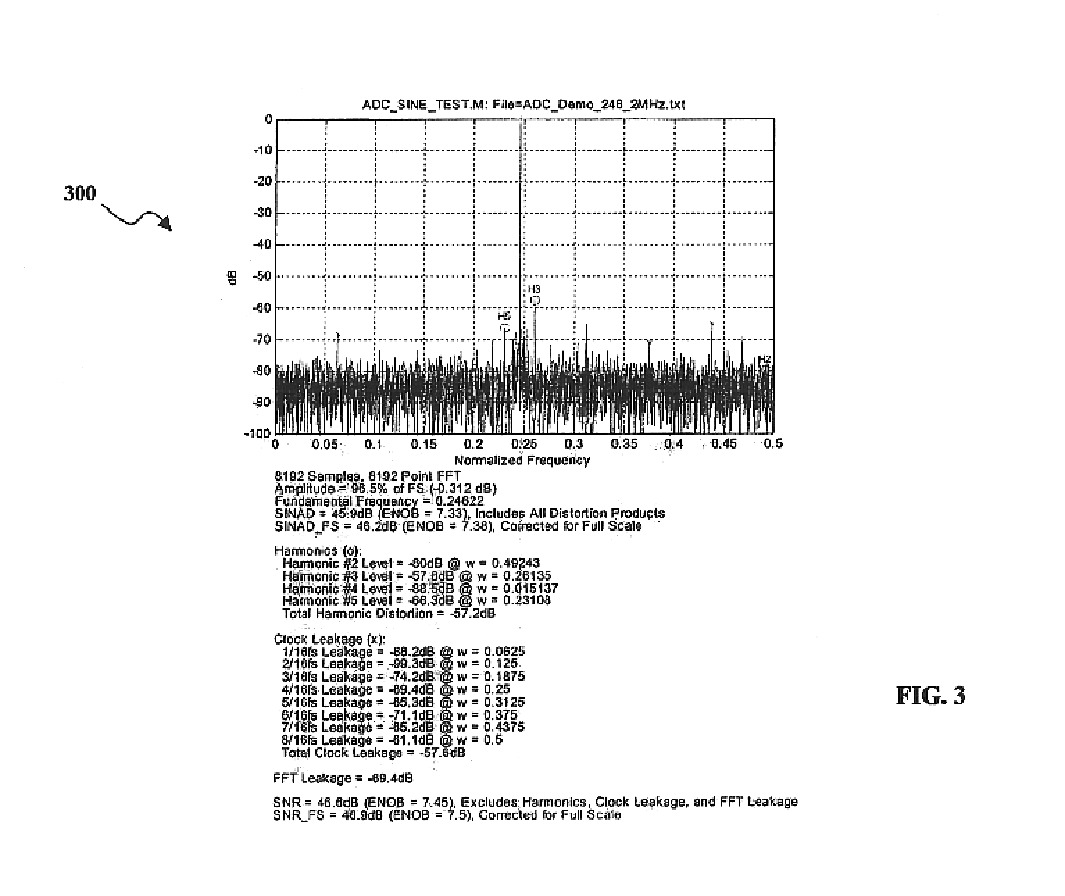
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
729 results about "Dither" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images. Dither is routinely used in processing of both digital audio and video data, and is often one of the last stages of mastering audio to a CD.
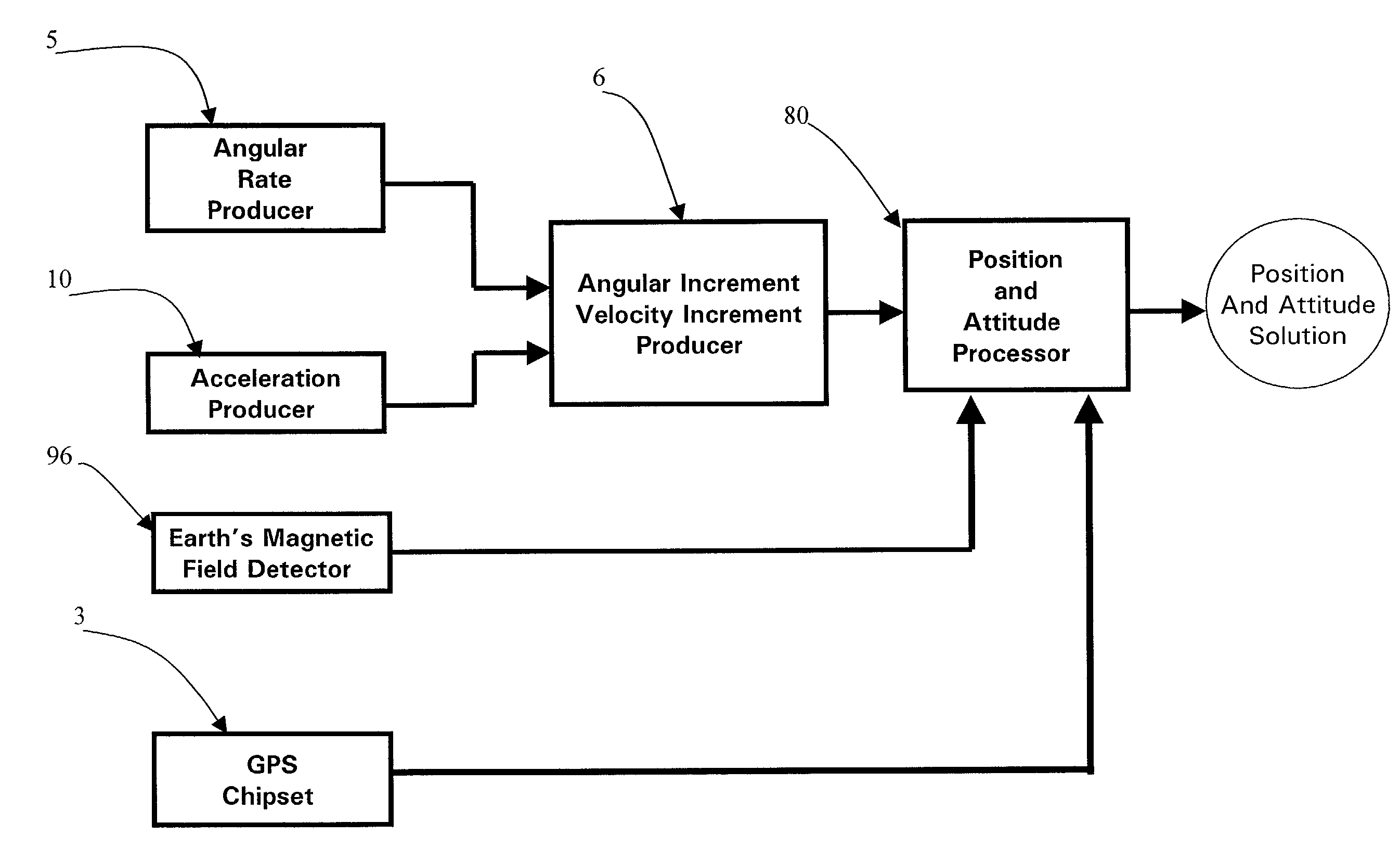
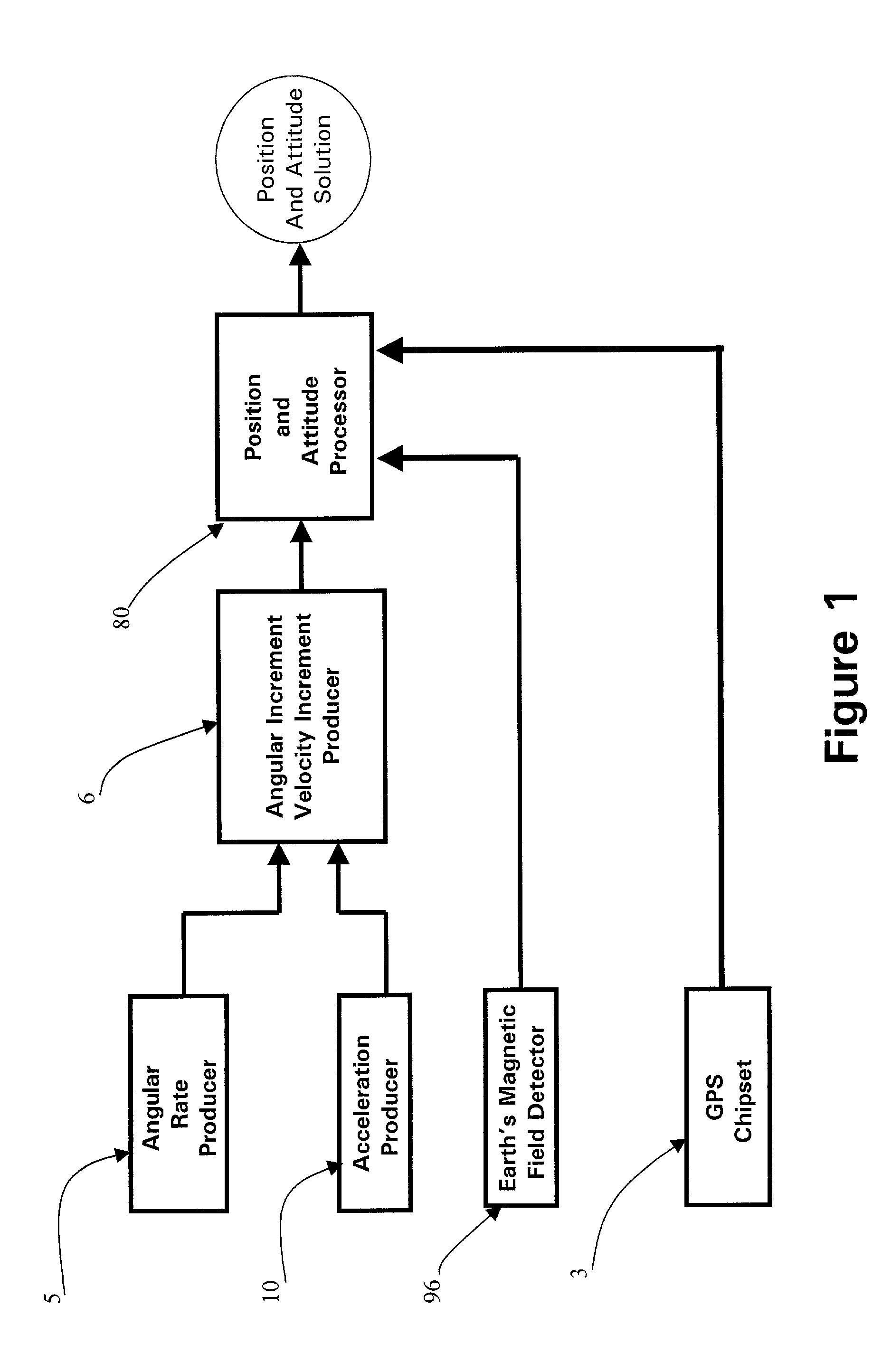
Micro integrated global positioning system/inertial measurement unit system
InactiveUS20020008661A1Precise positioningInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationCarrier signalClosed loop
A micro integrated Global Positioning System (GPS) / Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) System, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier and GPS measurements of the carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors, acceleration sensors, and GPS chipset, is employed with MEMS angular rate and acceleration sensors and GPS chipset. Compared with a conventional IMU / GPS system, the system of the present invention uses an integrated processing scheme by means of digital closed loop control of the dither driver signals for MEMS angular rate sensors, a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme of the IMU, digital temperature control and compensation, the earth's magnetic field-based heading damping, robust error estimator, and compact sensor and circuit architecture and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
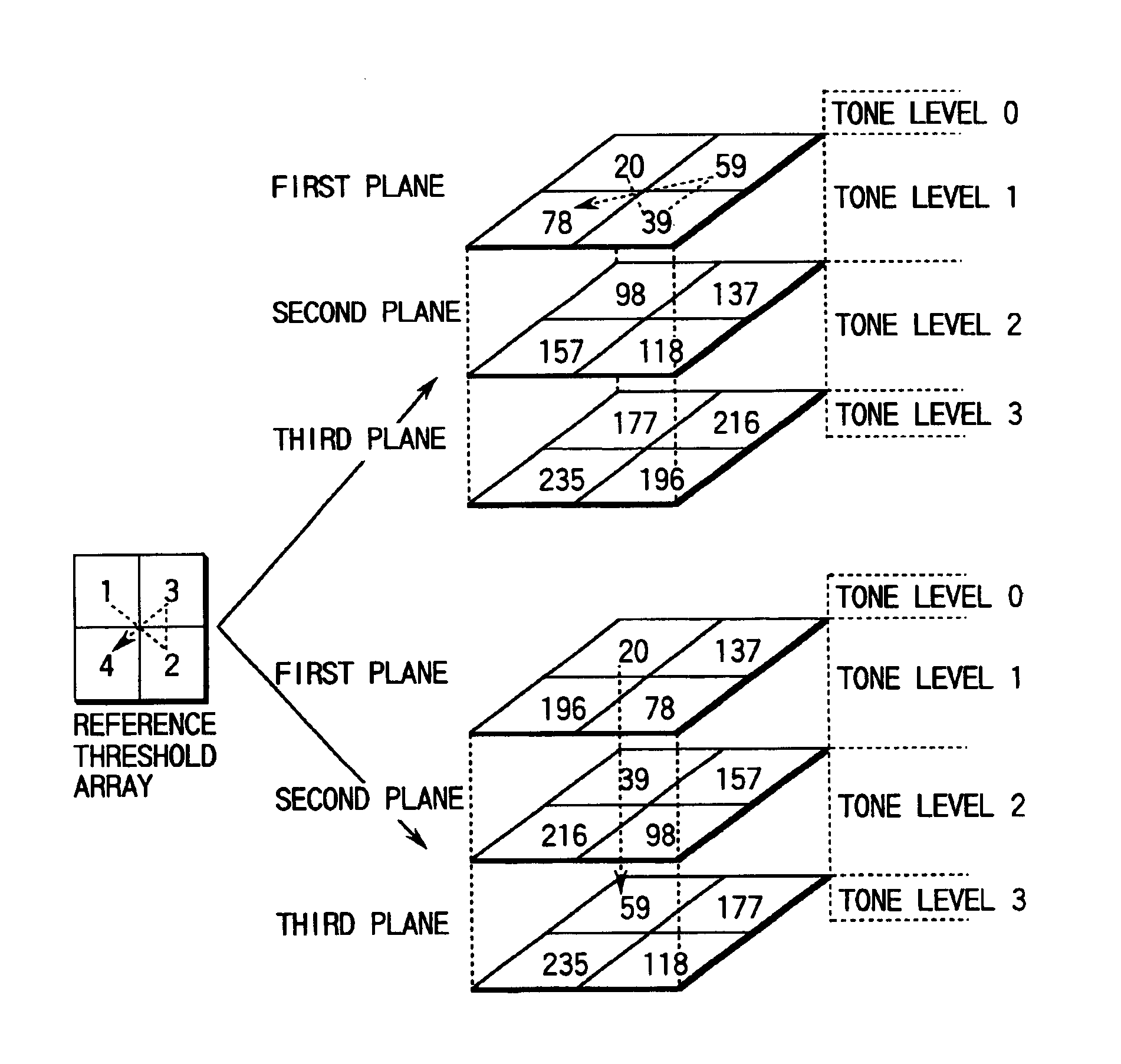
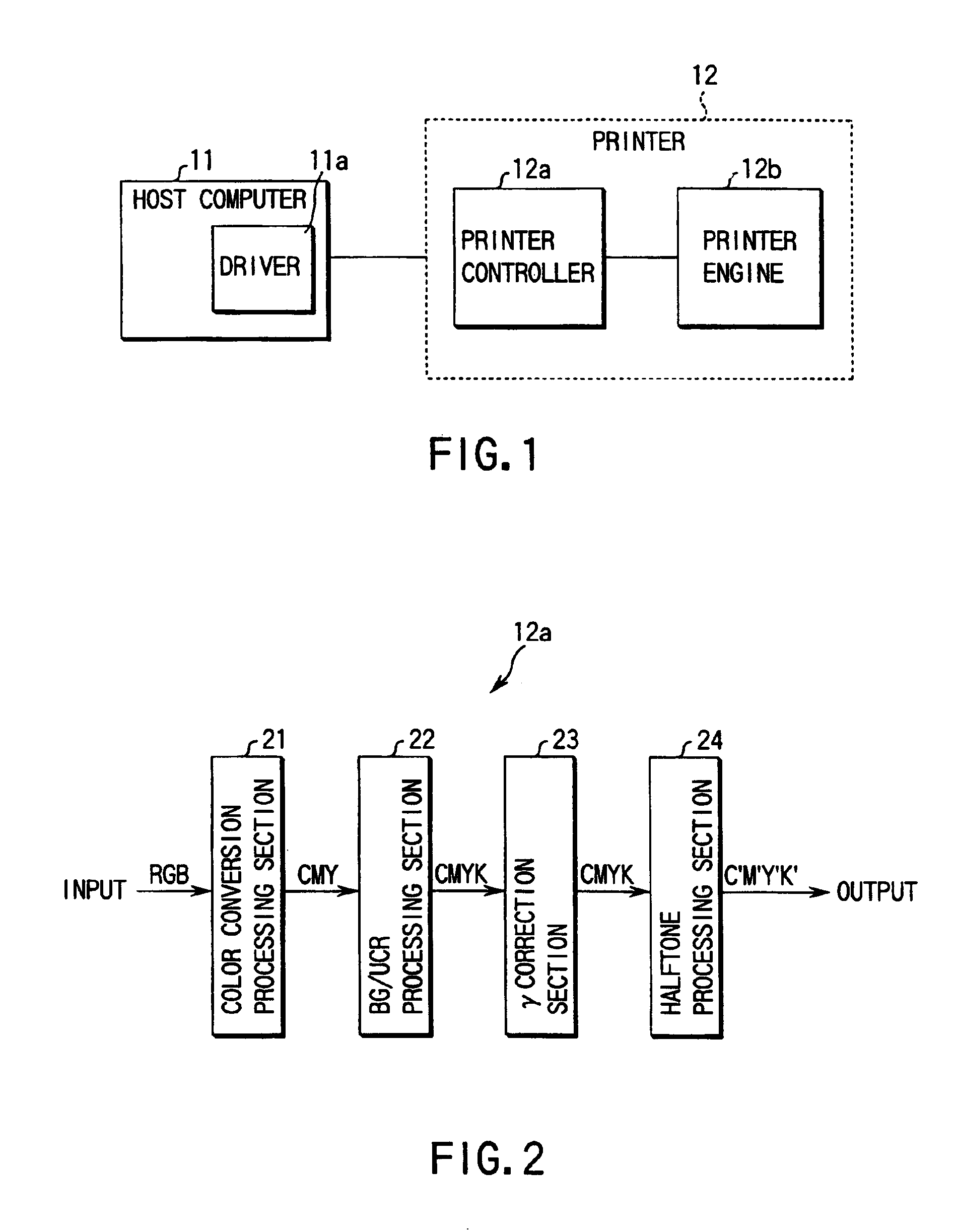
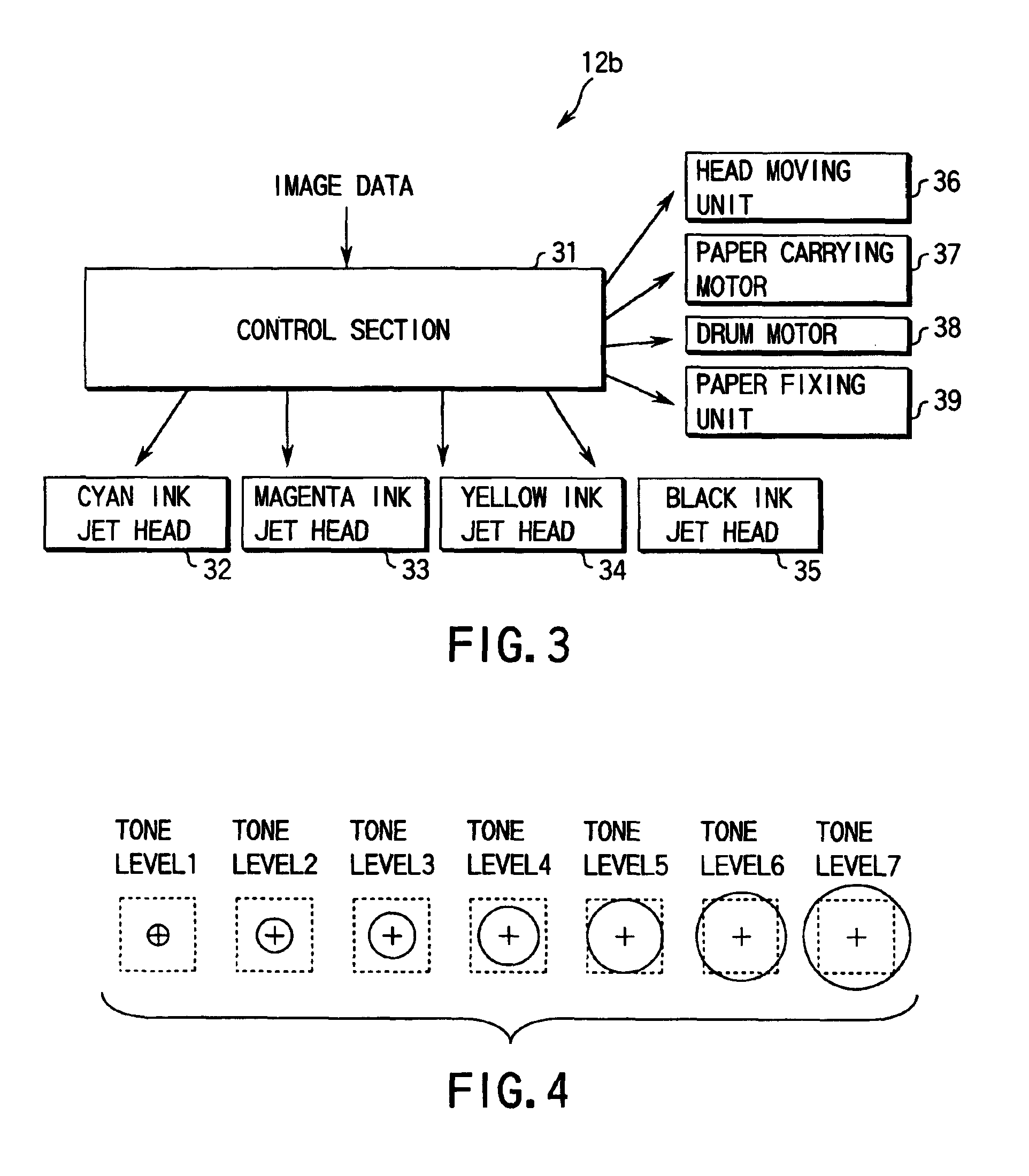
Image processor and color image processor
InactiveUS6906825B1Preventing deterioration of tone reproducibilityInhomogeneous suppressionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging dataDither
A halftone processing section halftone-processes input image data using a plurality of dither threshold planes. An image output section having different output position accuracies between a main scan direction and a sub-scan direction outputs an image corresponding to halftone-processed image data. Each of the dither threshold planes consists of a plurality of the same unit threshold matrixes. In the unit threshold matrix, a relatively medium to high threshold array in a predetermined threshold range corresponding to the entire tone range of the input image data is an aperiodic array and an anisotropic array with neighboring thresholds having close values, in a direction coincident with a scan direction, in which the output position accuracy of the image output means is low. With this configuration, the image output section outputs an image having serial medium and high tone dots in the scan direction.
Owner:TOSHIBA TEC KK
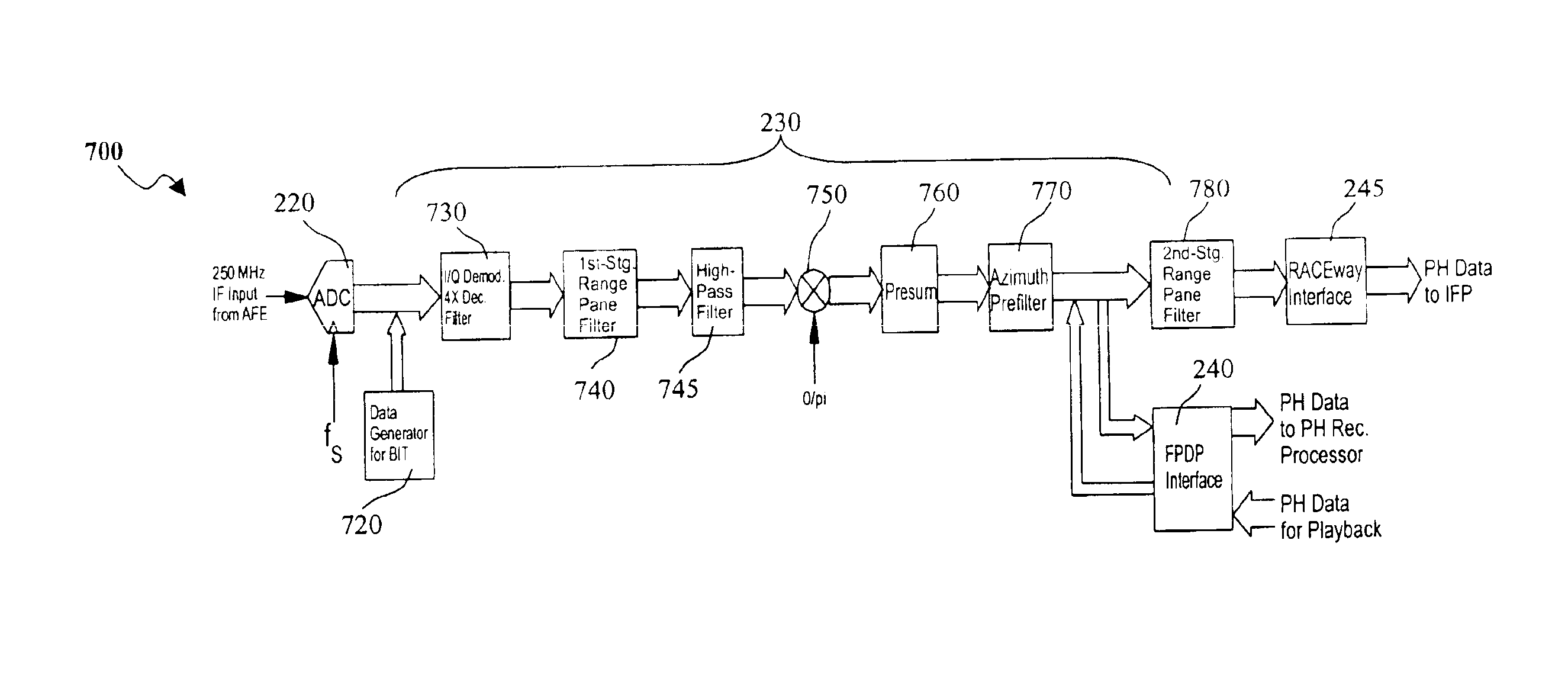
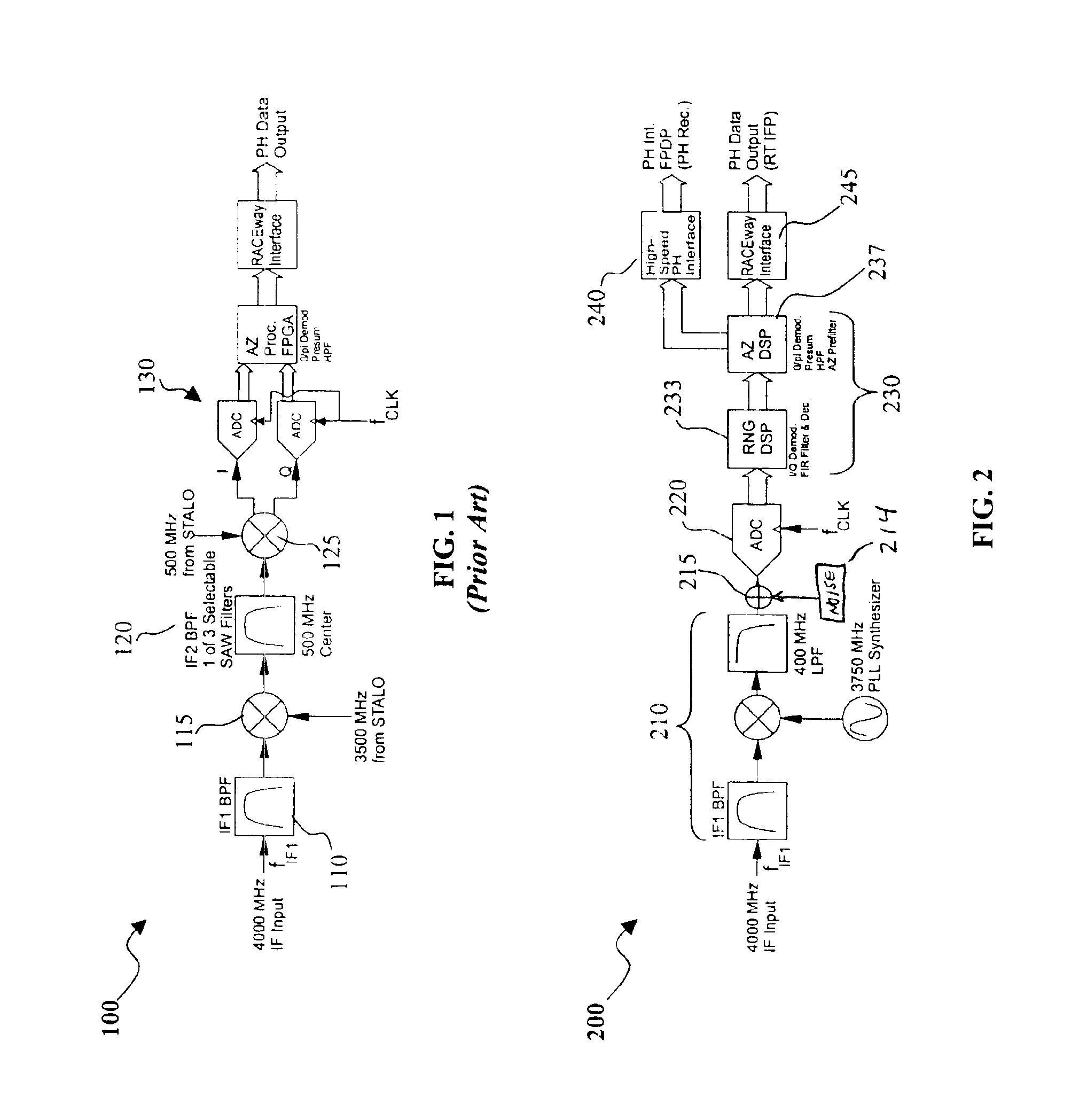
Digital intermediate frequency receiver module for use in airborne SAR applications
ActiveUS6864827B1Increase flexibilityIncrease spacingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
A digital IF receiver (DRX) module directly compatible with advanced radar systems such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems. The DRX can combine a 1 G-Sample / sec 8-bit ADC with high-speed digital signal processor, such as high gate-count FPGA technology or ASICs to realize a wideband IF receiver. DSP operations implemented in the DRX can include quadrature demodulation and multi-rate, variable-bandwidth IF filtering. Pulse-to-pulse (Doppler domain) filtering can also be implemented in the form of a presummer (accumulator) and an azimuth prefilter. An out of band noise source can be employed to provide a dither signal to the ADC, and later be removed by digital signal processing. Both the range and Doppler domain filtering operations can be implemented using a unique pane architecture which allows on-the-fly selection of the filter decimation factor, and hence, the filter bandwidth. The DRX module can include a standard VME-64 interface for control, status, and programming. An interface can provide phase history data to the real-time image formation processors. A third front-panel data port (FPDP) interface can send wide bandwidth, raw phase histories to a real-time phase history recorder for ground processing.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Control Method for a Robot
ActiveUS20070260356A1Reduce the effects of frictionFaster and accurate responseProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
An apparatus, a method and a control system for controlling an industrial robot with at least one axis of rotation and / or translation. The robot includes at least one actuator or motor at each of the axes for driving a movement of an arm of the robot and at least one sensor at each of the rotatable shafts. A dither-signal generator for generation of a periodic signal is used to provide a varying dither signal to a servo of the actuator. Automatic adaption of the dither signal is provided. A computer program for carrying out the method and a graphical user interface.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
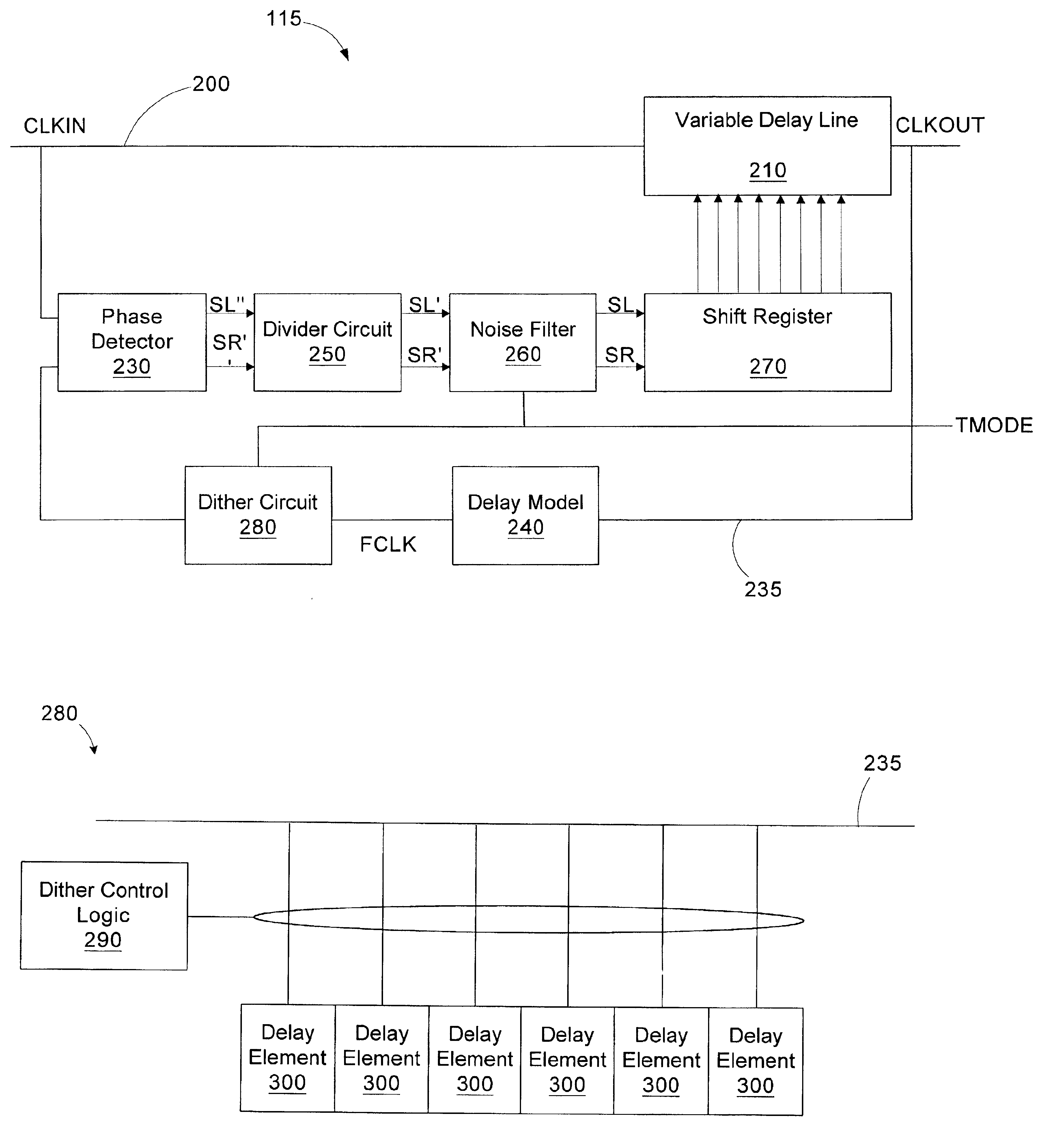
Method and apparatus for characterizing a delay locked loop
A delay locked loop includes a forward path, a feedback path, a phase detector, logic, and a dither circuit. The forward path includes a delay line configured to receive an input clock signal and delay the input clock signal by a time interval to generate an output clock signal. The feedback path is configured to provide a feedback clock signal based on the output clock signal. The phase detector is configured to compare the input clock signal and the feedback clock signal and generate a shift signal if the output clock signal is not in phase with the input clock signal. The logic is coupled to the delay line and configured to receive the shift signal and control the time interval based on the shift signal. The dither circuit is coupled to the delay line and configured to introduce a delay responsive to an assertion of a test mode enable signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
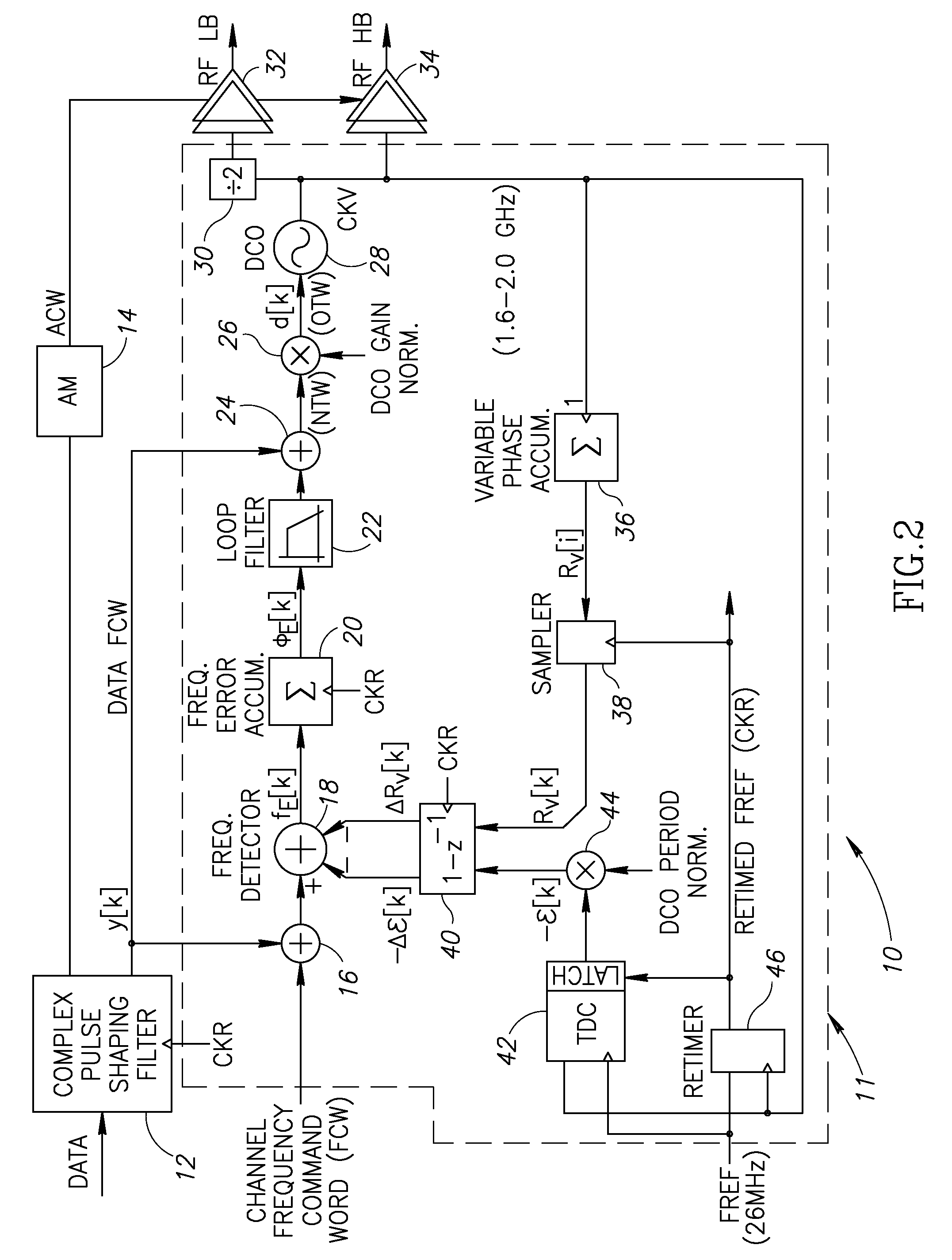
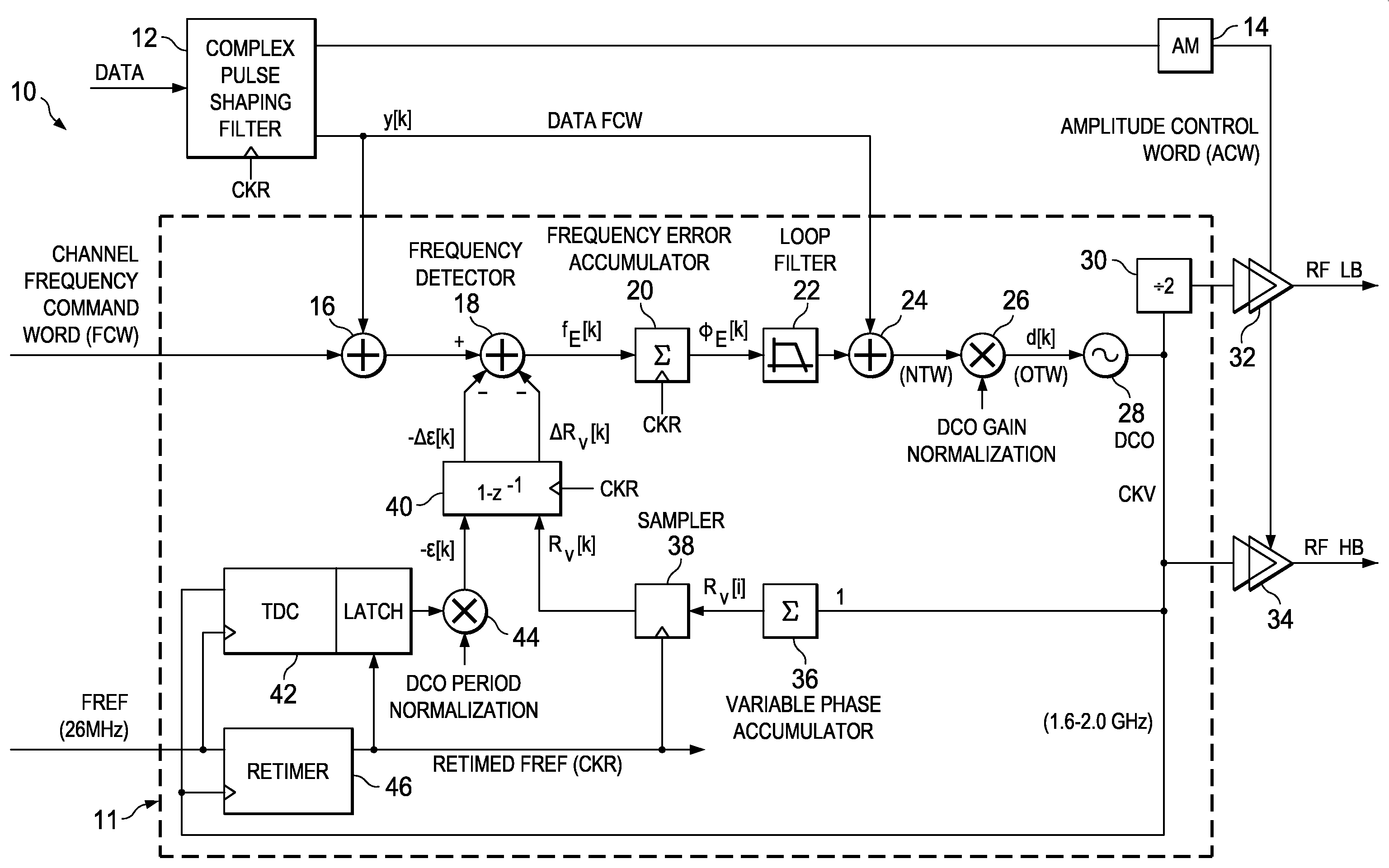
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS20080068236A1High resolutionHigh frequency noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
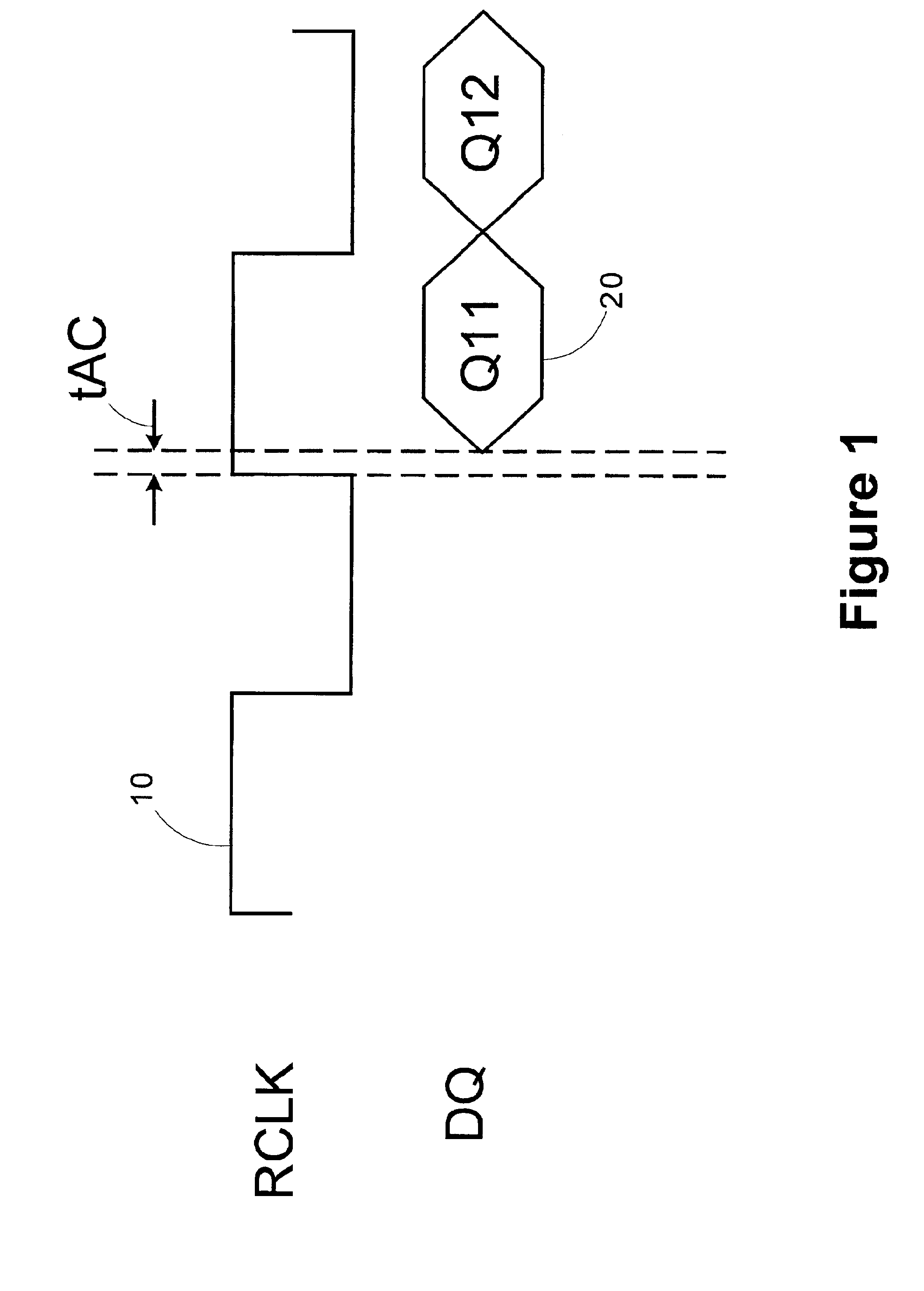
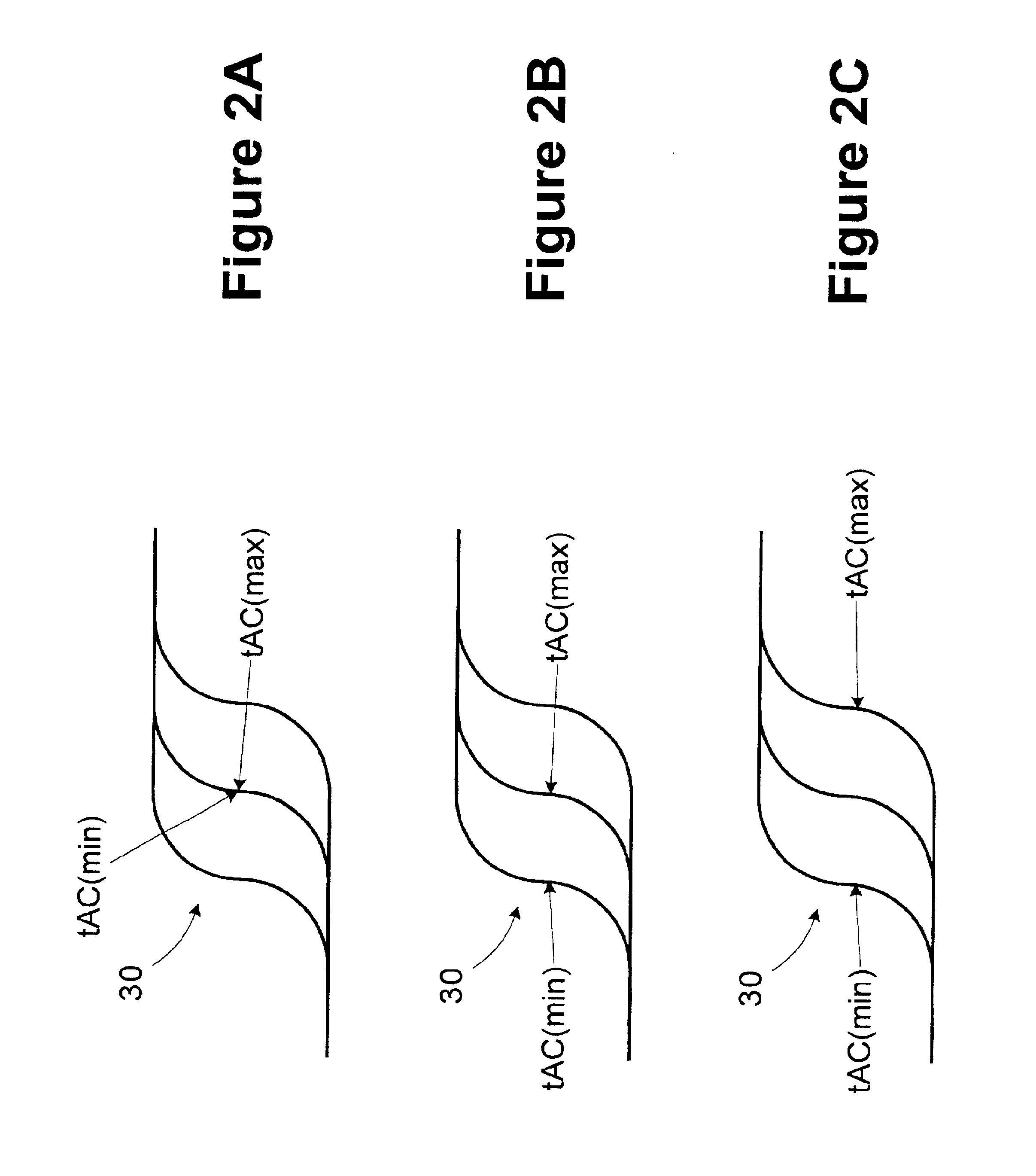
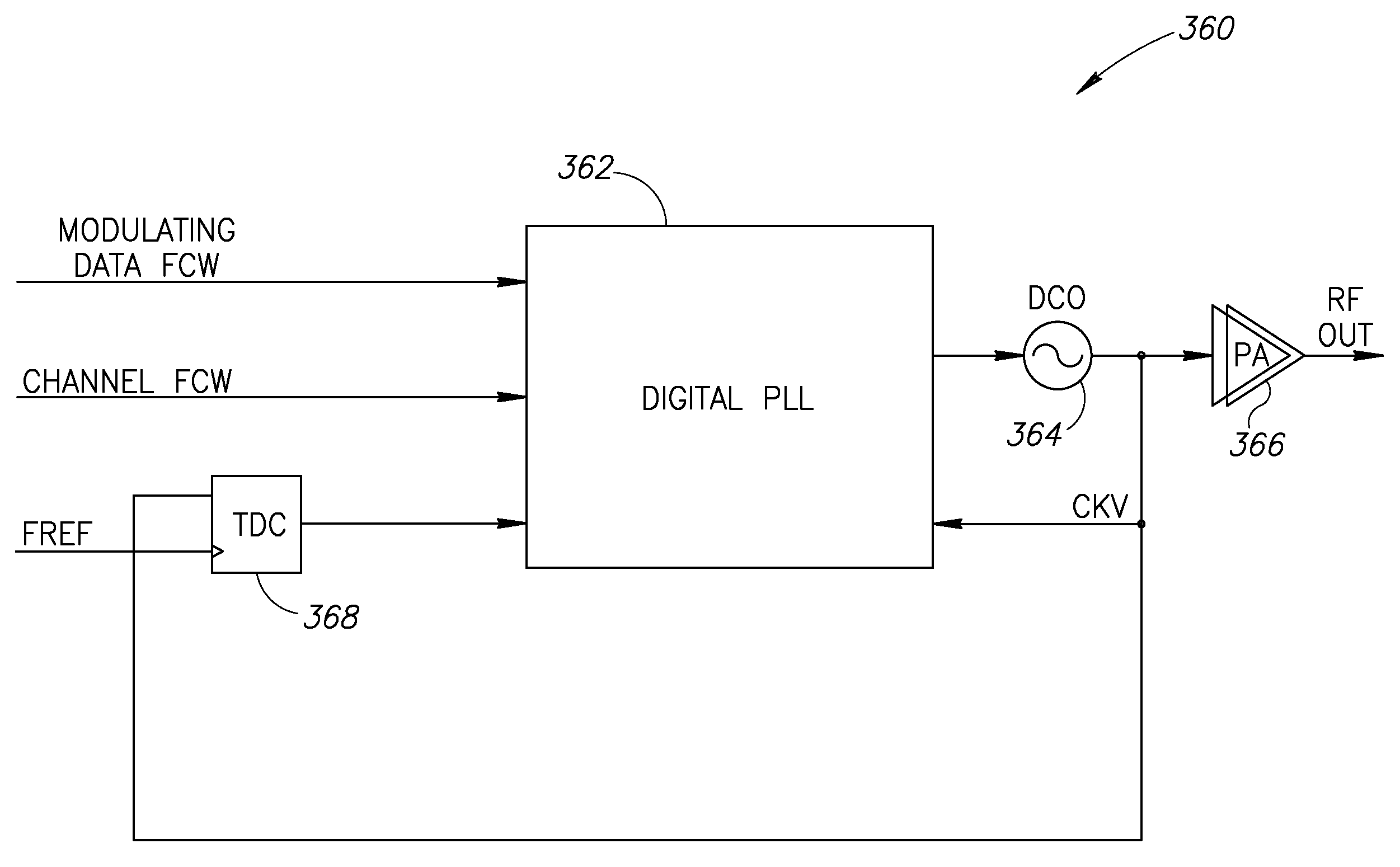
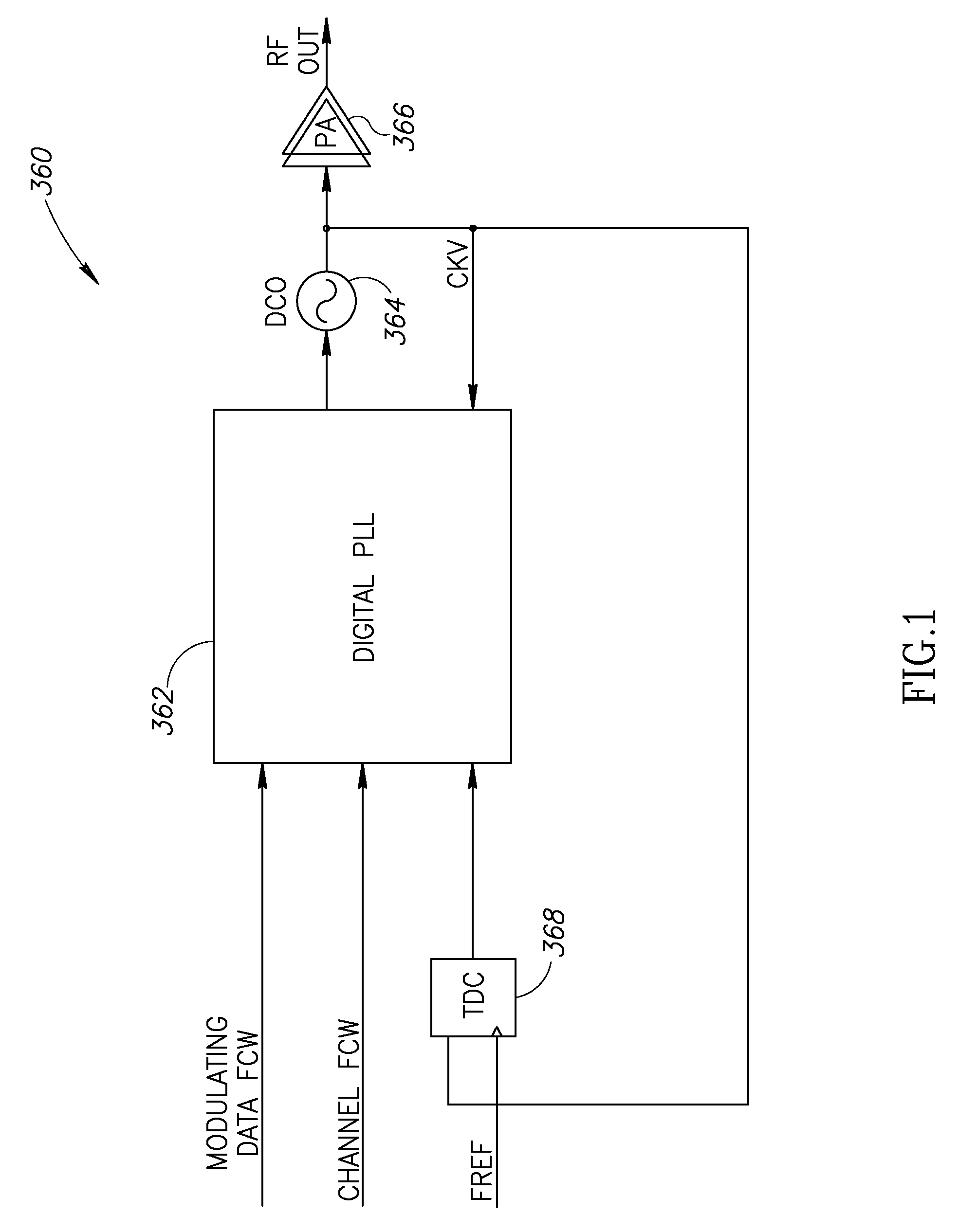
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of improving the quantization resolution of a time to digital converter in a digital PLL using noise shaping. The TDC quantization noise shaping scheme is effective to reduce the TDC quantization noise to acceptable levels especially in the case of integer-N channel operation. The mechanism monitors the output of the TDC circuit and adaptively generates a dither (i.e. delay) sequence based on the output. The dither sequence is applied to the frequency reference clock used in the TDC which adjusts the timing alignment between the edges of the frequency reference clock and the RF oscillator clock. The dynamic alignment changes effectively shape the quantization noise of the TDC. By shaping the quantization noise, a much finer in-band TDC resolution is achieved resulting in the quantization noise being pushed out to high frequencies where the PLL low pass characteristic effectively filters it out.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Laser spectral engineering for lithographic process
InactiveUS6853653B2Improved pattern resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionResistElectric discharge
An integrated circuit lithography technique called spectral engineering by Applicants, for bandwidth control of an electric discharge laser. In a preferred process, a computer model is used to model lithographic parameters to determine a desired laser spectrum needed to produce a desired lithographic result. A fast responding tuning mechanism is then used to adjust center wavelength of laser pulses in a burst of pulses to achieve an integrated spectrum for the burst of pulses approximating the desired laser spectrum. The laser beam bandwidth is controlled to produce an effective beam spectrum having at least two spectral peaks in order to produce improved pattern resolution in photo resist film. Line narrowing equipment is provided having at least one piezoelectric drive and a fast bandwidth detection control system having a time response of less than about 2.0 millisecond. In a preferred embodiment, a wavelength tuning mirror is dithered at dither rates of more than 500 dithers per second in phase with the repetition rate of the laser. In one case, the piezoelectric drive was driven with a square wave signal and in a second case it was driven with a sine wave signal. In another embodiment, the maximum displacement was matched on a one-to-one basis with the laser pulses in order to produce a desired average spectrum with two peaks for a series of laser pulses. Other preferred embodiments utilize three separate wavelength tuning positions producing a spectrum with three separate peaks.
Owner:CYMER INC
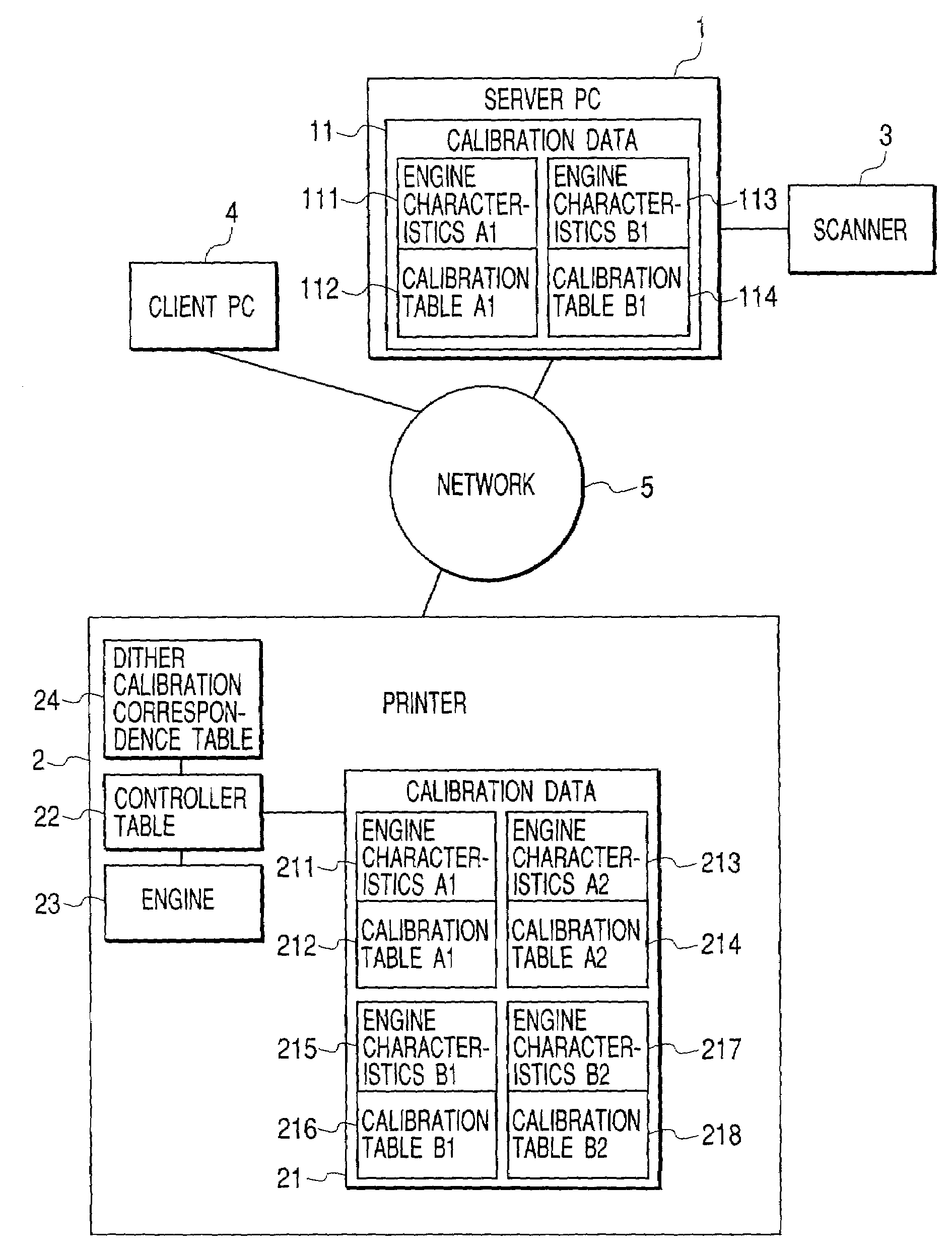
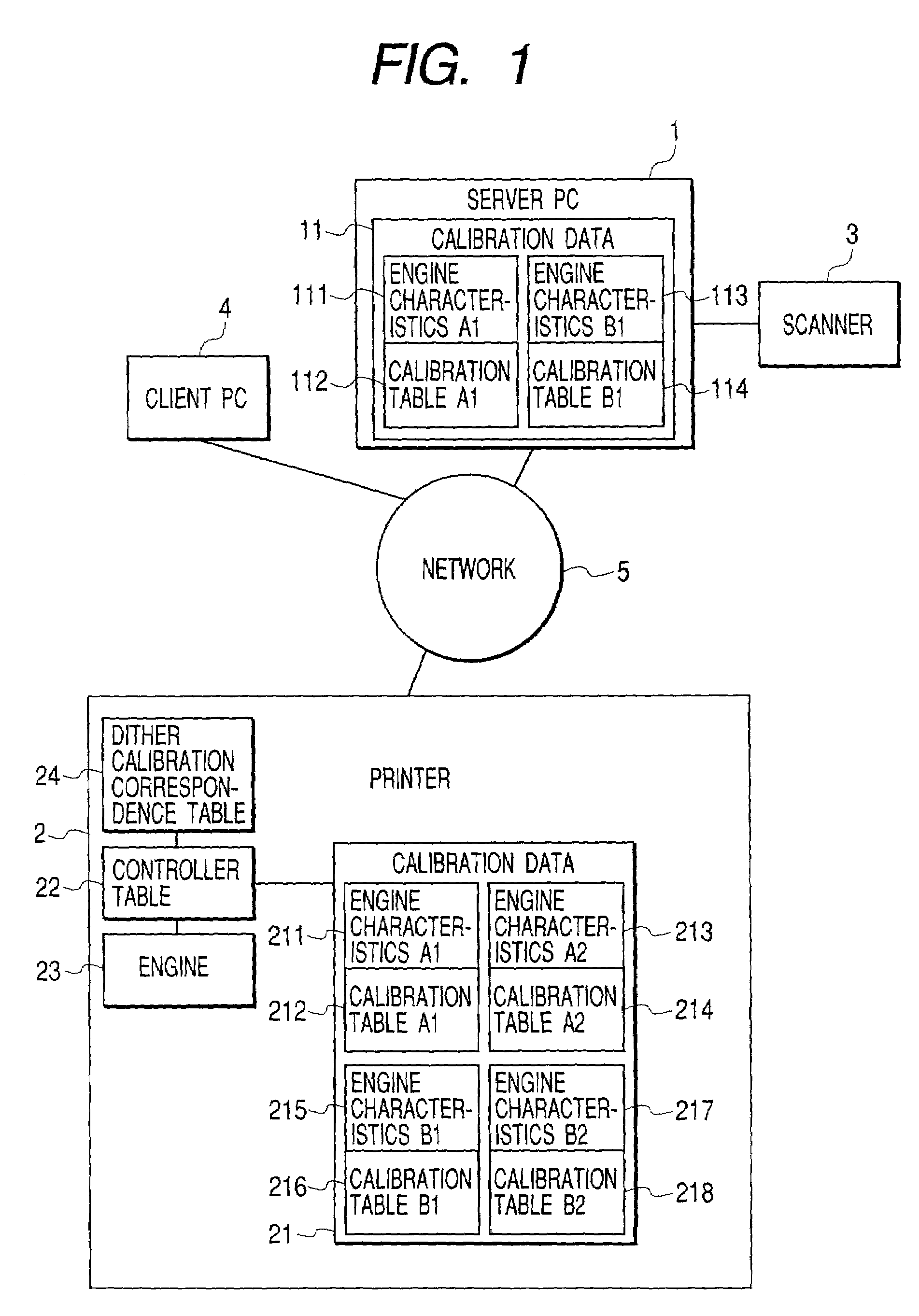
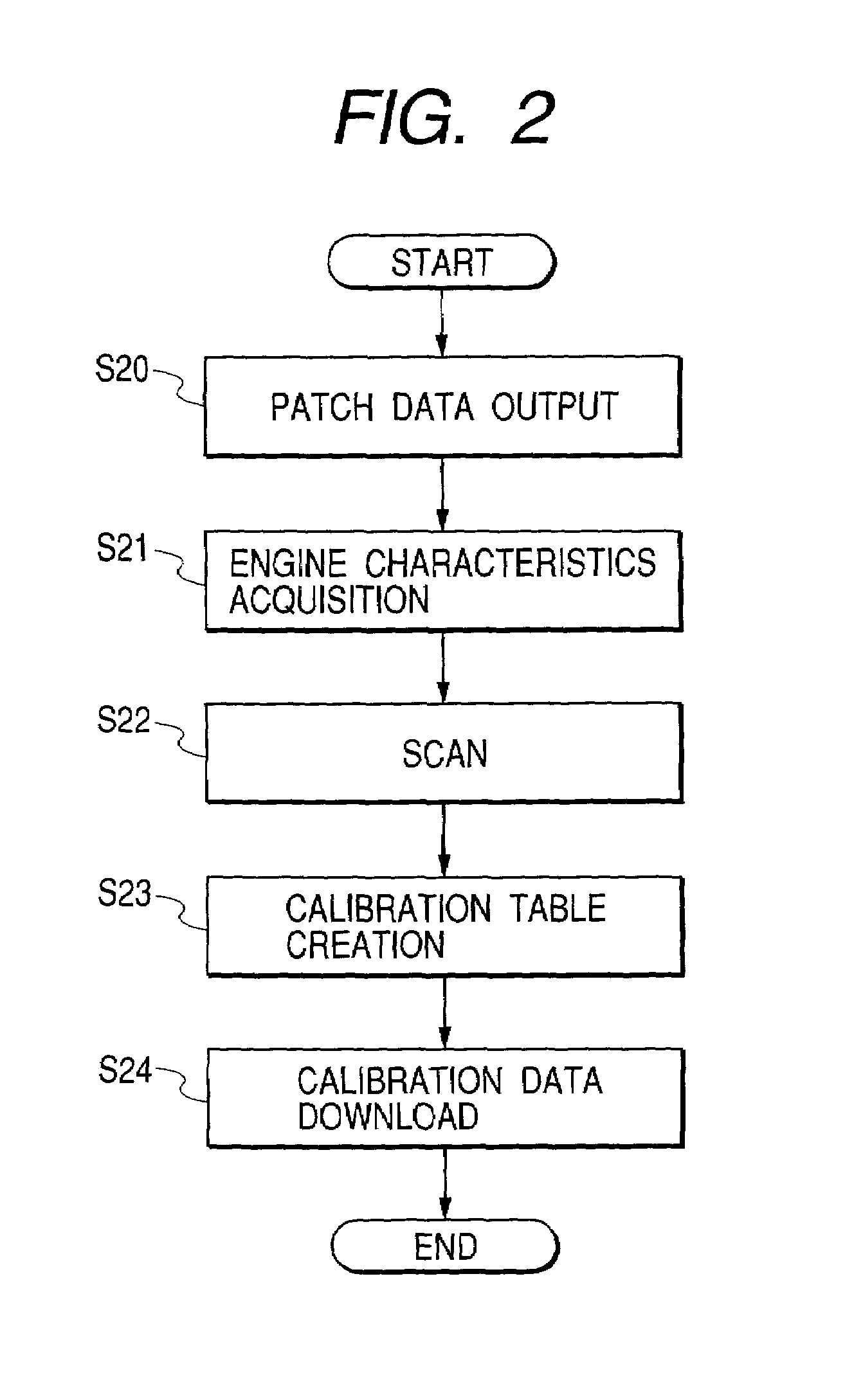
Calibration method for density in image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7061648B2Accurate CalibrationImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage formationVolumetric Mass Density
Calibration associated with output density correction of a printer is effected by software calibration manipulated by the user and device calibration automatically performed by the printer, and, regarding these calibrations, high accurate calibration in which dither patterns for binarizing processing are matched to each other is effected.In a system in which either one of halftone patterns A, B, C and D as dither patterns can be used, regarding fewer number of patterns A and B, second calibration tables are created by correcting first calibration tables based on the software calibration by using correction data of engine characteristics based on the device calibration. Among the usable halftone patterns, the calibration table corresponding to the pattern A or B is selected in accordance with the set halftone pattern, and the output density correction by using the selected table.
Owner:CANON KK
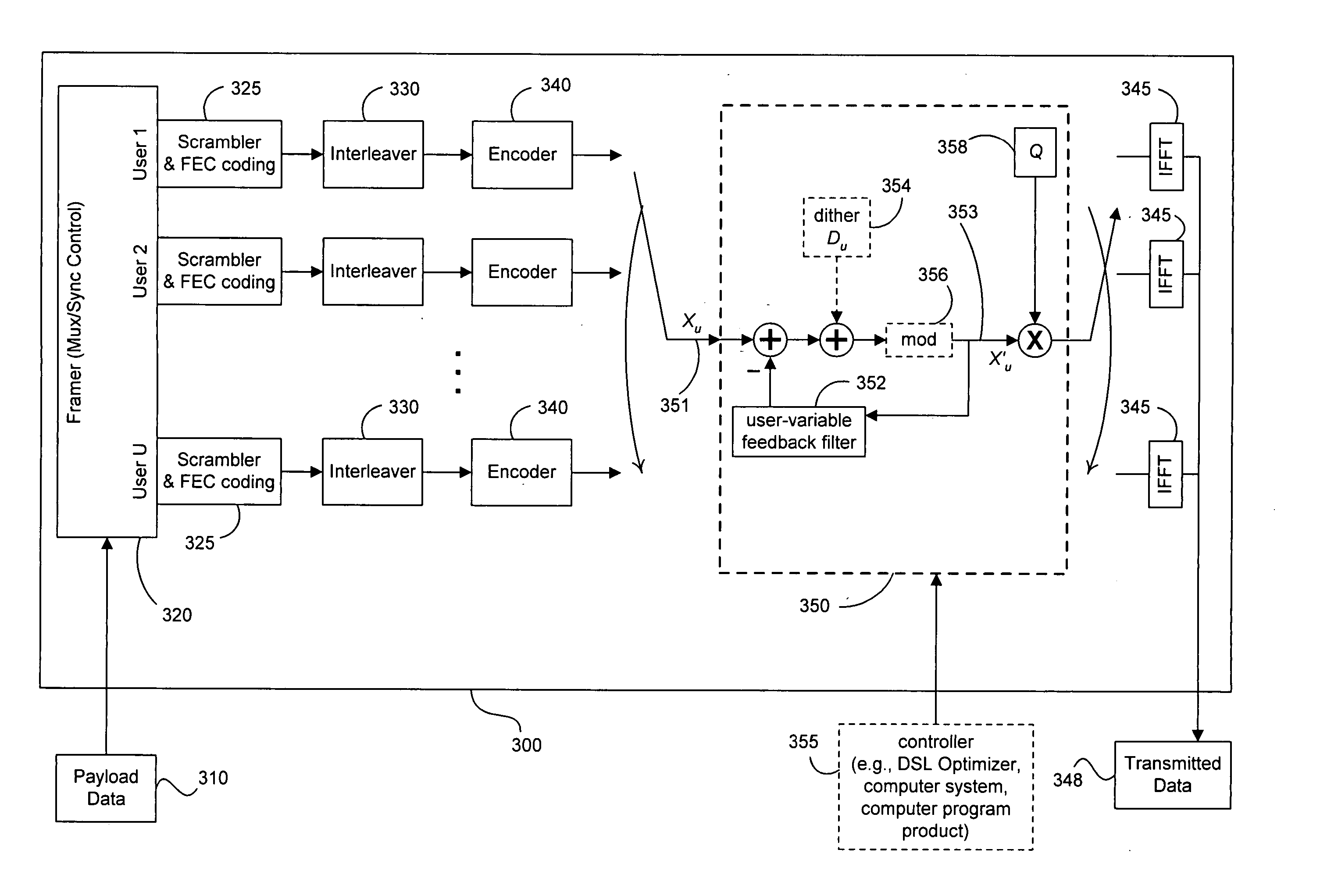
Tonal precoding
ActiveUS20060274825A1Mitigate and remove interference signalReduce removalDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQ-matrixPrecoding
Precoding mitigates or removes interference signals (especially crosstalk) among multiple users with interconnected transmitters in vectored DSL systems and the like. Efficient implementation is provided of the R matrix in RQ factorization that characterizes multi-user downstream vector channels (such as DMT VDSL one-sided or two-sided transmission channels). A set of precoder coefficients can vary with each tone used by each user and depend upon the encoding order of users selected for each tone. In adaptive operation, the coefficients of the R and Q matrices can be updated when changes occur to the transmission environment. Variable modulo arithmetic mitigates the power-enhancement problem, and the base of modular arithmetic also can vary with each user within a single precoder for a single tone. The user order of preceding need not be the same on each tone, and the modular arithmetic progression may thus also be different on each tone because multi-user situations create an unusual situation for precoding in that the modulo arithmetic used for each user can be different (thus imposing a larger power increase) and because digital duplexed or synchronized DMT systems can separately implement a precoder for each tone. Further, the precoding process terminates each DMT symbol, after processing up to the total number of users. An optional dither signal, known to both transmitter and receiver, can be added at the transmit side and removed at the receiver side to smooth the precoding process and ensure that aberrations in the transmitted constellation size and characteristics are consistent despite any unusual variations in the feedback signal that exits the feedback filter matrix G before being subtracted from the user signal of interest. Some embodiments use a “subtraction only” mode while other embodiments use a dither signal and / or modulo arithmetic, though embodiments of the present invention do not require use of identical constellations by both transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
Bit-depth extension of digital displays via the use of models of the impulse response of the visual system
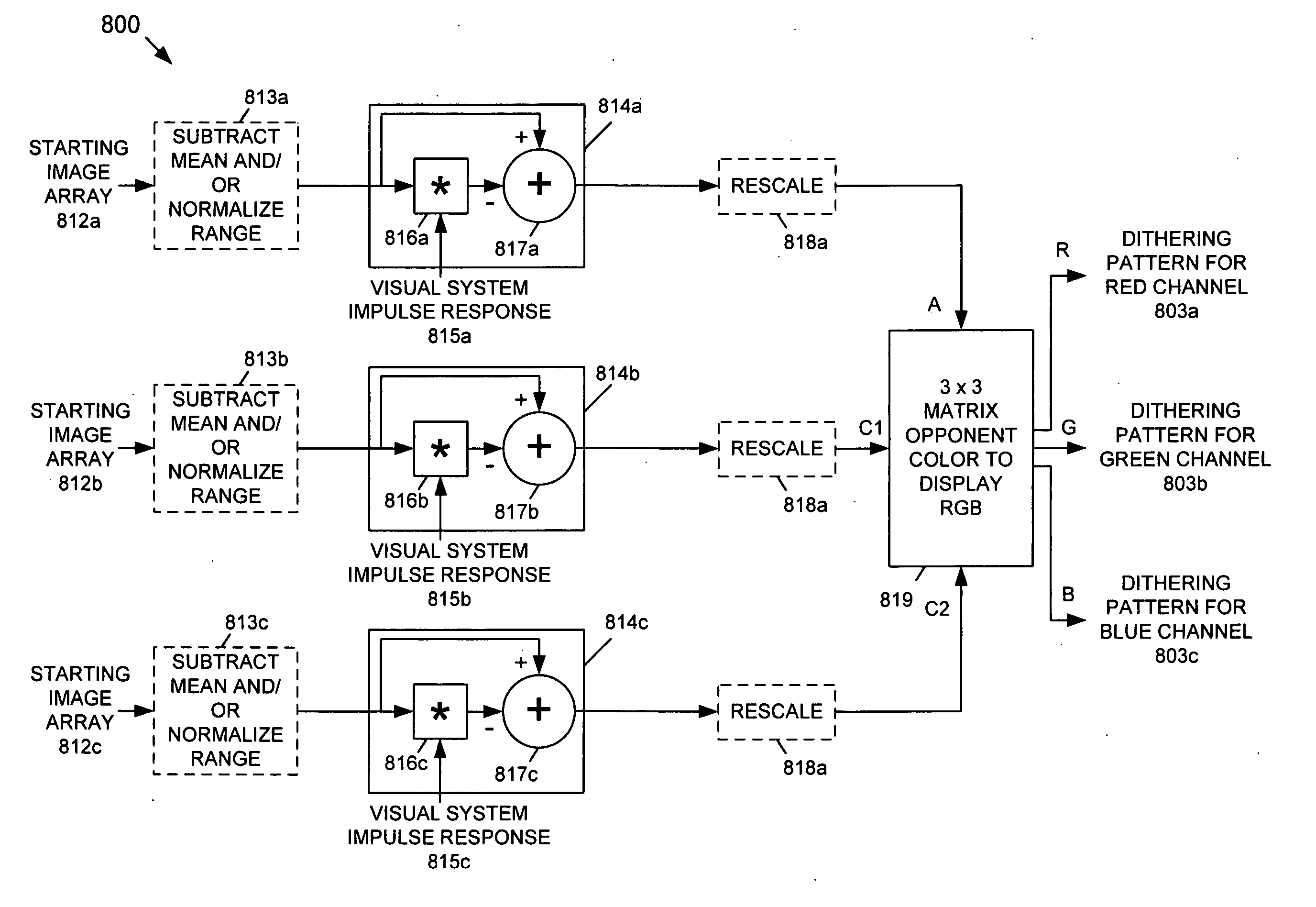
InactiveUS20060038826A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionDisplay device
A dithering pattern that is generated based on a spatial operation is used for a Bit-Depth Extension (BDE) technique for preventing contouring artifacts in an image displayed by a display having a bit-depth that-is less than the bit-depth of the image. The dithering pattern can be based on achromatic visual model or a spatio-chromatic visual model. The dither pattern is formed by shaping a pseudo-random noise signal by an equivalent noise visual model that is based on an array of pixels. Alternatively, the array of pixels is based on an image, or a determinate array of pixels.
Owner:SHARP KK
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS7570182B2Quantization noise resolutionReduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
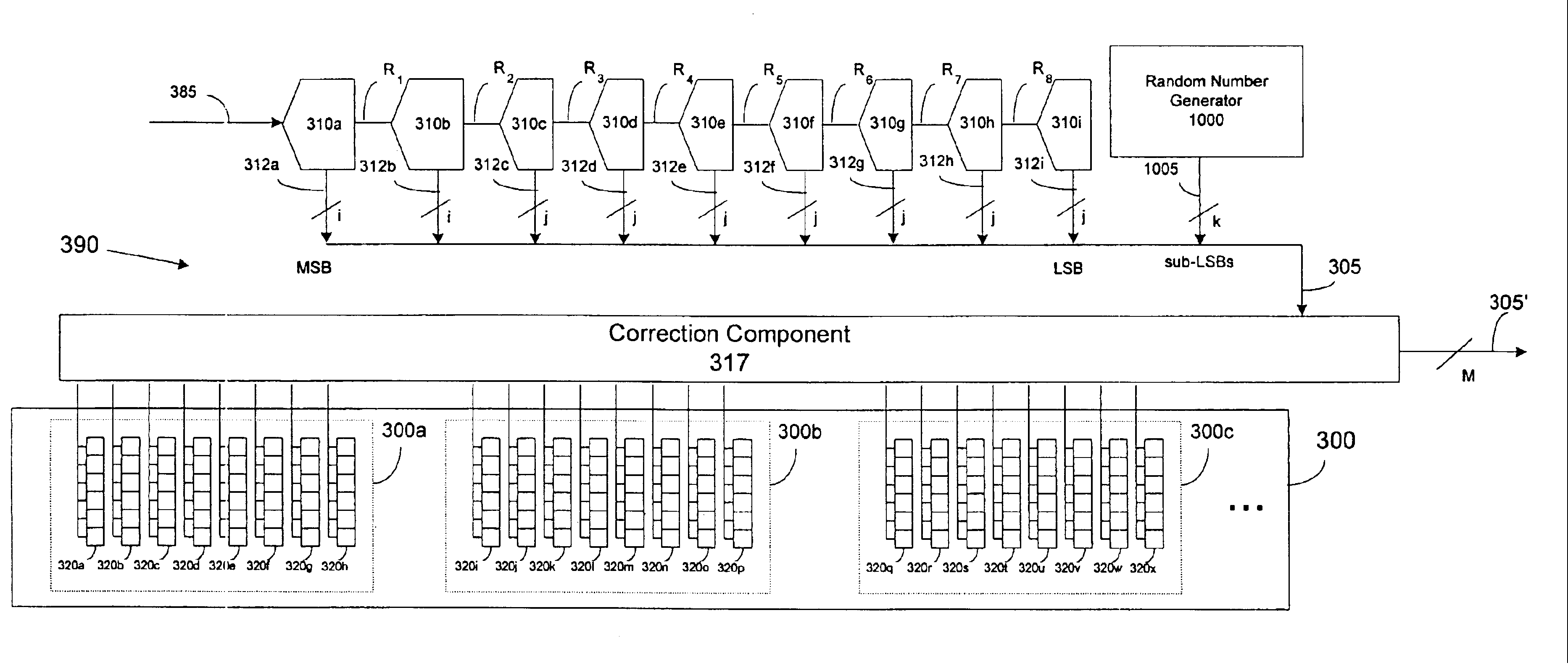
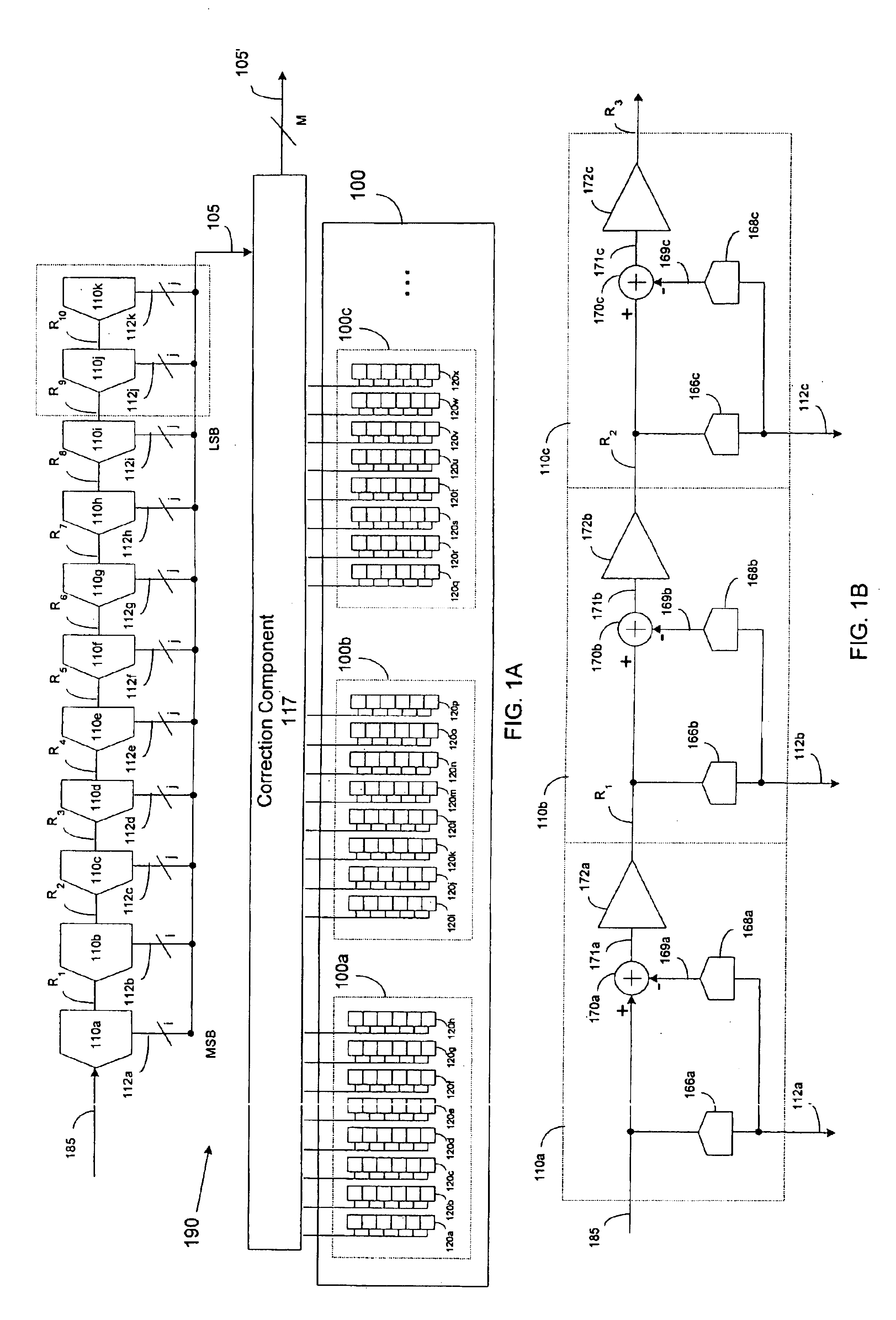
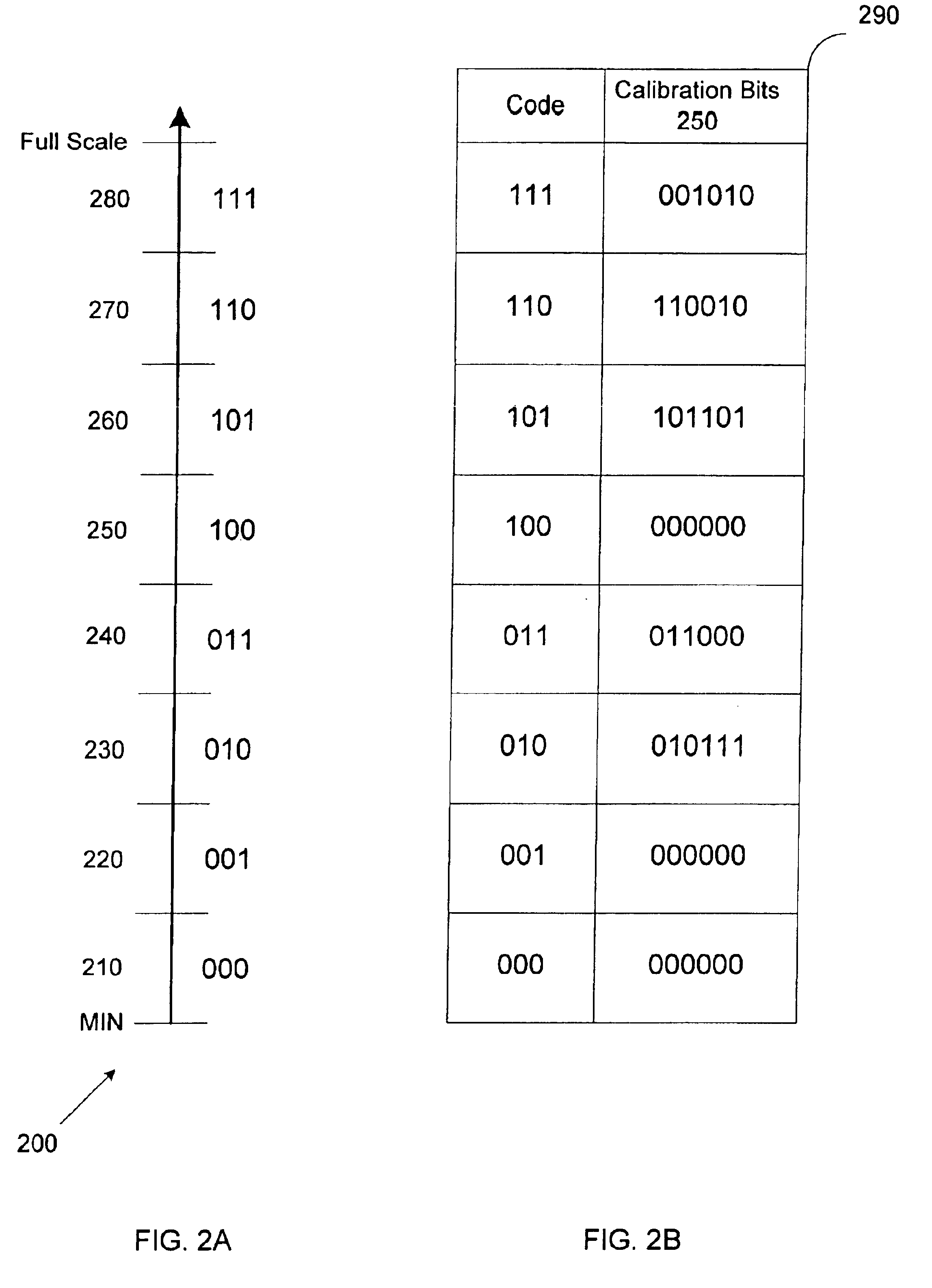
Pipeline ADC digital dithering for increased digital calibration resolution
ActiveUS6894631B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterImage resolution
An pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is provided that is capable of applying calibration at a resolution greater than the resolution of a digital output signal provided by the ADC. The ADC includes a calibration component adapted to apply calibration bits to digital output bits generated by stages of the pipeline and corresponding to samples of an analog input signal. The ADC also includes a random number generator that provides at least one random bit having a sub-LSB bit weight. The calibration bits and the at least one random bit are applied as a dither to the digital output bits such that, on average, the digital output signal provided by the ADC is calibrated at a sub-LSB resolution.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
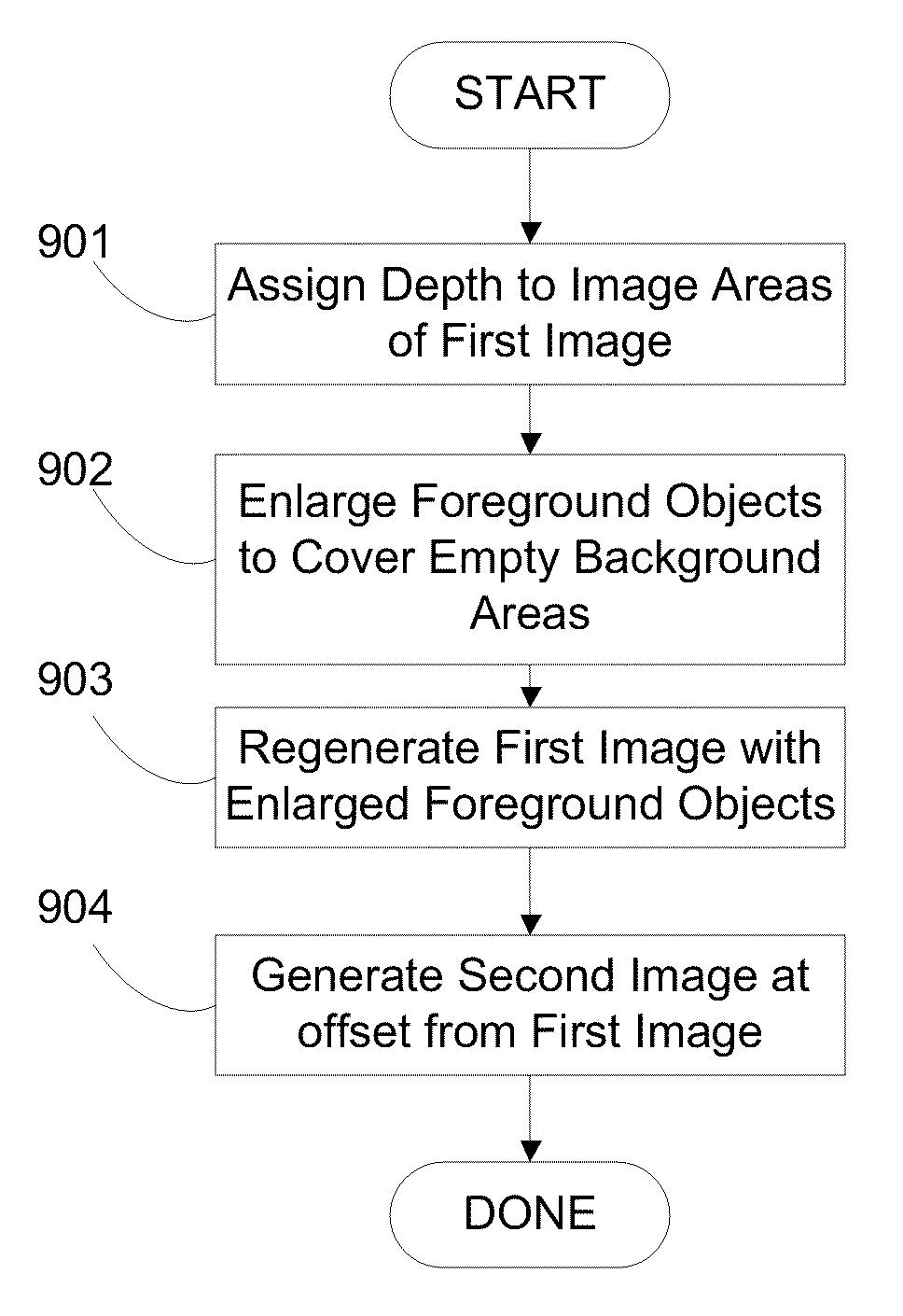
Image depth augmentation system and method
Image depth augmentation system and method for providing three-dimensional views from a two-dimensional image. Depth information is assigned by the system to areas of a first image via a depth map. Foreground objects are enlarged to cover empty areas in the background as seen from a second viewpoint at an offset distance from a first viewpoint of the first image. The enlarged objects are used to regenerate the first image and to generate the second image so that empty background areas are covered with the enlarged foreground objects. The resulting image pair may be viewed using any type of three-dimensional encoding and viewing apparatus. Can use existing masks from non-3D projects to perform depth augmentation and dither mask edges to provide for realistic soft edges for depth augmented objects.
Owner:PASSMORE CHARLES GREGORY
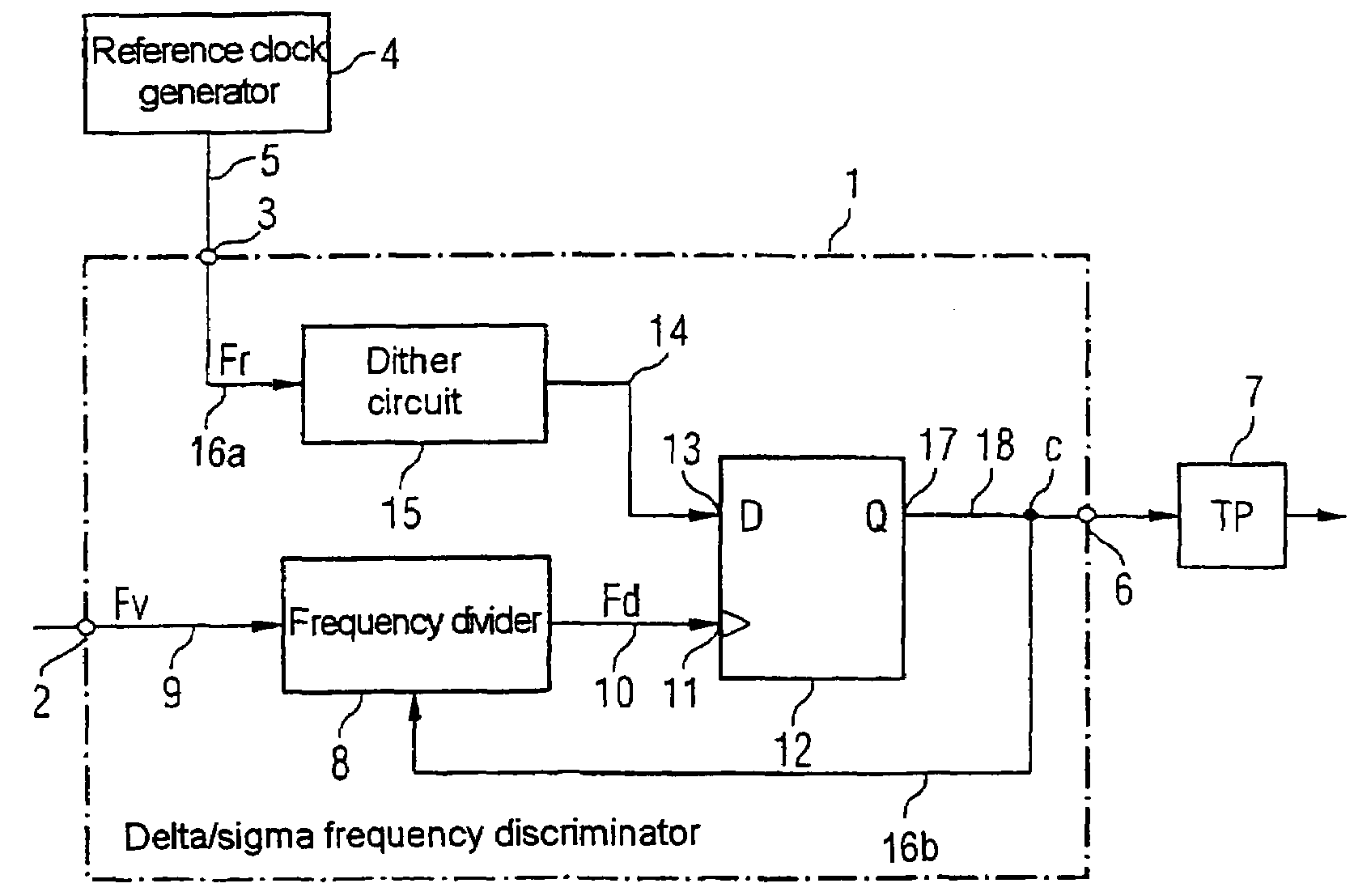
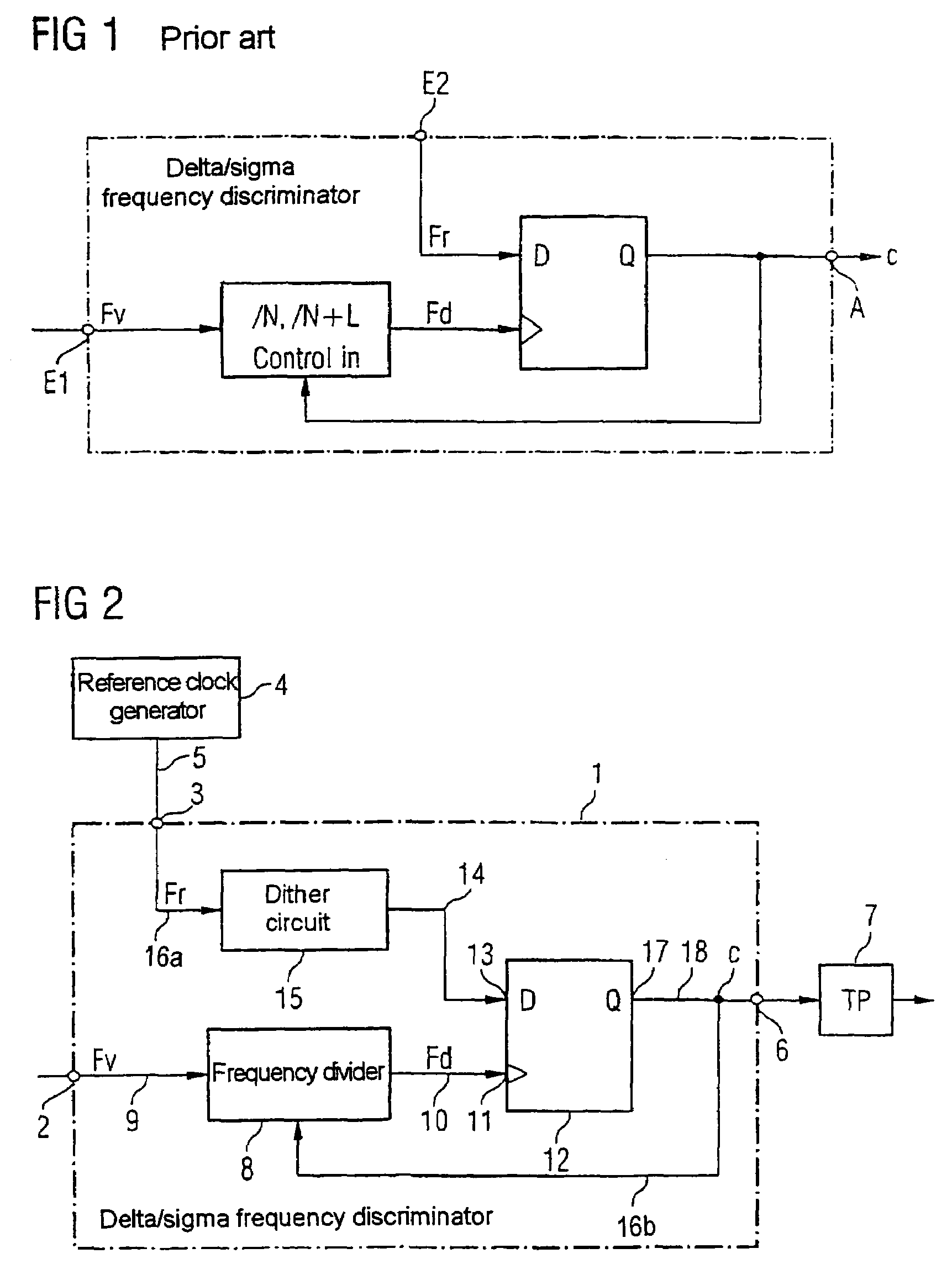
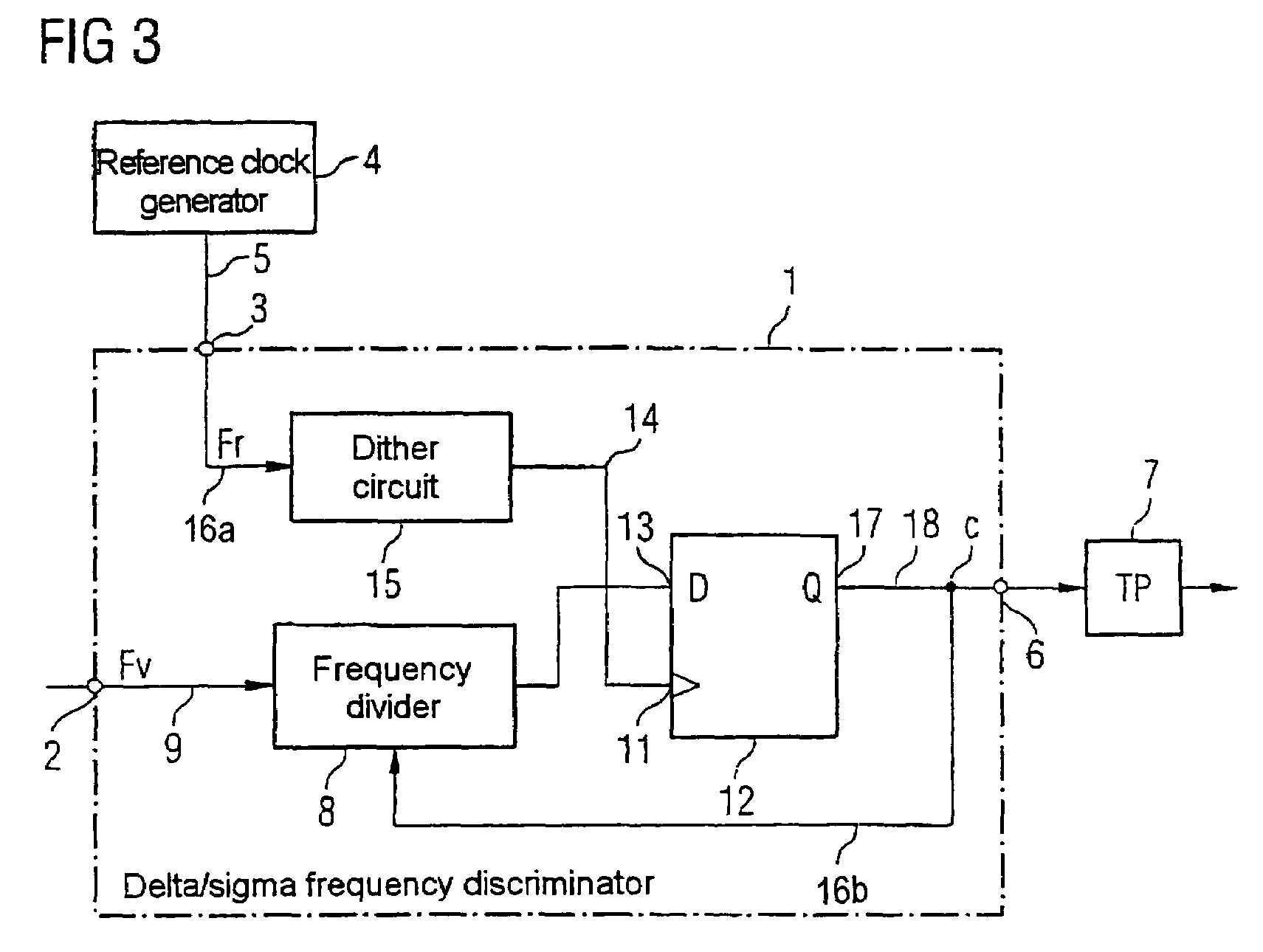
Delta/sigma frequency discriminator
ActiveUS7230458B2Little circuit complexityElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorFrequency spectrum
Delta / sigma frequency discriminator (1) for converting a frequency (Fv) of an input signal into a digital output signal (C) comprising a frequency divider (8) which divides the input signal at a frequency dividing ratio which can be switched in dependence on the digital output signal (C), with at least one sampling register (12) which samples the divided input signal by means of a reference clock signal for generating the digital output signal (C), and with a dither circuit (15) which varies the clock period (T) of the reference clock signal so that interfering modulation tones in the signal spectrum of the digital output signal (C) are suppressed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
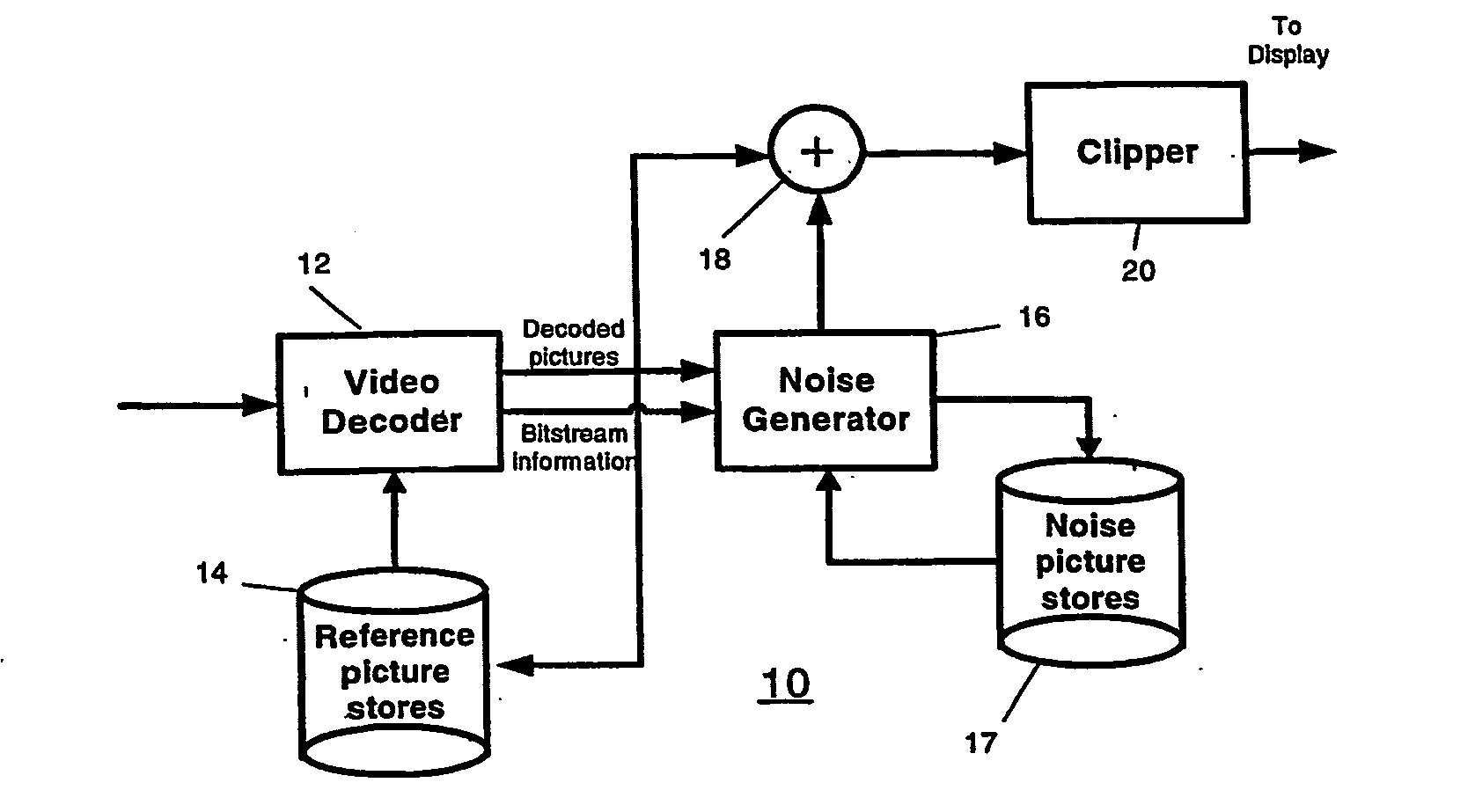
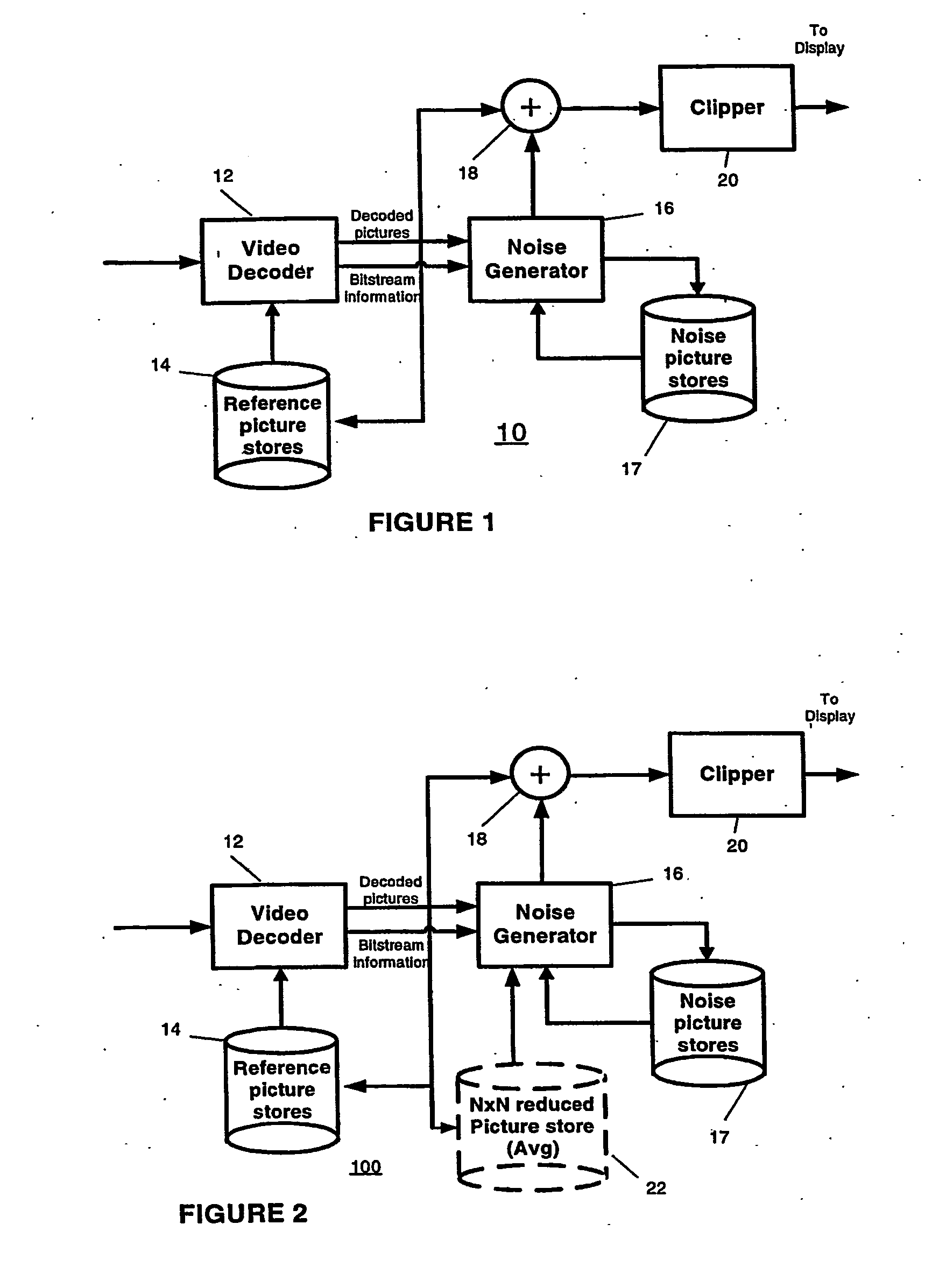
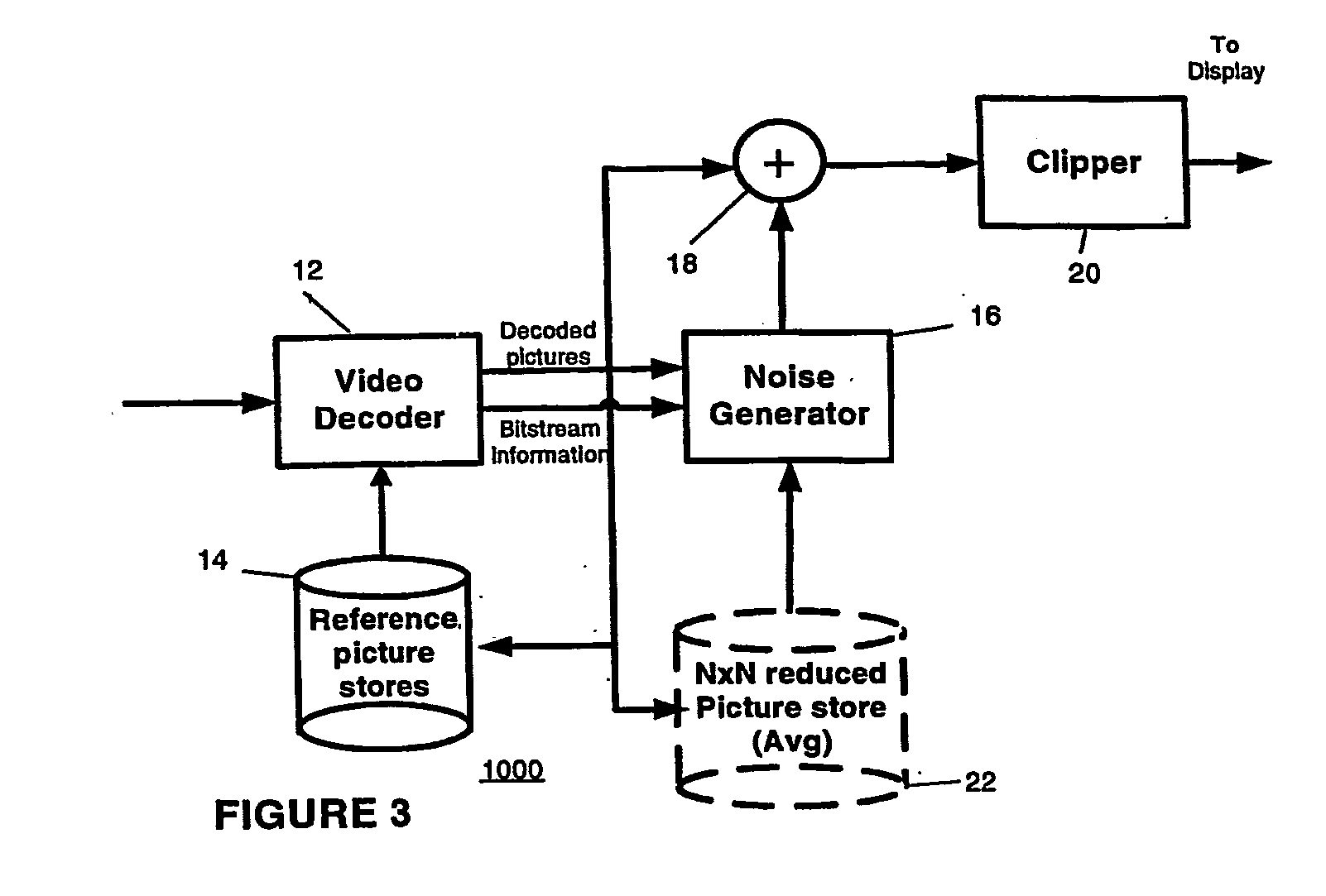
Video comfort noise addition technique
InactiveUS20070047658A1Reduce artifactsSignificant differenceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionComfort noise
A decoding arrangement for decoding pictures in an incoming video stream includes a noise generator for adding a dither signal containing random noise to the pictures after video decoding, to improve the subjective video quality. The noise generator adds noise to each pixel in an amount correlated to the luminance of at least a portion of the current picture.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
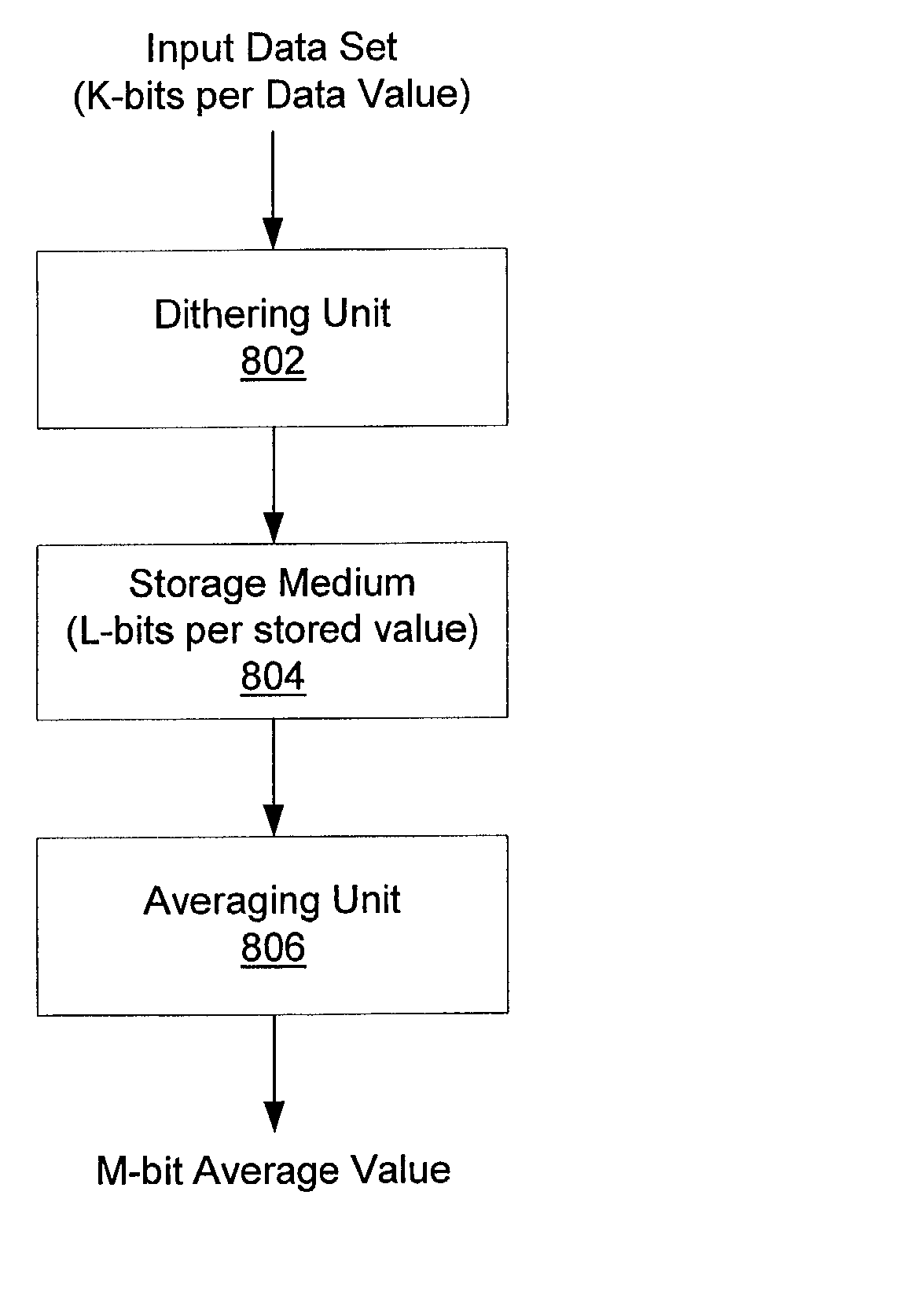
Recovering added precision from L-bit samples by dithering the samples prior to an averaging computation
InactiveUS20020005854A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGraphic system
A dithering system comprising a dithering unit, a storage medium, and an averaging unit. The dithering unit is configured to receive a set of data values, to add dither values to the data values, and to truncate the resultant addition values to L-bit truncated values. The storage medium is configured to store the L-bit truncated values. The averaging unit is configured to read the L-bit truncated values from the storage medium, and to compute an average value using at least a subset of the L-bit truncated values. The dither values may have an average value of approximately one-half. The dither values may approximate a uniform distribution of numbers between -A+½ and A+½, wherein A is greater than or equal to one. Alternatively, the dithering unit may receive a temporal stream of data values, and the average unit may perform a temporal average (e.g. an FIR filter). The dithering system may be incorporated in a graphics system. In this case, data values may represent rendered sample values (e.g. color or alpha).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
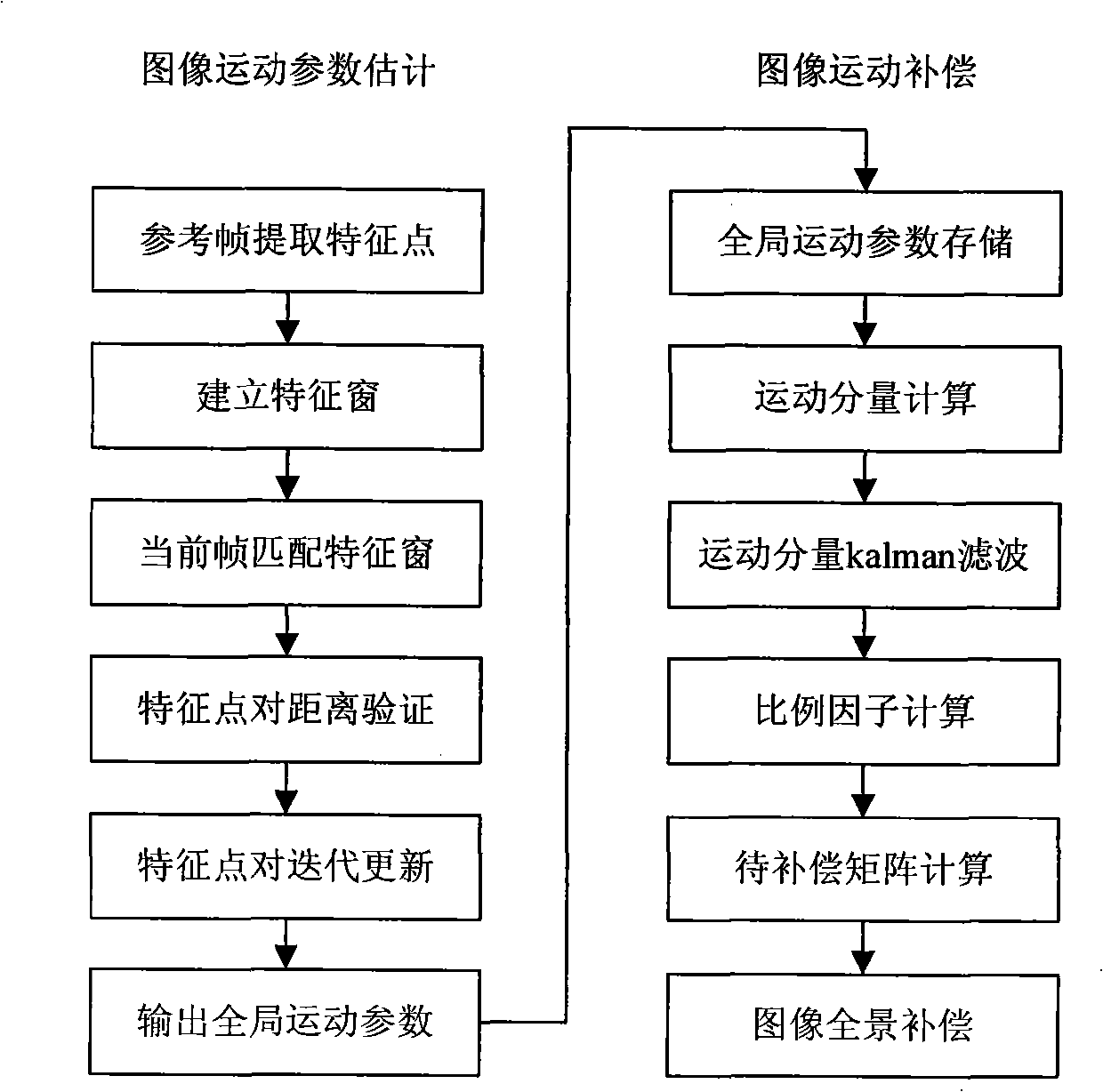
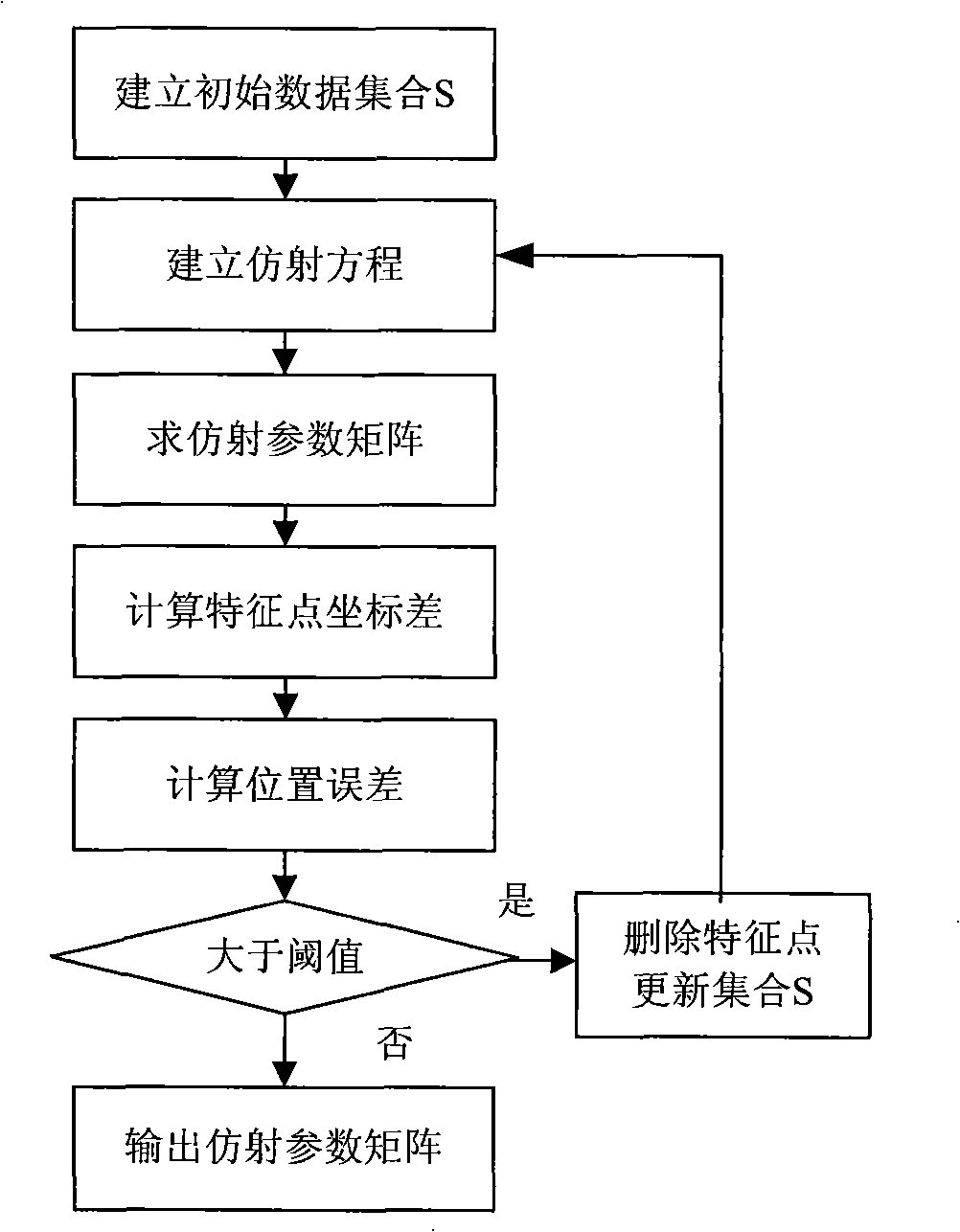
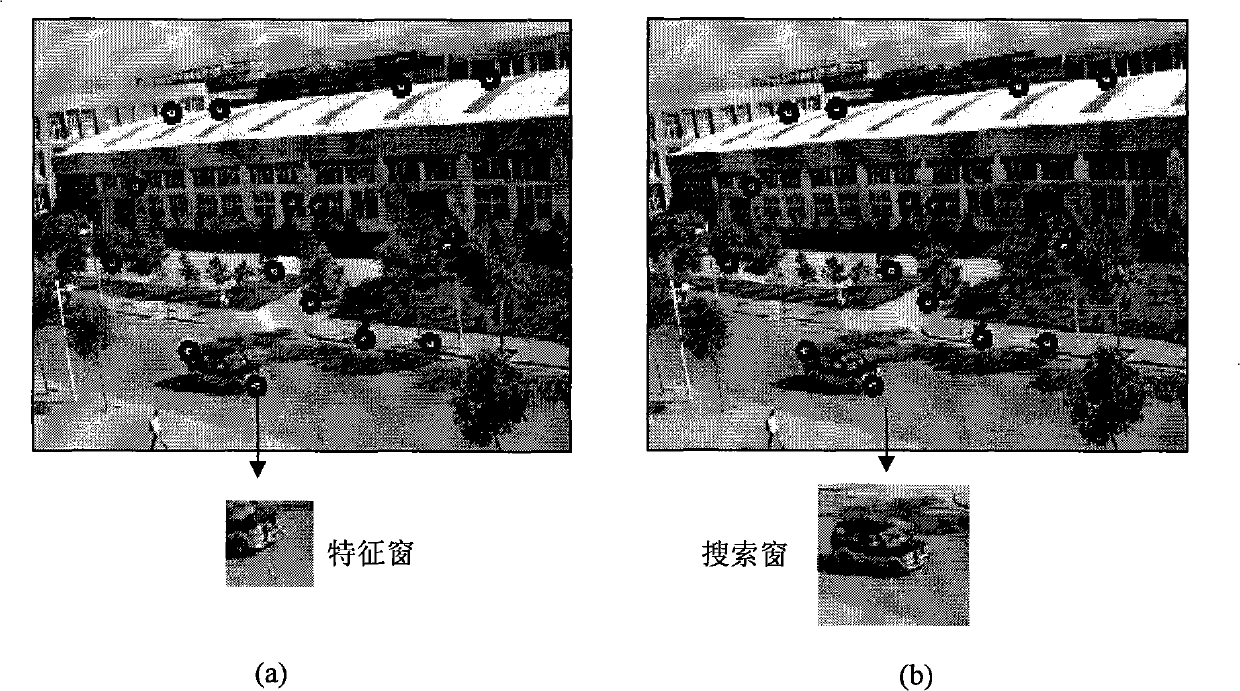
Full view stabilizing method based on global characteristic point iteration
InactiveCN101316368AImprove calculation accuracyHandle translation efficientlyImage analysisTelevision systemsVideo monitoringMotion parameter
The invention discloses a panorama image stabilization method based on the iteration of global characteristic points. The method of the invention includes two parts of the estimation of image motion parameters based on the iteration of characteristic points and the compensation of image motion based on the wave filtering. The estimation of global motion parameters includes that a Harries characteristic point which is the most stable in the image is combined with a characteristic window; local characteristic points are gradually deleted through the identification of the distance consistency and the updating of the iteration of characteristic points so that the global characteristic point set converges rapidly and the global motion parameters can be accurately obtained. The compensation of the motion image includes that the global motion parameters are filtered to acquire dither parameters, and actual dither parameters are compensated and the normal scanning motion of an image pickup system is retained; simultaneously, the image fusion is combined with the compensation to realize the output of a panorama image. The method of the invention can effectively process the dithers such as translation, rotation and zooming, etc., of the image pick-up system and more complex local motion of the scene, and can be used for removing the influence on the video sequence by a motion carrier so as to output a stable video and improve the observation effect of the video monitoring or tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
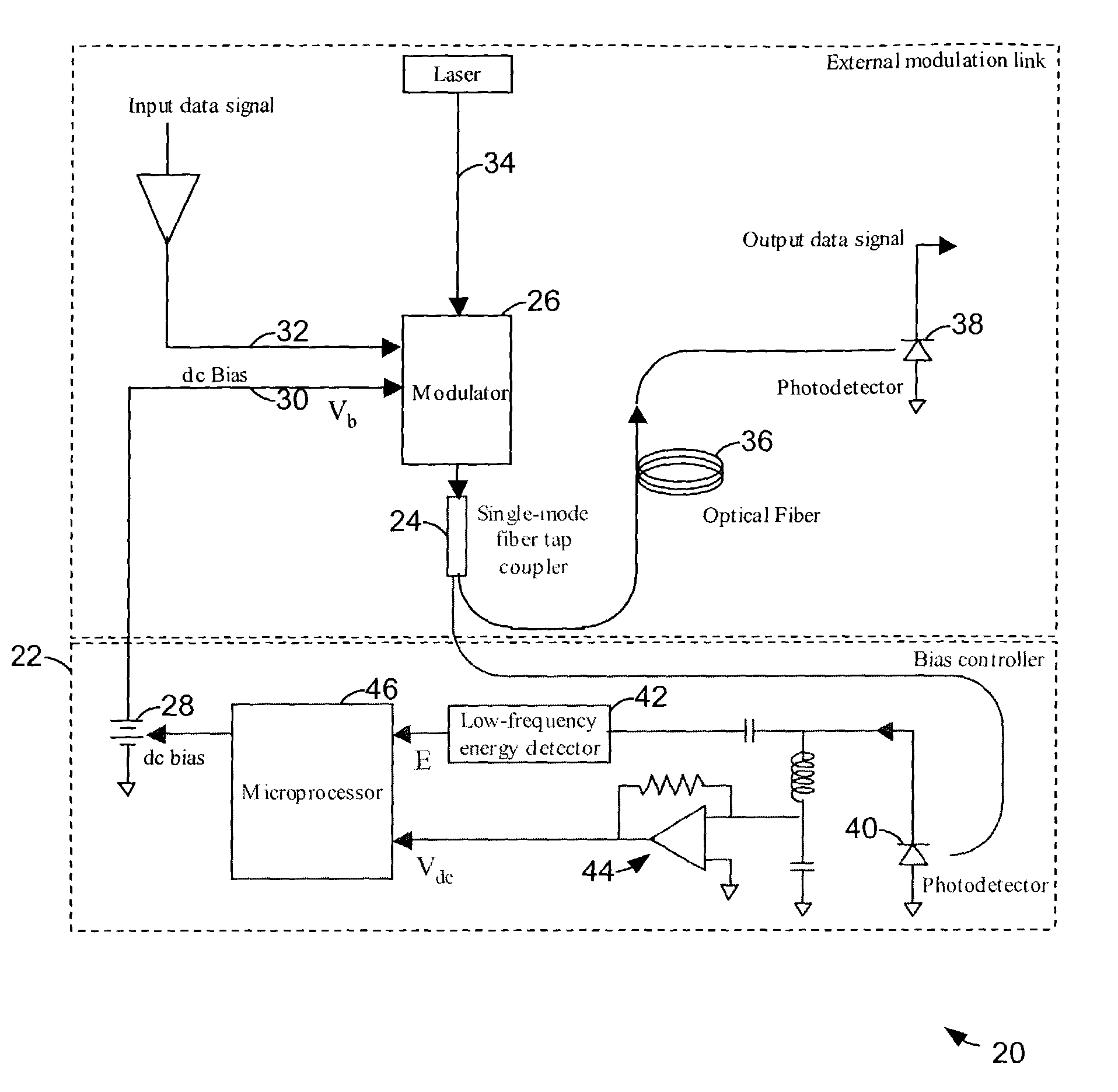
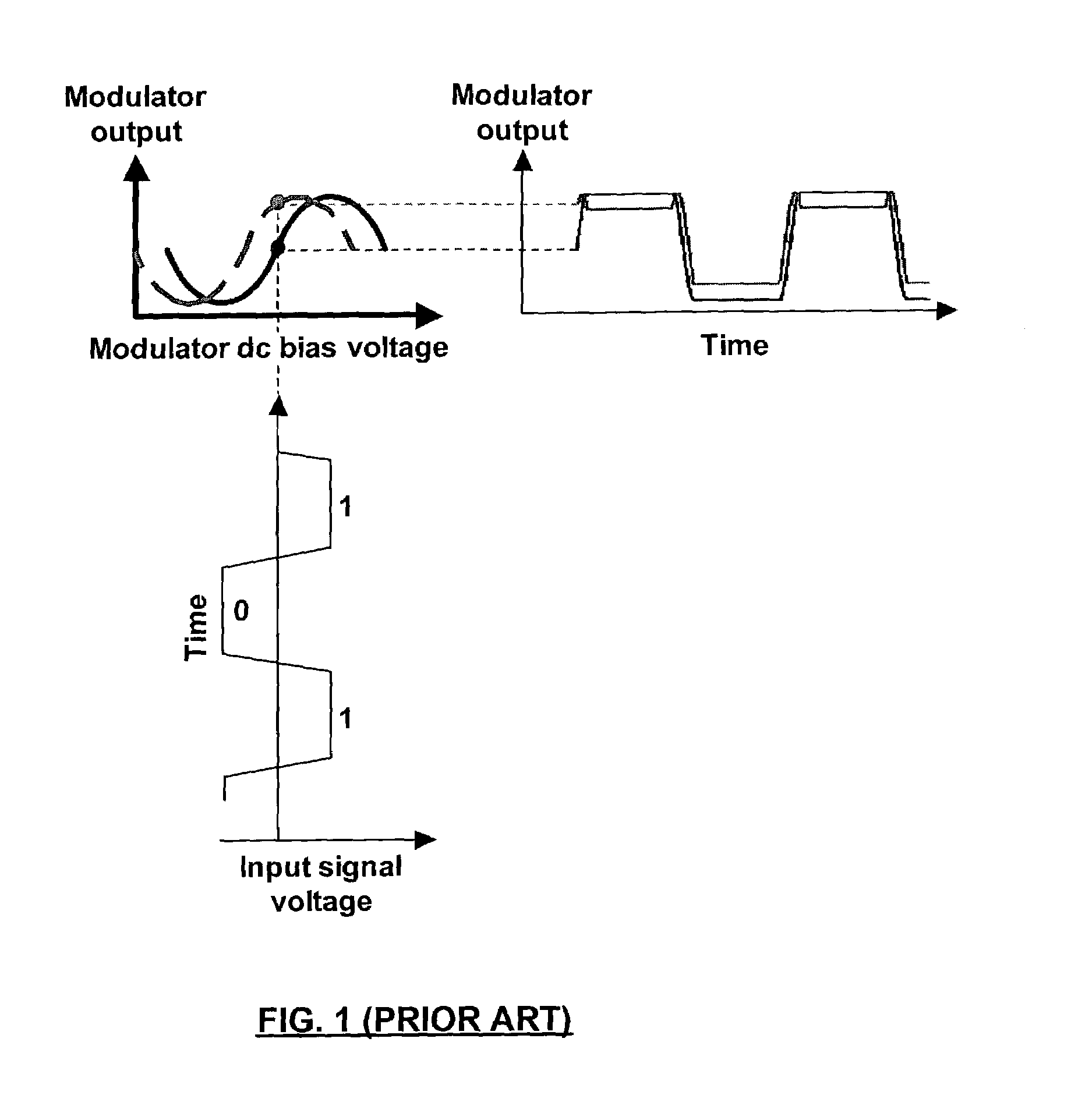
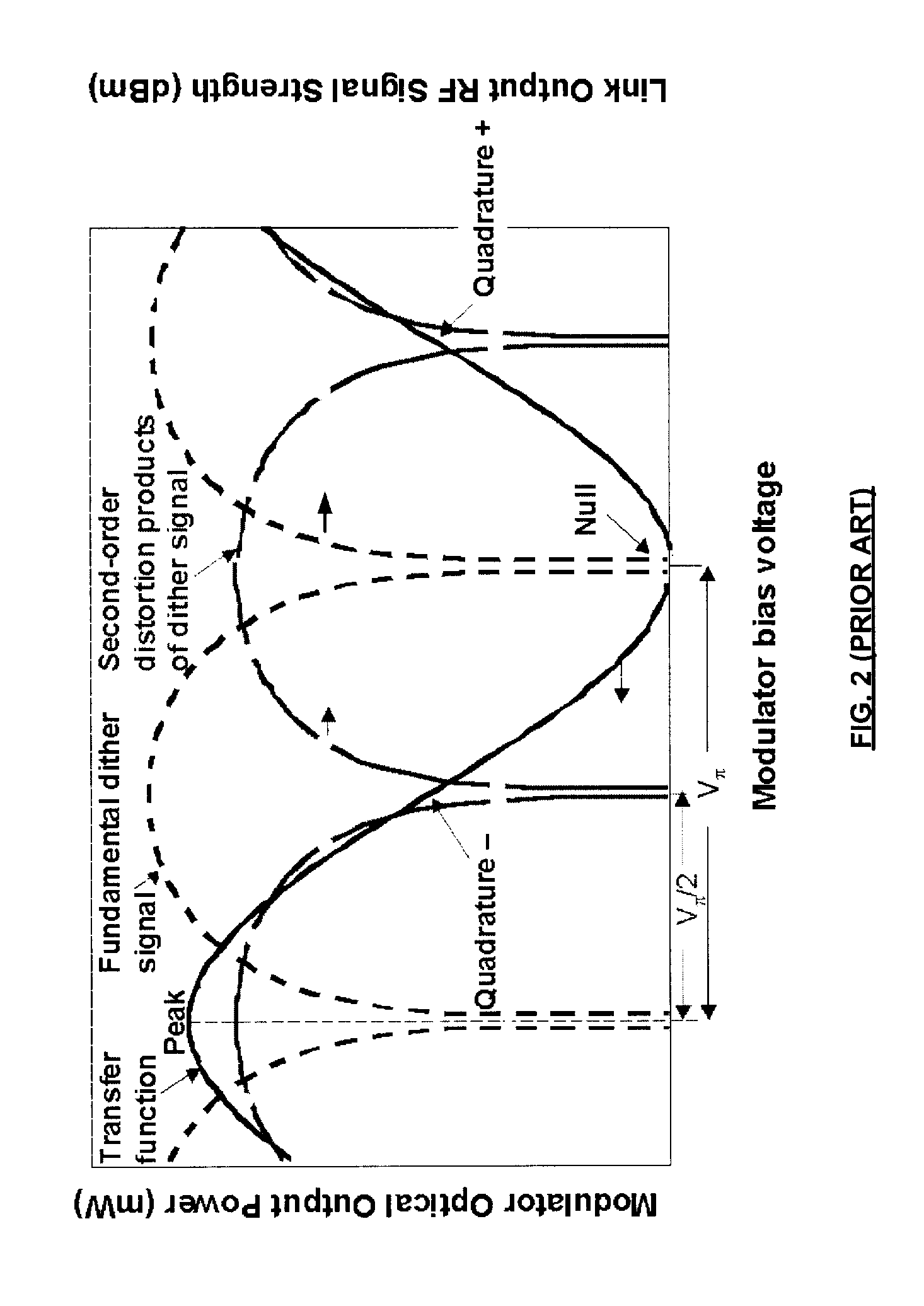
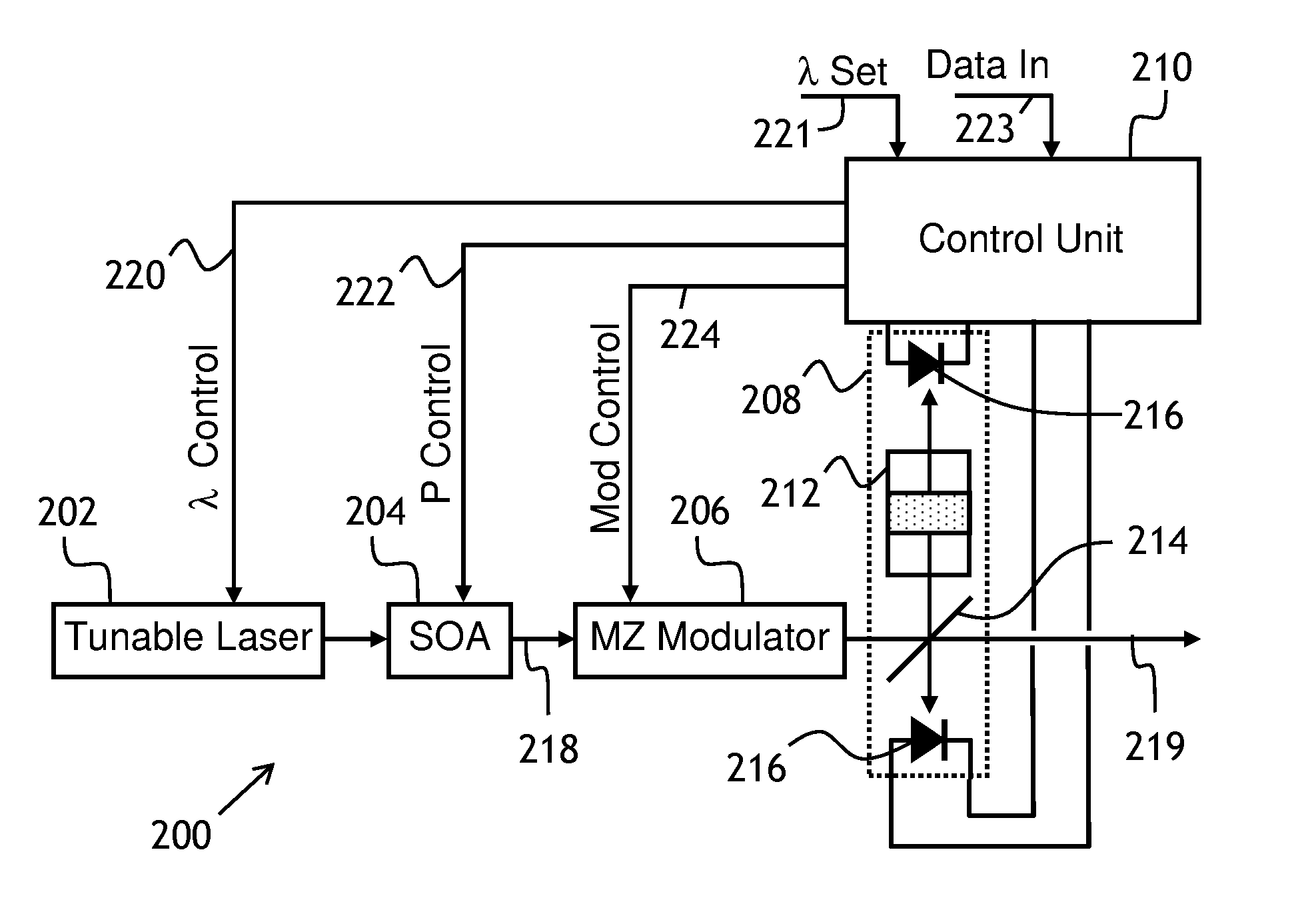
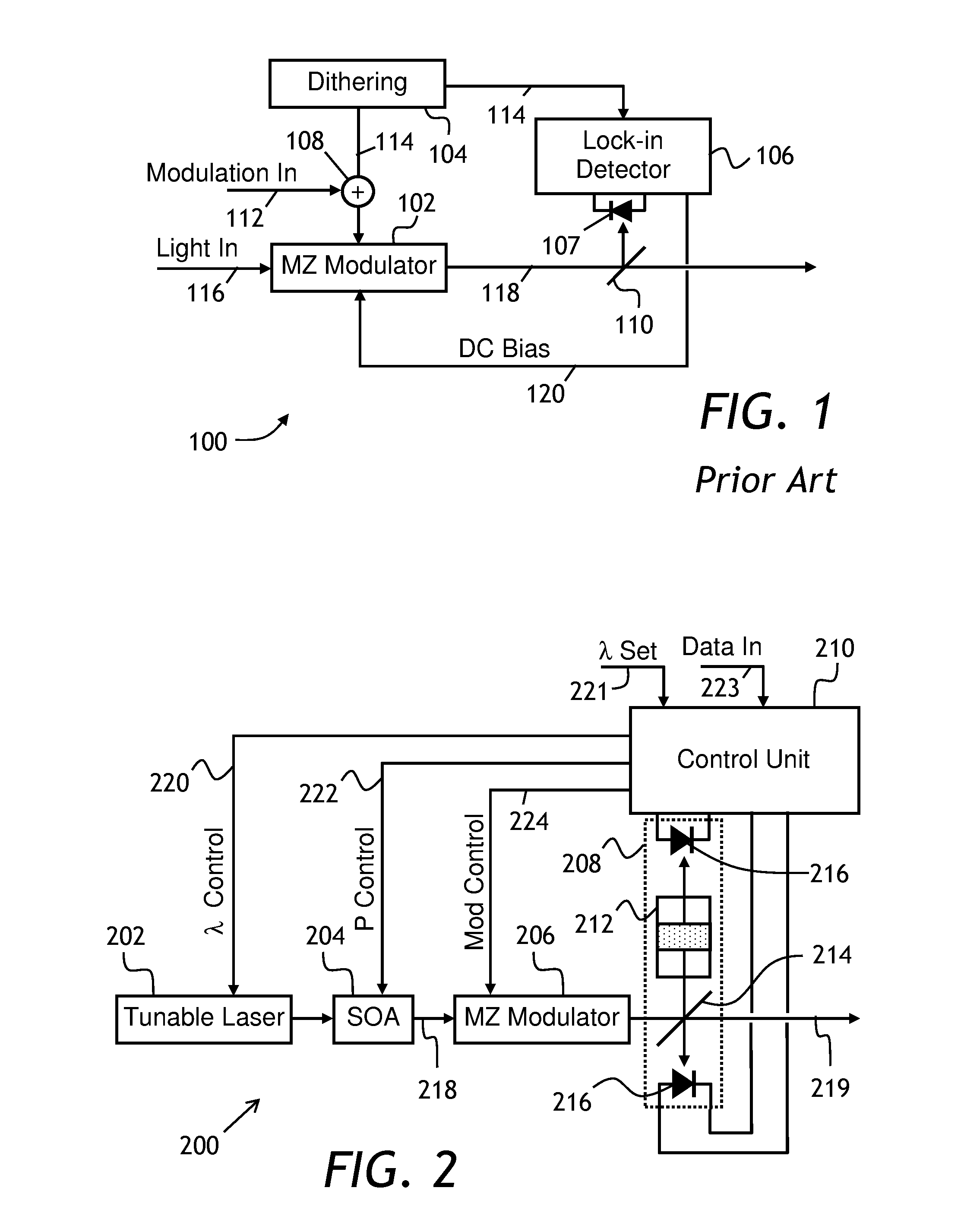
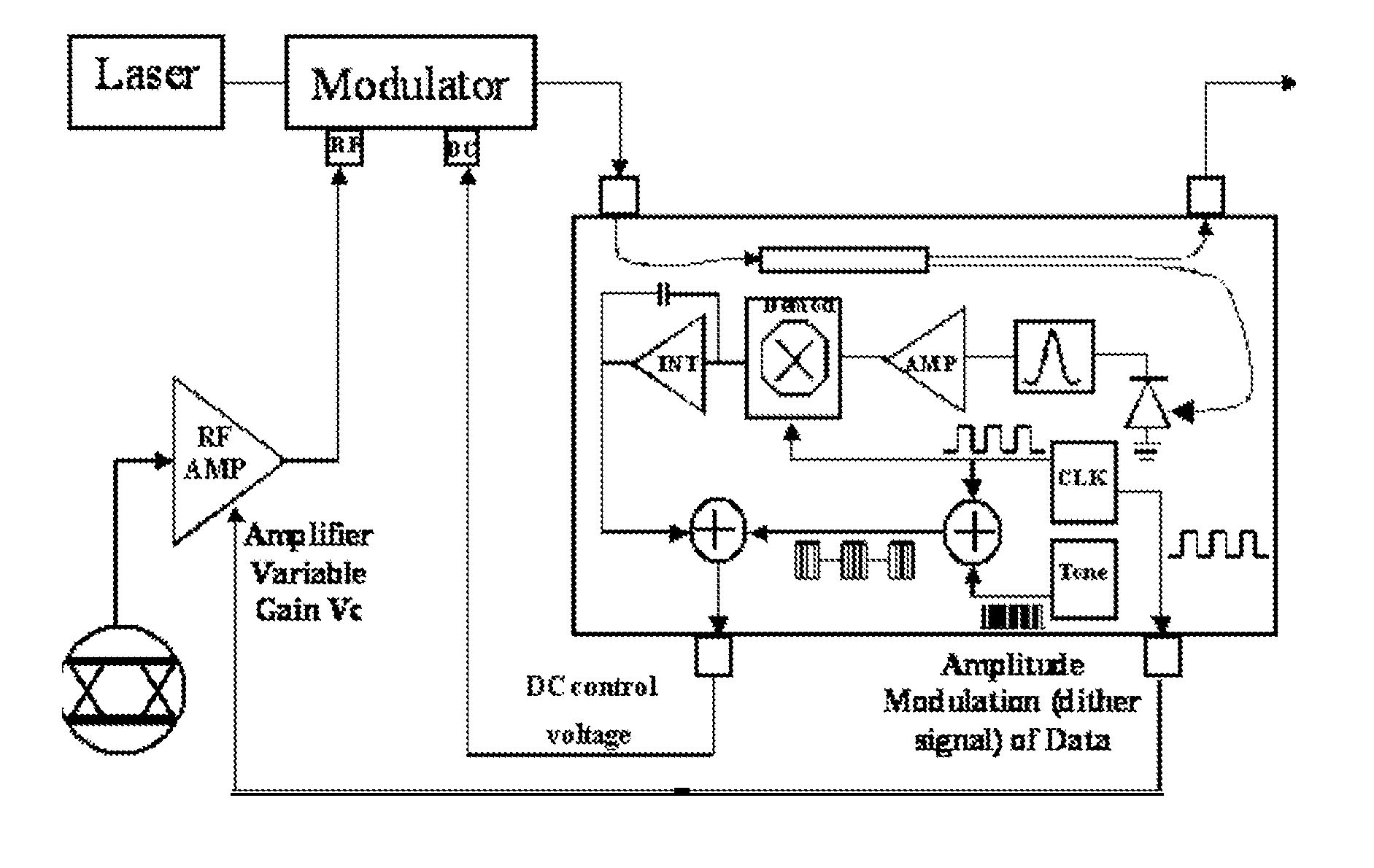
Modulator bias control
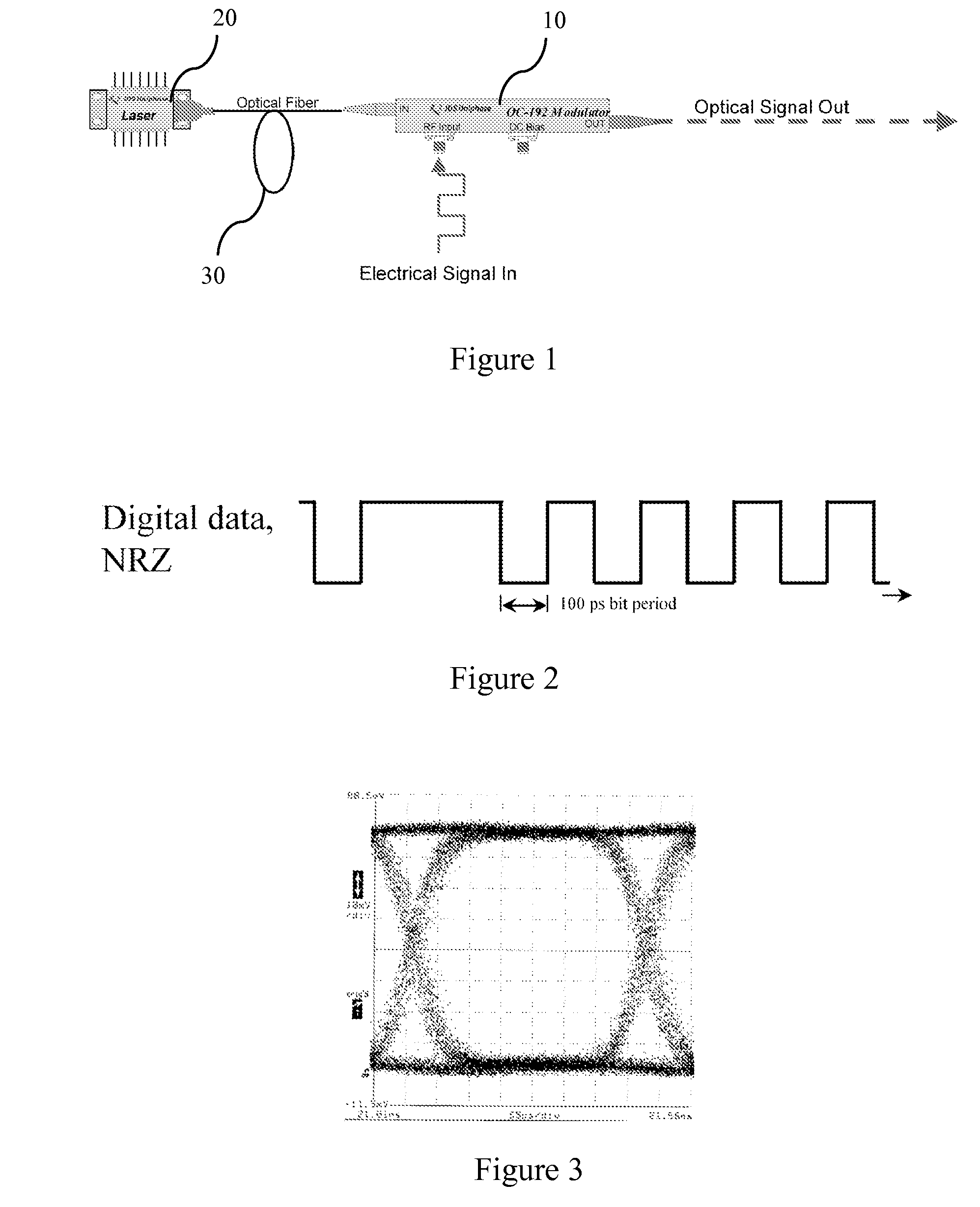
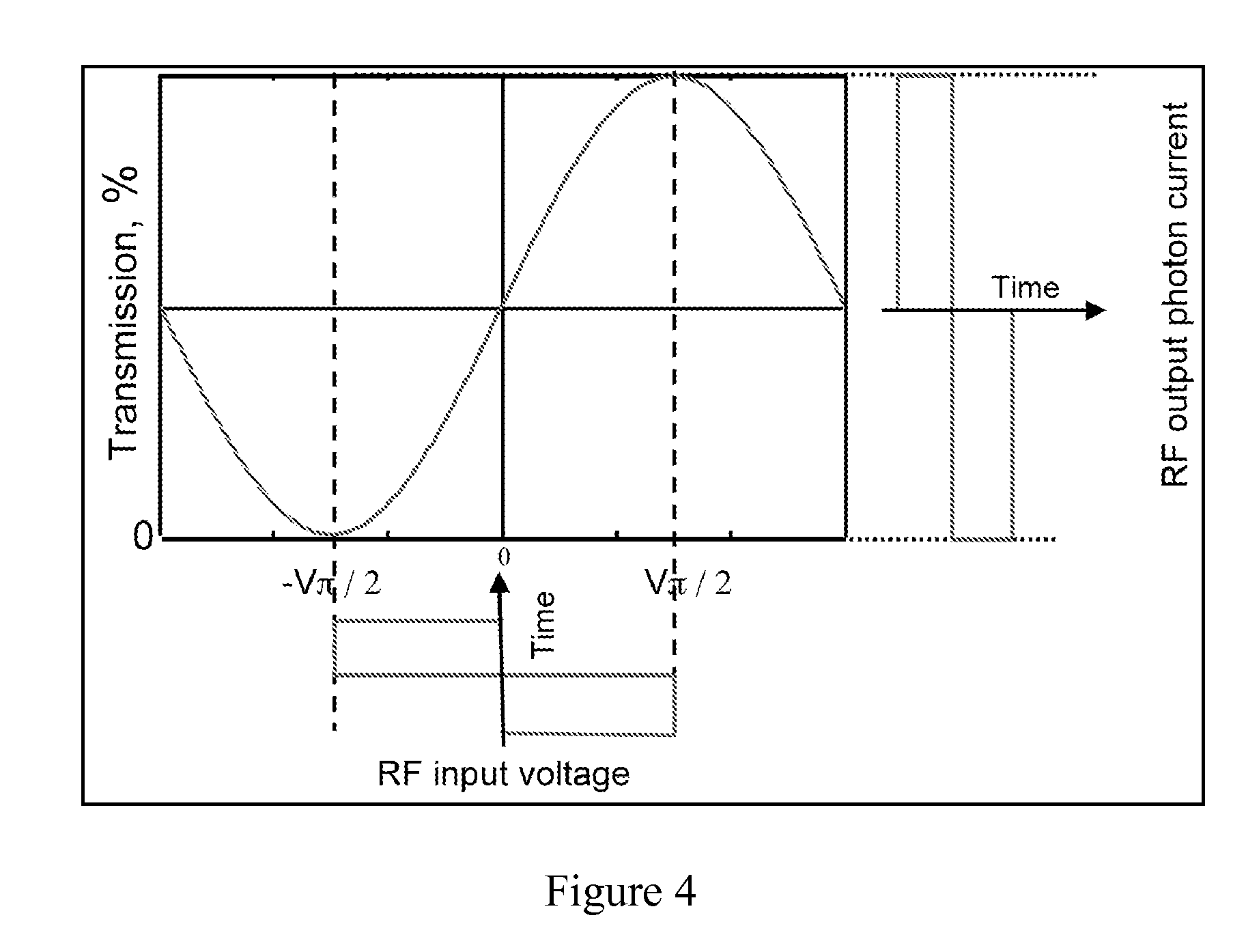
InactiveUS7369290B1Implementation is particularly straightforwardBetter bit error rateNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityCarrier signal
Approaches to bias control are disclosed for an optical modulator that modulates an optical carrier with a data input signal. In one embodiment an electrical bias input signal provided to the modulator is adjusted based on a characteristic of the data input signal detected from the modulated optical output signal. Another embodiment injects an additive dither signal into an optical modulator receiving a data input signal having a modulation depth of at least on the order of 50%. These embodiments can obtain and maintain a correct bias point on a modulator's transfer function curve when the modulation signal has a modulation depth on the order of 100%.
Owner:PHOTONICSYST
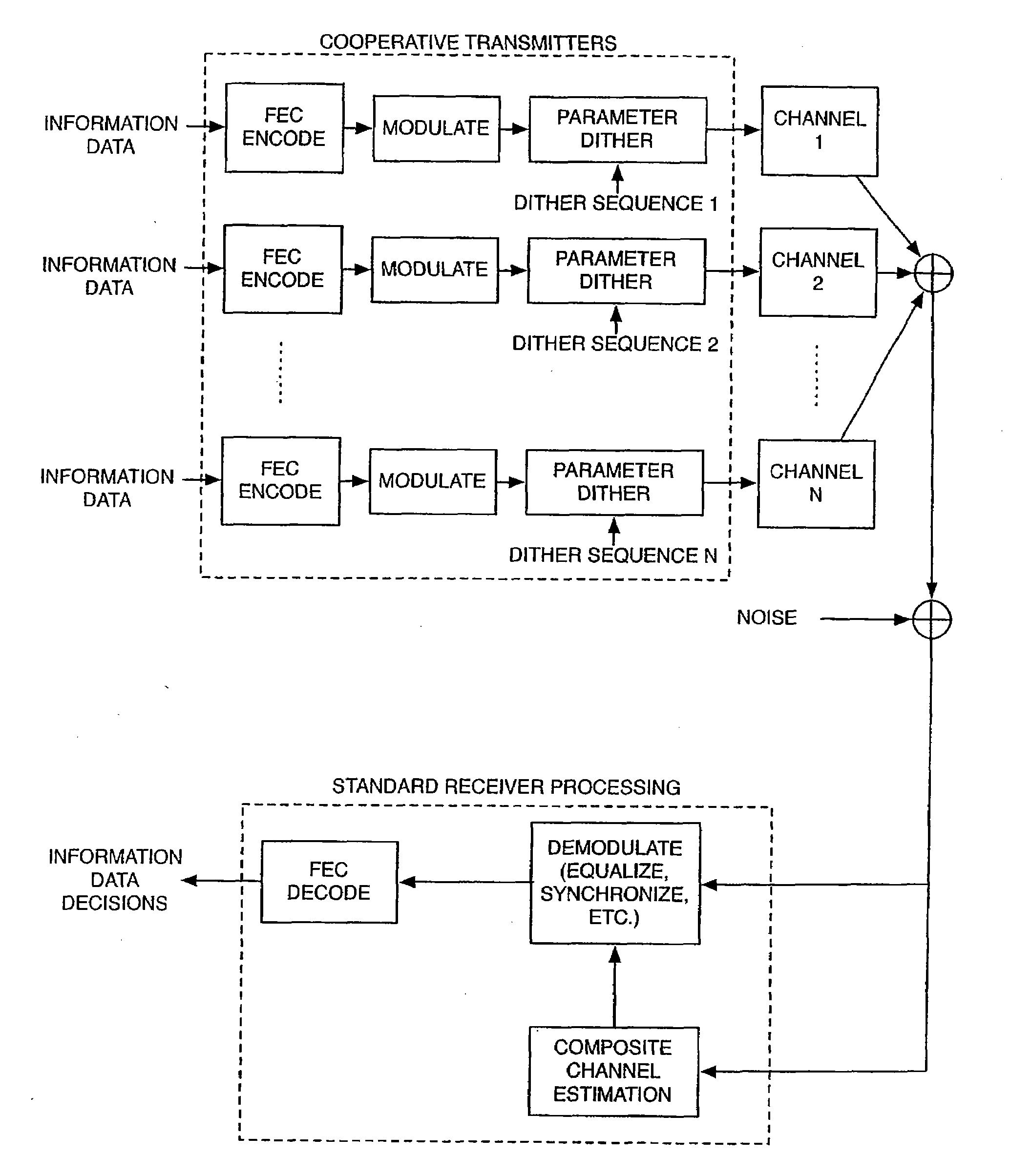
Method and System for Cooperative Communications with Minimal Coordination
ActiveUS20090313528A1Verify correctnessHigh data reliabilitySite diversityRandom number generatorsTemporal diversityCommunications system
A method and system are provided in a wireless communications system comprising a plurality of nodes (users) working cooperatively. The system provides cooperative diversity by allowing nodes to actively share their antennas and other resources to obtain spatial diversity. The nodes receive the same message (information data) from a common source. Each node enhances the reliability of the message with a modern forward error correction (FEC) code, converts the FEC encoded message into an ensemble of symbols, divides the ensemble of symbols into packets, modulates, dithers and transmits the packets to a receiving node. The dithering process is performed by varying the signal amplitude, phase, frequency and / or symbol timing of the modulated packets. A unique dither pattern is assigned to each node. The receiving node captures a composite signal comprising the transmitted packets of all or most of the transmitting nodes in the cooperative communications system. Because the transmitted packets are dithered independently in phase and / or amplitude, spatial diversity is transformed into temporal diversity.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
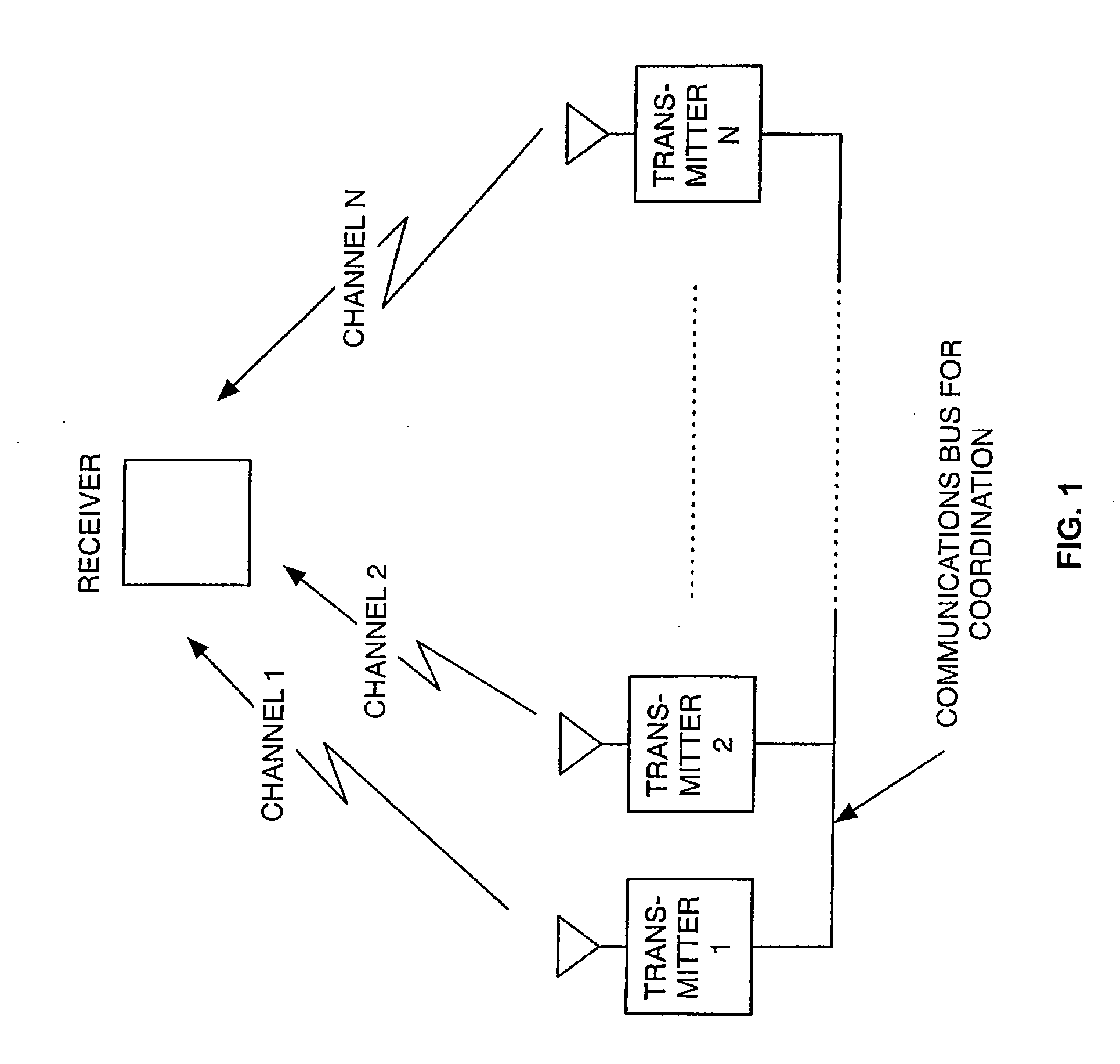
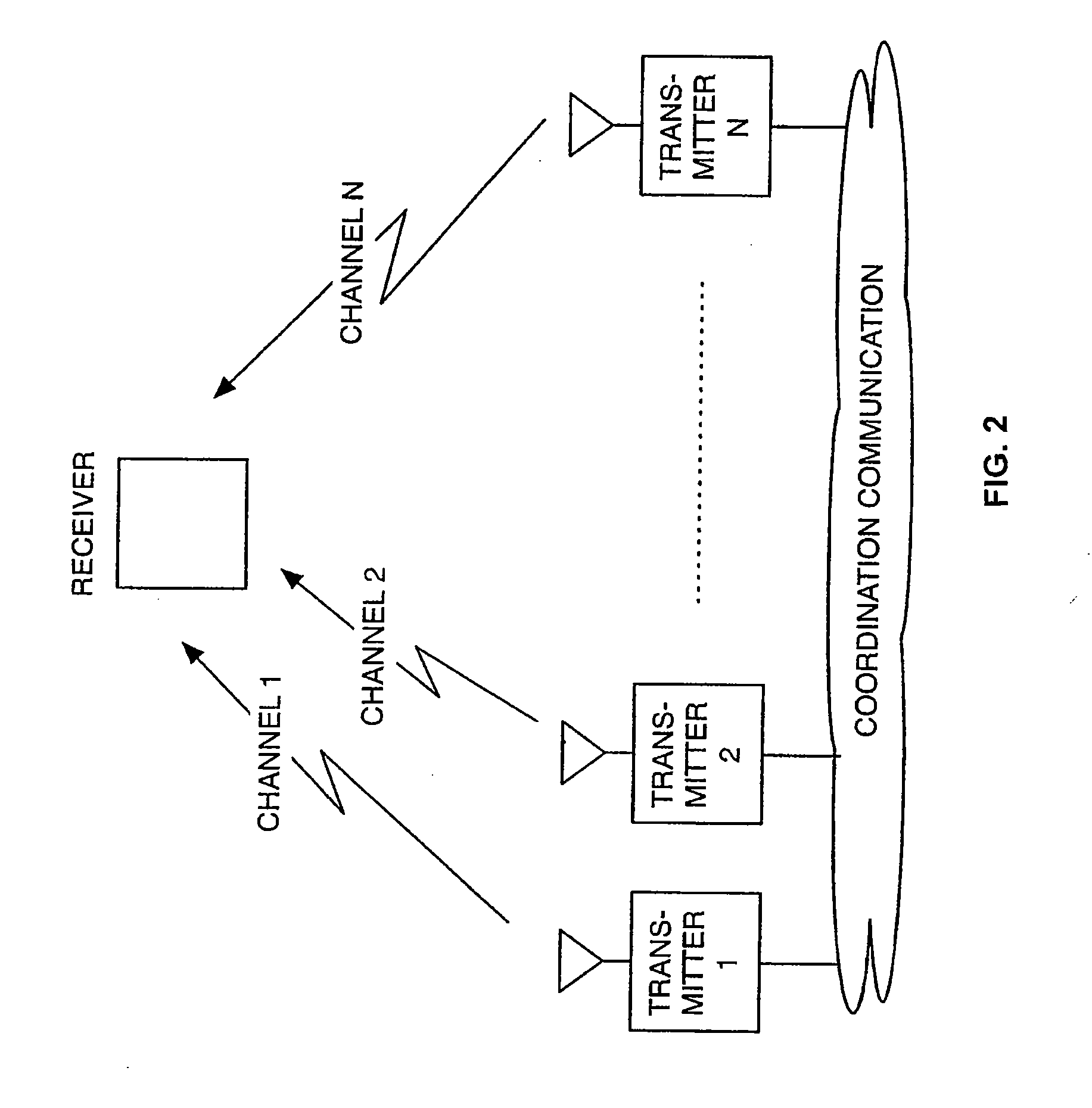
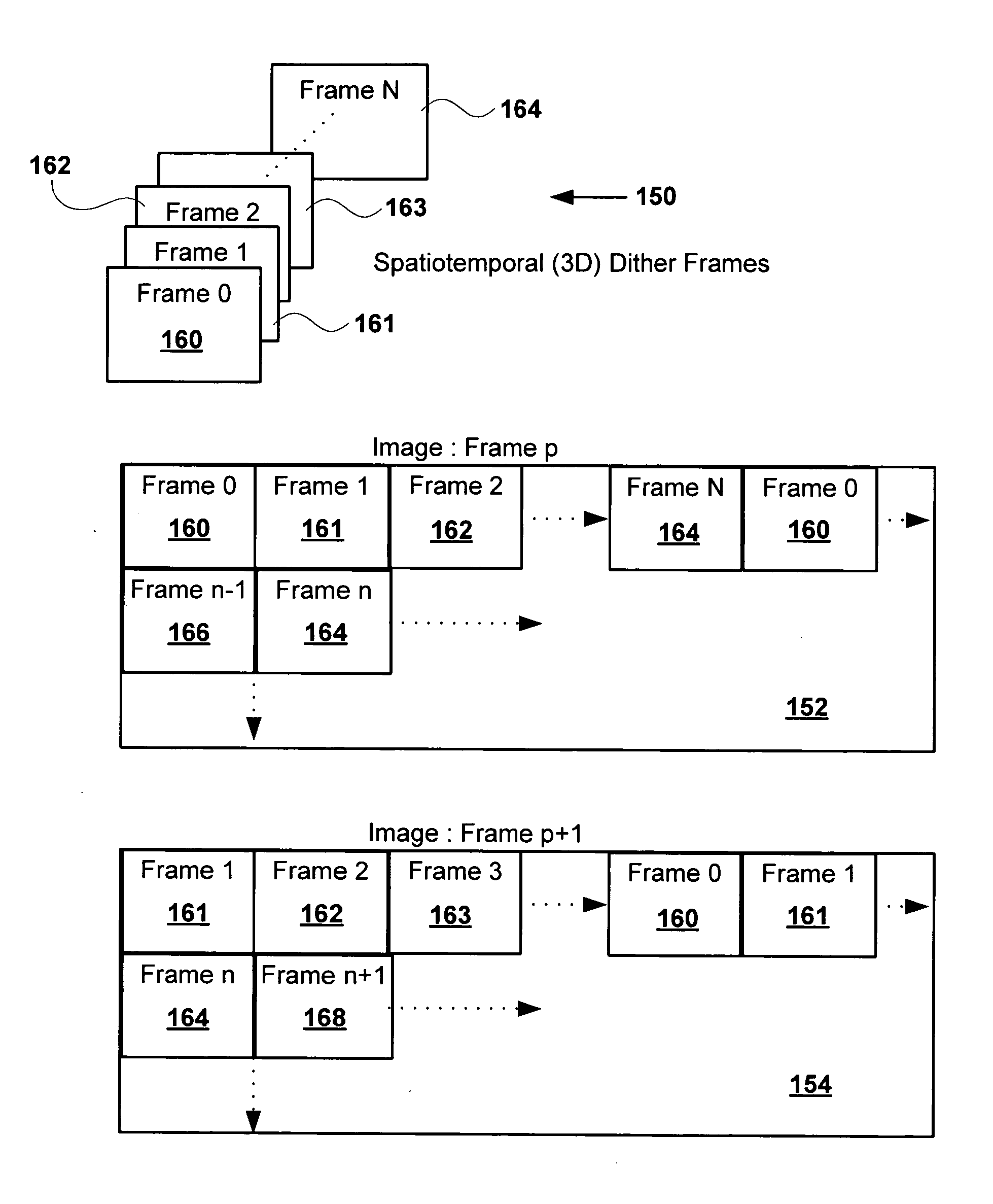
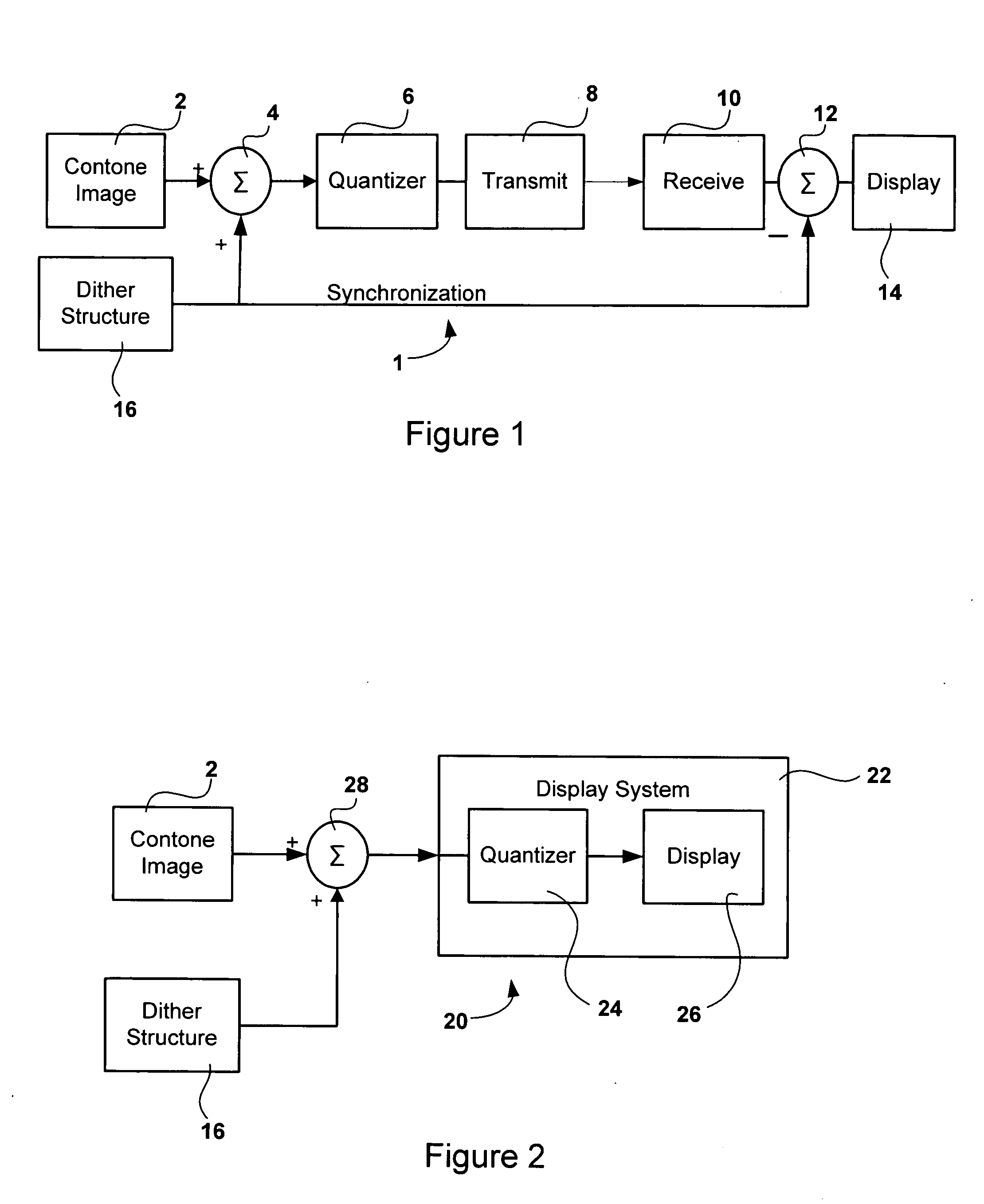
Systems and methods for multi-dimensional dither structure creation and application
InactiveUS20050068463A1Improve visibilityImage enhancementElectric signal transmission systemsMulti dimensionalComputer science
Embodiments of the present invention comprise systems and methods for creation, modification and implementation of dither pattern structures.
Owner:SHARP KK
Printing system and method of recording images
The present invention appropriately determines the on / off state of dots having different hues in a printer using at least two inks of different hues, thereby enhancing the quality of printing. The system of the present invention applies the systematic dither method to determine whether or not dots are to be formed by ink of a predetermined hue, for example, magenta. In the case of formation of dots by magenta ink, the system drives a piezoelectric element PE disposed on a head corresponding to the magenta ink to form magenta dots and calculates a resulting value MRST. In the case of non-formation of dots by the magenta ink, on the other hand, the resulting value MRST is set equal to zero. The system then applies the technique of error diffusion to determine whether or not dots are to be formed by cyan ink, based on the tone data of the cyan ink. The structure of the present invention enables a difference between density data M(x,y) of the magenta ink and its resulting value MRST to affect density data of the cyan ink. This makes it difficult to form dots of cyan ink in the vicinity of dots of magenta ink.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
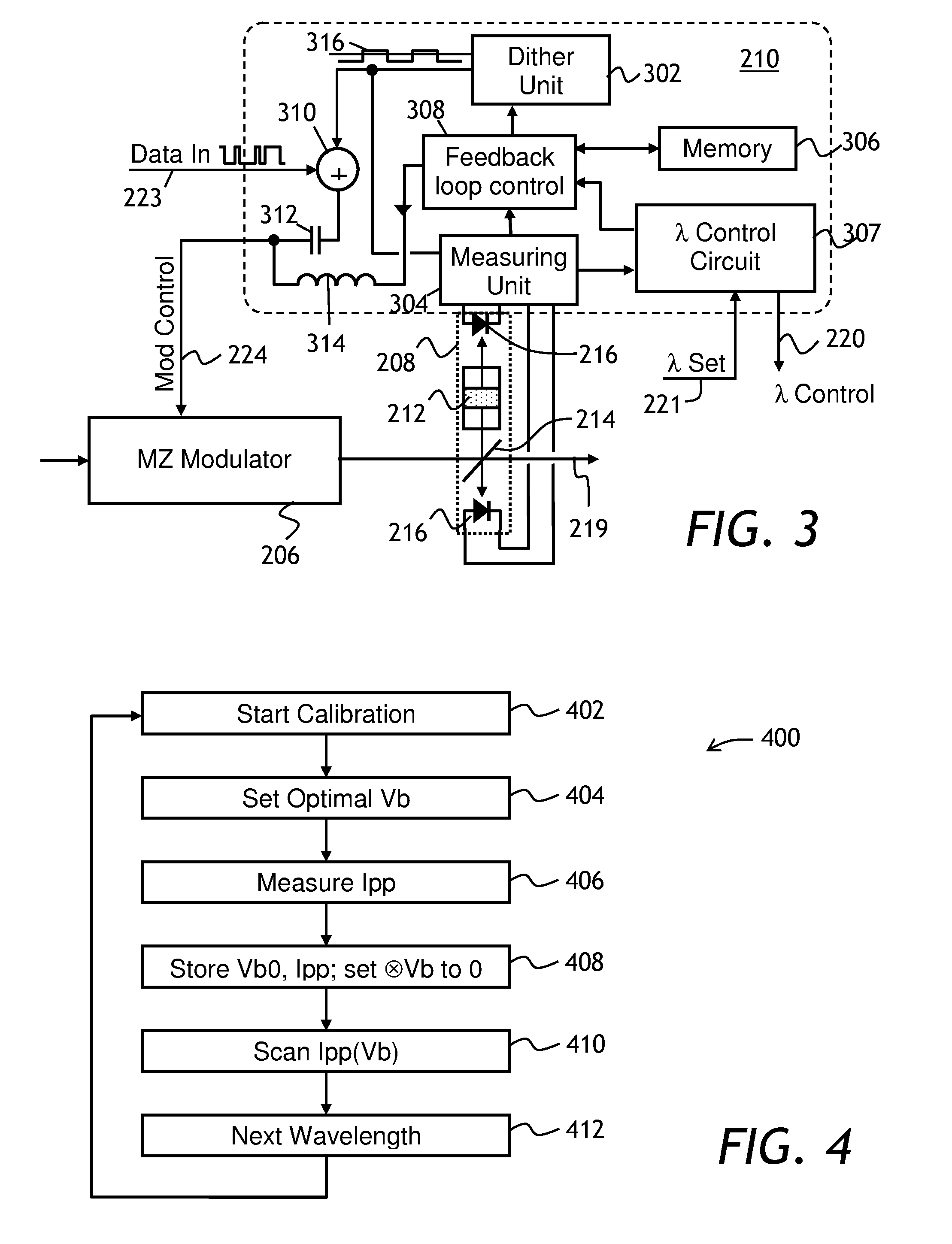
Bias control in an optical modulator and transmitter
ActiveUS20110206384A1Value can be obtainedReduce the differenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersLength waveDither
An apparatus and method for controlling bias in an optical modulator is disclosed. The method is particularly applicable to controlling multi-wavelength modulators and wavelength-tunable transmitters. At a calibration stage, a desired optical performance of the modulator is achieved, and an amplitude of a peak-to-peak variation of the output optical signal at a pre-determined amount of dither is stored in a memory as a reference. At operating stage, a controller of the optical modulator adjusts a bias voltage of the modulator until the measured peak-to-peak optical signal variation matches the reference value stored at the calibration stage. For multi-wavelength modulators and tunable transmitters, the calibration is repeated at each wavelength, and corresponding peak-to-peak optical signal variations are stored in the memory.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
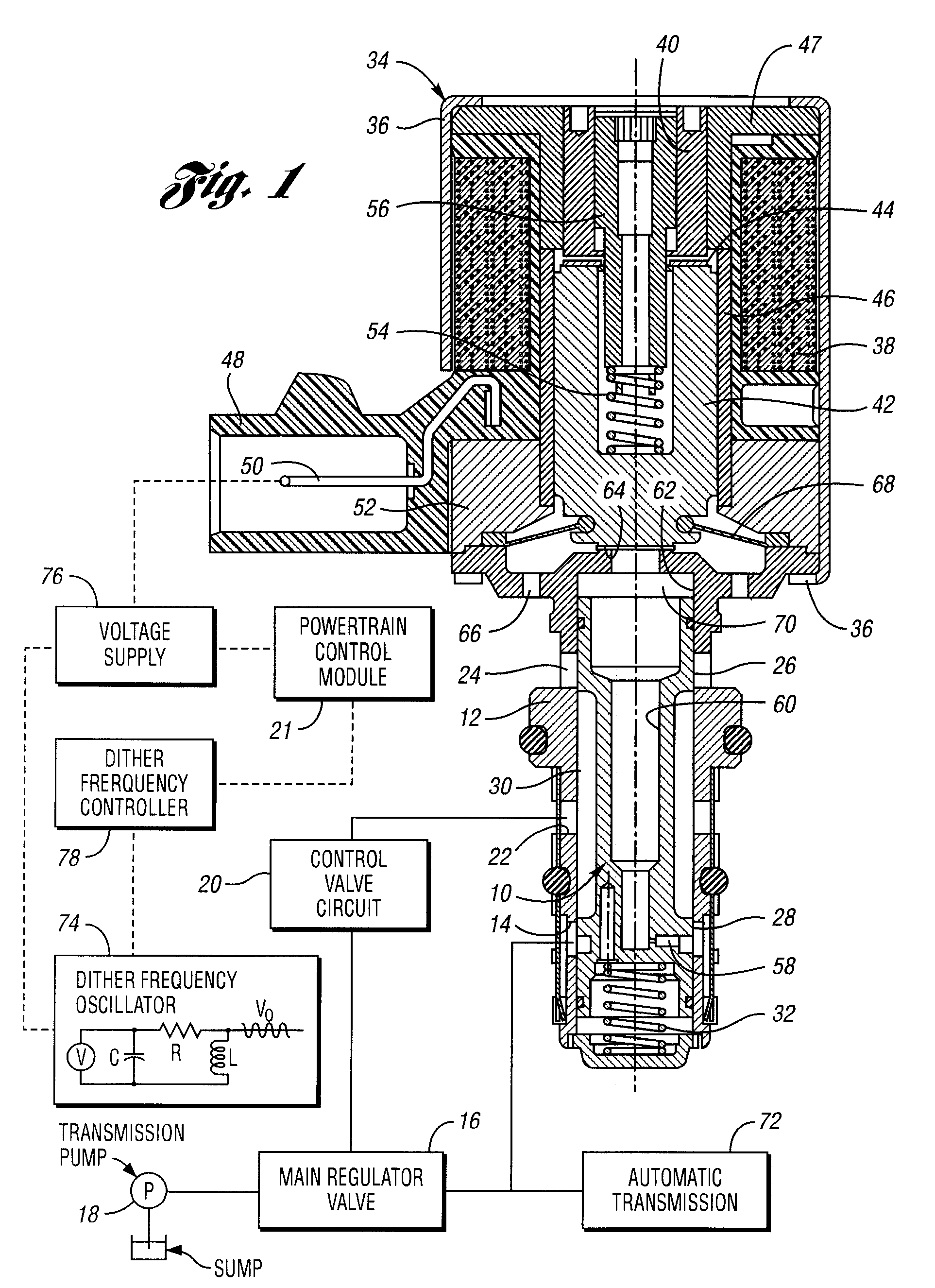
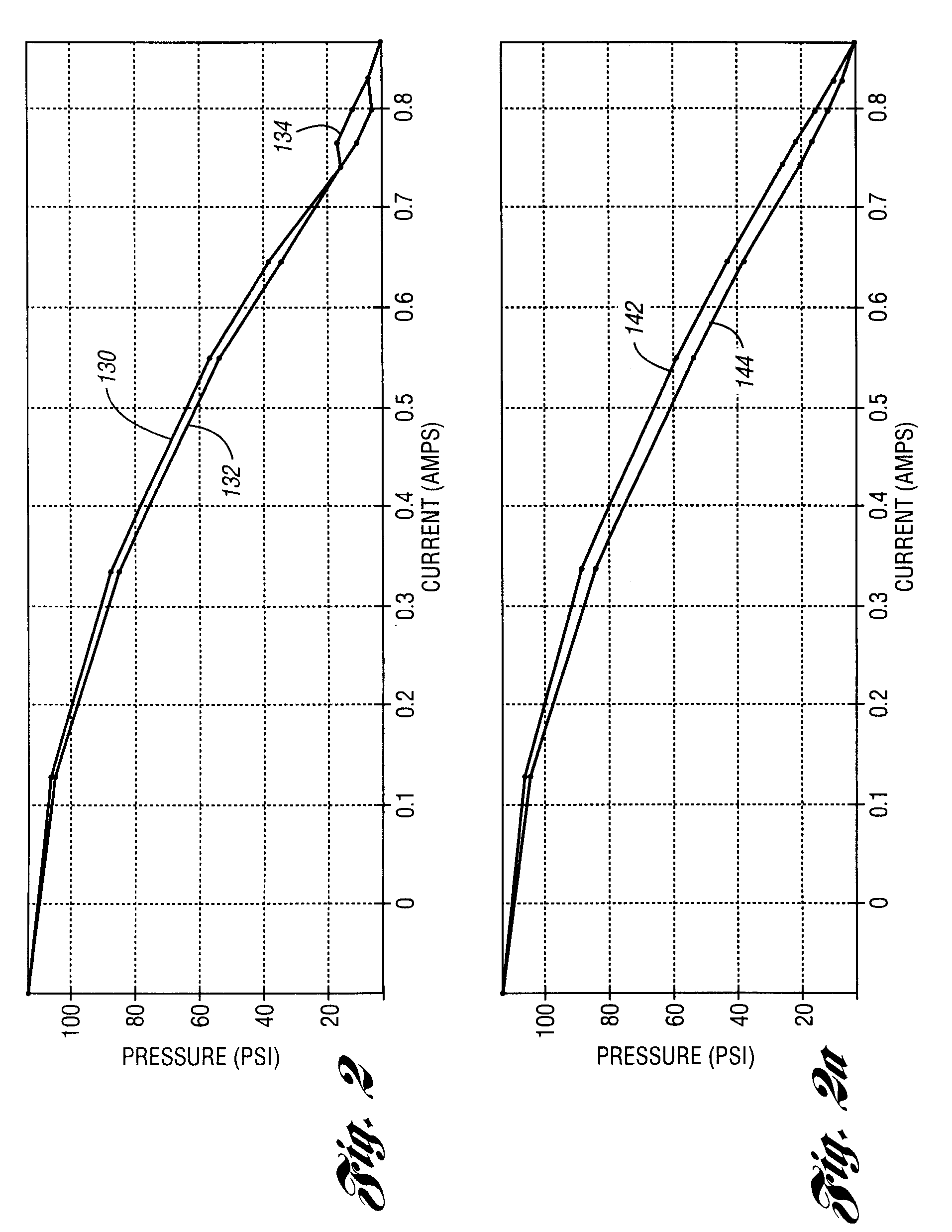
A control method and controller for a solenoid-operated electrohydraulic control valve
ActiveUS20060011878A1Reduce and to avoid undesirable transmission pressure control variationGreat pressure control accuracyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesThin material handlingInstabilityControl valves
A method and system for controlling a solenoid-operated pressure regulator valve to achieve high compliance with respect to a commanded current in accordance with a precalibrated transfer function. A dither frequency imposed on applied current is changed at precalibrated regulated pressure values to avoid dynamic instability.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
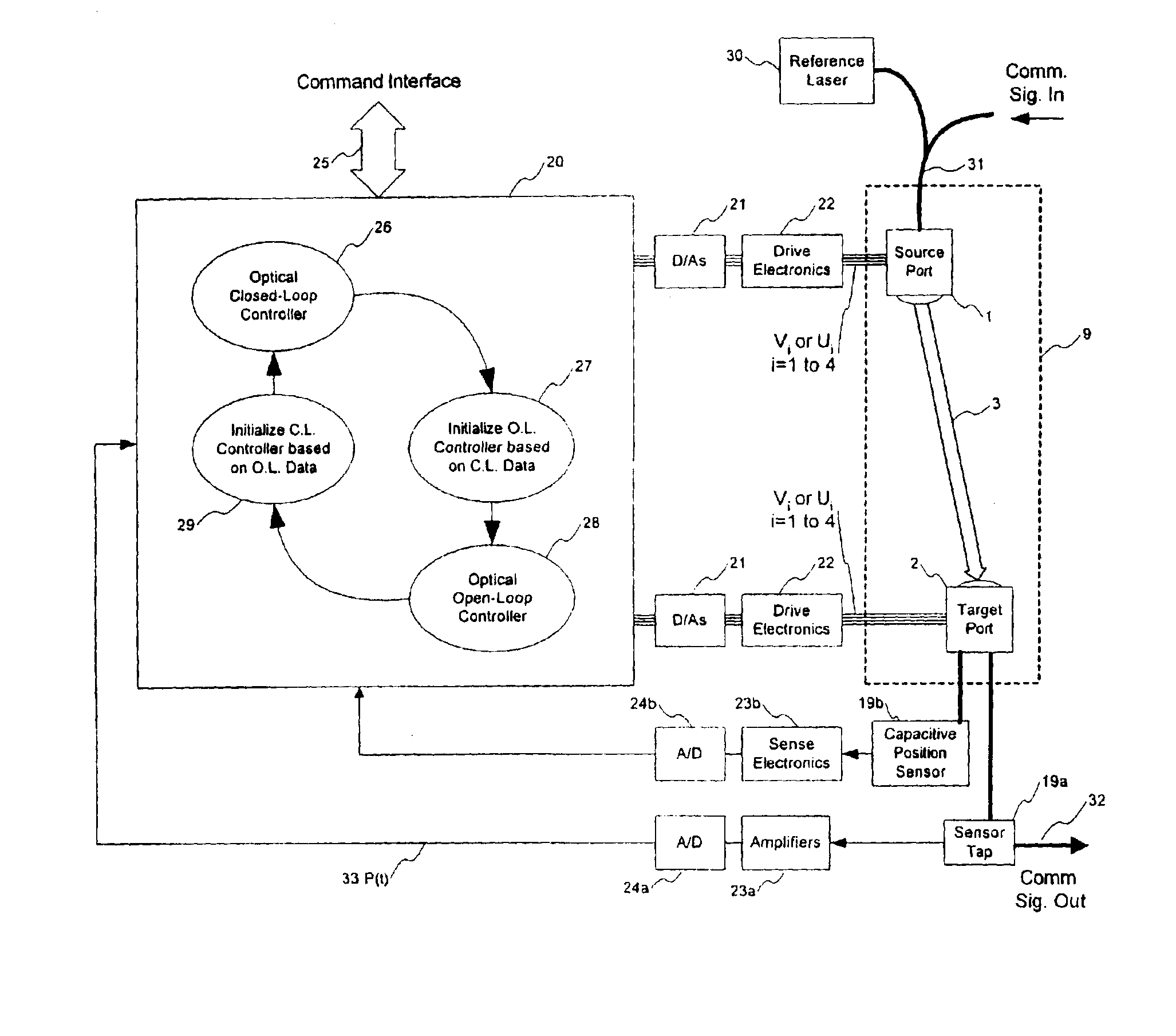
Multiple-axis control system for an optical switch
ActiveUS6975785B2Move fastRapidly tiltMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesFir systemLoop control
A free space optical switch that uses both an open loop control mode and a closed loop control mode. The open loop control mode is used to transition to a state where at least some light is sensed at a destination port. A closed loop control mode is then used, whereby a series of controlled dither signals are adjusted for system dynamics. Modifying the dither signals in this matter allows moving actuators at a rate that is much closer to the natural frequency of the underlying system, and hence speeds up the system convergence process. Variable modulation amplitudes may be employed on the dither signals to maximize convergence speed. In particular, changes in the dither signal can be made in accordance with the change in amplitude as a function of a gradient along a parabola that models the optical system response. According to still further aspects, the dither signals may be compensated for a desired and selectable attenuation level of output optical power.
Owner:POLATIS PHOTONICS INC
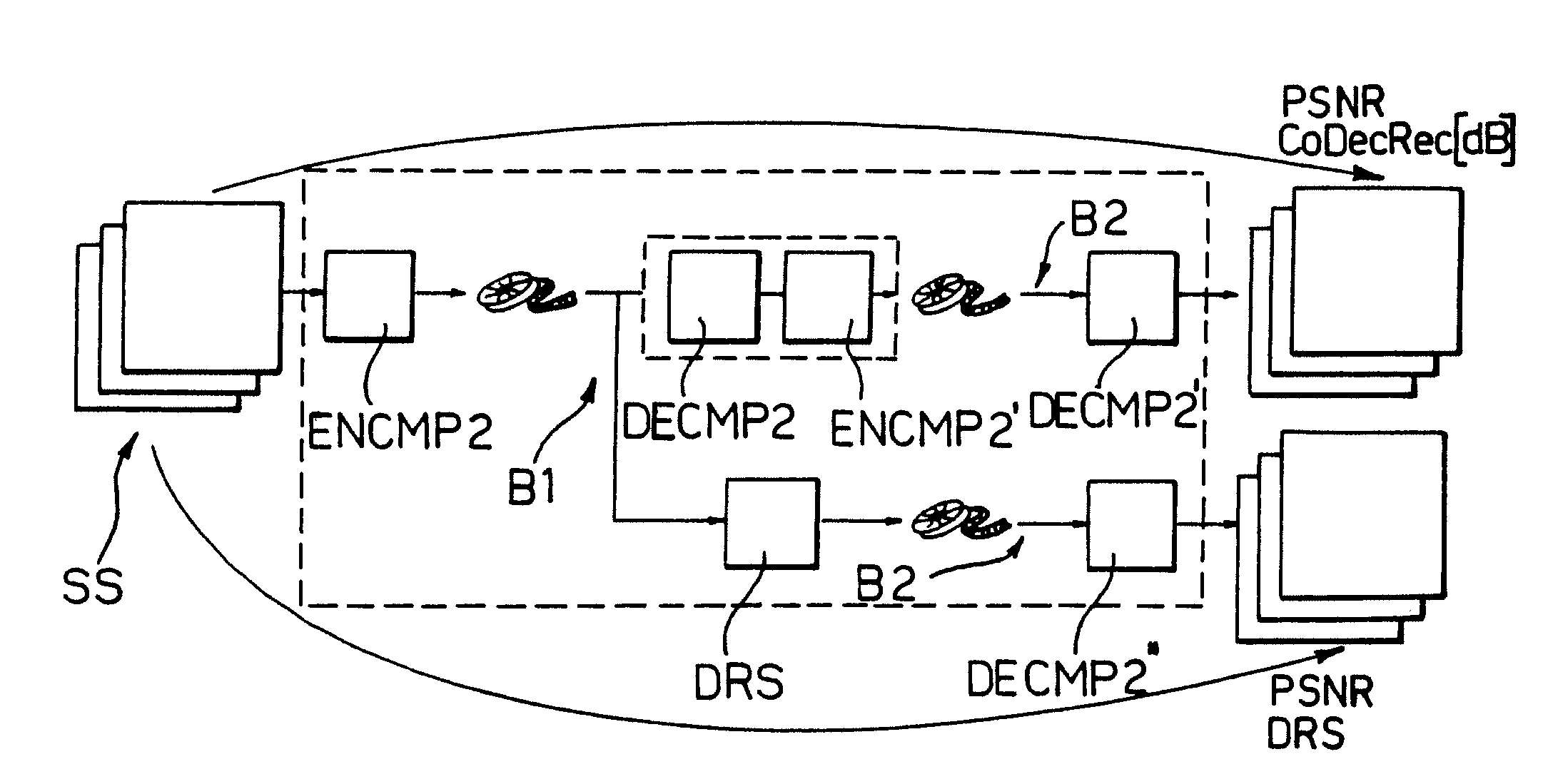
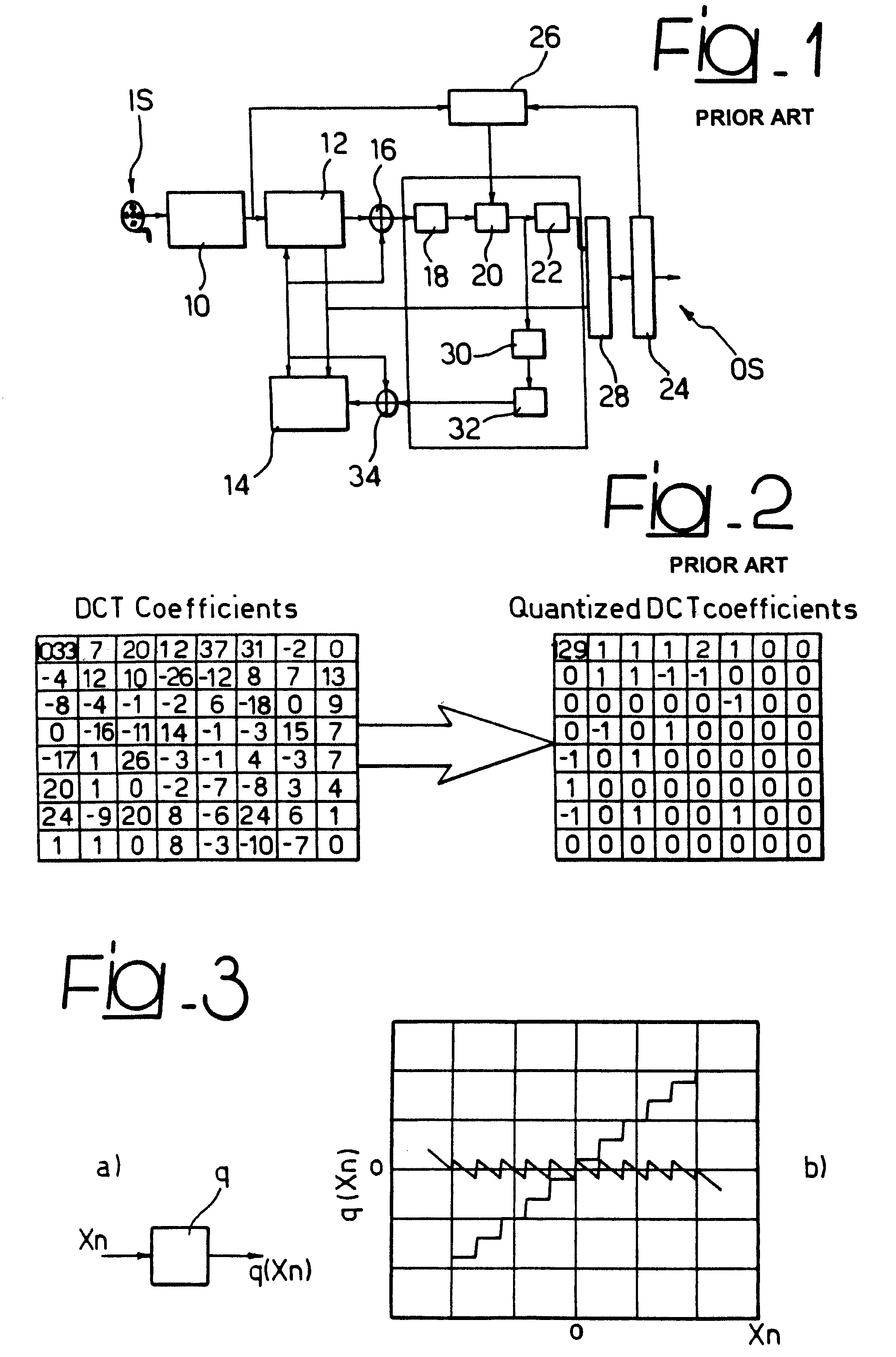
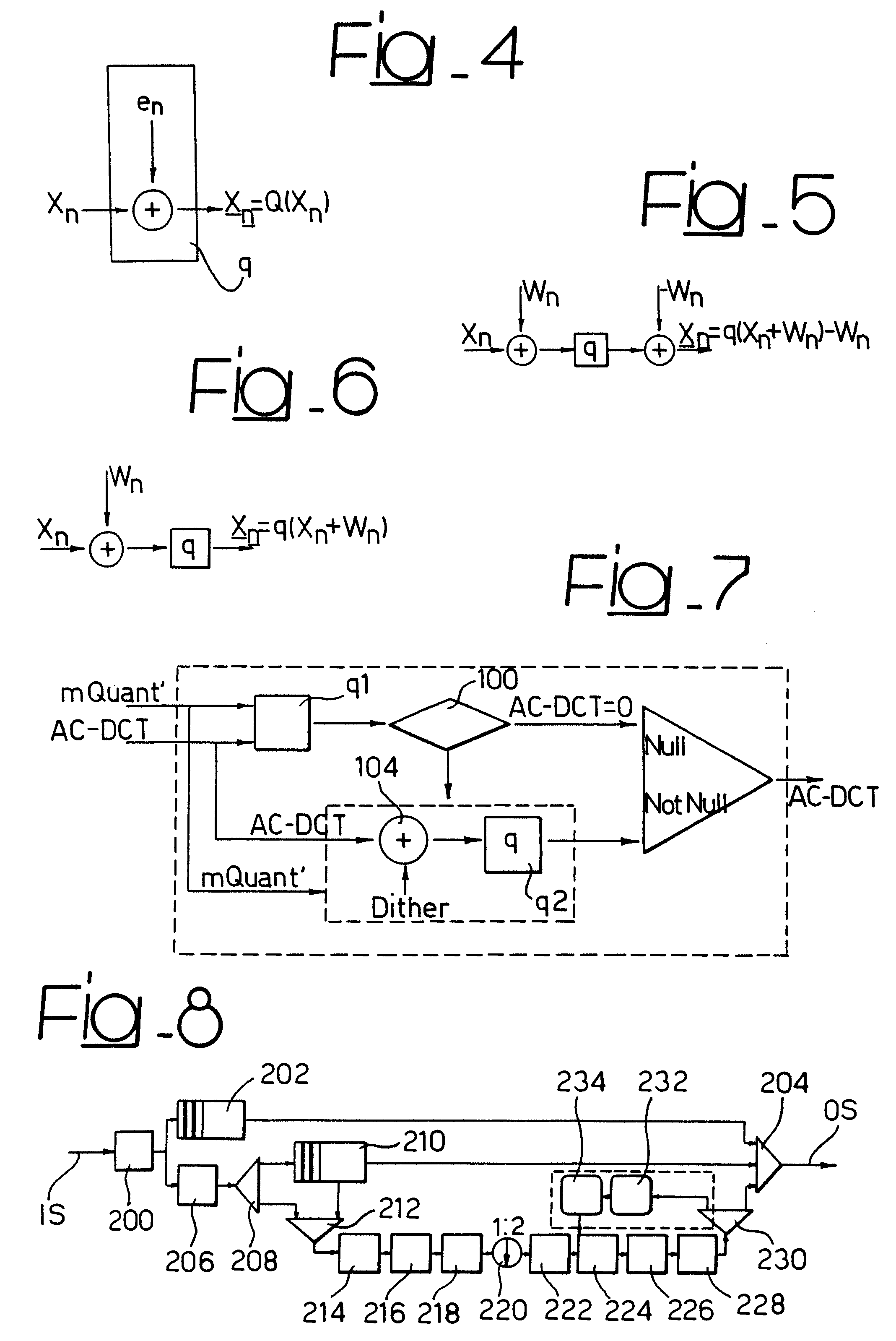
Quantization method and system for video MPEG applications and computer program product therefor
ActiveUS7301999B2Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationTranscodingDiscrete cosine transform
Digital signals are converted between a first and second format by a conversion process including generating coefficients representing the digital signals. The coefficients may be discrete cosine transform coefficient generated during encoding / transcoding of MPEG signals. The coefficients are subject to quantization by generating a dither signal that is added to the coefficients before quantization to generate a quantized signal. Preferably, each coefficient is first subject to a first quantization in the absence of any dither signal added to generate an undithered quantized coefficient. If the undithered quantized signal is equal to zero the undithered quantized coefficient is taken as the output quantized signal. If the undithered quantized coefficient is different from zero, the dither signal is added and the dithered coefficient thus obtained is subject to quantization to generate the output quantized signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Ditherless optical modulator control
ActiveUS20090232517A1Improve modulated optical output signalCreating qualityElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsSignal qualityEngineering
A method of controlling the operating parameters of an optical modulator, without using a dither signal, is provided. Past operating parameters are compared to present operating parameters using a quality of modulation signal obtained by cross-correlating the data modulation signal used to drive the optical modulator with the modulated optical signal output from the optical modulator. The quality of modulation signal is used to optimize the operating parameters (e.g., bias point) of the optical modulator, or other operating parameters of the arrangement, such as the modulator drive level, timing alignment, etc.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
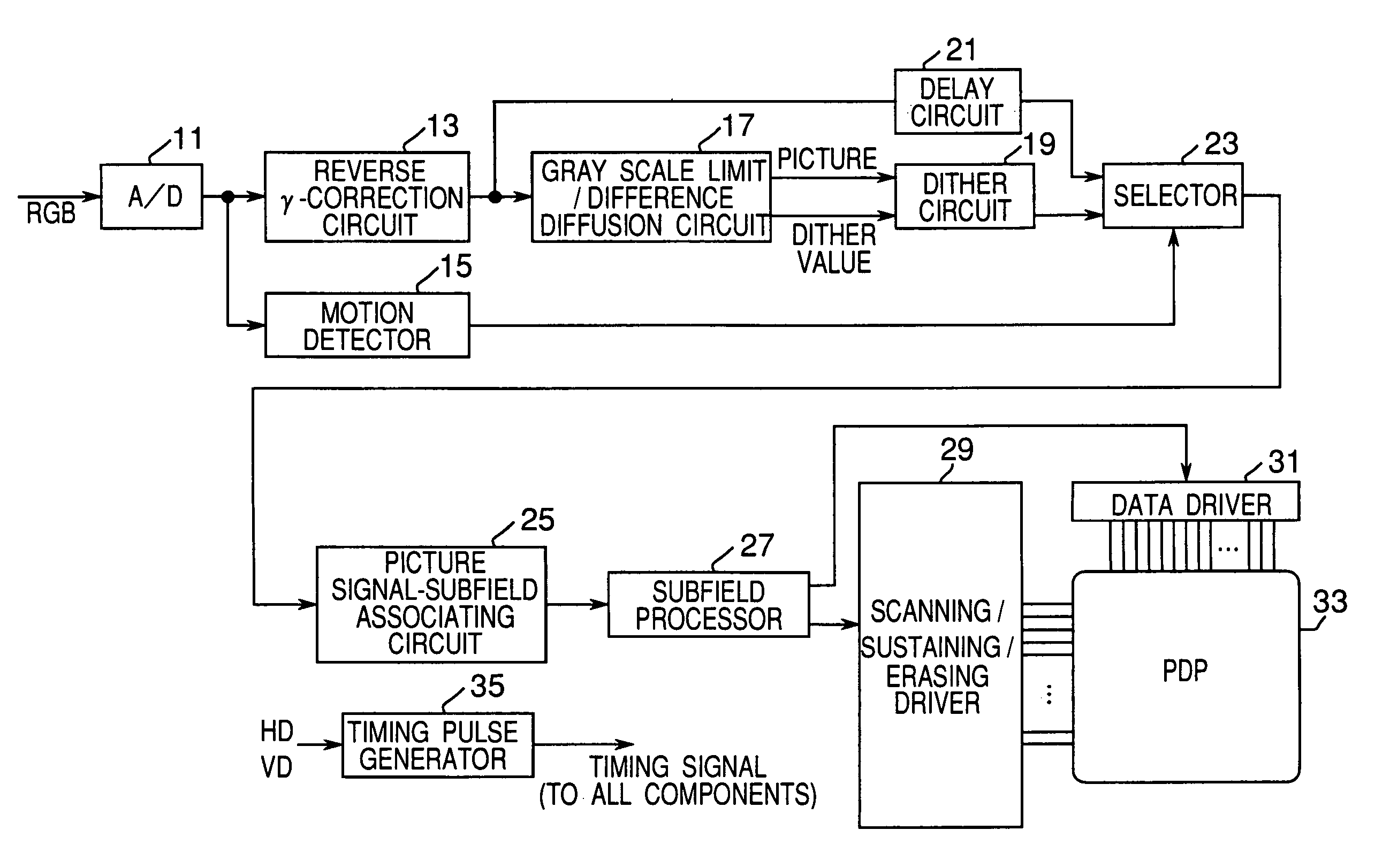
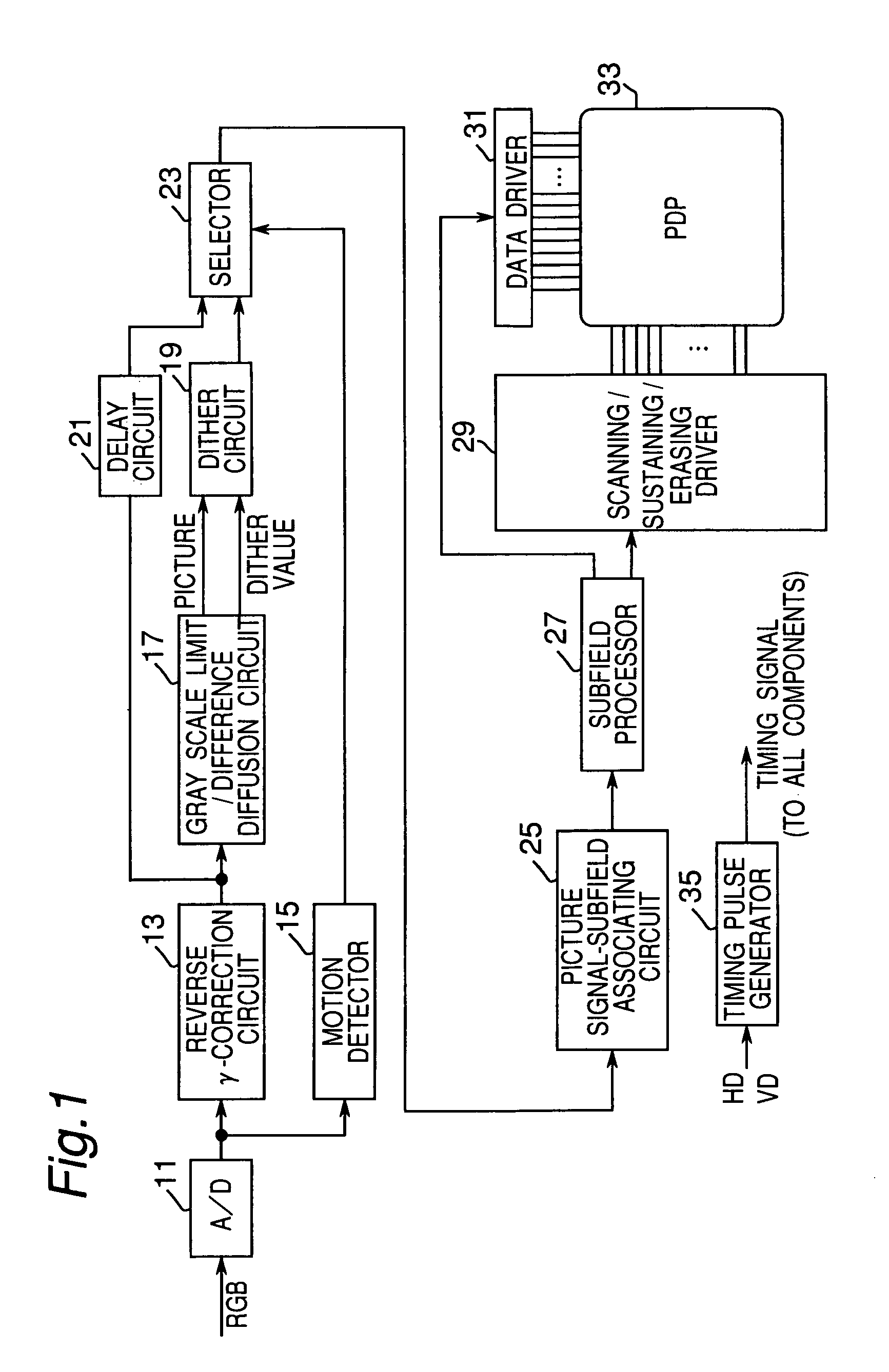
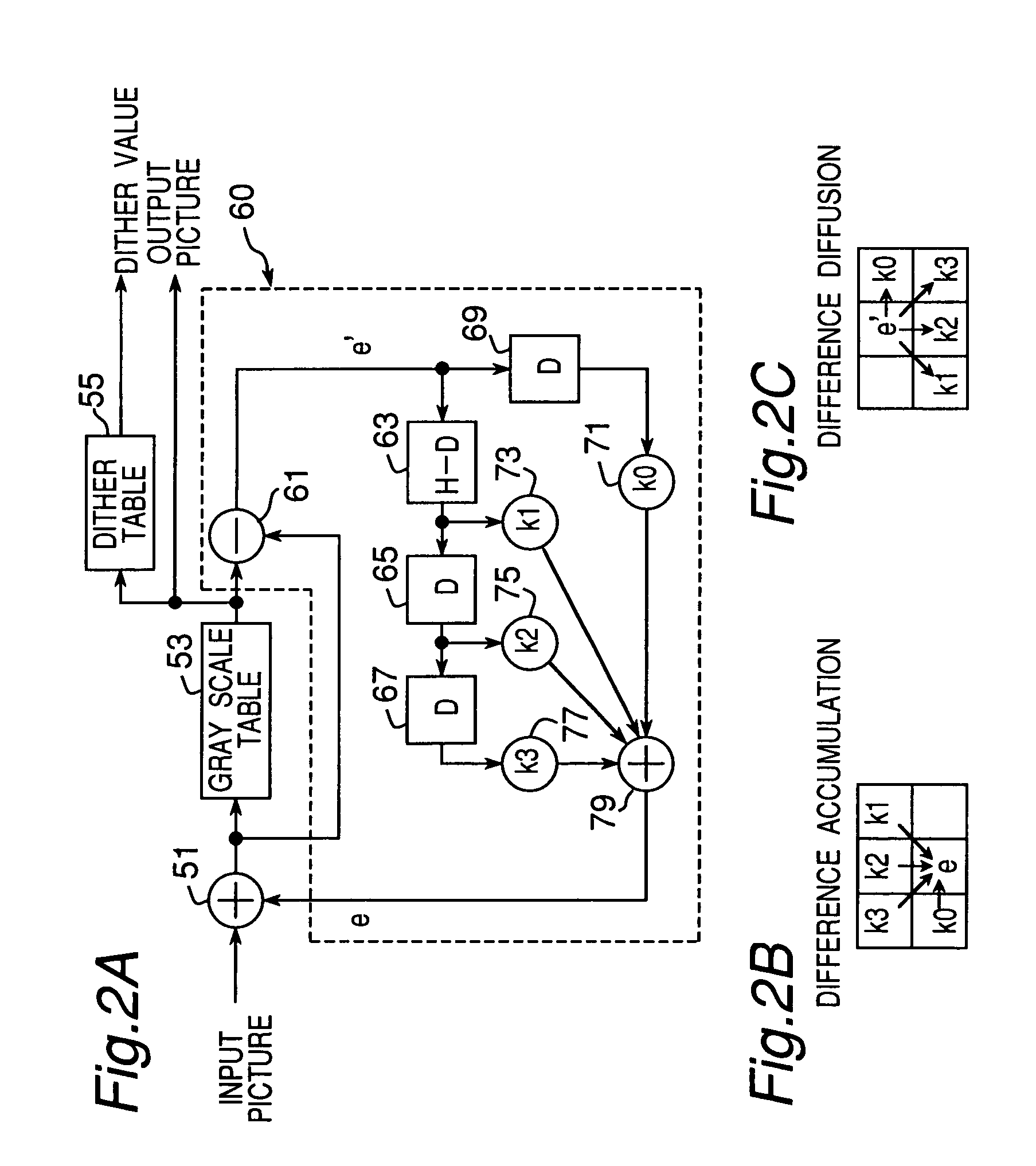
Apparatus and method for making a gray scale display with subframes
The invention provides an apparatus and a method applied to a plasma display panel or other display panel, achieving a gray scale display by using a plurality of weighted subfields. The apparatus comprises a gray scale limiting / difference diffusion circuit (17) for converting gray scale levels in a supplied image signal to specific gray scale levels that do not easily create pseudo contours in moving picture areas and to intermediate gray scale levels between the specific gray scale levels, and diffusing the difference between the converted gray scale level and the original gray scale level to adjacent pixels, and a dither circuit (19) for generating a video signal to display the converted gray scale level from the circuit (17) alternately in even and odd fields. The dither circuit (19) generates the video signal in which the gray scale levels offset the dither level above and below the dithered gray scale are alternately presented when the converted gray scale level is a dithered gray scale.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Content management based on dither-like watermark embedding
ActiveUS20160055607A1Easy to identify automaticallyEasy accessTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionContent managementContent management system
Methods, devices and computer program products allow embedding and detection of watermarks into and from a multimedia content. One watermark embedding method includes selecting a content segment that lacks inherent features for embedding of watermarks without producing perceptible artifacts, and obtaining a first dither pattern corresponding to a first watermark symbol of a watermark symbol alphabet, where each symbol is associated with a particular dither pattern. Further, each particular dither pattern, upon combination with the multimedia content segment that lacks inherent features, produces a composite content segment without perceptible artifacts. By combining the first dither pattern with the multimedia content segment that lacks inherent features, a first composite content segment with the first embedded watermark symbol is produced. The detection of watermarks messages can be carried out quickly by examining a small portions of the multimedia because even the featureless content segments include embedded watermarks.
Owner:VERANCE
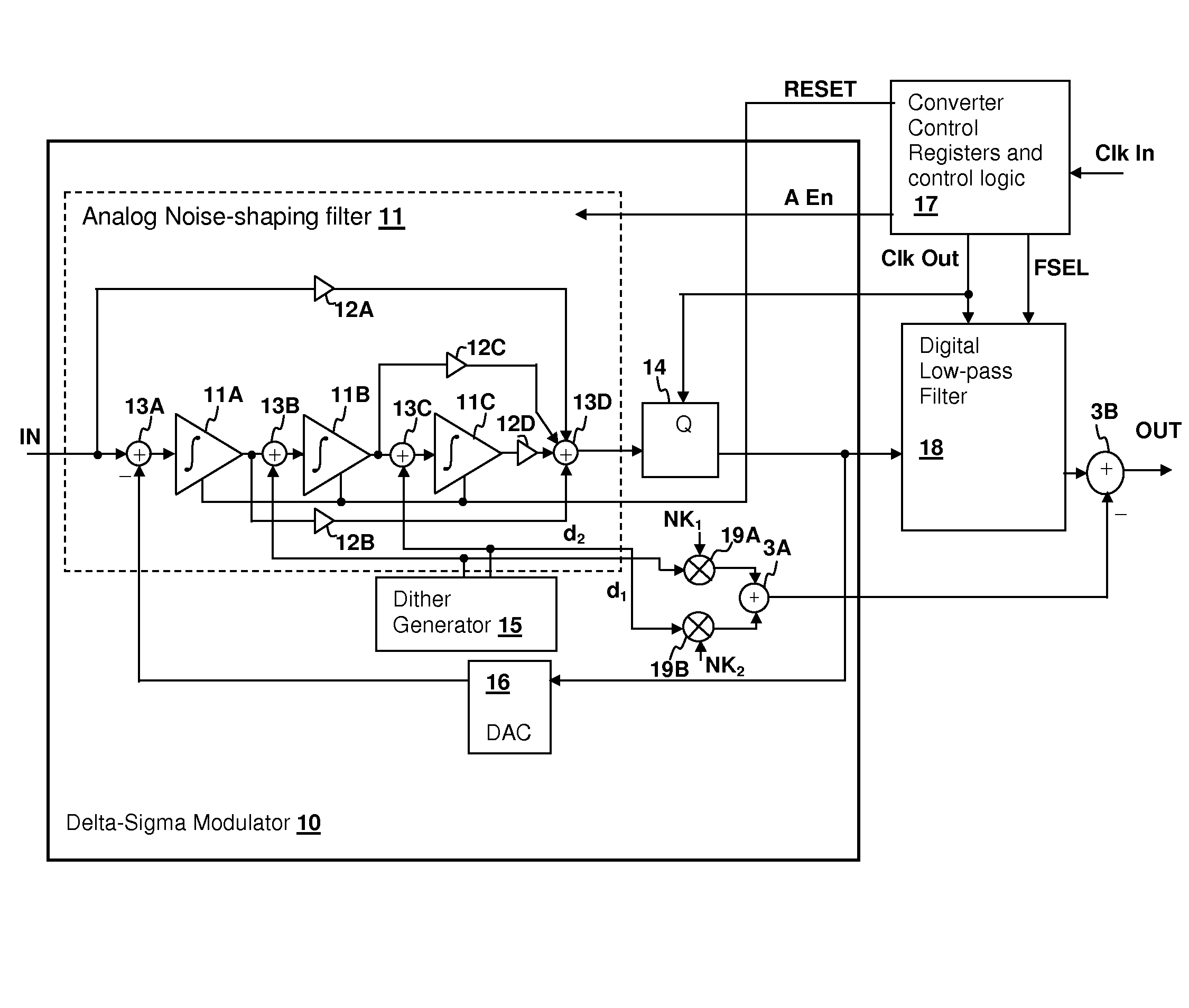
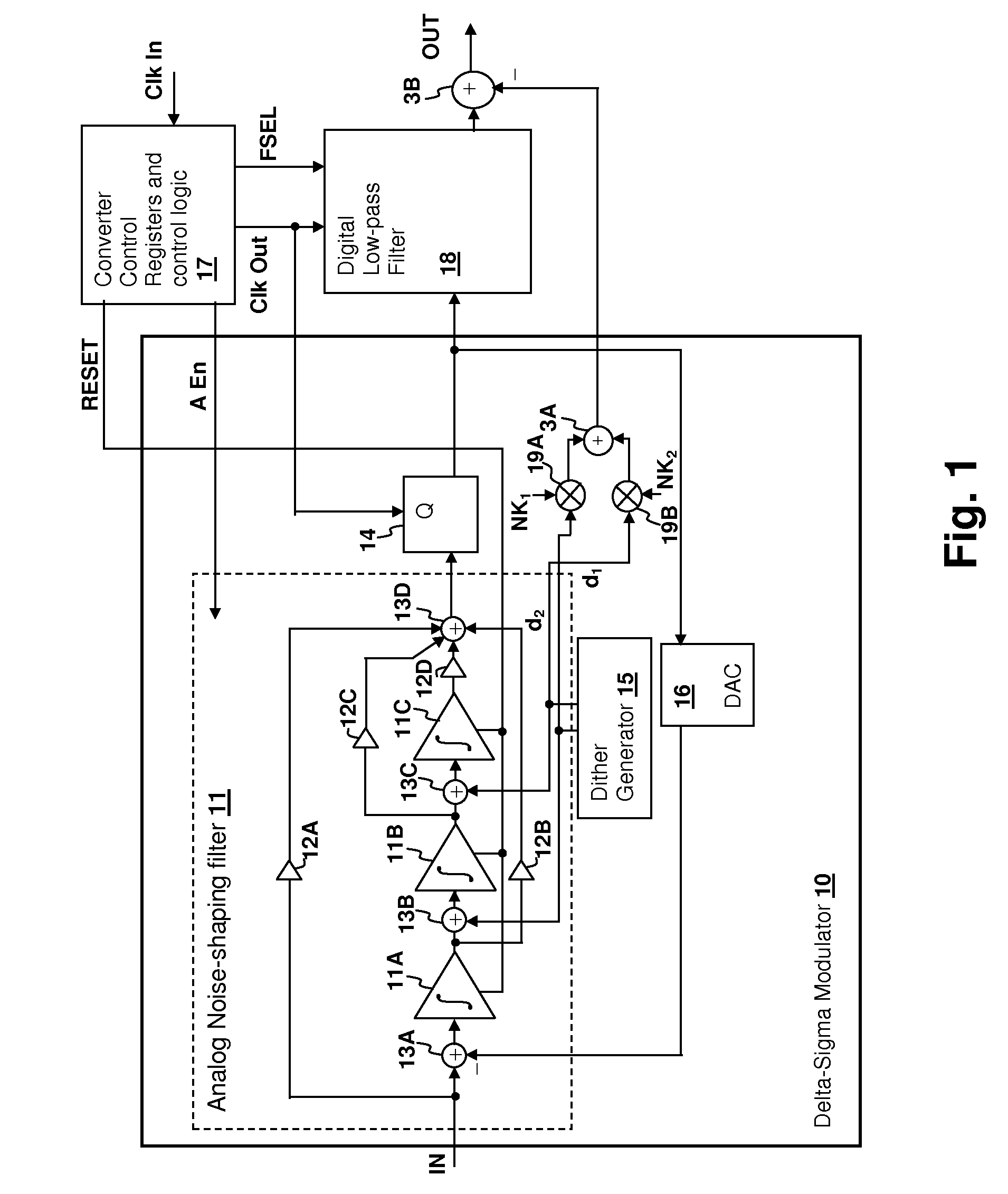
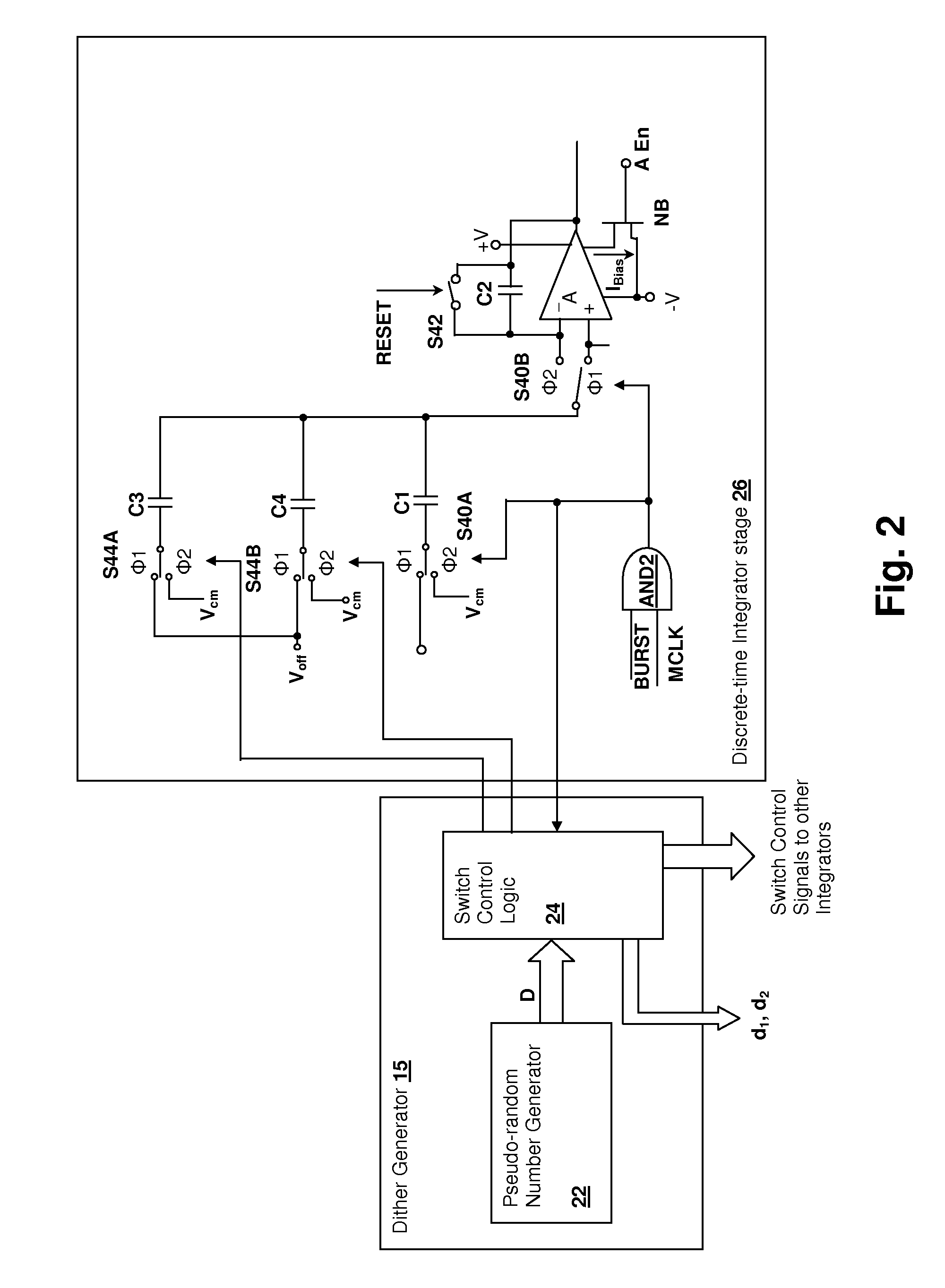
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) having integrator dither injection and quantizer output compensation
ActiveUS7411534B1Reduce in quantityLittle and no errorElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorAnalog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) having integrator dither injection and quantizer output compensation reduces the probability of unchanging code sequences that occur when the input signal and feedback signal are equal and thus no quantizer output change occurs. In particular, in modulators that are periodically reset, the dither reduces the probability of a stuck code sequence at startup. The effect of the dither is removed from the output of the ADC, either by subtracting an offset value from the result of filtering the quantizer output, or directly from the quantizer output itself.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
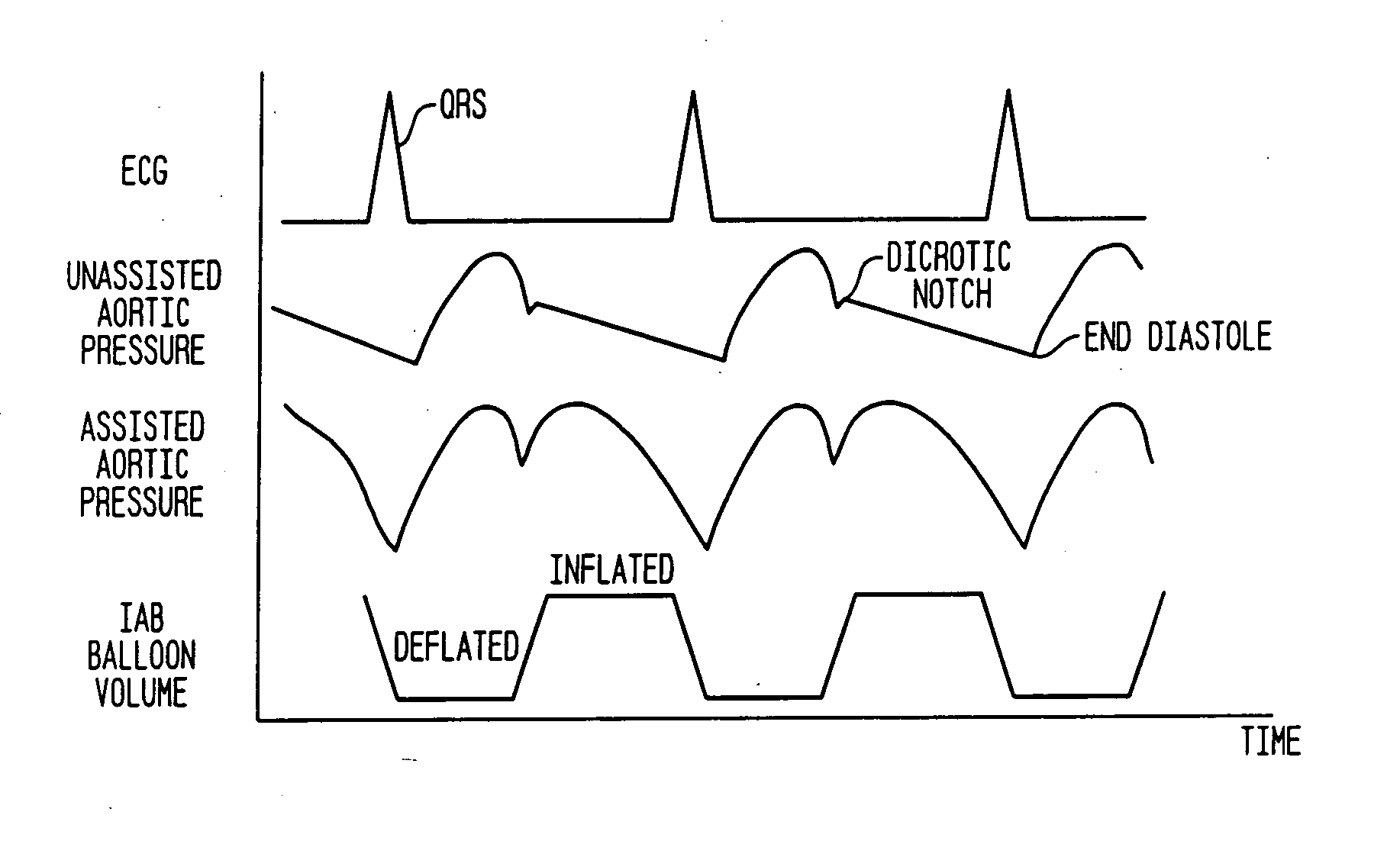
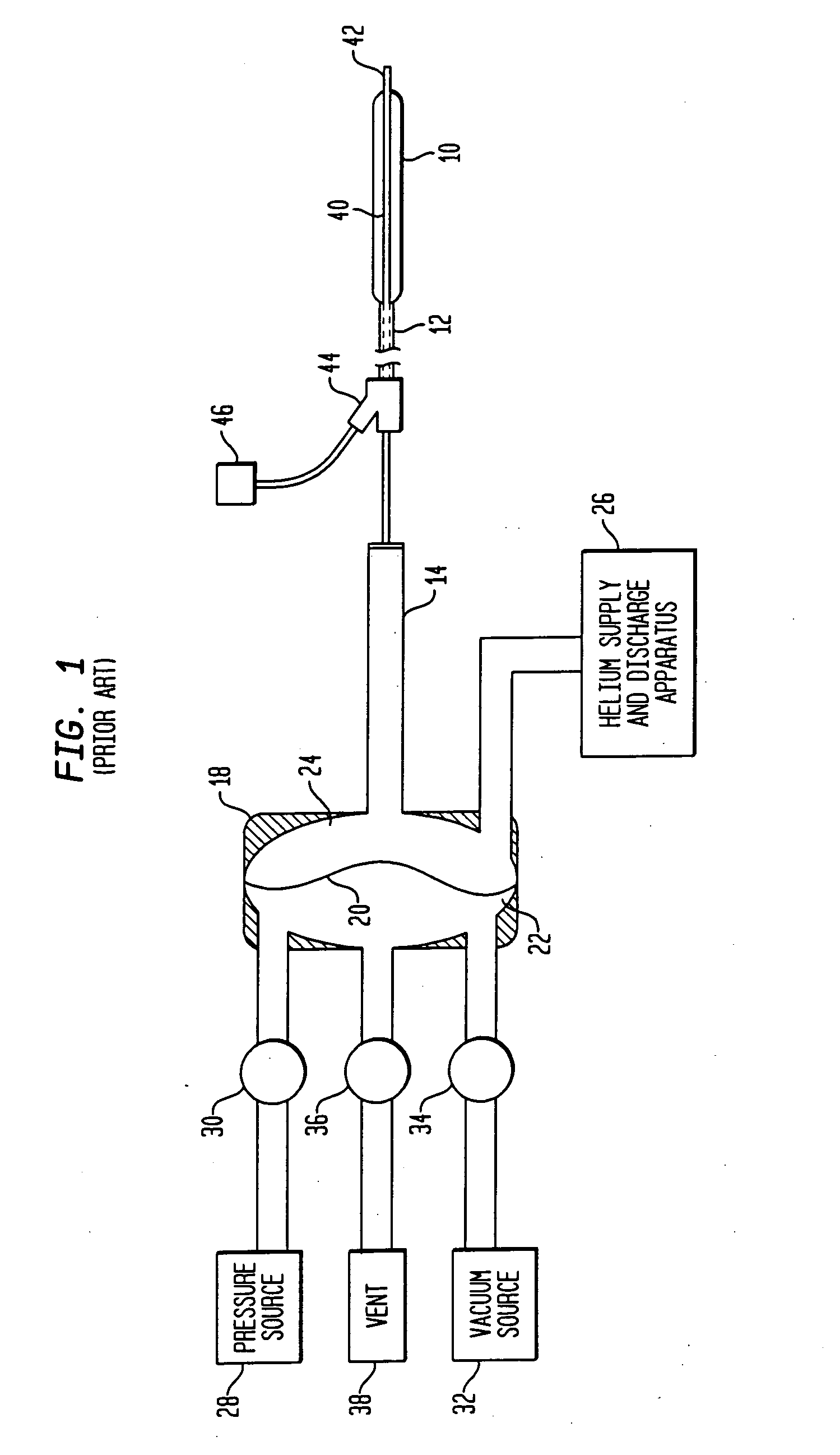
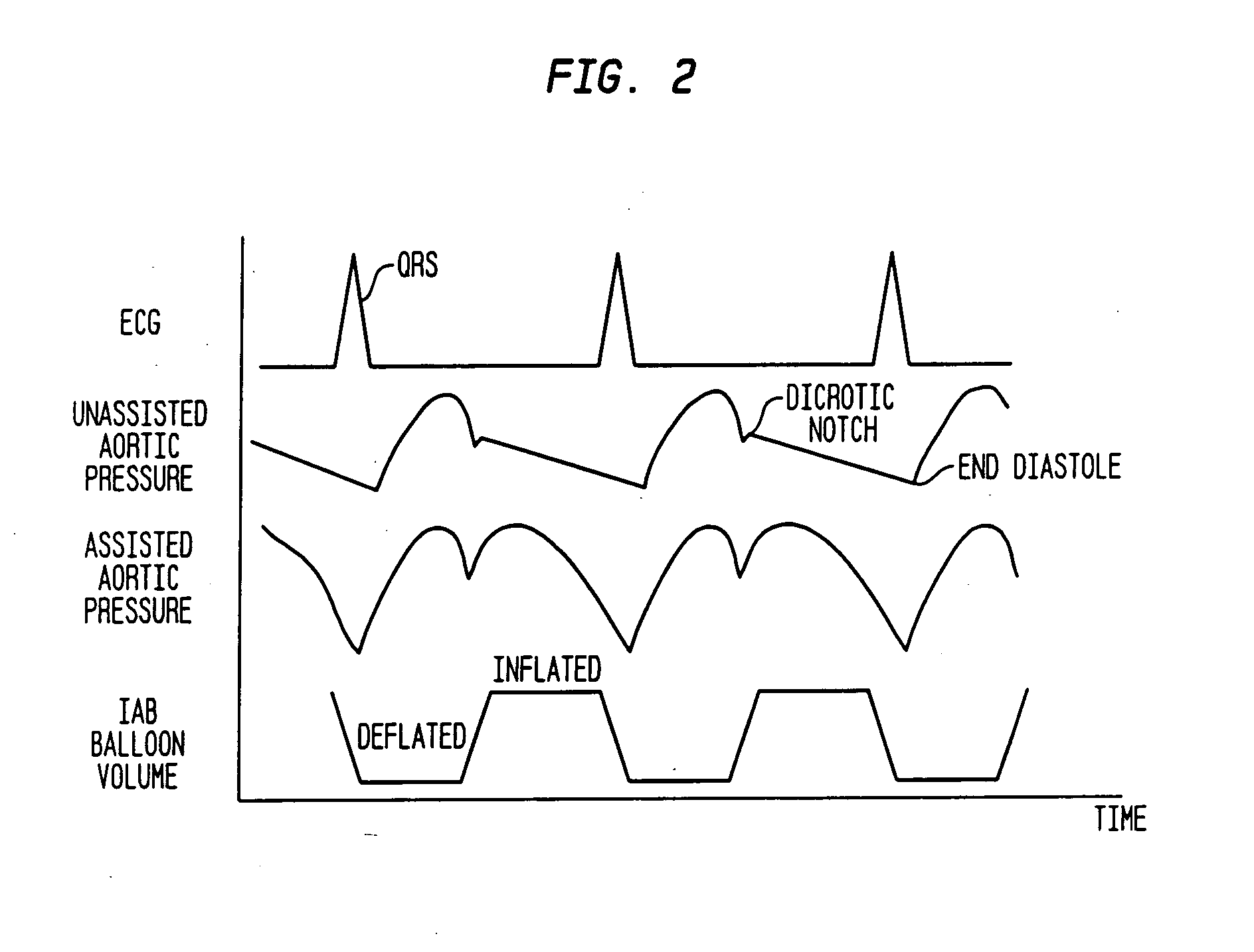
Timing of intra-aortic balloon pump therapy
ActiveUS20050148812A1Long durationAssist cardiac functionElectrocardiographyControl devicesTotal delayAortic balloon pump
In order to fully automate the inflation timing and deflation timing of an intra-aortic balloon pump, certain delays intrinsic in the system must be taken into account. A process for calculating these delays includes determining a nominal inflate command time, adding a dither time interval to the nominal inflate command time to obtain an actual inflate time, and determining a deflate command time. An inflation / deflation cycle is then processed in which the intra-aortic balloon pump is inflated at the actual inflate command time and deflated at the deflate command time. Blood pressure data is acquired from the patient during the inflation / deflation cycle, and is then analyzed to determine a realization time at which the effects of inflating the intra-aortic balloon are realized on the blood pressure waveform. From this the total delay time between the actual inflate command time and the realization time can be determined.
Owner:DATASCOPE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com