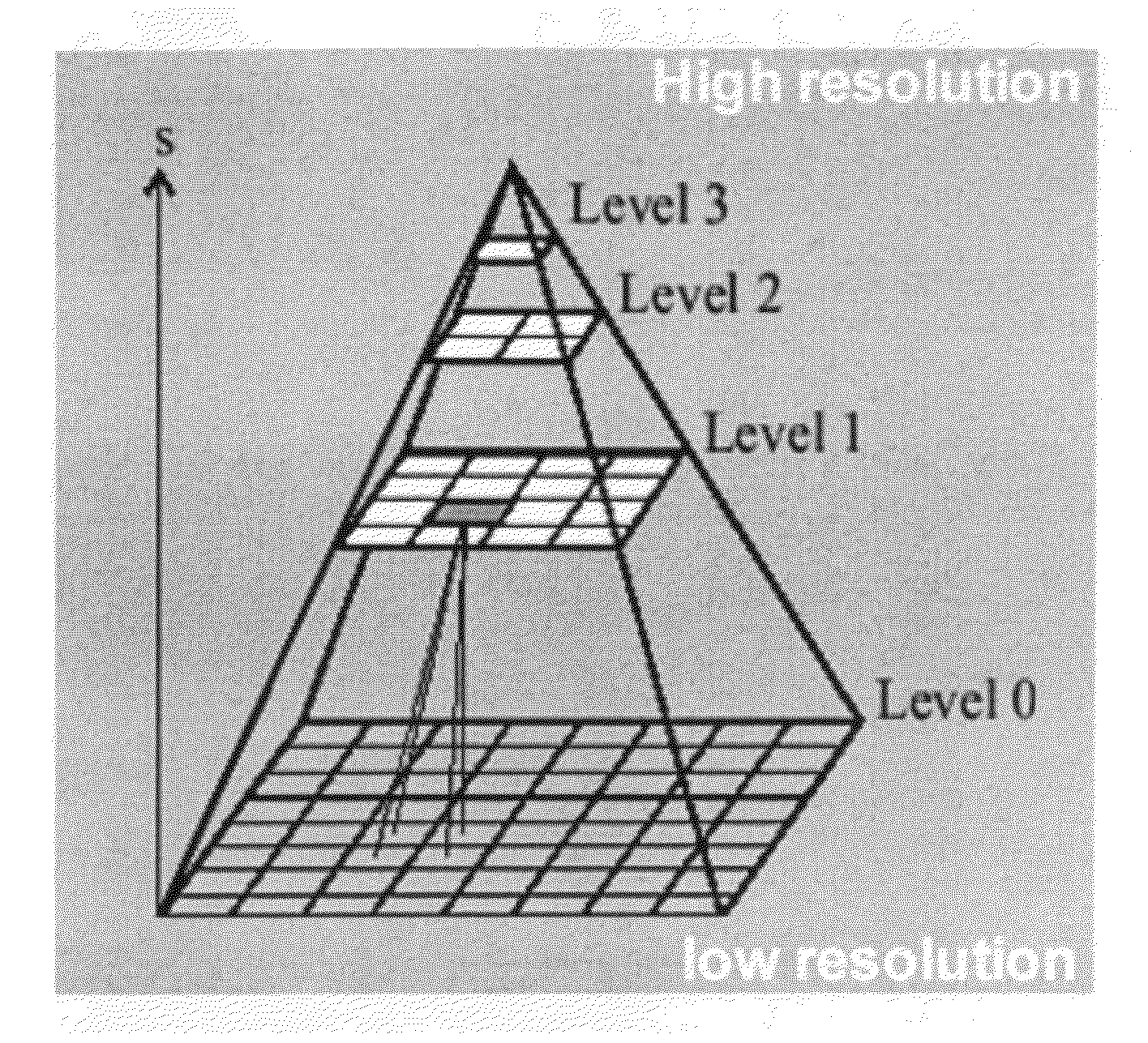Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278results about How to "Depth accurate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
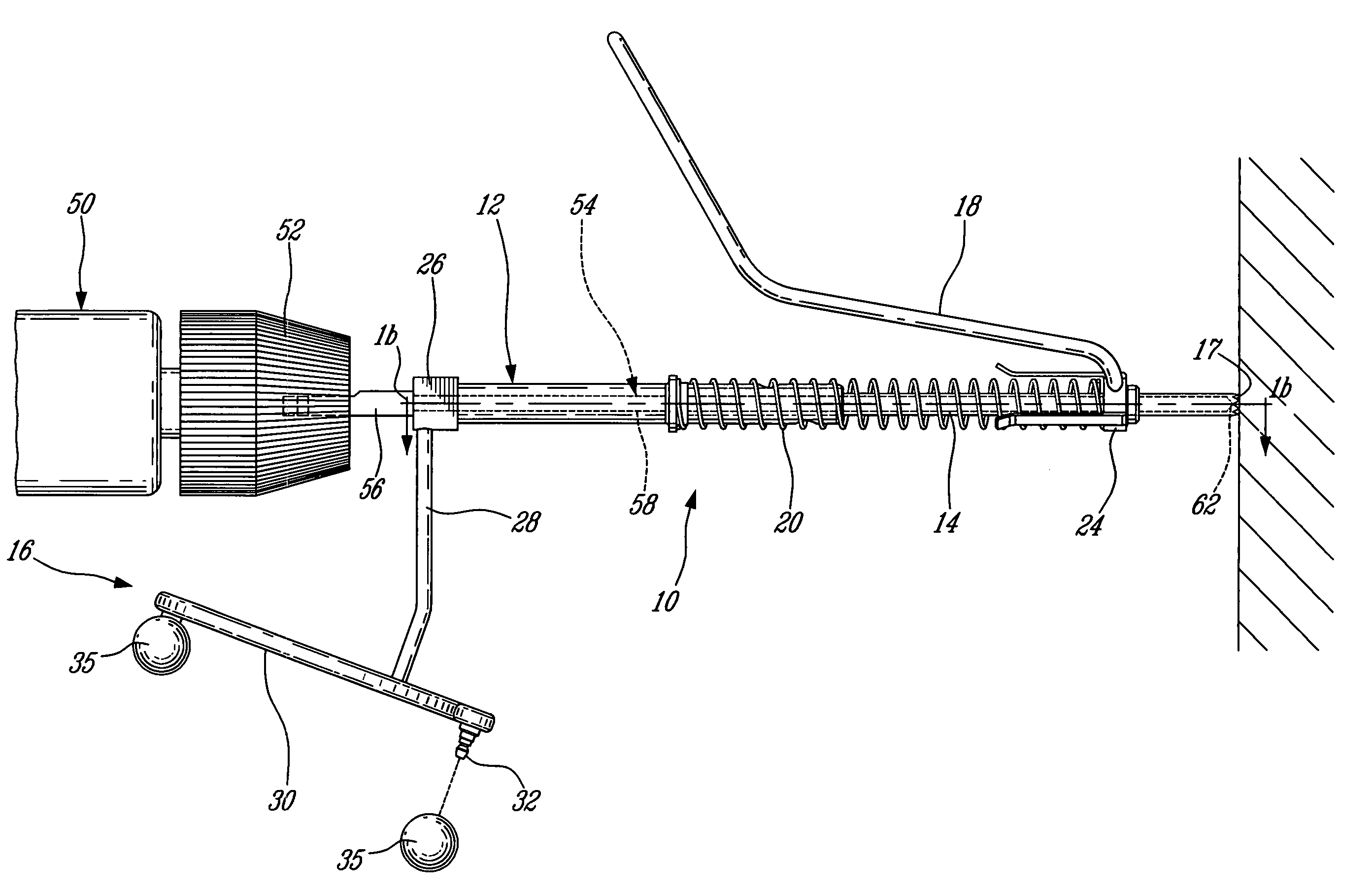
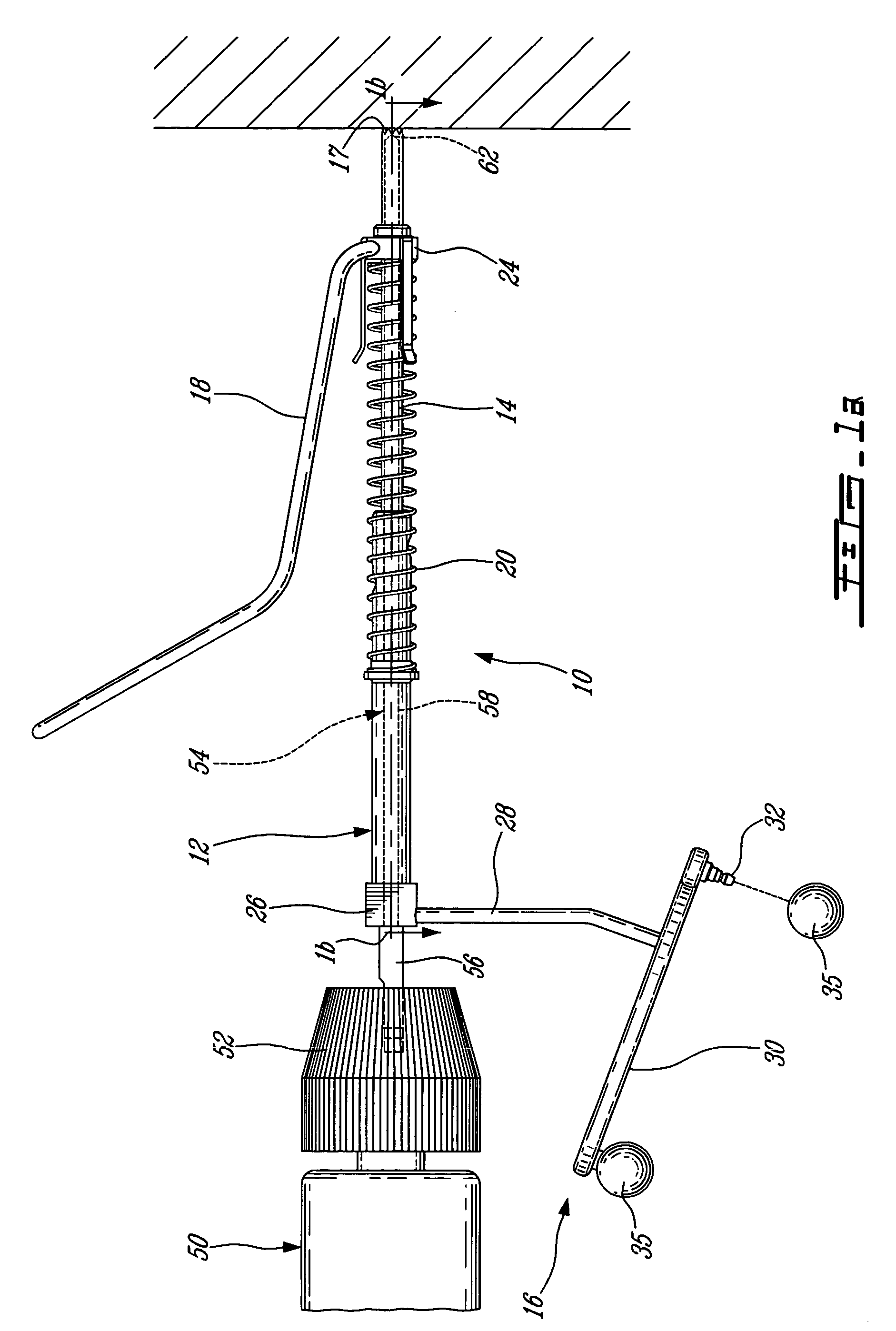
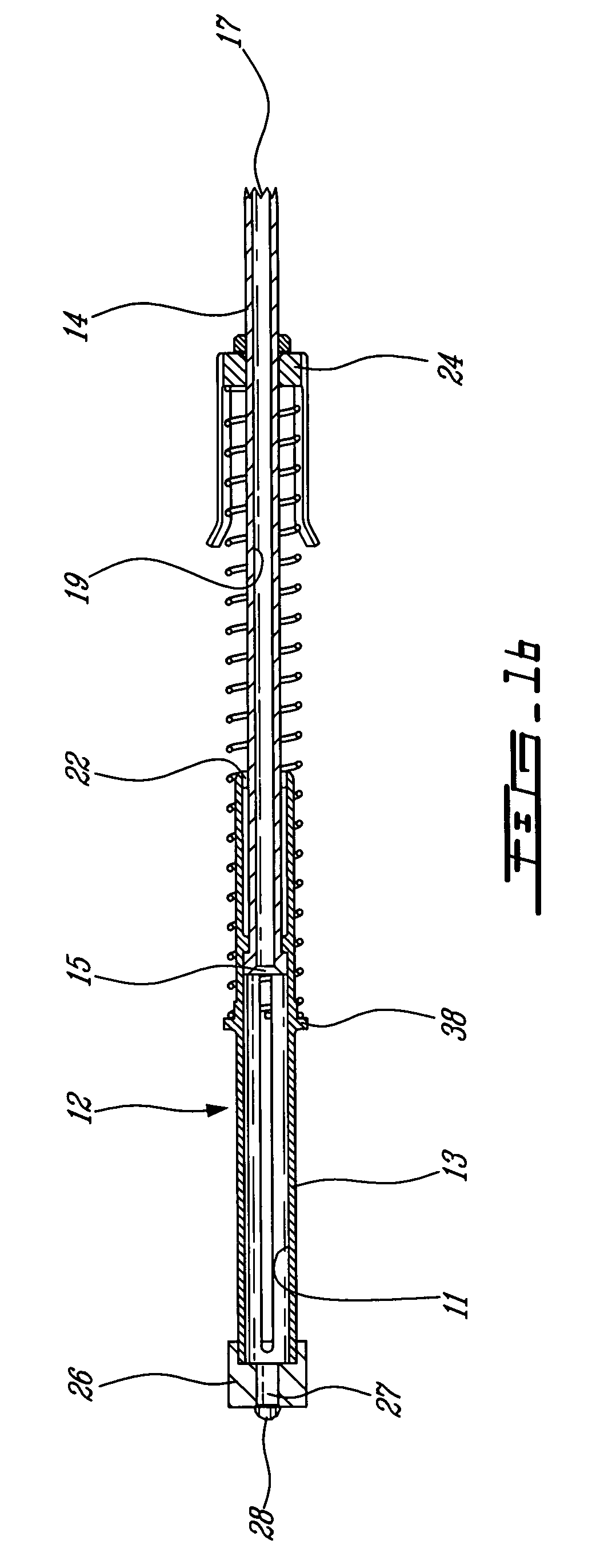
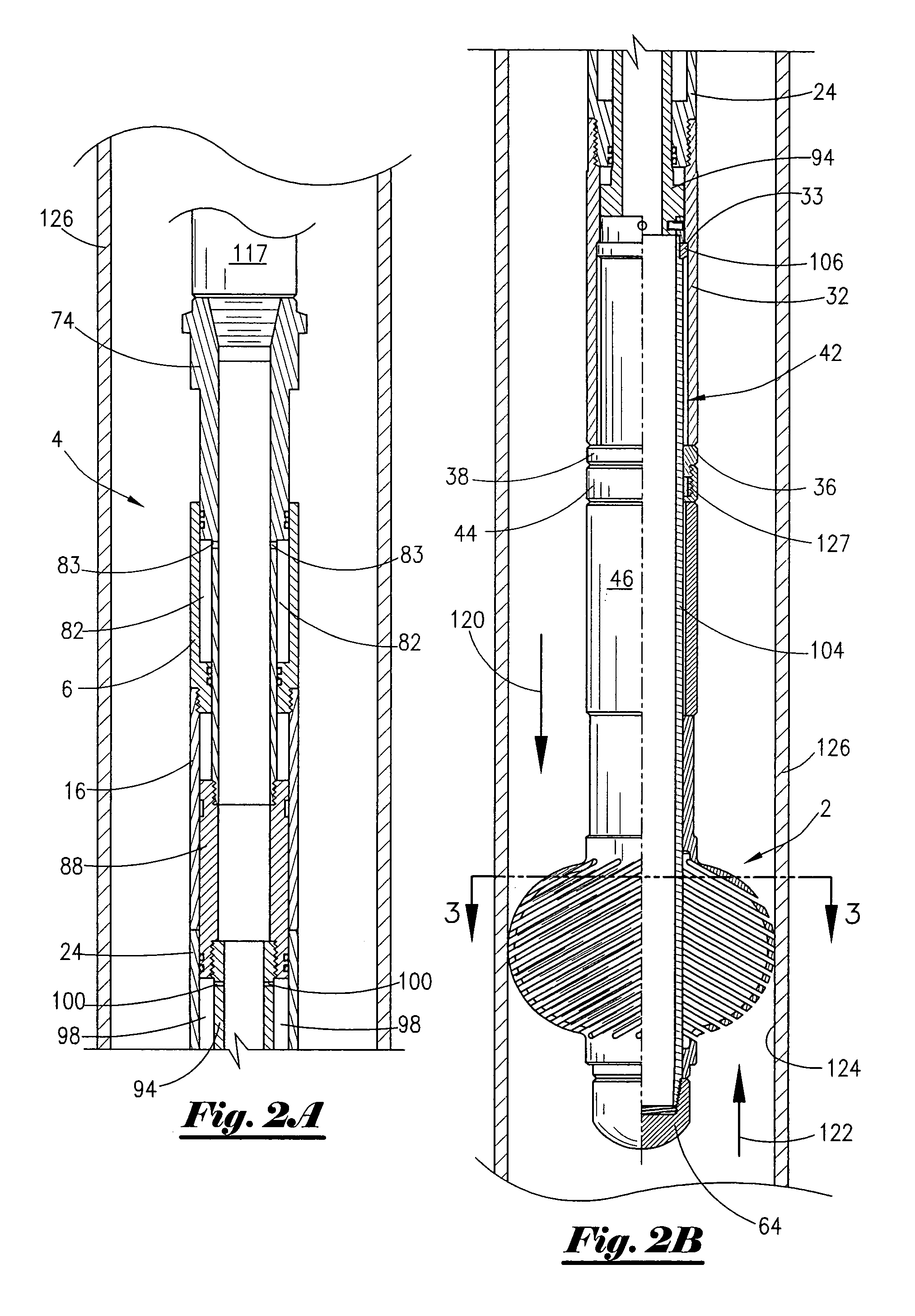
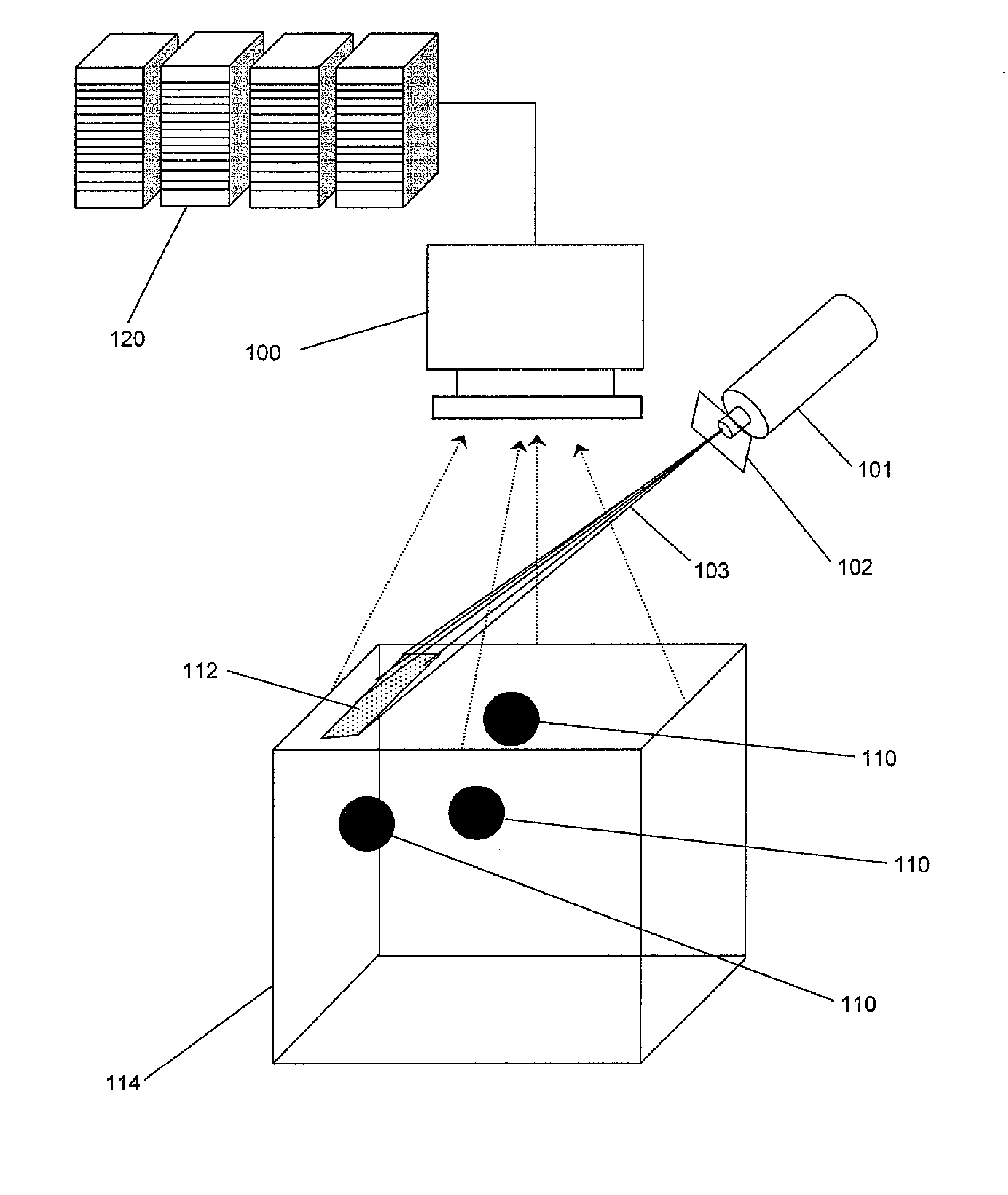
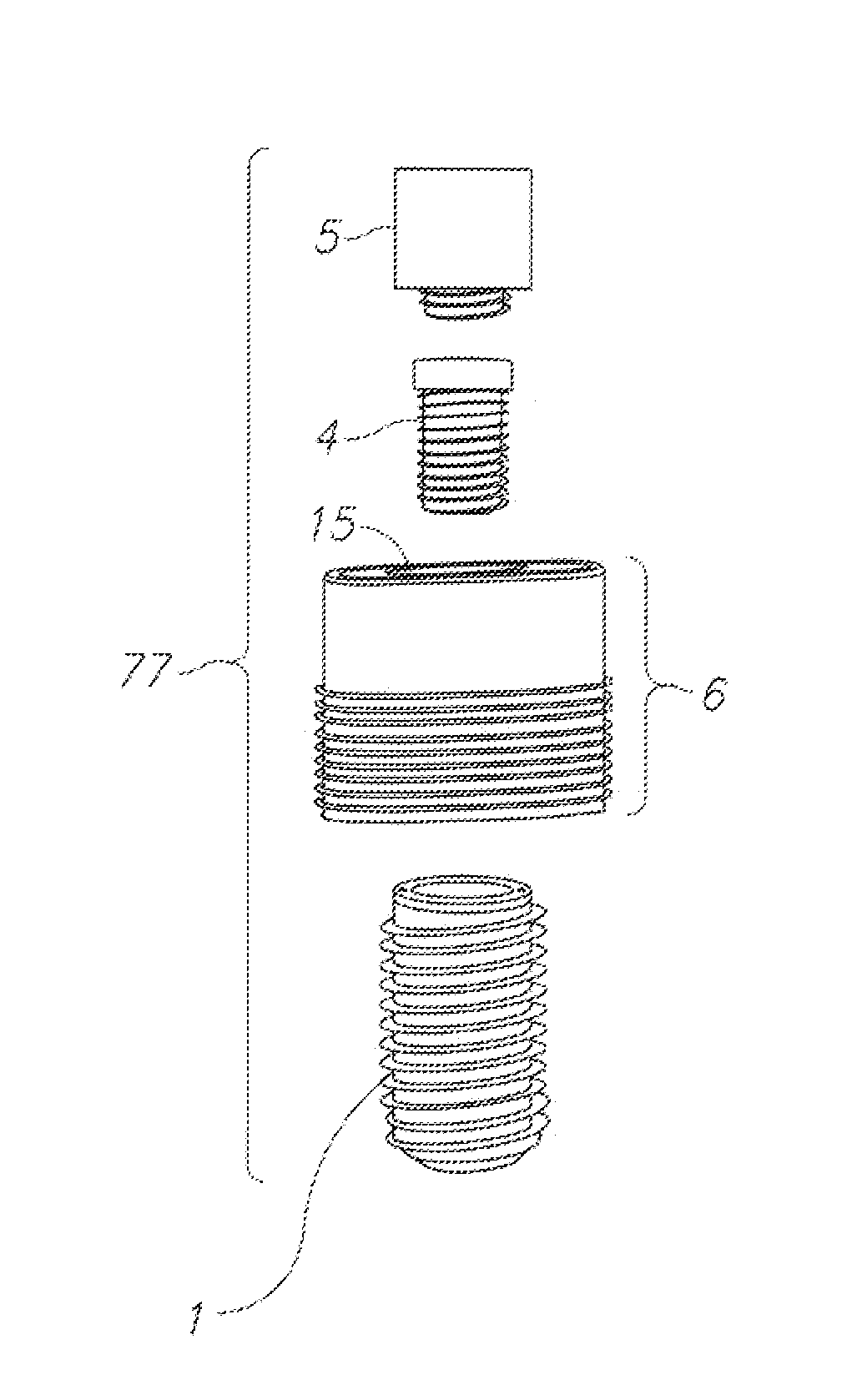
CAS drill guide and drill tracking system
InactiveUS6887247B1Accurate representationDepth accurateDrilling/boring measurement devicesThread cutting machinesThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
A drill guide assembly for a drilling tool having a chuck engaging a bit portion comprising a tip and a length extending from the chuck, the drill guide assembly comprising a first member, a second member and a trackable member. The first member is adapted to abut a workpiece surface and defines a central aperture therethrough adapted to receive the bit portion of the drilling tool. The second member is adapted to be axially displaced with respect to the first member and is axially biased therefrom, and defines a central aperture therethrough adapted to receive the bit portion of the drilling tool. The trackable member, fastened to the second member, comprises a detectable element adapted to be located and tracked in three dimensional space, thereby defining the position and movement of the second member and therefore that of the bit portion of the drilling tool.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
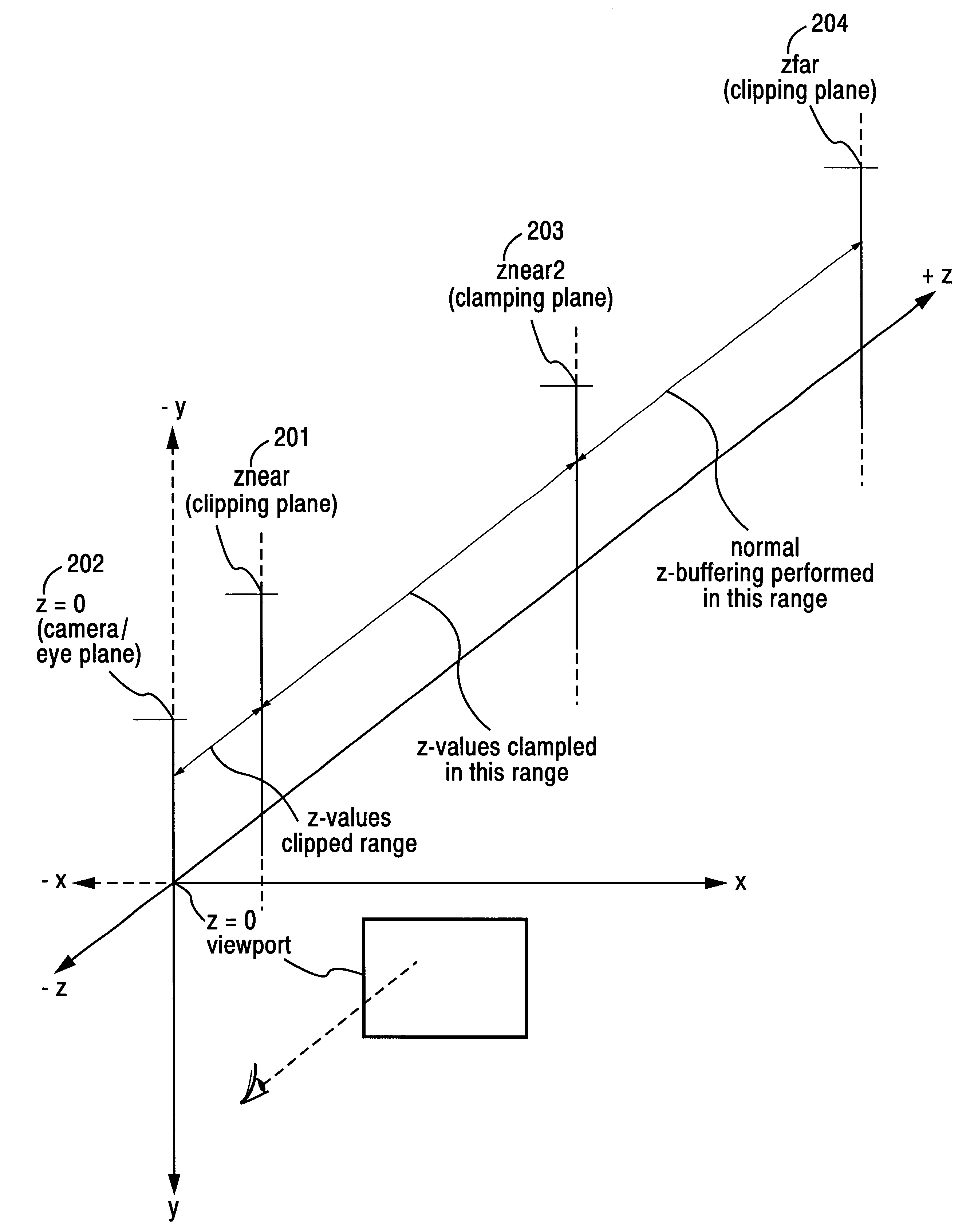
3D graphics rendering system for performing Z value clamping in near-Z range to maximize scene resolution of visually important Z components
InactiveUS6618048B1Improve precisionAvoid undesirable visual artifactCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationSurround soundImage resolution
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics pipeline performs Z-buffering and optionally provides memory efficient full scene anti-aliasing (FSAA). When the anti-aliasing rendering mode is selected, Z value bit compression is performed to more efficiently make use of the available Z buffer memory. A Z-clamping arrangement is used to improve the precision of visually important Z components by clamping Z values to zero of pixels that fall within a predetermined Z-axis range near the Z=0 eye / camera (viewport) plane. This allows a Z-clipping plane to be used very close to the eye / camera plane--to avoid undesirable visual artifacts produced when objects rendered near to the eye / camera plane are clipped--while preserving Z value precision for the remaining depth of the scene. In an example implementation, a Z value compression circuit provided in the graphics pipeline is enhanced to effectuate Z-clamping within the predetermined range of Z values. The enhanced circuitry includes an adder for left-shifting an input Z value one or more bits prior to compression and gates for masking out the most significant non-zero shifted bits to zero.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
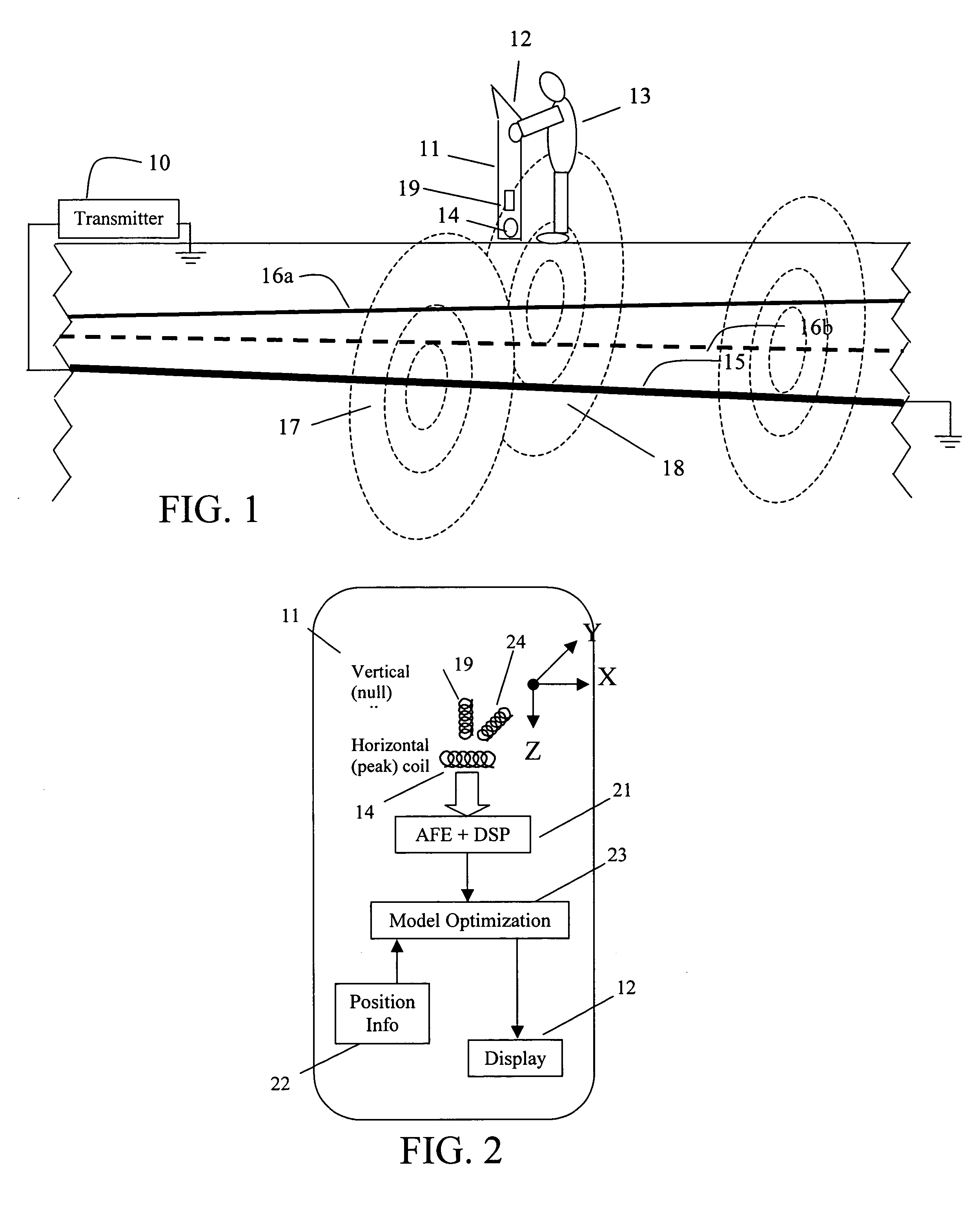
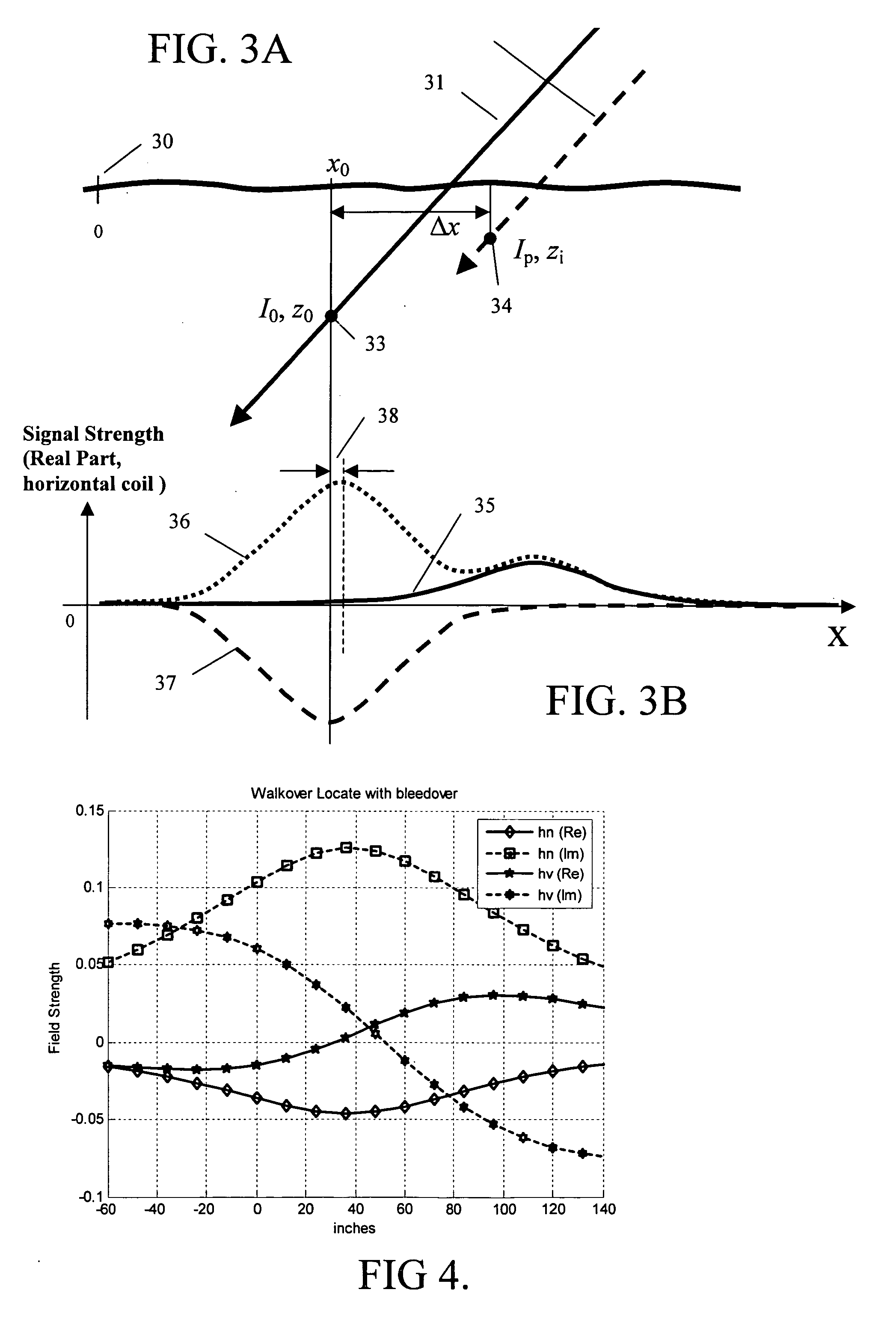
Precise location of buried metallic pipes and cables in the presence of signal distortion
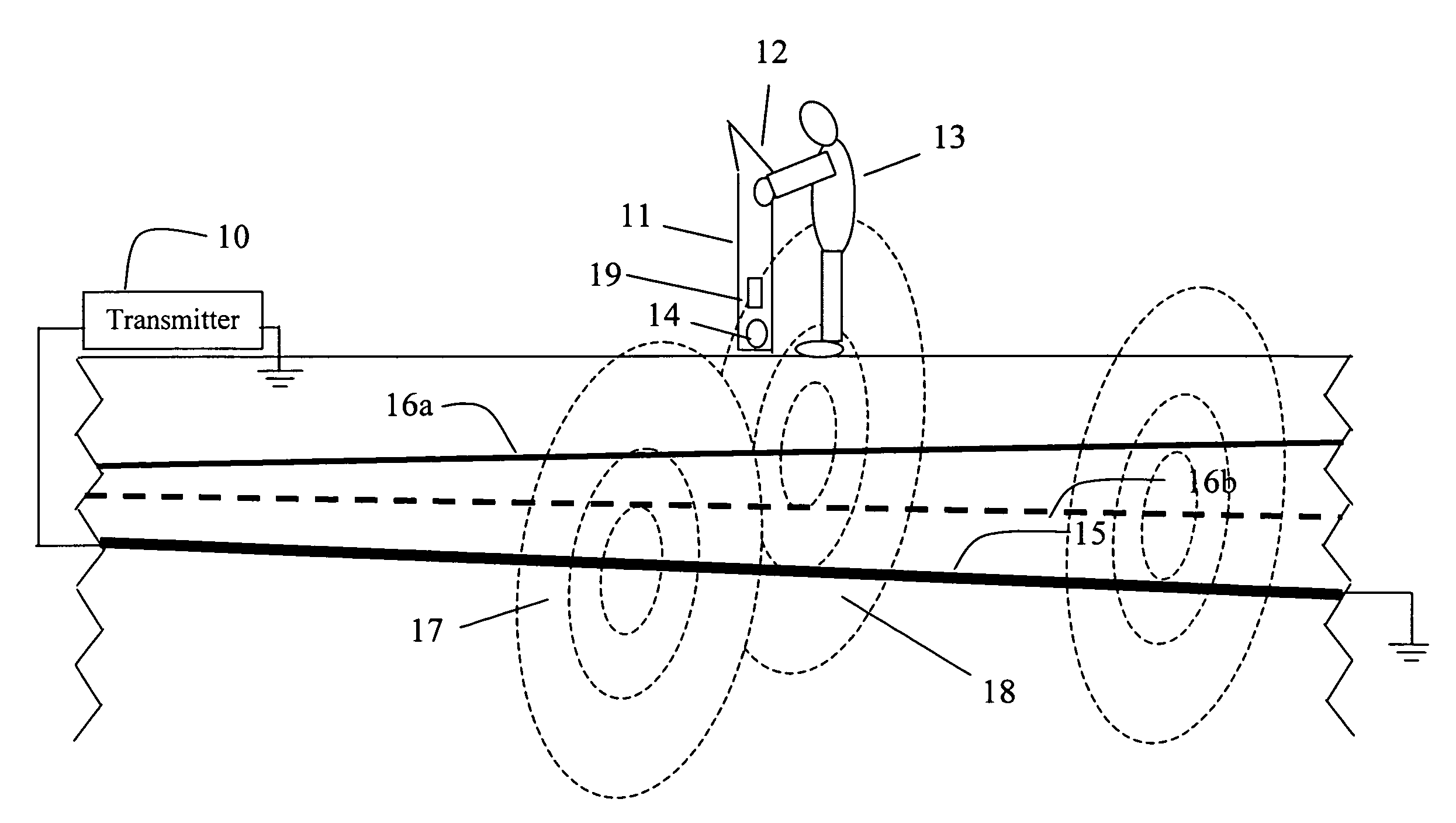
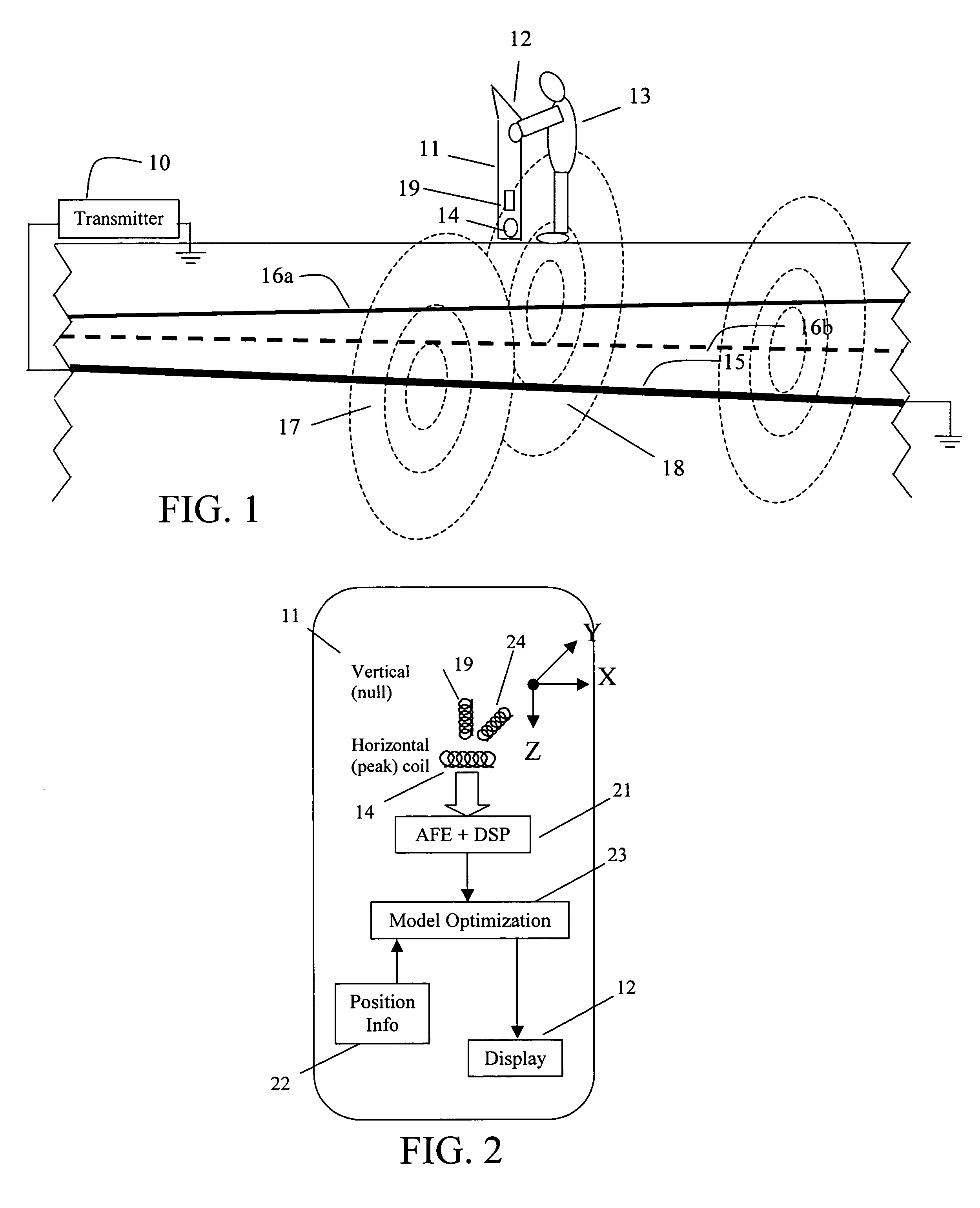
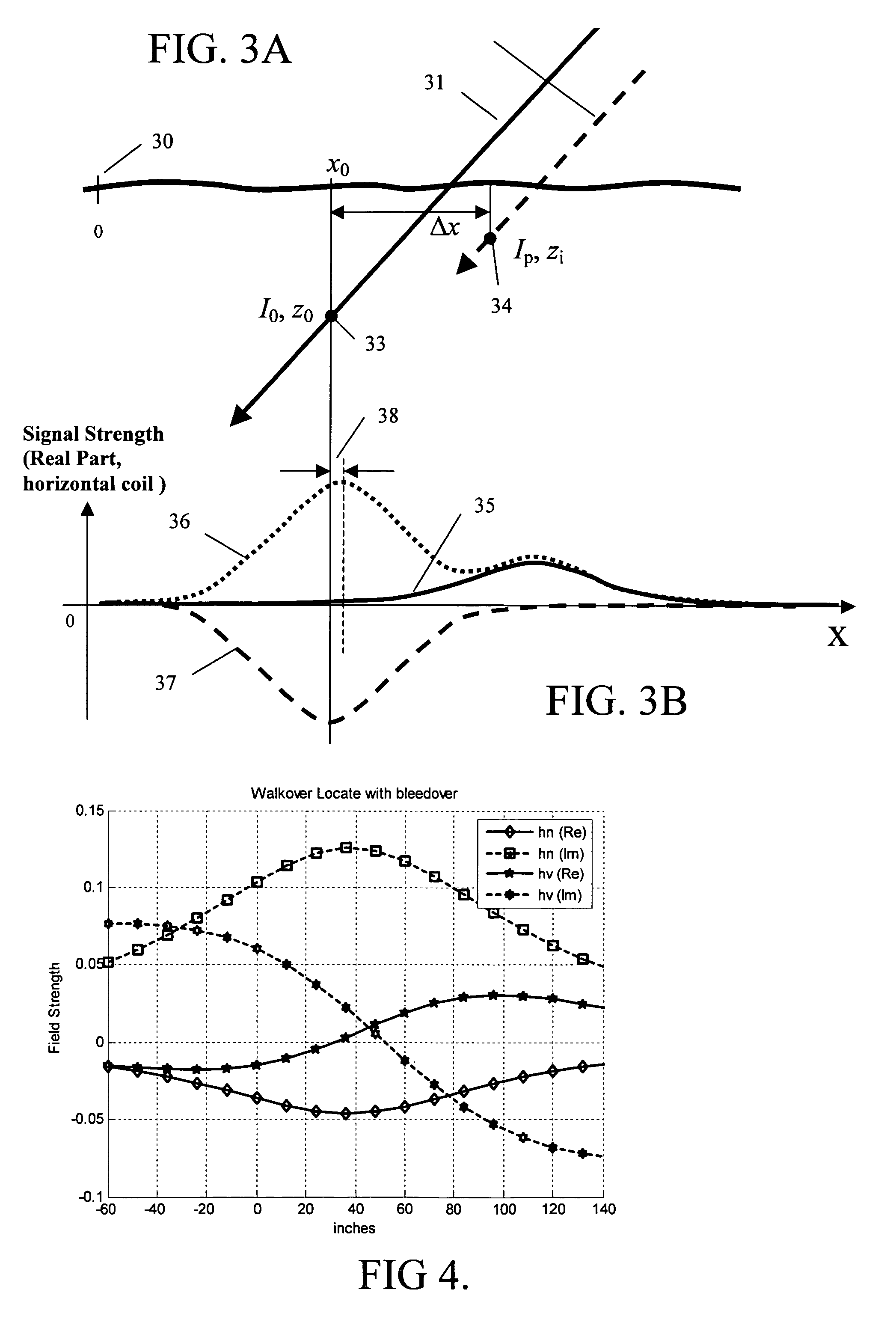
ActiveUS7356421B2Depth accurateCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic property measurementsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A new approach for locating an underground line described herein remains accurate in the face of bleedover by including both amplitude and phase from at least two magnetic field strength sensors in the measurement set. A numerical optimization step is introduced to deduce the positions and currents of each of several cables, of which one is the targeted cable and the others are termed bleedover cables. Furthermore, some embodiments of the method accounts for practical problems that exist in the field that relate to reliable estimation of cable positions, like the phase transfer function between transmitter and receiver, the estimation of confidence bounds for each estimate, and the rejection of false positive locates due to the presence of noise and interference.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
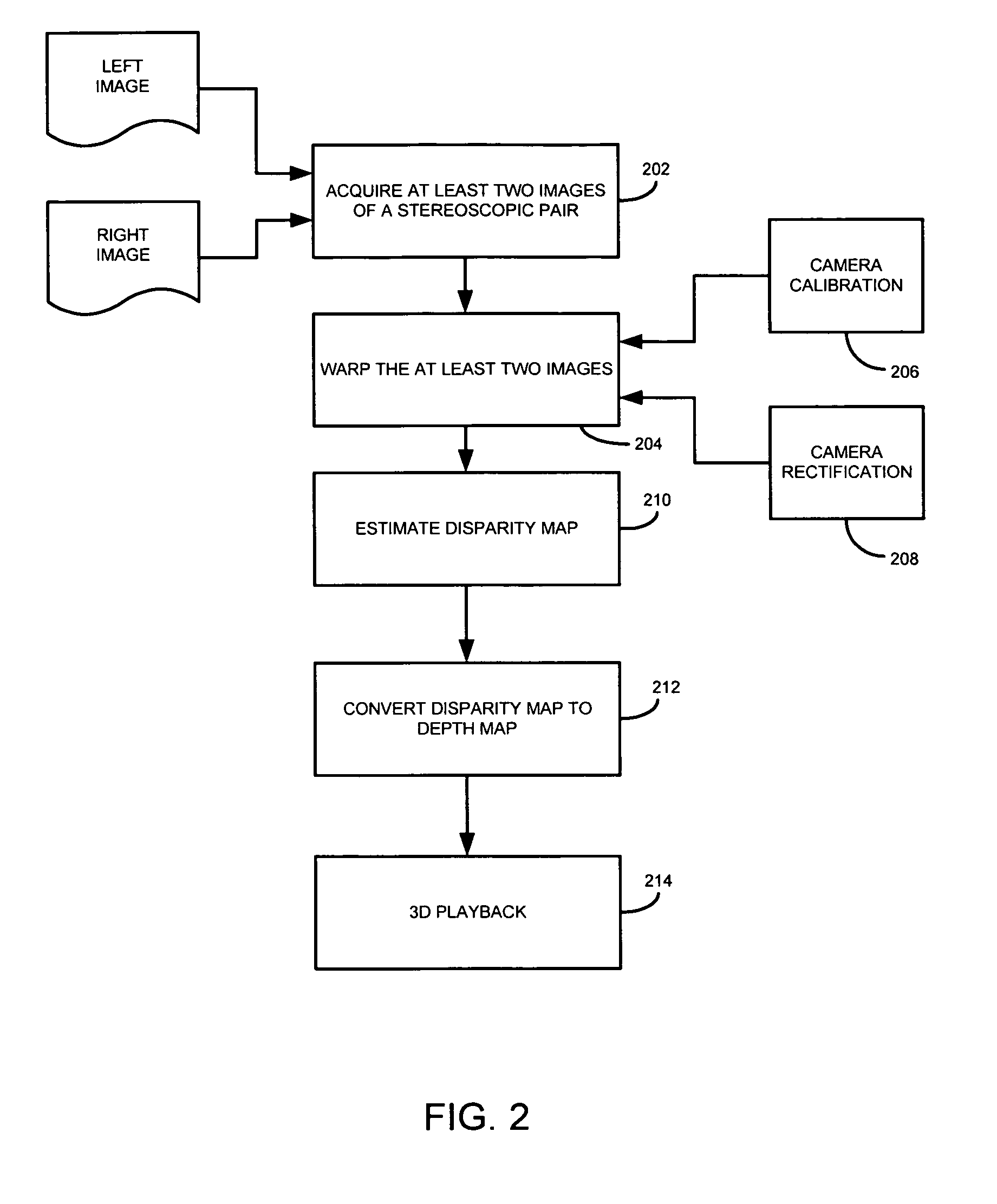
Method for conforming objects to a common depth perspective for converting two-dimensional images into three-dimensional images
InactiveUS7102633B2Depth accurateHighly realistic three-dimensional reproductionImage analysisGeometric image transformationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
Methods for converting two-dimensional images into three-dimensional images employing various interactive image processing tools that allow a user to apply any number or combination of image pixel repositioning depth contouring effects, algorithms or the like to create three-dimensional images.
Owner:REALD DDMG ACQUISITION LLC
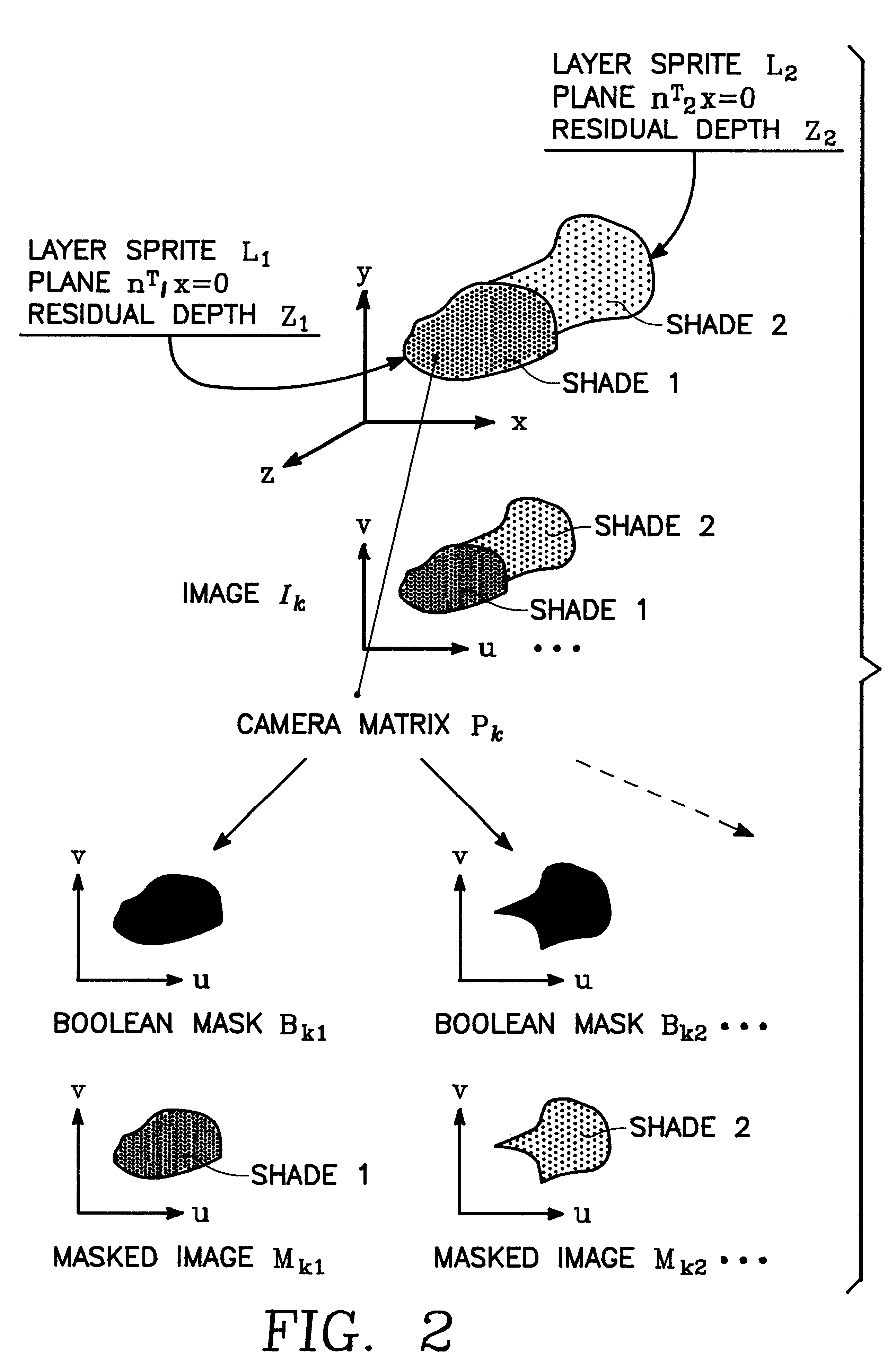
Stereo reconstruction employing a layered approach
InactiveUS6348918B1Improve performanceDepth accurateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A system and method for extracting structure from stereo that represents the scene as a collection of planar layers. Each layer optimally has an explicit 3D plane equation, a colored image with per-pixel opacity, and a per-pixel depth value relative to the plane. Initial estimates of the layers are recovered using techniques from parametric motion estimation. The combination of a global model (the plane) with a local correction to it (the per-pixel relative depth value) imposes enough local consistency to allow the recovery of shape in both textured and untextured regions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for conforming objects to a common depth perspective for converting two-dimensional images into three-dimensional images
InactiveUS20050099414A1Easy to createDepth accurateImage analysisGeometric image transformationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
Methods for converting two-dimensional images into three-dimensional images employing various interactive image processing tools that allow a user to apply any number or combination of image pixel repositioning depth contouring effects, algorithms or the like to create three-dimensional images.
Owner:REALD DDMG ACQUISITION LLC
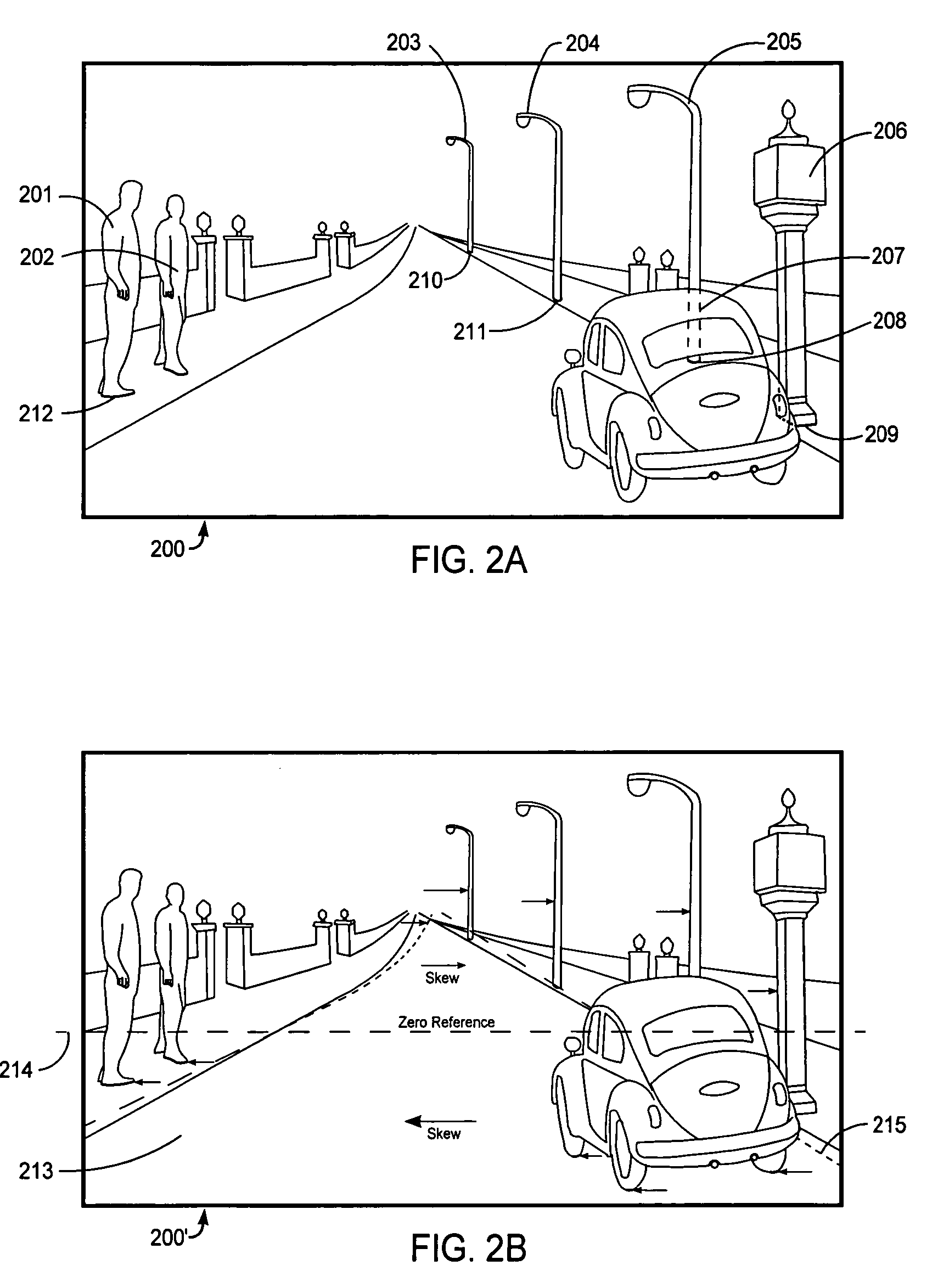
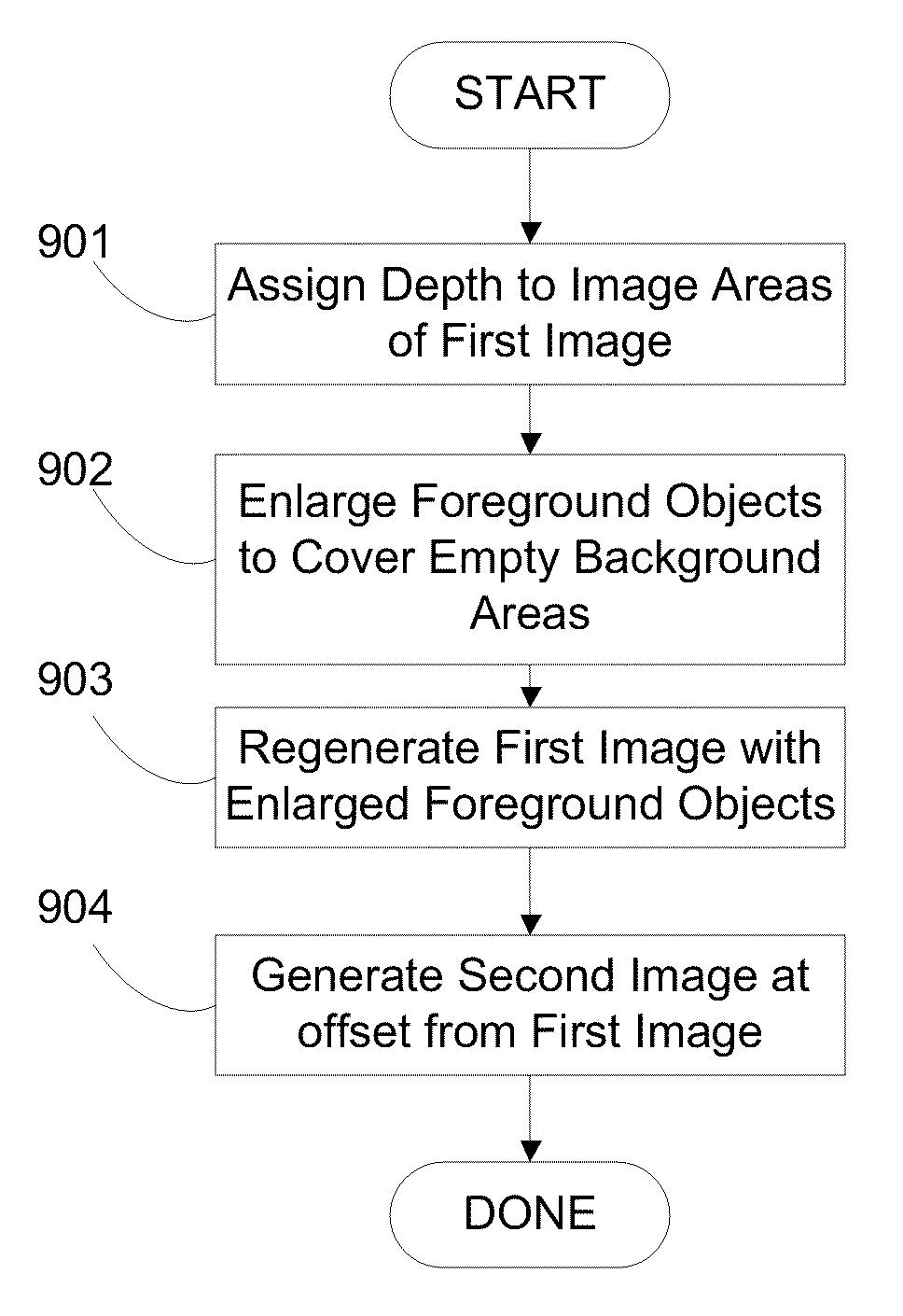
Image depth augmentation system and method
Image depth augmentation system and method for providing three-dimensional views from a two-dimensional image. Depth information is assigned by the system to areas of a first image via a depth map. Foreground objects are enlarged to cover empty areas in the background as seen from a second viewpoint at an offset distance from a first viewpoint of the first image. The enlarged objects are used to regenerate the first image and to generate the second image so that empty background areas are covered with the enlarged foreground objects. The resulting image pair may be viewed using any type of three-dimensional encoding and viewing apparatus. Can use existing masks from non-3D projects to perform depth augmentation and dither mask edges to provide for realistic soft edges for depth augmented objects.
Owner:PASSMORE CHARLES GREGORY
Precise location of buried metallic pipes and cables in the presence of signal distortion
ActiveUS20060036376A1Depth accurateCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic property measurementsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A new approach for locating an underground line described herein remains accurate in the face of bleedover by including both amplitude and phase from at least two magnetic field strength sensors in the measurement set. A numerical optimization step is introduced to deduce the positions and currents of each of several cables, of which one is the targeted cable and the others are termed bleedover cables. Furthermore, some embodiments of the method accounts for practical problems that exist in the field that relate to reliable estimation of cable positions, like the phase transfer function between transmitter and receiver, the estimation of confidence bounds for each estimate, and the rejection of false positive locates due to the presence of noise and interference.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
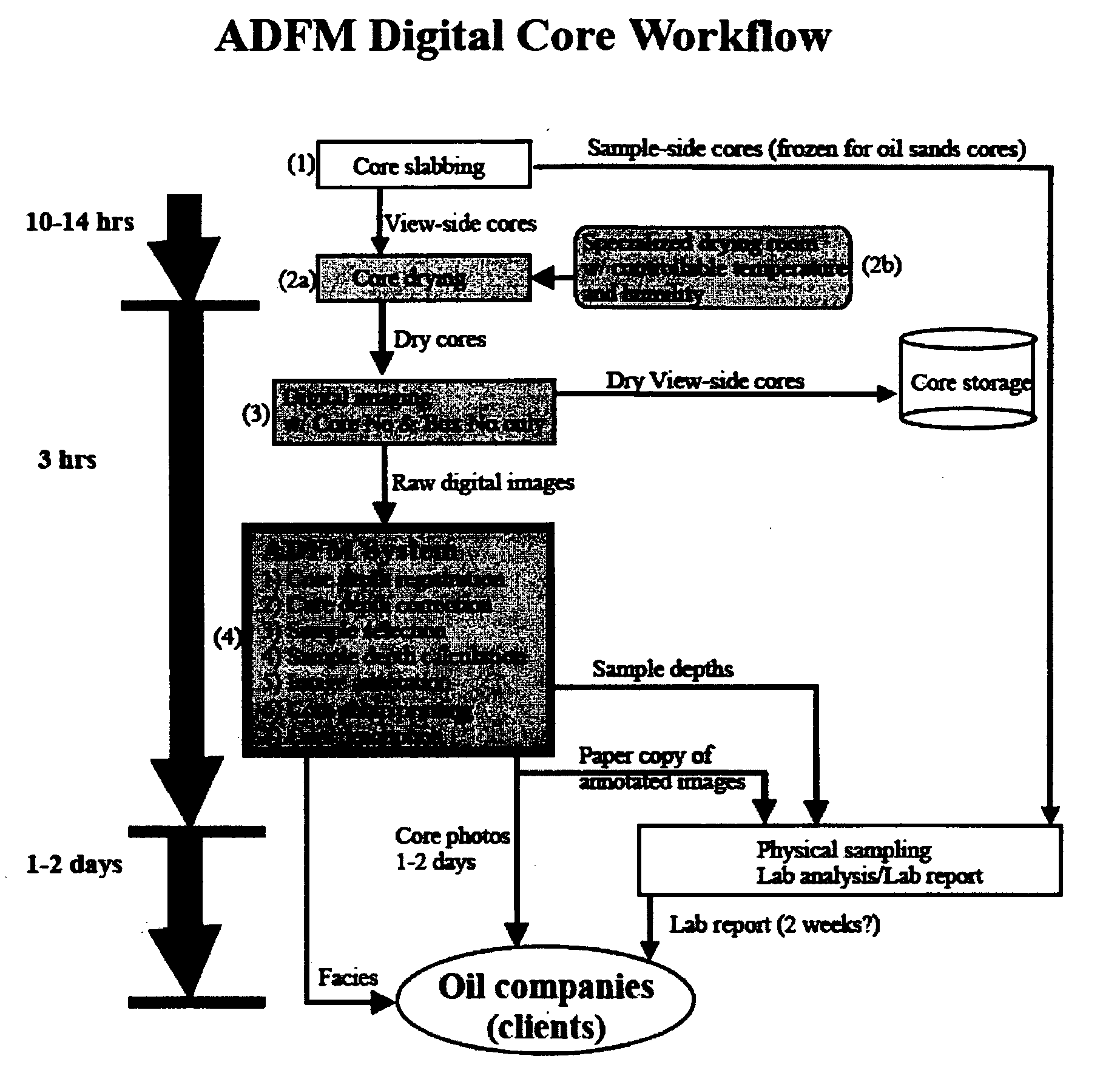
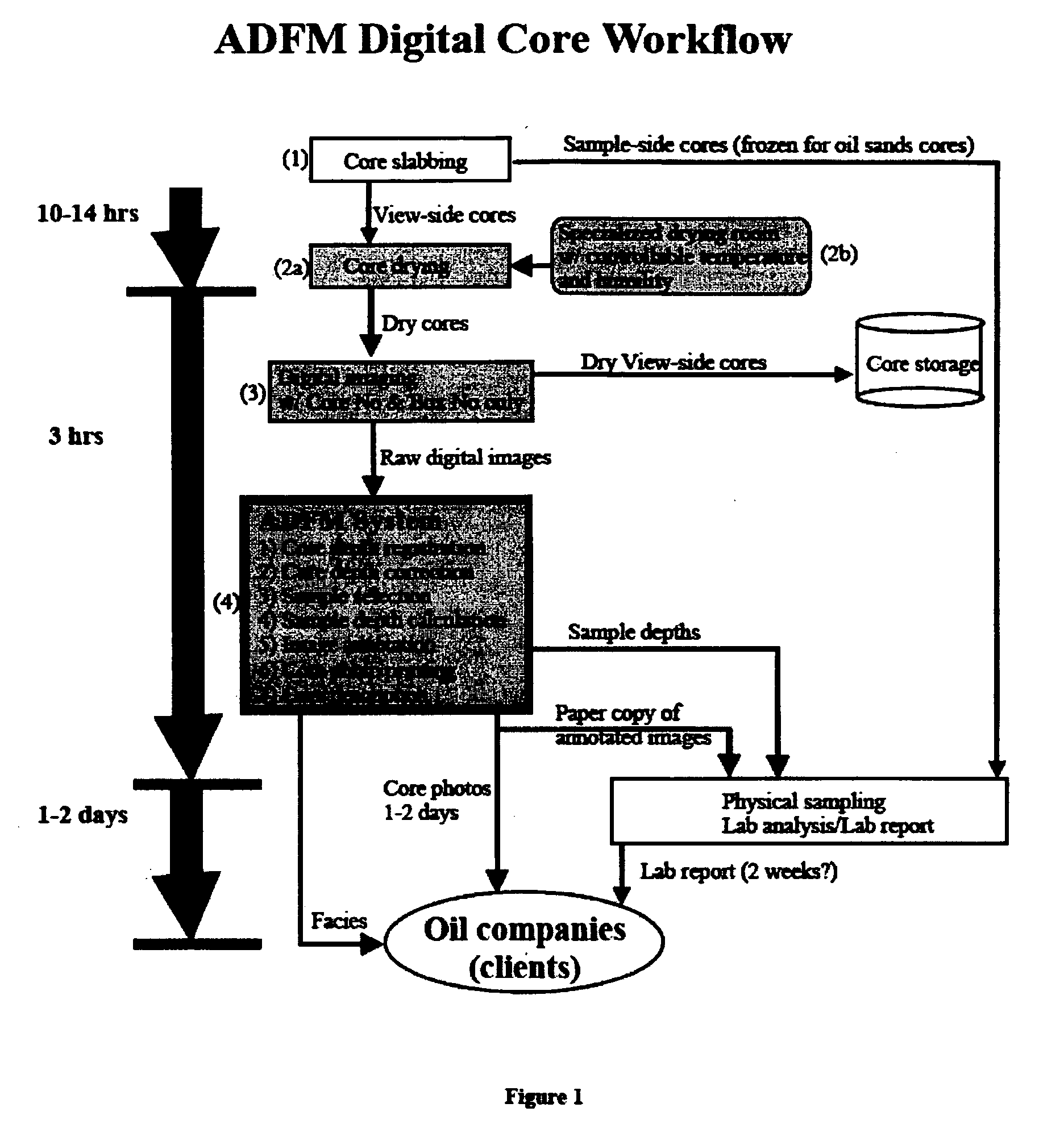
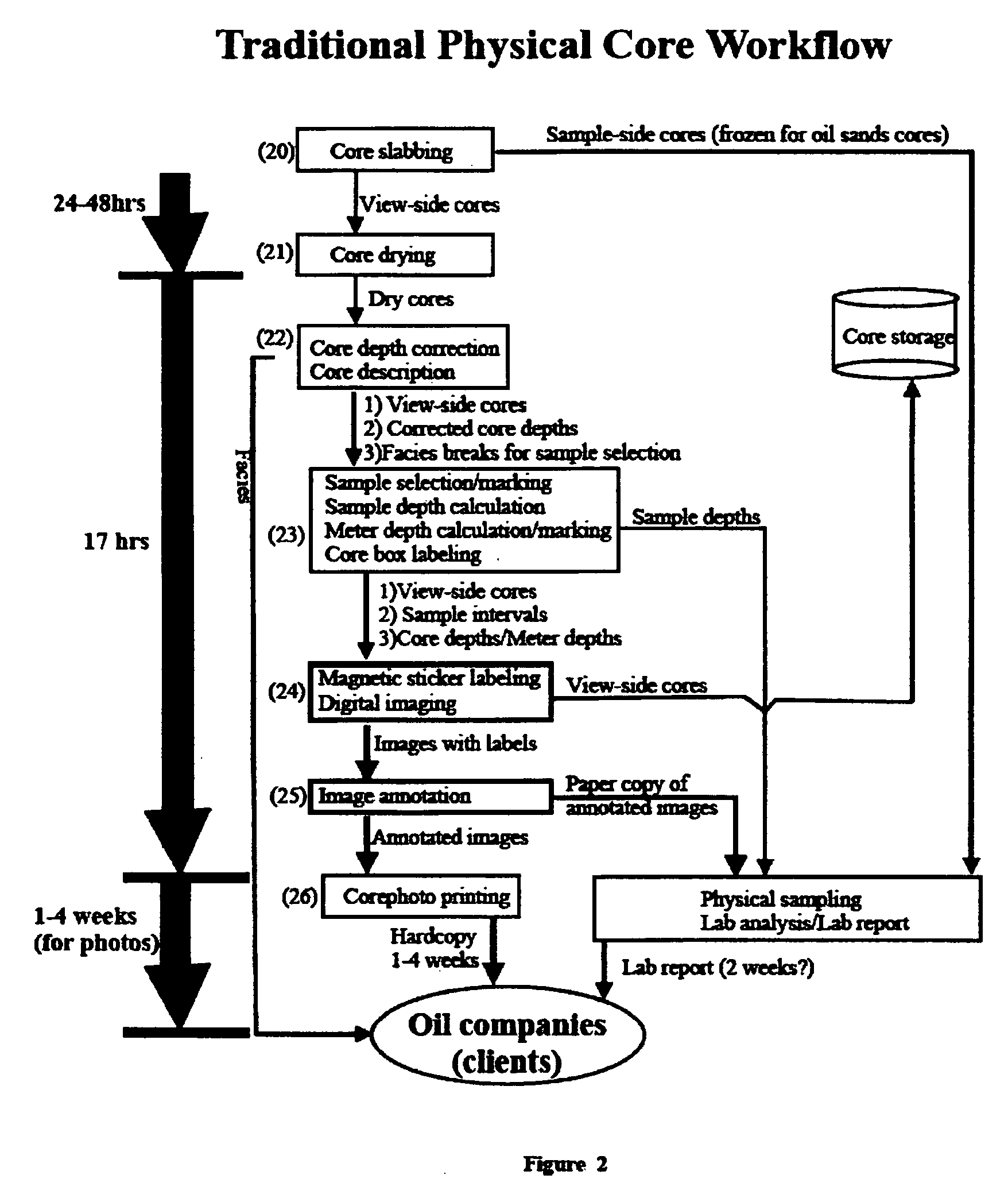
Digital core workflow method using digital core image
InactiveUS20070061079A1Many solutionsEasy to analyzeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyWell loggingField data
A method for registration and correction of downhole core depth information using digital core images. Digital core images are employed during depth registration, with top and base depths for a selected interval being determined by field data and a digital ruler which calculates an actual interval length based on the digital core image. Correction of the top and base depths is enabled by side-by-side display of the digital core image interval and corresponding well logging data, which displayed information can be manipulated by a user to provide more accurate depth information. The method further allows for shale volume calculations and facies interpretation, again employing the digital core images.
Owner:H & H CONSULTING
Auto-stereoscopic interpolation
ActiveUS20110134109A1Quicker and efficient and accurate three dimensional conversionHuge savingsSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingDepth mapComputer program
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for auto-stereoscopic interpolation. A first two dimensional image and a second two dimensional image are received. A reduced pixel image is generated for each of the first and second two dimensional images, wherein each reduced pixel image comprises a reduced pixel size that is less than the original pixel size. Boundary information is calculated for each of the first and second two dimensional images. A depth map is calculated for the first and second reduced pixel images, wherein the depth map comprises data indicative of three dimensional information for one or more objects in the first and second reduced pixel images. A depth map is calculated for the first and second two dimensional images based on the boundary information for each of the first and second two dimensional images and the depth map of the first and second reduced pixel images.
Owner:ALTER DOMUS US LLC
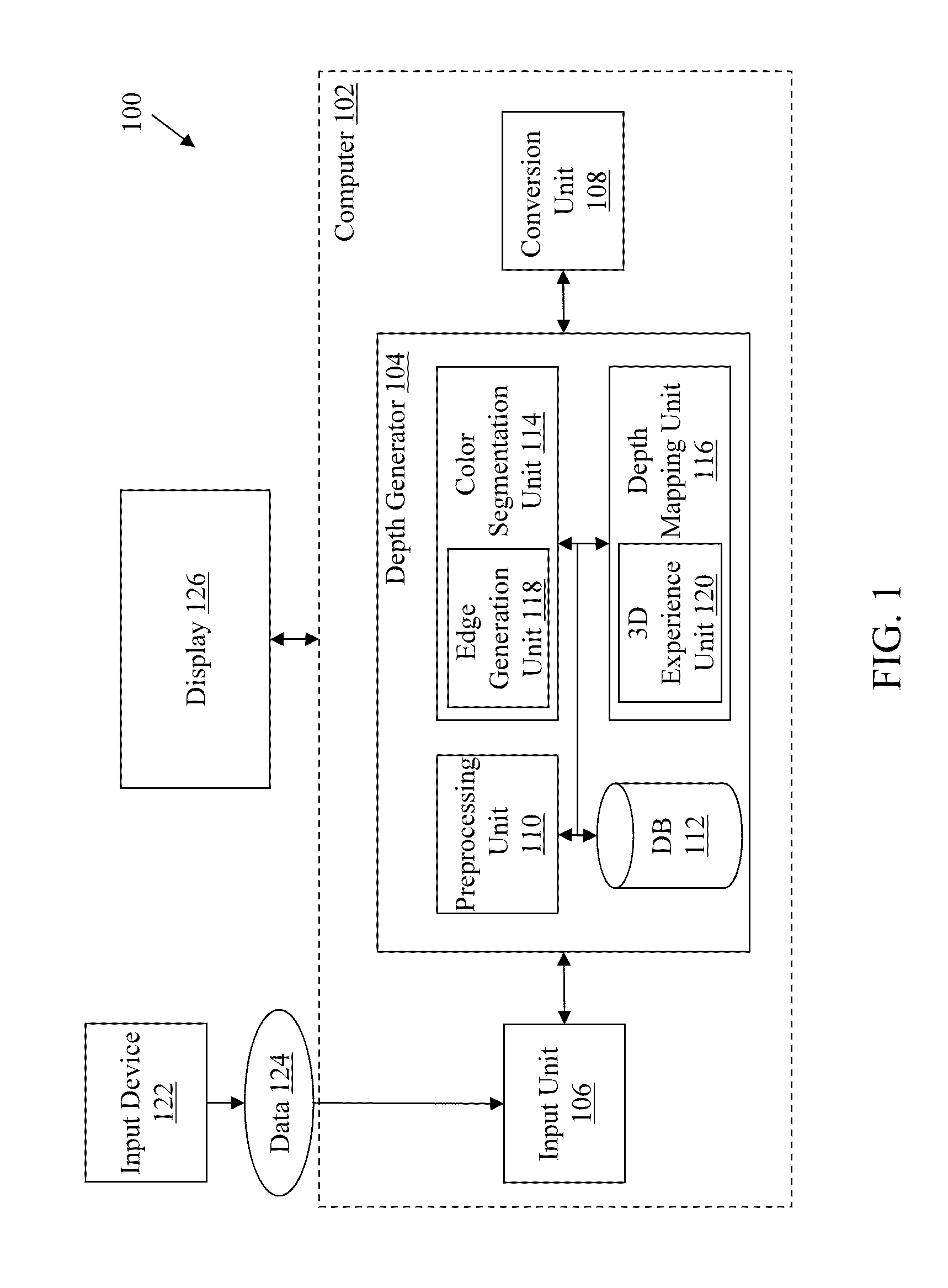
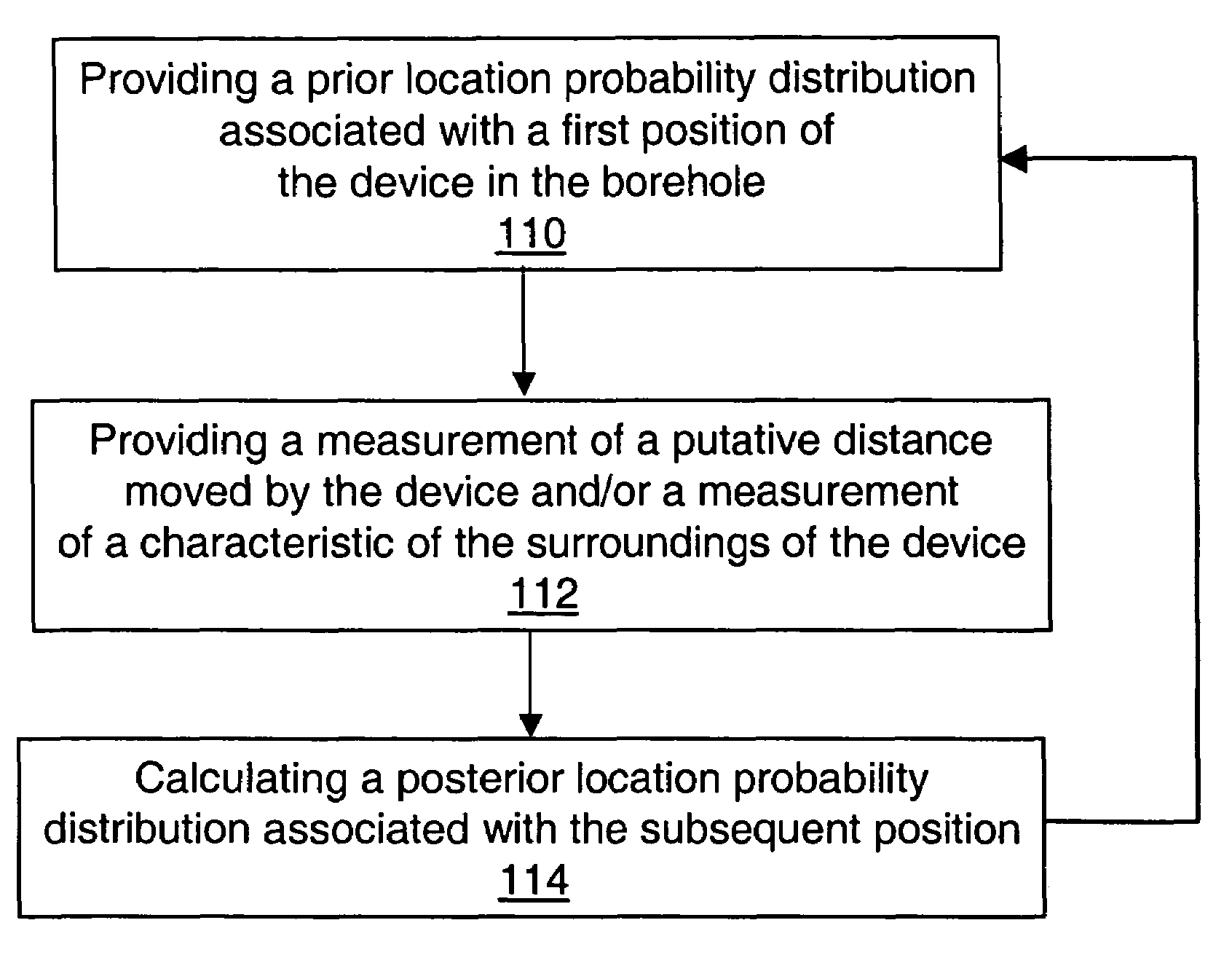
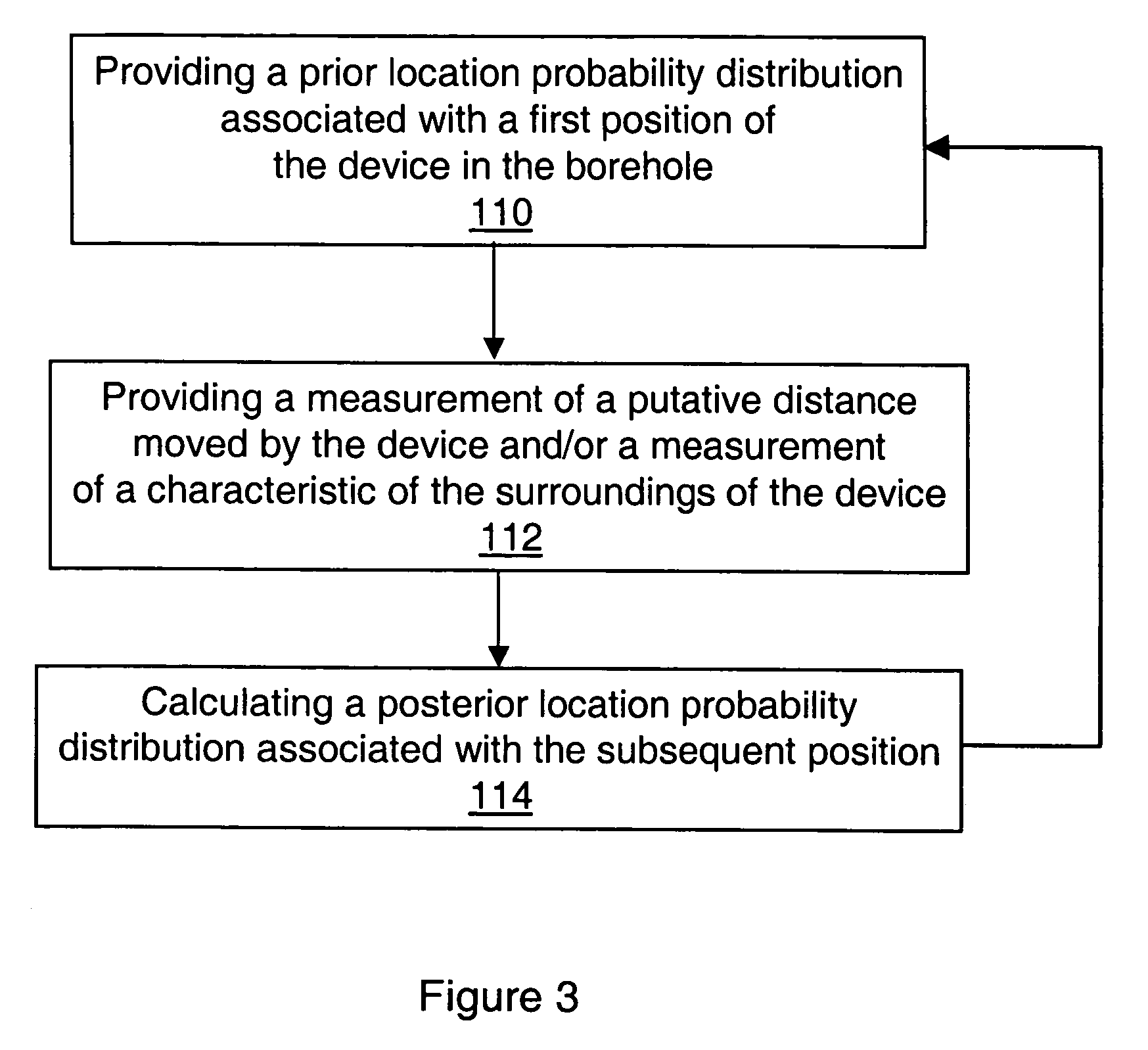
Method and system for estimating the position of a movable device in a borehole
InactiveUS7055601B2Improve accuracyConveniently combinedSurveyFluid removalPosition dependentComputer science
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
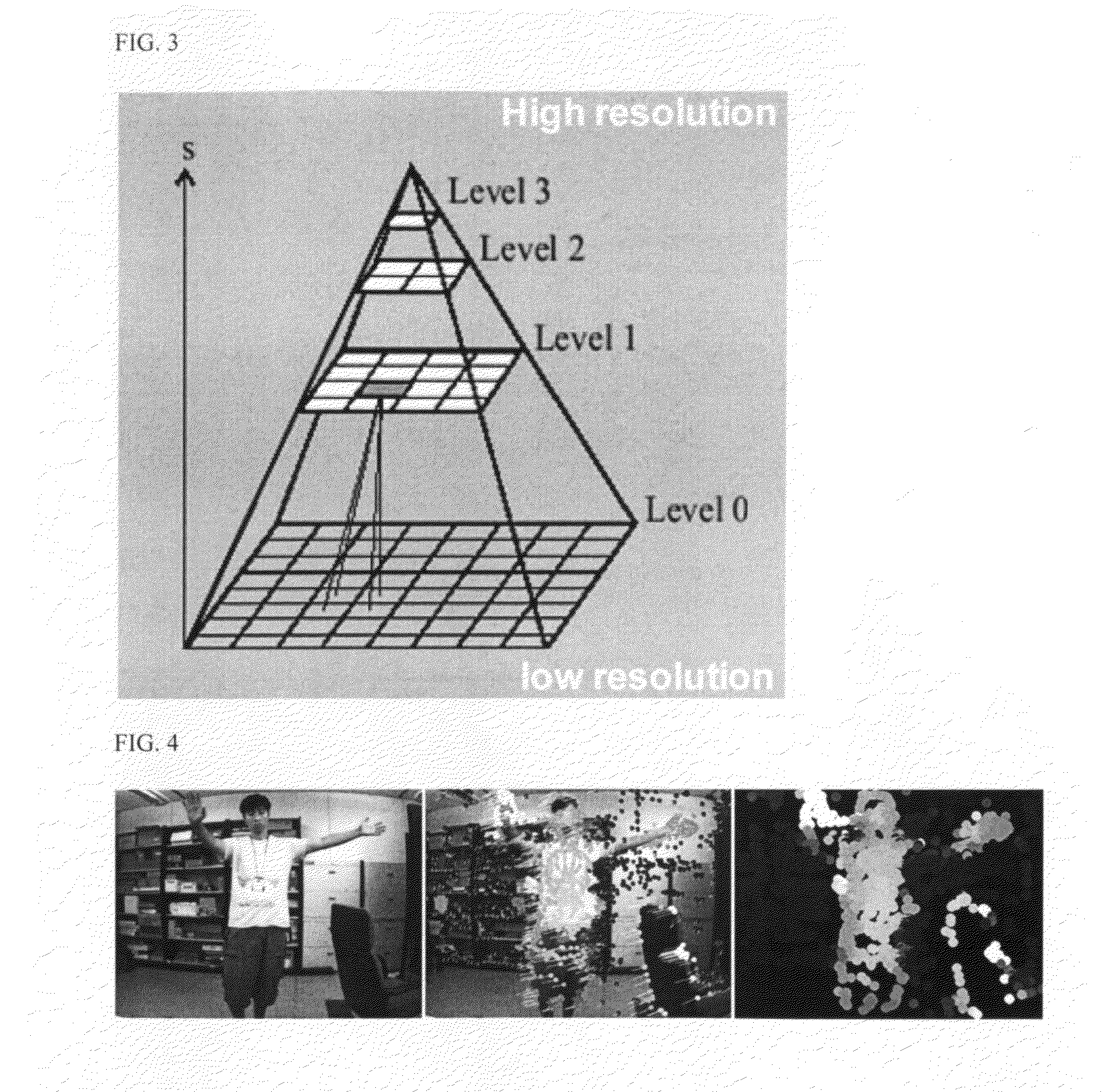
3D motion recognition method and apparatus
InactiveUS20120148097A1Depth accurateReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional motionOptical flow
Disclosed are a three-dimensional motion recognition method and an apparatus using a motion template method and an optical flow tracking method of feature points. The three dimensional (3D) motion recognition method through feature-based stereo matching according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure includes: obtaining a plurality of images from a plurality of cameras; extracting feature points from a single reference image; and comparing and tracking the feature points of the reference image and another comparison image photographed at the same time using an optical flow method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Spiral tubular tool and method
InactiveUS20050000692A1Depth accurateImprove anchoring abilityConstructionsInsulationBiomedical engineeringHelix
Owner:COOK ROBERT BRADLEY +1
Layered structures
InactiveUS20050118349A1Depth accurateHigh energyPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWide bandWide gap
A process of making a product which comprises at least two layers in contact with each other, each layer being of a wide-gap material and each layer differing from each other in at least one property, includes the steps of: (i) providing a substrate of a wide-band gap material having a surface and a region adjacent the surface having a particular characteristic, (ii) ion implanting the substrate through the surface to form a damaged layer below that surface, (iii) growing a layer of a wide-band gap material by chemical vapour deposition on at least a portion of the surface of the substrate through which ion implantation occurred, the material of the grown layer having a characteristic different to that of the region of the substrate adjacent the surface through which ion implantation occurred, and (iv) severing the substrate through the damaged layer. The wide-gap material is preferably diamond.
Owner:WHITEHEAD ANDREW JOHN +2
Centralized seed distribution system for planter
InactiveUS6494154B2Depth accurateReduce the overall heightSpadesAgricultural machinesDistribution systemGuide tube
Owner:KINZE MFG INC
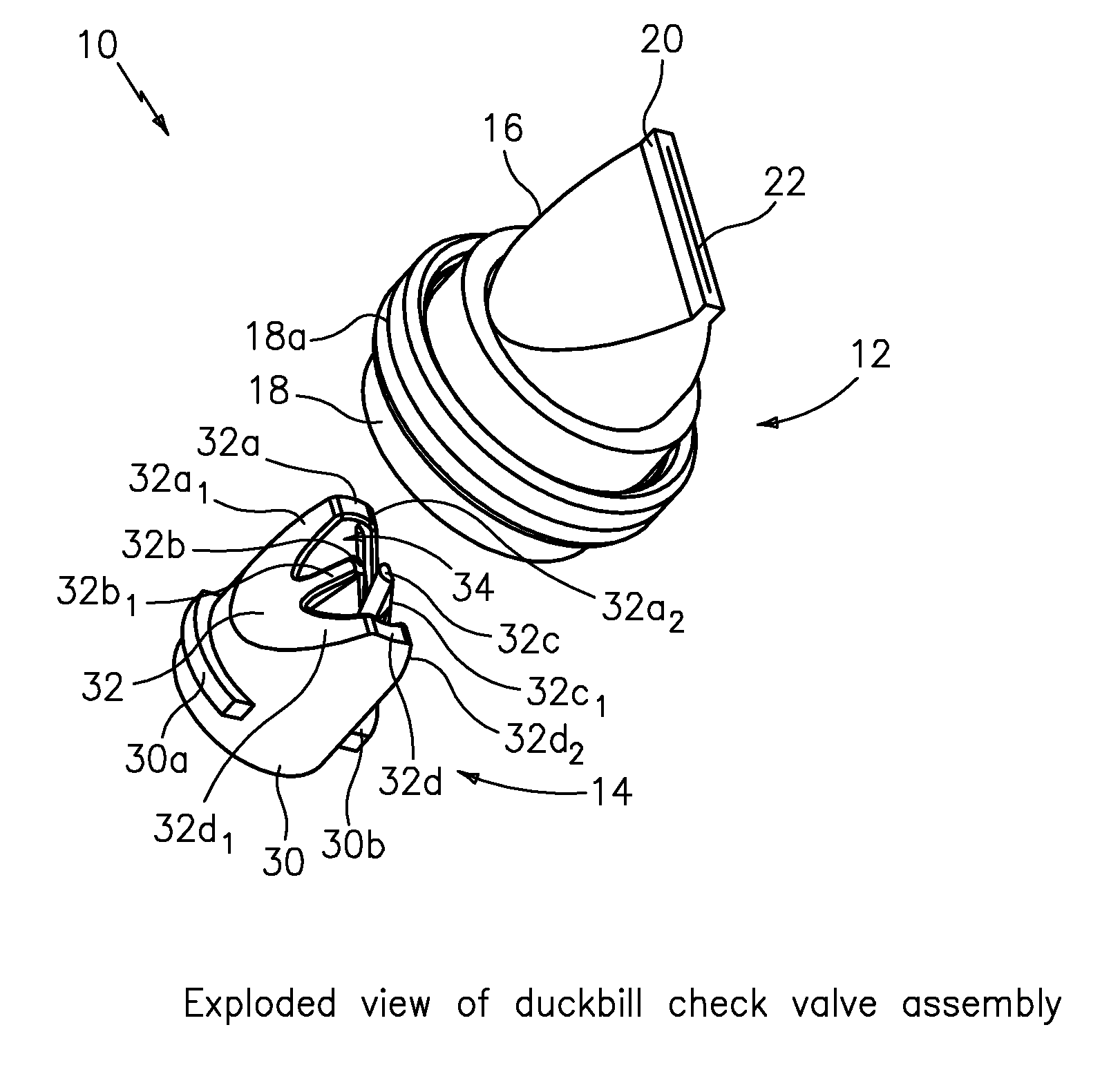
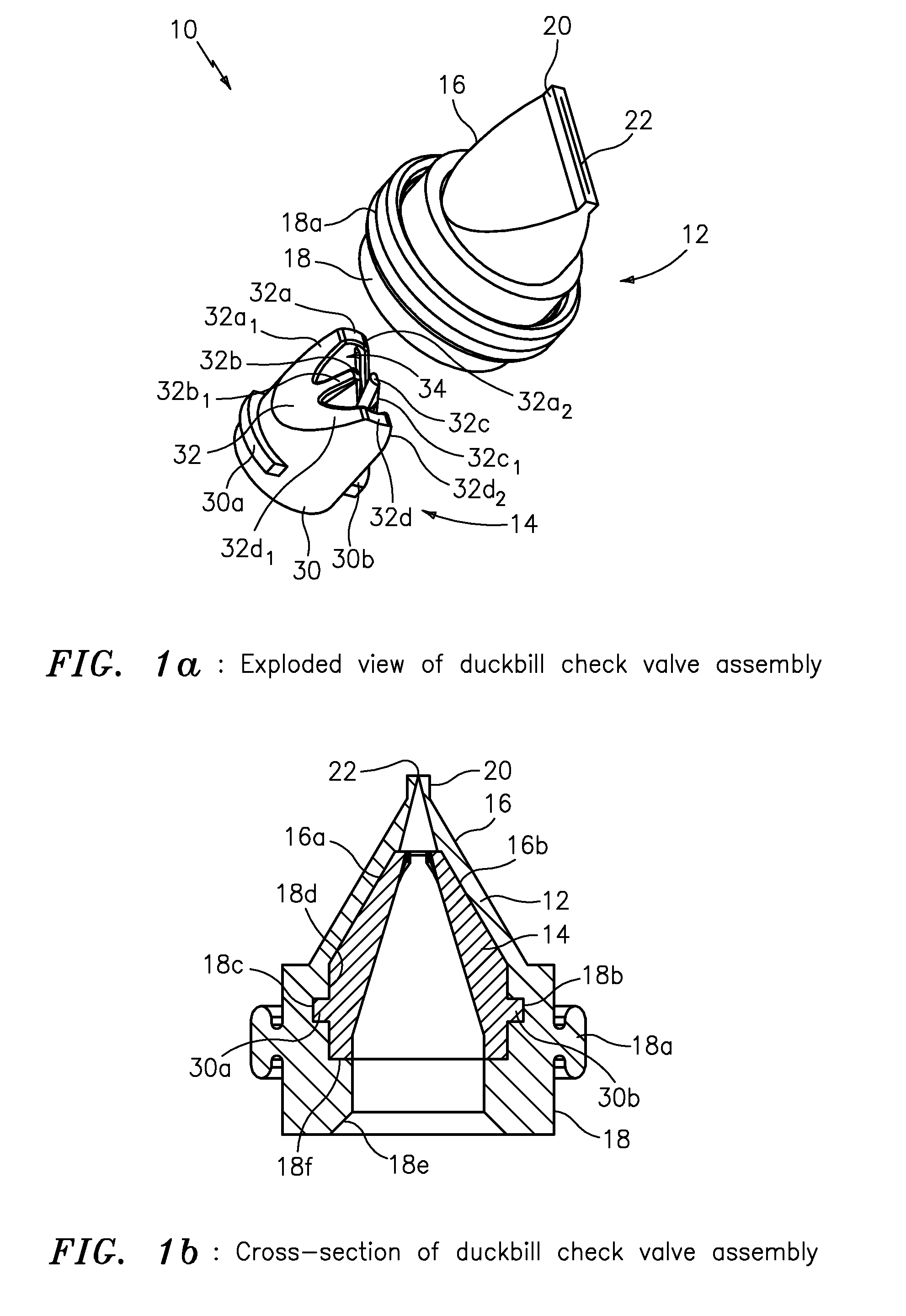
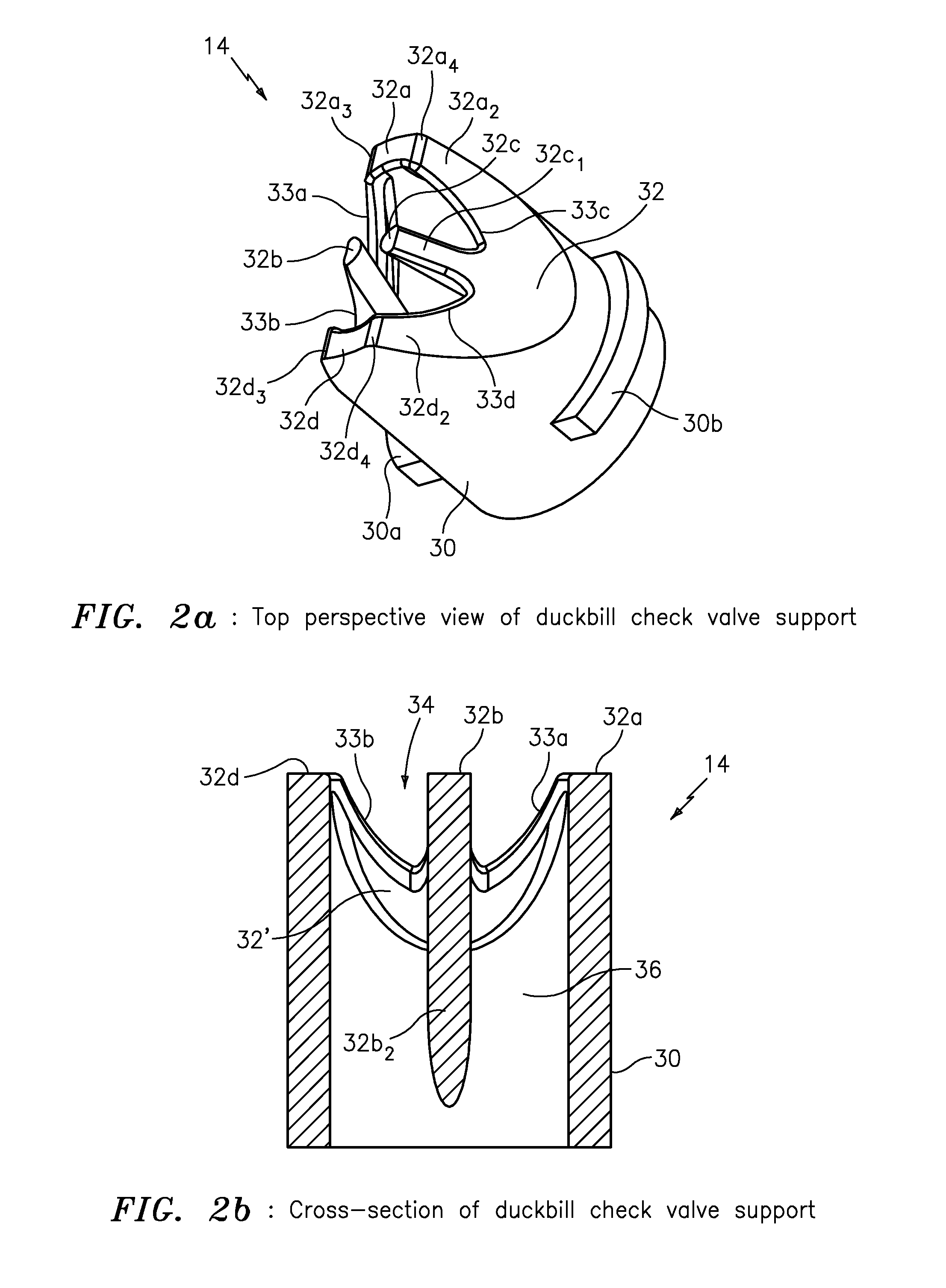
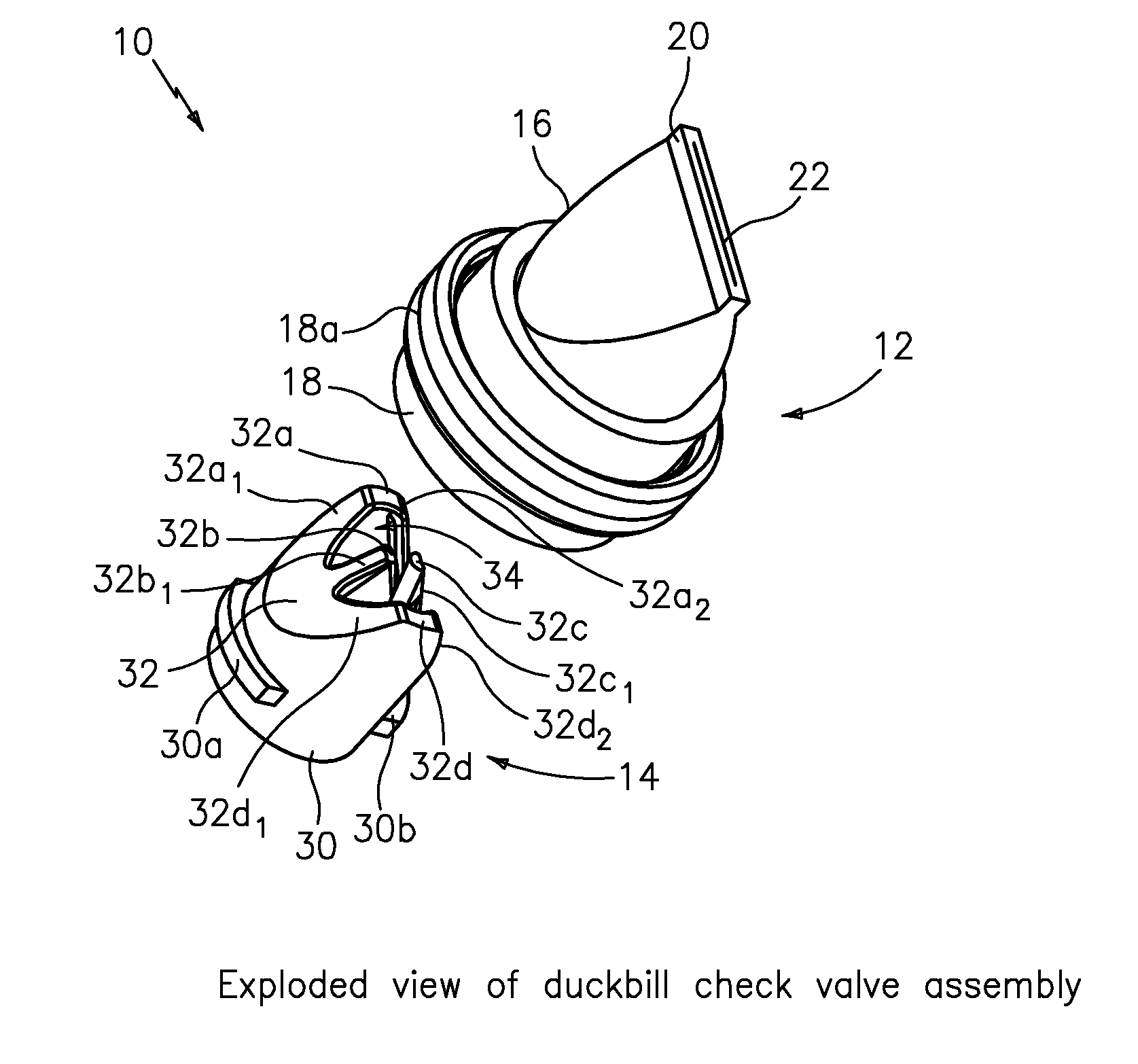
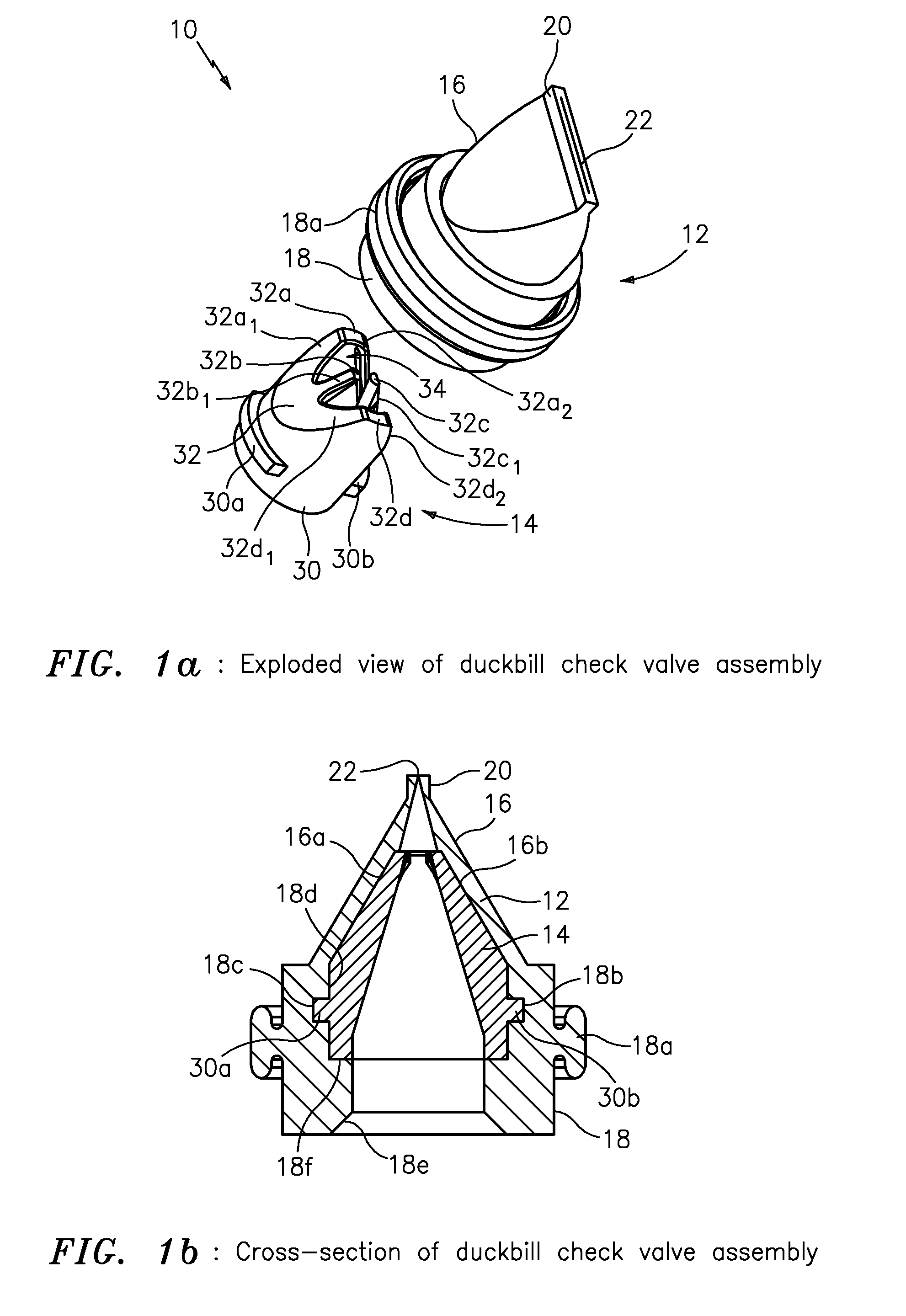
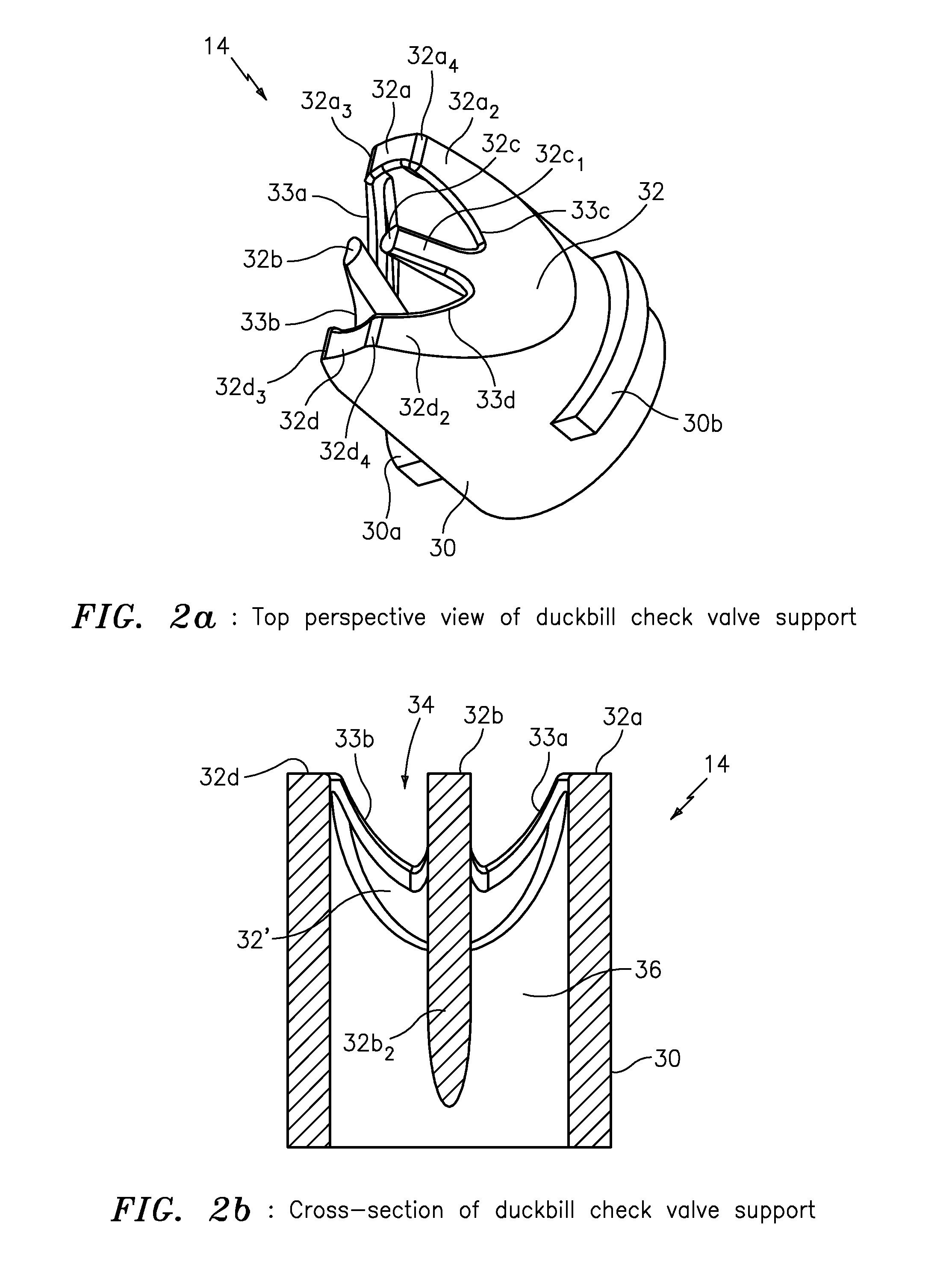
High pressure duckbill valve and insert
ActiveUS20110108139A1Large openingIncrease back pressureCheck valvesEqualizing valvesParticulatesEngineering
The present invention provides apparatus featuring a check valve featuring a duckbill valve configured to provide fluid and particulate; and an insert having a base portion configured to seat the insert inside the duckbill valve, and a W-shaped portion configured with an opening to pass the fluid and particulate through the duckbill valve and also configured to provide support for walls of the duckbill valve in response to back pressure caused by the fluid and particulate.
Owner:XYLEM IP HLDG
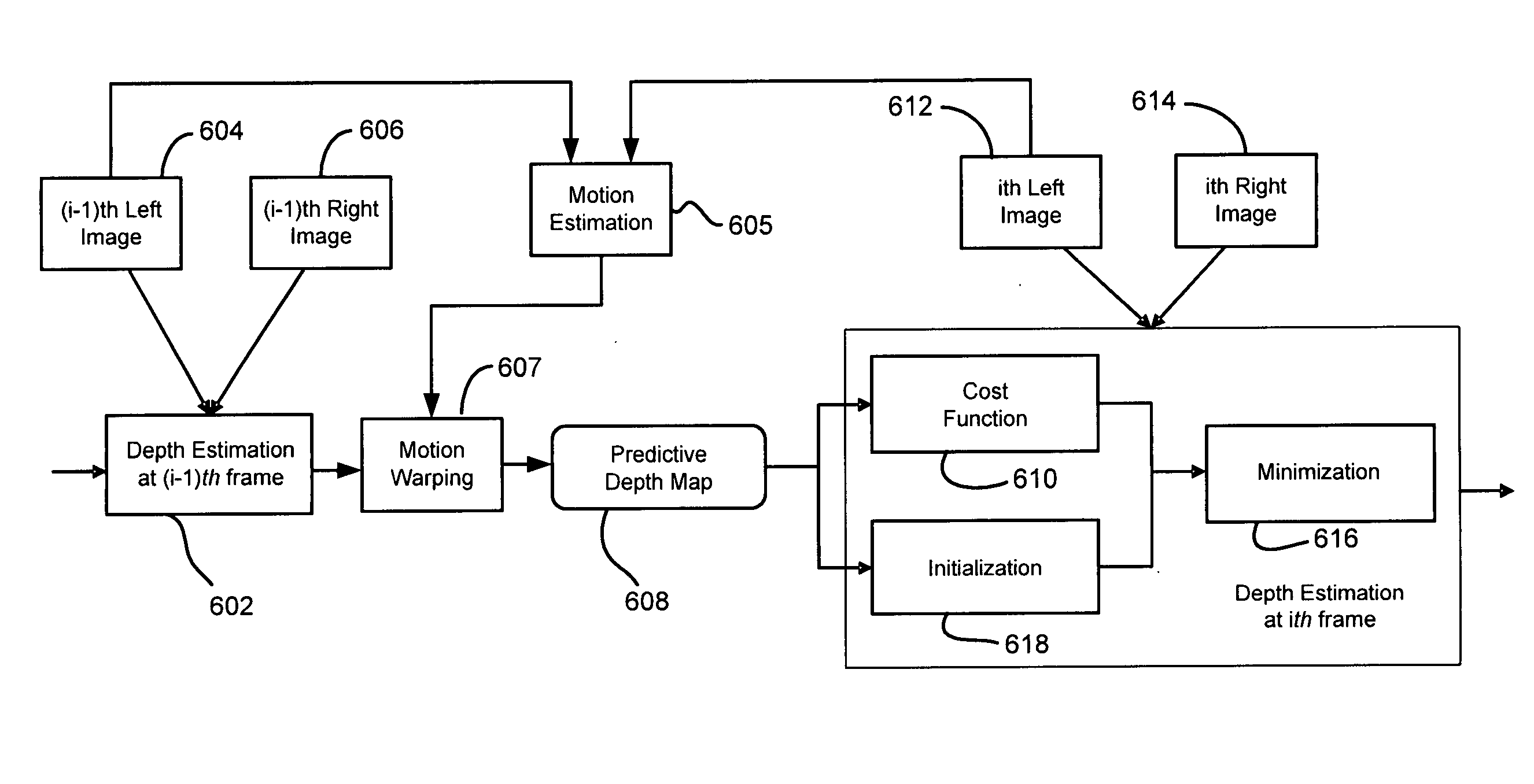
System and method for depth extraction of images with motion compensation
InactiveUS20110110583A1Depth accurateMinimizing disparityImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxFrame based
A system and method for spatiotemporal depth extraction of images are provided. The system and method provide for acquiring a sequence of images from a scene, the sequence including a plurality of successive frames of images, estimating the disparity of at least one point in a first image with at least one corresponding point in a second image for at least one frame, estimating motion of the at least one point in the first image, estimating the disparity of the at least one next successive frame based on the estimated disparity of at least one previous frame in a forward direction of the sequence, wherein the estimate disparity is compensated with the estimated motion, and minimizing the estimated disparity of each of the plurality of successive frames based on the estimated disparity of at least one previous frame in a backward direction of the sequence.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
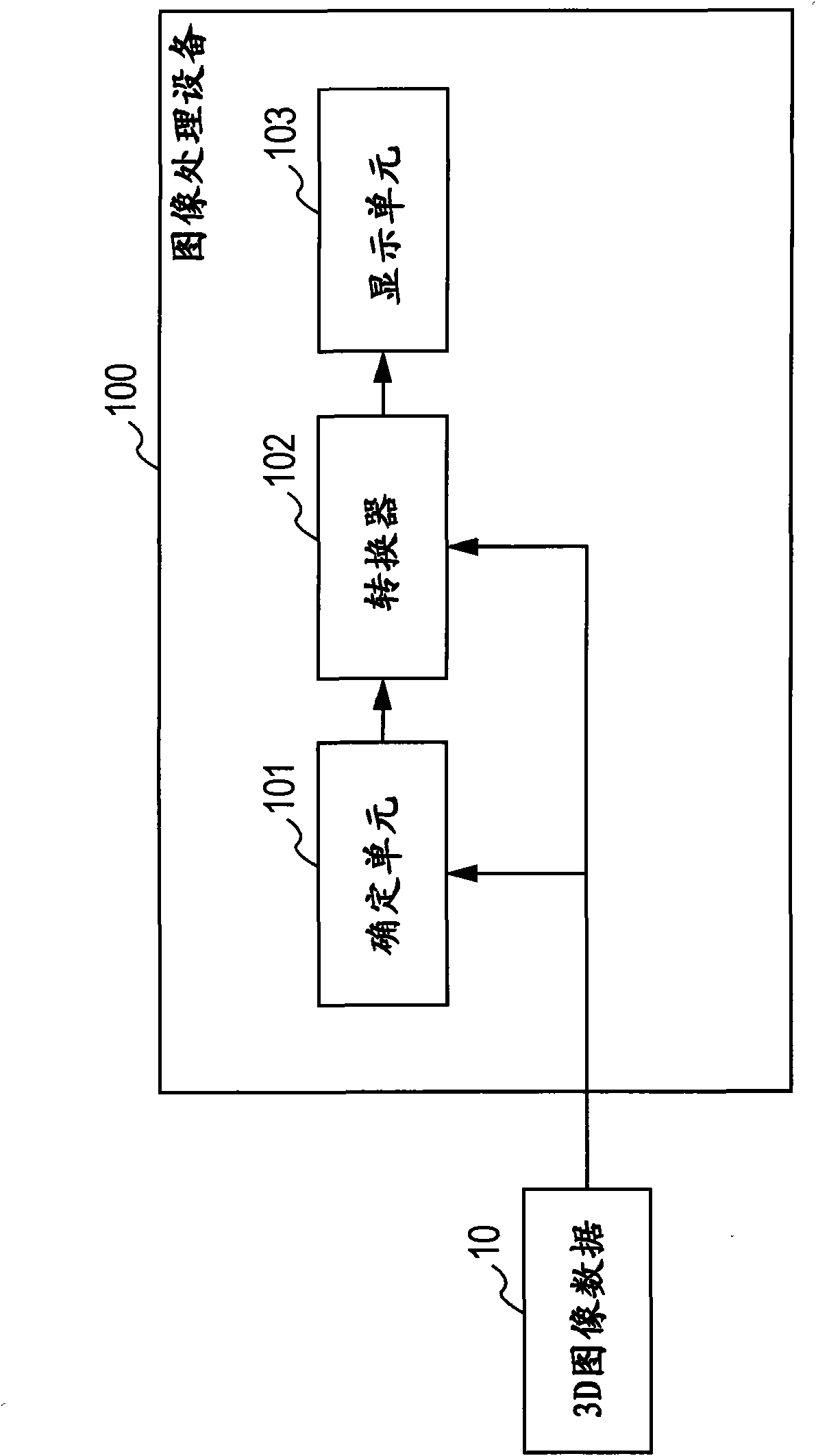
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
An image processing apparatus includes a determining unit, a converter, and a display unit. The determining unit receives image data for three-dimensional display as input, and determines the three-dimensional display format corresponding to the input data. The converter converts the input data in accordance with the determination results from the determining unit. The display unit displays the converted results from the converter.
Owner:SONY CORP
Spiral tubular tool and method
InactiveUS7104323B2Depth accurateImprove anchoring abilityCleaning apparatusFluid removalBiomedical engineeringHelix
Owner:COOK ROBERT BRADLEY +1
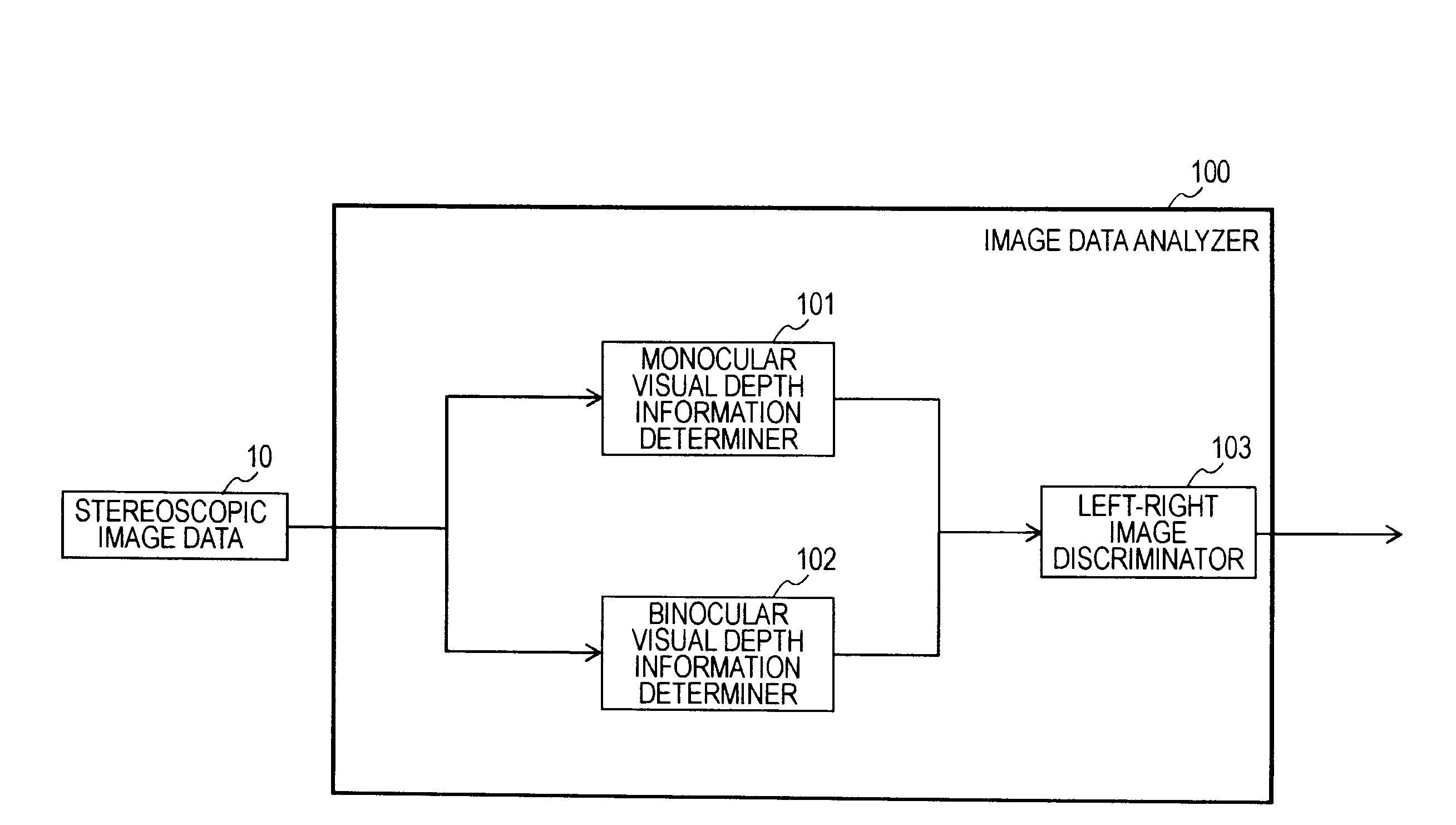
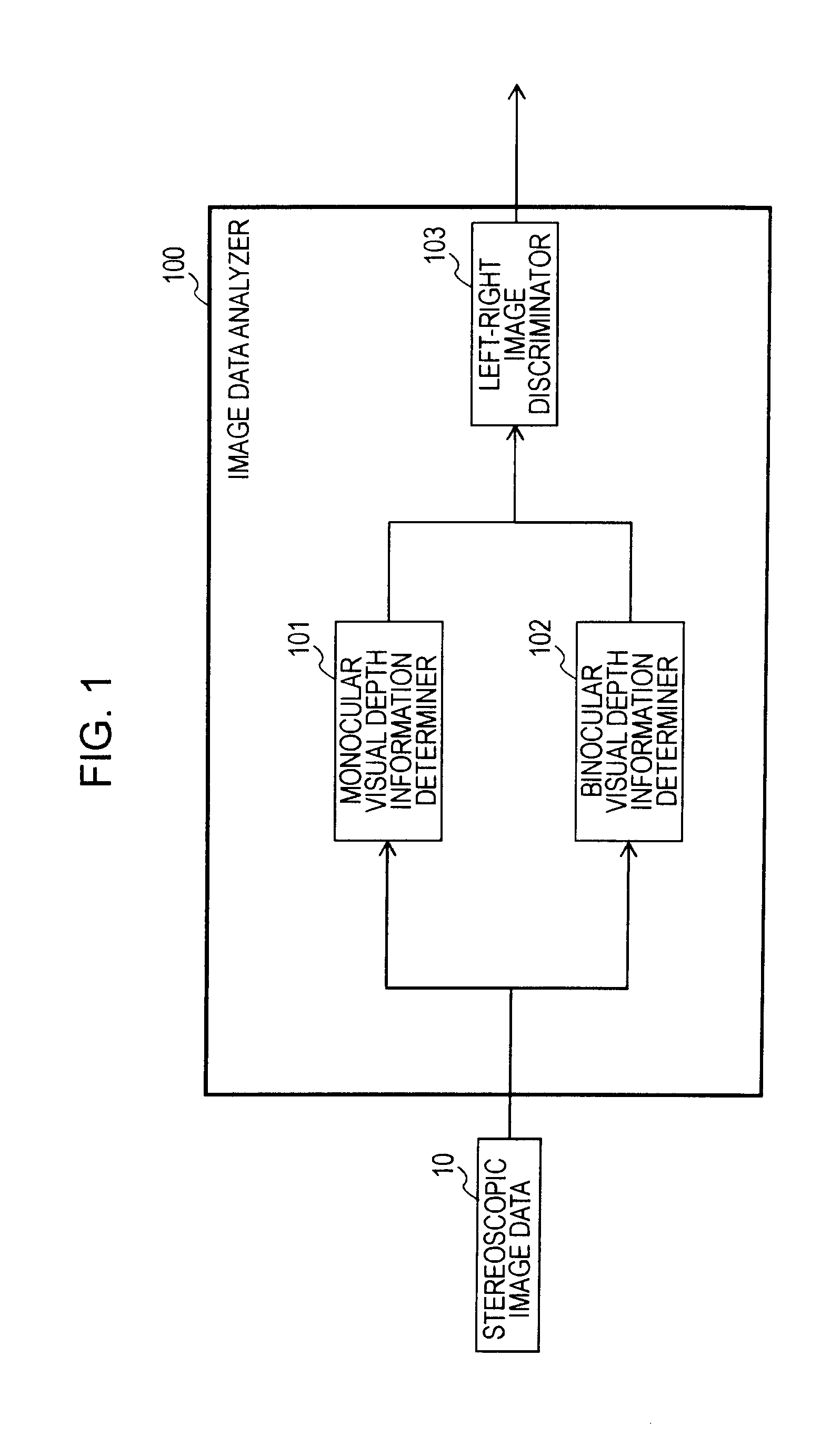
Apparatus, method, and computer program for analyzing image data
InactiveUS20100060720A1Accurately determineAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisDiscriminatorHigh rate
An image data analyzing apparatus includes a monocular visual depth information determiner for determining the anteroposterior relationship of regions contained in an image frame of one of a left image and a right image forming stereoscopic image data of time-division display type, a binocular visual depth information determiner for determining the anteroposterior relationship of regions contained in a plurality of images assumed to be the left image and right image, and a left-right image discriminator for outputting left-right image identification information in agreement with an assumption of the binocular visual depth information determiner if a pair of determination results show a high rate of agreement, and outputting left-right image identification information in agreement with a reverse setting of the assumption if the pair of determination results show a low rate of agreement.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods and Apparatus for Coded Time-of-Flight Camera
ActiveUS20150120241A1Accurate measurementDepth accurateOptical rangefindersMechanical depth measurementsWiener deconvolutionMultipath interference
In illustrative implementations, a time-of-flight camera robustly measures scene depths, despite multipath interference. The camera emits amplitude modulated light. An FPGA sends at least two electrical signals, the first being to control modulation of radiant power of a light source and the second being a reference signal to control modulation of pixel gain in a light sensor. These signals are identical, except for time delays. These signals comprise binary codes that are m-sequences or other broadband codes. The correlation waveform is not sinusoidal. During measurements, only one fundamental modulation frequency is used. One or more computer processors solve a linear system by deconvolution, in order to recover an environmental function. Sparse deconvolution is used if the scene has only a few objects at a finite depth. Another algorithm, such as Wiener deconvolution, is used is the scene has global illumination or a scattering media.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and System for Non-Contact Fluorescence Optical Tomography with Patterned Illumination
ActiveUS20070286468A1Depth accurateEfficiently obtainedMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical tomographyData set
A method and system for non-contact fluorescent optical tomography using patterned illumination is disclosed. The method comprises illuminating a surface of a medium with light from at least one excitation light source to project at least two patterns. Each pattern comprises at least one motif, wherein the medium comprises at least one fluorescent target. The method further comprises for each pattern, measuring excitation light reflected from the medium to generate an excitation data set. In addition, the method comprises, for each pattern, measuring fluorescence emitted from the at least one fluorescent target to generate a fluorescence data set. The method also comprises generating a 3D image of the at least one fluorescent target in the medium by applying iterative algorithm. The iterative algorithm minimizes the difference between a predicted data set based on a mathematical model, and each excitation data set and each fluorescence data set.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Tof camera system and a method for measuring a distance with the system
ActiveUS20170123067A1Exclude influenceAccurate depth mapElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging processingLight beam
The invention relates to a method for measuring a distance between an object of a scene and a Time-Of-Flight camera system, and providing a depth map of the object, the Time-Of-Flight camera system comprising an illumination unit, an imaging sensor having a matrix of pixels and image processing means, the method being characterized by the following steps: modifying in a discrete way the illumination of said illumination unit in order to illuminate elementary areas of the scene with different incident intensities, respectively, for distinguishing the direct incident light beams from the indirect incident light beams; receiving onto the pixels of the matrix of the sensor the beams reflected by said elementary areas and providing the image processing means with corresponding data; processing the said corresponding data for eliminating the influence of the indirect light beams in the depth map of the object.
Owner:SONY DEPTHSENSING SOLUTIONS SA NV
High pressure duckbill valve and insert
ActiveUS8276616B2Large openingIncrease back pressureCheck valvesEqualizing valvesParticulatesEngineering
The present invention provides apparatus featuring a check valve featuring a duckbill valve configured to provide fluid and particulate; and an insert having a base portion configured to seat the insert inside the duckbill valve, and a W-shaped portion configured with an opening to pass the fluid and particulate through the duckbill valve and also configured to provide support for walls of the duckbill valve in response to back pressure caused by the fluid and particulate.
Owner:XYLEM IP HLDG
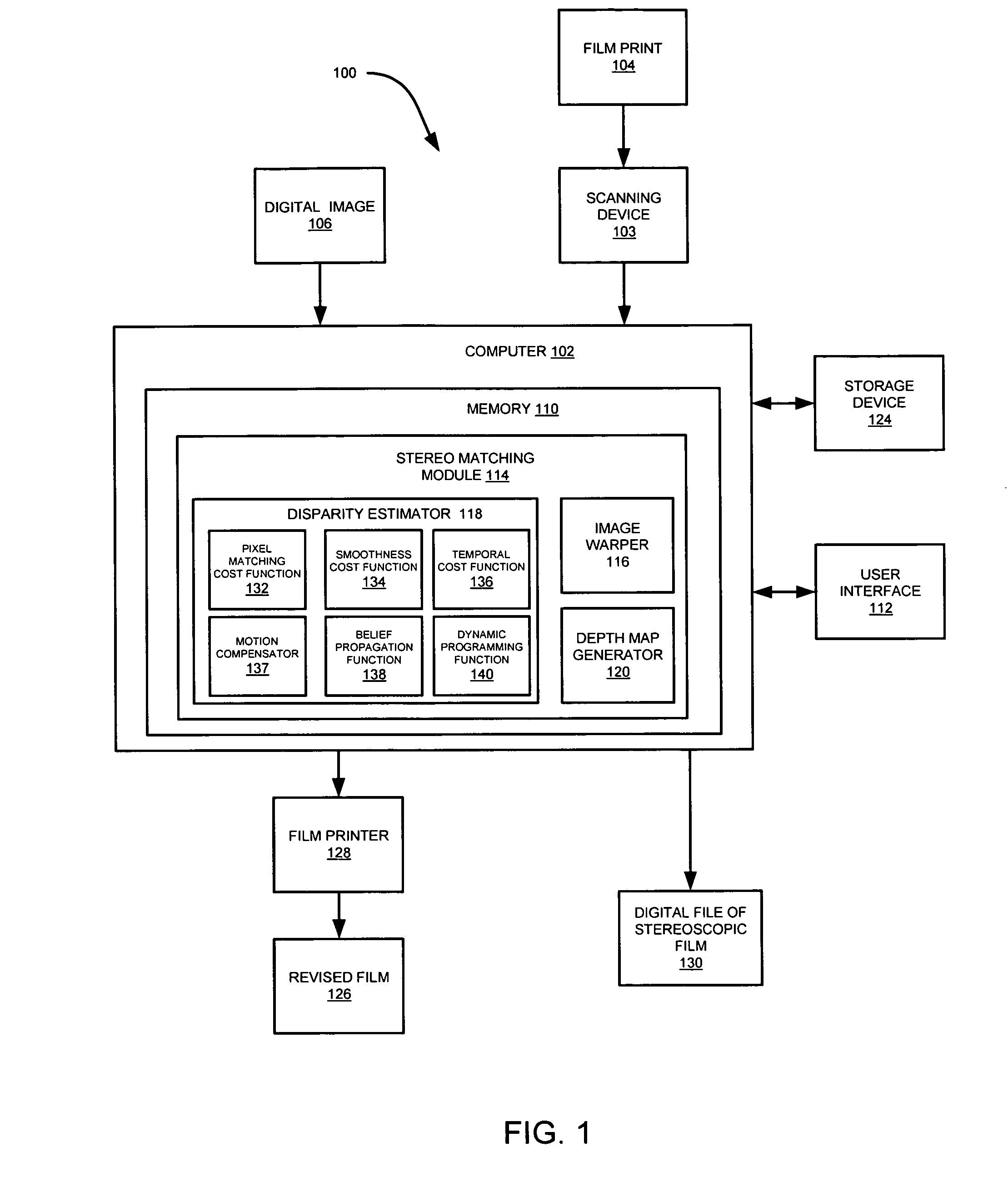
Pulling keys from color segmented images
ActiveUS20110135194A1Quicker and efficient and accurate three dimensional conversionHuge savingsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceDepth map
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for pulling keys from color segmented images. Data indicative of a two dimensional image is stored in a data storage device, the two dimensional image comprising a plurality of pixels. A plurality of color segmented frames are generated based on the two dimensional image, wherein each color segmented frame comprises one or more objects. For each of the color segmented frames, a key is generated based on the one or more objects. A depth map is calculated for the two dimensional image based on the keys, wherein the depth map comprises data indicative of three dimensional information for each pixel of the two dimensional image.
Owner:ALTER DOMUS US LLC
System, method and apparatus for implementing dental implants
ActiveUS20110287381A1Accurately and intimately coupledGreat frictional fitDental implantsDental toolsSelf limitingModular design
A system, apparatus, device, tools and method is provided for the insertion of improved anatomically corrected modular design anterior and posterior dental implants, the apparatus including a root component and a head / abutment component, wherein the root component is inserted into the jawbone using precision surgical guide tools in combination with self-limiting surgical templates and a precision adjustable clamping device.
Owner:MID
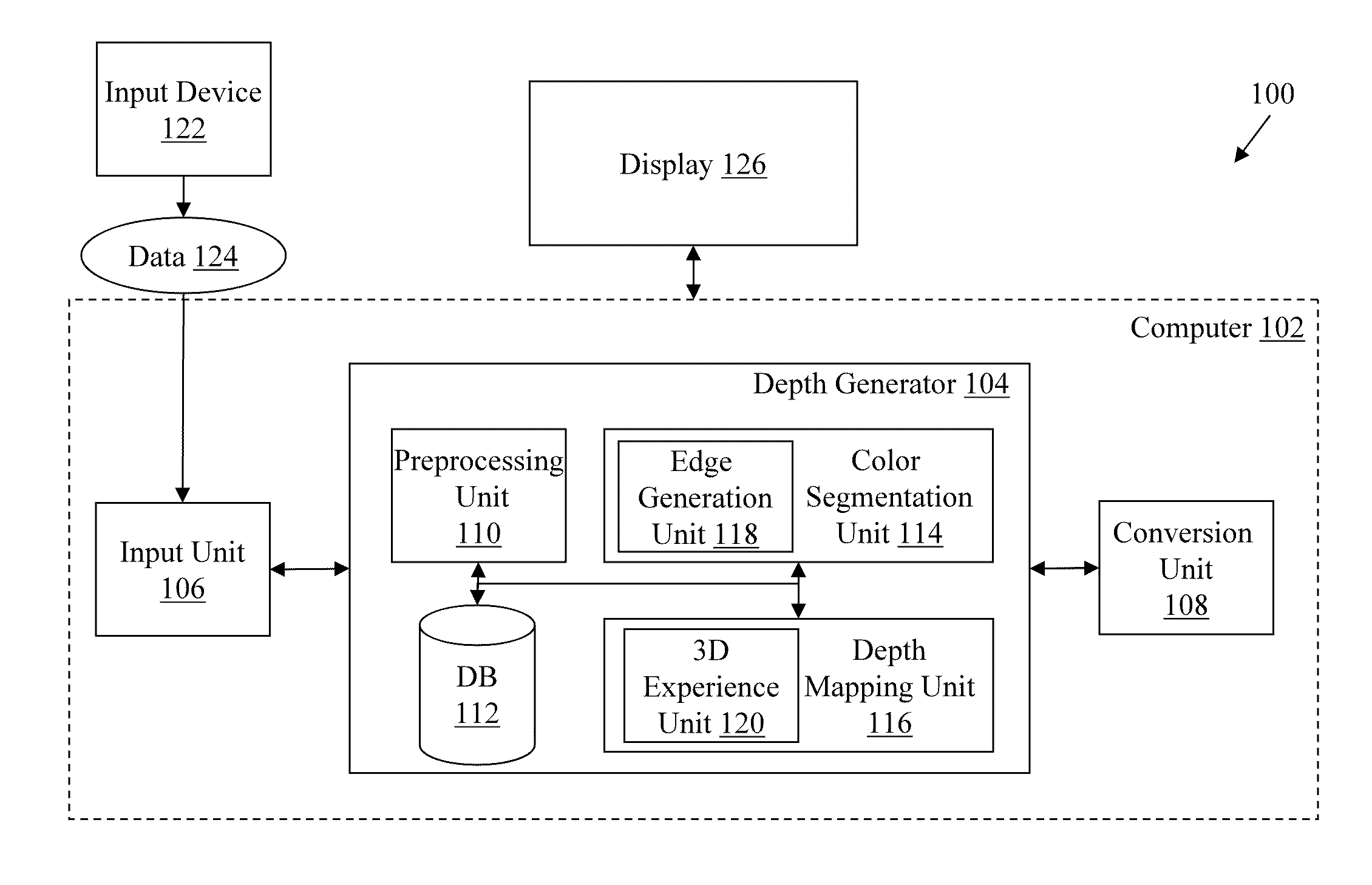
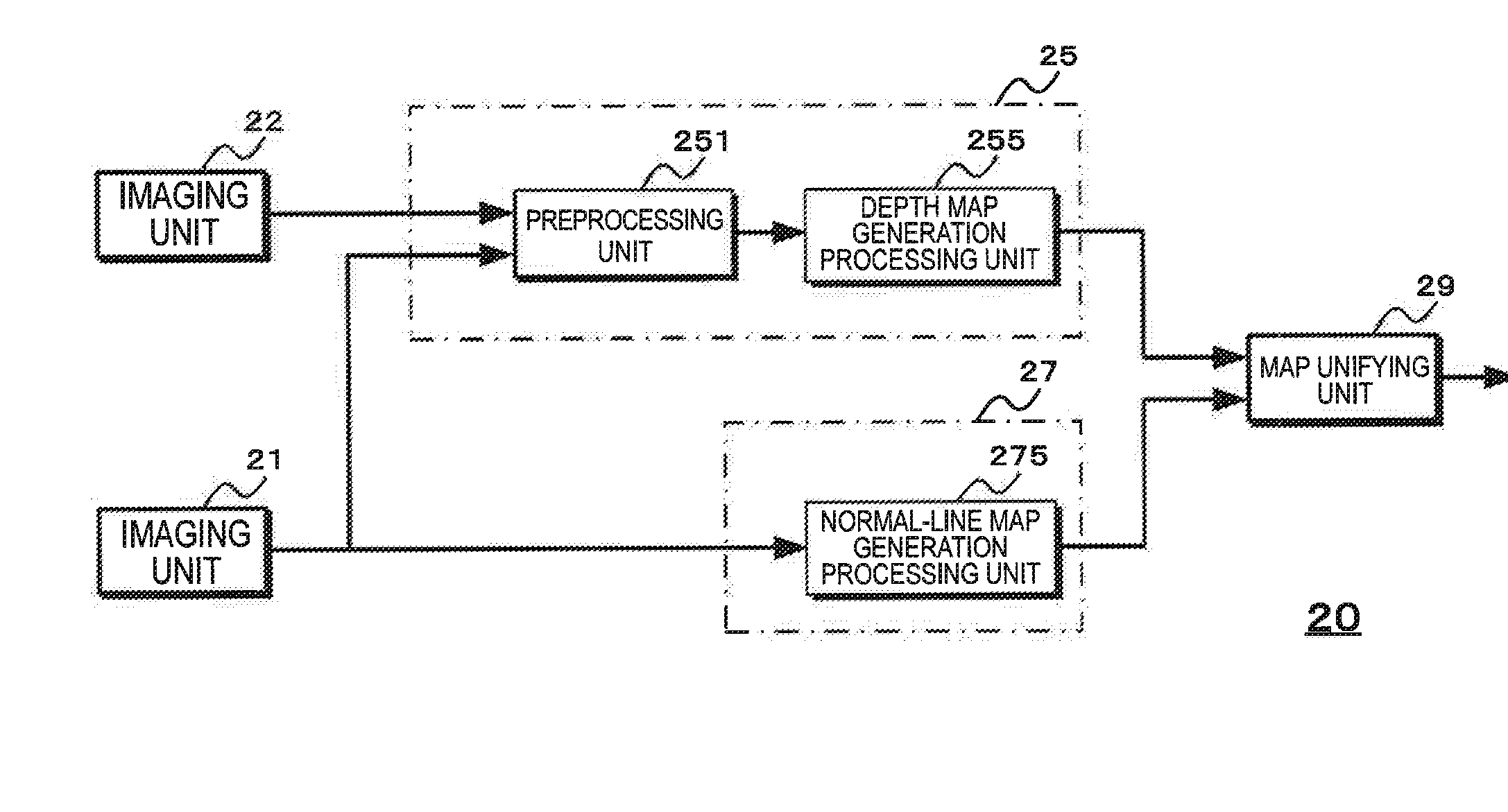
Image processing device, image processing method, and imaging device
ActiveUS20160261852A1Highly precise depth mapIncrease the number of pixelsImage analysisOptical rangefindersComputer scienceDepth map
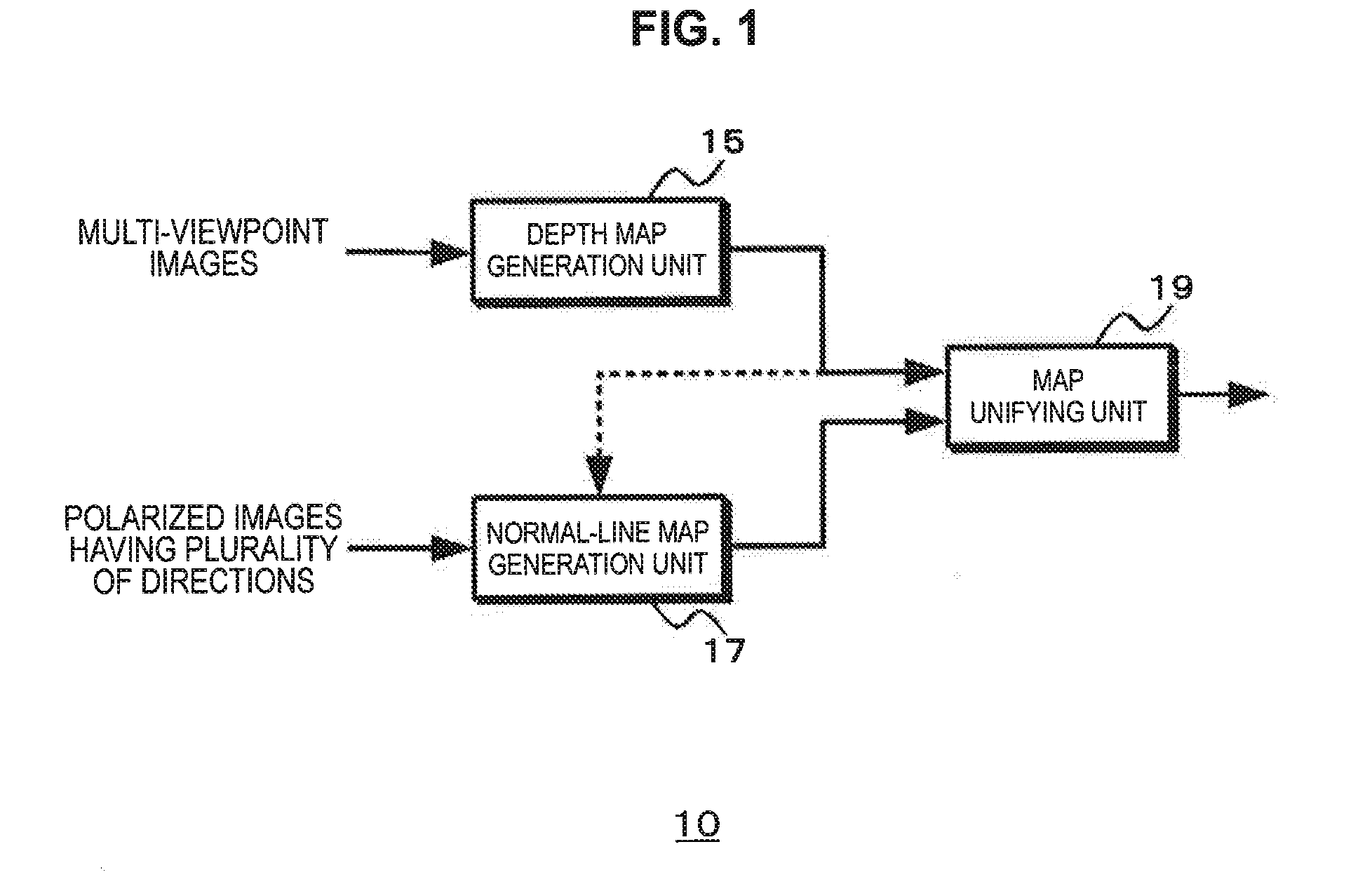
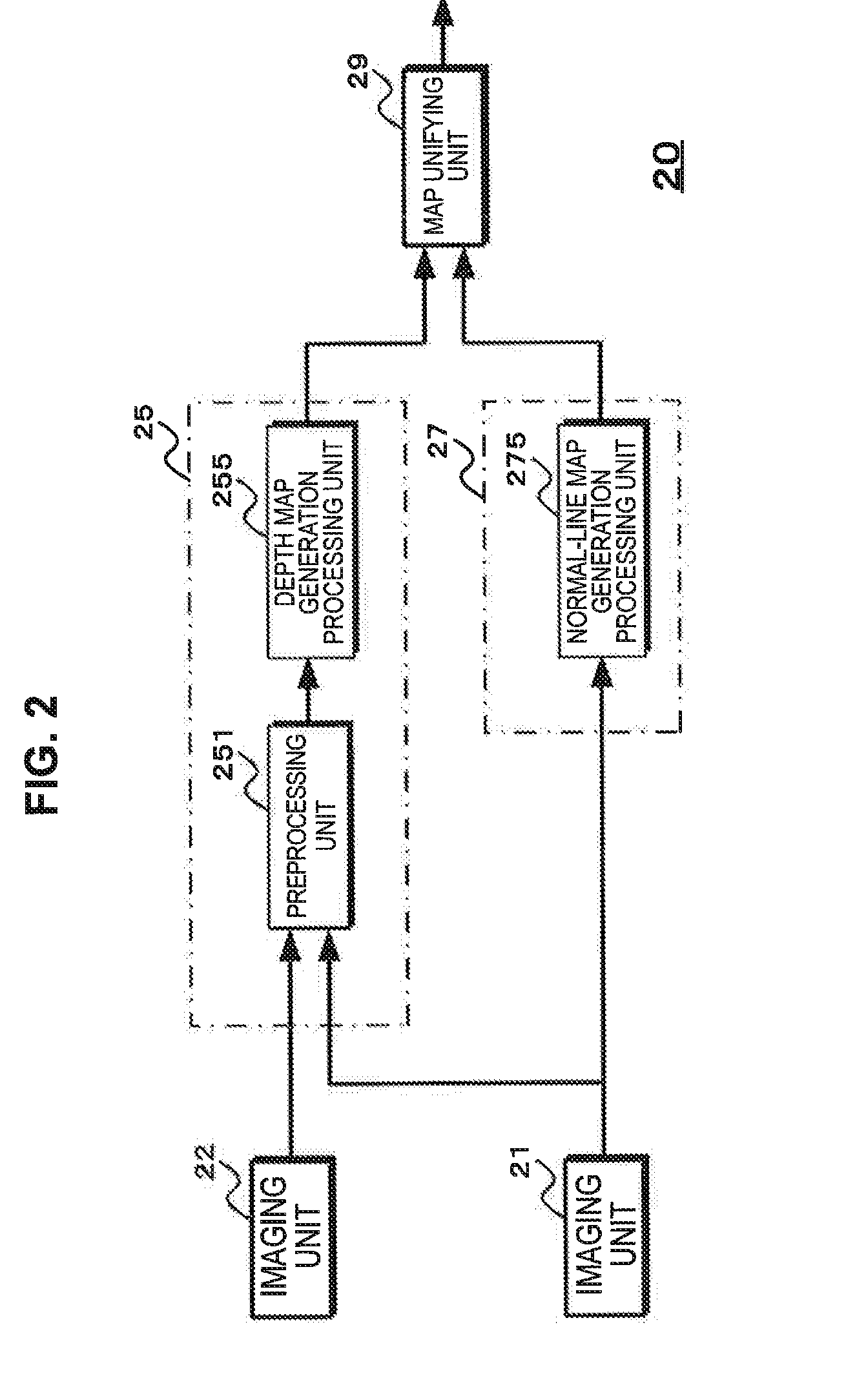
A depth map generation unit (15) generates a depth map through a matching process using a first image generated by a first imaging unit which has a pixel configuration including pixels having different polarization directions and a second image generated by a second imaging unit which has a different pixel configuration from the pixel configuration of the first imaging unit. A normal-line map generation unit (17) generates a normal-line map based on a polarization state of a polarized image of at least one of the first and second images. A map unifying unit (19) performs a process of unifying the generated depth map and the generated normal-line map and acquires an image in which the number of pixels is not reduced while generating the depth map with precision equal to or greater than the generated depth map. The image in which the number of pixels is not reduced can be acquired while generating the highly precise depth map.
Owner:SONY CORP
Centralized seed distribution system for planter
InactiveUS20020043194A1Increase storage capacityReduce amountSpadesPlantingDistribution systemAerospace engineering
An agricultural planter having left and right hinged wing sections includes seed storage tanks carried by the planter frame and feeding individual row units, mounted fore and aft of the main toolbar, by means of flexible conduits. The tanks are mounted to permit the wings to flex independently to follow ground contour while extending the tanks from a wing section onto the center frame section.
Owner:KINZE MFG INC
Compact array of imaging devices with supplemental imaging unit
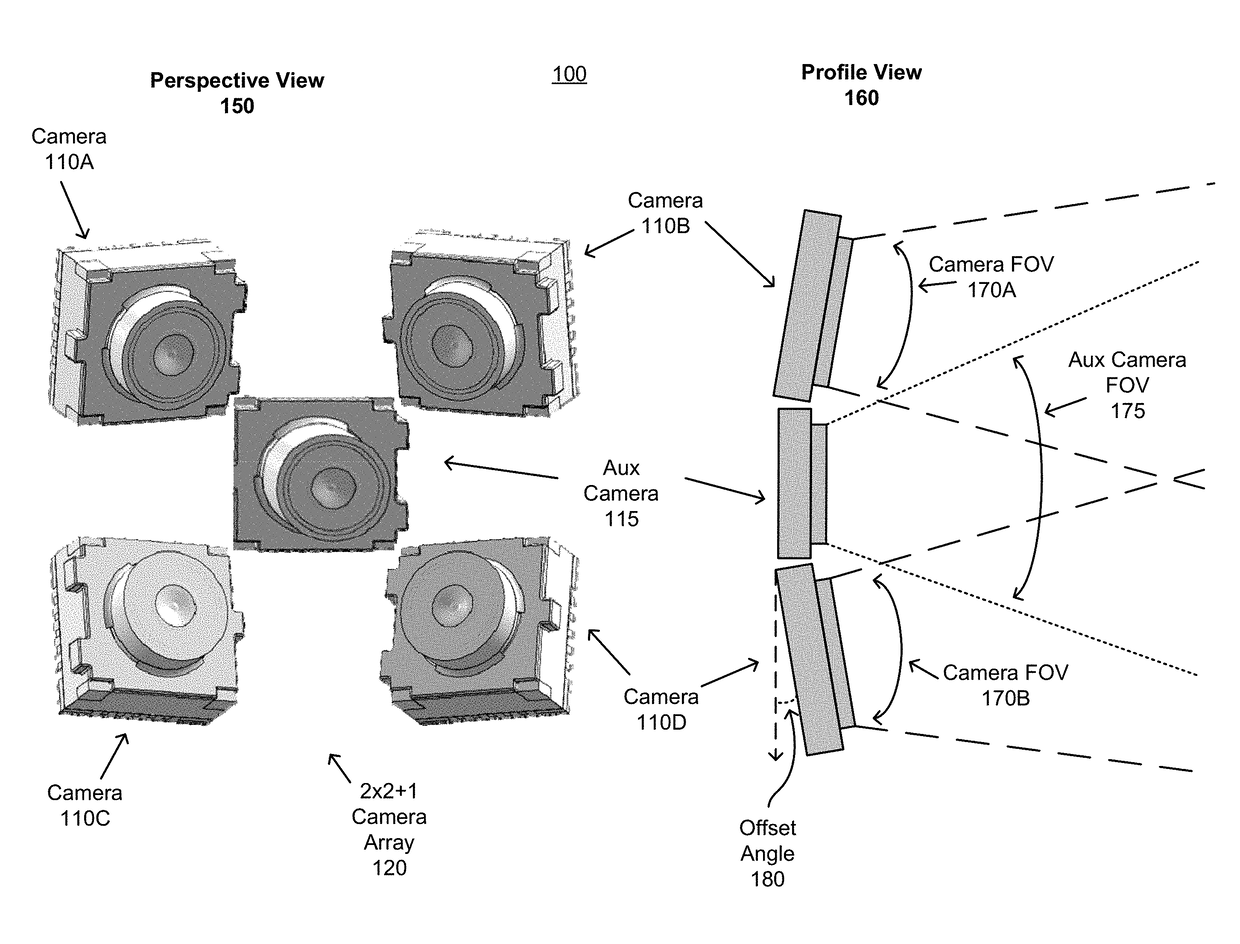
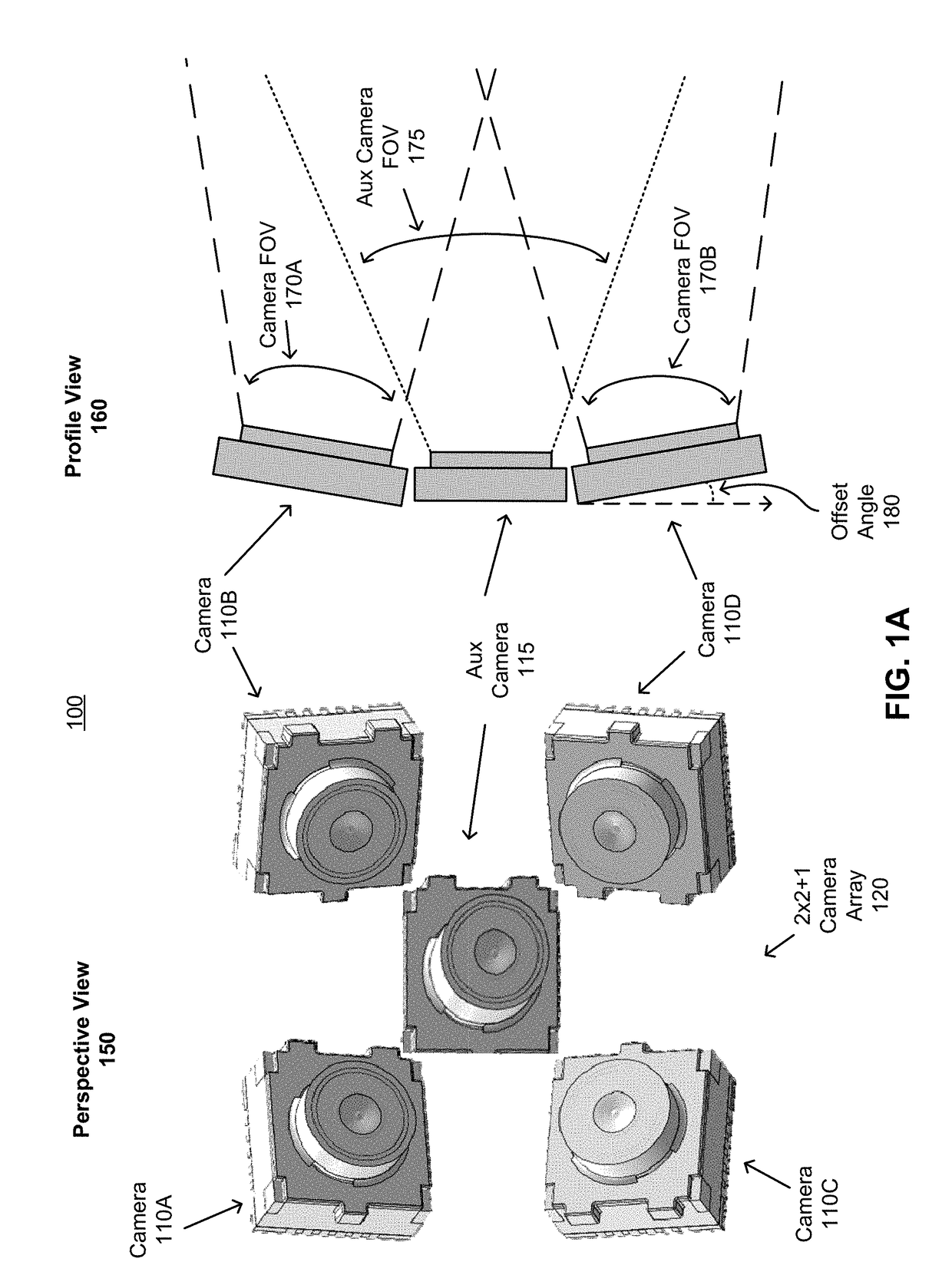
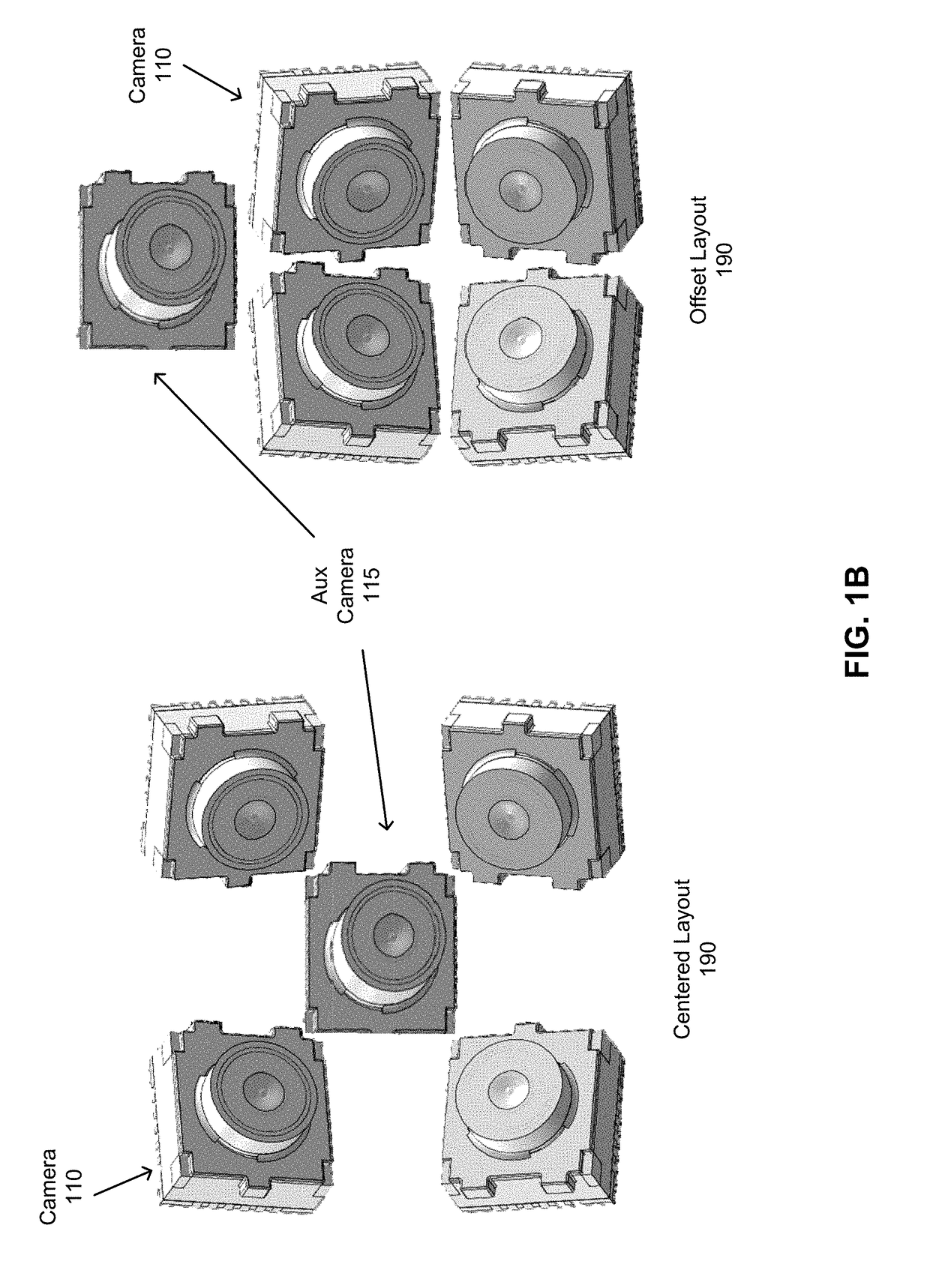
ActiveUS20180176541A1Depth accuratePrecise positioningImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionField of view
A method and system are described. The method includes capturing a set of images from a 2×2 array of cameras, each camera of the array of cameras having an overlapping field of view (FOV) with an adjacent camera of the array of cameras. The method further includes synchronously capturing a supplemental image from a fifth camera, the fifth camera having an at least partially overlapping FOV with every camera of the array of cameras. Supplemental information is extracted by comparing the supplemental image with the set of four images. Portions of the set of images are stitched based in part on the supplemental information to produce a combined stitched image, the combined stitched image having a higher resolution than each image of the set of images
Owner:GOPRO
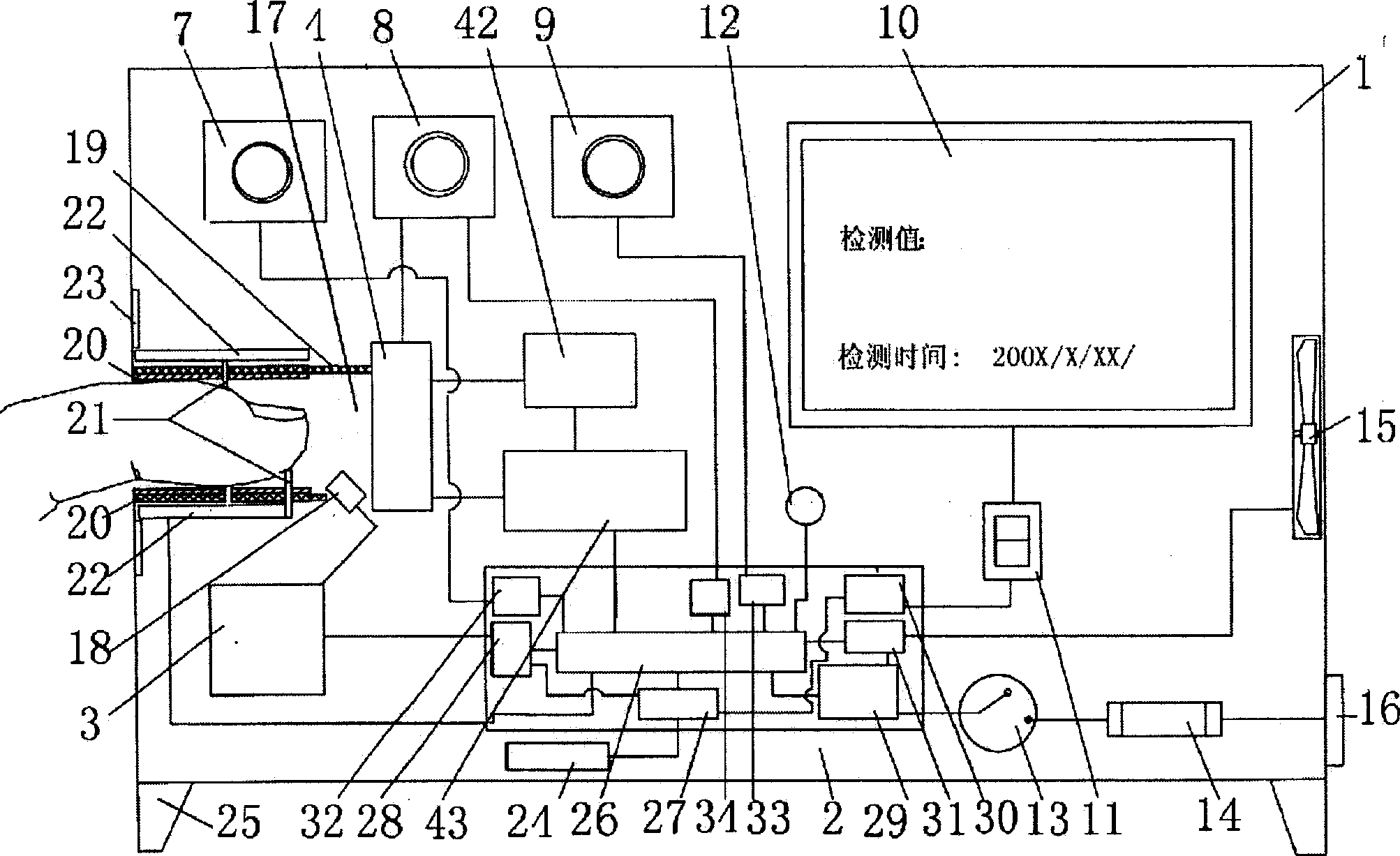
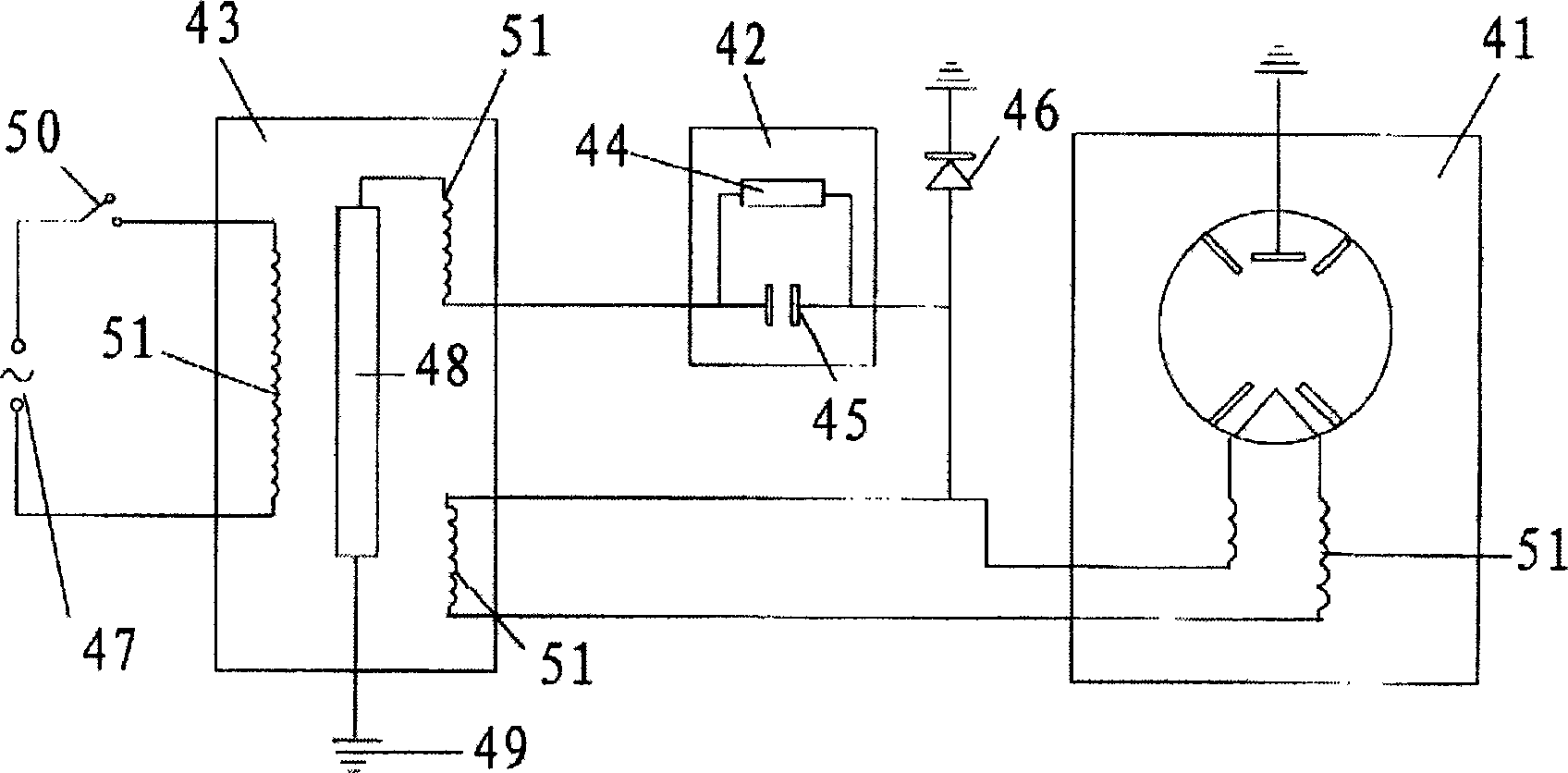
Method of dynamic detecting organism parameter and its medical detecting analyzer
InactiveCN1823683AMitigate the risk of exposure to unnecessary X-ray radiationReduce diagnostic costsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrowaveTemperature monitoring
Owner:BEIJING YINHEZHIZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com