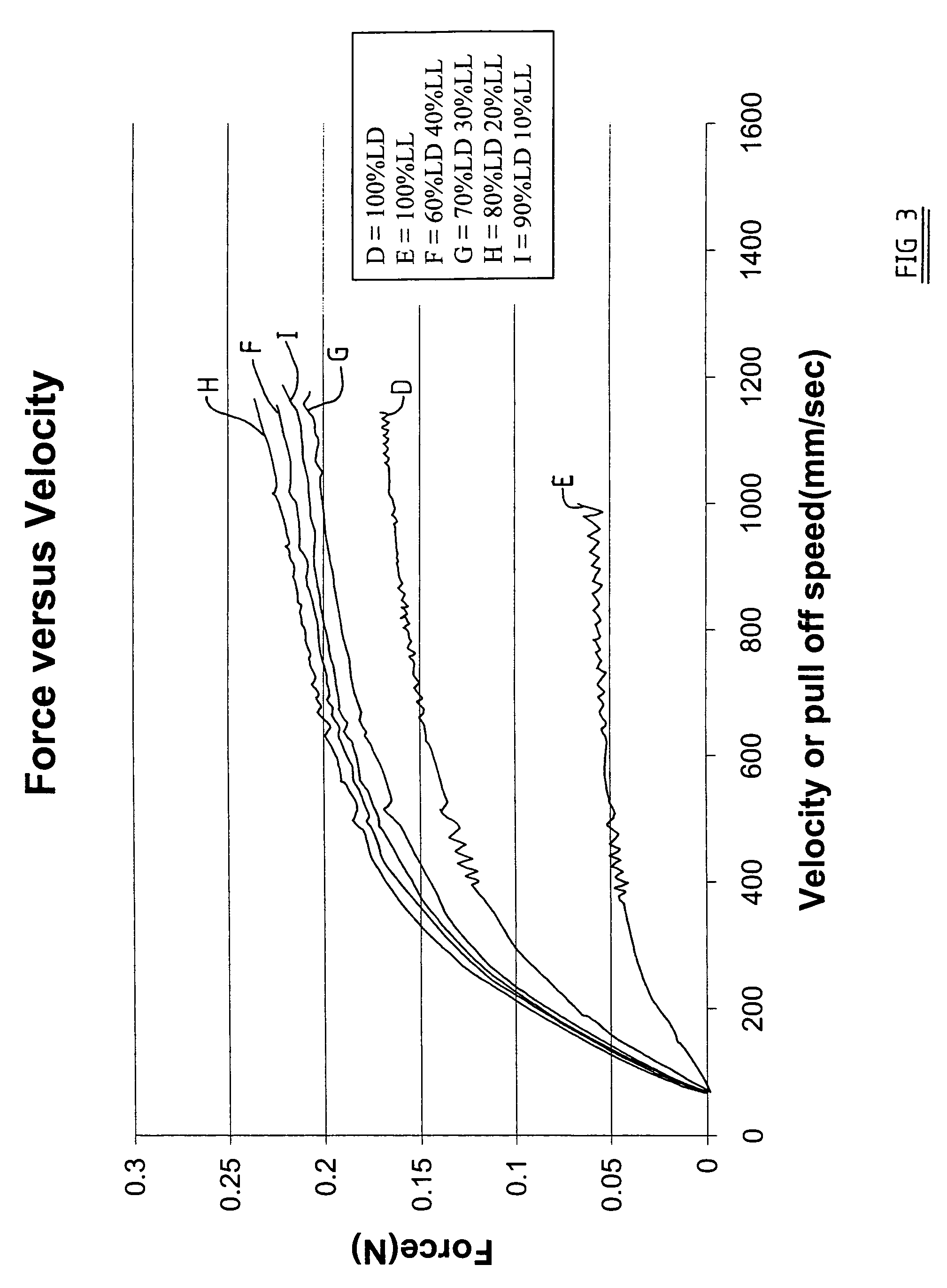
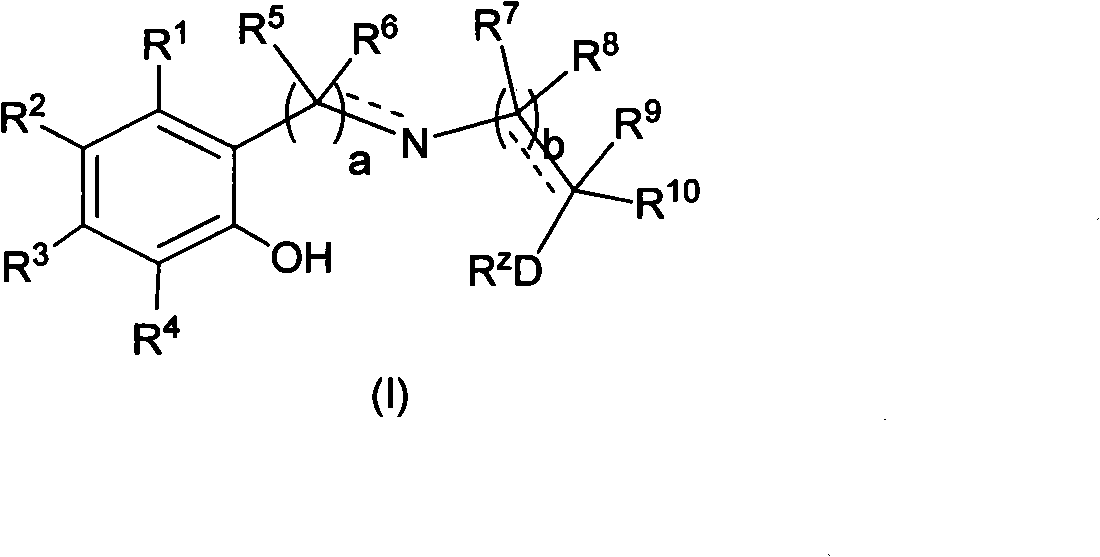
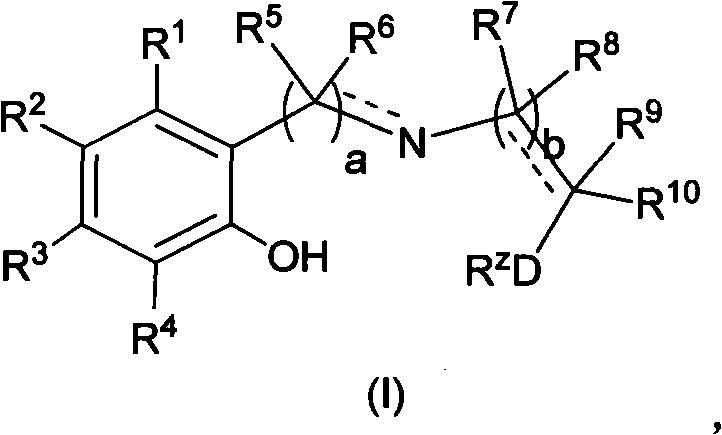
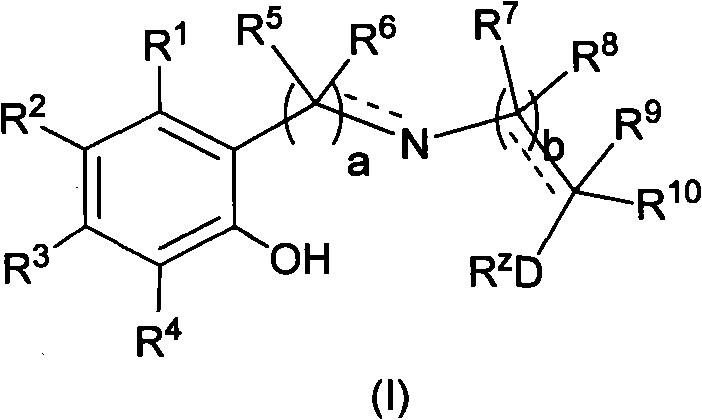
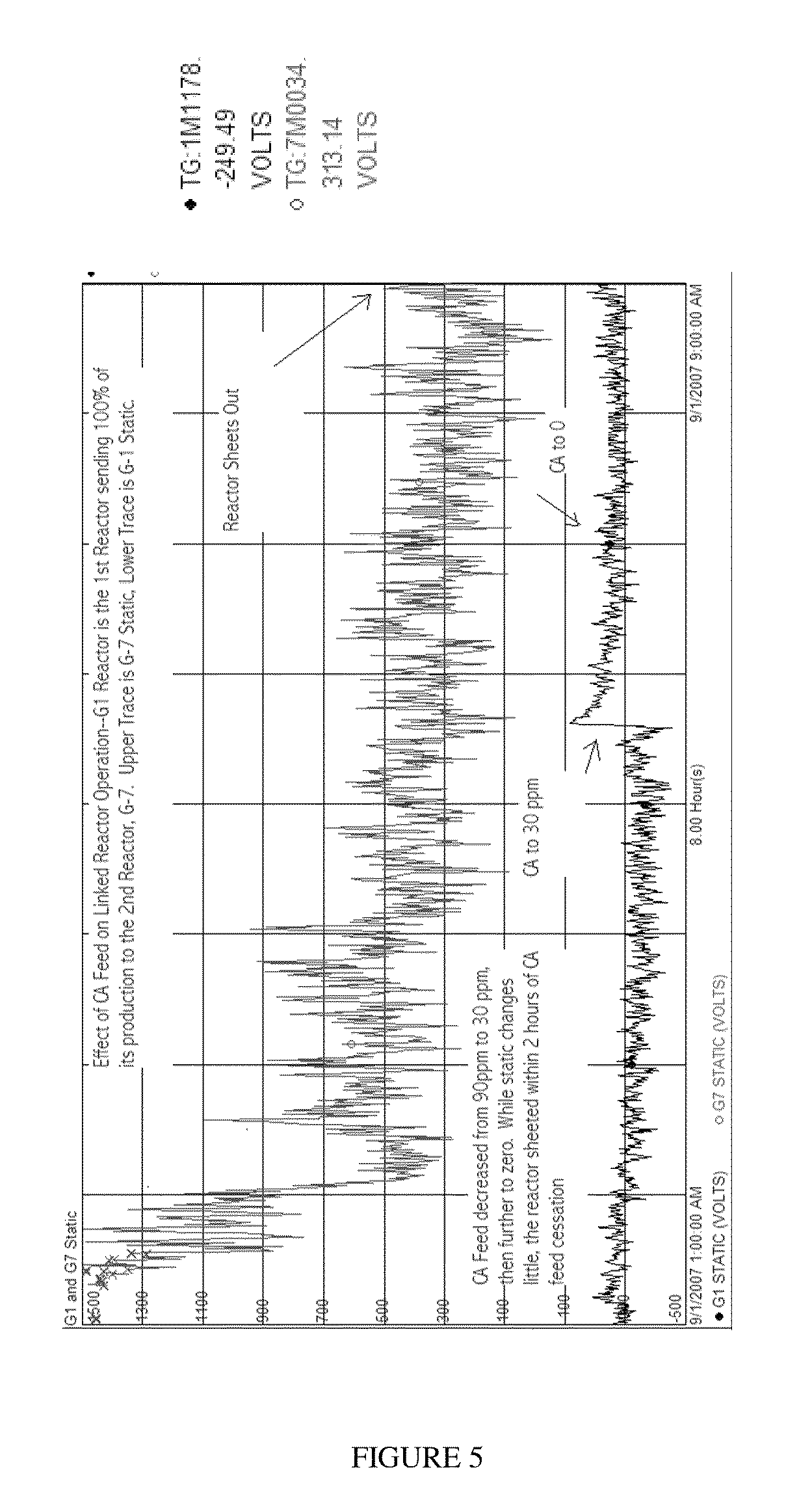
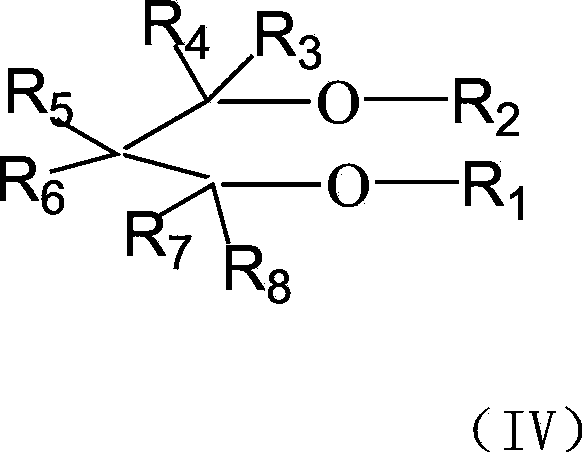
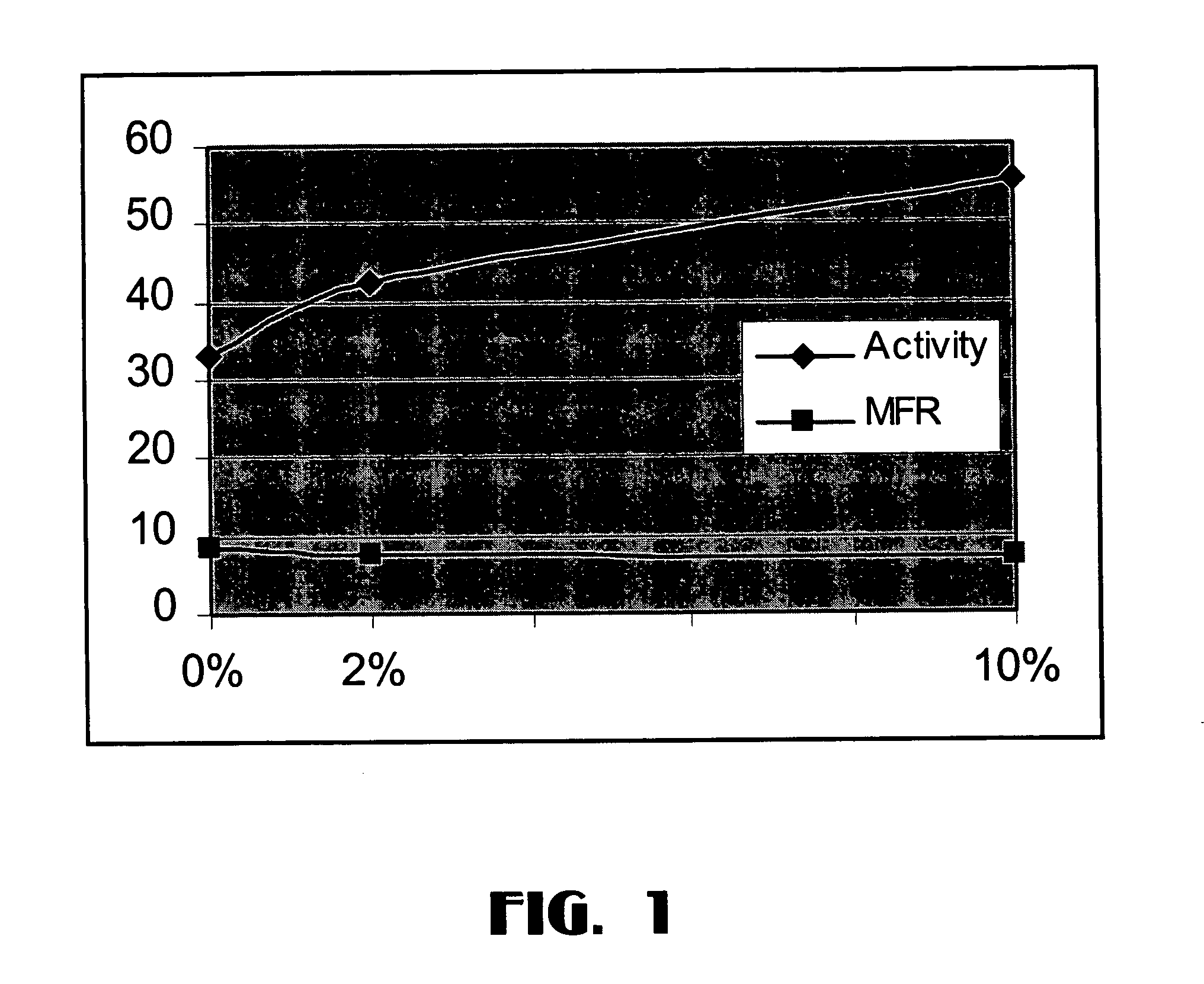
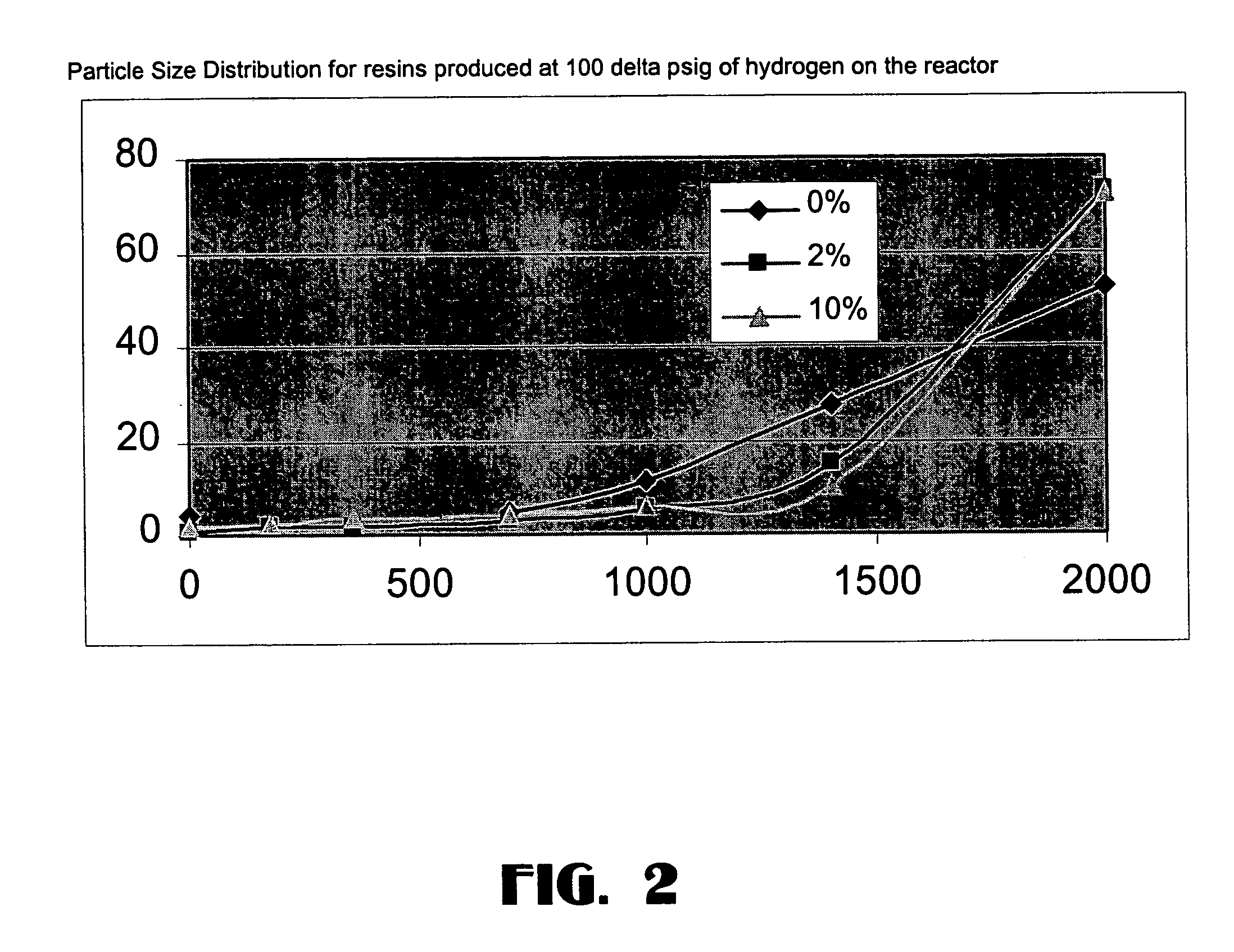
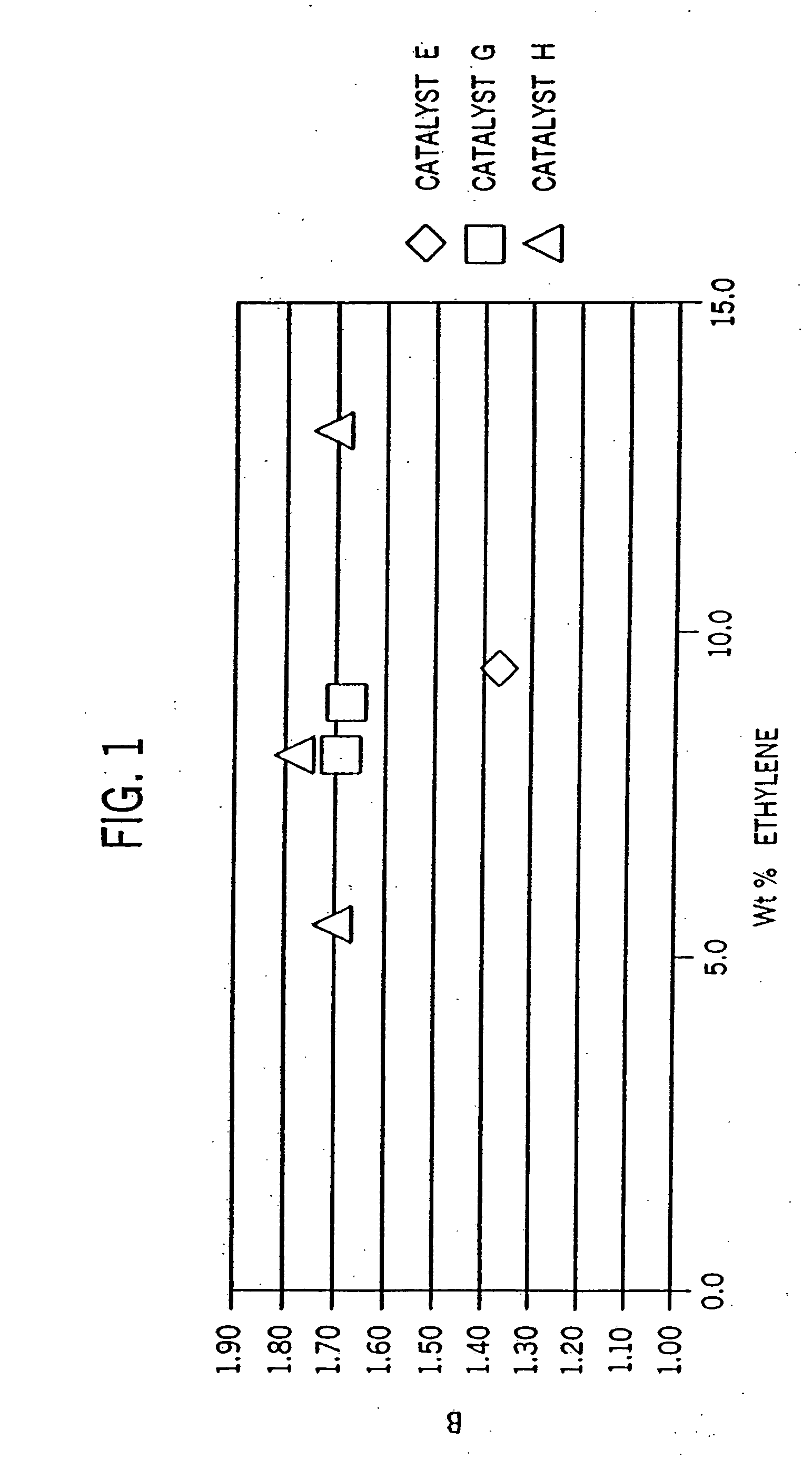
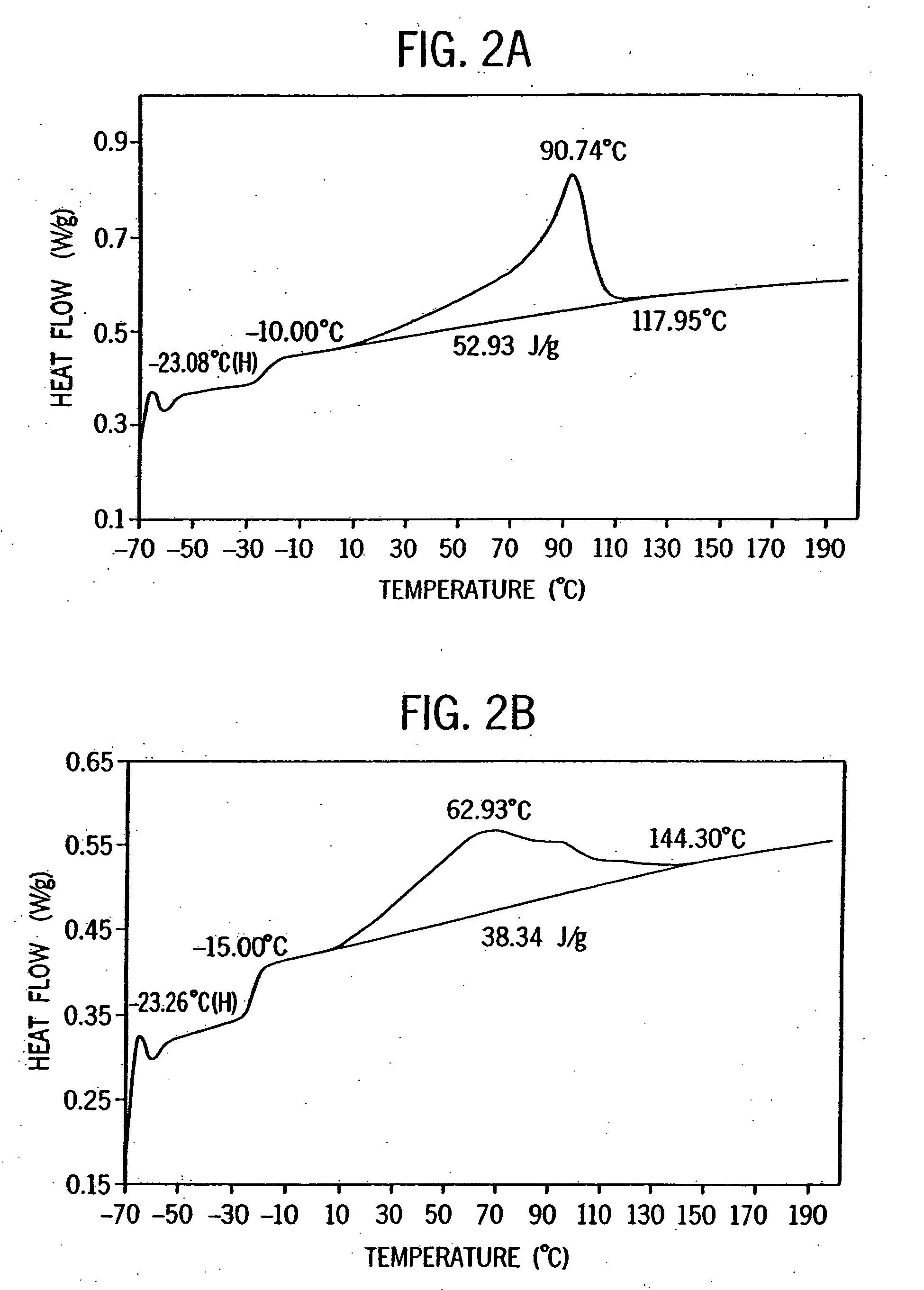
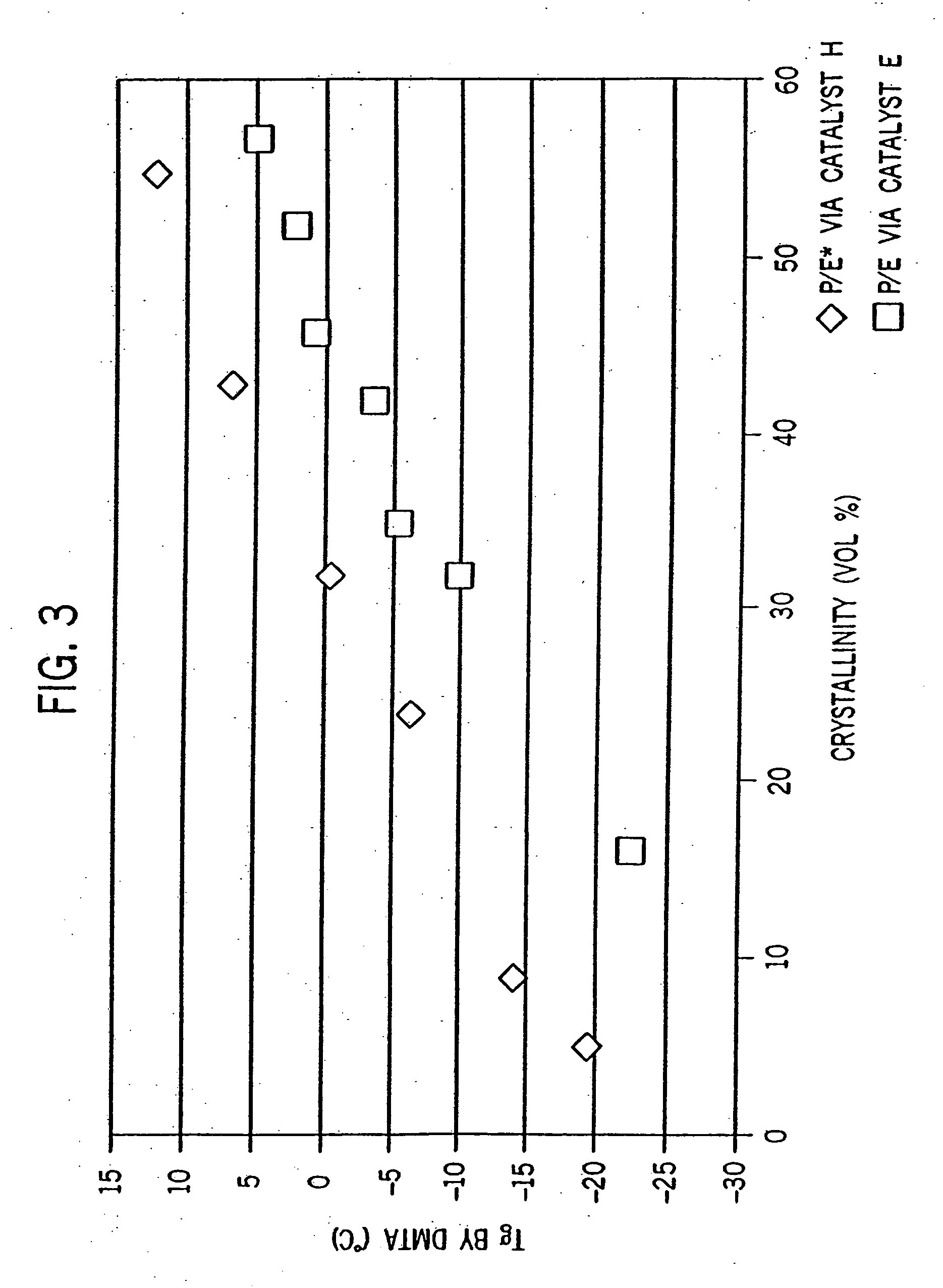
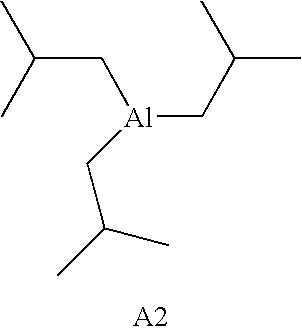
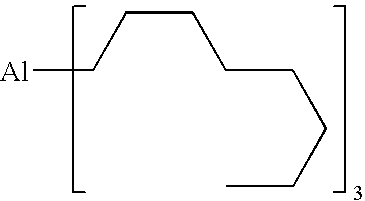
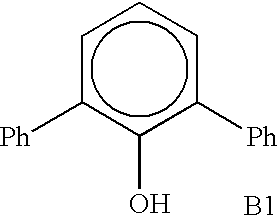
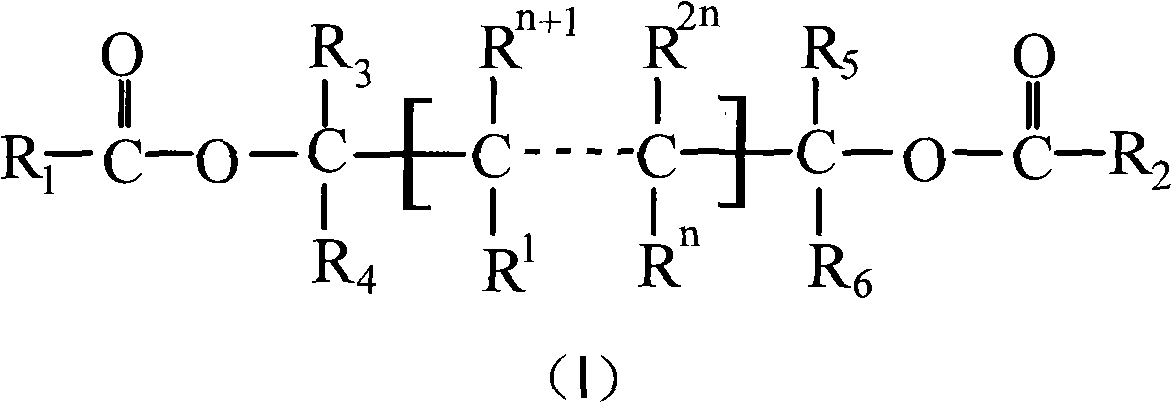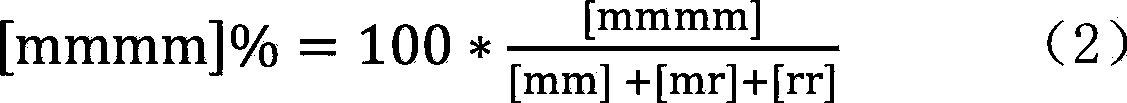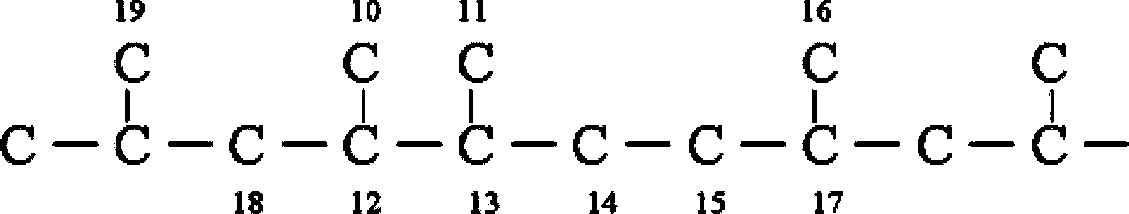Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
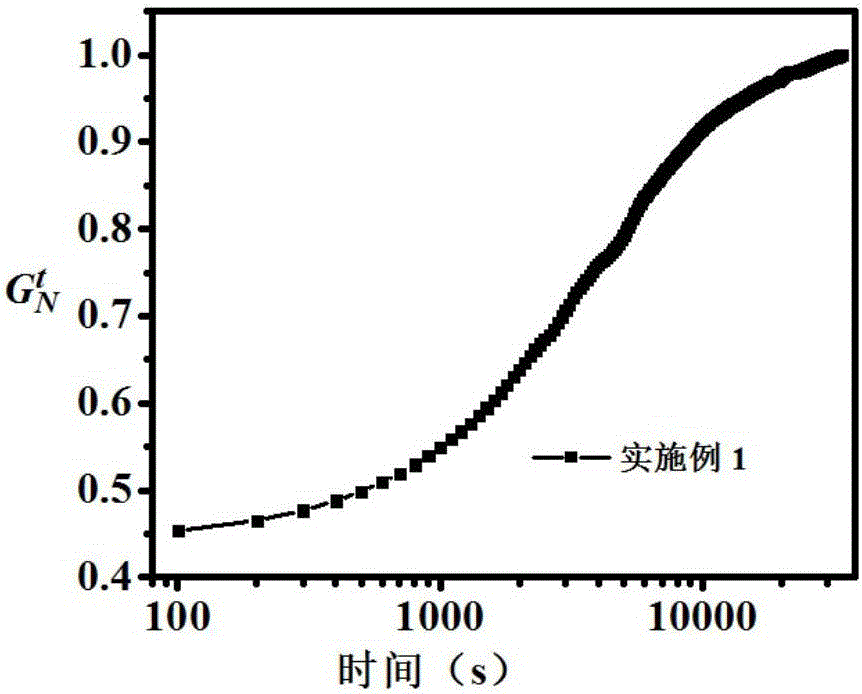
188 results about "Natta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natta is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Ferdinand Anton Franz Karsch in 1879. As of July 2019 it contains only two species, found only in Africa and Yemen: N. chionogaster and N. horizontalis.
Mono-active center Ziegler-Natta catalyst for olefinic polymerization
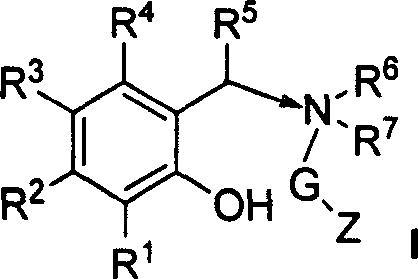
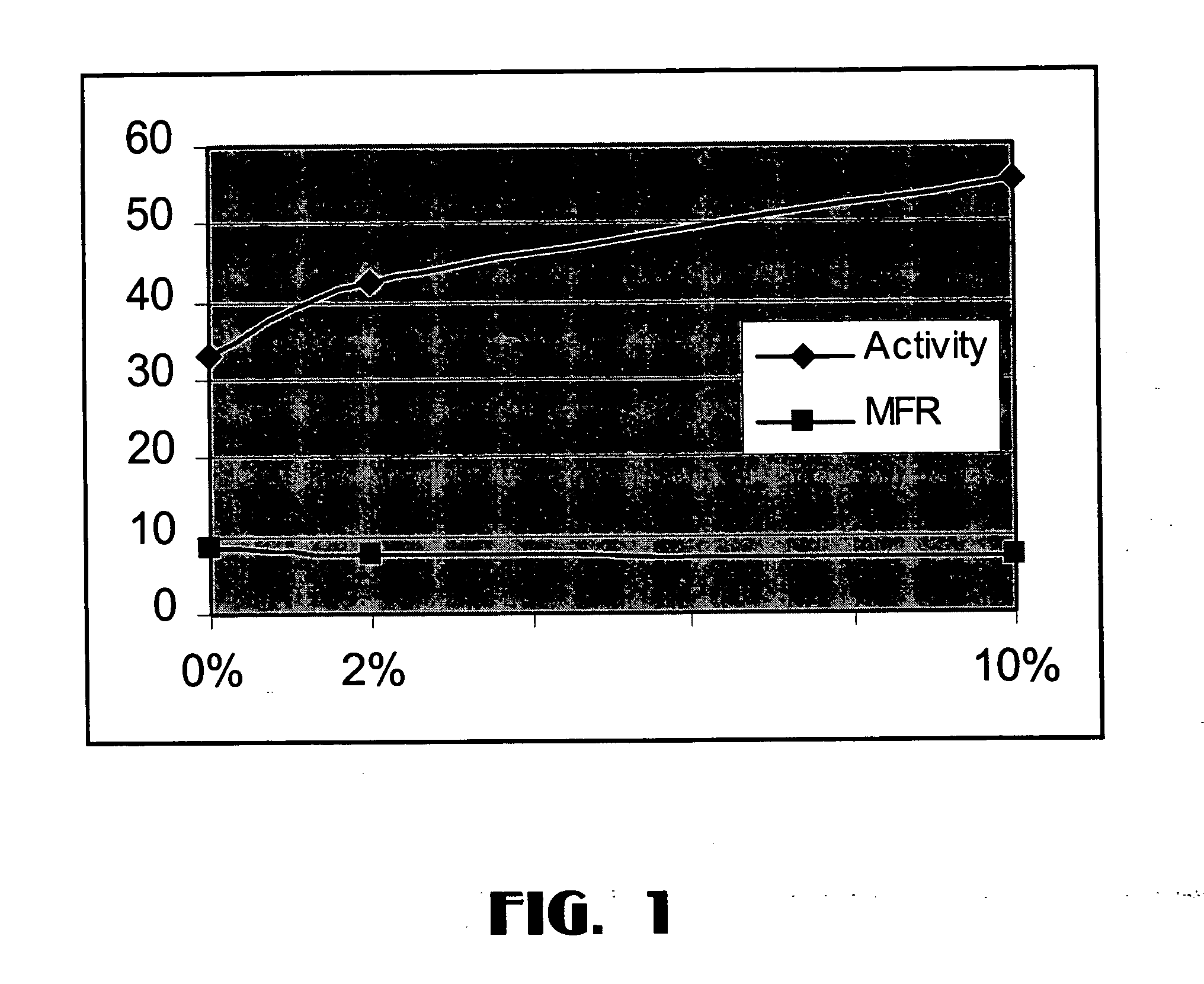
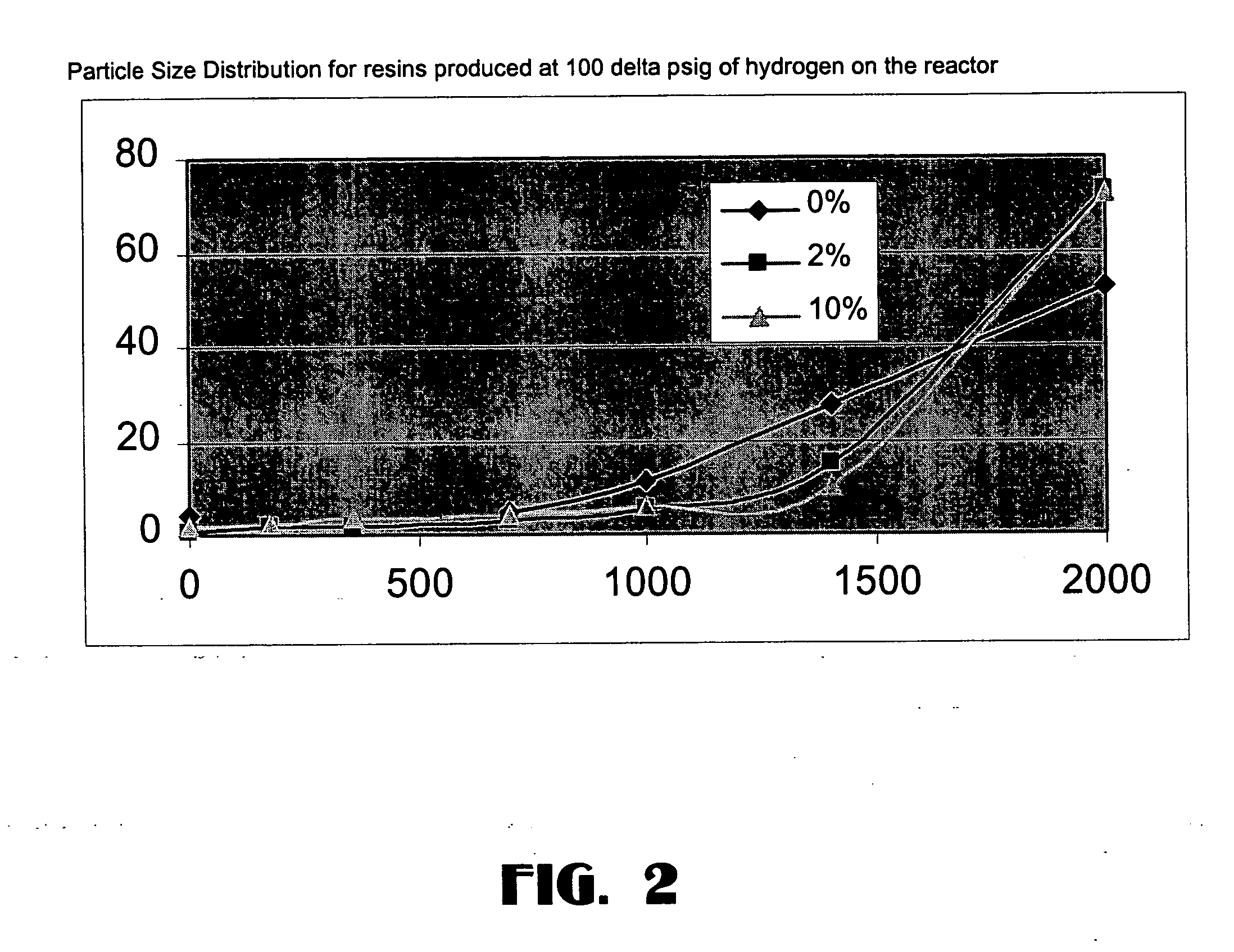
The invention relates to a new catalyst for single active central Ziegler-Natta alkene polymerization. Said catalyst takes salicylal containing dentate or substituted salicylal derivatives as electrons, and is prepared by adding pretreated carrier, metallic compound and electrons into magnesium compound / tetrahydrofuran solution. The catalyst can produce ethane homopolymer and copolymer with narrow molecular weight distribution (1.6-3.8) and even comonomer distribution, with high activity and under action of adjuvant catalyst of alkyl aluminium and alkyl aluminoxanes. The ethane polymerization, homopolymerization or combined polymerization of ethane and 1- olefin, ring olefin and polar monomer through slurry method or gas phase method by using said catalyst can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Blends and sealant compositions comprising isotactic propylene copolymers
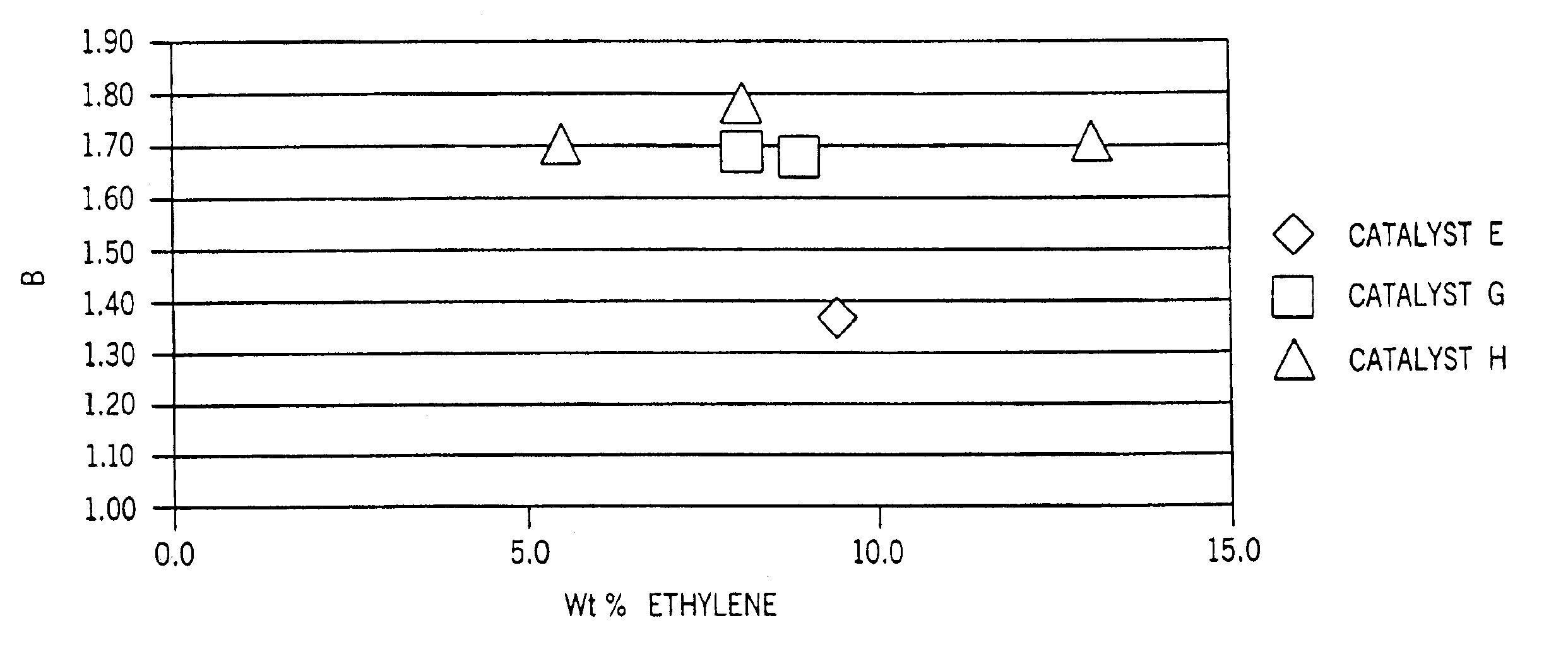
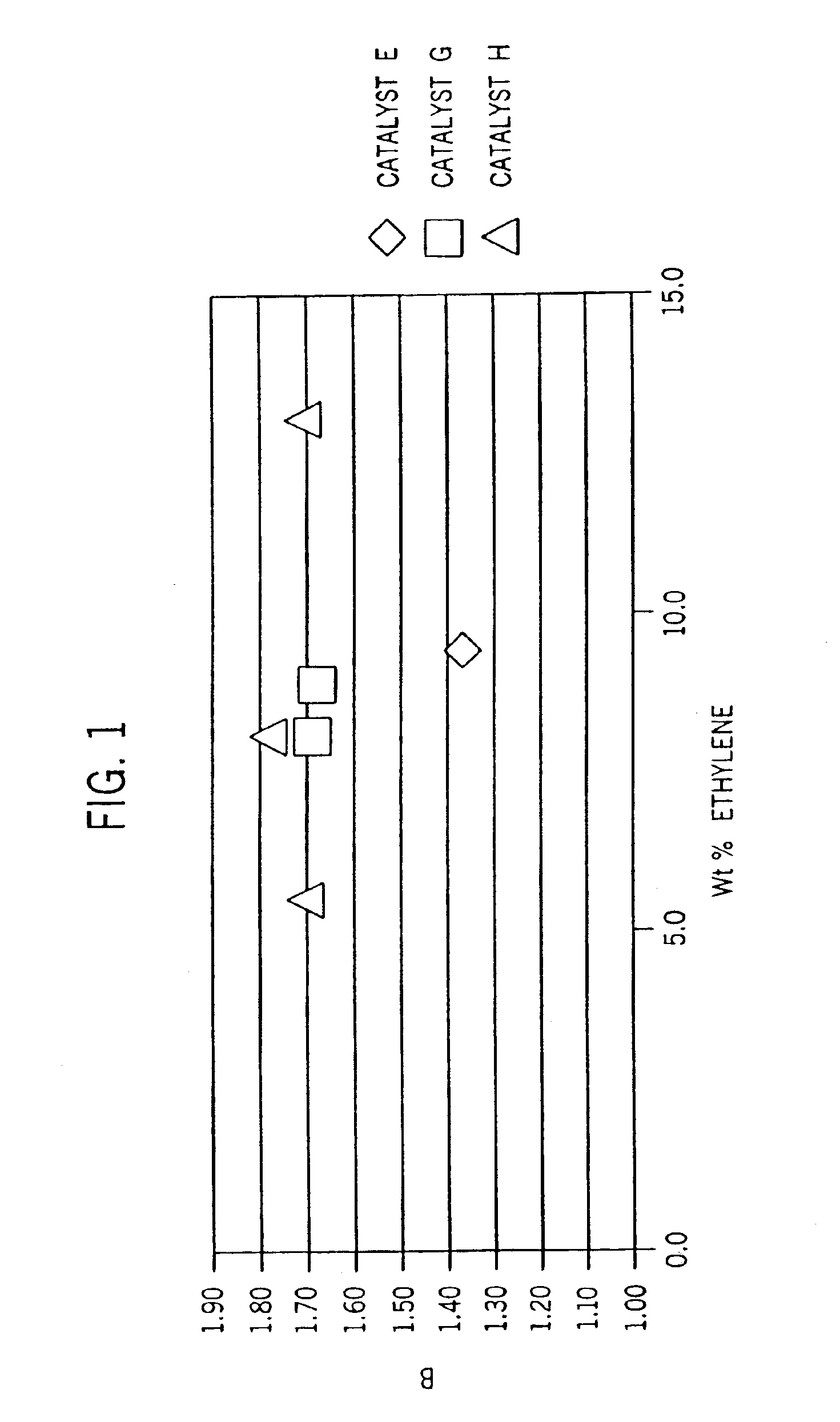
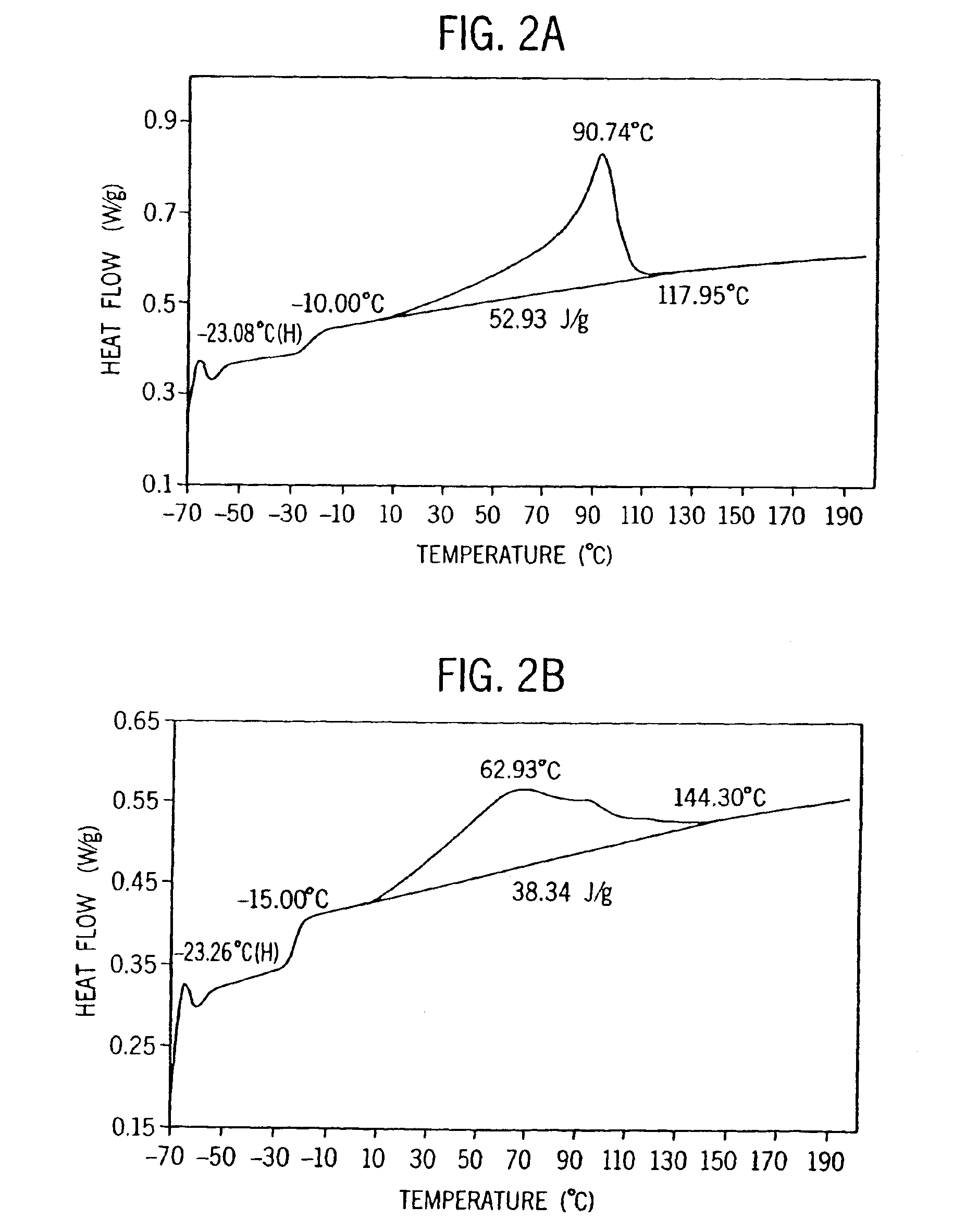
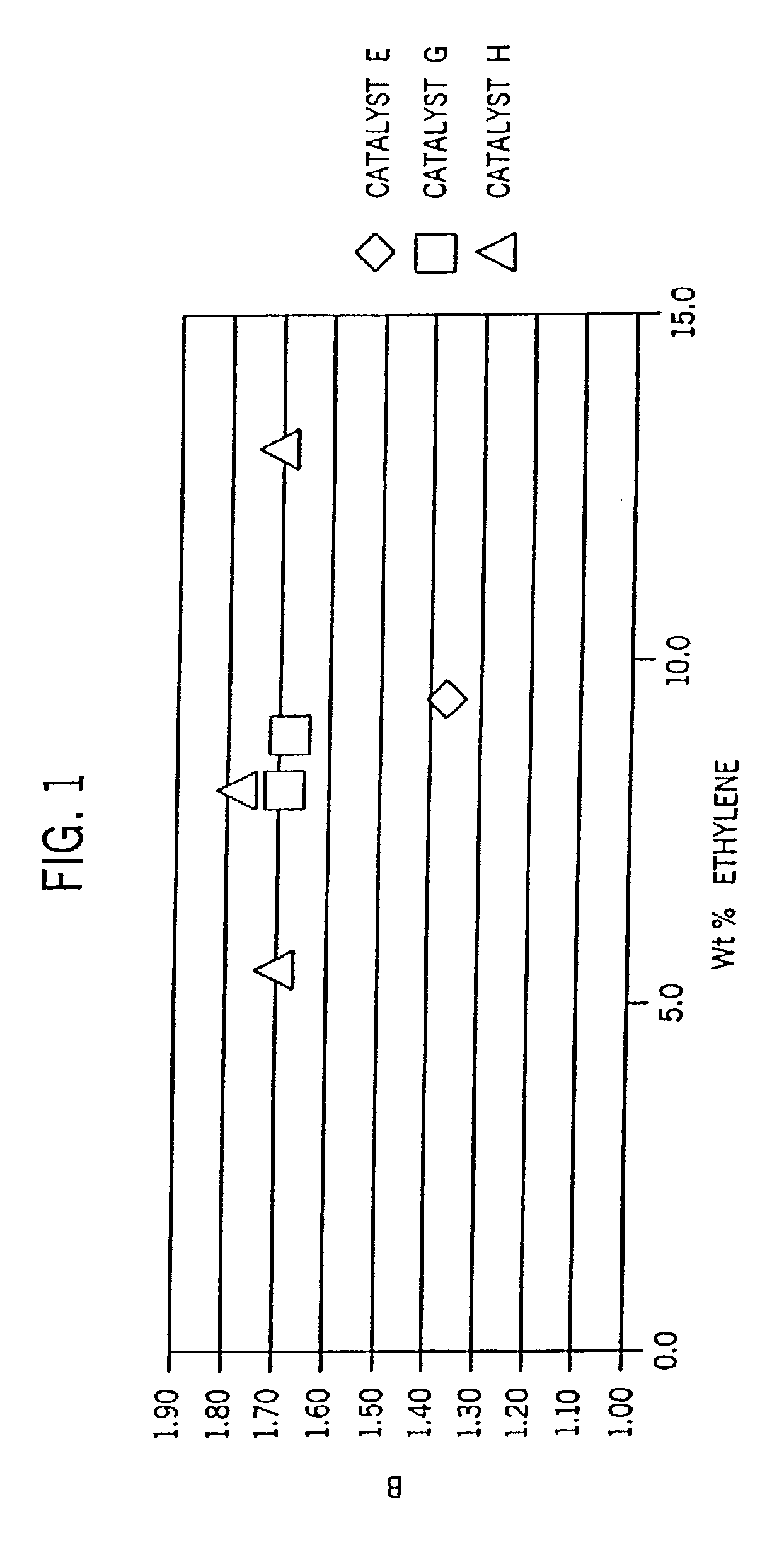
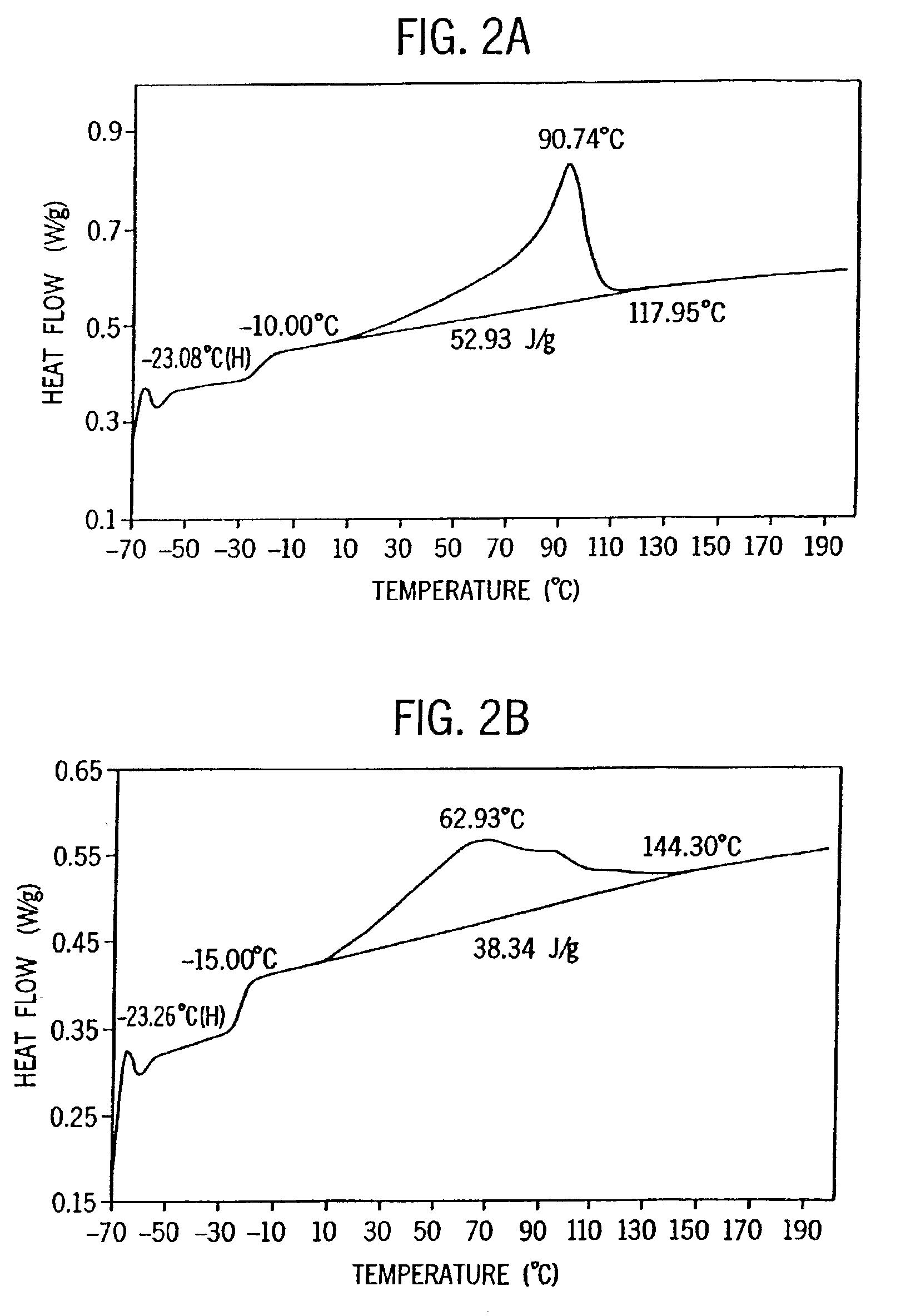
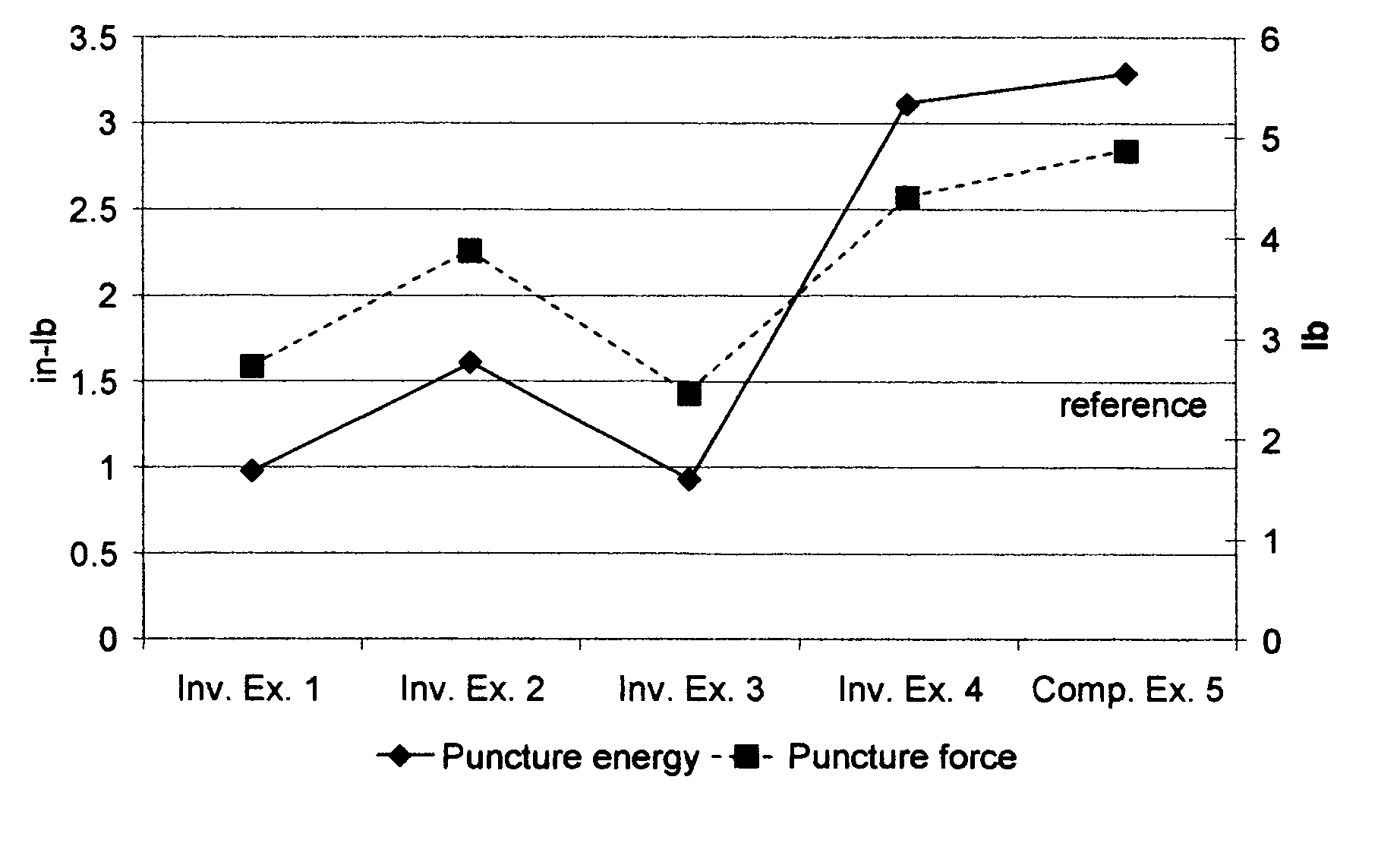
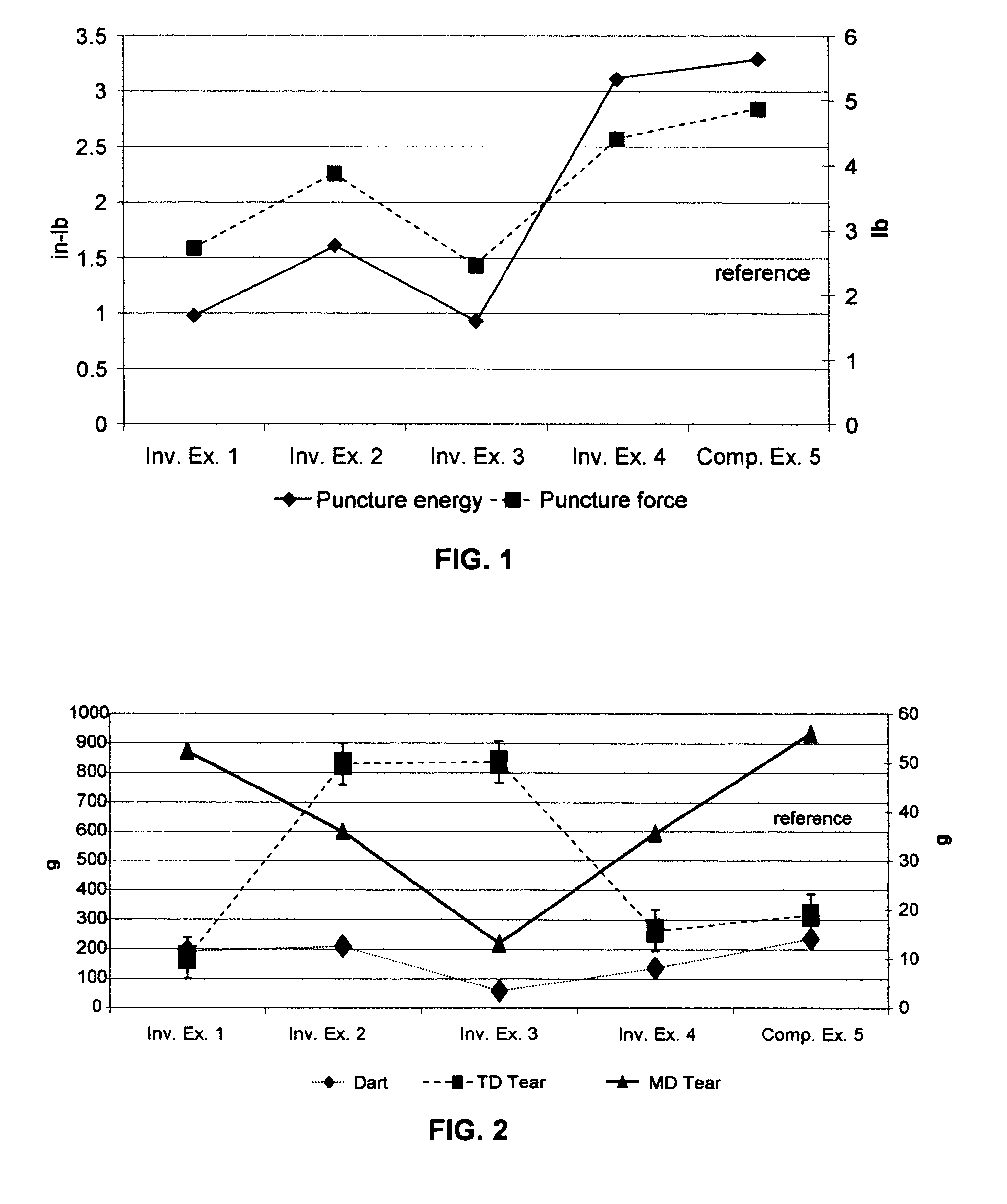
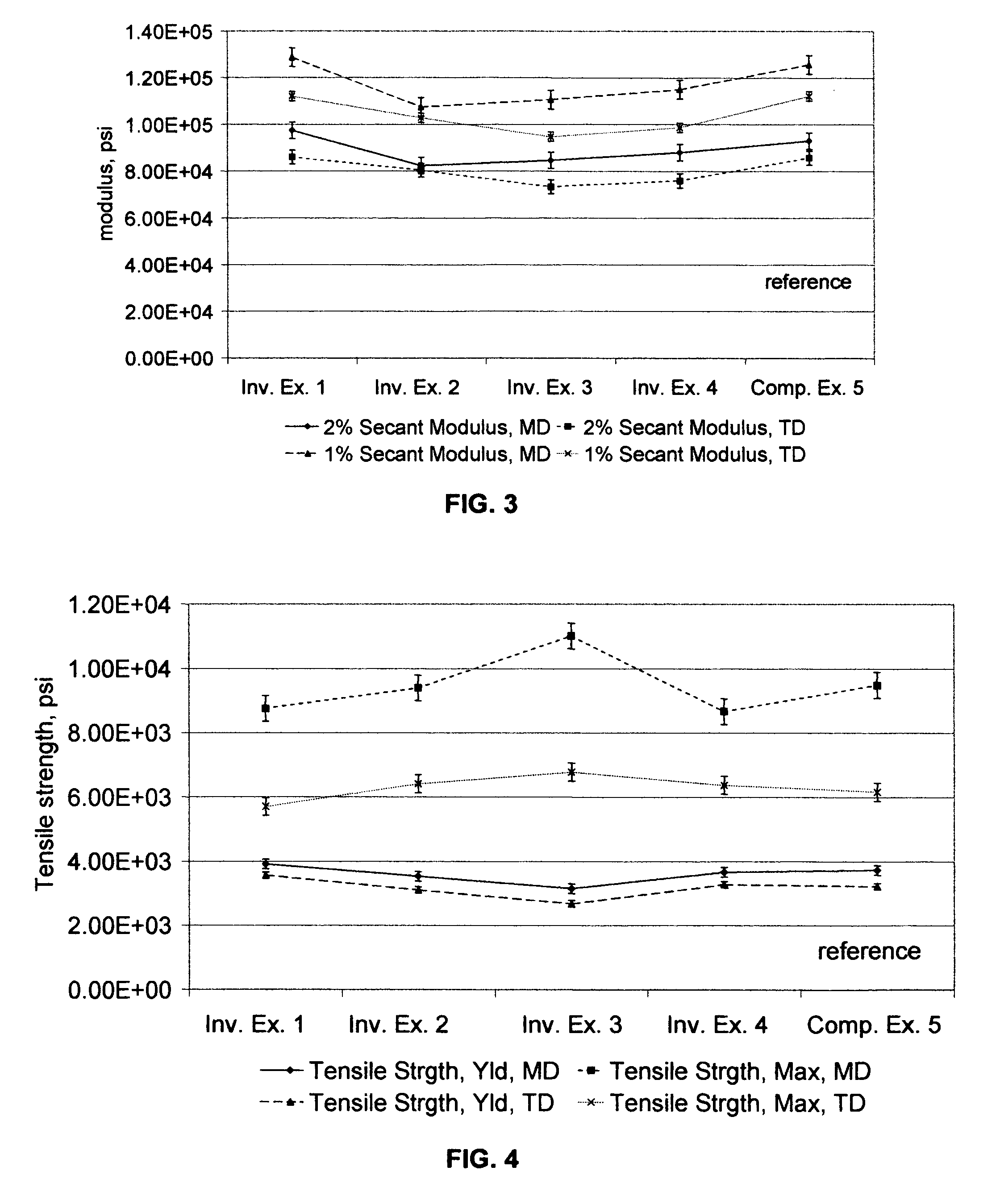
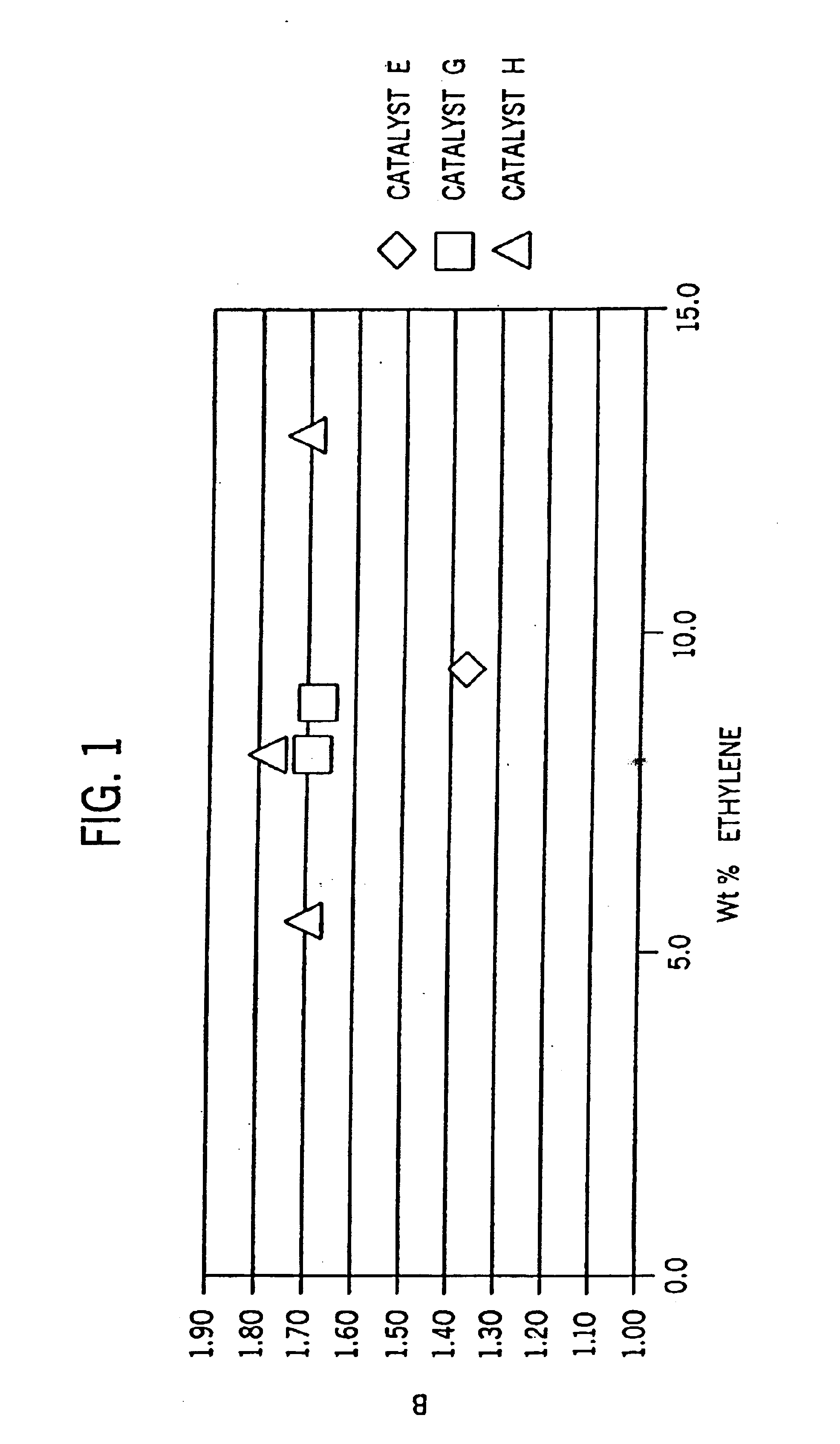
Films with excellent machine direction (MD) tear properties comprise at least one layer made from a polymer comprising:(A) at least 50 weight percent (wt %) propylene; and(B) at least 5 wt % ethylene and / or one or more unsaturated comonomers.Representative of component (B) unsatuarated comonomers are the C4-20 α-olefins, C4-20 dienes, styrenic compounds, and the like. Preferably, the film has at least one of a (i) haze value of less than about 10, (ii) 45 degree gloss of greater than about 65, and (iii) dart value of greater than about 100 g / mil. In one preferred embodiment, the layer comprises a compolymer characterized as having at least one of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content, i.e., the units derived from ethylene and / or the unsaturated comonomer(s), of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer, i.e., the units derived from ethylene and / or the unsaturated comonomer(s), in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Isotactic propylene copolymer fibers, their preparation and use
Fibers comprising a propylene homopolymer or a copolymer of propylene and at least one of ethylene and one or more unsaturated comonomers exhibit desirable properties. The homopolymers are characterized as having 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity. The copolymers are characterized as (A) comprising at least about 60 weight percent (wt %) of units derived from propylene, and (B) having at least one of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Self limiting catalyst composition and propylene polymerization process
ActiveUS7491670B2Poor surfaceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSelf limitingElectron donor
A catalyst composition for the polymerization of propylene comprising one or more Ziegler-Natta procatalyst compositions comprising one or more transition metal compounds and one or more esters of aromatic dicarboxylic acid internal electron donors; one or more aluminum containing cocatalysts; a selectivity control agent (SCA) comprising at least one silicon containing compound containing at least one C1-10 alkoxy group bonded to a silicon atom, and one or more activity limiting agent (ALA) compounds comprising one or more aliphatic or cycloaliphatic carboxylic acids; alkyl-, cycloalkyl- or alkyl(poly)(oxyalkyl)-(poly)ester derivatives thereof; or inertly substituted derivatives of the foregoing.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Alumoxane-enhanced, supported ziegler-natta polymerization catalysts, methods of making same, processes of using same and polymers produced therefrom
InactiveUS6124412AUseful and improved range of productivityGood physical propertiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationProduction rateAluminoxane
The present invention relates to a new olefin polymerization catalyst composition, and methods of preparing and methods of using the catalysts to polymerize various olefinic monomers in either gas or slurry phase reactions. The principal advance over the previous art of record involves using alumoxanes or combinations of alumoxanes as catalyst preactivators. Polymers prepared from these catalysts posses productivity increased as high as 40 percent. At the same time, the bulk density remains relatively constant. Additionally, the total amount of cocatalyst species needed to effectively practice the invention is relatively low.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
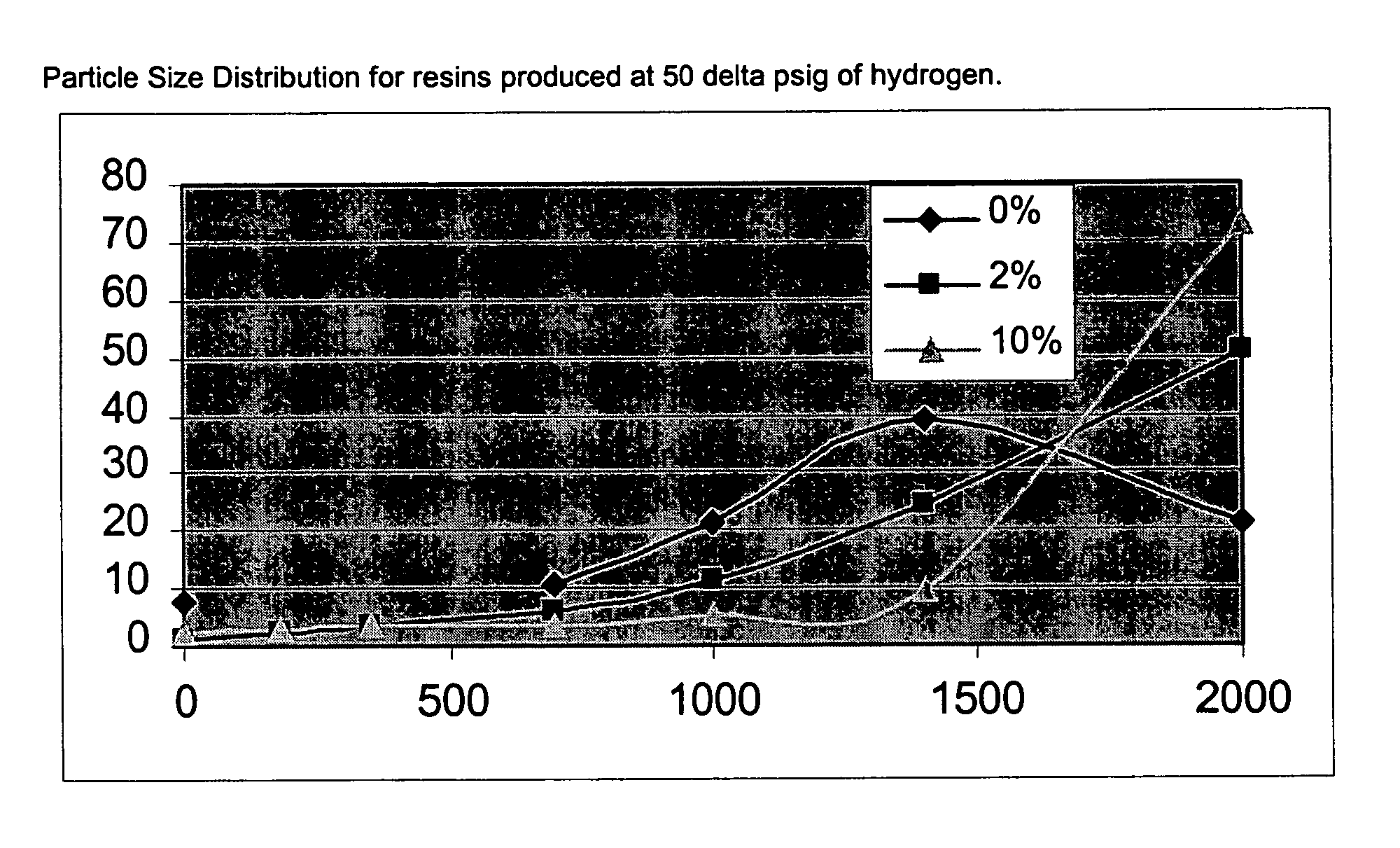
Suspension polymerization process for manufacturing ultra high molecular weight polyethylene, a multimodal ultra high molecular weight polyethylene homopolymeric or copolymeric composition, a ultra high molecular weight polyethylene, and their uses
InactiveUS20090163679A1Easy to processHigh molecular weightMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentFluidized bed dryingPolymer science
The present invention relates to a suspension polymerization process for the production of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene, wherein the operation is carried out in at least two reactors of the CSTR type (continuous stirring tank reactor), in a serial configuration, wherein the first reactor is fed with solvent, monomer and, optionally, comonomer; Ziegler-Natta type catalyst, said catalyst composition having a chloride concentration of at least 55%, based on its composition, and preferably more than 76%, chlorinated cocatalyst and chain growth regulator, said continuous stirring tank reactor being kept under a pressure between 0.1 to 2.0 MPa and temperature from 40° C. to 100° C., which contents of the first reactor are transferred to the subsequent reactor, by means of a pressure differential or through pumping, wherein said subsequent reactors are kept under a pressure between 0.1 to 2.0 MPa and temperature from 40° C. to 100° C., and fed with solvent, monomer, and, optionally, comonomer, catalyst, cocatalyst and chain growth regulator, the pressure and temperature in each of the reactors being different from one another up to the “nth” reactor, the number of reactors “n” varying from 2 to 4; the suspension thus obtained in reactor “n” being centrifugated for the removal of solvent and dried in a fluidized bed drier; thereby resulting in an ultra high molecular weight polyethylene homopolymeric or copolymeric composition with polydispersity greater than or equal to 6.
Owner:BRASKEM SA
Propylene homopolymer having high melt strength and preparation method thereof
The present invention provides a process for preparing high melt strength propylene polymer by direct polymerization, comprising that a propylene polymer with wide molecular weight distribution and containing “very high molecular weight fraction” can be prepared by controlling the species and ratios of the external electron donors in the Ziegler-Natta catalyst system at different reaction stages according to the requirment for different molecular weight fractions in the different propylene polymerization stage of the series operation, and said polymer has excellent mechnical properties, especially with very high melt strength. The present invention also provides a propylene homopolymer with high melt strength, comprising the following features: (1) the MFR is 0.2-10 g / 10 min at 230° C. with a load of 2.16 kg; (2) the molecular weight distribution Mw / Mn is 6-20; (3) the content of the fraction with a molecular weight higher than 5,000,000 is higher than or equal to 0.8 wt %; (4) Mz+1 / Mn is higher than or equal to 70. Said homopolymer can be used in the preparation of foam products, thermoforming products, biaxial stretching films, blown films and blow-molded products.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Co-extruded film structures of polypropylene impact copolymer with other polymers
InactiveUS20060147663A1Reduce smogHigh glossSynthetic resin layered productsBagsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
It has been discovered that the properties of sheet or film materials or structures can be improved by co-extruding a rubber-impact modified heterophasic copolymer core layer with at least a second polyolefin. The second polyolefin may be a Ziegler-Natta catalyzed polyethylene (ZN PE), Ziegler-Natta catalyzed polypropylene random copolymer (ZN PP RCP), a metallocene catalyzed polypropylene random copolymer (mPP RCP), a linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) and / or a metallocene catalyzed medium density polyethylene (mMDPE). Improvements include, but are not necessarily limited to, reduced haze and increased gloss. These sheet or film materials may be co-extruded with other resins or laminated with other materials after extrusion.
Owner:FINA TECH
Impact resistant polymer blends of crystalline polypropylene and partially crystalline, low molecular weight impact modifiers
InactiveUS6943215B2Group 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Polymer blends that exhibit good impact resistance comprise a crystalline polypropylene matrix and a partly crystalline copolymer impact modifier with a molecular weight lower than that of the matrix polymer. The matrix polymer can comprise any crystalline propylene homo- or copolymer. The impact modifying copolymers are characterized as comprising at least about 60 weight percent (wt %) of units derived from propylene and, in certain embodiments, as having at least one, preferably two or more, of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polyolefin foams and methods of making the same
A non-crosslinked polyolefin foam comprises a plastics component and a blowing agent. The plastics component comprises a first constituent and a second constituent. The first constituent is a Ziegler-Natta catalyzed linear low density polyolefin and the second constituent is a low density polyolefin in one embodiment. The Ziegler-Natta catalyzed linear low density polyolefin has a polydispersity of less than 10 and a melt flow index less than 10 g / 10 minutes. The second constituent may be a polypropylene.
Owner:PREGIS INNOVATIVE PACKAGING
Self limiting catalyst composition and propylene polymerization process
ActiveUS20070027275A1Poor surfaceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationElectron donorCarboxylic acid
A catalyst composition for the polymerization of propylene comprising one or more Ziegler-Natta procatalyst compositions comprising one or more transition metal compounds and one or more esters of aromatic dicarboxylic acid internal electron donors; one or more aluminum containing cocatalysts; a selectivity control agent (SCA) comprising at least one silicon containing compound containing at least one C1-10 alkoxy group bonded to a silicon atom, and one or more activity limiting agent (ALA) compounds comprising one or more aliphatic or cycloaliphatic carboxylic acids; alkyl-, cycloalkyl- or alkyl(poly)(oxyalkyl)-(poly)ester derivatives thereof; or inertly substituted derivatives of the foregoing.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Ziegler-Natta olefin polymerization catalysts with single-site center property
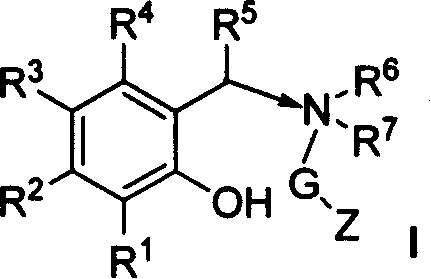
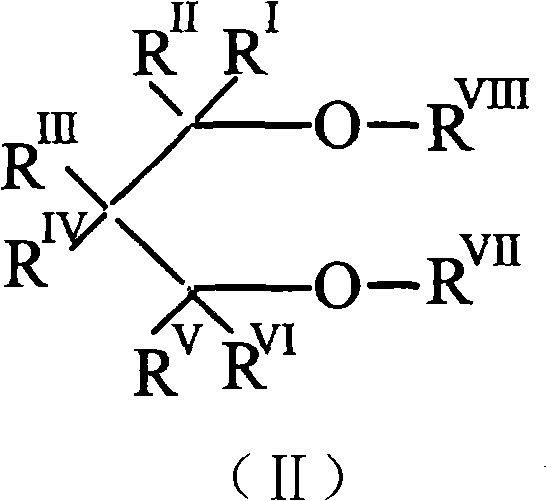
The invention relates to novel Ziegler-Natta olefin polymerization catalysts with single-site center property. The catalysts are characterized in that the catalysts are obtained by adopting a one-pot method and adding novel multidentate ligands (I), magnesium compounds, metal compounds and carriers to tetrahydrofuran solution for treatment. Under the action of alkylaluminium or alkylaluminoxane and other cocatalysts, the catalysts can obtain ethylene copolymer and homopolymer products with controllable molecular weight distribution (1.6-40) and uniformly distributed comonomers through high activity. The catalysts can realize catalytic ethylene polymerization, as well as the slurry-process or gas-phase-process homopolymerization or copolymerization of ethylene and 1-olefin, annular olefin, polar monomer and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
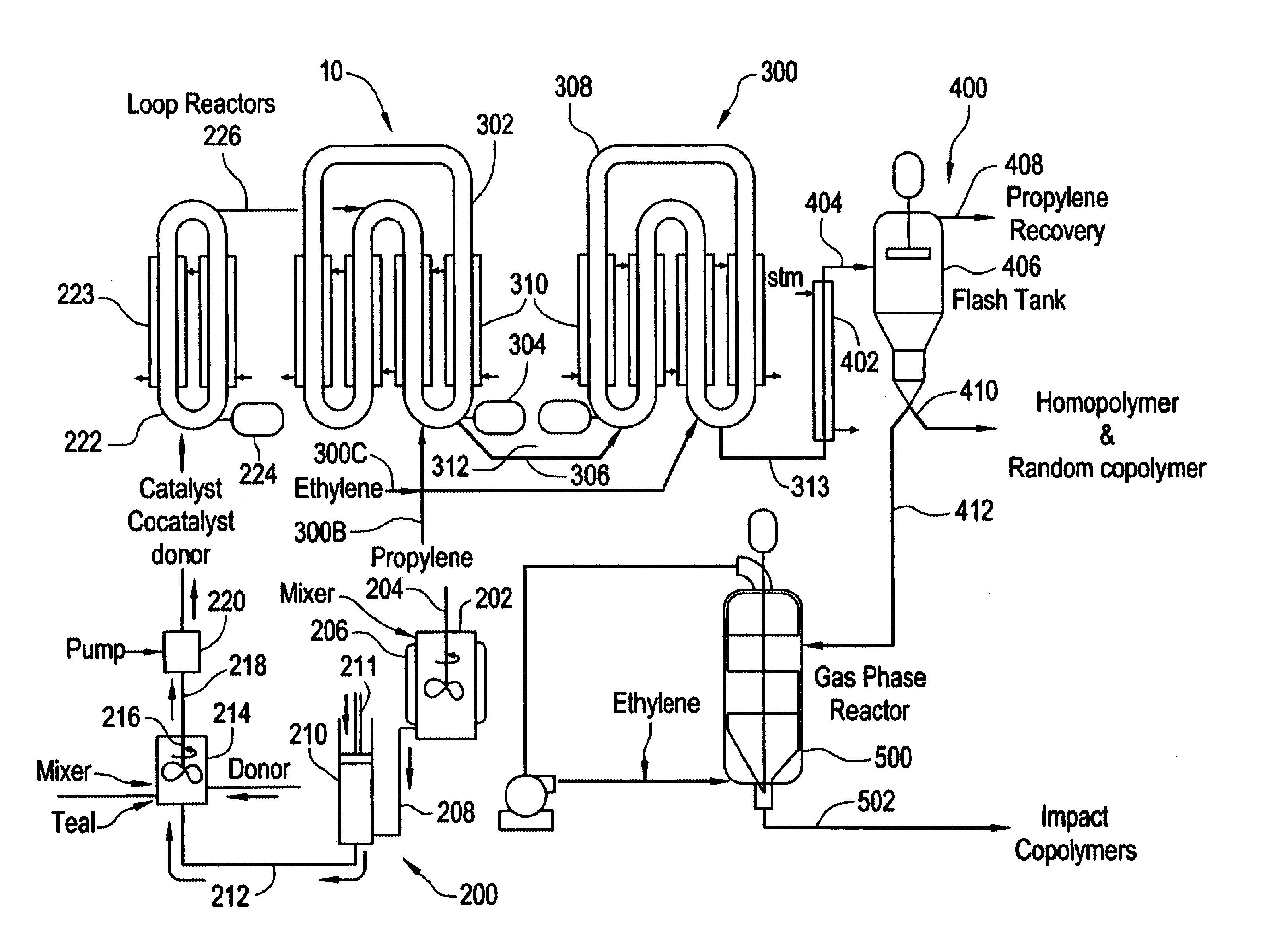
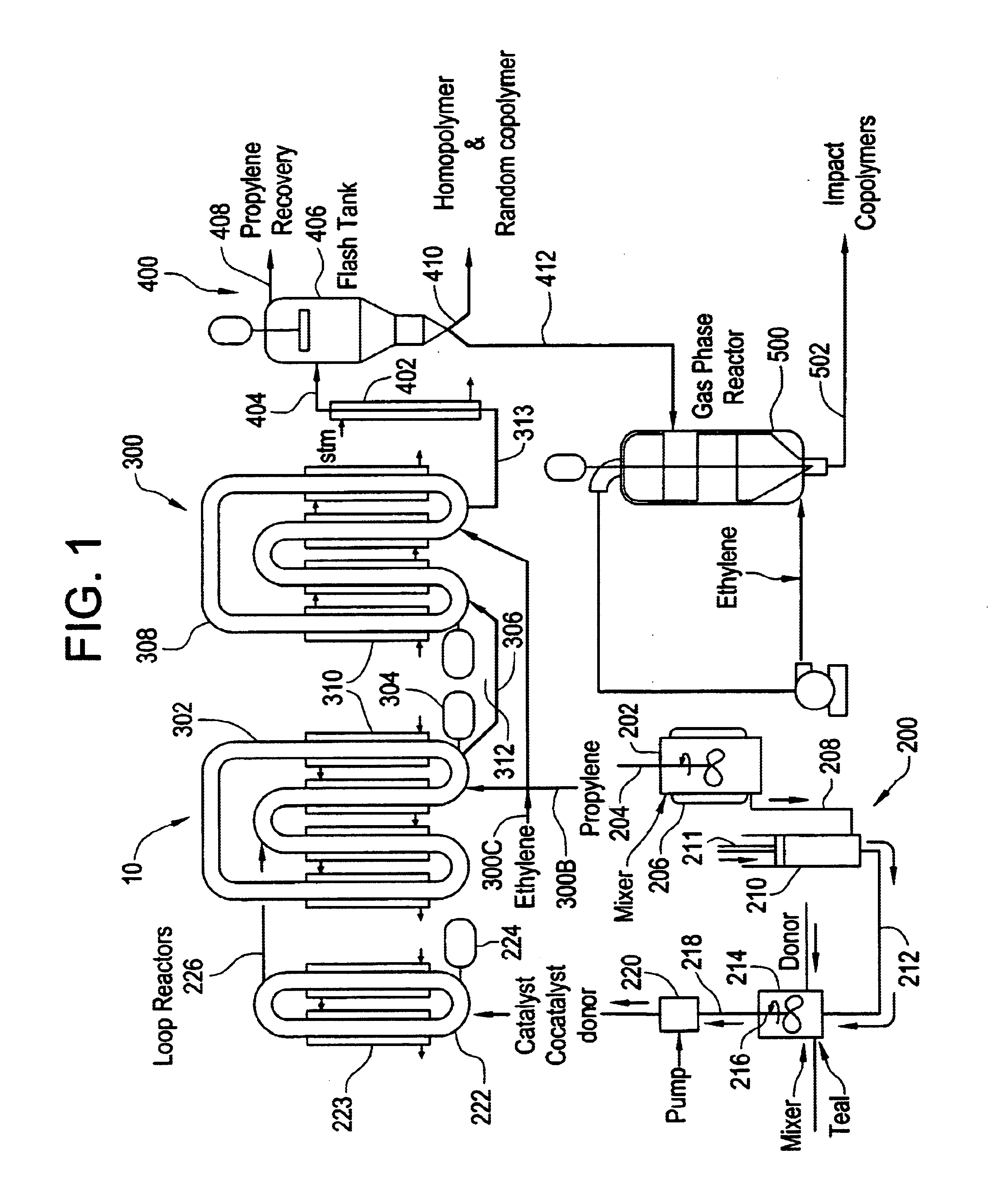
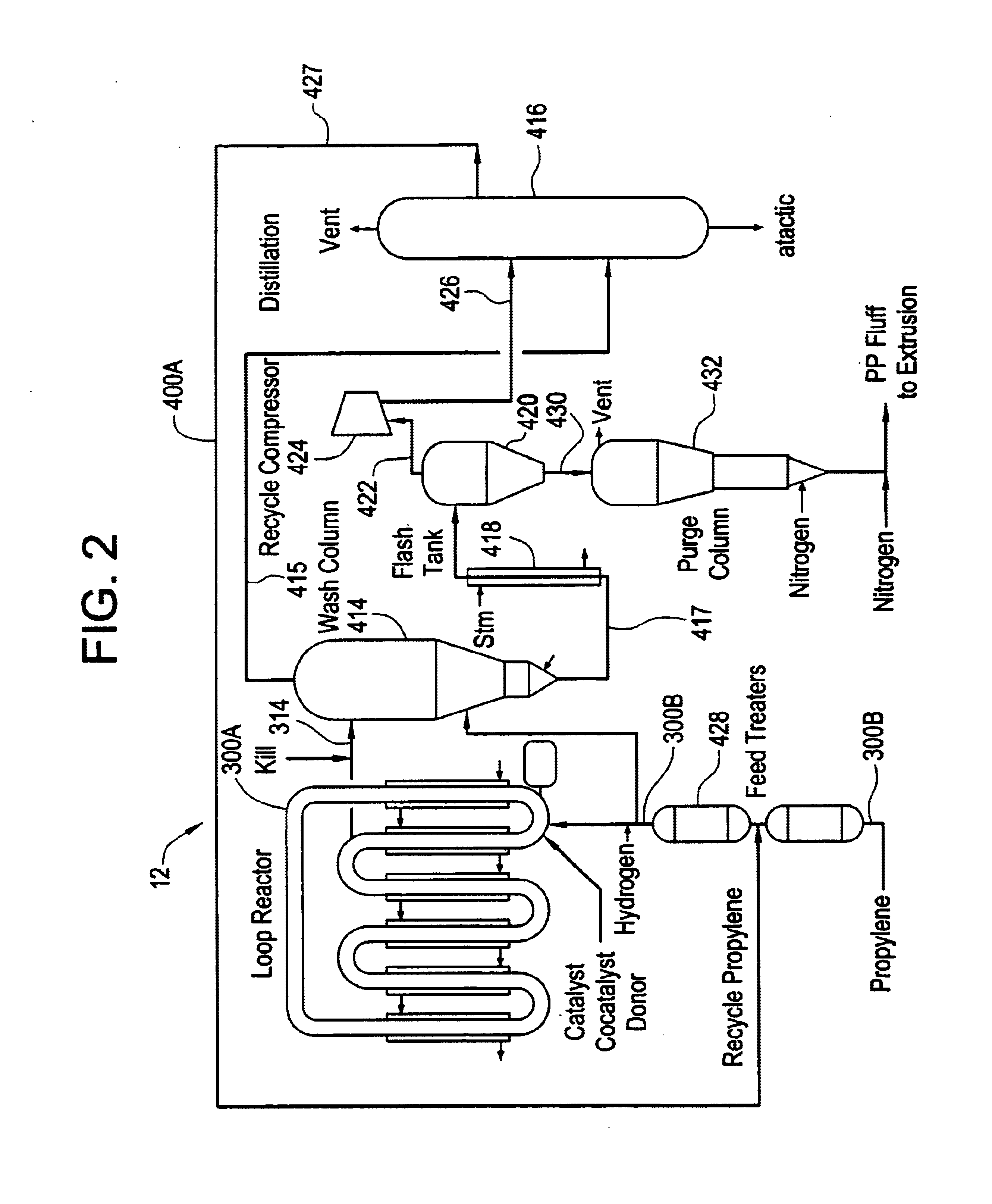
Method for transitioning between Ziegler-Natta and metallocene catalysts in a bulk loop reactor for the production of polypropylene
InactiveUS6916892B2High temperature rangeChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesFeed devicesScavengerZiegler–Natta catalyst
The present invention relates to propylene polymerization process in a bulk loop reactor, and particularly to propylene polymerization process for polymerizing commercial quantities of polypropylene in a bulk loop reactor by sequentially introducing Ziegler-Natta and metallocene catalyst systems into the bulk loop reactor. In one embodiment, separate catalyst mixing systems are used to introduce a quantity of metallocene catalyst and Ziegler-Natta catalyst into the bulk loop reactor. The frequency rate at which the quantity of metallocene catalyst is introduced into the bulk loop reactor may be higher than the frequency rate at which the quantity of Ziegler-Natta catalyst is introduced. In another embodiment, a method of polymerizing propylene in a bulk loop reactor is provided which includes contacting a quantity of supported metallocene catalyst with a first quantity of scavenger, such as TEAL and or TIBAL, prior to injecting the supported metallocene catalyst into the bulk loop reactor and contacting a quantity of Ziegler-Natta catalyst system with a second quantity of scavenger prior to injecting the Ziegler-Natta catalyst system into the bulk loop reactor, wherein the second quantity of scavenger is greater that the first quantity of scavenger. In another embodiment, a method of contacting a flow of metallocene with a flow of propylene is provided. This method includes directing the flow of metallocene towards a junction, directing the flow of propylene towards the junction and maintaining a portion of the flow of metallocene separate from a portion of the flow propylene within a portion of the junction downstream of the flow of propylene into the junction. In another embodiment, a method of introducing a quantity of antifouling agent into a catalyst mixing system is provided. In this embodiment a portion of the antifouling agent is introduced at or downstream of a point of contact of a stream of propylene with a stream of catalyst. The antifouling agent may be a member, alone or in combination with other members, selected from the group consisting of Stadis 450 Conductivity Improver, Synperonic antifouling agent, and Pluronic antifouling agent.
Owner:FINA TECH
Multi-metallic ziegler-natta procatalysts and cataysts prepared therefrom for olefin polymerizations
ActiveUS9255160B2Monocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentThin material handlingLinear low-density polyethyleneOlefin polymerization
Novel catalyst compositions comprising three or more transition metals are effective in increasing catalyst efficiency, reducing polydispersity, and increasing uniformity in molecular weight distribution when used in olefin, and particularly, linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), polymerizations. The resulting polymers may be used to form differentiated products including, for example, films that may exhibit improved optical and mechanical properties.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Gas-phase polymerization method and polymer of polybutene-1
The invention provides a gas-phase polymerization method of polybutene-1 for preparing high-quality butene-1 polymer, which comprises: performing homopolymerization of butene-1 serving as a monomer and a reaction medium or copolymerization of butene-1 and other alpha-olefins in a gas-phase polymerization reactor at a reaction temperature of 0 to 110 DEG C in the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst with high stereoselectivity, and standing for 1 to 6 hours optimally. The method is simple in process, easy in operation and low in cost. The prepared polybutene-1 product is sphere-like or spherical particles and contains little fine powder, thereby contributing to the long-term operation o devices.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process of making polymer blends
In a process for producing a polymer blend, at least one first monomer is polymerized in a first slurry phase reaction zone in the presence of a supported first catalyst comprising a Ziegler-Natta component to produce a thermoplastic first polymer having a crystallinity of at least 30%. At least part of said first polymer is then contacted with at least one second monomer different from said first monomer and at least one polyene in a second solution phase reaction zone in the presence of a second catalyst under conditions to produce and at least partially cross-link said second polymer such that said second polymer comprises at least a fraction which is insoluble in xylene and has a crystallinity of less than 20%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method of making a Ziegler-Natta catalyst
ActiveUS20060046927A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationZiegler–Natta catalystFumed silica
A method for making a Ziegler-Natta catalyst support includes the steps of contacting a fumed silica with a surface modifying agent such as a compound having the formula RMgX MgR′R″ wherein R, R′ and R″ are each individually a moiety selected from an alkyl group, cycloalkyl, aryl or alkaryl group, and X is a halogen selected from the group consisting of chlorine, bromine and iodine, to provide a pretreated silica seeding agent. The pretreated silica seeding agent is then dispersed in a non-aqueous liquid magnesium halide / alkanol complex, and the magnesium halide is crystallized onto the silica particles to form-catalyst support particles especially suitable for Ziegler-Natta catalysts.
Owner:LUMMUS NOVOLEN TECH
Processes for transitioning between metallocene and Ziegler-Natta polymerization catalysts
ActiveUS6949612B2Efficient activationReducing electricityZiegler–Natta catalystOlefin polymerization
Processes for transitioning among polymerization catalyst systems, preferably catalyst systems that are incompatible with each other. In particular, the processes relate to transitioning from olefin polymerizations utilizing metallocene catalyst systems to olefin polymerizations utilizing traditional Ziegler-Natta catalyst systems.
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
Magnesium chloride/mesoporous molecular sieve bisupported Ziegler-Natta polyethylene catalyst, preparation and use
The invention relates to a Ziegler-Natta polyethylene catalyst loaded by double carriers of magnesium chloride / mesoporous molecular sieve, a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst is made up by taking titanium tetrachloride as a main catalyst of active components and organic aluminum as a cocatalyst. The double carriers of the magnesium chloride / mesoporous molecular sieve are taken as a carrier; an organic reagent of magnesium is used, by the breaking and creation of chemical bonds, Si-O-Mg bond is generated so as to obtain a complex carrier with clear structure. The dried mesoporous molecular sieve is suspended in toluene and added with tetrahydrofuran solvent of methyl magnesium chloride; the methyl magnesium chloride on a surface is reacted with silanol group to form the Si-O-Mg bond; and an obtained complex carrier has the frame of the mesoporous molecular sieve and the surface of the magnesium chloride, and can possess the advantages of the double carriers. The active titanium is loaded on the double carriers of chloride / mesoporous molecular sieve to catalyze the polymerization of ethane, thereby obtaining polyethylene with a super molecular weight of 600 thousand to 7 million.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for polymerizing olefin-based polymers
A process for producing an olefin-based polymer, said process comprising polymerizing at least one monomer, in the gas phase, or in a slurry process, in the presence of at least the following components:A) at least one catalyst;B) at least one cocatalyst;C) a composition comprising at least one compound selected from formula (I), and / or at least one compound selected from formula (II):(R1CO2)2AlOH (I),(R2)xN(R3OH)y (II);wherein R1 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 13 to 25 carbons;R2 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 14 to 26 carbons;R3 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 1 to 4 carbons; andx+y=3, and x has a value of 1 or 2.A process for producing an olefin-based polymer, said process comprising polymerizing at least one monomer in the presence of at least the following components:A) a Ziegler Natta type catalyst comprising at least two transition metals;B) a trialkylaluminum compound;C) optionally a composition comprising at least one compound selected from formula (I), and / or at least one compound selected from formula (II):(R1CO2)2AlOH (I),(R2)xN(R3OH)y (II);wherein R1 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 13 to 25 carbons;R2 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 14 to 26 carbons;R3 is a hydrocarbon radical containing from 1 to 4 carbons; andx+y=3, and x has a value of 1 or 2.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polypropylene with narrow distribution of molecular weight
The invention relates to polypropylene with narrow distribution of molecular weight and a preparation method, and especially relates to a propylene polymer with narrow distribution of molecular weight by employing a Ziegler-Natta catalyst through direct reactor polymerization. The polymer has high and adjustable isotacticity, the molecular weight distribution is narrow, and the high-molecular trailing index is high. propylene is not contained in a locational isomeric structure, the melting point and crystallization temperature are high, compared with a traditional degradation method for producing the polypropylene with narrow distribution, the polypropylene with narrow distribution of molecular weight has the advantages of economy, energy saving and environmental protection. The product is especially suitable for the fields with high fluidity requirement such as spinning, injecting by a thin wall, casting the transparent material. In addition, due to characteristic of narrow distribution of molecular weight, the polymer has a certain advantage on transparency application aspect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
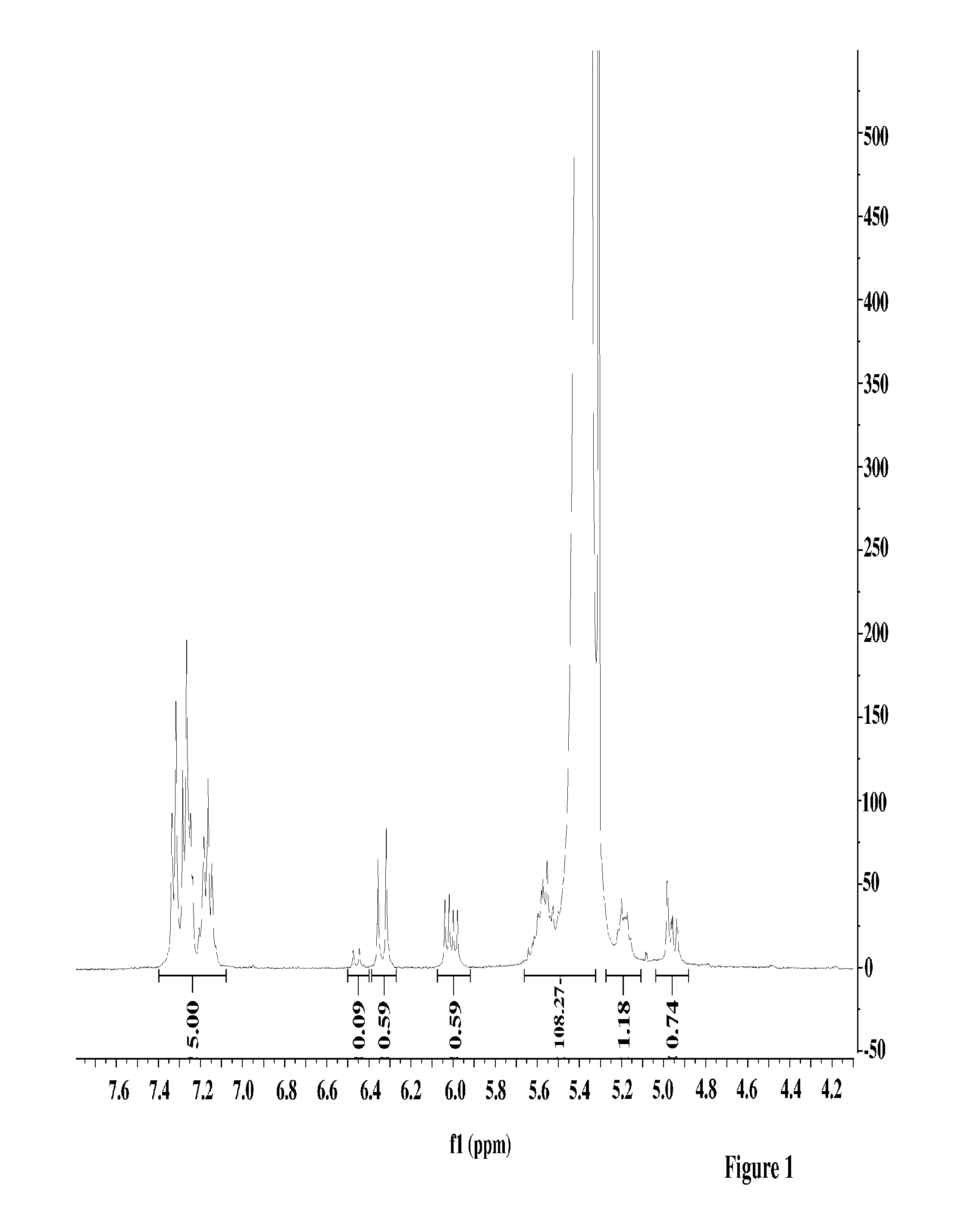
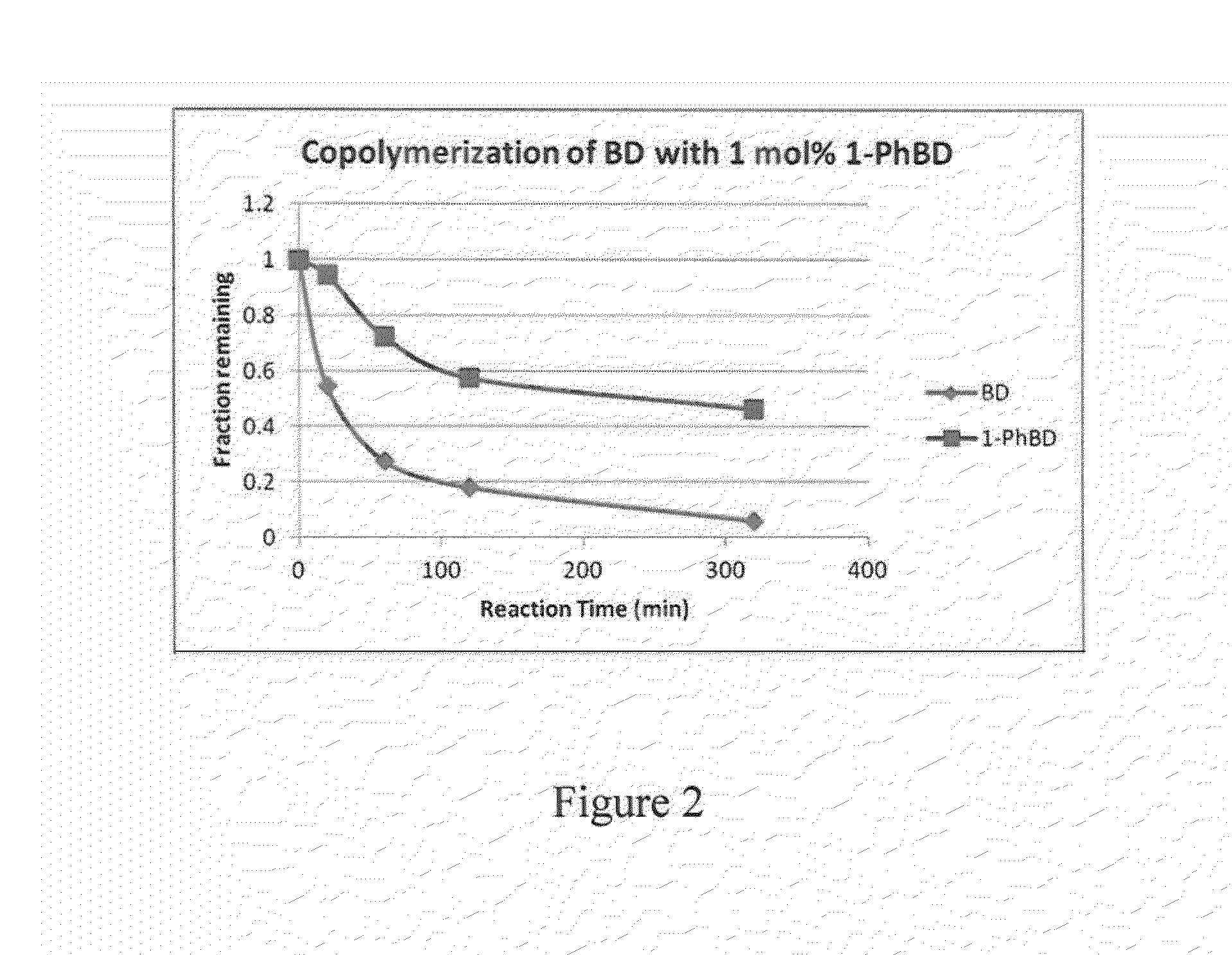
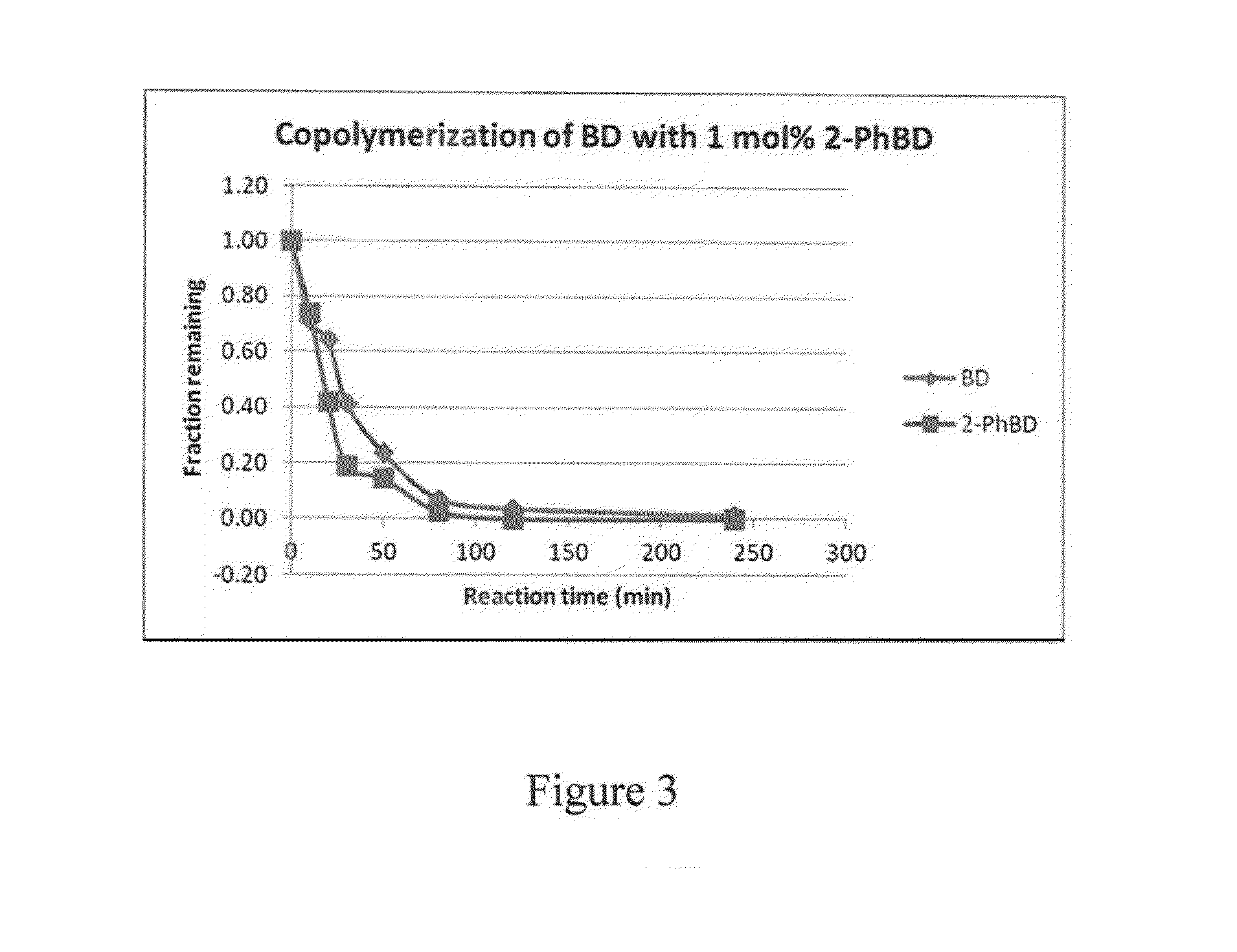
High cis diene/phenylbutadiene copolymers prepared using a Ziegler/Natta neodymium catalyst
The present invention is directed to a polymer comprising repeat units derived from 1,3-butadiene and a substituted butadiene of formula I or IIwherein R is hydrogen, an alkyl group, aryl group, or a fused cyclic group; andwherein at least 95 percent by weight of the repeat units have a cis-1, 4 microstructure. The invention is further directed to a rubber composition and pneumatic tire comprising the polymer, and a method for making the polymer using a neodymium catalyst system.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
High barrier multilayer film
InactiveUS6458470B1Improve moisture resistanceGood dimensional stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersZiegler–Natta catalystOptoelectronics
The present invention is a high barrier multilayer film particularly suitable for packaging. The high barrier multilayer film is a film including (a) a core substrate layer having an isotactic polypropylene produced from Ziegler-Natta catalysts, and (b) an adjacent layer on at least one surface of the core substrate layer, wherein the adjacent layer (b) comprises an isotactic polypropylene produced from metallocene catalysts; or the high barrier multilayer film includes (a') a core substrate layer having an isotactic polypropylene produced from metallocene catalysts, and (b') an adjacent layer on at east one surface of the core substrate layer, wherein the adjacent layer (b') comprises an isotactic polypropylene produced from Ziegler-Natta catalysts.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Method of making a ziegler-natta catalyst
ActiveUS7071137B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationZiegler–Natta catalystFumed silica
A method for making a Ziegler-Natta catalyst support includes the steps of contacting a fumed silica with a surface modifying agent such as a compound having the formula RMgX MgR′R″ wherein R, R′ and R″ are each individually a moiety selected from an alkyl group, cycloalkyl, aryl or alkaryl group, and X is a halogen selected from the group consisting of chlorine, bromine and iodine, to provide a pretreated silica seeding agent. The pretreated silica seeding agent is then dispersed in a non-aqueous liquid magnesium halide / alkanol complex, and the magnesium halide is crystallized onto the silica particles to form catalyst support particles especially suitable for Ziegler-Natta catalysts.
Owner:LUMMUS NOVOLEN TECH
Multi-metallic ziegler-natta procatalysts and cataysts prepared therefrom for olefin polymerizations
ActiveUS20140080970A1High densityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationLinear low-density polyethyleneOlefin polymerization
Novel catalyst compositions comprising three or more transition metals are effective in increasing catalyst efficiency, reducing polydispersity, and increasing uniformity in molecular weight distribution when used in olefin, and particularly, linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), polymerizations. The resulting polymers may be used to form differentiated products including, for example, films that may exhibit improved optical and mechanical properties.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Impact resistant polymer blends of crystalline polypropylene and partially crystalline, low molecular weight impact modifiers
InactiveUS20060142497A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesX-rayPolypropylene
Polymer blends that exhibit good impact resistance comprise a crystalline polypropylene matrix and a partly crystalline copolymer impact modifier with a molecular weight lower than that of the matrix polymer. The matrix polymer can comprise any crystalline propylene homo- or copolymer. The impact modifying copolymers are characterized as comprising at least about 60 weight percent (wt %) of units derived from propylene and, in certain embodiments, as having at least one, preferably two or more, of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for ziegler-natta research
InactiveUS20070224641A1Reduce contentAvoid lostSequential/parallel process reactionsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCombined methodAlkene
A combinatorial method for identifying a catalyst composition for use in the heterogeneous Ziegler-Natta addition polymerization of an olefin monomer, said catalyst composition comprising a compound of a metal of Group 2 of the Periodic Table of the Elements.
Owner:CAMPBELL RICHARD E
Preparation method of Ziegler-Natta catalyst for efficiently preparing low entanglement polyethylene and application
ActiveCN106543301AElimination of bimetallic deactivationHigh polymerization activityPolymer scienceZiegler–Natta catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst for efficiently preparing low entanglement polyethylene and an application. The preparation method comprises the following steps that a prepared alcohol absorbing porous carrier and a prepared polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane molecule / Mg mixture are stirred in tetrahydrofuran and filtered, solid powder is dried until the solid powder flows freely, and a carrier used for preparing the low entanglement polyethylene catalyst is obtained; then, a carrier of an aluminium alkyl modified catalyst is prepared through the aluminium alkyl; and finally, a TiC14 tetrahydrofuran solution is added into the carrier of the aluminium alkyl modified catalyst, after stirring, the solid powder is washed by means of the tetrahydrofuran solution and dried until the solid powder flows freely, and the Ziegler-Natta catalyst for efficiently preparing the low entanglement polyethylene is obtained. POSS can be assembled into a microsphere with particle diameter being 20-100 nm in a pore passage of the porous carrier. The active points are divided effectively. The intervals between active centers are increased. The occurrence of chain overlapping in the polymerization process is restrained. The low entanglement polyethylene Ziegler-Natta can be prepared efficiently with the polymerizing temperature being higher than or equal to 60 DEG C.
Owner:宁波链增新材料科技有限公司
Self-extinguishing catalyst composition with monocarboxylic acid ester internal door and propylene polymerization process
InactiveUS7420021B2Good self-extinguishingNarrow molecular weight distributionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSilane compoundsElectron donor
A catalyst composition for the polymerization of propylene comprising one or more Ziegler-Natta procatalyst compositions comprising one or more transition metal compounds and one or more monoesters of aromatic carboxylic acid internal electron donors; one or more aluminum containing cocatalysts; and a mixture of two or more different selectivity control agents, said SCA mixture comprising from 98.0 to 99.9 mol percent of one or more esters of one or more aromatic monocarboxylic acids or substituted derivatives thereof, and from 2.0 to 0.1 mol percent of one or more alkoxysilane compounds.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
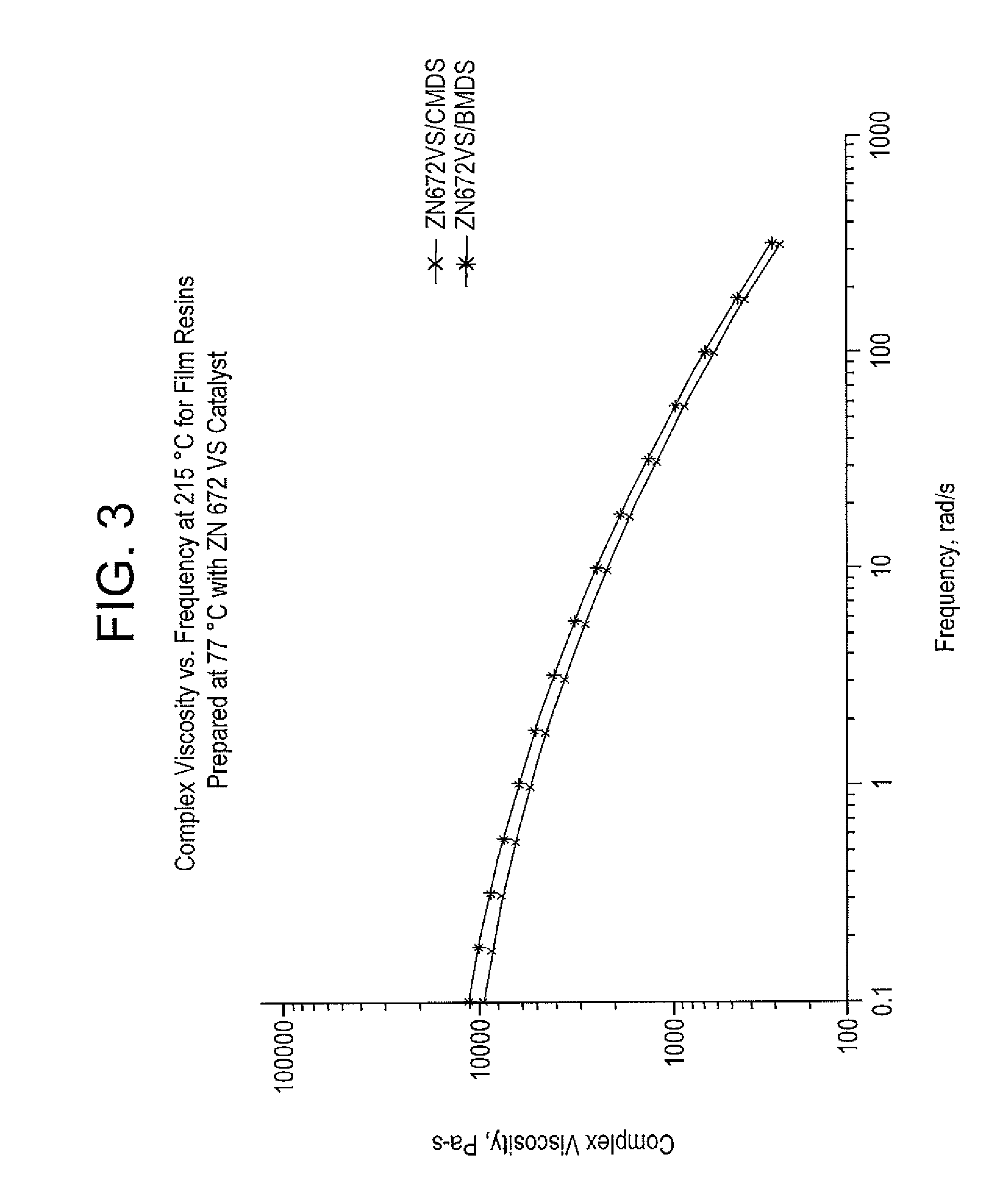
Succinate-Containing Polymerization Catalyst System Using n-Butylmethyldimethoxysilane for Preparation of Polypropylene Film Grade Resins
InactiveUS20080161515A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationZiegler–Natta catalystElectron donor
It has been discovered that using n-butylmethyldimethoxysilane (BMDS) as an external electron donor for succinate-containing Ziegler-Natta catalysts can provide a catalyst system that may prepare polypropylene films with improved properties. The catalyst systems of the invention provide for controlled chain defects / defect distribution and thus a regulated microtacticity along with broadened molecular weight distribution.
Owner:FINA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com