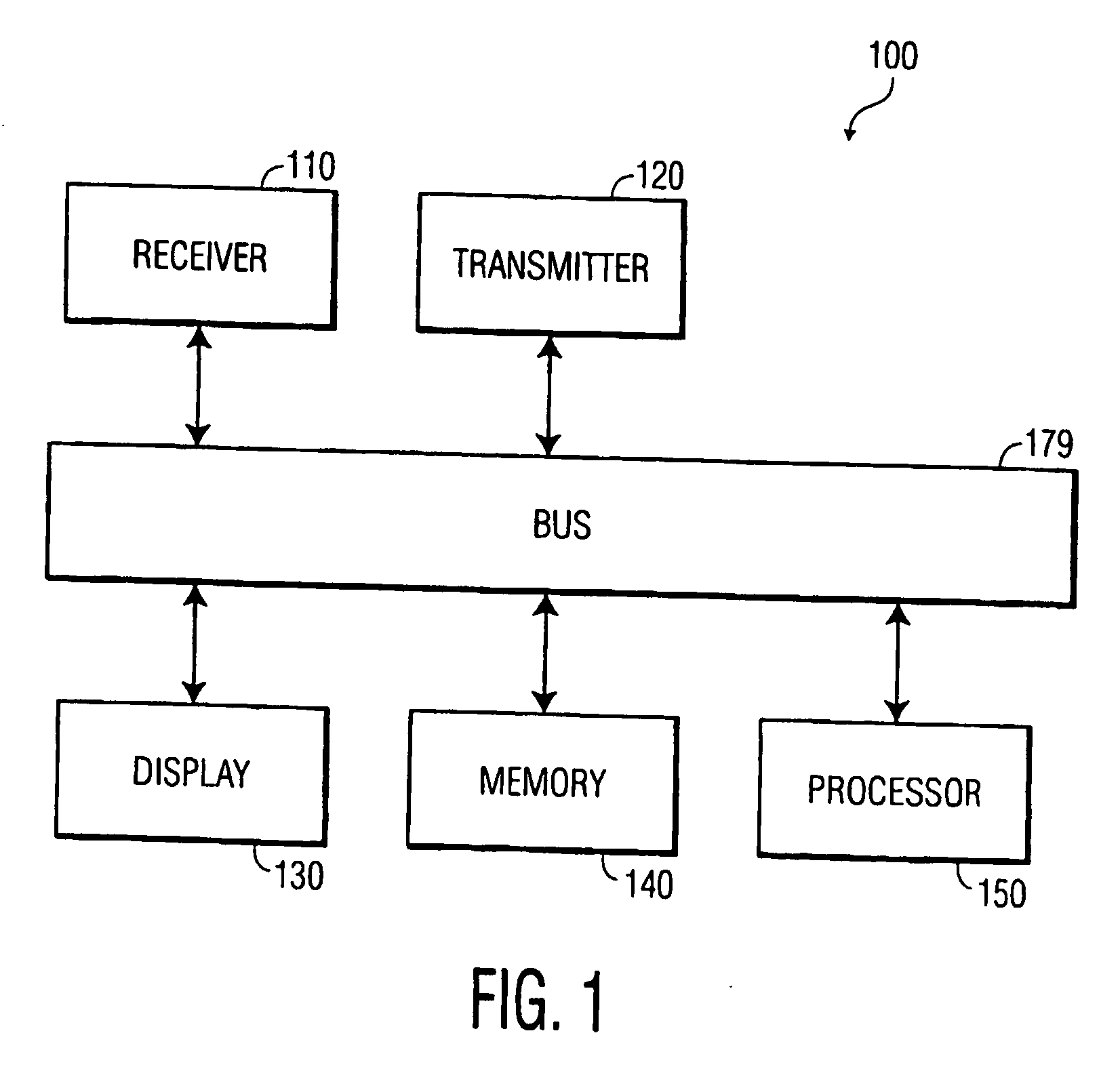
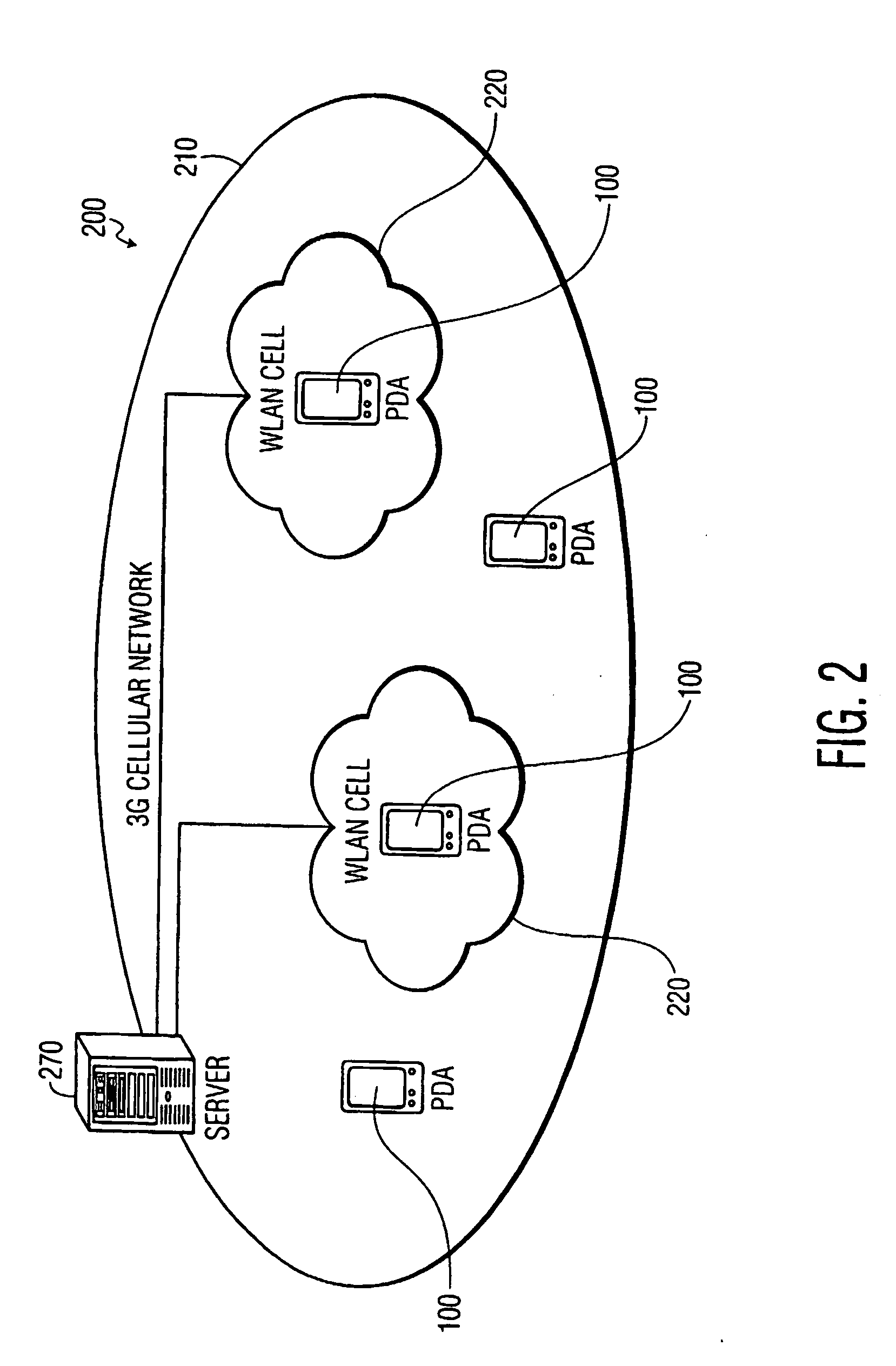
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
InactiveUS20030052911A1Reduce data transfer rateMoreData processing applicationsImage analysisUser deviceQuality level
A method for transmitting a stream of multi-media content from provider server to a user device includes transmitting multi-media content from the provider server to the user device via a communication network and outputting the multi-media content from the user device to a user via an output on the user device such that the multi-media content is delivered from the provider server to the user in real-time. A degree of attention that the user directs to the output of the user device is continuously determined during the transmission and a parameter adjusting module at the provider server adjusts a parameter of the multi-media content in response to the degree of attention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
InactiveUS7284201B2Reduce data transfer rateMoreImage analysisData processing applicationsUser deviceEngineering
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
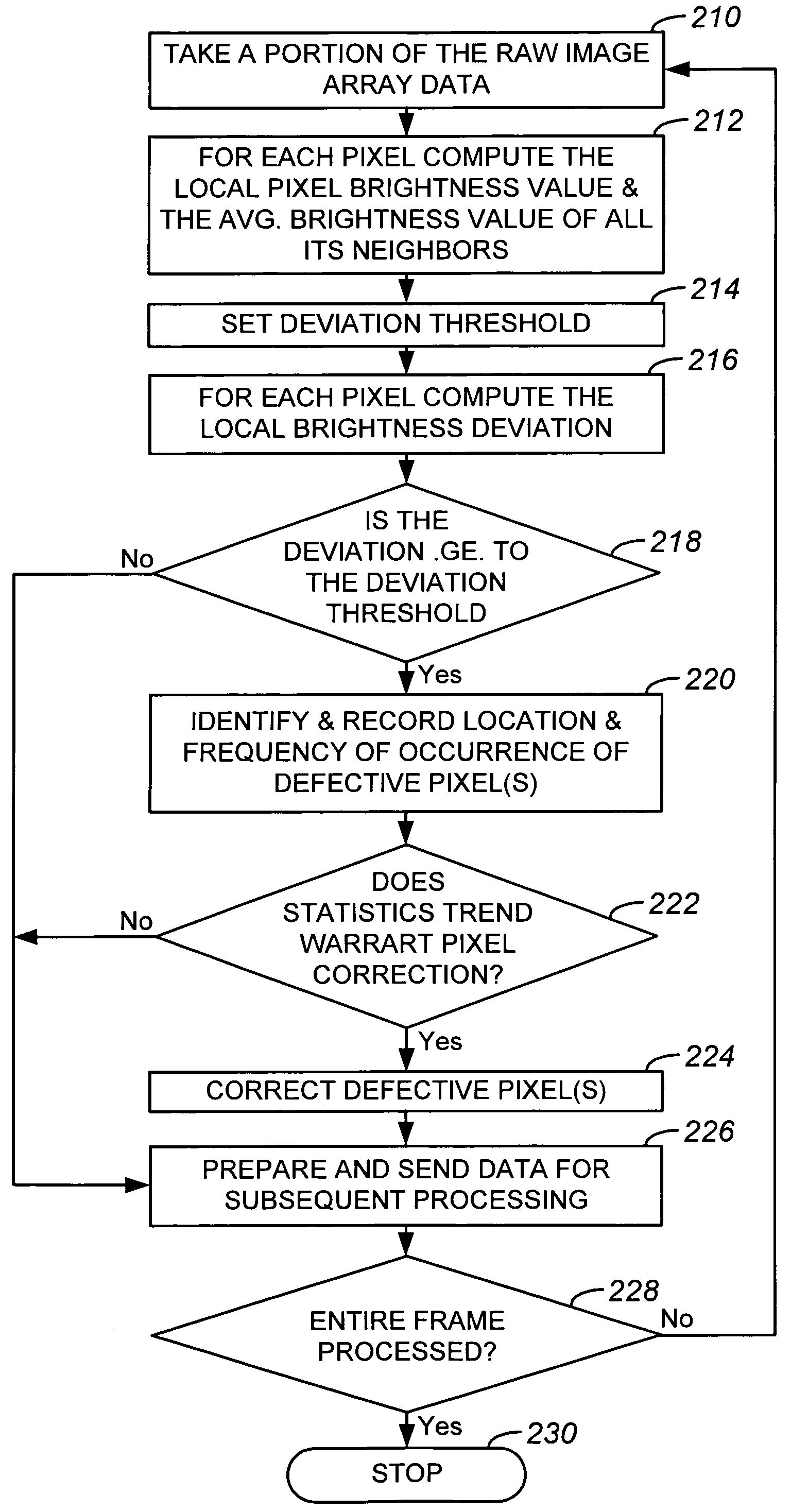
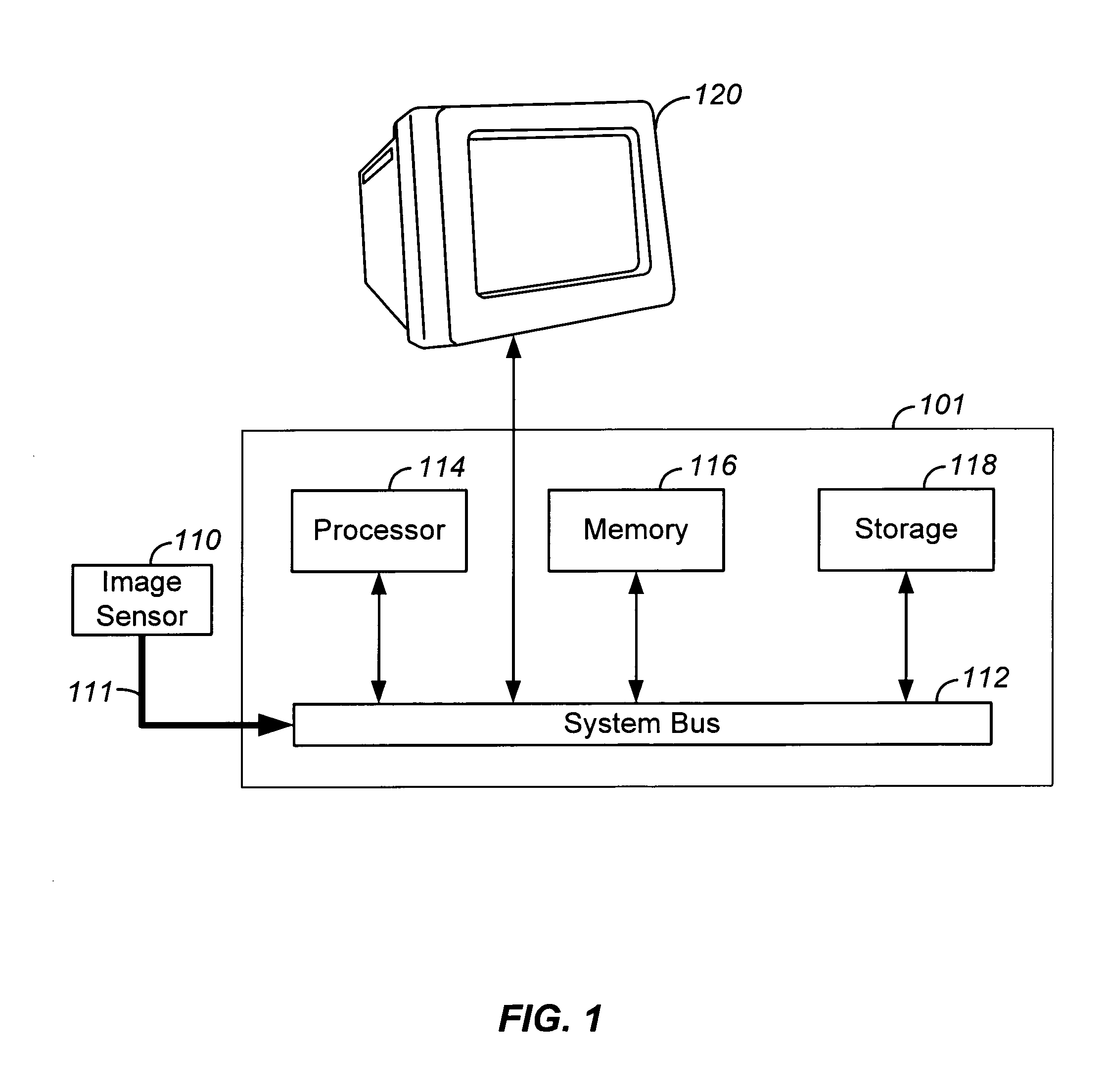
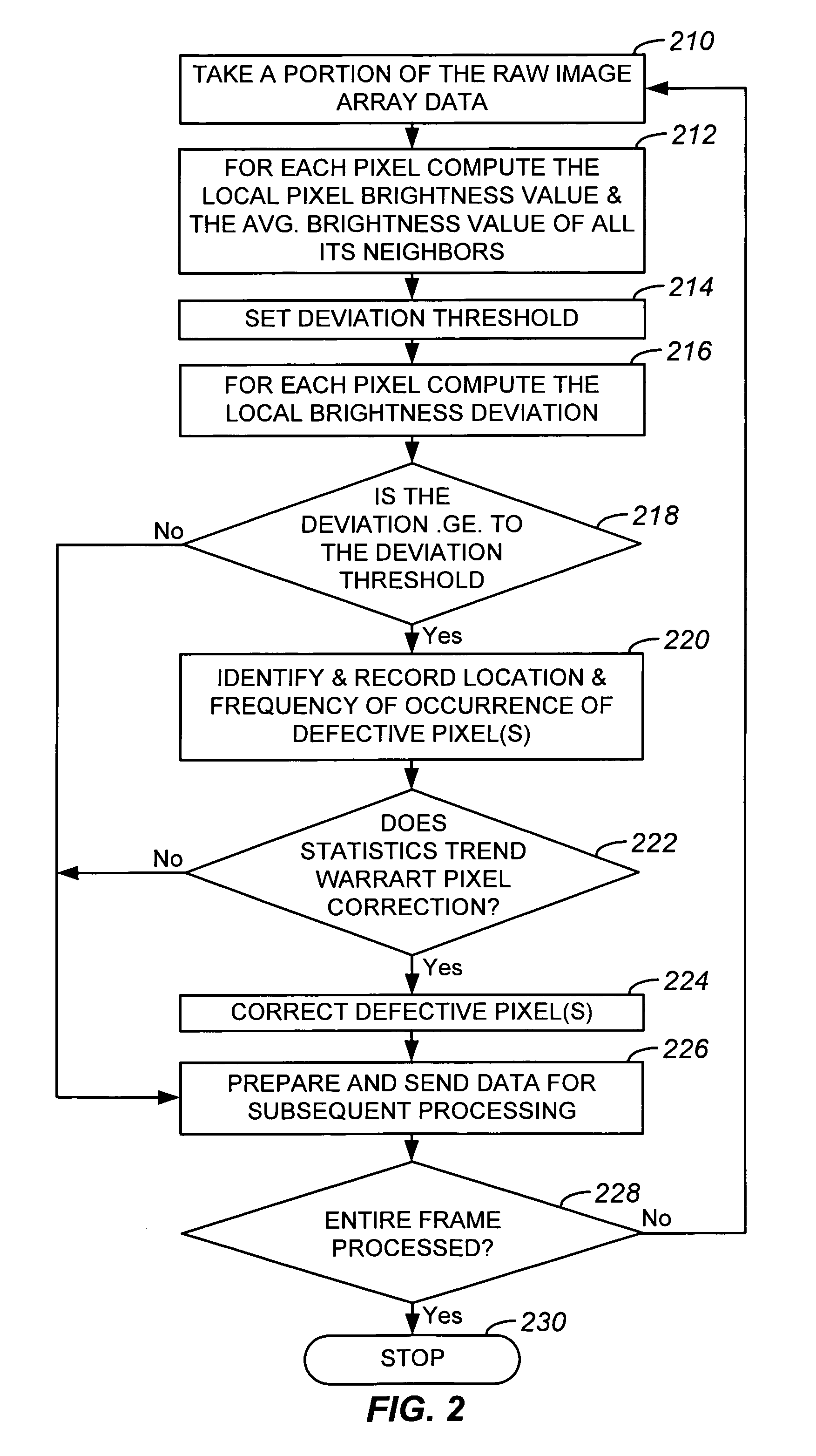
Dynamic anomalous pixel detection and correction
InactiveUS7009644B1Minimally affectedImpact rateTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionCMOS sensor
A method and a system for dynamically detecting and correcting anomalous pixels in the raw data taken from an image sensor array such as a CCD or a CMOS sensor array, thus allowing the use of dumb cameras to capture digital images for subsequent use by an intelligent host—such as being displayed on a computer monitor. This invention uses software algorithms running on an intelligent host processor to dynamically correct the anomalous pixels in the raw data taken from an image sensor array typical of those in a digital still or a video camera. Using the combination of a dumb camera which provides raw data to an intelligent host, which does all the subsequent image processing, the system works by scanning an image frame for pixels that vary more than a specified amount in their brightness value from their neighboring pixels and designating those as defective pixels. The location and frequency of the photosites sending the defective pixels are stored in a statistical database in the computer's memory. The brightness value of a defective pixel is then replaced by a local brightness value obtained from the defective pixel's neighboring pixels. The process includes video subsampling, meaning that the defective pixel detection is carried out and repeated at a pre-specified frame rate to ensure optimum detection and correction at a minimal level of scanning. A statistical database is kept so that truly anomalous pixels can over time be distinguished from false detection of true anomalies in the target image, lighting or other environmentally induced anomalies.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
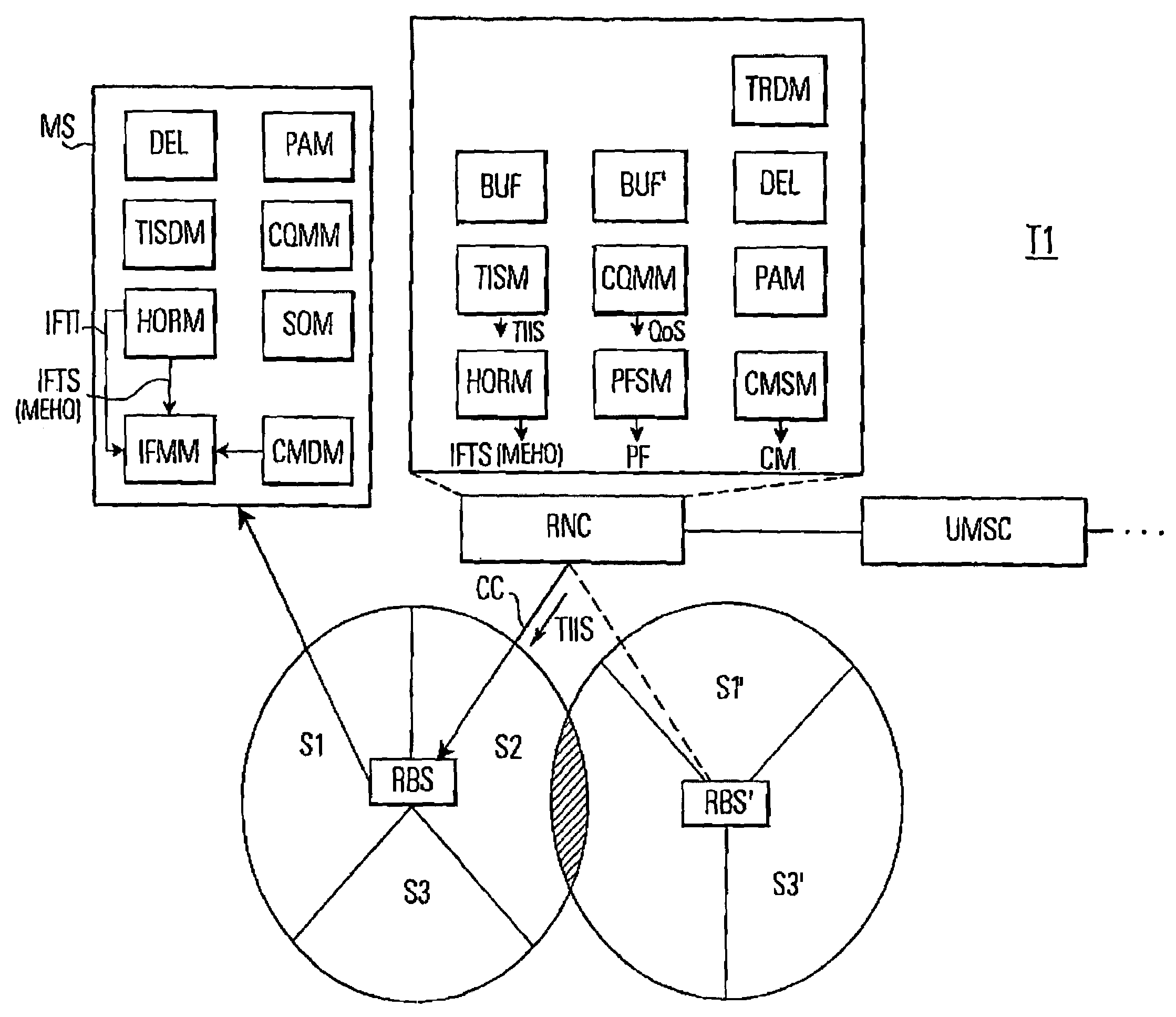
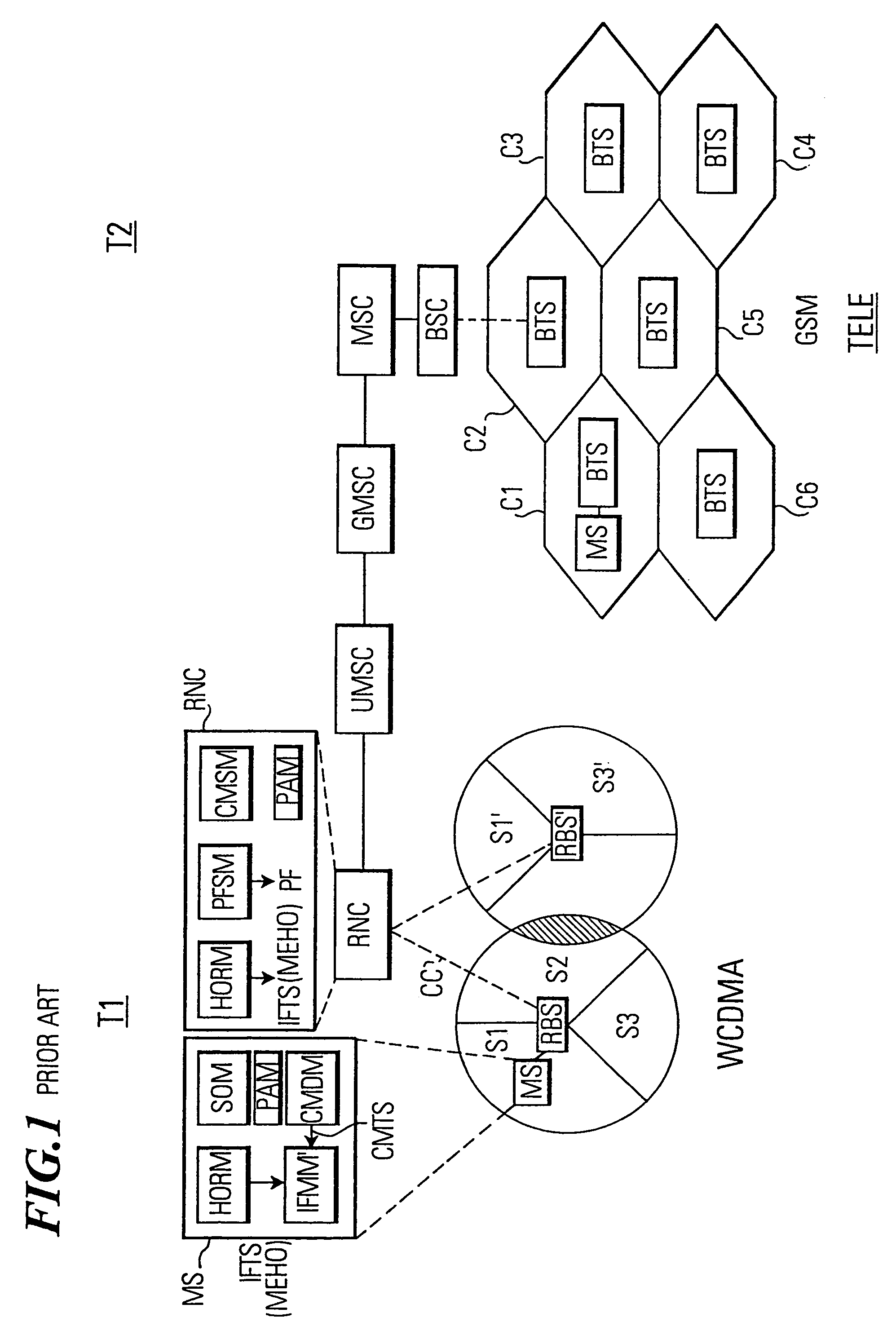
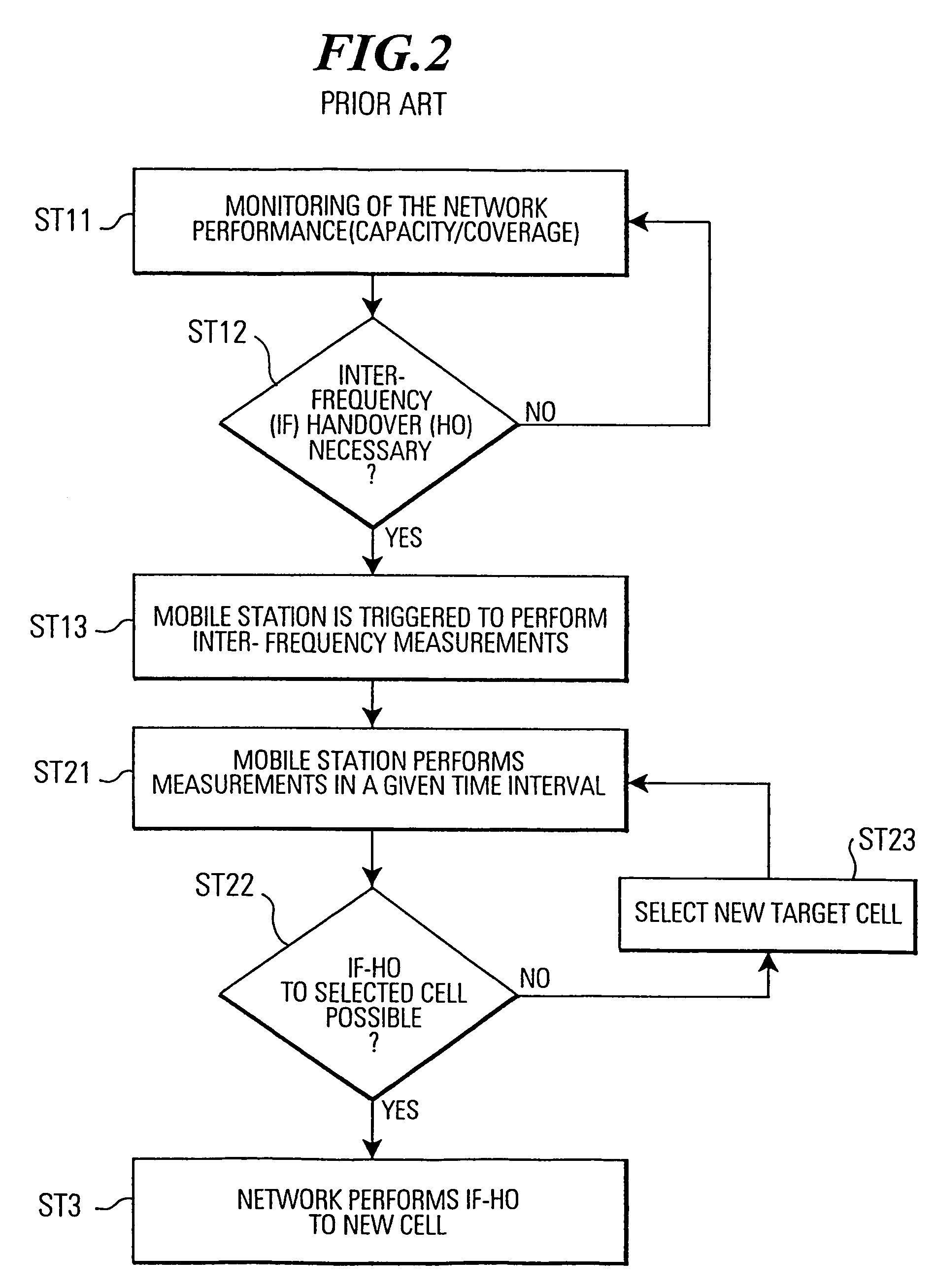
Subscriber station, network control means and method for carrying out inter-frequency measurements in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7016320B1Maintain qualityEasy to measurePower managementTransmission control/equalisingIdle timeFrequency measurements
In a mobile communication system (T1) a time interval selection means (TISM) in a network control means (RNC) determines a time interval and sends an indication about this time interval to a subscriber station (MS) in a time interval indication signal. A time interval signal determining means (TISDM) in the subscriber station (MS) detects the time interval and an IF measurement means (IFMM) carries out inter-frequency / inter-system measurements in the detected time interval specified by the network control means (RNC). In this time interval the temporary reduction of the quality of service QoS on the communication connection (CC) is planed by the network control means (RNC). However, independent as to whether a delay-sensitive or loss-sensitive data transmission is carried out, the network control means (RNC) can make provisions in order to compensate the temporary reduction of the quality of service. Such procedure is superior to performing IF measurements in an idle time interval of a compressed time slot in which a temporary degradation of the quality of service must always be accepted due to a compressed mode of operation.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
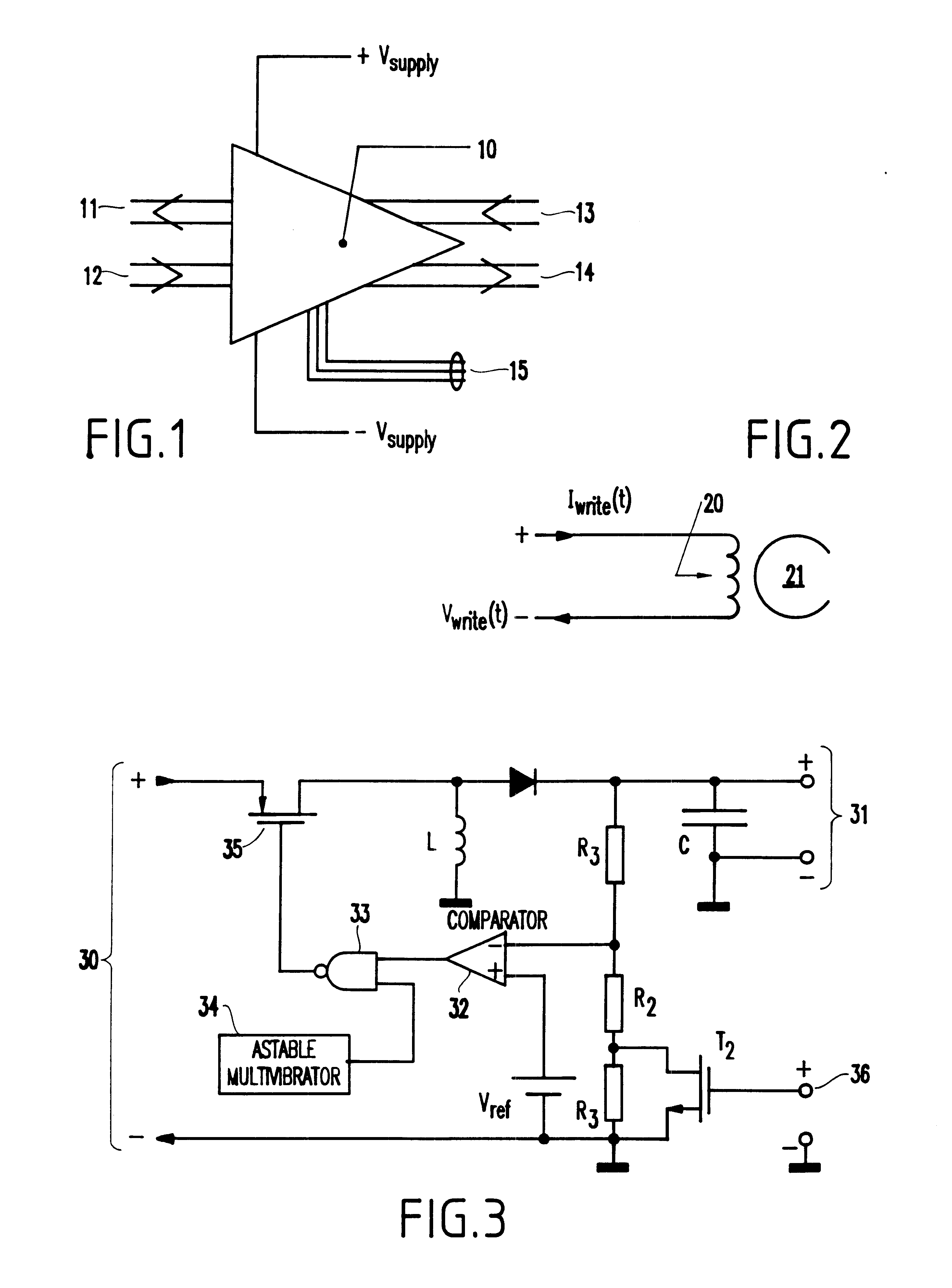
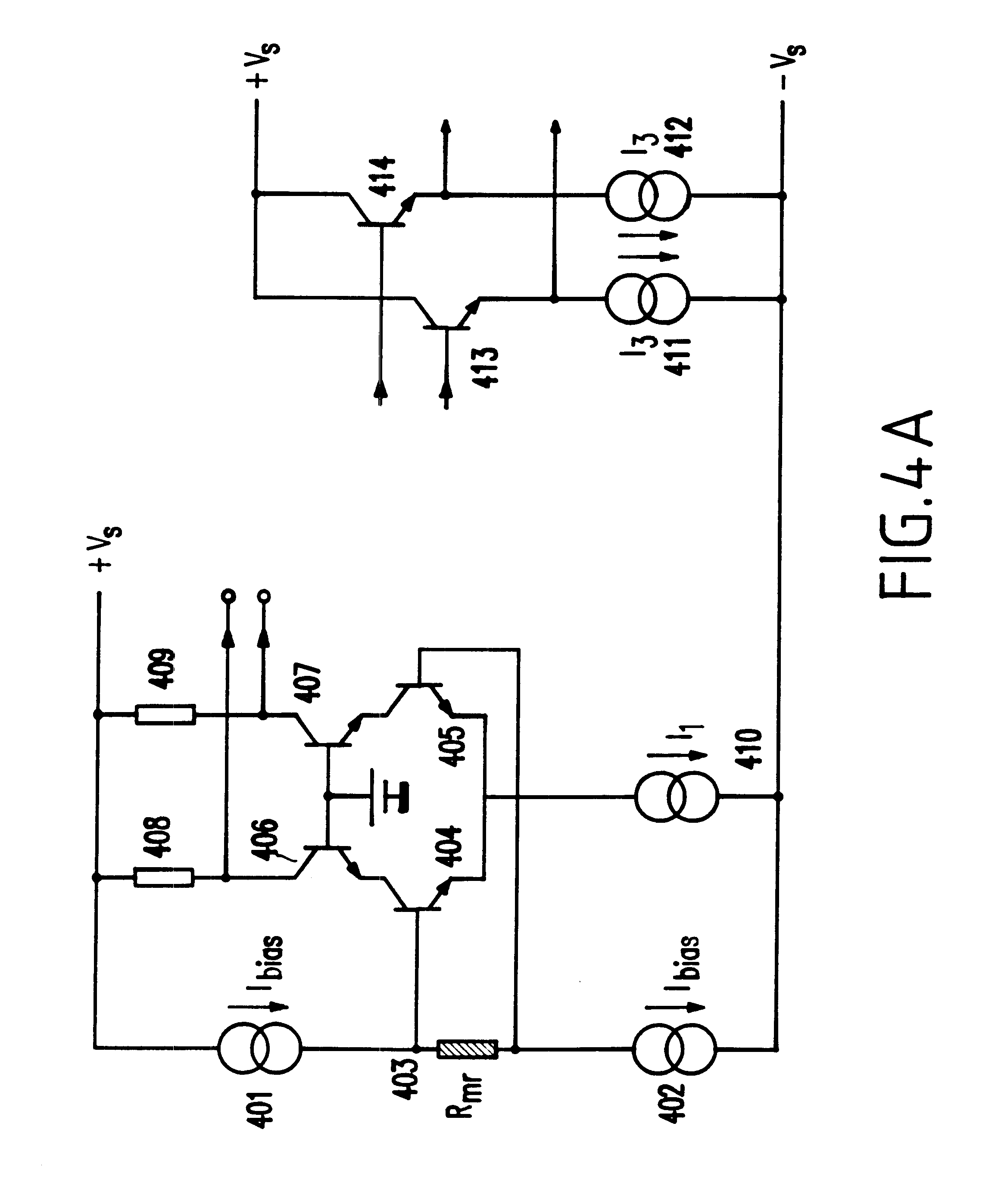
Data storage device having selectable performance modes for use in dual powered portable devices
InactiveUS6622252B1Reduce rateShorten speedEnergy efficient ICTFilamentary/web record carriersAudio power amplifierElectrical battery
A portable computer includes a battery and a connection to an external power source, a two-speed data storage device being supplied power from one or more of the battery and the external power source, and a controller attached to the storage device. With the invention, when the storage device is powered by the internal battery, the controller not only reduces the rotation speed and the clock rate of the storage device, but also reduces the power consumption of the read / write electronics module inside the disk drive by lowering the power supply voltage for the write driver inside said module and lowering the tail currents for the amplifier stages in the readback amplifier inside said module. When the storage device is powered by an external power source, the controller will run the storage device at full speed and highest clock rate, and will provide the write driver inside the read / write electronics module with a power supply voltage high enough to accommodate the resulting higher data rate, and will provide tail currents in the amplifier stages of the readback amplifier high enough to accommodate the higher required bandwidth for the readback amplifier.
Owner:IBM CORP
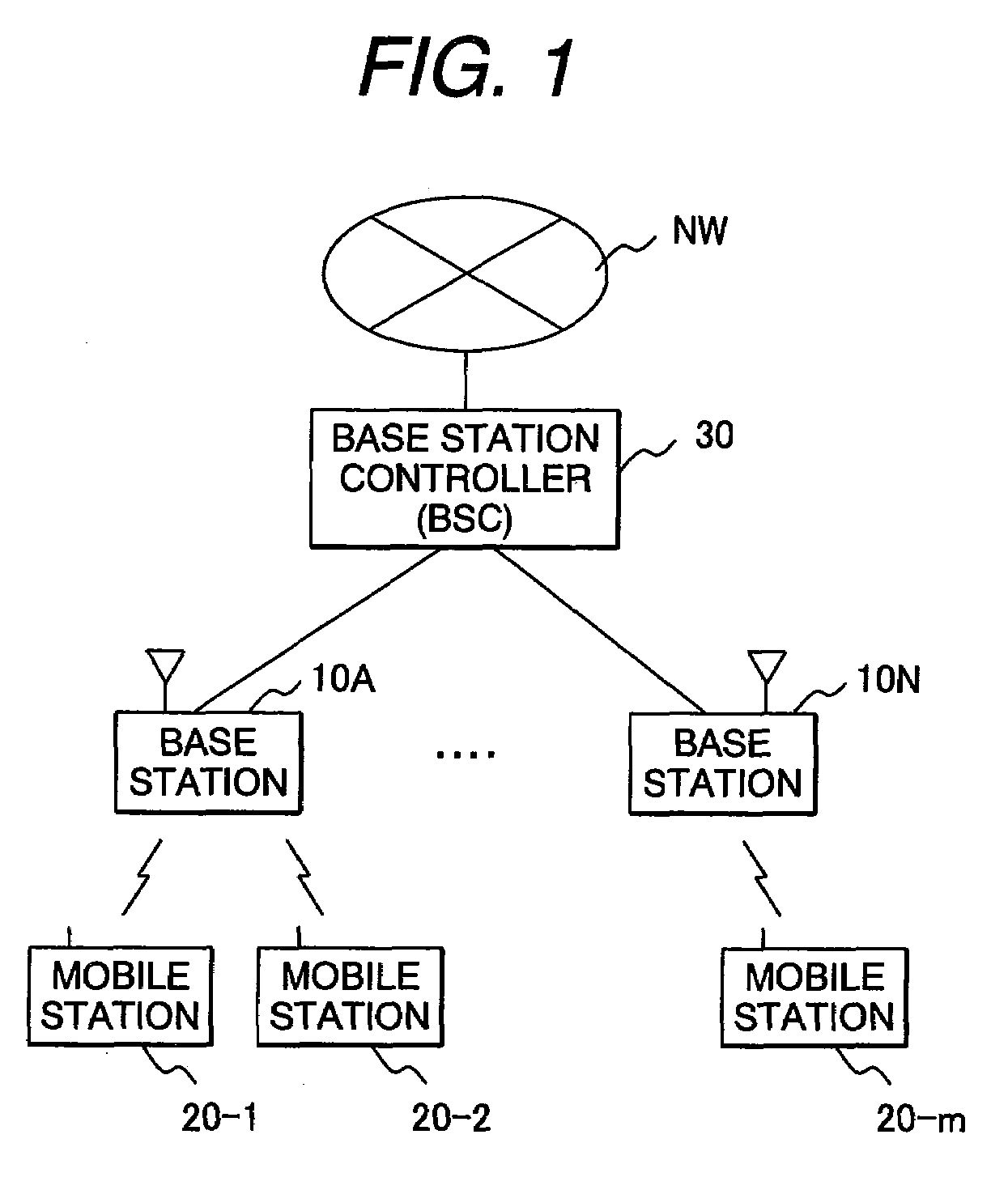
High-speed data transmission in a digital mobile communication system
InactiveUS6148209AReduce data transfer rateLow data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile communication systemsMobile station
A data transmission in a digital mobile communication system employing a so-called multi-channel access technique, in which one or more traffic channels may be allocated to a mobile station for data transmission in accordance with the data transfer rate required by the application using the mobile station. Upon establishing a data call, the mobile station indicates to the mobile communication network the maximum and optionally the minimum requirements for the user data transfer rate. The mobile communication network assigns the mobile station for a data call a channel configuration consisting of one or more traffic channels in connection with call set-up or handover, the channel configuration depending on the resources currently available in the mobile communication network and enabling performance of the data channel, which is not lower than the minimum requirement and not higher than the maximum requirement.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
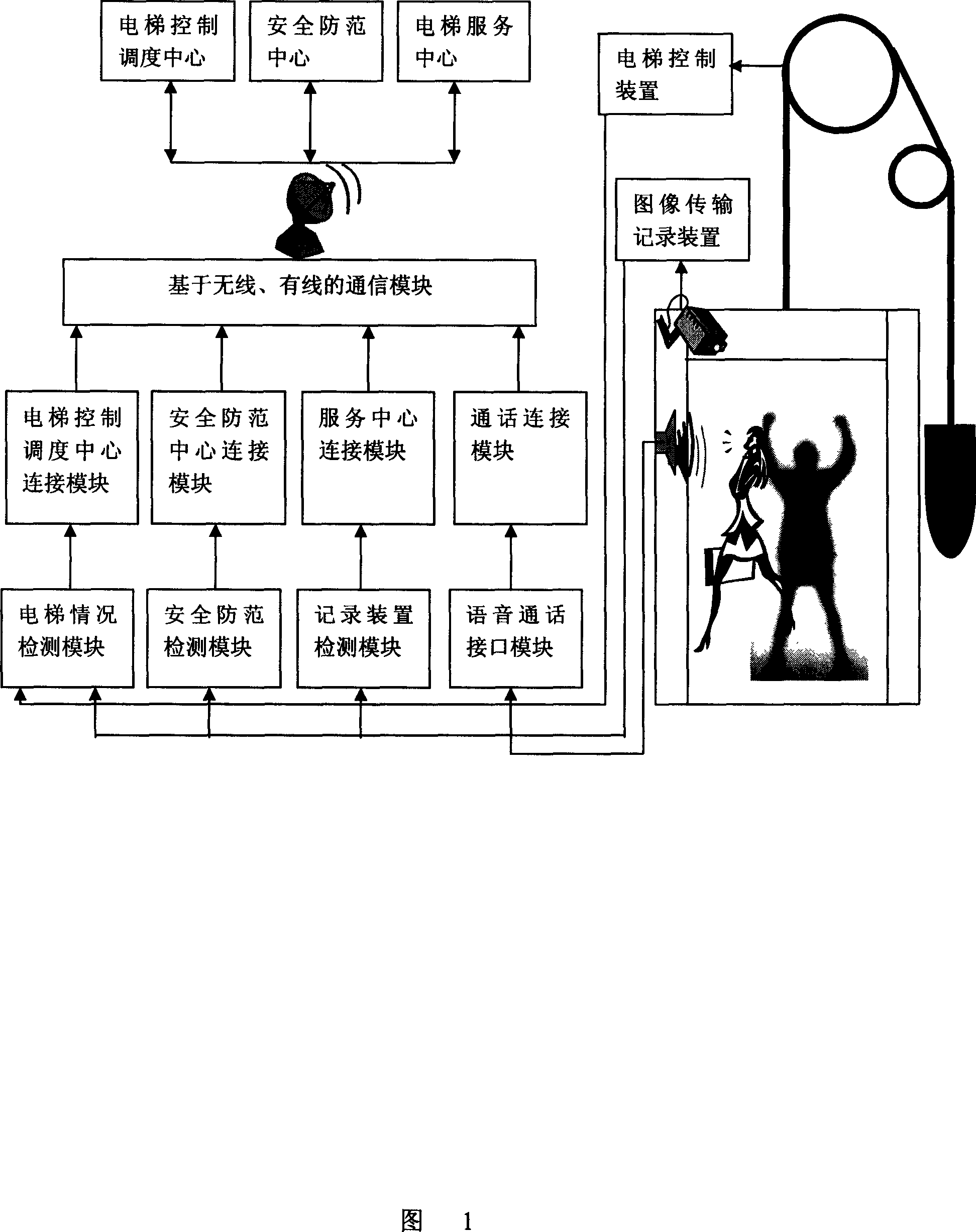
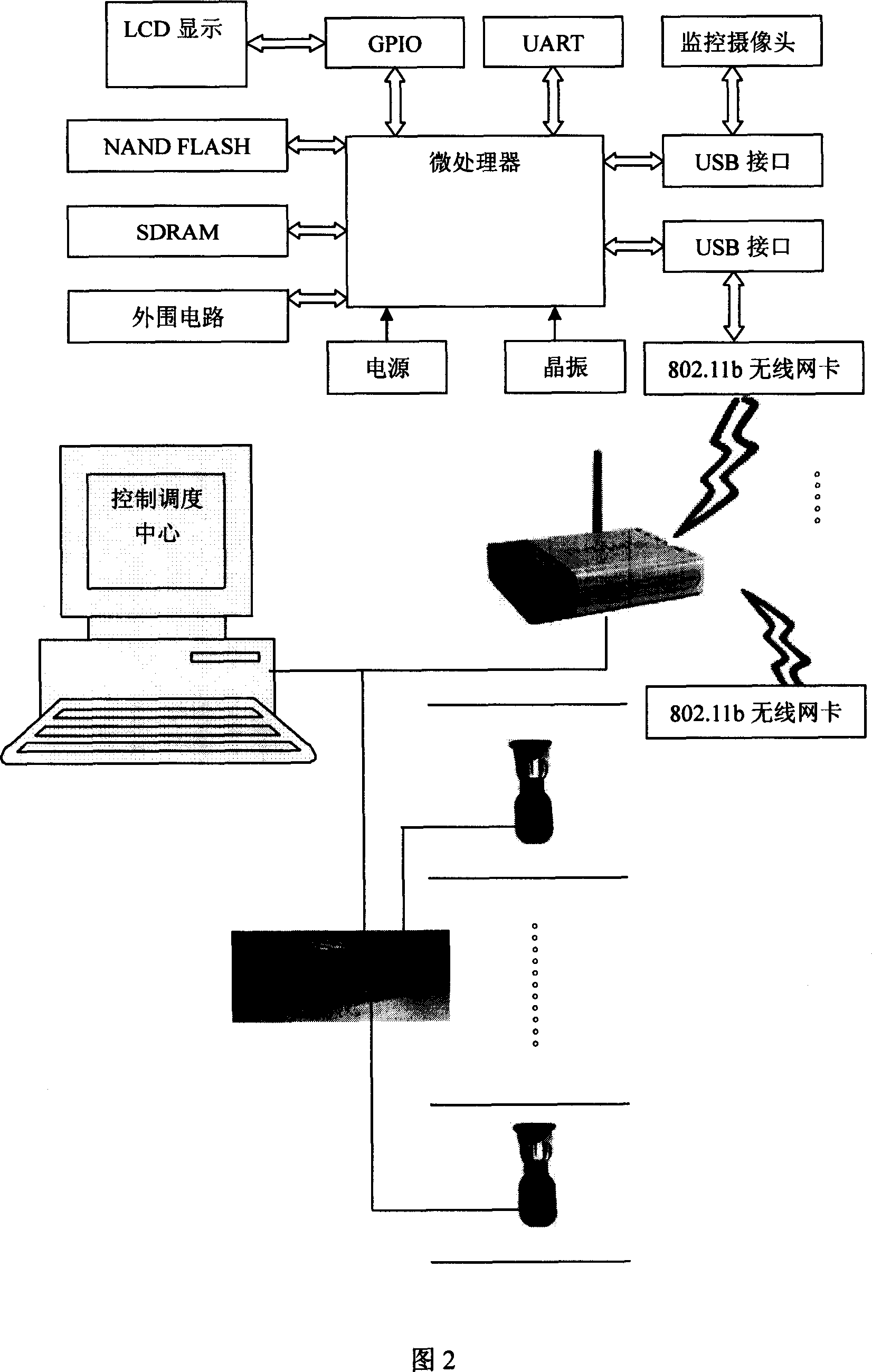
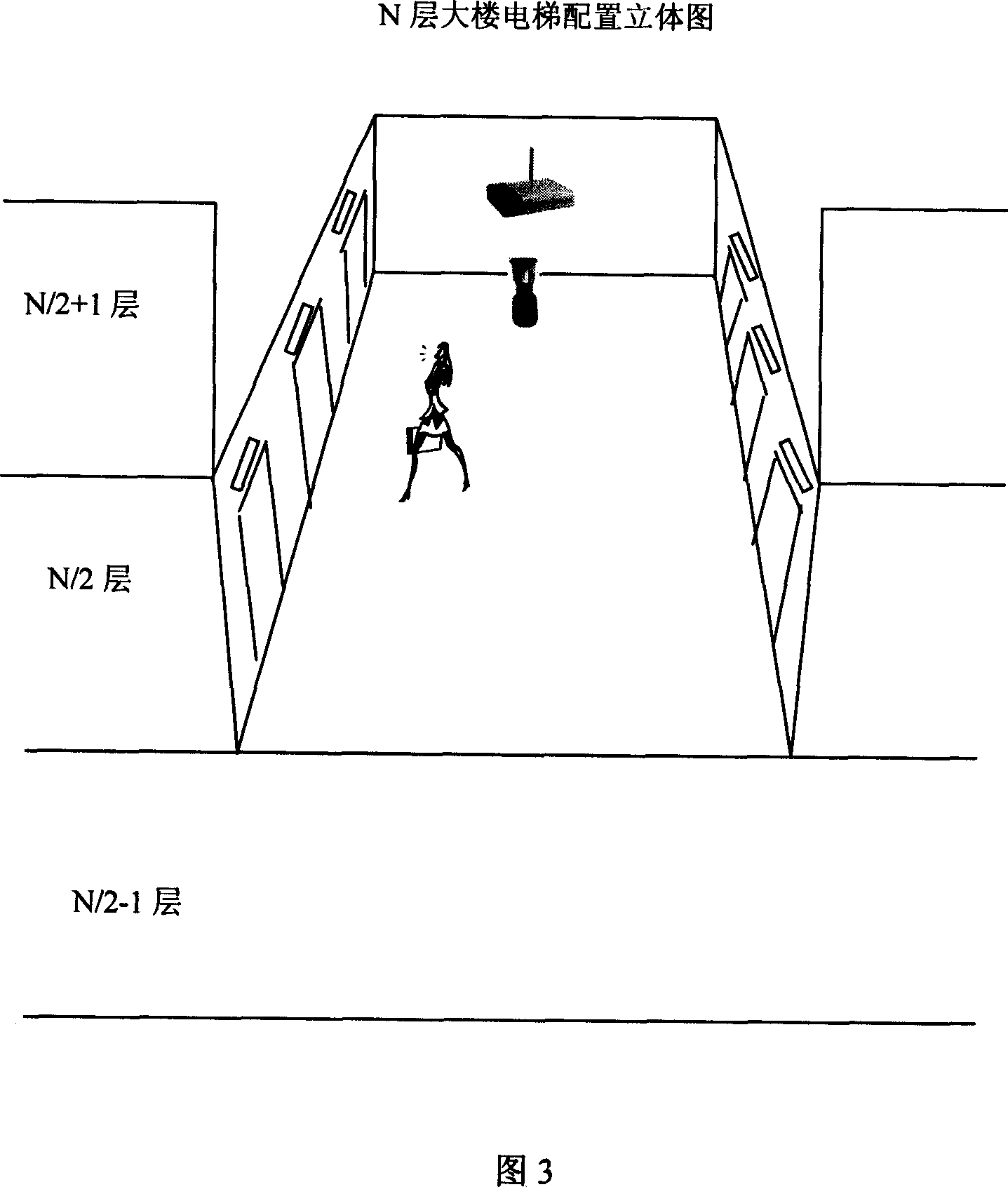
Elevator safety apparatus based on image recognition technique
The invention discloses an elevator safeguard device based on image recognizing technology, which comprises the following parts: video sensor on the top of elevator wagon, monitor center computer, display mode to connect display device, wherein the video sensor connects wireless data of monitor center computer through wireless network exchanging equipment, which is the center of LAN in the building, the monitor computer contains safeguard microprocessor, which analyzes trapped person in the elevator through video information and detects accident of elevator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
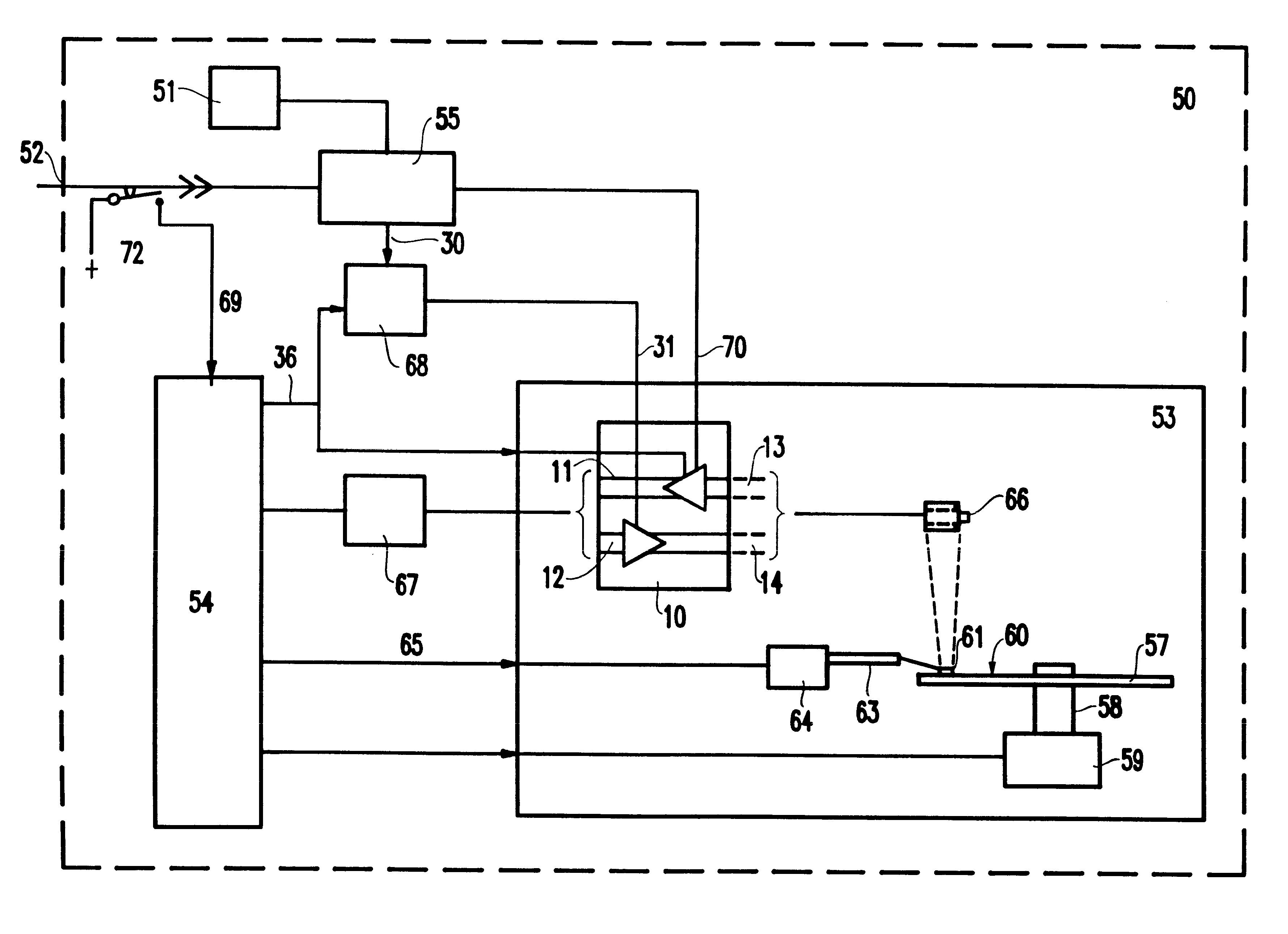
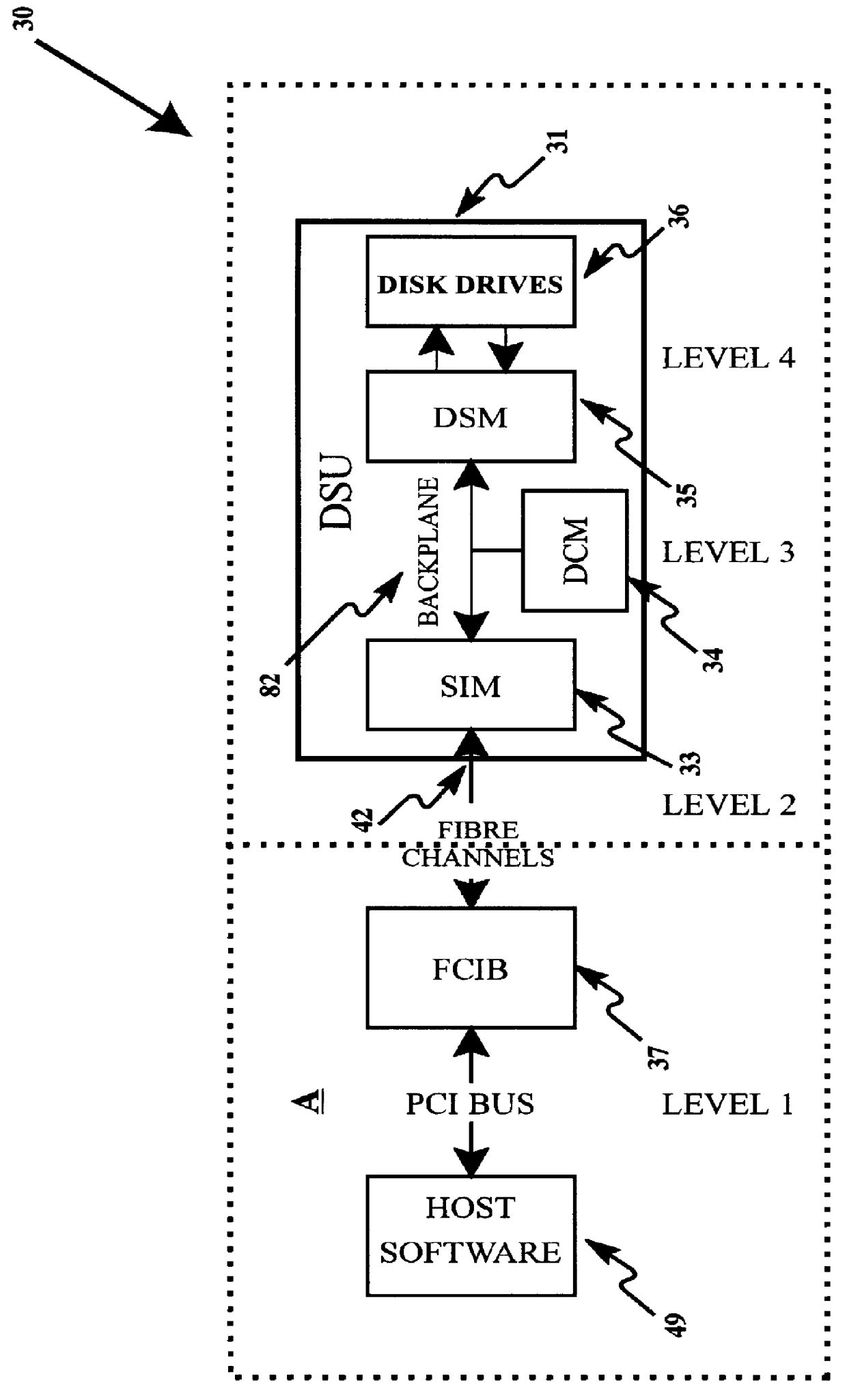
Modular disk memory apparatus with high transfer rate
InactiveUS6112276AIncrease chanceLarge capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsFiberHard disc drive
A modular disk memory apparatus provides a modularly expandable, multi-gigabyte auxiliary memory for a computer or other host electronic device, and includes multiple, parallel serial data channels to maximize bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and the host device. Maximization of READ / WRITE data transfer rates within the apparatus is achieved by utilizing a large number of small hard disk drives, typically eight 2.5-inch drives on each of a plurality of Disk Storage Modules, each including a plug-in printed circuit board capable of holding two 5-+E,fra 1 / 4+EE inch drives, thereby increasing the maximum data transfer rate per unit volume of the modules by a factor of two. Maximization of bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and host device over that attainable using a single serial data channel such as a coaxial, quadaxial or fiber optic cable, is achieved by parsing or demultiplexing data to be transmitted from a single parallel channel onto p paralleled cables, thereby increasing the maximum transmittal rate by p. Data received over the parallel data channels is multiplexed or concatenated to comprise a data stream on a single parallel channel. Reconstruction data is embedded in data contained in the p parallel data channels specifying the number q of channels employed, where 1< / =q< / =p thereby configuring the demultiplexer to concatenate that number of data channels onto a single parallel data bus.
Owner:SIGNATEC
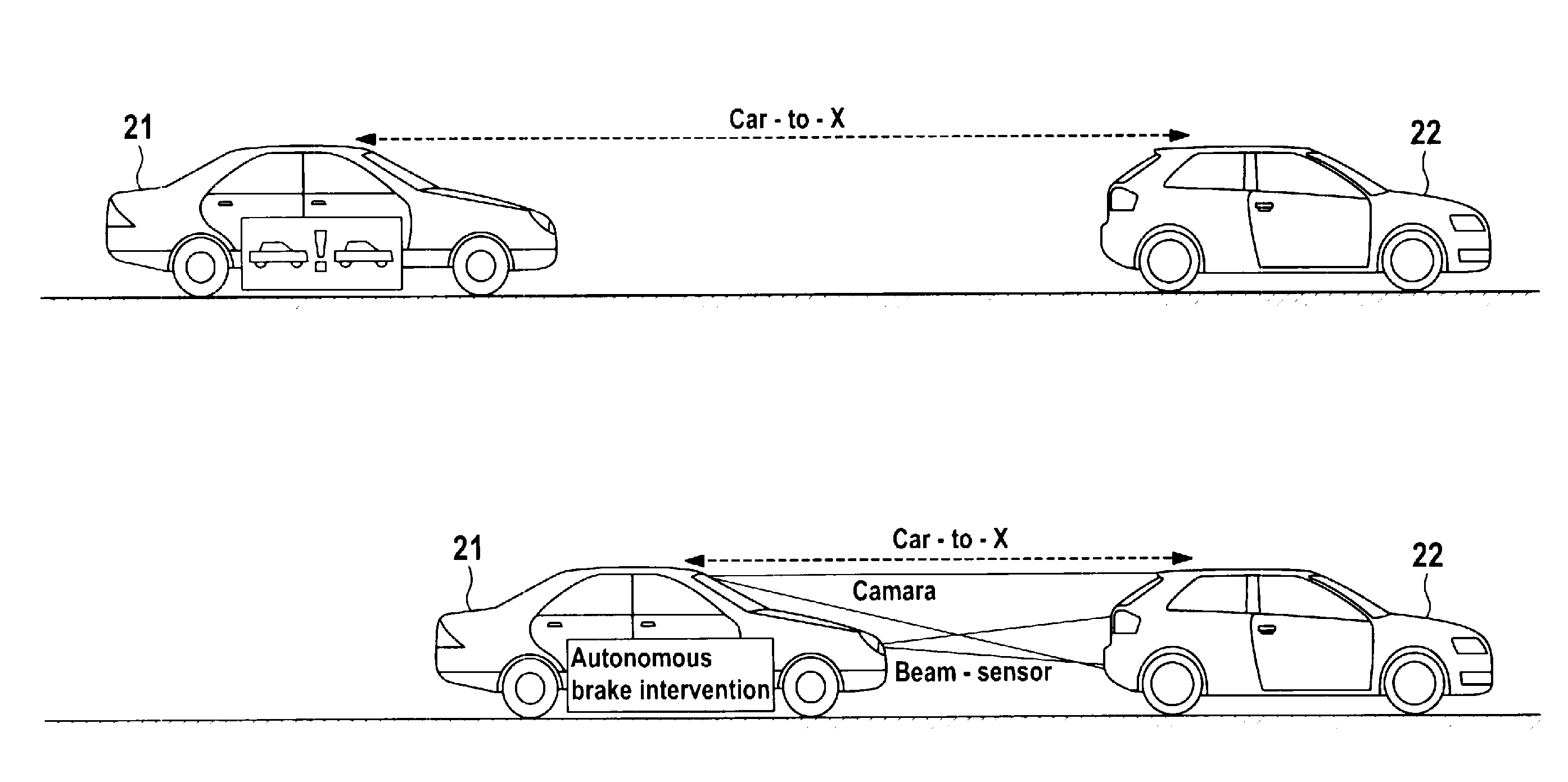
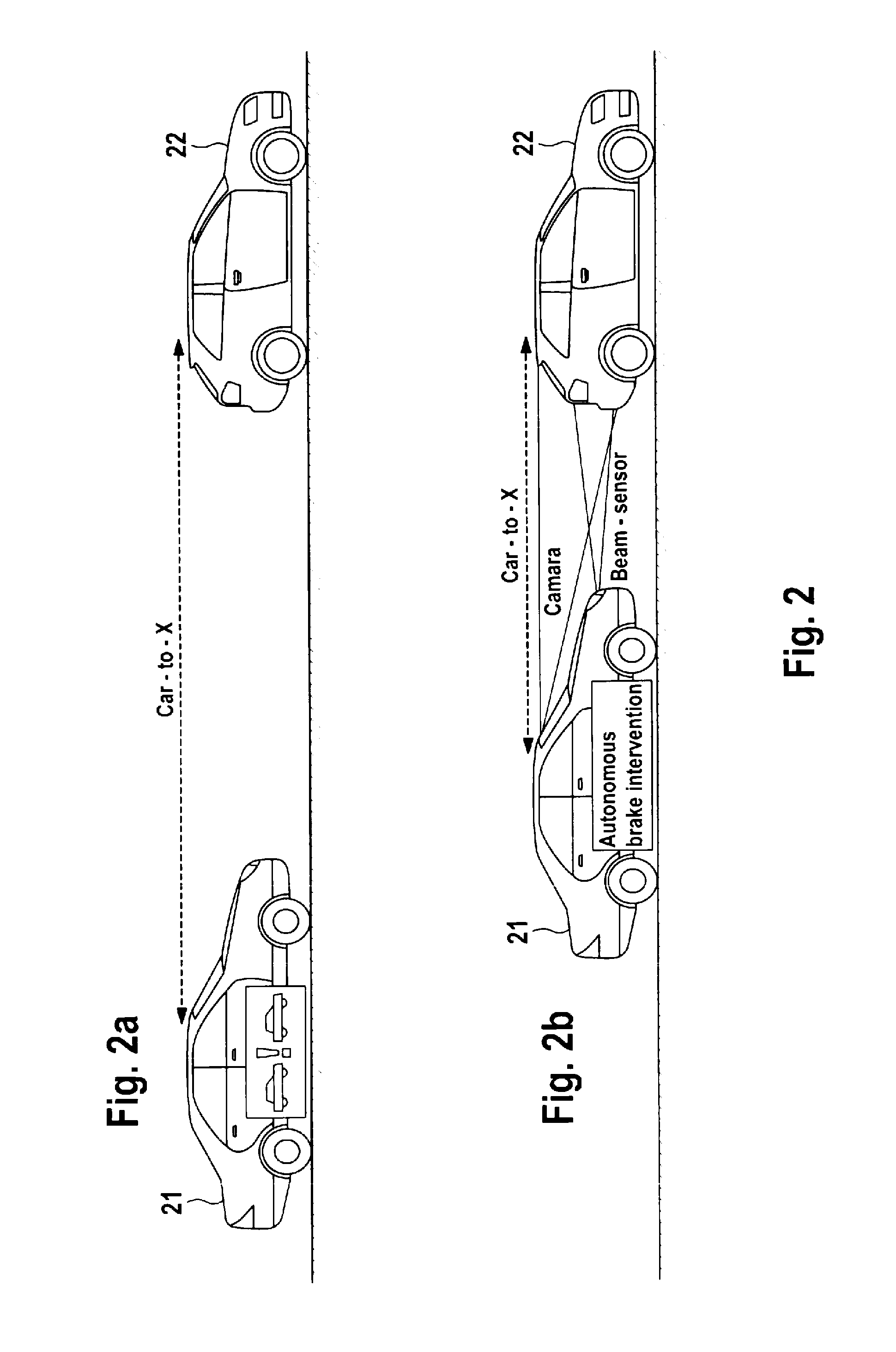
Method and System for Accelerated Object Recognition and/or Accelerated Object Attribute Recognition and Use of Said Method
ActiveUS20130158852A1Quick checkImprove reliabilityVehicle testingAnti-collision systemsCommunication deviceObject detection
A method for accelerated object detection or for accelerated object attribute detection, wherein a first information item is acquired by a vehicle-to-X communication device, and describes at least one object or at least one object attribute in an evaluated data form. A second information item is acquired by at least one individual sensor or by a sensor group, and describes the at least one object or the at least one object attribute in sensor raw data form, and an object detection algorithm and / or an object attribute detection algorithm is applied to sensor raw data of the second information item. The method is defined in that a threshold value of the object detection algorithm or of the object attribute detection algorithm for detecting the at least one object or at least one object attribute described by the first information item is reduced in the sensor raw data of the second information item.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
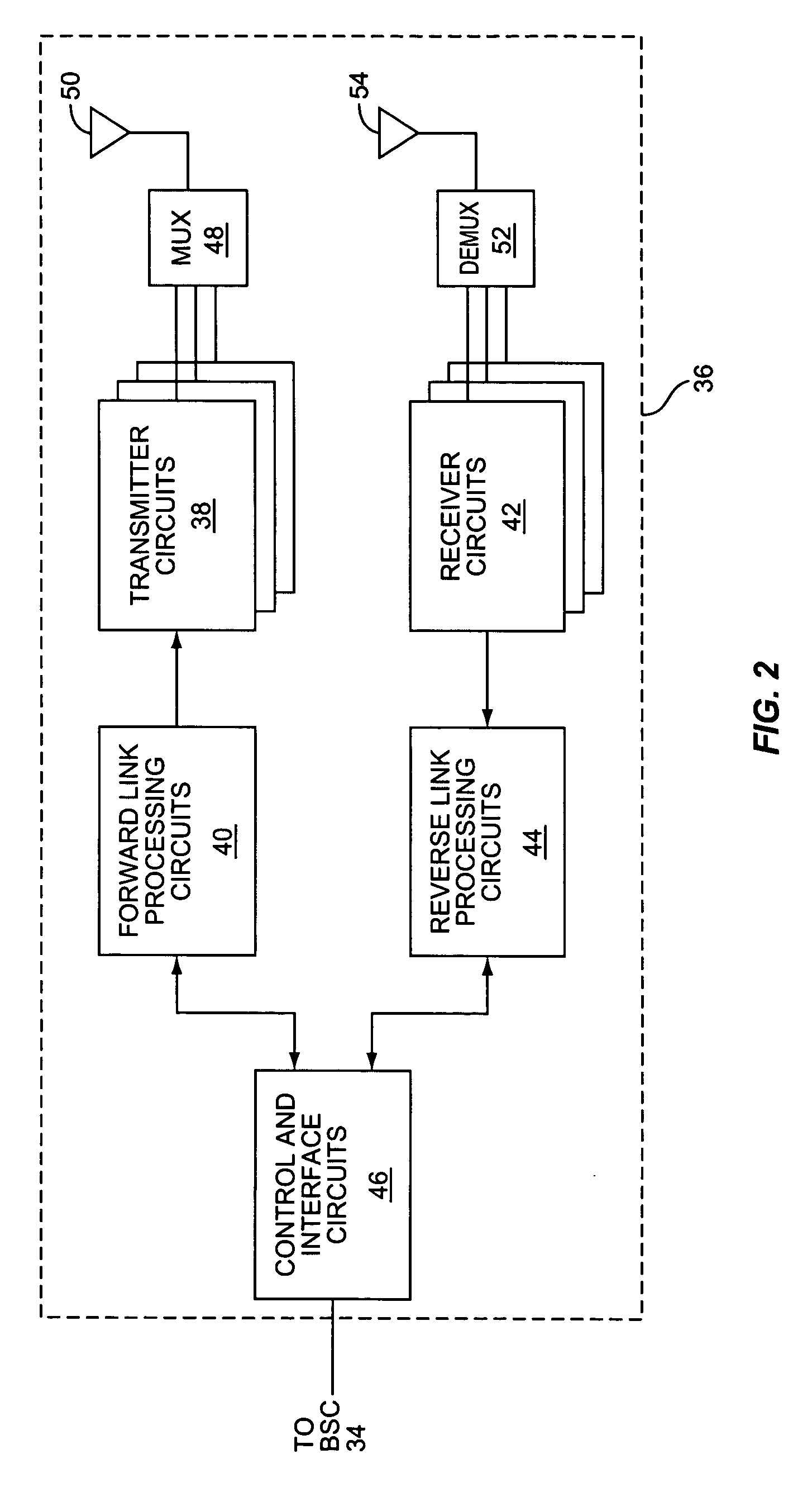
Forward and reverse link channels dynamic processing gain
InactiveUS7058400B2Increase probabilityDetrimental to environmentEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementDouble data rateTransmitted power
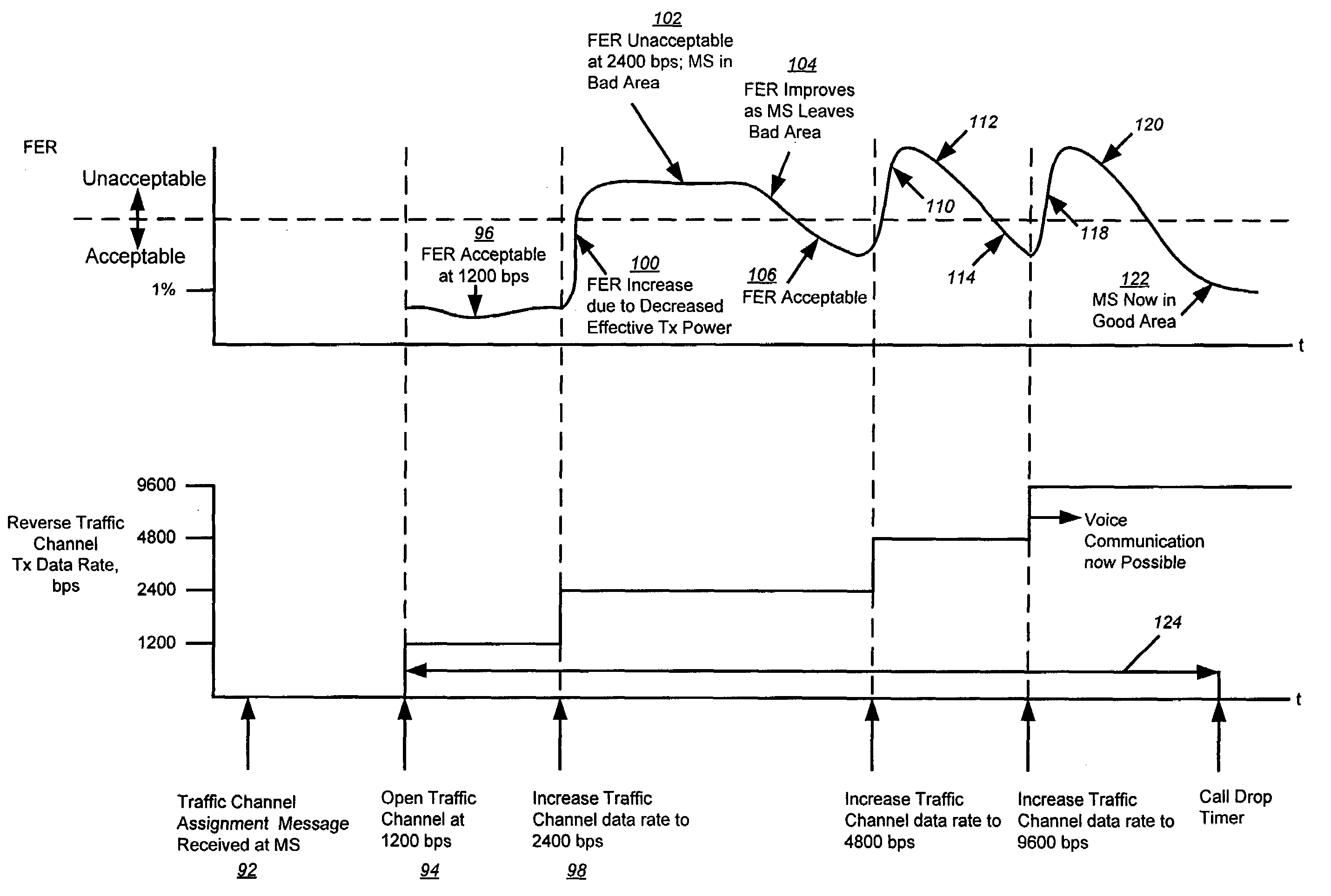
A method and apparatus for dynamically controlling forward and reverse link channel processing gain to minimize dropped connections and improve the reliability of hard handoffs is disclosed. The transmission bit stream of a forward or reverse link channel is allowed to become dynamic under controlled conditions in such a way as to take advantage of the inherit strengths that the concept of processing gain provides and thereby improve the probability of establishing and maintaining a forward or reverse link traffic channel. Dropped connections due to reverse link fades and dropped connections during call origination are minimized by allowing a MS to transmit reverse traffic channel data using dynamically adjustable data rates to increase the processing gain and the effective transmit power level. In addition, dropped connections during hard handoffs are minimized by using a special code channel and dynamically adjustable data rates to evaluate the proposed new link.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Base station and mobile station for ofdma cellular system
InactiveUS20090232236A1Reduce signal interferenceImprove robustnessPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCellular radioCommunications system
In a cellular radio communication system, a base station or a mobile station has a TA (Time Alignment)-range-out detection function, so that when a TA-range-out state that is unable to compensate with a guard interval is detected, the transmission condition of an uplink signal at the mobile station is changed by the mobile station autonomously or by the base station and the mobile station cooperatively.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for controlling a plurality of transmitters
ActiveUS20070135130A1Avoiding packet transmission collisionReduce data transfer rateRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionMobile communication networkPacket transmission
Mobile station transmits a scheduling request message to base station to request a grant for transmitting packets in a cellular mobile communication network. Base station transmits at least a deactivation scheduling grant message to mobile station to deactivate packet transmission of mobile station. Mobile station fails to receive the first grant message but successfully receives the second grant message. Upon receiving a scheduling grant confirmation message responding the second grant message from mobile station, base station transmits an activation scheduling grant message to mobile station.
Owner:NEC CORP
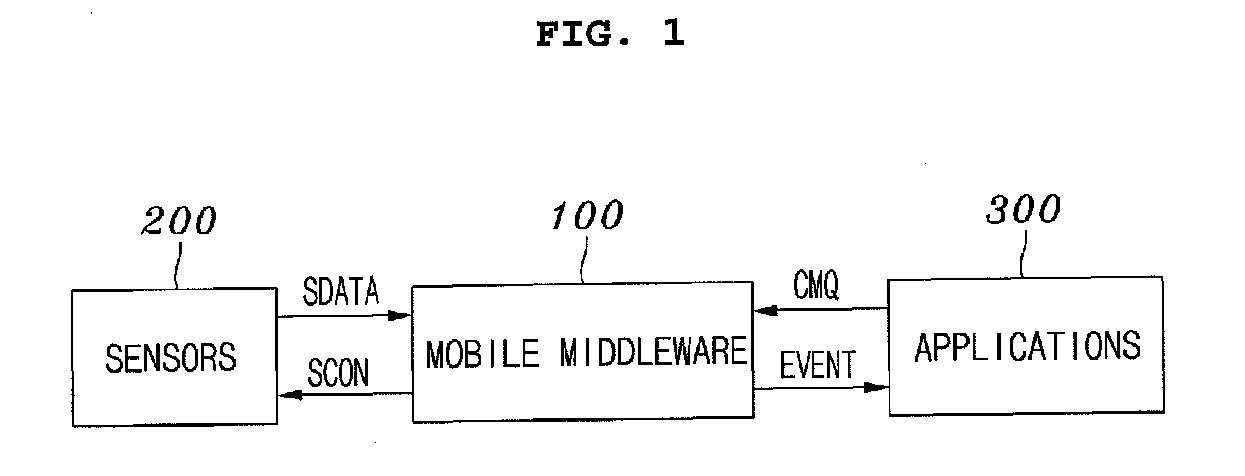
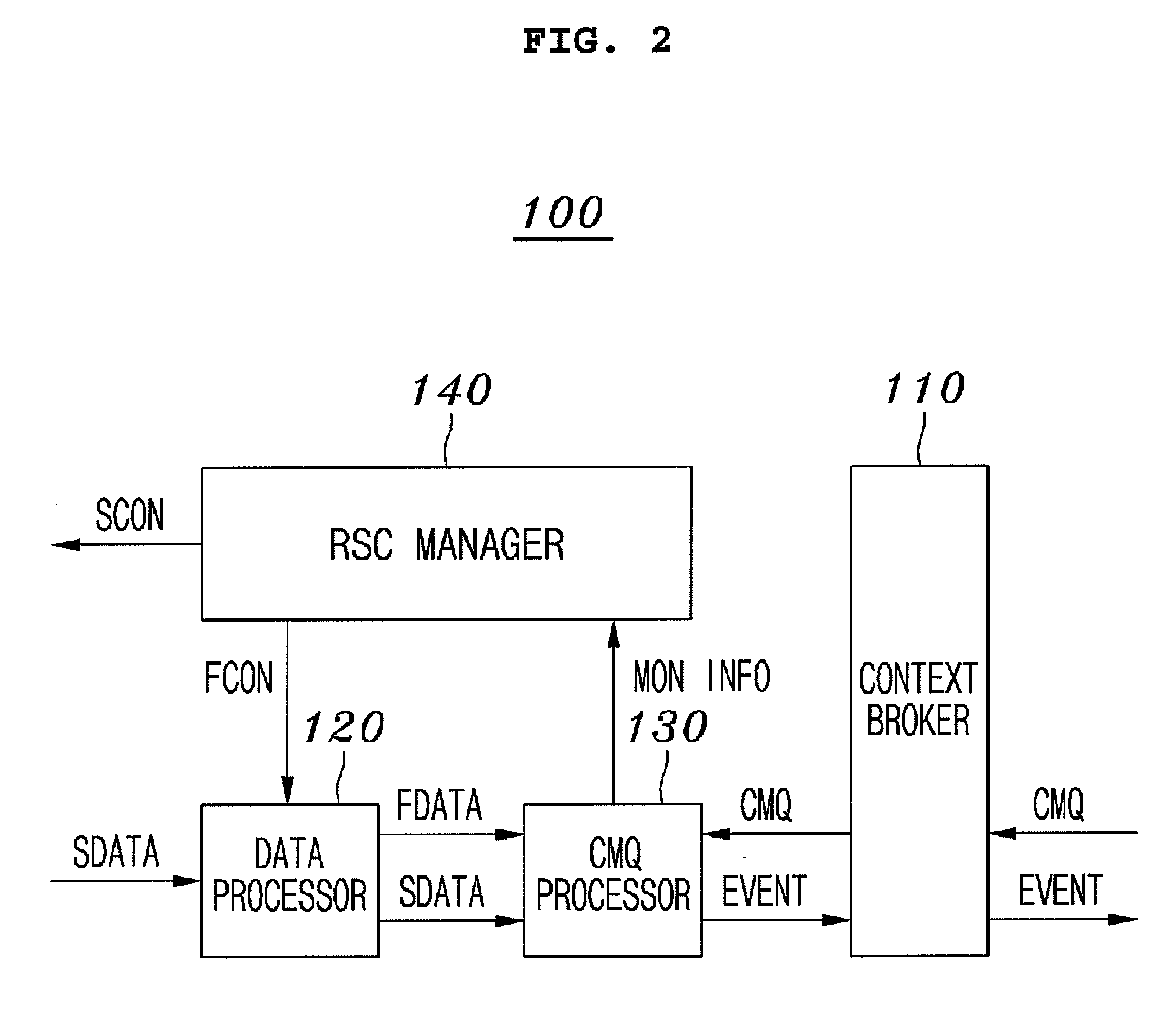
Mobile middleware supporting context monitoring and context monitoring method using the same
ActiveUS20080248789A1Energy efficientStop operationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTApplication softwareContext monitoring
Disclosed herein is mobile middleware, a context monitoring method, a context-aware system, and a context-aware service provision method, which support energy-efficient context monitoring. The mobile middleware receives a request for a CMQ from context-aware application programs, receives sensor data from sensors, monitors whether the CMQ is satisfied, and transmits an event to the context-aware application programs according to results of the monitoring. In this case, the mobile middleware controls the sensors so that only sensor data required to determine whether the CMQ is satisfied needs to be transmitted so as to reduce energy consumption during the performance of the monitoring. Therefore, the mobile middleware can perform energy-efficient context monitoring, required by the context-aware application programs.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Common rate control method for reverse link channels in CDMA networks
ActiveUS20050111407A1Reduce volatilityReduce data transfer rateError preventionTransmission systemsMobile stationRadio Base Station
A radio base station transmits periodic load indications based on the measured reverse link load to a plurality of mobile stations transmitting on a reverse link channel. If the measure reverse link load is within a first predetermined range, the radio base stations transmits a load indication instructing mobile stations transmitting on the reverse link to change their transmission rate probabilistically. If the reverse link load is within second predetermined range outside the first predetermined range, the radio base station transmits a load indication instructing mobile stations transmitting on the reverse link to change their transmission rate deterministically.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Scheduling of voice over IP data
InactiveUS20100202376A1Reduce data transfer rateConveniently changedWireless commuication servicesTransmissionResource blockVoice over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) transfer is provided over radio links between mobile stations and base stations with a mechanism to schedule initial transmission within voice spurts when semi-persistent allocation of radio resources is employed. The radio link is changed during the voice spurt by allocating different physical resource blocks or by changing transmission parameters with given rescheduling intervals. The scheduling is informed from the base station to involved MS by using data link layer VoIP packet padding bits. The radio link can also be changed per initiative of the MS so that the MS codes a predetermined request into data link layer padding bits of an uplink VoIP packet. The requests from the MS typically involve a change of audio coding mode or informing of the present packet buffer status for VoIP packets at the MS.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Network system, adjusting method of data transmission rate and computer program product thereof
InactiveUS20100110892A1Reduce data transfer rateFast decayError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetworked systemData transmission
A network system, an adjusting method of a data transmission rate of the network system, and a computer program product thereof are disclosed. The network system comprises a transmitting apparatus and a receiving apparatus. The transmitting apparatus is configured to transmit a packet train at a transmission rate to the receiving apparatus. The receiving apparatus is configured to receive the packet train and to compute at least one factor related to the received packet train to evaluate whether the transmission rate is suitable for the network system. The receiving apparatus is further configured to transmit an adjustment signal according to the at least one factor, such that the transmitting apparatus appropriately adjusts the transmission rate in response to the adjusting signal.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Wireless communication device and method of displaying wireless communication state
InactiveUS20090290628A1Increase data rateReduce data transfer rateNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission monitoringTelecommunicationsData rate
Provided is a wireless communication device that receives at least one communication packet containing data rate information, including: a storage unit that receives the at least one communication packet and stores, in a memory unit, the data rate information contained in the at least one communication packet; a display data generation unit that generates display data rate information to be used for display, based on the data rate information stored in the memory unit; and a display unit that displays the display data rate information generated by the display data generation unit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
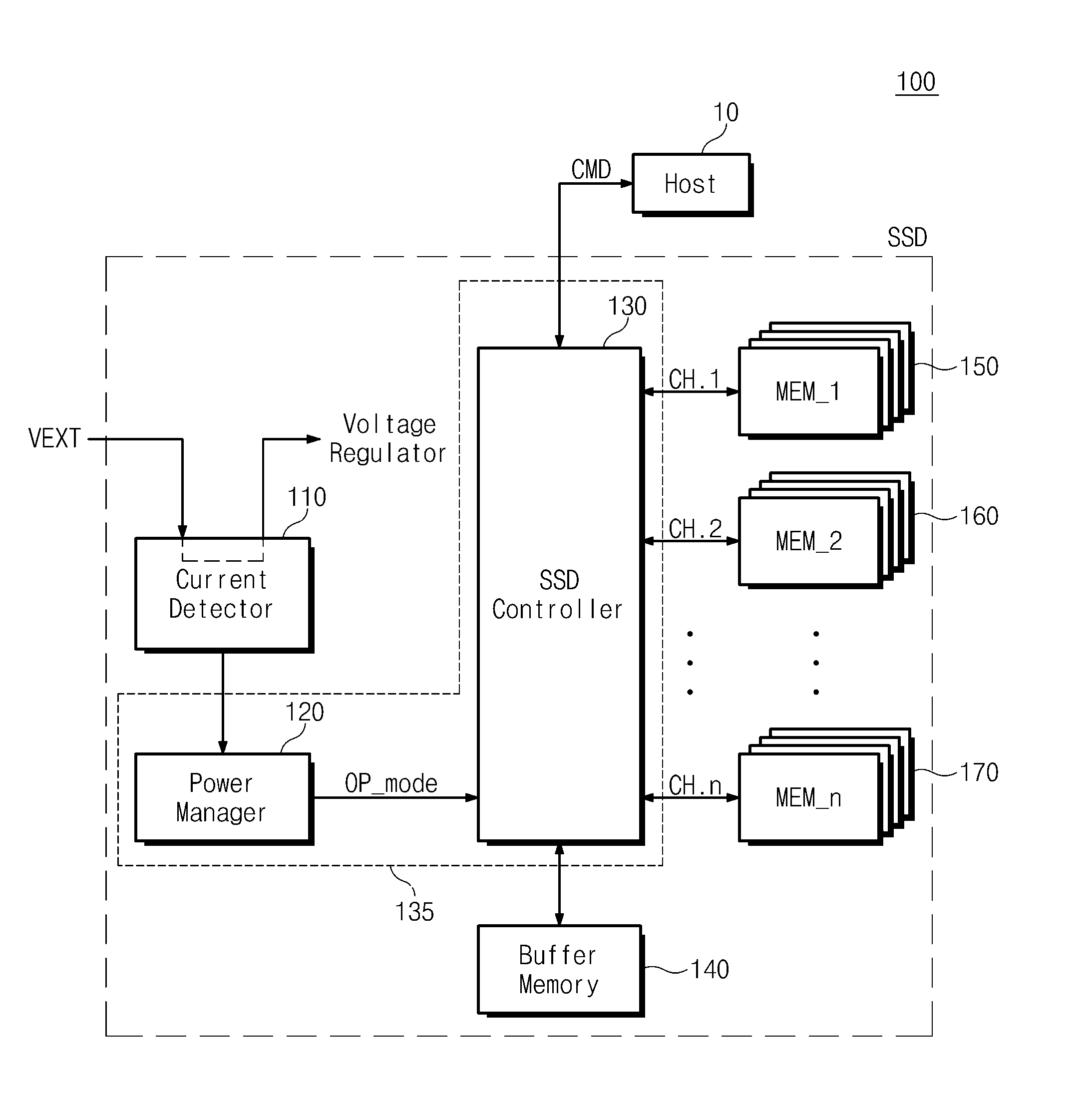
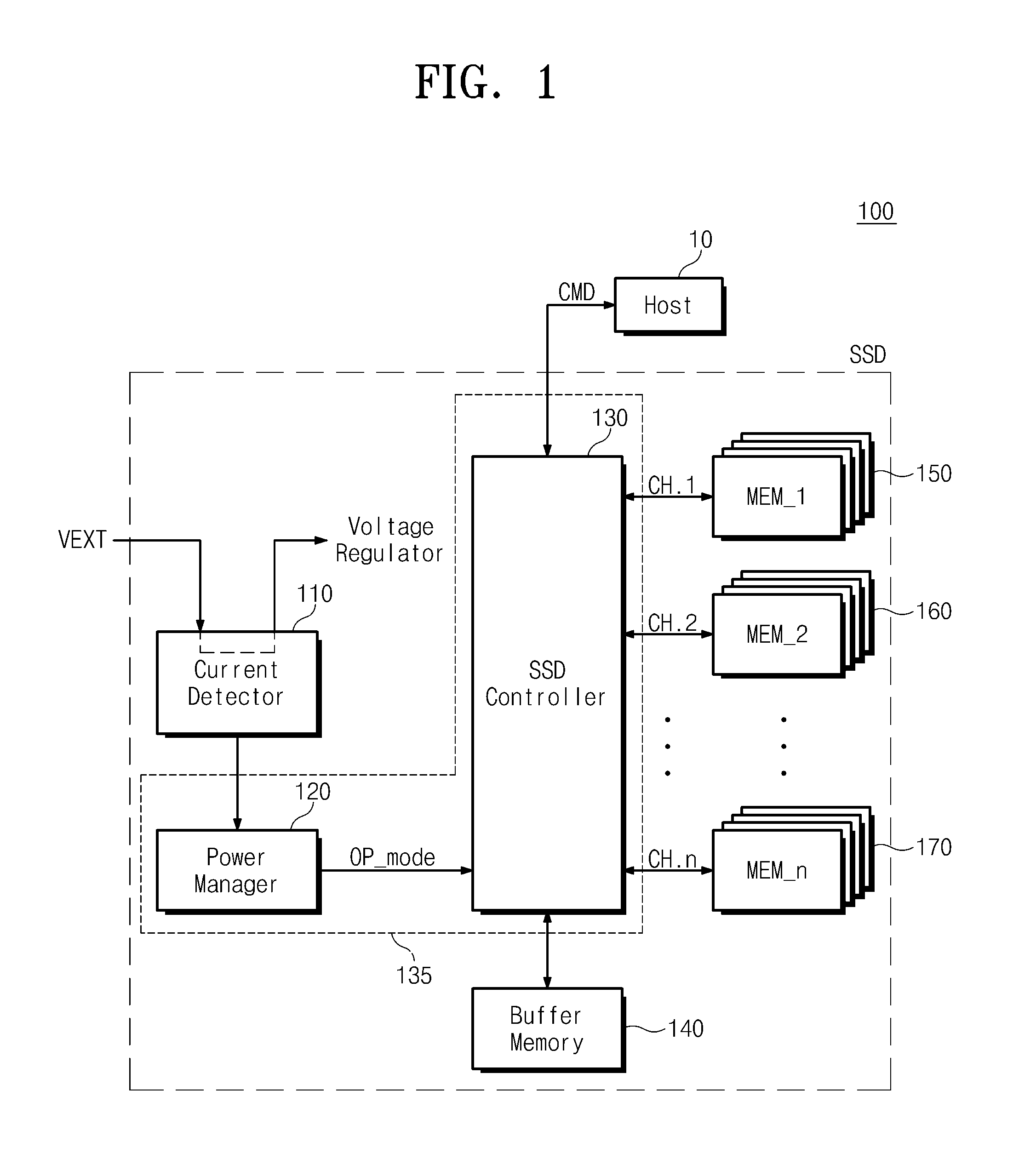
Data storage device including current detector
ActiveUS20100275050A1Reduce data transfer rateVolume/mass flow measurementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer scienceElectrical current
Provided is a data storage device including a current detector. The data storage device includes a plurality of memory devices, a detector, and a power manager. The detector detects a current inputted from a power source. The power manager manages consumption power of the plurality of memory devices according to a result of the detection provided from the detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ever-decreasing network qos requirements for stored video streaming in a mobile wireless interworking environment
InactiveUS20060156365A1Reduce data transfer rateLow costPulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio access networkData transmission
A method for downloading and displaying a video program using a mobile terminal that includes a first radio access network having a first data transfer rate and a second radio access network having a second data transfer rate faster than the first data transfer rate. The downloaded video program is displayed at a predetermined playback rate. Excess portions of the downloaded video program that result when a rate at which the video program is downloaded exceeds the predetermined playback rate are buffered. A third data transfer rate that is lower than the first transfer rate is calculated in response to the predetermined playback rate, the buffered excess portions and the time duration of the remainder of the video program. The third data transfer rate is negotiated with the first network for downloading the video program when the difference between the first and third data transfer rates exceeds a threshold level.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Integrated antenna system for imaging microsatellites
ActiveUS20120154585A1Maximize efficiencyAvailable spaceCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesData transmissionRadiation pattern
Examples of imaging microsatellites are described that have an imaging system and antenna system disposed within the microsatellite body when the microsatellite is in a non-deployed state. The properties of the antenna system can be adjusted such that the antenna system does not impact, contact, or displace the imaging system when the microsatellite is in the non-deployed state. The properties of the antenna system can be adjusted such that the antenna system does not contact or impact the body of the microsatellite or any other structure when the microsatellite transitions to a deployed state. The antenna system can be configured to achieve a desired gain and / or data transmission rate by adjusting properties of the antenna system based on the radiation pattern of an antenna feed and geometric constraints imposed by the imaging system. Examples of methods for designing such imaging microsatellites are provided.
Owner:PLANET LABS PBC
CQI information receiving method, transmitting method, receiving device, and transmitting device
ActiveCN106559171AHigh data transmission reliabilityReduce data transfer rateError prevention/detection by using return channelAssess restrictionData transmissionComputer hardware
The invention provides a CQI information receiving method, transmitting method, receiving device, and transmitting device. The CQI information receiving method includes sending high-level configuration signaling to a terminal; and receiving the CQI information from the terminal, wherein the CQI information is determined based on a CQI form which is obtained based on the high-level configuration signaling. According to the invention, the problem that the high data transmission reliability, low data transmission rate, and low system spectral efficiency cannot satisfy the coverage of the enhanced MTC terminal in the prior art is solved, and the effects of high data transmission reliability, low data transmission rate, and low system spectral efficiency required by the coverage of the enhanced MTC terminal can be achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Broadband dual-polarized OMNI-directional antenna and feeding method using the same
ActiveUS20130215832A1Good polarization isolation effectImprove data transfer ratePolarised antenna unit combinationsWireless commuication servicesIsolation effectElectrical conductor
A broadband dual-polarized omni-directional antenna and a feeding method using the same are provided. By setting a vertically polarized antenna and a horizontally polarized antenna each in co-axial, the horizontally polarized antenna is attached to an upper surface and a lower surface of the attaching plate respectively by two arms of a folded dipole and the two arms connect to an inner conductor and an outer conductor of a feed line so that the dual-polarized antenna may have a comparatively broad bandwidth. At the same time, since the dual-polarized ceiling antenna has a good isolation effect and coverage balance, it may work as the MIMO antenna in the LTE and WLAN systems effectively and may be used in the 2G and 3G networks to improve the data transmission rate.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP DESIGN INST
Driving method for electro-optical device, driving circuit therefor, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20030156128A1Reduce data transfer rateReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingData transmissionComputer science
To reduce the data transfer rate in one subfield while suppressing display nonuniformity, a pixel positioned corresponding to each intersection between a plurality of scanning lines and a plurality of data lines is turned on or off in subfields sf1 to sf17, into which one field (1f) is divided, according to weighting of gray scale data (dcba) indicating the gray scale level of that pixel, and the reference time of weighting for the gray scale data is shifted every scanning line and every subfield.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Relay device, electronic control unit, and vehicle-mounted system
ActiveUS20180203685A1Smooth upgradeSuppressing communication loadProgramme controlComputer controlNon targetedNon target
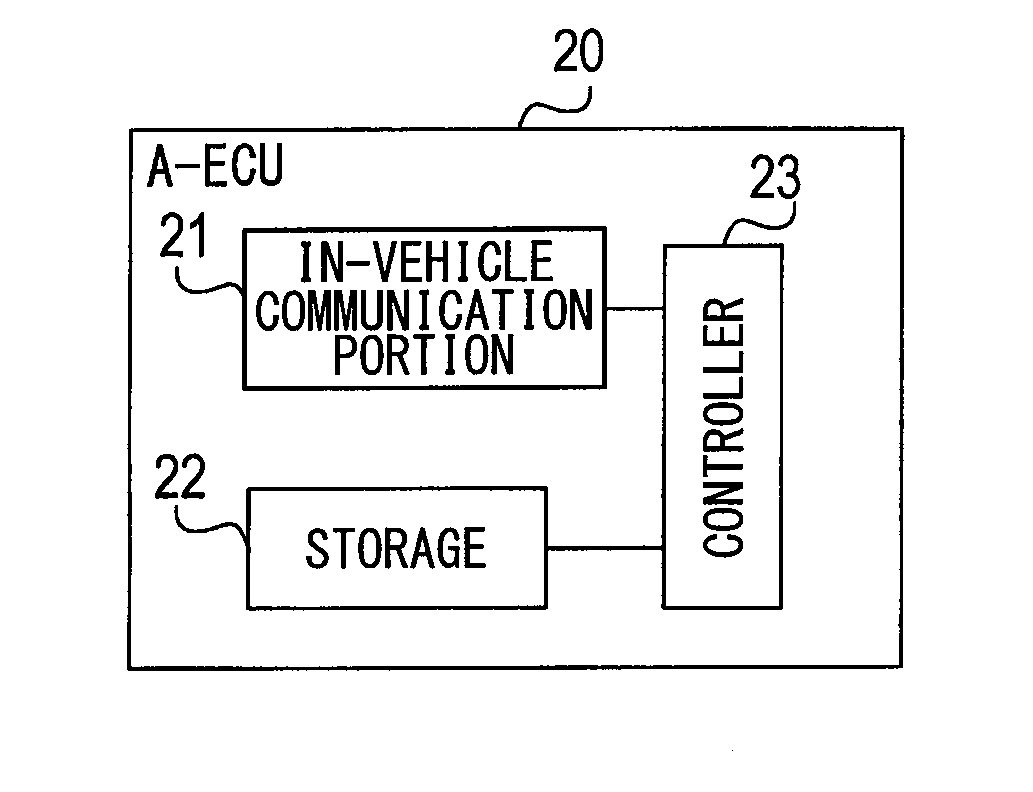
A relay device is provided. The relay device includes: an acquisition unit acquiring data necessary for an upgrade processing from an upgrading tool, which performs the upgrading processing to an ECU connected to a vehicle-mounted network; a relay unit providing the data, via the vehicle-mounted network, to a target ECU which is subject to the upgrade processing; a suspend instructing unit transmitting, via the vehicle-mounted network, a suspend command which instructs the non-target ECU to shift to a suspend state in which a transmission of other data to the non-target ECU via the vehicle-mounted network is suspended in response to a start of the upgrade processing; and a cancel instructing unit instructing, via the vehicle-mounted network, the non-target ECU to cancel the suspend state when the upgrade processing is completed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Aggregate rate transparent LAN service for closed user groups over optical rings
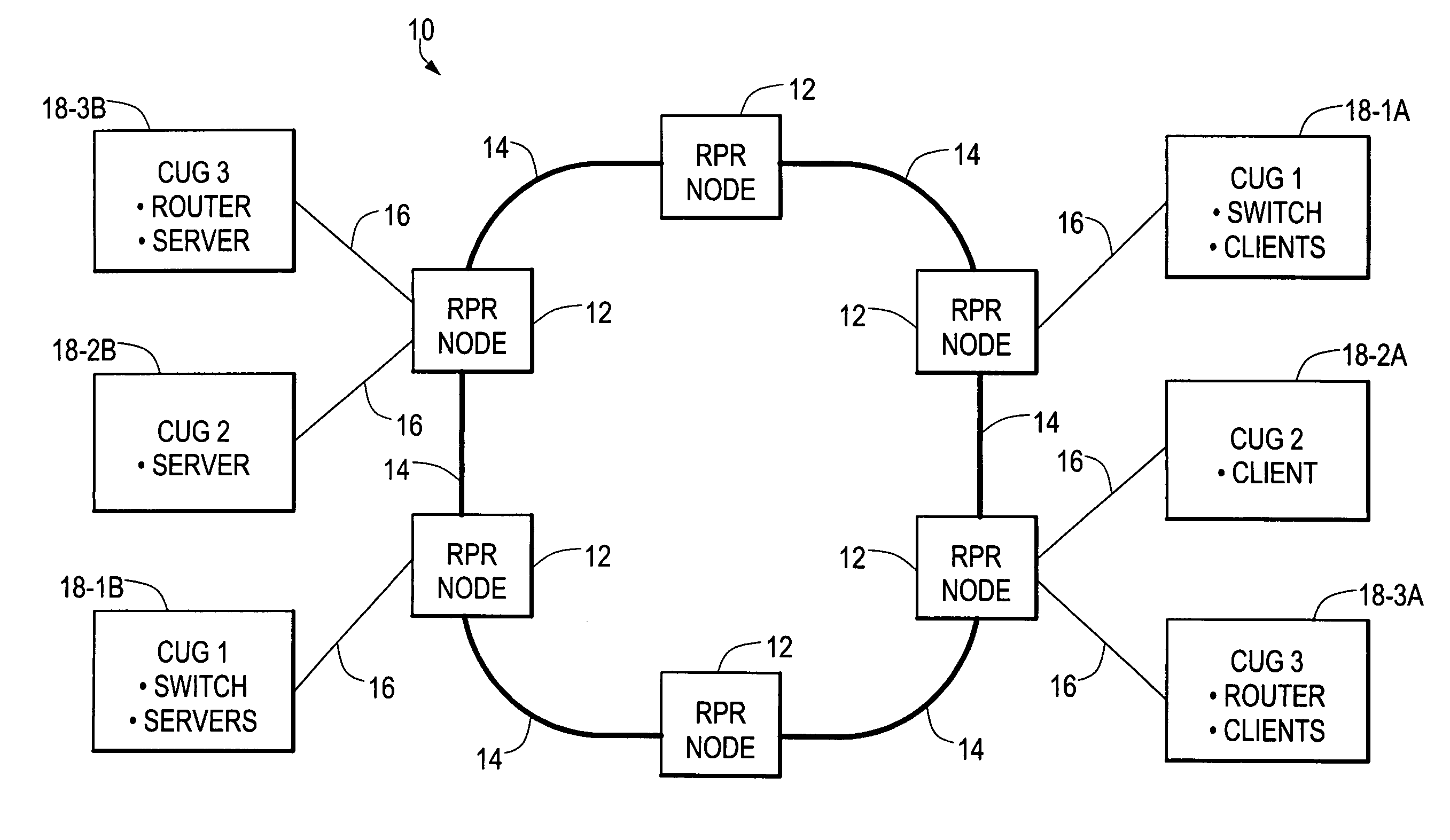
ActiveUS7102997B2Lighten the configuration burdenReduce data transfer rateEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsRing networkClient-side
A ring network provides transparent local area network (LAN) service by allocating respective proportions of data transmission capacity of the ring to different closed user groups (CUGs), each including a plurality of LAN clients. At each node of the ring, the use of a connected segment of the ring is monitored for both pass-through and locally-generated traffic by the LAN clients on a per-CUG basis. When it is detected that use of the connected segment for a CUG is approaching the allocated proportion, an active LAN client of the CUG is selected and sent a throttle message indicating that the LAN client is to reduce its data transmission rate. Rate monitoring for is accomplished using a “leaky bucket” mechanism. A “rate cache” identifying the active senders and their transmission rates can also be used in selecting a LAN client for receiving the throttle message.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Detection of visible light communication sources over a high dynamic range
ActiveUS10193627B1High imagingGood durationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLed arrayLight signal
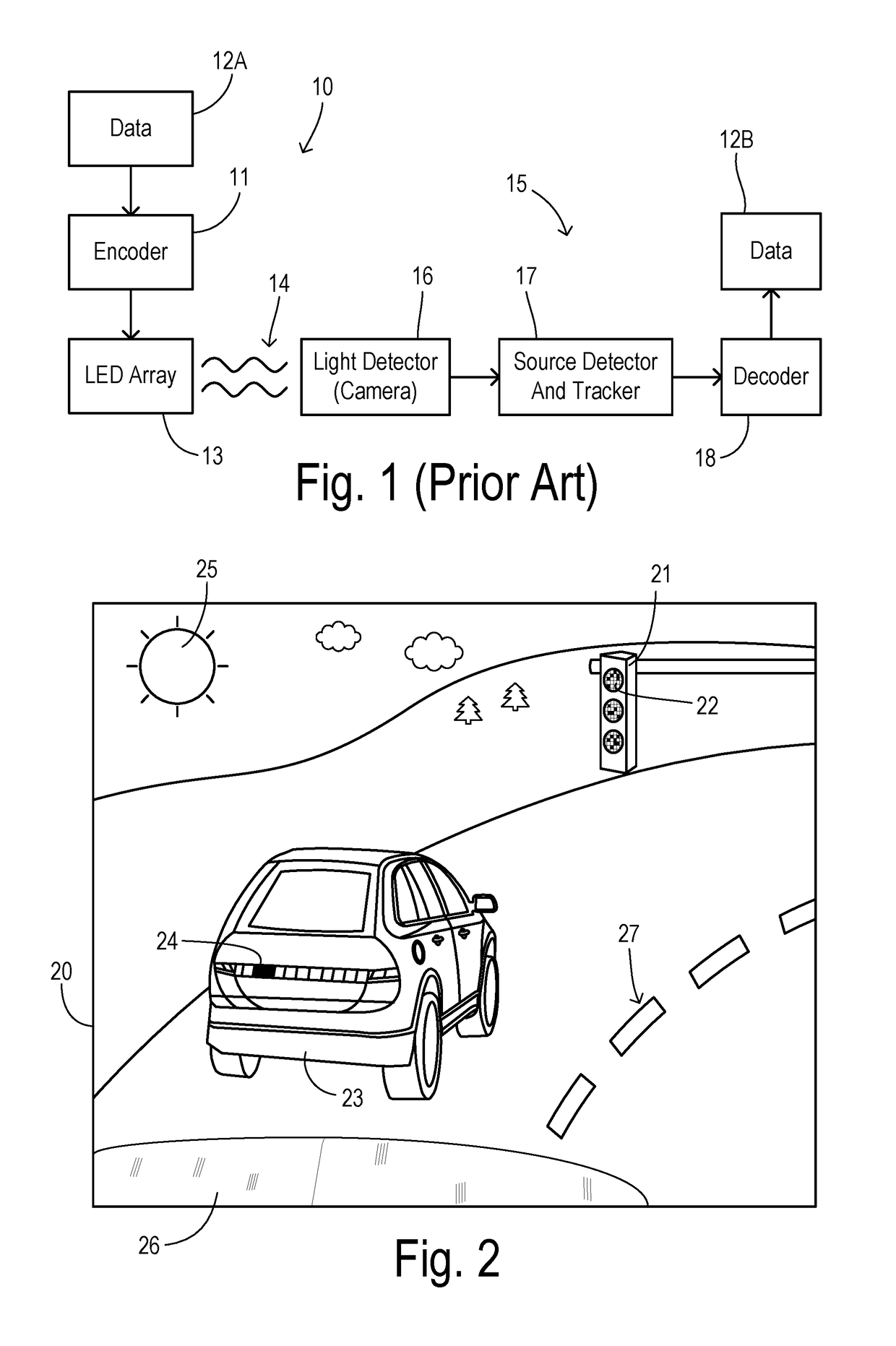
A visible light communication (VLC) receiver captures frames of a scene with a camera to detect flashing light signals from a VLC transmitter such as an array of LEDs. The method assembles an enhanced dynamic range image sequence from the frames. At least one VLC source is detected in the enhanced sequence, wherein the source occupies a respective subwindow within the scene. An imaging exposure such as the exposure time used for capturing images at the subwindow is optimized according to a brightness of the respective VLC source. Then a plurality of subwindow images are captured using the optimized exposure. VLC data visible in the subwindow images is then decoded.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
High noise immunity emergency resonder communication system
InactiveUS20090052714A1Improve noise immunityImprove immunityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesNear-field systems with portable transmittersModem deviceCommunications system
High noise immunity communication systems are provided for voice communications among emergency responders, in which first and second wireless devices employ near field spread spectrum data modems to transfer digital audio data between a responder mask or helmet and a secondary device affixed to the responder's clothing or uniform to allow the responder to broadcast messages to other responders and to hear broadcasts from other responders.
Owner:UNDERSEA SENSOR SYST
Intelligent energy-saving system for controlling wireless networking of office building environment and control method thereof
InactiveCN101706663AReduce power consumptionLow costEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesWireless controlEngineering
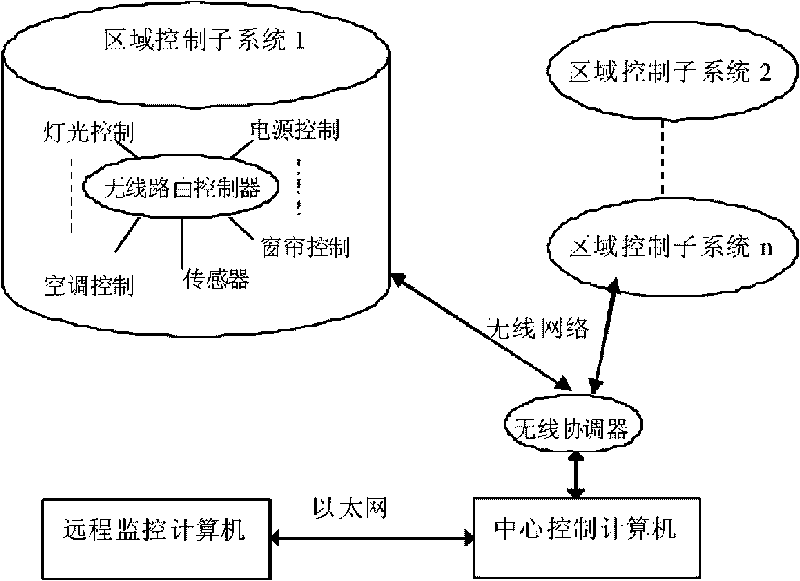
The invention discloses an intelligent energy-saving system for controlling the wireless internetworking of office building environment, which comprises a central controller and area control subsystems. End control equipment is arranged in each area control subsystem; the central controller is connected with a wireless coordinator; each end control equipment is in signal connection with a wireless routing controller which is in signal connection with the wireless coordinator; and the end control equipment, the wireless routing controller and the wireless coordinator are all based on a ZigBee communication protocol and meet IEEE802.15.4 standard. The intelligent energy-saving system solves the technical problem that a relatively larger measurement and control network cannot be formed in a conventional wireless control system, also solves the problems of the high power consumption, low rate and high cost of the conventional building intelligent control system, ensures that manual control is effective when equipment communication or control is at fault and avoids the paralysis of the whole system.
Owner:欧阳东 +2
Ultra-wideband communication protocol
ActiveUS20050058121A1High and low data transfer rate capabilityFast data transferTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexUltra-widebandSubject matter
A communication protocol for ultra-wideband communications is provided. The present invention provides compatibility and interoperability between ultra-wideband communications devices within various types of networks. In one embodiment, combined, or interleaved data frames having both high and low data transfer rate capability are provided. The low data transfer rate may be used for initial discovery of the type of network that is being accessed, and the high data transfer rate may be used to quickly transfer data within networks that have a high data transfer rate capability. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Multicarrier communication with variable overhead rate
InactiveUS20030007509A1Reduce rateImprove data transfer rateTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationData transmissionEngineering
In the present invention, the overhead data transmission rate in a multicarrier communication system (1) may be changed and / or selected. More specifically, this rate may be selected during an initial negotiation process and / or during a steady state mode of operation.
Owner:AWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com