Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
828 results about "Metadata management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metadata management involves managing metadata about other data, whereby this "other data" is generally referred to as content data. The term is used most often in relation to digital media, but older forms of metadata are catalogs, dictionaries, and taxonomies. For example, the Dewey Decimal Classification is a metadata management systems developed in 1876 for libraries.
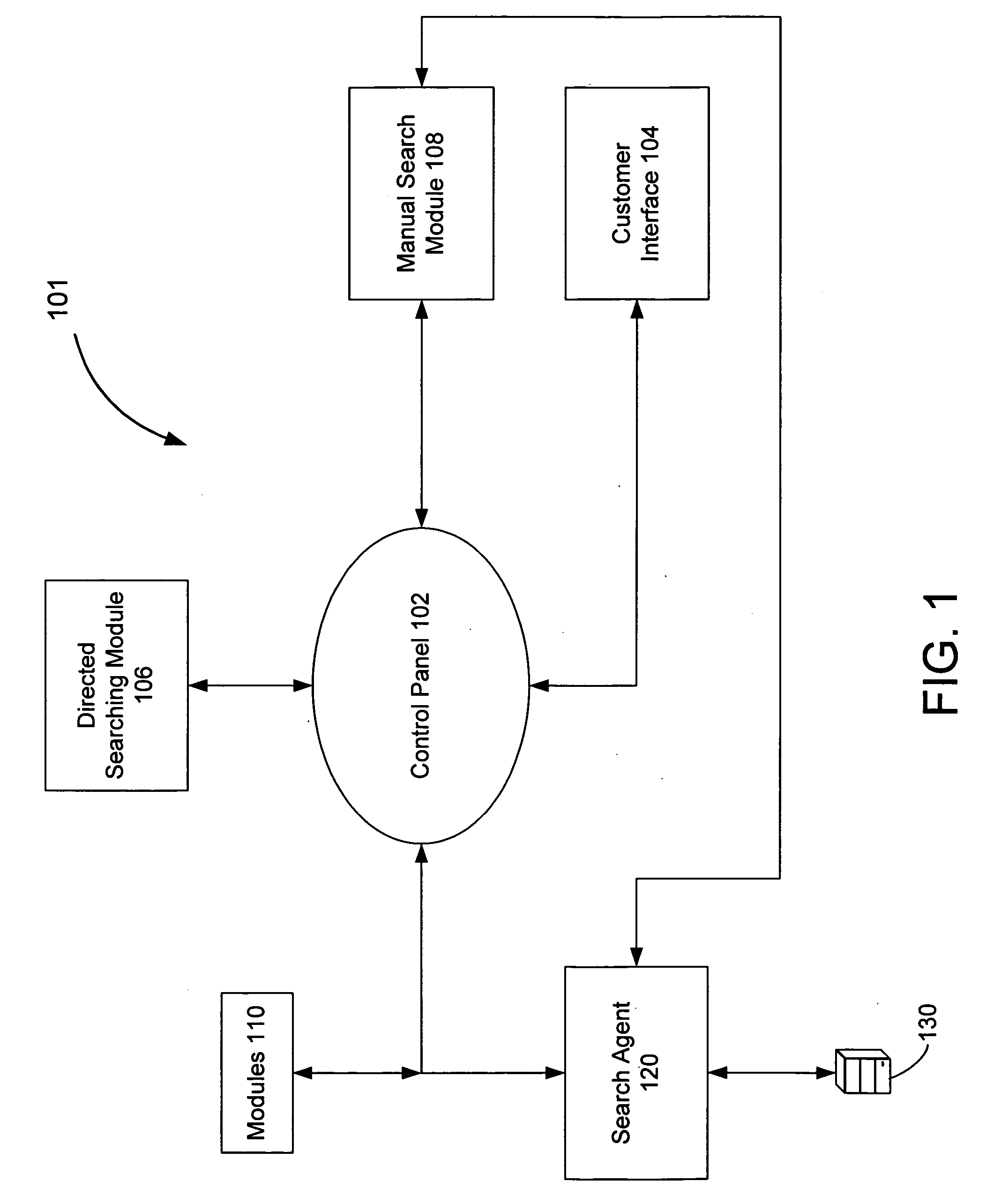
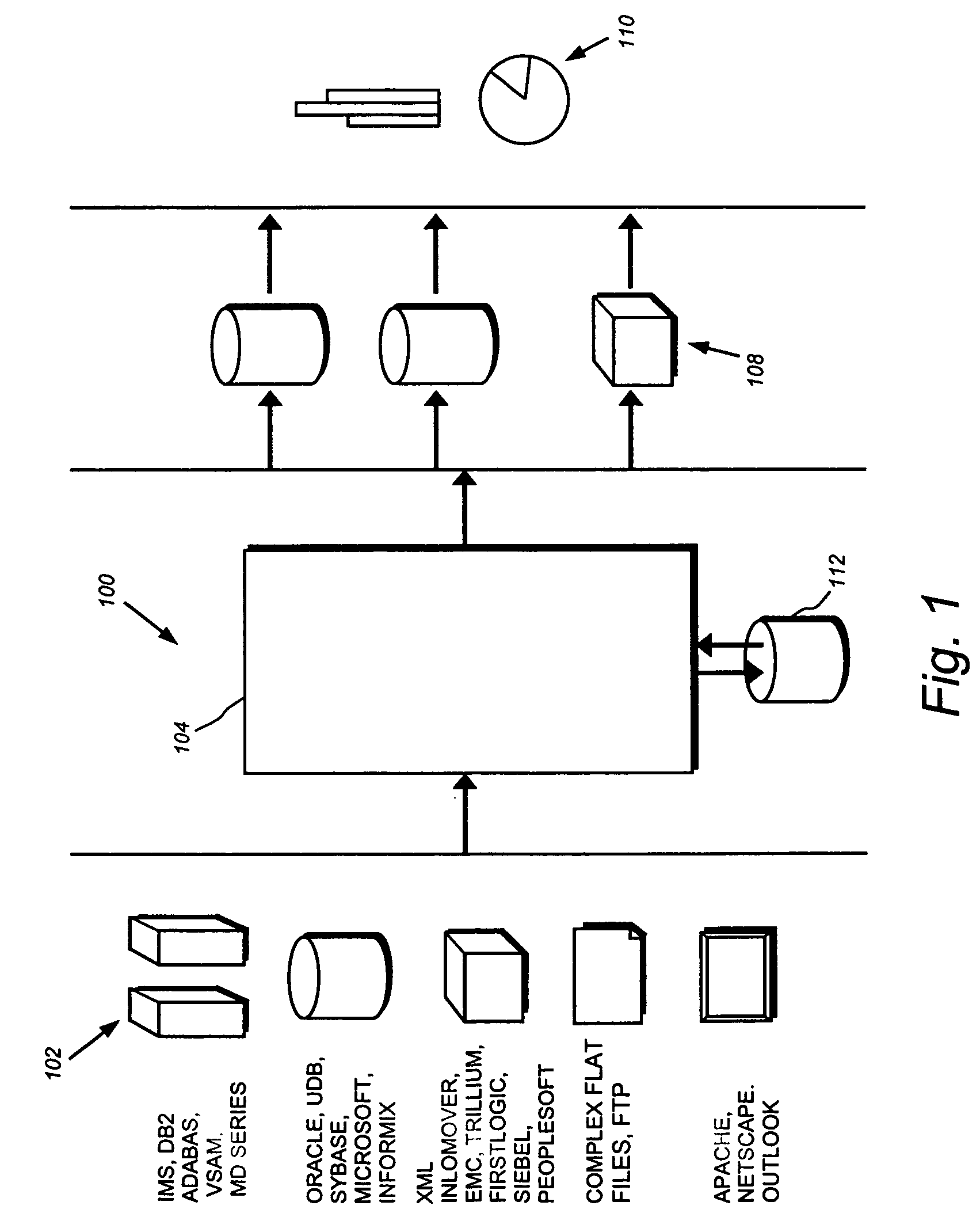
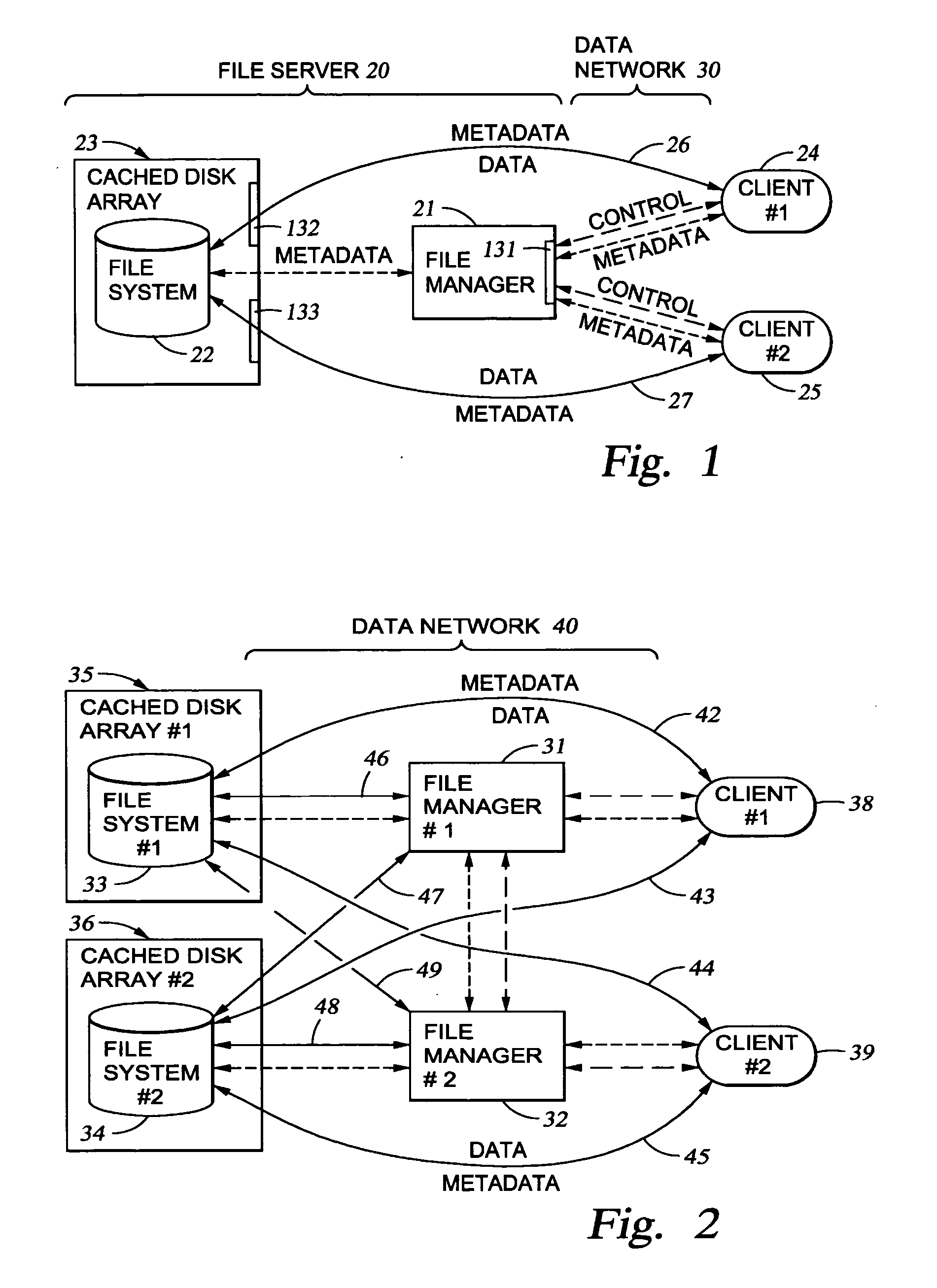
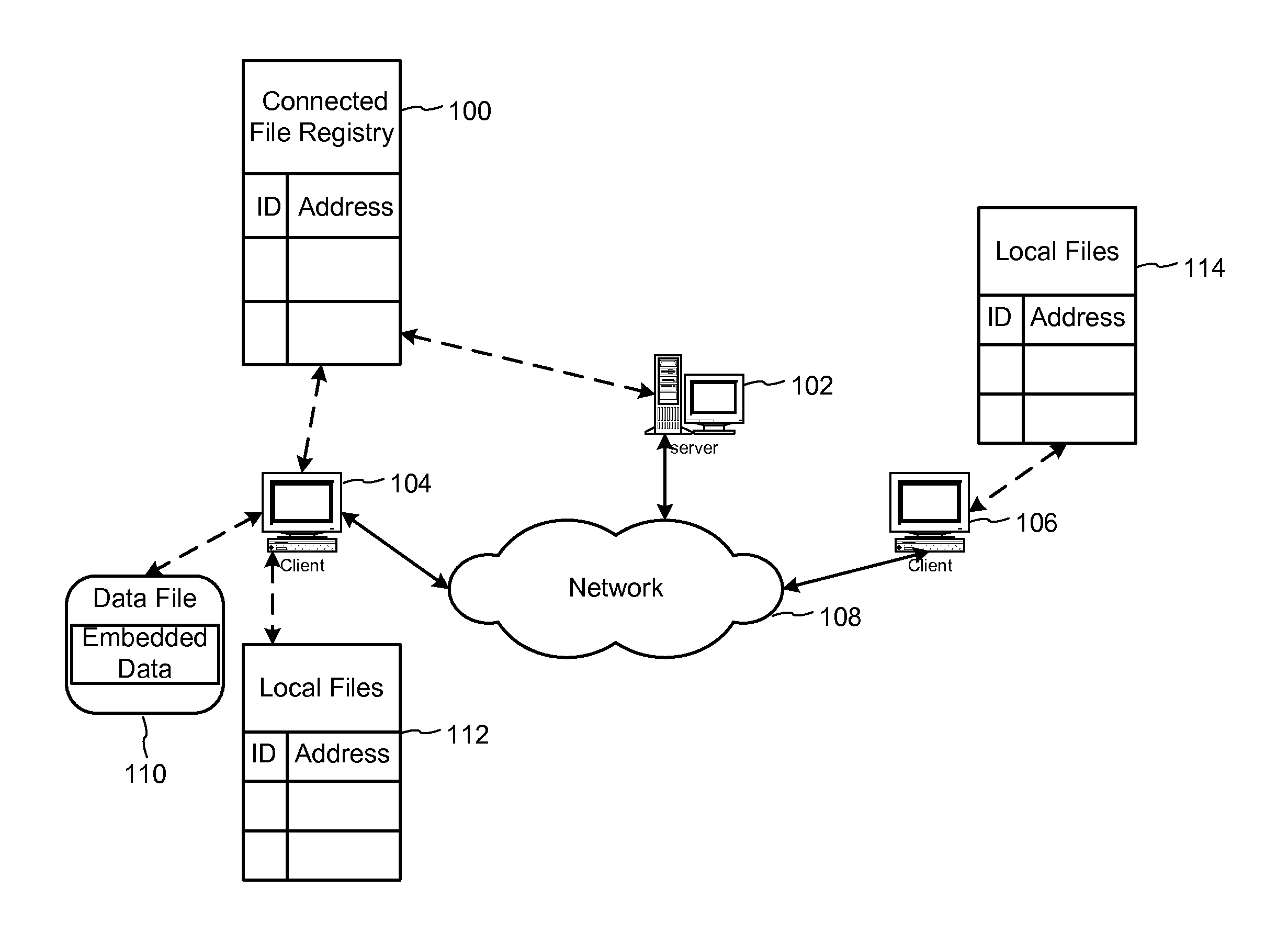
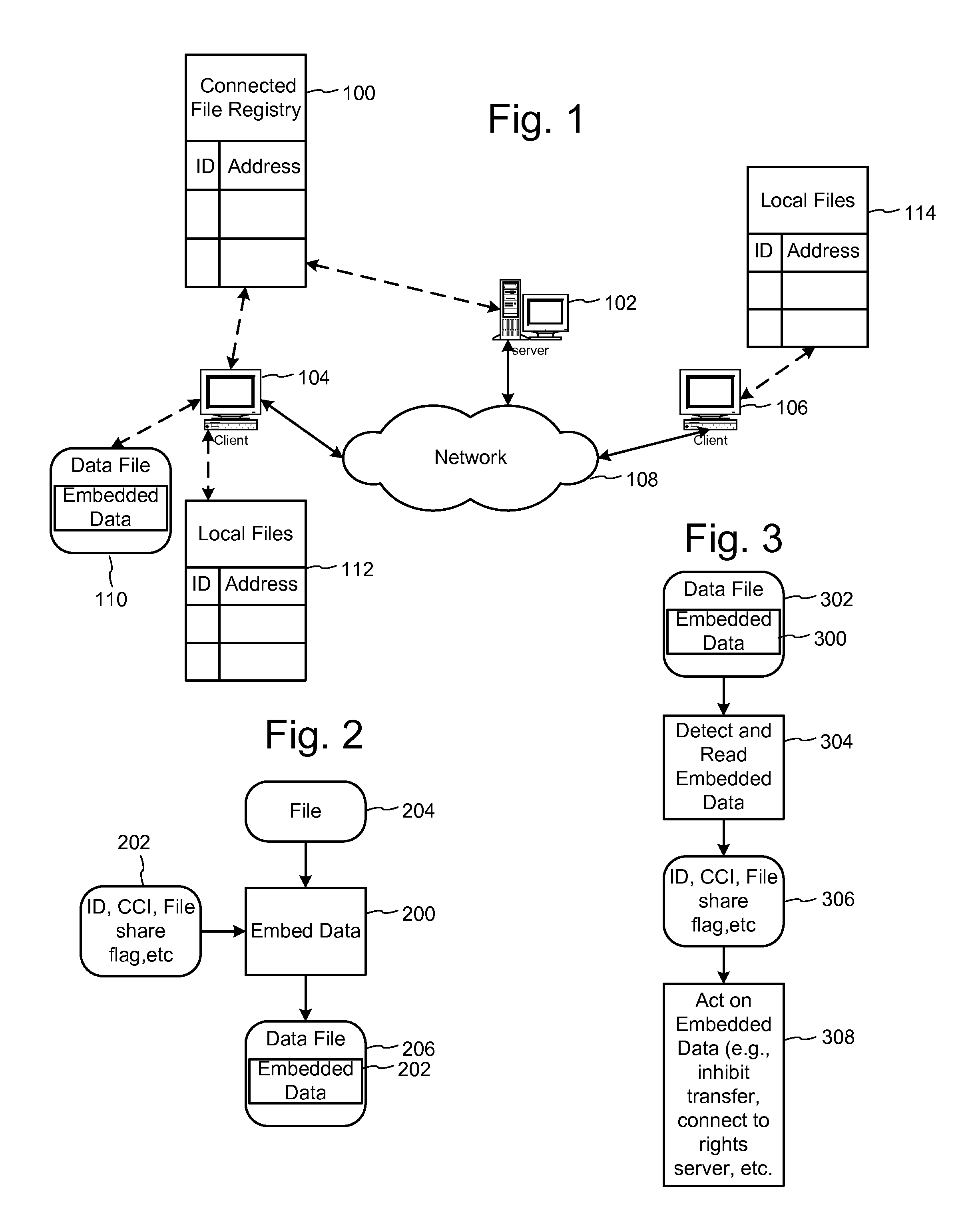
Metadata management system for an information dispersed storage system
ActiveUS20070079083A1Less usableImprove privacyComputer security arrangementsMemory systemsInformation dispersalMetadata management
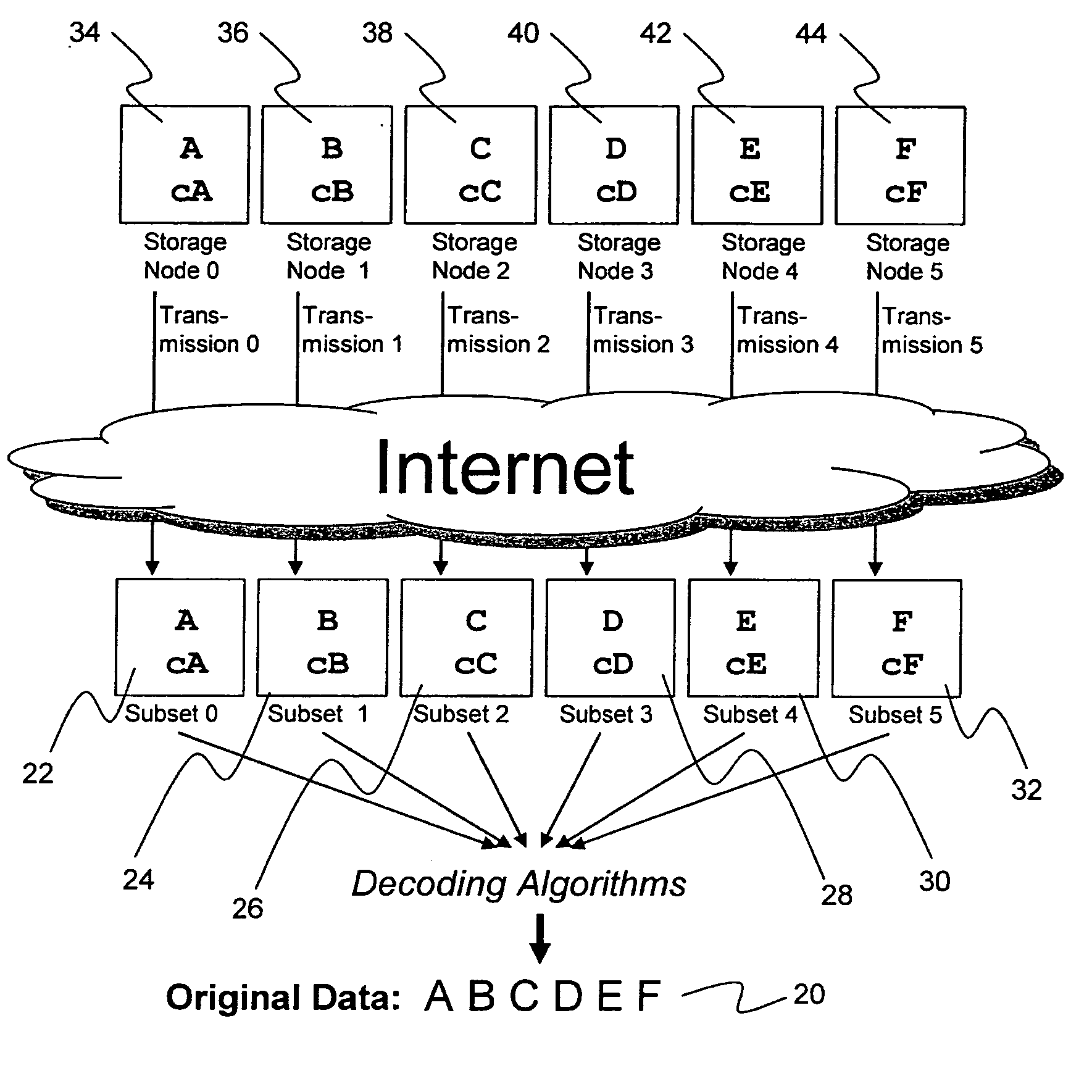
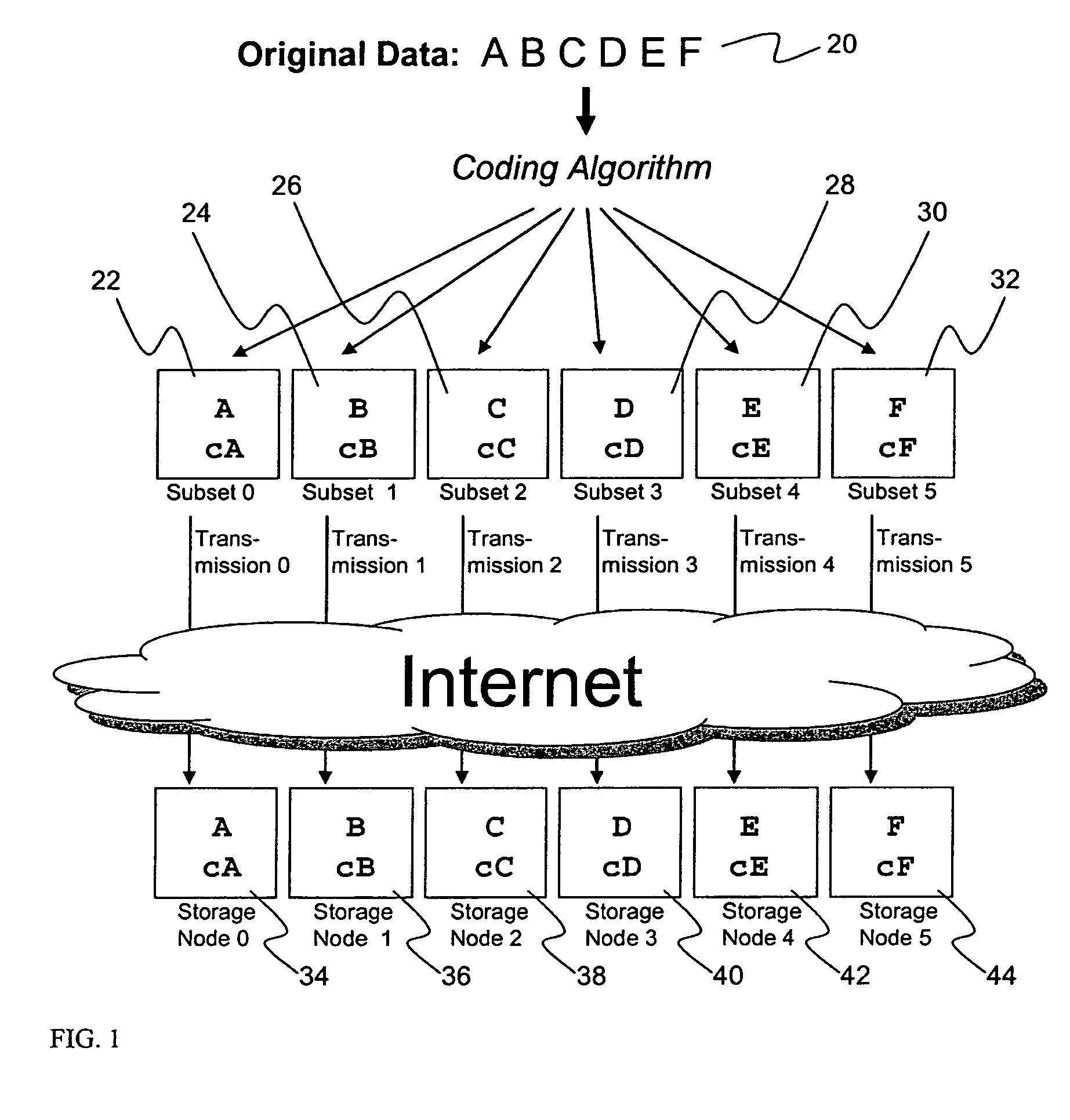
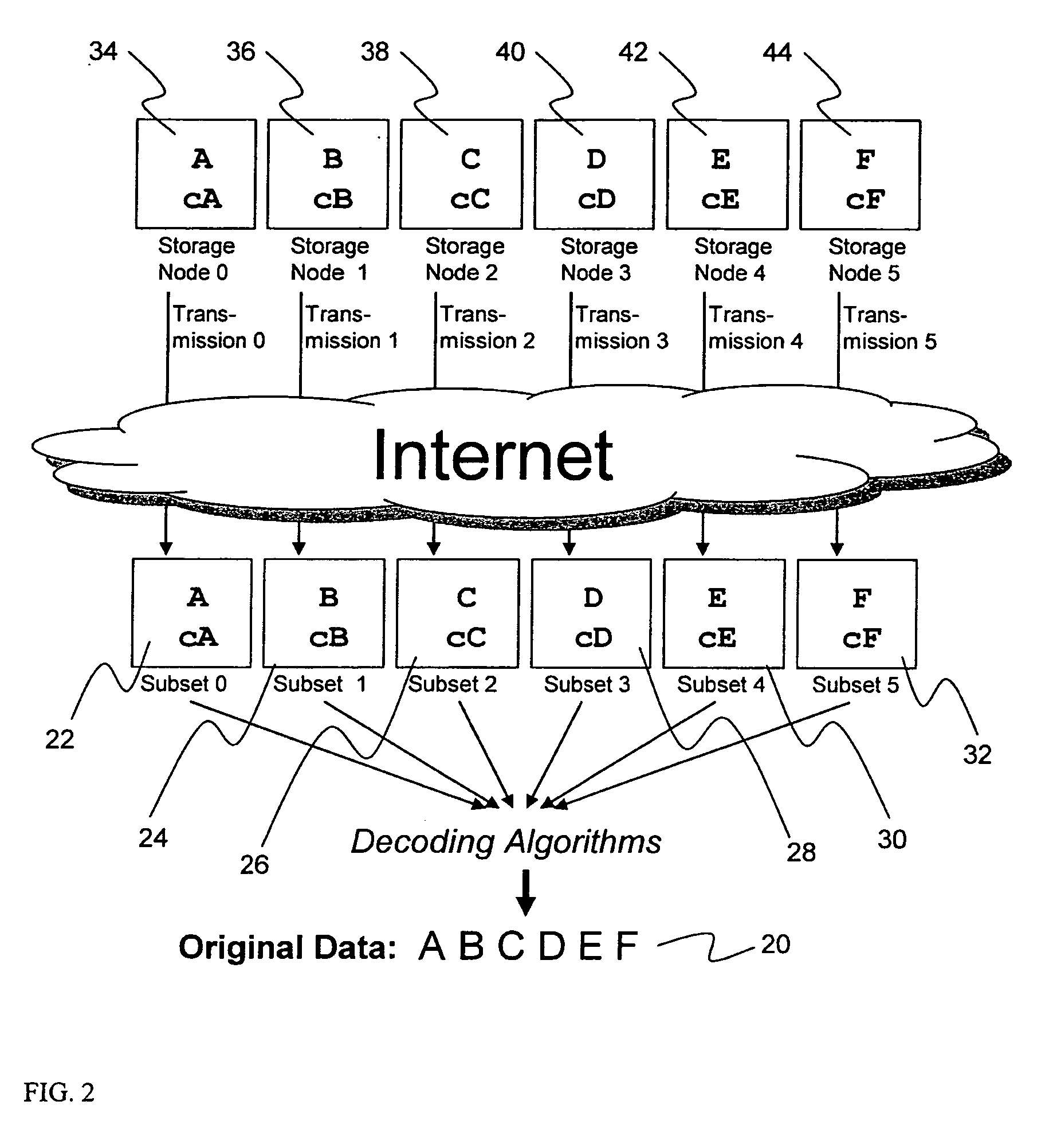
Briefly, the present invention relates to an information dispersal sytem in which original data to be stored is separated into a number of data “slices” in such a manner that the data in each subset is less usable or less recognizable or completely unusable or completely unrecognizable by itself except when combined with some or all of the other data subsets. These data subsets are stored on separate storage devices as a way of increasing privacy and security. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention, a metadata management system stores and indexes user files across all of the storage nodes. A number of applications run on the servers supporting these storage nodes and are responsible for controlling the metadata. Metadata is the information about the data, the data slices or data subsets and the way in which these data subsets are dispersed among different storage nodes running over the network. As used herein, metadata includes data source names, their size, last modification date, authentication information etc. This information is required to keep track of dispersed data subsets among all the nodes in the system. Every time new data subsets are stored and old ones are removed from the storage nodes, the metadata is updated. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention, the metadata management system stores metadata for dispersed data where: The dispersed data is in several pieces. The metadata is in a separate dataspace from the dispersed data. Accordingly, the metadata management system is able to manage the metadata in a manner that is computationally efficient relative to known systems in order to enable broad use of the invention using the types of computers generally used by businesses, consumers and other organizations currently.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS20050120025A1Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
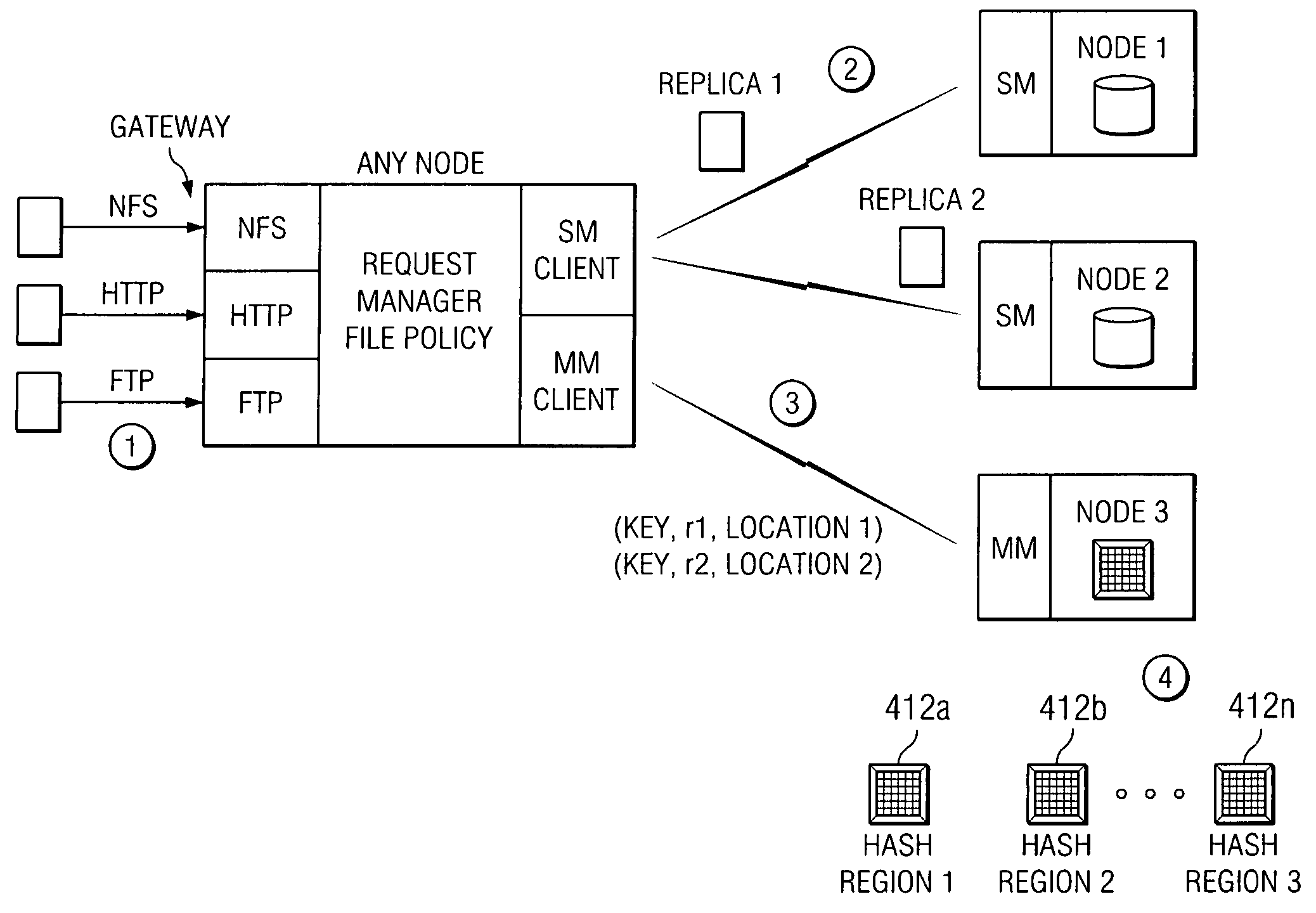
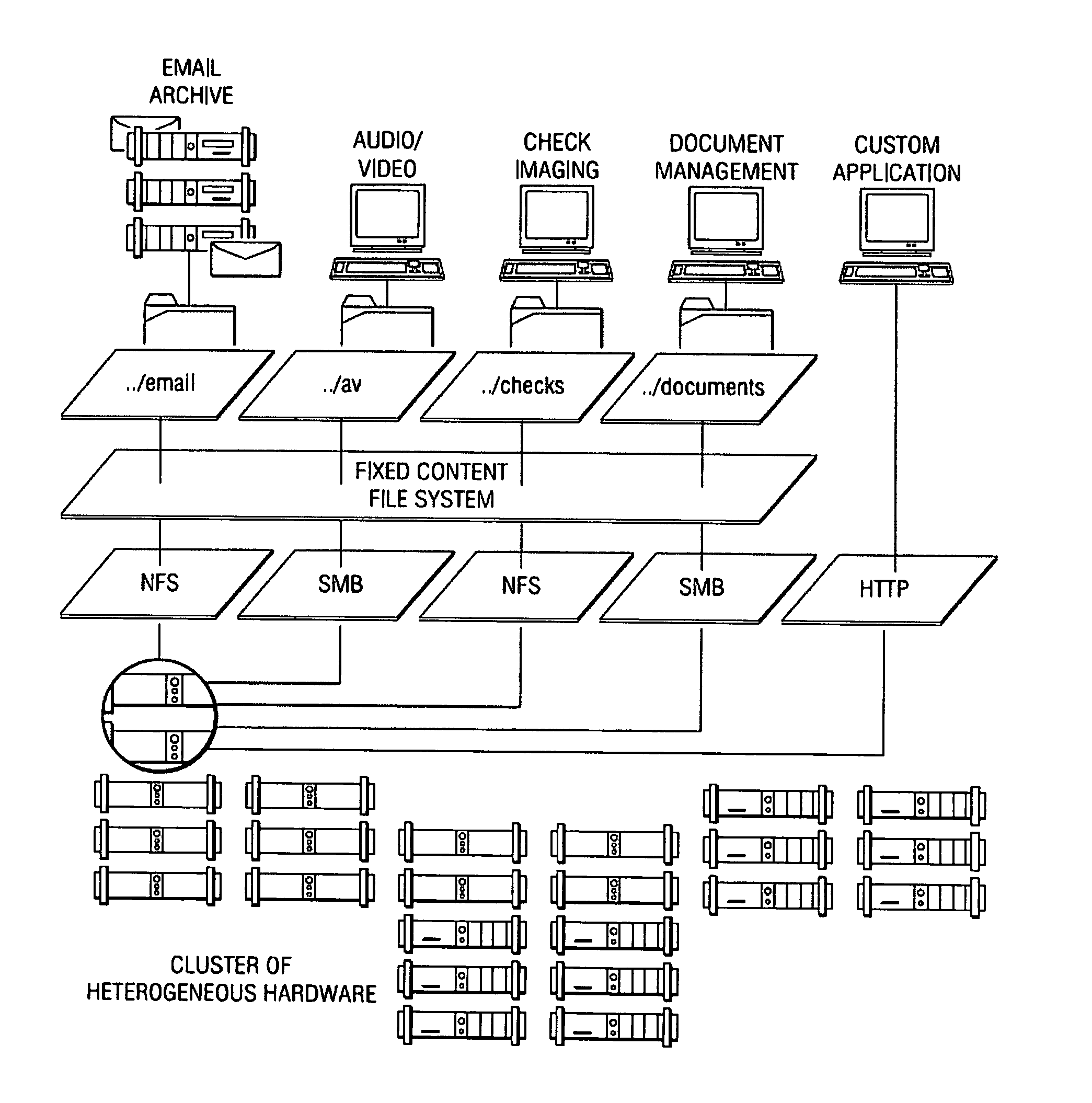
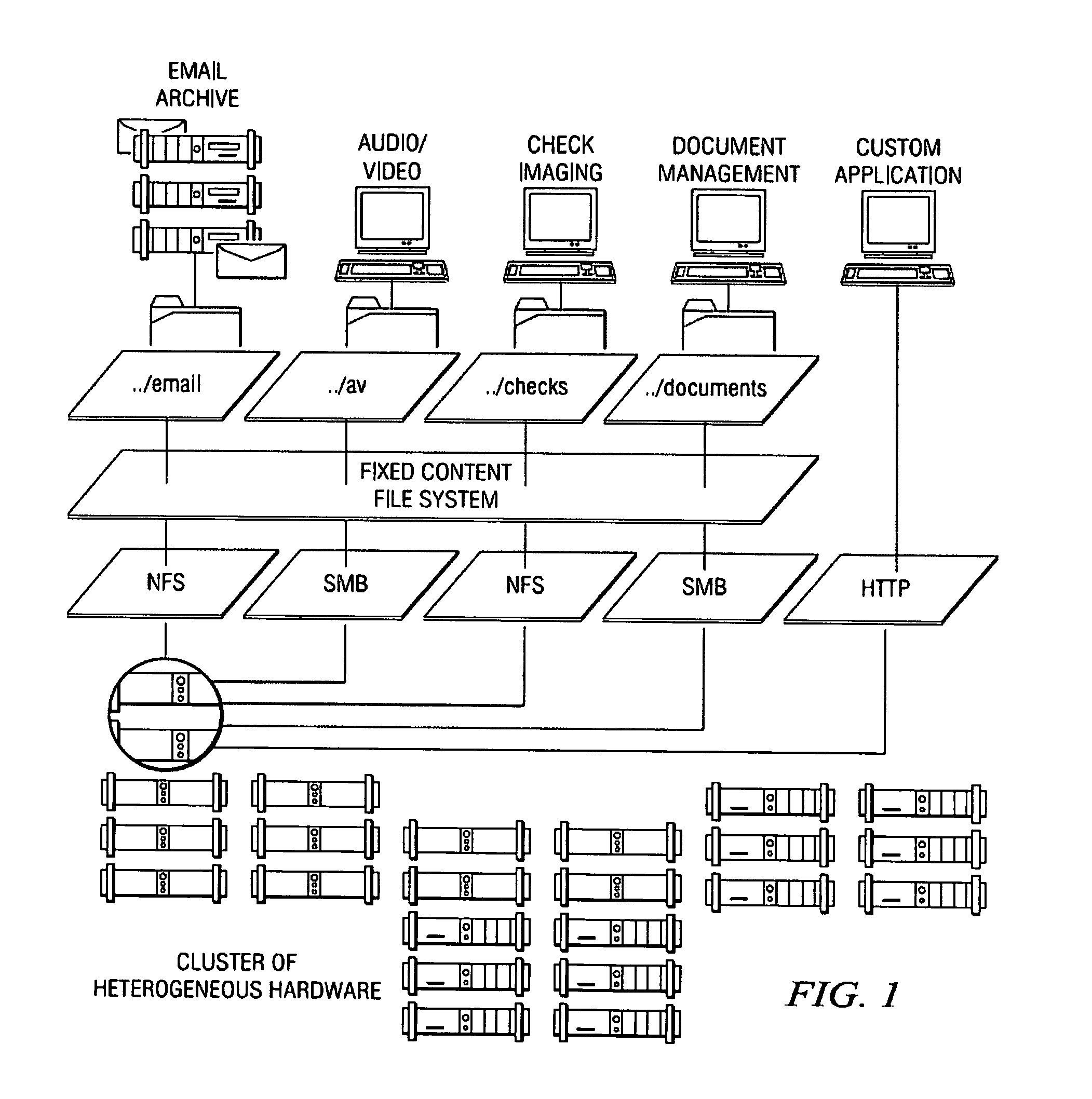
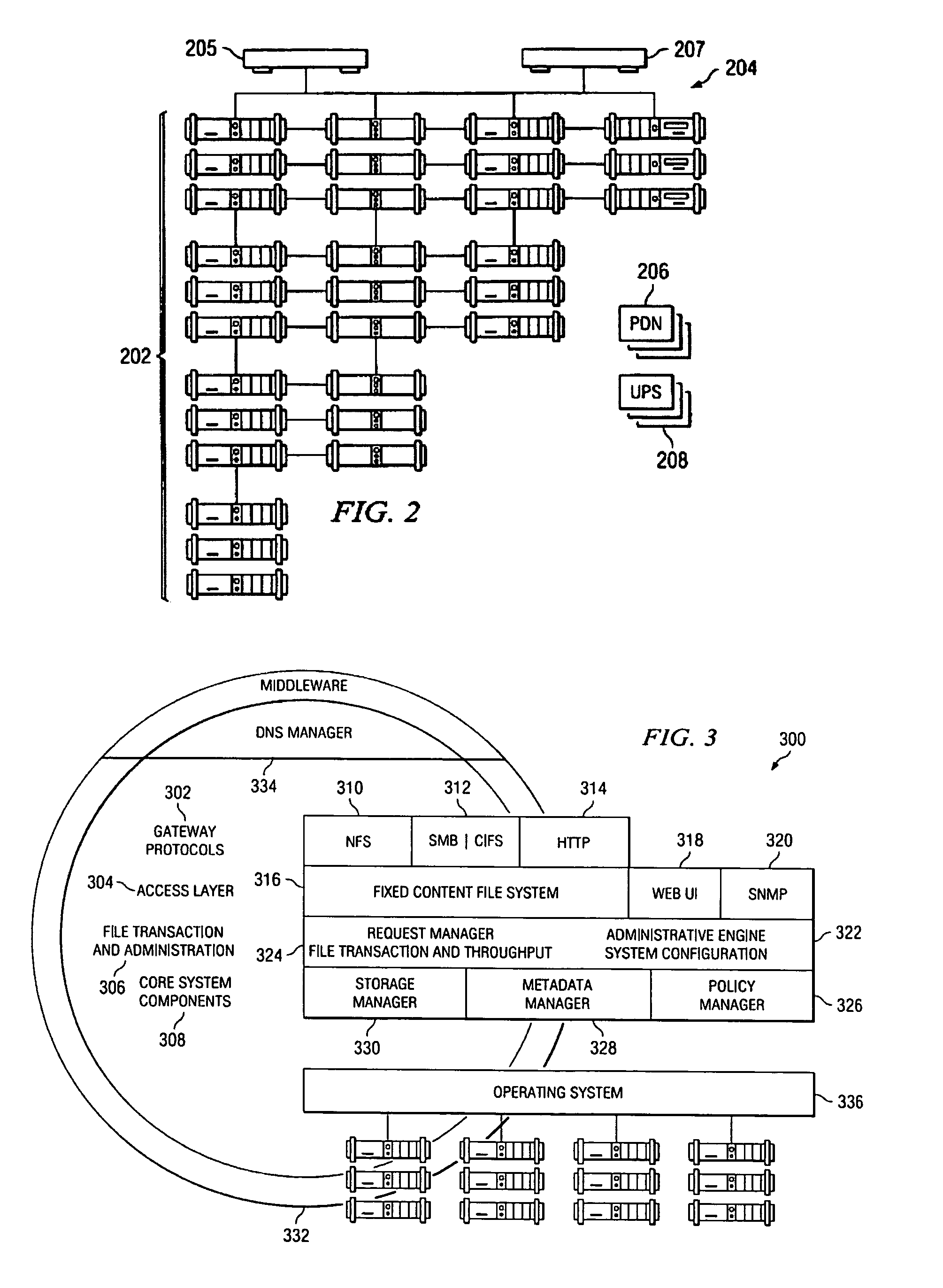
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS7155466B2Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Metadata management and generation using digital watermarks
ActiveUS20060115108A1Difficult to controlDifficult to trackMultimedia data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionWeb browserMetadata management
The present invention provides methods and systems to improve network searching for watermarked content. In some implementations we employ keyword searching to narrow the universe of possible URL candidates. A resulting URL list is searched for digital watermarking. A system is provided to allow customer input. For example, a customer enters keywords or network locations. The keywords or network locations are provided to a watermark-enabled web browser which accesses locations associated with the keywords or network locations. Some implementations of the present invention employ a plurality of distributed watermark-enabled web browsers. Other aspects of the invention provide methods and system to facilitate desktop searching and automated metadata gathering and generating. In one implementation a digital watermark is used to determine whether metadata associated with an image or audio file is current or fresh. The metadata is updated when it is out of date. Watermarks can also be used to link to or facilitate so-called on-line “blogs” (or online conversations).
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Metadata Management for fixed content distributed data storage
ActiveUS20060026219A1Improve usabilityDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionMetadata managementDistributed data store
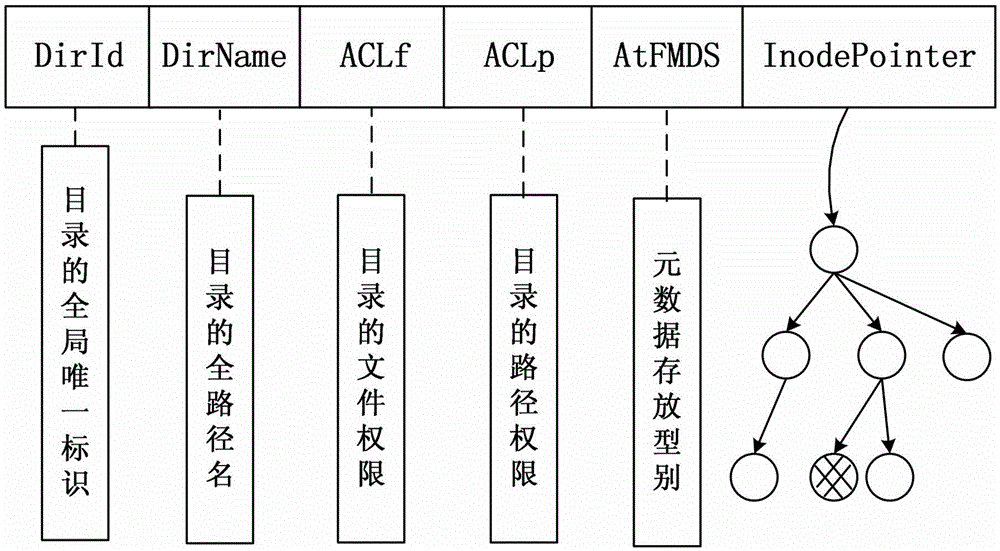
An archival storage cluster of preferably symmetric nodes includes a metadata management system that organizes and provides access to given metadata, preferably in the form of metadata objects. Each metadata object may have a unique name, and metadata objects are organized into regions. Preferably, a region is selected by hashing one or more object attributes (e.g., the object's name) and extracting a given number of bits of the resulting hash value. The number of bits may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Each region is stored redundantly. A region comprises a set of region copies. In particular, there is one authoritative copy of the region, and zero or more backup copies. The number of backup copies may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Region copies are distributed across the nodes of the cluster so as to balance the number of authoritative region copies per node, as well as the number of total region copies per node. Backup region copies are maintained synchronized to their associated authoritative region copy.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Method for loosely coupling metadata and data in a storage array
InactiveUS7032125B2Maximizing input/output (I/O) performanceAdjustable sizeInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionMetadata managementDatabase
The present invention is a method and system for associating metadata with user data in a storage array in a manner that provides independence between metadata management and a storage controller's cache block size. Metadata may be associated with user data according to multiple fashions in order to provide a desired performance benefit. In one example, the metadata may be associated according to a segment basis to maximize random I / O performance and may be associated according to a stripe basis to maximize sequential I / O performance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
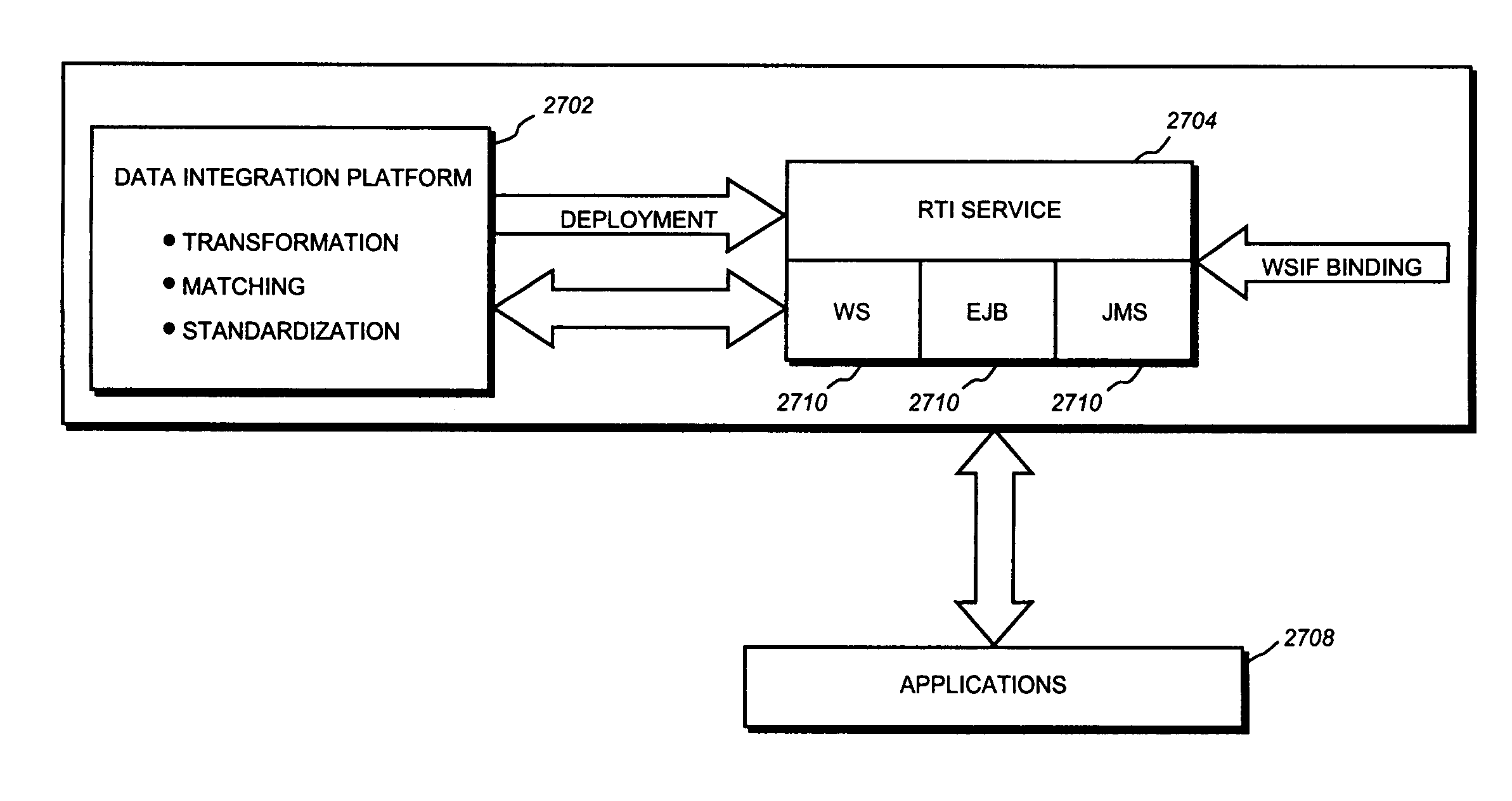
Multiple service bindings for a real time data integration service
InactiveUS7814470B2Easy accessSimple interfaceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData transformationMetadata management
Real time data integration jobs are deployed in a services oriented architecture as services that allow multiple service bindings. In one aspect, a method includes providing a code module executing a data integration job and a registry of services for storing the code module. When the code module is identified in the registry, access is provided to the code module in the registry of services, in real time wherein the code module may be accessed by more than one type of service binding such that different applications can utilize the real-time integration service using different protocols to invoke the real-time integration service. At least one of the types of service bindings may be an EJB binding, a SOAP binding, a JMS binding, and a web service binding. The data integration job may include an extraction job, a data transformation job, a loading job, a metadata management job, and a data quality job.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Metadata management convergence platforms, systems and methods
InactiveUS20050203931A1Convenience to workWeb data indexingSemi-structured data queryingMetadata managementAcademic library
Metadata management convergence platforms, systems, and methods to organize a community of users' data records. More specifically, methods managing metadata records related to content housed in unique, disparate or federated holdings in centralized or distributed environments. Also systems and methods for creating and managing metadata records using domain specific language, vocabulary and metadata schema accepted by a community of users of unique, disparate or federated databases in centralized or distributed environments. Such environments can include content repositories including but not limited to: vehicle fleet information systems; government document holdings; insurance and underwriting information holdings; academic library collections; and entertainment archives.
Owner:PINGREE ROBERT W
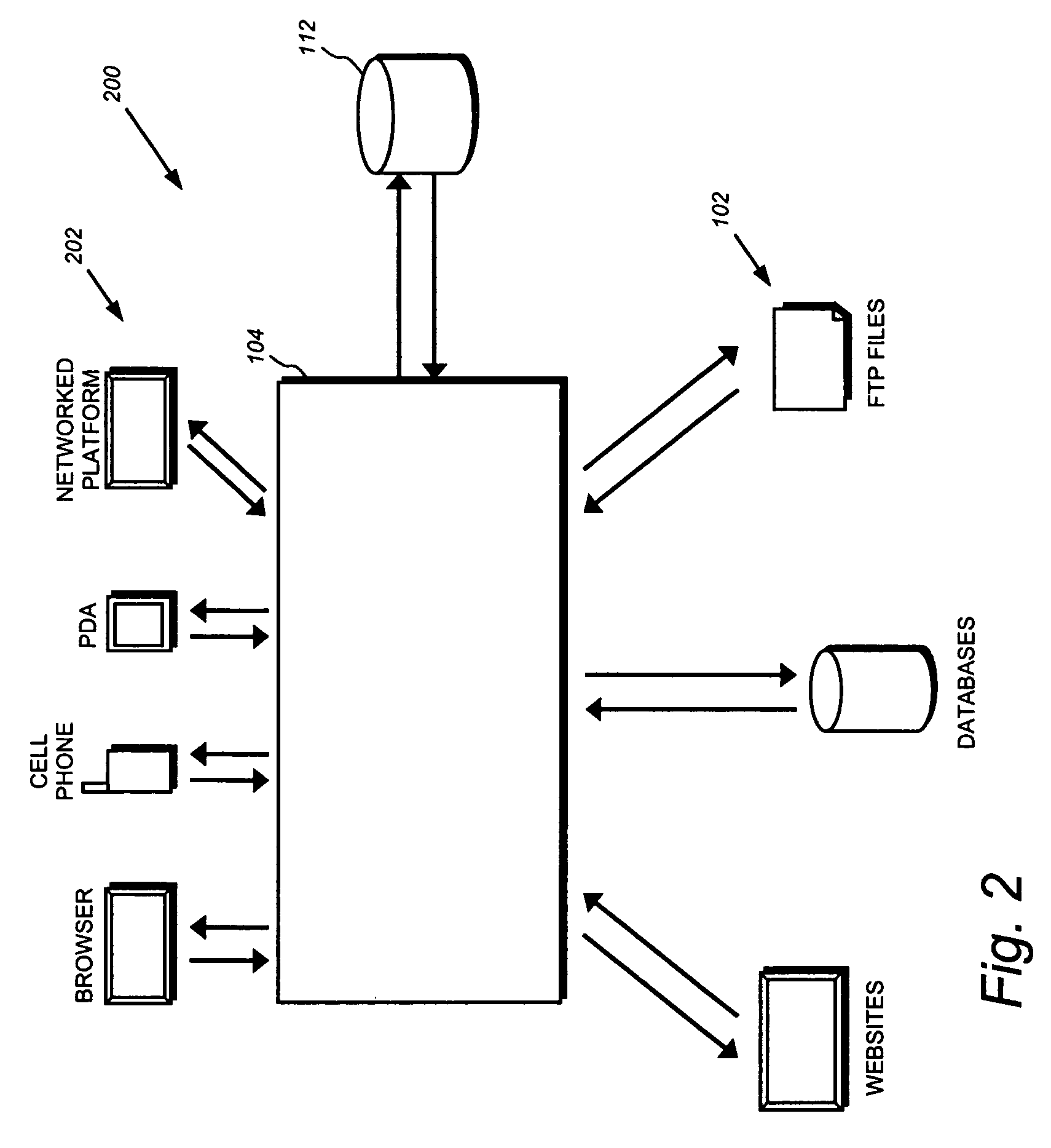
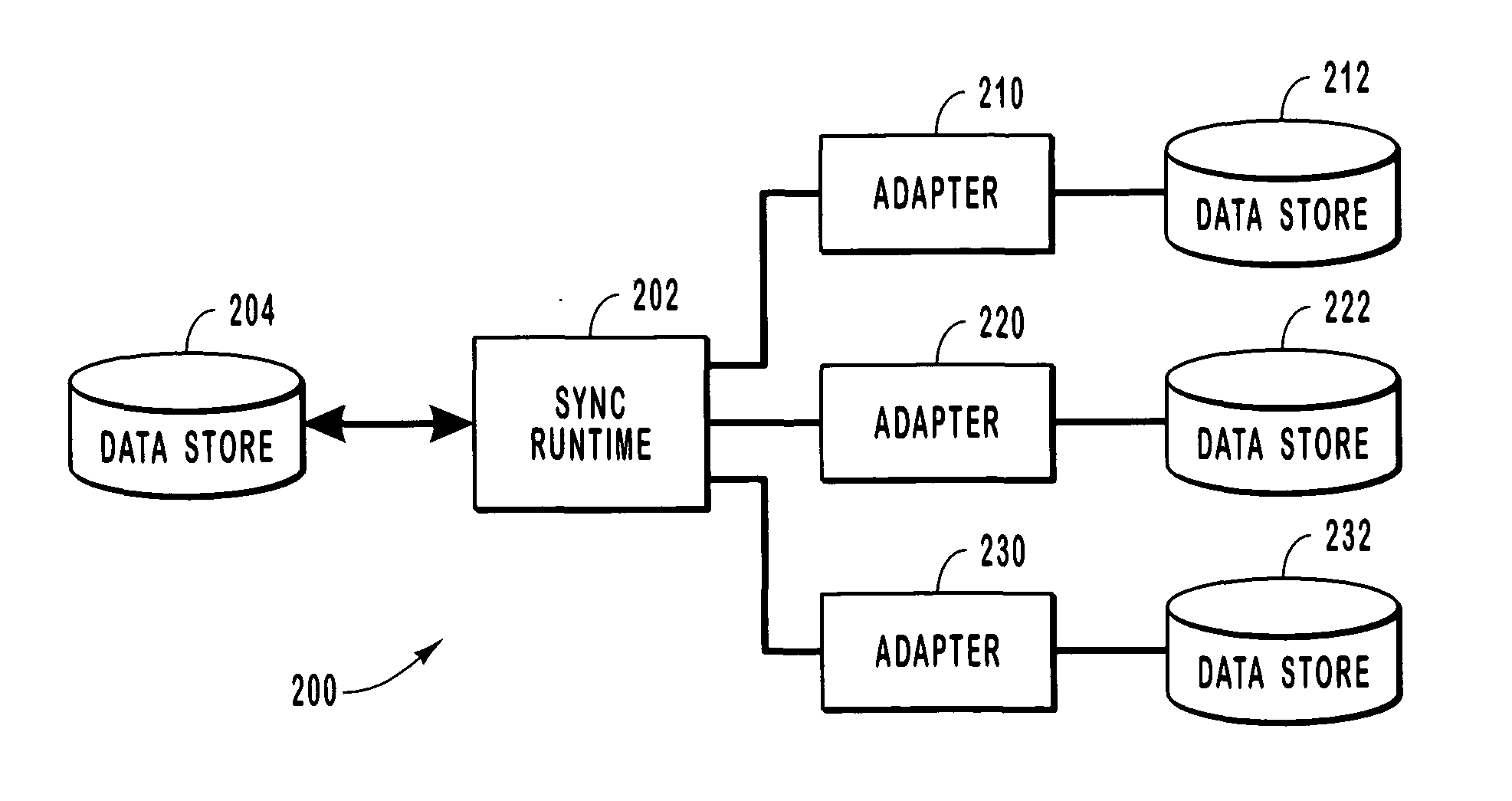
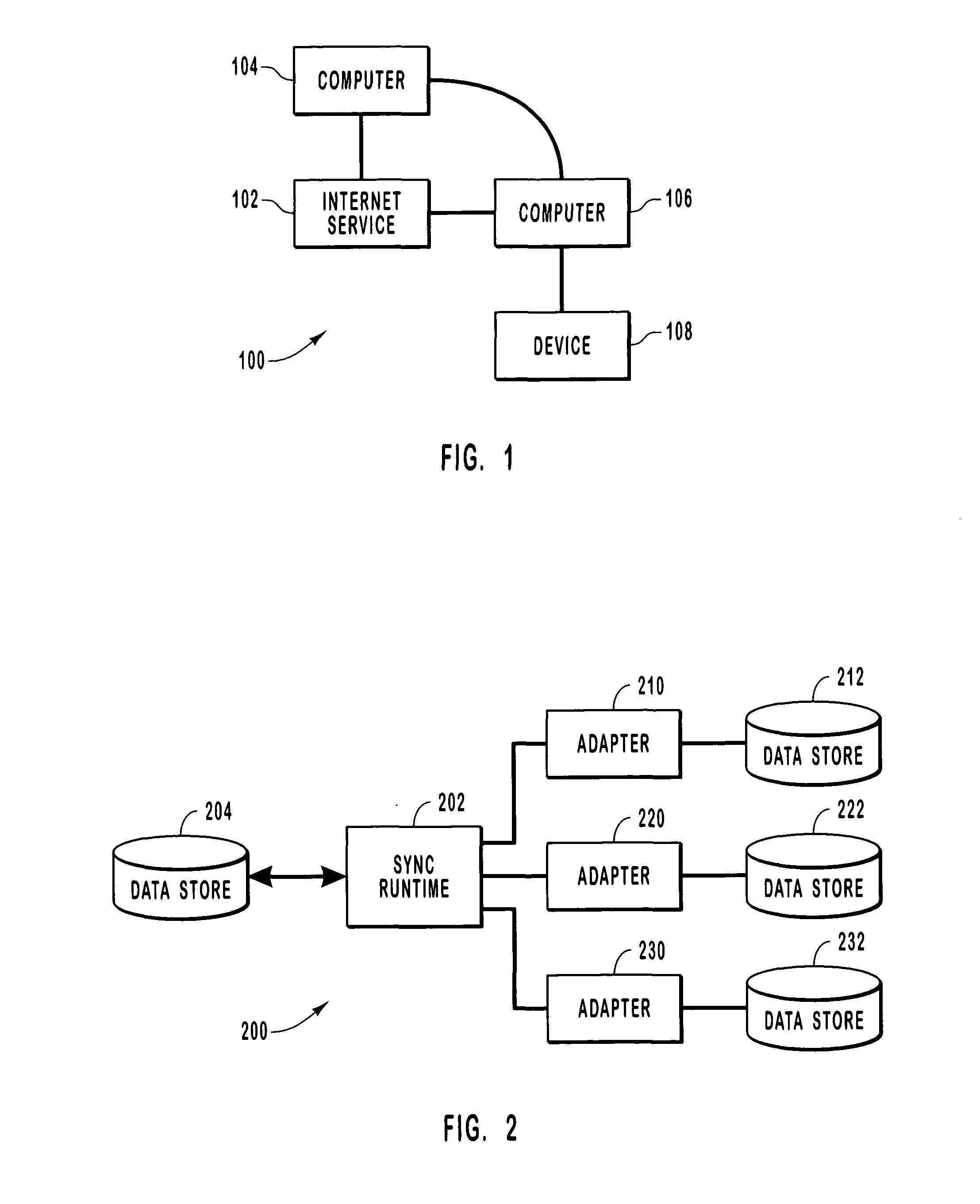
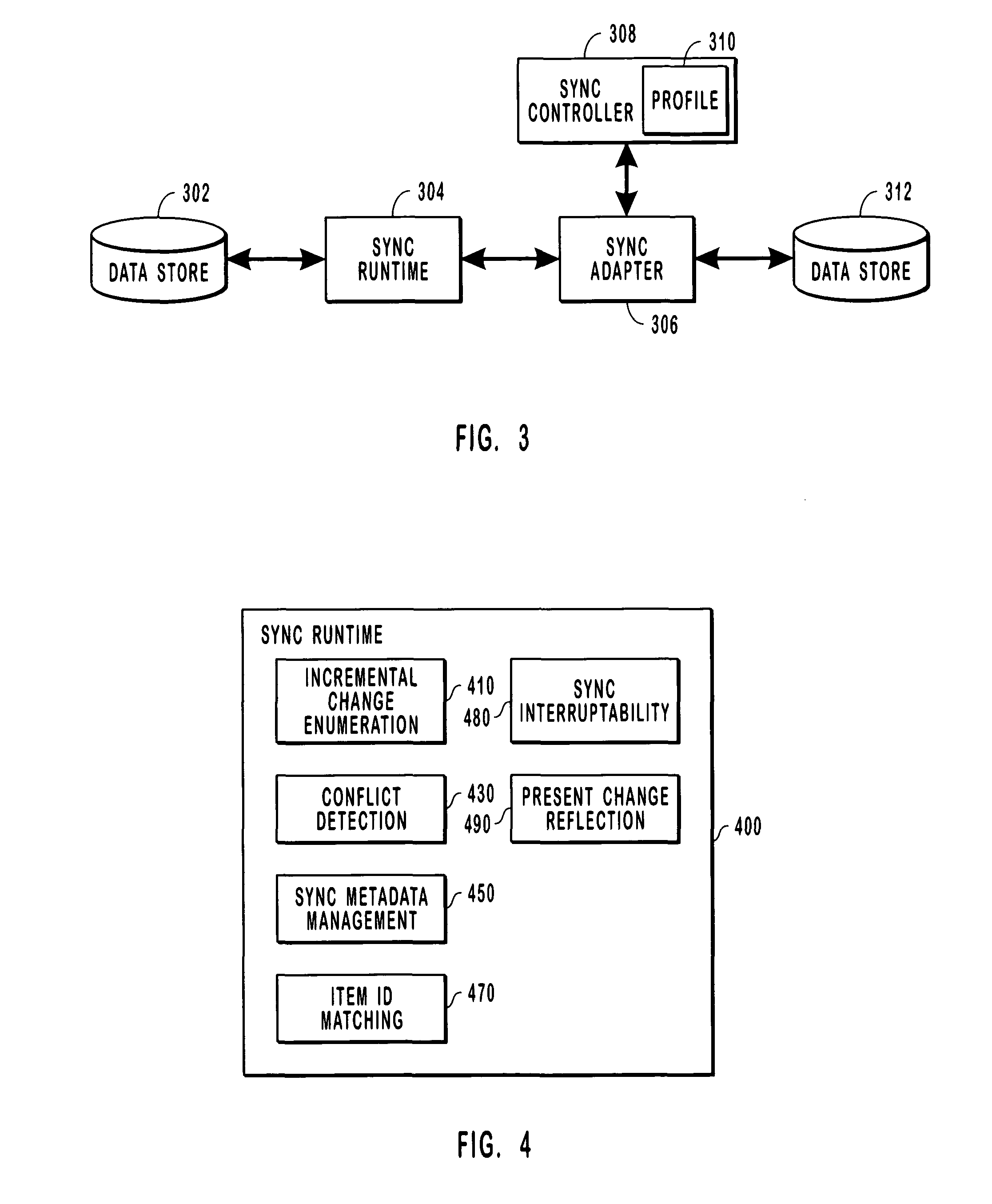
Systems and methods for synchronizing with multiple data stores
ActiveUS20050027755A1Overcome limitationsDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsMetadata managementApplication programming interface
Systems and methods for synchronizing data stores. A framework including a sync runtime enables consistent and manageable synchronization between a data store and multiple, diverse back end data stores. The sync runtime provides services such as change enumeration, conflict detection, metadata management, item ID matching, sync interruptability, and the like that are accessible to configurable adapters over an application programming interface. Each synchronizing data store can uses a sync controller to initialize an adapter that can access the services provided by the sync runtime. The sync controller can use a profile to configure each adapter. The profile can identify conflict resolution policies, synchronization filters, source and destination folders, sync direction, and the like.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
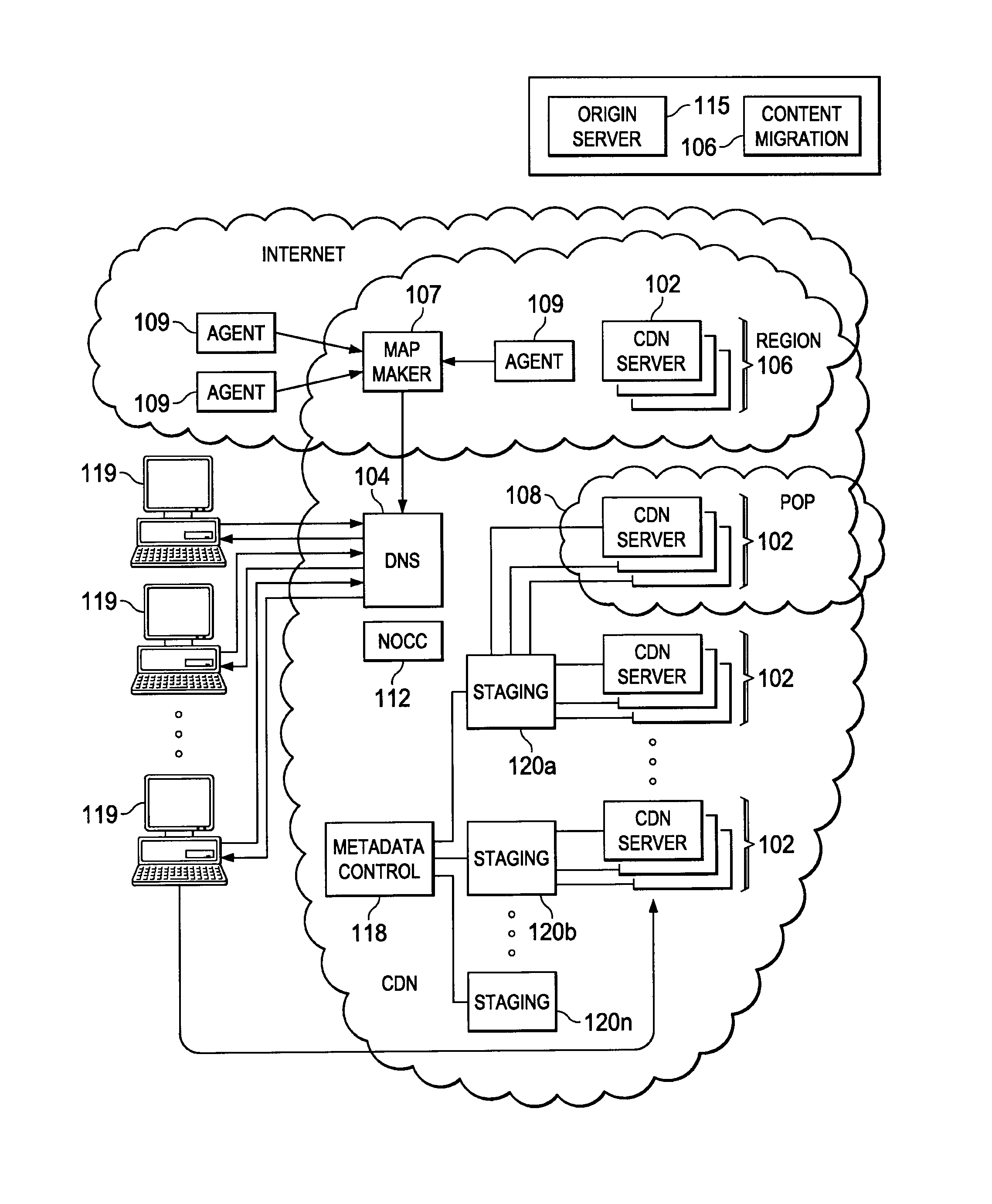
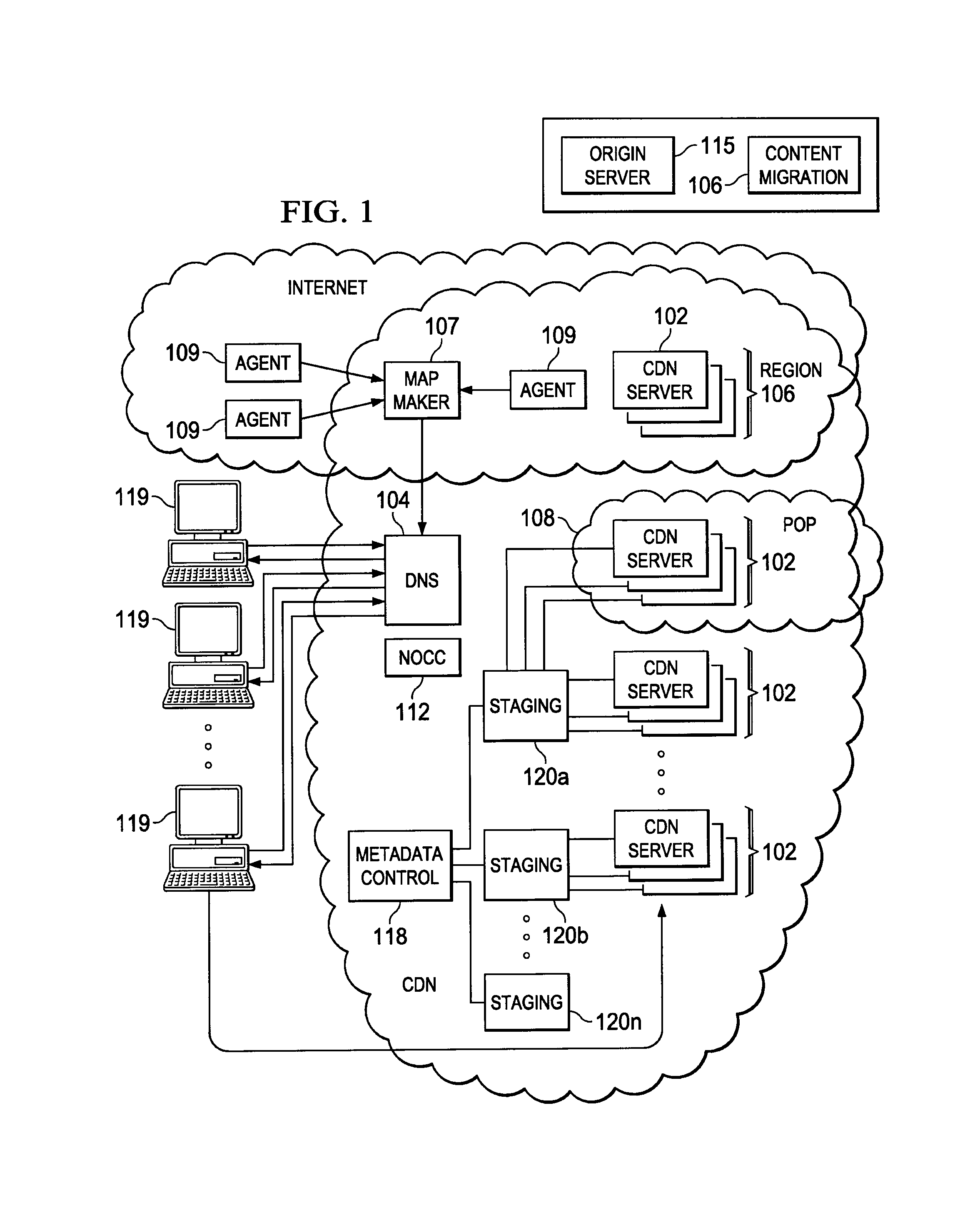
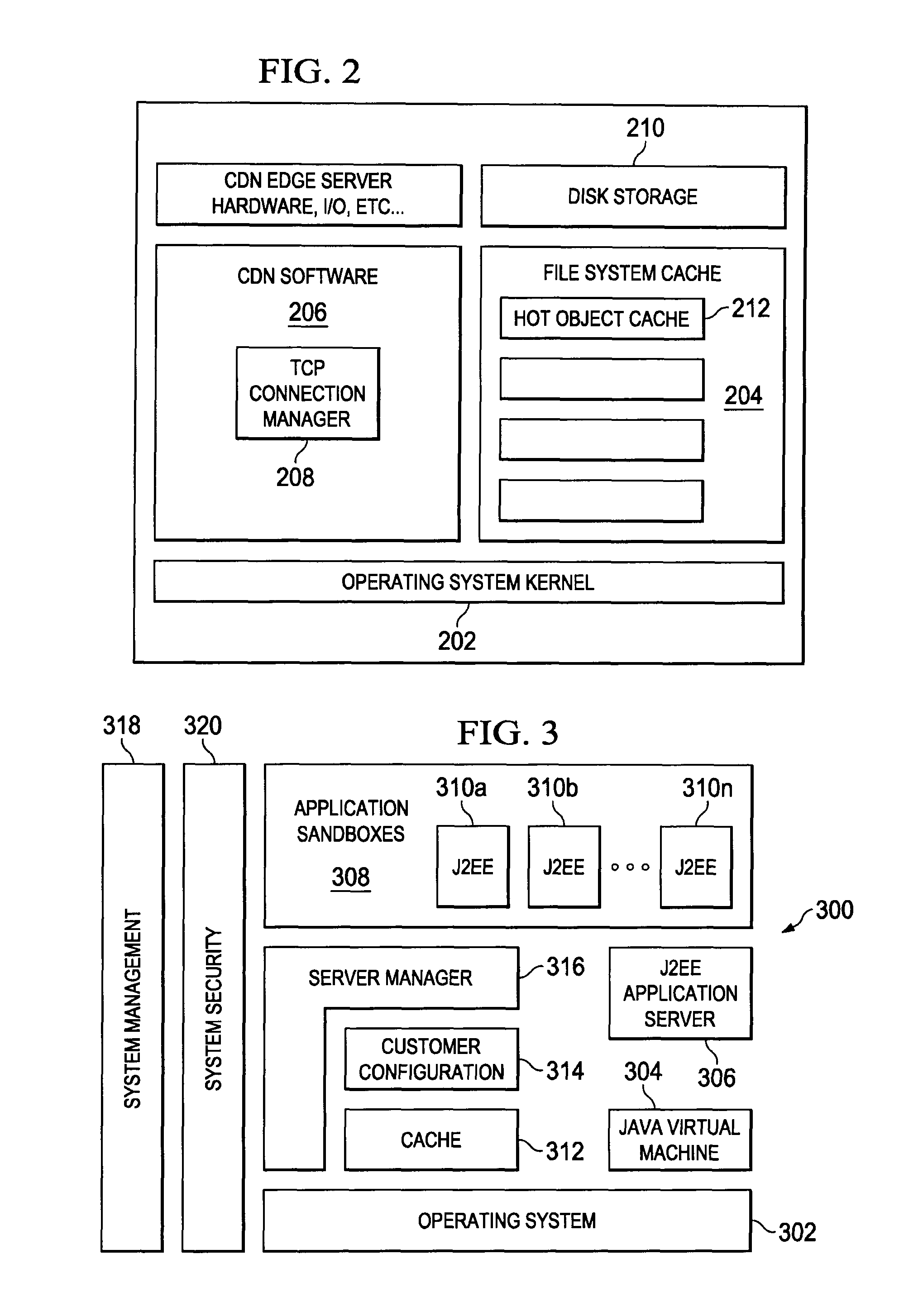
Forward request queuing in a distributed edge processing environment
An edge server in a distributed processing environment includes at least one process that manages incoming client requests and selectively forwards given service requests to other servers in the distributed network. According to the invention, the edge server includes storage (e.g., disk and / or memory) in which at least one forwarding queue is established. The server includes code for aggregating service requests in the forwarding queue and then selectively releasing the service requests, or some of them, to another server. The forward request queuing mechanism preferably is managed by metadata, which, for example, controls how many service requests may be placed in the queue, how long a given service request may remain in the queue, what action to take in response to a client request if the forwarding queue's capacity is reached, and the like. In one embodiment, the server generates an estimate of a current load on an origin server (to which it is sending forwarding requests) and instantiates the forward request queuing when that current load is reached.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
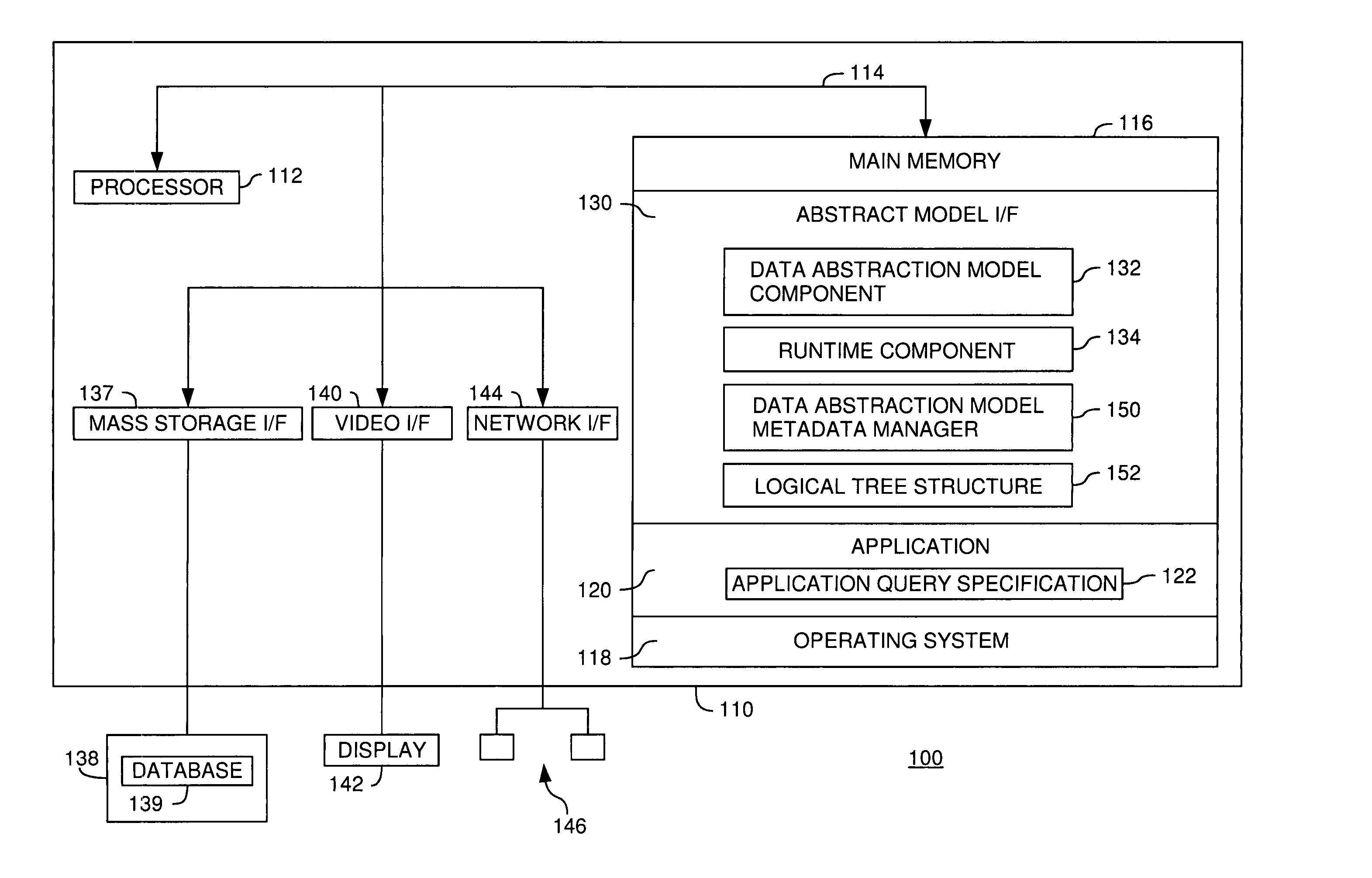
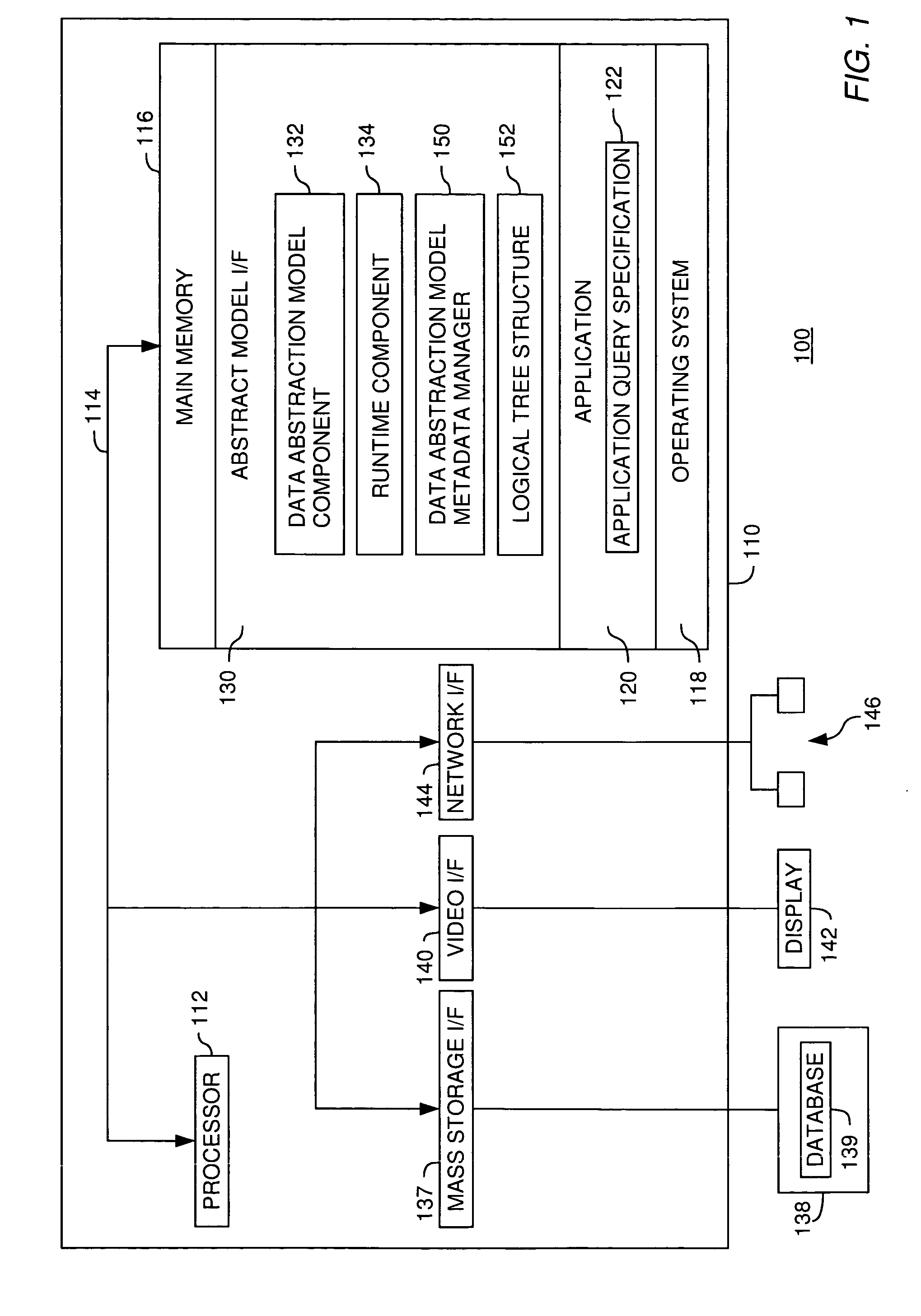
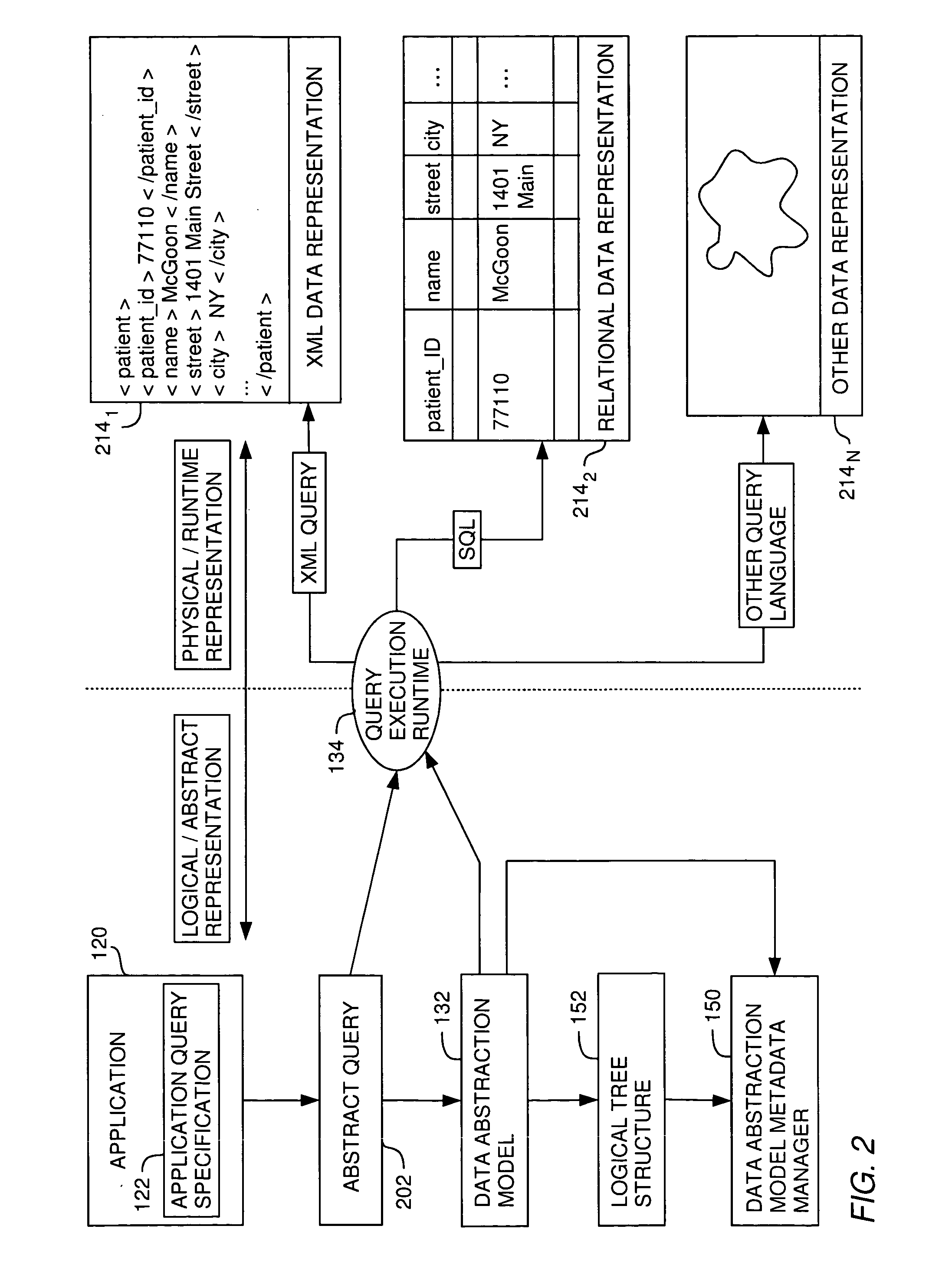
Metadata management for a data abstraction model
InactiveUS20060074953A1Data processing applicationsHospital data managementData abstractionMetadata management
A method, system and article of manufacture for managing metadata associated with a data abstraction model abstractly describing data in a database. One embodiment provides a method of managing metadata describing objects of a data abstraction model with logical fields that define abstract views of physical data in a database. The method comprises traversing a logical tree structure representing the data abstraction model. The logical tree structure has a plurality of nodes, each representing a logical field or a category of logical fields of the data abstraction model. The method further comprises identifying metadata describing logical fields or categories represented by the plurality of nodes. The identified metadata is stored in a queryable database. A user is allowed to query the database to identify objects in the data abstraction model that may be used to construct an abstract query.
Owner:IBM CORP
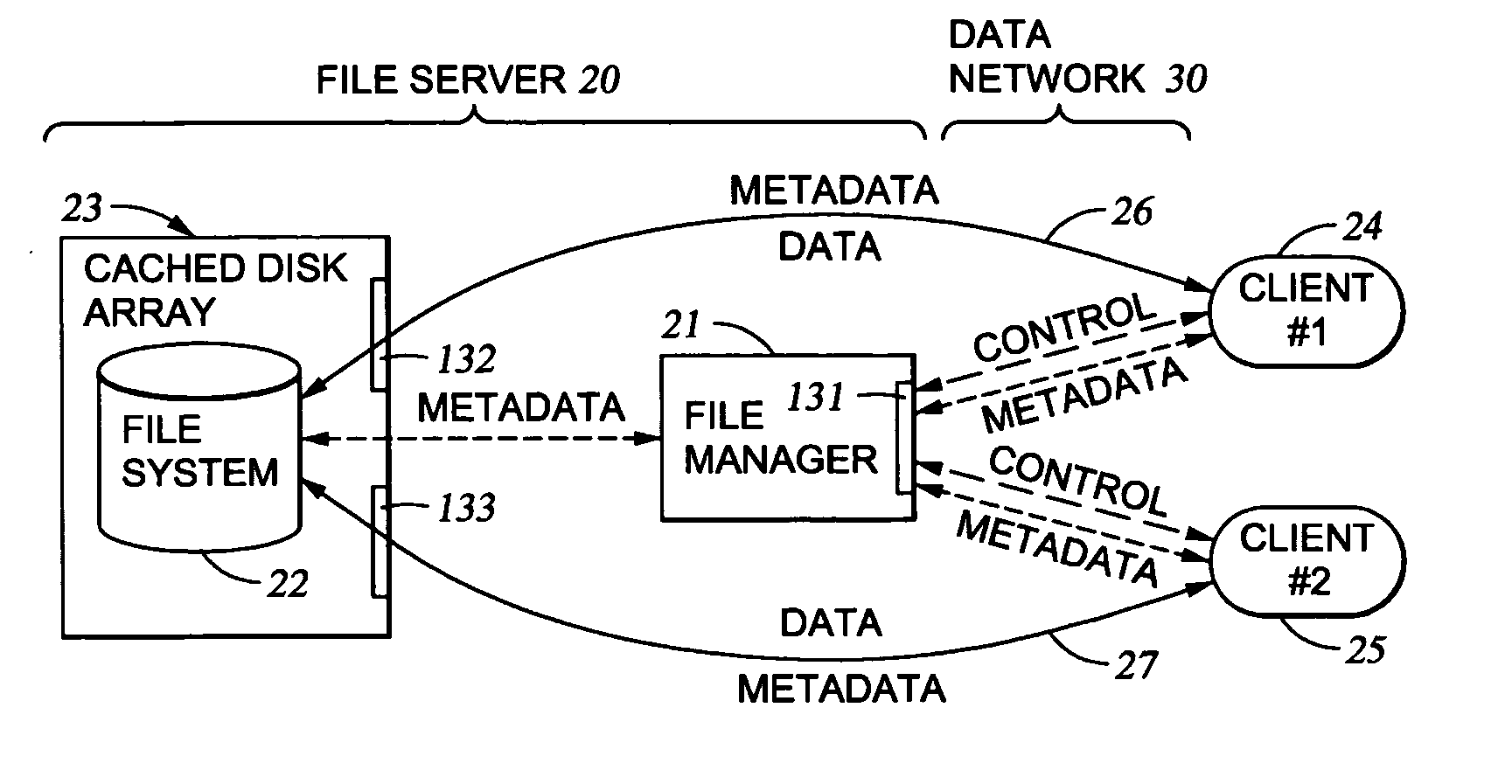
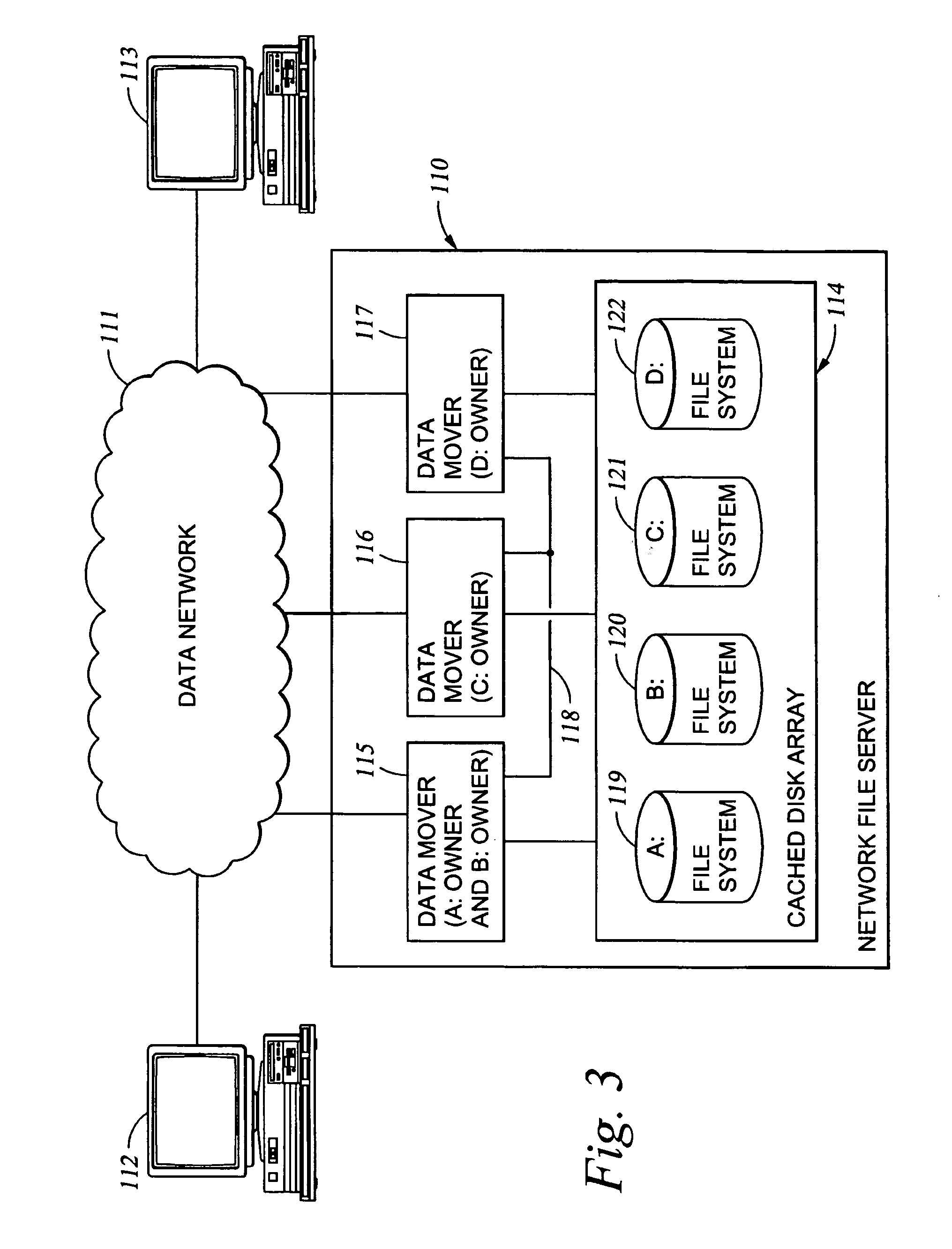
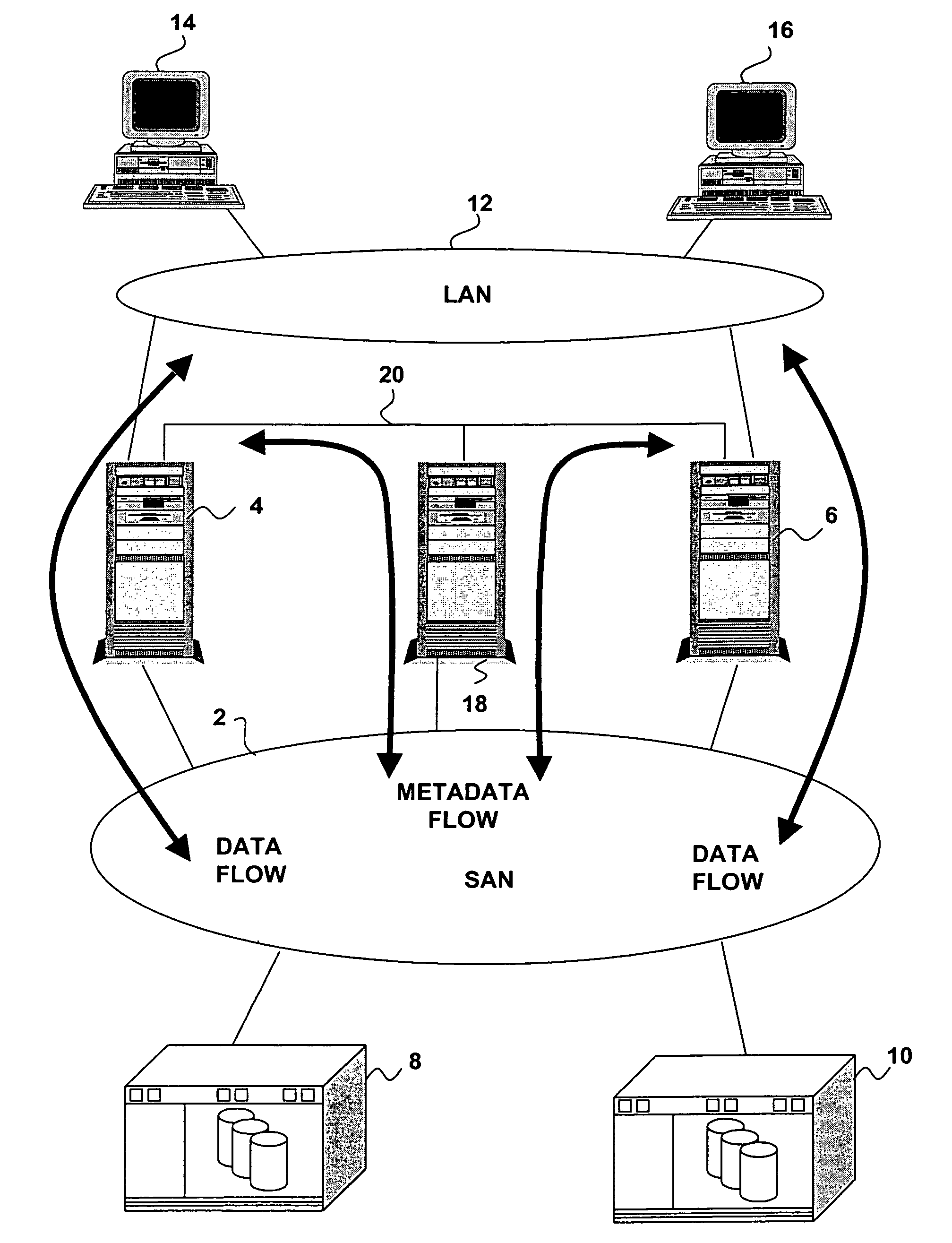
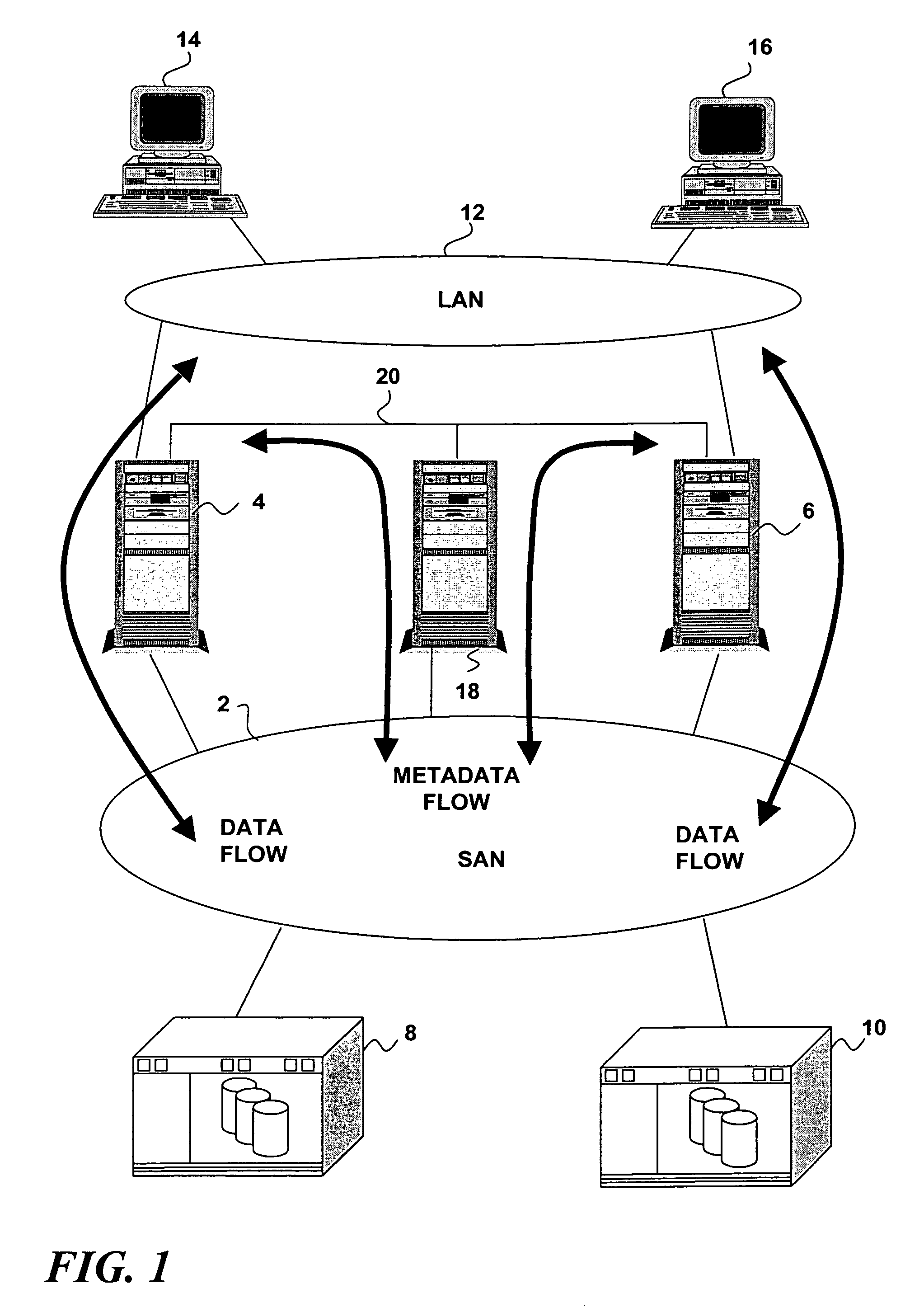
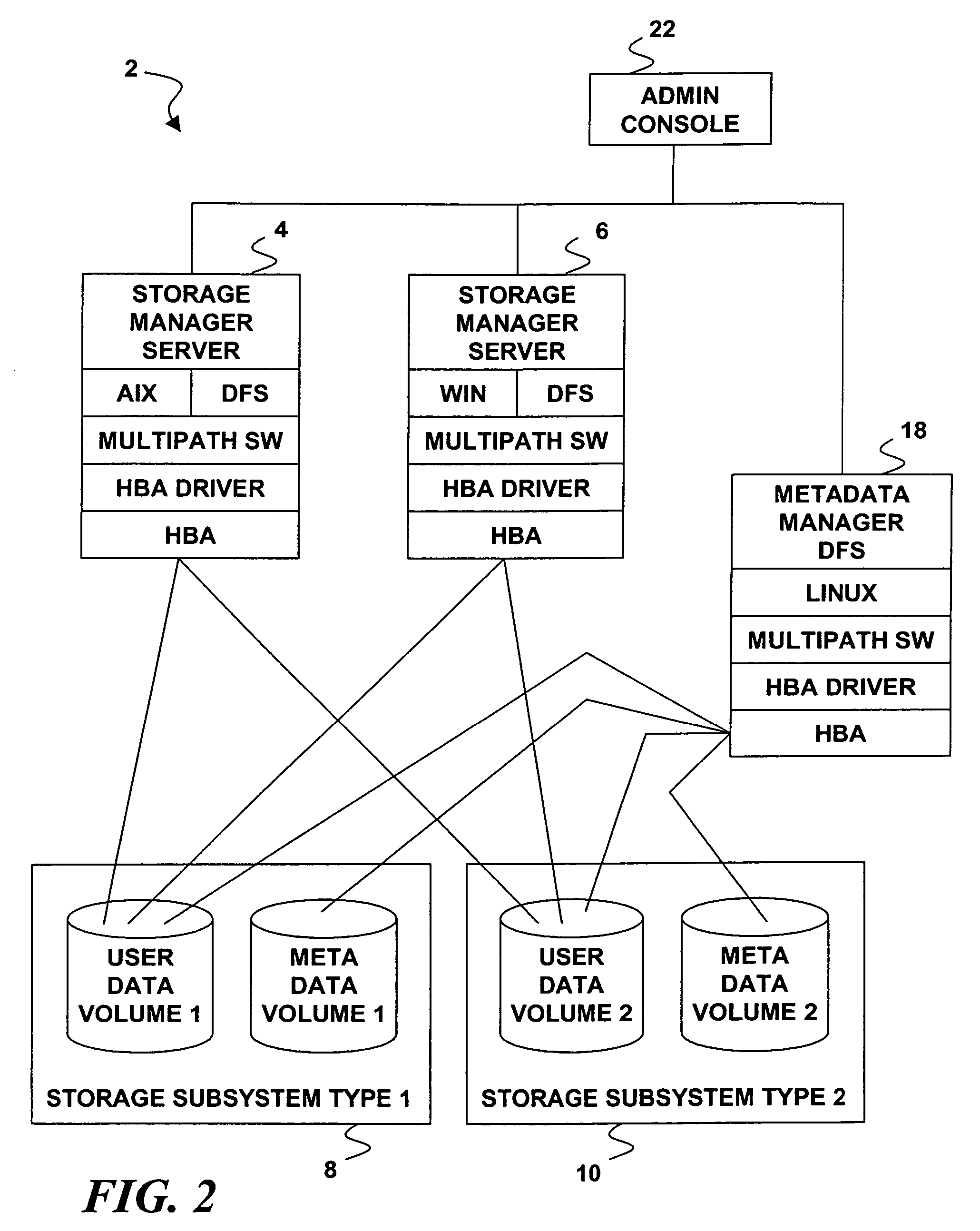
Delegation of metadata management in a storage system by leasing of free file system blocks from a file system owner
InactiveUS20050240628A1Reduce amountAvoid adjustmentData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMetadata managementData management
Metadata management in a file server or storage network is delegated from a primary data processor to a secondary data processor in order to reduce data traffic between the primary data processor and the secondary data processor. The primary data processor retains responsibility for managing locks upon objects in the file system that it owns, and also retains responsibility for allocation of free blocks and inodes of the file system. By leasing free blocks and inodes to the secondary and granting locks to the secondary, the secondary can perform the other metadata management tasks such as appending blocks to a file, truncating a file, creating a file, and deleting a file.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
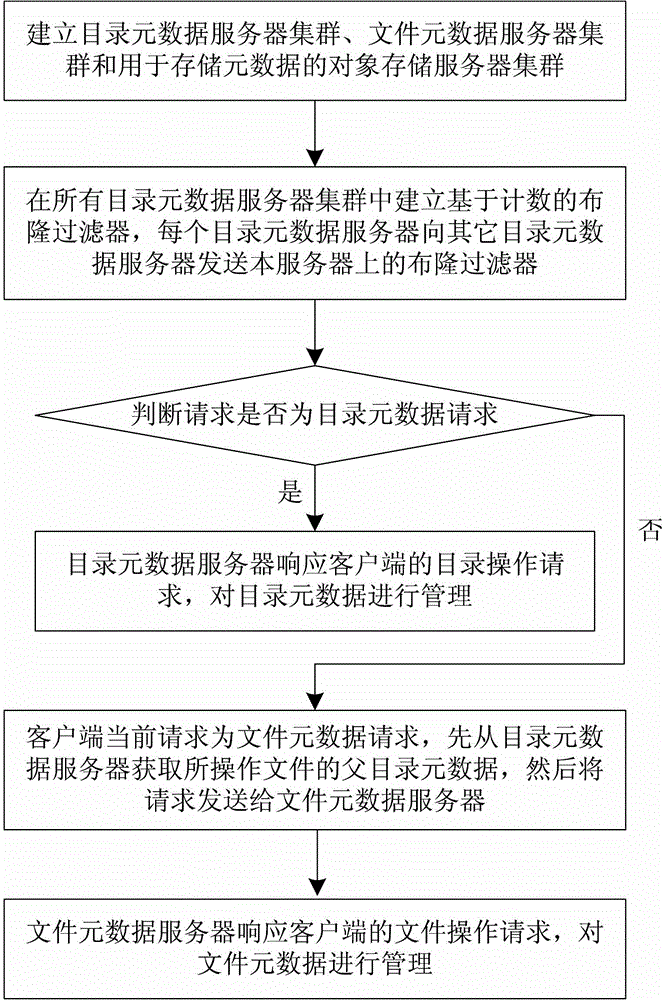
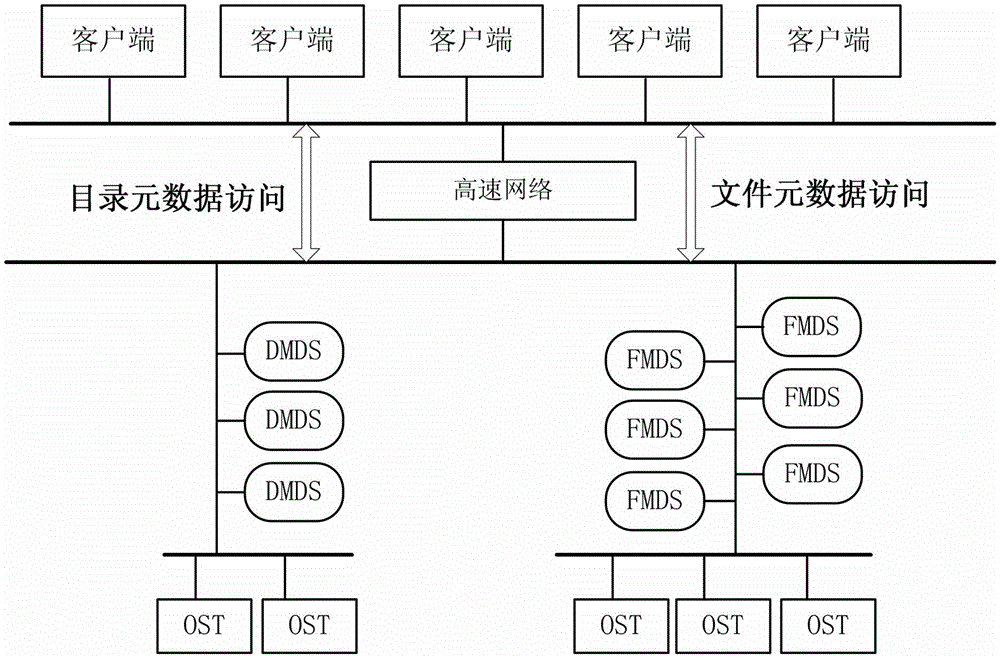
Distributed file system metadata management method facing to high-performance calculation
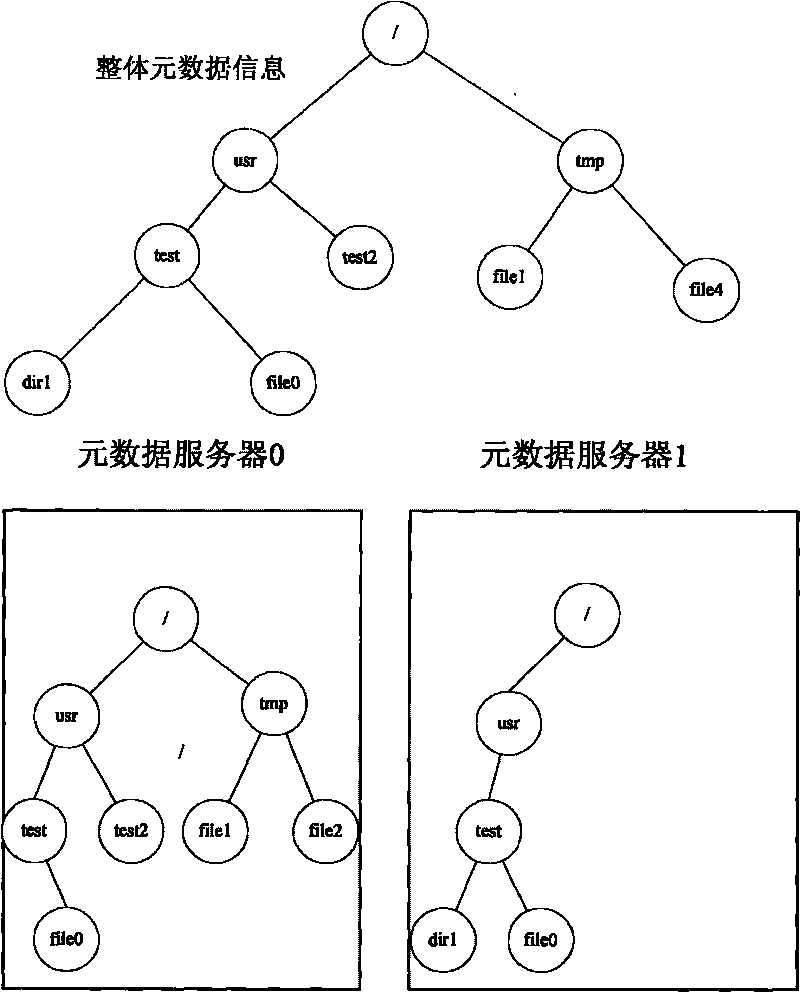
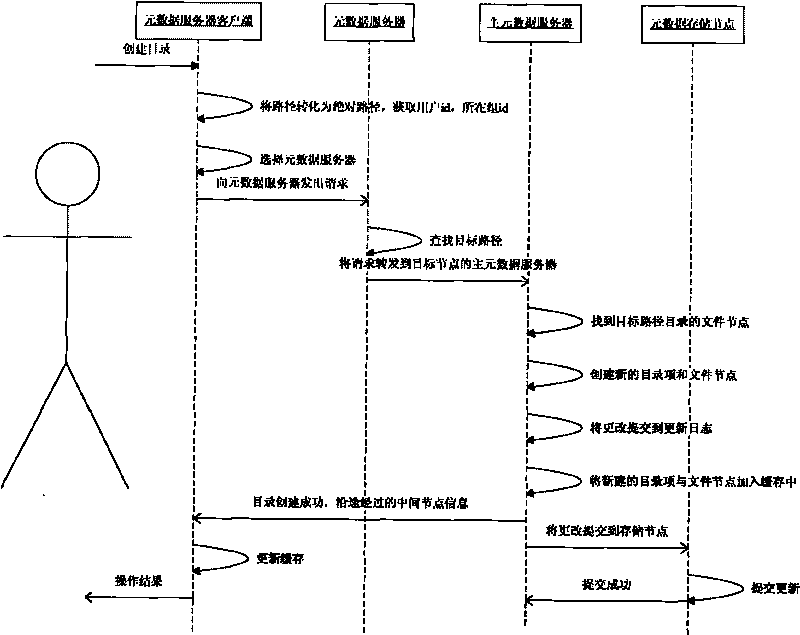
ActiveCN103150394AInhibit migrationLoad balancingTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed File SystemMetadata management
The invention discloses a distributed file system metadata management method facing to high-performance calculation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) establishing a catalogue metadata server cluster, a file metadata server cluster and an object storage server cluster; 2) establishing a global counting-based bloom filter in the catalogue metadata server cluster; 3) when the operation request of a client side arrives, skipping to execute step 4) or 5); 4) enabling the catalogue metadata server cluster to respond to the catalogue operation request of the client side to manage the catalogue metadata; and 5) enabling the file metadata server cluster to respond to the file operation request of the client side to manage the file metadata data. According to the distributed file system metadata management method disclosed by the invention, the metadata transferring problem brought by catalogue renaming can be effectively solved, and the distributed file system metadata management method has the advantages of high storage performance, small maintenance expenditure, high load, no bottleneck, good expansibility and balanced load.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Metadata management for fixed content distributed data storage
ActiveUS7657581B2Improve usabilityError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsMetadata managementData mining
An archival storage cluster of preferably symmetric nodes includes a metadata management system that organizes and provides access to given metadata, preferably in the form of metadata objects. Each metadata object may have a unique name, and metadata objects are organized into regions. Preferably, a region is selected by hashing one or more object attributes (e.g., the object's name) and extracting a given number of bits of the resulting hash value. The number of bits may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Each region is stored redundantly. A region comprises a set of region copies. In particular, there is one authoritative copy of the region, and zero or more backup copies. The number of backup copies may be controlled by a configuration parameter. Region copies are distributed across the nodes of the cluster so as to balance the number of authoritative region copies per node, as well as the number of total region copies per node. Backup region copies are maintained synchronized to their associated authoritative region copy.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
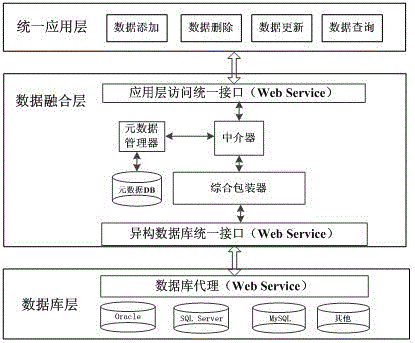
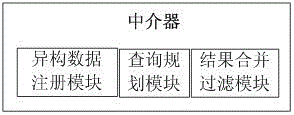
Multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and data query method thereof
InactiveCN104008135AAchieve integrationEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsMetadata managementSystem maintenance
The invention provides a multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and a data query method thereof. The system comprises a database layer, a data fusion layer and a uniform application layer. The database layer is composed of heterogeneous databases and agencies of the heterogeneous databases. The data fusion layer is used for fusing information of all heterogeneous data sources, and is responsible for data access of the heterogeneous data sources and coordinating the information of all the data sources, and specifically comprises a metadata data base (DB), a metadata manager, a comprehensive wrapper, a mediator, an application layer access uniform interface and a heterogeneous database uniform interface. The uniform application layer is the user of the heterogeneous database fusion system and can have access to shared data resources of the heterogeneous databases by fusing middle layers. The multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and the data query method of the multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system solve the problems in heterogeneous database fusion and overcome the defects of an existing database fusion technology. The system can conduct transparent query on all the heterogeneous databases on the condition that local databases are not affected, and the maintenance cost of the system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Delegation of metadata management in a storage system by leasing of free file system blocks and i-nodes from a file system owner
ActiveUS20030191745A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMetadata managementInode
Metadata management in a file server or storage network is delegated from a primary data processor to a secondary data processor in order to reduce data traffic between the primary data processor and the secondary data processor. The primary data processor retains responsibility for managing locks upon objects in the file system that it owns, and also retains responsibility for allocation of free blocks and inodes of the file system. By leasing free blocks and inodes to the secondary and granting locks to the secondary, the secondary can perform the other metadata management tasks such as appending blocks to a file, truncating a file, creating a file, and deleting a file.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
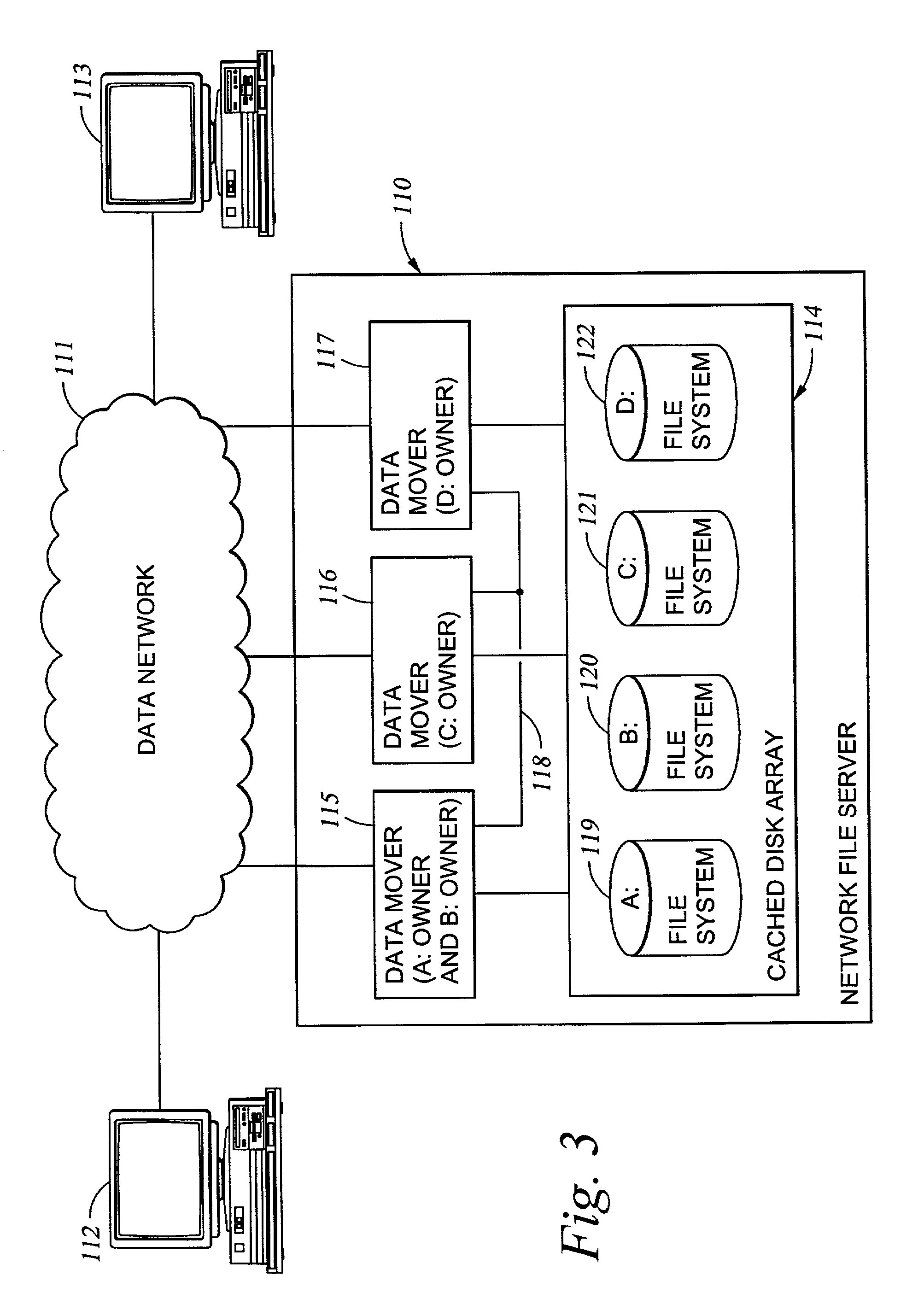
File system architecture requiring no direct access to user data from a metadata manager
InactiveUS7617321B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDistributed File SystemFile system
A system, method and computer program product for implementing a distributed file system architecture requiring no direct access to user data from a metadata manager in a data storage network. Metadata operations requiring user volume access are performed via a proxy on a storage manager server that is a distributed file system client. Management of metadata can be isolated from user data because the metadata manager requires no capability to see the storage for user volumes. This allows for a distributed file management system to support heterogeneous environments without requiring any single point in the system to see all the storage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus of hierarchical storage management based on data value
InactiveUS20060015529A1Manage data volumesMinimal costData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamMetadata management
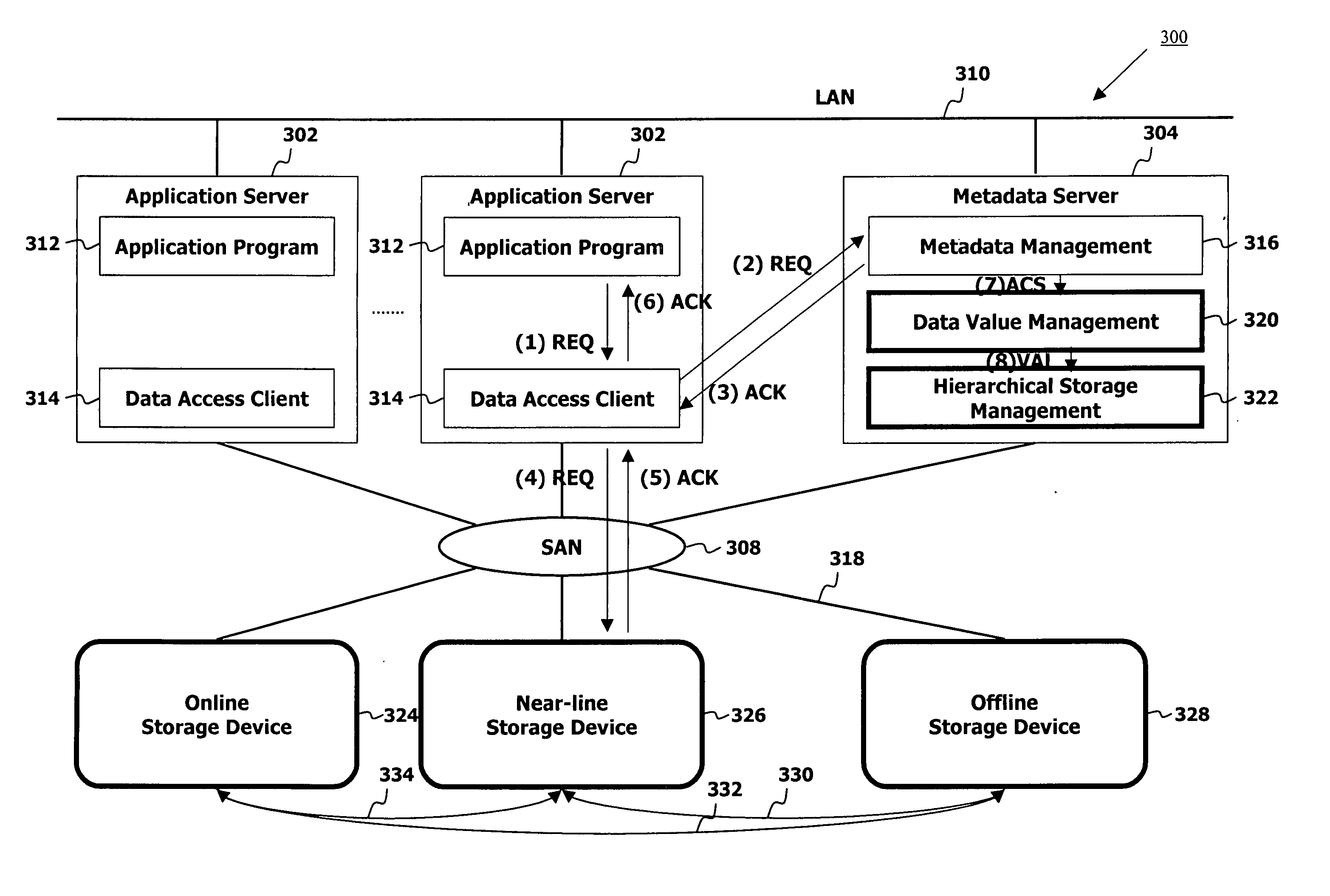
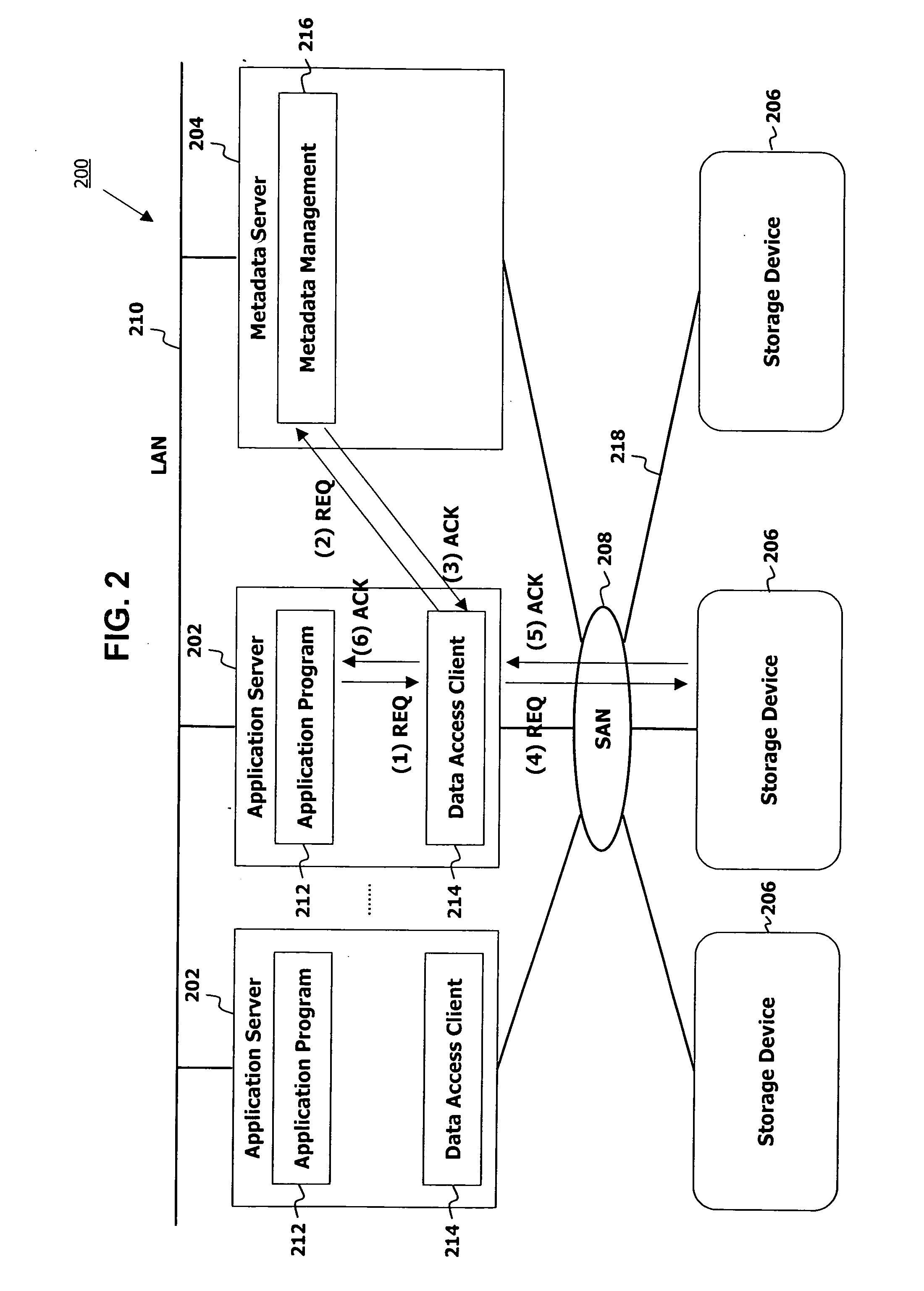
A hierarchical storage data management system includes application servers, a metadata server interconnected with the application servers through a local area network, storage devices interconnected through data flow paths, and a storage network connecting the storage devices to the application servers and to the metadata server. The metadata server including a metadata management element, a data value management unit, and a hierarchical storage management element calculates a data value for each of stores data objects in the system, assigns a storage cost value for each of storage areas in the system, normalizes calculated data values and assigned storage costs to an identical value range, compares normalized data values with normalized storage costs thereby determining whether to relocate the data objects to different storage areas, and relocates data objects to storage areas with storage cost values identical with data values of the data objects.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for dynamically managing metadata of distributed file system
InactiveCN101697168ASmooth expansionLoad balancingTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsExtensibilityDistributed File System
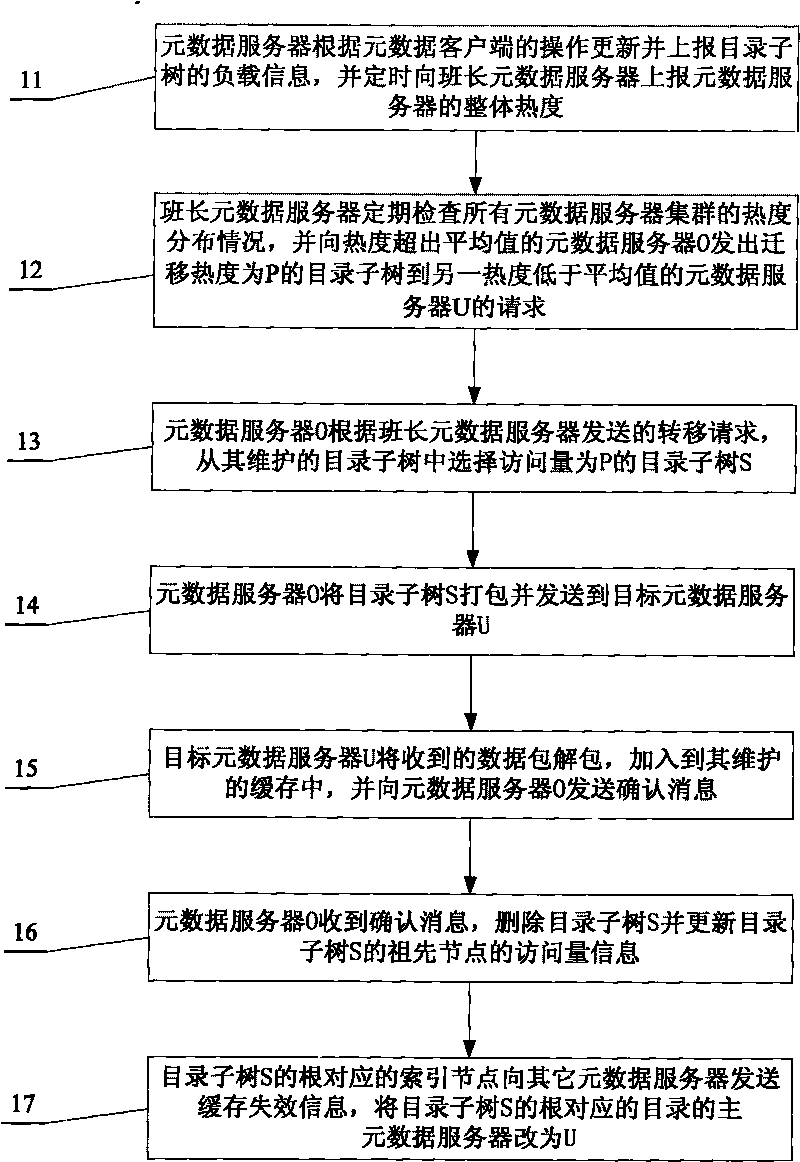
The invention relates to a method and a system for dynamically managing metadata of a distributed file system in order to solve the problems that a metadata management method cannot dynamically adjust the distribution of the metadata according to the load change, smoothly extend a metadata server, process the access to a hot content and well deal with the access to a single hot file. The method comprises that: the metadata server dynamically divides the distribution of the metadata on each metadata server according to the access condition of the metadata and manages the dynamically divided metadata according to the operation request of a client. The method and the system solve the problems of extensibility and load balance of the metadata server through dynamic division and the problem of consistency of the metadata through the management of the dynamically divided metadata.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Programming environment and metadata management for programmable multimedia controller
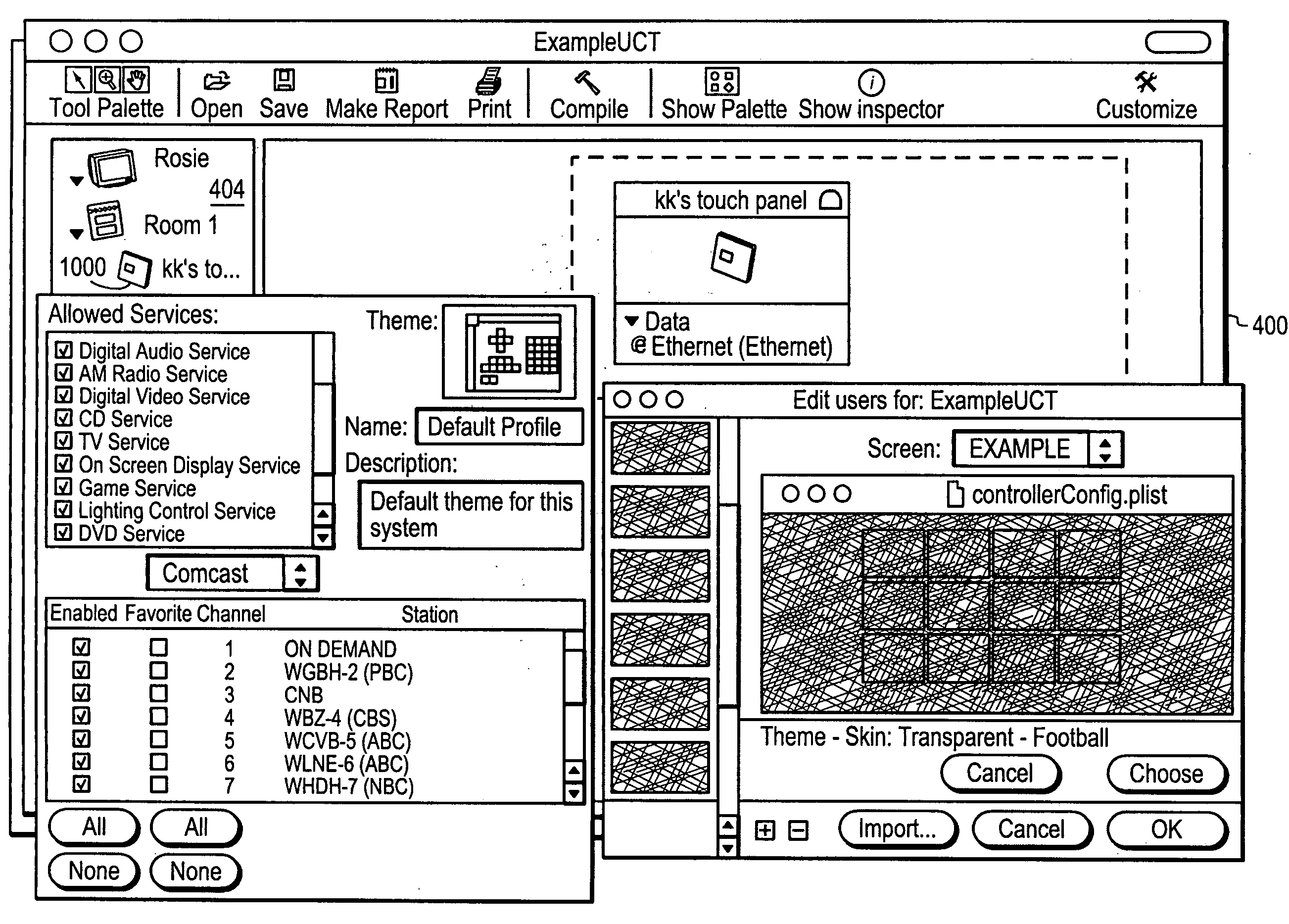
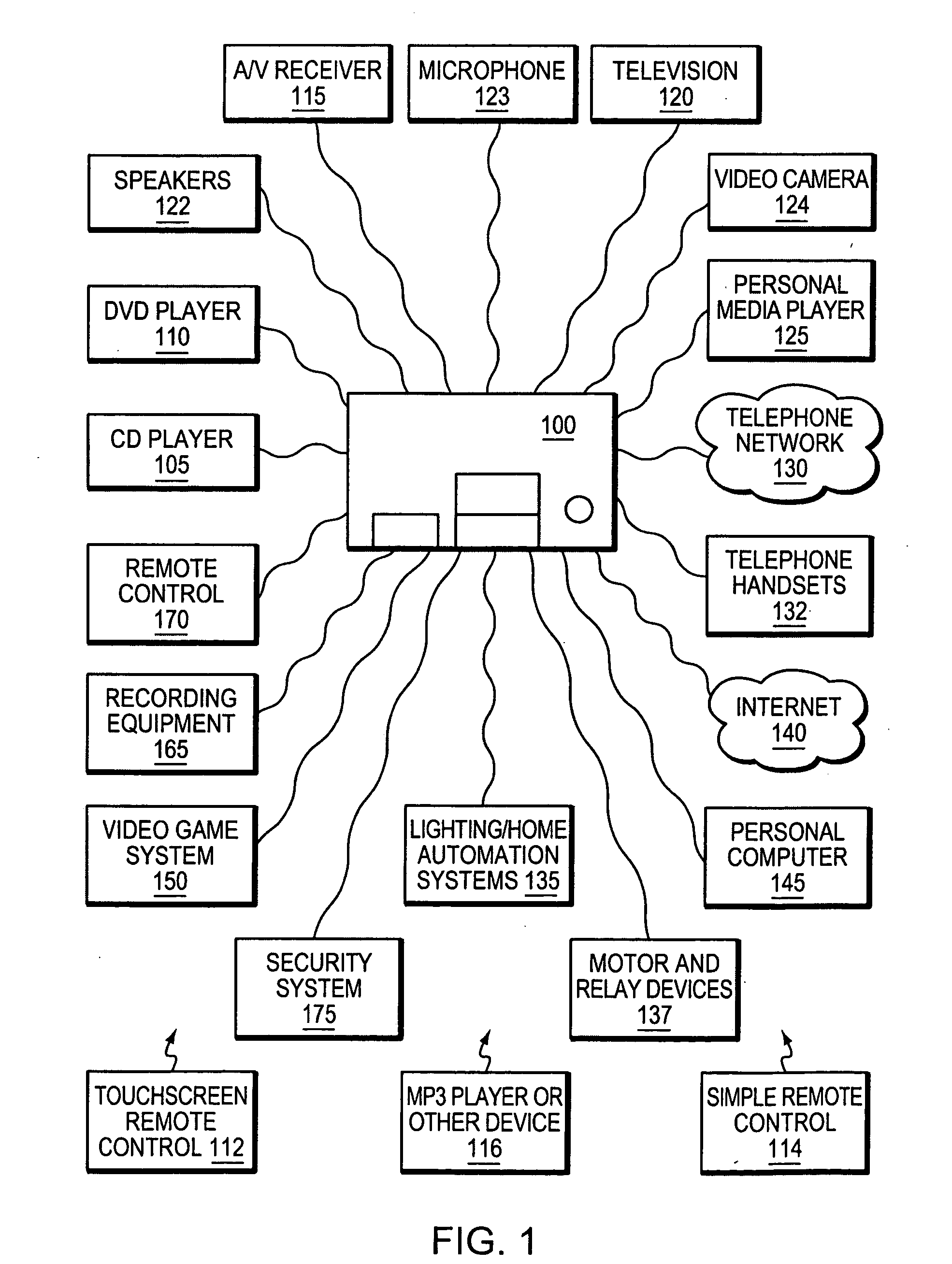
ActiveUS20080127063A1Television system detailsTemperature control using digital meansGraphicsGraphical user interface
A multimedia controller, based on a general purpose computer, which is capable of interfacing with, controlling or managing a wide variety of audio, video, telecommunications, data communications or other devices. A configuration tool, based on a graphical user interface, provides a simple, schematic way to configure even highly complex systems having numerous components or devices which are to be interconnected with or interfaced to the multimedia controller. A user interface programming tool enables a user to customize the appearance and functionality of a graphical user interface to the multimedia controller. A metadata manager automatically collects metadata that is available within the multimedia controller, automatically detects the presence of new media and collects metadata from it, and may also access web resources to locate additional pertinent metadata.
Owner:SAVANT SYST INC
Method and system for load balancing of metadata management in distributed file system
InactiveCN101697526AIncrease profitSmooth expansionData switching networksDistributed File SystemMetadata management
The invention relates to a method and a system for load balancing of metadata management in a distributed file system. When the data structure of metadata, i.e. a directory tree, becomes hotspot metadata, the access heat degree of the directory tree is updated through adopting a mode of copying the metadata; when the load balancing degrees of service nodes of the metadata exceeds a preset value, partial working loads are transferred to underload nodes from overload nodes through adopting a mode of transferring the metadata; and the loading balancing among a plurality of the metadata service nodes is realized through the two modes. The system comprises an information communication module, a metadata operation module, a metadata service node management module, a metadata management module, a metadata strategy implementation nodule and a working load acquisition module. The invention improves the utilization rate of metadata service resources through the two modes of copying and transferring the metadata so as to achieve the purpose of load balancing, thus a metadata service system can be smoothly expanded.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A great magnitude of data hierarchical storage method
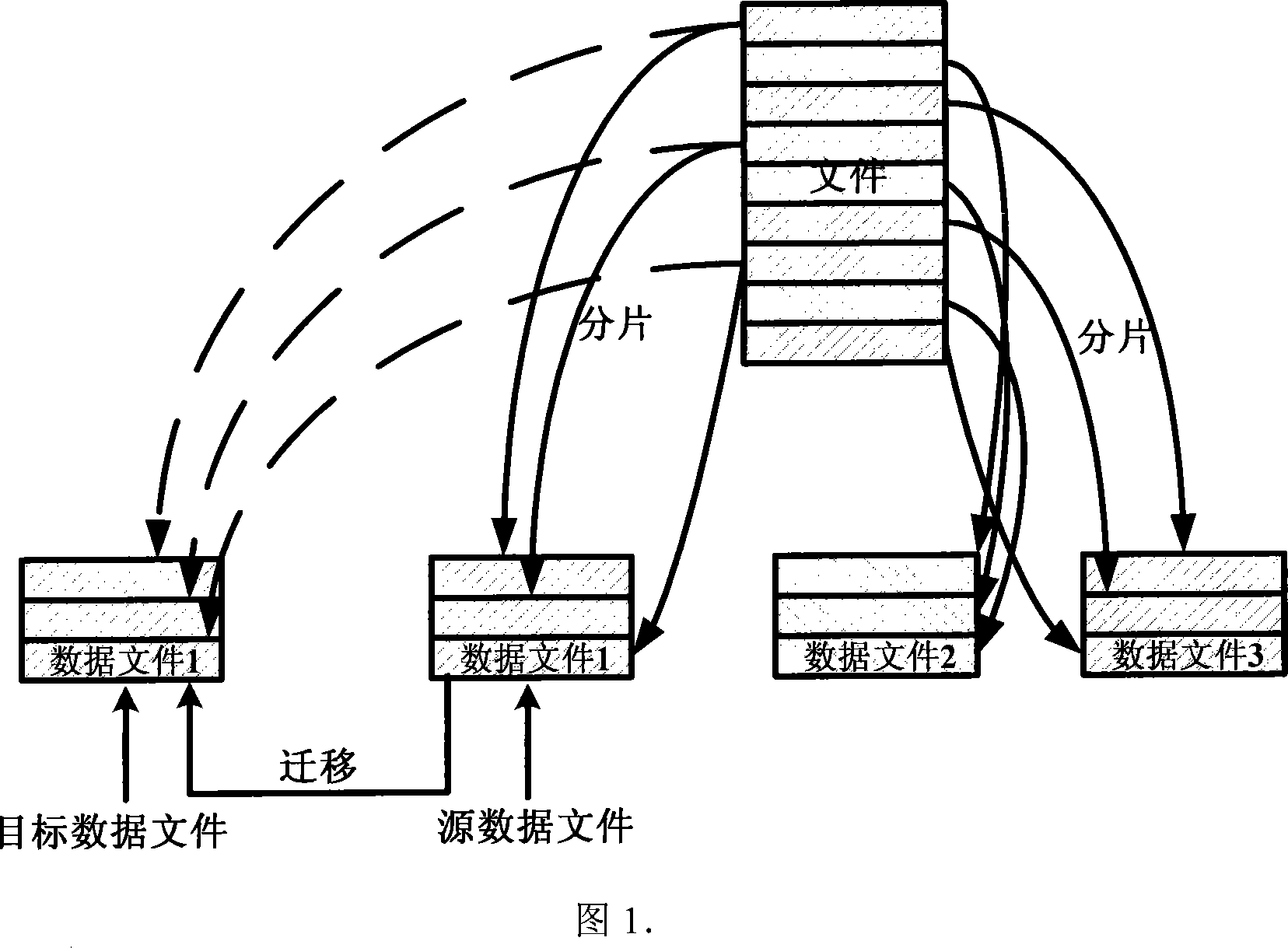
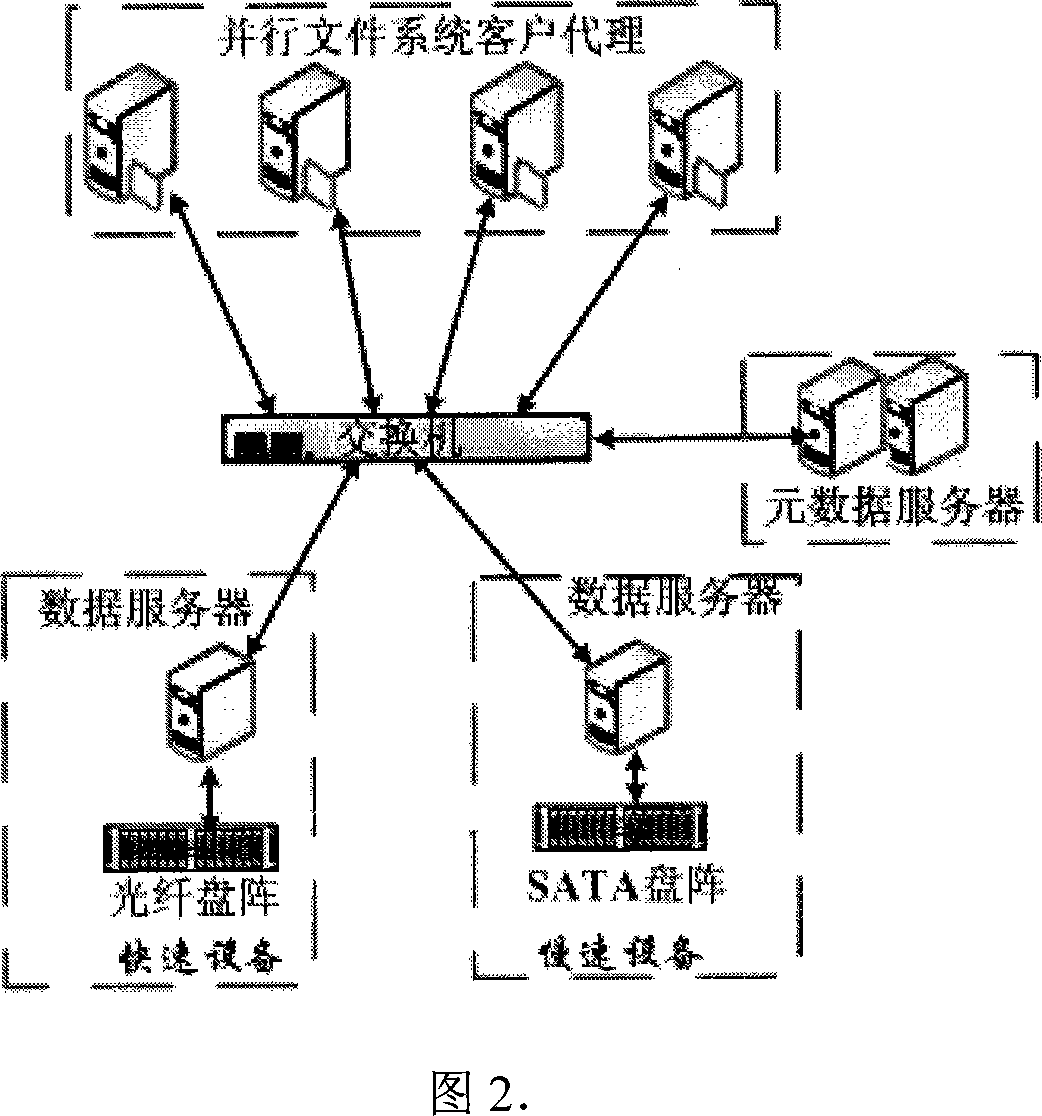
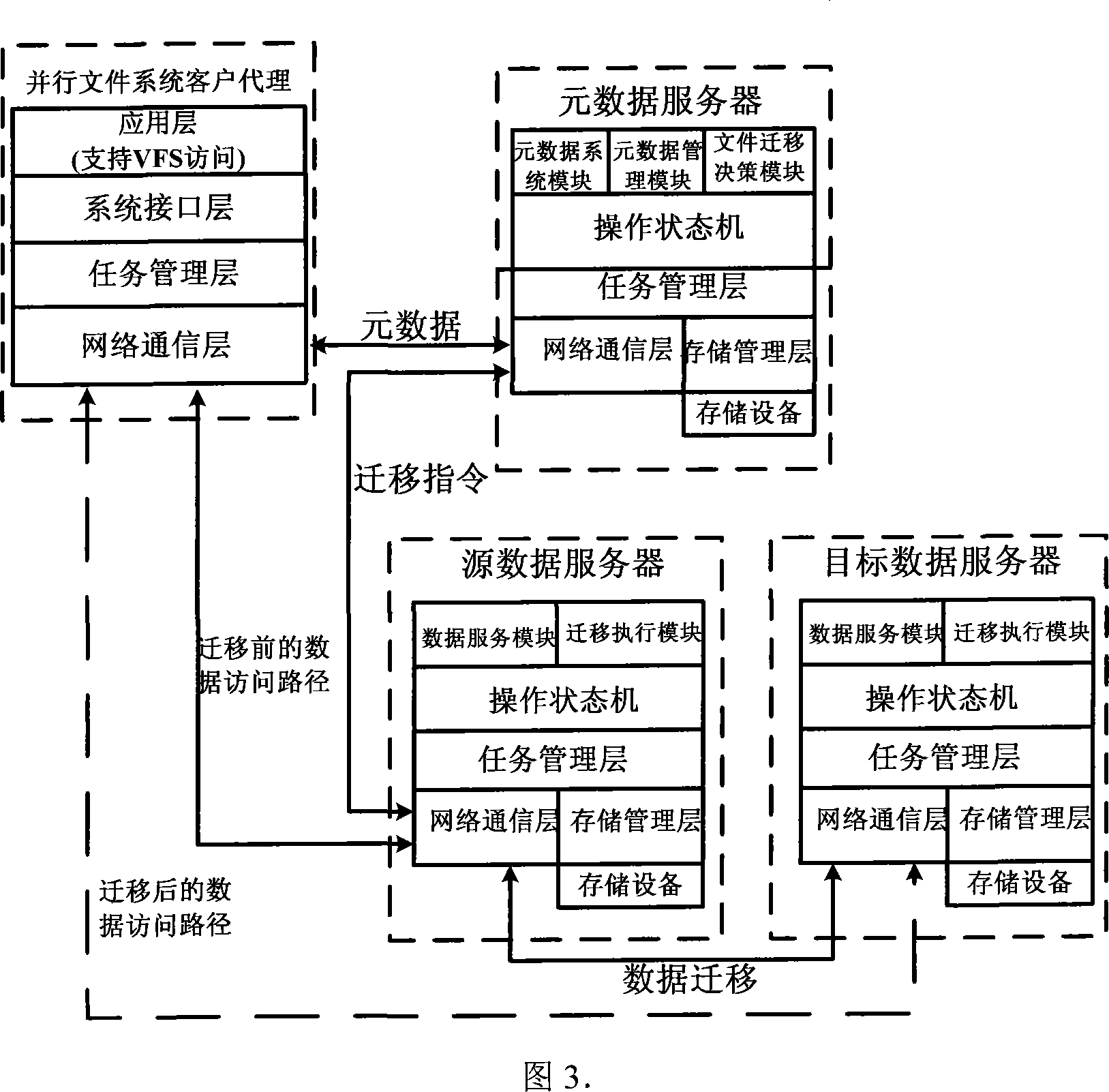
InactiveCN101079902ANo need to scanAvoid front-end application impactTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsMetadata managementFile system
This invention relates to a graded storing method for mass data characterizing that the customer proxy software of parallel file systems on front hosts realizes support to VFS access by system interface sub-modules and sub-modules of the VFS layer, a metadata server is responsible for organizing data files on different data servers to a unified parallel file system view, and a metadata management module provides operations of accessing metadata, a file migration deciding module gets file access information from the data server periodically and makes decision to file migration according to file system load and grade situation of equipment and an executing module of the data server executes migration.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
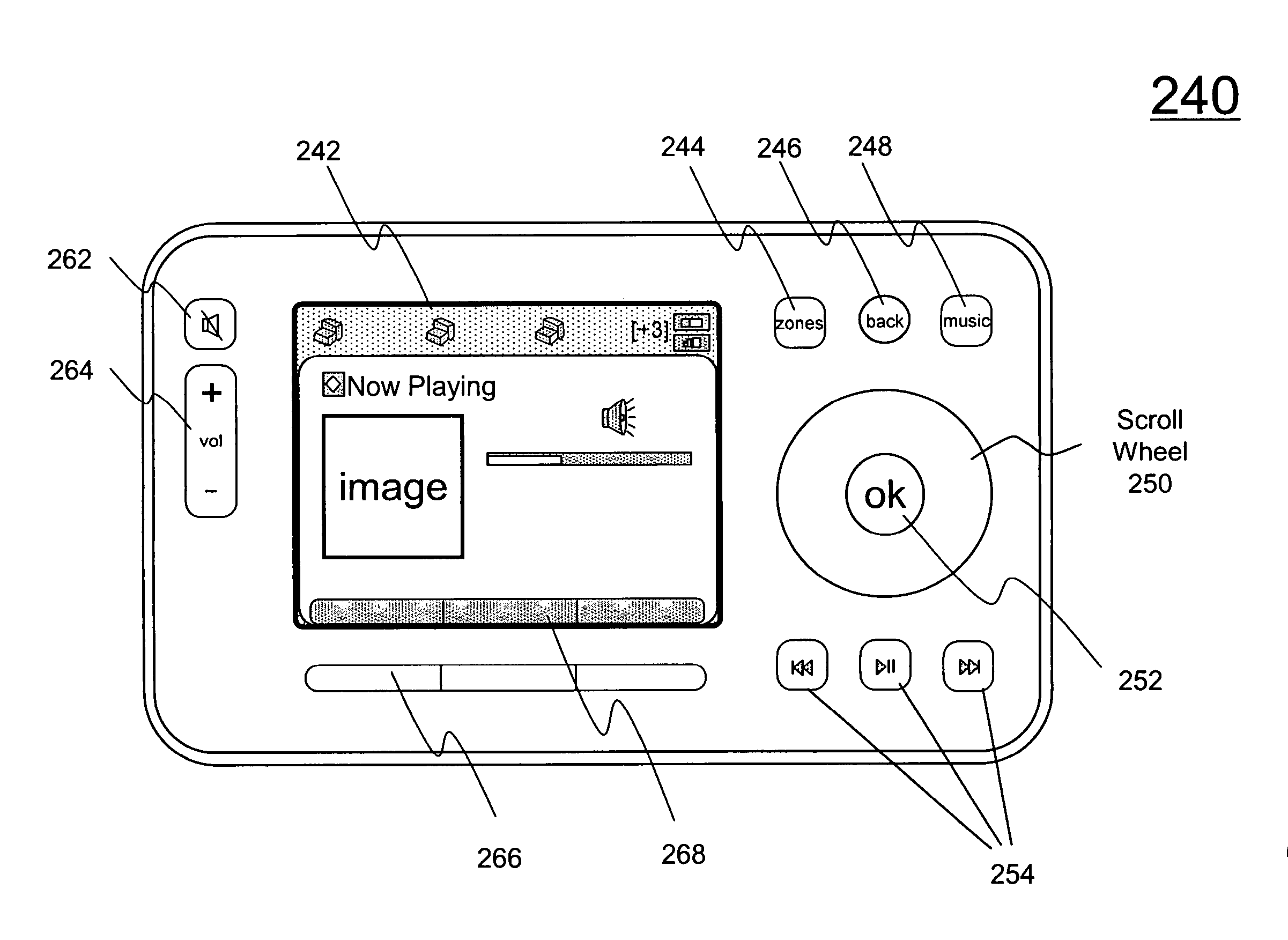
Method and apparatus for managing a playlist by metadata
ActiveUS20130191749A1Sacrificing manageabilityImprove memory usageInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsMetadata managementSingle item
Techniques for managing a playlist in a multimedia system are disclosed. According to one aspect of the techniques, the playlist is structured to be able to include as many items as desired. To facilitate the manageability of such playlist, the playlist is built with a plurality of items. Each of the items is associated with metadata that includes information related to, for example, artist, album, genre, composer, and track number. The metadata for each item may be parsed, updated or logically operated upon to facilitate the management of the playlist. In another embodiment, each of the items is either a single item or a group item. A single item contains metadata of a corresponding source. A group item contains metadata of accessing other constituent items, which again may be single items or group items. As a result, the playlist can accommodate as many items as desired in a limited memory space without compromising the manageability of the playlist. Each of the items can be removed from, added to, or moved around in the playlist without concerning that an item may further include many items therein.
Owner:SONOS
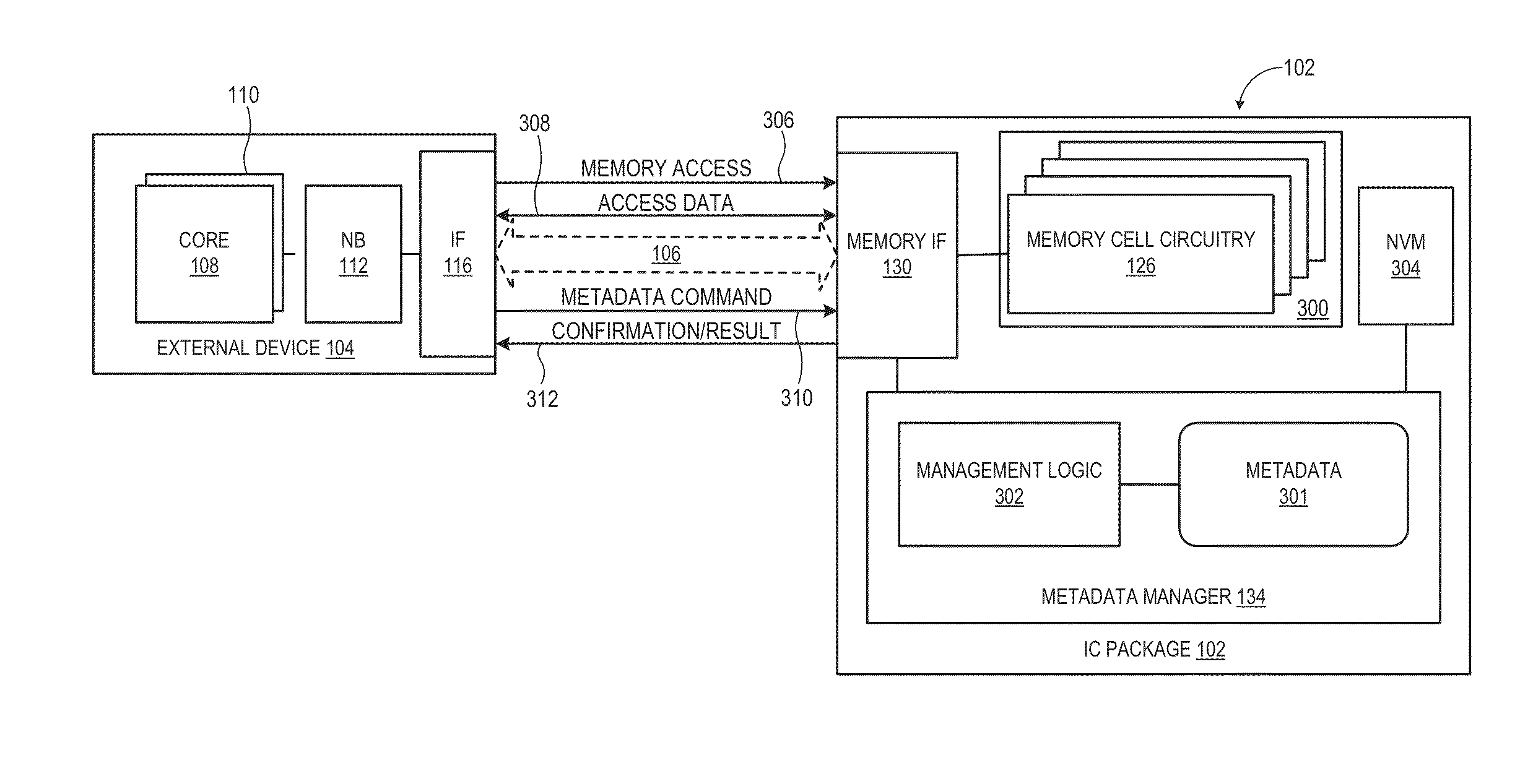
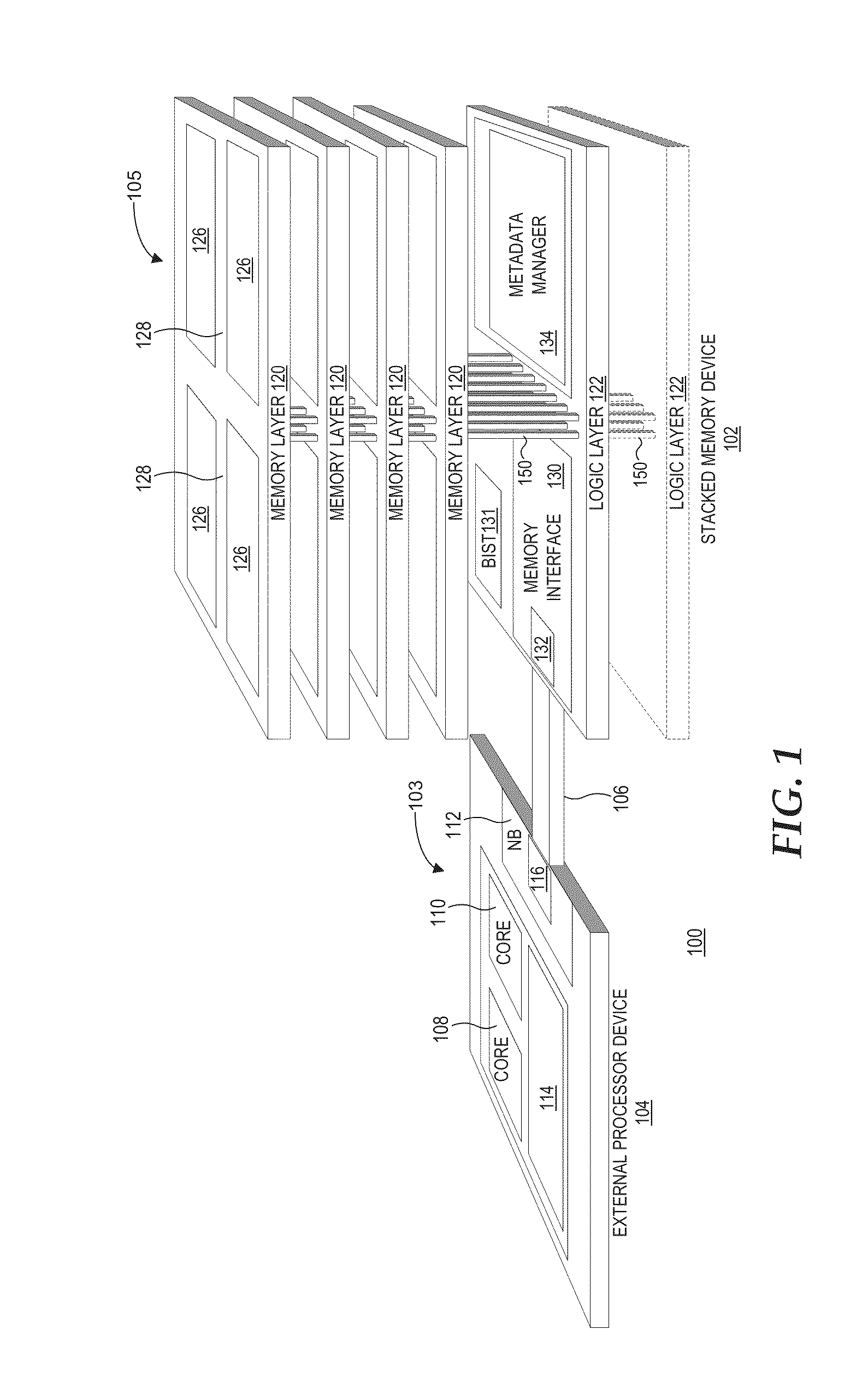
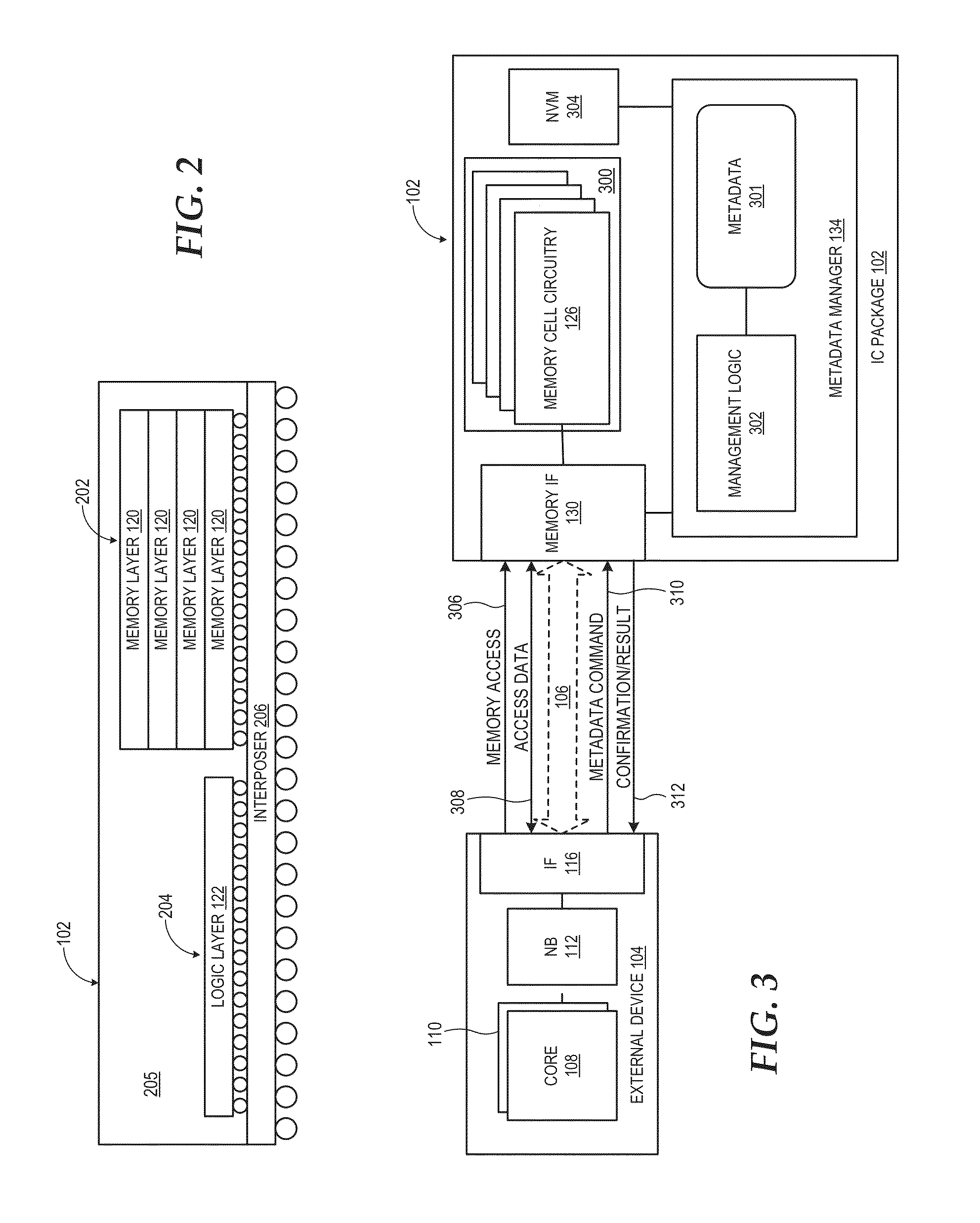
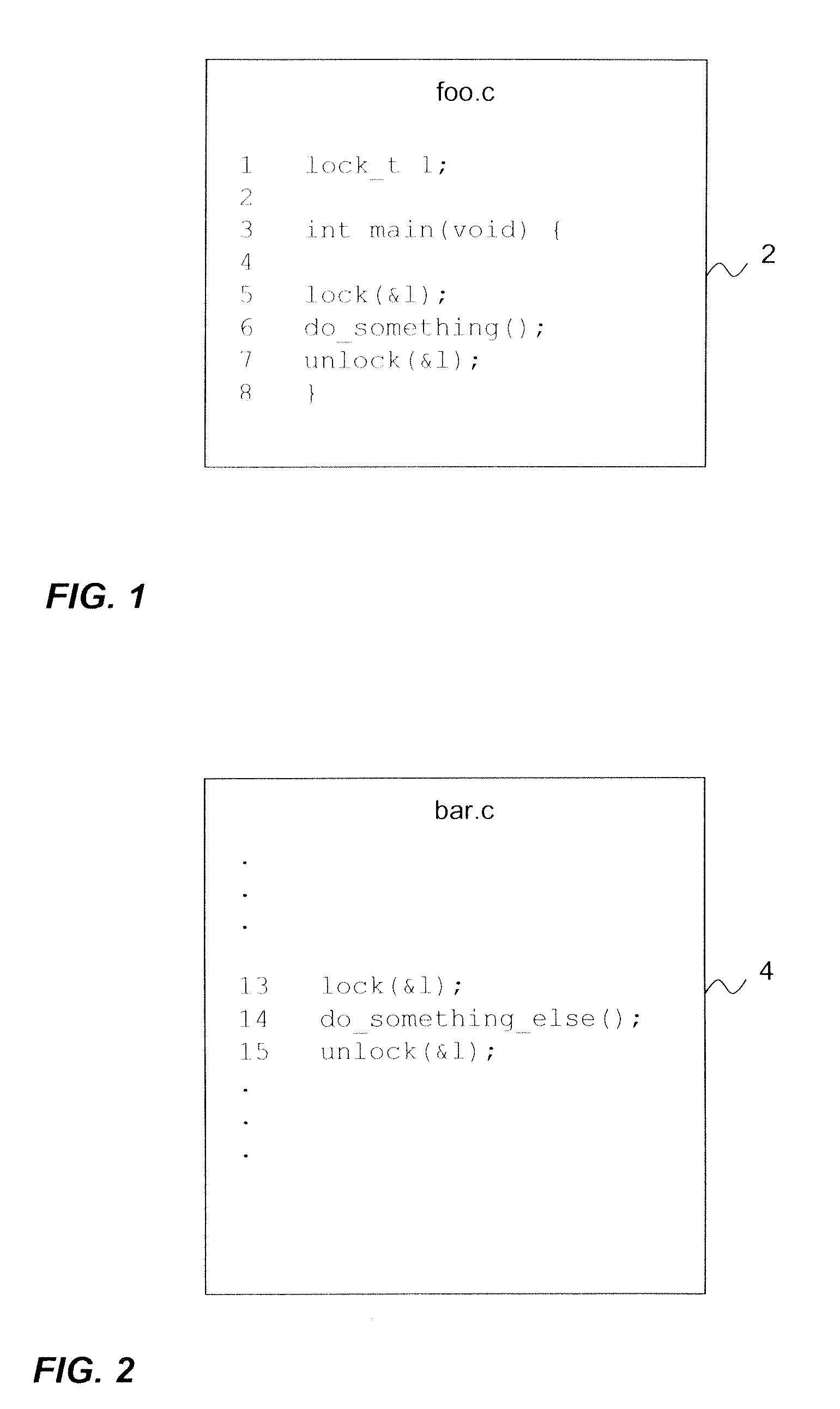
Stacked memory device with metadata mangement
ActiveUS20140040698A1Relatively large bandwidthLatency significantMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCode conversionMetadata managementMemory interface
A processing system comprises one or more processor devices and other system components coupled to a stacked memory device having a set of stacked memory layers and a set of one or more logic layers. The set of logic layers implements a metadata manager that offloads metadata management from the other system components. The set of logic layers also includes a memory interface coupled to memory cell circuitry implemented in the set of stacked memory layers and coupleable to the devices external to the stacked memory device. The memory interface operates to perform memory accesses for the external devices and for the metadata manager. By virtue of the metadata manager's tight integration with the stacked memory layers, the metadata manager may perform certain memory-intensive metadata management operations more efficiently than could be performed by the external devices.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Managing source annotation metadata
ActiveUS20090119576A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingMetadata managementAnnotation
A method, system and computer program product for managing source annotation metadata. The metadata management technique may include maintaining a set of metadata, maintaining data / metadata relationships between individual units of the metadata and individual units of the source data, and maintaining metadata / metadata relationships between individual units of the metadata. The metadata / metadata relationships define two or more intersecting search pathways through the metadata that intersect at one or more metadata units belonging to more than one search domain.
Owner:IBM CORP
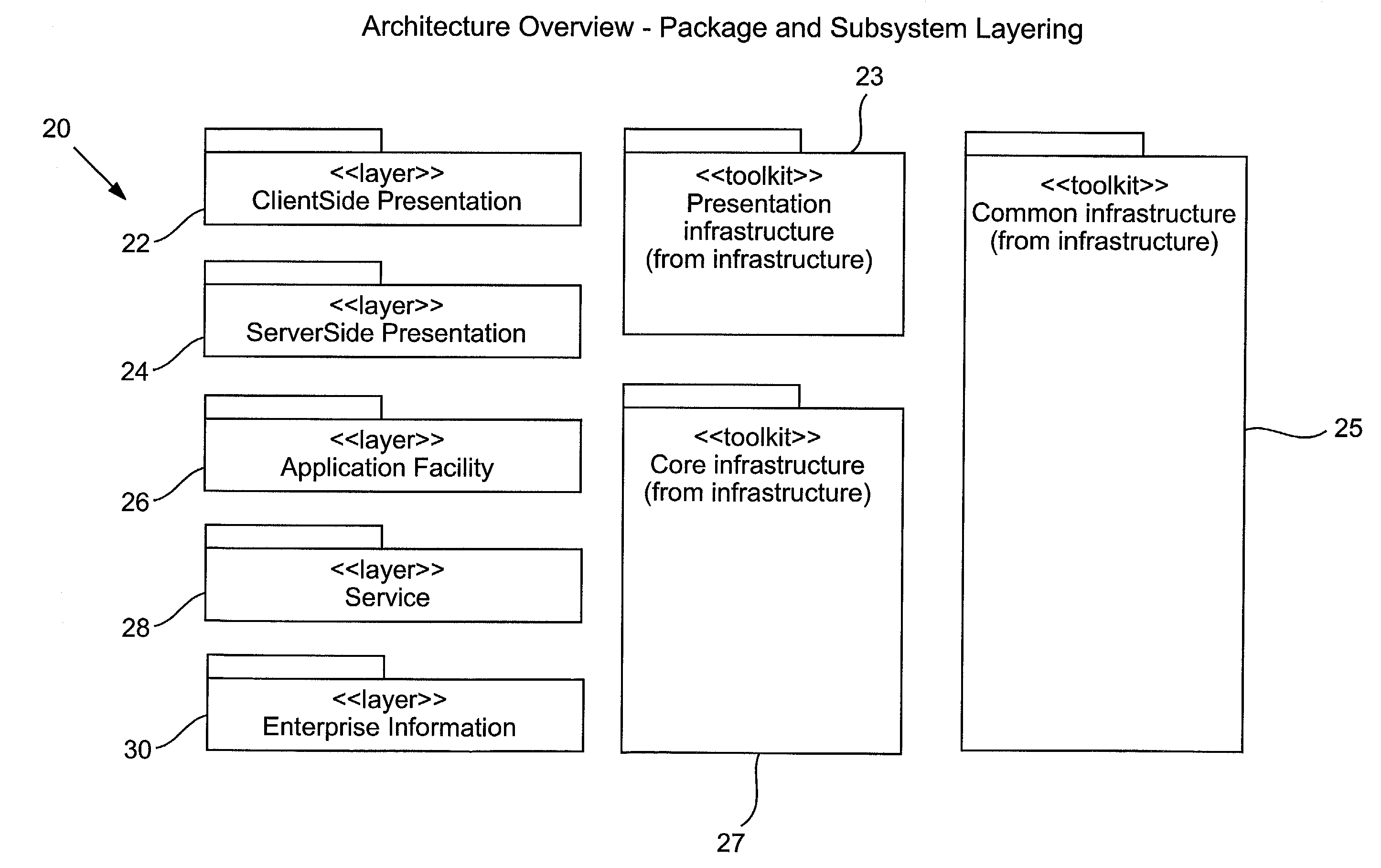
Enterprise framework and applications supporting meta-data and data traceability requirements
InactiveUS7016919B2Anchor value chainSignificant richnessDigital data processing detailsOffice automationMetadata managementData source
An application adapted to run within an enterprise wide, web-based framework which provides reusable services and facilities such as security, meta-data management and traceability of data and a framework supporting the same. The framework supports decision making across the value chain, with an emphasis on the meta-data needed for decision making. The framework can support the activities of a virtual organization (internal or external) and the inevitable variations in data types, file formats etc. without requiring massive integration between the various sources of data involved.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
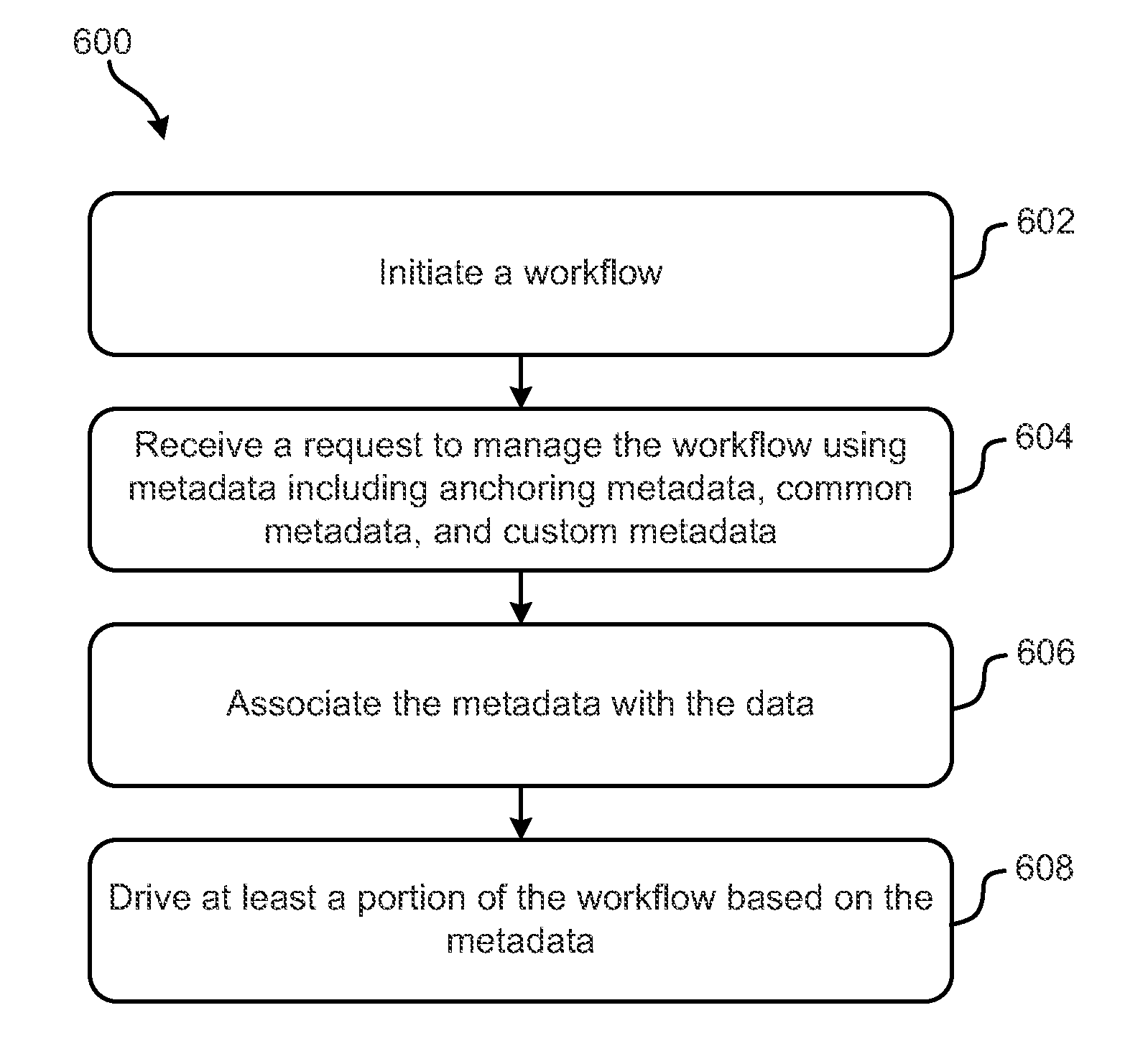
Metadata-driven workflows and integration with genomic data processing systems and techniques
ActiveUS20150286495A1Metadata text retrievalMultimedia data retrievalData processing systemProgram instruction
Systems, methods and computer program products configured to provide and perform metadata-based workflow management are disclosed. The inventive subject matter includes a computer readable storage medium having computer readable program instructions embodied therewith. The computer readable program instructions are configured to: initiate a workflow configured to process data; associate the data with metadata; and drive at least a portion of the workflow based on at least some of the metadata. The metadata include anchoring metadata; common metadata; and custom metadata. Inventive subject matter also encompasses a method for managing genomic data processing workflows using metadata includes: initiating a workflow; receiving a request to manage the workflow using metadata comprising: anchoring metadata, common metadata, and custom metadata, associating the metadata with the data; and driving at least a portion of the workflow based on the metadata. The workflow involves genomic analyses.
Owner:IBM CORP
Metadata-configurable systems and methods for network services
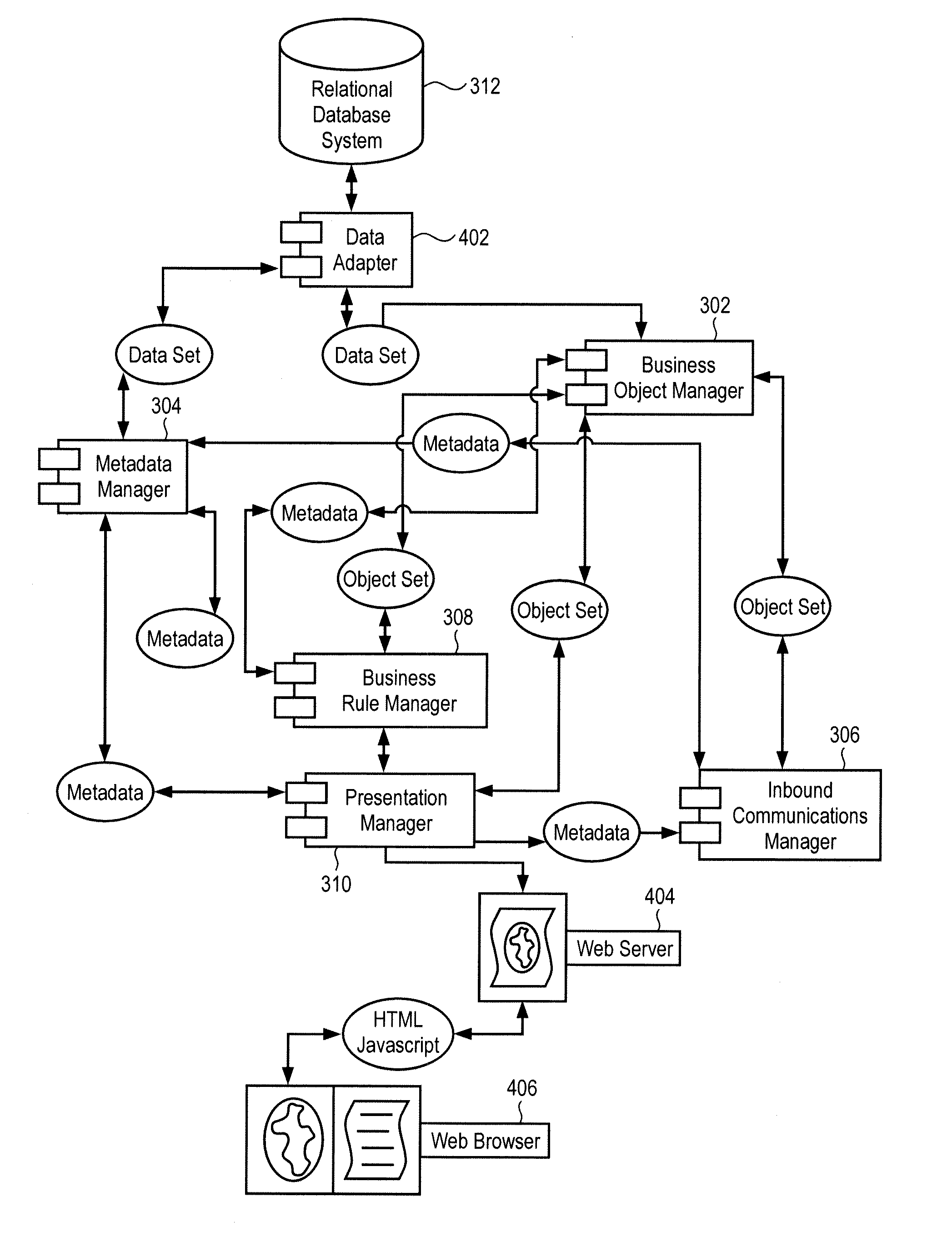
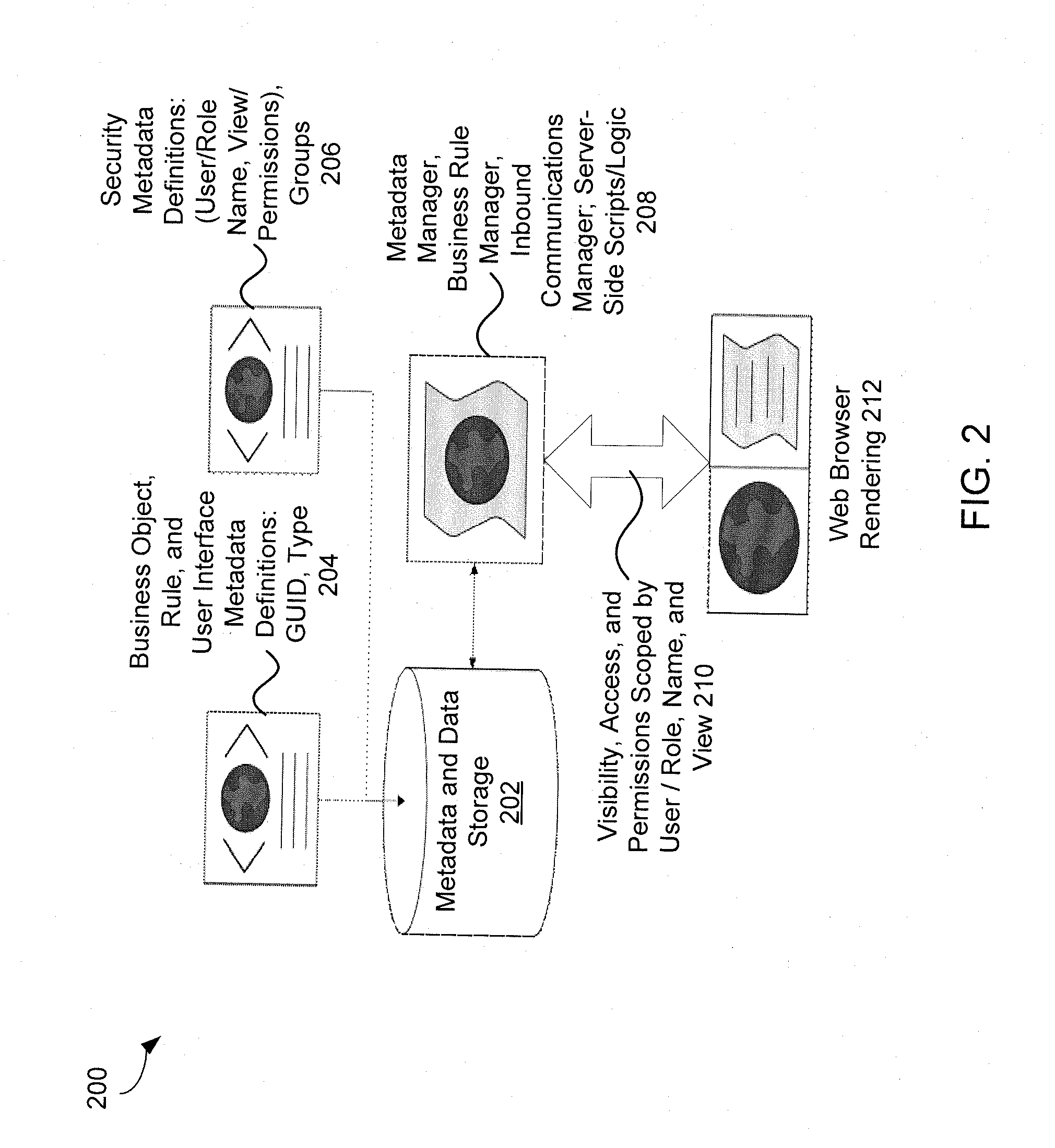
ActiveUS20110179110A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsMetadata managementPresentation Manager
In some embodiments, the presentation manager is configured to provide an interface requesting information regarding a proposal from a digital device over a network and receive the information from the digital device. The business object manager is configured to instantiate a business object based on the received information and store the instantiated business object within a data structure residing in a computer readable medium. The business rule manager is configured to generate a business rule associated with the business object, the business rule comprising instructions to perform an operation, the instructions being conditional based on the instantiated business object. The metadata manager is configured to generate metadata associated with the instantiated business object, store the generated metadata in the computer readable medium, perform the operation based on the business rule and the generated metadata, and instruct the presentation manager to provide a second interface indicating a status of the proposal.
Owner:VERSAIC
RDF Object Type and Reification in the Database
ActiveUS20080126397A1Digital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesGraphicsMetadata management
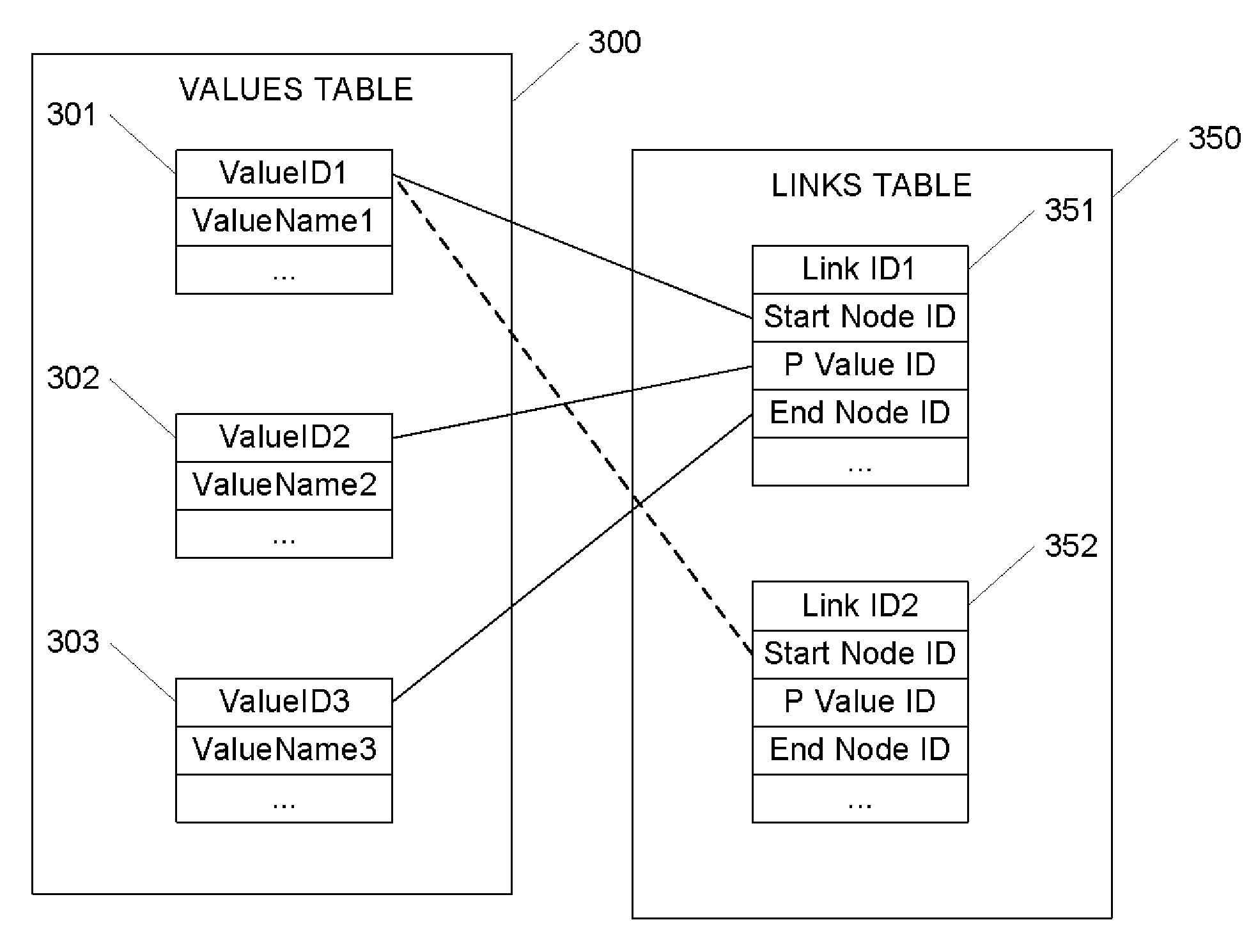
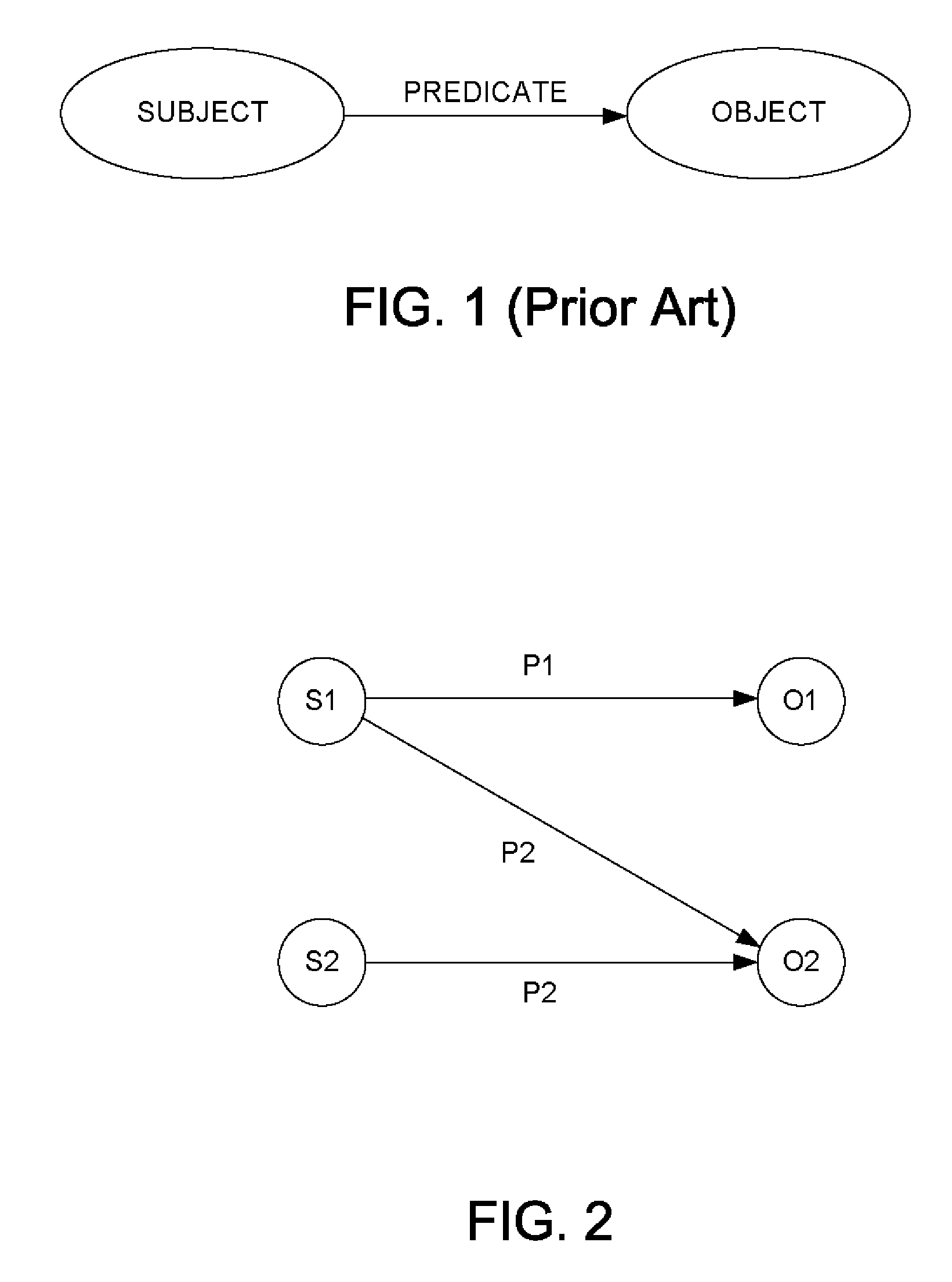
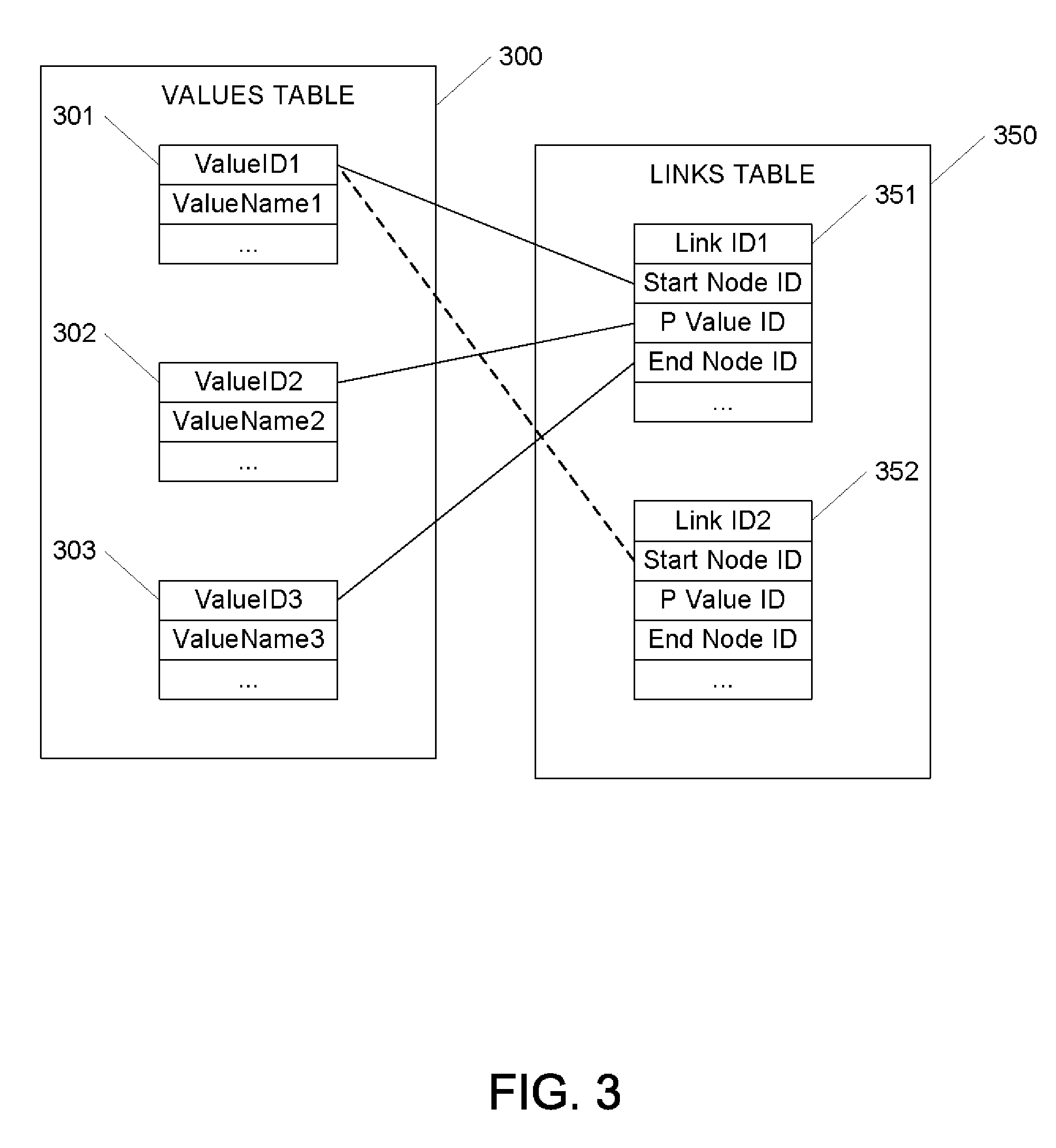
A method for representing RDF data in a database provides a new RDF data type built on top of a network data model (NDM), where a network or graph captures relationships between objects using connectivity. This exposes the NDM functionality to RDF data, allowing RDF data to be managed as objects and analyzed as networks. In this network, the subject and objects of triples are mapped to nodes, and the predicates are mapped to links that have subject start-nodes and object end-nodes. A link, therefore, represents a complete RDF triple. The nodes are stored only once, regardless of the number of times they participate in triples. But a new link is created whenever a new triple is inserted. A streamlined approach to representing reified RDF data is also provided for faster retrievals. An RDF object type and reification in the database thus provide a basic infrastructure for effective metadata management.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Content identification and management in content distribution networks
InactiveUS20100306257A1Easy to liftFacilitates and enhances authorized file sharingDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsContent distributionMetadata management
Peer-to-peer file sharing and uploading of content to content server systems is increasing in popularity on the Internet. Content signals can be edited and combined with other content programming, and or altered in ways that make it difficult to identify using conventional techniques. Content identification based on content fingerprints is used to retrieve related metadata, which in turn, is used to manage use of the content signal in content distribution systems. The content signal is uploaded to a computer within a network of computers in the content distribution system. A content fingerprint of the content signal is computed and sent to a database to look up related metadata. The metadata is received and used to manage use of the content signal in the content distribution system based on the metadata. This can include blocking uploading or rendering of audio or video, controlling streaming of audio or video, linking to a licensing server, which provides usage control rules, etc.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com