Patents
Literature
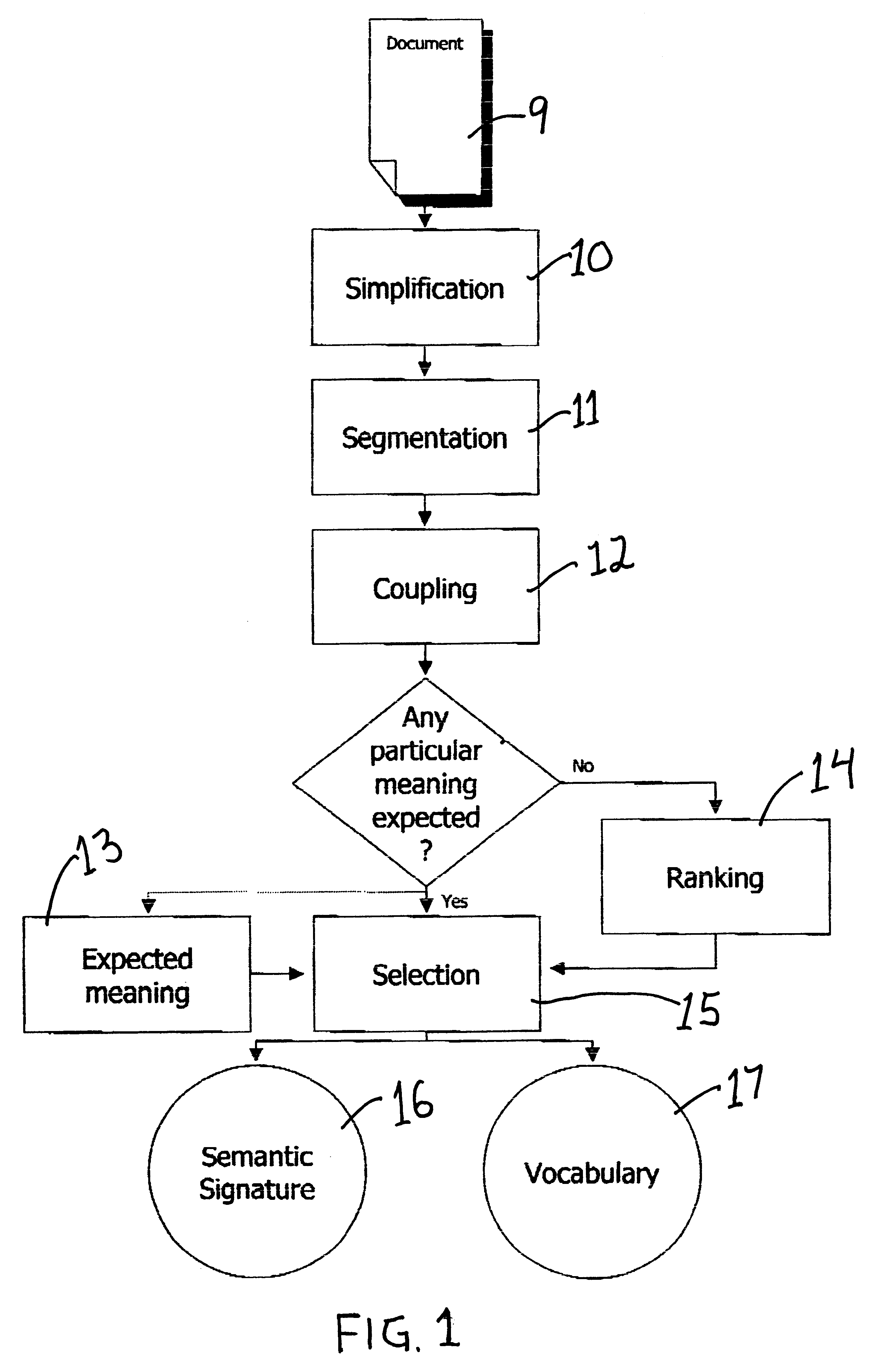
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
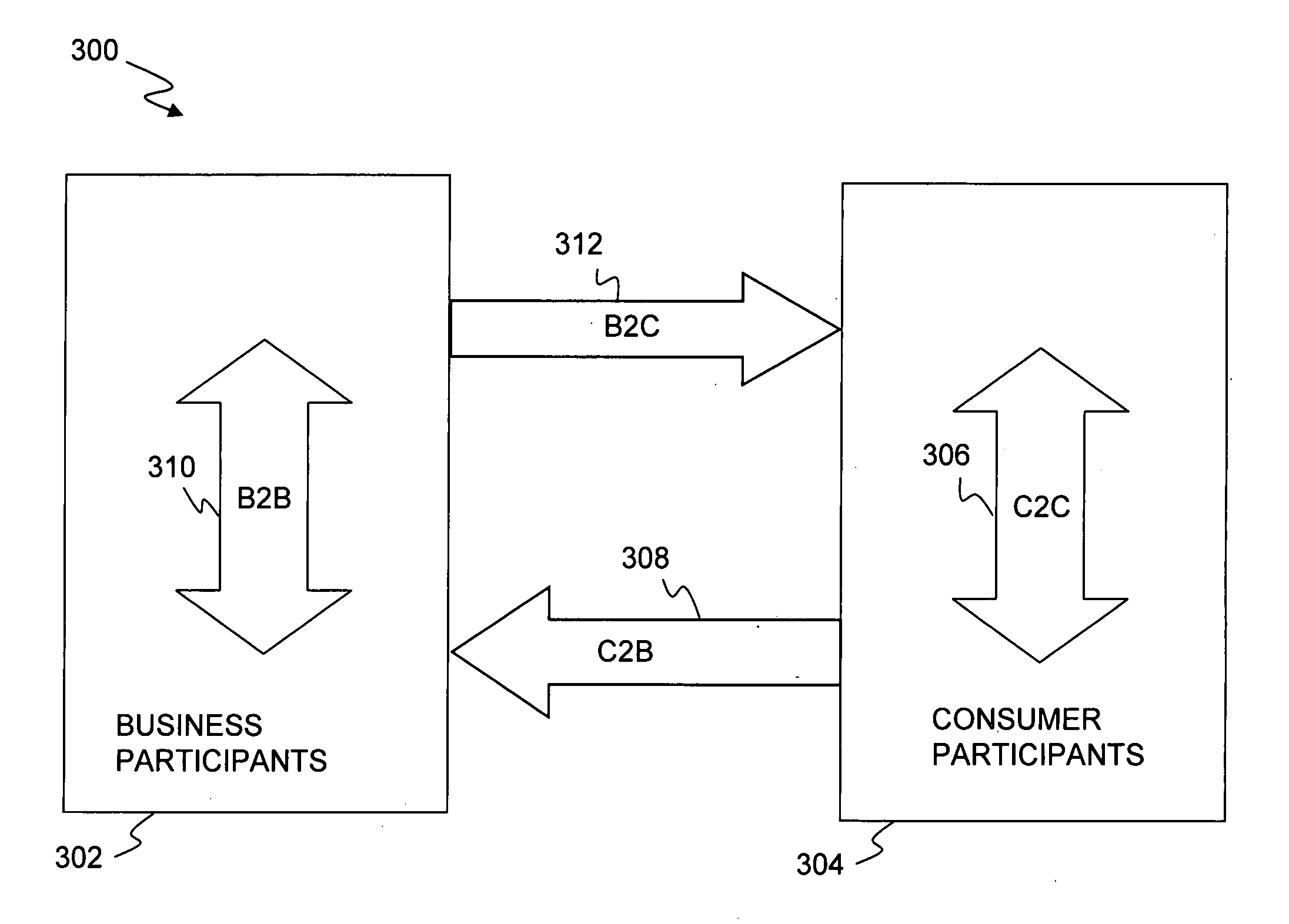
2142 results about "Distributed database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
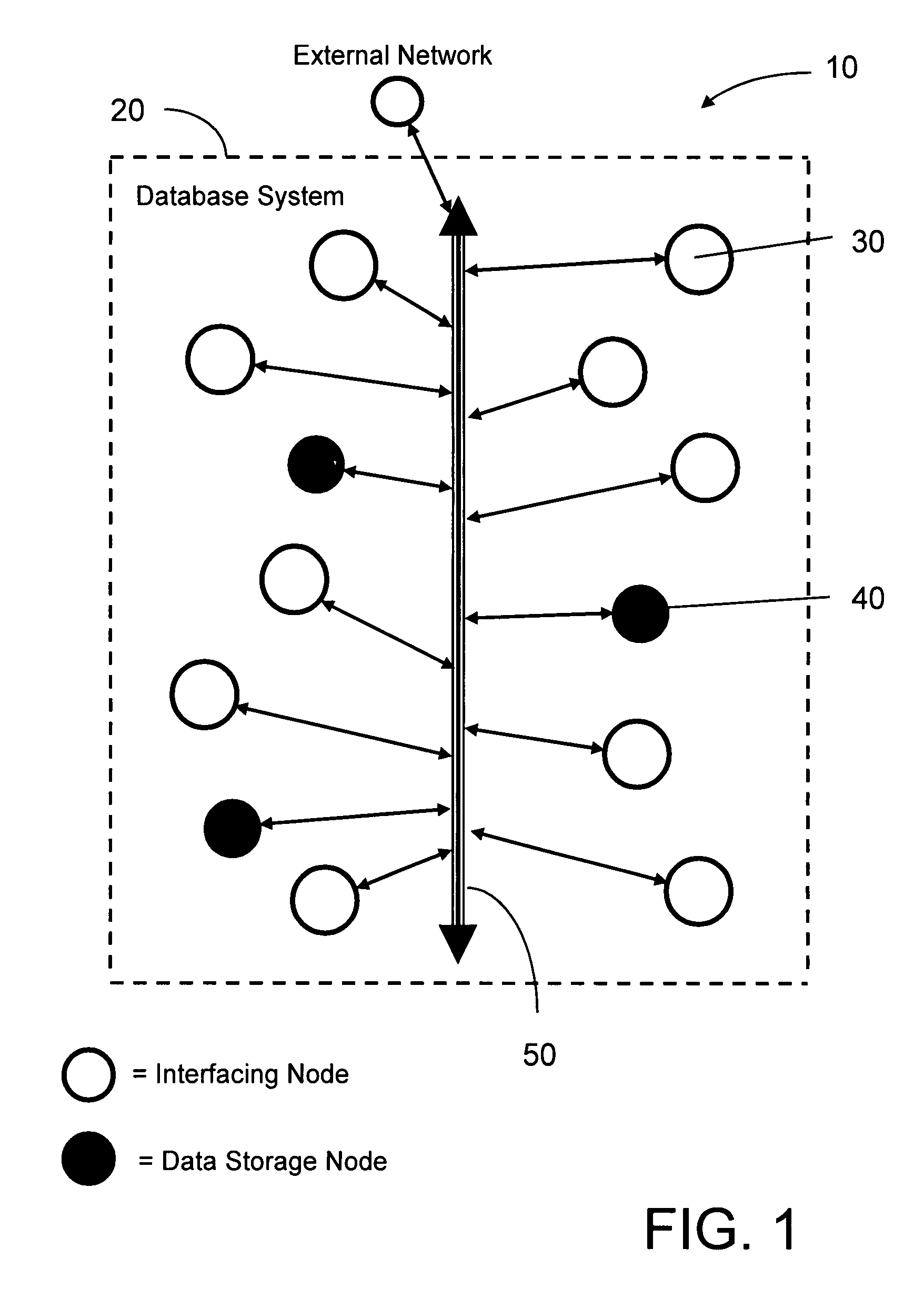
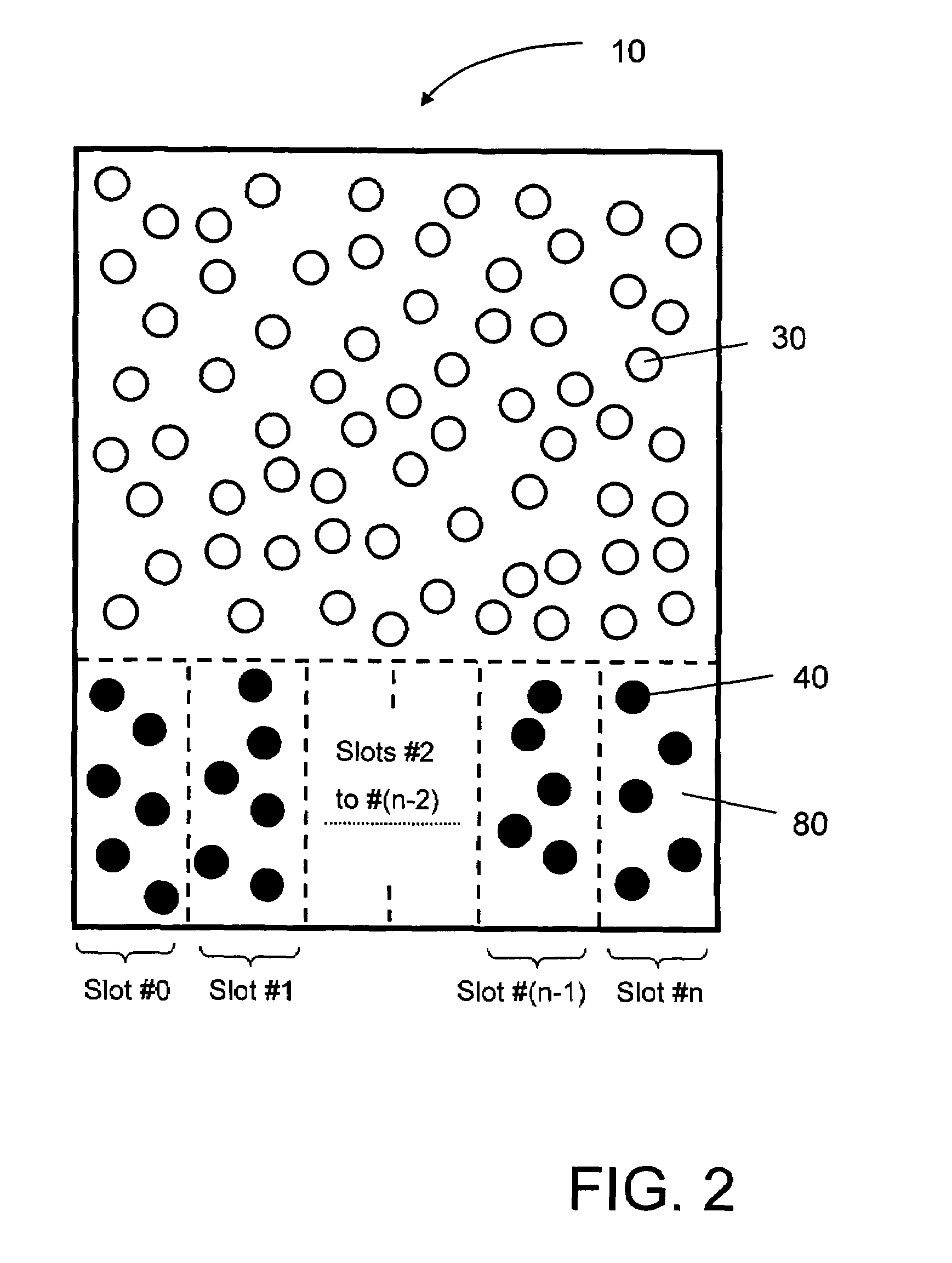
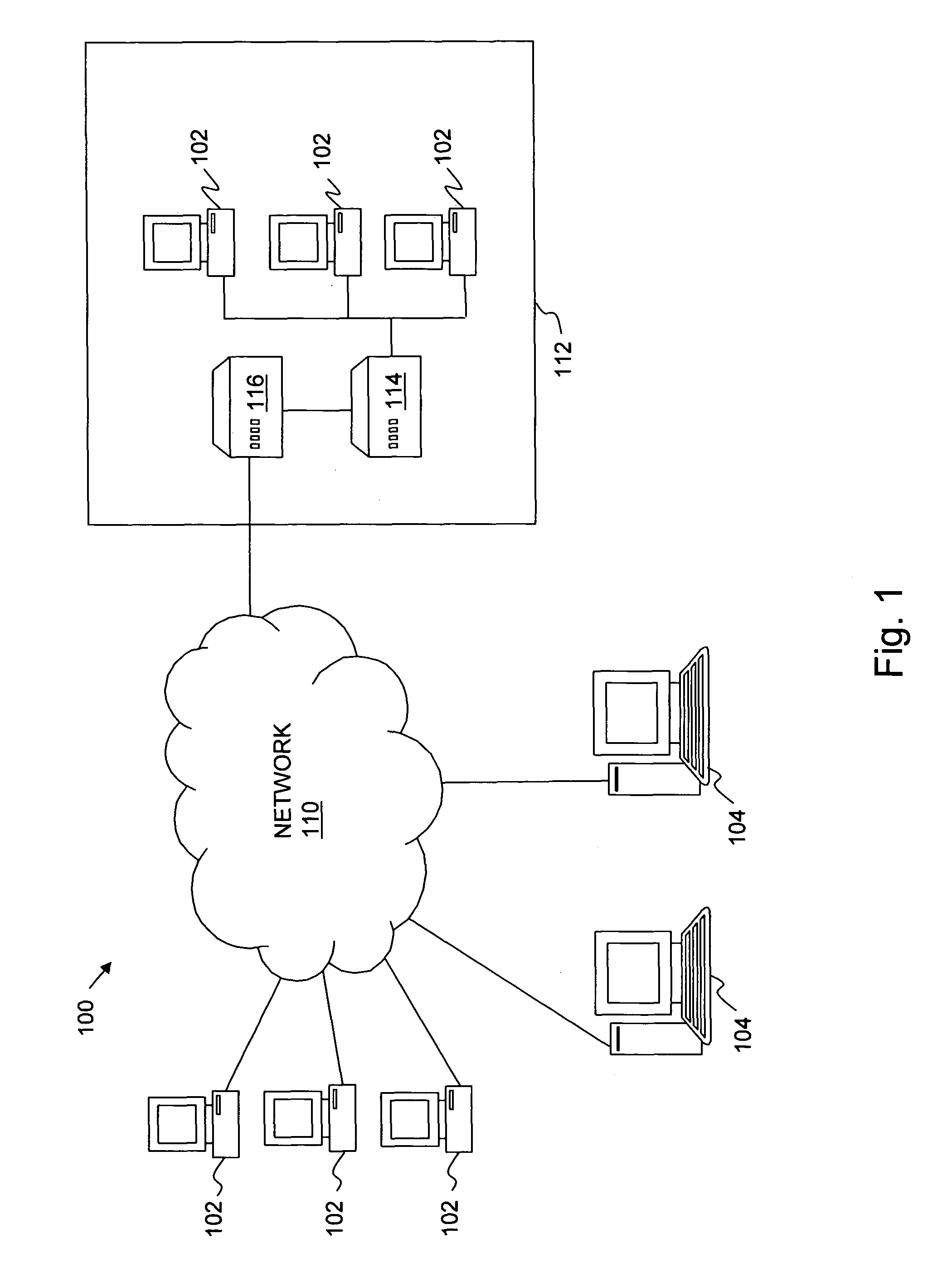
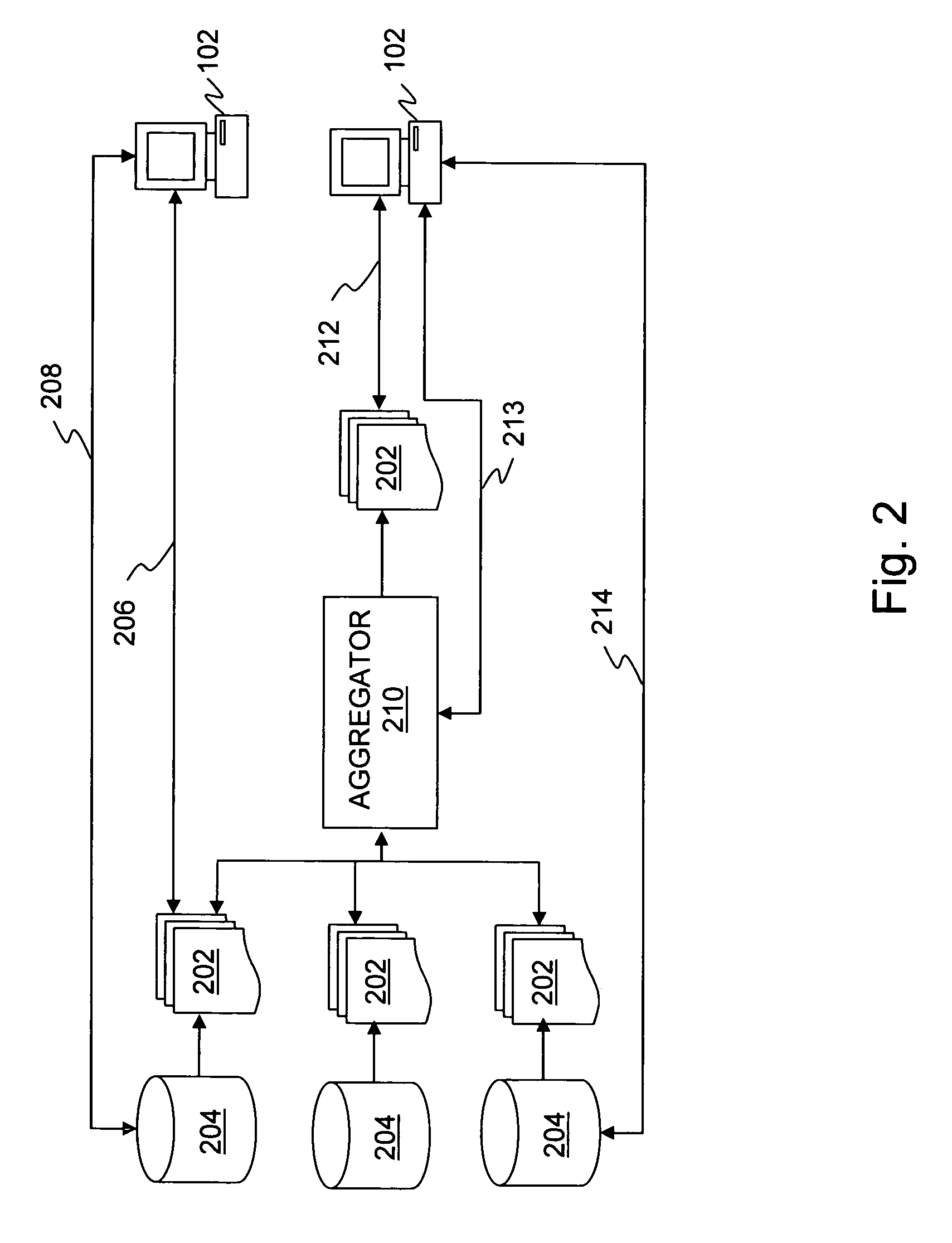
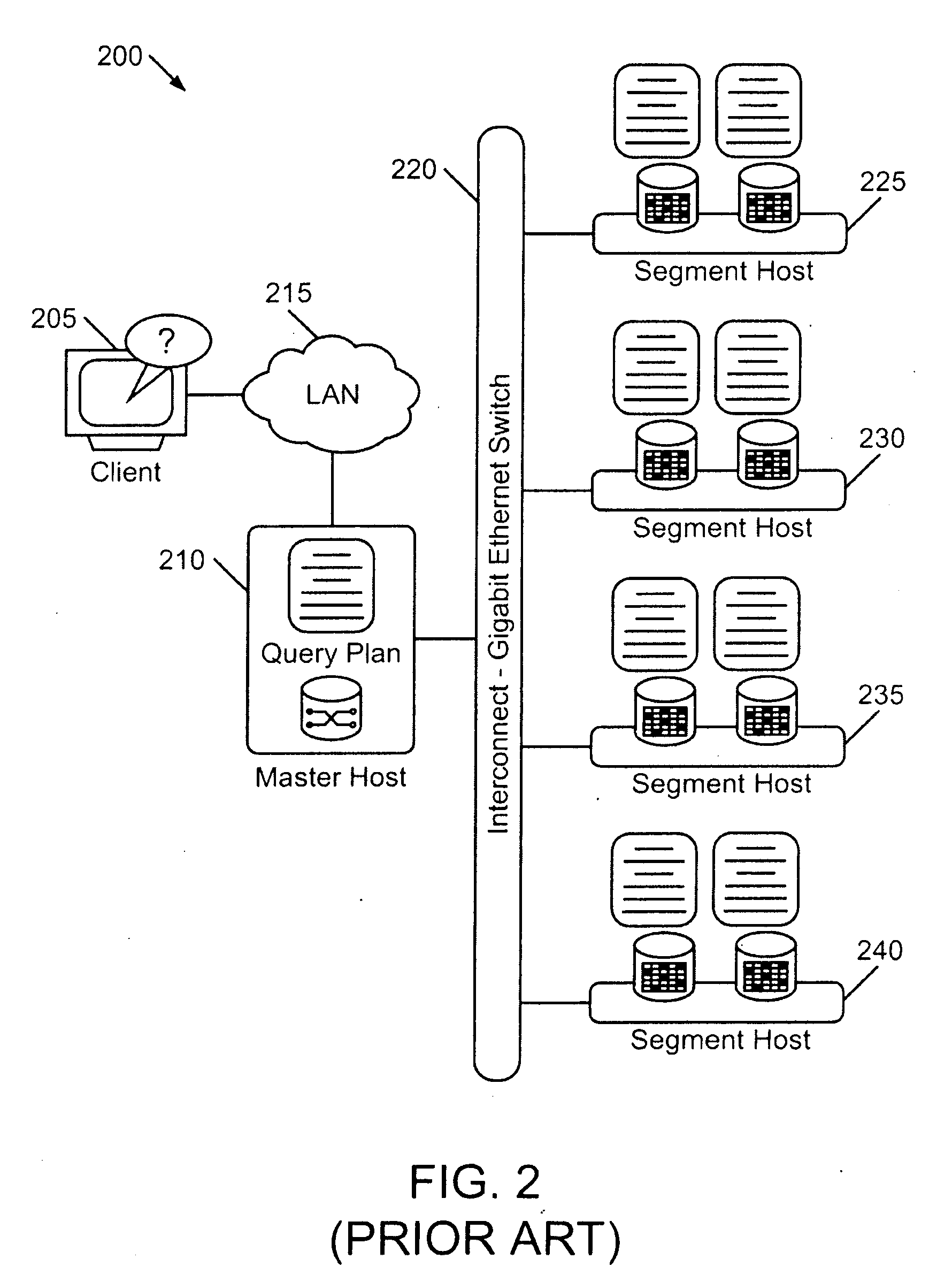
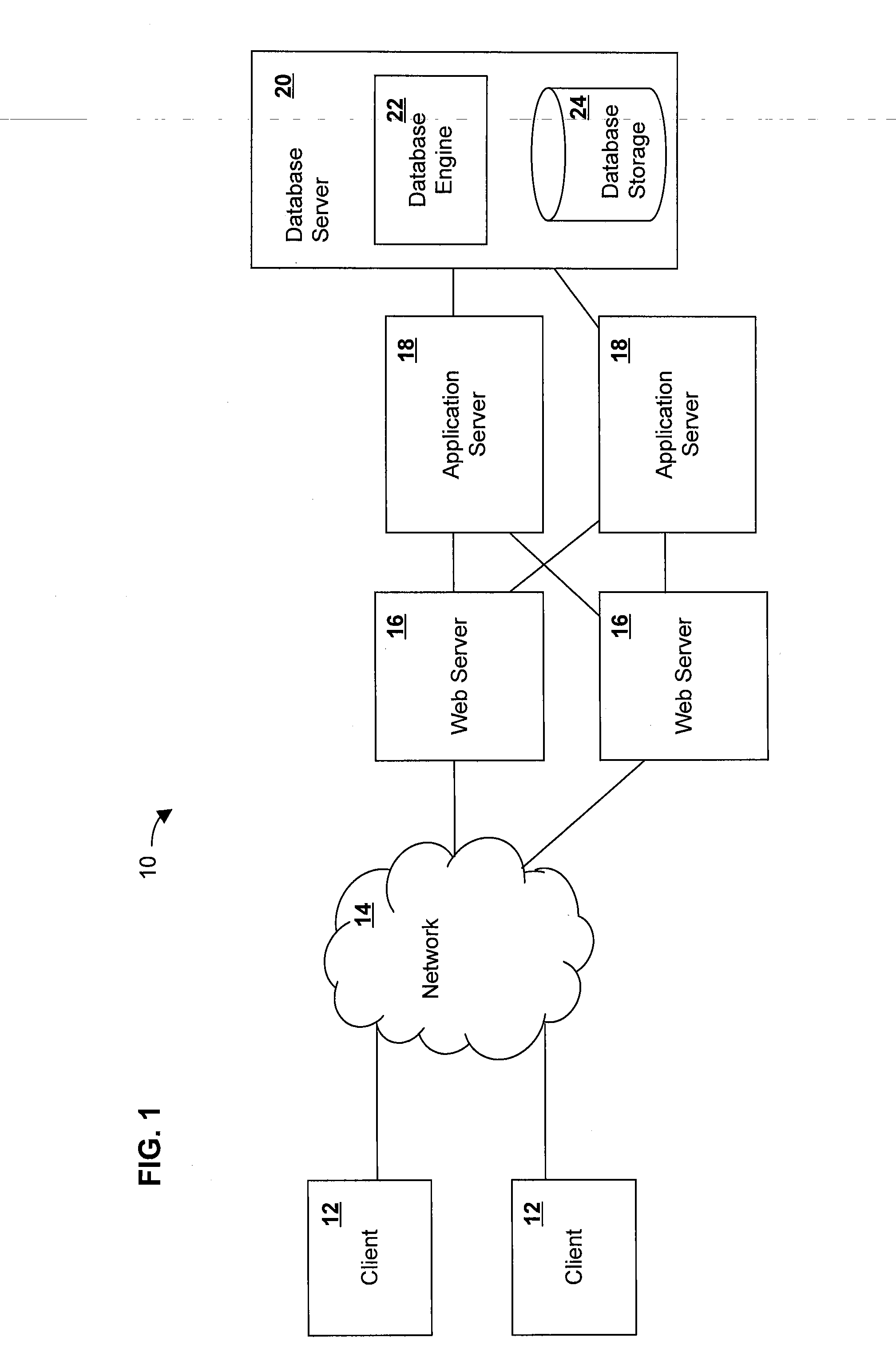
A distributed database is a database in which not all storage devices are attached to a common processor. It may be stored in multiple computers, located in the same physical location; or may be dispersed over a network of interconnected computers. Unlike parallel systems, in which the processors are tightly coupled and constitute a single database system, a distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical components.
Systems and methods for use of structured and unstructured distributed data
InactiveUS20070061487A1Increase flexibilityDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationDistributed databaseComputer science
The invention relates to hardware, software and electronic service components and systems to provide large-scale, reliable, and secure foundations for distributed databases and content management systems, combining unstructured and structured data, and allowing post-input reorganization to achieve a high degree of flexibility.
Owner:NEWSILIKE MEDIA GROUP
Disaster management using an enhanced syndication platform
InactiveUS20060265489A1Increase flexibilityDigital computer detailsData switching networksData feedDistributed database
The invention relates to hardware, software and electronic service components and systems to provide large-scale, reliable, and secure foundations for distributed databases and content management systems, combining unstructured and structured data, and allowing post-input reorganization to achieve a high degree of flexibility. This system may be combined with various syndication techniques to provide a platform for disaster preparation, response, and relief The invention described herein may allow disaster relief data to be stored in a syndication format, processed, and published through a plurality of disaster management data feeds. The syndicated content may be used by disaster relief participants in the preparation, response and relief efforts associated with a disaster.
Owner:NEWSILIKE MEDIA GROUP
Security systems and methods for use with structured and unstructured data
InactiveUS20130104251A1Increase flexibilityEasy accessDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsUnstructured dataDistributed database
Disclosed herein are systems and methods including hardware, software and electronic service components and systems to provide large-scale, reliable, and secure foundations for distributed databases and content management systems combining unstructured and structured data, and allowing post-input reorganization to achieve a high degree of flexibility.
Owner:NEWSILIKE MEDIA GROUP
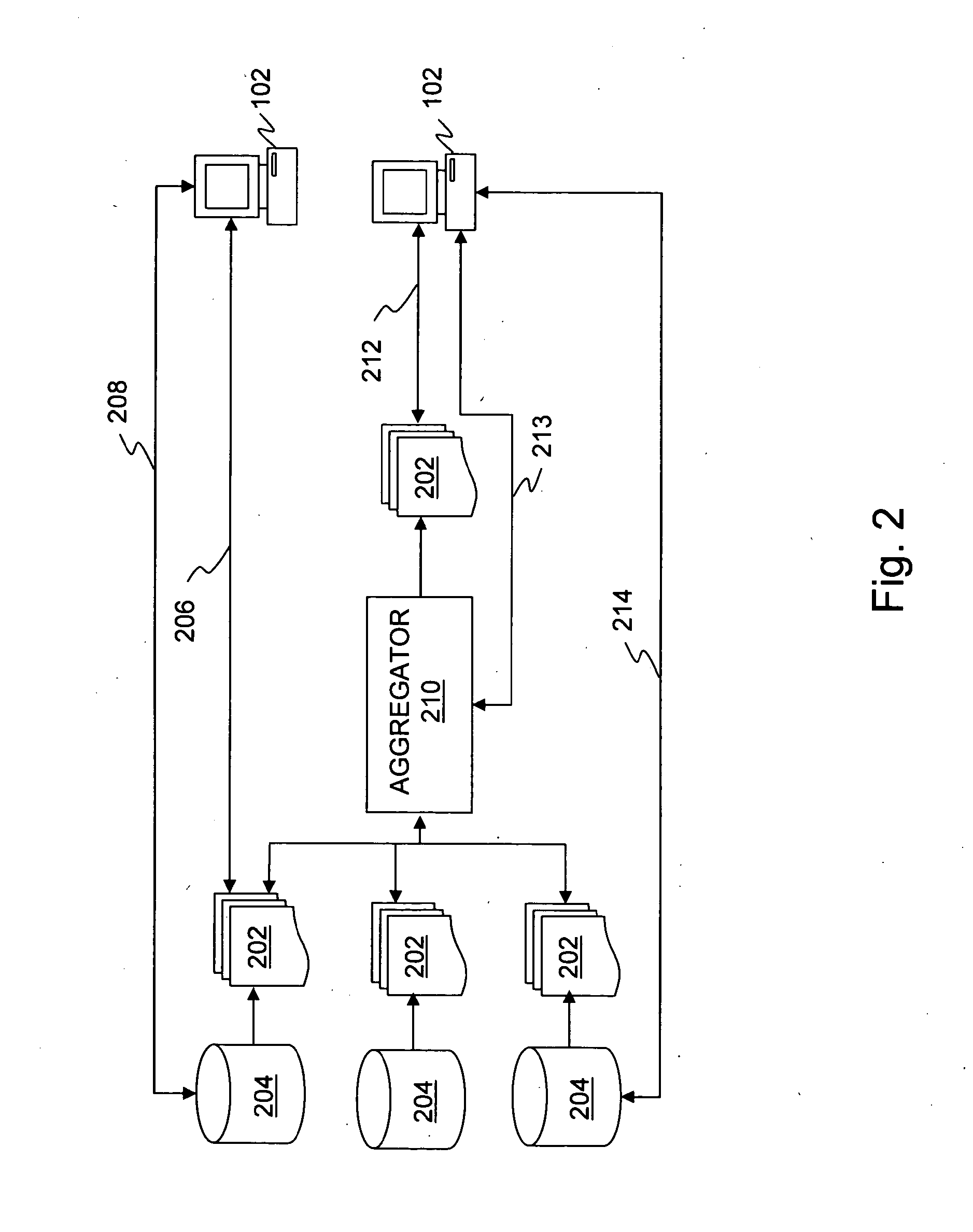
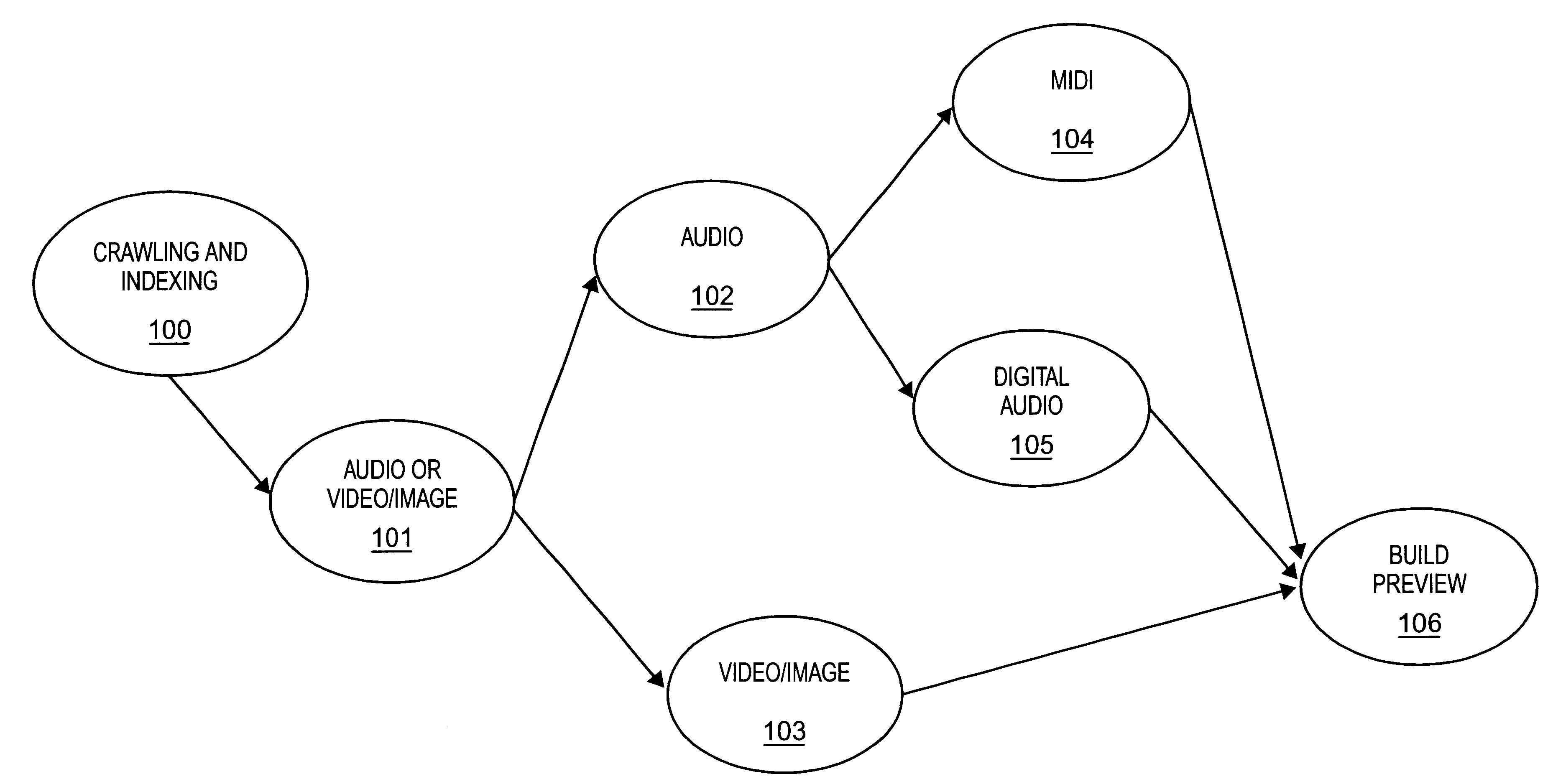
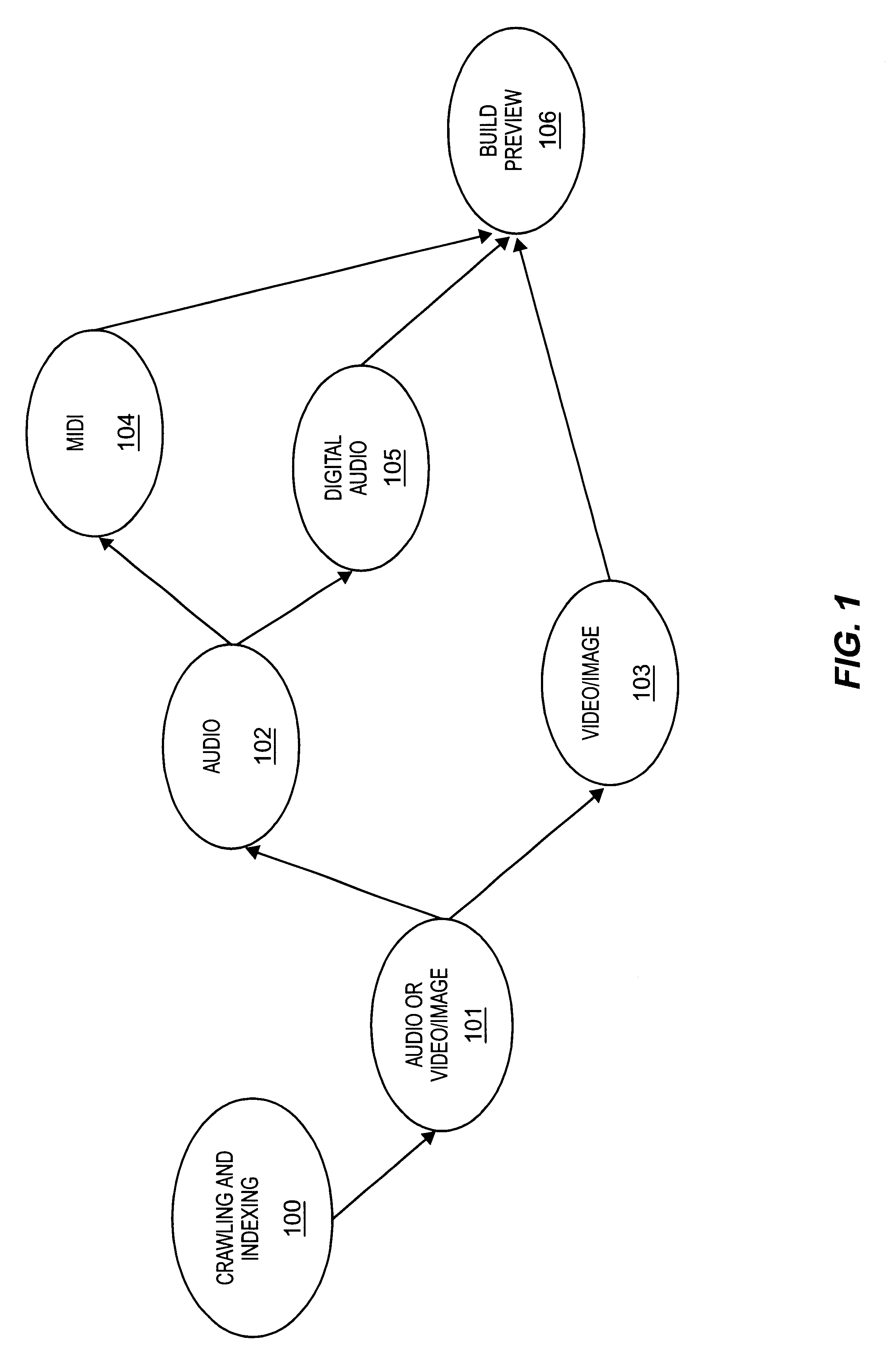
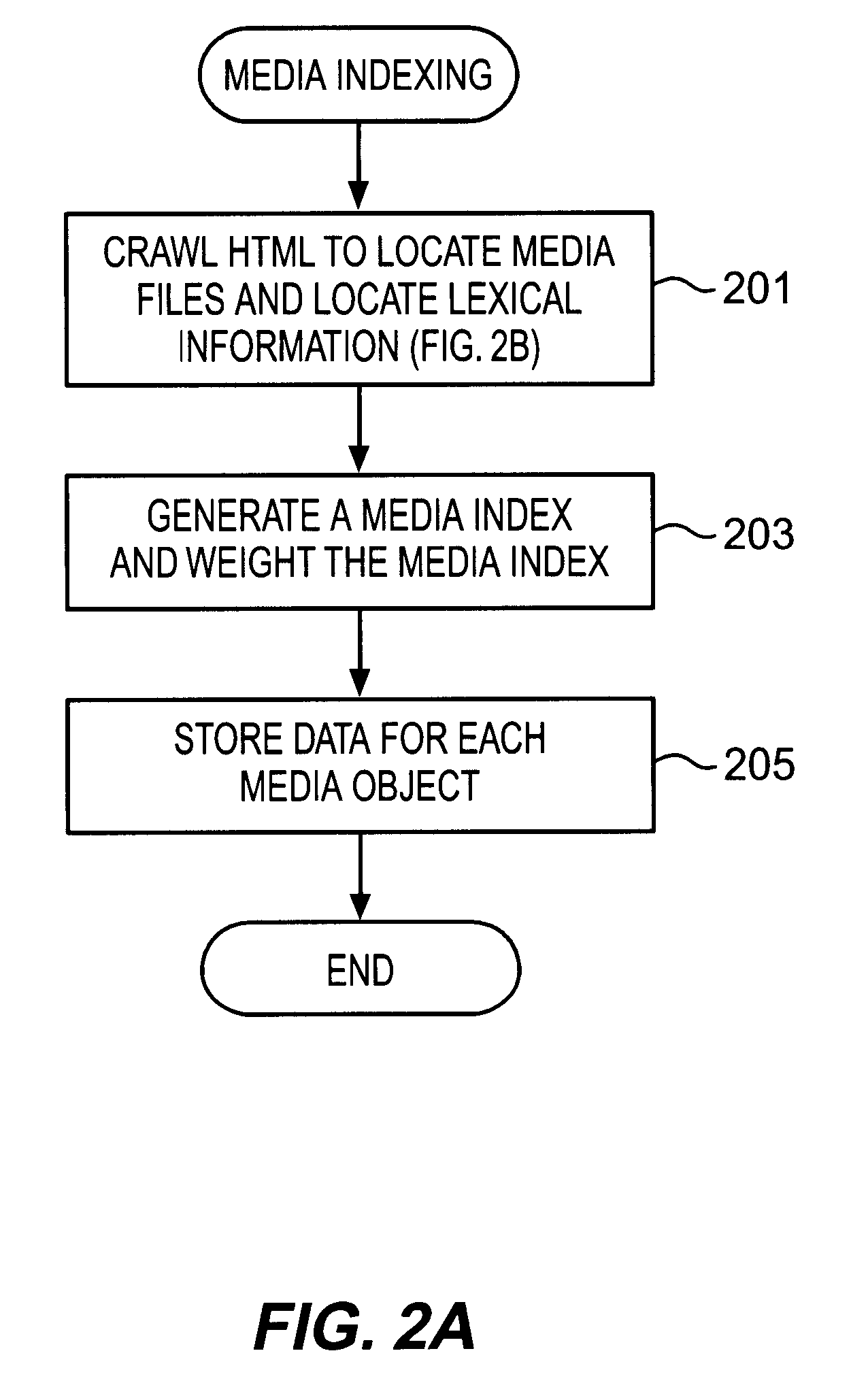
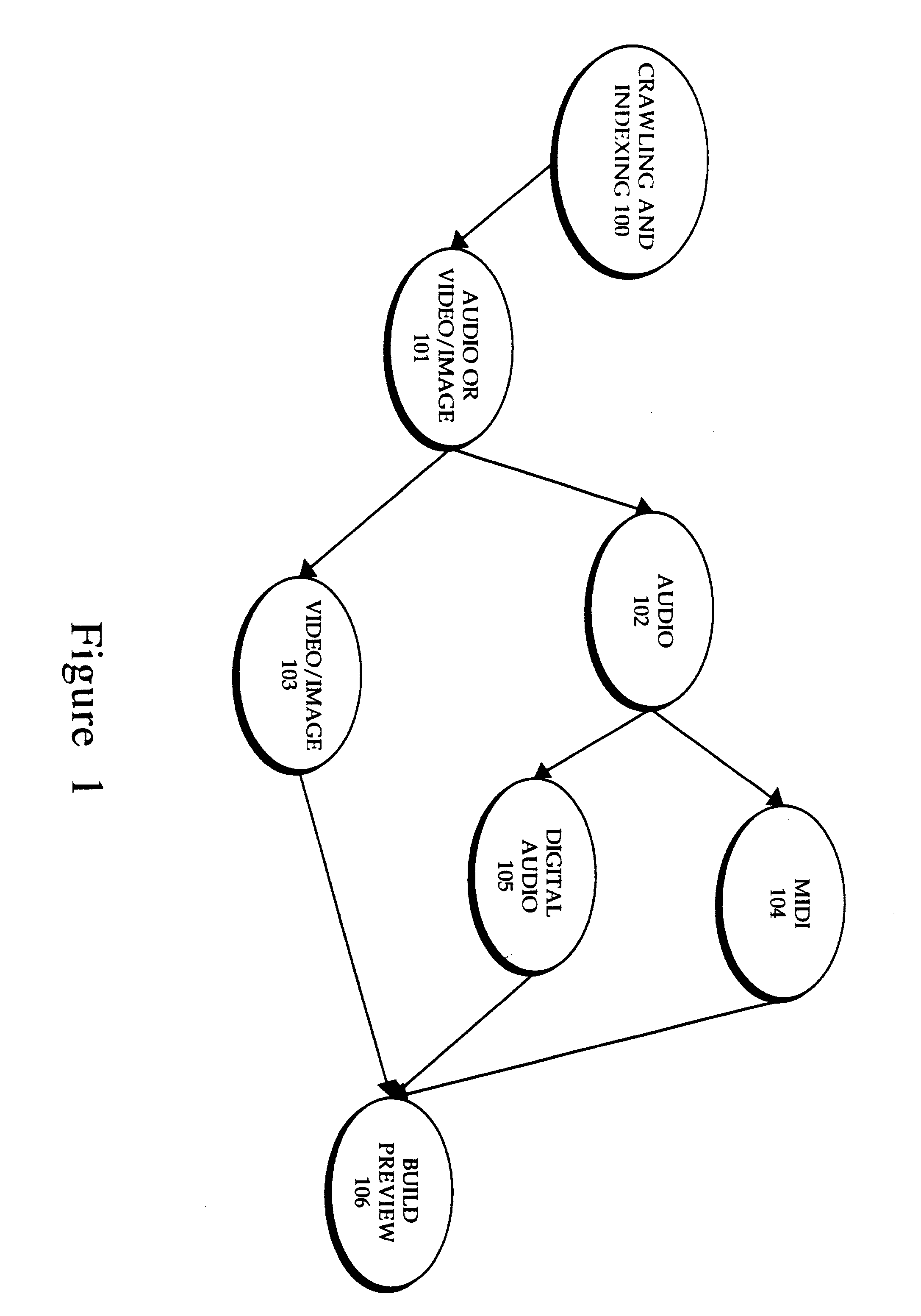
Display of media previews
A method and apparatus for searching for multimedia files in a distributed database and for displaying results of the search based on the context and content of the multimedia files.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
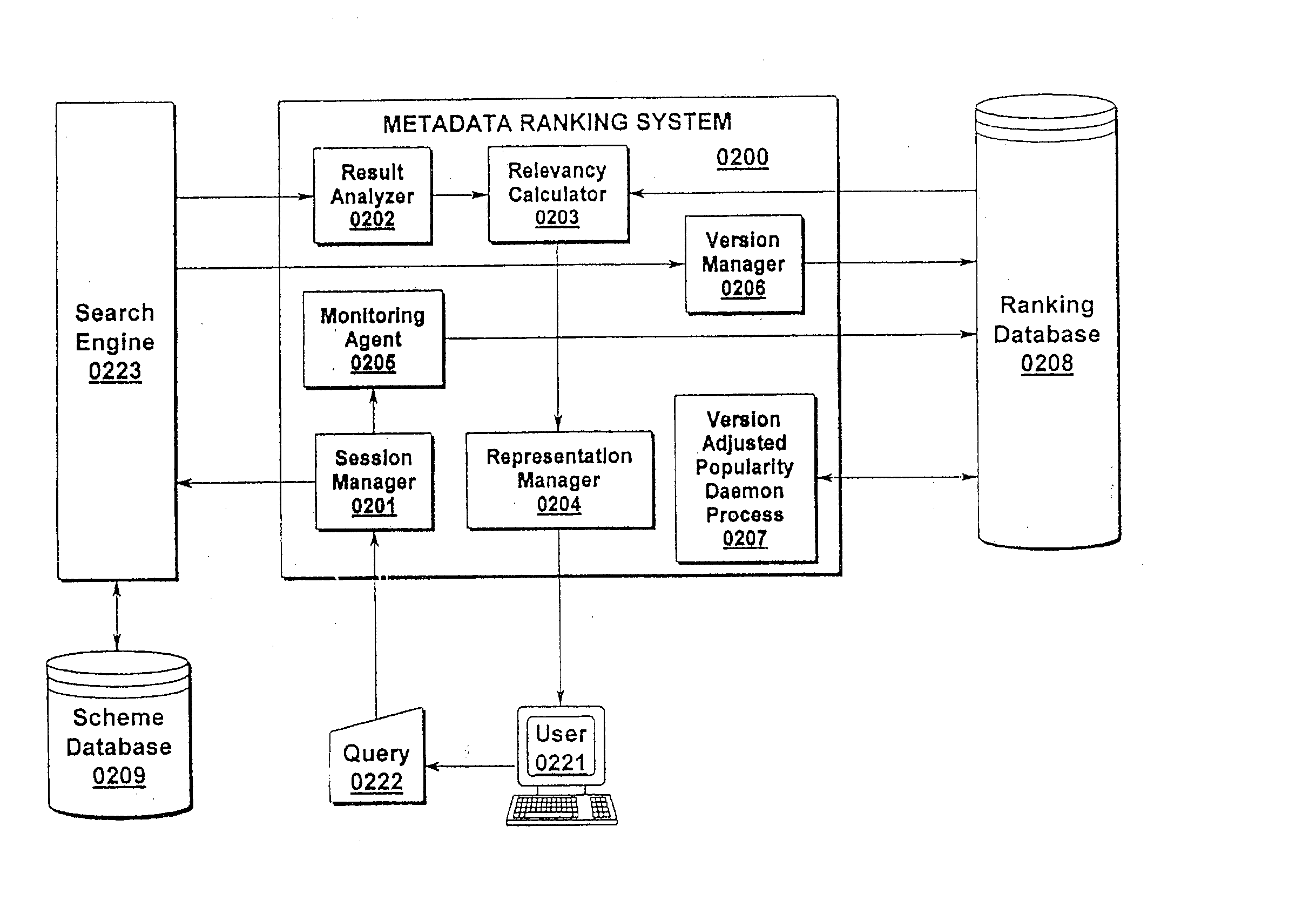
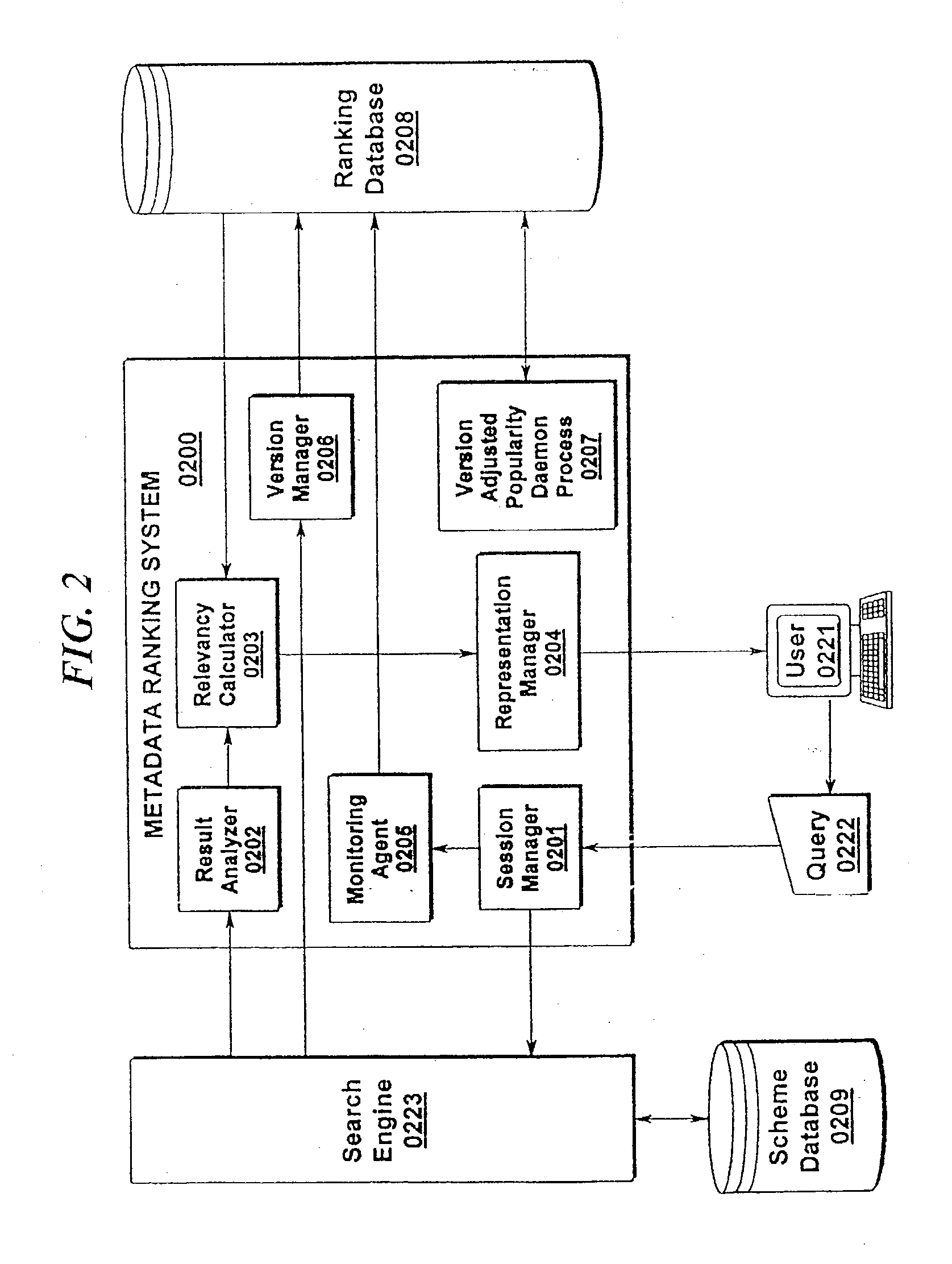
Metadata search results ranking system
InactiveUS20030120654A1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingThe InternetDistributed database
A system and method of metadata search ranking is disclosed. The present invention utilizes a combination of popularity and / or relevancy to determine a search ranking for a given search result association. Given the exponential growth rate currently being experienced in the Internet community, the present invention provides one of the few methods by which searches of this vast distributed database can produce useful results ranked and sorted by usefulness to the searching web surfer. The present invention permits embodiments incorporating a Ranking System / Method (0100) further comprising a Session Manager (0101), Query Manager (0102), Popularity Sorter (0103), and Association (0104) functions. These components may be augmented in some preferred embodiments via the use of a Query Entry means (0155), Search Engine (0156); Data Repository (0157), Query Database (0158), and / or a Resource List (0159).
Owner:IBM CORP
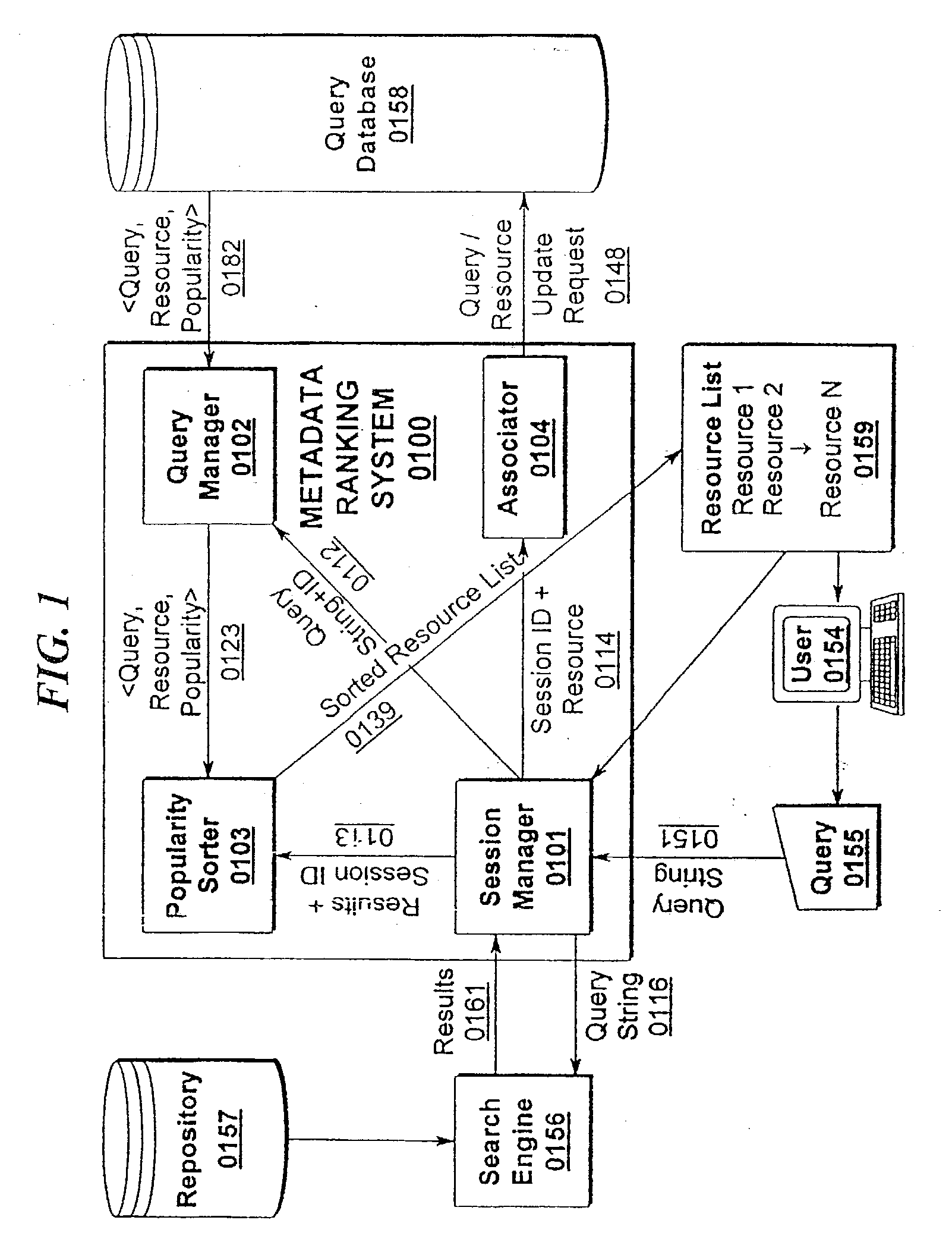
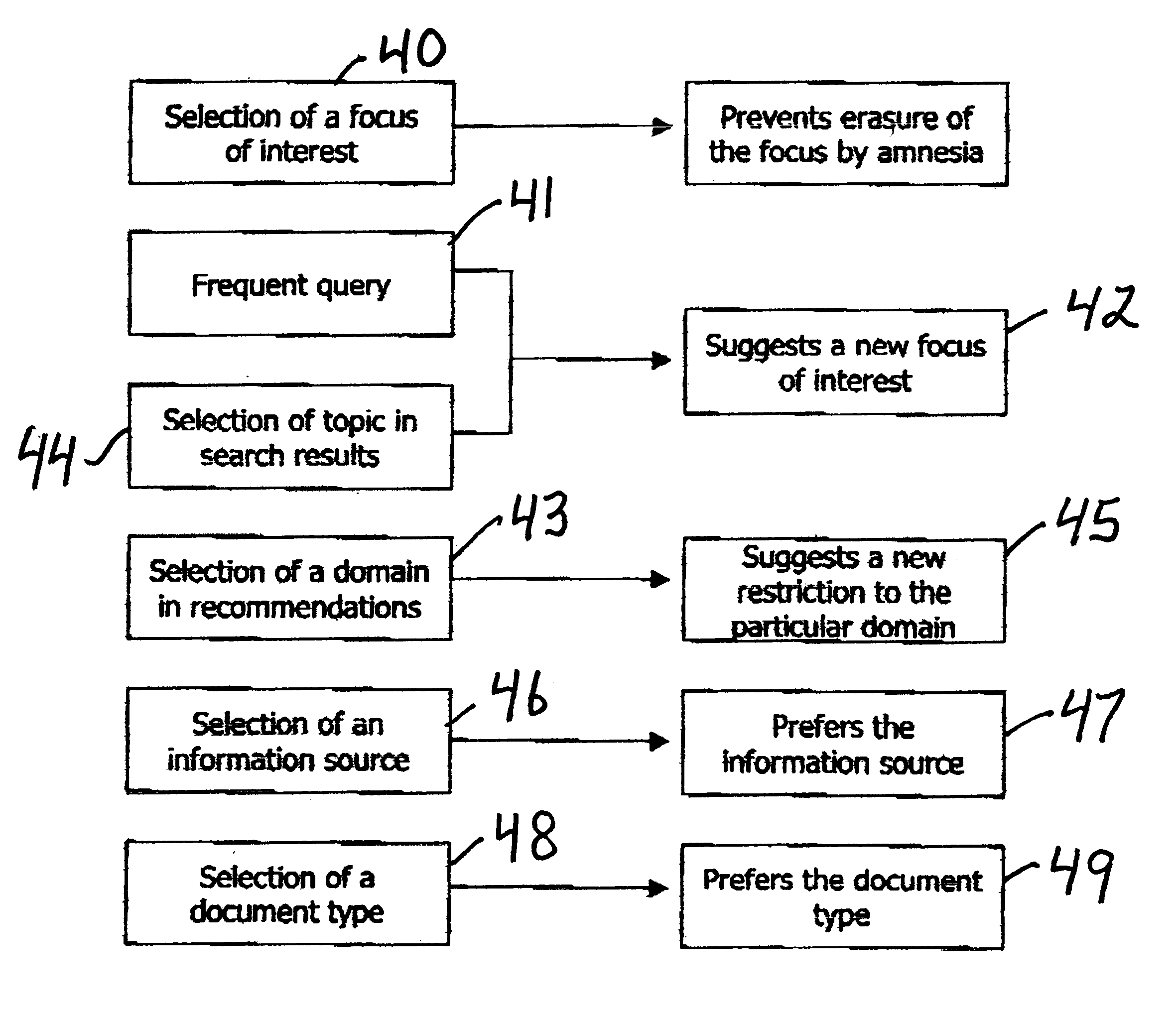
System and method for searching databases employing user profiles
InactiveUS6564210B1Enhanced informationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDocument preparationUser profile
A computer program method enables a user to find the most relevant documents by searching of distributed databases, i.e., the World Wide Web. The program employs the user's profile, based on the user's foci of interest, the user's query and a semantic analysis of the query and documents. In one embodiment, the retrieved documents are ranked according to relevancy based on the user's profile and query.
Owner:VIRTUAL SELF
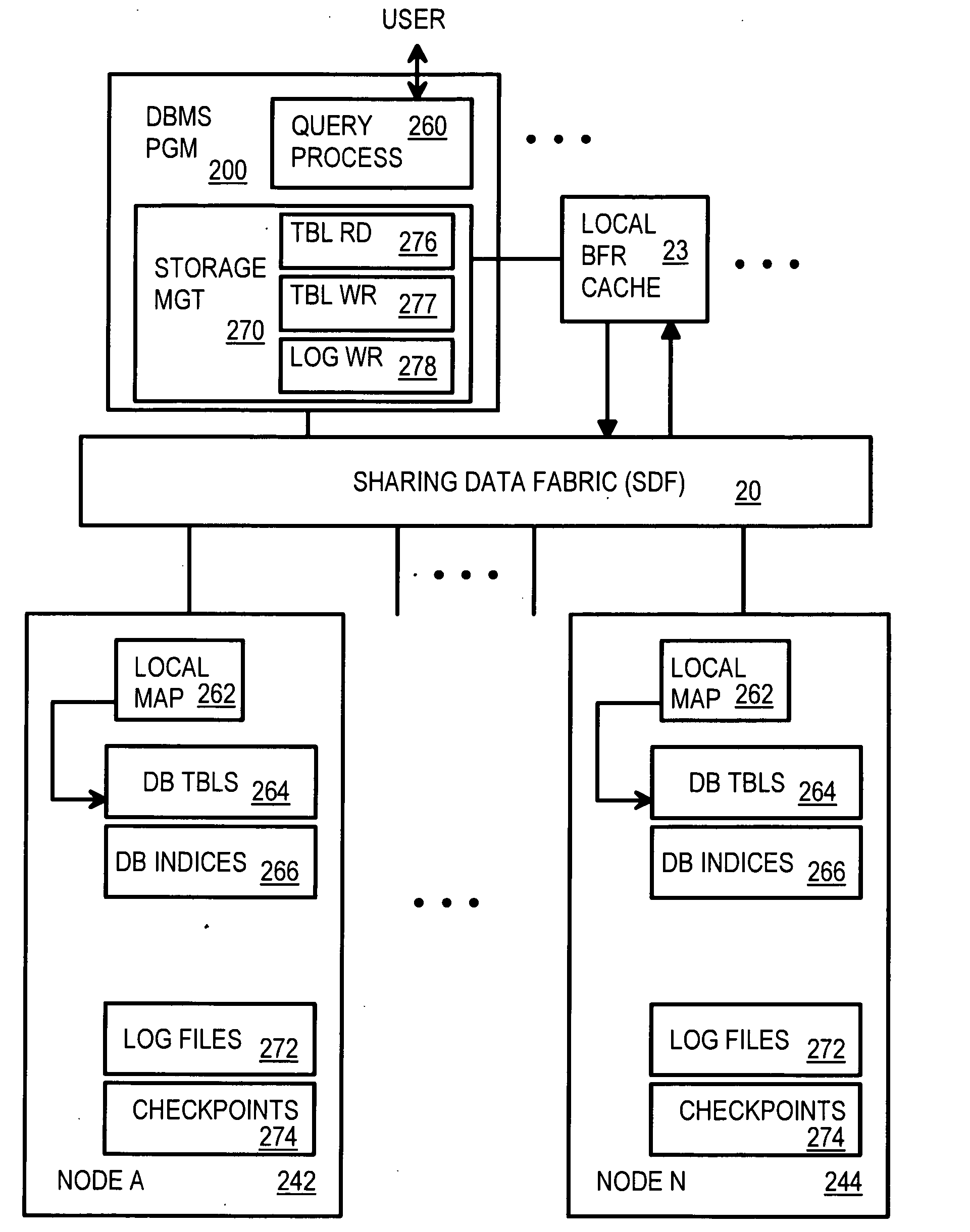
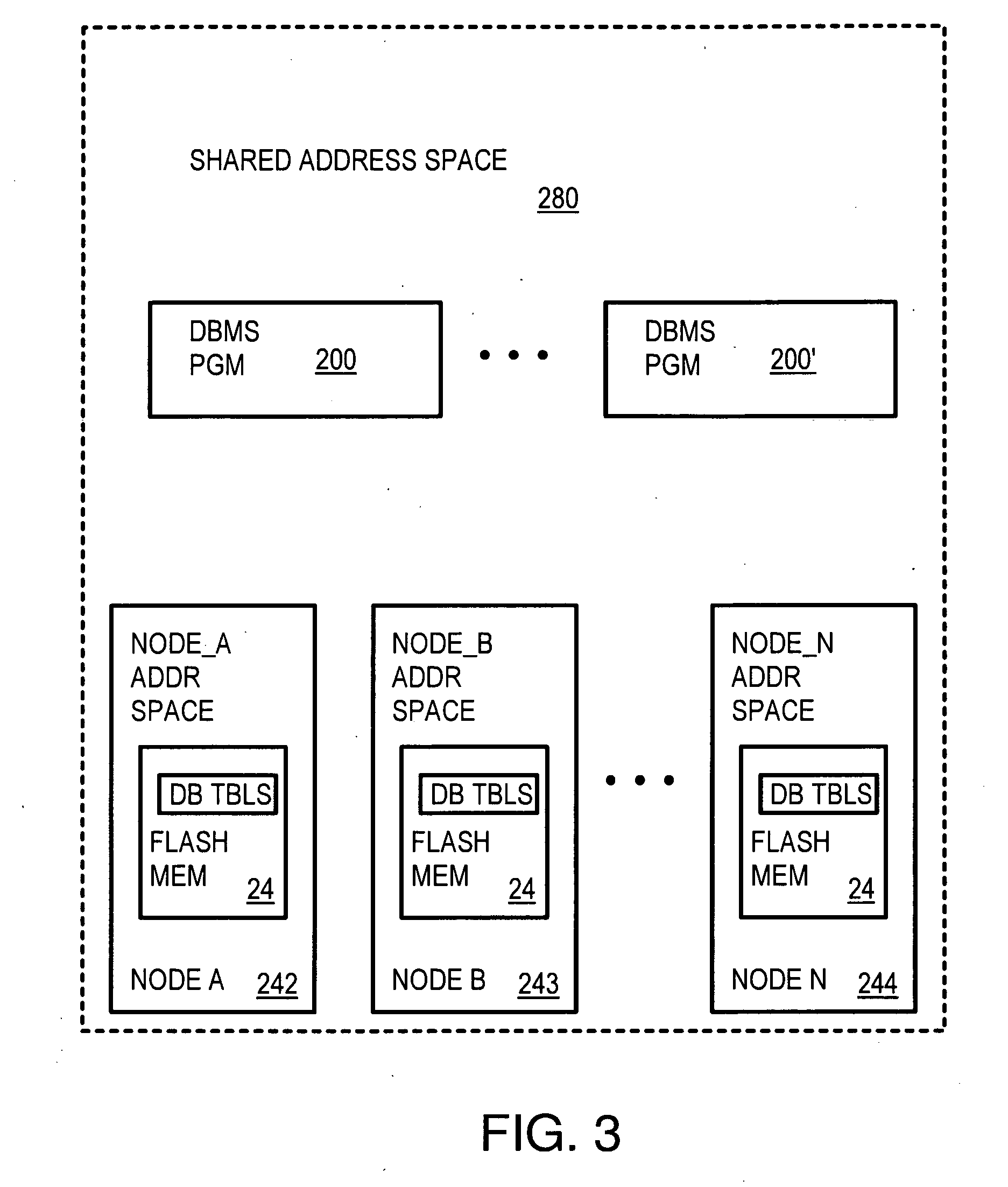
Scalable Database Management Software on a Cluster of Nodes Using a Shared-Distributed Flash Memory
ActiveUS20090240664A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel computingDistributed database
A distributed database system has multiple compute nodes each running an instance of a database management system (DBMS) program that accesses database records in a local buffer cache. Records are persistently stored in distributed flash memory on multiple storage nodes. A Sharing Data Fabric (SDF) is a middleware layer between the DBMS programs and the storage nodes and has API functions called by the DBMS programs when a requested record is not present in the local buffer cache. The SDF fetches the requested record from flash memory and loads a copy into the local buffer cache. The SDF has threads on a home storage node that locate database records using a node map. A global cache directory locks and pins records to local buffer caches for updating by a node's DBMS program. DBMS operations are grouped into transactions that are committed or aborted together as a unit.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Remote database technique
InactiveUS20060116991A1Optimize data processingMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsData storingDistributed database
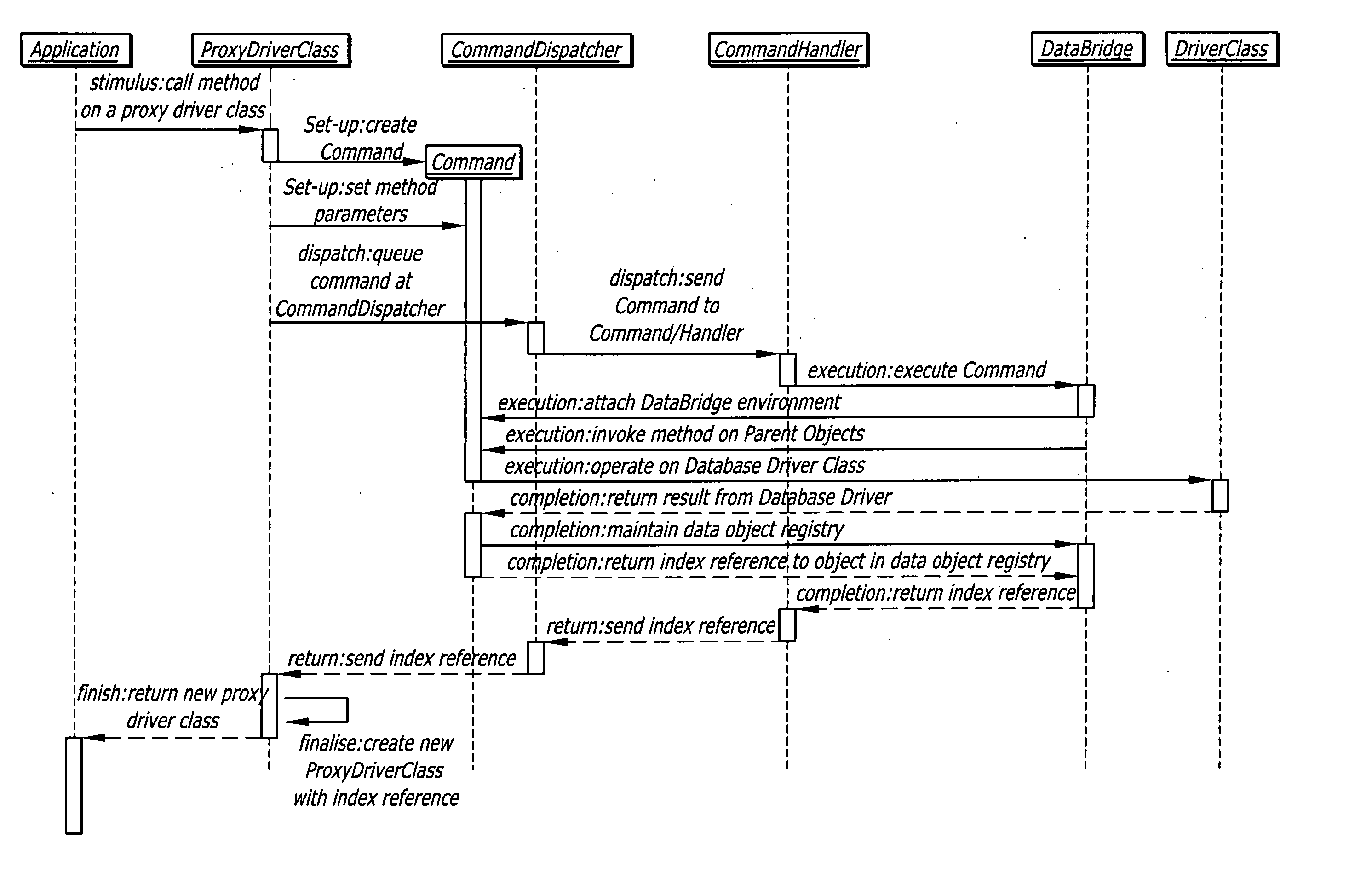
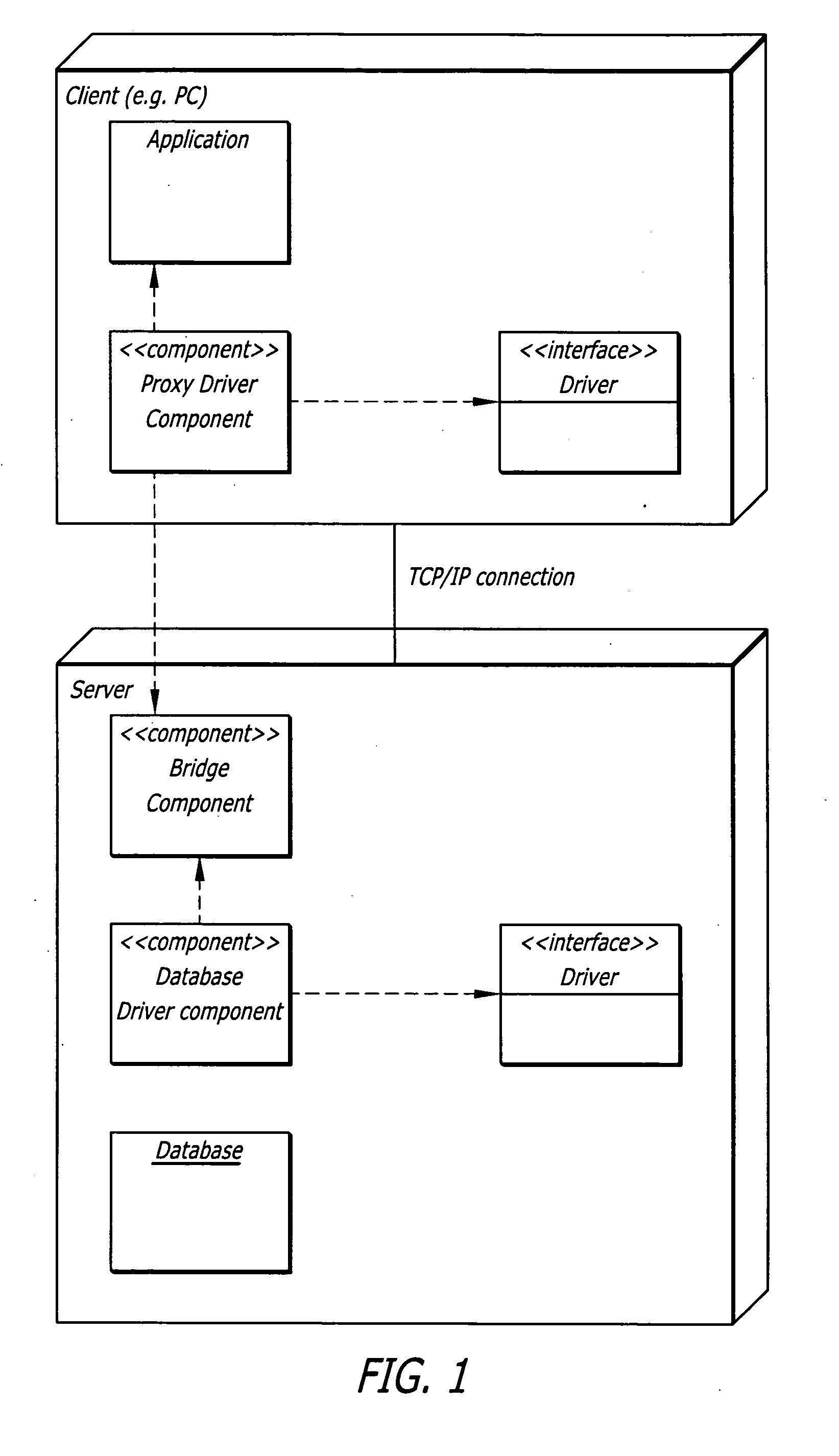
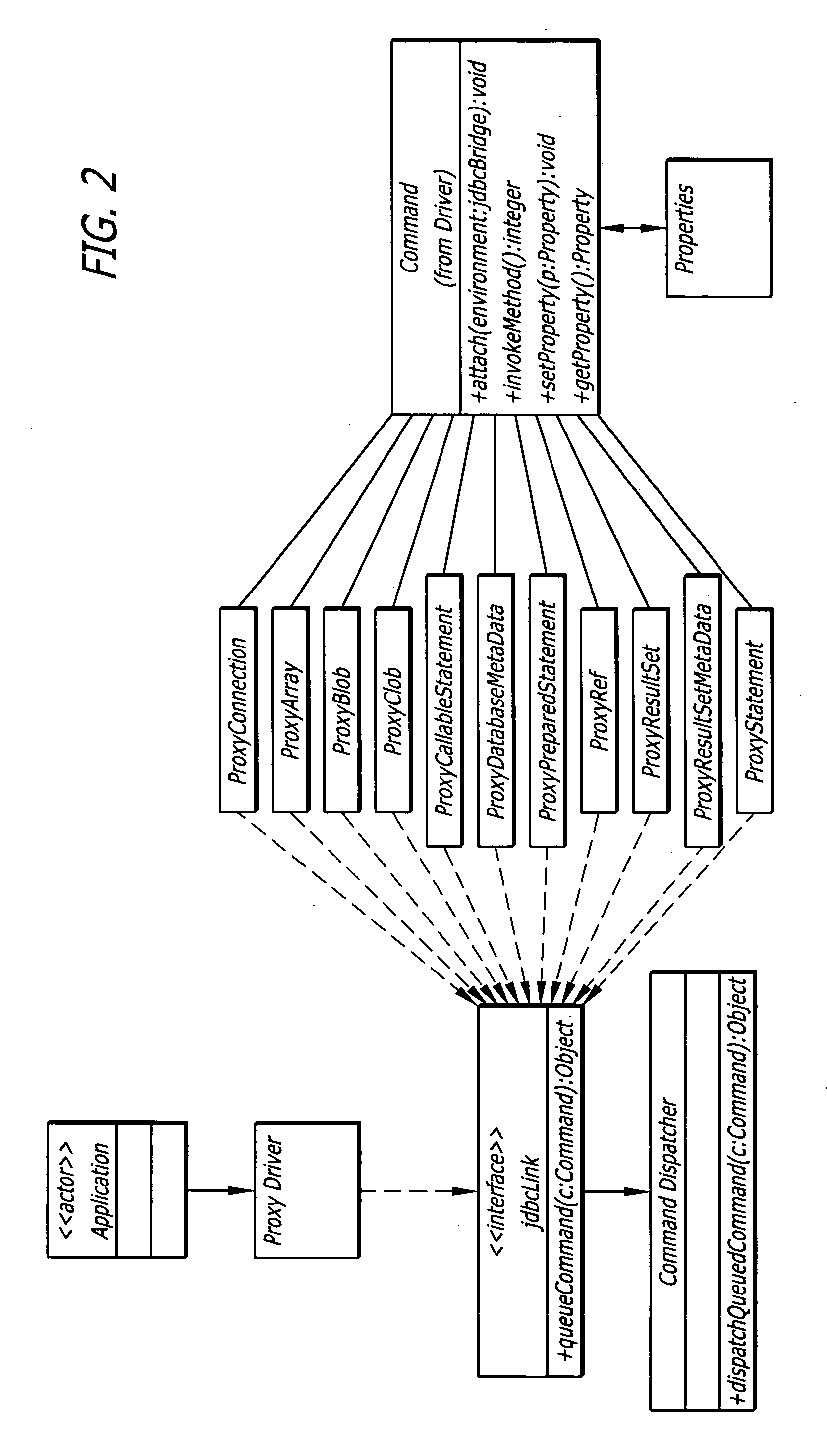
Systems, methods, software applications and virtual machines for creating, holding, referencing and / or accessing data objects from an application on a remote machine. The system allows a software application to read, write and perform transactions using data stored in one or more distributed databases. Methods are described for accessing a data object of a resource from an application located remotely from the resource. Methods are also described for issuing and servicing a method call from an application to a data object in a remote database. A virtual machine is yet further described for running a software application implemented using an object-oriented language for performing an operation on a plurality of data objects of a remote virtual machine. Still further described is a software application implemented using an object-oriented language to instantiate, store and access data objects on a remote virtual machine.
Owner:CIPHERGRID
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS20050120025A1Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
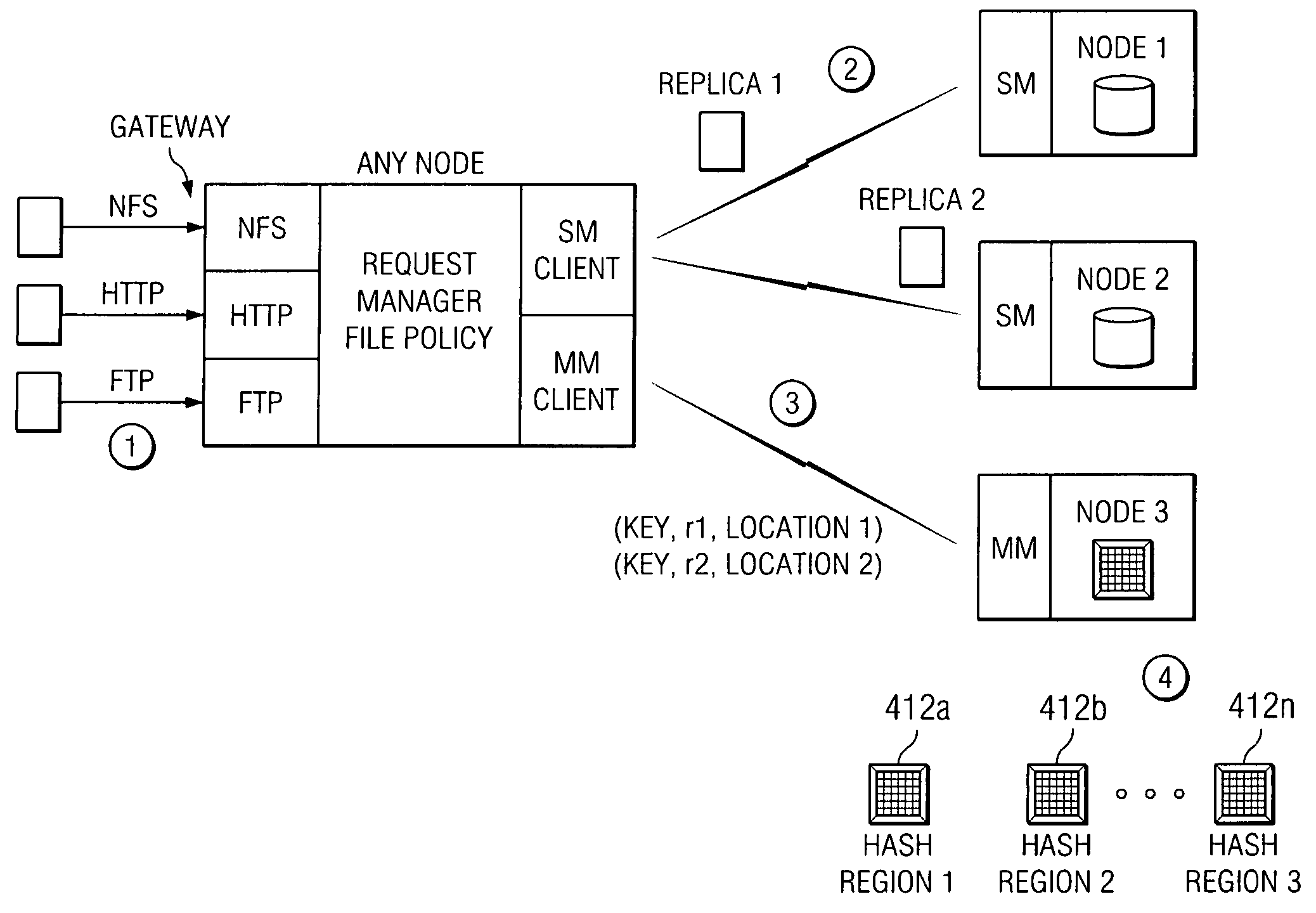
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS7155466B2Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Display of media previews
A method and apparatus for searching for multimedia files in a distributed database and for displaying results of the search based on the context and content of the multimedia files.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
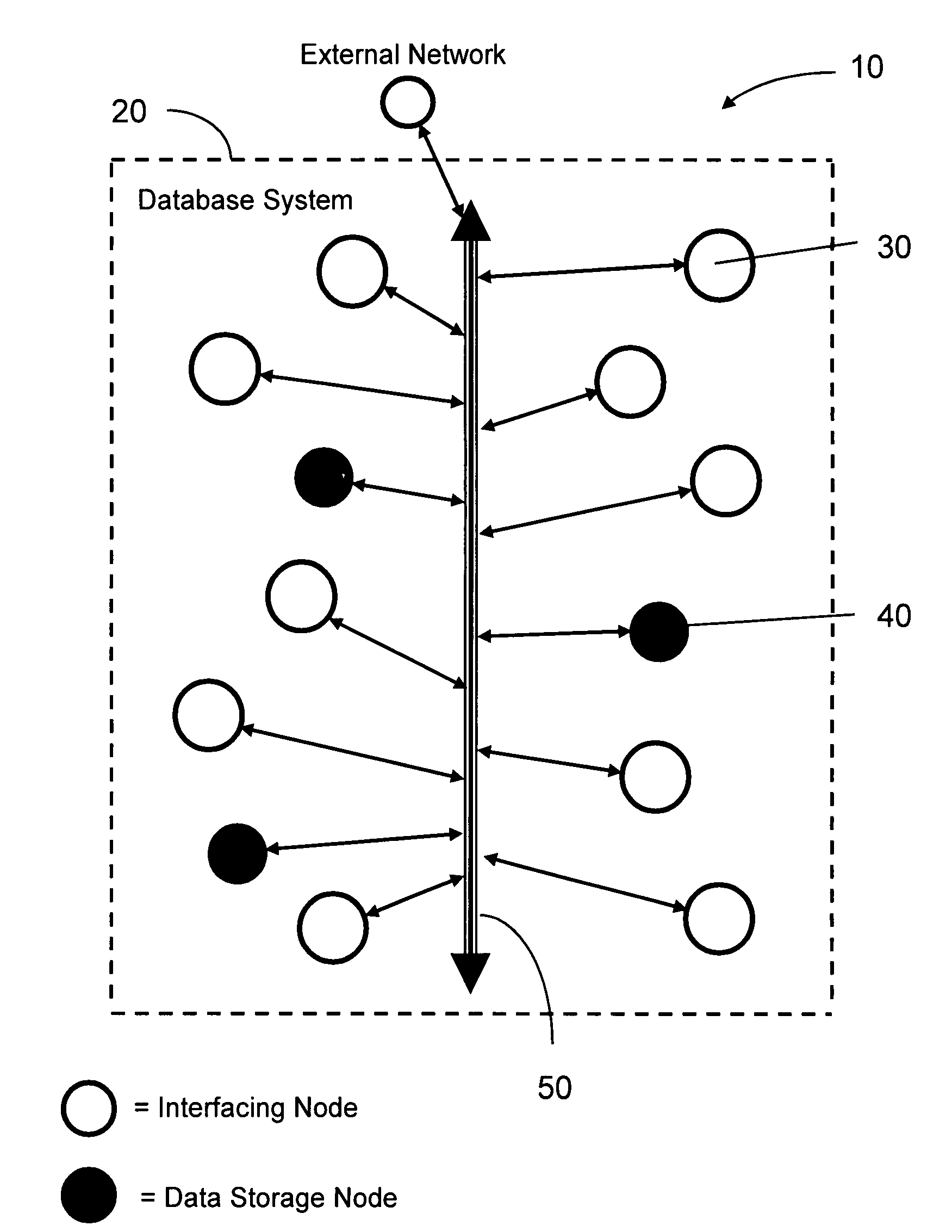
Distributed database system and method having nodes co-ordinated in a decentralized manner
InactiveUS7480658B2Function increaseEnhanced database systemDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationCo ordinateDistributed database
Owner:SKYPE
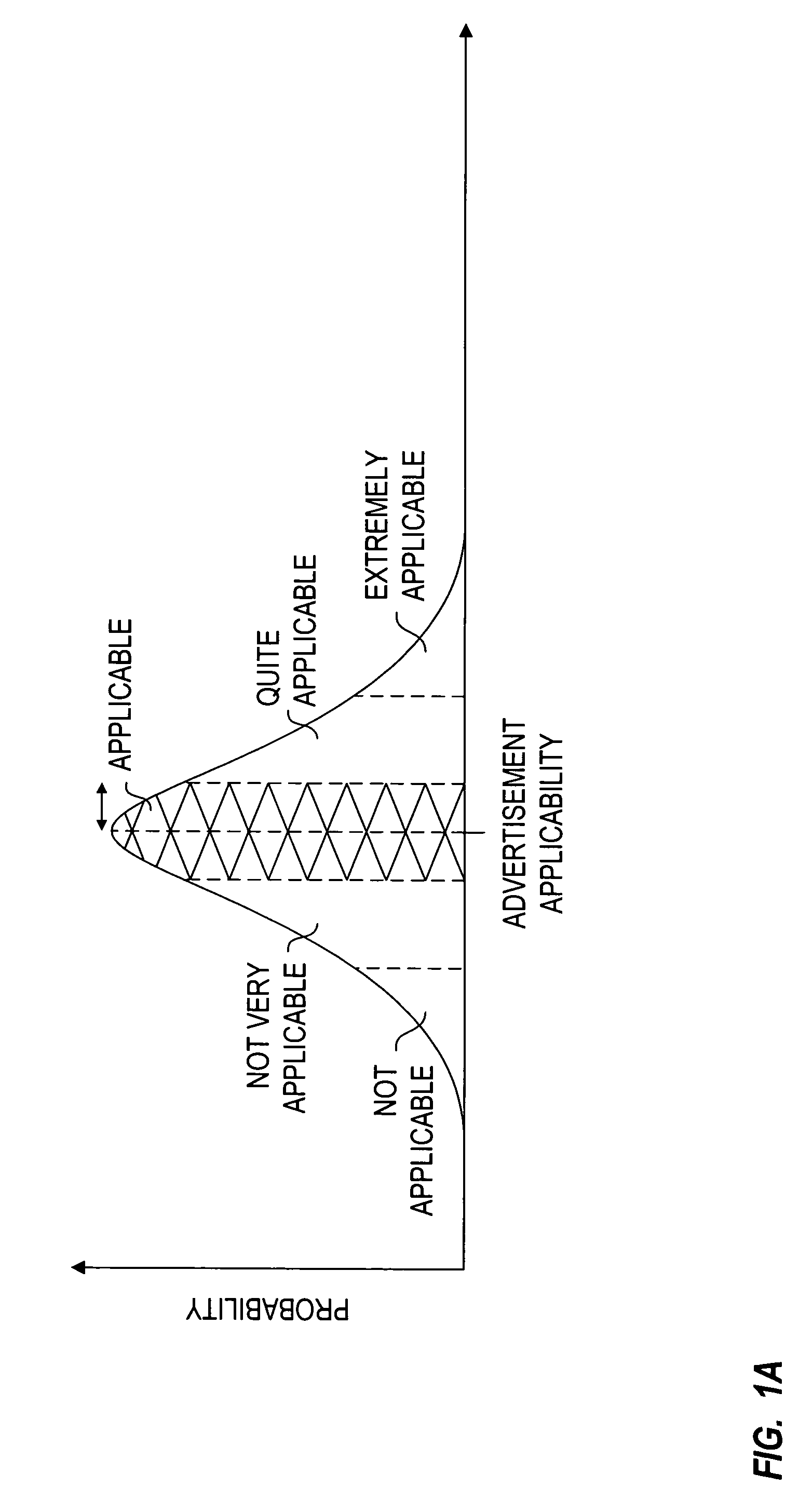
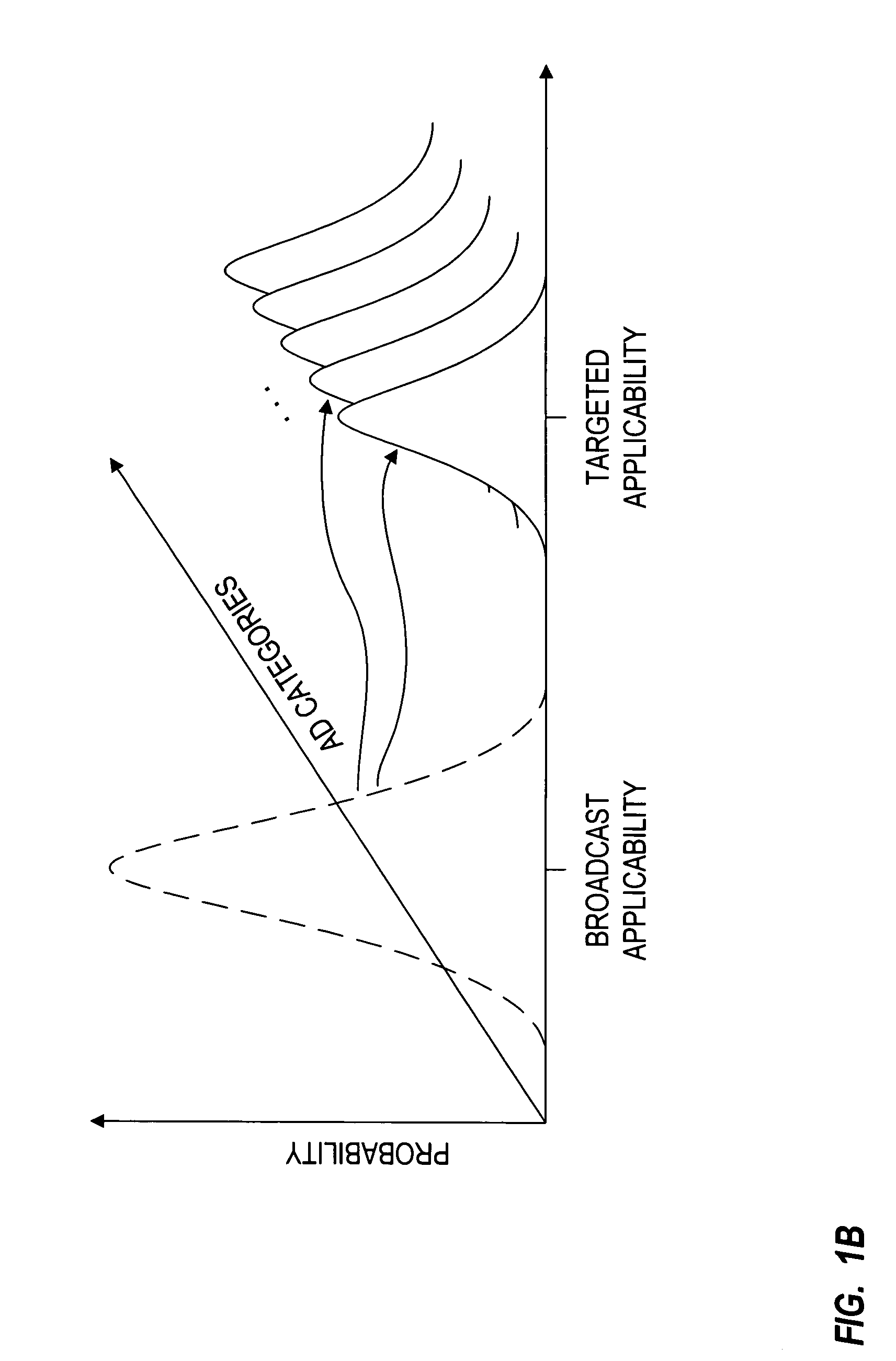
Privacy-protected advertising system
InactiveUS7949565B1Easy to usePermit targetingBroadcast-related systemsBroadcast information switching/replacementPrivacy protectionDemographic data
A database of consumer profiles is generated from multiple sources of information including demographic databases identifying demographic attributes of the consumers and transaction records for the consumers. The transaction records are processed to generate transaction attributes and interests of the consumer. The consumer profiles identify deterministic and probabilistic attributes about the consumer, but do not contain privacy violating information such as raw transaction records. The consumer profiles may be maintained in a plurality of distributed databases. Advertisers generate profiles that identify attributes of an intended target market of the advertisement. The advertisement profiles are in the form of operators that can be applied to the database of consumer profiles to determine applicability of advertisements to the subscribers. The operators may only be applied to or make measurements on certain “observables”. The operators will not be able to obtain private information from the database of consumer profiles.
Owner:PRIME RES ALLIANCE E LLC
Security systems and methods for use with structured and unstructured data
InactiveUS8347088B2Increase flexibilityEasy accessData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsUnstructured dataDistributed database
Disclosed herein are systems and methods including hardware, software and electronic service components and systems to provide large-scale, reliable, and secure foundations for distributed databases and content management systems combining unstructured and structured data, and allowing post-input reorganization to achieve a high degree of flexibility.
Owner:NEWSILIKE MEDIA GROUP
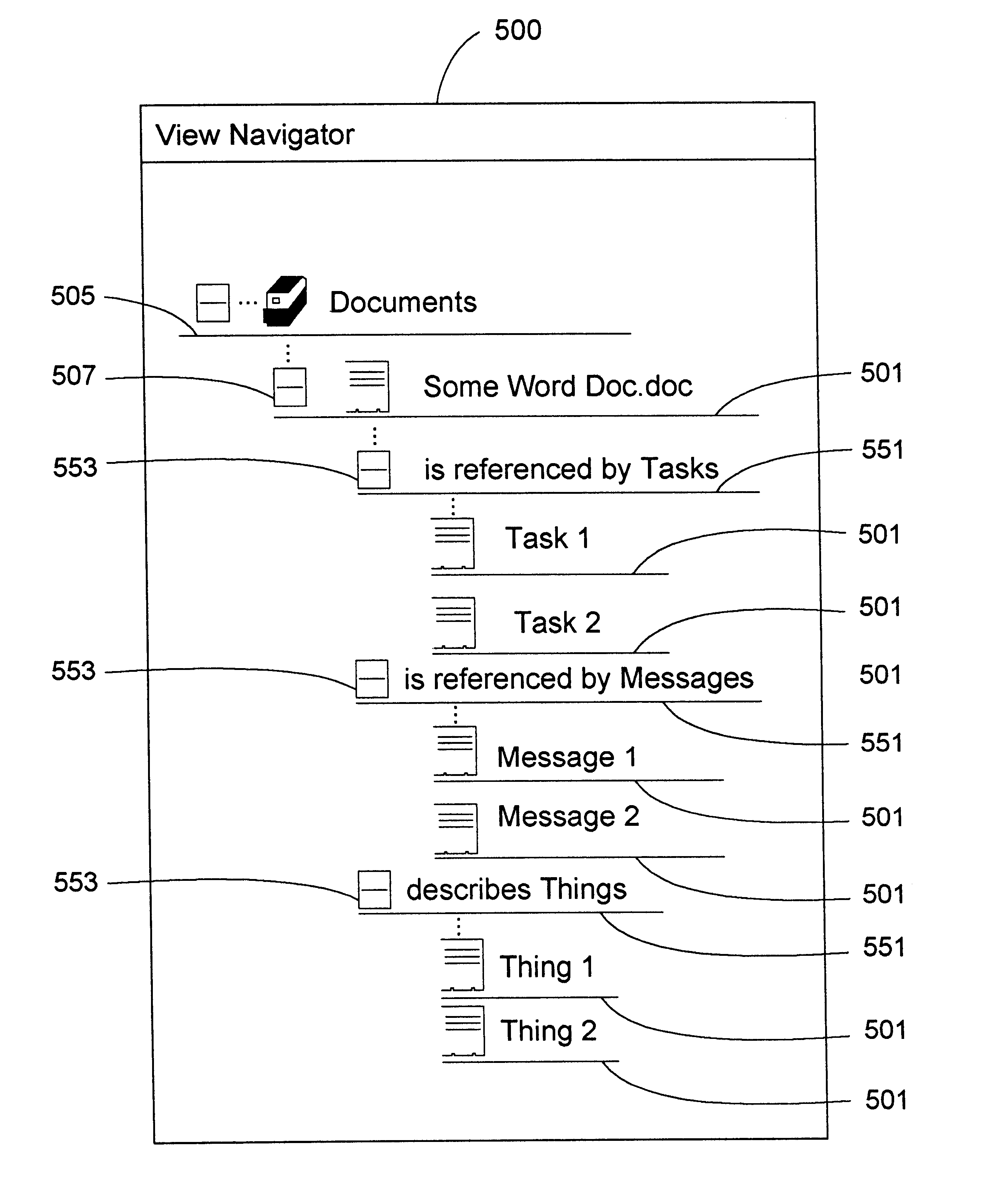
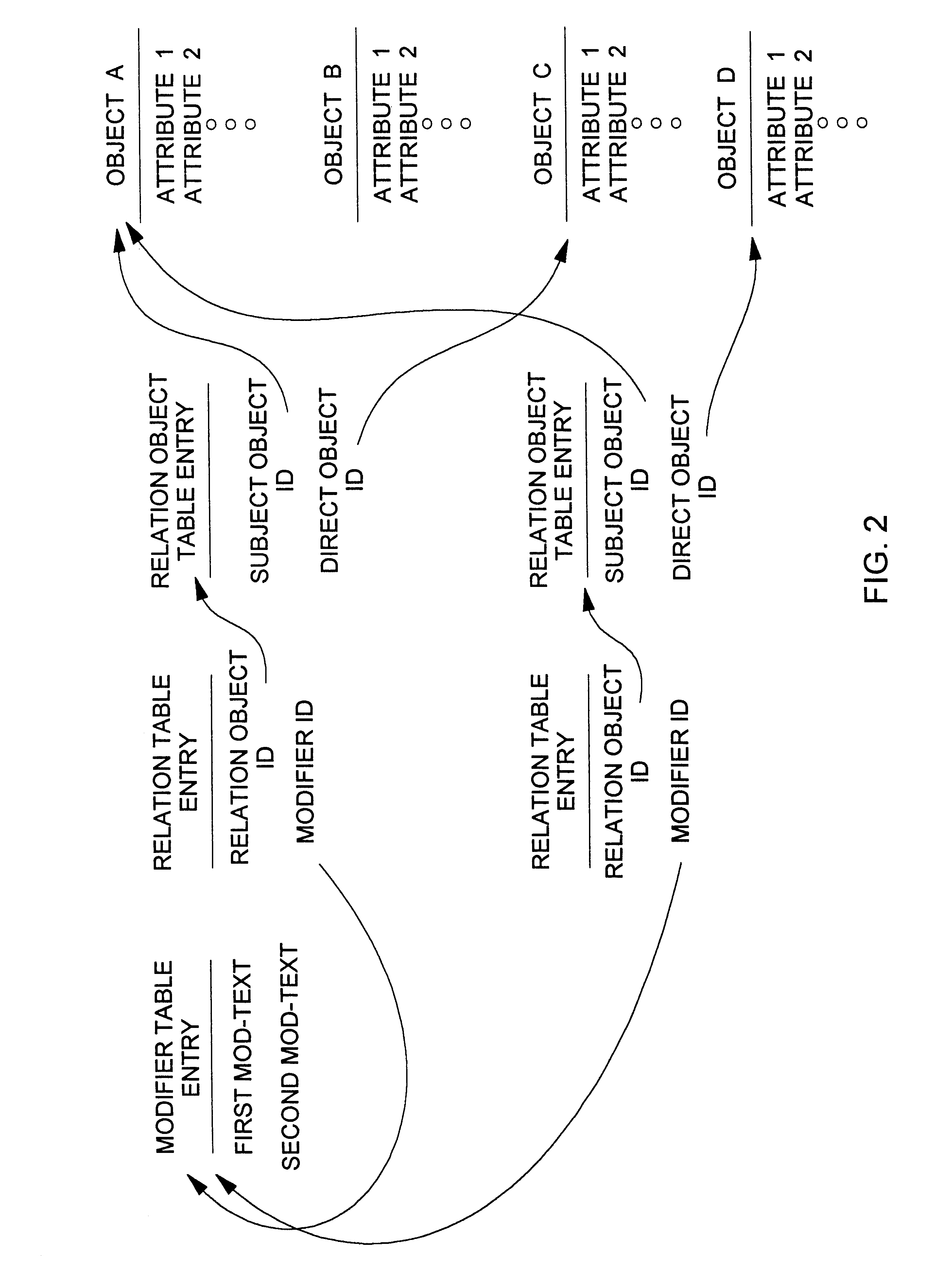
Database query handler supporting querying of textual annotations of relations between data objects
InactiveUS6618732B1EffectivelySave storage spaceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabase queryCustomer relationship management
An improved command handler (and database system utilizing the improved command handler) interfaces to a datastore storing item data for a plurality of items and bi-directional modifier data, corresponding to a relation between at least one first item and at least one second item, that represents first text characterizing semantics of a relationship of the at least one first item to the at least one second item, and represents second text characterizing semantics of a relationship of the at least one second item to the at least one first item. The command handler operates, in response to receiving a first-type query command that specifies at least one given item, to access the datastore to identify i) at least one related item that is related to the given item, and identify ii) either the first text or the second text characterizing semantics of the relation between the given item and the at least one related item. The command hander returns i) data corresponding to the at least one related item; and ii) data corresponding to the identified first text and or second text characterizing semantics of the relation between the given item and the at least one related item. Preferably, the data returned in response to the first-type query command identifies the at least one related item. and identifies the first text or second text characterizing semantics of the relation between the given item and the at least one related item. In addition, the command handler preferably supports additional commands that retrieve from the datastore information related to specified objects, object types, and relations.The command handler (and database system) of the present invention may be used in a wide assortment of software applications, including enterprise applications (such as e-business applications, supply chain management applications, customer relationship management applications, decision support applications), the file system in operating systems, web browsers, e-mail applications and personal information management applications. Importantly, the command handler (and database system) provides an efficient mechanism to query the organization of the data elements (and the relationships therebetween) stored and accessed in such software applications, in a manner that efficient and readily adaptable to client-server database systems or other distributed database systems.
Owner:REVELINK
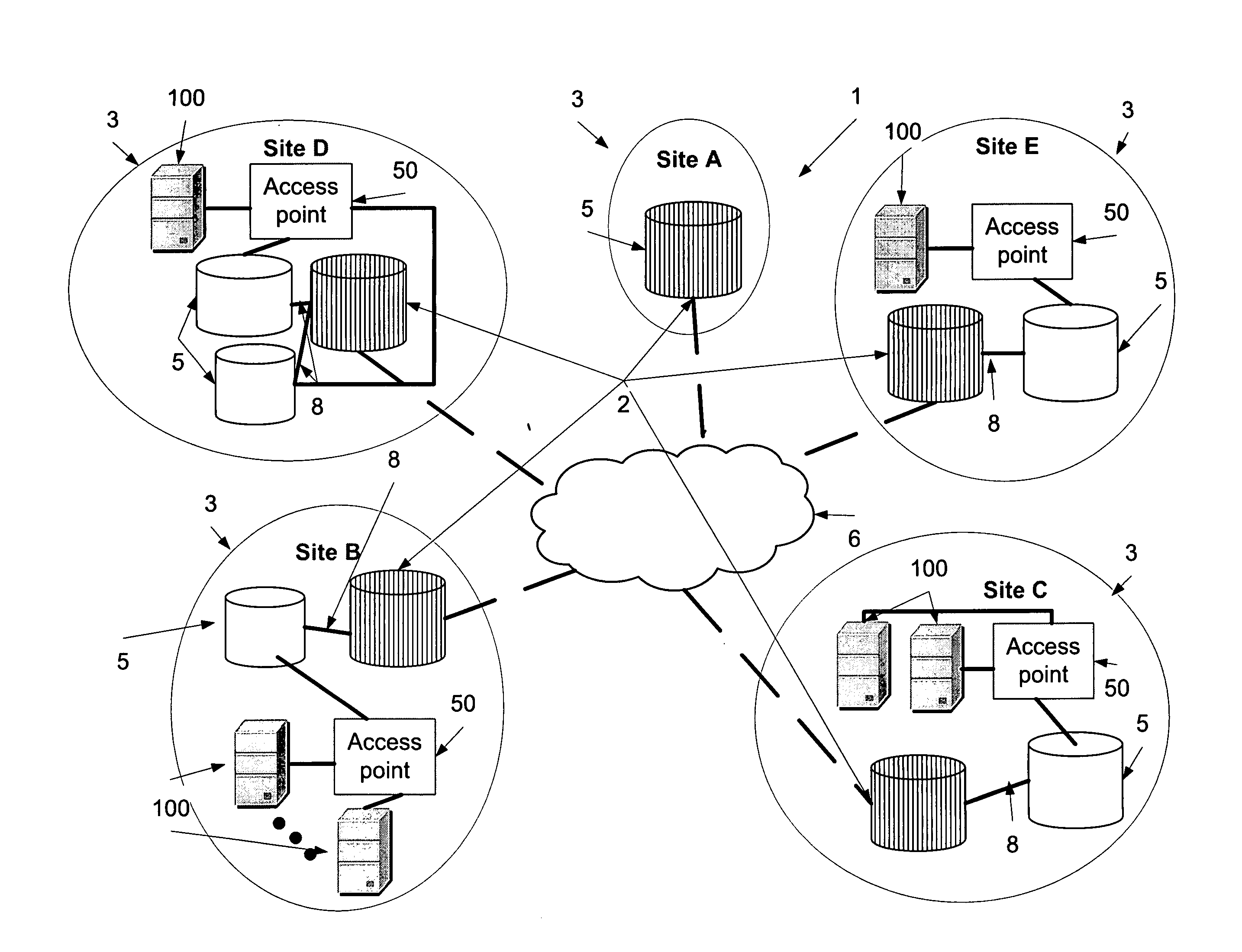
Apparatus and method for a distributed storage global database
InactiveUS20090070337A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData managementData element
A geographically distributed storage system for managing the distribution of data elements wherein requests for given data elements incur a geographic inertia. The geographically distributed storage system comprises geographically distributed sites, each comprises a site storage unit for locally storing a portion of a globally coherent distributed database that includes the data elements and a local access point for receiving requests relating to ones of the data elements. The and geographically distributed storage system comprises a data management module for forwarding at least one requested data element to the local access point at a first of the geographically distributed sites from which the request is received and storing the at least one requested data element at the first site, thereby to provide local accessibility to the data element for future requests from the first site while maintaining the globally coherency of the distributed database.
Owner:NORTHEND NETWORKS
Distributed metadata searching system and method
InactiveUS6434548B1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingWeb search engineInternet communication
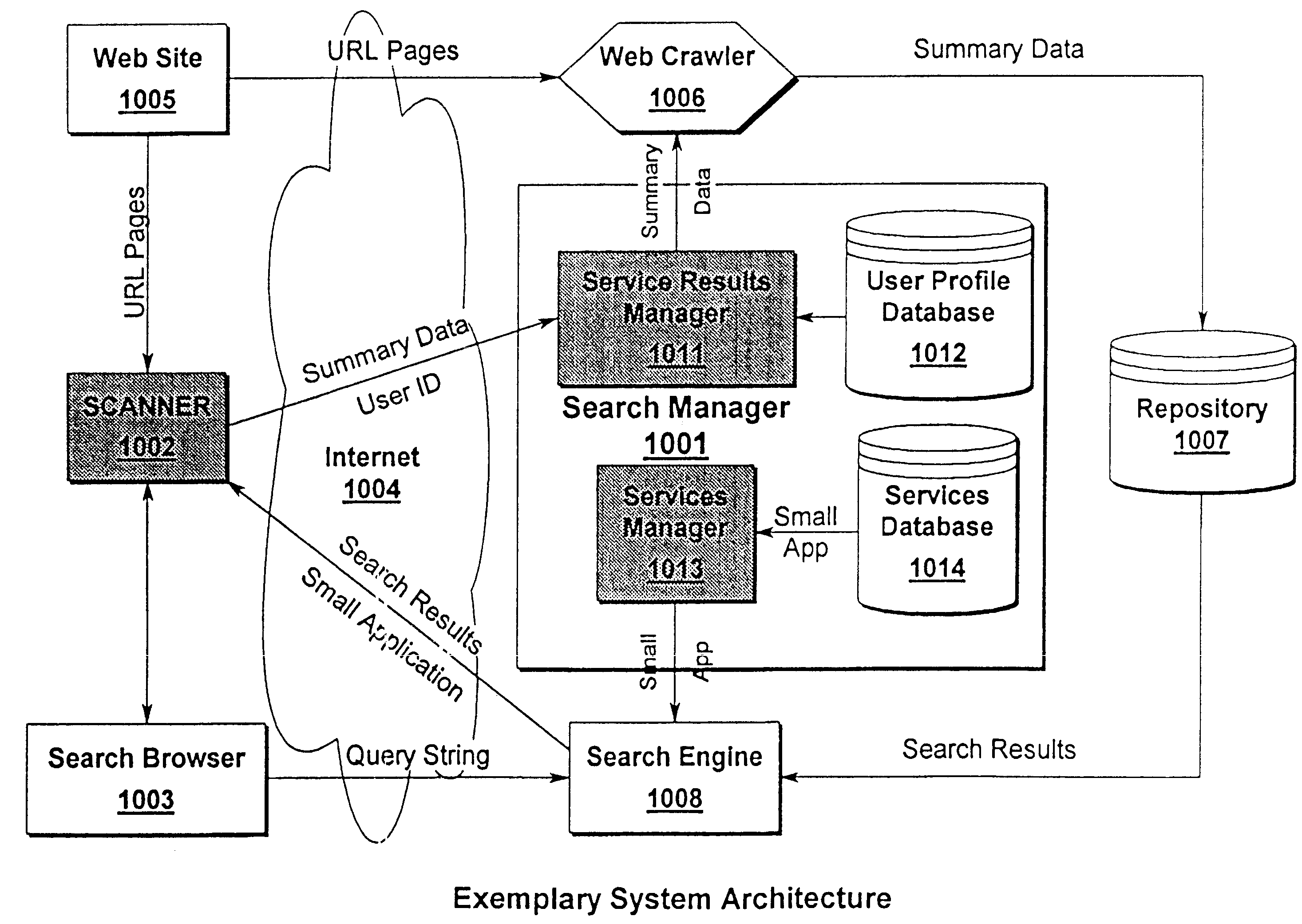
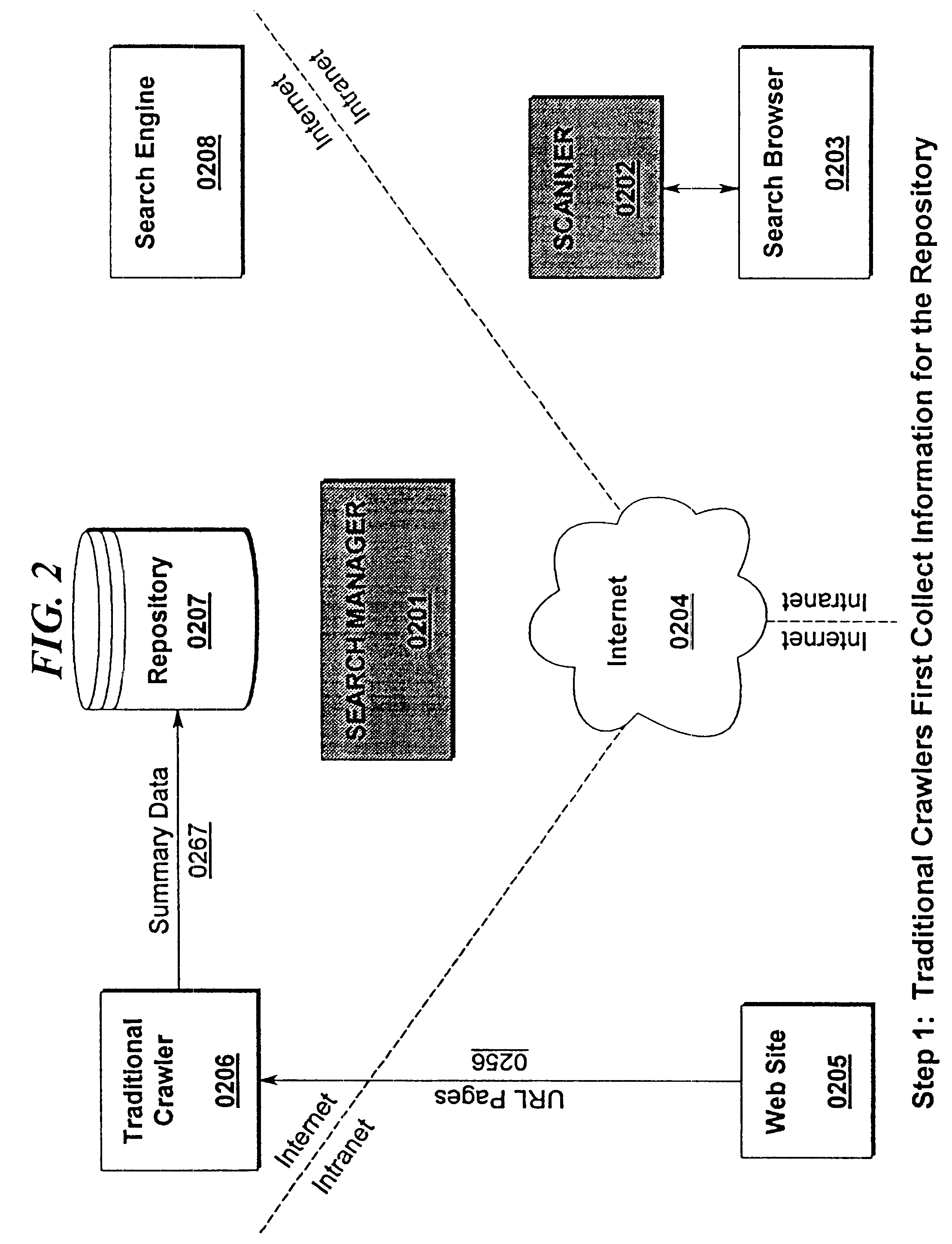
A system and method of distributed metadata searching is disclosed. The present invention permits an extension of the searching and retrieval functions of existing Internet web search engines by utilizing computational resources embodied in user computer systems and search browsers. By distributing the searching and scanning functions to the user level, the present invention reduces the computational and communications burden on Internet web search engines and crawlers, resulting in lower computational resource utilization by Internet search engine providers. Given the exponential growth rate currently being experienced in the Internet community, the present invention provides one of the few methods by which complete searches of this vast distributed database may be performed. The present invention permits embodiments incorporating a Search Manger (1001) further comprising a Service Results Manager (1013), User Profile Database (1012), Service Manager(1013), and Service Database (1014); a Light Weight Application SCANNER (1002); and a Search Engine (1008). These components may be augmented in some preferred embodiments via the use of a Search Browser (1003), Internet Communications (1004); Web Site(s) (1005), Web Crawler(s) (1006), and a Repository Database (1007).
Owner:IBM CORP
Techniques for sharing network security event information
ActiveUS20150207813A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInformation sharingPrivate network
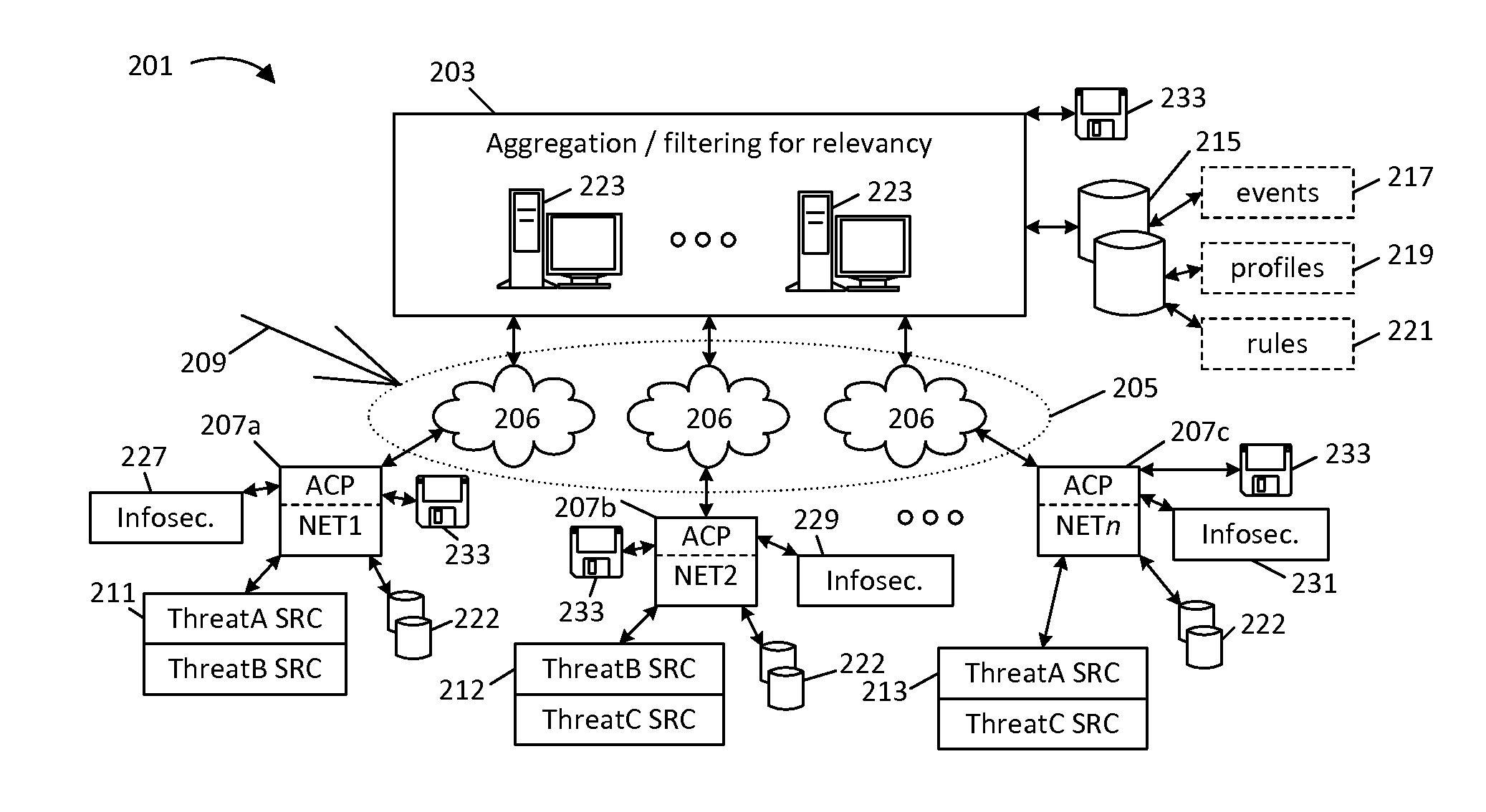
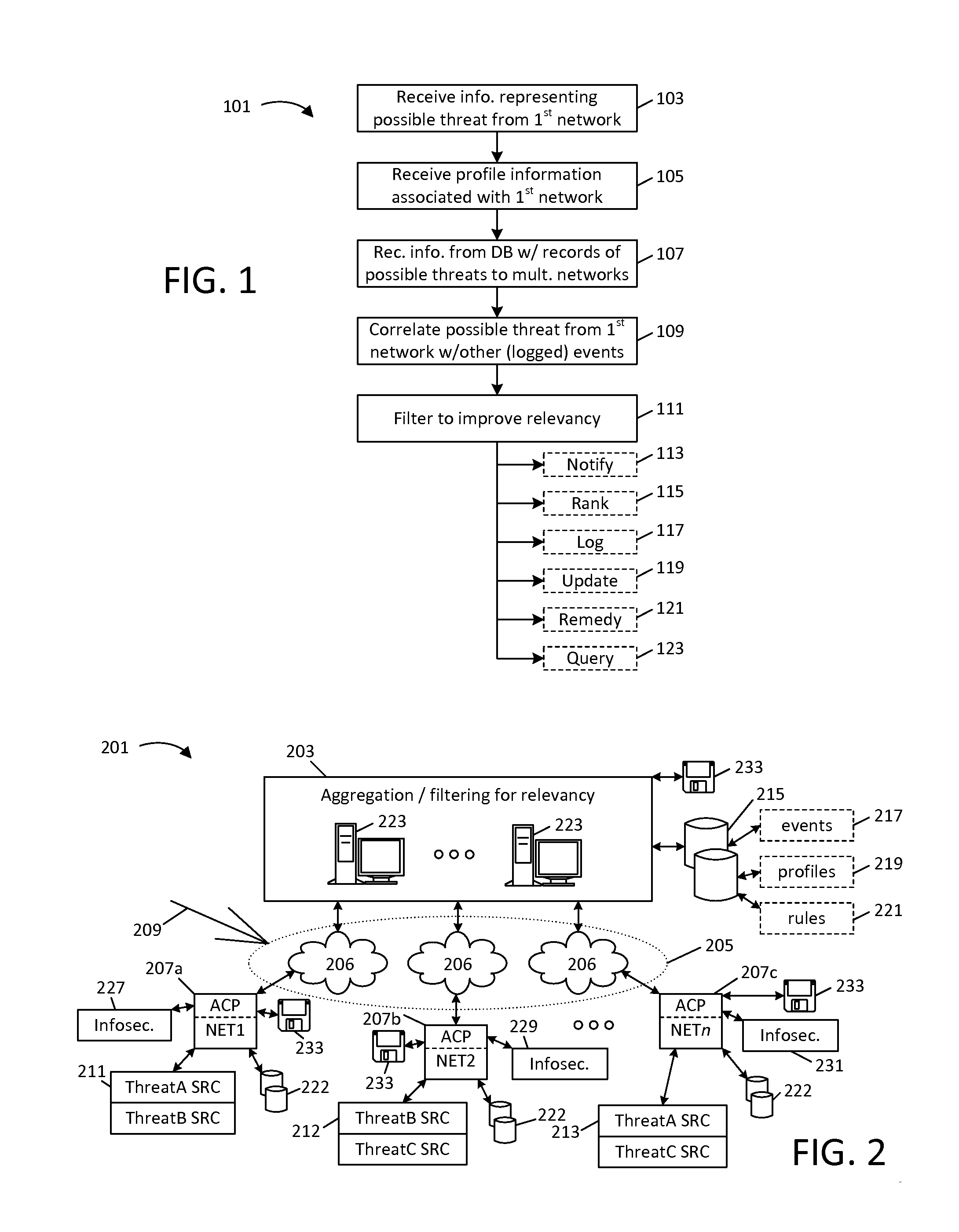
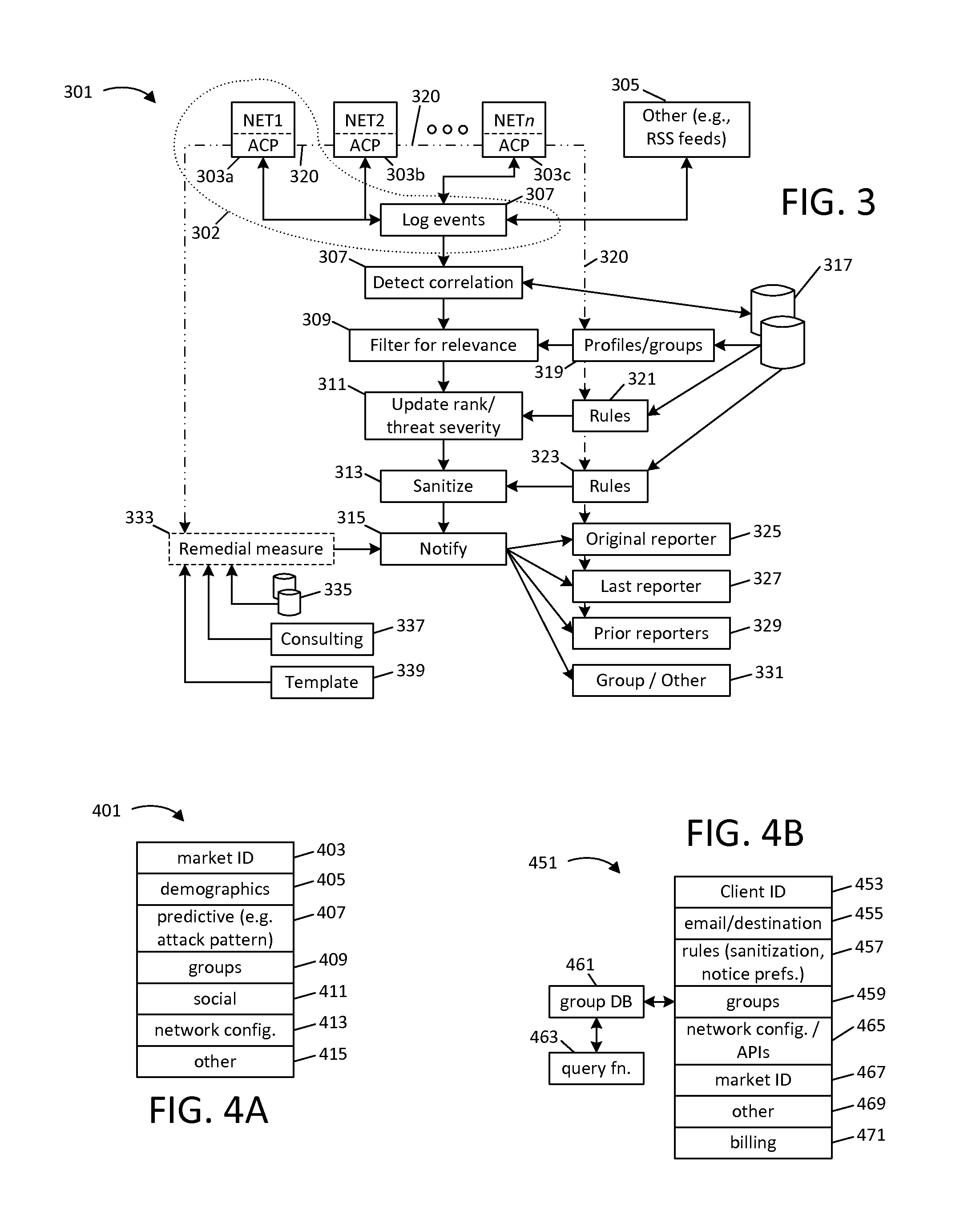
This disclosure provides techniques for pooling and searching network security events reported by multiple sources. As information representing a security event is received from one source, it is searched against a central or distributed database representing events reported from multiple, diverse sources (e.g., different client networks). Either the search or correlated results can be filtered and / or routed according at least one characteristic associated with the networks, for example, to limit correlation to events reported by what are presumed to be similarly situated networks. The disclosed techniques facilitate faster identification of high-relevancy security event information, and thereby help facilitate faster threat identification and mitigation. Various techniques can be implemented as standalone software (e.g., for use by a private network) or for a central pooling and / or query service. This disclosure also provides different examples of actions that can be taken in response to search results.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
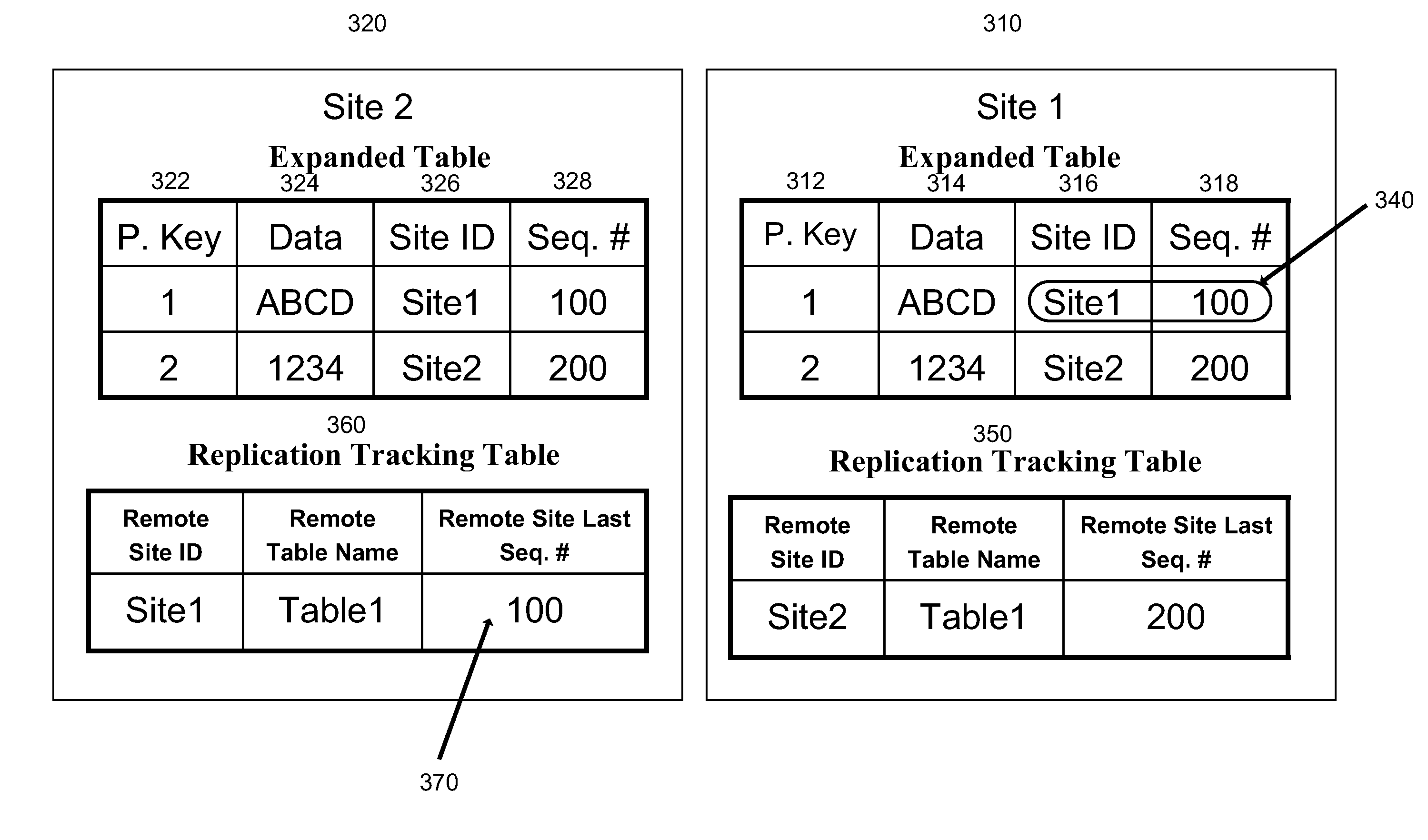
Data Replication Across Enterprise Boundaries
ActiveUS20110161289A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData fieldUnique identifier
Systems and methods for synchronizing verification data in a distributed database including client and server databases. The server database may exchange verification data regarding one-time passwords to multiple client databases. An update to the server database may be initiated based on information stored in the client database by pushing updated verification information from the client database to the server database via an SSL tunnel. An update to the client database may be initiated based on information stored in the server database by pulling updated verification data from the server database to the client database via an SSL tunnel. The client database and the server database may include a two-dimensional data field including the verification data and an associated key identifier, and a site ID. The site ID may include a unique identifier to identify the respective database in which it is included. The data field may include a sequence number assigned to each row of data that increases every time the row of information is updated. The client database and the server database may also include a replication tracking table including a record of the last known update to a remote database. Data fields that require updating may be determined based on the site ID and a comparison of the sequence numbers from the replication tracking table and the server's database.
Owner:CA TECH INC
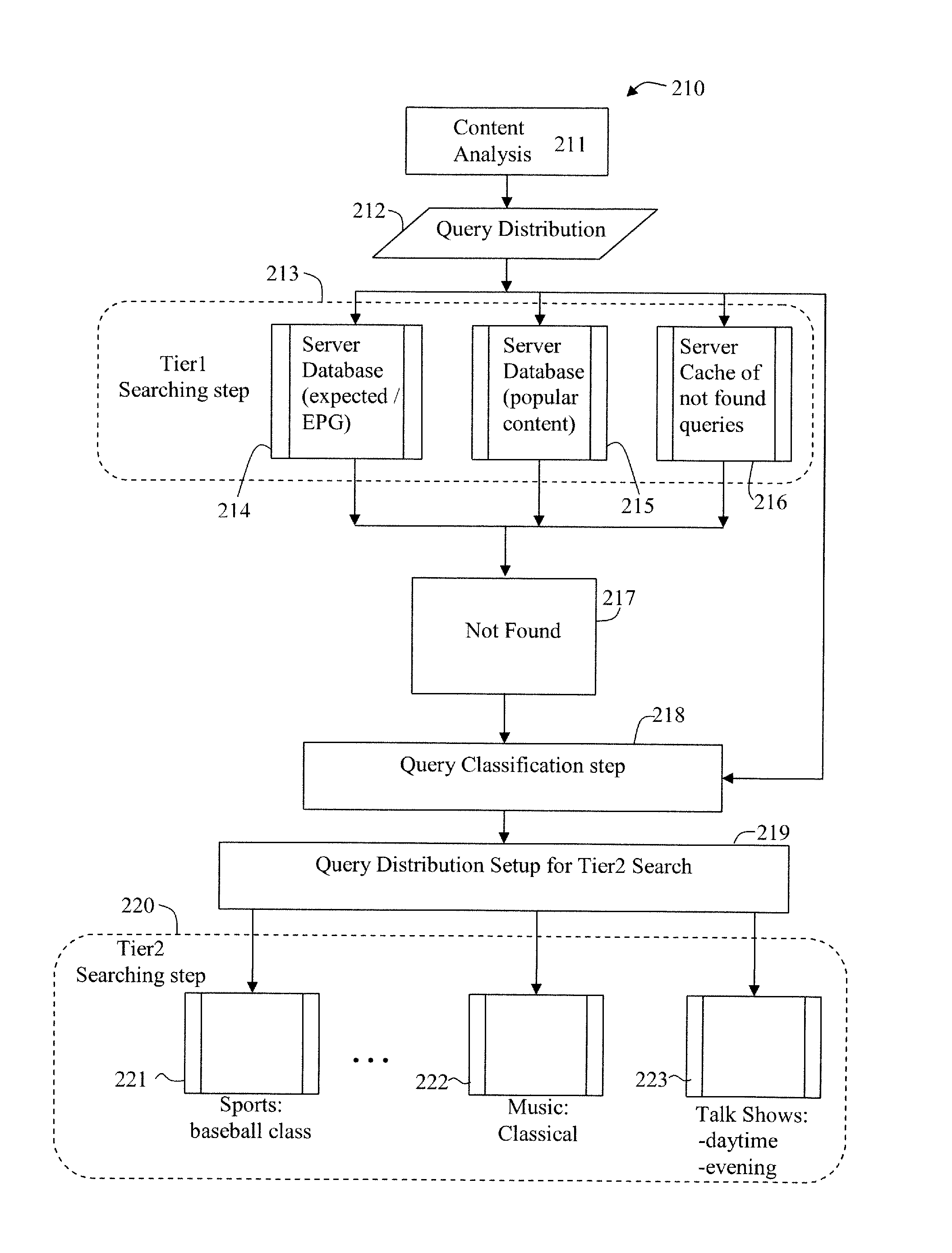
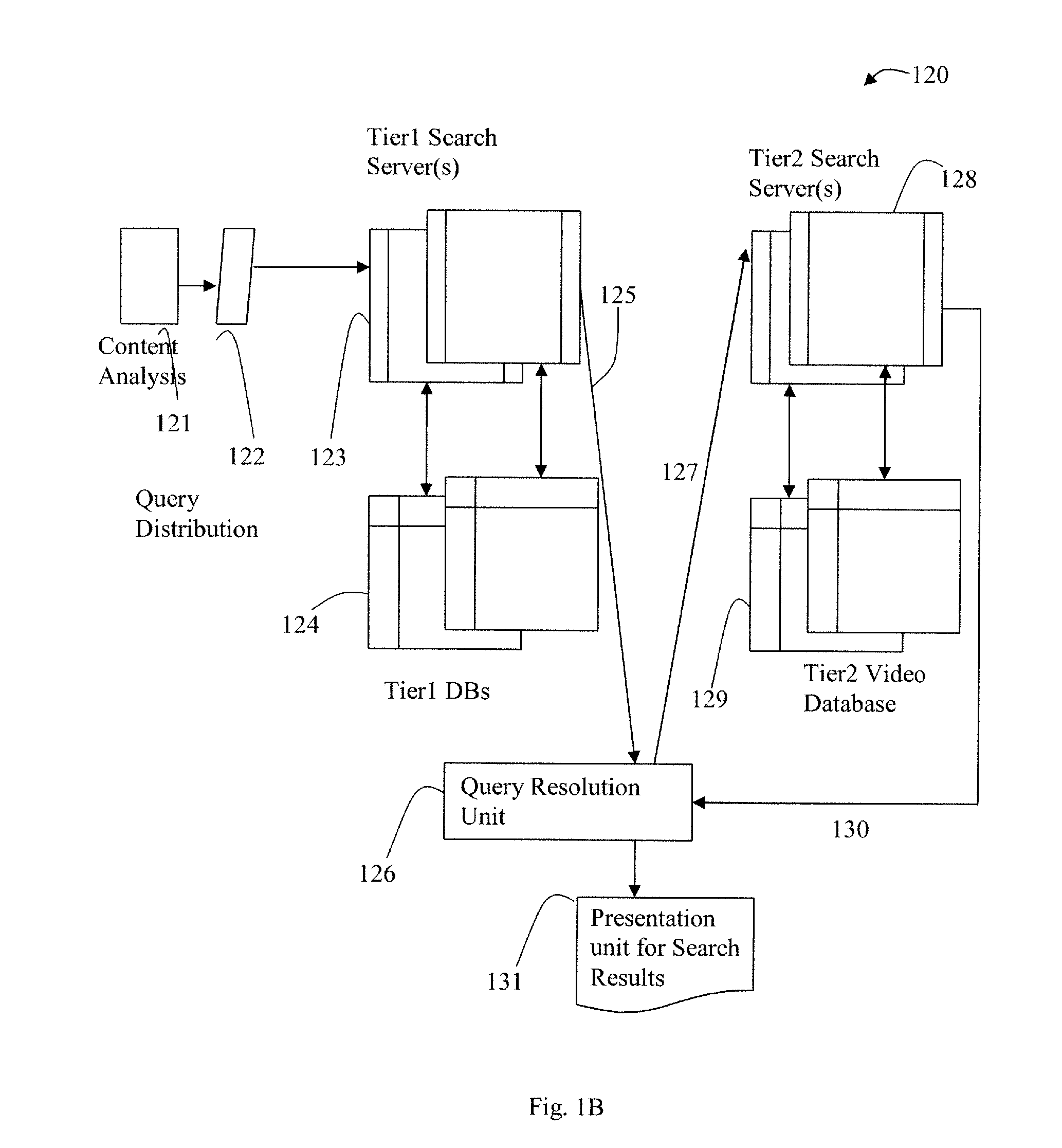
Distributed and Tiered Architecture for Content Search and Content Monitoring
ActiveUS20120095958A1Multimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsTime segmentSchema for Object-Oriented XML
An efficient large scale search system for video and multi-media content using a distributed database and search, and tiered search servers is described. Selected content is stored at the distributed local database and tier1 search server(s). Content matching frequent queries, and frequent unidentified queries are cached at various levels in the search system. Content is classified using feature descriptors and geographical aspects, at feature level and in time segments. Queries not identified at clients and tier1 search server(s) are queried against tier2 or lower search server(s). Search servers use classification and geographical partitioning to reduce search cost. Methods for content tracking and local content searching are executed on clients. The client performs local search, monitoring and / or tracking of the query content with the reference content and local search with a database of reference fingerprints. This shifts the content search workload from central servers to the distributed monitoring clients.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
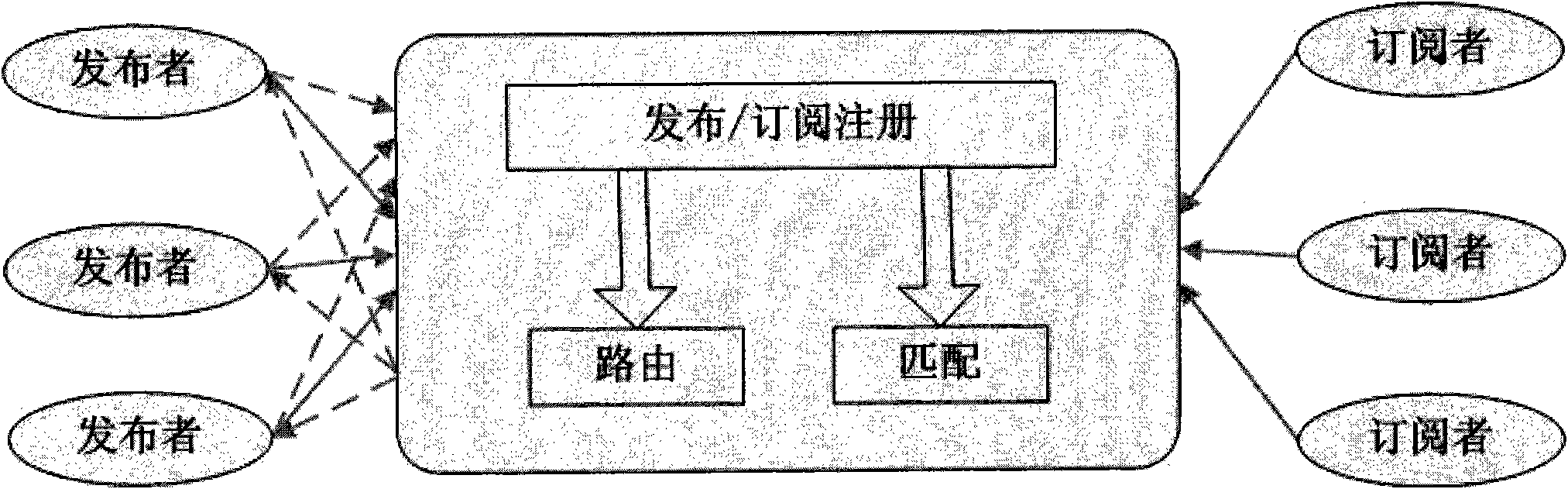
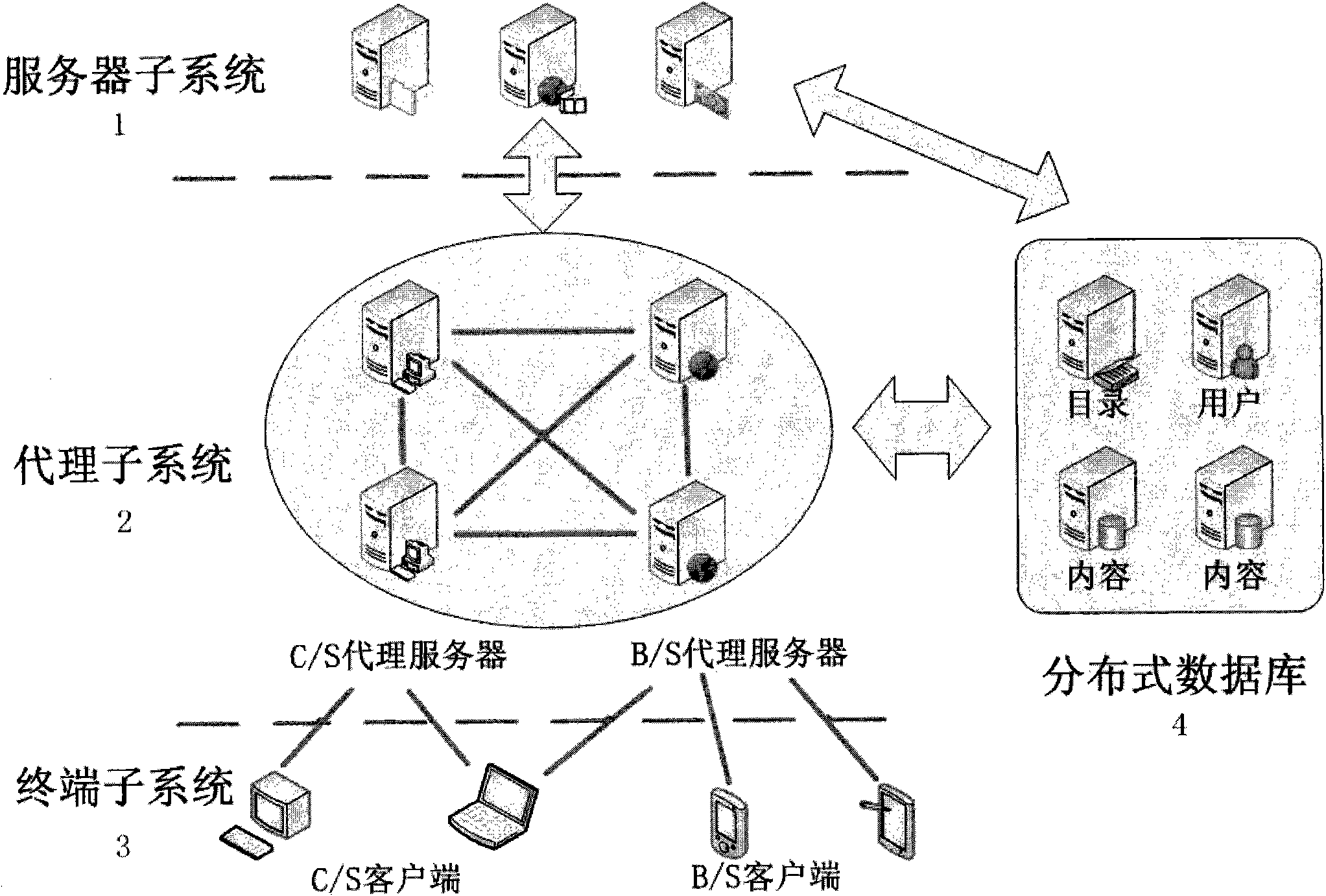
Real-time data distribution system with distributed network architecture and working method thereof
InactiveCN101848236AImplement hierarchical configurationFlexible accessData switching networksGeolocationNetwork architecture
The invention relates to a real-time data distribution system with a distributed network architecture and a working method thereof, the system adopts a publication / subscription communication mechanism to transfer information in Internet and a mobile network, and the system comprises a server sub-system, a proxy sub-system, a terminal sub-system and a distributed database, wherein, the server sub-system is used for completing the operations of topic storage, topic matching and the like; the proxy sub-system is used for completing the operations of receiving a topic from a terminal, transmitting a matching event to a subscriber, submitting the publication / subscription topic and the like; the terminal sub-system is used for completing the publication / subscription information of a user; and a distributed database which is used for storing the publication / subscription information and the system information. The system can automatically, quickly and safely provide real-time data transmission service against the subscription information of the user, provide the publication / subscription service of a variety of types of data, such as text information, streaming media, geographic position information and the like, provide up to 20 QoS control parameters, realize the QoS hierarchy configuration of an application layer and provide the convenience for function expansion of the data distribution system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
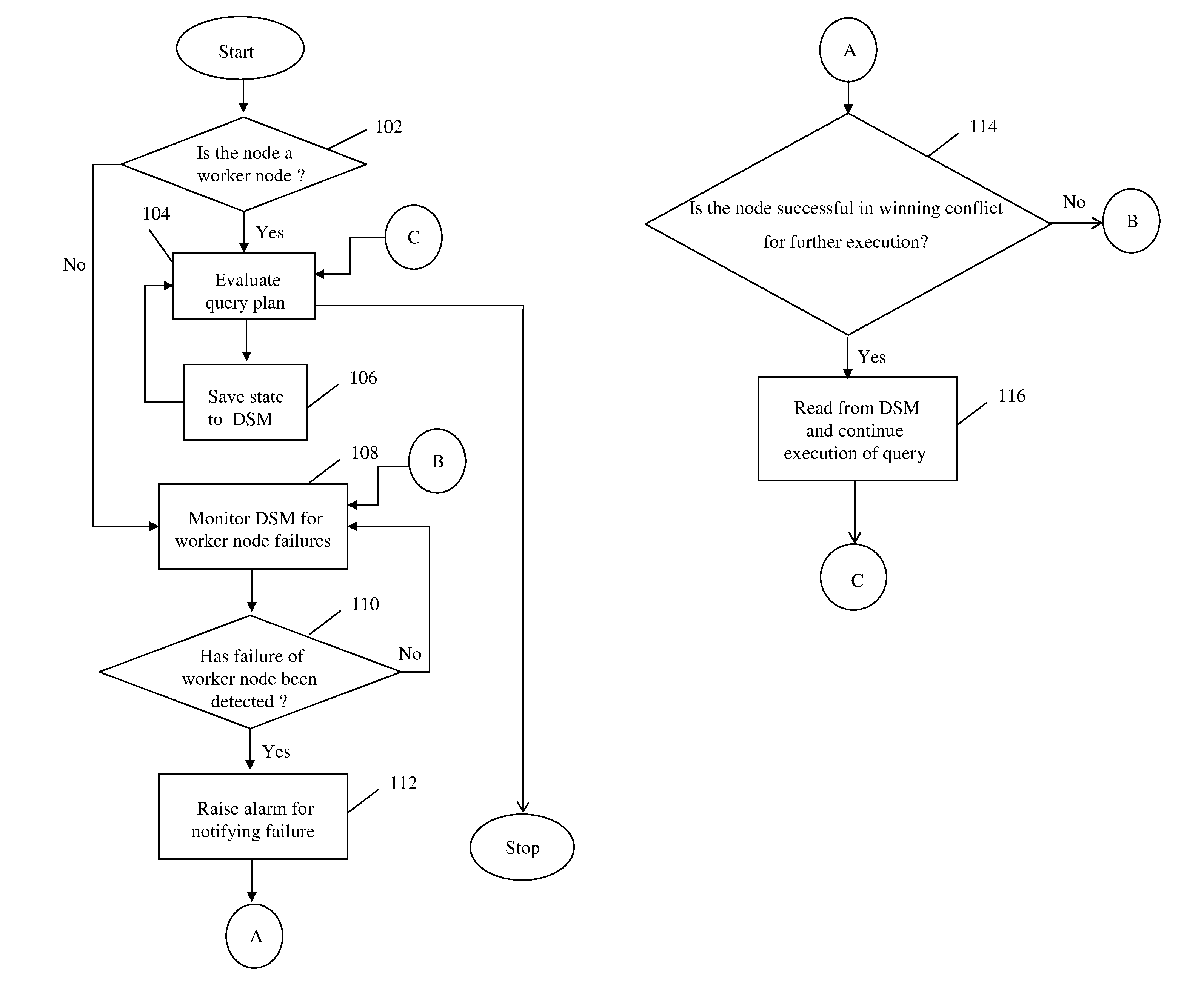
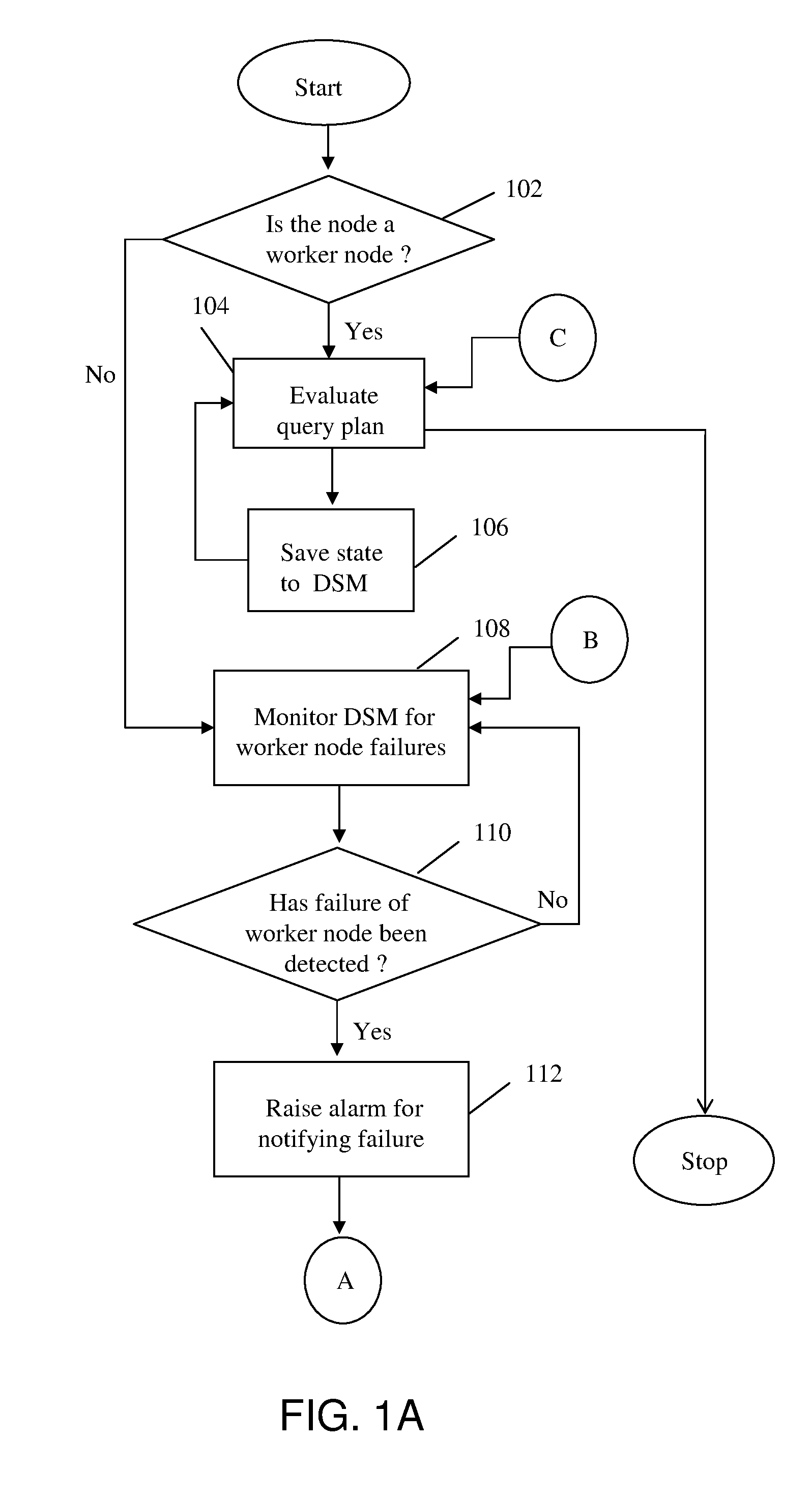
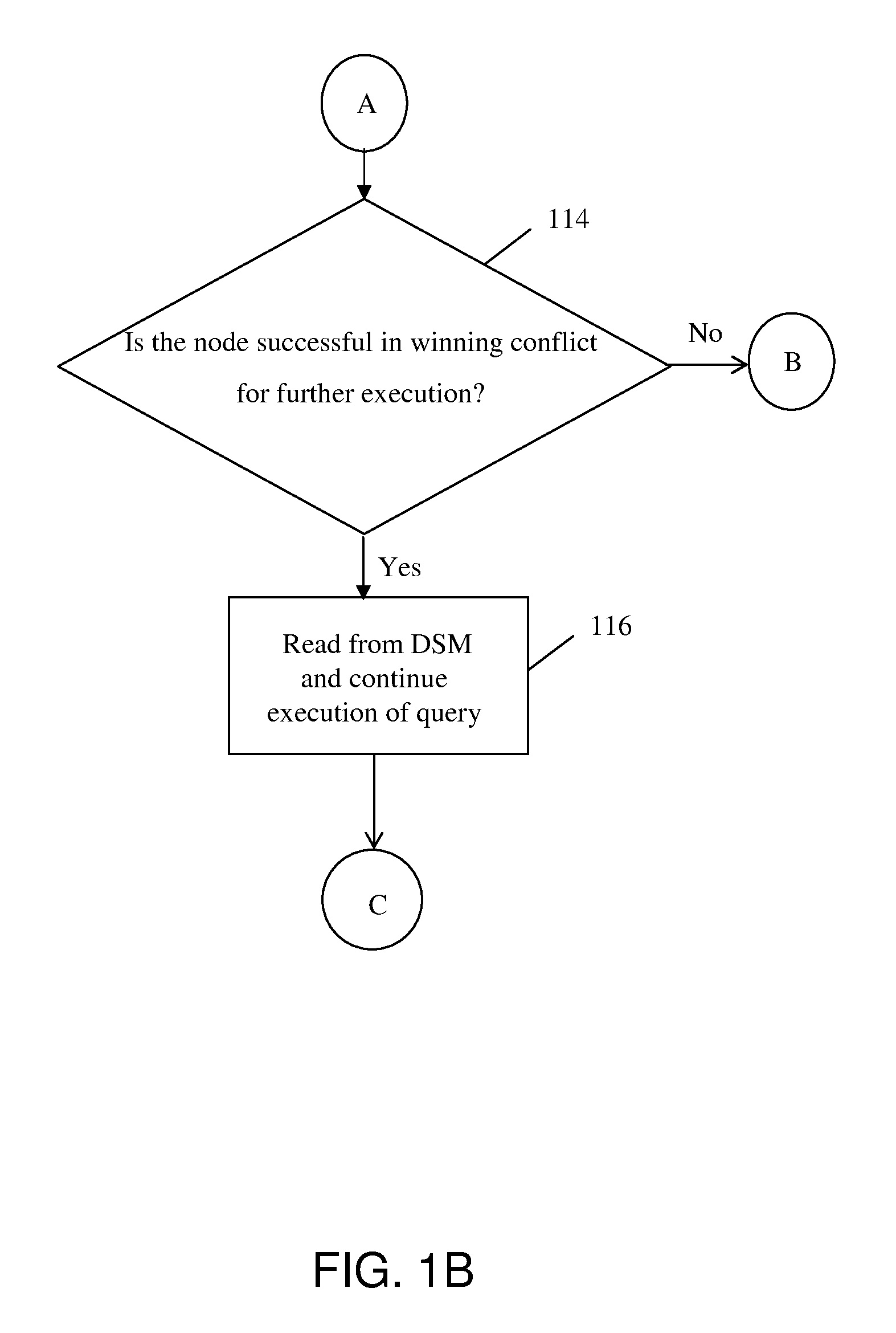
Method and system for automatic failover of distributed query processing using distributed shared memory
A method and system for implementing automatic recovery from failure of resources in a grid-based distributed database is provided. The method includes determining the category of each node in the subgroup of nodes, where the determination identifies each node as at least one of a worker node and an idle node. The method further includes saving state of each worker node engaged in execution of a task in a shared memory at pre-determined time intervals. Each worker node is monitored by one or more idle nodes in each sub-group. Upon detection of no change in state of worker node for a pre-determined period of time, a failure notification is raised by one or more idle nodes that have detected failure of the worker node.
Owner:INFOSYS LTD
Systems and methods for use of structured and unstructured distributed data
InactiveUS8200700B2Increase flexibilityDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationDistributed databaseContent management system
Owner:NEWSILIKE MEDIA GROUP
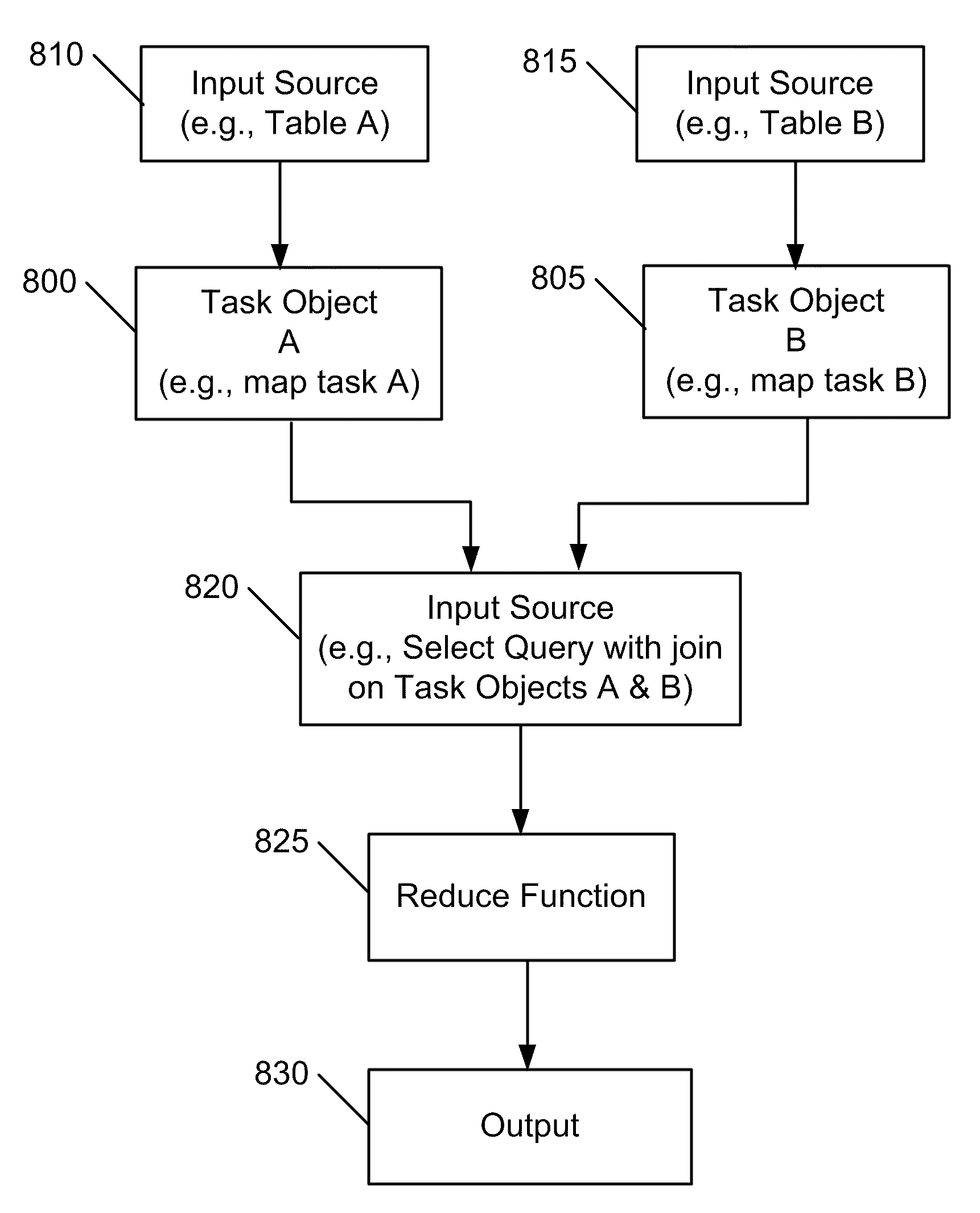
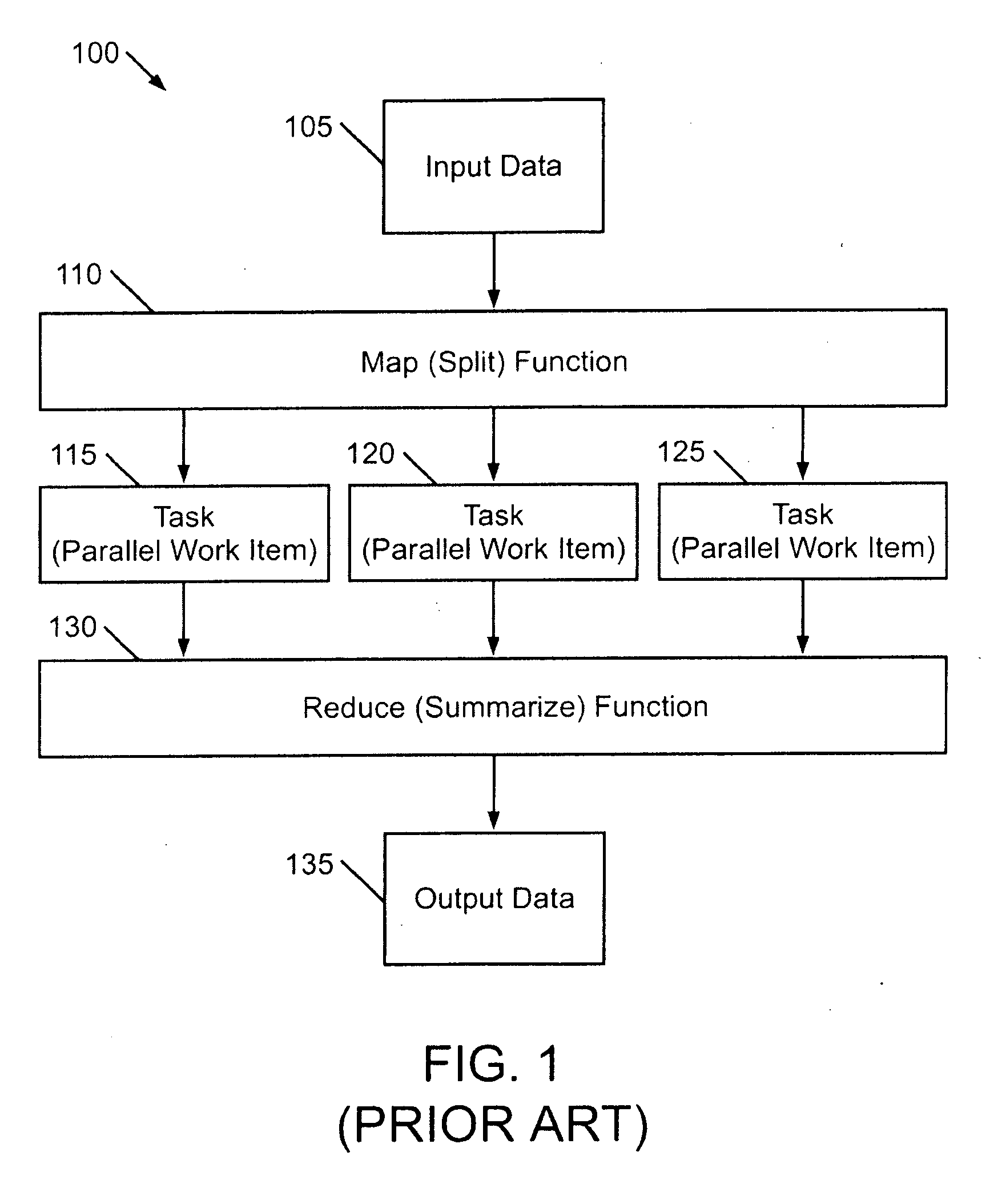
Apparatus and method for integrating map-reduce into a distributed relational database
ActiveUS20100257198A1Database management systemsDigital data processing detailsMap reduceRelational database
A computer readable storage medium includes executable instructions to define a map-reduce document that coordinates processing of data in a distributed database. The map-reduce document complies with a map-reduce specification that integrates map-reduce functions with queries in a query language. The operations specified by the map-reduce document are executed in the distributed database.
Owner:GOPIVOTAL
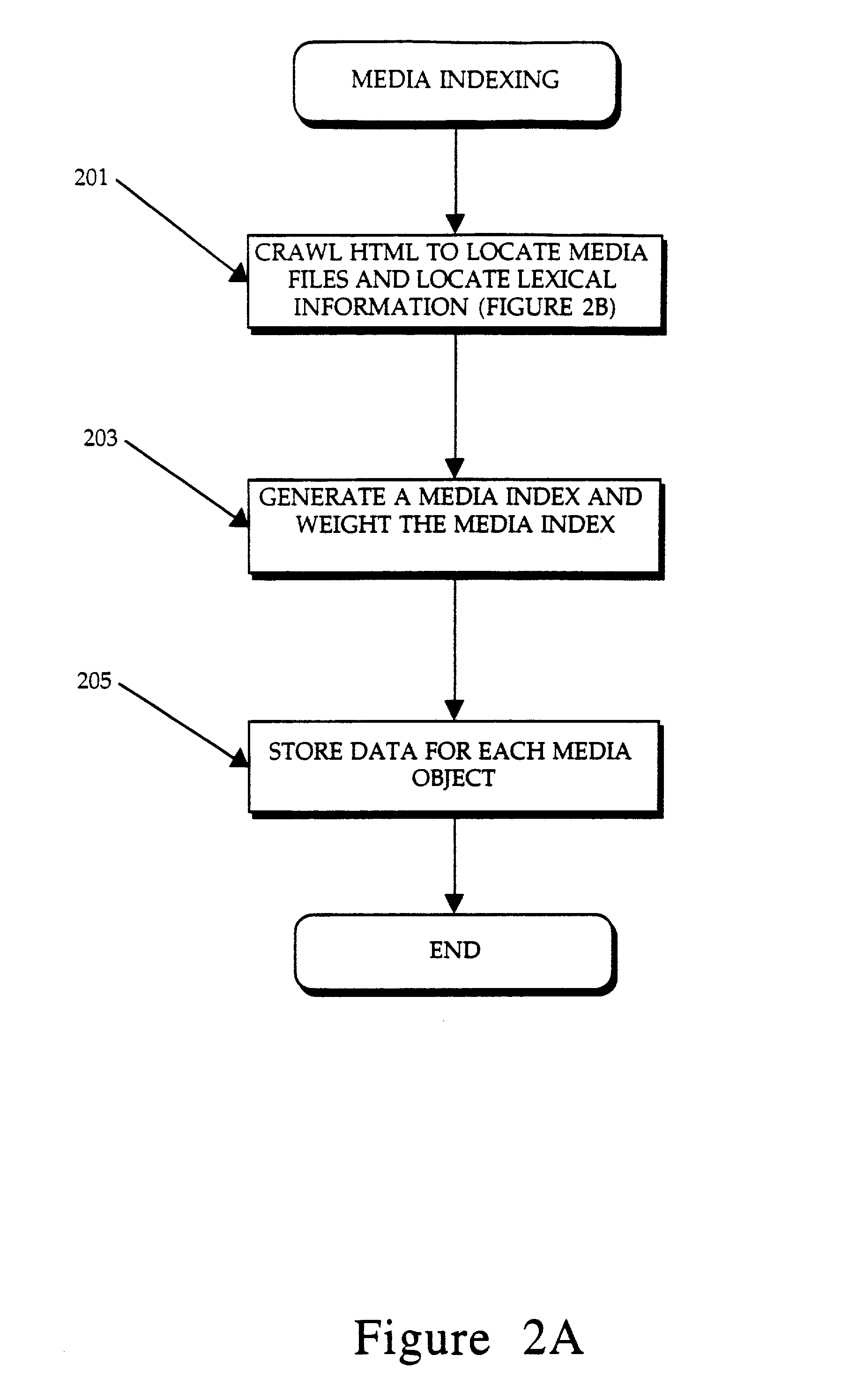
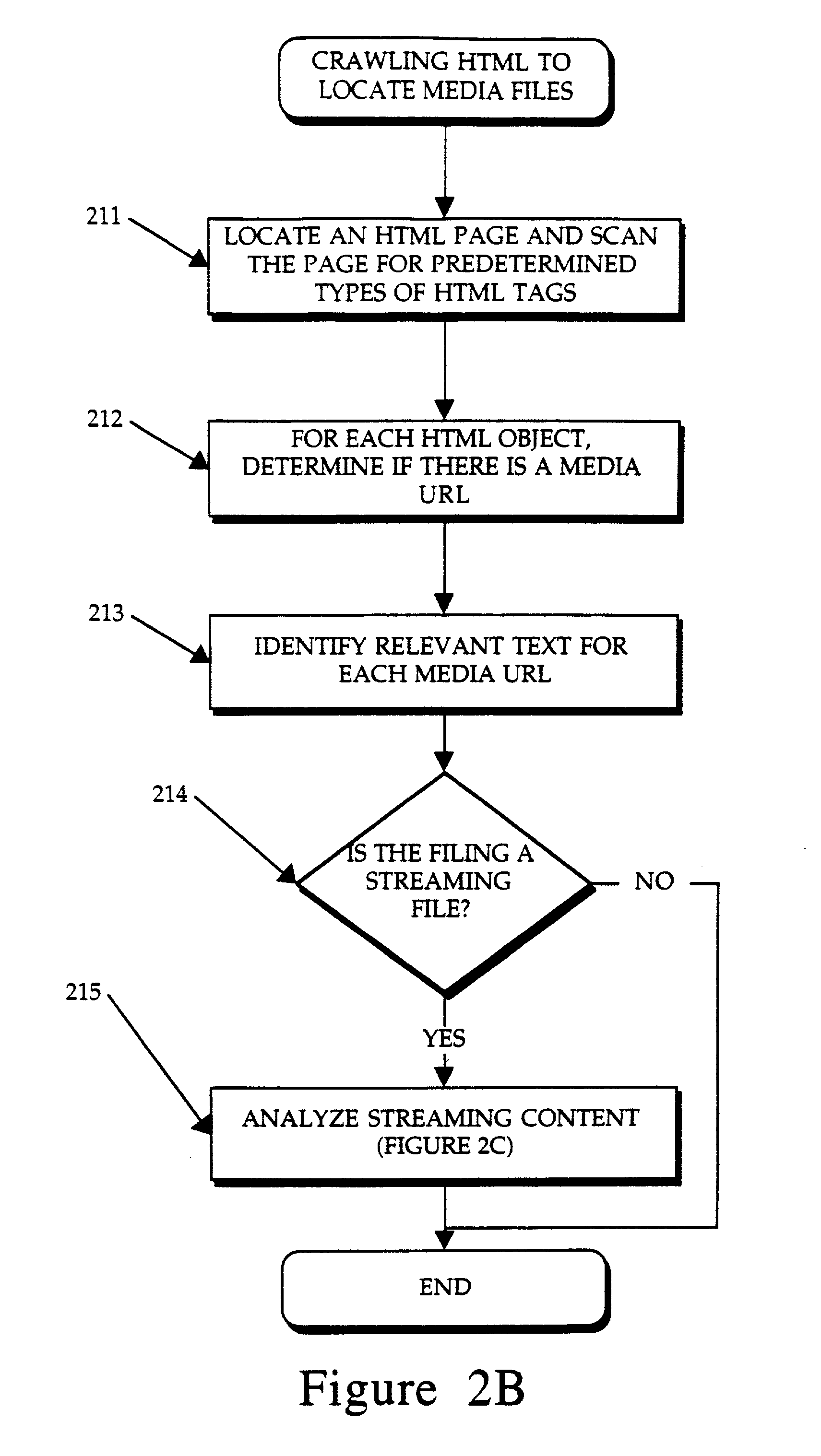
Method and apparatus for categorizing and presenting documents of a distributed database
InactiveUS7231395B2Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingDocumentation procedureDocument preparation
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Method and System for Load Balancing a Distributed Database
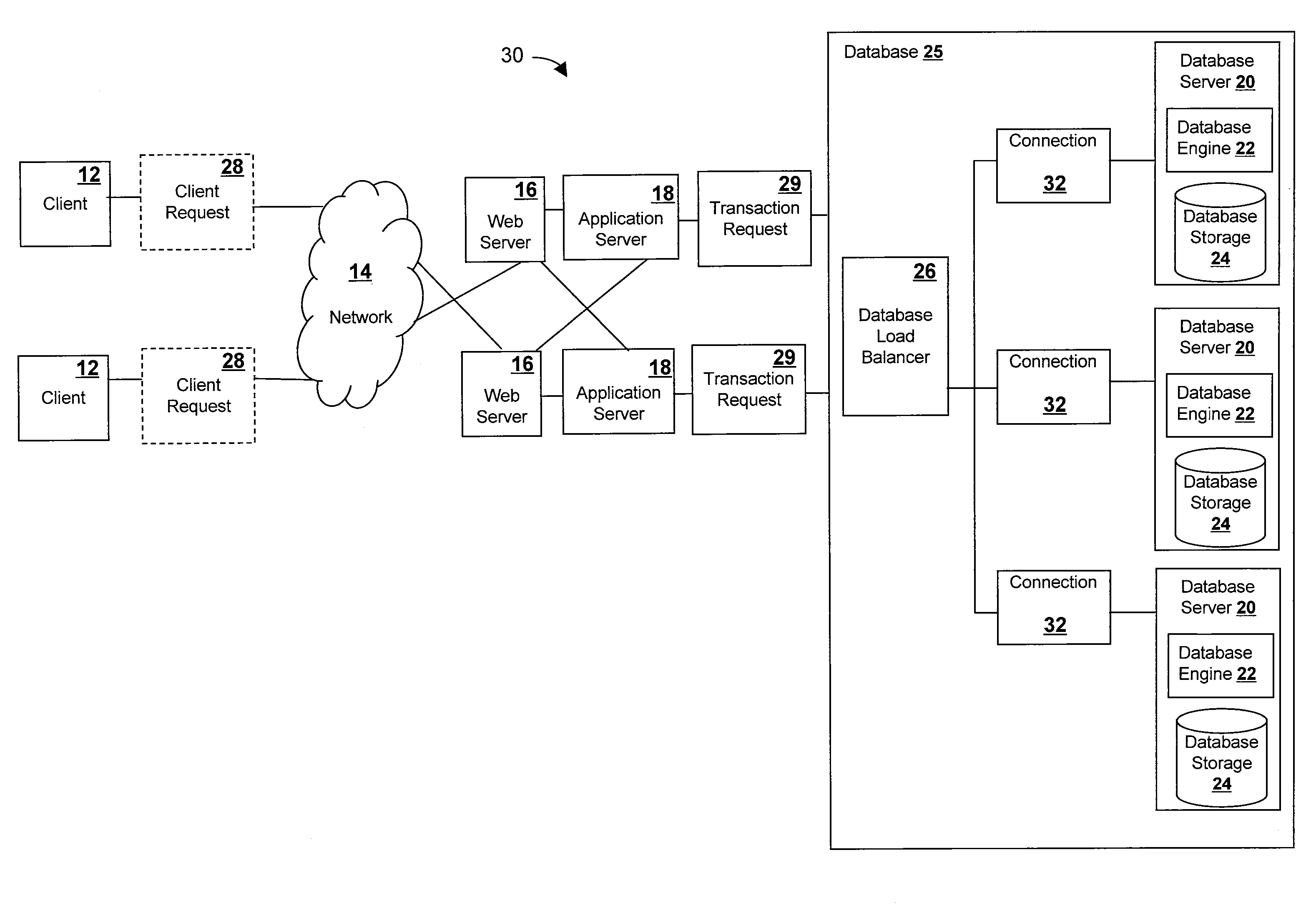
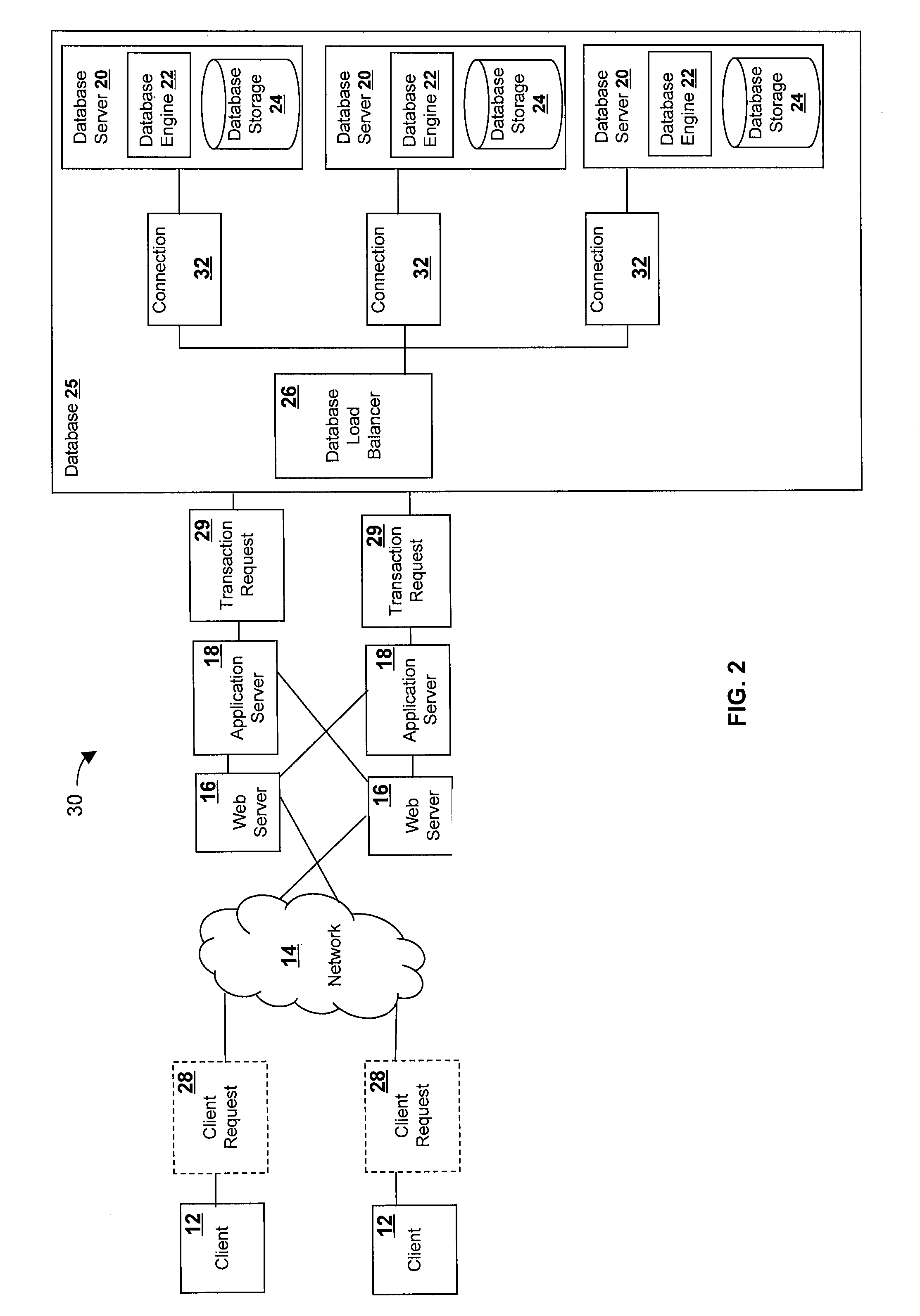
ActiveUS20070203910A1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationDatabase serverDistributed database
A method of processing a transaction request at a database load balancer. The method comprises receiving the transaction request, where the transaction request is comprised of one or more operations; analyzing the transaction request to determine the one or more operations; associating one or more database locks with each of the one or more operations; analyzing one or more of the database locks to determine the one or more sequence numbers associated with each of the one or more operations; and transmitting the one or more operations with the associated database locks and the sequence numbers to one or more databases servers accessible to the database load balancer.
Owner:TERADATA US +1
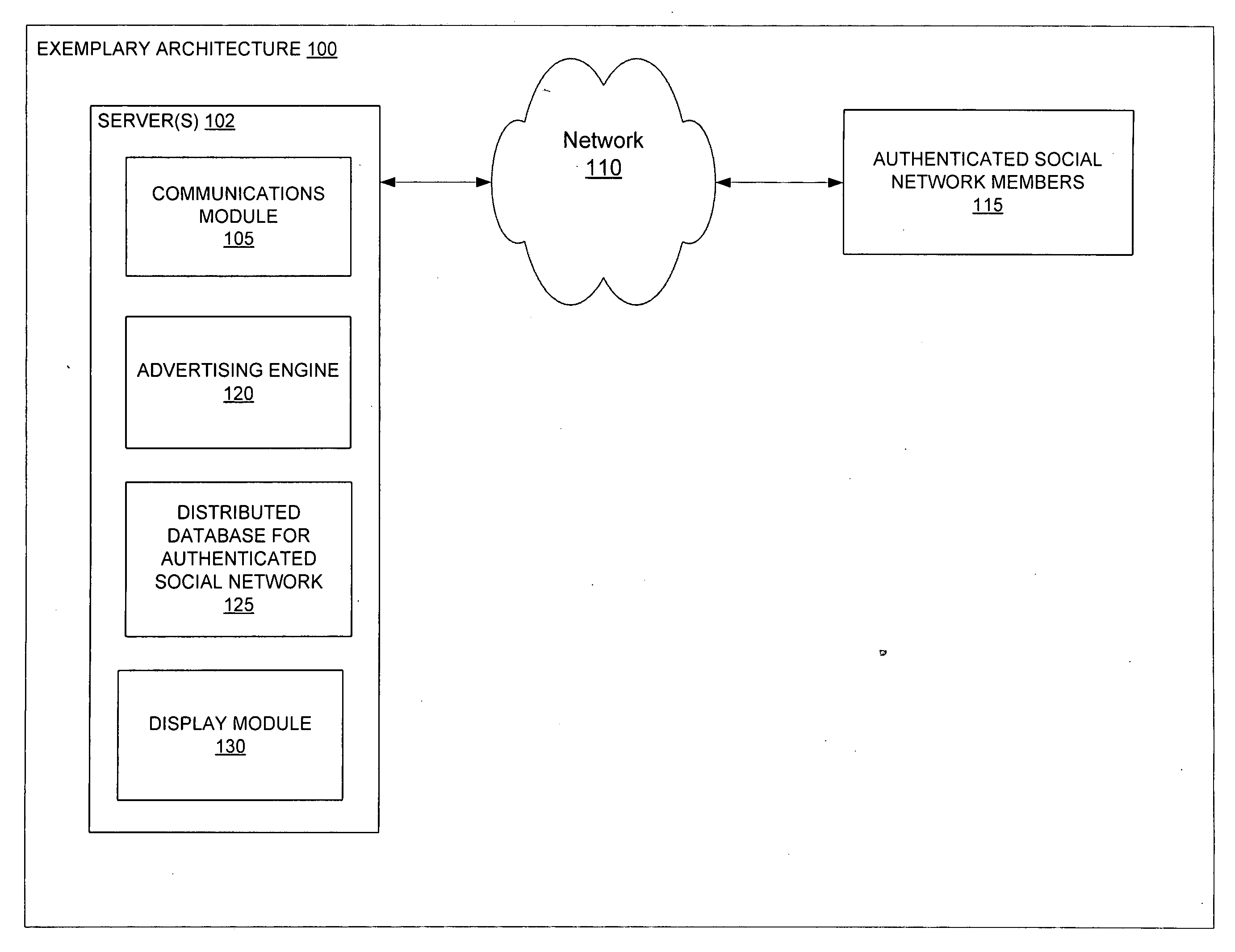
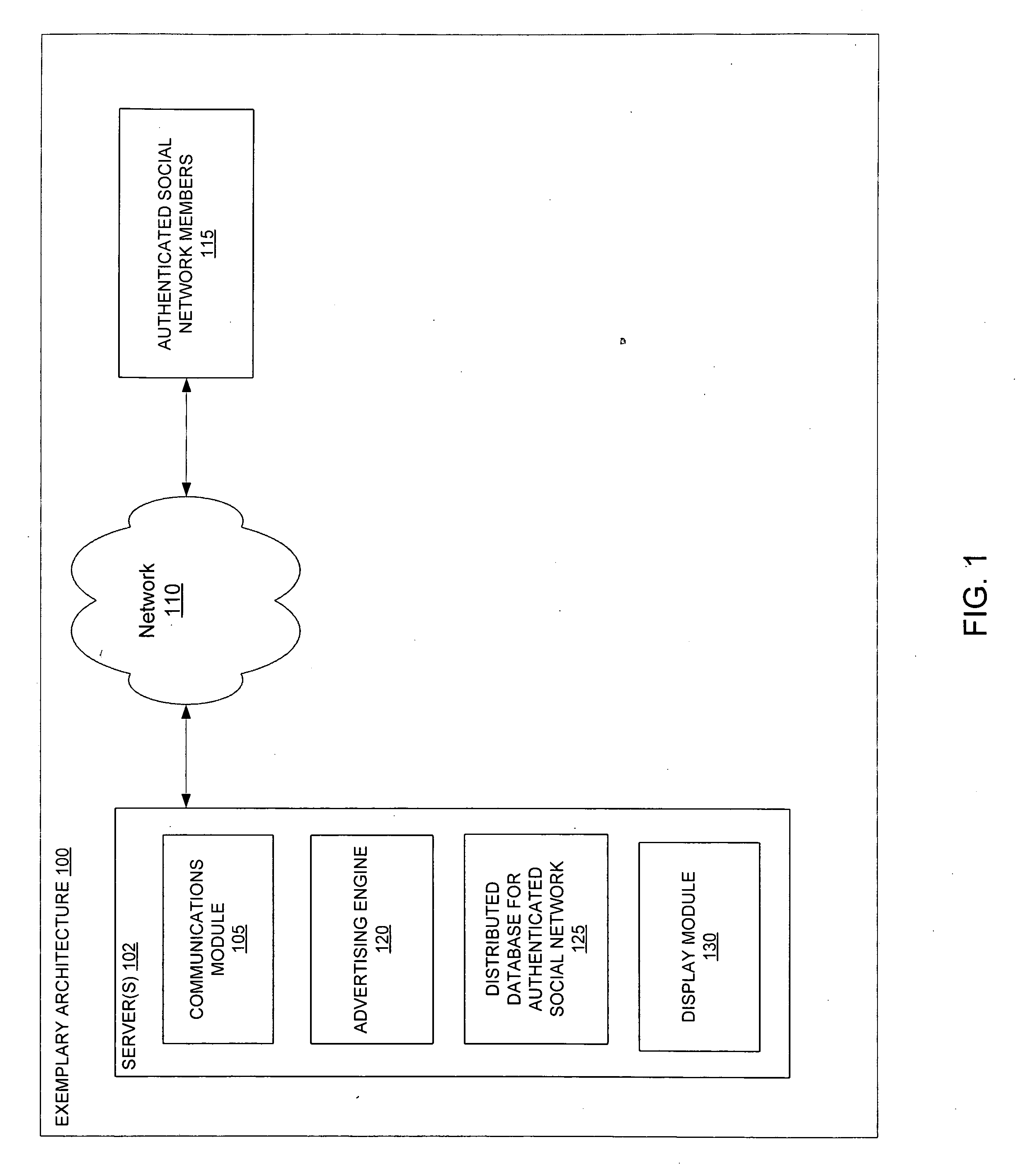
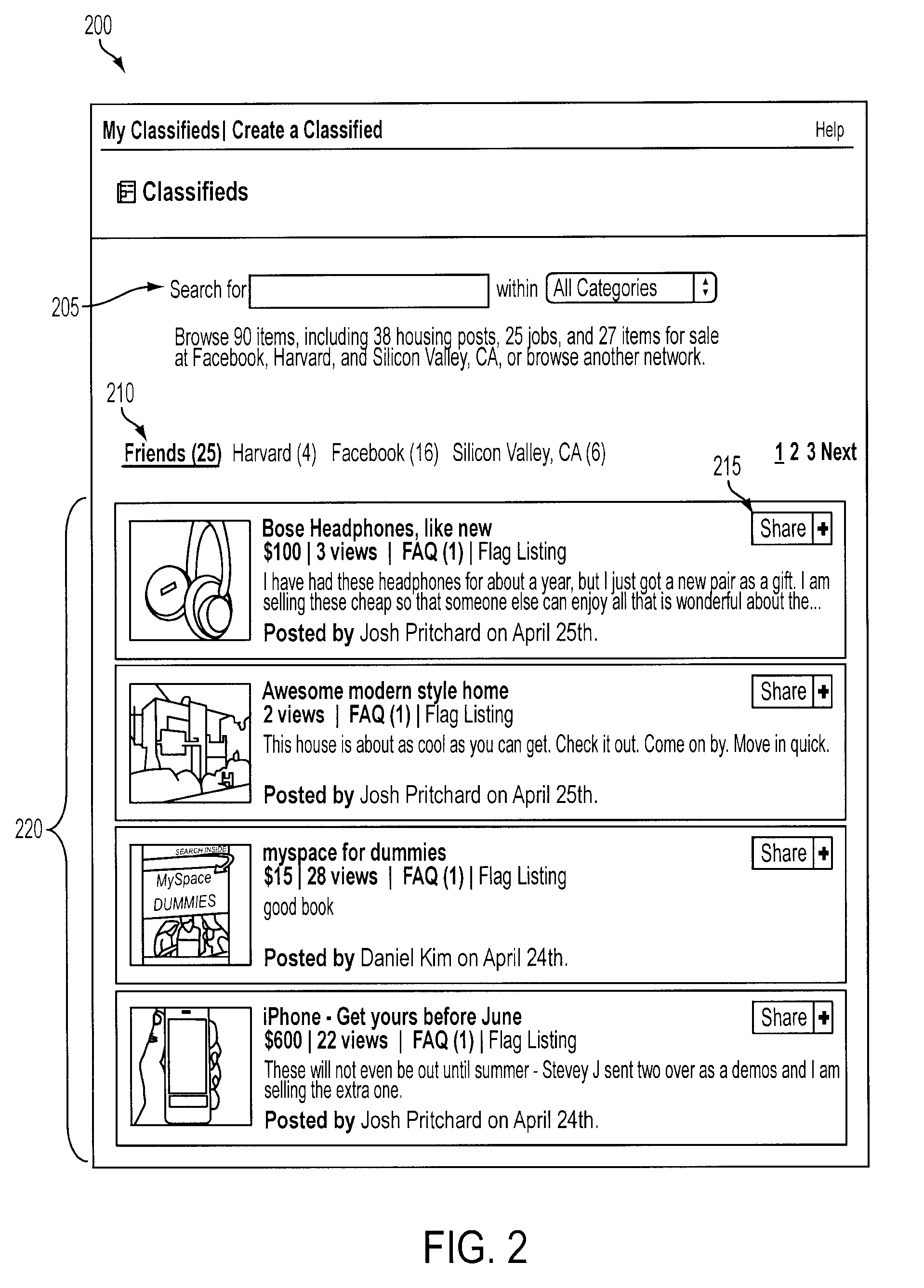
Systems and methods for classified advertising in an authenticated web-based social network
Exemplary systems and methods are provided for advertising on an authenticated web-based social network. Such methods include providing a screen for creation of a classified advertisement, receiving the classified advertisement from an advertising member, and displaying the classified advertisement on a user network in the authenticated web-based social network with information about a relationship between the advertising member and a member of the authenticated web-based social network viewing the classified advertisement. Exemplary systems include an advertising engine configured to generate a screen for creation of a classified advertisement, a communications module configured to receive the classified advertisement from an advertising member, a distributed database configured with a user network and relationship information, and a display module configured to display the classified advertisement on the user network with the relationship information.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
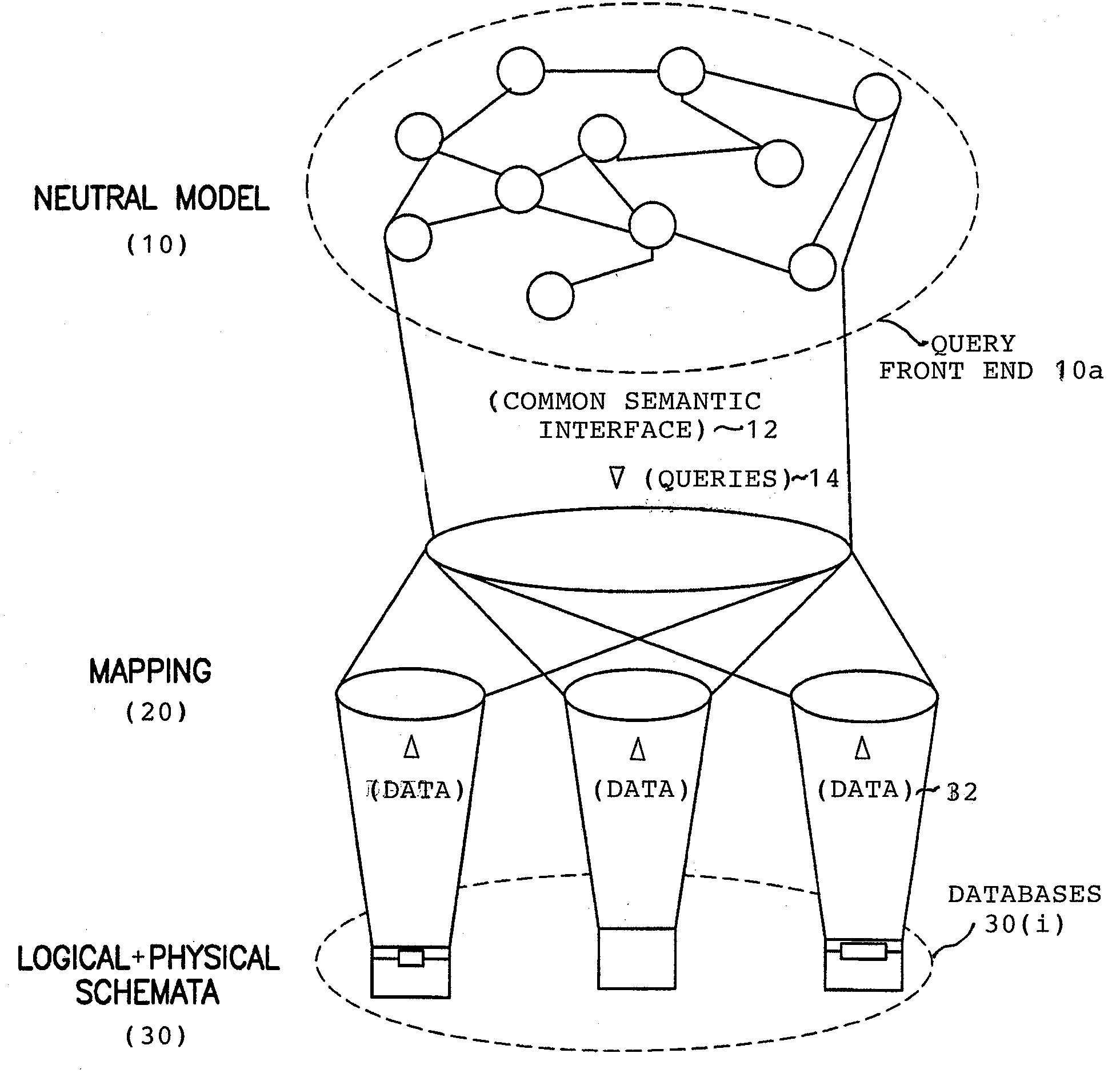
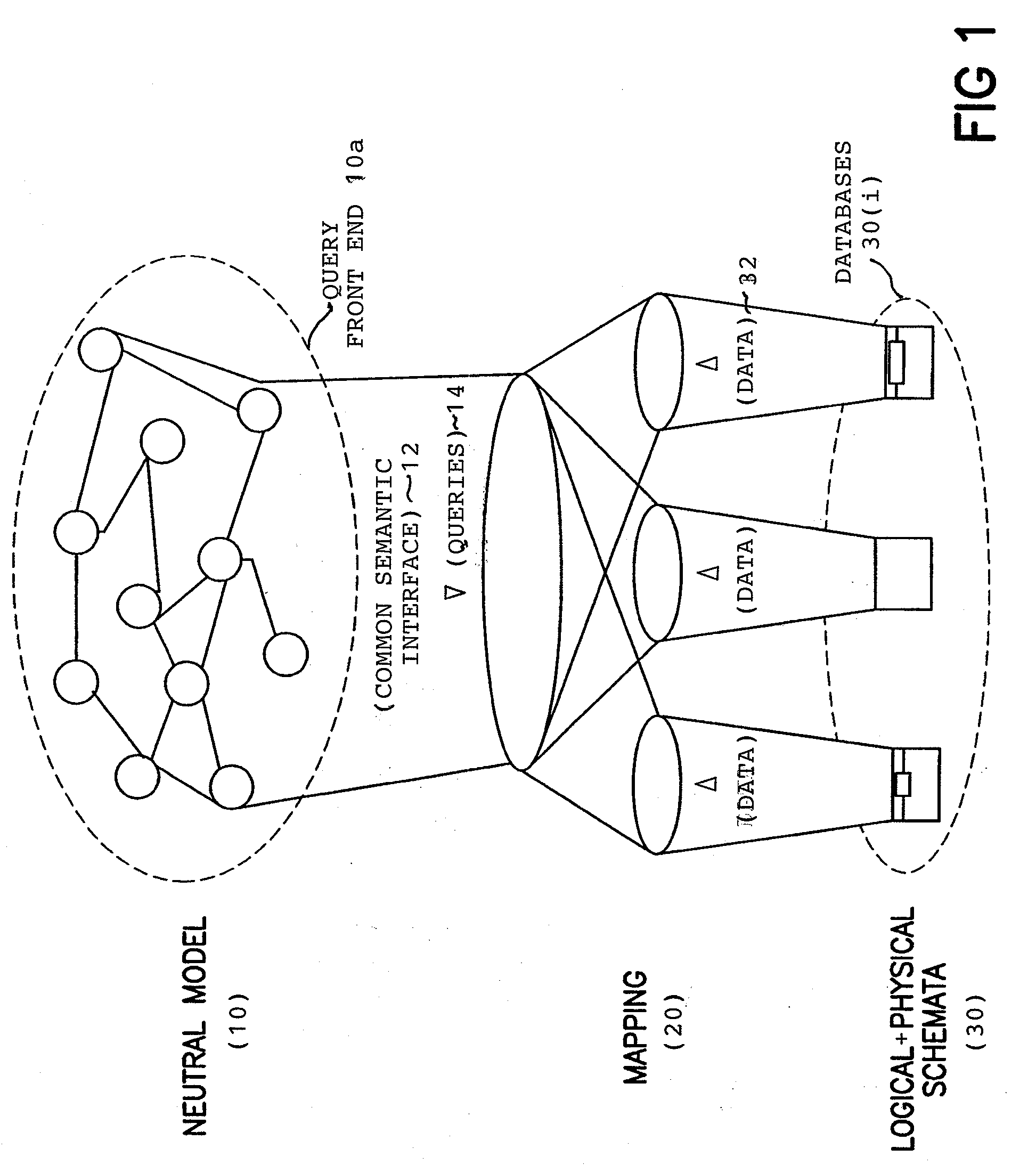
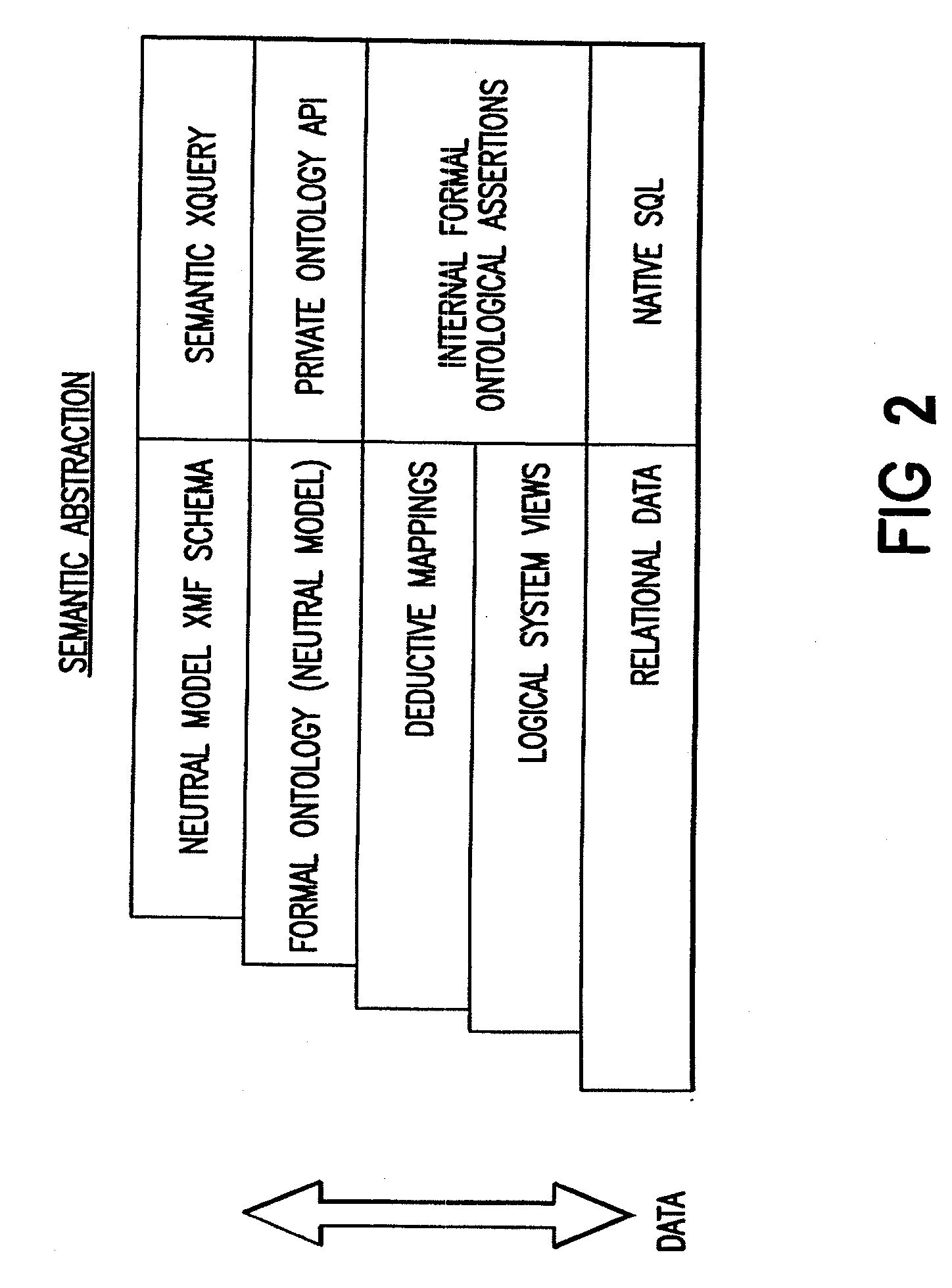
Querying of distributed databases using neutral ontology model for query front end
ActiveUS20080077598A1Reduce riskInherent riskDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsOntology schemaDistributed database
According to an embodiment, a method includes constructing a neutral ontology model of a query front end characterized by ontology schemata which subsume the plurality of different databases on the network in order to provide a common semantic interface for use in generating queries for data from any of the different databases, importing respective database metadata representing logical and physical structures of each database subscribed for receiving queries for data from the database using the query front end, constructing mappings of the database metadata representing the logical and physical structures of each subscribed database to the ontology schemata of the query front end, and storing the constructed mappings for use by the query front end for queries through the common semantic interface of the neutral ontology model for data from any of the different databases.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
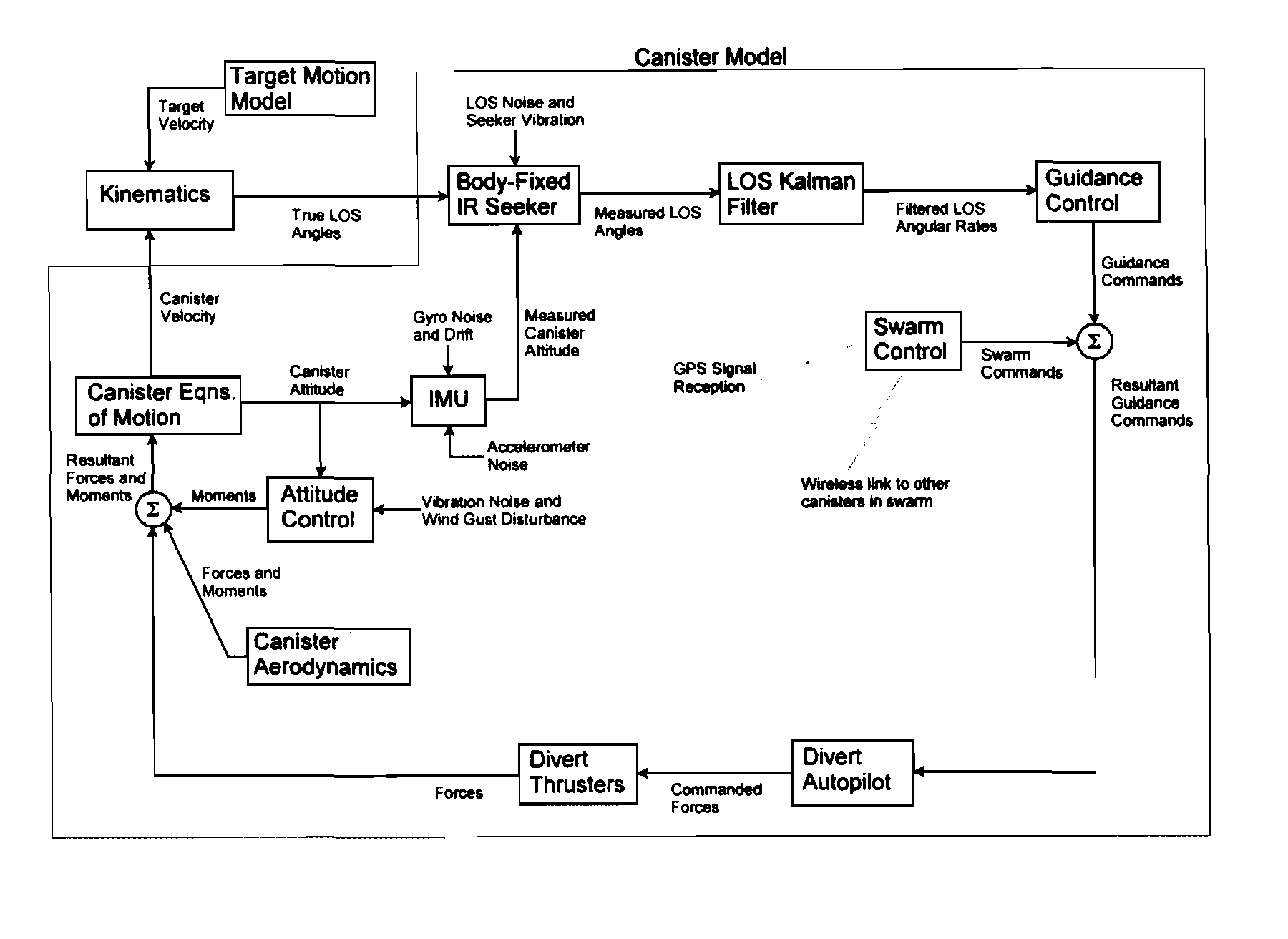
Smart counter asymmetric threat micromunition with autonomous target selection and homing
InactiveUS7631833B1Avoid redundant targetingEnhance probability of missionAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersLand basedSubject matter
The present invention provides an unpowered low-cost “smart” micromunition unit for a weapon system for defense against an asymmetric attack upon ships and sea or land based facilities. A plurality of air dropped micromunition units are each capable of detecting and tracking a plurality of maneuvering targets and of establishing a fast acting local area wireless communication network among themselves to create a distributed database stored in each deployed micromunition unit for sharing target and micromunition unit data. Each micromunition unit autonomously applies stored algorithms to data from the distributed database to select a single target for intercept and to follow an intercept trajectory to the selected target. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope of the claims.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Systems and methods for interfacing with digital history data
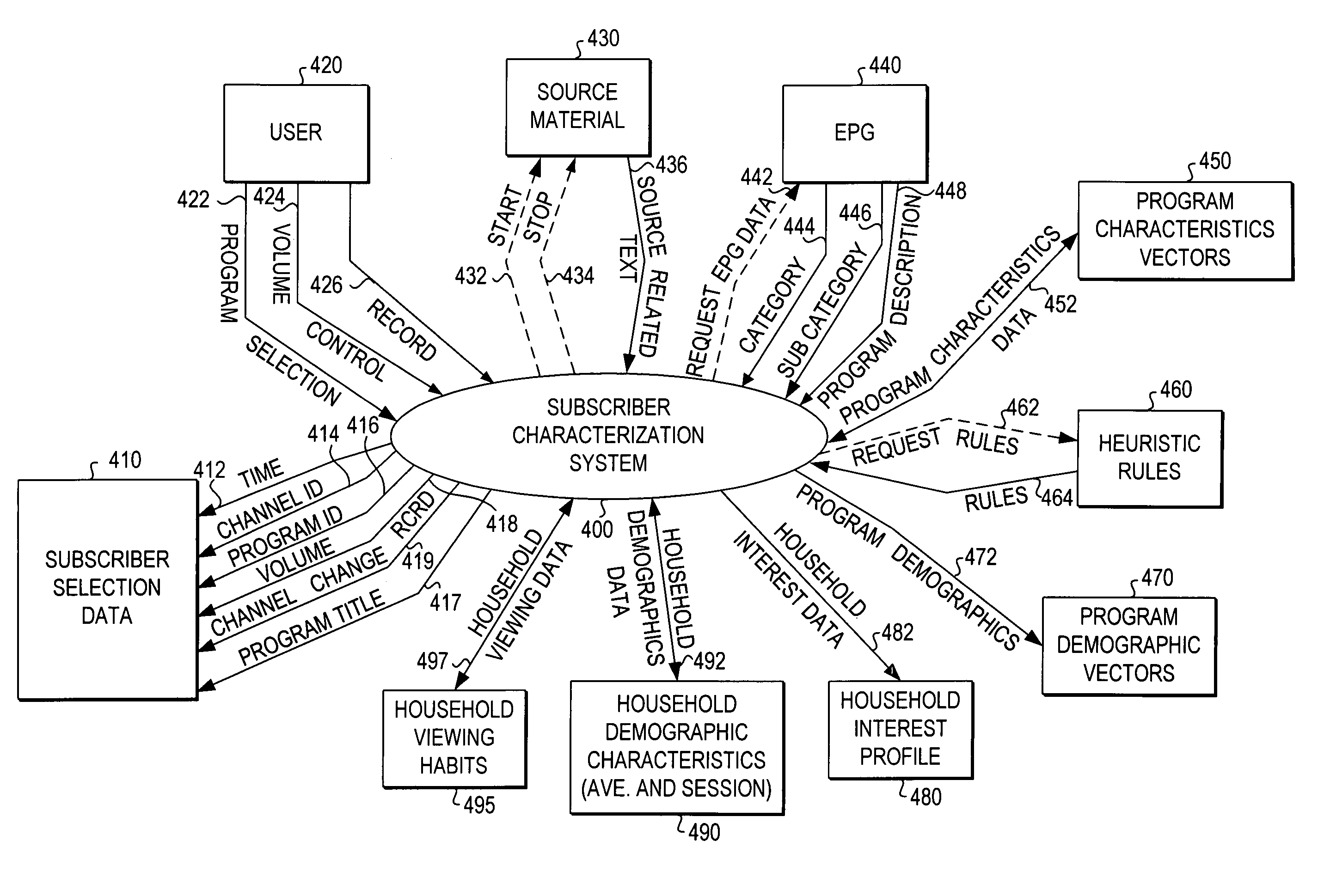
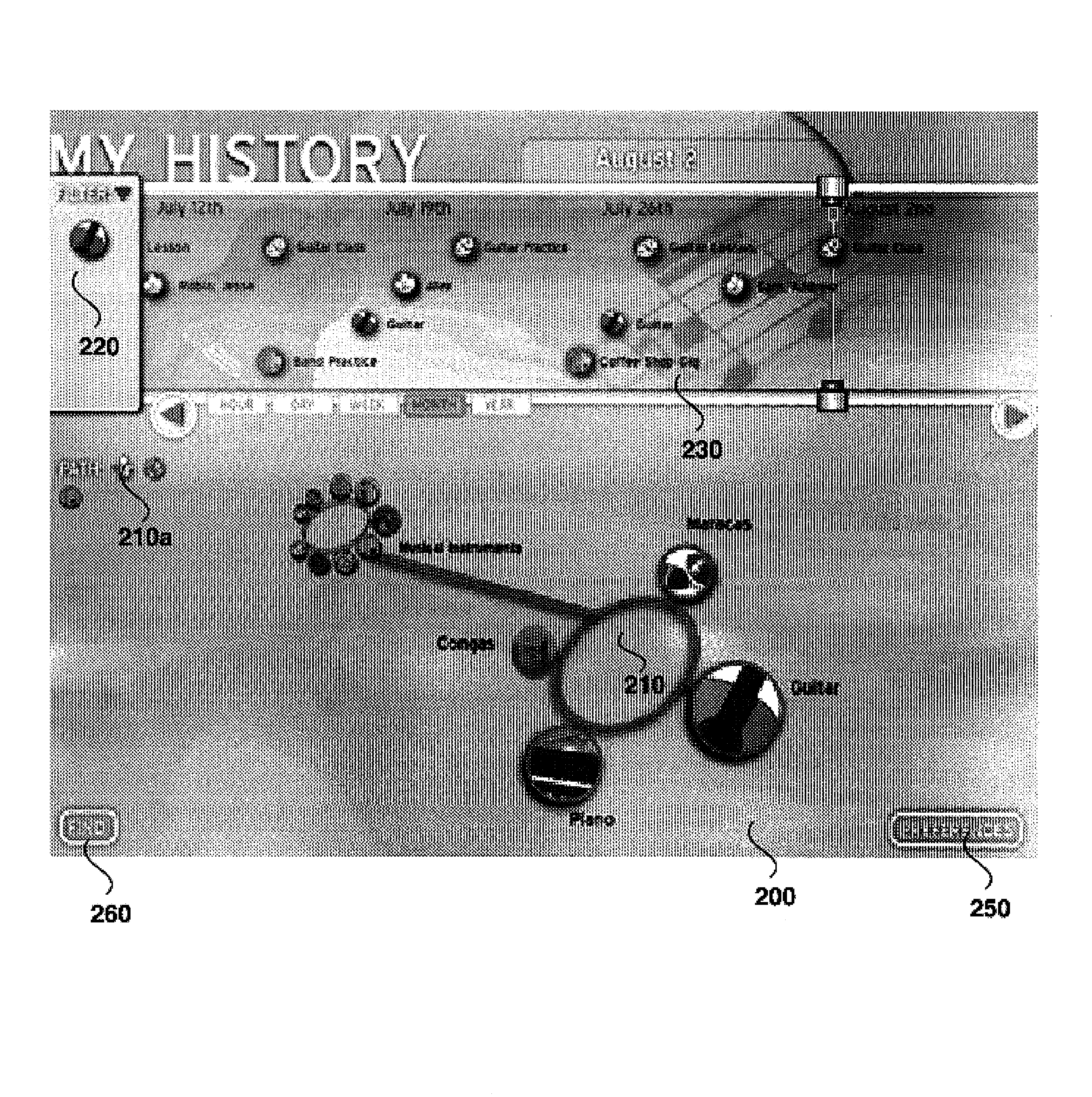
InactiveUS7146574B2Other databases browsing/visualisationWeb data navigationTime segmentAccess history
Systems and methods for accessing historical data are provided. Based upon user interaction, a time period of interest and historical data, the systems and methods perform cross-correlation algorithms and interpret which items are to be accessed and displayed to the user via a user interface vis-a-vis a timeline portion and navigation region. Based on frequency and recency usage patterns, and / or user preferences, items are assigned relative weights and displayed accordingly in the timeline portion and navigation region of the user interface. Each item that can be displayed within the system has a unique identification, which may be translated to one or more visual symbols within the user interface. In various non-limiting embodiments, the system leverages a distributed database store which stores and indexes items that make up a digital history. When a request is made to the database, items, such as events, places, people and things, are automatically cross-referenced and correlations are drawn based on filtering criteria.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com