Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2145 results about "File server" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
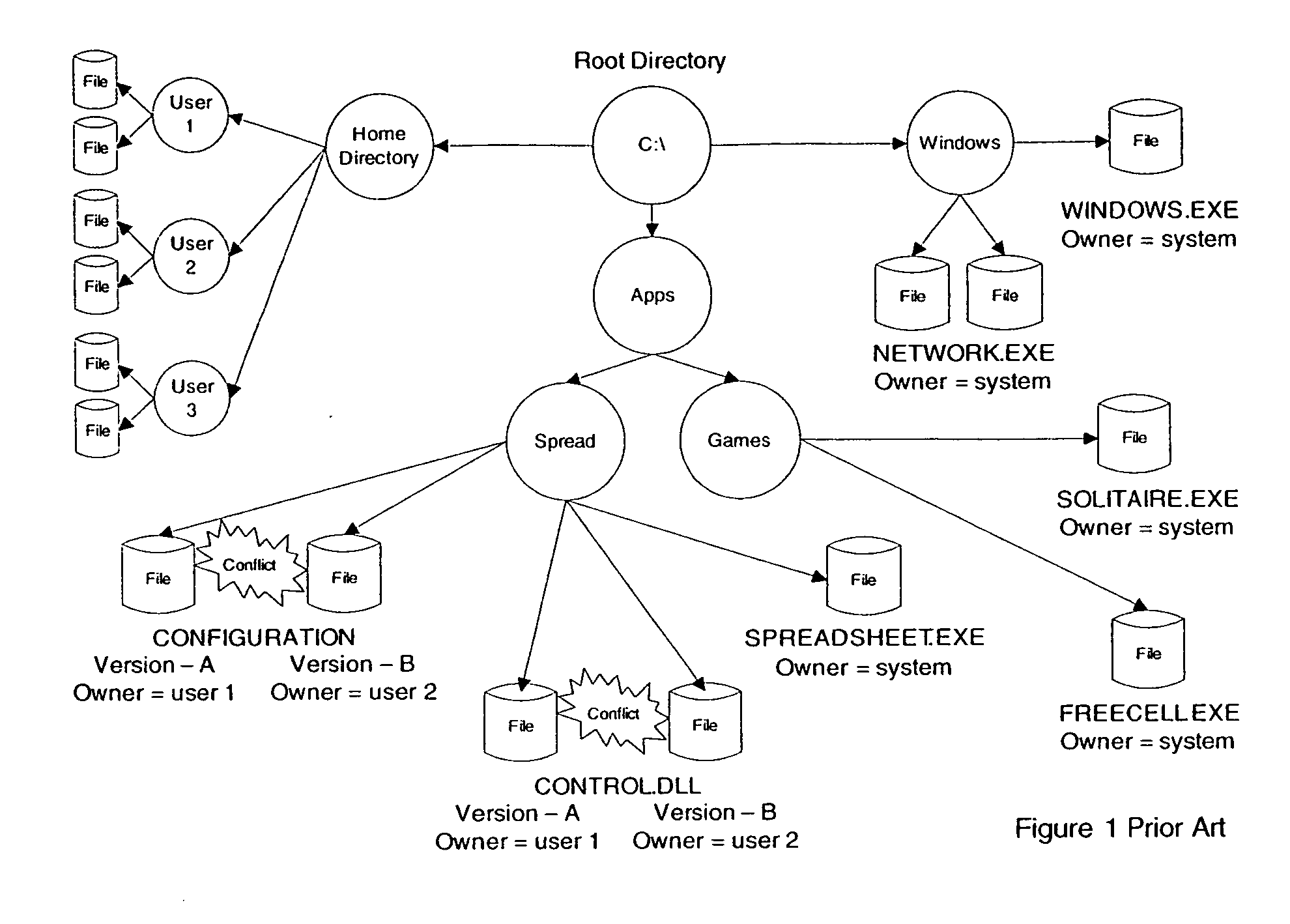
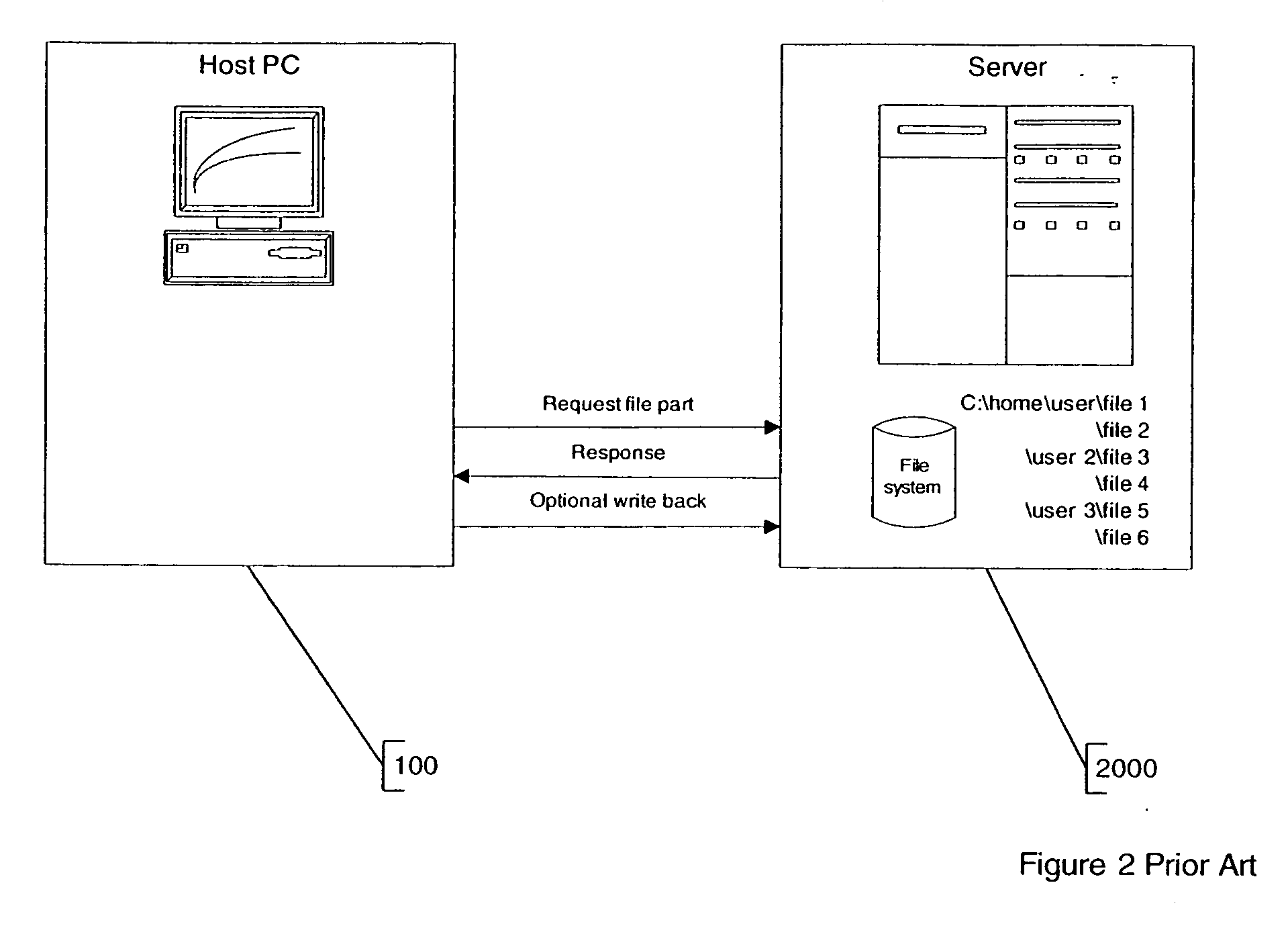
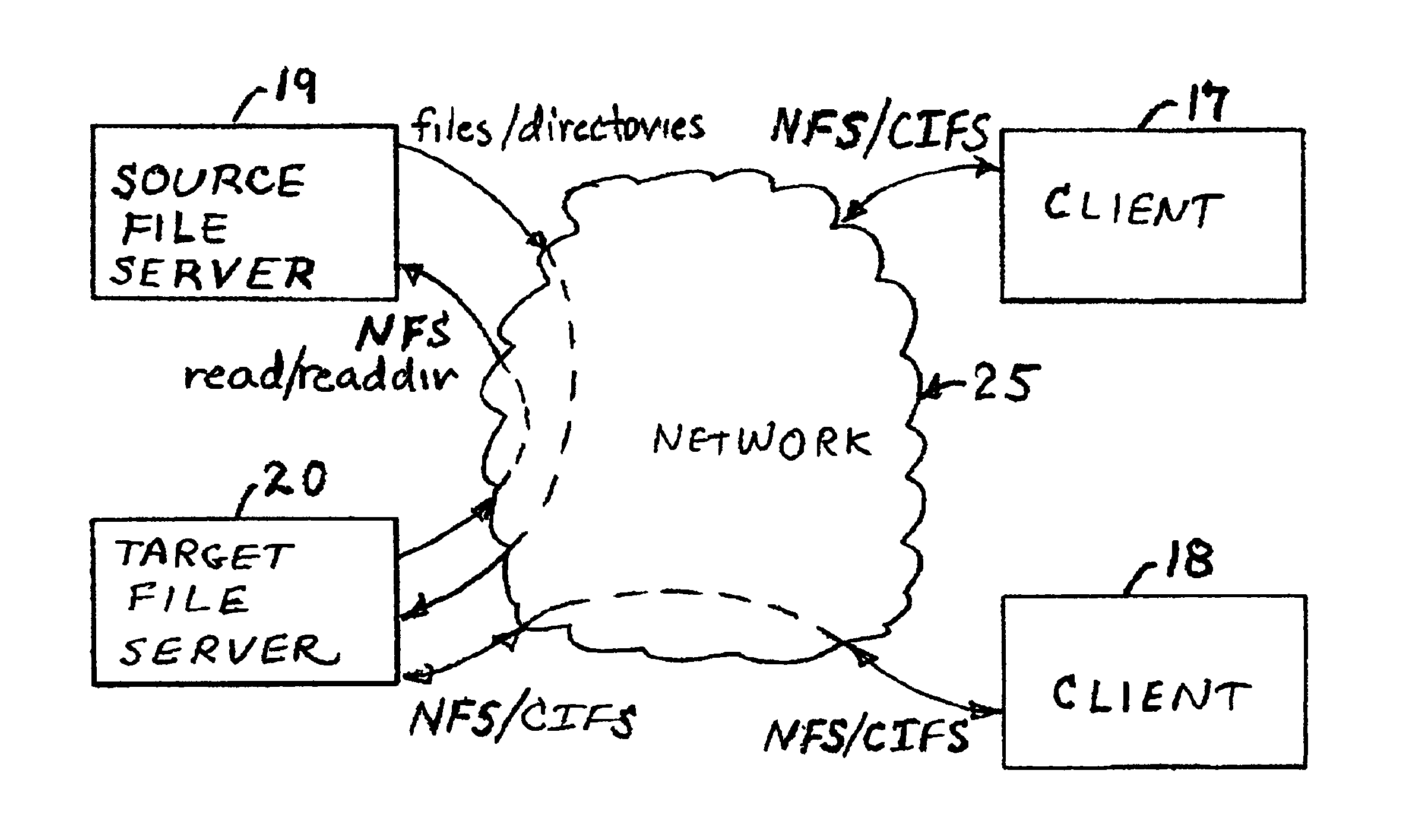
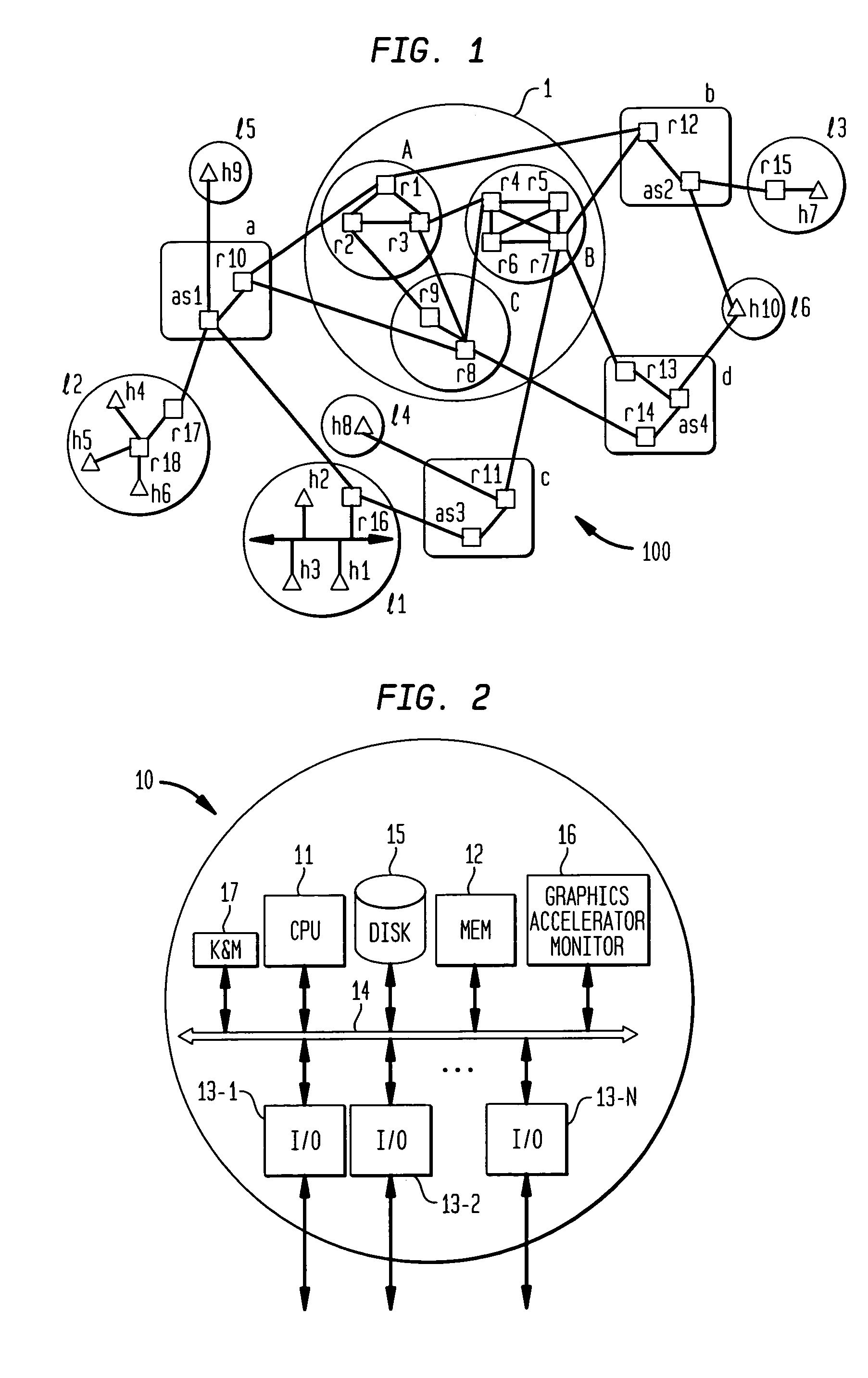
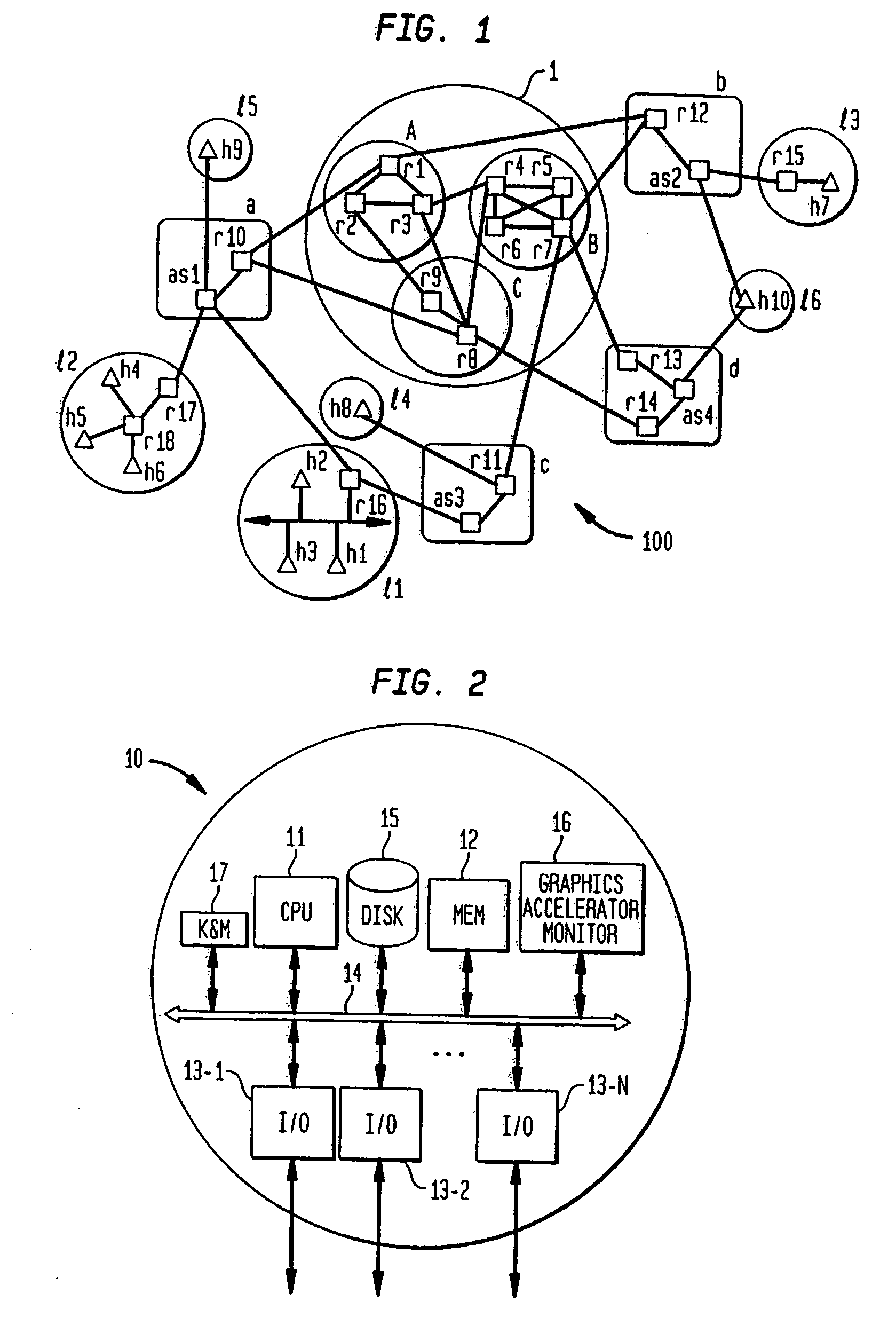
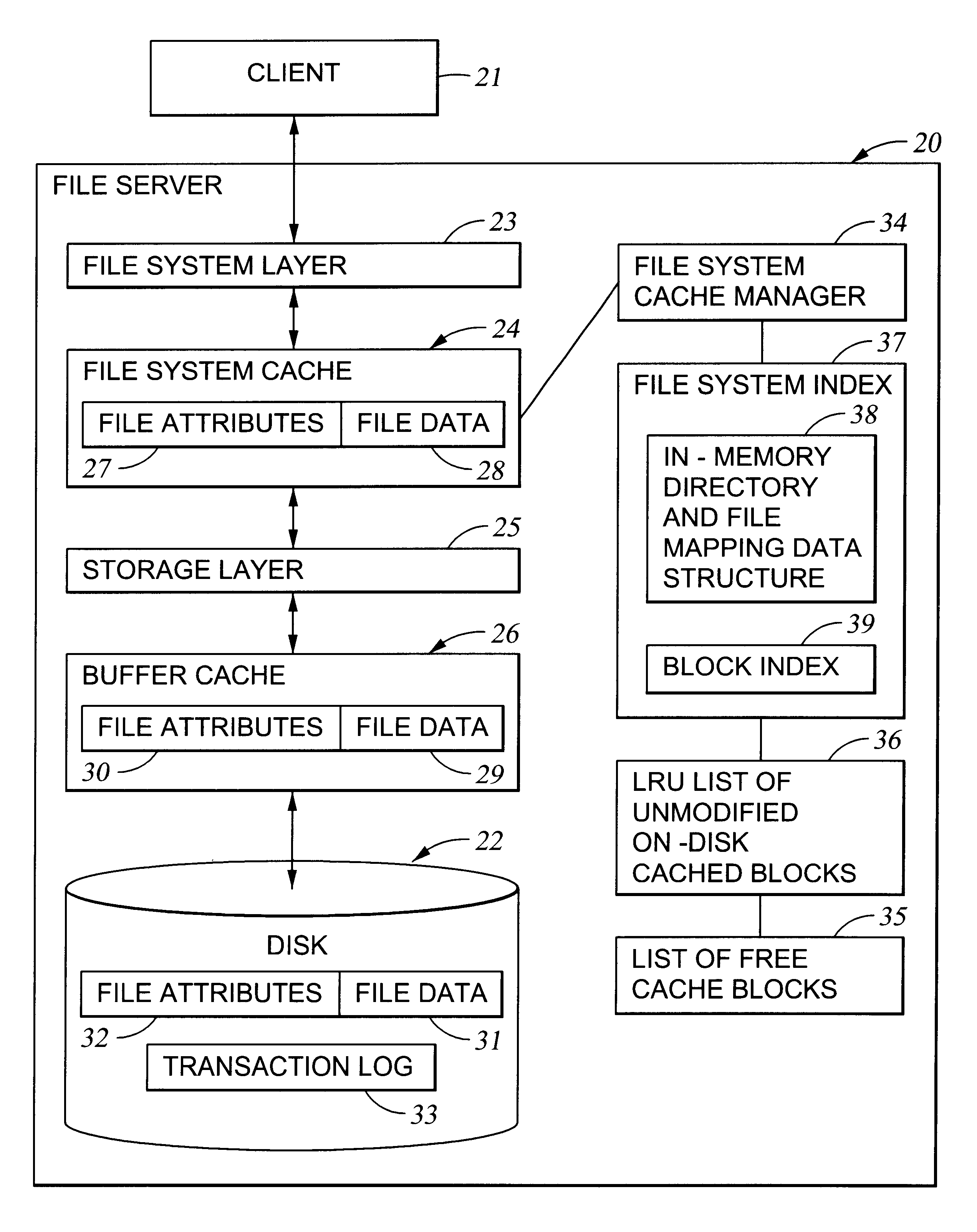
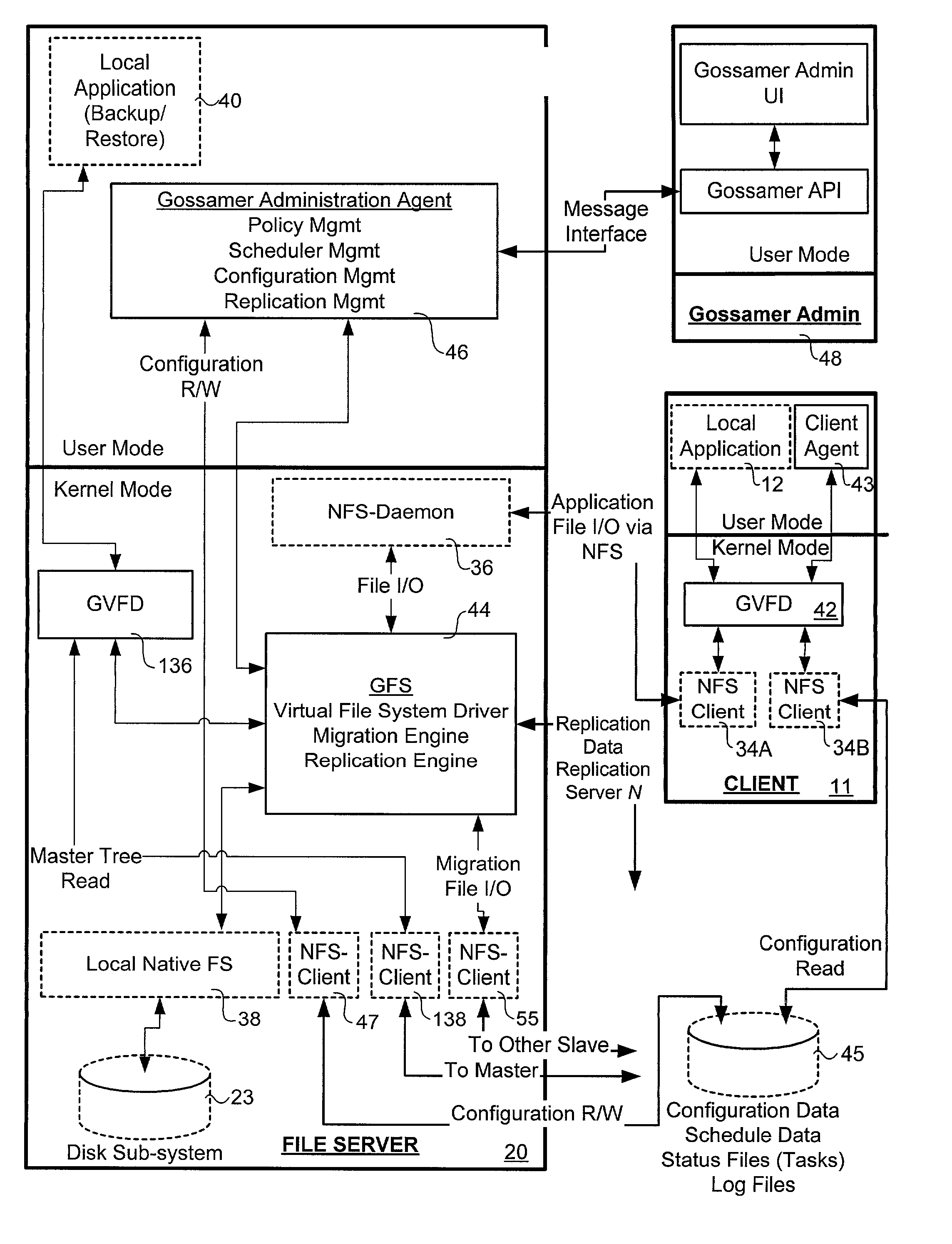
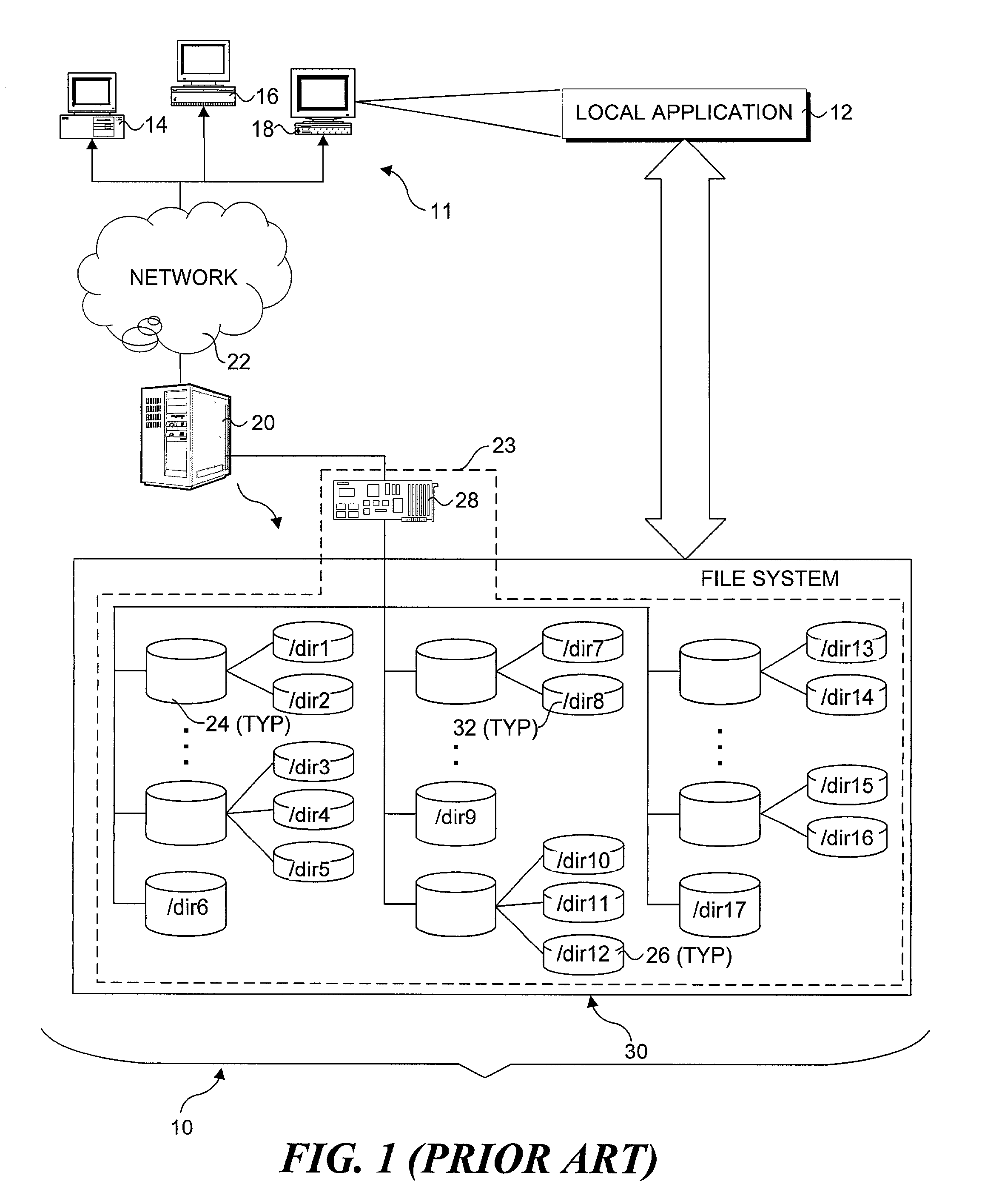
In computing, a file server (or fileserver) is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for never shared disk access, i.e.storage of computer files (such as text, image, sound, video) that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the client–server owner, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. It is common that a workstations.
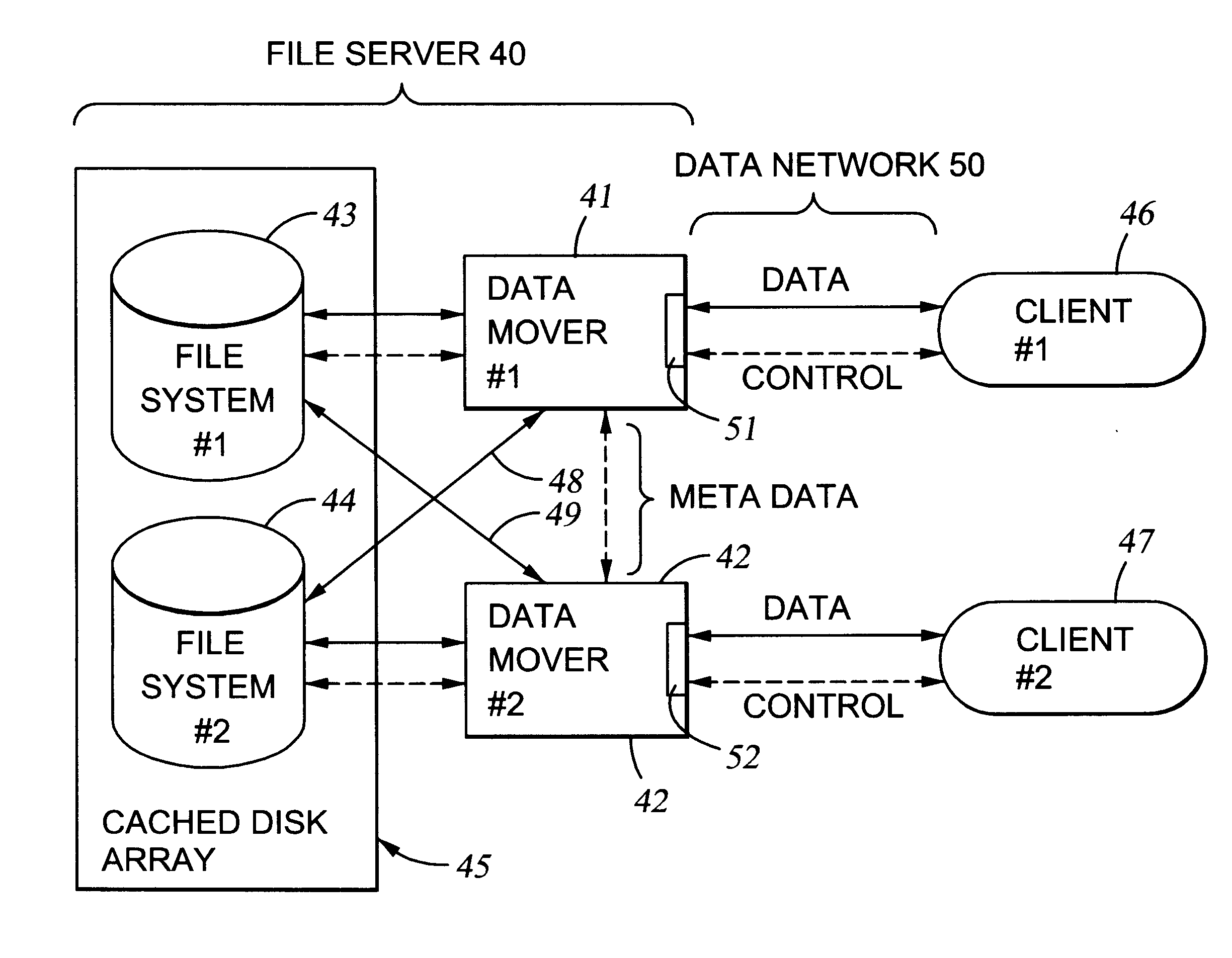
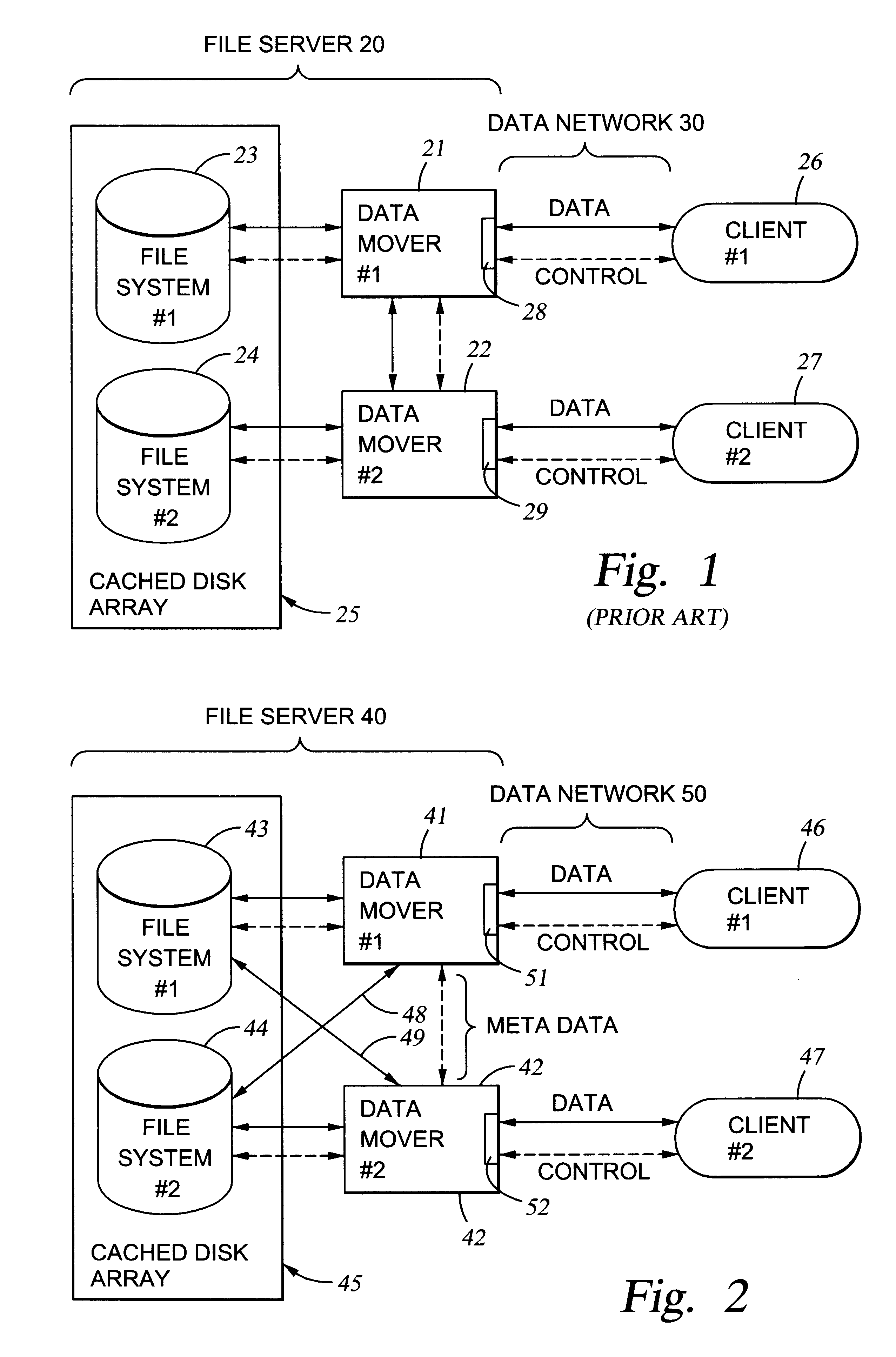
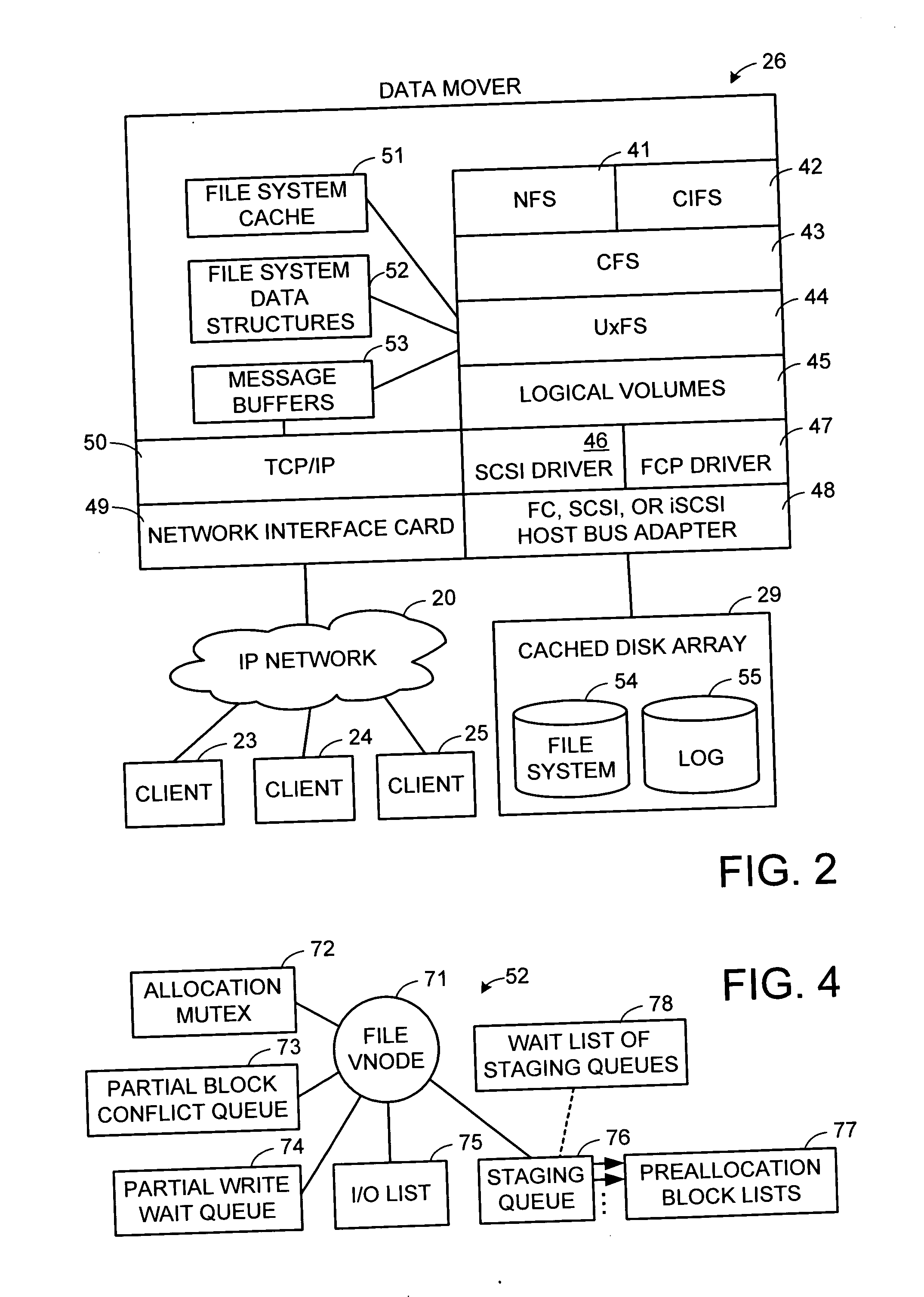
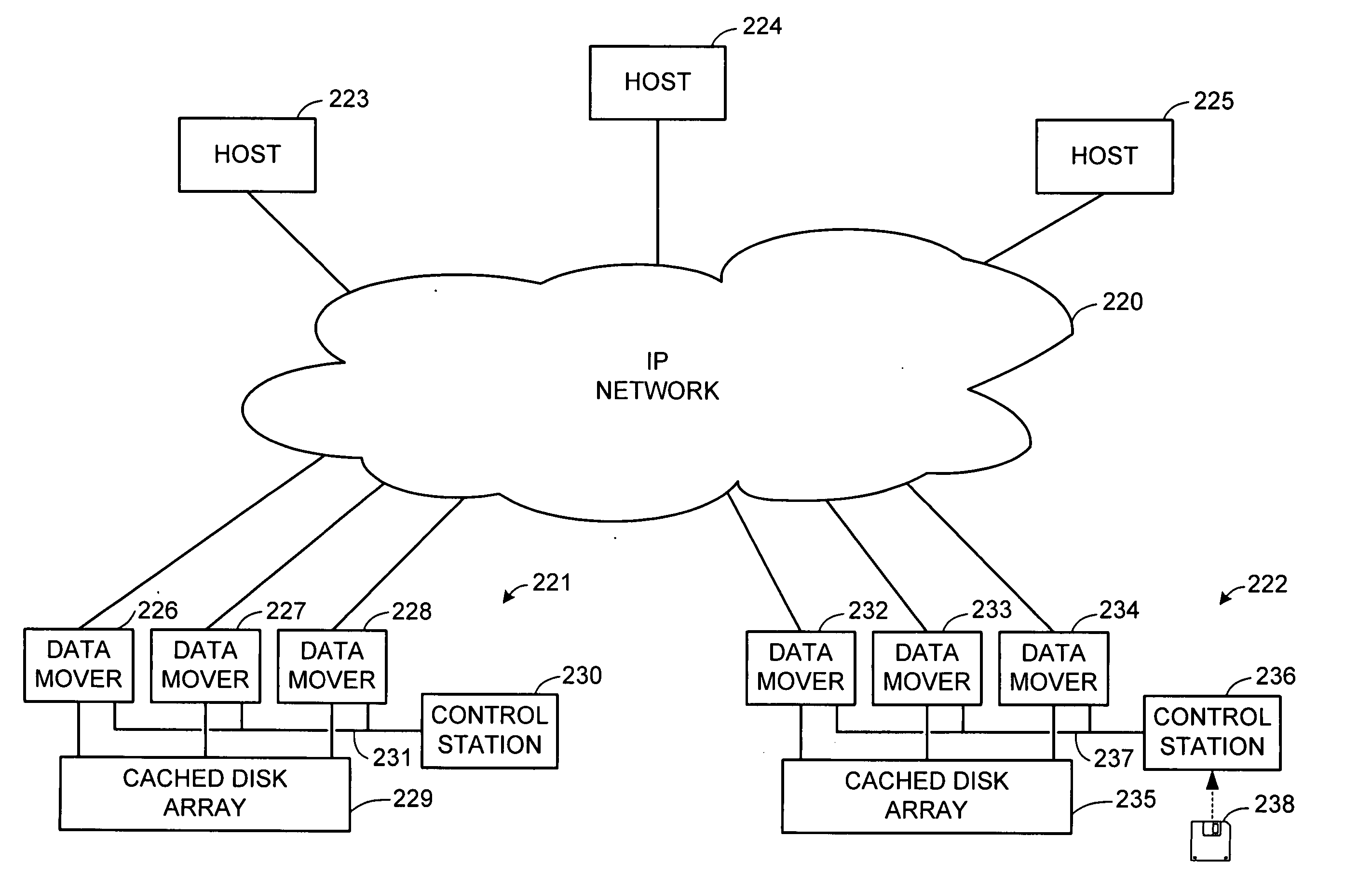
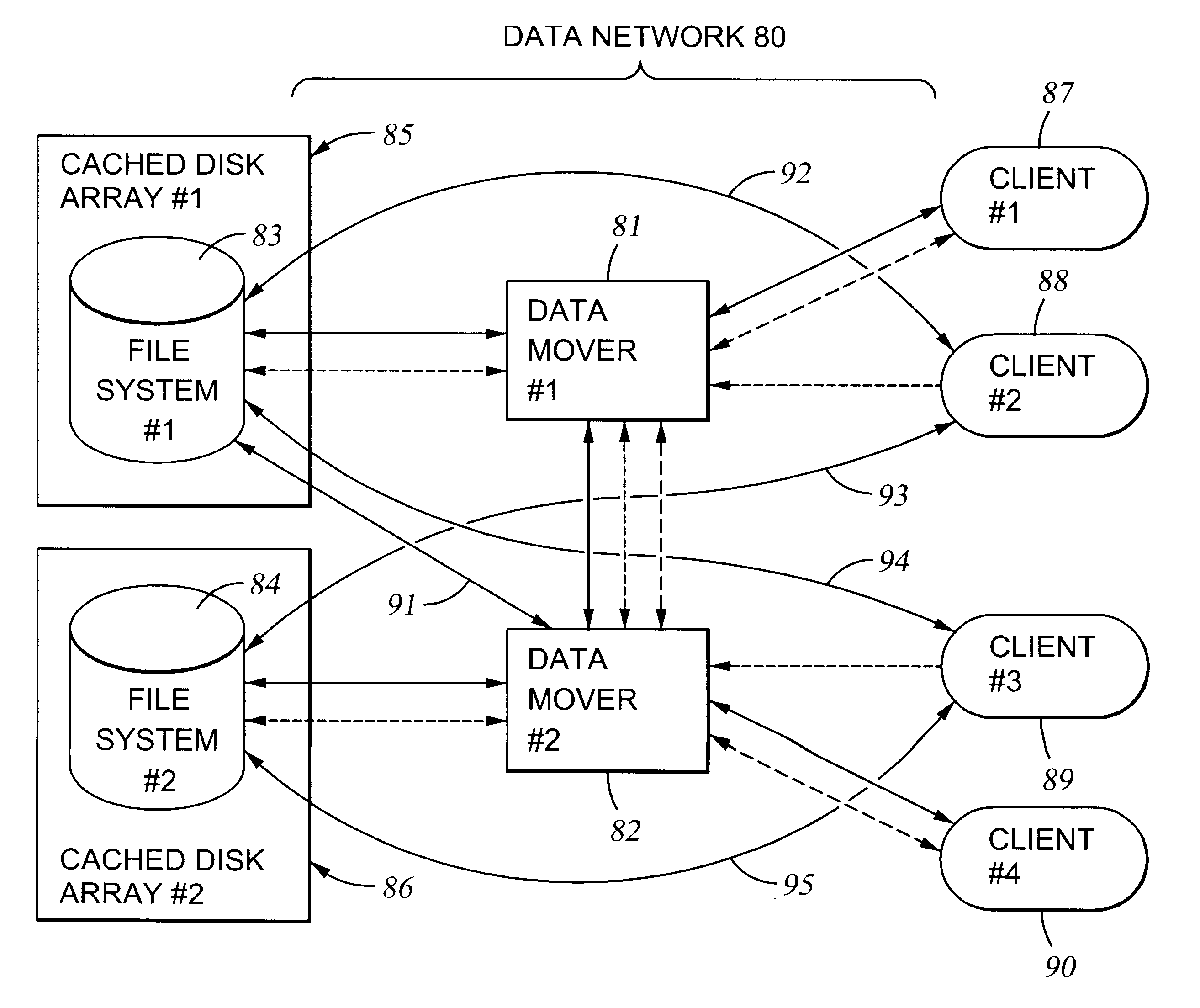
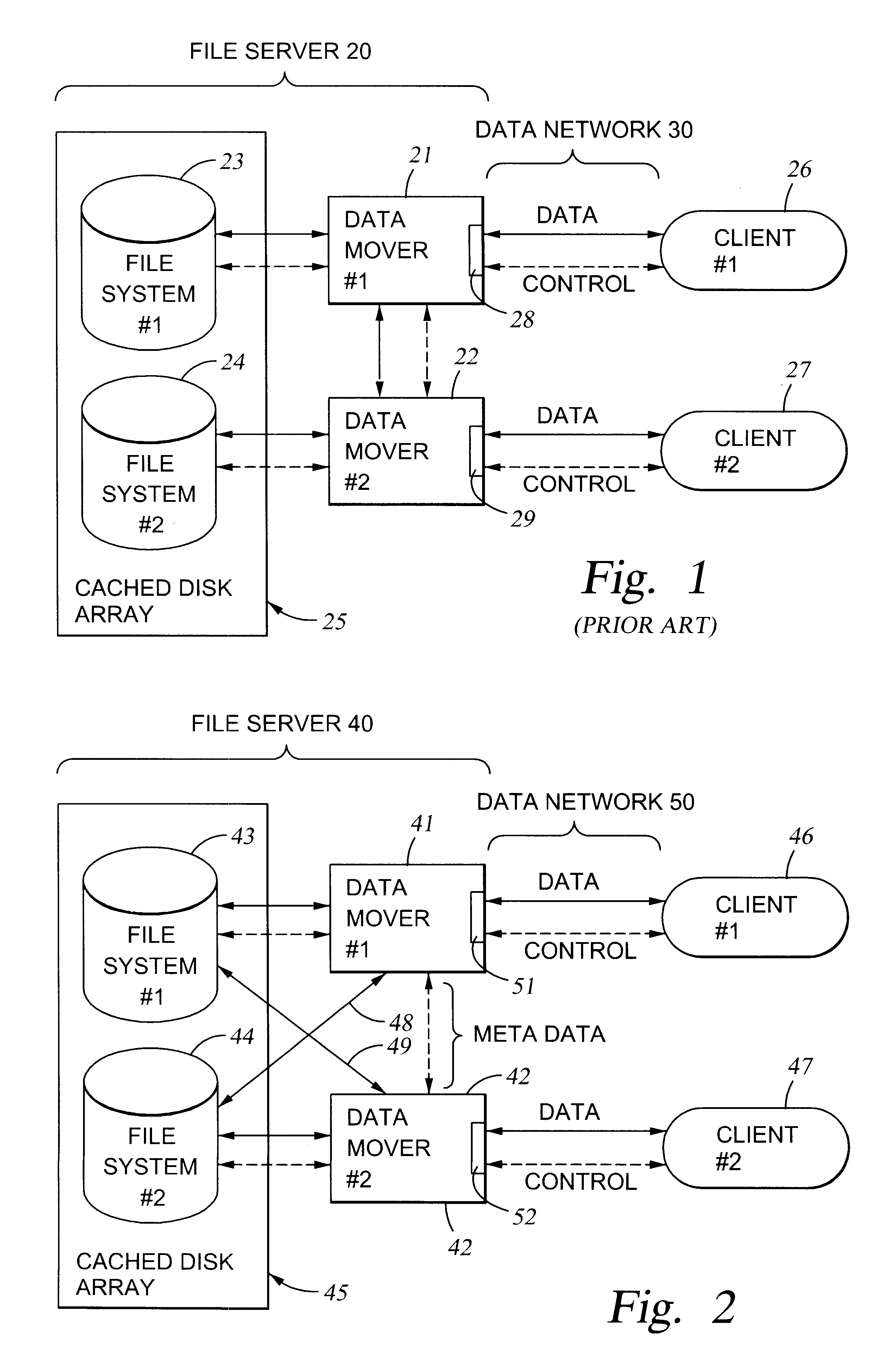
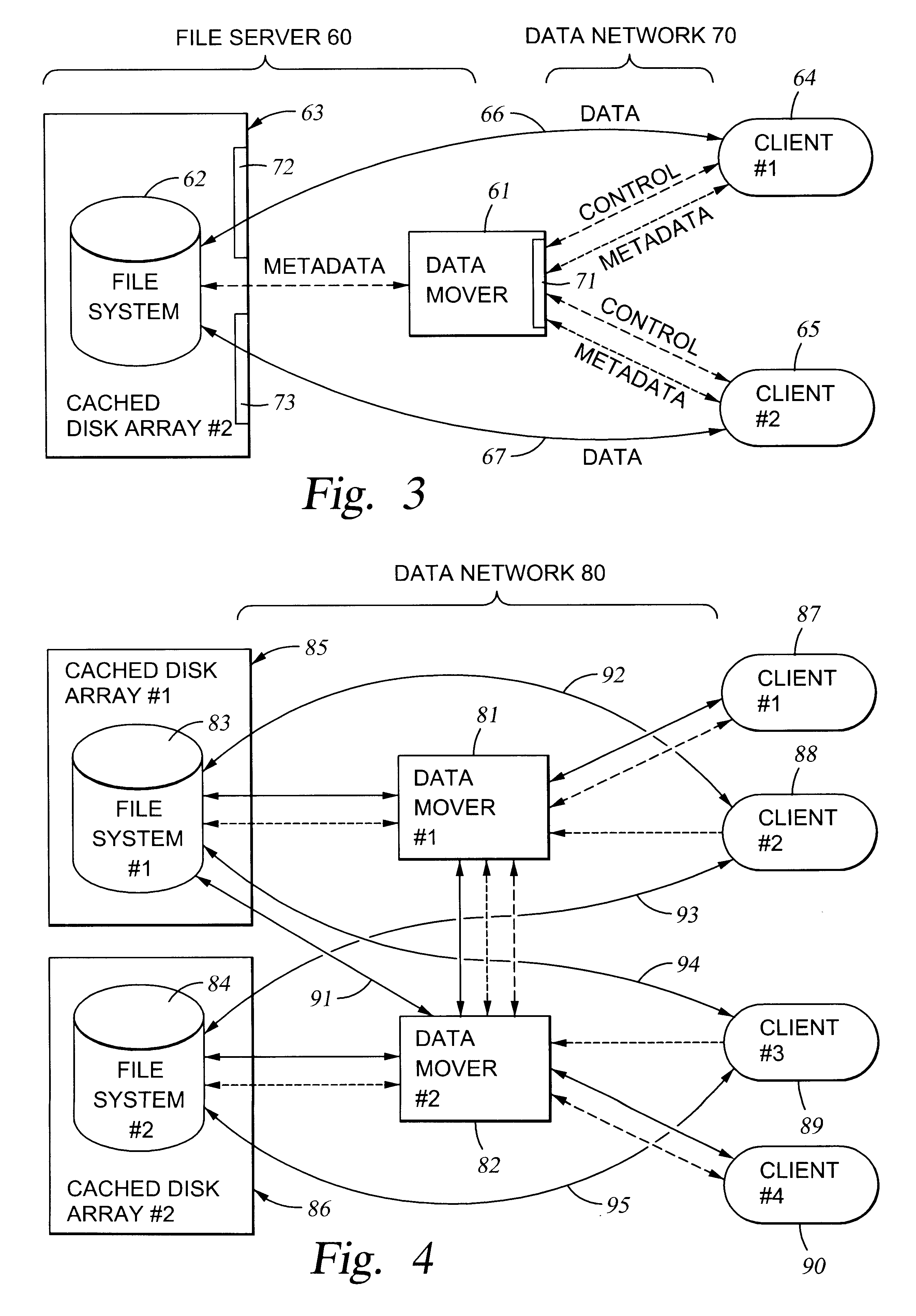
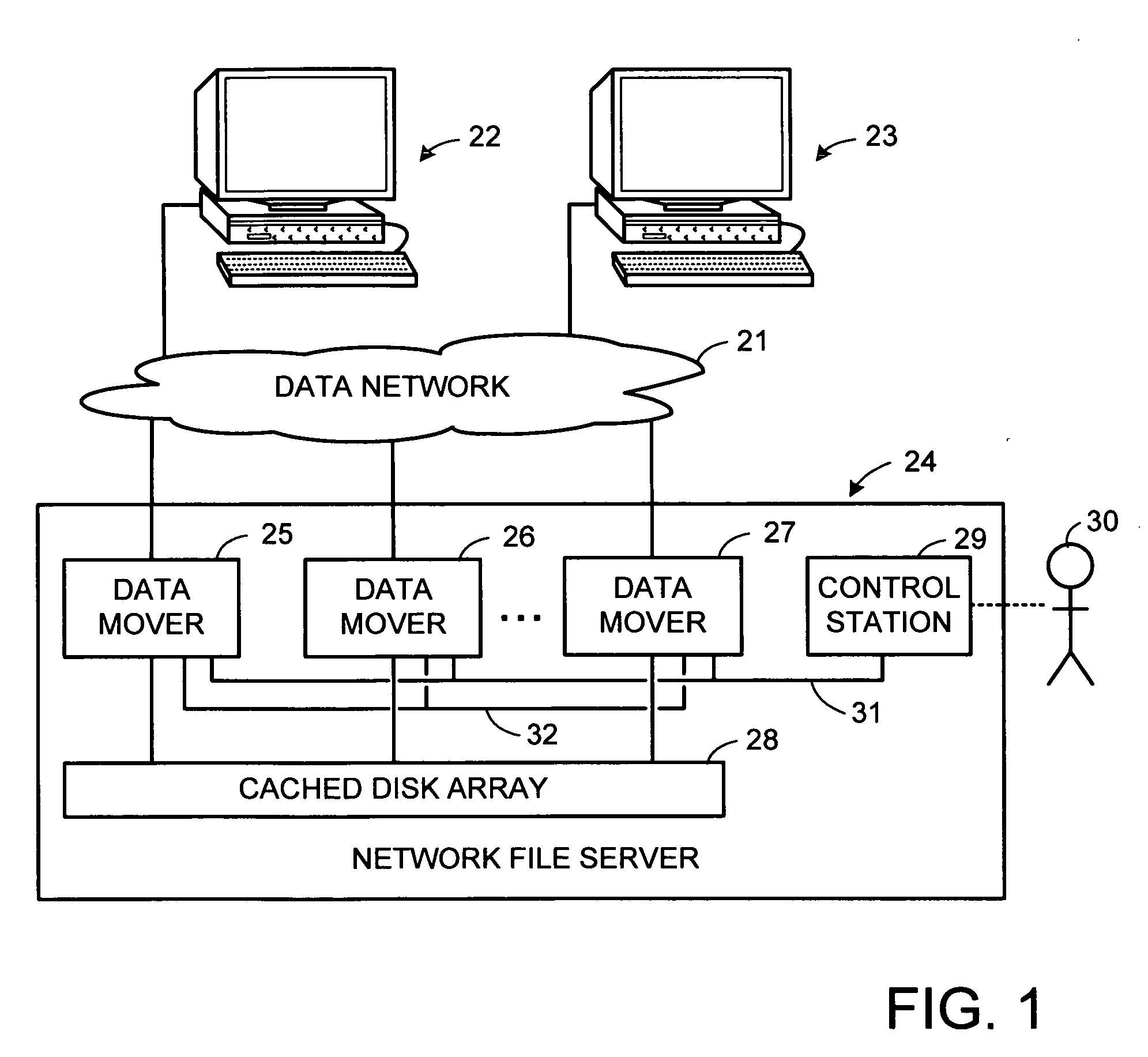
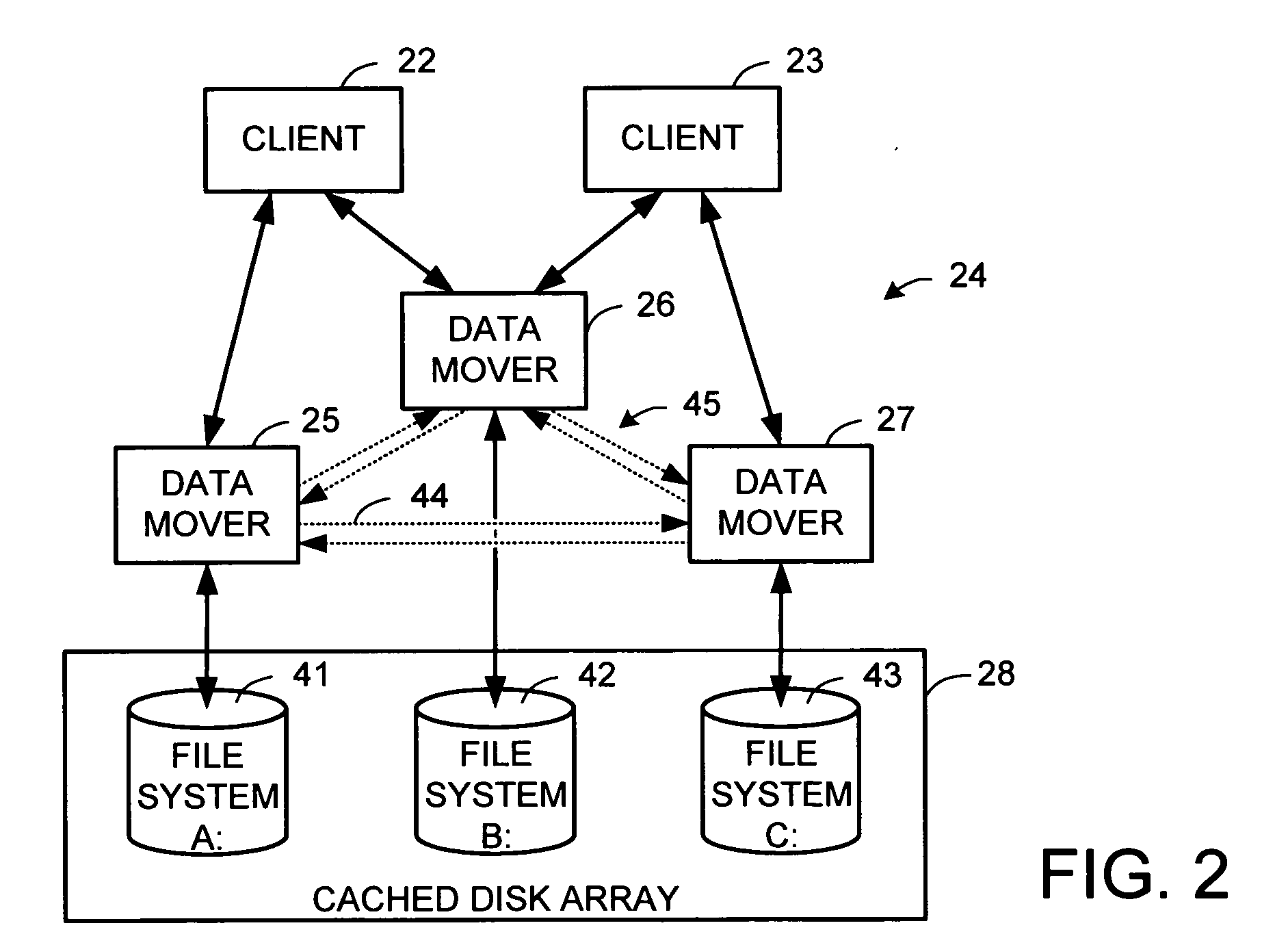
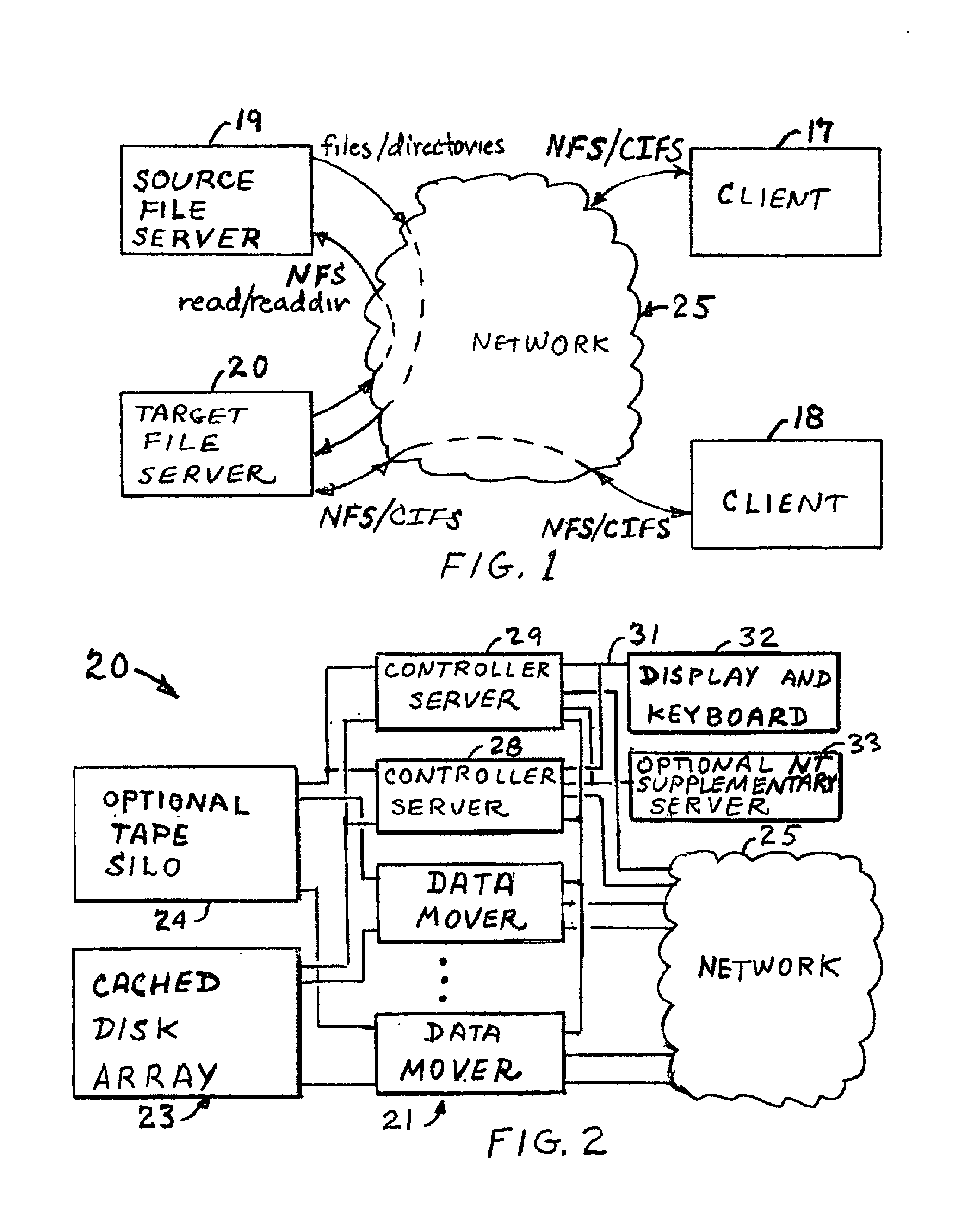
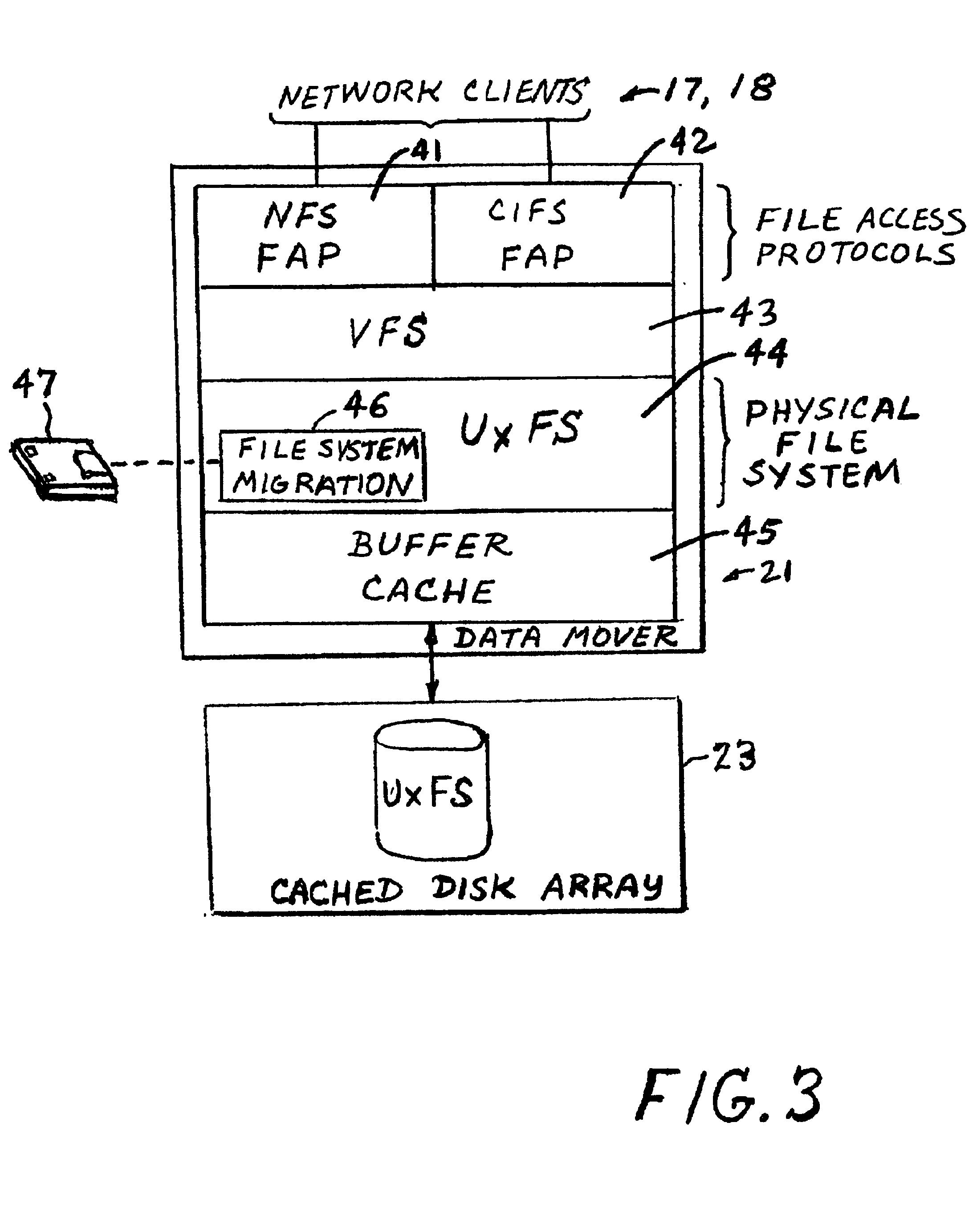
File server system using file system storage, data movers, and an exchange of meta data among data movers for file locking and direct access to shared file systems
InactiveUS6324581B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemData access
A plurality of data mover computers control access to respective file systems in data storage. A network client serviced by any of the data movers can access each of the file systems. If a data mover receives a client request for access to a file in a file system to which access is controlled by another data mover, then the data mover that received the client request sends a metadata request to the data mover that controls access to the file system. The data mover that controls access to the file system responds by placing a lock on the file and returning metadata of the file. The data mover that received the client request uses the metadata to formulate a data access command that is used to access the file data in the file system over a bypass data path that bypasses the data mover computer that controls access to the file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Peer-to-Peer Redundant File Server System and Methods
InactiveUS20090271412A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsHash functionFile system
Peer-to-peer redundant file server system and methods include clients that determine a target storage provider to contact for a particular storage transaction based on a pathname provided by the filesystem and a predetermined scheme such as a hash function applied to a portion of the pathname. Servers use the same scheme to determine where to store relevant file information so that the clients can locate the file information. The target storage provider may store the file itself and / or may store metadata that identifies one or more other storage providers where the file is stored. A file may be replicated in multiple storage providers, and the metadata may include a list of storage providers from which the clients can select (e.g., randomly) in order to access the file.
Owner:OVERLAND STORAGE
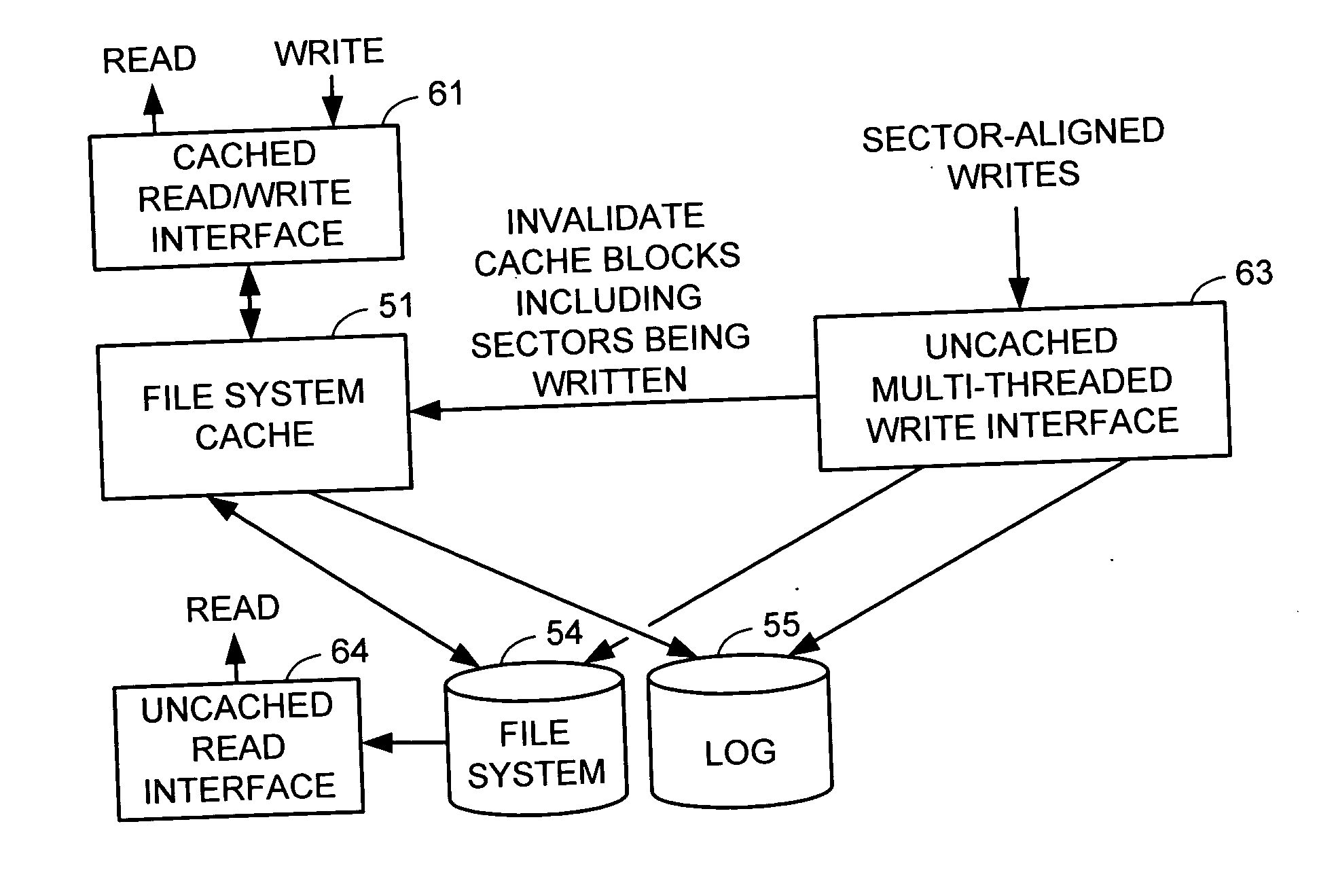
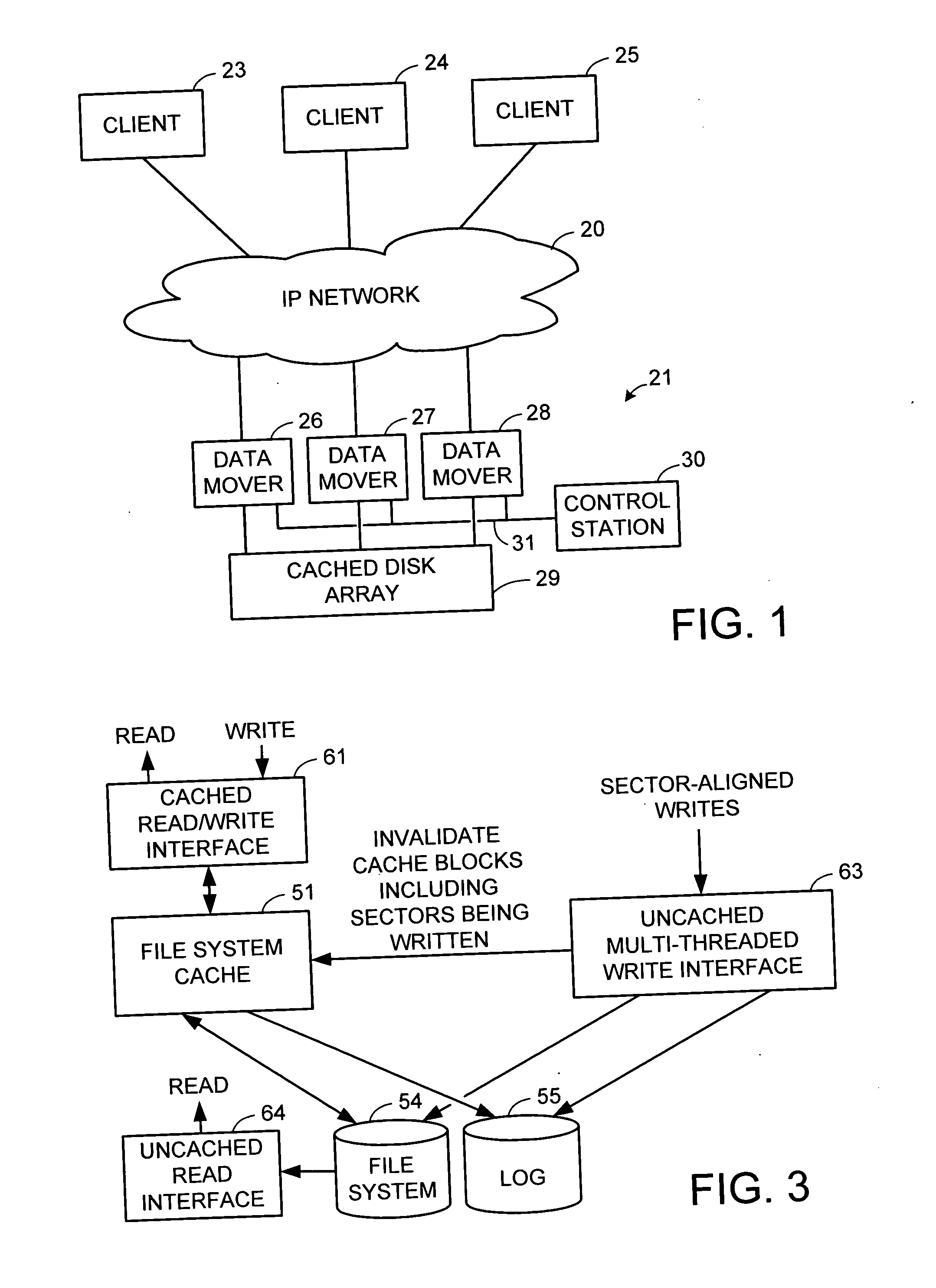
Multi-threaded write interface and methods for increasing the single file read and write throughput of a file server
ActiveUS20050066095A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData integrityFile allocation
A write interface in a file server provides permission management for concurrent access to data blocks of a file, ensures correct use and update of indirect blocks in a tree of the file, preallocates file blocks when the file is extended, solves access conflicts for concurrent reads and writes to the same block, and permits the use of pipelined processors. For example, a write operation includes obtaining a per file allocation mutex (mutually exclusive lock), preallocating a metadata block, releasing the allocation mutex, issuing an asynchronous write request for writing to the file, waiting for the asynchronous write request to complete, obtaining the allocation mutex, committing the preallocated metadata block, and releasing the allocation mutex. Since no locks are held during the writing of data to the on-disk storage and this data write takes the majority of the time, the method enhances concurrency while maintaining data integrity.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
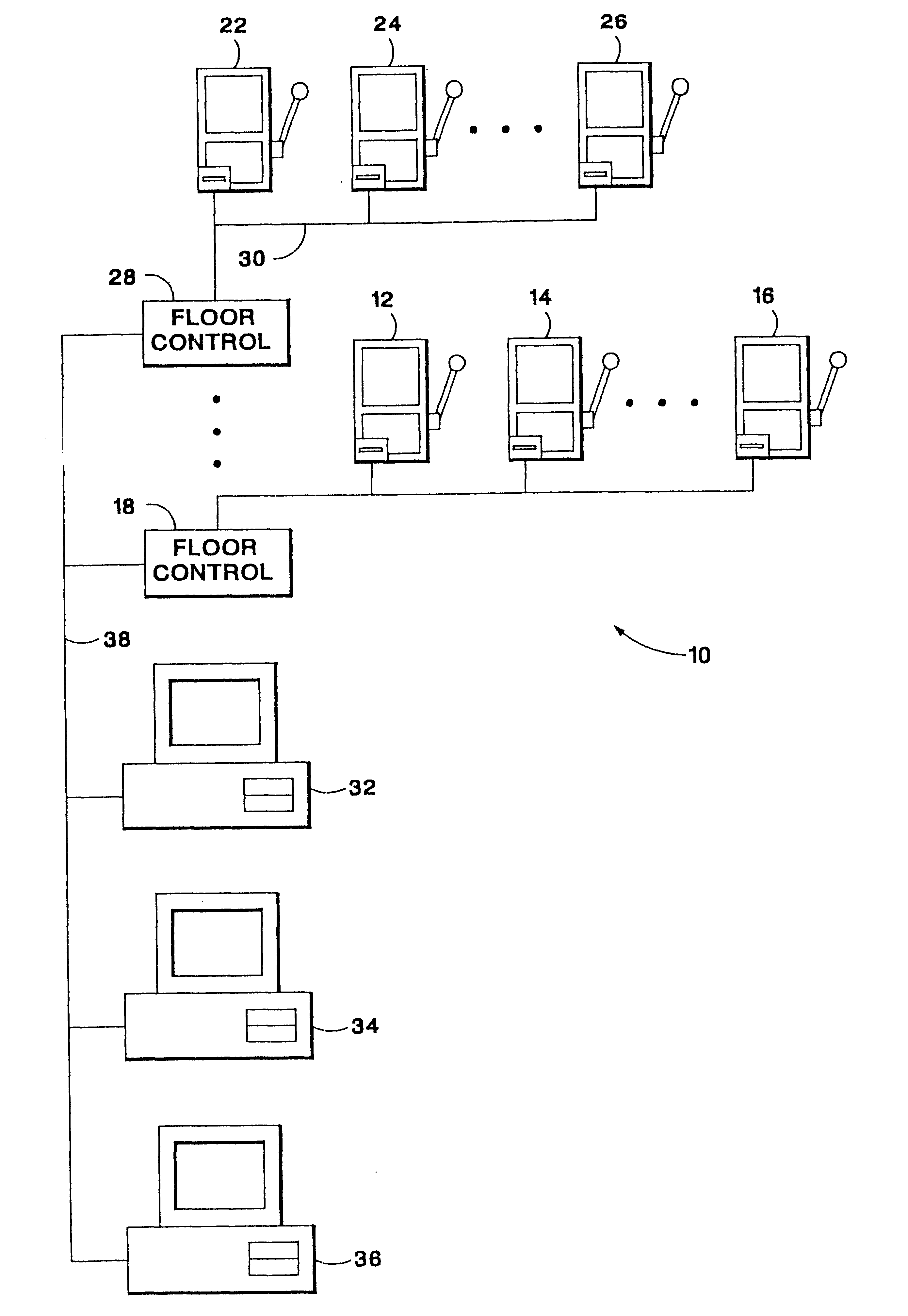
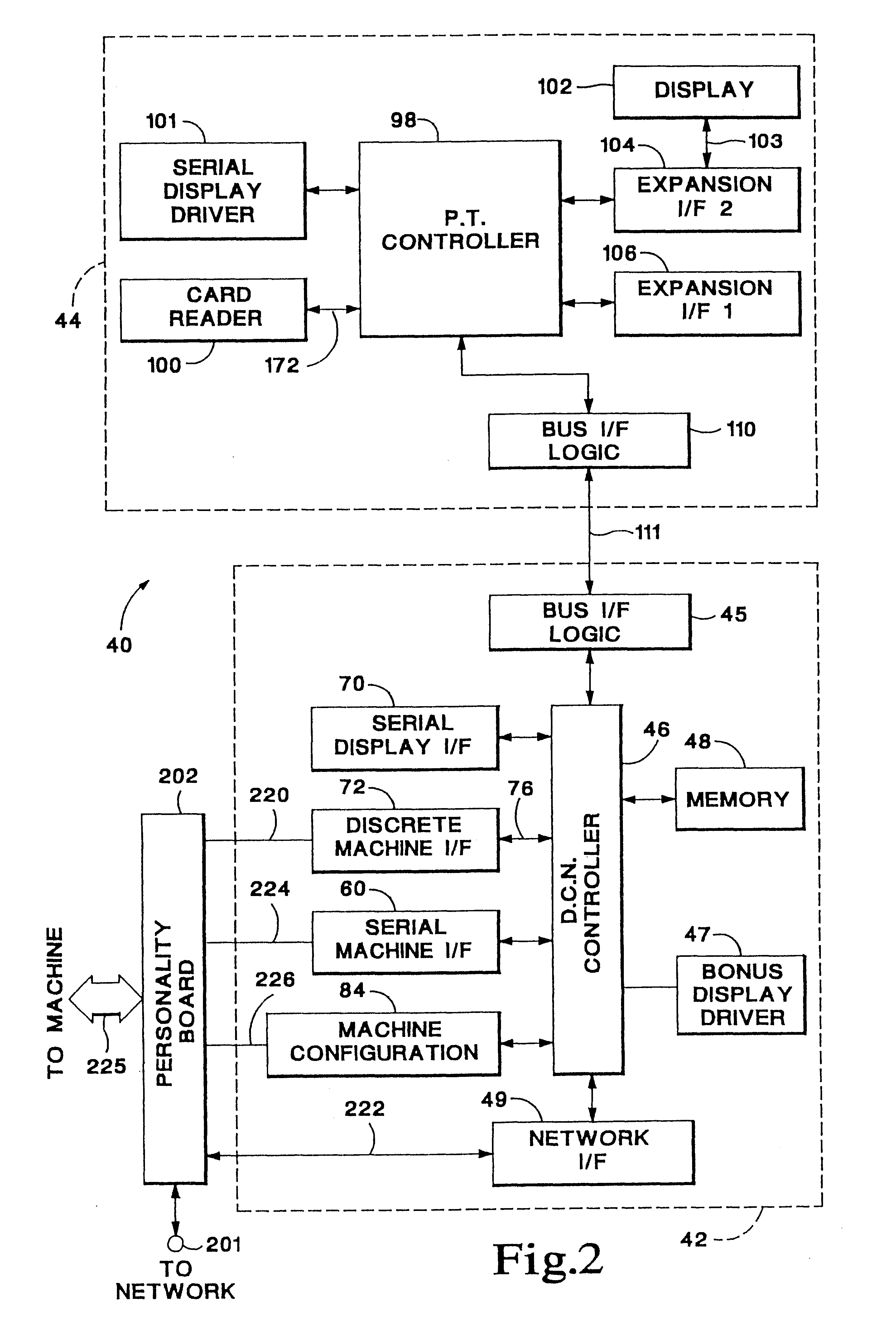
Method and apparatus for operating networked gaming devices
InactiveUSRE37885E1Coin countersApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingComputer moduleComputer terminal
A system for monitoring and configuring gaming devices interconnected over a high-speed network is disclosed. The system can support a file server, one or more floor controllers, one or more pit terminals, and other terminals all interconnected over the network. Each gaming device includes an electronic module which allows the gaming device to communicate with a floor controller over a current loop network. The electronic module includes a player tracking module and a data communication node. The player tracking module includes a card reader for detecting a player tracking card inserted therein which identifies the player. The data communication node communicates with both the floor controller and the gaming device. The data communication node communicates with the gaming device over a serial interface through which the data communication node transmits reconfiguration commands. The gaming device reconfigures its payout schedule responsive to the reconfiguration commands to provide a variety of promotional bonuses such as multiple jackpot bonuses, mystery jackpot bonuses, progressive jackpot bonuses, or player specific bonuses.
Owner:IGT
Network manager for cable television system headends
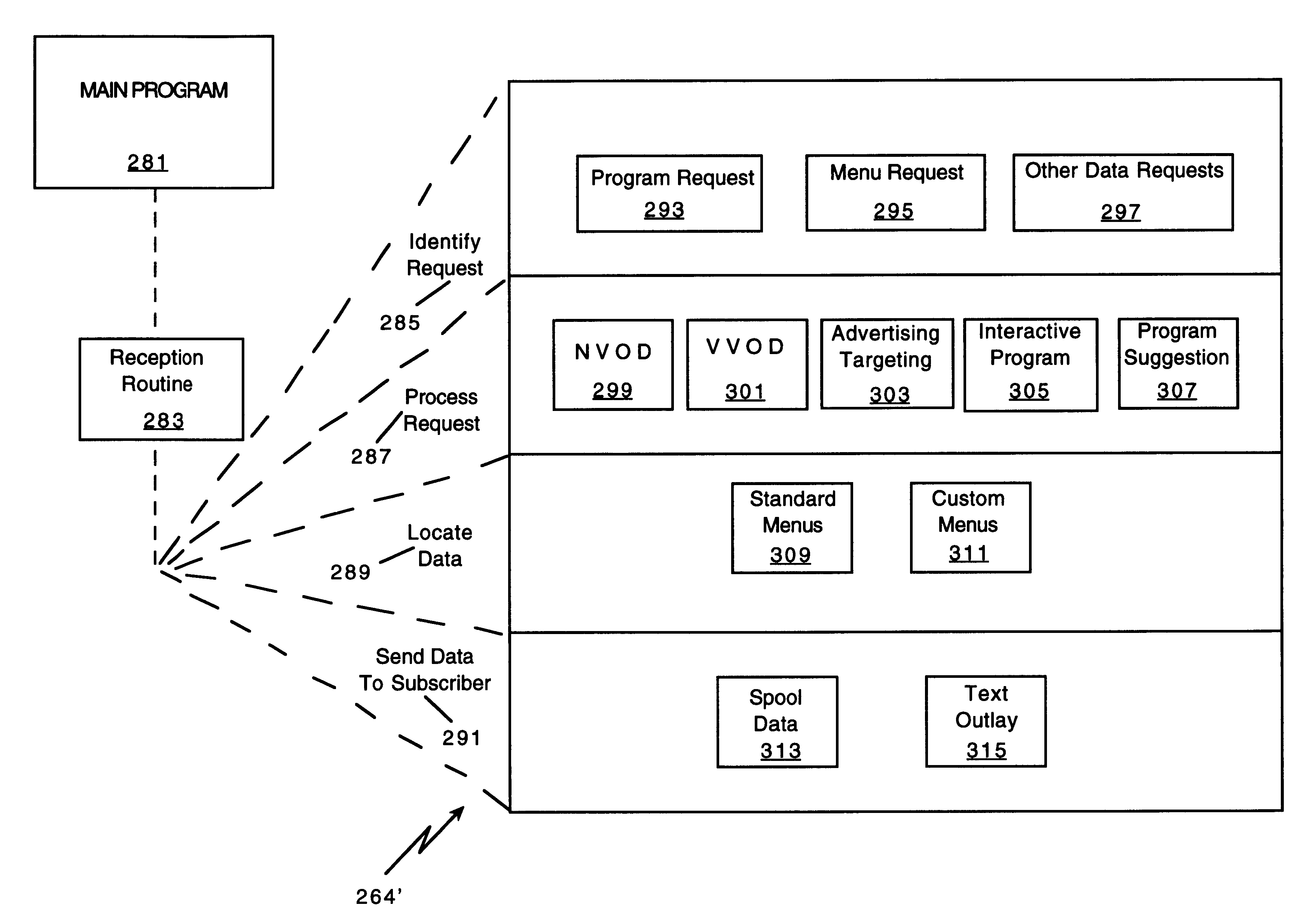
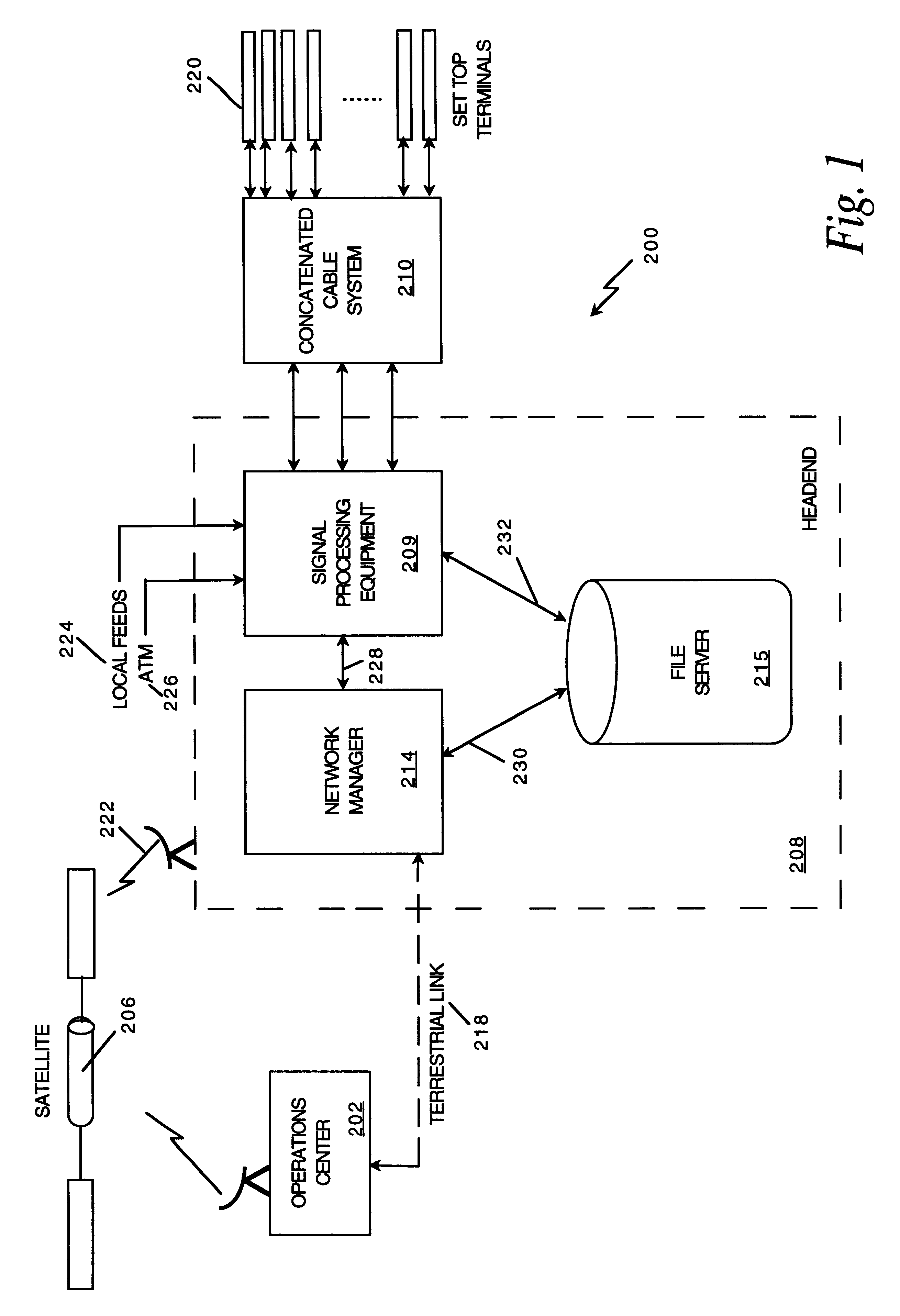
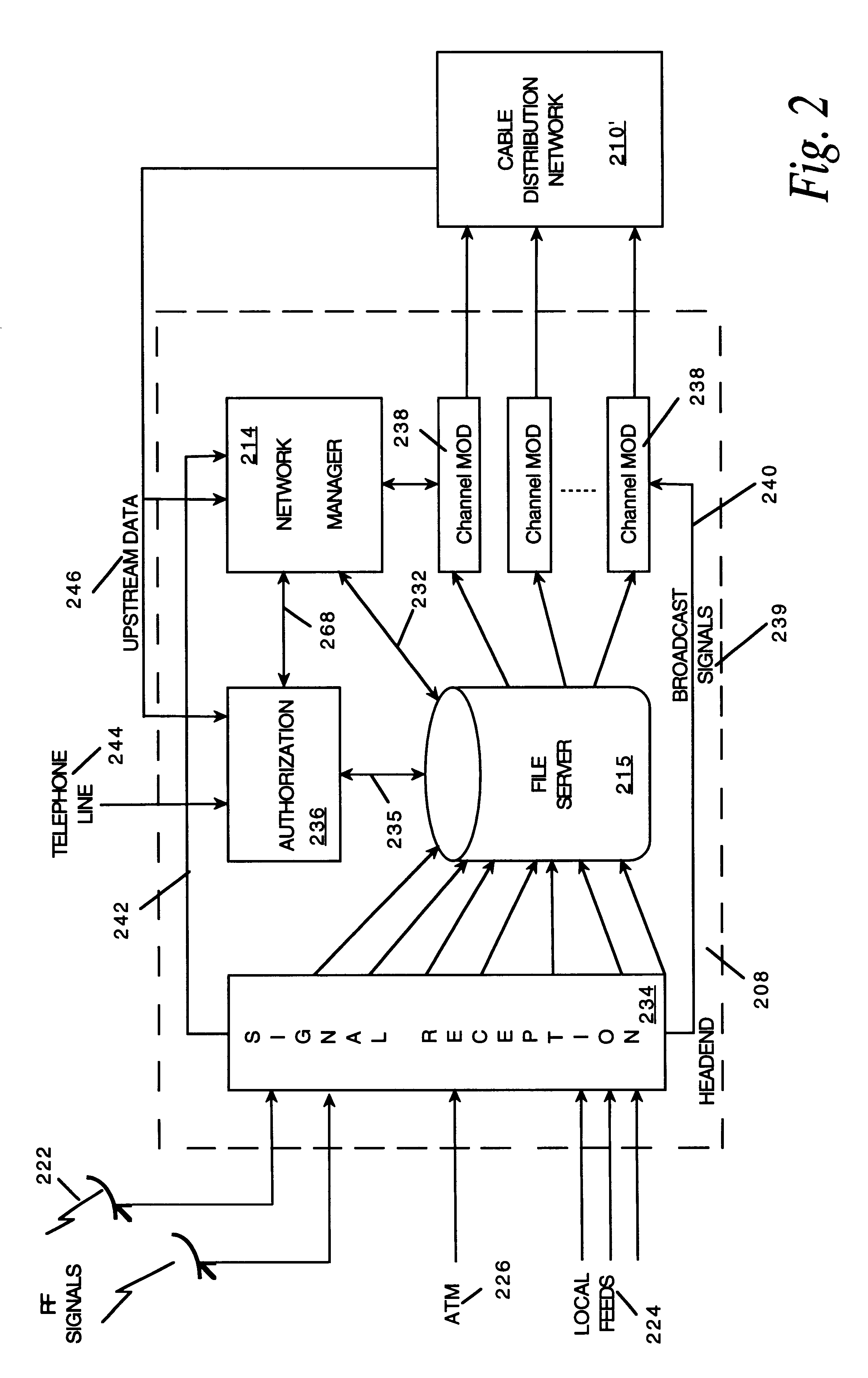
InactiveUS6201536B1Increase flexibilityImprove rendering capabilitiesTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInformation processingInstruction memory
A novel network manager for use with a cable television system headend capable of monitoring and managing headend components and set top terminals in a television delivery system is described. The invention relates to methods and apparatus that manage and coordinate the reception of various programming and control signals at a headend. The invention manages and coordinates the storage of such signals for intelligent selection and distribution to set top terminals. The invention makes use of a receiver or set of receivers, a work station, a program control information processing component, a network management CPU, databases, control software and an instruction memory. The invention uses these components to manage and monitor certain headend components, such as signal reception equipment, an authorization component, a file server, MPEG decoders, a digital buffer with frame repeat and channel modulators. The invention is particularly useful in processing and responding to upstream information and subscriber communications received from set top terminals. In so doing, the invention accommodates various system services, including (1) near video on demand (NVOD), (2) virtual video on demand (VVOD), (3) video on demand (VOD), (4) interactive program services, (5) program suggestion features, (6) advertisement targeting, (7) generation of standard and custom menus, and (8) data spooling and text overlaying.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
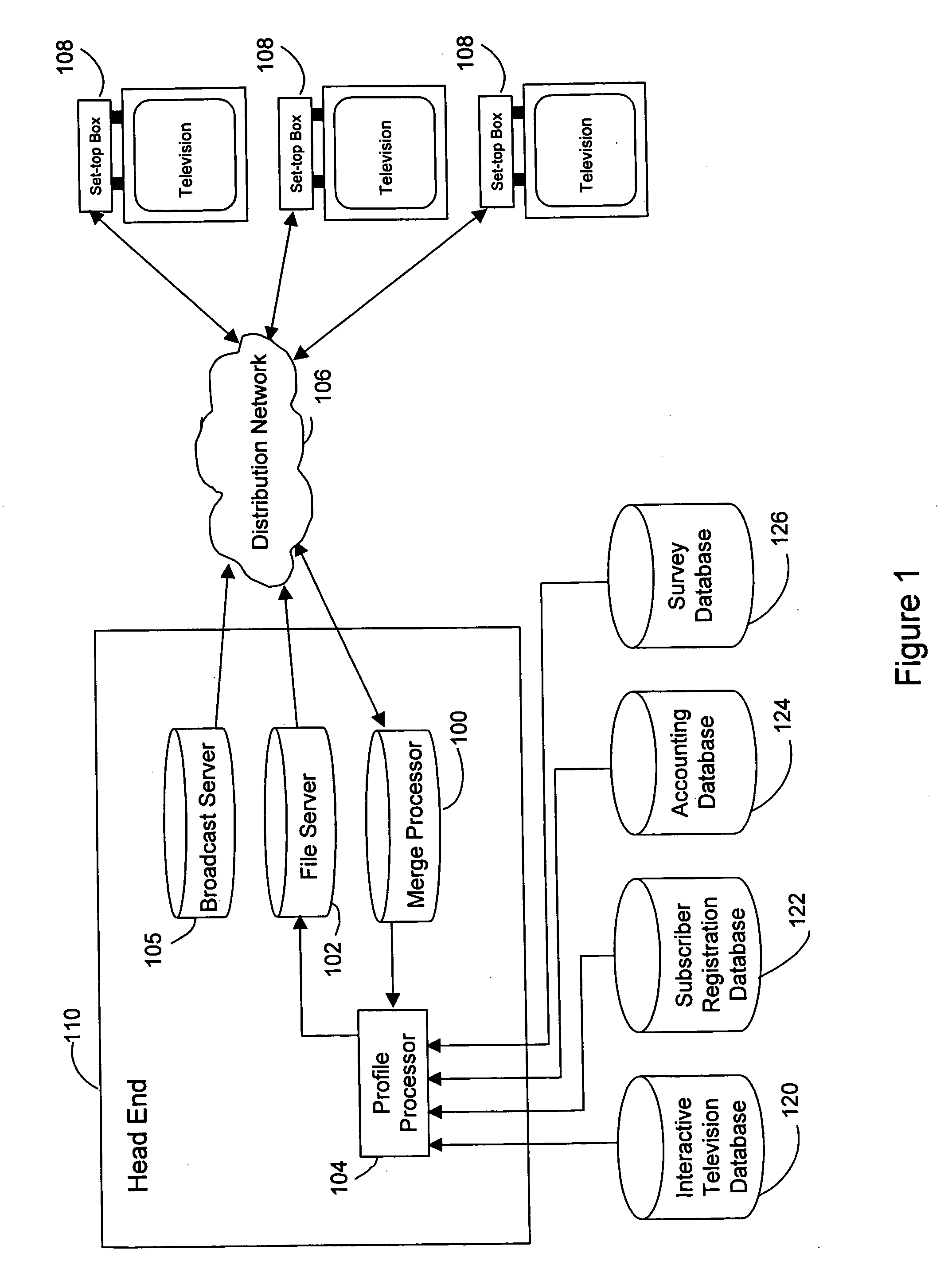
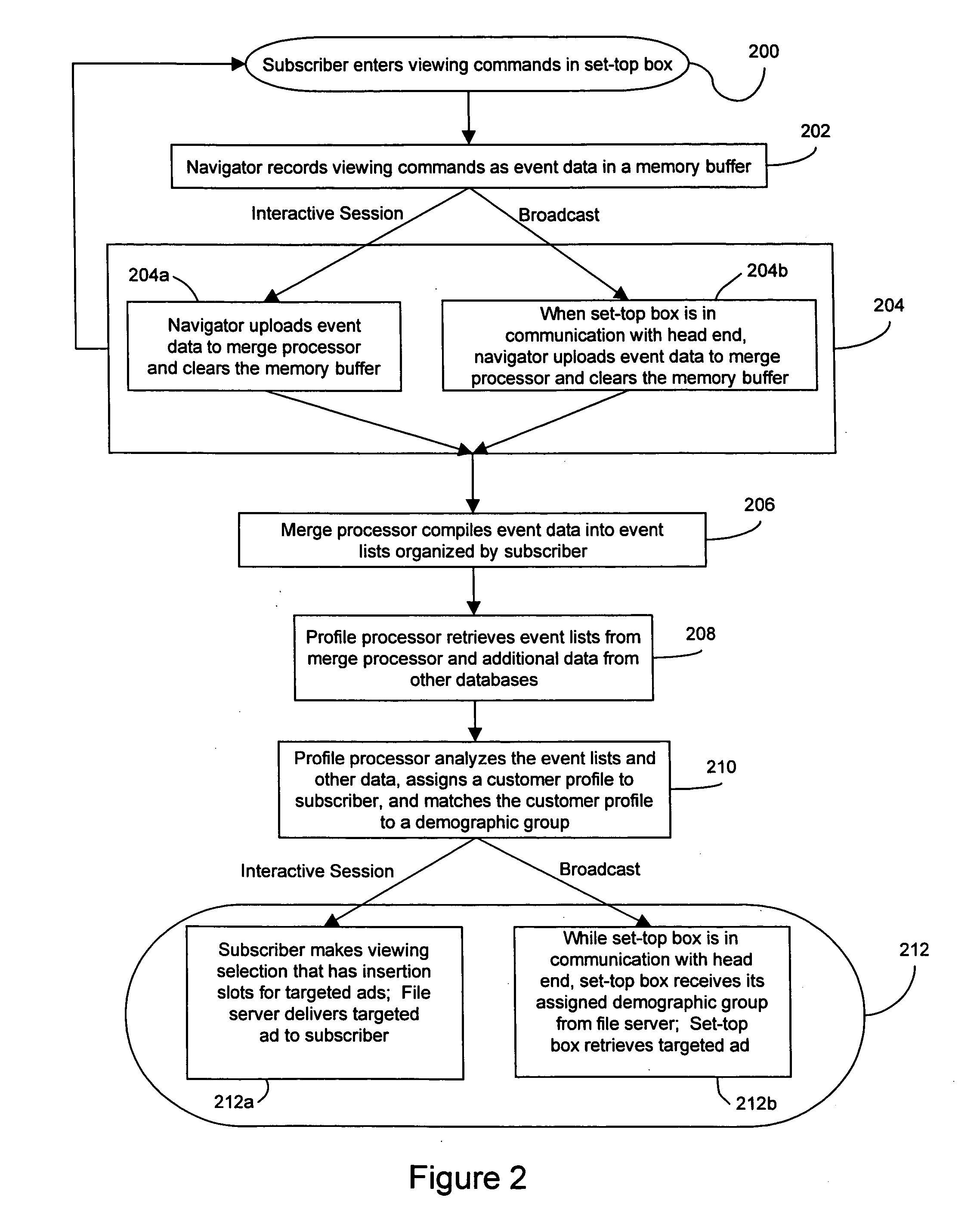
Method and system for providing targeted advertisements
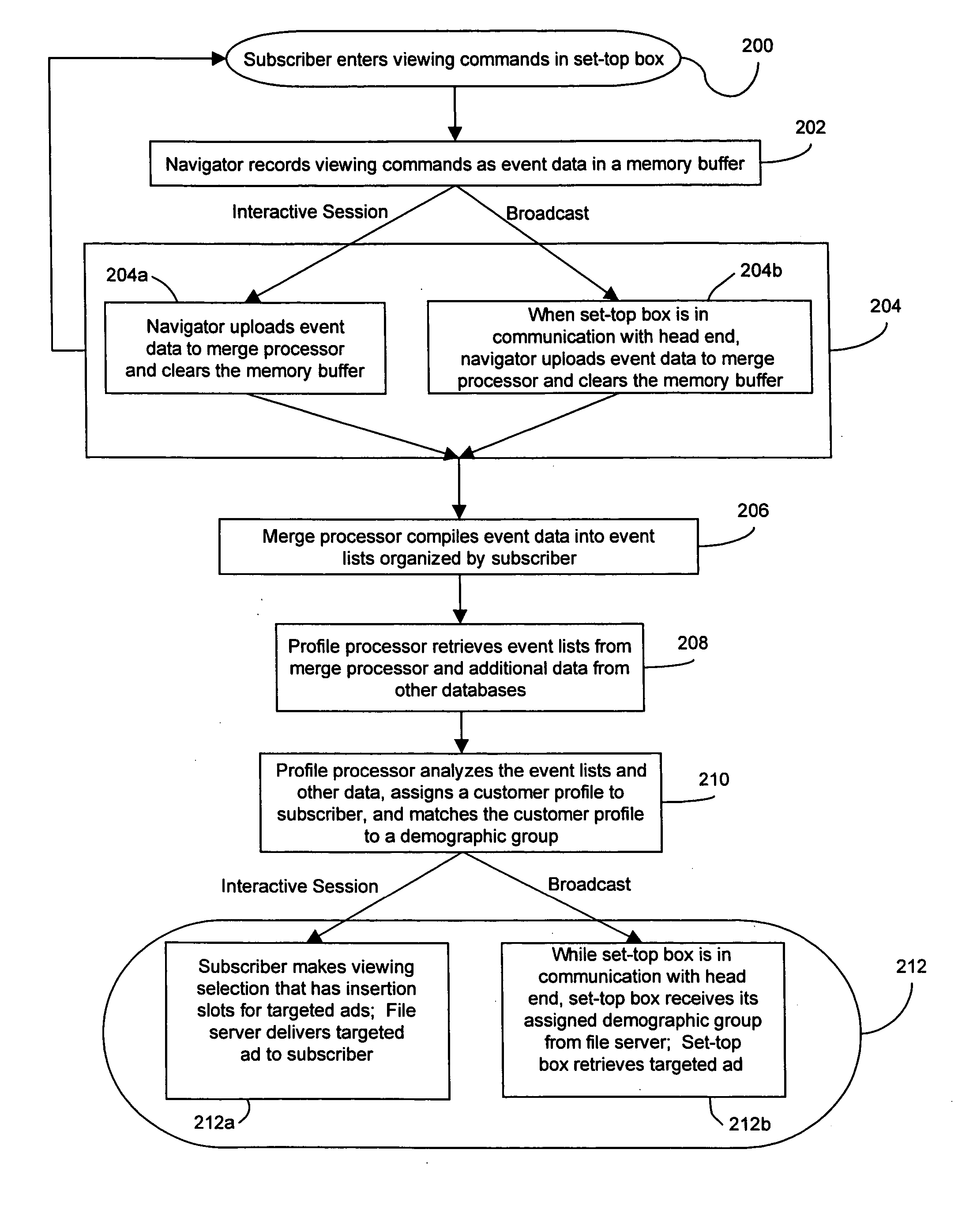
InactiveUS20040163101A1Receiver side switchingAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive televisionNetwork media
A method and system for providing targeted advertisements over a networked media delivery system, especially interactive television networks, the system comprising tracking and storing viewer selections, analyzing the selections, and delivering targeted advertisements that appeal to the particular subscriber making the selections, the system including a merge processor, a file server, a profile processor, and a broadcast server contained in a head end in communication with a plurality of set-top boxes through a distribution network. Based on a subscriber's viewing habits and account information, the present invention delivers different, customized advertisements to different viewers watching the same program or channel. The present invention delivers the advertisements as either still frame bit maps or as video streams advertisement insertion in a playlist or a broadcast media program.
Owner:ALPHONSO
Apparatus and method for remotely monitoring a computer network
InactiveUS20060031476A1Easy to provideMinimize the possibilityDigital computer detailsTransmissionAnti virusPrivate network
There is provided an apparatus for remotely monitoring a computer network. Monitoring is performed using an inside out approach from behind firewalls and other security devices. The monitoring appliance is shipped to a client site preconfigured and typically requires no technically trained person for installation. Collected network data is periodically transmitted to a remote monitoring facility where it is recorded and analyzed. Both the monitoring appliance and the remote center maintain the configuration data. Typically, no client data is transmitted to the remote monitoring site. If the monitoring appliance fails, a completely configured replacement may be shipped to the site and easily installed. The monitoring appliance is optionally equipped to provide network services. Services such as web hosting, file server, print server, virtual private network (VPN), shared Internet access, web content filtering, anti-virus, spam e-mail elimination, and IP telephony services as well as other such services may be easily provided.
Owner:MATHES MARVIN LEE +1
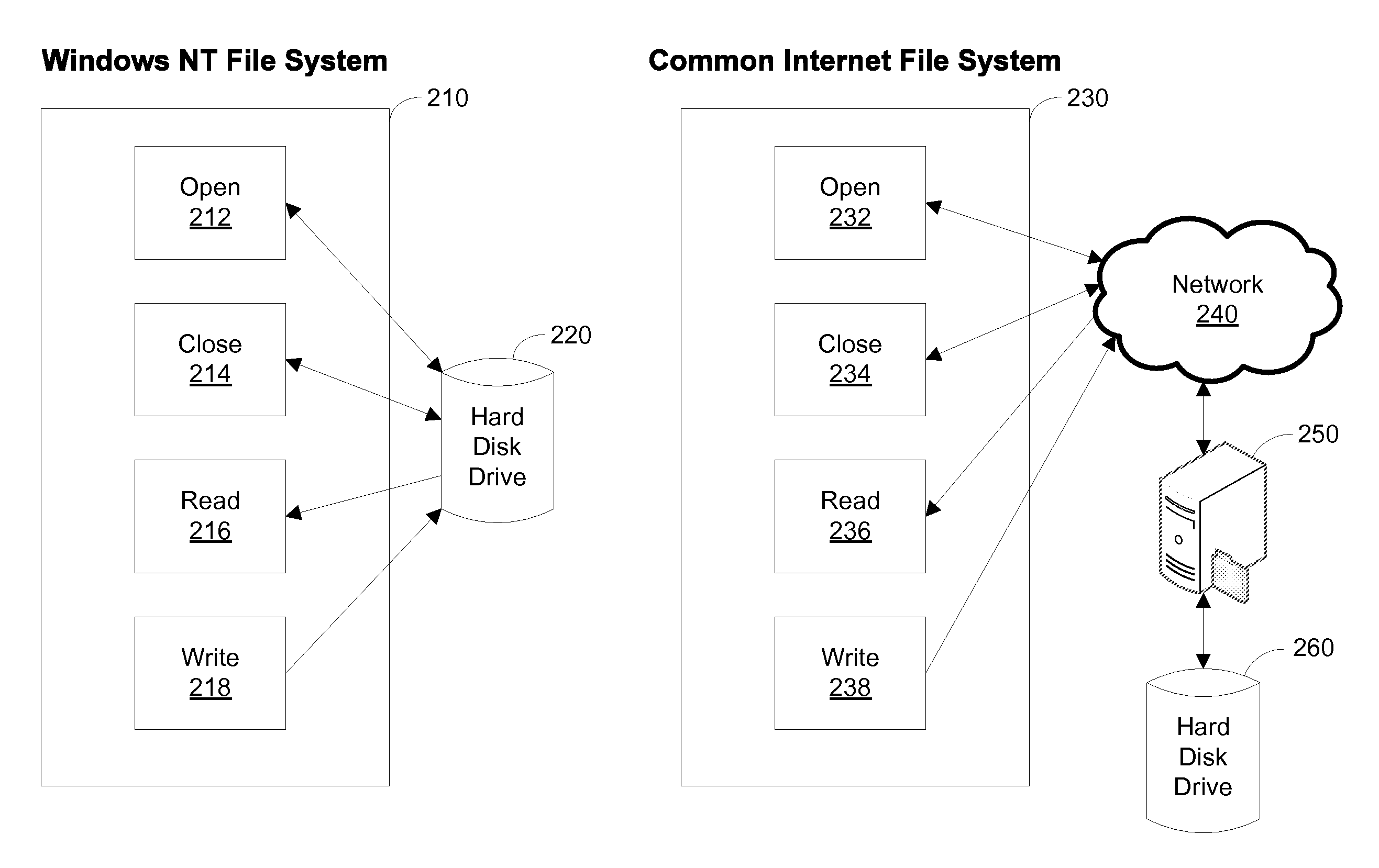
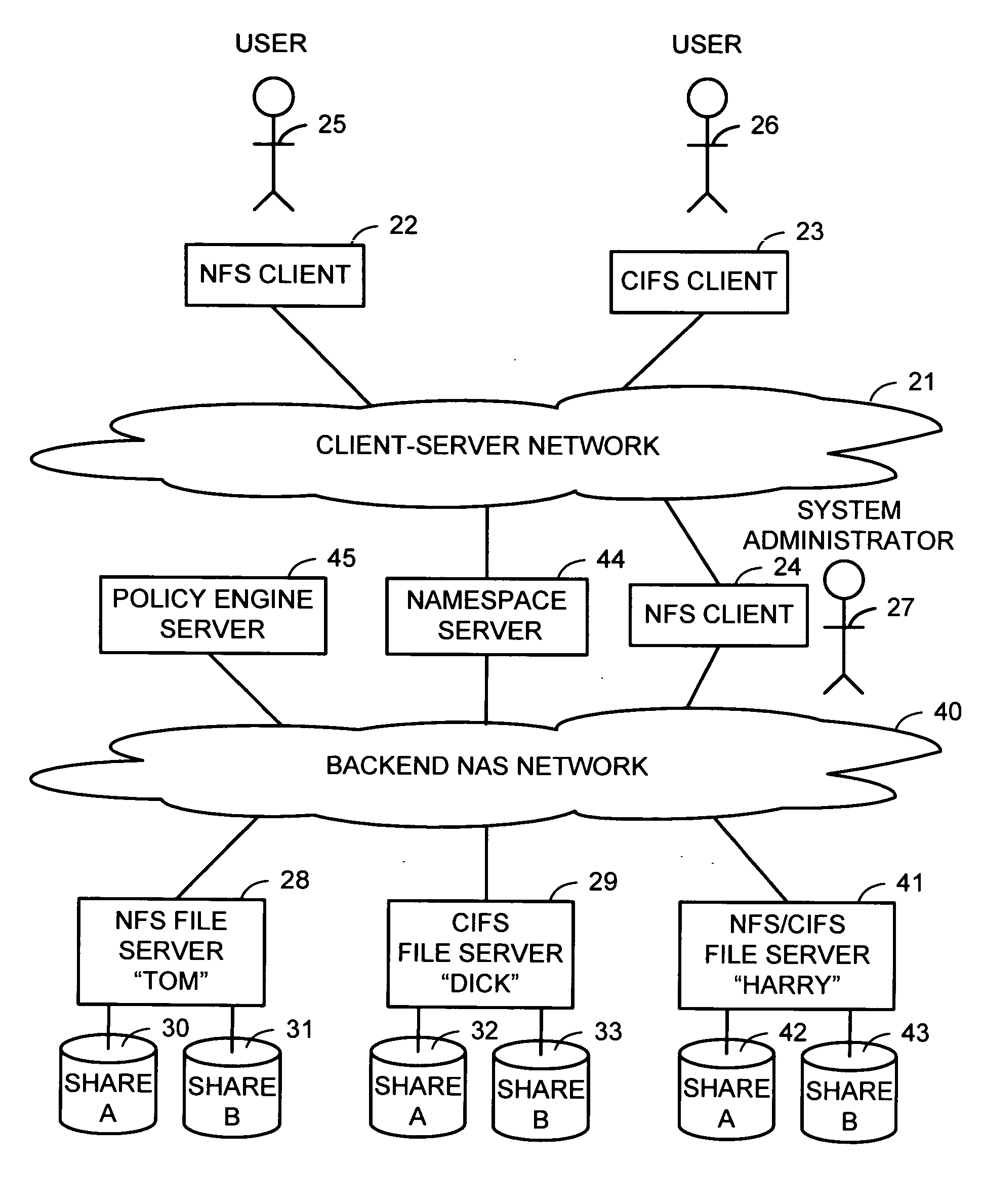
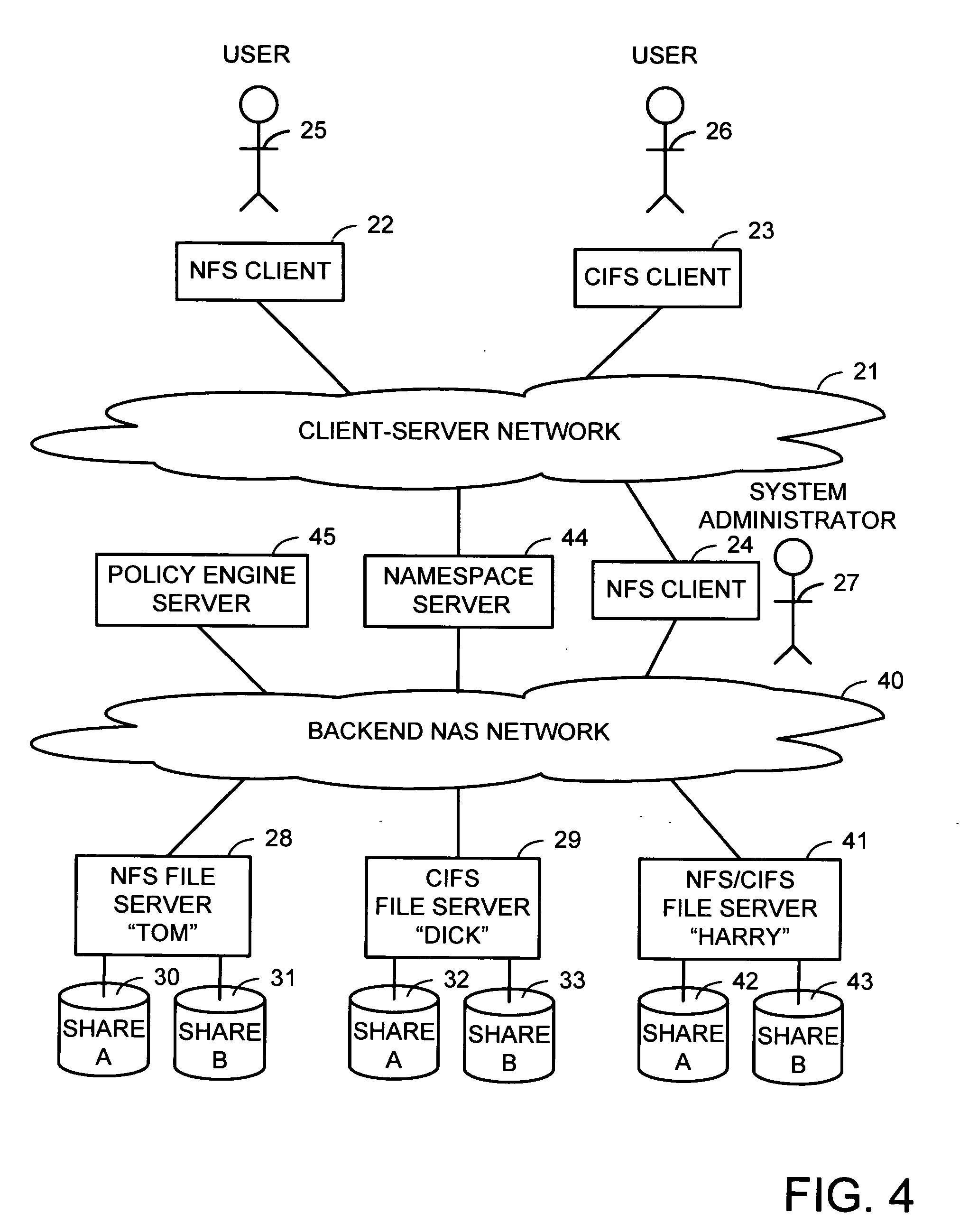
Intelligent network client for multi-protocol namespace redirection
InactiveUS20070088702A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionIntelligent NetworkEngineering
An intelligent network client has the capability of accessing a first network server in accordance with a first high-level file access protocol, and responding to a redirection reply from the first network server by accessing a second network server in accordance with a second high-level file access protocol. For example, the intelligent network client can be redirected from a CIFS / DFS server to a NFS server, and from an NFSv4 server to a CIFS server. Once redirected, the intelligent network client performs a directory mounting operation so that a subsequent client access to the same directory goes directly to the second network server. For example, the first network server is a namespace server for translating pathnames in a client-server network namespace into pathnames in a NAS network namespace, and the second network server is a file server in the NAS network namespace.
Owner:EMC CORP
Internet protocol based disaster recovery of a server
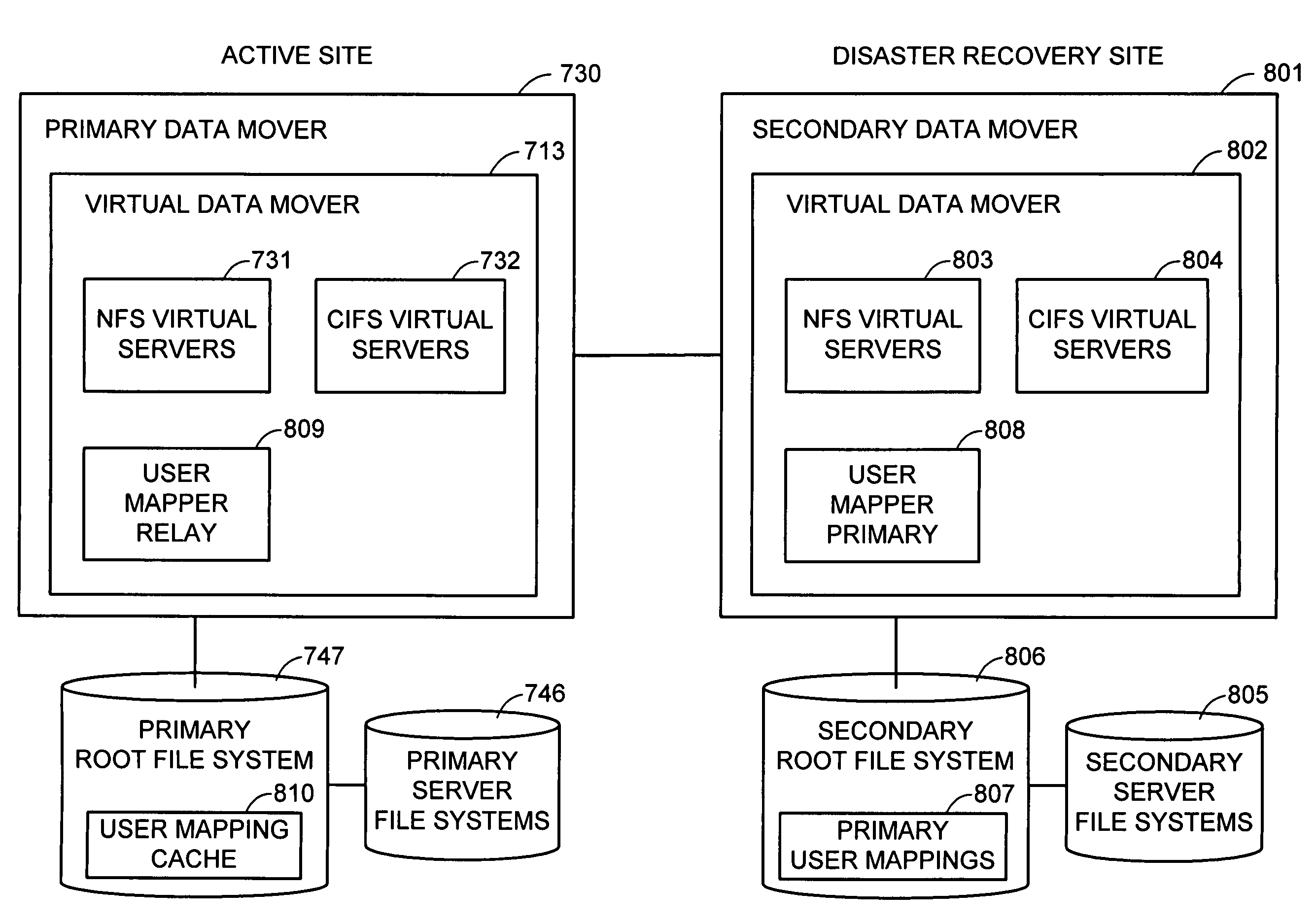
For disaster recovery of a file server at an active site, the files that define the user environment of the file server are replicated to a virtual server at a disaster recovery site. To switch over user access from the active site to the disaster recovery site, the disaster recovery system determines whether there are sufficient network interfaces and file system mounts at the disaster recovery site. If so, the required resources are reserved, and user access is switched over. If not, an operator is given a list of missing resources or discrepancies, and a choice of termination or forced failover. Interruptions during the failover can be avoided by maintaining a copy of user mappings and a copy of session information at the disaster recovery site, and keeping alive client-server connections and re-directing client requests from the active site to the disaster recovery site.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Double-proxy remote data access system
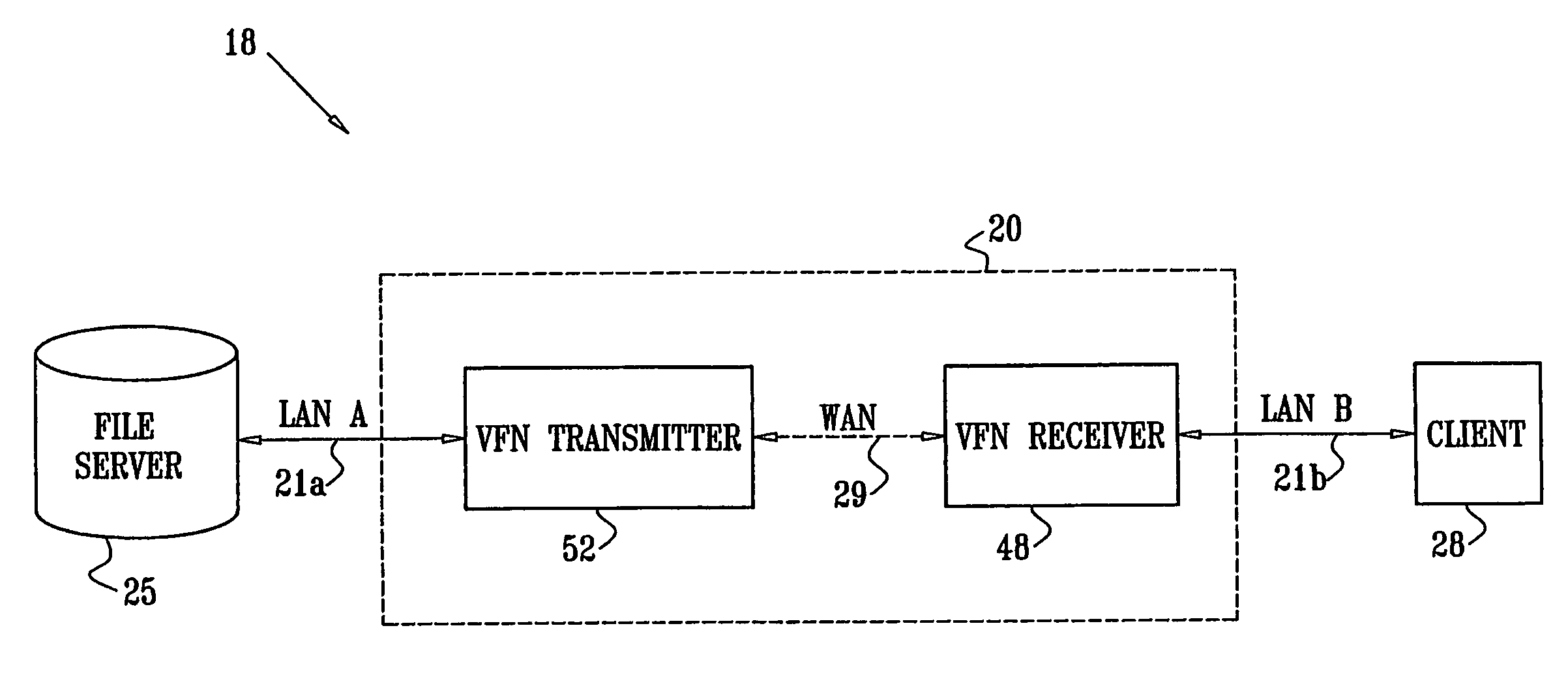
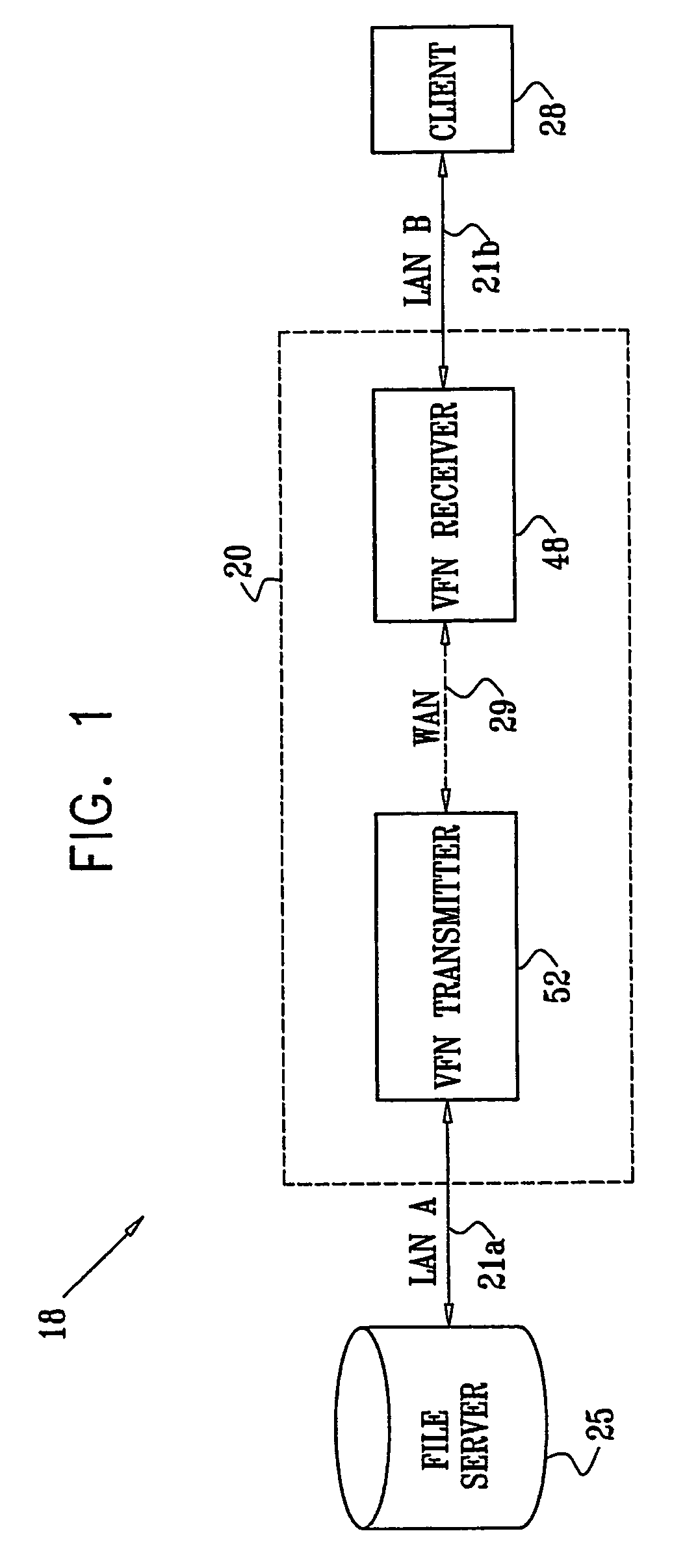
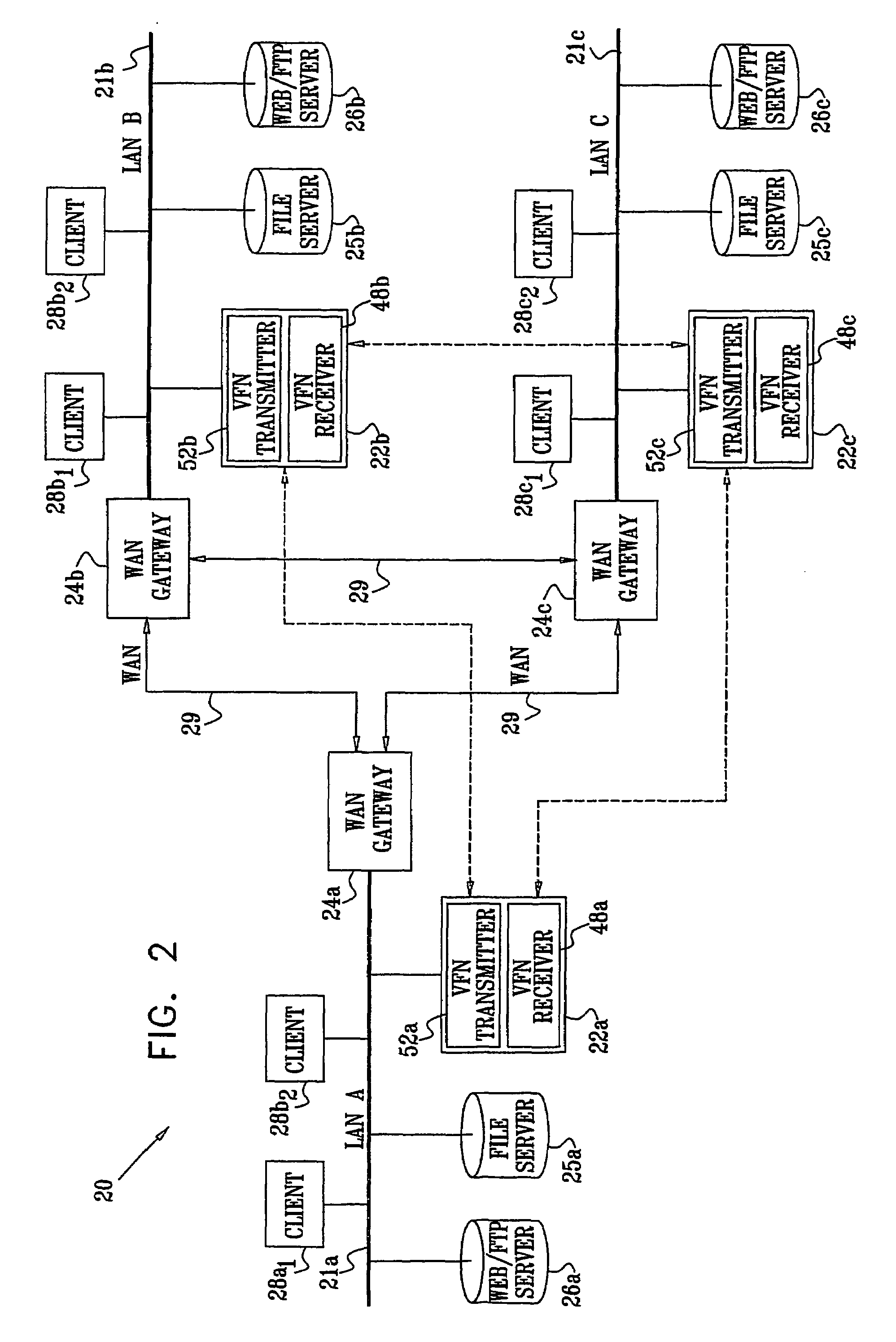
InactiveUS7139811B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData accessClient-side
A method for enabling access to a data resource, which is held on a file server (25) on a first local area network (LAN) (21a), by a client (28) on a second LAN (21b). A proxy receiver (48) on the second LAN (21b) intercepts a request for the data resource submitted by the client (28) and transmits a message via a wide area network (WAN) (29) to a proxy transmitter (52) on the first LAN (21a), requesting the data resource. The proxy transmitter (52) retrieves a replica of the data resource from the file server (25) and conveys the replica of the data resource over the WAN (29) to the proxy receiver (48), which serves the replica of the data resource from the proxy receiver (48) to the client (28) over the second LAN (21b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
File server system using connection-oriented protocol and sharing data sets among data movers
InactiveUS6453354B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsMultiplexingData set
A first data mover computer services data access requests from a network client, and a second data mover computer is coupled to the first data mover computer for servicing data access requests from the first data mover computer. The first data mover computer uses a connection-oriented protocol to obtain client context information and to respond to a session setup request from the client by authenticating the client. Then the first data mover computer responds to a file system connection request from the client by forwarding the client context information and the file system connection request to the second data mover computer. Then the first data mover computer maintains a connection between the first data mover computer and the second data mover computer when the client accesses the file system and the first data mover computer passes file access requests from the client to the second data mover computer and returns responses to the file access requests from the second data mover computer to the client. In a preferred embodiment, the connection-oriented protocol is the Common Internet File System (CIFS) Protocol, and multiple clients share a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection between the first data mover computer and the second data mover computer by allocation of virtual channels within the shared TCP connection and multiplexing of data packets of the virtual channels over the shared TCP connection.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
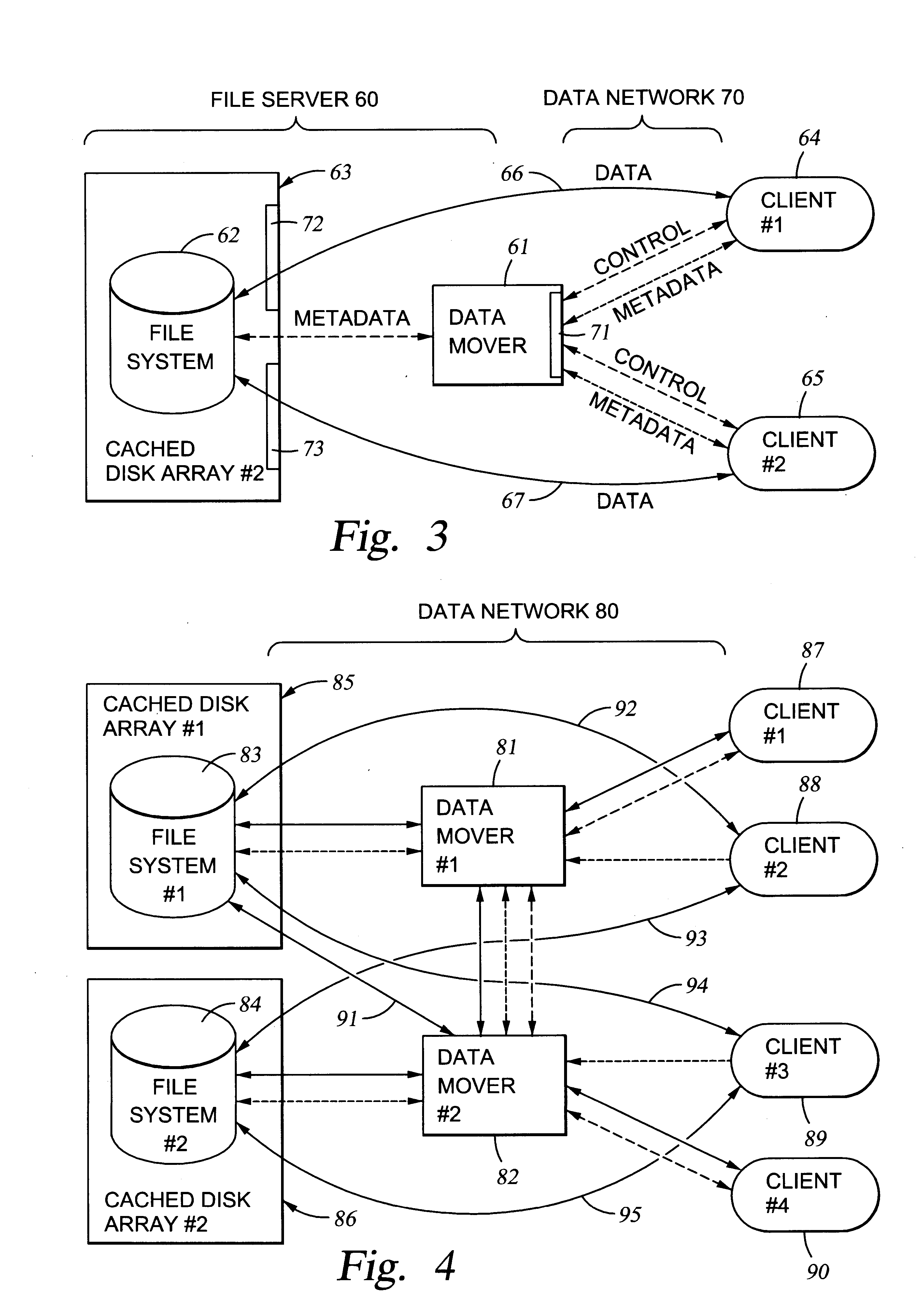
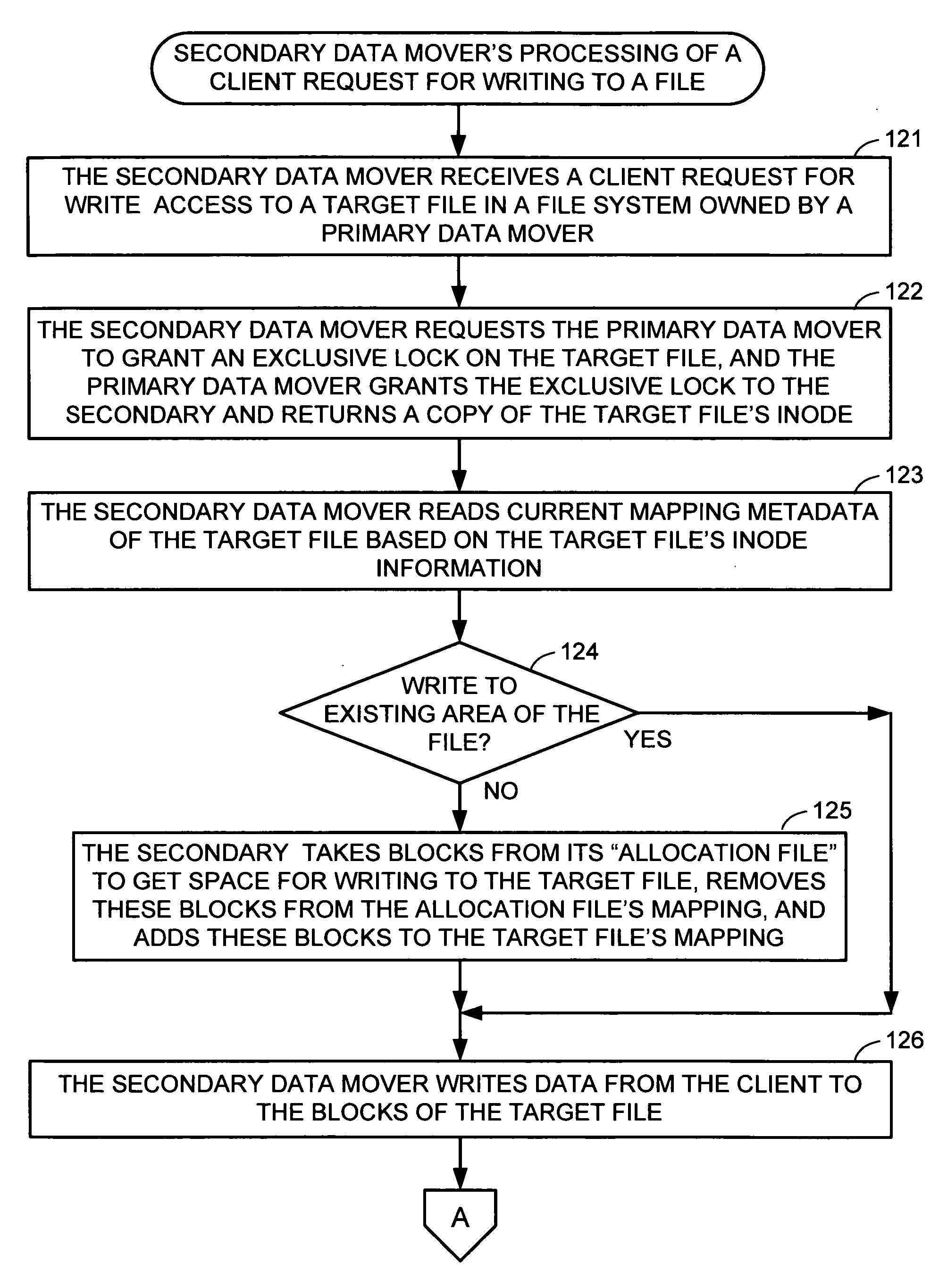
Metadata offload for a file server cluster
ActiveUS20070055702A1Promote recoveryReduce processDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemData treatment
A file server system has a cluster of server computers that share access to a file system in shared storage. One of the server computers has primary responsibility for management of access to the file system. In order to reduce the possibility of primary server overload when a large number of the clients happen to concurrently access the same file system, most metadata processing operations are offloaded to secondary server computers. This also facilitates recovery from failure of a primary server computer since only a fraction of the ongoing metadata operations of a primary server computer is interrupted by a failure of the primary server computer. For example, a secondary data mover may truncate, delete, create, or rename a file in response to a client request.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Policy based composite file system and method
InactiveUS20060259949A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemConfigfs
A policy configurable file system includes a computer system upon which the policy configurable file system operates, a policy source for providing the configuration policies, and one or more file servers. The computer system includes software for enforcing one or more configuration policies. The policy source is typically either a policy server such that the policy is derived from the policy server, or a policy configurable file system, such that the policy is embedded in the policy configurable file system. The one or more file servers each uses a protocol, wherein the protocols of the one or more file servers are not all the same. In one case, the one or more of the configurable policies are separable from the policy configurable file system. In another case, the one or more configurable policies are downloadable to the computer system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
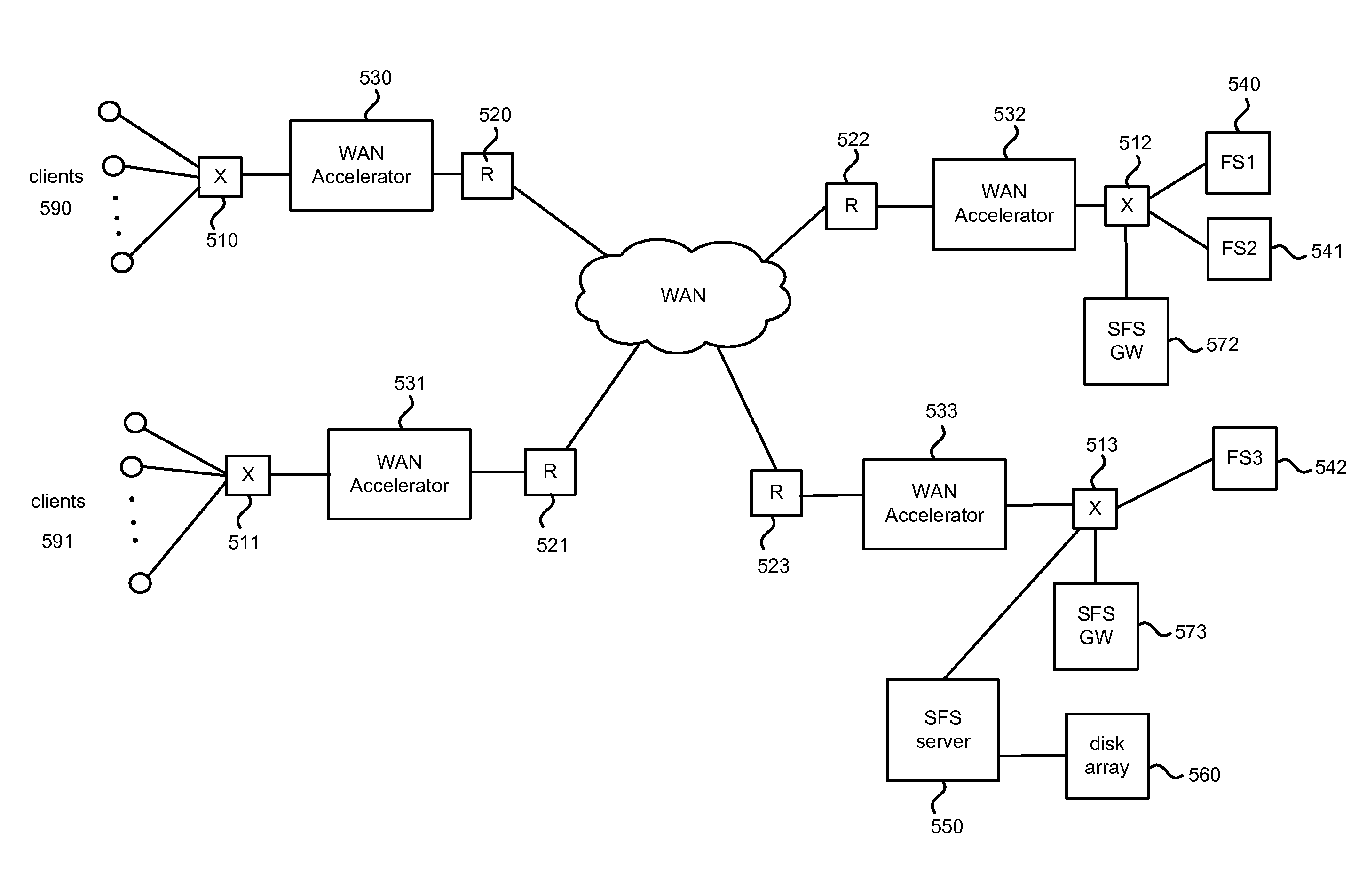
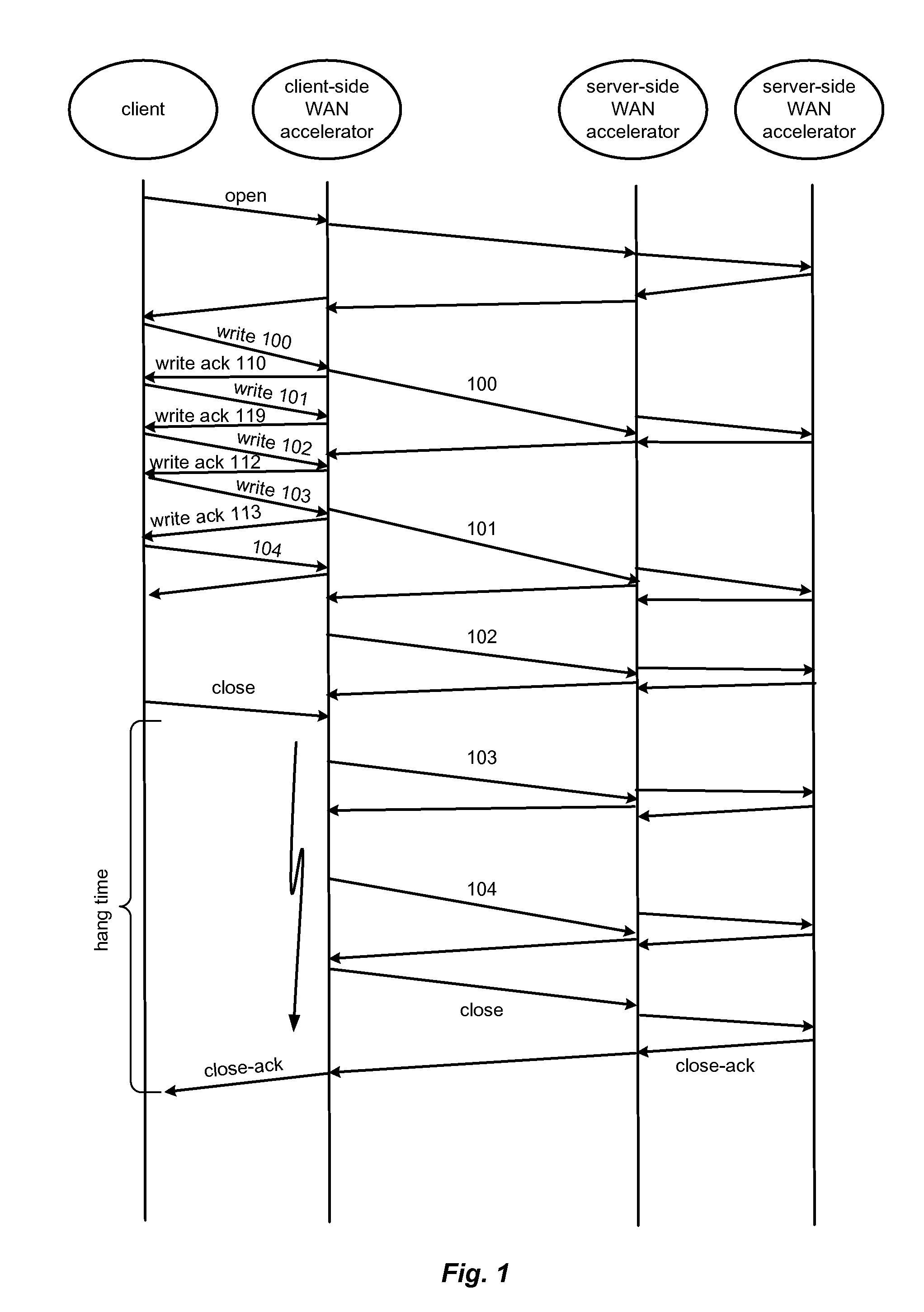
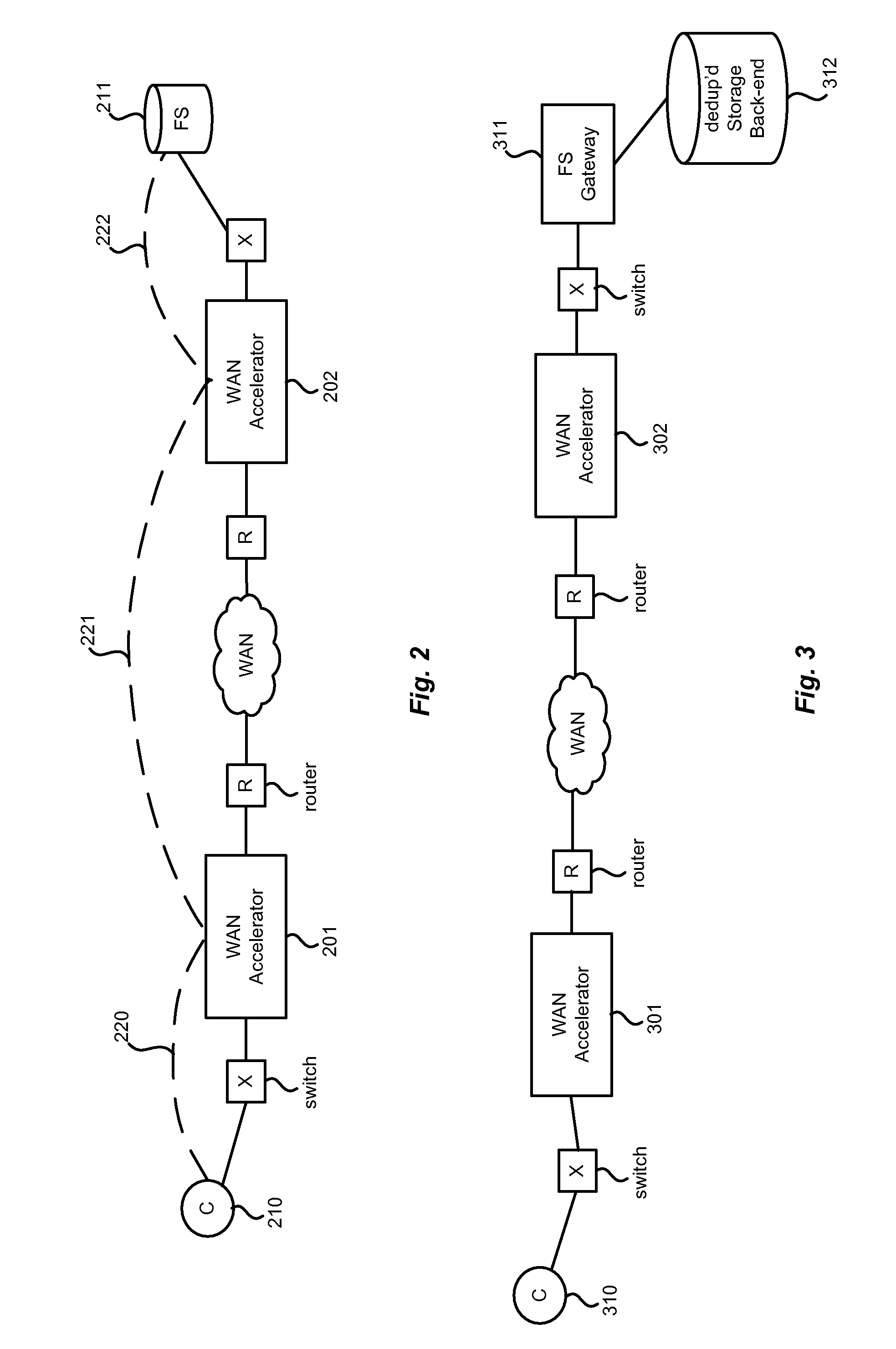
Hybrid segment-oriented file server and wan accelerator
ActiveUS20080281908A1Error detection/correctionComputer security arrangementsFile serverProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
In a network including WAN accelerators and segment-oriented file servers, a method comprises responding to a client request to manipulate a file via a network file protocol by receiving a first request at a first WAN accelerator, wherein the request is a request to open a file located at a file server that is a segment-oriented file server, sending a local request for the file, corresponding to the first request, from the WAN accelerator to the file server, using a segment-aware network request protocol, returning at least a portion of the requested file in the form of a representation of a data map corresponding to the at least a portion of the requested file stored on the file server and using a data map for reconstruction of the requested file.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
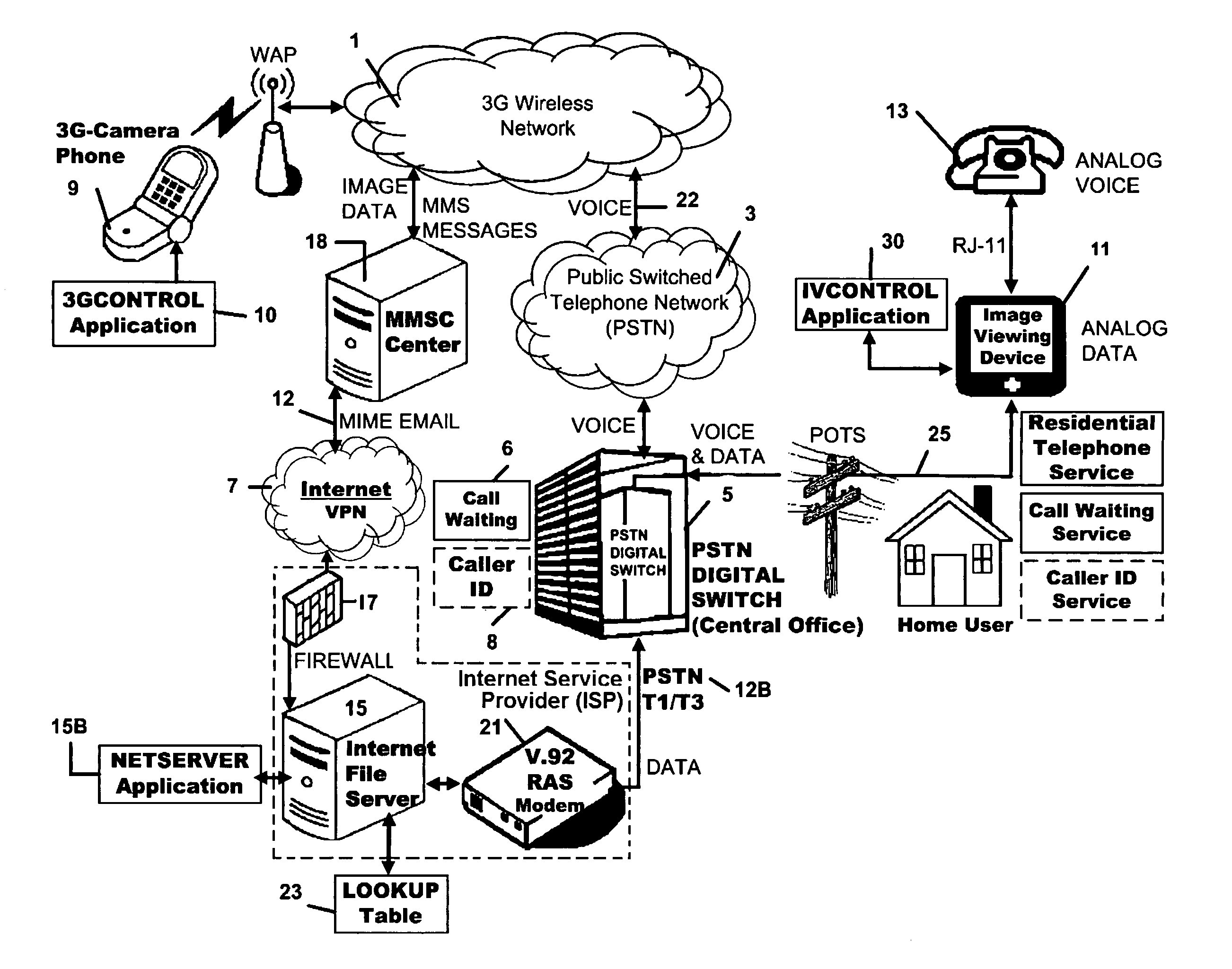
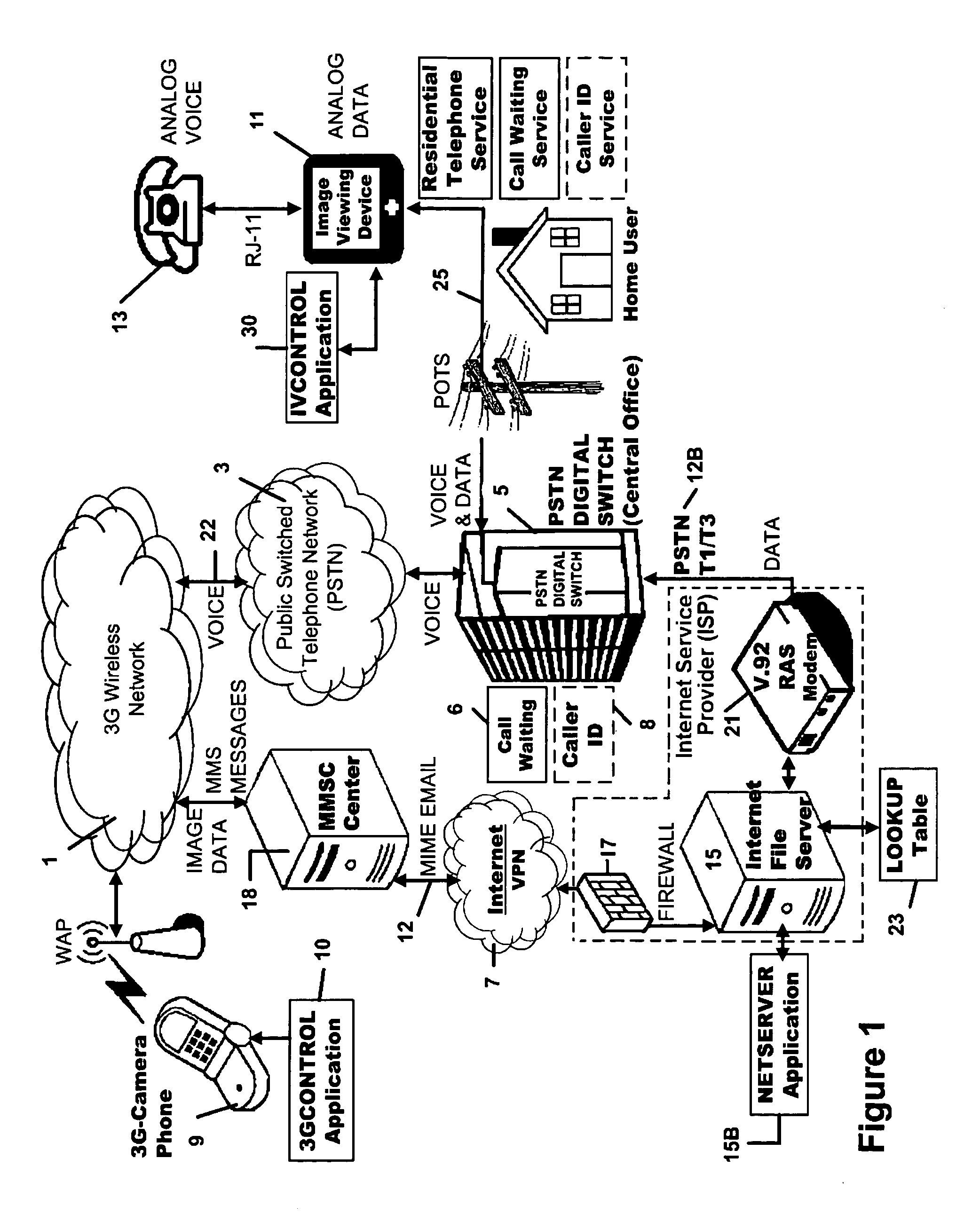
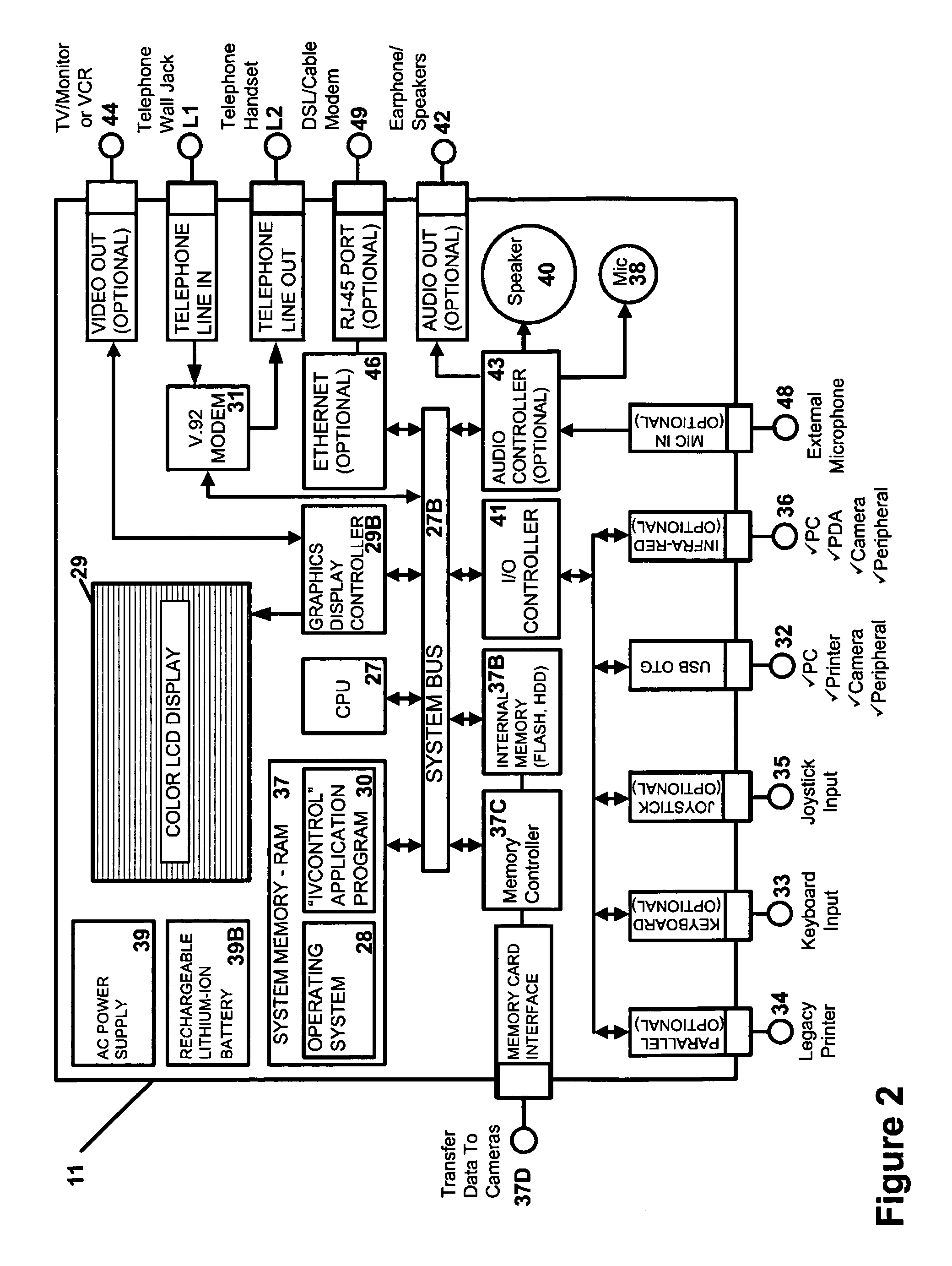
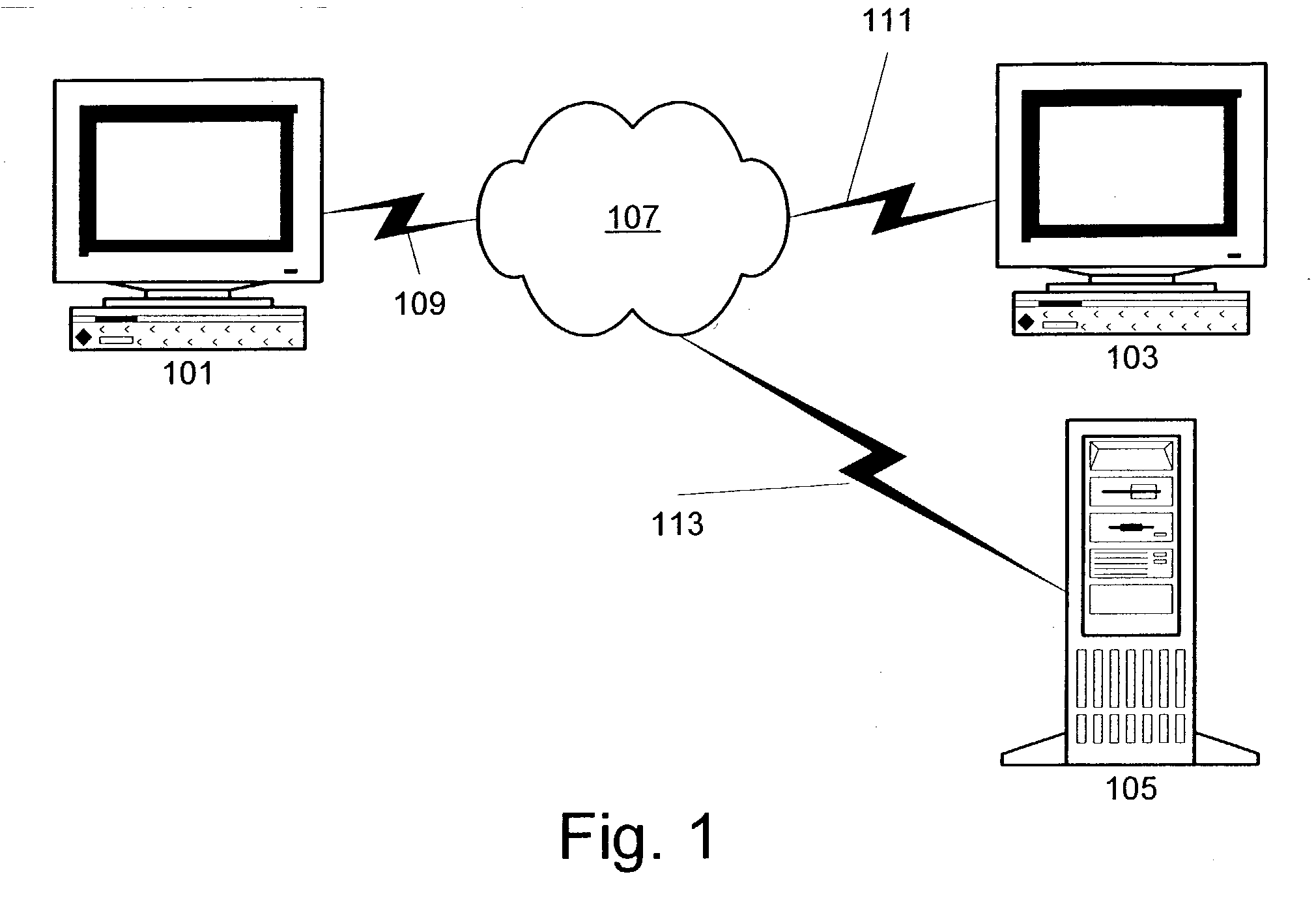
Picture transmission and display between wireless and wireline telephone systems
InactiveUS20060033809A1Accurate operationInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCamera phoneImage transfer
A 3G-camera phone (9) user may transfer photographic images from 3G-camera phone to an image viewing device (11) associated with a residential telephone (13) accessible on the PSTN telephone network (3). Both the image viewing device (11) and telephone (13) are connected to narrowband PTSN POTS telephone line (25). Through use of a call waiting (6) feature of the networks, data transfer is performed over a single narrowband PTSN POTS line with the voice conversation put on hold. Reciprocal image transmission is also possible. Like data transfers may also be made to telephone users having broadband DSL (45, 47 FIGS. 8 &10) or CATV (54, 57 FIGS. 9 &11) or VoIP (82, FIGS. 10 &11) services. An Internet (7) connected fileserver (15) uses a lookup table (23) to determine the kind of line to which the image viewing device is connected and select the appropriate routing for the image transfer.
Owner:FARLEY MARK A +1
Remote Network Access Via Virtual Machine
ActiveUS20070300220A1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkSoftware engineering
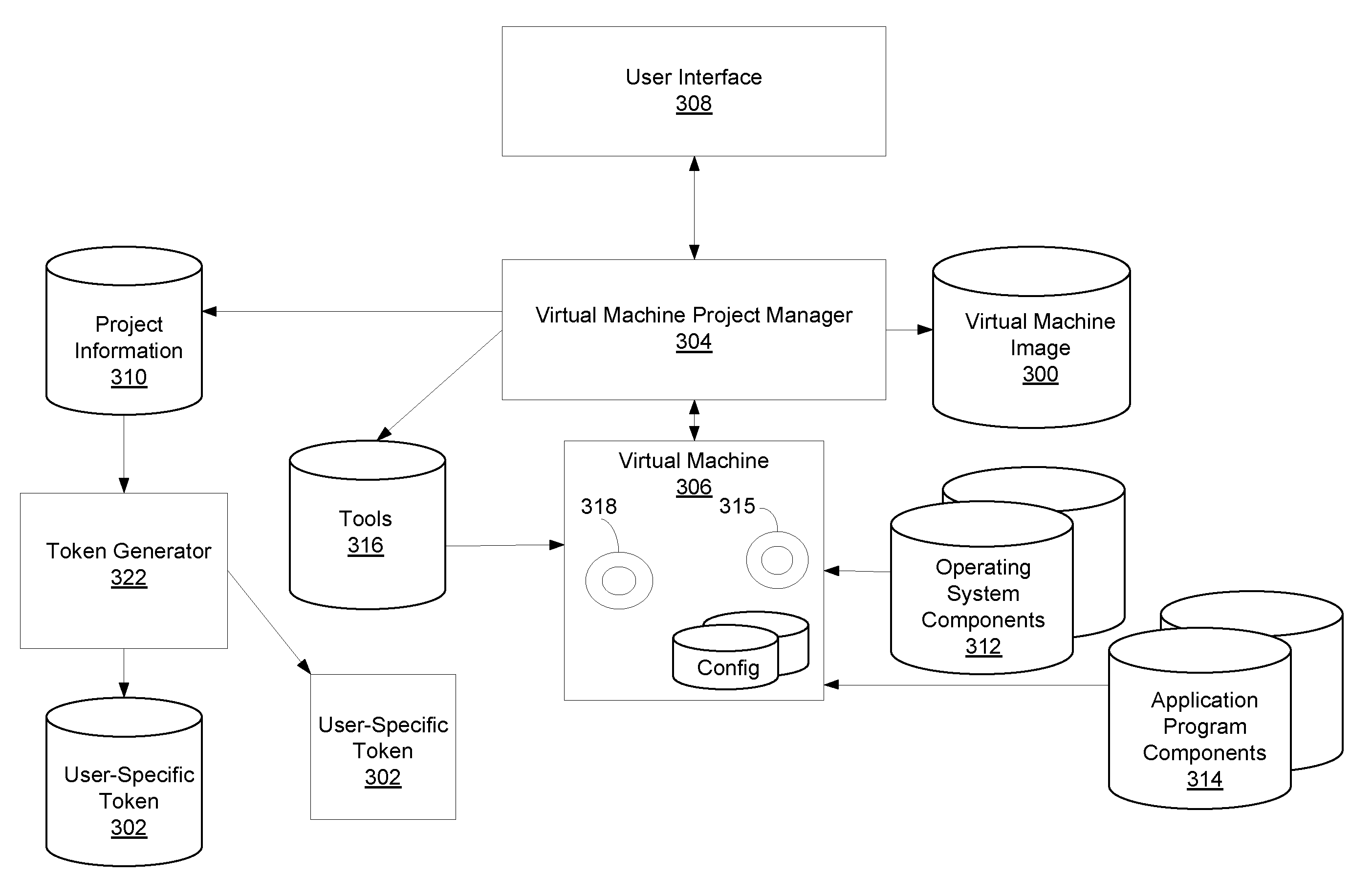
A virtual machine project manager creates a generic, i.e., not user-specific, virtual machine image file. Copies of this image file may be distributed to one or more users, each of whom may then use an automated procedure to generate a user-specific virtual machine image file and, thus, a user-specific virtual machine on his / her remote host computer. The generic virtual machine image file may be distributed on computer-readable media, such as a DVD disks, or the file may be stored on a server and downloaded (such as via the Internet) by the users. Each user also receives or downloads a token, which contains a small amount of user-specific information that is used by the automated procedure to provision the generic virtual machine image file for the particular user. A virtual machine accesses a security token connected to a host computer to automatically authenticate or re-authenticate a user, such as when a virtual private network connection is restarted. Substantially identical session identifiers are used by a host computer and a virtual machine, or by two or more virtual machines and, when communicating with an integrated access server. A file server stores virtual machine images that are accessed by a plurality of host computers.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
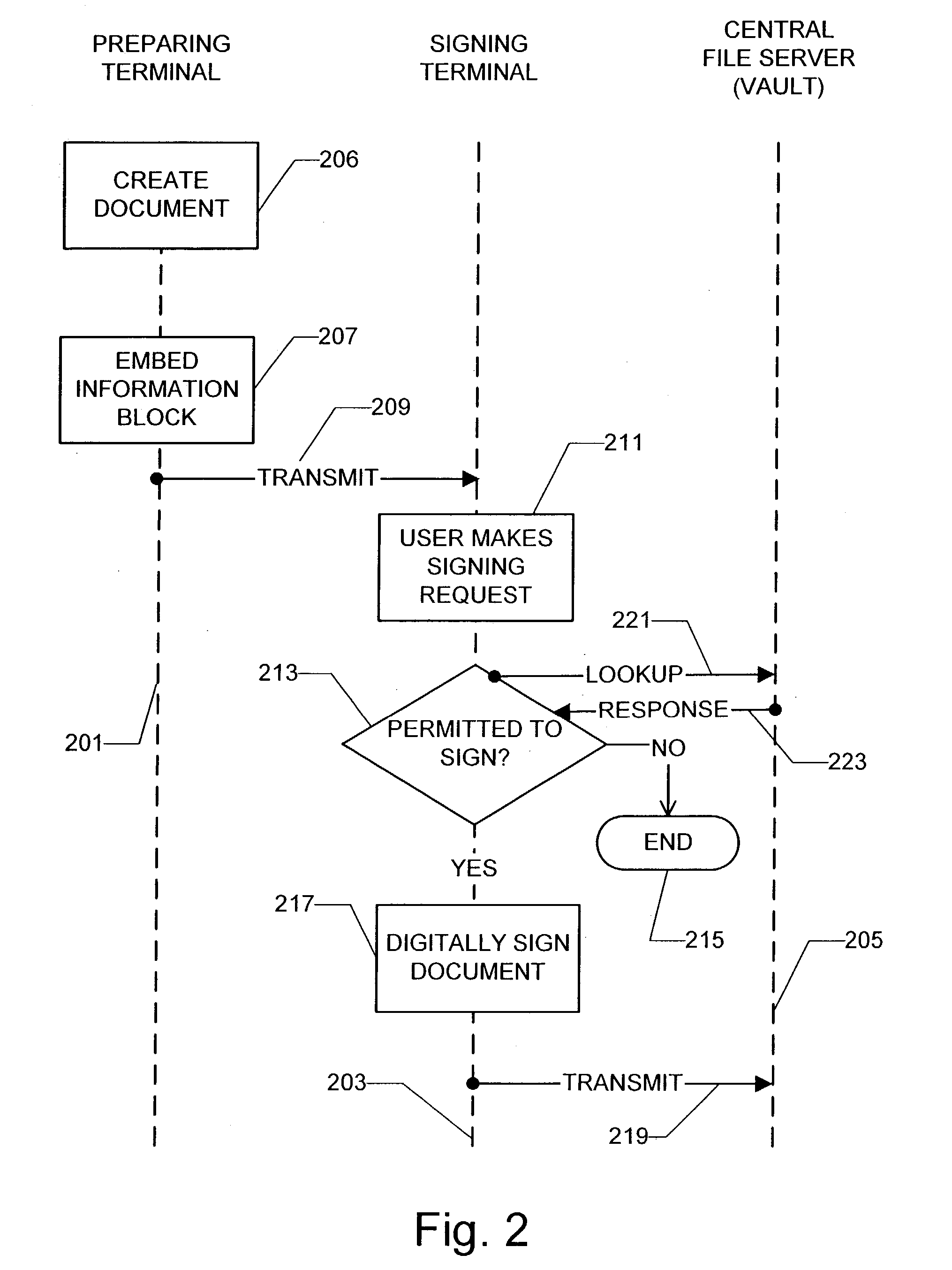
Method and system for electronically signing and processing digital documents
InactiveUS20030078880A1FinanceUser identity/authority verificationElectronic documentInternet privacy
A method and system for managing the electronic signing of digital documents is disclosed. An electronic document created and prepared for signing by associating certain signing constraints with the document. Indicia of the signing constraints are encoded into a document information block or blocks that are embedded into the document. The information block may include indicia of a database record at a central server that stores indicia of the signing constraints in addition to or in lieu of including the signing constraint indicia in the document information block or blocks. Upon receiving the prepared document at a signing terminal, the information blocks are extracted and the signing constraints tested. If the user desires to sign the document, and if the user is permitted to sign, the document is electronically signed and transmitted to the central file server for storage.
Owner:WAVE SYST
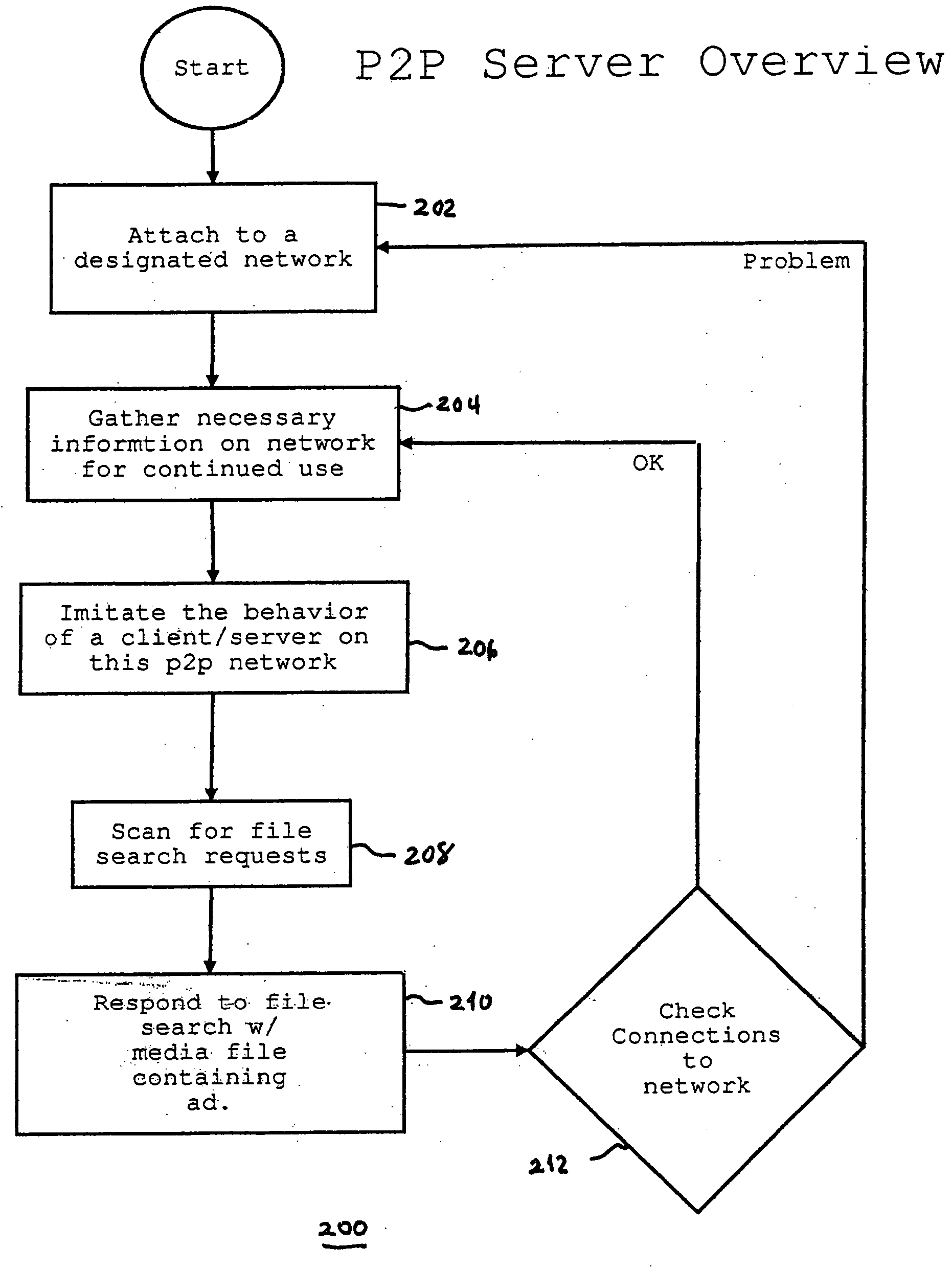
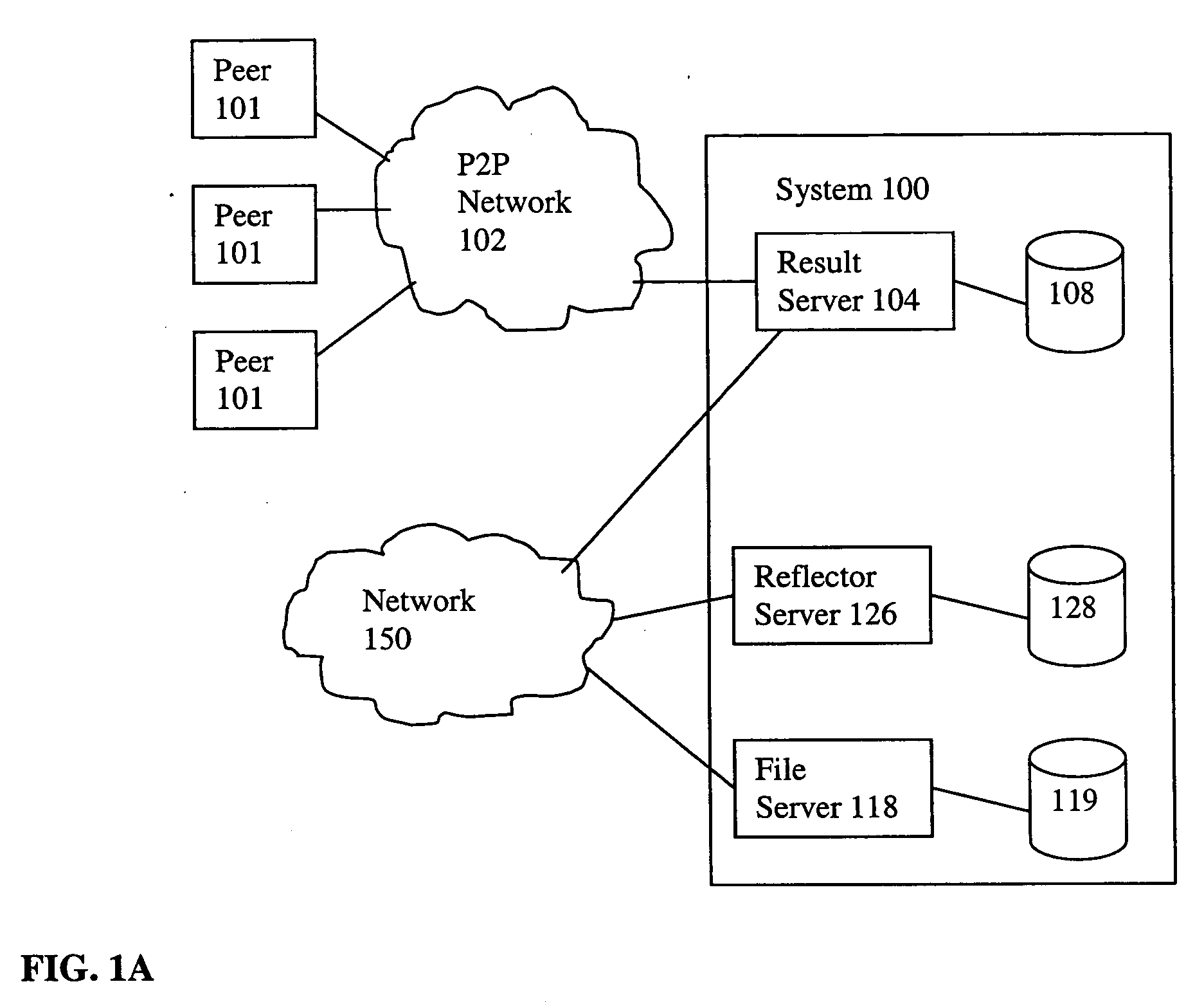
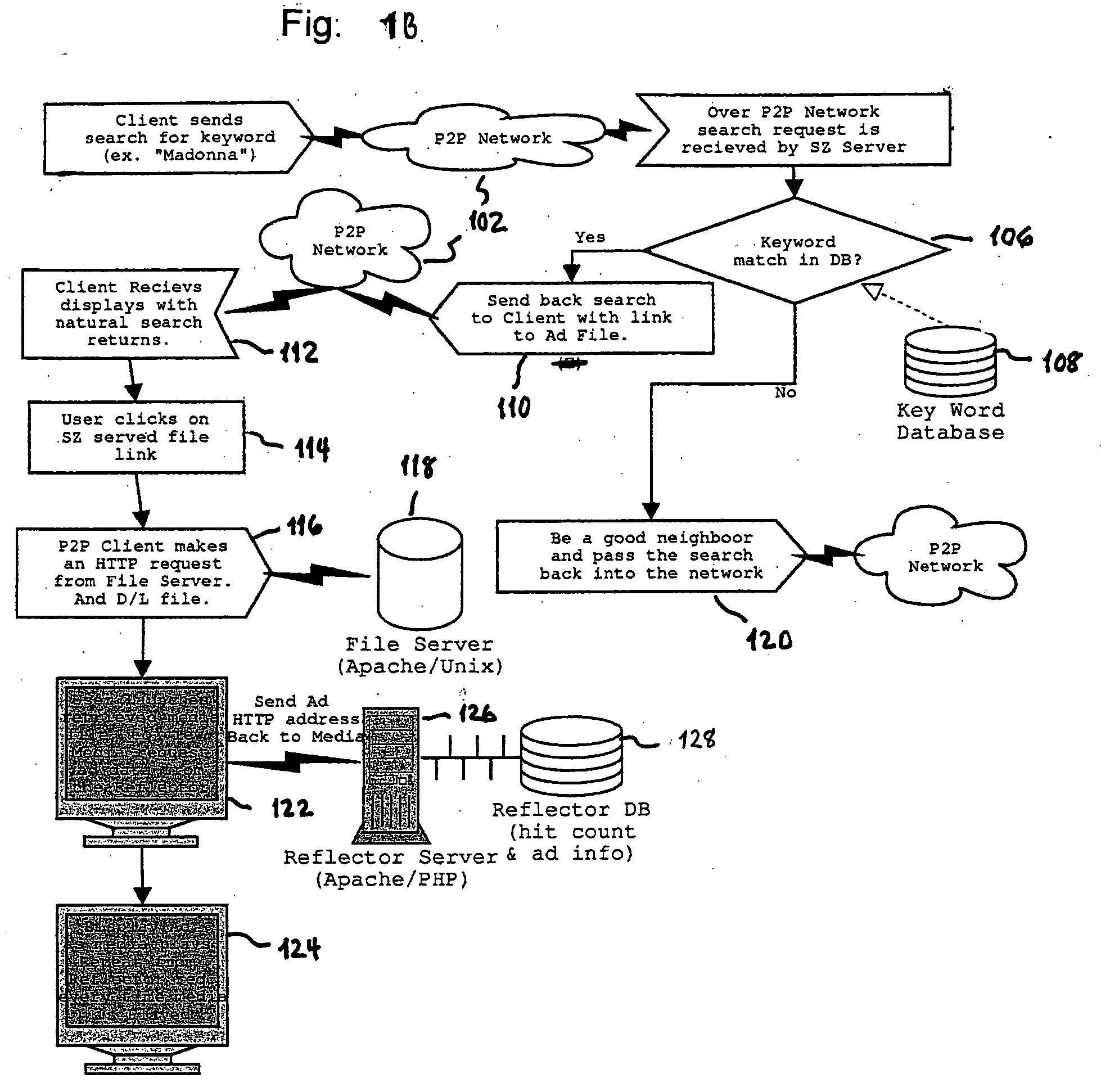
System and methods for direct targeted media advertising over peer-to-peer networks
An information handling system according to the invention comprises an input for receiving search requests seeking one or more specified files; a search engine for searching a database for names of files satisfying a received search request; and server logic for serving a results page comprising the names of files satisfying a received search request and a hyperlink associated with each file name. Each hyperlink in the results, when activated causes transmission of a request for the selected file that is associated with the link. The request for the selected file is directed to a file server controlling a database of files including the selected file. The file server responds to the request by serving a content (or media) file comprising a copy of the selected file with an embedded request for information for presentation to the person from whom the search request was received. When the user runs the downloaded content file the content file sends a request for service to a site (e.g., a reflector server) that responds by serving information such as advertising to the requester.
Owner:MOGANSTEIN DAVID MR
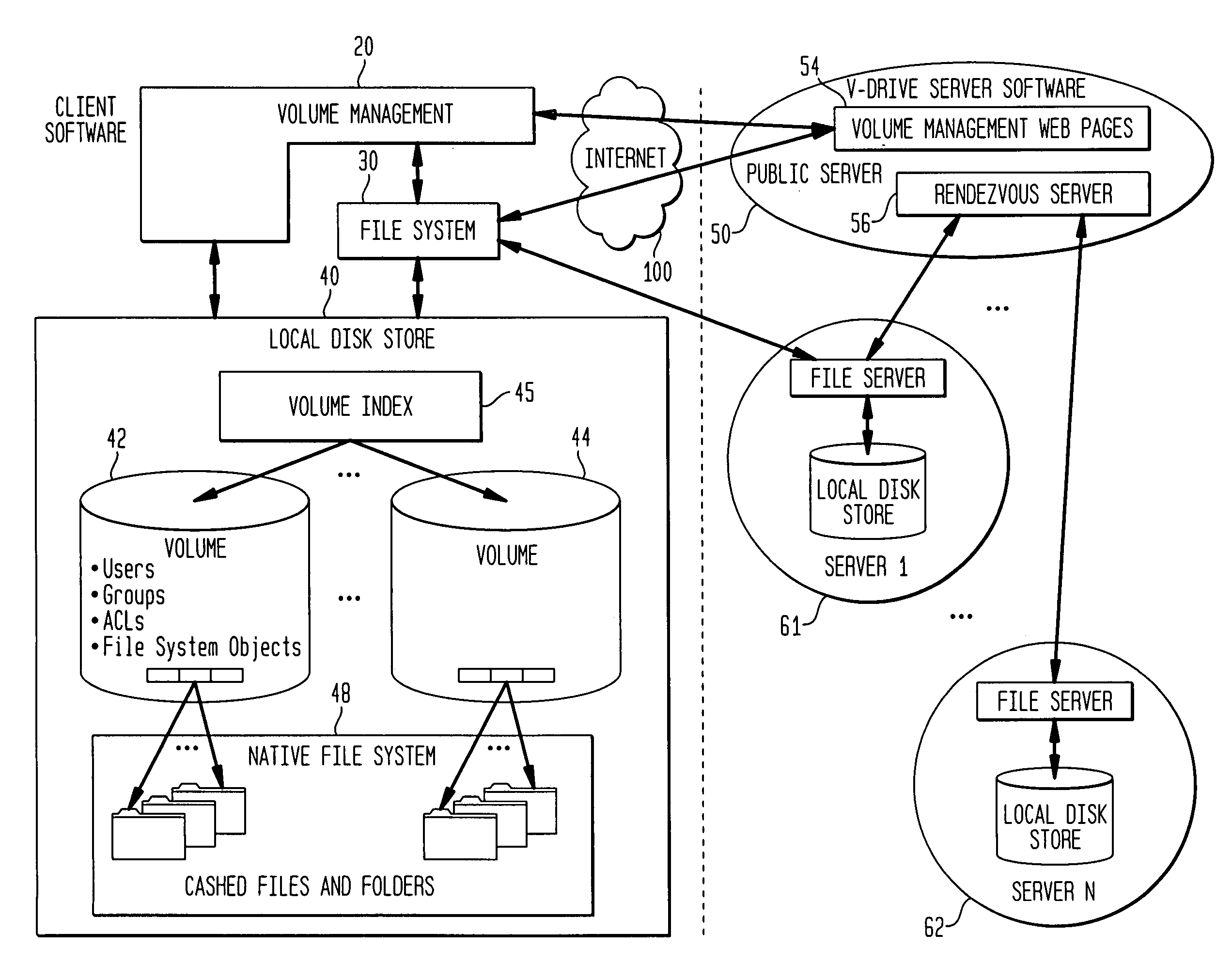
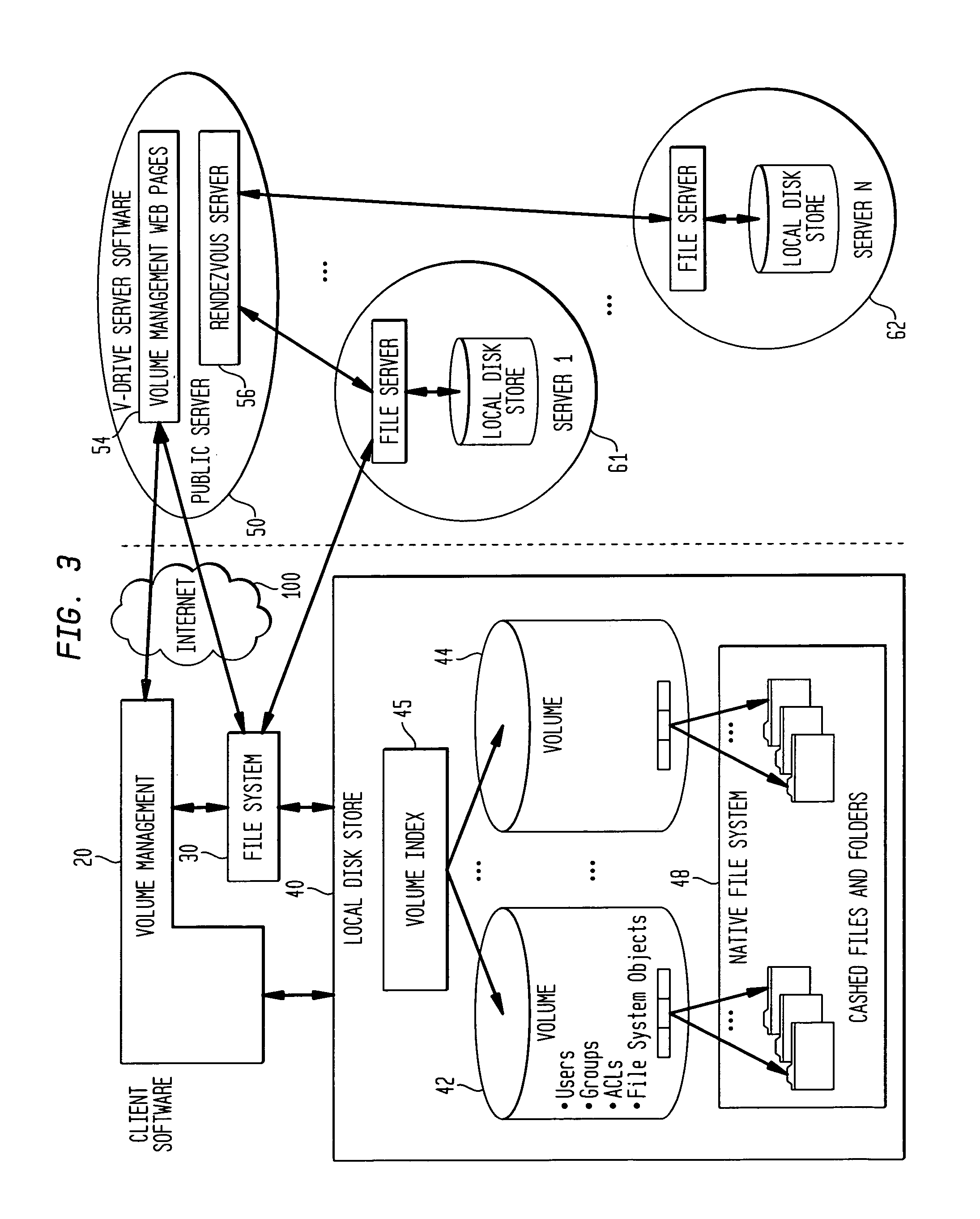
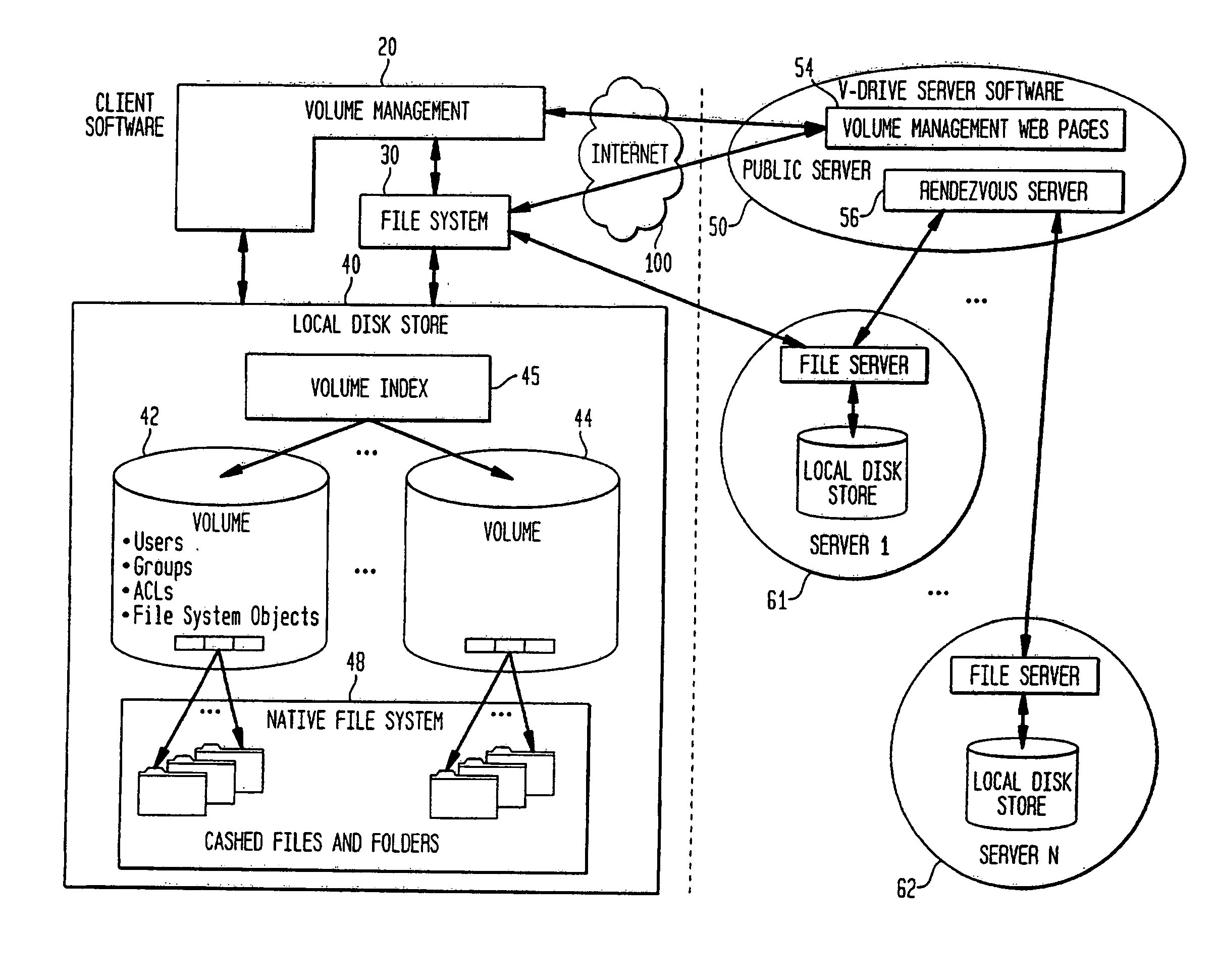
Internet-based shared file service with native PC client access and semantics and distributed access control
InactiveUS7136903B1Web data retrievalPublic key for secure communicationWide area networkAccess control
A multi-user file storage service and system enable each user of a pre-subscribed user group to communicate with a remote file server node via a wide area network and to access the files of the file group via the respective client node. More than one user of the pre-subscribed user group is permitted to access the file group at the remote file server node simultaneously. Integrity of the files at the remote file server node are maintained by controlling each access to each file at the remote file server node so that each access to files at the remote file server is performed, if at all, on a respective portion of each file as most recently updated at the remote file server node. Additionally, an encrypted key is transferred from the file server node to a particular client node via a secure channel. The encrypted key uses an encryption function and a decryption function not known locally at the remote file server. Furthermore, both privileged access control rights and file sharing mode access control to a particular file of the group of files are delegated to one or more distributed nodes other than the remote file server node which provides the data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Concurrent file across at a target file server during migration of file systems between file servers using a network file system access protocol
InactiveUS6938039B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile systemNetwork File System
A file system is migrated from a source file server to a target file server in a data network while permitting clients to have concurrent read / write access to the file system. The target file server issues directory read requests and file read requests to the source file server in accordance with a network file access protocol to transfer the file system from the source file server to the target file server. Concurrent with the transfer of the file system from the source file server to the target file server, the target file server responds to client read / write requests for access to the file system. In a preferred embodiment, the target file server maintains a hierarchy of on-line nodes off-line nodes. The online nodes represent file system objects that have been completely migrated, and the offline nodes representing file system objects that have not been completely migrated. The target file server executes a background process that walks through the hierarchy in order to migrate the objects of the offline nodes. When an object has been completely migrated, the target file server changes the offline node for the object to an online node for the object.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
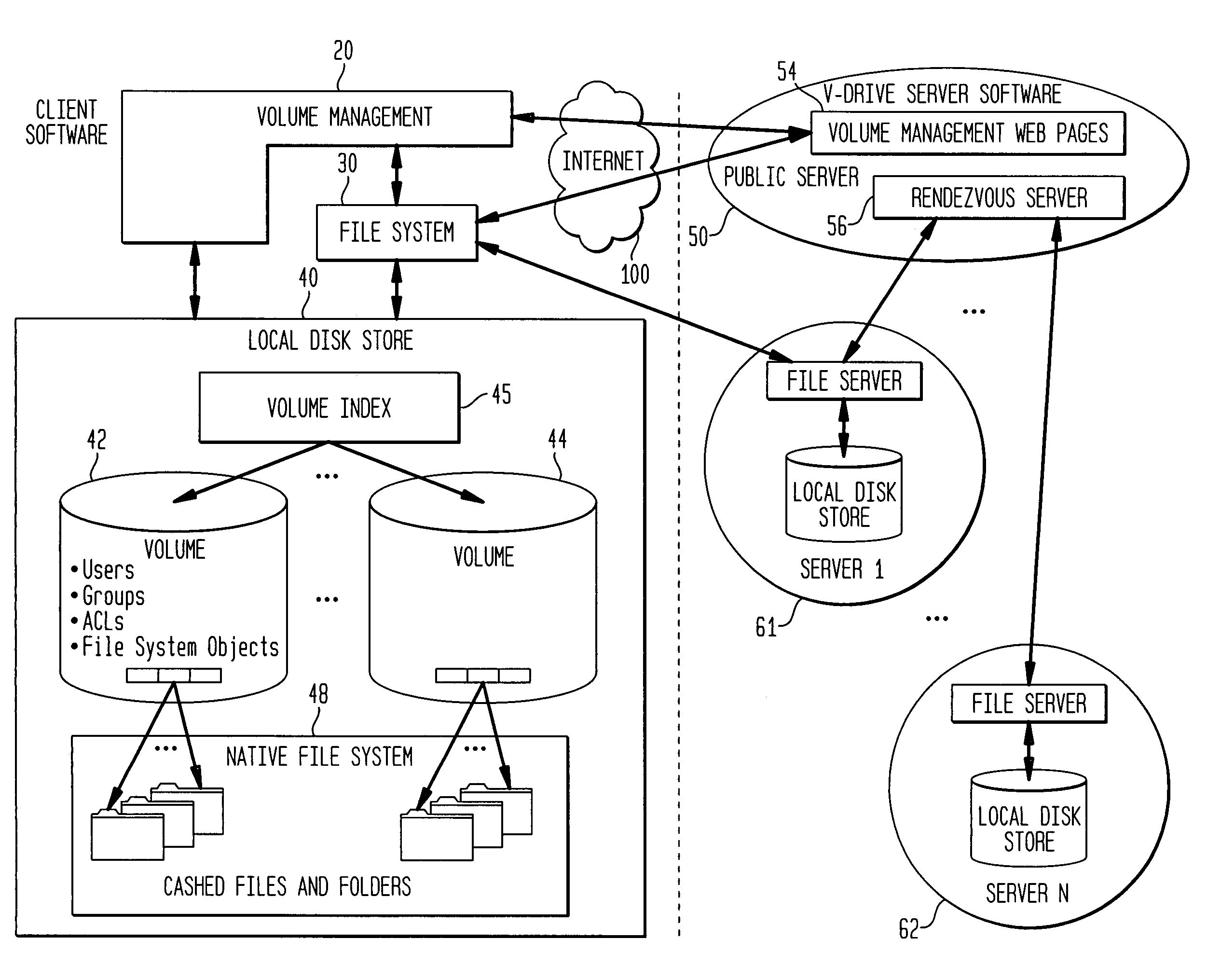
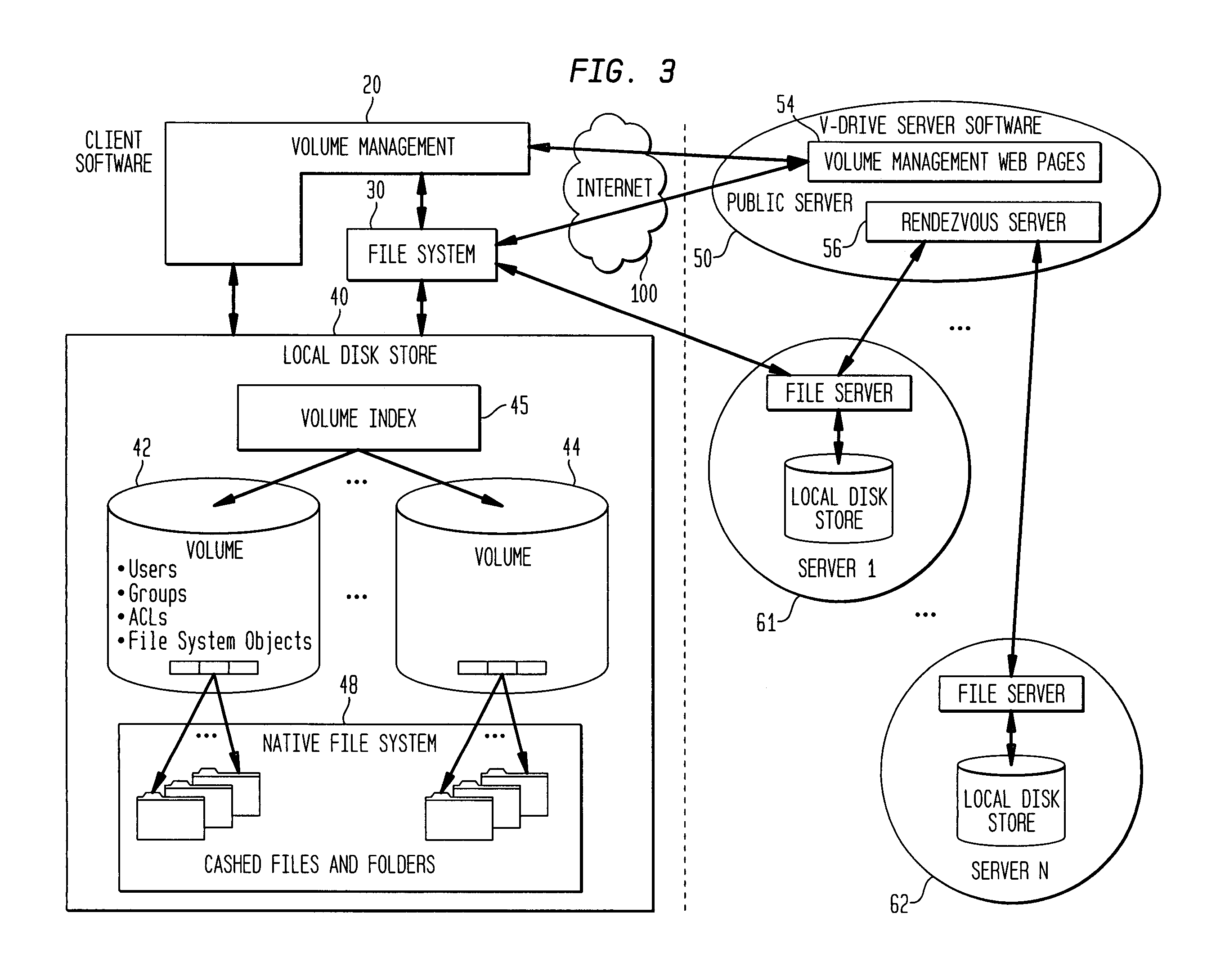
Internet-based shared file service with native PC client access and semantics
A multi-user file storage service and system enables each user of a user group to operate an arbitrary client node at an arbitrary geographic location to communicate with a remote file server node via a wide area network. More than one user of the user group is permitted to access the file group at the remote file server node simultaneously, but the integrity of the files is maintained by controlling access so that each access to one of the files at the remote file server is performed, if at all, on a respective portion of that file as most recently updated at the remote file server node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Internet-based shared file service with native PC client access and semantics and distributed version control
InactiveUS20060129627A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionOperational systemWide area network
A multi-user file storage service and system enable each user of a pre-subscribed user group to operate an arbitrary client node at an arbitrary geographic location, to communicate with a remote file server node via a wide area network and to access the files of the file group via the respective client node in communication with the remote file server node via the wide area network. More than one user of the pre-subscribed user group is permitted to access the file group at the remote file server node simultaneously. Illustratively, the integrity of the files at the remote file server node are maintained by controlling each access to each file at the remote file server node so that each access to files at the remote file server is performed, if at all, on a respective portion of each file as most recently updated at the remote file server node. Thus, all native operating system application programming interfaces operate as if all multi-user applications accessing the files function as if the remote server and client nodes were on the same local area network. Illustratively, an interface is provided for adapting file access one of the client nodes. The interface designates at the client node each accessible file of the group as stored on a virtual storage device. The interface enables access to the designated files in a fashion which is indistinguishable, by users of, and applications executing at, the client node, with access to one or more files stored on a physical storage device that is locally present at the client node. Illustratively, an encrypted key is transferred from the remote file server node to one of the client nodes via a secure channel. The key is encrypted using an encryption function not known locally at the remote file server node. The transferred key is decrypted at the client node. The key is used at the client node to decrypt information of the files downloaded from the remote file server node or to encrypt information of the files prior to uploading for storage at the remote file server node. Access control to a particular one of the files of the group can be delegated to an access control node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
File storage system, cache appliance, and method
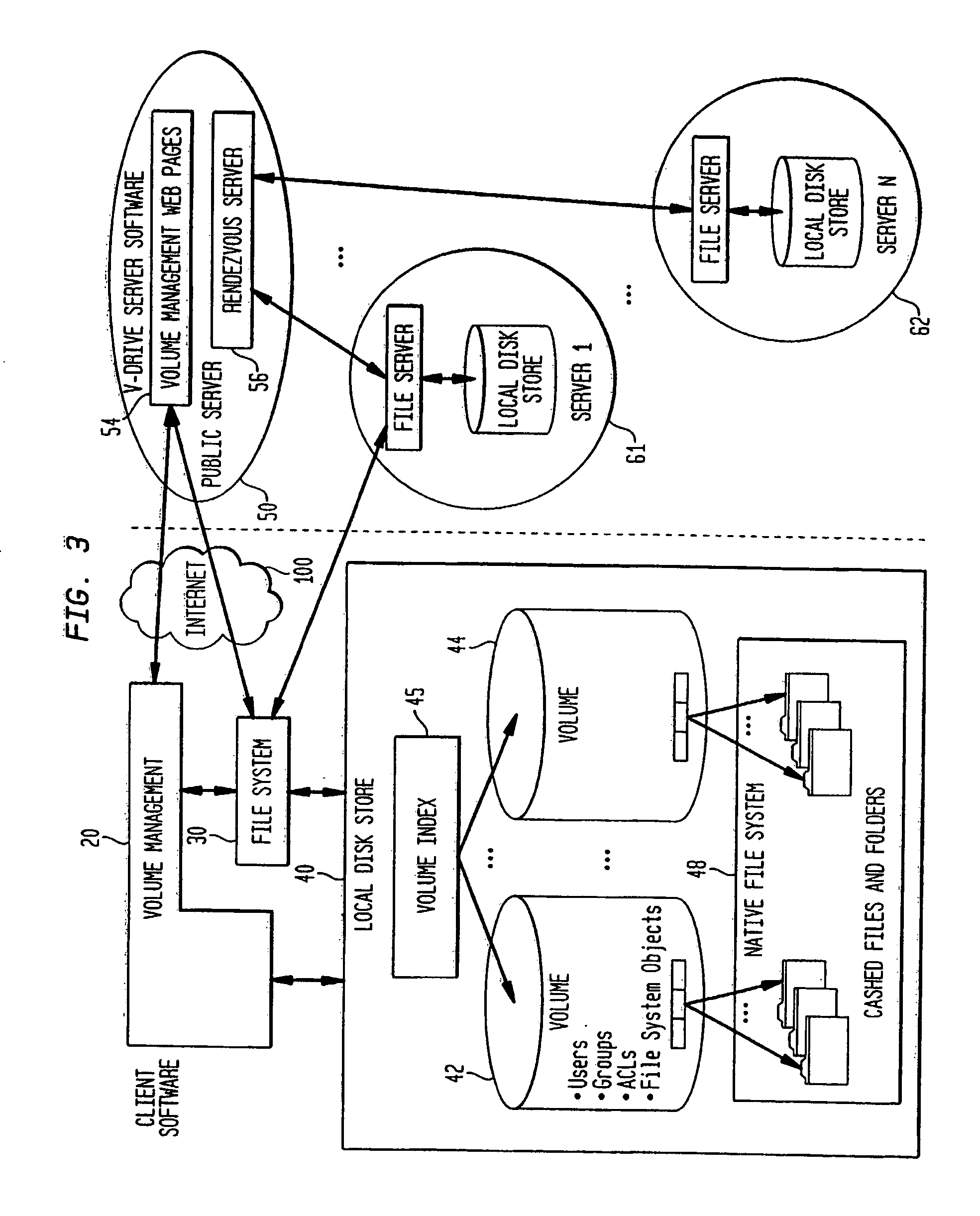
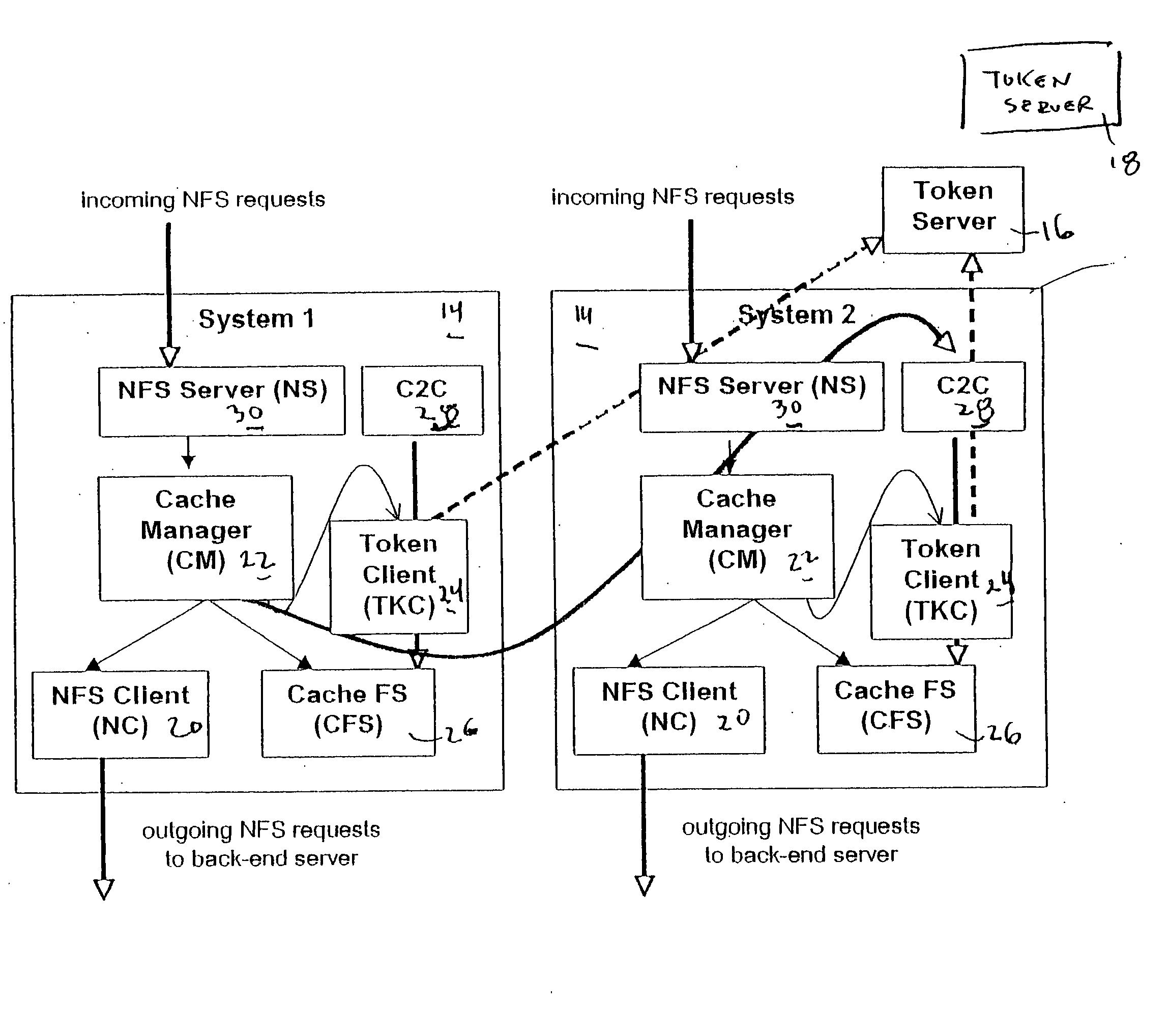
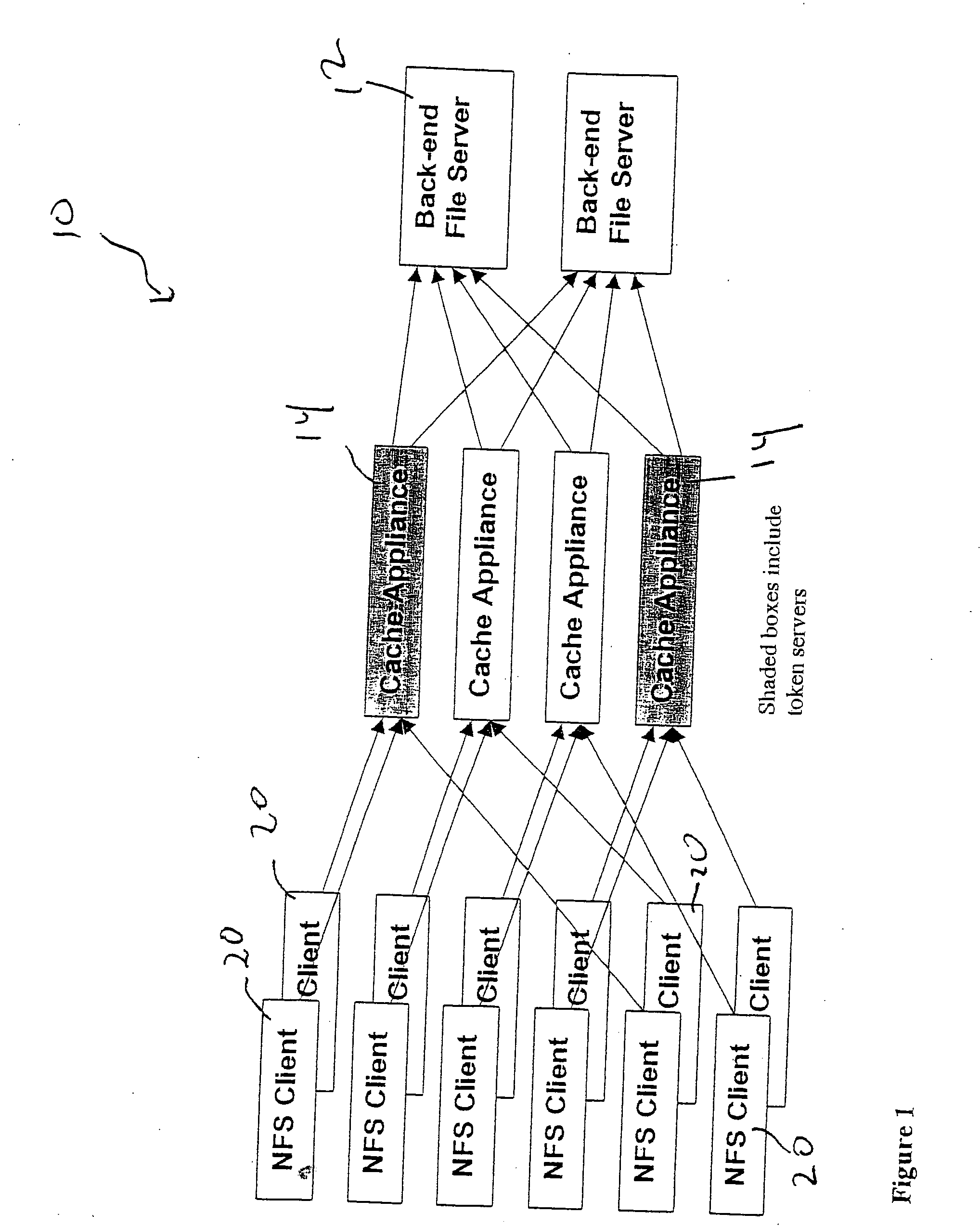
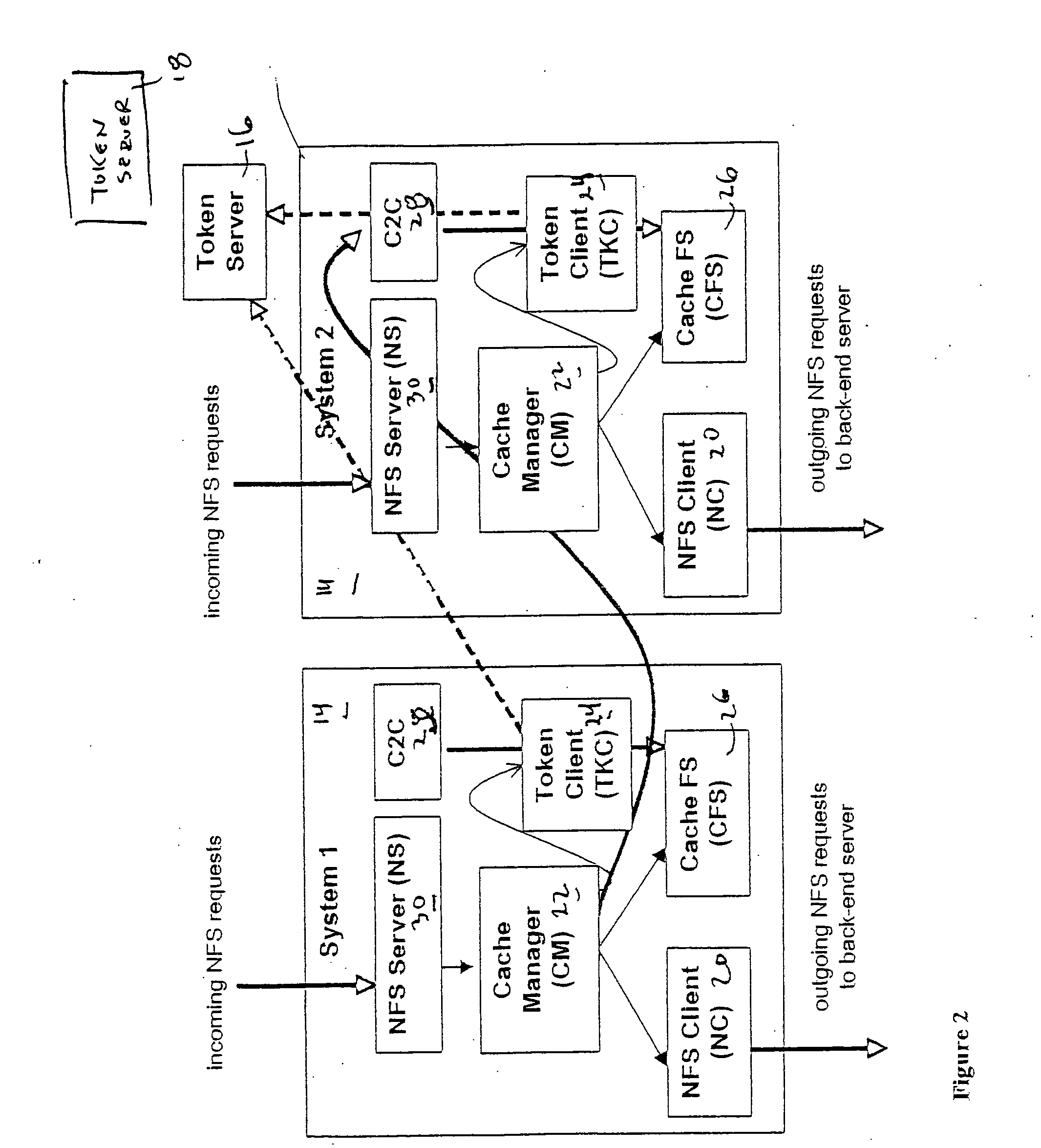
ActiveUS20100094806A1Increase profitLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsFile systemBack end server
A file storage system for storing data of a file received from a client includes a back-end file server in which the data is stored. The system includes a cache appliance in communication with the file server, such that the appliance stores portions of the data or attributes of the file, and uses the stored data or attributes to process file system requests received from the client, and which reads and writes data and attributes to the back-end file server independently. A system for responding to a file system protocol request in regard to a back-end server includes a token server. The system includes a plurality of cache appliances in communication with the token server, each of which receives tokens from the token server to synchronize access to data and attributes caches of the cache appliances, and reading and writing data and attributes to the back-end servers when tokens are revoked, the cache appliance having persistent storage in which data are stored, and the token server having persistent storage in which tokens are stored. A storage system includes a plurality of backend servers. The system includes a token server which grants permission to read and write file attributes and data system, and includes a plurality of cache appliances in communication with at least one of the backend servers and the token server for processing an incoming NFS request to the one backend server. Each cache appliance comprises an NFS server which converts incoming NFS requests into cache manager operations; a token client module in communication with the token server having a cache of tokens obtained from the token server; a cache manager that caches data and attributes and uses tokens from the token client module to ensure that the cached data or attributes are the most recent data or attributes, and an NFS client which sends outgoing NFS requests to the back-end file server. Methods for storing data of a file received from a client.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
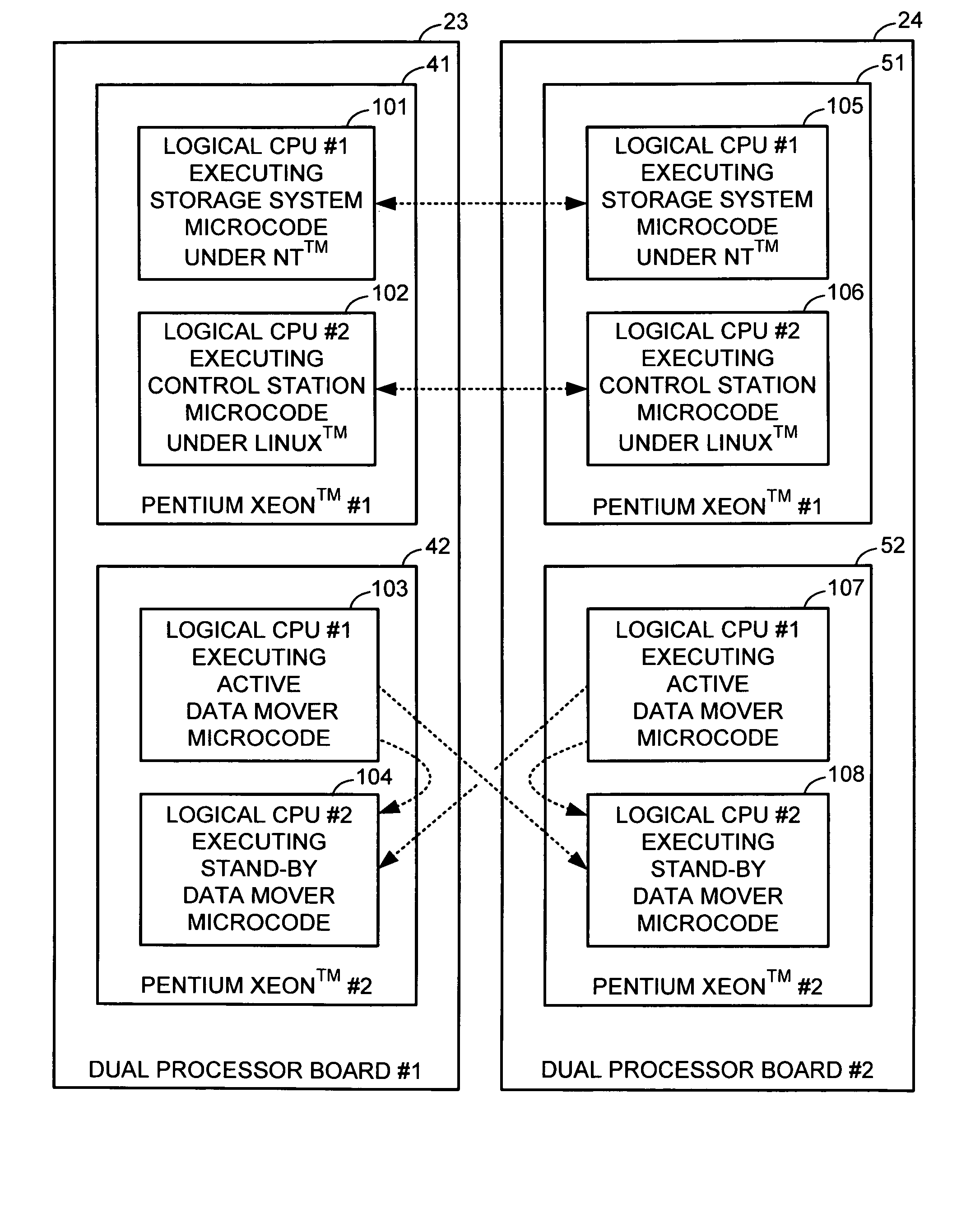
Redundant multi-processor and logical processor configuration for a file server
A redundant file server includes at least two dual processor boards. Each physical processor has two logical processors. The first logical processor of the first physical processor of each board executes storage system code under the Microsoft NT™ operating system. The second logical processor of the first physical processor of each board executes control station code under the Linux operating system. The first logical processor of the second physical processor of each board executes data mover code. The second logical processor of the second physical processor of each board is kept in a stand-by mode for assuming data mover functions upon failure of the first logical processor of the second physical processor on the first or second board.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
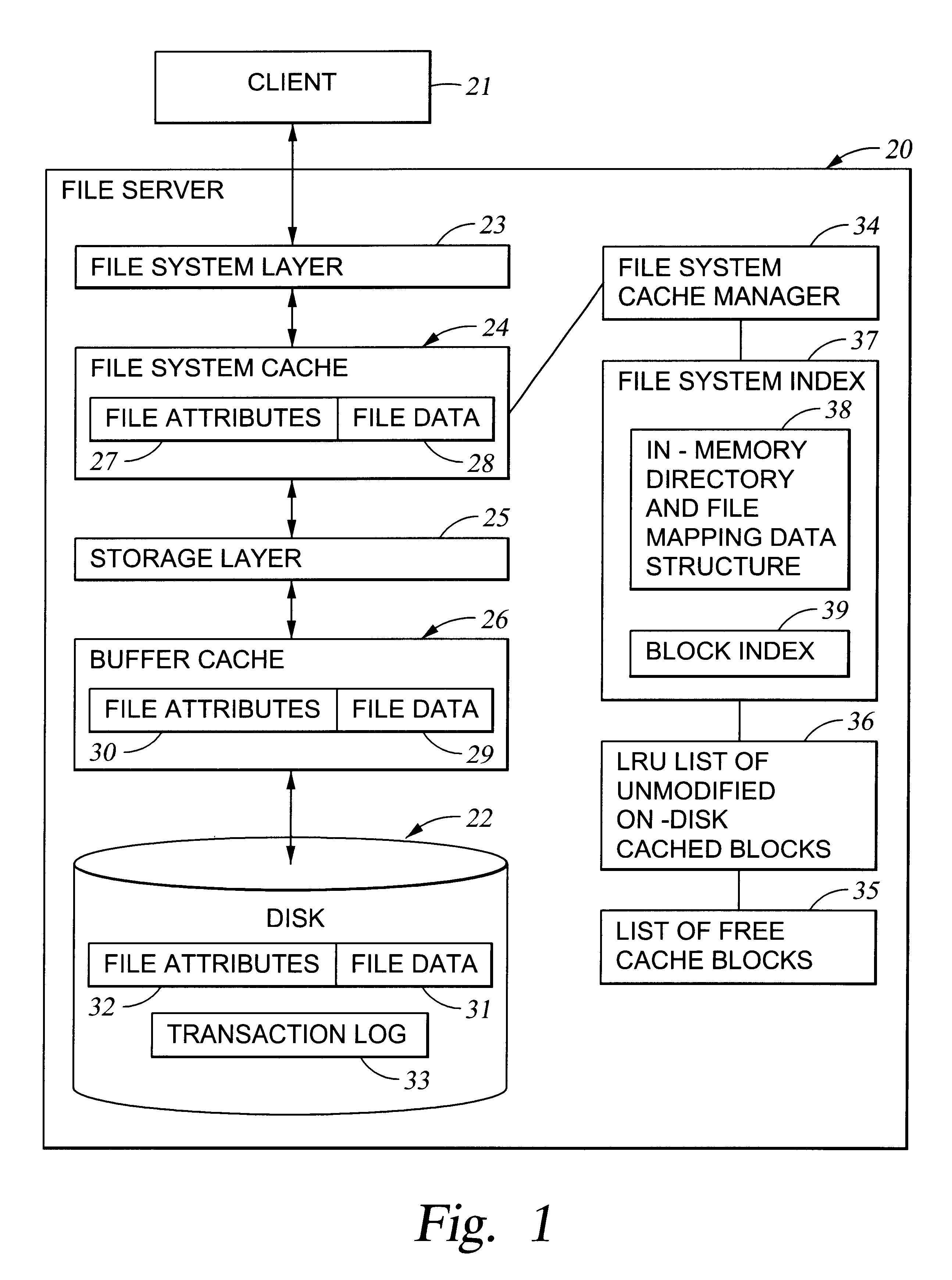
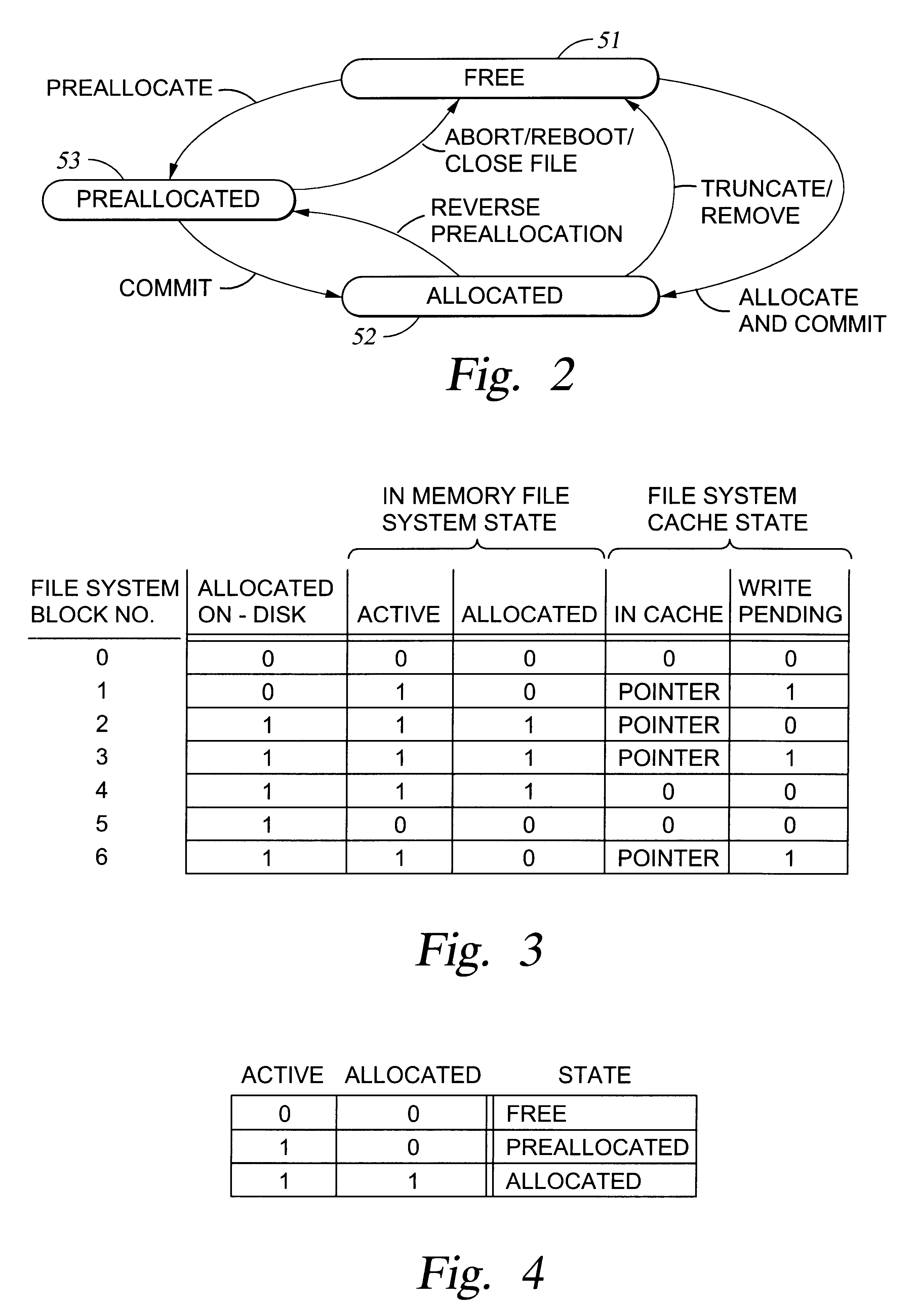
Preallocation of file system cache blocks in a data storage system
InactiveUS6571259B1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemTransaction log
A file server provides transaction processing capabilities previously supplied by the operating system of a host computer. On-disk file system metadata is changed only at commit time, and a transaction log protects the transition. The disk state can only be a consistent state, resulting from a commit operation. All disk-block reservation and pre-allocation mapping are in the memory, and after a crash, they are automatically discarded. The file server therefore relieves the client of processing burden and also reduces network traffic. In addition, the file server can more efficiently perform the transaction processing capabilities and reduce the frequency of access to storage by judicious allocation of file system blocks and transfer of file system blocks between file system objects, cache memory, and the transaction log. The differentiation between preallocation states and allocation states of in-memory file system blocks also permits application programs to more efficiently transfer data between files.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
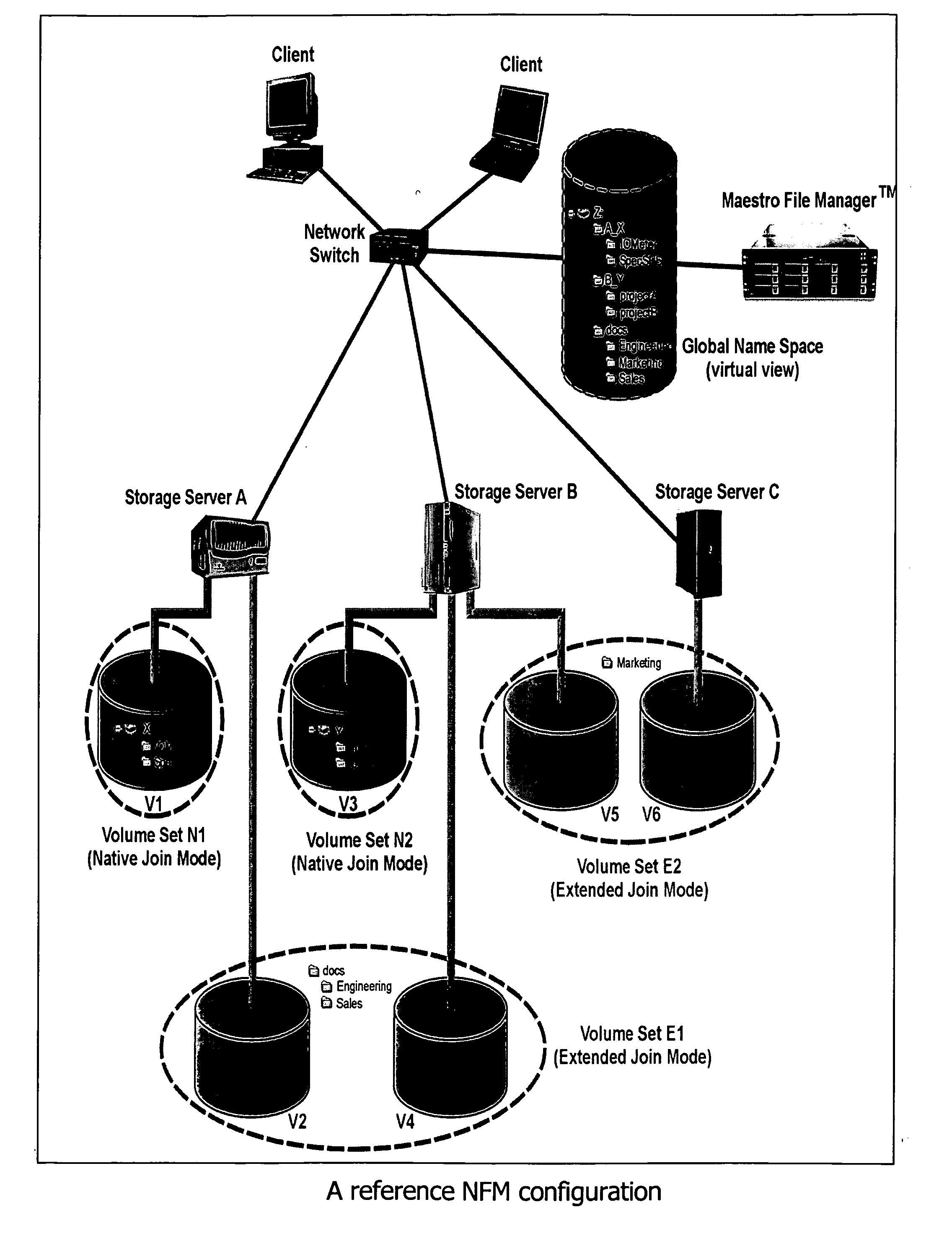
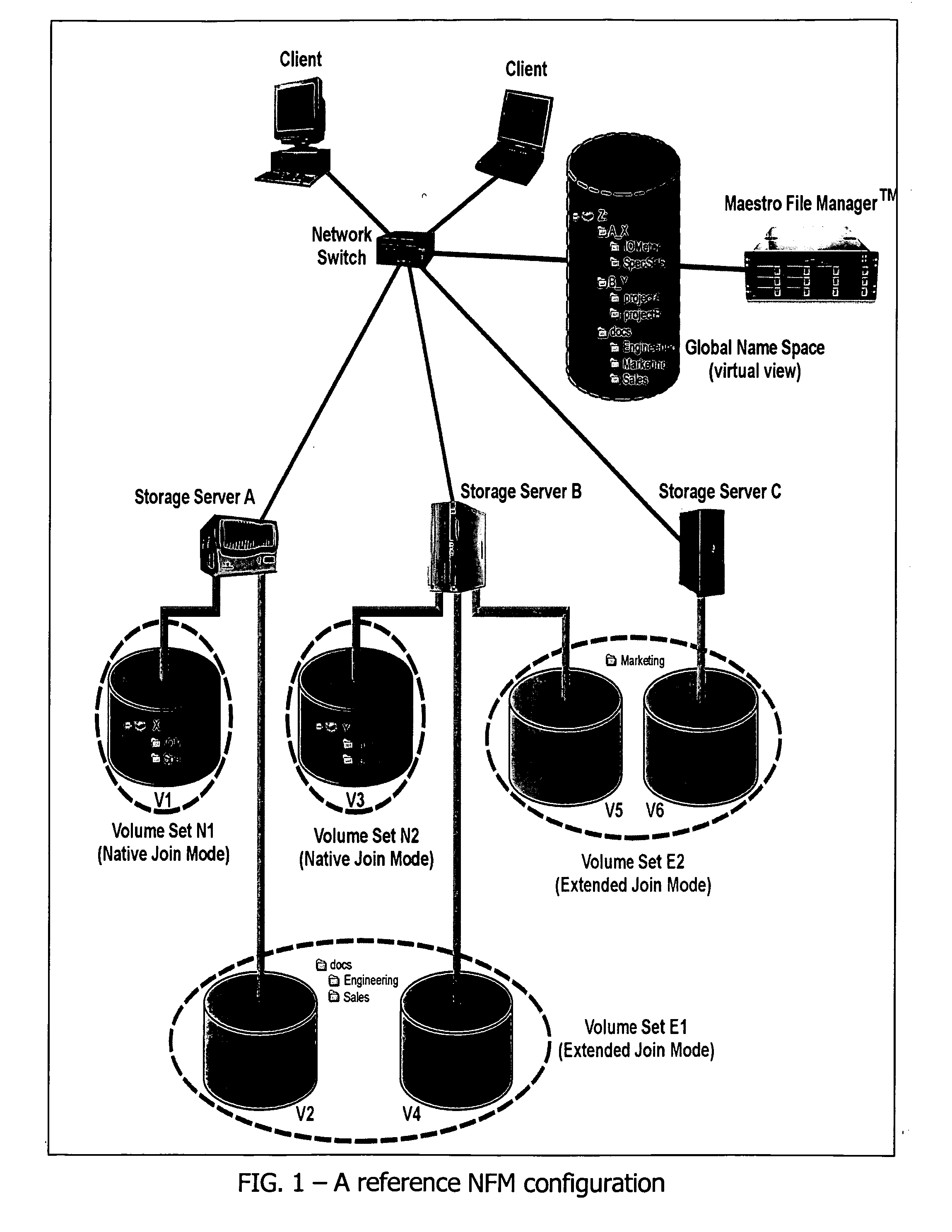
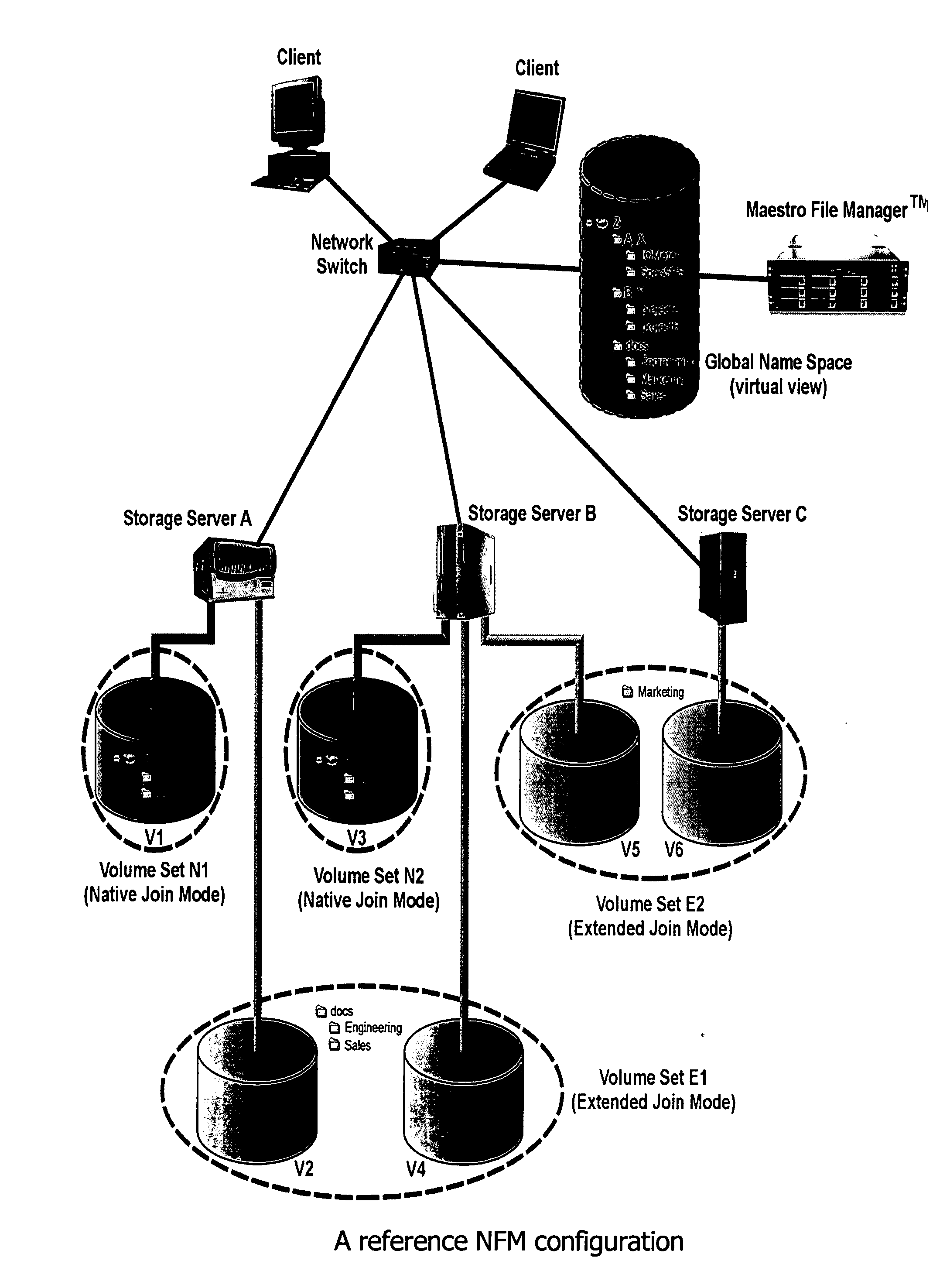
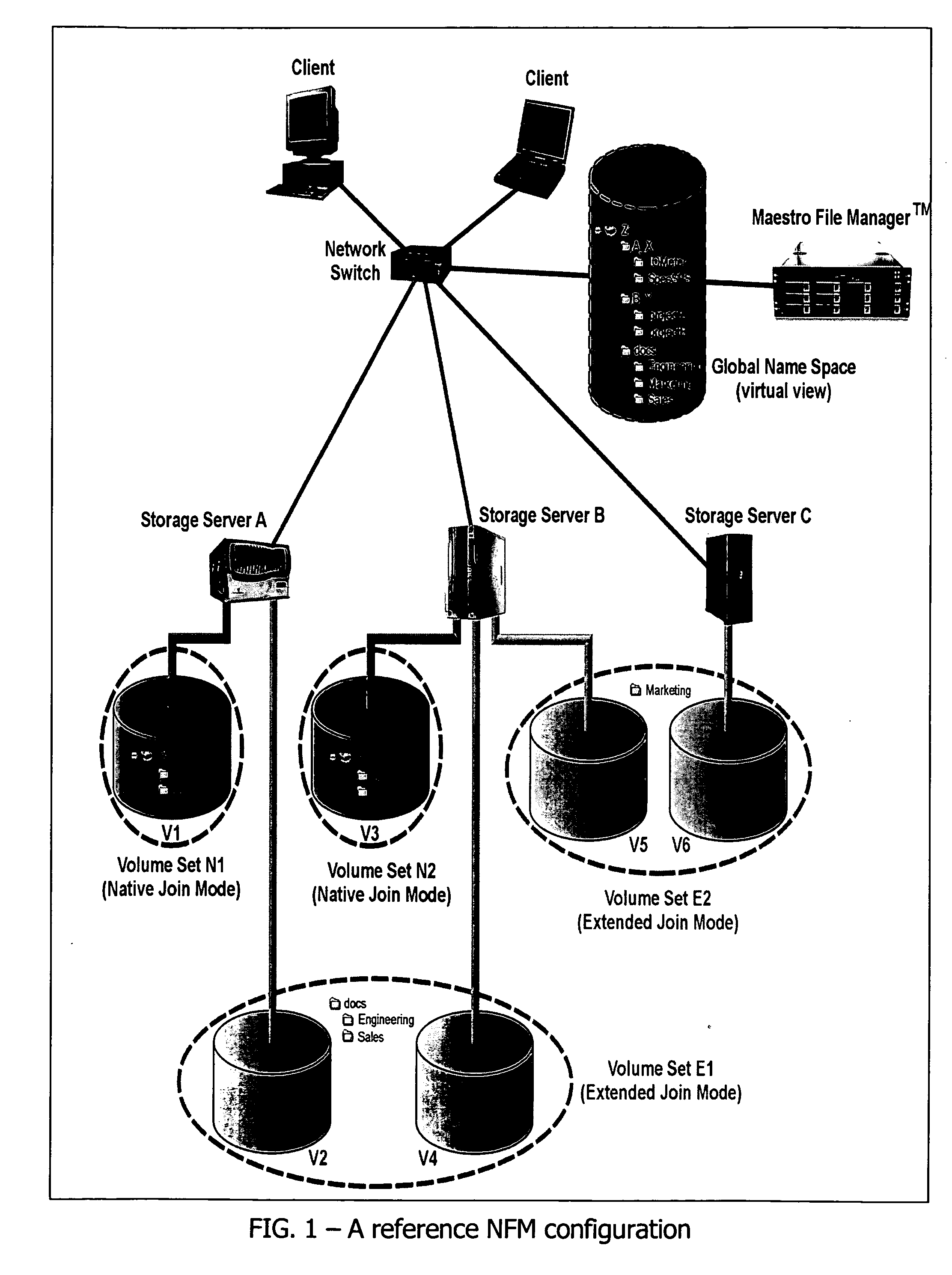
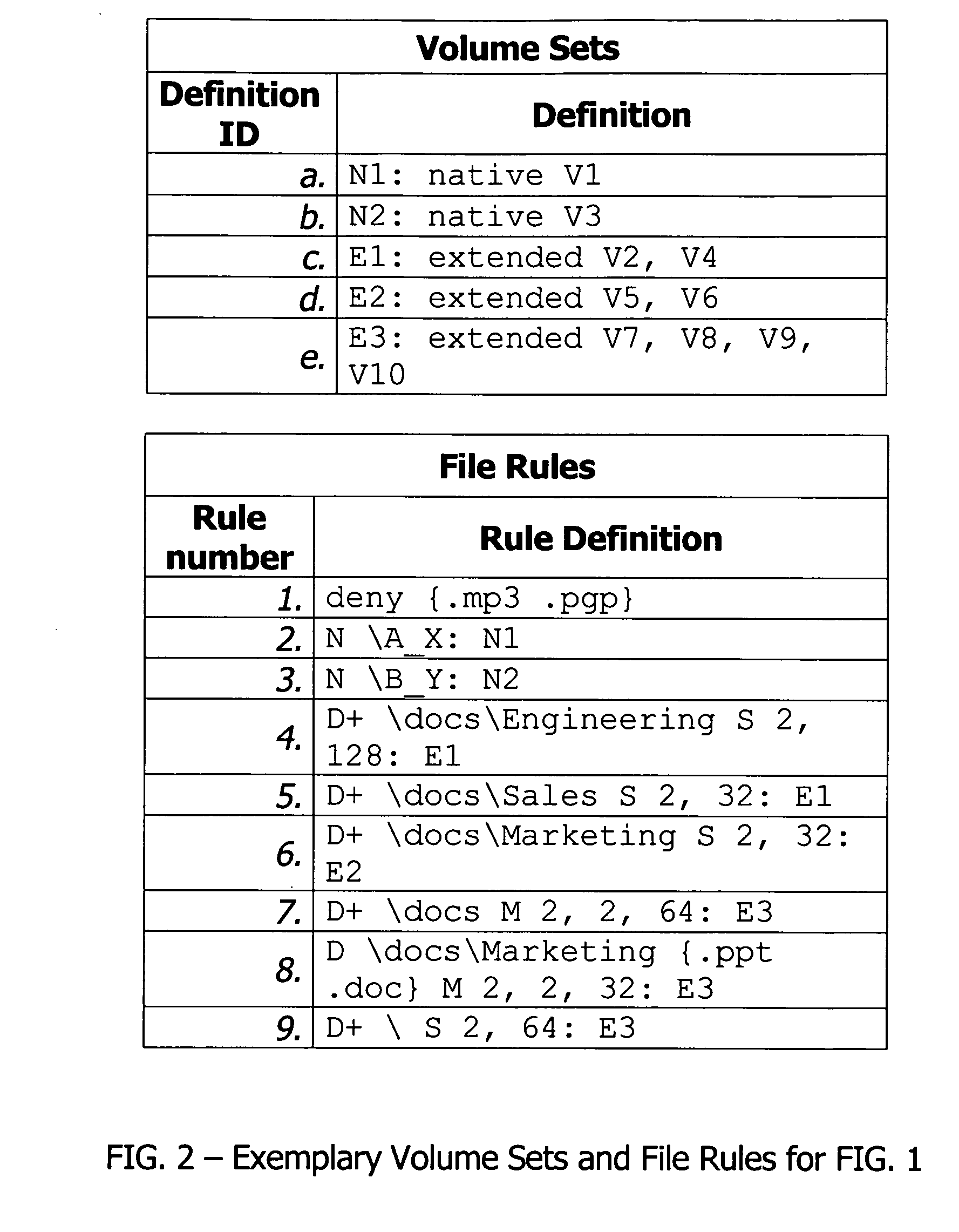
File Aggregation in a Switched File System
InactiveUS20090077097A1Digital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionFile systemGlobal file system
In a switched file system, a file switching device is logically positioned between clients and file servers and communicates with the clients and the file servers using standard network file protocols. The file switching device appears as a server to the client devices and as a client to the file servers. The file switching device aggregates storage from multiple file servers into a global filesystem and presents a global namespace to the client devices. The file switching device typically supports a “native” mode for integrating legacy files into the global namespace and an “extended” mode for actively managing files across one or more file servers. Typically, native-mode files may be accessed directly or indirectly via the file switching device, while extended-mode files may be accessed only through the file switching device. The file switching device may manage file storage using various types of rules, e.g., for managing multiple storage tiers or for applying different types of encoding schemes to files. Rules may be applied to pre-existing files.
Owner:RPX CORP
Virtual file system
InactiveUS7024427B2Function increaseDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersGlobal file systemData file
A virtual file system and method. The system architecture enables a plurality of underlying file systems running on various file servers to be “virtualized” into one or more “virtual volumes” that appear as a local file system to clients that access the virtual volumes. The system also enables the storage spaces of the underlying file systems to be aggregated into a single virtual storage space, which can be dynamically scaled by adding or removing file servers without taking any of the file systems offline and in a manner transparent to the clients. This functionality is enabled through a software “virtualization” filter on the client that intercepts file system requests and a virtual file system driver on each file server. The system also provides for load balancing file accesses by distributing files across the various file servers in the system, through migration of data files between servers.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
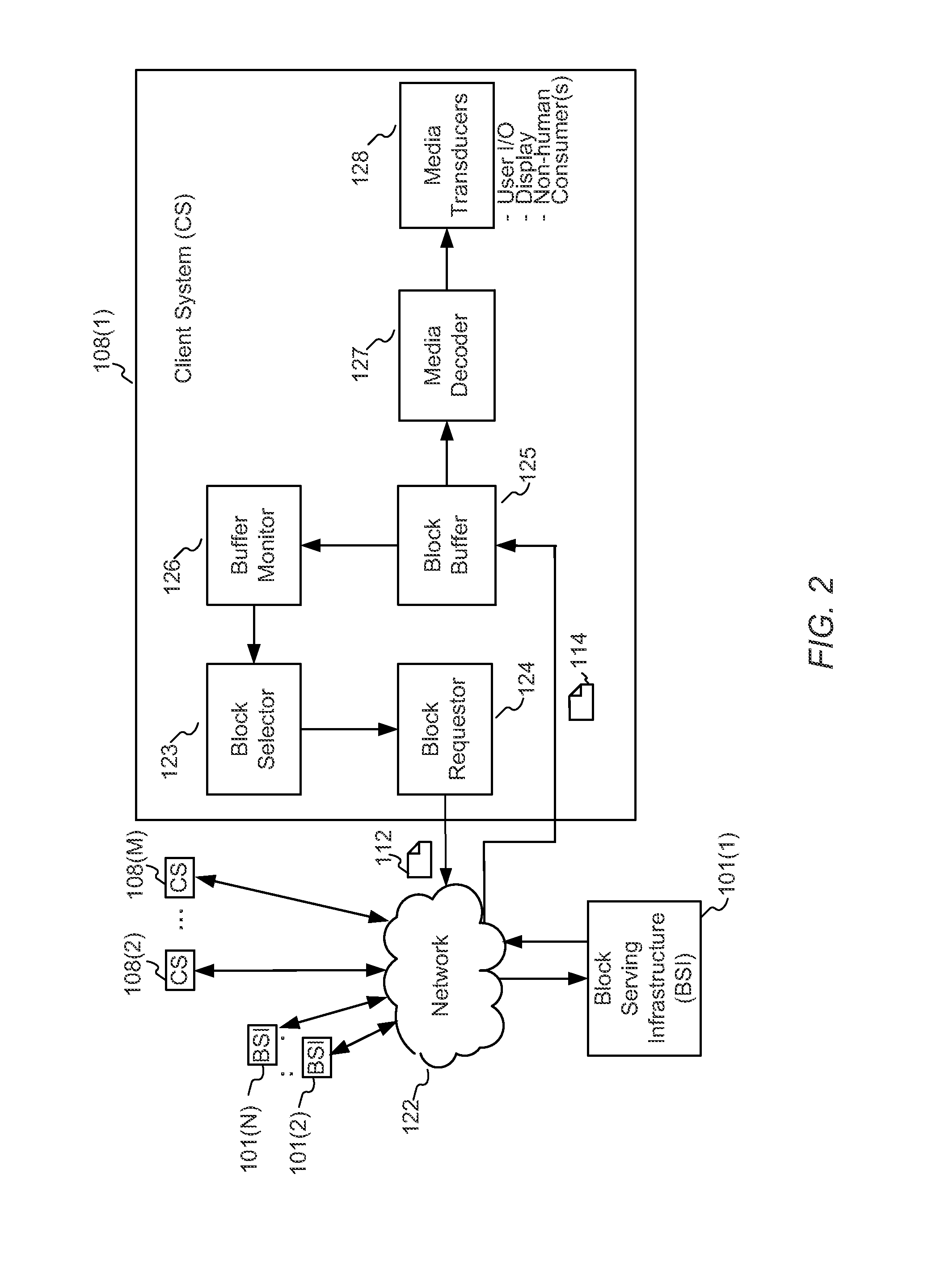
Enhanced block-request streaming system using signaling or block creation
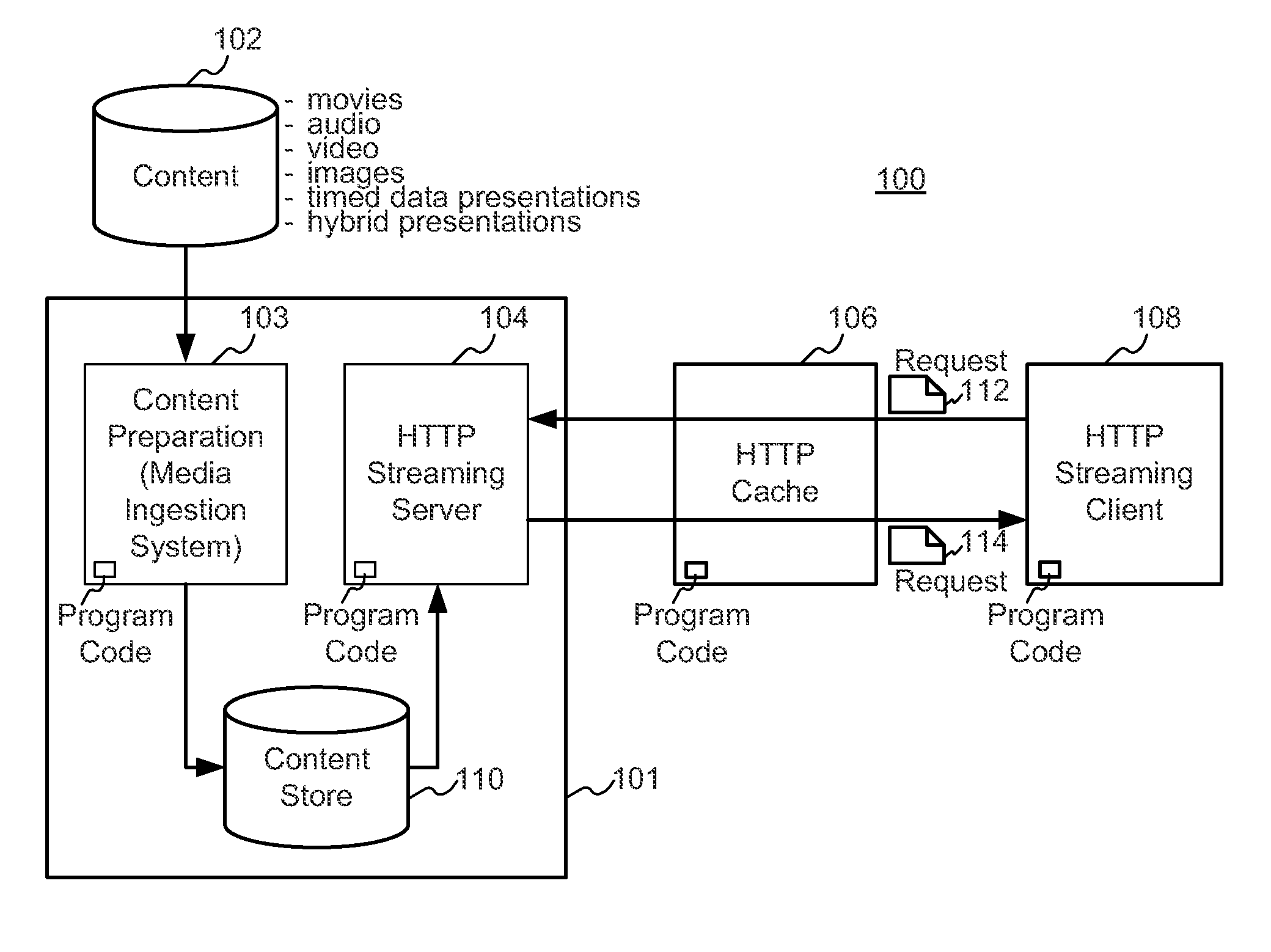
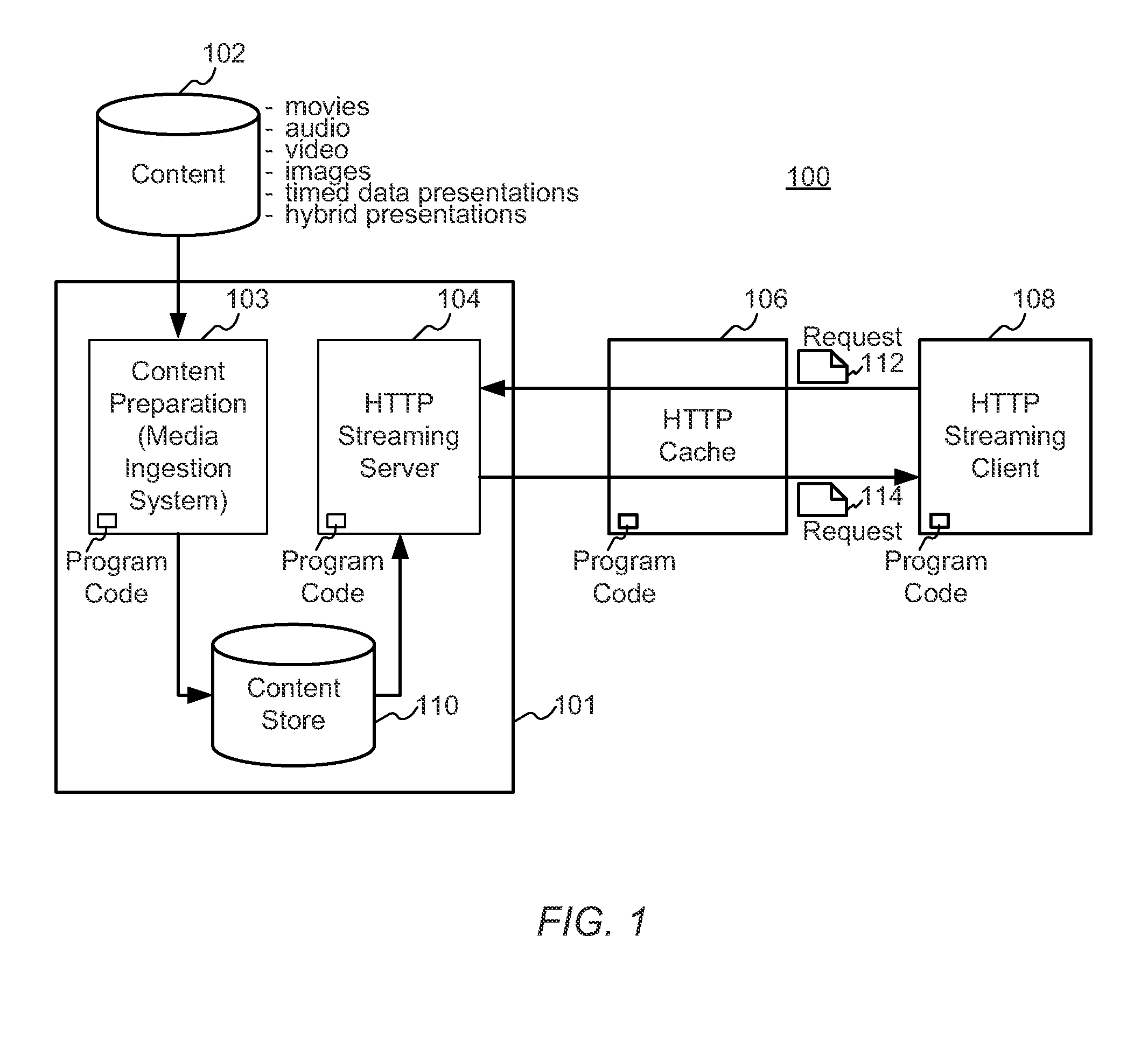
ActiveUS20110238789A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyImprove user experiencePulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransport systemPoint placement
A block-request streaming system provides for improvements in the user experience and bandwidth efficiency of such systems, typically using an ingestion system that generates data in a form to be served by a conventional file server (HTTP, FTP, or the like), wherein the ingestion system intakes content and prepares it as files or data elements to be served by the file server. The system might include controlling the sequence, timing and construction of block requests, time based indexing, variable block sizing, optimal block partitioning, control of random access point placement, including across multiple presentation versions, dynamically updating presentation data, and / or efficiently presenting live content and time shifting.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
File Aggregation in a Switched File System
InactiveUS20090106255A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionGlobal file systemFile system
In a switched file system, a file switching device is logically positioned between clients and file servers and communicates with the clients and the file servers using standard network file protocols. The file switching device appears as a server to the client devices and as a client to the file servers. The file switching device aggregates storage from multiple file servers into a global filesystem and presents a global namespace to the client devices. The file switching device typically supports a “native” mode for integrating legacy files into the global namespace and an “extended” mode for actively managing files across one or more file servers. Typically, native-mode files may be accessed directly or indirectly via the file switching device, while extended-mode files may be accessed only through the file switching device. The file switching device may manage file storage using various types of rules, e.g., for managing multiple storage tiers or for applying different types of encoding schemes to files. Rules may be applied to pre-existing files.
Owner:RPX CORP
Internet protocol based disaster recovery of a server
For disaster recovery of a file server at an active site, the files that define the user environment of the file server are replicated to a virtual server at a disaster recovery site. To switch over user access from the active site to the disaster recovery site, the disaster recovery system determines whether there are sufficient network interfaces and file system mounts at the disaster recovery site. If so, the required resources are reserved, and user access is switched over. If not, an operator is given a list of missing resources or discrepancies, and a choice of termination or forced failover. Interruptions during the failover can be avoided by maintaining a copy of user mappings and a copy of session information at the disaster recovery site, and keeping alive client-server connections and re-directing client requests from the active site to the disaster recovery site.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com