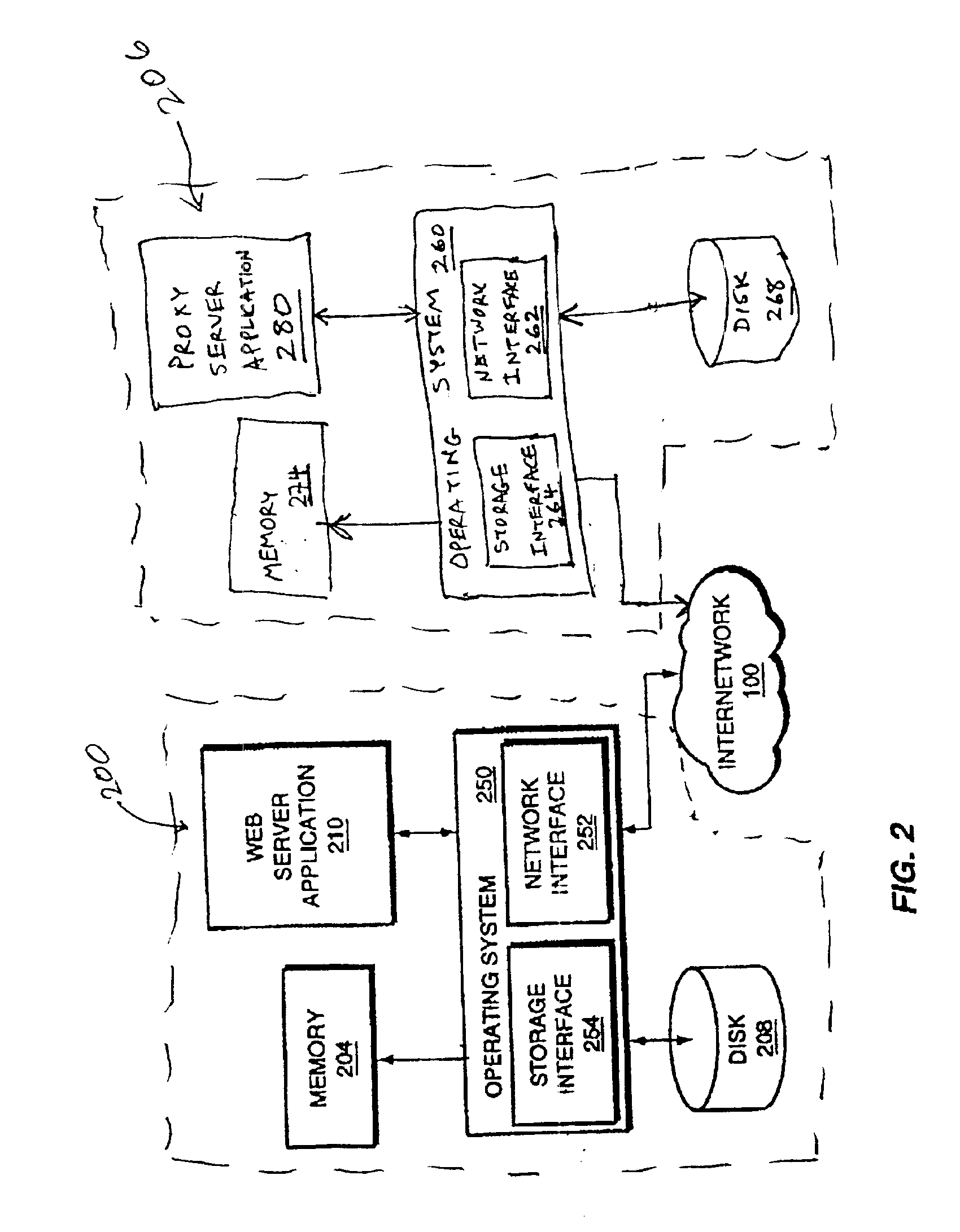
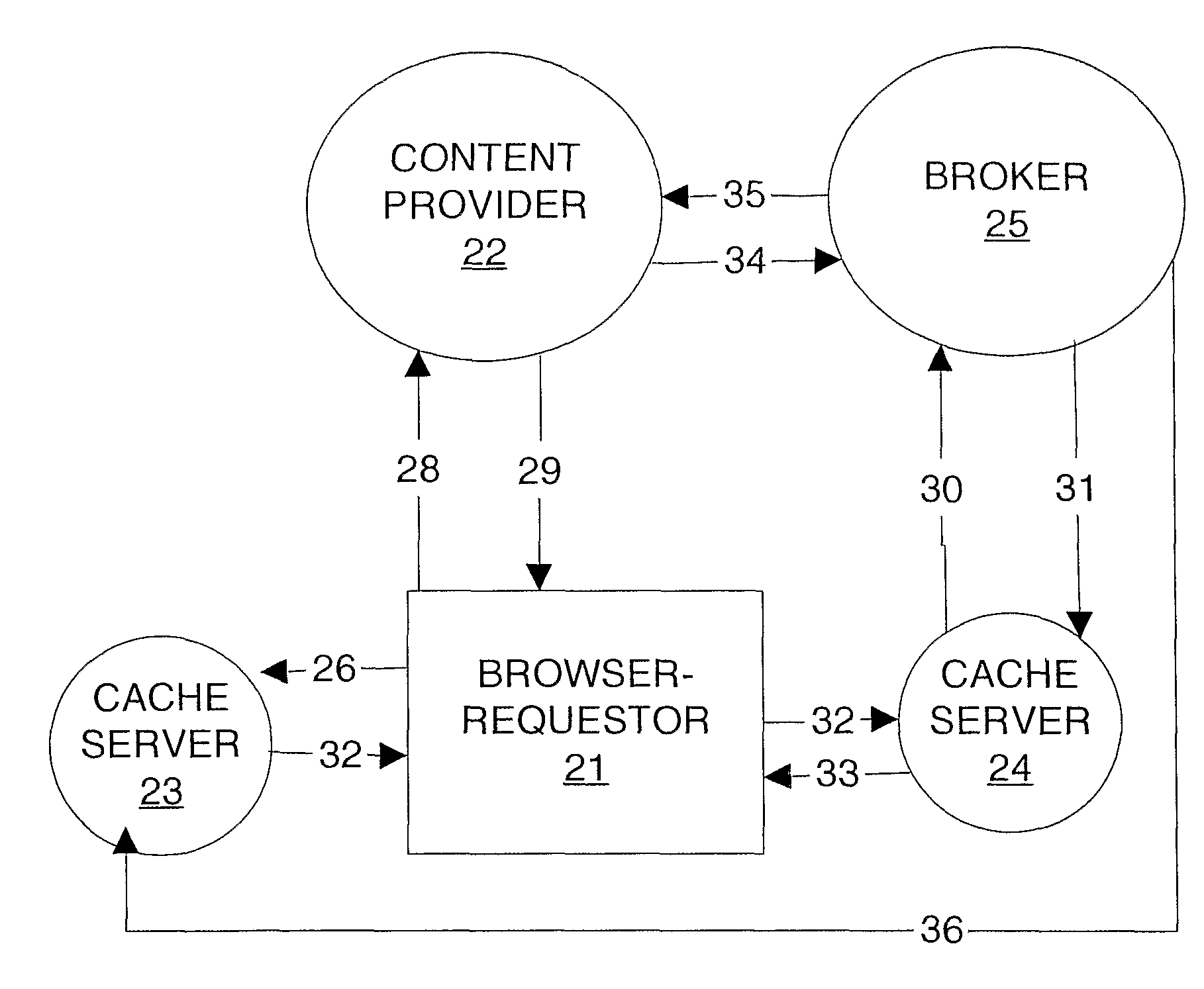
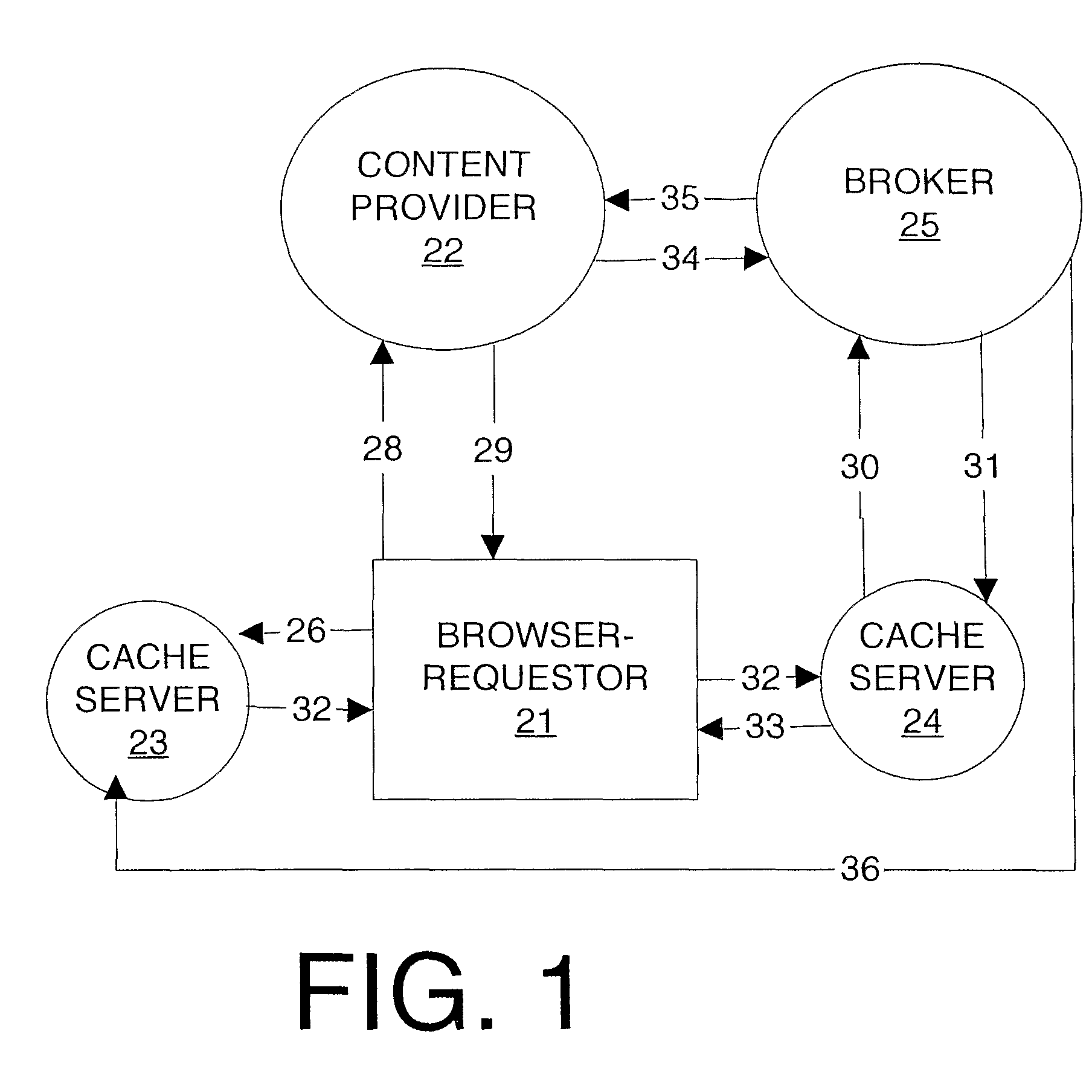
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1379 results about "Cache server" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
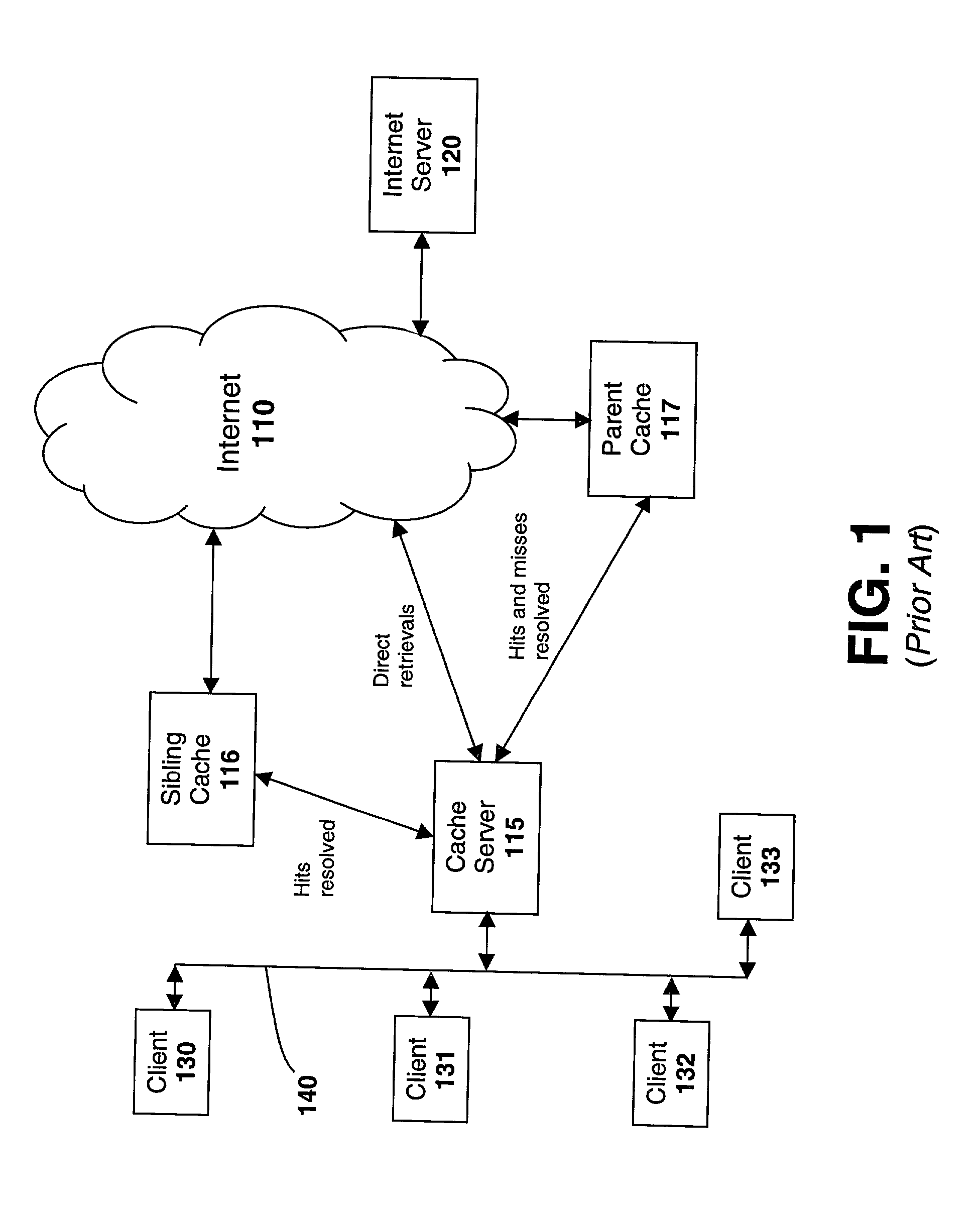
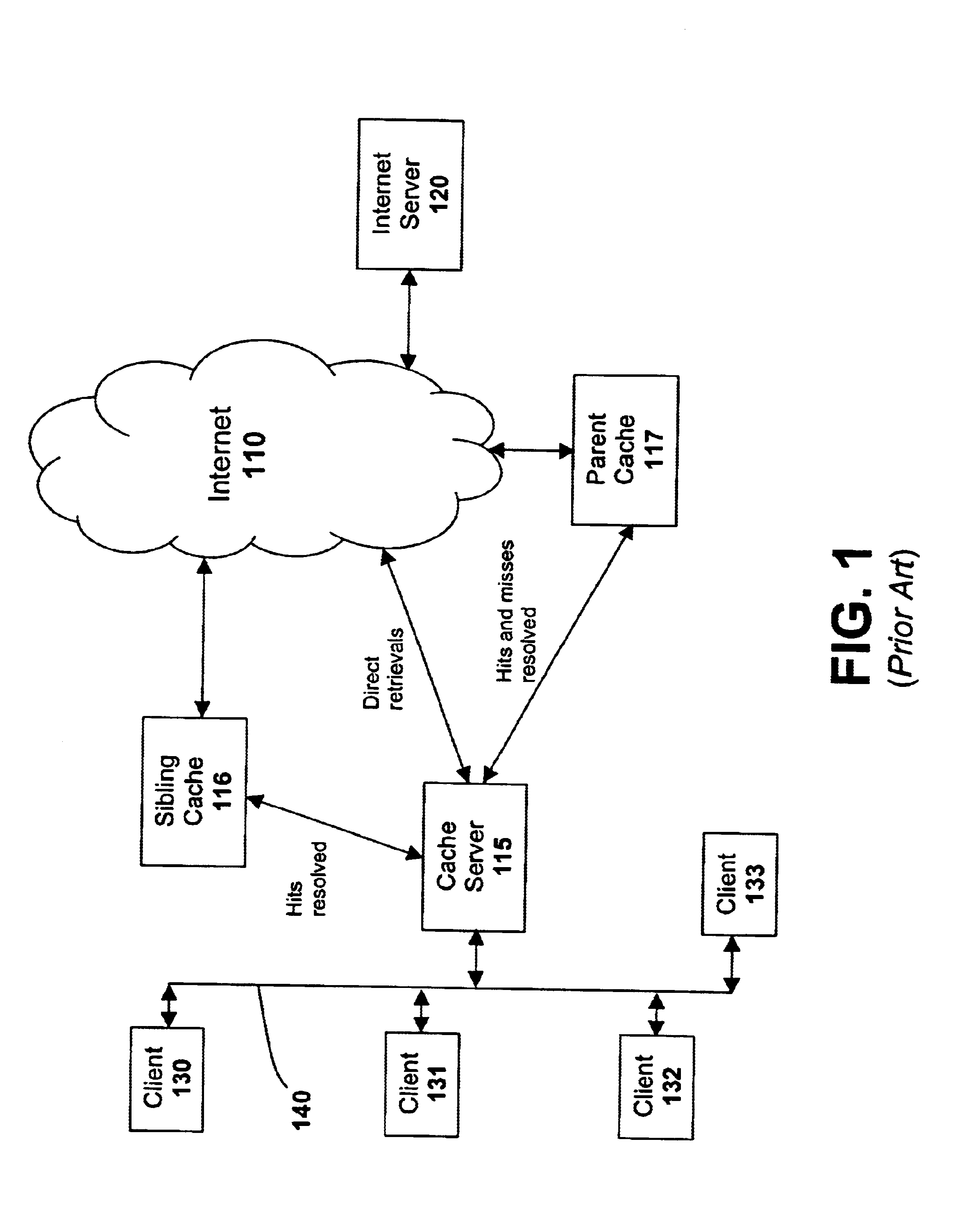
A cache server is sometimes called a "cache engine. ". ... A cache server is almost always also a proxy server, which is a server that "represents" users by intercepting their Internet requests and managing them for users.
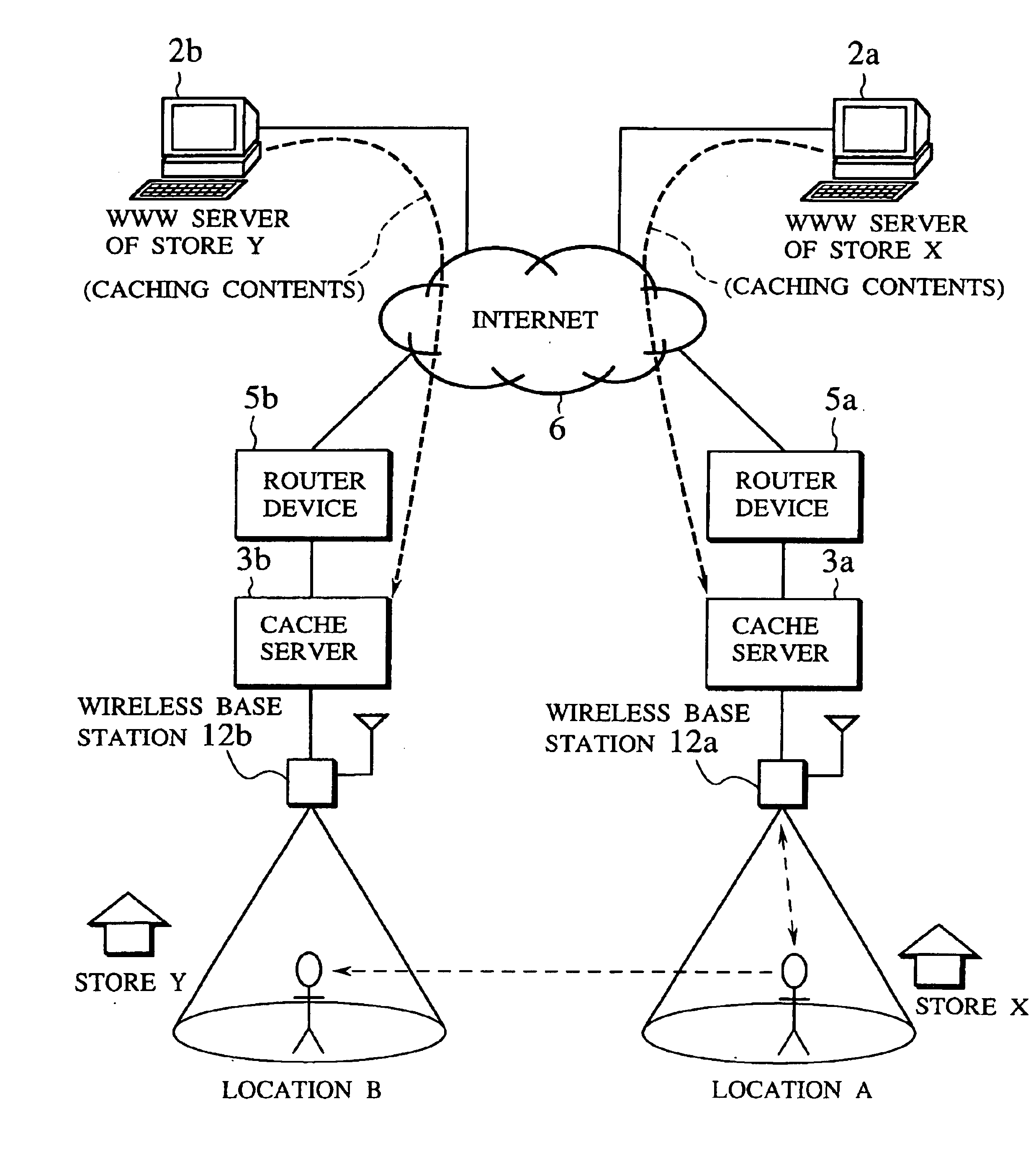
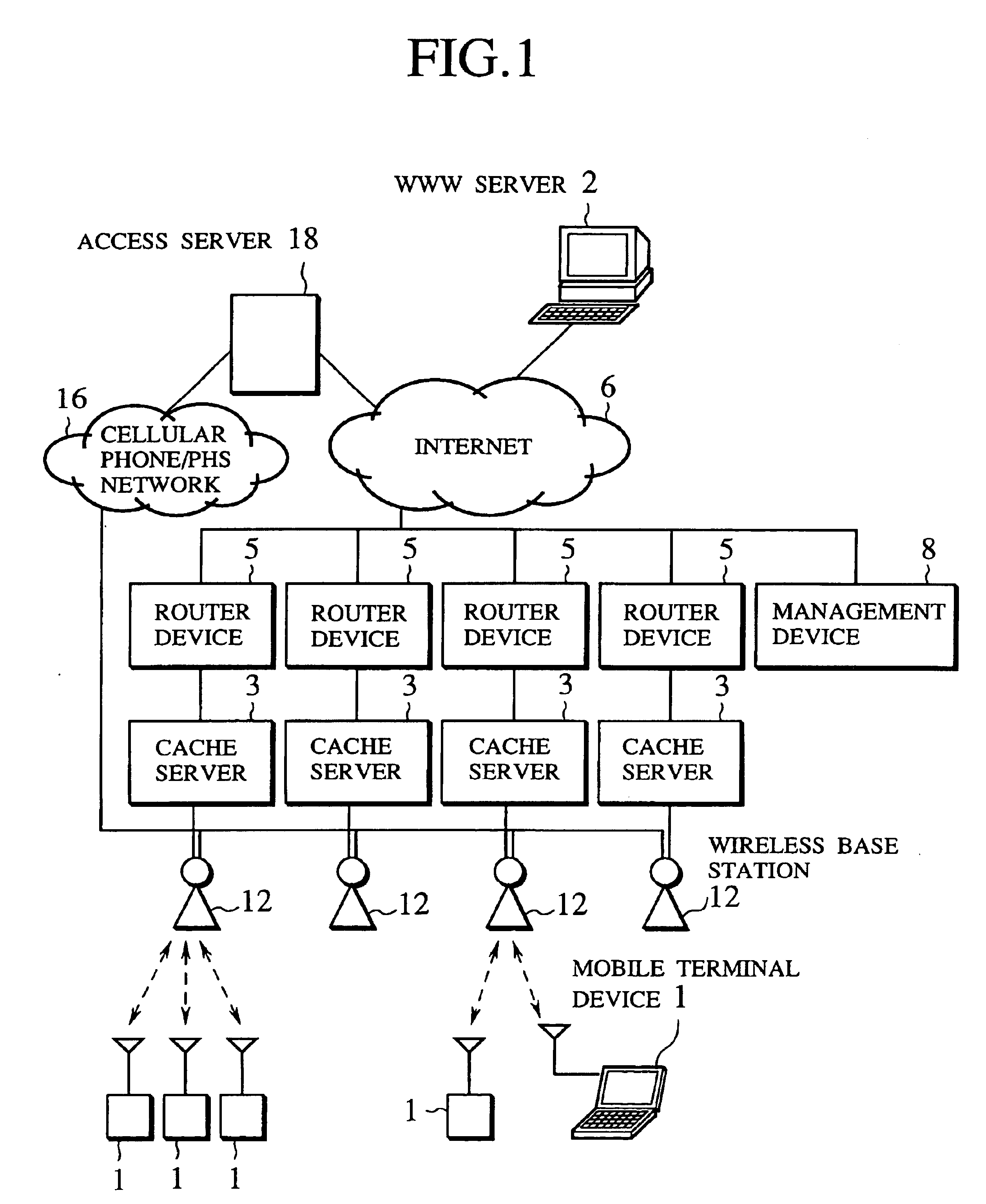
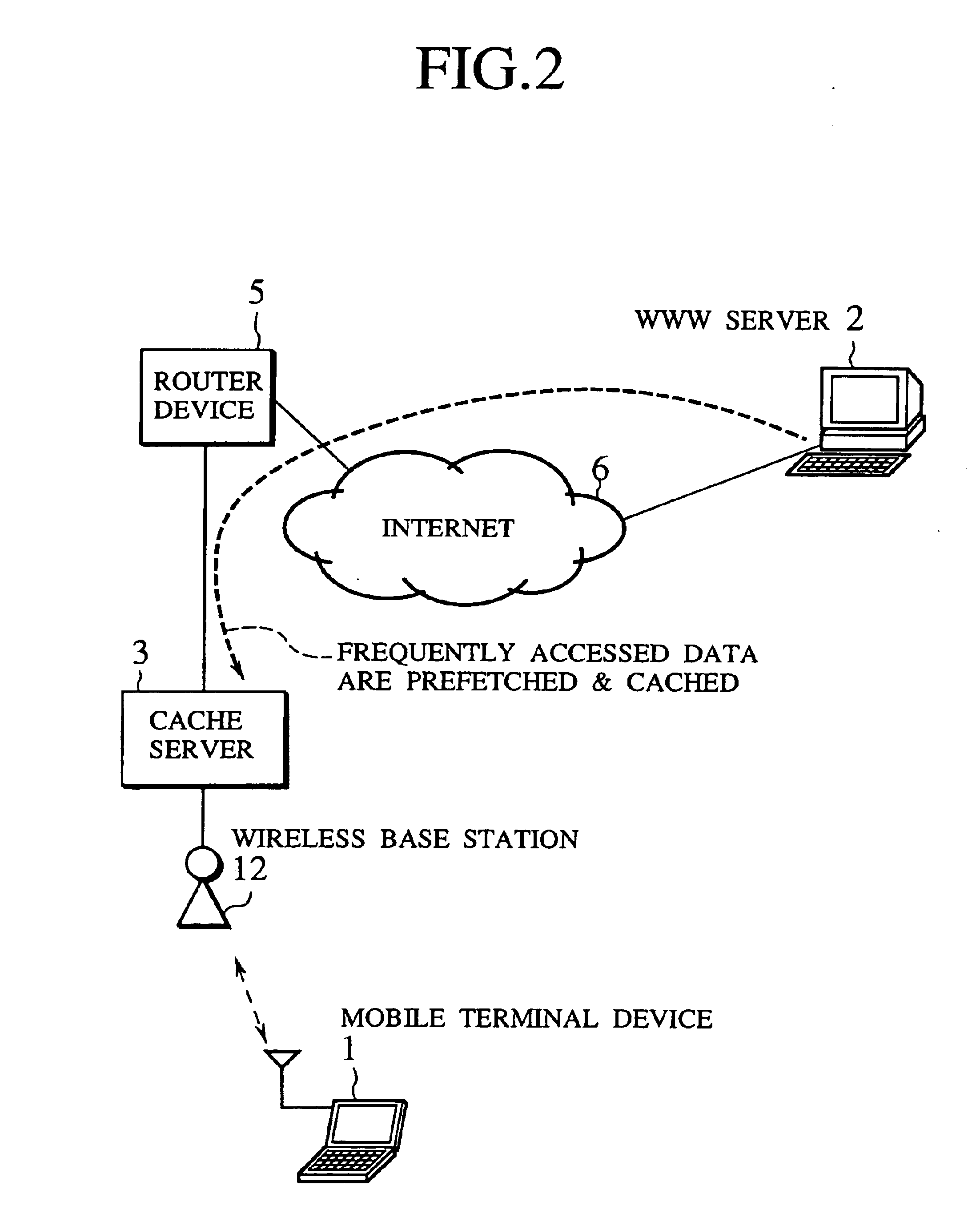
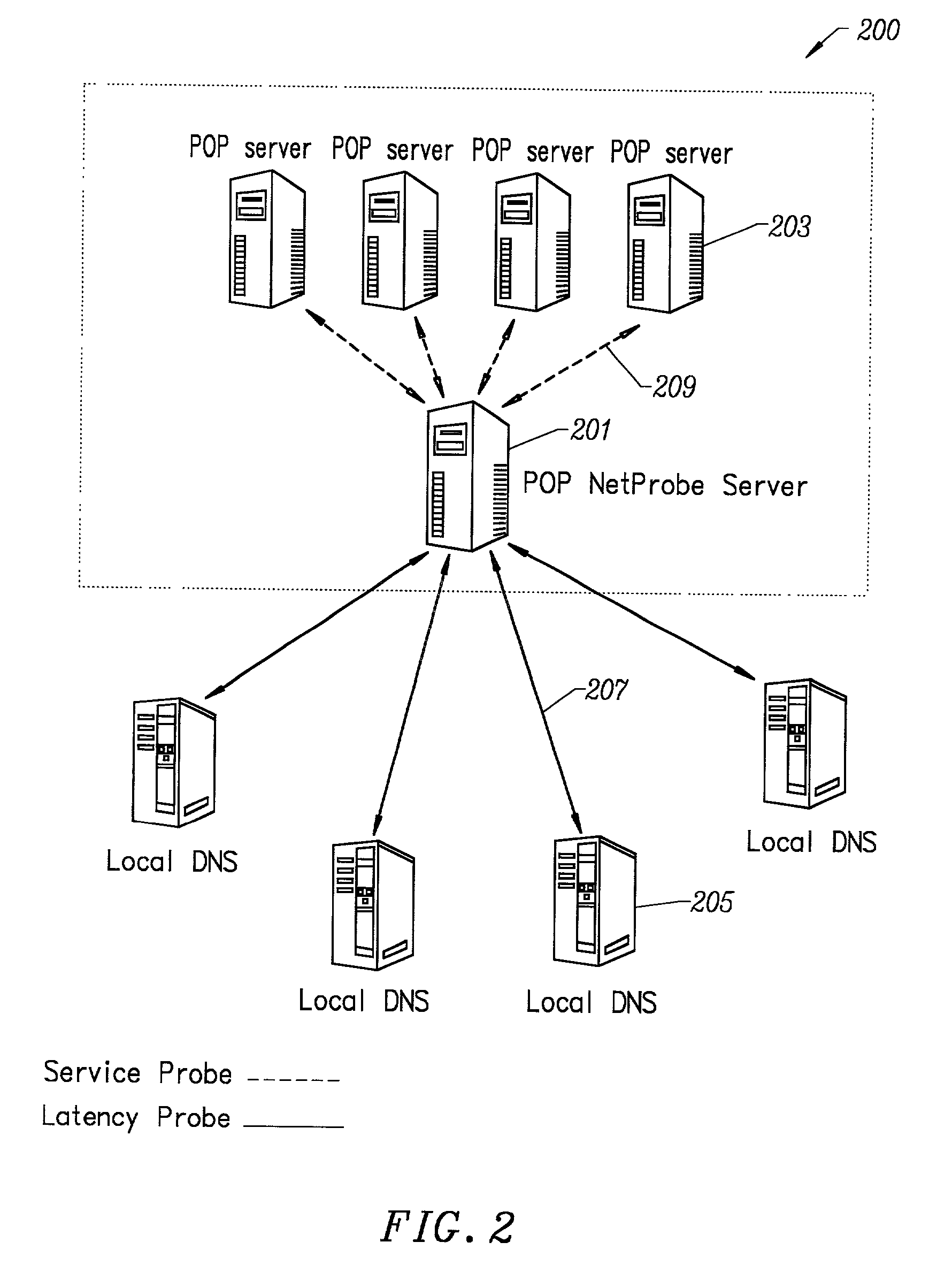
Scheme for information delivery to mobile computers using cache servers
InactiveUS6874017B1Effective cachingEasy accessSpecial service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalCache serverThe Internet
In the disclosed information delivery scheme for delivering WWW information provided by information servers on the Internet to mobile computers connected to the Internet through a wireless network, a plurality of cache servers capable of caching WWW information provided by the information servers are provided in association with the wireless network. The cache servers can be managed by receiving a message indicating at least a connected location of a mobile computer in the wireless network from the mobile computer, selecting one or more cache servers located nearby the mobile computer according to the message, and controlling these one or more cache servers to cache selected WWW information selected for the mobile computer, so as to enable faster accesses to the selected WWW information by the mobile computer. Also, the cache servers can be managed by selecting one or more cache servers located within a geographic range defined for an information provider who provides WWW information from an information server, and controlling these one or more cache servers to cache selected WWW information selected for the information provider, so as to enable faster accesses to the selected WWW information by the mobile computer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
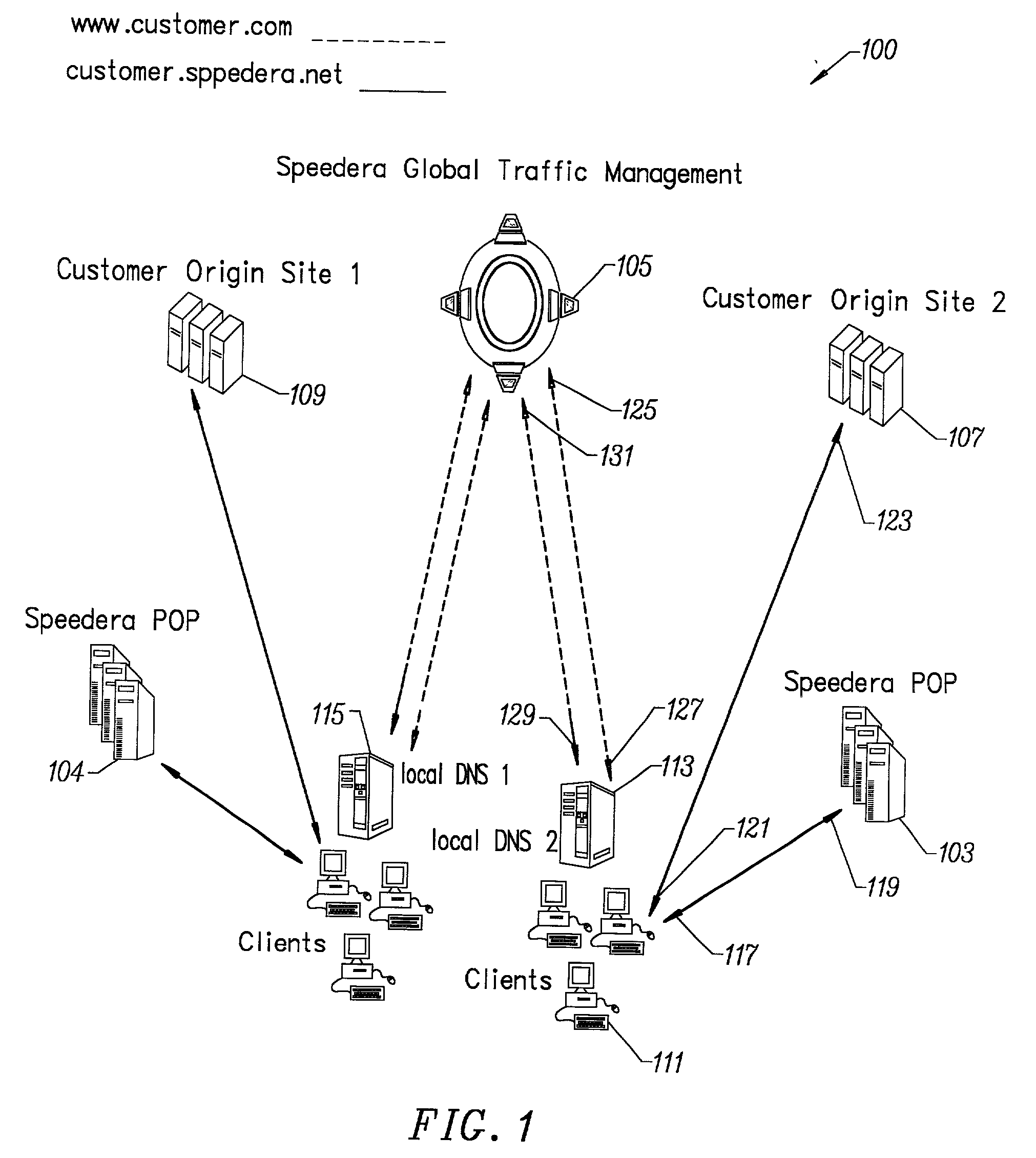
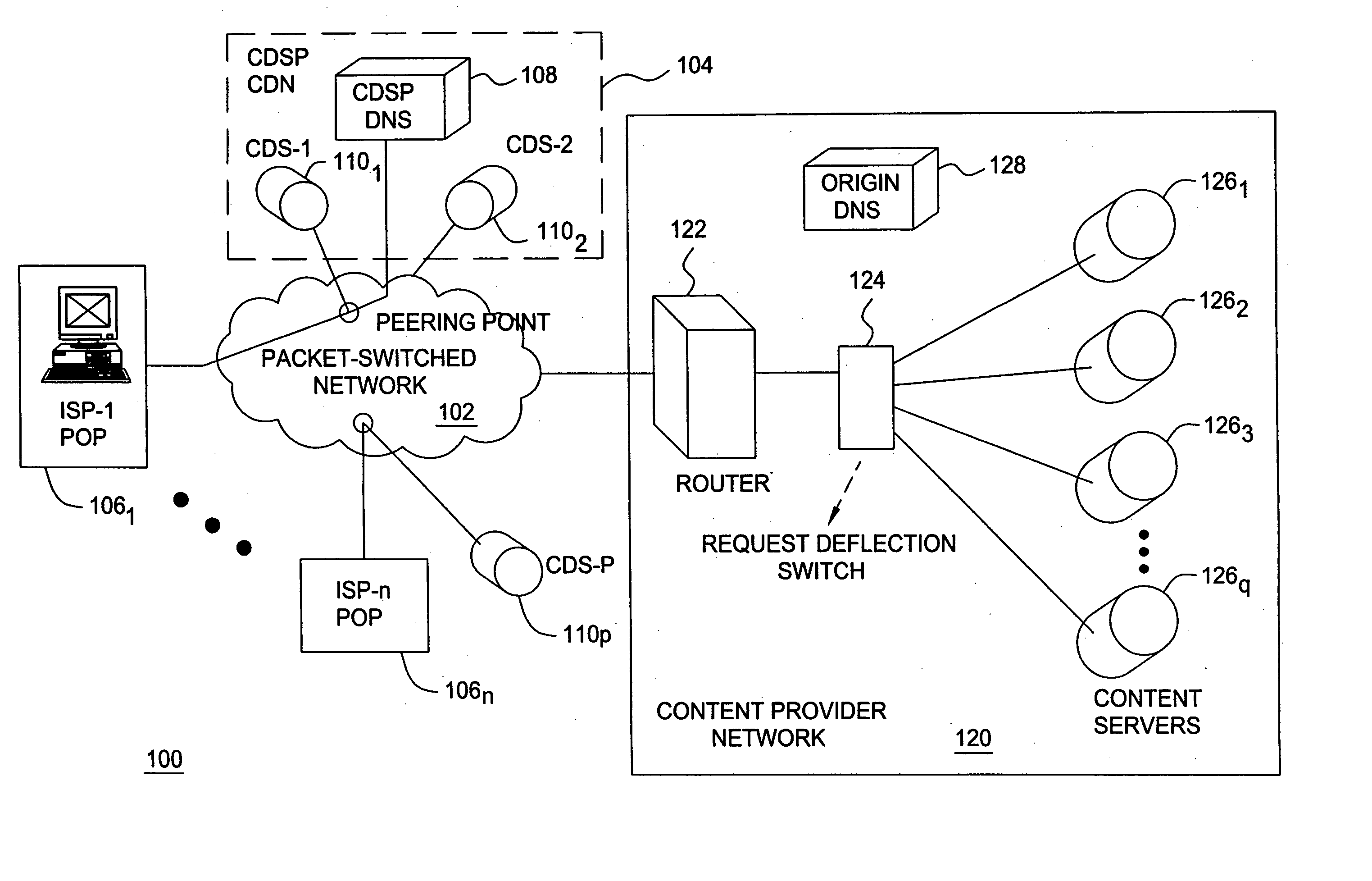
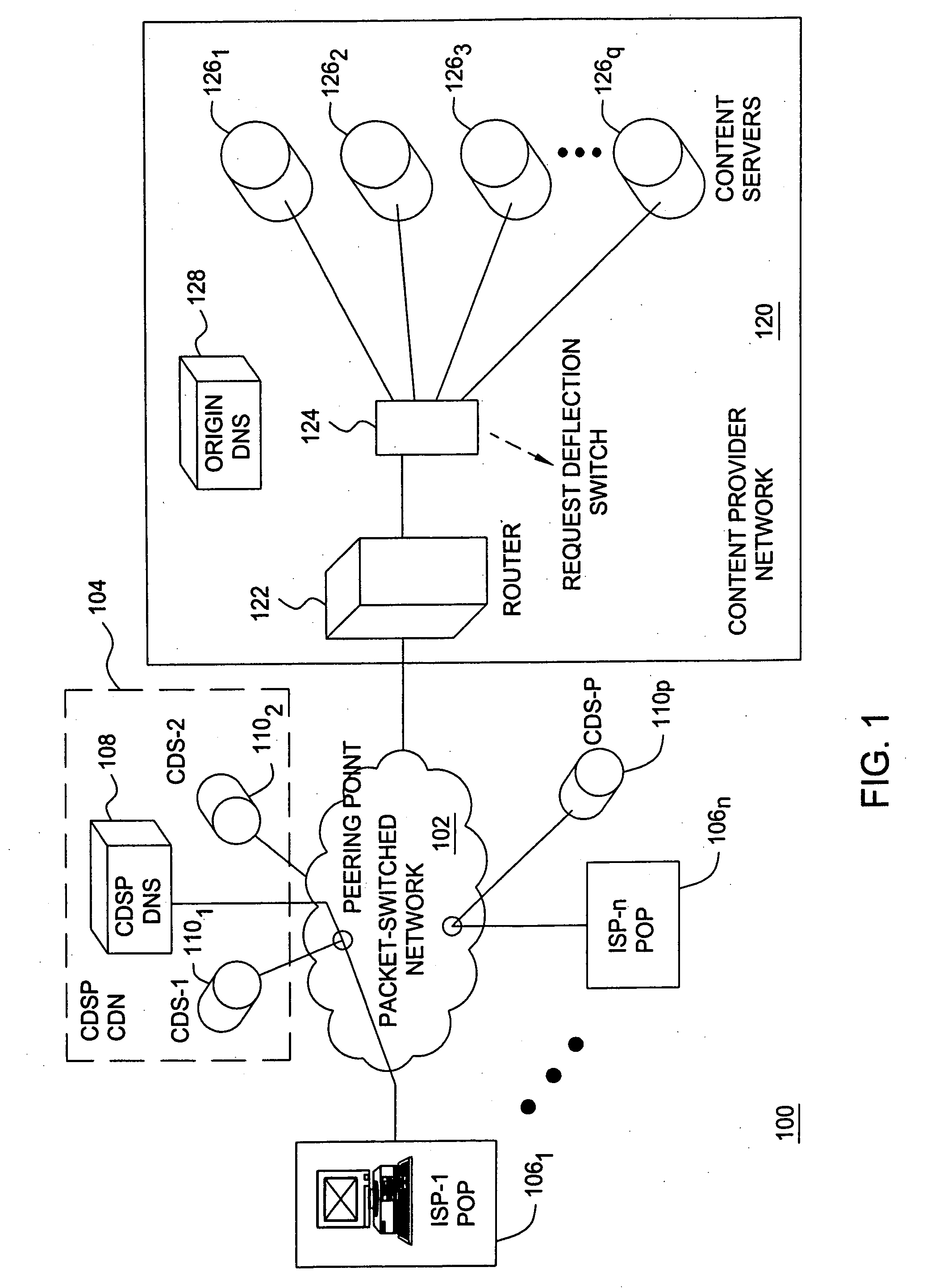
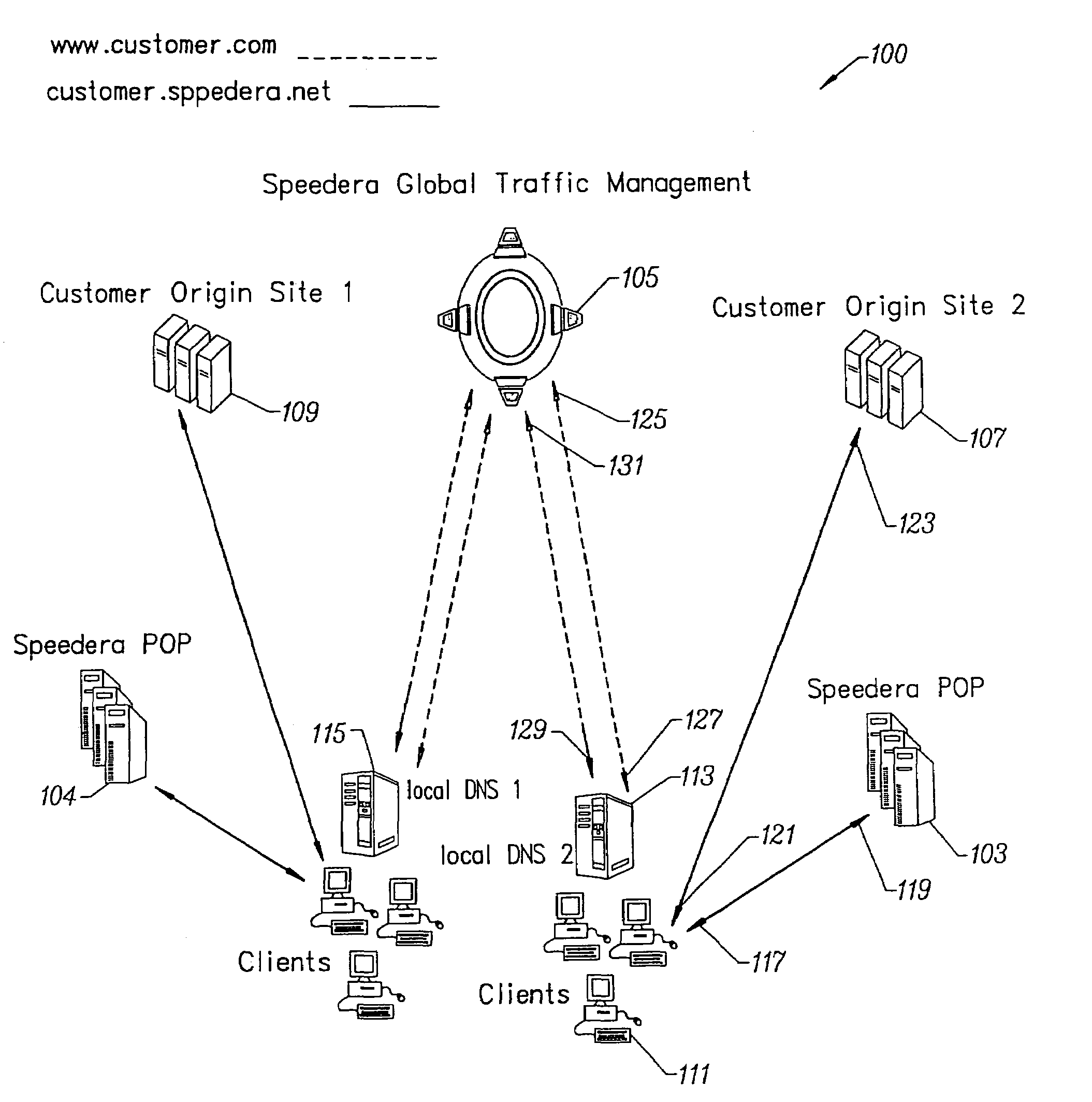
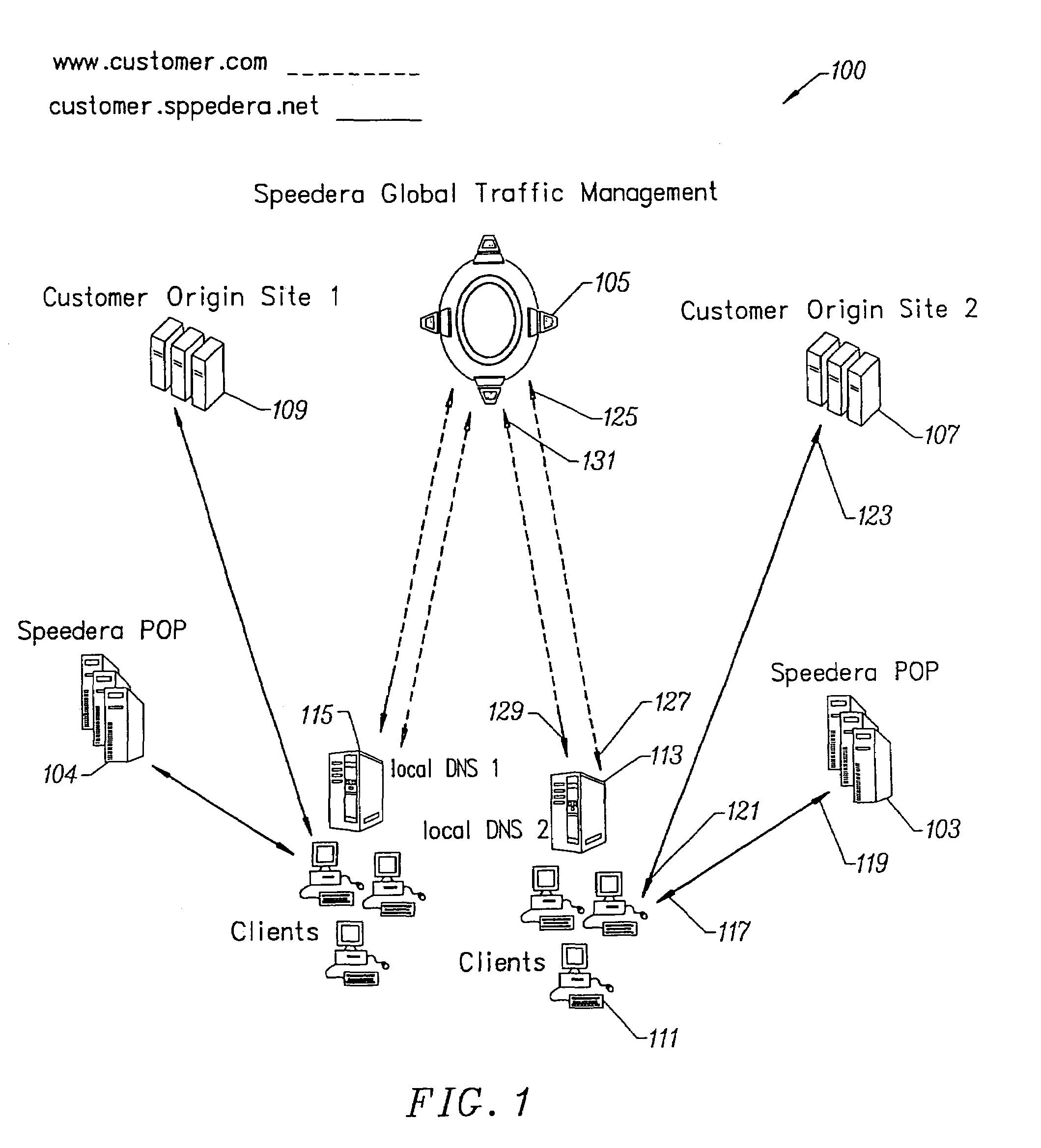
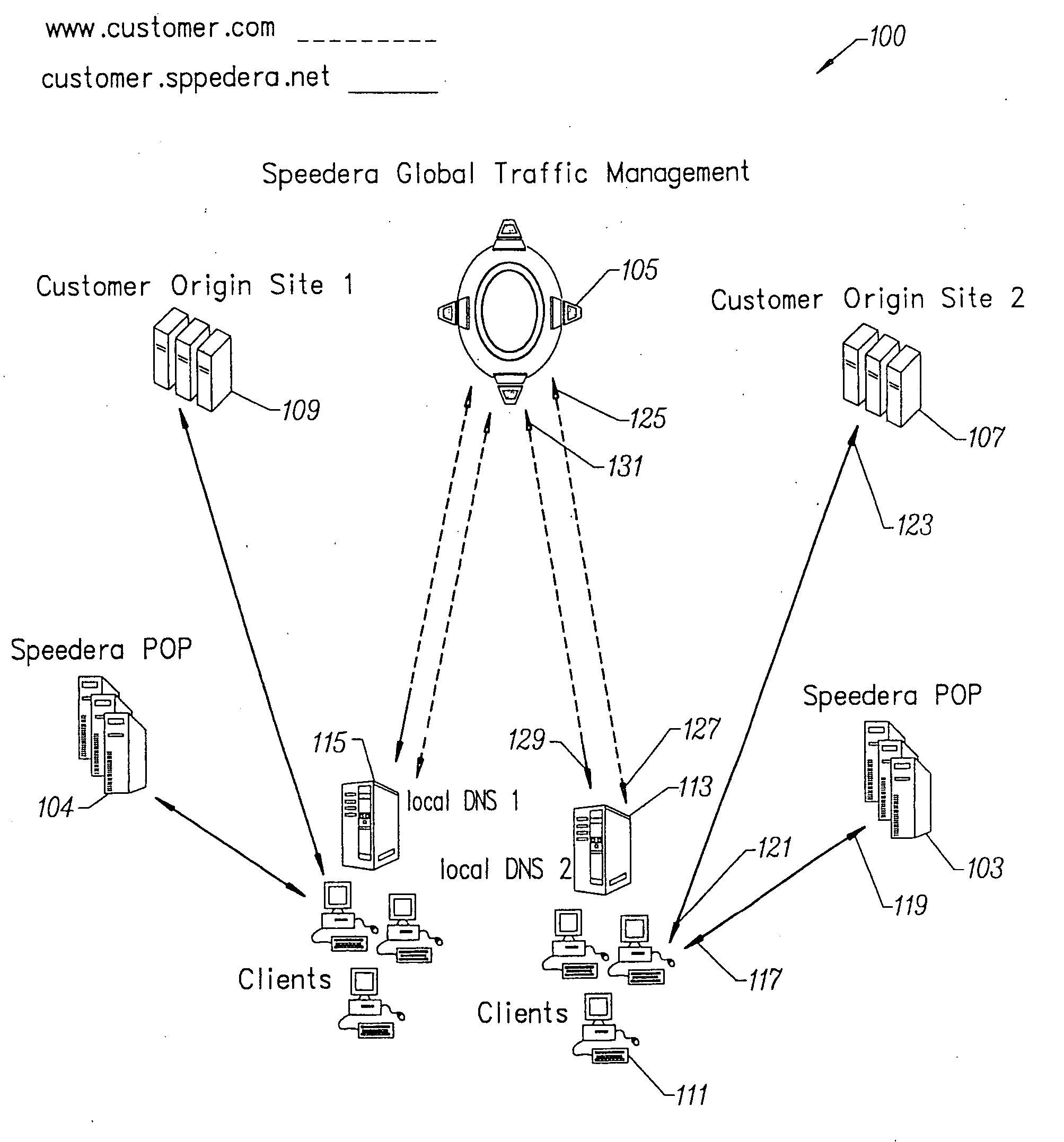
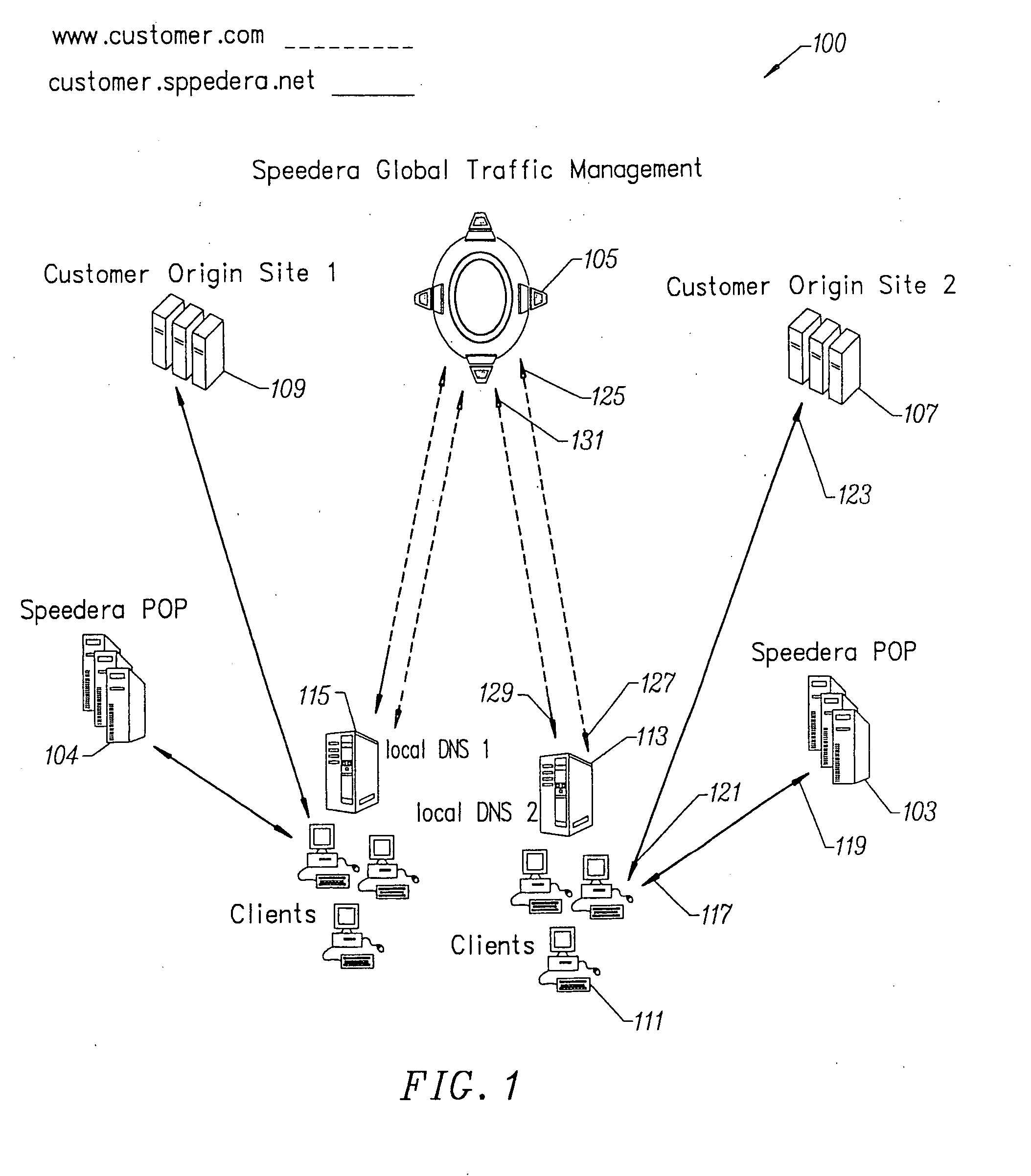
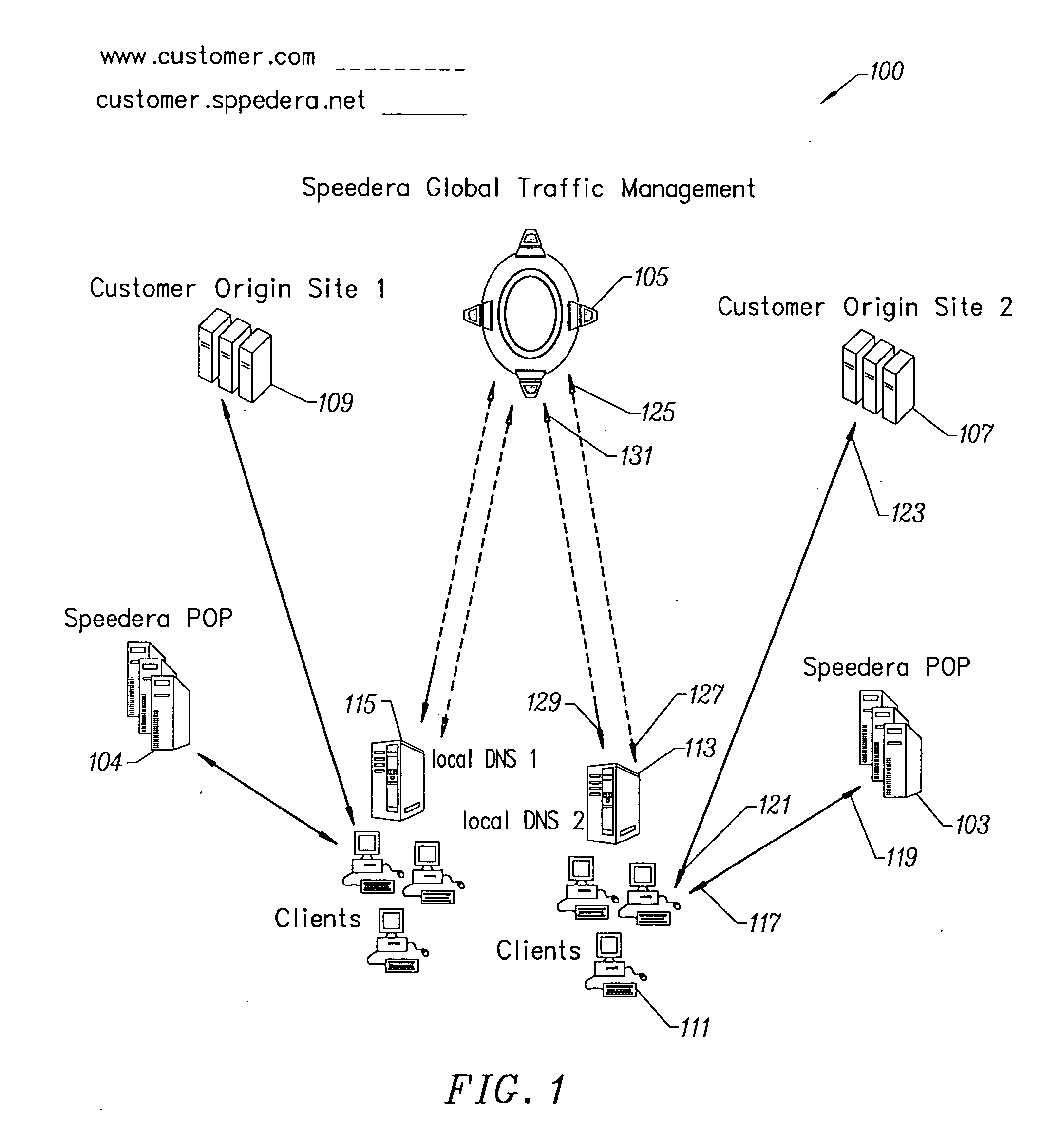
Content delivery and global traffic management network system
InactiveUS20020052942A1Meet cutting requirementsReduce trafficMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionWeb serviceCache server
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
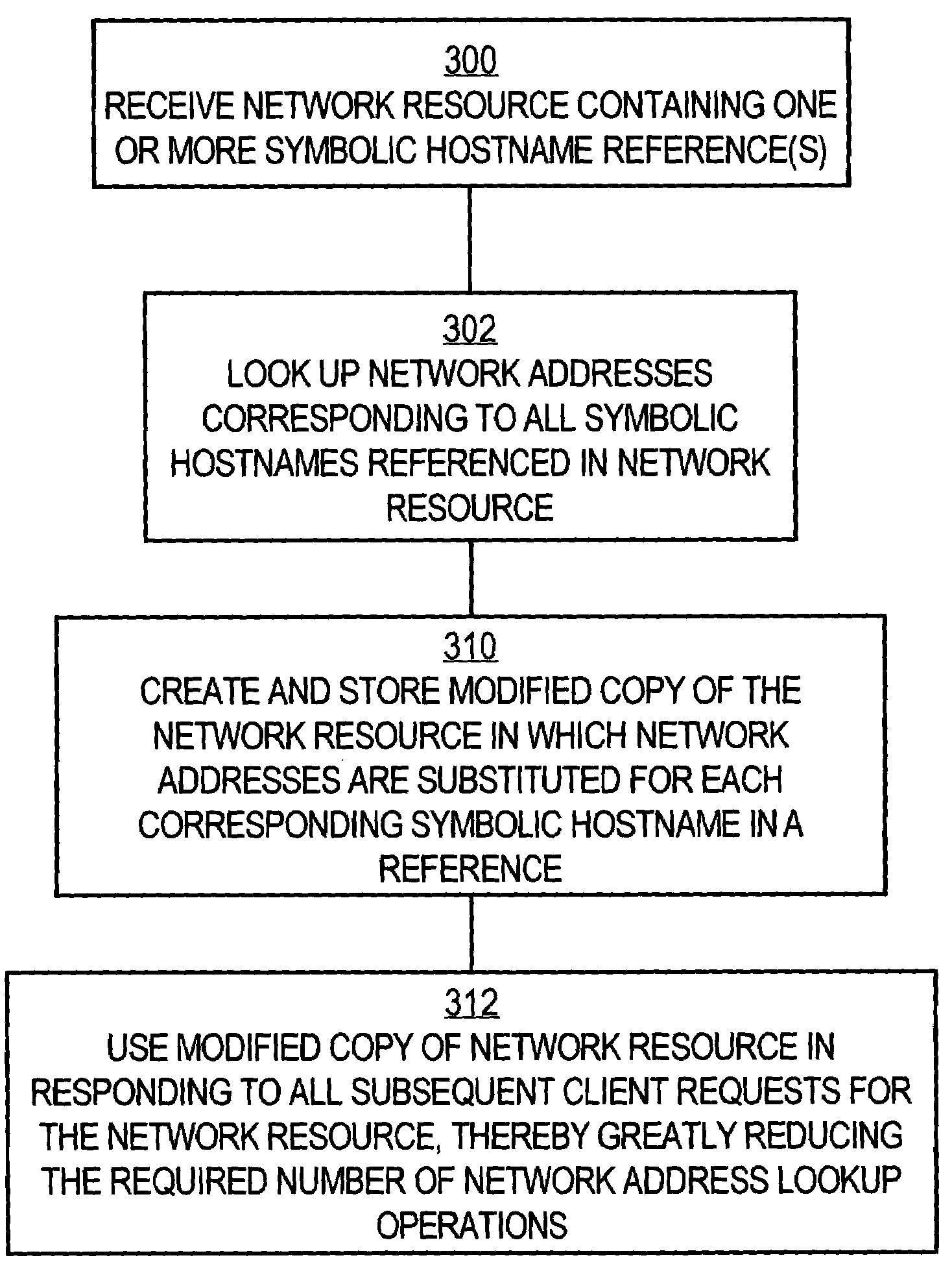
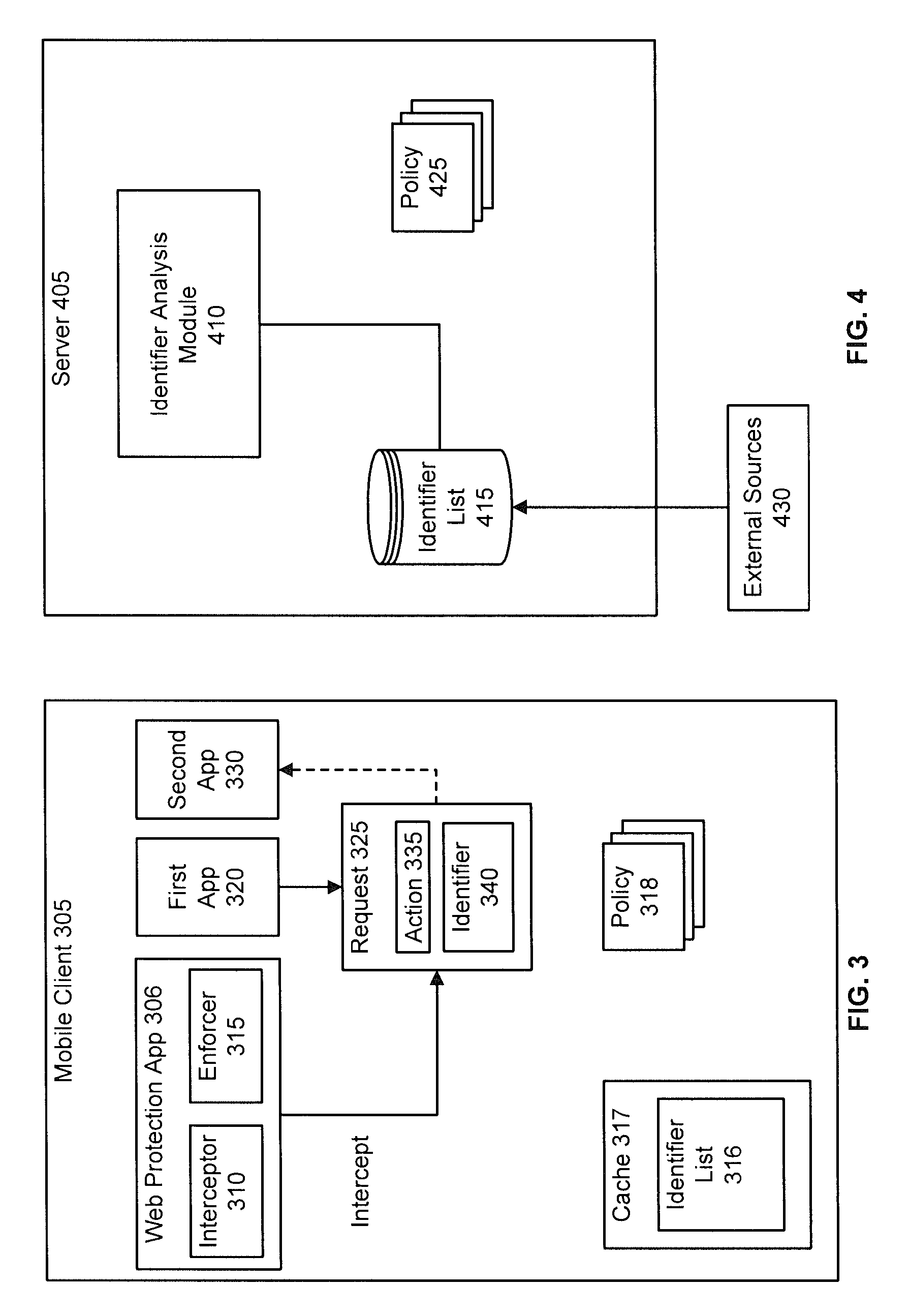
System and method of optimizing retrieval of network resources by identifying and substituting embedded symbolic host name references with network addresses in accordance with substitution policies
InactiveUS7082476B1Reduce in quantityEasy accessMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionCache serverNetwork addressing
A method and apparatus are provided for optimizing retrieval of network resources. In one embodiment, a method of optimizing access to a network resource is implemented in a computer program executed by a router, cache server, or proxy server. A network resource that contains one or more embedded symbolic host name references is received. A network address corresponding to each of the embedded symbolic host name references is determined. A modified copy of the network resource is created and stored; in the modified copy, a network address is substituted for each corresponding embedded symbolic host name reference. Thereafter, the modified copy of the network resource in responding to all subsequent client requests for the network resource, thereby greatly reducing the required number of network address lookup operations. In one specific embodiment, IP addresses are determined using DNS queries for the hostname portion of all URLs that are embedded in a Web page using image, applet, object, or embed tags. The IP addresses are stored in place of the hostname portions in a modified copy of the Web page, typically in a cache. As a result, when the modified page is subsequently served to clients, the clients need not carry out DNS resolution of all the embedded URLs, resulting in reduced network message traffic and more rapid page display.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
User specific request redirection in a content delivery network
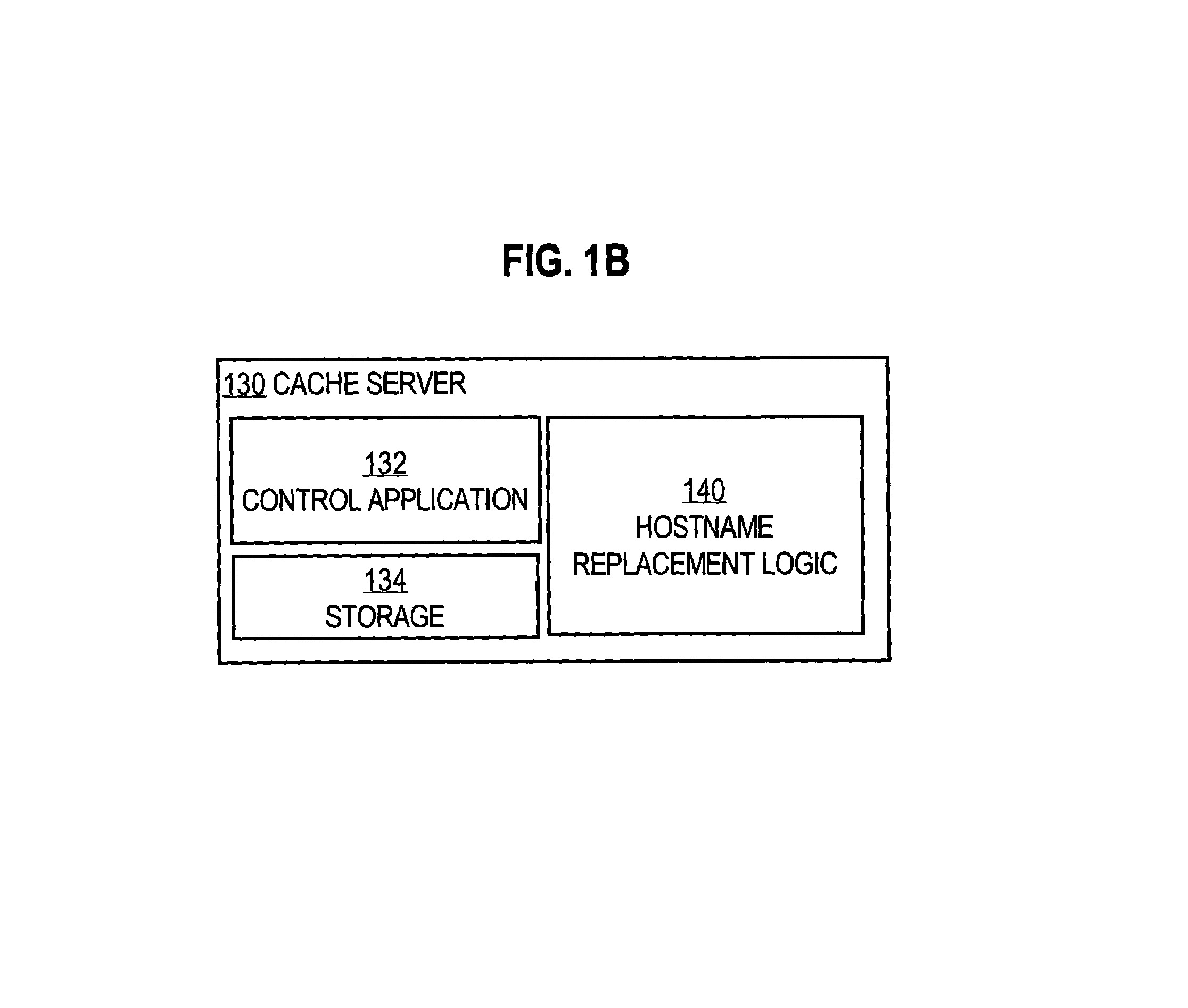
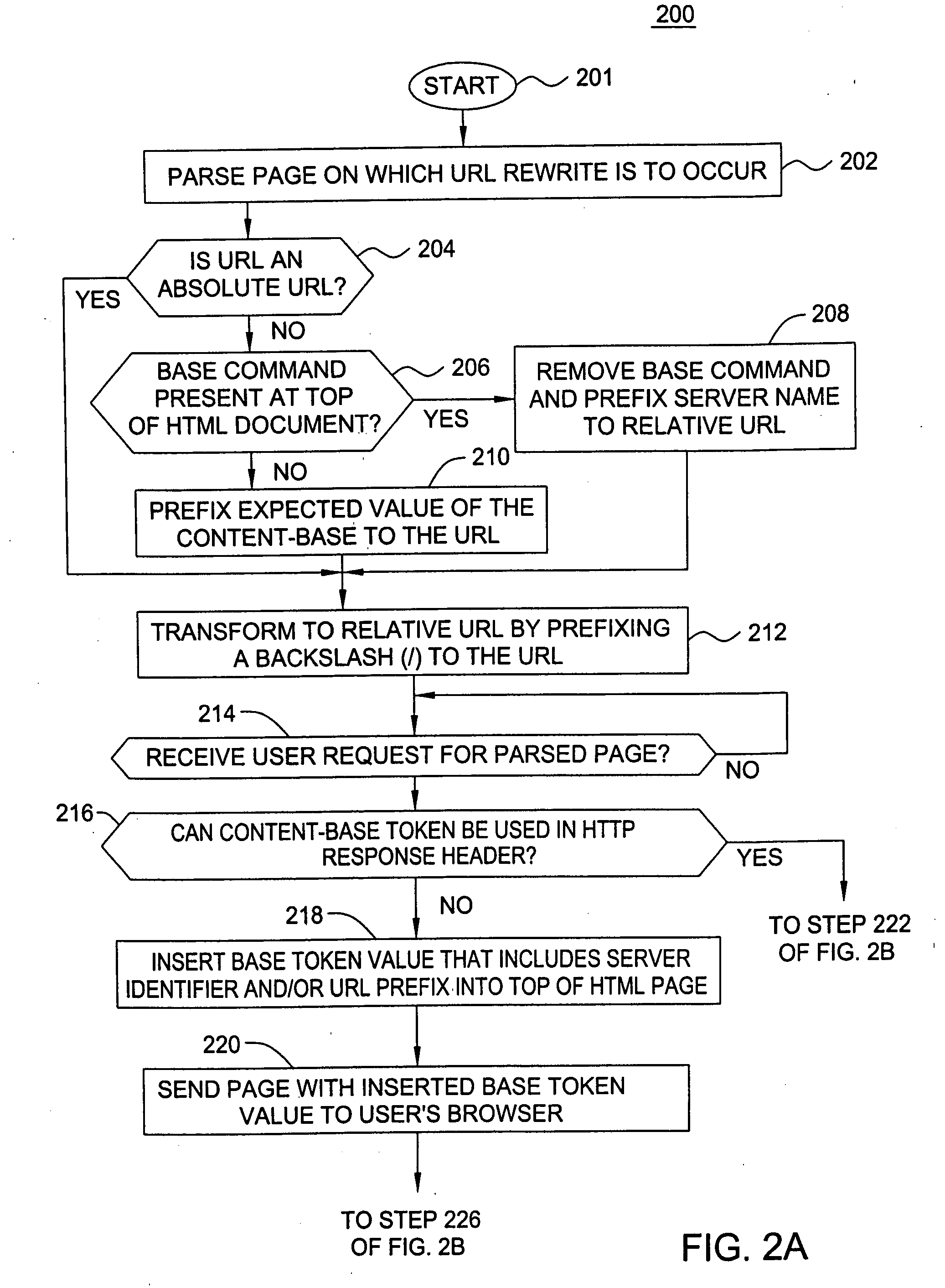
A method and apparatus for providing user specific request redirection in a content delivery network includes parsing a page having embedded objects intended for redirection to at least one cache server, and transforming the embedded objects into relative uniform resource locators (URLs). A content-base token is inserted into an HTTP response header in response to a user request for the page. In an instance where the content-base token is not supported by the server and / or client devices, a base token is inserted into the page in response to a user request for the page. The content-base token and base token provide identification of a server or URL prefix where the embedded objects in the page are to be retrieved. The requested page is then sent to the user's browser. The browser constructs absolute URLs from the embedded URLs using either the received content-base token or base token, to retrieve embedded objects from the server.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Network caching using resource redirection
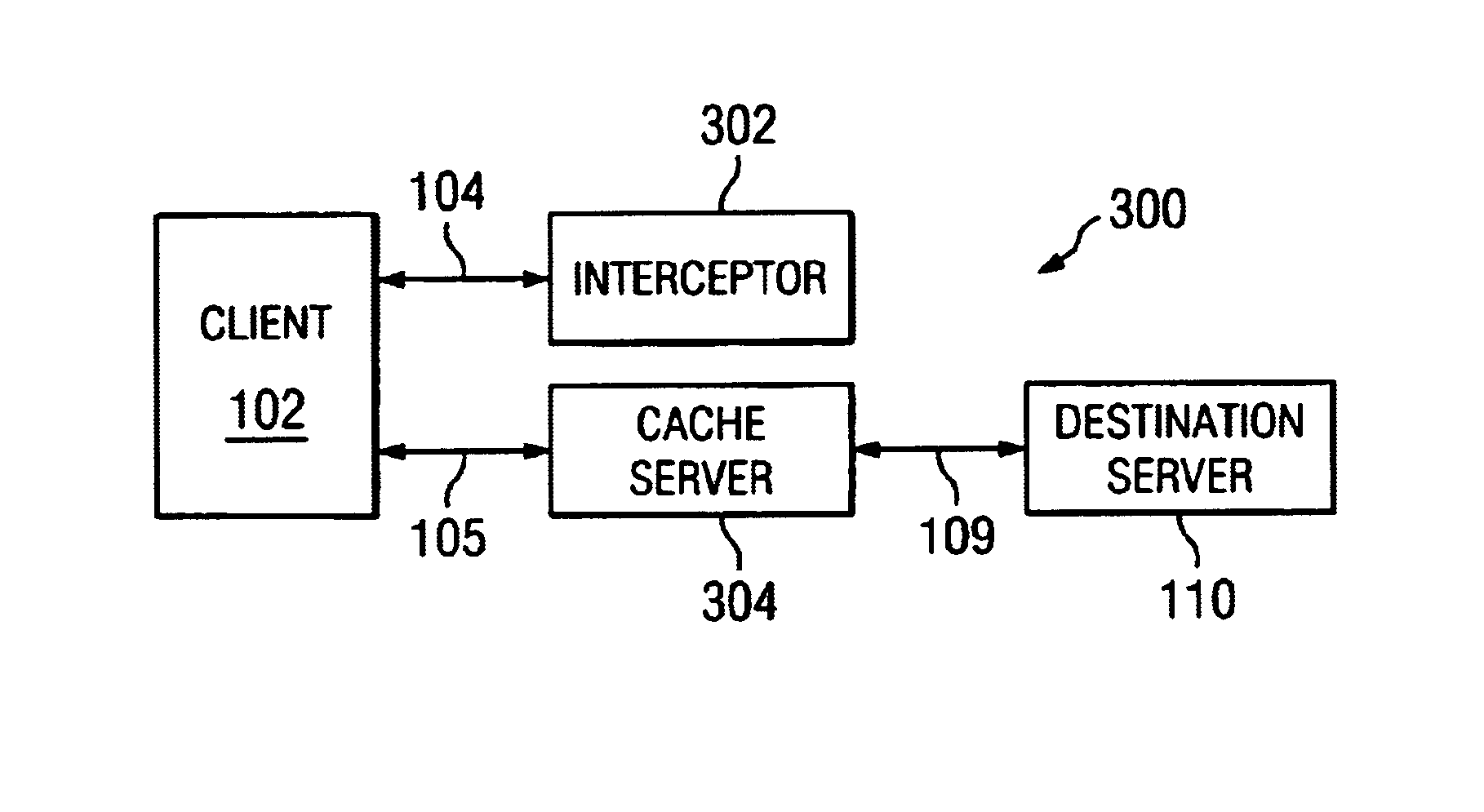
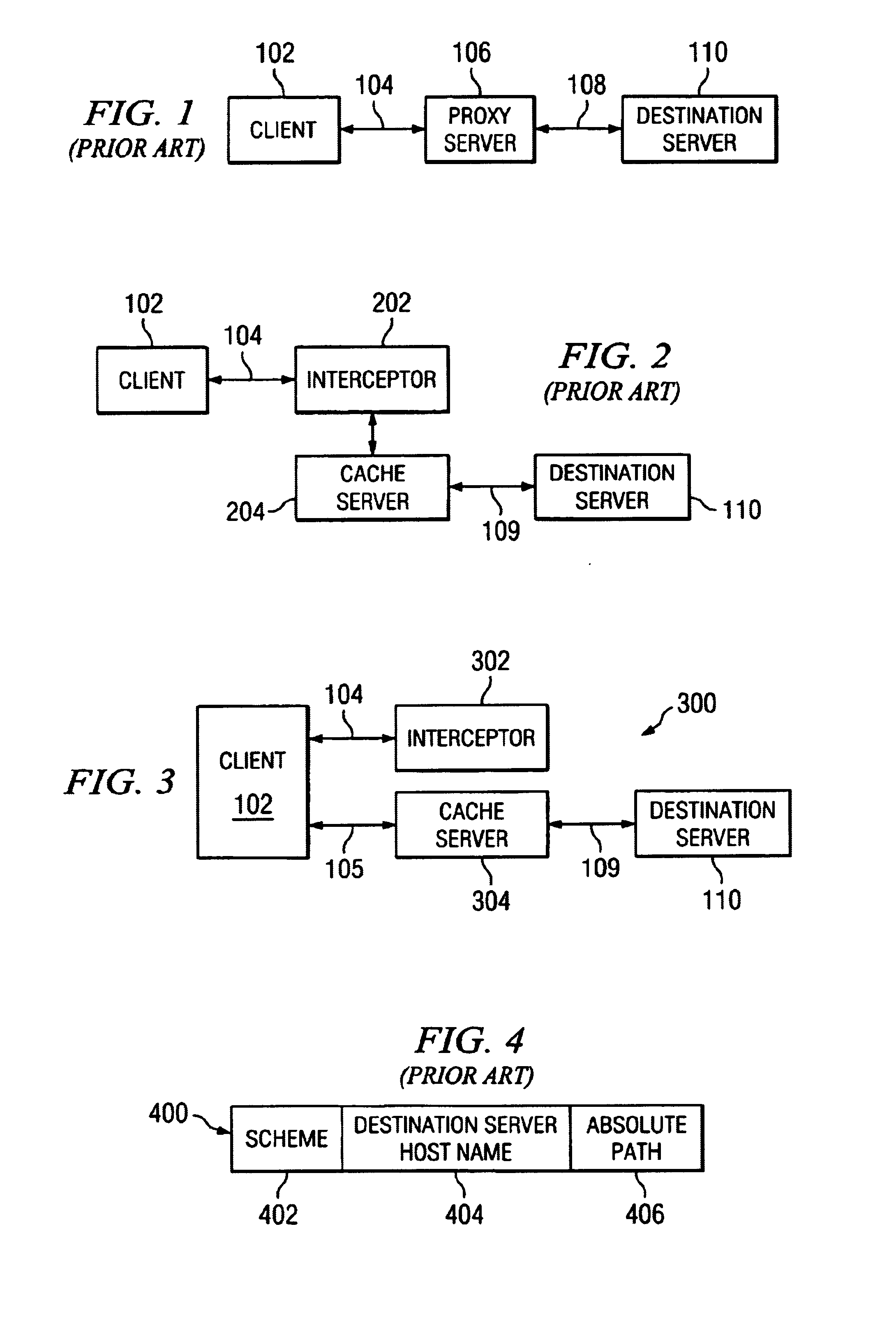
InactiveUS7080158B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCache serverClient-side
A caching technique uses an interceptor situated between the client and the destination server to redirect client requests to a cache server. Specifically, the client transmits a request message that includes a reference to the intended destination server. The interceptor receives the client request and, based on the intended destination server, selects an appropriate cache server to handle the request. The interceptor then sends a response to the client including references to the cache server and to the intended destination server. Upon receiving the response, the client contacts the cache server directly using the reference included in the response.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Load balancing service
InactiveUS7346676B1Efficient executionMeet cutting requirementsDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsCache serverWeb service
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
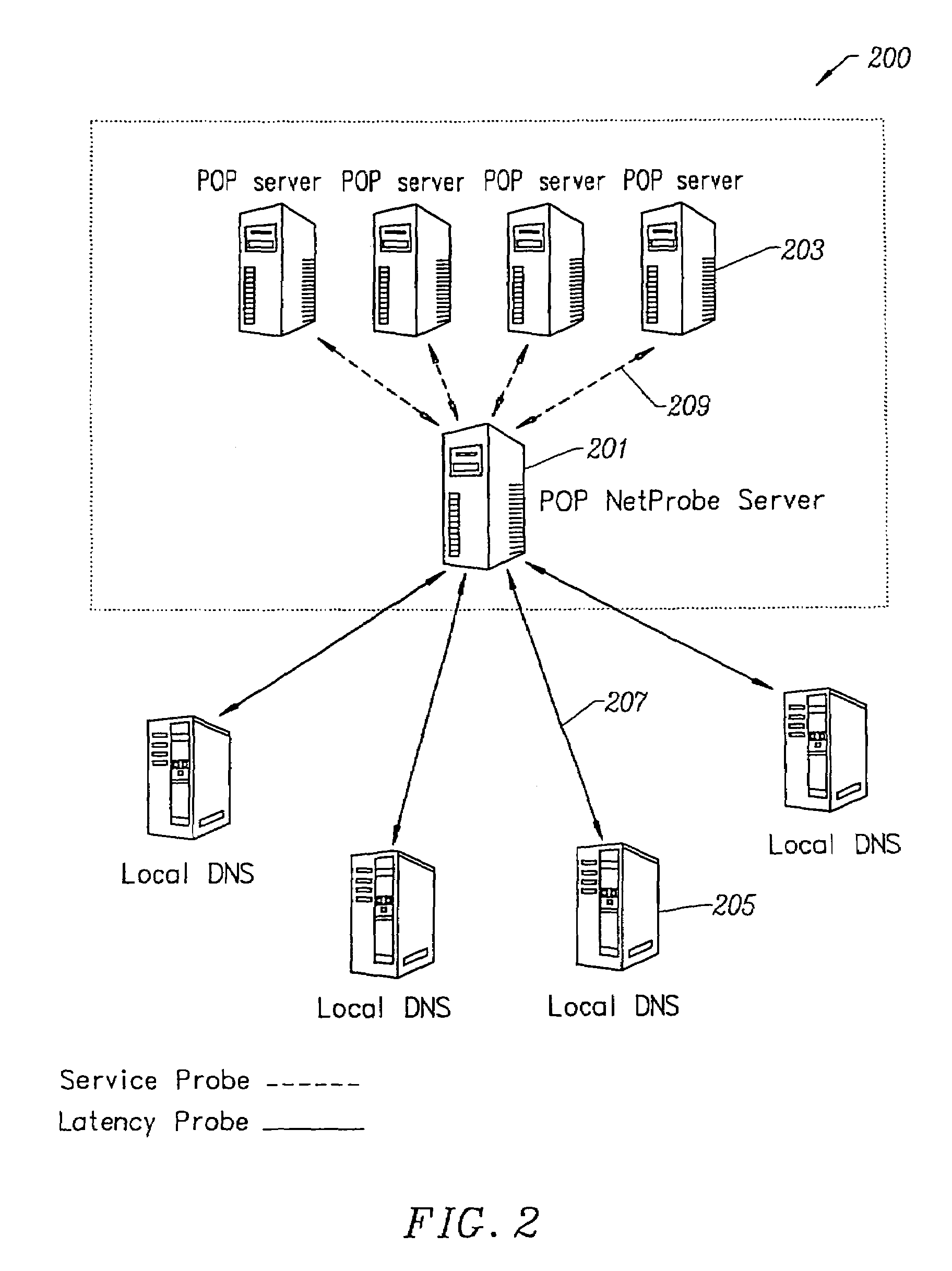
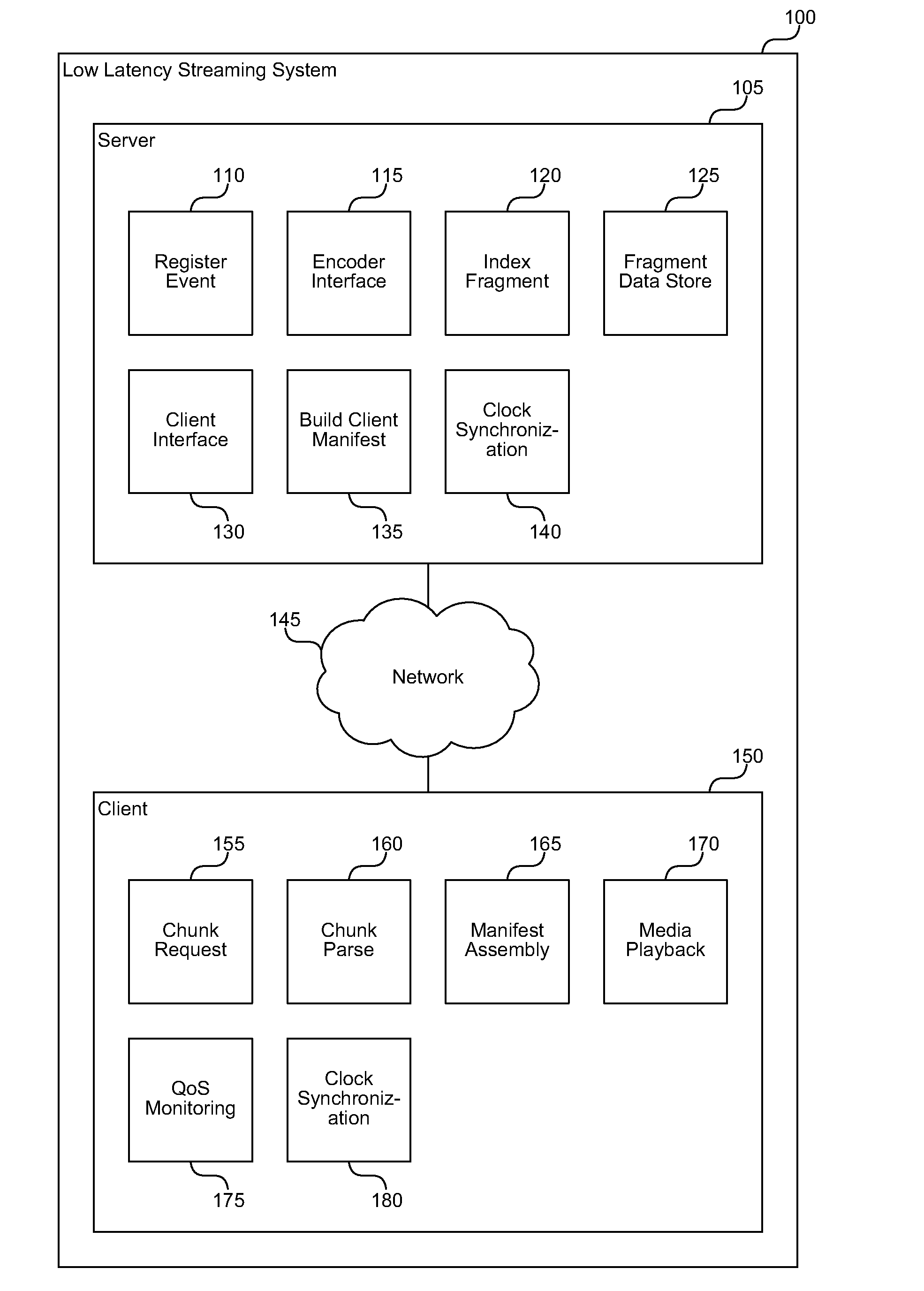
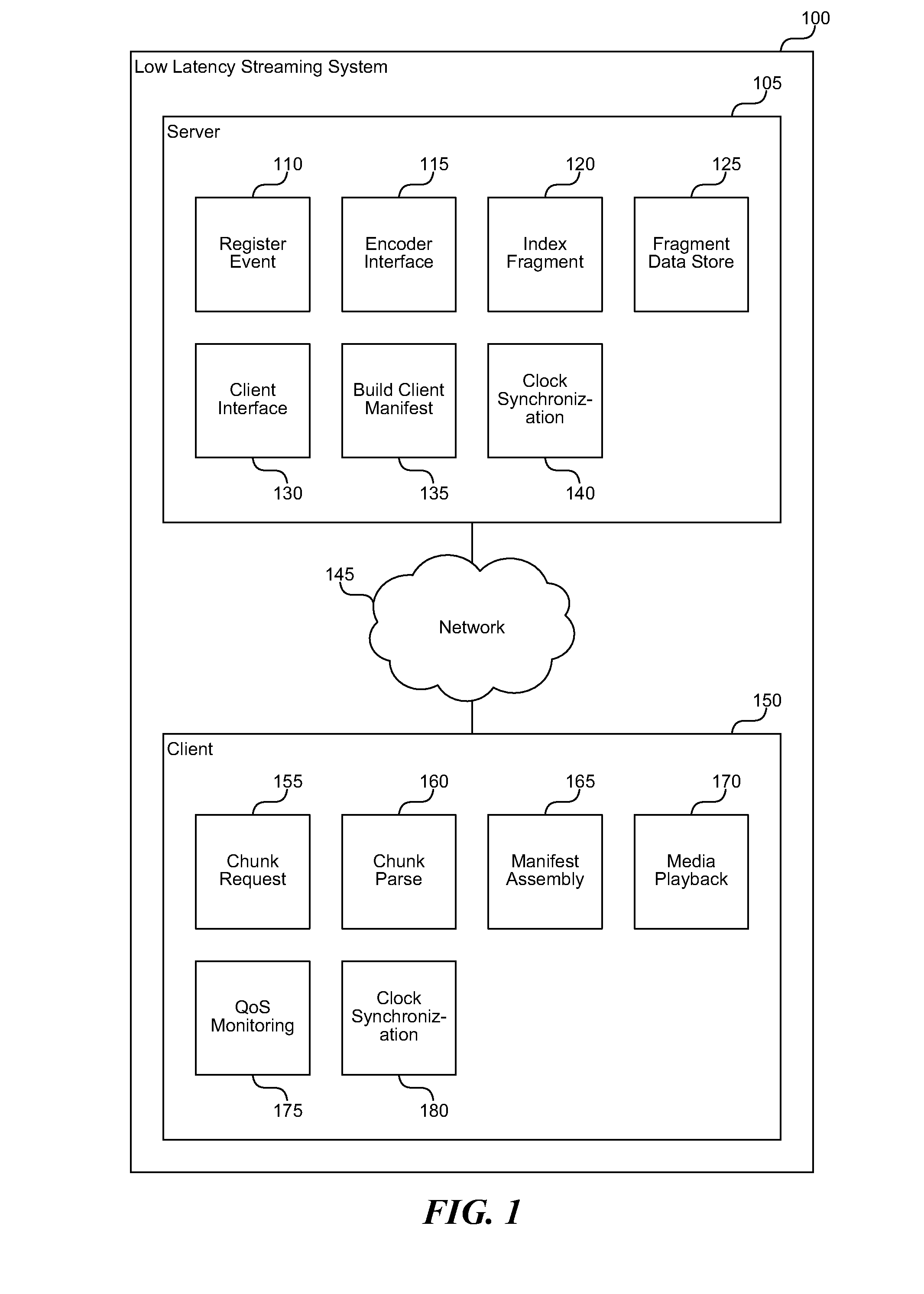
Low latency cacheable media streaming
ActiveUS20110080940A1Lower latencyRaise the possibilityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningGroup of picturesCache server
A low latency streaming system provides a stateless protocol between a client and server with reduced latency. The server embeds incremental information in media fragments that eliminates the usage of a typical control channel. In addition, the server provides uniform media fragment responses to media fragment requests, thereby allowing existing Internet cache infrastructure to cache streaming media data. Each fragment has a distinguished Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that allows the fragment to be identified and cached by both Internet cache servers and the client's browser cache. The system reduces latency using various techniques, such as sending fragments that contain less than a full group of pictures (GOP), encoding media without dependencies on subsequent frames, and by allowing clients to request subsequent frames with only information about previous frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
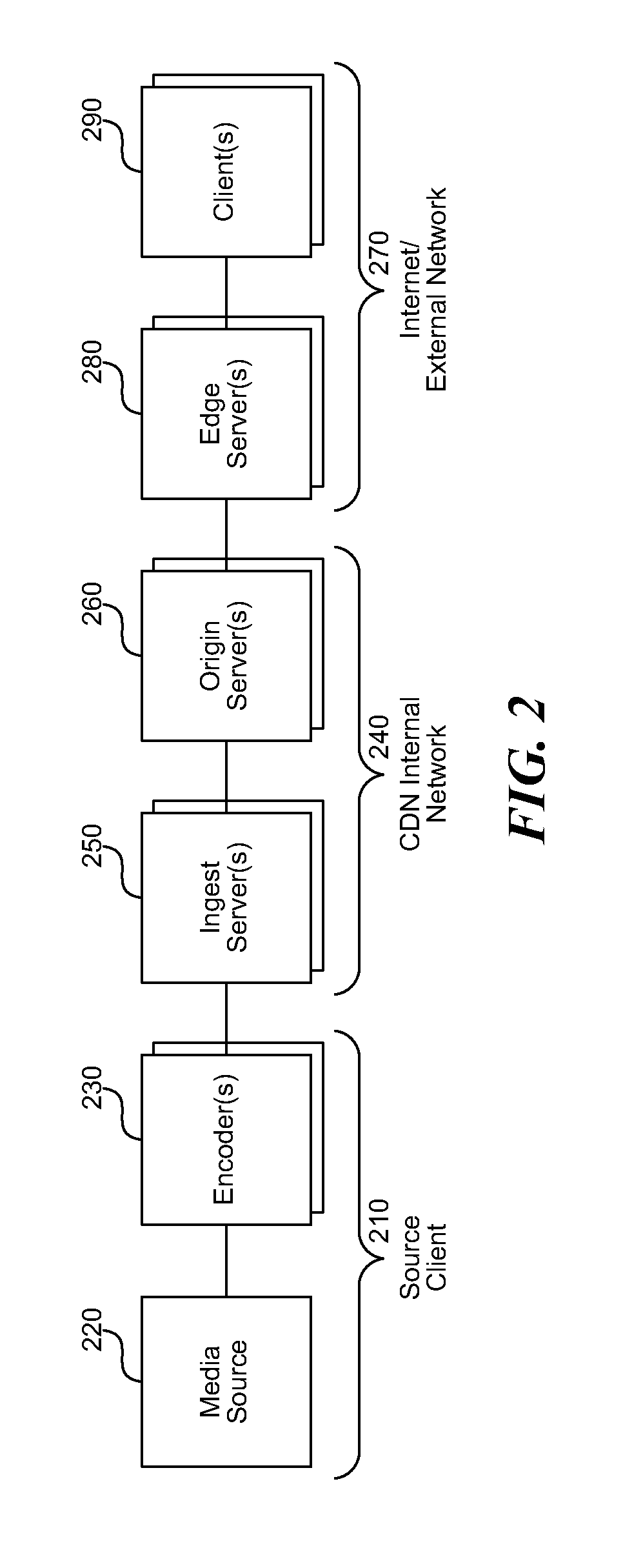
Content delivery and global traffic management network system
InactiveUS20070174426A1Effective distributionFast response timeMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsMultiprogramming arrangementsBalancing networkWeb service
A content delivery and global traffic management network system provides a plurality of caching servers connected to a network. The caching servers host customer content that can be cached and stored, and respond to requests for Web content from clients. If the requested content does not exist in memory or on disk, it generates a request to an origin site to obtain the content. A DNS Server load balances network requests among customer Web servers and directs client requests for hosted customer content to the appropriate caching server. The customer pays a service that provides the content delivery and global traffic management network system a fee for usage of the content delivery and global traffic management network system.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
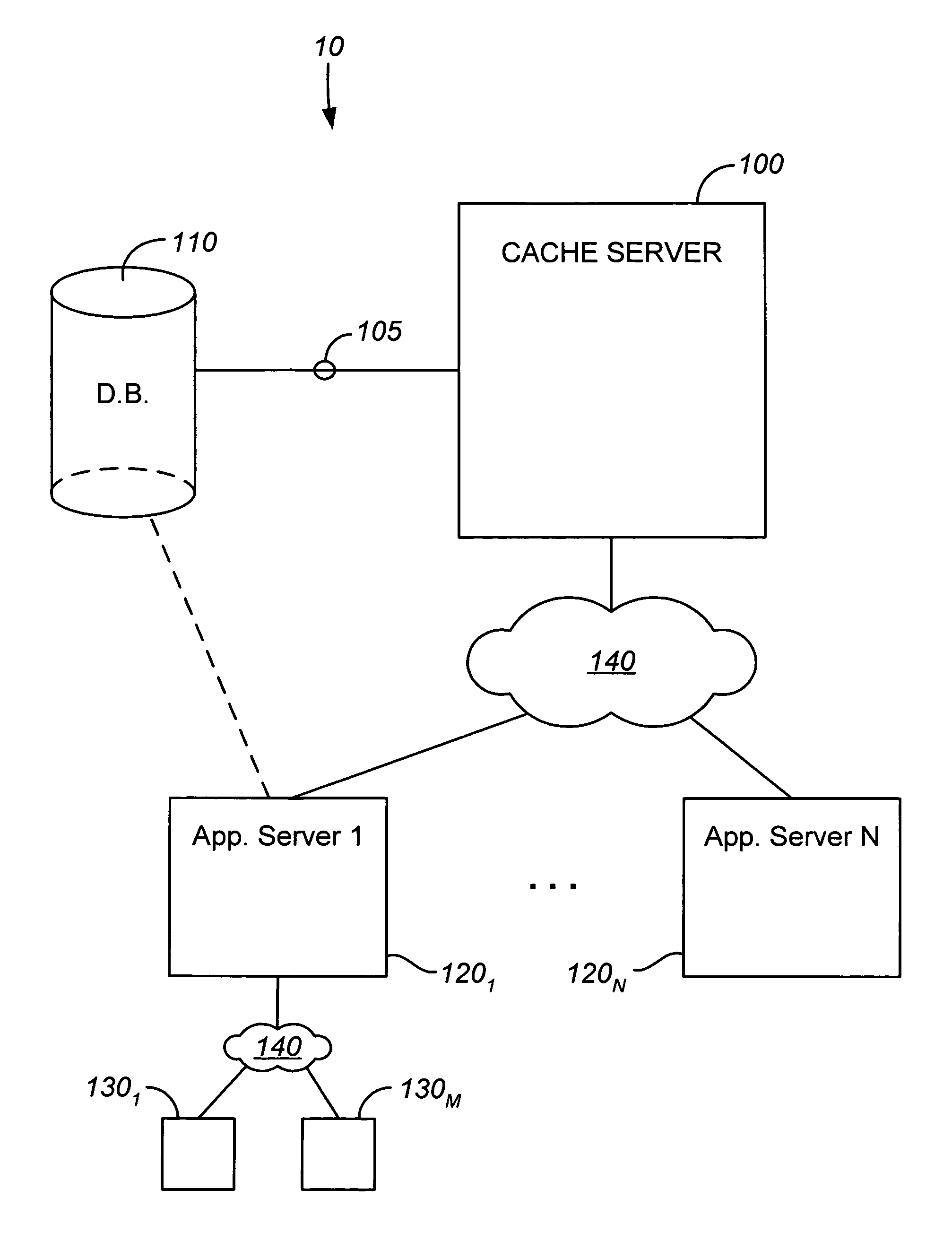
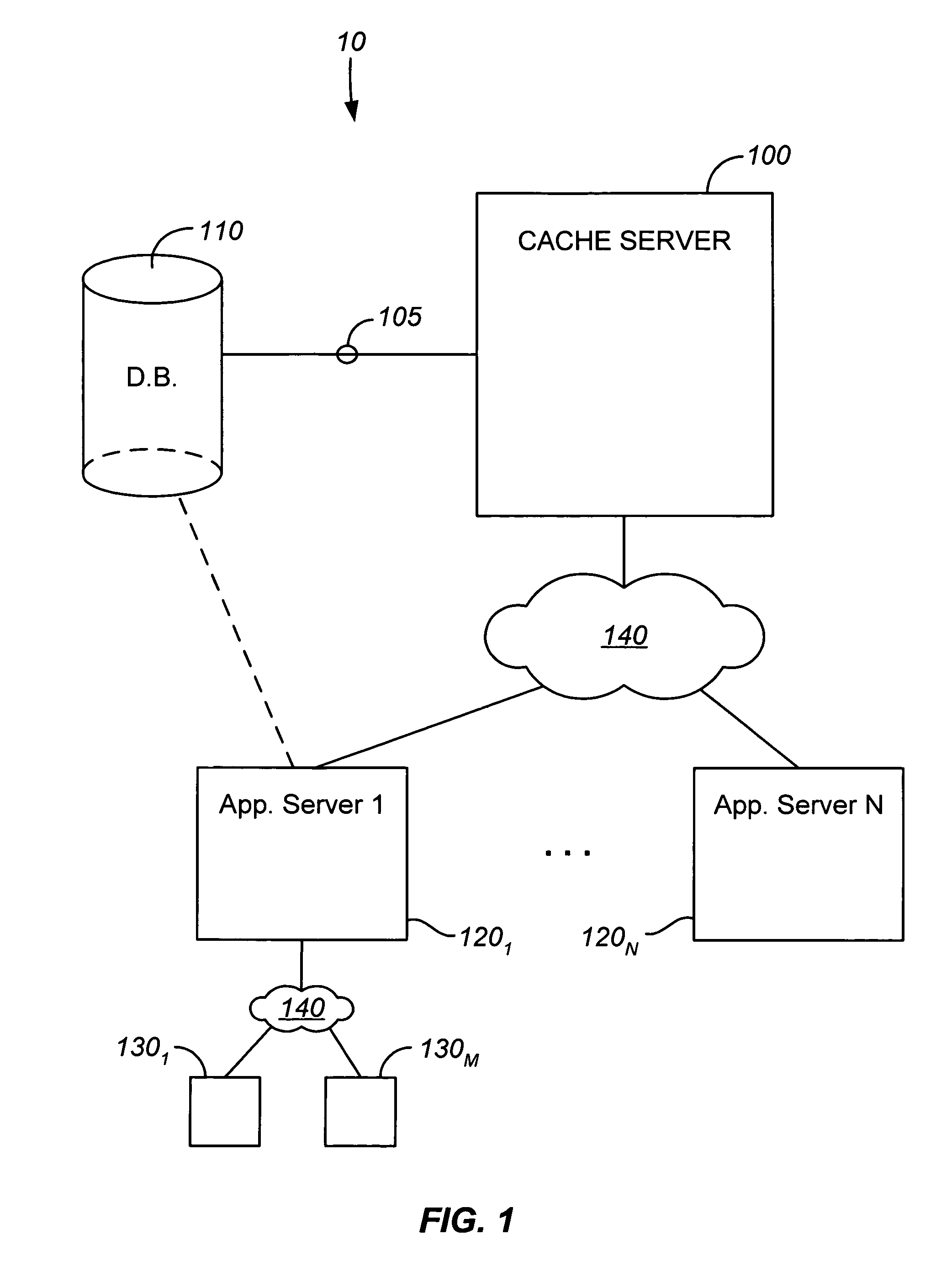
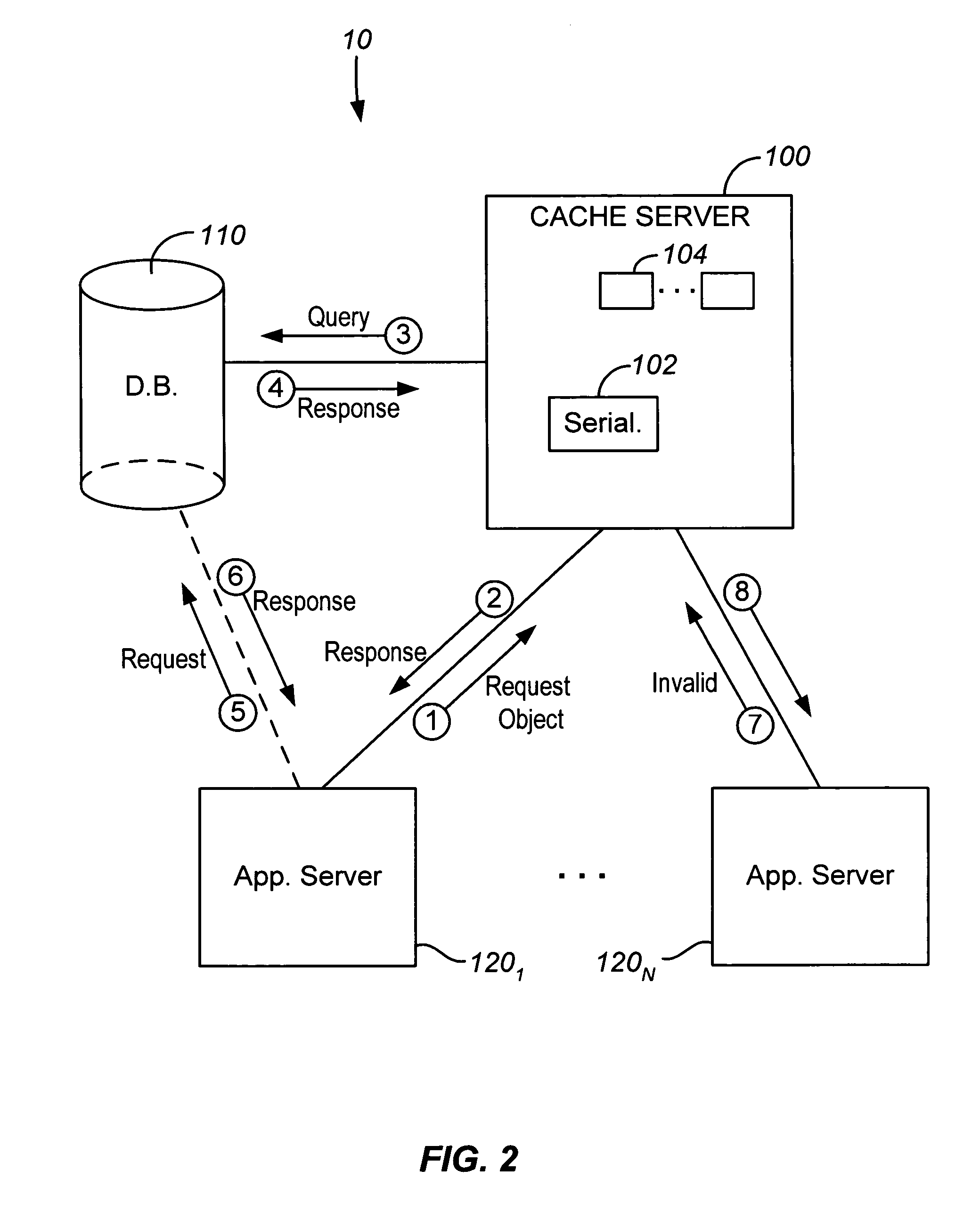
Java object cache server for databases
ActiveUS7209929B2Reduce loadReduce processing loadData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsApplication serverCache server
A cache server is provided in a network for storing Java objects for retrieval by one or multiple application servers. Application server(s) are configured to request an object from the cache server, rather than requesting the Java object directly from a database, so as to reduce processing load on the database and free up database resources. Responsive to a request for a Java object from an application server, e.g., in an HTTP request, the cache server determines if the object is stored in memory and if so, serializes the requested object and sends the serialized object to the requesting server, e.g., in an HTTP response. The requesting server then deserializes the Java object. If the object is not stored in memory, the cache server instantiates the object (typically by requesting the object from the database), serializes the instantiated object and sends it to the requesting server. Cache coherency methods are also provided.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Load balancing service
InactiveUS20050033858A1Efficient executionMeet cutting requirementsError preventionTransmission systemsLoad SheddingCache server
A load balancing service for a plurality of customers performs load balancing among a plurality of customer Web servers. Requests for Web content are load balanced across the customer Web servers. The load balancing service provider charges a fee to the customers for the load balancing service. A caching service is also provided that comprises a plurality of caching servers connected to a network. The caching servers host customer content that can be cached and stored, e.g., images, video, text, and / or software. The caching servers respond to requests for Web content from clients. The load balancing service provider charges a fee to the customers for the Web caching service
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
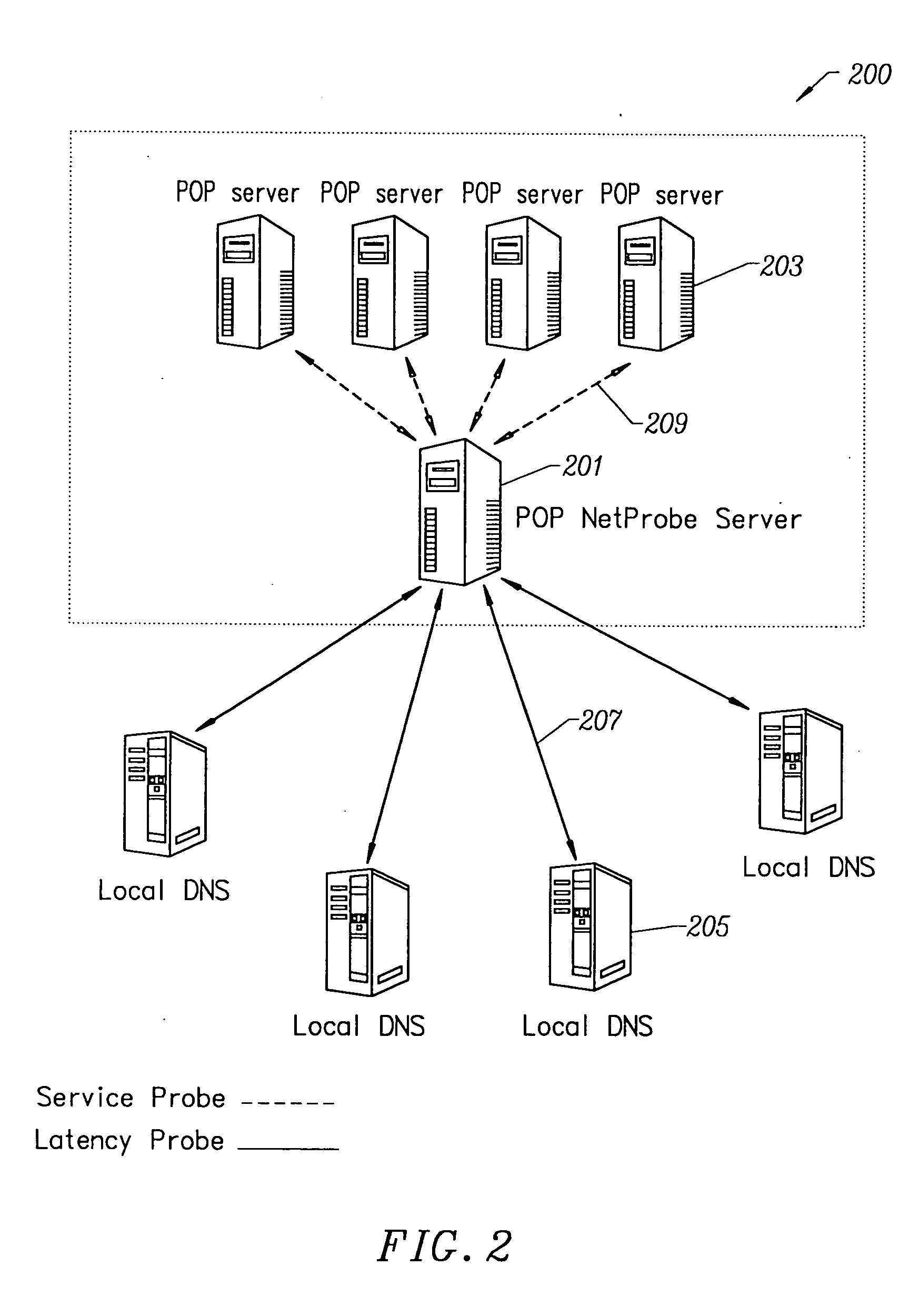
Method for network-aware clustering of clients in a network
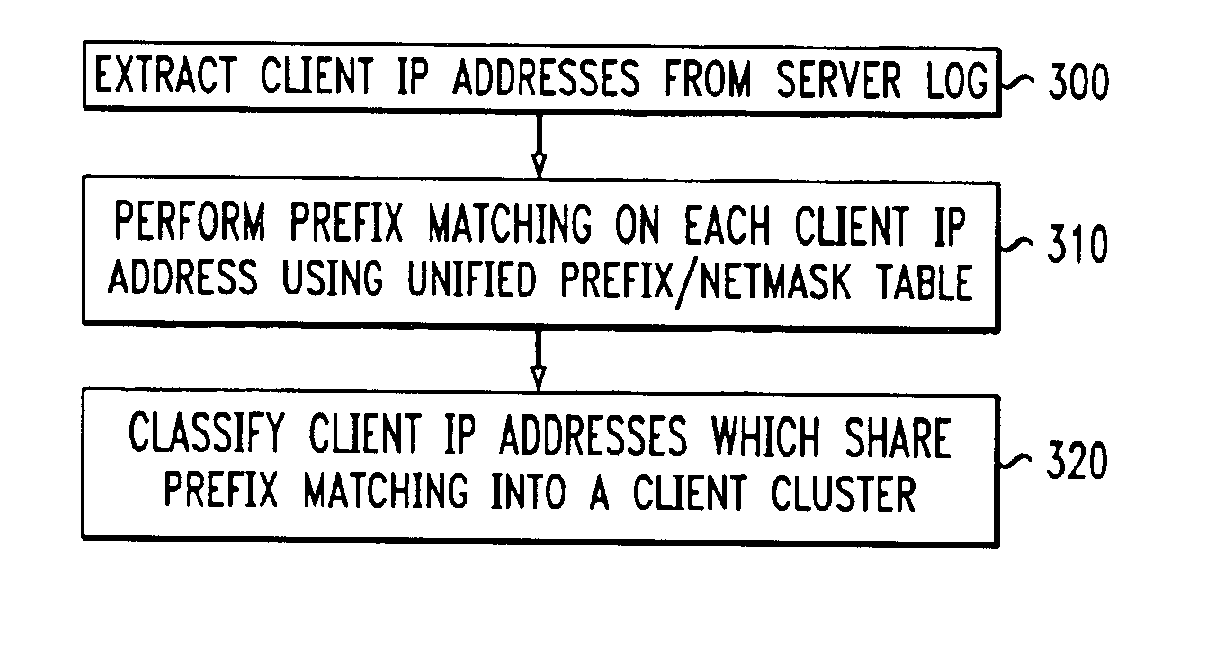
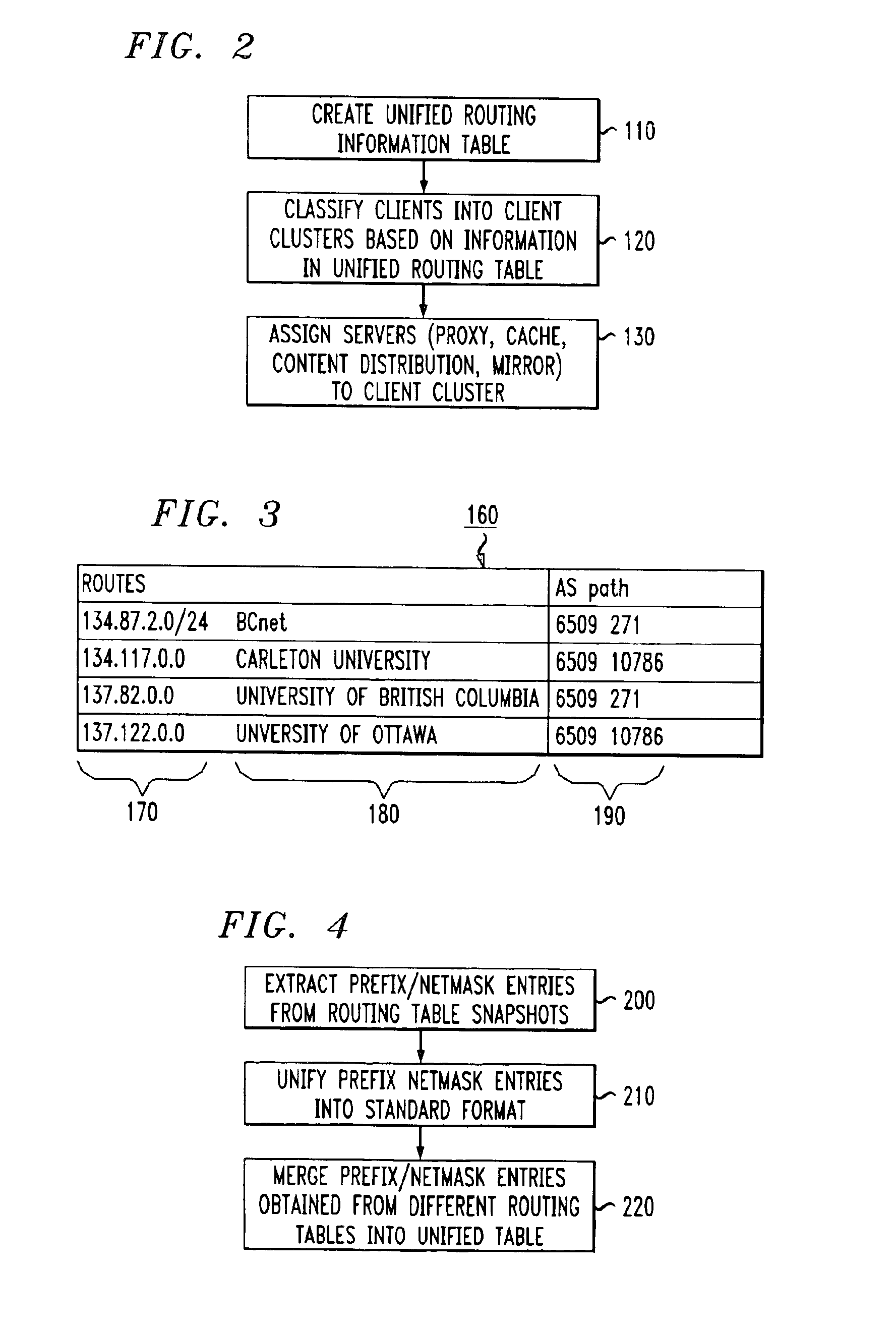
InactiveUS6928485B1Relational databasesMultiple digital computer combinationsServer logContent distribution
A method for clustering together network clients for guiding of placement of network servers is disclosed. A number of routing table prefix / netmask entries are aggregated and unified into a tubular format. The routing table entries may be converted into a singular format. A network server log is used to extract a number of client IP addresses which are compared to the entries within the unified routing table. A common prefix shared by a number of the client IP addresses and an entry in the unified routing table is determined and used to cluster the clients together in a client cluster. Network servers, such as proxy server, cache servers, content distribution servers and mirror server may be placed in the network according to the client clusters.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
File bundling for cache servers of content delivery networks
InactiveUS20110276623A1Easy data accessReduce read operationsDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveCache server
Data access time in content delivery networks is improved by storing files in cache servers as file bundles. A cache server determines that multiple files are requested by the same client based on information available in the request including the IP address of the client, a URL of a webpage referring to the file, and / or a cookie stored at a client. The cache server stores multiple files requested by the same client on the hard drive as a file bundle with meta data associating the files with one another, such that they can be accessed together. A future request from the client for a file in a file bundle results in multiple files from the file bundle being loaded in the memory. If the client requests another file from the file bundle, the file is accessed directly from the memory instead of the hard drive, resulting in improved performance.
Owner:CDNETWORKS HLDG SINGAPORE PTE LTD
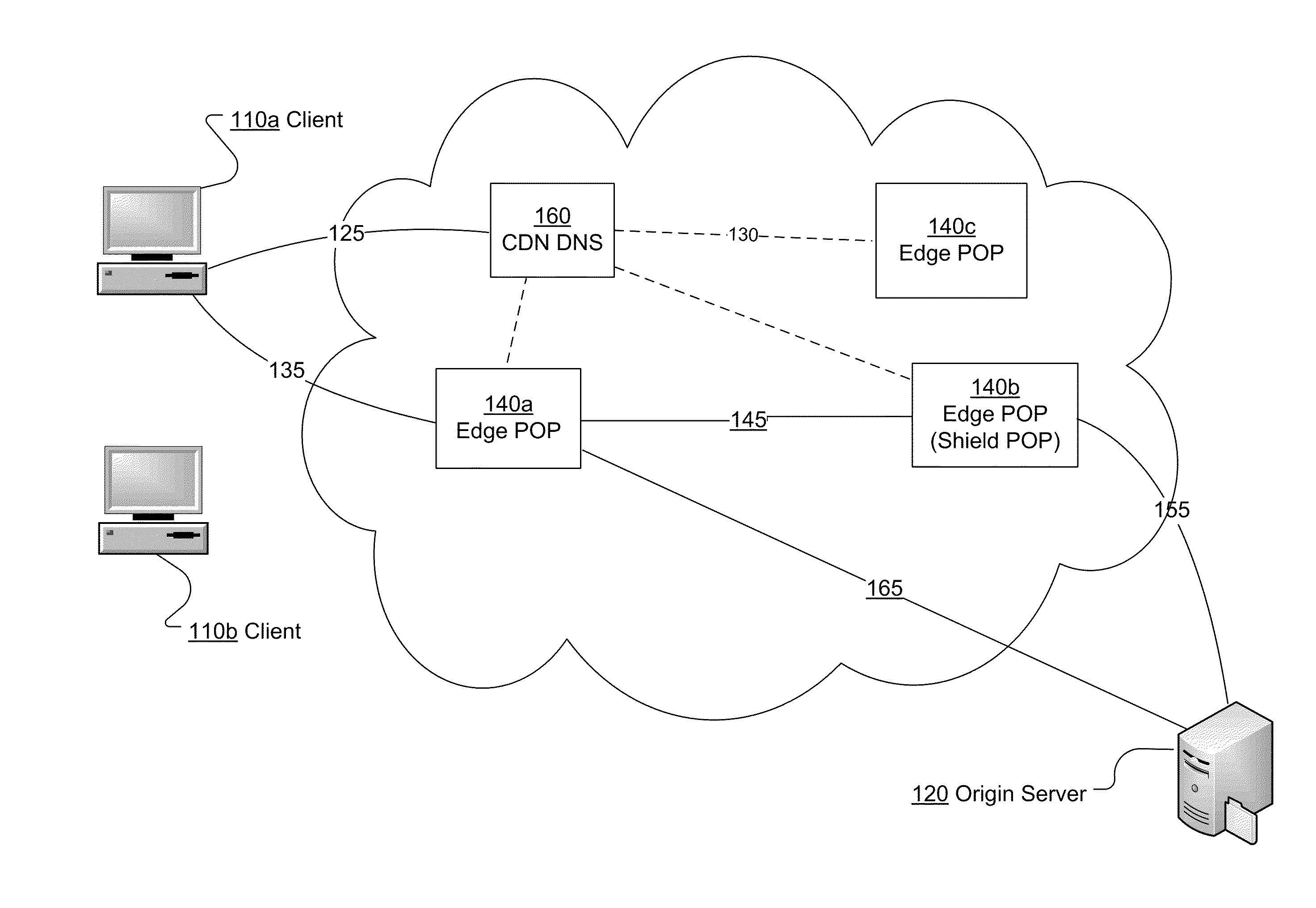
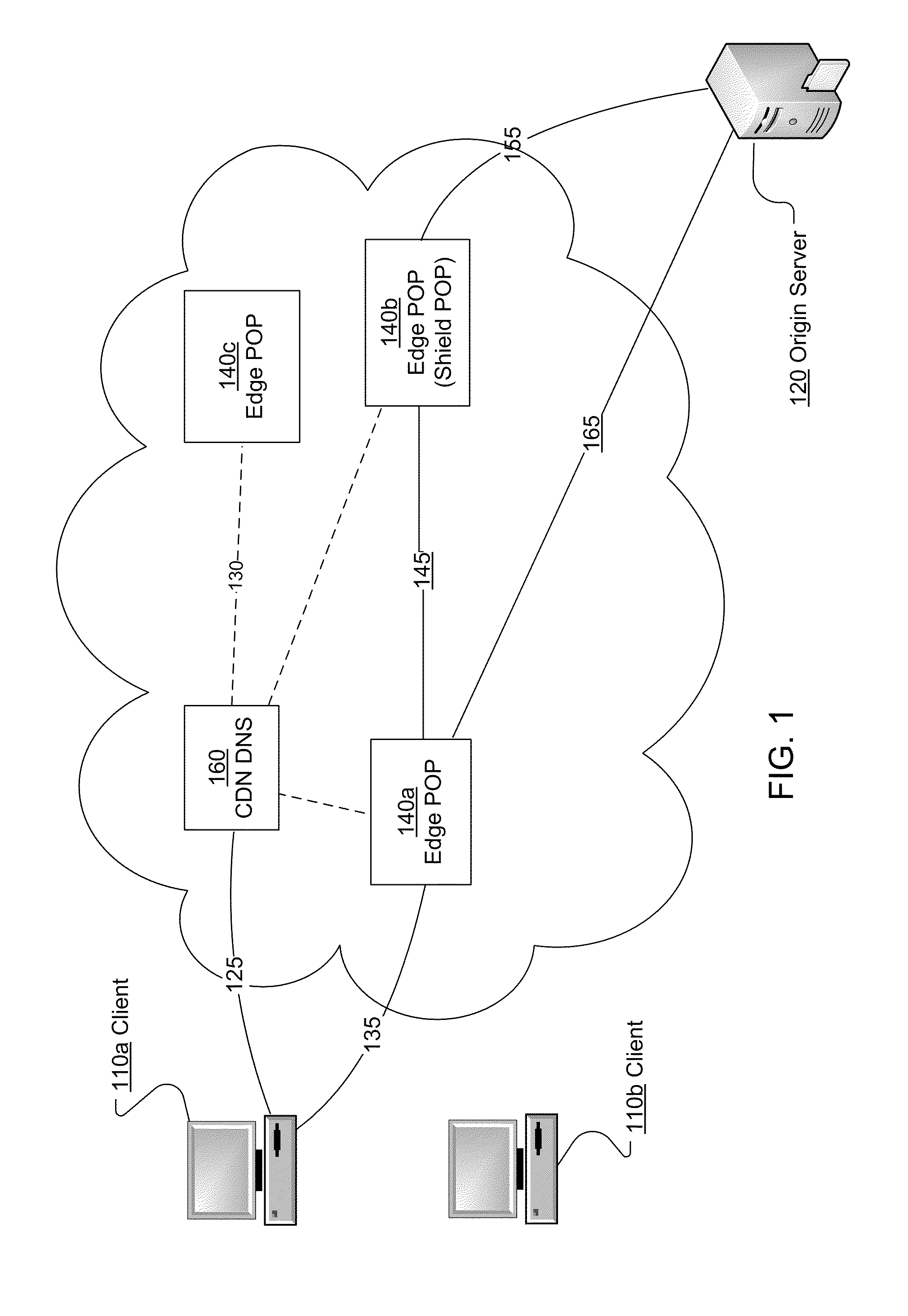
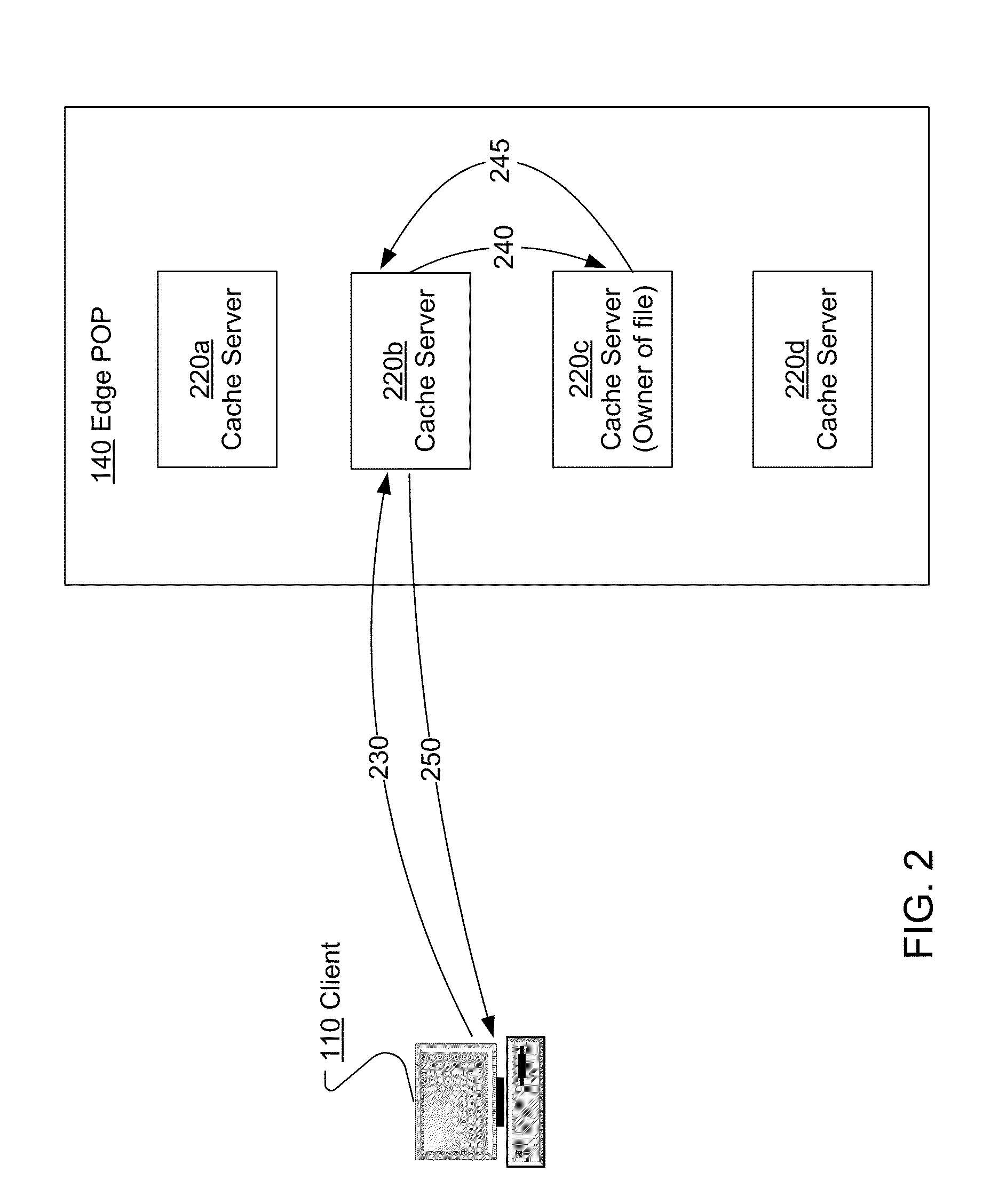
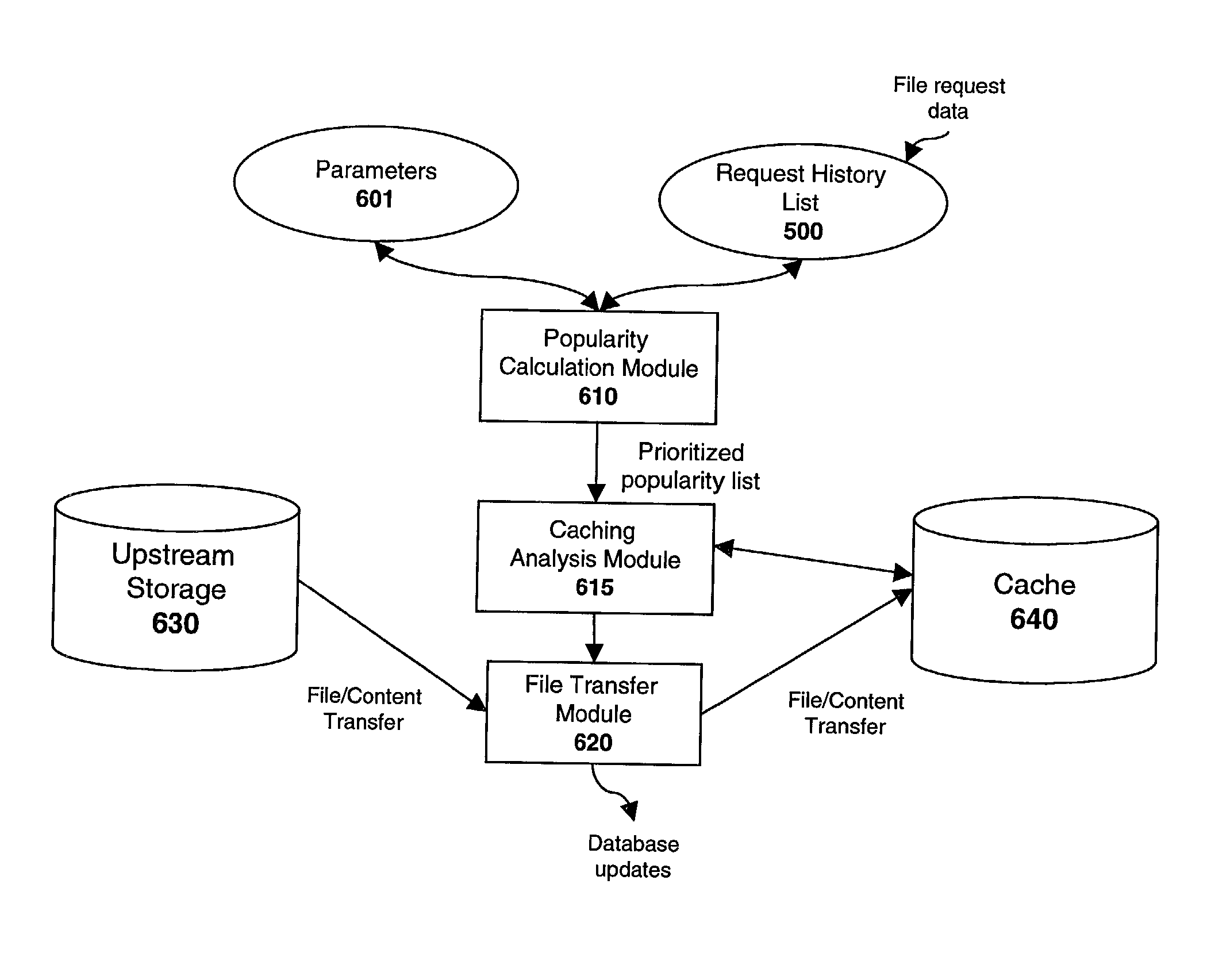
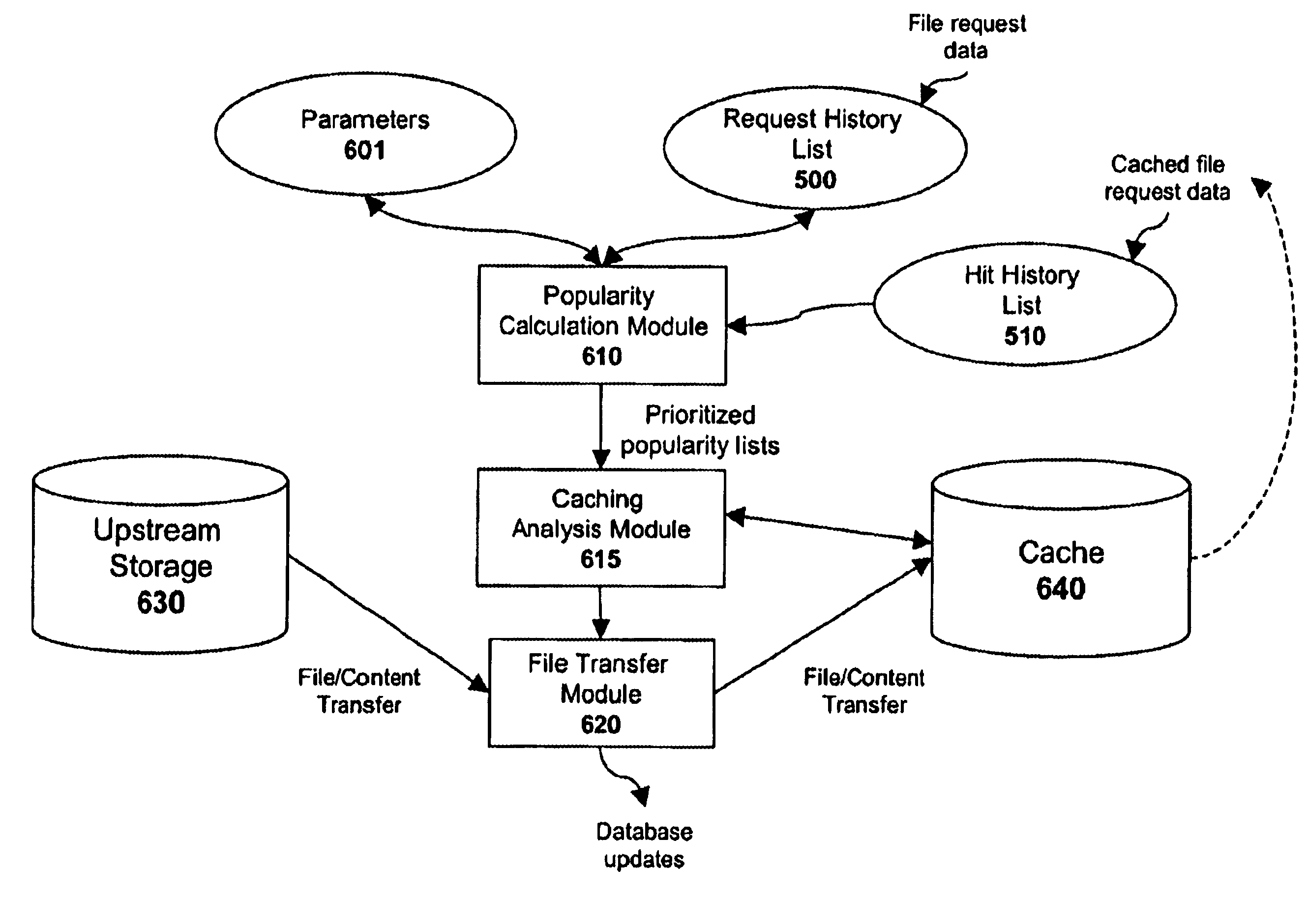
System and method for populating cache servers with popular media contents
InactiveUS20020087797A1Digital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCache serverDatabase
A system and method for caching files is disclosed. Popularity values are calculated for a plurality of files over a period of time. The popularity values are then used to determine which files should be cached at various remote sites. Once the caches are filled, the popularity values associated with the cached files are periodically compared with the popularity values of uncached content. Generally, if the popularity of an uncached file is greater than the popularity of a cached file, then the cached file will be replaced. However, numerous different variables may be factored into the caching determination including, for example, the size of the file, the required bitrate of the file, the identity of the owner of the file, and / or the type of file.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Proxy-based cache content distribution and affinity
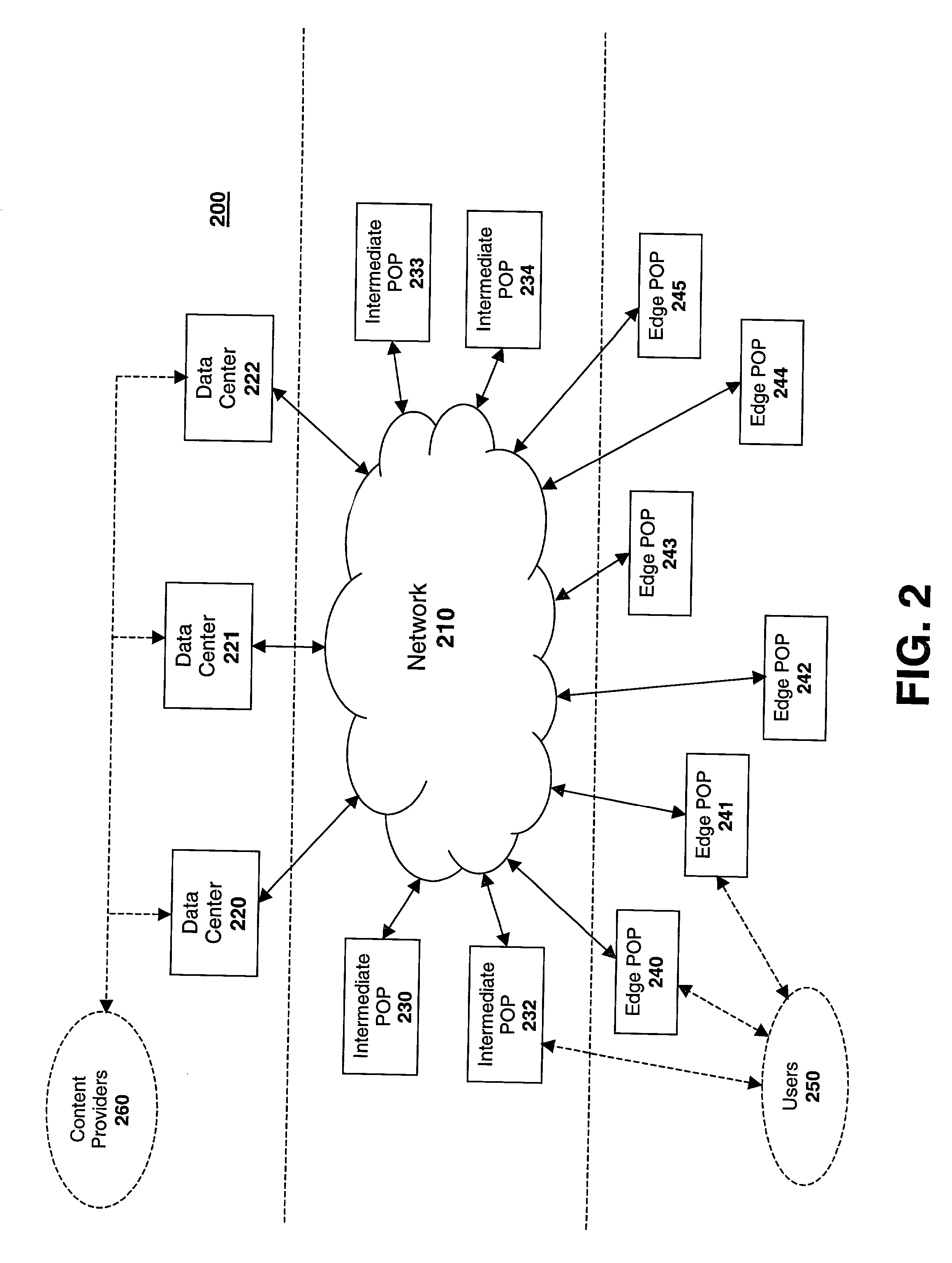
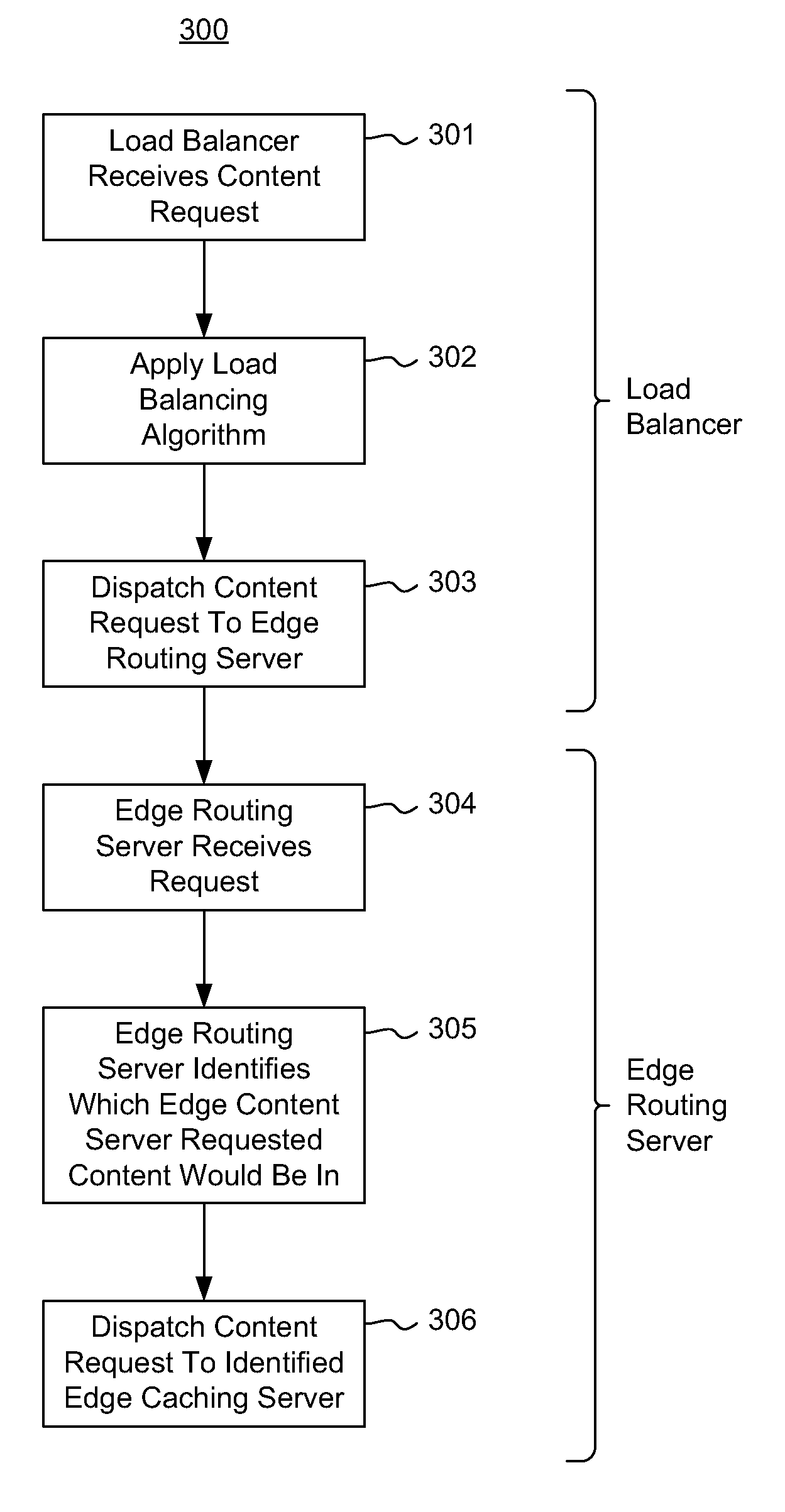
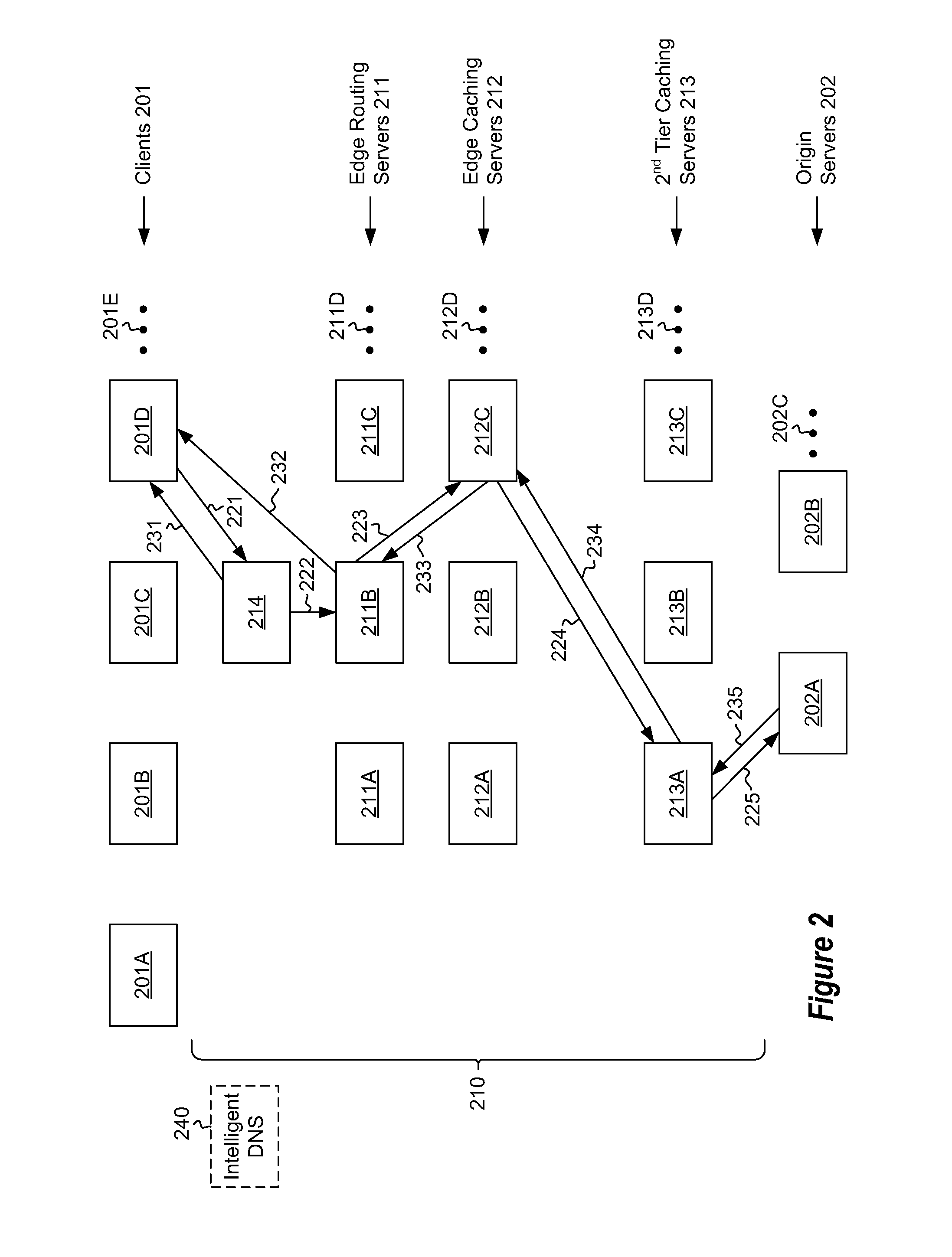
ActiveUS8612550B2Maximize likelihoodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent distributionMultiple edges
A distributed caching hierarchy that includes multiple edge routing servers, at least some of which receiving content requests from client computing systems via a load balancer. When receiving a content request, an edge routing server identifies which of the edge caching servers the requested content would be in if the requested content were to be cached within the edge caching servers, and distributes the content request to the identified edge caching server in a deterministic and predictable manner to increase the likelihood of increasing a cache-hit ratio.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for automatically updating content stored on servers connected by a network
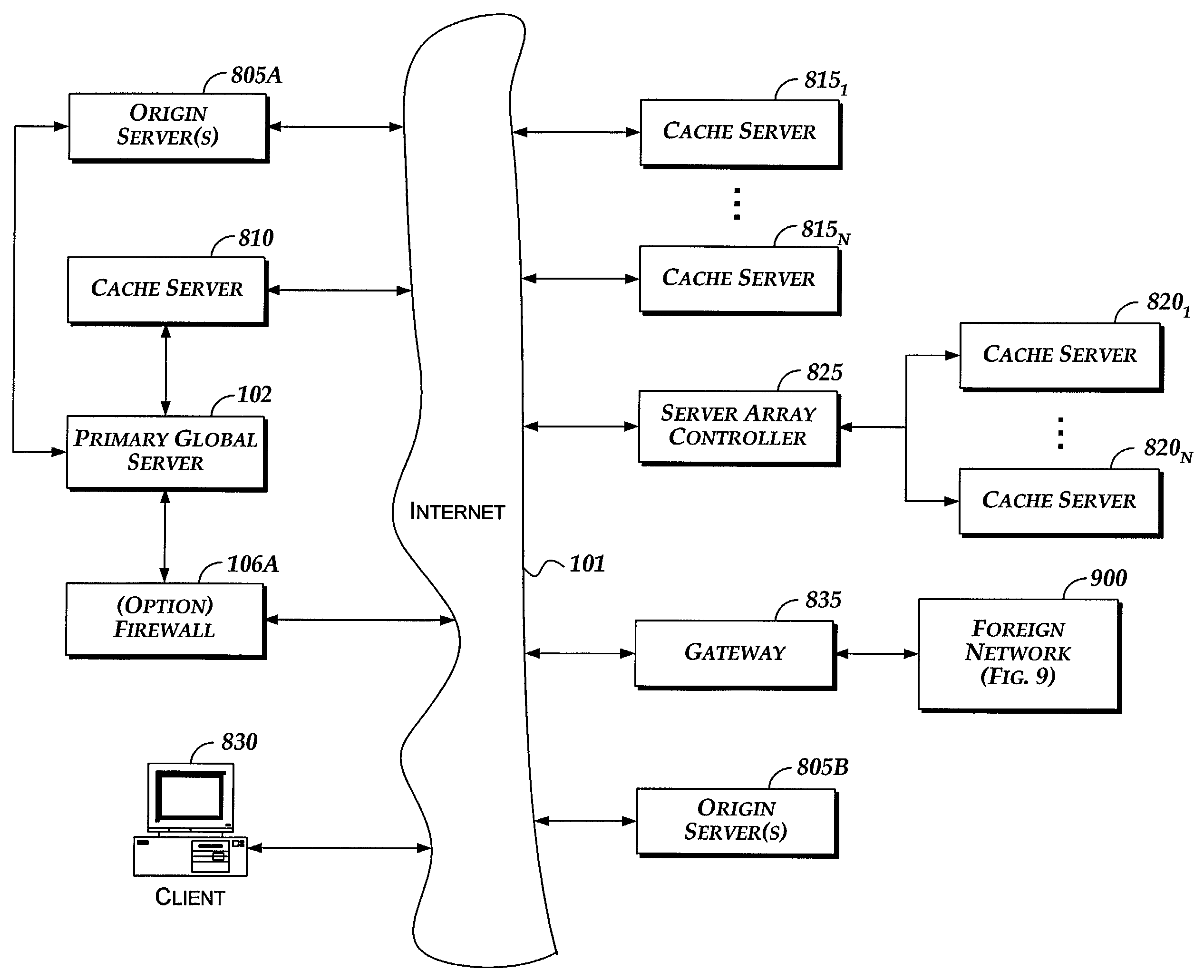
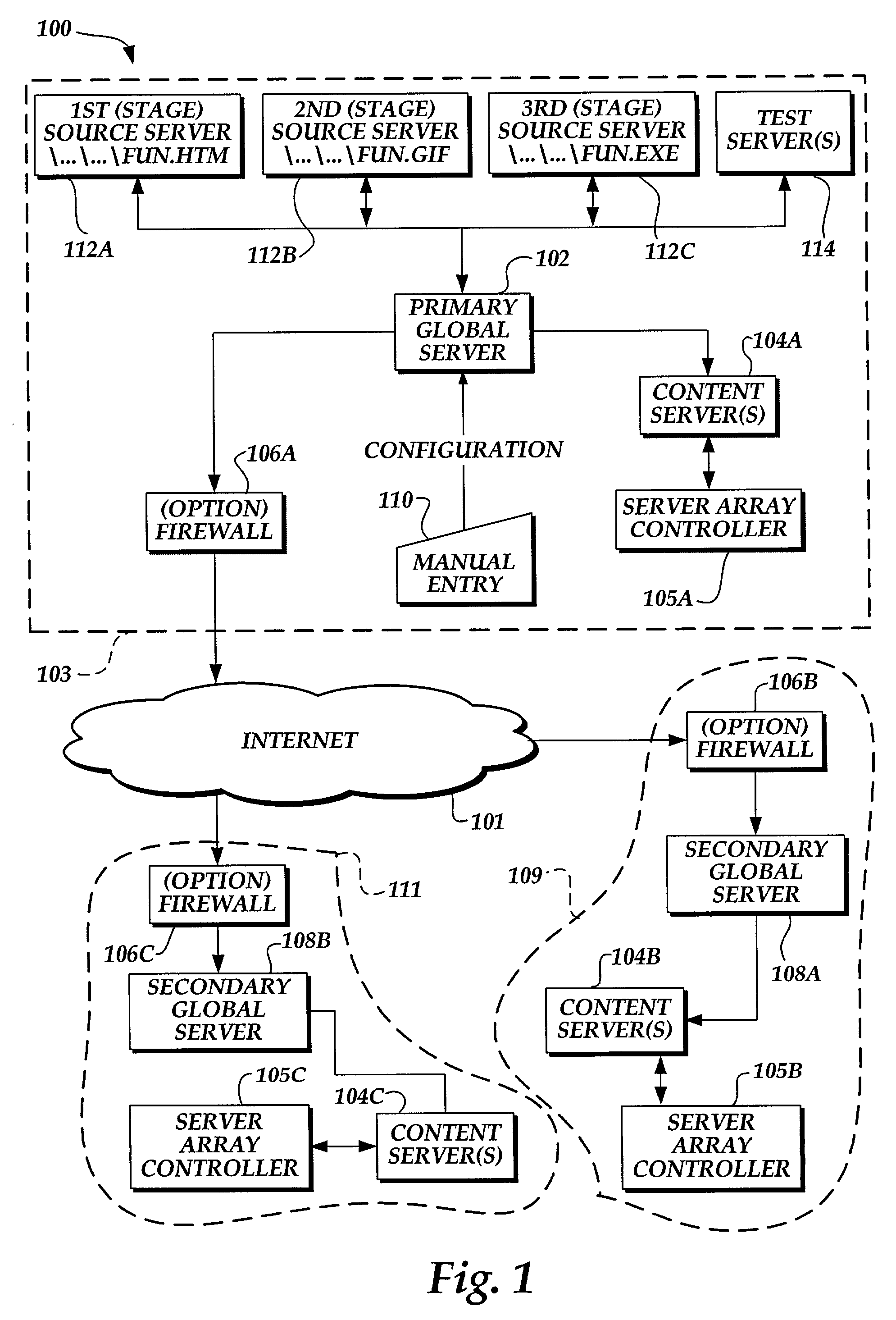
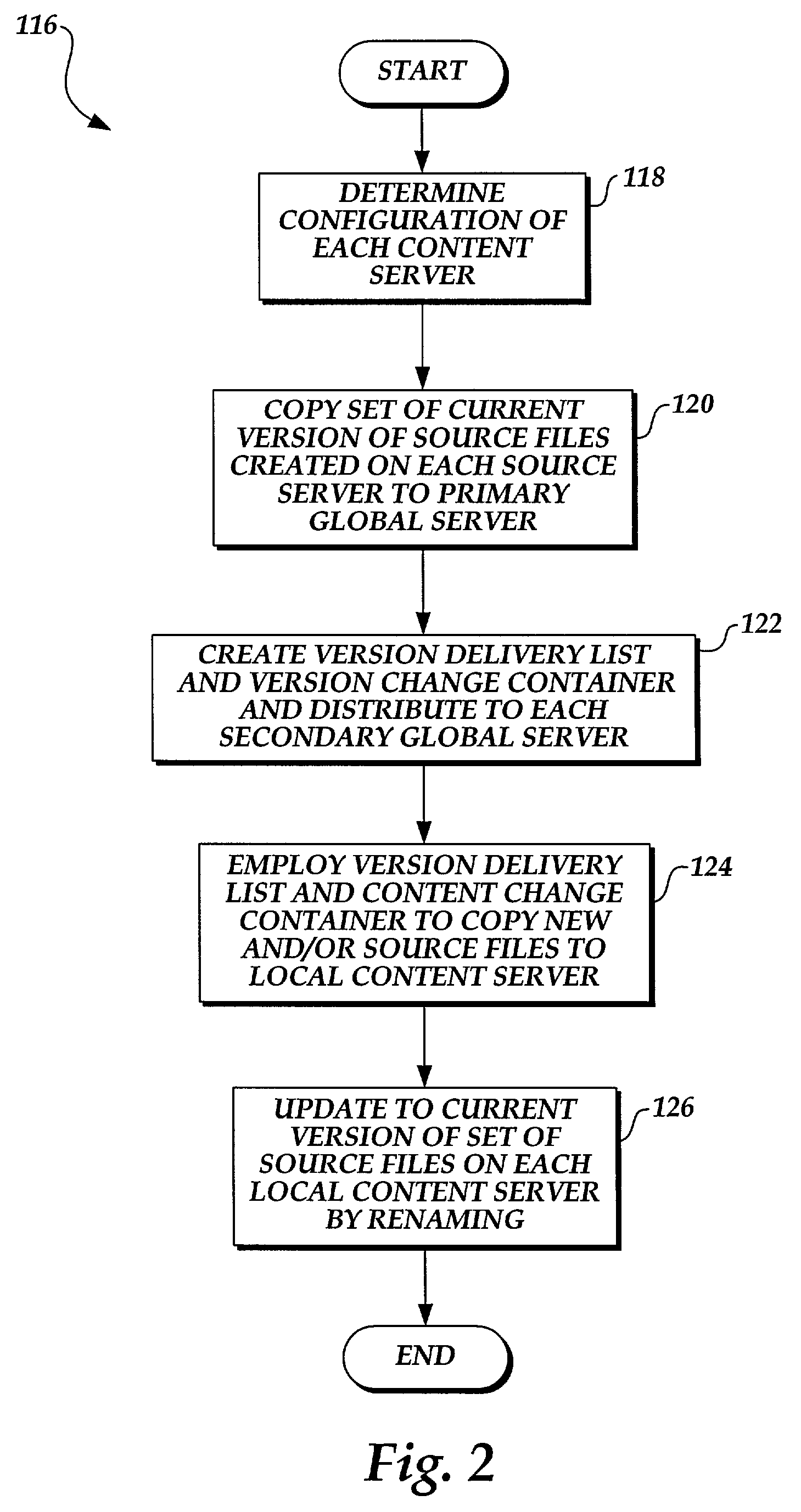
InactiveUS7113962B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalCache serverNetwork connection
A system and computer implementable method for updating content on servers coupled to a network. The method includes updating an origin server with a version of files used to provide content, retrieving data that indicates an action to be performed on one or more cache servers in conjunction with updating the origin server, and performing the action to update entries in the one or more cache servers. Each entry in each cache server is associated with a subset of the content on the origin server and may include an expiration field and / or a time to live field. An example of a subset of content to which a cache entry may be associated is a Web page. Cache servers are not required to poll origin servers to determine whether new content is available. Cache servers may be pre-populated using push or pull techniques.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
Method and apparatus for efficient SQL processing in an n-tier architecture
ActiveUS7580971B1Efficient processingFree of ChargeDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsData setCache server
A method and apparatus for efficiently processing data requests in a network oriented n-tier database environment is presented. According to one embodiment of the invention, certain or all data from the tables of a database server device can be maintained in tables on the client device in a client side database cache server system. This local cache allows the network oriented n-tier database system to eliminate the expense of repetitive network transmissions to respond to duplicate queries for the same information. Additionally, the local client device may also keep track of what data is cached on peer network nodes. This allows the client to request that data from a peer database cache server and off load that burden from the database server device. Moreover, the local client may also keep statistics regarding the frequency of requested data in order to optimize the data set maintained in the local database cache server.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
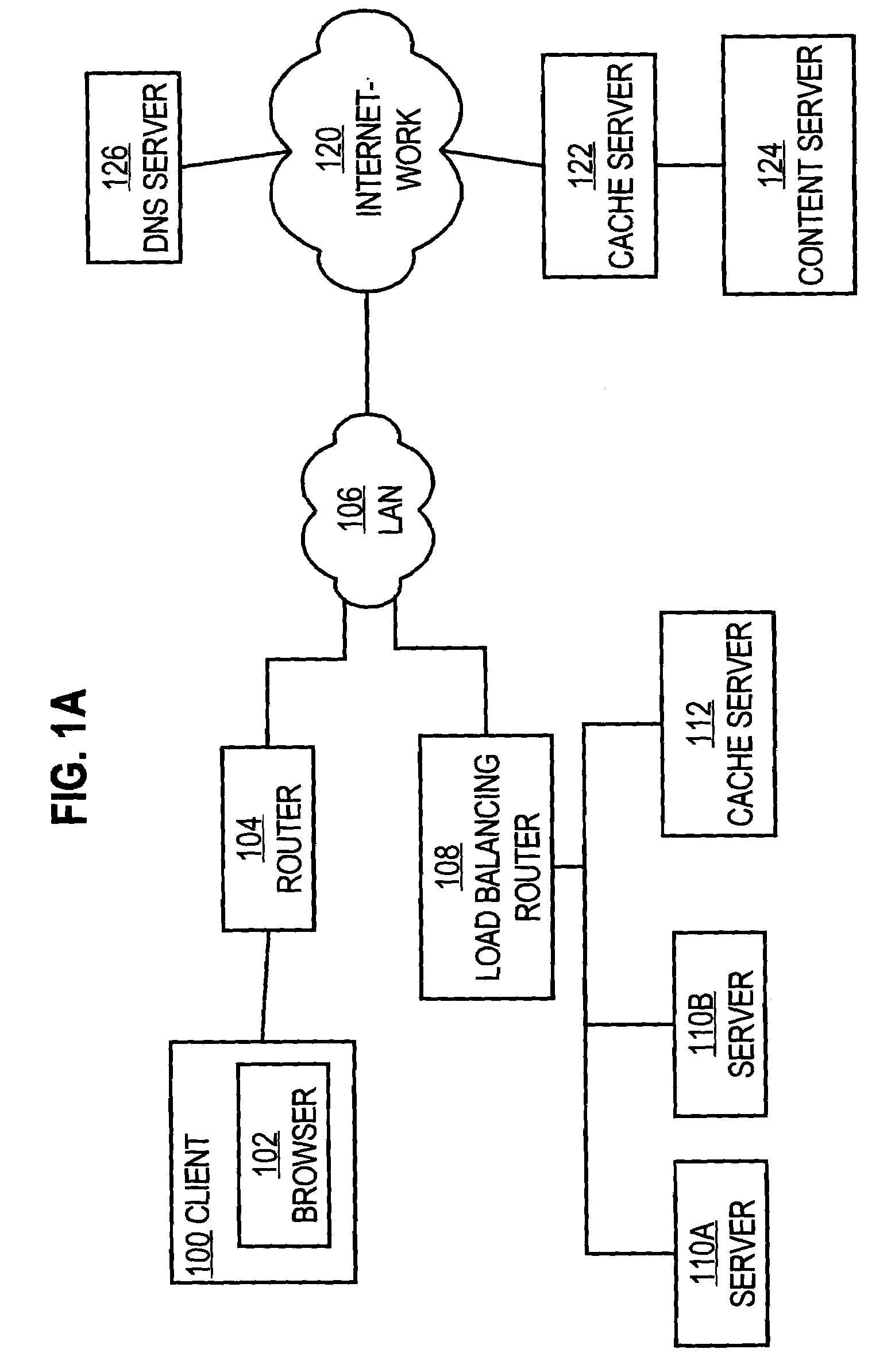
System and method for delivering high-performance online multimedia services
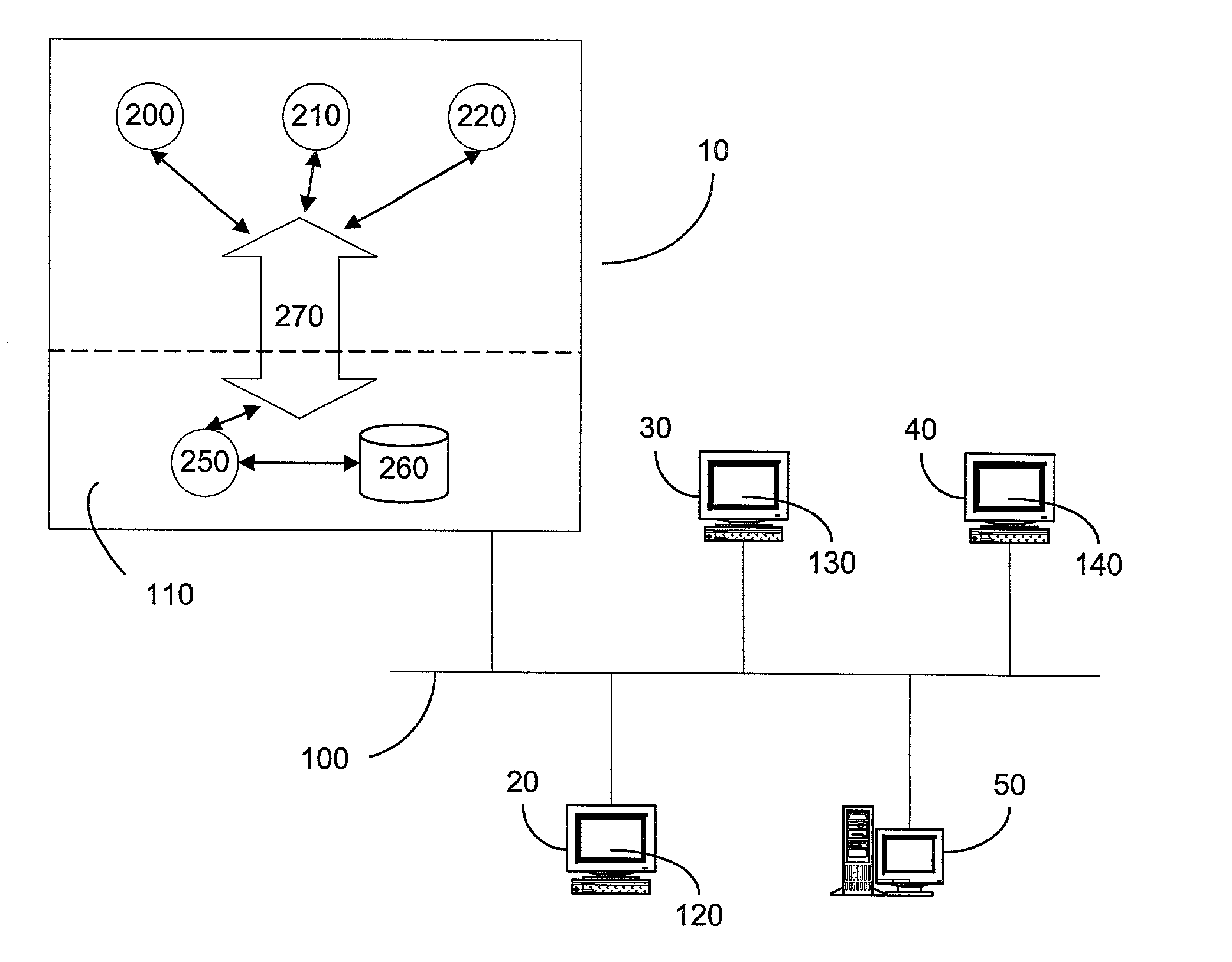
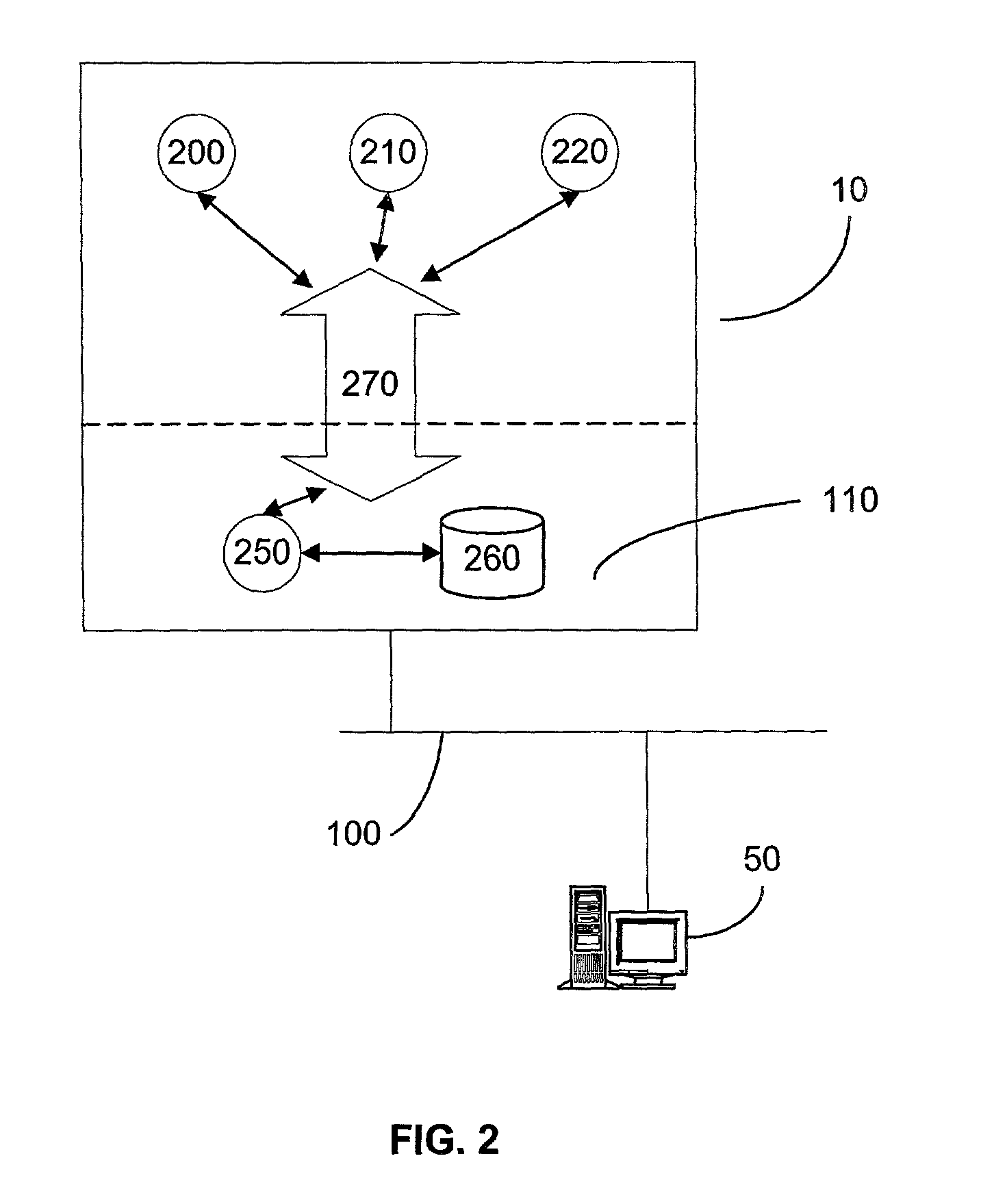
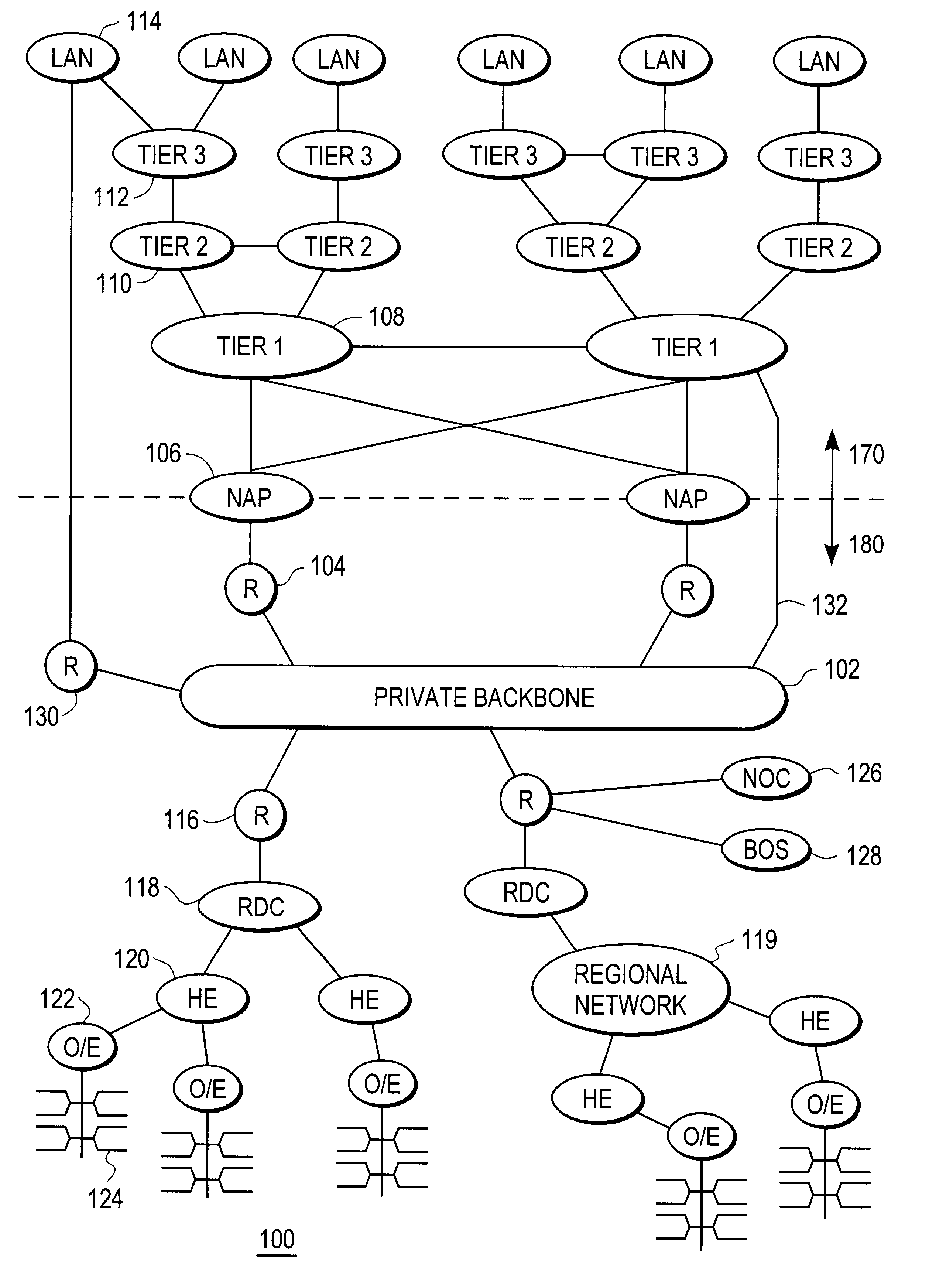
InactiveUS6370571B1Easy to scaleIncrease speedSpecial service provision for substationResource allocationFiberCoaxial cable
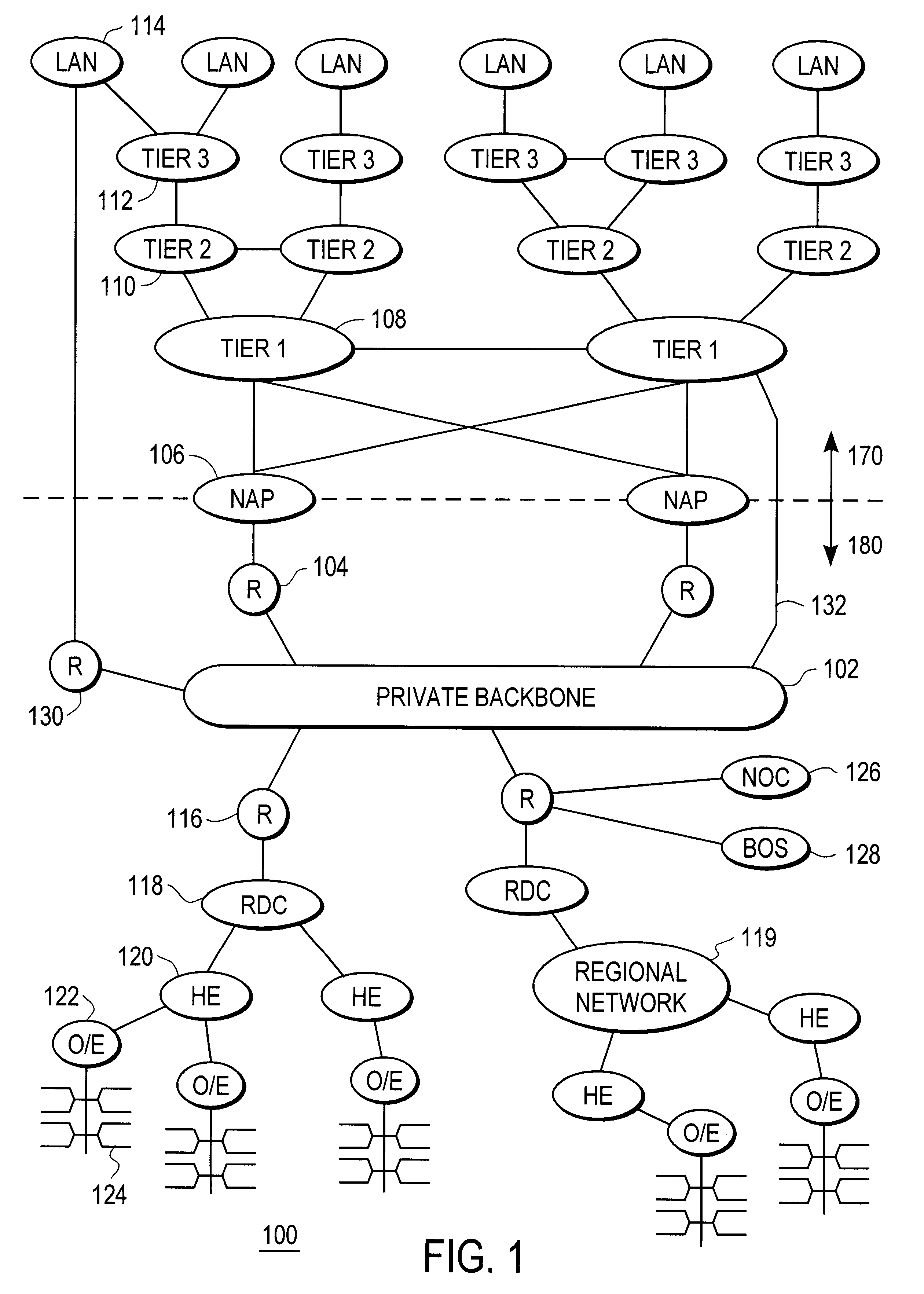
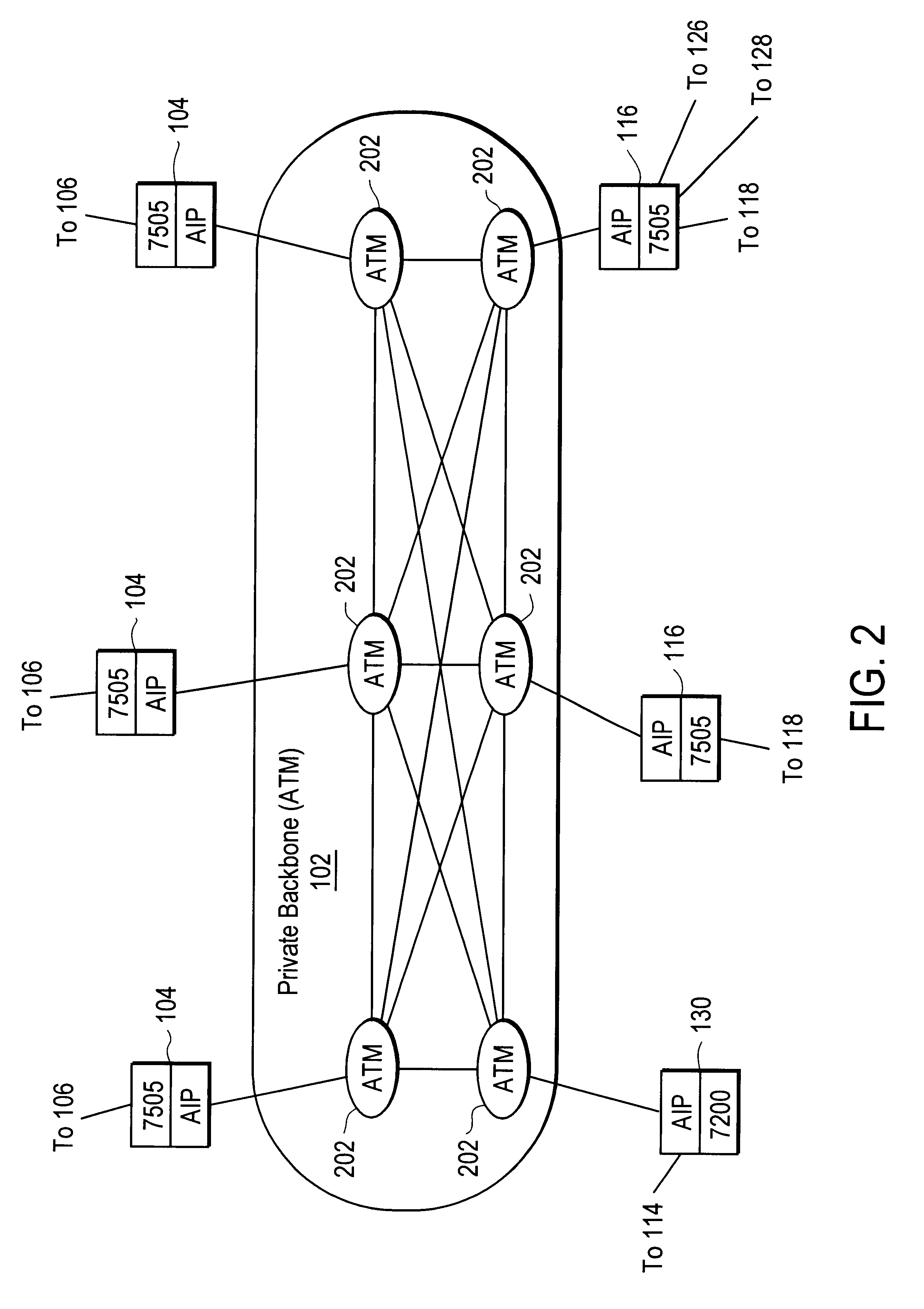
Disclosed is a scalable, hierarchical, distributed network architecture and processes for the delivery of high-performance, end-to-end online multimedia services, including Internet services such as World Wide Web access. The network architecture connects a high-speed private backbone to multiple network access points of the Internet, to a network operation center, to a back office system, and to multiple regional servers in regional data centers. Each of the regional servers connects to several caching servers in modified head-ends, which in turn connect via fiber optics to many neighborhood nodes. Finally, each node connects via coaxial cable to multiple end-user systems. The processes include those for replicating and caching frequently-accessed content, and multicasting content customized per region or locality.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
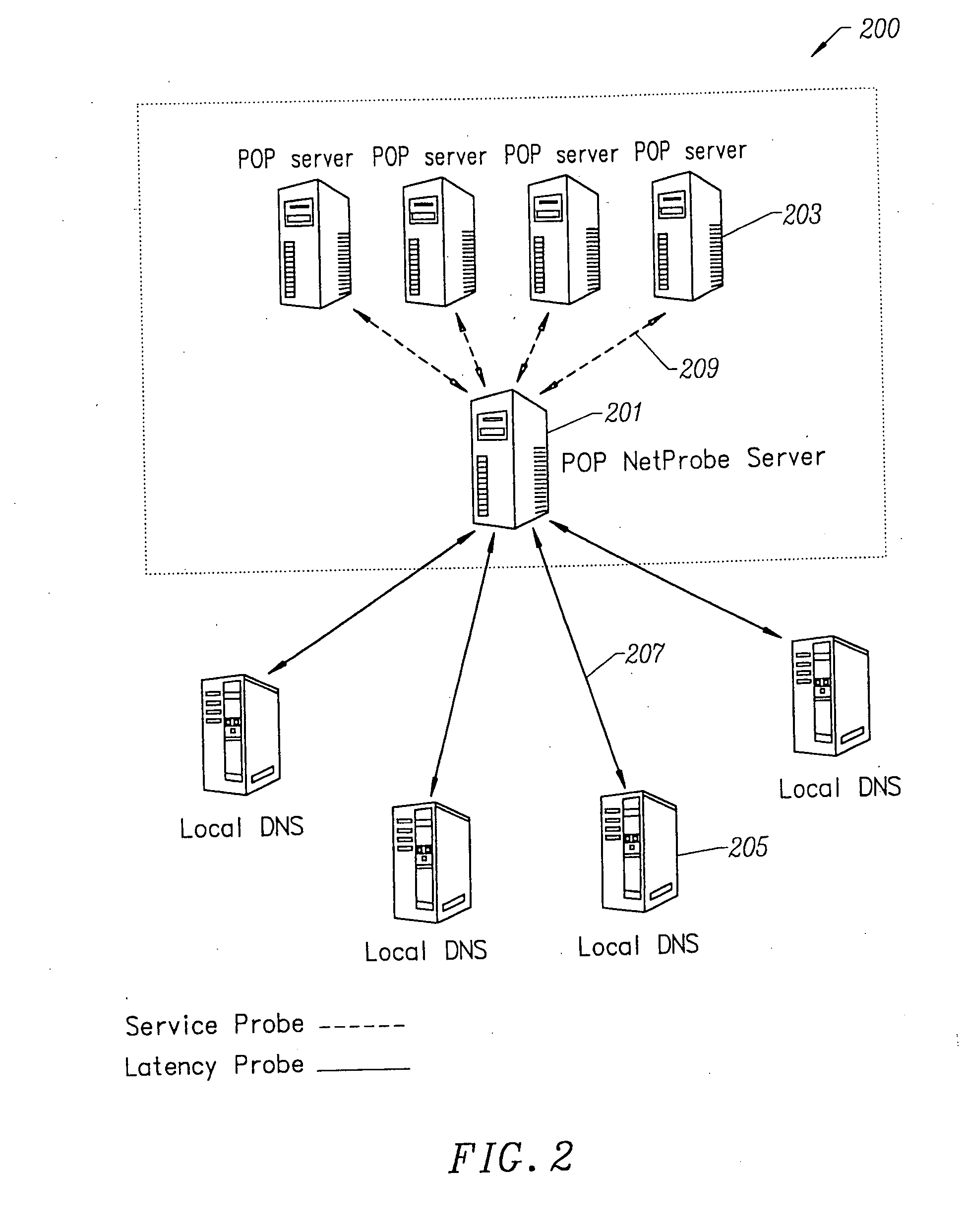
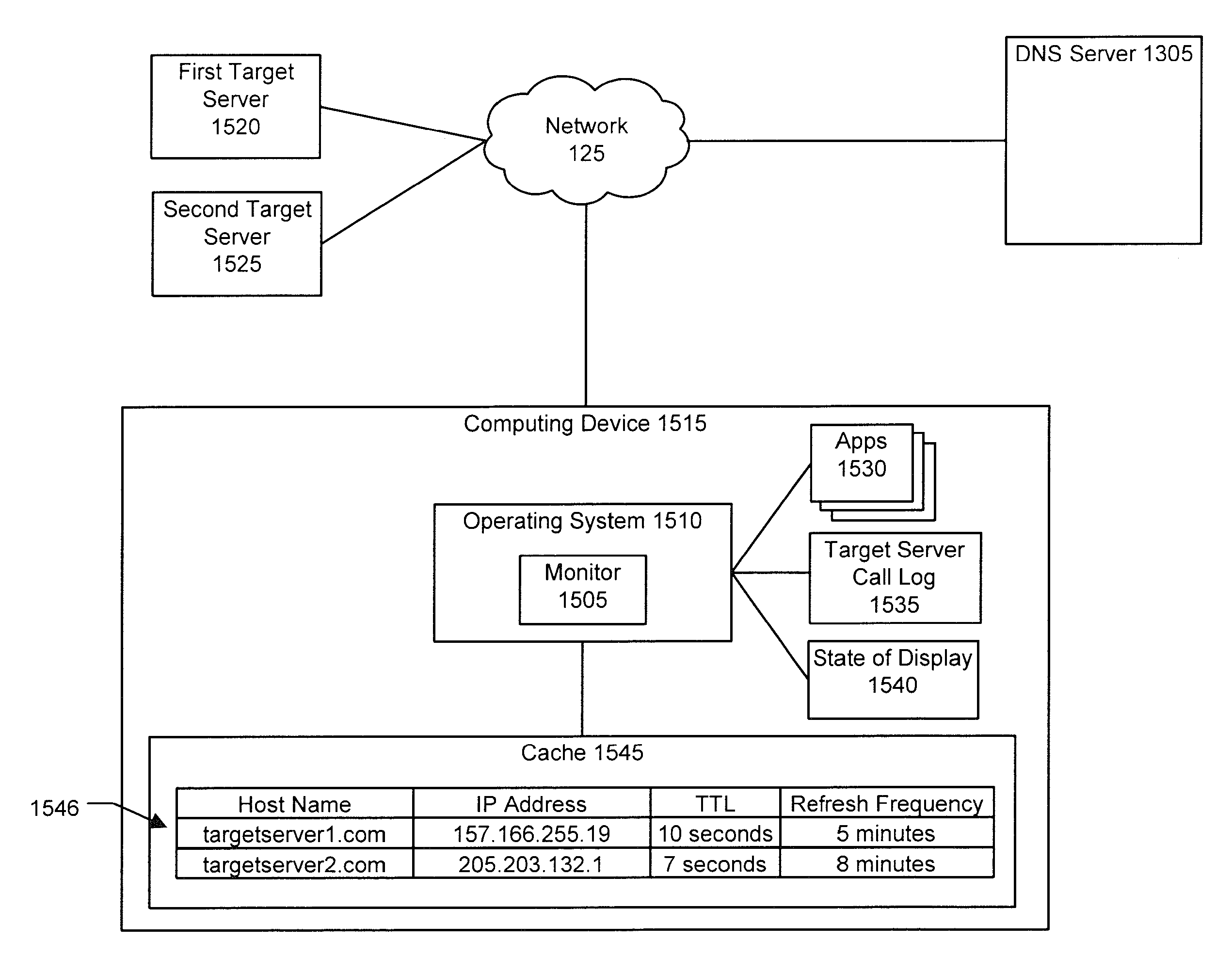
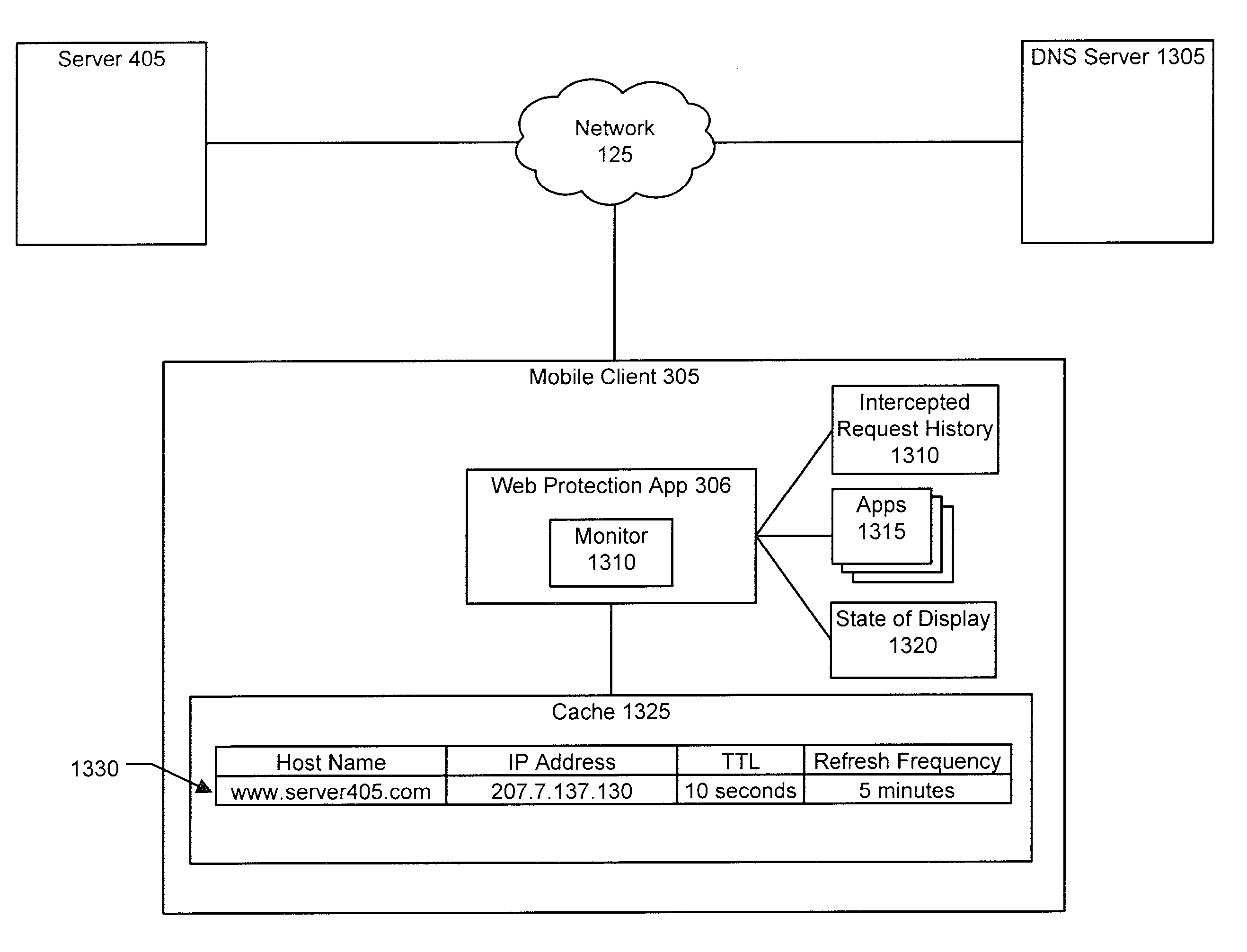
Mobile device DNS optimization
When a mobile device interacts with a network service, synchronous DNS resolution can significantly impact user experience due to lossy or moderate-high latency conditions. Network services that rely on low-TTL DNS records for failover require a client to frequently resolve the service's host name. It is undesirable to block on these frequent resolutions. In an implementation, user activity on a mobile device is monitored to determine whether the user is engaged in an activity that would contact a server. If such an activity is in progress, then DNS requests to resolve the server's host name are periodically generated to make sure the server's IP address is cached. In an implementation, if a request to communicate with a server fails, the DNS cache expires the entry for that server so that a new DNS request can resolve the server's IP address in case the server's IP address has changed.
Owner:LOOKOUT MOBILE SECURITY
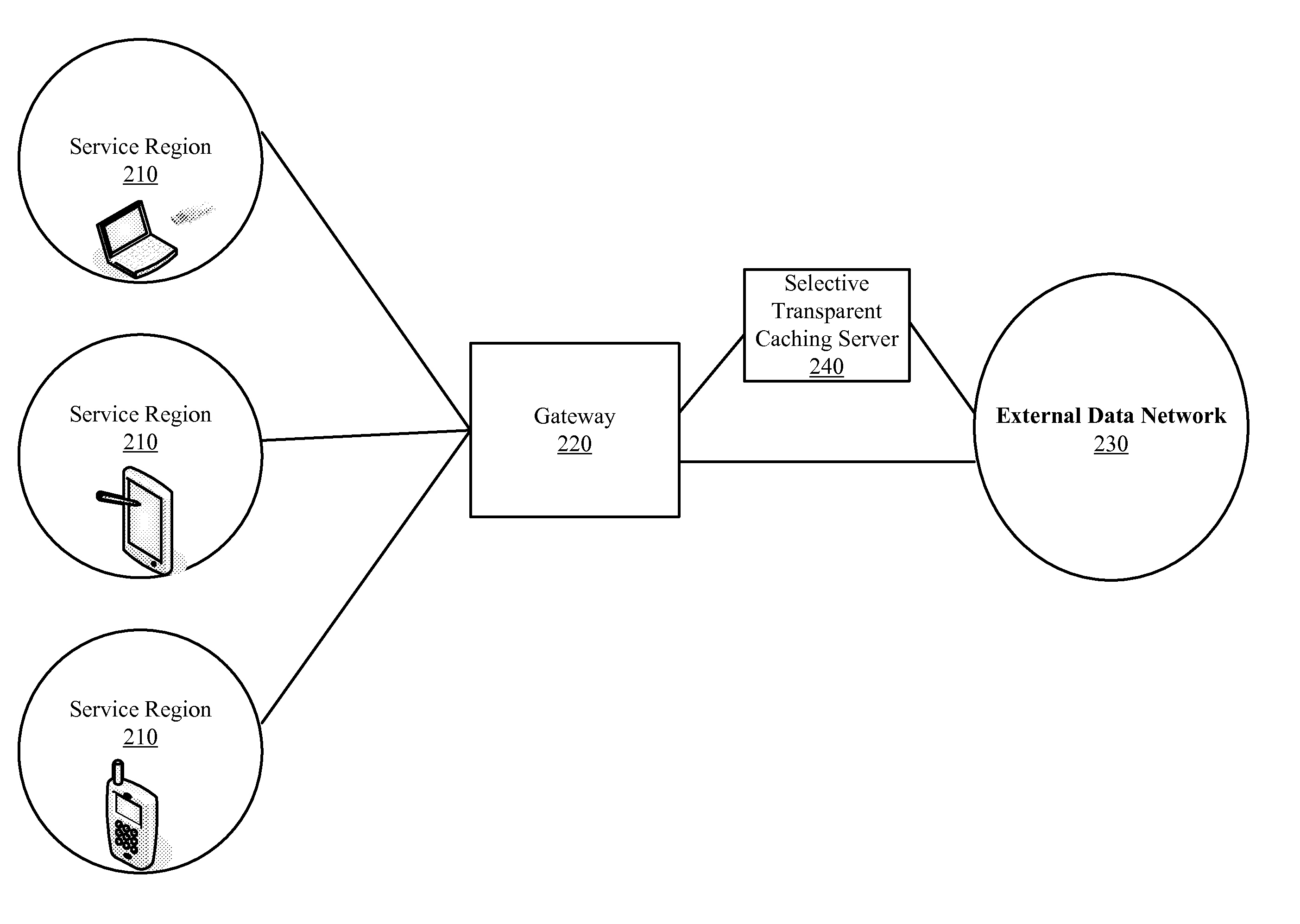
Discrete Mapping for Targeted Caching
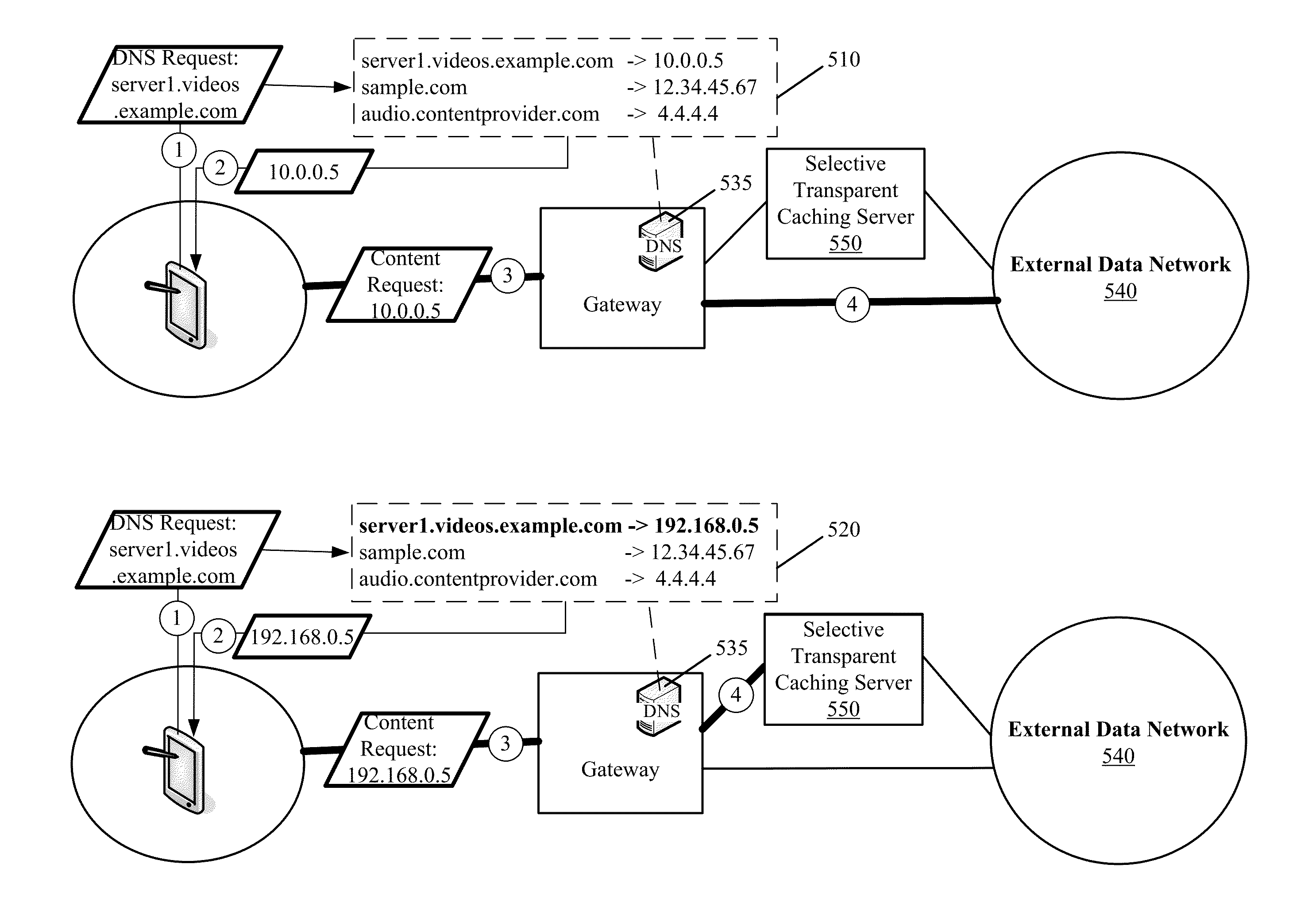
Some embodiments provide systems and methods for implementing discrete mapping for targeted caching in a carrier network. In some embodiments, discrete mapping is implemented using a method that caches content from a content provider to a caching server. The method modifies a DNS entry at a particular DNS server to resolve a request that identifies either a hostname or a domain for the content provider to an address of the caching server so that the requested content is passed from the cached content of the caching server and not the source content provider. In some embodiments, the particular DNS server is a recursive DNS server, a local DNS server of the carrier network, or a DNS server that is not authoritative for the hostname or domain of the content provider.
Owner:EDGIO INC
Discrete mapping for targeted caching
Owner:EDGIO INC
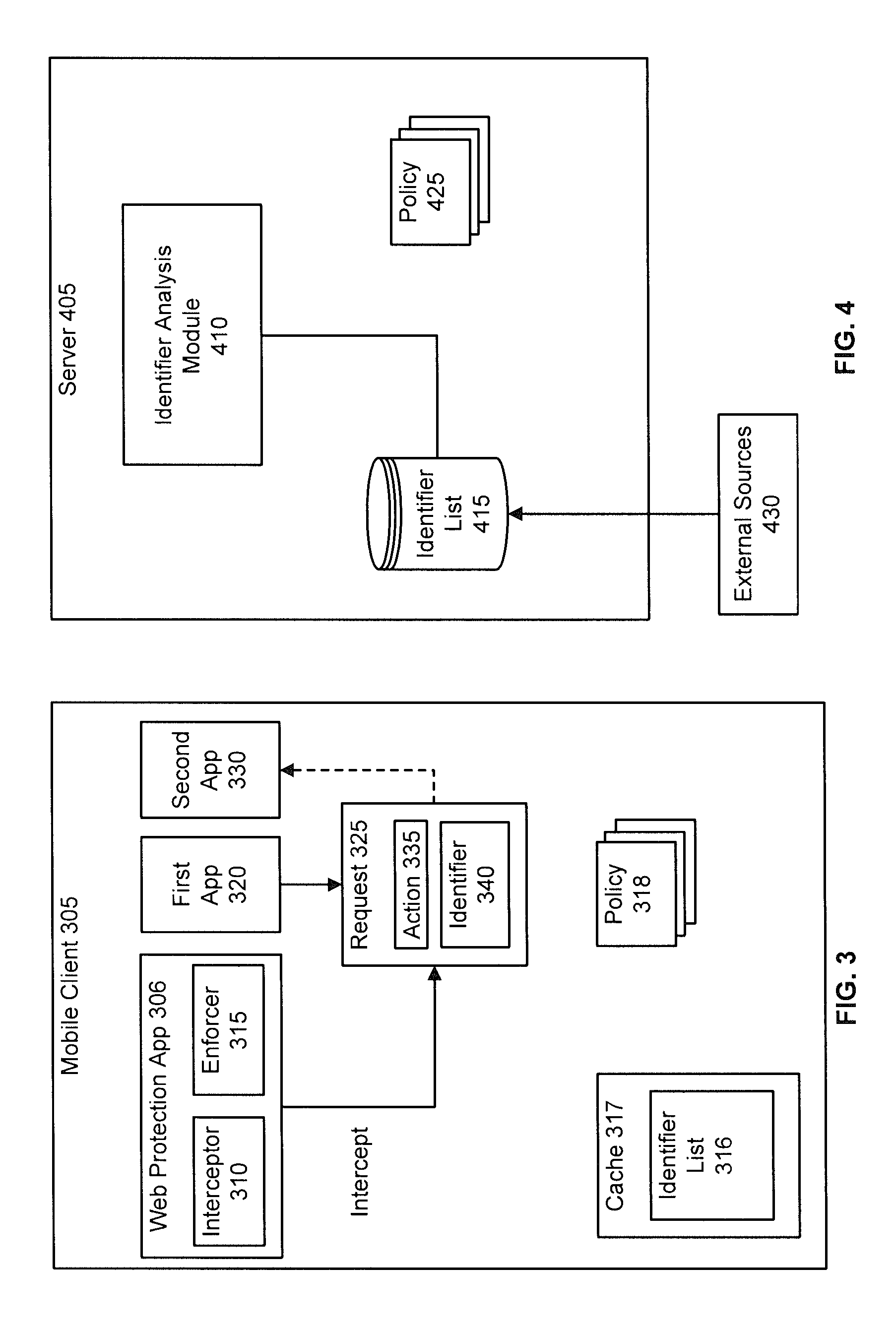
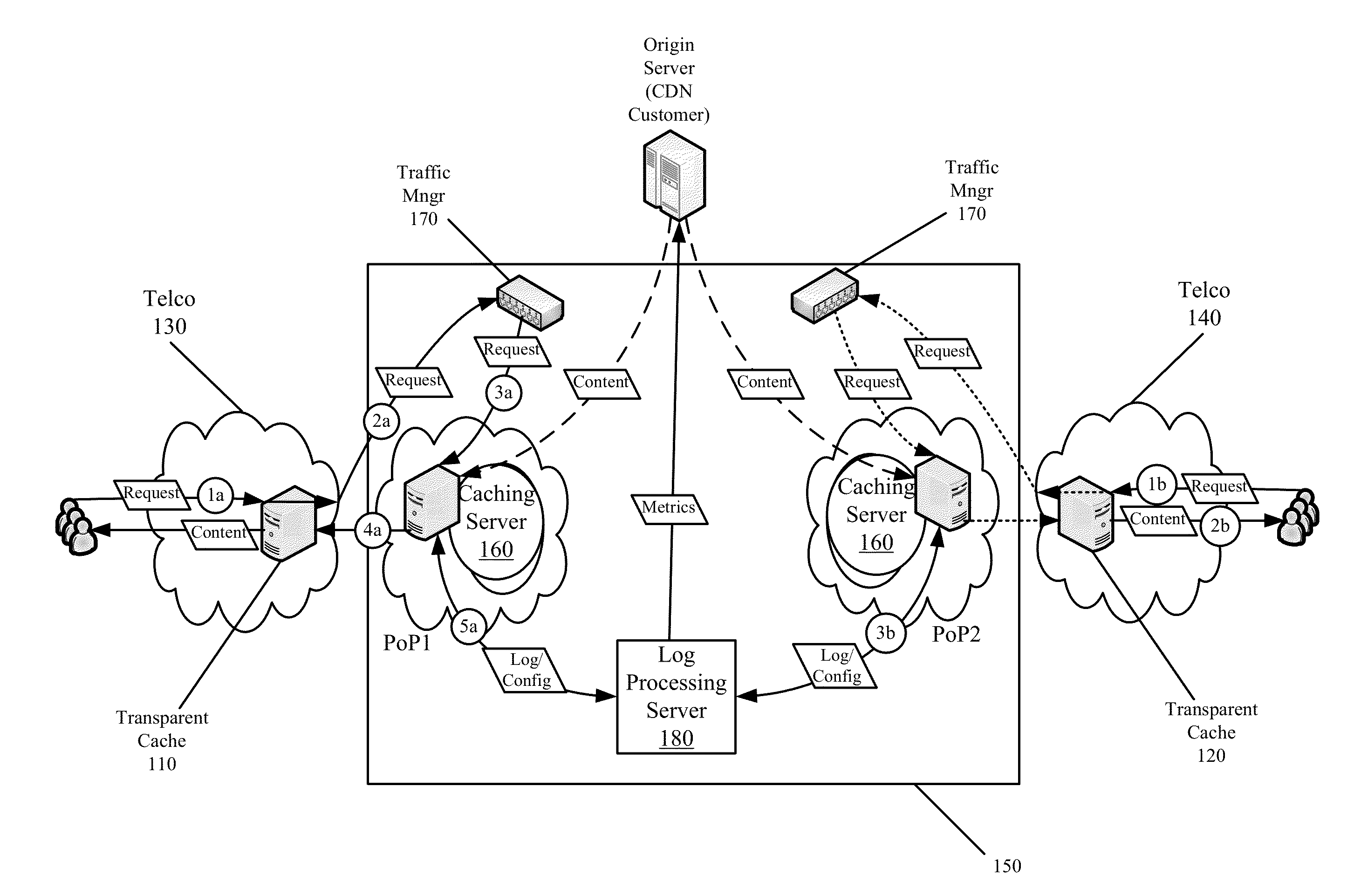
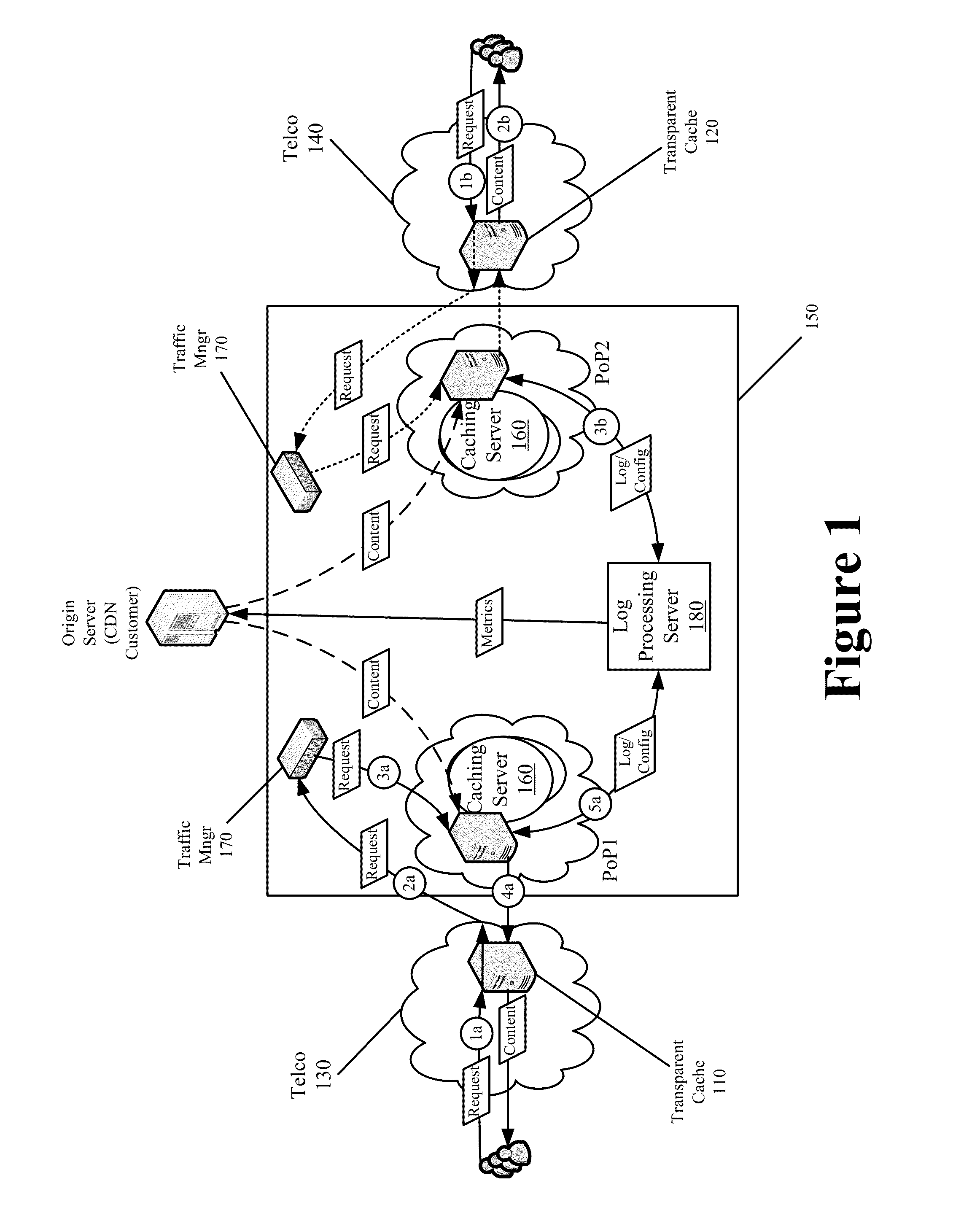
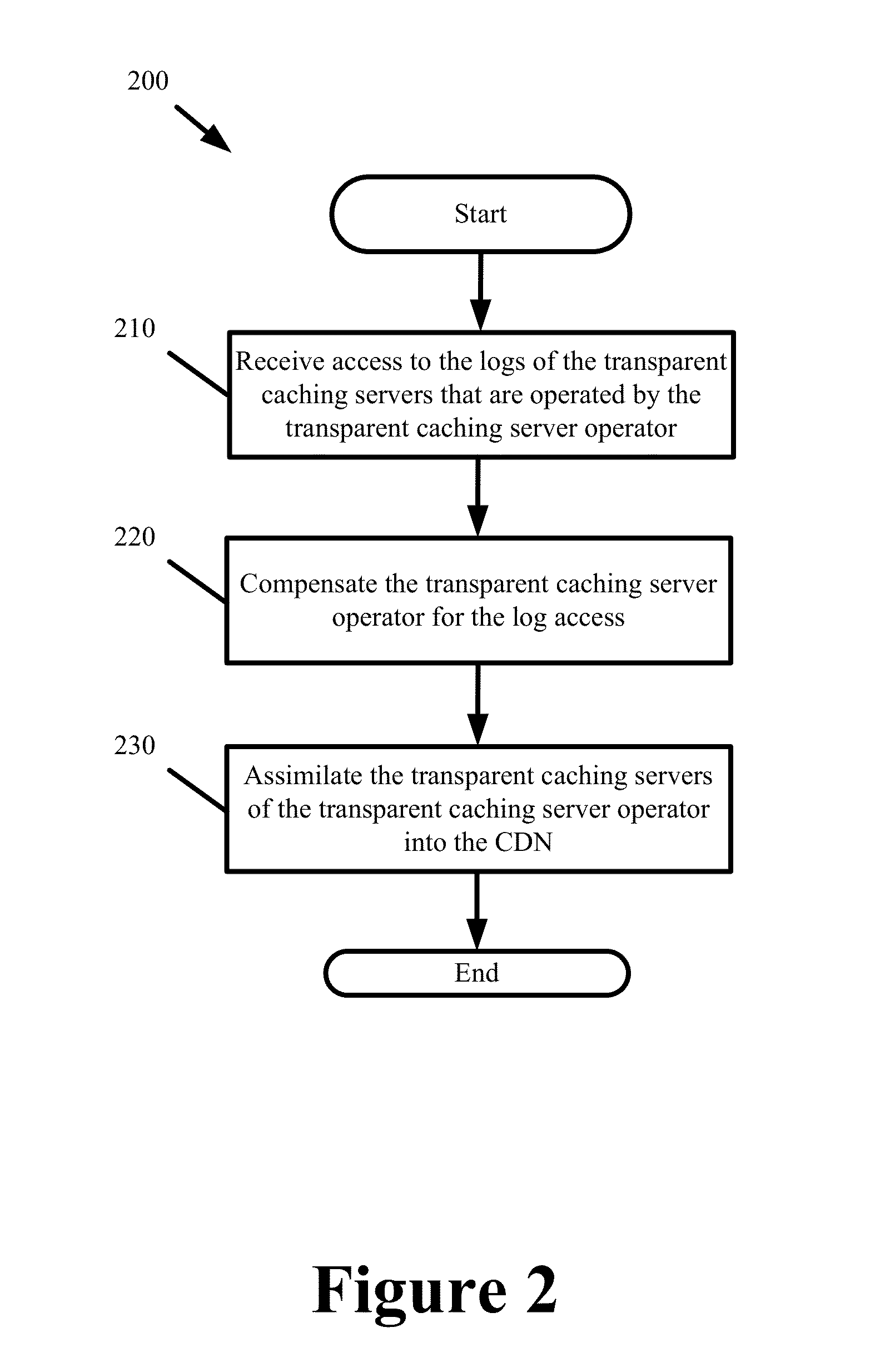
End-to-End Content Delivery Network Incorporating Independently Operated Transparent Caches and Proxy Caches
ActiveUS20130046883A1Accurately and comprehensively track and report metricImproves content deliveryDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsServer logCache server
Some embodiments provide an end-to-end federated CDN solution that assimilates a transparent caching server that is operated by a transparent caching server operator into a CDN that independently operates CDN caching servers. Specifically, the logs from the transparent caching server are assimilated into the CDN by aggregating the logs from the transparent caching server and processing the transparent caching server logs to identify network usage for content of a CDN content provider customer that is delivered by the transparent caching server. The network usage is then combined with the network usage that tracked by the CDN caching servers in order to provide comprehensive report metrics for the content provider customer and to bill the content provider customer for all network usage related to delivering the content provider customer's content irrespective of whether the content was delivered by a transparent caching server or a CDN caching server.
Owner:EDGIO INC
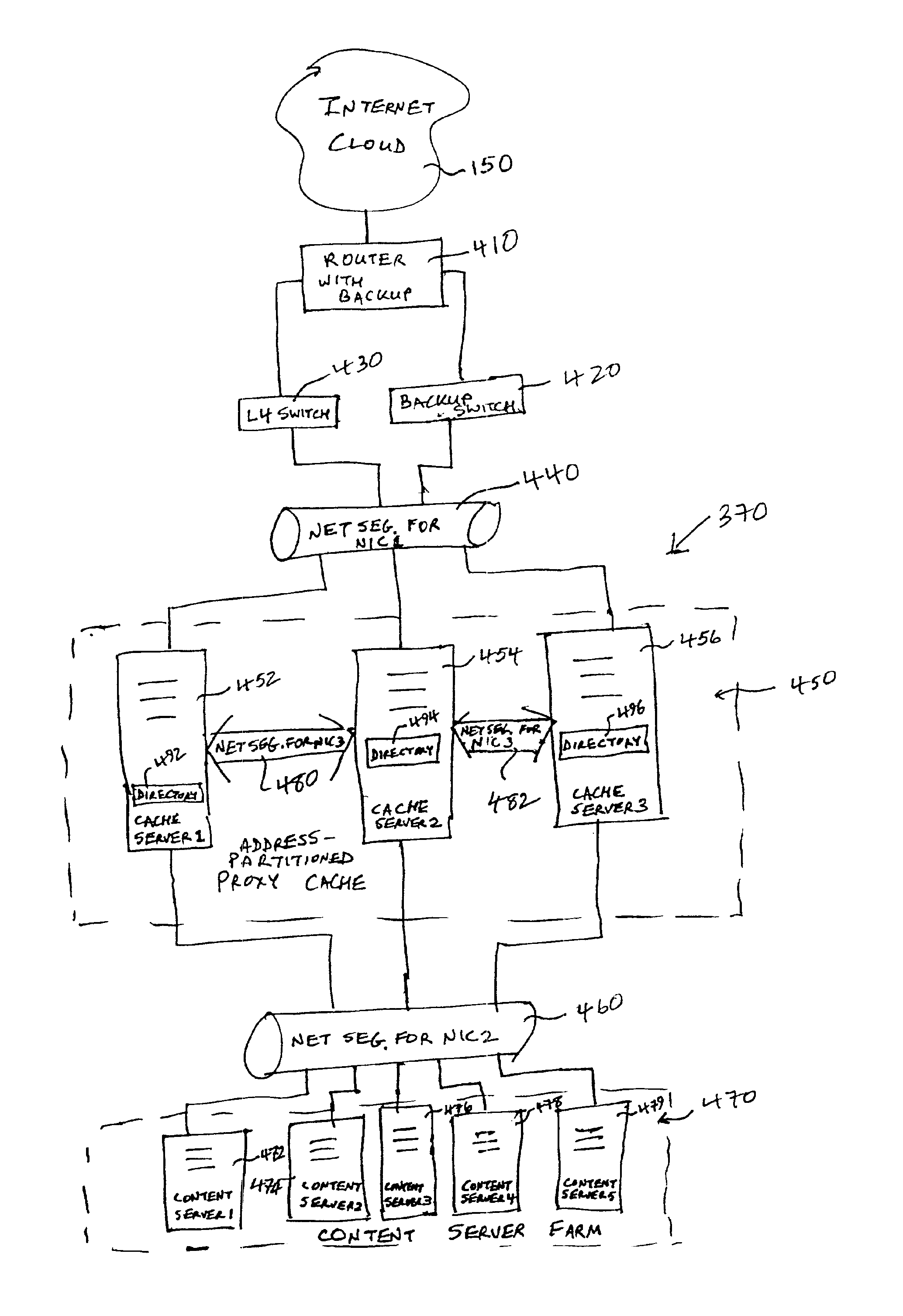
System and method for partitioning address space in a proxy cache server cluster
InactiveUS6862606B1Overcome disadvantagesReduce congestionMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationCache serverParallel computing
A proxy partition cache (PPC) architecture and a technique for address-partitioning a proxy cache consisting of a grouping of discrete, cooperating caches (servers) is provided. Client requests for objects (files) of a given size are redirected or reassigned to a single cache in the grouping, notwithstanding the cache to which the request is made by the load-balancing mechanism (such as a Layer 4 switch) based upon load-balancing considerations. The file is then returned to the switch via the switch-designated cache for vending to the requesting client. The redirection / reassignment occurs according to a function within the cache to which the request is directed so that the switch remains freed from additional tasks that can compromise speed.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
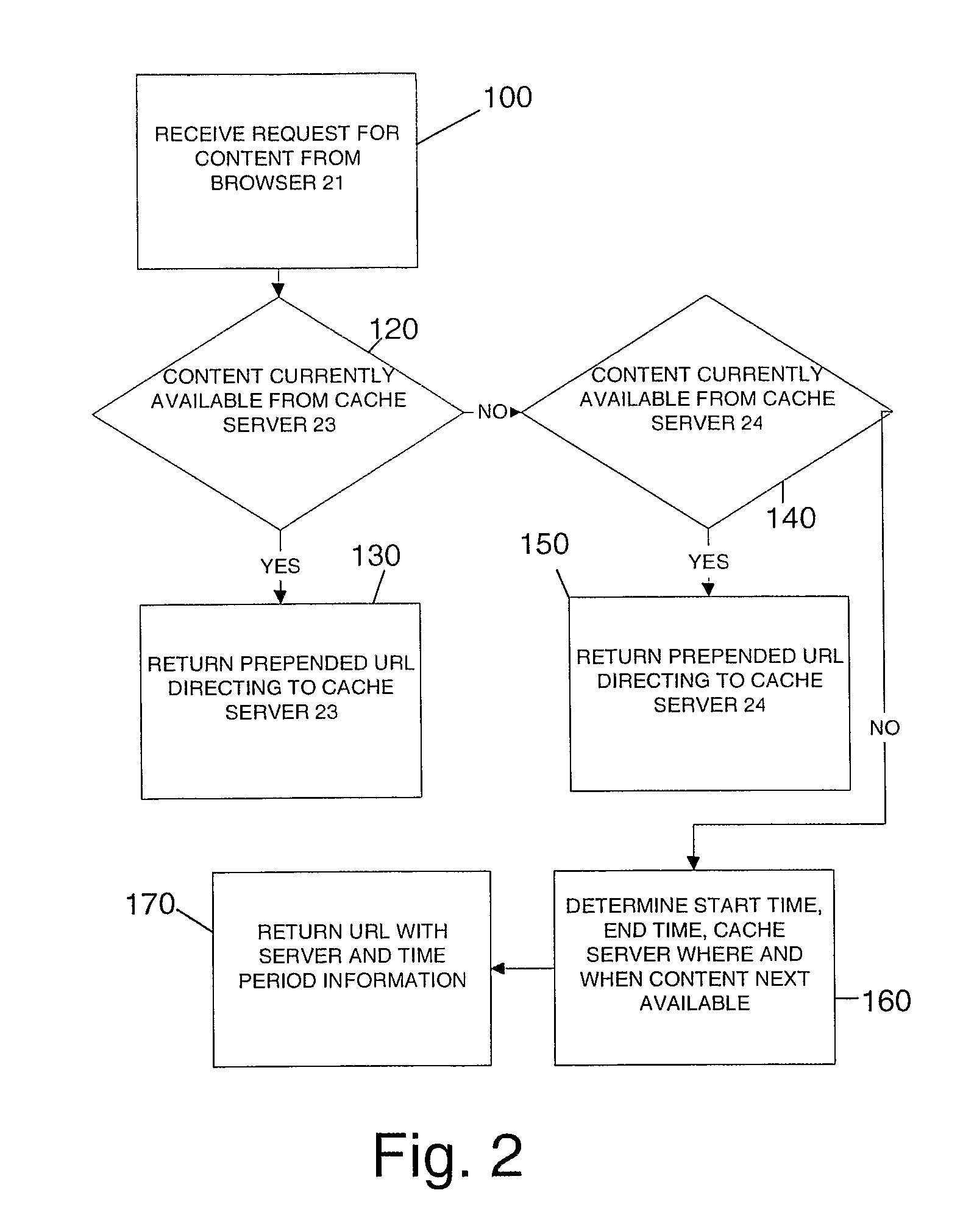
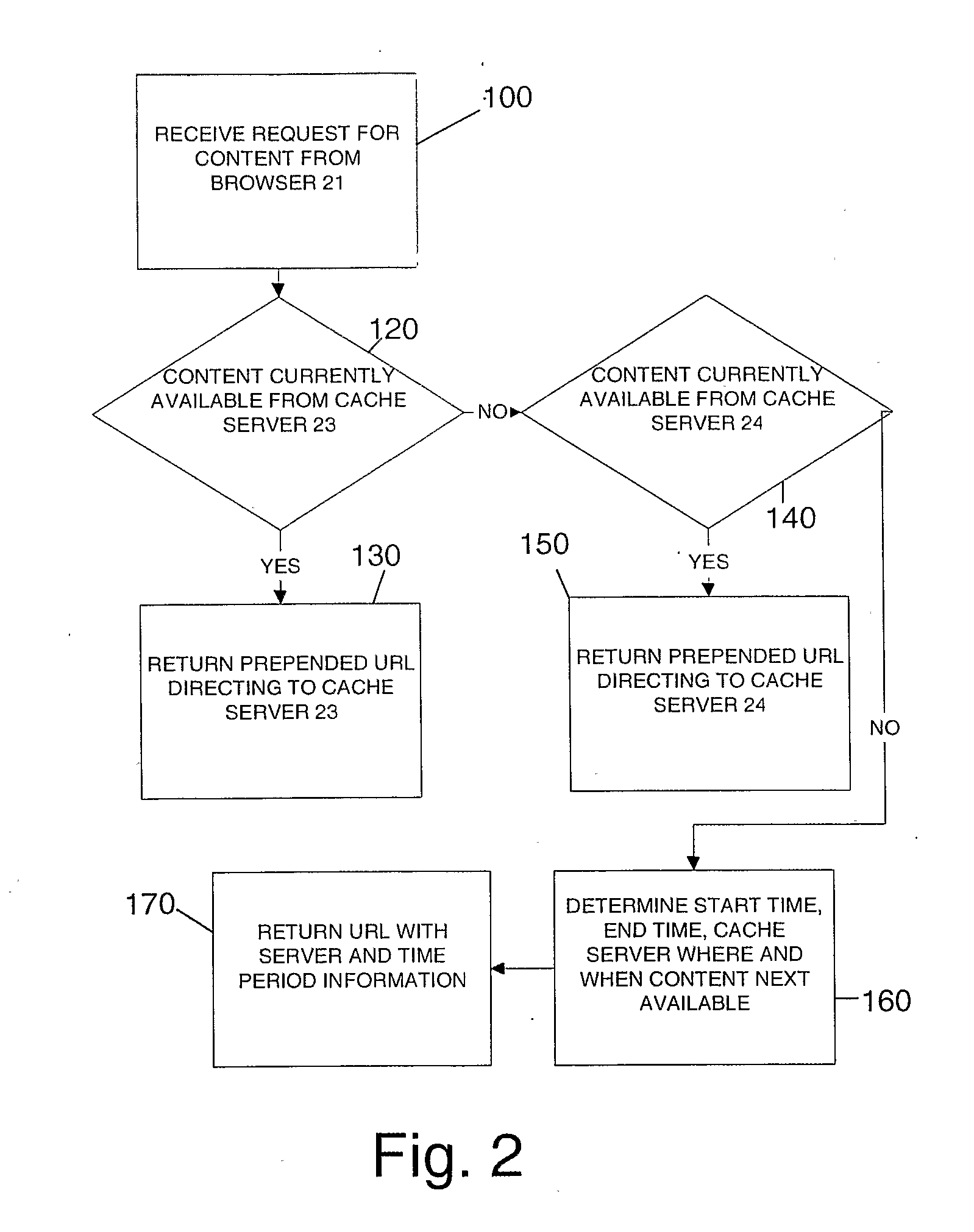
Content timing method and system
A computer method and related apparatus for delivering content files to a client computer are disclosed wherein a request for a content file on a content server is received from a client; a future time period during which the content file will be available on a cache server is determined; and a rewritten uniform resource locator comprising time period availability information, or a link to a file comprising the time period availability information, is returned from the server to the client. The client can use the information to obtain the content file in the determined future time period.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Mobile device DNS optimization
ActiveUS8738765B2Multiple digital computer combinationsMobile application execution environmentsFailoverCache server
When a mobile device interacts with a network service, synchronous DNS resolution can significantly impact user experience due to lossy or moderate-high latency conditions. Network services that rely on low-TTL DNS records for failover require a client to frequently resolve the service's host name. It is undesirable to block on these frequent resolutions. In an implementation, user activity on a mobile device is monitored to determine whether the user is engaged in an activity that would contact a server. If such an activity is in progress, then DNS requests to resolve the server's host name are periodically generated to make sure the server's IP address is cached. In an implementation, if a request to communicate with a server fails, the DNS cache expires the entry for that server so that a new DNS request can resolve the server's IP address in case the server's IP address has changed.
Owner:LOOKOUT MOBILE SECURITY
Distributed type dynamic cache expanding method and system supporting load balancing
InactiveCN102244685AReduce overheadImprove performanceData switching networksTraffic capacityCache server
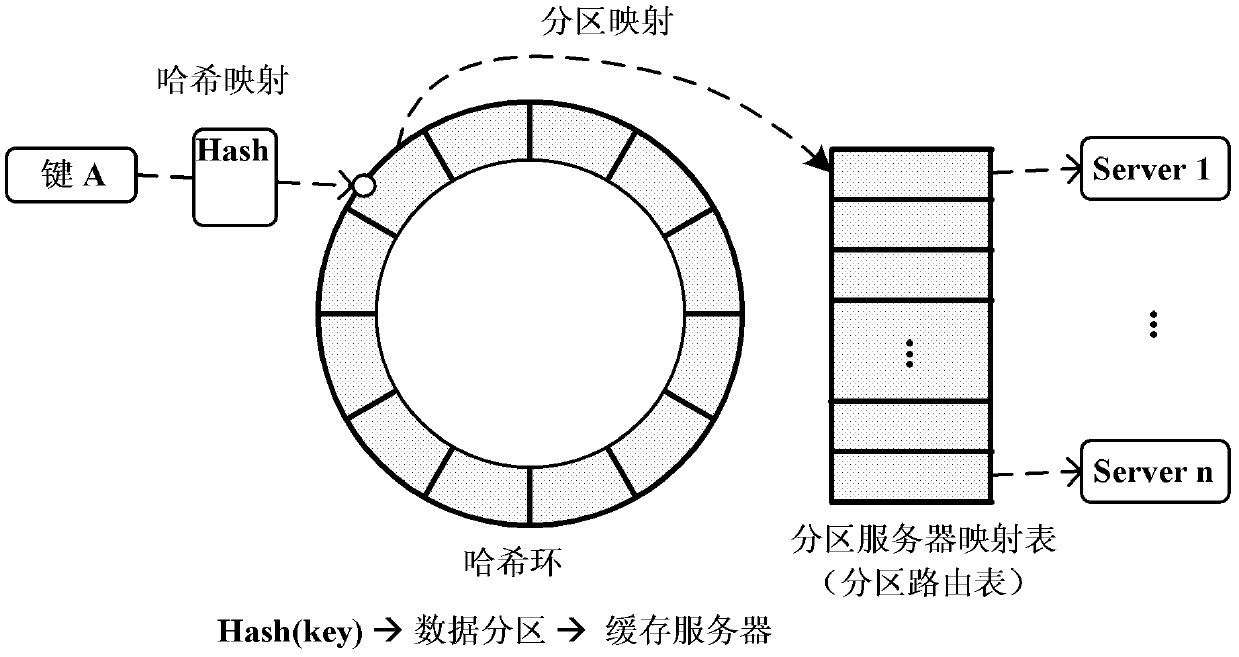
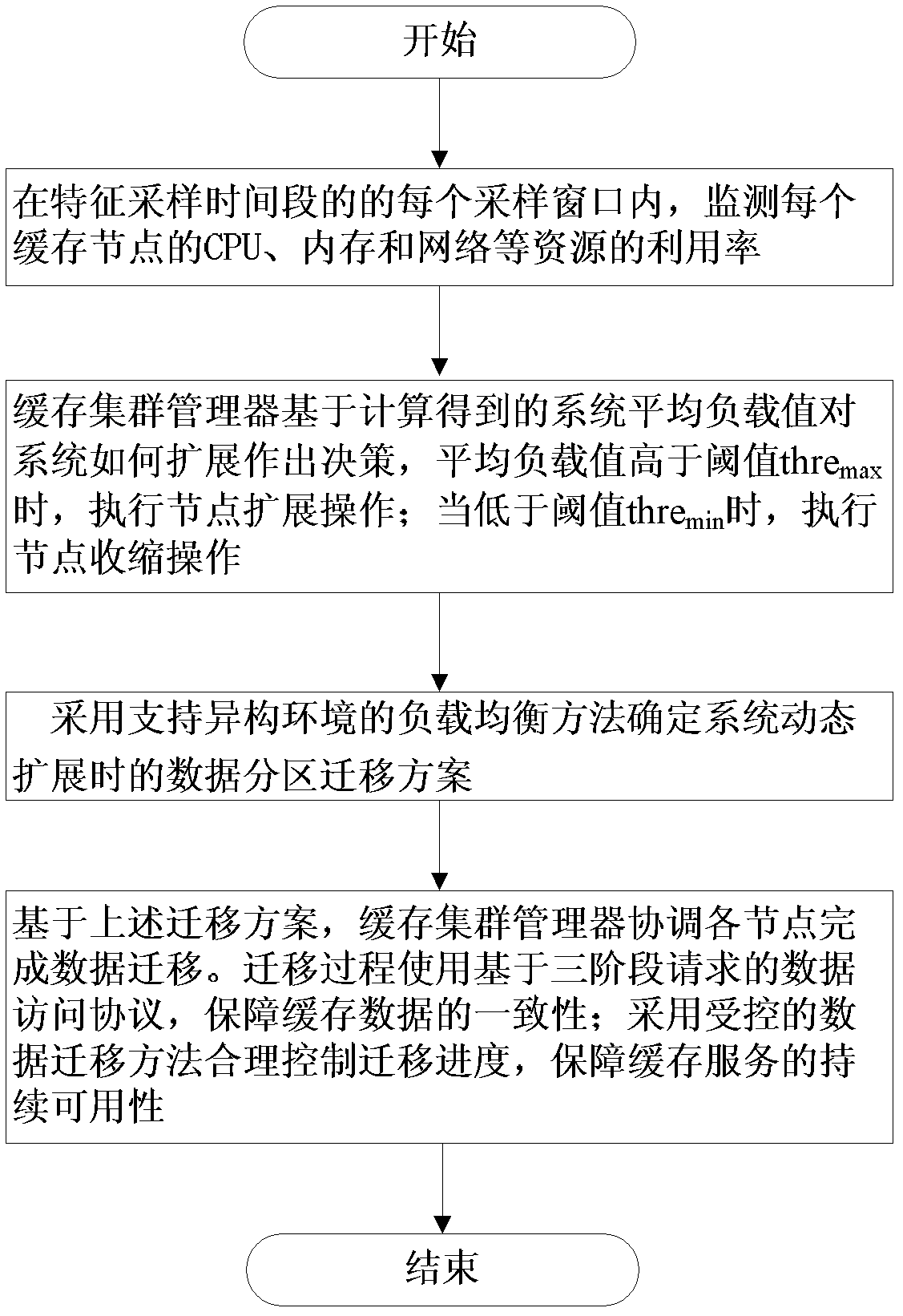
The invention discloses a distributed type dynamic cache expanding method and system supporting load balancing, which belong to the technical field of software. The method comprises steps of: 1) monitoring respective resource utilization rate at regular intervals by each cache server; 2) calculating respective weighing load value Li according to the current monitored resource utilization rate, and sending the weighting load value Li to a cache clustering manager by each cache server; 3) calculating current average load value of a distributed cache system by the cache clustering manager according to the weighting load value Li, and executing expansion operation when the current average load value is higher than a threshold thremax; and executing shrink operation when the current average load value is lower than a set threshold thremin. The system comprises the cache servers, a cache client side and the cache clustering manager, wherein the cache servers are connected with the cache client side and the cache clustering manager through the network. The invention ensures the uniform distribution of the network flow among the cache nodes, optimizes the utilization rate of system resources, and solves the problems of ensuring data consistency and continuous availability of services.
Owner:济南君安泰投资集团有限公司
Content timing method and system
A computer method and related apparatus for delivering content files to a client computer are disclosed wherein a request for a content file on a content server is received from a client; a future time period during which the content file will be available on a cache server is determined; and a rewritten uniform resource locator comprising time period availability information, or a link to a file comprising the time period availability information, is returned from the server to the client. The client can use the information to obtain the content file in the determined future time period.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
System and method for populating cache servers with popular media contents
A system and method for caching files is disclosed. Popularity values are calculated for a plurality of files over a period of time. The popularity values are then used to determine which files should be cached at various remote sites. Once the caches are filled, the popularity values associated with the cached files are periodically compared with the popularity values of uncached content. Generally, if the popularity of an uncached file is greater than the popularity of a cached file, then the cached file will be replaced. However, numerous different variables may be factored into the caching determination including, for example, the size of the file, the required bitrate of the file, the identity of the owner of the file, and / or the type of file.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Internet home page data acquisition method
InactiveUS6868453B1Shorten unnecessary wait timeWeb data retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsCache serverHome page
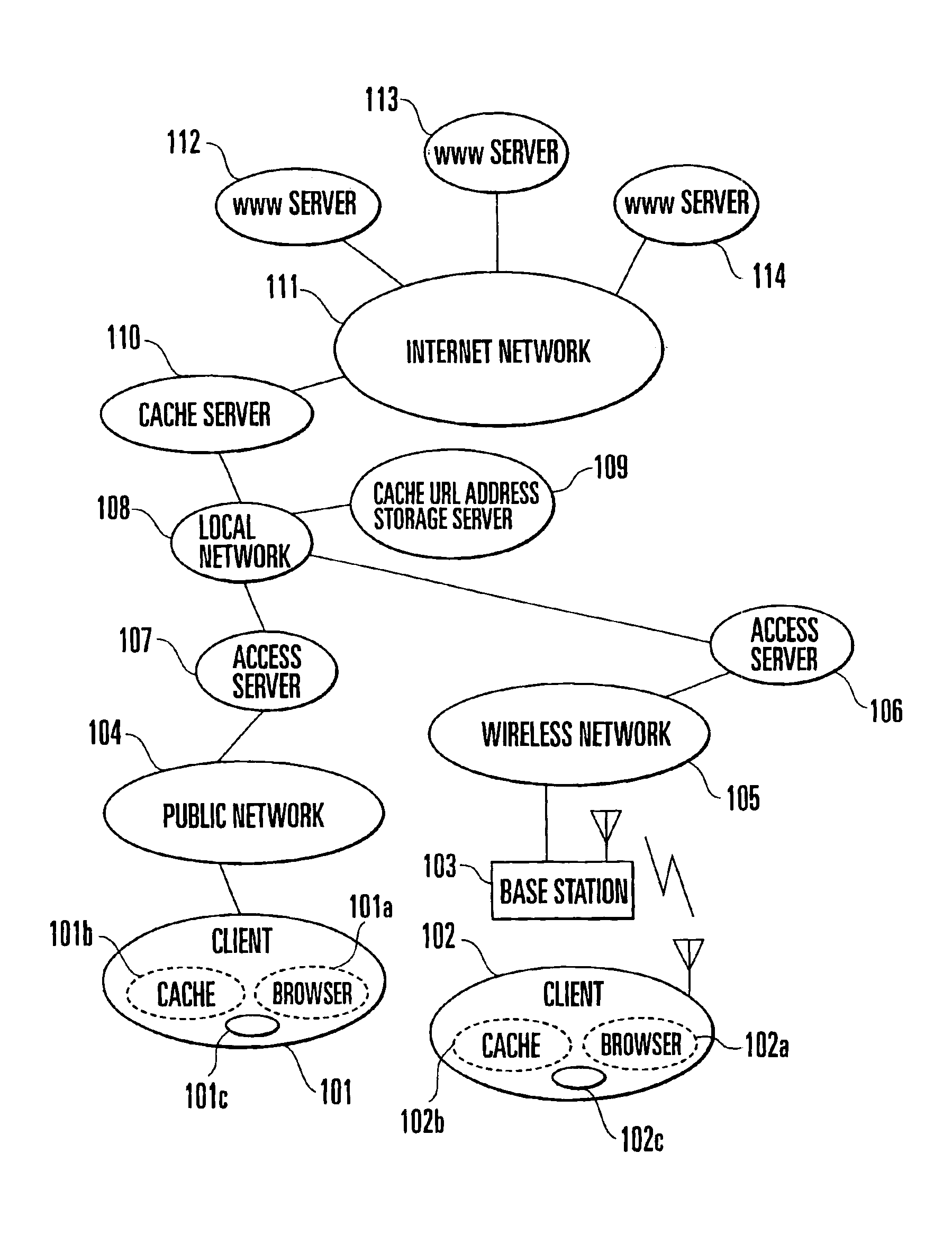
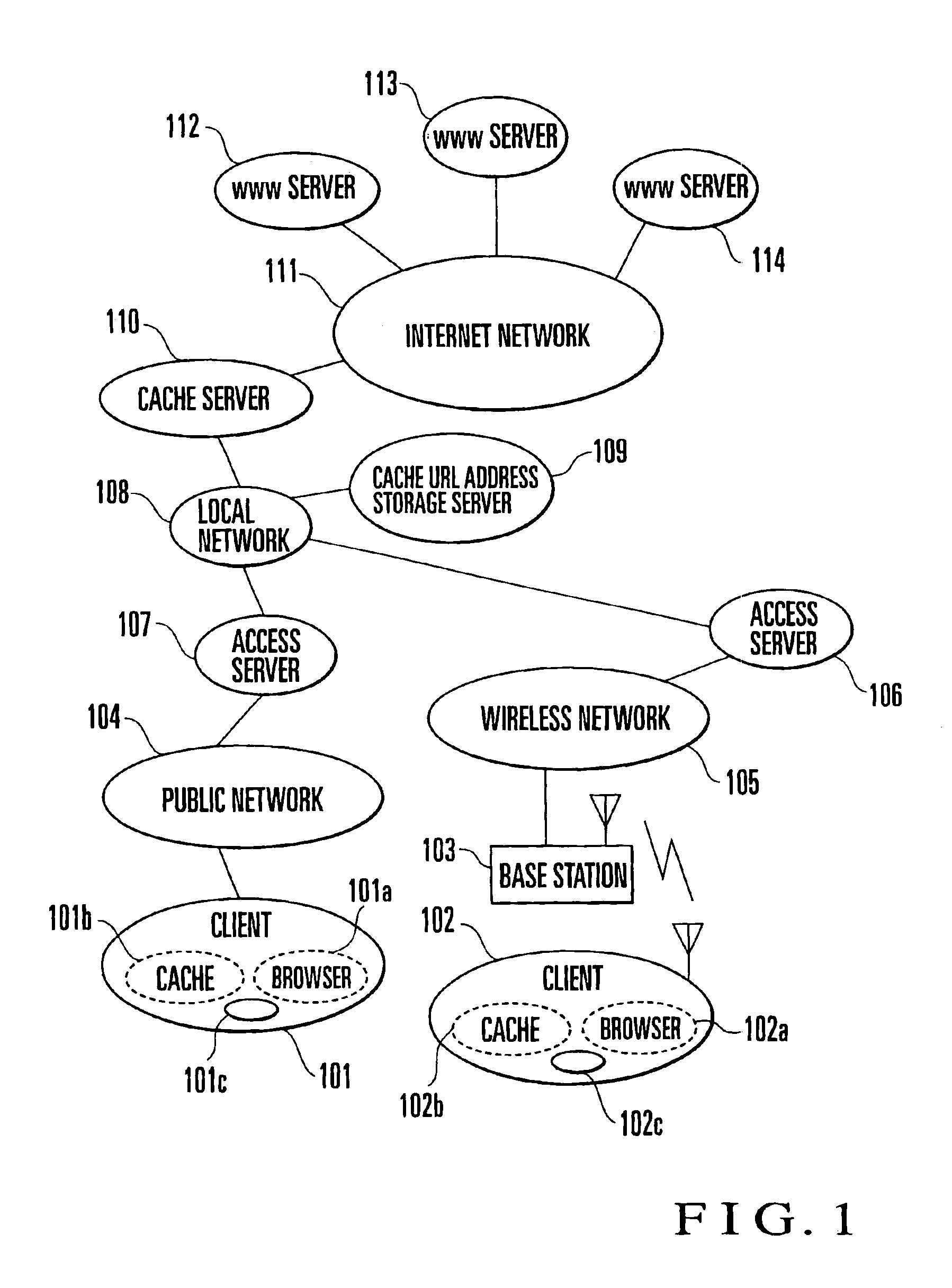
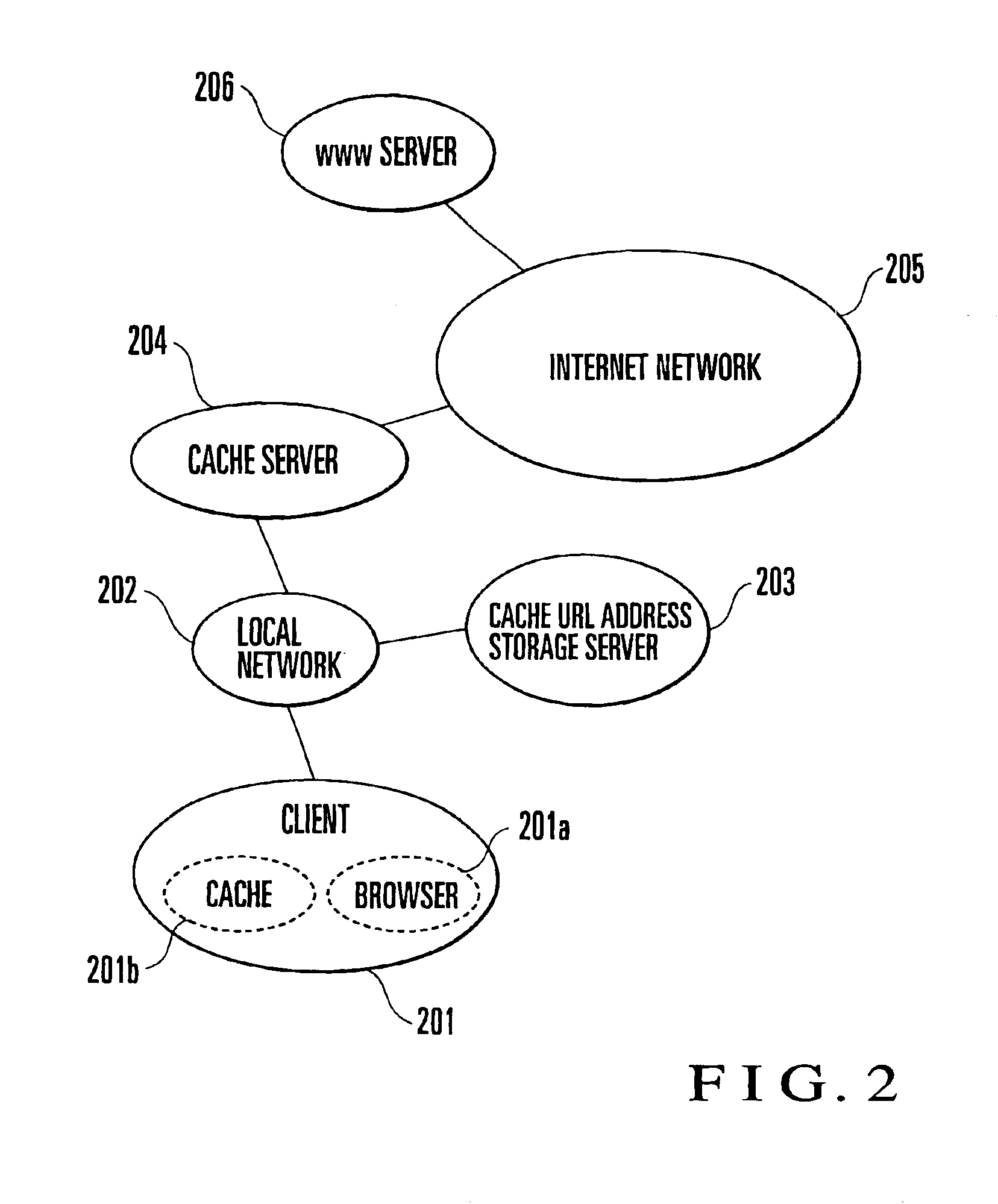
In an Internet home page data acquisition method, an access list held by a client is transferred to a cache URL address storage server. Home page data is acquired by a cache server on the basis of the transferred access list. The acquired home page data is transferred from the cache server to the client upon completion of acquisition of the home page data.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Caching media data using content sensitive object identifiers
InactiveUS20050165828A1Efficient and economicalMemory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsCache serverClient-side
Techniques for caching media data, including streaming media data, using content-sensitive identifiers. The content-sensitive identifiers enable a caching proxy or a caching server to unambiguously determine the version or contents of media data cached by the caching proxy for a particular data pointer or data reference (e.g., a URL) such that an appropriate version of the media data can be served to a requesting client system in an efficient and economical manner.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
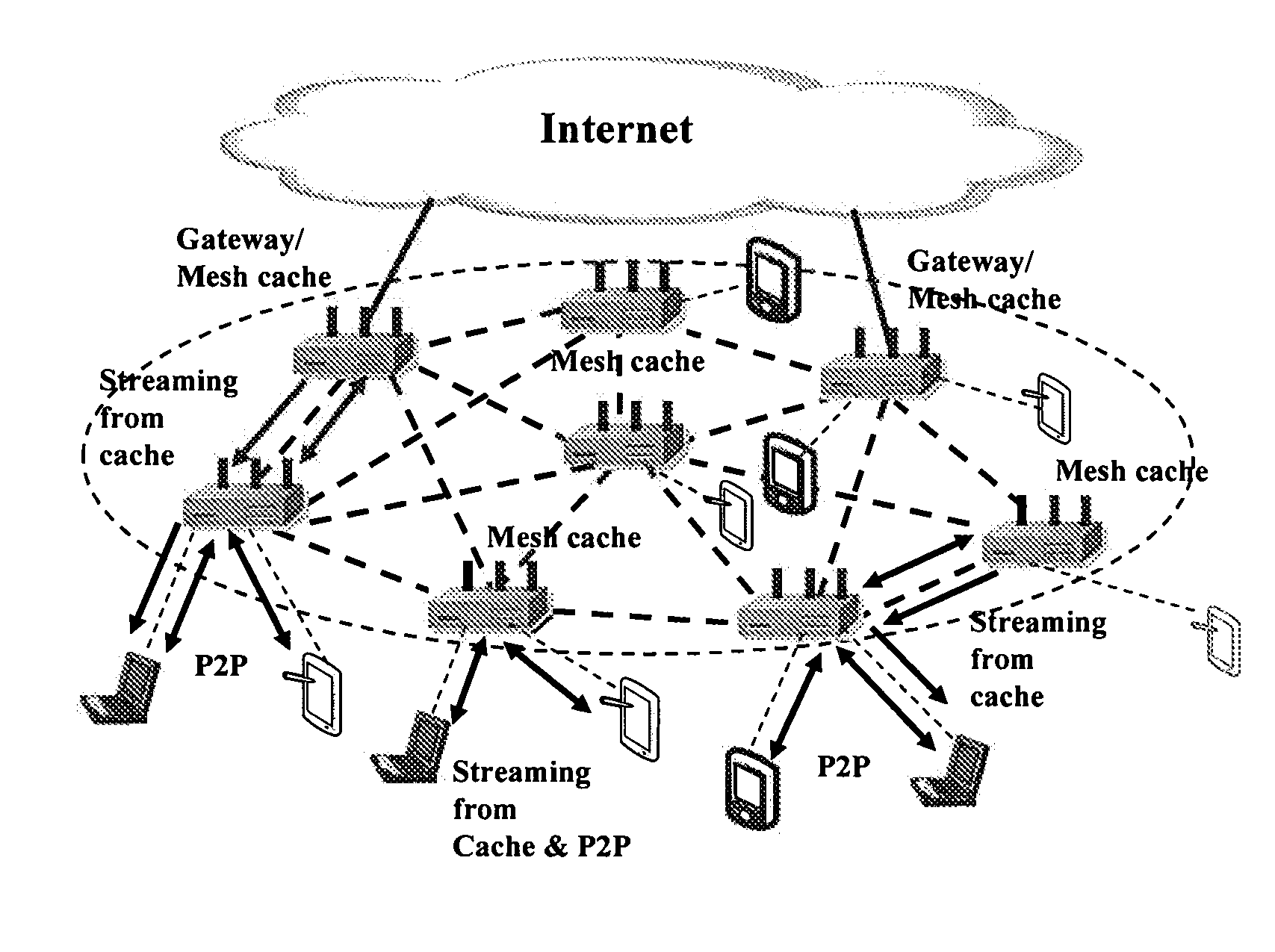
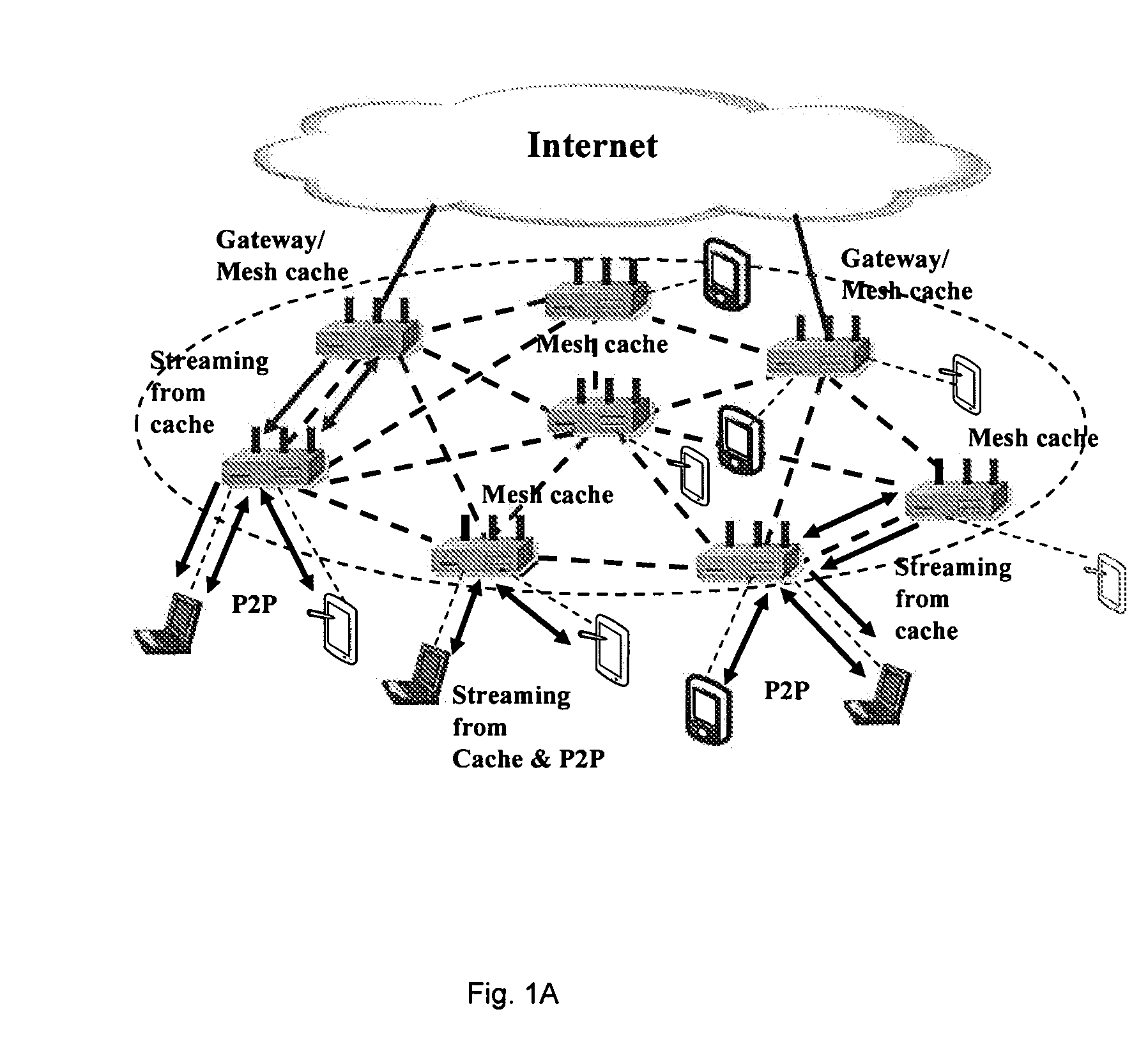
Unified cache and peer-to-peer method and apparatus for streaming media in wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20110225312A1Reduce in quantityImprove good performanceSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceMissing data
A method and apparatus are described including determining a number of clips to be streamed, requesting a selection of a mesh cache server to meet quality of service requirements for streaming the determined number of clips, establishing a streaming route responsive to the mesh cache server selection, receiving the number of streamed clips from the selected mesh cache server if the request is granted, joining a peer-to-peer network, downloading a next clip via the peer-to-peer network, requesting a selection of a mesh cache server to meet quality of service requirements for complimentary streaming any data missing from the next clip, receiving any data missing from the next clip via complimentary streaming if the request for complimentary streaming is granted and continuing to download any missing data of the next clip that has at least one of not passed its playback deadline and not been requested via complimentary streaming.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com