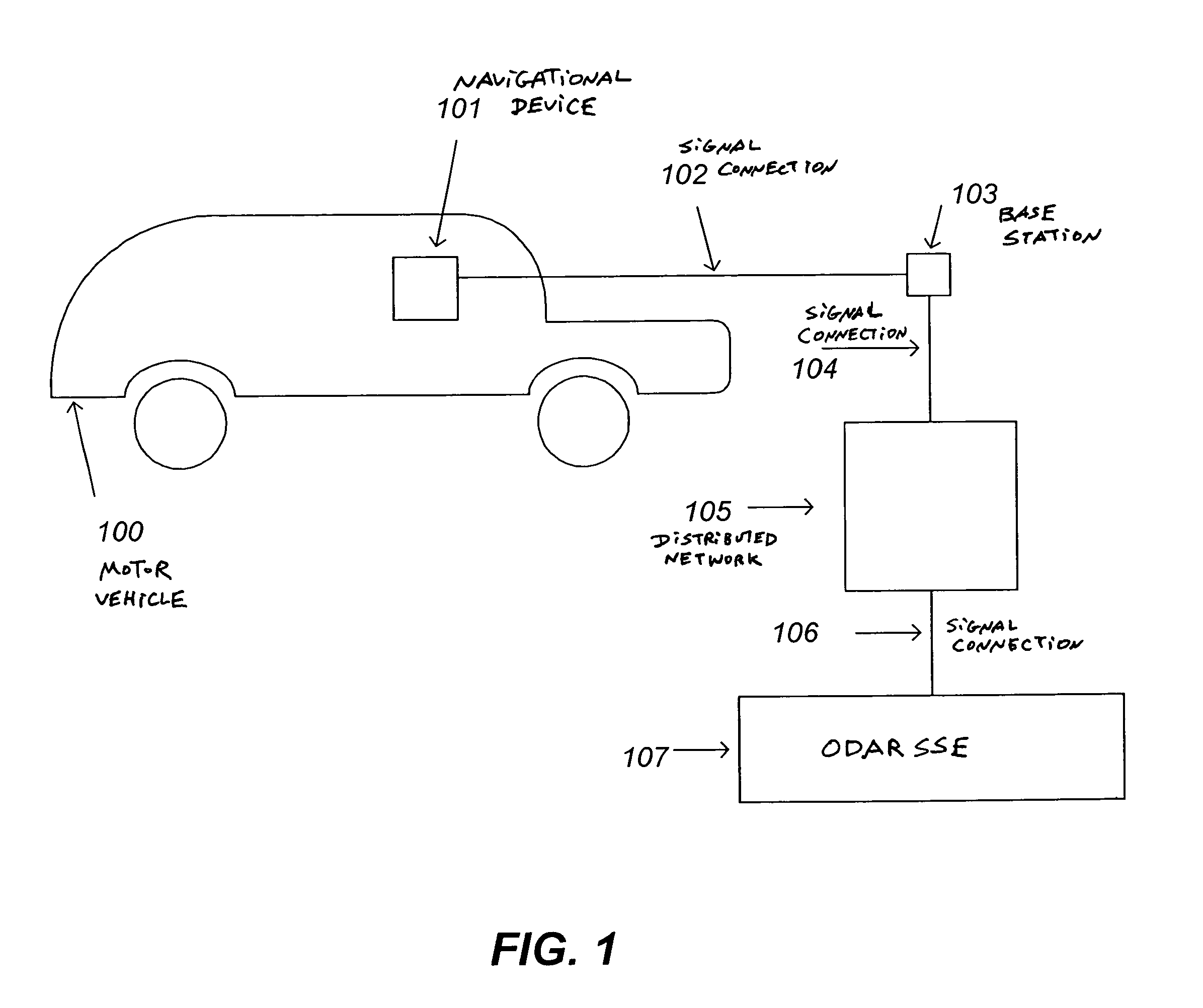
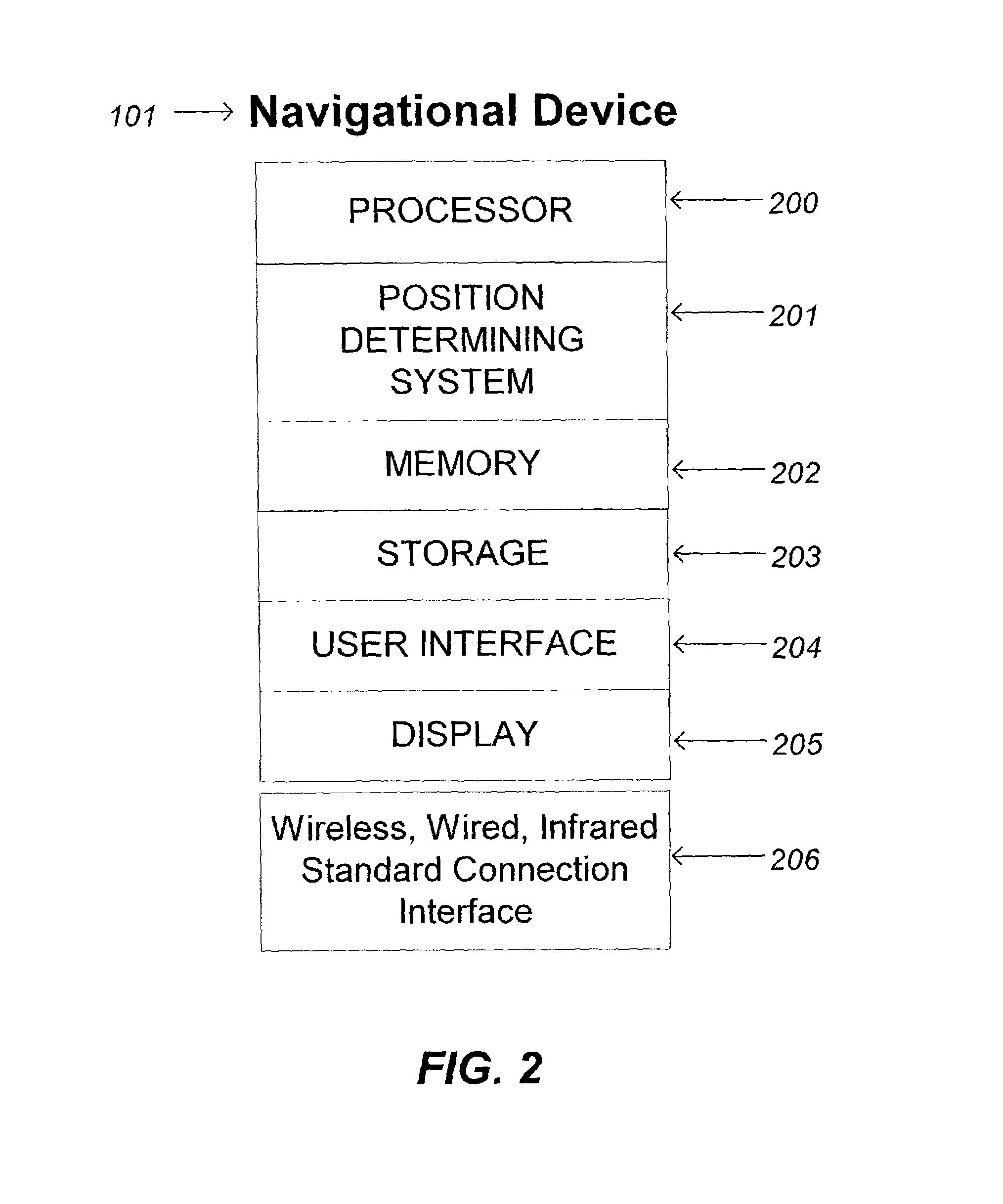
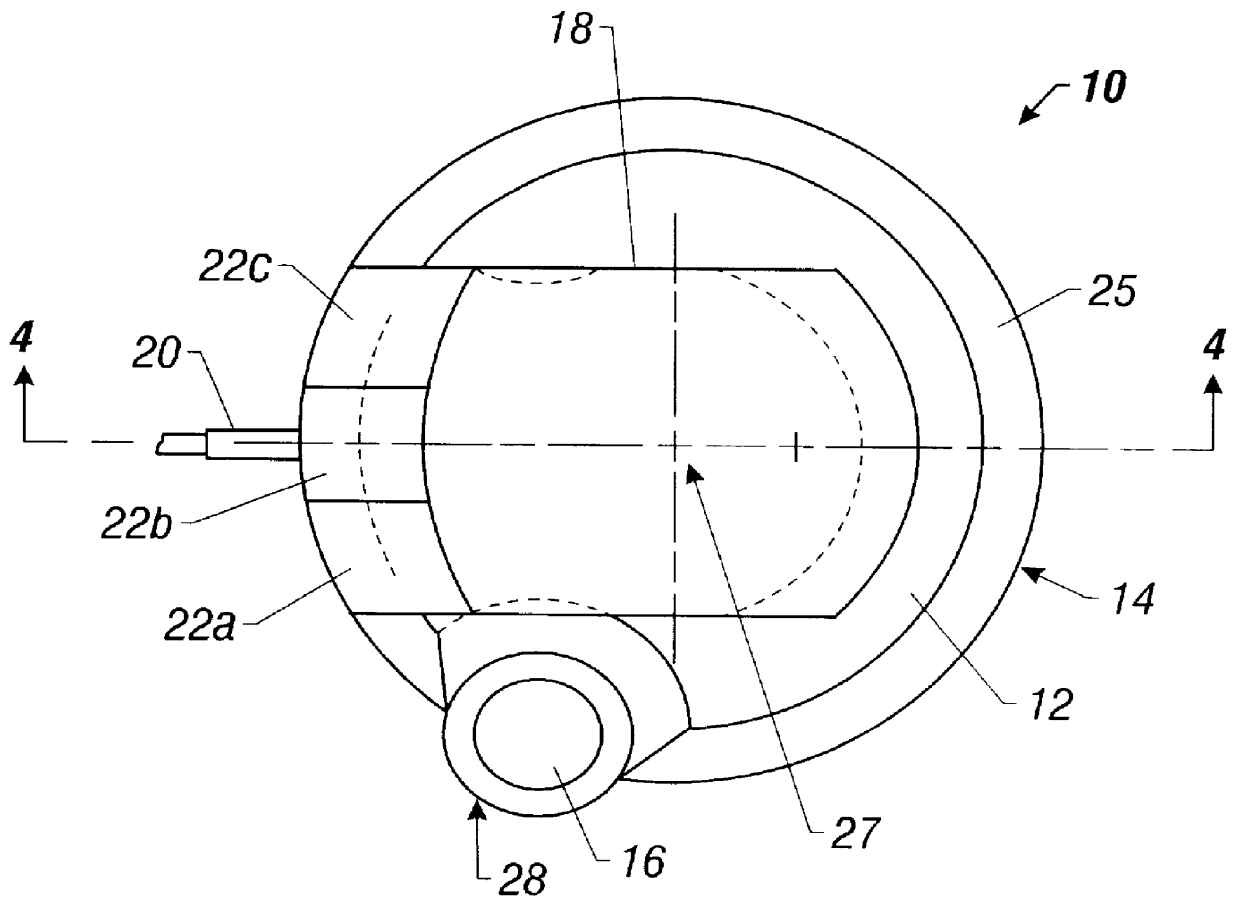
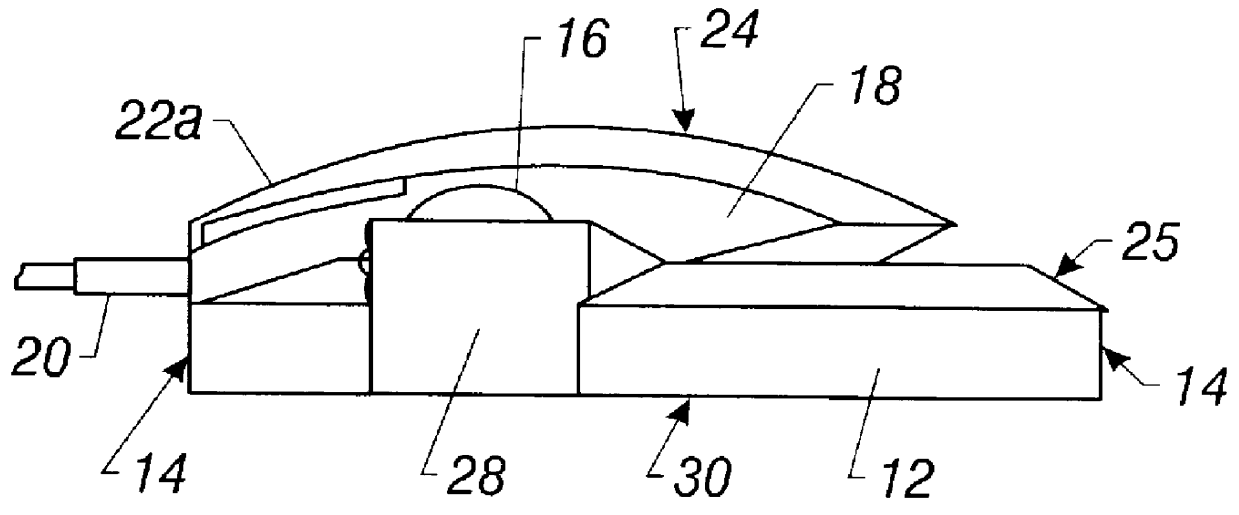
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6891 results about "System information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
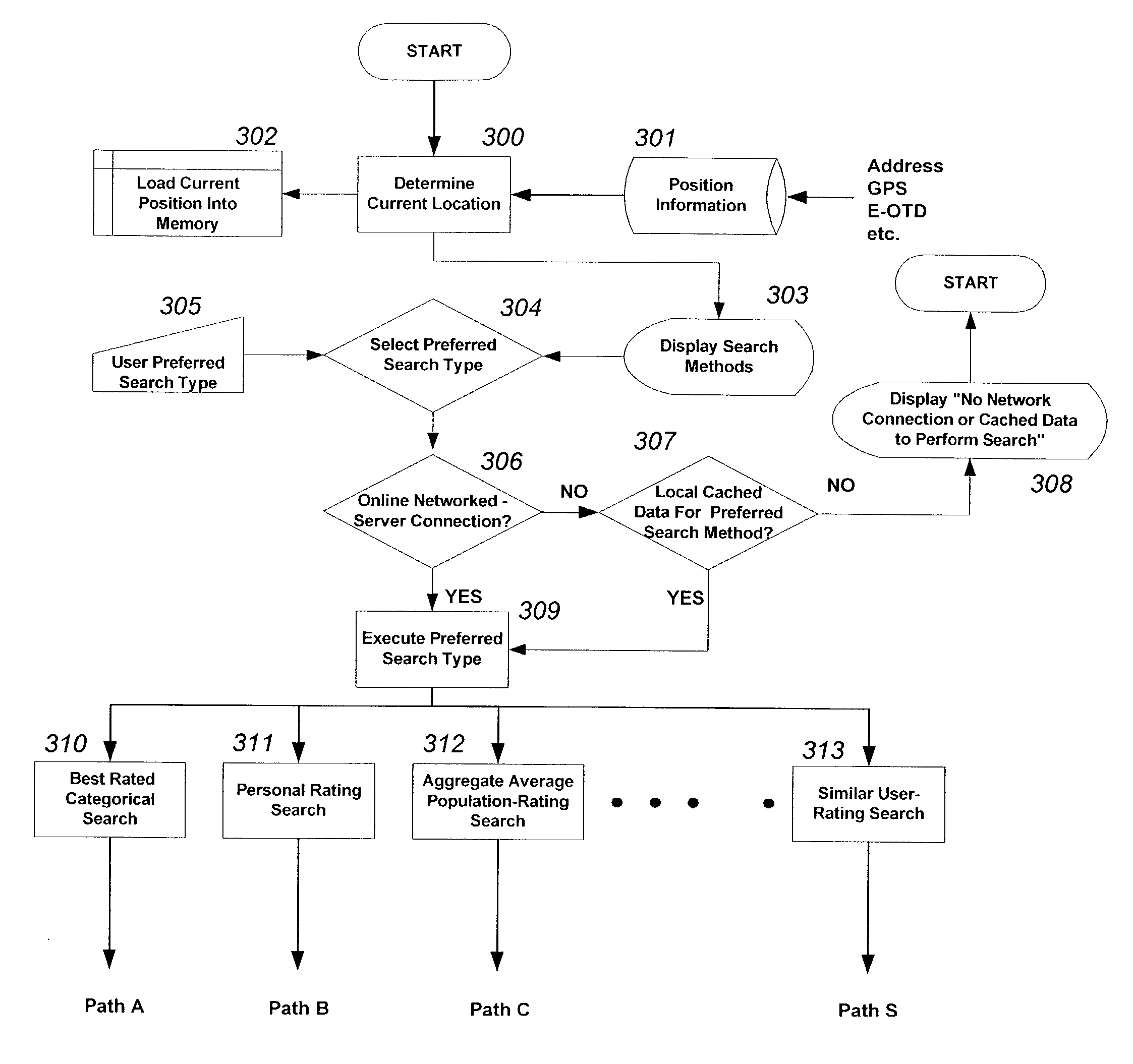
Point of interest spatial rating search method and system
InactiveUS20030036848A1Aid accuracyAid efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlData miningData science
The present invention is directed to a system and method for searching and retrieving location information associated with one or more points of interests, whereby the search criteria can be dependent upon the location of a point of interest with respect to the the real-time position of the user, and any preferences or search restrictions selected by the user, such as rating information about the point of interest. Upon selecting a point of interest from the search result, the user is then given further information regarding the selected point of interest, including but not limited to directions for traveling to the point of interest. Additionally, the present invention can provide to the user a proximity notification once the user is within a certain distance from the point interest. Finally, while at a point of interest, the user can provide to the system information regarding the point of interest, such as rating of the food of a restaurant, without having to specifically identify the point of interest as the system can self-identify the point of interest by using the position information of the user.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Distributed antenna system using overhead power lines
InactiveUS20090079660A1Great contributionReadily apparentPower distribution line transmissionBroadcast transmission systemsTransport systemDistributed antenna system
A distributed antenna system having a transport portion including at least one overhead power line for transmitting system information along its length, and a distribution portion including at least one local access point disposed along the length of the power line for providing local access to information transported by the transport portion.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
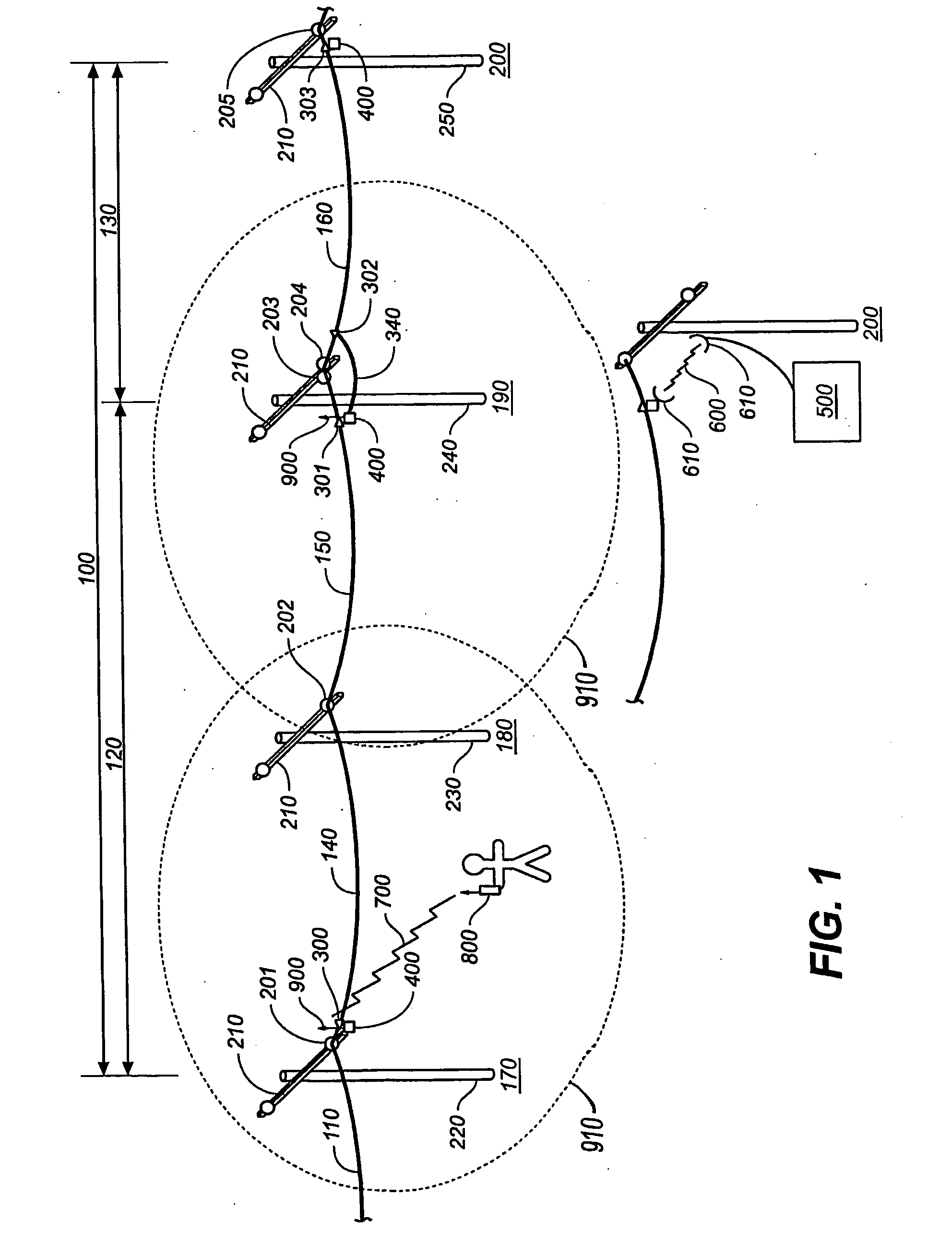
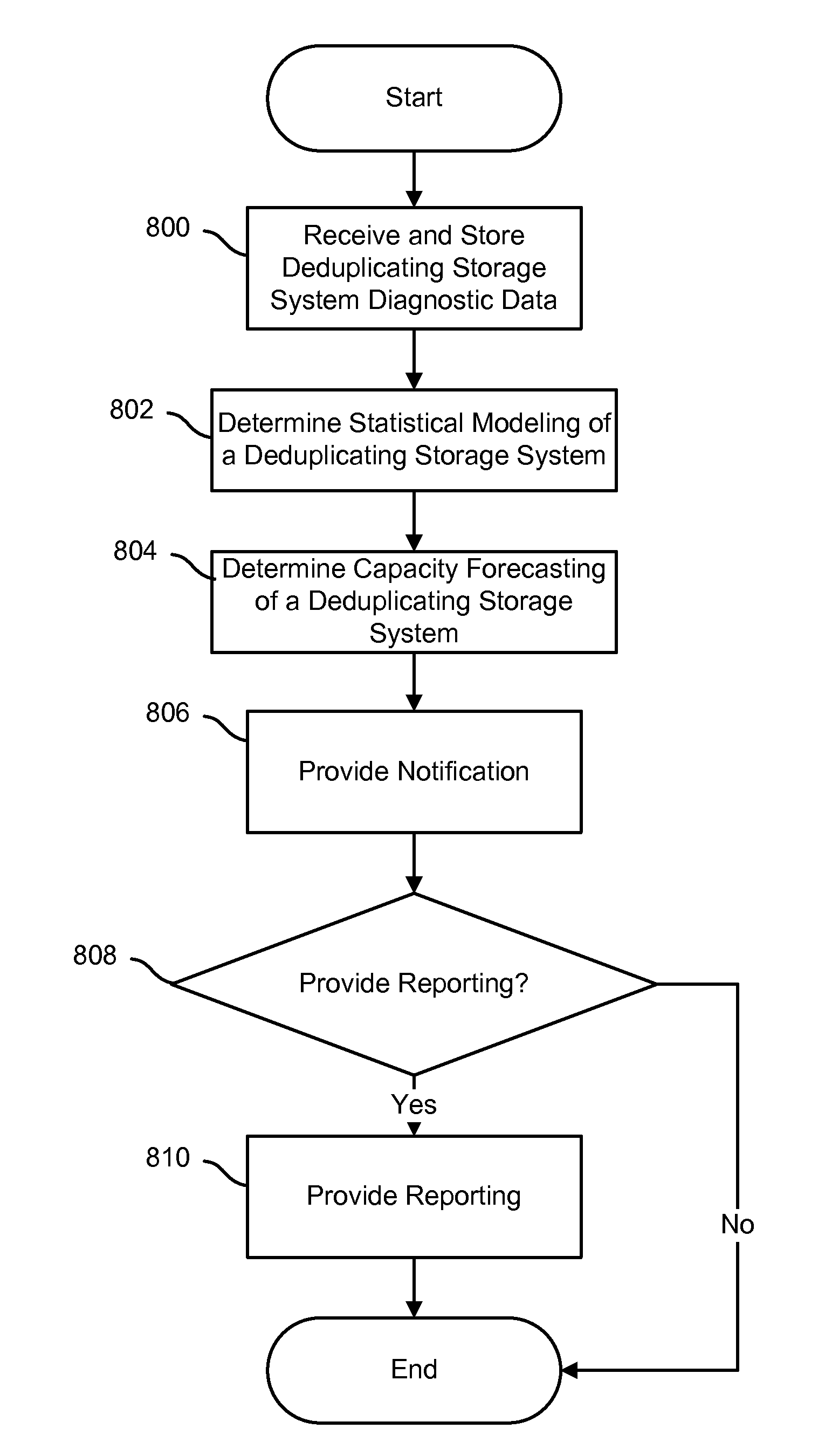
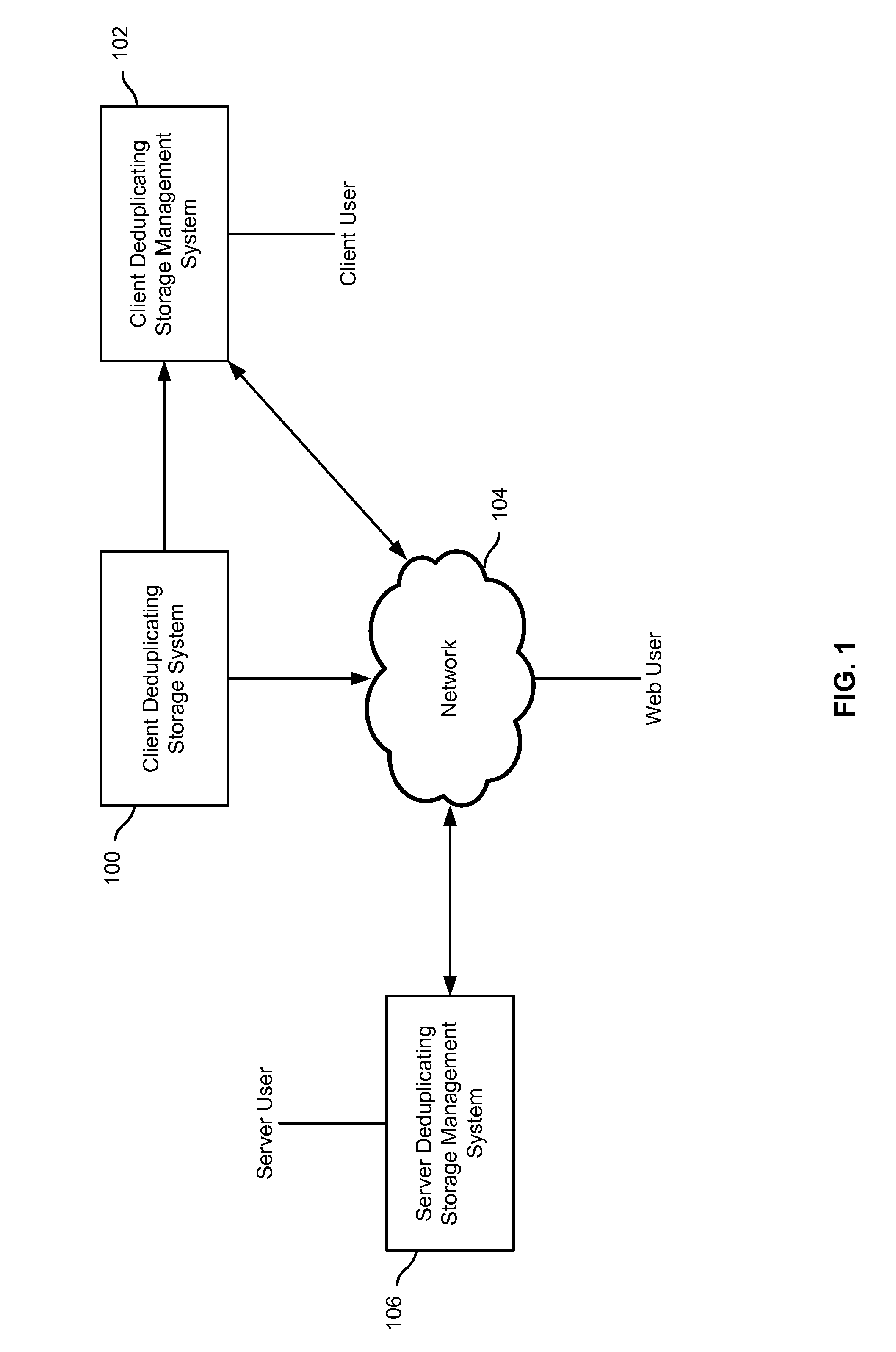
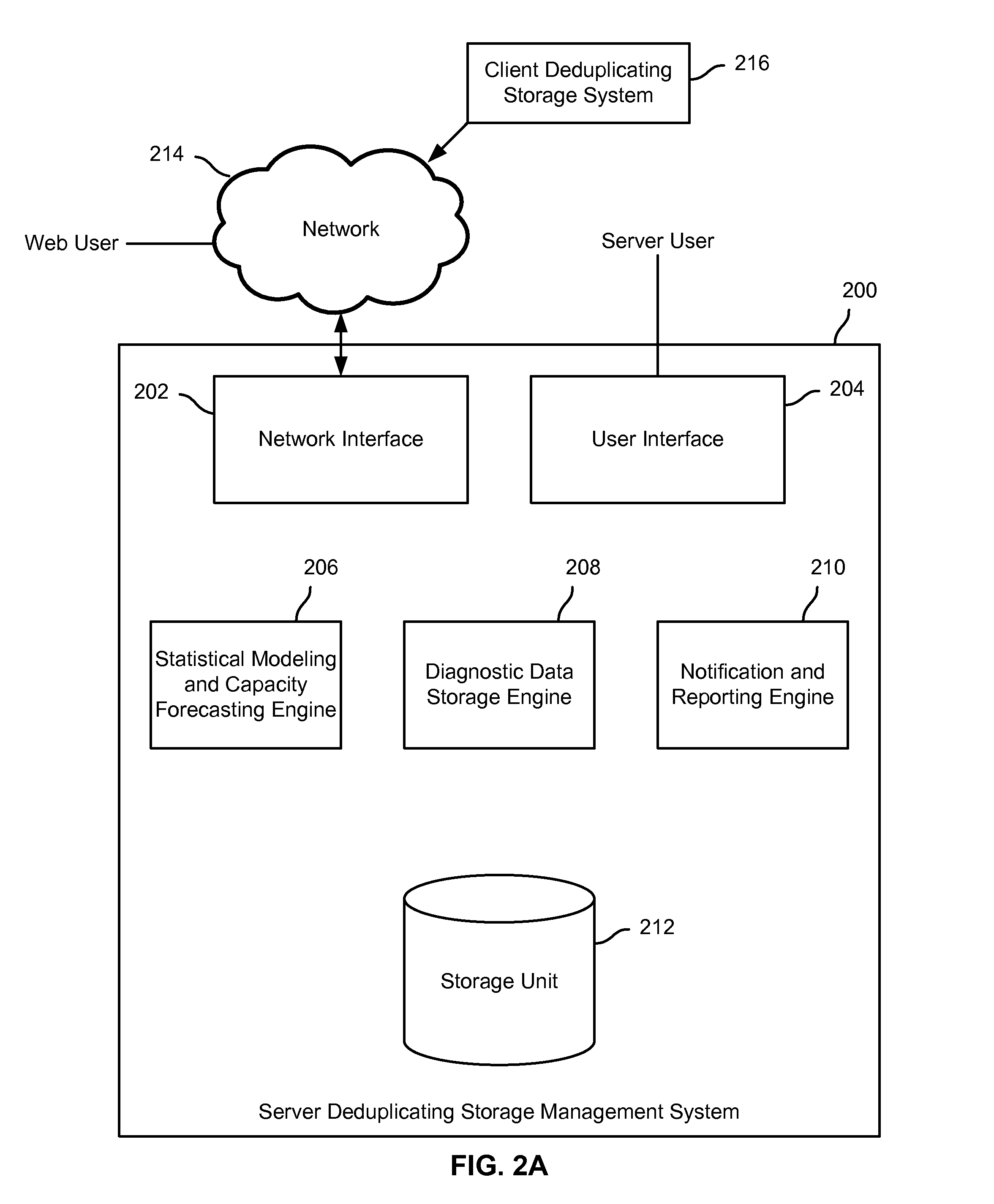
Capacity forecasting for a deduplicating storage system
ActiveUS8751463B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSystem informationData deduplication
A system for managing a storage system comprises a processor and a memory. The processor is configured to receive storage system information from a deduplicating storage system. The processor is further configured to determine a capacity forecast based at least in part on the storage system information. The processor is further configured to provide a compression forecast. The memory is coupled to the processor and configured to provide the processor with instructions.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
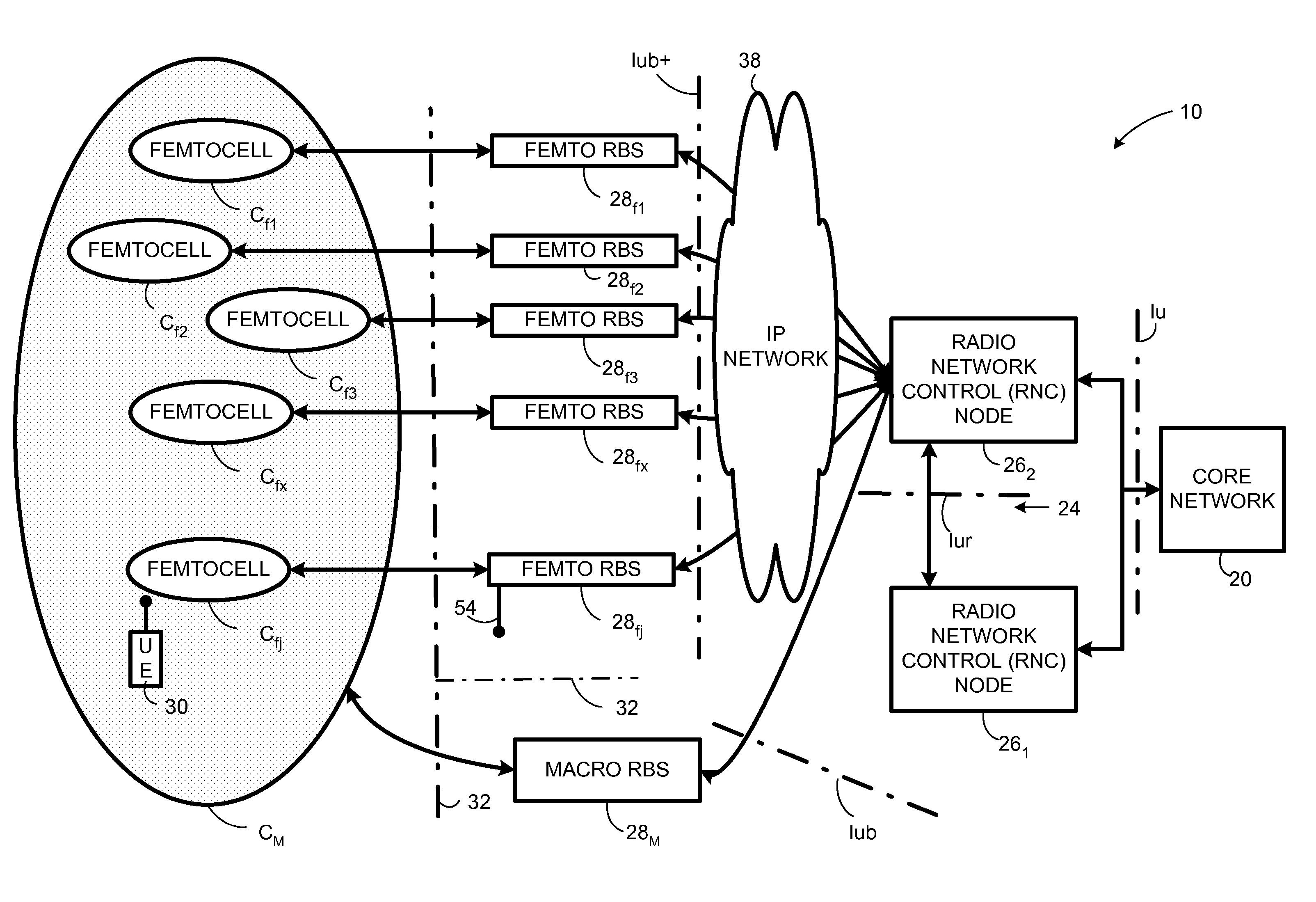
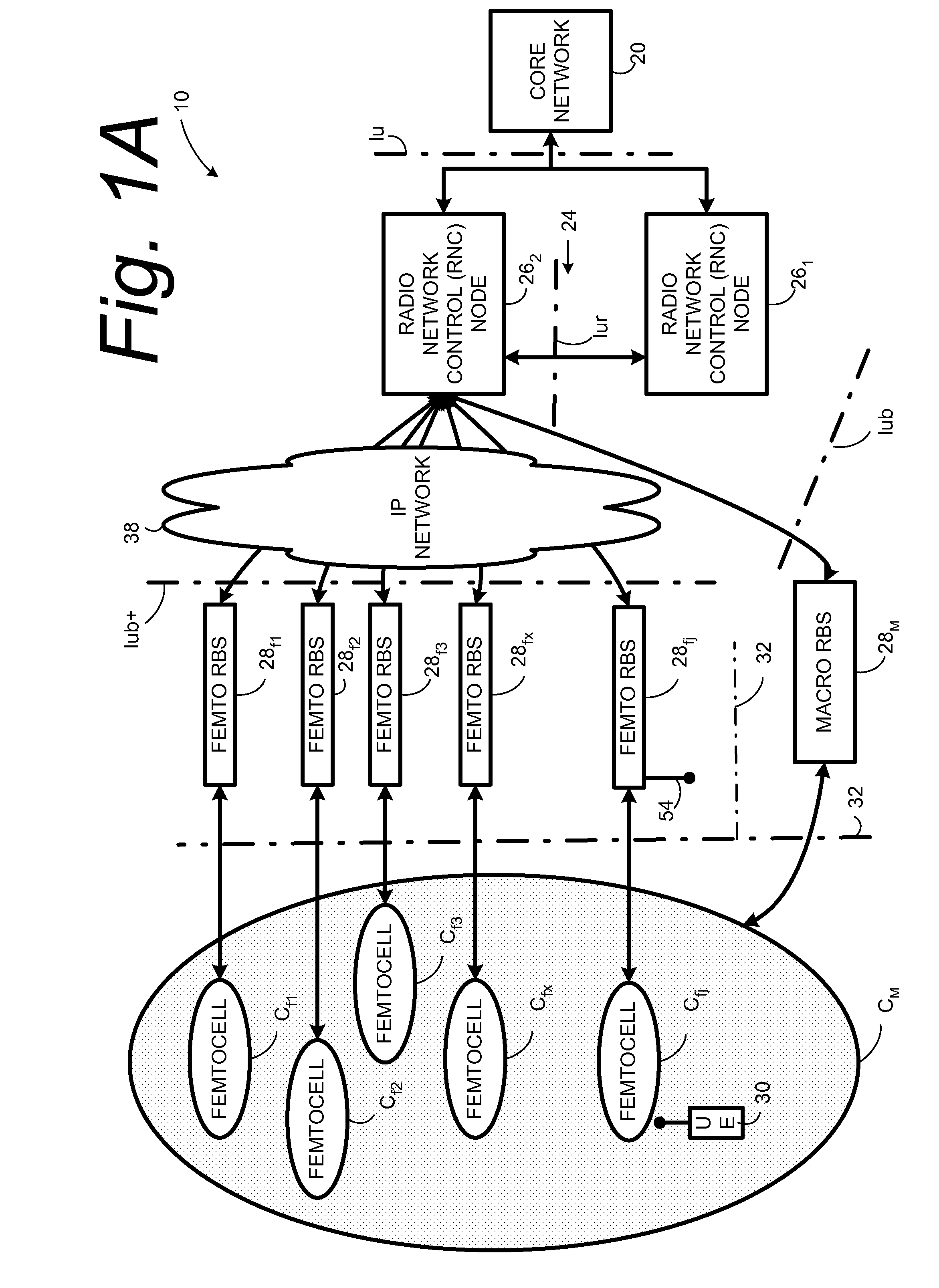
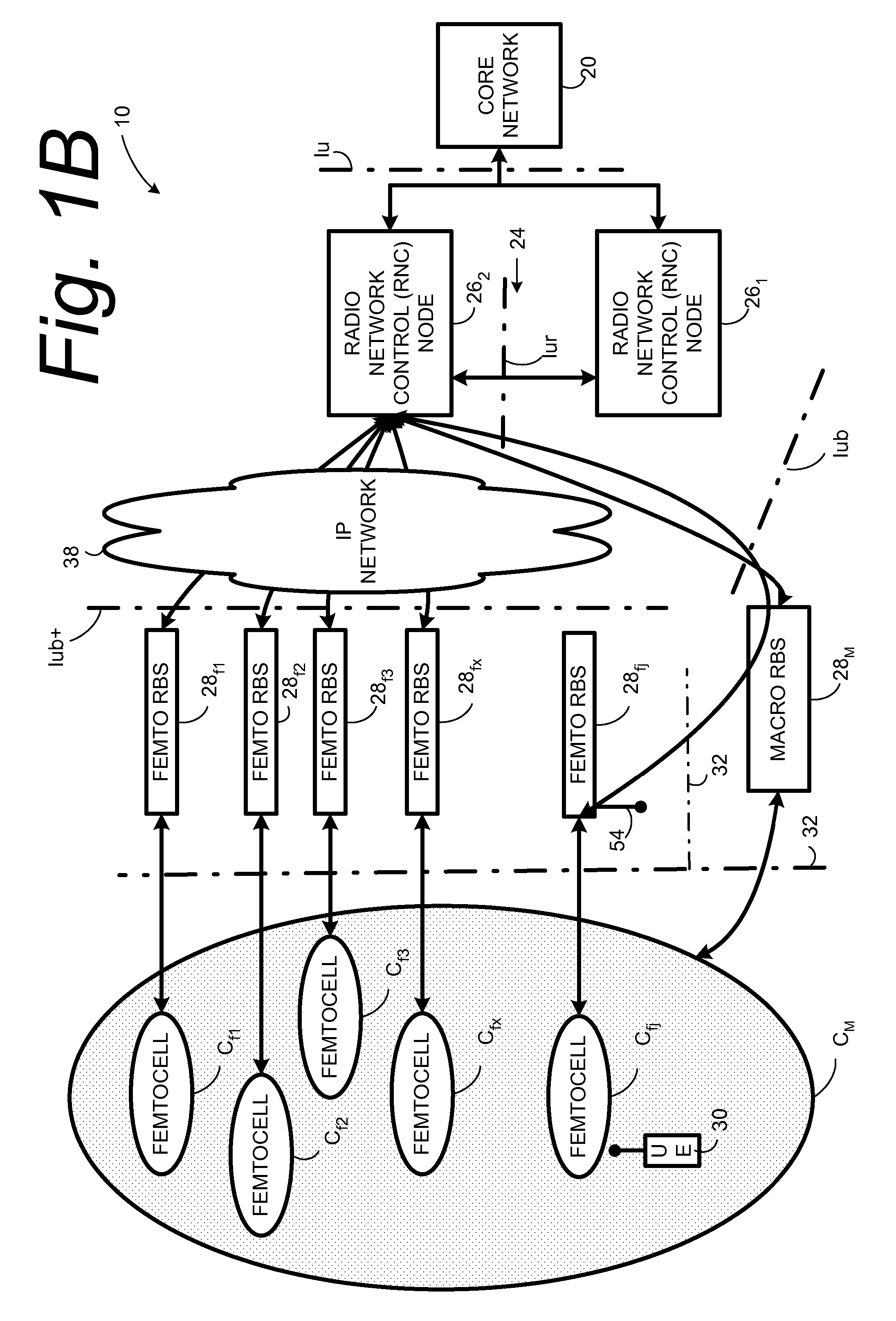
Automatic building of neighbor lists in mobile system
In a radio access network (24) a femto radio base station (28f) comprises a resident receiver (54) which acquires system information broadcast in a radio access network (24). At least part of the system information is used for building, at the femto radio base station (28f), a neighbor data structure (59) comprising information for neighboring cells. The neighbor data structure (59) is then used for building a neighbor list. The neighbor list is subsequently transmitted from the femto radio base station (28f) to a user equipment unit (30) served by the femto radio base station (28f). In some example embodiments and modes, the femto radio base station (28f) reports the neighbor data structure to a network node (26, 100) other than the femto radio base station. The other node (26, 100) uses the neighbor data structure for building the neighbor list at the other node. In some example embodiments and modes, acquisition of the system information comprises scanning a surrounding macro coverage area of the femto radio base station for obtaining cell identity information for detected cells. In other example embodiments and modes, the acquisition of the system information can additionally comprise camping on a macro cell and using / consulting at least one system information block in the camped-on macro cell is consulted / used for obtaining information about at least one neighboring cell.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Point of interest spatial rating search method and system
InactiveUS7082365B2Improve matchInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlData miningData science
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Pointing device with biometric sensor
InactiveUS6148094ACathode-ray tube indicatorsInternal/peripheral component protectionComputerized systemPointing device
A pointing device incorporates a biometric sensor at a location such that when operating the pointing device in a normal manner, a user's hand rests naturally in a position to place a finger of the user's hand in proximity to and readable by the biometric sensor. In one embodiment, a computer trackball pointing device includes a fingerprint sensor which is equally well suitable for use by either a right-handed or a left-handed user. Along with positional information from a position sensor and user selection information from at least one user-depressable button, the pointing device also conveys to an attached computer system information associated with the user's identity detected by the fingerprint sensor. Such a pointing device is well suited to both transparent verification as well as continuous verification, for if a user removes his or her hand from the natural position when using the device, the user's fingerprint will no longer be detectable by the fingerprint sensor, and the computer system to which the pointing device is attached can be alerted as to the need to re-authenticate any additional attempts at using the pointing device.
Owner:DALTON PATRICK ENTERPRISES
Method for optimizing the random access procedures in the cdma cellular networks
InactiveUS20030076812A1Limit collisionSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCellular networkSystem information
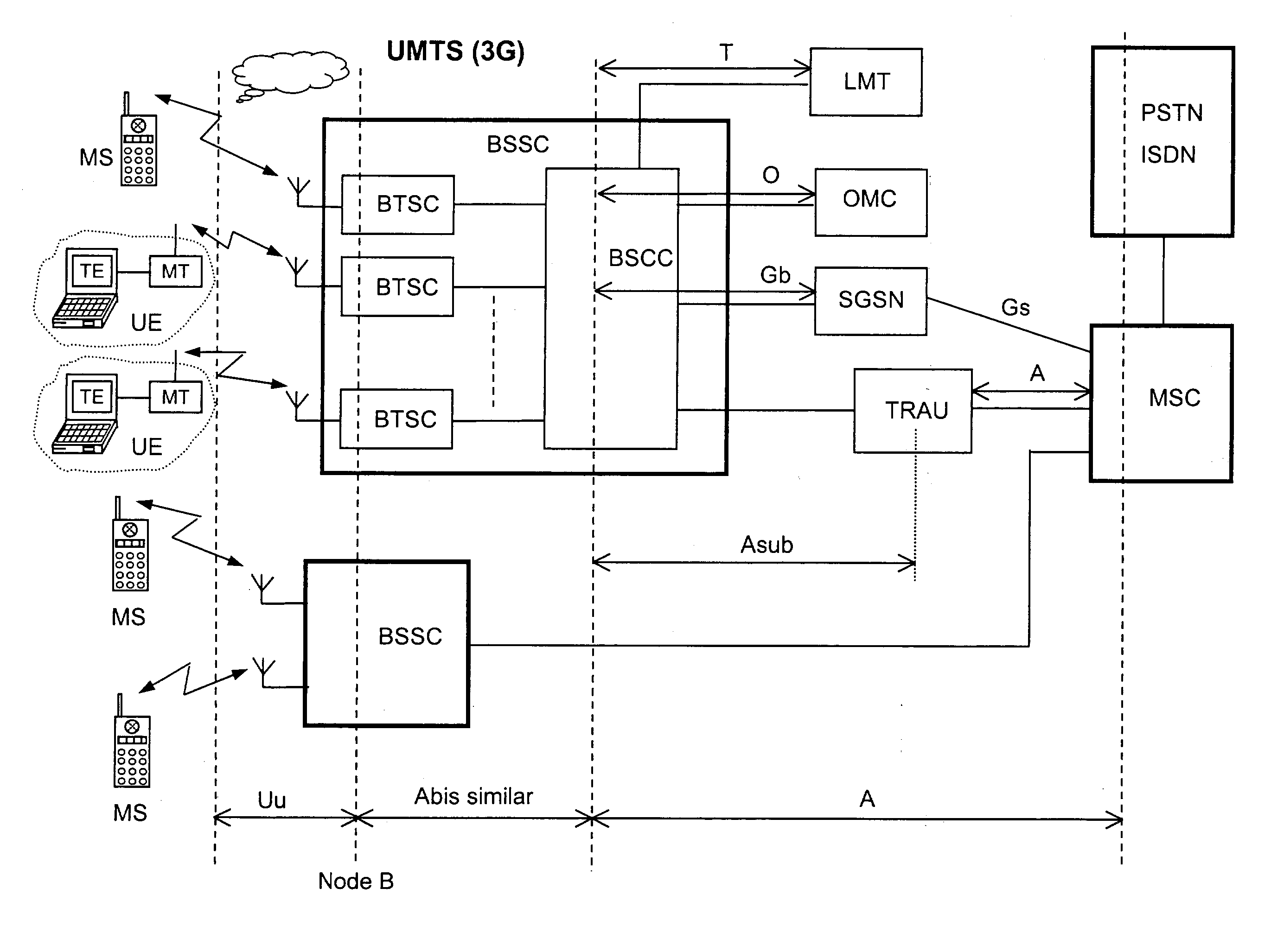
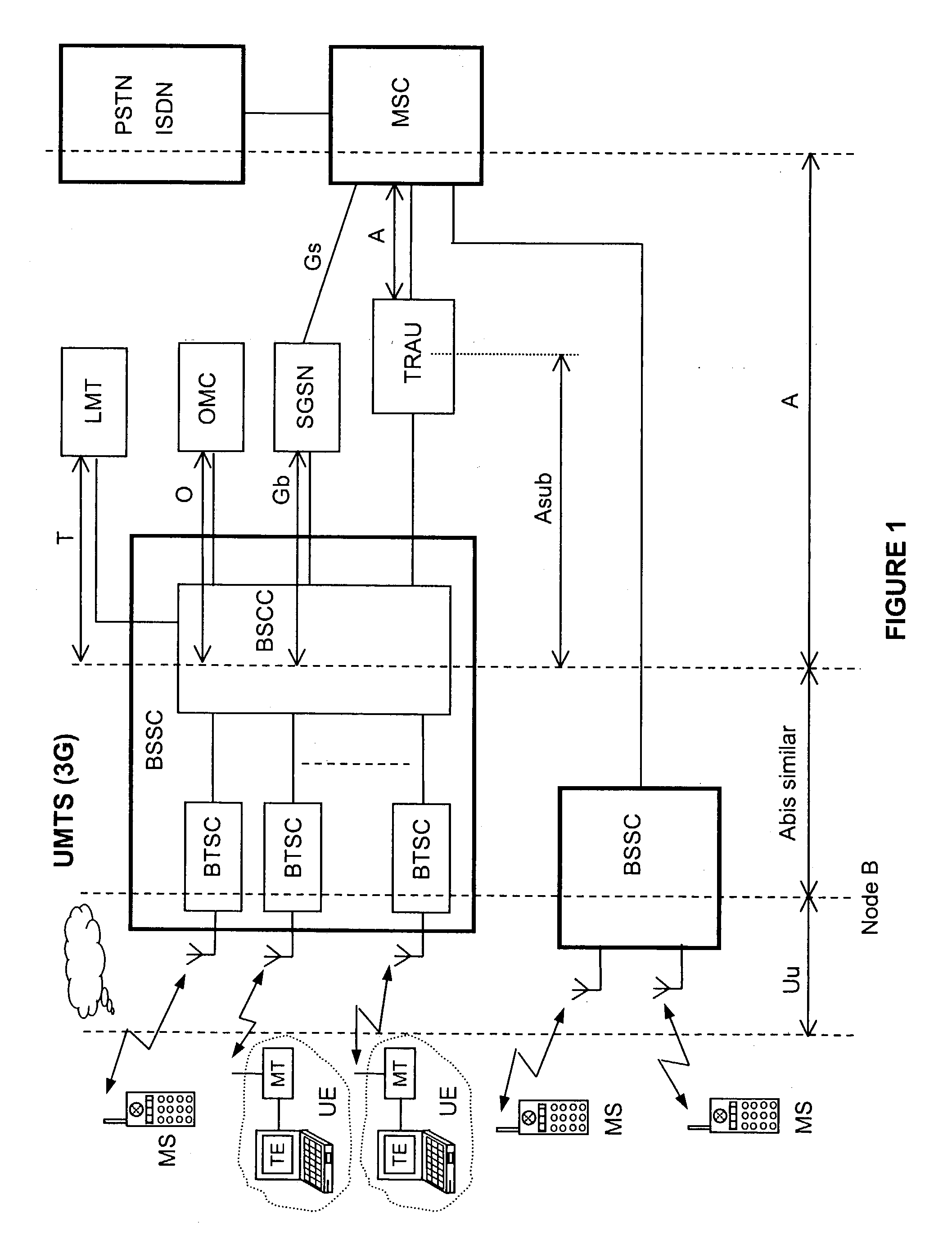
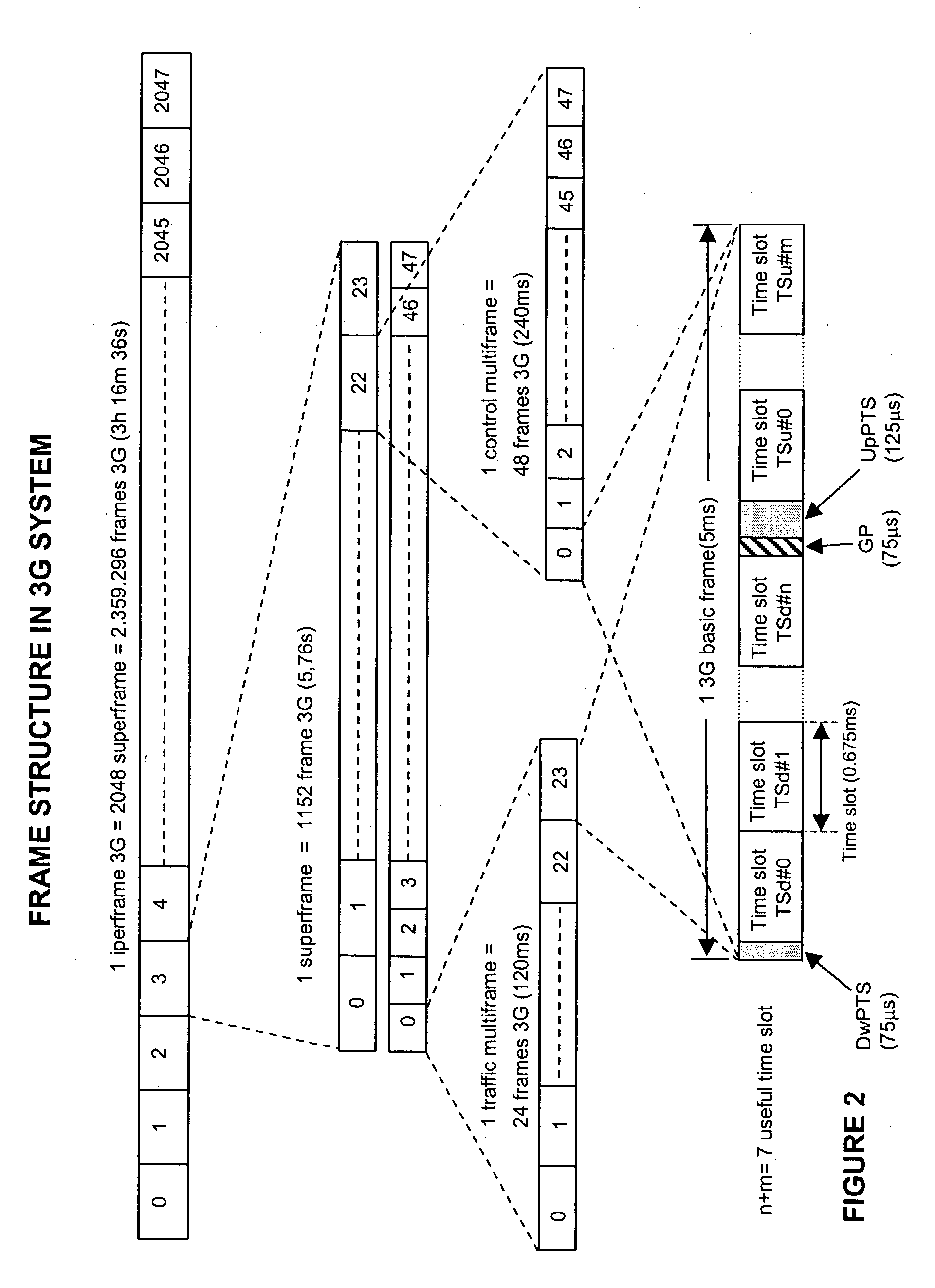
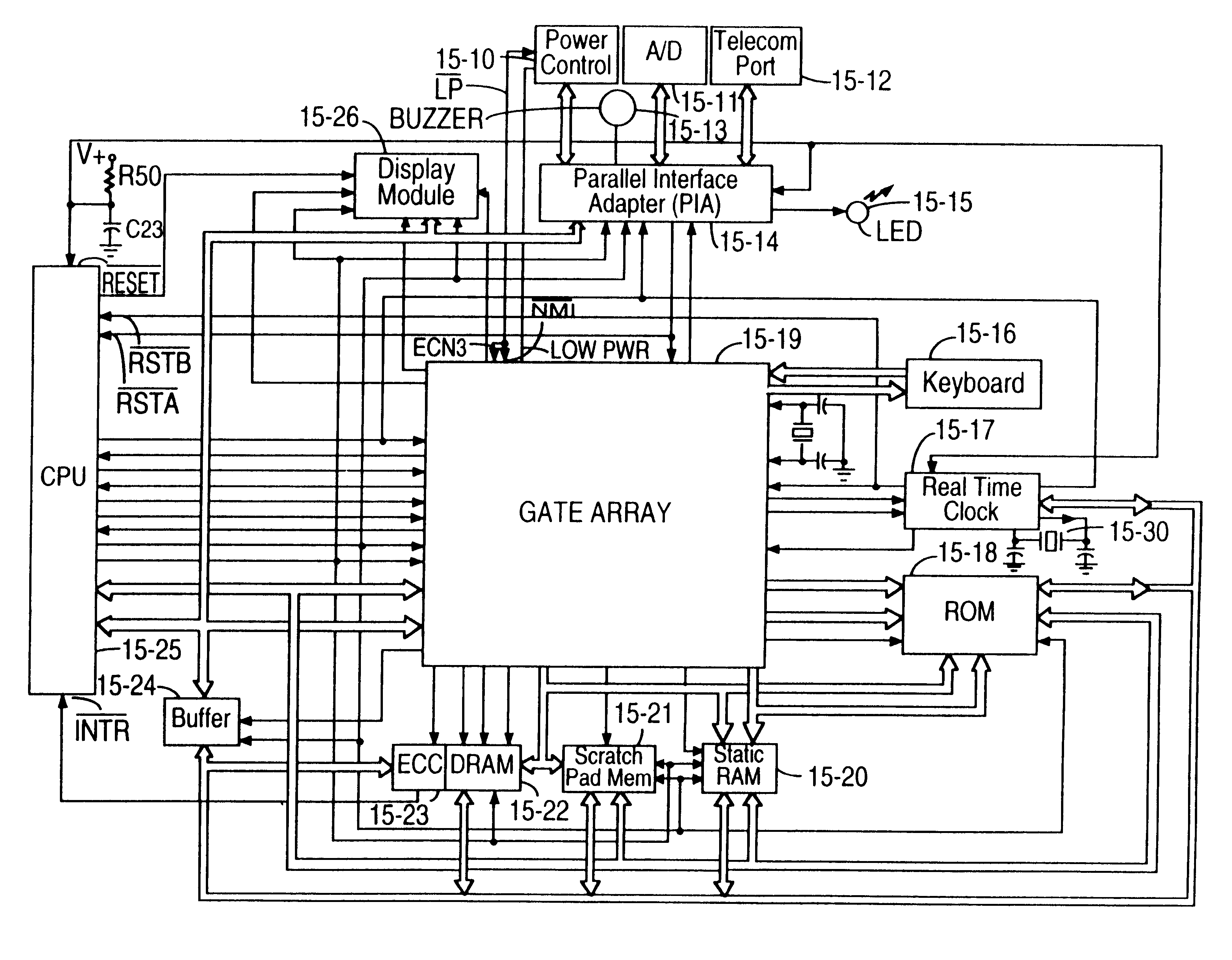
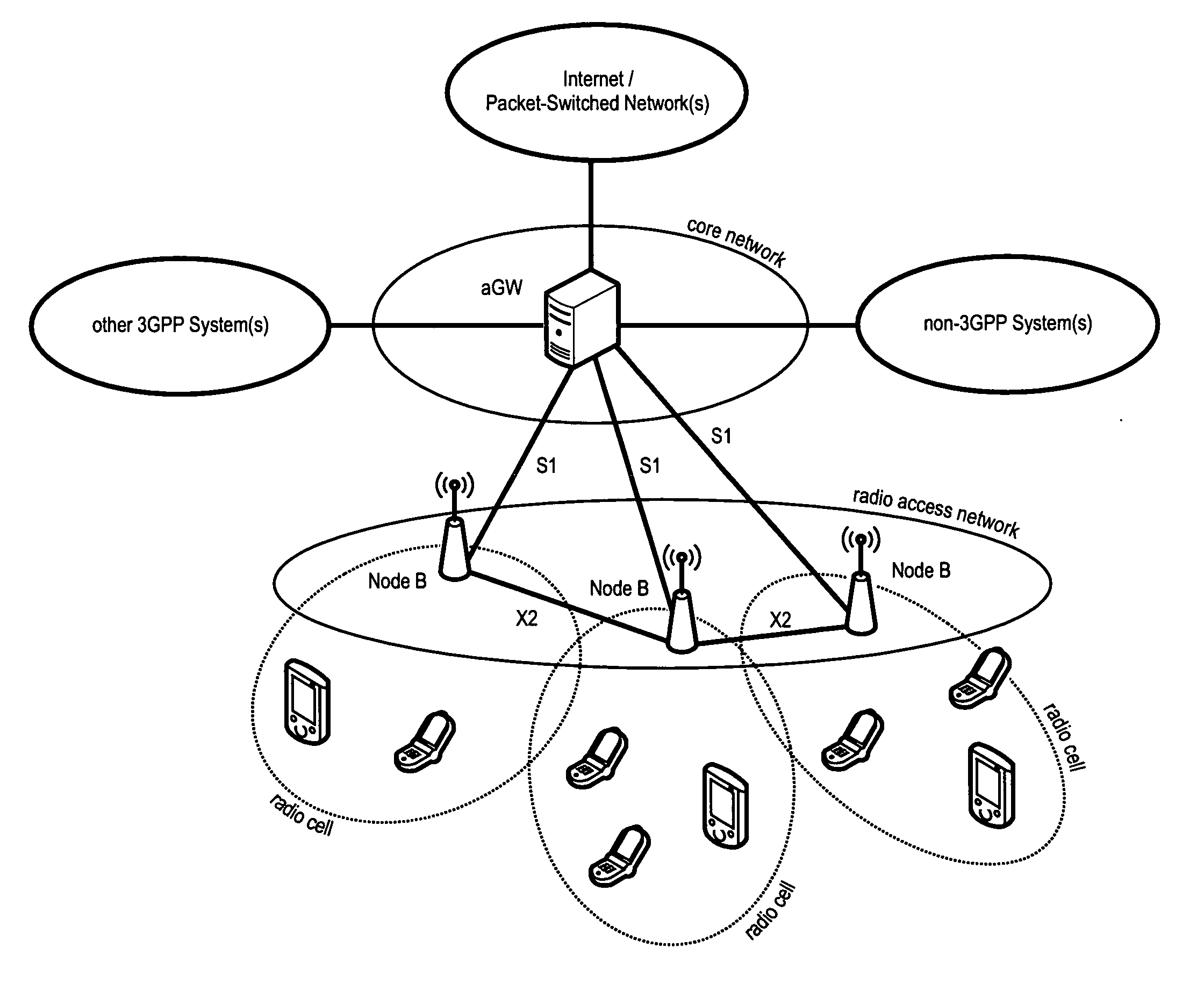
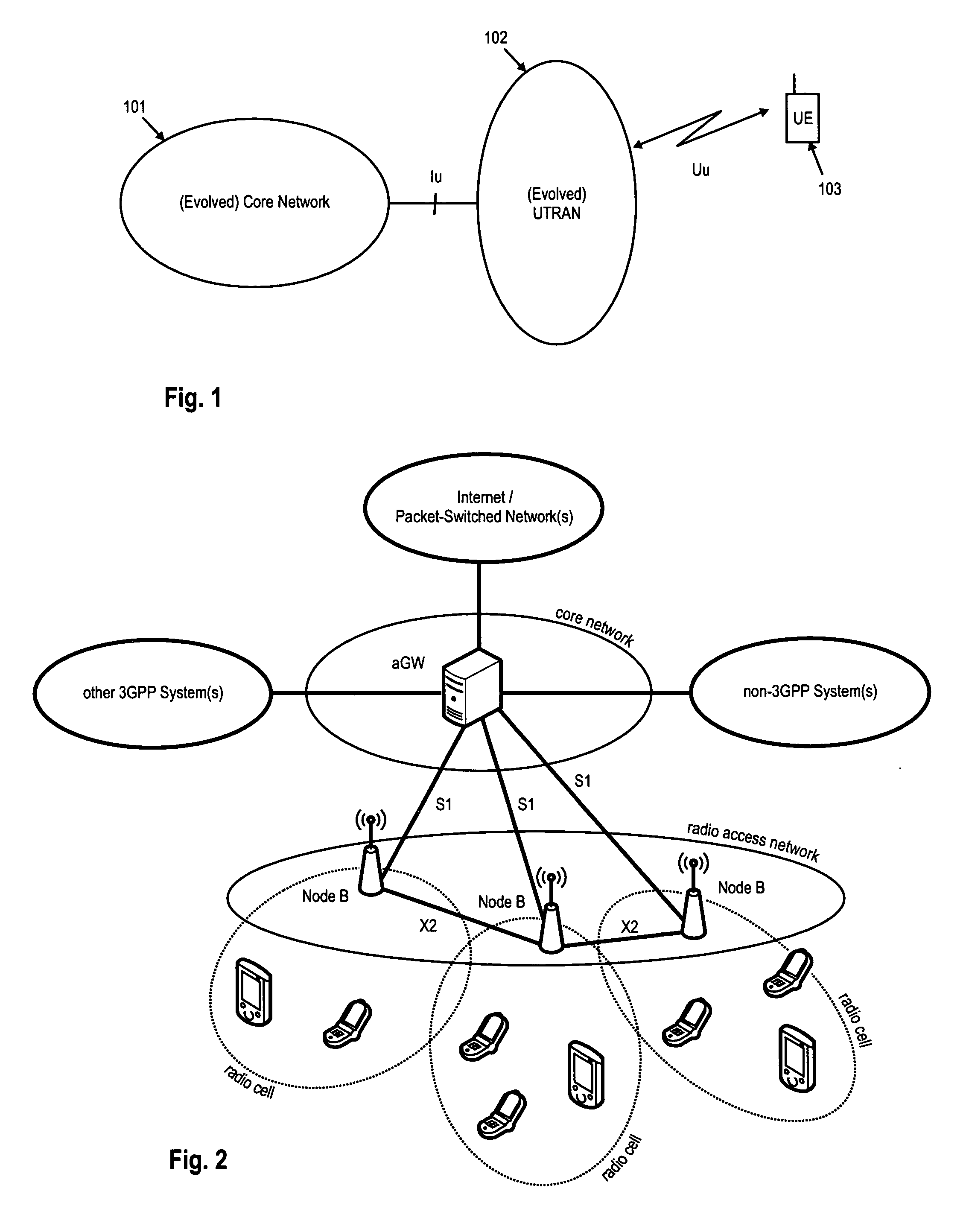
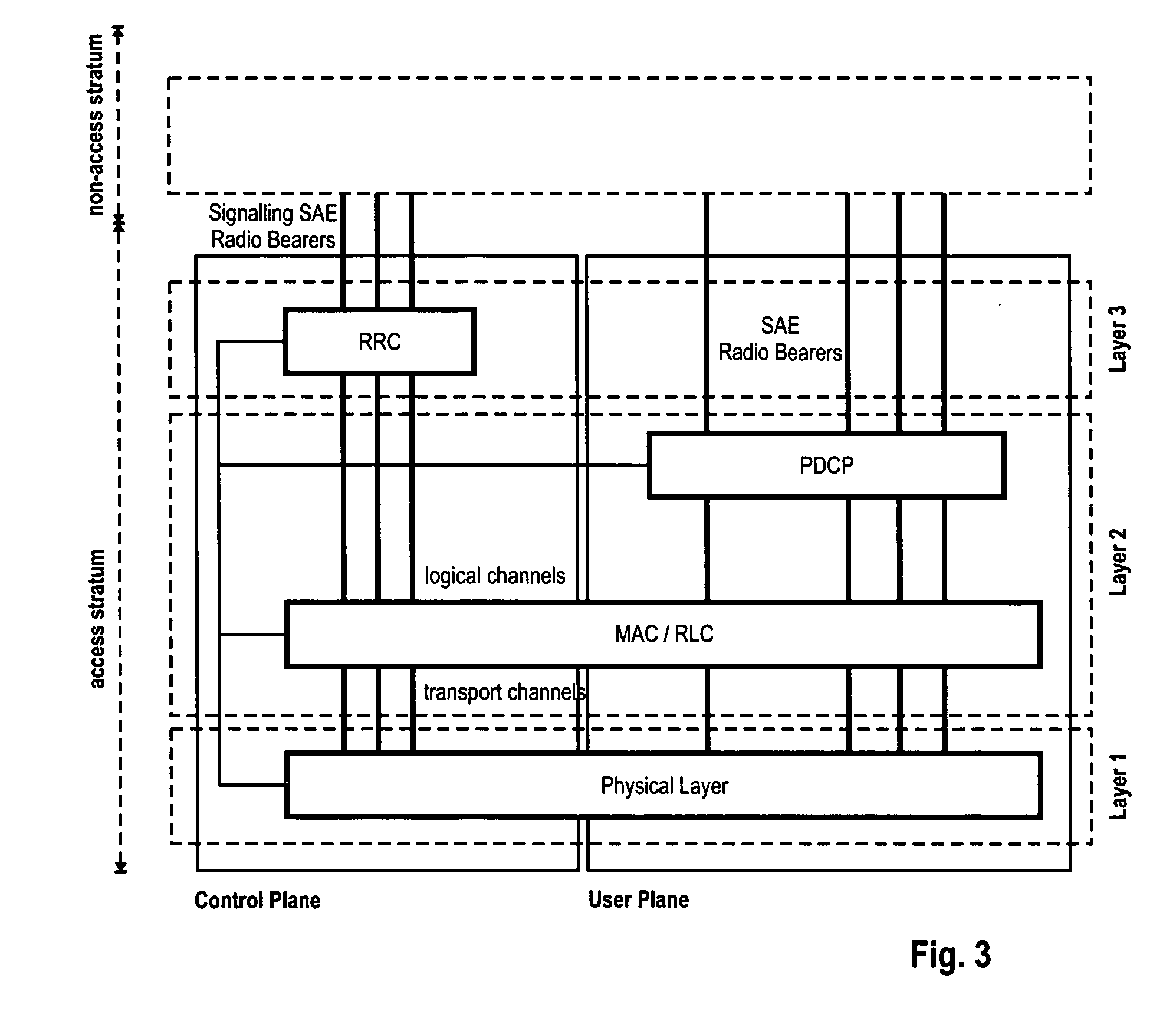
The disclosed invention is referred to a method for optimising the random access procedures in third generation CDMA cellular telephony systems. The particular embodiment of the example concerns a TD-SCDMA-TDD synchronous realization. The disclosed procedure includes a preliminary part charged to the network (BSSC, MSC) only for establishing the following associations between the configuration parameters of the involved physical channels: one signature burst (SYNC1) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to avoid any, ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected acknowledgement from the network; one random access common channel (P-RACH) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to reduce collision on the latter (P-RACH); one access grant channel (P / S-CCPCH, AGCH) only is associated to one random access common channel (P-RACH), in order to avoid any ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected answer from the network with the indication of the dedicated service channels (DPCH); and each complete associative link binding the involved physical channels is included in the system information and broadcasted into the serving cell to be read by the mobile stations (MS, UE) when entering an actual part of the procedure charged to exchange protocol messages with the network (BSSC, MSC) through said associative links that being signalling at once to the mobile stations the route towards the services offered by the network, simplifying the access procedure consequently. Suitable groupings among: Downlink pilot sequences, Uplink pilot sequences, scrambling codes, basic midambles, are carried out in a cell-discriminating way and broadcasted into the cell to simplify the serving cell selection procedure (<cross-reference target="DRAWINGS">FIG. 1< / cross-reference>).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Battery pack having memory
InactiveUS6307349B1Reduce eliminateDecreasing the turn on potentialCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingElectrical batteryCombined use
In an exemplary embodiment, a battery conditioning system monitors battery conditioning and includes a memory for storing data based thereon; for example, data may be stored representative of available battery capacity as measured during a deep discharge cycle. With a microprocessor monitoring battery operation of a portable unit, a measure of remaining battery capacity can be calculated and displayed. Where the microprocessor and battery conditioning system memory are permanently secured to the battery so as to receive operating power therefrom during storage and handling, the performance of a given battery in actual use can be accurately judged since the battery system can itself maintain a count of accumulated hours of use and other relevant parameters. In the case of a nonportable conditioning system, two-way communication may be established with a memory associated with the portable unit so that the portable unit can transmit to the conditioning system information concerning battery parameters (e.g. rated battery capacity) and / or battery usage (e.g. numbers of shallow discharge and recharge cycles), and after a conditioning operation, the conditioning system can transmit to the portable unit a measured value of battery capacity, for example. A battery pack having memory stores battery history and identifying data to be retrieved by a portable battery powered device. Battery status information may be utilized in conjunction with characteristic battery history data in order to optimize charging and discharging functions and to maximize the useful life of a battery pack.
Owner:INTERMEC
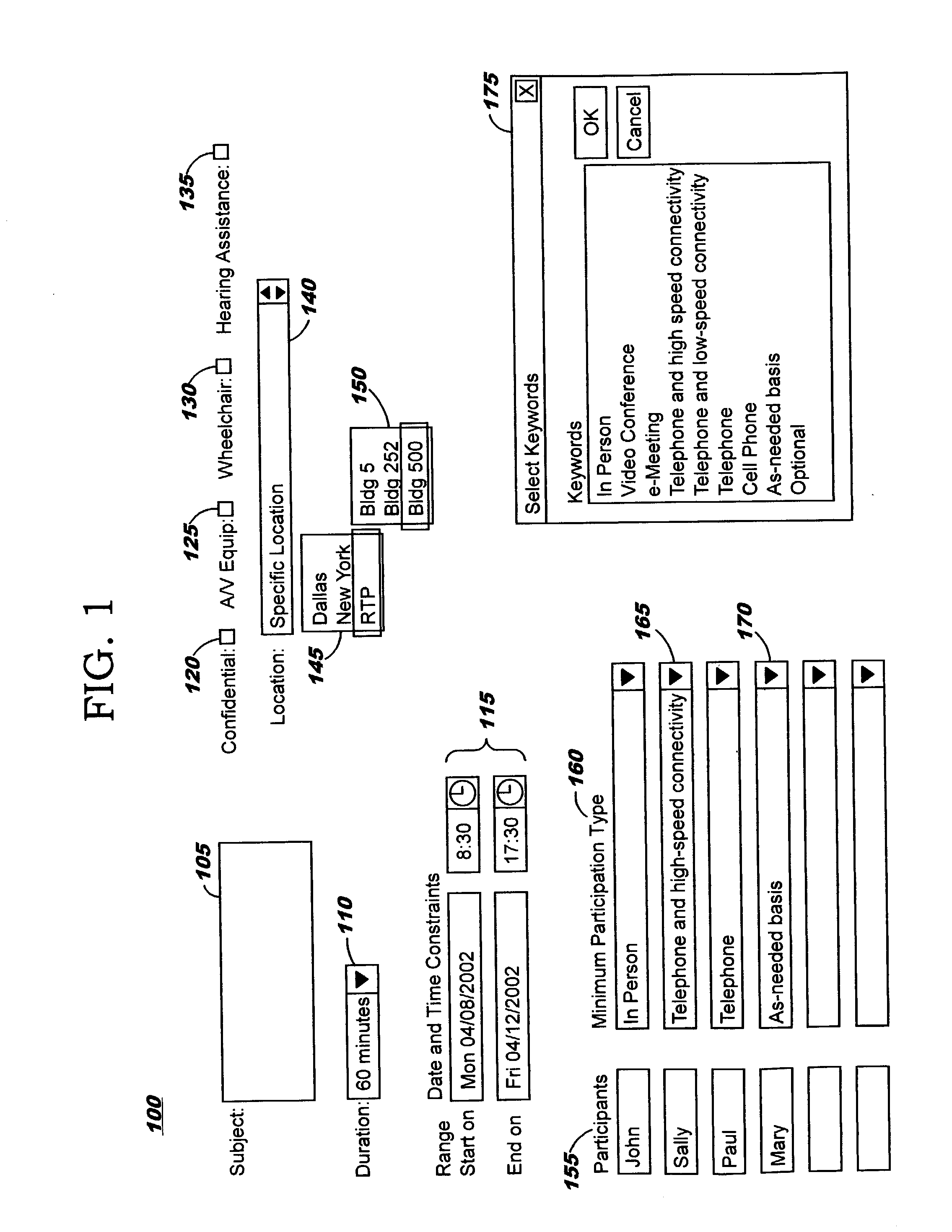
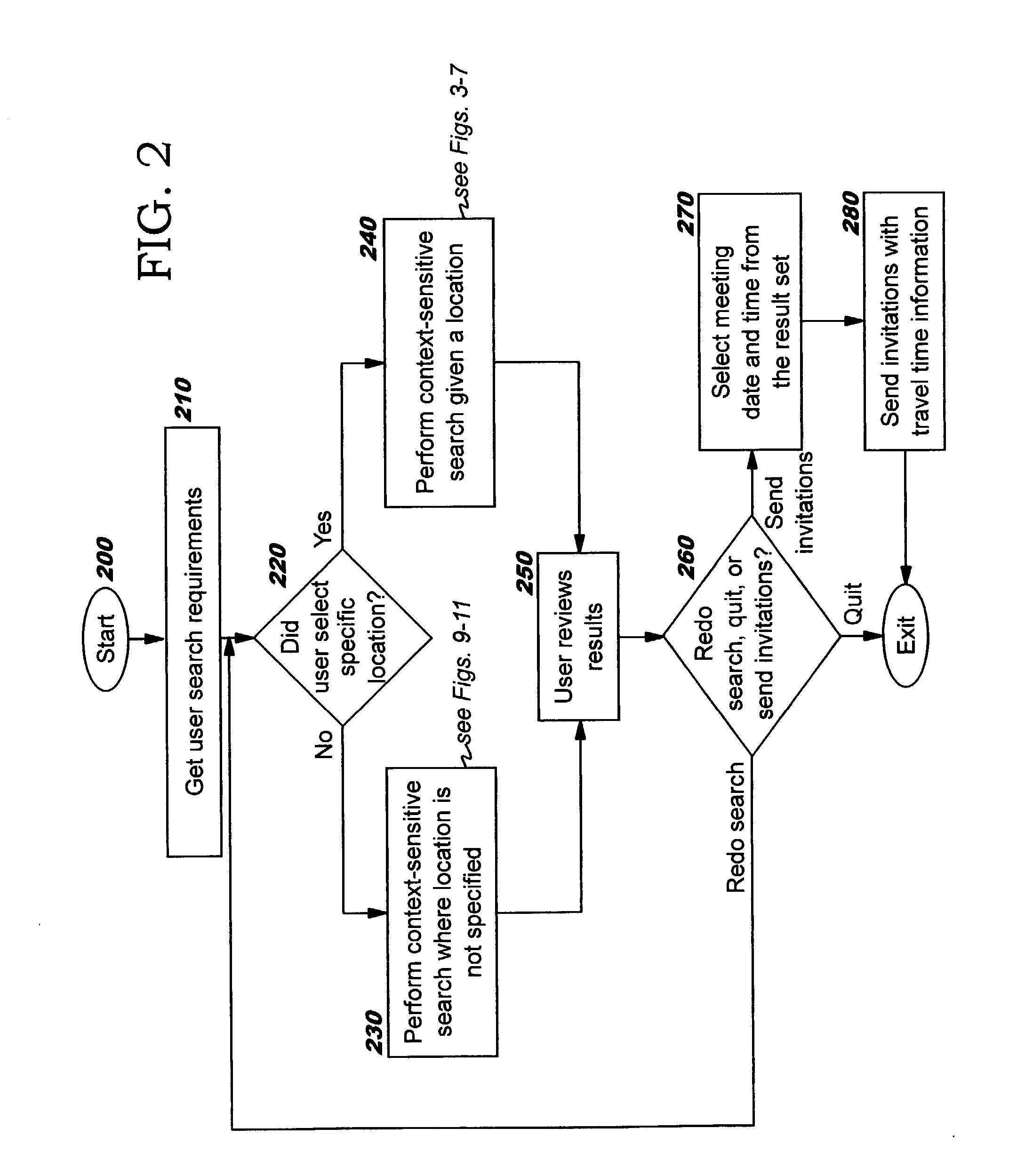
Intelligent free-time search
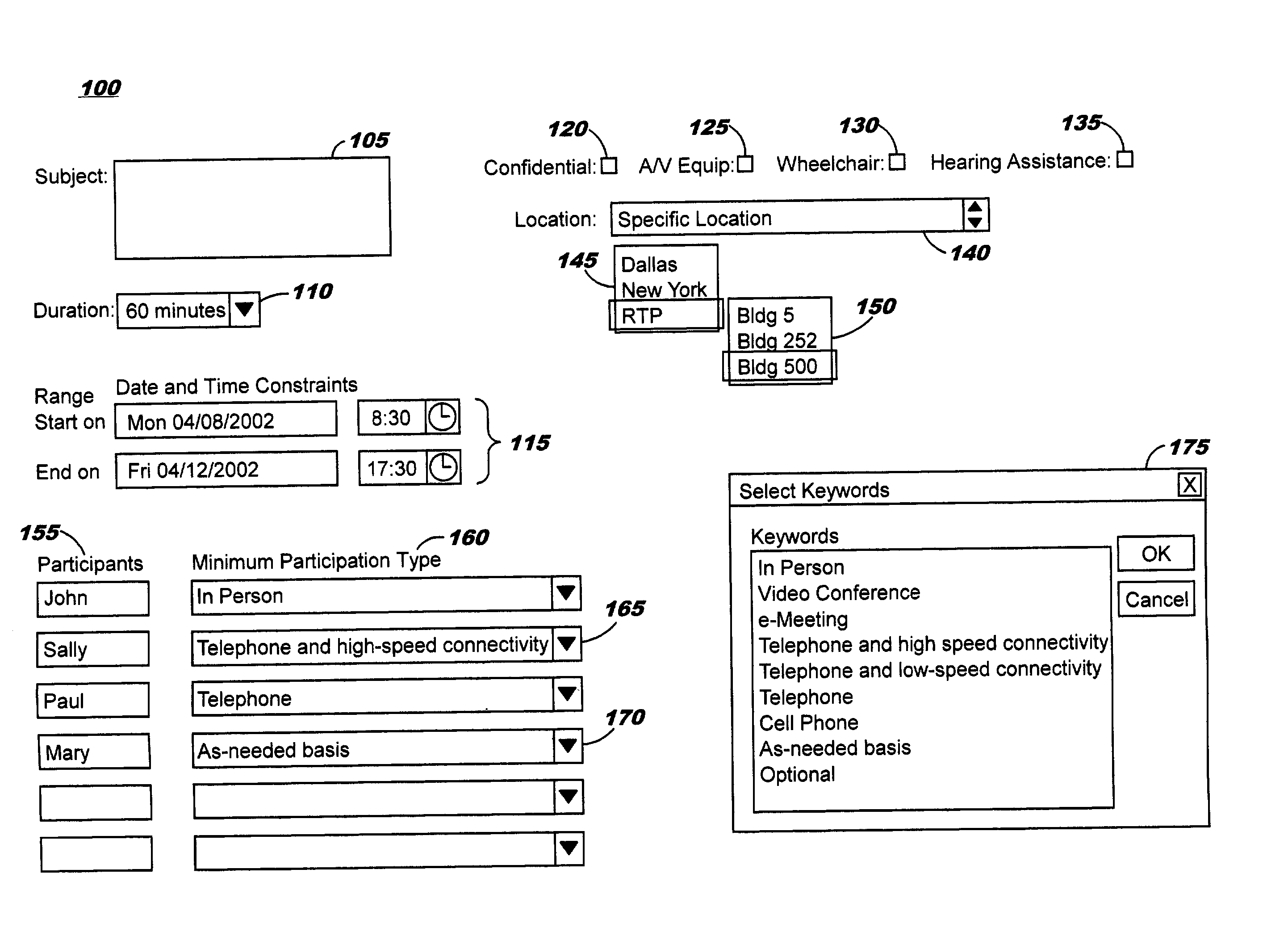
Techniques are disclosed for performing free-time searches that exploit information of the type used with electronic calendars. By leveraging advanced calendaring system information and using location, other context information such as corporate policy, legal constraints, and technology constraints, and user-specific preferences to provide a complete picture of a person's availability, the functionality (and therefore the value) of scheduling systems in increased, resulting in an ability to schedule meetings with more accuracy and less rework. Various allowable participation types for meeting invitees may be specified, and each invitee's availability is determined accordingly. Location-sensitive travel times (including optional user-specific travel time adjustments) are used in preferred embodiments when in-person participation is required.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for transacting an automated patient communications session
InactiveUS20050171411A1Facilitates gathering and storage and analysisBurden to of minimizedMedical communicationData processing applicationsSpoken languagePatient characteristics
A system and method for transacting an automated patient communications session is described. A patent health condition is monitored by regularly collecting physiological measures through an implantable medical device. A patient communications session is activated through a patient communications interface, including an implantable microphone and an implantable speaker in response to a patient-provided activation code. An identification of the patient is authenticated based on pre-defined uniquely identifying patient characteristics. Spoken patient information is received through the implantable microphone and verbal system information is played through the implantable speaker. The patient communications session is terminated by closing the patient communications interface. The physiological measures and the spoken patient information are sent.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
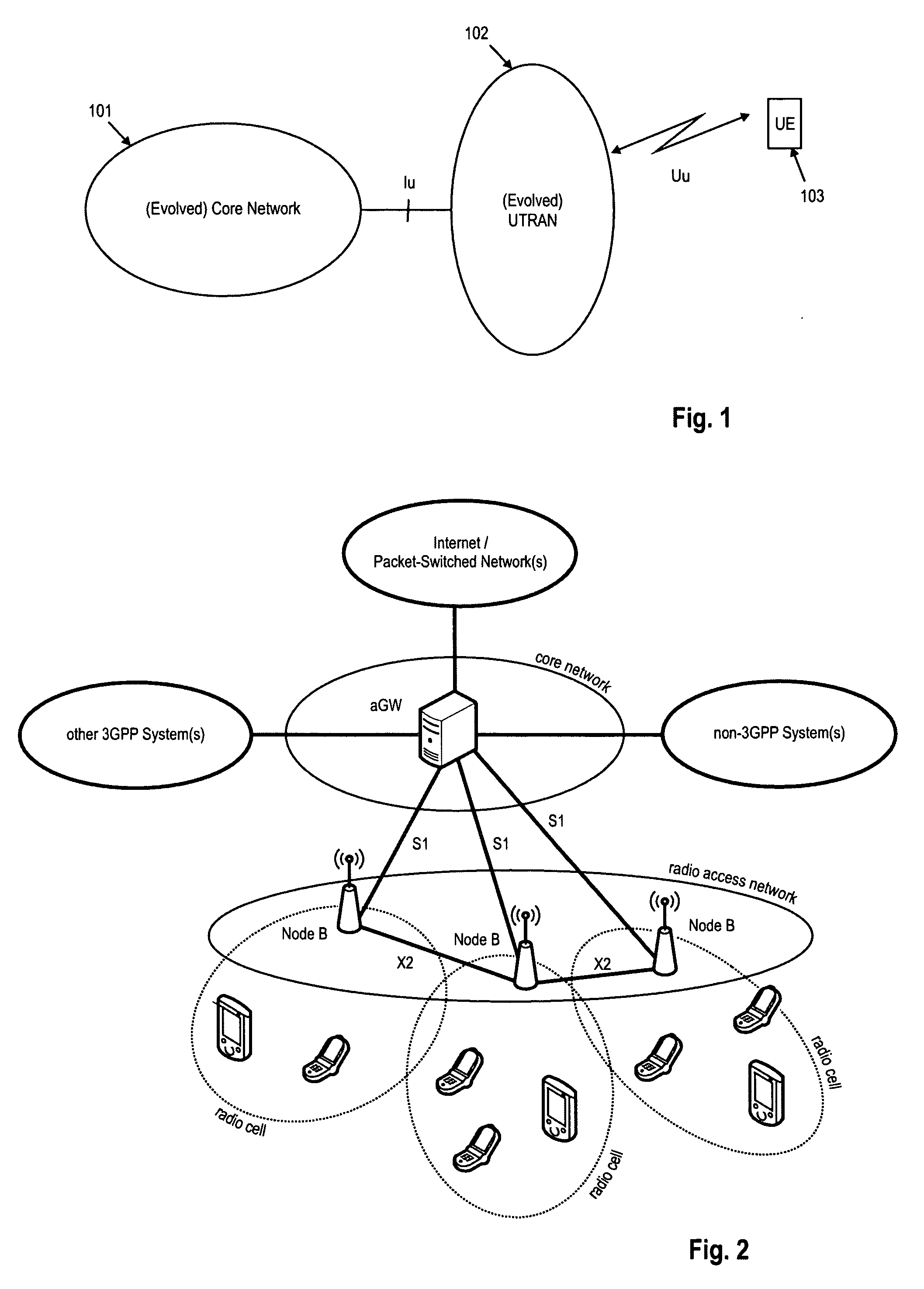
Apparatus and method for supporting mobility in a heterogeneous wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110294508A1Minimizes service interruptionShorten the timeConnection managementCurrent cellCommunications system
An apparatus and method in a heterogeneous wireless communication system reconnect a Mobile Station (MS) to a previously connected cell upon occurrence of a Radio Link Failure (RLF) in a current cell when a portion of a coverage of the second cell is included in a coverage of the first cell. A Mobile Station (MS) stores system information of a first Base Station (BS) of a first cell when performing handover from the first cell to a second cell. When changed system information of the first BS is received from a second BS of the second cell, the MS updates the stored system information using the changed system information. When detecting that a connection with the second cell is lost prior to a handover from the second cell, the MS performs reconnection to the first BS using the stored system information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
User equipment and power control method for random access
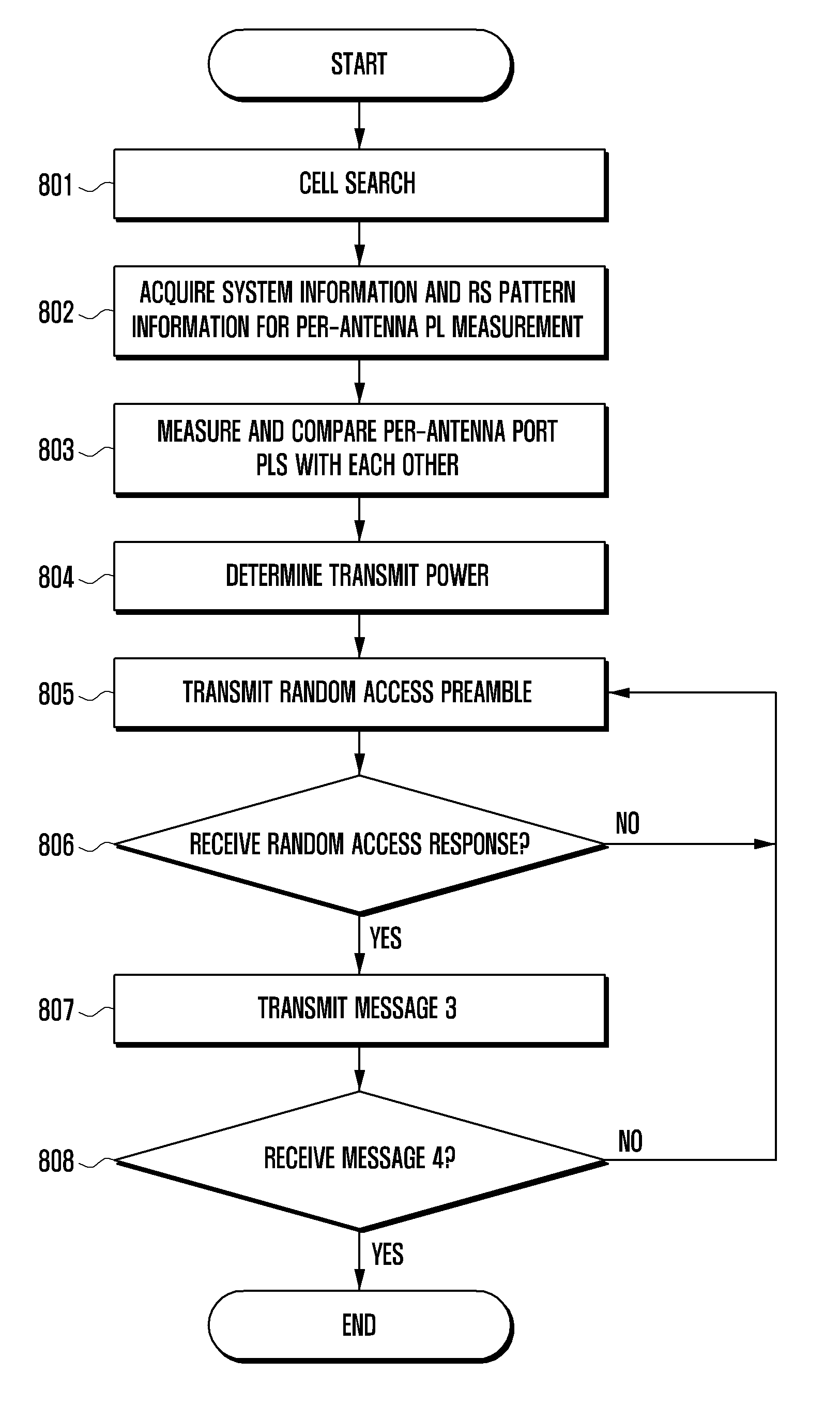
An improved power control method and apparatus of a mobile terminal is provided for facilitating random access procedure in a mobile communication system based on a distributed antenna system. A method includes receiving, by the terminal, system information from a base station, the system information including transmit power information for transmitting a random access preamble; calculating a transmit power using the transmit power information; and transmitting the random access preamble using with the calculated transmit power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for controlled distribution of contact information over a network
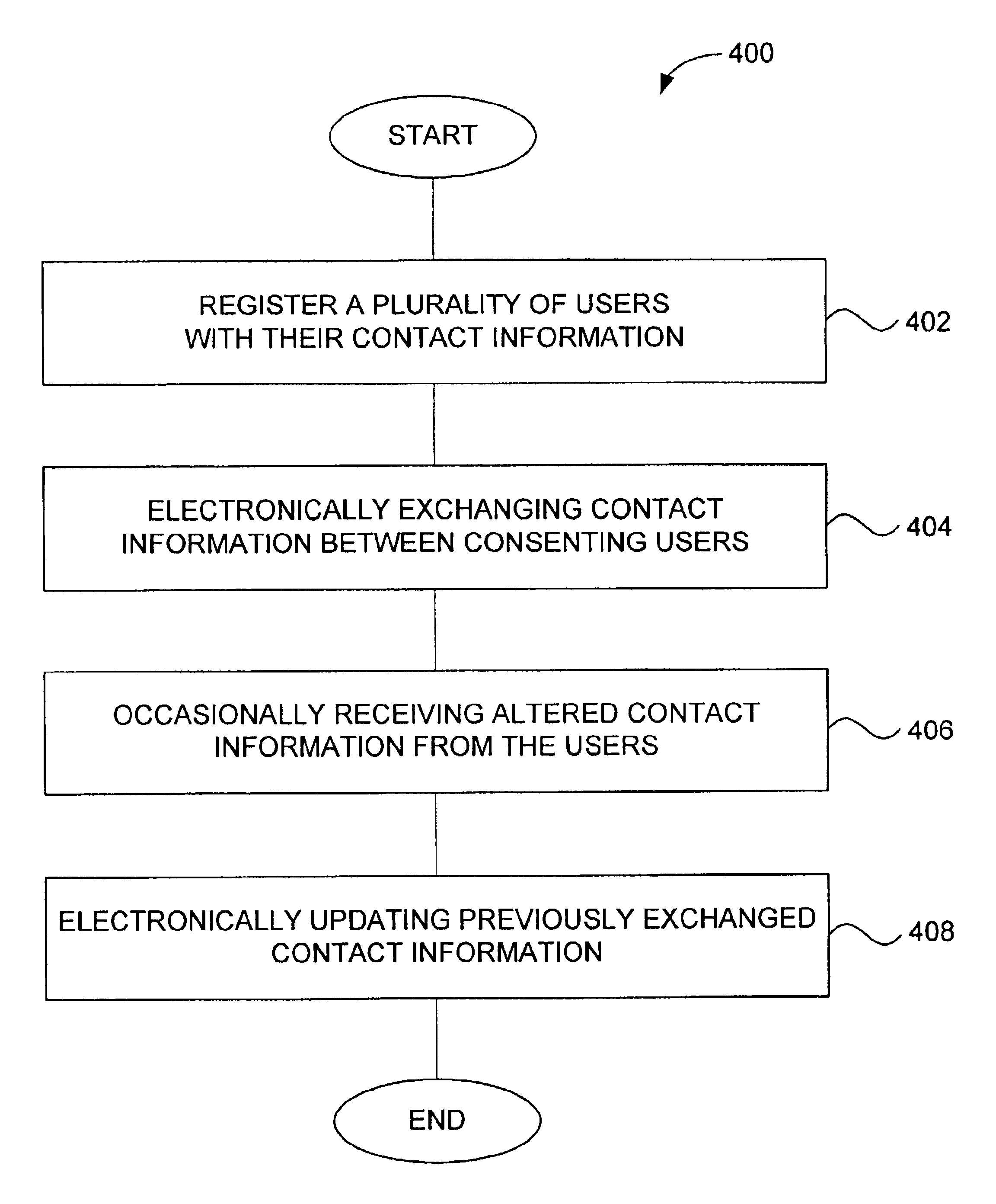
InactiveUS7003546B1Effective contactAutomate updatesMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationNetwork controlDistribution system
An information management and distribution system is disclosed. The information management and distribution system includes a client-side application and a server application that interact to facilitate the controlled exchange of contact information over a network. The client-side application can provide creation and design, rolodex, exchange, and update features. The information management and distribution system can also include a corporate administrator application. Still another aspect of the invention is that contact information can be distributed to registered users in a common format.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
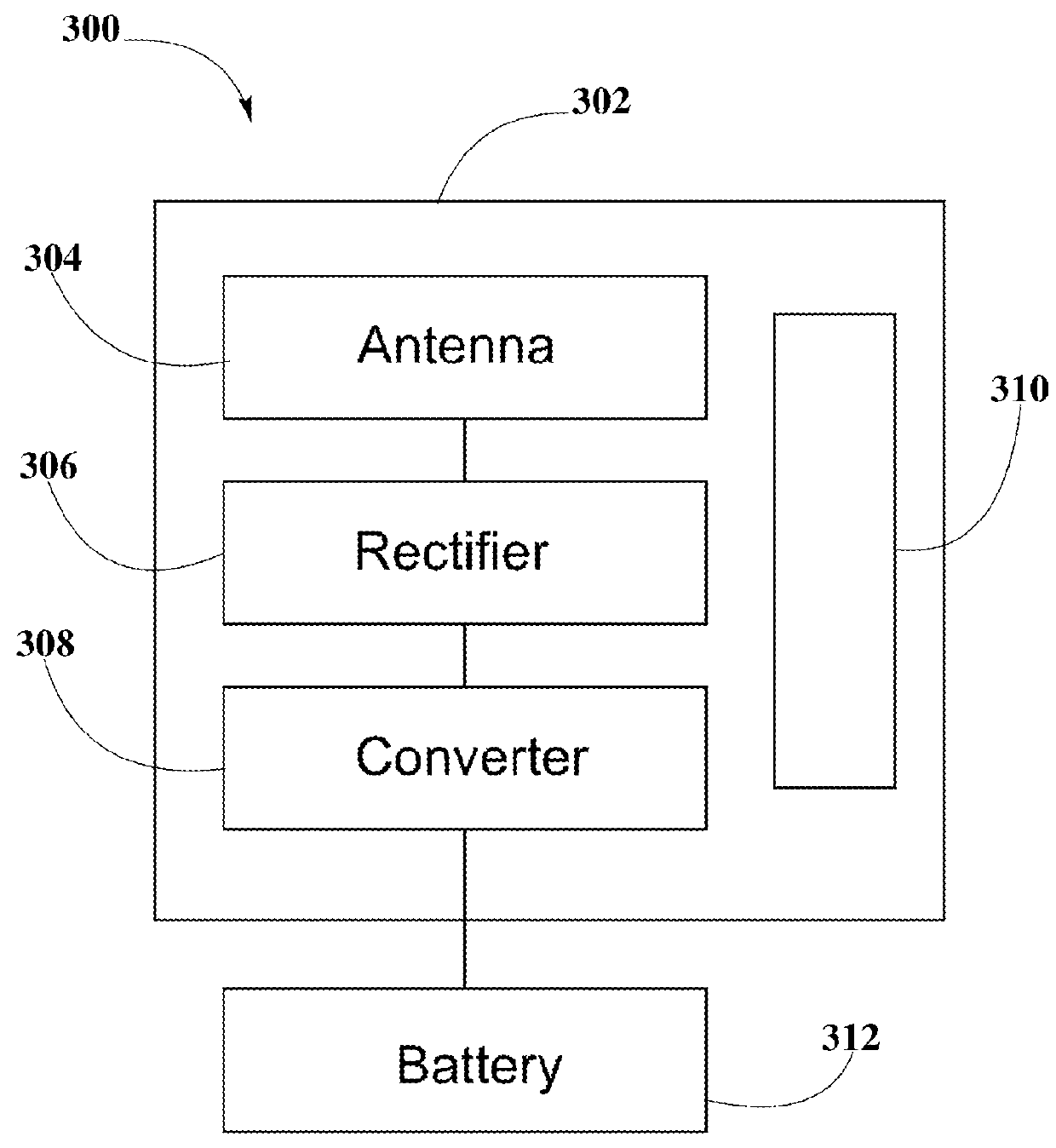
Systems and Methods for Tracking the Status and Usage Information of a Wireless Power Transmission System
InactiveUS20160056635A1Improve concentrationImprove accuracyVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingElectric power transmissionElectric force
Disclosed here are methods and systems to generate and distribute information about the status and usage of a wireless power transmission system. Specifically, the present disclosure may describe a process to generate information through various software running in different components of the wireless power transmission system. Additionally, the disclosure may also include a wireless power transmission system architecture which may include components, such as a remote information service, a remote information service manager, a remote information service database, one or more authorized computing devices, and a plurality of system information generators. System information generator may refer to components, such as wireless power transmitters, computing devices / non computing devices (coupled with power receiver devices), a system management service, and distributed system database. The aforementioned components within the wireless power transmission system may be used to automatically and autonomously generate, store, transmit, and distribute system status, usage, and statistics or metrics information in order to be edited or reported by authorized and authenticated users. The information may also be used to increase the accuracy of strategic marketing, sales focus, to alert customer service of system problems and performance issues, and for billing end users.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
Improved acquisition of system information of another cell
InactiveUS20090274086A1Reduce the necessary timeSave resourcesAssess restrictionBroadcast transmission systemsAcquisition timeComputer science
Method for informing a mobile terminal (MN), which is located in a first cell, on system information of a second cell. In particular, pointers to the system information are transmitted from the base station of the first cell to the mobile node, while the mobile node is located in the first cell. The MN processes said pointer, comprising e.g. information on the transmission format and timing of system information in the second cell. Using an acquisition gap assigned by the network, the MN changes the frequency to the second frequency so as to acquire the system information based on the previously received scheduling information. Thus, the acquisition time for important system information may be reduced, as no Master Information Block on the second frequency has to be processed first, in order to acquire the system information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
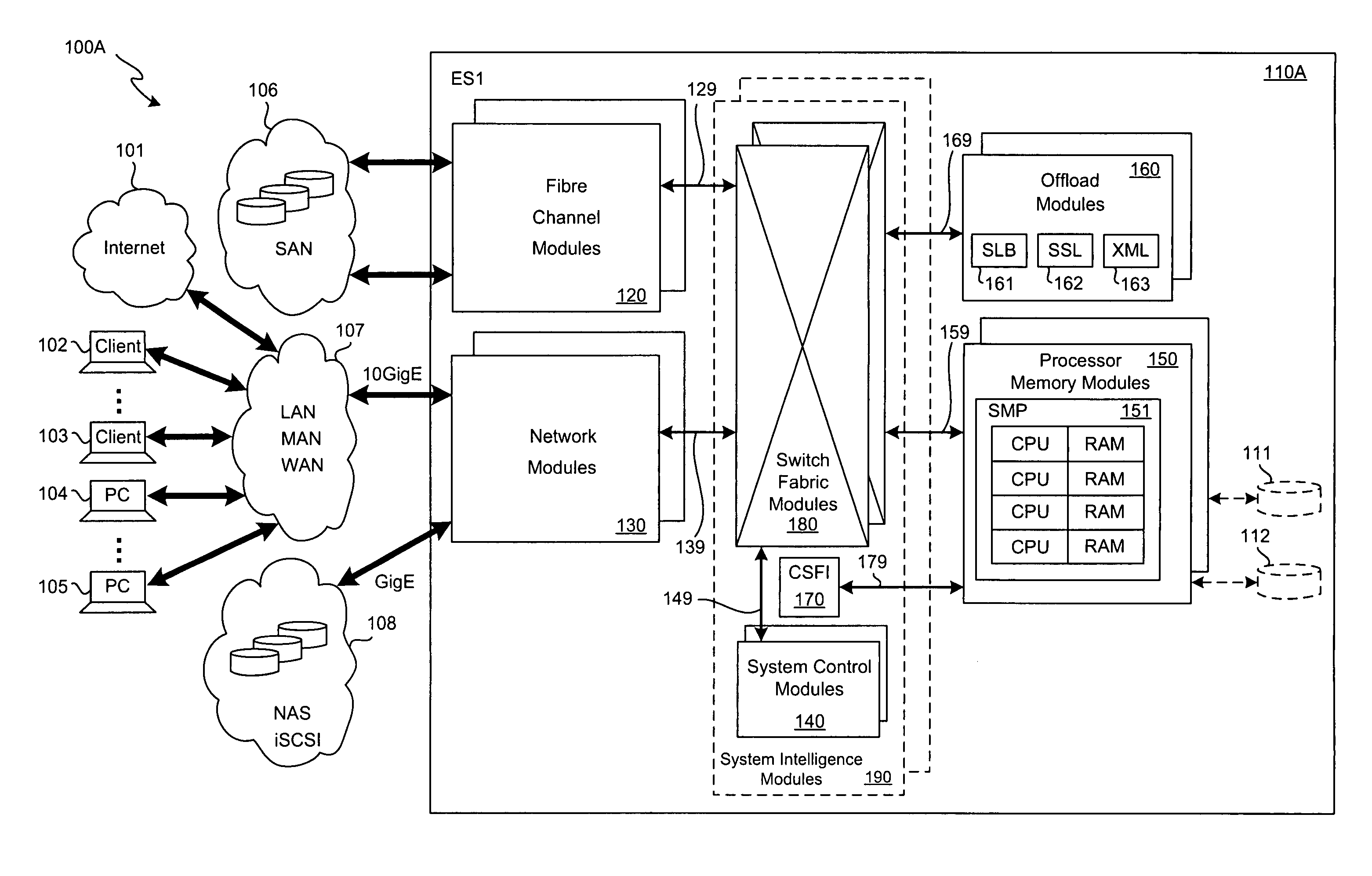
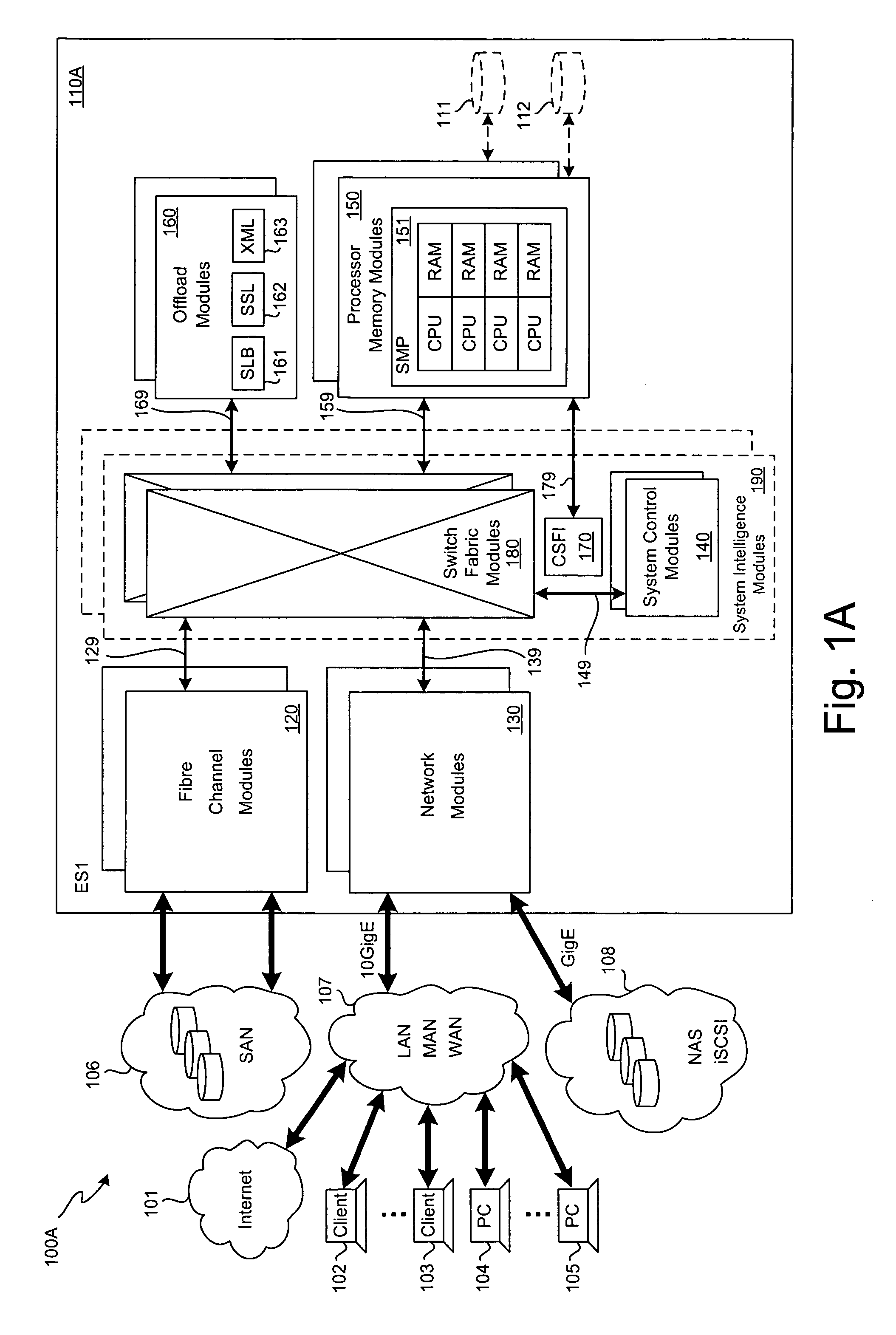
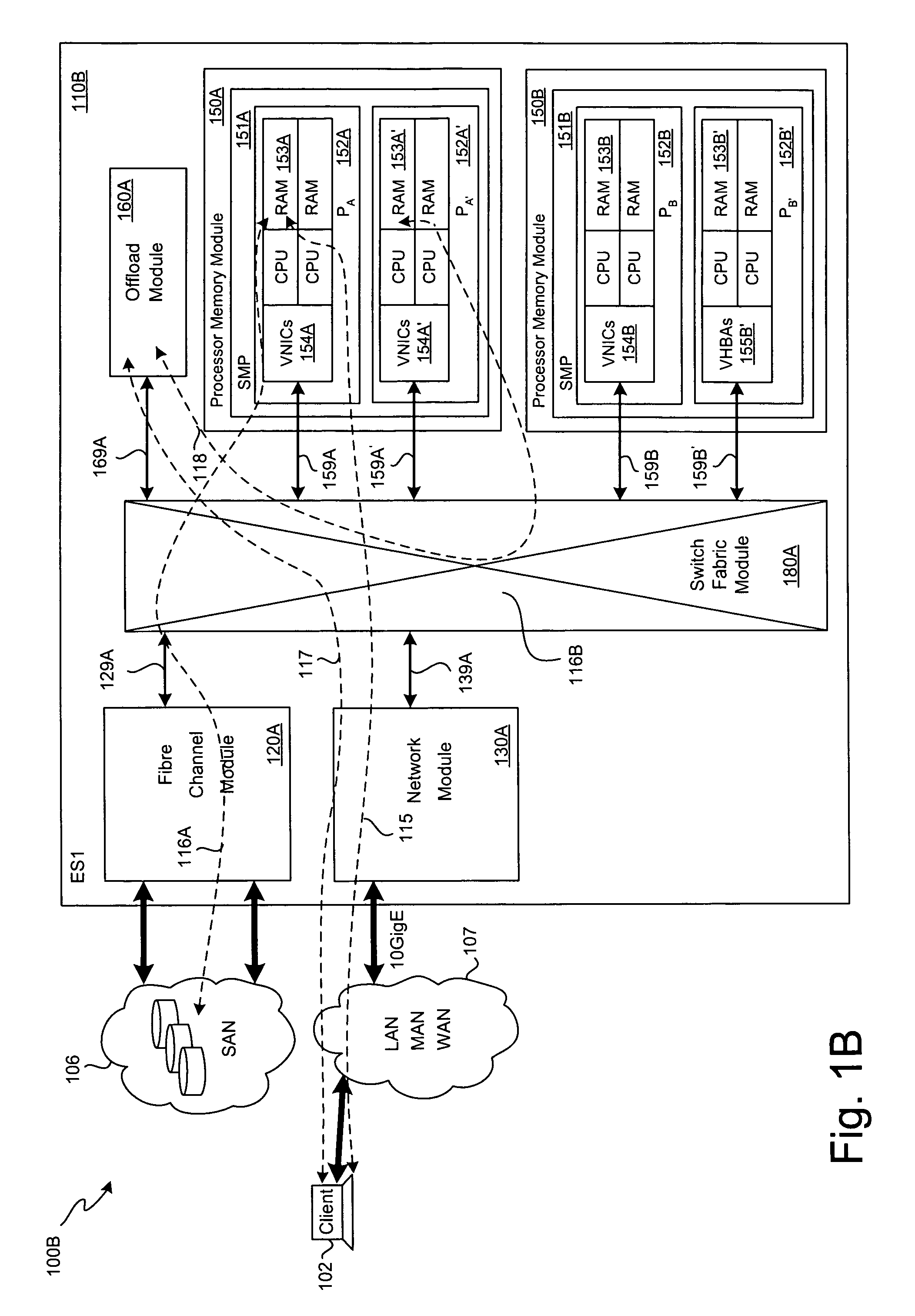
SCSI transport for fabric-backplane enterprise servers
ActiveUS7633955B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationSCSI initiator and targetFiber
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) transport for fabric backplane enterprise servers provides for local and remote communication of storage system information between storage sub-system elements of an ES system and other elements of an ES system via a storage interface. The transport includes encapsulation of information for communication via a reliable transport implemented in part across a cellifying switch fabric. The transport may optionally include communication via Ethernet frames over any of a local network or the Internet. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Direct Data Placement (DDP) protocols are used to communicate the information (commands, responses, and data) between SCSI initiator and target end-points. A Fibre Channel Module (FCM) may be operated as a SCSI target providing a storage interface to any of a Processor Memory Module (PMM), a System Control Module (SCM), and an OffLoad Module (OLM) operated as a SCSI initiator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
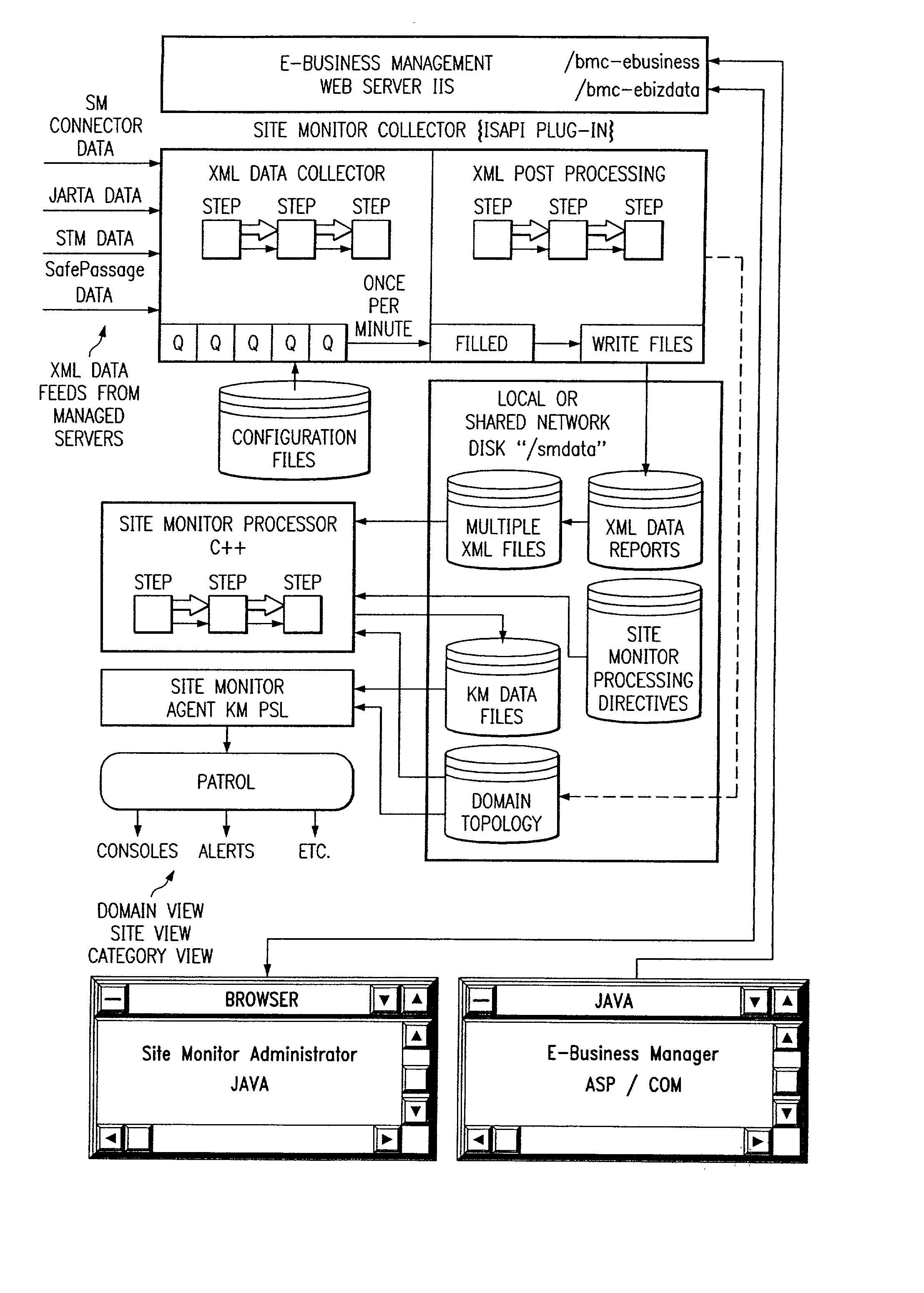
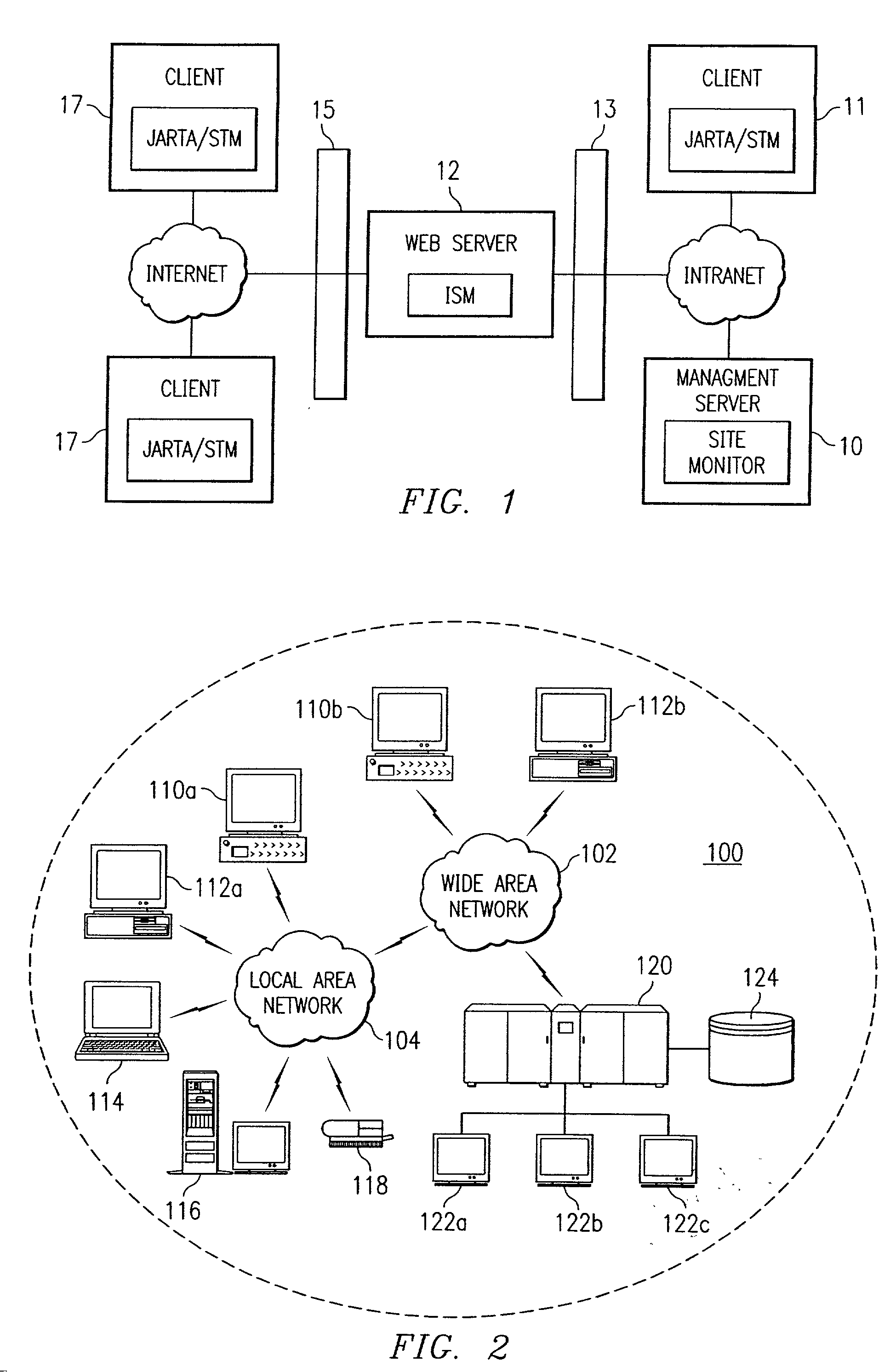
Site monitor
Systems and methods for network service management, wherein the internet service management system includes one or more components which collectively enable an administrator to obtain a site-wide view of network activities on servers such as web servers, FTP servers, e-mail servers, domain name servers, etc. In addition to collecting information relating to web server latency and processing time, the internet service management system may collect actual user transaction information and system information from end users on client computers. The internet service management system may provide domain summary information for a domain, or it may provide management information organized by "categories" according to how a site manager wants to view and manage his business; e.g., byline of business (books, auctions, music, etc.), by site function (searches, shopping cart, support, quotes, sales automation), or most any other categorization customers may choose.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
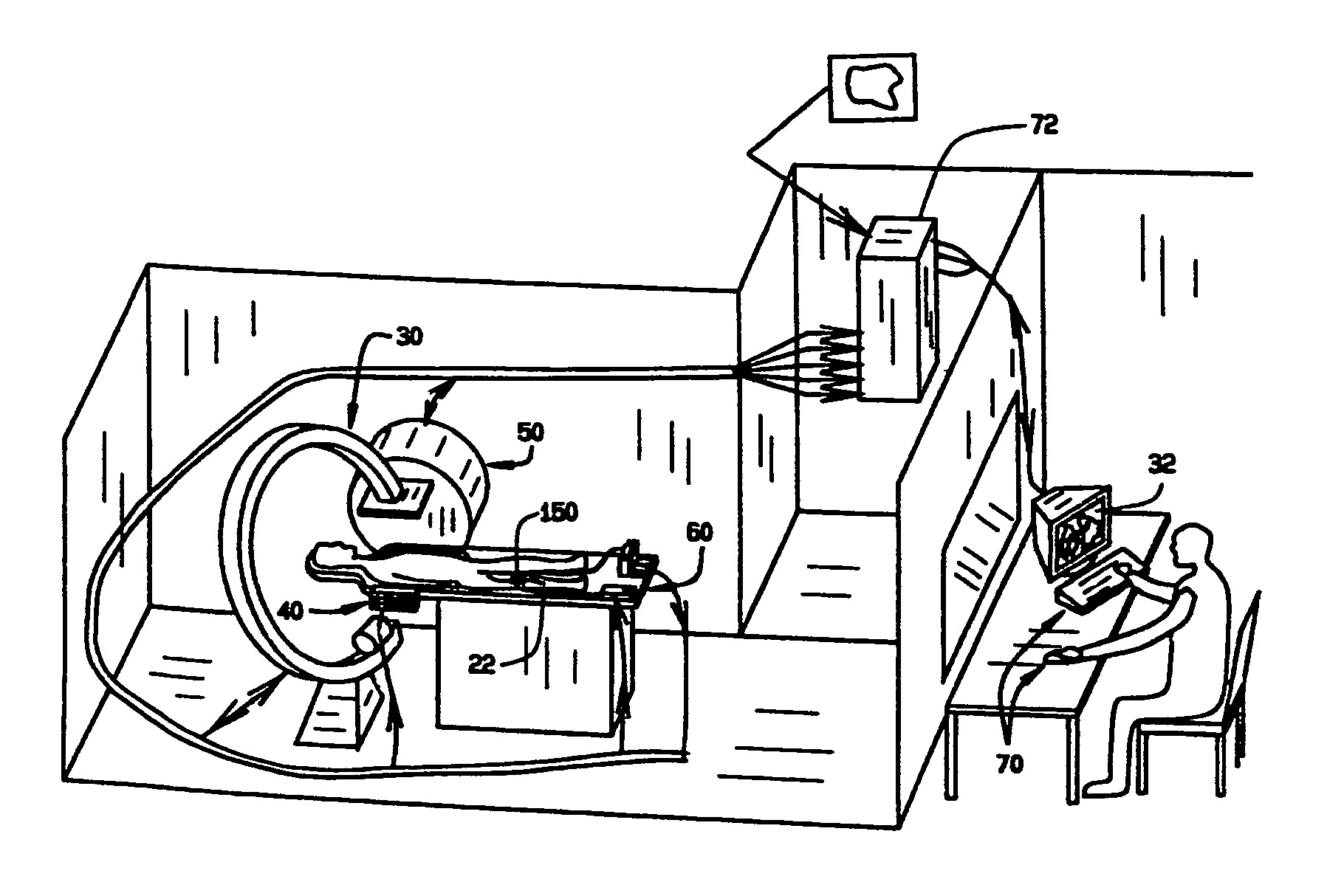
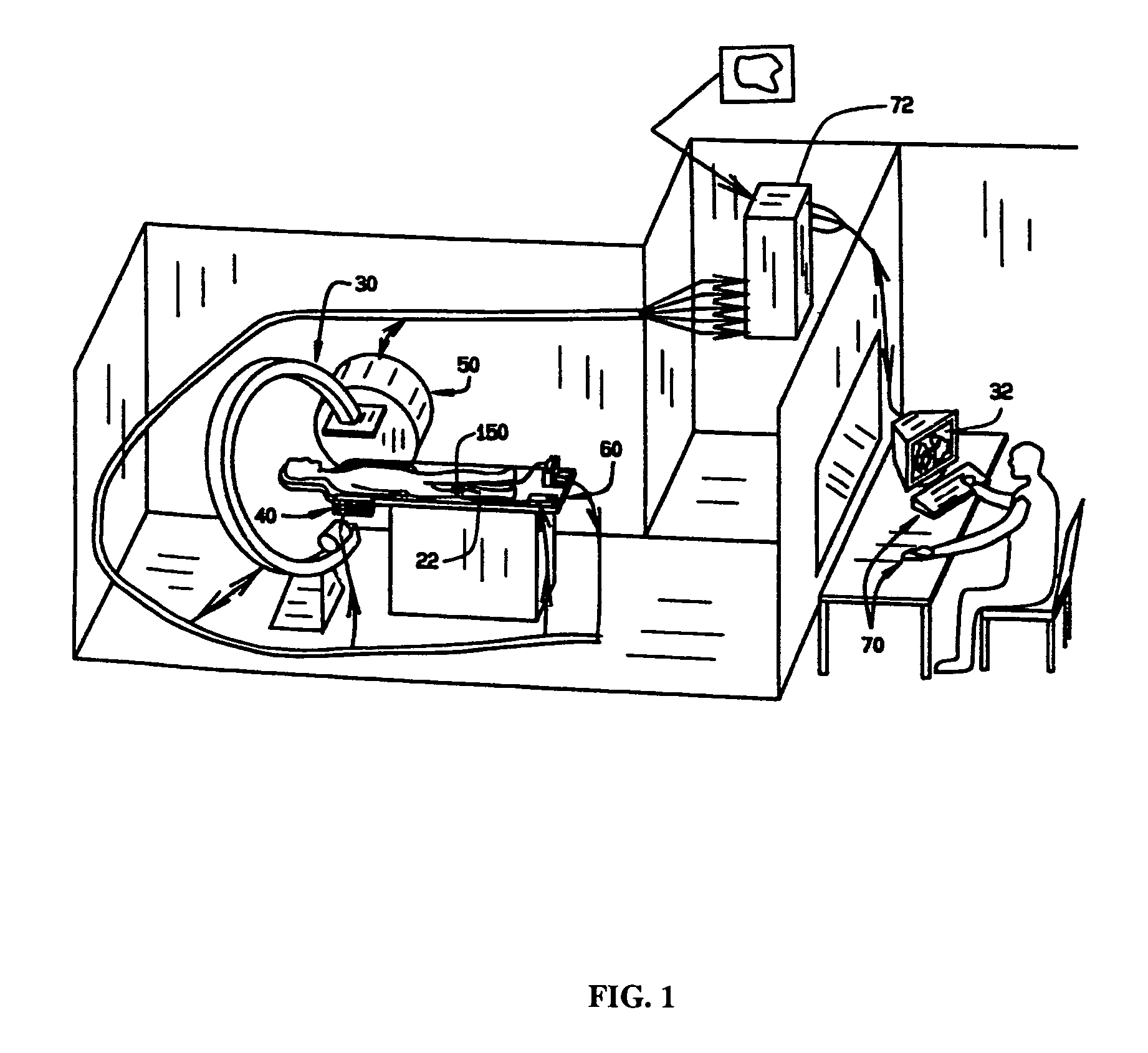
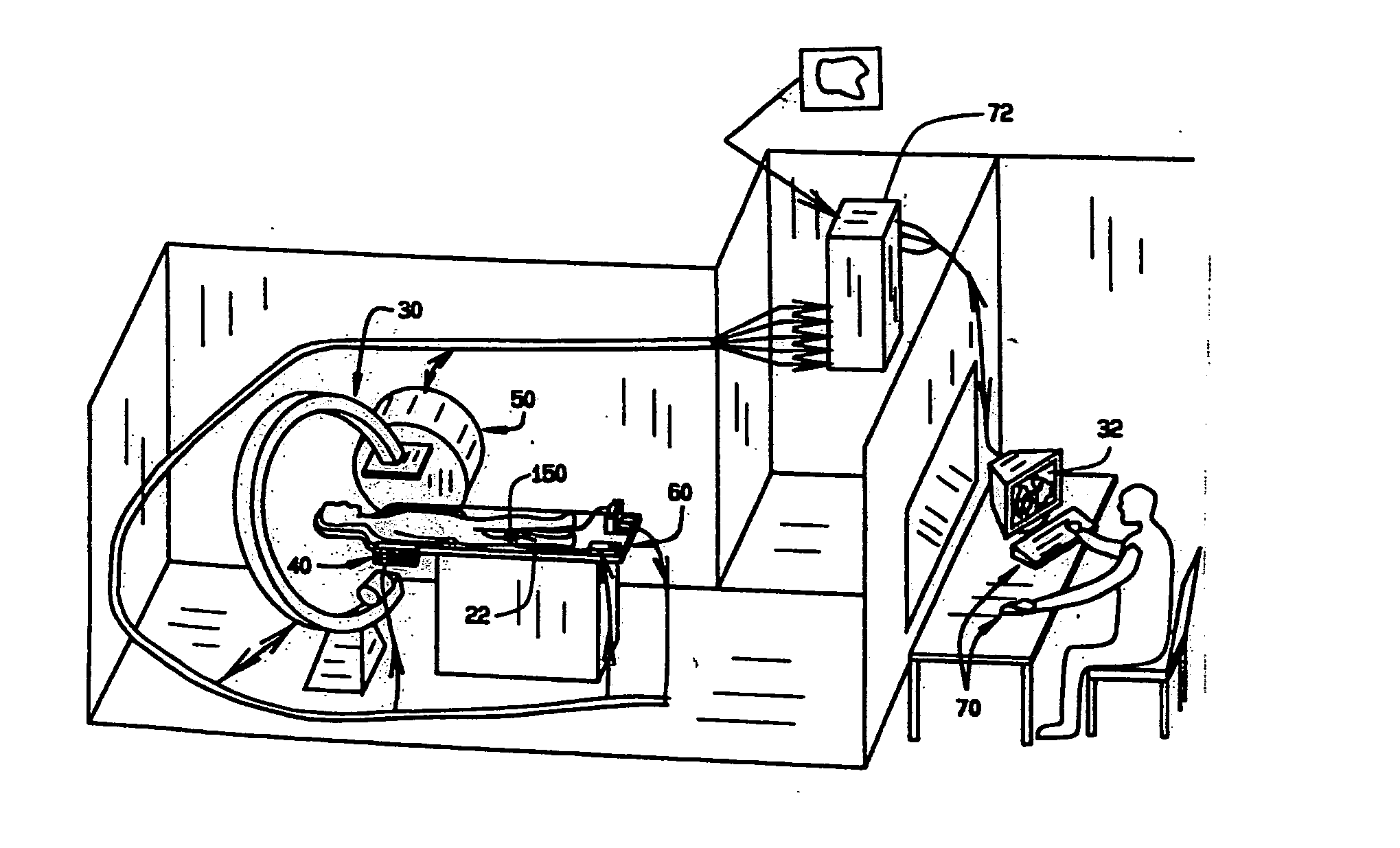
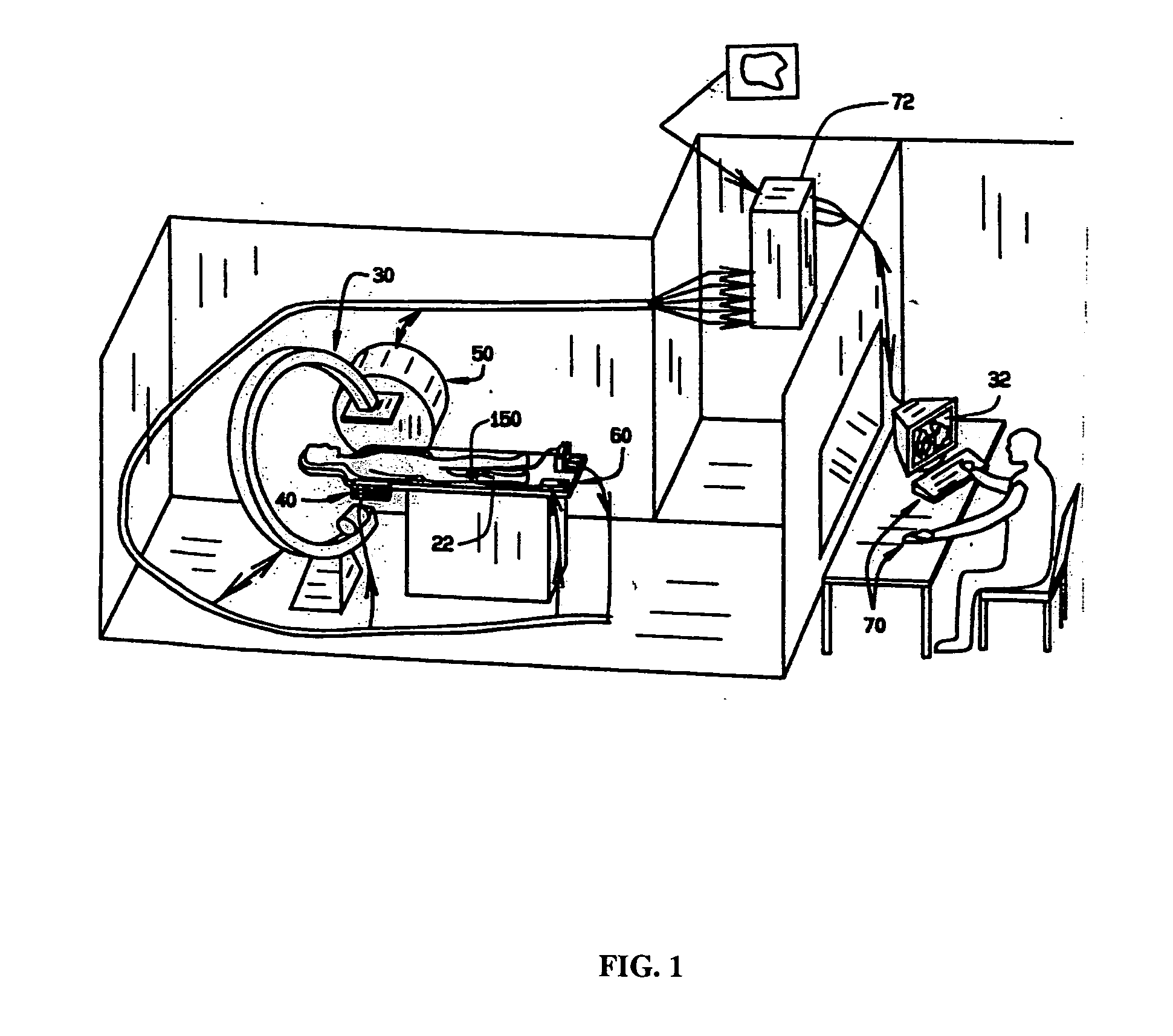
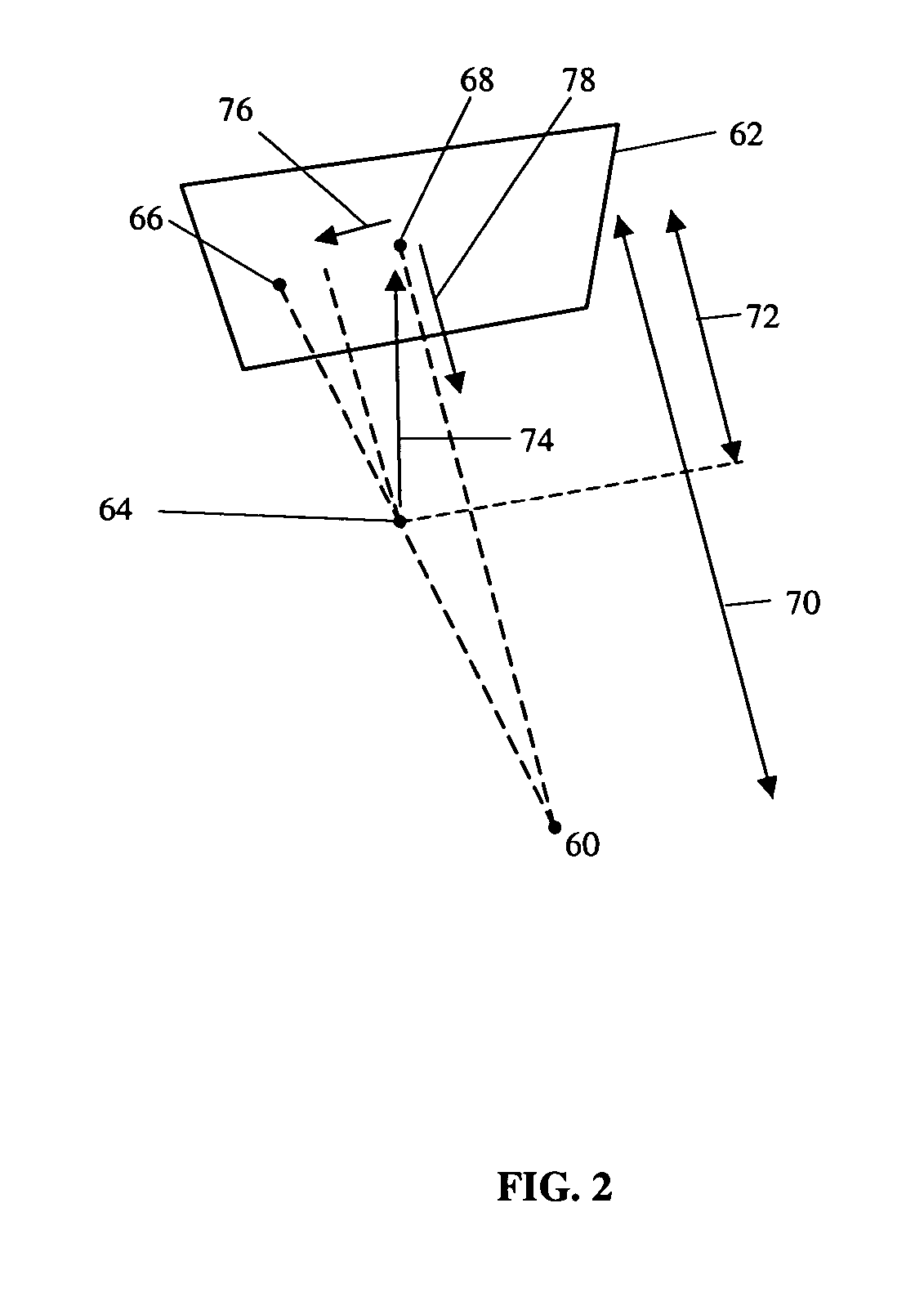
System and method of surgical imagining with anatomical overlay for navigation of surgical devices
ActiveUS7831294B2Improve the display effectPrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
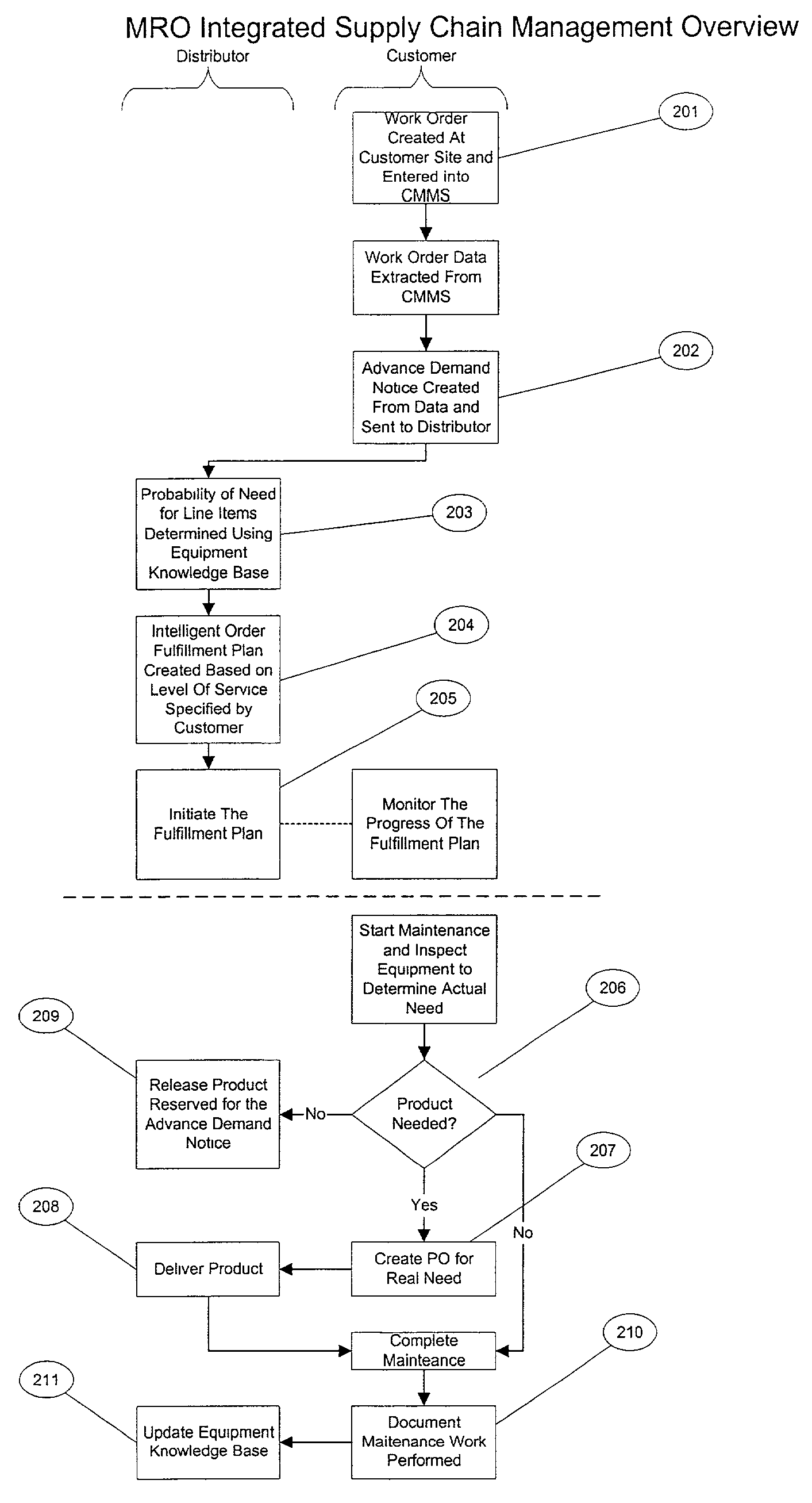
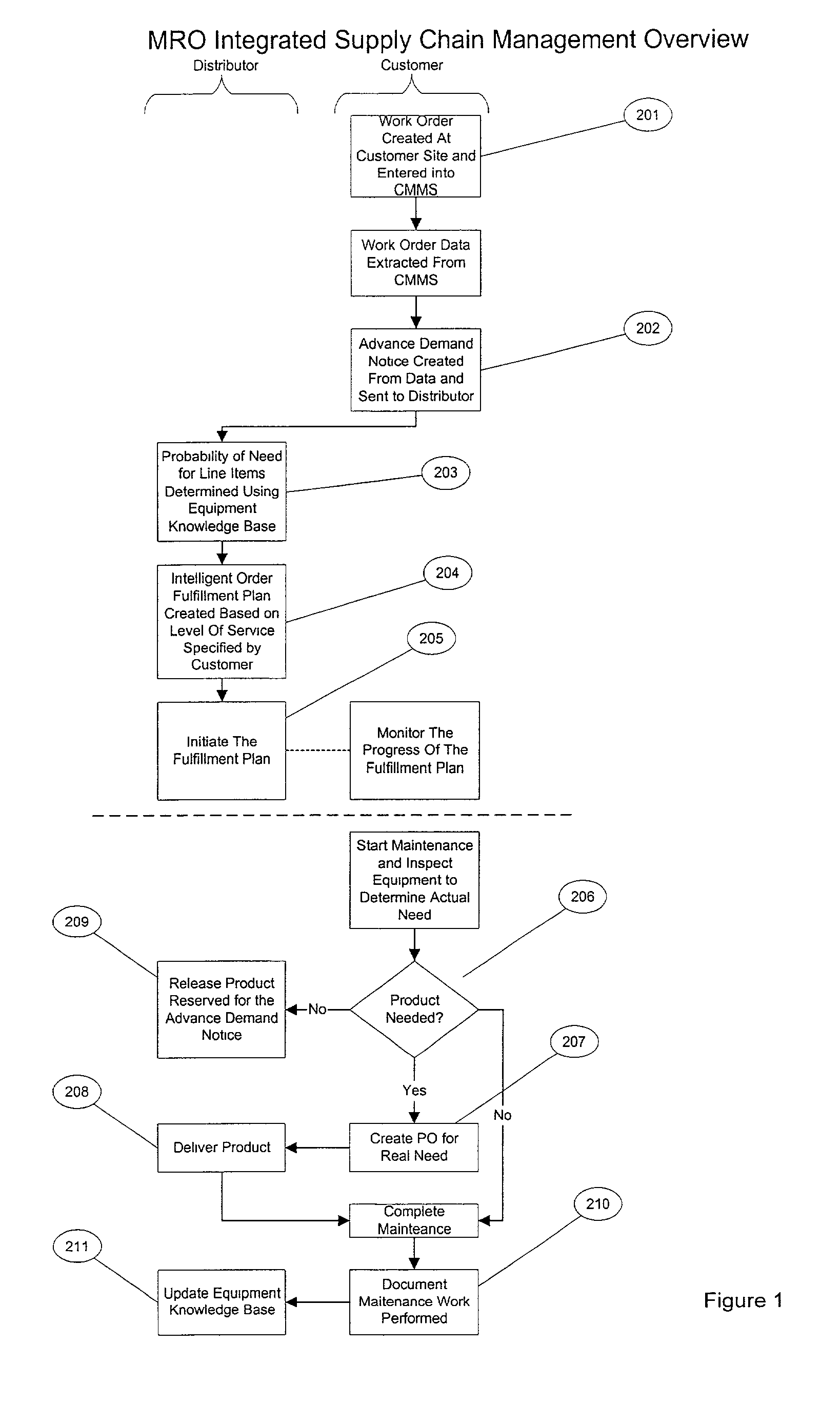
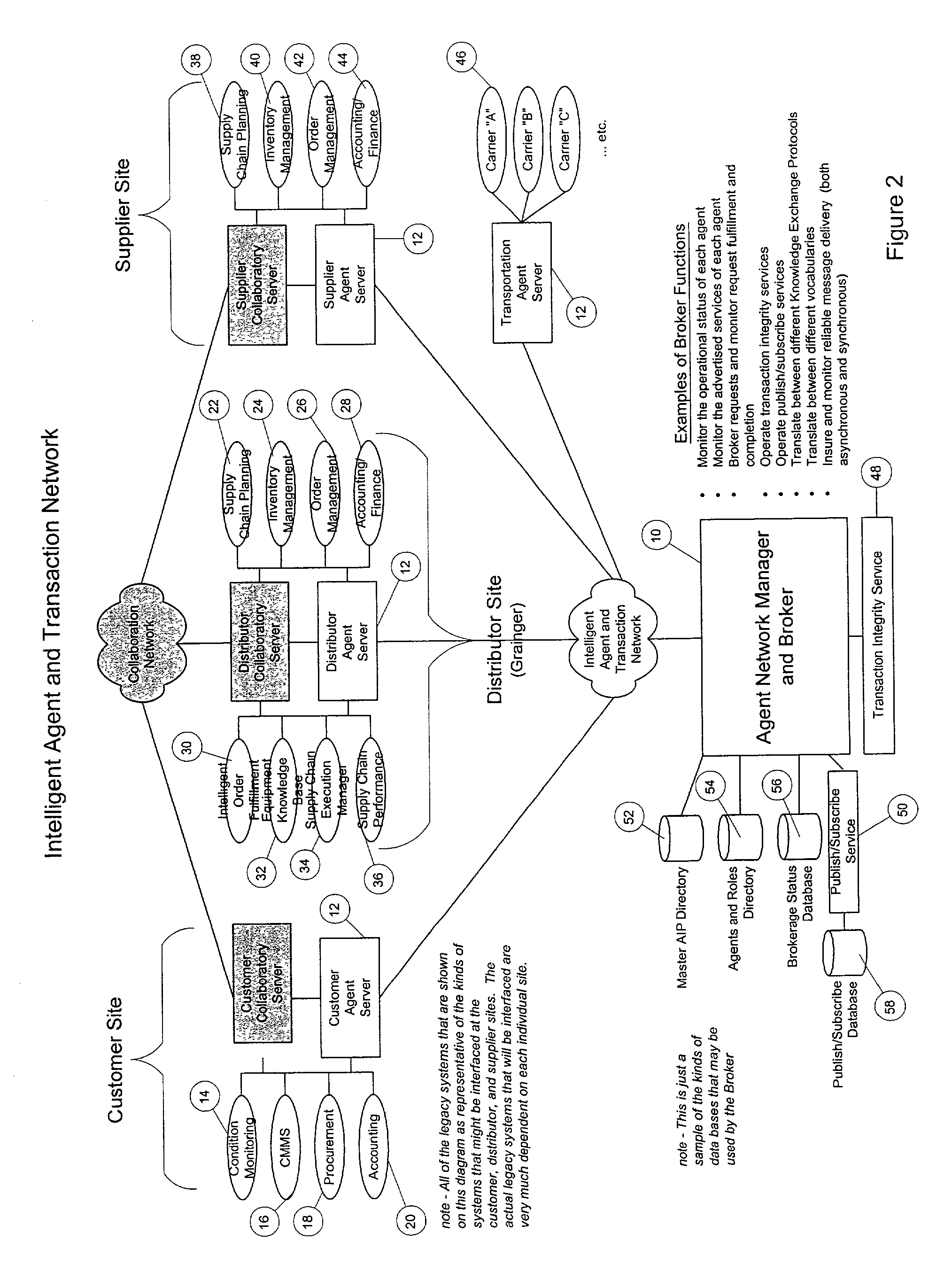
Method for fulfilling an order in an integrated supply chain management system
A method for fulfilling an order in a supply chain. The method is performed by extracting from a customer system information pertaining to the work order that specifies a piece of equipment to be repaired and items expected to be used during the repair procedure, determining, using an equipment knowledge base, a probability that each of the items will be needed to effect the repair procedure, and using the determined probability to stage the items within the supply chain whereby the items are made ready for use in the repair procedure. Further steps can include extracting from the customer system information pertaining to a completion of the repair procedure and using the information pertaining to the completion of the repair procedure to populate the equipment knowledge base for use in future probability of need calculations.
Owner:W W GRAINGER
Surgical navigation with overlay on anatomical images
ActiveUS20060079745A1Enhance displayed imagePrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
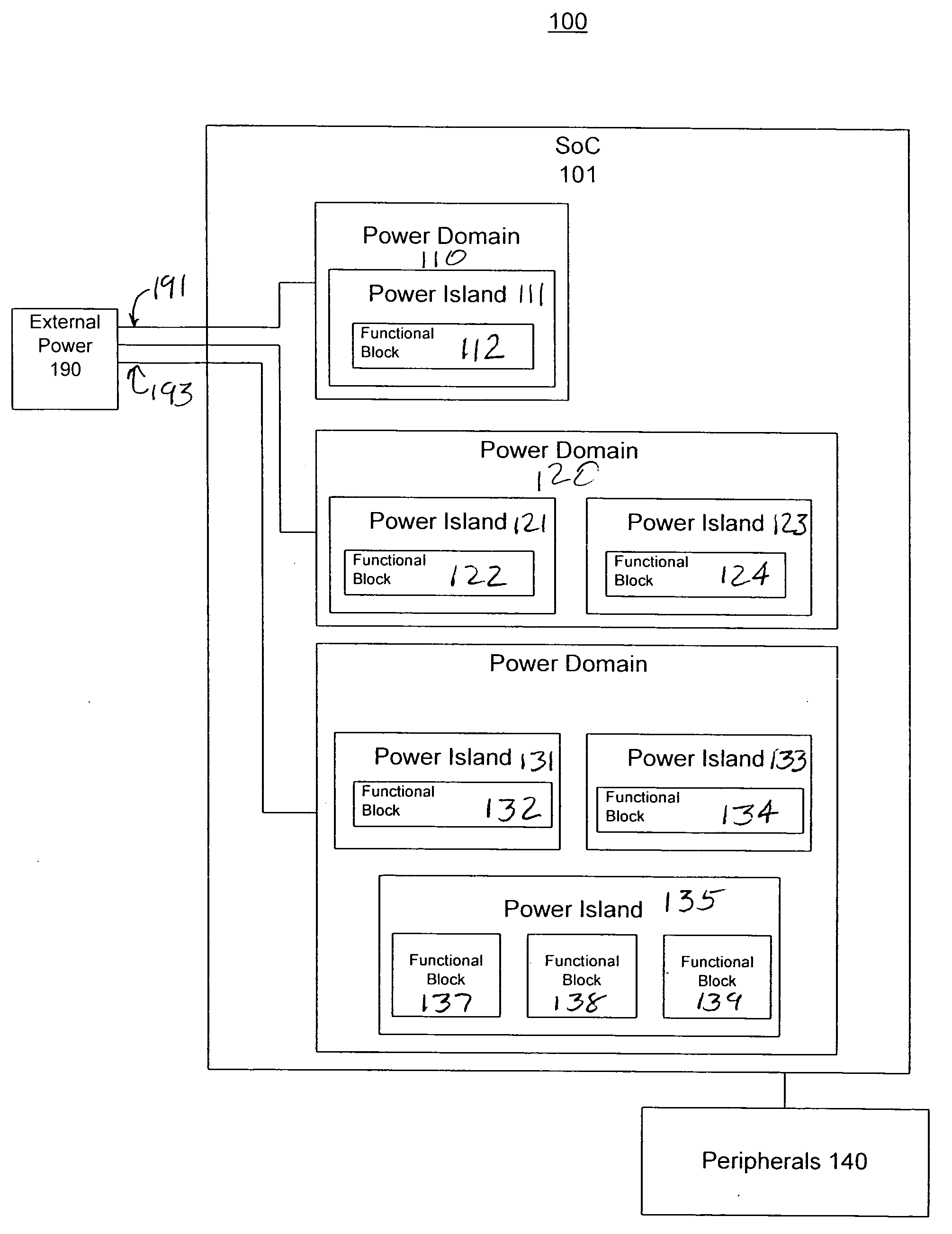
Power control system and method
An efficient and effective power control system method are described with expedited recovery from a reduced power state. In one embodiment, a present invention power control system includes performing a reduced power detection process for detecting a reduced power state, wherein the reduced power state is associated with an expedited recovery; performing a reduced power state entry process; performing a recovery detection process for detecting a recover indication event; and performing an expedited recovery process in accordance with detection of a recovery indication event. The reduced power state entry process comprises saving an expedited recovery information in registers of an always on domain and putting an external memory in self refresh mode to preserve a system context while a chip is turned off. The expedited recovery process comprises determining whether to proceed with the expedited recovery process; initializing memory controller registers and directing memory controller to exit self refresh; validating system context recovered from memory using keys stored in an always on domain; jumping to recovery instructions in memory; restoring operating system information and returning to operating system control.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
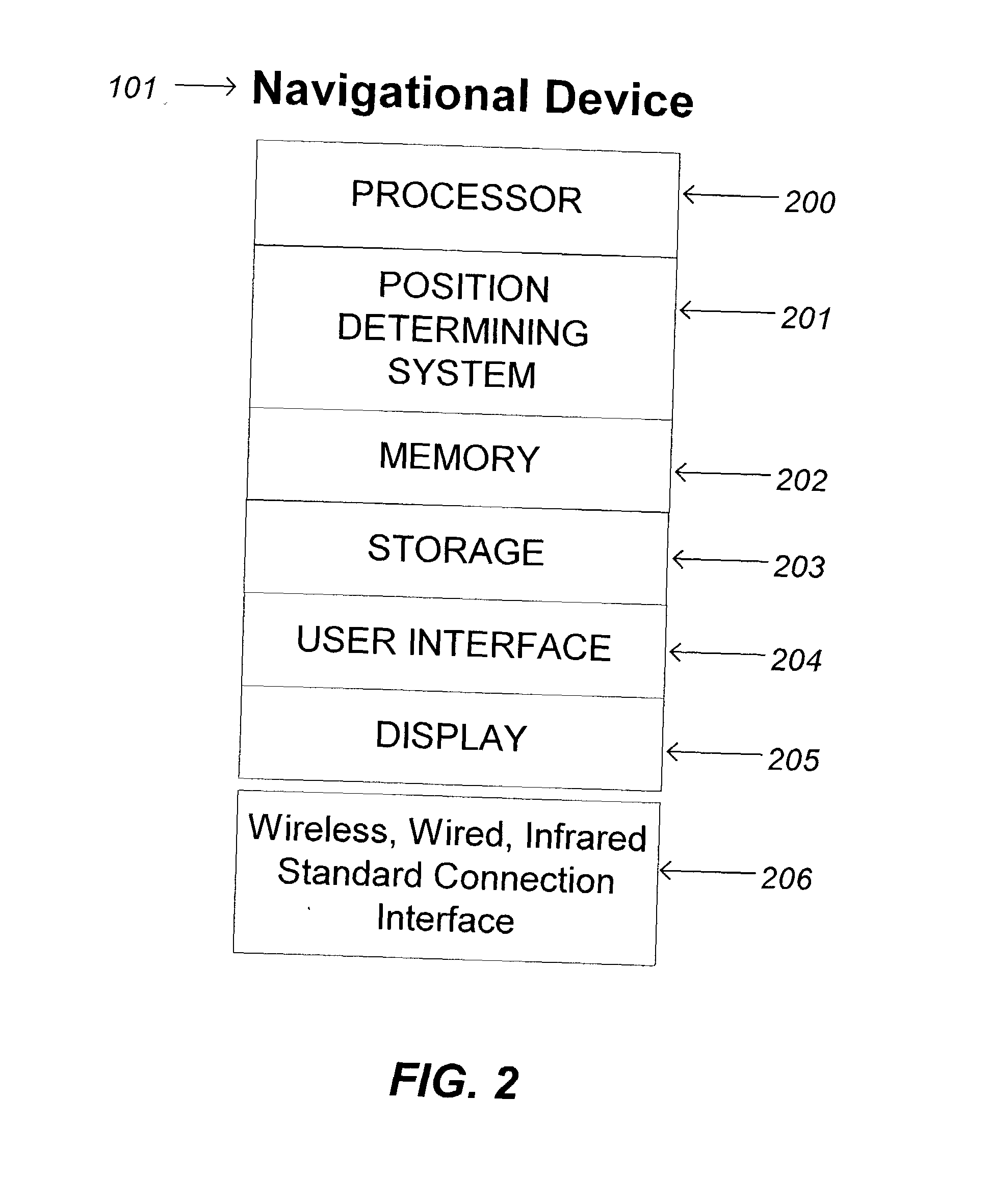
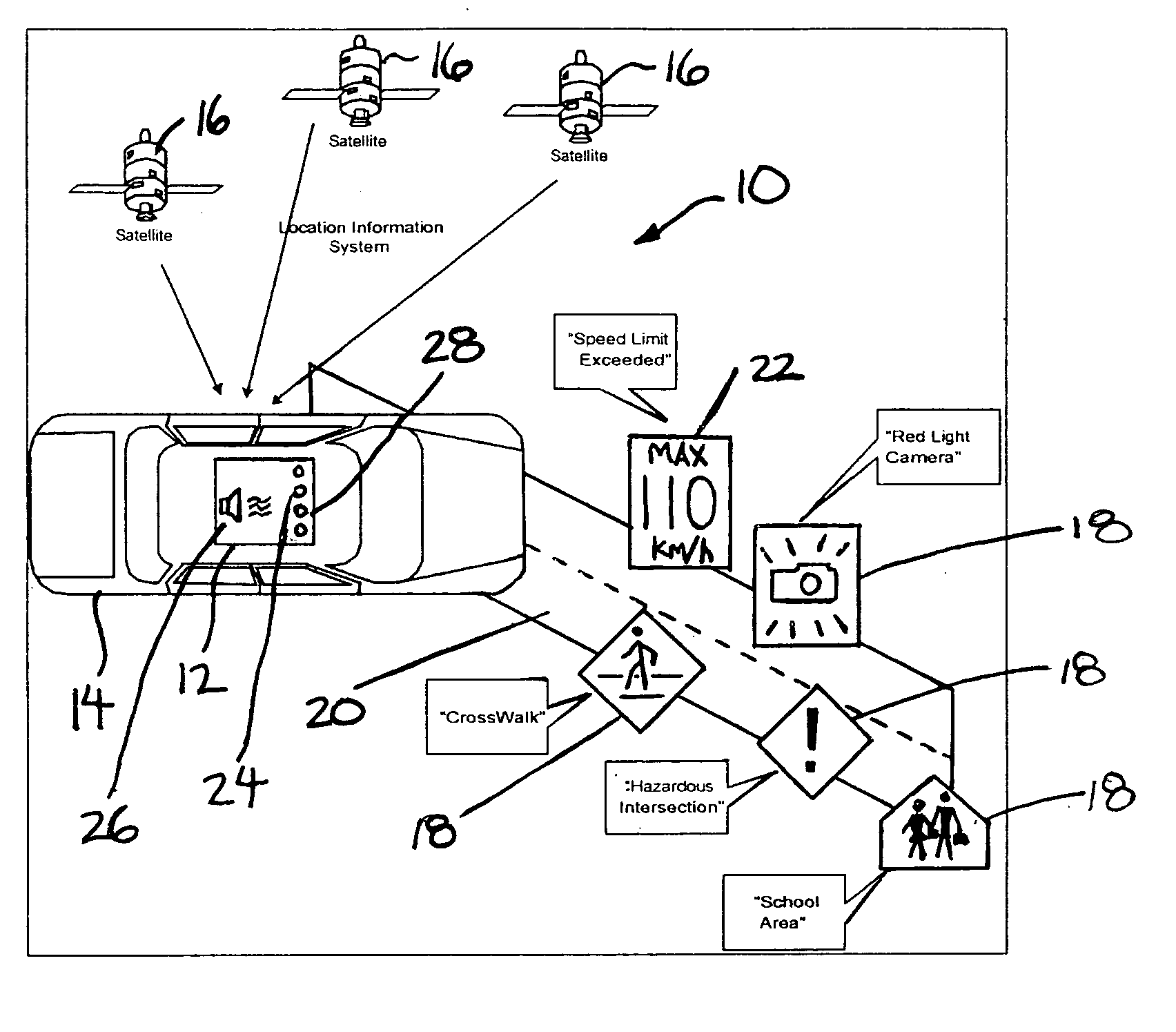
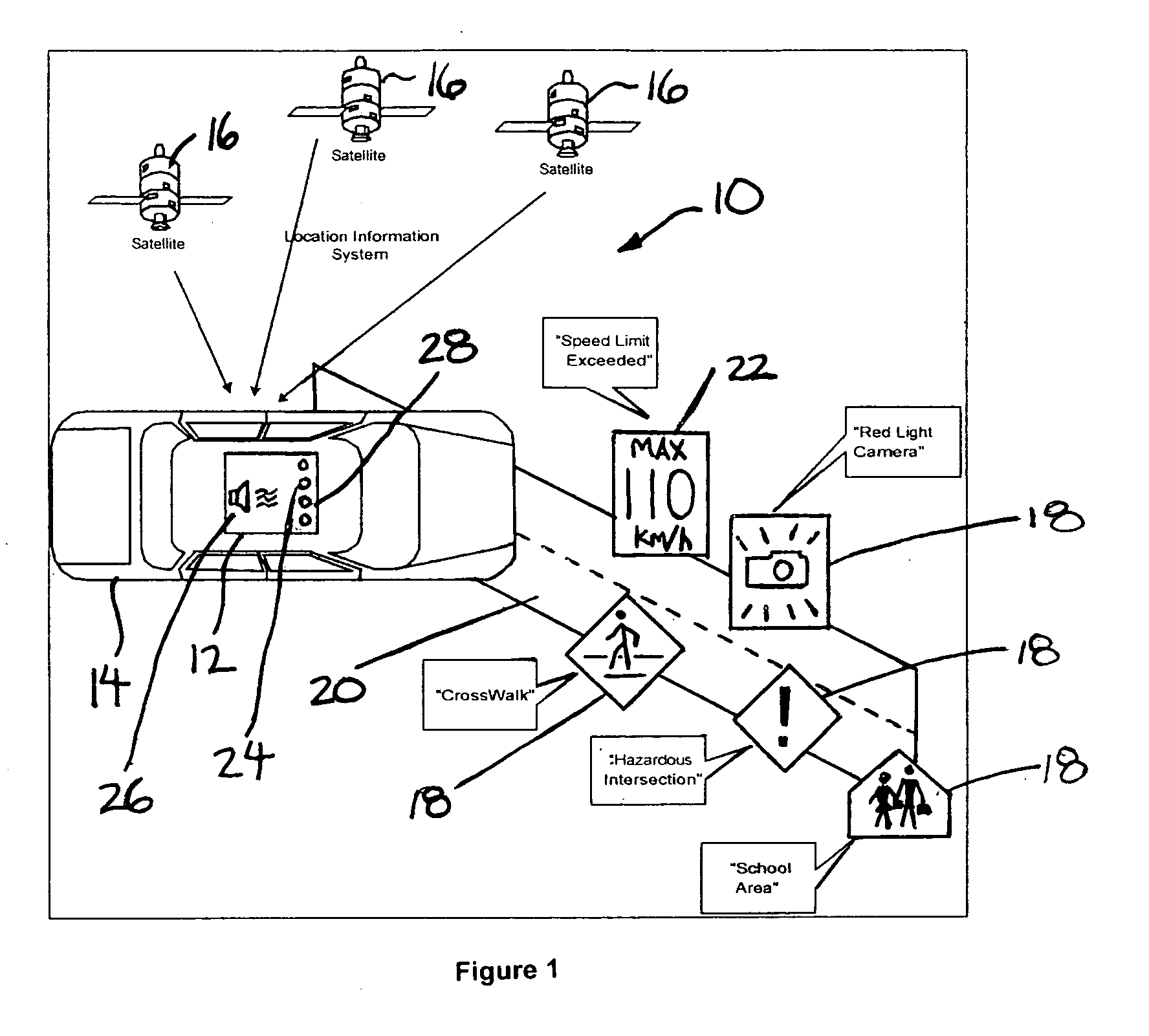
Vehicle warning system
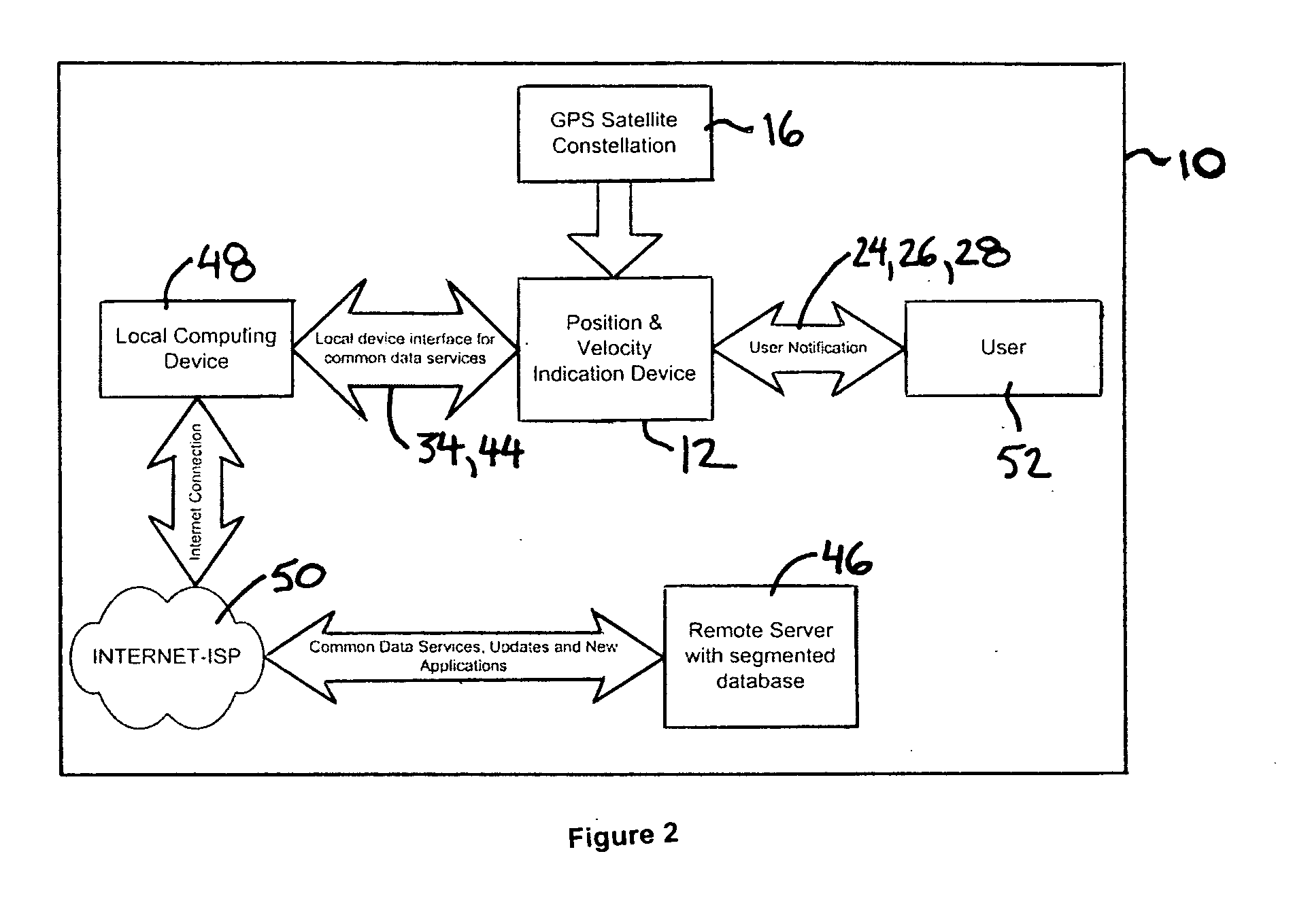
ActiveUS20050264404A1Easy to configureEasy to updateVehicle fittingsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsPersonalizationCommunication interface
A vehicle warning system is responsive to vehicle speed and position as determined by GPS or other location based system information to alert a vehicle operator of potentially unsafe conditions when either exceeding the speed limit on a given road segment or when approaching coordinates of a designated location alert point. The system comprises a portable device, a simple device personalization process using a single physical data communications interface to a local computing device connected to the Internet, and a remote server with a segmented database that provides access to common data services, positional data updates, and device personalization functionality.
Owner:PERSEN TECH
Method and system for searching an information retrieval system according to user-specified location information
InactiveUS7376640B1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsGeolocationInformation searching
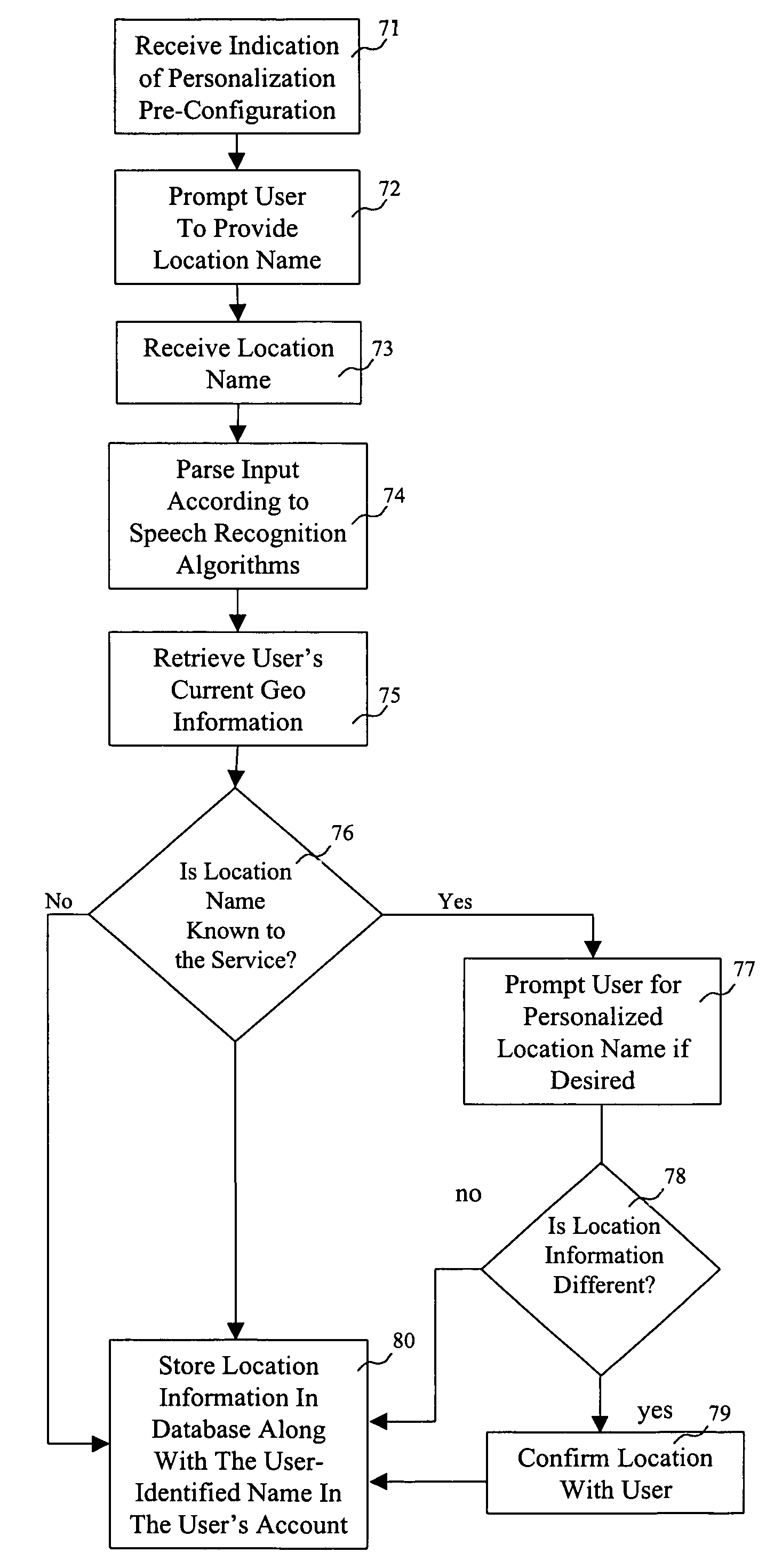
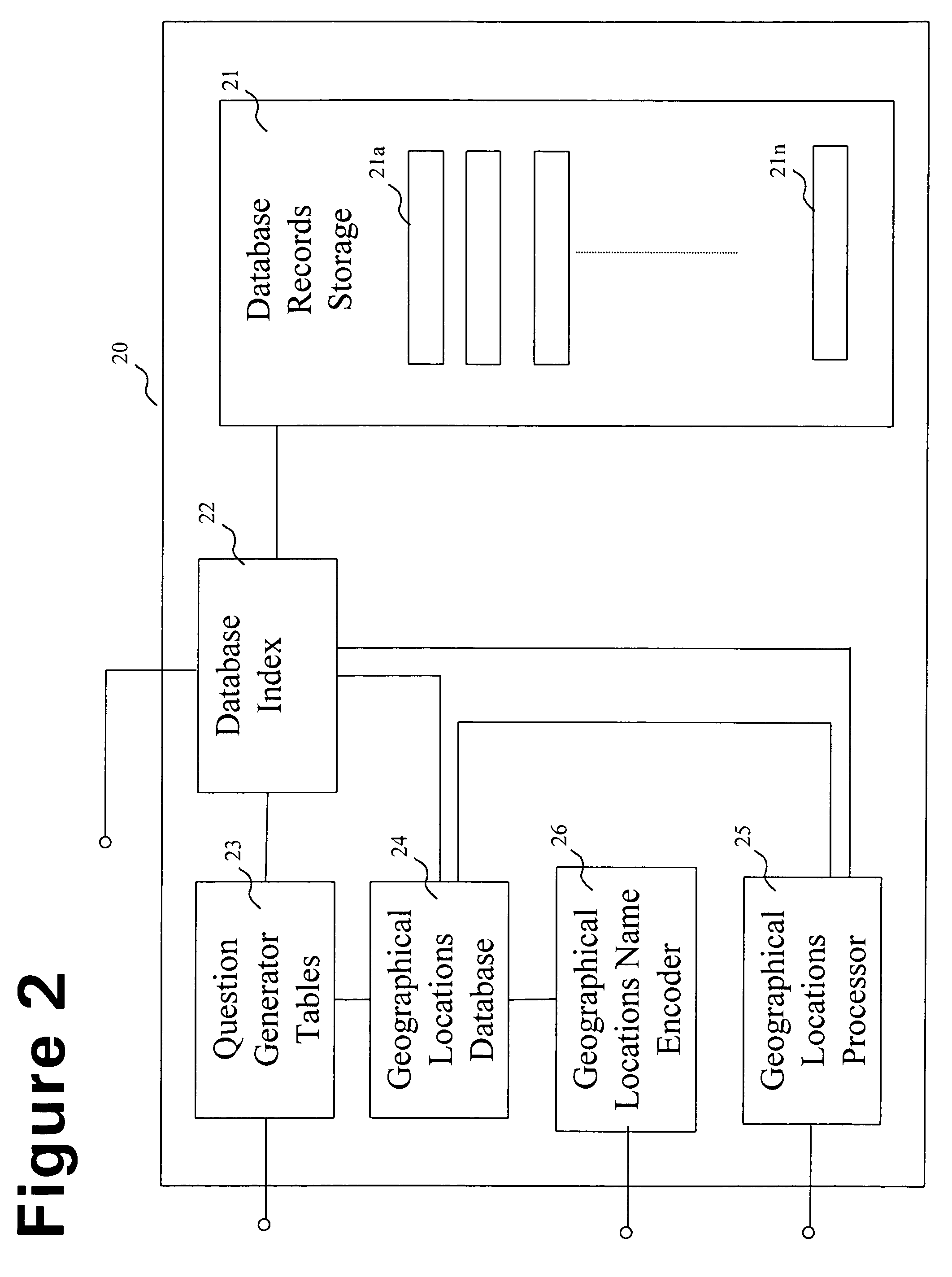
A method and system for searching an information retrieval system for items of interest that are in proximity to geographical locations provided by the user. The information retrieval system can perform a search for specified types of businesses or items of interest that surround or are in close proximity to the user's present geographical location, or a geographical location that the user has pre-configured in a database. The system receives geographical location information concerning the user's position from the wireless network carrier, which tracks the location of the user's mobile communications device. When the user desires to store a geographical location and geographical name for a future search, the information is entered into the pre-configured database. When conducting an information search at a later time, the user can narrow a search request to a geographical area in the vicinity of the stored geographical location.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Methods and systems for mobile device messaging
ActiveUS20050164721A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentWeb serviceMobile device
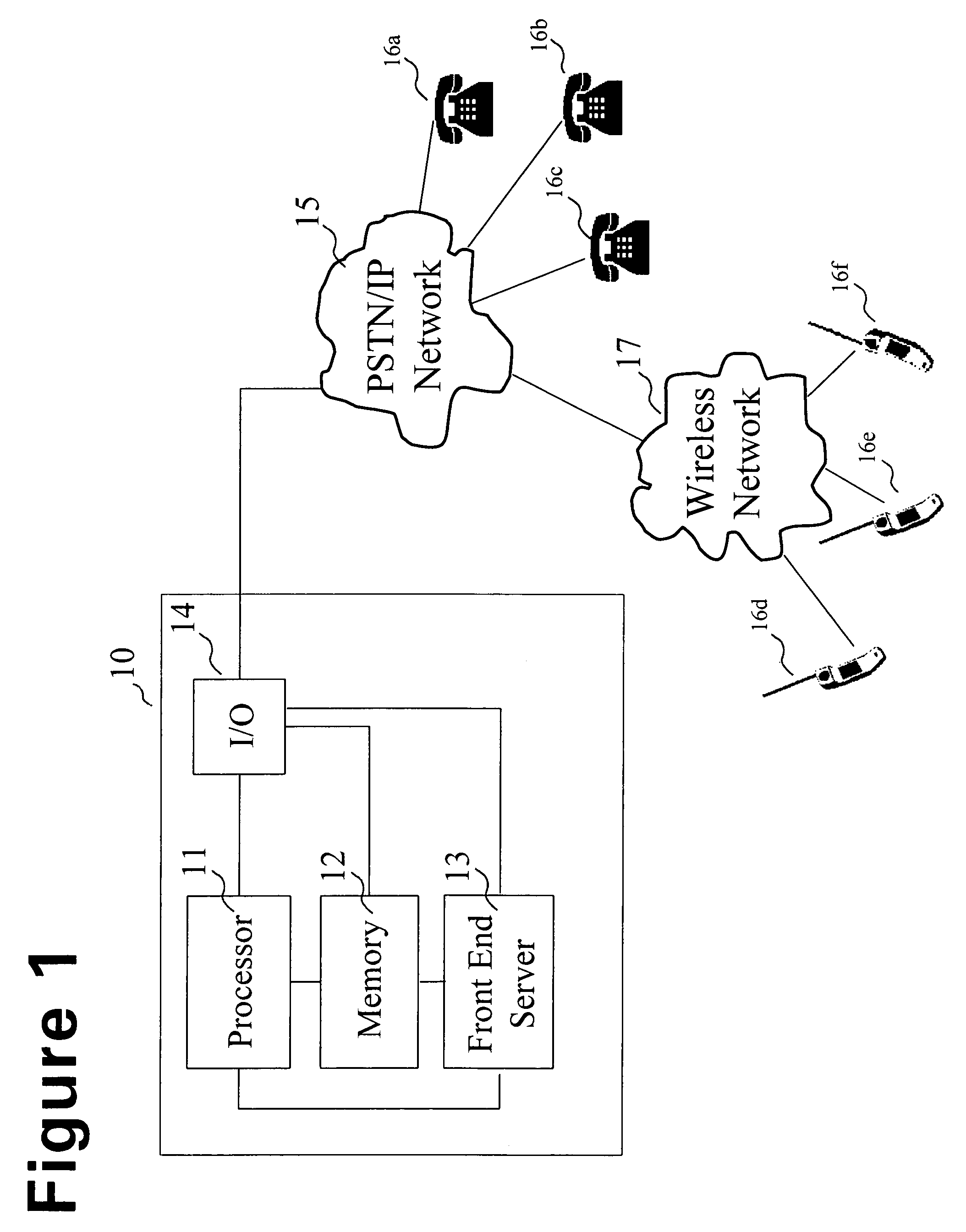
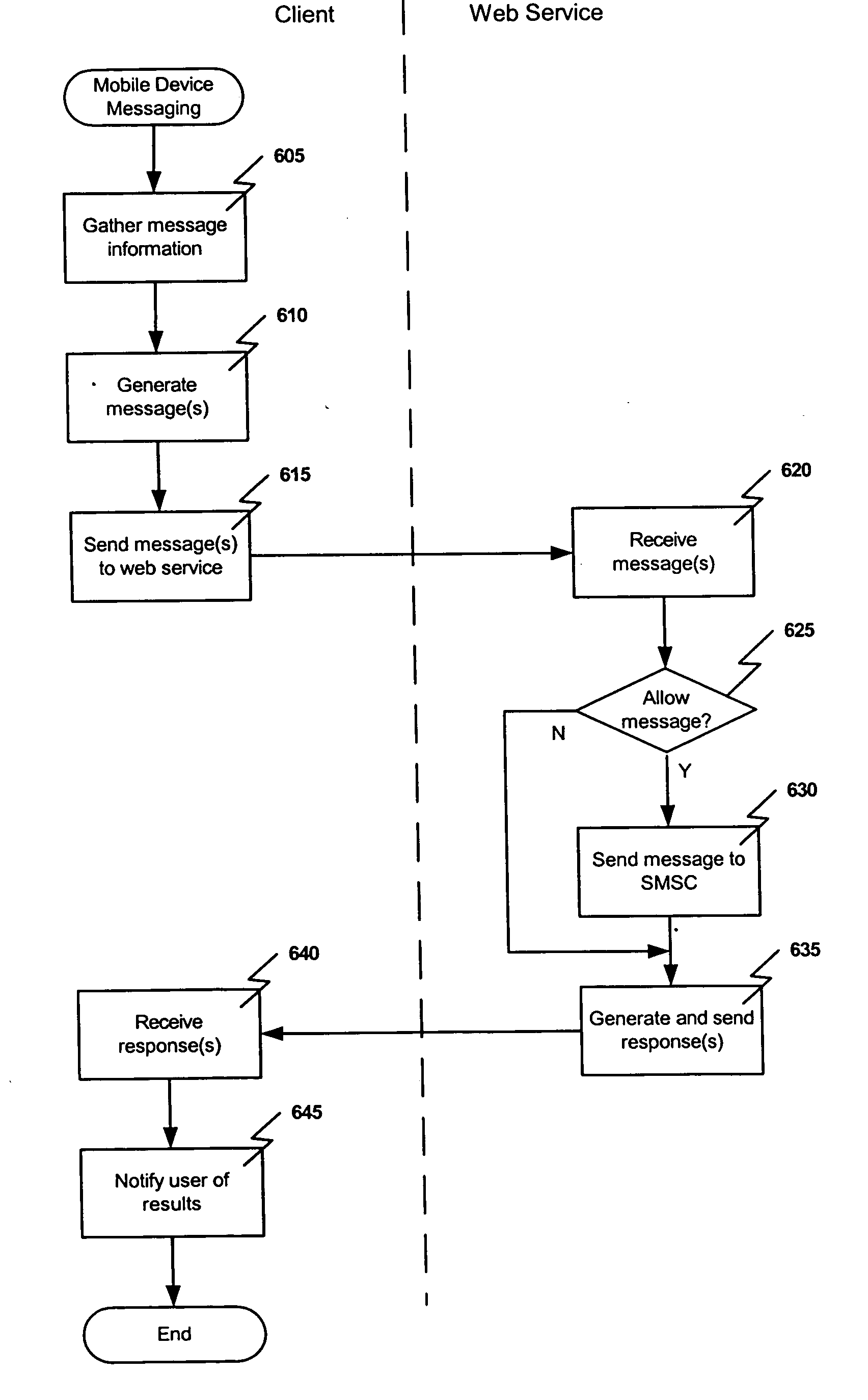
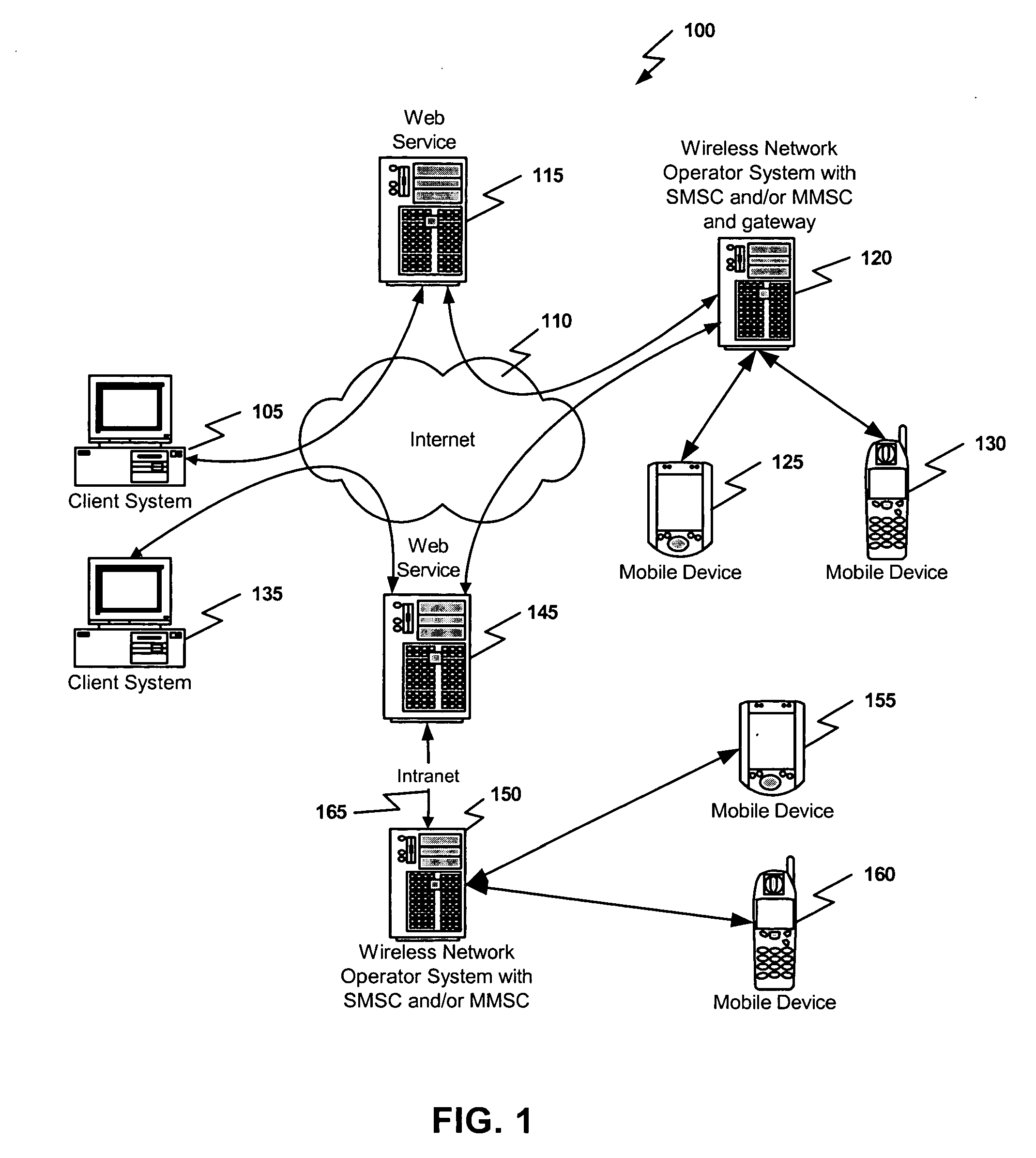
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods, systems, and computer-readable media for mobile device messaging. Mobile device messaging comprises collecting from an originating system information including content data to be sent to the mobile device. One or more short messages are generating for encapsulating the content data. The one or more short messages are formatted to be readable by a web service and the content data is formatted to be readable by the mobile device. The one or more short messages are sent to the web service for delivery to the mobile device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
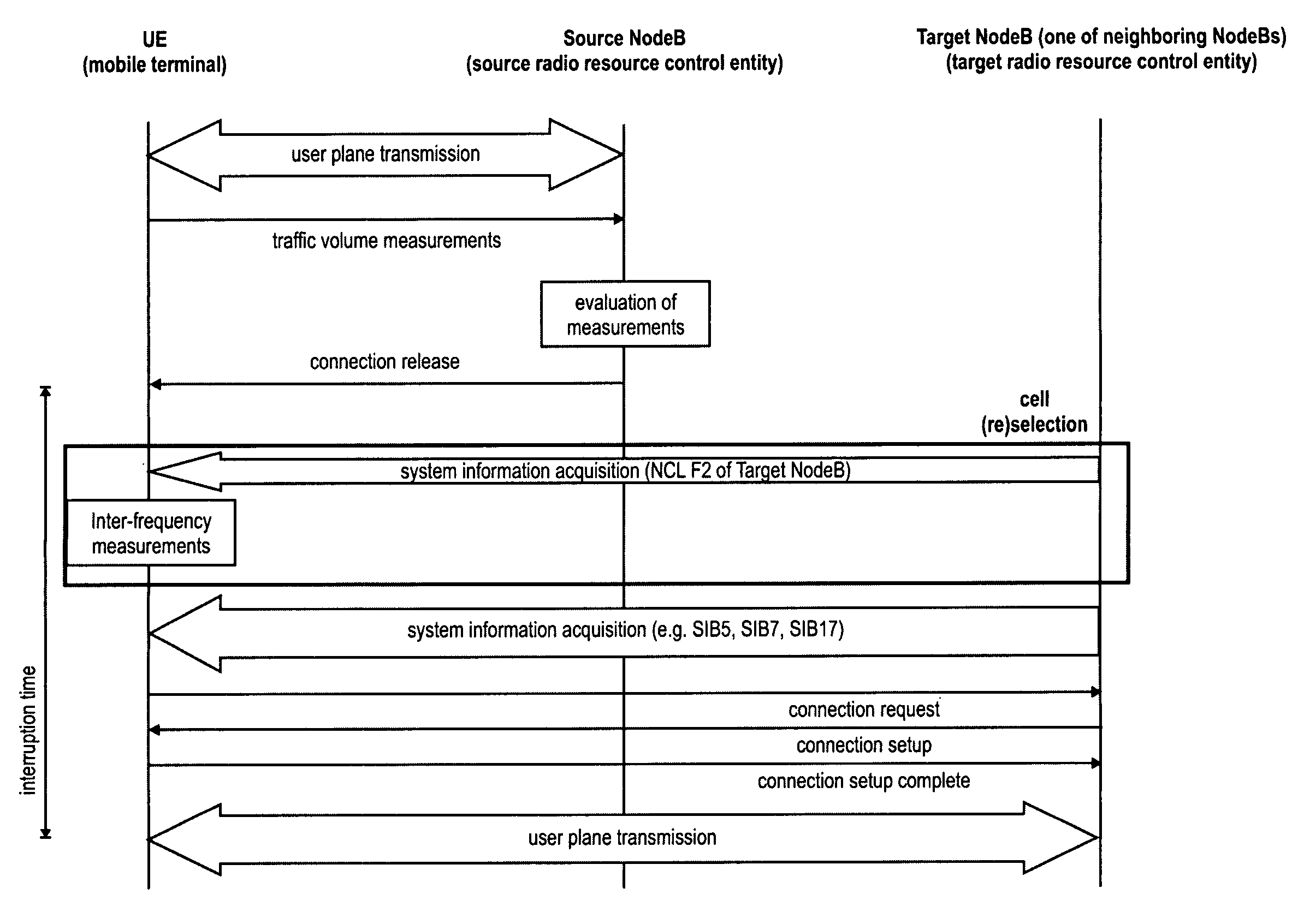
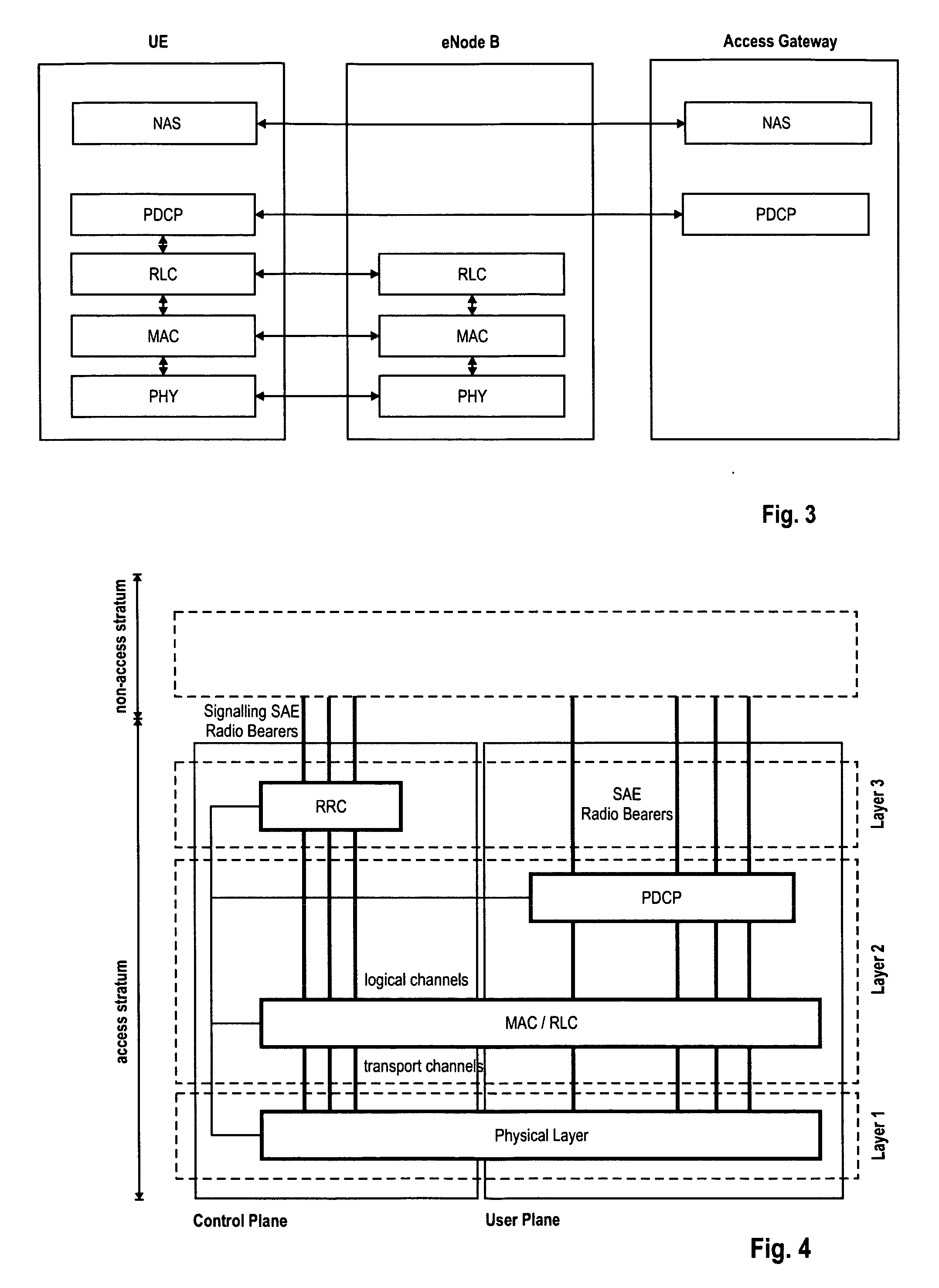
Transmission and reception of system information upon changing connectivity or point of attachment in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20100022250A1Reduce downtimeIncrease flexibilityAssess restrictionOrthogonal multiplexCell specificMobile communication systems
Method for informing a mobile terminal on target cell-specific system information to facilitate a mobility procedure such as handover or cell reselection in a mobile communication network. Further a radio resource control apparatus, a mobile terminal and a system comprising the radio resource control apparatus and the mobile terminal are provided. The invention suggests improvements to current mobility procedures so as to reduce the interruption time implied by the procedures. More specifically, it is proposed to include at least one pointer to target cell-specific system information to a control message, such as a handover indication or connection release message, pointing the mobile terminal to system information in the target cell relevant for system access and / or to perform mobility procedures. Further, a portion of the target cell-specific system information may also be comprised in the control message.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for monitoring and managing system assets and asset configurations
InactiveUS6973491B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksWeb serviceApplication software
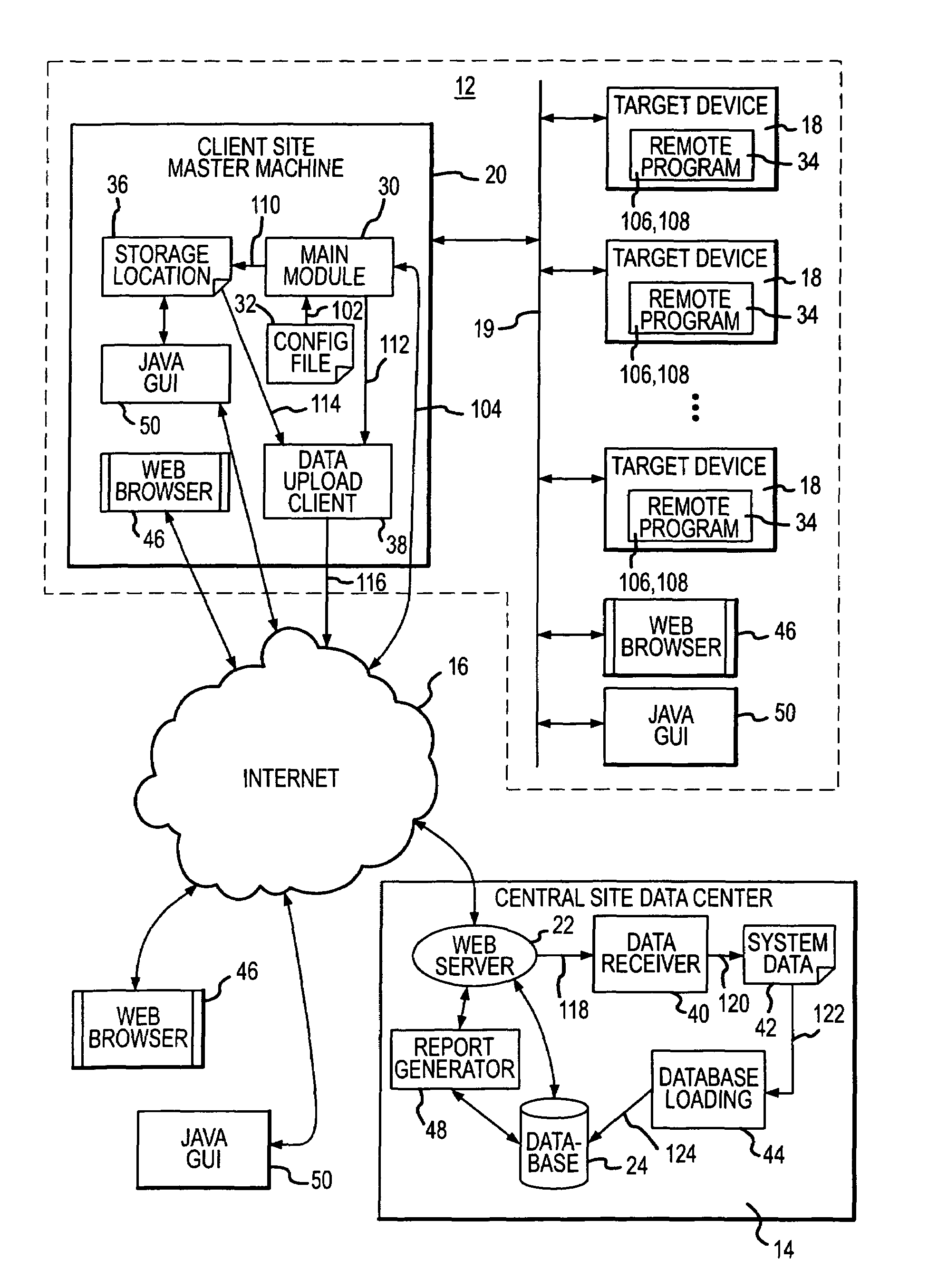
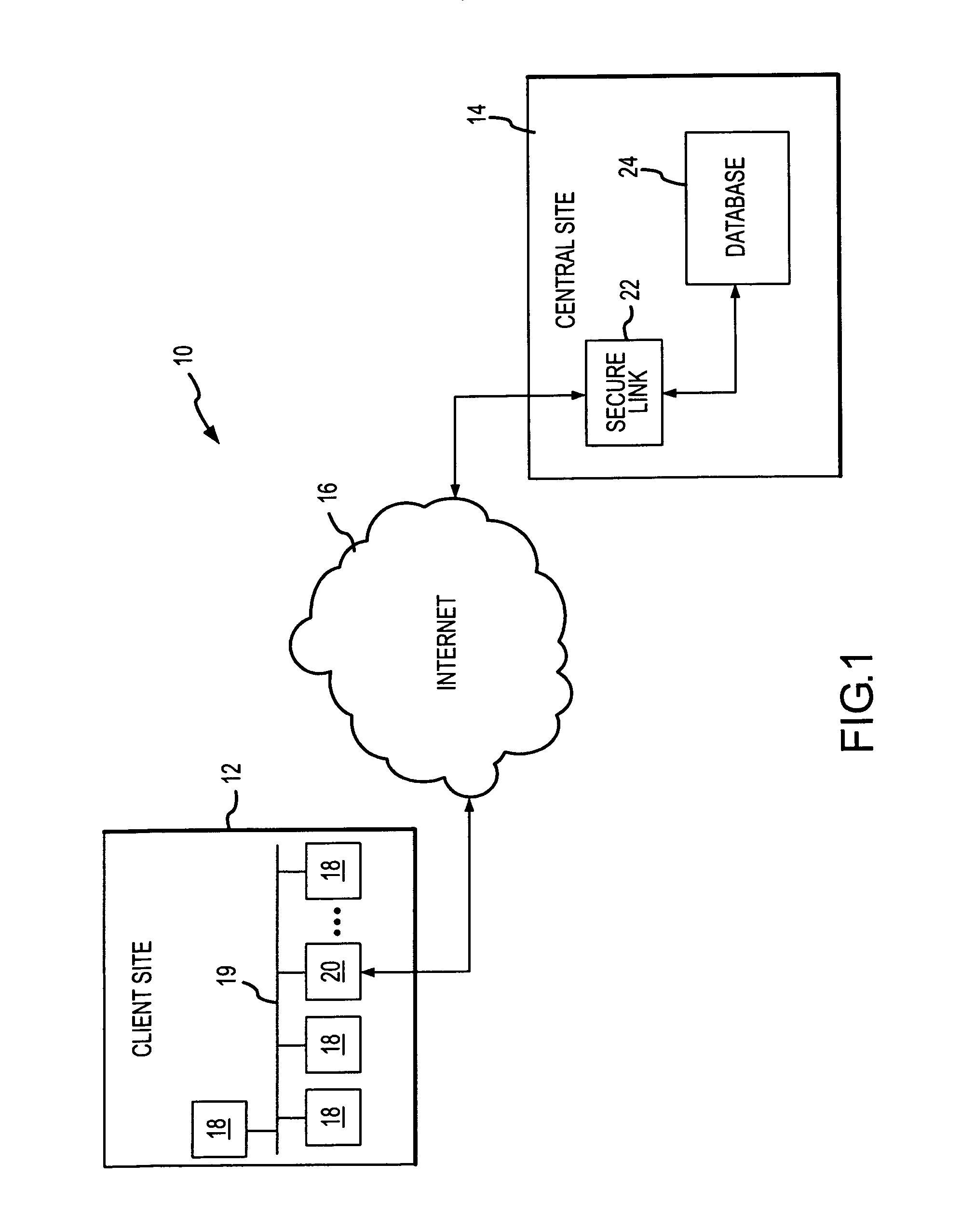
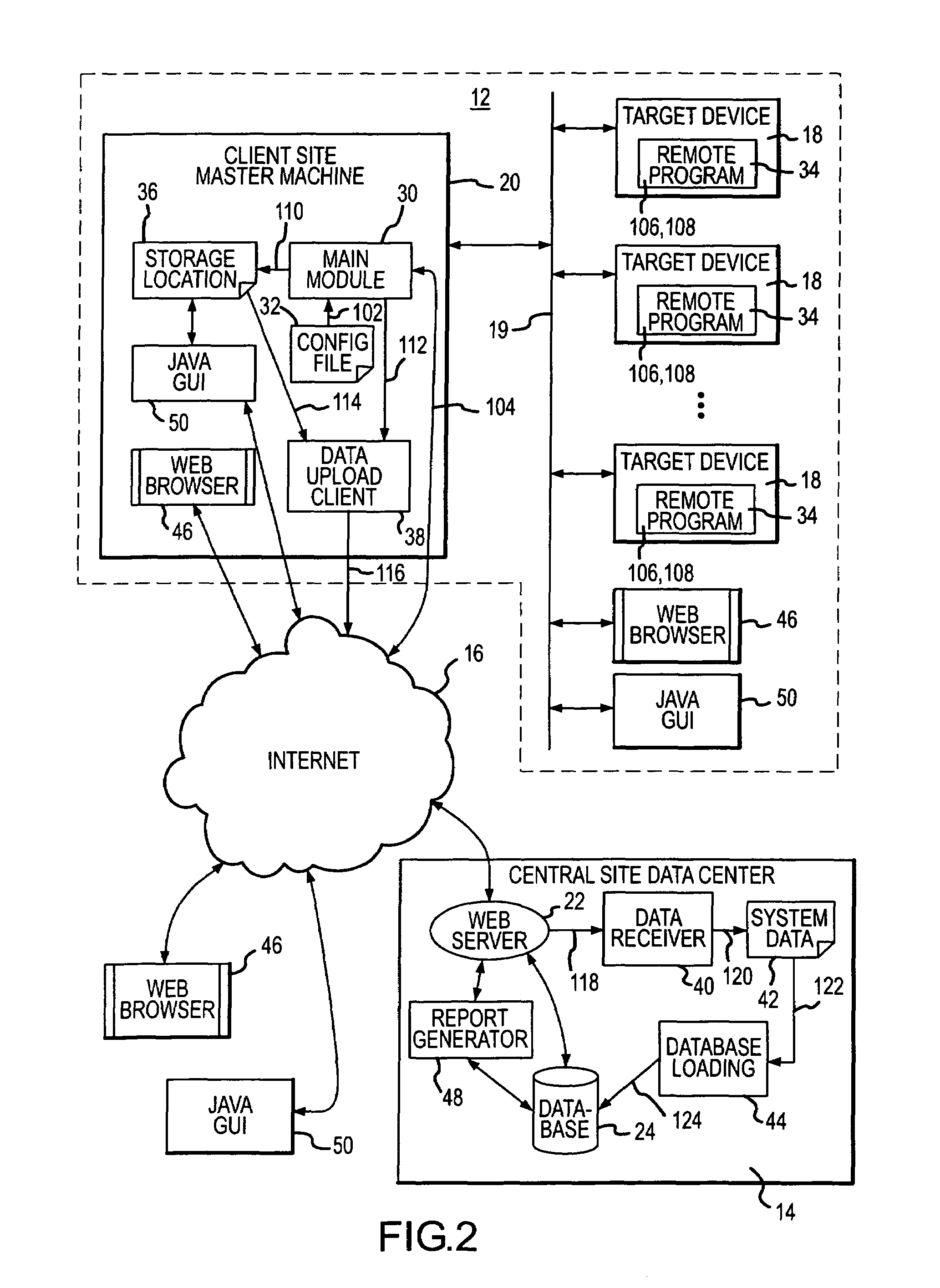
A system and method for monitoring the configuration and / or status of target devices on a network. The system comprises a monitoring application that can be run on a first network device. The monitoring application is configured to monitor one or more target devices on the network using data collector modules that run on the target devices. The data collector modules are launched on the target devices by the monitoring application and are configured to collect configuration and / or status information about the target devices. After collecting the data, the data collector modules preferably pass the data back to the first network device, where a data upload application receives the data and uploads it to a central site. The data at the central site is placed in a database for access by users or clients. Users can access the data in the database by communicating with the central site, for example, via a dial-up connection or via the Internet. Once connected to the central site, a user can retrieve system information using a graphical user interface, or can submit report requests to the central site. The interface used to access information at the central site may be a web browser communicating through a web server at the central site.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
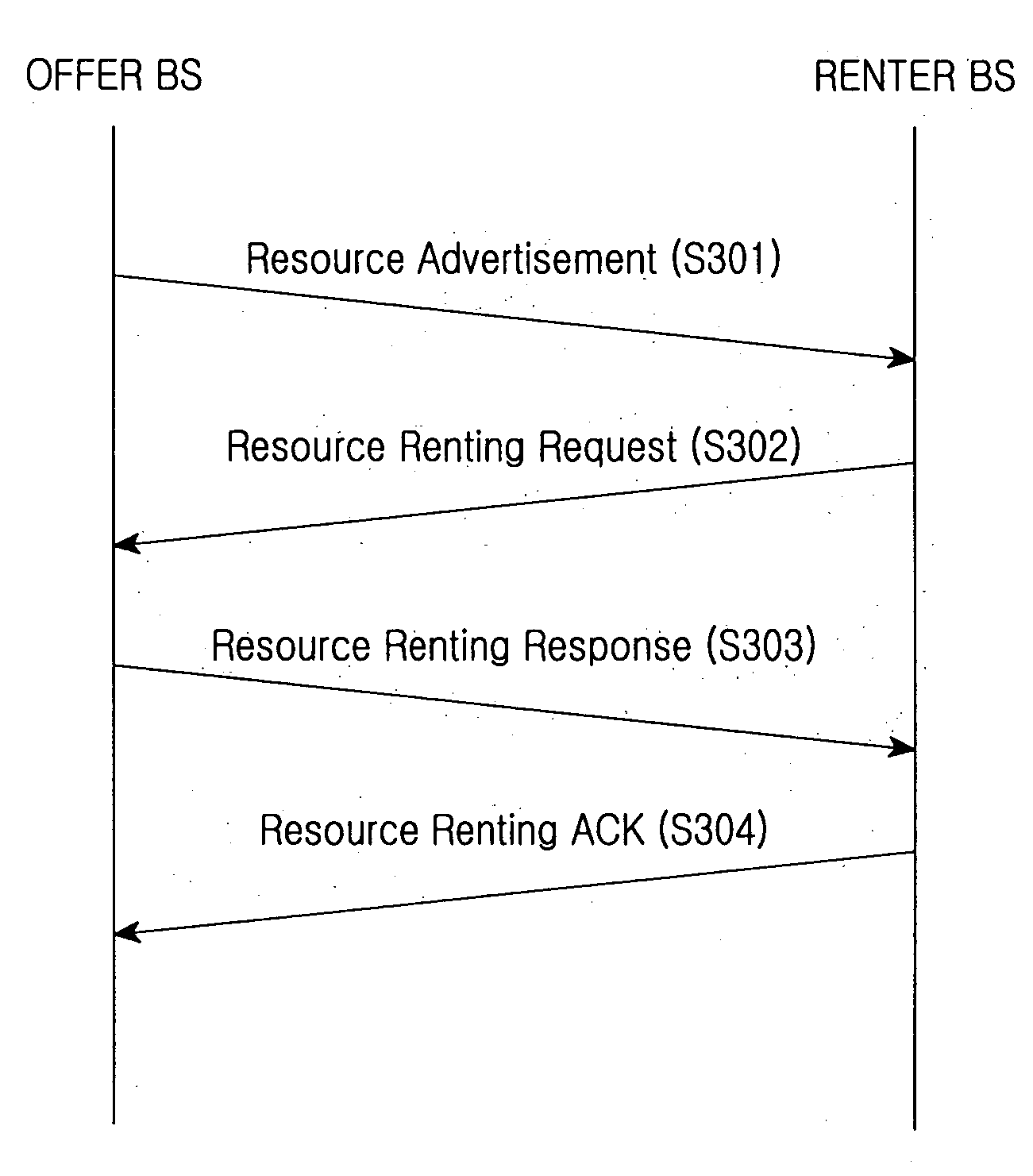
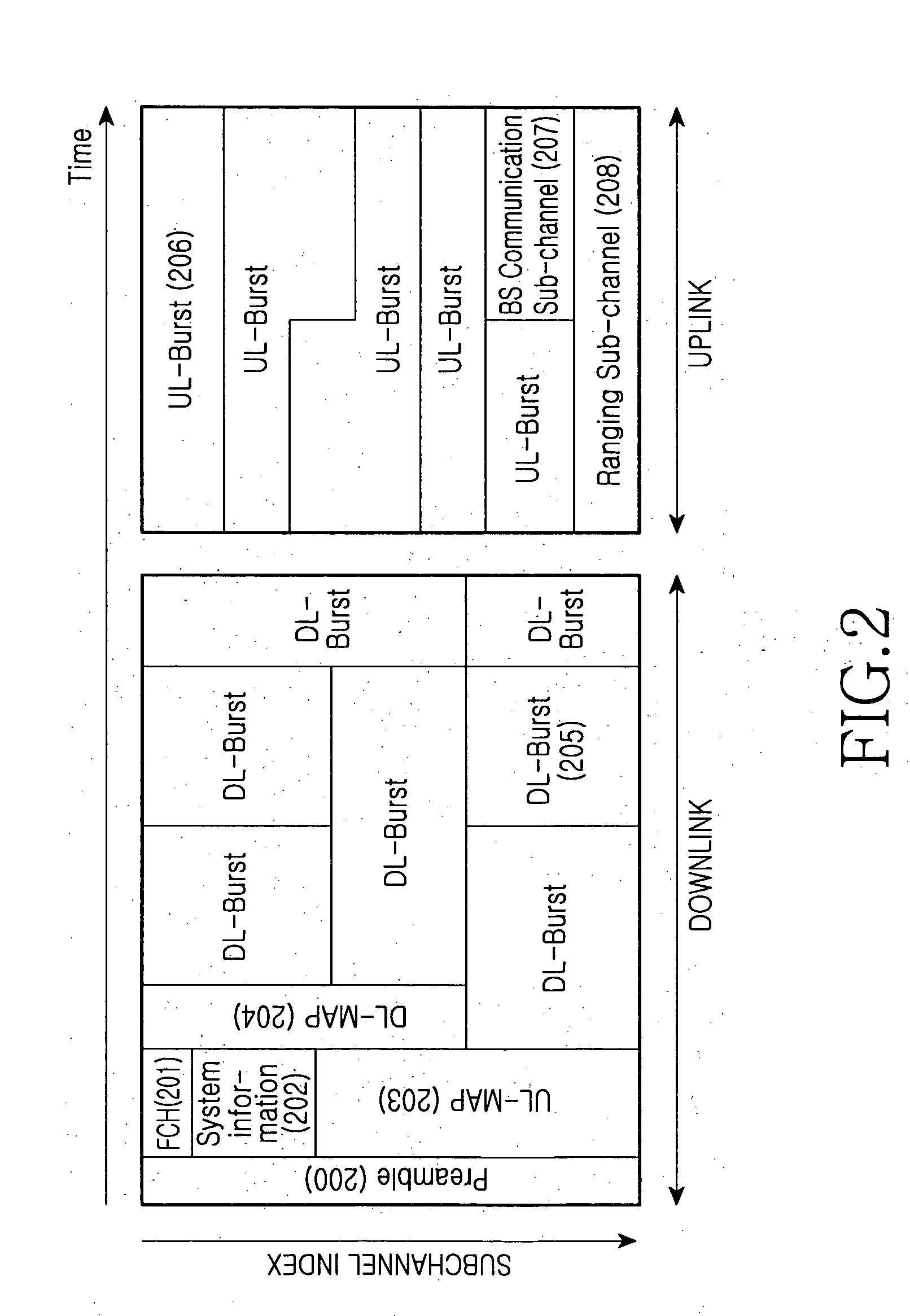
Method of managing resources in a cognitive radio communication system
InactiveUS20070117537A1Efficient methodBroadcast service distributionAutomatic exchangesCommunications systemResource information
A resource management method in a Cognitive Radio communication system where at least two Base Stations of heterogeneous networks provide a connection service to Mobile Stations within their service areas is provided. In the method, at least one BS having candidate resources broadcasts its candidate resource information on the downlink of a system information channel. At least one BS lacking in resources searches the downlinks of system information channels from neighbor heterogeneous networks, selects an offer BS among the BSs having candidate resources, and rents resources from the selected offer BS by negotiations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
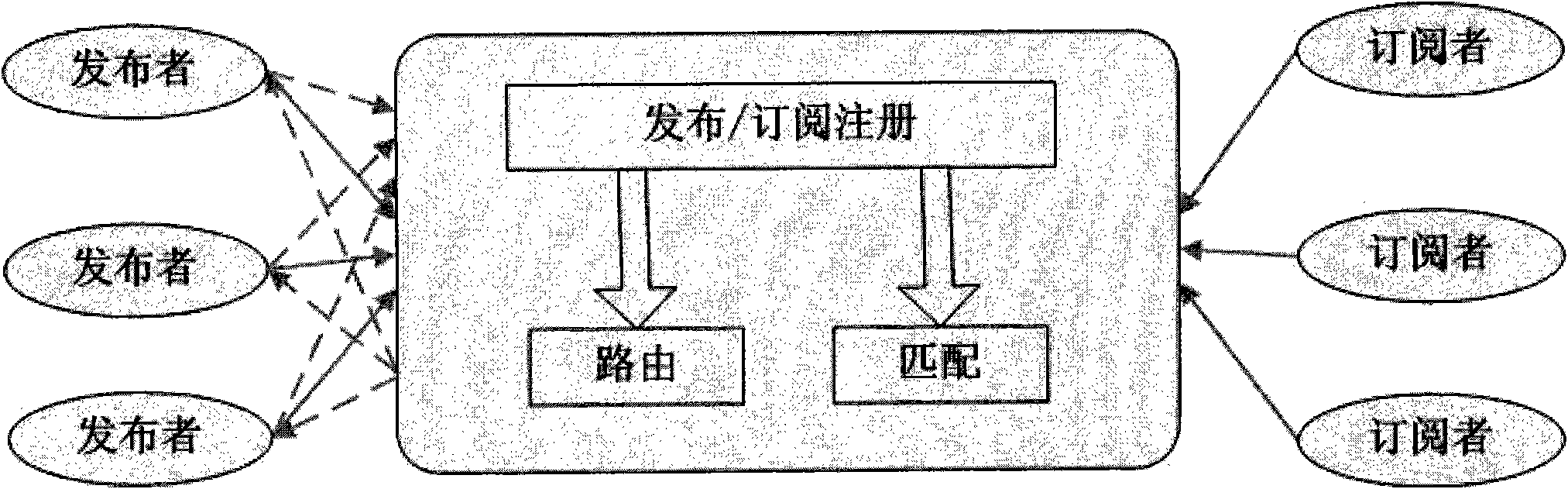
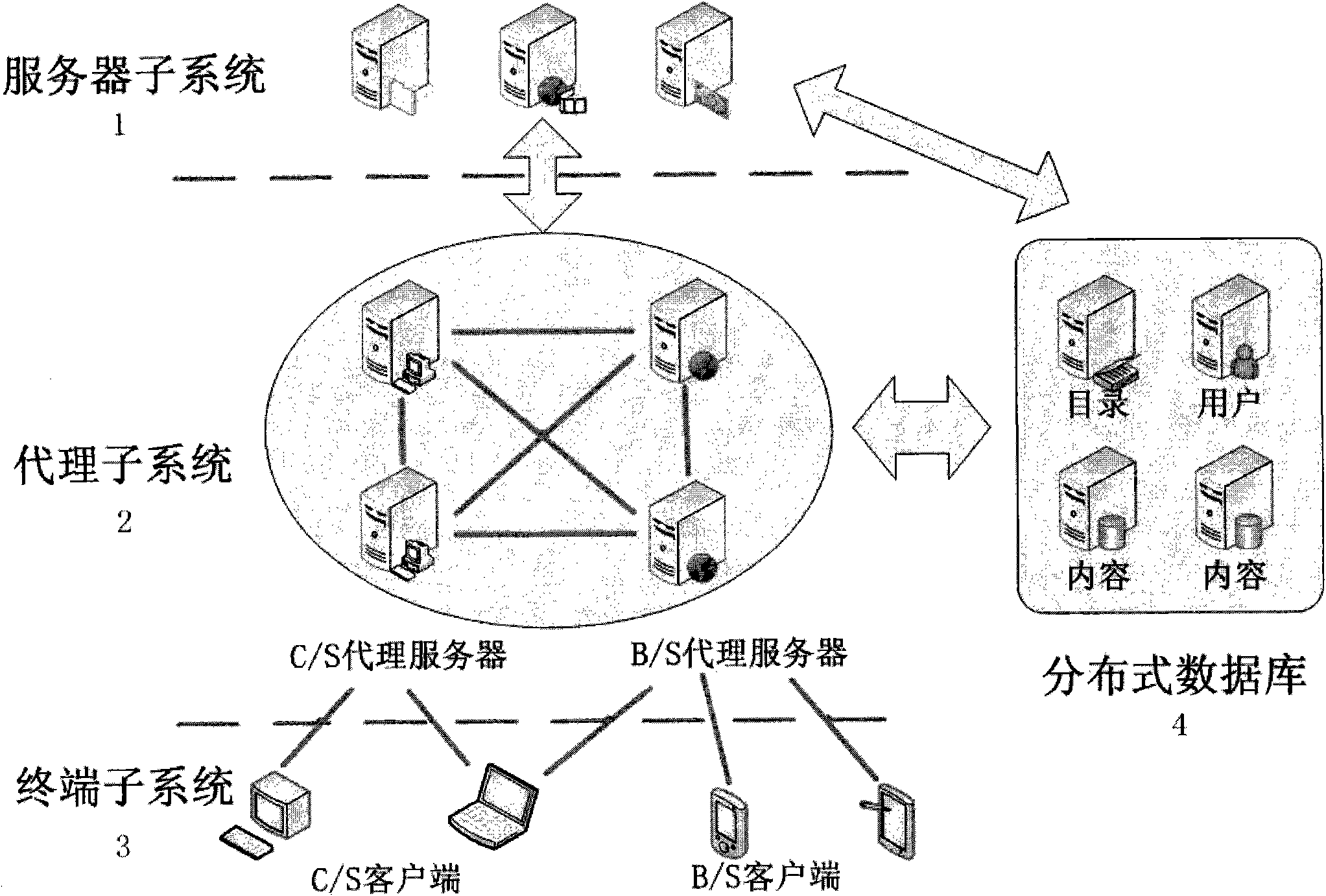
Real-time data distribution system with distributed network architecture and working method thereof
InactiveCN101848236AImplement hierarchical configurationFlexible accessData switching networksGeolocationNetwork architecture
The invention relates to a real-time data distribution system with a distributed network architecture and a working method thereof, the system adopts a publication / subscription communication mechanism to transfer information in Internet and a mobile network, and the system comprises a server sub-system, a proxy sub-system, a terminal sub-system and a distributed database, wherein, the server sub-system is used for completing the operations of topic storage, topic matching and the like; the proxy sub-system is used for completing the operations of receiving a topic from a terminal, transmitting a matching event to a subscriber, submitting the publication / subscription topic and the like; the terminal sub-system is used for completing the publication / subscription information of a user; and a distributed database which is used for storing the publication / subscription information and the system information. The system can automatically, quickly and safely provide real-time data transmission service against the subscription information of the user, provide the publication / subscription service of a variety of types of data, such as text information, streaming media, geographic position information and the like, provide up to 20 QoS control parameters, realize the QoS hierarchy configuration of an application layer and provide the convenience for function expansion of the data distribution system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method system and article of manufacture for performing real time currency conversion
A currency converter consisting of a source of exchange rate information with either an object performing the role of currency selection, exchange rate information retrieval, and price display, or objects undertaking currency selection and exchange rate information retrieval and price display. Prices embedded within the document or environment are displayed in the default or selected currency. The appropriate currency for price display is selected by using methods such as a menu used by the user, or by reading system information to choose the currency. The exchange rate information is retrieved from the source of exchange rate information and is then passed to any other price display object or objects, and optionally, any other currency selection and exchange rate retrieval objects or currency selection, exchange rate information retrieval, and price display objects in the document or environment.
Owner:TUMBLEWEED HLDG LLC
Cell reselection process for wireless communications
InactiveUS20080227453A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemBlack list
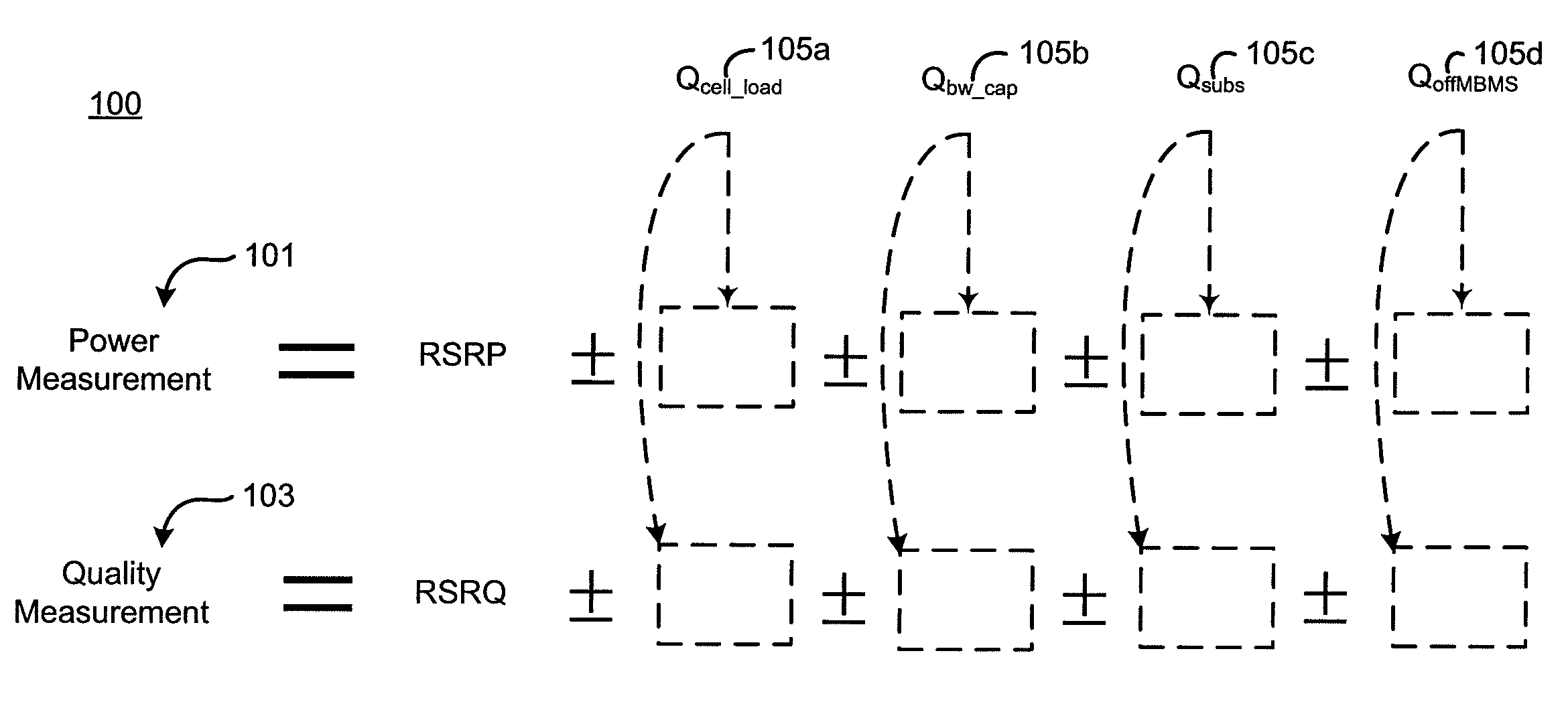
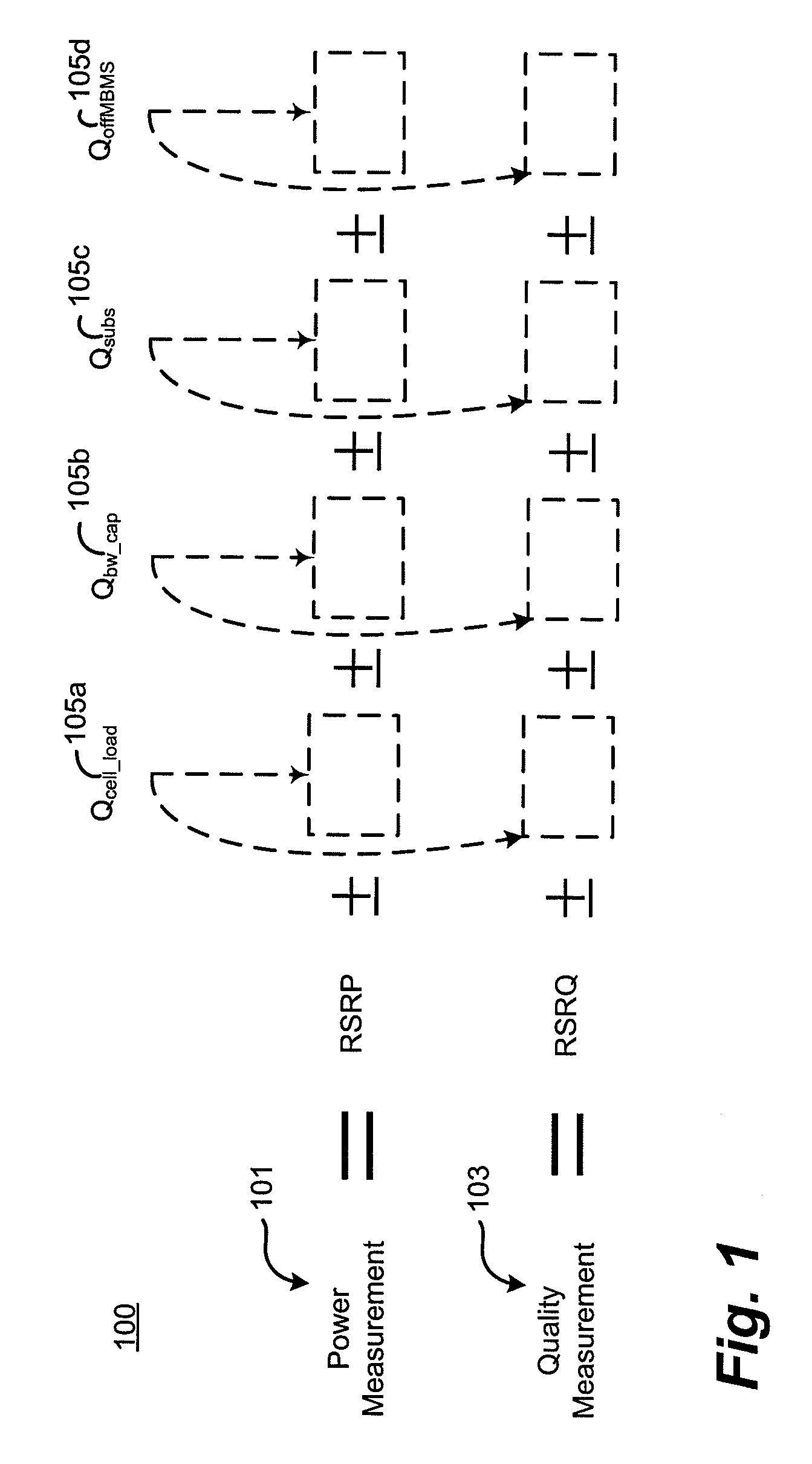
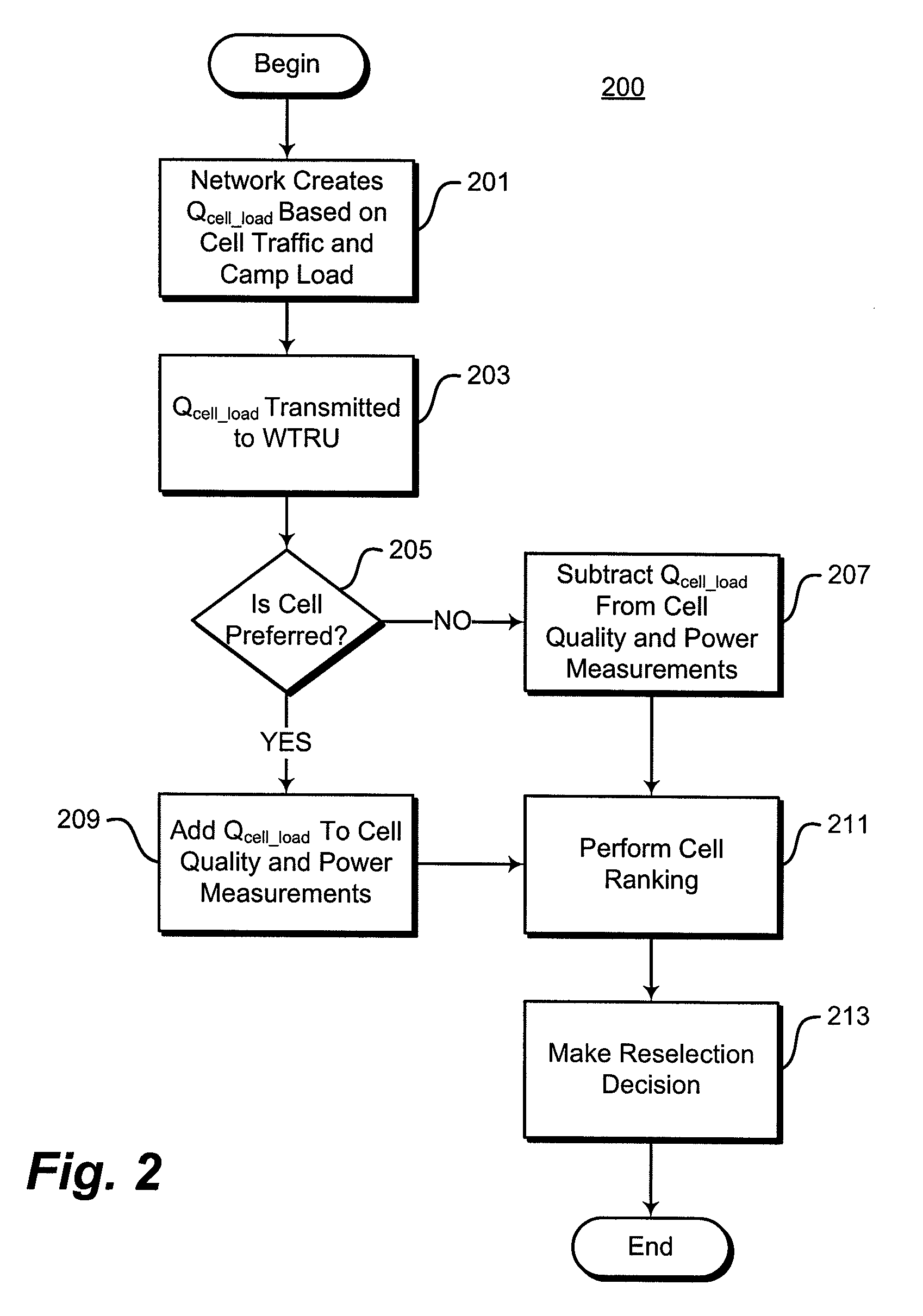
A method of cell reselection in a wireless communications system where parameters are transmitted by the network in system information blocks to WTRU's on the network. Parameters are either added or subtracted from an equation representing the signal power and / or quality of a cell. Parameters may be prioritized. The results of the calculations are used to rank the servicing cell and neighboring cells. If a neighboring cell has a higher quality than the servicing cell, then the WTRU reselects the better cell. The network may transmit a blacklist of cells where the WTRU cannot camp as well as a barring timer for each cell where if the timer expires, the cell may again be considered for reselection. Information germane to the reselection decision may be transmitted and used by the network.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com