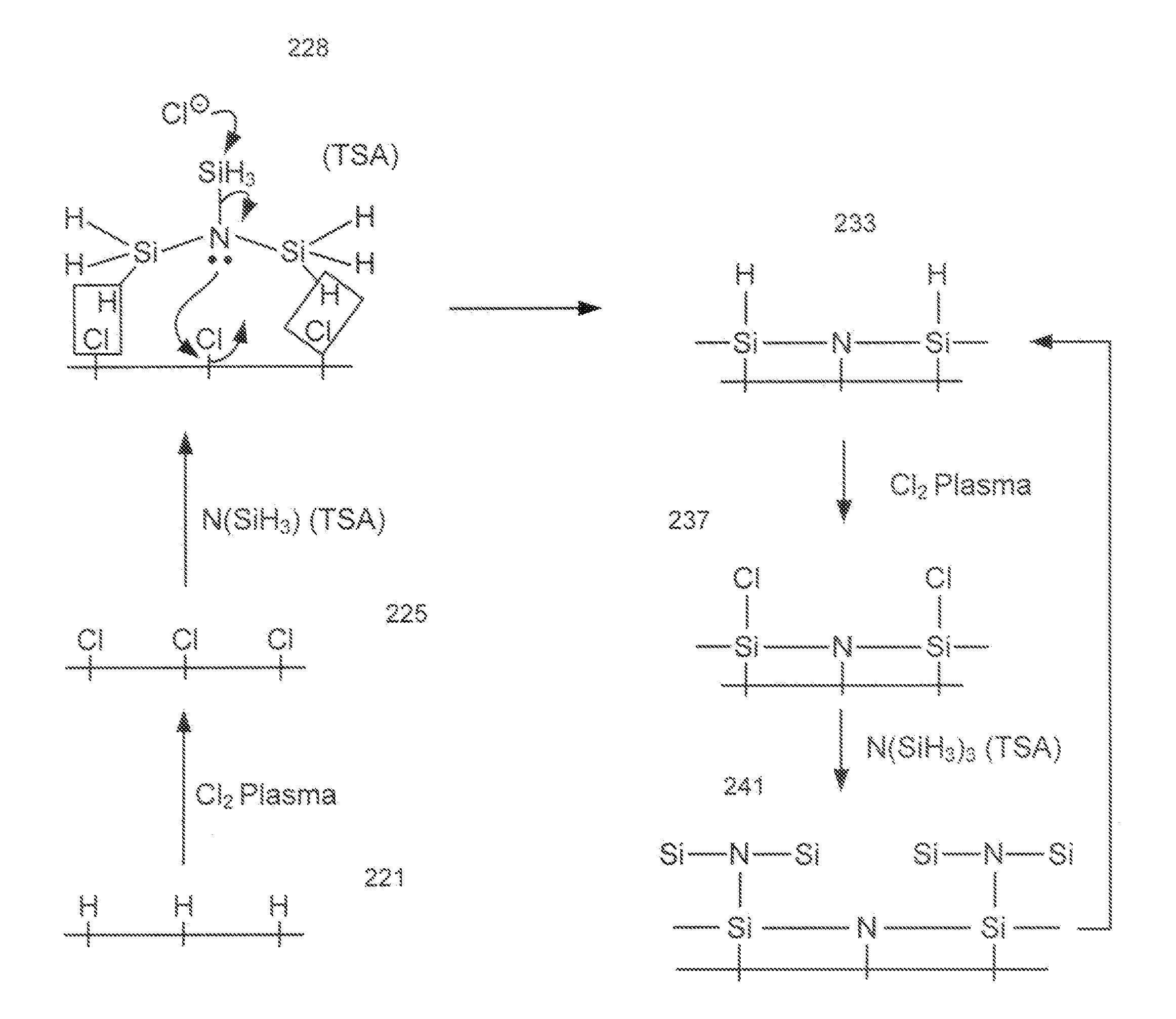Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
422 results about "Self limiting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Self-limiting (biology) In biology, a self-limiting organism or colony of organisms limits its own growth by its actions. For example, a single organism may have a maximum size determined by genetics, or a colony of organisms may release waste which is ultimately toxic to the colony once it exceeds a certain population.
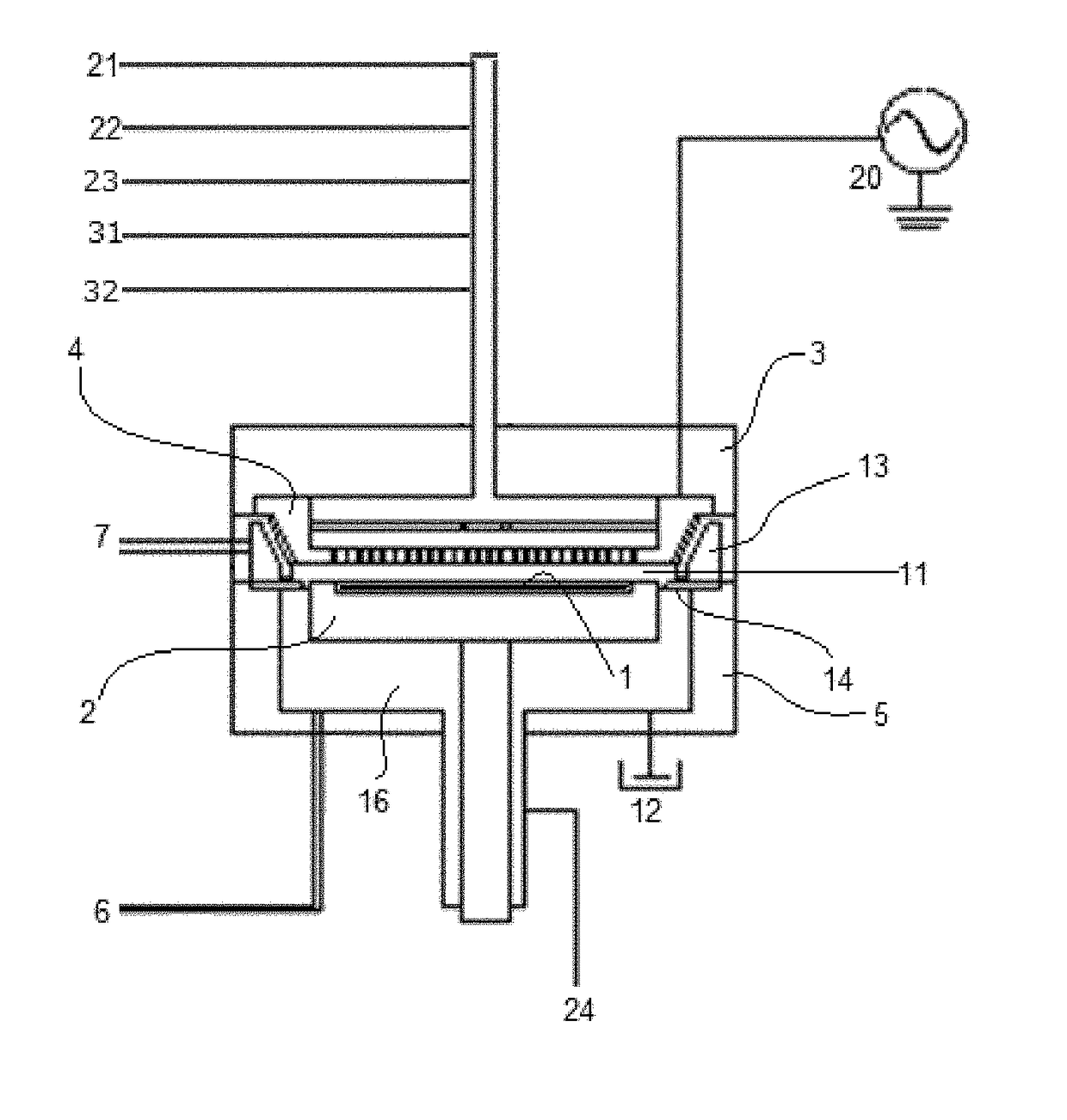
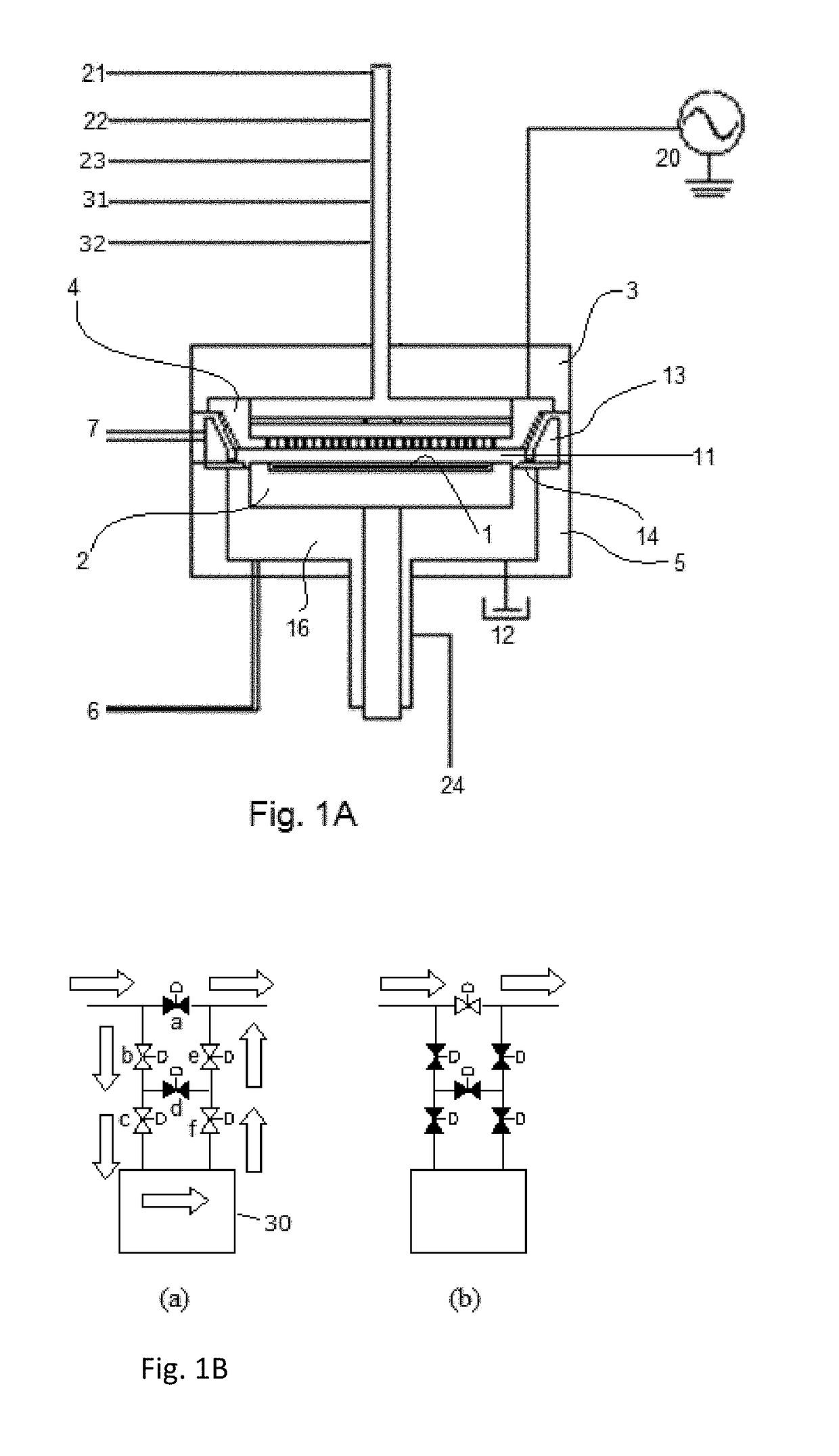
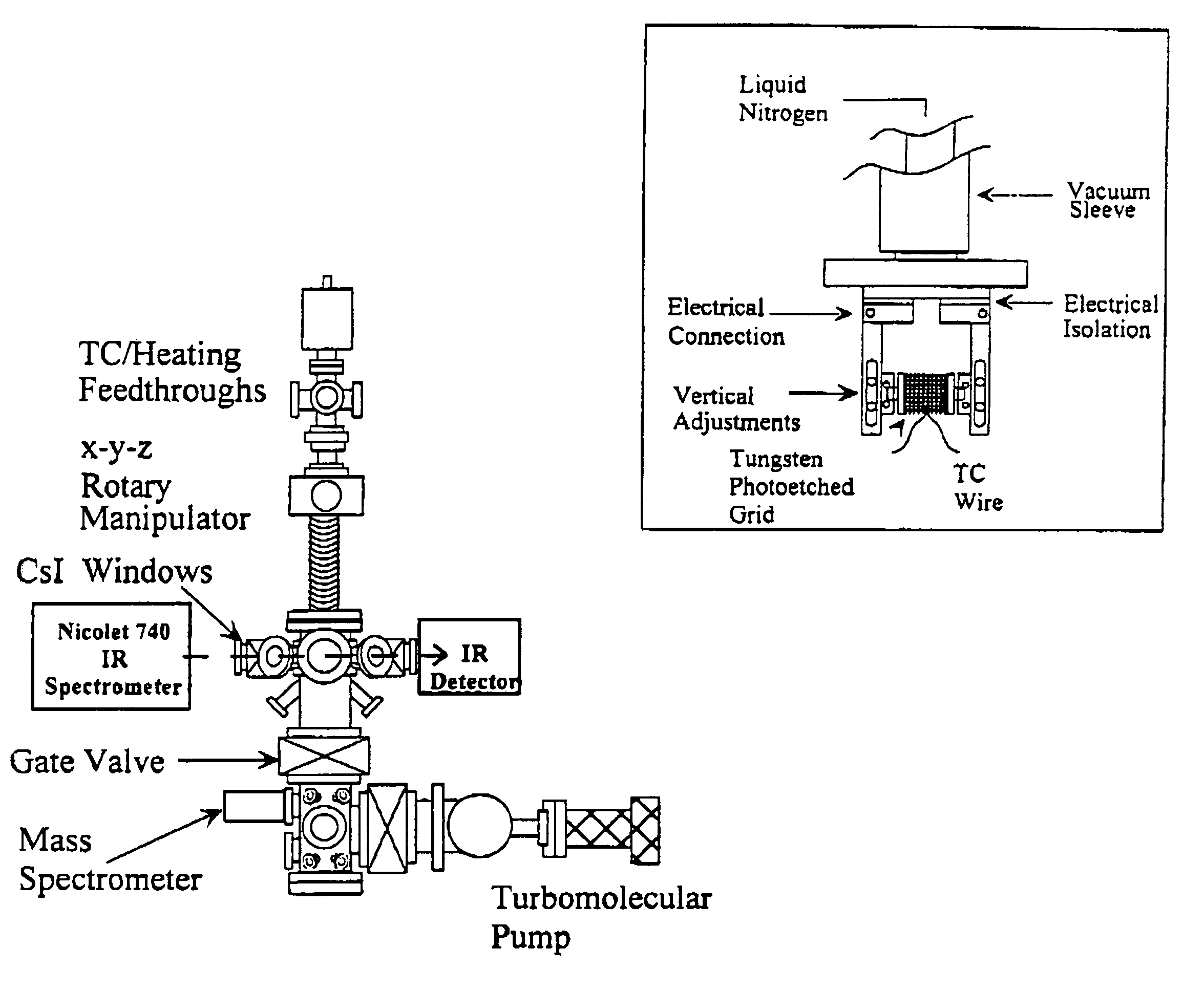
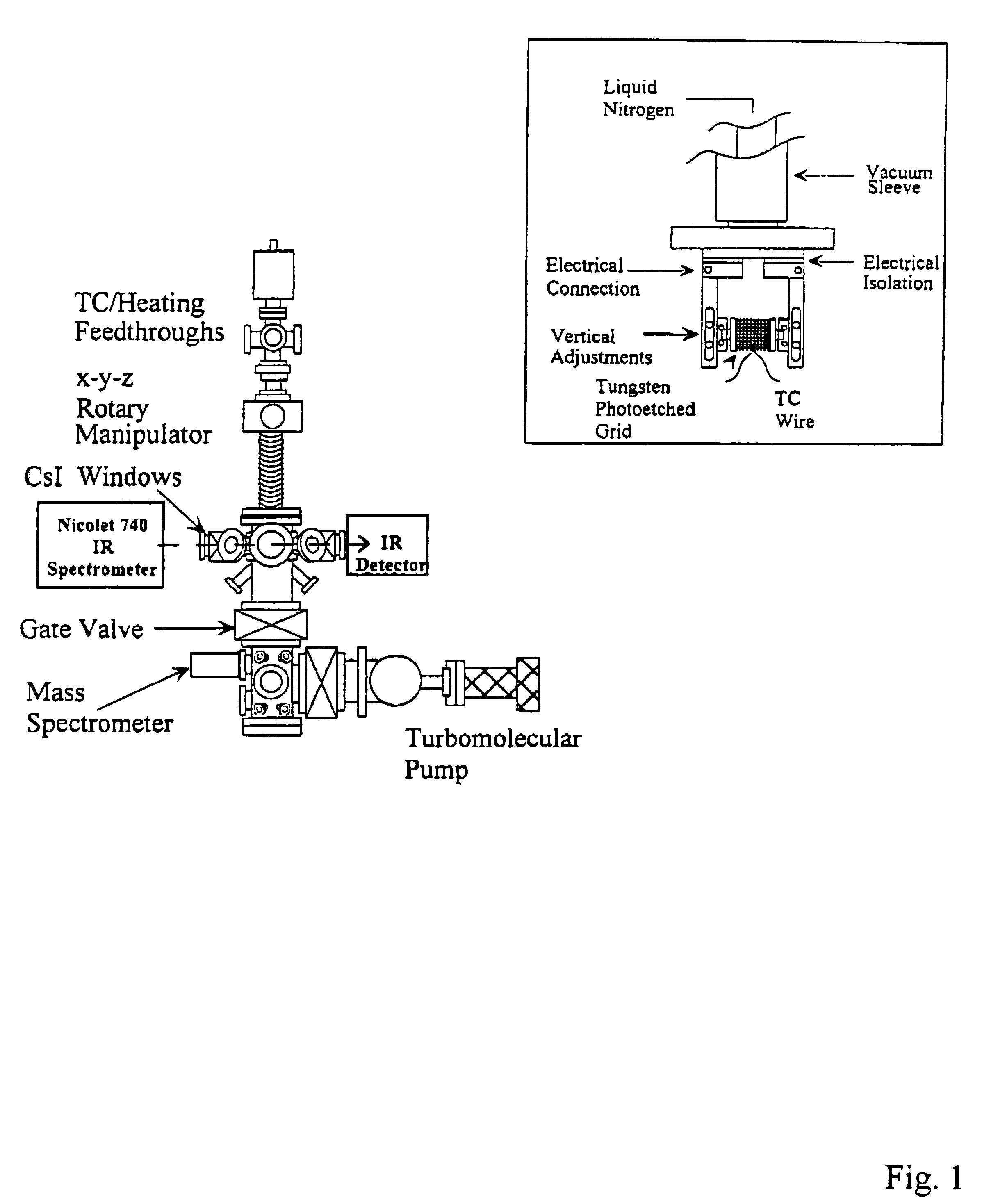
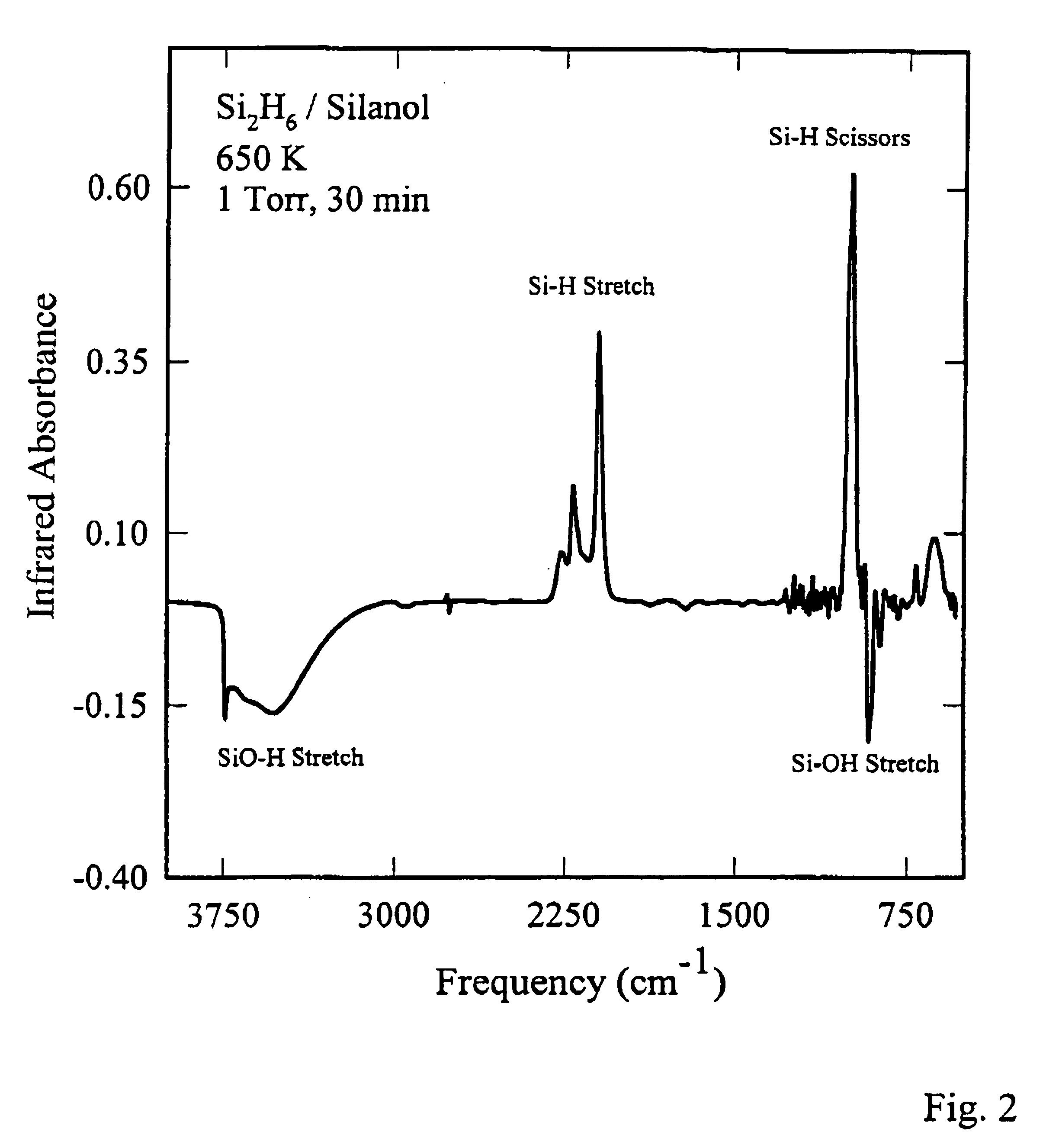
Methods of removing silicon oxide and gaseous mixtures for achieving same
ActiveUS20090275205A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentPartial oxidation
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Thin films
InactiveUS20050181555A1Quality improvementHigh dielectric constantSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon oxide
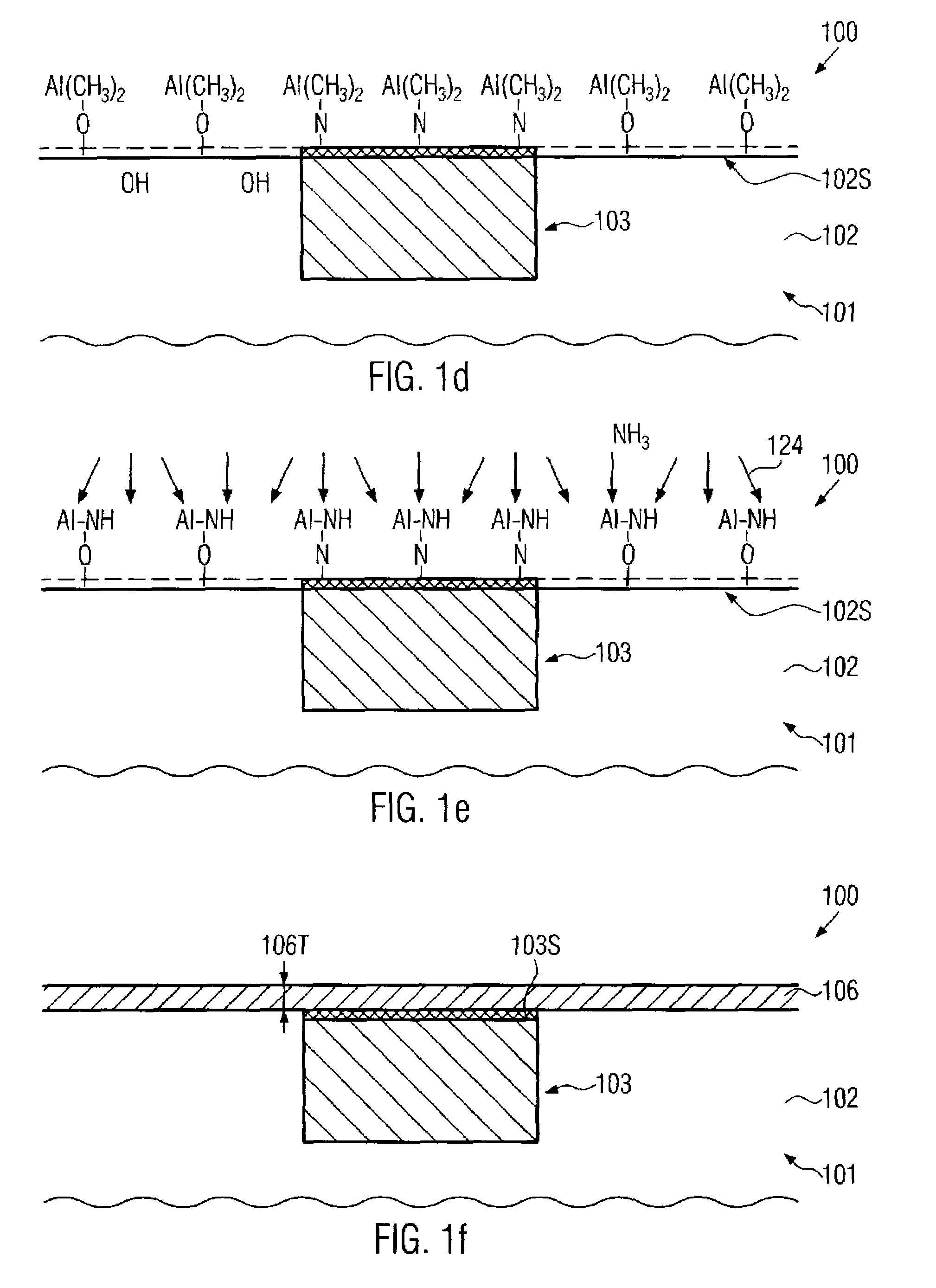
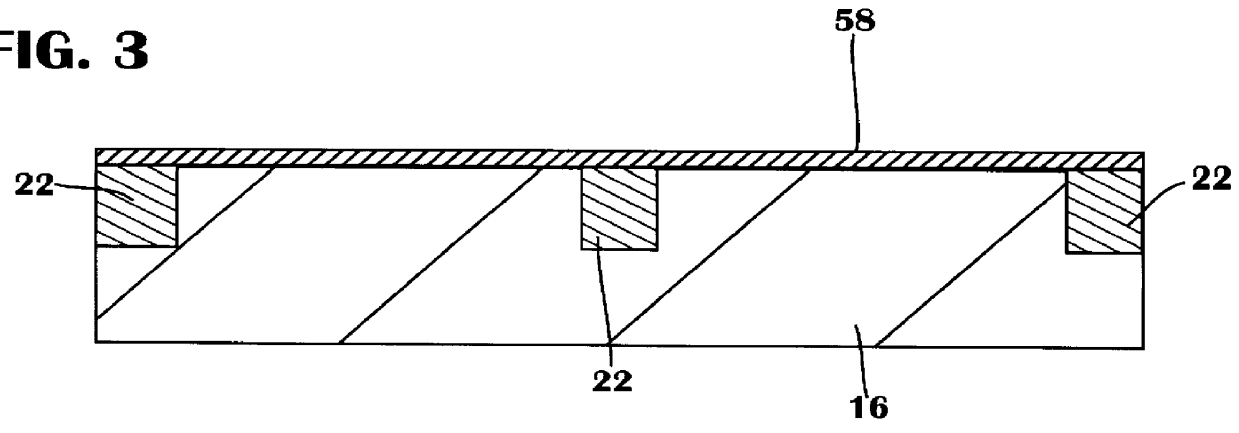
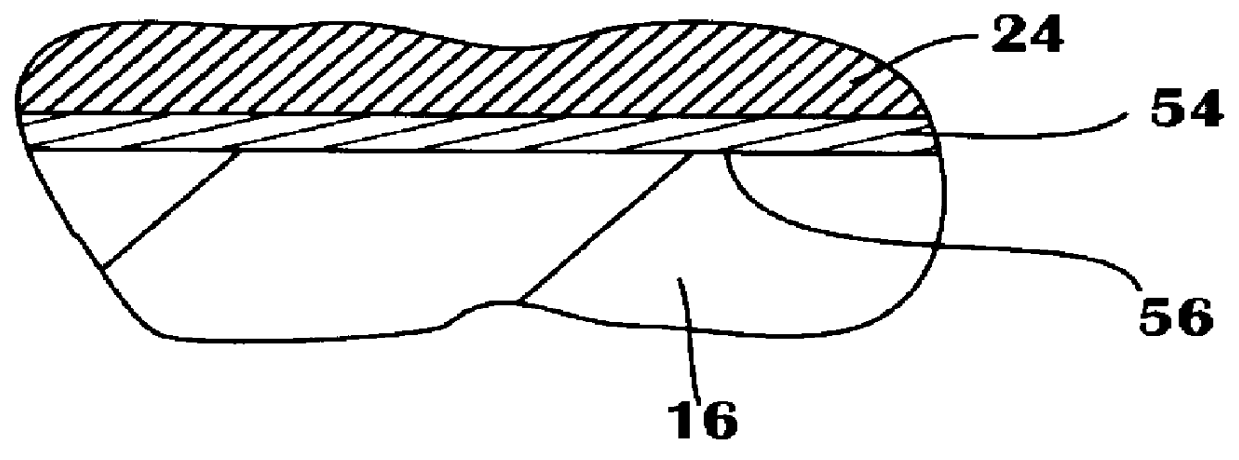
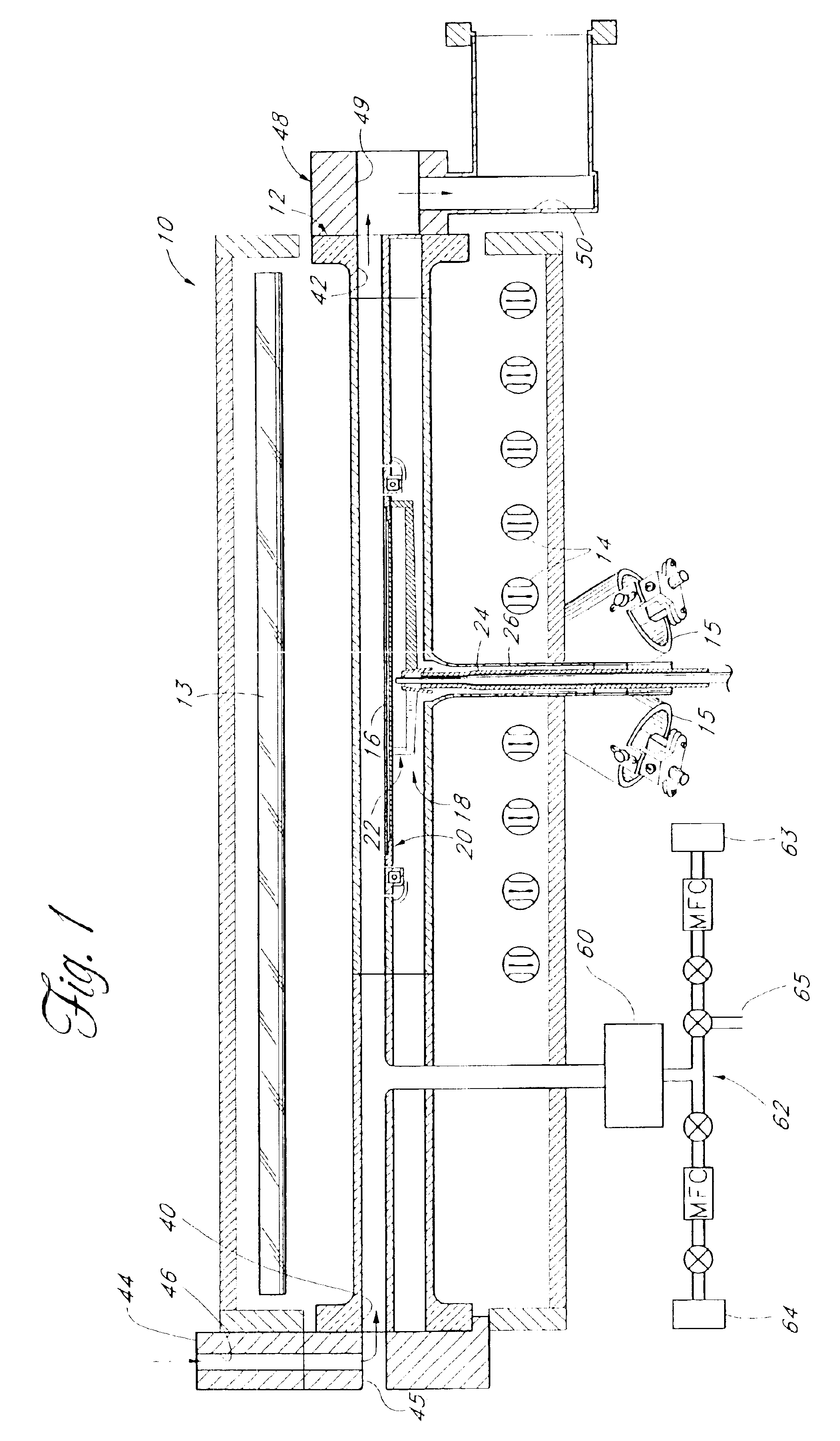
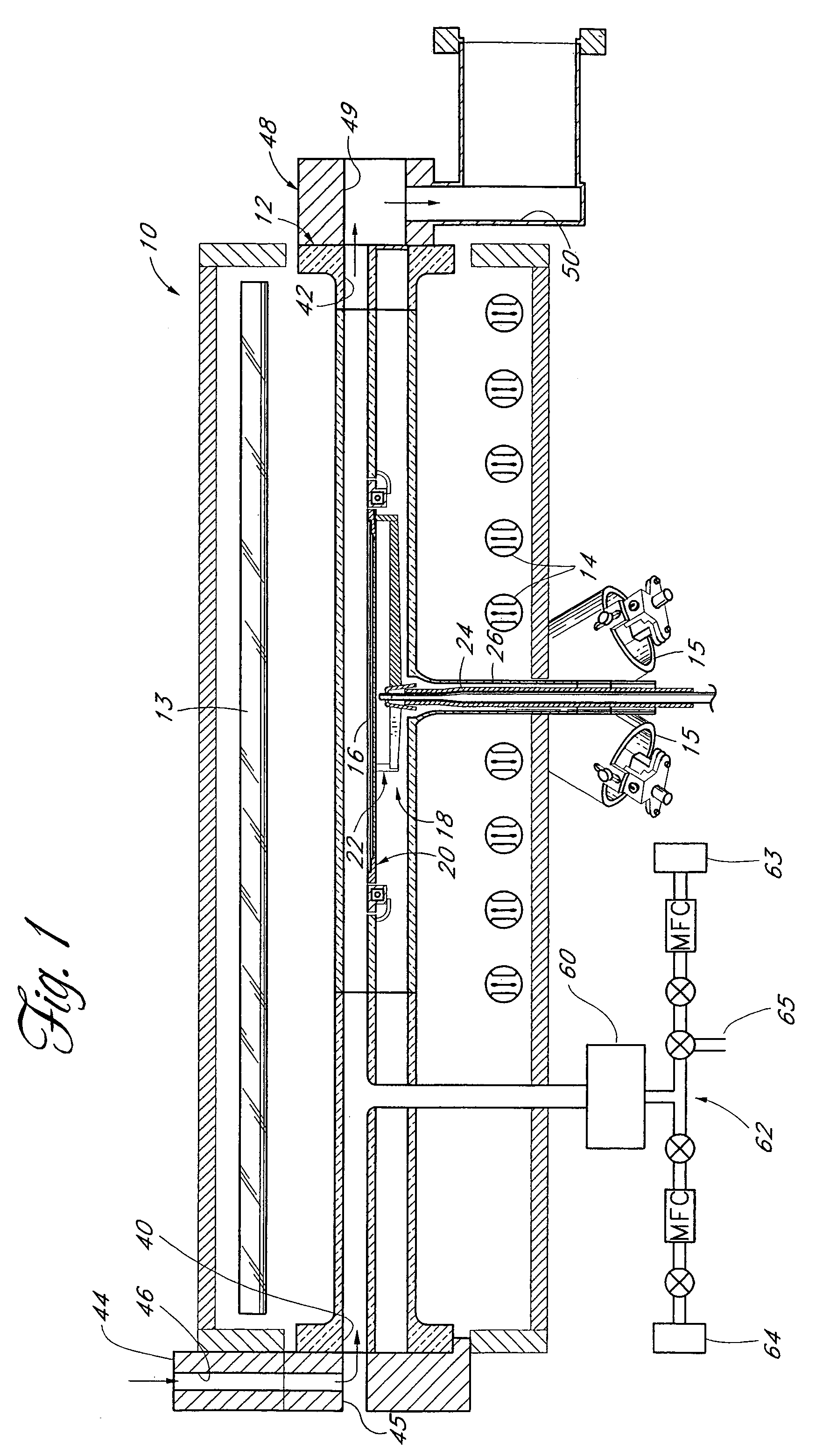
Thin films are formed by formed by atomic layer deposition, whereby the composition of the film can be varied from monolayer to monolayer during cycles including alternating pulses of self-limiting chemistries. In the illustrated embodiments, varying amounts of impurity sources are introduced during the cyclical process. A graded gate dielectric is thereby provided, even for extremely thin layers. The gate dielectric as thin as 2 nm can be varied from pure silicon oxide to oxynitride to silicon nitride. Similarly, the gate dielectric can be varied from aluminum oxide to mixtures of aluminum oxide and a higher dielectric material (e.g., ZrO2) to pure high k material and back to aluminum oxide. In another embodiment, metal nitride (e.g., WN) is first formed as a barrier for lining dual damascene trenches and vias. During the alternating deposition process, copper can be introduced, e.g., in separate pulses, and the copper source pulses can gradually increase in frequency, forming a transition region, until pure copper is formed at the upper surface. Advantageously, graded compositions in these and a variety of other contexts help to avoid such problems as etch rate control, electromigration and non-ohmic electrical contact that can occur at sharp material interfaces. In some embodiments additional seed layers or additional transition layers are provided.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Plasma pre-treating surfaces for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS7498242B2Improve barrier propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingSelf limitingAtomic layer deposition
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Adsorption based material removal process
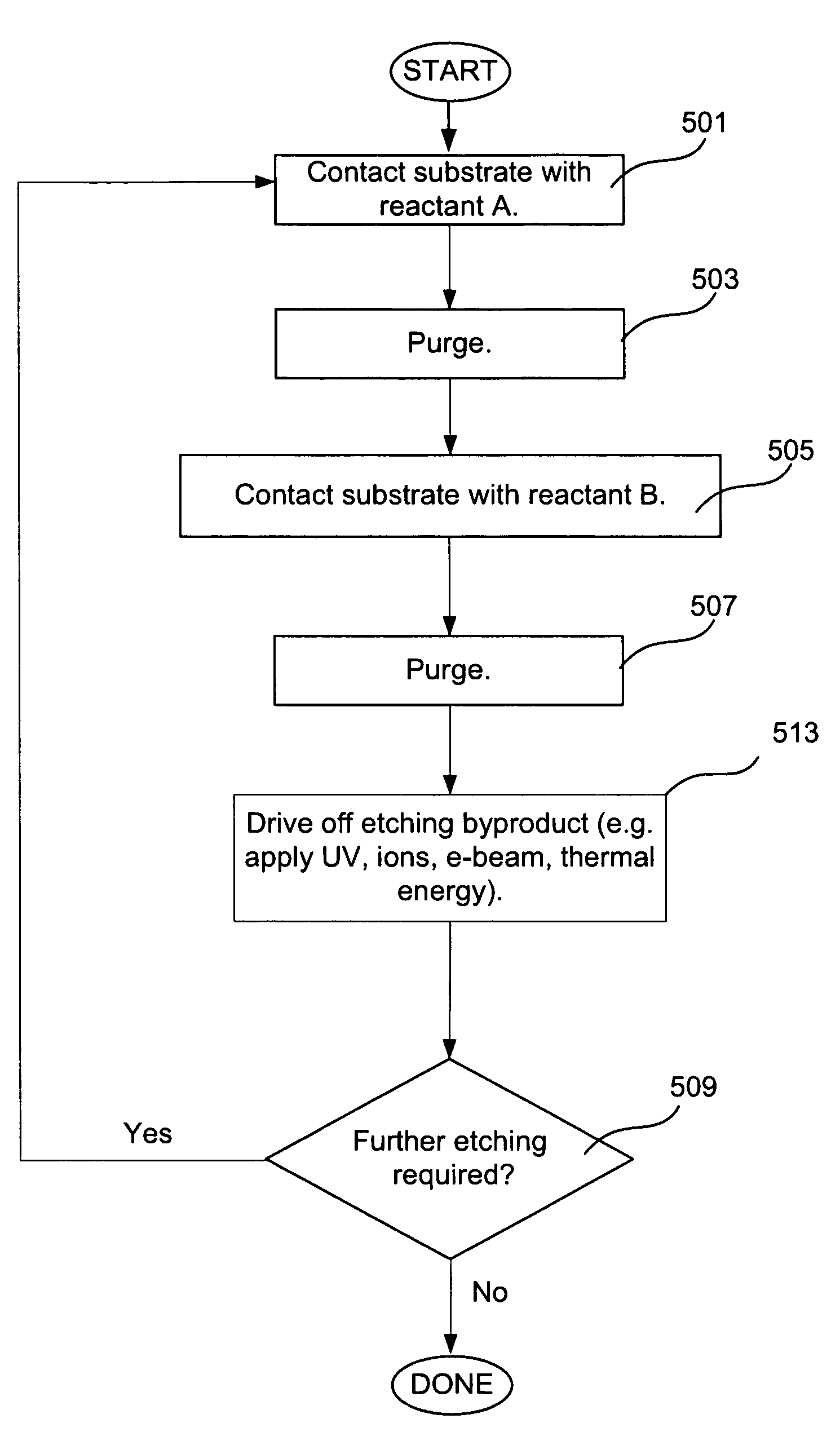
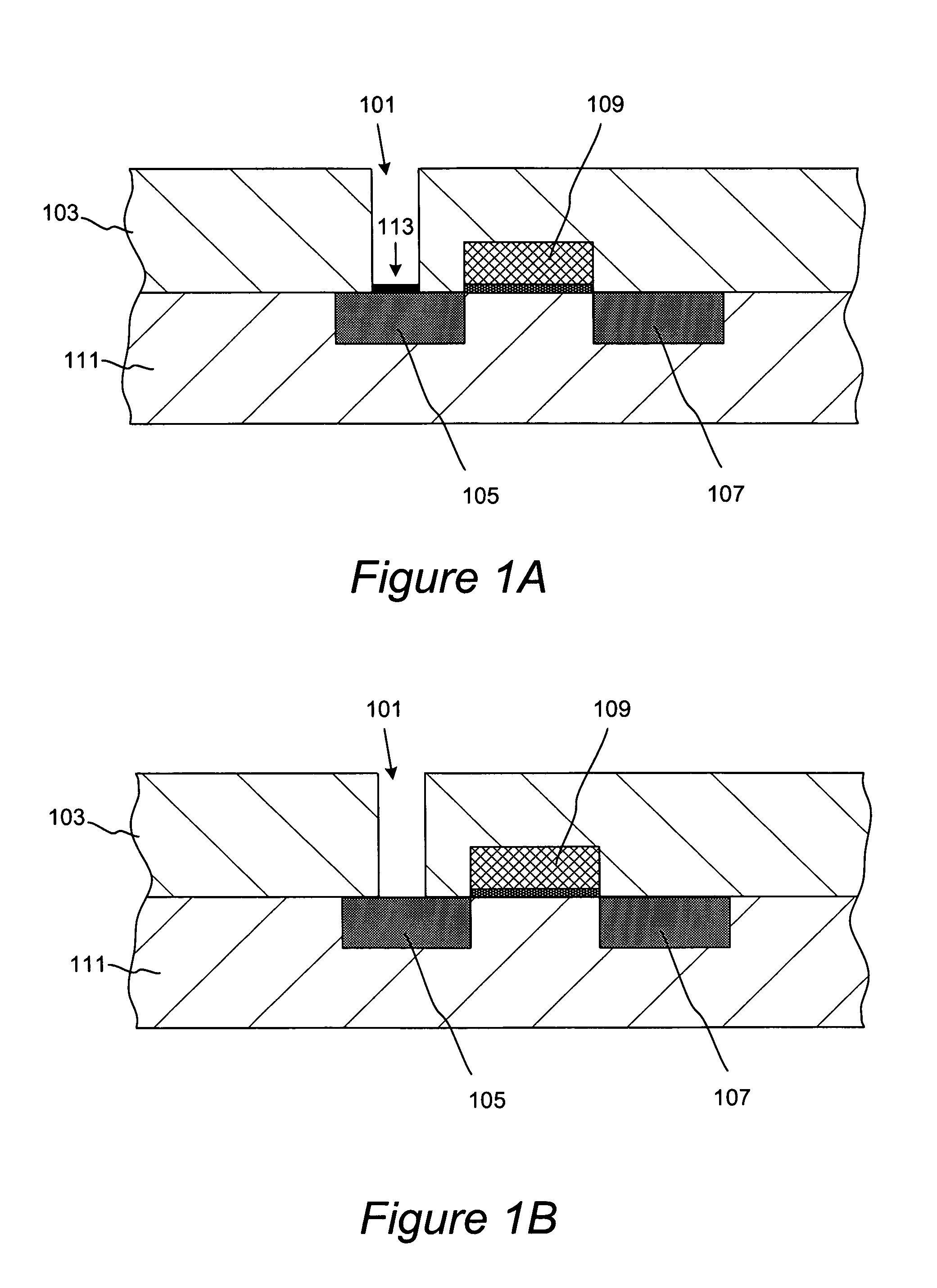
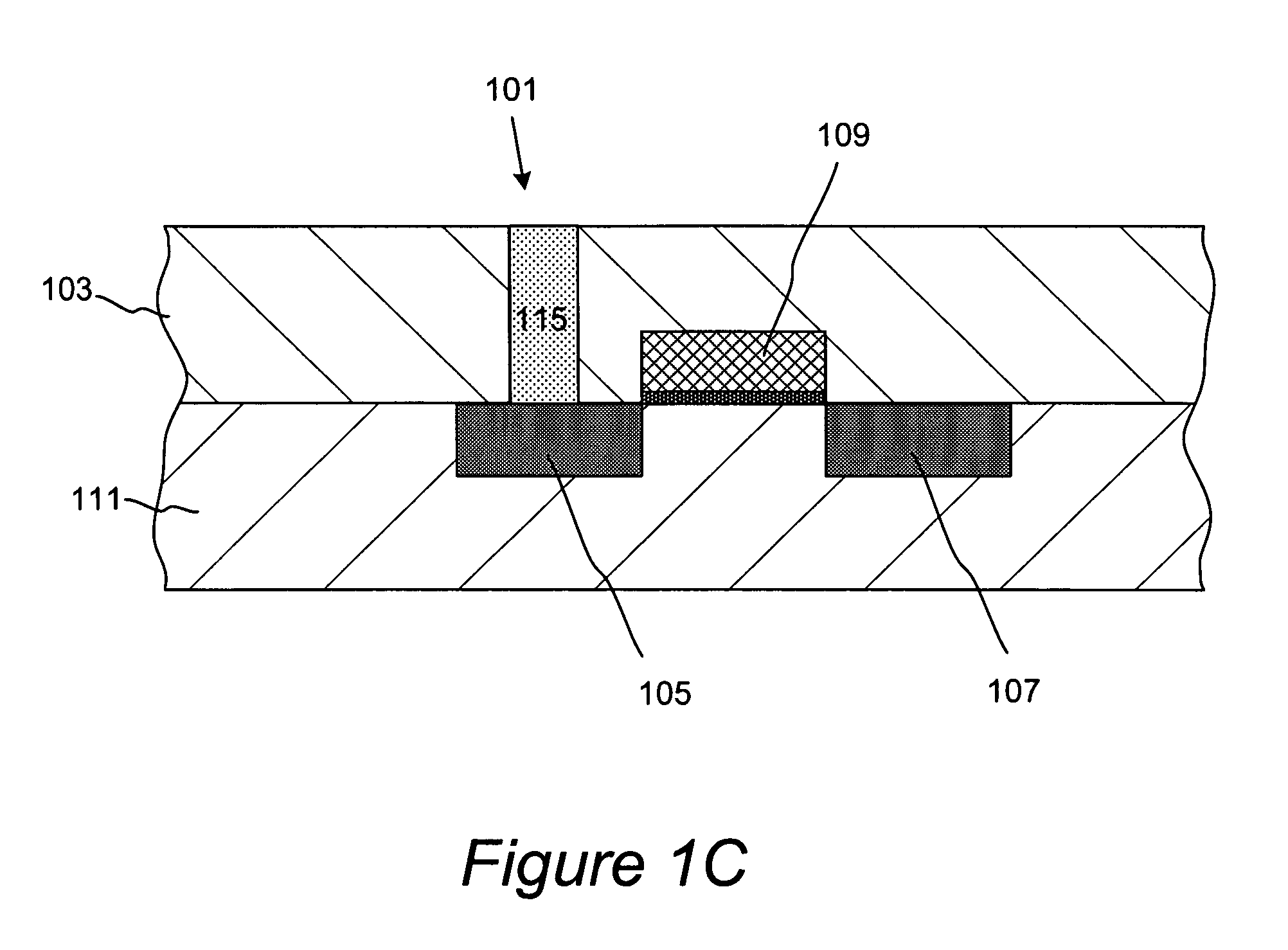
InactiveUS8043972B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingEtching
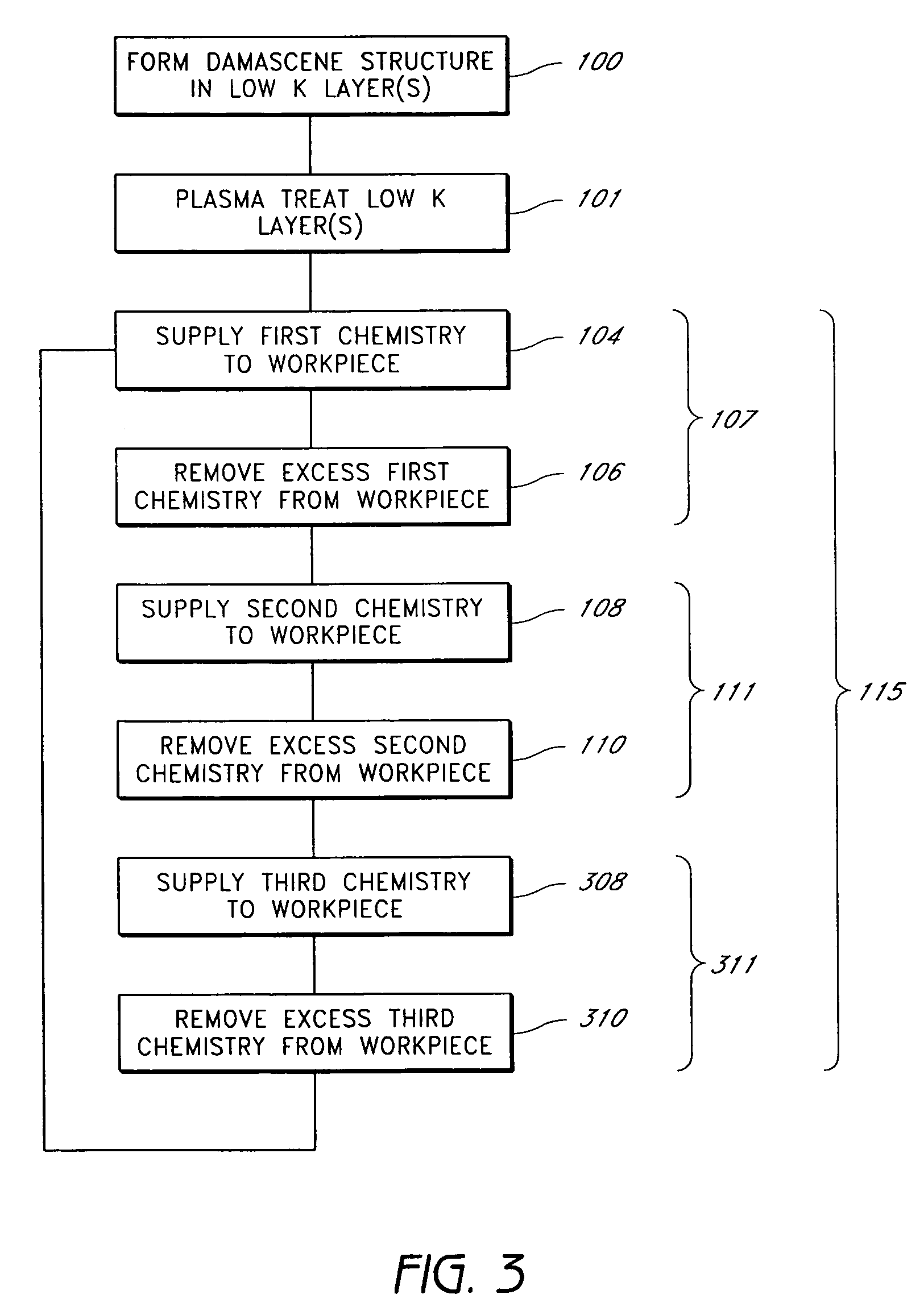
Methods for accurate and conformal removal of atomic layers of materials make use of the self-limiting nature of adsorption of at least one reactant on the substrate surface. In certain embodiments, a first reactant is introduced to the substrate in step (a) and is adsorbed on the substrate surface until the surface is partially or fully saturated. A second reactant is then added in step (b), reacting with the adsorbed layer of the first reactant to form an etchant. The amount of an etchant, and, consequently, the amount of etched material is limited by the amount of adsorbed first reactant. By repeating steps (a) and (b), controlled atomic-scale etching of material is achieved. These methods may be used in interconnect pre-clean applications, gate dielectric processing, manufacturing of memory devices, or any other applications where removal of one or multiple atomic layers of material is desired.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Adsorption based material removal process
Methods for accurate and conformal removal of atomic layers of materials make use of the self-limiting nature of adsorption of at least one reactant on the substrate surface. In certain embodiments, a first reactant is introduced to the substrate in step (a) and is adsorbed on the substrate surface until the surface is partially or fully saturated. A second reactant is then added in step (b), reacting with the adsorbed layer of the first reactant to form an etchant. The amount of an etchant, and, consequently, the amount of etched material is limited by the amount of adsorbed first reactant. By repeating steps (a) and (b), controlled atomic-scale etching of material is achieved. These methods may be used in interconnect pre-clean applications, gate dielectric processing, manufacturing of memory devices, or any other applications where removal of one or multiple atomic layers of material is desired.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
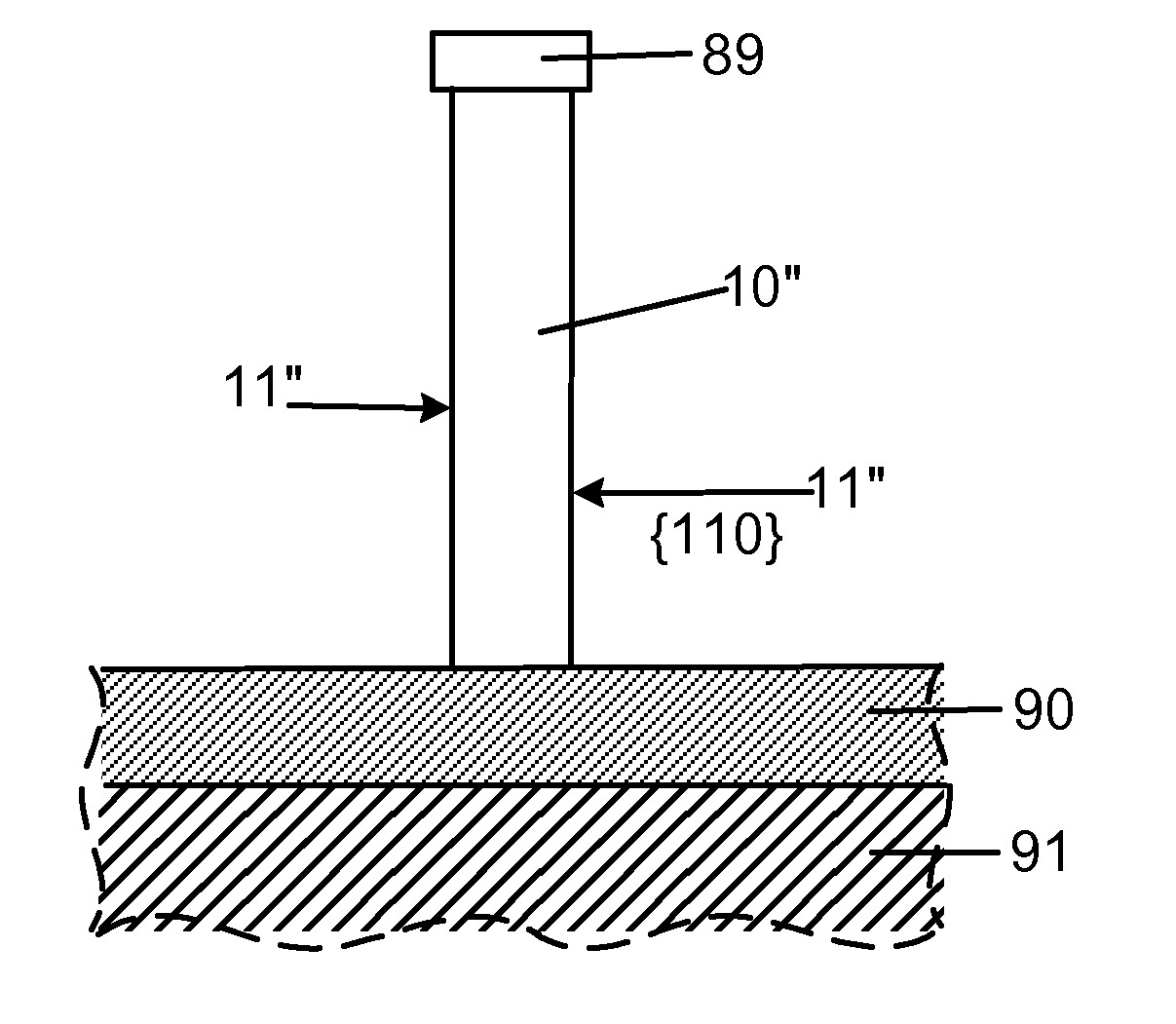
Smooth and vertical semiconductor fin structure
InactiveUS20100048027A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingCrystal orientation
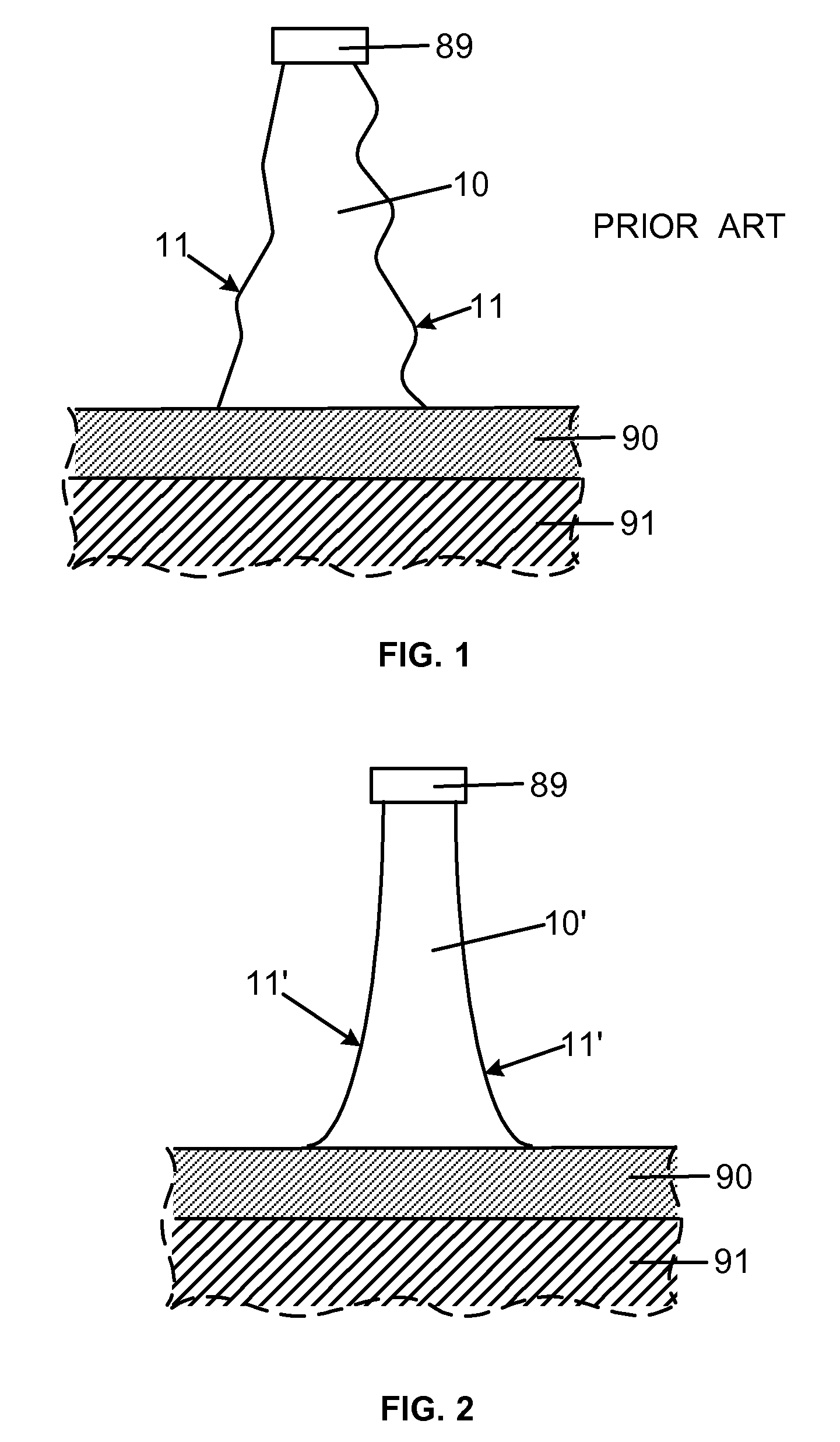
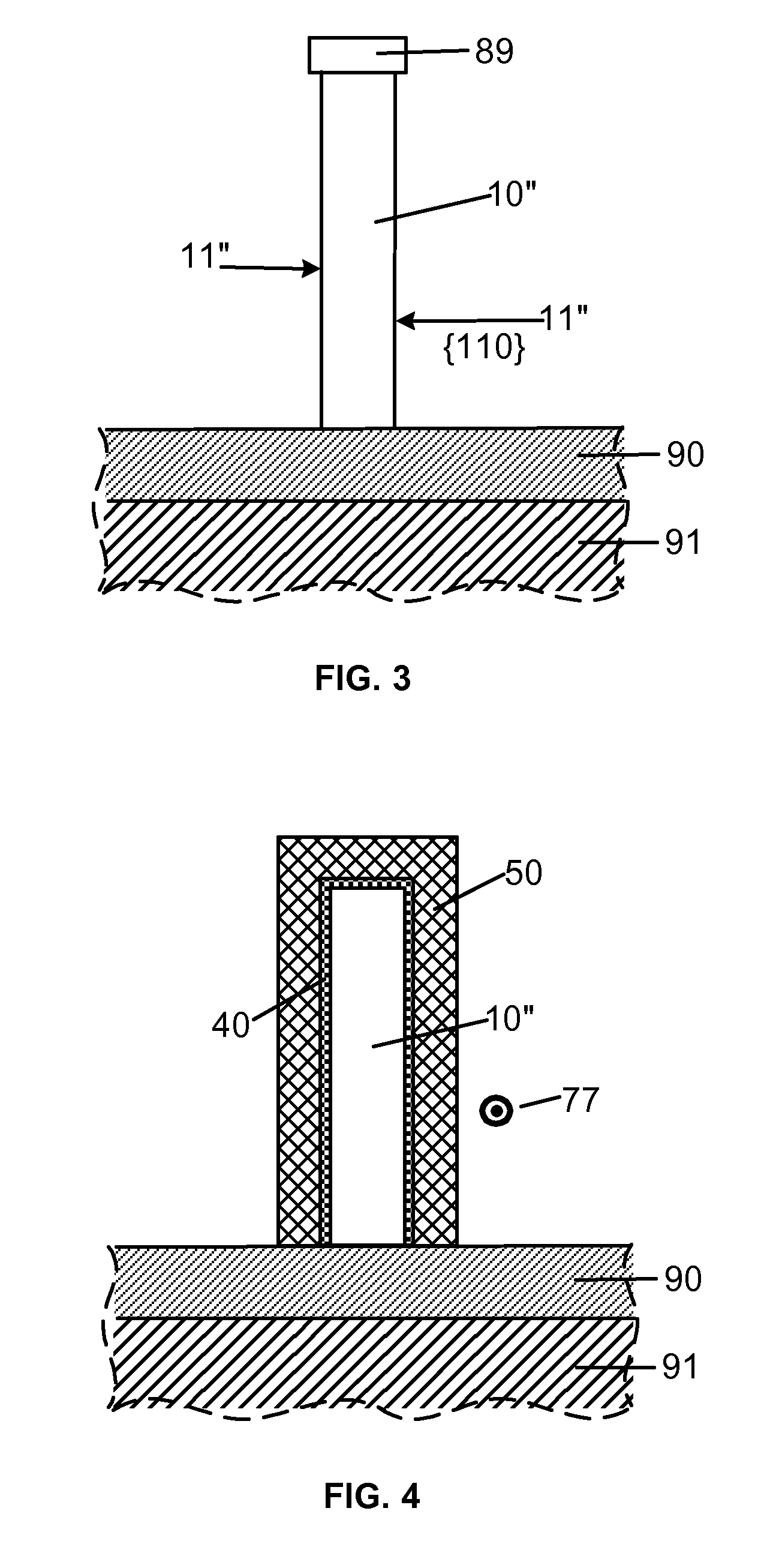
A method for processing a semiconductor fin structure is disclosed. The method includes thermal annealing a fin structure in an ambient containing an isotope of hydrogen. Following the thermal annealing step, the fin structure is etched in a crystal-orientation dependent, self-limiting, manner. The crystal-orientation dependent etch may be selected to be an aqueous solution containing ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). The completed fin structure has smooth sidewalls and a uniform thickness profile. The fin structure sidewalls are {110} planes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of manufracturing increasing reliability of copper-based metallization structures in a microstructure device by using aluminum nitride
ActiveUS7829460B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSelf limitingPermittivity
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Atomic layer removal process with higher etch amount
InactiveUS8058179B1Easy to controlLimit amount of materialSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingLayer removal
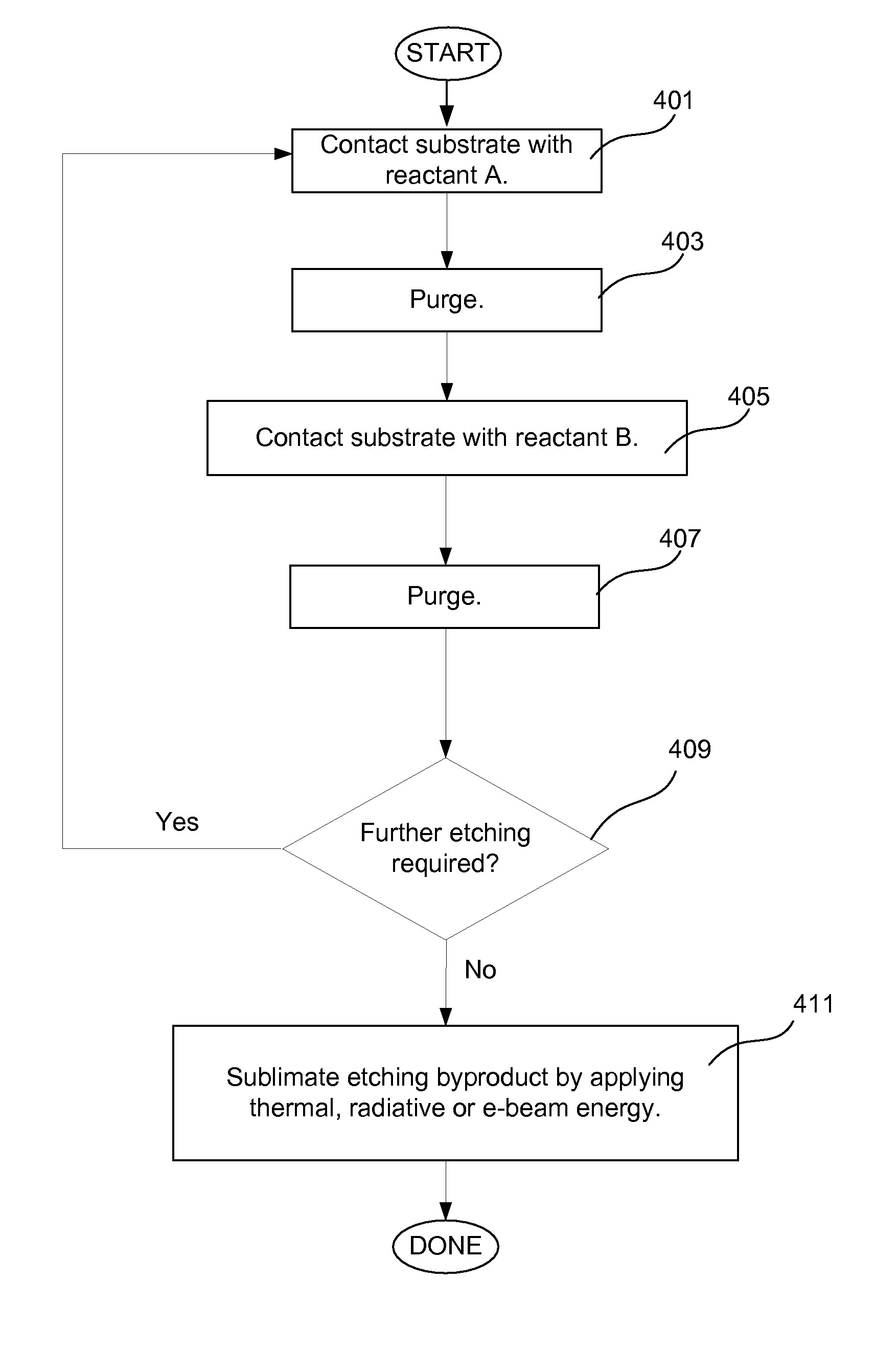
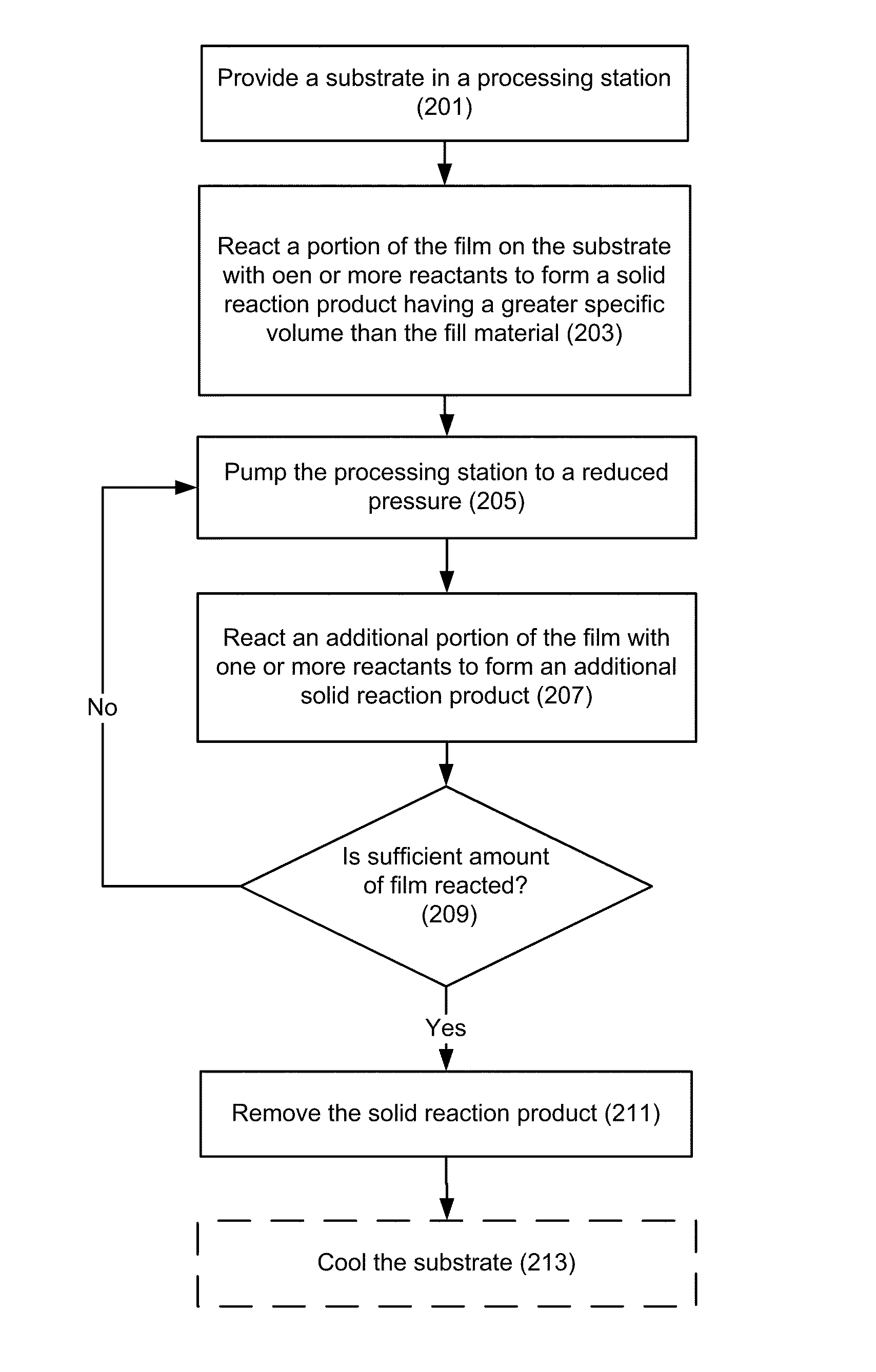
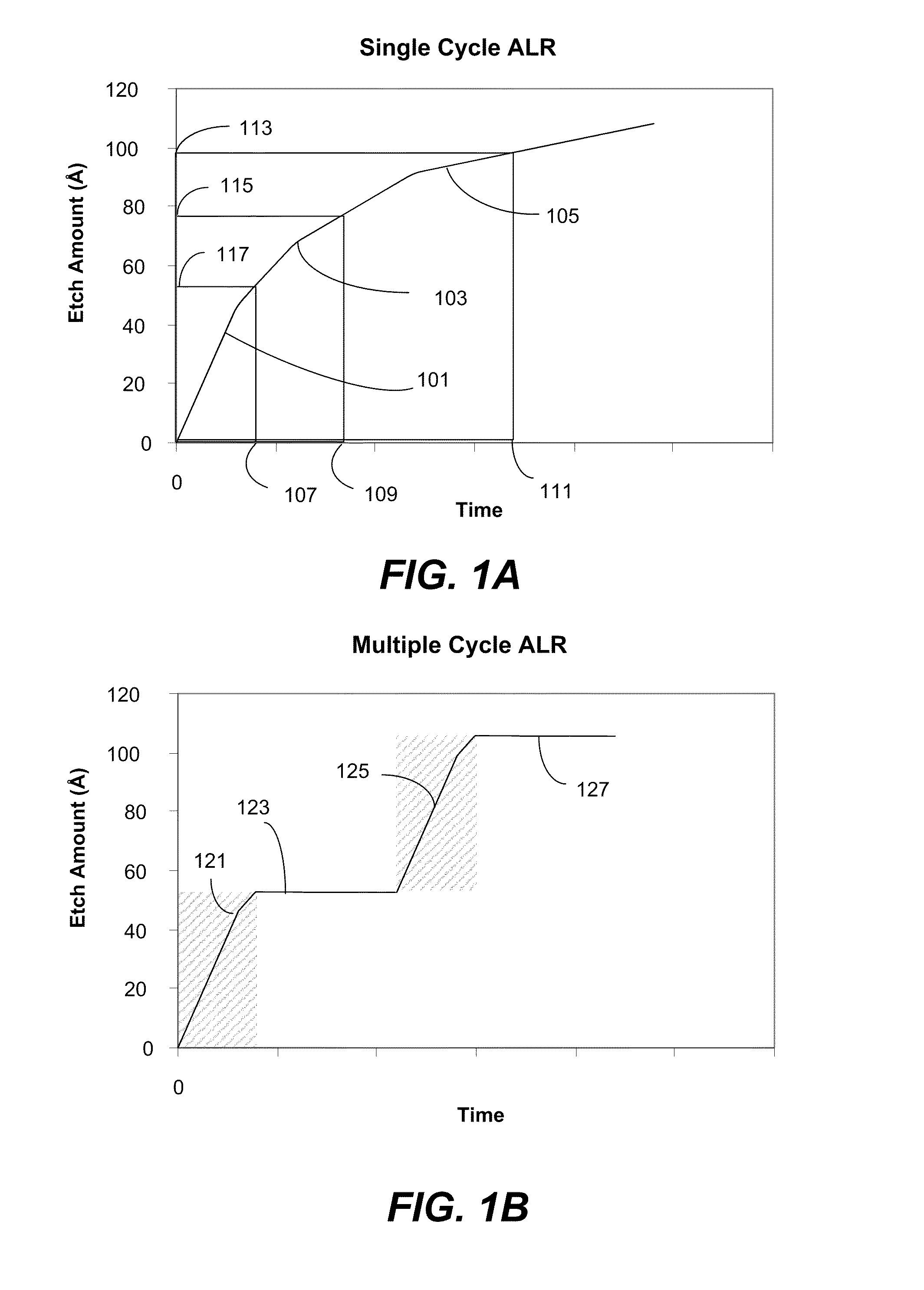
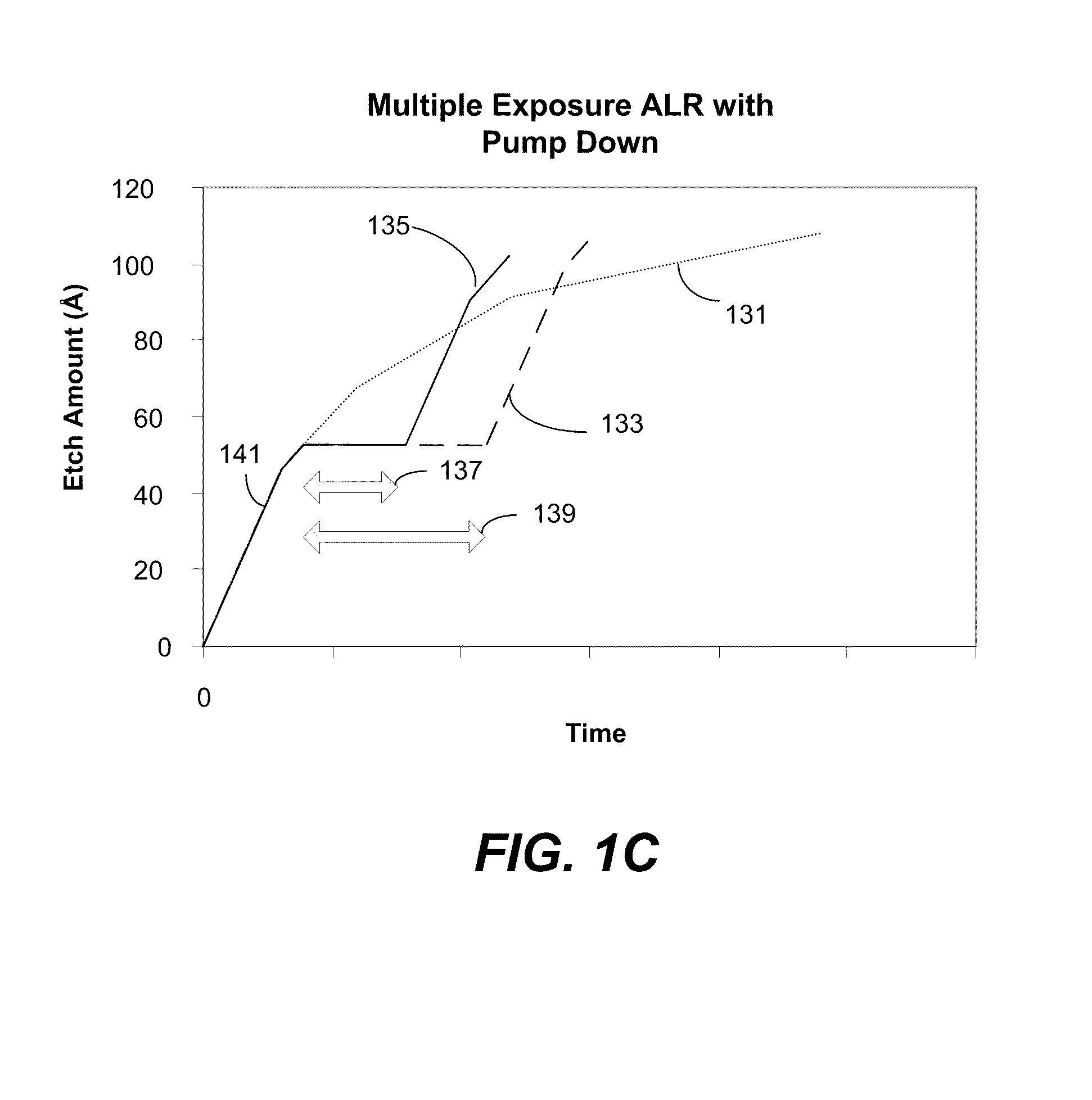
Higher overall etch rate and throughput for atomic layer removal (ALR) is achieved. The reaction is a self-limiting process, thus limiting the total amount of material that may be etched per cycle. By pumping down the process station between reacting operations, the reaction is partially “reset.” A higher overall etch rate is achieved by a multiple exposure with pump down ALR process.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Single-electron floating-gate MOS memory
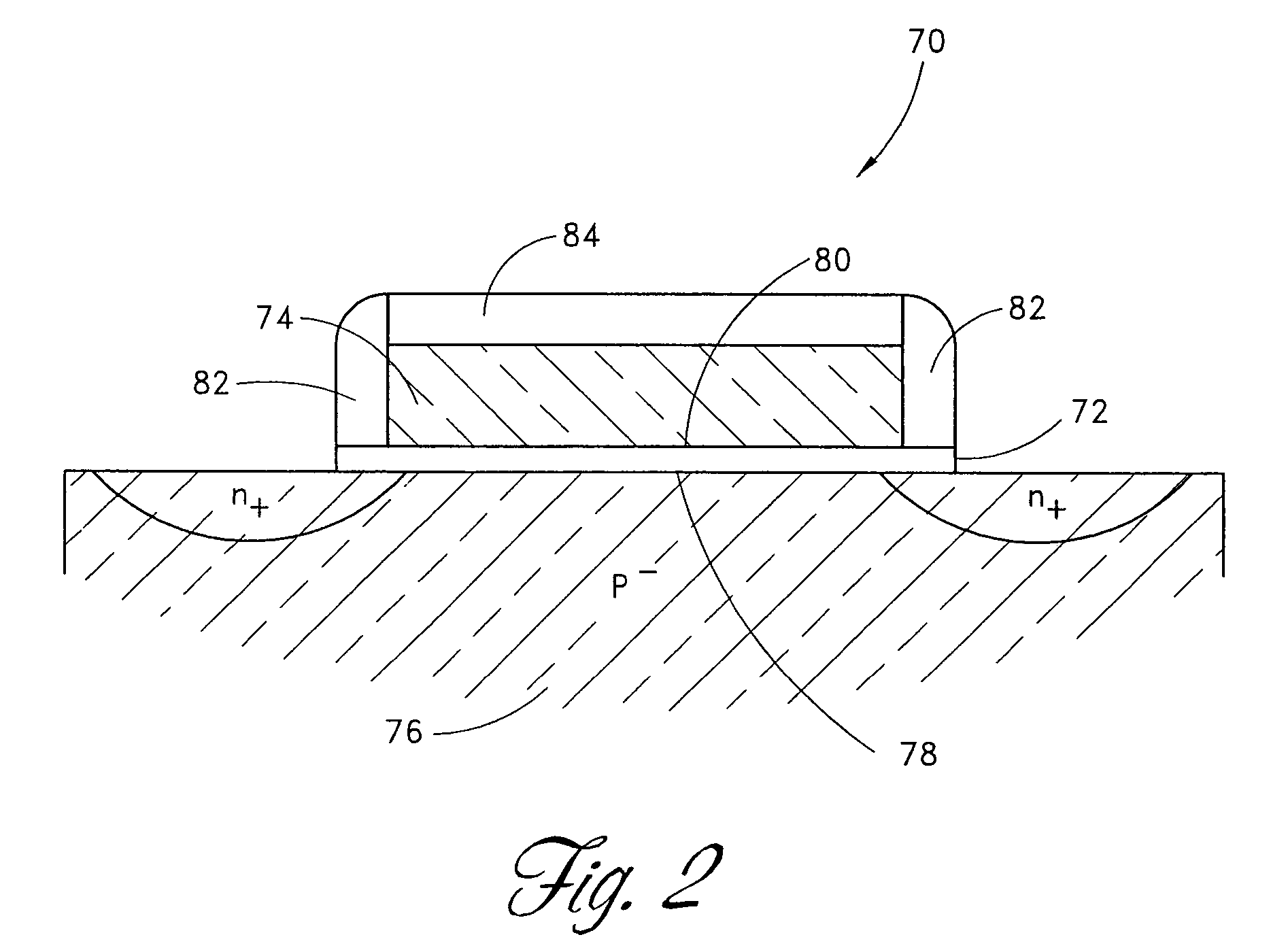
A Single Electron MOS Memory (SEMM), in which one bit of information is represented by storing only one electron, has been demonstrated at room temperature. The SEMM is a floating gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) transistor in silicon with a channel width (about 10 nanometers) which is smaller than the Debye screening length of a single electron stored on the floating gate, and a nanoscale polysilicon dot (about 7 nanometers by 7 nanometers by 2 nanometers) as the floating gate which is positioned between the channel and the control gate. An electron stored on the floating gate can screen the entire channel from the potential on the control gate, and lead to: (i) a discrete shift in the threshold voltage; (ii) a staircase relation between the charging voltage and the shift; and (iii) a self-limiting charging process. The structure and fabrication of the SEMM is well adapted to the manufacture of ultra large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
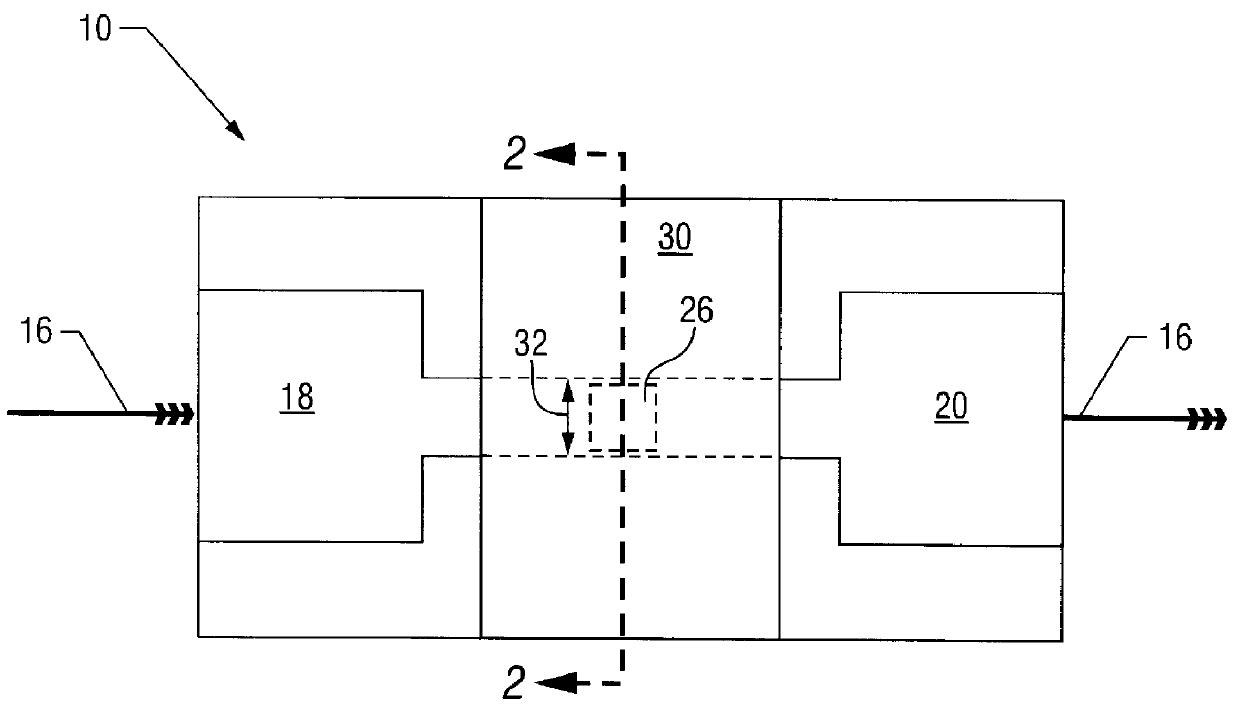
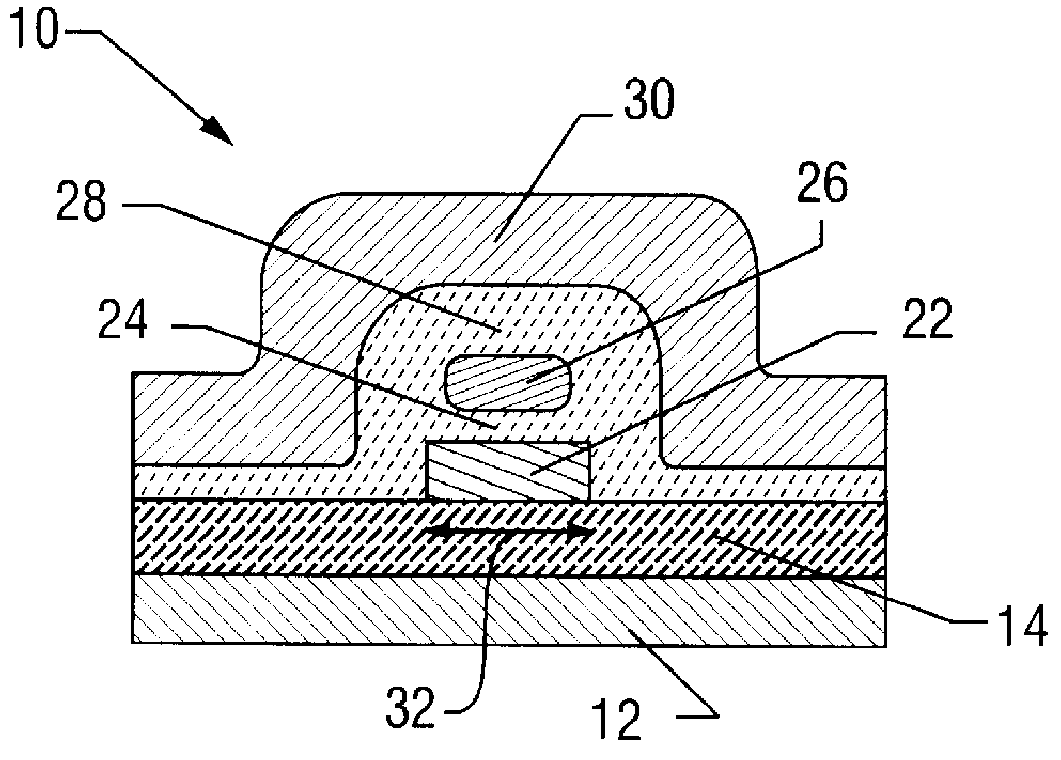
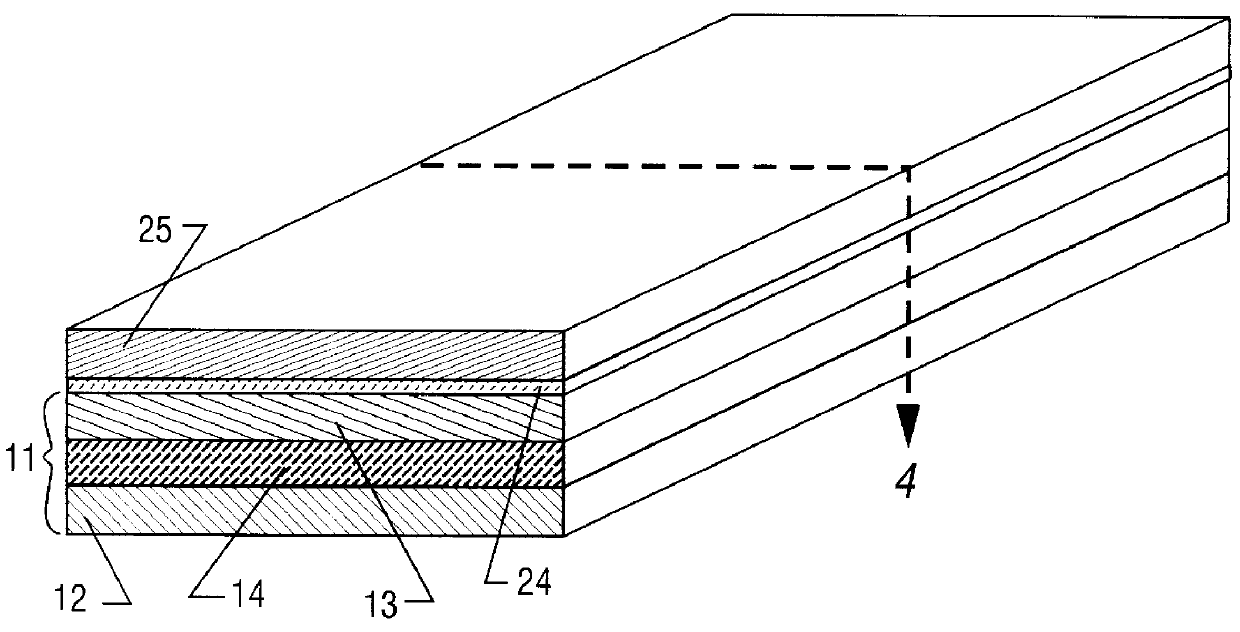
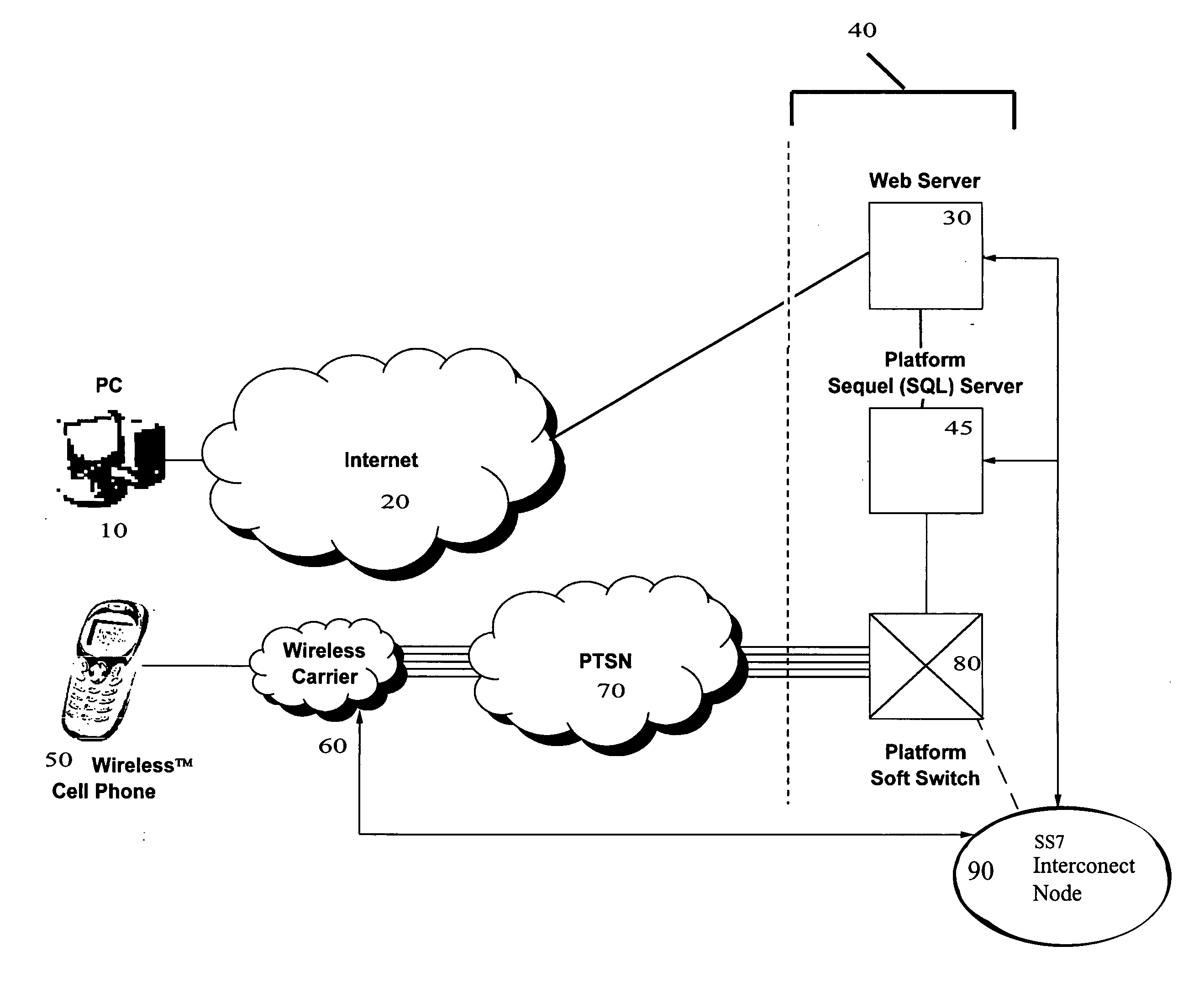
System and method for secure web-based mobile phone parental controls
InactiveUS20060293057A1Unwanted useGraded-service arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWeb siteSelf limiting
A wireless system and method for implementing call controls (such as parental controls) for wireless telephones via a call-intercept platform (including a soft switch and / or an SS7 interconnection node, and SQL database), and a conventional mobile phone that makes and receives all outgoing calls through the call intercept platform. The call intercept platform includes secure web server to provide a secure website point of entry for allowing parents to specify a ruleset of parental controls that is stored in the SQL database. Every outgoing call from the mobile phone is routed into the call-intercept platform, which logs the call, crosschecks the mobile phone and outgoing call number against the stored ruleset for that phone / user, and selectively screens te calls. Incoming calls are automatically forwarded from the wireless carrier to the call intercept platform and are logged, cross-checked and selectively screened. The secure web portal allows parents and guardians or other individuals who desire to self-limit call usage to thoroughly manage their dependent's or their own phone, inclusive of viewing calls, activating and deactivating controls, customizing controls, as well as purchasing prepaid minutes and managing their accounts.
Owner:CLOSECALL AMERICA
Method to remove capping layer of insulation dielectric in interconnect structures
ActiveUS20110143542A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSelf limitingInsulation layer
A method for patterning an insulation layer and selectively removing a capping layer overlying the insulation layer is described. The method utilizes a dry non-plasma removal process. The dry non-plasma removal process may include a self-limiting process.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
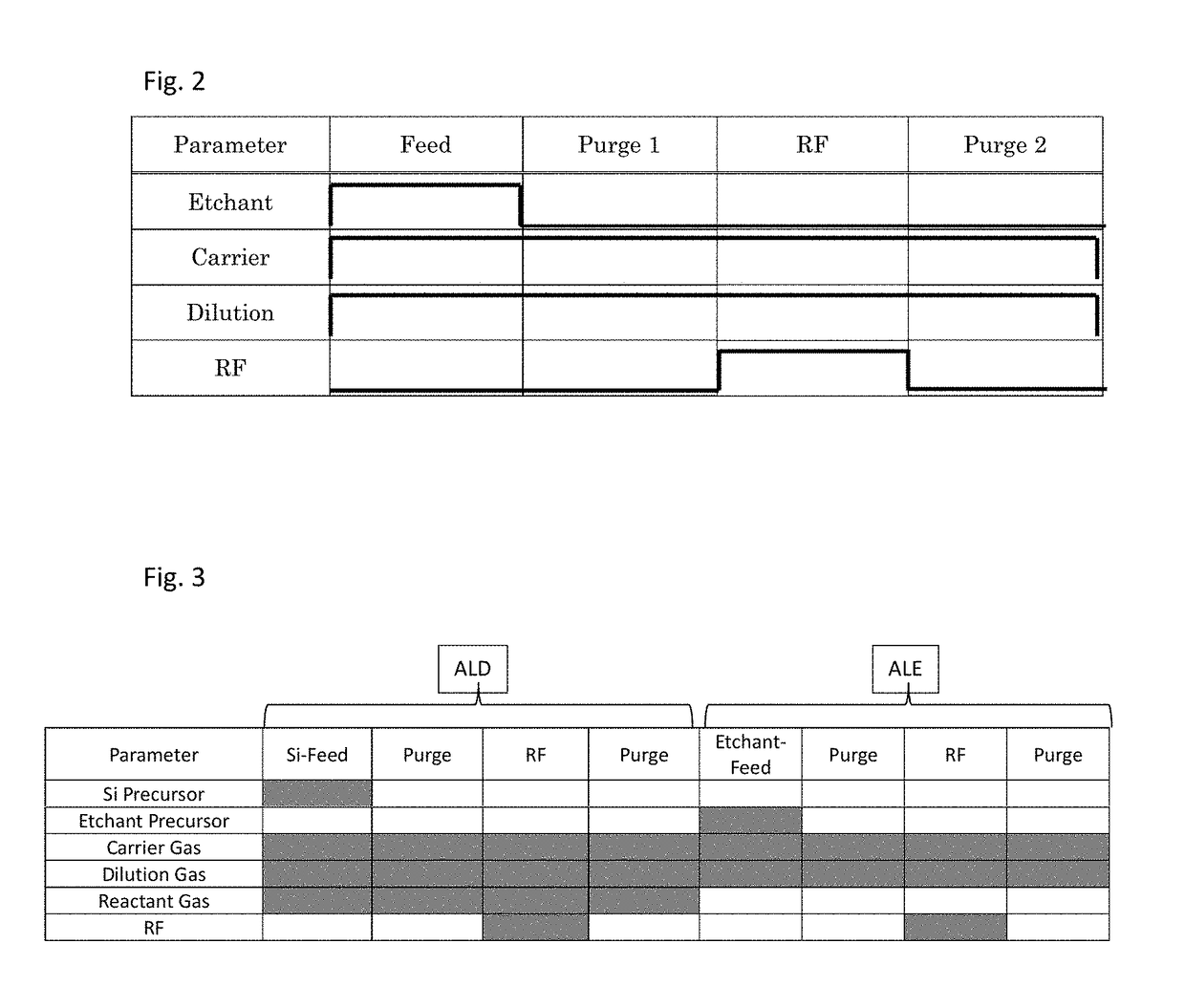
Method of atomic layer etching using functional group-containing fluorocarbon
ActiveUS20170186621A1Improve in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingNoble gas
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Atomic layer deposition of silicon nitride using dual-source precursor and interleaved plasma
InactiveUS20120213940A1Reduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesSelf limitingSilicon nitride
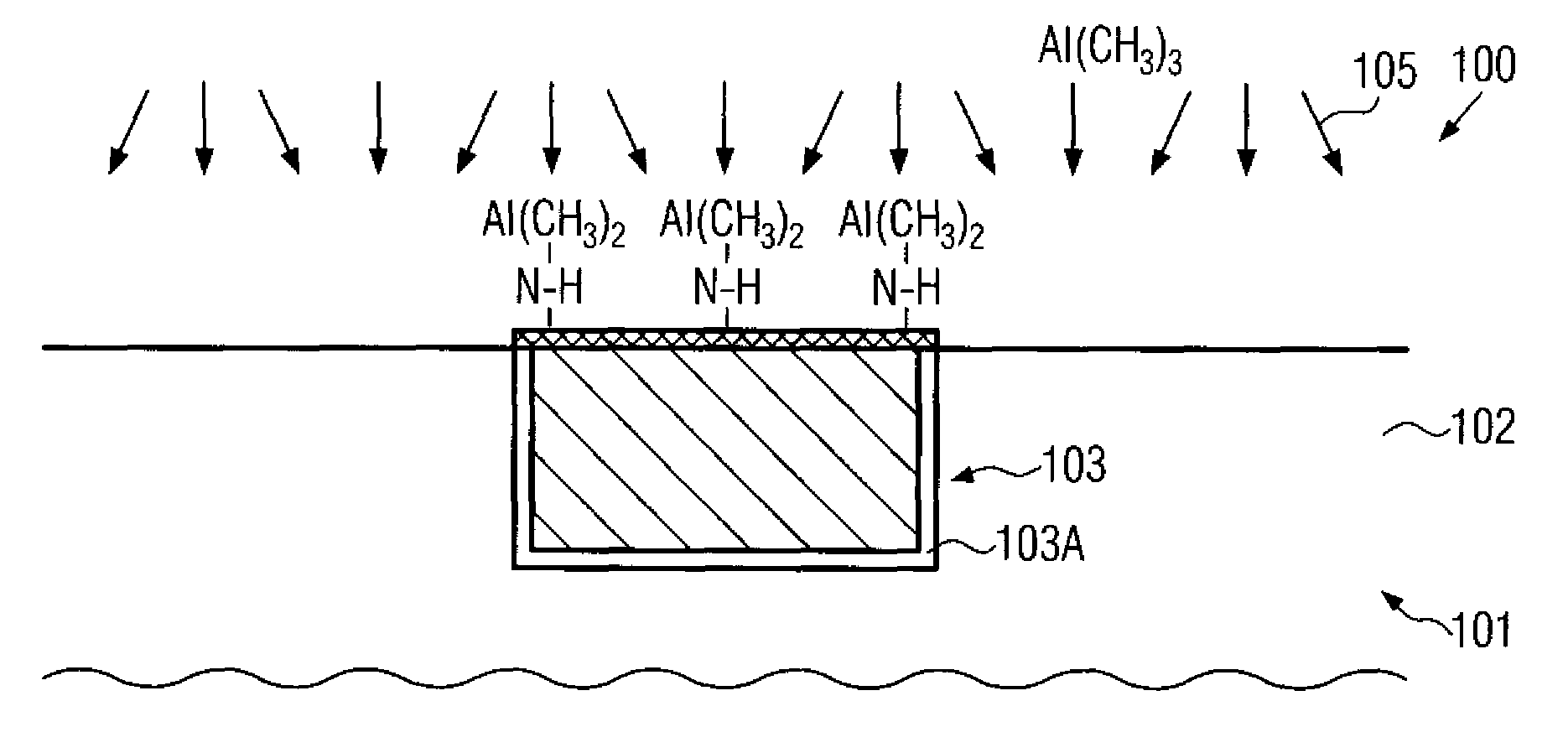
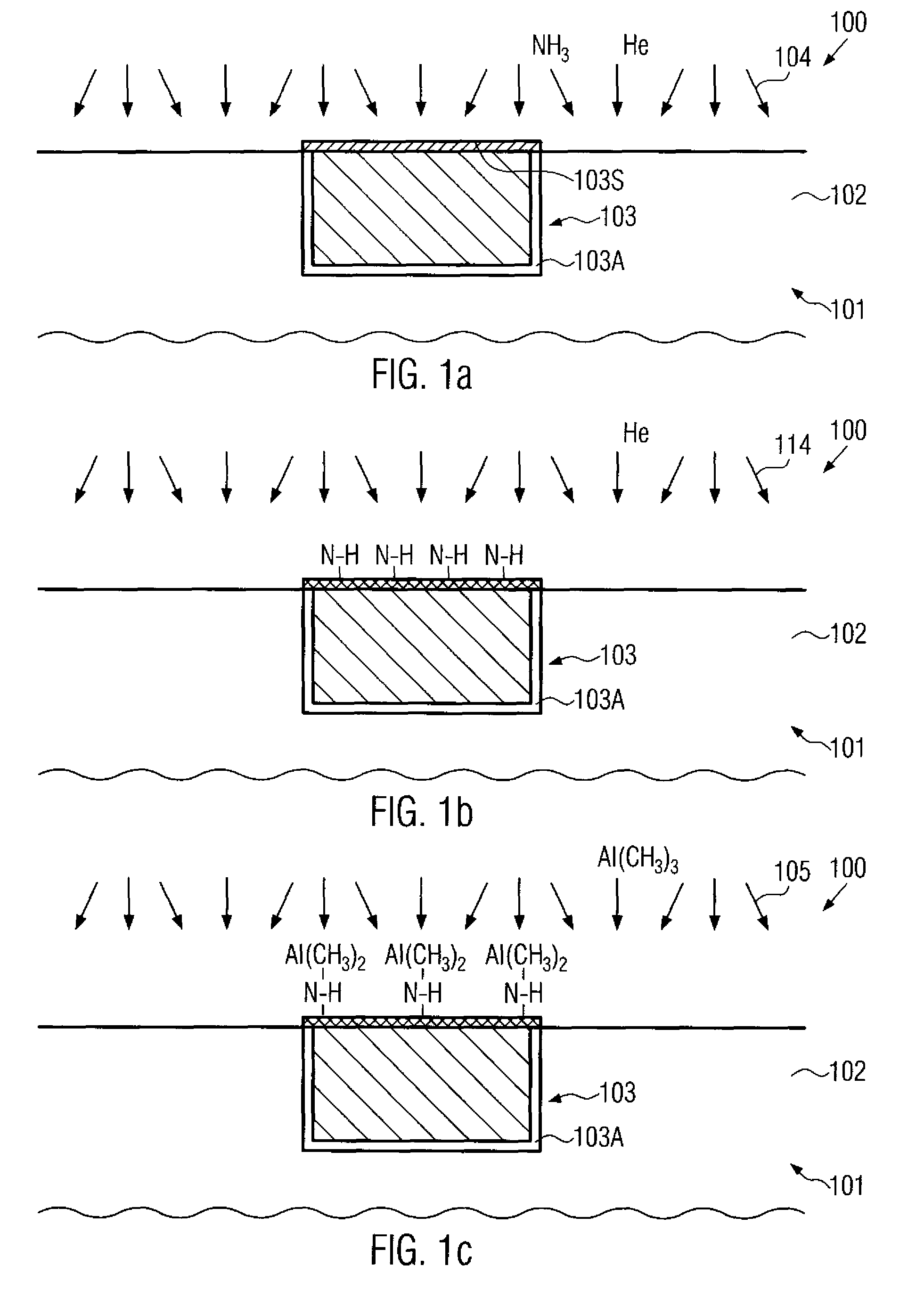
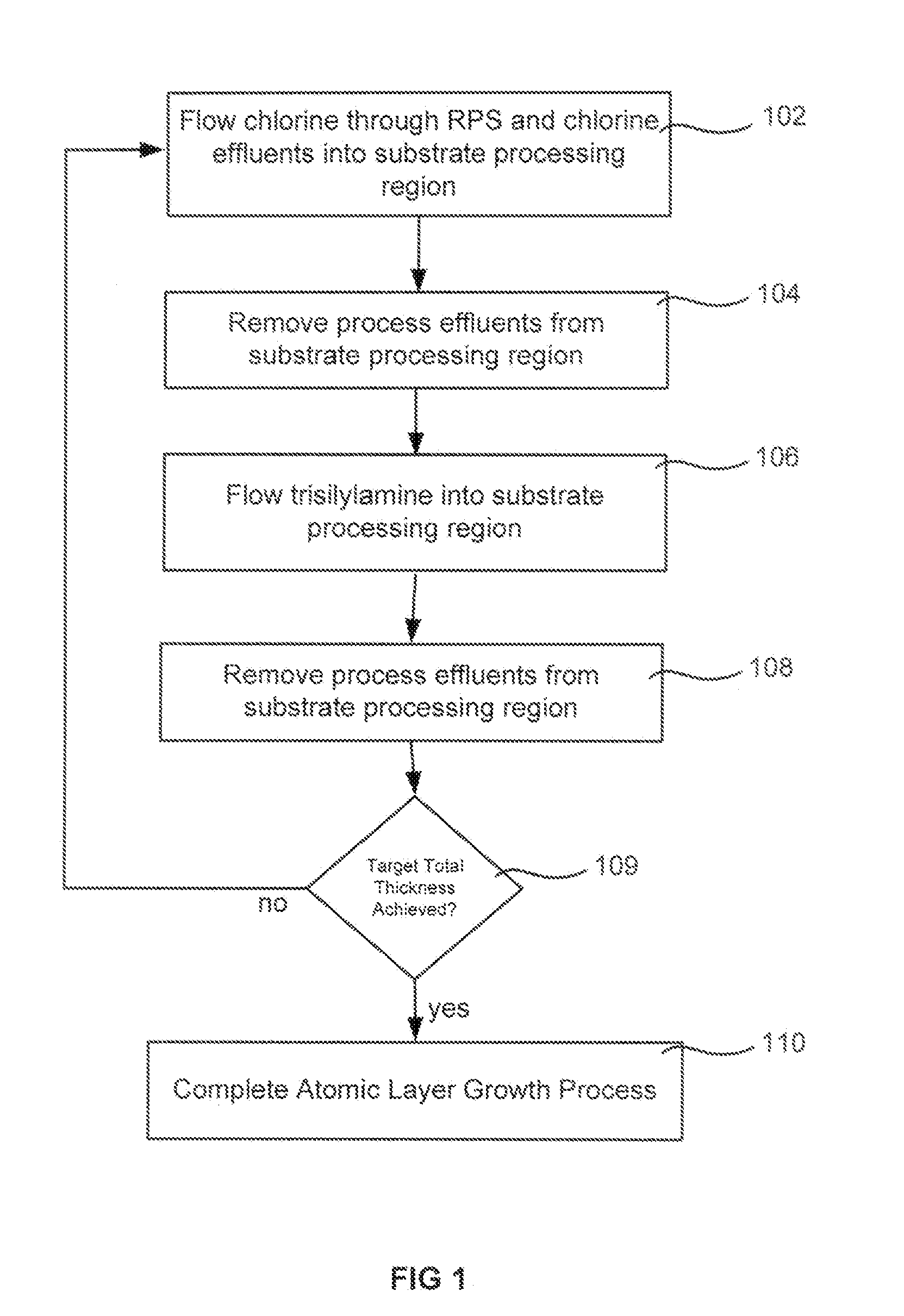
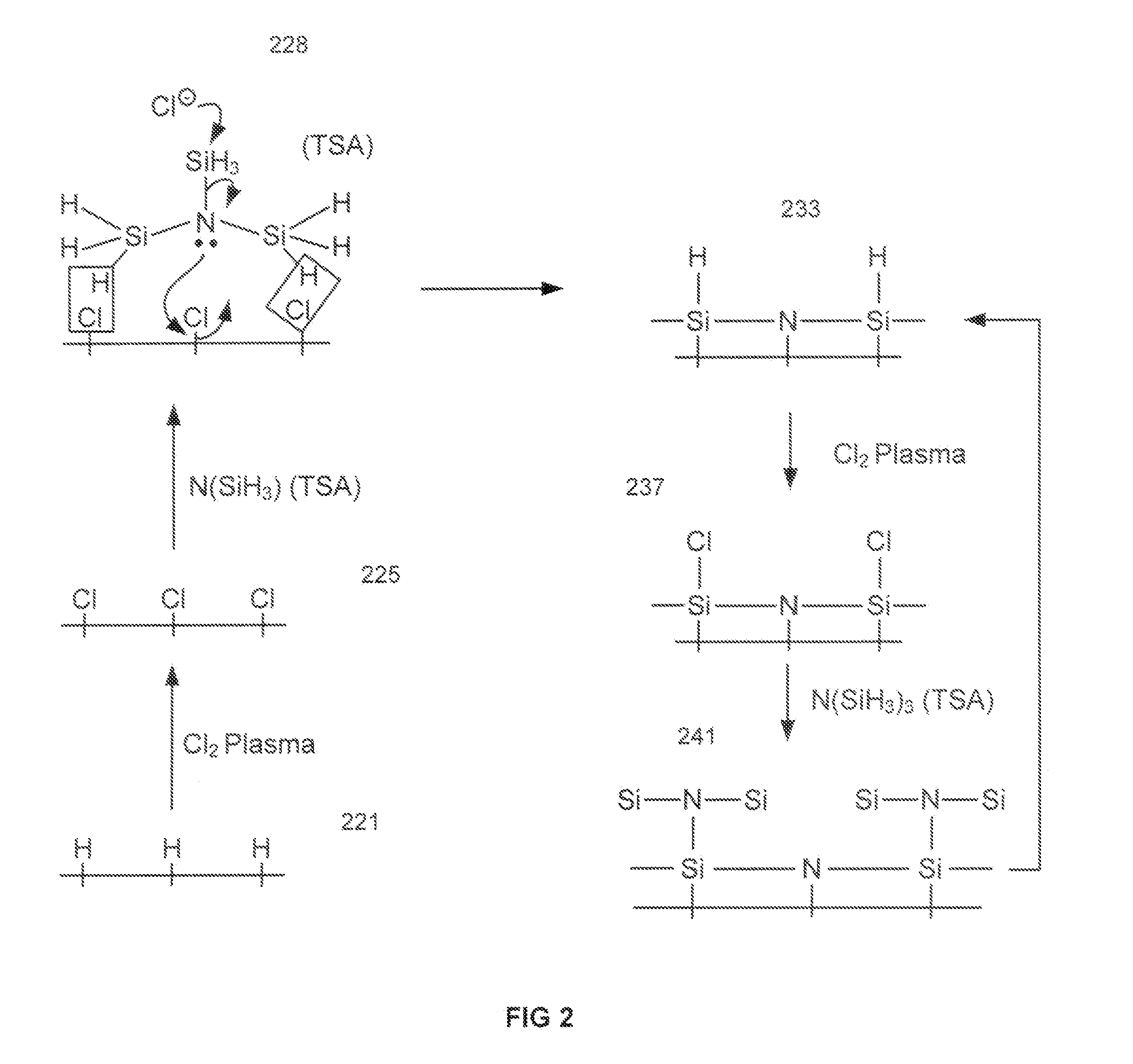
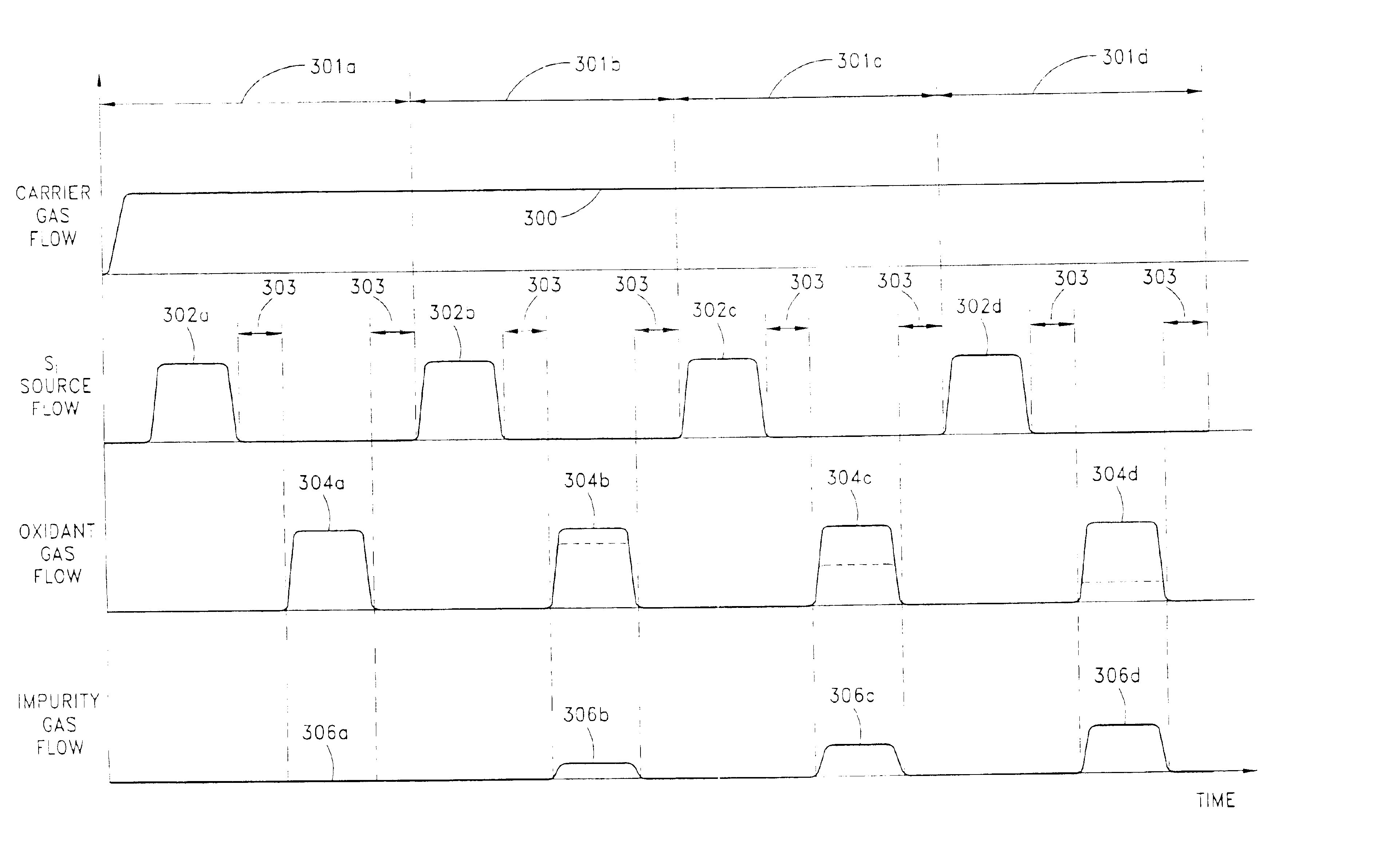
Atomic layer deposition using a precursor having both nitrogen and silicon components is described. The deposition precursor contains molecules which supply both nitrogen and silicon to a growing film of silicon nitride. Silicon-nitrogen bonds may be present in the precursor molecule, but hydrogen and / or halogens may also be present. The growth substrate may be terminated in a variety of ways and exposure to the deposition precursor displaces species from the outer layer of the growth substrate, replacing them with an atomic-scale silicon-and-nitrogen-containing layer. The silicon-and-nitrogen-containing layer grows until one complete layer is produced and then stops (self-limiting growth kinetics). Subsequent exposure to a plasma excited gas modifies the chemical termination of the surface so the growth step may be repeated. The presence of both silicon and nitrogen in the deposition precursor molecule increases the deposition per cycle thereby reducing the number of precursor exposures to grow a film of the same thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Formation of CIGS absorber layer materials using atomic layer deposition and high throughput surface treatment
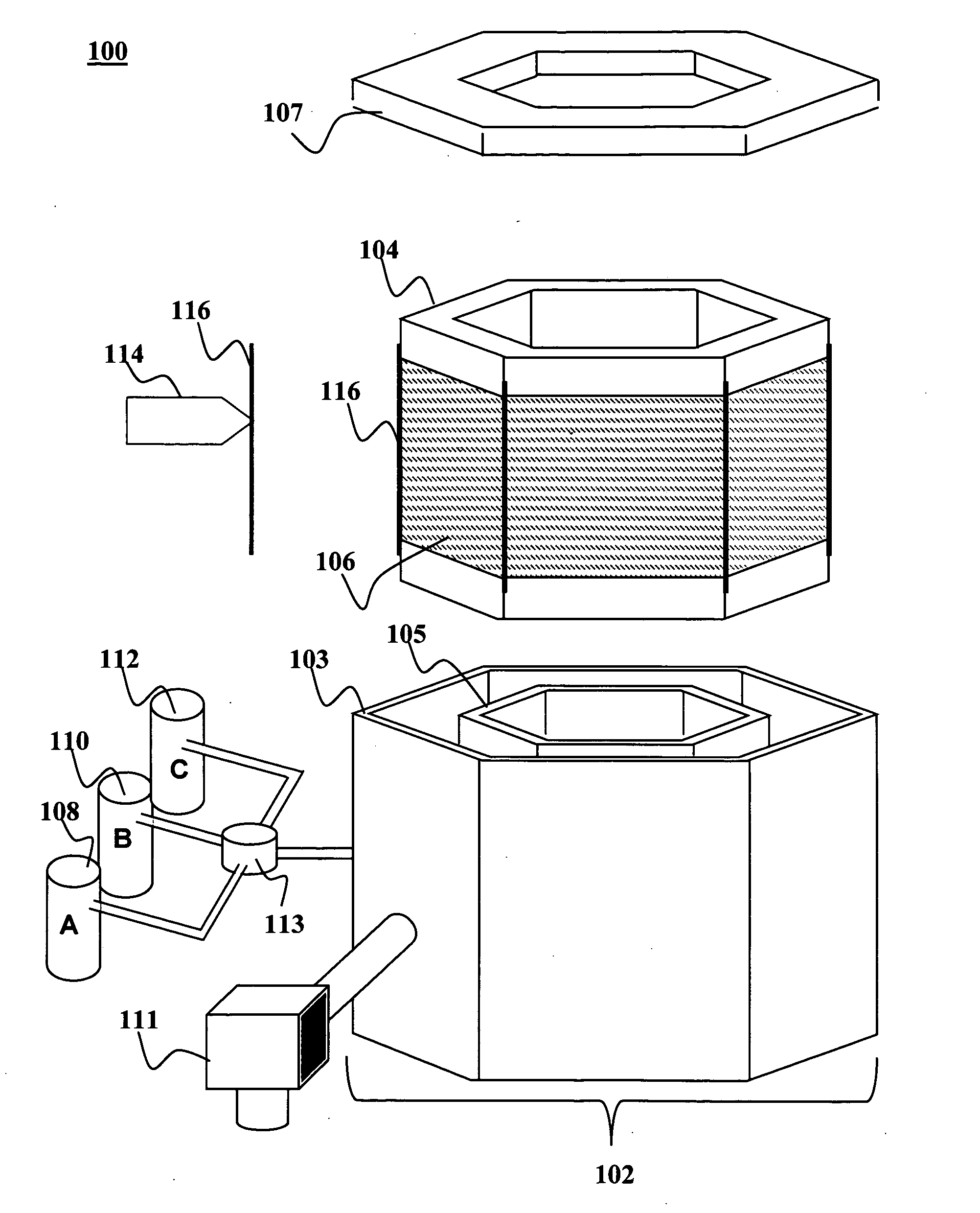
An absorber layer may be formed on on a substrate using atomic layer deposition reactions. An absorber layer containing elements of groups IB, IIIA and VIB may be formed by placing a substrate in a treatment chamber and performing atomic layer deposition of a group IB element and / or one or more group IIIA elements from separate sources onto a substrate to form a film. A group VIA element is then incorporated into the film and annealed to form the absorber layer. The absorber layer may be greater than about 25 nm thick. The substrate may be coiled into one or more coils in such a way that adjacent turns of the coils do not touch one another. The coiled substrate may be placed in a treatment chamber where substantially an entire surface of the one or more coiled substrates may be treated by an atomic layer deposition process. One or more group IB elements and / or one or more group IIIA elements may be deposited onto the substrate in a stoichiometrically controlled ratio by atomic layer deposition using one or more self limiting reactions.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Method of making an ultra thin silicon nitride film
InactiveUS6150286ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingThin oxide
Various methods of fabricating a circuit structure utilizing silicon nitride are provided. In one aspect, a method of fabricating a circuit structure is provided that includes forming a silicon nitride film on a silicon surface, annealing the silicon nitride film in an ammonia ambient and annealing the silicon nitride film in a nitrous oxide ambient to form a thin oxide layer at an interface between the silicon nitride film and the silicon surface. The process of the present invention enables the manufacture of thin silicon nitride films with highly uniform morphology for use as gate dielectrics or other purposes. The thin oxide film is self-limiting in thickness and improves differential mechanical stresses.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Graded thin films
InactiveUS6933225B2Reduce the temperatureDesirable interface propertySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon oxide
Thin films are formed by atomic layer deposition, whereby the composition of the film can be varied from monolayer to monolayer during cycles including alternating pulses of self-limiting chemistries. In the illustrated embodiments, varying amounts of impurity sources are introduced during the cyclical process. A graded gate dielectric is thereby provided, even for extremely thin layers. The gate dielectric as thin as 2 nm can be varied from pure silicon oxide to oxynitride to silicon nitride. Similarly, the gate dielectric can be varied from aluminum oxide to mixtures of aluminum oxide and a higher dielectric material (e.g., ZrO2) to pure high k material and back to aluminum oxide. In another embodiment, metal nitride (e.g., WN) is first formed as a barrier for lining dual damascene trenches and vias. During the alternating deposition process, copper can be introduced, e.g., in separate pulses, and the copper source pulses can gradually increase in frequency, forming a graded transition region, until pure copper is formed at the upper surface. Advantageously, graded compositions in these and a variety of other contexts help to avoid such problems as etch rate control, electromigration and non-ohmic electrical contact that can occur at sharp material interfaces.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
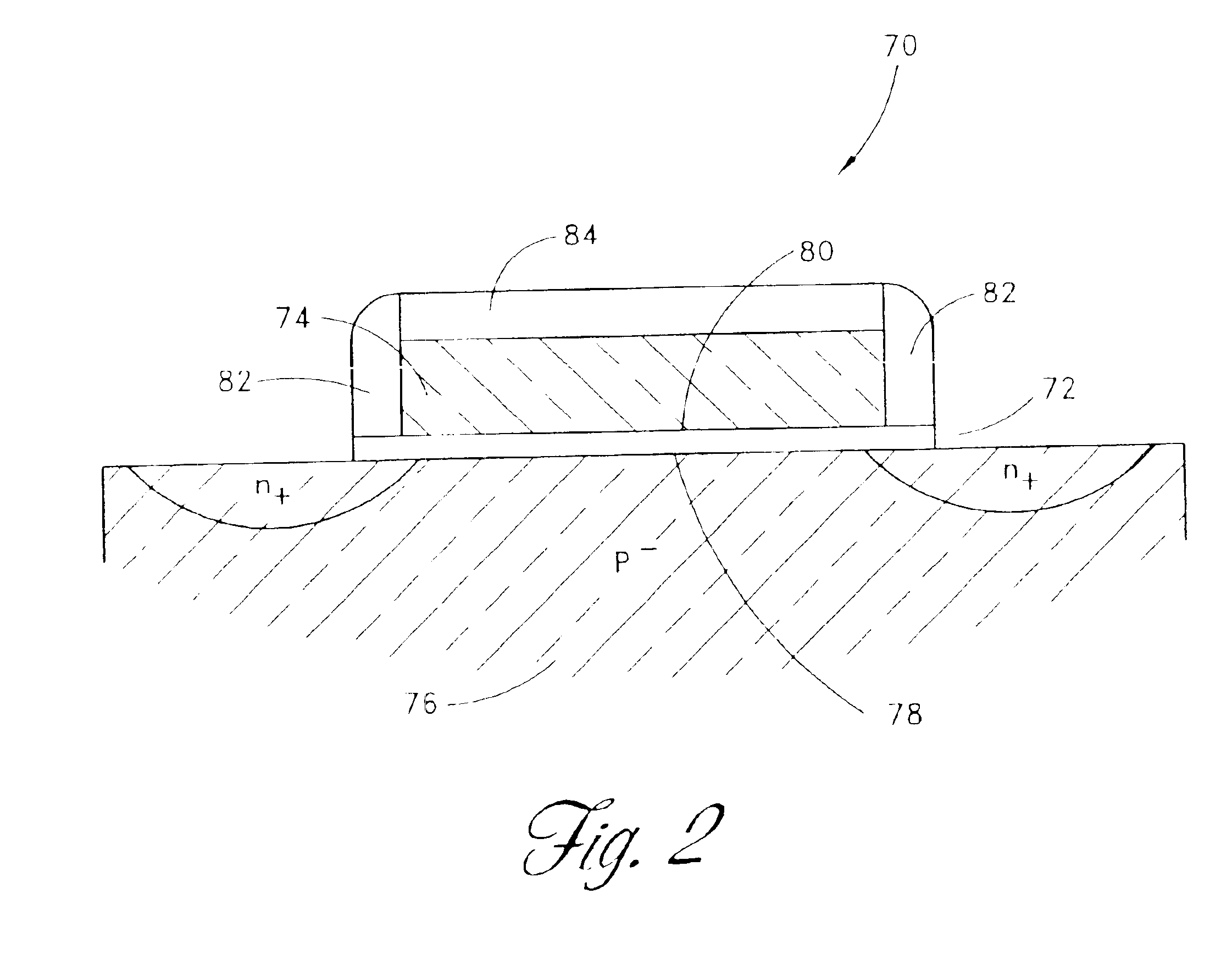
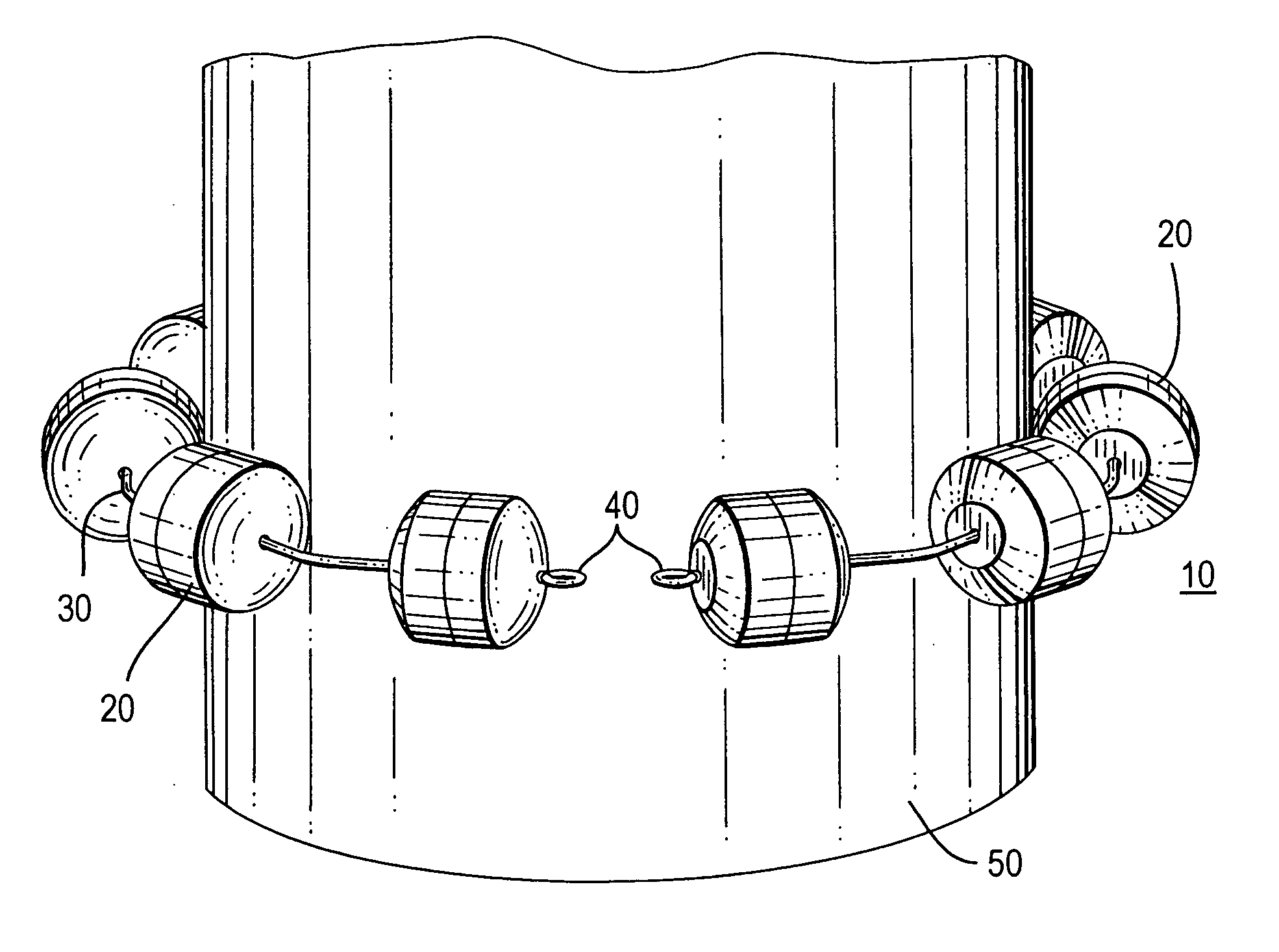
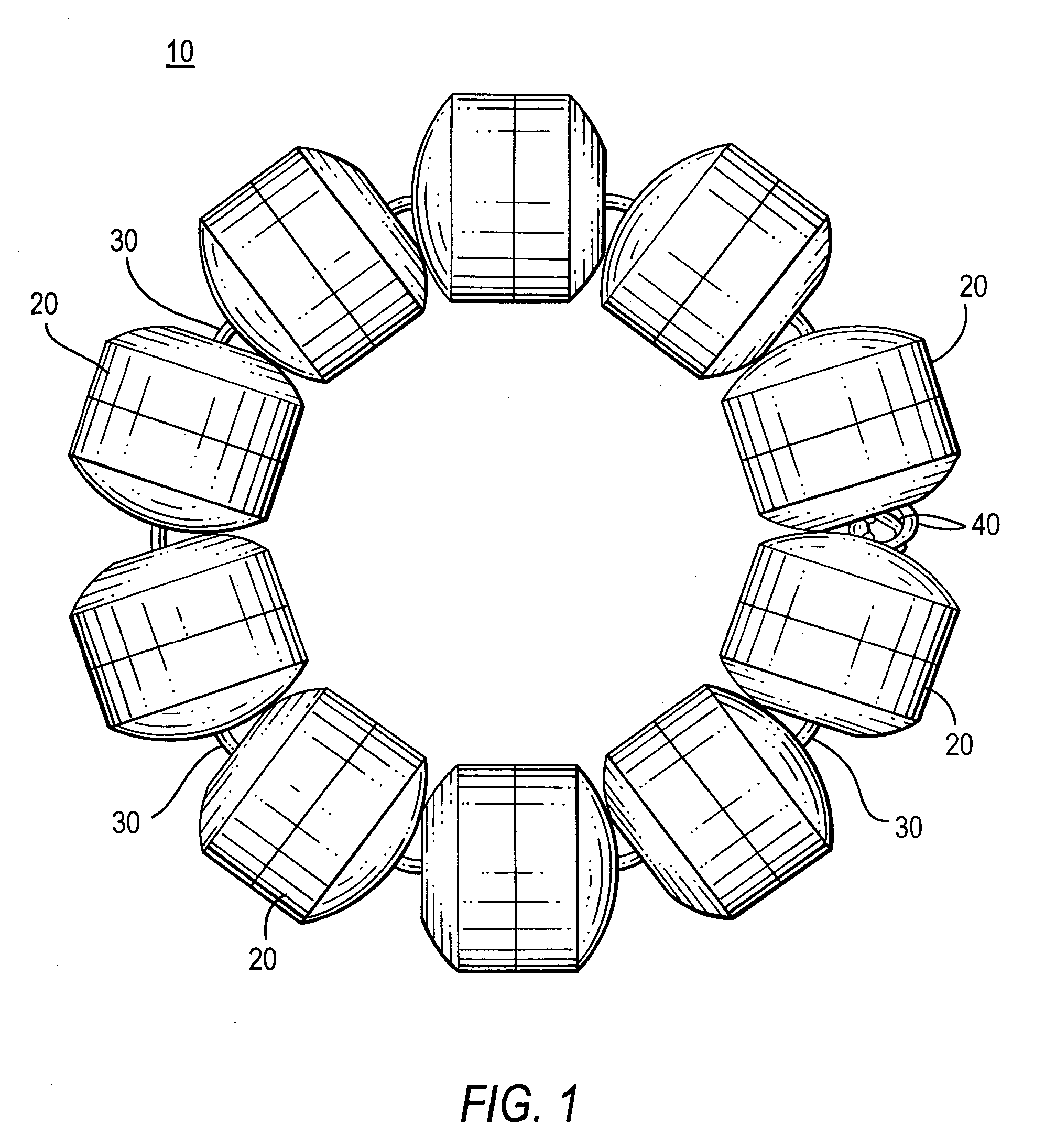
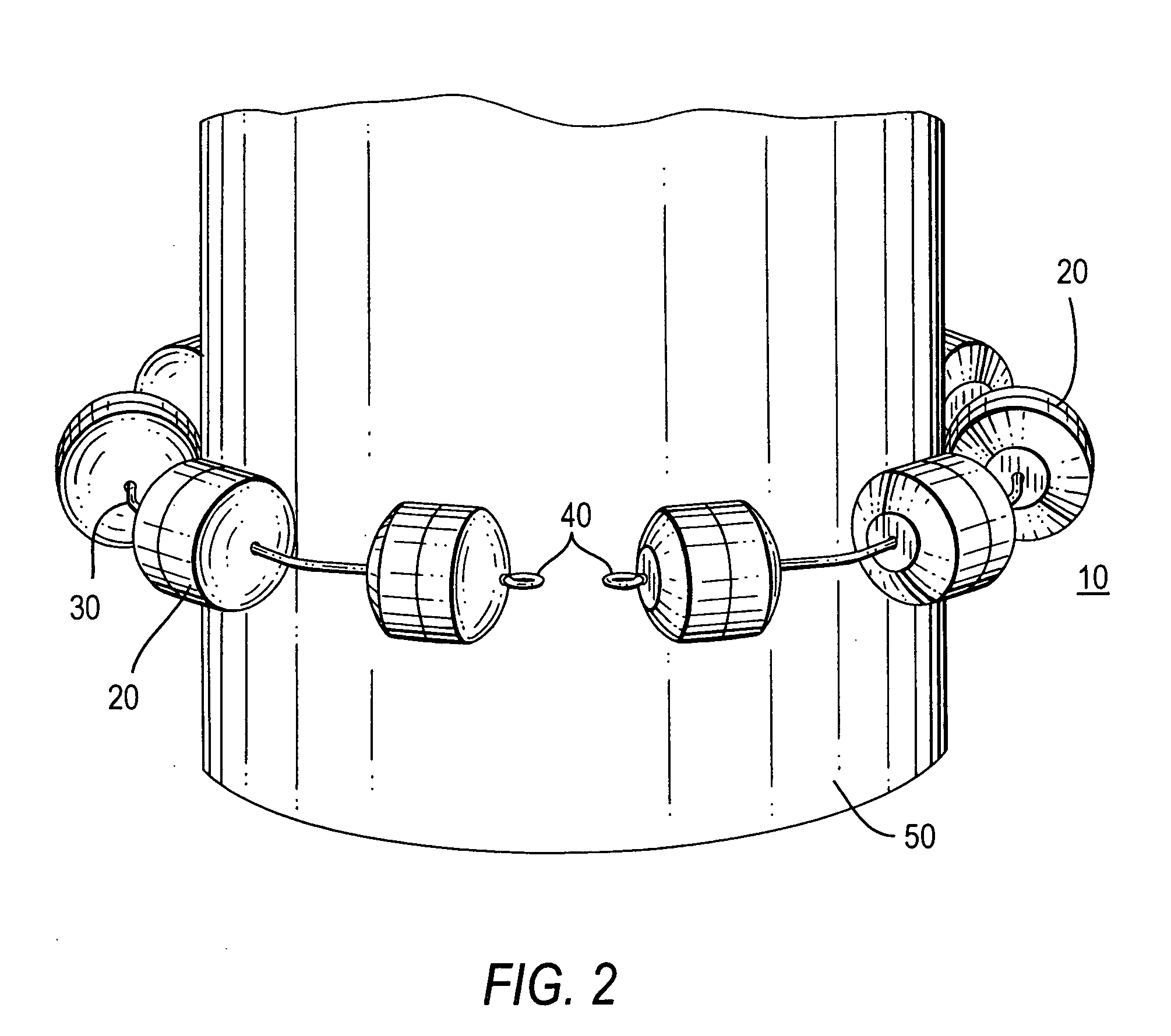
Methods and apparatus for treating body tissue sphincters and the like
ActiveUS20050283235A1Excellent toneSimple structureAnti-incontinence devicesSurgerySelf limitingSphincter
A plurality of structures that resiliently attract one another are provided for implanting in a patient around a body tissue structure of the patient. For example, the body tissue structure may be the esophagus, and the plurality of structures may be implanted in an annulus around the outside of the esophagus, the annulus being substantially coaxial with the esophagus. The attraction may be between annularly adjacent ones of the structures in the annulus, and it may be provided, for example, by magnets or springs. The array of structures is preferably self-limiting with respect to the smallest area that it can encompass, and this smallest area is preferably large enough to prevent the apparatus from applying excessive pressure to tissue passing through that area.
Owner:TORAX MEDICAL
Method of trimming a gate electrode structure
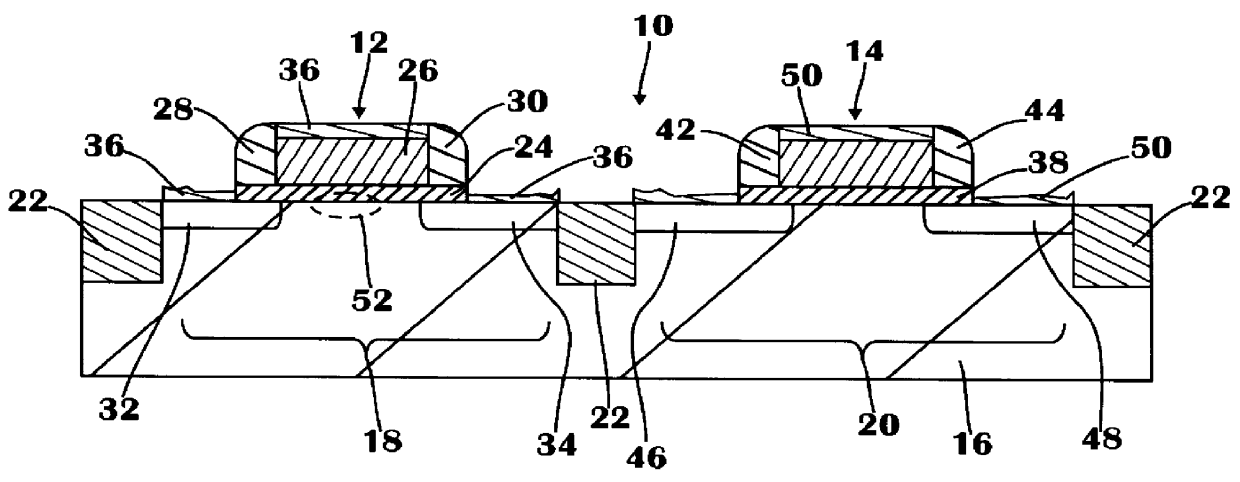
ActiveUS6852584B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingReaction layer
A method and processing tool are provided for trimming a gate electrode structure containing a gate electrode layer with a first dimension. A reaction layer is formed through reaction with the gate electrode structure. The reaction layer is the selectively removed from the unreacted portion of the gate electrode structure by chemical etching, thereby forming a trimmed gate electrode structure with a second dimension that is smaller than the first dimension. The trimming process can be carried out under process conditions where formation of the reaction layer is substantially self-limiting. The trimming process can be repeated to further reduce the dimension of the gate electrode structure.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
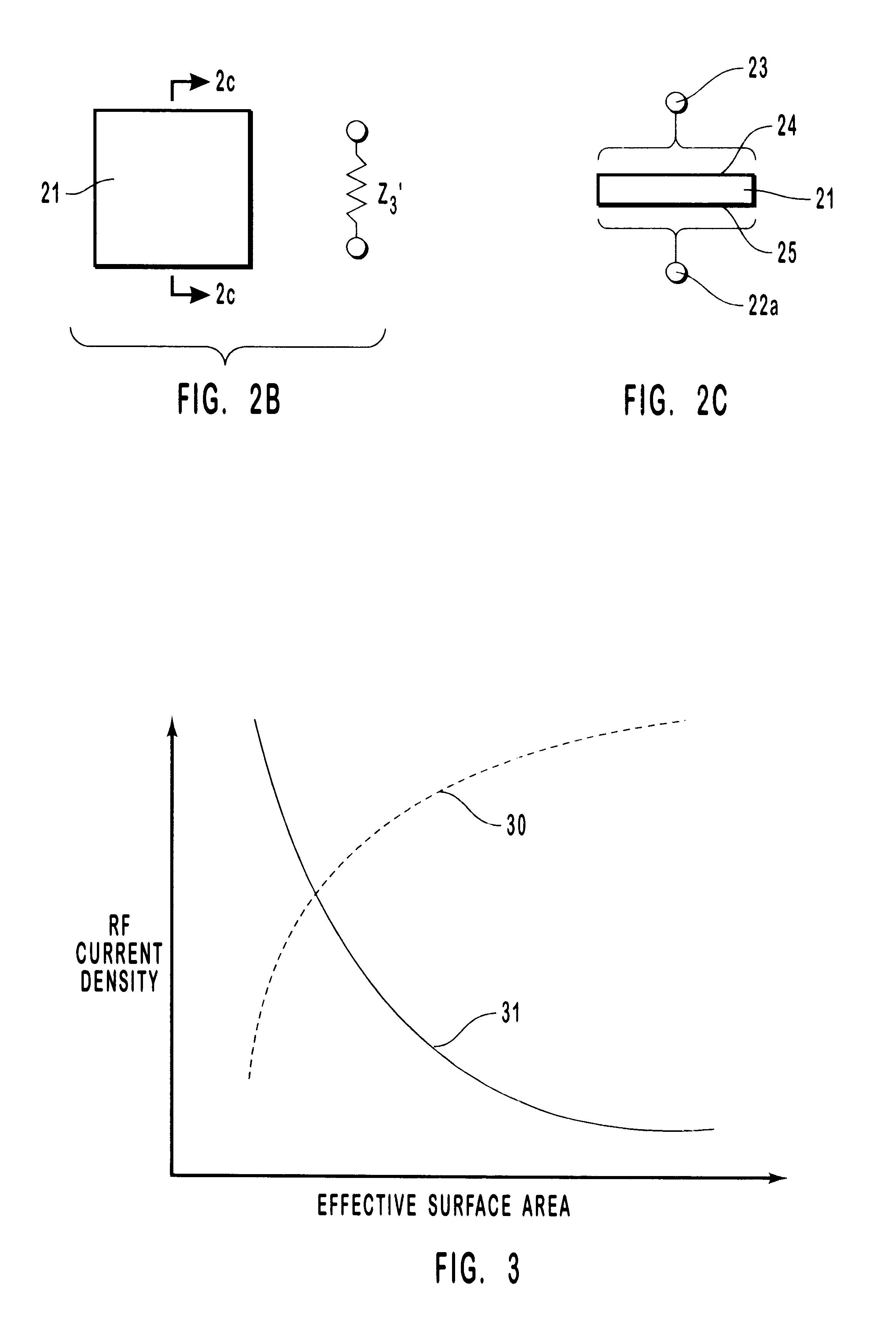
Self-limiting electrosurgical return electrode
InactiveUS6454764B1Eliminate burnsReduce the possibilityElectrotherapyDiagnosticsCapacitanceElectrical connection
A self-limiting electrosurgical return electrode for use with electrosurgery. Through the selection of impedance characteristics for the electrode materials of the principal body of the electrode, and through tailoring of electrode geometries, the return electrode of the present invention is self-regulating and self-limiting as to current density and temperature rise so as to prevent patient trauma. The electrosurgical return electrode includes a sheet of material having an effective bulk impedance equal to or greater than about 4,000 OMEGA.cm and one or more connectors for making electrical connection to the sheet. The effective bulk impedance of the sheet may arise from resistive components, capacitive components, inductive components, or combinations thereof. The configuration of the presently described return electrode allows the electrode to self-limit the electrode's current densities, thereby preventing burning of a patient during surgery. Furthermore, through employment of washable surface areas, the electrode is made readily cleanable, disinfectable, sterilizable, and reusable. An optional sleeve is provided for cooperative use with the electrode.
Owner:MEGADYNE MED PROD INC US
Method of treating vulnerable plaque
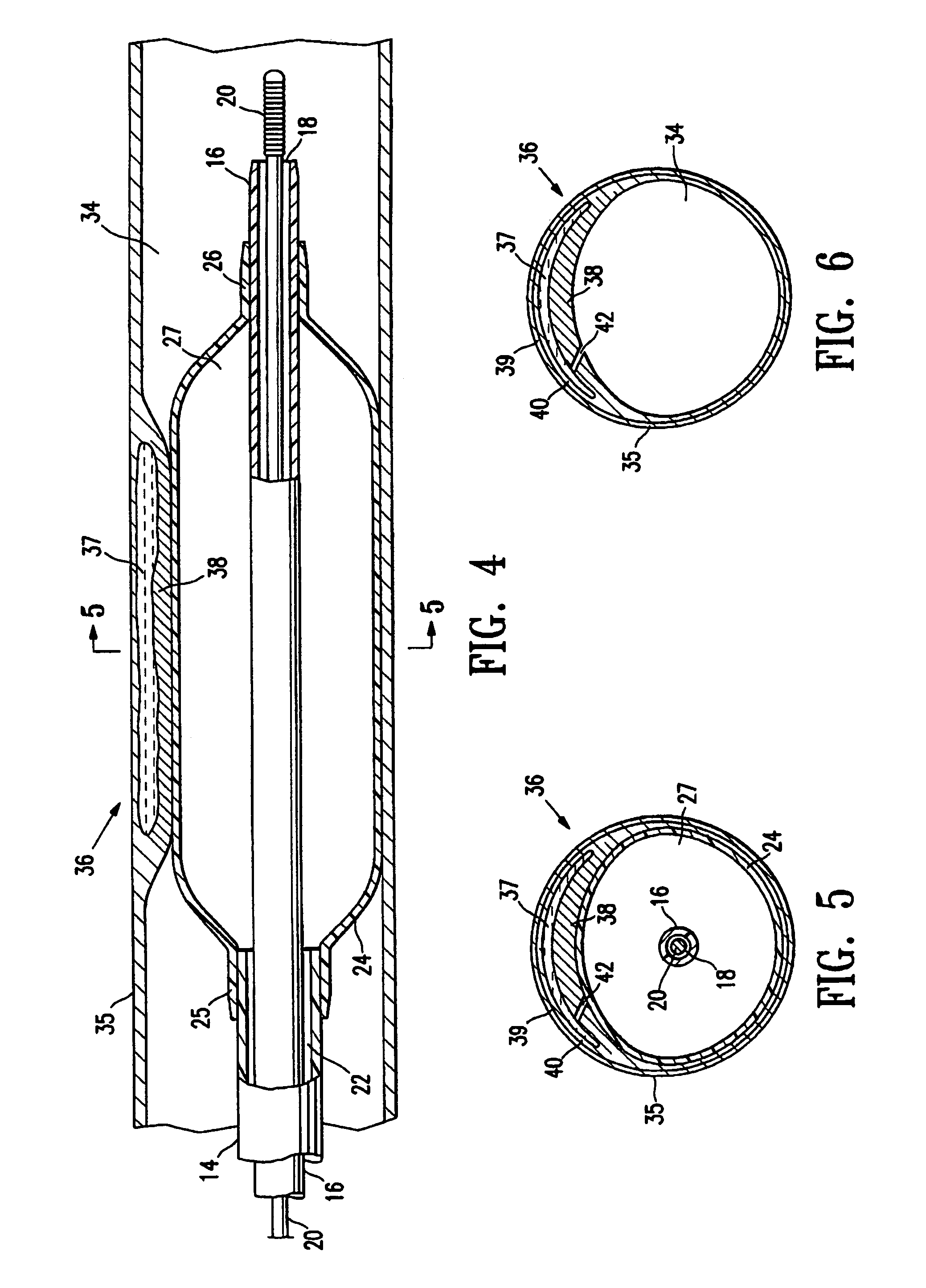
InactiveUS6972024B1Minimizing avoiding damageIncrease synthesisStentsEar treatmentSelf limitingVulnerable plaque
A method of treating vulnerable plaque comprising intentionally damaging or rupturing the vulnerable plaque using a wingless balloon which is inflated from a wingless unexpanded diameter to a limited expanded diameter. This process produces significant increase in ECM synthesis at the site of the damage or rupture. As a result, the method strengthens the vulnerable plaque while minimizing or avoiding damage to the surrounding wall of the body lumen or damaging a stable plaque mistakenly believed to be a vulnerable plaque. The method of the invention is particularly useful in treating a fibroatheroma type of vulnerable plaque. In one embodiment, the balloon is self-limiting such that it expands compliantly at initial inflation pressures, and above nominal pressure it expands noncompliantly. In an alternative embodiment, the balloon is inflated using a diameter-limiting device, such as a device which limits the inflation pressure or the volume of inflation fluid in the balloon.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Solid material comprising a thin metal film on its surface and methods for producing the same
InactiveUS6958174B1Reduce percentageVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSelf limitingMetallurgy
The present invention provides a solid material comprising a solid substrate having a thin metal film and methods for producing the same. The method generally involves using a plurality self-limiting reactions to control the thickness of the metal film.
Owner:UNIV TECH
Modification of selectivity for sensing for nanostructure device arrays
InactiveUS6905655B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSelf limitingChemical species
An electronic system for selectively detecting and identifying a plurality of chemical species, which comprises an array of nanostructure sensing devices, is disclosed. Within the array, there are at least two different selectivities for sensing among the nanostructure sensing devices. Methods for fabricating the electronic system are also disclosed. The methods involve modifiying nanostructures within the devices to have different selectivity for sensing chemical species. Modification can involve chemical, electrochemical, and self-limiting point defect reactions. Reactants for these reactions can be supplied using a bath method or a chemical jet method. Methods for using the arrays of nanostructure sensing devices to detect and identify a plurality of chemical species are also provided. The methods involve comparing signals from nanostructure sensing devices that have not been exposed to the chemical species of interest with signals from nanostructure sensing devices that have been exposed to the chemical species of interest. Nanostructure sensing device array structures that can measure and subtract out environmental factors are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOMIX INC
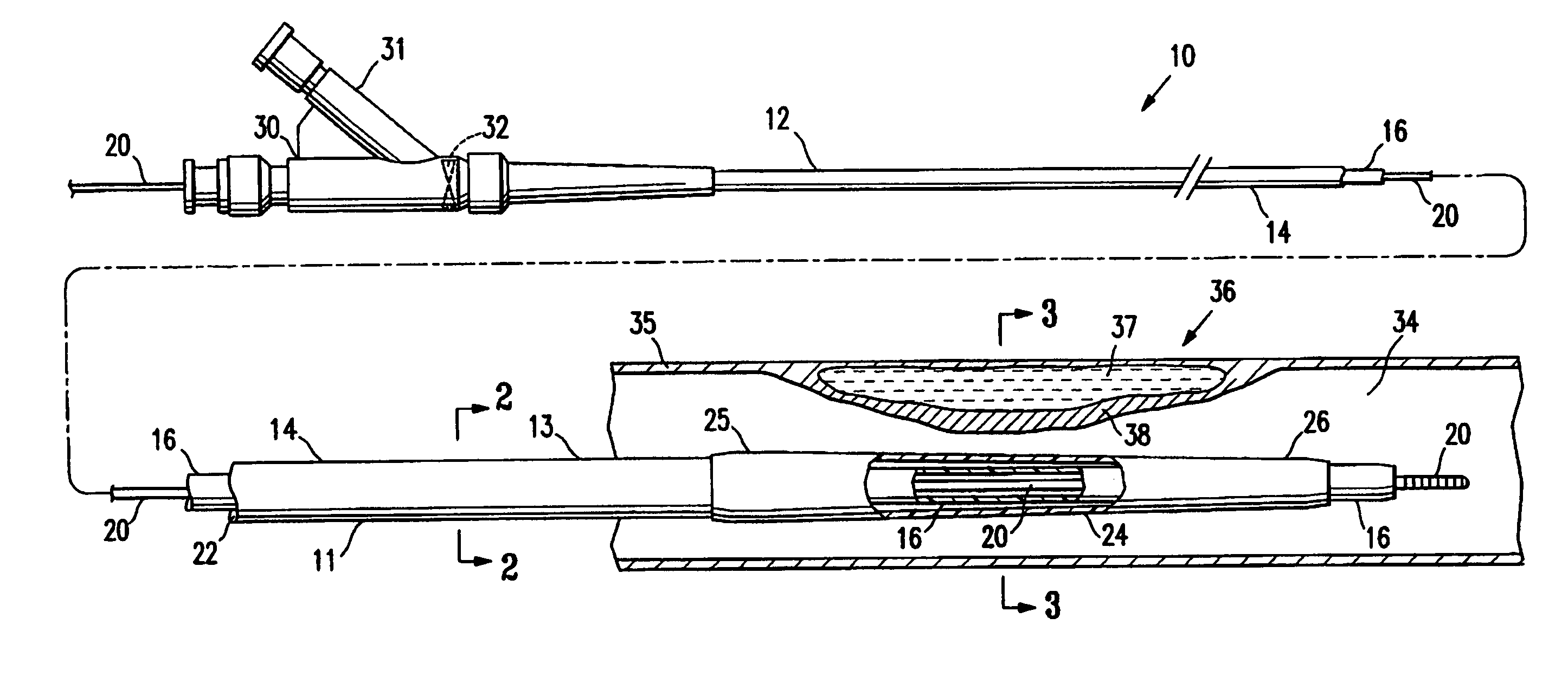
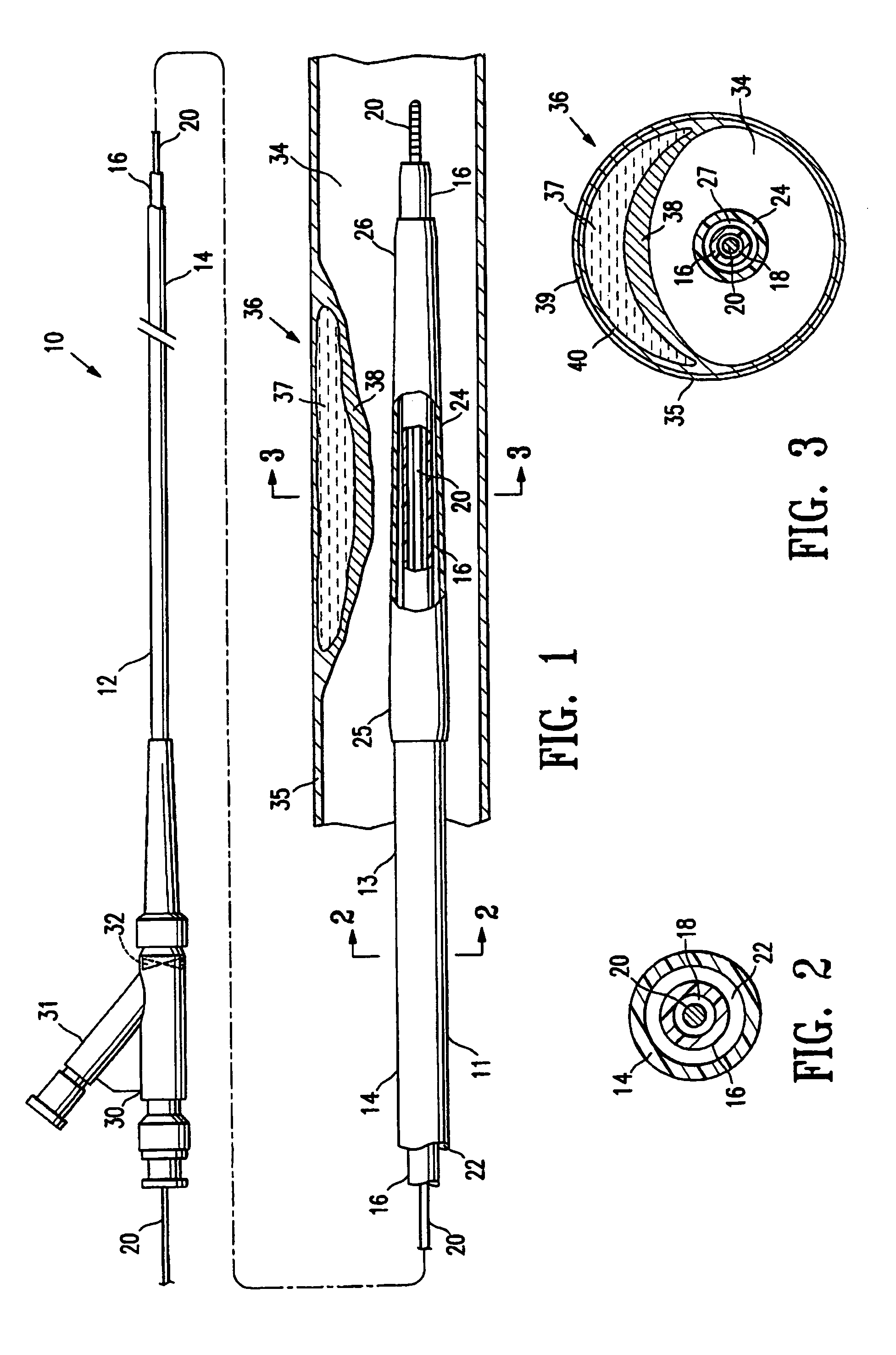
Proximal catheter assembly having a self-limiting aspiration valve
InactiveUS7004931B2Efficient removalIncrease chanceCatheterExcision instrumentsSelf limitingHigh rate
The present invention is directed to a proximal catheter assembly configured to facilitate natural or suction-assisted aspiration through a catheter lumen. The proximal catheter assembly comprises a multi-function valve configured to perform functions associated with conventional check valves and relief valves. The valve is configured to regulate the direction of fluid flow, and further configured to regulate the rate of suction-assisted aspiration provided through the lumen of the catheter. When the rate of suction-assisted aspiration exceeds a predetermined threshold, the valve opens to allow fluid to be drawn from tubing coupled to the proximal catheter assembly, thereby mitigating excessively high rates of aspiration imposed upon the patient's vessel.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Nanolayer deposition process
InactiveUS7713592B2High energyIncrease powerMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSelf limitingDeposition process
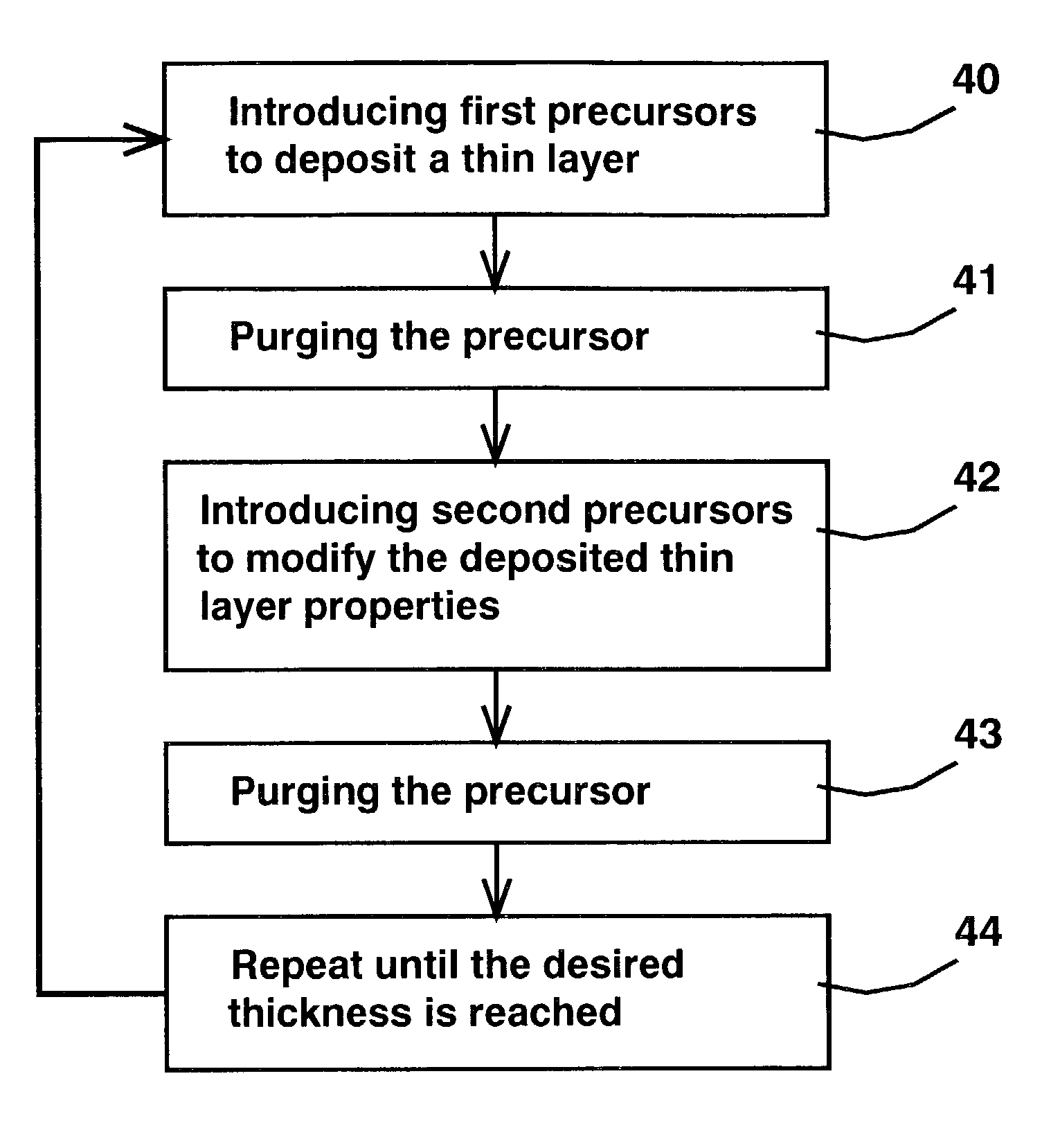
A hybrid deposition process of CVD and ALD, called NanoLayer Deposition (NLD) is provided. The nanolayer deposition process is a cyclic sequential deposition process, comprising the first step of introducing a first plurality of precursors to deposit a thin film with the deposition process not self limiting, then a second step of purging the first set of precursors and a third step of introducing a second plurality of precursors to modify the deposited thin film. The deposition step in the NLD process using the first set of precursors is not self limiting and is a function of substrate temperature and process time. The second set of precursors modifies the already deposited film characteristics. The second set of precursors can treat the deposited film such as a modification of film composition, a doping or a removal of impurities from the deposited film. The second set of precursors can also deposit another layer on the deposited film. The additional layer can react with the existing layer to form a compound layer, or can have minimum reaction to form a nanolaminate film.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Thin films
InactiveUS7419903B2Desirable interface propertyQuality improvementSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon oxide
Thin films are formed by formed by atomic layer deposition, whereby the composition of the film can be varied from monolayer to monolayer during cycles including alternating pulses of self-limiting chemistries. In the illustrated embodiments, varying amounts of impurity sources are introduced during the cyclical process. A graded gate dielectric is thereby provided, even for extremely thin layers. The gate dielectric as thin as 2 nm can be varied from pure silicon oxide to oxynitride to silicon nitride. Similarly, the gate dielectric can be varied from aluminum oxide to mixtures of aluminum oxide and a higher dielectric material (e.g., ZrO2) to pure high k material and back to aluminum oxide. In another embodiment, metal nitride (e.g., WN) is first formed as a barrier for lining dual damascene trenches and vias. During the alternating deposition process, copper can be introduced, e.g., in separate pulses, and the copper source pulses can gradually increase in frequency, forming a transition region, until pure copper is formed at the upper surface. Advantageously, graded compositions in these and a variety of other contexts help to avoid such problems as etch rate control, electromigration and non-ohmic electrical contact that can occur at sharp material interfaces. In some embodiments additional seed layers or additional transition layers are provided.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Microstructures and method for treating and conditioning skin which cause less irritation during exfoliation
An improved method is provided to enhance skin appearance and health, in which skin is cleaned (or exfoliated) and conditioned by use of microelements affixed to a base element or hand-held patch. For the microstructure used in the improved method, the dimensions of the microelements are controlled so as to remove a certain number of layers of skin cells and to accumulate and retain those skin cells, along with other foreign substances, into areas between the microelements. In another embodiment of the improved method, a conditioning compound or therapeutic active can be applied to the exfoliated skin to enhance the skin. Moreover, the amount of skin cells accumulated using the improved method represents a self-limiting maximum quantity that cannot be substantially exceeded regardless of the number of attempts by a user to re-use the microstructure apparatus associated with the improved method. Some of the microelement shapes are purposefully designed with distal ends that exhibit sharp edges rather than sharp tips to reduce skin irritation resulting from use of the improved method.
Owner:CORIUM PHARMA SOLUTIONS INC
Carbon nanoarchitectures with ultrathin, conformal polymer coatings for electrochemical capacitors
ActiveUS20050153130A1Hybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrolysis componentsSelf limitingPolymer science
A composite having an electroactive polymer coating on a porous carbon structure is disclosed. The composite may be used in capacitor electrodes. The composite may be made by self-limiting electropolymerization of a monomer on the carbon structure.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Plasma pre-treating surfaces for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20060216932A1Improve barrier propertiesBarrier propertySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingSelf limitingAtomic layer deposition
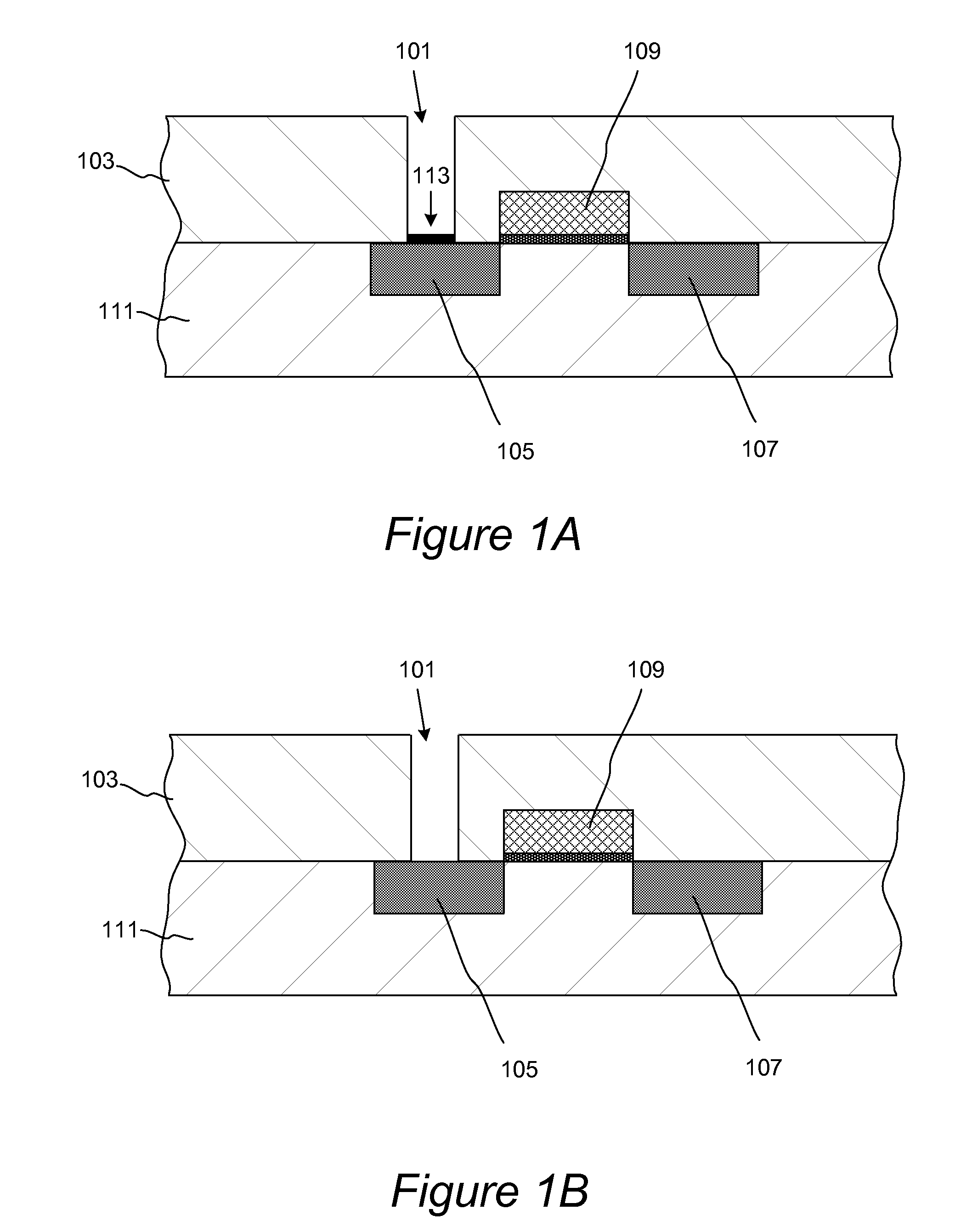
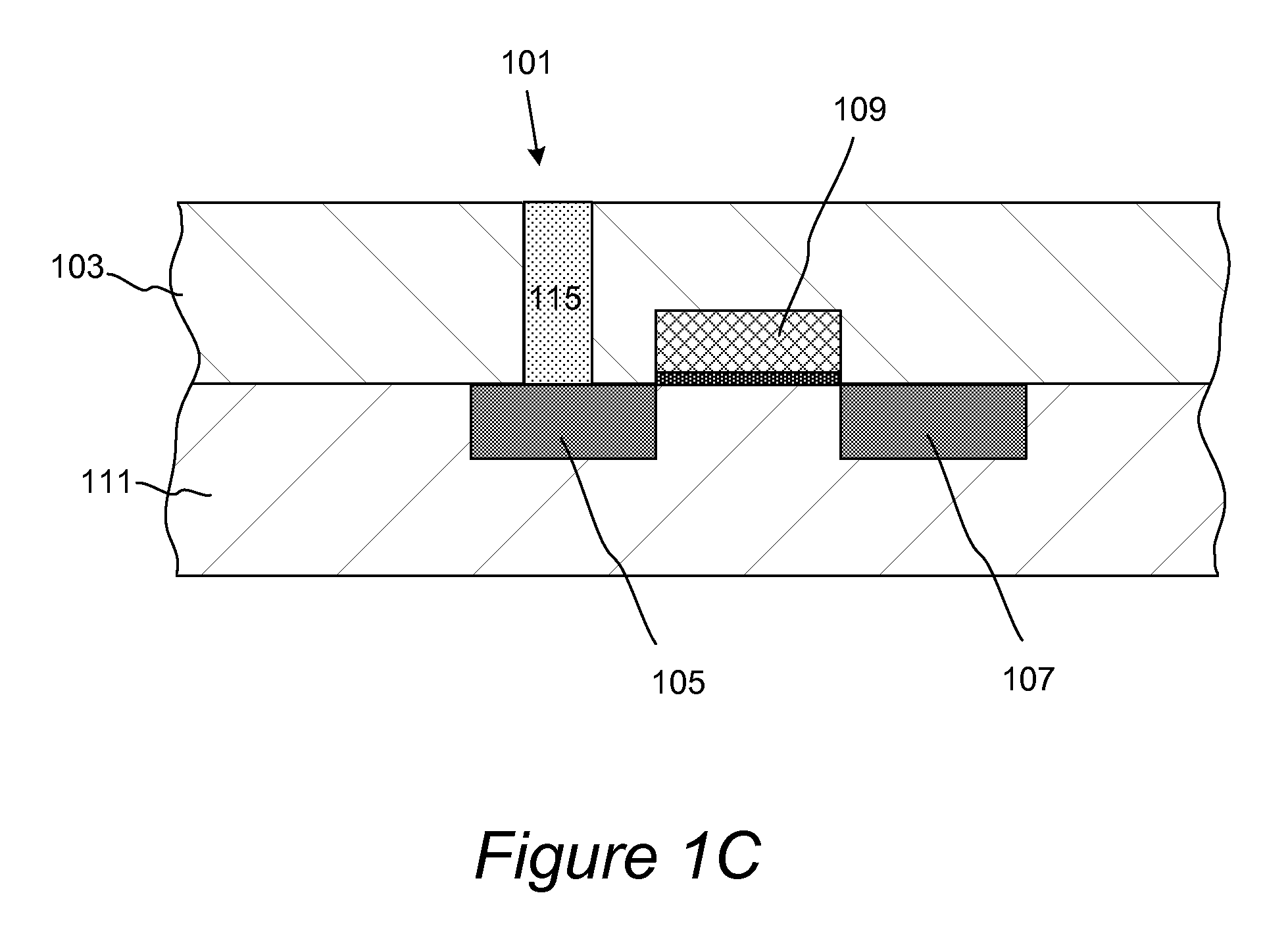
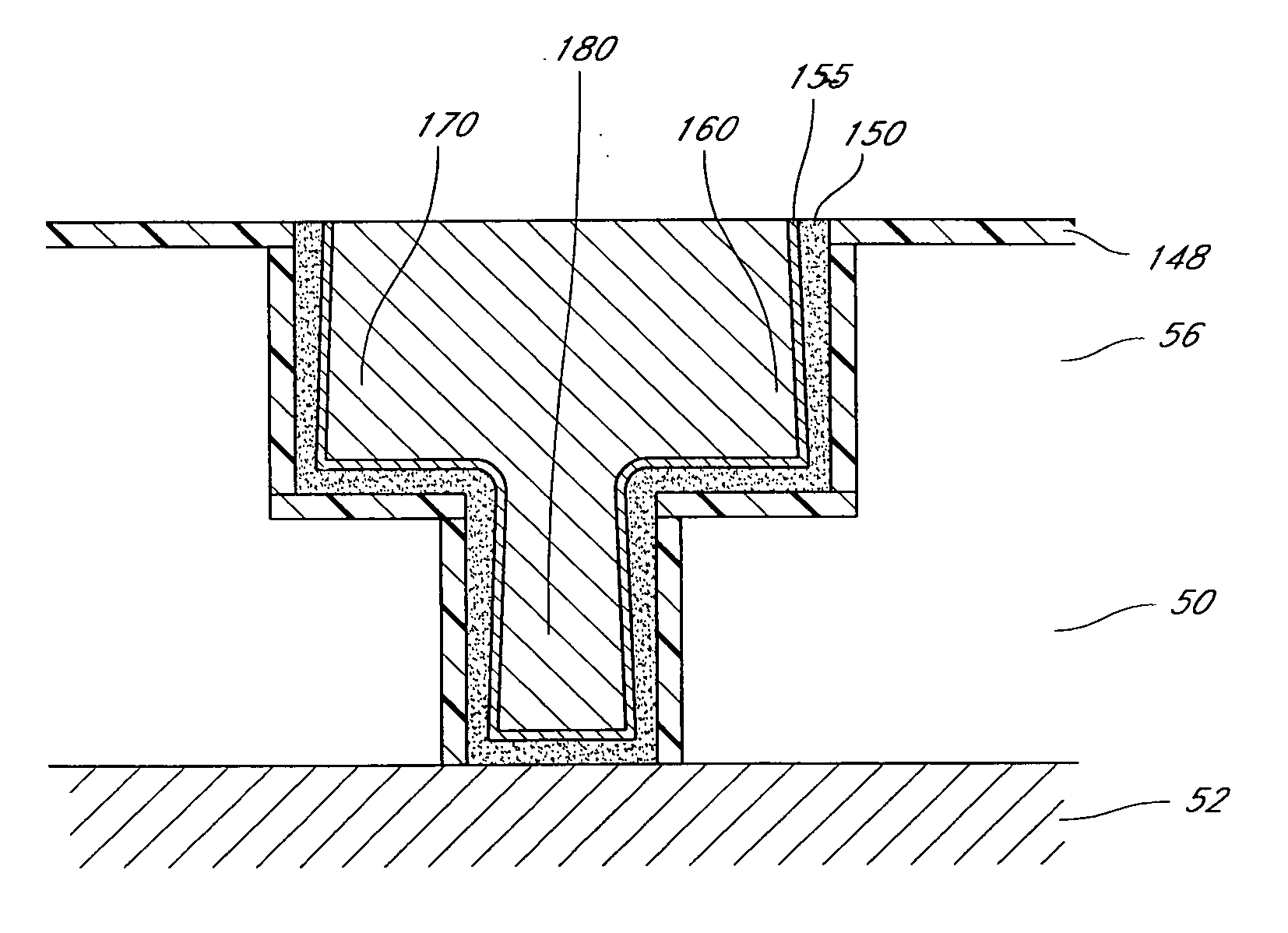
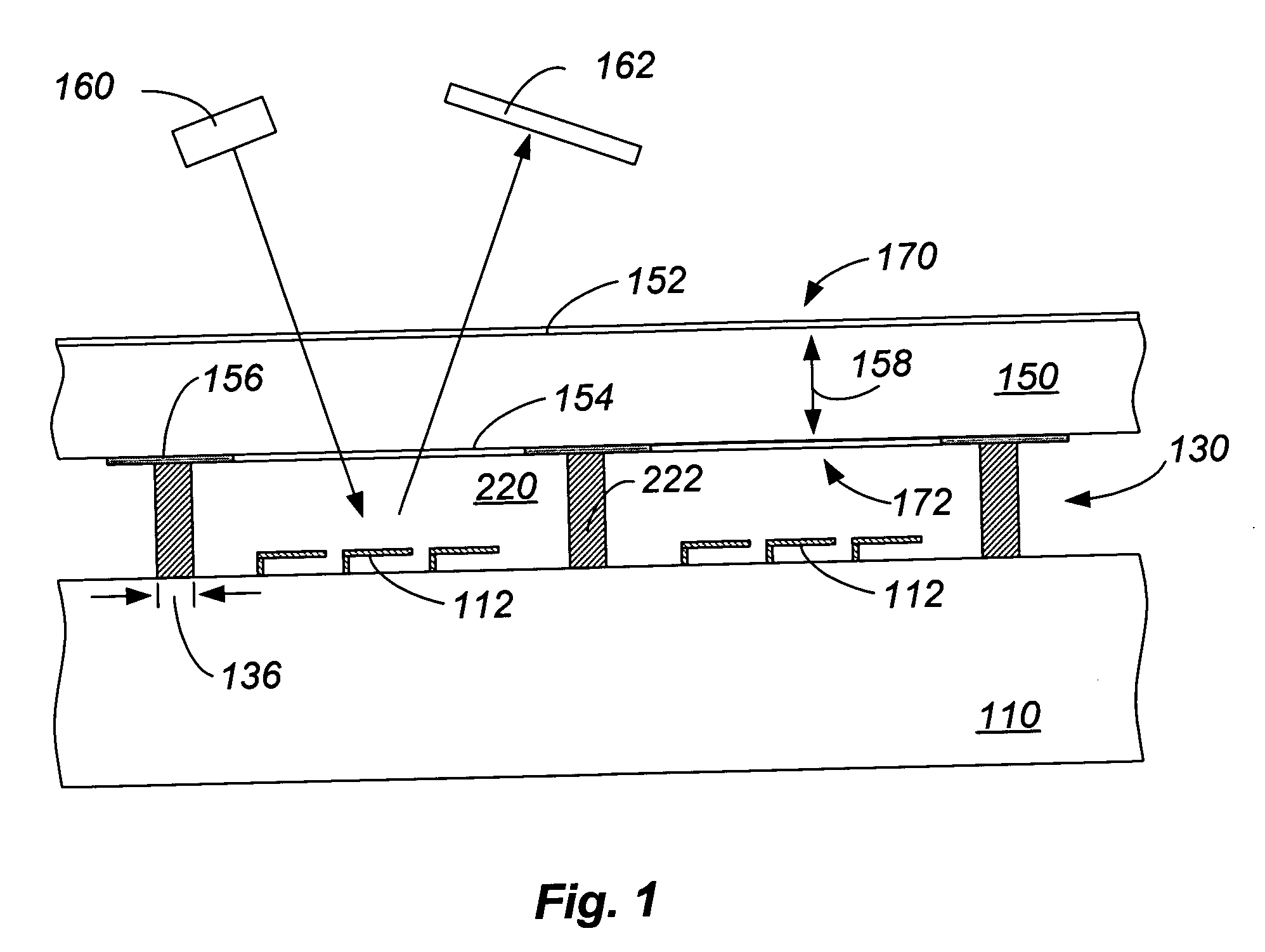
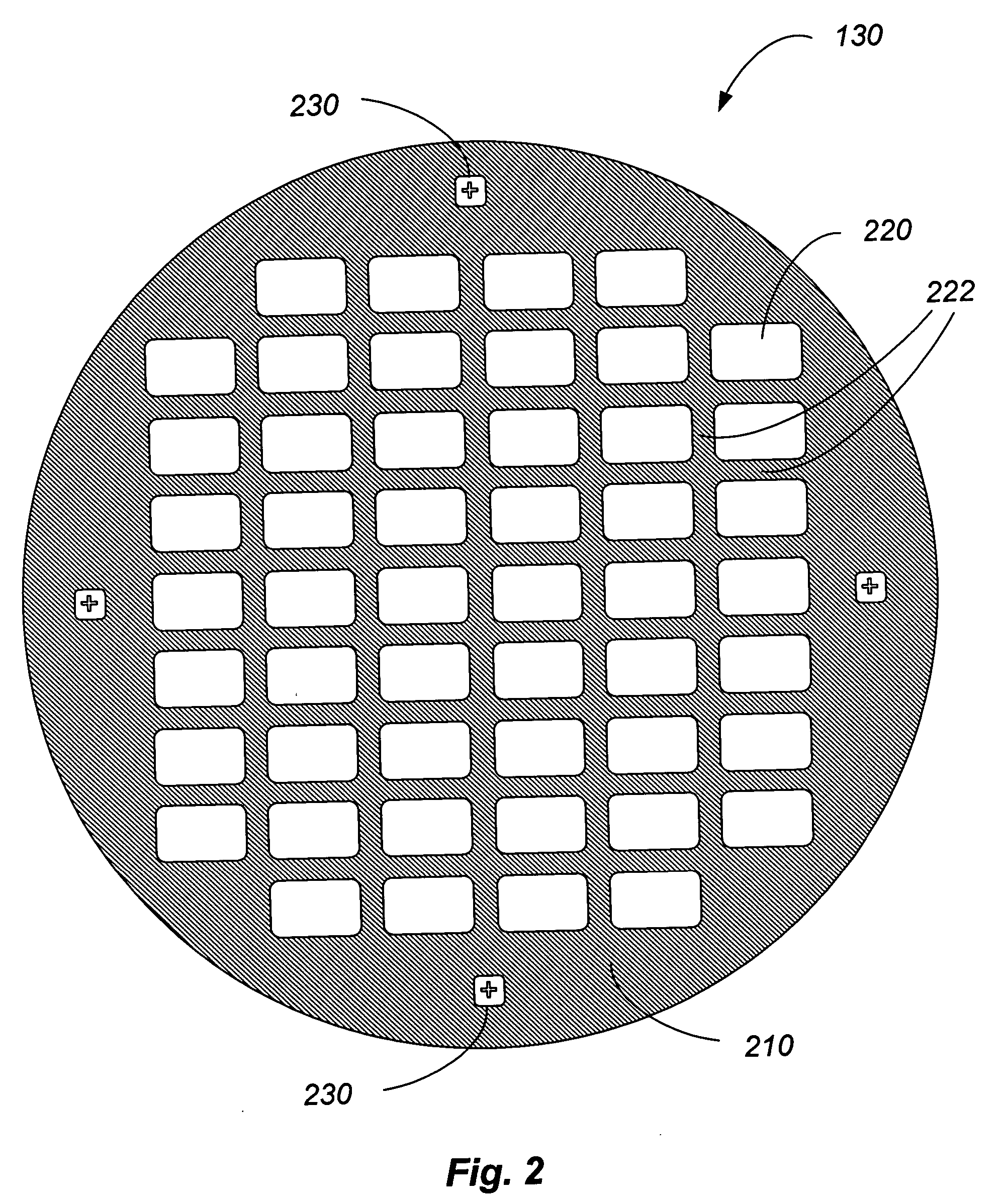
Method and structures are provided for conformal lining of dual damascene structures in integrated circuits. Preferred embodiments are directed to providing conformal lining over openings formed in porous materials. Trenches are formed in, preferably, insulating layers. The layers are then adequately treated with a particular plasma process. Following this plasma treatment a self-limiting, self-saturating atomic layer deposition (ALD) reaction can occur without significantly filling the pores forming improved interconnects.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Self limiting catalyst composition and propylene polymerization process
ActiveUS7491670B2Poor surfaceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSelf limitingElectron donor
A catalyst composition for the polymerization of propylene comprising one or more Ziegler-Natta procatalyst compositions comprising one or more transition metal compounds and one or more esters of aromatic dicarboxylic acid internal electron donors; one or more aluminum containing cocatalysts; a selectivity control agent (SCA) comprising at least one silicon containing compound containing at least one C1-10 alkoxy group bonded to a silicon atom, and one or more activity limiting agent (ALA) compounds comprising one or more aliphatic or cycloaliphatic carboxylic acids; alkyl-, cycloalkyl- or alkyl(poly)(oxyalkyl)-(poly)ester derivatives thereof; or inertly substituted derivatives of the foregoing.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Triple alignment substrate method and structure for packaging devices
ActiveUS20060270179A1Easy to useHigh device yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSelf limitingEtching
A method for aligning multiple substrates. The method includes providing a handle substrate, providing a spacer substrate, and forming a plurality of first alignment marks on a first surface of the handle substrate. The method also includes forming a plurality of self-limiting alignment marks on a first surface of the spacer substrate and forming a plurality of openings in the spacer substrate, each of the plurality of openings surrounded by standoff regions. The method further includes aligning the first surface of the handle substrate and the first surface of the spacer substrate using the first alignment marks and the self-limiting alignment marks and bonding the handle substrate to the spacer substrate to form a composite substrate structure. In a specific embodiment, the plurality of self-limiting alignment marks and the plurality of openings are formed using an anisotropic wet etching process that preferentially etches the spacer substrate.
Owner:MIRADIA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com