Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
321results about How to "Improve in-plane uniformity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
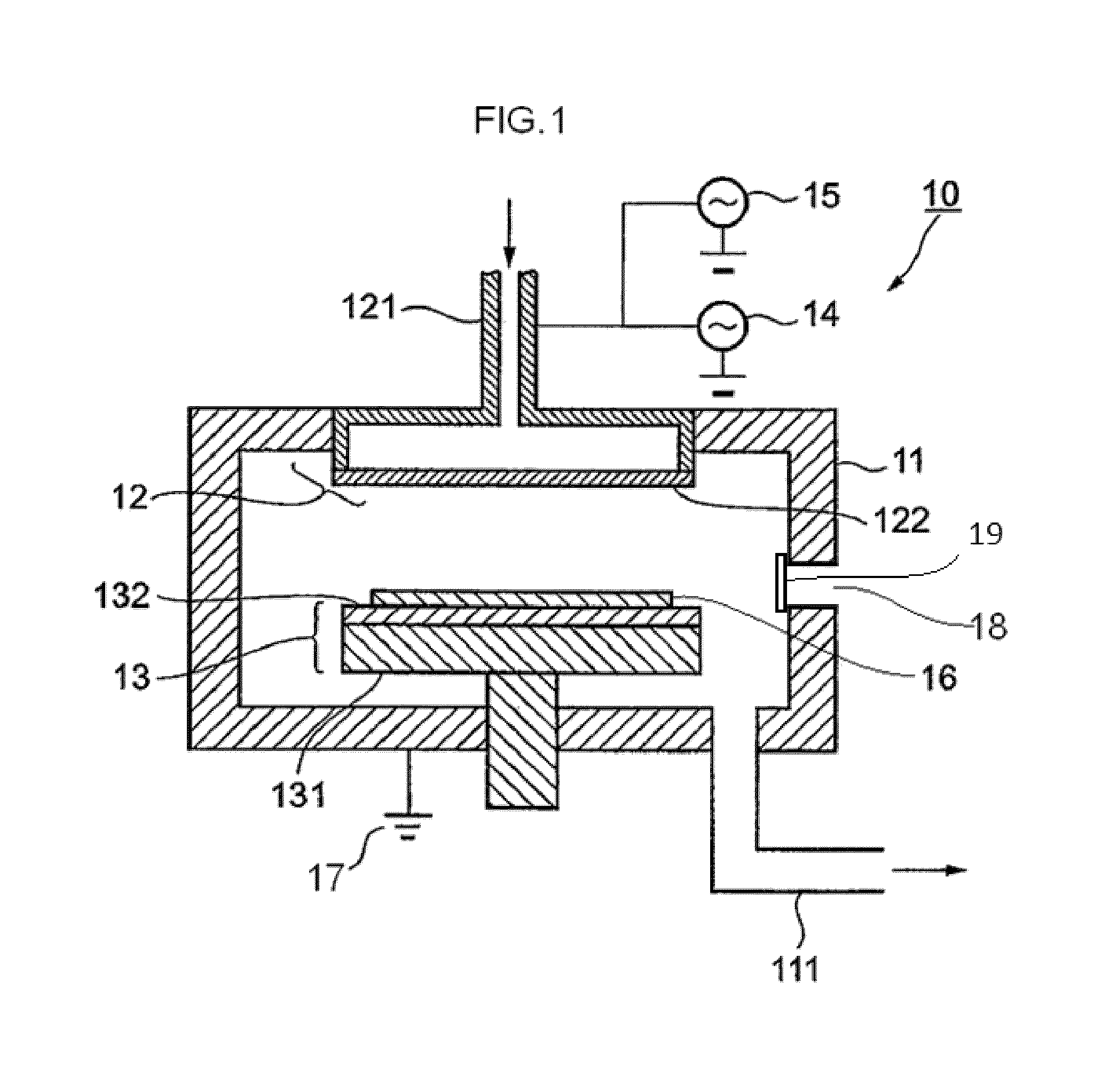
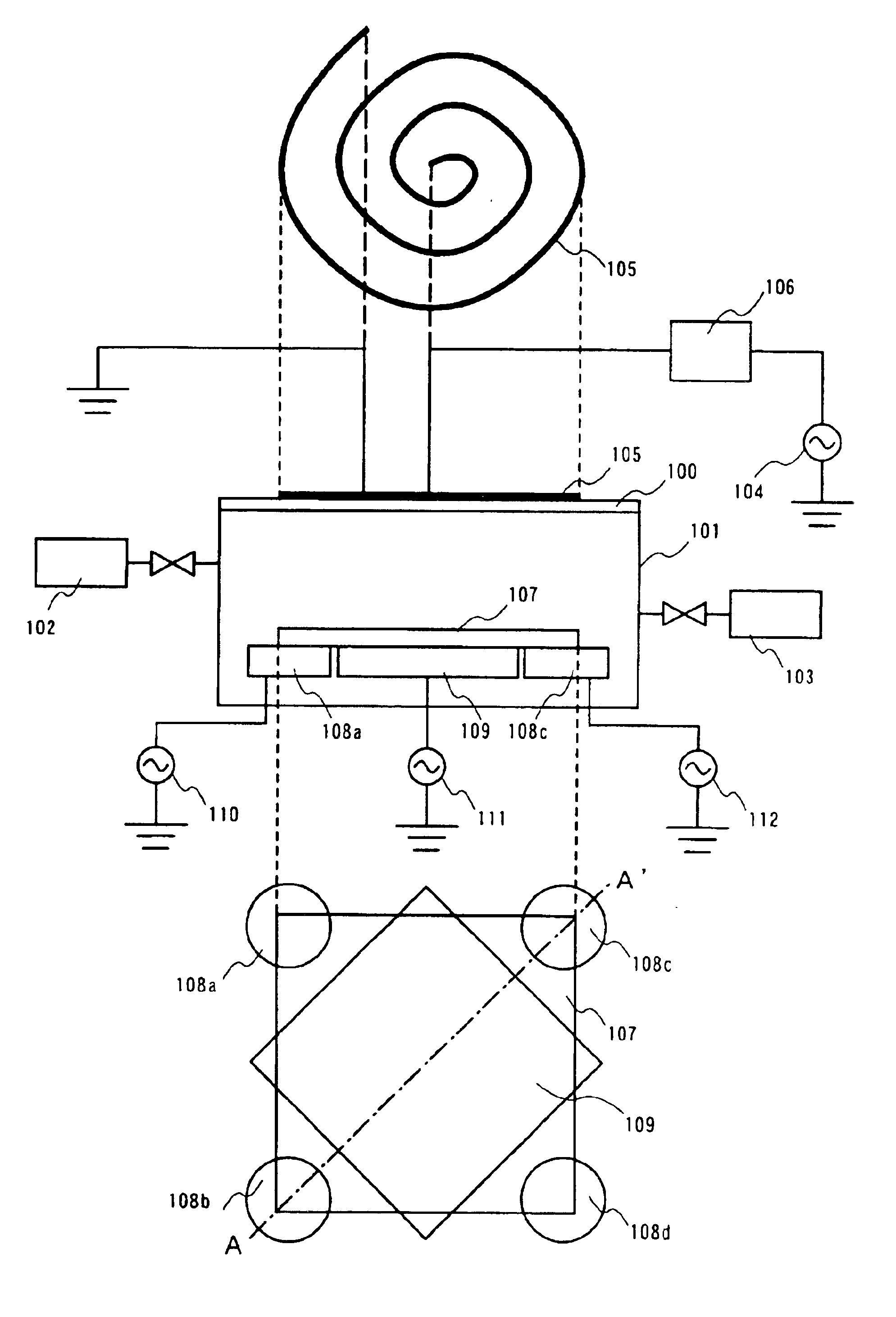
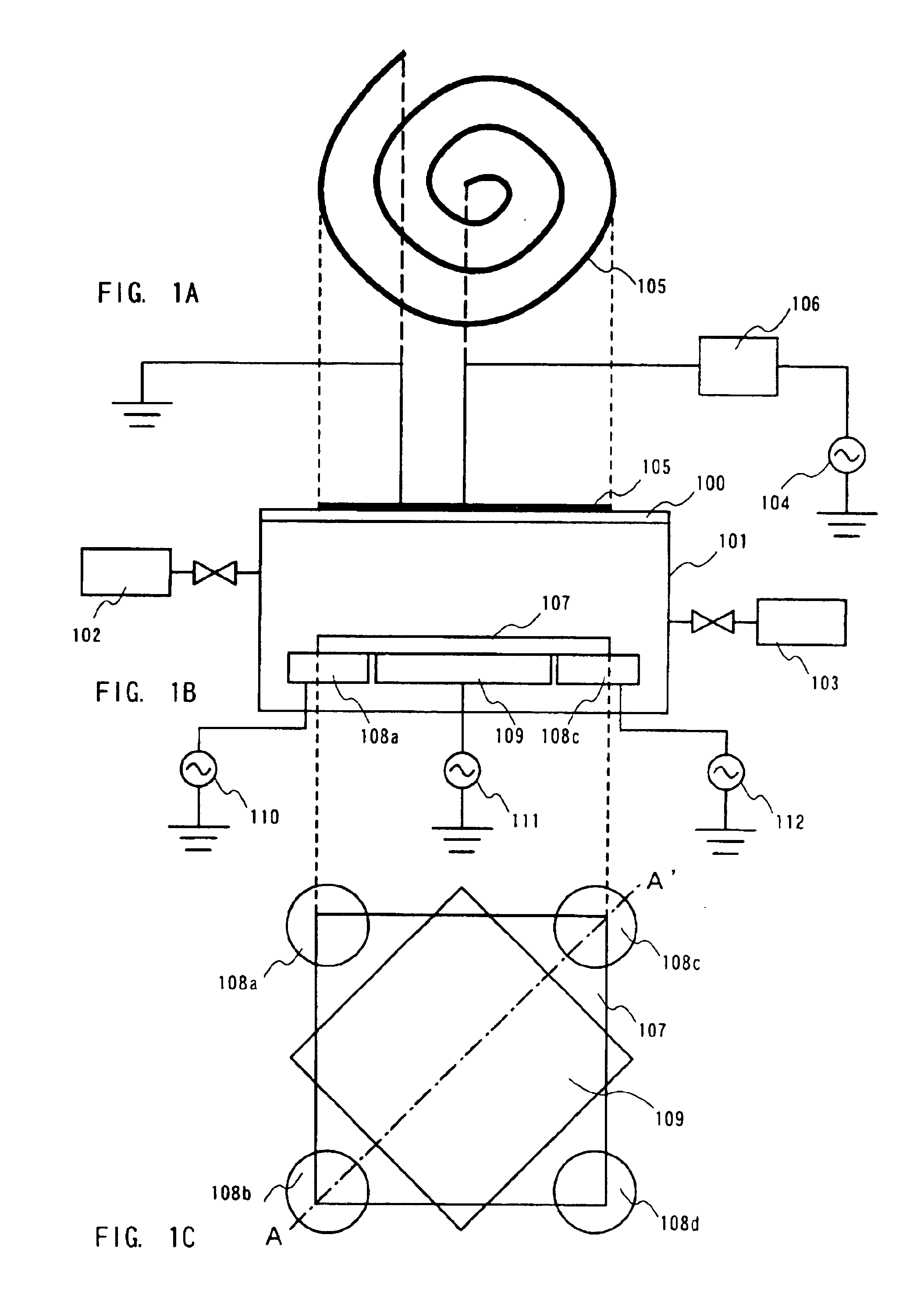
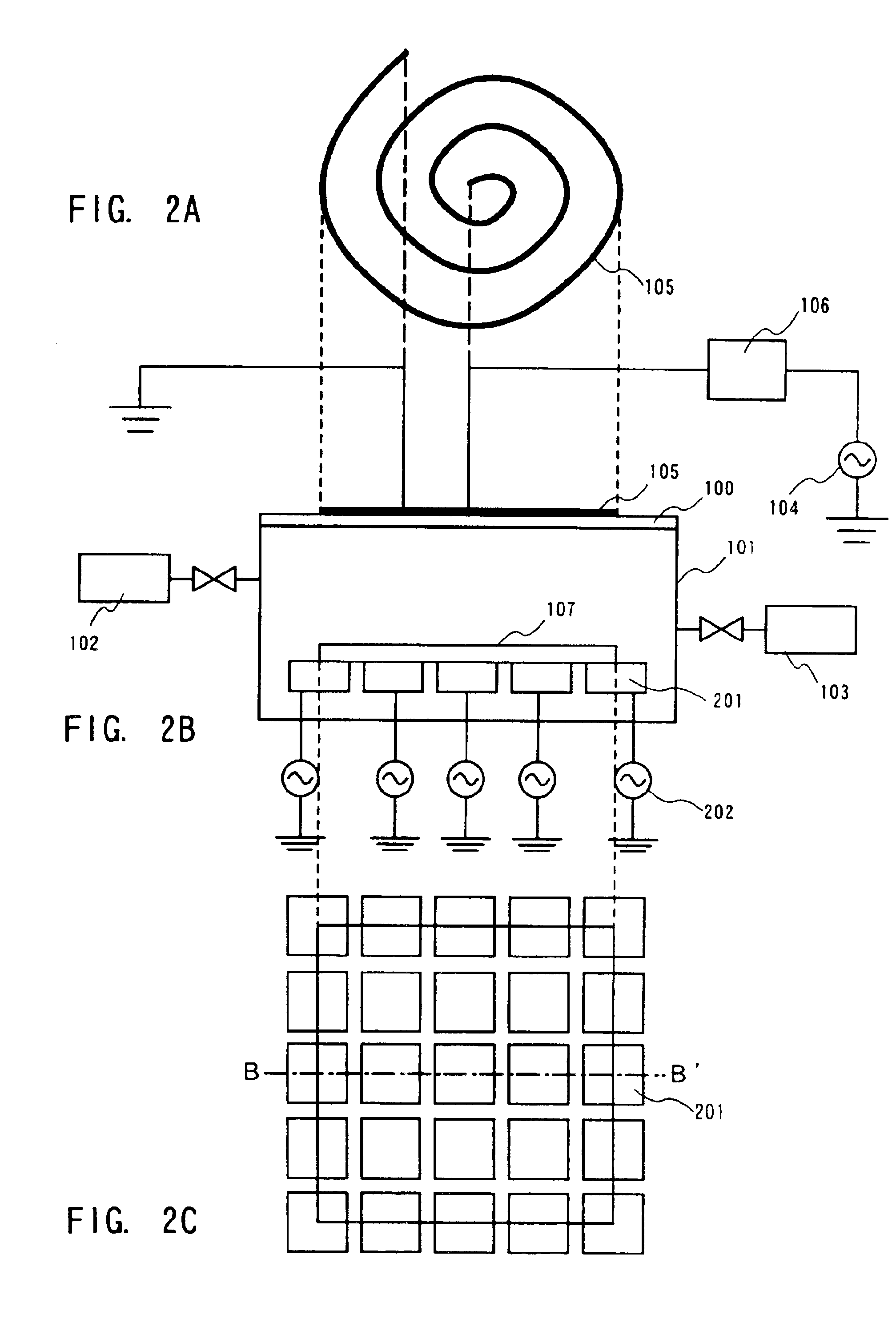
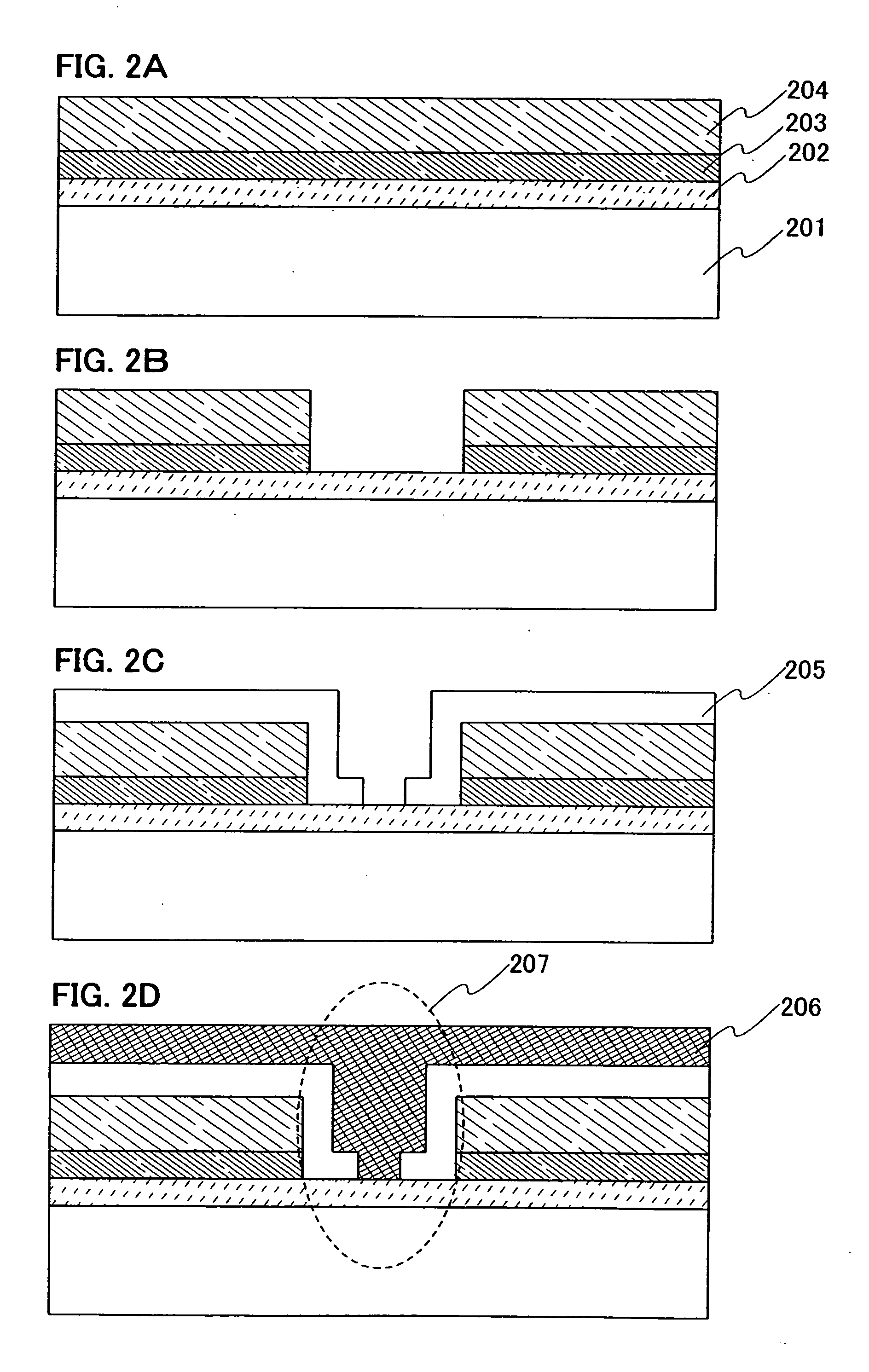
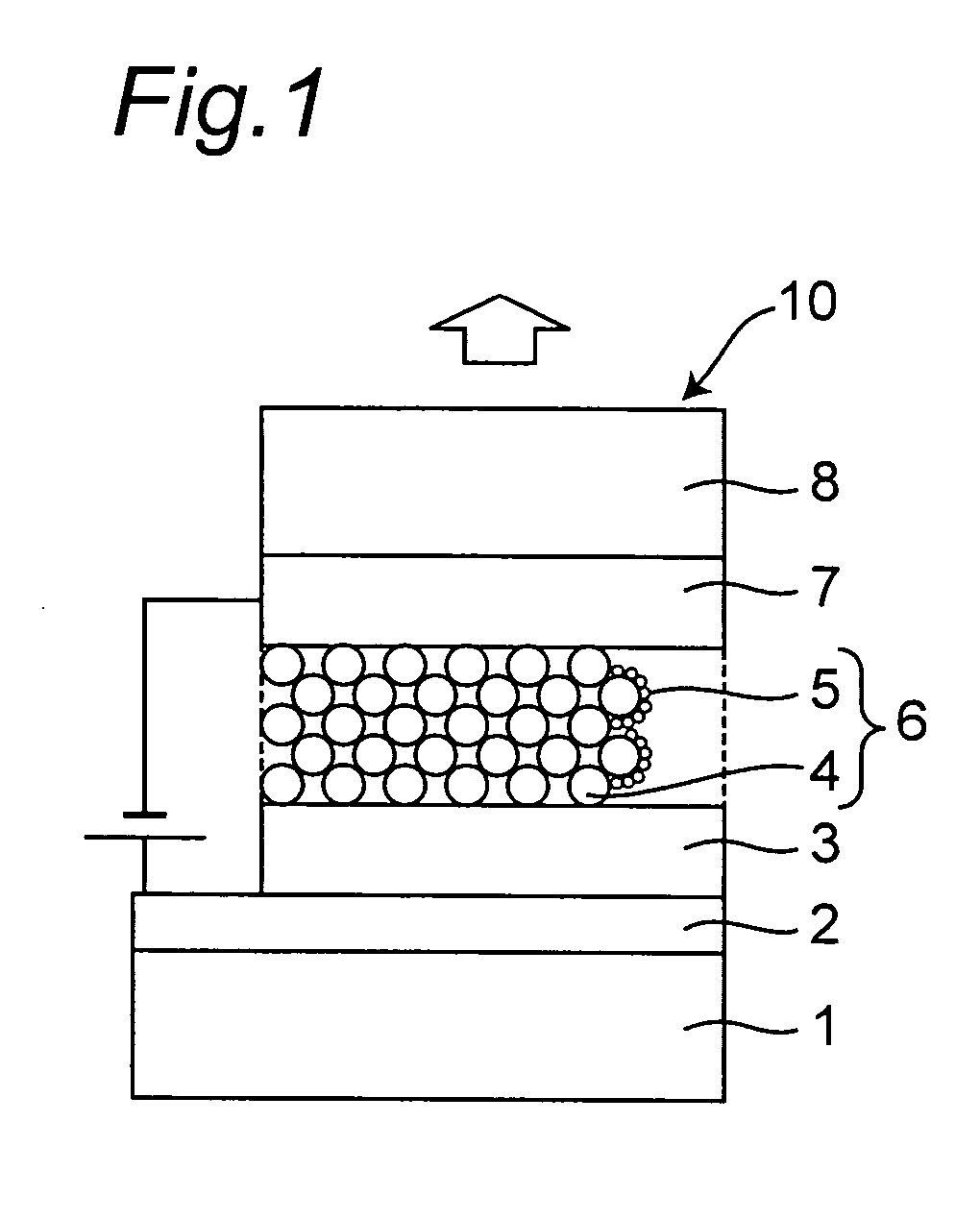
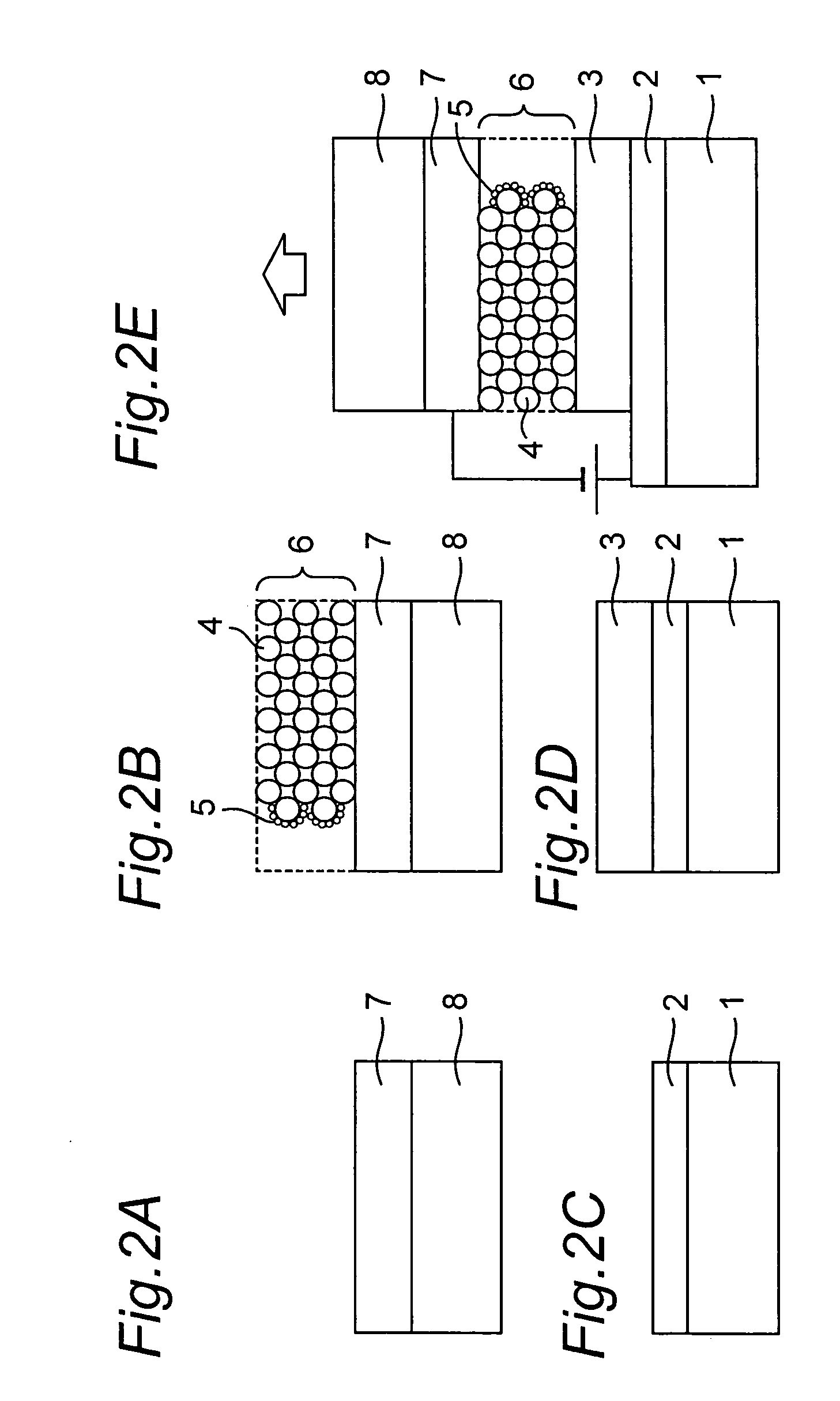
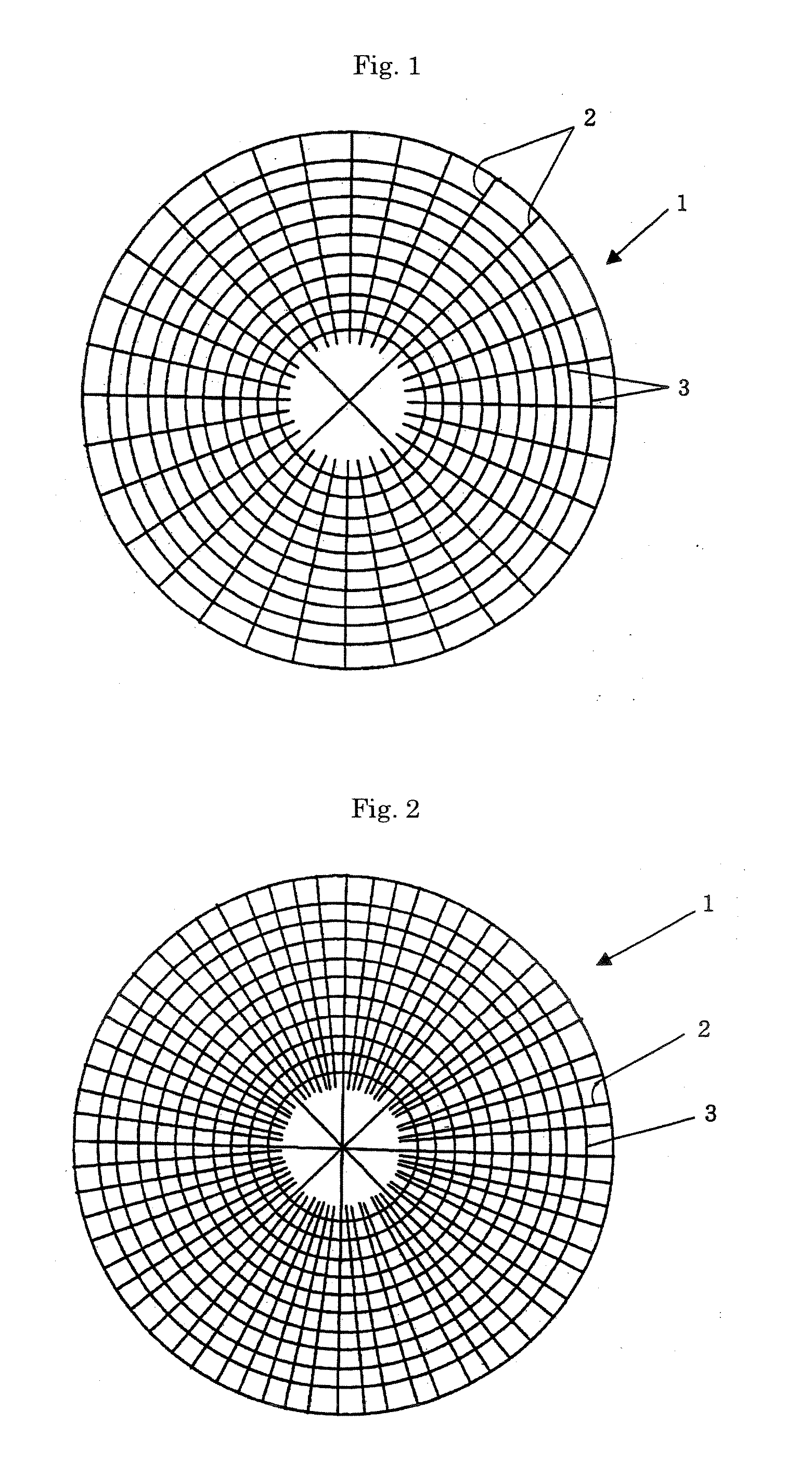
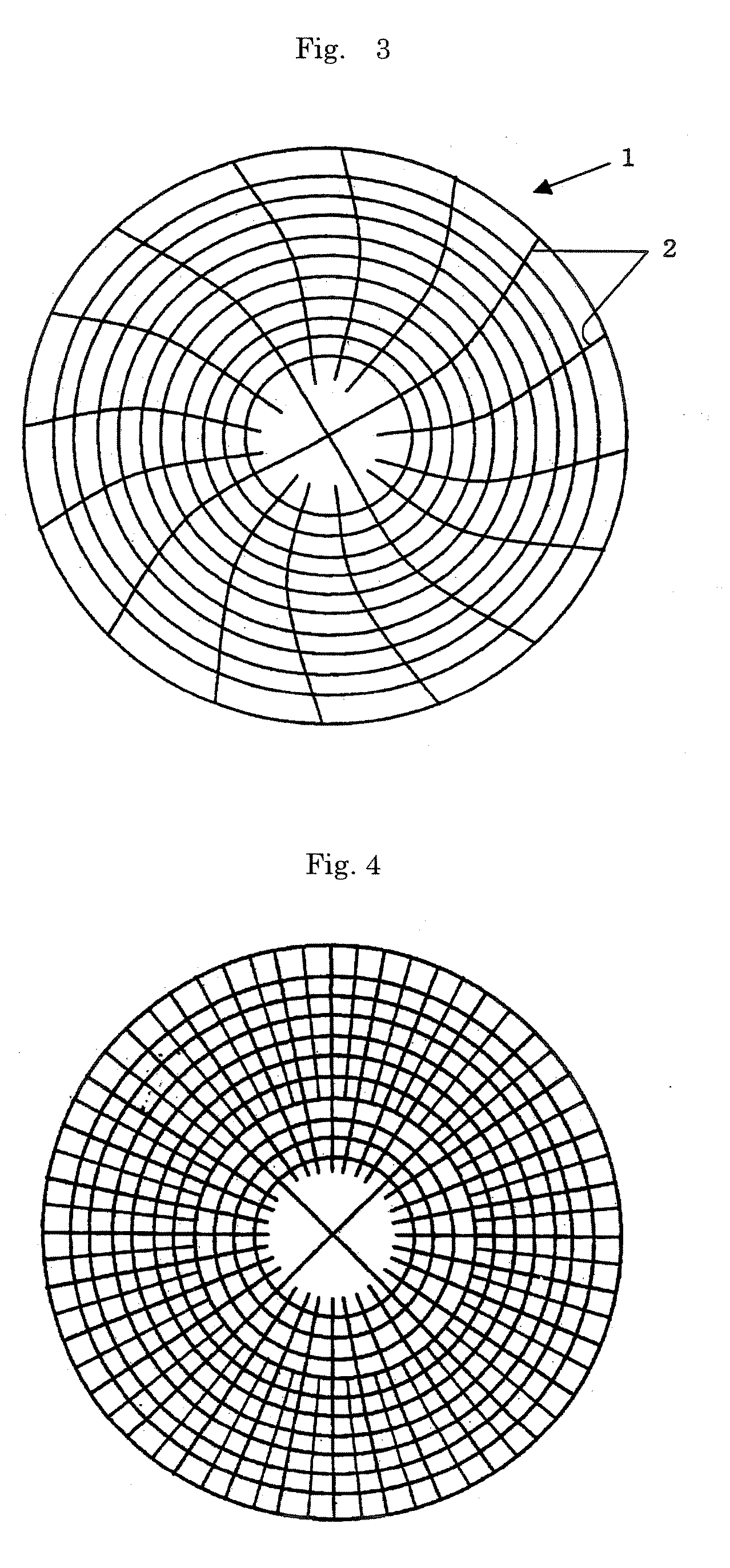
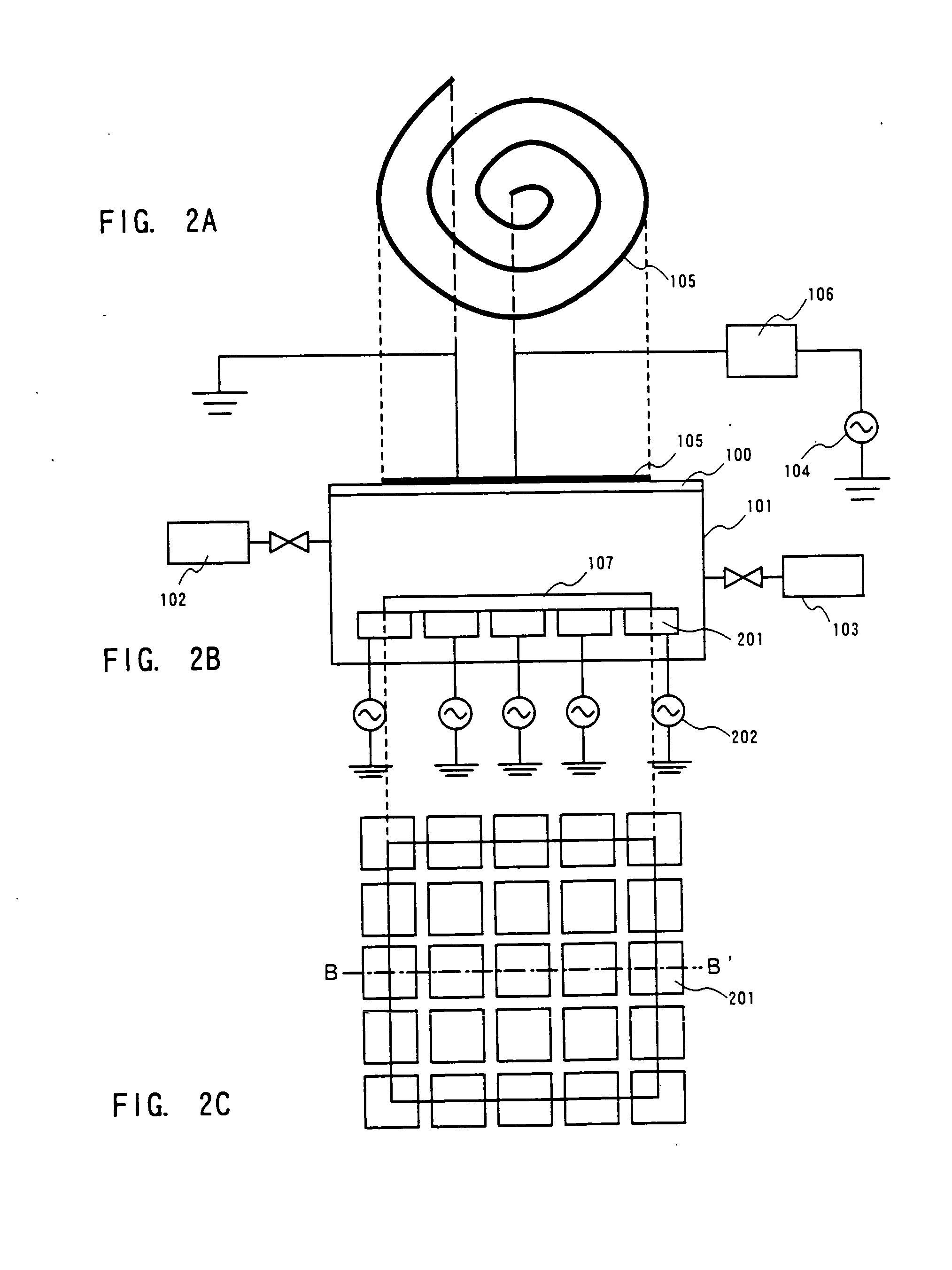
Method of depositing film by atomic layer deposition with pulse-time-modulated plasma
ActiveUS8465811B2Improve in-plane uniformityUniform supplyPretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingPulse time modulationAtomic layer deposition
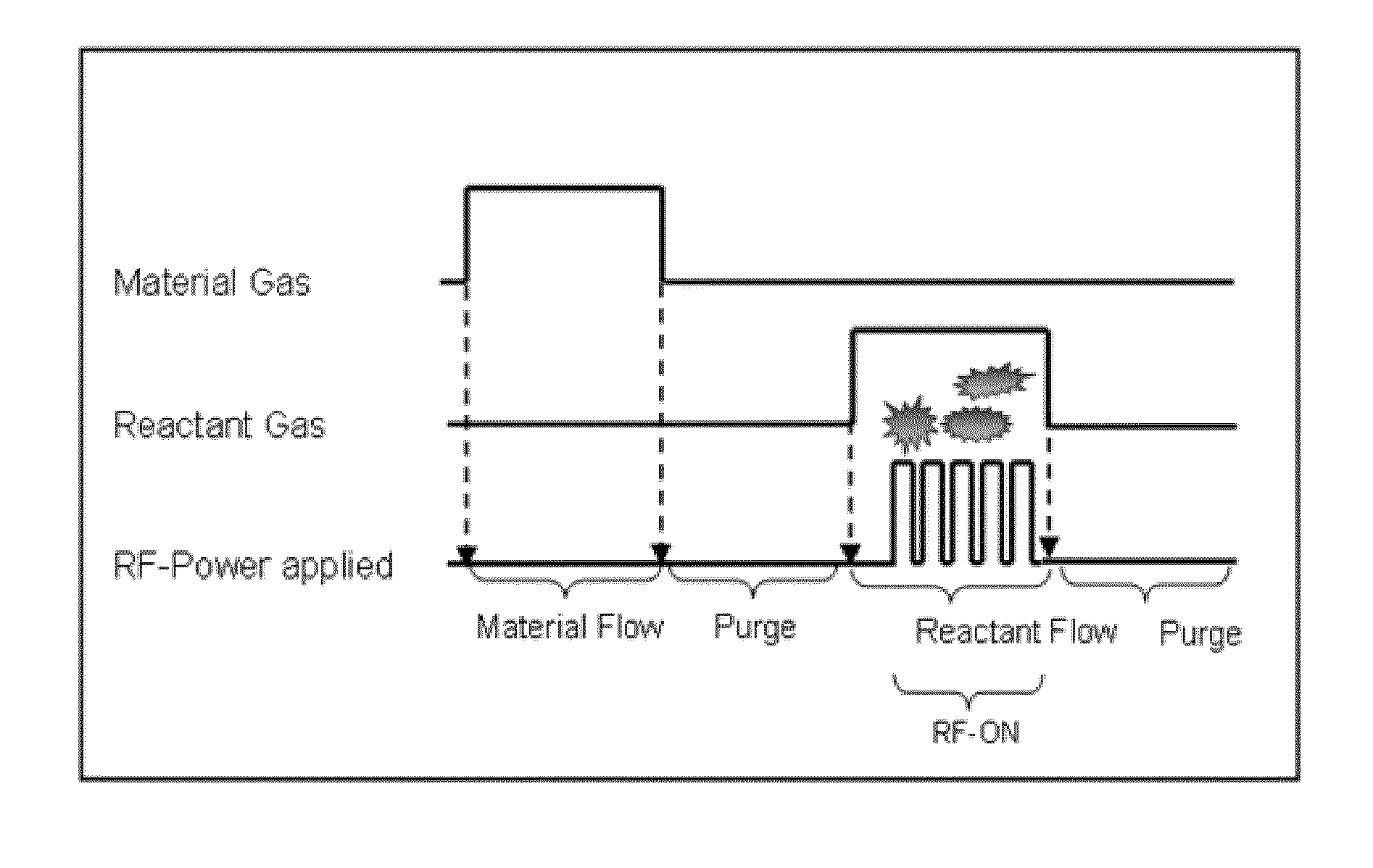
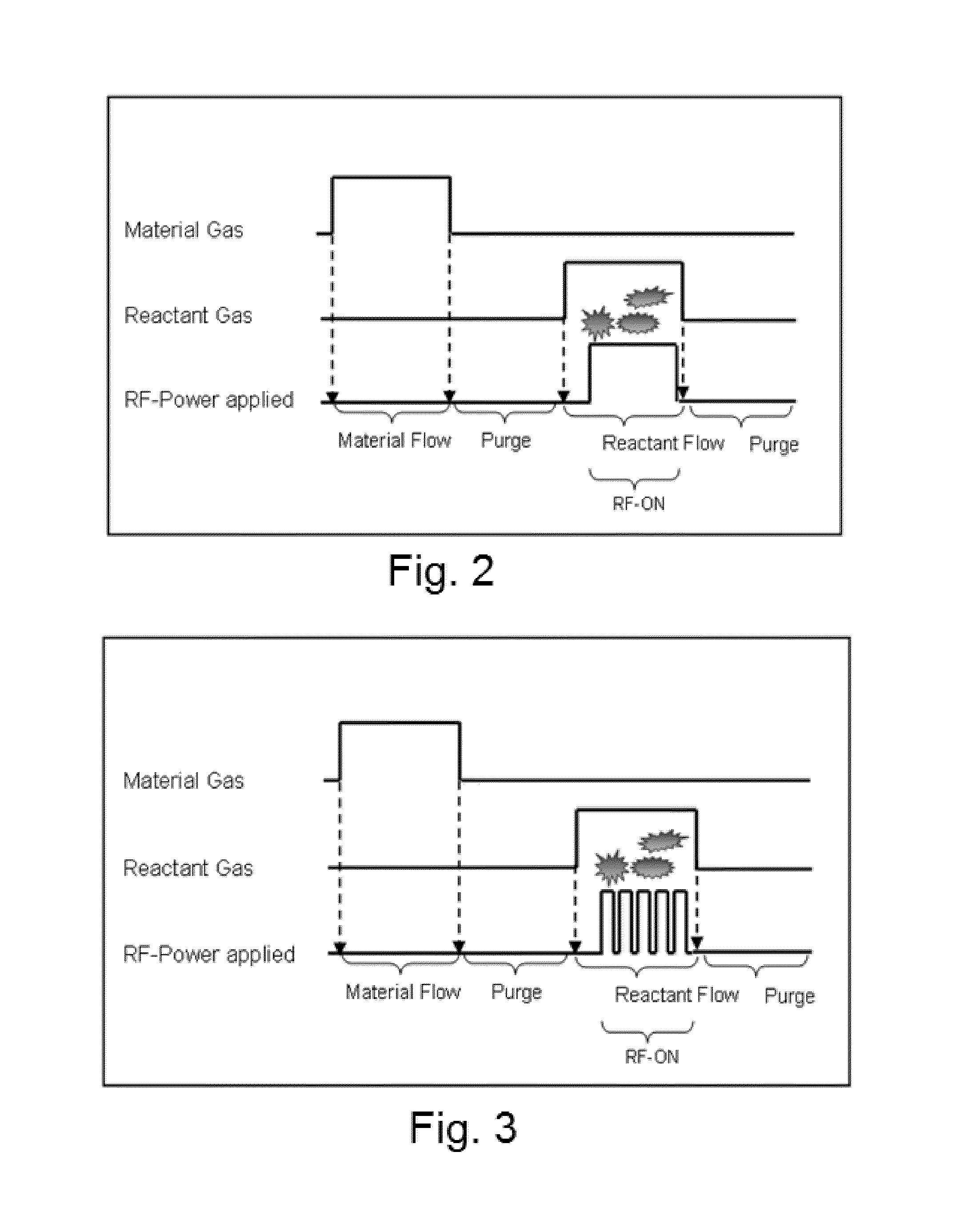
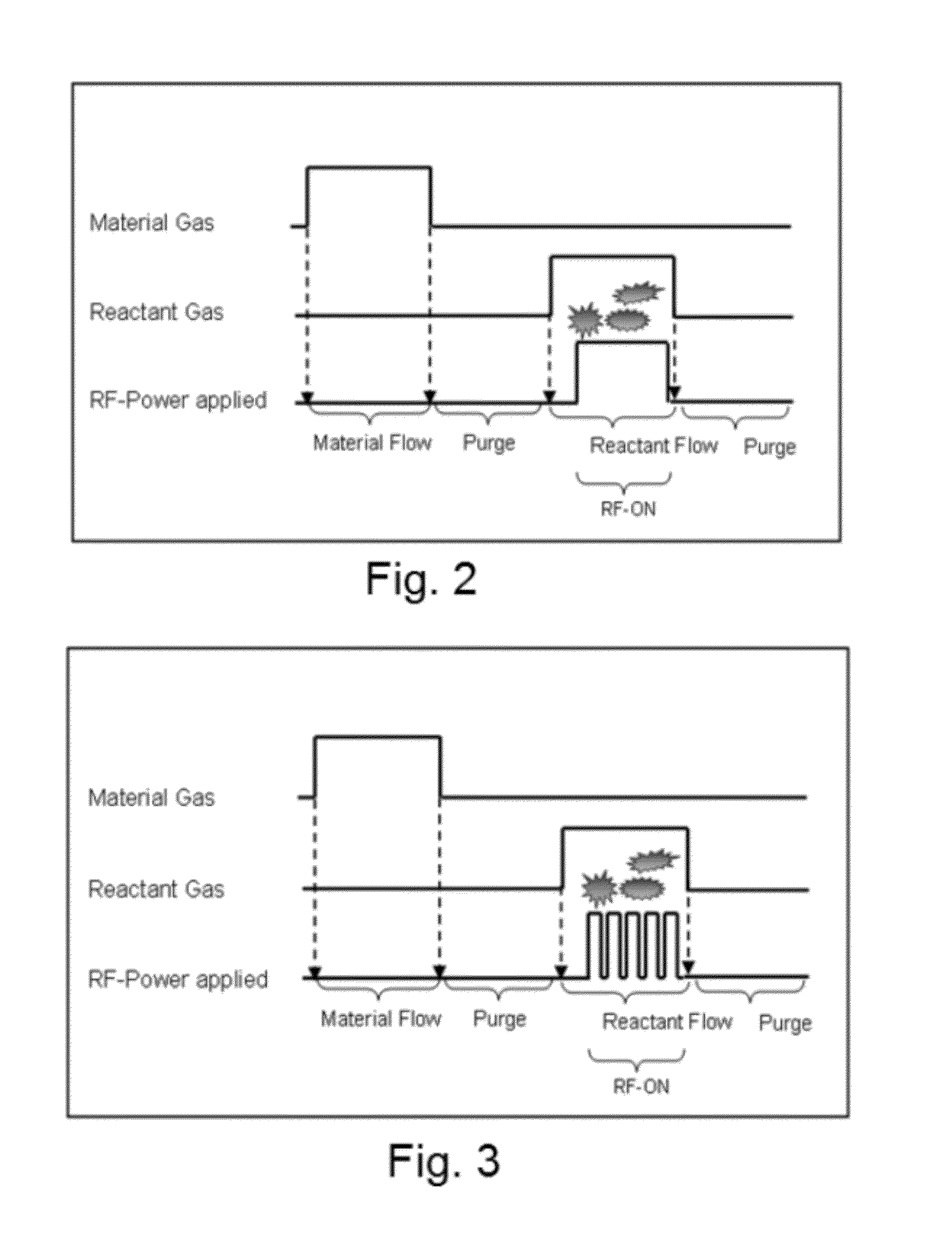
A thin film is formed by alternating multiple times, respectively, a process of adsorbing a precursor onto a substrate and a process of treating the adsorbed surface using a reactant gas and a plasma, wherein the reactant gas is supplied substantially uniformly over the substrate, and the plasma is pulse-time-modulated and applied in the process of supplying the reactant gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Shower plate having different aperture dimensions and/or distributions
ActiveUS8845806B2Improve uniformityUniform propertyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorMechanical engineering
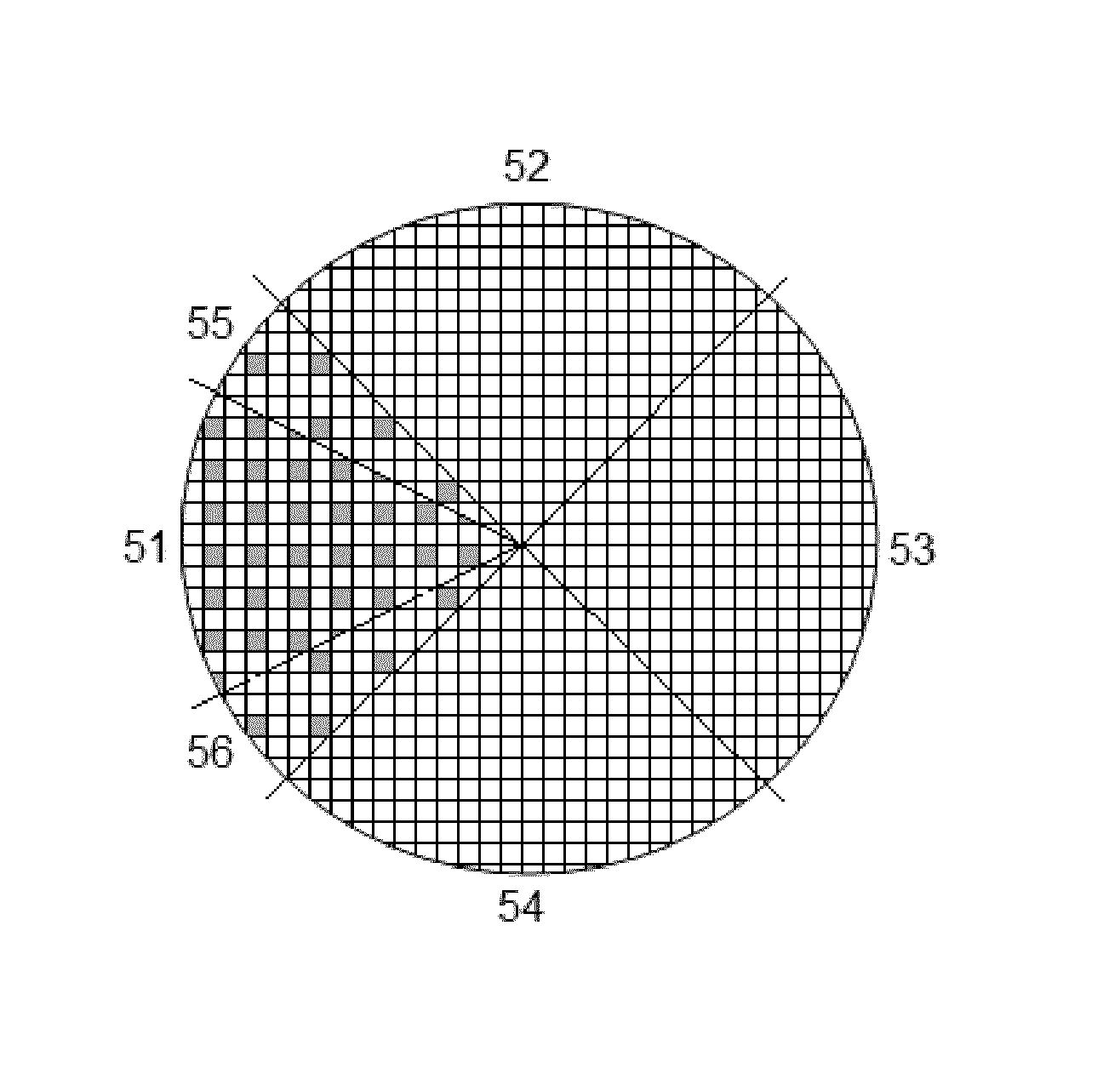
A shower plate is adapted to be attached to the showerhead and includes a front surface adapted to face the susceptor; and a rear surface opposite to the front surface. The shower plate has multiple apertures each extending from the rear surface to the front surface for passing gas therethrough in this direction, and the shower plate has at least one quadrant section defined by radii, wherein the one quadrant section has an opening ratio of a total volume of openings of all the apertures distributed in the section to a total volume of the one quadrant section, which opening ratio is substantially smaller than an opening ratio of another quadrant section of the shower plate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of depositing film by atomic layer deposition with pulse-time-modulated plasma
ActiveUS20120196048A1Effective controlImprove in-plane uniformityPretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingAnalytical chemistryAtomic layer deposition
A thin film is formed by alternating multiple times, respectively, a process of adsorbing a precursor onto a substrate and a process of treating the adsorbed surface using a reactant gas and a plasma, wherein the reactant gas is supplied substantially uniformly over the substrate, and the plasma is pulse-time-modulated and applied in the process of supplying the reactant gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
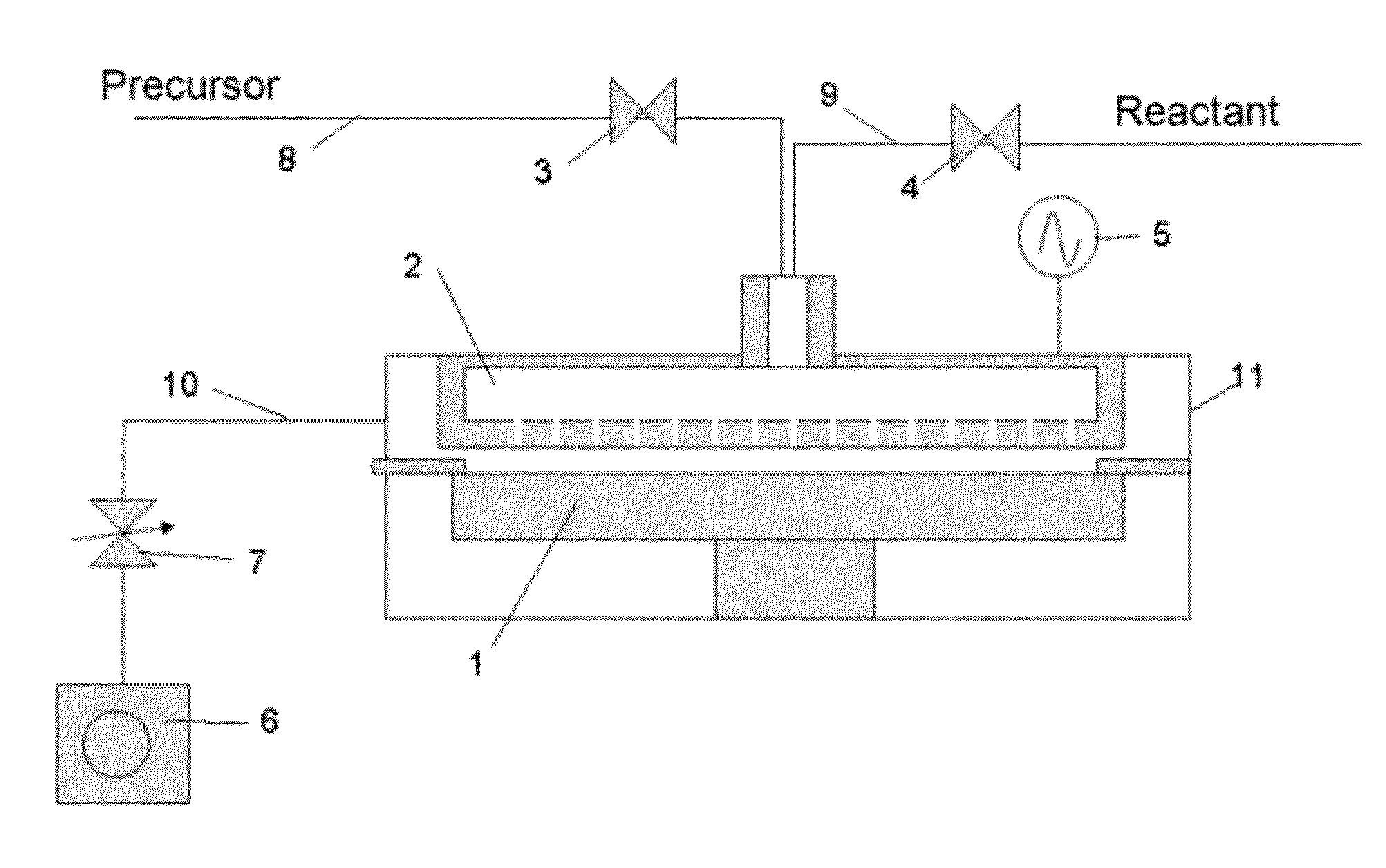
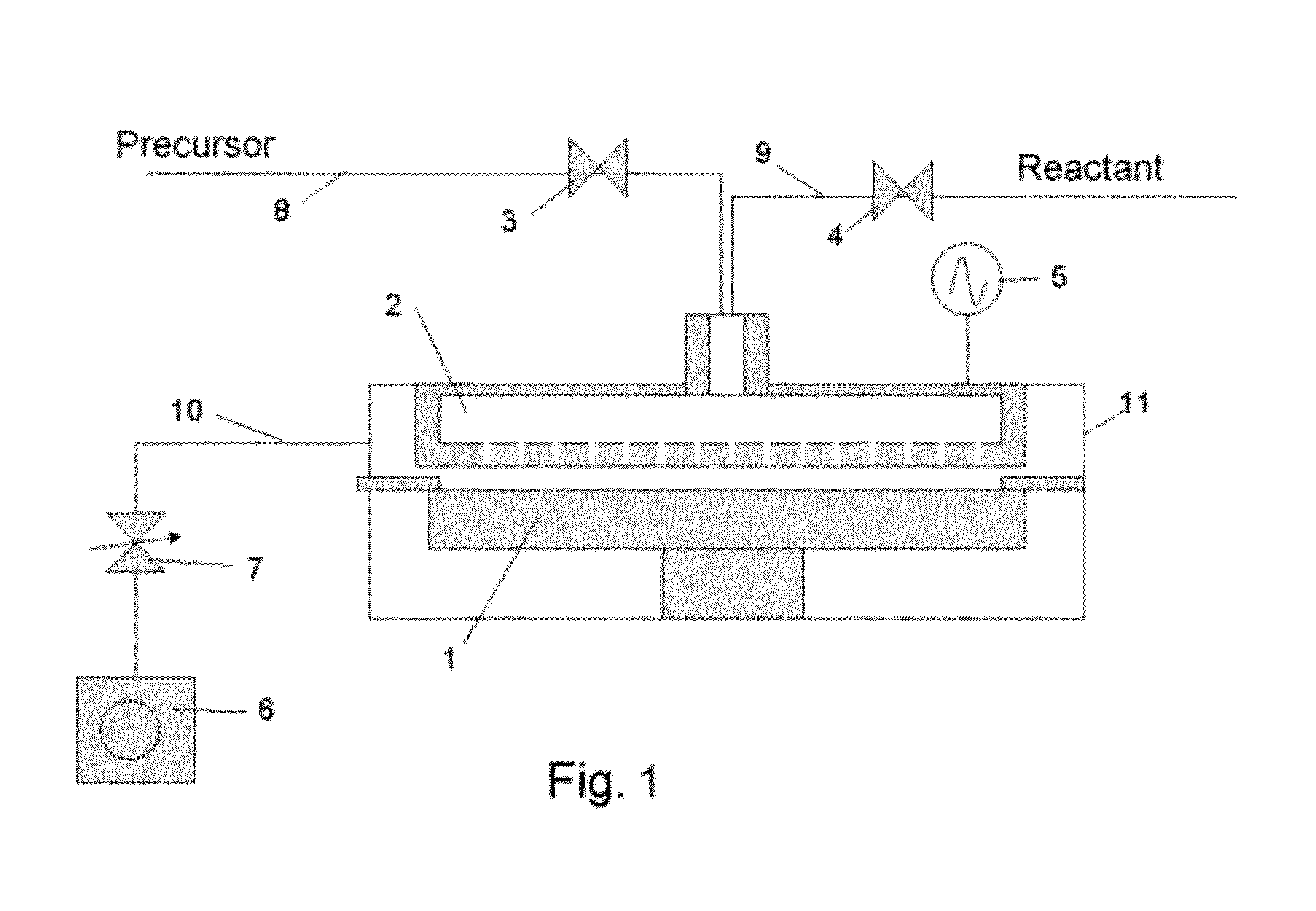
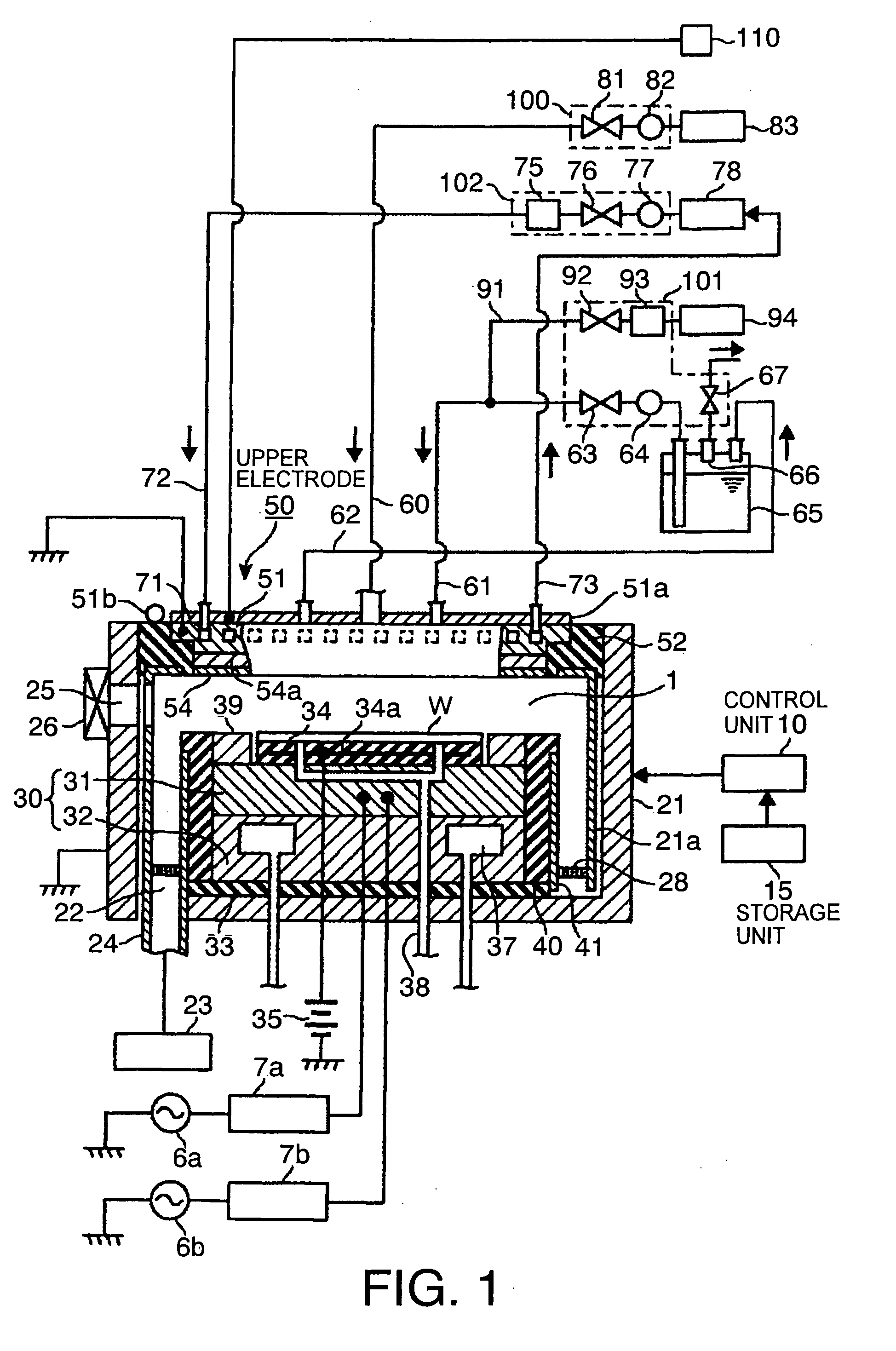
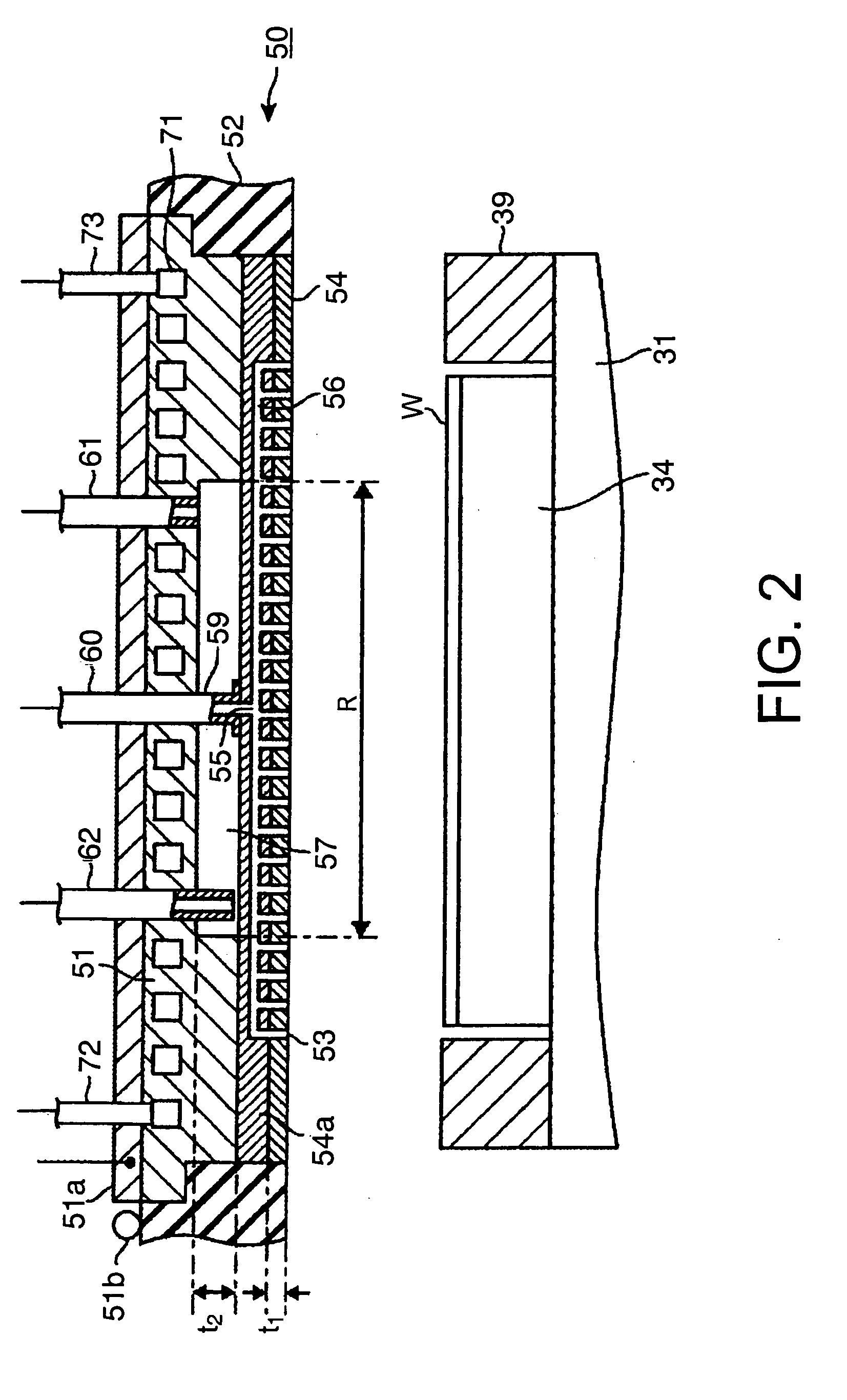
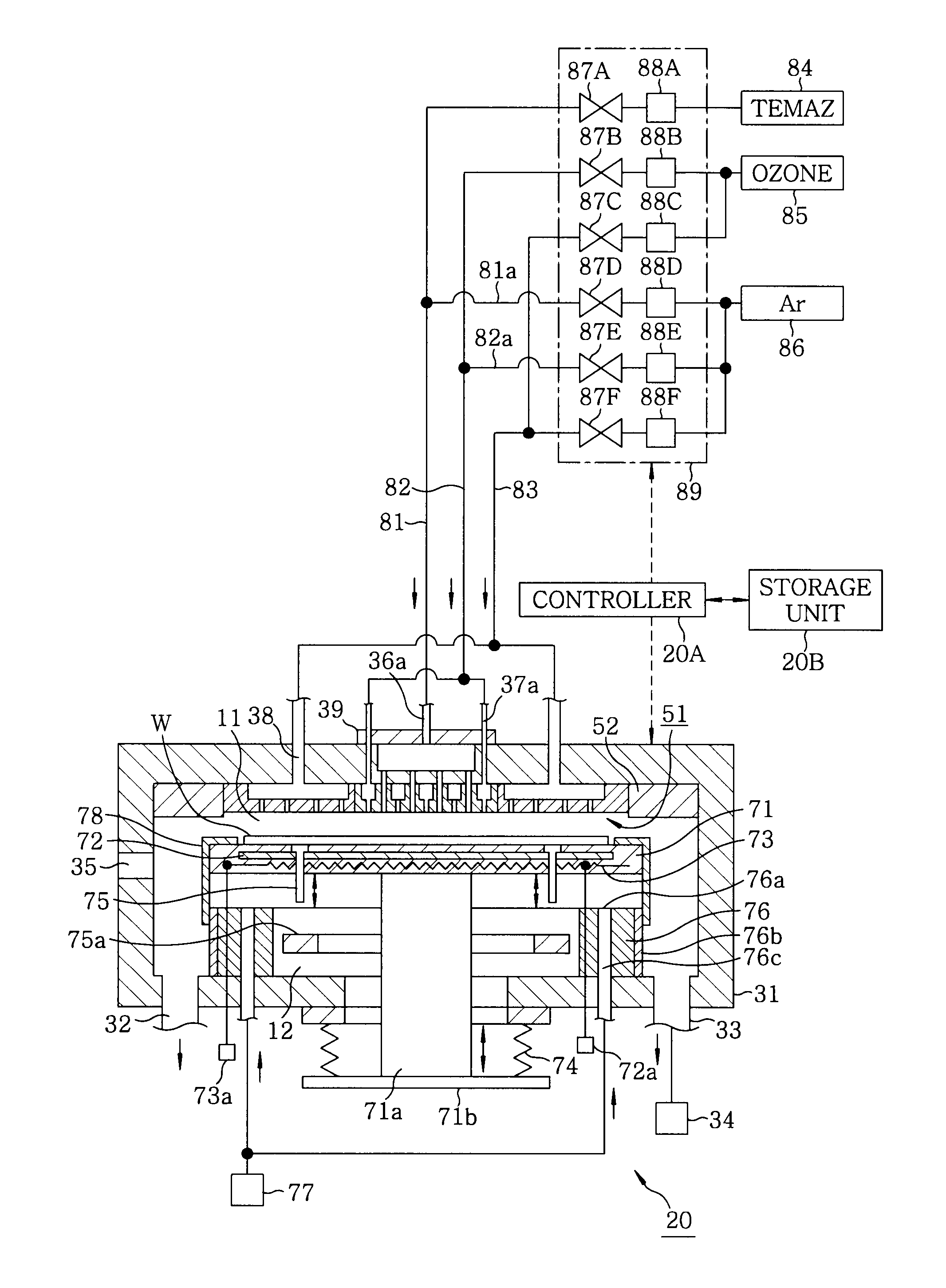
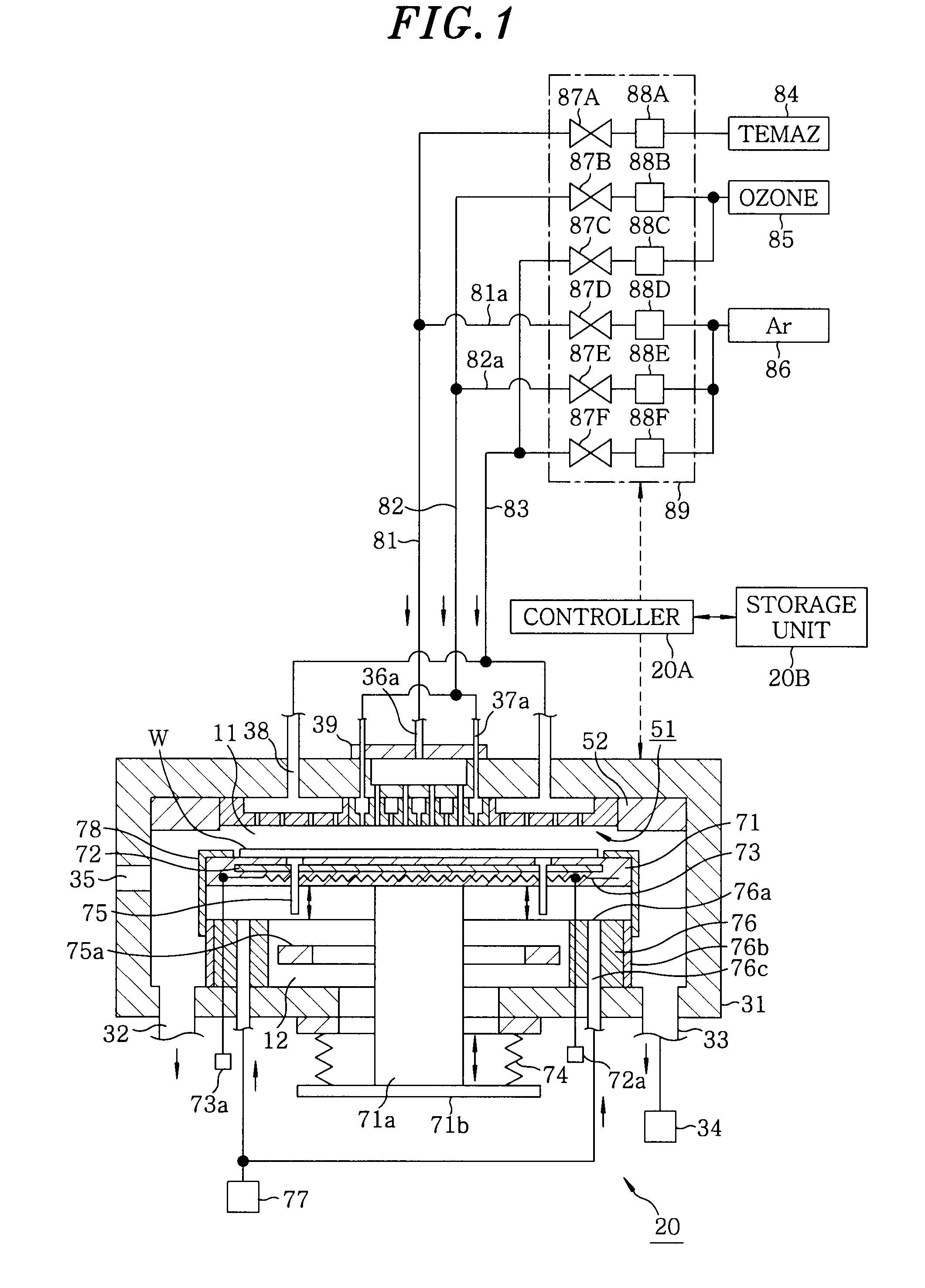
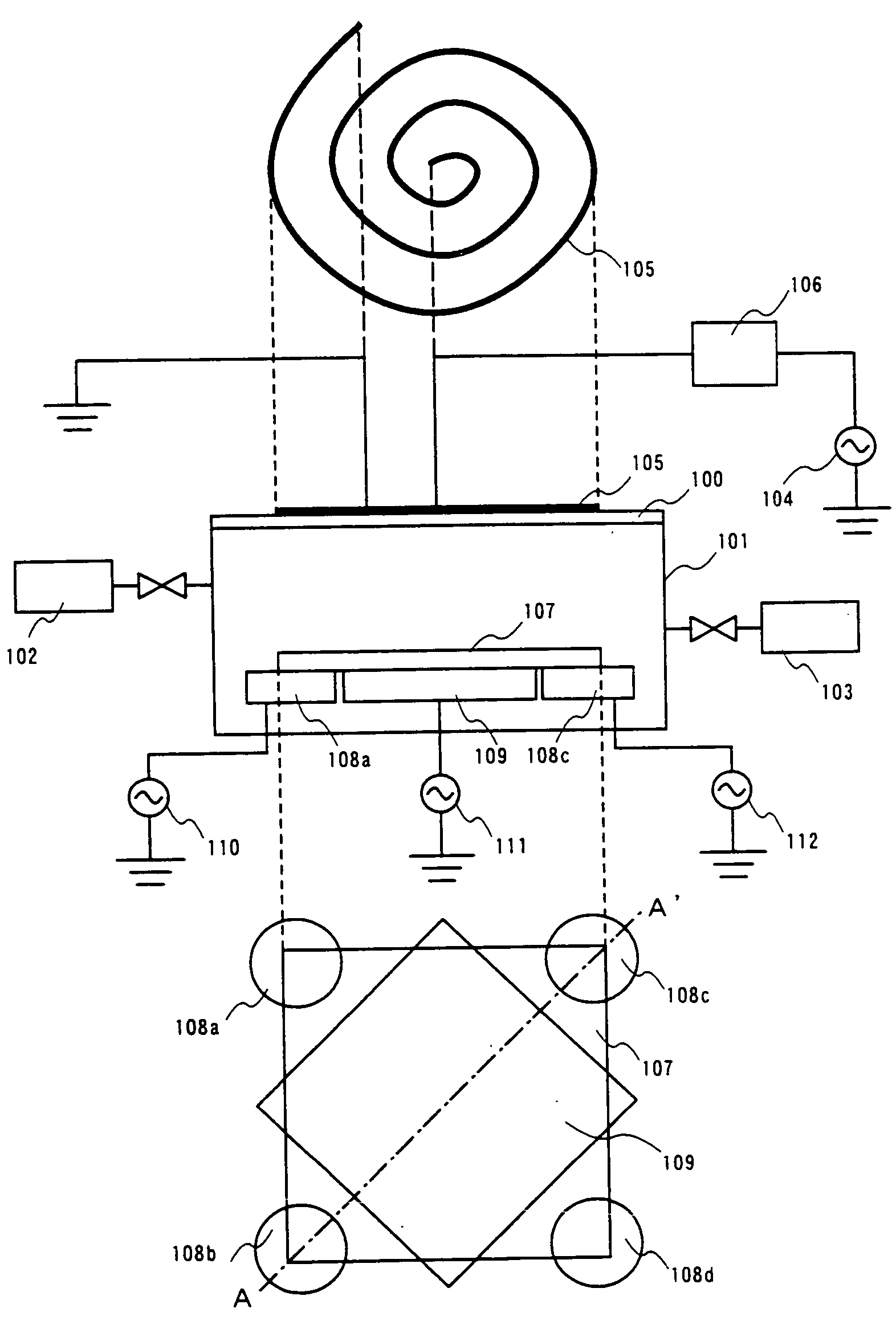
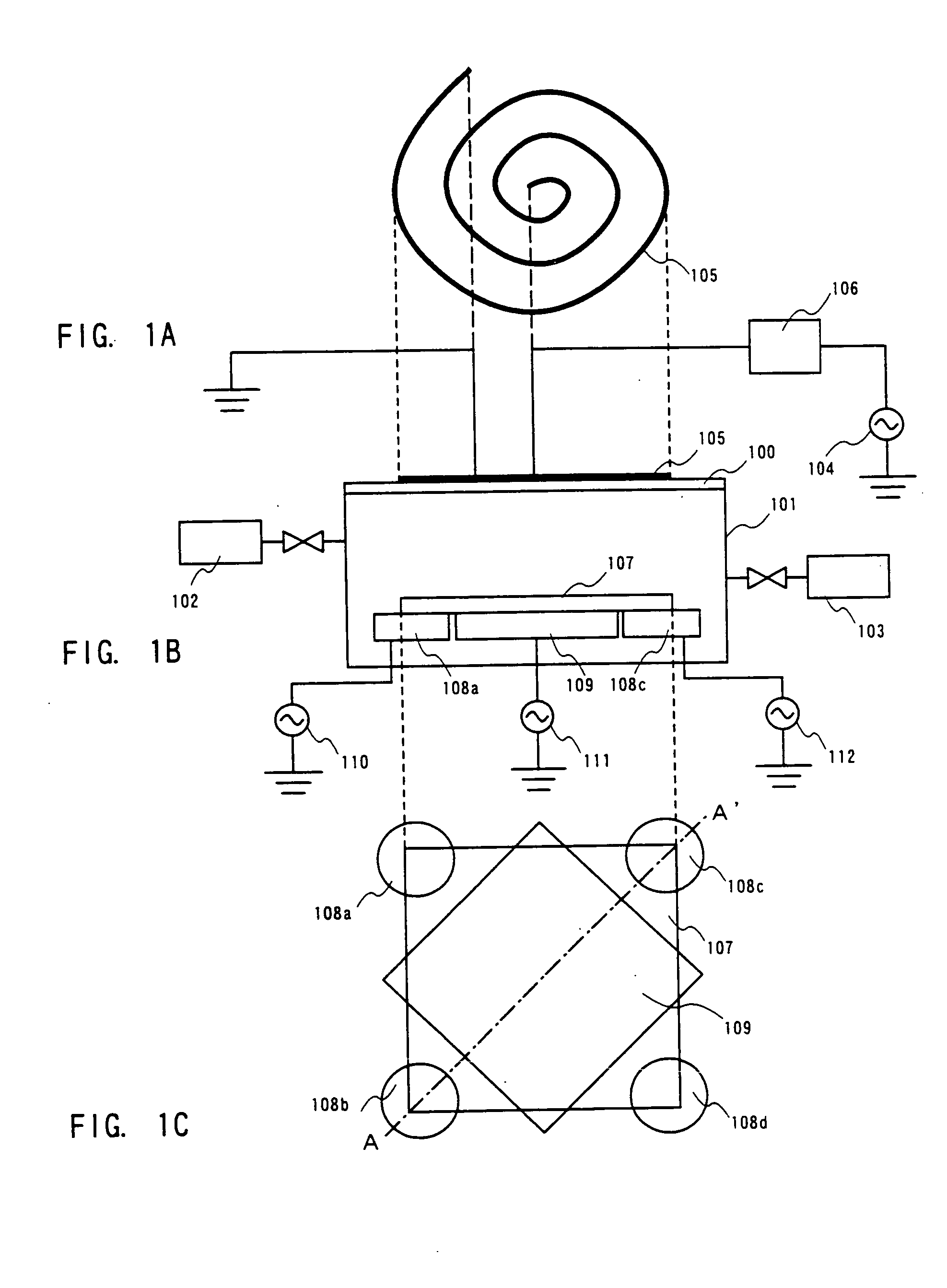
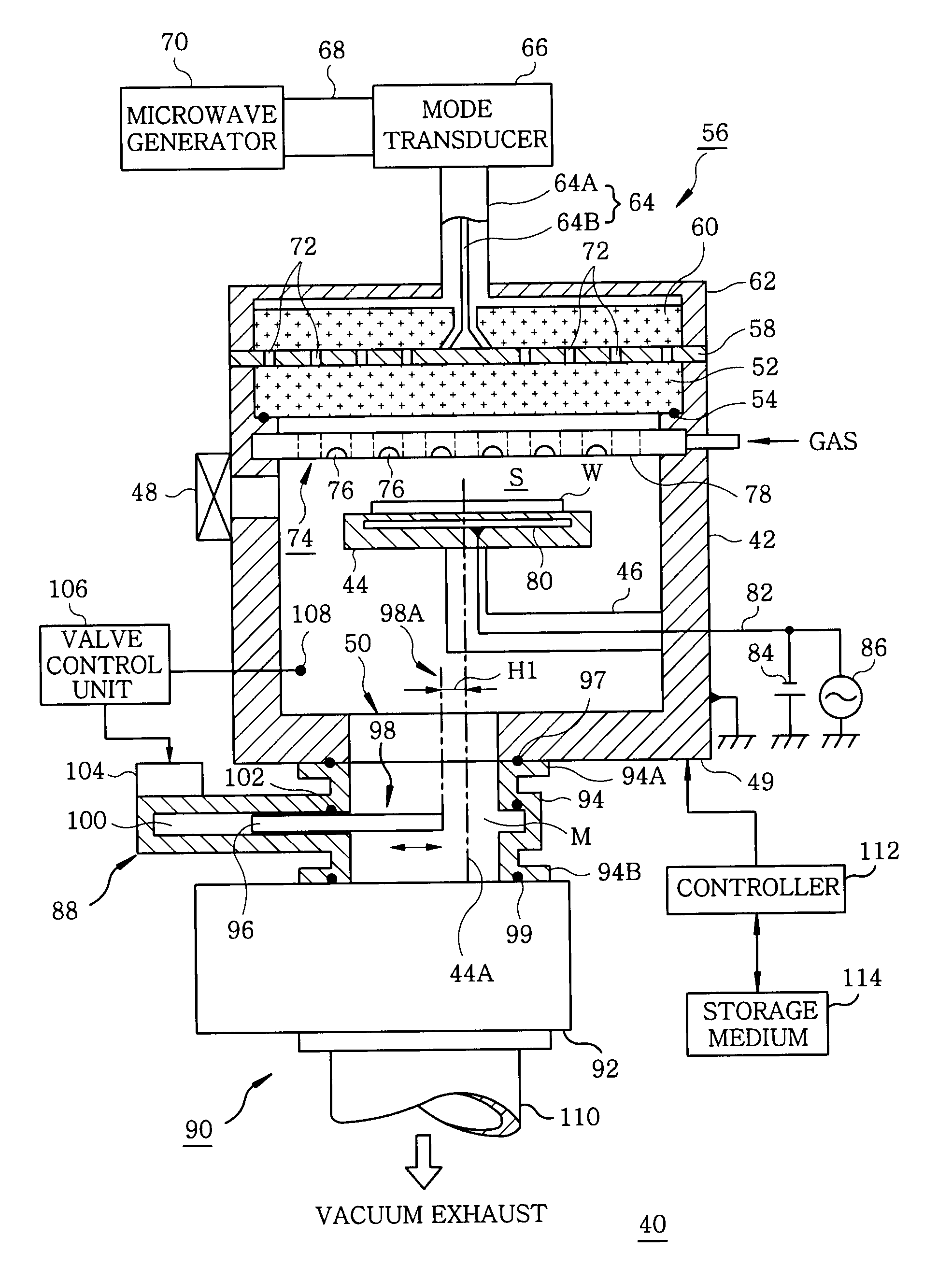
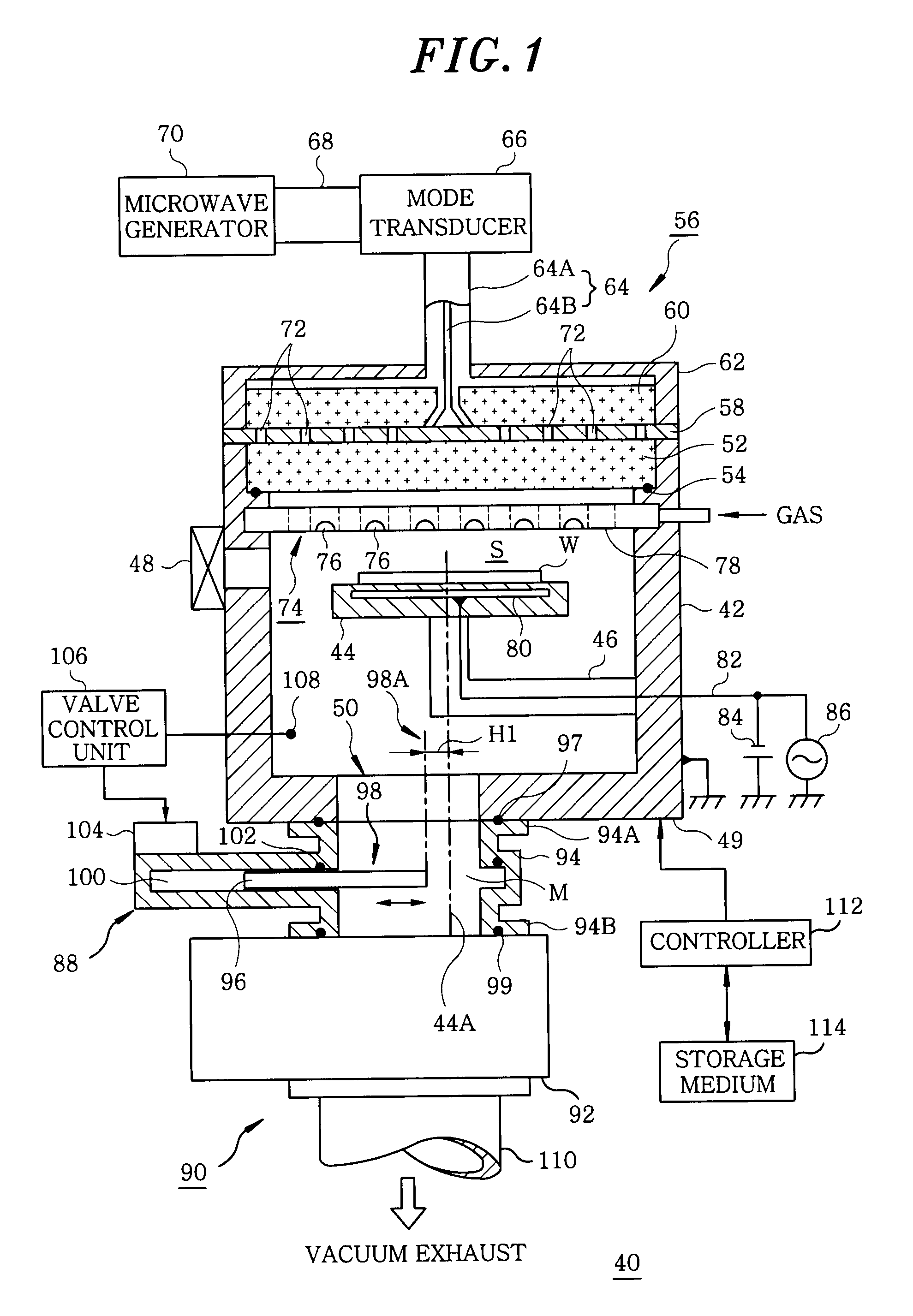
Film forming apparatus, film forming method and storage medium
ActiveUS20100119727A1Reduce gas volumeShorten the timeComputer controlPretreated surfacesEnergy supplyProduct gas
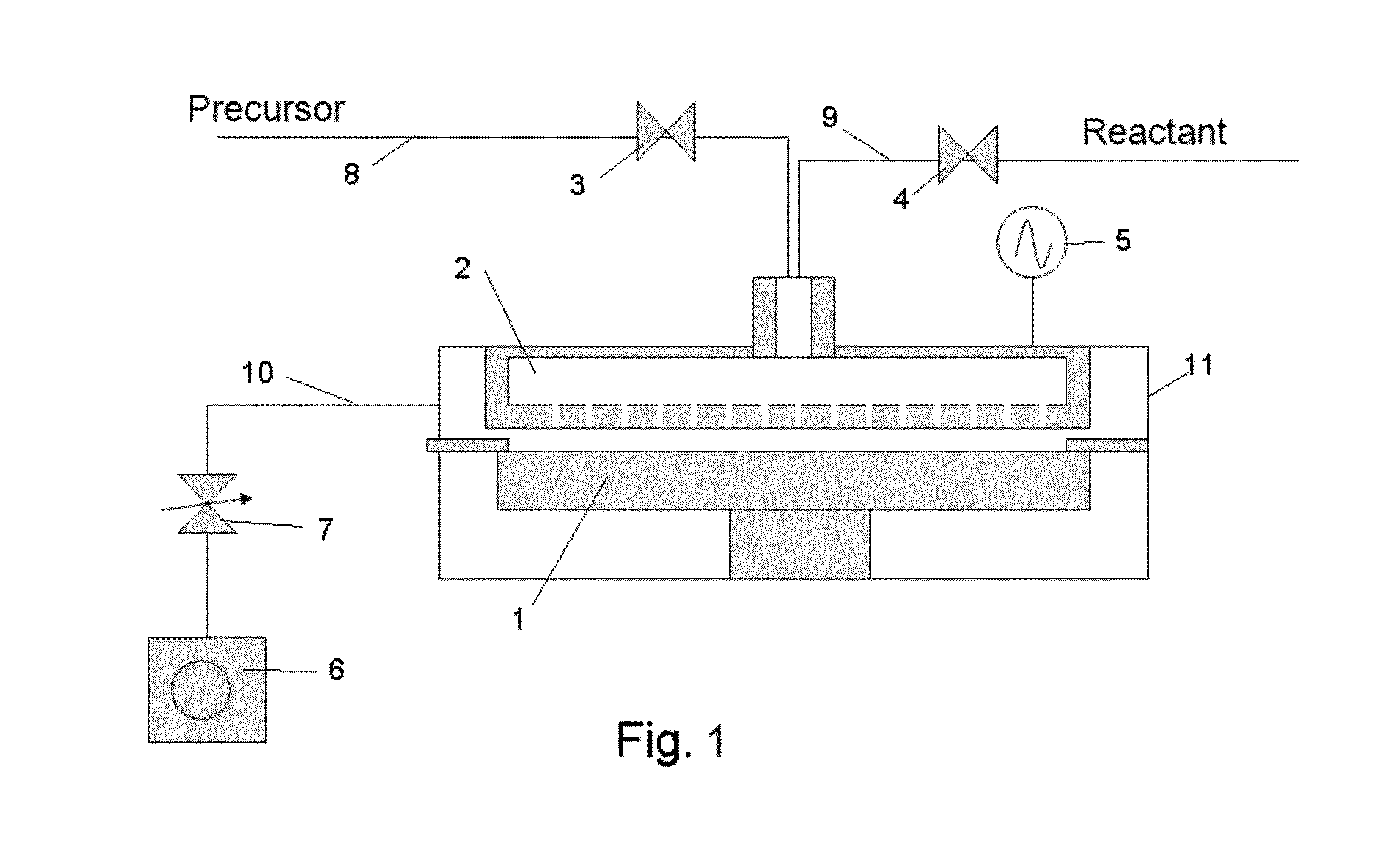
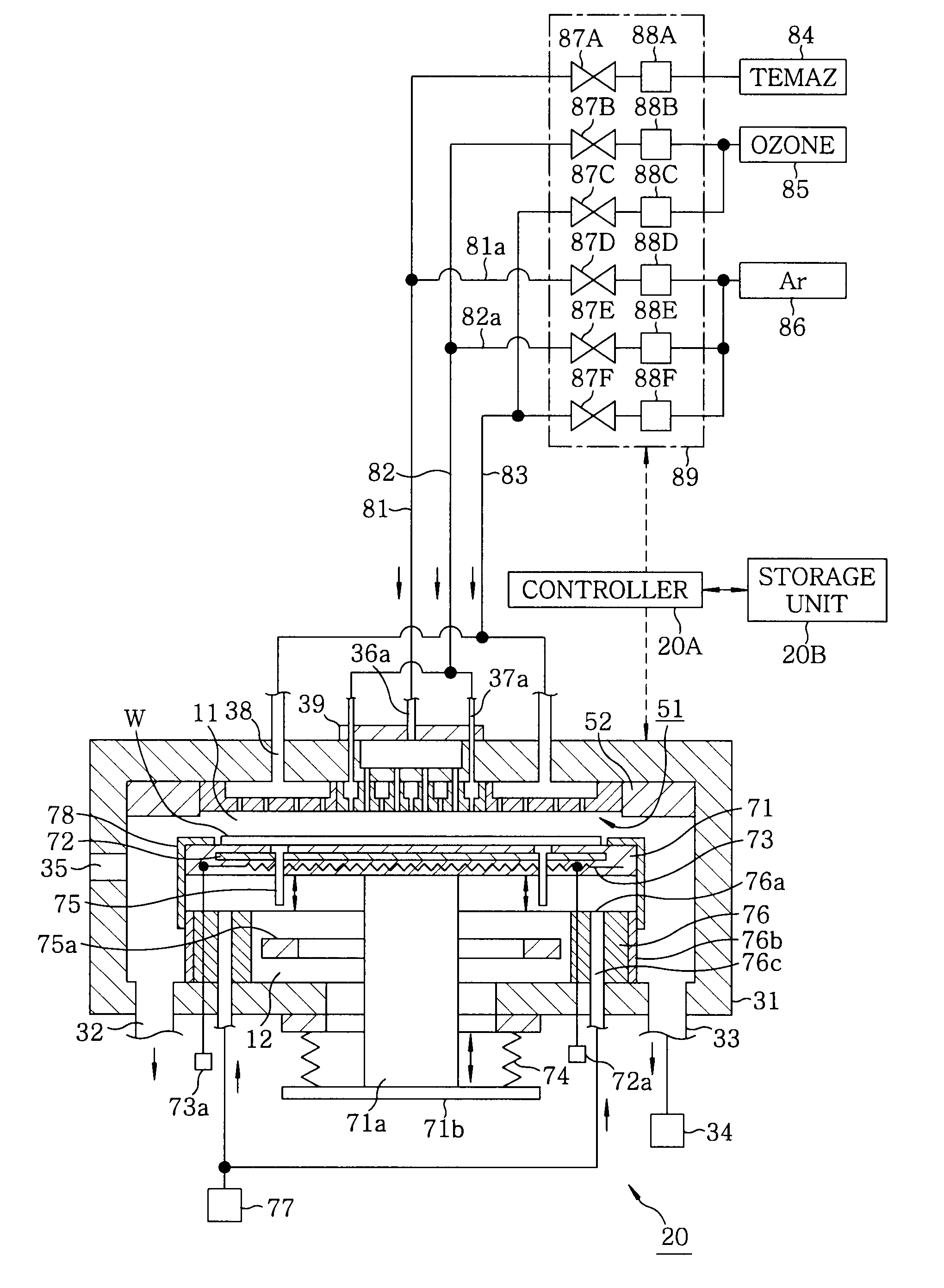
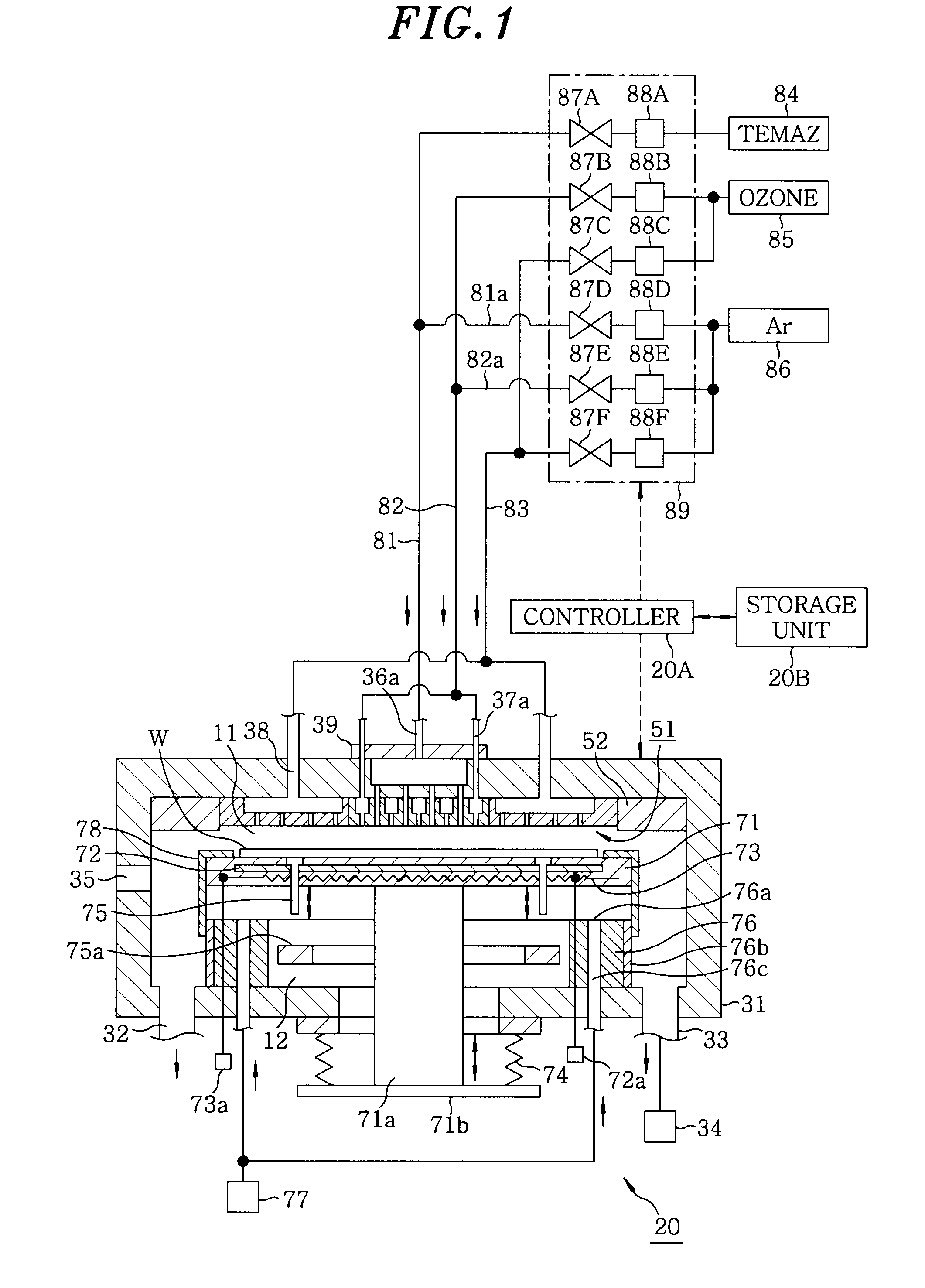
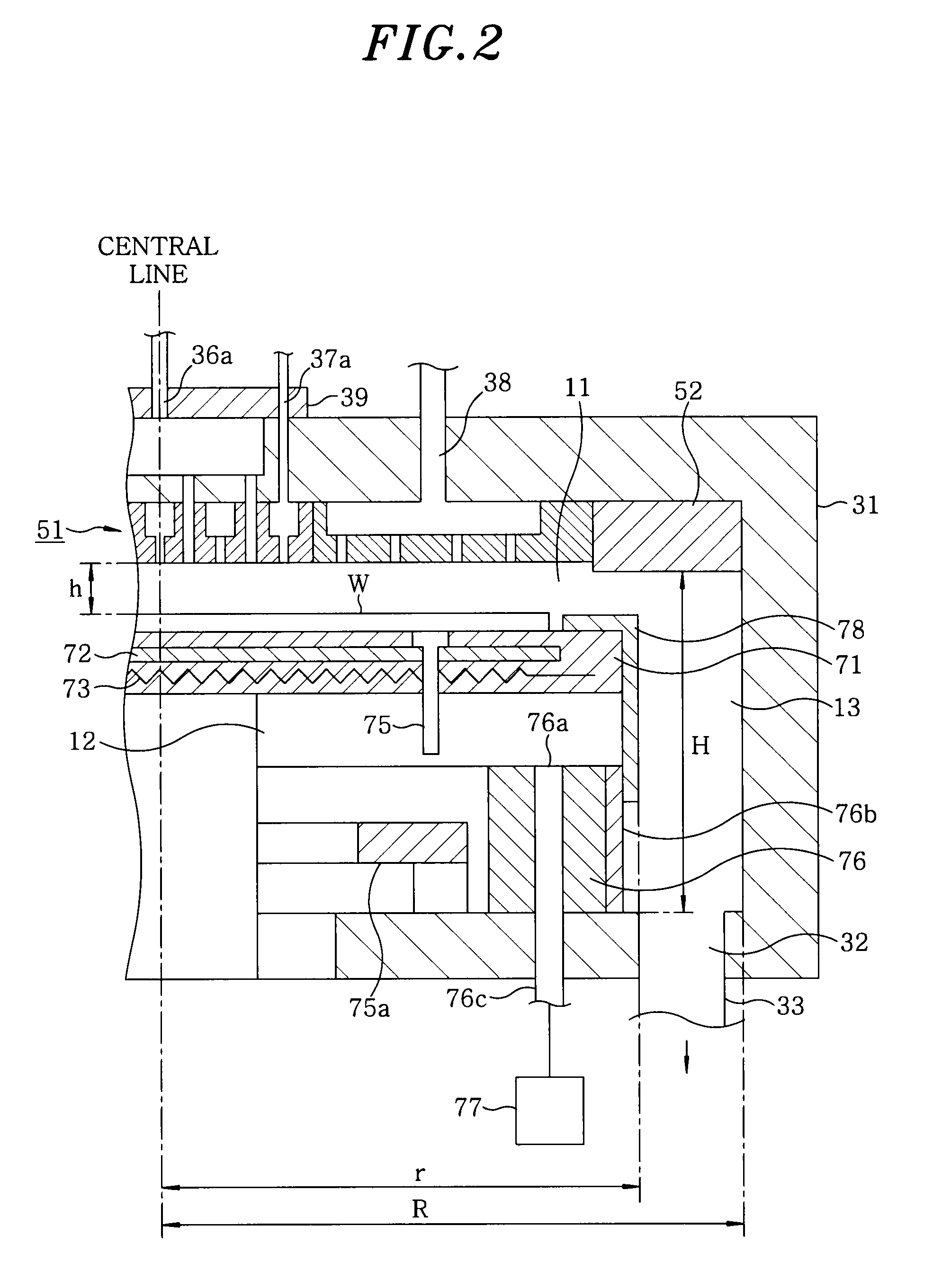
A film forming apparatus includes a processing chamber, and a mounting table disposed in the processing chamber to mount a substrate thereon. The film forming apparatus further includes a gas shower head having gas supply holes and including a central region facing a central portion of the substrate and a peripheral region facing a peripheral portion of the substrate, a first processing gas supply unit for supplying a first processing gas to the central region, a second processing gas supply unit for supplying a second processing gas to the central region, an energy supply unit for supplying energy to react the first processing gas with the second processing gas on the substrate, and a purge gas supply unit for supplying a purge gas to the central region and the peripheral region when one of the first and the second processing gas is switched by the other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
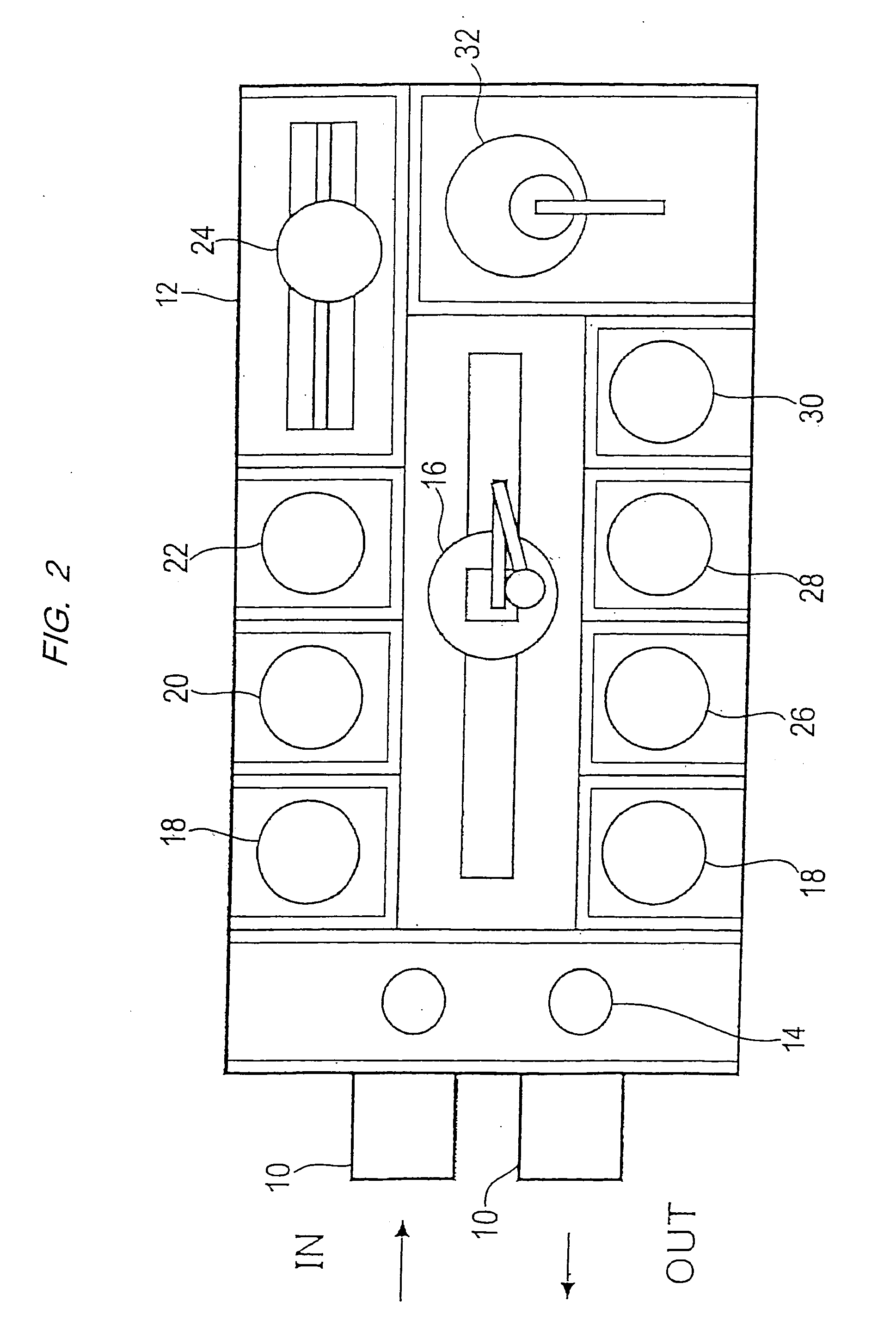
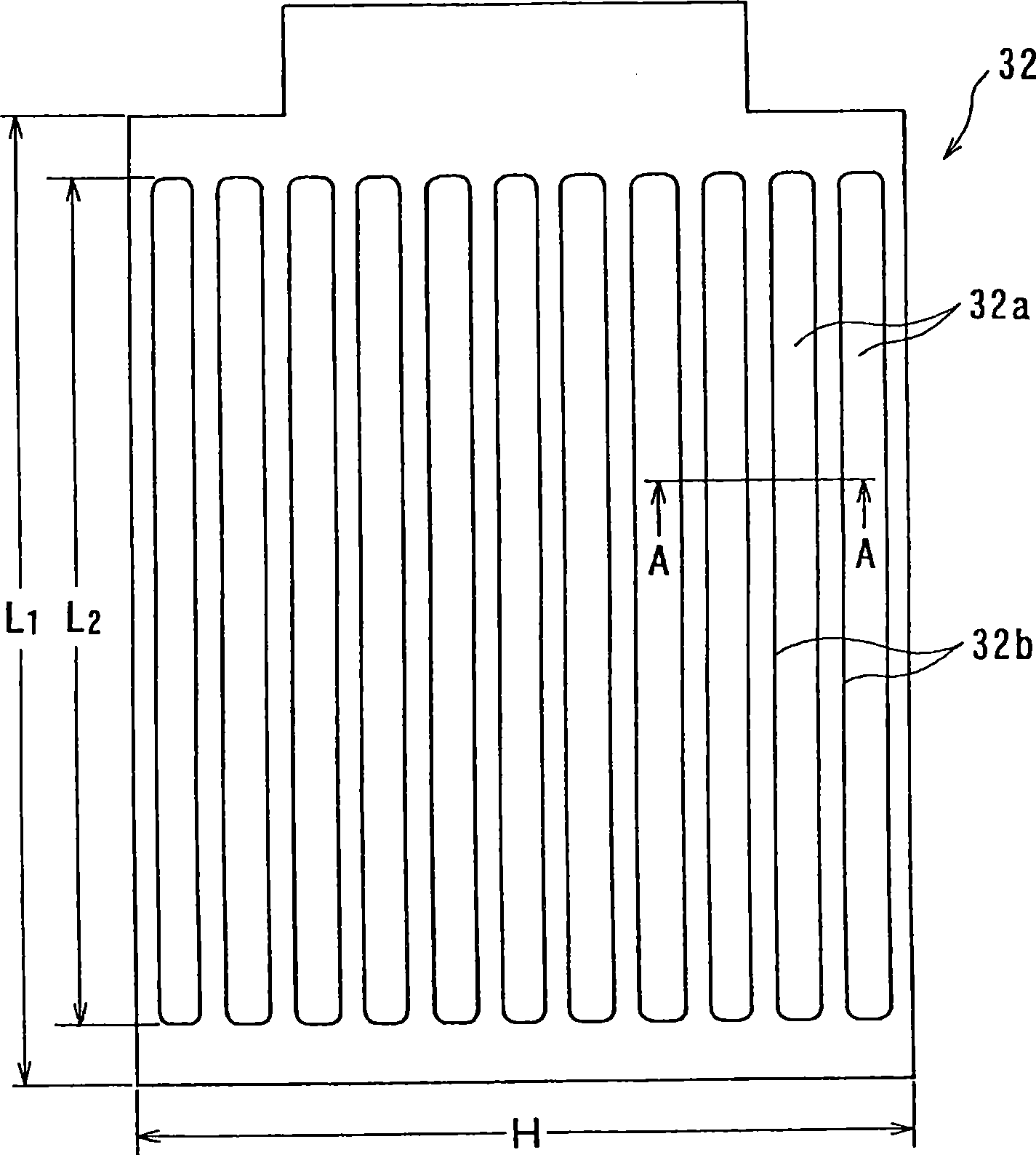
Dry etching apparatus, etching method, and method of forming a wiring
InactiveUS6930047B2Improve in-plane uniformityUniformity of selection ratioTransistorElectric discharge tubesIn planeHigh frequency power
An etching apparatus is provided, in which a plurality of electrodes are disposed for placing a substrate, high-frequency power sources as many as electrodes are provided, and the electrodes and the high-frequency power sources are connected to each other independently. Among a plurality of electrodes, a high-frequency power applied to an electrode disposed below the central portion of the substrate and a high-frequency power applied to electrodes disposed below comer portions of the substrate are controlled respectively, whereby in-plane uniformity of etching can be enhanced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electrode for plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method and storage medium
InactiveUS20090221151A1Uniformity of intensity can be improvedHigh in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricIn plane
The present invention provides an upper electrode used in an etching apparatus and the etching apparatus including the upper electrode, both of which can properly reduce intensity of electric field of plasma around a central portion of a substrate to be processed, thus enhancing in-plane uniformity of a plasma process. In this apparatus, a recess, serving as a space for allowing a dielectric to be injected therein, is provided around a central portion of the upper electrode. A dielectric supply passage configured for supplying the dielectric into the space and a dielectric discharge passage configured for discharging the dielectric from the space are connected with the space, respectively. With such configuration, the dielectric can be controllably supplied into the recess, such that in-plane distribution of the intensity of the electric field can be uniformed, corresponding to in-plane distribution of the intensity of the electric field of the plasma generated under various process conditions, such as a kind of each wafer that will be etched, each processing gas that will be used, and the like.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Lighting device
ActiveUS20050258436A1Improve in-plane uniformitySmall and lightPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusEffect lightVoltage drop
An object of the invention is to provide a lighting device which can suppress luminance nonuniformity in a light emitting region when the lighting device has large area. A layer including a light emitting material is formed between a first electrode and a second electrode, and a third electrode is formed to connect to the first electrode through an opening formed in the second electrode and the layer including a light emitting material. An effect of voltage drop due to relatively high resistivity of the first electrode can be reduced by electrically connecting the third electrode to the first electrode through the opening.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Plating apparatus and plating method
InactiveUS20070238265A1Improve thickness uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsElectrolysis componentsHigh resistanceEngineering
A plating apparatus can form a plated film having a more uniform thickness over an entire surface of a substrate and can securely fill interconnect recesses with the metal without forming voids in the embedded metal even when the substrate has a high sheet resistance in the surface. The plating apparatus includes a substrate holder for holding a substrate, a cathode portion including a cathode for contact with the substrate held by the substrate holder to feed electricity to the substrate, and an anode, partly or wholly having a high resistance, disposed opposite a surface of the substrate held by the substrate holder, wherein plating of the surface of the substrate is carried out while filling between the anode and the substrate held by the substrate holder with a plating solution.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Light-emitting device, method for producing same, and display
InactiveUS20070007538A1Increase brightnessImprove in-plane uniformityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight emitting device
Disclosed herein is a light-emitting device comprising a transparent or semi-transparent first substrate, a second substrate provided opposite to the first substrate, a transparent or semi-transparent first electrode provided on the first substrate, a second electrode provided on the second substrate so as to be opposite to the first electrode, and a light-emitting layer which contains a metal oxide semiconductor porous body, by the surface of which an organic light-emitting material is supported, and is provided between the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
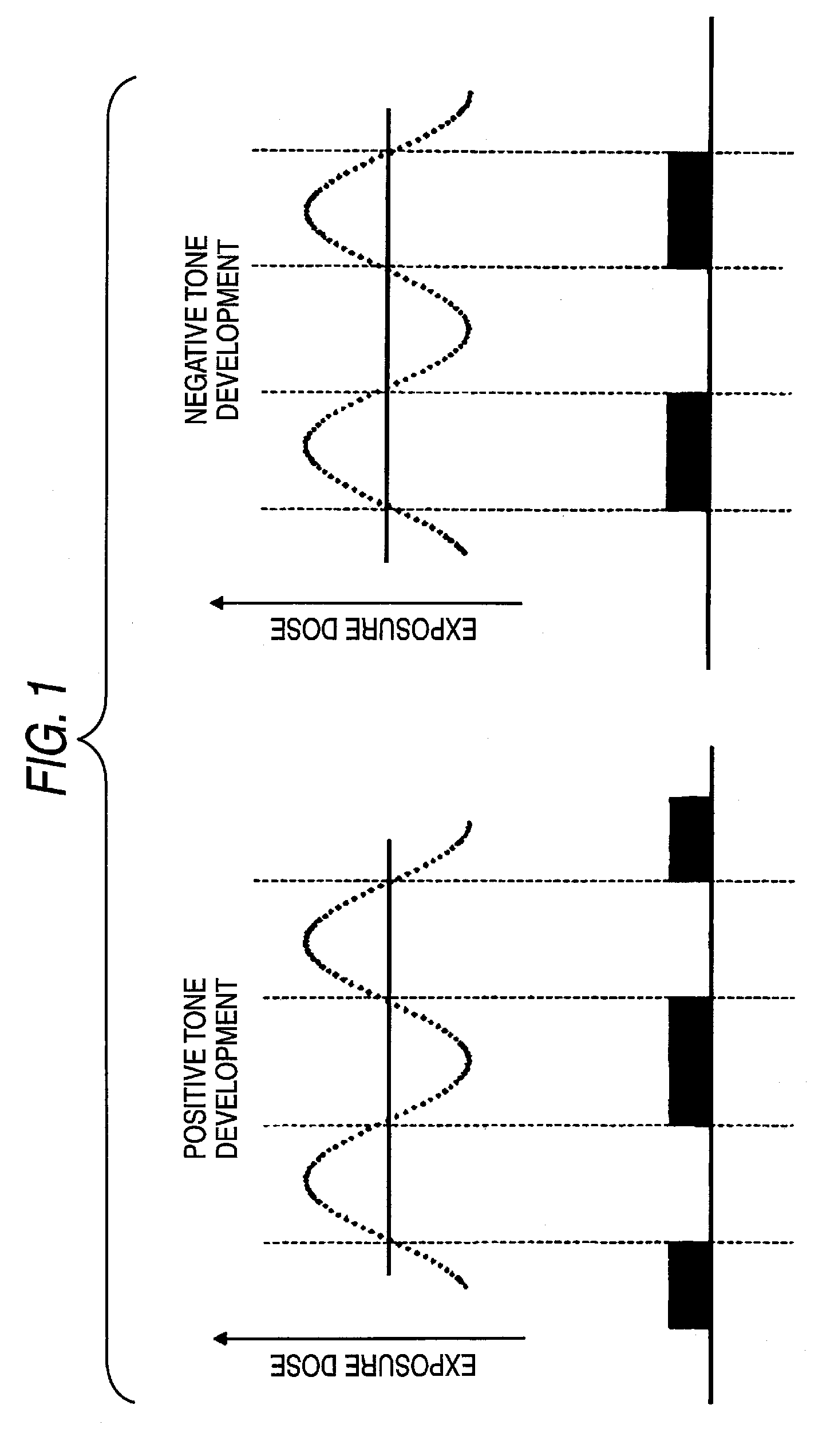
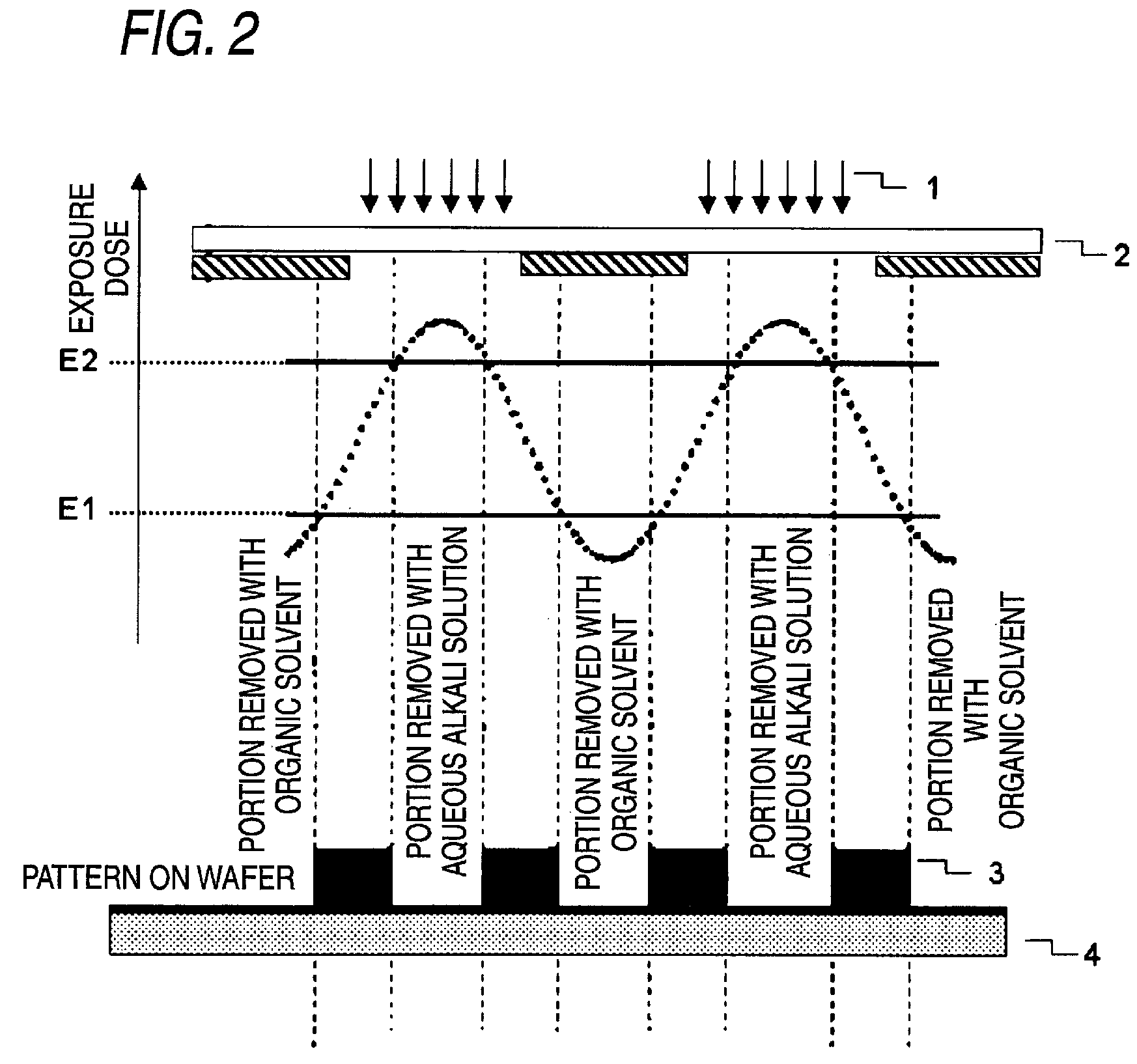
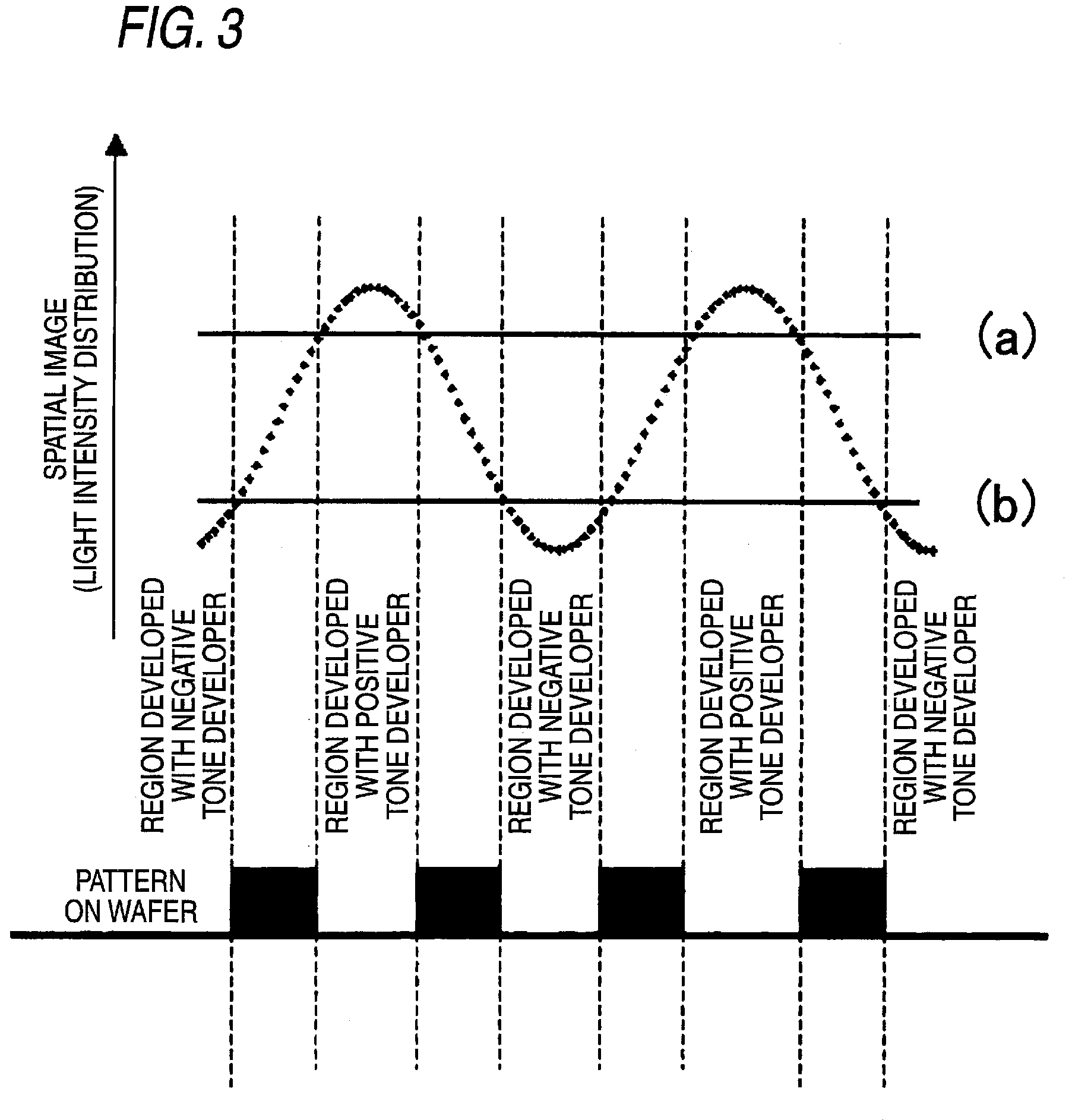
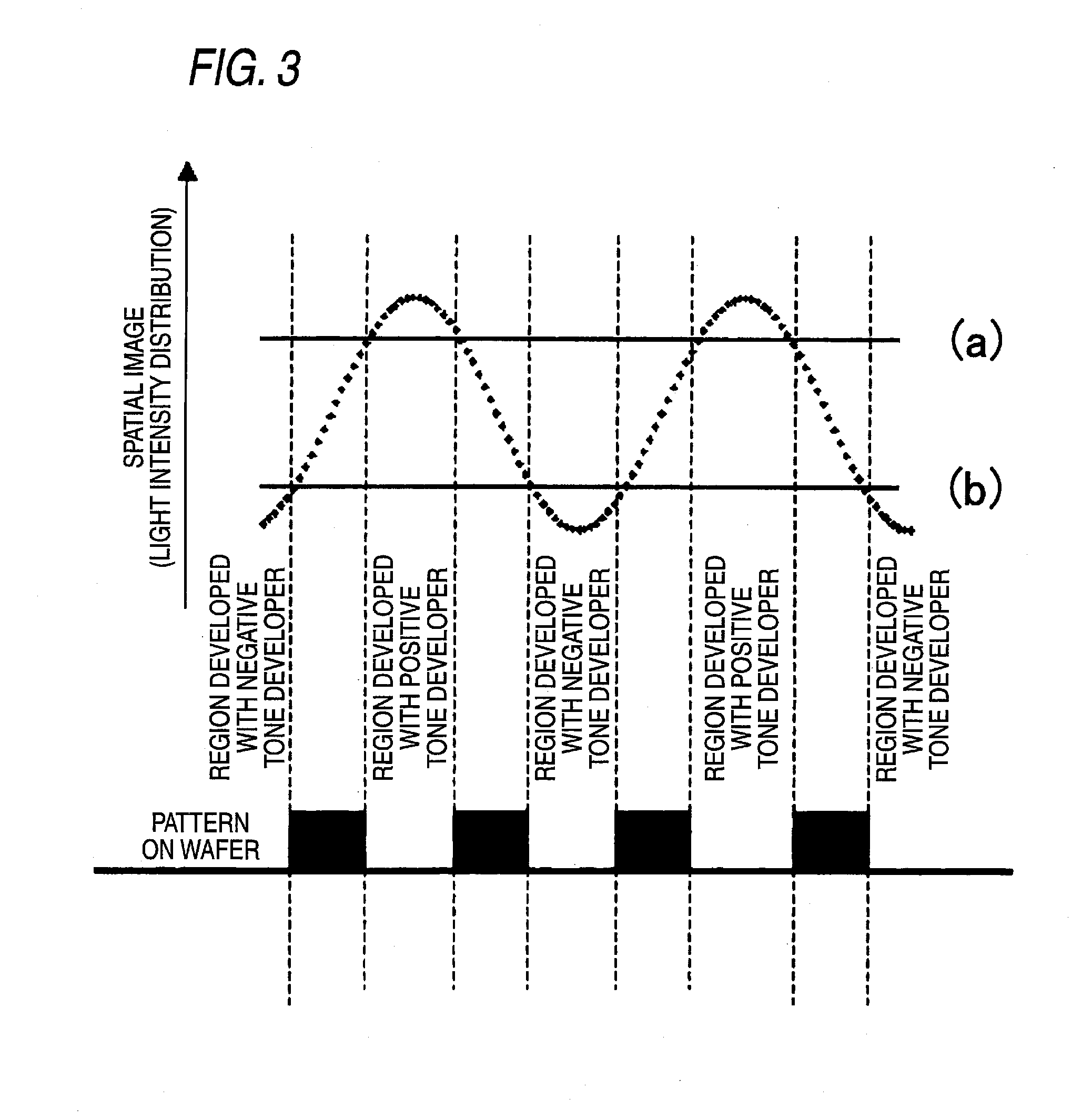
Resist composition for negative tone development and pattern forming method using the same
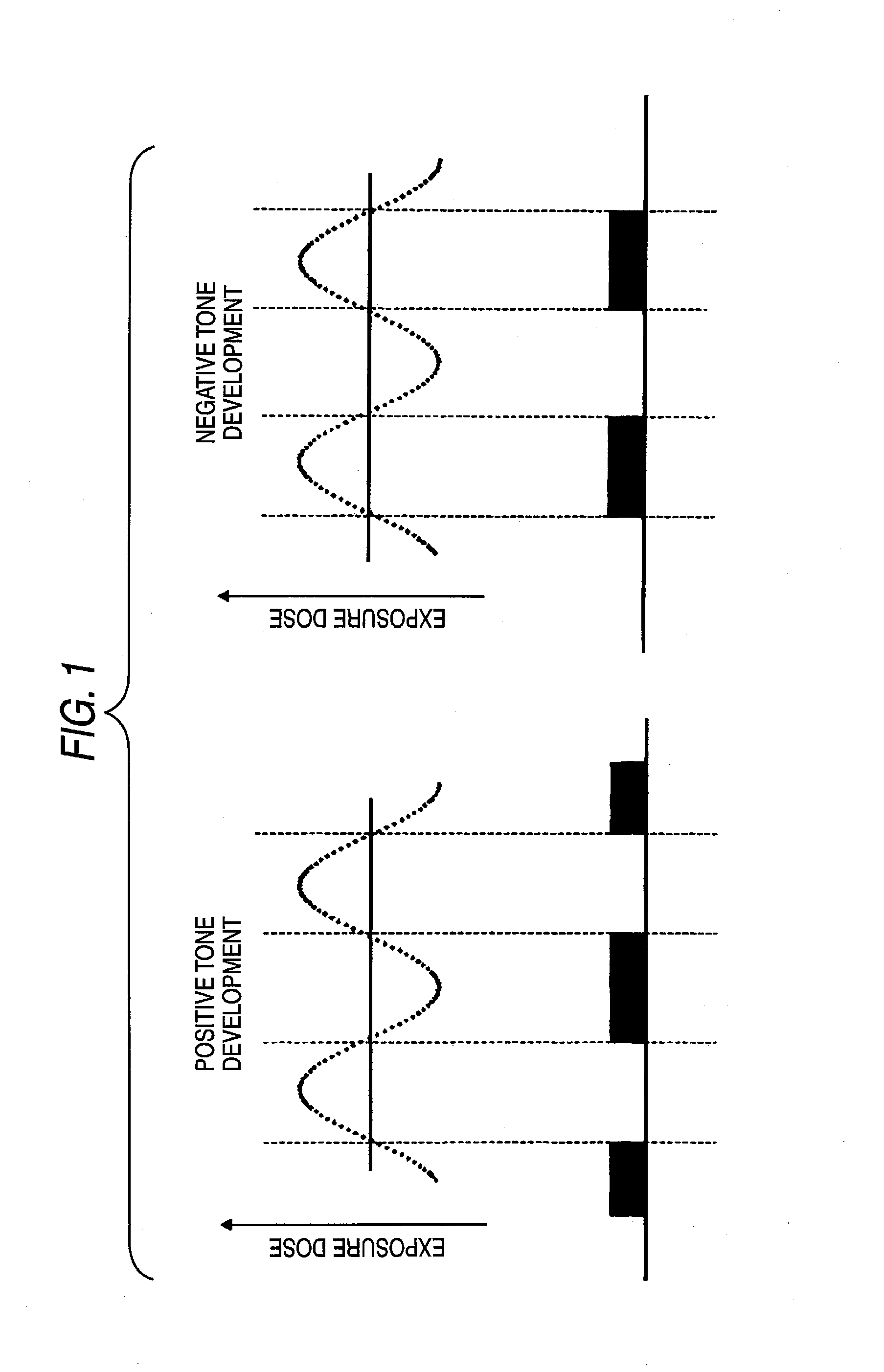
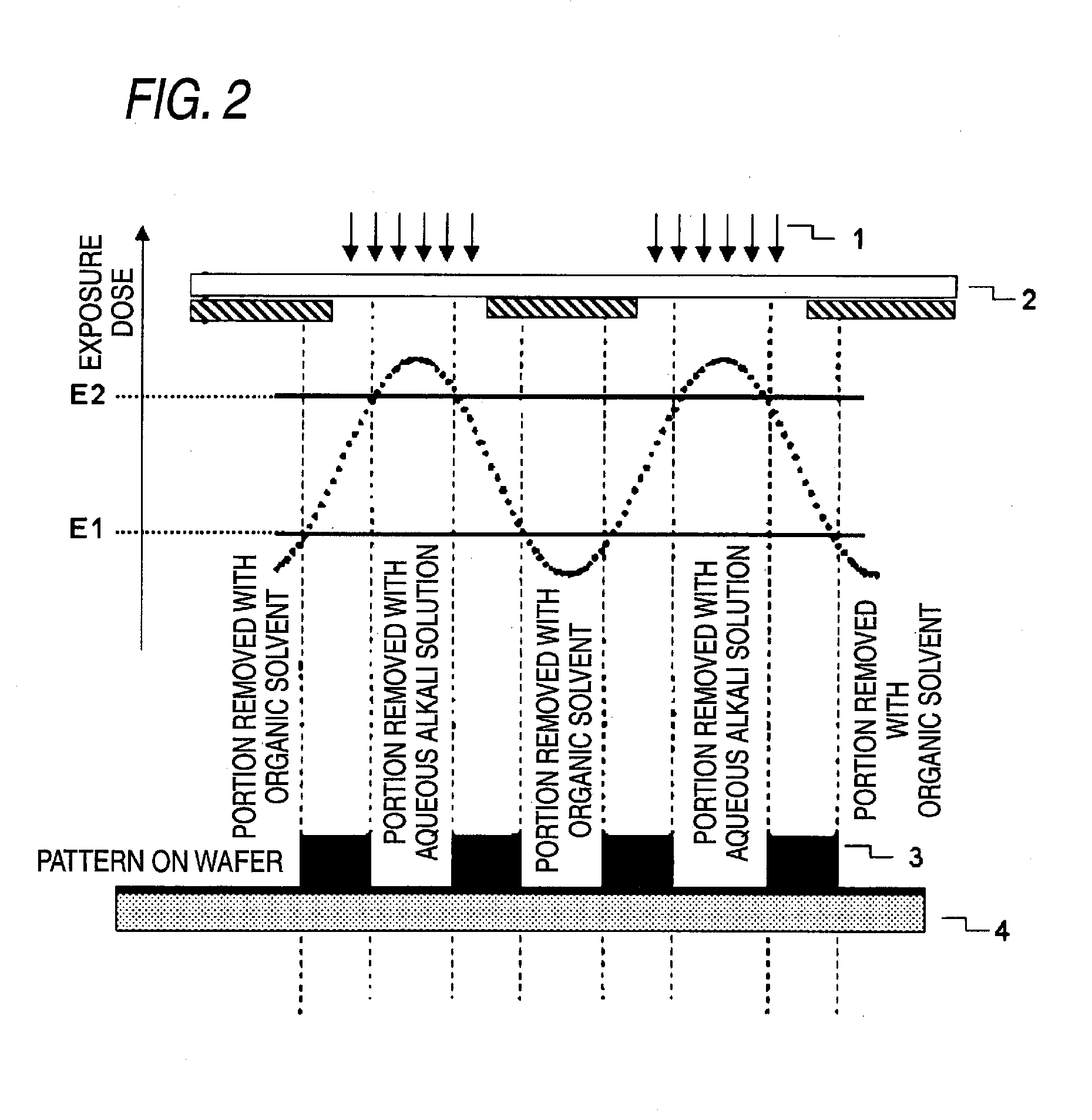
InactiveUS7851140B2Enhance the imageImprove in-plane uniformityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsIn planeActinic Rays
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
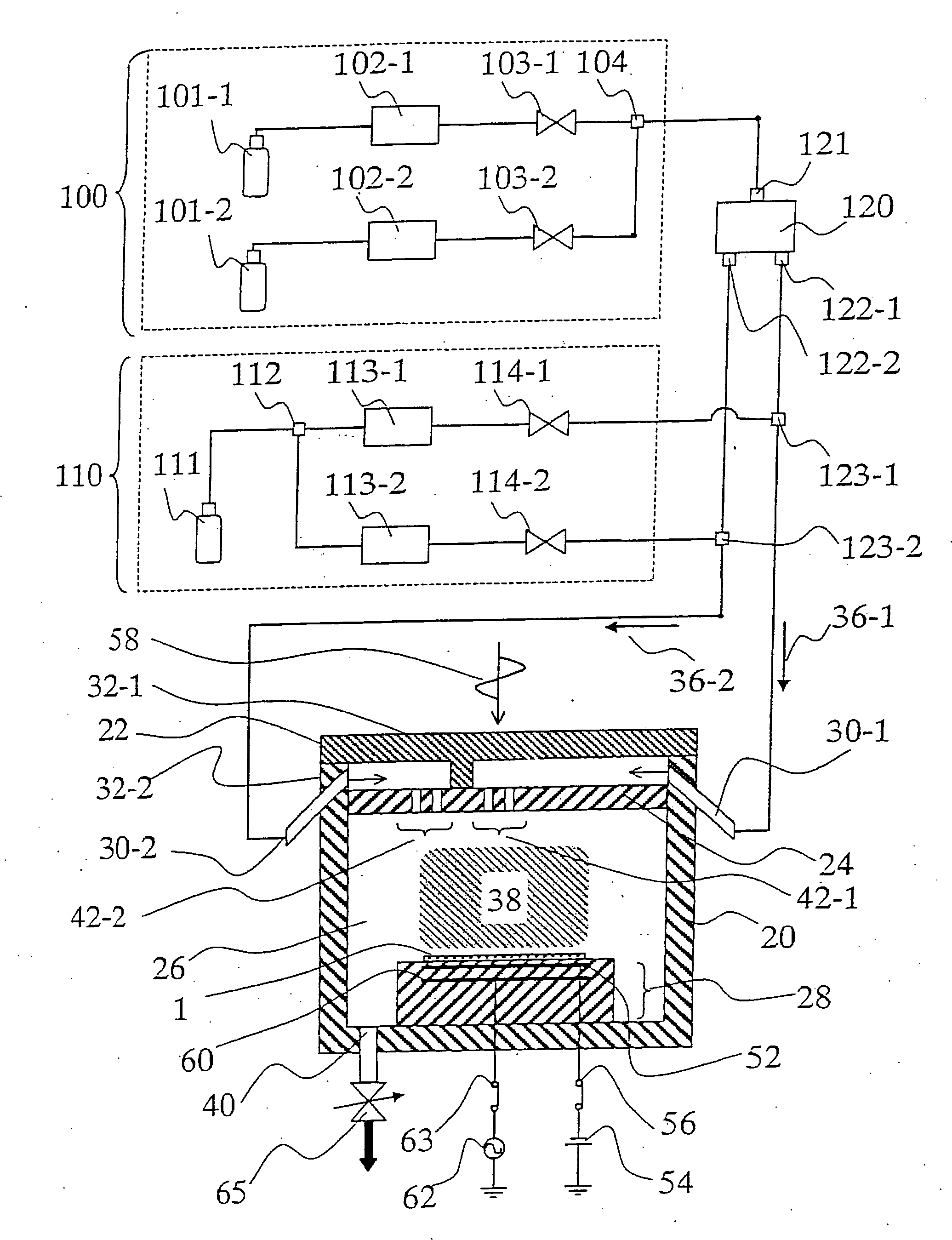
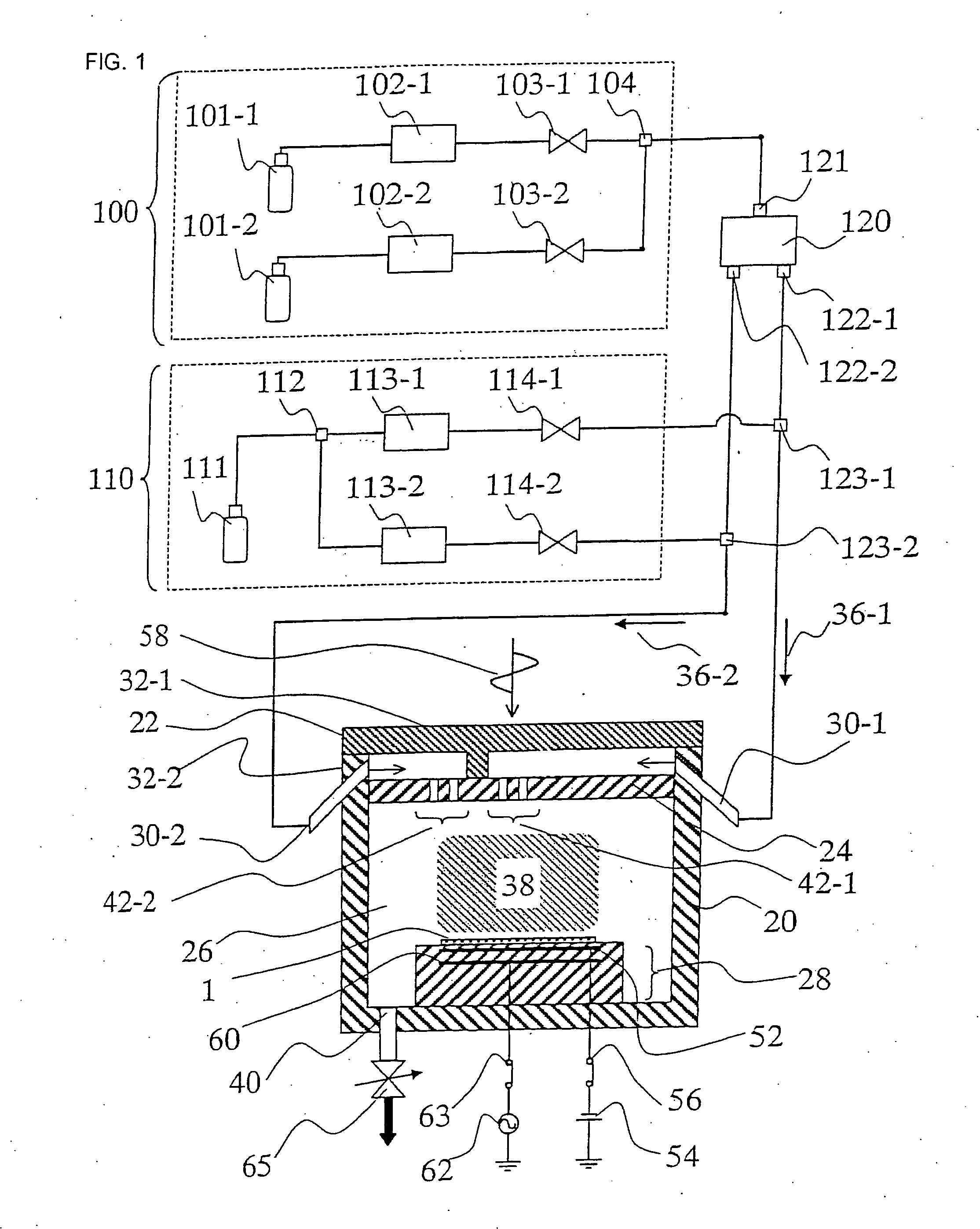
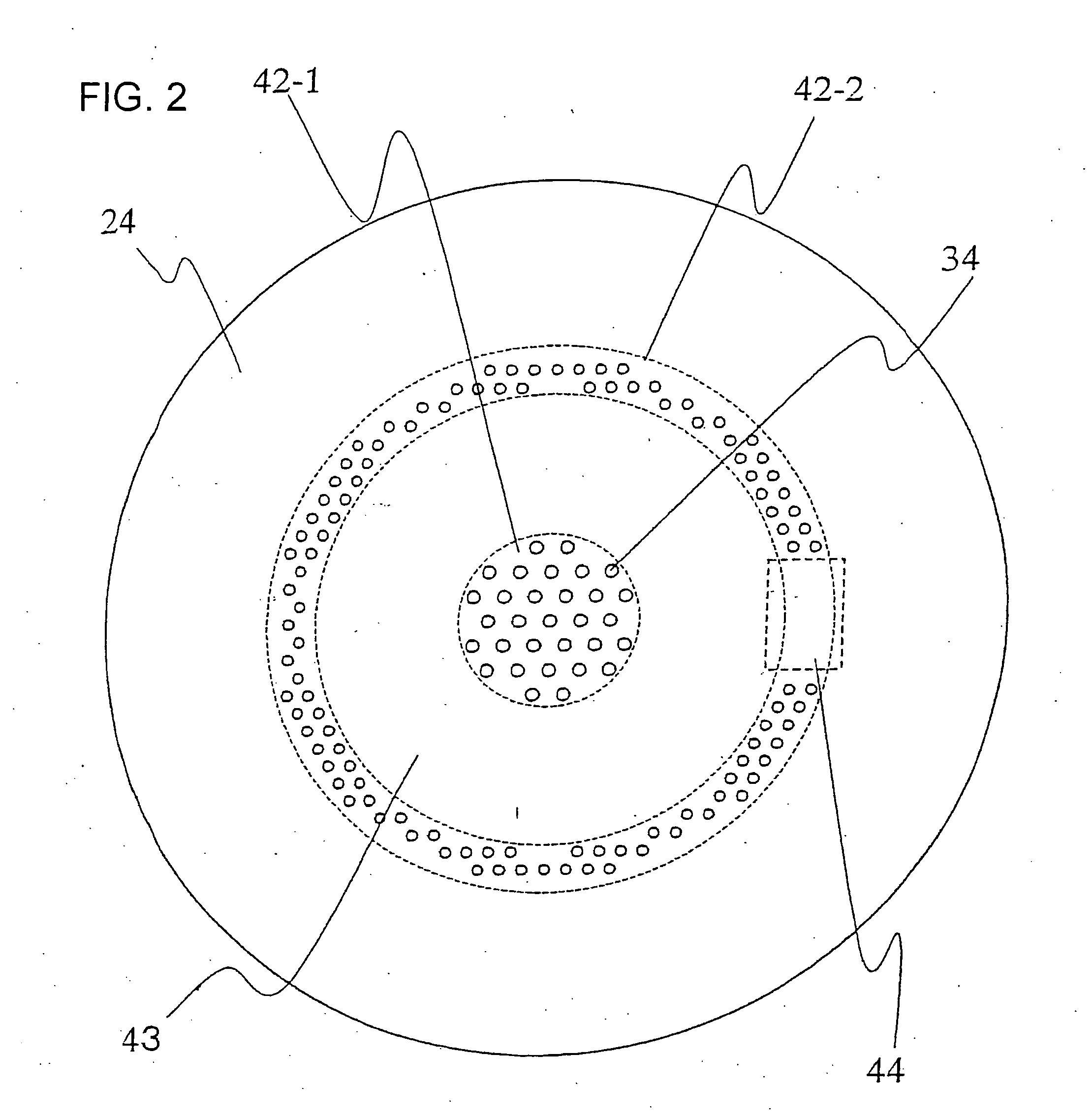
Plasma etching apparatus and plasma etching method
InactiveUS20060169671A1High in-plane uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsIn planeProcess engineering
To provide a plasma etching apparatus that achieves a high in-plane uniformity of the CD shift. A plasma etching apparatus includes: a process chamber 26 in which a plasma etching process is performed on a process target object 1; A first gas supply source 100 for supplying a first process gas; a second gas supply source 110 for supplying a second process gas; a first gas introduction area 42-1 having a first gas introduction port for introducing the first process gas into the process chamber 26; a second gas introduction area 42-2 having a second gas introduction port 3 for introducing the second process gas into the process chamber 26; flow controllers 102, 113 for adjusting the flow rates of the process gasses; and a gas flow divider 120 for dividing the process gas into a plurality of gas flows, in which the first gas introduction port and the second gas introduction port are provided substantially in the same plane, and the first gas introduction area 42-1 and the second gas introduction area 42-2 are separated from each other.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Group-iii nitride compound semiconductor device and production method thereof, group-iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, and lamp
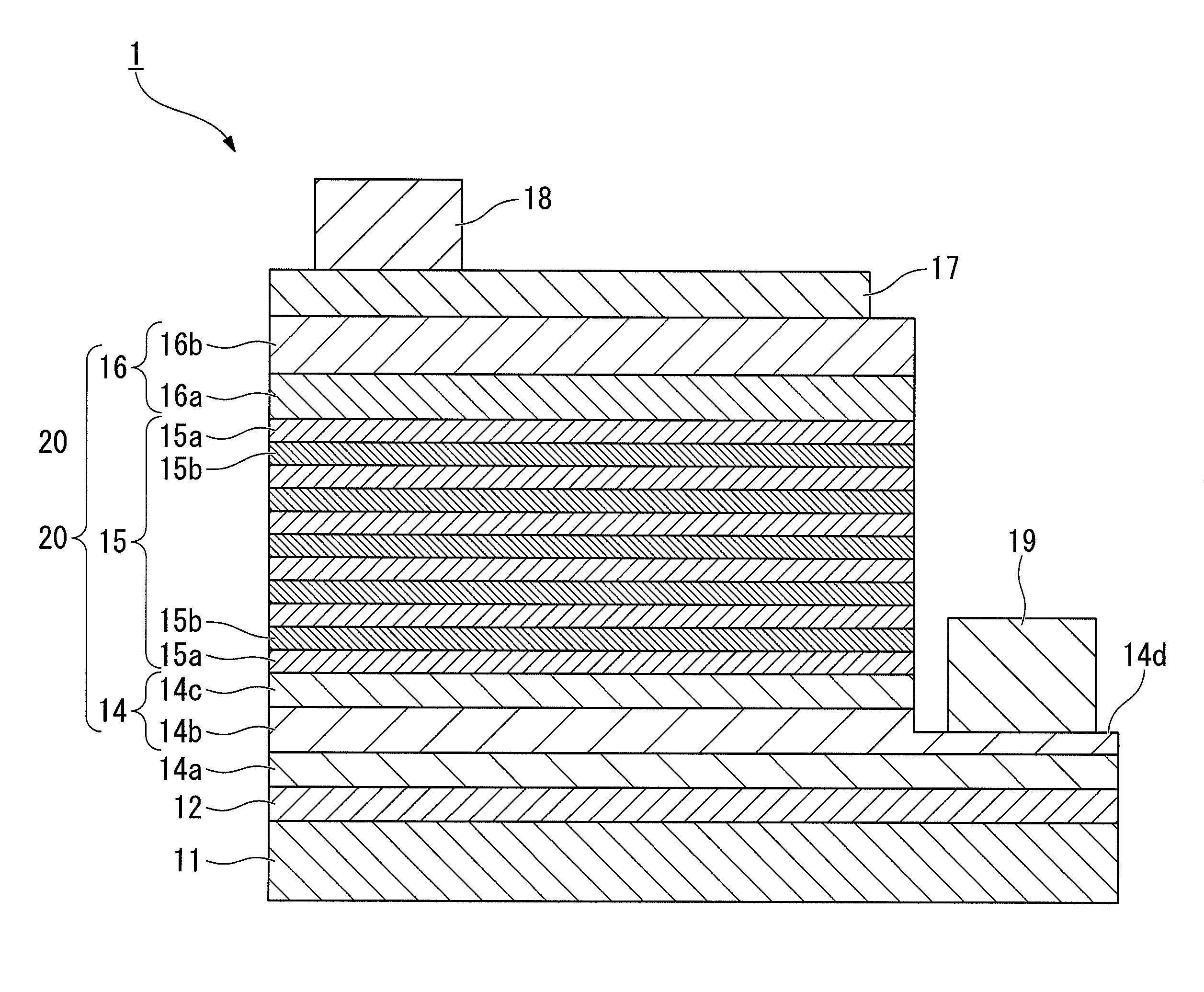
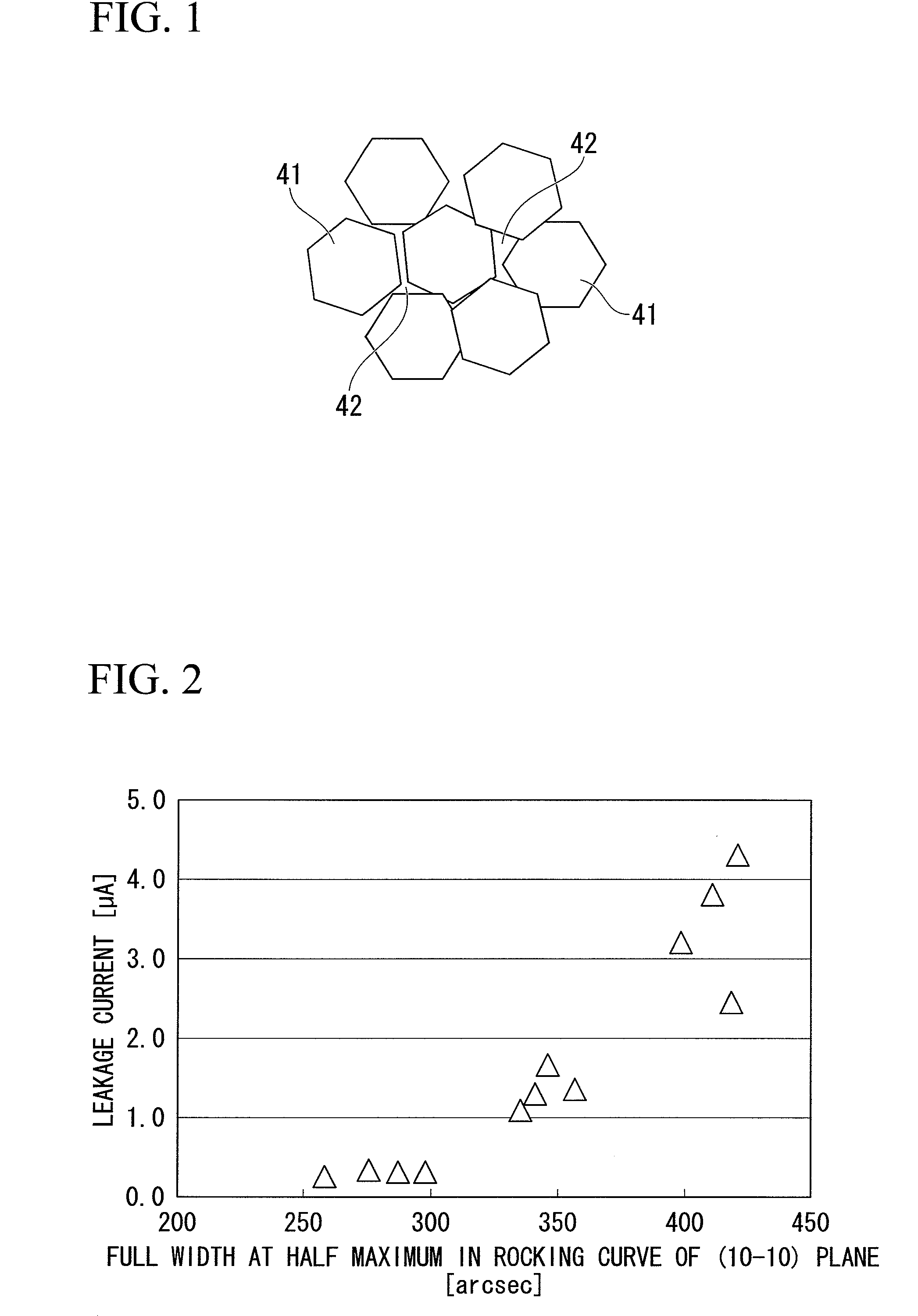
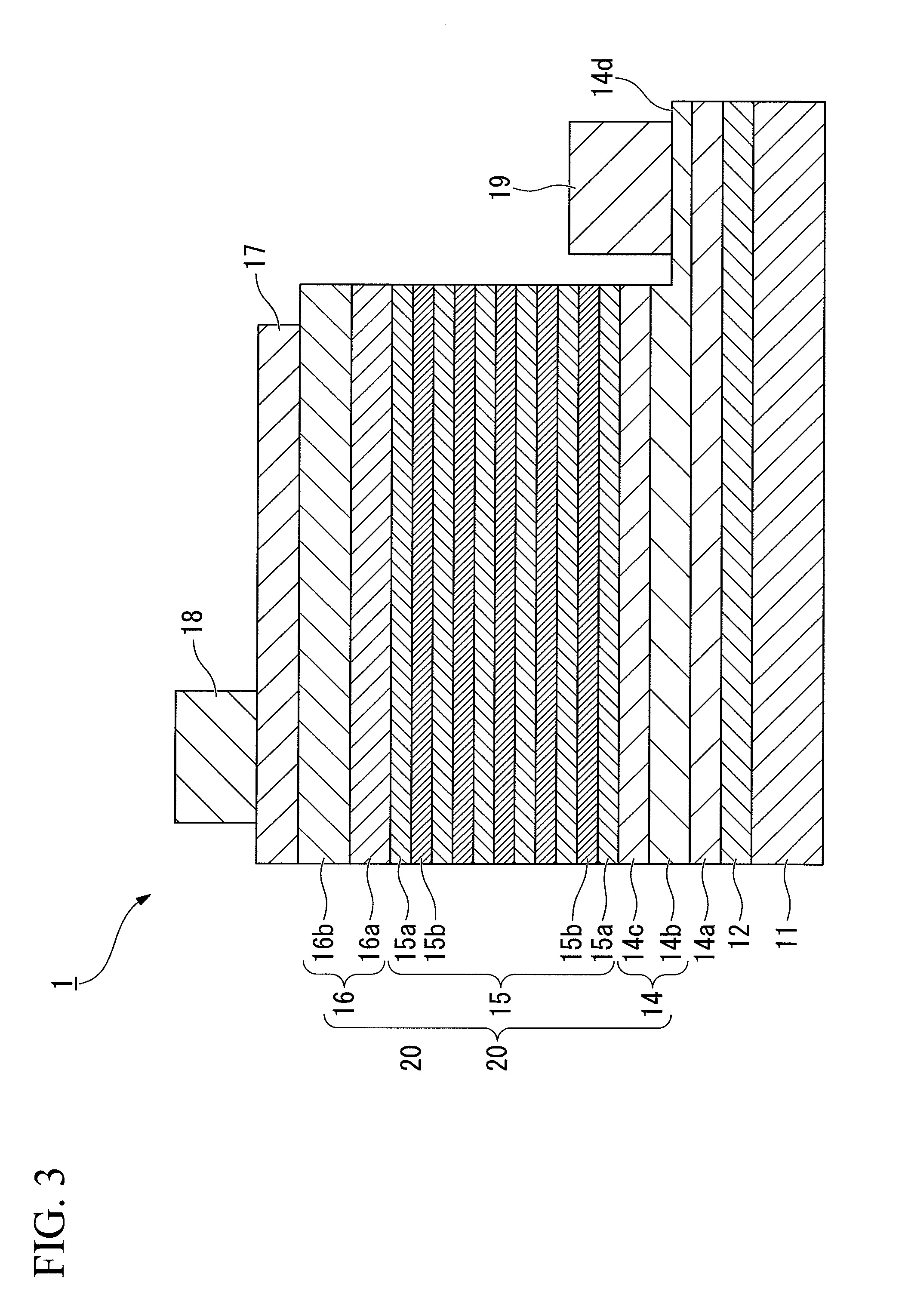
InactiveUS20090194784A1Improve in-plane uniformityLower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingRocking curveInter layer
A group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises a substrate, an intermediate layer provided on the substrate, and a base layer provided on the intermediate layer in which a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (0002) plane is 100 arcsec or lower and a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (10-10) plane is 300 arcsec or lower. Also, a production method of a group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises forming the intermediate layer by using a sputtering method.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Integrated semiconductor light-emitting device and its manufacturing method
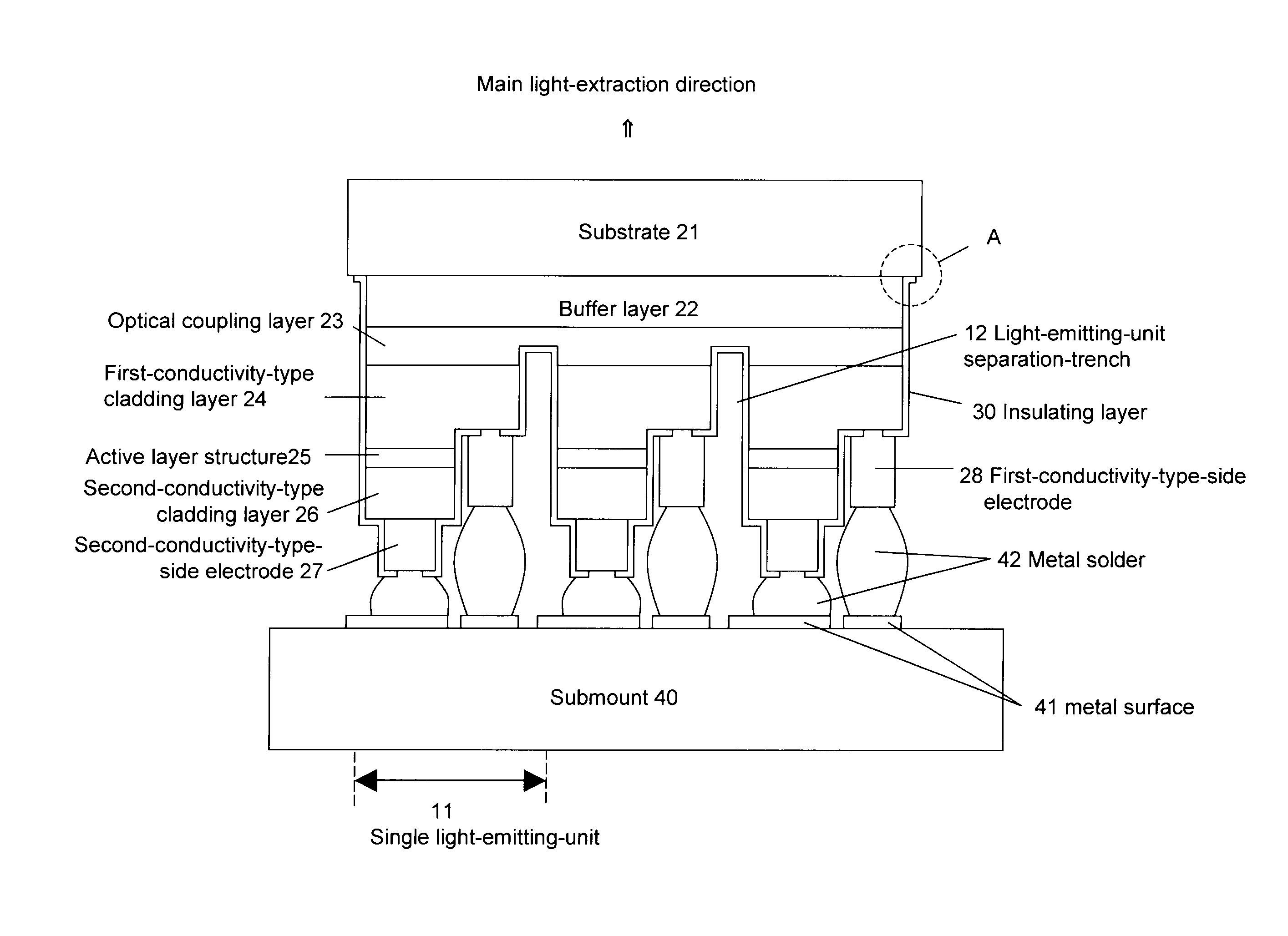
InactiveUS20100320488A1Improve in-plane uniformityImprove uniformitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical couplingLight emitting device
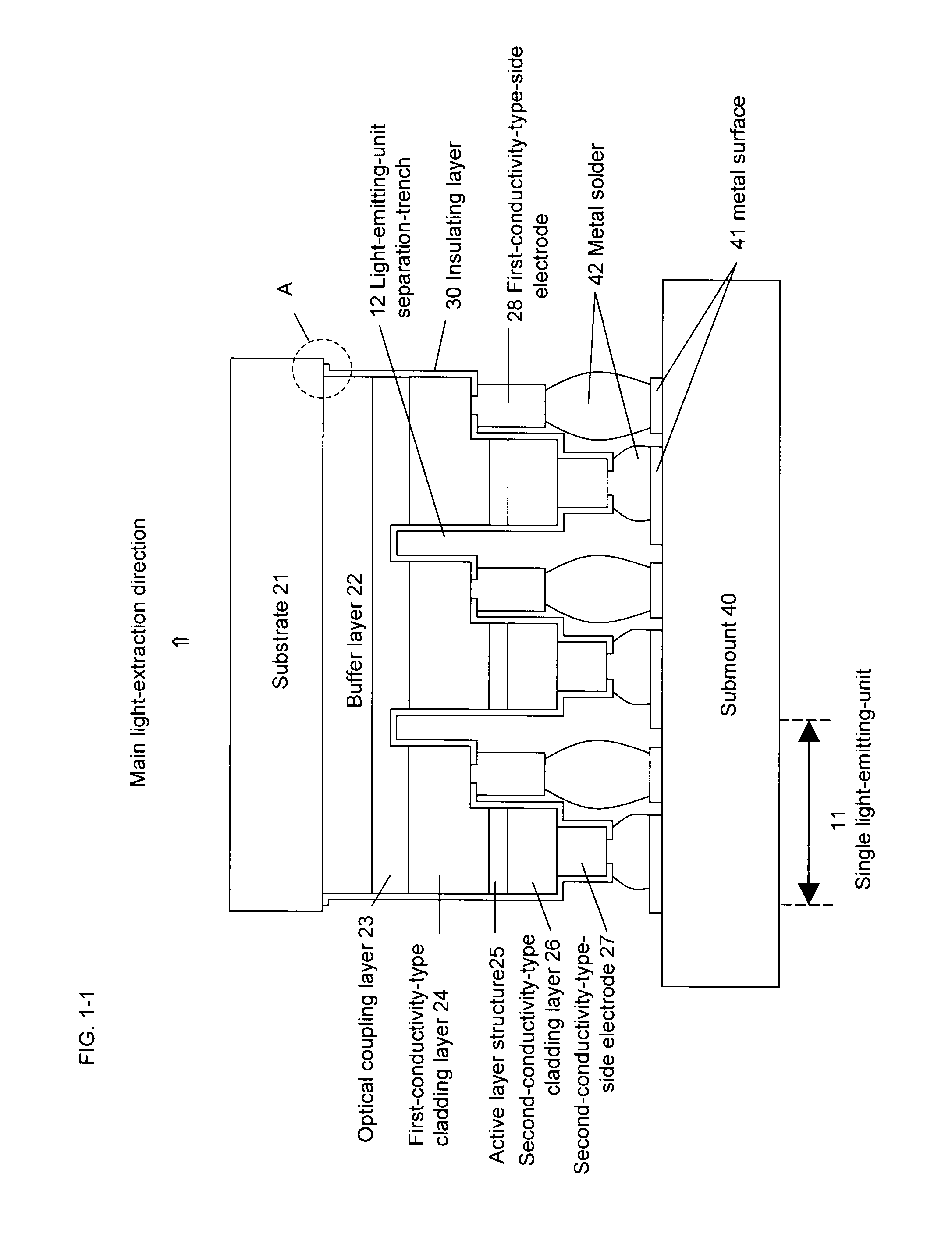
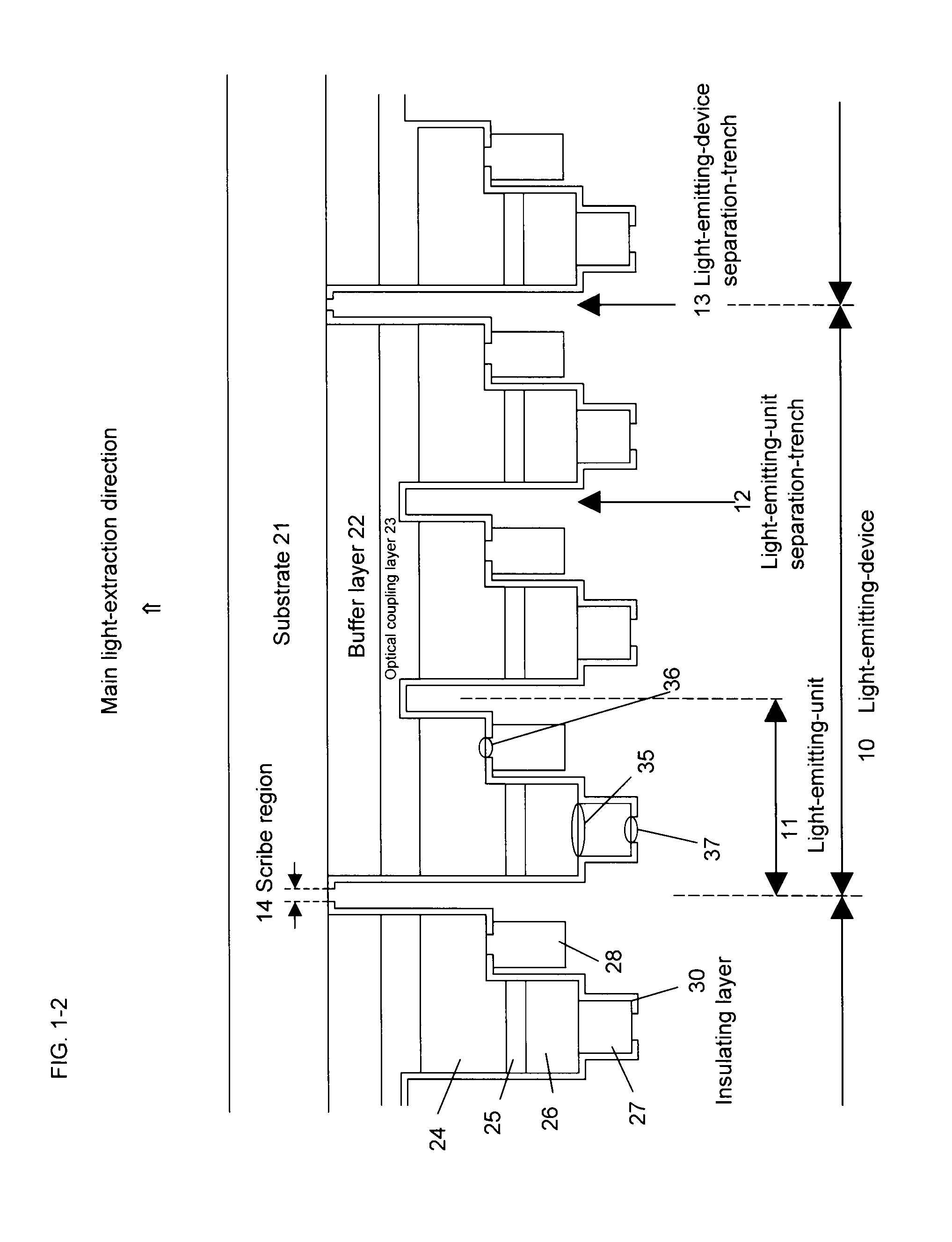
An integrated compound semiconductor light-emitting-device capable of emitting light as a large-area plane light source. The light-emitting-device includes plural light-emitting-units formed over a substrate, the light-emitting-units having a compound semiconductor thin-film crystal layer, first and second-conductivity-type-side electrodes, a main light-extraction direction is the side of the substrate, and the first and the second-conductivity-type-side electrodes are formed on the opposite side to the light-extraction direction. The light-emitting-units are electrically separated from each other by a light-emitting-unit separation-trench. An optical coupling layer is formed between the substrate and the first-conductivity-type semiconductor layer. The optical coupling layer is common to the plurality of light-emitting-units, and capable of optical coupling of the plurality of light-emitting-units and distributing a light to the entire light-emitting-device.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Resist composition for negative tone development and pattern forming method using the same
InactiveUS20100167201A1Reduced line edge roughnessImprove in-plane uniformityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsIn planeActinic Rays
To provide a resist composition for negative tone development, which can form a pattern having a good profile improved in the pattern undercut and moreover, can reduce the line edge roughness and enhance the in-plane uniformity of the pattern dimension, and a pattern forming method using the same.A resist composition for negative tone development, comprising (A) a resin capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid to increase the solubility in a positive tone developer and decrease the solubility in a negative tone developer, (B) a compound capable of generating an acid having an acid dissociation index pKa of −4.0 or less upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, and (C) a solvent; and a pattern forming method using the same.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
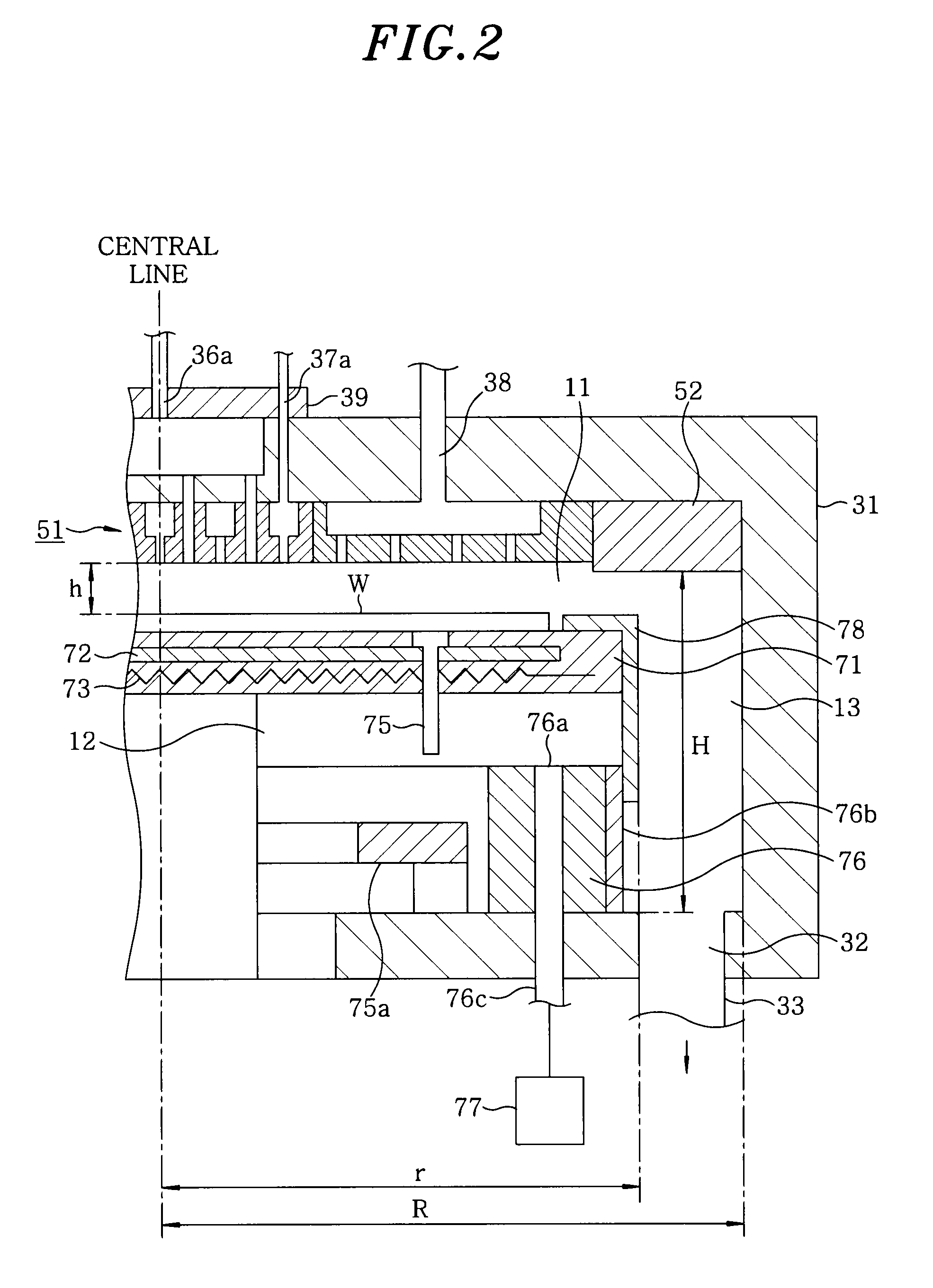
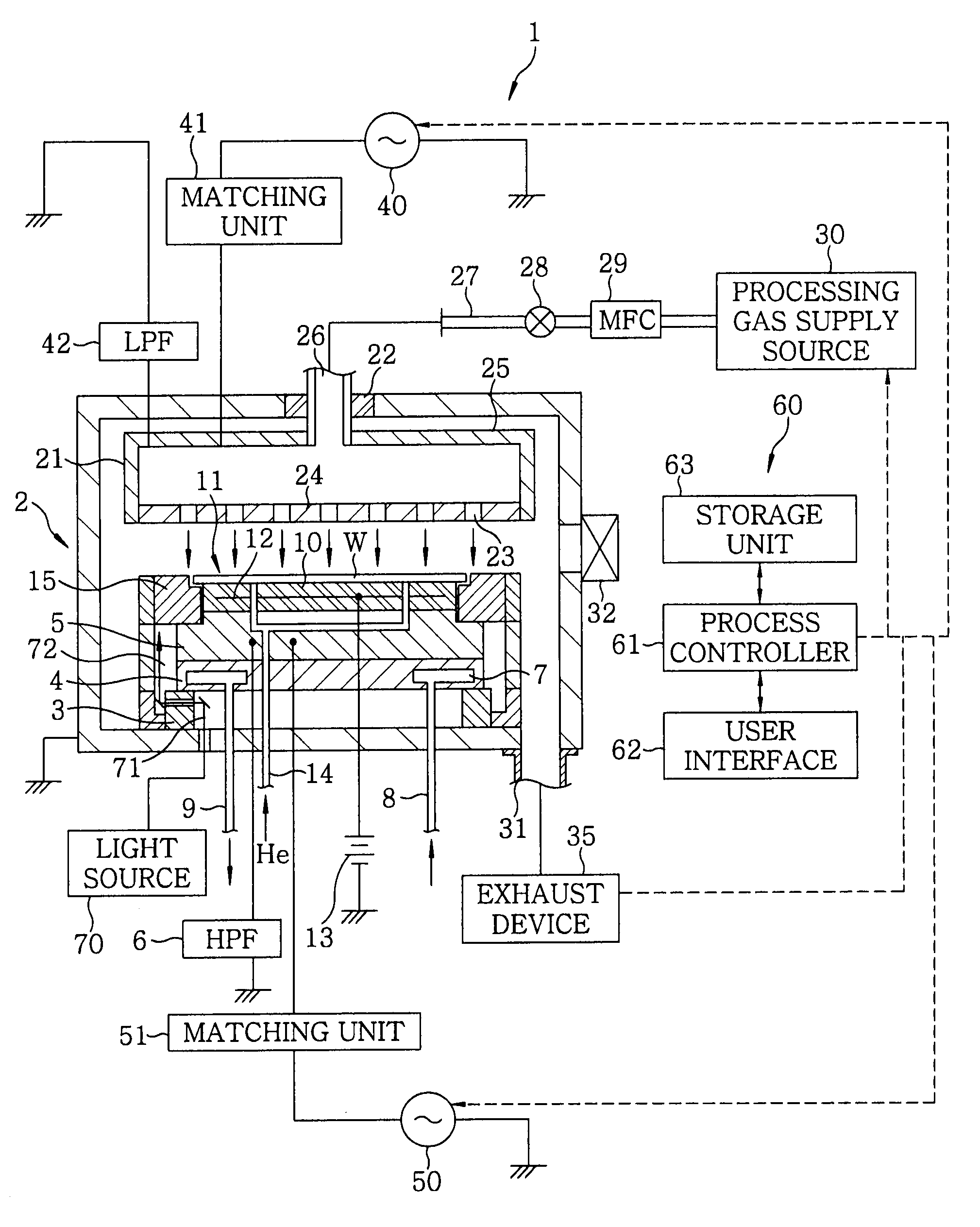
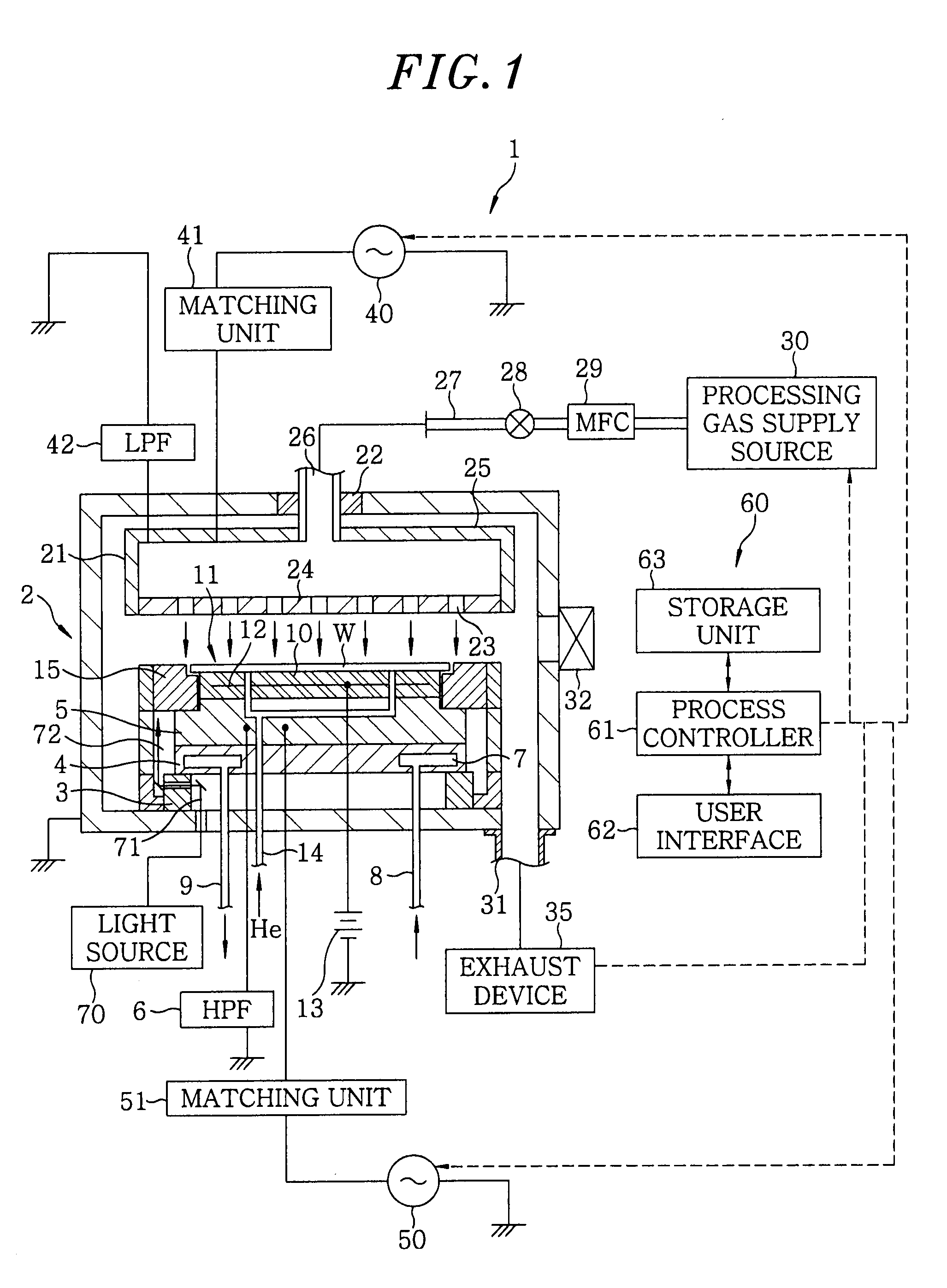
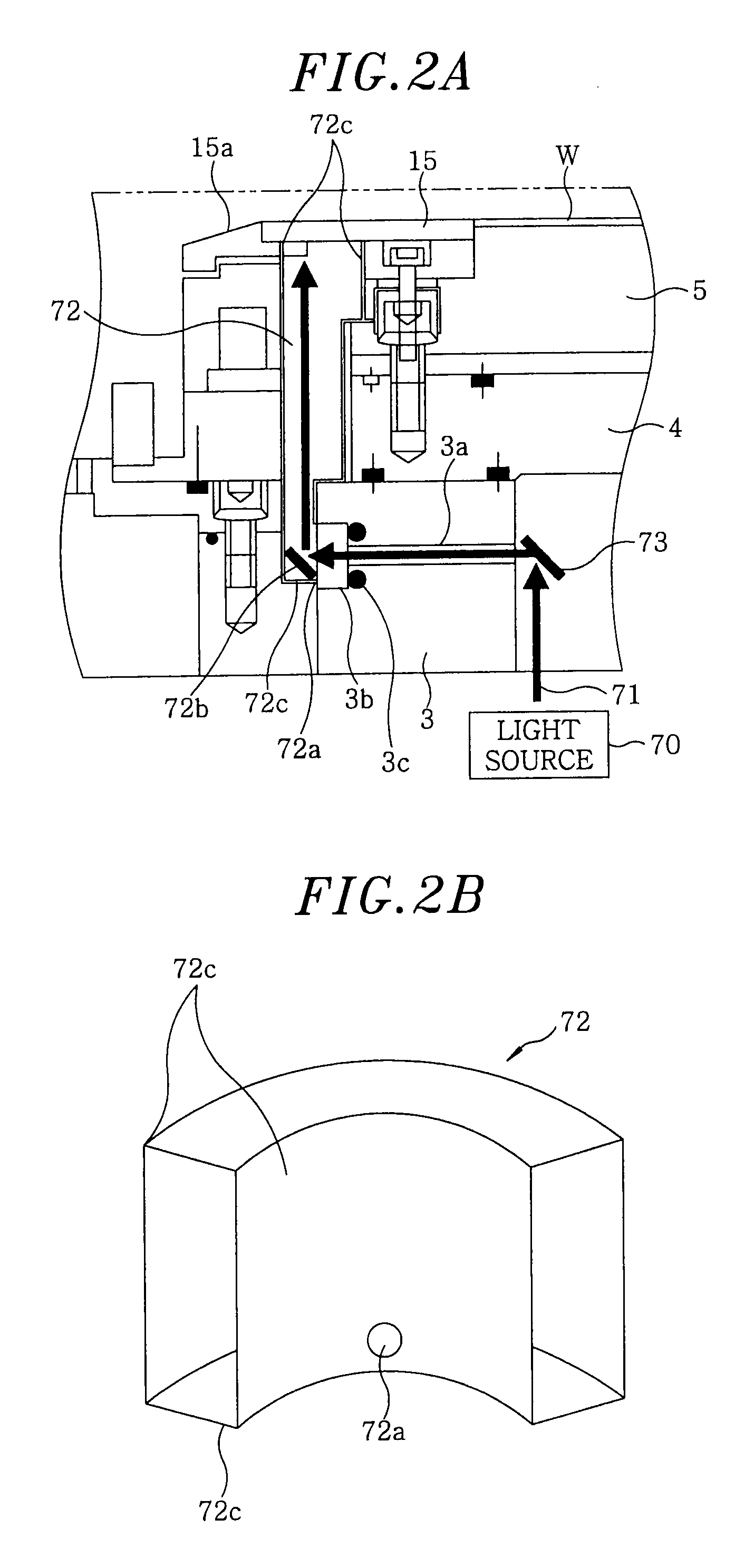
Plasma treatment device and structure of reaction vessel for plasma treatment
ActiveUS11225718B2Improve uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingMechanical engineeringMaterials science
Owner:CORTECH +1
Wet processing method and processing apparatus of substrate
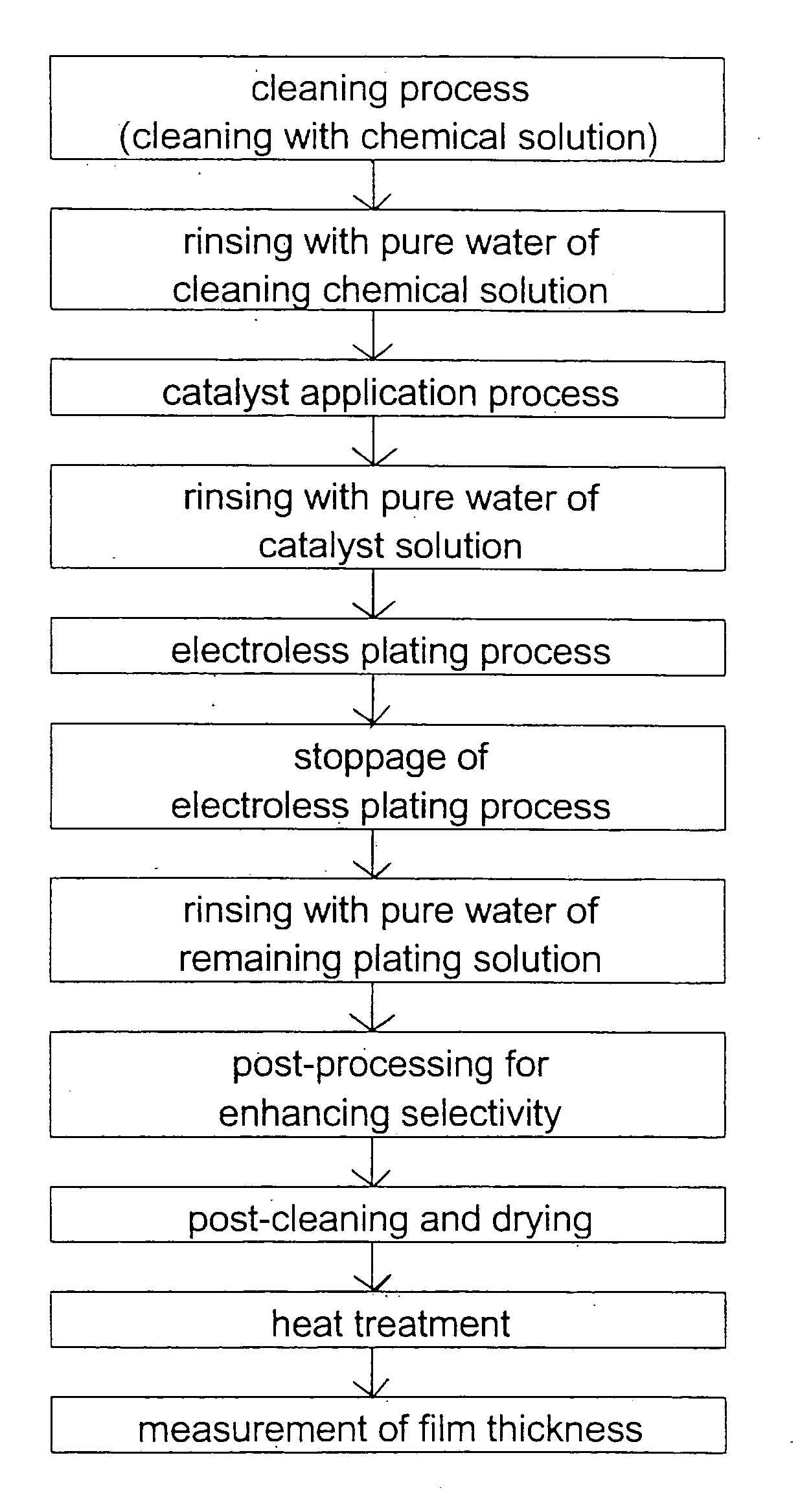
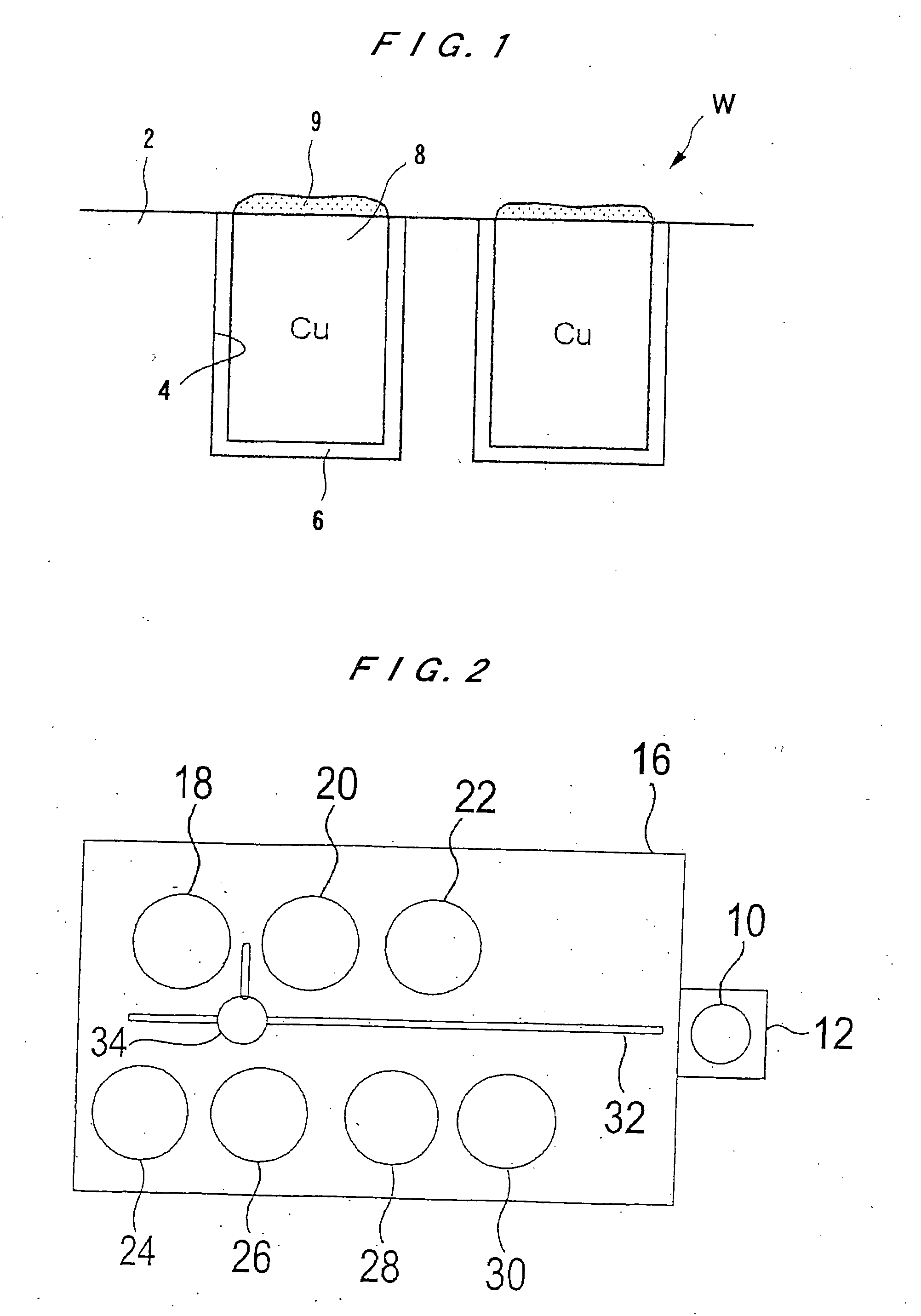
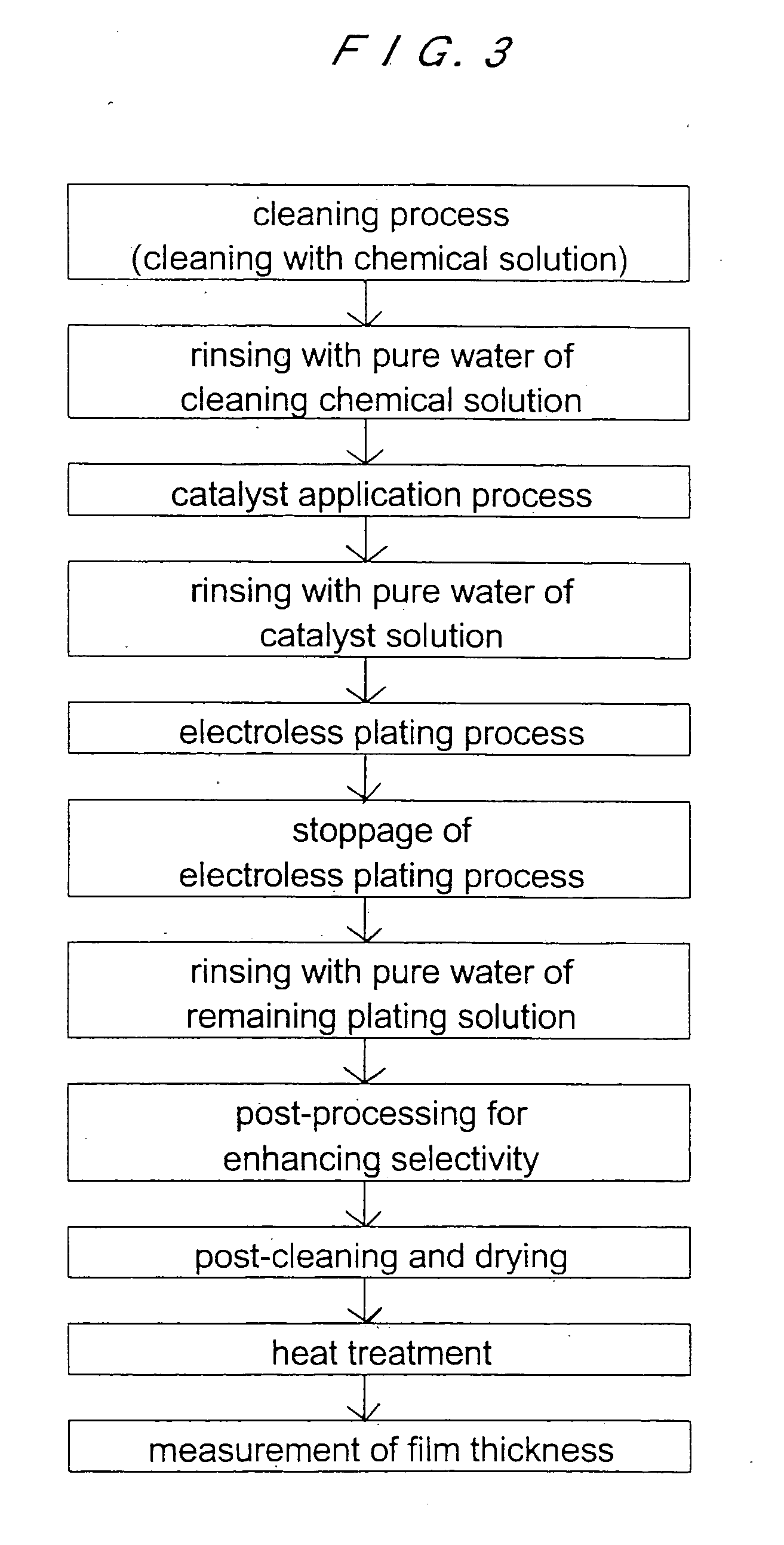
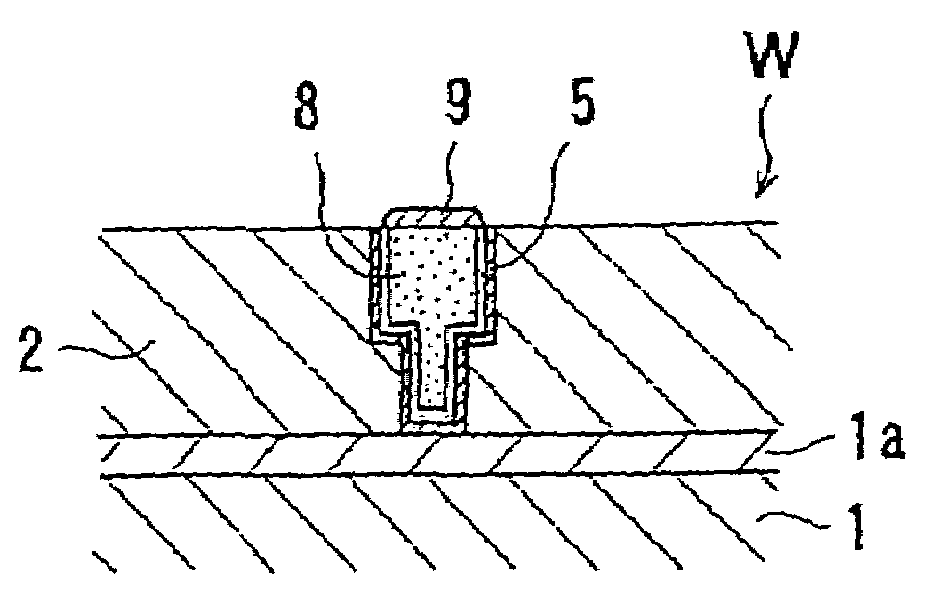
InactiveUS20050208774A1Easy to solveSimple wayElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentChemical solution
A substrate wet-processing method can carry out uniform chemical processing of the surface of a substrate while easily preventing a gas from remaining on the surface of the substrate and preventing difference in the concentration and the temperature of a chemical solution between the end portion and the central portion of the substrate. The substrate wet-processing method includes: providing an acidic solution whose concentration is previously adjusted within a predetermined concentration range; continuously spraying the acidic solution having the adjusted concentration toward a substrate at a predetermined pressure to bring it into contact with a surface of the substrate; and then forming a film of an insulating material, a metal or an alloy on the exposed surface of a metal formed in the surface of the substrate.
Owner:EBARA CORP
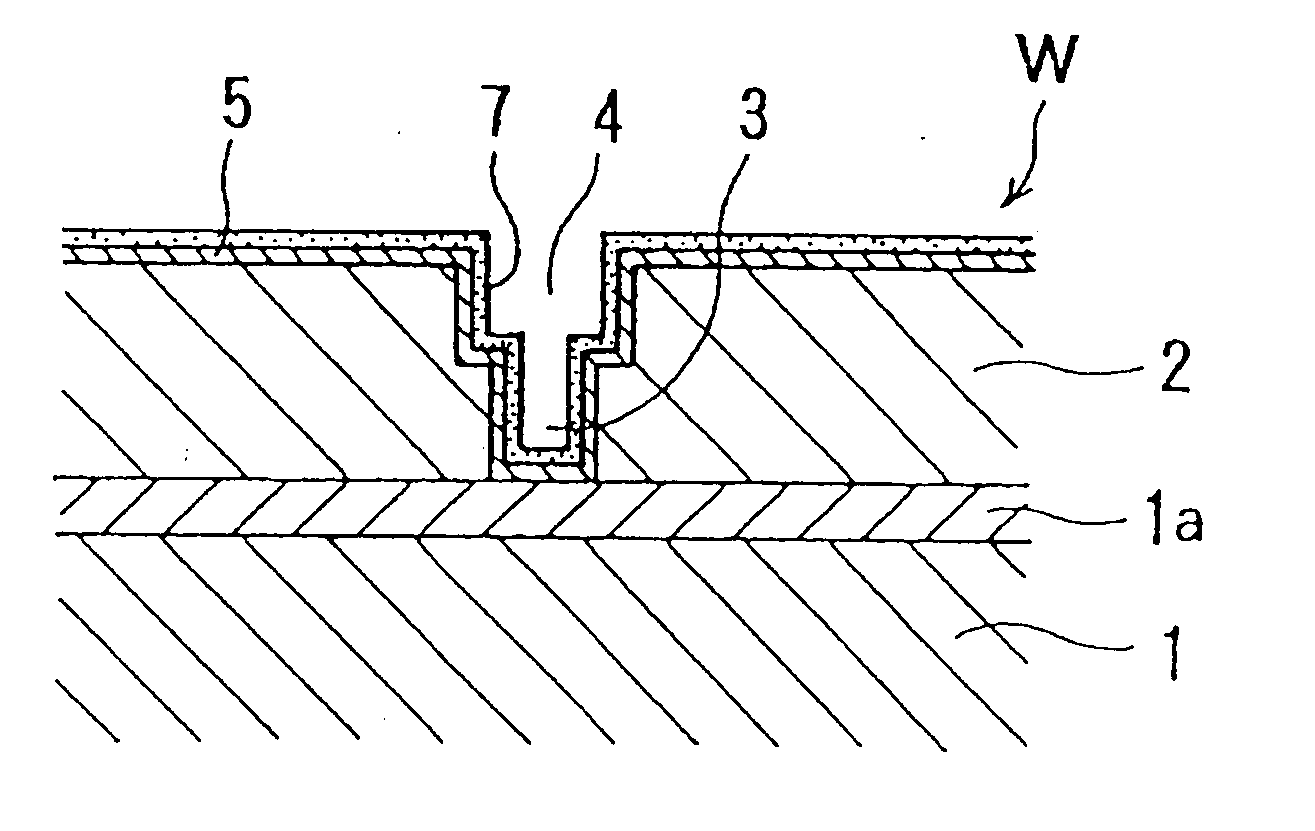
Plating method and plating apparatus
ActiveUS7169705B2Improve in-plane uniformityGood embedding effectElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic acidIn plane
A plating method is capable of depositing a plated film having excellent in-plane uniformity with respect to a thin seed layer and excellent embeddability with respect to fine damascene structures. The plating method includes: positioning an electric resistor between a conductive layer formed on at least a portion of a surface of a substrate and an anode; introducing respectively a plating solution into a space between the conductive layer and the anode on a conductive layer side, and an anode solution into a space between the conductive layer and the anode on an anode side, thereby filling the space with a plating bath composed of the plating solution and the anode solution, with the plating solution containing 25 to 75 g / L of copper ions and at least 0.4 mole / L of an organic acid or an inorganic acid, and the anode solution being of the same composition as the plating solution, or containing 0 to 75 g / L of copper ions and at most 0.6 mole / L of an organic acid or an inorganic acid; and applying a voltage between the conductive layer and the anode to plate a surface of the conductive layer.
Owner:EBARA CORP
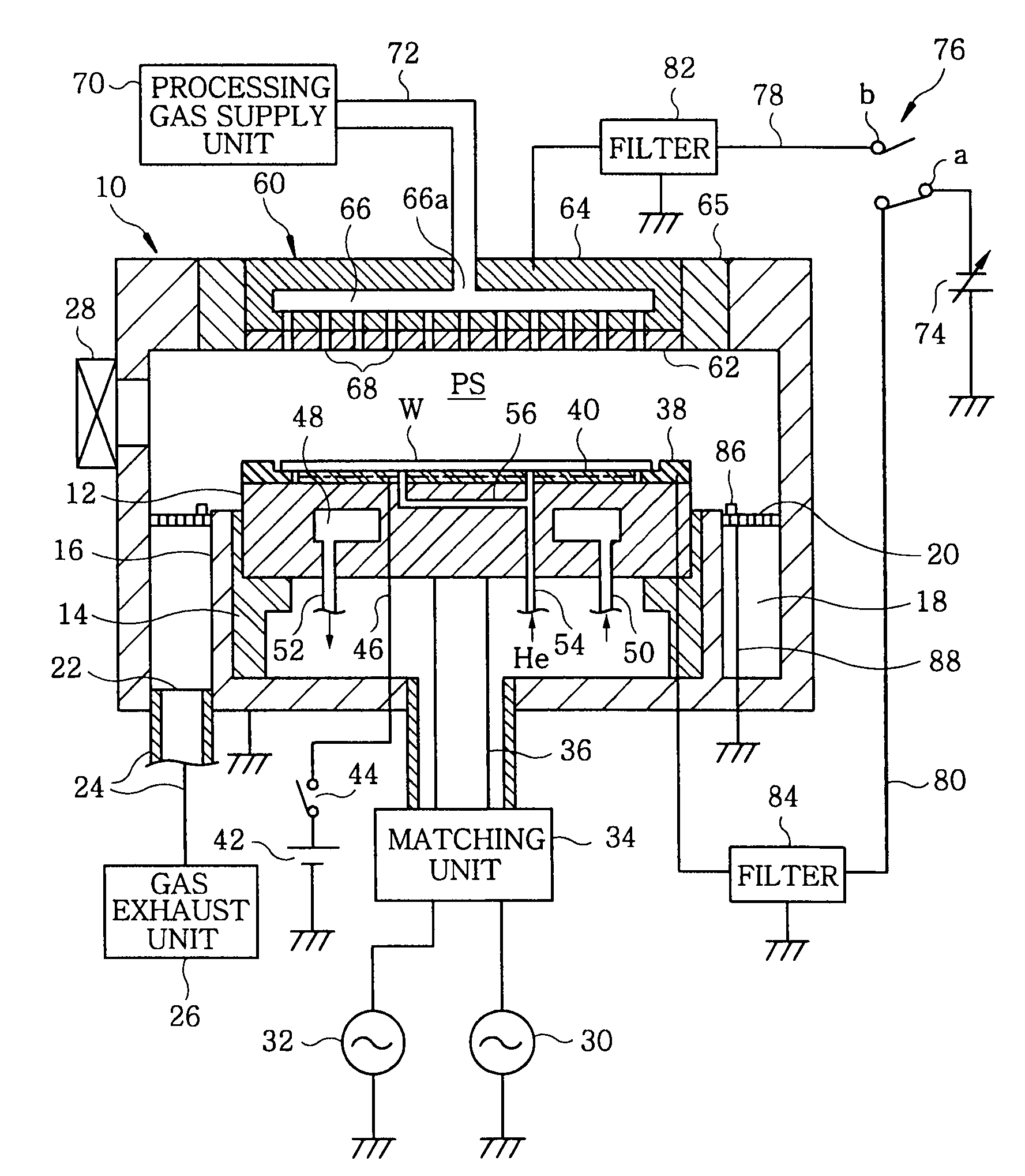
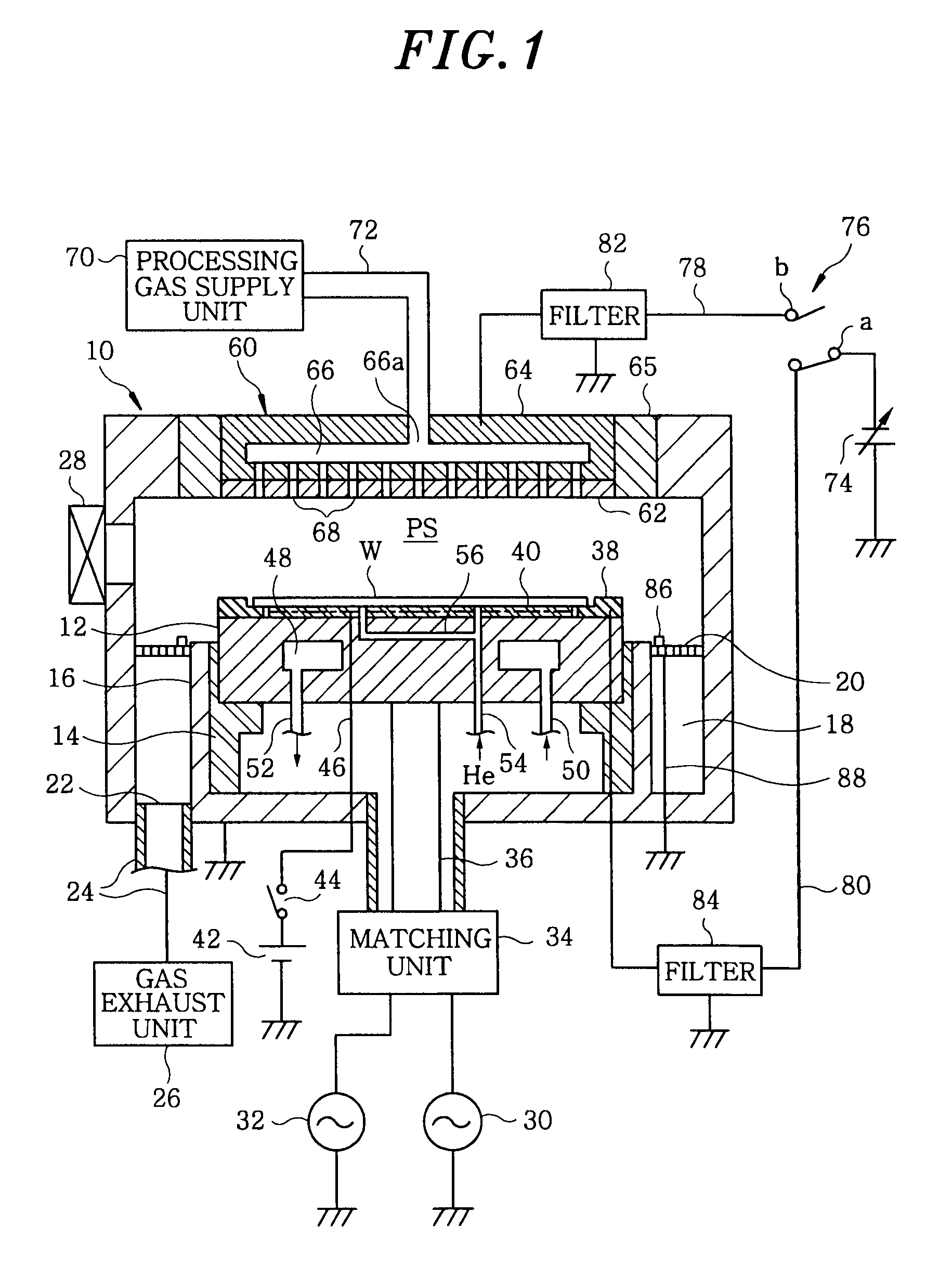
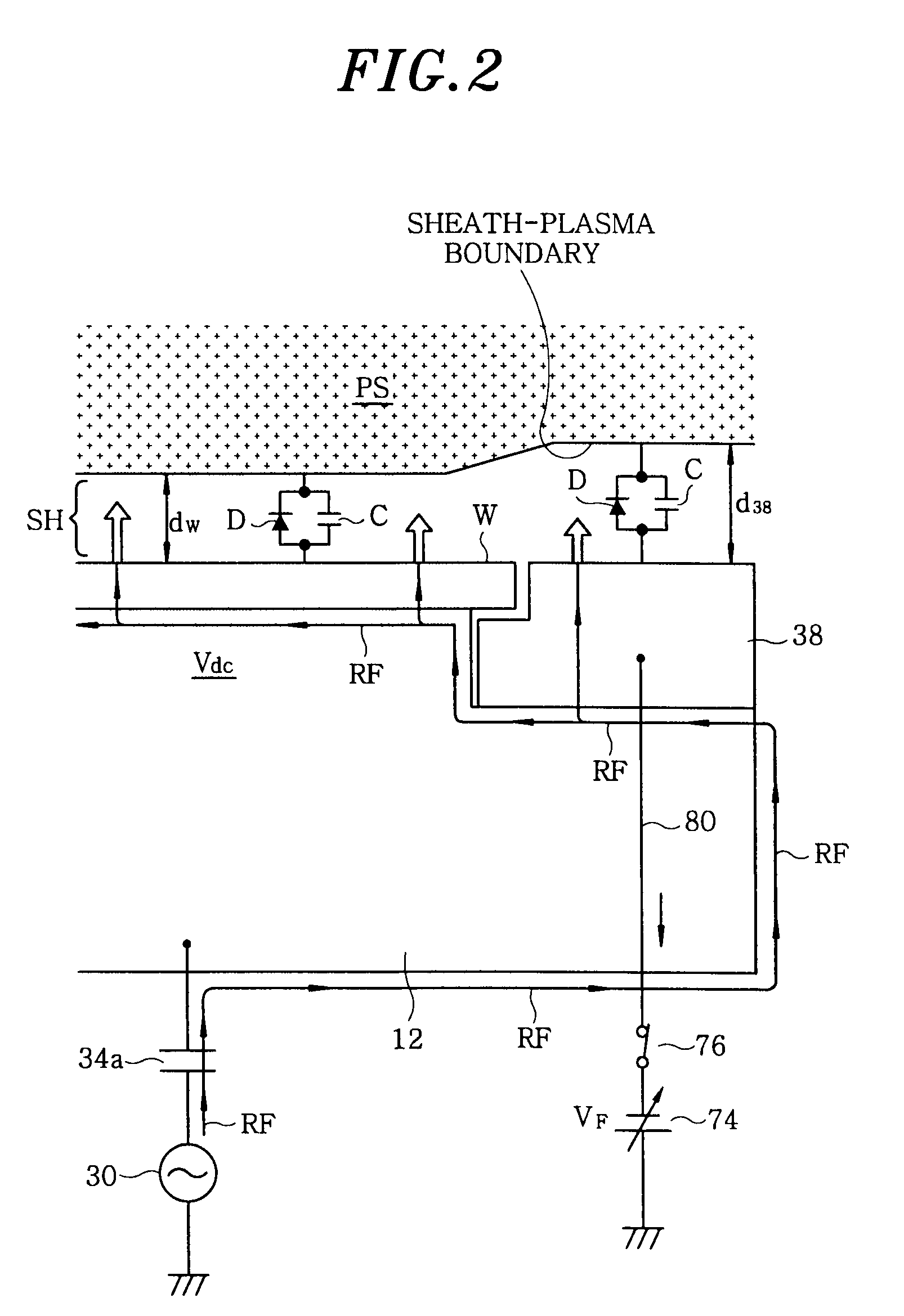
Plasma etching apparatus and method, and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20090242127A1Simply and effectively correcting or solvingExcellent characteristicsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadio frequency
A plasma etching apparatus includes a processing vessel; a lower electrode on which a target substrate is mounted in the processing vessel; an upper electrode disposed in the processing vessel to face the lower electrode in parallel; a processing gas supply unit configured to supply a processing gas into a processing space between the upper and the lower electrode; a first radio frequency power supply unit configured to apply, to the lower electrode, a first radio frequency power for generating plasma of the processing gas; a focus ring covering a top surface peripheral portion of the lower electrode protruding toward a radial outside of the substrate; a DC power supply configured to output a variable DC voltage; and a DC voltage supply network that connects the DC power supply to either one of the focus ring and the upper electrode or both depending on processing conditions of plasma etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
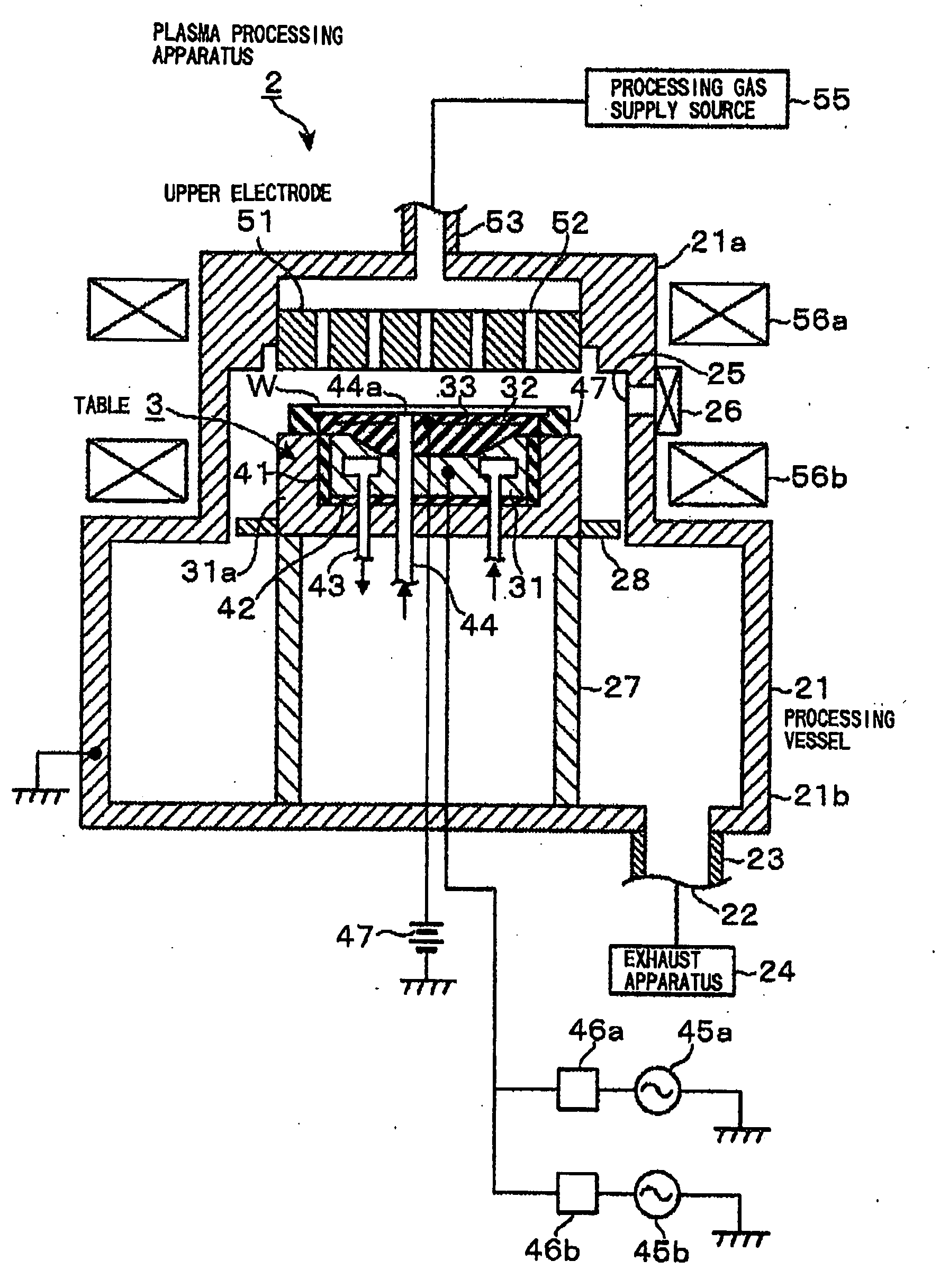
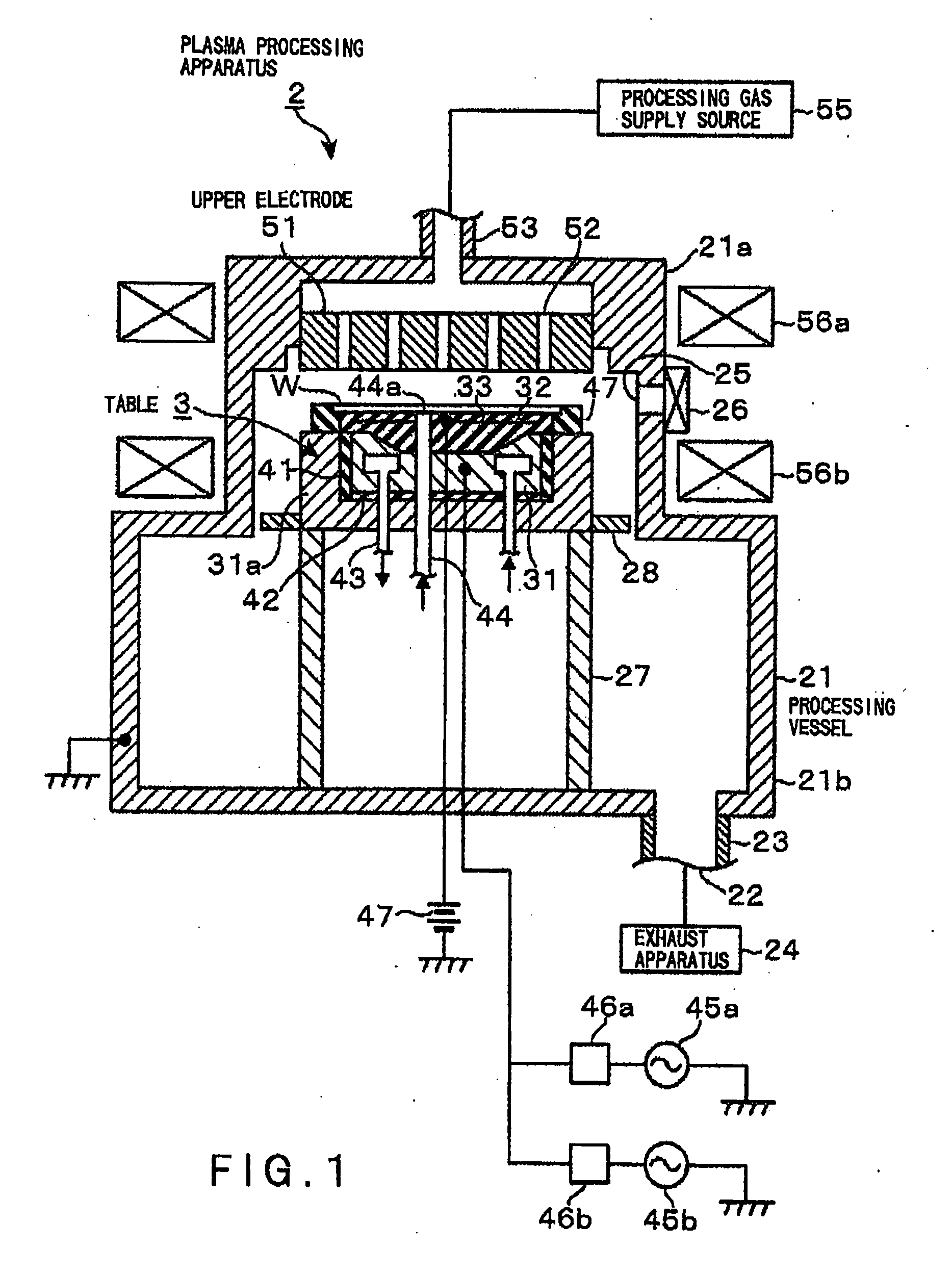
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20090236043A1Improve in-plane uniformityWide power rangeCellsElectric discharge tubesRf dischargeRadio frequency
A plasma processing apparatus includes a processing gas supplying unit for supplying a desired processing gas to a processing space between an upper electrode and a lower electrode which are disposed facing each other in an evacuable processing chamber. The plasma processing apparatus further includes a radio frequency (RF) power supply unit for applying an RF power to one of the lower and the upper electrode to generate plasma of the processing gas by RF discharge and an electrically conductive RF ground member which covers a periphery portion of the electrode to which the RF power is applied to receive RF power emitted outwardly in radial directions from the periphery portion of the electrode to which the RF power is applied and send the received RF power to a ground line.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
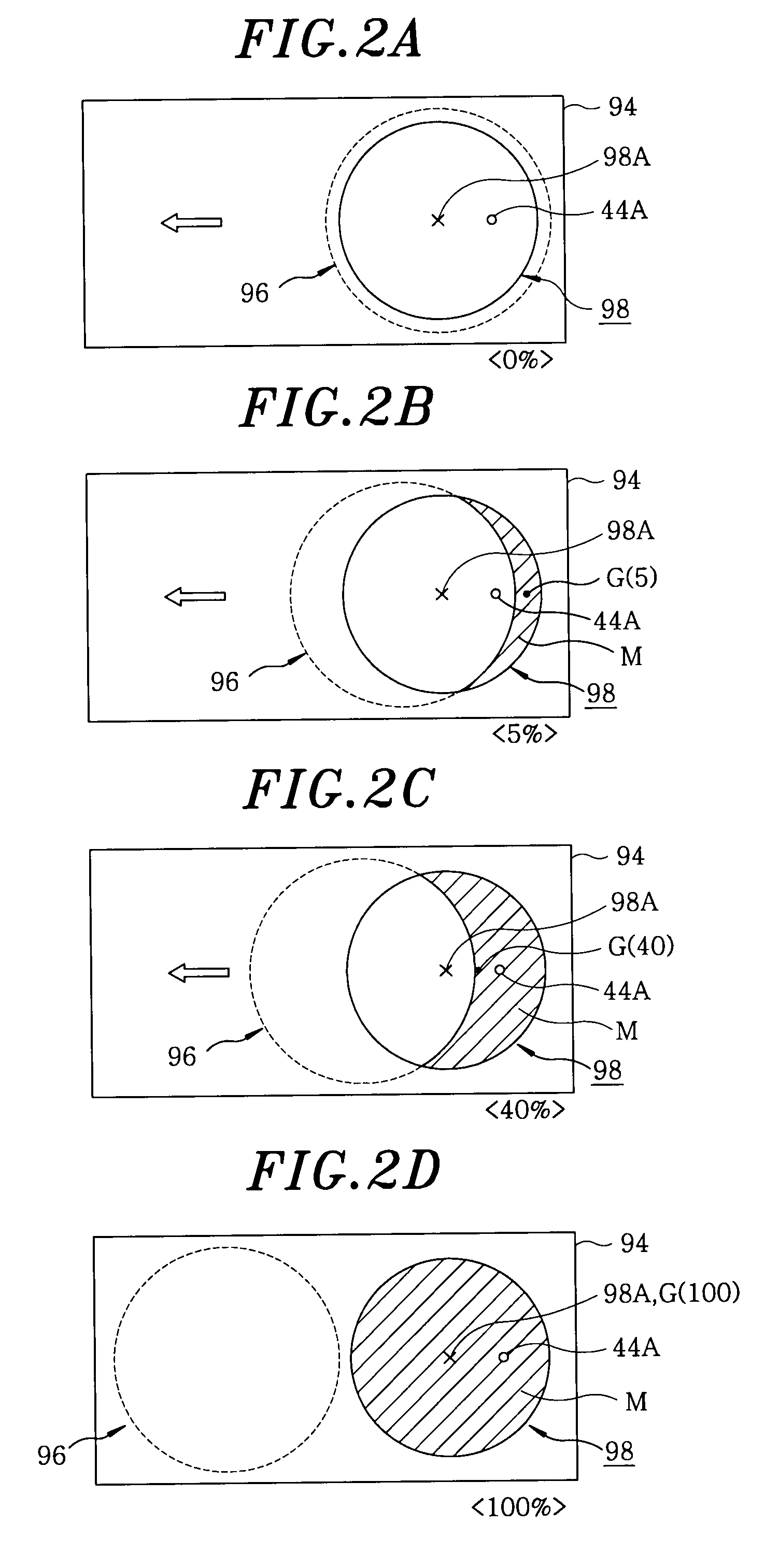
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveCN101451264AExcellent in-plane uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityCellsSolid-state devicesHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Film forming apparatus, film forming method and storage medium
ActiveUS8539908B2Reduce gas volumeShorten the timeComputer controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEnergy supplyProcess engineering
A film forming apparatus includes a processing chamber, and a mounting table disposed in the processing chamber to mount a substrate thereon. The film forming apparatus further includes a gas shower head having gas supply holes and including a central region facing a central portion of the substrate and a peripheral region facing a peripheral portion of the substrate, a first processing gas supply unit for supplying a first processing gas to the central region, a second processing gas supply unit for supplying a second processing gas to the central region, an energy supply unit for supplying energy to react the first processing gas with the second processing gas on the substrate, and a purge gas supply unit for supplying a purge gas to the central region and the peripheral region when one of the first and the second processing gas is switched by the other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
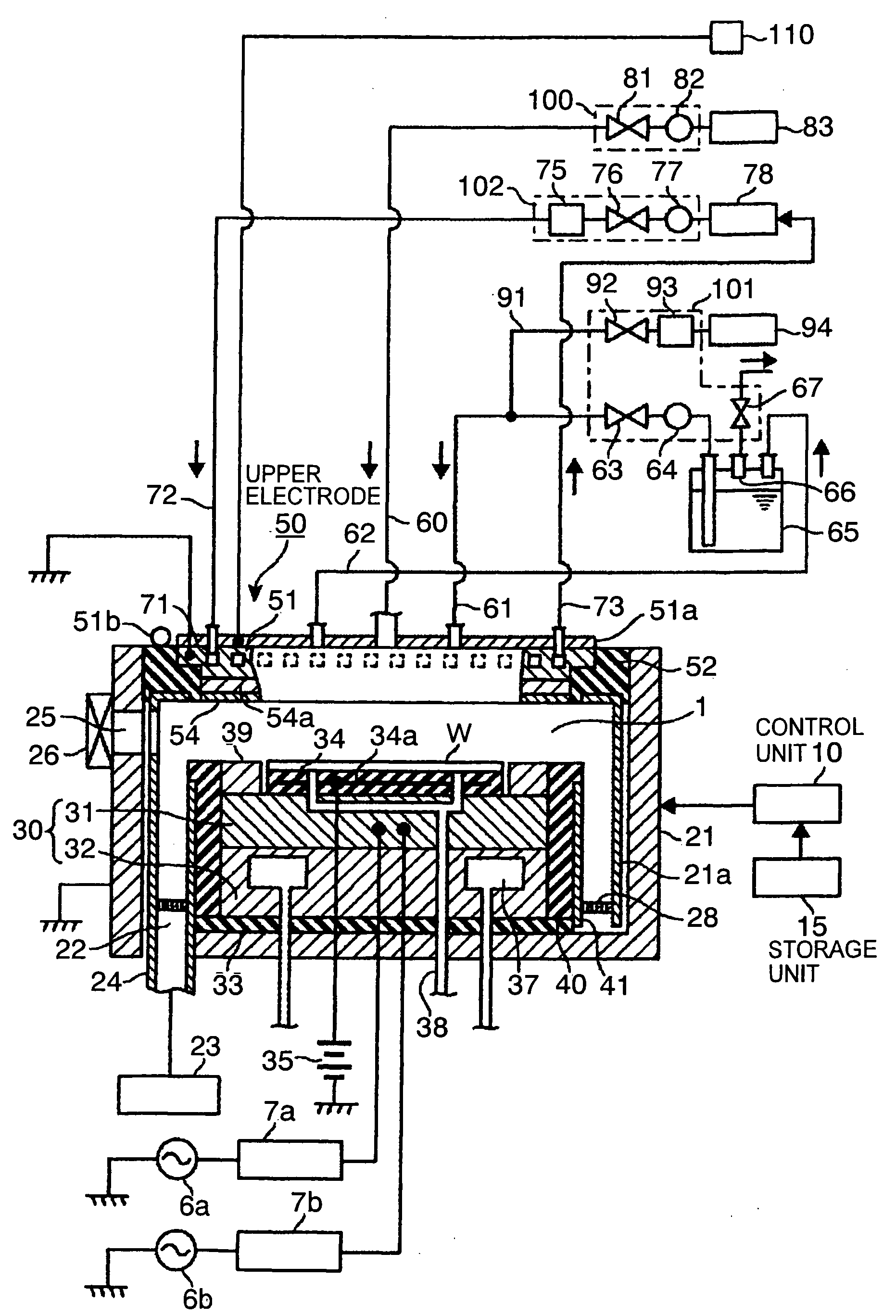
Focus ring heating method, plasma etching apparatus, and plasma etching method
ActiveUS20100213171A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple structureElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHigh frequency powerEngineering
There are provided a method of heating a focus ring and a plasma etching apparatus, capable of simplifying a structure of a heating mechanism without a dummy substrate. The plasma etching apparatus includes a vacuum processing chamber; a lower electrode serving as a mounting table for mounting a substrate thereon; an upper electrode provided to face the lower electrode; a gas supply unit for supplying a processing gas; a high frequency power supply for supplying a high frequency power to the lower electrode to generate a plasma of the processing gas; and a focus ring provided on the lower electrode to surround a periphery of the substrate. In the plasma etching apparatus, the focus ring is heated by irradiating a heating light thereto from a light source provided outside the vacuum processing chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Chemical mechanical polishing pad and chemical mechanical polishing method
ActiveUS7357703B2High rateImprove in-plane uniformityAbrasion apparatusLapping machinesIn planeEngineering
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Chemical mechanical polishing pad and chemical mechanical polishing method
ActiveUS20070149096A1High polishing rateImprove in-plane uniformityAbrasion apparatusLapping machinesCompound (substance)Engineering
A chemical mechanical polishing pad of the present invention has the following two groups of grooves on the polishing surface: (i) a group of first grooves intersect a single virtual straight light extending from the center toward the periphery of the polishing surface and have a land ratio represented by the following equation of 6 to 30: Land ratio=(P−W)÷W (P is the distance between adjacent intersections between the virtual straight line and the first grooves, and W is the width of the first grooves); and (ii) a group of second grooves extend from the center portion toward the peripheral portion of the polishing surface and consist of second grooves which are in contact with one another in the area of the center portion and second grooves which are not in contact with any other second grooves in the area of the center portion. The chemical mechanical polishing pad of the present invention has a high polishing rate and excellent in-plane uniformity in the amount of polishing of the surface to be polished even when the amount of an aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing is made small.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Dry etching apparatus, etching method, and method of forming a wiring
InactiveUS20060048894A1Improve in-plane uniformityUniformity of selection ratioTransistorElectric discharge tubesIn planeHigh frequency power
An etching apparatus is provided, in which a plurality of electrodes are disposed for placing a substrate, high-frequency power sources as many as electrodes are provided, and the electrodes and the high-frequency power sources are connected to each other independently. Among a plurality of electrodes, a high-frequency power applied to an electrode disposed below the central portion of the substrate and a high-frequency power applied to electrodes disposed below corner portions of the substrate are controlled respectively, whereby in-plane uniformity of etching can be enhanced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Processing device
InactiveUS20090008369A1Improve in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringControl valves
In a processing apparatus for performing a specified process on a target object at a predetermined process pressure, the apparatus includes an evacuable processing chamber having a gas exhaust port formed in a bottom portion thereof; a mounting table provided within the processing chamber for holding the target object; a pressure control valve connected to the gas exhaust port, the pressure control valve including a slide-type valve body for changing an area of an opening region of a valve port; and a gas exhaust system connected to the pressure control valve. The pressure control valve is eccentrically arranged such that a center axis of the mounting table lies within an opening region of the pressure control valve formed over a practical use region of a valve opening degree of the pressure control valve.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
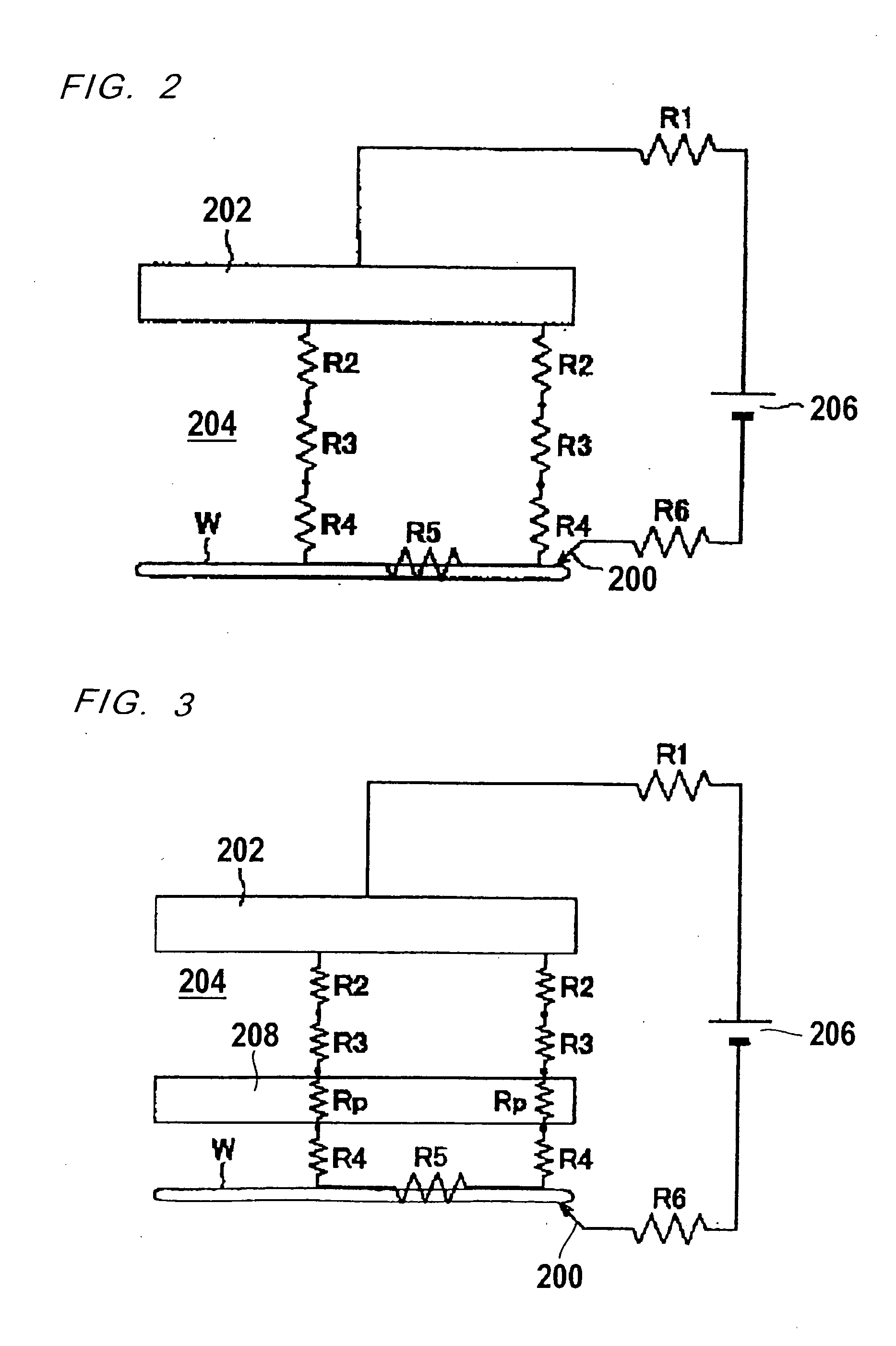
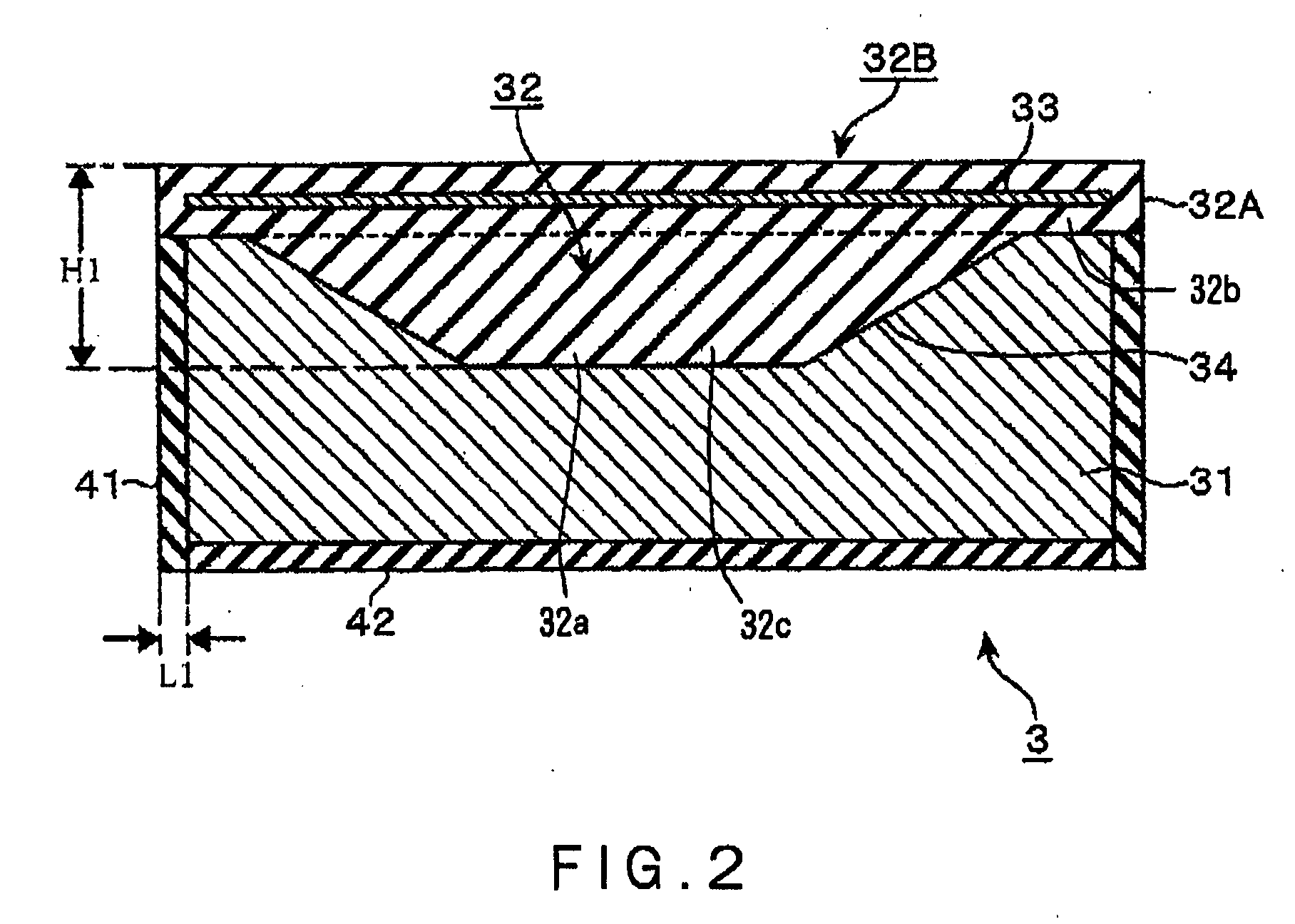
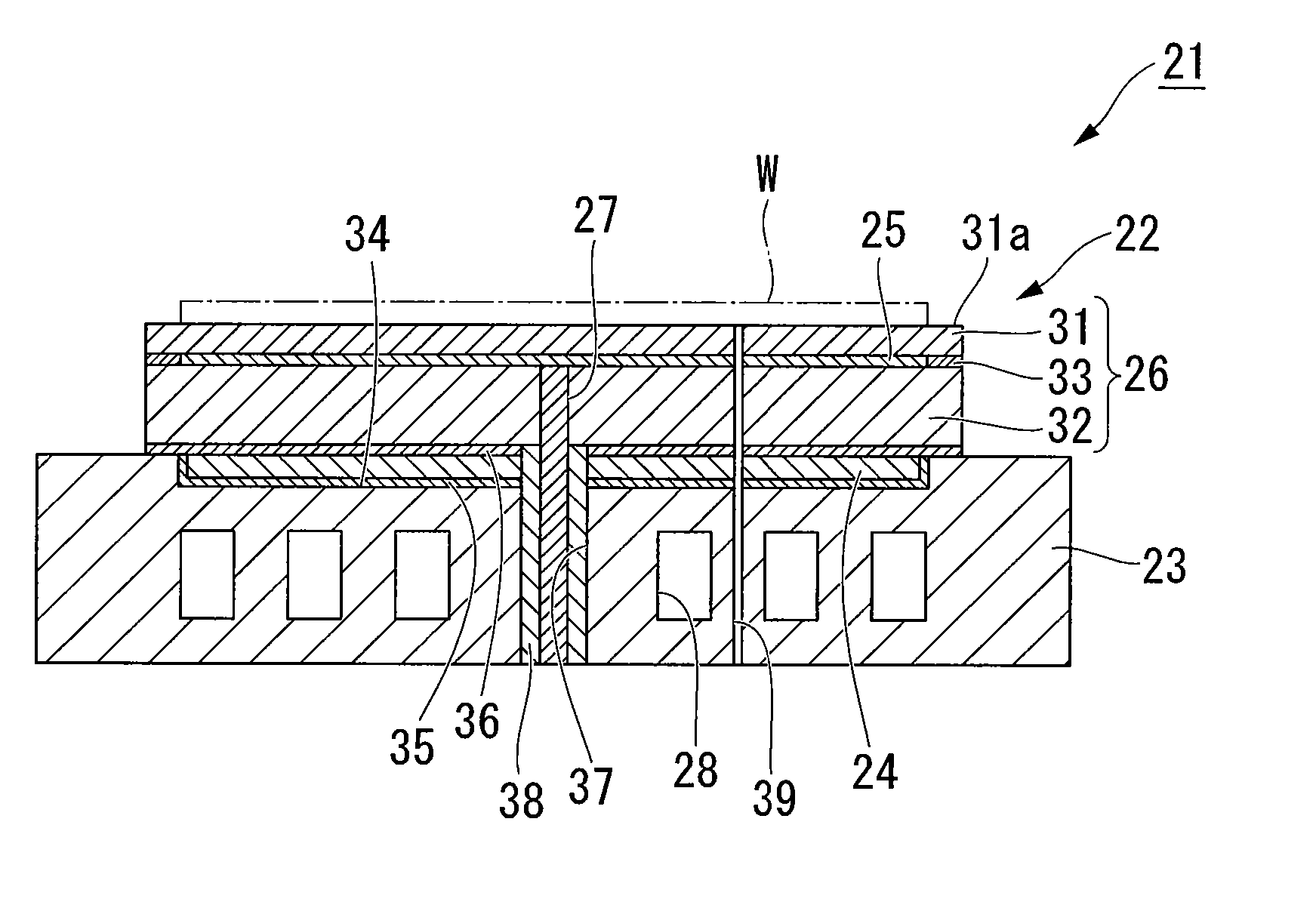
Table for plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20090101284A1Avoiding and suppressing damageUniform density distributionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeHigh frequency power
An object of the present invention is to suppress damage of an electrostatic chuck, by controlling stress exerted on each part of a table, which includes an electrically conductive material, i.e., an electrode for generating plasma, a dielectric layer for enhancing the in-plane uniformity of a plasma process, and an electrostatic chuck. The table for a plasma processing apparatus includes an electrically conductive member connected with a high frequency power source and adapted for plasma generation, for drawing ions present in the plasma, or for both thereof; a dielectric layer provided on a top face of the electrically conductive member, having a central portion and a peripheral portion that are different in thickness relative to each other, and adapted for providing uniformity of high frequency electric field intensity in a plane over the substrate to be processed; and an electrode film for an electrostatic chuck, provided in the dielectric layer and adapted for electrostatically chucking the substrate onto a top face of the dielectric layer. With such configuration, the stress exerted on the electrostatic chuck due to temperature change can be controlled.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Electrostatic chuck device
ActiveUS20080062611A1Easy to adjustInhibit currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic adsorptionDielectric plate
An electrostatic chuck device includes an electrostatic chuck section, a metal base section, and a dielectric plate. The electrostatic chuck section has a substrate, a main surface of which serves as a mounting surface for a plate-like sample, an electrostatic-adsorption inner electrode built in the substrate, and a power supply terminal for applying a DC voltage to the electrostatic-adsorption inner electrode. Here, a dielectric plate is fixed to a concave portion formed in the metal base section. The dielectric plate and the electrostatic chuck section are adhesively bonded to each other with an insulating adhesive bonding layer interposed therebetween. The dielectric plate and the concave portion are adhesively bonded to each other with a conductive adhesive bonding layer interposed therebetween, the volume resistivity of which is 1.0×10−2Ωcm or less.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
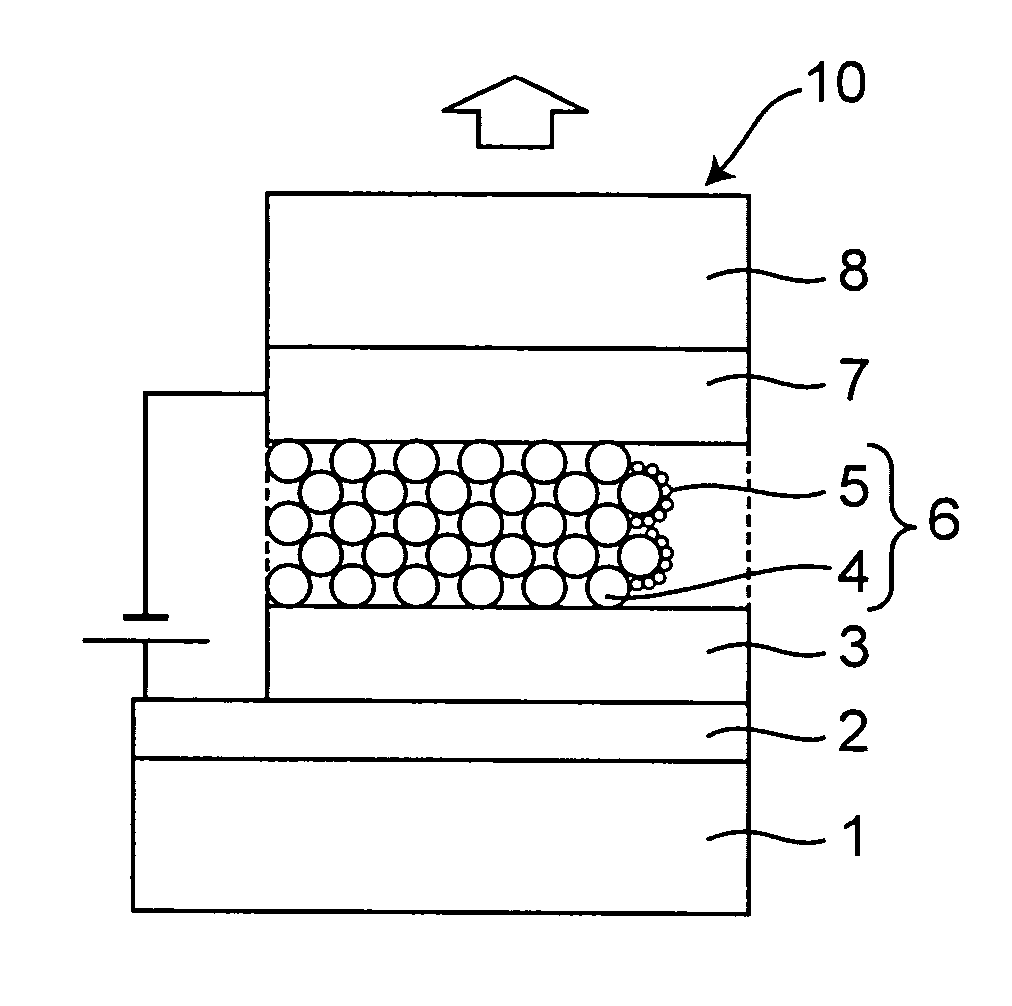
Microstructures, method for producing microstructures, and optical field amplifying device
InactiveCN101319994AEffective electric field enhancement effectNot easy to peel offRaman scatteringFluorescence/phosphorescenceElectricityDielectric
Manufacture of a microstructure that exhibits electric field amplification effects having high planar uniformity is enabled by a simple process. The microstructure 1 is formed on a conductor (13). The microstructure (1) is equipped with a dielectric base material (11), in which a great number of fine holes (12) having substantially the same shape in plan view are formed. The fine holes (12) are open at the surface (11s) of the dielectric base material (11), and are substantially uniformly provided therein. A plurality of micro metal members (20) are fixed to the dielectric base material (11).The micro metal members (20) include filling portions (21) that fill one or more of the fine holes (12), and protruding portions (22) that protrude from the surface (11s) of the dielectric base material (11) and are of diameters greater than the fine holes (12), capable of inducing local plasmon. The plurality of micro metal members (20) include those that have different numbers of filling portions (21).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method and storage medium
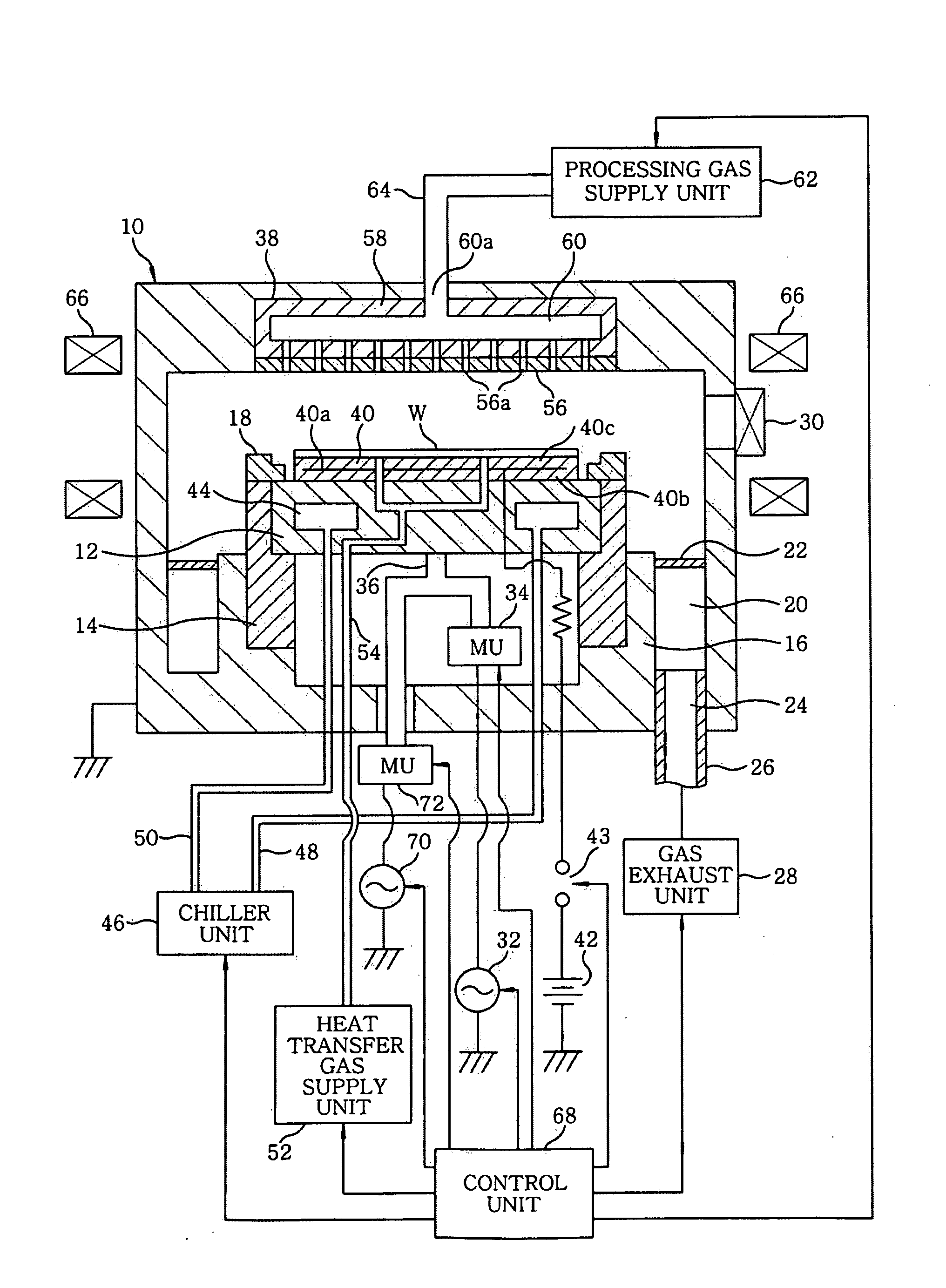
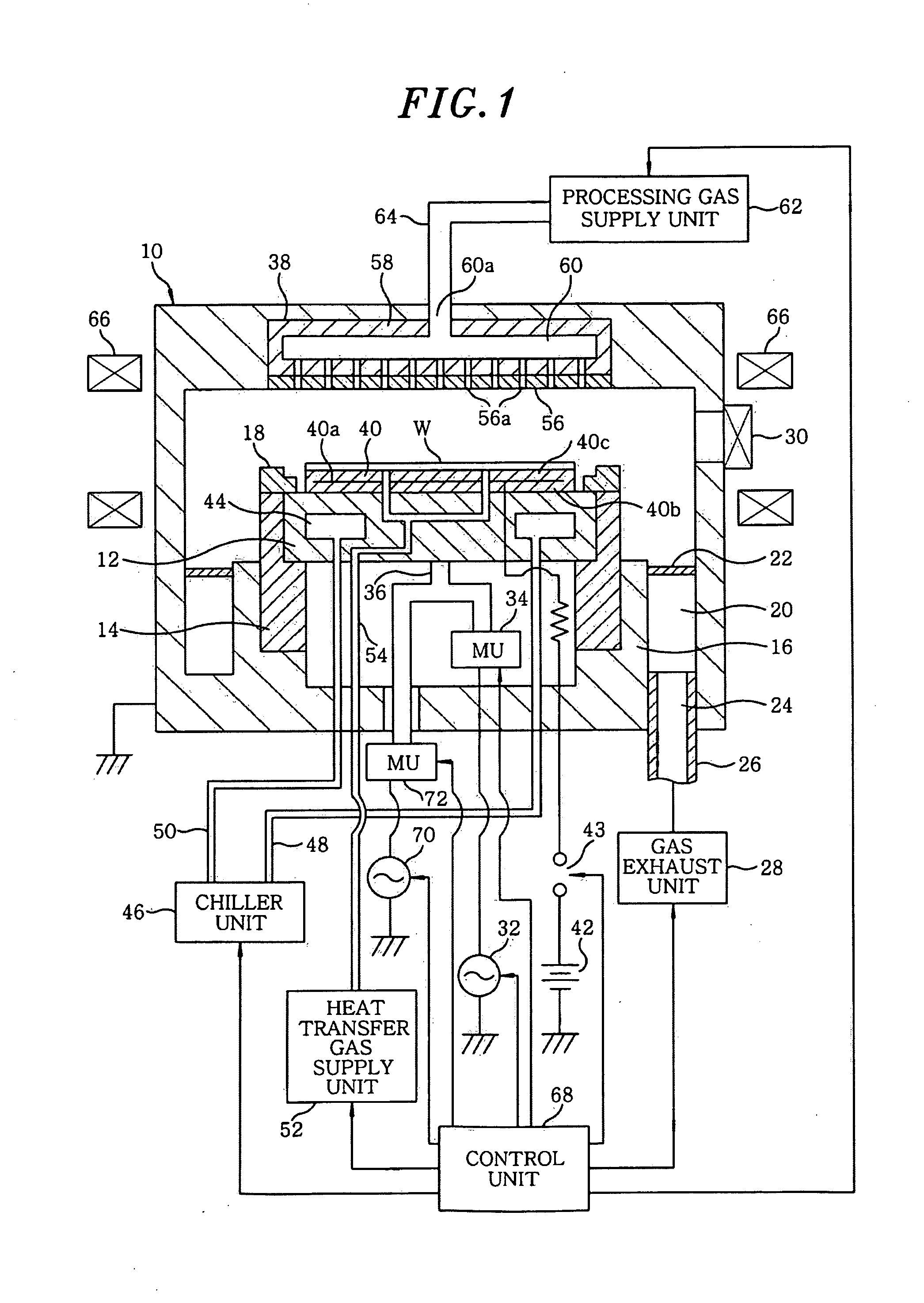
InactiveUS20090047795A1Effectively preventing charging damageImproving stability and reliabilityCellsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringRadio frequency
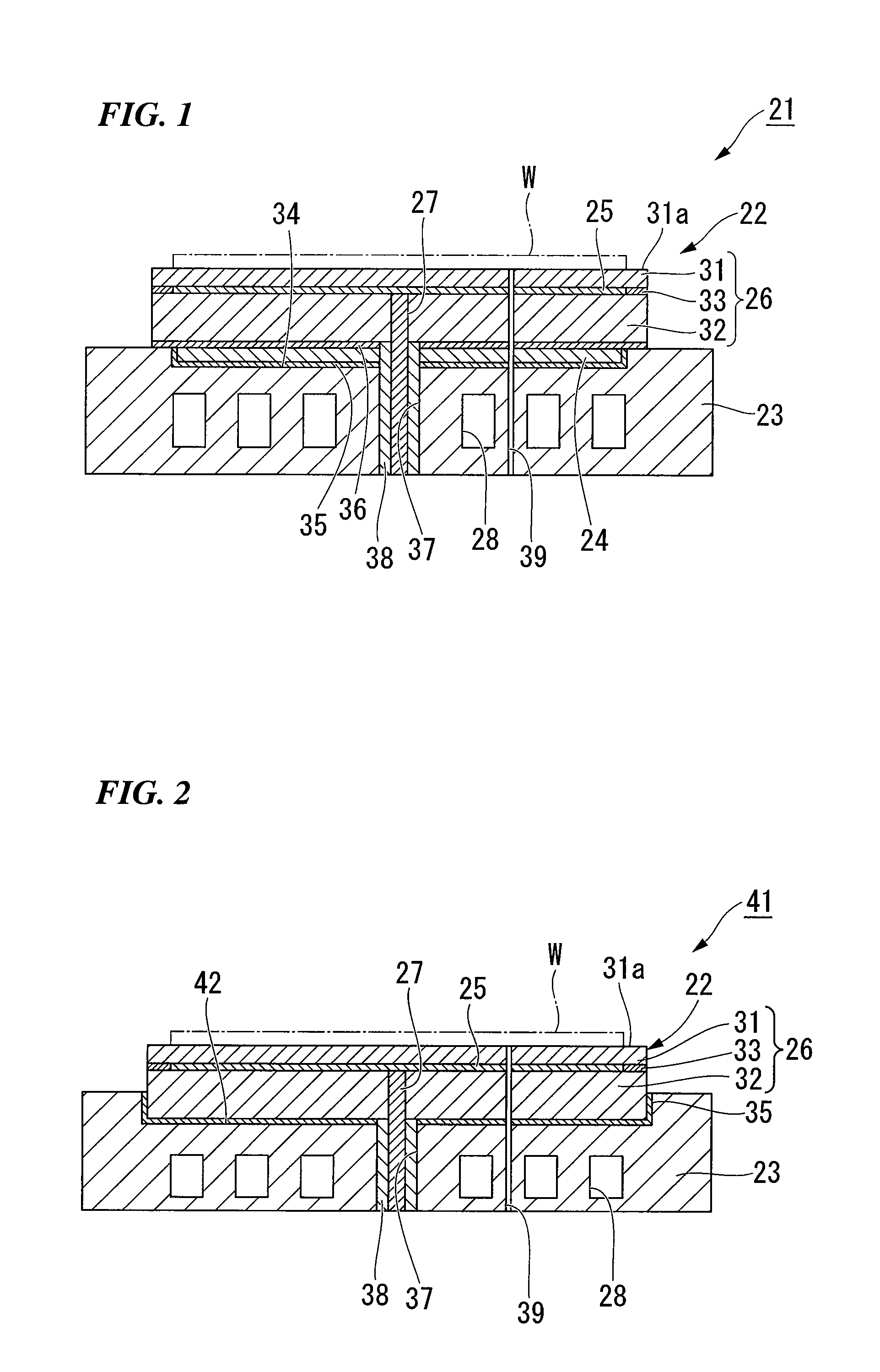
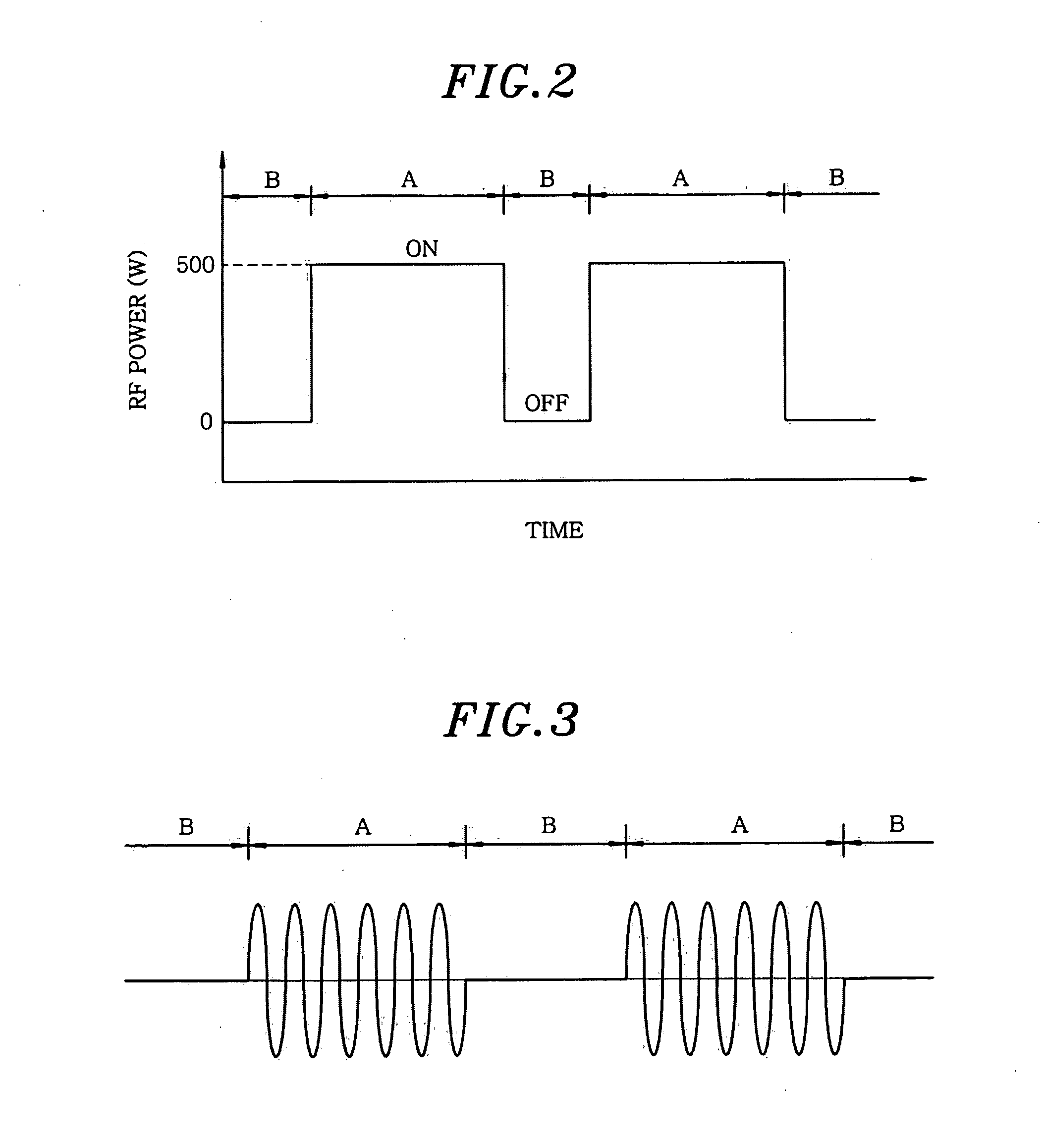
A plasma processing apparatus includes a first radio frequency (RF) power supply unit for applying a first RF power for generating a plasma from a processing gas to at least one of a first and a second electrode which are disposed facing each other in an evacuable processing chamber. The first RF power supply unit is controlled by a control unit so that a first phase at which the first RF power has a first amplitude for generating a plasma and a second phase at which the first RF power has a second amplitude for generating substantially no plasma are alternately repeated at predetermined intervals.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com