Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
499results about How to "Avoid artifacts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
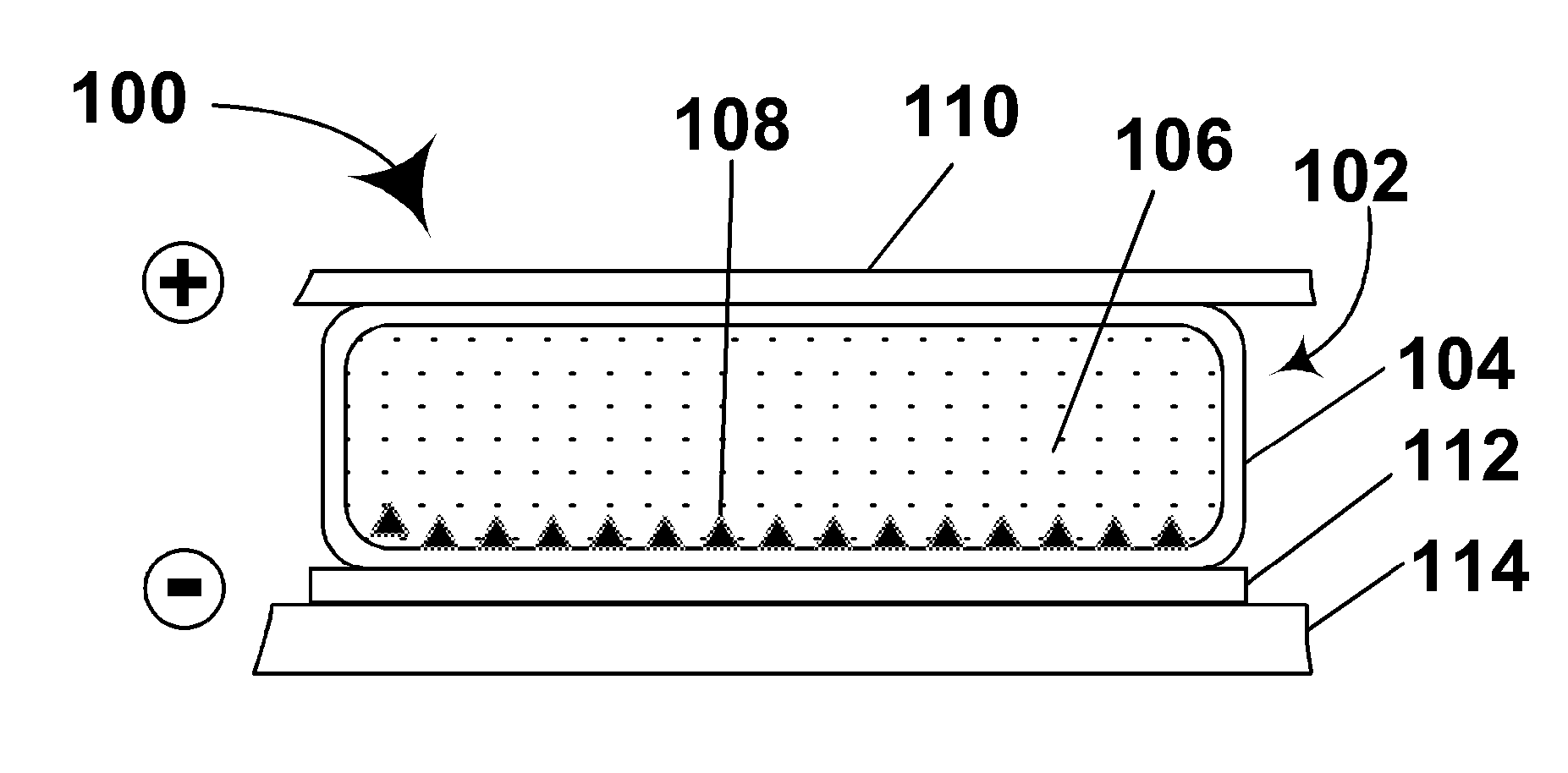
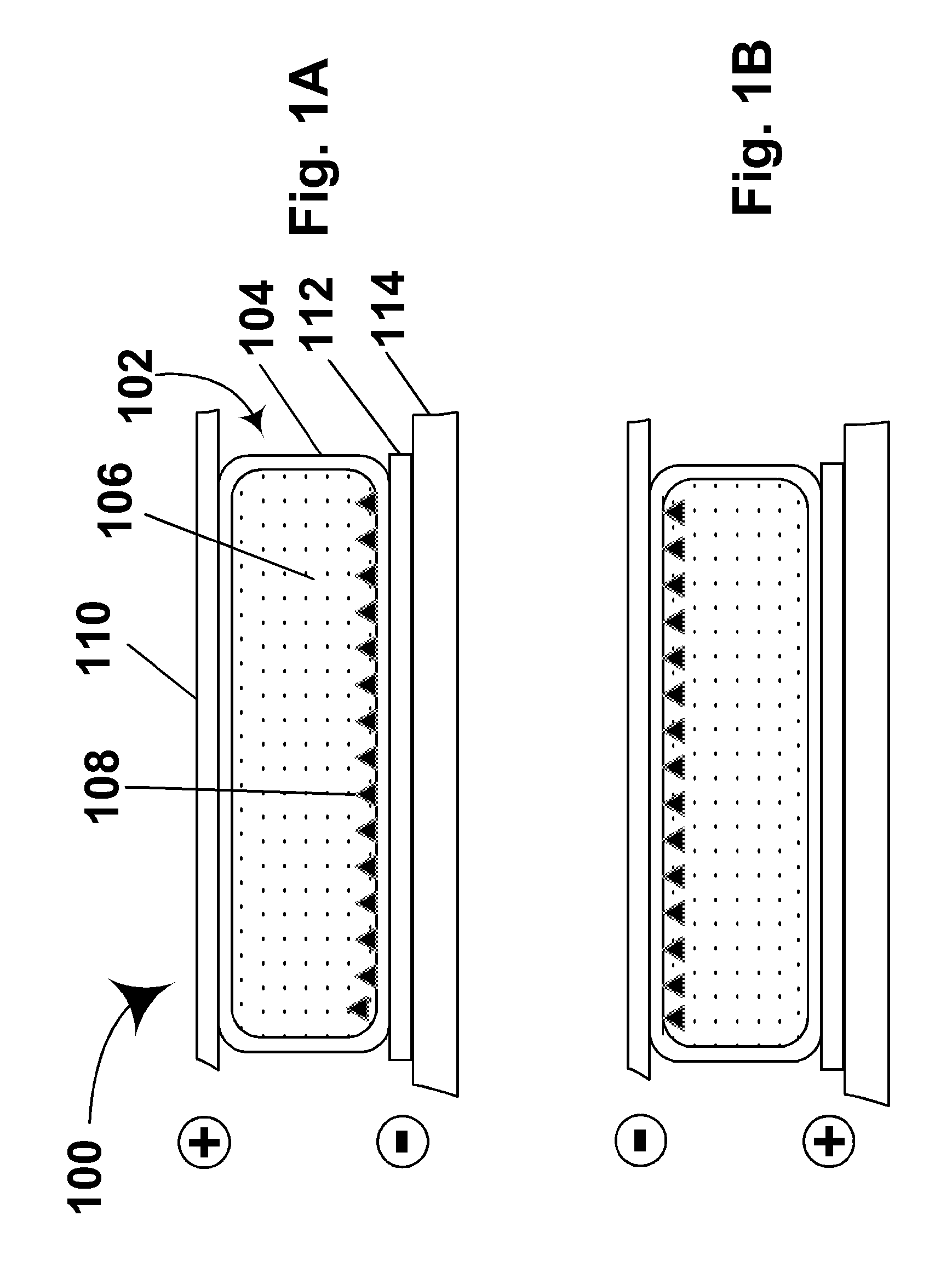
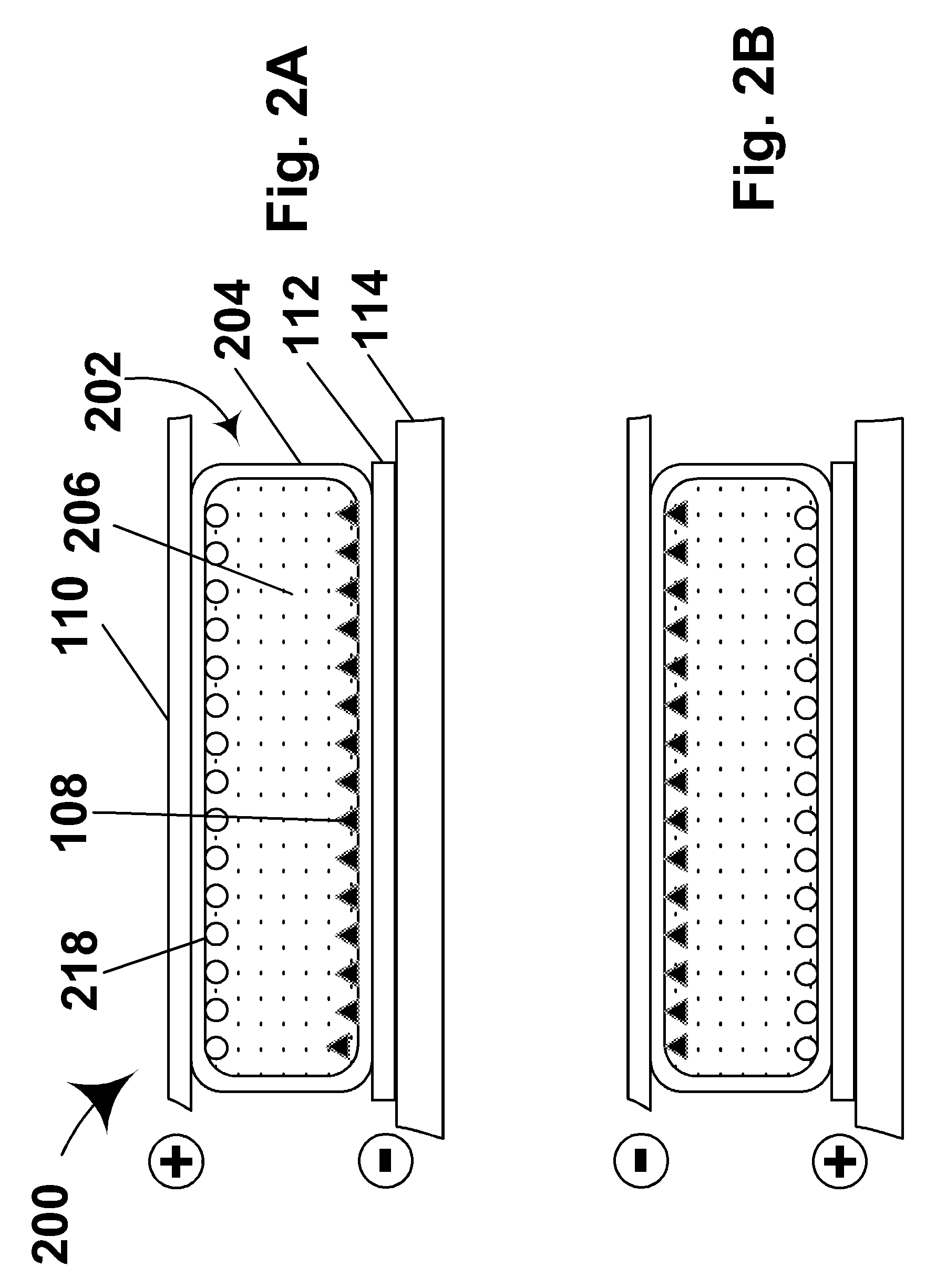
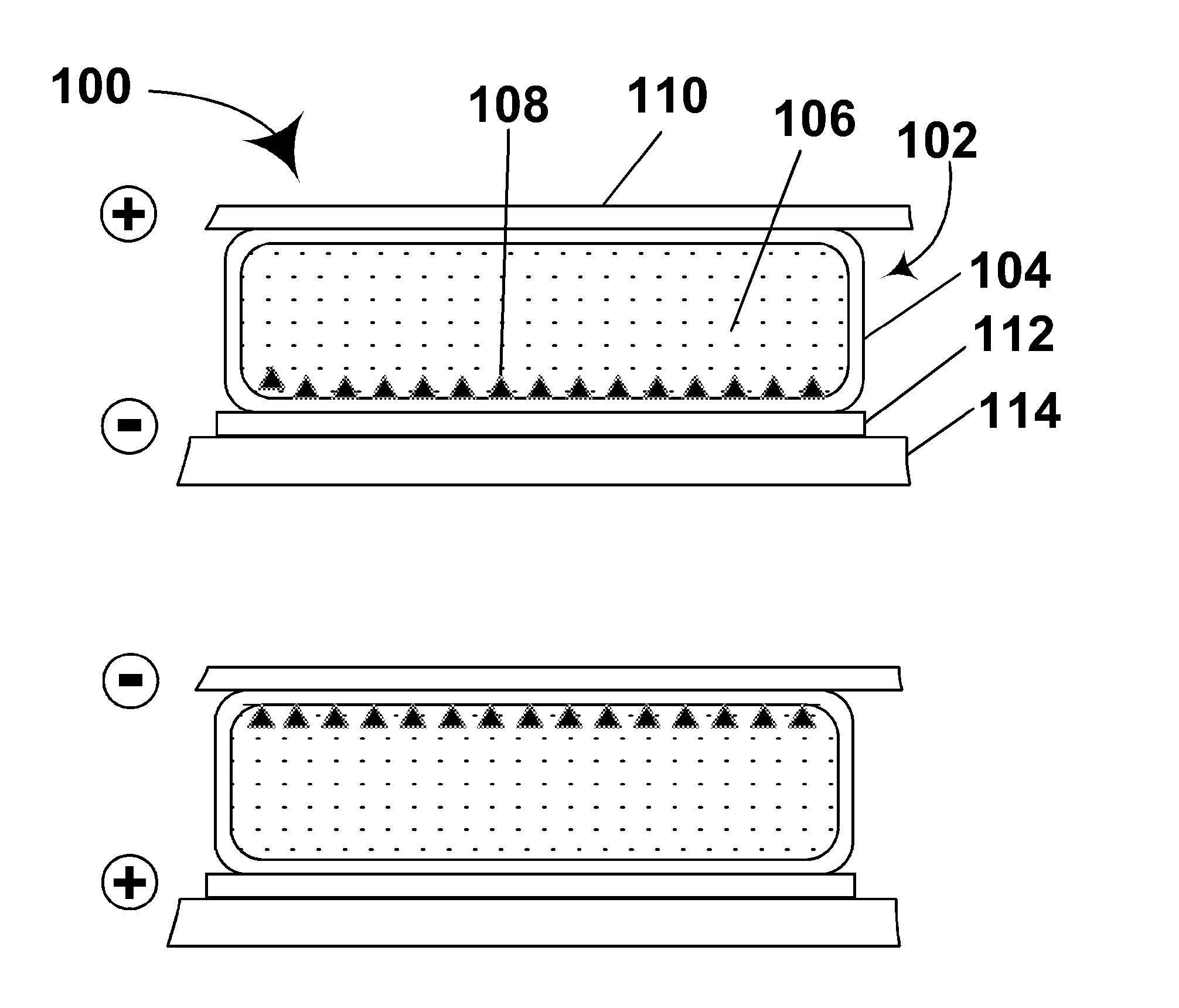
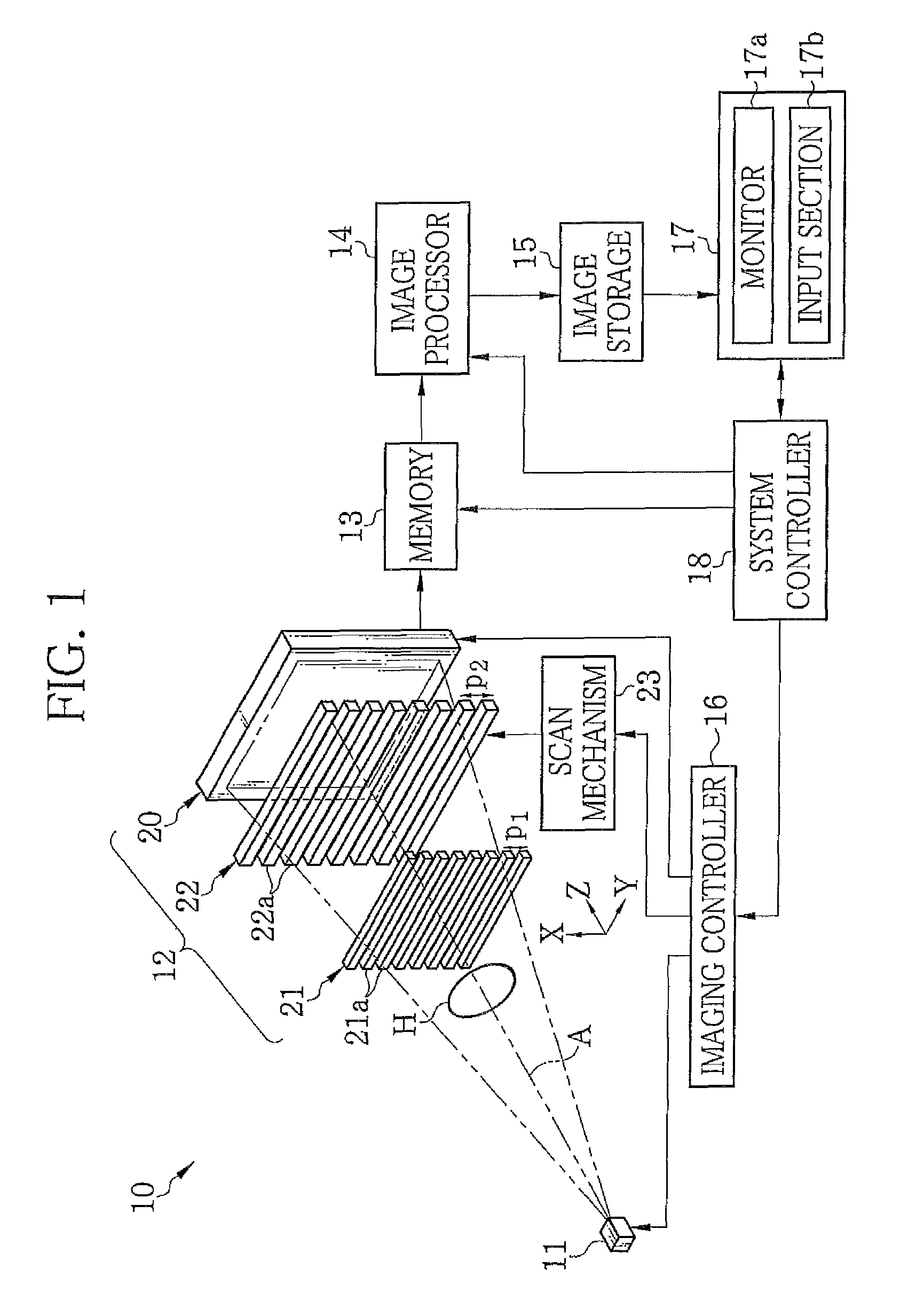
Electrophoretic displays with controlled amounts of pigment
InactiveUS20050012980A1Good optical performanceAvoid artifactsNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic medium has walls defining a microcavity containing an internal phase. This internal phase comprises electrophoretic particles suspended in a suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the electrophoretic medium. The average height of the microcavity differs by not more than about 5 μm from the saturated particle thickness of the electrophoretic particle divided by the volume fraction of the electrophoretic particles in the internal phase.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
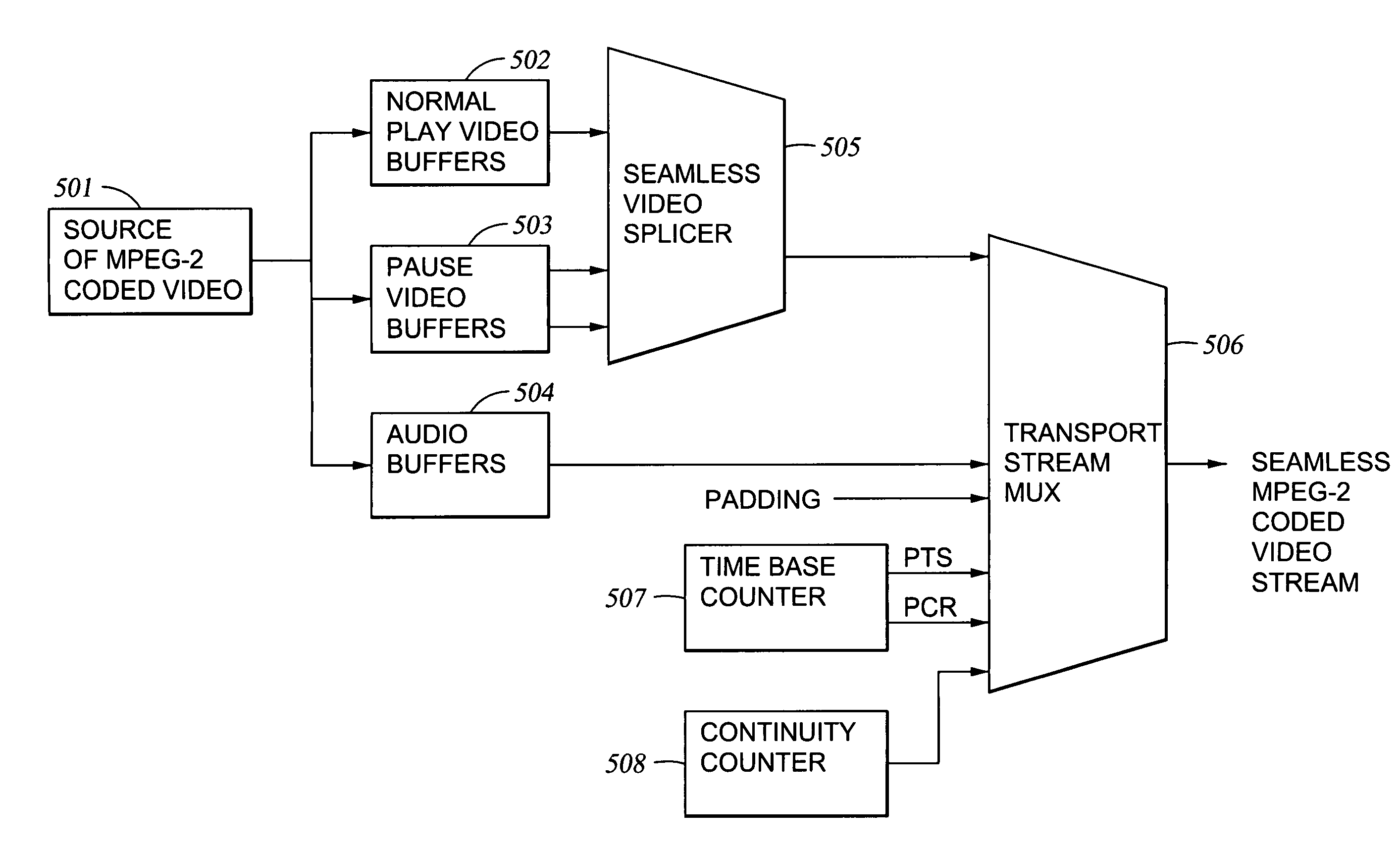
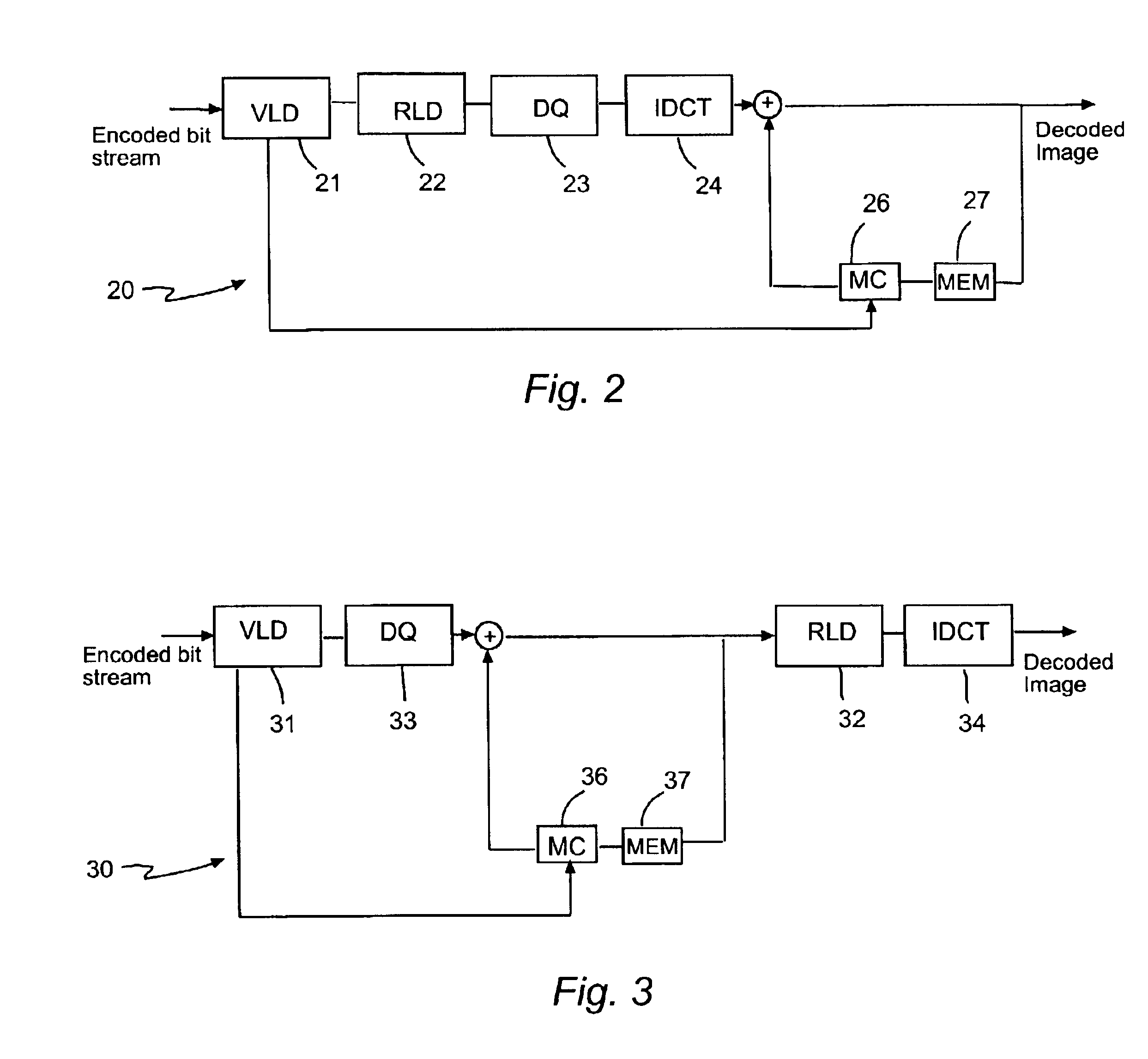
Method of pausing an MPEG coded video stream
ActiveUS7023924B1Avoid artifactsMaintaining synchronizationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionGroup of picturesMPEG encoding
To produce a paused MPEG coded video stream from an original MPEG coded video stream, an I frame is extracted from the original stream, and a Group of Pictures for a “pause” (a pause GOP) is constructed containing the extracted I frame, some “frozen” frames, and padding. Each “frozen” frame is a P frame that repeats the I frame. When a pause is requested in the original stream, a seamless transition is made from the I frame to the pause GOP, and the pause GOP is played in a loop until a resume is requested. To resume, the pause GOP is completed and a seamless transition is made to continue in the original stream from the I frame where the pause had begun.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
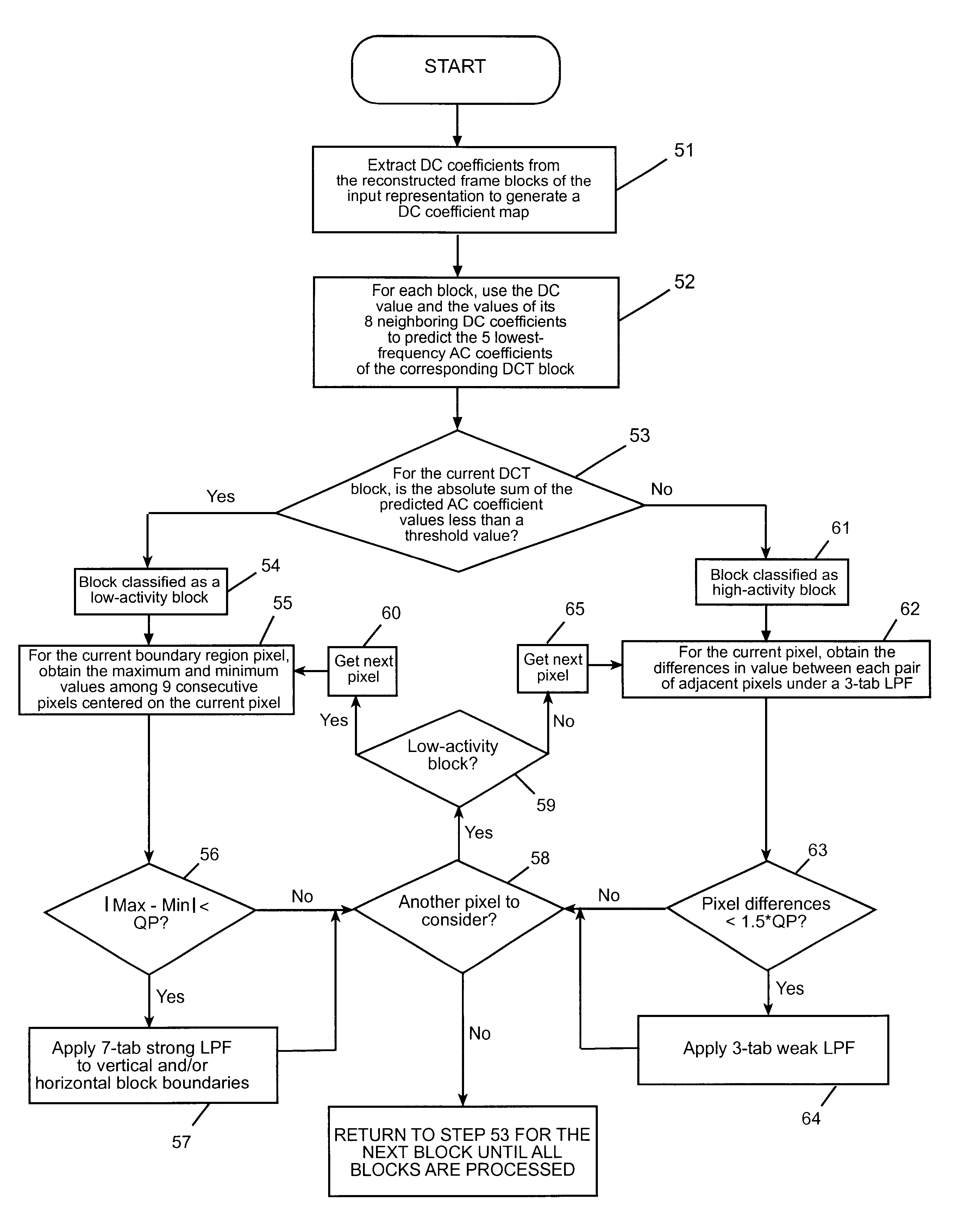
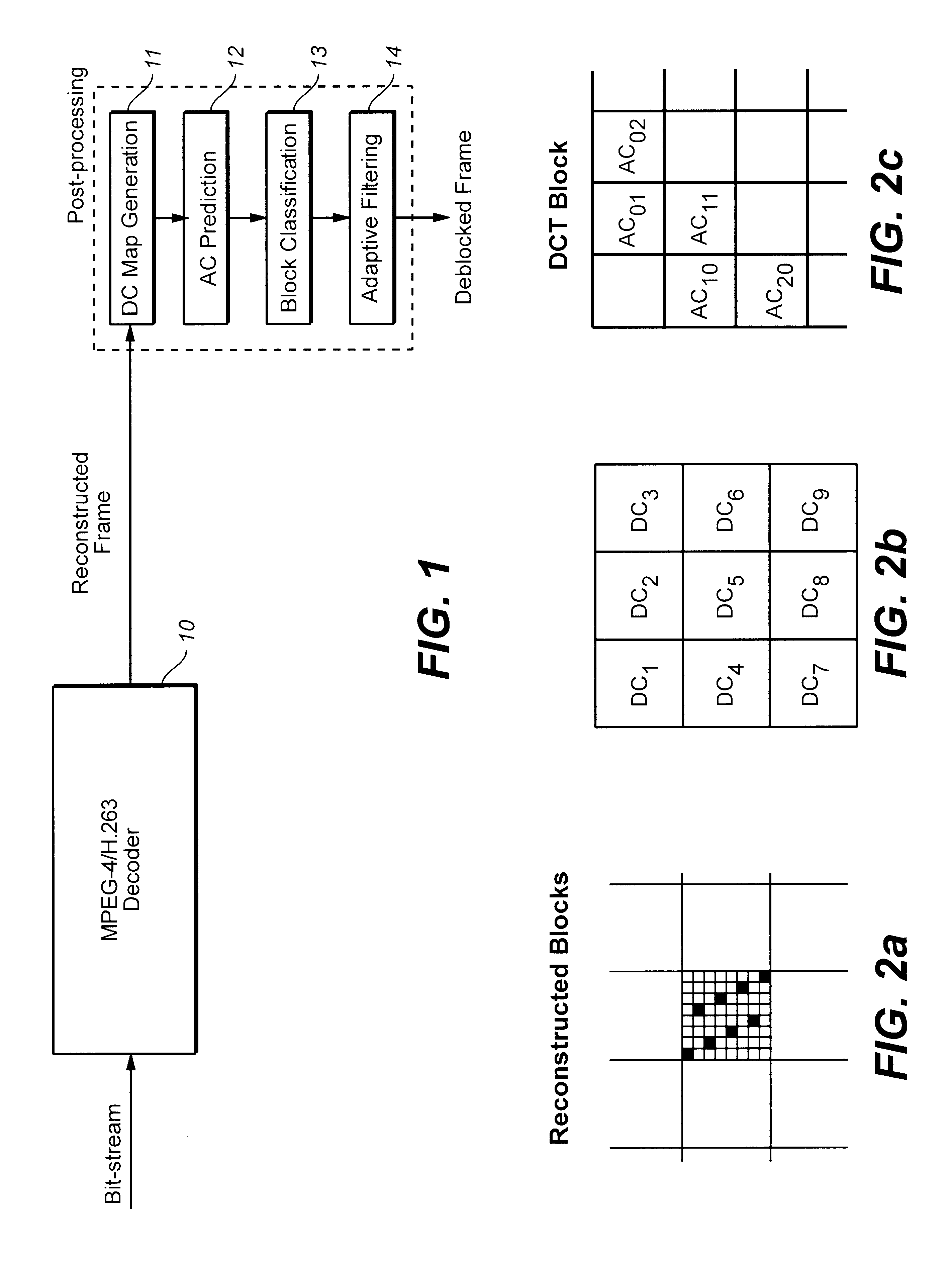
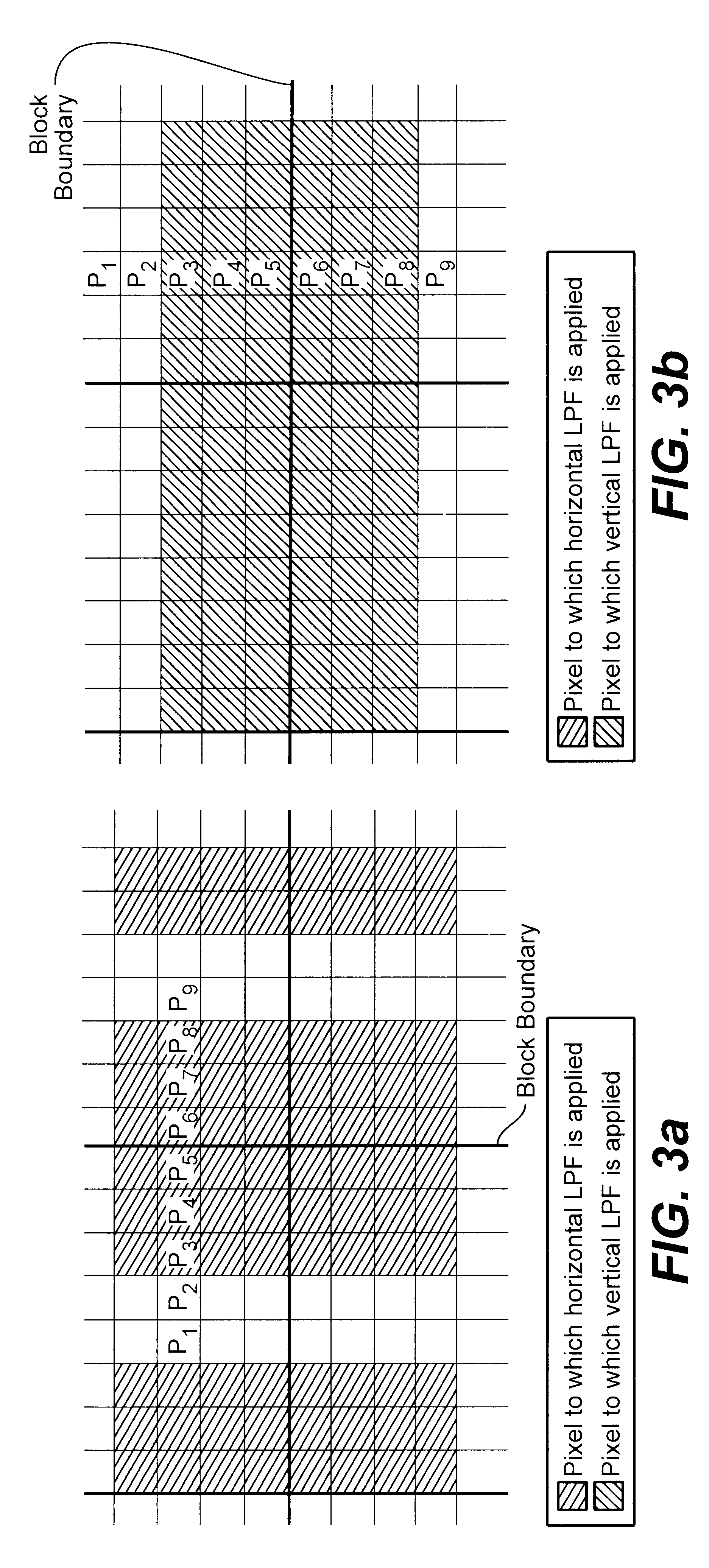
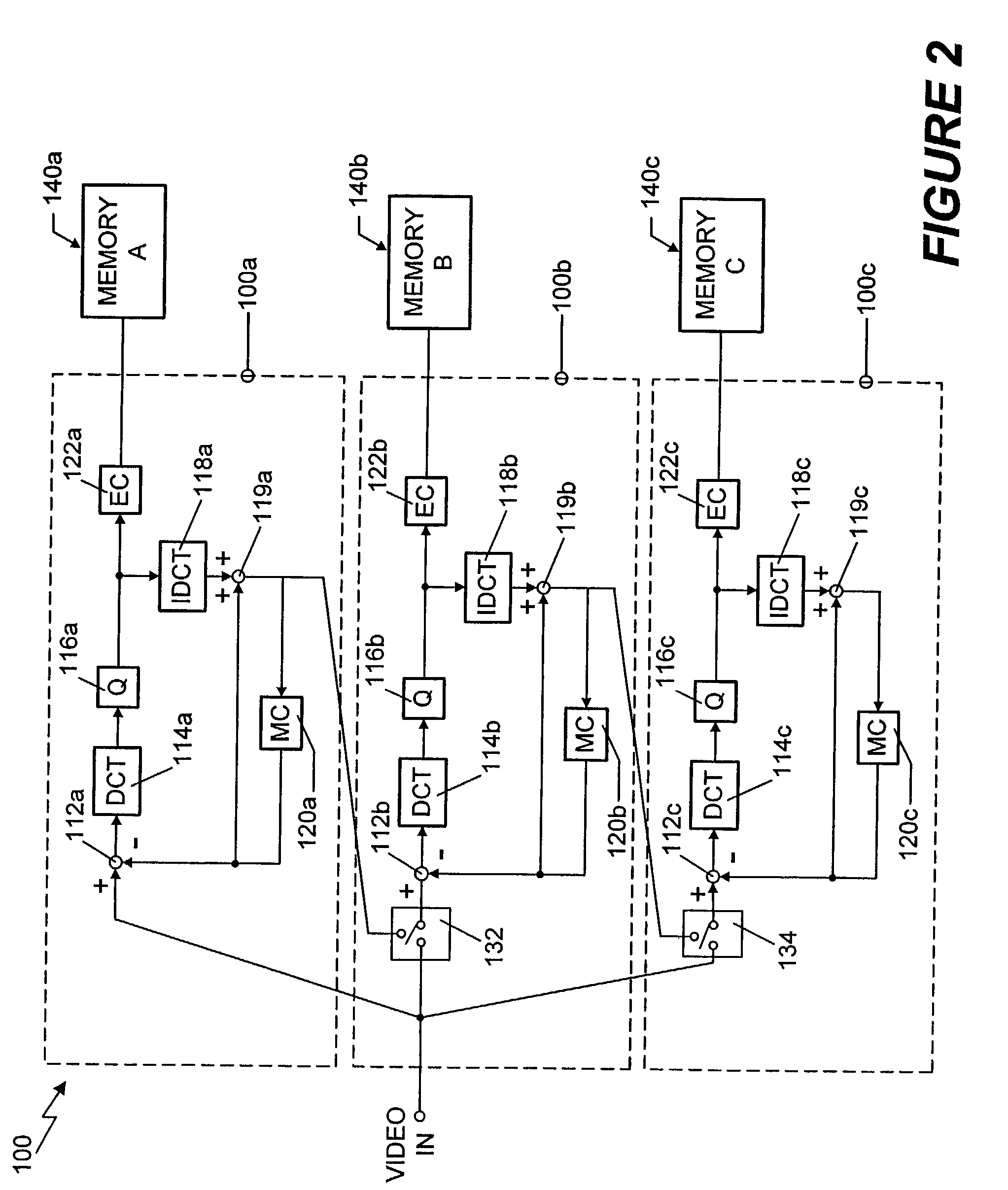
Reducing blocking and ringing artifacts in low-bit-rate coding
InactiveUS6983079B2Increase speedReducing blocking and artifactPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLow activity
A technique to reduce blocking and ringing artifacts in low bit-rate block-based video coding is applied to each reconstructed frame output from the decoder. For each pixel block of a reconstructed frame, its DC value and DC values of the surrounding eight neighbor blocks are exploited to predict AC coefficients which might be lost in the quantization stage in the encoding process. The predicted AC coefficients are used to classify each reconstructed block as either a low-activity or a high-activity block. Low-pass filtering is then adaptively applied according to the classification of the block. Strong low-pass filtering is applied in low-activity blocks where the blocking artifacts are most noticeable, whereas weak low-pass filtering is applied in high-activity blocks where ringing noise as well as blocking artifacts may exist. The adaptive filtering reduces ringing noise as well as blocking artifacts without introducing undesired blur. In low activity blocks, the blocking artifacts are reduced by one dimensional horizontal and vertical low-pass filters which are selectively applied in either the horizontal and / or vertical direction depending on the locations and absolute values of the predicted AC coefficients. In high activity blocks, de-blocking and de-ringing is conducted by a single filter, applied horizontally and / or vertically, which makes the architecture simple.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
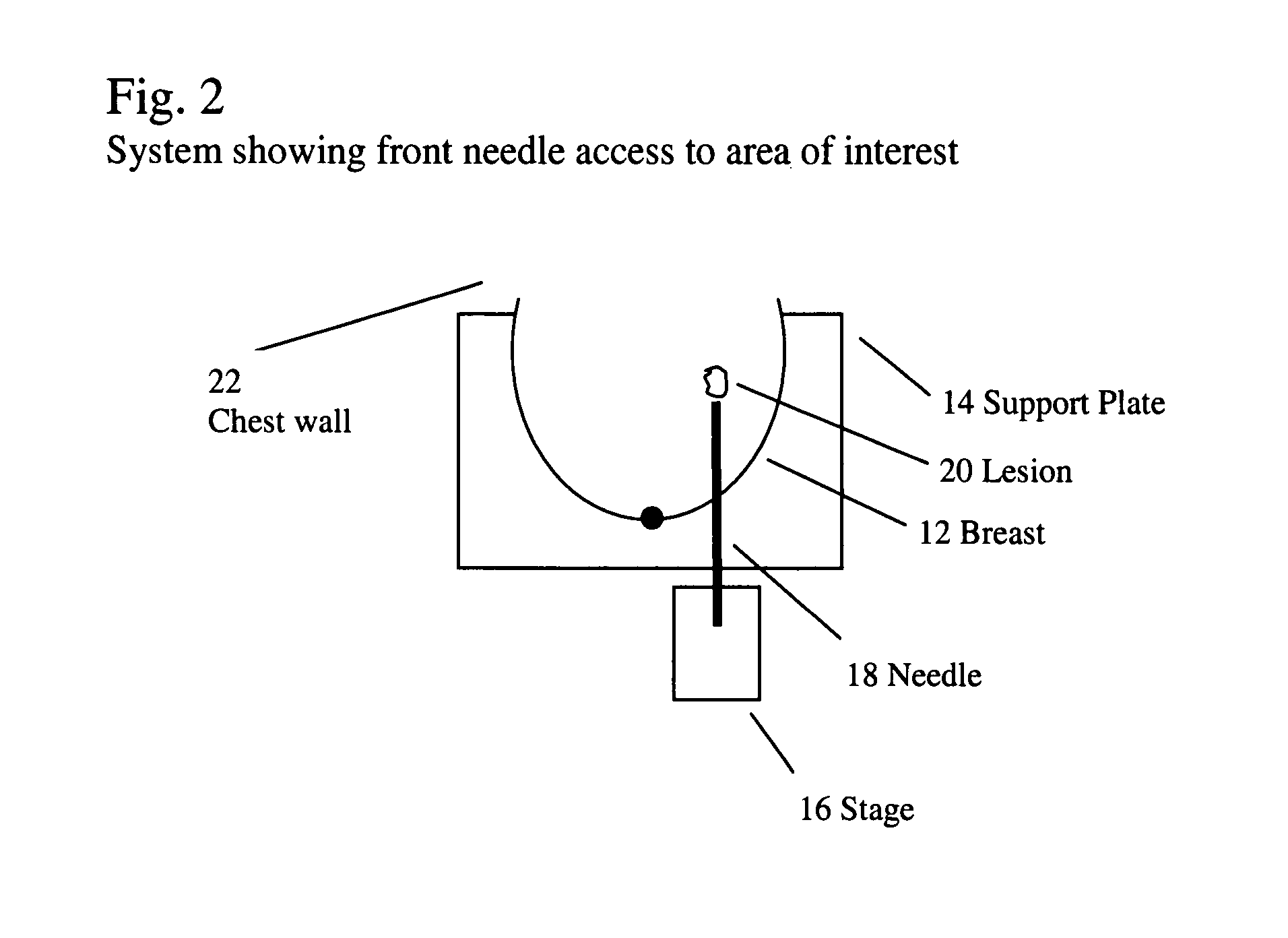
Breast biopsy and needle localization using tomosynthesis systems
ActiveUS20080045833A1High contrast visibilityImprove visibilityTomosynthesisVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTomosynthesisNeedle localization
Methods, devices, apparatuses and systems are disclosed for performing mammography, such as utilizing tomosynthesis in combination with breast biopsy.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
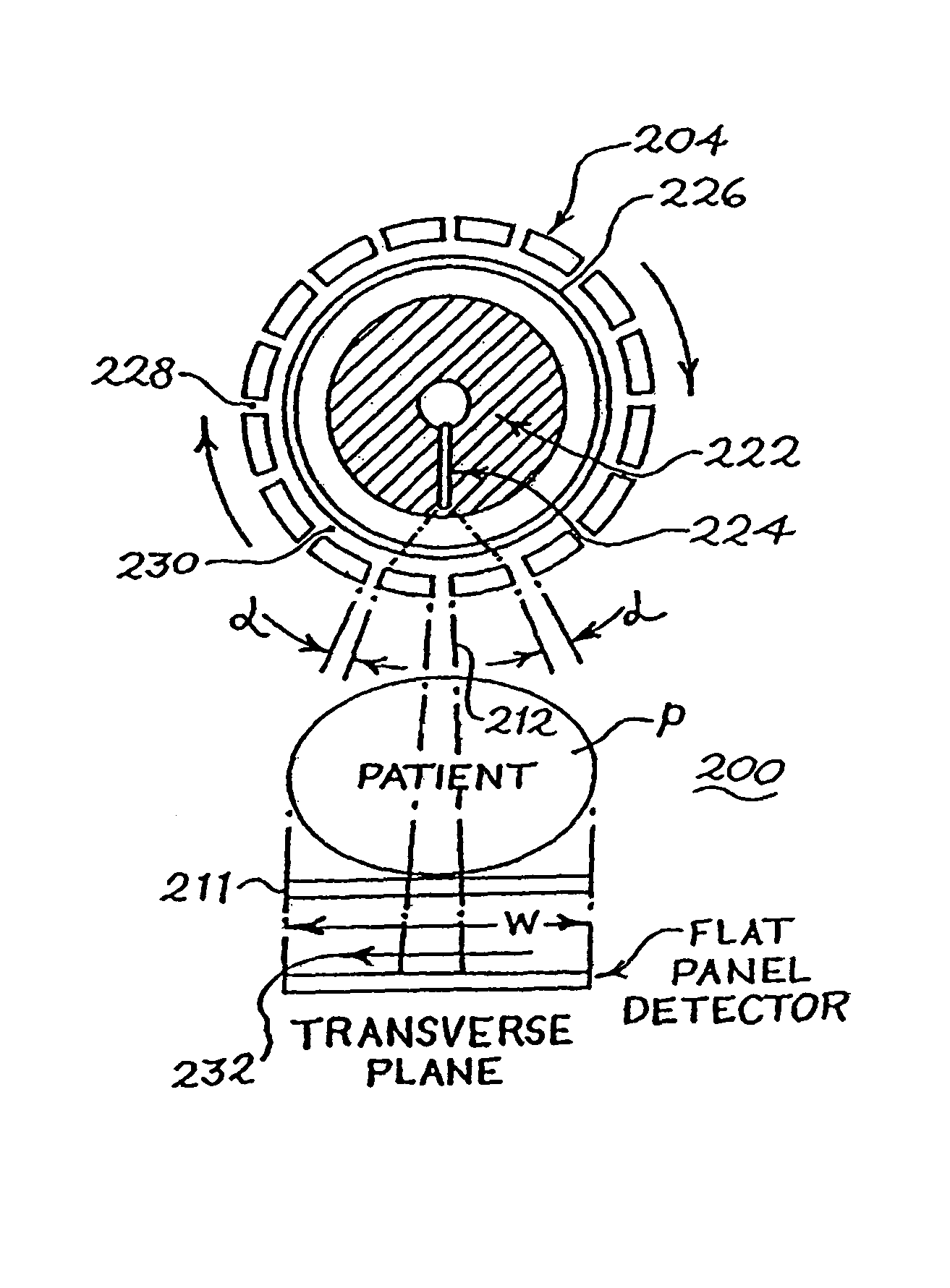
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
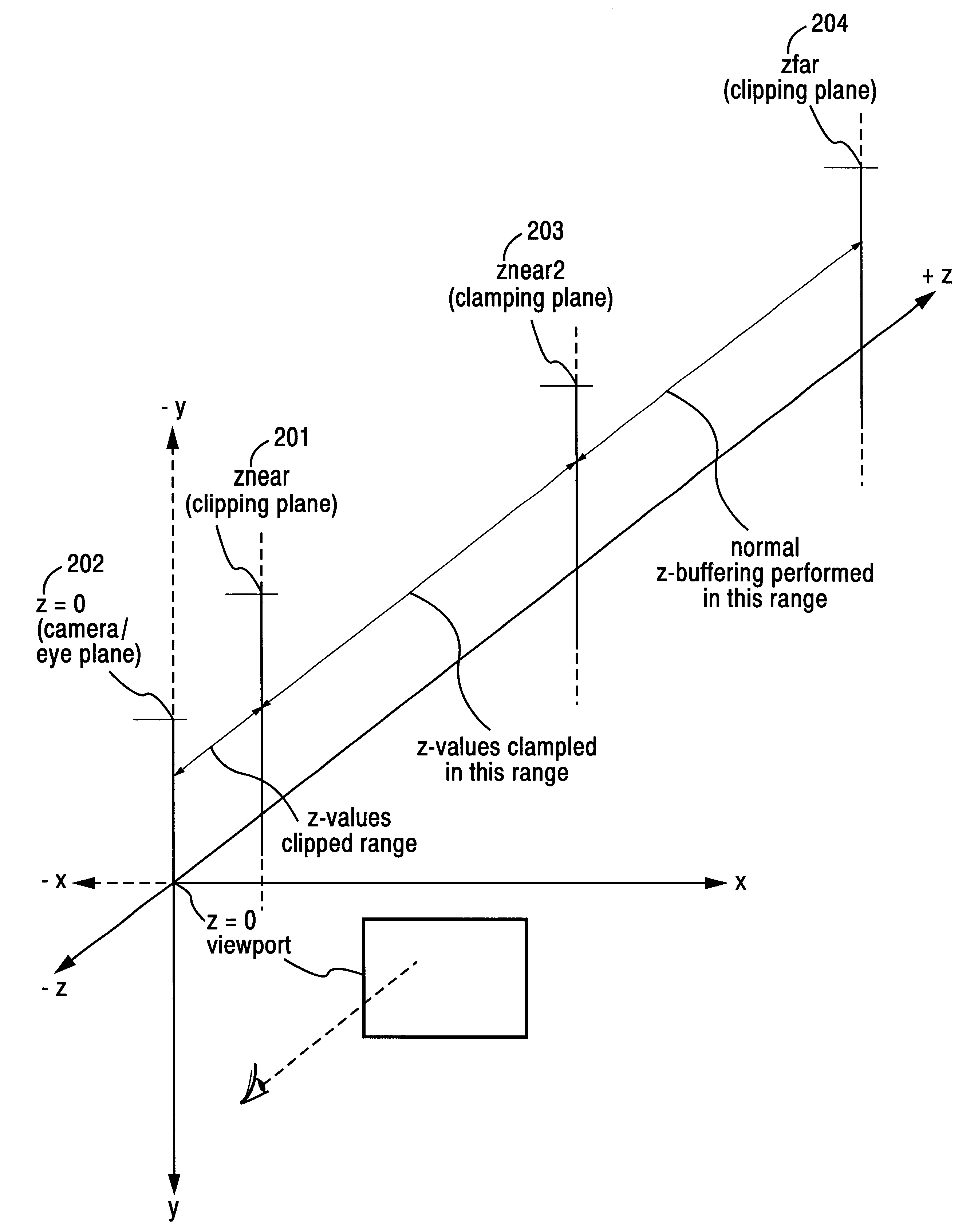
3D graphics rendering system for performing Z value clamping in near-Z range to maximize scene resolution of visually important Z components
InactiveUS6618048B1Improve precisionAvoid undesirable visual artifactCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationSurround soundImage resolution
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics pipeline performs Z-buffering and optionally provides memory efficient full scene anti-aliasing (FSAA). When the anti-aliasing rendering mode is selected, Z value bit compression is performed to more efficiently make use of the available Z buffer memory. A Z-clamping arrangement is used to improve the precision of visually important Z components by clamping Z values to zero of pixels that fall within a predetermined Z-axis range near the Z=0 eye / camera (viewport) plane. This allows a Z-clipping plane to be used very close to the eye / camera plane--to avoid undesirable visual artifacts produced when objects rendered near to the eye / camera plane are clipped--while preserving Z value precision for the remaining depth of the scene. In an example implementation, a Z value compression circuit provided in the graphics pipeline is enhanced to effectuate Z-clamping within the predetermined range of Z values. The enhanced circuitry includes an adder for left-shifting an input Z value one or more bits prior to compression and gates for masking out the most significant non-zero shifted bits to zero.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
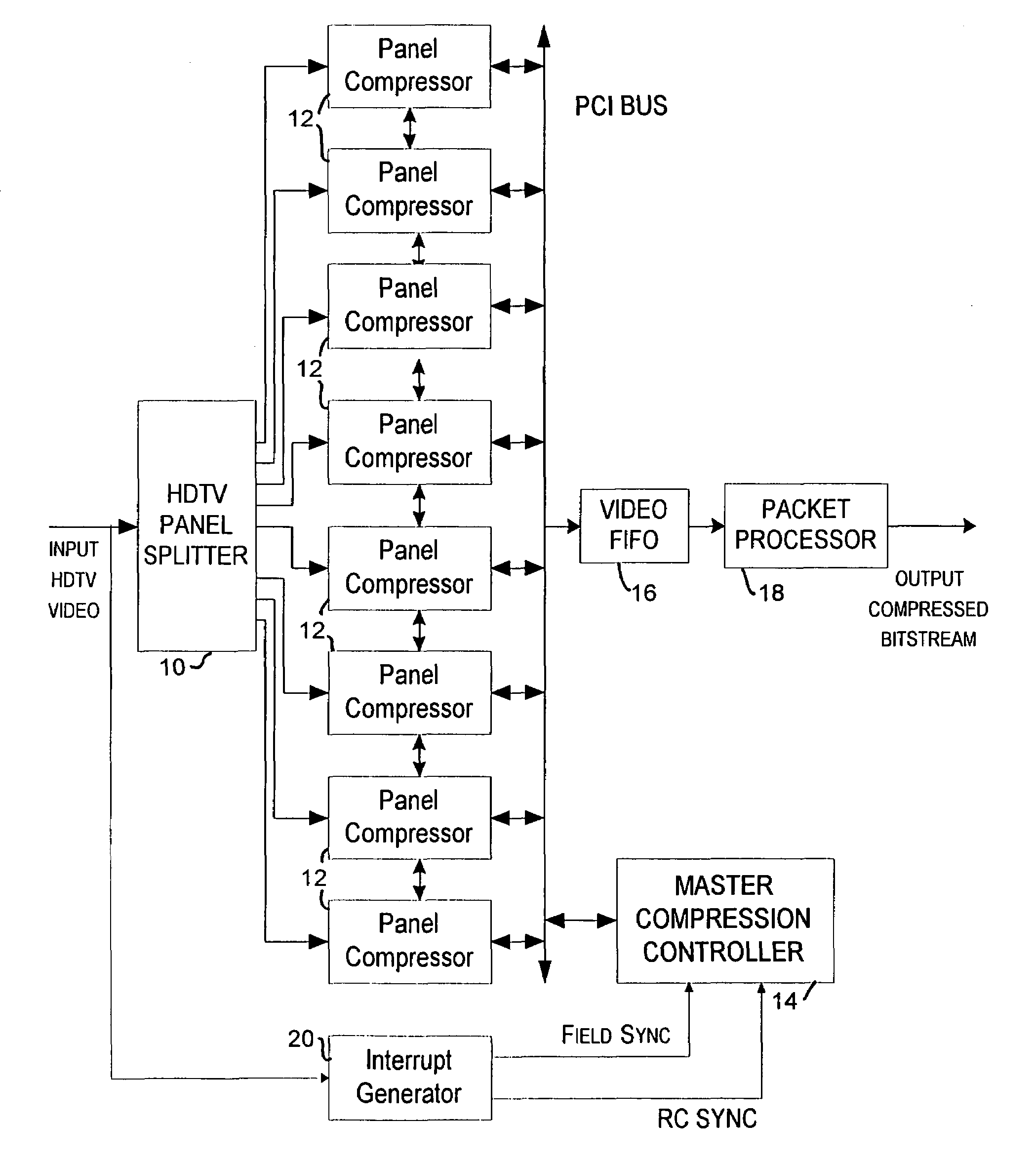
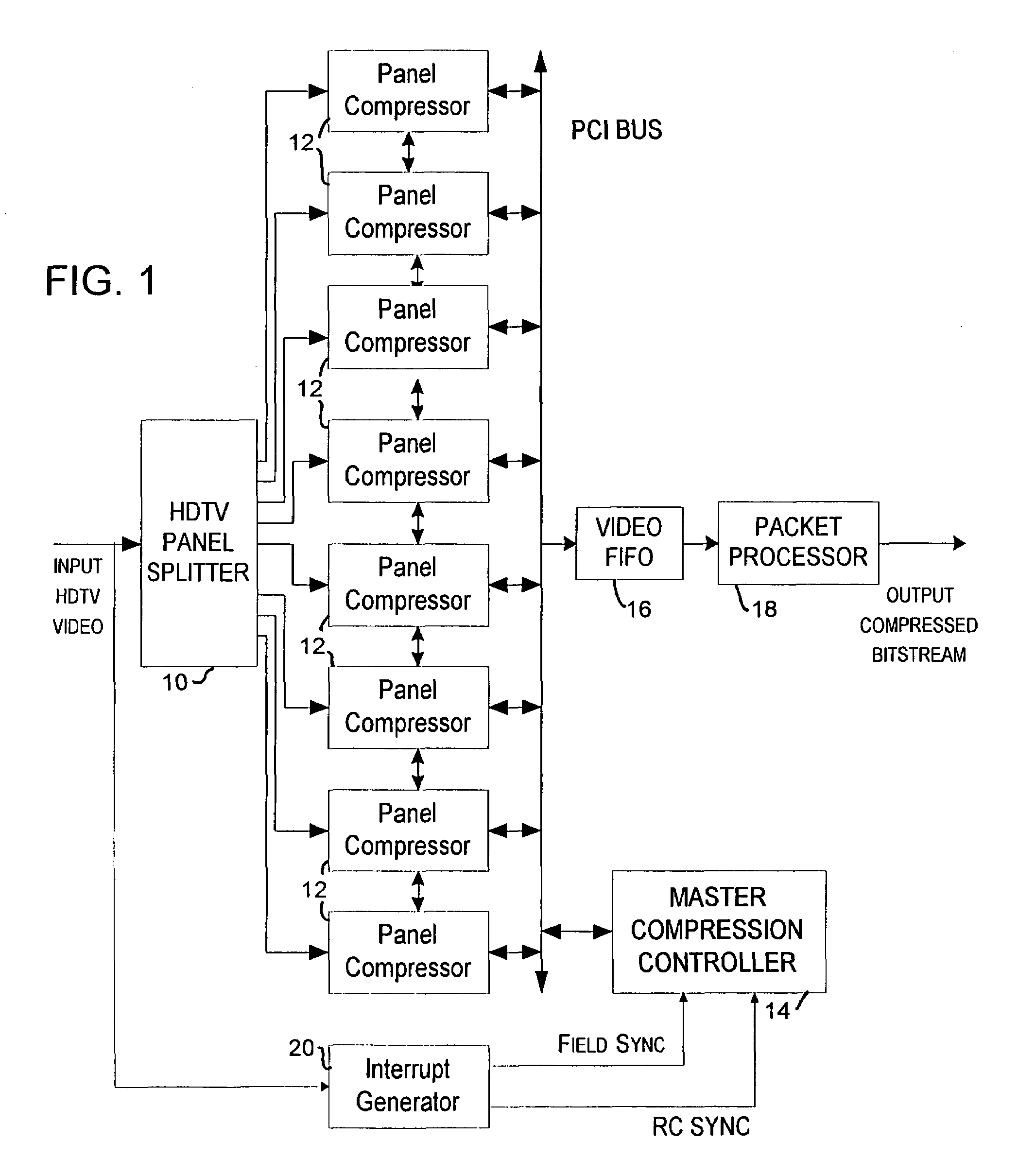
Method and apparatus for providing rate control in a video encoder
InactiveUS6963608B1Avoids visible artifactAvoid artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoVideo encoding
A method and apparatus are provided for controlling the quantization level in a digital video encoder that comprises a plurality of parallel compression engines (12). The input picture is partitioned into a number of panels (10) and each panel is processed by a distinct compression engine (12). A reference quantizer scale is determined before encoding a frame of video. The reference quantizer scale is used at the first slice of every video image panel being processed by the video encoder. The quantizer scale at the last slice of the image panel is then forced to be the same as the first slice. The forcing step can use a piecewise-linear feedback formula. A group of pictures (GOP) target bit rate is adjusted based on the number of film pictures and non-film pictures currently in the processing pipeline of at least one of the compression engines. A higher target bit rate is provided for non-film pictures. A buffer (16) level of the video encoder is used to control the start of a new group of pictures (GOP). The start of a new GOP is delayed if the buffer (16) does not have sufficient space to accommodate an intra-coded (I) frame for the new GOP.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
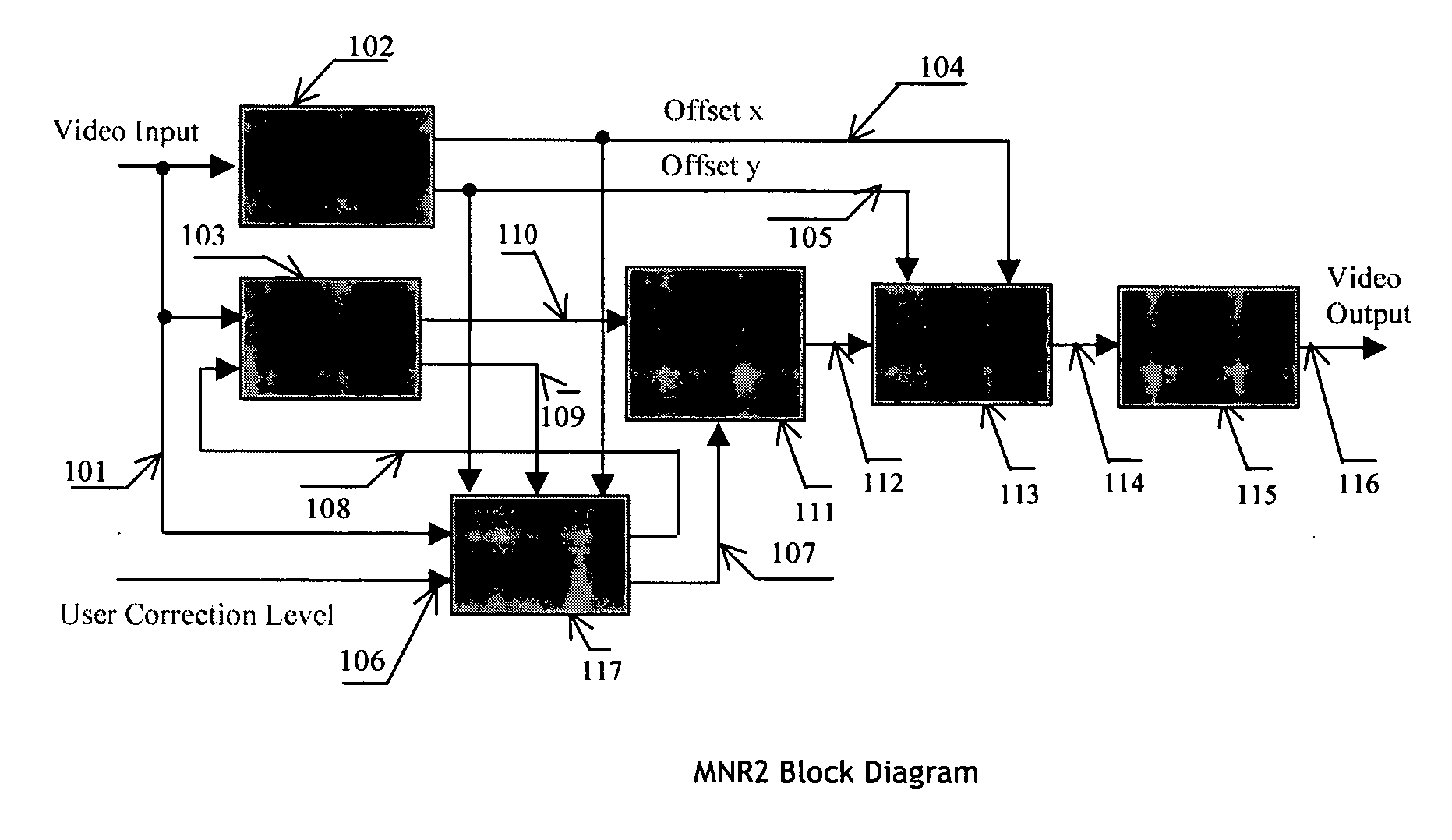
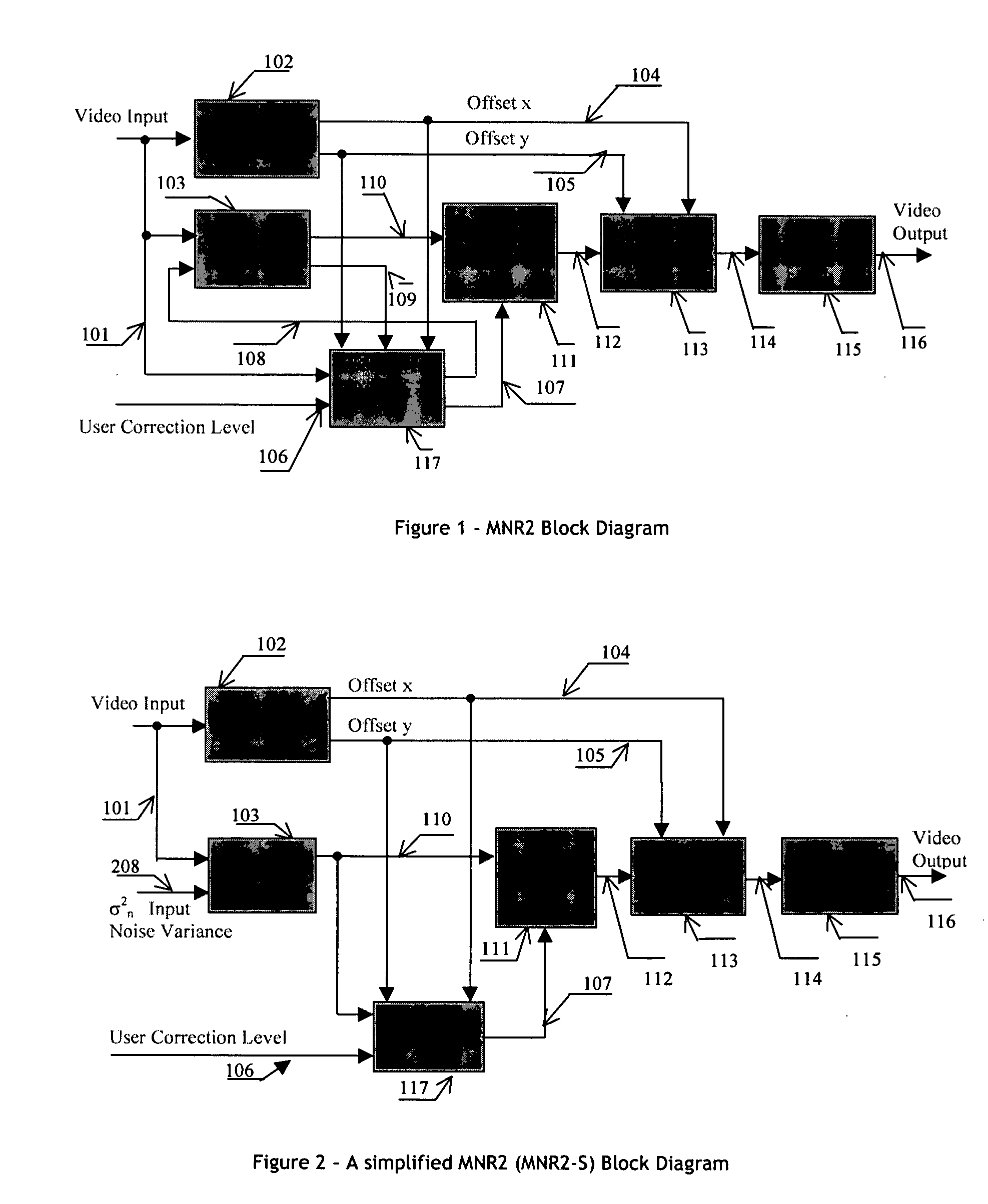
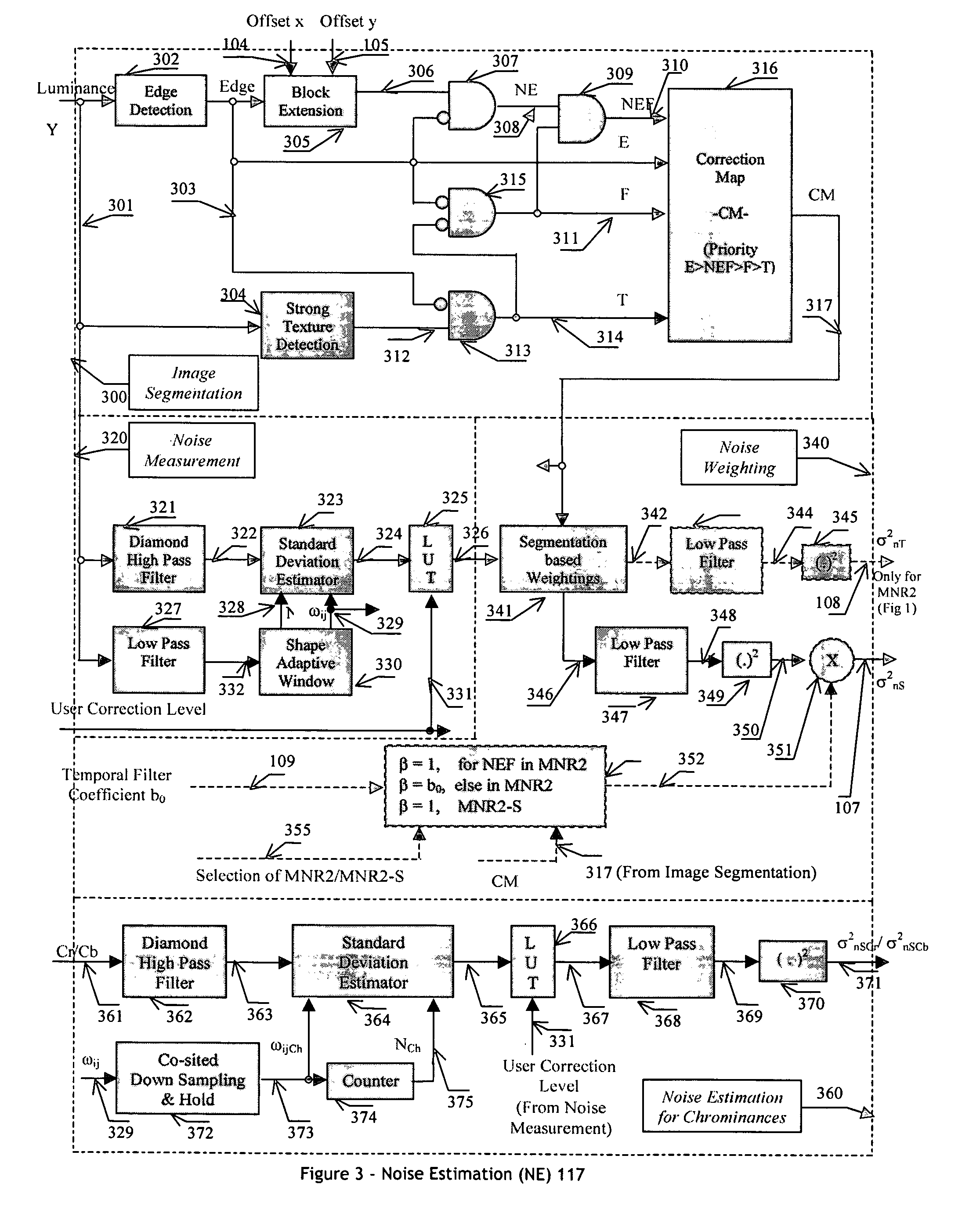
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
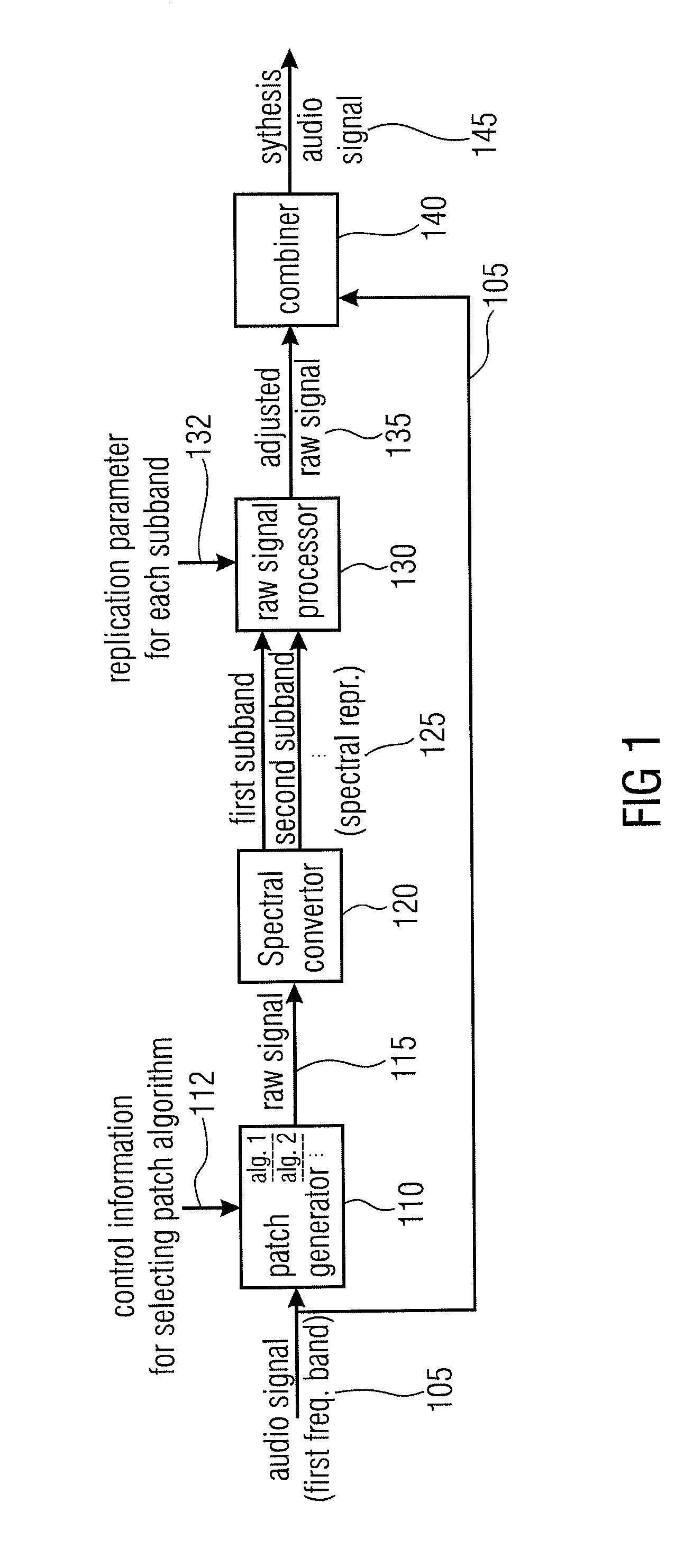
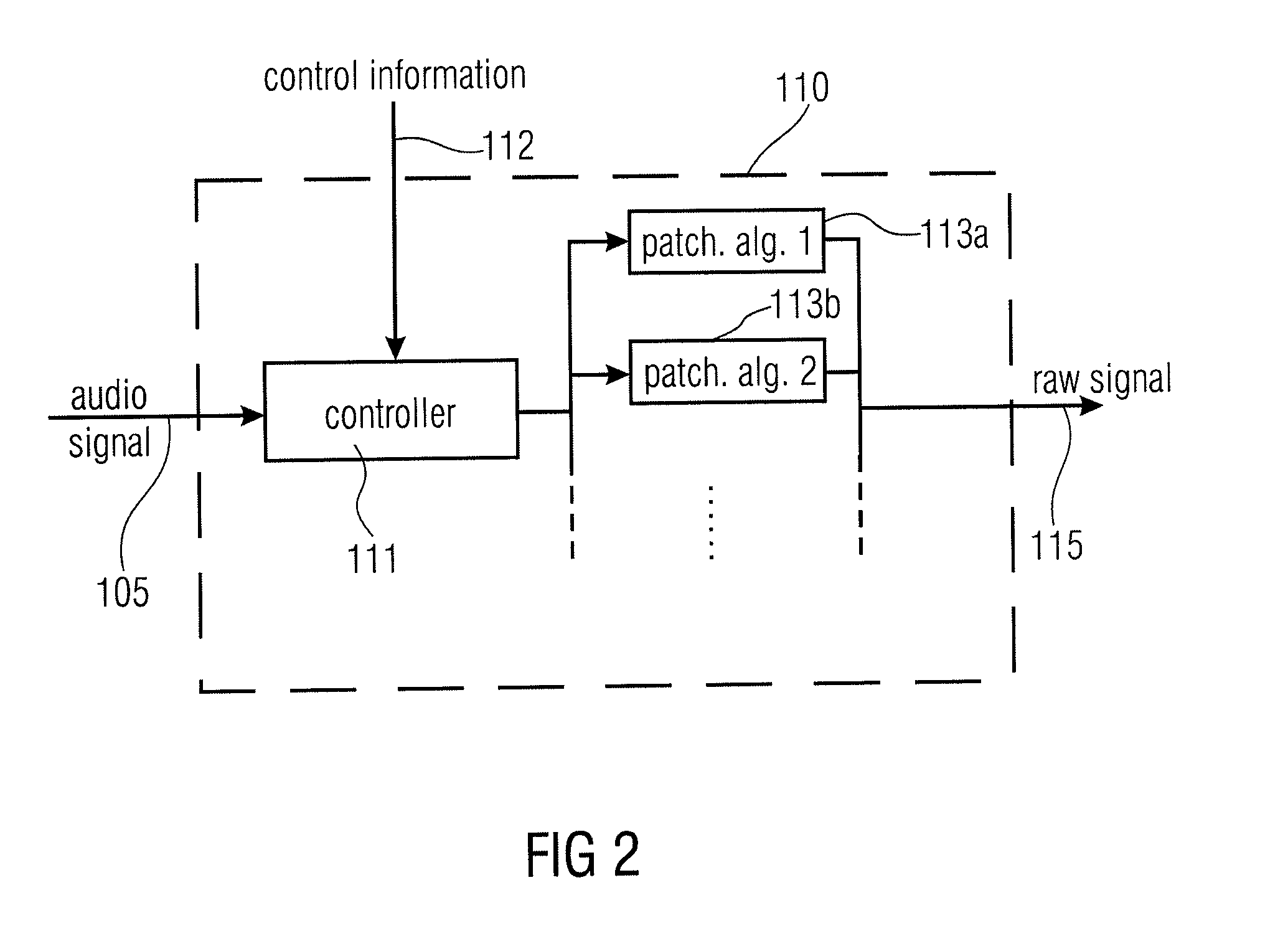
Audio Signal Synthesizer and Audio Signal Encoder
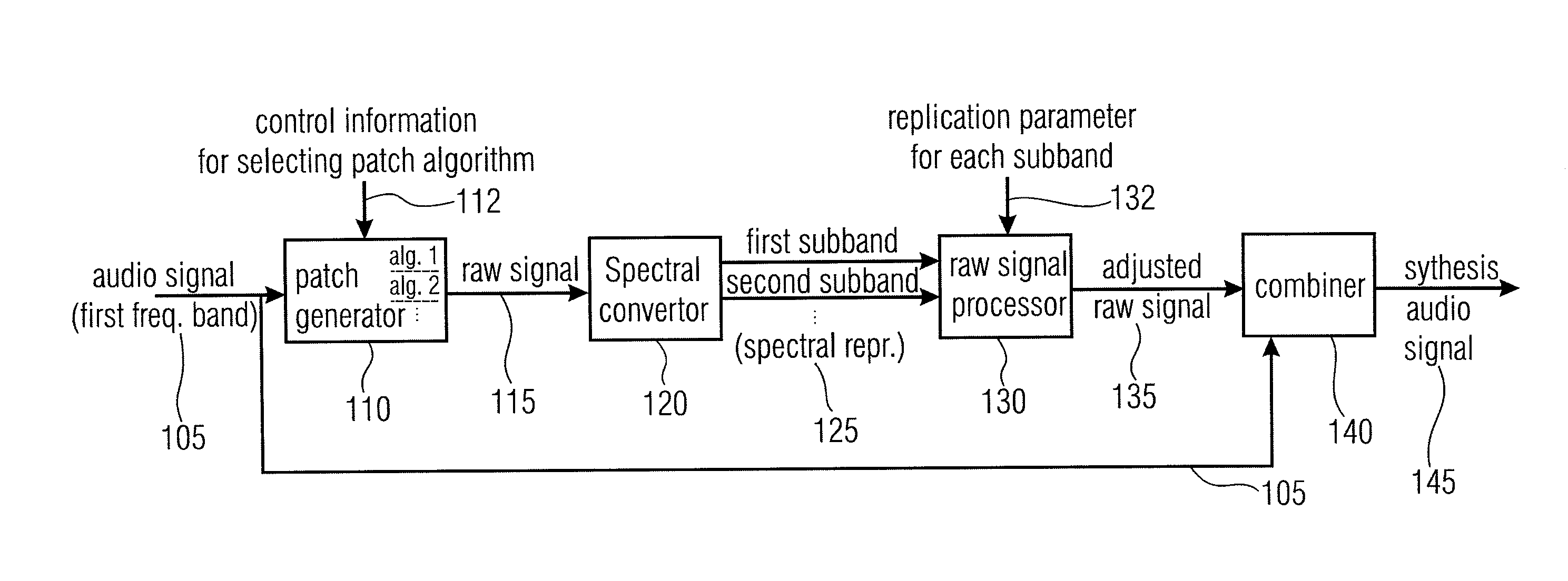
ActiveUS20110173006A1Quality improvementAvoid artifactsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumSpectral domain
An audio signal synthesizer generates a synthesis audio signal having a first frequency band and a second synthesized frequency band derived from the first frequency band and comprises a patch generator, a spectral converter, a raw signal processor and a combiner. The patch generator performs at least two different patching algorithms, each patching algorithm generating a raw signal. The patch generator is adapted to select one of the at least two different patching algorithms in response to a control information. The spectral converter converts the raw signal into a raw signal spectral representation. The raw signal processor processes the raw signal spectral representation in response to spectral domain spectral band replication parameters to obtain an adjusted raw signal spectral representation.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
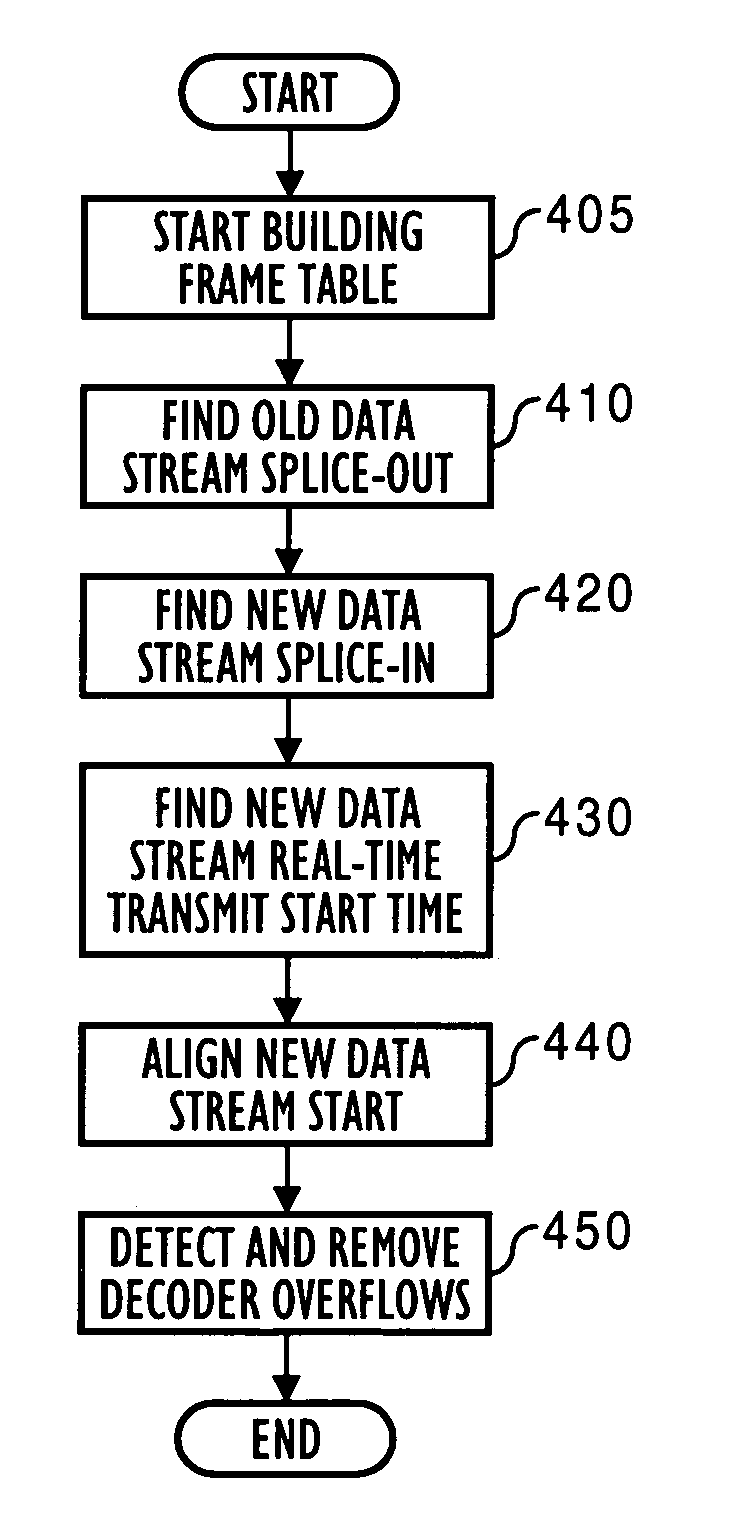
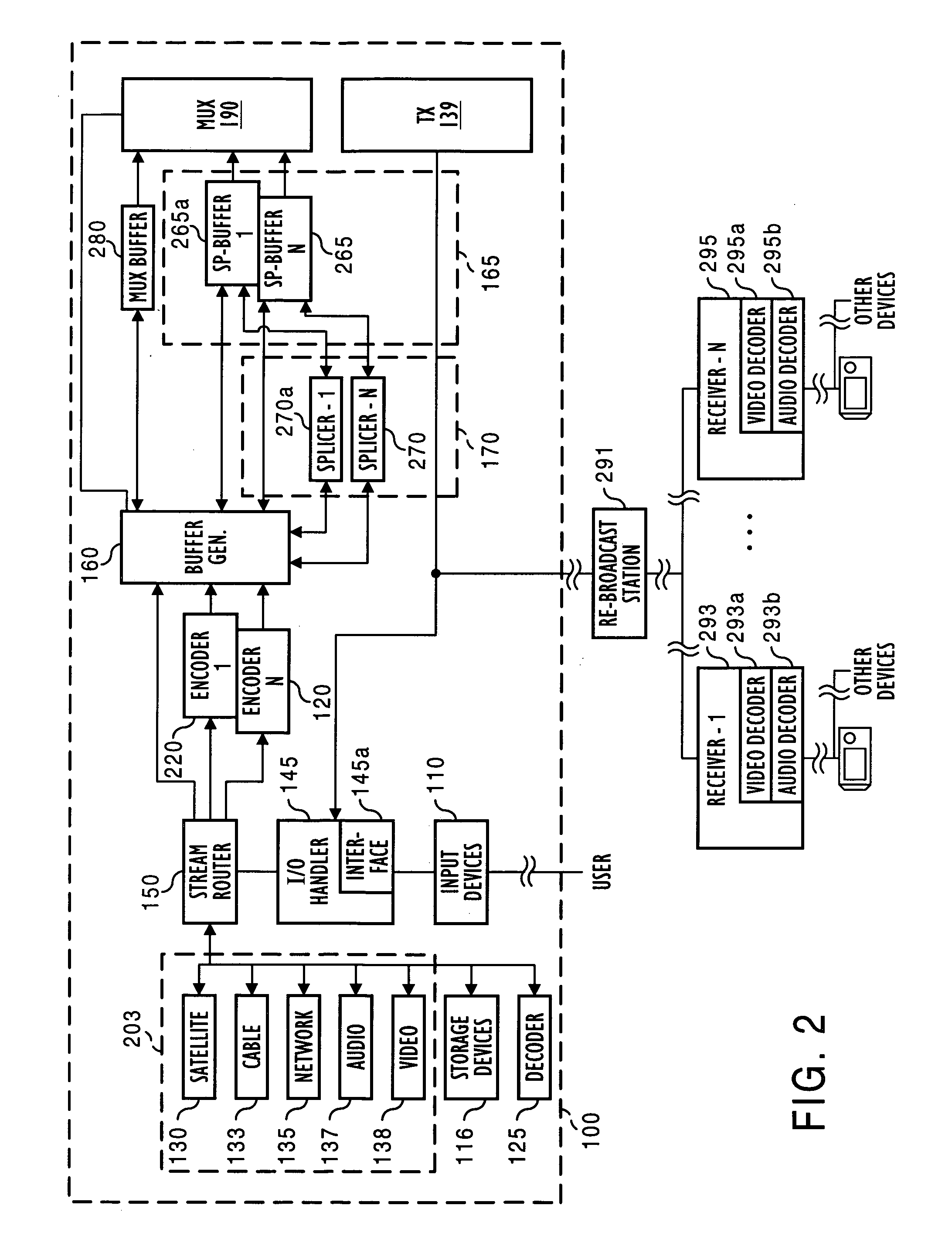
Apparatus and method of splicing digital video streams
InactiveUS7031348B1Avoid expensesAvoiding visual artifactTelevision system detailsLighting and heating apparatusDigital videoProgram clock reference
A splicing system includes a splicer for seamlessly splicing togther digitally encoded data streams. In a preferred embodiment, the splicer preferably parses successive splice buffers of data stream data for a splice-out point and a splice-in point, closing an initial group of pictures GOP if needed. The preferred splicer further finds a new data stream real-time program clock reference PCR value for aligning new data stream decode / presentation, and aligns the new data stream start time. Concurrently, the splicer preferably uses a frame table to detect overflow and corrects such overflow by adding null packets, thereby delaying portions of data stream data. The splicer also preferably restores data stream encoding by deleting null packets, and thereby accelerating a portion of data stream data. In a further preferred embodiment, the splicer preferably uses a bit-clock schedule offset to delay or accelerate portions of data stream data.
Owner:OPTIBASE TECH +1
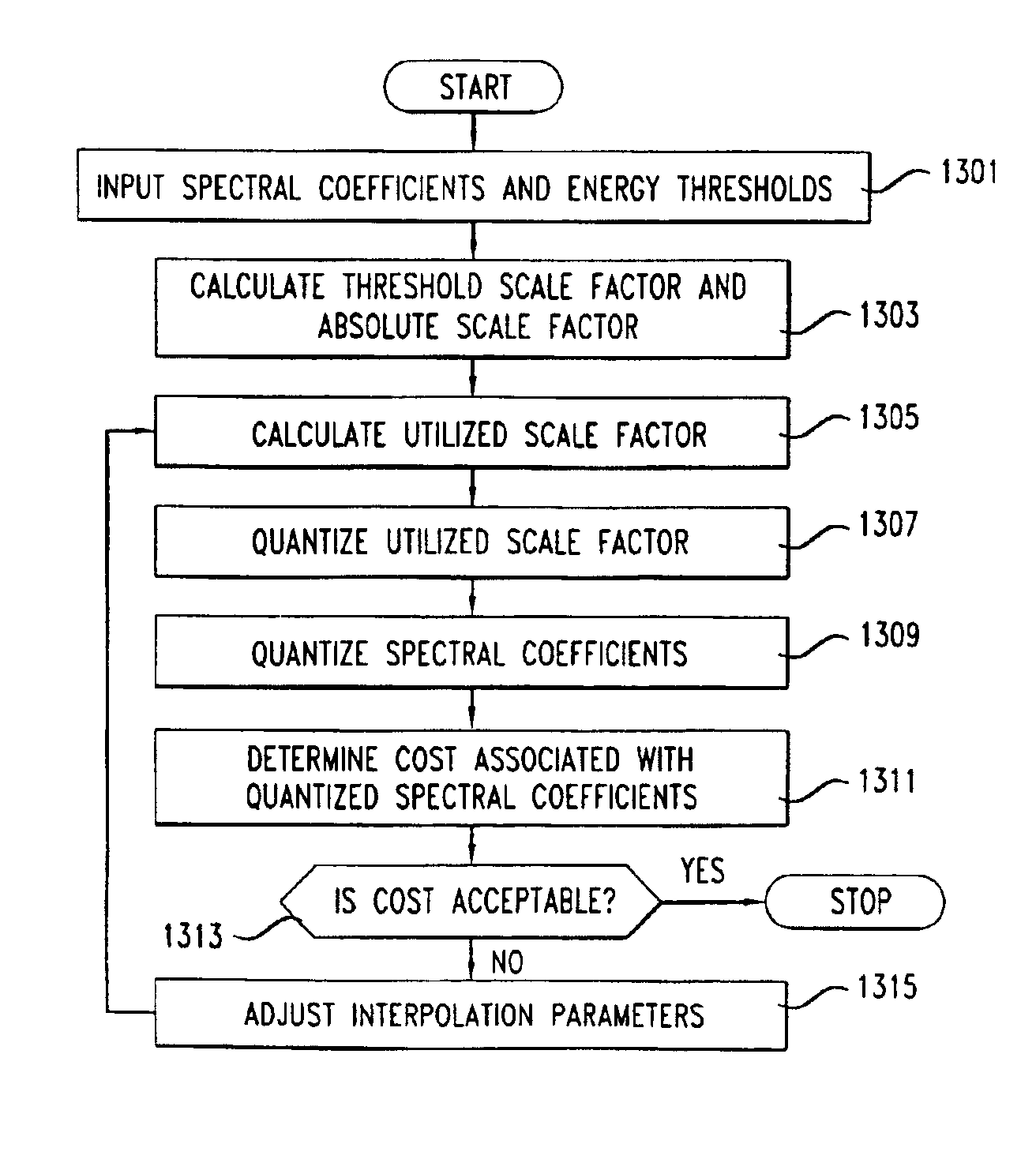
Rate loop processor for perceptual encoder/decoder
InactiveUSRE39080E1Easy to compressWithout degrading audio qualitySpeech analysisAnalogue-digital convertersHearing perceptionComputer science
A method and apparatus for quantizing audio signals is disclosed which advantageously produces a quantized audio signal which can be encoded within an acceptable range. Advantageously, the quantizer uses a scale factor which is interpolated between a threshold based on the calculated threshold of hearing at a given frequency and the absolute threshold of hearing at the same frequency.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
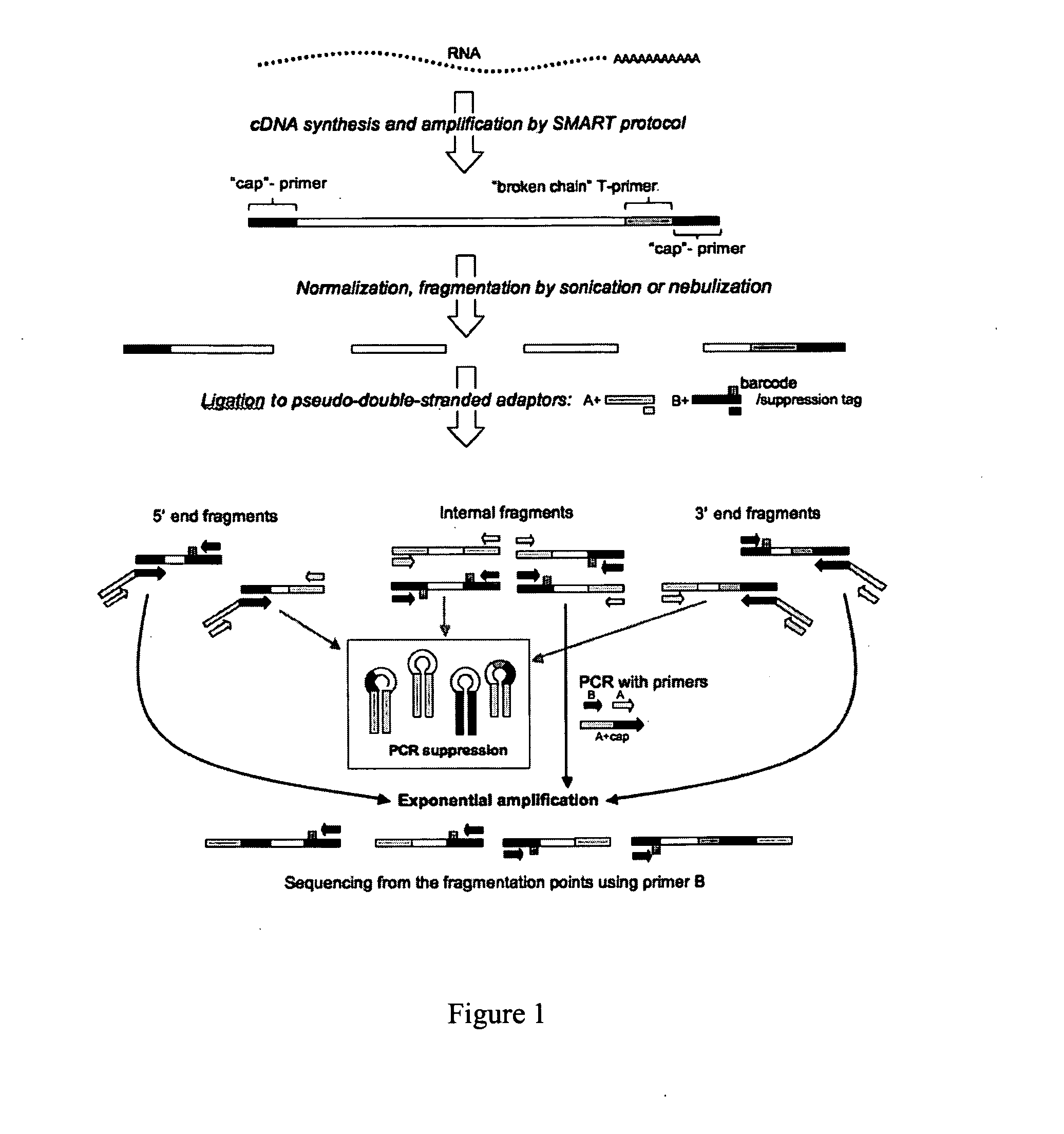
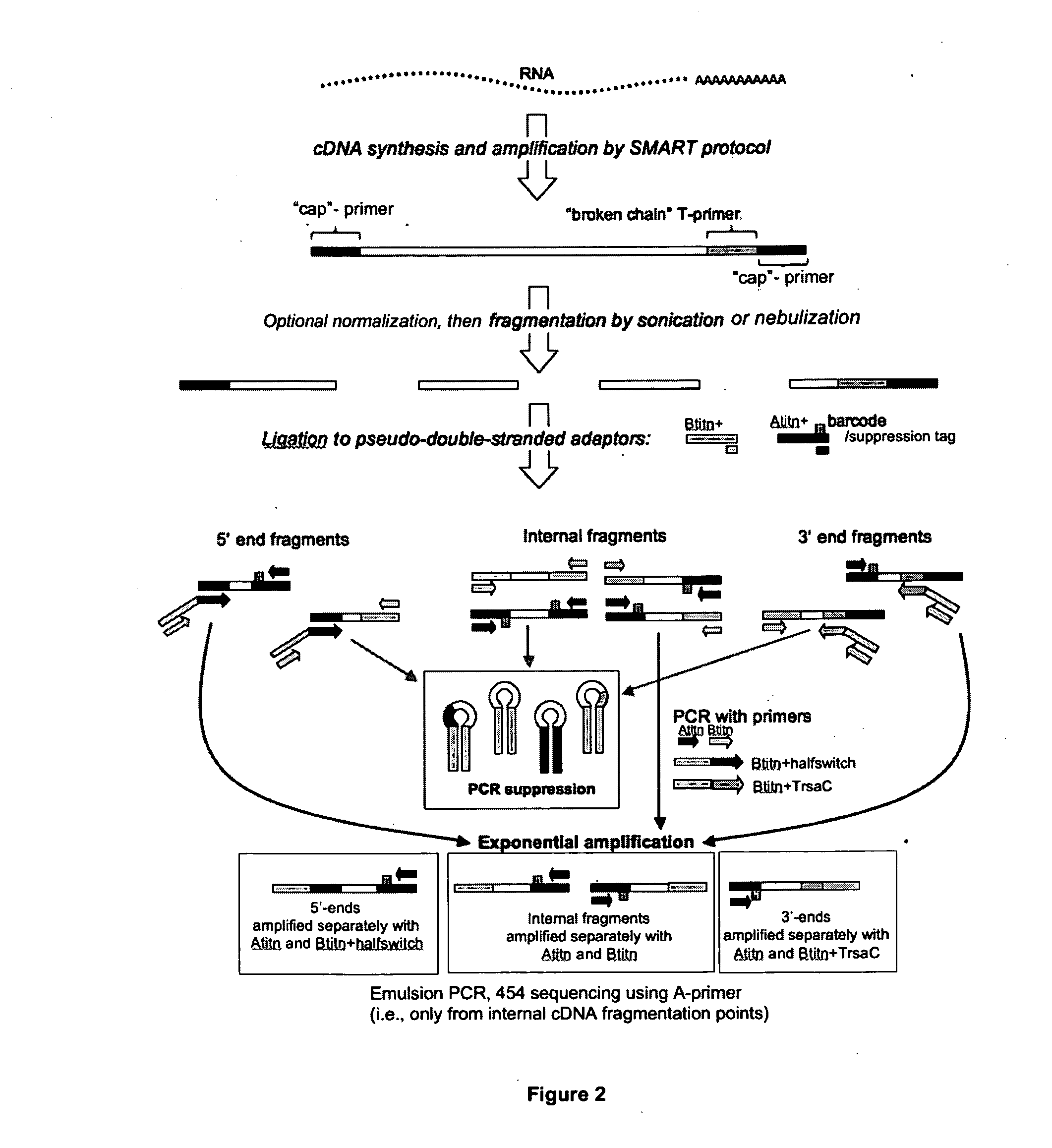
Methods and compositions for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20100120097A1Improve nucleic acid sequencingDecreased fractionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingOligonucleotide
The present invention includes novel compositions and method for nucleic acid sequencing. The methods and compositions permit a very large number of independent sequencing reactions to be arrayed in parallel, permitting simultaneous sequencing of a very large number of different oligonucleotides with superior output and quality.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
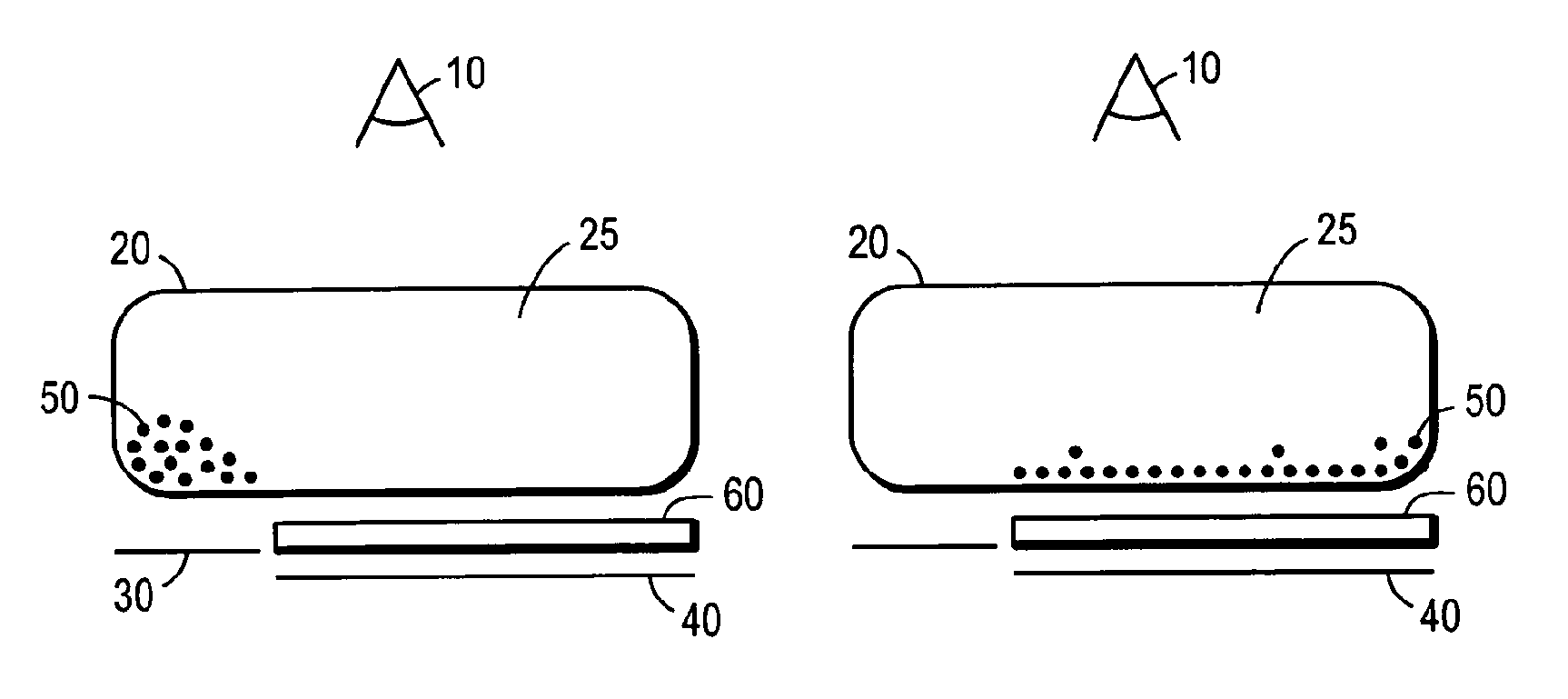
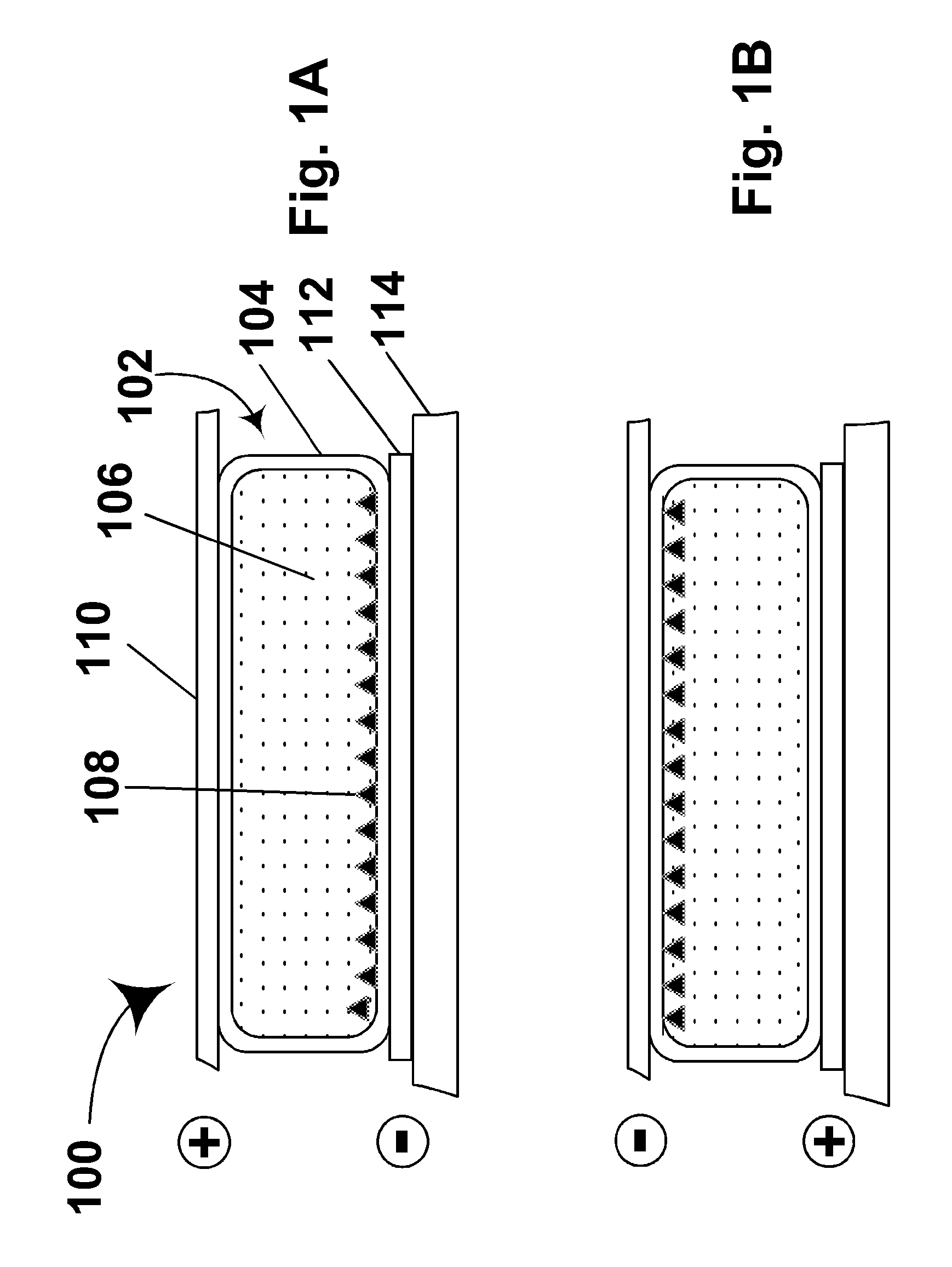
Electrophoretic displays with controlled amounts of pigment
ActiveUS20080266245A1Simplifies positionAvoids visible artifactStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsChemistryElectric field
An electrophoretic medium has walls defining a microcavity containing an internal phase. This internal phase comprises electrophoretic particles suspended in a suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the electrophoretic medium. The average height of the microcavity differs by not more than about 5 μm from the saturated particle thickness of the electrophoretic particle divided by the volume fraction of the electrophoretic particles in the internal phase.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
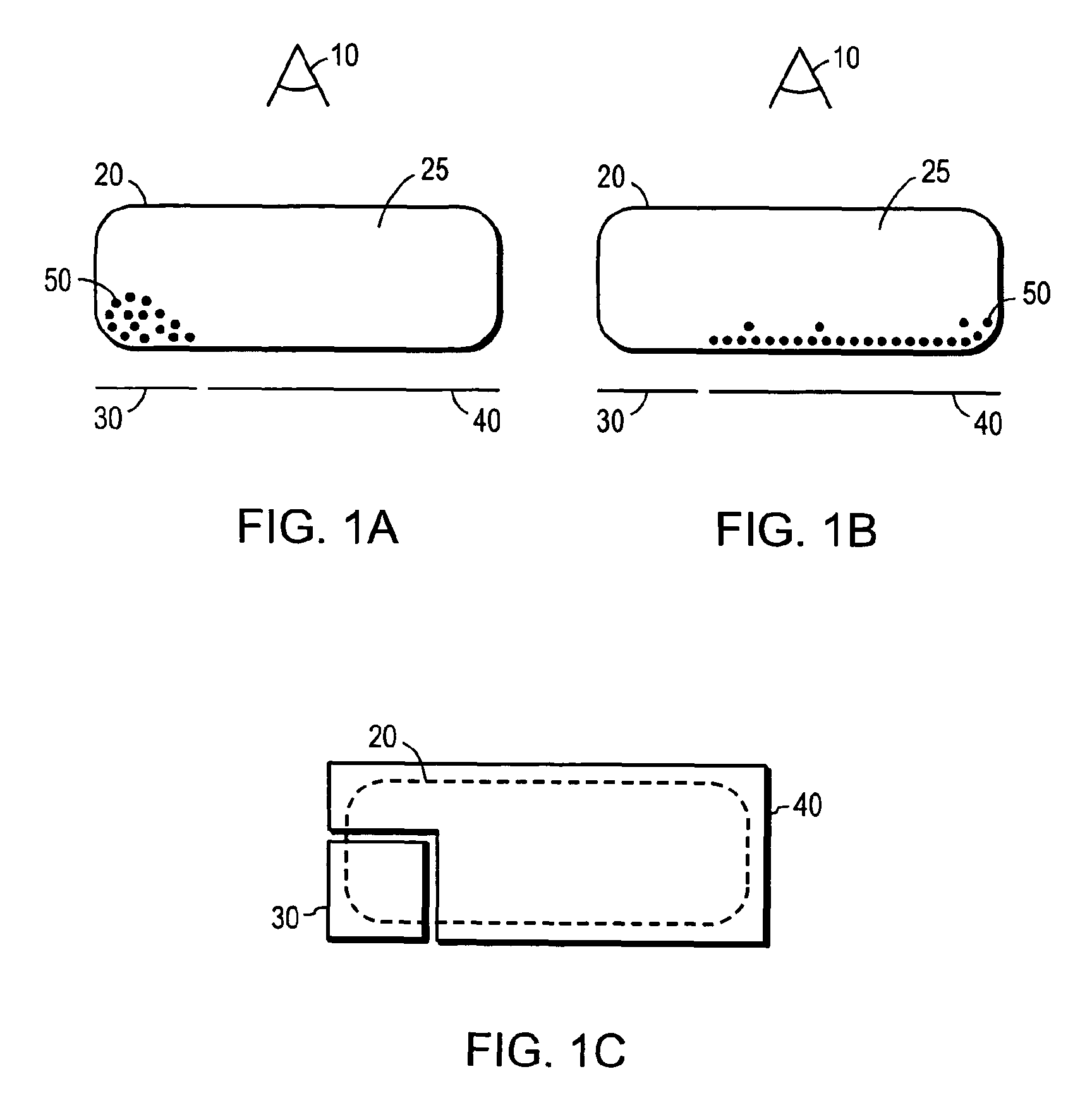
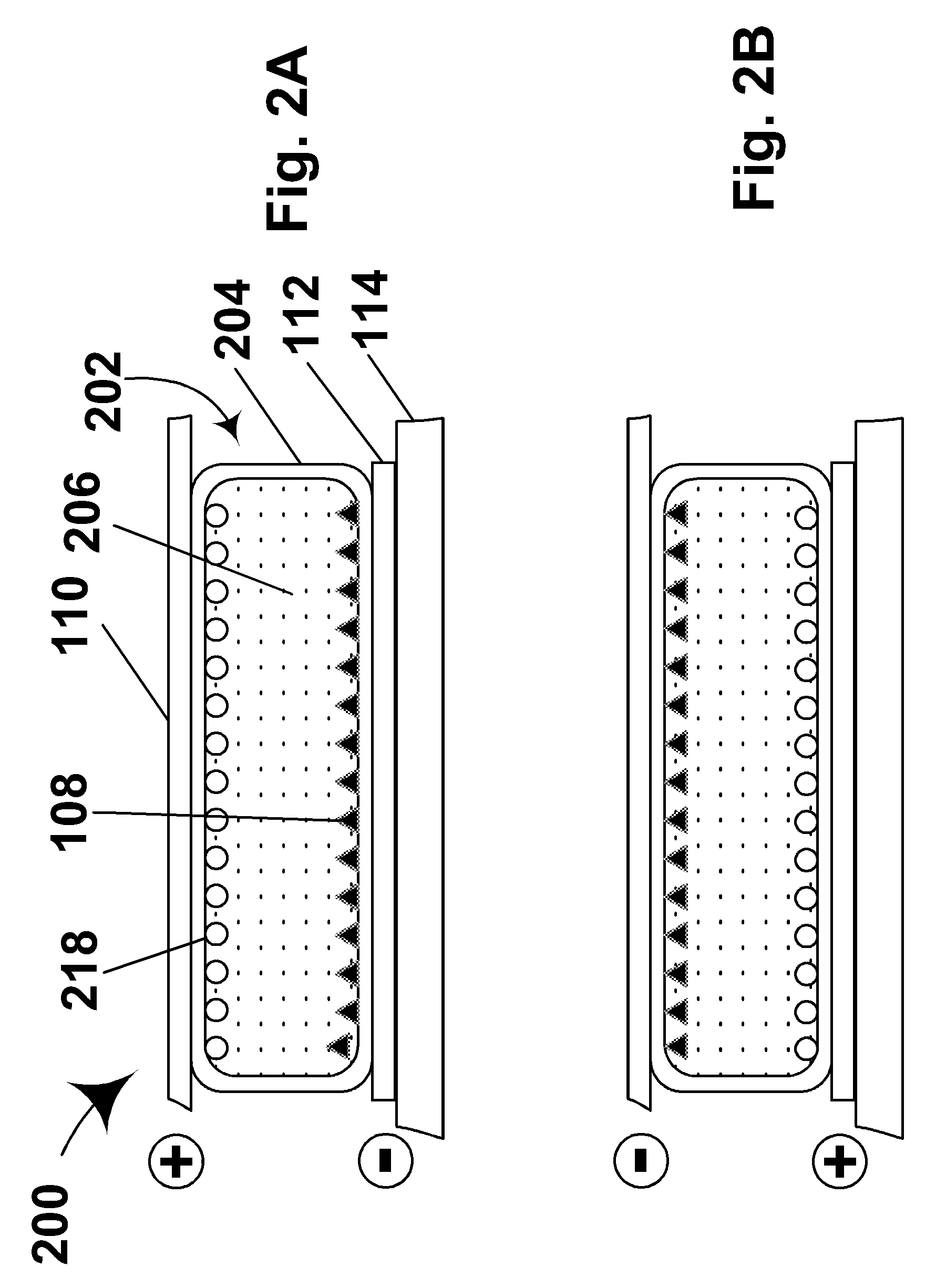
Electrophoretic displays with controlled amounts of pigment
InactiveUS7848006B2Avoid artifactsPrecise positioningStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
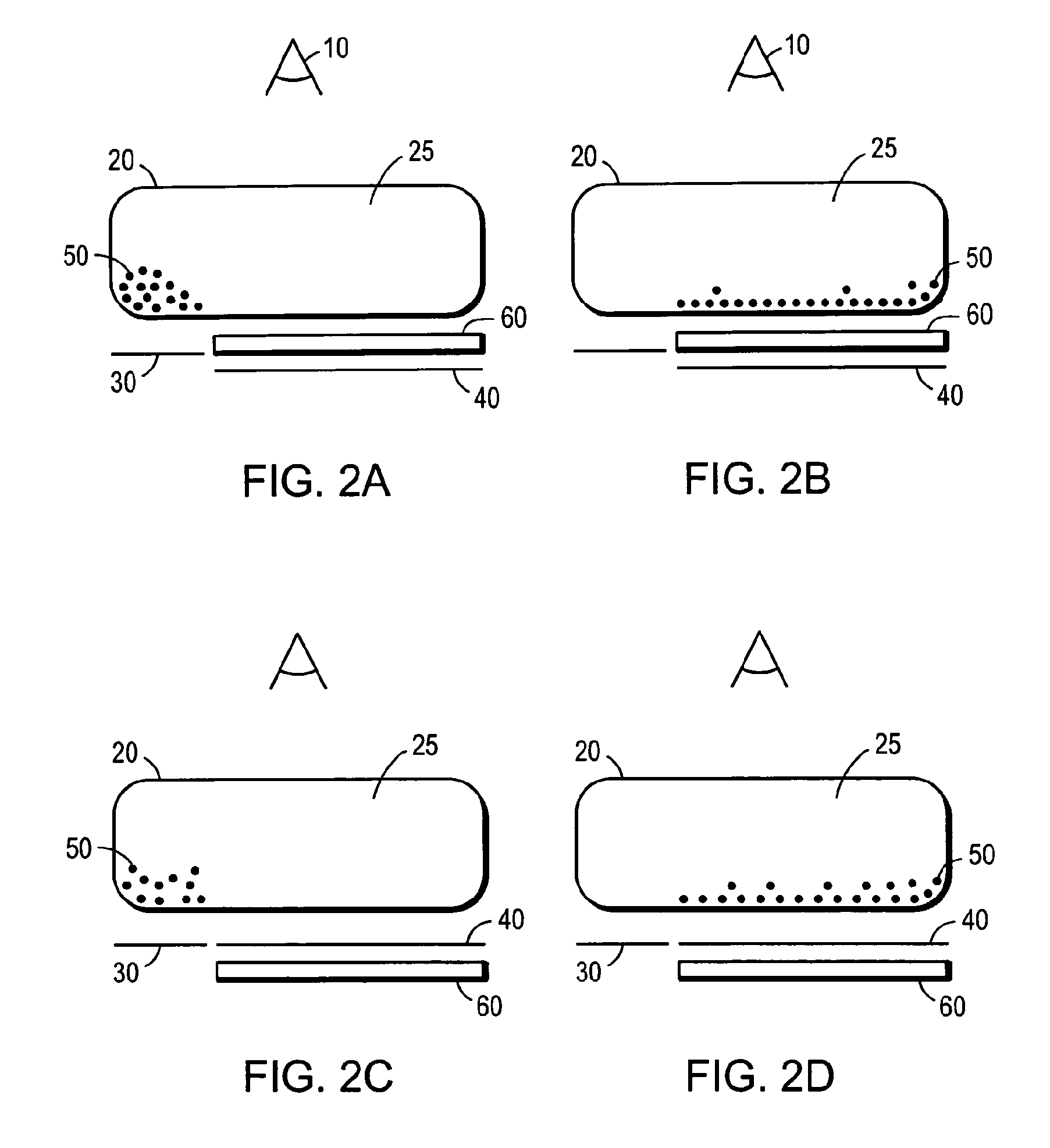
Electrophoretic displays with controlled amounts of pigment
ActiveUS8390918B2Avoid artifactsPrecise positioningNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic medium has walls defining a microcavity containing an internal phase. This internal phase comprises electrophoretic particles suspended in a suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the electrophoretic medium. The average height of the microcavity differs by not more than about 5 μm from the saturated particle thickness of the electrophoretic particle divided by the volume fraction of the electrophoretic particles in the internal phase.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
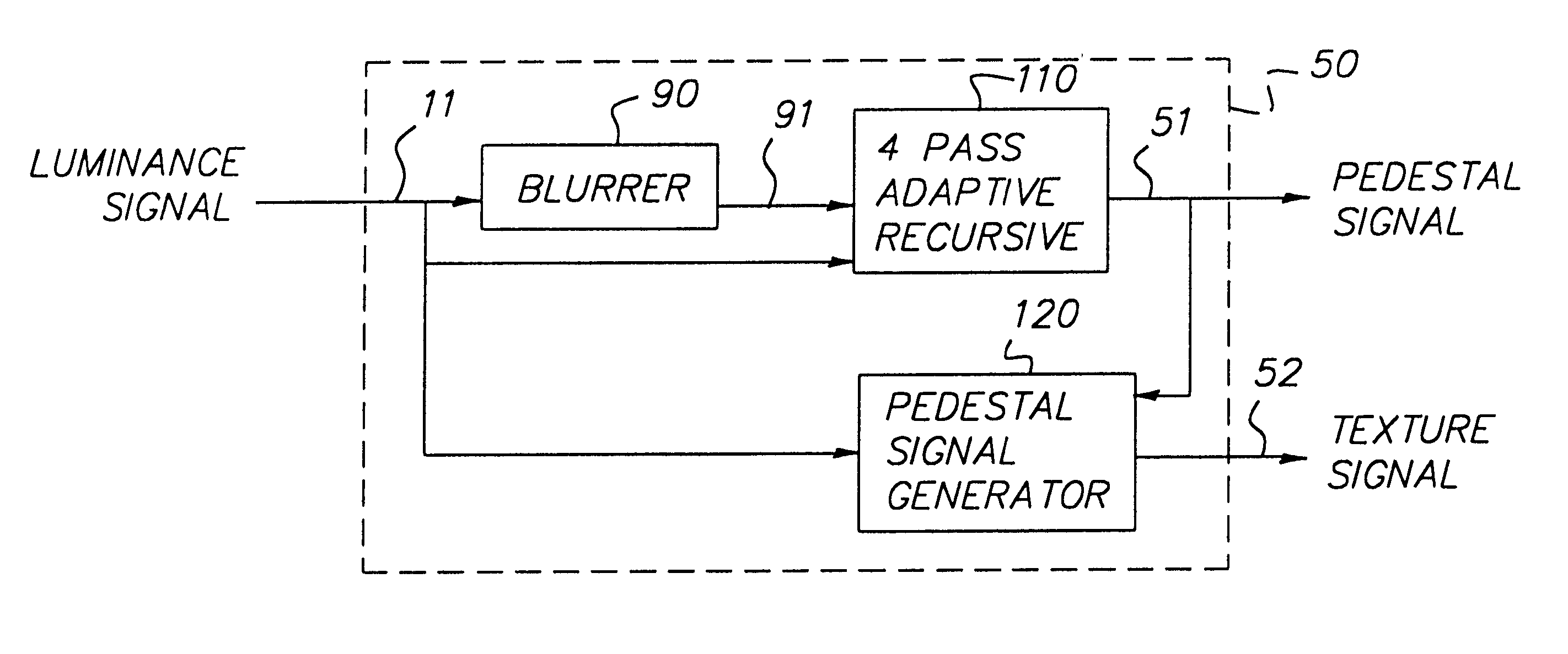
Adjusting the contrast of a digital image with an adaptive recursive filter
InactiveUS6728416B1Fast processingAvoid artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementFilter tuningDigital image
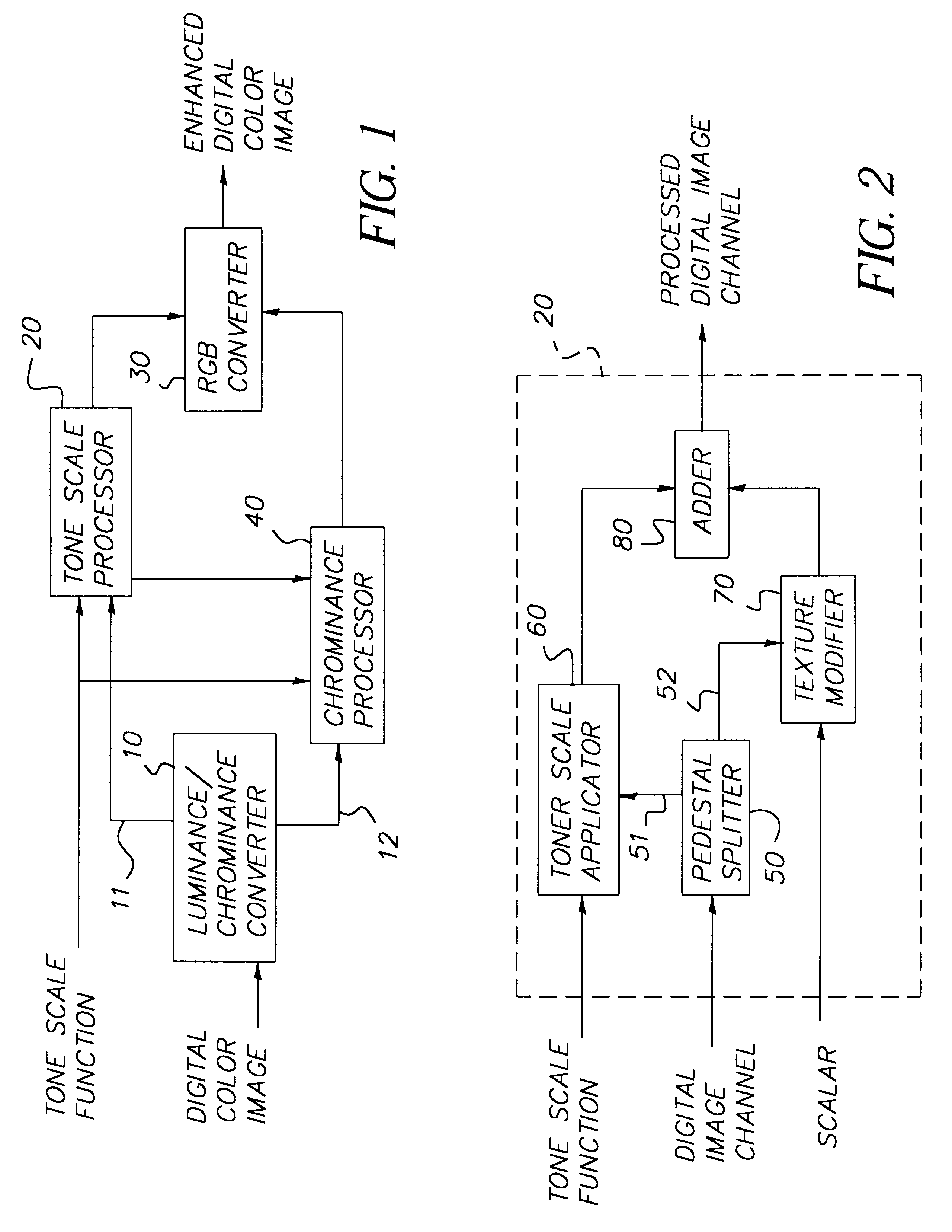
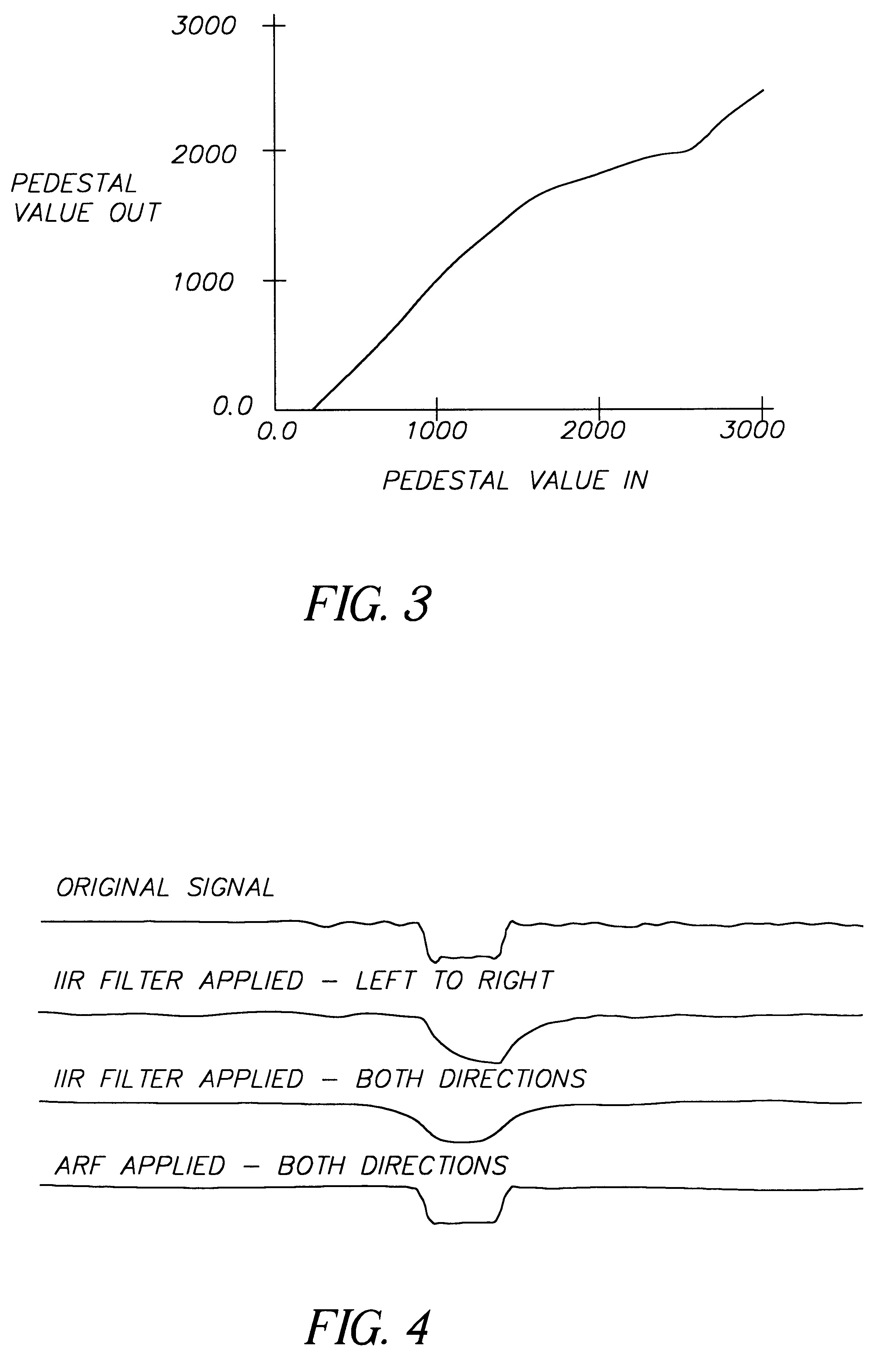
A method and structure for adjusting the contrast of a digital image includes inputting an image, dividing the image into a pedestal signal and a texture signal, applying a tone scale function to the pedestal signal to produce a modified pedestal signal, and adding the texture signal to the modified pedestal signal to produce a processed digital image channel. The dividing filters a pixel of the image using weighting that is dependent upon coefficients of neighboring pixels adjacent the pixel. The filtering blurs the pedestal signal such that flat areas of the image are blurred more that discontinuities in the image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and apparatus for providing scalable pre-compressed digital video with reduced quantization based artifacts
InactiveUS7075986B2Avoid artifactsQuick searchPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
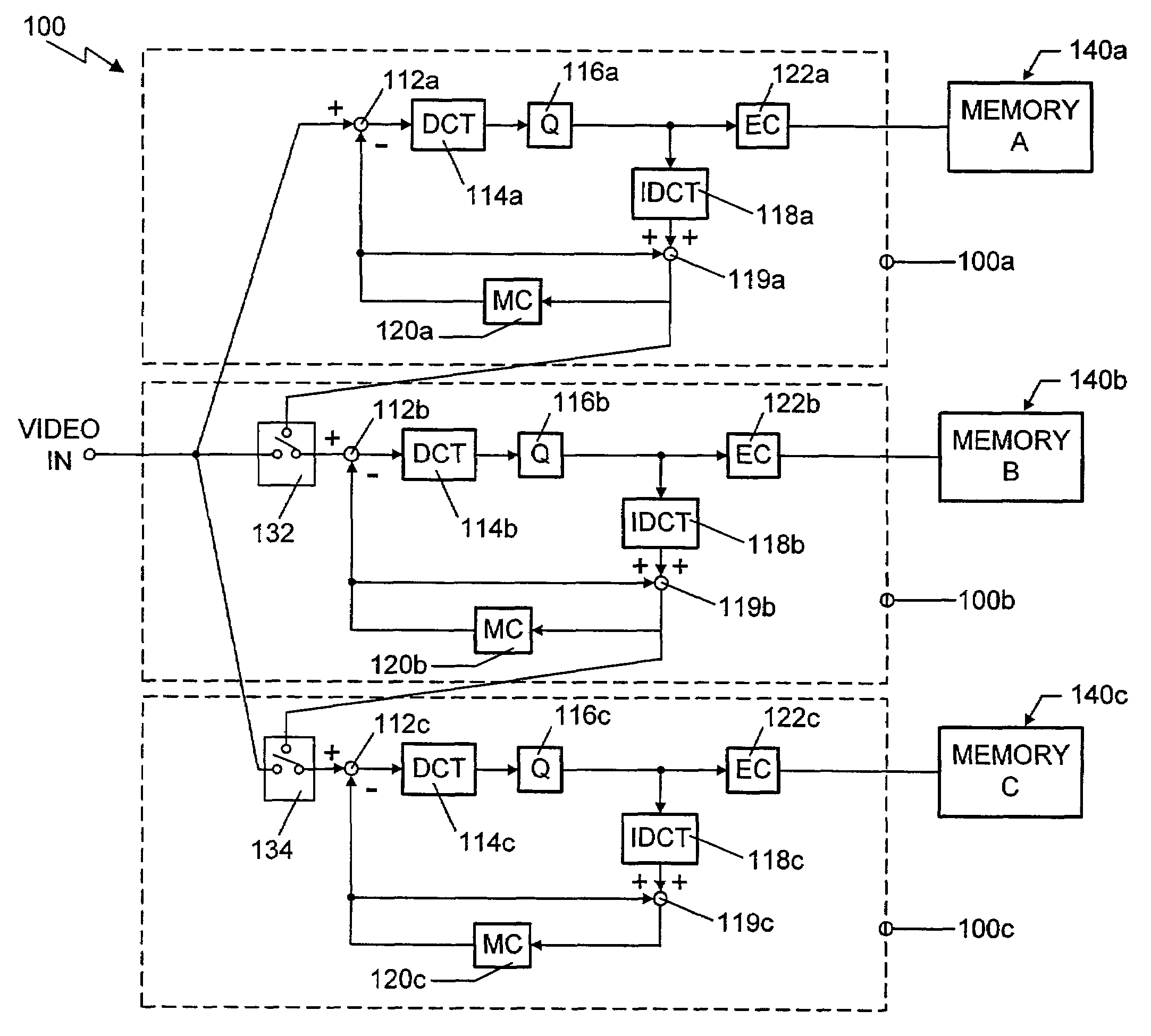
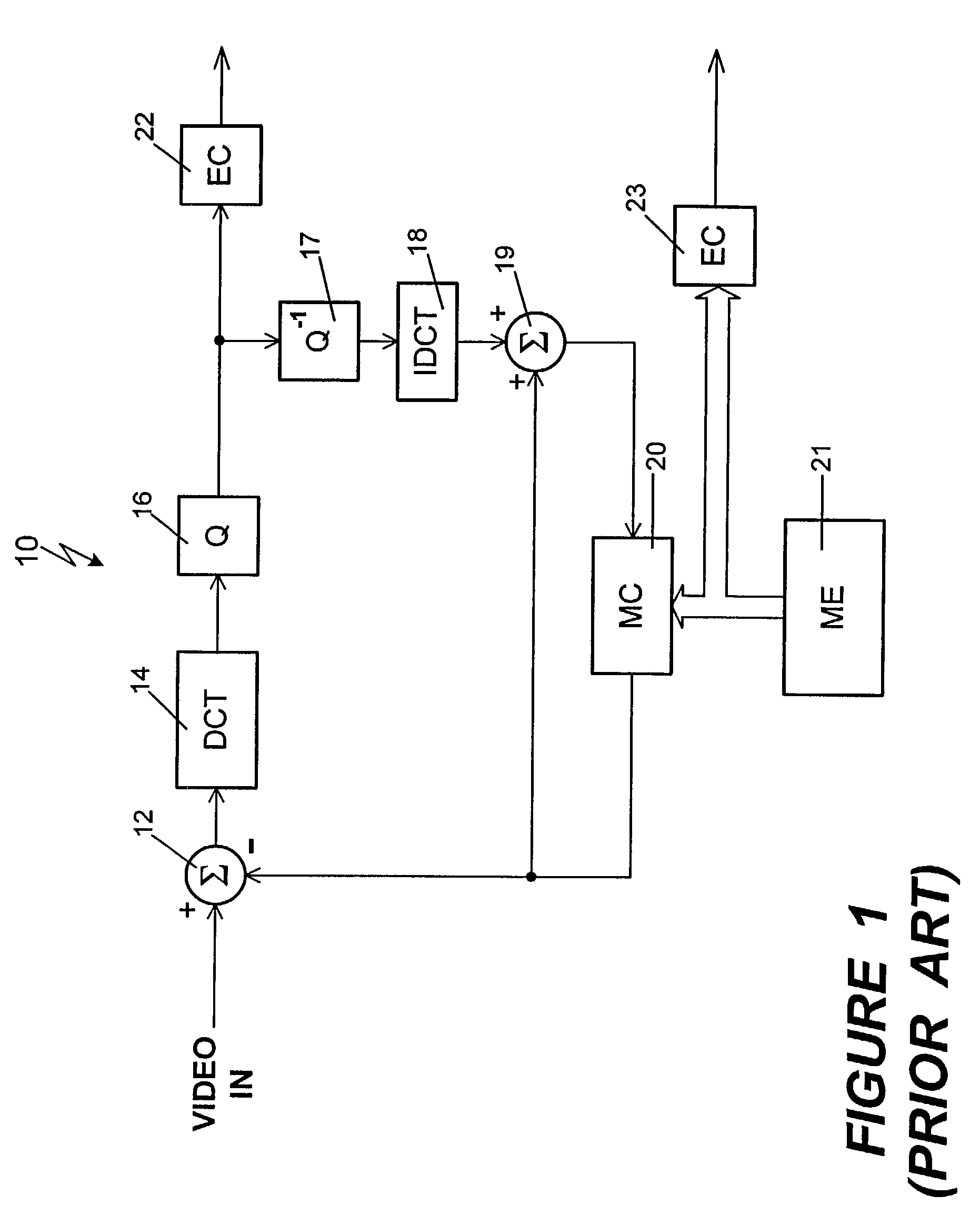
A method for generating a digital motion video sequence at a plurality of bit rates uses a transitional coding source when switching between bitstreams having different bit rates during transmission of a video sequence. The transitional data may be frames coded using reconstructed frames reconstructed for a first bitstream using the characteristics of the second bitstream. These “low bit rate insert frames,” or LBIFs, contain the image characteristics of a signal coded at the lower bit rate. With a bitstream having a higher bit rate being periodically coded using an LBIF, a point of image continuity between the two bitstreams is provided. Thus, switching from one bitstream to the other at this point in the video sequence minimizes the production of artifacts caused by differences in bit rate. In another embodiment of the invention, a separate set of transitional data is created, taking the form of “switch” frames, or S-frames. The S-frames are typically the difference between a frame of a first bitstream and a frame of a second bitstream. These frames are inserted into the decoded bitstream during the transition from one bitstream to the other, and compensate for any visual artifacts that might otherwise occur due to the difference in bit rate of the two bitstreams.
Owner:INTEL CORP
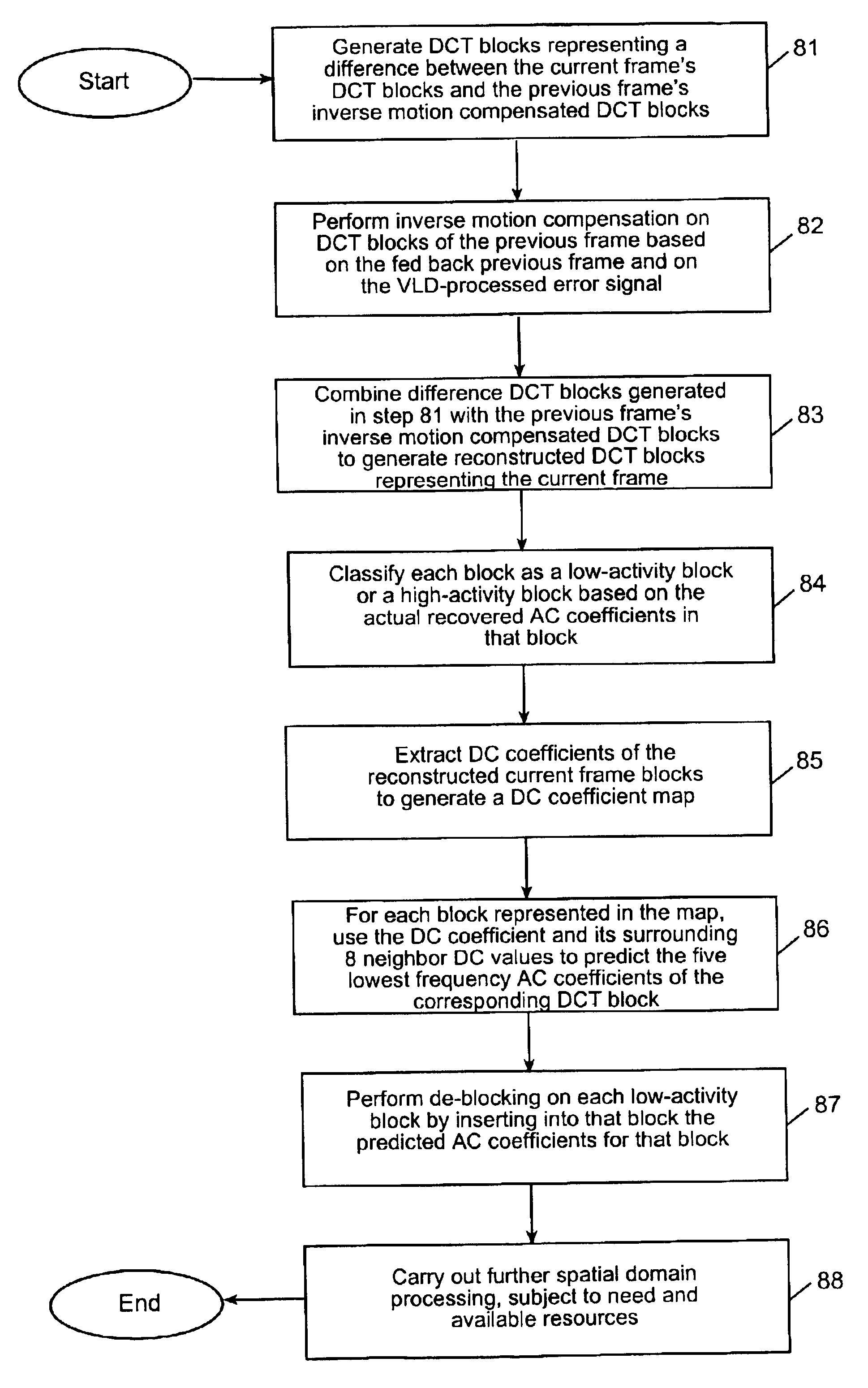
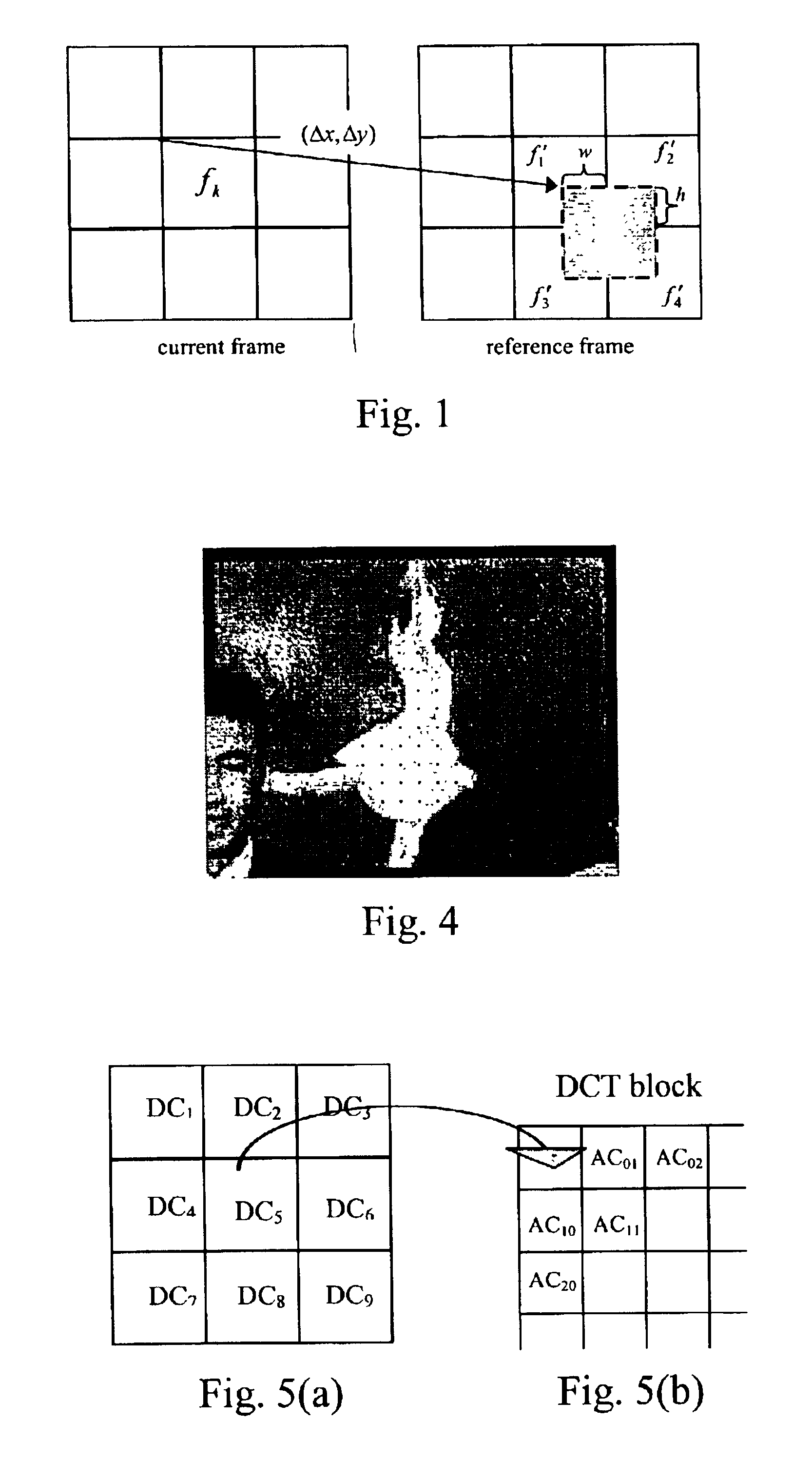
Hybrid technique for reducing blocking and ringing artifacts in low-bit-rate coding
ActiveUS6950473B2Efficient and effective power-scalableReduce blockingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionLow activityDct coefficient
A power-scalable hybrid technique to reduce blocking and ringing artifacts in low bit-rate block-based video coding is employed in connection with a modified decoder structure. Fast inverse motion compensation is applied directly in the compressed domain, so that the transform (e.g., DCT) coefficients of the current frame can be reconstructed from those of the previous frame. The spatial characteristics of each block is calculated from the DCT coefficients, and each block is classified as either low-activity or high-activity. For each low-activity block, its DC coefficient value and the DC coefficient values of the surrounding eight neighbor blocks are exploited to predict low frequency AC coefficients which reflect the original coefficients before quantization in the encoding stage. The predicted AC coefficients are inserted into the low activity blocks where blocking artifacts are most noticeable. Subject to available resources, this may be followed by spatial domain post-processing, in which two kinds of low-pass filters are adaptively applied, on a block-by-block basis, according to the classification of the particular block. Strong low-pass filtering is applied in low-activity blocks where the blocking artifacts are most noticeable, whereas weak low-pass filtering is applied in high-activity blocks where ringing noise as well as blocking artifacts may exist. In low activity blocks, the blocking artifacts are reduced by one dimensional horizontal and vertical low-pass filters which are selectively applied in either the horizontal and / or vertical direction depending on the locations and absolute values of the predicted AC coefficients. In high activity blocks, de-blocking and de-ringing is conducted by 2- or 3-tap filters, applied horizontally and / or vertically, which makes the architecture simple.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus for deblocking-filtering video data
InactiveUS20080170629A1Avoid problemsAvoid artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionImaging processingDeblocking filter
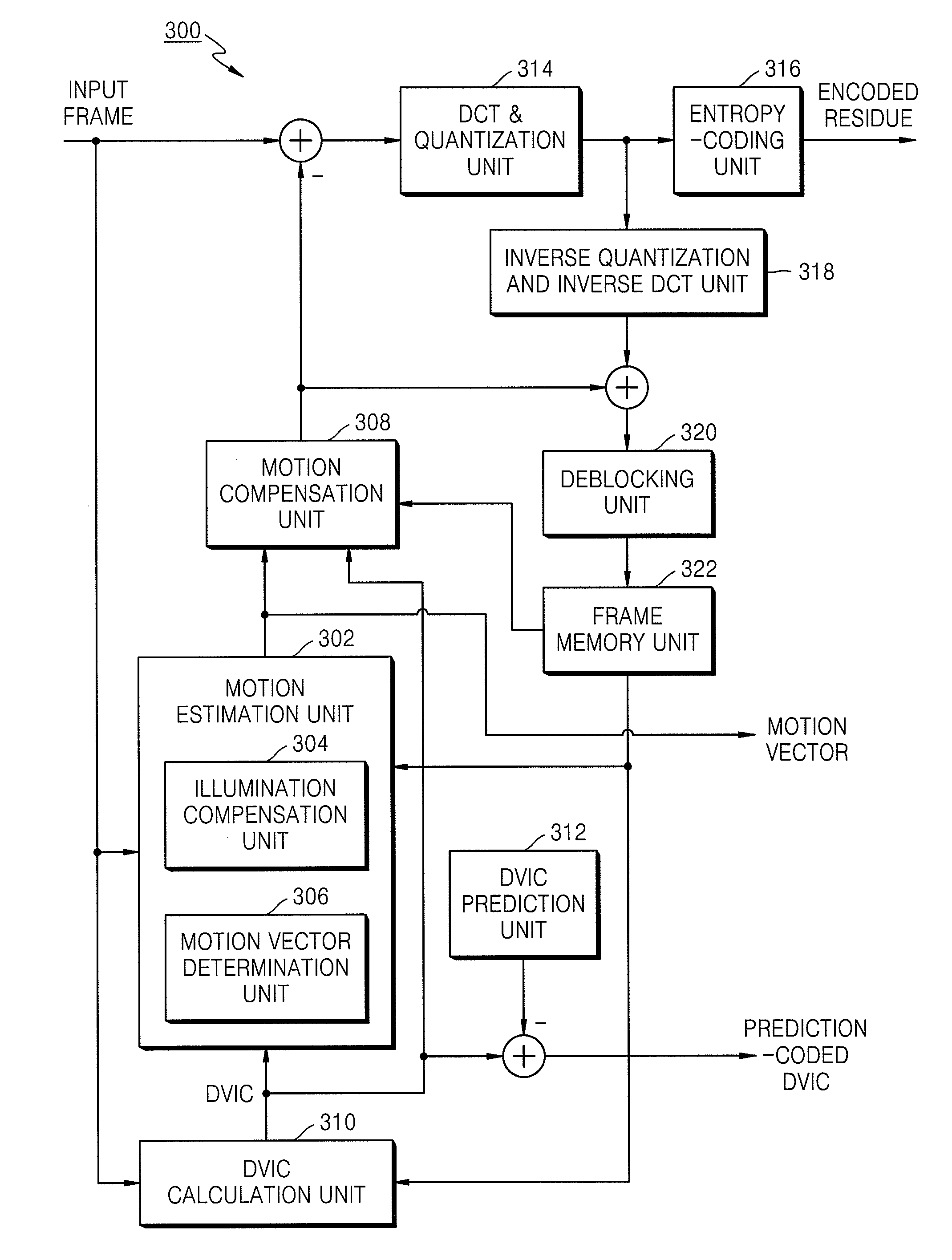
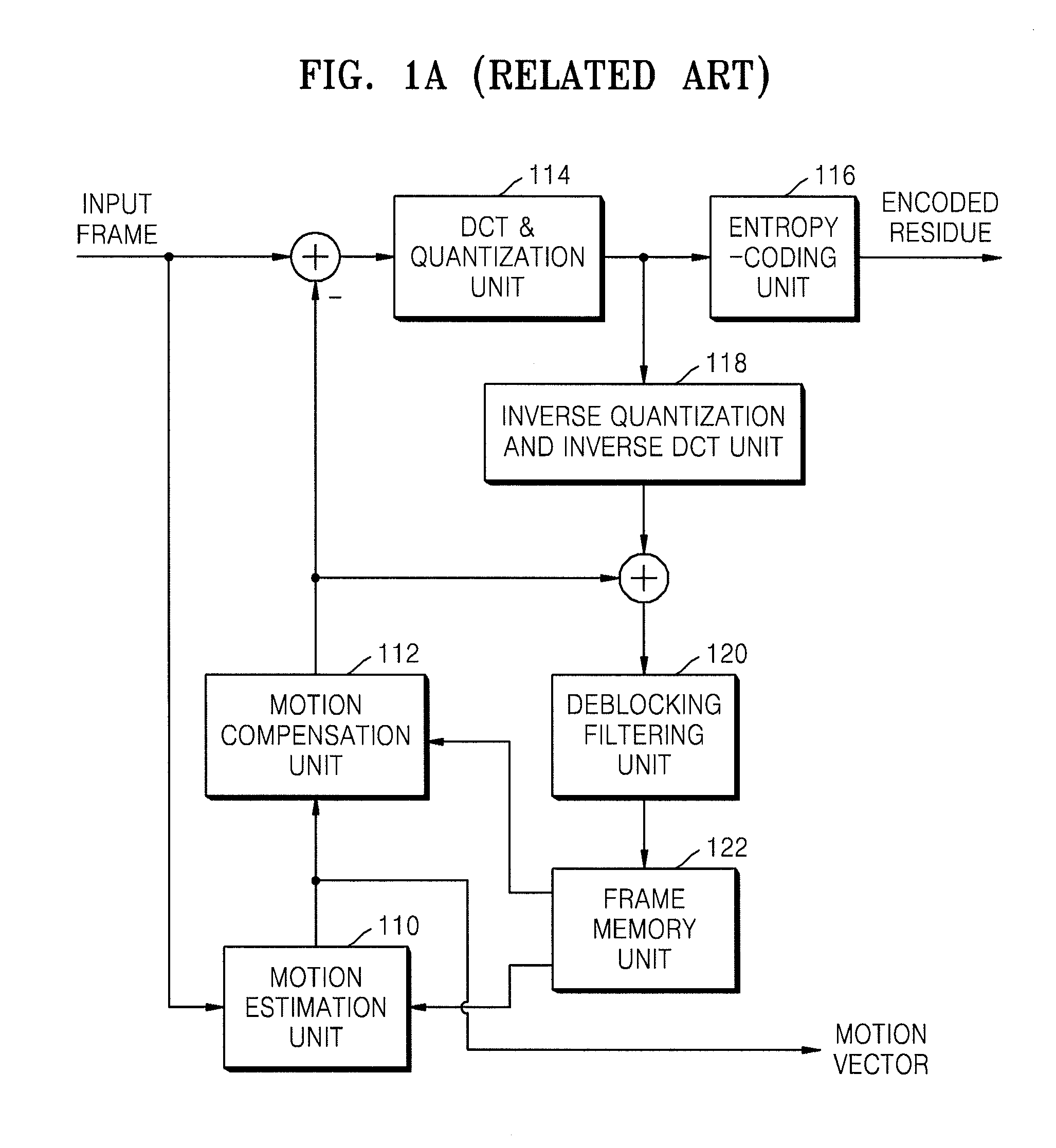
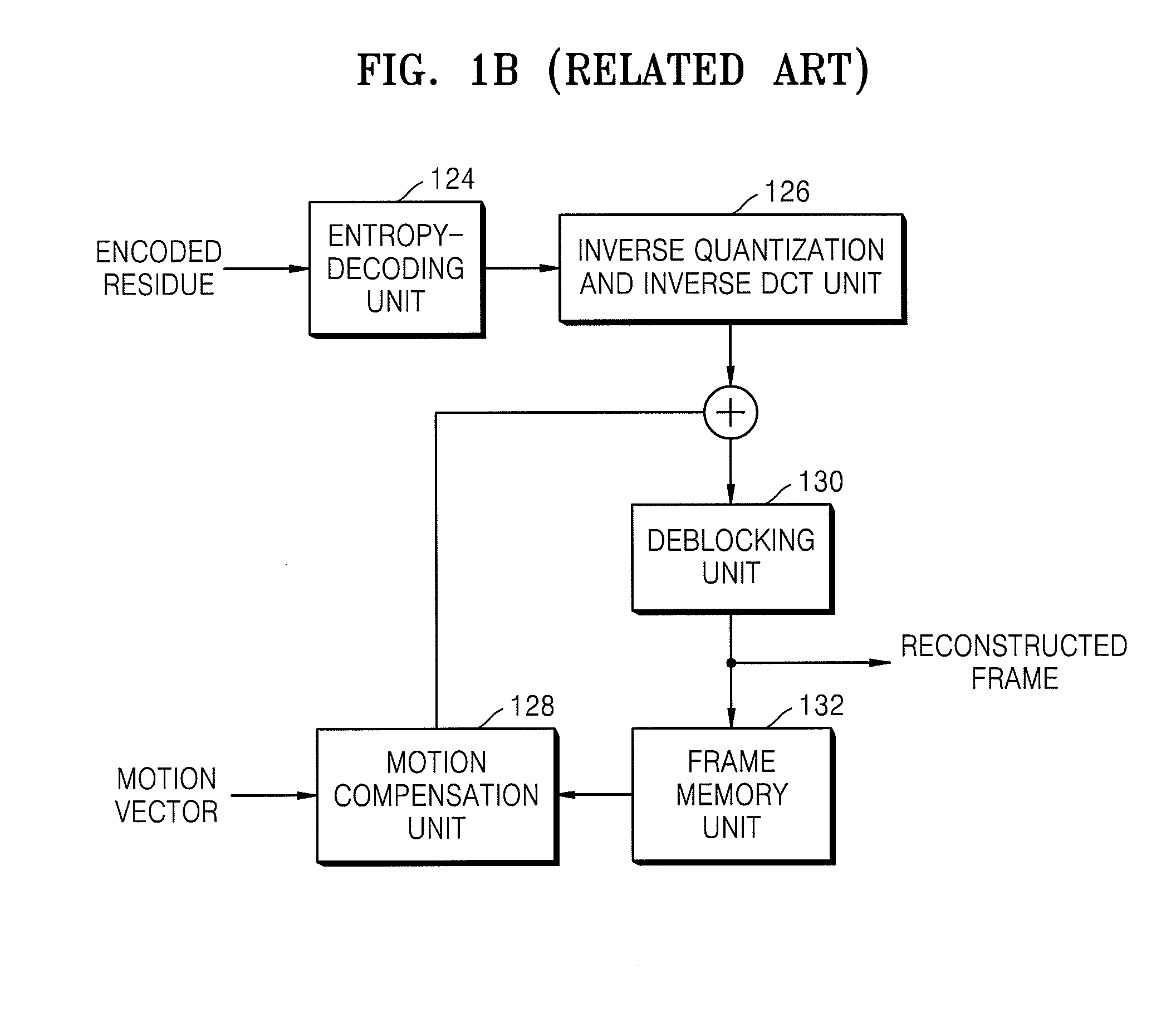
Provided are a method and an apparatus for filtering video data. The method includes determining whether a difference value of illumination change (DVIC) of a current image processing unit containing a current block is different from a DVIC of an image processing unit that is adjacent to the current image processing unit and based on the determining, adjusting a filtering strength of a deblocking filter and performing deblocking filtering on a boundary of the current block using the filter with the adjusted filtering strength.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coding method and image coding device for the compression of an image sequence
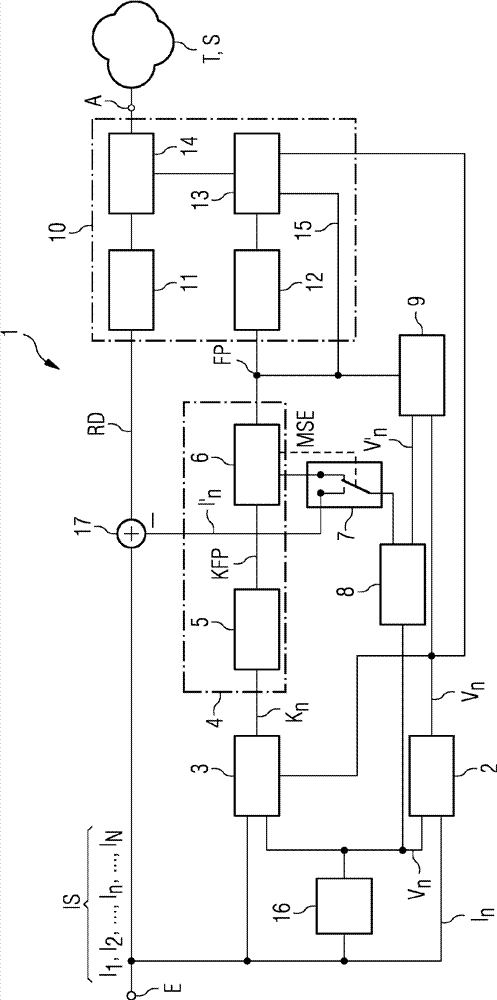
InactiveCN103370937AAvoid artifactsGood residual error coding methodTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorVector field
The method (100) involves determining a dense motion vector field (Vn) for an actual image area (In) of an image sequence by comparison with an image area (In-1) of the image sequence. A confidence vector field (Kn) is determined for the actual image area, which indicates a confidence value for a motion vector for the motion vector field. Motion vector field reconstruction parameters (FP) for the actual image area are determined based on the motion and confidence vector fields. The motion vector field is reconstructed by using the reconstruction parameters. Independent claims are also included for the following: (1) a method for decoding an image sequence (2) a method for transmission and / or storage of an image sequence (3) an image coding device (4) an image decoding device (5) a system for transmission and / or storage of an image sequence (6) a computer program comprising instructions for executing a method for compression of image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
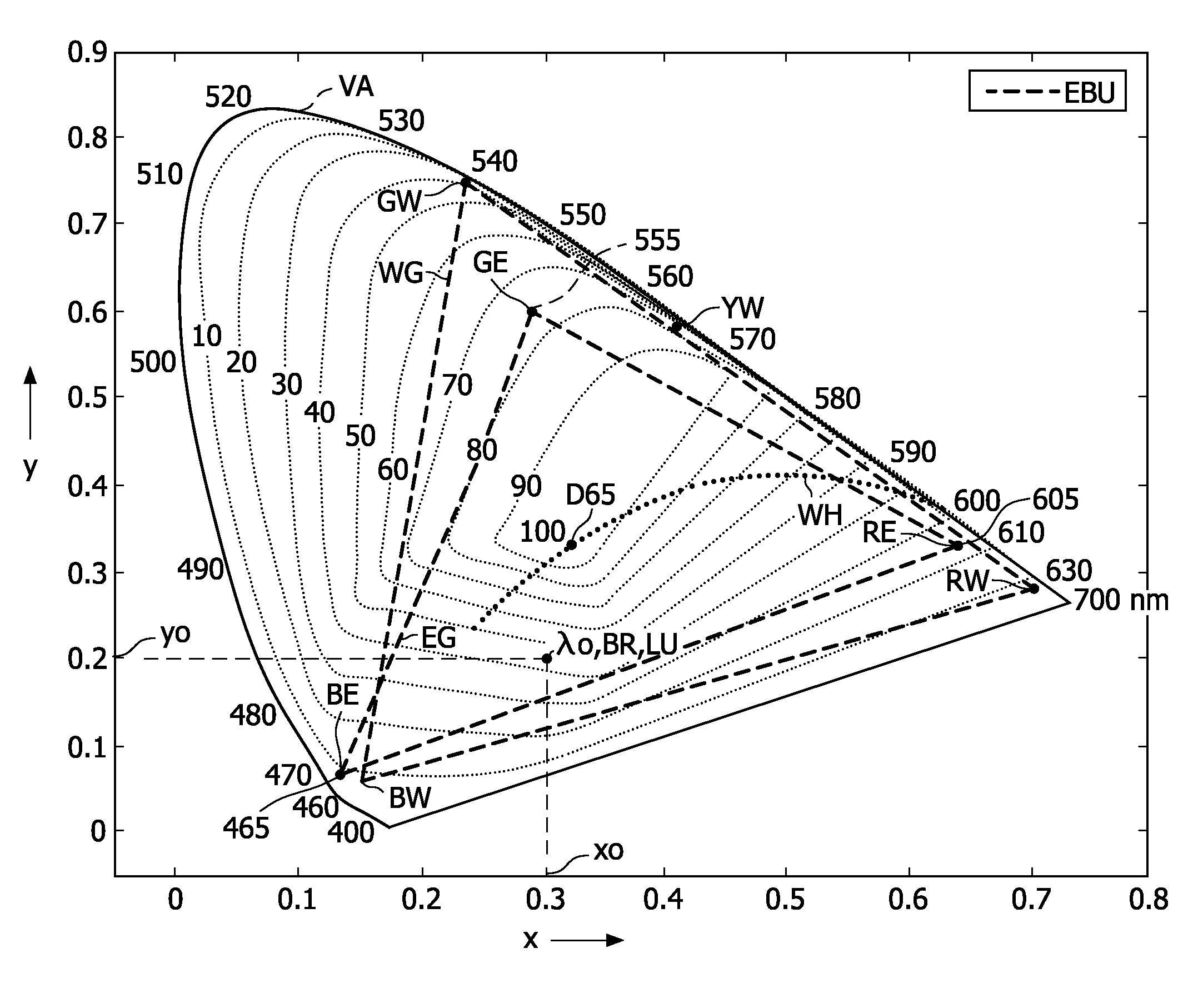
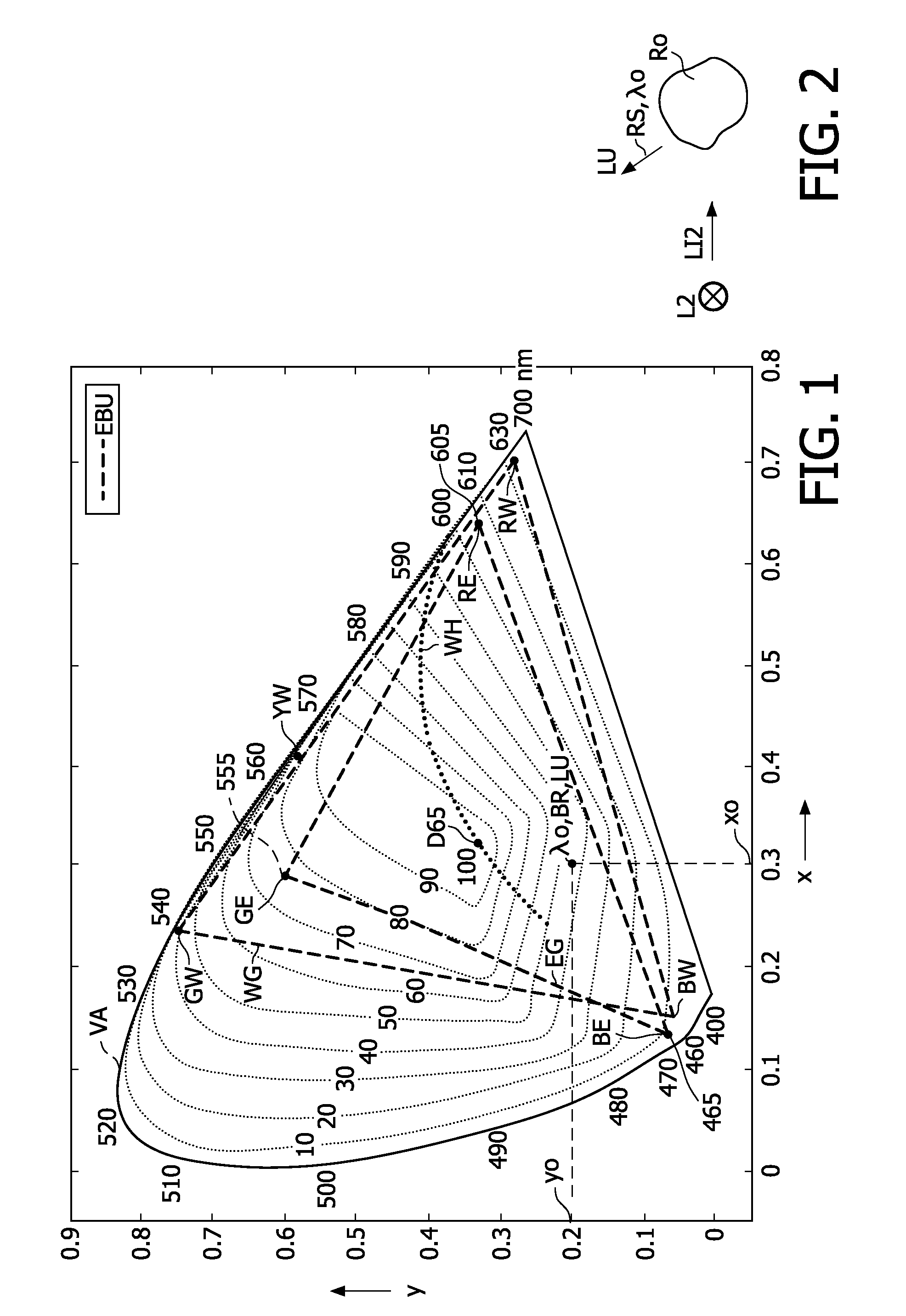
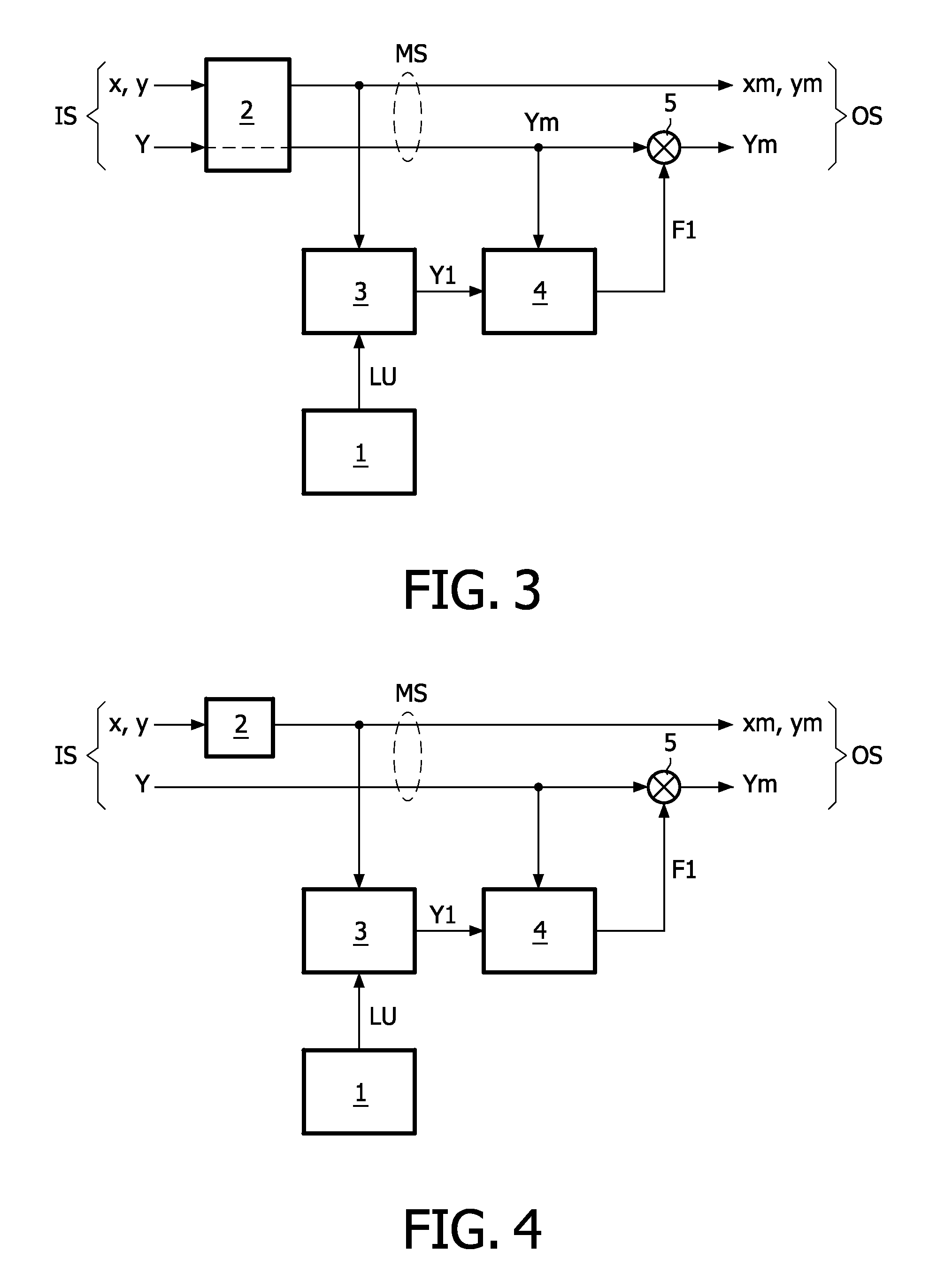
Color mapping method
ActiveUS20100103200A1Improve color reproductionHigh color reproductionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsReflectivityPixel color
A color mapping method maps an input image signal (IS) into an output image signal (OS) for a display (DD) with display pixels (Pi) having sub-pixels (RP, GP, BP, YP) with primary colors (RW, GW, BW, YW) defining a display color gamut (WG). A look-up table (1) comprises stored luminances (LU) of reflective spectra (RS) at different chromaticities (λO) within the display color gamut (WG). The reflective spectra (RS) are spectra of reflective objects (RO) having a substantial maximum reflectivity at the corresponding chromaticities (λO). The color mapping method comprises a gamut mapping (2), retrieving (3) a looked-up luminance (Y1), a factor determination (4), and adapting the mapped luminance (Ym; Y). The gamut mapping (2) maps the input image signal (IS) having input pixel colors defined by an input luminance (Y) and an input chromaticity (x, y) into a mapped image signal (MS) having corresponding mapped pixel colors defined by a mapped luminance (Ym; Y) and a mapped chromaticity (xm, ym). The input pixel colors lie within an input color gamut different than the display color gamut (WG). The looked-up luminance (Y1) is retrieved (3) by looking up the stored luminance (LU) in the look-up table (1) at the mapped chromaticity (xm, ym). The factor (F) is determined (4) from a difference between the looked-up luminance (Y1) and the mapped luminance (Ym; Y). The mapped luminance (Ym; Y) is adapted (5) by using the factor (F; G) to obtain an output luminance (Ys) nearer to the looked-up luminance (Y1) than the mapped luminance (Ym). The image output signal (OS) is defined by the mapped chromaticity (xm, ym) and the output luminance (Ys).
Owner:TOP VICTORY INVESTMENTS
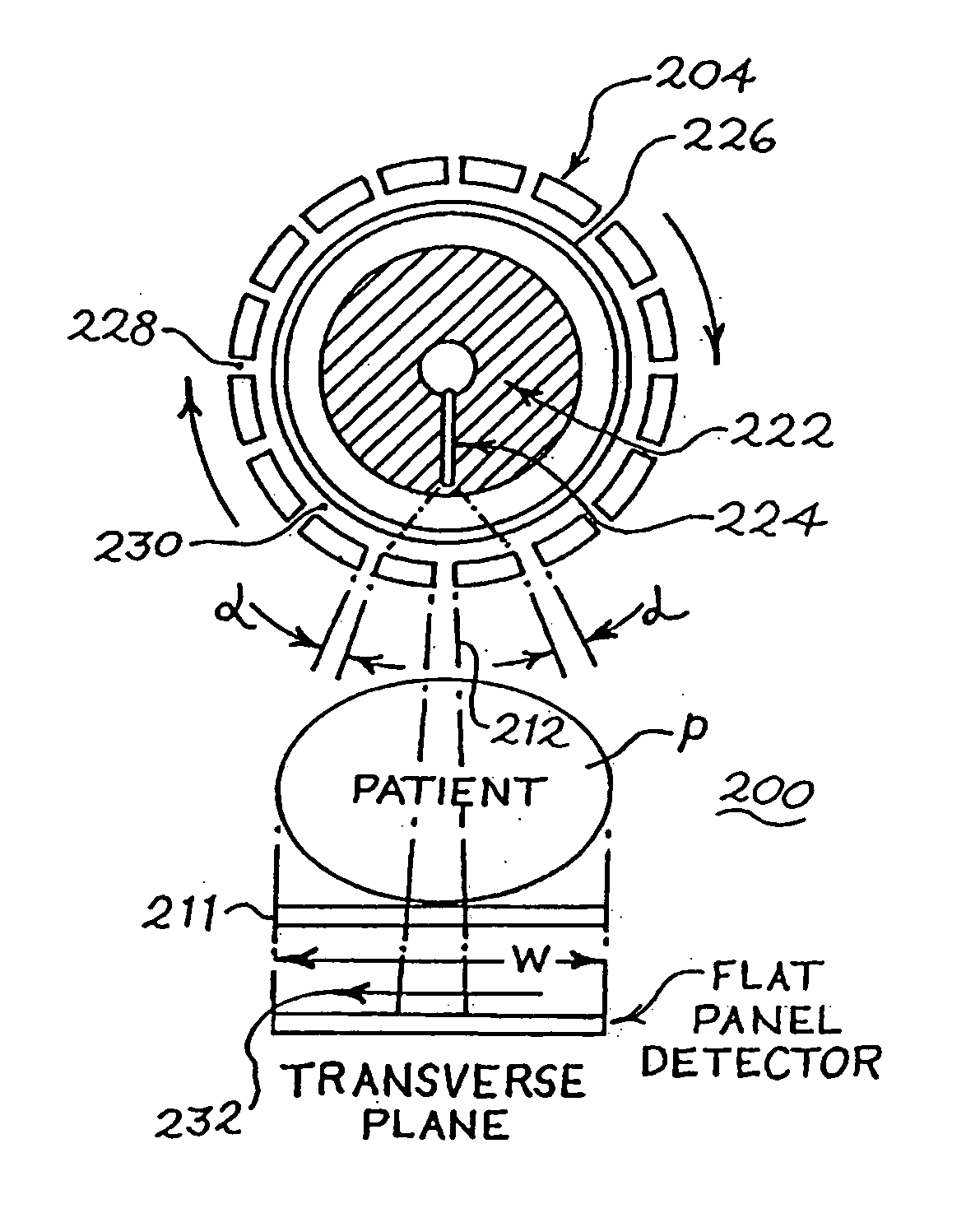
Scanning slot cone-beam computed tomography and scanning focus spot cone-beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20070280408A1Minimize radiation doseAvoid artifactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhysicsTomography
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Computed tomography (CT) scanning heterogeneous model testing system
ActiveCN102095740AImprove mechanical propertiesPeel-resistantPermeability/surface area analysisMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFluid saturationComputed tomography
The invention relates to a computed tomography (CT) scanning heterogeneous model testing system. The system comprises a CT scanning system, a displacement system, an overburden pressure system, a pressure measurement system, a heterogeneous multilayer core clamp holder and a metering system, wherein the heterogeneous multilayer core clamp holder consists of a shell, a rubber cylinder, a core left plug, a core right plug, a left fixing sleeve, a right fixing sleeve, a left fastening sleeve, a right fastening sleeve and a fixed bracket; the core right plug is provided with a plurality of liquid outlets; each liquid outlet is respectively aligned with one layer of core model; and a strip liquid outlet sealing gasket is formed on the core right plug, which correspond to a seam between two adjacent layers of core models, so that liquid flow passing through each layer of core model flows out from the corresponding liquid outlet of each layer of core model, and thus, intraformational heterogeneous water displacing oil layered measurement is realized. By the CT scanning system, the real-time on-line monitoring of the on-way distribution of saturation of fluid on each layer section in a heterosphere is realized so as to observe the interlayer communication phenomenon.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Visual processing device, visual processing method, program, display device, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS7894684B2Avoid artifactsImprove image qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsVision processingDisplay device
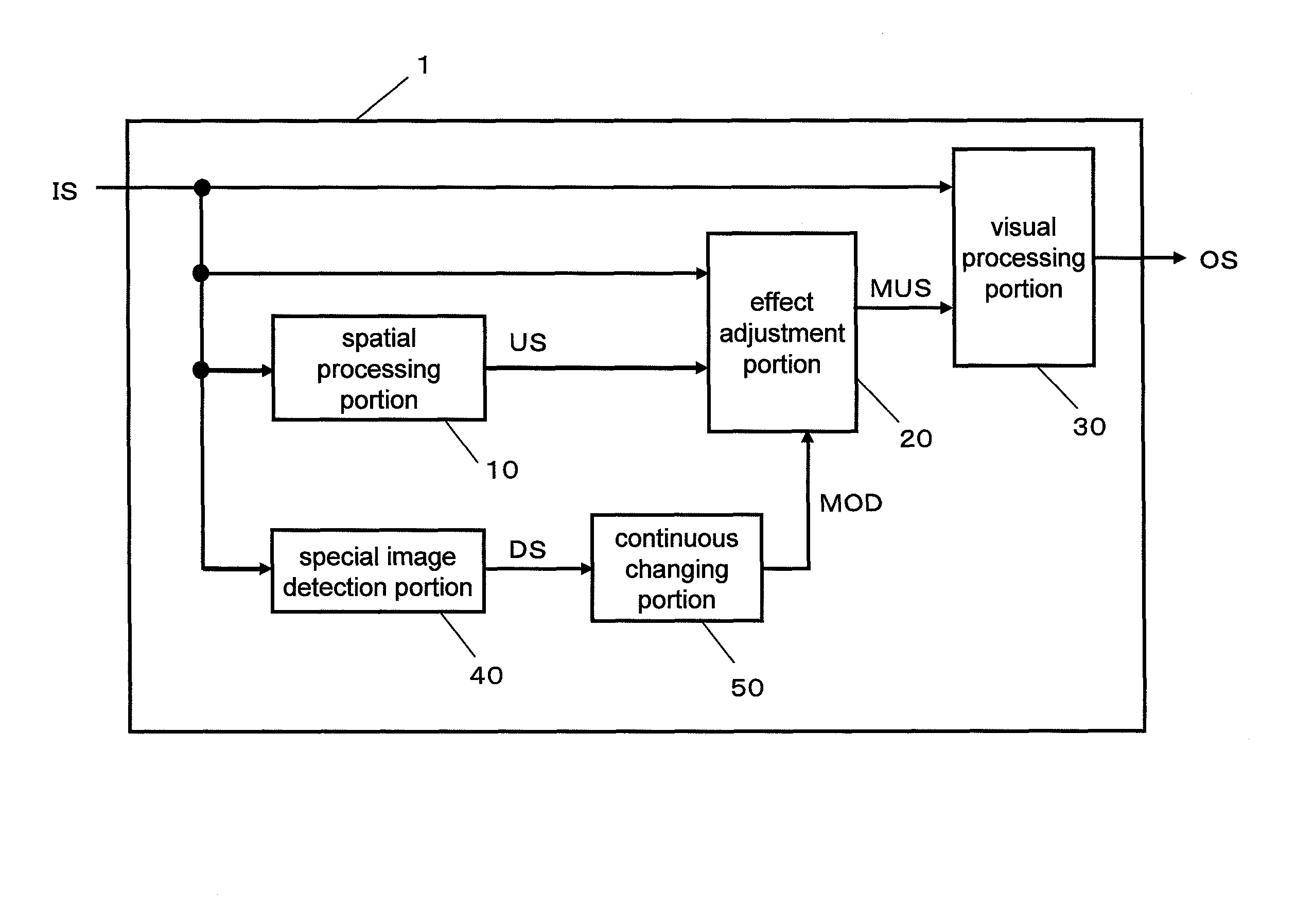
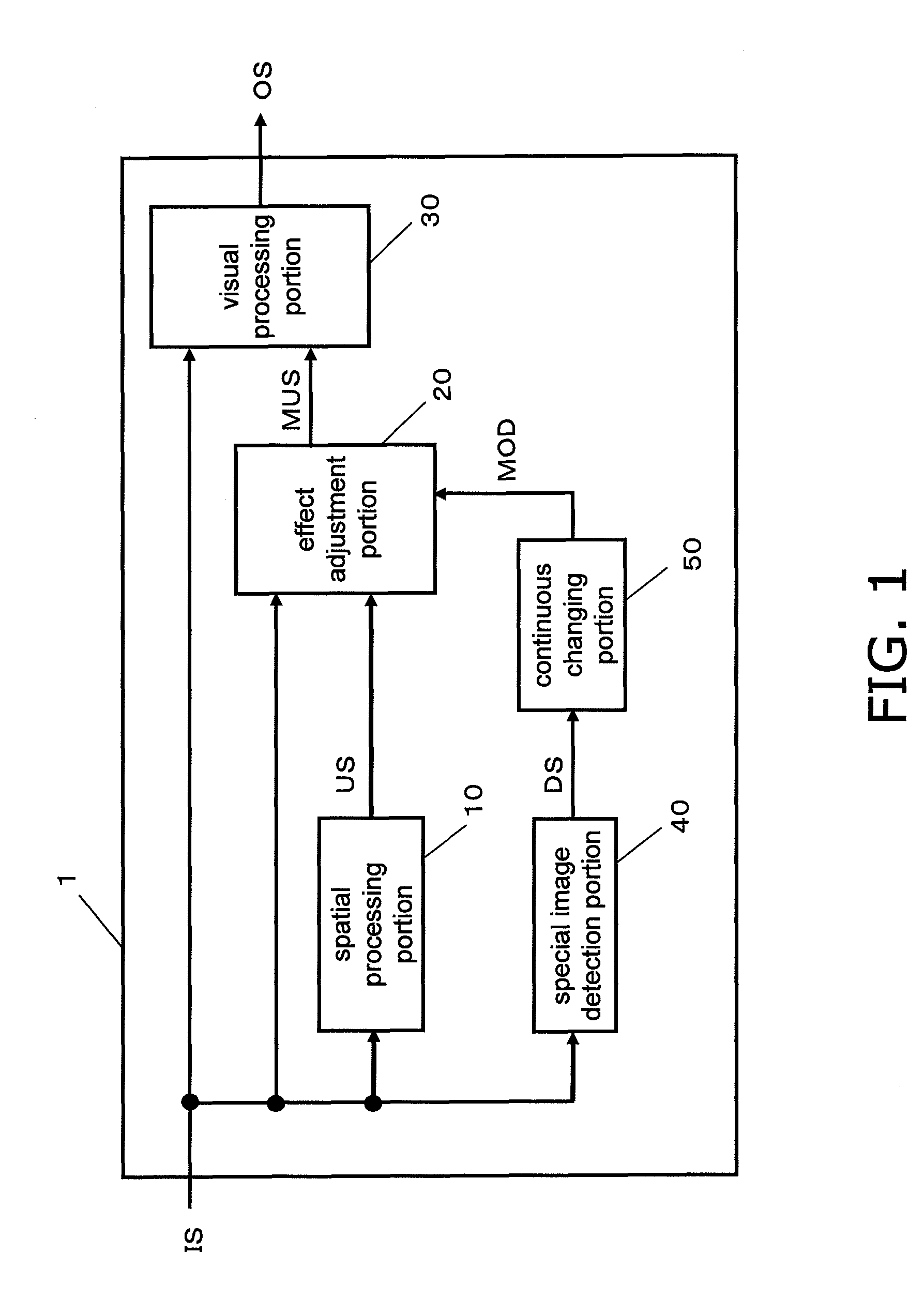
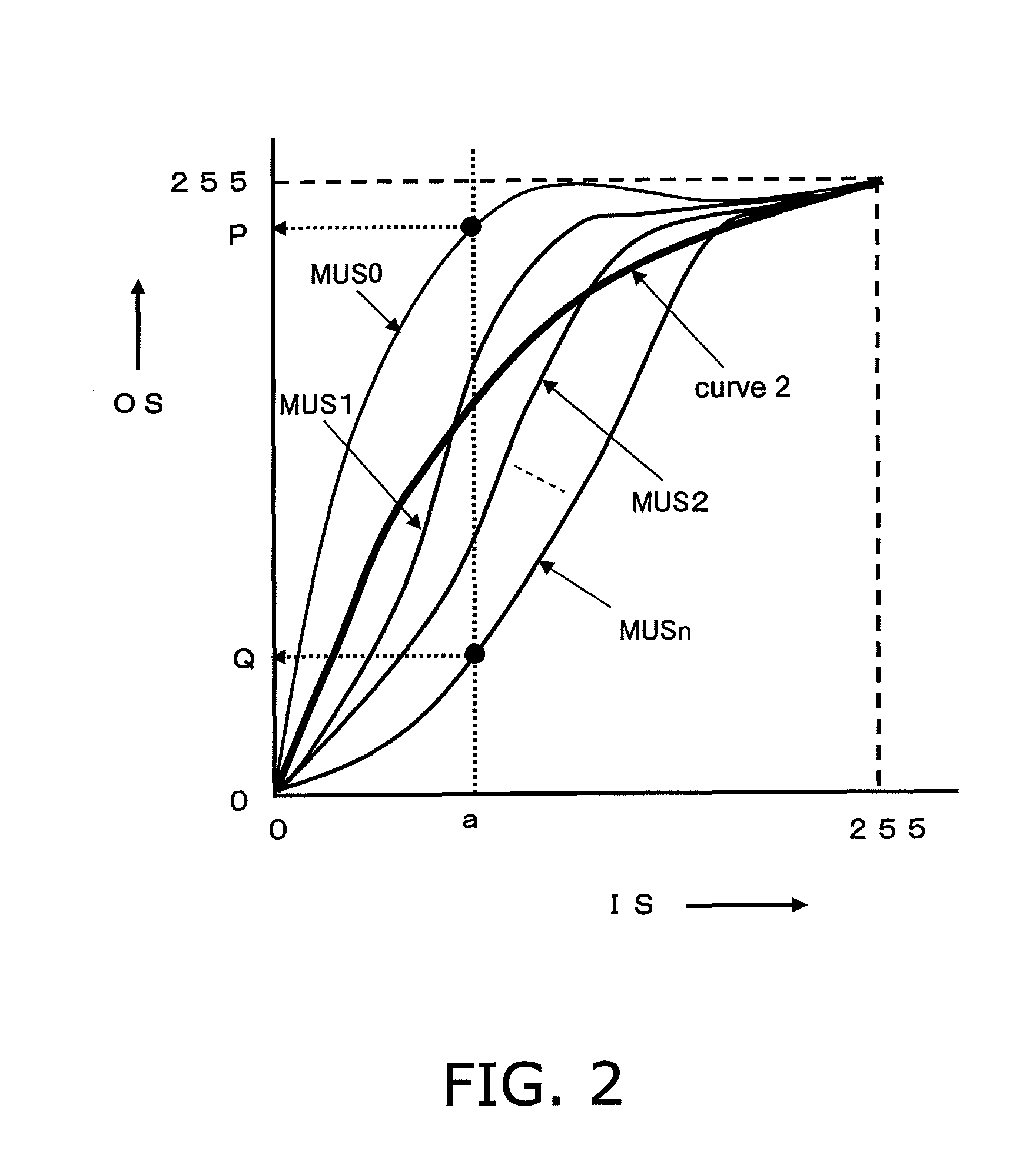
In order to inhibit artifacts (even when a special image has been input) a visual processing device is provided with a spatial processing portion extracting surrounding image information US from an input image signal IS, and a special image detection portion outputting a special image effect adjustment signal DS according to a degree of a statistical bias of the image signal IS. The visual processing device also includes a continuous changing portion outputting an effect adjustment signal MOD in which the special image effect adjustment signal DS is continuously changed between frames, an effect adjustment portion outputting a synthesized signal MUS in which the effect of the visual processing differs depending on the effect adjustment signal MOD, and a visual processing portion outputting a processed signal OS obtained by visually processing the image signal IS based on the image signal IS and the synthesized signal MUS.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Timing scheme for touch screen supporting variable refresh rate
ActiveUS20160370915A1Reduce the required powerAvoid display artifactStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingSensing dataTouch Senses
Various timing schemes can be used to synchronizing display functions with touch and / or stylus sensing functions for devices including a variable refresh rate (VRR) display. In a continuous-touch mode, for example, extended blanking can result in frame judder due to mismatch or latency between reporting of sensing data and the display. To minimize these issues, sensing operations can reset to re-synchronize with the display operation, and unreported data from sensing scans can be discarded or ignored. In some examples, a display frame can be divided into two sub-frames, and a system can be configured to perform a touch sensing scan during the first sub-frame of a display frame. At the conclusion of extended blanking, the sensing operations can reset to re-synchronize with the display. The touch sensing scan can be completed in one intra-frame pause and can begin at the start of the display frame.
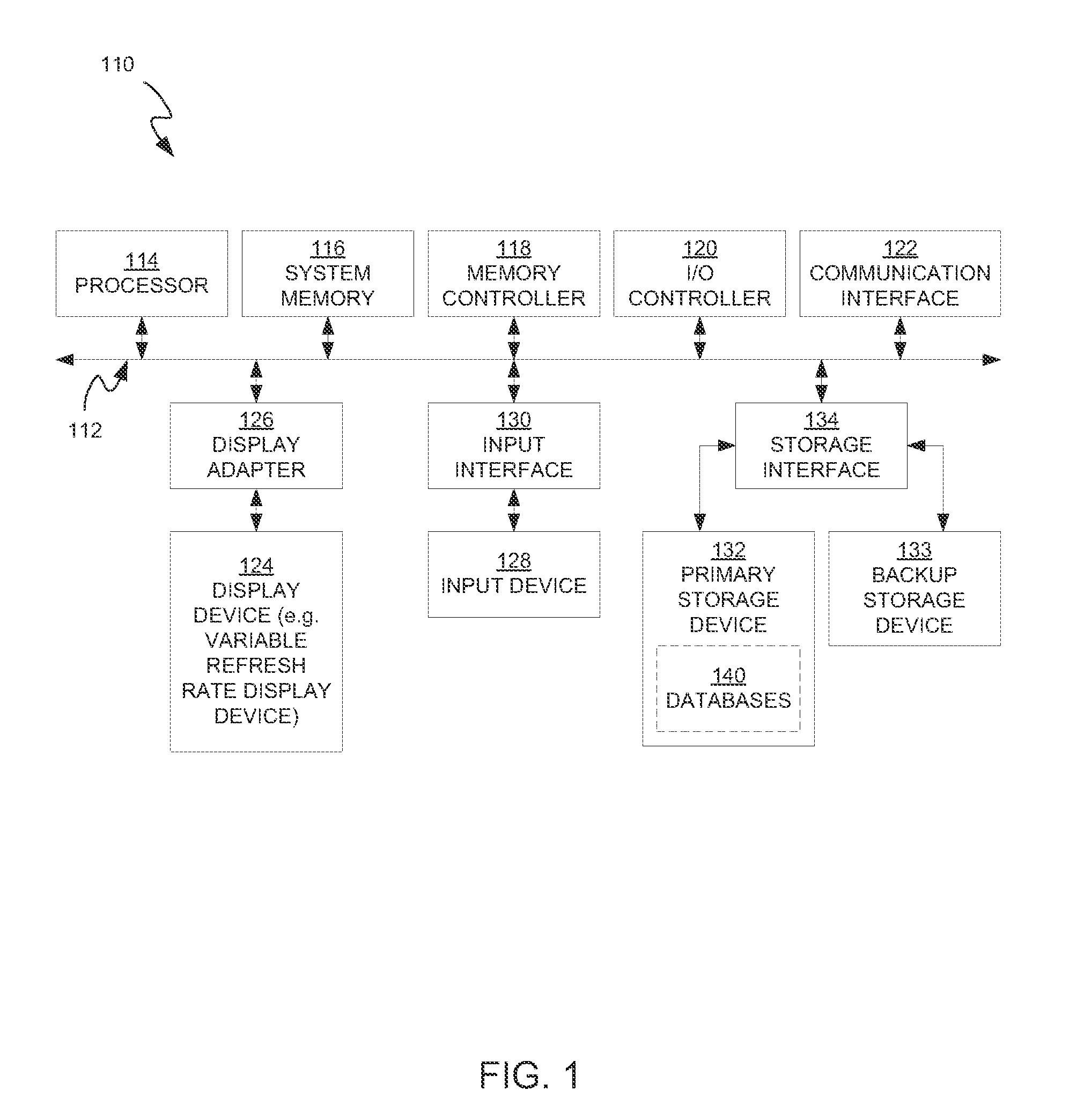
Owner:APPLE INC
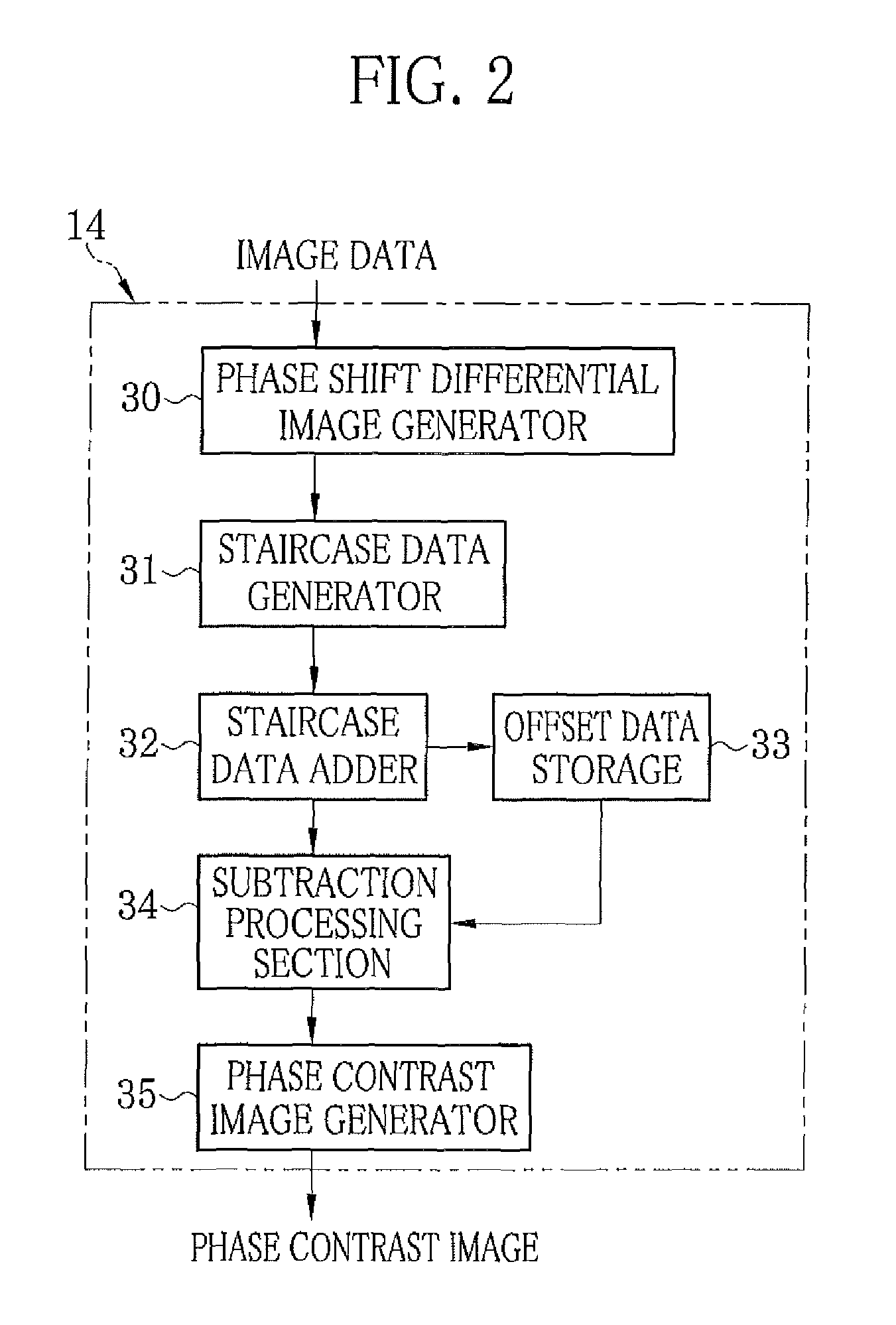
Radiation imaging system and image processing method
InactiveUS8824629B2Avoid artifactsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsPhase shiftedImaging processing
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Tomographic scanning X-ray inspection system using transmitted and Compton scattered radiation
InactiveUS7072440B2Avoid artifactsThe effect is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansSoft x rayRadiation x
X-ray radiation is transmitted through and scattered from an object under inspection to detect weapons, narcotics, explosives or other contraband. Relatively fast scintillators are employed for faster X-ray detection efficiency and significantly improved image resolution. Detector design is improved by the use of optically adiabatic scintillators. Switching between photon-counting and photon integration modes reduces noise and significantly increases overall image quality.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
Tomographic scanning X-ray inspection system using transmitted and compton scattered radiation
InactiveUS20050089140A1Avoid artifactsThe effect is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansImaging qualityEngineering
X-ray radiation is transmitted through and scattered from an object under inspection to detect weapons, narcotics, explosives or other contraband. Relatively fast scintillators are employed for faster X-ray detection efficiency and significantly improved image resolution. Detector design is improved by the use of optically adiabatic scintillators. Switching between photon-counting and photon integration modes reduces noise and significantly increases overall image quality.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
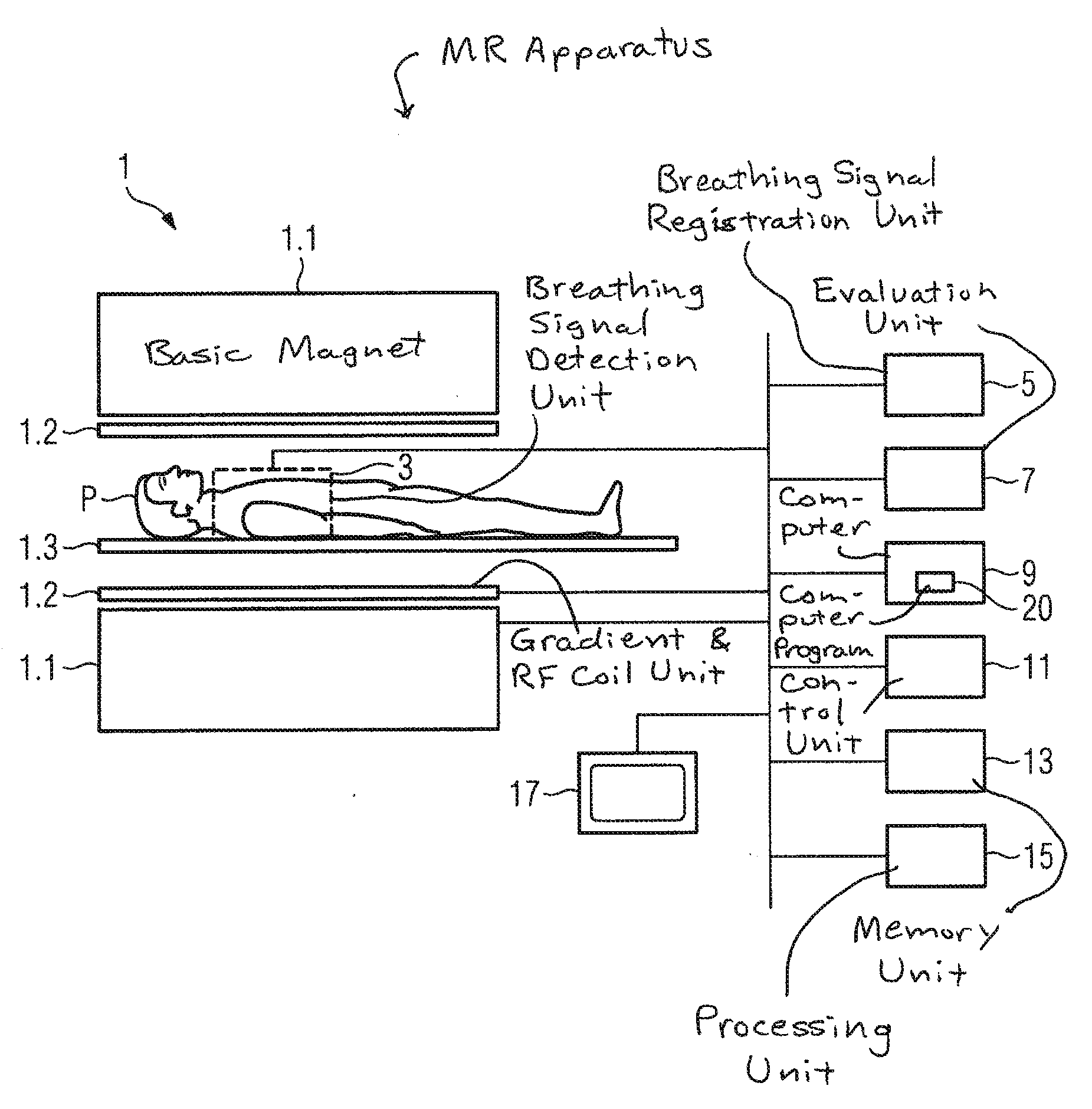
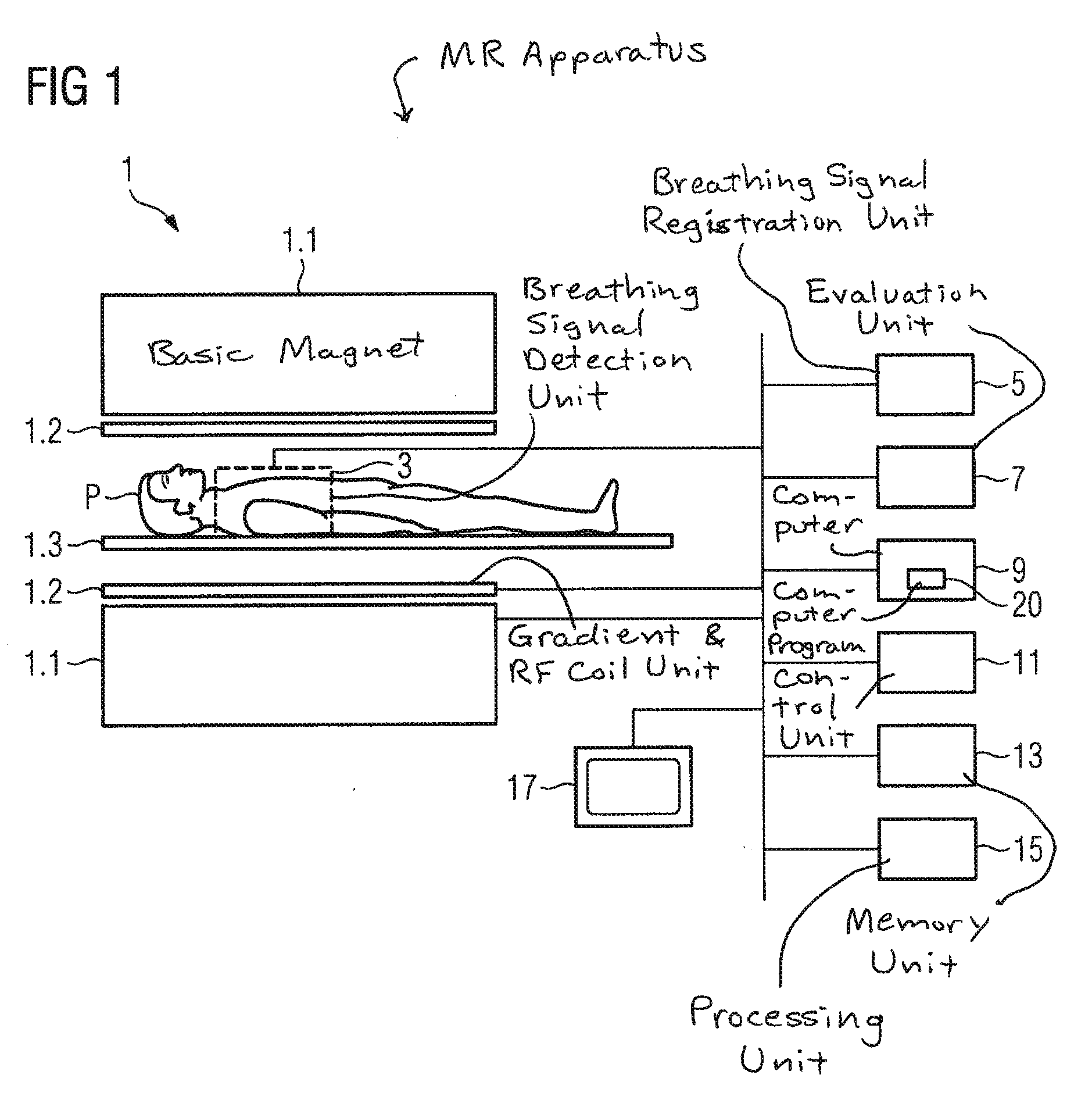
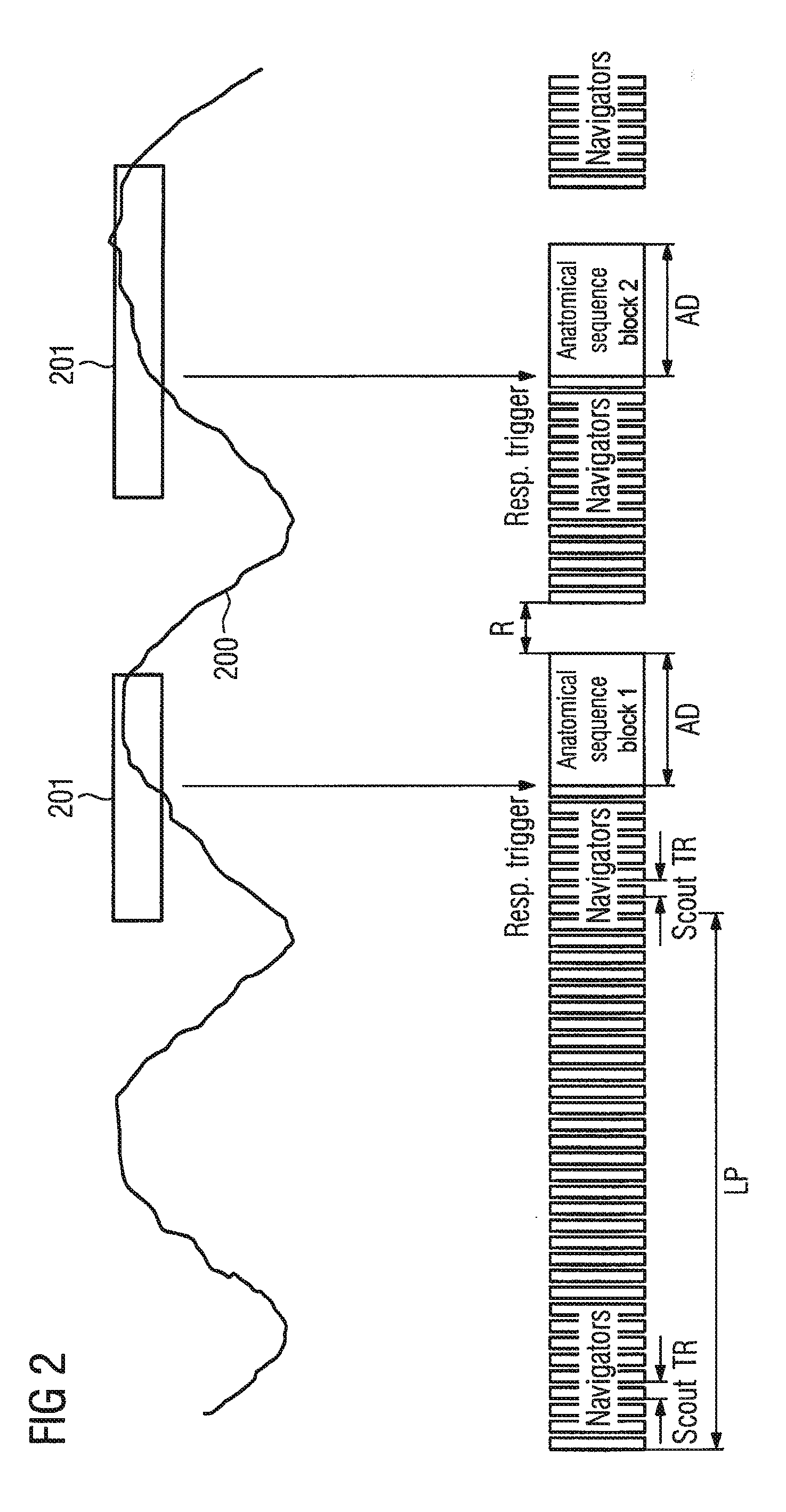
Method to acquire measurement data of a breathing examination subject by magnetic resonance technology, and associated computer program
ActiveUS20110130644A1Reduce Motion ArtifactsEasy to measureMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineResonance
A method for the acquisition of measurement data of a breathing examination subject by magnetic resonance includes the following steps: (a) detect the physiological breathing signal of the examination subject with a breathing signal detection unit, (b) evaluate the detected breathing signal in an evaluation unit, (c) based on the evaluated breathing signal, calculate in a computer at least one parameter affecting the type of acquisition of measurement data by means of magnetic resonance, (d) detect a current physiological breathing signal with the breathing signal detection unit, (e) compare the last detected breathing signals with at least one trigger condition, (f) initiate the acquisition of measurement data using the calculated parameter from step (c) upon satisfaction of the trigger conditions from step (e), (g) repeat the steps (d) through (f) until all desired measurement data have been acquired, and (h) store and / or process the acquired measurement data in a memory and / or processing unit. After the evaluation of the detected breathing signal, at least one parameter of a following acquisition of measurement data is thus determined automatically without an input by an operator of the MR apparatus in use being required.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
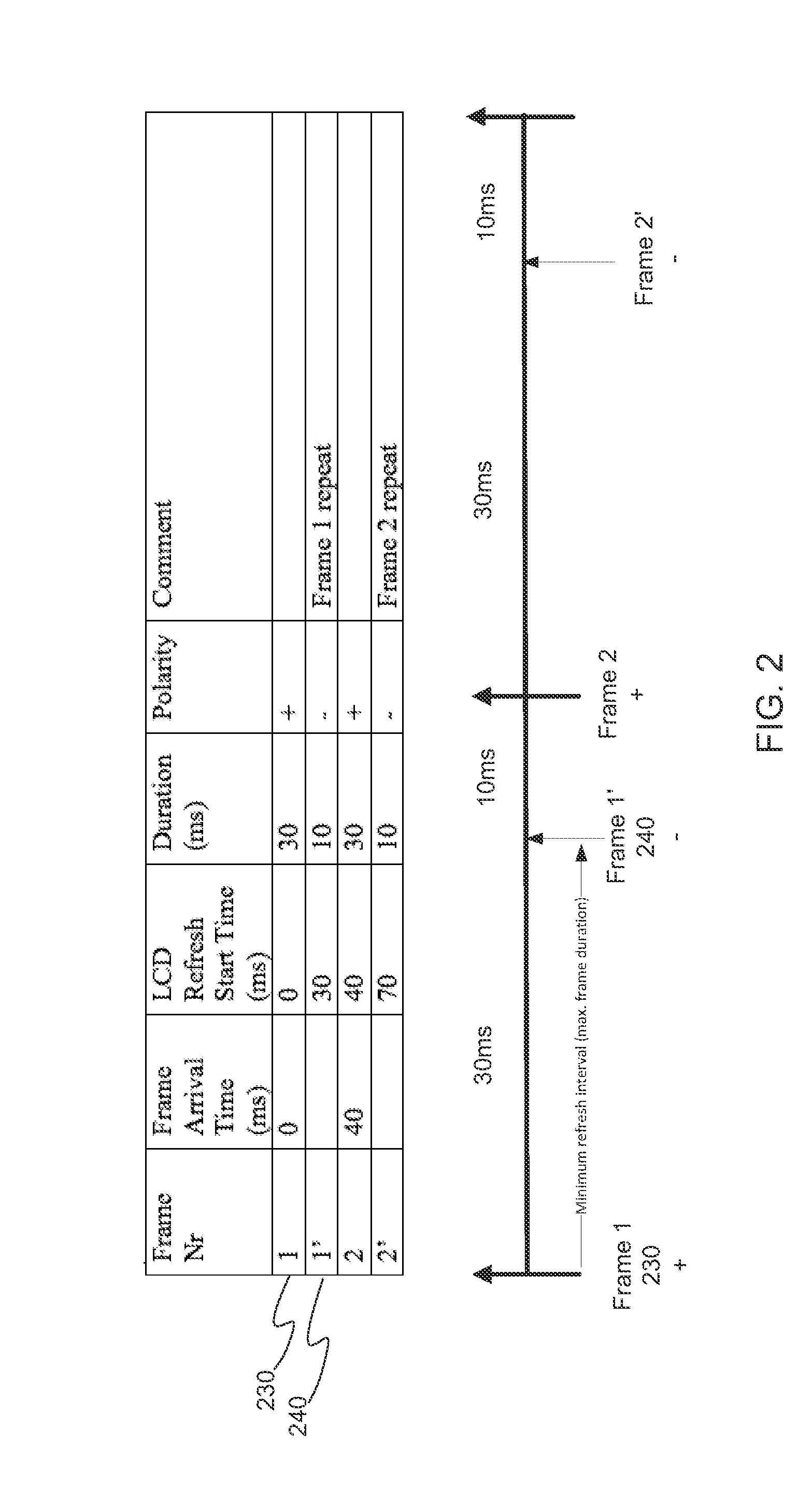
Techniques for avoiding and remedying DC bias buildup on a flat panel variable refresh rate display
ActiveUS20150243233A1Avoid charge accumulationAvoiding resultant visual artifactStatic indicating devicesCountermeasureDisplay device
A method for driving a display panel having a variable refresh rate is disclosed. The method comprises receiving a current input frame from an image source. Next, it comprises determining a number of re-scanned frames to insert between the current input frame and a subsequent input frame, wherein the re-scanned frames repeat the input frame, and wherein the number of re-scanned frames depends on the minimum refresh interval (MRI) of the display panel. Further, it comprises calculating respective intervals at which to insert the re-scanned frames between the current input frame and the subsequent input frame. Subsequently, it comprises determining if a charge accumulation in pixels of the display panel has crossed over a predetermined threshold value. Finally, responsive to a determination that the charge accumulation has crossed over a predetermined threshold value, it comprises performing a counter-measure to remediate the charge accumulation.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com