Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
738 results about "Group of pictures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
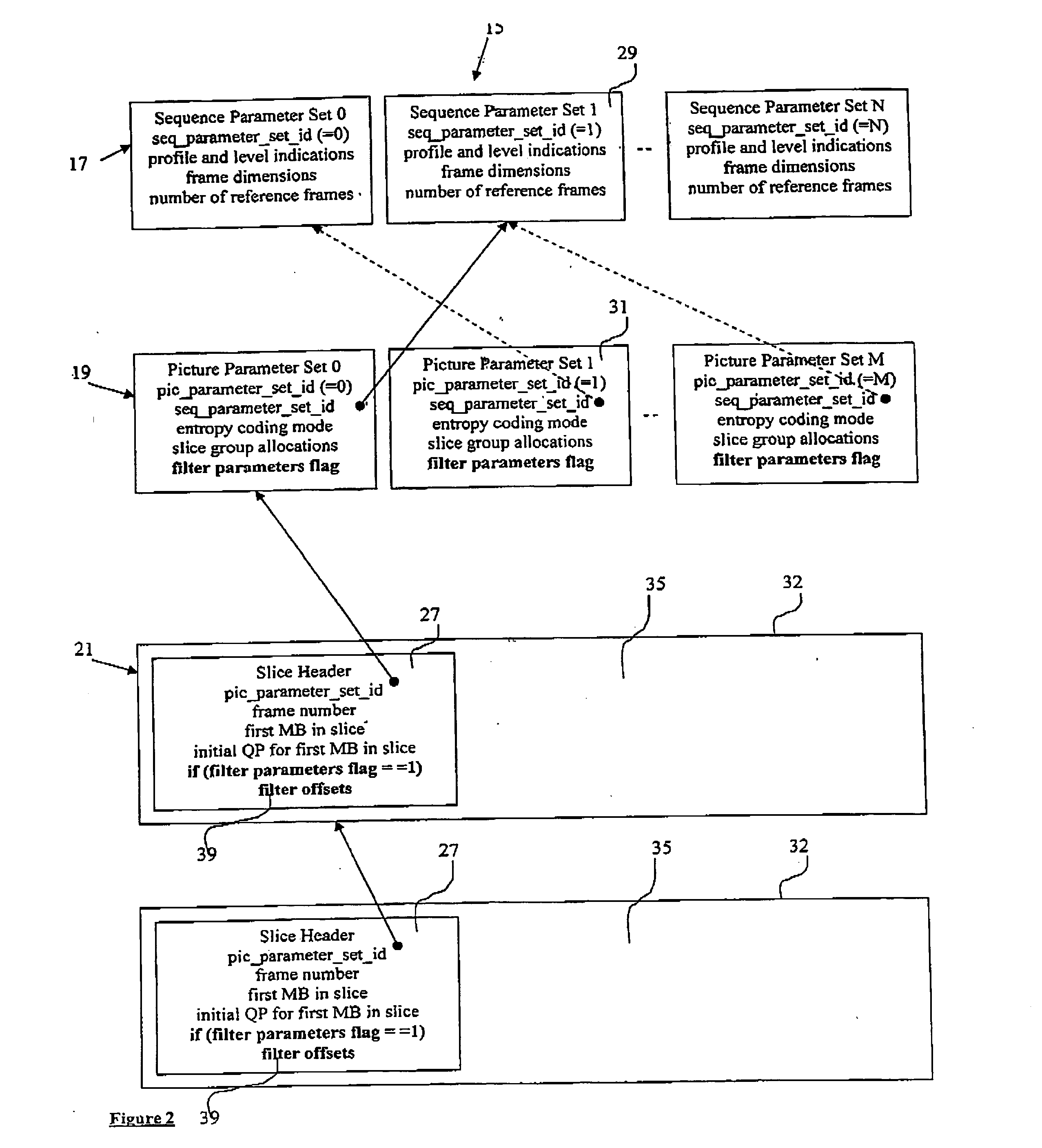
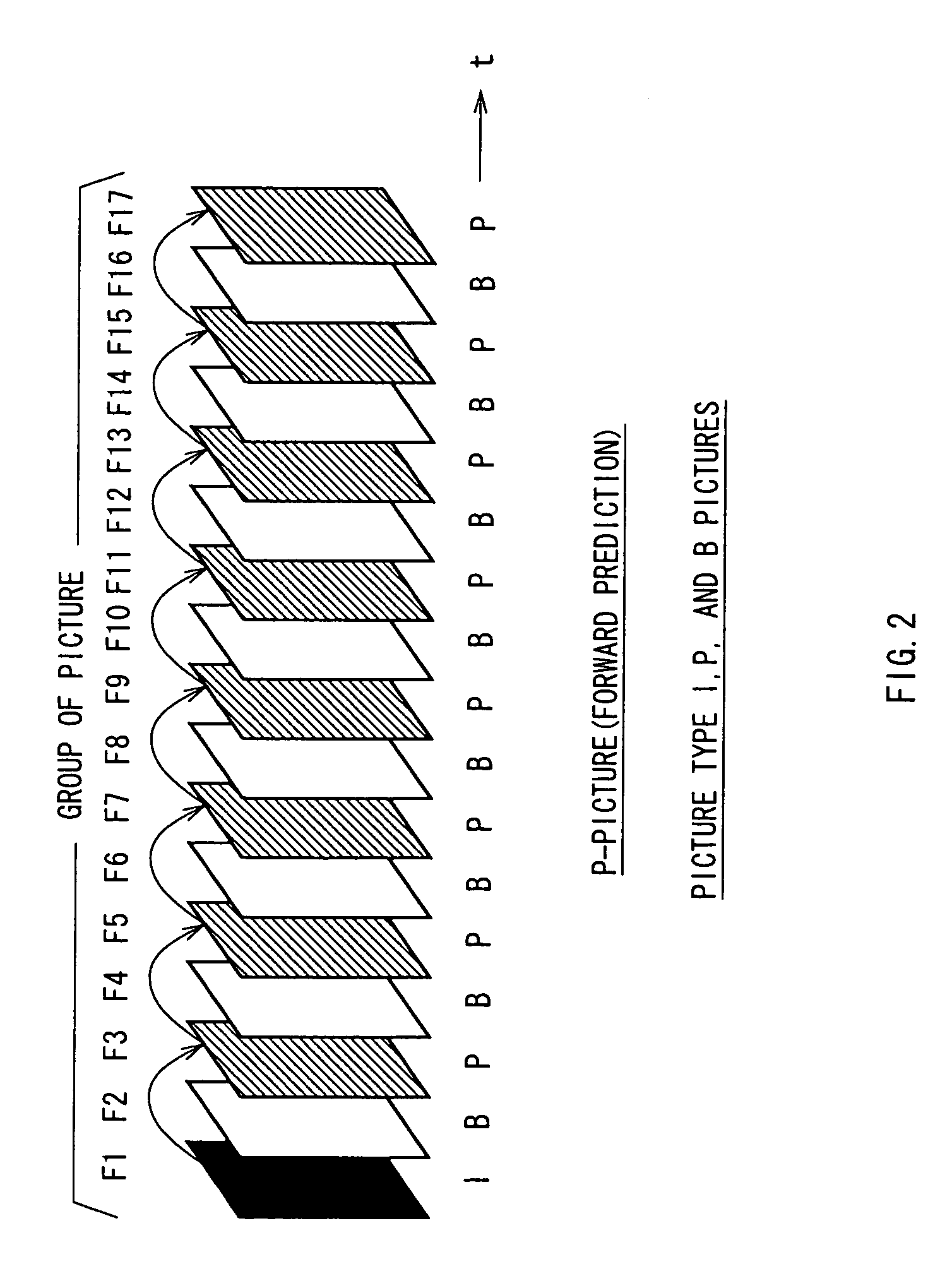
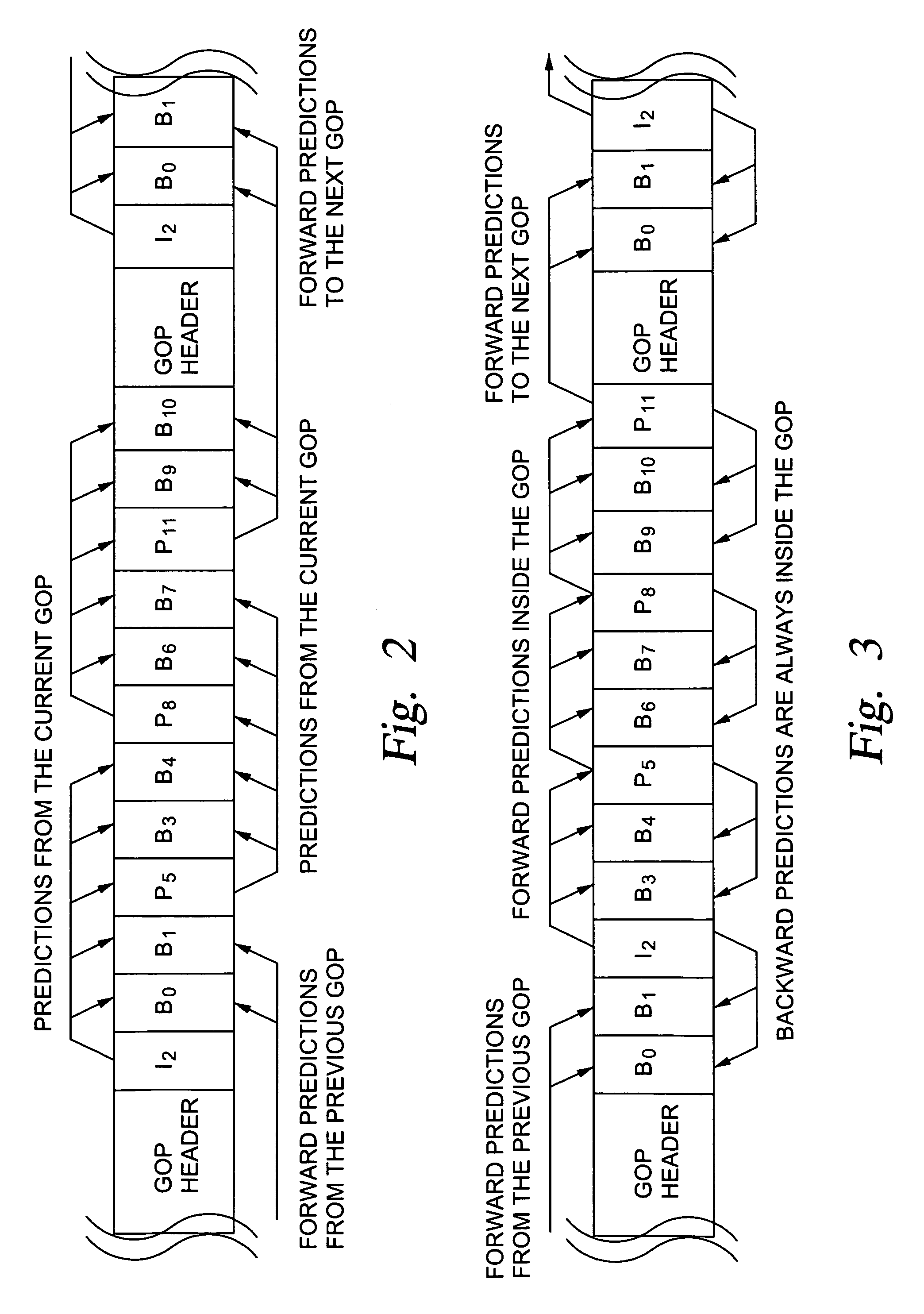
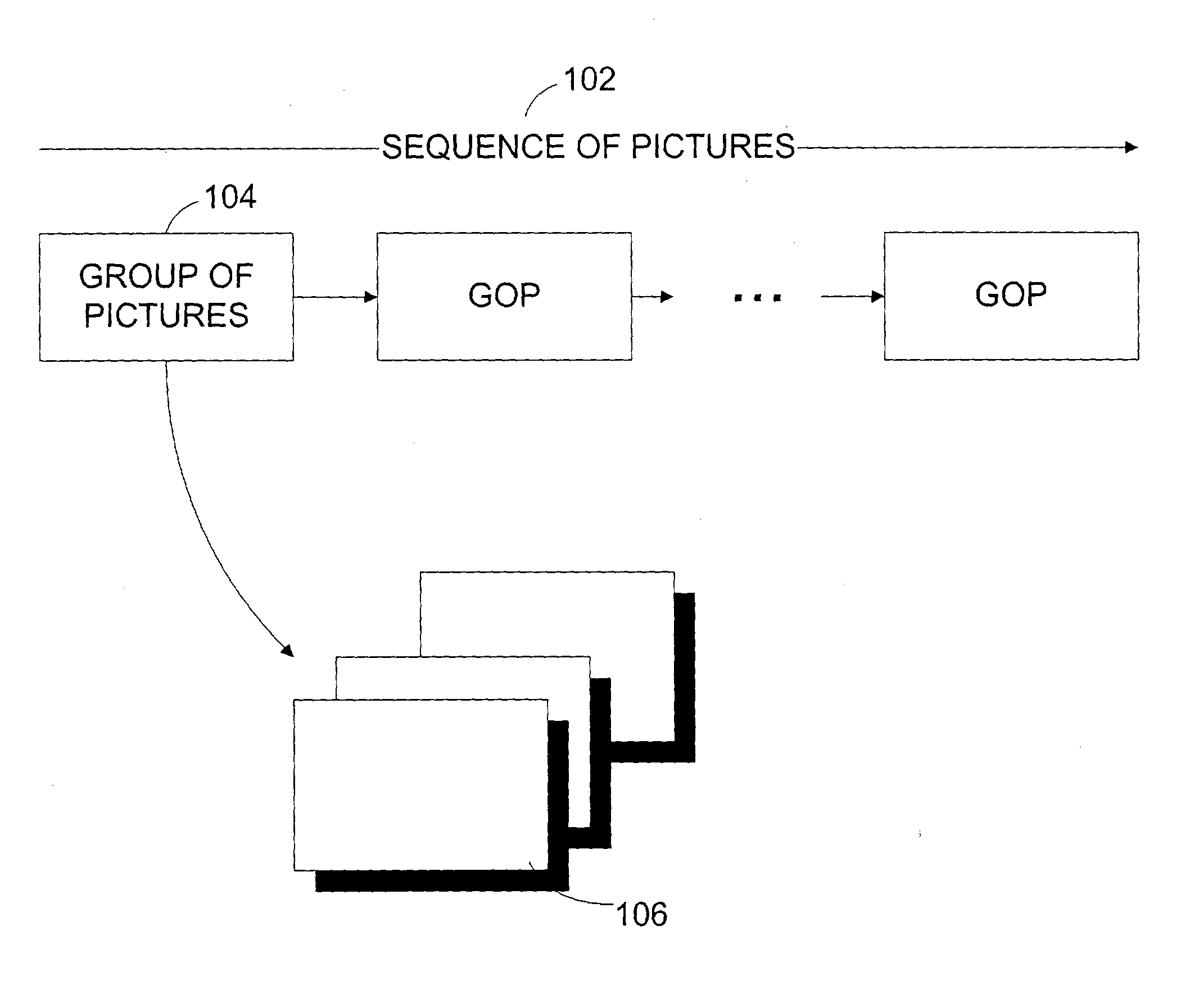
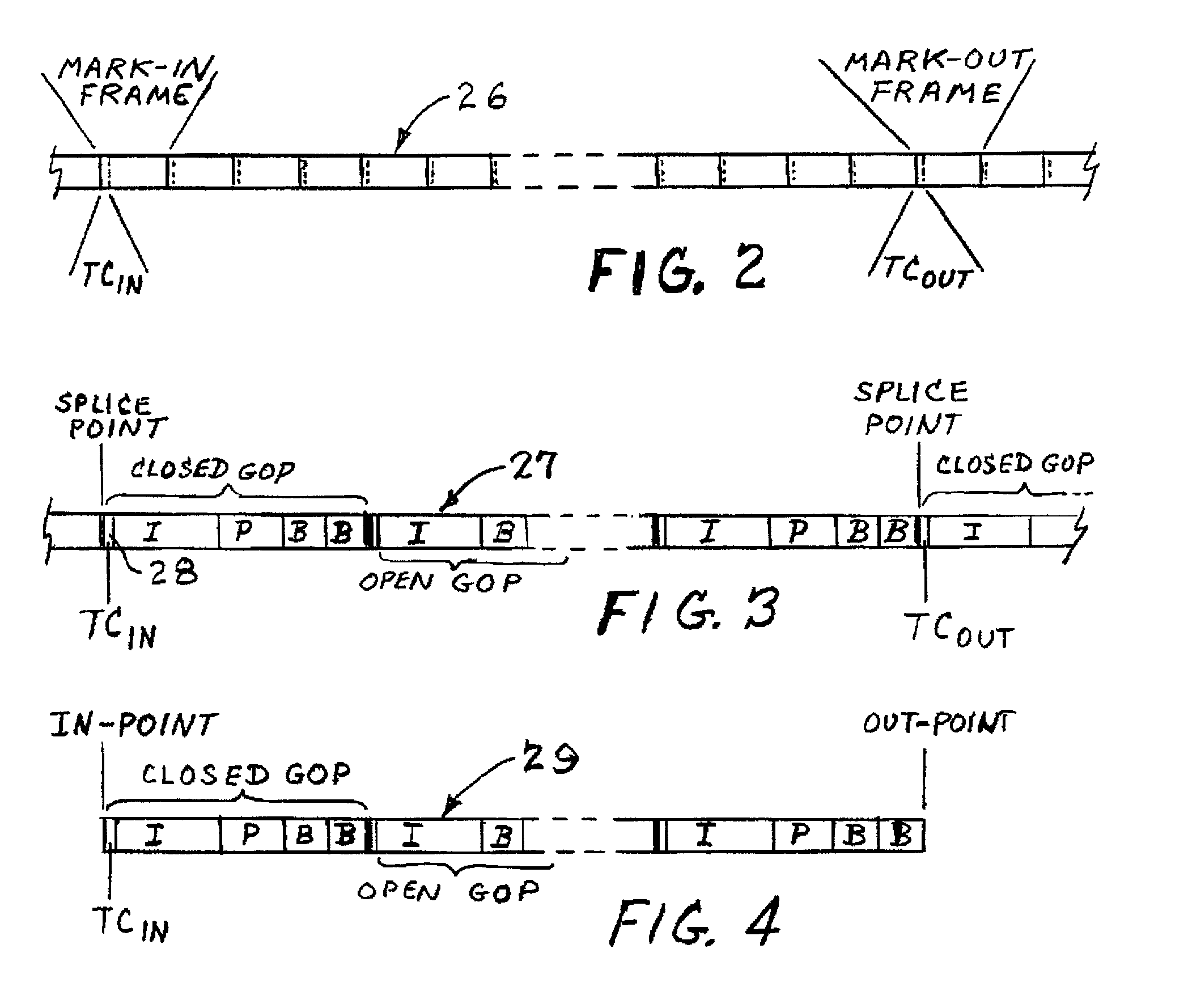
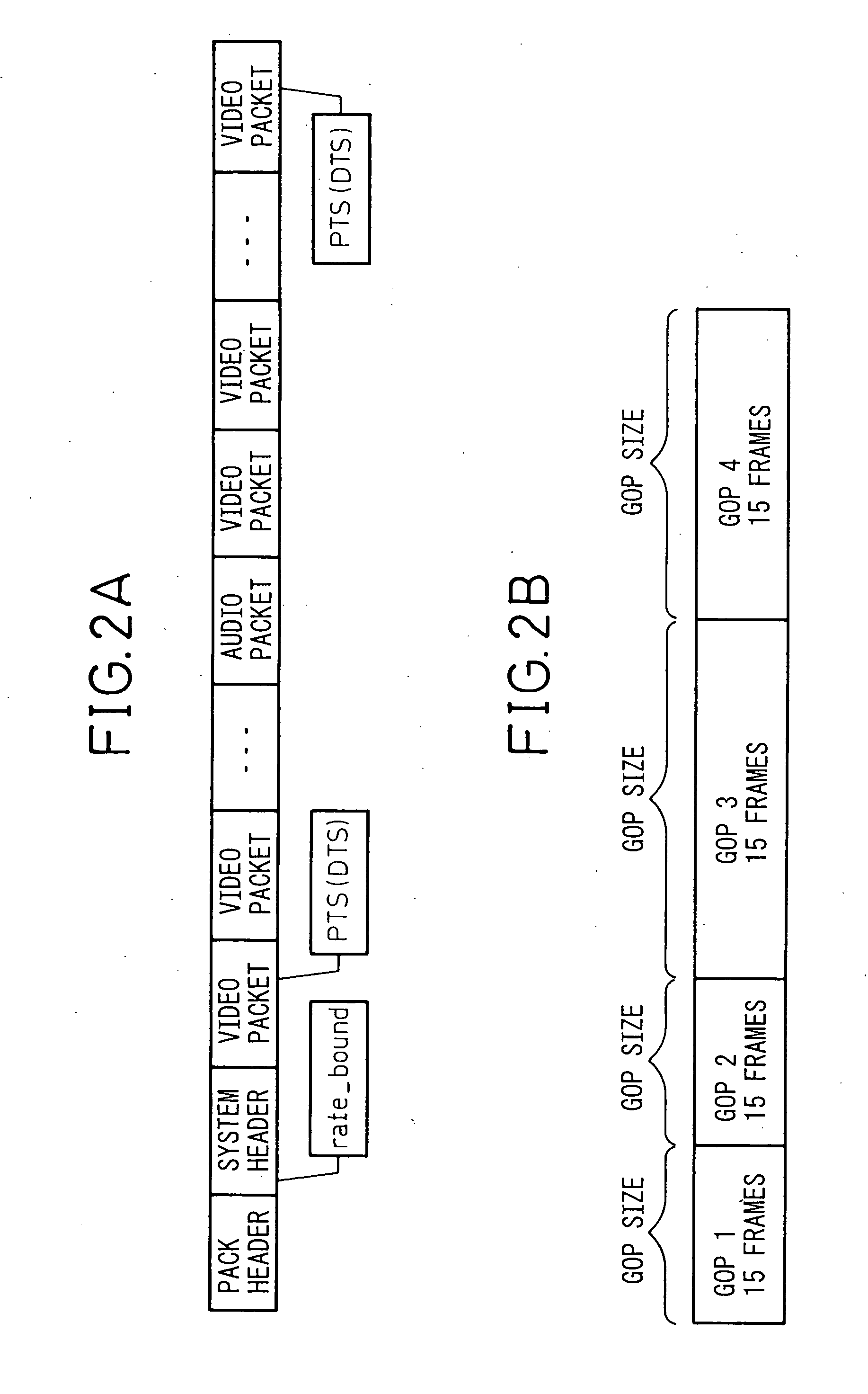
In video coding, a group of pictures, or GOP structure, specifies the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. The GOP is a collection of successive pictures within a coded video stream. Each coded video stream consists of successive GOPs, from which the visible frames are generated. Encountering a new GOP in a compressed video stream means that the decoder doesn't need any previous frames in order to decode the next ones, and allows fast seeking through the video.
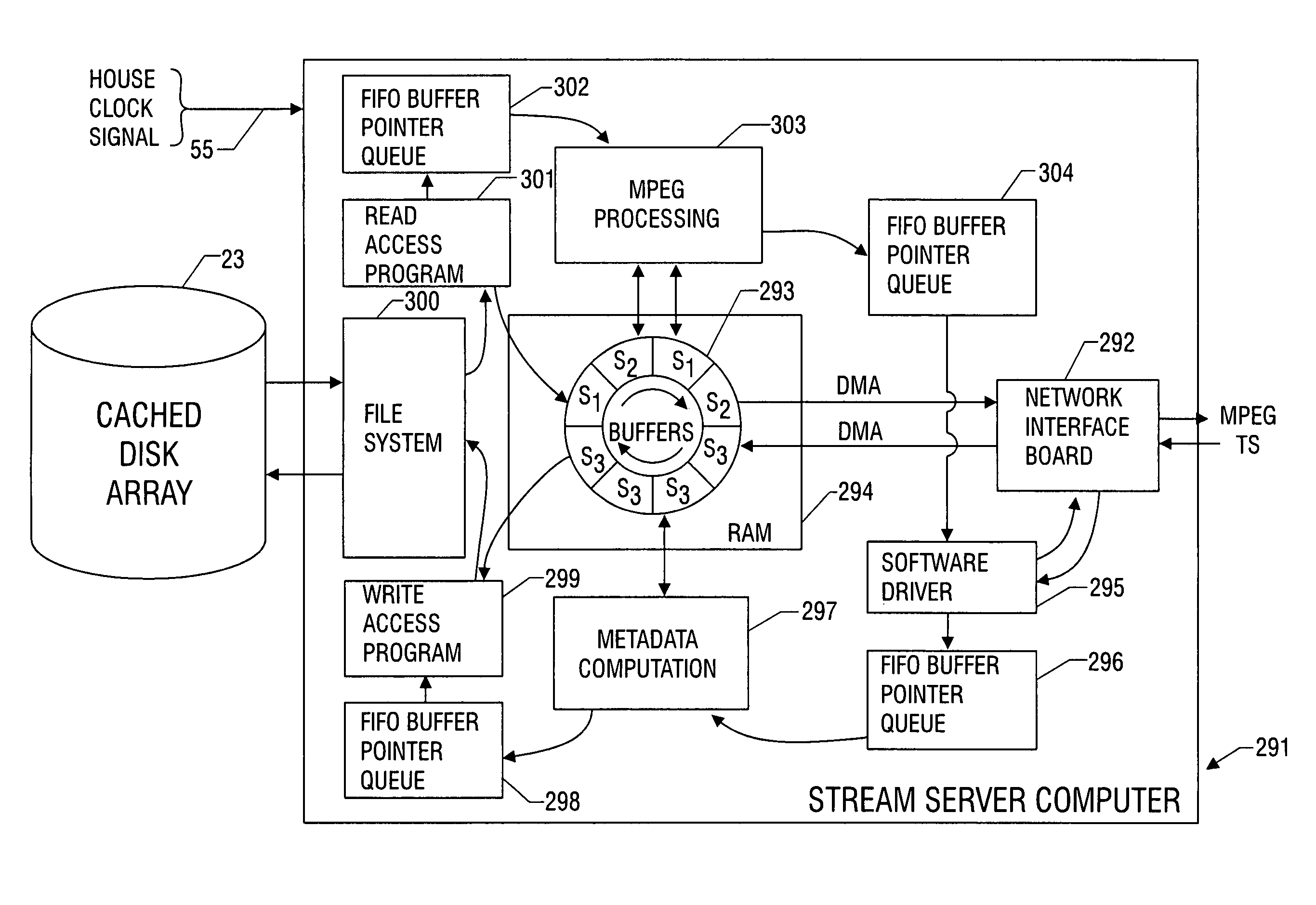
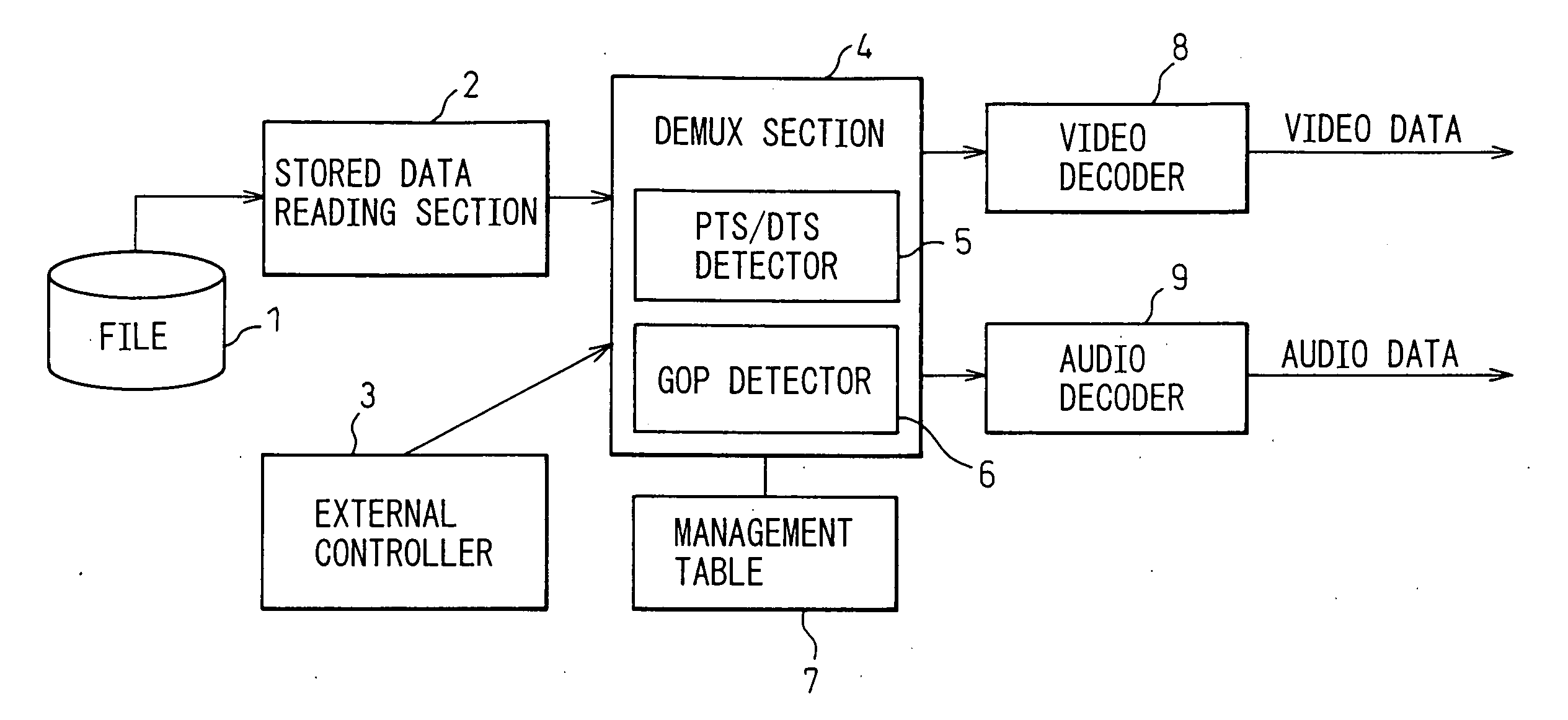
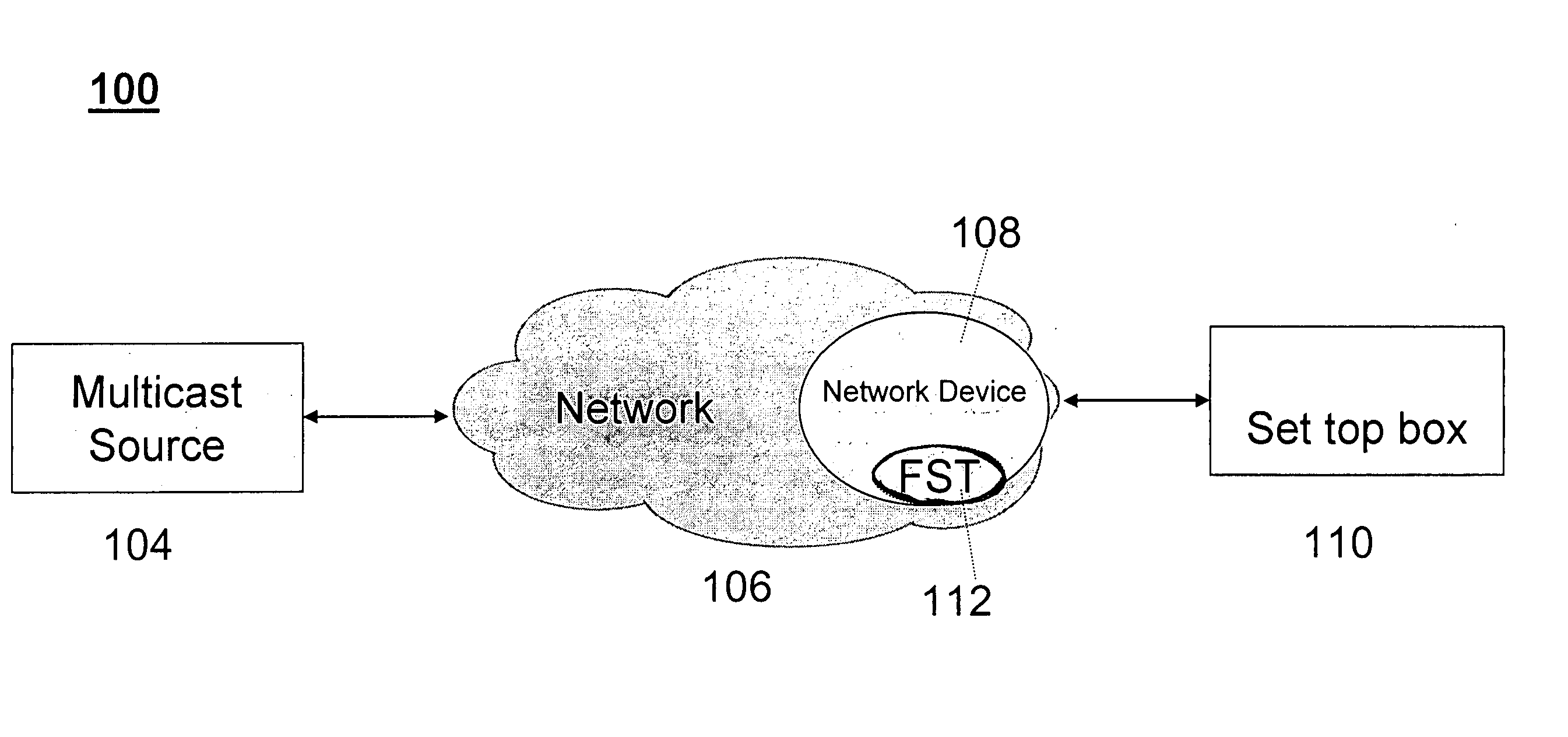
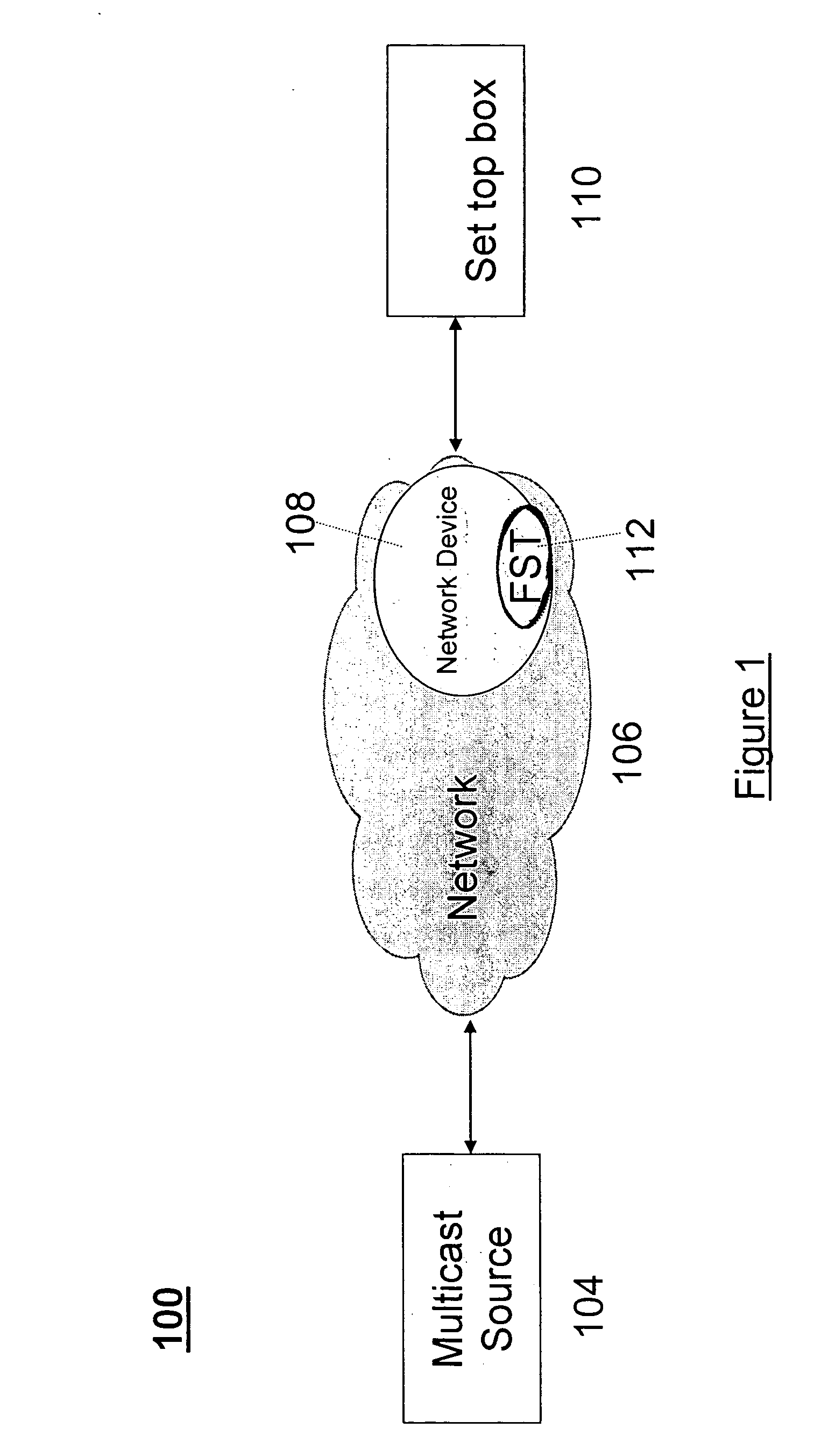
Preparation of metadata for splicing of encoded MPEG video and audio
InactiveUS7096481B1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningMPEG transport streamData stream
Metadata for splicing of an encoded digital motion video stream (such as an MPEG Transport Stream) is prepared in real time while recording at the encoding bit rate and faster than encoded bit rate for off line encoding independent of the bit rate and mechanisms for ingestion of the data stream into data storage. Preprocessing is performed during a metered file transfer protocol (FTP) and includes pseudo real-time encoding. The preprocessing includes Group of Pictures (GOP) level pre-processing of splicing In Points and results in an intimate linkage between metadata and the file system in which the video data is stored. The preferred file system enables access to metadata in parallel to writing the data on disk. The pre-processing is performed simultaneous to writing the data to the disk using a carousel type buffer mechanism.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC +1
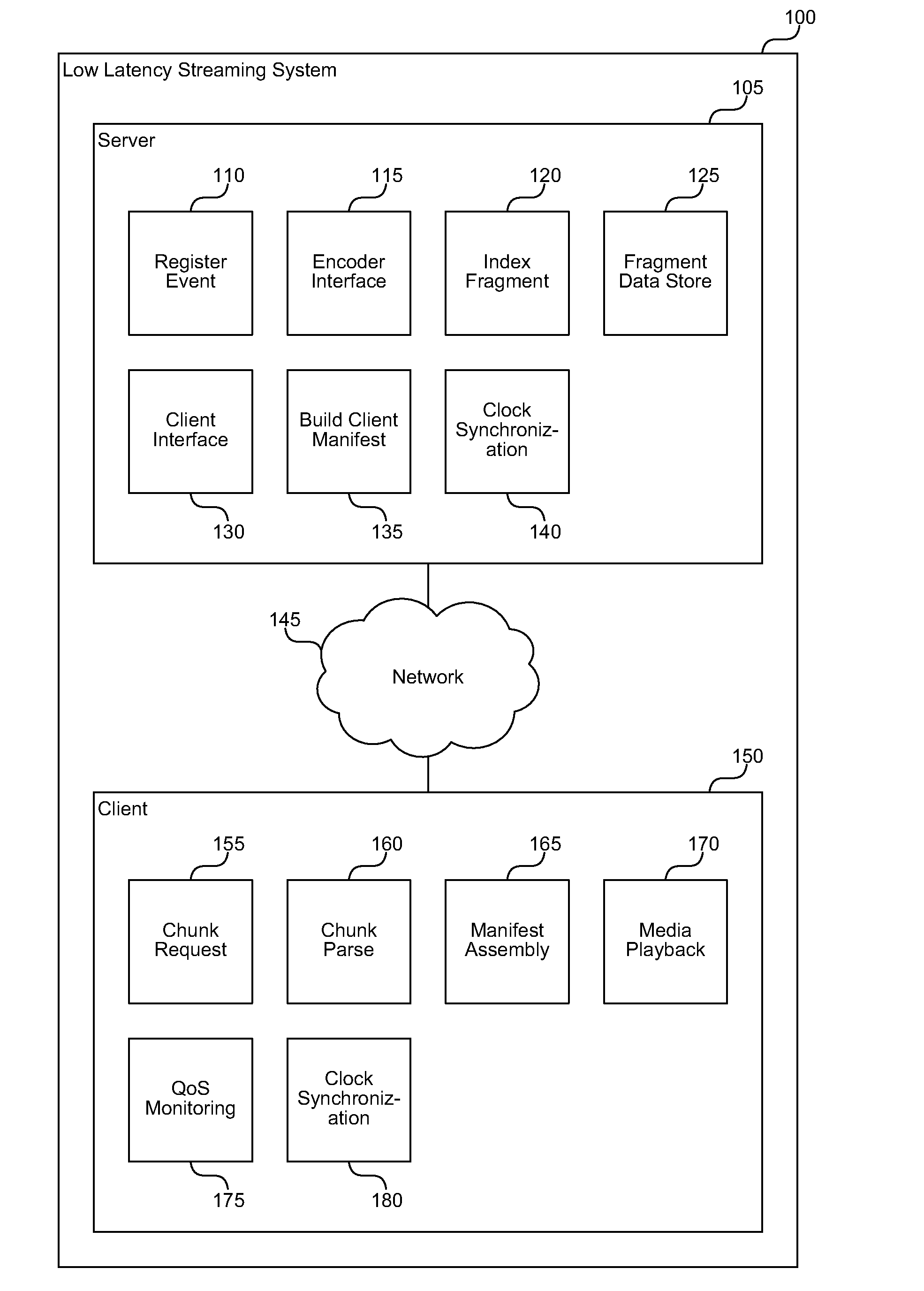
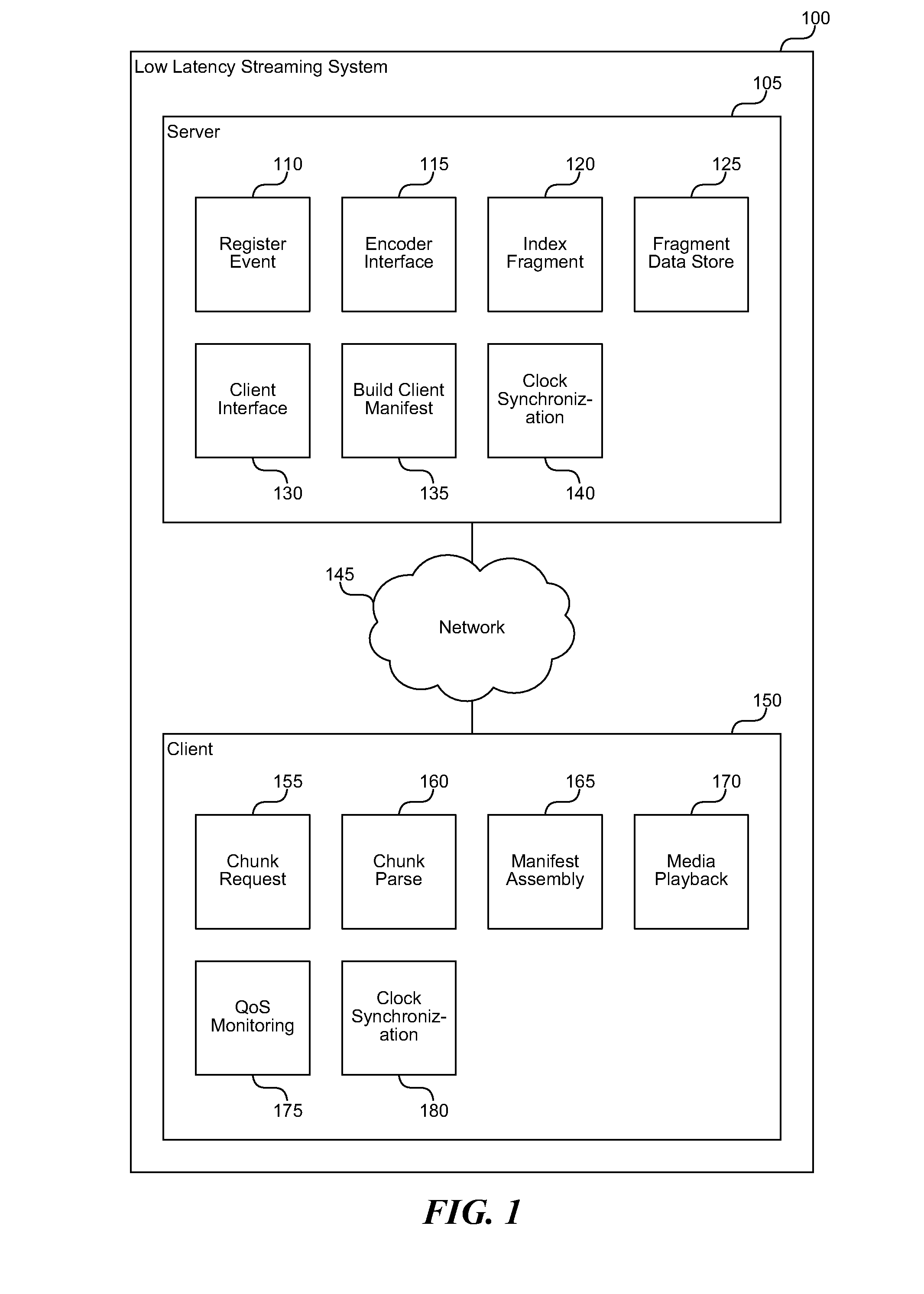
Low latency cacheable media streaming
ActiveUS20110080940A1Lower latencyRaise the possibilityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningGroup of picturesCache server
A low latency streaming system provides a stateless protocol between a client and server with reduced latency. The server embeds incremental information in media fragments that eliminates the usage of a typical control channel. In addition, the server provides uniform media fragment responses to media fragment requests, thereby allowing existing Internet cache infrastructure to cache streaming media data. Each fragment has a distinguished Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that allows the fragment to be identified and cached by both Internet cache servers and the client's browser cache. The system reduces latency using various techniques, such as sending fragments that contain less than a full group of pictures (GOP), encoding media without dependencies on subsequent frames, and by allowing clients to request subsequent frames with only information about previous frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Low-complexity motion vector prediction for video codec with two lists of reference pictures
ActiveUS20050117646A1Expand selectionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLow complexityMotion vector
A method of motion vector prediction for use in differential motion vector coding within a block motion-compensation-based video coder. The video coder employs a generalized multiple reference picture buffer which may contain multiple reference pictures in both the forward and backward temporal direction from the current picture. For the purpose of coding selections of reference pictures within the buffer, the pictures are organized into two, potentially overlapping, lists of reference pictures. The prediction of a motion vector that selects a reference picture using a given reference picture list is not dependent upon any motion vectors that select their reference pictures using the other reference picture list. The values of spatially neighbouring motion vectors that use the same list of reference pictures as the notion vector being predicted are used for prediction, regardless of the relative temporal direction of the current and neighbouring motion vectors.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
System and method for media stream indexing
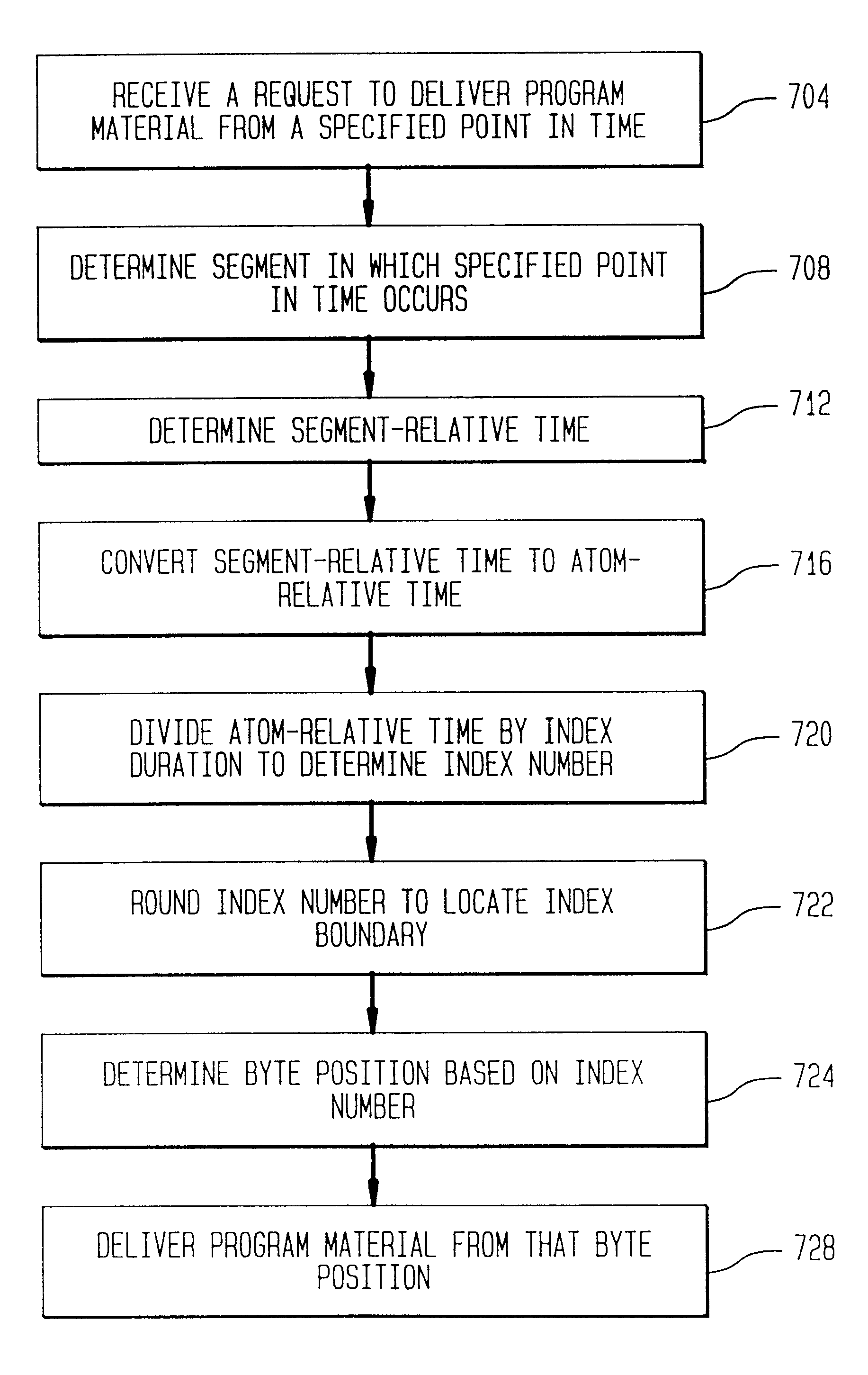
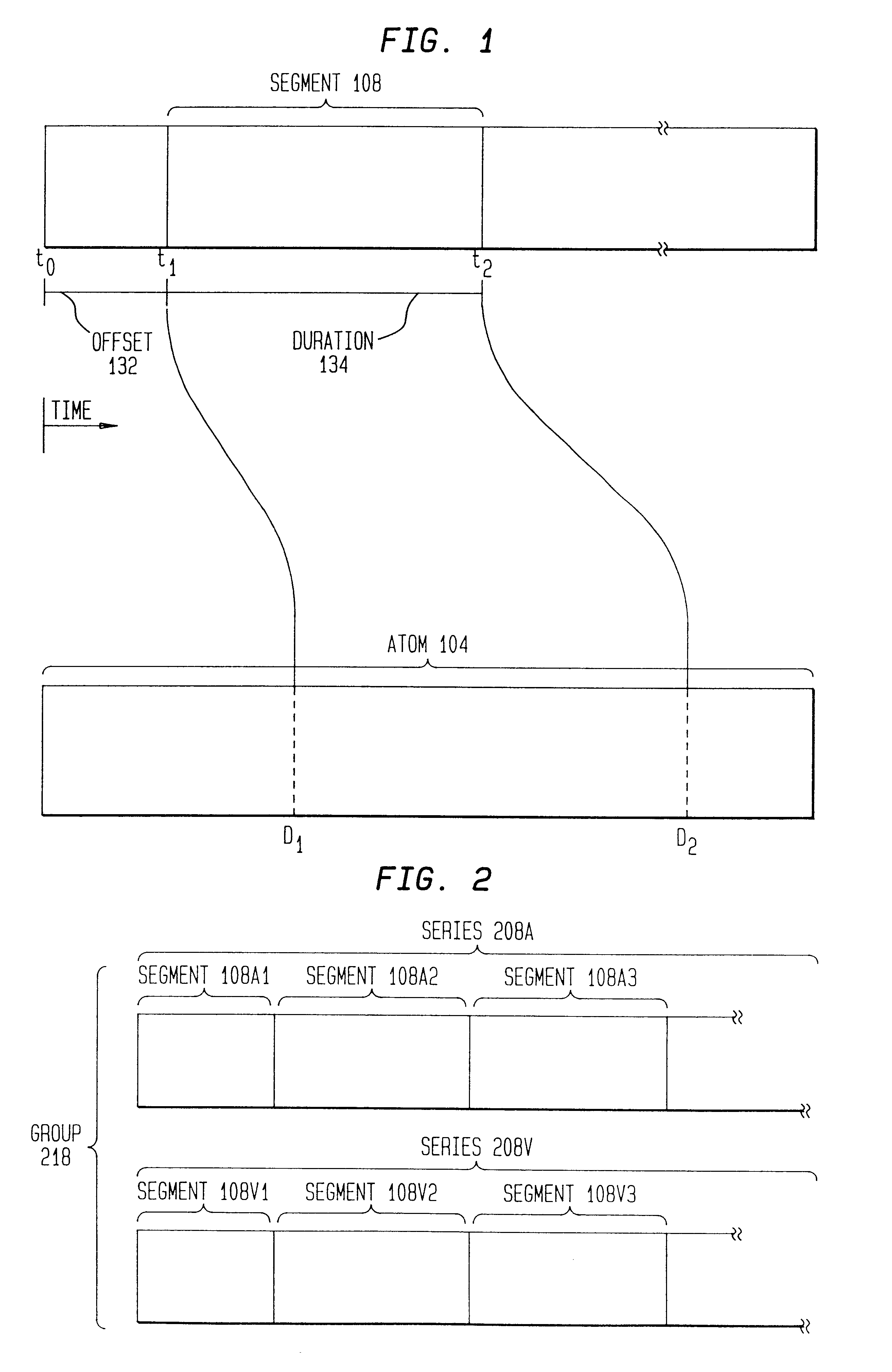
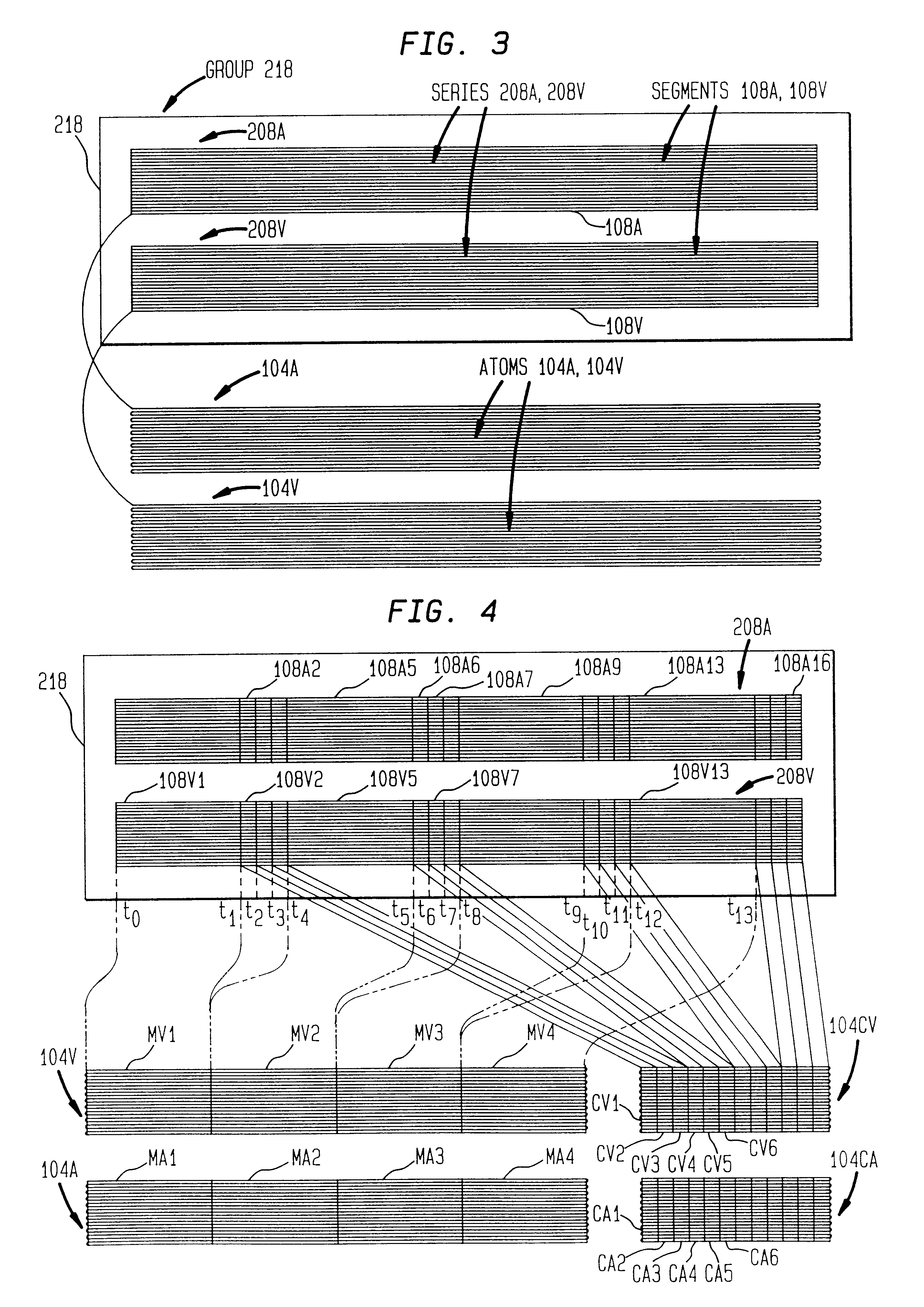
An indexing method for allowing a viewer to control the mode of delivery of program material. By mapping from time to data position, data delivery can begin at any selected time in the program material. The indexing method also provides for controlling data delivery to begin at the beginning of a frame of data. A synchronizing method is provided to minimize a time offset between audio and video data, particularly in environments using groups of pictures.
Owner:ESPIAL
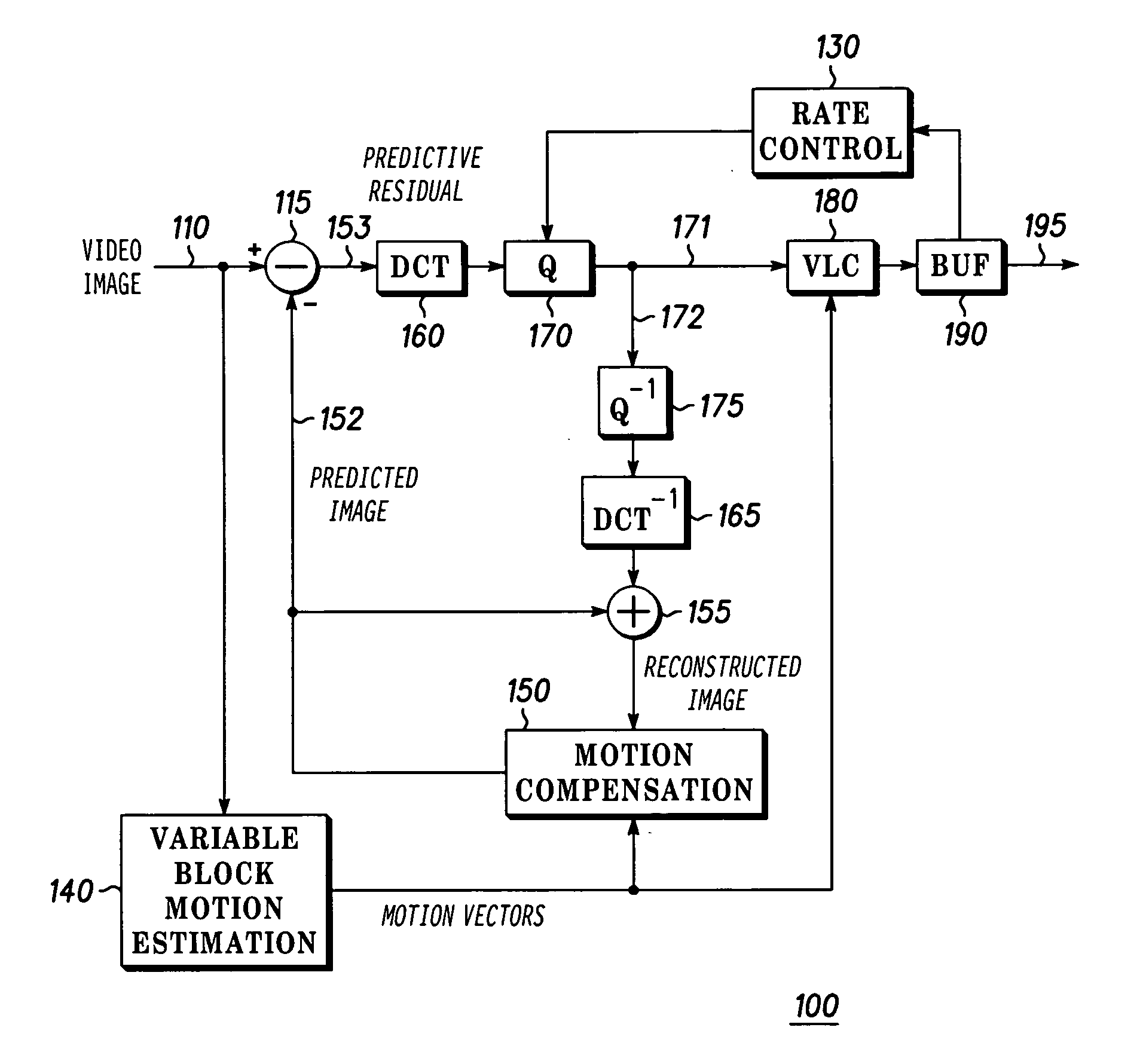
Method and apparatus for providing rate control in a video encoder
InactiveUS6963608B1Avoids visible artifactAvoid artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoVideo encoding
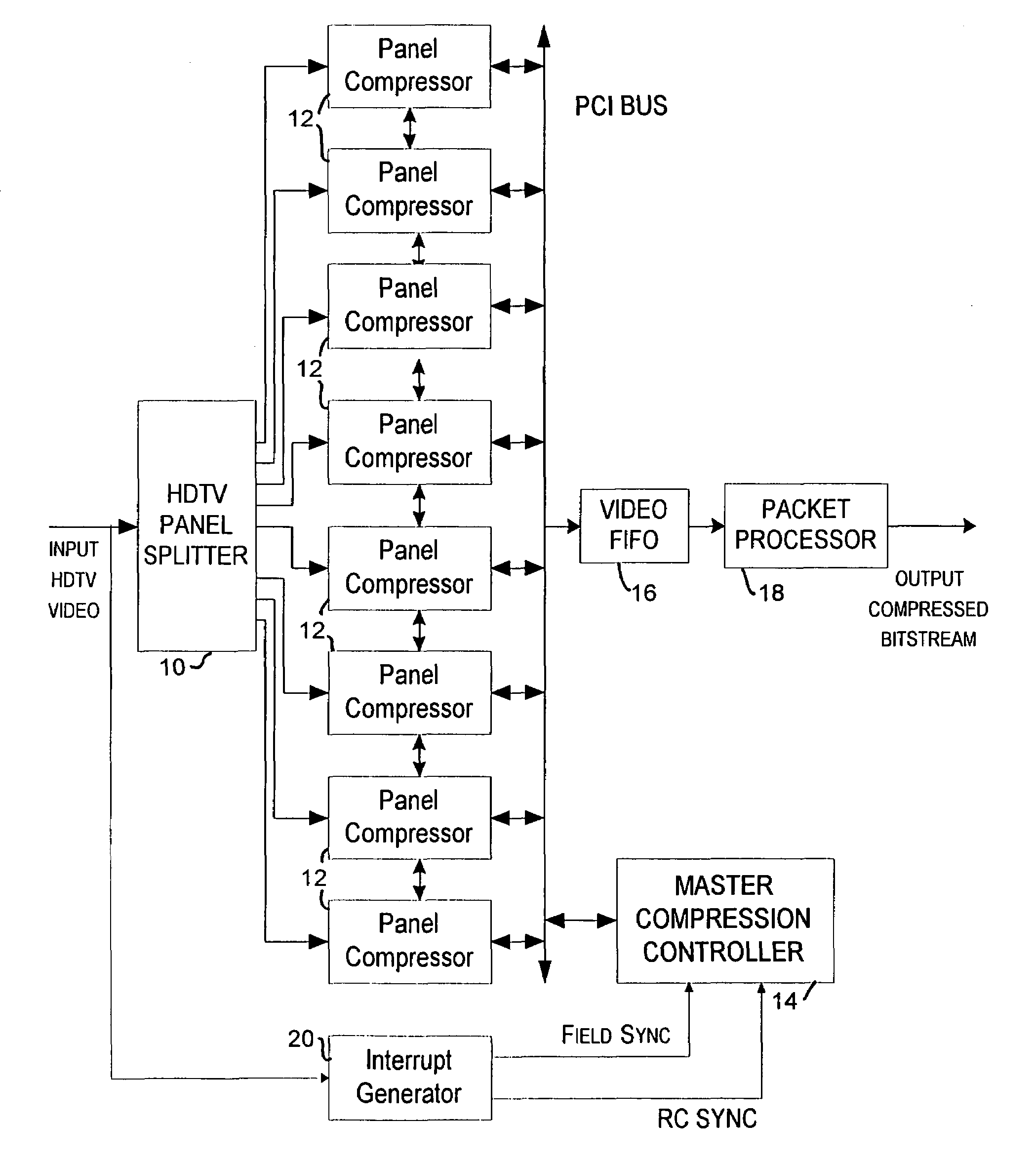
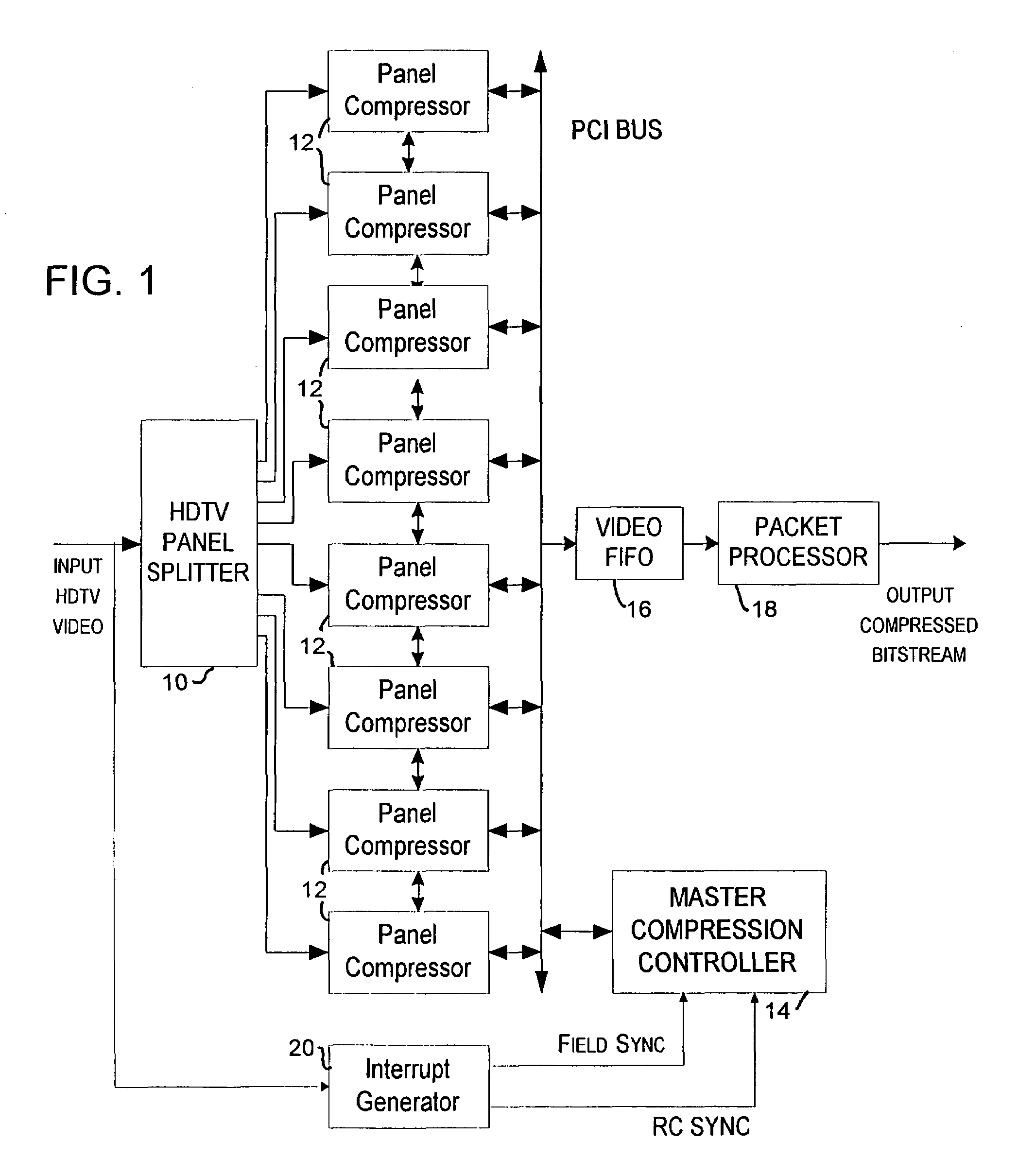
A method and apparatus are provided for controlling the quantization level in a digital video encoder that comprises a plurality of parallel compression engines (12). The input picture is partitioned into a number of panels (10) and each panel is processed by a distinct compression engine (12). A reference quantizer scale is determined before encoding a frame of video. The reference quantizer scale is used at the first slice of every video image panel being processed by the video encoder. The quantizer scale at the last slice of the image panel is then forced to be the same as the first slice. The forcing step can use a piecewise-linear feedback formula. A group of pictures (GOP) target bit rate is adjusted based on the number of film pictures and non-film pictures currently in the processing pipeline of at least one of the compression engines. A higher target bit rate is provided for non-film pictures. A buffer (16) level of the video encoder is used to control the start of a new group of pictures (GOP). The start of a new GOP is delayed if the buffer (16) does not have sufficient space to accommodate an intra-coded (I) frame for the new GOP.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method and apparatus for playing an MPEG data file backward
InactiveUS6353700B1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsReverse orderComputer graphics (images)
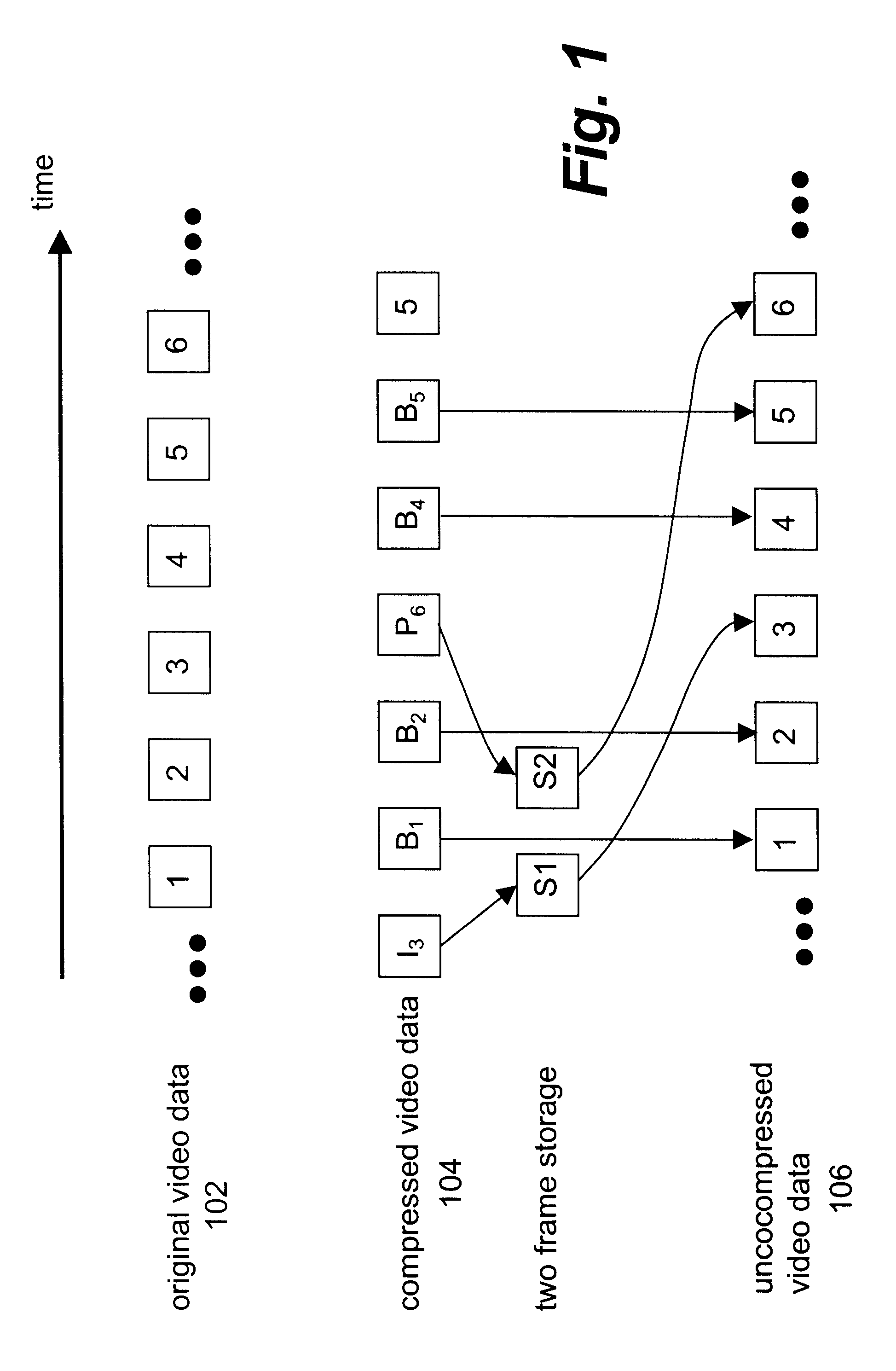
The present invention has been made in consideration of linear reverse playback of MPEG video data and has particular applications to video special effect editing. According to one aspect of the present invention, the disclosed system uses a minimum number of frame storage to buffer decompressed I and P frames so as to decompress B frames in a reverse order and subsequently display the B frames. Every time, it comes to display the decompressed I and P frames buffered in the frame storage, an I frame or a P frame in a group of picture (GOP) prior to current GOP is decompressed and buffered into one of the frame storage that becomes available when the content therein has been retrieved for display. The cyclic use of the frame storage and the time that would be otherwise spent for decompressing B frames guarantees a linear reverse playback of MPEG video data without showing retardant visual effects that often result from non-even decoding processes in displaying compressed frames.
Owner:WOMBLE MULTIMEDIA +1
Data structure and methods for providing an interactive program guide
InactiveUS6584153B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPattern recognitionGroup of pictures
A data structure suited to efficiently representing a plurality of image streams including common and non-common portions. Specifically, a plurality of similar group of picture (GOP) data structures representing the corresponding plurality of image streams including common and non-common portions is adapted to provide a first encoded stream comprising only P-picture and B-picture access units of one of the similar GOP data structures, and a corresponding plurality of encoded streams comprising only respective I-picture access units of the similar GOP data structures. In this manner, the redundant P-picture and B-picture access units within the encoded streams are eliminated, thereby greatly reducing the bandwidth or memory resources needed to transmit or store the plurality of image streams.
Owner:TIVO CORP
Recording medium, reproduction device, recording method, program, and reproduction method
ActiveUS20060188223A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsLow bandwidthTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer hardwareGraphics
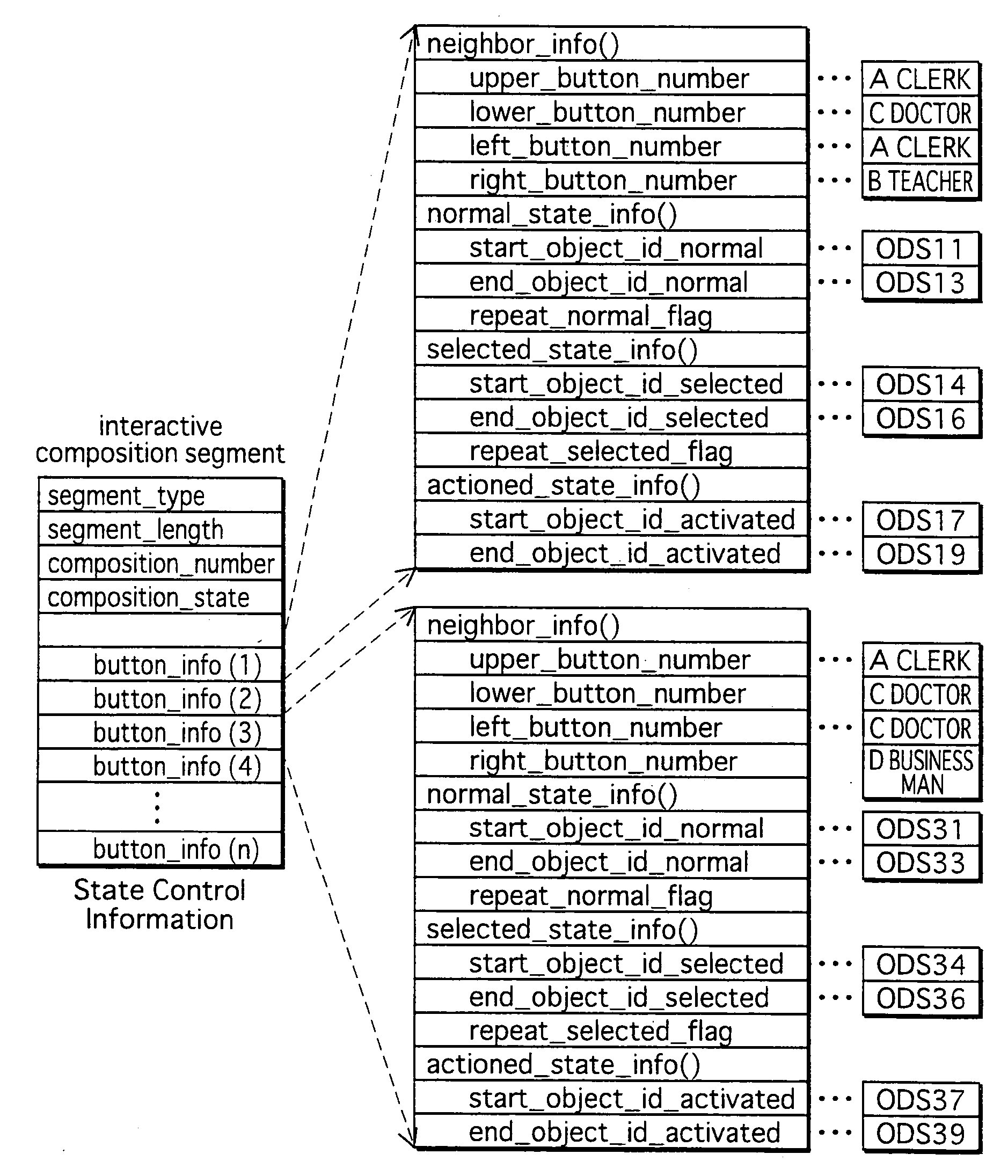
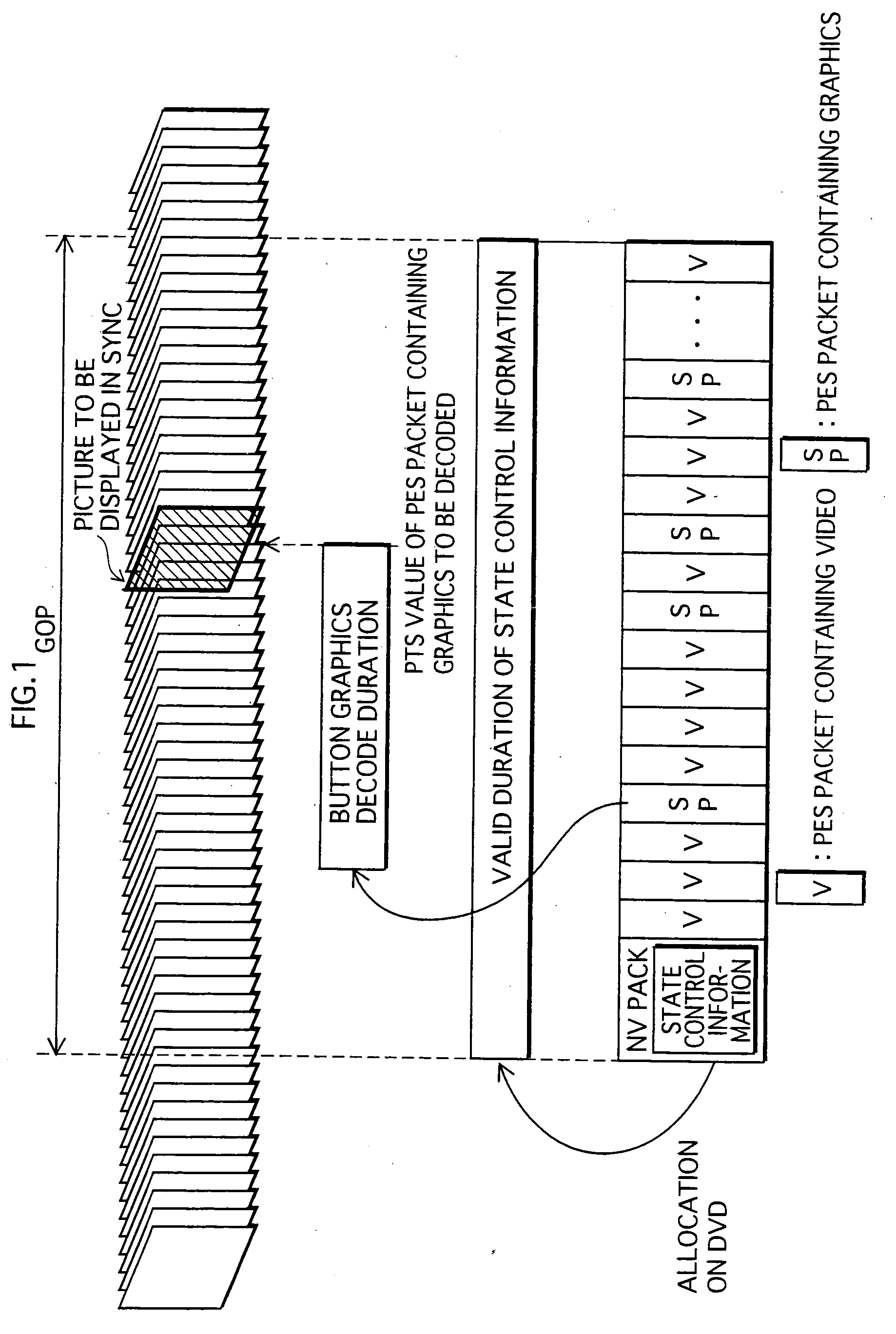
On a BD-ROM, there is recorded is a digital stream into which video and audio streams are multiplexed. The video stream is composed of a plurality of pictures that together represent video. The graphics stream includes a PES packet storing state control information (ICS) and PES packets containing graphics data (ODSs). The graphics data constructs an interactive display. The state control information defines the control so as to change the states of buttons presented on the interactive display according to the reproduction proceeding and user operations. The ICS is attached with a PTS showing the display timing of a picture to be synchronized with the interactive display. The ODS is attached with a PTS showing the timing for decoding the graphics data. The timing shown in the ODS is prior to the display timing.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus and method of splicing digital video streams
InactiveUS7031348B1Avoid expensesAvoiding visual artifactTelevision system detailsLighting and heating apparatusDigital videoProgram clock reference
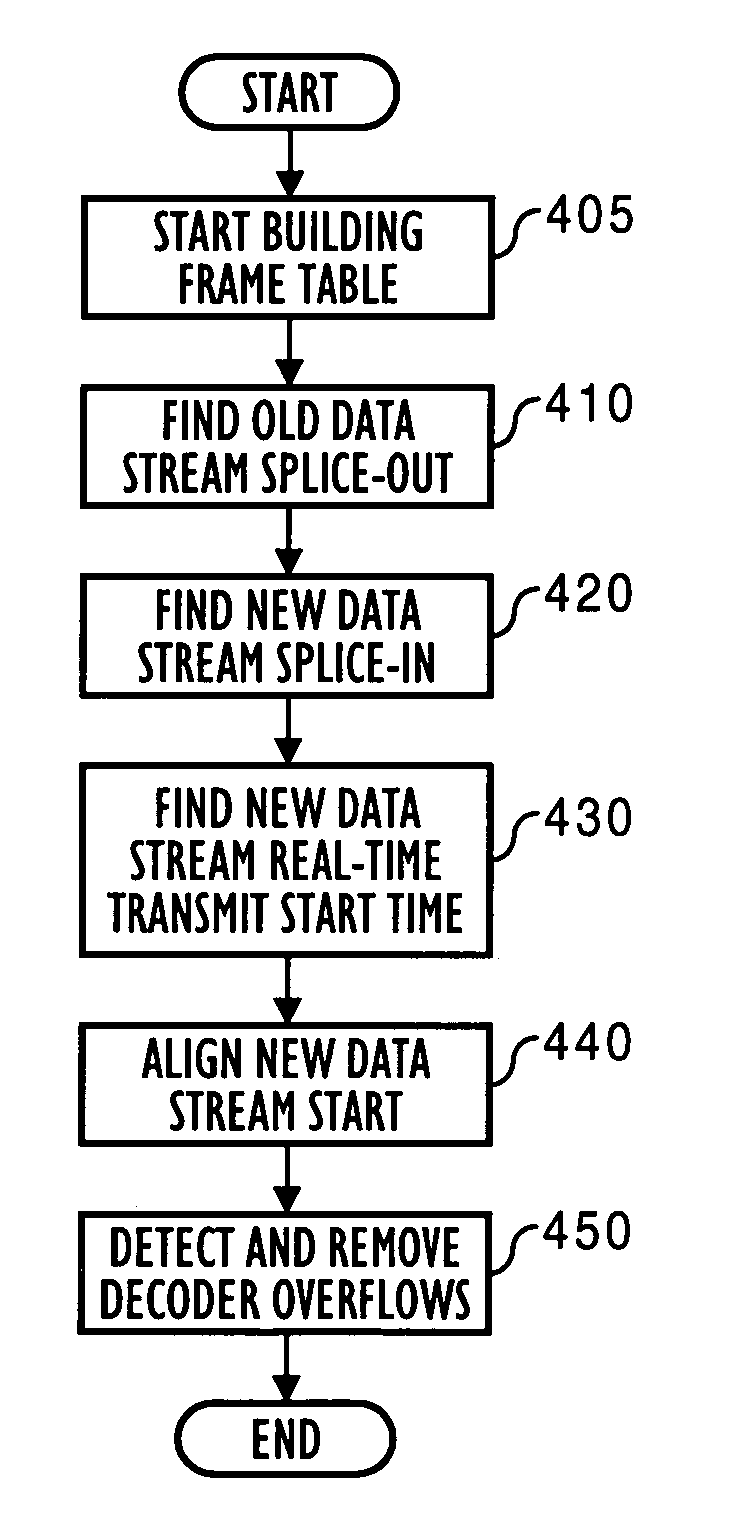
A splicing system includes a splicer for seamlessly splicing togther digitally encoded data streams. In a preferred embodiment, the splicer preferably parses successive splice buffers of data stream data for a splice-out point and a splice-in point, closing an initial group of pictures GOP if needed. The preferred splicer further finds a new data stream real-time program clock reference PCR value for aligning new data stream decode / presentation, and aligns the new data stream start time. Concurrently, the splicer preferably uses a frame table to detect overflow and corrects such overflow by adding null packets, thereby delaying portions of data stream data. The splicer also preferably restores data stream encoding by deleting null packets, and thereby accelerating a portion of data stream data. In a further preferred embodiment, the splicer preferably uses a bit-clock schedule offset to delay or accelerate portions of data stream data.
Owner:OPTIBASE TECH +1
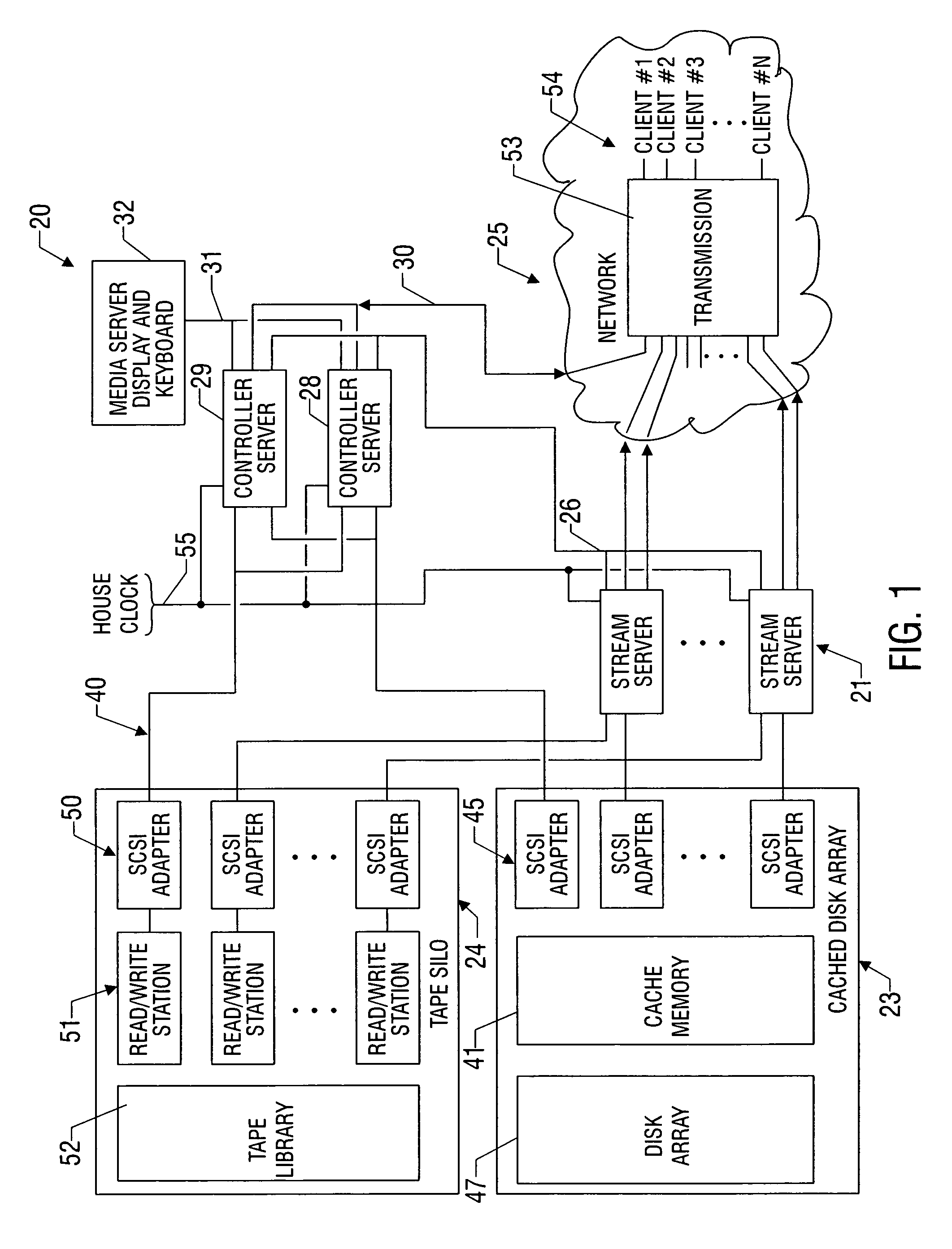
MPEG dual-channel decoder data and control protocols for real-time video streaming
ActiveUS20030021346A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGroup of picturesChannel decoder
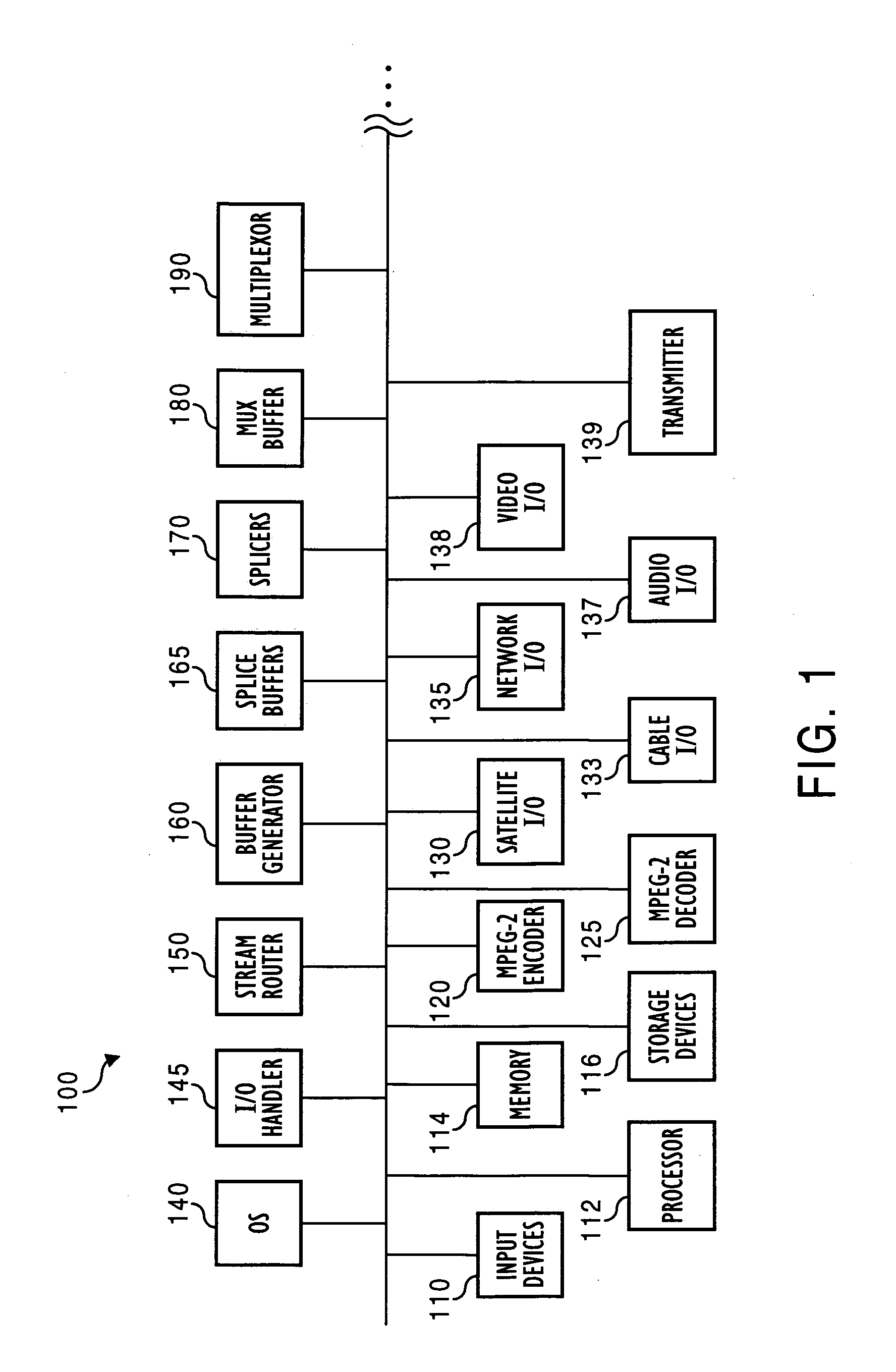
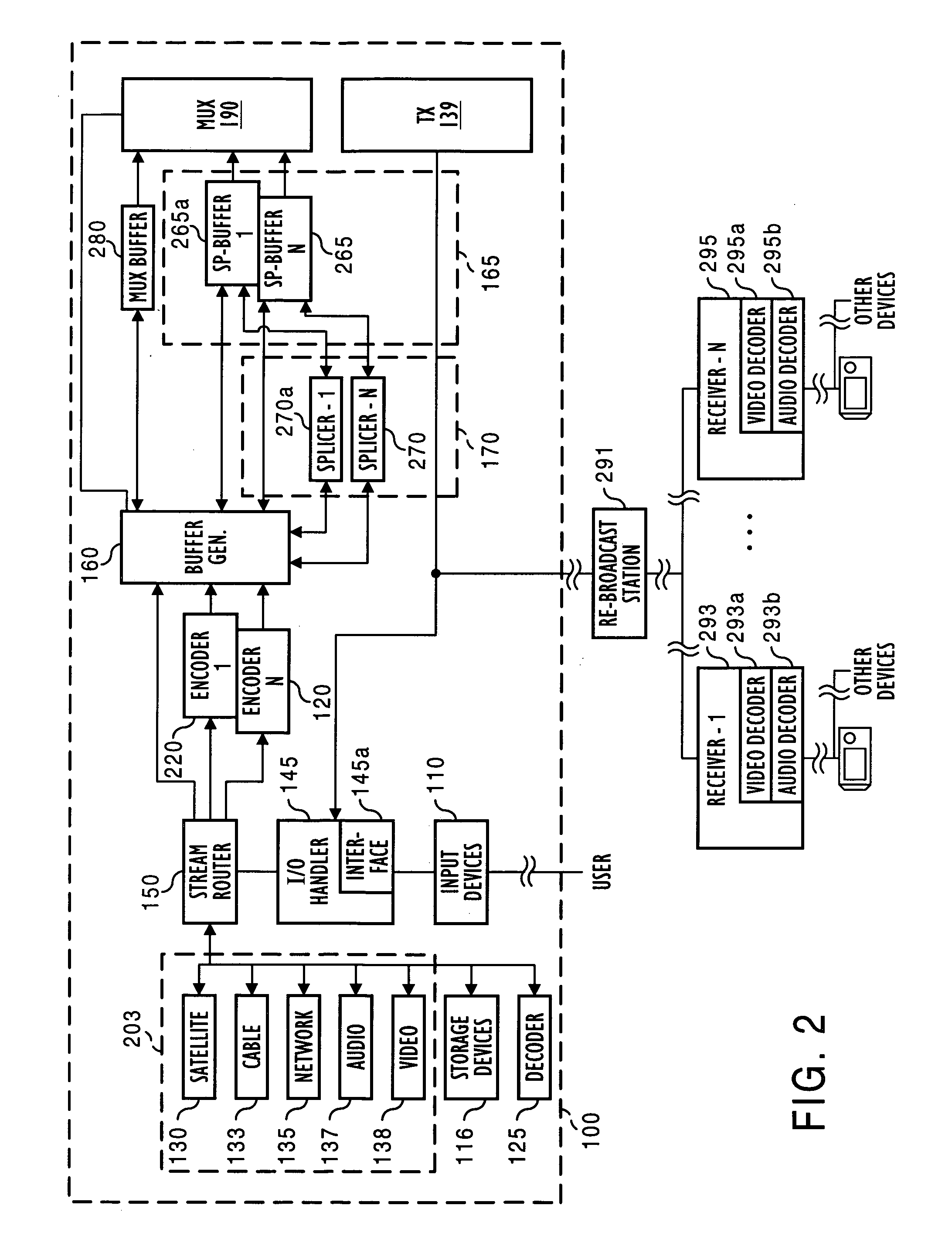
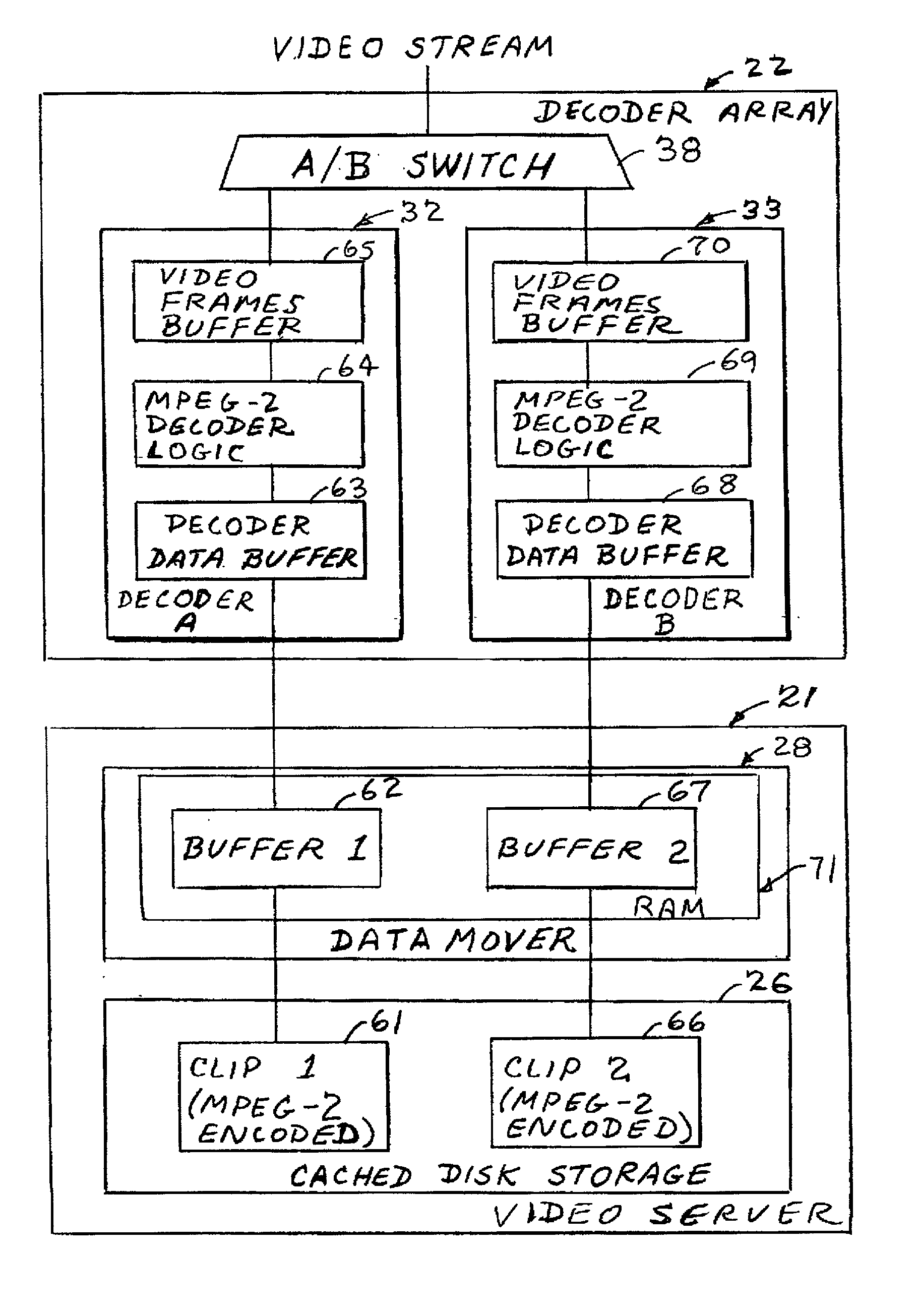
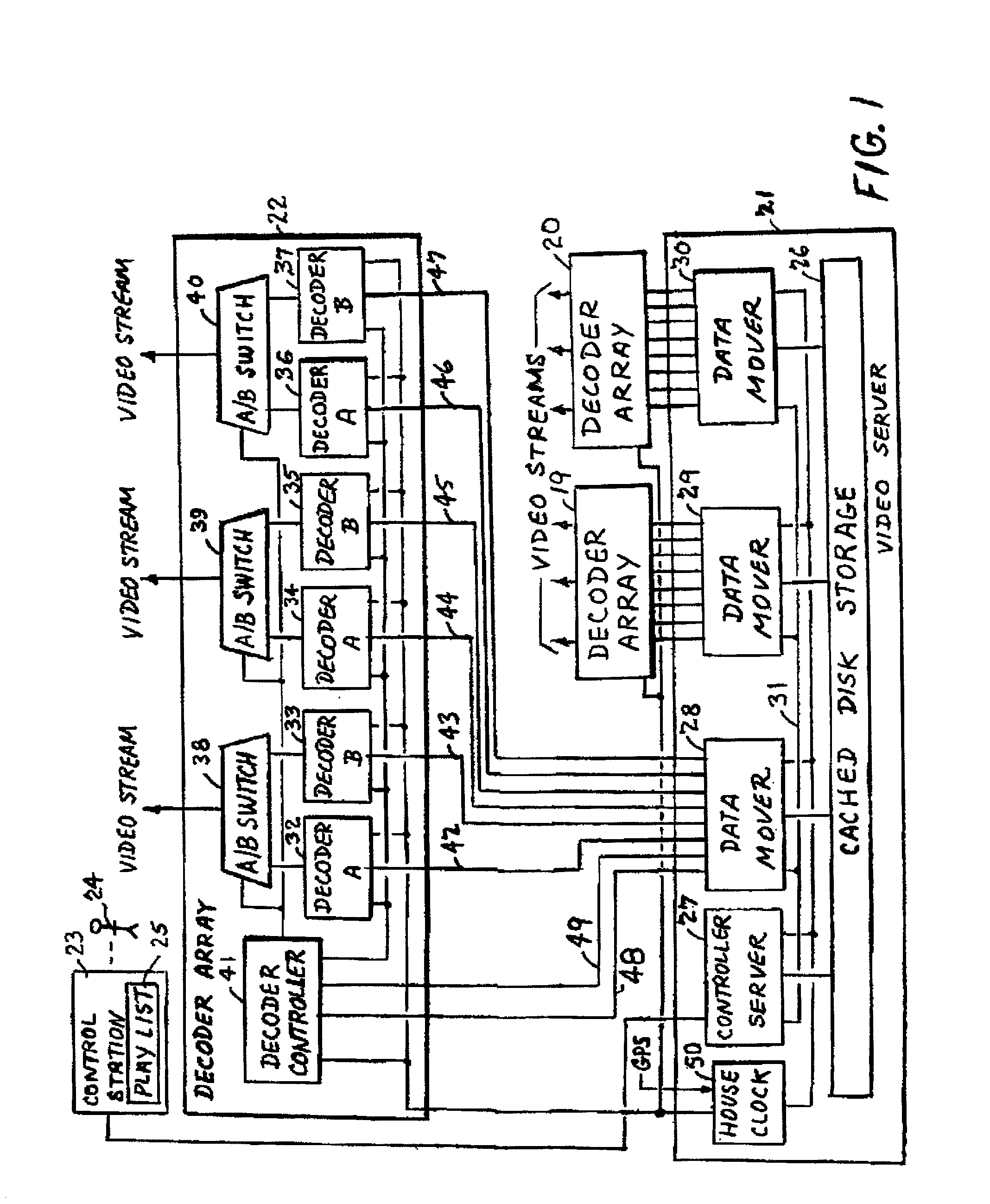
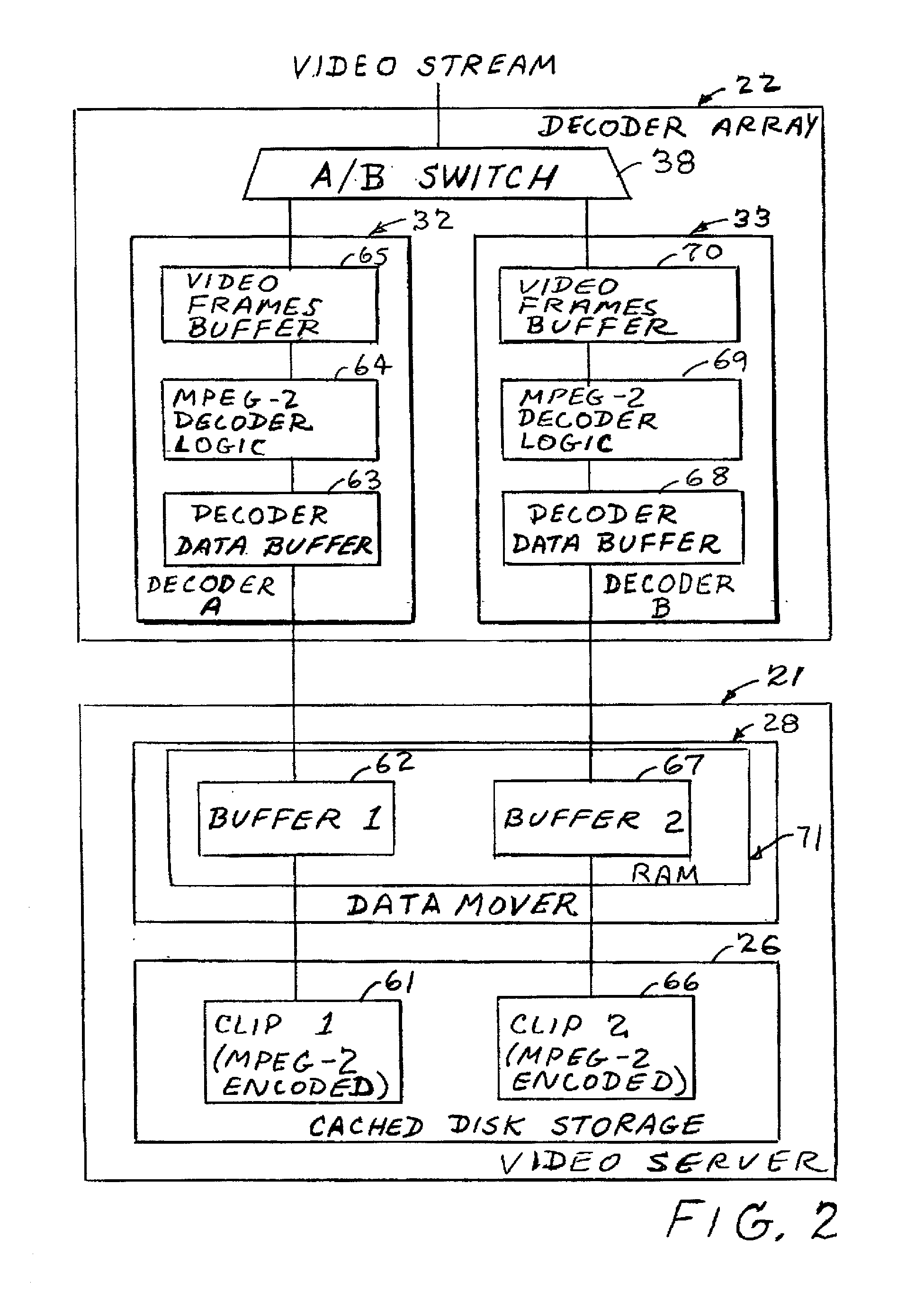
A system for producing multiple concurrent real-time video streams from stored MPEG video clips includes a video server and at least one MPEG decoder array. The decoder array has multiple decoder pairs, each pair having a video switch for switching from one decoder in the pair to the other at a specified time. Switching may occur from a specified Out-point frame to a specified In-point frame, and the specified frames can be any frame type at any location in the group of pictures (GOP) structure. In a preferred construction, the video server has a controller server linked to a series of data mover computers, each controlling one or more respective decoder arrays. The data mover computers use a control protocol to control the decoder arrays, and each decoder uses a data protocol to request data from a respective data mover computer.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Coding system and its method, coding device and its method, decoding device and its method, recording device and its method, and reproducing device and its method
InactiveUS7236526B1Quality improvementMinimize degradation of image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging qualityGroup of pictures
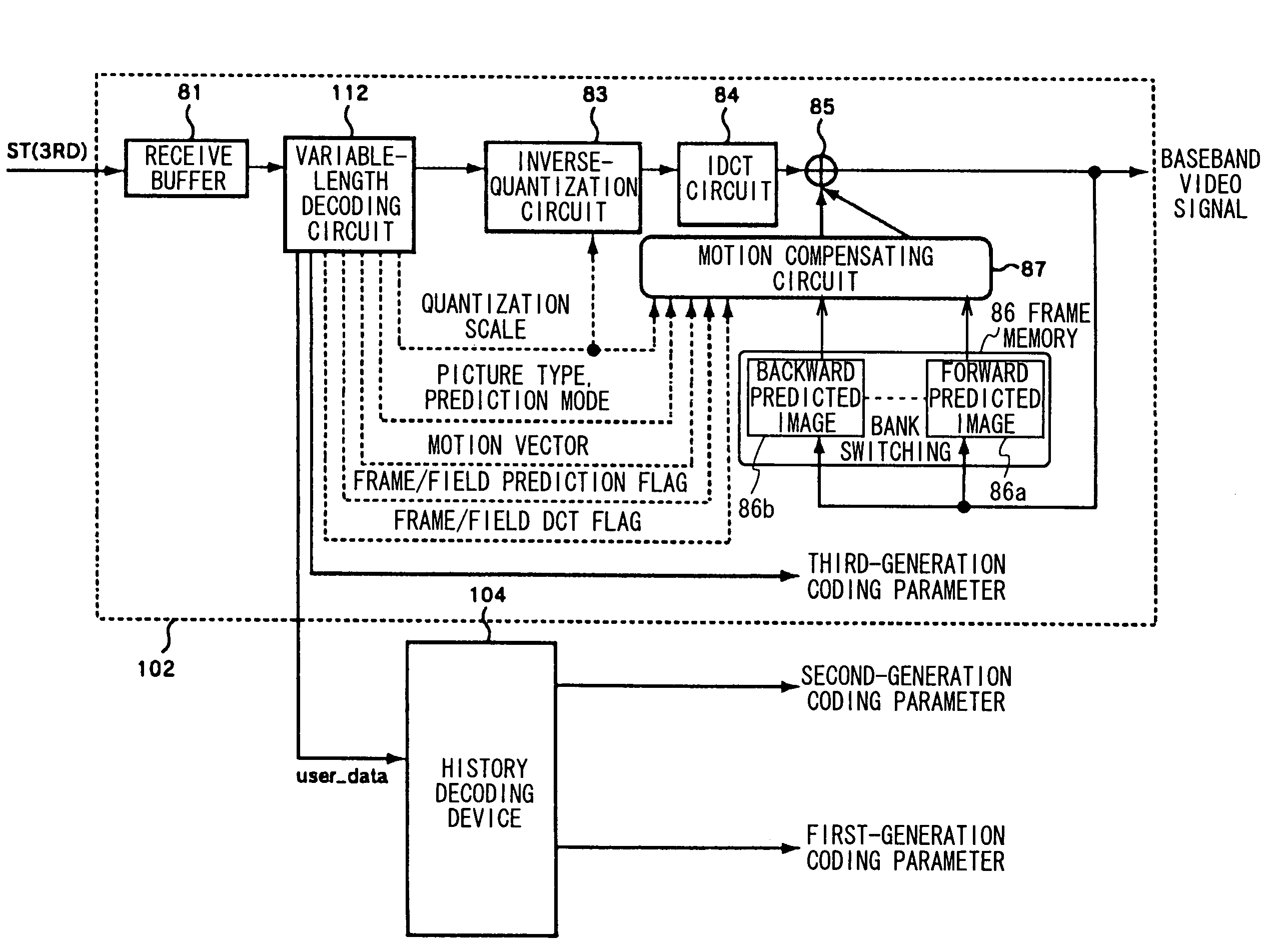
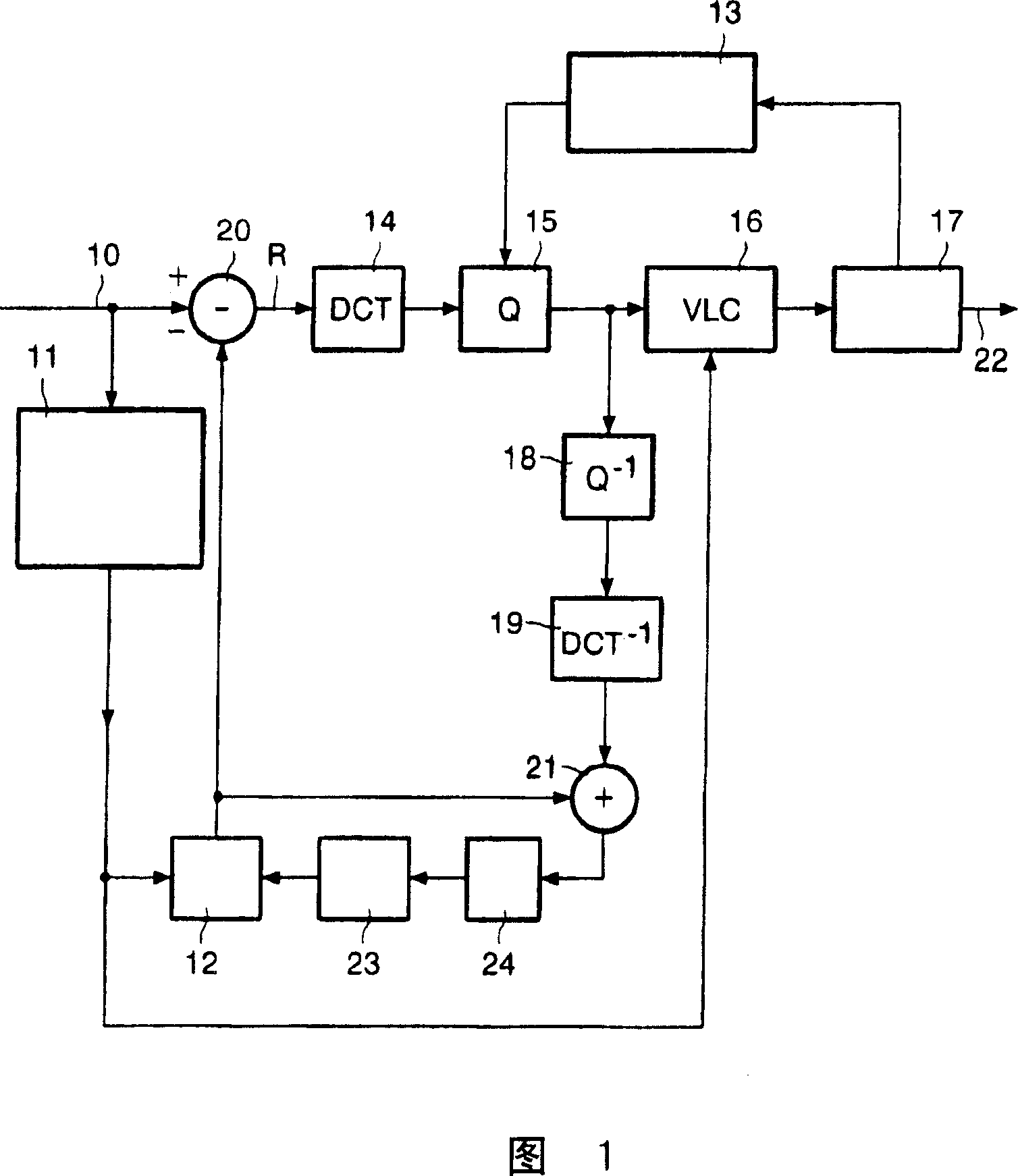
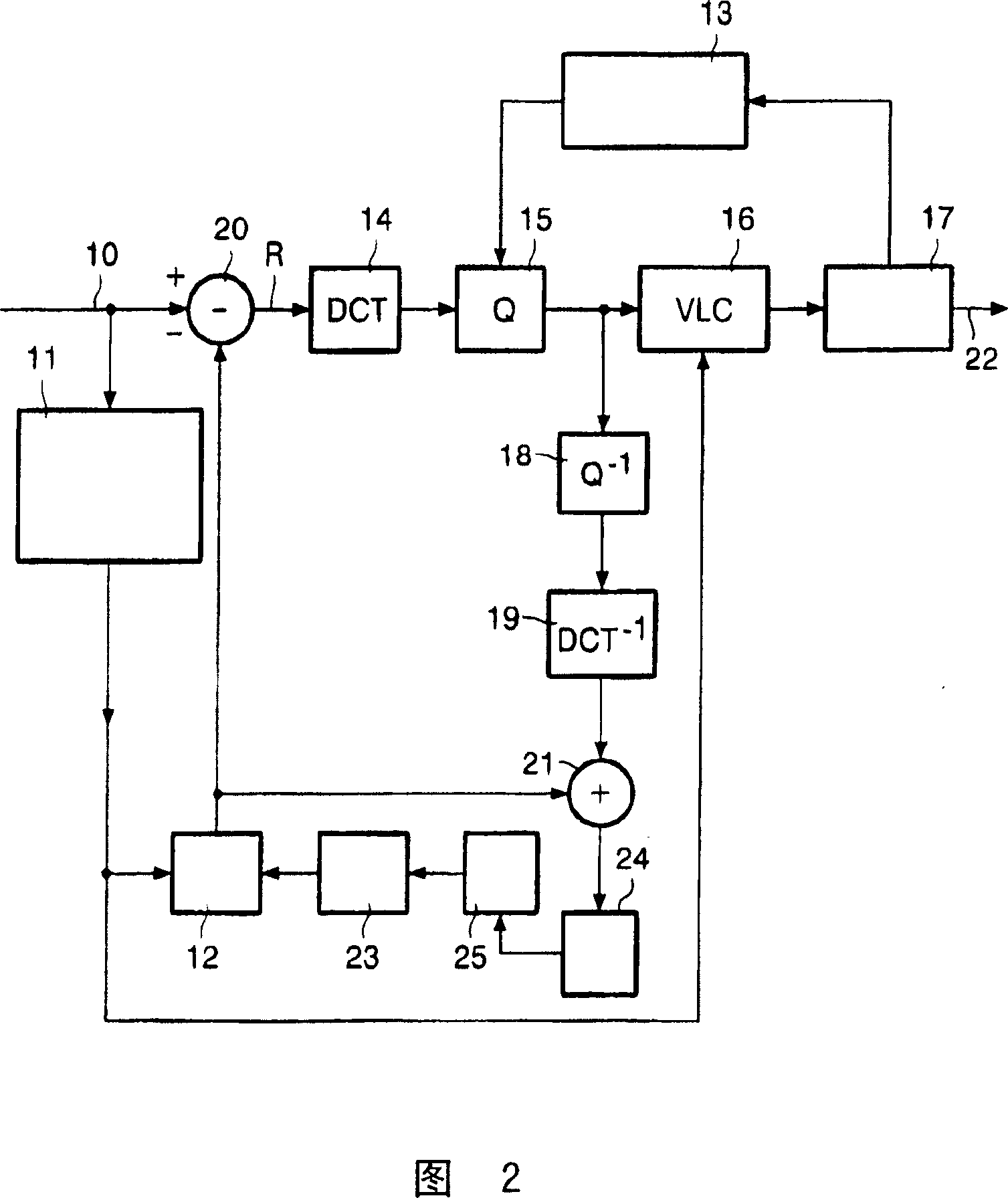
The present invention relates to a transcoder for executing a re-coding process on an encoded stream generated based on an MPEG standard in order to generate a re-coded stream having a different GOP (Group of Pictures) structure or bit rate.Specifically, a decoding device of a transcoder 106 decodes a source encoded stream to generate decoded video data and extracts past coding parameters superposed in the encoded stream as history_stream( ). In this case, the decoding device extracts the past coding parameters based on information superposed in the encoded stream as re_coding_stream_info( ).An encoding device receives the decoded video data and the past coding parameters and uses the past coding parameters to carry out an encoding process in a manner such that this process will not degrade image quality, thereby generating a re-coded stream. Further, the encoding device selects one of the past coding parameters which are optimal for an application connectively following the encoding device and describes only the selected past coding parameters in the encoded stream as history_stream( ). The encoding device superposes, as re_coding_stream_info( ), information indicating the selected past coding parameters so that the following application can properly extract the coding parameters for the history_stream( ) from the re-coded stream.
Owner:SONY CORP
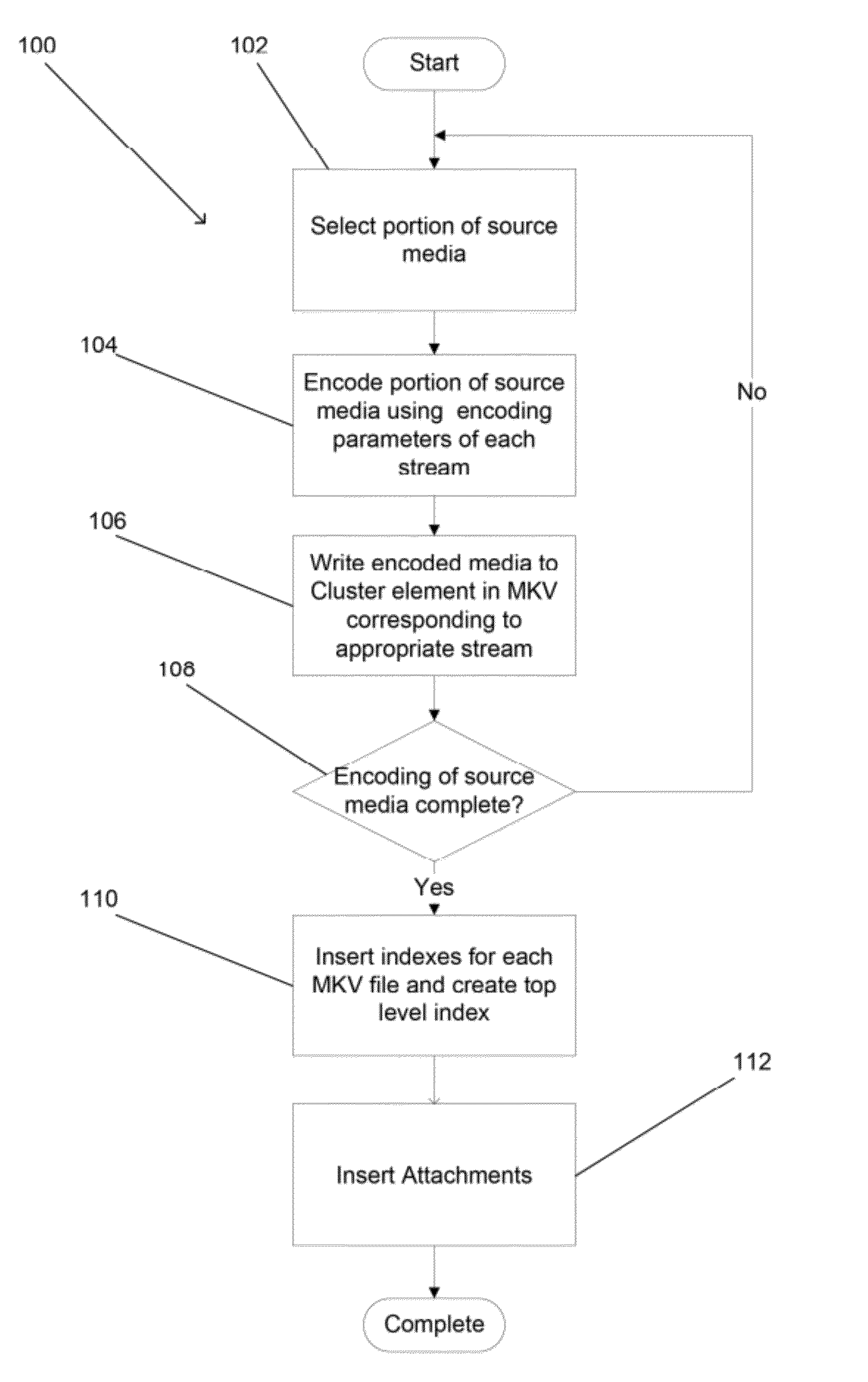
Systems and methods for encoding media including subtitles for adaptive bitrate streaming
ActiveUS20120170643A1Small sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSelf adaptiveGroup of pictures
Systems and methods for adaptive bitrate streaming of media including subtitles utilizing HTTP in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention includes selecting a portion of the source media using the source encoder, transcoding the selected portion of the source media into a plurality of alternative portions of encoded video, where each alternative portion is encoded using a different set of encoding parameters and commences with an intra frame at the start of a closed group of pictures (GOP), writing each of the alternative portions of encoded video to a separate container file using the source encoder, writing a subtitle stream segment from each subtitle track corresponding to the selected portion of the source media to a separate container file using the source encoder, and associating a font file with at least one of the container files containing subtitle stream segments.
Owner:DIVX INC
Method and device for encoding digital video data
InactiveCN1957617AReduce or eliminate the flare effectPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationDigital videoGroup of pictures
The invention relates to a method and device for encoding digital video data corresponding to an original sequence of images and available in the form of a video stream consisting of successive pictures which are either INTRA pictures or INTER pictures. The INTRA pictures are called I-pictures and encoded by means of a so-called INTRA mode without any reference to any past or future picture. The INTER pictures are either monodirectionally predicted pictures, called P-pictures and encoded with reference to a past or future reference picture which is an INTRA or INTER picture, or bidirectionally predicted pictures, called B-pictures and encoded with reference to one or more reference picture(s). The INTRA pictures themselves comprise either I-pictures placed at the beginning of a new group of pictures corresponding to a scene change, where no temporal redundancy is available, and called scene change I-pictures, or I-pictures placed in other locations, where some temporal redundancy is available, and called refresh pictures. According to the invention, the method is characterized in that, before being quantized and encoded in INTRA mode, said INTRA refresh pictures are replaced by an INTER picture having quality and artefacts substantially similar to those of the last encoded INTER picture(s).
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
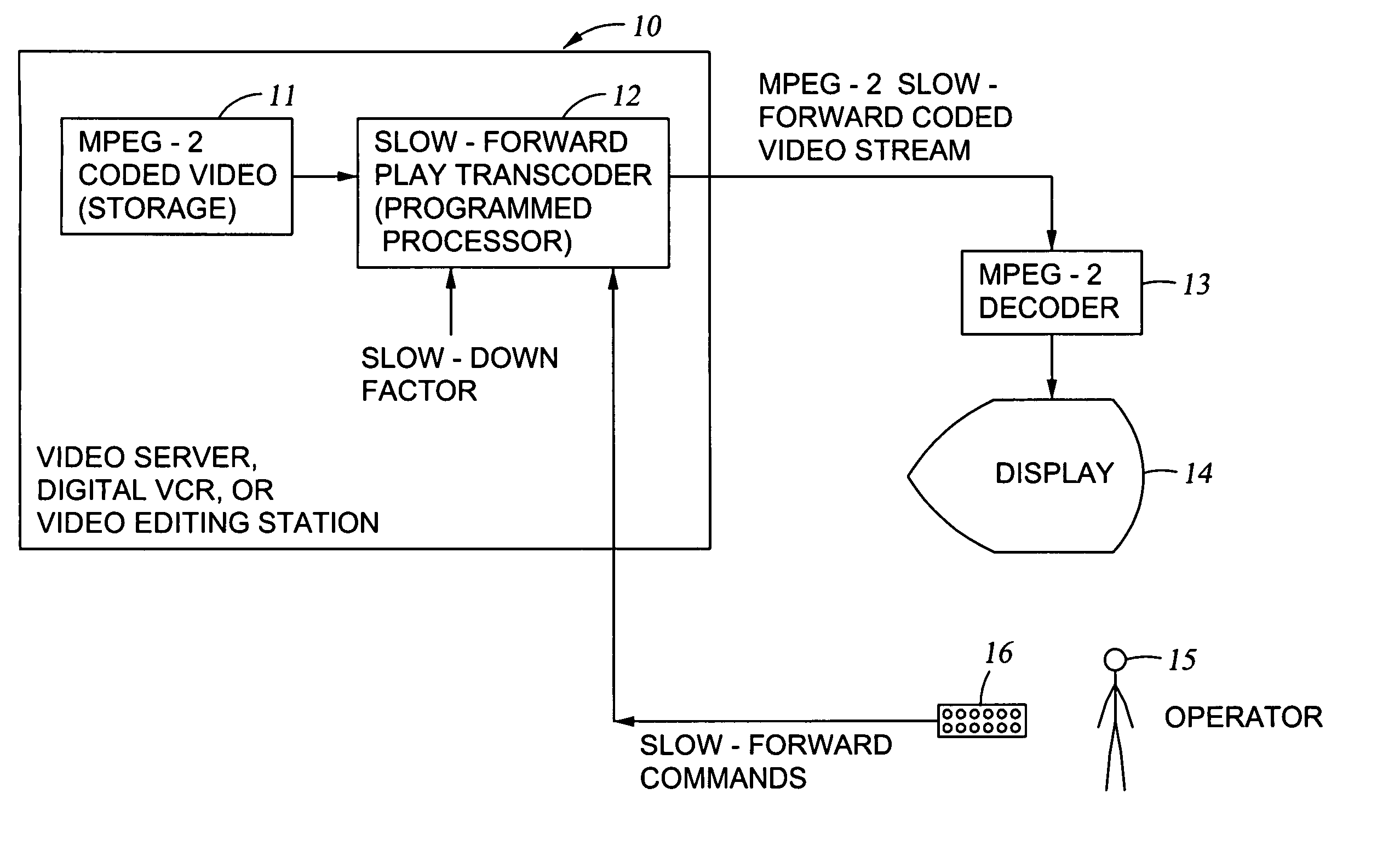
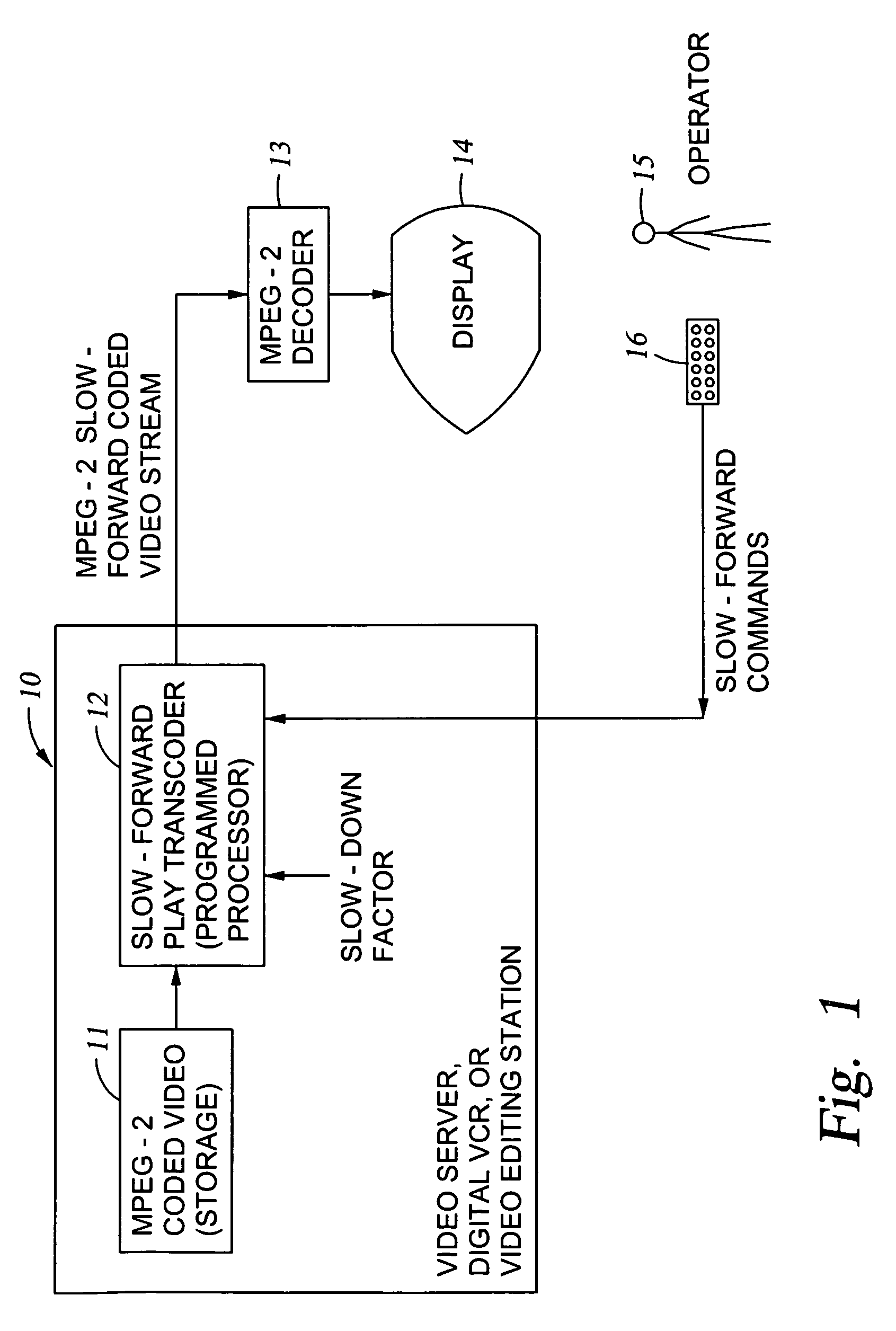
Generation of MPEG slow motion playout
InactiveUS6980594B2Minimal costGuaranteed preservation qualityTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersGroup of picturesComputer graphics (images)
MPEG coded video data includes groups of pictures (GOPs). Each group of pictures includes one or more I-frames and a plurality of B- or P-frames. To produce an MPEG slow-forward coded video stream, the coding type of each frame in the MPEG coded video data is identified, and freeze frames are inserted as a predefined function of the identified coding type and as a predefined function of a desired slow down factor. In a preferred implementation, for a slow-down factor of n, for each original I- or P-frame, (n−1) backward-predicted freeze frames are inserted, and for each original B-frame, (n−1) copies of the original B-frames are added, and a selected amount of padding is added to each copy of each original B-frame in order to obtain a normal play bit rate and avoid video buffer overflow or underflow.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Systems and methods for resetting rate control state variables upon the detection of a scene change within a group of pictures
ActiveUS7197072B1Improve picture qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that advantageously improve picture quality in a video encoder, such as an MPEG video encoder. Scene changes typically occur relatively frequently in picture sequences, such as movies. One embodiment of the invention detects a scene change within a group of pictures and allocates bits within the group of pictures in response to the detected scene change without changing a predetermined structure for the group of pictures.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
Method and system for structural similarity based rate-distortion optimization for perceptual video coding
ActiveUS20140119432A1Minimize cost functionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionGroup of pictures
There is disclosed a system and method for video coding, and more particularly to video coding that uses structural similarity (SSIM) based rate-distortion optimization methods to improve the perceptual quality of decoded video without increasing data rate, or to reduce the data rate of compressed video stream without sacrificing perceived quality of the decoded video. In an embodiment, the video coding system and method may be a SSIM-based rate-distortion optimization approach that involves minimizing a joint cost function defined as the sum of a data rate term and a distortion functions. The distortion function may be defined to be monotonically increasing with the decrease of SSIM and a Lagrange parameter may be utilized to control the trade-off between rate and distortion. The optimal Lagrange parameter may be found by utilizing the ratio between a reduced-reference SSIM model with respect to quantization step, and a data rate model with respect to quantization step. In an embodiment, a group-of-picture (GOP) level quantization parameter (QP) adjustment method may be used in multi-pass encoding to reduce the bit-rate while keeping similar perceptual video quality. In another embodiment, a frame level QP adjustment method may be used in single-pass encoding to achieve constant SSIM quality. In accordance with an embodiment, the present invention may be implemented entirely at the encoder side and may or may not require any change at the decoder, and may be made compatible with existing video coding standards.
Owner:SSIMWAVE INC
Method and an apparatus for controlling the rate of a video sequence; a video encoding device
ActiveUS7876821B2Reduced burst effectWithout obvious degradation in perceptual motion smoothnessColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareVideo encoding
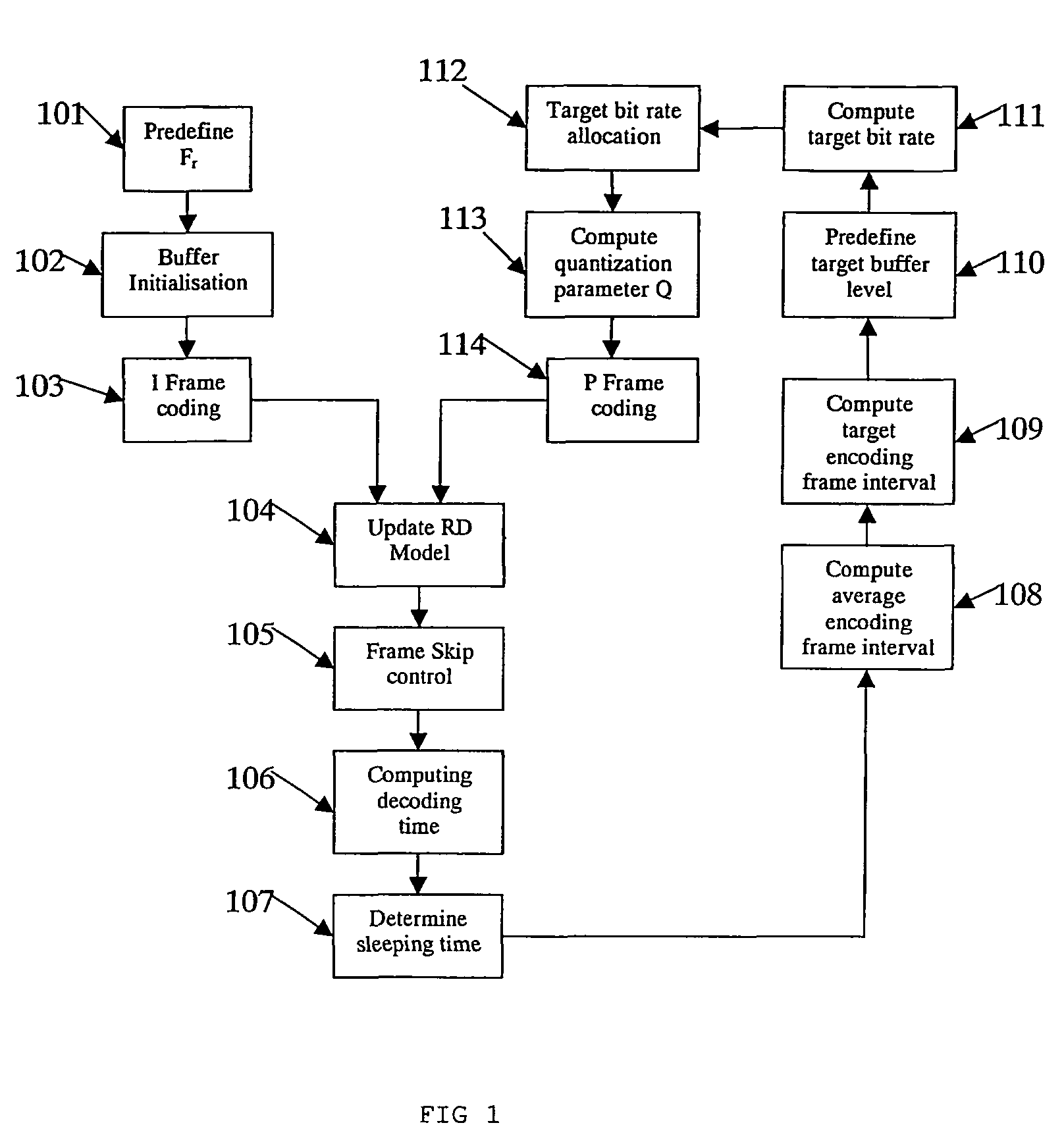
A method for rate control for encoding video sequence, wherein the video sequence includes a plurality of Group Of Pictures, wherein each Group of Picture includes at least and I-frame and an Inter-frame, where the rate control method includes the following steps for the encoding of the Inter-frame in the Group of Picture: determining a desired frame rate based on an available bandwidth of a channel for transmitting the video sequence and an available computational resources for the encoding process; determining a target buffer level based on the desired frame rate and the position of the Inter-frame with respect to the I-frame; and determining a target bit rate based on the target buffer level and the available channel bandwidth, wherein the target bit rate is used for controlling the rate of encoding the video sequence.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Graphical user interface utilizing three-dimensional scatter plots for visual navigation of pictures in a picture database
InactiveUS6948124B2Metadata still image retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
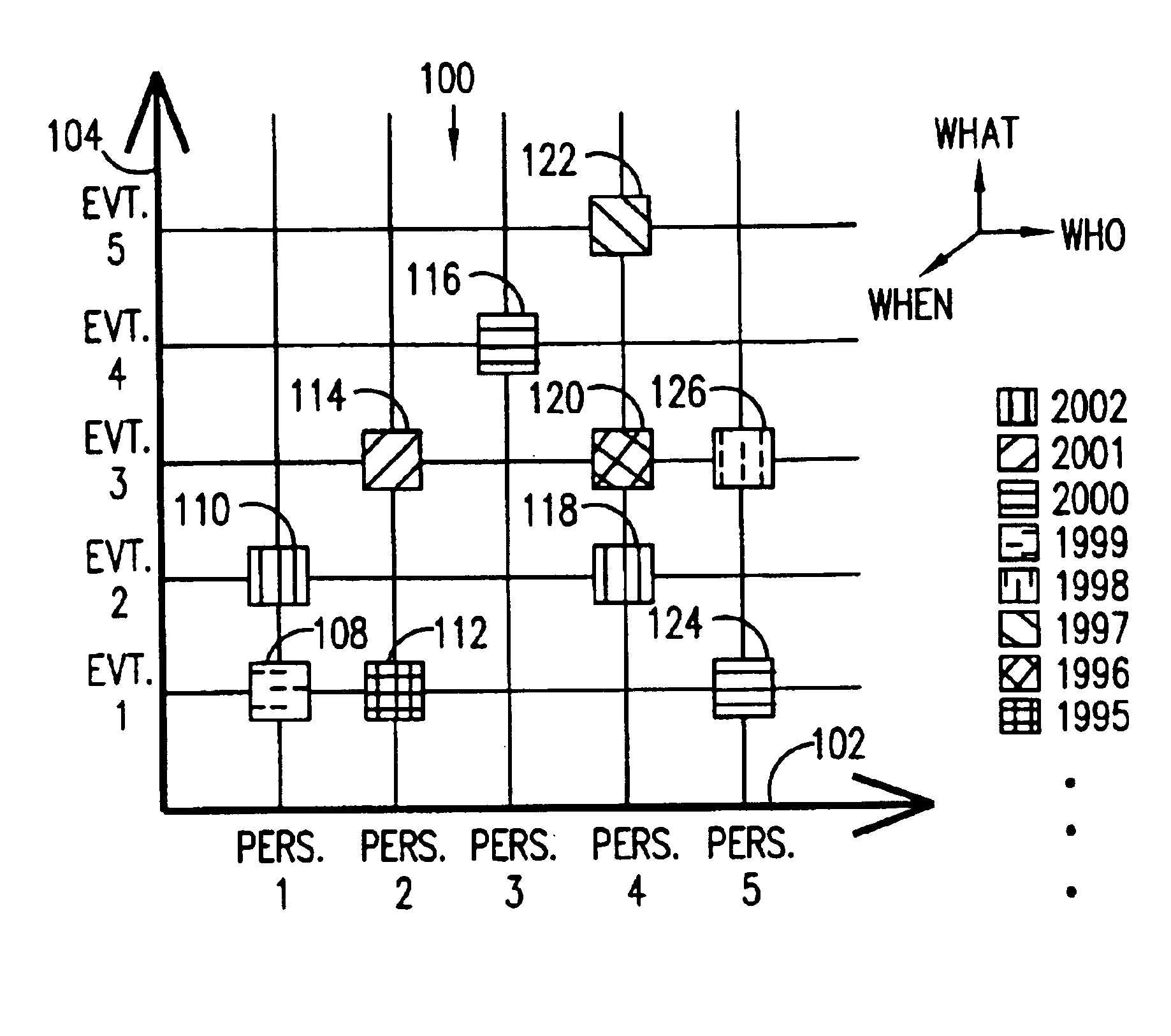
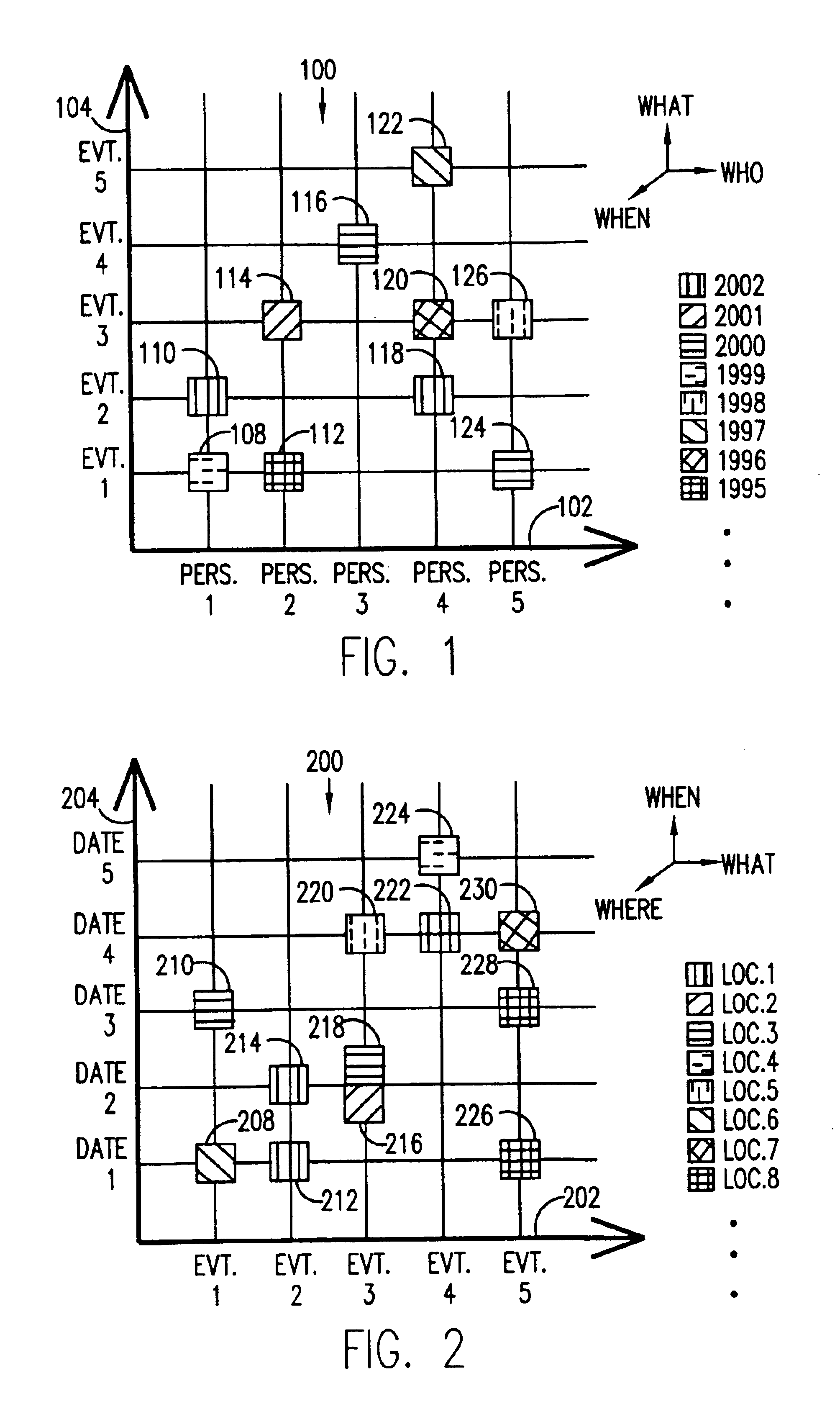
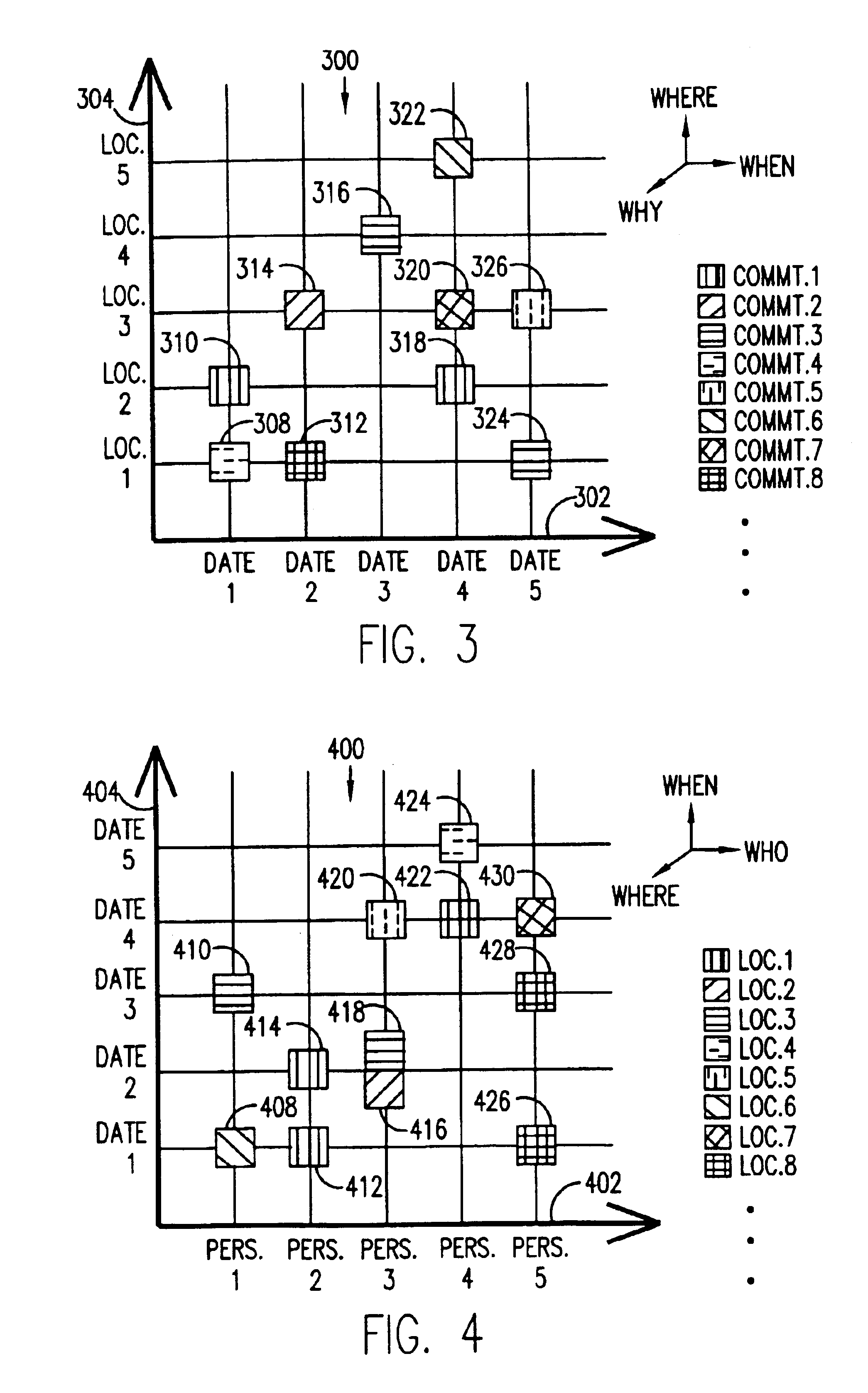
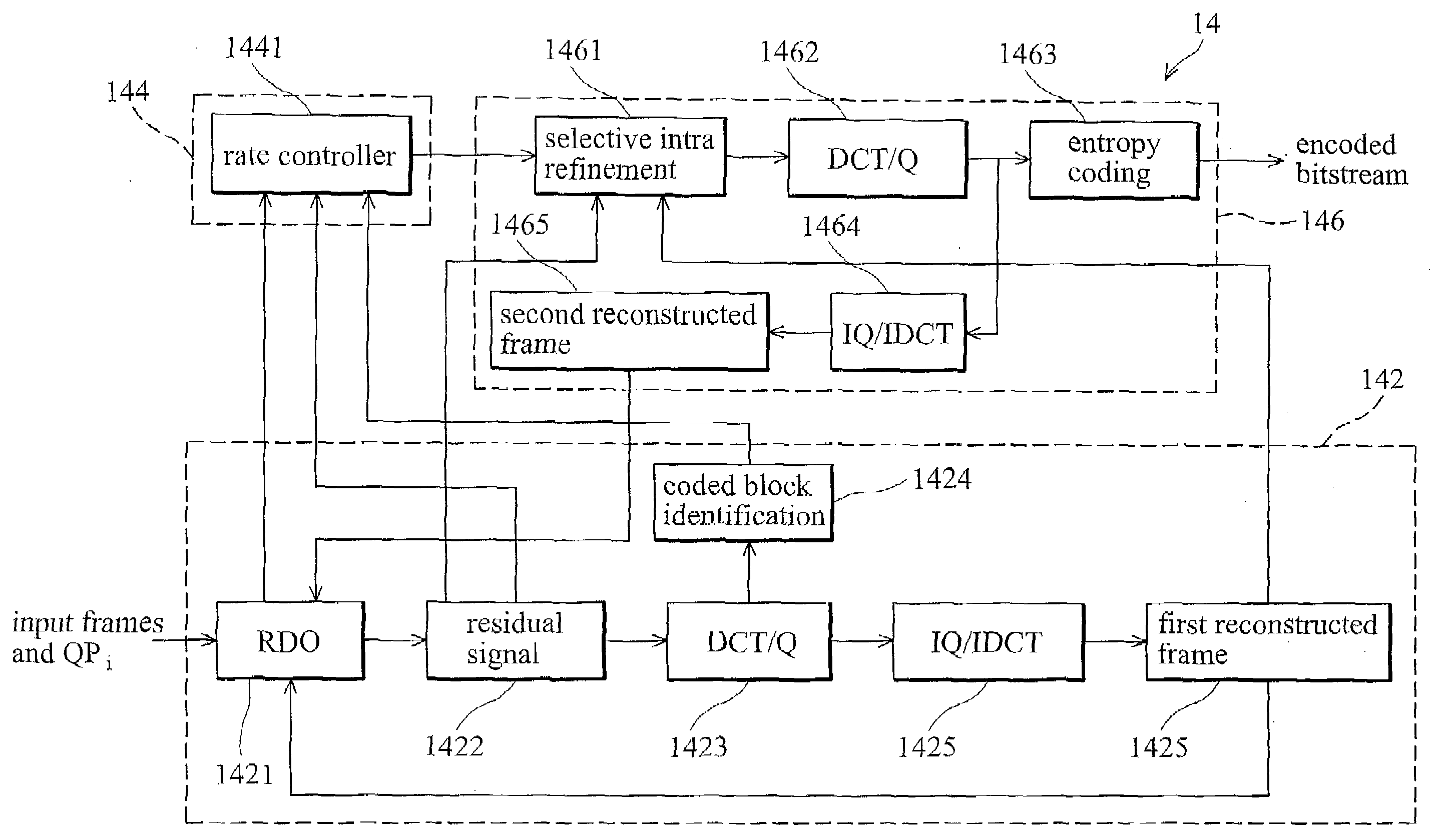
A novel graphical user interface (GUI) using metadata, generates three-dimensional scatter plots (100, 200, 300, 400) for the efficient and aesthetic navigation and retrieval of pictures in a picture database. The first and second dimensions (102, 104, 202, 204, 302, 304, 402, 404) represent abscissas and ordinates corresponding to two picture characteristics chosen by the user. Distinguishing characteristics of icons (108-126, 208-230, 308-326, 408-430) in the scatter plot (100, 200, 300, 400), which icons represent groups of pictures, indicate the third dimension, also chosen by the user. In the preferred embodiment, the third dimension is indicated by the color of the icon (108-126, 208-230, 308-326, 408-430). Along with many other possibilities, the three dimensions of a scatter plot (100, 200, 300, 400) can represent combinations of “Who,”“What,”“When,”“Where,” and “Why” picture characteristic information contained in the picture metadata. Activating an icon (108-126, 208-230, 308-326, 408-430) produces a thumbnail of the pictures in the group represented by the particular icon (108-126, 208-230, 308-326, 408-430). Updating one display dimension dynamically updates the other display dimensions.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Rate control method with frame-layer bit allocation and video encoder
ActiveUS20080063051A1Improve video qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareBit allocation
A video encoder controlling rate of each frame in a current frame set (Group of Picture, GOP), and method thereof. The video encoder comprises a frame grouping device, a GOP initialization device, and a GOP encoding device. The frame grouping device allocates a target bit budget RGOP to the current frame set. The GOP initialization device is coupled to the frame grouping device, and estimates a first quantization parameter QP1 based on the target bit budget RGOP and complexity of the current frame set. The GOP encoding device is coupled to the GOP initialization device, and encoding a frame in the current frame set with the second quantization parameter QP2 to generate output data.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
MPEG encoder control protocol for on-line encoding and MPEG data storage
ActiveUS20020172281A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Remote control
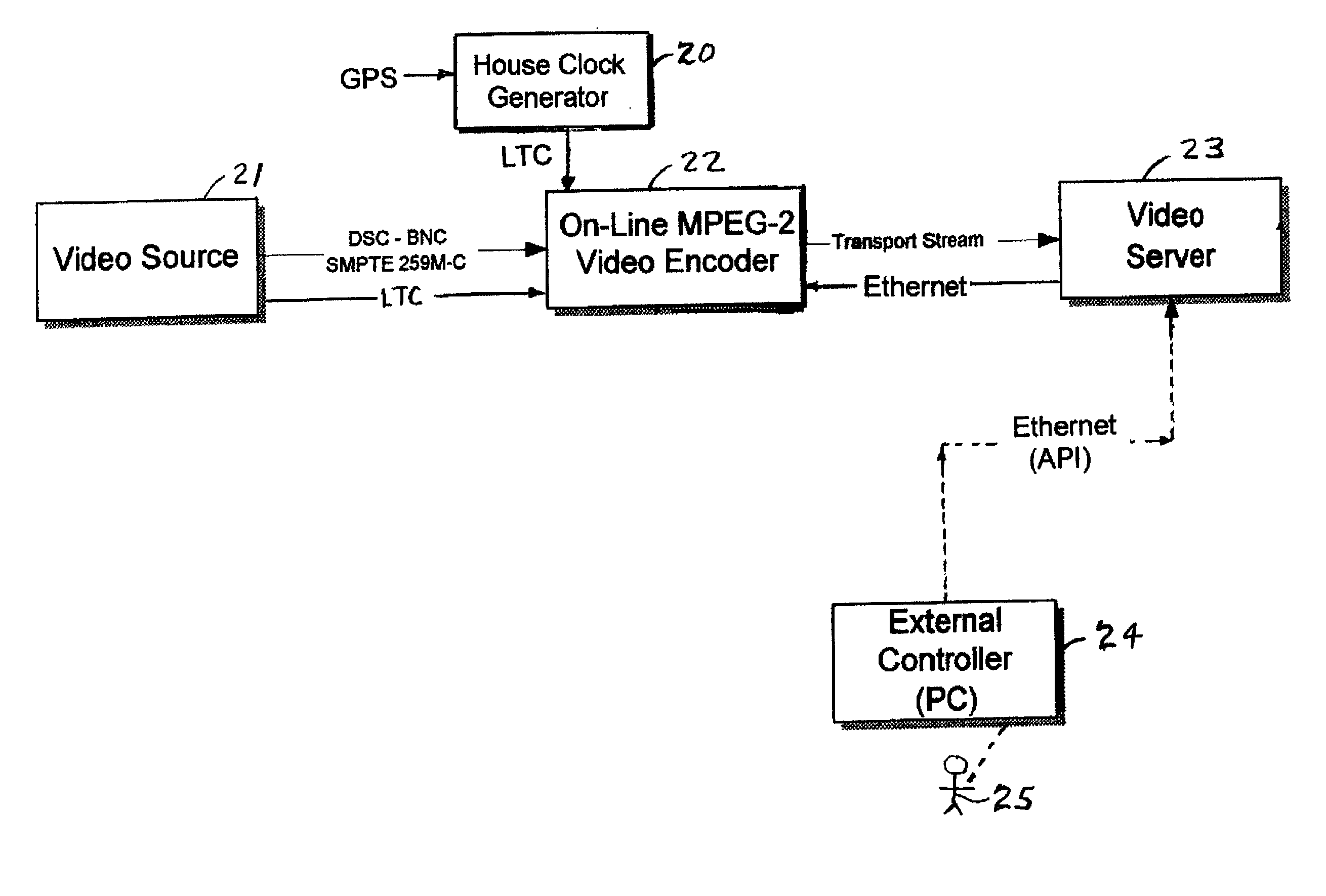
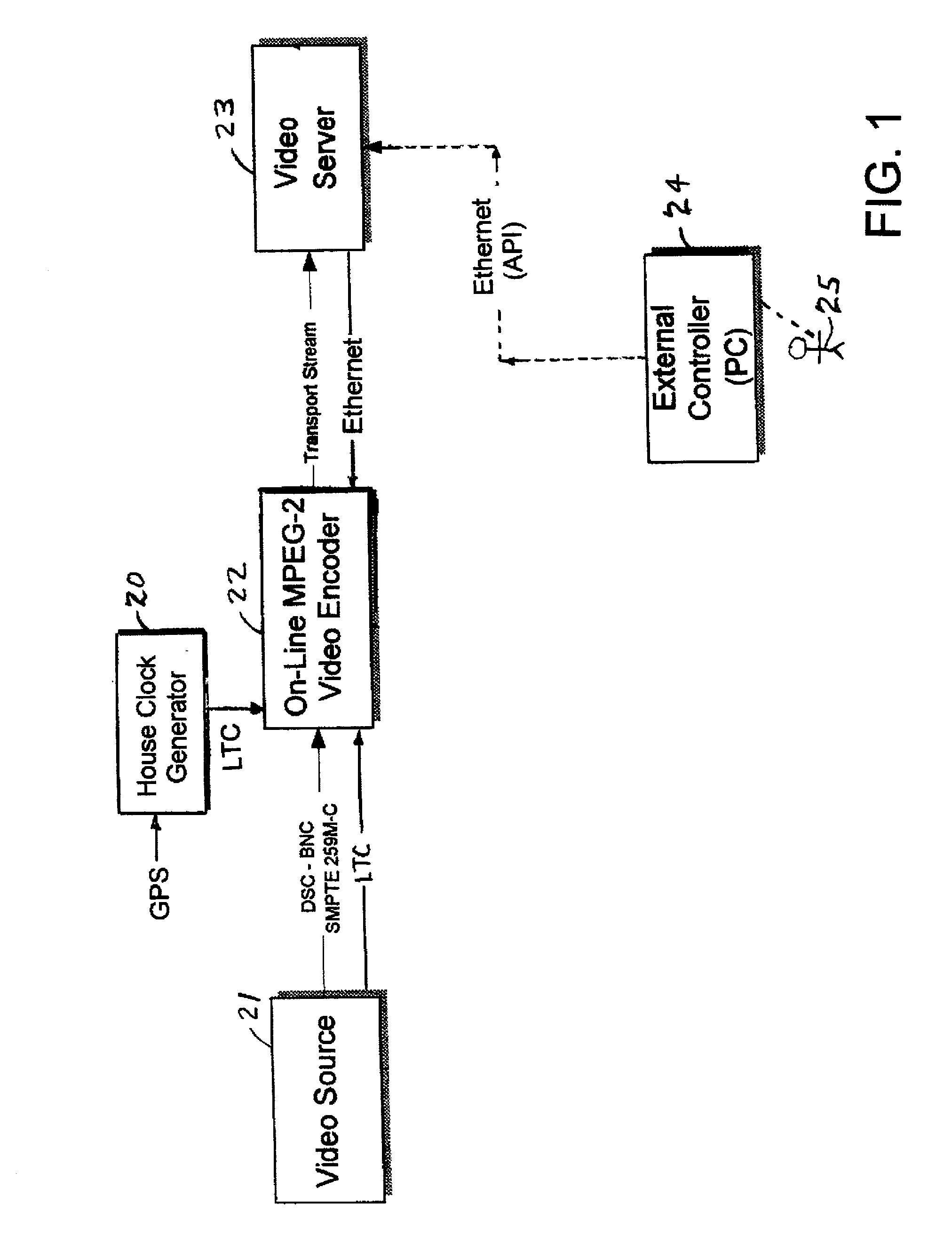
Coded video from an on-line MPEG video encoder is stored as a clip in a video server or is otherwise received in the video server and prepared or used for splicing. In order to reduce apparent frame inaccuracy that may result from the splicing process, the on-line MPEG video encoder and the server are coordinated so that the group-of-picture (GOP) structure in the encoder provides specified In-points and Out-points that are valid and desirable for splicing. An encoder control protocol is also provided for remote control of the on-line MPEG video encoder in order to coordinate the on-line MPEG video encoder with the video server.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Network constructing method for human face identification, identification method and system
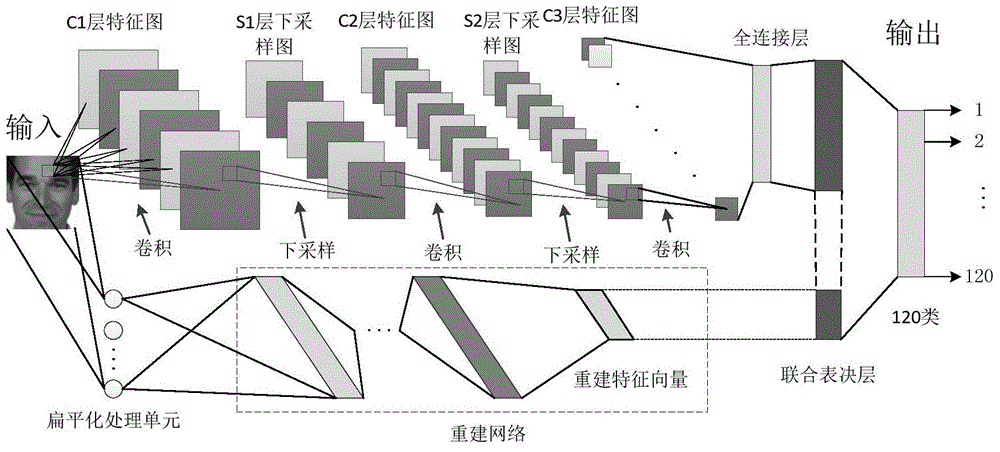
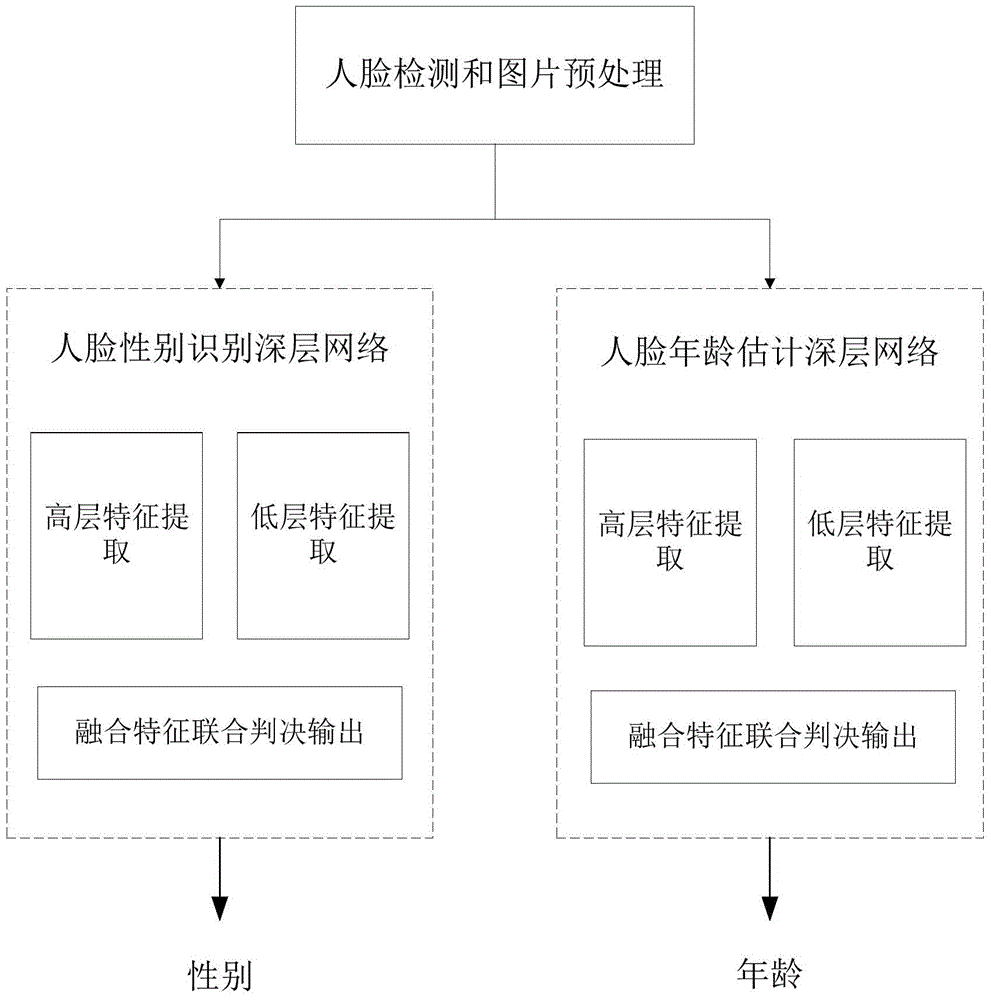
ActiveCN105095833AImprove learning abilityImprove generalization abilityBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionAge estimationGroup of pictures
The invention discloses a deeper layer network constructing method used for gender identification or age estimation based on human face. The method includes a step (101) dividing all training pictures into a plurality of groups; (102) extracting high layer features of a group of pictures based on a convolution neural network and thereby obtaining a first matrix composed of the high layer feature vectors, and extracting low layer and global features of the same group of the training images based on an artificial neural network and thereby obtaining a second matrix composed of the low layer feature vectors, obtaining a group of gender identification or age estimation results based on the extract first matrix, the second matrix and the defined judgment formula, wherein the values of a first weight matrix W1, a second weight matrix w2, an offset matrix b and an adjusting weight beta in the defined judgment formula are updated by utilizing an error back propagation algorithm and the final values of the parameters are obtained and the network construction is completed. Judgment of age and gender of a human face is performed based on the judgment formula determined according to the values of the parameters when the network construction is completed.
Owner:HENGFENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for playing-back moving image data
InactiveUS20050147383A1Improve search accuracyQuick and accurate searchingTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersTime informationGroup of pictures
The invention is directed to the provision of a moving image data playback method, and more particularly, an MPEG data playback method that can randomly access MPEG data stored at a VBR. The playback method comprises: storing in a table an average bit rate computed from time information at the beginning and end of stored moving image data; detecting and storing the time information and position information of randomly accessible picture groups one at the beginning of the moving image data and the other at the end thereof, and computing a picture group unit time from the number of frames between adjacent picture groups and storing the result in the table; computing a point to be accessed, based on the average bit rate and other information stored in the table; and starting playback from the computed point to be accessed, and storing in the table the time information and position information of the picture groups detected during the playback and the average bit rate between each picture group computed from the detected time information and position information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Systems and methods for encoding media including subtitles for adaptive bitrate streaming
ActiveUS9025659B2Small sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningGroup of picturesIntra-frame
Systems and methods for adaptive bitrate streaming of media including subtitles utilizing HTTP in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention includes selecting a portion of the source media using the source encoder, transcoding the selected portion of the source media into a plurality of alternative portions of encoded video, where each alternative portion is encoded using a different set of encoding parameters and commences with an intra frame at the start of a closed group of pictures (GOP), writing each of the alternative portions of encoded video to a separate container file using the source encoder, writing a subtitle stream segment from each subtitle track corresponding to the selected portion of the source media to a separate container file using the source encoder, and associating a font file with at least one of the container files containing subtitle stream segments.
Owner:DIVX INC
Method for reducing channel change startup delays for multicast digital video streams
ActiveUS20070214490A1Reduce start-up delayPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoVideo transmission
Methods and systems for reducing channel change startup delays for multicast digital video streams are described. Packets of a multicast digital video transport stream having a plurality of normal Group of Pictures are received. Further, a channel change request is received and a speed-up Group of Pictures is inserted in the stream in response to the channel change request. In one embodiment, video stream specific information is also inserted in the stream. The packets are processed and transmitted.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
Living body human face recognition method and device
ActiveCN105184277AImprove anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove securityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFixation point
The invention relates to the technical field of identity verification, and particularly relates to a living body human face recognition method, a device and a system. The method comprises steps: multiple human face images are acquired instantly; according to the human face images, a fixation point of at least one eye in each human face image or a motion track of the fixation point is acquired; according to the fixation point of the eye or the motion track of the fixation point, whether the eye moves according to a hint is judged; if yes, living body verification is passed. According to the method, when a user carries out facial feature verification, the eye moves according to the hint; as facial features and eye moving data are extracted from the same picture or one group of pictures or video, an illegal logon person can not cheat the verification device by using a face image or video prepared in advance, and thus, the method can judge that the user agrees to the face features, and the face information is from the living body in reality.
Owner:杨晴虹 +2
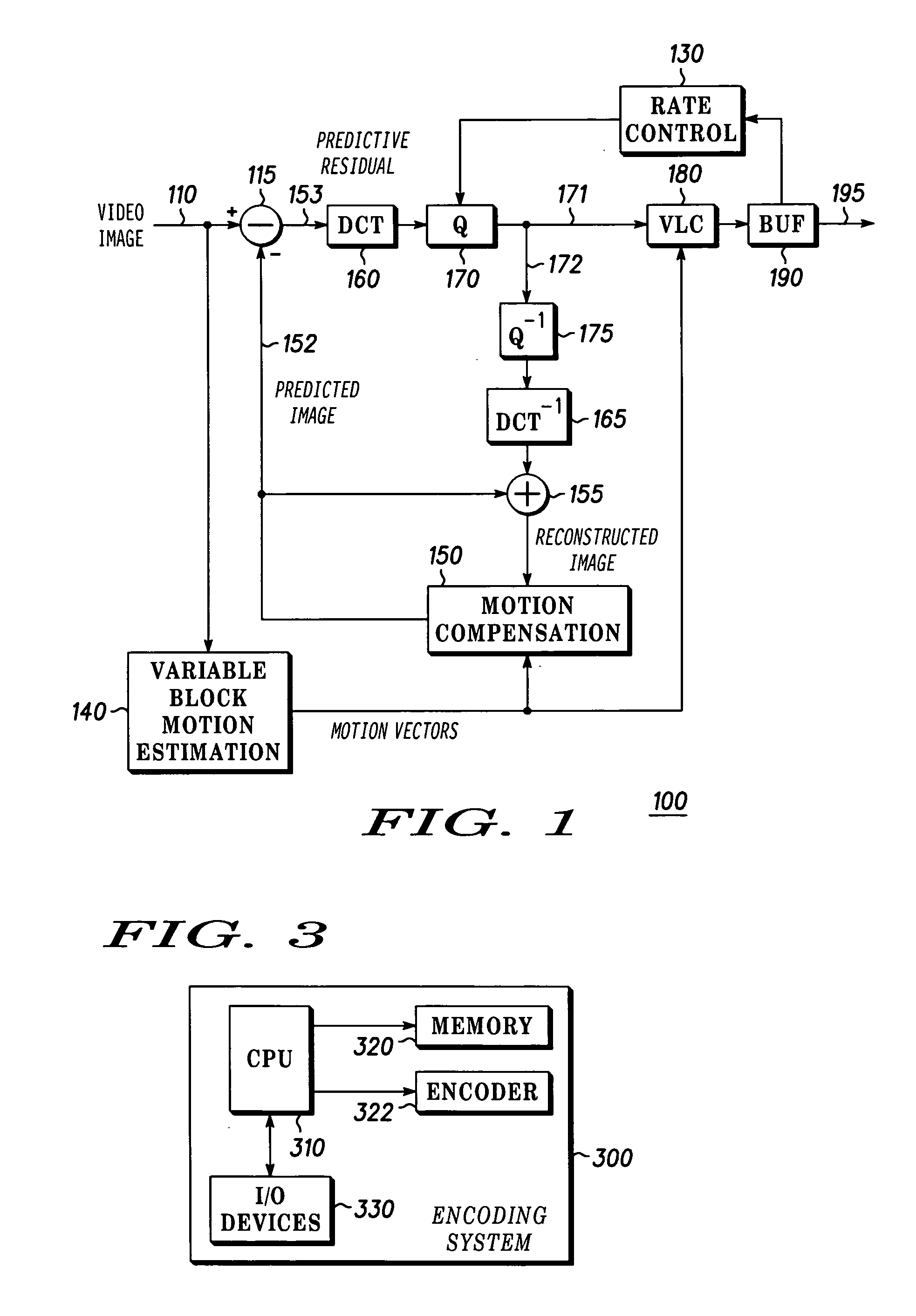
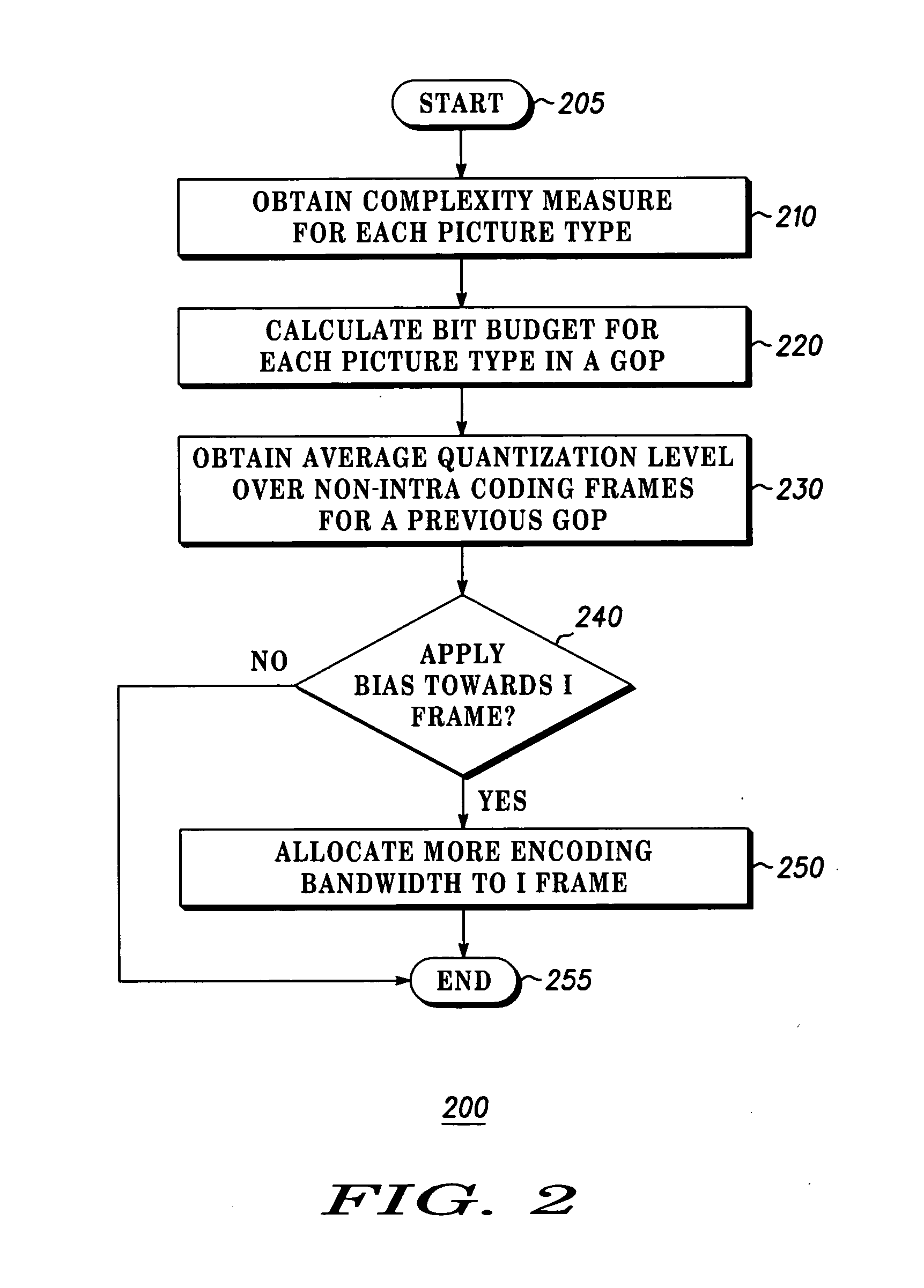
Method and apparatus for providing intra coding frame bit budget
InactiveUS20060140267A1Improve picture qualityOptimizationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGroup of pictures
The present invention discloses a system and method for adaptive adjustment of bit budget that favors the allocation of bits to intra coding frames (I frames). Namely, an encoder is able to dynamically adjust the bit budget for each picture type in an image sequence, thereby effecting proper usage of the available transmission bandwidth and improving the picture quality. In one embodiment, the present invention will allocate more encoding bandwidth to a current Intra coding frame when the average quantization level of inter coding frames (e.g., P and B frames) of a previous group of pictures is relatively high.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
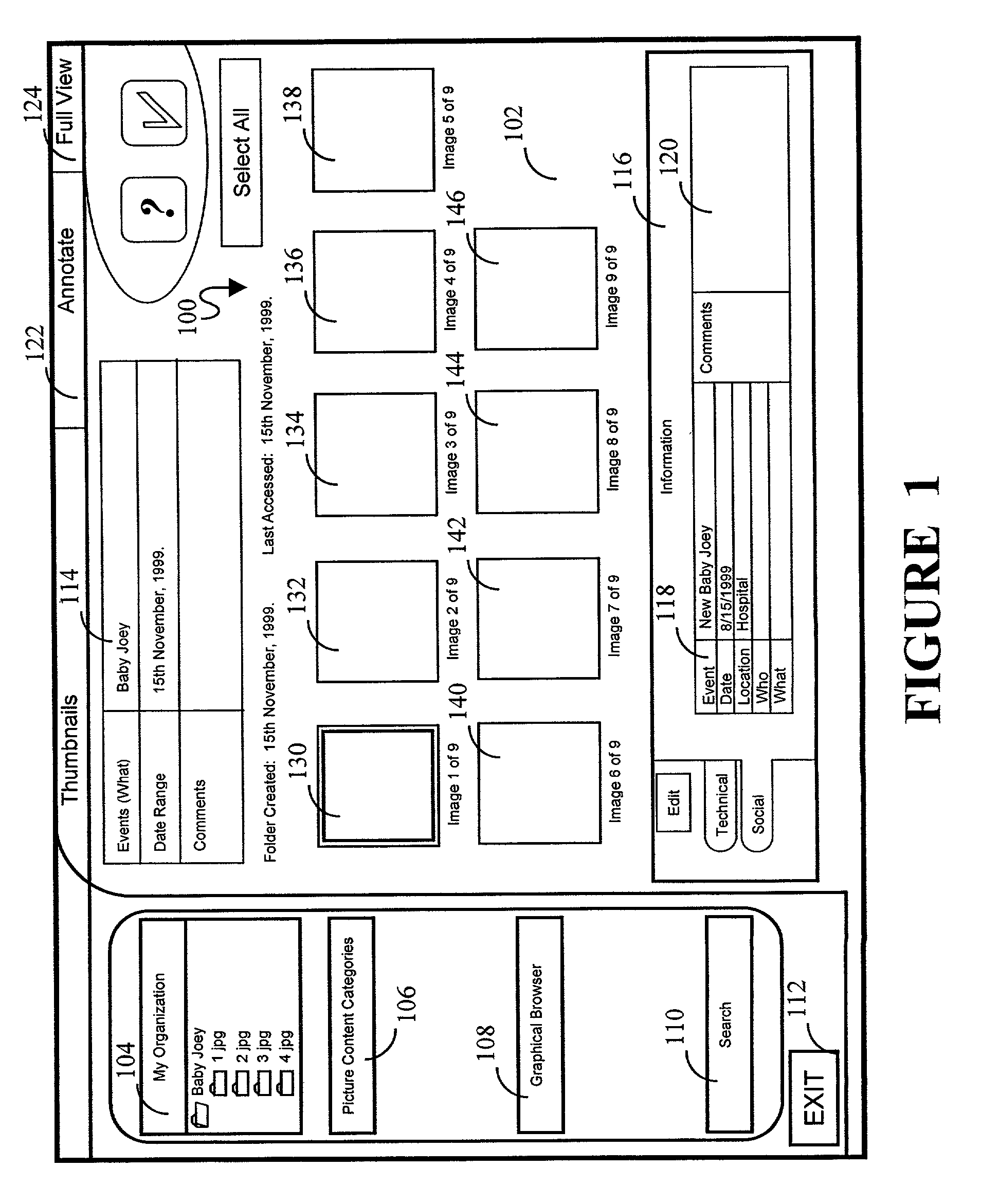
Graphical user interface adapted to allow scene content annotation of groups of pictures in a picture database to promote efficient database browsing
InactiveUS7032182B2Multimedia data retrievalStill image data indexingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A graphical user interface (GUI) allows a picture database user to enter metadata serving to annotate digital pictures to promote efficient picture database browsing. The annotation is permitted, not just for individual pictures, but for groups of pictures. The annotation information can be entered quickly, via a user-friendly interface (200, 204, 206), and can contain “social” information (via 116, 118 and 120) about groups of pictures (130–146), such as capture location, date and time, people or objects featured in groups of pictures, and events recorded by a group of pictures.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, and scalable video encoder and decoder
InactiveUS20050047509A1Slow changeEliminate spaceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGroup of pictures
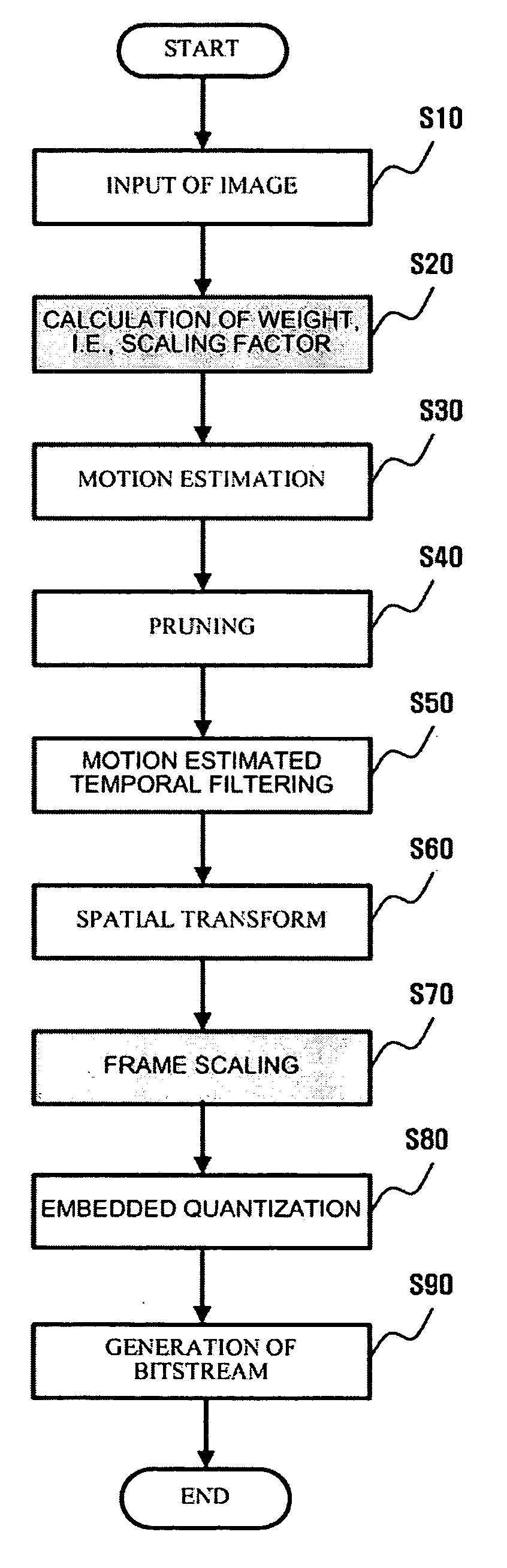
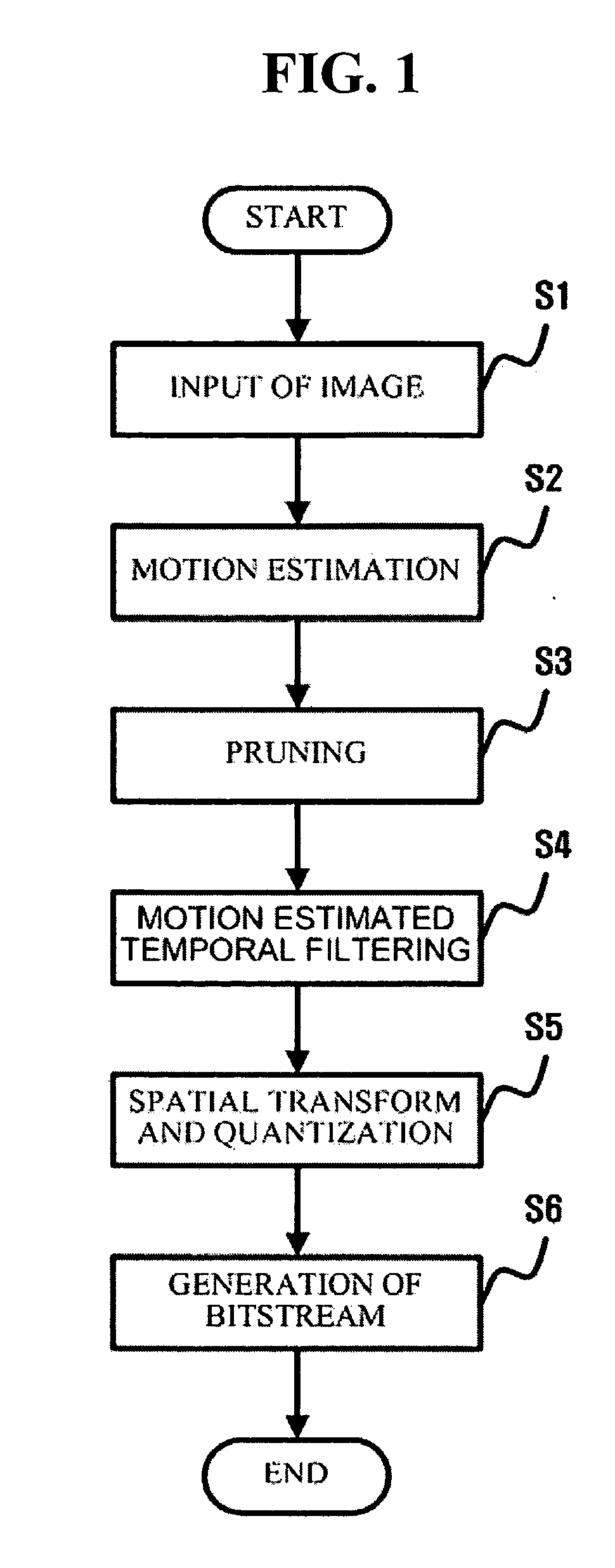
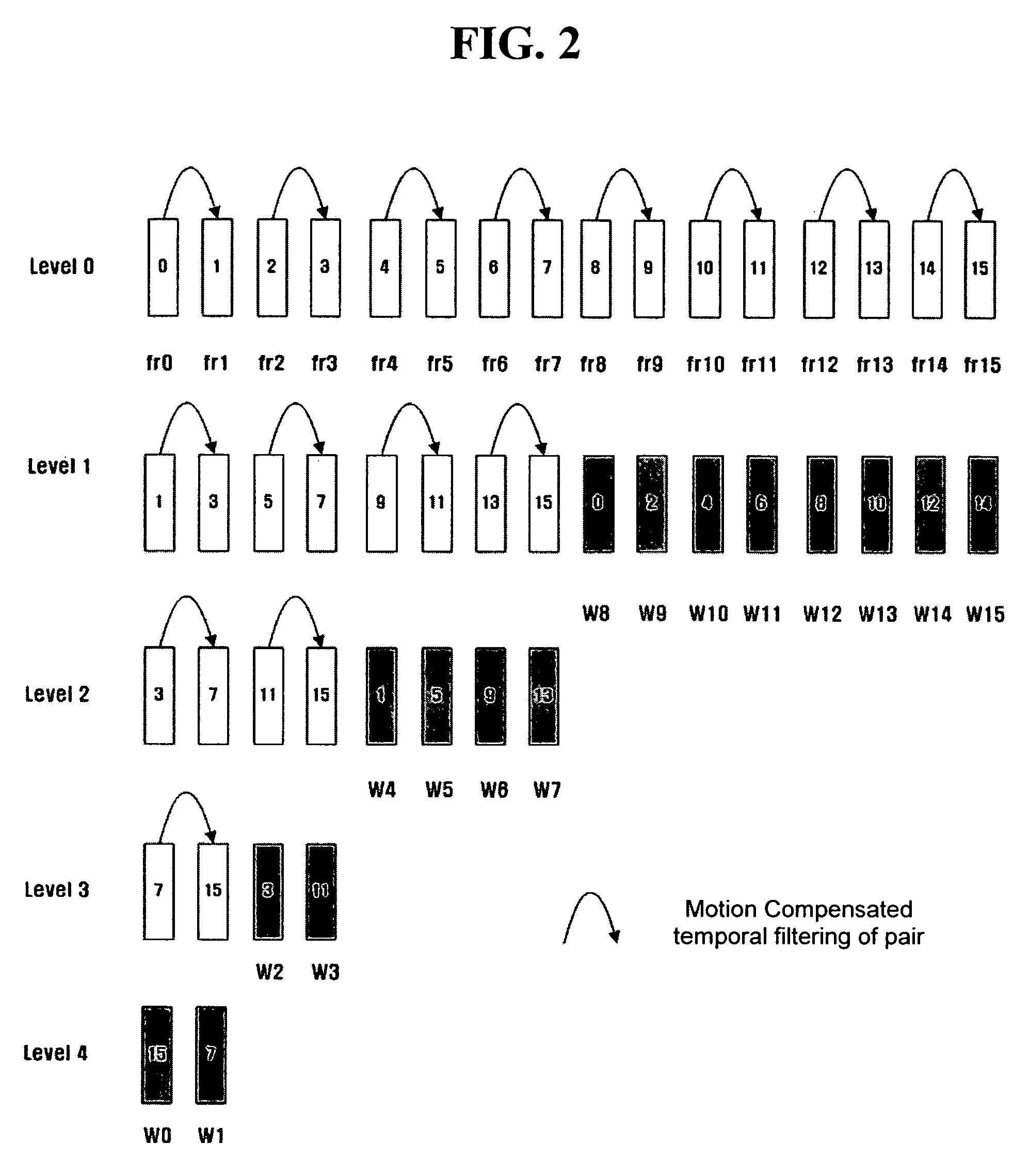
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, a scalable video encoder, and a scalable video decoder. The scalable video coding method includes receiving a GOP, performing temporal filtering and spatial transformation thereon, quantizing and generating a bitstream. The scalable video encoder for performing the scalable video coding method includes a weight determination block which determines a weight for scaling. The scalable video decoding method includes dequantizing the coded image information obtained from a received bitstream, performing descaling, inverse spatial transformation, and inverse temporal filtering on the scaled transform coefficients, thereby recovering video frames. The scalable video decoder for performing the scalable video decoding method includes an inverse weighting block. The standard deviation of Peak Signal to Noise Ratios (PSNRs) of frames included in a group of pictures (GOP) is reduced so that video coding performance can be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
P2P-based broadcast system and method using the same
InactiveUS20080160911A1Quality improvementReceive the video contents more efficientlyRepeater circuitsSelective content distributionGroup of picturesSystems management
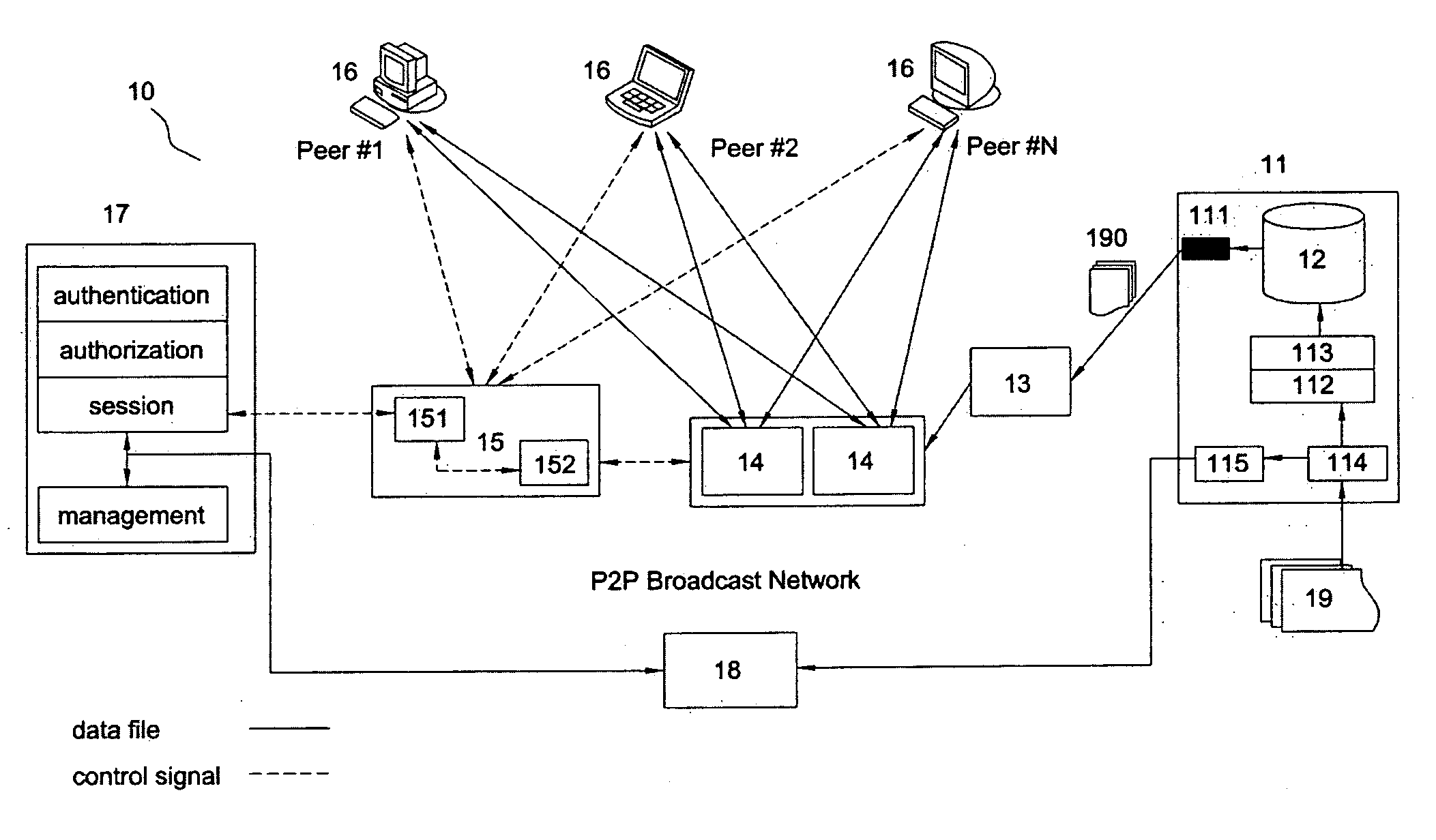
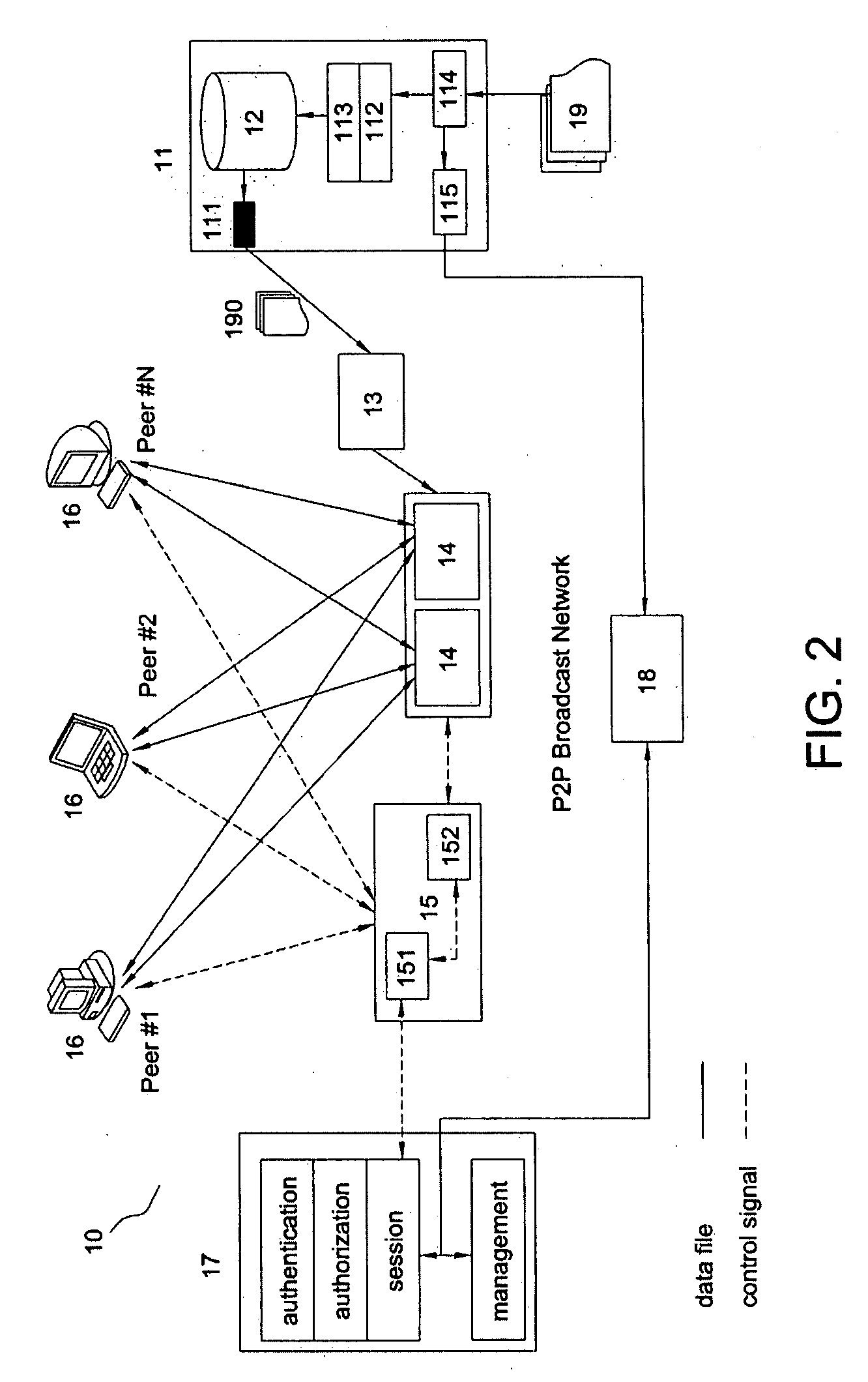
The present invention is to disclose a peer-to-peer based broadcast system for broadcasting video contents, comprising at least one video head-end means for receiving a plurality of original video contents, said video head-end means comprising a splitter to split each original video content into a plurality of video files for each video file being formed of a group of pictures (GOPs) based on said GOPs' boundaries, and said video head-end means further comprising at least one content repository means for storing said video files corresponding to each of original video contents; at least one relay means for receiving and broadcasting some of said video files (190) from the video head-end means; a plurality of peers for receiving and broadcasting some of said video files; at least one super seed means for receiving said video files from said relay means and / or said peers, and broadcasting said files to some of said peers; at least one network management means for managing connections among said super seed means and said peers, said network management means comprising at least one tracking means for storing all required location information of said video files; and at least one system management means for providing authentication and authorization for clients on said peers to access to said P2P based broadcast system; wherein said each peer comprising a player for processing said video files so as to play said original video contents when said video files being received.
Owner:GOOSEAN MEDIA
Method and device for correlation channel estimation
InactiveUS20130266078A1Accurate channel estimationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionSide information
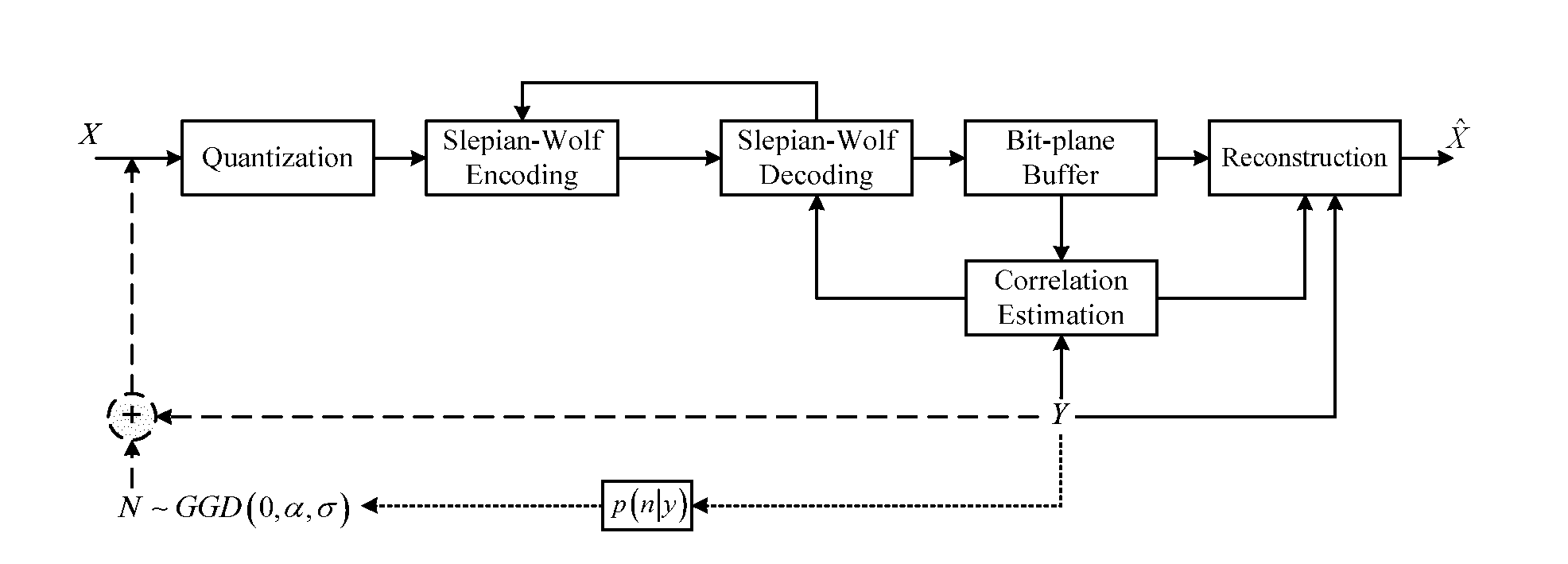
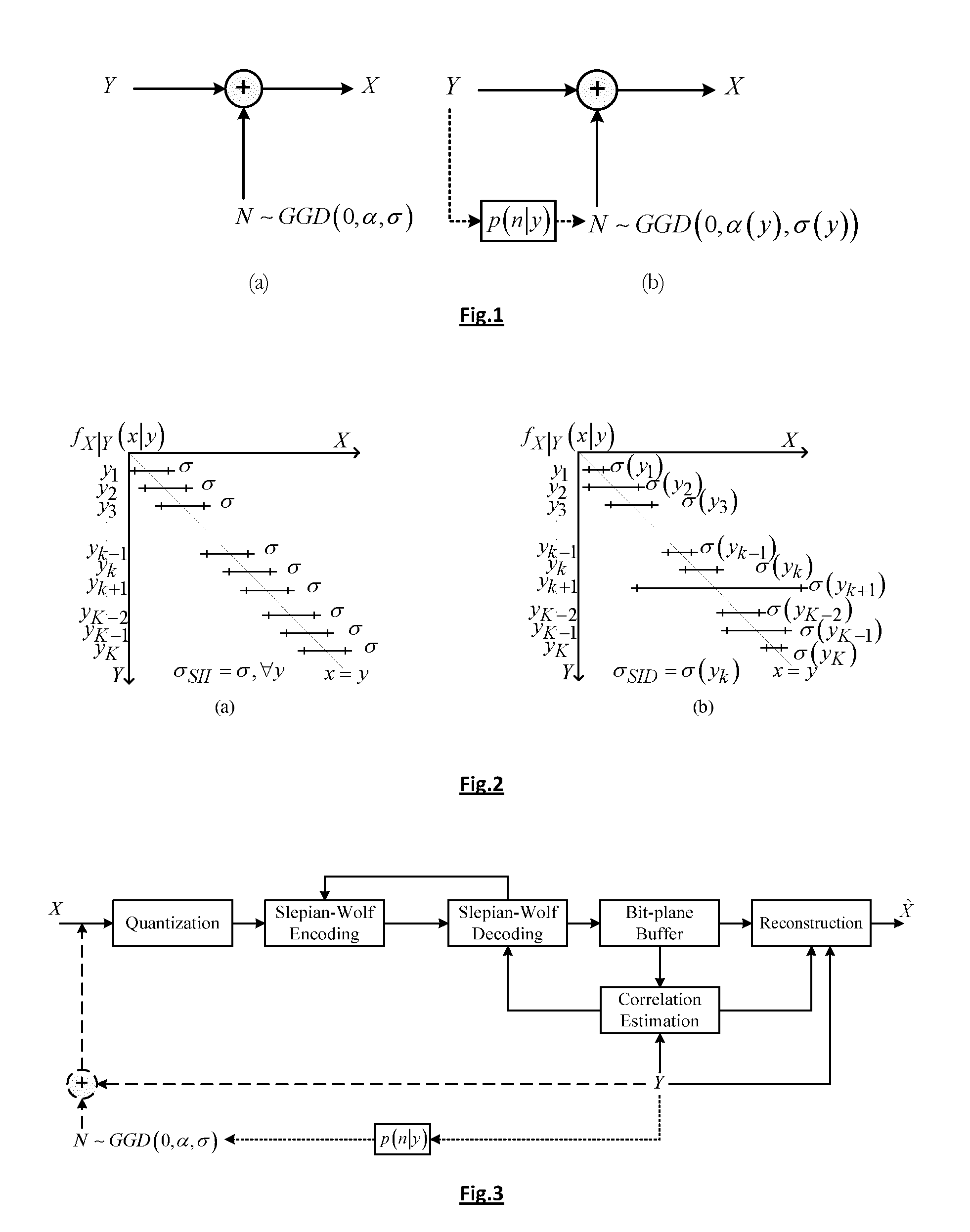
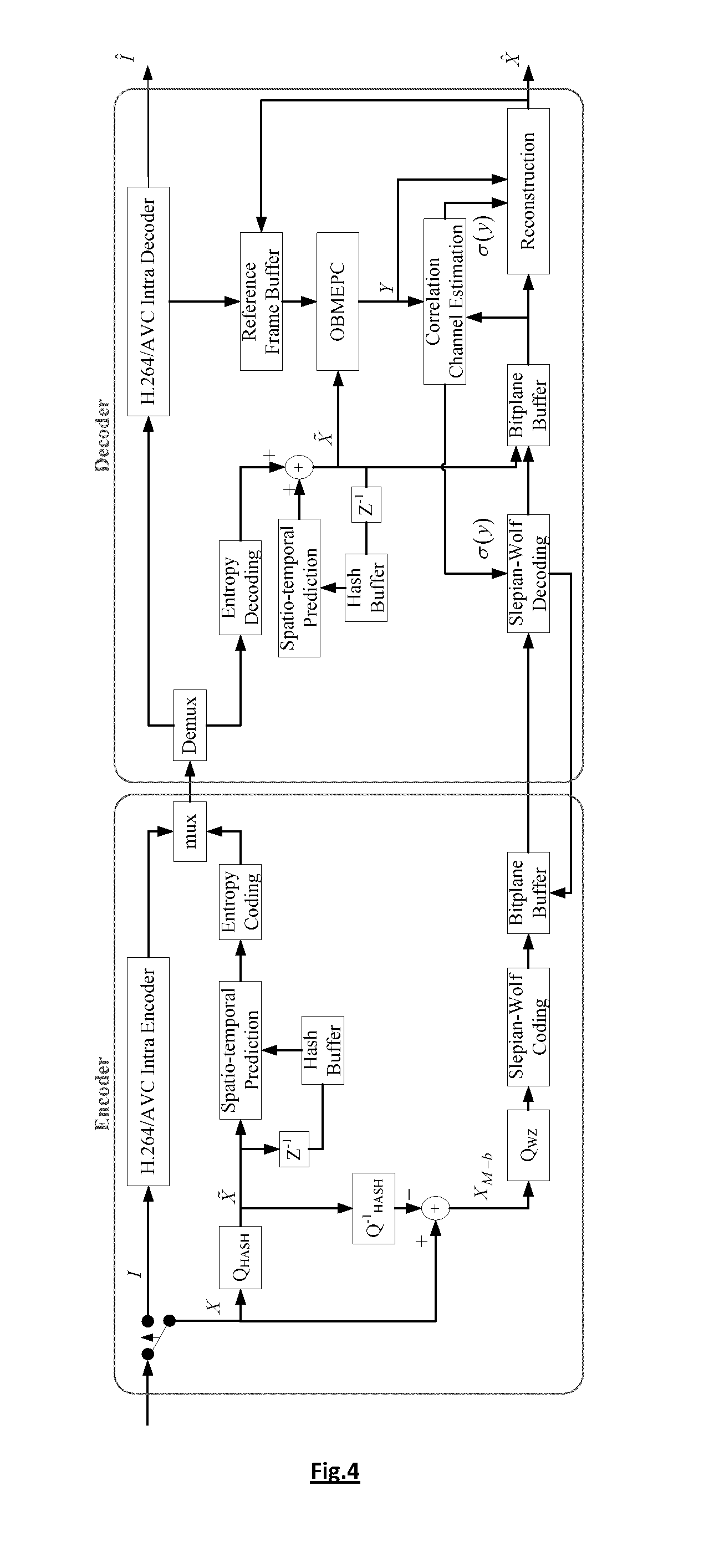
A hash-based distributed video coding architecture has an encoder with an input video sequence organized in Groups of Pictures (GOPs) decomposed into key frames using H264 / AVC Intra frame coding. The Wyner-Ziv (WZ) frames are encoded in two parts, a hash layer and a WZ layer. The WZ frames are quantized and each and then decorrelated using spatio-temporal prediction and entropy coded. The intra bit stream is H264 / AVC decoded and the intra frames are stored in a reference frame buffer. The hash is decoded by inverting the tasks applied at the encoder, and the obtained bit planes are stored. Overlapped Block Motion Estimation and Probalistic Compensation (OBMEPC) is used to estimate the missing bit planes in the side-information. The decoder utilizes the hash information and the side information frame created by OBMEPC to perform online estimation of the correlation channel, and produces soft estimates used to decode the WZ bit planes.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com