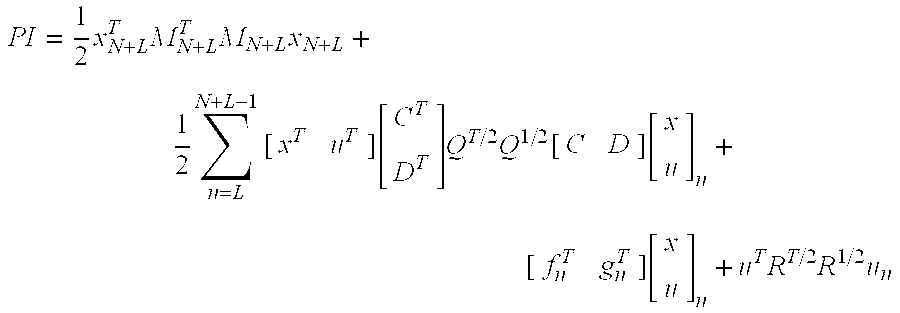Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2415 results about "System maintenance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
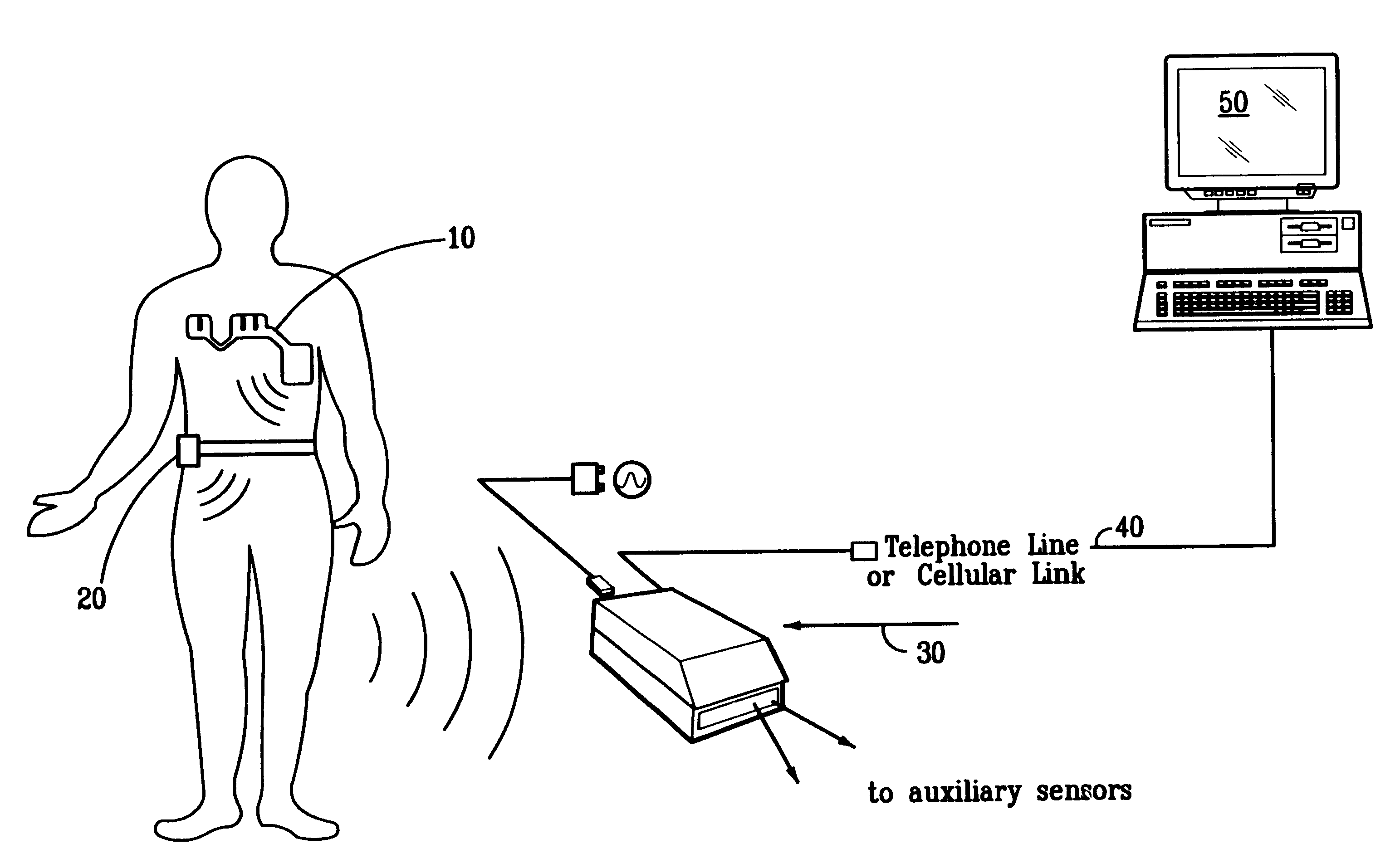
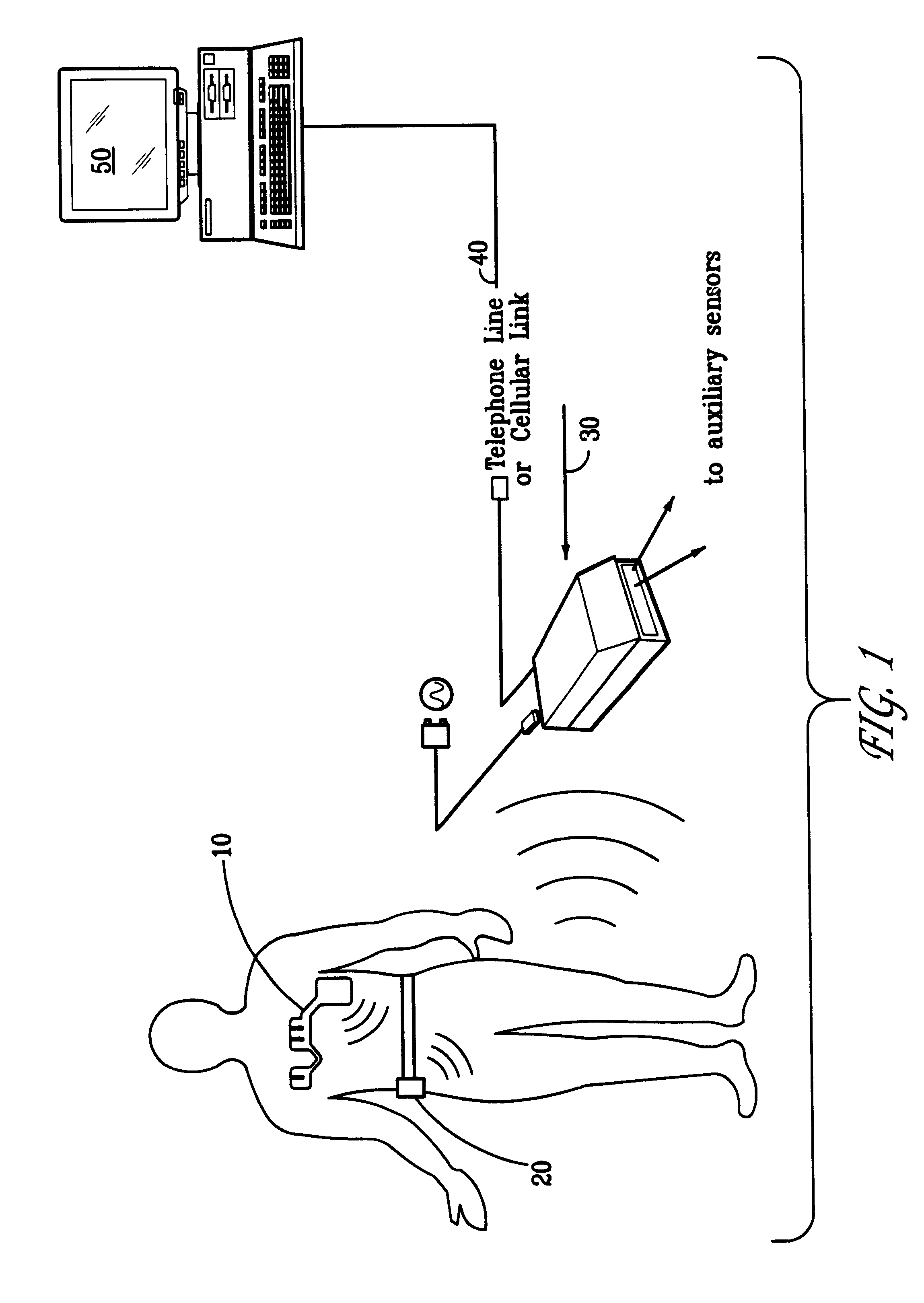
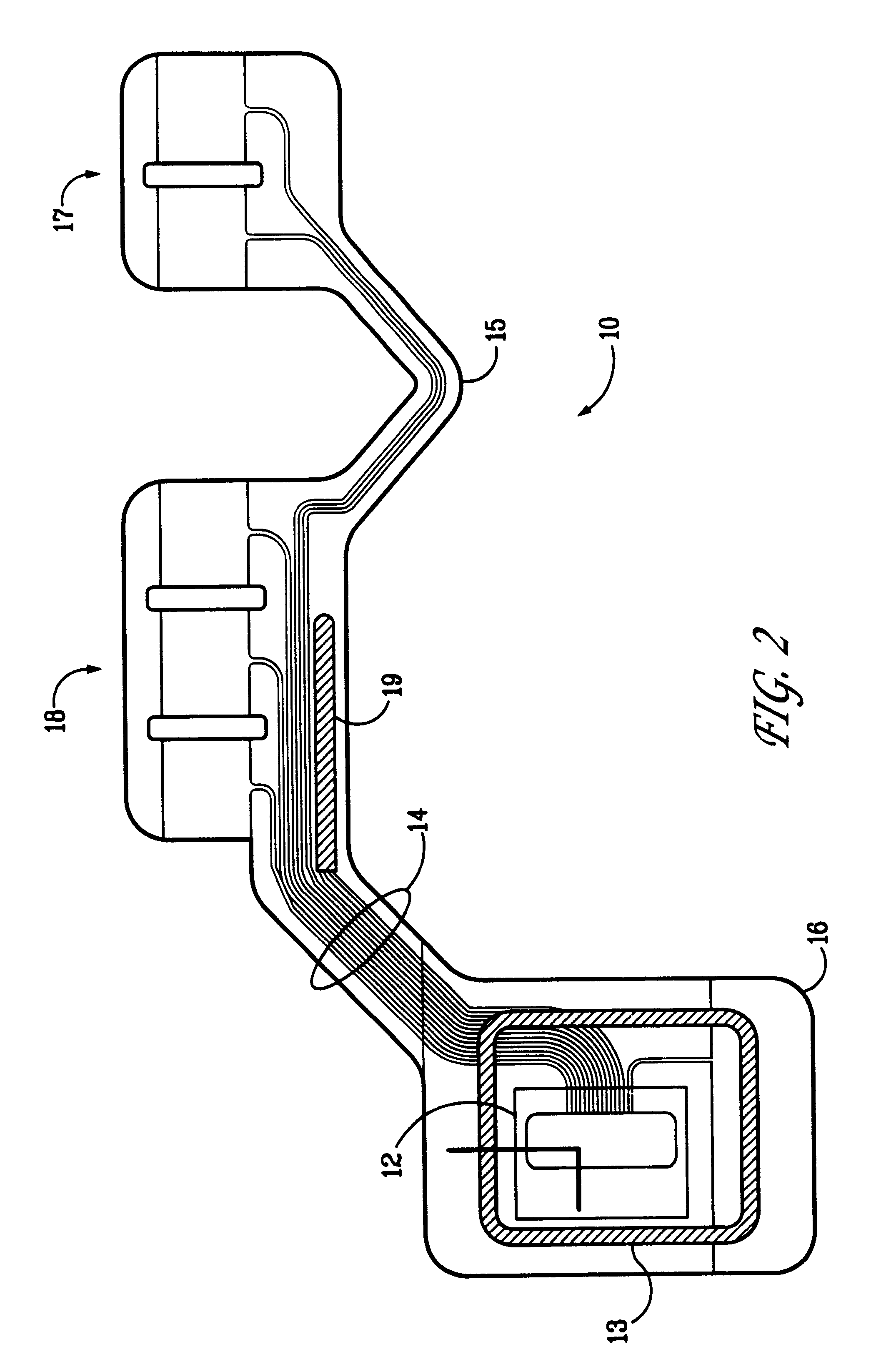
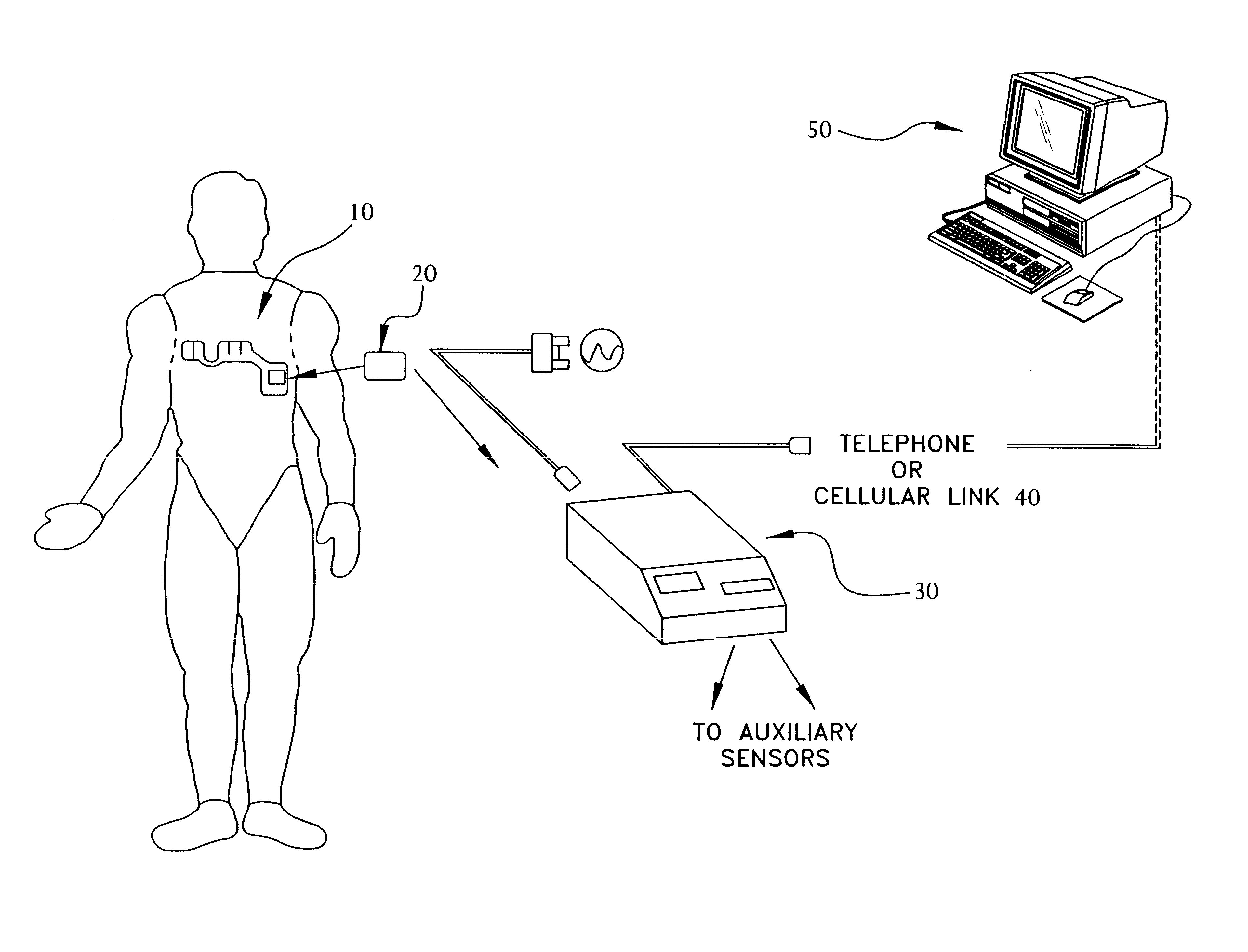
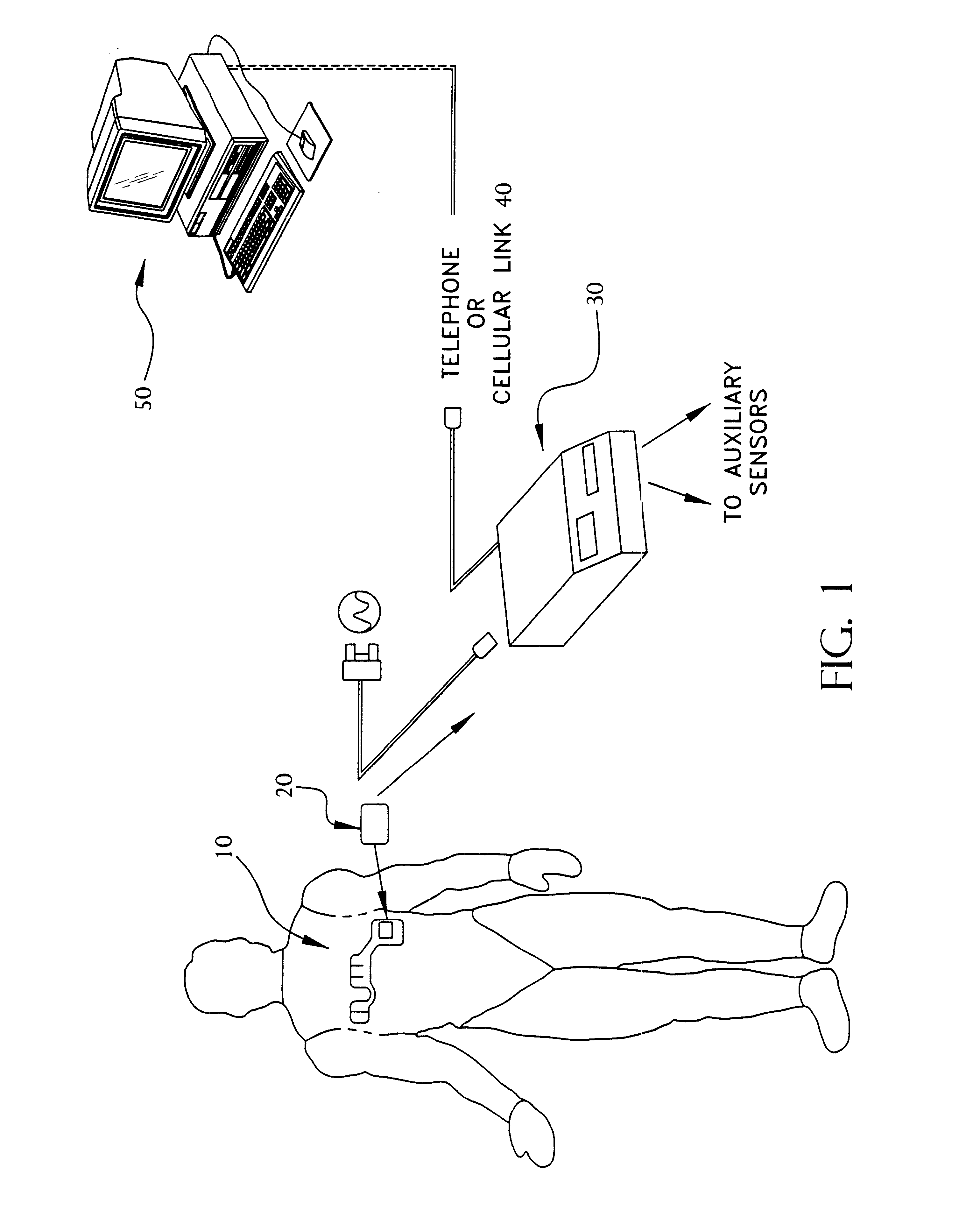
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system
A system and method for monitoring vital signs and capturing data from a patient remotely using radiotelemetry techniques. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors form measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and transmission circuitry for the detection and transmission of vital signs data of the patient. A small signal transfer unit that can either be worn by the patient, e.g., on his or her belt, or positioned nearby receives data from the sensor band, which it then forwards by e.g., radio transmission to a base station that can be located up to 60 meters away. The base station receives data transmissions from the signal transfer unit and is designed to connect to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Patient safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g., ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. Such events are indicated to the physician and could be indicated to the patient by reverse transmission to the signal transfer unit. A remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of patient clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
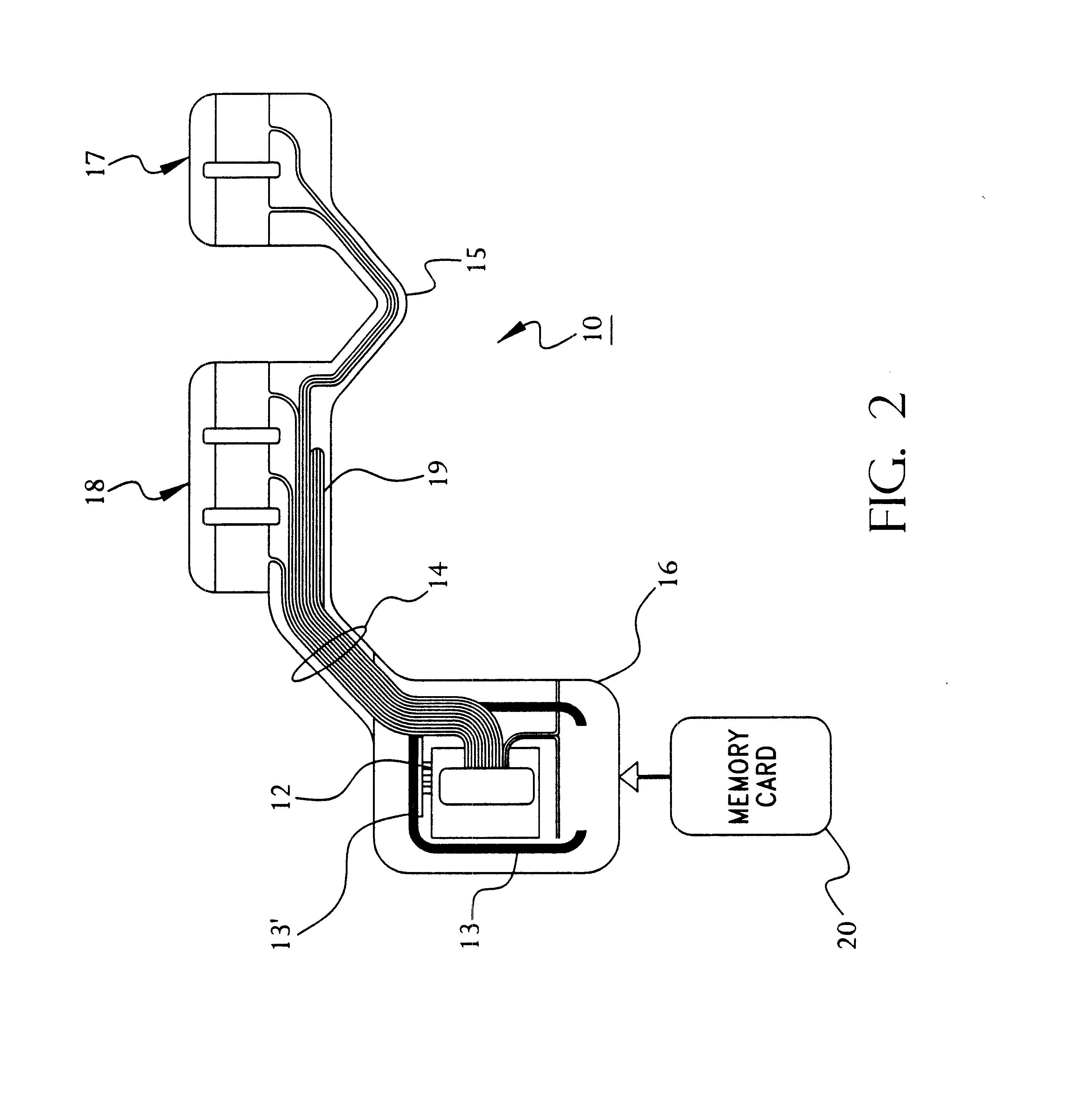
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system using a memory card or smart card
InactiveUS6454708B1Low costIncrease the number ofSurgeryRespiratory organ evaluationSmart cardFull waveform
A system and method for monitoring health parameters and capturing data from a subject. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors for measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and a connector which accepts a memory card or a smart card for storage of the measured data. After a predetermined period of time, such as when the sensor band is removed, the memory card or smart card is removed and inserted into a monitoring device which reads the stored health parameter data of the subject. The monitoring device includes a base station that includes a memory / smart card reader and is connected to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Subject safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g. ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. The remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. In alternative embodiments, a smart card includes the sensor band's electronics and / or signal transmission circuitry in conjunction with a portable data logger so that the electronics may be reused from one disposable sensor band to the next without limiting the patient's range of movement. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of subject clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of subjects with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
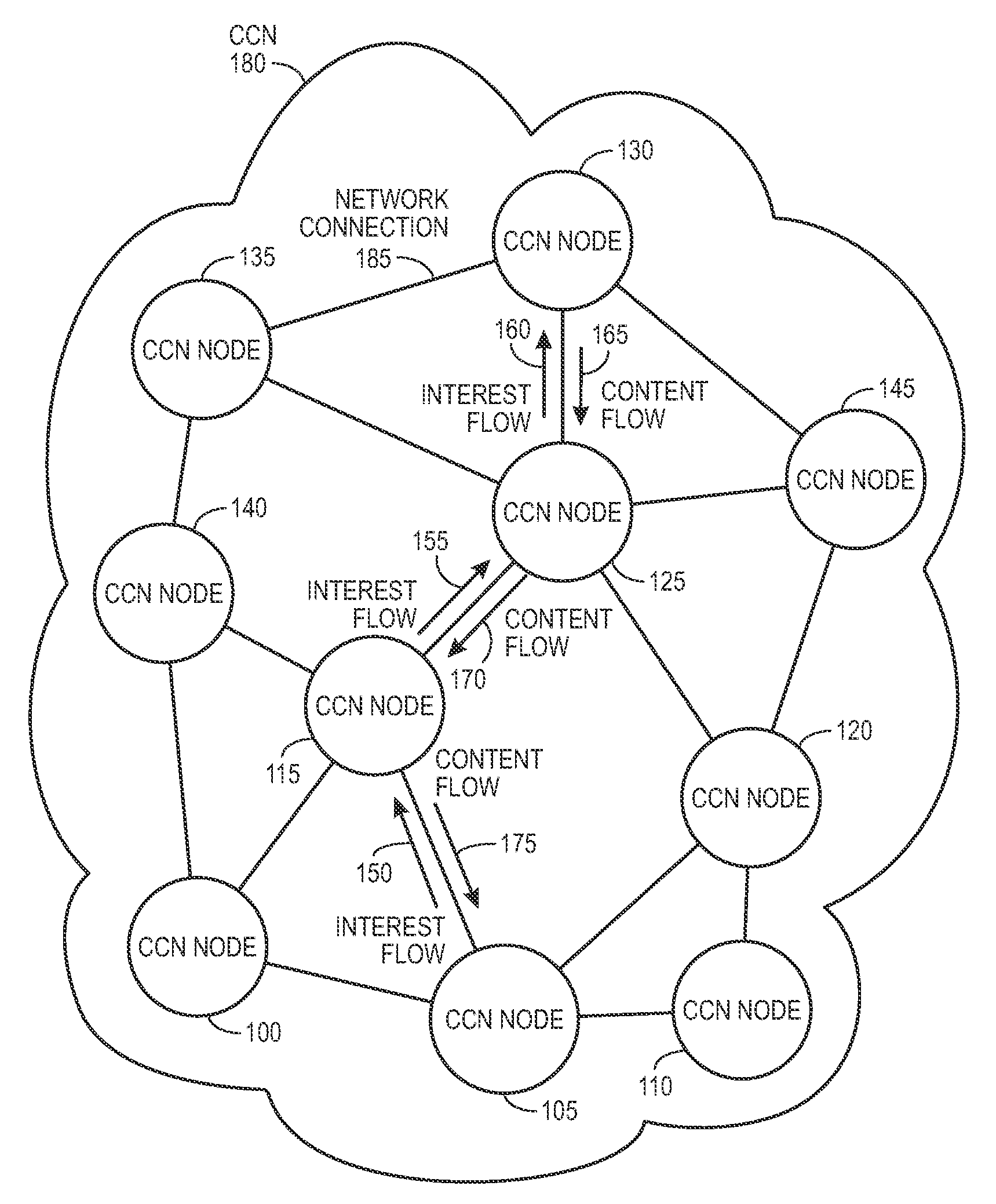
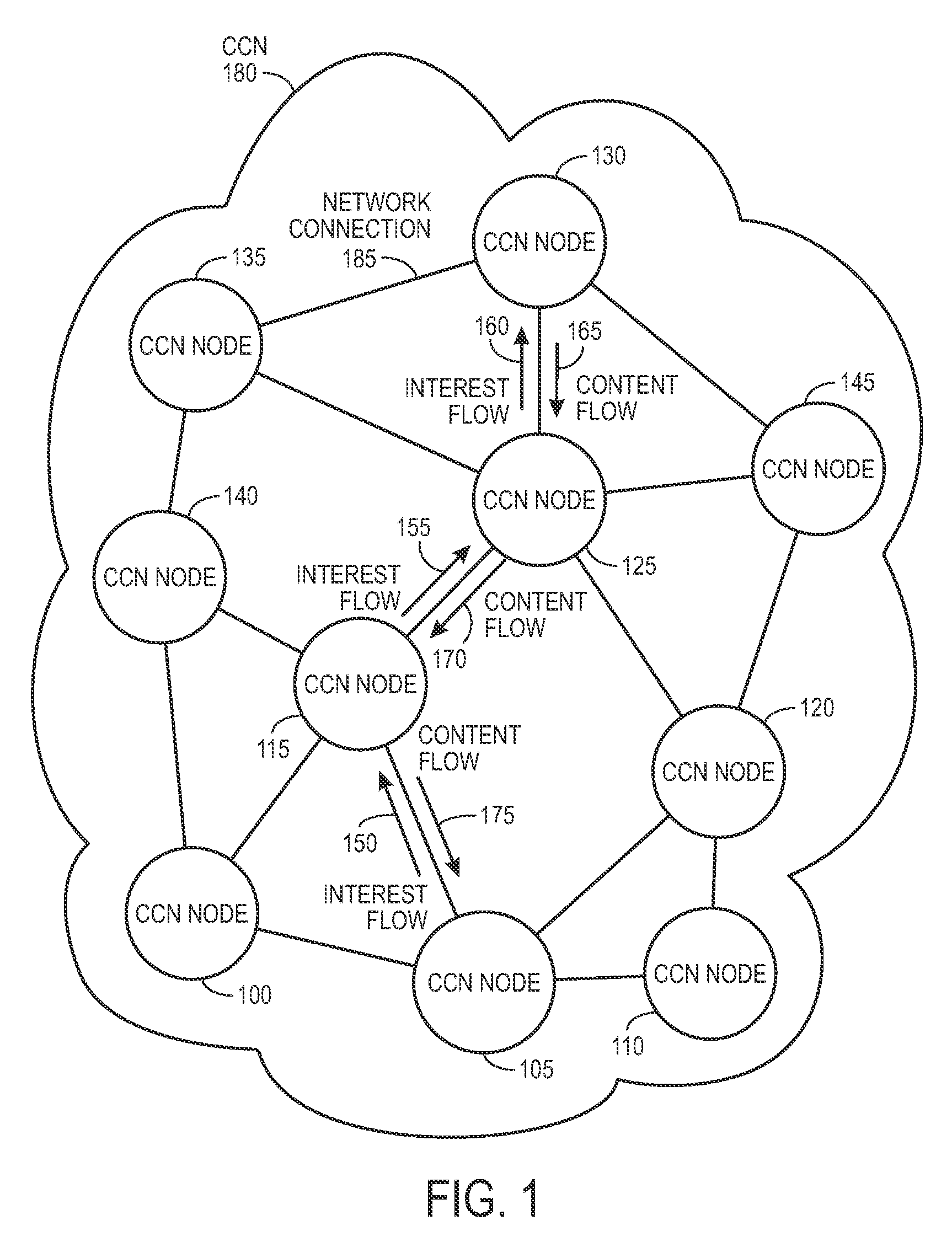
Controlling the spread of interests and content in a content centric network
ActiveUS20090288163A1Easy flow controlExpected levelMemory loss protectionMultiple keys/algorithms usageContent centricSystem maintenance
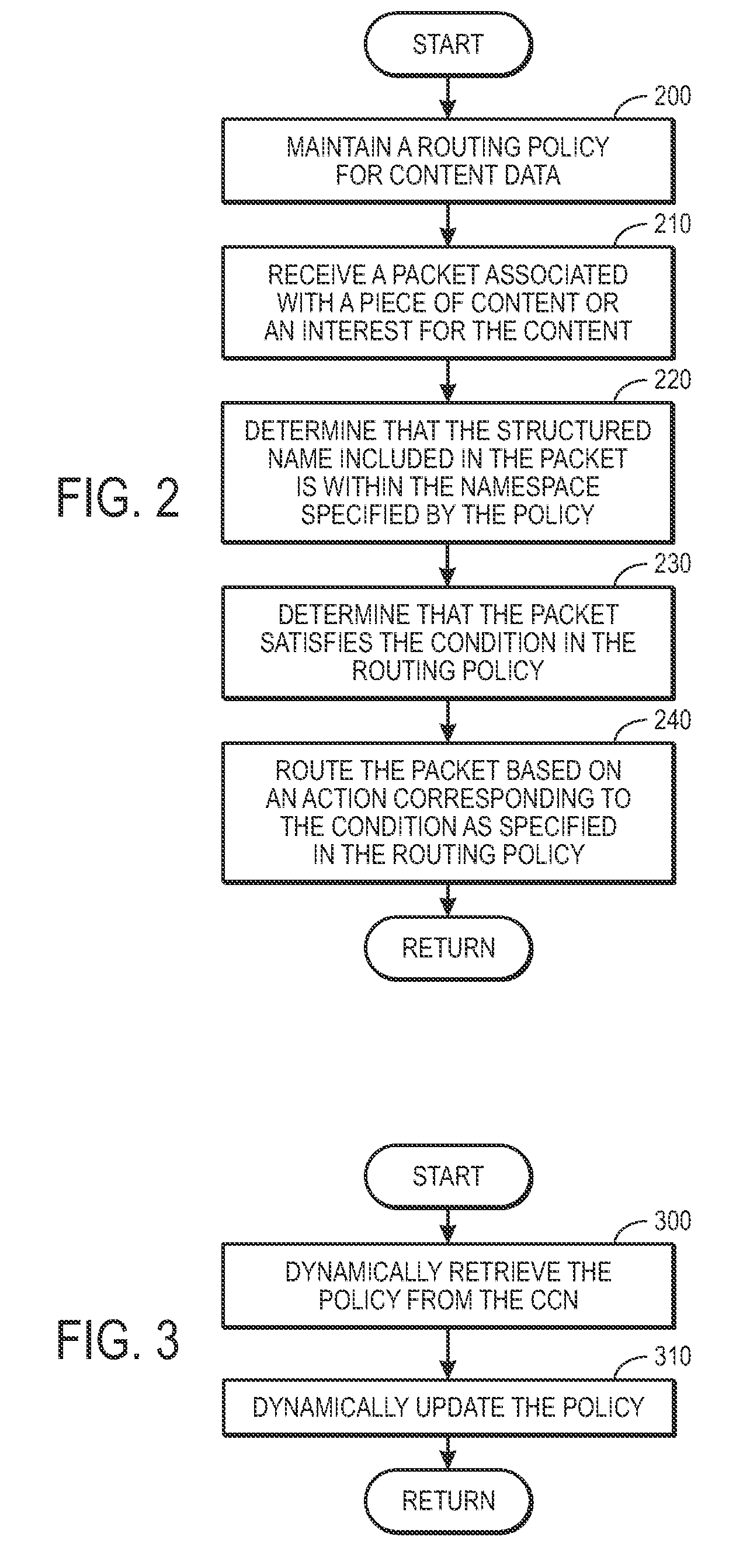
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for controlling the spread of interests and content in a content centric network (CCN). During operation, the system maintains a routing policy for content data. The system also receives a packet associated with a piece of content or an interest for the content. Next, the system determines that the structured name included in the packet is within the namespace specified in the routing policy. The system further determines that the packet satisfies the condition in the routing policy. Subsequently, the system routes the packet based on in part the action corresponding to the condition as specified in the routing policy.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System for controlled provisioning of telecommunications services
InactiveUS6622016B1Special service for subscribersConnection managementProcessing InstructionComputer science
A method and system for controlled provisioning of a desired set of service logic for a subscriber of group of subscribers. In response to a designated stimulus, such as a time-event, a location-event or a threshold-event, a network entity modifies the subscriber profile maintained by a serving system, so as to include in the profile one or more desired parameters. One such modification may be the inclusion in the profile of a trigger that directs the serving system to query a designated network entity for call handling instructions. The designated network entity may then provide a special set of services for the subscriber or group. Further, a mechanism is provided to help ensure that once such a service overlay is imposed, it remains imposed if desired.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
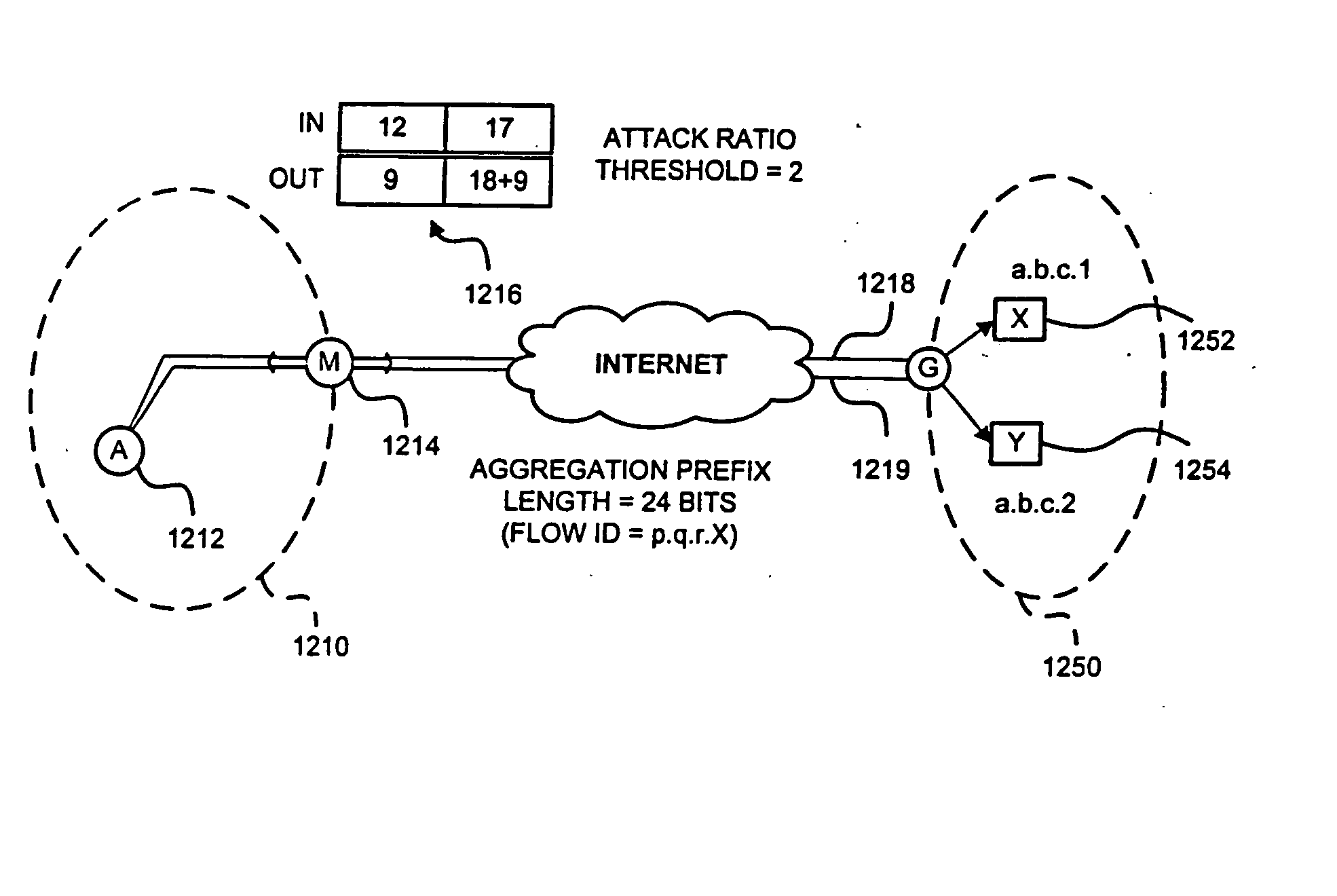
Detection of Distributed Denial of Service Attacks in Autonomous System Domains
A denial-of-service network attack detection system is deployable in single-homed and multi-homed stub networks. The detection system maintains state information of flows entering and leaving the stub domain to determine if exiting traffic exceeds traffic entering the system. Monitors perform simple processing tasks on sampled packets at individual routers in the network at line speed and perform more intensive processing at the routers periodically. The monitors at the routers form an overlay network and communicate pertinent traffic state information between nodes. The state information is collected and analyzed to determine the presence of an attack.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
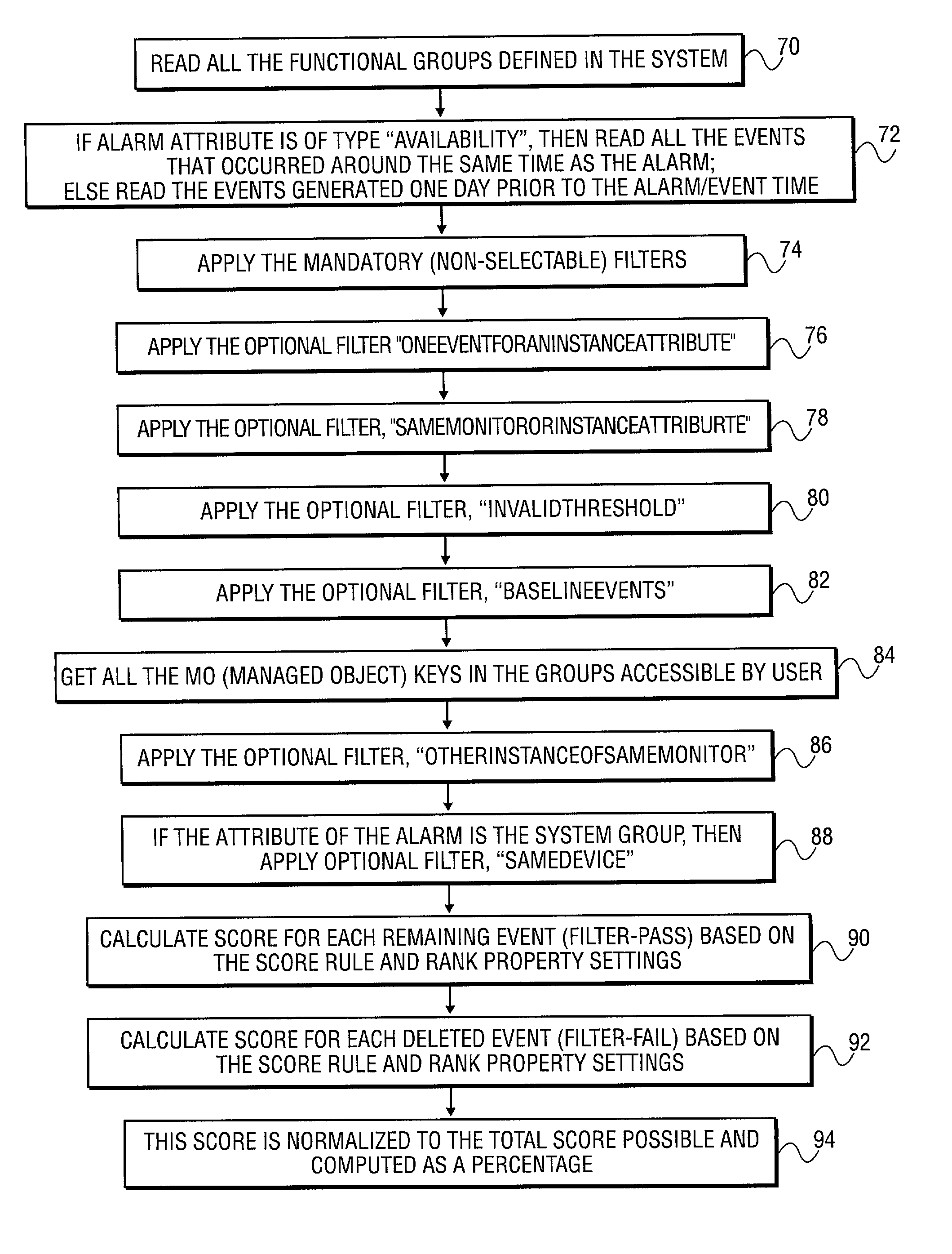
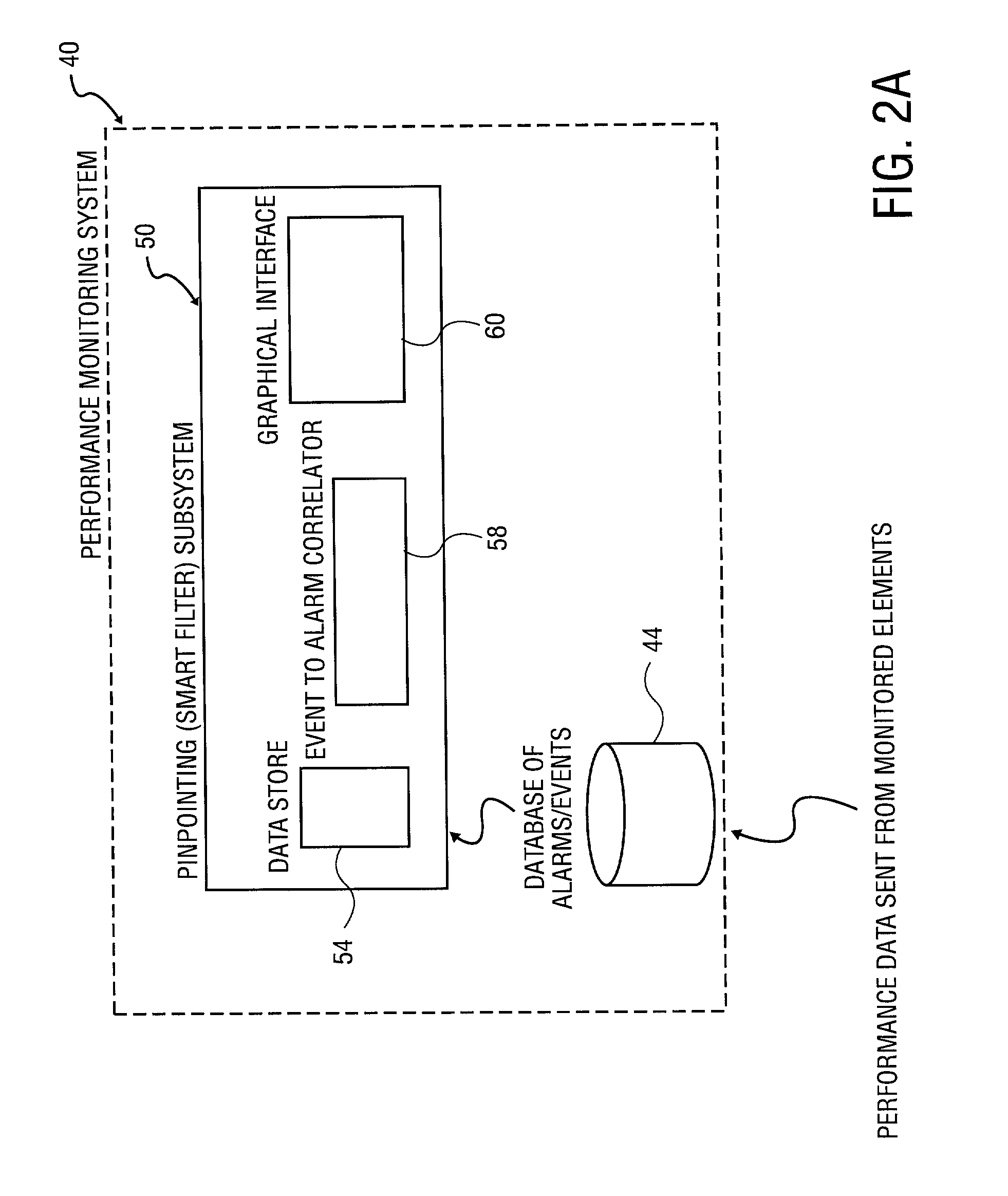
Method and system to correlate a specific alarm to one or more events to identify a possible cause of the alarm
A system is provided to monitor network performances. The system maintains a database of performance abnormalities, alarms and events from a system of monitored elements. The system automatically identifies a possible cause of a specific alarm by correlating the specific alarm with a plurality of events using the database. The system displays the cause of the specific alarm. The database includes alarms and events of network devices, network systems, and network applications. The specific alarm consists of a notification of an occurrence of the plurality of events.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
Continuous upgrading of computers in a load balanced environment
ActiveUS20110276695A1Reduce riskLimit riskMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlOperating systemLoad Shedding
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
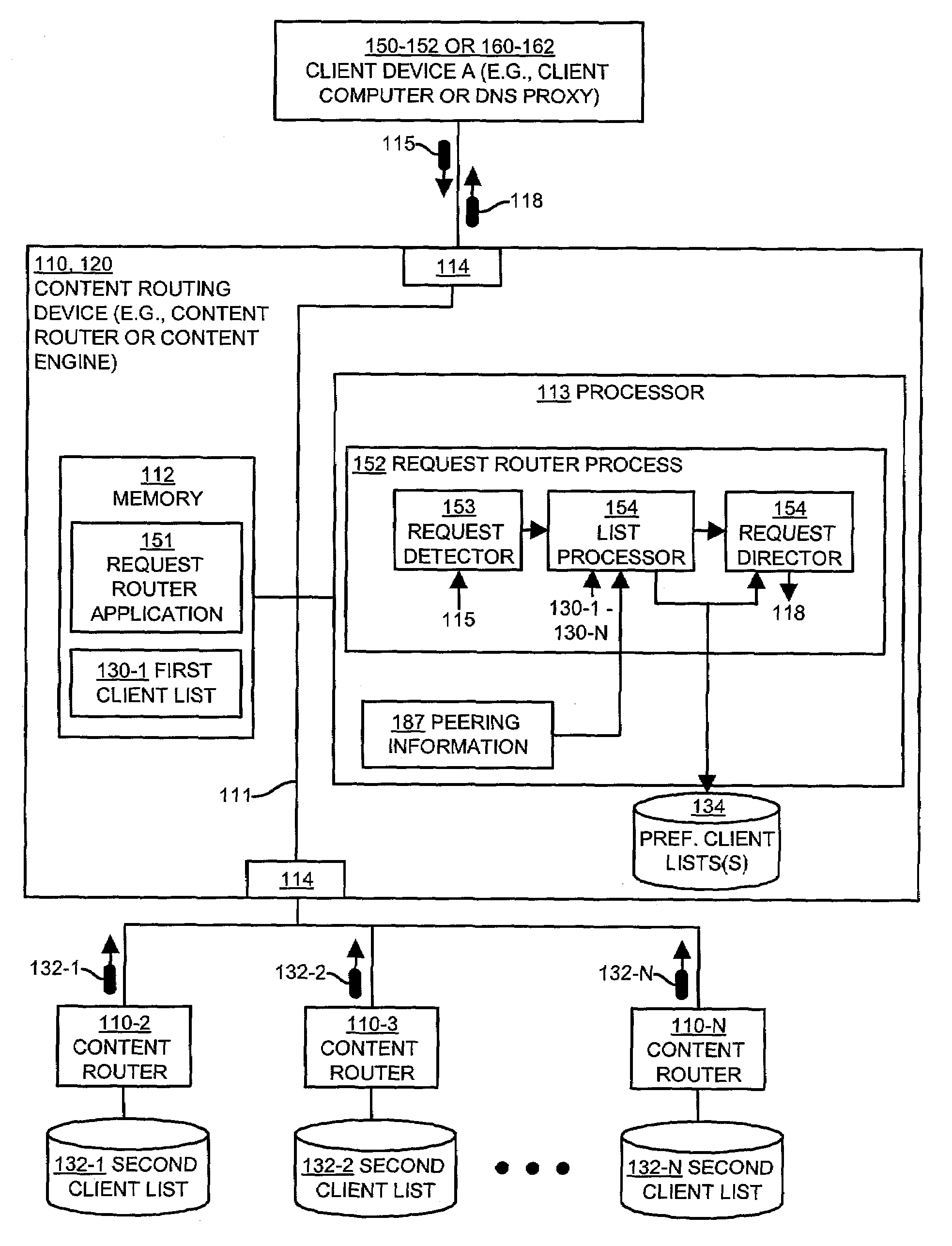
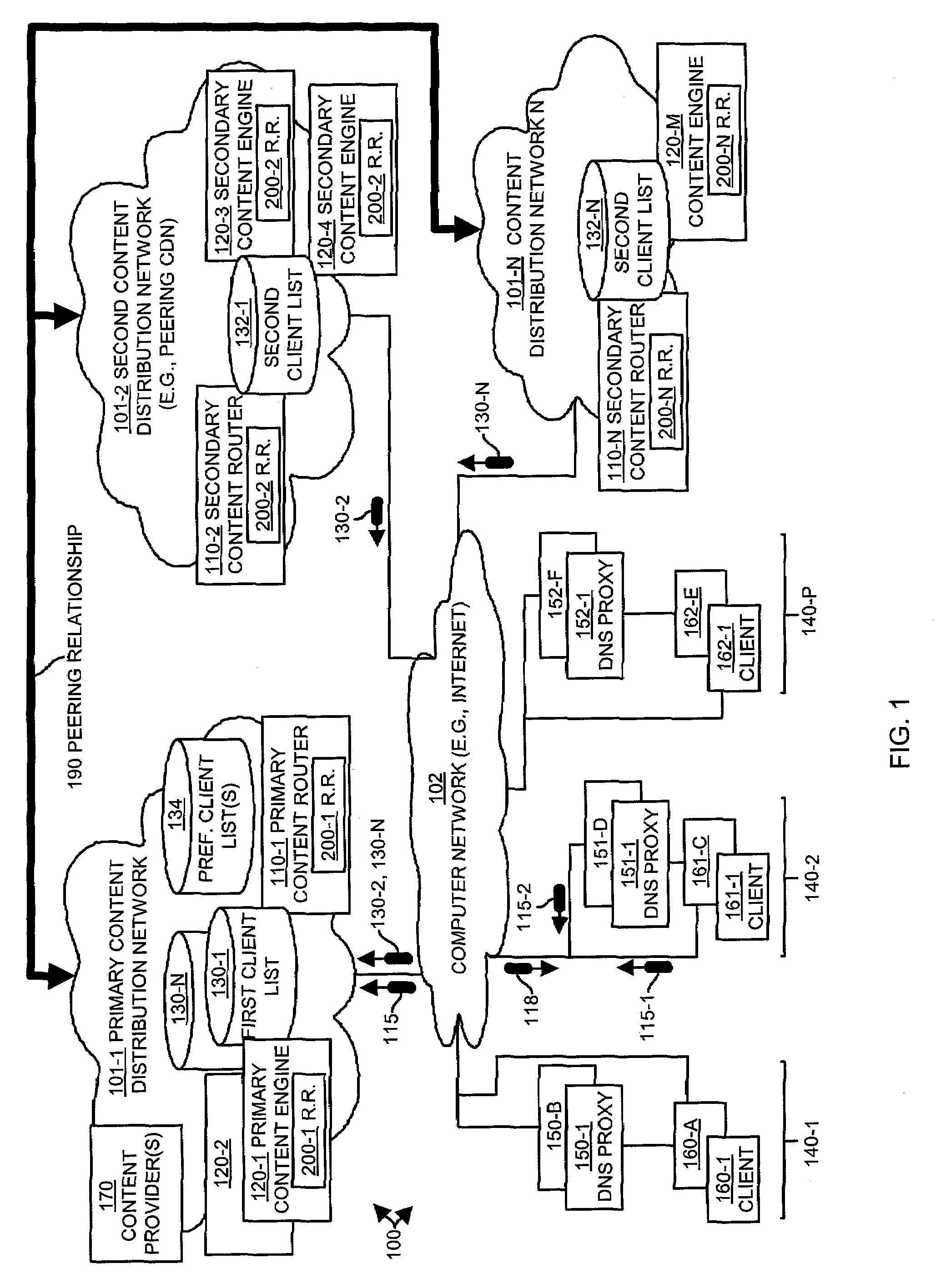
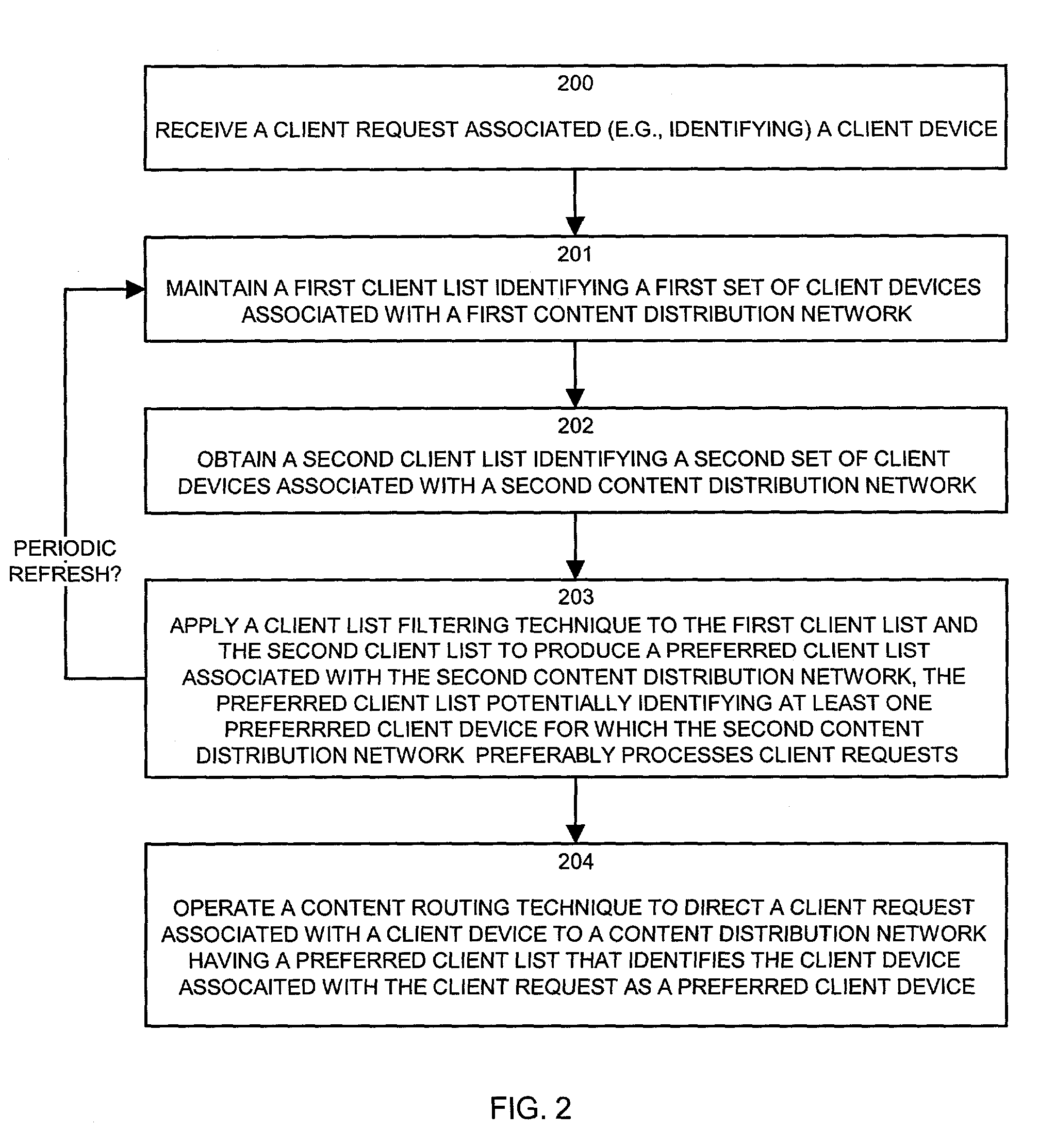
Methods and apparatus for processing client requests in a content distribution network using client lists
InactiveUS7260598B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsContent distributionSystem maintenance
Mechanisms and techniques operating in a content distribution network in a peering relationship with a second content distribution network. The system maintains a first client list identifying a first set of client devices associated with a first content distribution network. The system also obtains a second client list identifying a second set of client devices associated with a second content distribution network. The system applies a client list filtering technique to the first client list and the second client list to produce a preferred client list associated with the second content distribution network. The preferred client list potentially identifies at least one preferred client device for which the second content distribution network preferably processes client requests. The system then operates a content routing technique to direct a client request associated with a client device to a content distribution network having a preferred client list that identifies the client device associated with the client request as a preferred client device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
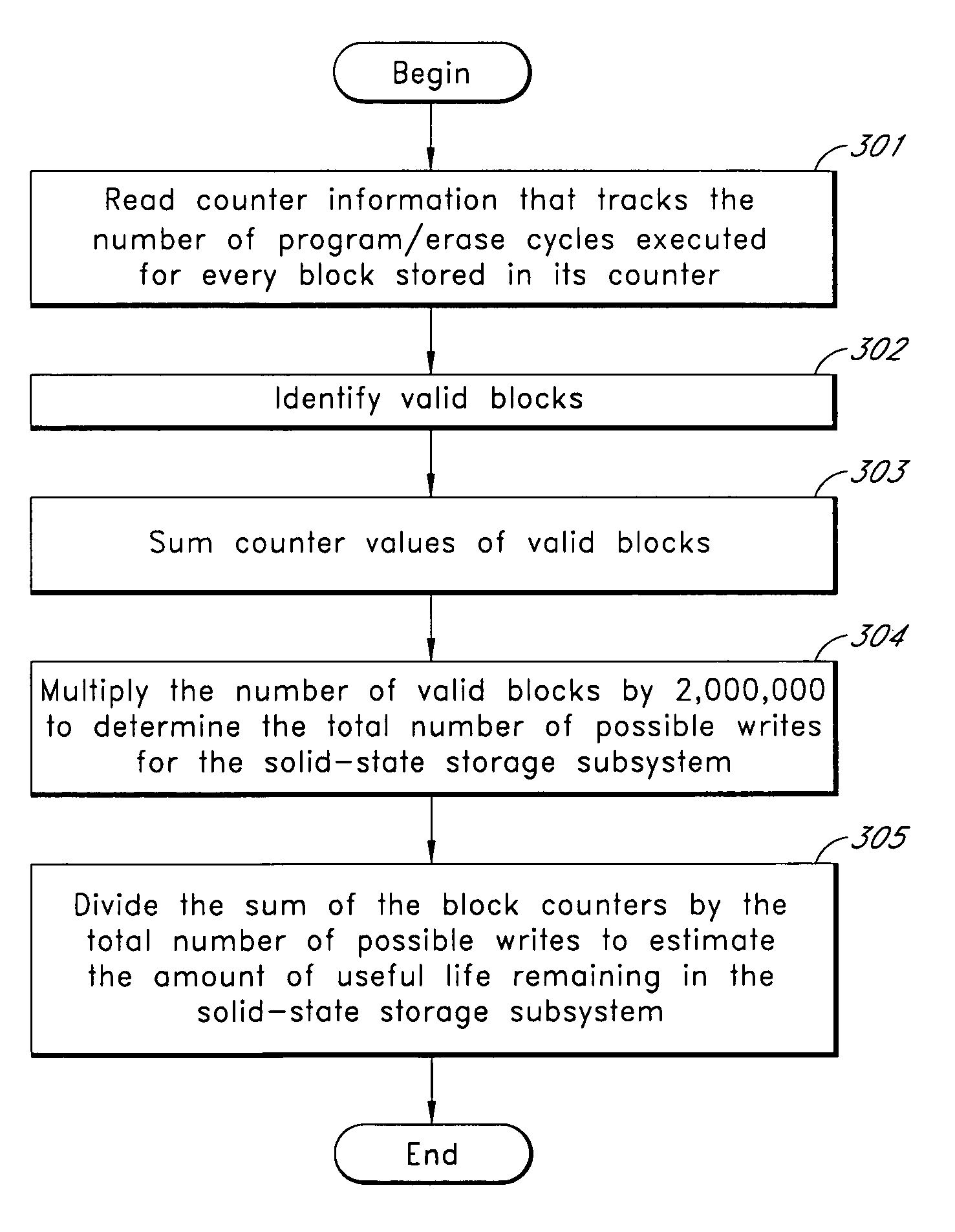
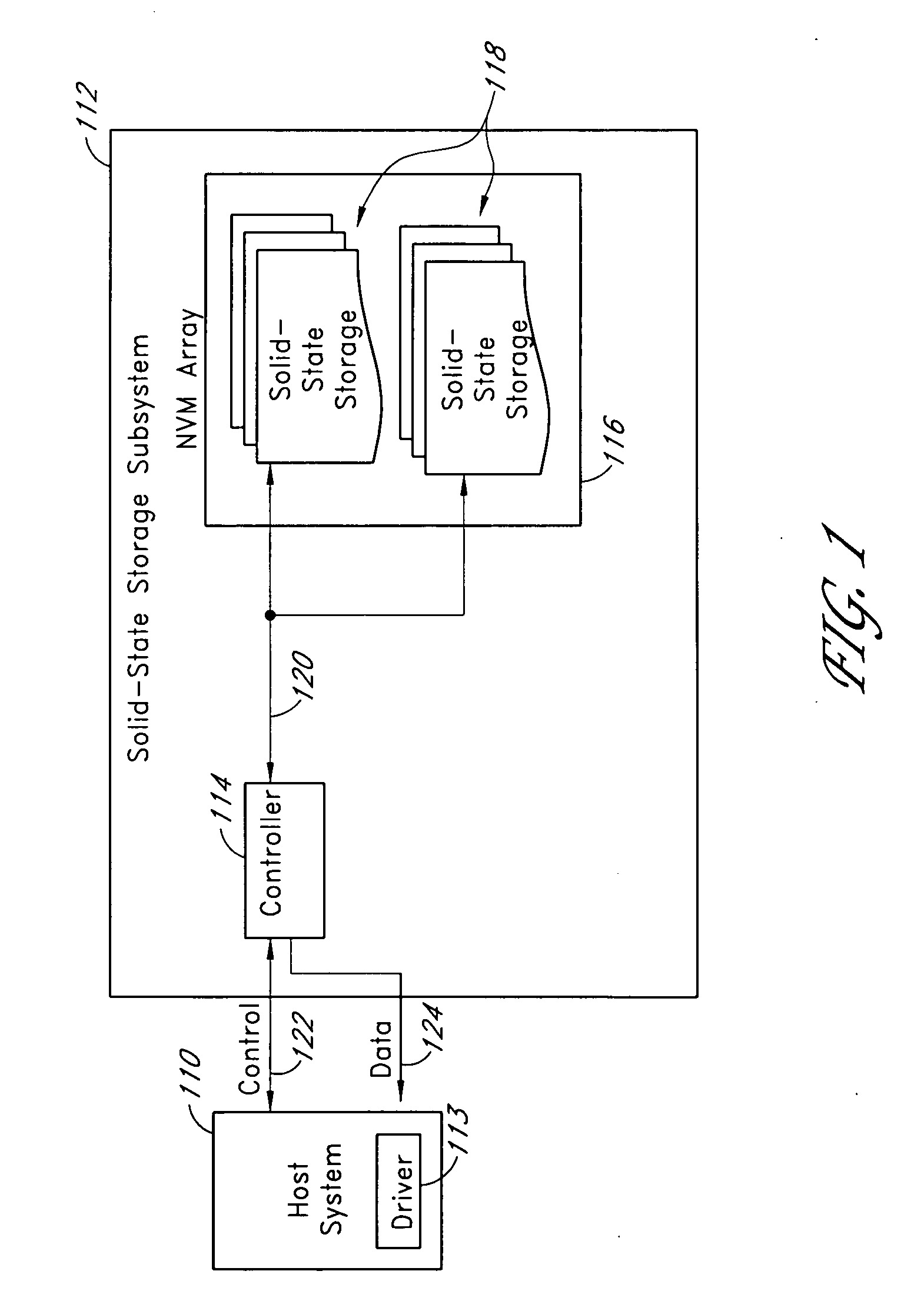
Systems and methods for measuring the useful life of solid-state storage devices
ActiveUS20070260811A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageSystem maintenance
A non-volatile solid-state storage subsystem, such as a non-volatile memory device, maintains usage statistics reflective of the wear state, and thus the remaining useful life, of the subsystem's memory array. A host system reads the usage statistics information, or data derived therefrom, from the subsystem to evaluate the subsystem's remaining life expectancy. The host system may use this information for various purposes, such as to (a) display or report information regarding the remaining life of the subsystem; (b) adjust the frequency with which data is written to the subsystem; and / or (c) select the type(s) of data written to the subsystem.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Consistency methods and systems
InactiveUS20070214194A1Maintain data consistencyError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsTimestampDistributed data store
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods for maintaining data consistency of data blocks during migration or reconfiguration of a current configuration within a distributed data-storage system to a new configuration. In one embodiment of the present invention, the current configuration is first determined to be reconfigured. The new configuration is then initialized, and data blocks are copied from the current configuration to the new configuration. Then, the configuration states maintained by component data-storage systems that store data blocks of the current and new configurations are synchronized. Finally, the current configuration is deallocated. In a second embodiment of the present invention, a current configuration is determined to be reconfigured, and, while carrying out continuing READ and WRITE operations directed to data blocks of the current configuration in a data-consistent manner, the new configuration is initialized, data blocks are copied from the current configuration to the new configuration, and the timestamp and data states for the data blocks of the current and new configurations are synchronized.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
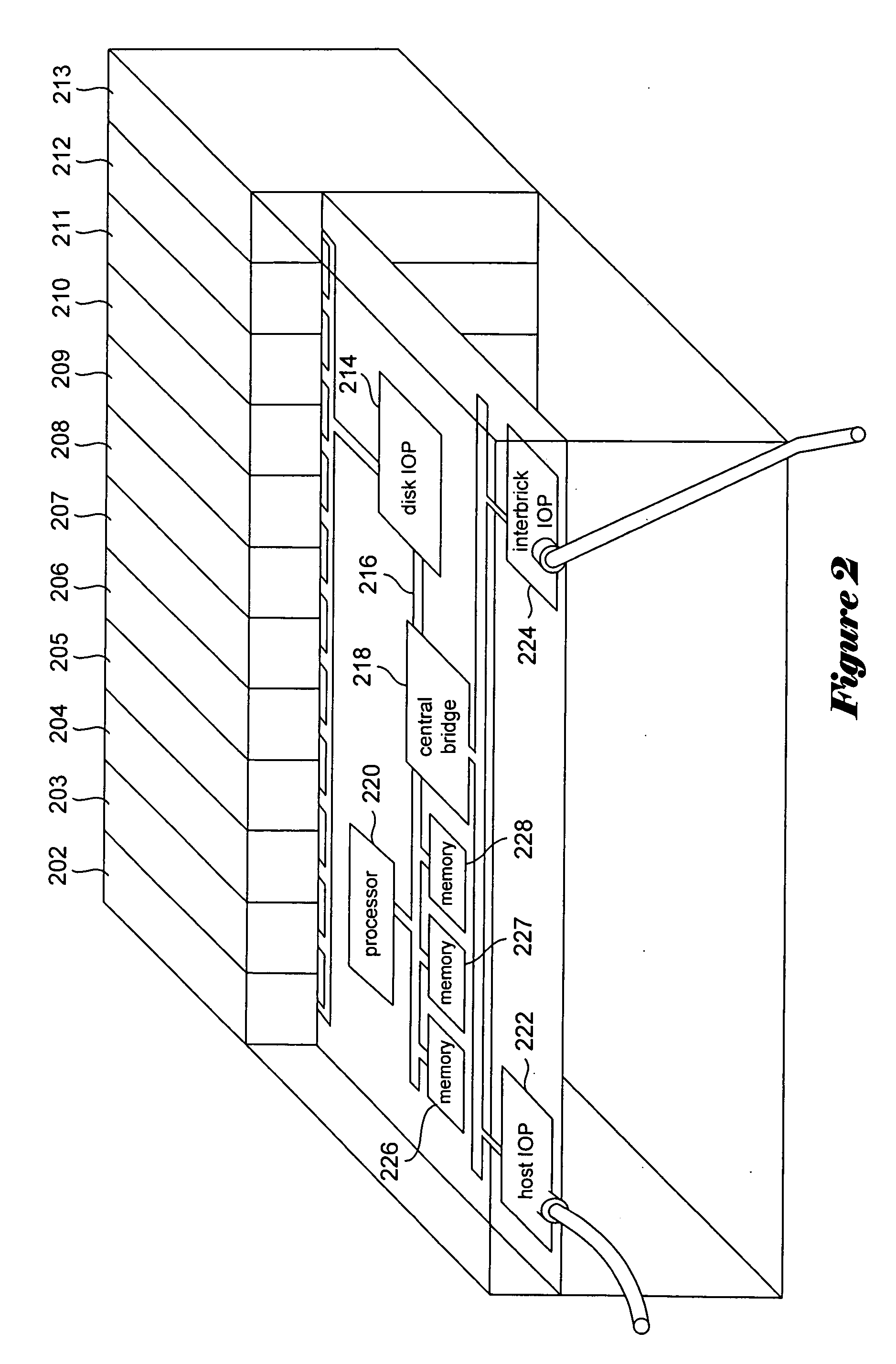
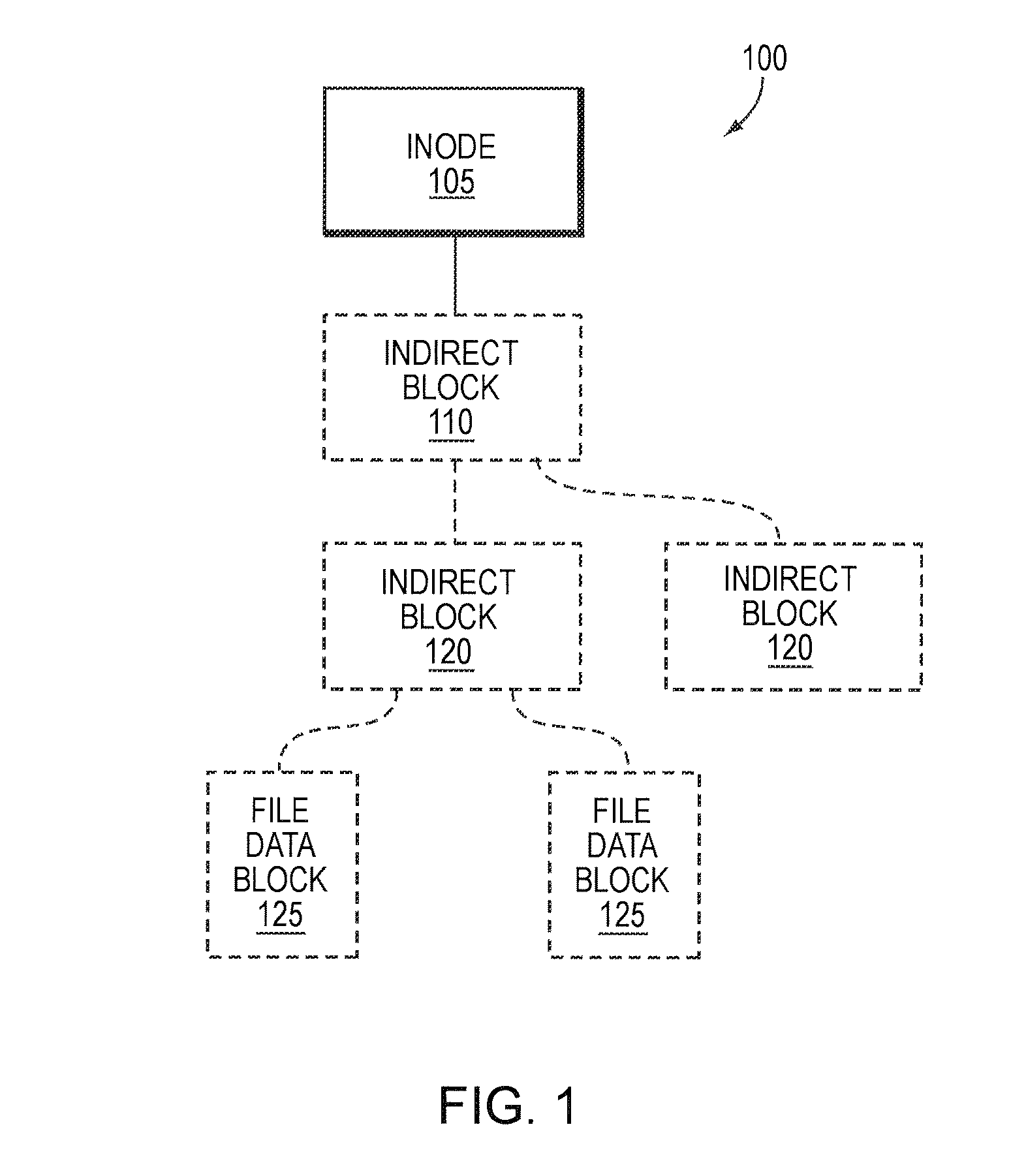
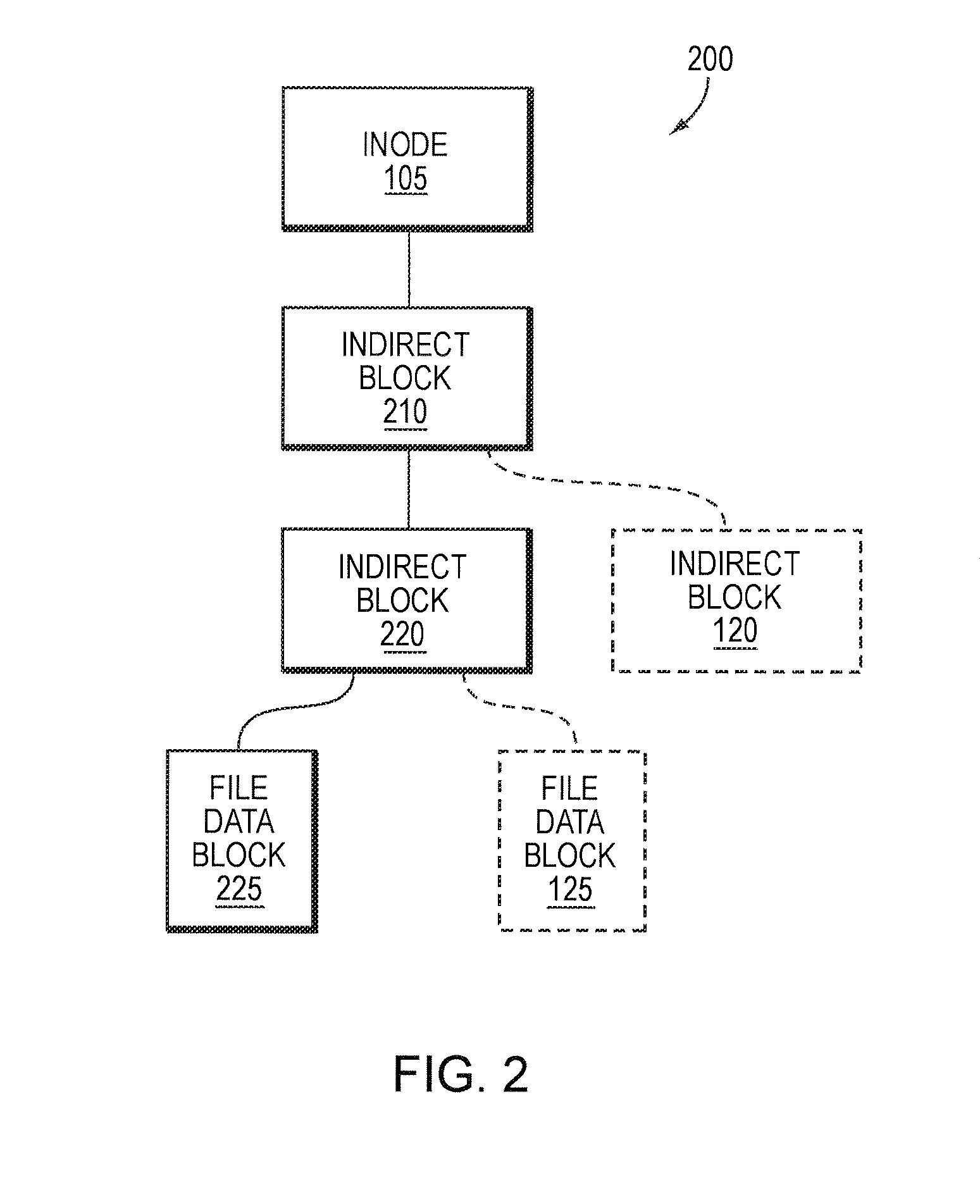
Storage system-based hole punching for reclaiming unused space from a data container
ActiveUS8086652B1Maintain integrityOvercome disadvantagesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemSystem maintenance
A system and method reclaims unused storage space from a data container, such as a logical unit number (LUN) of a storage system. In particular, a novel technique is provided that allows a storage system to reclaim storage space not used by a client file system for which the storage system maintains storage, without requiring assistance from the client file system to determine storage usage. In other words, storage system may independently reclaim storage space not used by the client file system, without that file system's intervention.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Online markerplace for real estate transactions
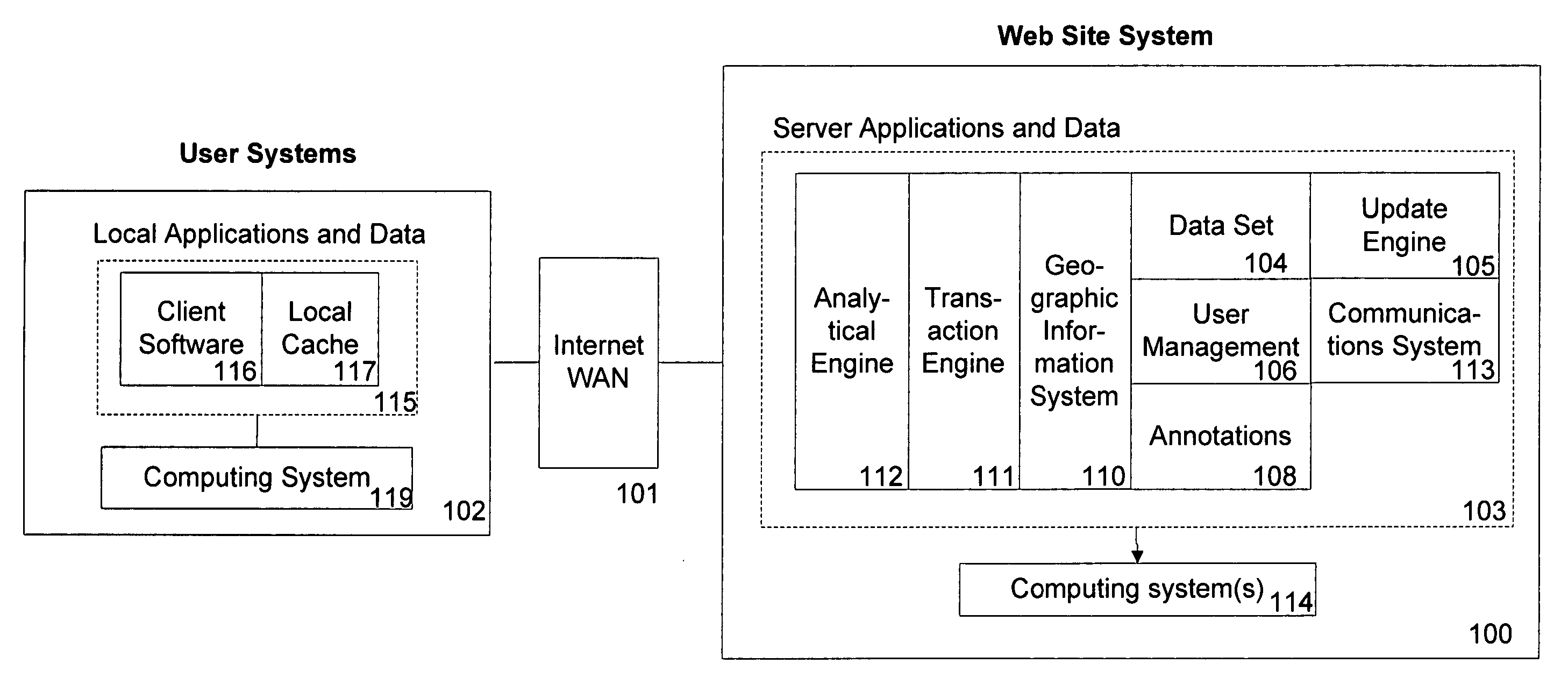
ActiveUS20050288958A1Facilitates online collaborationGood choiceCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteGeographic regions
Under an embodiment of the invention, a web site system maintains a real estate web page. The web page has an aerial image map of a geographic region that can be navigated by a user. The web site system facilitates online collaboration for real estate transactions. When the user registers, the system creates a user account for real estate information. Real estate agents and / or other real estate service providers selected by the user are granted shared access to the user's account by the web site system.
Owner:REDFIN CORP
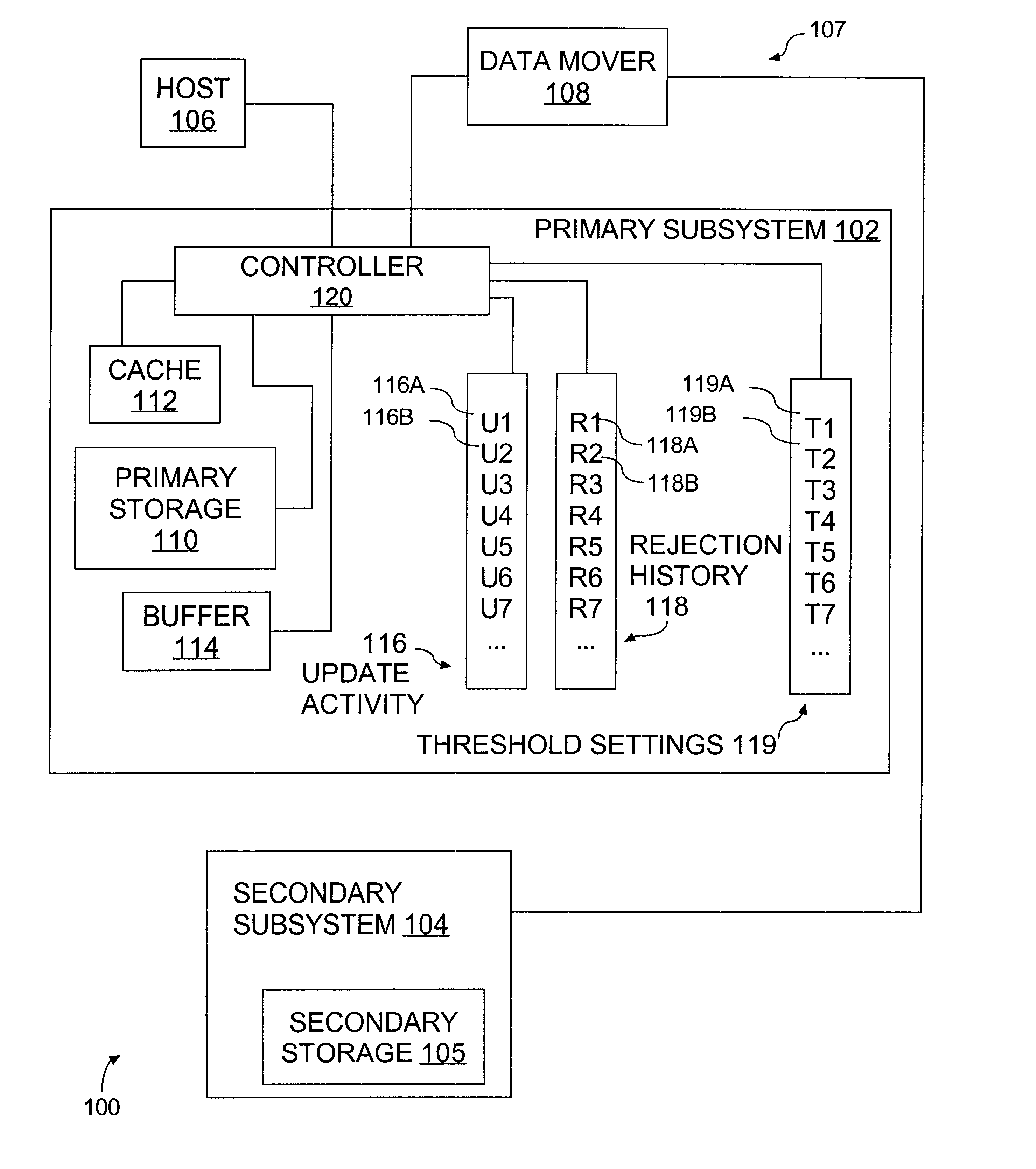
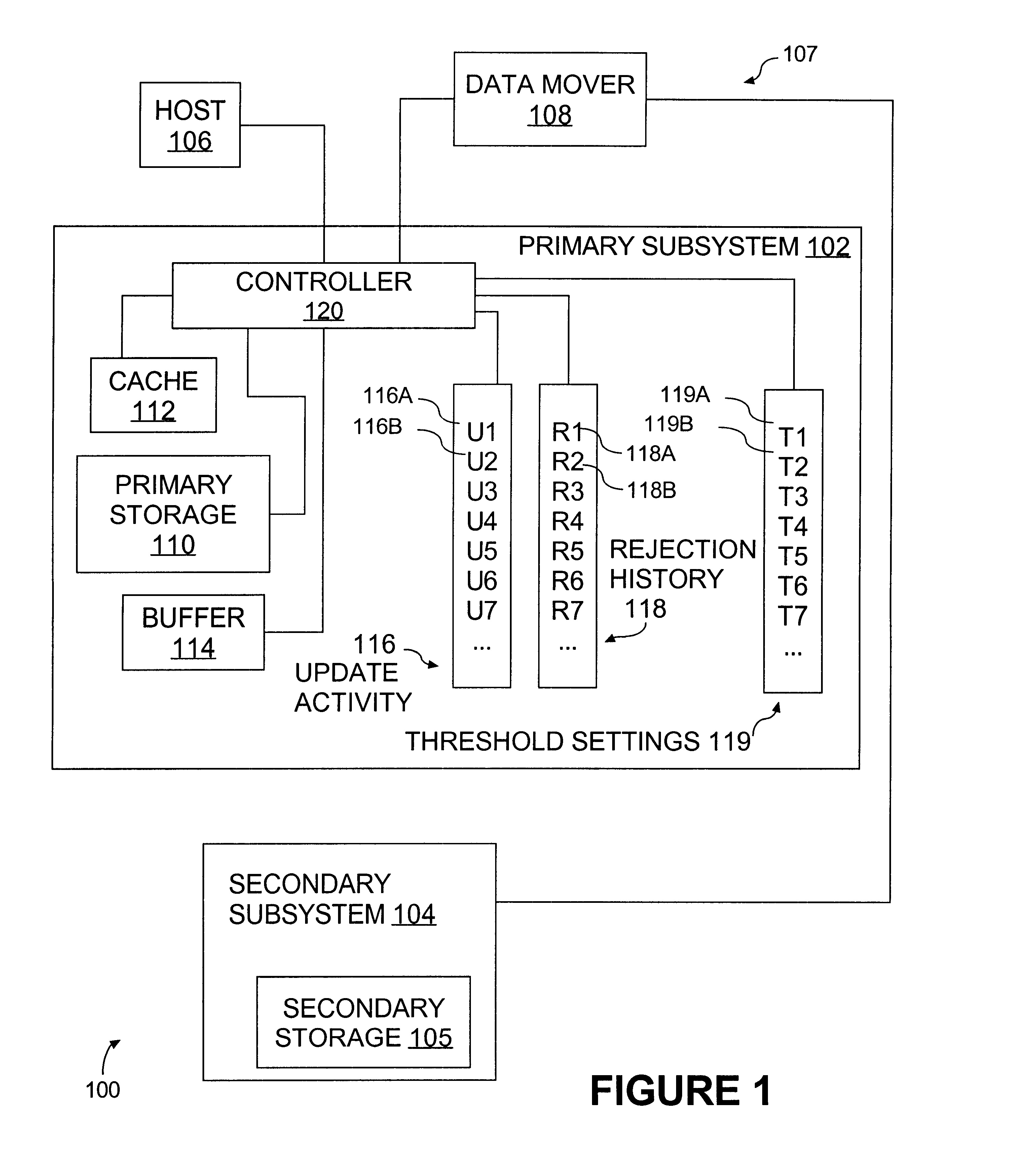
Data storage subsystem with fairness-driven update blocking
InactiveUS6487645B1Input/output to record carriersData processing applicationsComputer hardwareSystem maintenance
Owner:IBM CORP
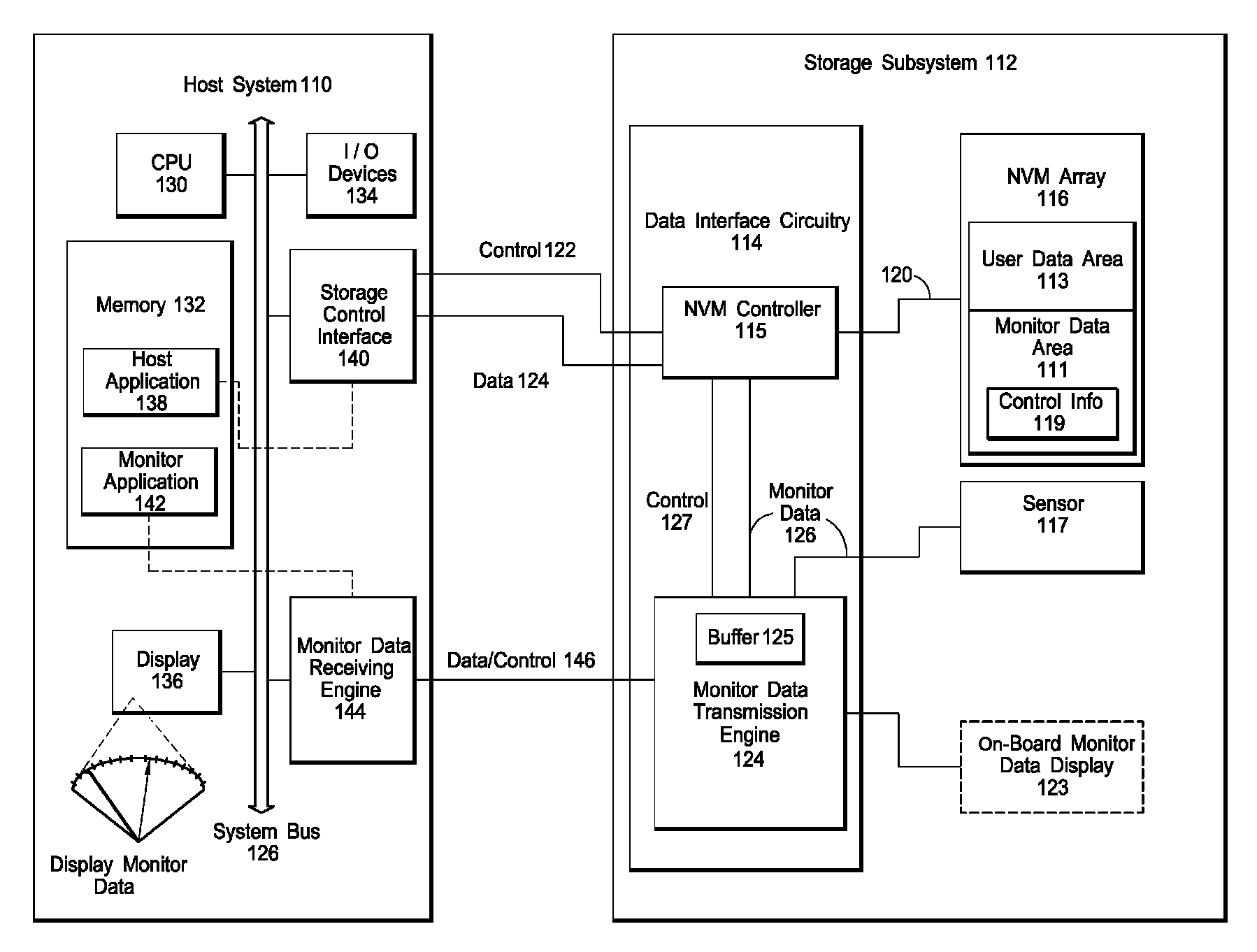
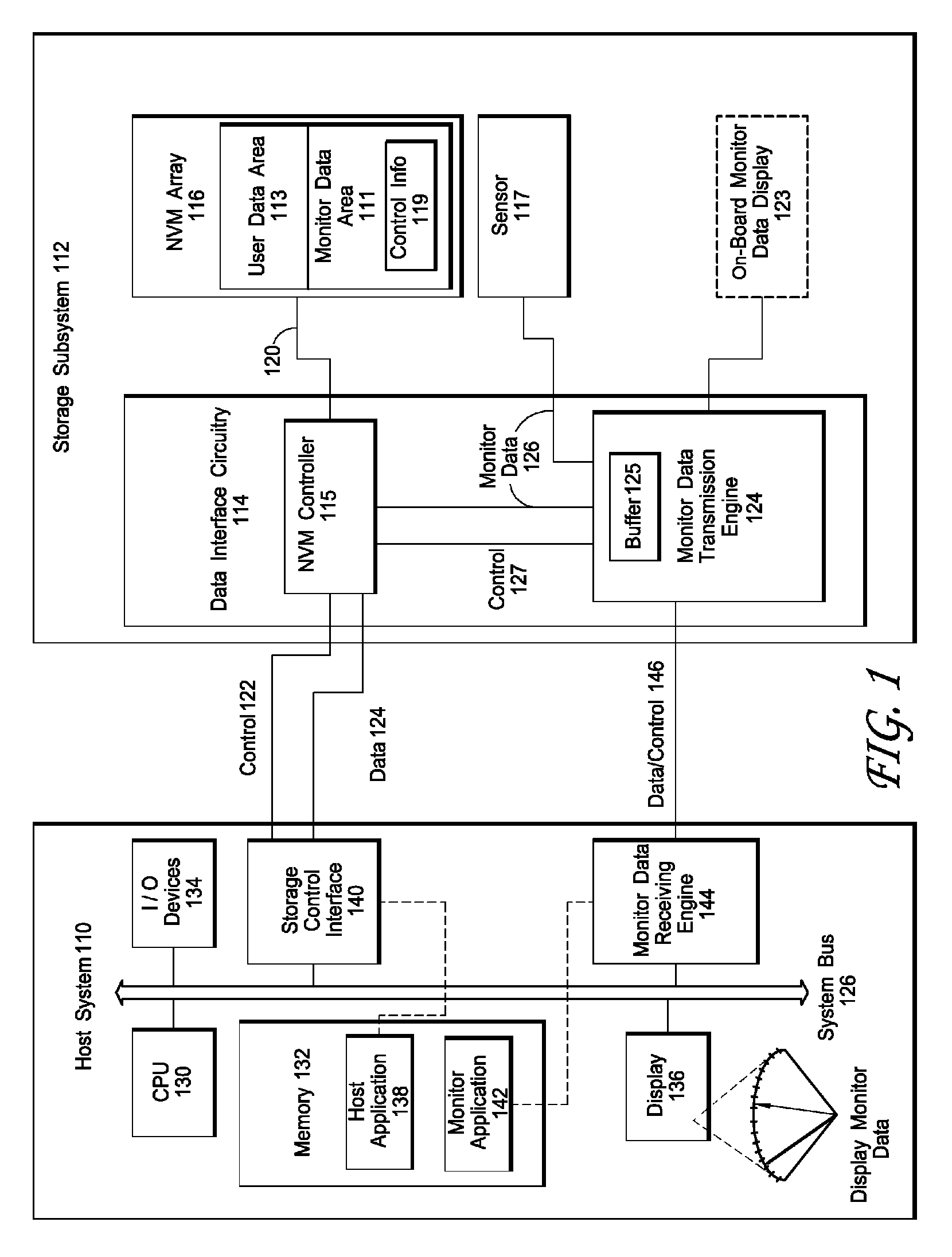
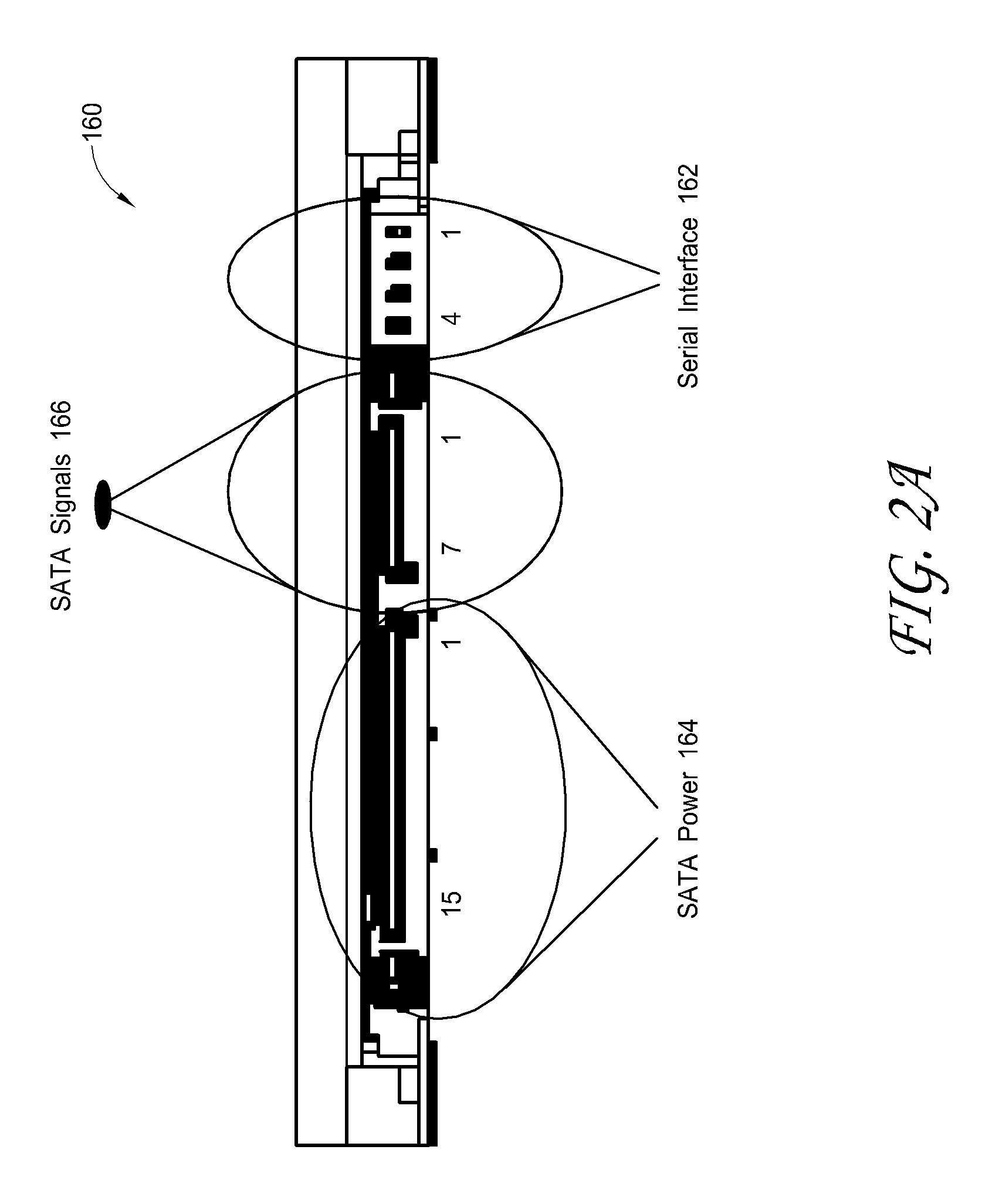
Interface for enabling a host computer to retrieve device monitor data from a solid state storage subsystem
ActiveUS7962792B2Reduce eliminateReduce the possibilityReliability/availability analysisInput/output processes for data processingSolid-state storageDevice Monitor
A non-volatile storage subsystem maintains, and makes available to a host system, monitor data reflective of a likelihood of a data error occurring. The monitor data may, for example, include usage statistics and / or sensor data. The storage subsystem transfers the monitor data to the host system over a signal interface that is separate from the signal interface used for standard storage operations. This interface may be implemented using otherwise unused pins / signal lines of a standard connector, such as a CompactFlash or SATA connector. Special hardware may be provided in the storage subsystem and host system for transferring the monitor data over these signal lines, so that the transfers occur with little or no need for host-software intervention. The disclosed design reduces or eliminates the need for host software that uses non-standard or “vendor-specific” commands to retrieve the monitor data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
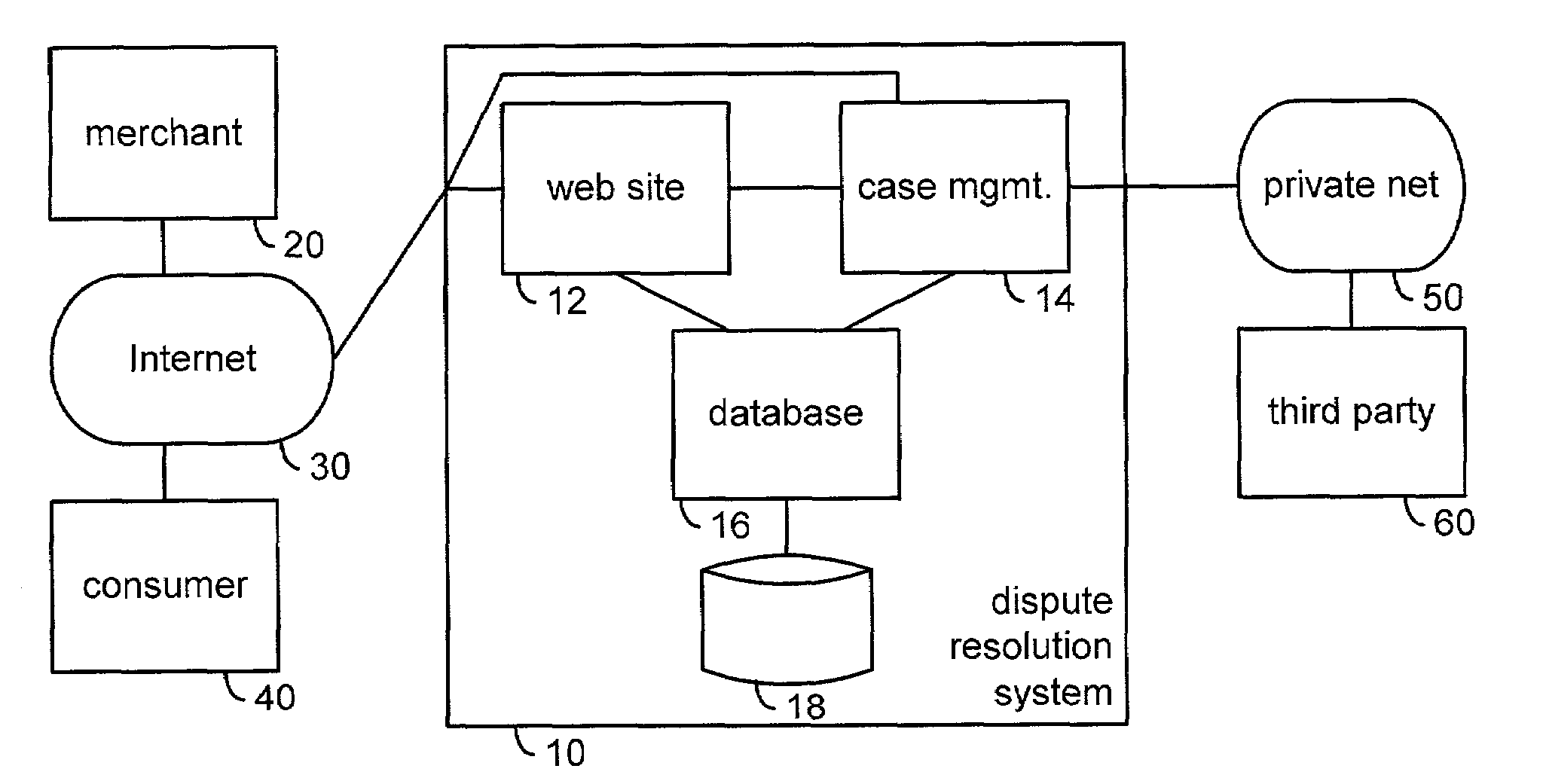
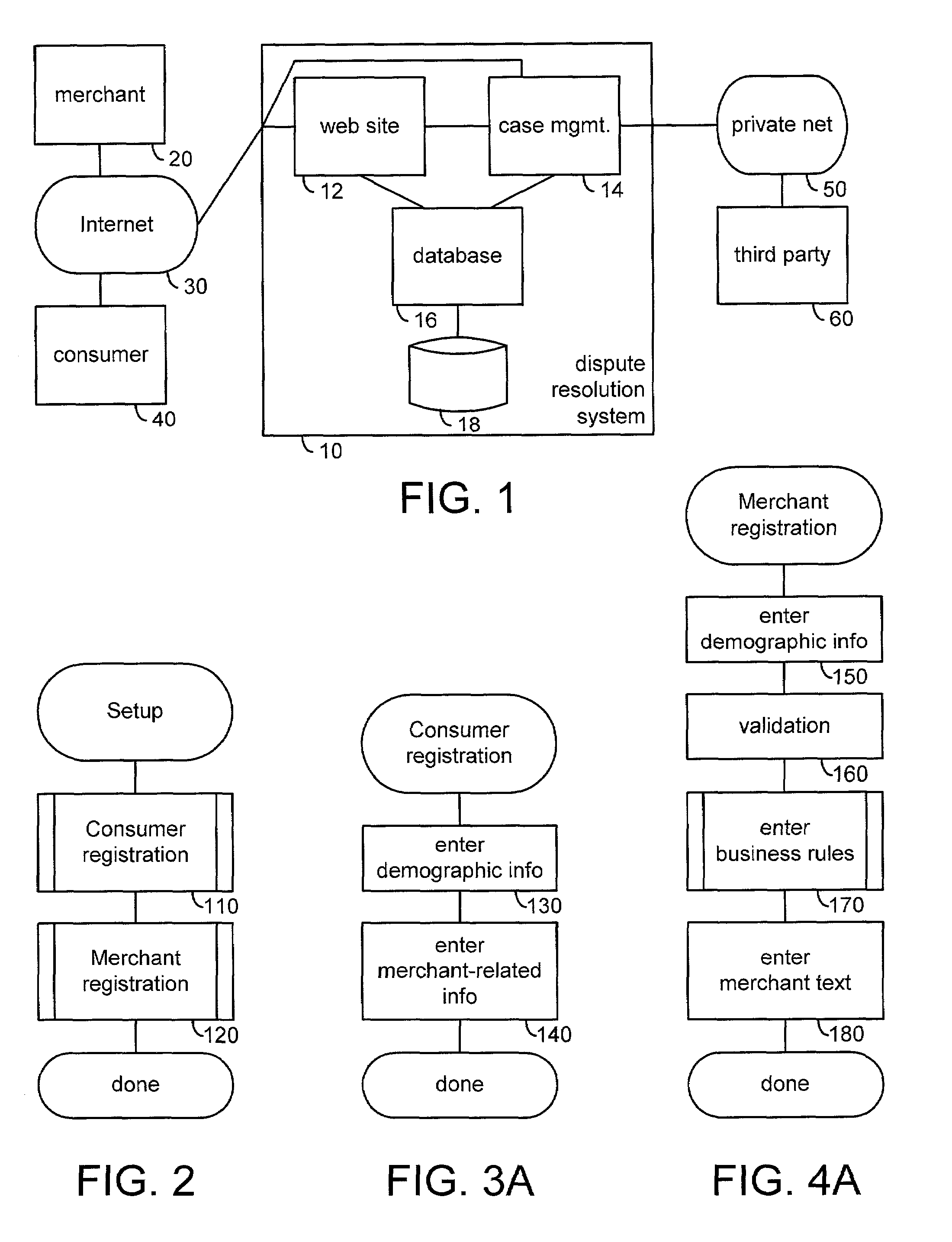
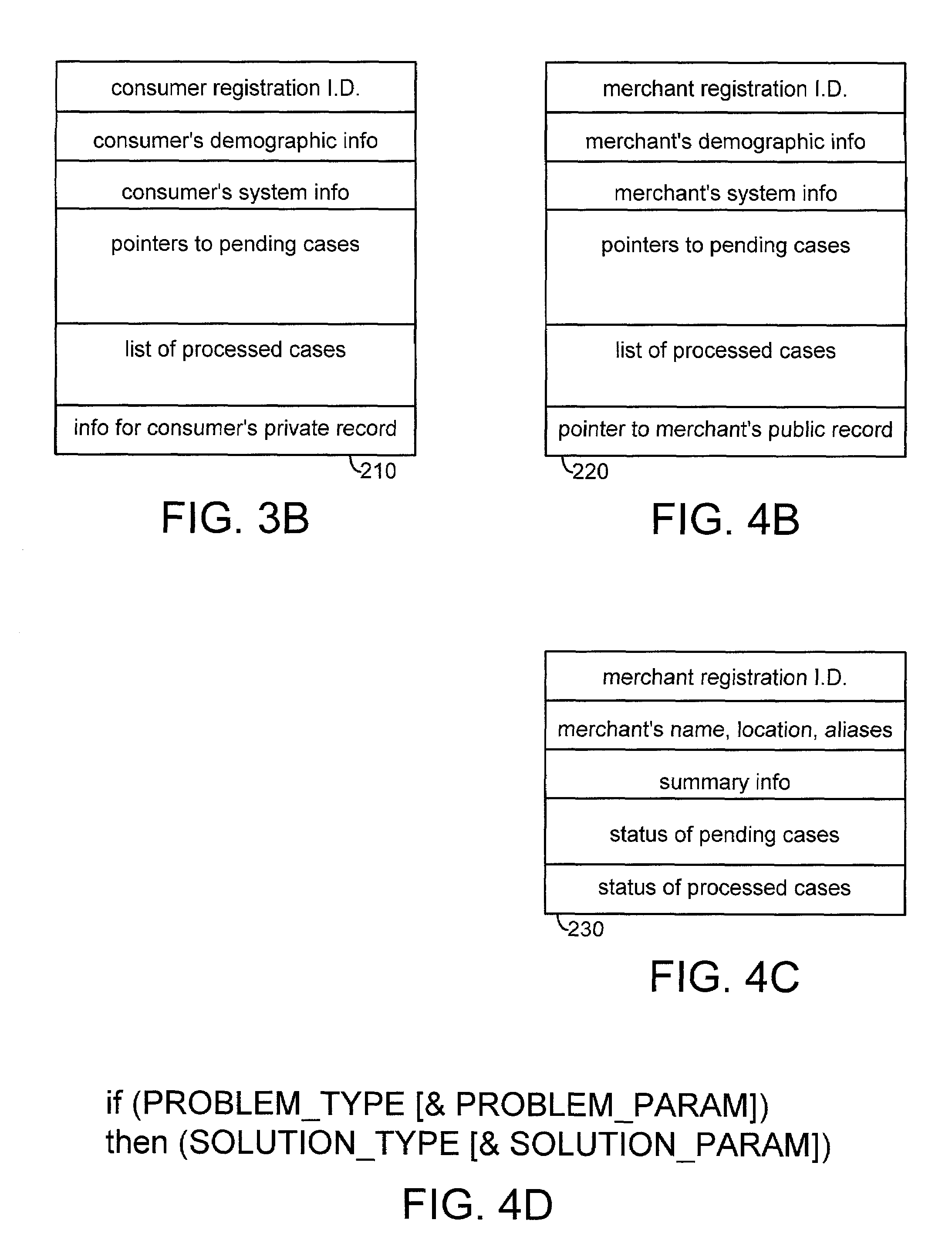
Automated complaint resolution system
A complaint resolution system, also referred to as a disputes system, enables registered consumers to file a complaint against a merchant. During complaint preparation, the disputes system advises the consumer of relevant cases and other information, allows the consumer to vent their emotions, and prepares a well-formed complaint on behalf of the consumer. After the consumer approves filing of the complaint, the complaint is compared with the merchant's stored business rules. If the merchant's solution for the problem and the consumer's desired solution match, then the disputes system automatically forms an agreement. The disputes system monitors compliance with the agreement by the merchant and consumer. If the merchant has specified a business rule for the problem, but the merchant's solution for the problem and the consumer's desired solution differ, then the disputes system initiates automated mediation, automatically preparing an Answer comprising the solution from the merchant's business rule as the merchant's starting negotiating position. If the merchant has not specified a business rule for the consumer's problem, then the disputes system initiates automated mediation, asking the merchant for his or her Answer to the consumer's complaint. During processing of the consumer's complaint, the disputes system maintains and updates a detailed case record. At the conclusion of the case, the disputes system automatically prepares an anonymized case summary, and adds the anonymized case summary to a database of anonymized case summaries.
Owner:POMERANCE BRENDA
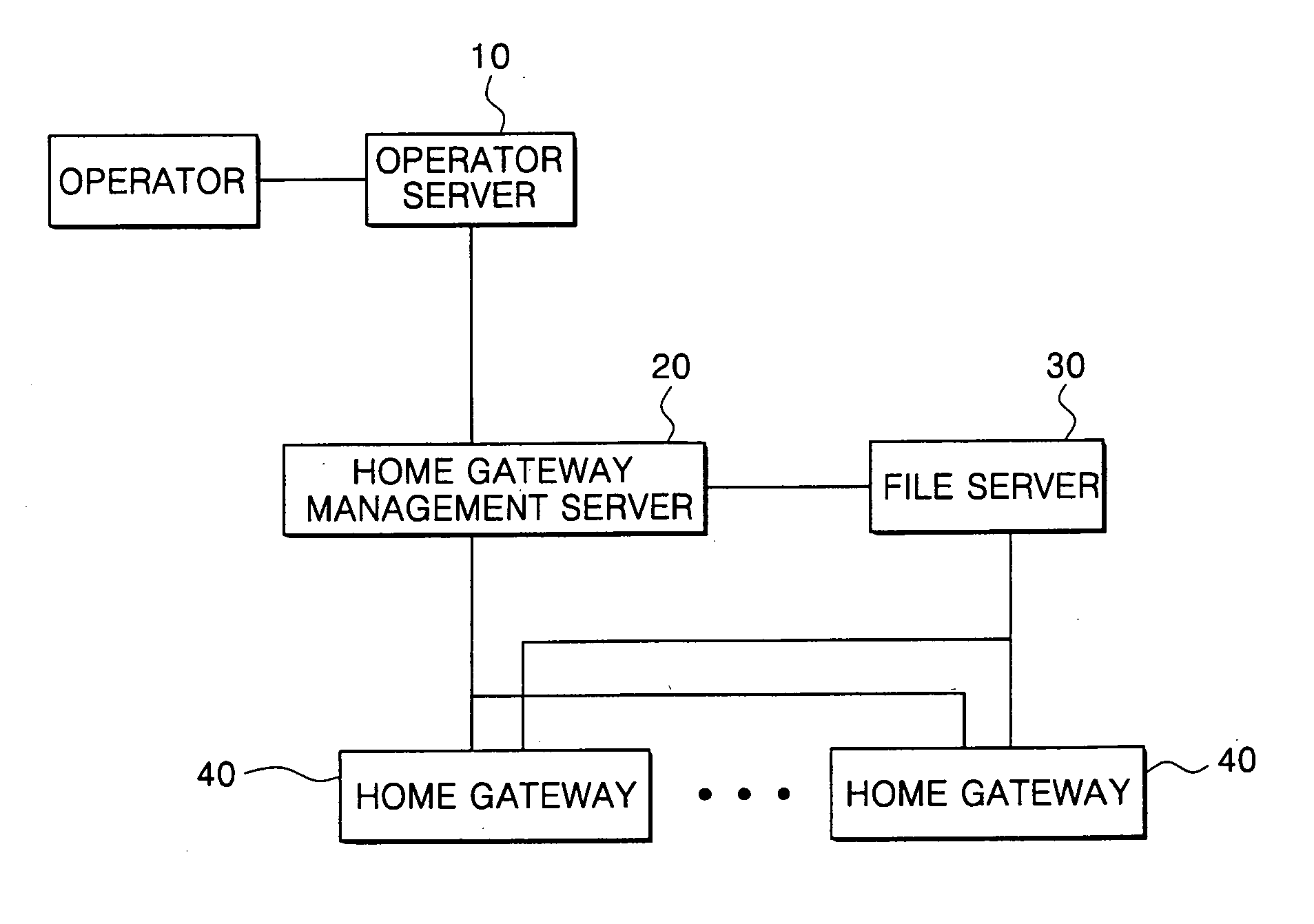
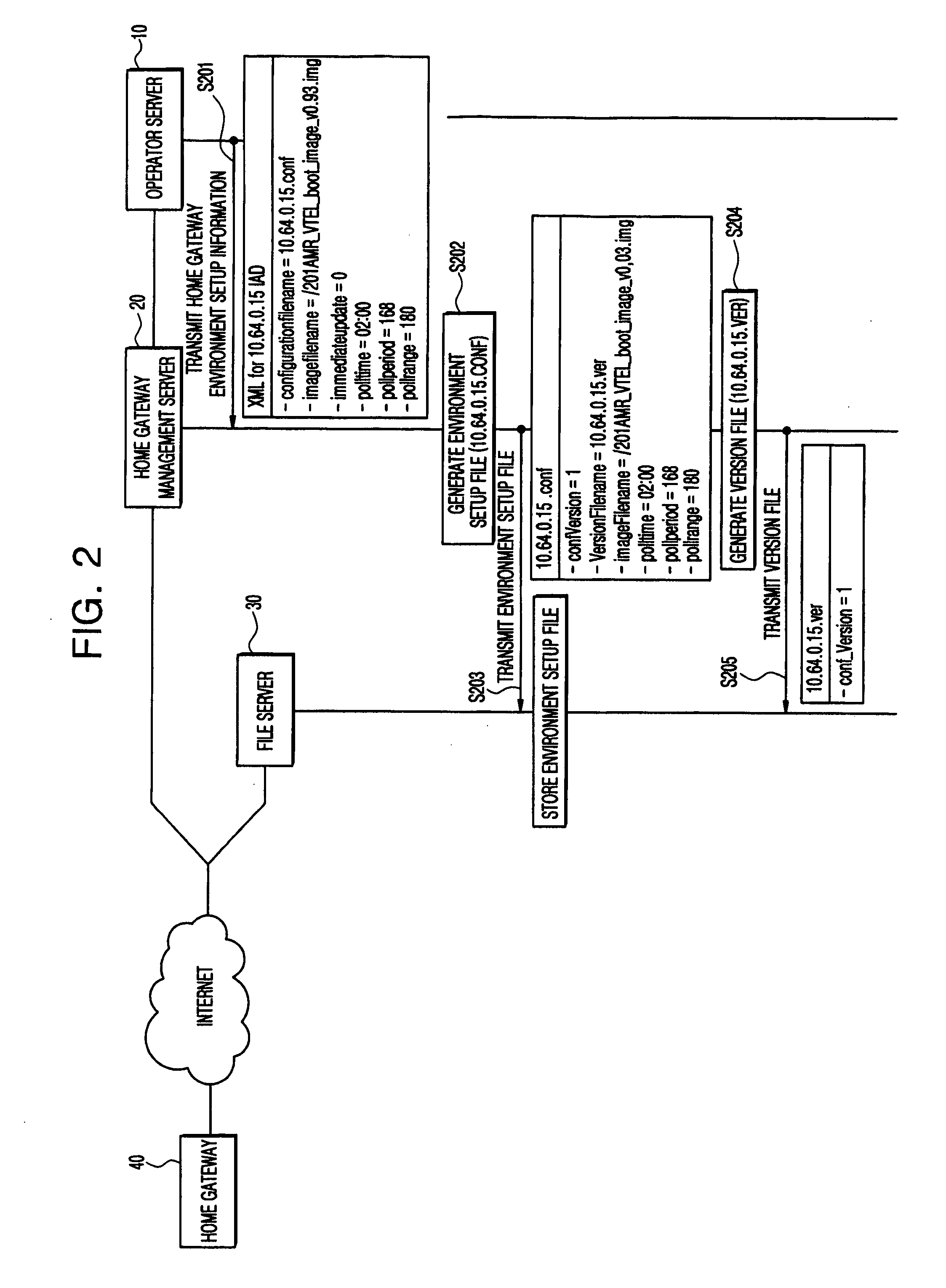
Environment setup apparatus and method for home gateway system
InactiveUS20070061430A1Simple methodSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsSystem maintenanceFile server
An environment setup apparatus and method for a home gateway system for a home gateway that provides triple play service. Even though a user does not manually operate the home gateway, the home gateway automatically downloads and installs an application program from a file server on a network to provide environment setup information and service. This can facilitate home gateway's environment setup and ensure systematic maintenance of the home gateway as well.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
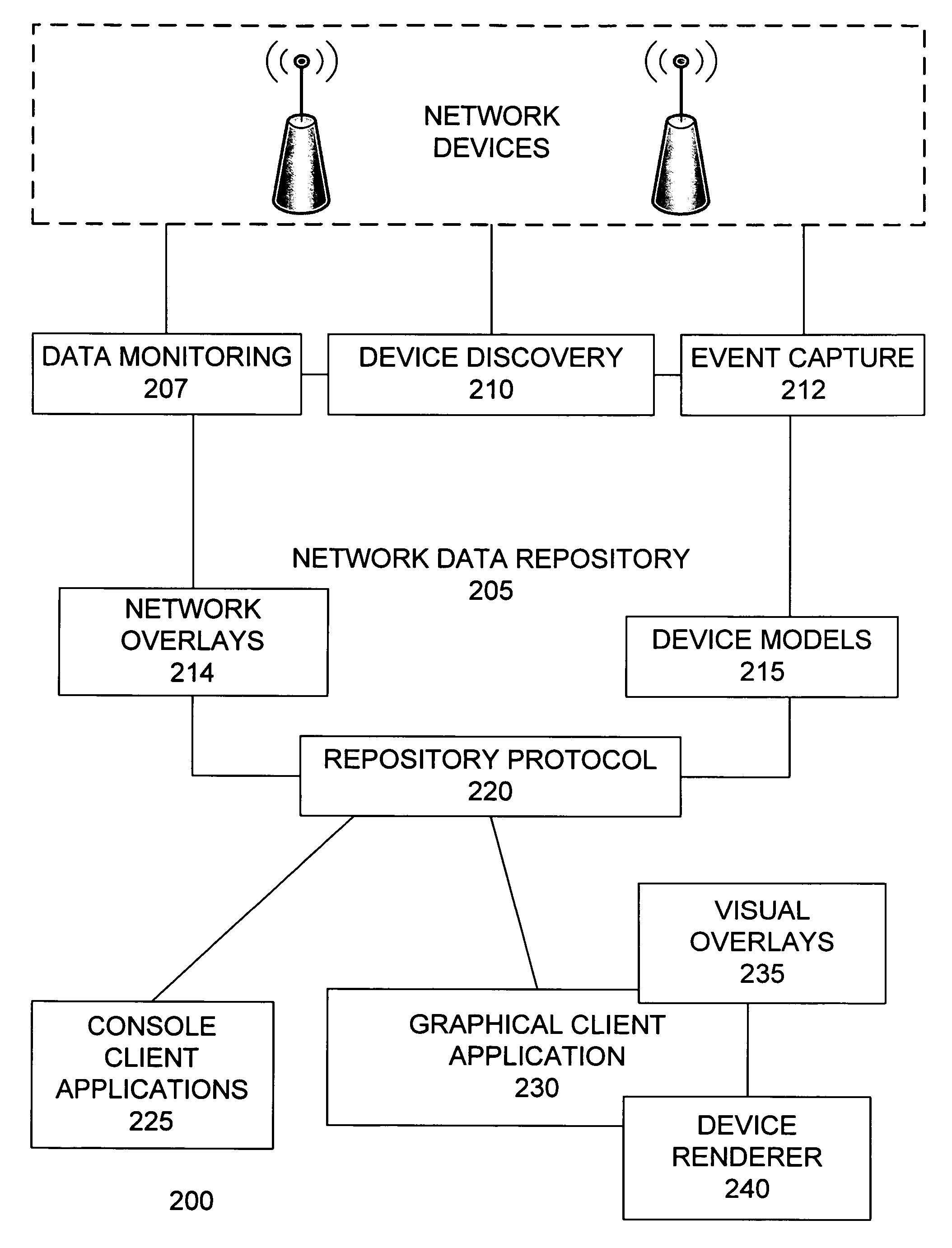
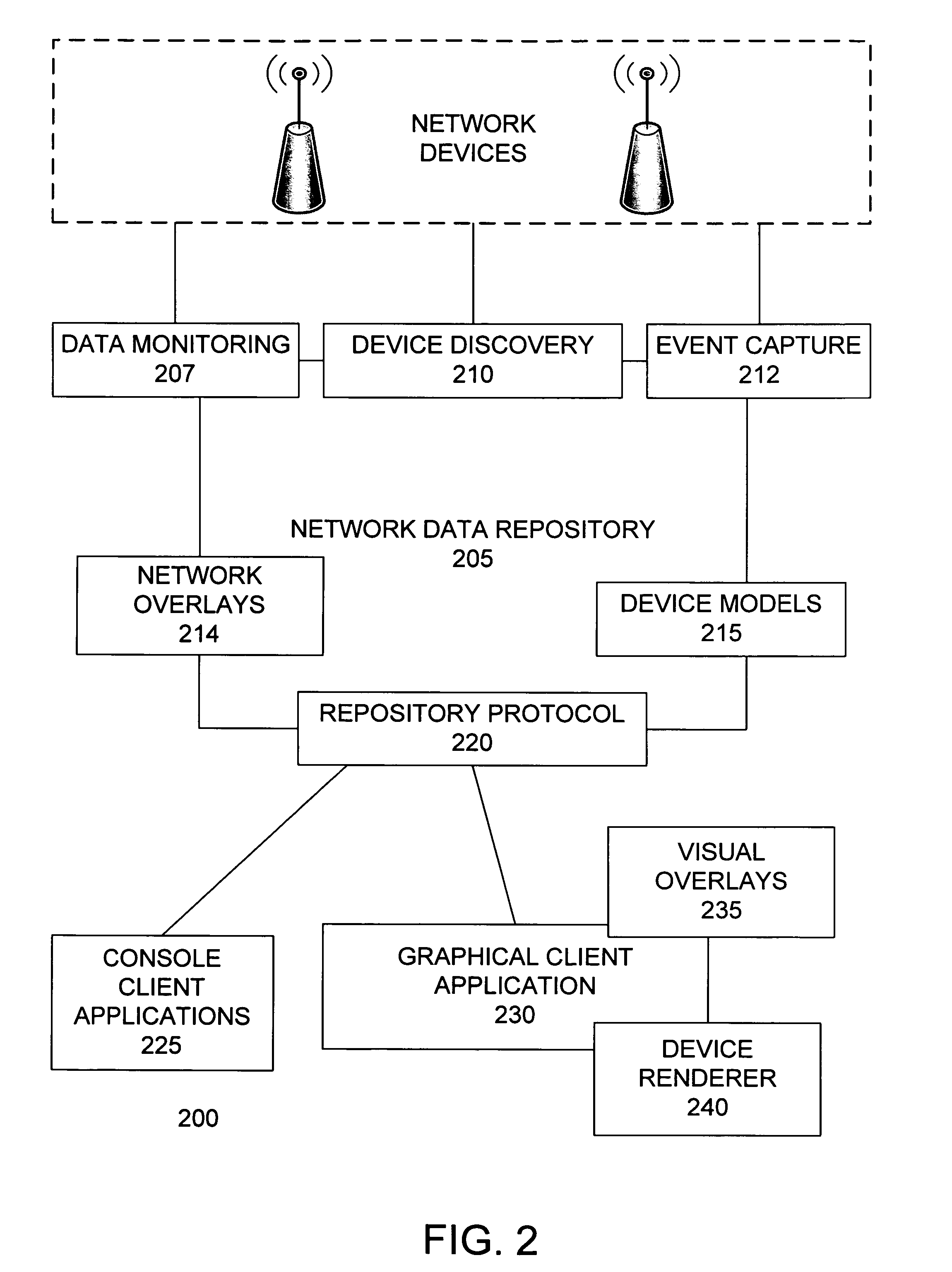
Network monitoring device
ActiveUS20070014248A1CommunicationData switching by path configurationMonitoring systemSystem maintenance
A network monitoring system monitors a data network and enables observation of the data network state in the present or any arbitrary previous time. The system maintains an object-oriented network model that mirrors the state of network devices. A network data repository stores and maintains the network model. The network model retains a history of network events, enabling the system to reconstruct the state of all or a portion of the devices in the network at any previous time. The network data repository detects network devices on the data network to be monitored, communicates with network devices, monitors the state of network devices, receives and records network events, provides device and network state information to client applications, and manages data storage. Client applications can rewind and replay the history of the network model, allowing the observation of network devices and all of their state data at any prior time.
Owner:CHANNEL IP BV
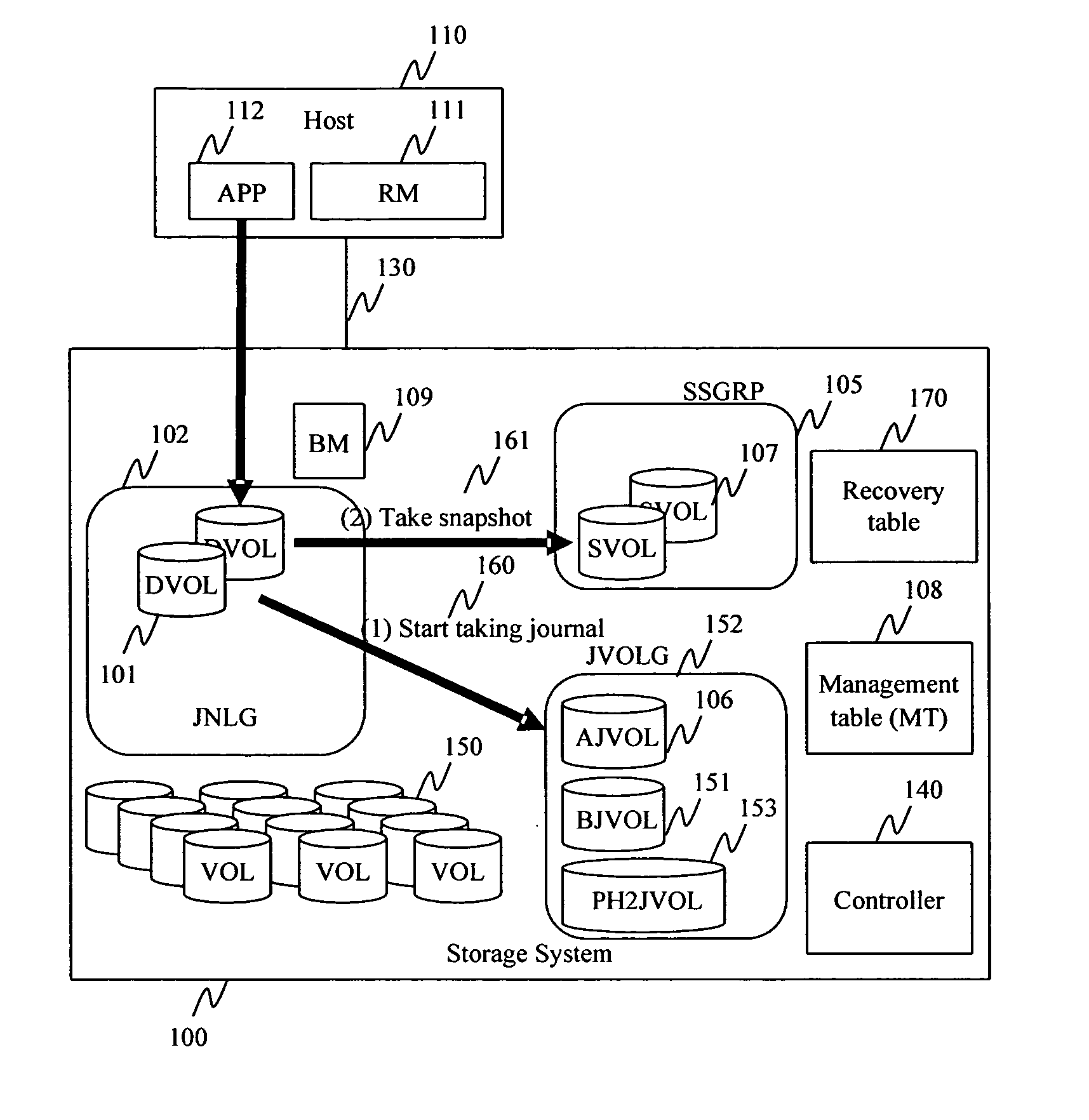
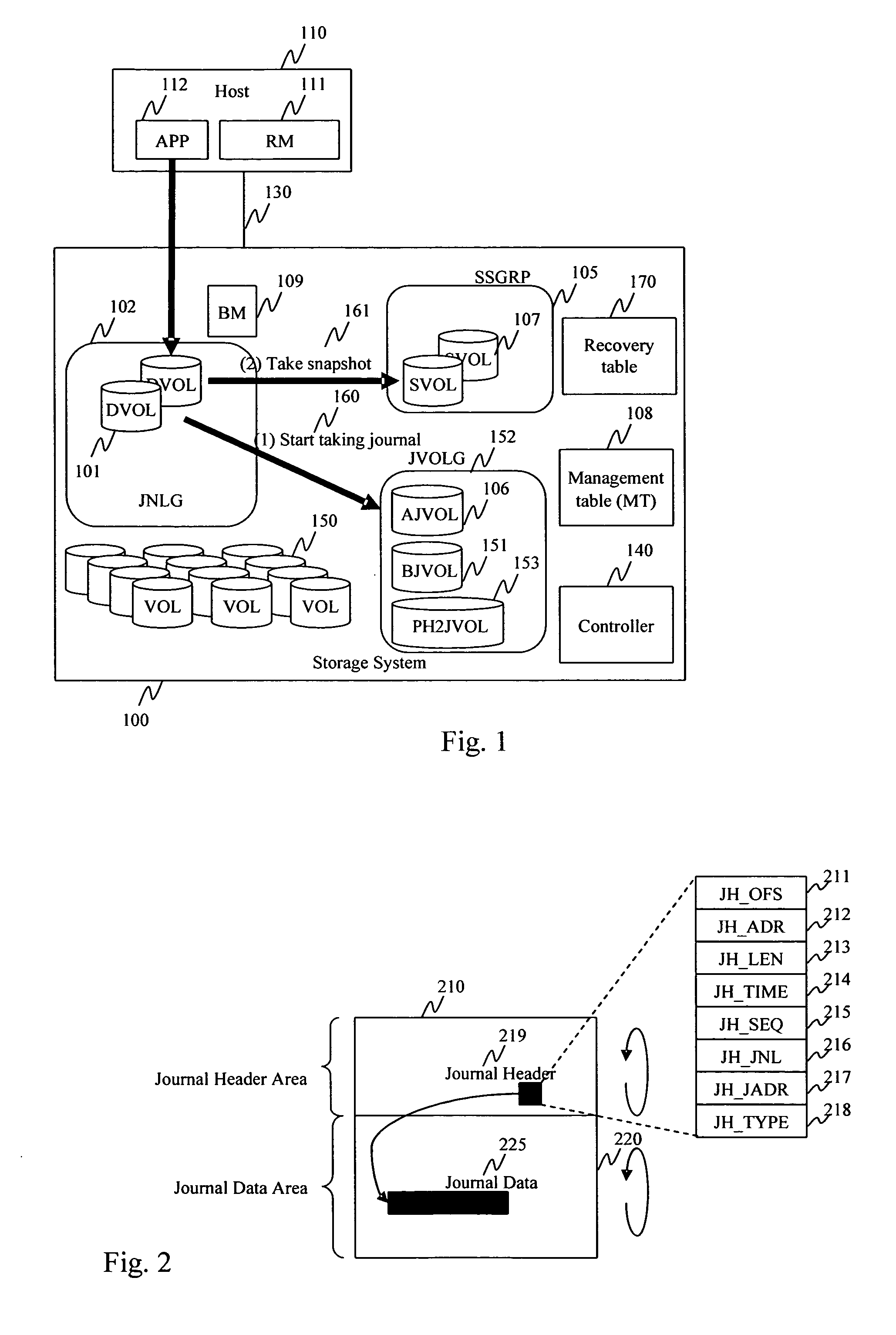
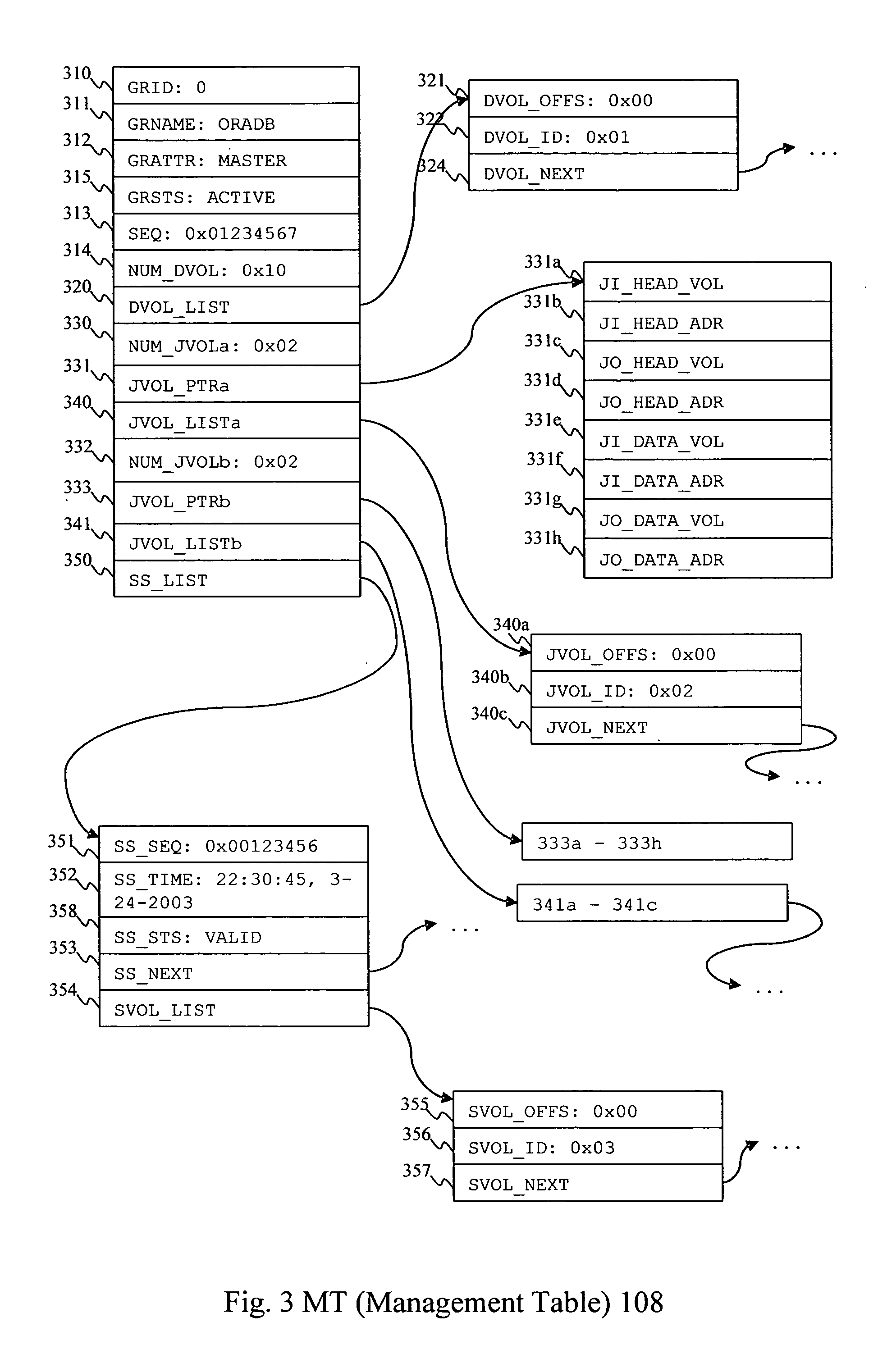
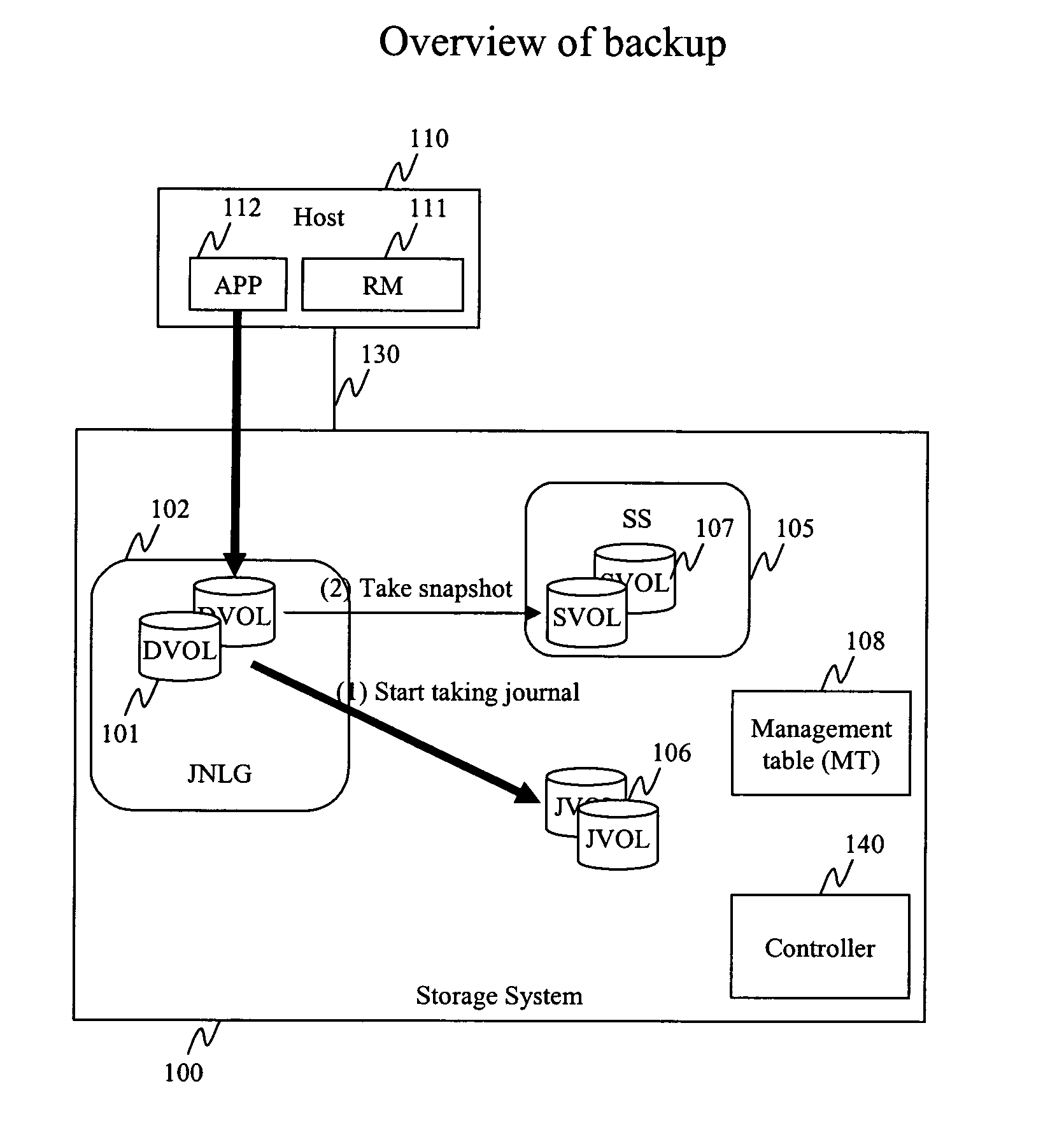
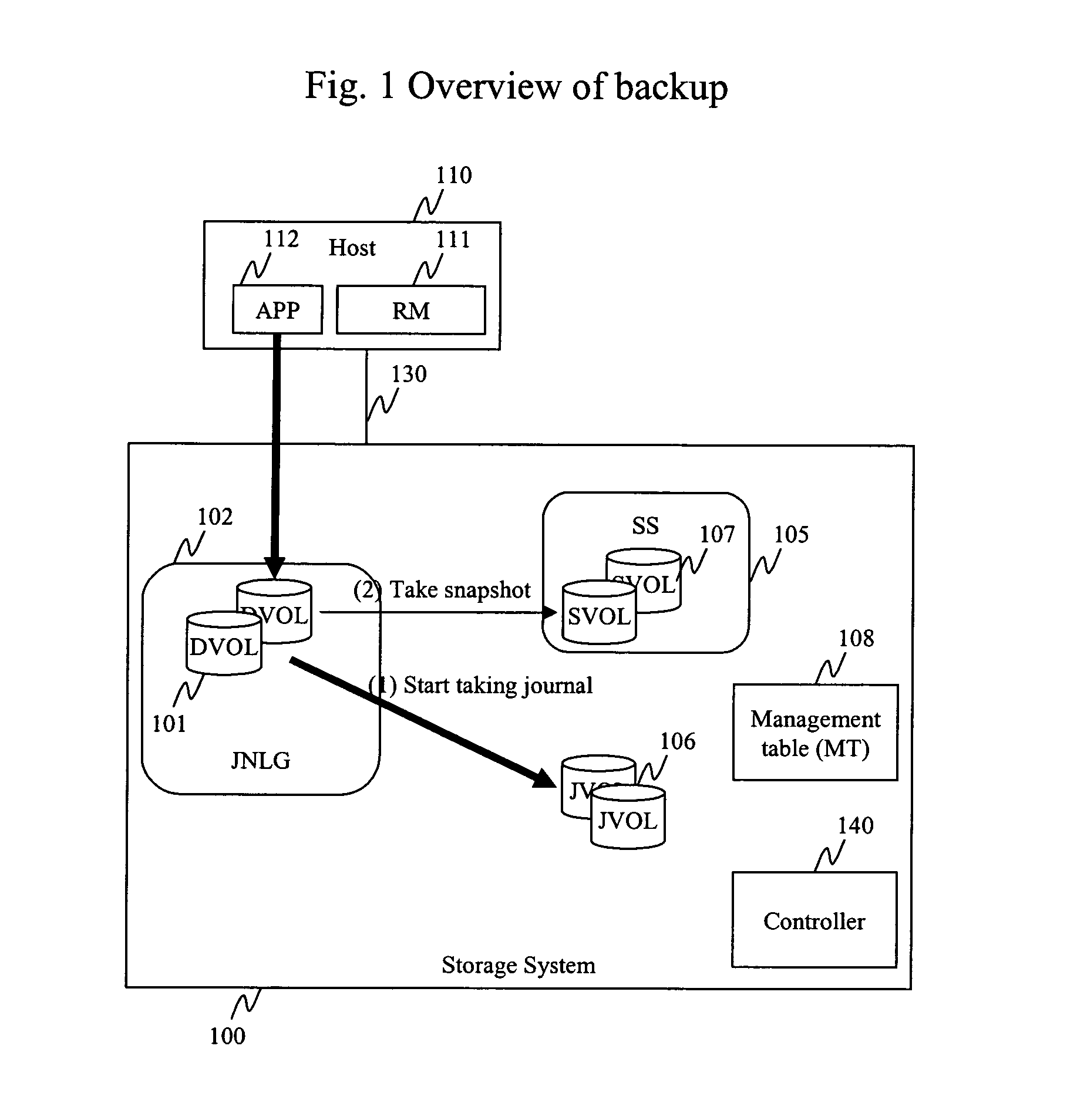
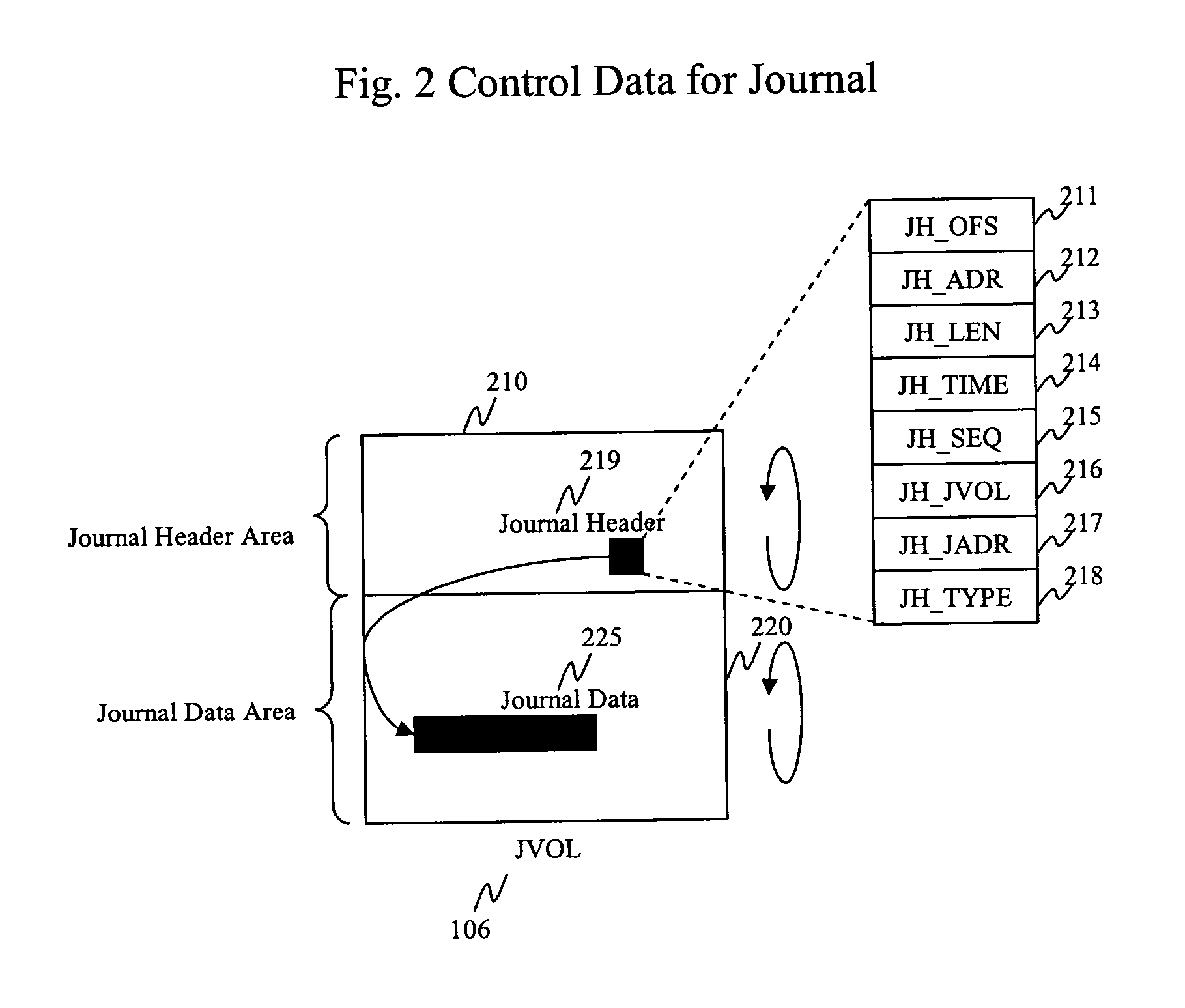
Method and apparatus for data recovery system using storage based journaling
InactiveUS20050028022A1Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionSystem maintenanceDatabase
A storage system maintains a journal and a snapshot of one or more data volumes. Two journal entry types are maintained, an AFTER journal entry and a BEFORE journal entry. Two modes of data recovery are provided: “fast” recovery and “undo-able” recovery. A combination of both recovery modes allows the user to quickly recover a targeted data state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for data recovery using storage based journaling
InactiveUS20050015416A1Resume normal operationError detection/correctionMemory systemsSystem maintenanceComputer science
A storage system maintains a journal and a snapshot of one or more data volumes. Two journal entry types are maintained, an AFTER journal entry and a BEFORE journal entry. Two modes of data recovery are provided: “fast” recovery and “undo-able” recovery. A combination of both recovery modes allows the user to quickly recover a targeted data state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
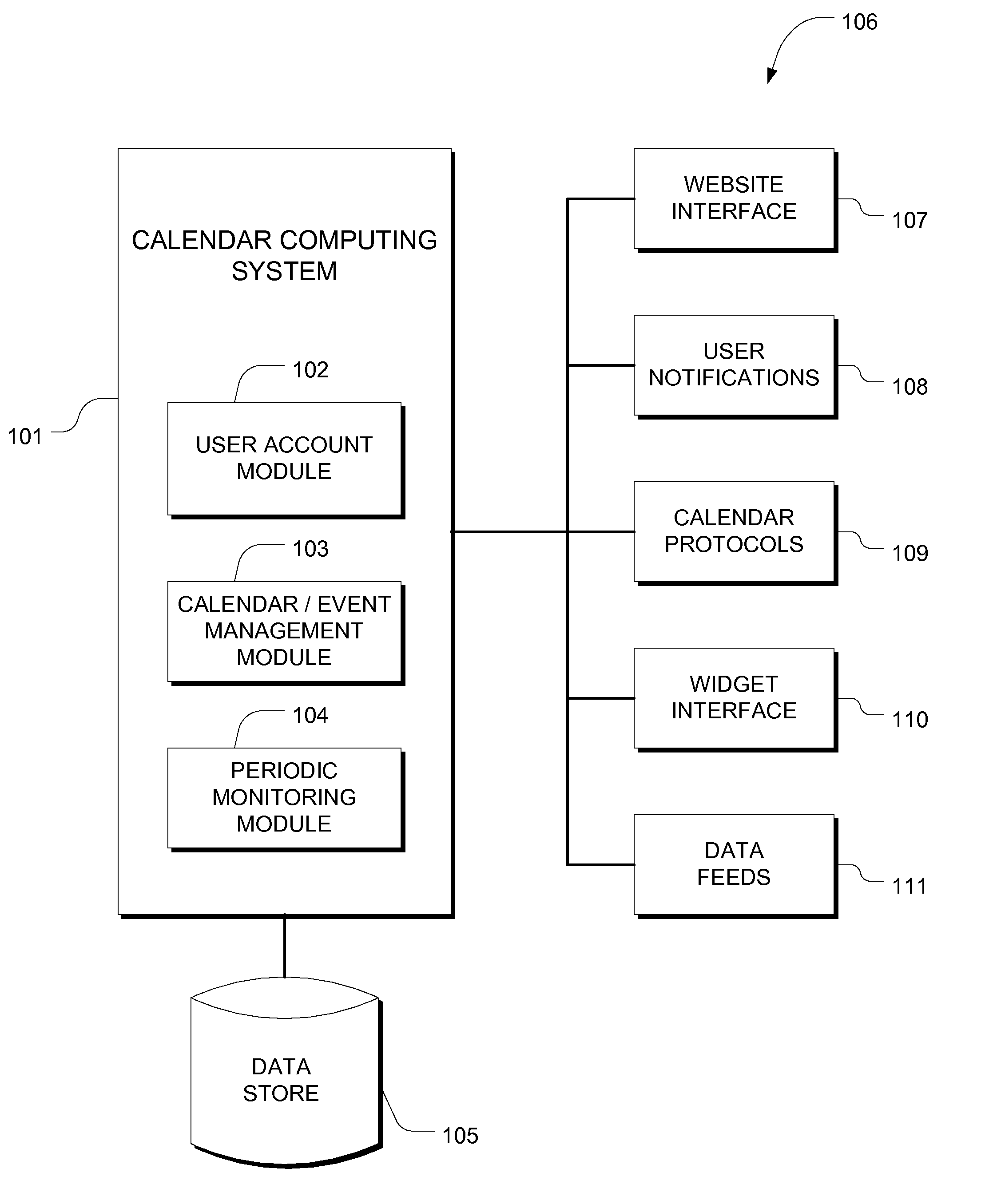
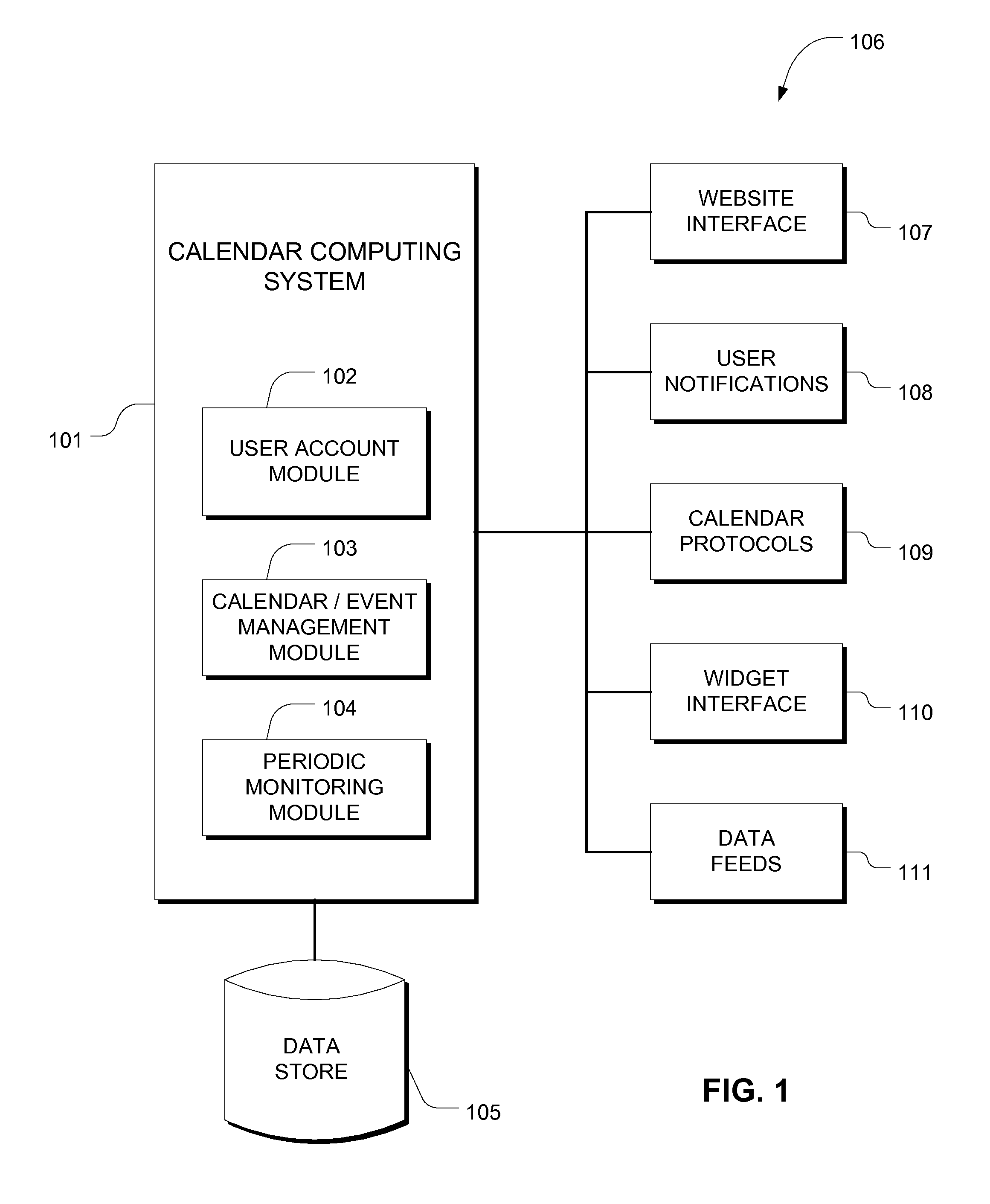
Systems and methods for managing event-related information
InactiveUS20130036369A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsRelevant informationSystem maintenance
An embodiment of the invention is a method of integrating public and private calendars on a user-specific basis, such that a user is able to view multiple shared calendars created by different users. A system maintains event data relating to a future event, and receives a request to add that event to one of the user's calendars. The system creates a link between that event and the calendar, configuring the link so that updates to the event are automatically reflected on the calendar. It further enables the user to modify attributes associated with the event.
Owner:SQUAREDOUT
System for policy-based management of software updates
ActiveUS20050262076A1Program loading/initiatingSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware updateSystem maintenance
A computer system configured for policy-based management of software updates is disclosed. The system maintains group-policy objects, with which groups of computers are associated. The system obtains identities of software updates from a source of software updates. The system also obtains filter criteria for each update, for determining whether the update should be applied to a particular computer or not. The system assigns newly available updates to respective selected group-policy objects and adds the obtained filter criteria to each such group-policy object. The system performs necessary installations of updates by, for each group-policy object, determining whether, for each combination of a computer belonging to a group associated with that policy object and an update assigned to that policy object, the computer satisfies the filter criteria for the update, and if so, applying the update to that computer, but if not, refraining from applying the update.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
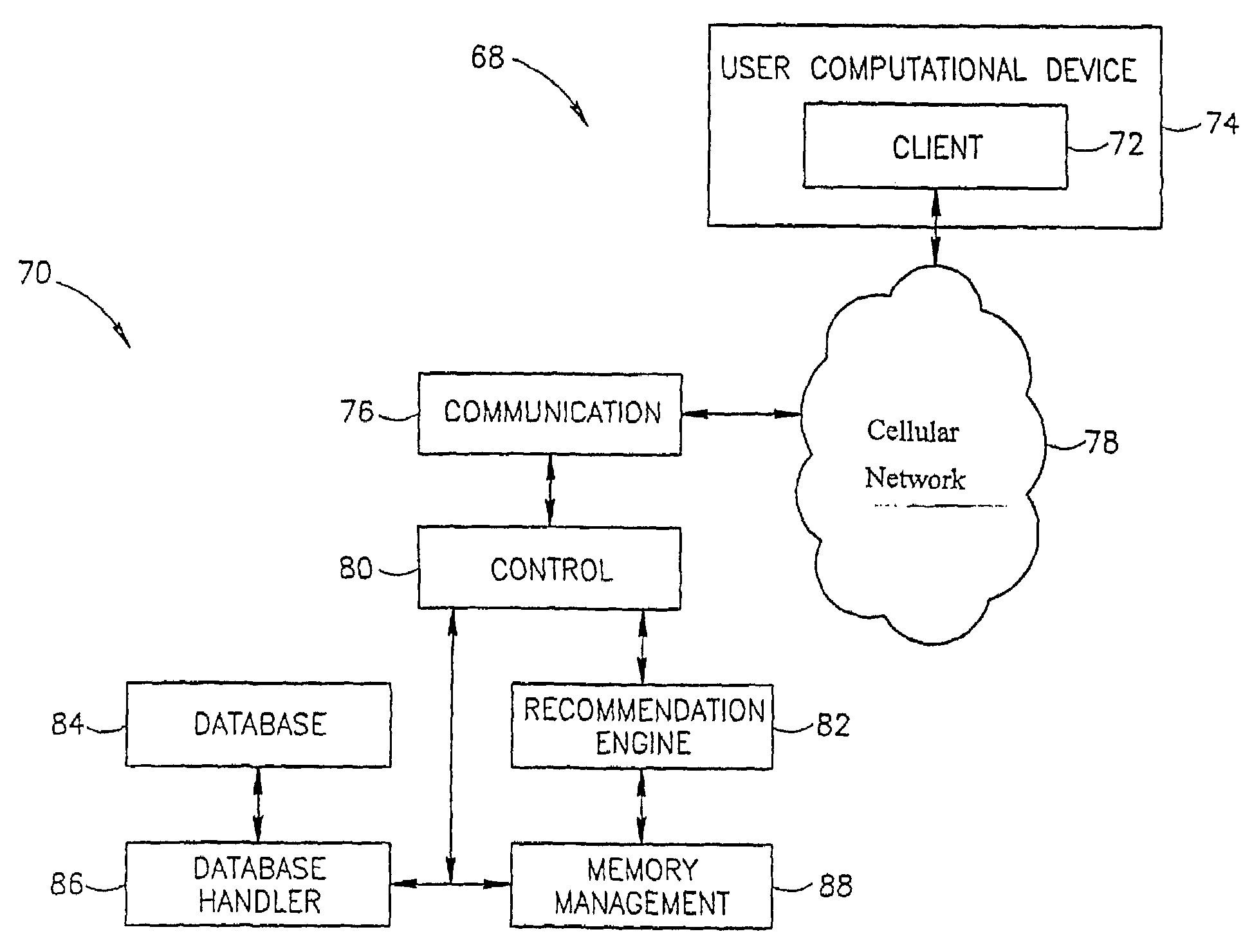
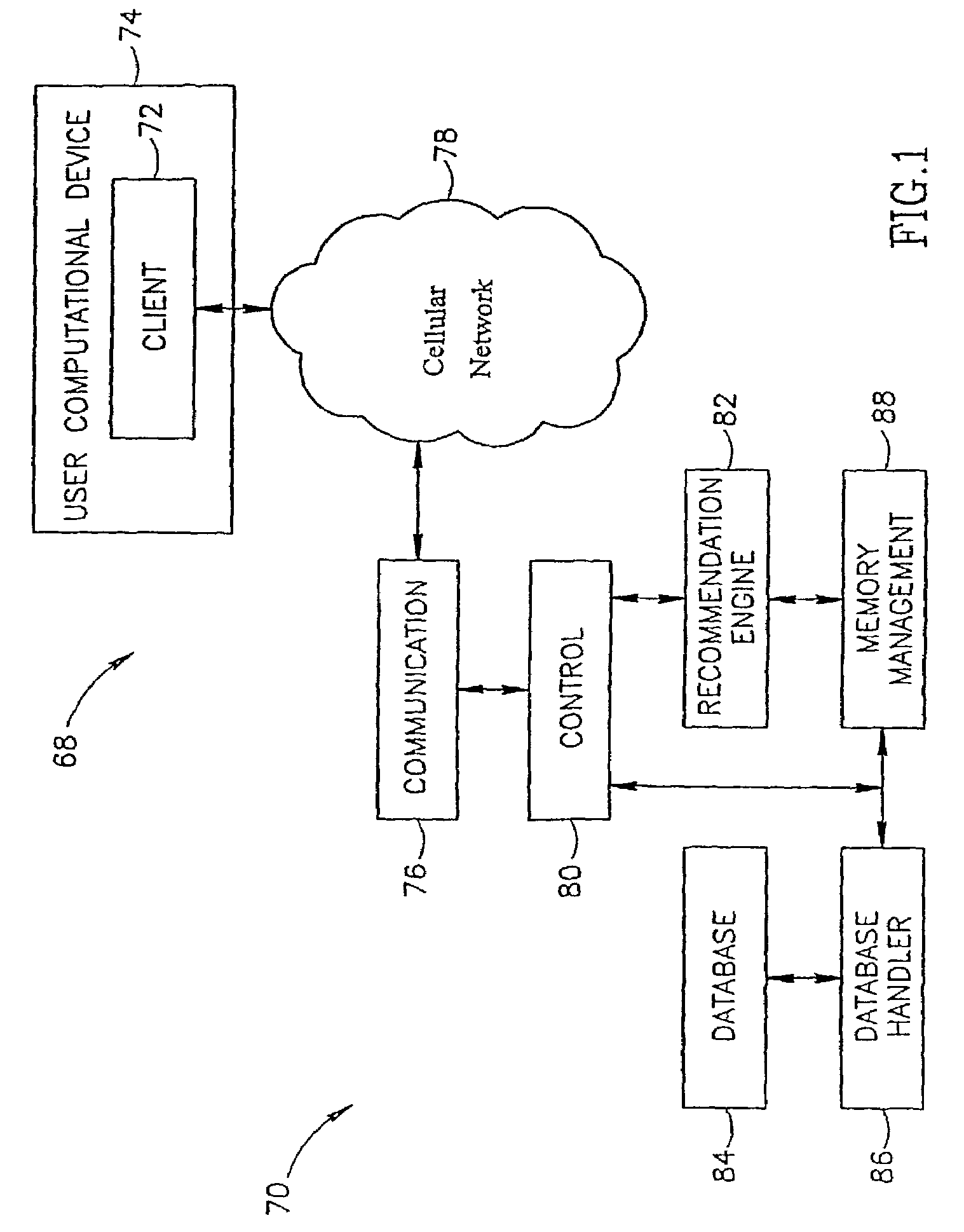
Using a system for prediction of musical preferences for the distribution of musical content over cellular networks
InactiveUS7102067B2Accurate predictionElectrophonic musical instrumentsMultimedia data retrievalMusical toneSystem maintenance
A system and a method for predicting the musical taste and / or preferences of the user and its integration into services provided by a wireless network provider. Although the present application is directed toward implementations with wireless providers, the present invention can also be implemented on a regular, i.e., wireline network. The core of the present invention is a system capable of predicting whether a given user, i.e., customer, likes or does not like a specific song from a pre-analyzed catalog. Once such a prediction has been performed, those items that are predicted to be liked best by the user may be forwarded to the mobile device of the user on the cellular (or other wireless) network. The system maintains a database containing propriety information about the songs in the catalog and, most important, a description (profile) of the musical taste of each of its customers, identified by their cellular telephone number.
Owner:PANDORA MEDIA
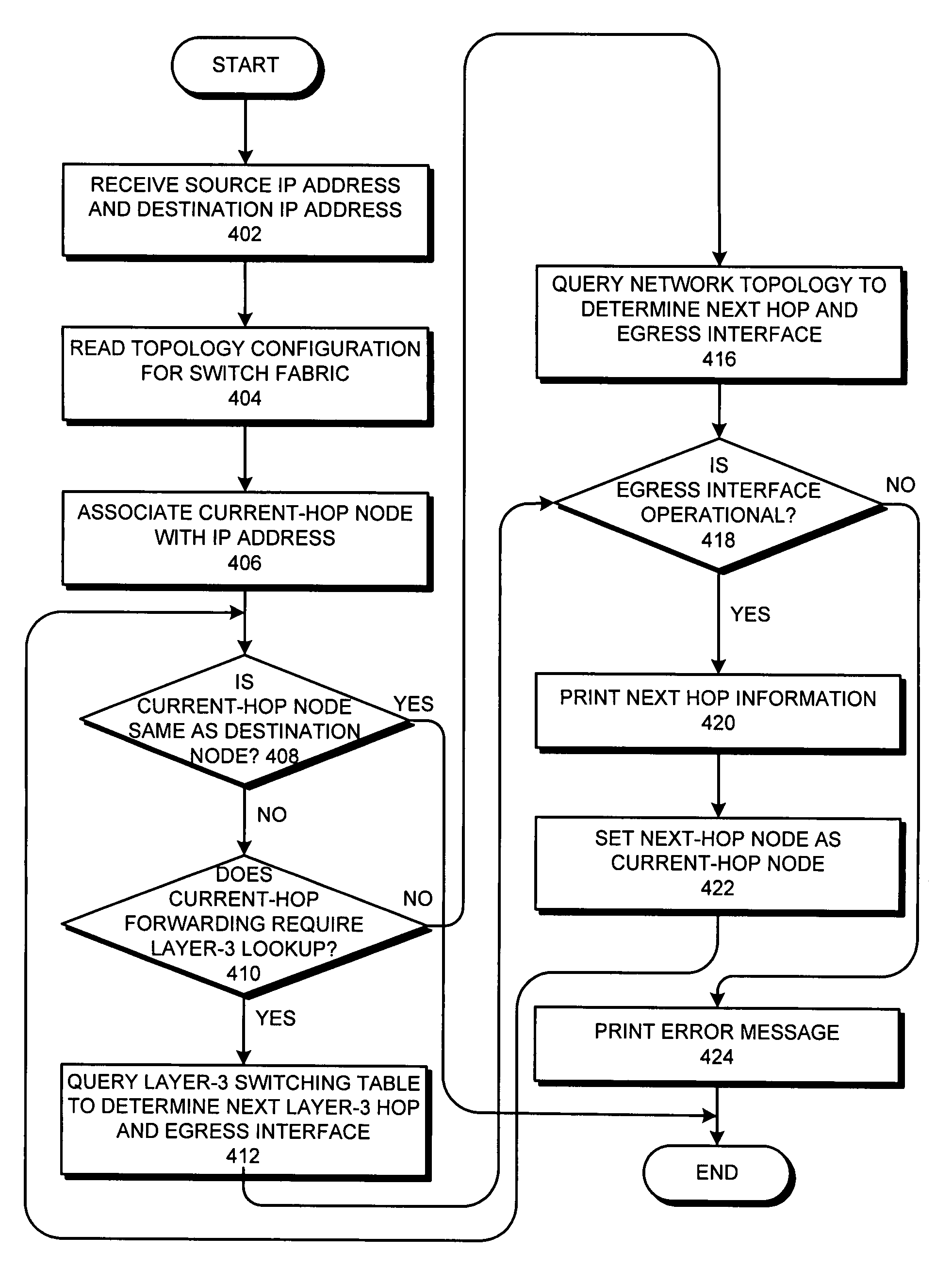
Method and system for discovering network paths
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that identifies network switches along a path. During operation, the system receives an address of a source node and an address of a destination node. The system maintains a set of topology information for a network. The system further simulates a data packet originated at the source node and destined for the destination node. During the simulation, the system determines whether a current-hop node performs layer-3, layer-2, or sub-layer-2 switching. The system sends a query to the current-hop node over a separate control channel to determine the status of the current-hop node and discover a next-hop node. The system then receives a reply. The system determines the next-hop node based on the reply and sets the next-hop node as the current-hop node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Efficient system and method for running and analyzing multi-channel, multi-modal applications
InactiveUS7174534B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer moduleSystem maintenance
A system for developing, running and analyzing multi-modal applications includes a development platform, a run-time engine, and a data-mining module. Once a mobile application is built and tested on the development platform, it can be automatically deployed on the run-time system, which maintains and manages the application. Further, the data-mining system allows access to reporting and analysis tools that aid in understanding end-user behavior and preferences. This data can be used to further enhance applications by redesigning and redeploying them in a rapid and efficient manner.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
System & Method For Compiling Intellectual Property Asset Data
ActiveUS20120191757A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsIntellectual propertyThe Internet
An access server computing system scrapes a set of records maintained by a target computing system in a database which is only made accessible over the Internet with a limited protocol query and an access challenge. The access server accesses the target computing system through an Internet browser interface based on emulating a user query made through the limited protocol, including by automatically passing locator identifier fields to retrieve a corresponding set of record which are stored in the first database.
Owner:J NICHOLAS & KRISTIN GROSS TRUST U A D APRIL 13 2010
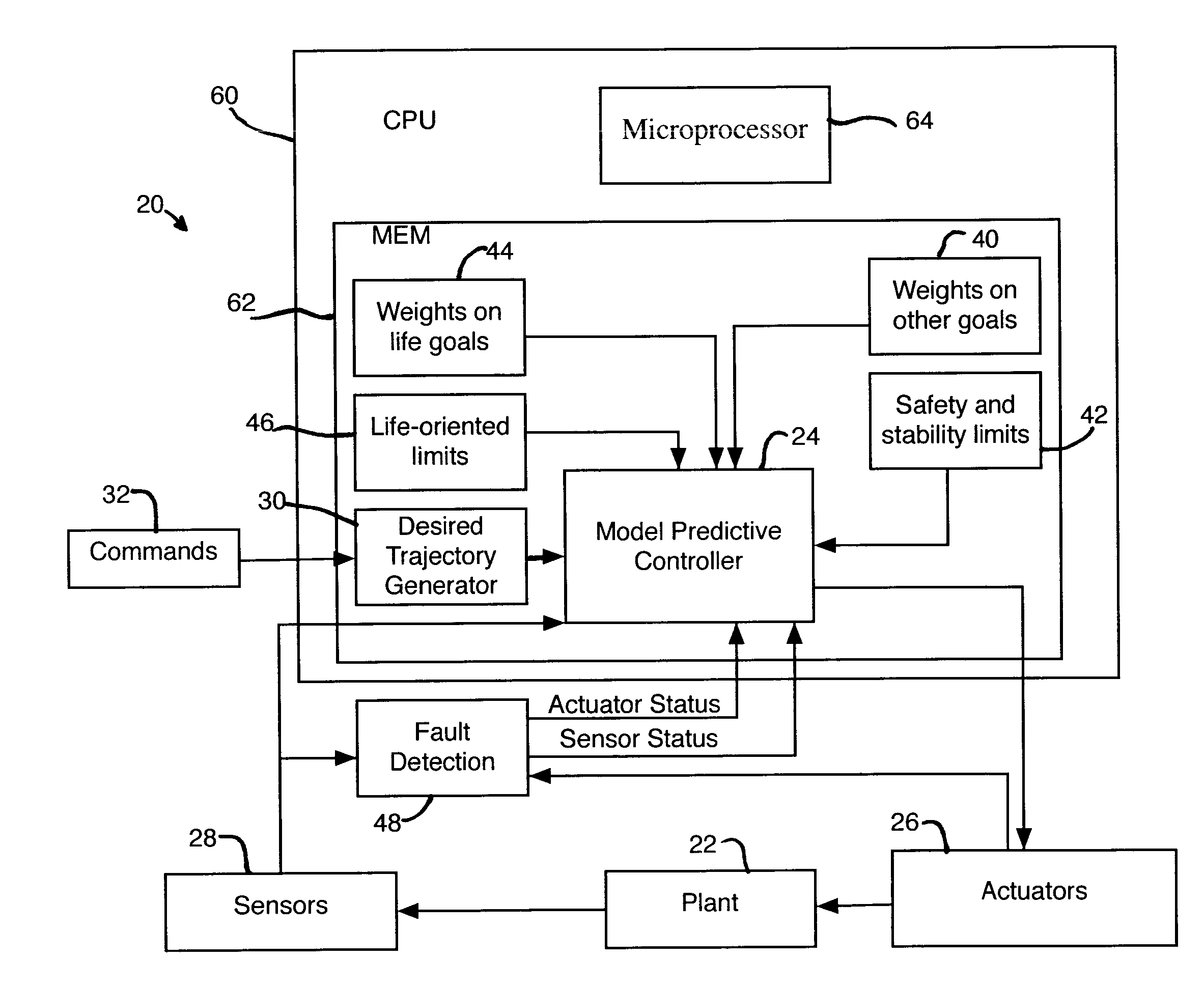
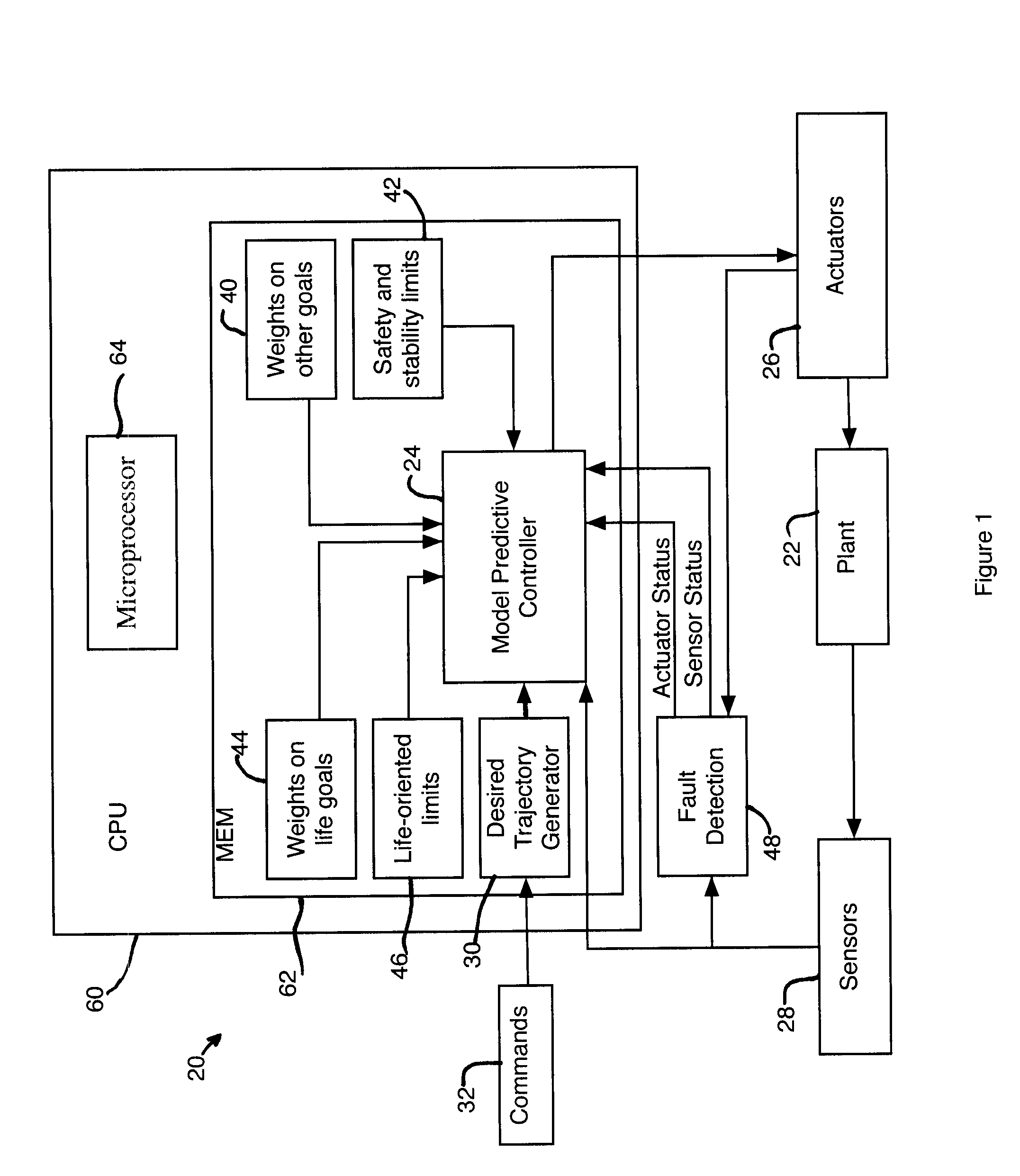
Model predictive controller with life extending control
ActiveUS7203554B2Reduce in quantityProlong lifeElectric testing/monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsControl systemPredictive controller
An MPC Control system provides a life extending control that includes life-extending goals in the performance index of the MPC controller and limits in the inequality equations. The MPC controller performs the normal functions of a control system for a physical system, but does so in a manner that extends the life or time-to-next maintenance or reduces the number of parts that need to be replaced. If the life extending functions do not degrade other control functions, they can be always enabled, making the system less expensive to maintain. If the life extending functions degrade some other control functions, they can be adjusted in-the-field or on-the-fly to stretch the time-until-maintenance until it is more convenient, but with some impact on performance.
Owner:RTX CORP
Apparatus and method for building distributed fault-tolerant/high-availability computed applications
InactiveUS6865591B1Multiple failureOptimal hardware utilizationMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionOperational systemSystem maintenance
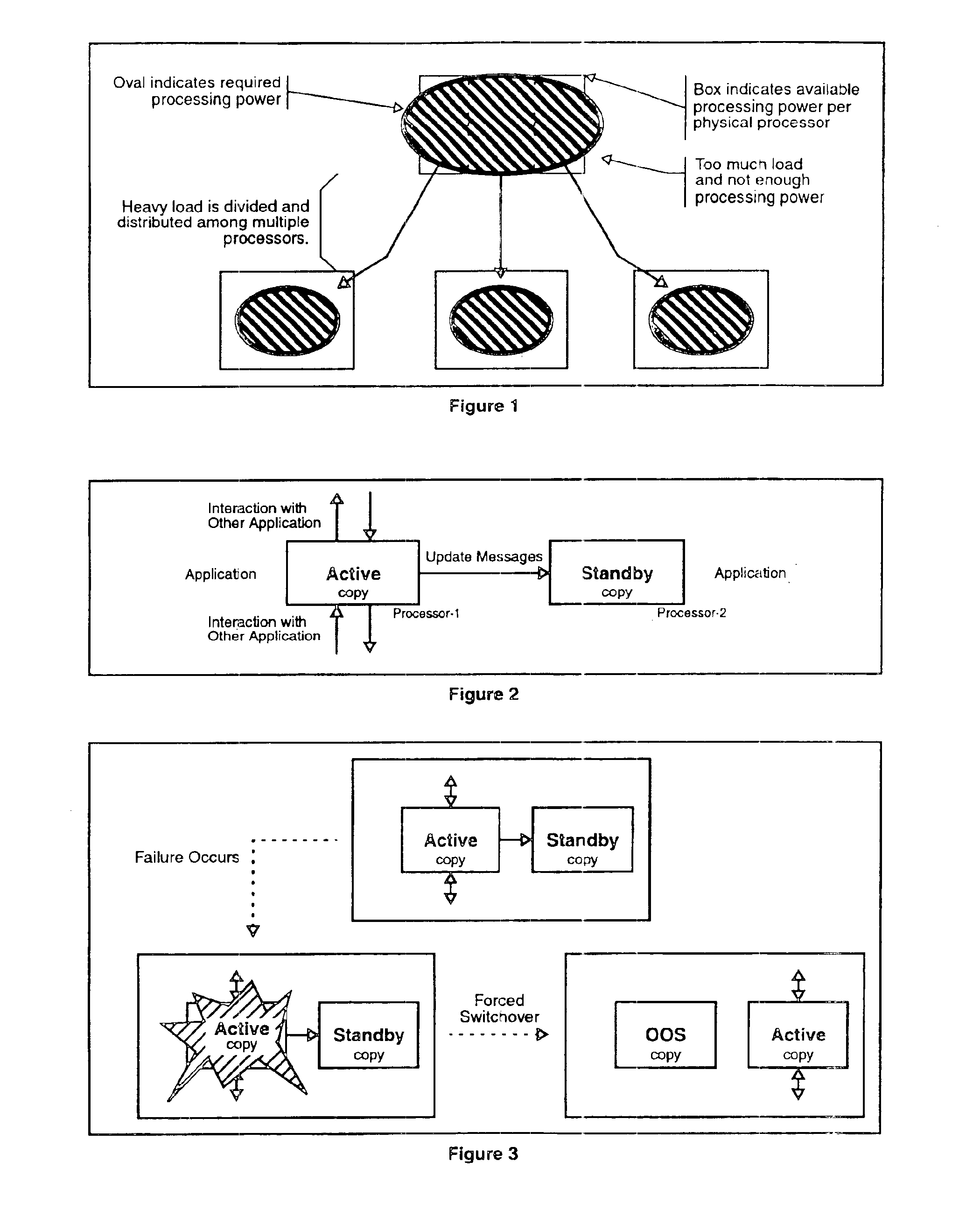
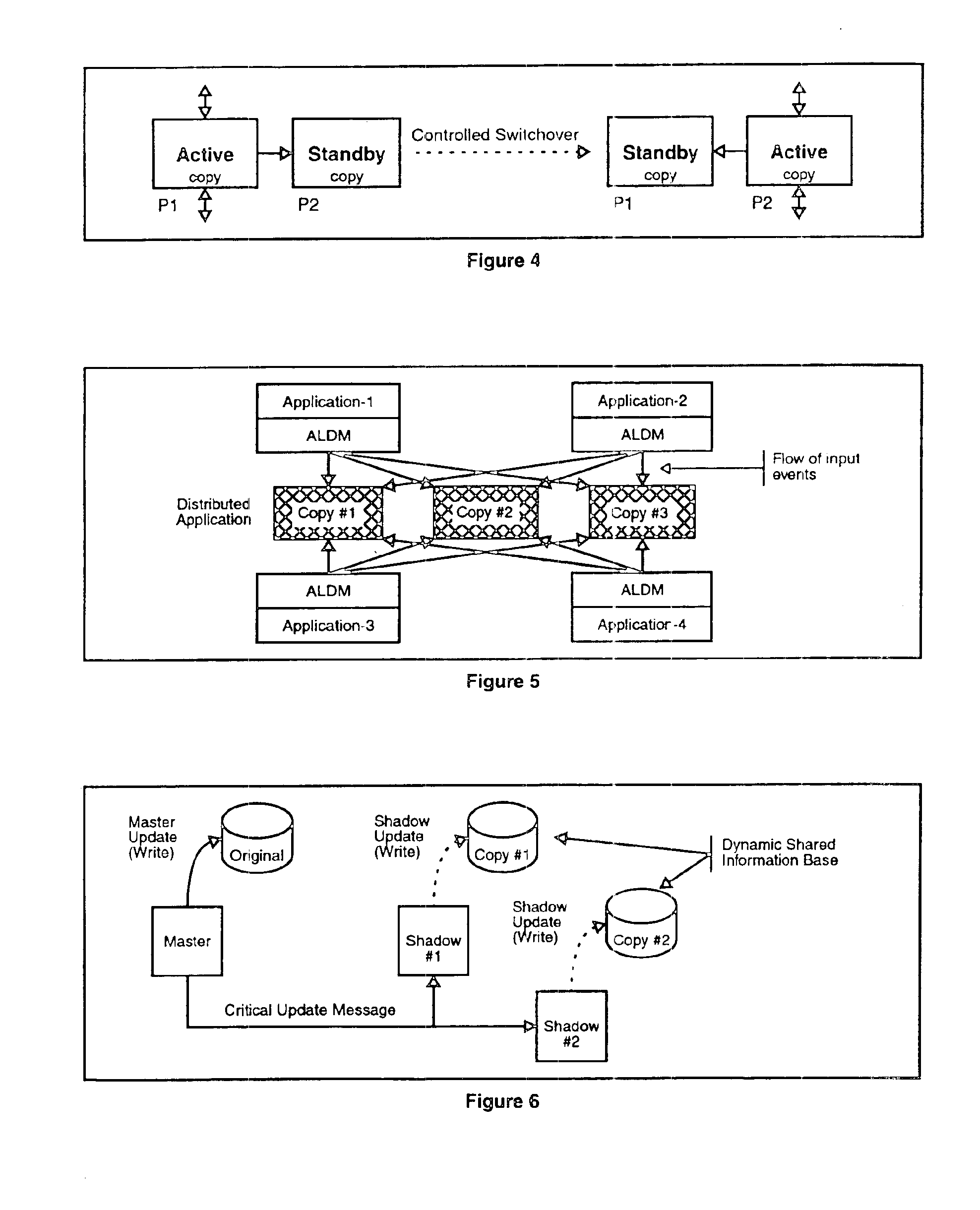
Software architecture for developing distributed fault-tolerant systems independent of the underlying hardware architecture and operating system. Systems built using architecture components are scalable and allow a set of computer applications to operate in fault-tolerant / high-availability mode, distributed processing mode, or many possible combinations of distributed and fault-tolerant modes in the same system without any modification to the architecture components. The software architecture defines system components that are modular and address problems in present systems. The architecture uses a System Controller, which controls system activation, initial load distribution, fault recovery, load redistribution, and system topology, and implements system maintenance procedures. An Application Distributed Fault-Tolerant / High-Availability Support Module (ADSM) enables an applications( ) to operate in various distributed fault-tolerant modes. The System Controller uses ADSM's well-defined API to control the state of the application in these modes. The Router architecture component provides transparent communication between applications during fault recovery and topology changes. An Application Load Distribution Module (ALDM) component distributes incoming external events towards the distributed application. The architecture allows for a Load Manager, which monitors load on various copies of the application and maximizes the hardware usage by providing dynamic load balancing. The architecture also allows for a Fault Manager, which performs fault detection, fault location, and fault isolation, and uses the System Controller's API to initiate fault recovery. These architecture components can be used to achieve a variety of distributed processing high-availability system configurations, which results in a reduction of cost and development time.
Owner:TRILLIUM DIGITAL SYST
Multipath switching over multiple storage systems
ActiveUS20120131289A1Memory loss protectionDigital computer detailsSystem maintenanceComputer science
A system comprises a first storage system, a second storage system, a plurality of switches, and a server connected with the first storage system via a first group of switches and connected with the second storage system via a second group of switches. The first group and the second group have at least one switch which is not included in both the first and second groups. The first storage system receives I / O commands targeted to first logical units from the server via the first group of switches. The first storage system maintains first information regarding the ports of both the first and second storage systems. The first information is used to generate multipath communication between the server and the first storage system, including at least one path which passes through the second storage system and at least one other path which does not pass through the second storage system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
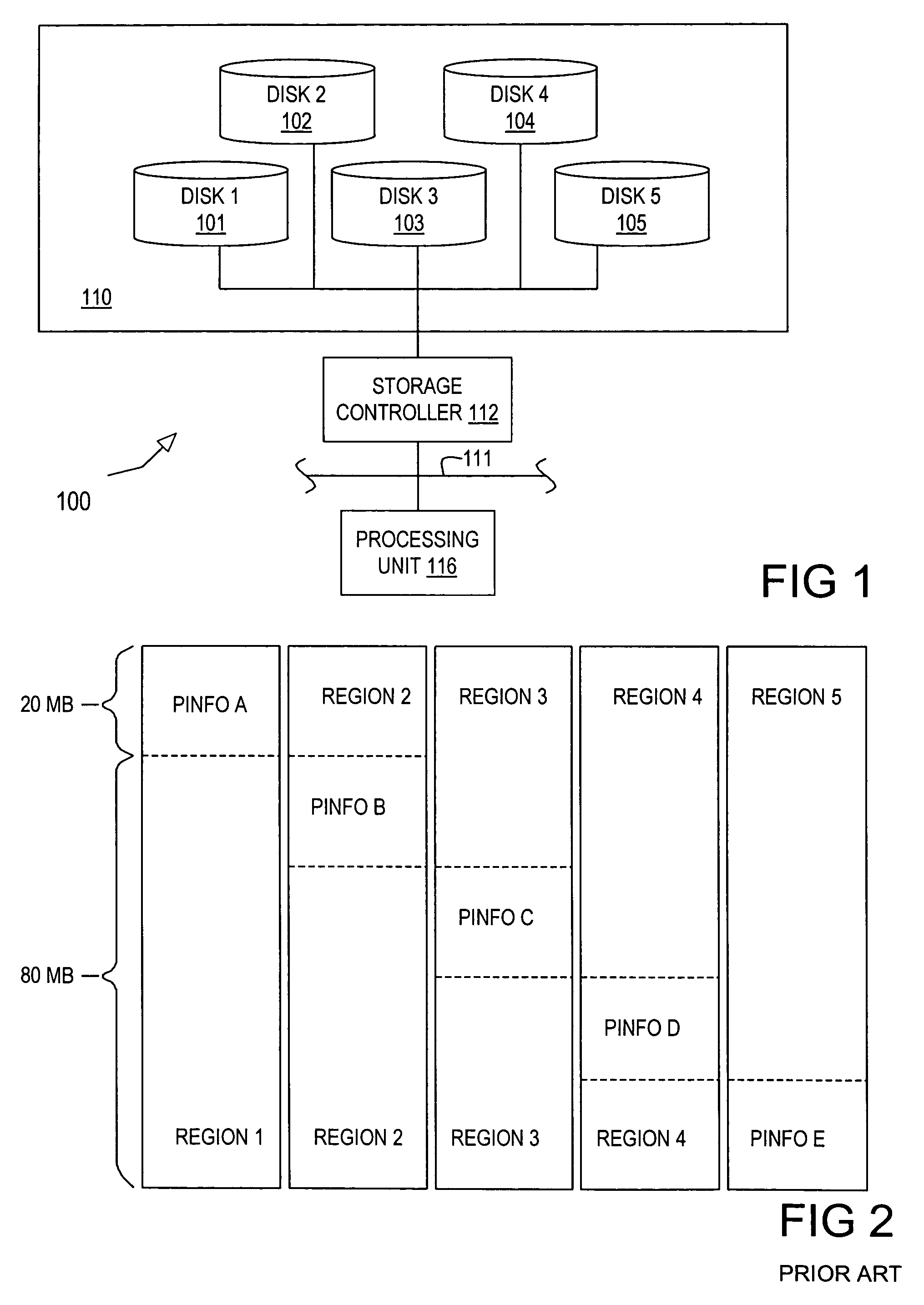
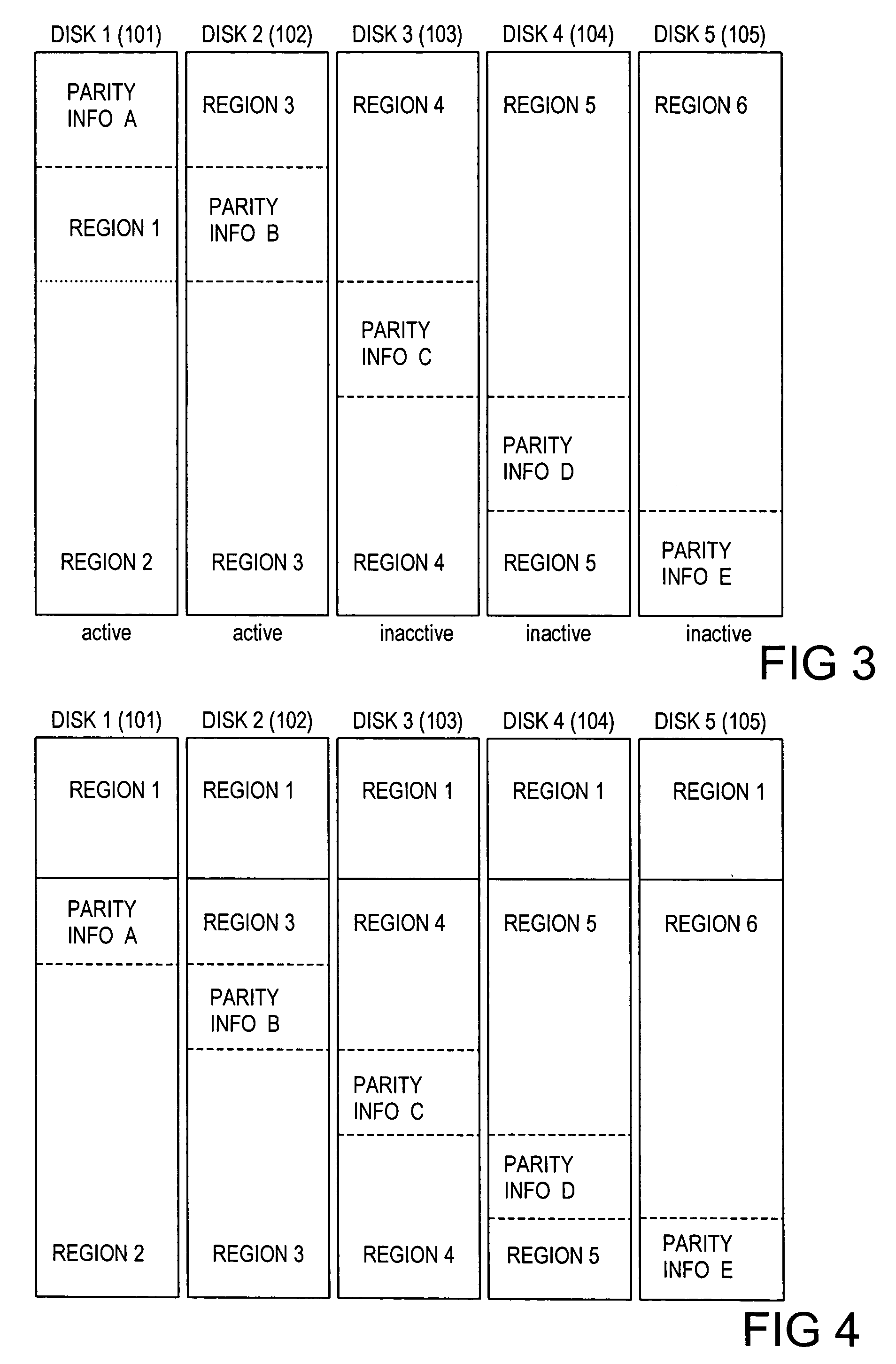
Multiple disk data storage system for reducing power consumption
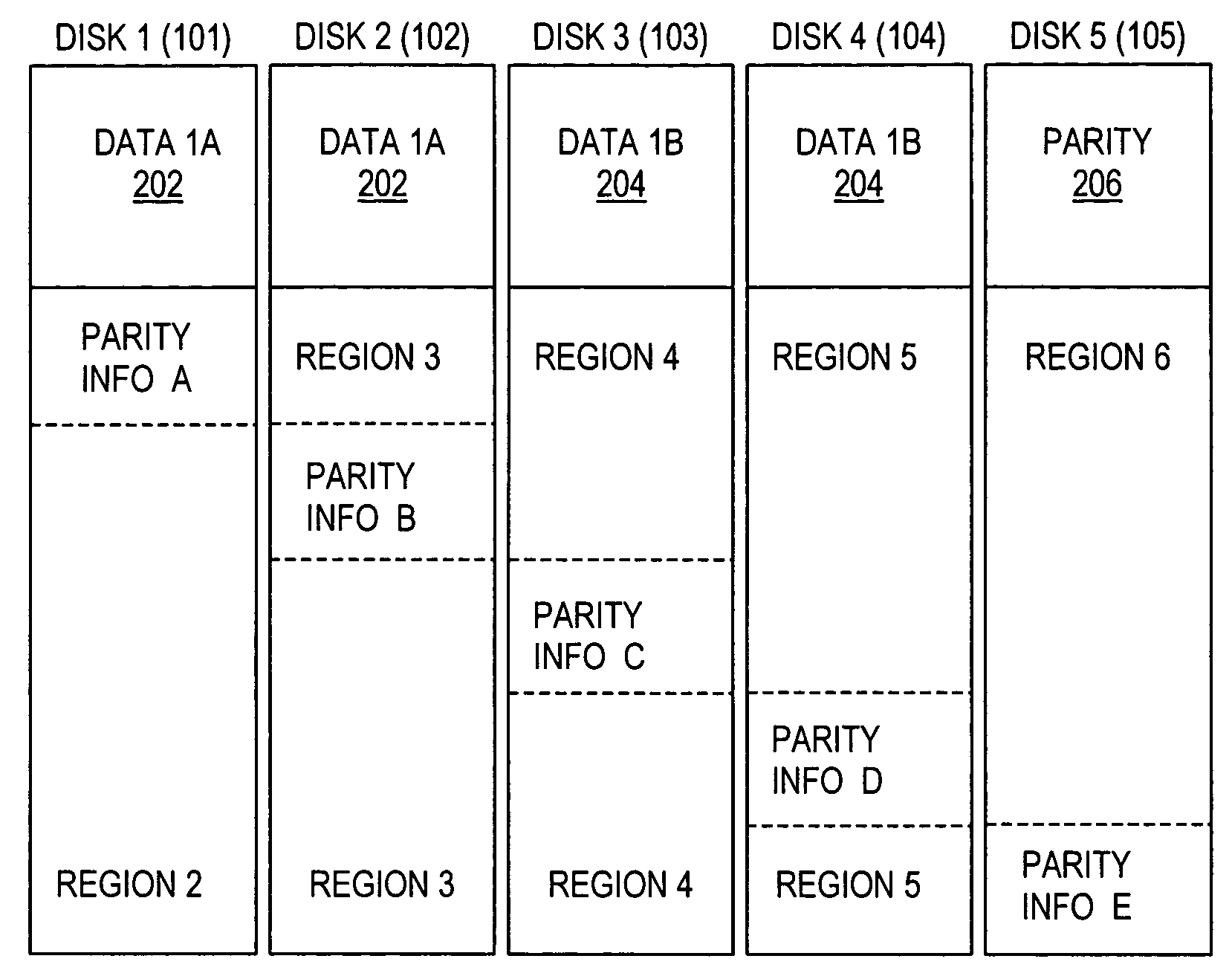
InactiveUS7234074B2Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDisk controllerSystem maintenance
A data storage system in which each of a set of disks has a first portion for either popular data or error correction information (parity or Reed-Solomon code symbols) associated with the popular data, and a second portion used for other data. A disk controller connected to the set of disks maintains a first popular data block in the first portion of a first of the set of disks and a second popular data block in the first portion of a second of the set of disks. The system maintains at least two of the disks in an active state. The active disks are selected to insure that any data in the popular data blocks can be determined from data stored in the active disks. An additional disk is maintained in an active state if write access is permitted or if there is an additional popular data block.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and data query method thereof
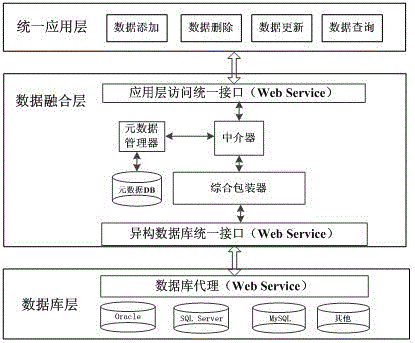
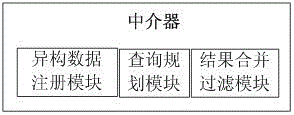
InactiveCN104008135AAchieve integrationEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsMetadata managementSystem maintenance
The invention provides a multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and a data query method thereof. The system comprises a database layer, a data fusion layer and a uniform application layer. The database layer is composed of heterogeneous databases and agencies of the heterogeneous databases. The data fusion layer is used for fusing information of all heterogeneous data sources, and is responsible for data access of the heterogeneous data sources and coordinating the information of all the data sources, and specifically comprises a metadata data base (DB), a metadata manager, a comprehensive wrapper, a mediator, an application layer access uniform interface and a heterogeneous database uniform interface. The uniform application layer is the user of the heterogeneous database fusion system and can have access to shared data resources of the heterogeneous databases by fusing middle layers. The multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and the data query method of the multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system solve the problems in heterogeneous database fusion and overcome the defects of an existing database fusion technology. The system can conduct transparent query on all the heterogeneous databases on the condition that local databases are not affected, and the maintenance cost of the system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com