Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6622 results about "Data query" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
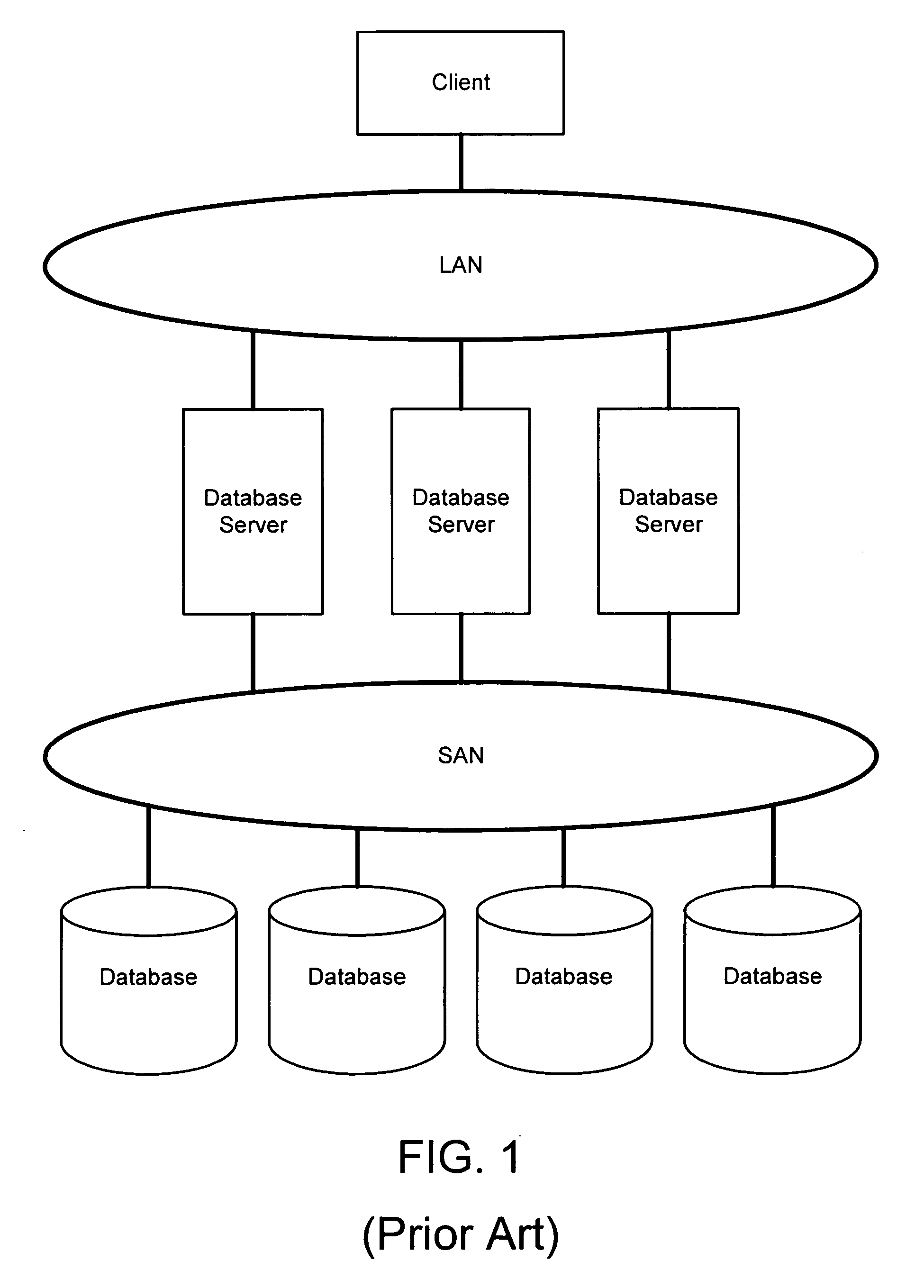
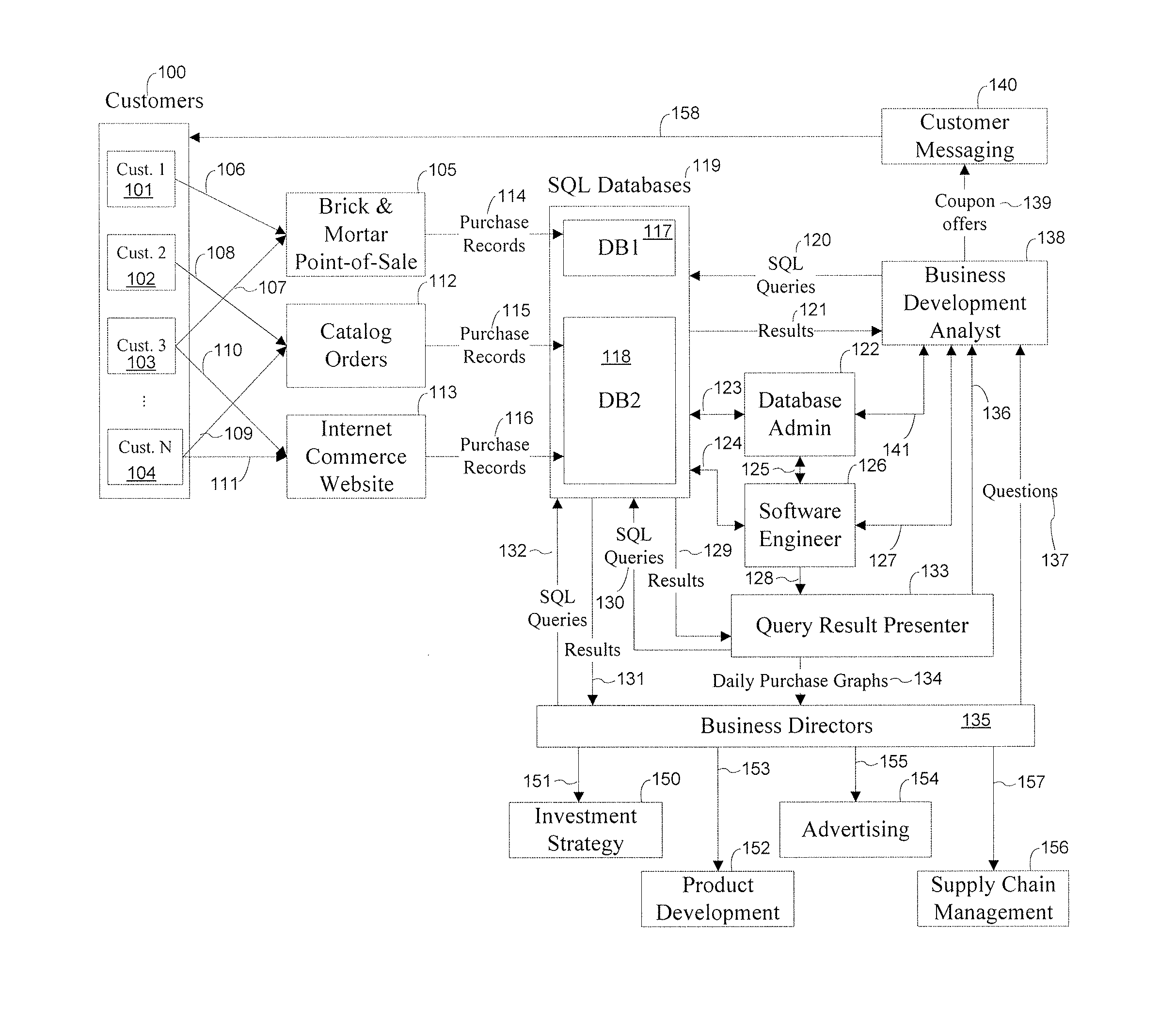
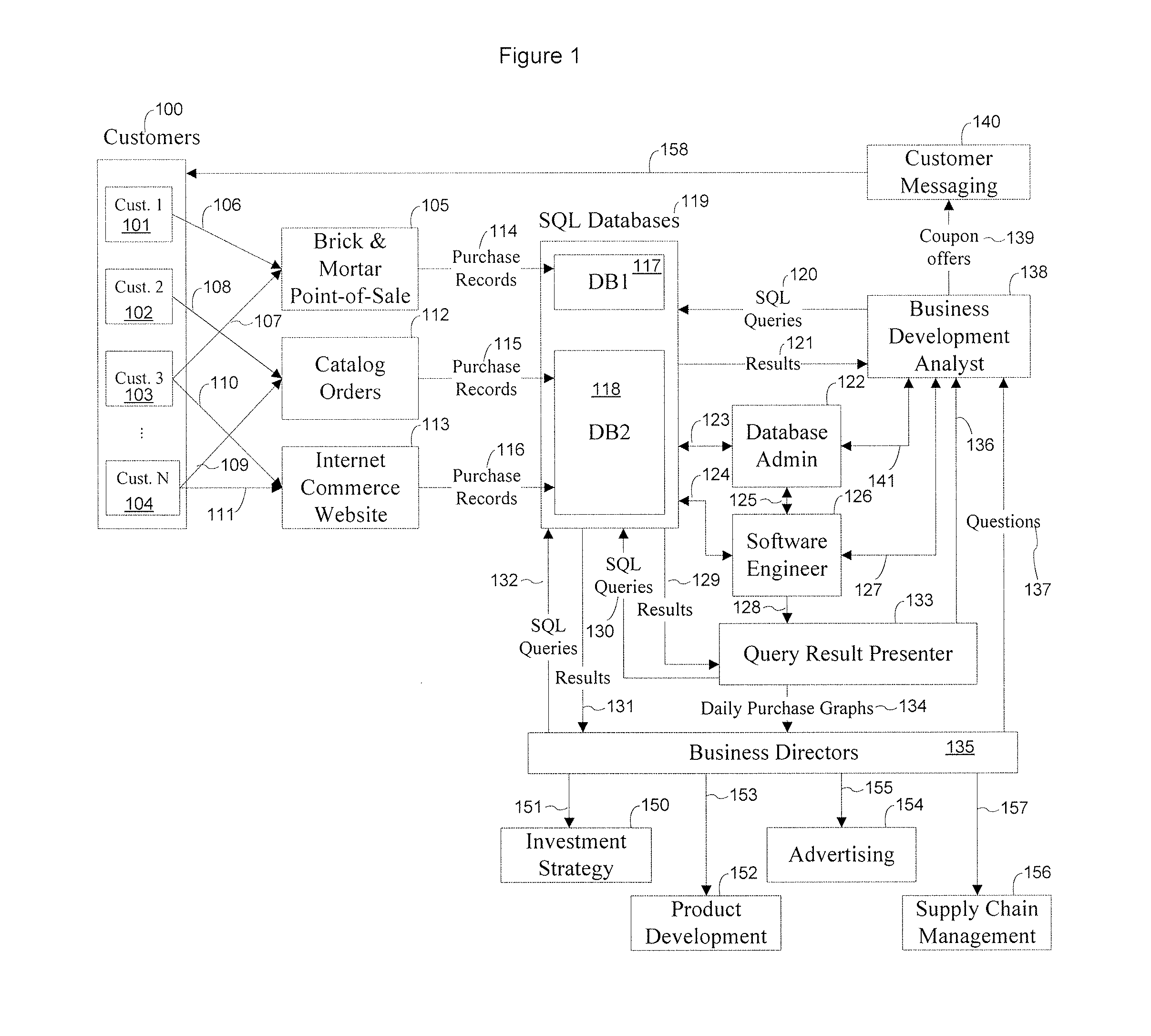
A query is a request for data or information from a database table or combination of tables. This data may be generated as results returned by Structured Query Language (SQL) or as pictorials, graphs or complex results, e.g., trend analyses from data-mining tools.
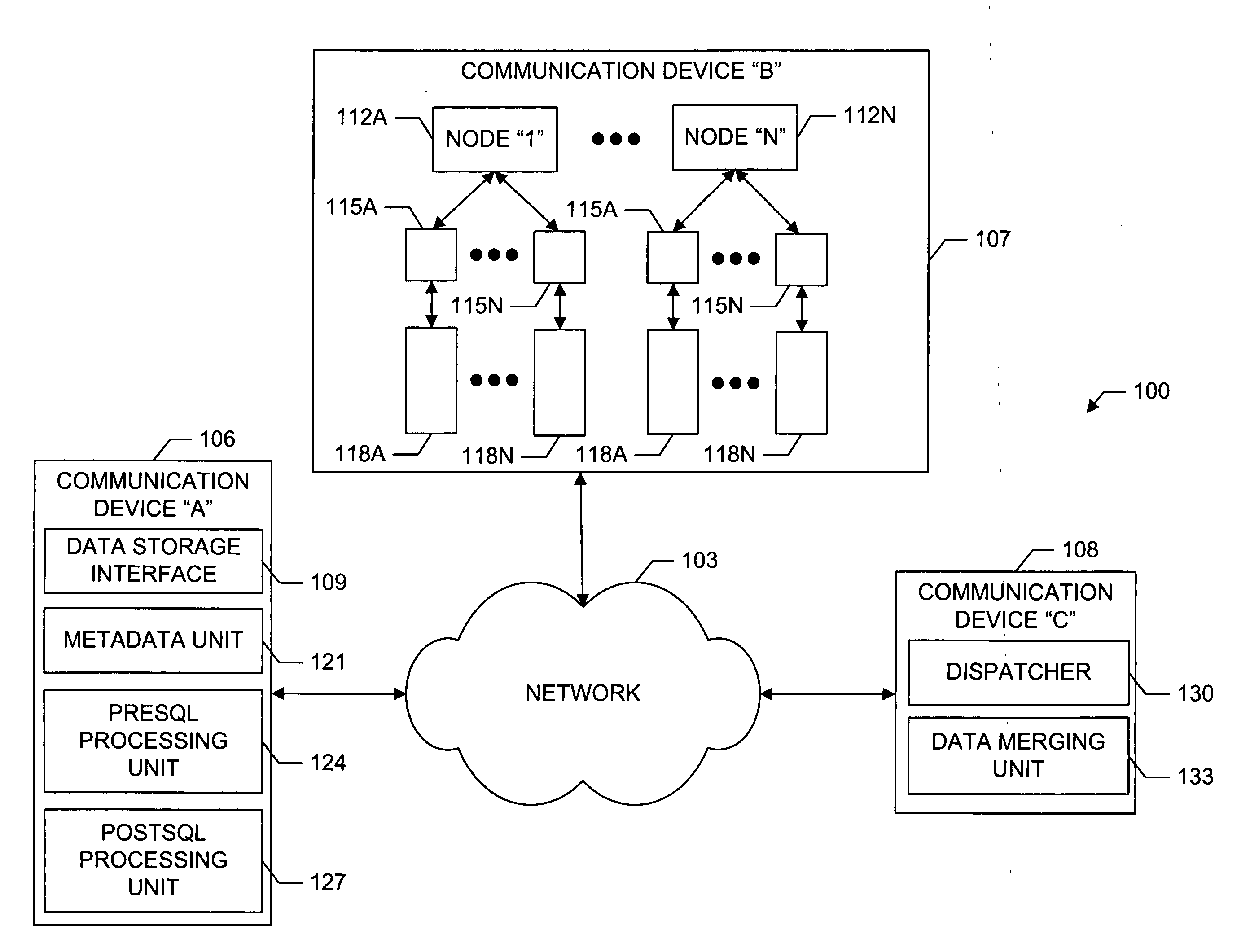
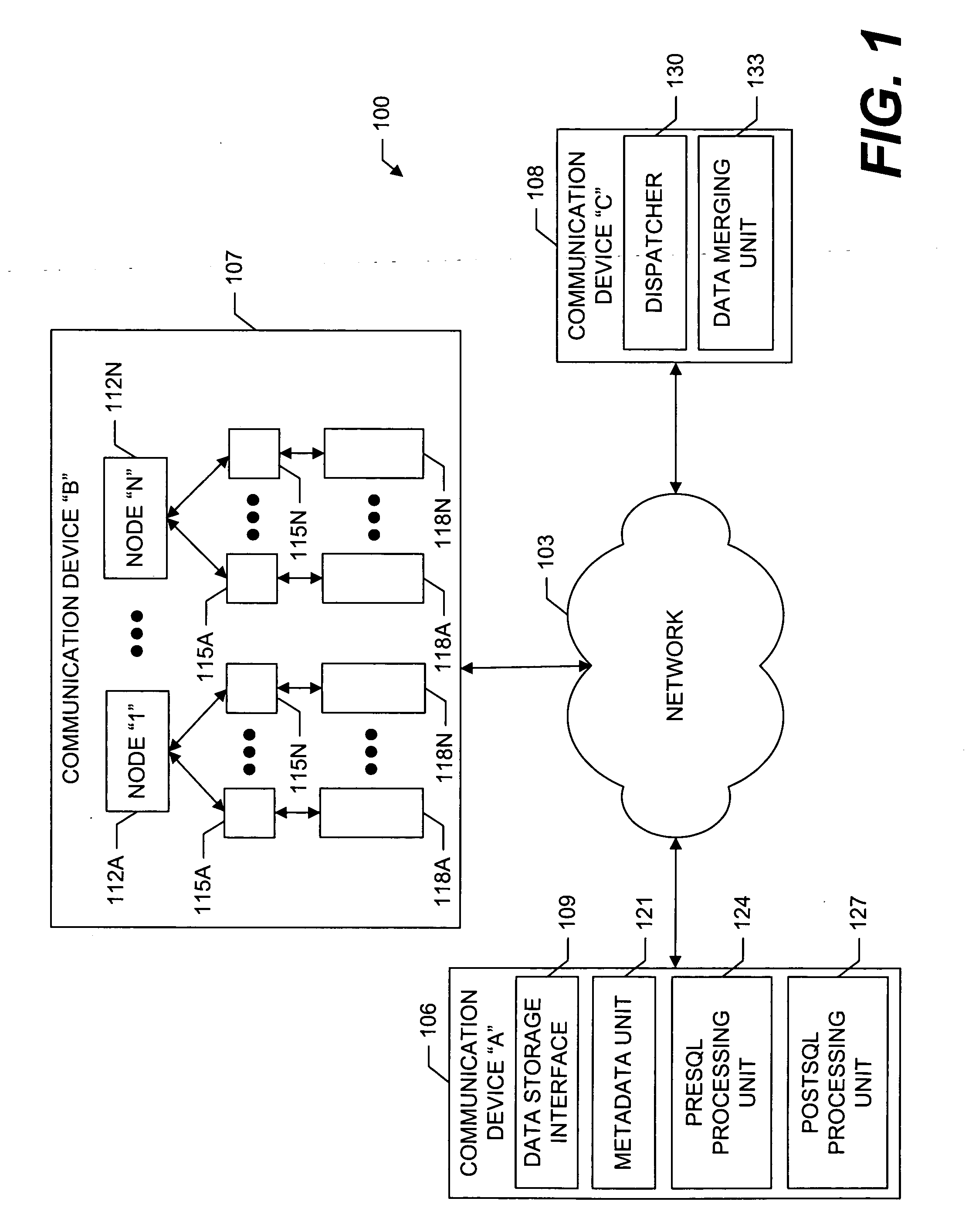
System and methods for facilitating a linear grid database with data organization by dimension
InactiveUS20060224603A1Data processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesGrid managementData storing
A system and methods for organizing and querying data within a linear grid management system. Data having multiple dimensions is associated with physical locations, where a first dimension is associated with a node and a second dimension is associated with a data storage identifier of a memory storage device. The data may have a third dimension which provides a field for ordering data within the memory storage device. Metadata may be used to map a logical table to data stored in the memory storage device. The data query may be divided into multiple subqueries, wherein each subquery is related directly to one node associated with a data storage identifier related to a memory storage device. A preSQL and postSQL process may be generated to access an external database. A dispatcher may manage data subrequests and a node may generate a unique and efficient parsing process from the received data subrequest.
Owner:WALMART APOLLO LLC
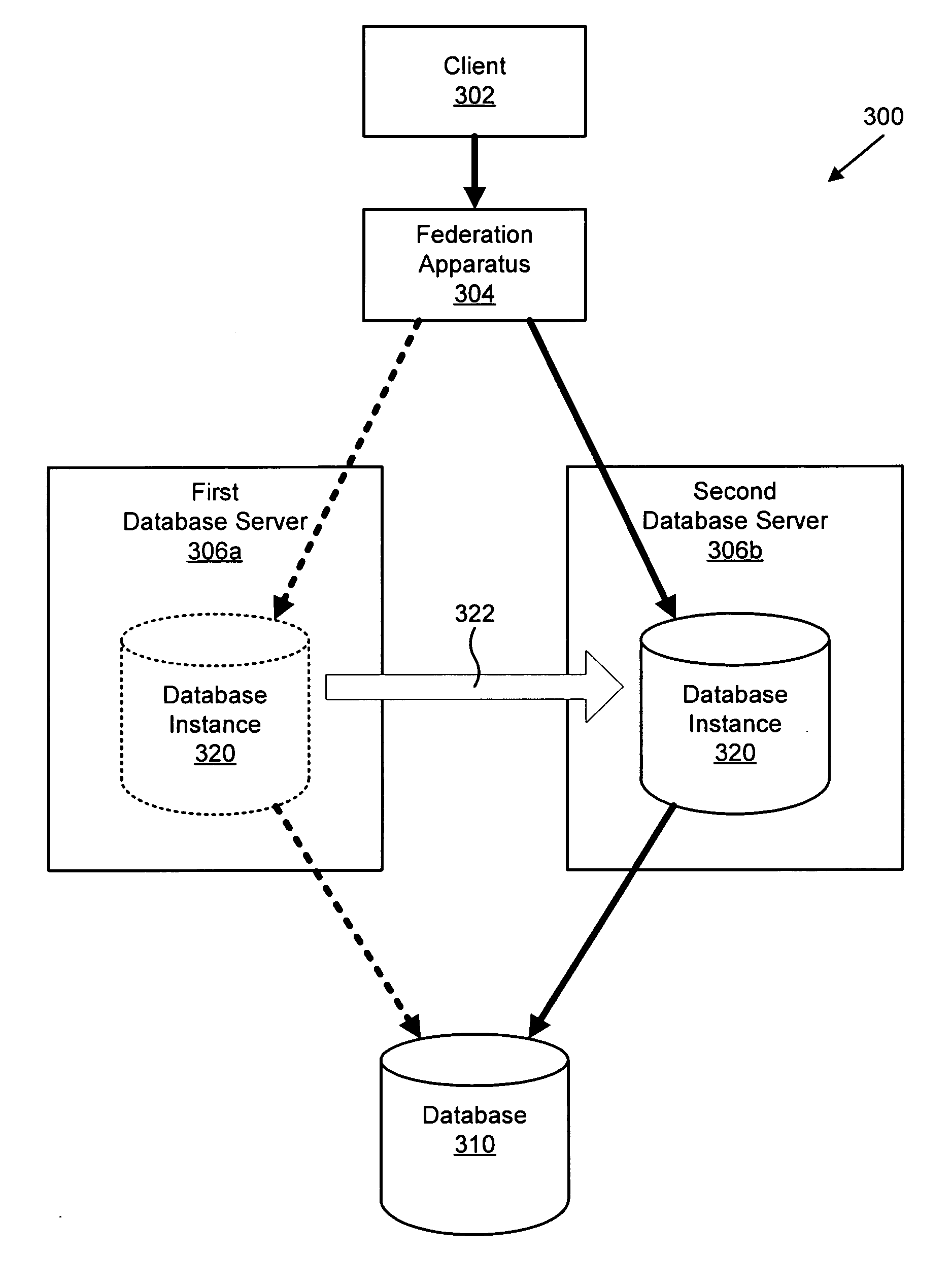
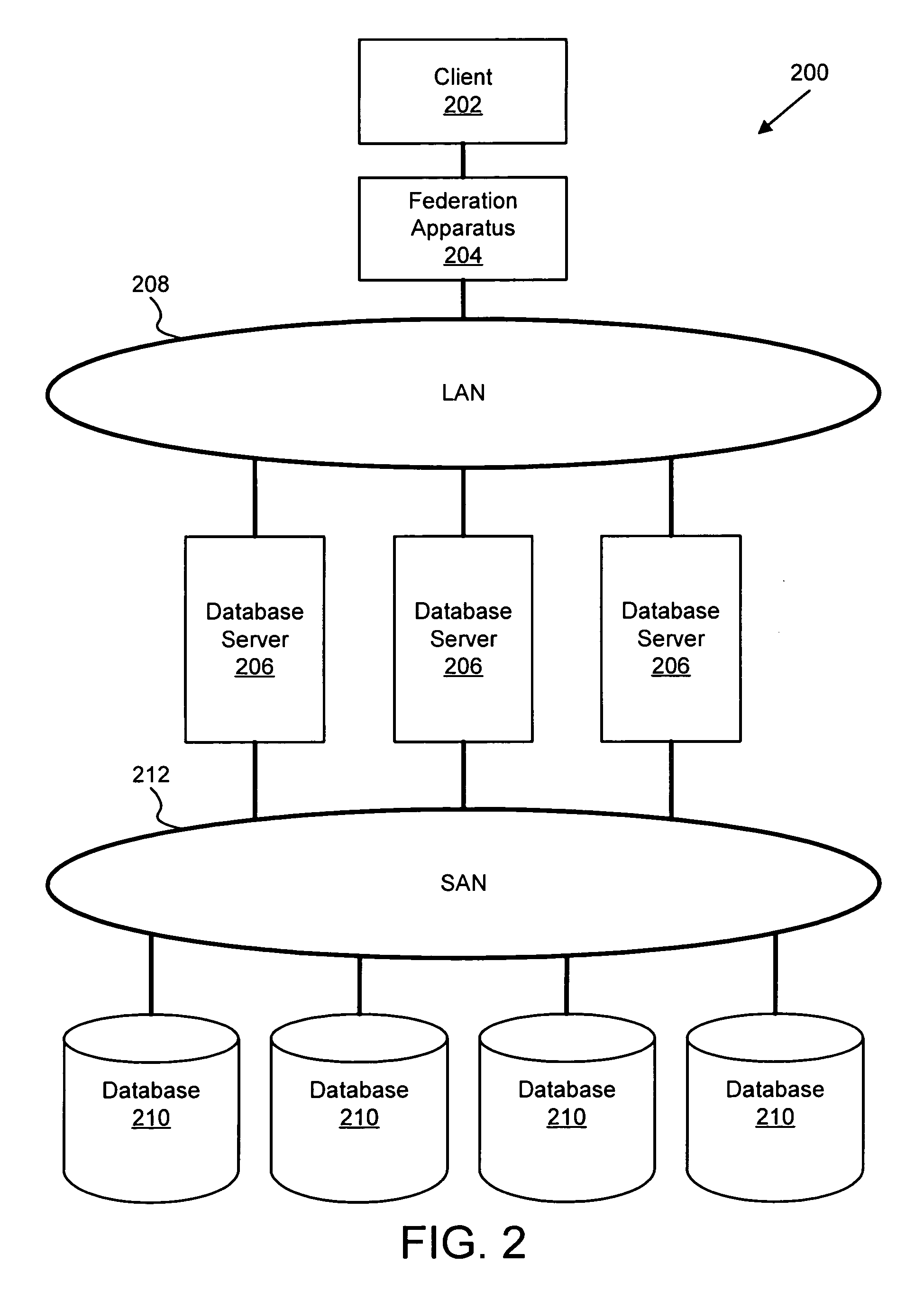
Apparatus, system, and method for database provisioning
ActiveUS20060136448A1Overcomes shortcomingDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsApplication softwareClient-side
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for provisioning database resource within a grid database system. The federation apparatus includes an analysis module and a provision module. The analysis module analyzes a data query stream from an application to a database instance and determines if the data query stream exhibits a predetermined performance attribute. The provision module provisions a database resource in response to a determination that the data query stream exhibits the predetermined performance attribute. The provisioned database resource may be a database instance or a cache. The provisioning of the new database resource advantageously is substantially transparent to a client on the database system.
Owner:TWITTER INC
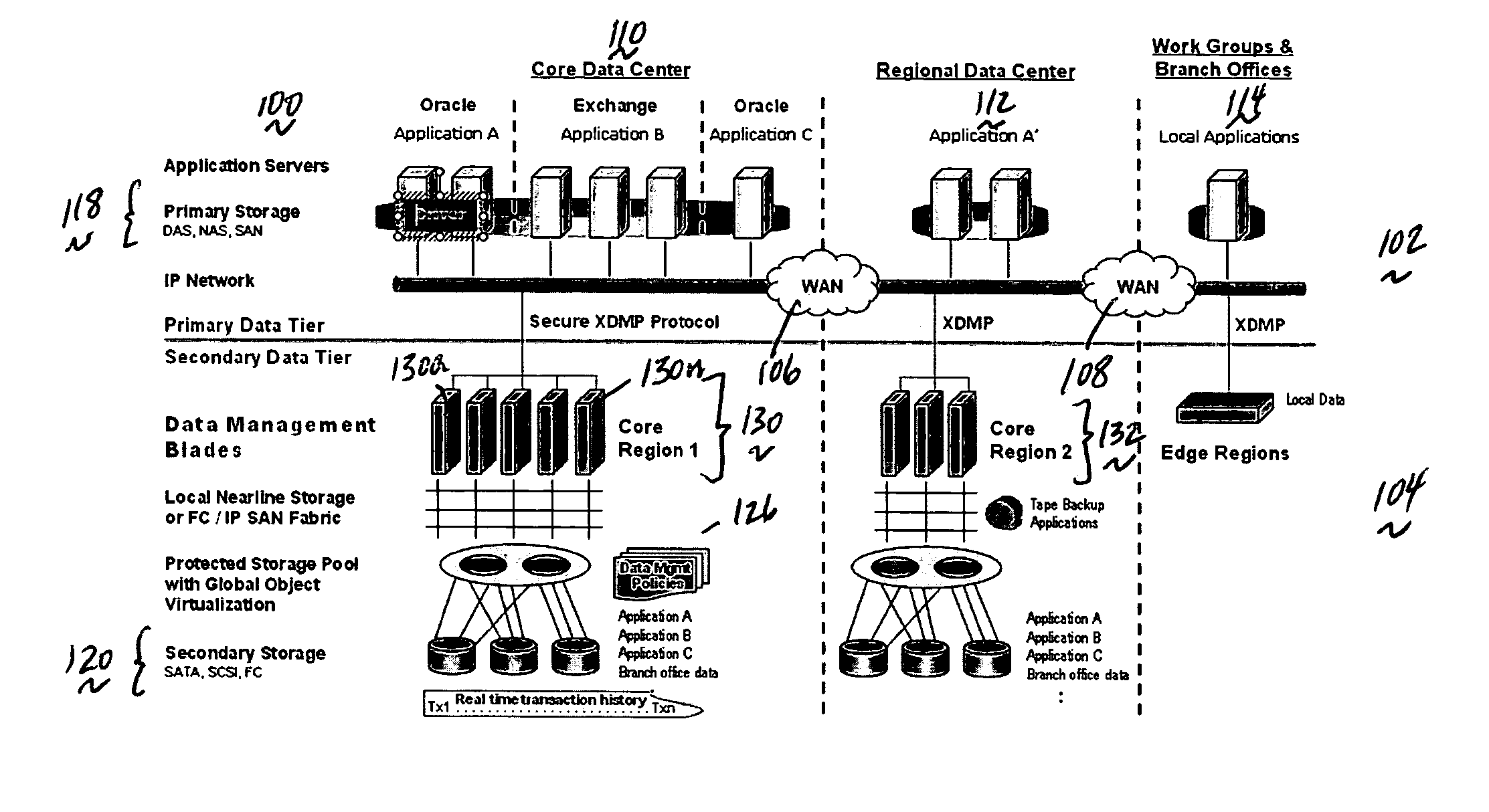
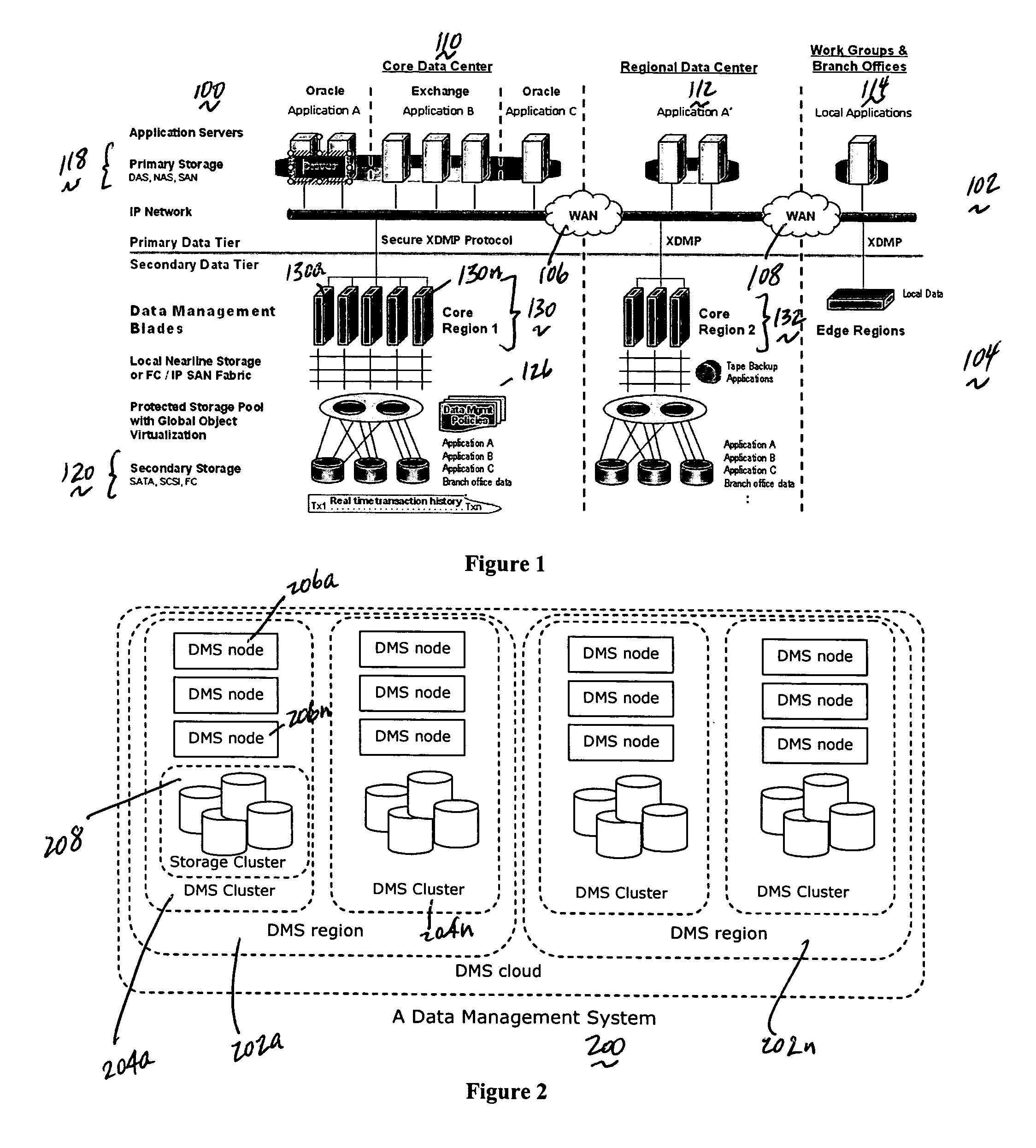
System for moving real-time data events across a plurality of devices in a network for simultaneous data protection, replication, and access services
ActiveUS20050262097A1Efficiently parallel processEfficiently route application-aware data changeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData connectionData stream
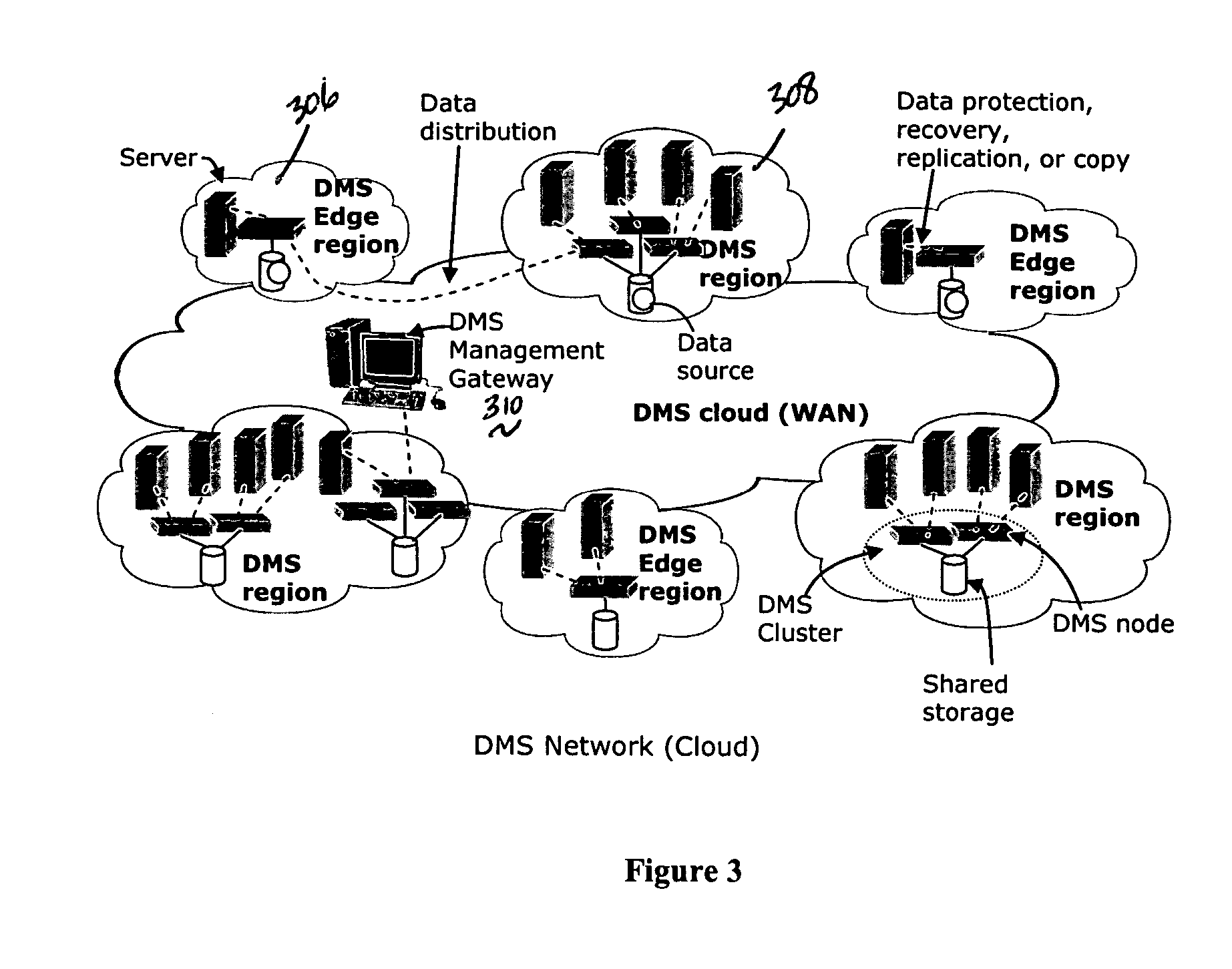
A data management system or “DMS” provides a wide range of data services to data sources associated with a set of application host servers. The data management system typically comprises one or more regions, with each region having one or more clusters. A given cluster has one or more nodes that share storage. To facilitate the data service, a host driver embedded in an application server connects an application and its data to a cluster. The host driver provides a method and apparatus for capturing real-time data transactions in the form of an event journal that is provided to the data management system. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. Using the streams generated in this manner, the DMS offers a wide range of data services that include, by way of example only: data protection (and recovery), disaster recovery (data distribution and data replication), data copy, and data query and access.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Authenticated access to internet based research and data services
InactiveUS6185567B1Data processing applicationsComputer security arrangementsData queryWeb authentication
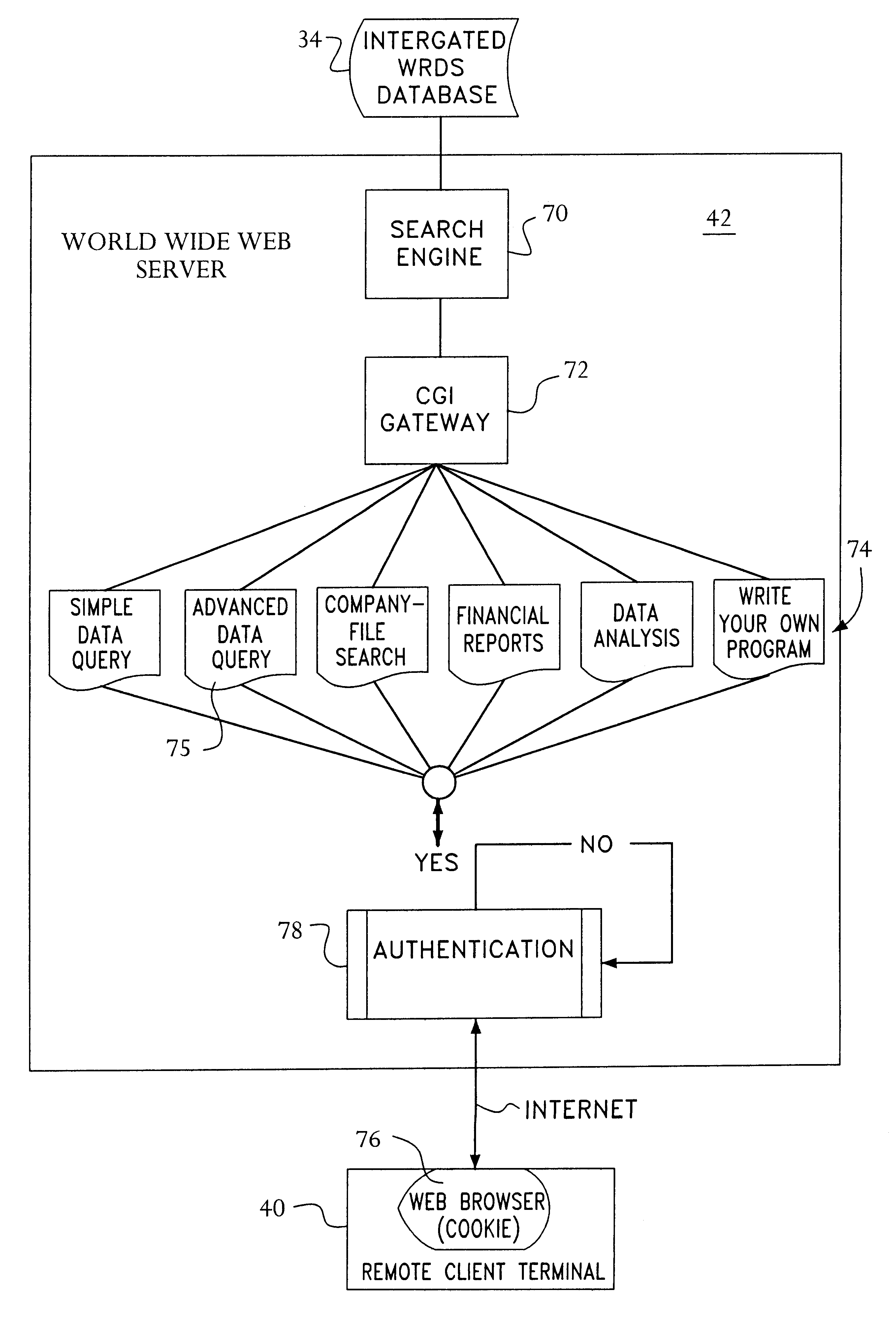
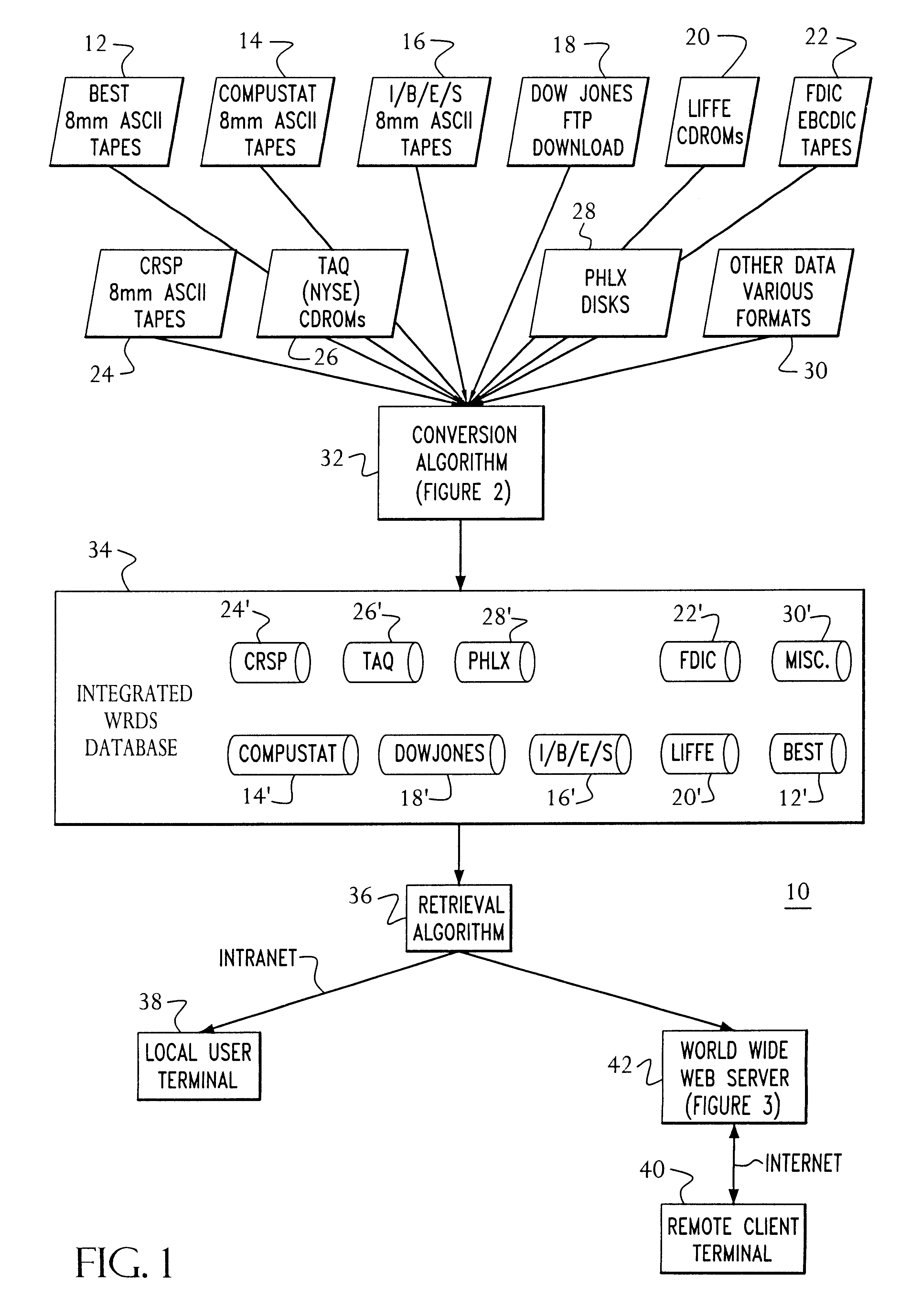
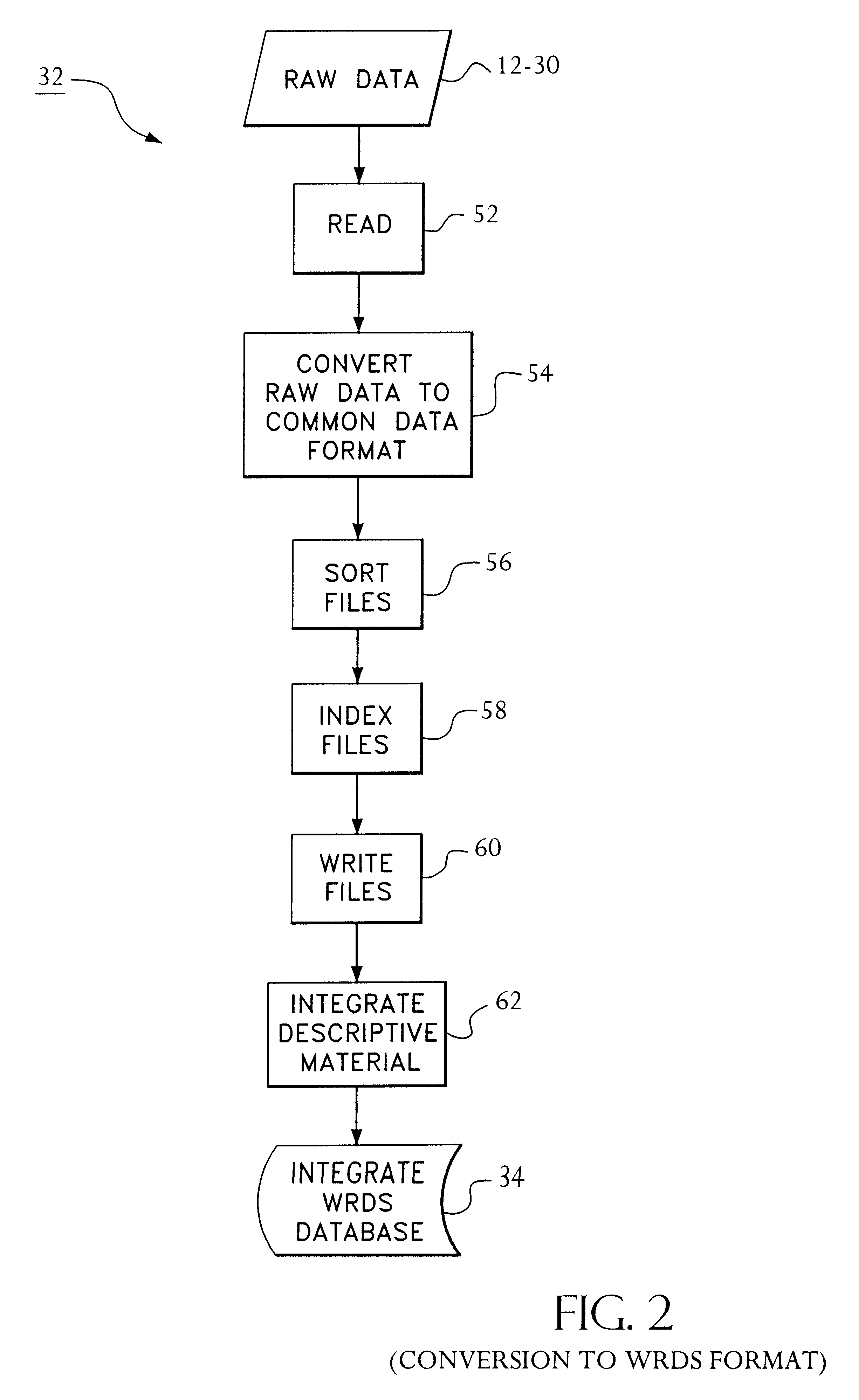
Access to a database is provided via the Internet using a World Wide Web server including a search engine, a CGI gateway and user selectable data queries for extracting data, generating reports, and the like. Access by the user is authenticated by querying the user's central machine for authentication. The authentication process operates by sending a page request from the web browser through three checkpoints before the requested page can be served to the web browser. The first checkpoint determines if the requested page is protected. If not, the requested page is served to the web browser. However, if the requested page is protected, the authentication process on the web server checks the host name of the system where the page request is coming from. If the domain of the requesting host is the same domain specified in the web authentication configuration, then the requested page is served to the web browser. However, if the page request is determined to come from outside of the domain of the web server, then the authentication process checks a "cookie" from the web browser to determine if the requesting user has been authenticated as an authorized user earlier in the same session. If the cookie has been "set" during the login procedure, then the requested page is served to the web browser. Otherwise, the user is prompted with a login page. After the user ends the web browser session, the cookie is cleared. Data Query software at the web server permits queries initiated via a web browser to be completed off-line and the results e-mailed to the initiator of the request.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Query language for unstructed data
InactiveUS20150019530A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRDF query languageUnstructured data
A system and methods are provided for interactive construction of data queries. One method comprises: generating a query based upon a plurality of user-identified data items, wherein the user-identified data items are data items representing desired results from a query, and wherein information related to the user-identified data items is included in a “given” clause of the query, assigning received input data to a hierarchical set of categories, presenting to a user a plurality of new query results, wherein the plurality of new query results are determined by scanning the received input data to find data elements in the same hierarchical categories as those in the “given” query clause and not in the same hierarchical categories as those of an “unlike” clause of the query, receiving from the user an indication as to whether each query result of the presented plurality of new query results is a desirable query result, adding query results indicated by the user as desirable to the “given” clause of the query, adding query results indicated by the user as undesirable to the “unlike” clause of the query, evaluating a metric indicative of the accuracy of the query, and responsive to a determination that the query achieves a predetermined threshold level of accuracy, storing the query.
Owner:COGNITIVE ELECTRONICS INC
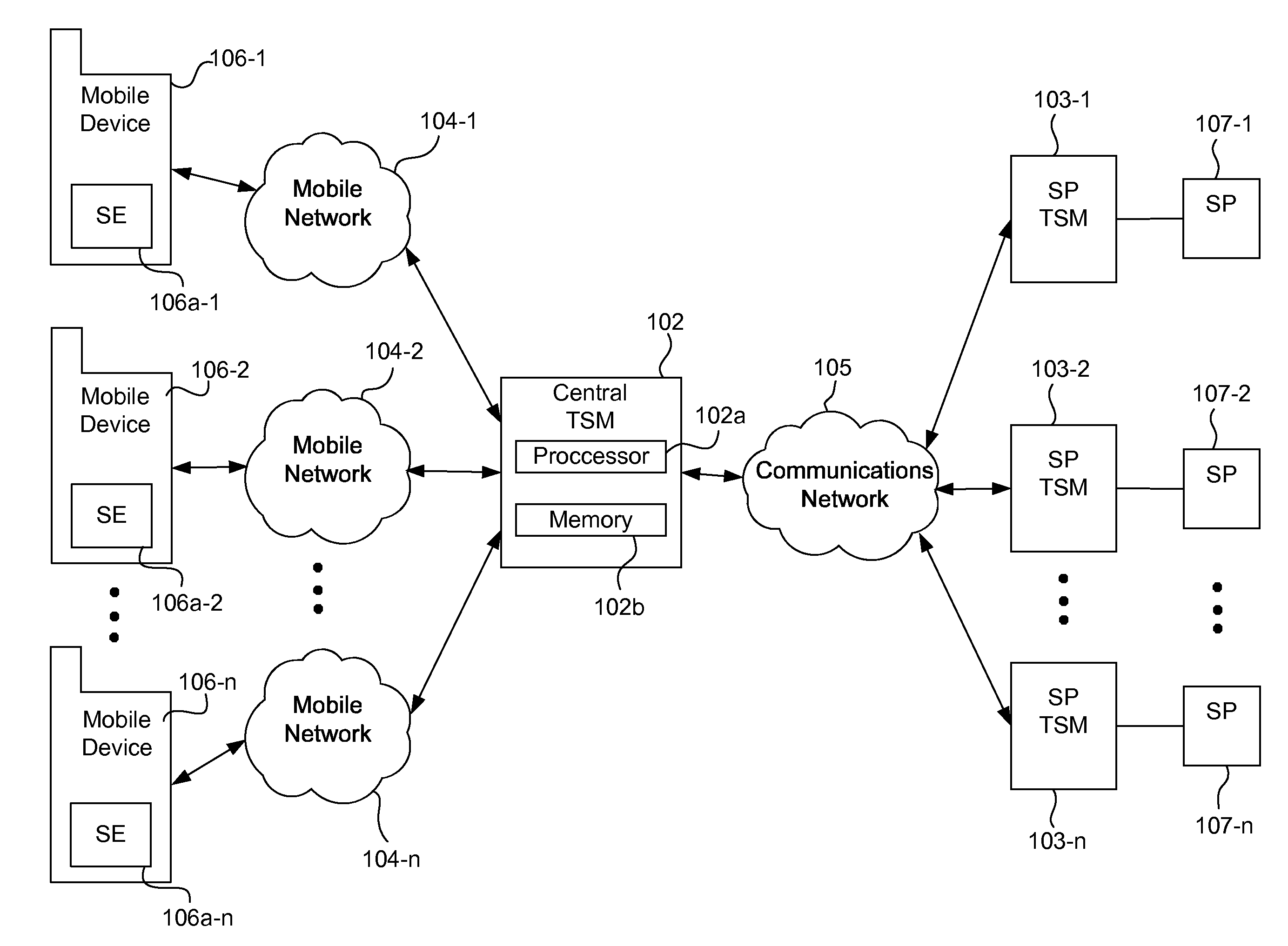
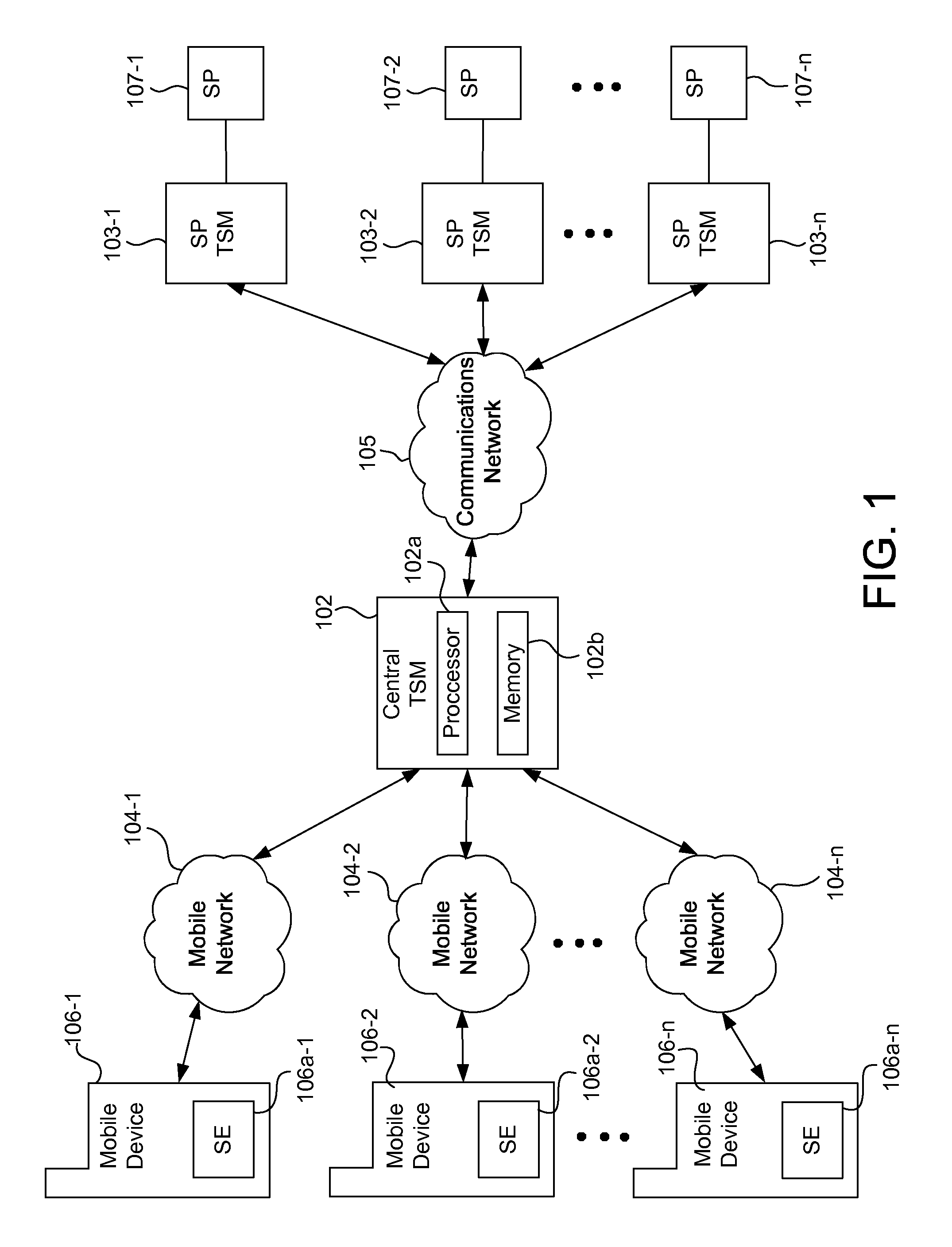
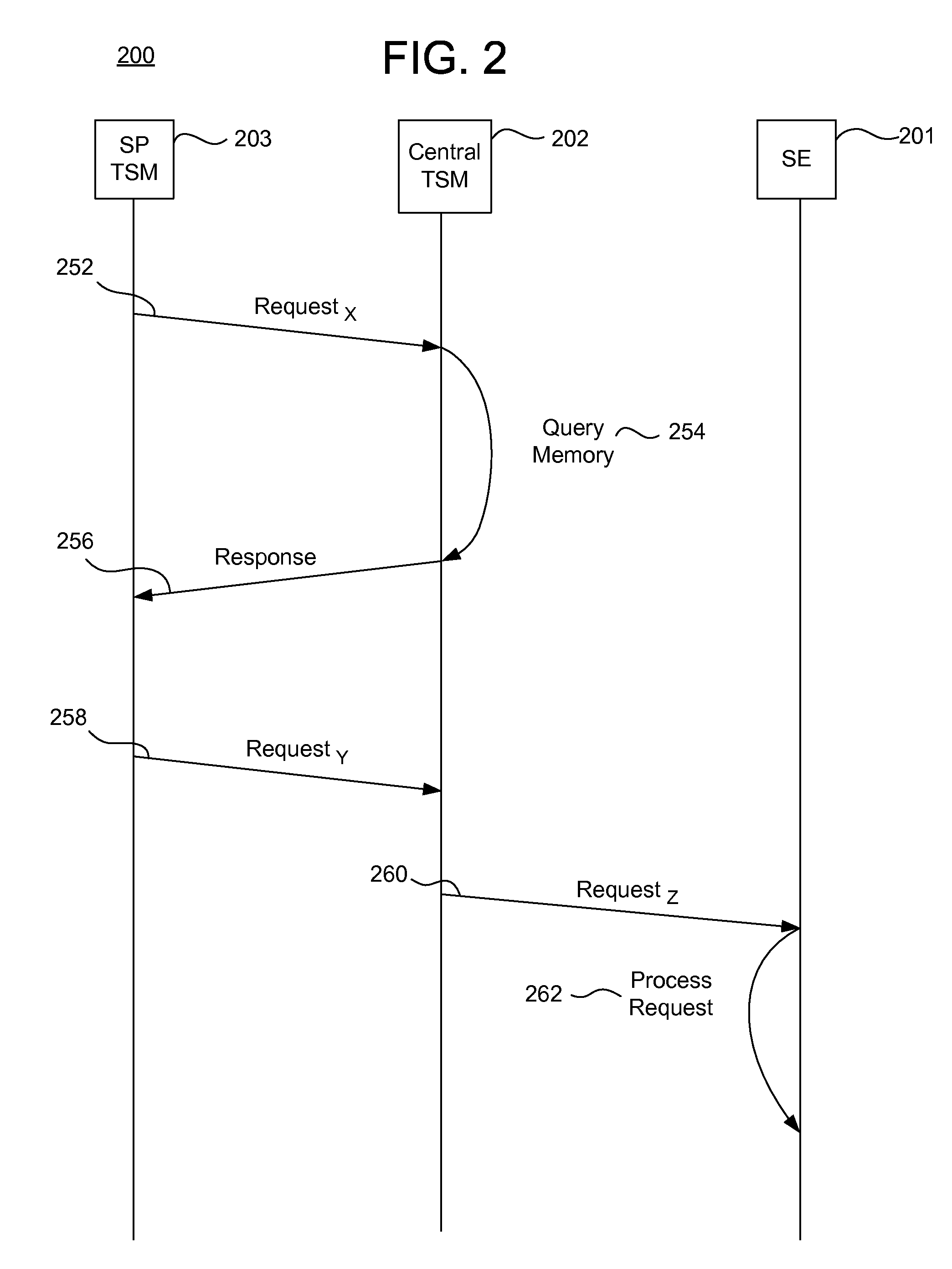
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interfacing multiple service provider trusted service managers and secure elements
ActiveUS20130111599A1Easily and securely communicateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer networkTerm memory
System, methods, and computer program products are provided for interfacing between one of a plurality of service provider (SP) trusted service managers (TSM) and one of a plurality of secure elements (SE). A first request including a mobile subscription identifier (MSI) is received from an SP TSM over a communications network. At least one memory is queried for SE data including an SE identifier corresponding to the MSI. The SE data is transmitted to the SP TSM over the communications network. A second request based on the SE data is received from the SP TSM over the communications network. A third request, based on the second request, is transmitted, over a mobile network, to an SE corresponding to the SE data. The mobile network is selected from multiple mobile networks, and is determined based on the SE data queried from the memory.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
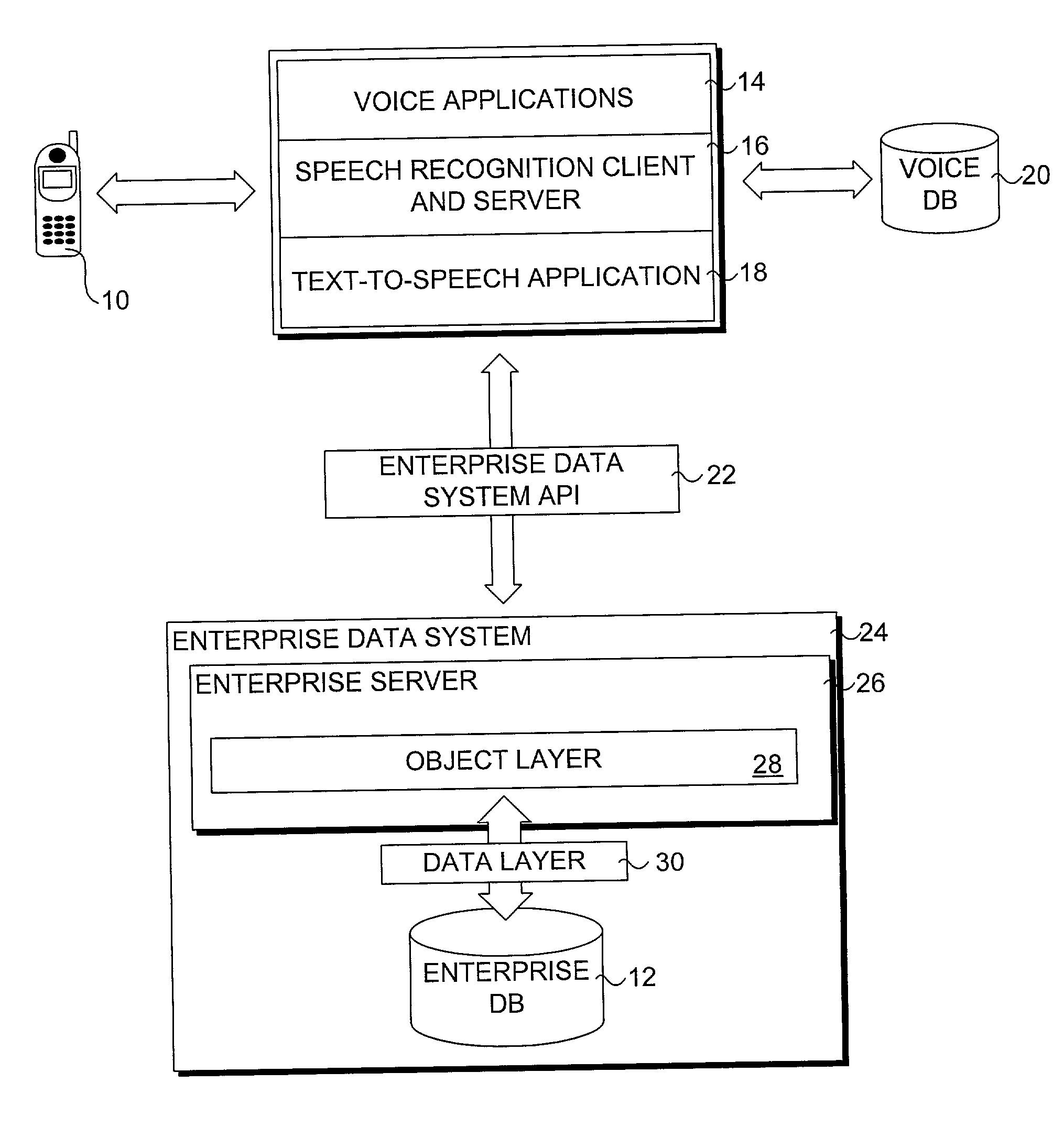
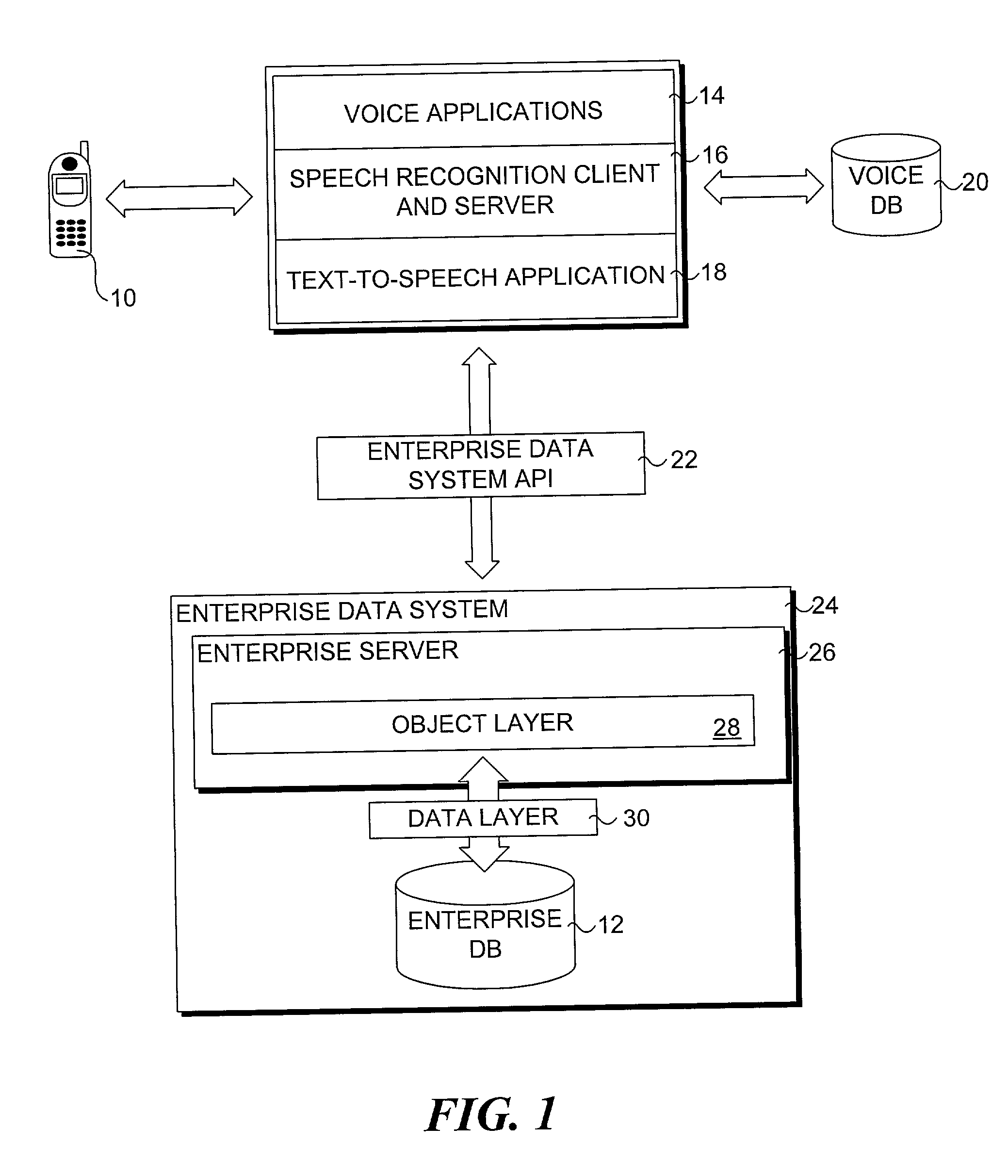
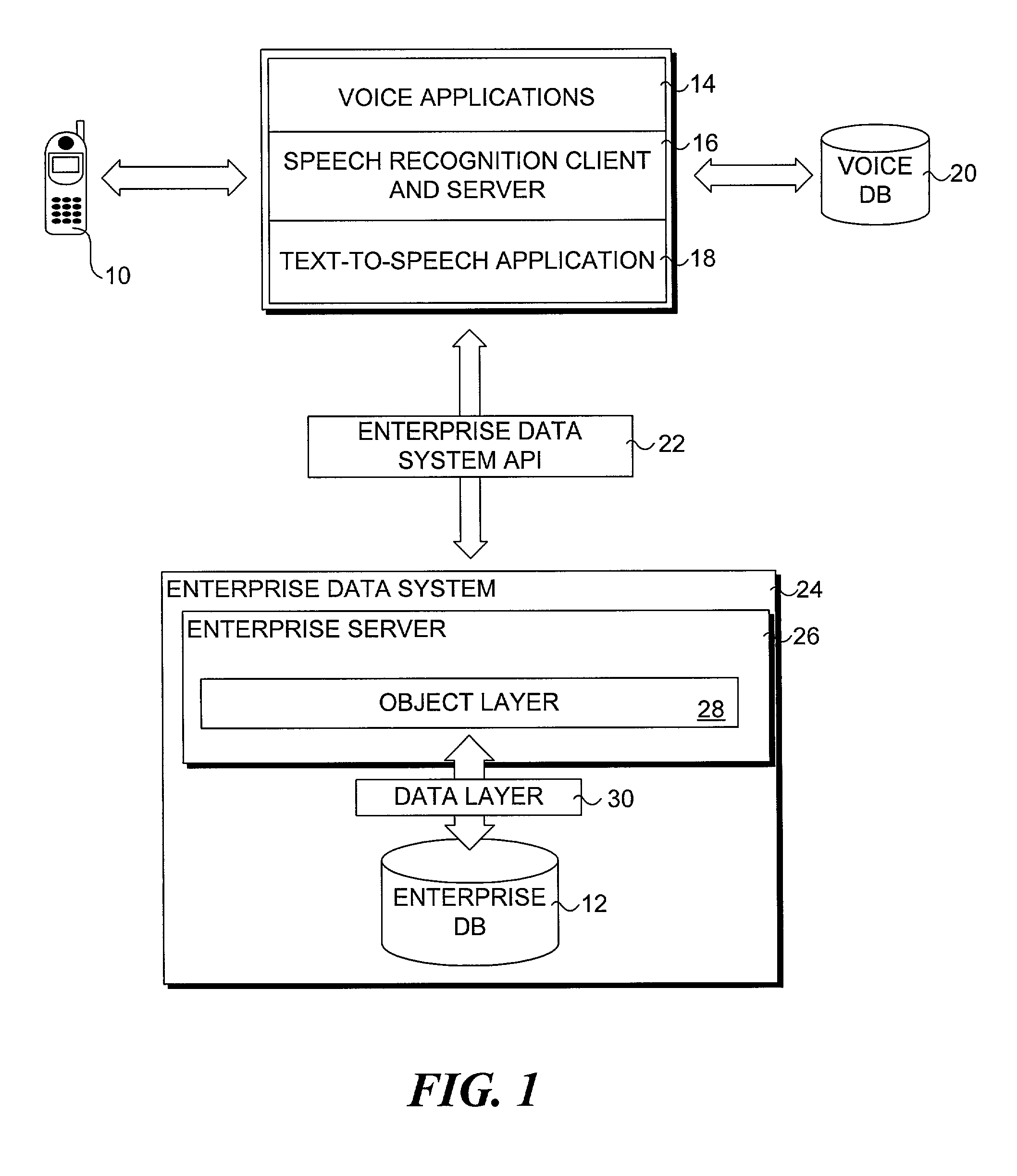
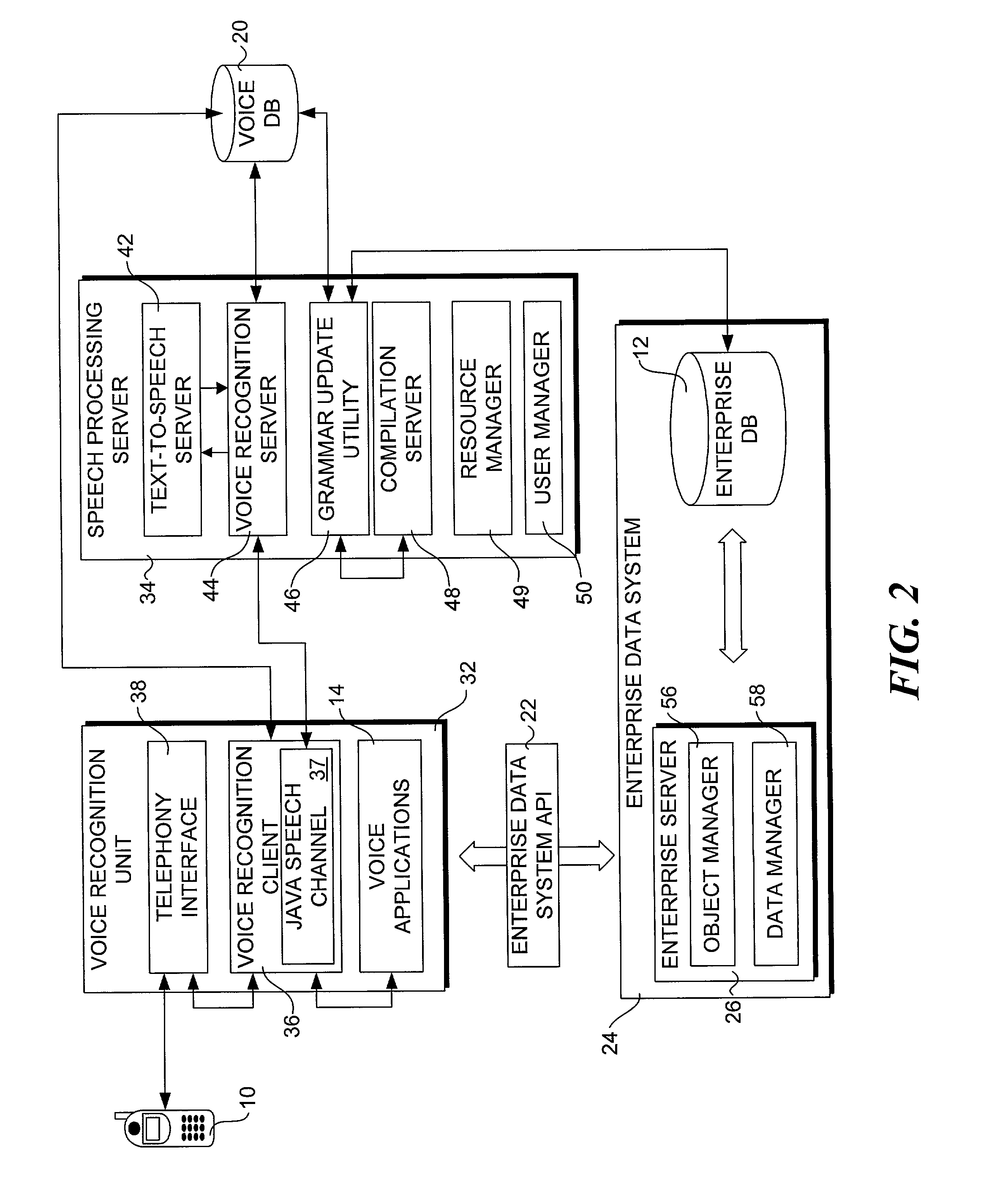
Method for accessing data via voice
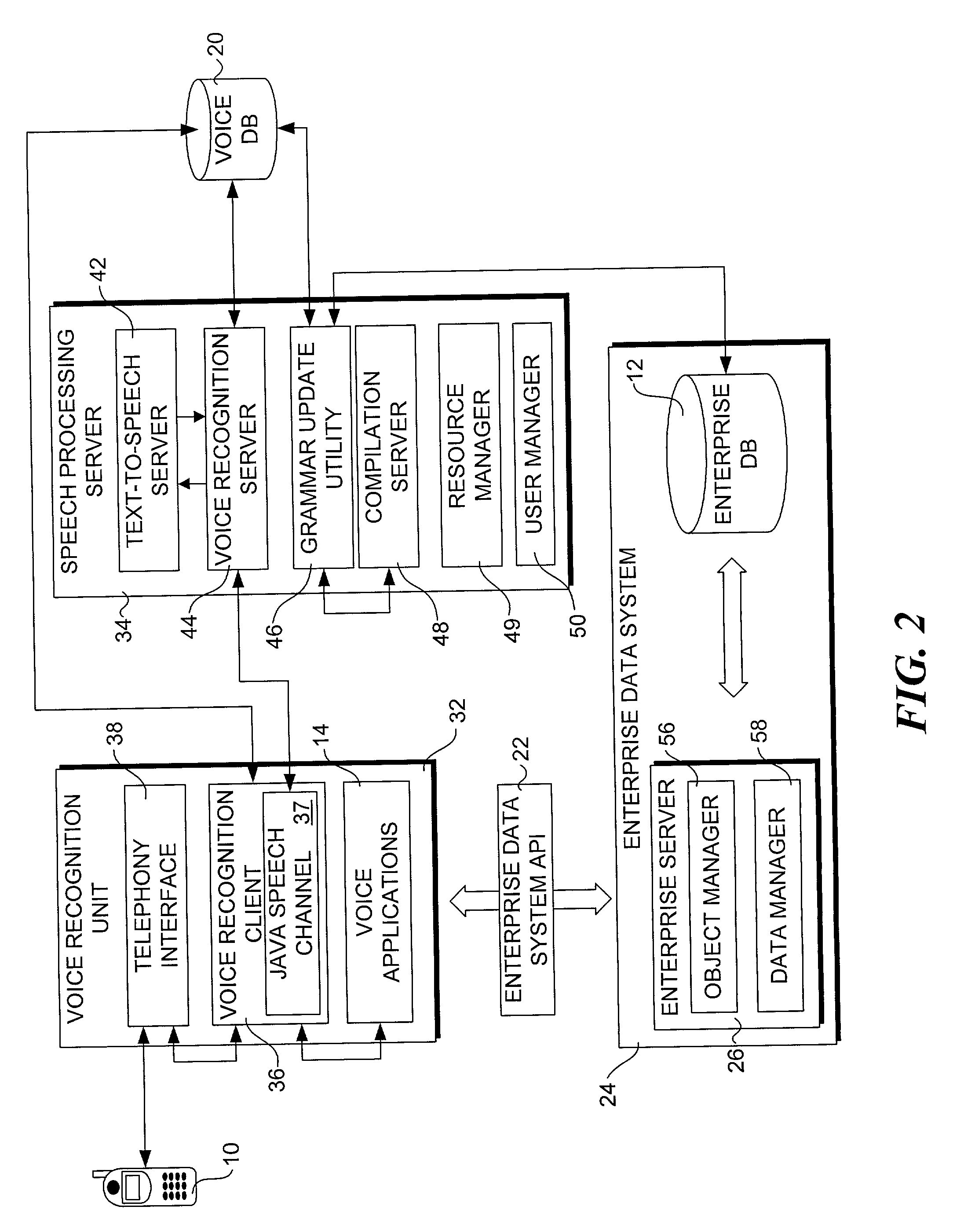
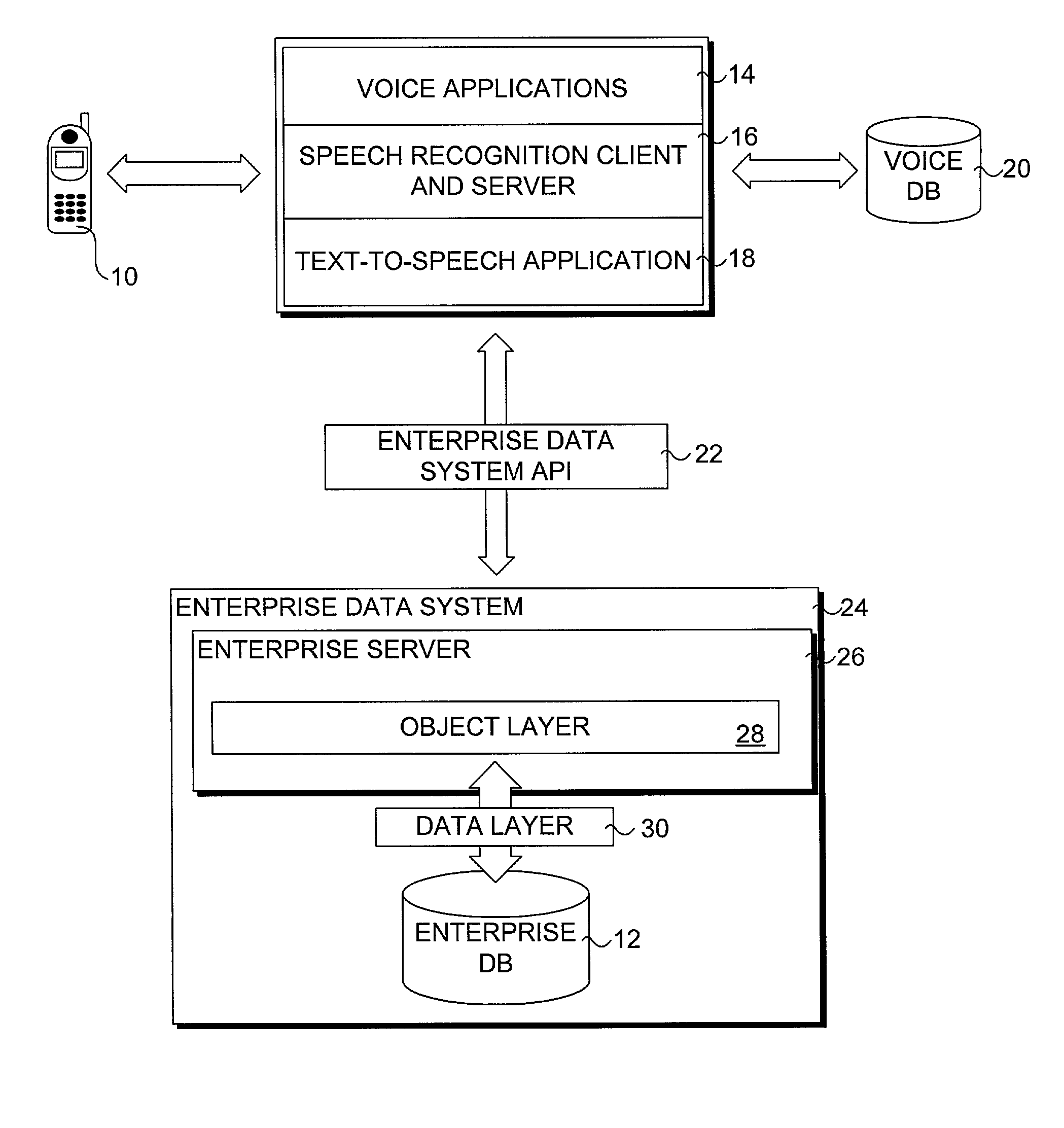
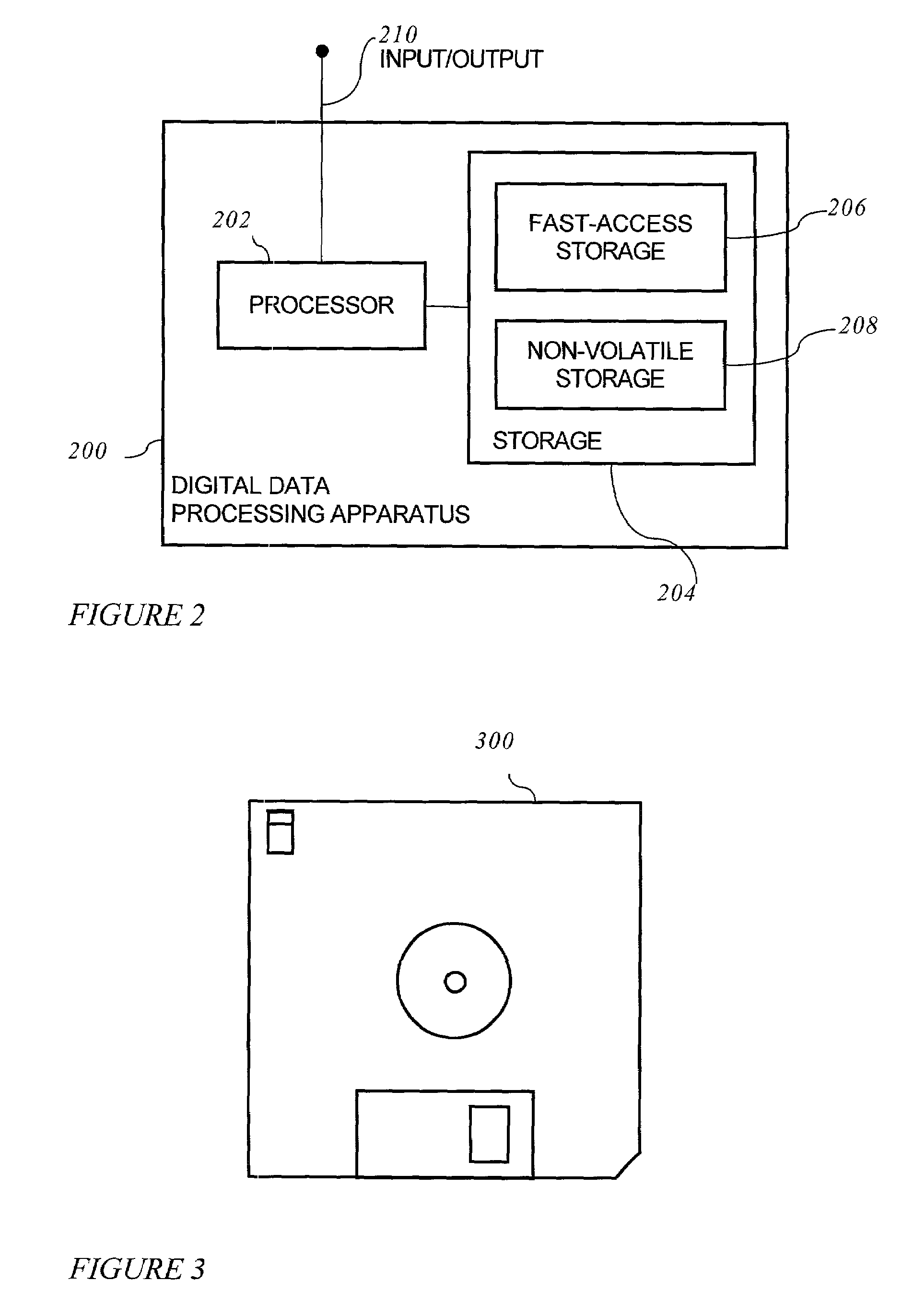
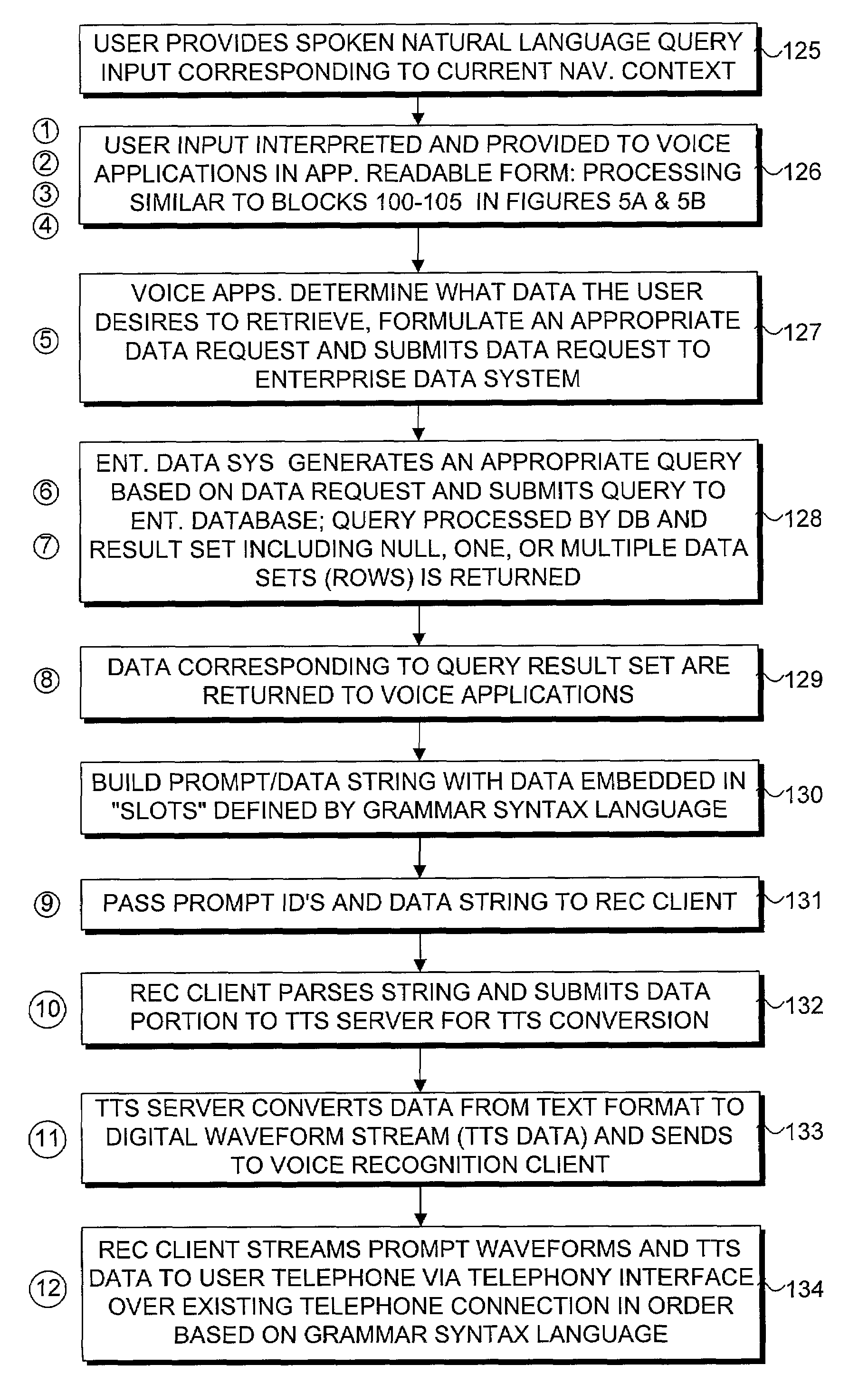
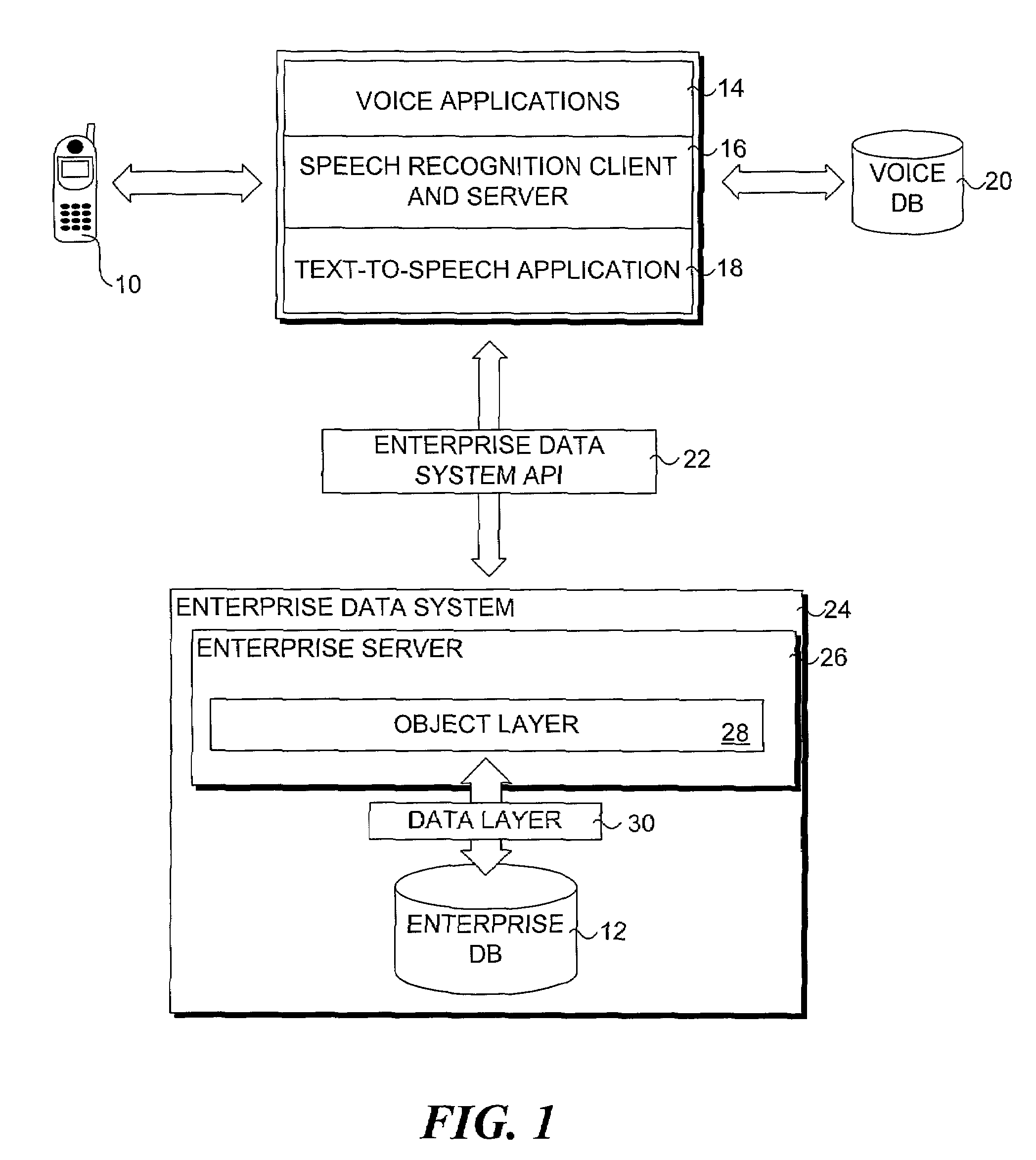
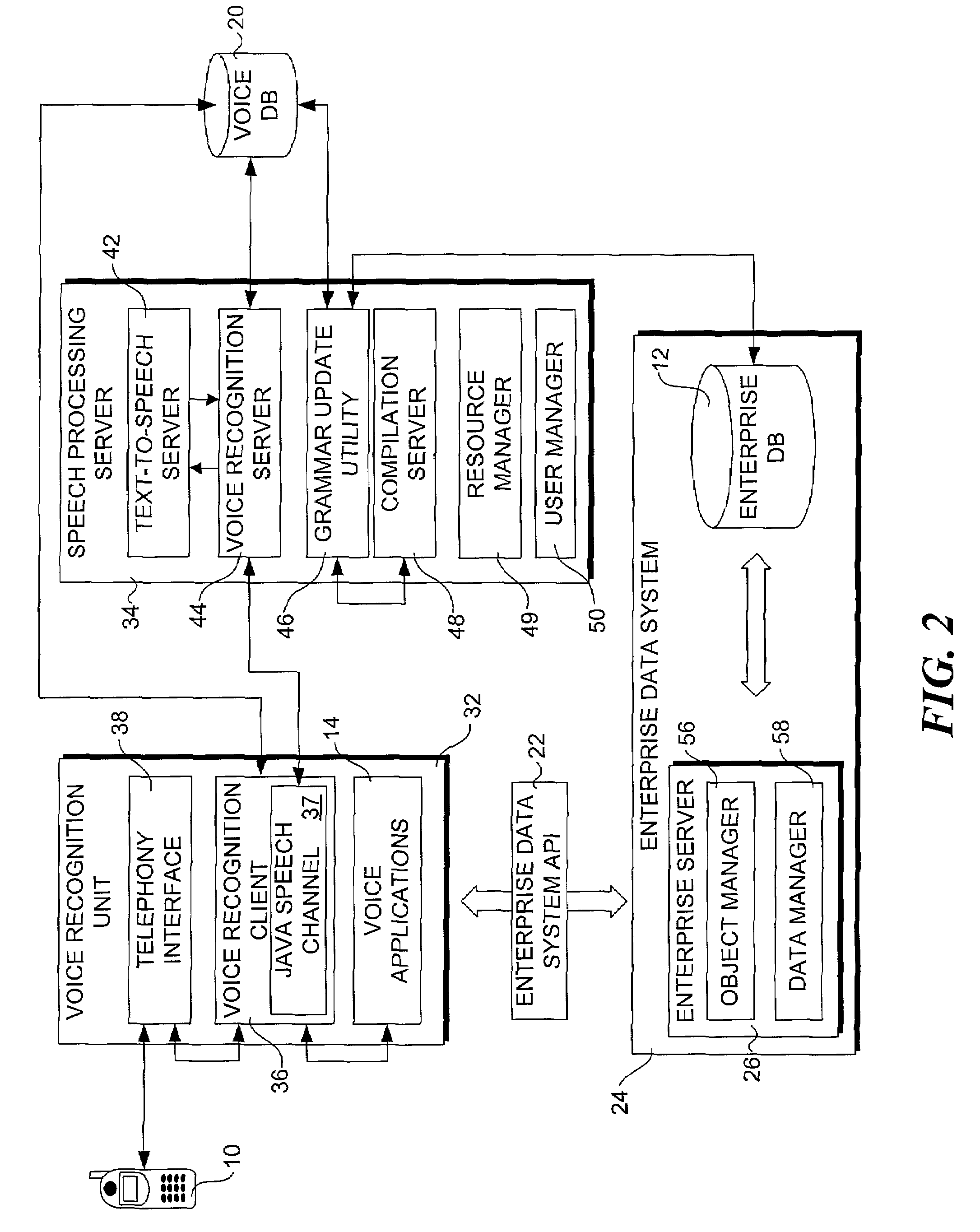
InactiveUS20070198267A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingData setSystem usage
A method for providing access to data via a voice interface. In one embodiment, the system includes a voice recognition unit and a speech processing server that work together to enable users to interact with the system using voice commands guided by navigation context sensitive voice prompts, and provide user-requested data in a verbalized format back to the users. Digitized voice waveform data are processed to determine the voice commands of the user. The system also uses a “grammar” that enables users to retrieve data using intuitive natural language speech queries. In response to such a query, a corresponding data query is generated by the system to retrieve one or more data sets corresponding to the query. The user is then enabled to browse the data that are returned through voice command navigation, wherein the system “reads” the data back to the user using text-to-speech (TTS) conversion and system prompts.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Weighted term ranking for on-line query tool
Disclosed is a system for performing online data queries. The system for performing online data queries is a distributed computer system with a plurality of server nodes each fully redundant and capable of processing a user query request. Each server node includes a data query cache and other caches that may be used in performing data queries. The data query, as well as request allocation, is performed in accordance with an adaptive partitioning technique with a bias towards an initial partitioning scheme. Generic objects are created and used to represent business listings upon which the user may perform queries. Various data processing and integration techniques are included which enhance data queries. An update technique is used for synchronizing data updates as needed in updating the plurality of server nodes. A multi-media data transfer technique is used to transfer non-text or multi-media data between various components of the online query tool. Optimizations for searching, such as the common term optimization, are included for those commonly performed data queries. Also disclosed is a system for targeting advertisements that are displayed to a user of the system.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for accessing data in disparate information sources
InactiveUS7668798B2Metadata text retrievalData processing applicationsRelevant informationData field
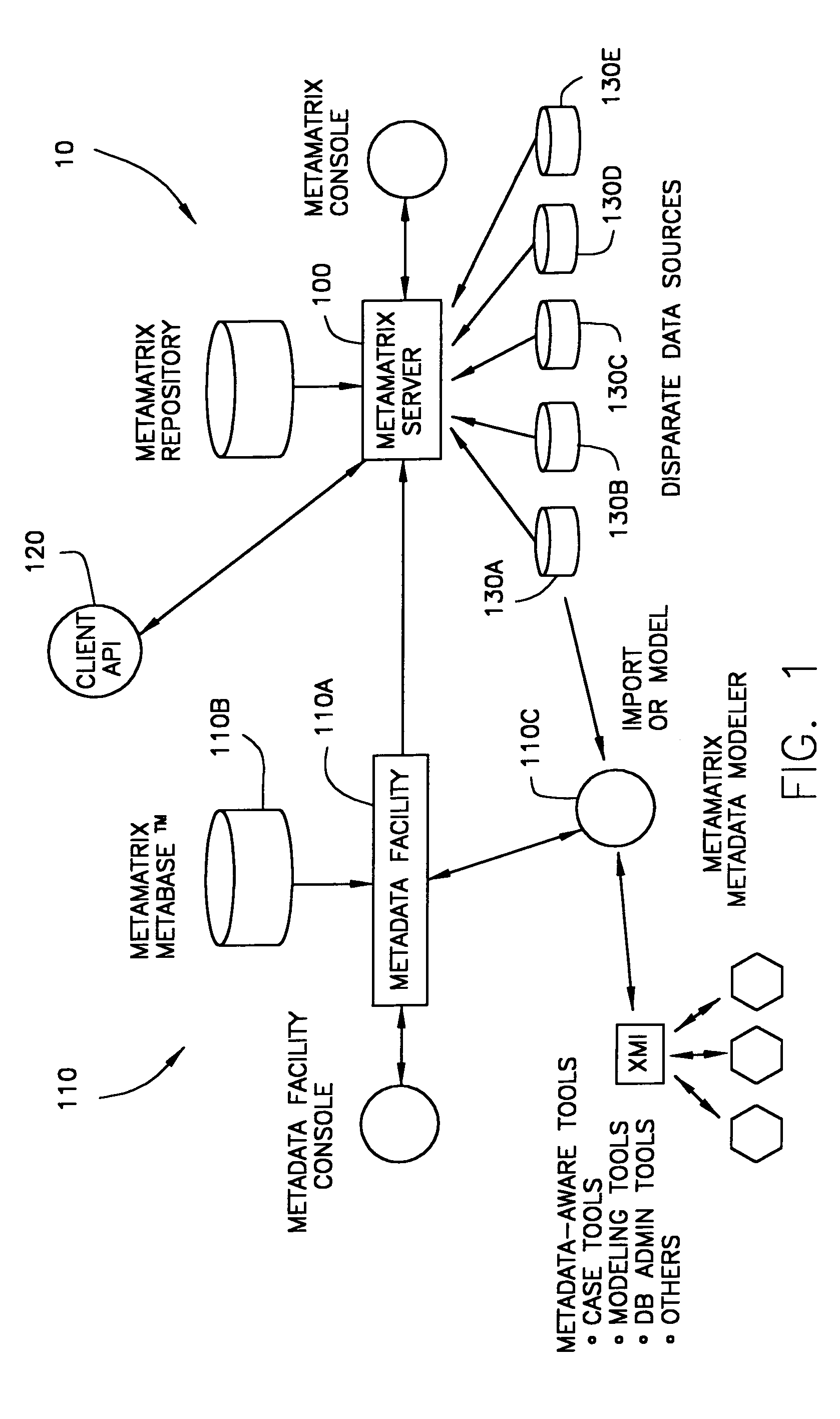
The present invention relates to a system (10) for generating and maintaining virtual and physical metadata layers in a MetaBase metadata repository (110b) in order to simplify and optimize the retrieval of data from a plurality of disparate information sources (130a-130c). The system stores in a physical metadata layer of a MetaBase metadata repository a plurality of physical metadata elements, wherein each one of the physical metadata elements corresponds to the metadata elements in the plurality of information sources. Logical metadata elements are stored in the virtual metadata layer and are linked to the physical metadata elements in order to maintain the relationships therebetween. By maintaining the relationships between the physical metadata elements, users can initiate a data query request for data corresponding to a logical metadata element, and the system is configurated to retrieve the desired data from the relevant information sources, even in the event that relevant information sources maintain the data in fields having different data field names, that the information sources employ incompatible data formats, and that the relevant information sources employ different query languages.
Owner:RED HAT
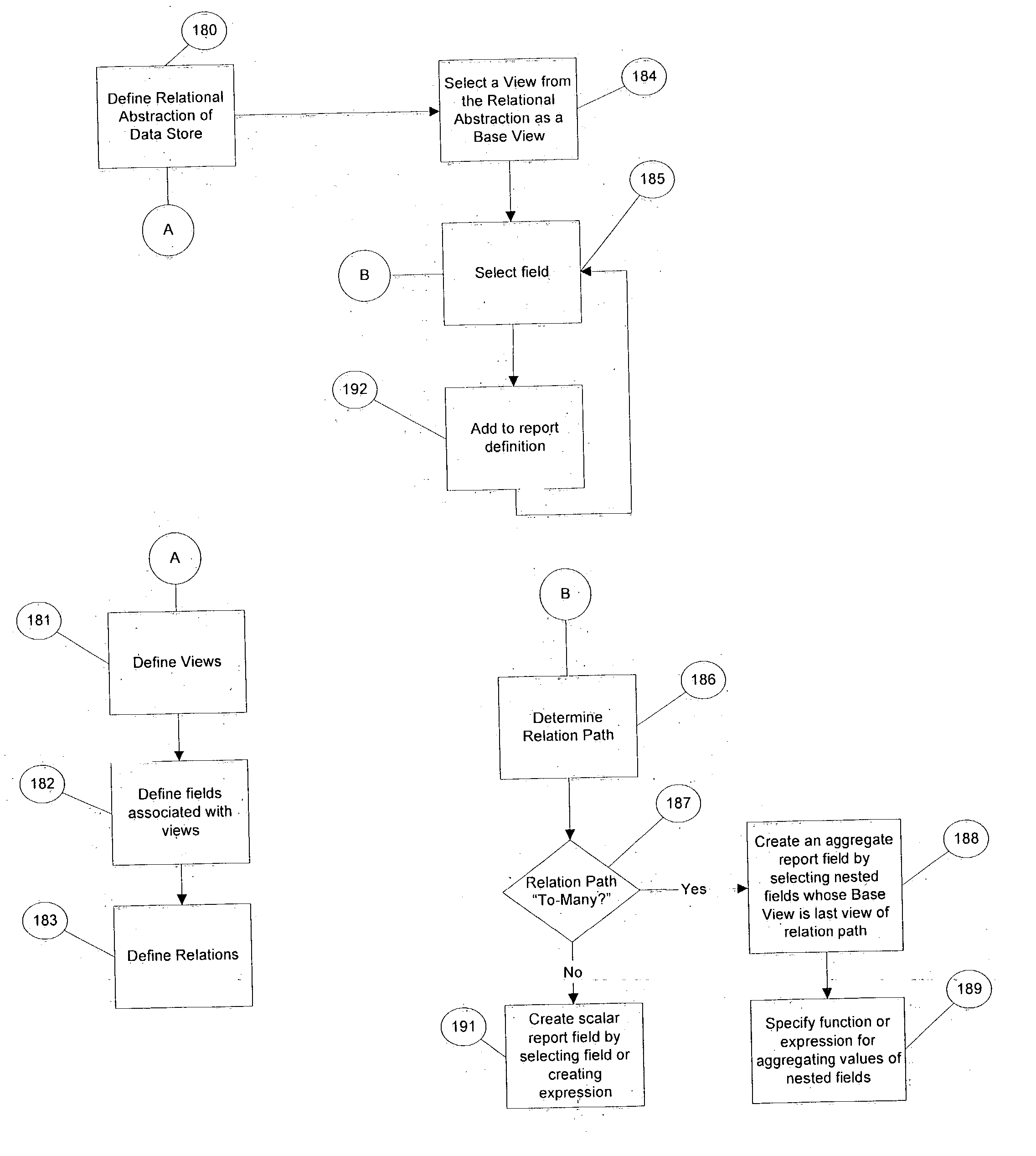
Method and system for building a report for execution against a data store
ActiveUS20050039033A1Minimizes learning curveQuickly and easily understandDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer usersData access
A data query and reporting method and system are provided. The method and system allow non-technical computer users to build and execute complex database queries. The method and system accommodate the need for a simple, easy-to-understand interactive and iterative means for generating and validating database queries. The method and system reduce the complexity and costs associated with retrieving useful information for organizations of all sizes, especially smaller businesses. The method and system support a robust security model, enabling organizations to protect sensitive data while providing broad data access.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
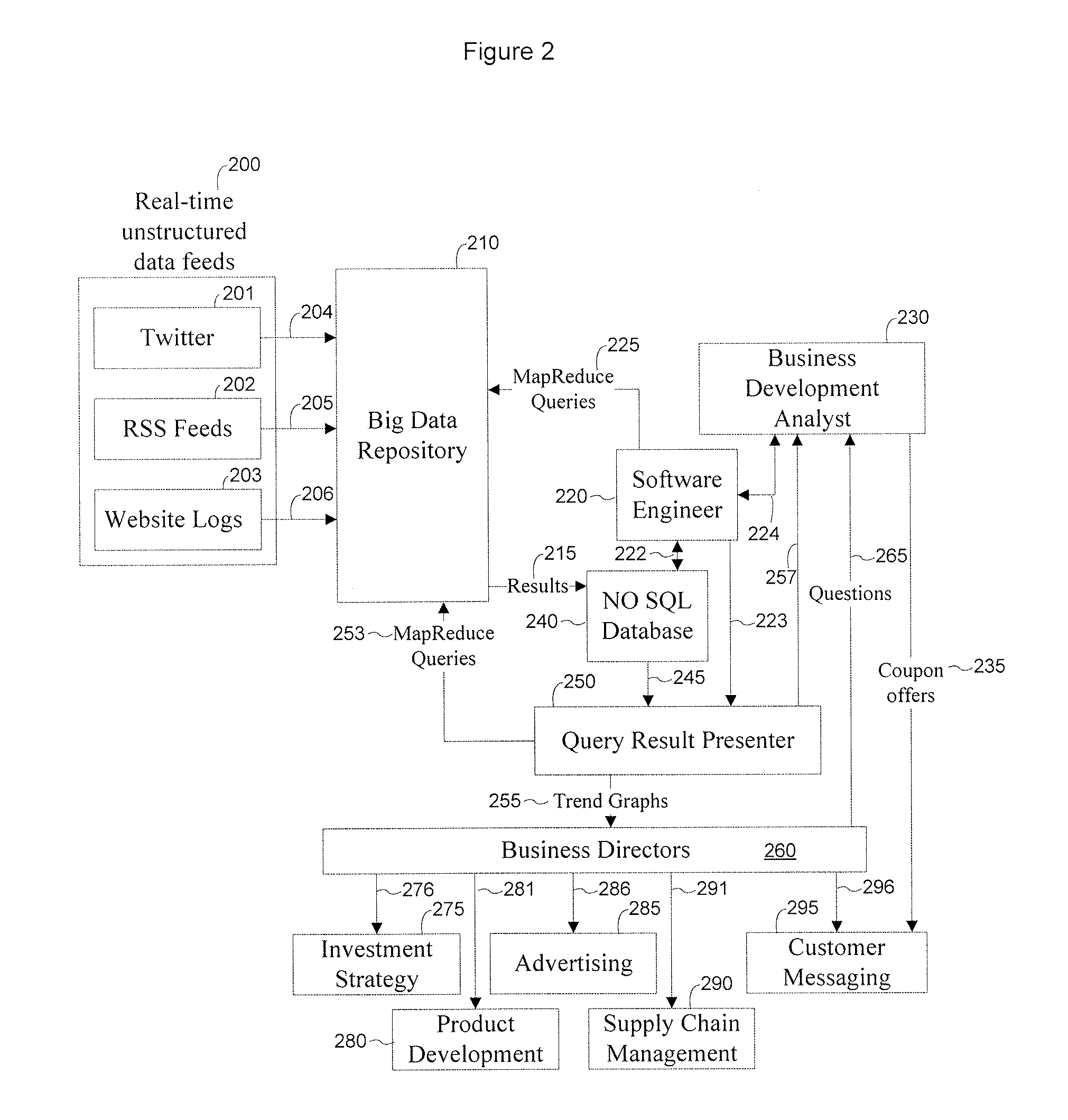
System and method for behavioural and contextual data analytics
ActiveUS20110264663A1Easy to customizeUseful for promotionDigital data processing detailsVisual data miningData packContext data
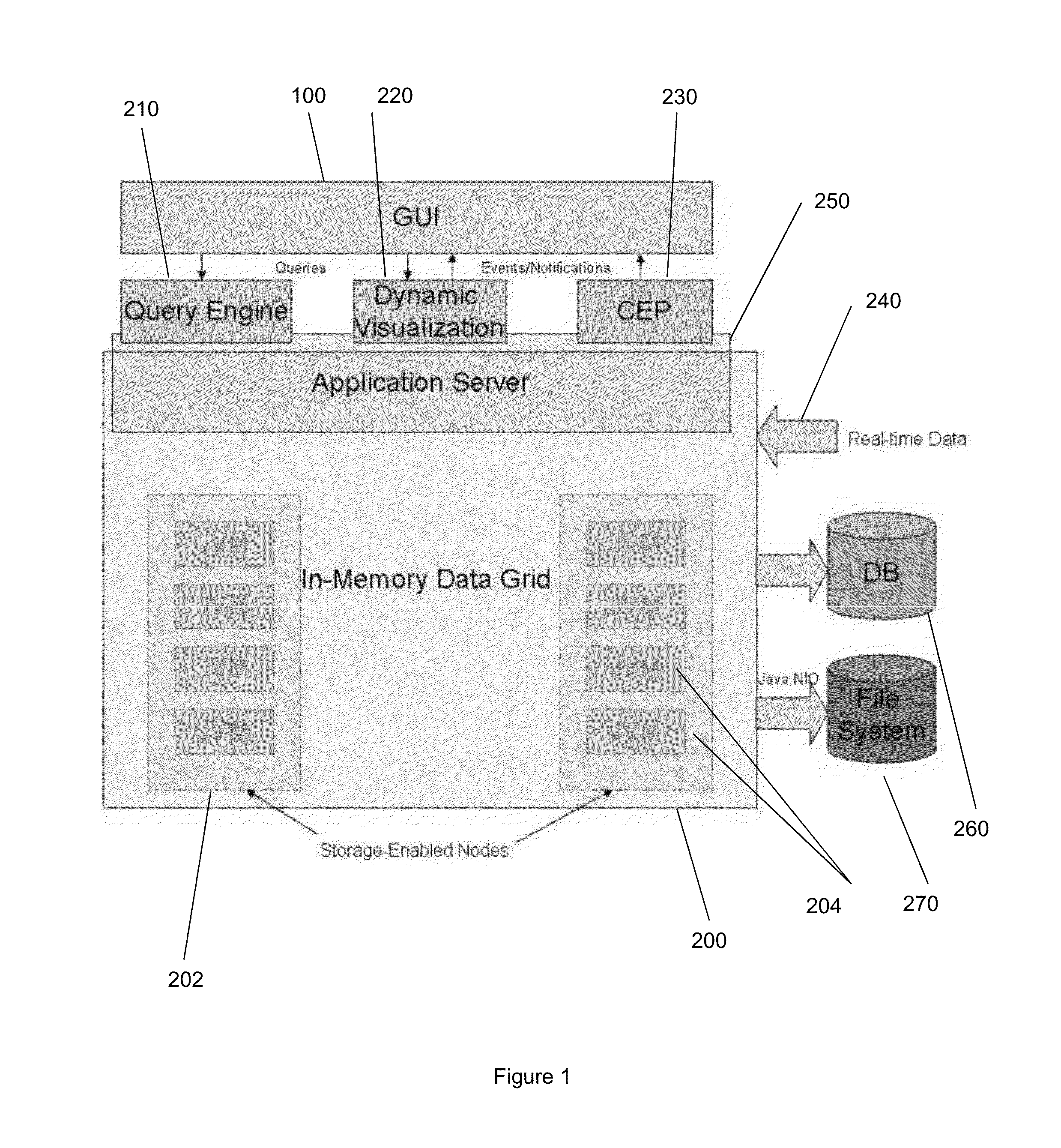
A server arrangement for managing observation data of wireless devices, including data input logic for obtaining observation data from wireless devices, the obtained data including behavioral and contextual raw data relative to the wireless devices, data mining logic for establishing a number of derived data elements, on the basis of processing and analyzing the obtained observation and optional supplementary data, the processing and analyzing incorporating aggregation procedures. At least one derived data element includes usage metrics with contextual dimension relative to applications or other features of wireless devices and users, data storage for storing the obtained data and the number of derived information elements, and a data distribution logic providing derived data. The distribution logic may serve a data query constructed by an external entity through provision of derived information from derived data elements according to the query parameters. A corresponding method for execution by the server arrangement is presented.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC
Block chain-based credit investigation data sharing and trading system
InactiveCN106651346APerfect risk control levelSolve imperfectionsPayment protocolsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsRisk ControlData provider
The invention relates to a block chain-based credit investigation data sharing and trading system. The credit investigation data sharing and trading system comprises at least two P2P network nodes; each network node comprises an underlying block chain system and a credit investigation data sharing platform running in the underlying block chain system; and the credit investigation data sharing platform comprises a data sharing module, a data query trading module, a member management module and a block chain adaption layer. According to the credit investigation data sharing and trading system, a trusted credit investigation data sharing and trading platform is established by using a block chain technology; and special data sharing mechanism, data query mechanism and data trading mechanism are used, so that credit investigation data owners and credit investigation data demanders can be attracted to perform use, credit investigation data providers can perform data trading under the condition that data is protected, and credit investigation data queriers can obtain the credit investigation data to improve risk control levels of themselves.
Owner:上海凯岸信息科技有限公司
Apparatus and method for producing video drive-by data corresponding to a geographic location
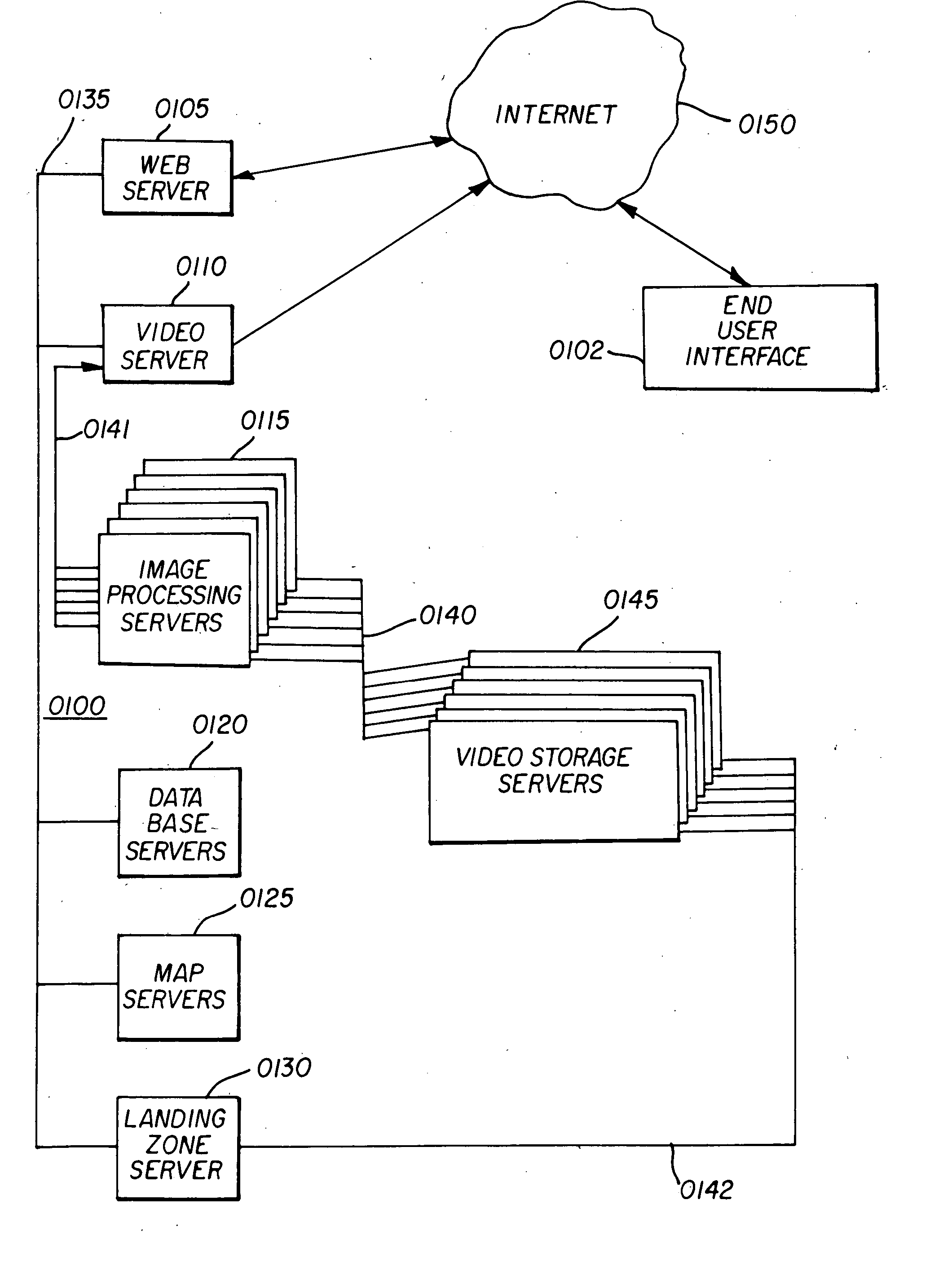
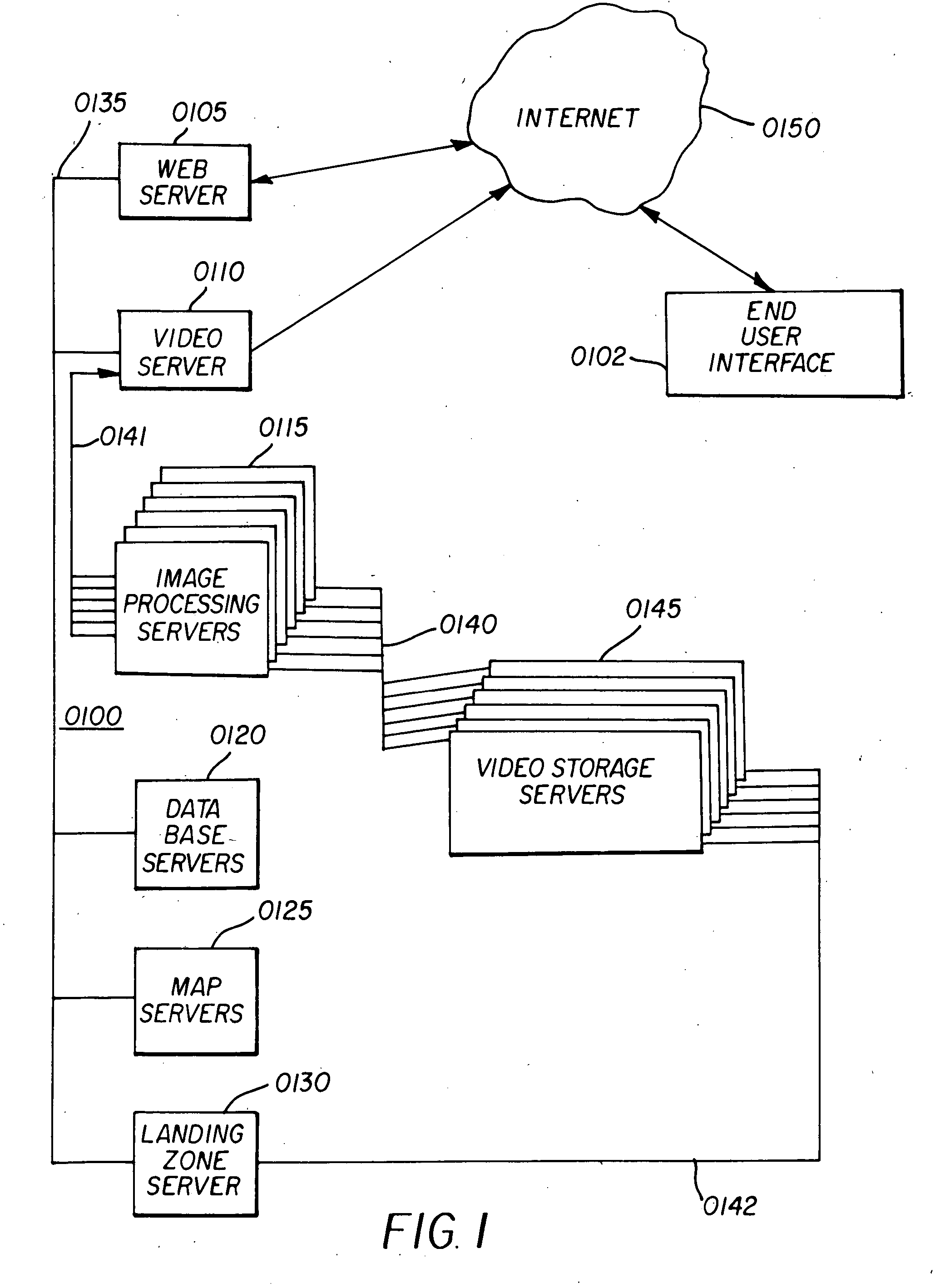
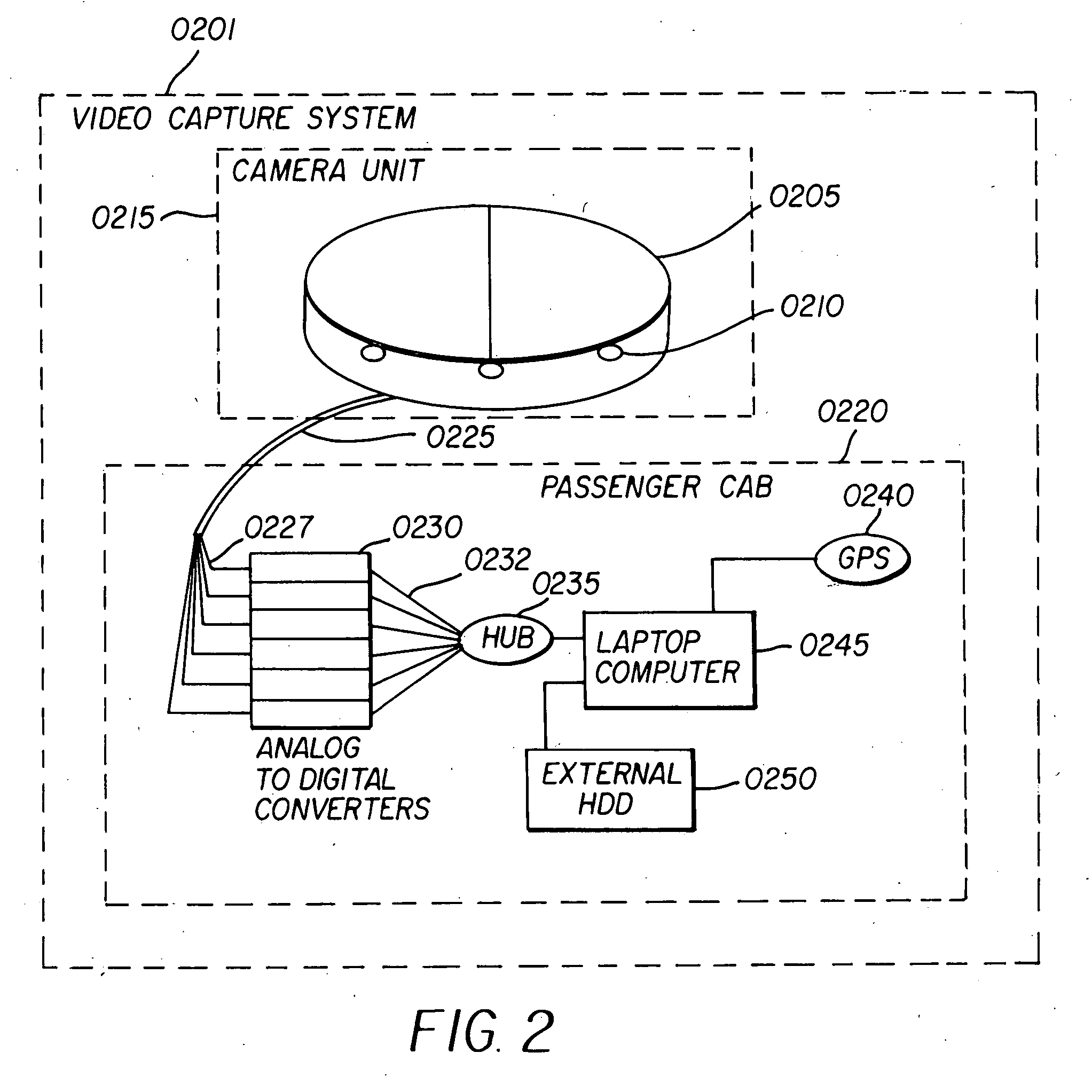
InactiveUS20060075442A1Low costImprove efficiencyMetadata video data retrievalNavigation instrumentsVideo storageImaging processing
A system and method of providing video drive-by data is provided to enable a street level view of a neighborhood surrounding a selected geographic location. The system includes a video and data server farm incorporation at least one video storage server that stores video image files containing video drive-by data that corresponds to a geographic location, a database server that processes a data query received from a user over the Internet that corresponds to a geographic location of interest, and an image processing server. In operation, the database server identifies video image files stored in the video storage server that correspond to the geographic location of interest contained in the data query, and transfers the video image files over a pre-processing network to the image processing server. The image processing server converts the video drive-by data to post processed video data corresponding to a desired image format, and transfers the post processed video data via post-processing network to the Internet response to the query.
Owner:VISUAL REAL ESTATE +2
Method and system for processing data queries
ActiveUS20130262443A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGranularityContinuous flow
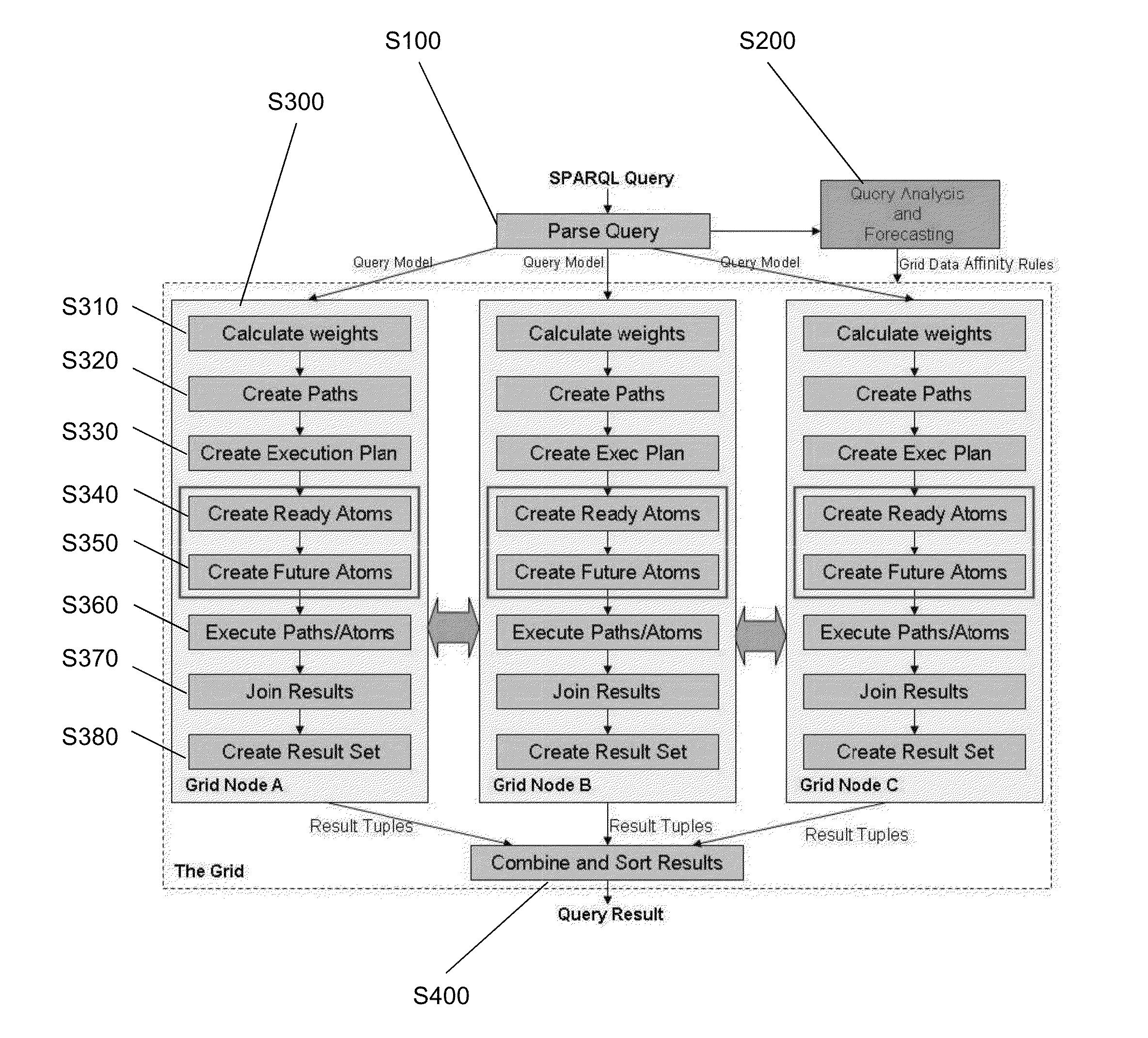
The invention relates to a method and system that provide a high performance and extremely scalable triple store within the Resource Description Framework (or alternative data models), with optimized query execution. An embodiment of the invention provides a data storage and analysis system to support scalable monitoring and analysis of business processes along multiple configurable perspectives and levels of granularity. This embodiment analyses data from processes that have been already executed and from ongoing processes, as a continuous flow of information. This embodiment provides defining and monitoring processes based on no initial domain knowledge about the process and such that the process will be built only from the incoming flow of information. Another embodiment of the invention provides a grid infrastructure that allows storage of data across many grid nodes and distribution of the workload, avoiding the bottleneck represented by constantly querying a database.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
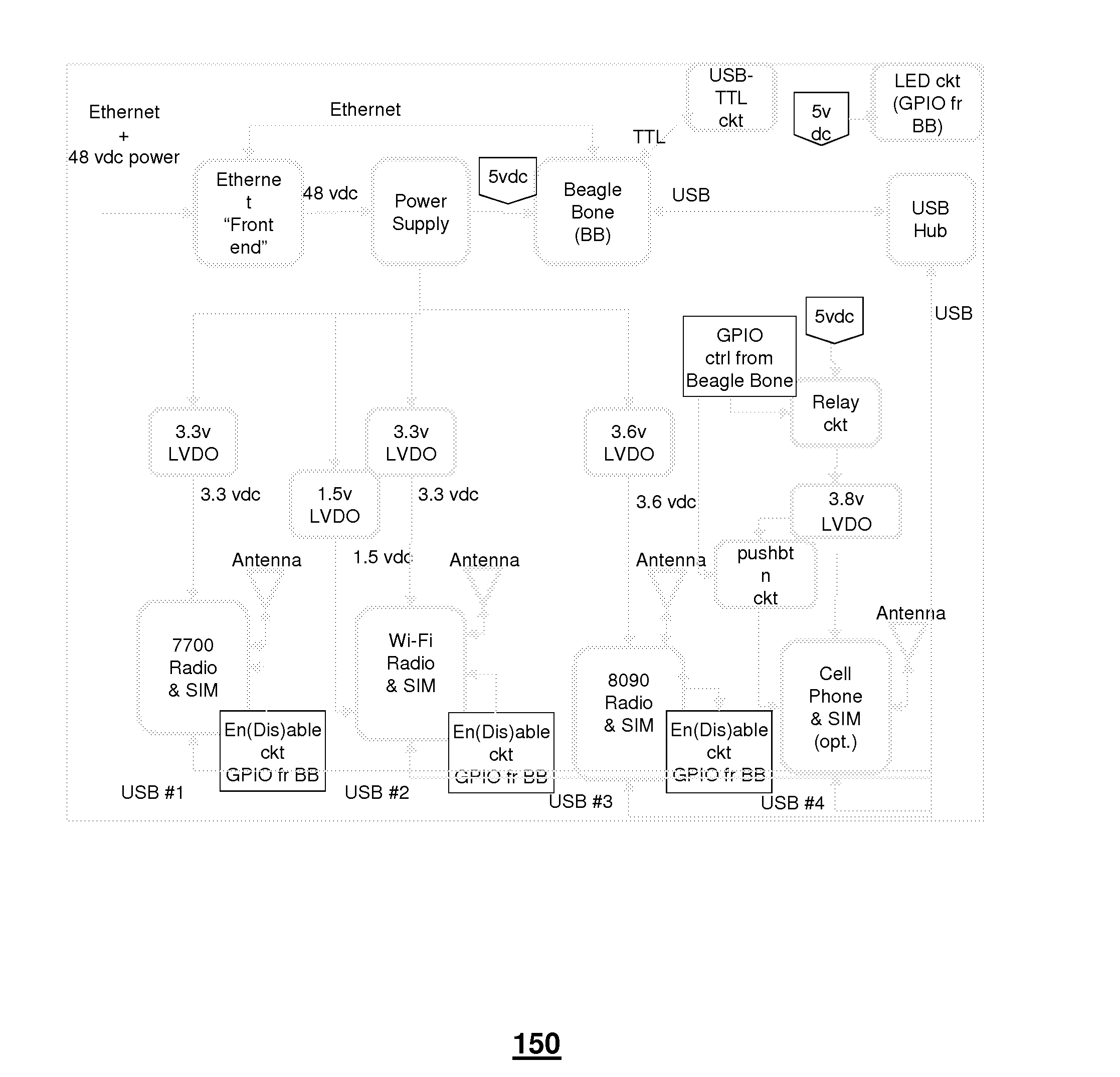
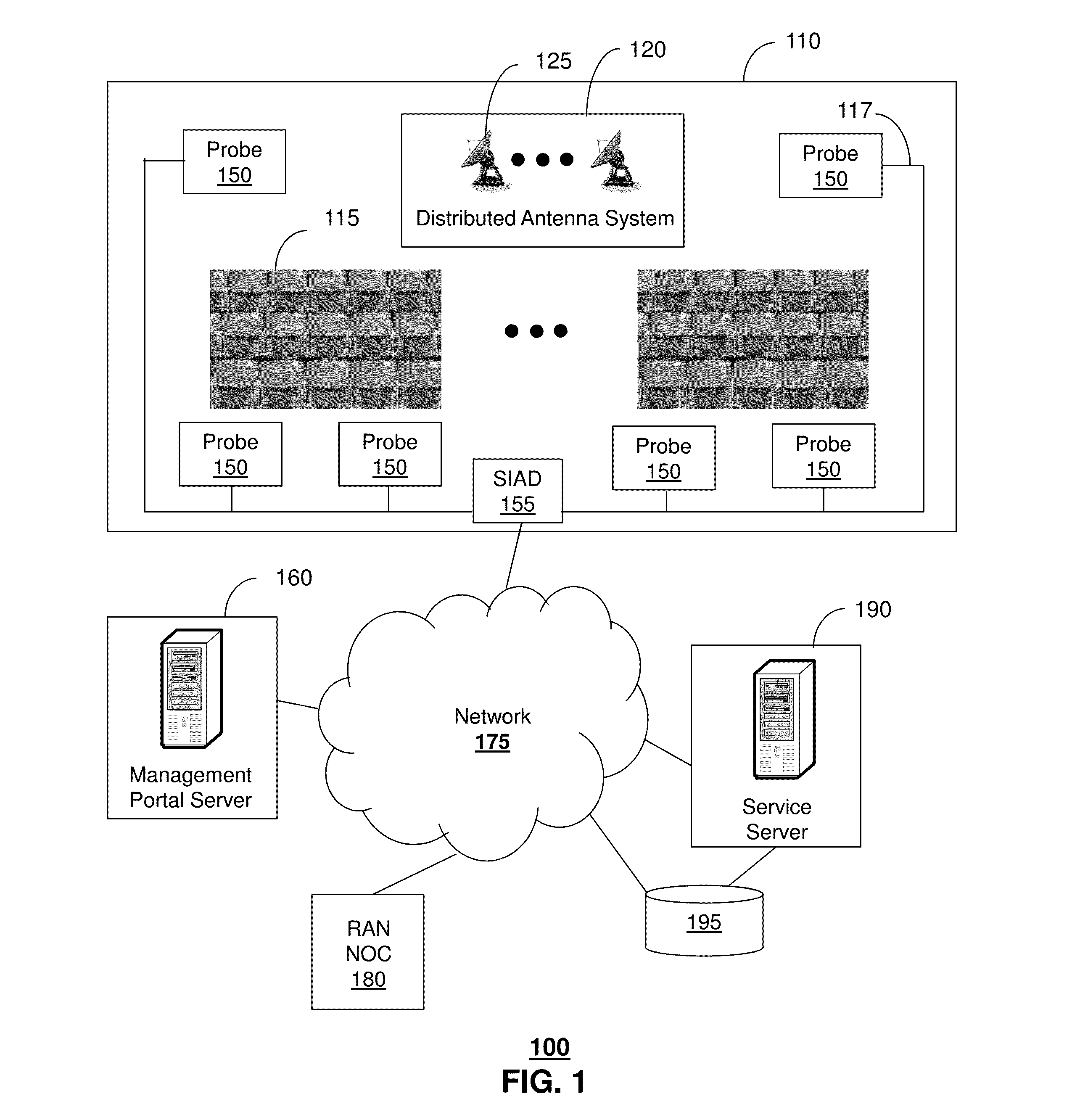
Method and apparatus for managing wireless probe devices
Aspects of the subject disclosure may include, for example, providing testing criteria to a probe device located at a venue enabling the probe device to perform testing of first communication services via a first wireless access technology utilizing a distributed antenna system of the venue and testing of second communication services via a second wireless access technology utilizing the distributed antenna system according to the testing criteria, and receiving performance data from a database server responsive to the data query, where the performance data is representative of test results generated from the testing of the first and second communication services by the probe device. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
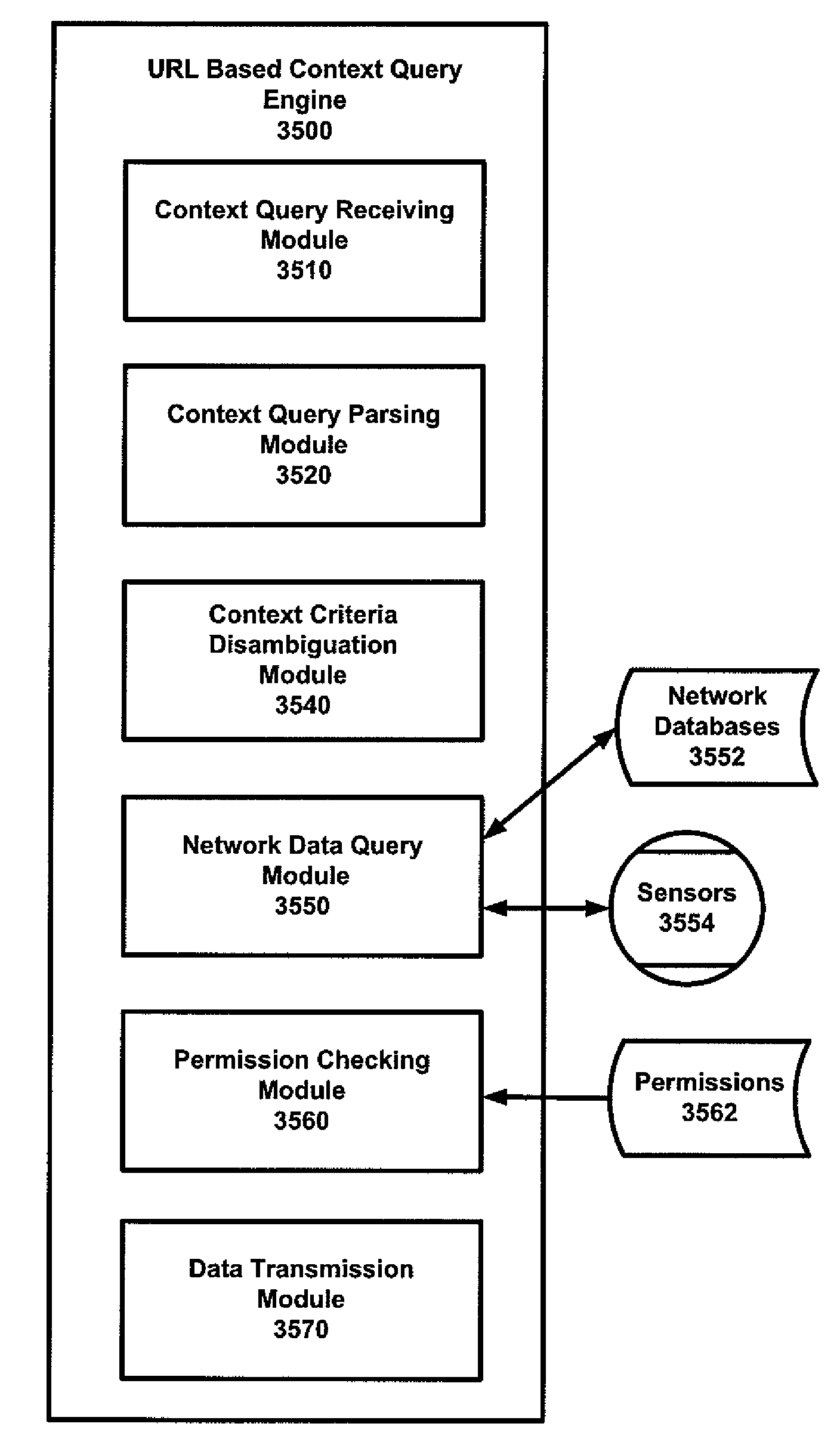
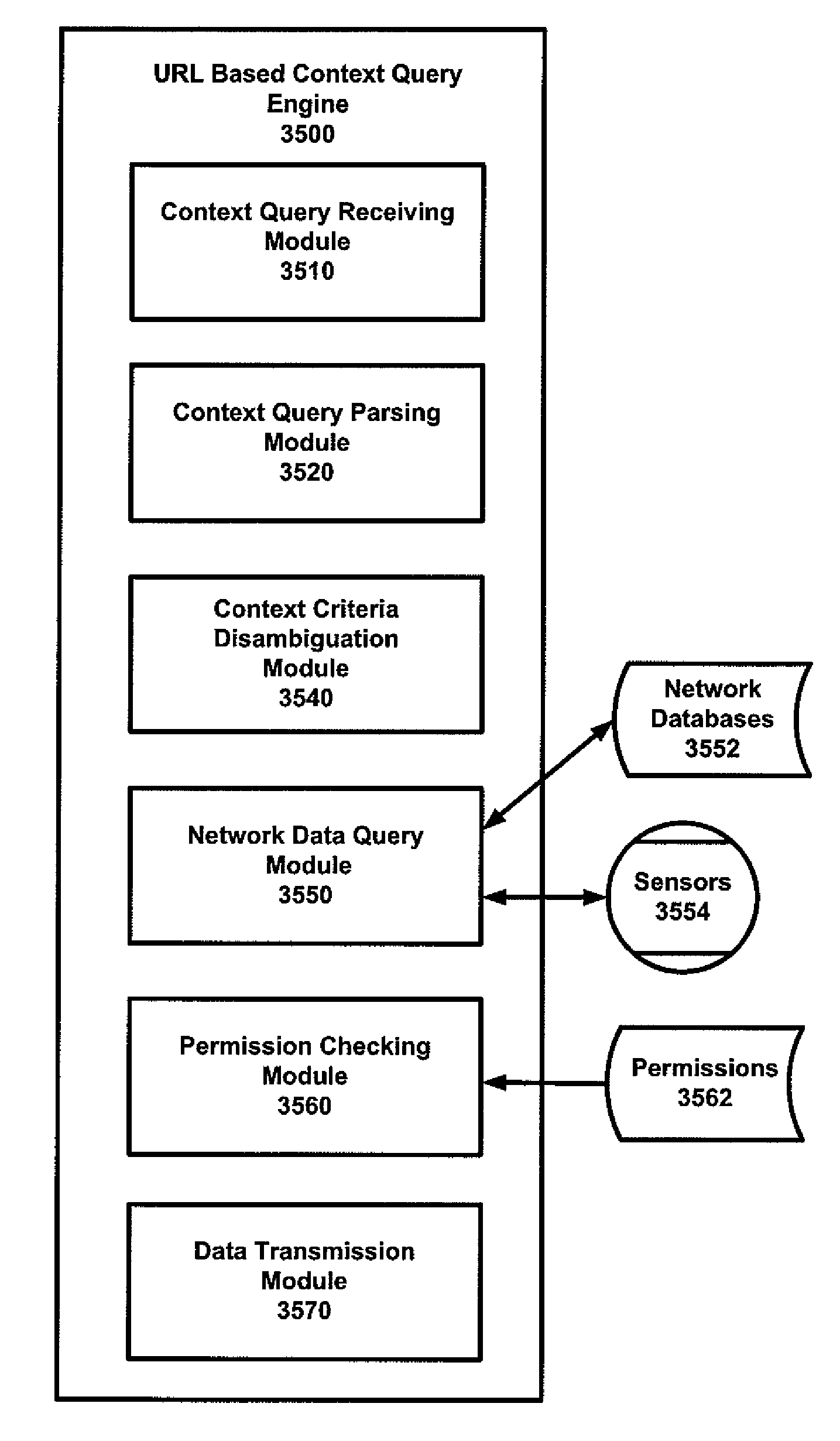
System and method for URL based query for retrieving data related to a context
ActiveUS20100125604A1Sufficient informationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContext basedNetwork data
A system and method for URL based query for retrieving data related to a context. A request is received over a network from a user for data related to a context, wherein the request is a URL comprising a context query comprising at least one context criteria. The context criteria are parsed and translated and disambiguated. A network data query is formulated based on the context criteria so as to search, via the network, for user profile data, social network data, spatial data, temporal data and topical data that is available via the network and relates to the context query so as to identify at least one data object that relates to context criteria. Permissions relating to the identified data objects are checked and references to the data objects are transmitted over the network to the user.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Computer-related method, system, and program product for controlling data visualization in external dimension(s)
InactiveUS6480194B1Change can be observedSimple equipmentDrawing from basic elementsDigital data information retrievalData queryHuman–computer interaction
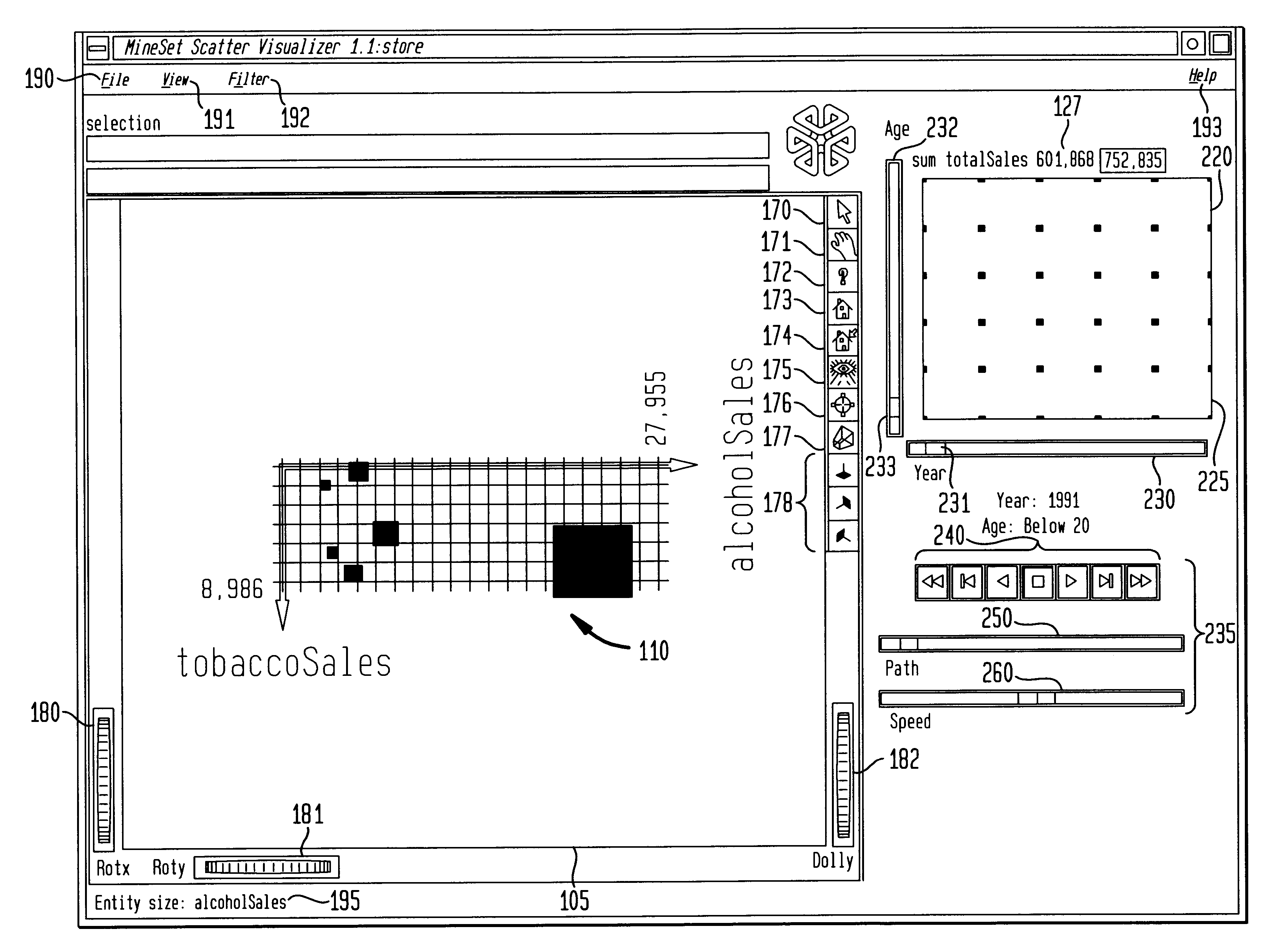
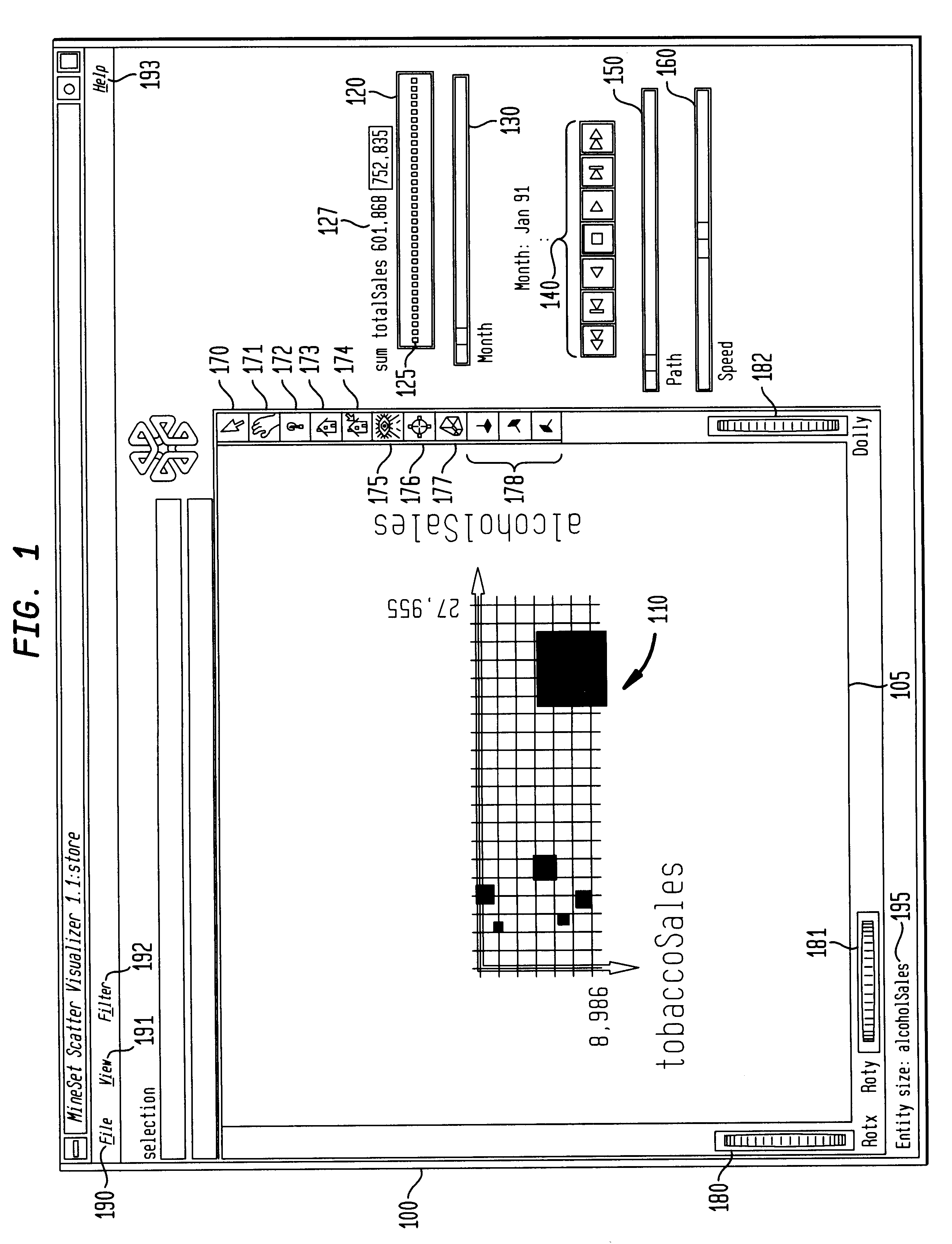
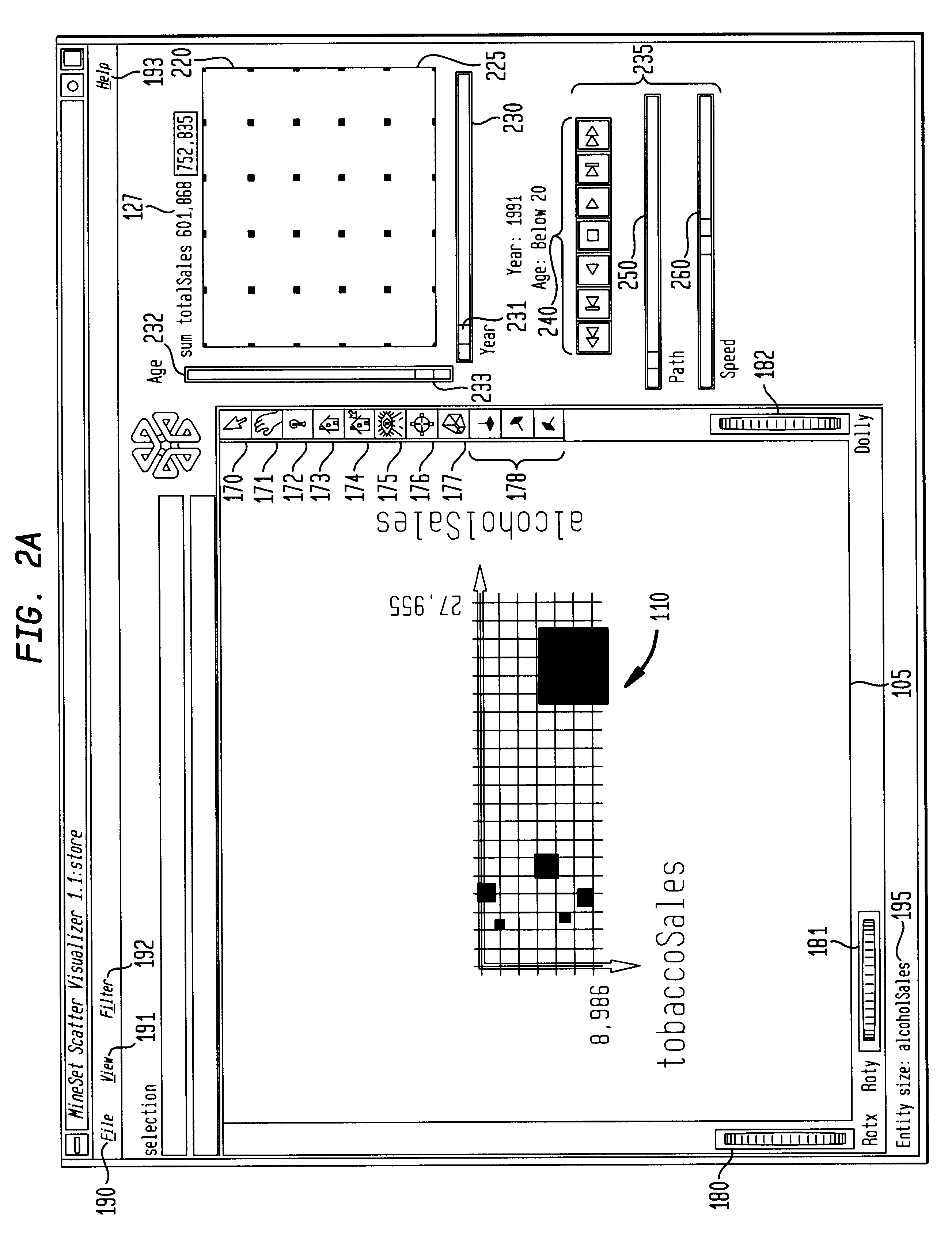
A computer graphics display method and system for controlling data visualization in at least one external dimension is provided which allows better querying and navigation of data in external dimension space. A data visualization is displayed in a first display window. A summary window provides summary information on data for the data visualization across one or more external dimensions. First and second controllers are displayed for controlling the variation of the data visualization in respective first and second external dimensions. A user queries the data visualization in the first and second external dimensions by selecting a point in the summary window. A user navigates through the data visualization in the first and second external dimensions by defining a path in the summary window. Grid points are also displayed in the summary window to facilitate data queries and navigation based on actual data points. The first and second controllers can be first and second sliders, such as, slide buttons, dials, or any other type of input. An animation control panel, including tape-drive controls, a path control, and a speed control, controls an animation of the data visualization over a selected navigation path through external dimension space.
Owner:RPX CORP
System for accessing data via voice
ActiveUS7194069B1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersData setData query
A system for providing access to data via a voice interface. In one embodiment, the system includes a voice recognition unit and a speech processing server that work together to enable users to interact with the system using voice commands guided by navigation context sensitive voice prompts, and provide user-requested data in a verbalized format back to the users. Digitized voice waveform data are processed to determine the voice commands of the user. The system also uses a “grammar” that enables users to retrieve data using intuitive natural language speech queries. In response to such a query, a corresponding data query is generated by the system to retrieve one or more data sets corresponding to the query. The user is then enabled to browse the data that are returned through voice command navigation, wherein the system “reads” the data back to the user using text-to-speech (TTS) conversion and system prompts.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
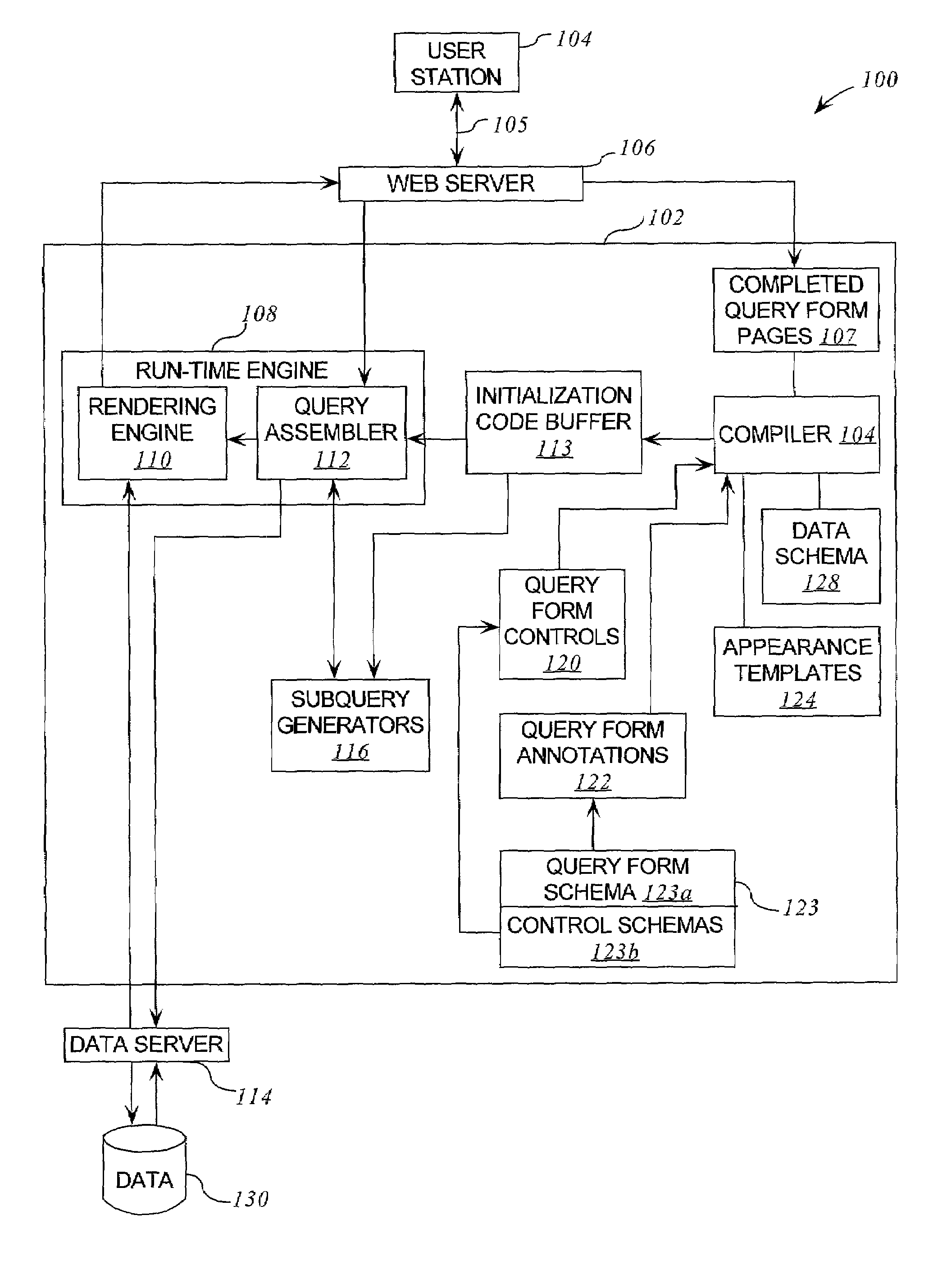
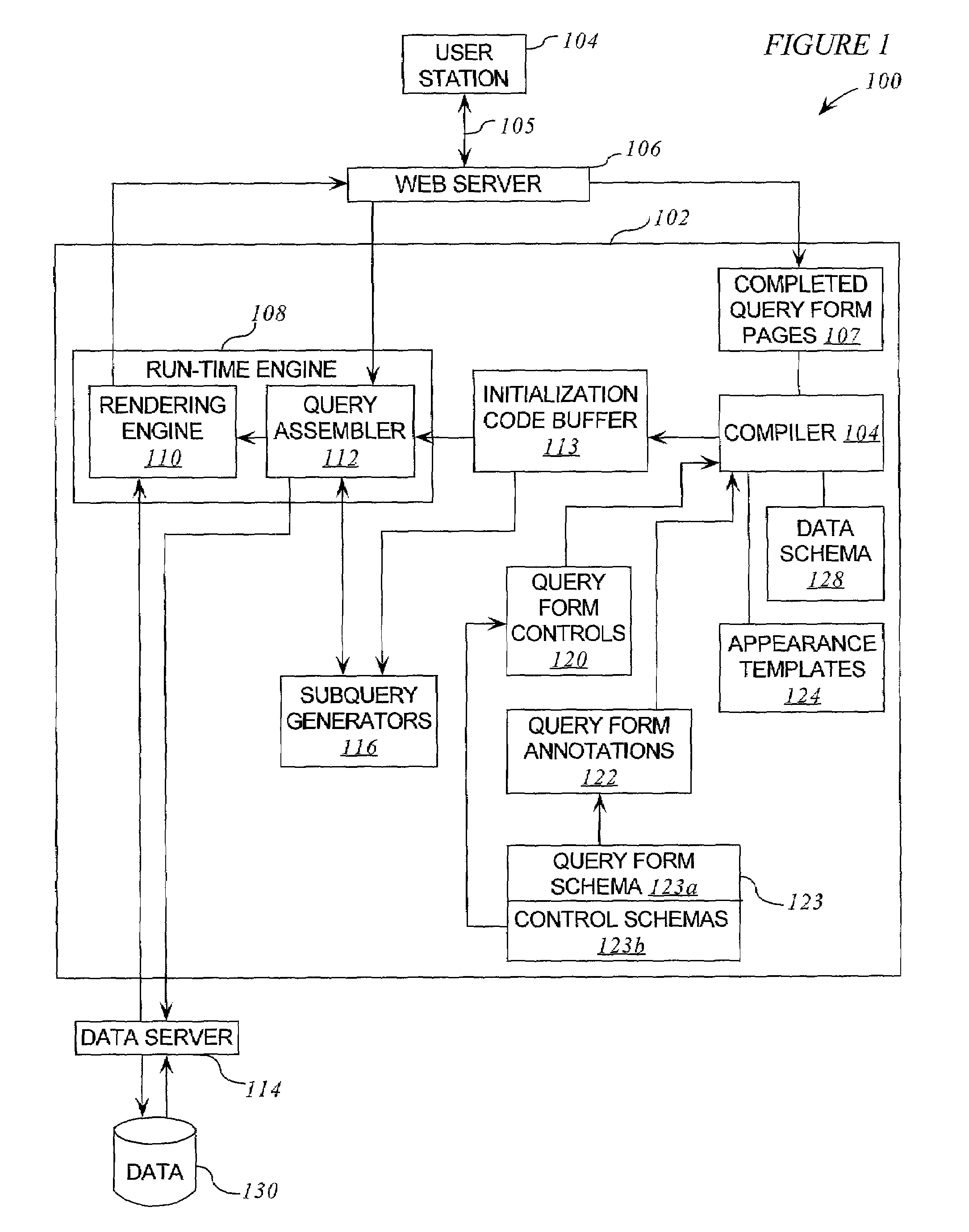
Reconfigurable query generation system for web browsers
ActiveUS7203678B1Simple procedureAvoid time-consuming reprogrammingData processing applicationsWeb data indexingWeb browserData query
A reconfigurable web-browser compatible data query system. The invention provides an XML platform enabling web-based forms that query data modeled by data schemas. This platform comprises a collection of query form controls, an annotation scheme for attaching these controls to the data schema, a compiler for creating a web-browser-compatible representation of the query form, and a run-time engine for constructing queries against the data and rendering query results.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for accessing data via voice
InactiveUS7493259B2Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingData setSystem usage
A method for providing access to data via a voice interface. In one embodiment, the system includes a voice recognition unit and a speech processing server that work together to enable users to interact with the system using voice commands guided by navigation context sensitive voice prompts, and provide user-requested data in a verbalized format back to the users. Digitized voice waveform data are processed to determine the voice commands of the user. The system also uses a “grammar” that enables users to retrieve data using intuitive natural language speech queries. In response to such a query, a corresponding data query is generated by the system to retrieve one or more data sets corresponding to the query. The user is then enabled to browse the data that are returned through voice command navigation, wherein the system “reads” the data back to the user using text-to-speech (TTS) conversion and system prompts.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for facilitating the refinement of data queries
InactiveUS6954750B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRankingDocument preparation
Refining a current query. Receiving information regarding the relevancy of documents retrieved from a document collection in response to a current query. Ranking the retrieved documents in accordance with the relevancy information. Forming a candidate query based on the rankings and analysis of locations of the retrieved documents in a latent semantic index vector space formed from the retrieved document. Applying the candidate query to the document collection. Ranking the documents retrieved in response to the candidate query in accordance with the received relevancy information. Comparing the ranking of documents retrieved in response to the candidate query and the ranking of documents retrieved in response to the current query with the received relevancy information. Choosing the query that produces the best ranking.
Owner:RELATIVITY ODA LLC
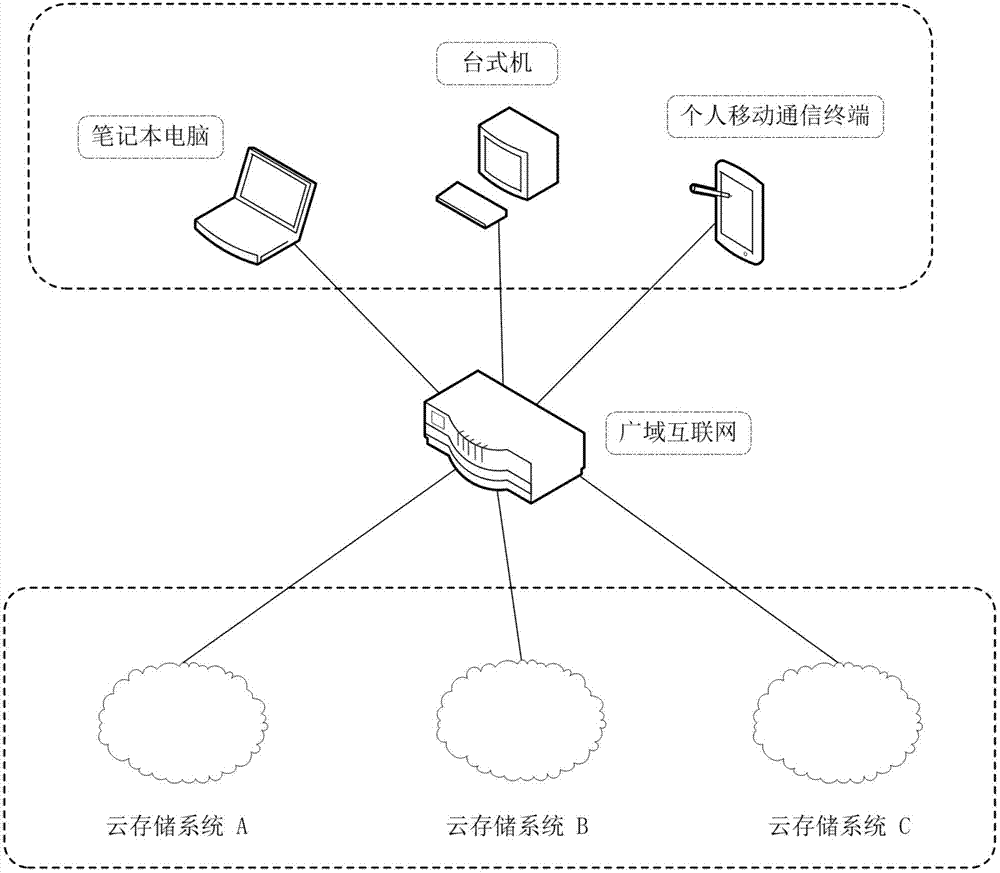
Safe storage method based on a plurality of cloud storage systems and system thereof
InactiveCN103118089AImprove fault toleranceAvoid inaccessibilityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCode moduleCiphertext
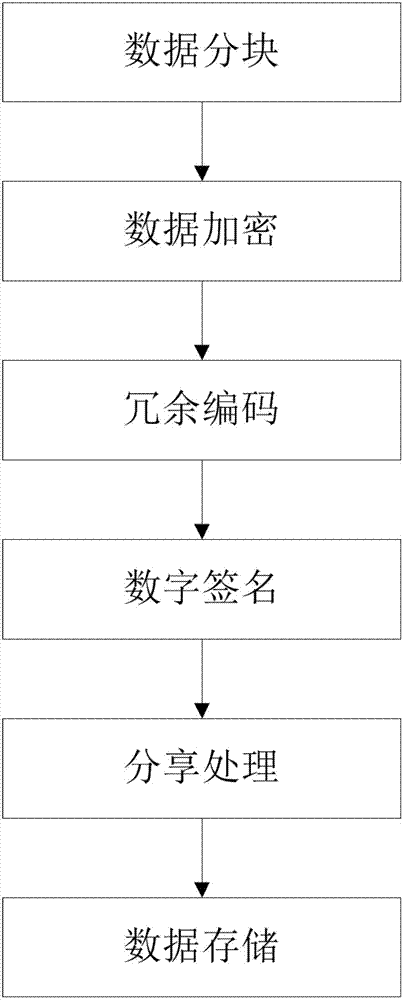
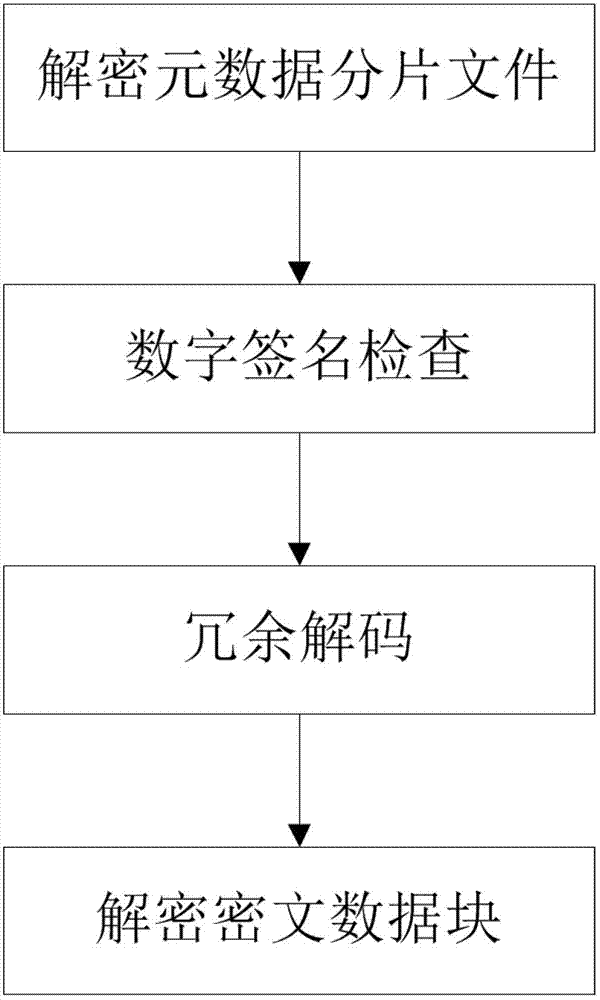
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer storage, and provides a safe storage method based on a plurality of cloud storage systems and a system thereof. The method and the system can achieve the purpose that in the plurality of existing cloud storage systems, safety of data and metadata can be guaranteed at the same time. The safe storage method comprises a step of data writing operation and a step of data reading operation, wherein the step of data writing operation comprises the sub-steps of data partitioning, data encryption, redundancy encoding, digital signature, sharing processing, and data storage. The step of data reading operation comprises the sub-steps of metadata partition file decryption, digital signature inspection, redundancy decoding and cipher text data block decryption. The safe storage system comprises an encryption and decryption coding module, a redundancy encoding module, a secret sharing module and a digital signature module. By means of the method and the system, metadata privacy and high availability can be guaranteed, and meanwhile, a user does not need to store any metadata information for indexing and data query.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for URL based query for retrieving data related to a context
InactiveUS8032508B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContext basedUniform resource locator
A system and method for URL based query for retrieving data related to a context. A request is received over a network from a user for data related to a context, wherein the request is a URL comprising a context query comprising at least one context criteria. The context criteria are parsed and translated and disambiguated. A network data query is formulated based on the context criteria so as to search, via the network, for user profile data, social network data, spatial data, temporal data and topical data that is available via the network and relates to the context query so as to identify at least one data object that relates to context criteria. Permissions relating to the identified data objects are checked and references to the data objects are transmitted over the network to the user.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
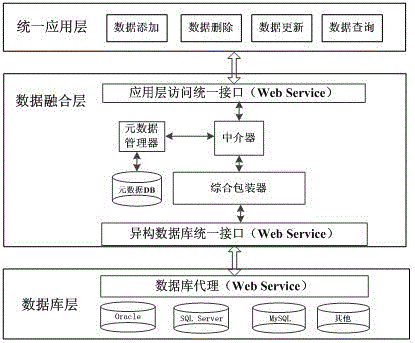
Multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and data query method thereof
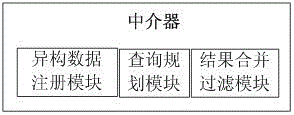
InactiveCN104008135AAchieve integrationEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsMetadata managementSystem maintenance
The invention provides a multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and a data query method thereof. The system comprises a database layer, a data fusion layer and a uniform application layer. The database layer is composed of heterogeneous databases and agencies of the heterogeneous databases. The data fusion layer is used for fusing information of all heterogeneous data sources, and is responsible for data access of the heterogeneous data sources and coordinating the information of all the data sources, and specifically comprises a metadata data base (DB), a metadata manager, a comprehensive wrapper, a mediator, an application layer access uniform interface and a heterogeneous database uniform interface. The uniform application layer is the user of the heterogeneous database fusion system and can have access to shared data resources of the heterogeneous databases by fusing middle layers. The multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system and the data query method of the multi-source heterogeneous database fusion system solve the problems in heterogeneous database fusion and overcome the defects of an existing database fusion technology. The system can conduct transparent query on all the heterogeneous databases on the condition that local databases are not affected, and the maintenance cost of the system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
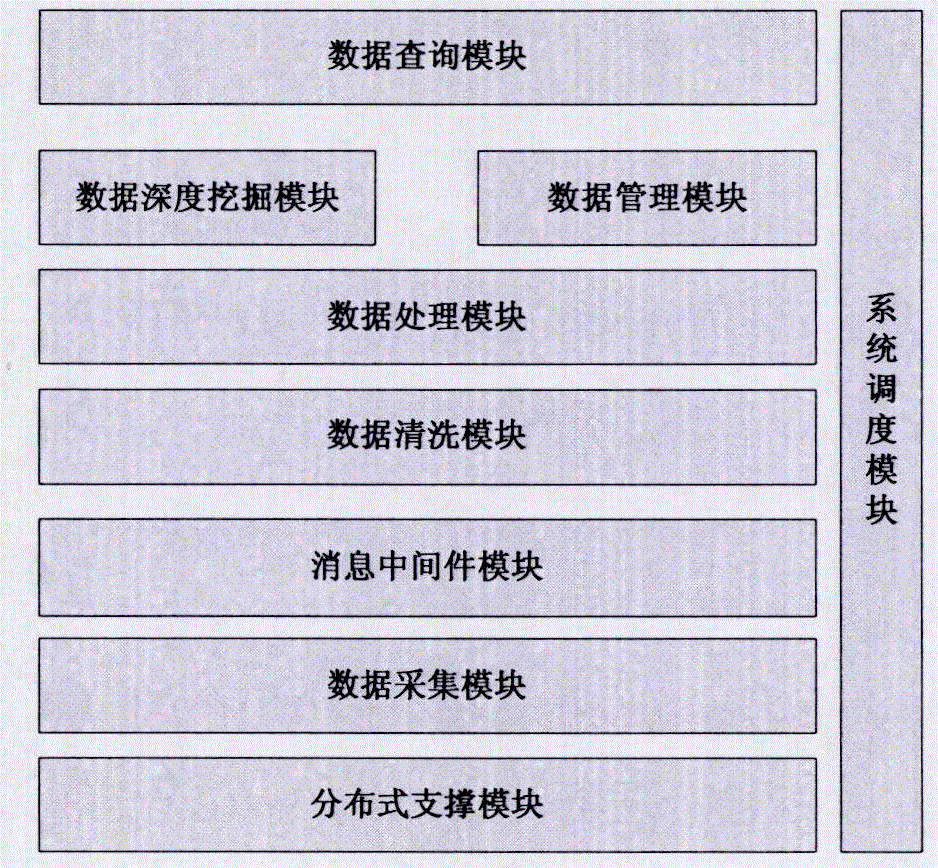
Big data real-time storage, processing and querying system
InactiveCN106815338AImprove real-time performanceQuick responseSpecial data processing applicationsData acquisitionMessage oriented middleware
A big data real-time storage, processing and querying system includes a distributed support module, a data acquisition module, a message-oriented middleware module, a data cleaning module, a data processing module, a data deep mining module, a data management module, a data querying module, and a system scheduling module; all the modules run under the coordination of the system scheduling module, and scheduling and circulation of data flows among all the modules can be achieved Processing flows among all the modules can be coordinated, and the date real-time performance is improved; effective improvement is performed for high throughput, mass data, fast response messages and data high availability; and then the comprehensive ability of a big data real-time data service system can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGHAI INVESTMENT MANAGEMENT CO LTD
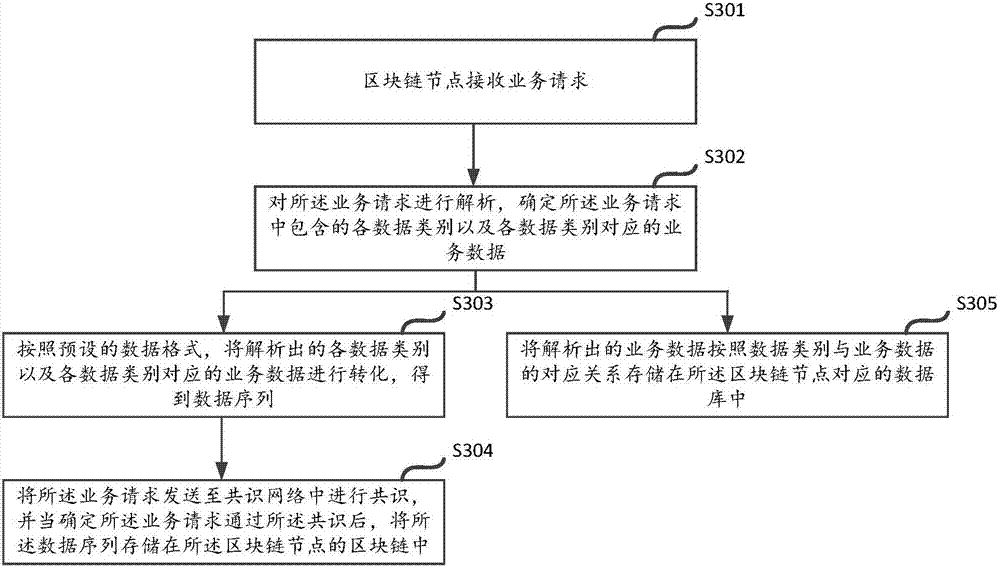
Data storage and query method and device based on block chain
ActiveCN107239479AIncrease flexibilityImprove query efficiencyDatabase queryingDatabase distribution/replicationData queryData library
The application discloses a data storage and query method and device based on a block chain. The method comprises the following steps: after receiving a service request sent by a user, a block chain node can resolve each data category and service data corresponding to each data category from the service request, and stores the resolved service data in a database corresponding to the block chain node according to a corresponding relation of the data category and the service data. By resolving the service data, the service data can be stored to the database corresponding to the block chain node according to the corresponding relation between the data category and the service data; therefore, the user can realize the query based on the corresponding relation in the database when querying the service data, a problem existent in the query based on the query in the existing block chain is avoided, the flexibility of the data query in the block chain is increased, and the data query efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
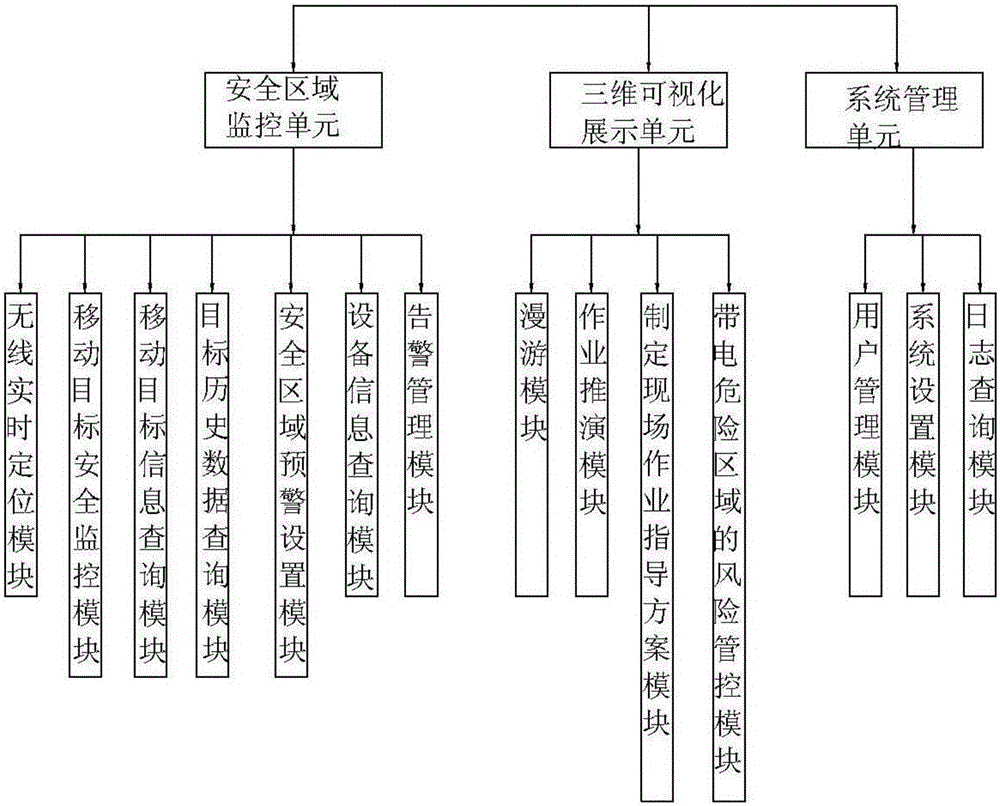
Transformer station three-dimensional real scene simulation system and implementation method
ActiveCN105956232ARealize 3D dynamic displayAvoid missingData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationSystems managementTransformer
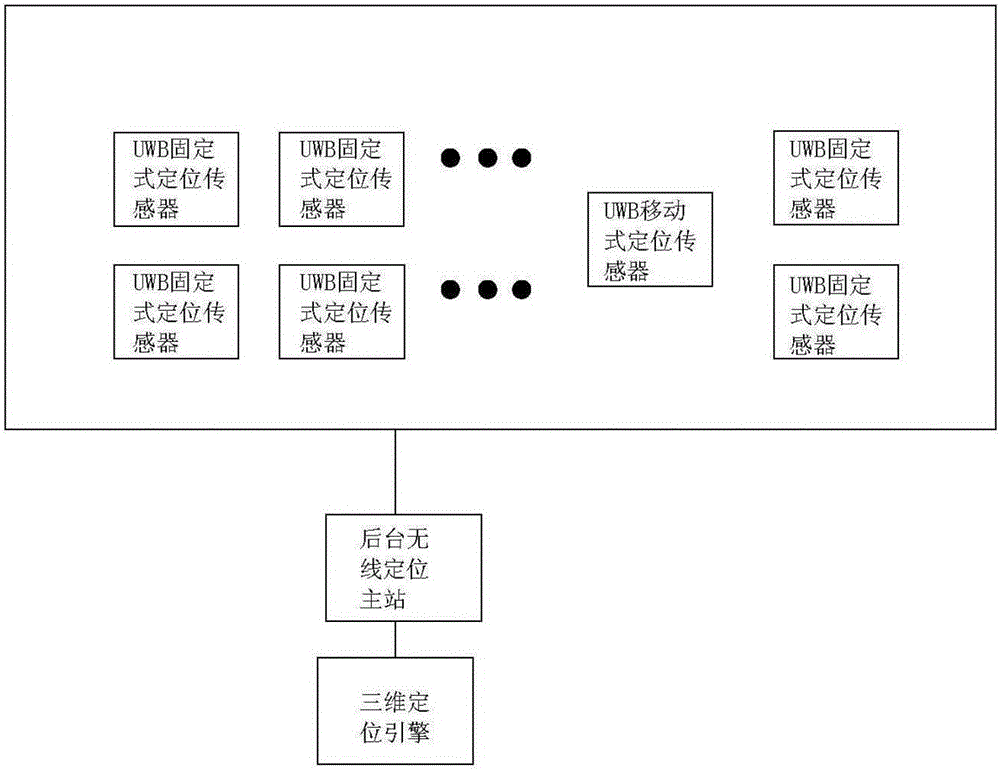
The invention relates to a transformer station three-dimensional real scene simulation system and an implementation method. The system comprises a safety region monitoring unit, a three-dimensional visualization display unit, and a system management unit. The safety region monitoring unit comprises a wireless real-time positioning module using a UWB positioning technology, a moving target security monitoring module, a moving target information query module, a target historical data query module, a safety region early warning setting module, an equipment information query module, and an alarm management module. The three-dimensional visualization display unit comprises a roaming module, an operation deduction module, a field operation instruction scheme making module, and a risk management and control module of an electrified dangerous region. The system management unit comprises a user management module, a system setting module, and a log query module. The system realizes functions of daily inspection and maintenance visual management of a transformer station, operating personnel daily inspection and maintenance process real-time tracking and monitoring, security alert alarm and intelligent recording management.
Owner:WUHAN NARI LIABILITY OF STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Interactive large data analysis query processing method
InactiveCN105279286AImprove query efficiencyImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsDatabase queryData set
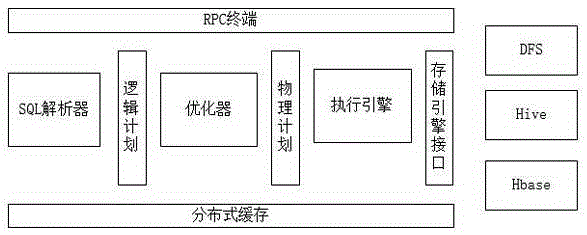
The invention provides an interactive large data analysis query processing method. The interactive large data analysis query processing method comprises steps that, 1), a query request generated by a user or a machine is submitted to an SQL query analyzer; 2), the query quest is analyzed by the SQL query analyzer into a logic plan; 3), the logic plan is read by an optimizer and is converted into a physical plan, and interaction between a storage engine and a specific data source is realized; and 4), the physical plan is performed by a performing engine, and meta-data information is provided based on a meta-database query performing framework. For real-time interactive large data set analysis blank, P-byte data is processed under the condition of low delay response through the method according to design, multiple functions of other SQL-on-Hadoop engines are integrated, the query speed is greatly improved, and thereby Hadoop data query and enterprise-level large data analysis can be rapidly and efficiently carried out for enterprise users.
Owner:陕西艾特智慧信息技术有限公司
Systems and methods for querying column oriented databases
InactiveUS20120303633A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData storingData query
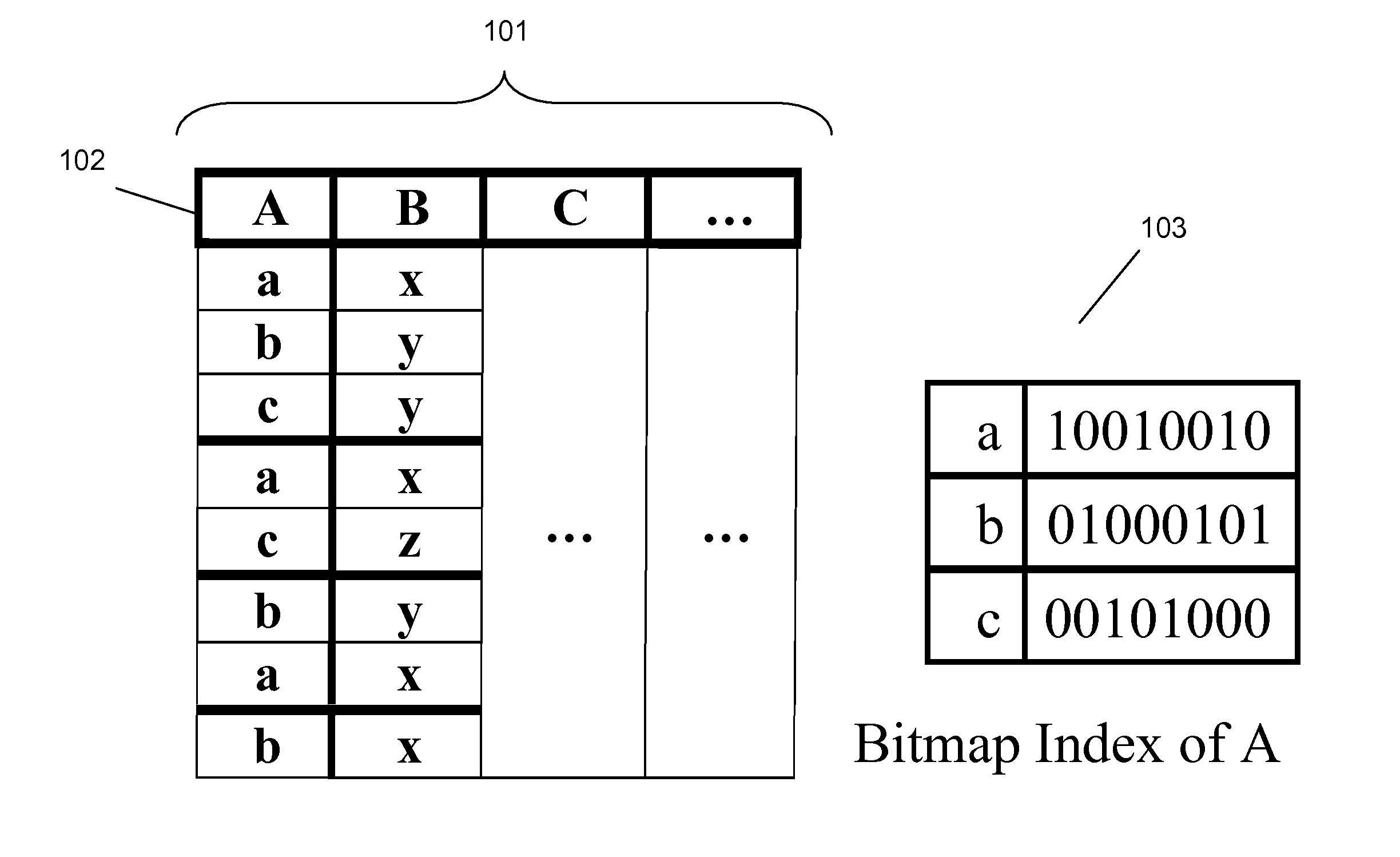
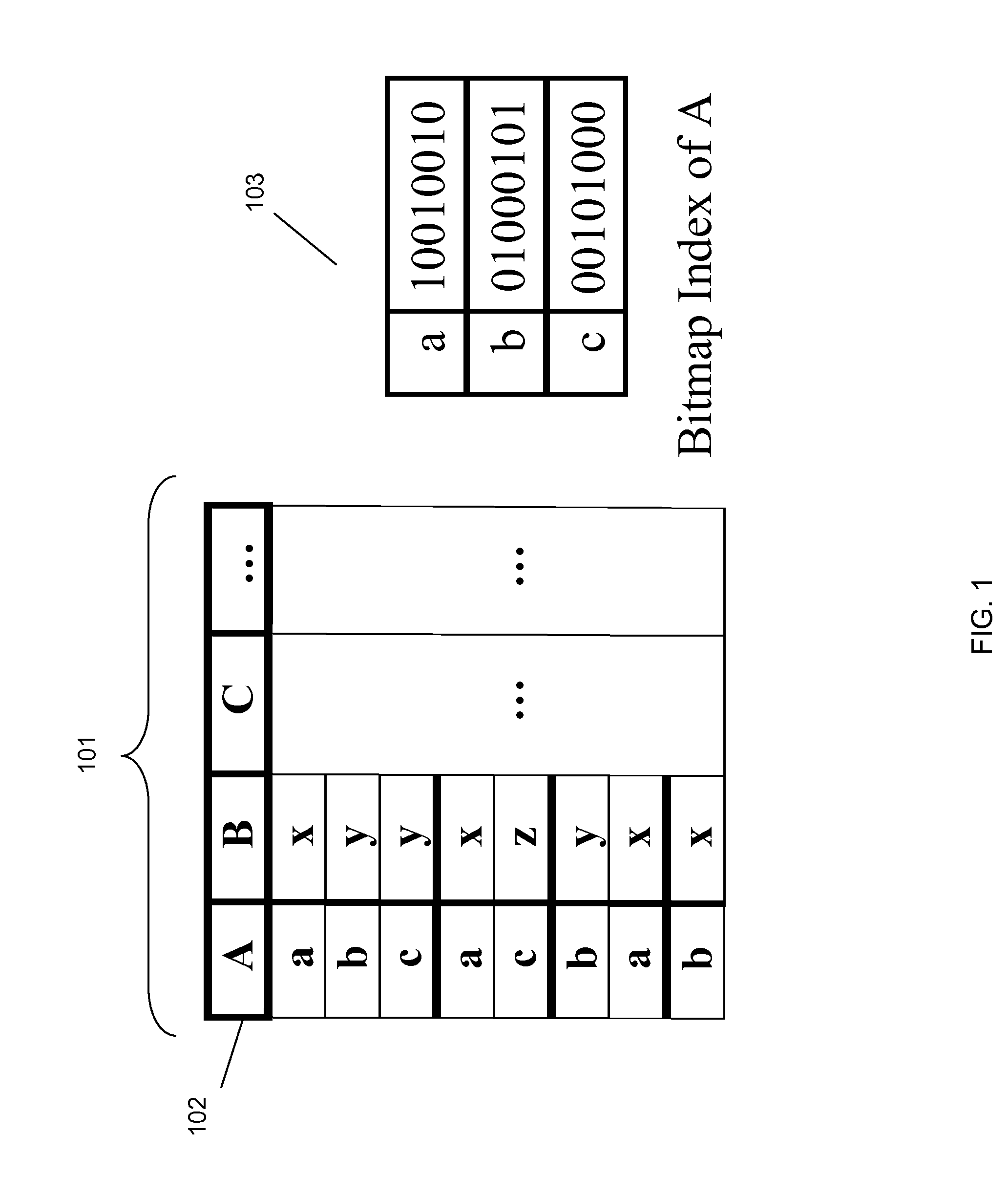
Systems and methods for accessing data stored in a data array, mapping the data using a bitmap index, and processing data queries by determining positions of query attributes in the bitmap index and locating values corresponding to the positions in the data array are described herein.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data caching system and data query method
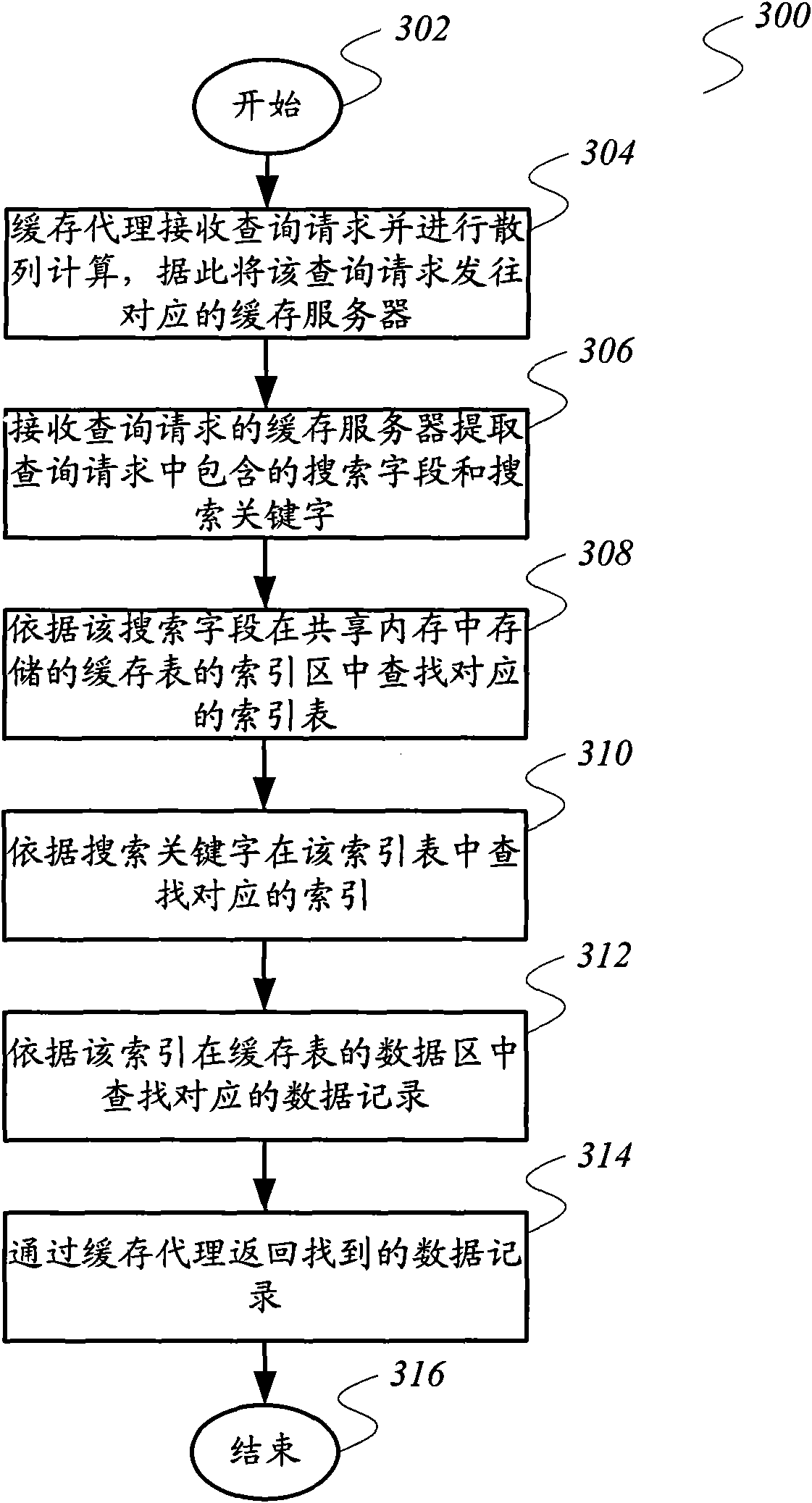
InactiveCN102117309AEasy to manageEasy to useTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsCache serverDependability
The invention relates to the cache technique, and provides a data caching system and a data query method, in order to overcome the disadvantages that the existing Memcached system does not support multi-index and the like. The data caching system comprises a cache proxy, and at least one cache server in communication connection with the cache proxy, wherein the cache proxy is used for receiving aquery quest and carrying out hash calculation, and sending the query quest to the corresponding cache server; and the cache server is used for extracting the search field and the search keyword contained in the query quest, searching the corresponding index table in an index region of a cache table of the search field stored in a shared memory, searching the corresponding index in the index tableaccording to the search keyword, searching the corresponding data record in a data region in the cache table according to the index, and returning to the searched data record through the cache proxy.The invention also provides a data query method. The technical scheme provided by the invention is helpful in improving the overall reliability and the security of the data caching system.
Owner:卓望数码技术(深圳)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com