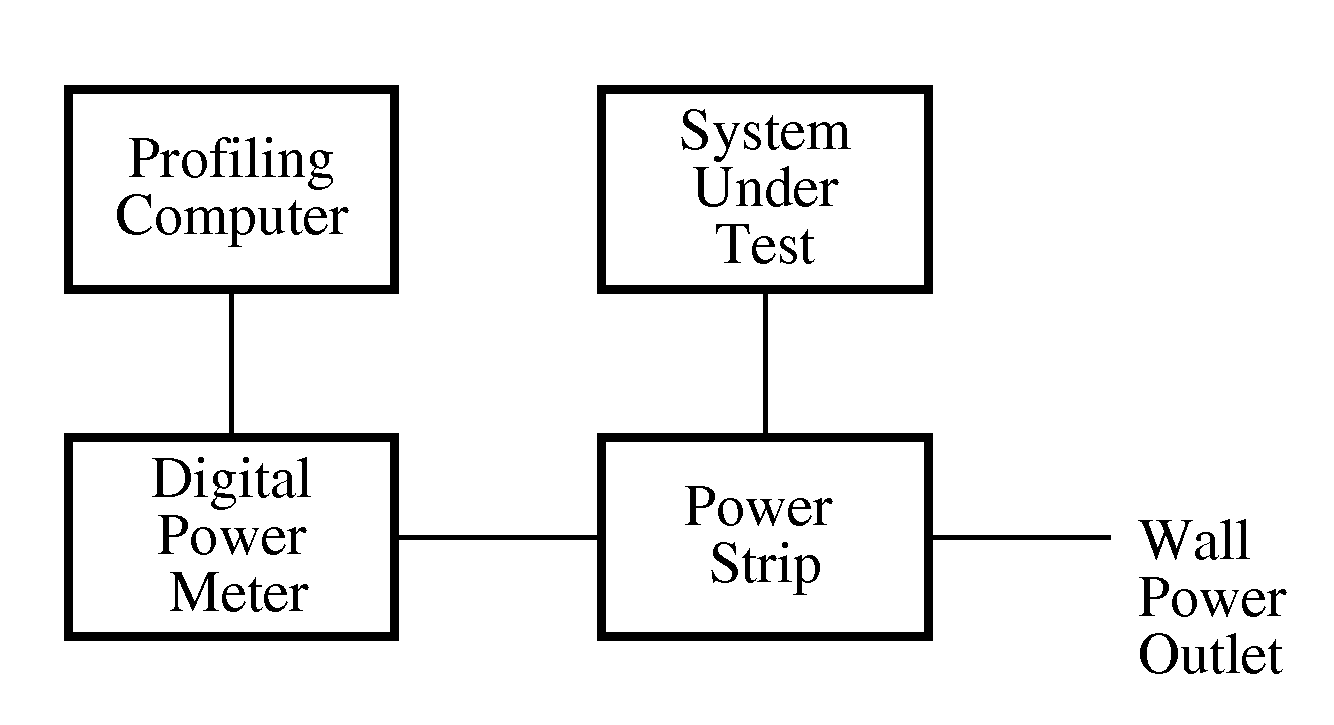
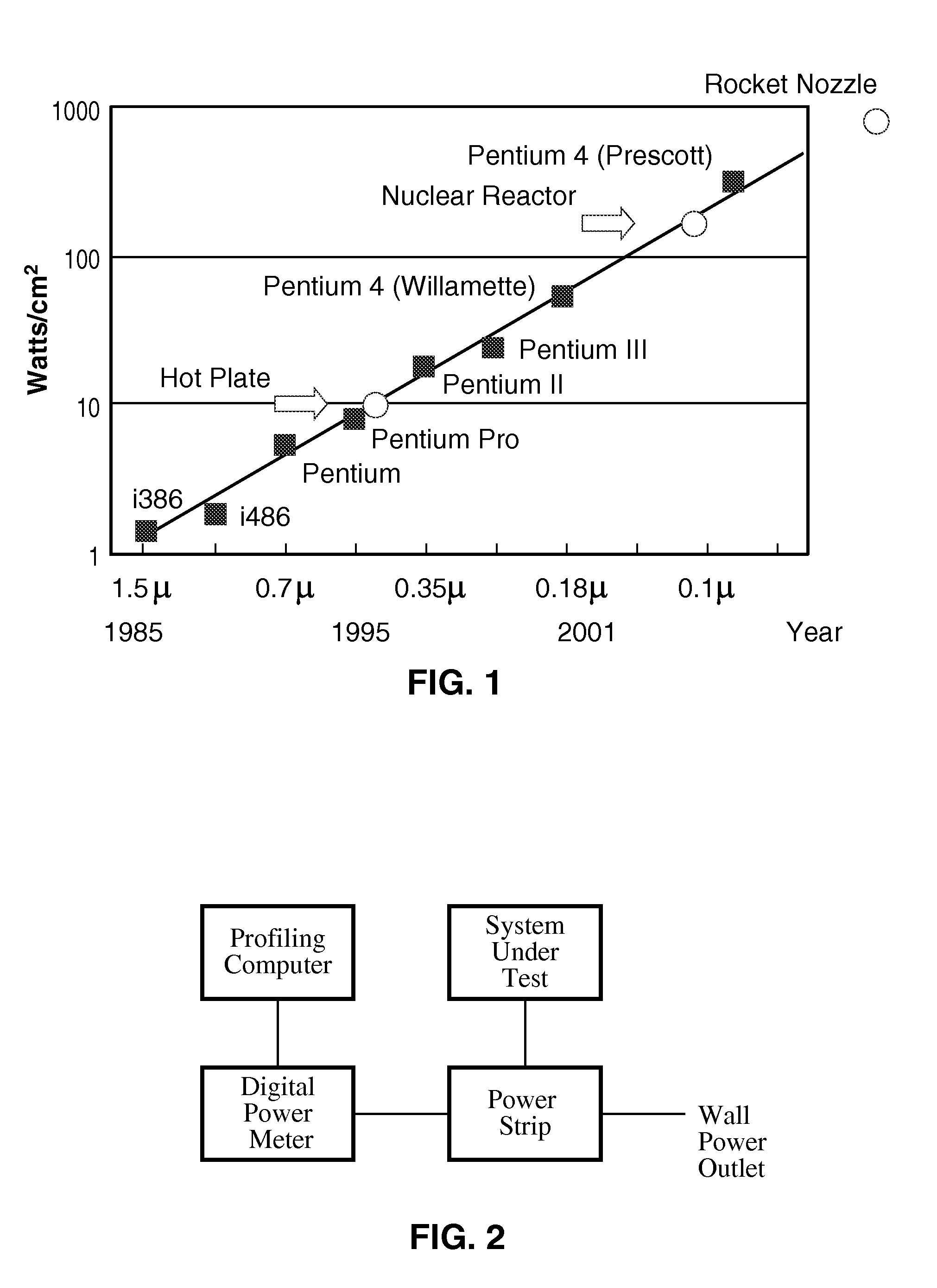
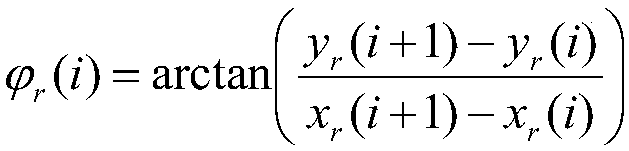Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Fir system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for manufacturing
ActiveUS8298054B2Increase capacityLess expensiveDomestic stoves or rangesSpace heating and ventilationFir systemOn board
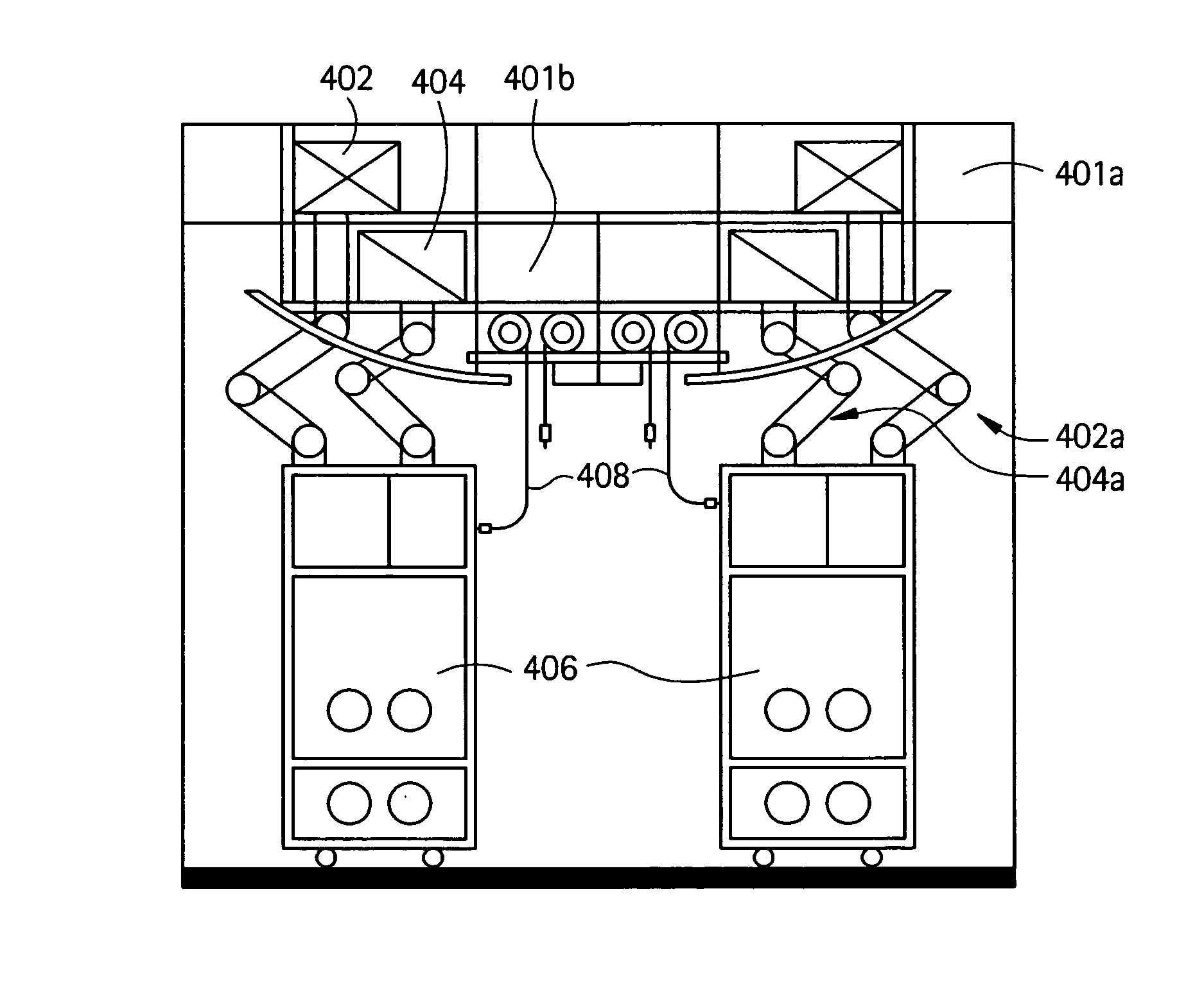
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a customizable bio-manufacturing system which includes a manufacturing space having a first air handling system for providing supply air and a second air handling system for handling exhaust air, the supply air system being optionally provided with at least one of filtration, heating, cooling and or humidity control and a plurality of portable modules provided within the manufacturing space. At least one module having an interior capable of being interconnected with another module interior and each module's interior includes one or more components to perform at least one specific task of a biological, chemical, and / or pharmaceutical manufacturing process. At least one module includes an on-board environmental control system for controlling an environment within the module and a connection means for interconnecting the module interior with another module interior. The system also includes a central controller operating to at least perform one or more of operation and information collection for the operation of at least one of the system and one or more modules.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method and apparatus for system monitoring and maintenance
InactiveUS20060126608A1Vehicle testingMultiplex system selection arrangementsFir systemComputer science
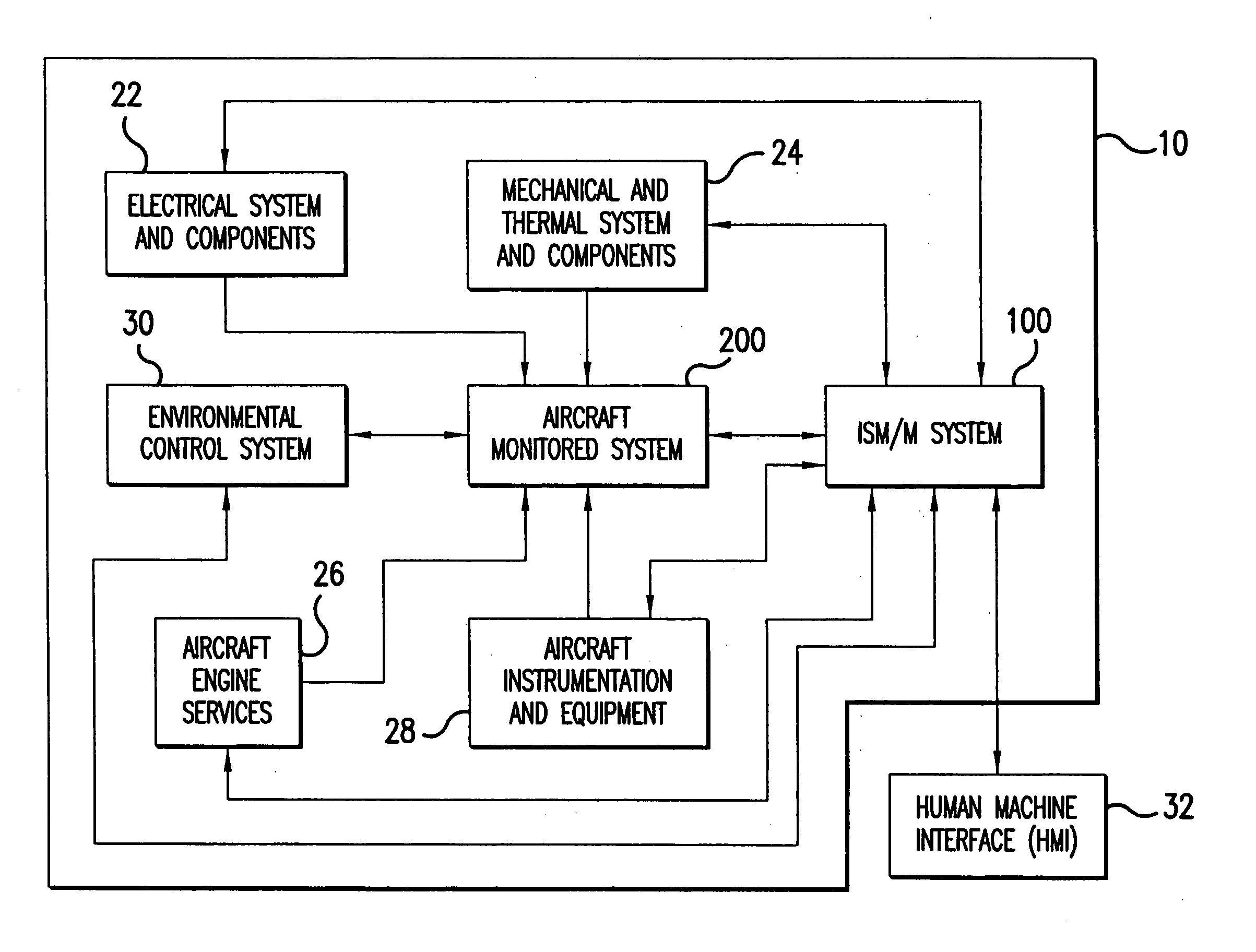
A method and an apparatus provide intelligent monitoring and maintenance of a system. The method according to one embodiment accesses data relating to functional components of the system; extracts parameter information for functional components of the system, the step of extracting parameter information including performing inferential processing and trend recognition of the data using previous knowledge about the system, and simulating performance of the system using models of the system and previous knowledge about the system; identifies new information about the system present in extracted parameter information; and provides the new information to the step of extracting parameter information, to be used as previous knowledge.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
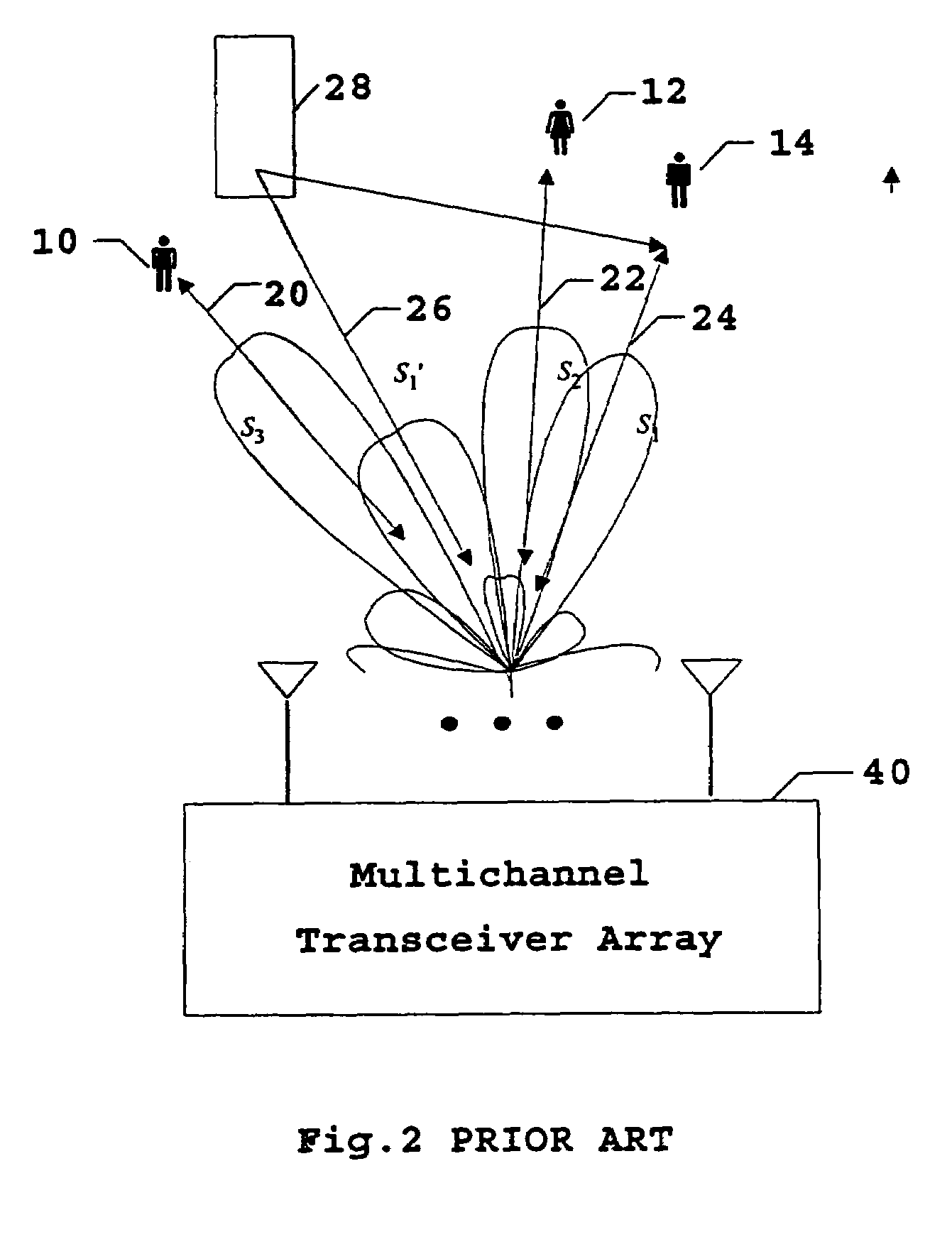
Smart antenna CDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS6980527B1Increase capacityImprove performanceSynchronisation arrangementSpatial transmit diversityFir systemDownlink beamforming
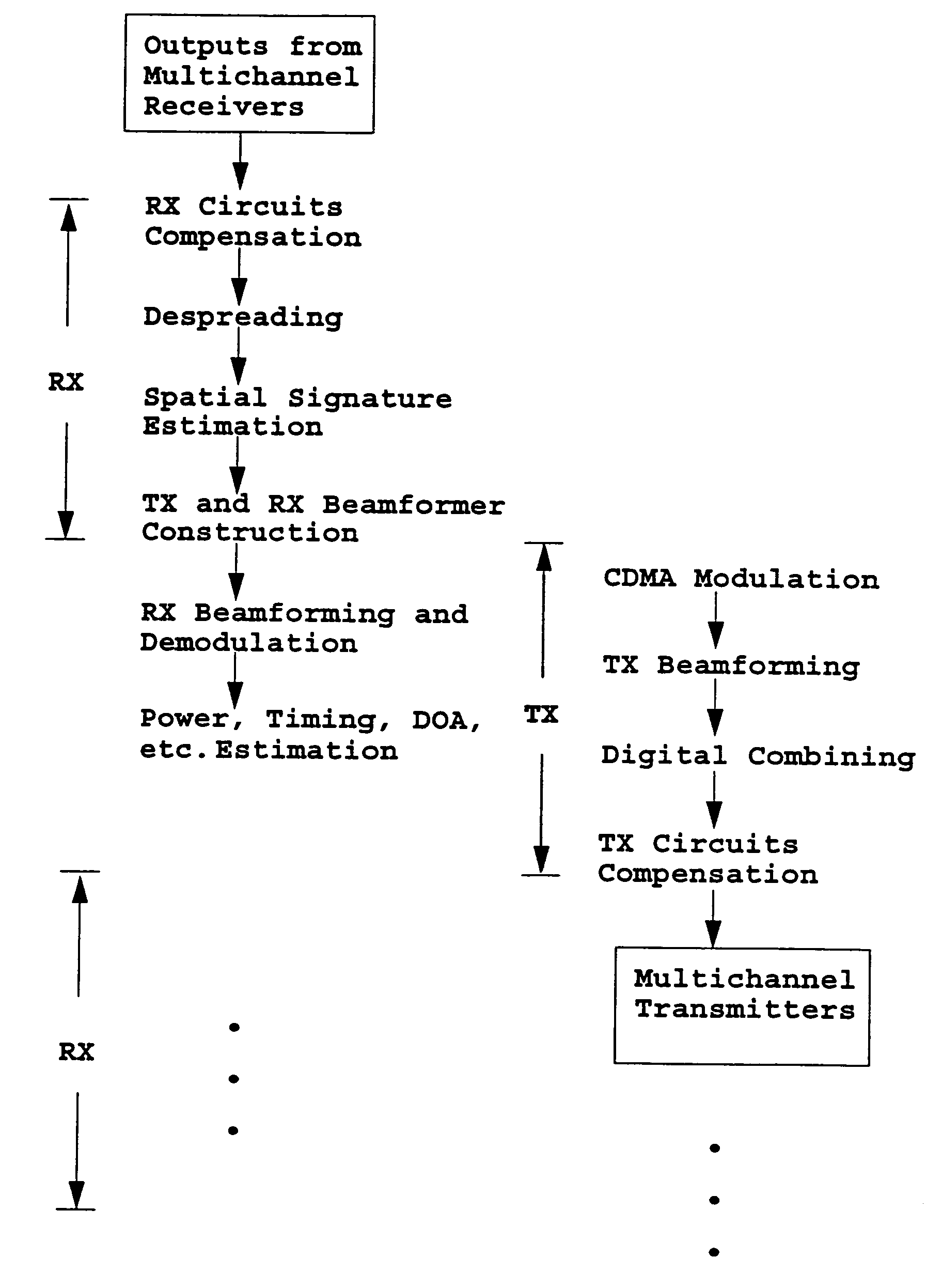
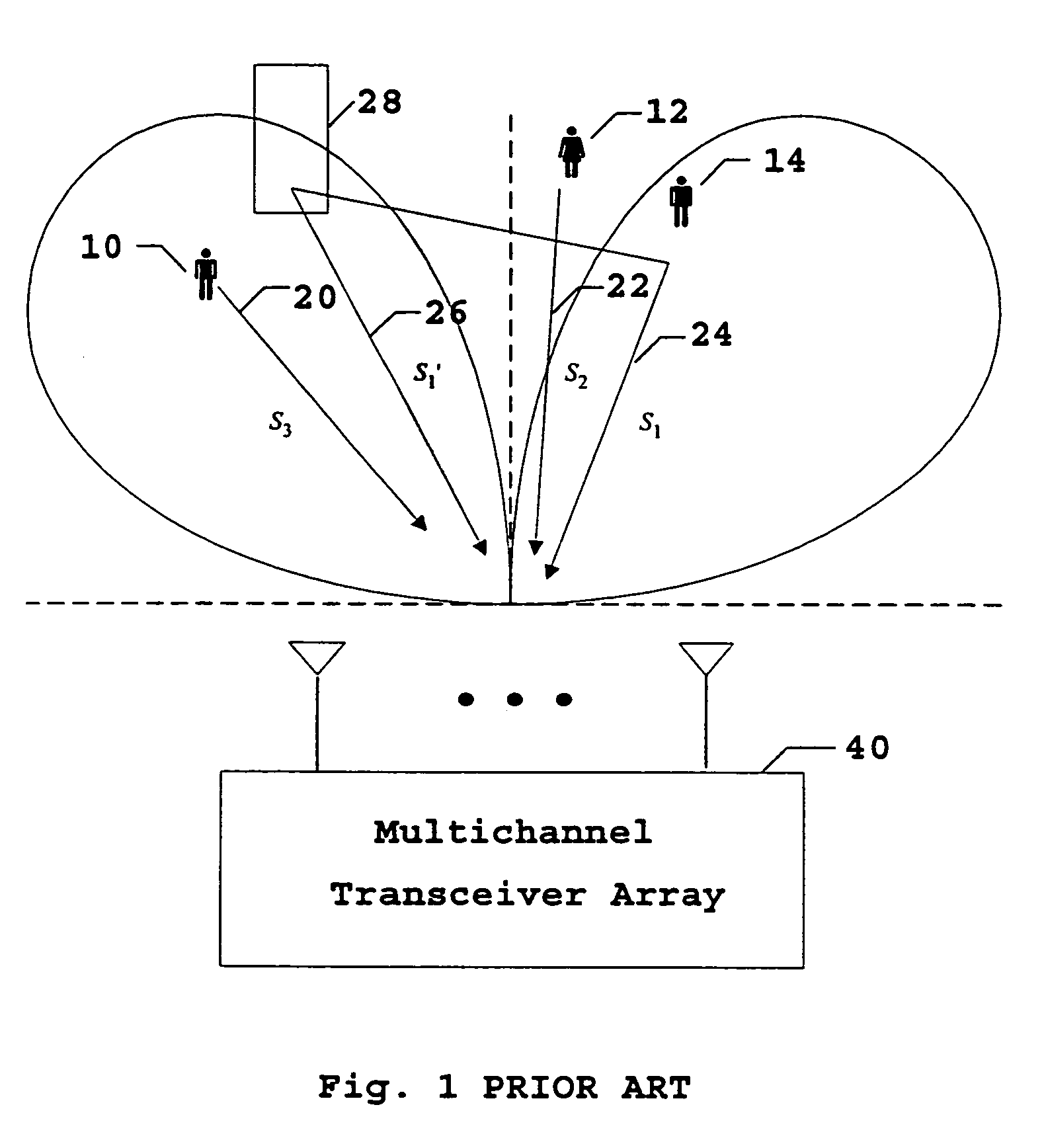
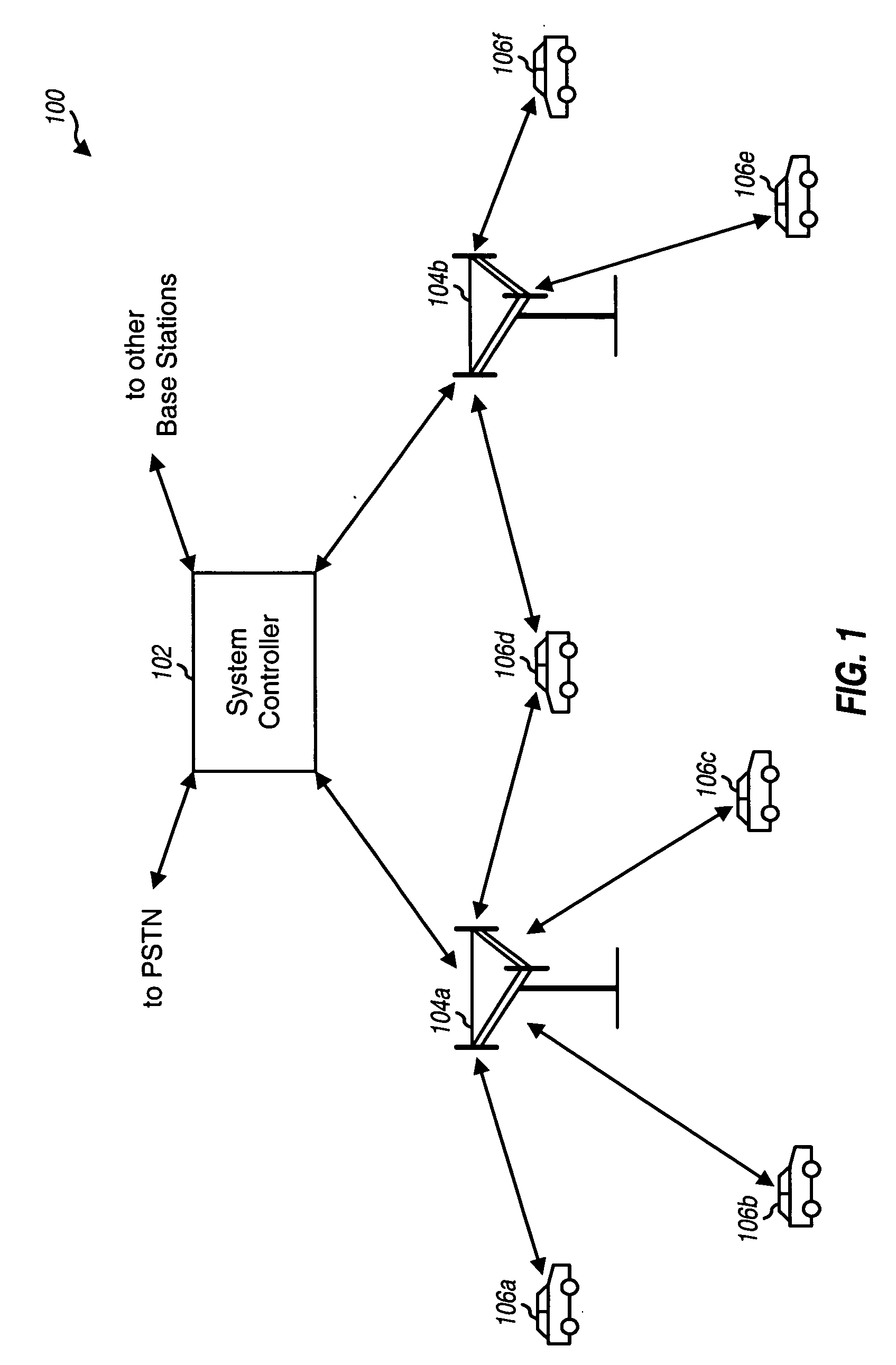
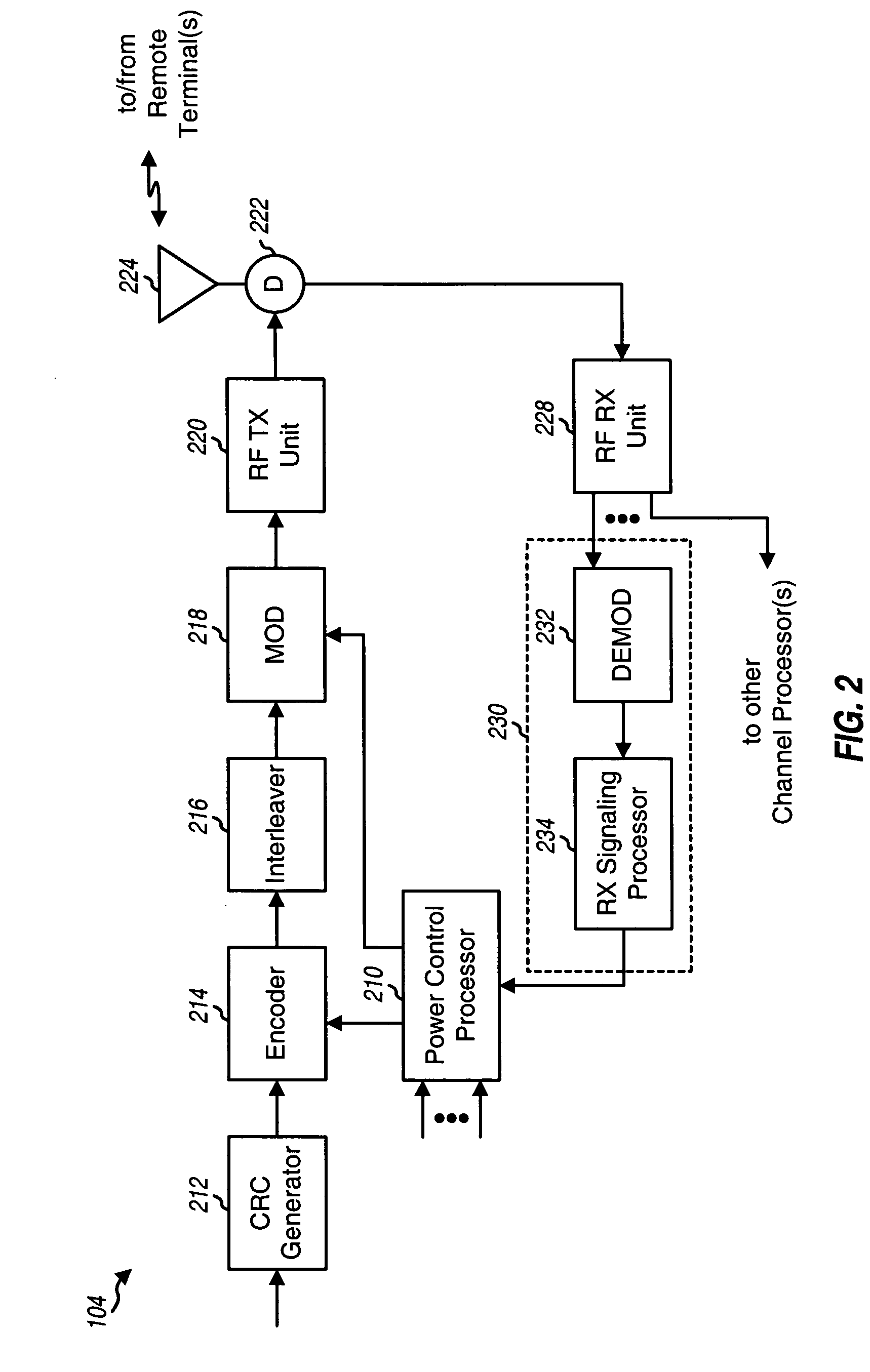
A TDD antenna array S-CDMA system for increasing the capacity and quality of a wireless communications is disclosed. By simultaneous exploiting the spatial and code diversities, high performance communications between a plurality of remote terminals and a base station is achieved without sacrificing system flexibility and robustness. The time-division-duplex mode together with the inherent interference immunity of S-CDMA signals allow the spatial diversity to be exploited using simple and robust beamforming rather than demanding nulling. Measurements from an array of receiving antennas at the base station are utilized to estimate spatial signatures, timing offsets, transmission powers and other propagation parameters associated with a plurality of S-CDMA terminals. Such information is then used for system synchronization, downlink beamforming, as well as handoff management. In an examplary embodiment, the aforementioned processing is accomplished with minimum computations, thereby allowing the disclosed system to be applicable to a rapidly varying environment. Among many other inherent benefits of the present invention are large capacity and power efficiency, strong interference / fading resistance, robustness power control, and easy hand-off.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
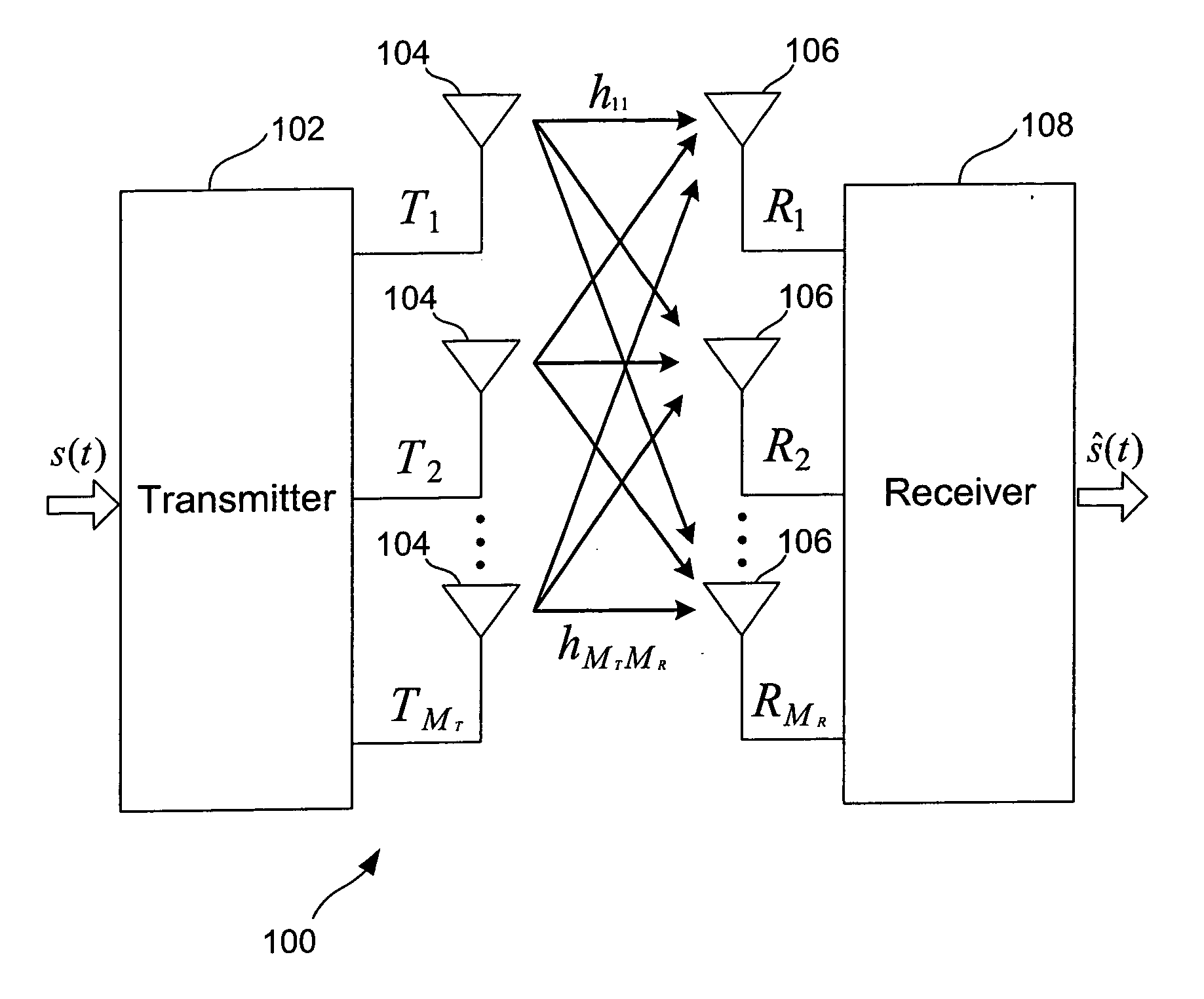
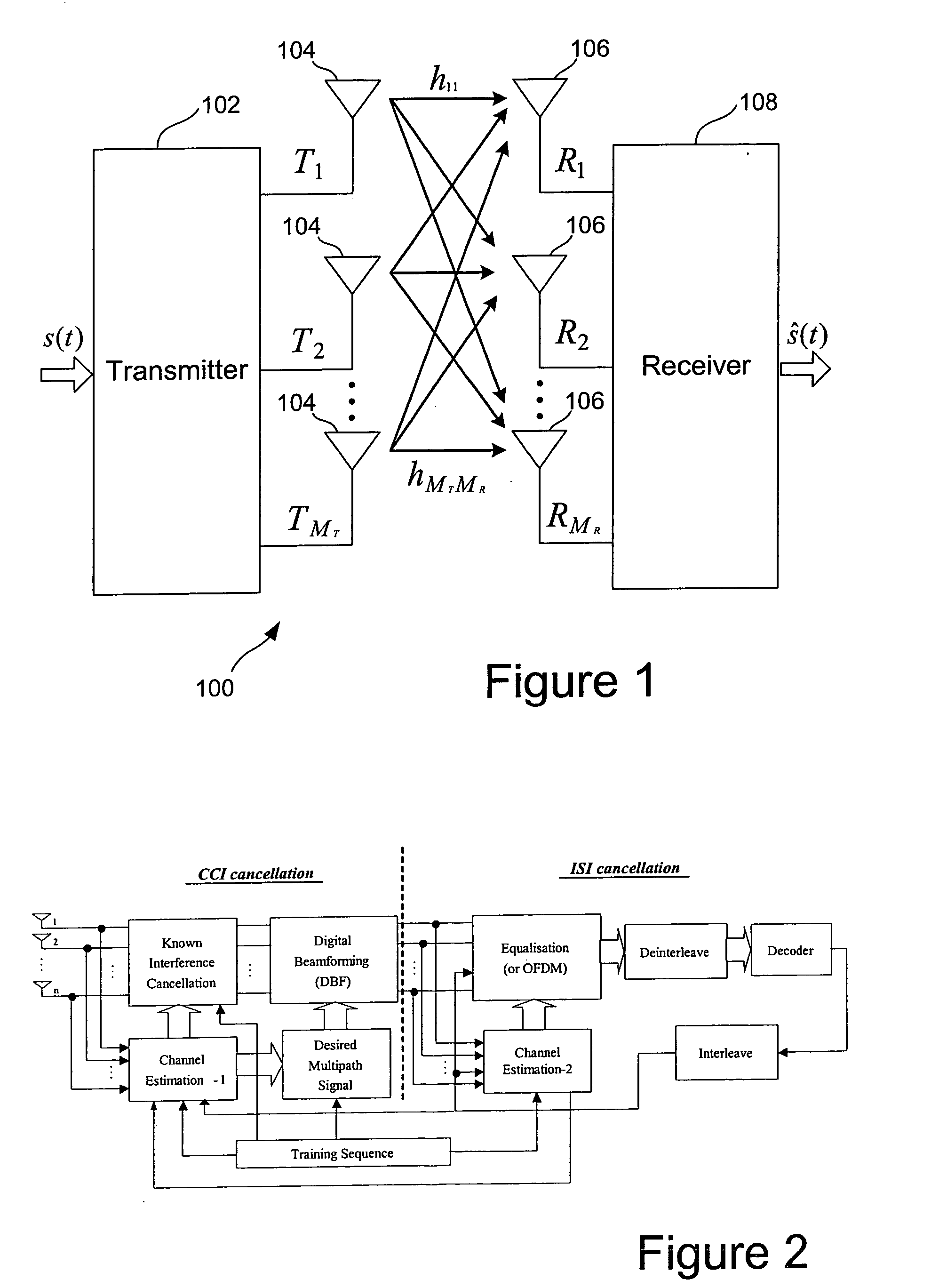
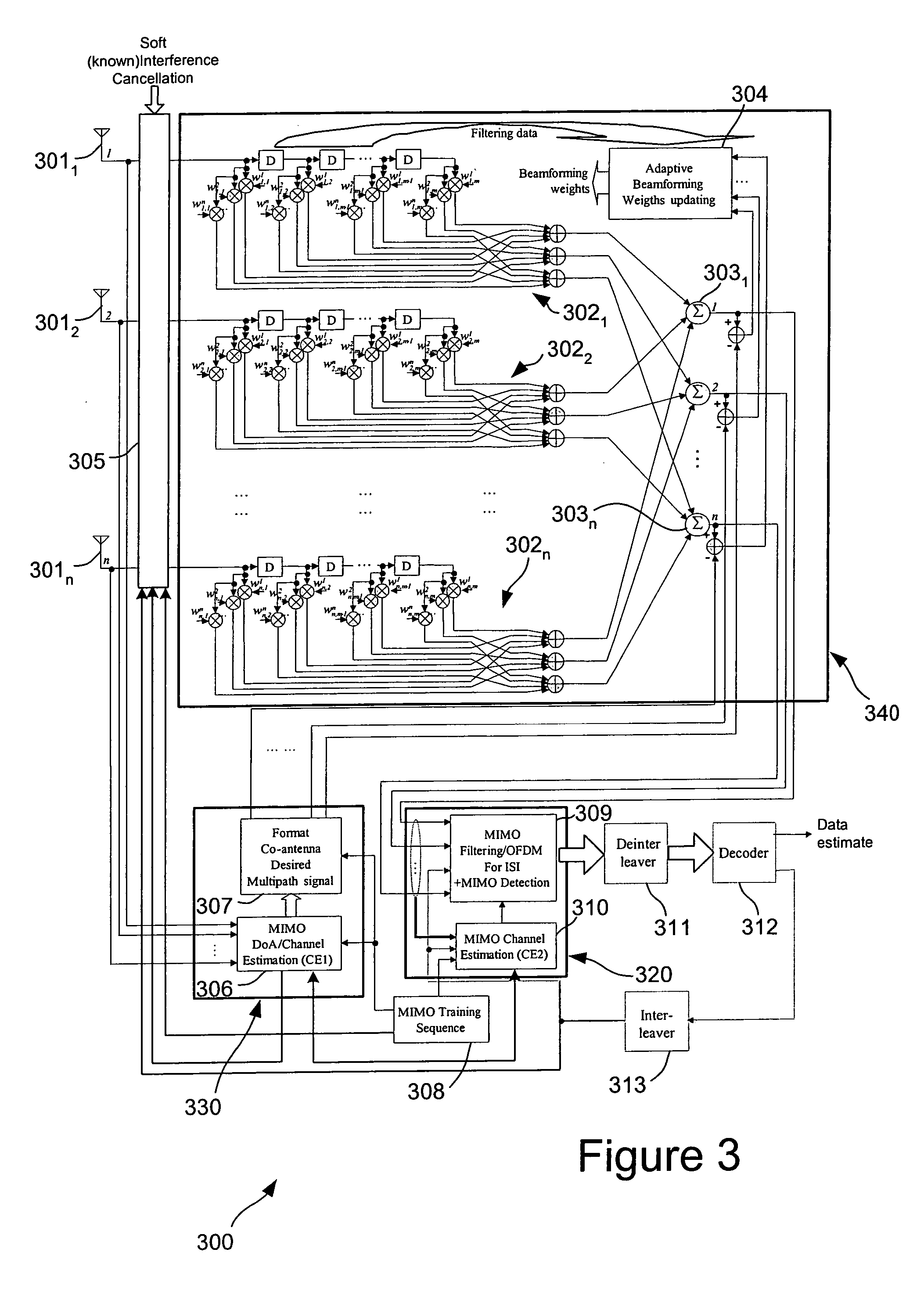
MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20050107057A1Improve performanceEstimate and ISI filtering is considerably improvedSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationFir systemCommunications system
The invention provides a generic and comprehensive architecture to optimise several space-time adaptive algorithms and their applications for both CCI and ISI interference cancellation for MIMO systems. The basic idea of this invention is to optimise space-only processes and time-only processes and their combination to take account of the varying affects of CCI and ISI in a given environment. This maximises the efficiency of adaptive algorithms. The invention is targeting on unknown CCI or co-antenna interference of other operating system at the same frequency band.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
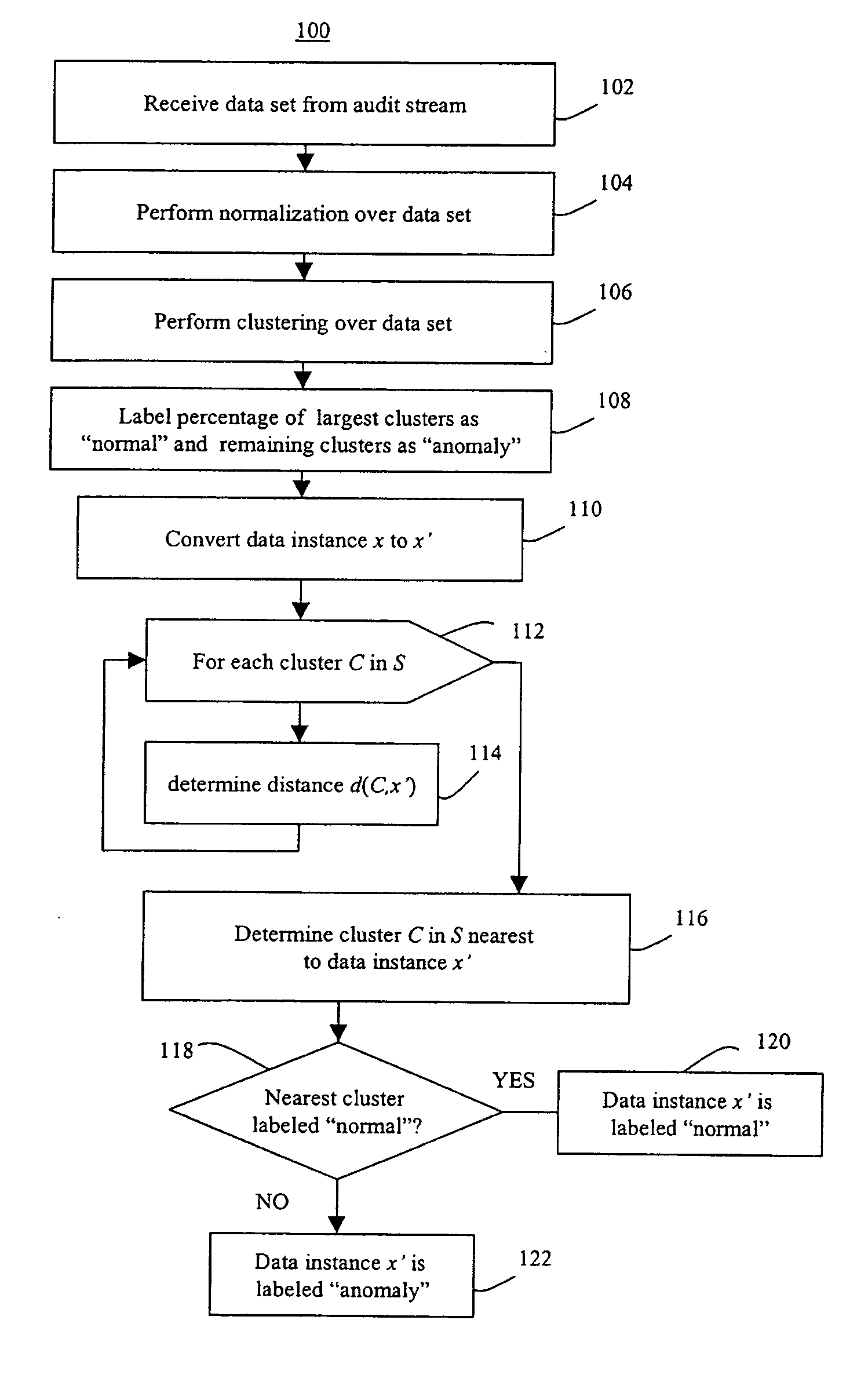
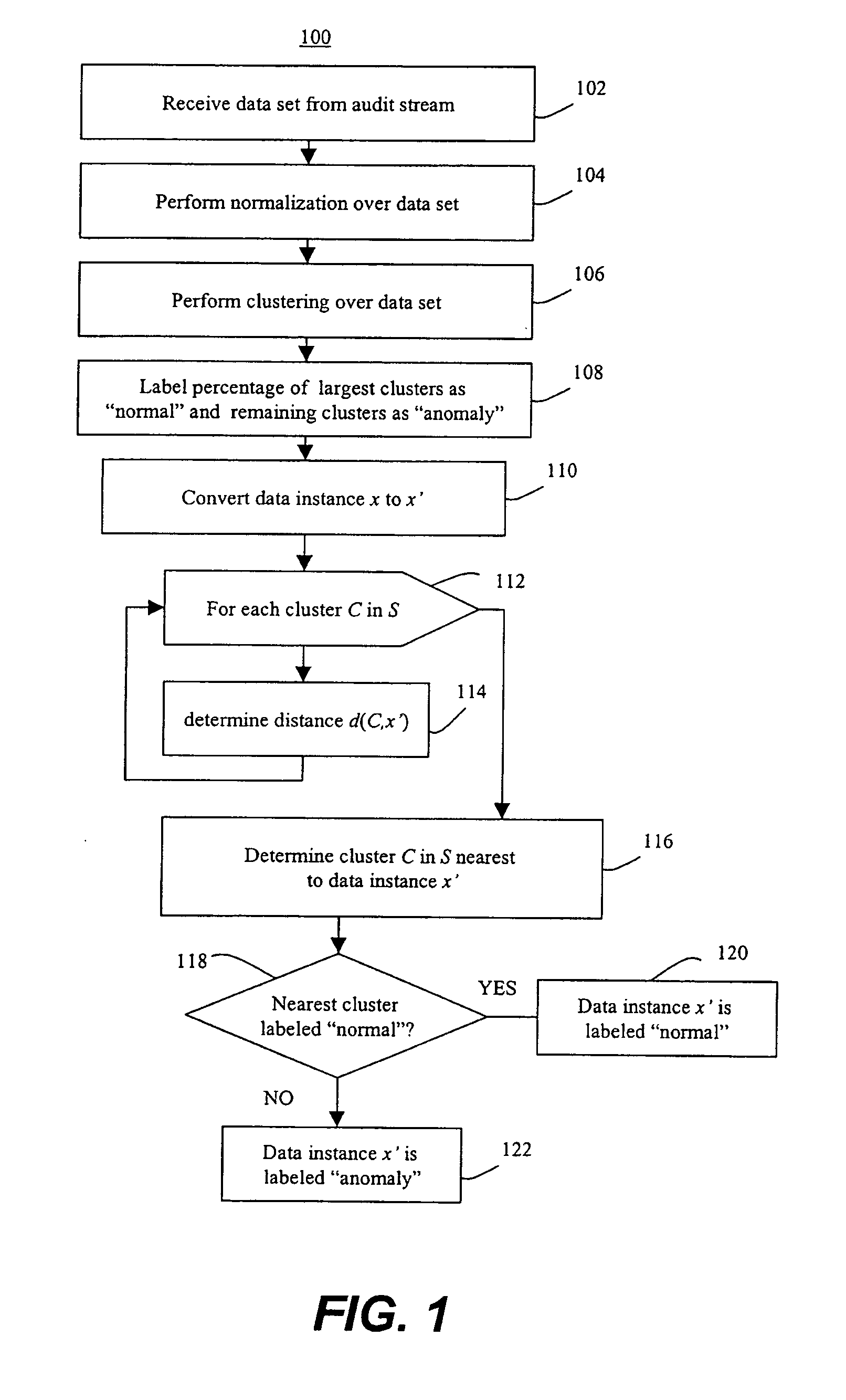
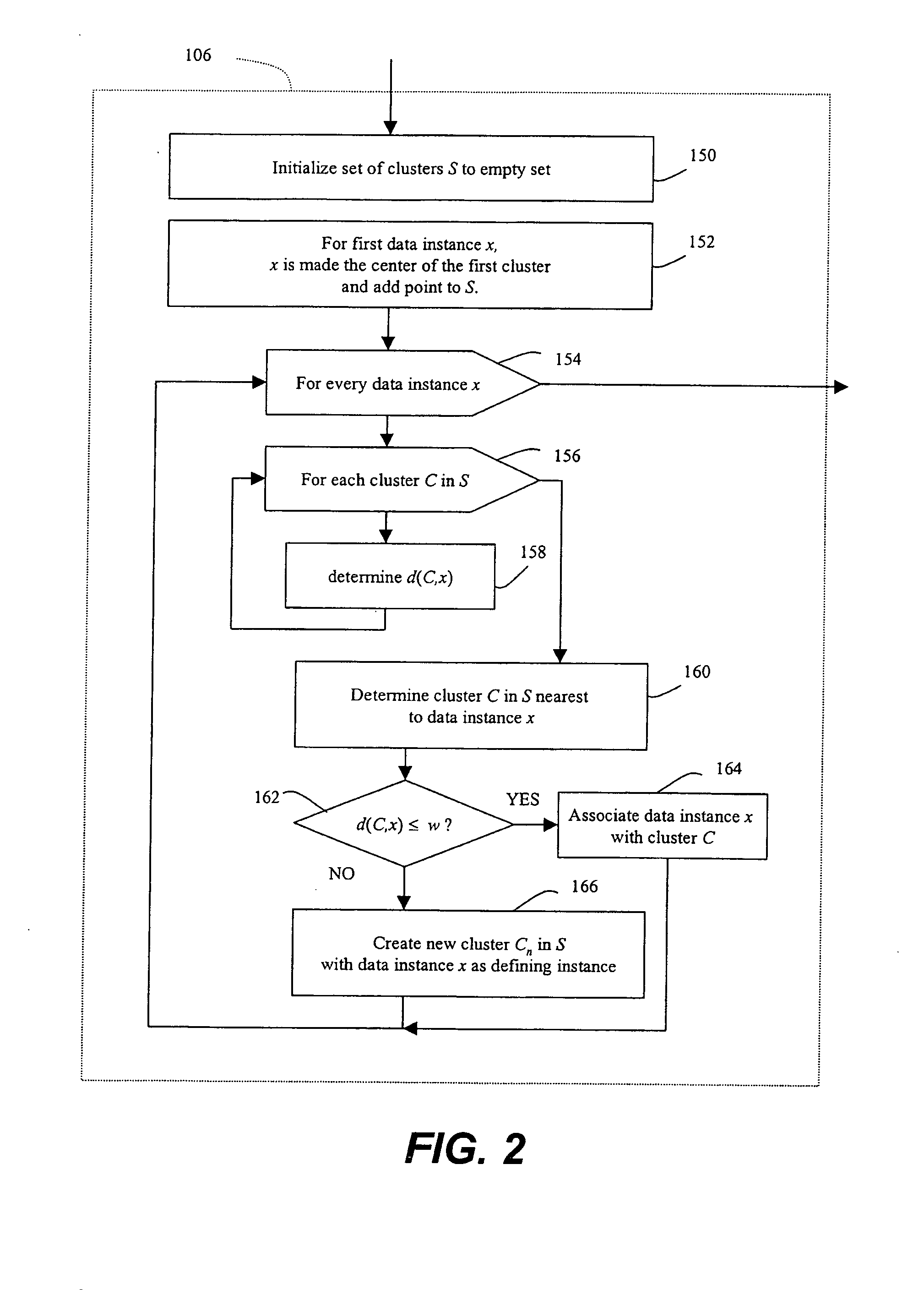
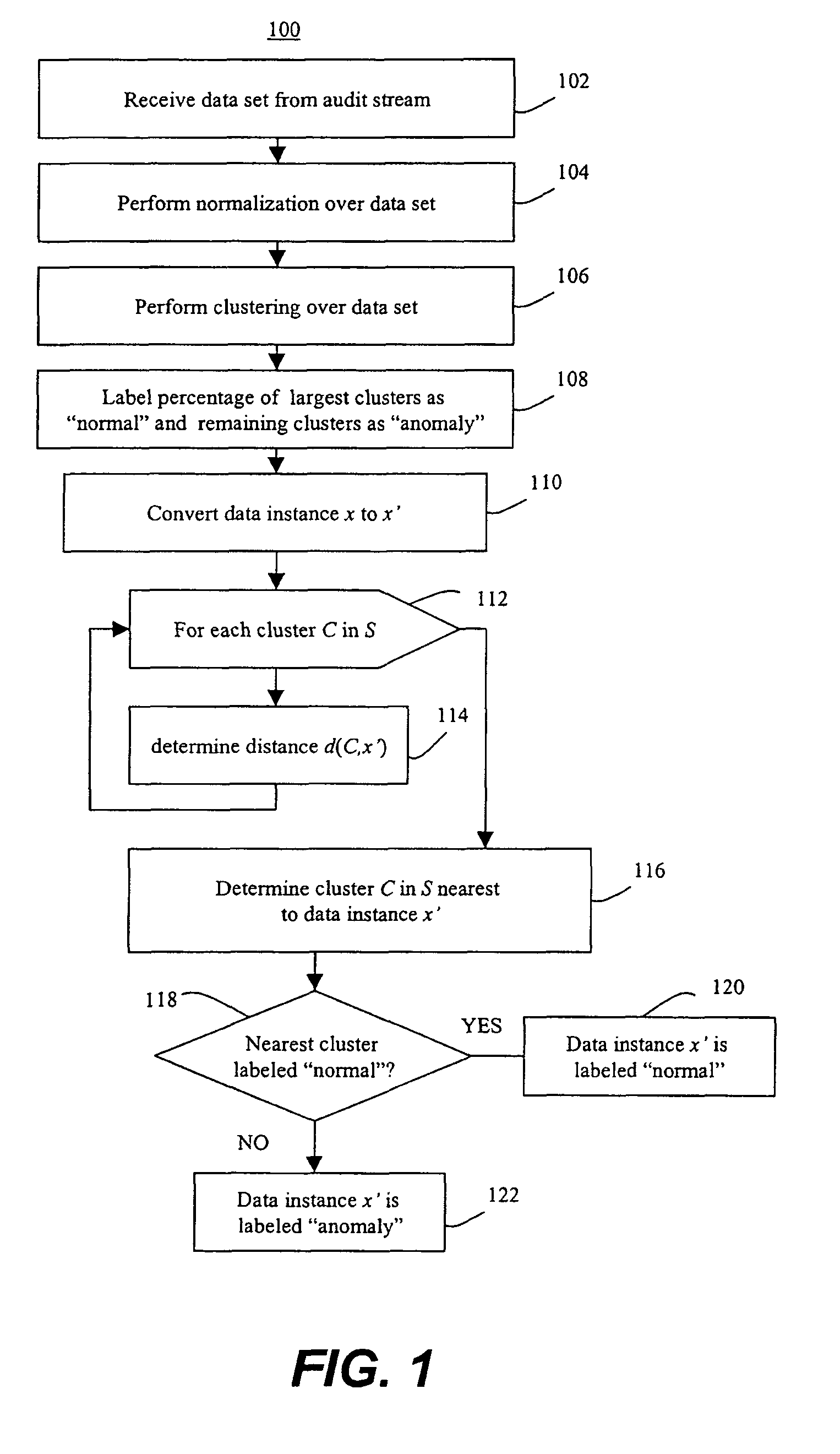
Methods of unsupervised anomaly detection using a geometric framework
InactiveUS20150058982A1Easy to operateMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionFir systemFrequency spectrum
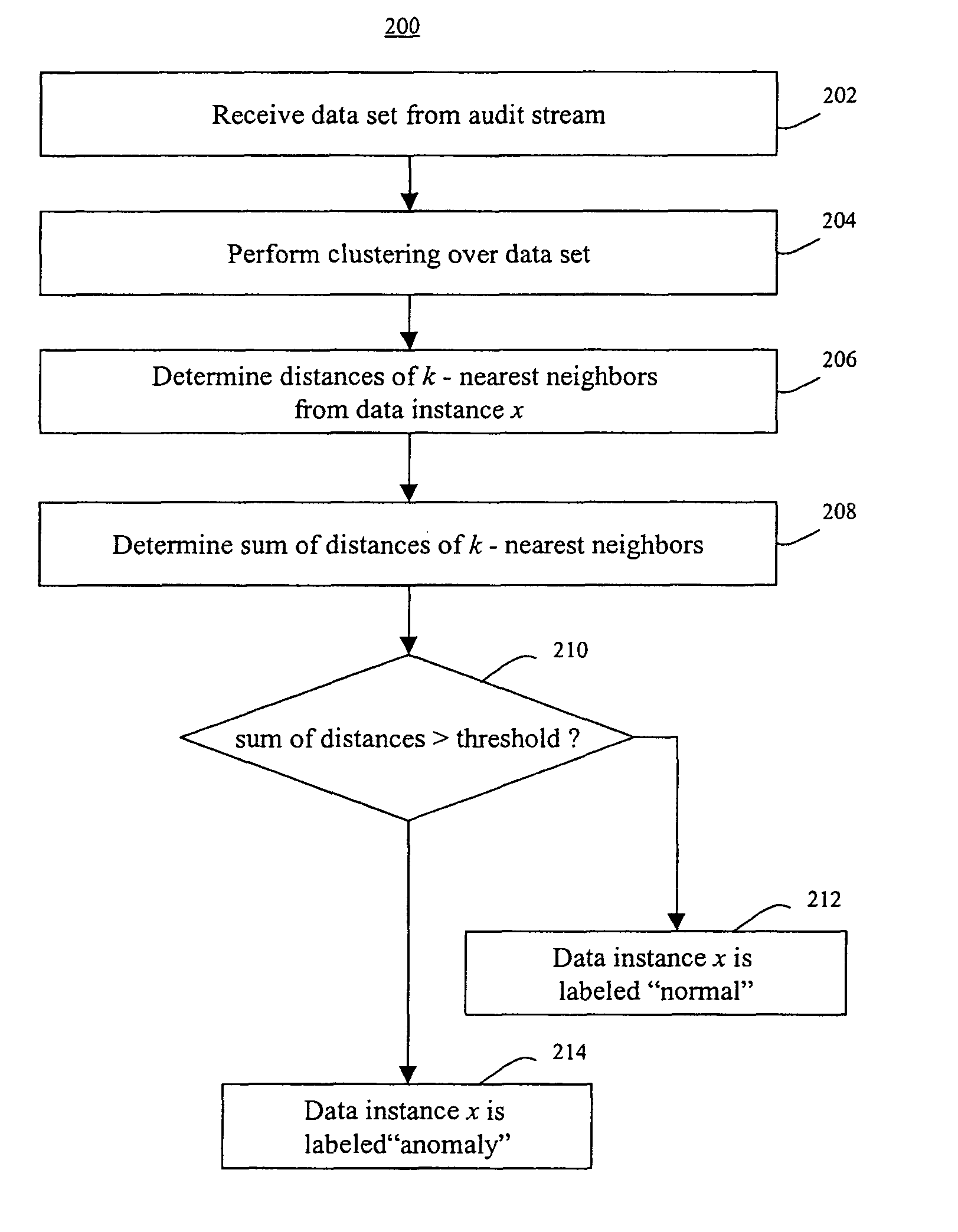
A method for unsupervised anomaly detection, which are algorithms that are designed to process unlabeled data. Data elements are mapped to a feature space which is typically a vector space d. Anomalies are detected by determining which points lies in sparse regions of the feature space. Two feature maps are used for mapping data elements to a feature apace. A first map is a data-dependent normalization feature map which we apply to network connections. A second feature map is a spectrum kernel which we apply to system call traces.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
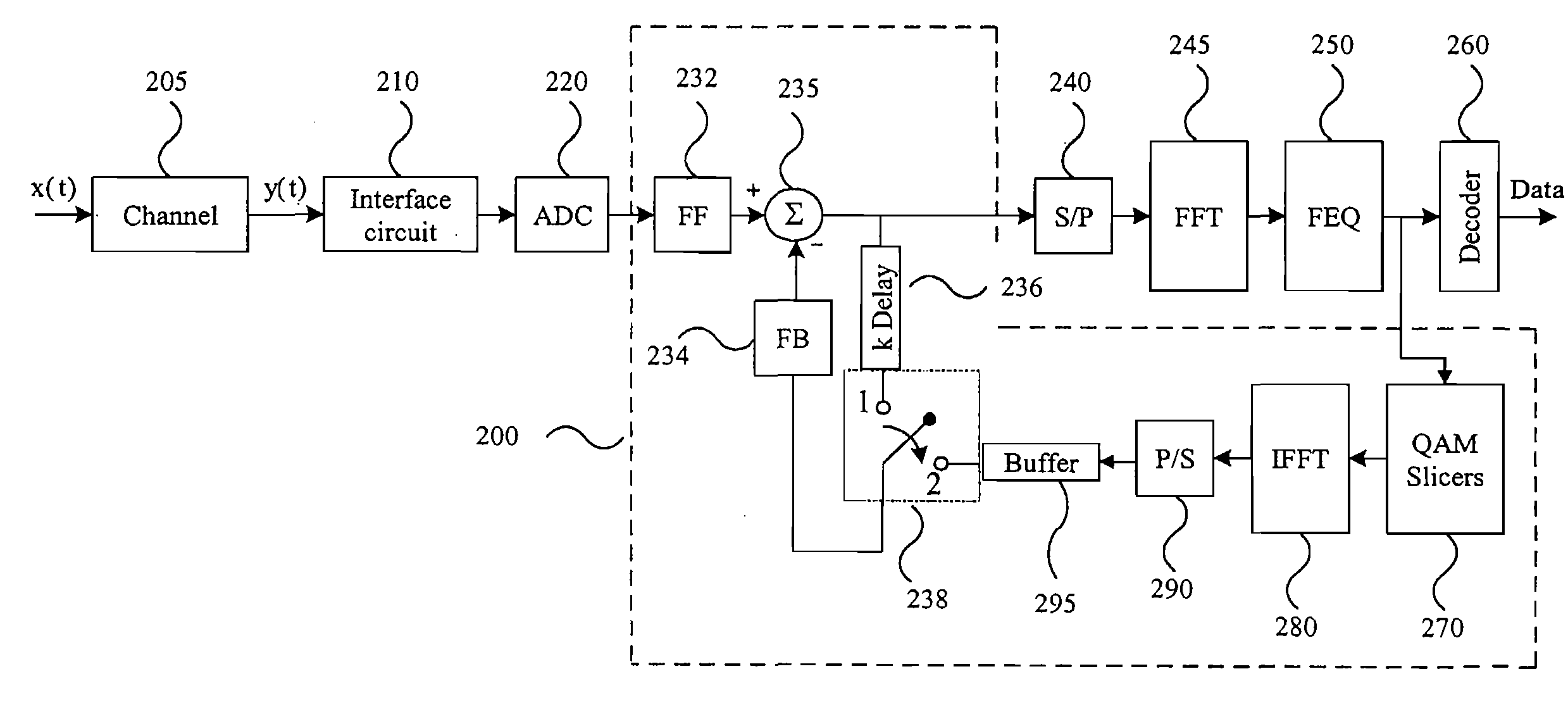
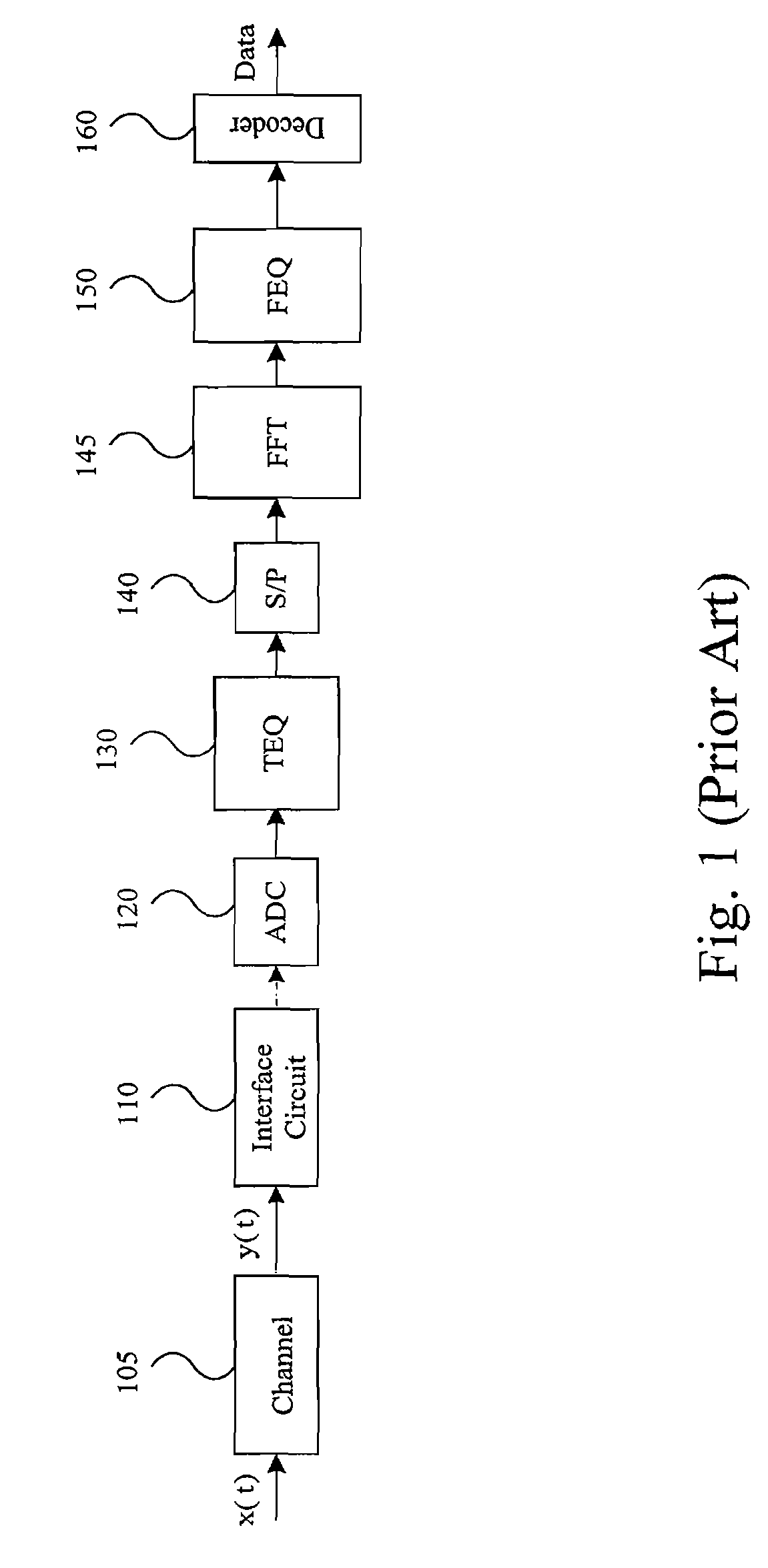
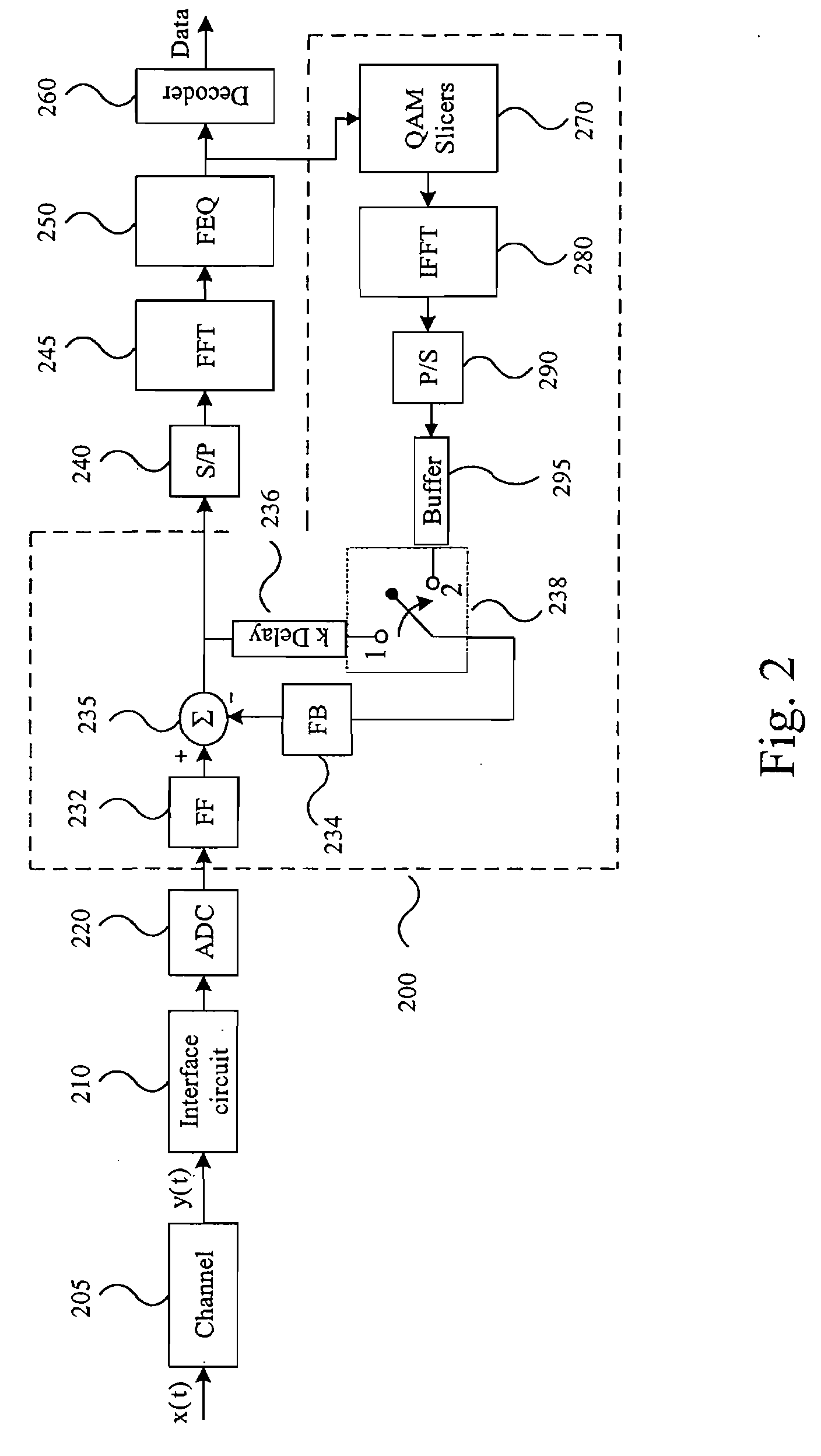
System and Method for Time-Domain Equalization in Discrete Multi-tone Systems
InactiveUS20070121718A1Minimal lengthAvoid Intersymbol InterferenceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainFir system
A novel time-domain equalizer (TEQ) is provided for the receiver of a Discrete Multi-tone (DMT) system to shorten the length of the effective channel impulse response. The TEQ is based on a variant of the conventional decision-feedback equalizer (DFE) structure along with a training method for the TEQ settings. By using this DFE-based TEQ for DMT systems, the data symbols transmitted through the effective shortened channel would be more reliable.
Owner:PROSCEND COMM
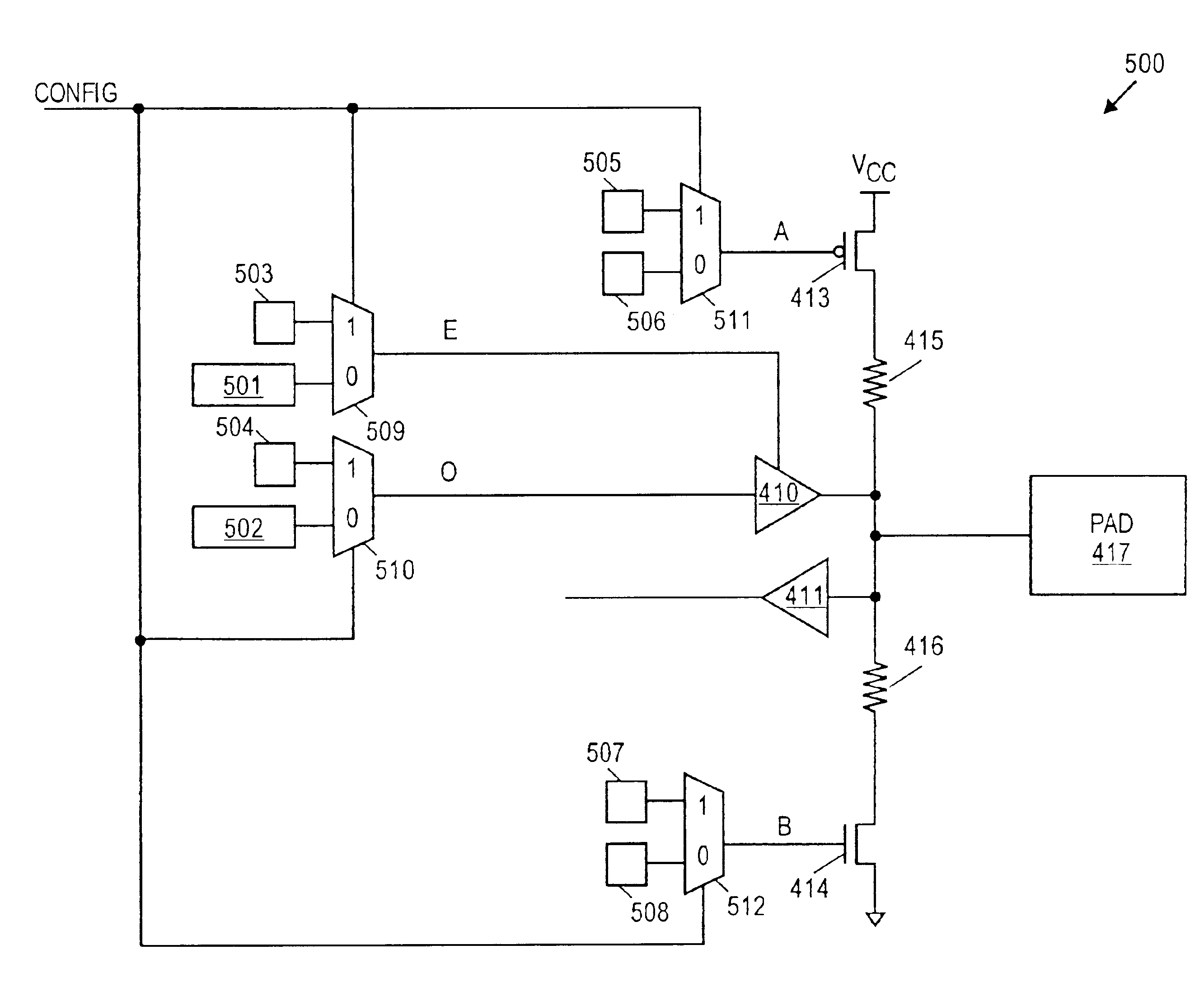
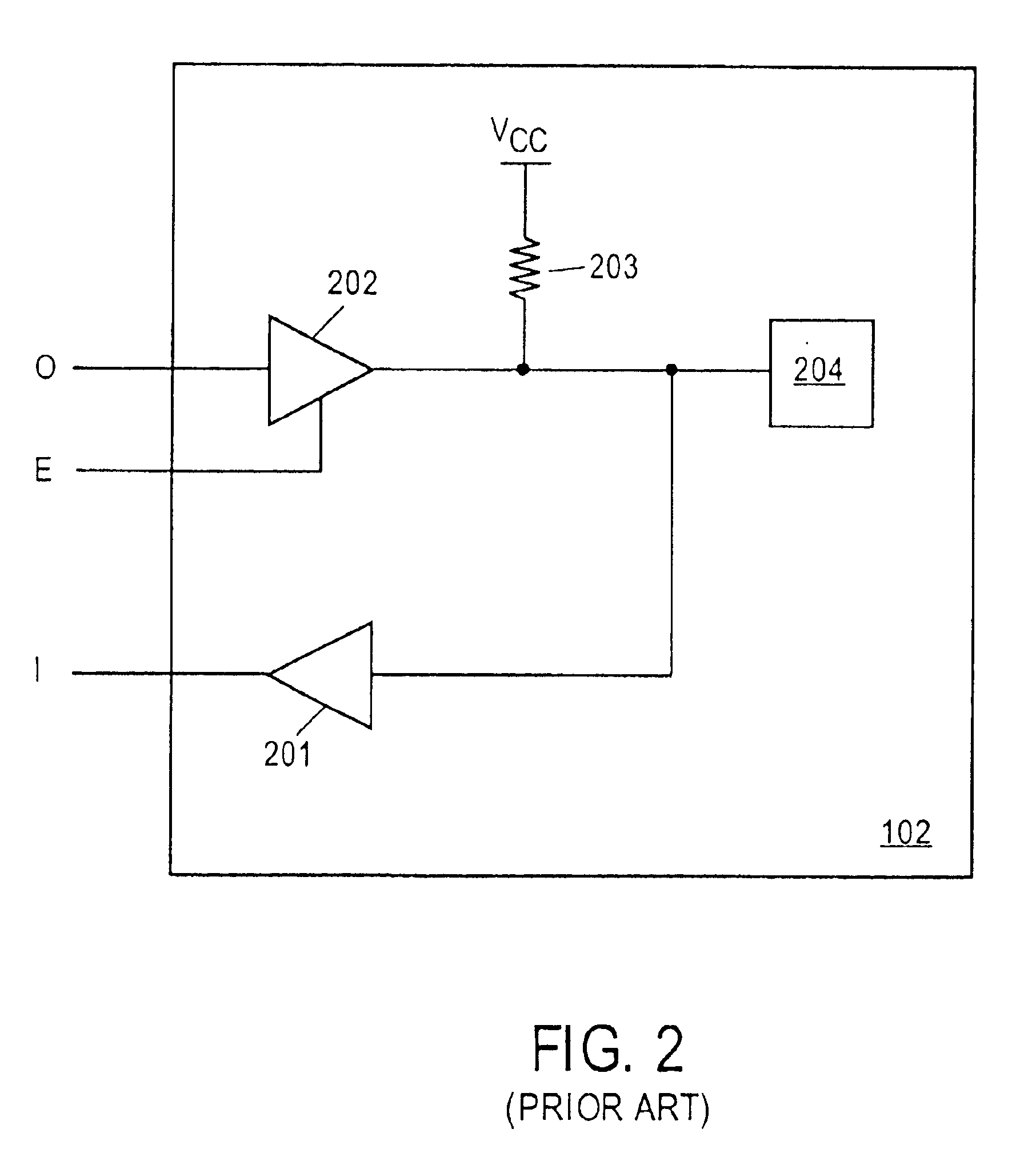
Input/output circuit with user programmable functions
InactiveUS6870397B1Increase flexibilityImprove performanceSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsPropagation delayFir system
The I / O circuit of the present invention provides optimal flexibility and performance using a number of different structures and methods. The present invention provides a signal follower circuit for an input pad. In one embodiment, the output buffer is capable of injecting a constant onto a pad during reconfiguration of a configurable system logic circuit. The present invention also provides a circuit for generating a programmable data propagation delay, thereby guaranteeing zero hold time for an arbitrary input register. Zero hold time is accomplished by allowing the user to optimally characterize clock delay to a given input / output circuit. The present invention also provides fast switching between input pads, thereby minimizing data propagation delay between the input pads. Additionally, the present invention reduces time spent in production product test by facilitating the testing of multiple routes with one test configuration. A circuit expanding the number of data input channels available to system routing is provided. Lastly, a plurality of identical input / output block tiles (IOBTs) is disclosed, thereby enabling each I / O circuit to provide the same signals regardless of the IOBTs location in the I / O circuit.
Owner:XILINX INC
Adaptive real-time methodology for optimizing energy-efficient computing
Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) is an effective way to reduce energy and power consumption in microprocessor units. Current implementations of DVFS suffer from inaccurate modeling of power requirements and usage, and from inaccurate characterization of the relationships between the applicable variables. A system and method is proposed that adjusts CPU frequency and voltage based on run-time calculations of the workload processing time, as well as a calculation of performance sensitivity with respect to CPU frequency. The system and method are processor independent, and can be applied to either an entire system as a unit, or individually to each process running on a system.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
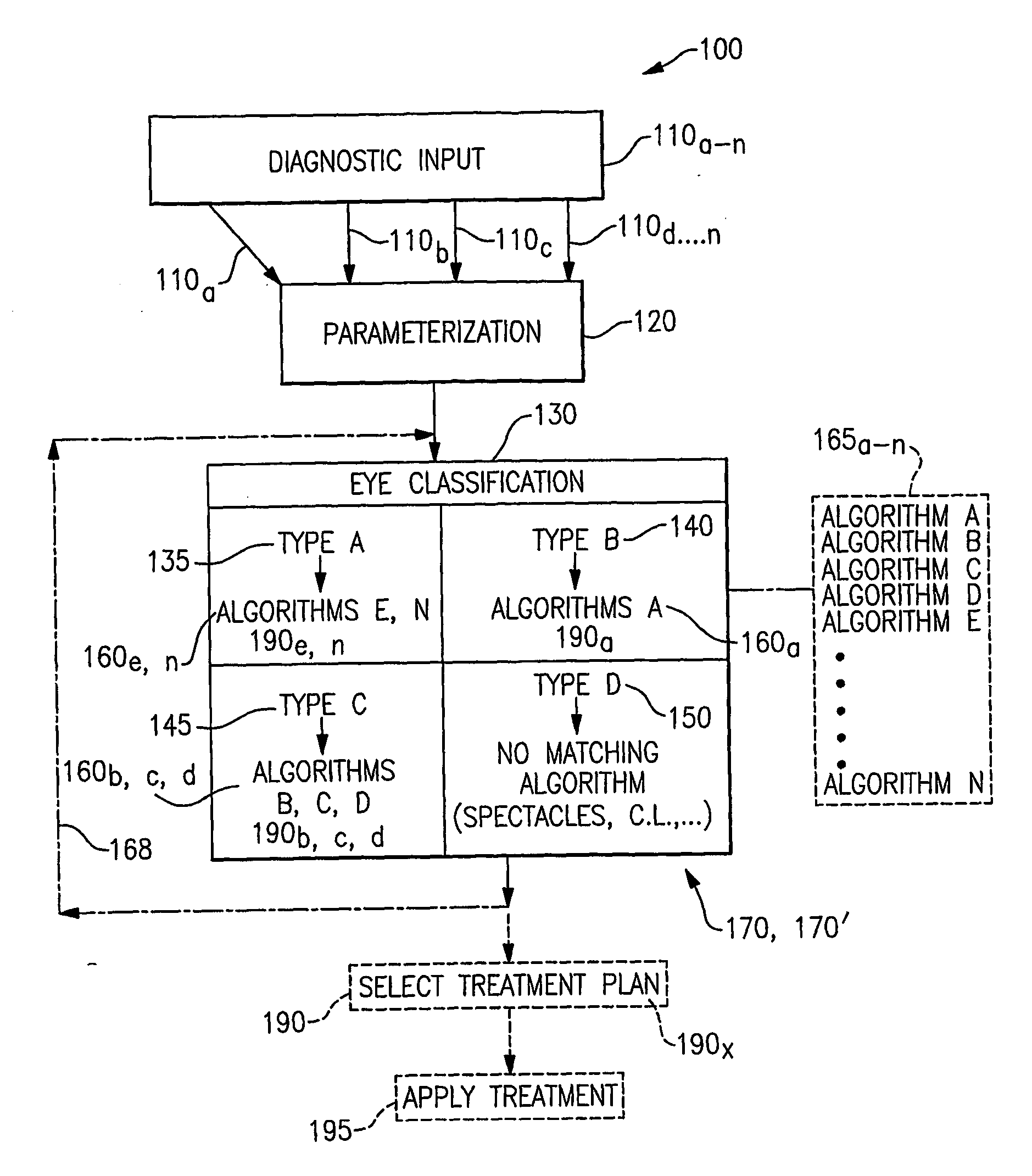
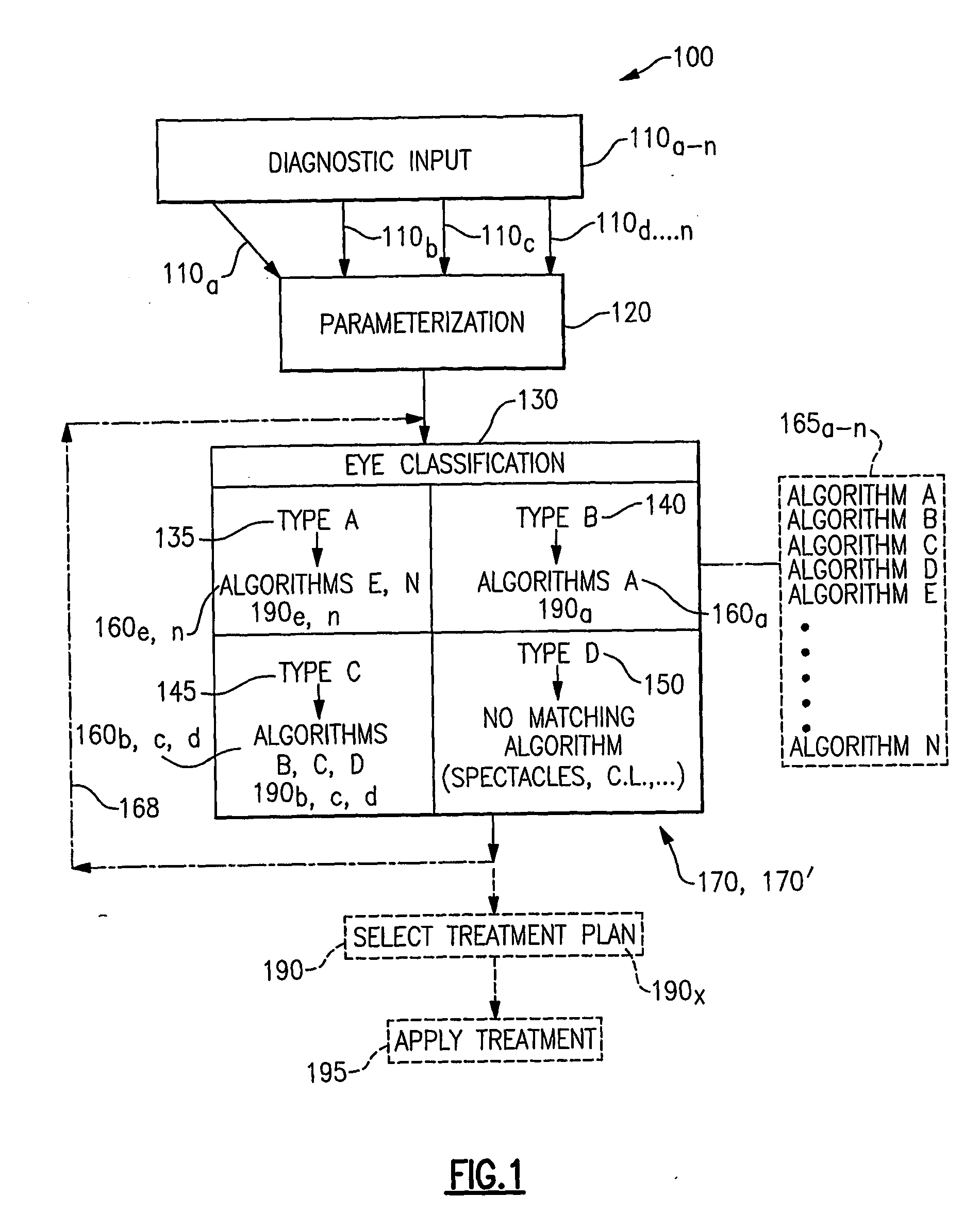
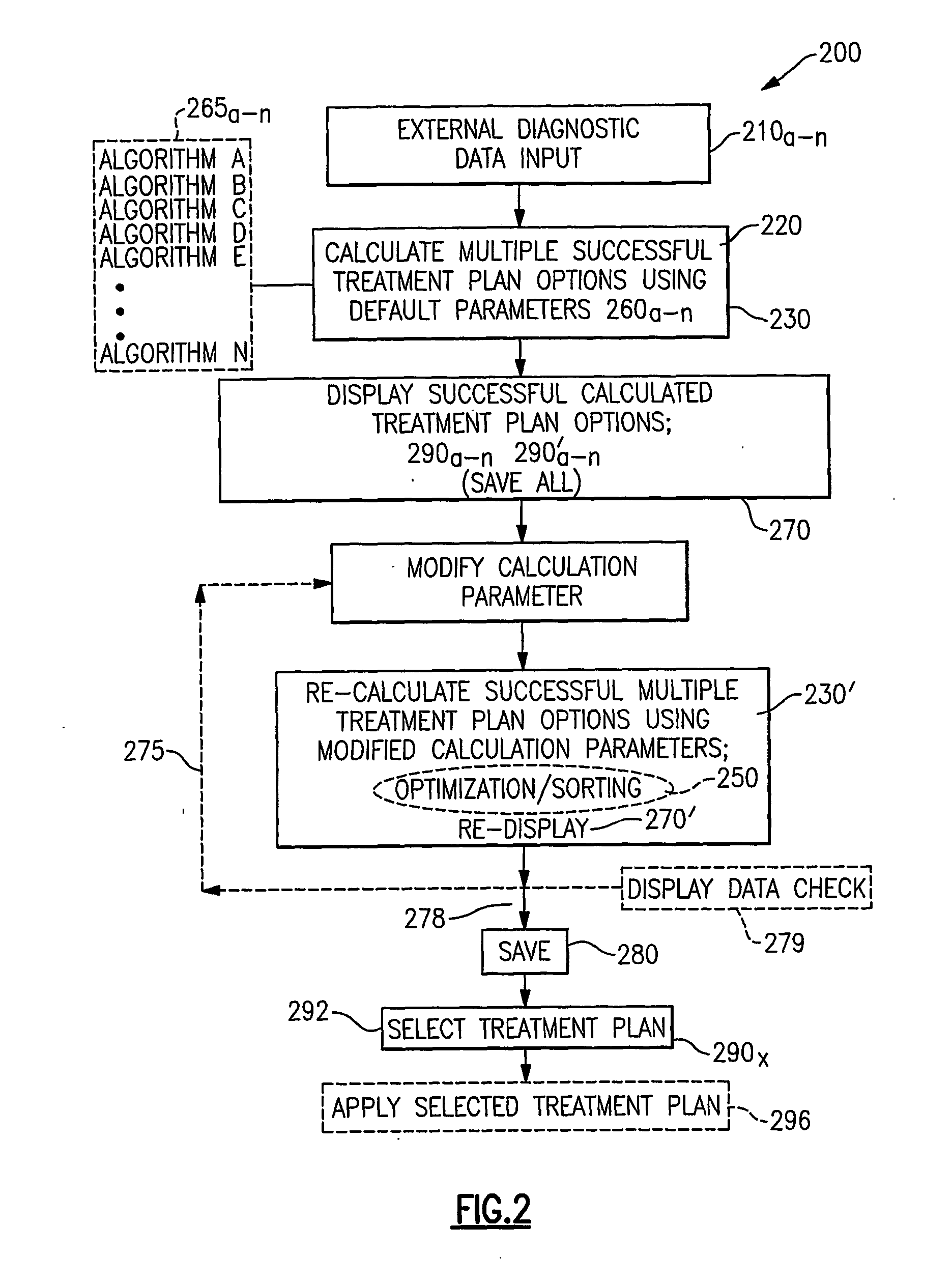
Method, system and algorithm related to treatment planning for vision correction
InactiveUS20070161972A1Convenient reviewEasy to modifyPhysical therapies and activitiesLaser surgeryGraphicsFir system
The invention is directed to a system and methods for automatically determining a multiple number of viable treatment plans for correcting a patient's vision via photoablative refractive surgery. Embodiments of the invention rely on selected various diagnostic input about the patient's eye to classify the eye as being particularly suitable for treatment by several different treatment algorithms. The invention is further directed to the simultaneous presentation of various treatment plans based upon selected input data and available treatment algorithms that can be reviewed, modified, and ultimately selected for application. A system embodiment according to the invention includes a component for receiving the diagnostic input data about the patient's vision, for analyzing the input data and determining the potentially usable treatment algorithms, and for processing the potentially usable treatment algorithms based upon the input data, and a component for displaying the multilevel graphical user interface which facilitates review, modification, and selection of viable treatment plans for correcting the patient's vision. The system is further operably associated with a storage medium for storing calculated and selected treatment plans which include executable instructions for a photoablative laser component of the system to deliver a selected treatment plan to the patient's eye.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
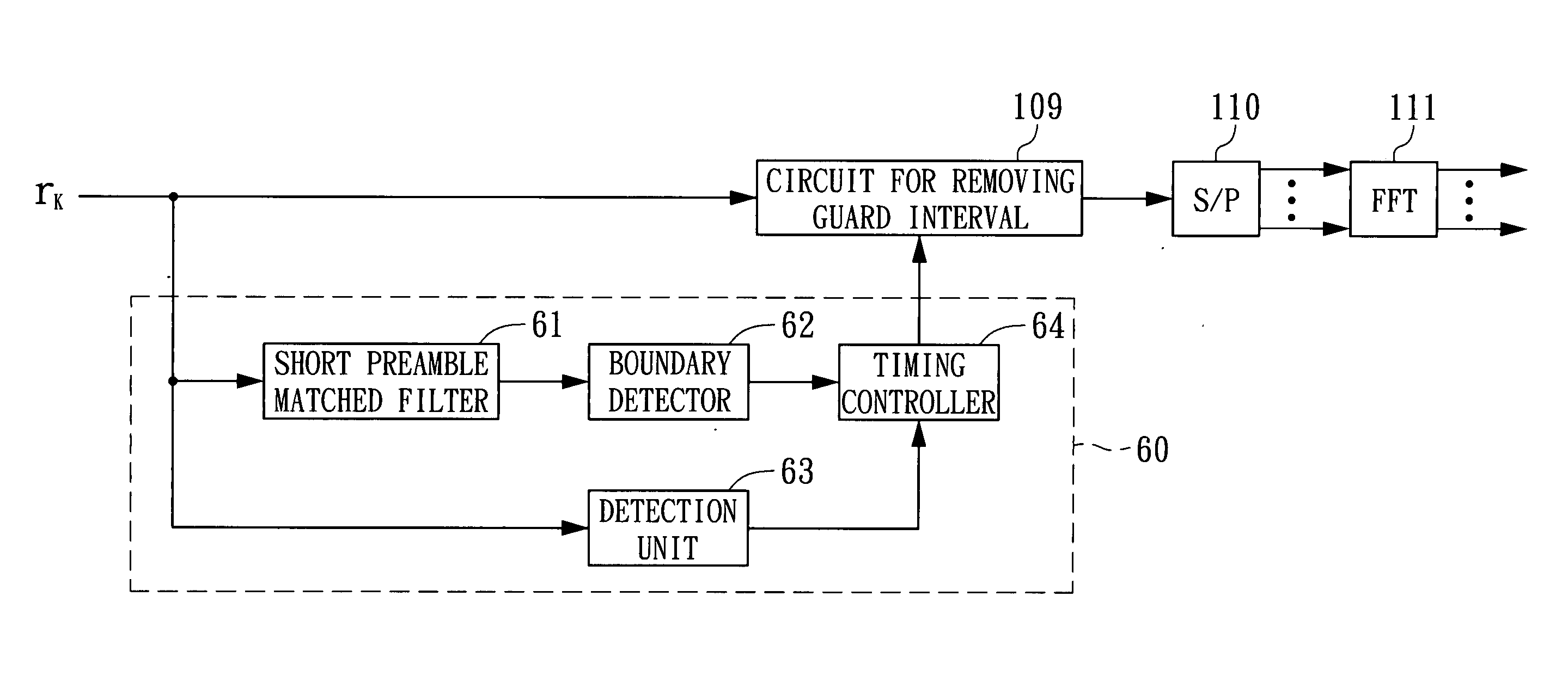
Symbol boundary detection device and method for use in OFDM system
ActiveUS20050008088A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationFir systemCommunications system
A symbol boundary detection device and a method thereof for use in a receiver of a multi-channel communication system. The device utilizes a threshold to make an auxiliary judgement so as to select a proper symbol boundary reference point within an early range. The threshold may be flexibly set in response to different characteristics of the systems. In addition, a pilot symbol guard interval matched filter is further utilized to determine whether a pilot symbol guard interval is received.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
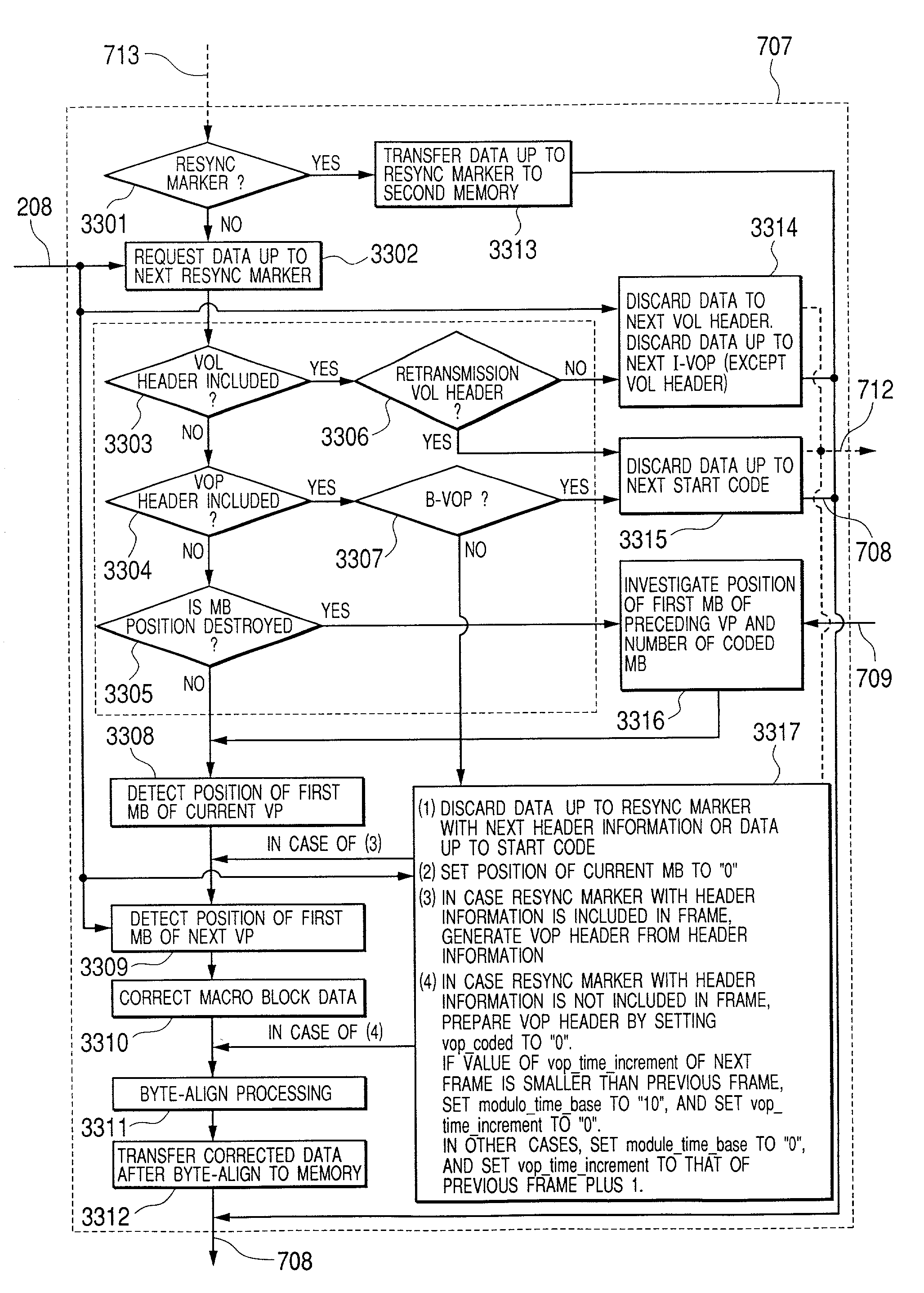
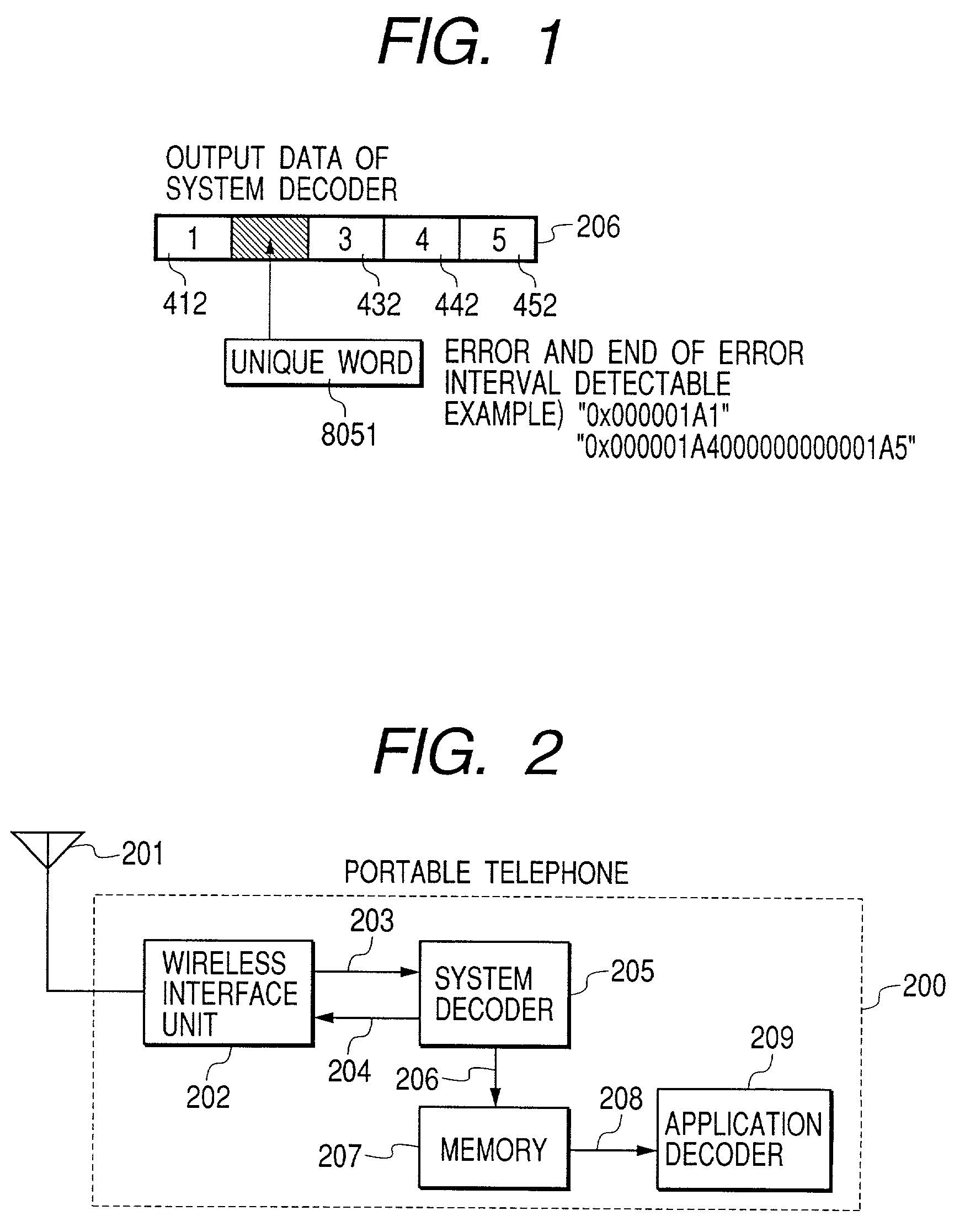
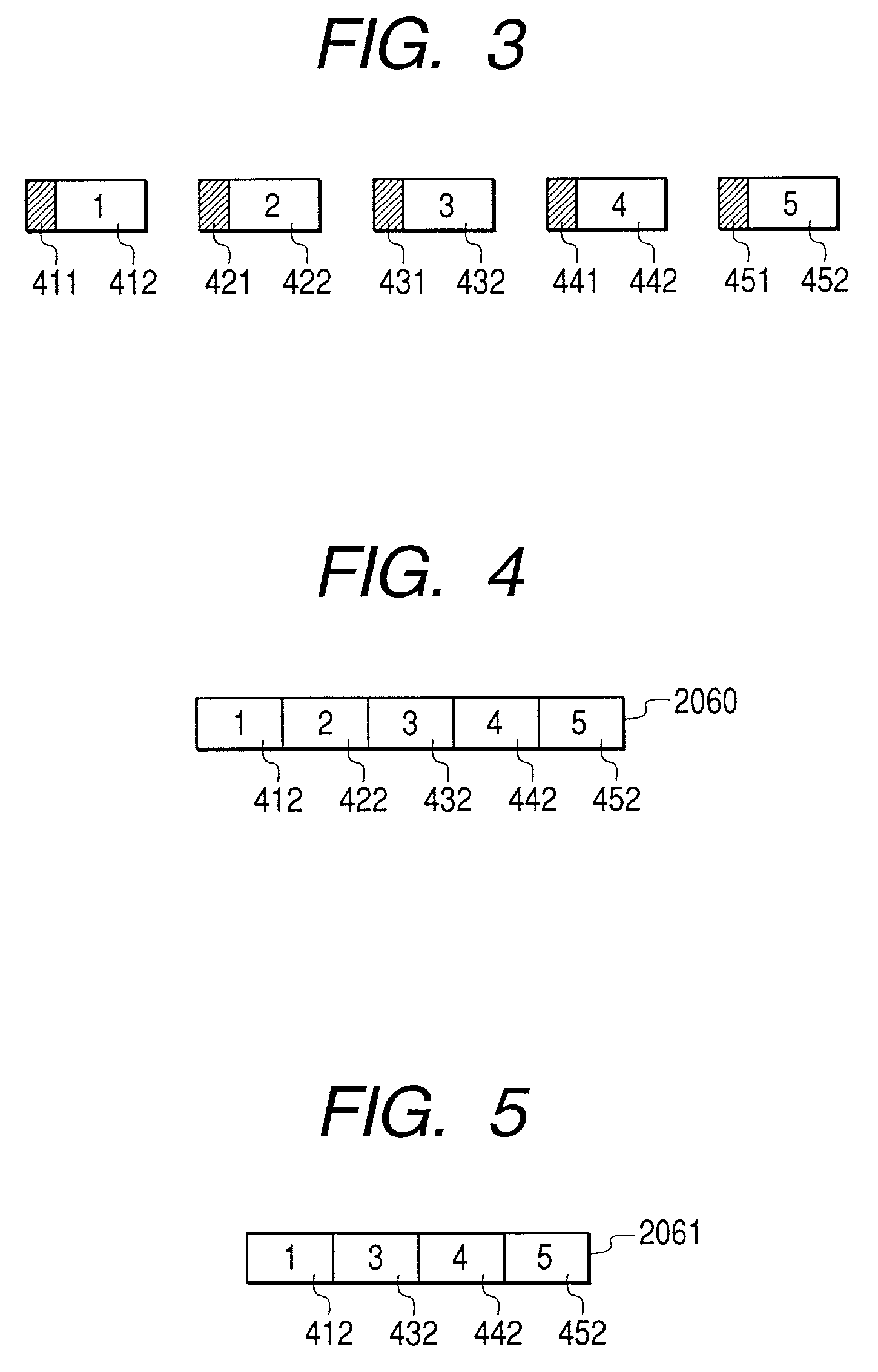
Apparatus for system decoder and method for error correction of packet data
InactiveUS7131048B2Precise positioningReduce the burden onError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsFir systemComputer hardware
When a non-error-resilient application decoder receives a data stream containing syntax error due to transmission errors, such as packet losses in wireless communication, an application decoder cannot usually continue decoding the stream data anymore. According to the present invention, the data stream containing syntax error along with error correction data generated by error-detectable transmission system is inputted into an error correction part before inputted into the application decoder. The error correction part detects the error position in the data stream using the error detection data, corrects the syntax error in the stream data, and generates a stream data which is possible to be decoded by the application decoder. As a result, the data stream containing syntax error can continue decoding or be decoded in better quality by a non-error-resilient application decoder, without adding any error correcting function in the existing application decoder.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
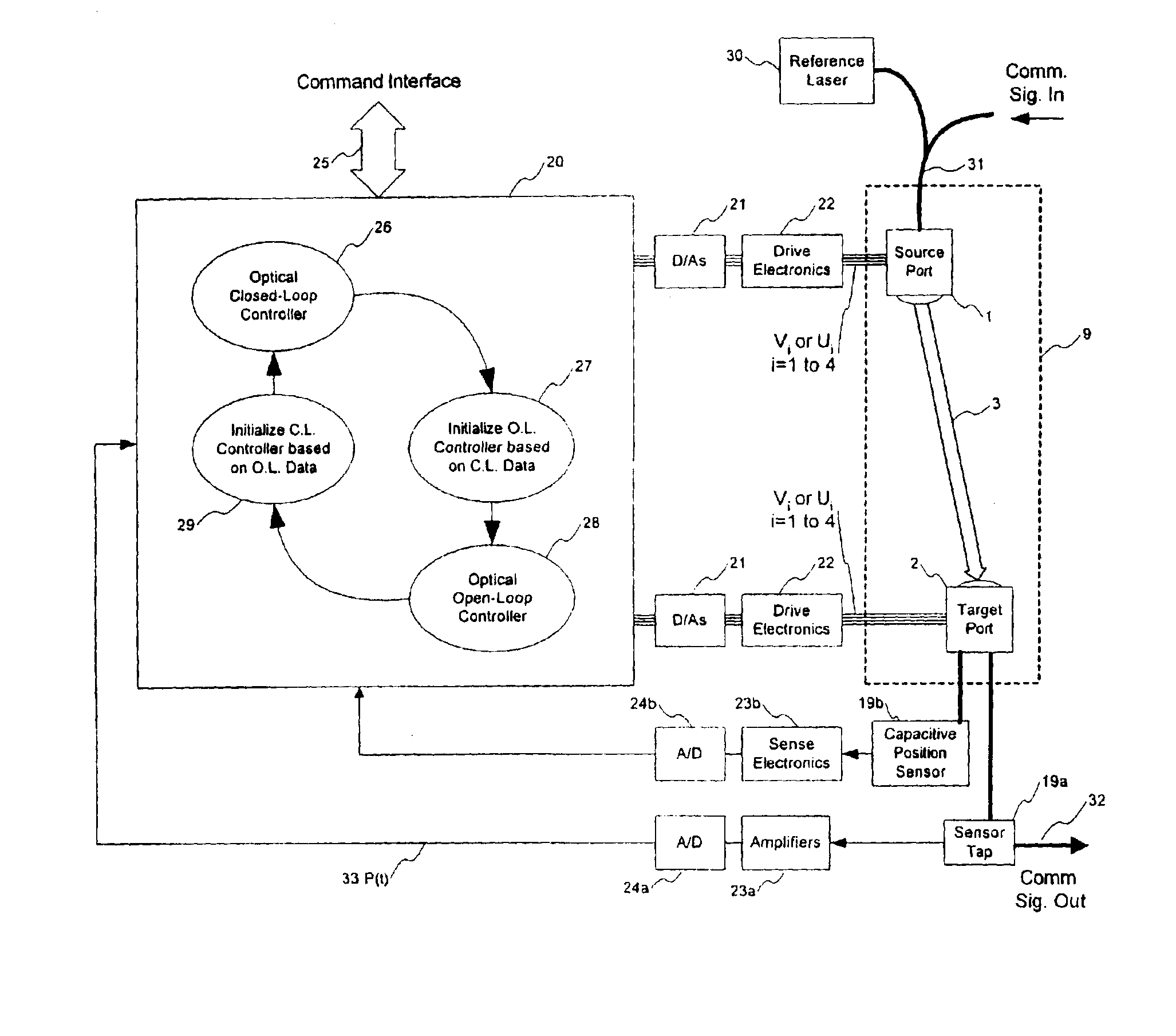
Multiple-axis control system for an optical switch
ActiveUS6975785B2Move fastRapidly tiltMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesFir systemLoop control
A free space optical switch that uses both an open loop control mode and a closed loop control mode. The open loop control mode is used to transition to a state where at least some light is sensed at a destination port. A closed loop control mode is then used, whereby a series of controlled dither signals are adjusted for system dynamics. Modifying the dither signals in this matter allows moving actuators at a rate that is much closer to the natural frequency of the underlying system, and hence speeds up the system convergence process. Variable modulation amplitudes may be employed on the dither signals to maximize convergence speed. In particular, changes in the dither signal can be made in accordance with the change in amplitude as a function of a gradient along a parabola that models the optical system response. According to still further aspects, the dither signals may be compensated for a desired and selectable attenuation level of output optical power.
Owner:POLATIS PHOTONICS INC
Receiver spatial processing for eigenmode transmission in a MIMO system
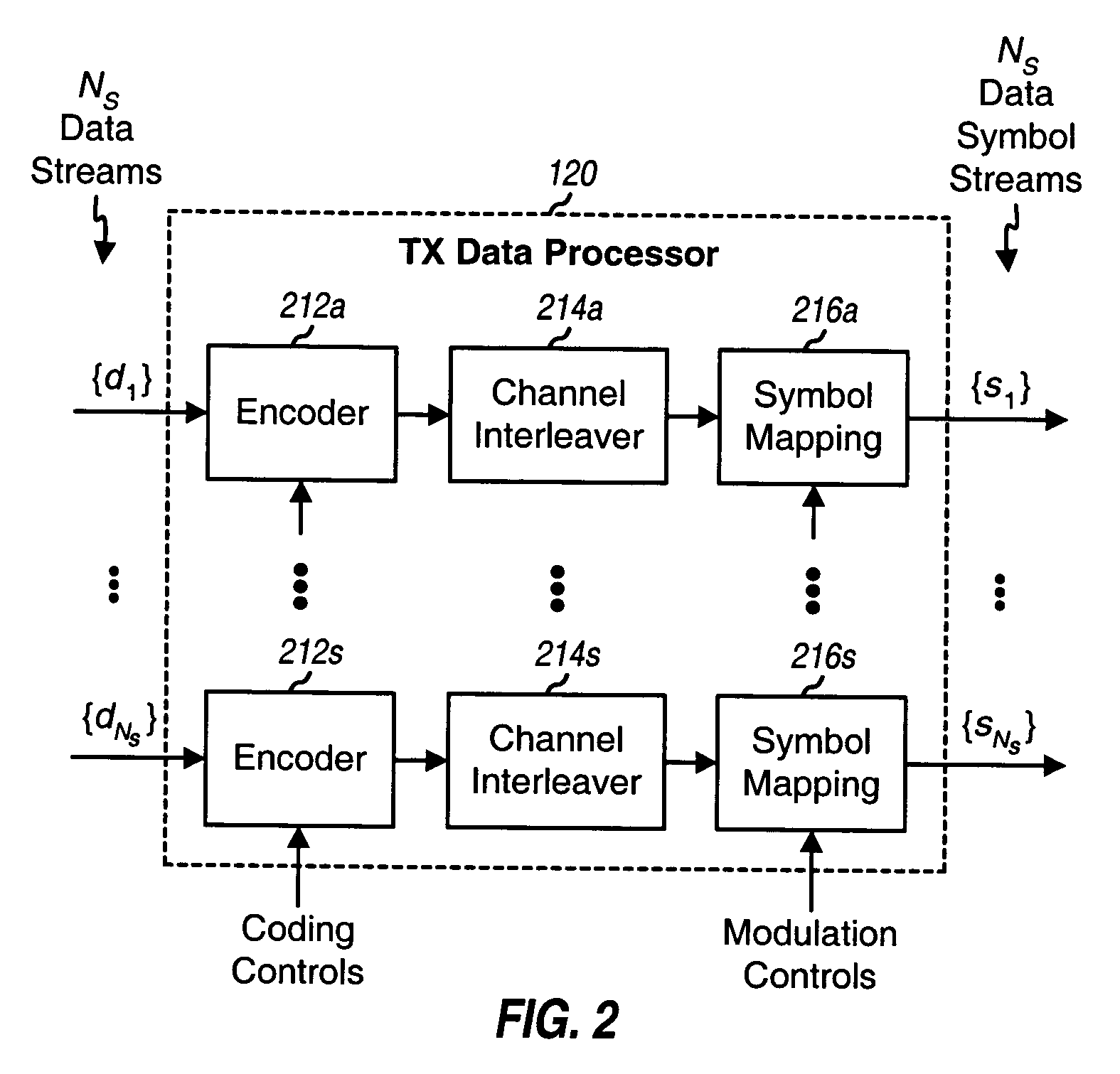
ActiveUS20050078762A1Reduce crosstalkImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFir systemData stream
For eigenmode transmission with minimum mean square error (MMSE) receiver spatial processing, a transmitter performs spatial processing on NS data symbol streams with steering vectors to transmit the streams on NS spatial channels of a MIMO channel. The steering vectors are estimates of transmitter steering vectors required to orthogonalize the spatial channels. A receiver derives a spatial filter based on an MMSE criterion and with an estimate of the MIMO channel response and the steering vectors. The receiver (1) obtains NR received symbol streams from NR receive antennas, (2) performs spatial processing on the received symbol streams with the spatial filter to obtain NS filtered symbol streams, (3) performs signal scaling on the filtered symbol streams with a scaling matrix to obtain NS recovered symbol streams, and (4) processes the NS recovered symbol streams to obtain NS decoded data streams for the NS data streams sent by the transmitter.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
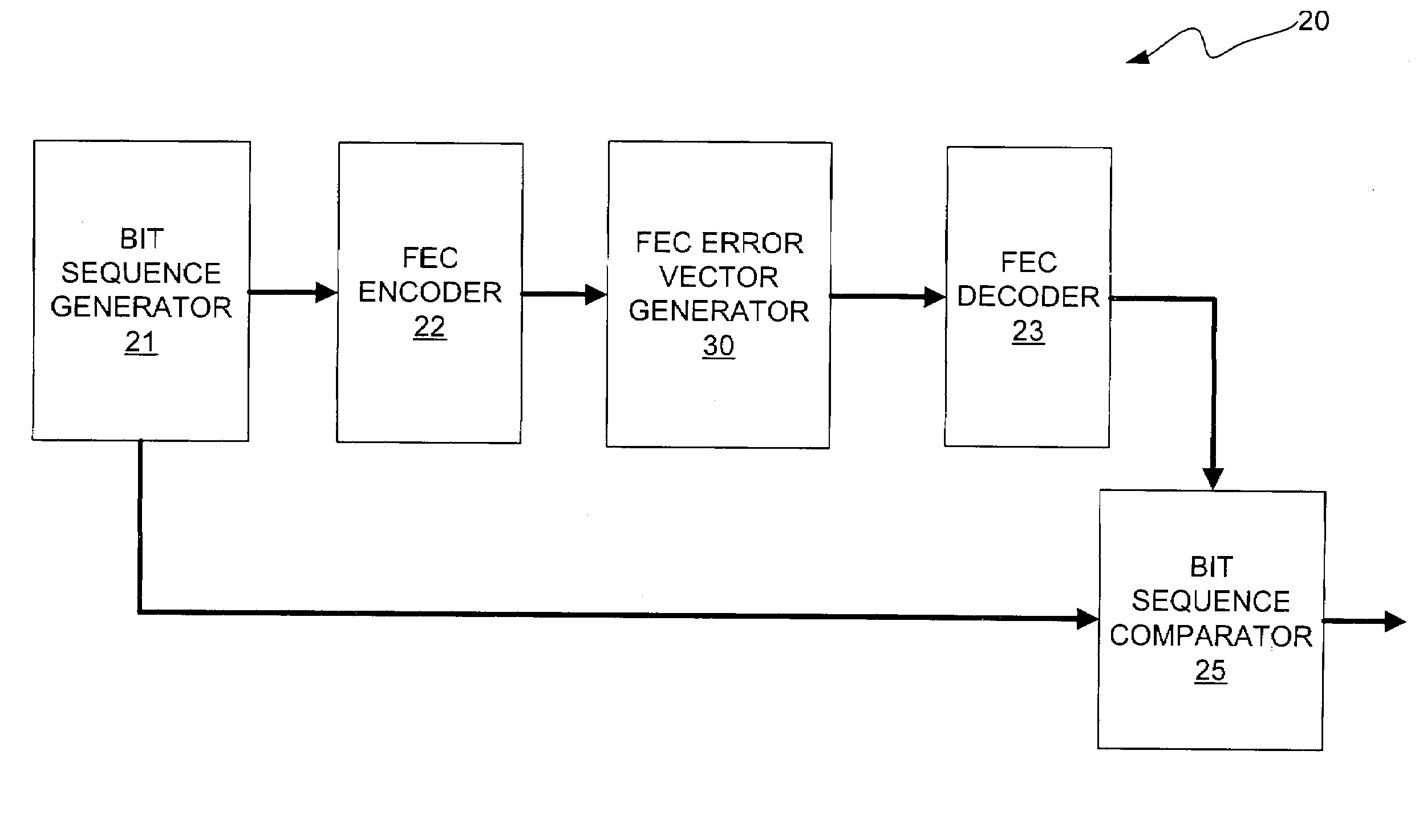
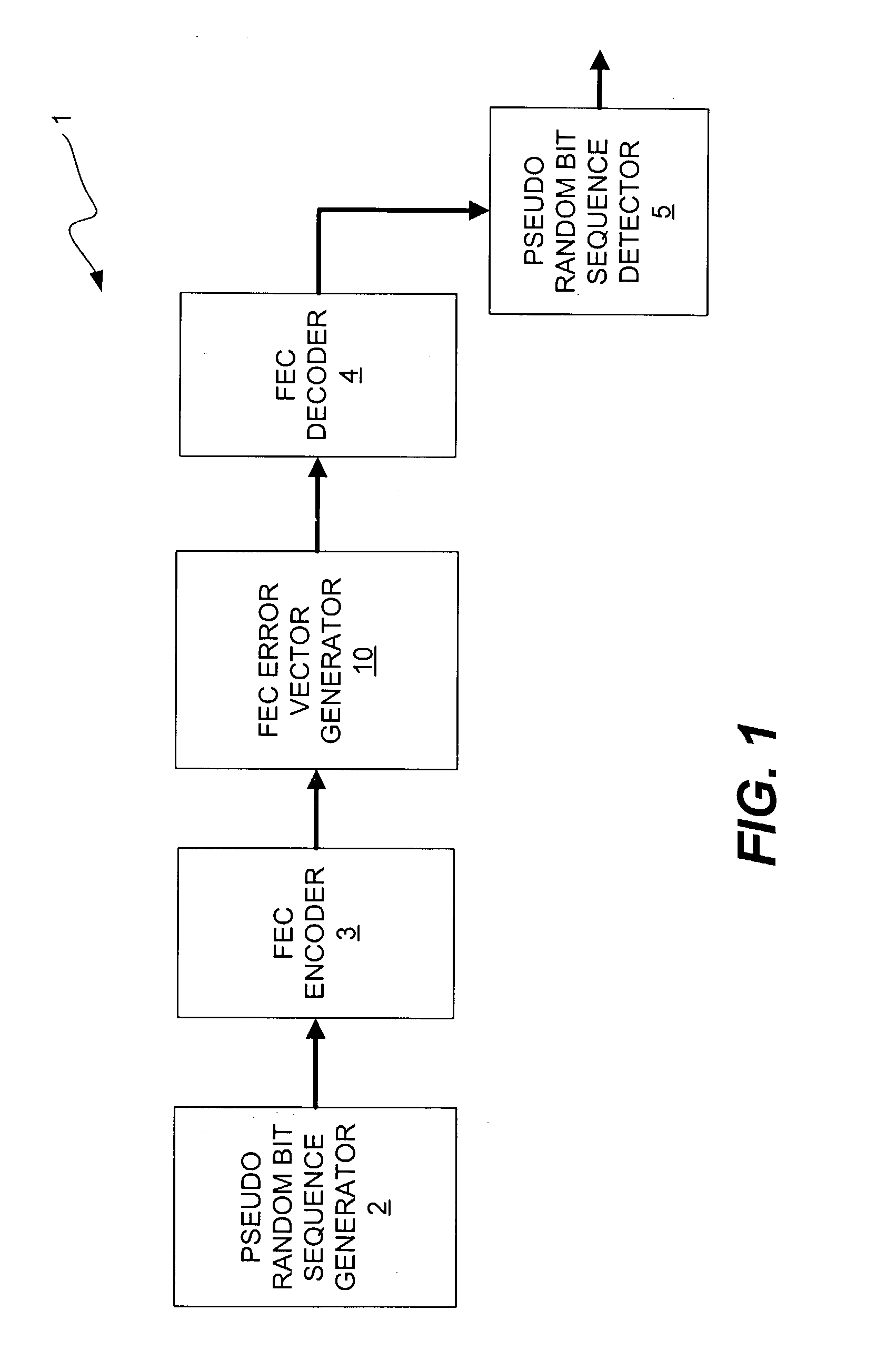
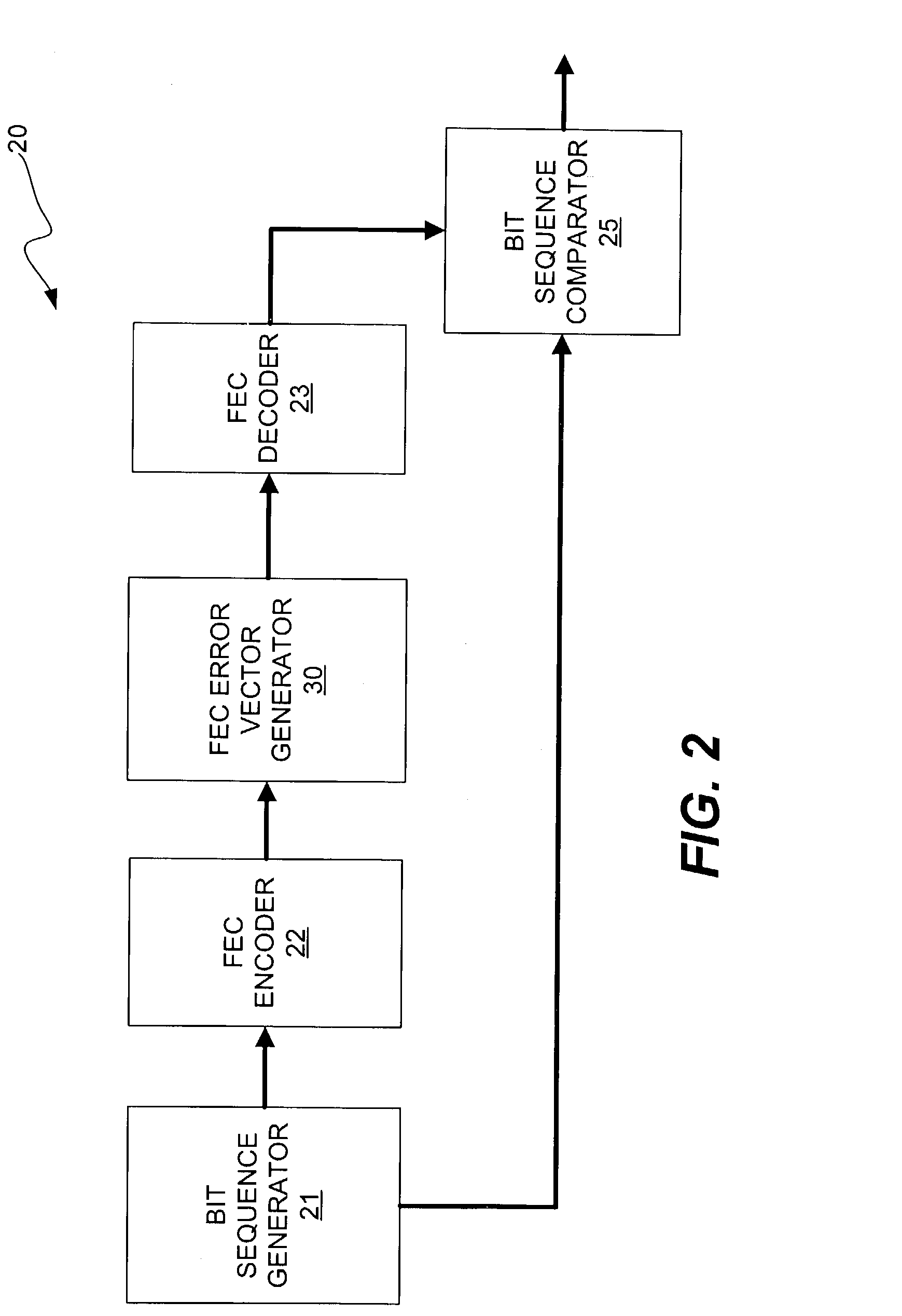
Method and apparatus for generating bit errors in a forward error correction (FEC) system to estimate power dissipation characteristics of the system
ActiveUS7073117B1Precision productionPower dissipationData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionFir systemForward error correction
A method and apparatus for generating and inserting bit errors in data words that have been encoded in a forward error correction (FEC) system in order to estimate power dissipation. In accordance with the present invention, it has been determined that a burst error generator that is capable of erroring the maximum number of correctable data bits in every FEC encoded frame, which allows the designer to accurately produce test vectors that are suitable for use in commercially available power estimation tools. In addition, after the IC is produced, the burst error generator of the present invention can be enabled to provide real-time FEC power dissipation data for use in system thermal modeling, thus obviating the need to use costly external devices that emulate a given error rate. Furthermore, the power dissipation data obtained in real-time may be used to refine the initial design power estimate, which will then allow the designer to develop a more accurate prediction of power consumption for future IC designs. Thus, the burst error generator of the present invention is capable of reducing iterations of IC designs by accurately estimating the worst-case power dissipation of FEC decoders.
Owner:CIENA
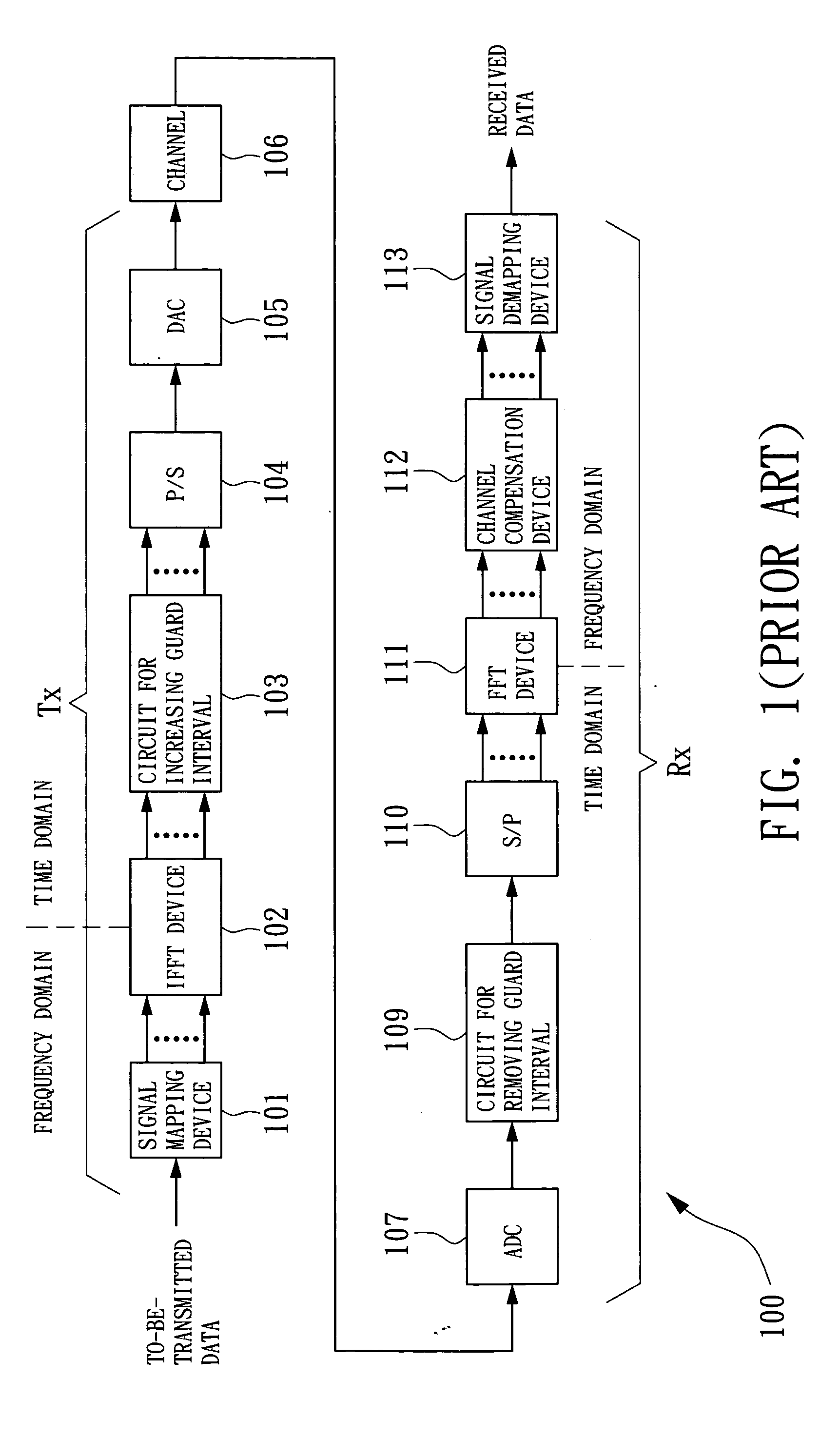
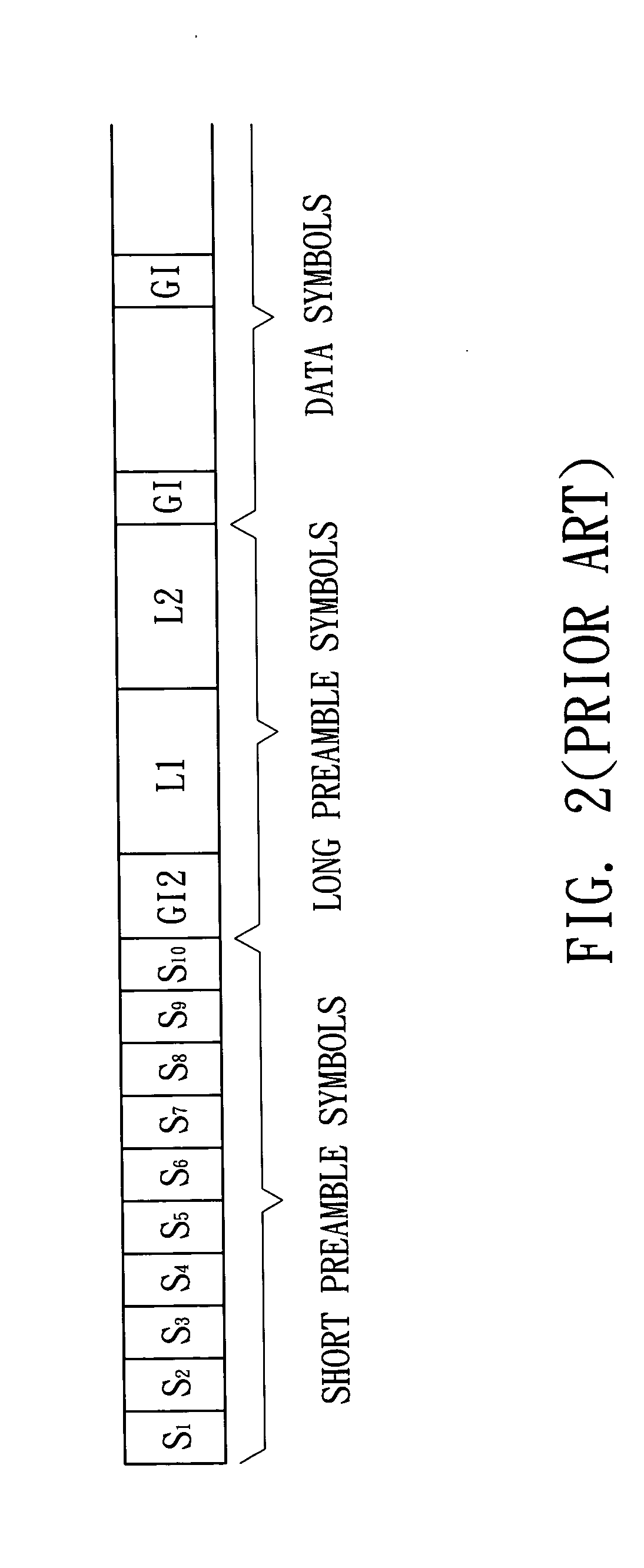
Scalable and backwards compatible preamble for OFDM systems
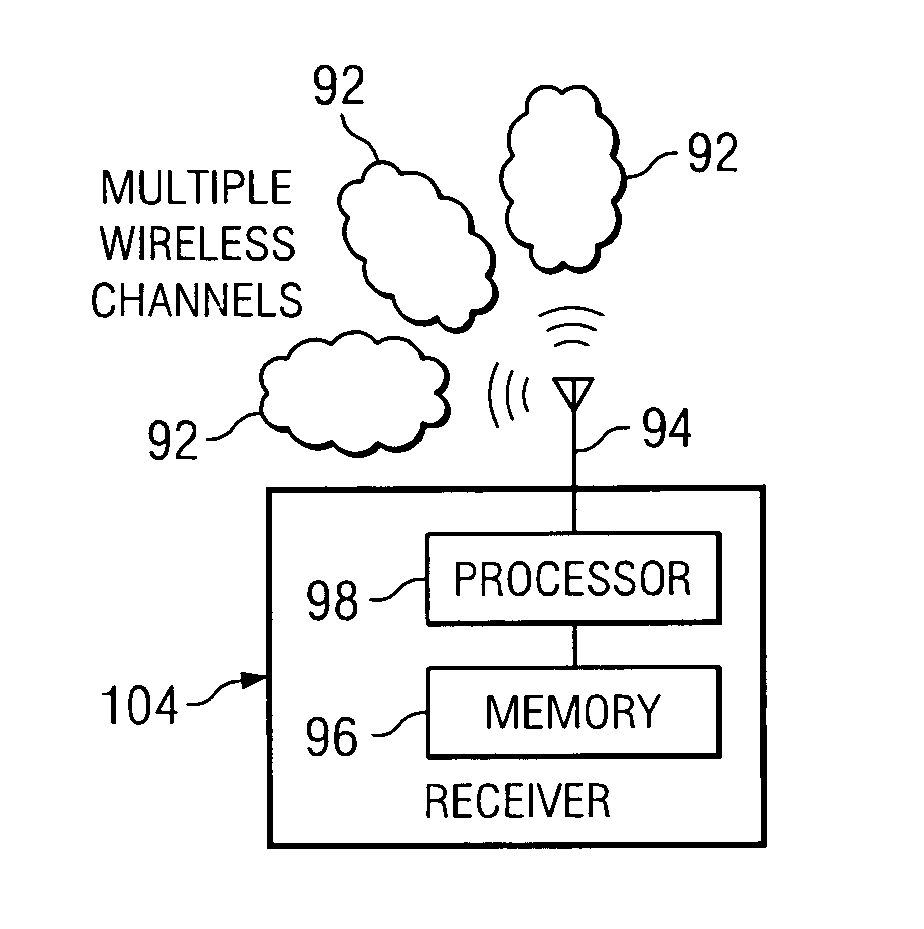
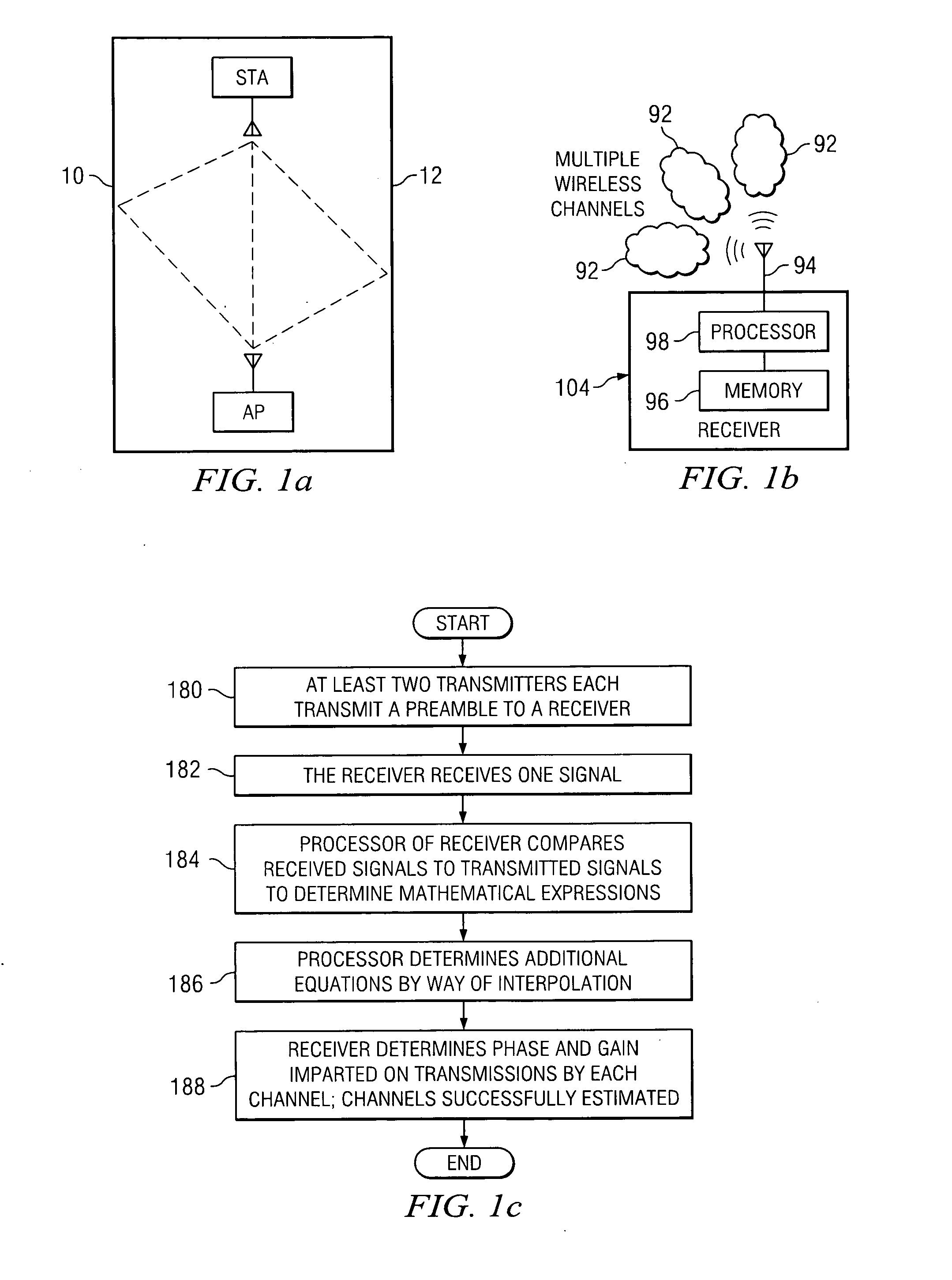
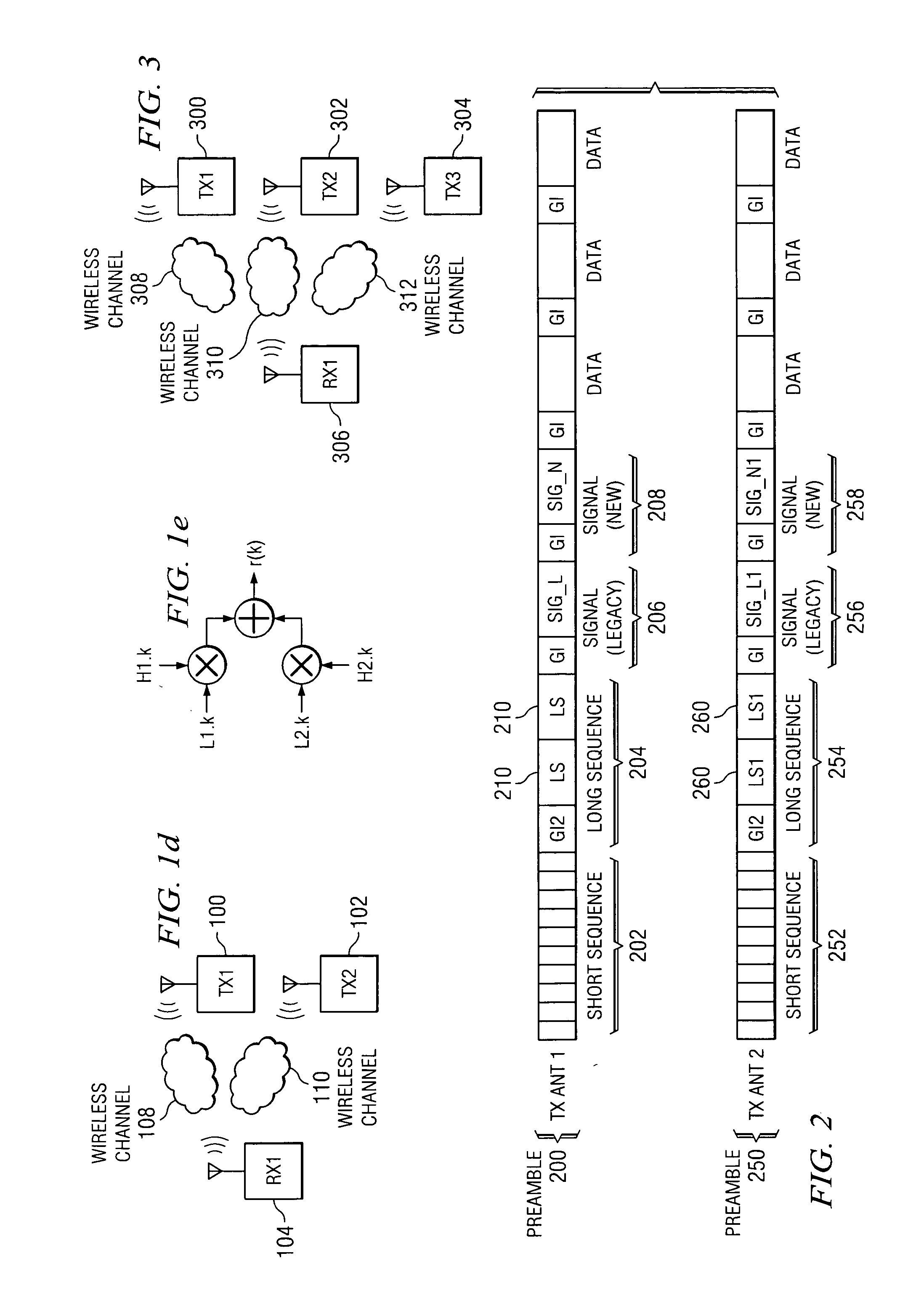
ActiveUS20050054313A1Eliminate signal distortionEfficiently estimating channelsSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringFir systemTelecommunications
A method comprising encoding a plurality of signals according to a predetermined negation scheme and transmitting the plurality of signals, wherein each signal is transmitted by way of a wireless channel. The method further comprises receiving a signal, wherein the received signal is a combination of the plurality of transmitted signals, and interpolating between data in the received signal to generate a plurality of systems of equations. The method further comprises solving the plurality of systems of equations to determine a gain and phase shift applied to each of the plurality of transmitted signals by a corresponding wireless channel.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for adjusting power control setpoint in a wireless communication system
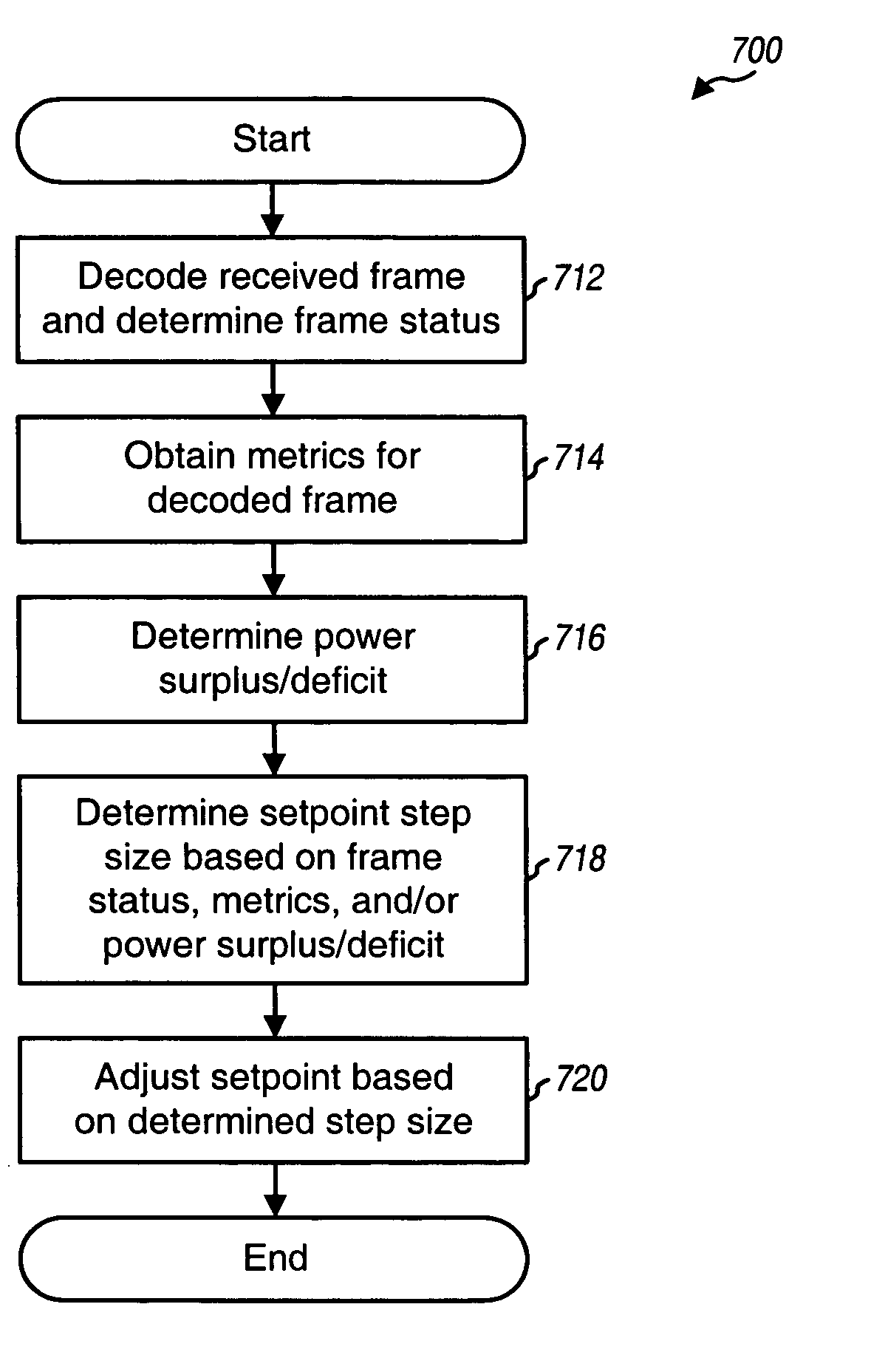
InactiveUS20050003848A1Effective regulationEasy to adjustPower managementSafety arrangmentsFir systemCommunications system
Techniques to adjust the setpoint of a power control loop in a wireless communication system. The setpoint may be adjusted based on frame status indicative of erased / good decoded frames, one or more (typically soft) metrics indicative of the confidence in the decoded results, power surplus / deficit indicative of the difference between the received signal quality and the setpoint, setpoint surplus / deficit indicative of the difference between the setpoint and a threshold Eb / Nt needed for the desired level of performance, or a combination thereof. The metrics may include re-encoded symbol error rate, re-encoded power metric, modified Yamamoto metric, minimum or average LLR among decoded bits, number of decoding iterations, and possibly others. The setpoint may be adjusted in different manners and / or by different amounts depending on the above-noted factors. The techniques may be employed for forward and / or reverse links in CDMA systems.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Residual frequency, phase, timing offset and signal amplitude variation tracking apparatus and methods for OFDM systems
InactiveUS20060133527A1Improve performanceIncrease speedError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionFir systemTime domain
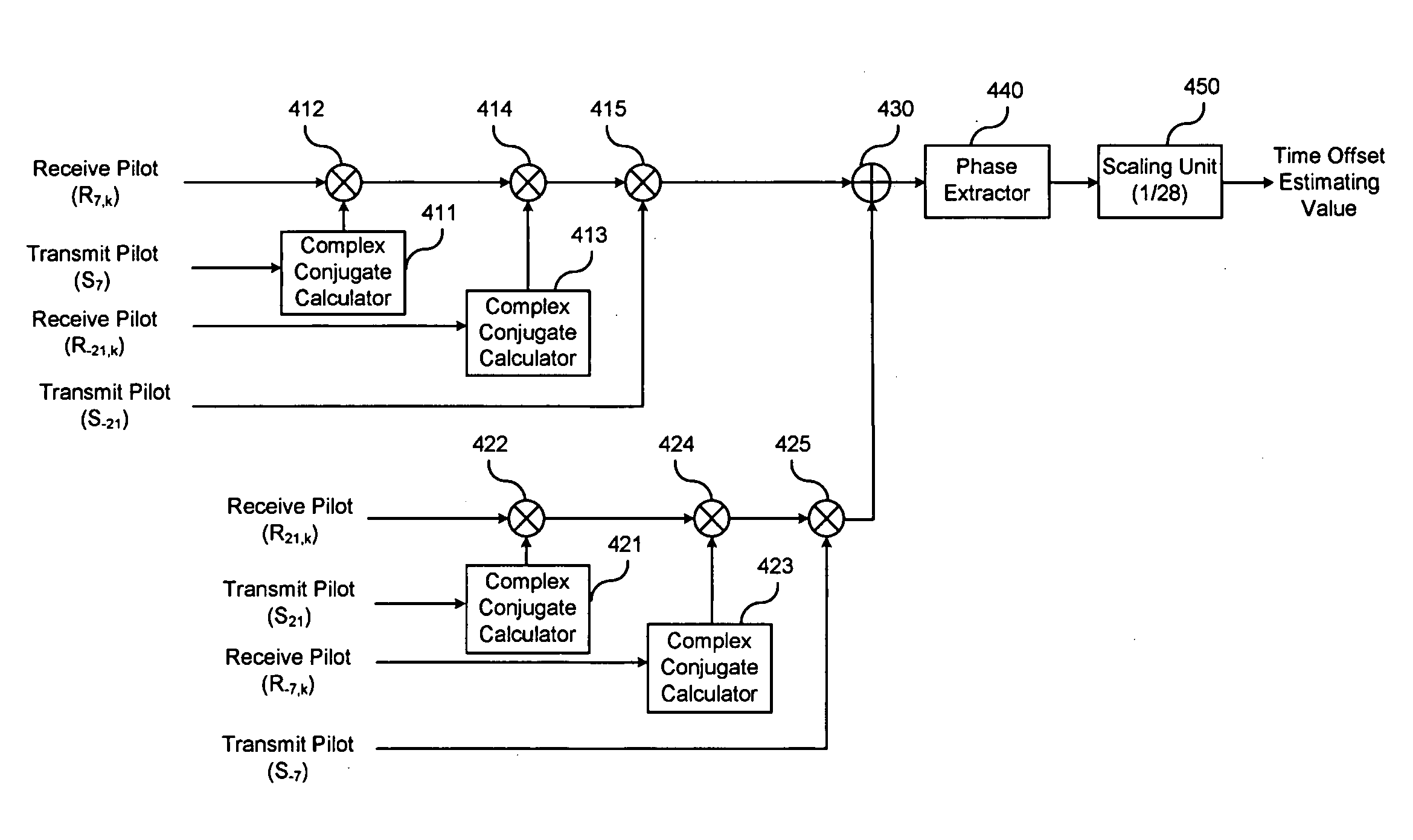
An error tracking apparatus and method for tracking a residual frequency error, a phase error, a timing error, and a signal amplitude variation to enhance a phase error tracking performance and a tracking speed in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system is provided. The error tracking apparatus and method include: a frequency error corrector for correcting a frequency at a time domain by adding a tracking carrier error estimating value to an initial carrier frequency error estimating value; a signal amplitude tracking corrector for controlling a signal amplitude by multiplying an input signal converted by a fast Fourier transform (FFT) by an output value corresponding to a calculated power of a receive pilot signal; a channel corrector for outputting a channel correcting signal by multiplying the receive pilot signal by a complex conjugate of a frequency channel response of the receive pilot signal; a carrier frequency error estimator for estimating a carrier frequency error parameter using the channel-corrected pilot and providing the tracking carrier frequency error estimating value; a time offset estimator for estimating a time offset parameter using the channel-corrected pilot; and a carrier phase error estimator for estimating a carrier phase error parameter using the channel-corrected pilot.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Unified MMSE equalization and multi-user detection approach for use in a CDMA system
ActiveUS20050094713A1Radio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFir systemMulti user detection
A unified minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalization / multi-user detection (MUD) approach for demodulating direct sequence CDMA (DS-CDMA) signals is described. In at least one embodiment, the unified approach is capable of generating a variety of cost-effective receiver demodulation techniques that may range from, for example, a low cost linear MMSE equalization technique to a relatively high complexity MMSE MUD.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method for selective antenna activation and per antenna or antenna group power assignments in cooperative signaling wireless MIMO systems
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for selective antenna activation in cooperative signaling wireless systems. In one embodiment, the method is for use in a cooperative signaling MIMO system in which antennas are located a plurality of different locations across a geographic area, the system comprising a plurality of different cooperative MIMO controllers and a plurality of antennas that can be communicably coupled to each of the controllers, the method comprising: at different transmission instances, selectively activating one or more antennas in the cooperative signaling MIMO system to vary which subset of antennas are active among antennas that can be used for each of the controllers in the system, including applying a power pattern which specifies per antenna or per antenna group power assignments for the one or more antennas being selectively activated, and performing cooperative MIMO transmission under control of at each controller in conformance with antenna activation and antenna power assignments assigned for each transmission time.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
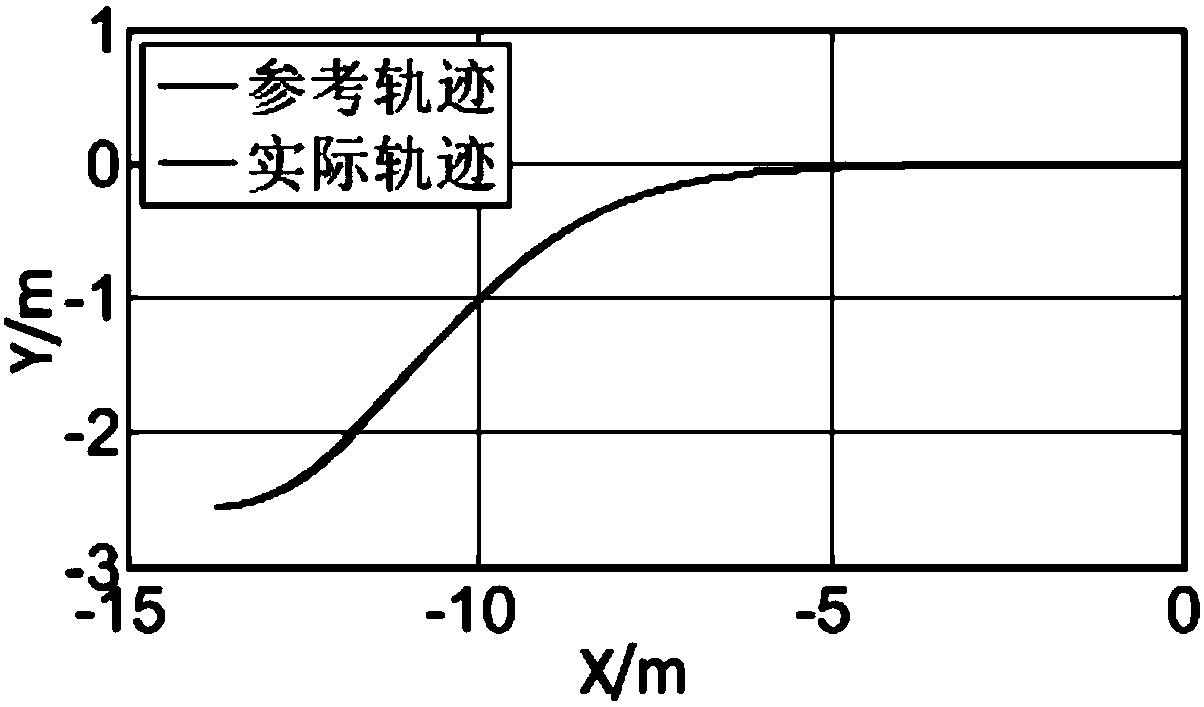
Unmanned vehicle path tracking control method based on soft constraint quadratic programming MPC
ActiveCN108334086AAdjust control parameters in real timeAccurate path followingPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesControl parametersPath tracing
The invention relates to an unmanned vehicle path tracking control method based on a soft constraint quadratic programming MPC. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a new reference path pointset Prset is calculated and established according to known reference path points; secondly, output from a kth sampling point to future Np sampling moments is predicted; thirdly, a control increment offuture Nc sampling moments is calculated by using an optimization method with soft constraint quadratic programming, and therefore a control amount at the current moment is obtained; finally, the control amount at the current moment is applied to a system, and the steps above are repeated until path tracking is completed. According to the method, through a rolling optimization strategy, global optimization is replaced by local optimization, feedback correction is conducted by utilizing actually-measured information, control parameters can be adjusted in the control process in real time, and path tracking is more accurate.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
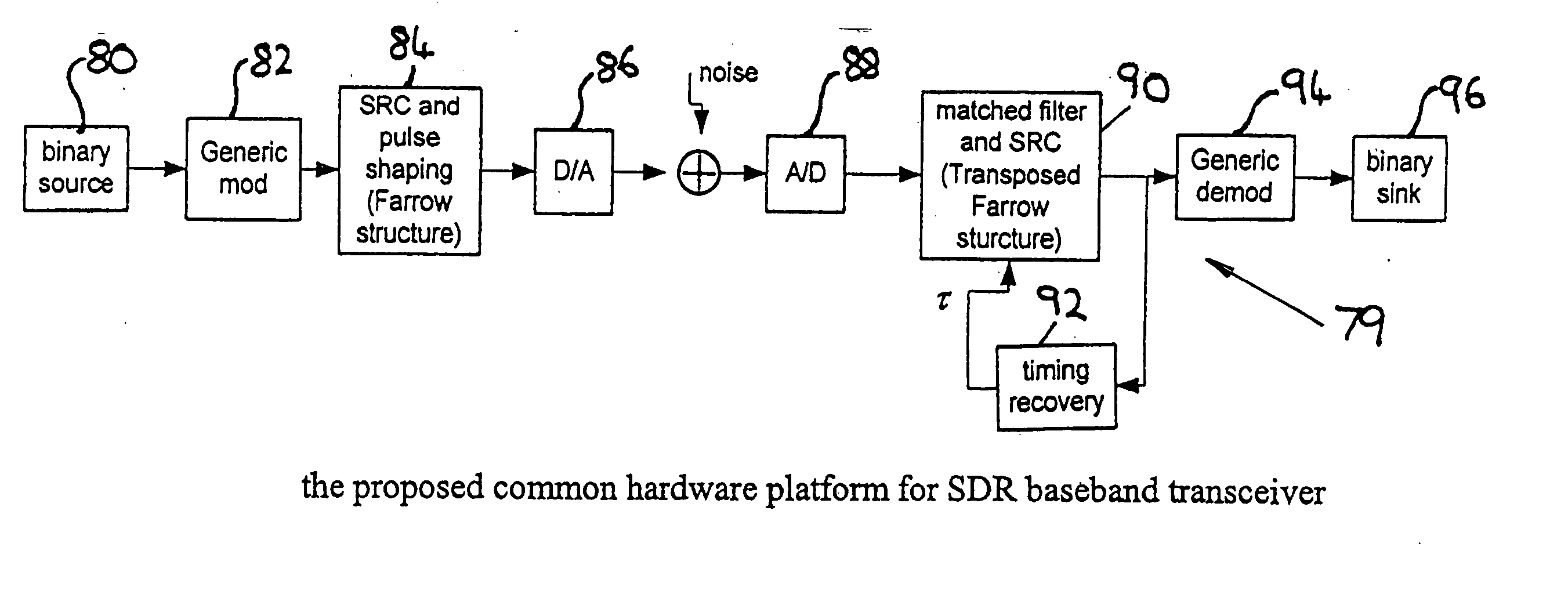
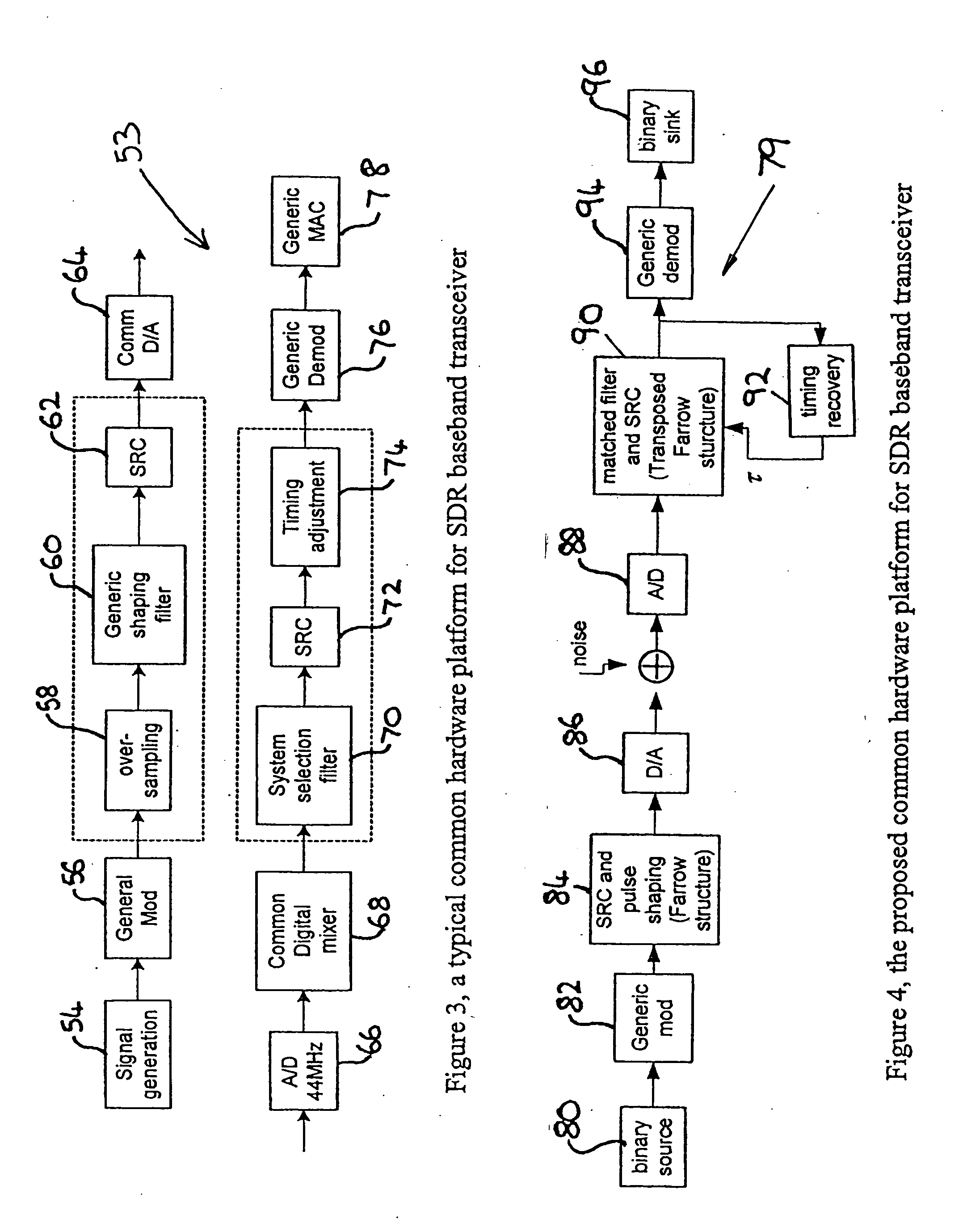
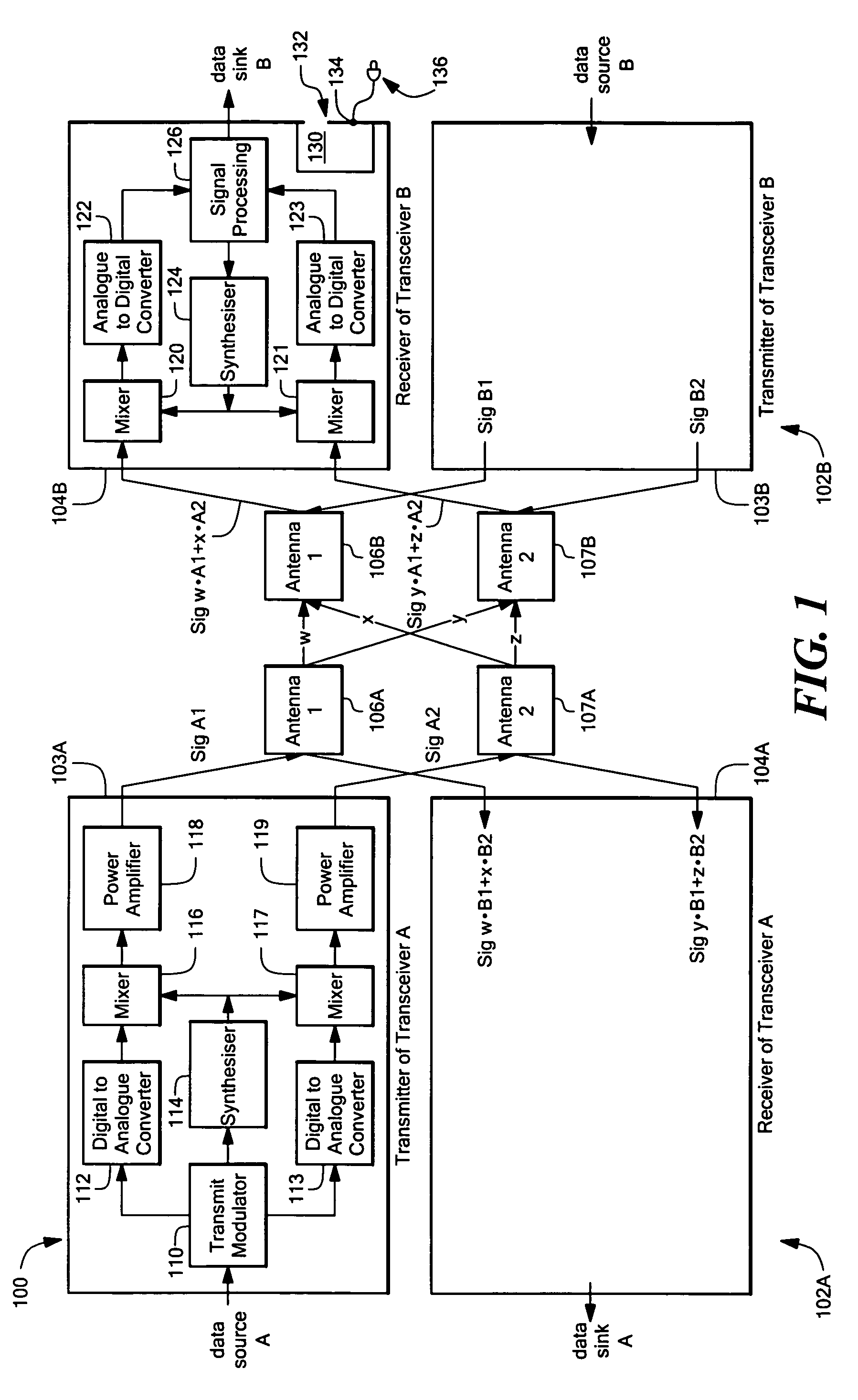
Methods for processing a received signal in a software defined radio (SDR) system, a transceiver for an SDR system and a receiver for an SDR system
InactiveUS20050243952A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationFir systemTransceiver
A receiver for a software defined radio system comprises an input stage for receiving a transmitted signal, an analogue-to-digital converter having a sample rate, a filter matched to the received transmitted signal, and a sample rate converter for converting the digital signal output from the filter from an input sequence having the sample rate of the analogue-to-digital converter to an output sequence having an output sample rate defined by the received transmitted signal. The input and output sequences comprise respectively a number of input samples and a number of output samples. A controller controls the output sample rate and a demodulator coupled to the output of the sample rate converter recovers the transmitted signal. The sample rate converter is implemented by a transposed Farrow structure. The controller is arranged to reset the output sequence from the sample rate converter when any one of said number of input samples and any one of said number of output samples pass through coincidence in time.
Owner:OKI TECHNO CENT SINGAPORE PTE
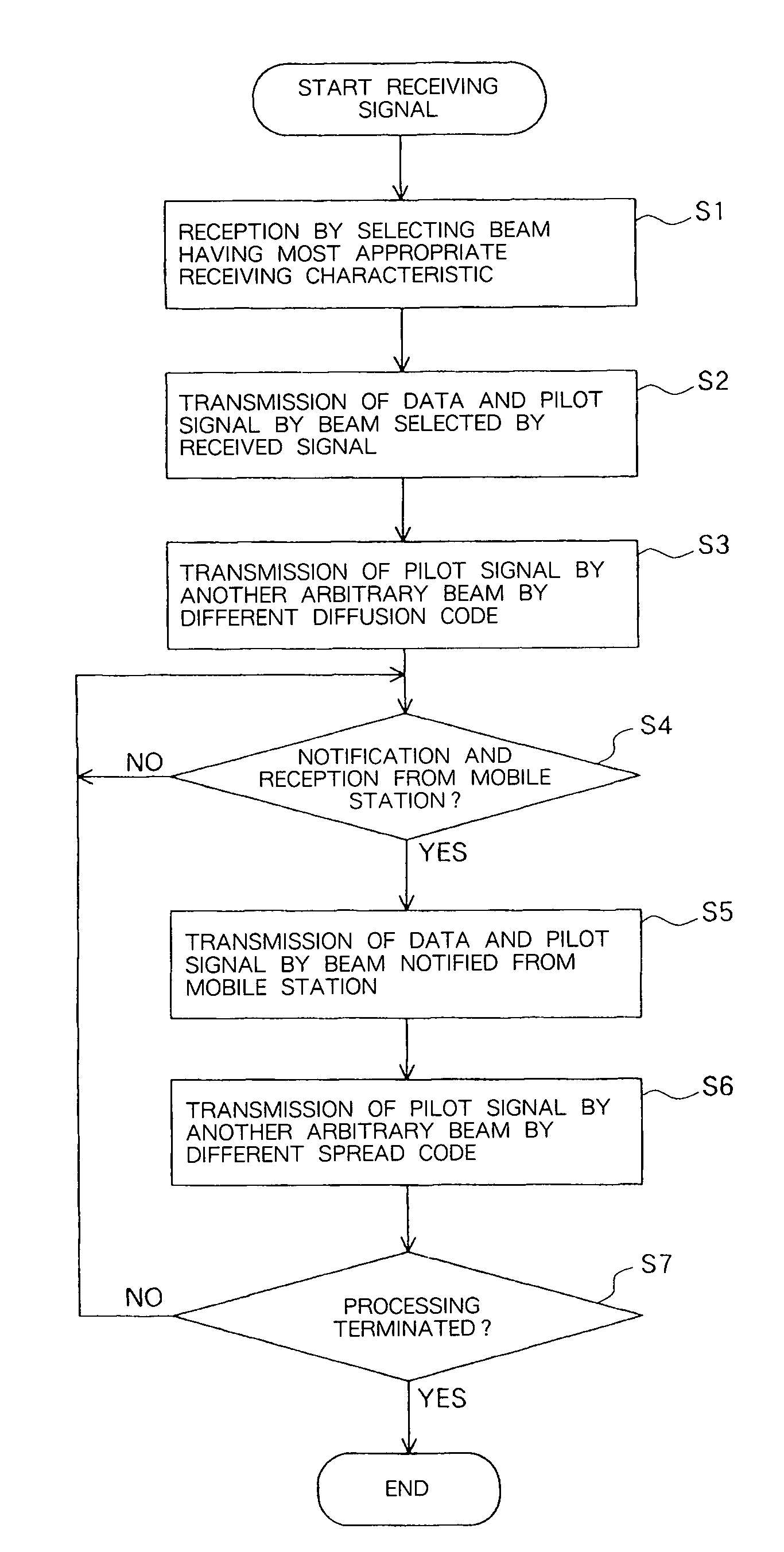
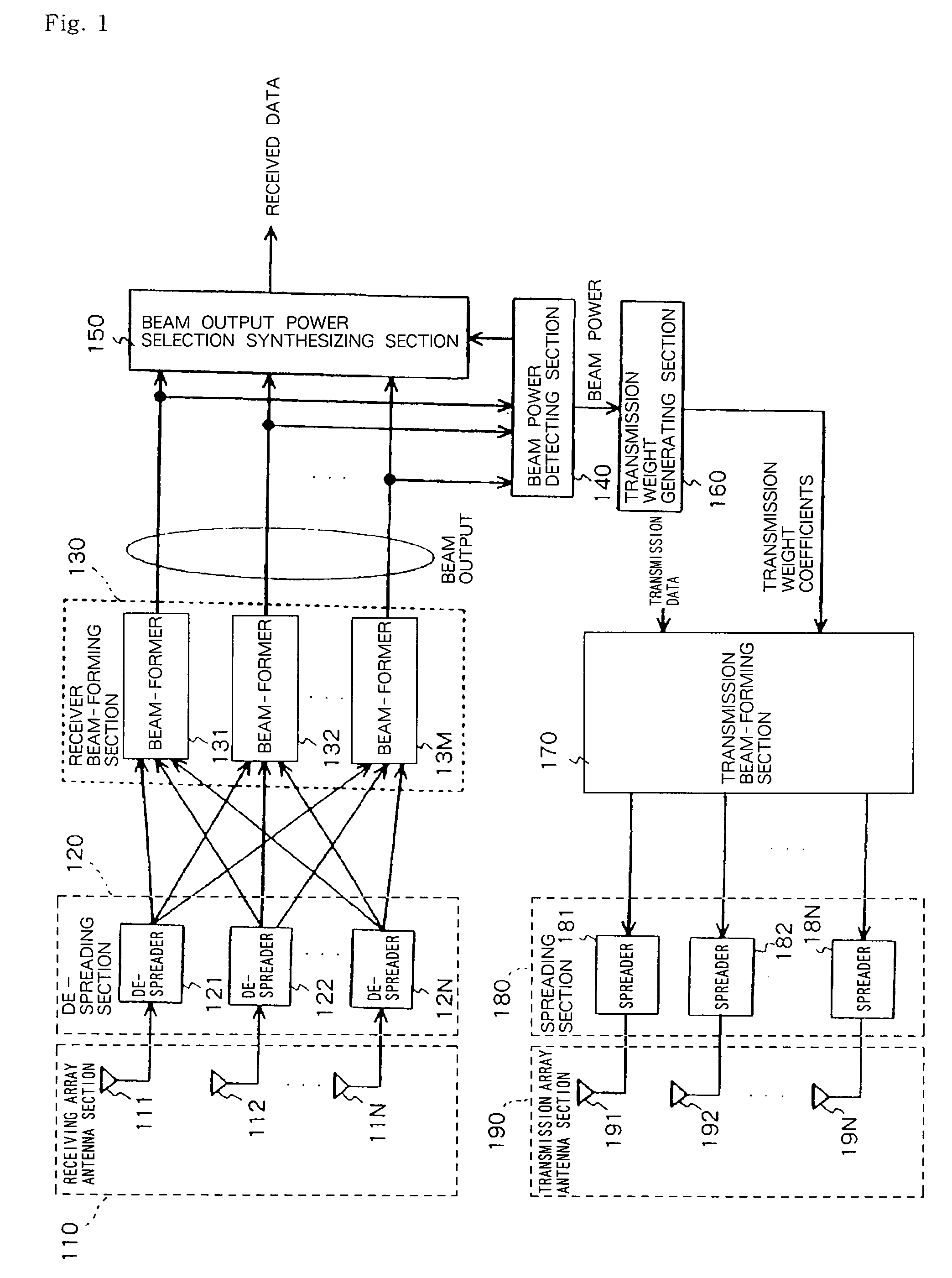
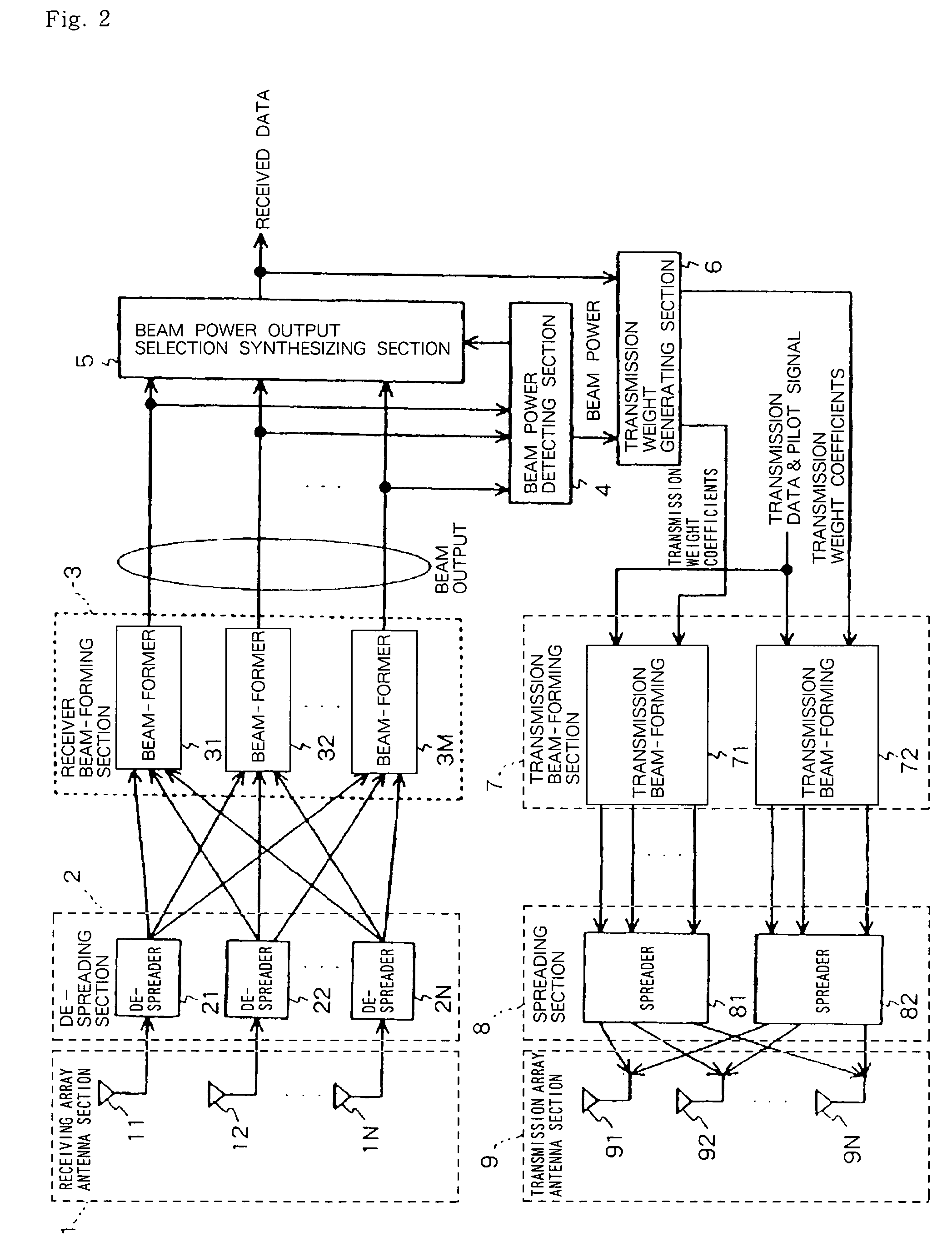
Transmission Directional Antenna Control System, Base Station, And Transmission Directional Antenna Control Method Used For System And Base Station
To provide a base station capable of selecting an optimum beam from among transmitted ones of multi-beams. In the arrangement, a beam power determining part (4) determines M received signal powers of multi-beams, and a beam output selecting part (5) selects, based on the information of the received powers from the beam power determining part (4), a beam of the largest power from among M outputs of beam formers (31-3M), and receives the selected beam. A transmission weight generating part (6) selects, based on the received information, a beam corresponding to the signal of a spread code selected by a mobile station and also selects another any beam to notify their respective transmission weighting coefficients. A transmitted beam forming part (7) weights transmitted data corresponding to transmission array antenna elements (91-9N) with the transmission weighting coefficients. Spreaders (81,82) use respective different spread codes to spread input signals, and the transmission array antenna elements (91-9N) send the beam-formed signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
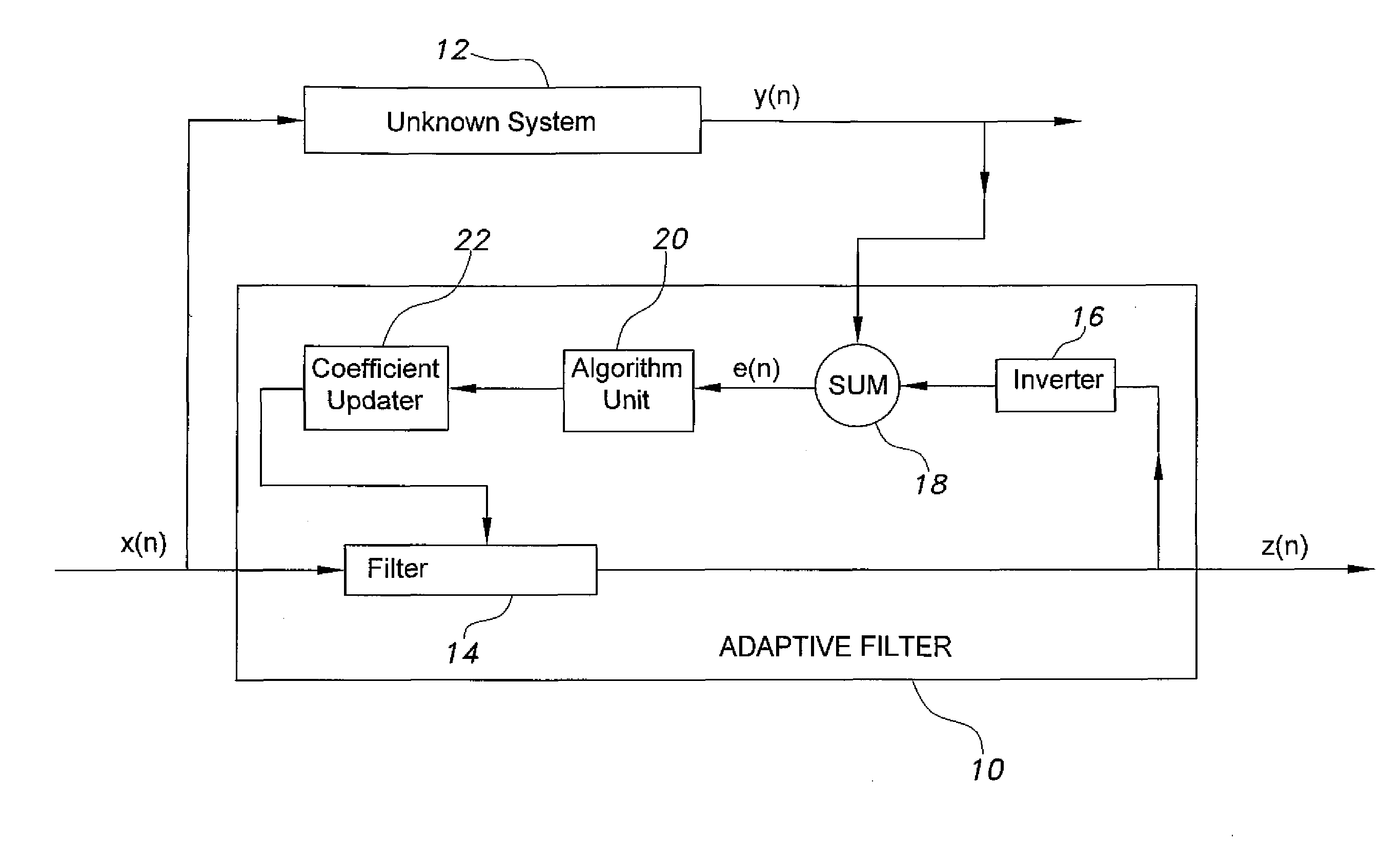
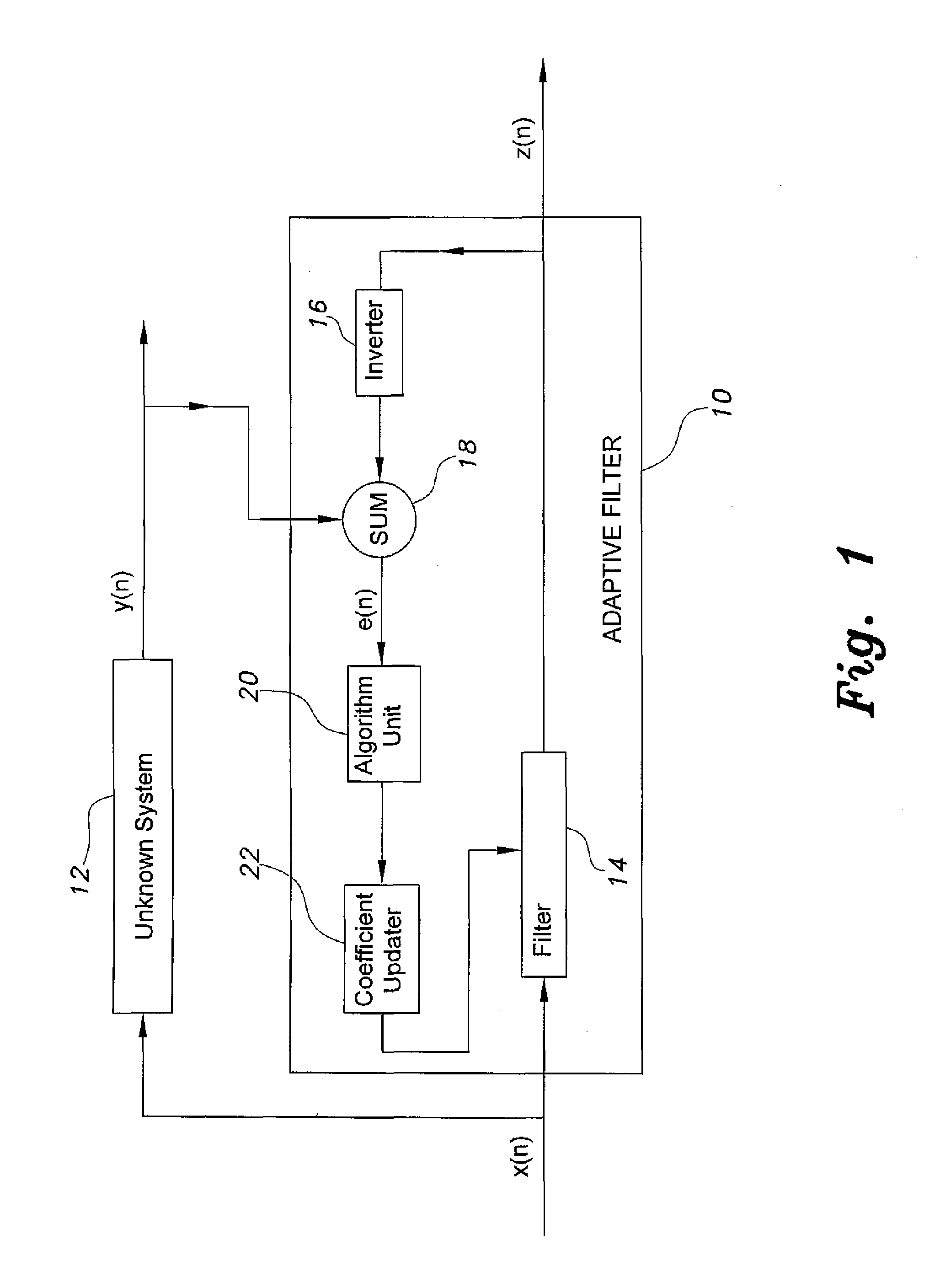
Adaptive filter for system identification
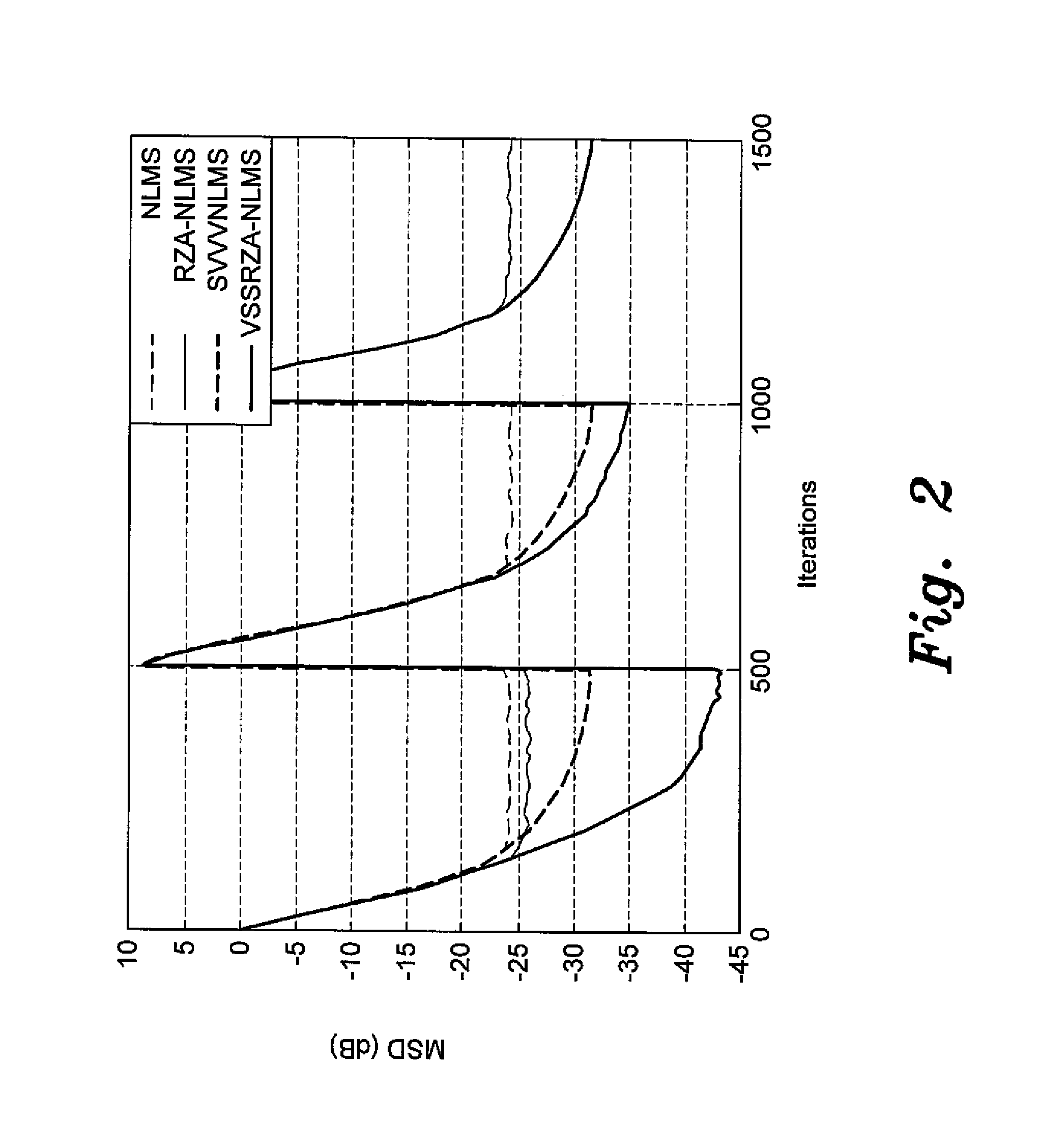
InactiveUS20140310326A1Improve performanceReadily apparentAdaptive networkComplex mathematical operationsFir systemMean square
The adaptive filter for system identification is an adaptive filter that uses an algorithm in the feedback loop that is designed to provide better performance when the unknown system model has sparse input, i.e., when the filter has only a few non-zero coefficients, such as digital TV transmission channels and echo paths. In a first embodiment, the algorithm is the Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithm in which the filter coefficients are updated at each iteration according to:w(i+1)=w(i)+μ(i)e(i)uT(i)u(i)2,where the step size μ is varied according to μ(i+1)=αμ(i)+γ|e(i)|. In a second embodiment, the algorithm is a Reweighted Zero Attracting LMS (RZA-LMS) algorithm in which the filter coefficients are updated at each iteration according to:w(i+1)=w(i)+μ(i)e(i)uT(i)u(i)2-ρsgn(w(i))1+ɛw(i),where the step size μ is varied according to μ(i+1)=αμ(i)+γ|e(i)|. The adaptive filter may be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP), an ASIC, or by FPGAs.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
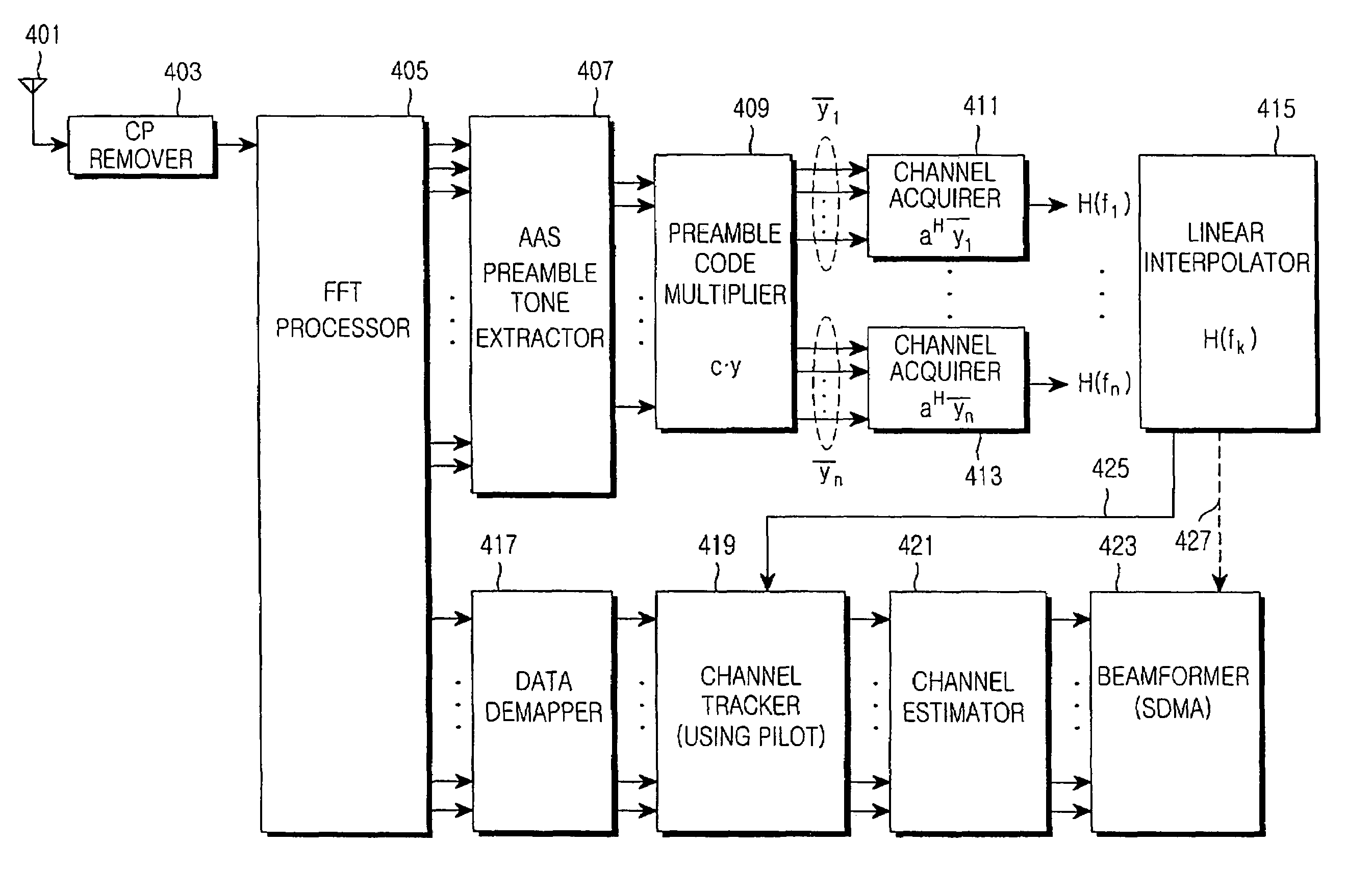
Apparatus and method for channel estimation in an SDMA-OFDM system
Provided is a channel estimation apparatus and method in a broadband wireless communications system using a smart antenna are provided. In the channel estimation apparatus, an FFT processor converts a received time-domain signal into a frequency-domain signal by FFT-processing the received time-domain signal. A channel acquirer estimates a first channel information for an SDMA user using a preamble signal allocated to the SDMA user in the frequency-domain signal. A channel tracker estimates a second channel information for the SDMA user using pilots in a data area allocated to the SDMA user in the frequency-domain signal. A channel estimator estimates a final channel information by weighting the first channel information and the second channel information according to a channel change rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for system selection
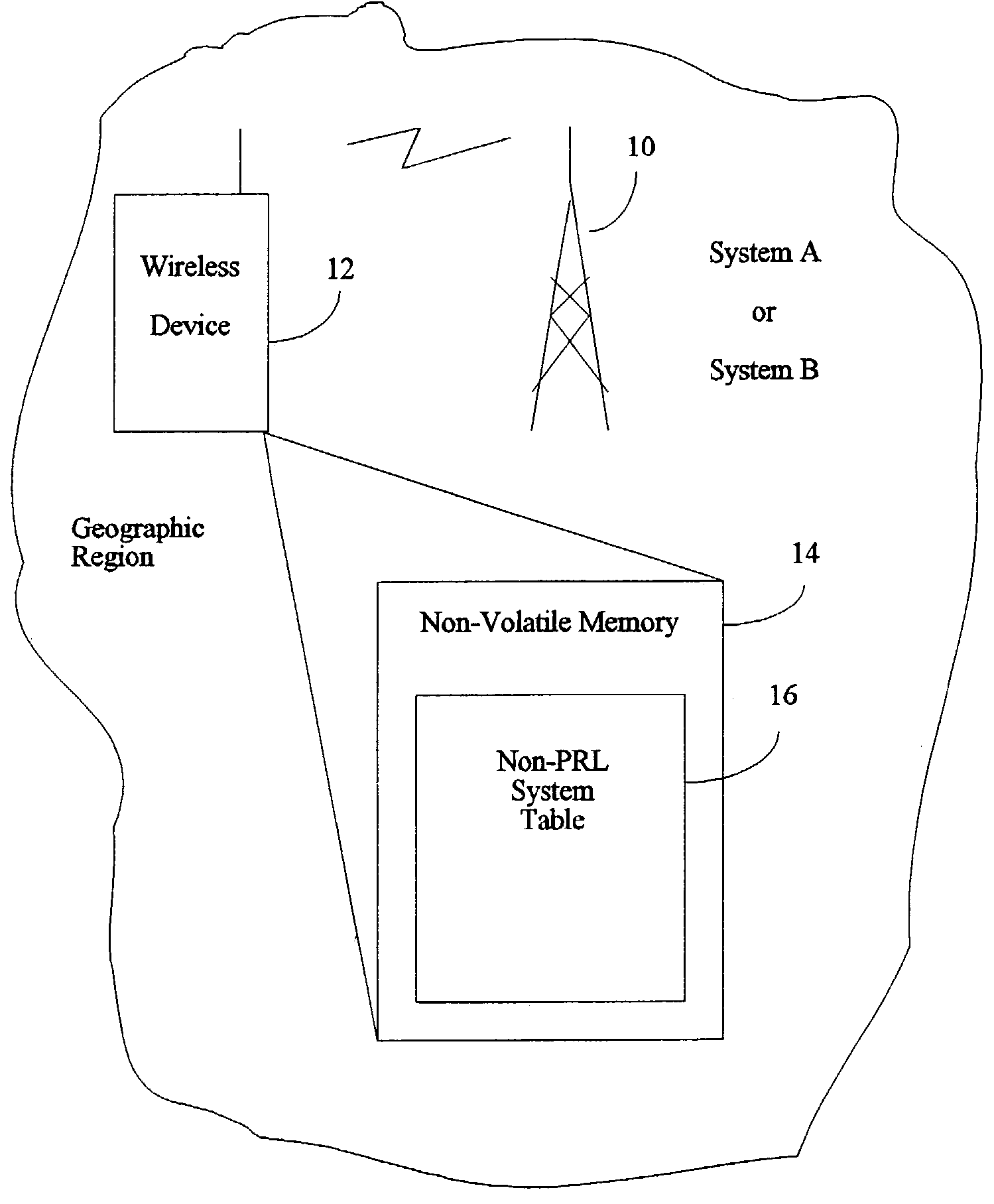
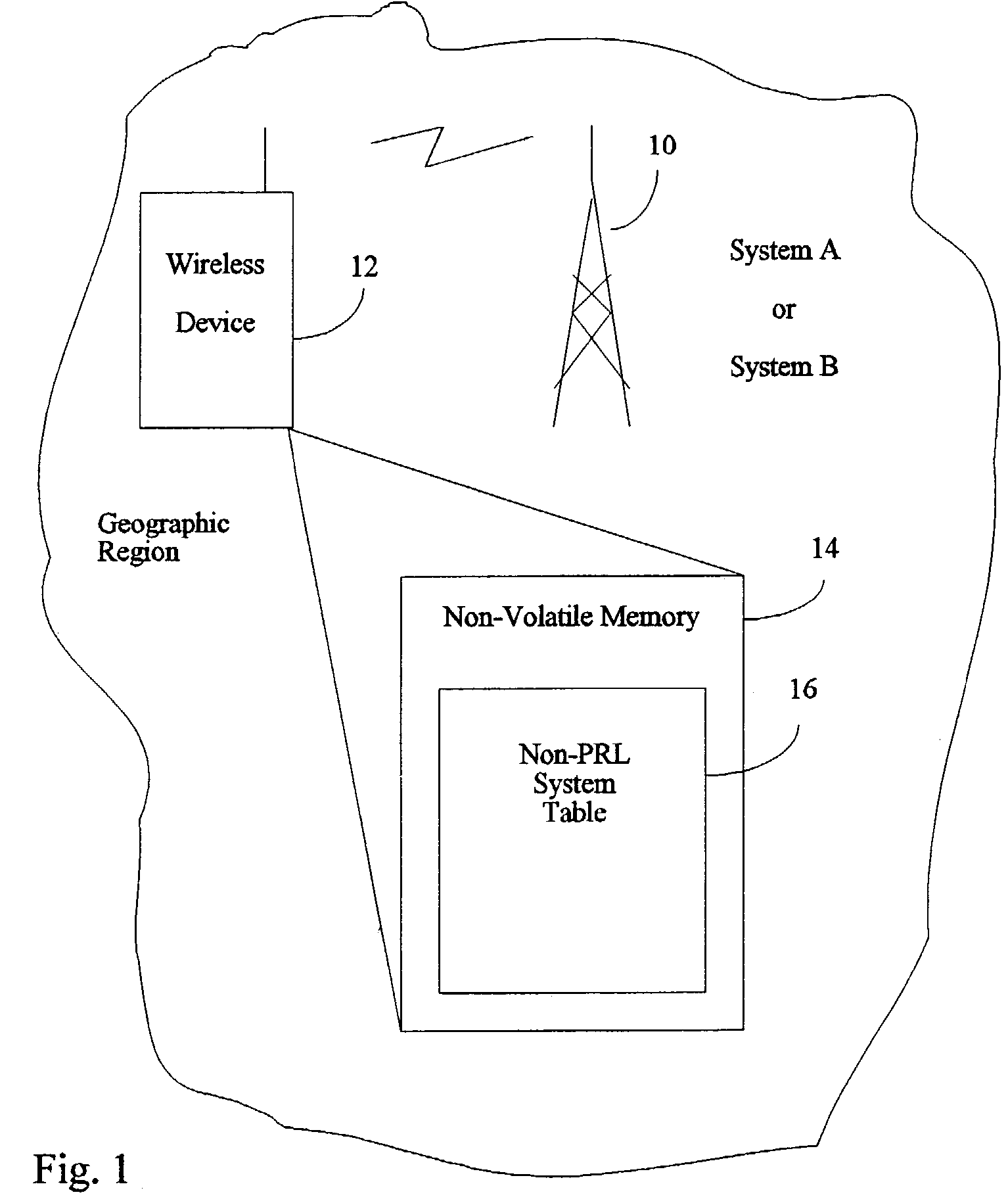
InactiveUS7139587B2Short acquisition timeNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionFir systemCommunications system
In a wireless communication device which is transportable between plural geographic region, wherein each geographic region has preferred and non-preferred communication systems for the wireless communication device, a method of selecting an appropriate communication system, including providing the wireless communication device with a non-PRL system table for storing acquisition parameters, including a communication system identification, a band class designation for a band class, a channel designation for a channel in the band class, and geographic region identification; making entries in the non-PRL system table when the wireless communication device acquire an appropriate channel in a geographic region; searching the non-PRL system table when the wireless communication device next changes geographic regions; and selecting a communication system based on the acquisition parameters in the non-PRL system table as a result of the searching.
Owner:SHARP KK
Synchronization method and apparatus for OFDM systems
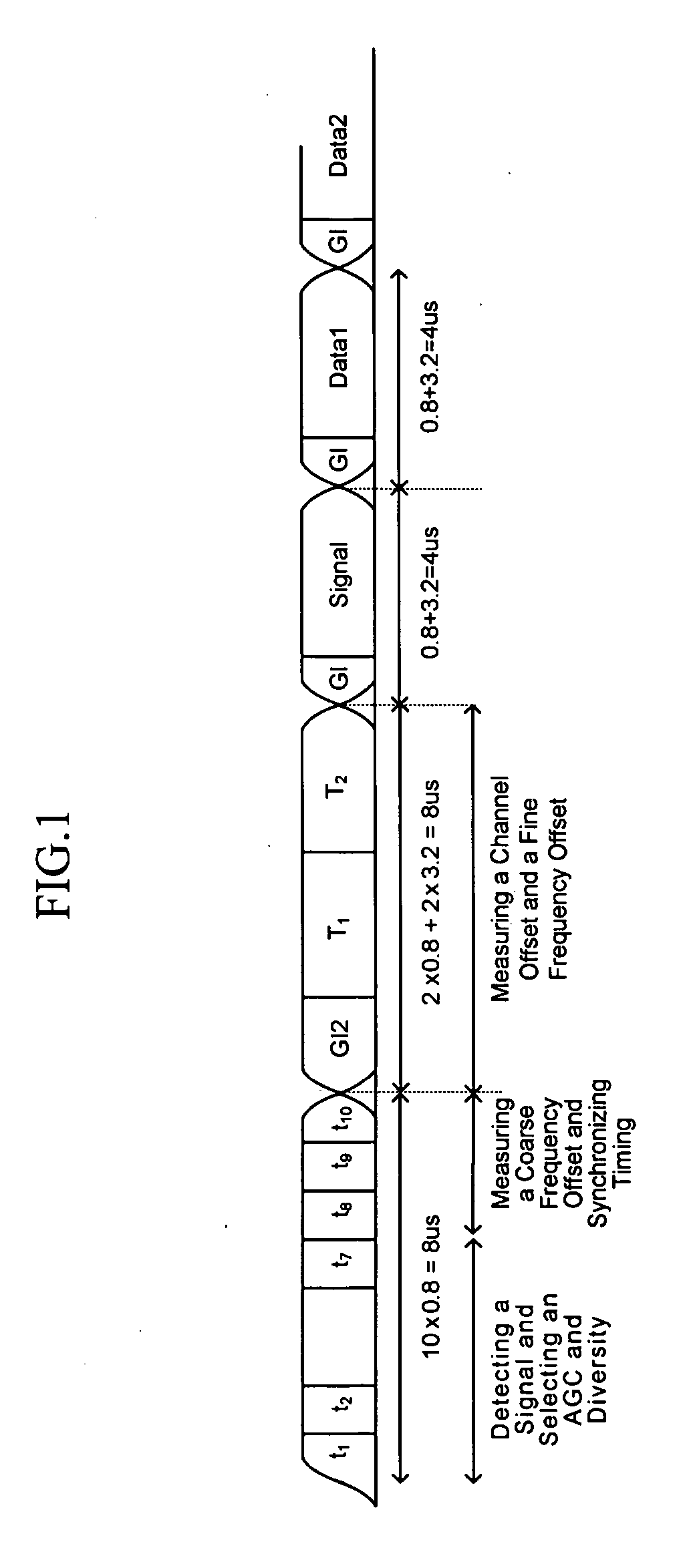
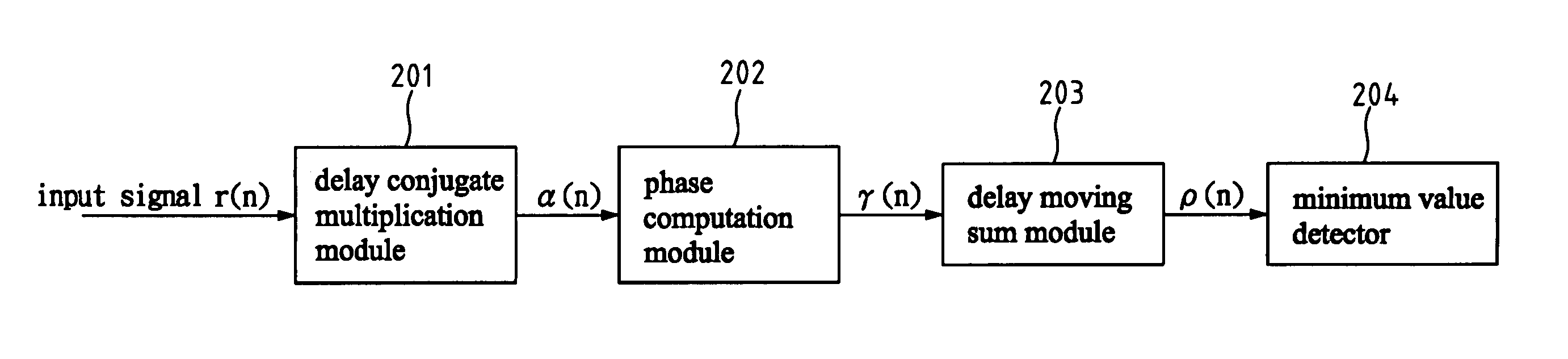
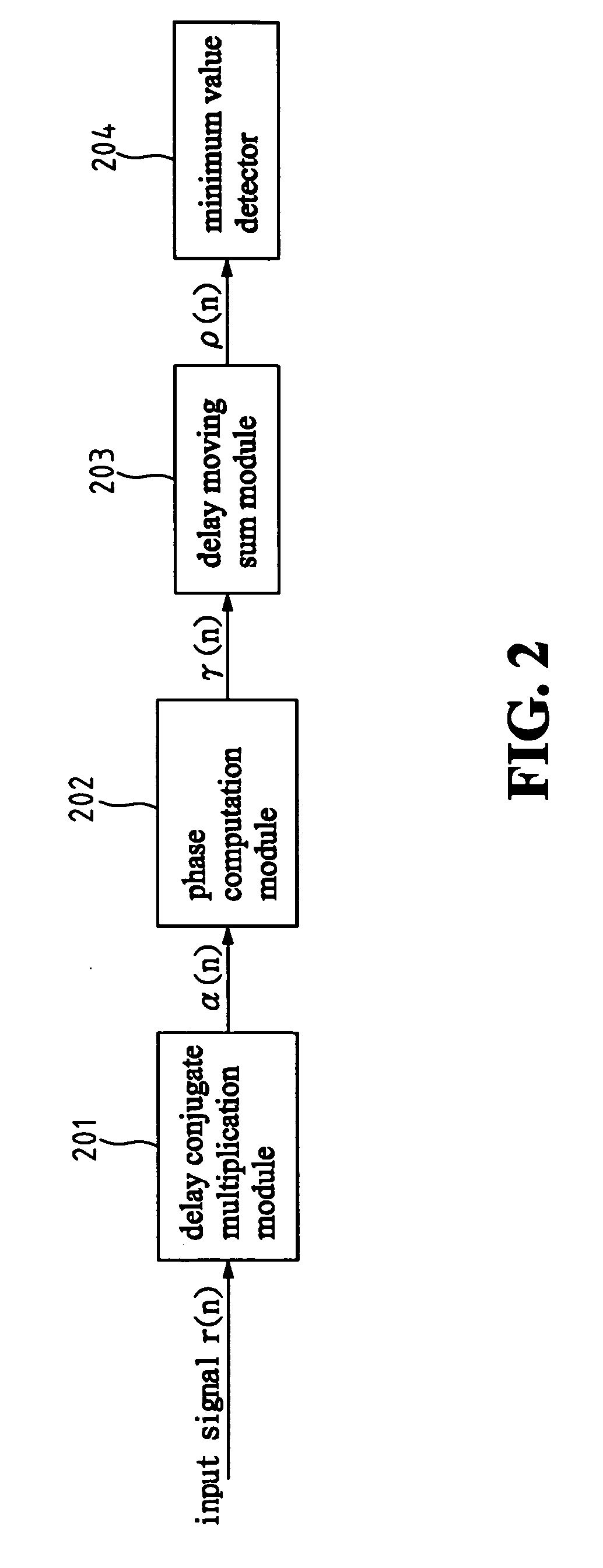
ActiveUS20070025457A1Improve accuracyPrevents conventional misjudgeTime-division multiplexSecret communicationDigital videoFir system
A synchronization apparatus and method for an OFDM system includes four portions: delay conjugate multiplication, phase processing, delay moving sum and minimum value detection. The invention performs the correlation phase operation and finds out the location of abnormal change for the phase difference of the output signal. The location is used for the reference of symbol synchronization. It overcomes the problems of incorrect judge about synchronization location due to the channel fading or noise. The invention can be applied to wire / wireless communications or digital video broadcasting-terrestrial systems, specialized in symbol synchronization at a receiving end.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and system for 80 and 160 gigabit-per-second QRZ transmission in 100 GHz optical bandwidth with enhanced receiver performance
InactiveUS20060228118A1High receptionHigh transmissionPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFir system
Owner:TERADVANCE COMM
Wireless communication system, receiver, demodulation method used for the system and receiver, and program thereof
InactiveUS20060165192A1Steadily calculating bit likelihoodMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsFir systemCommunications system
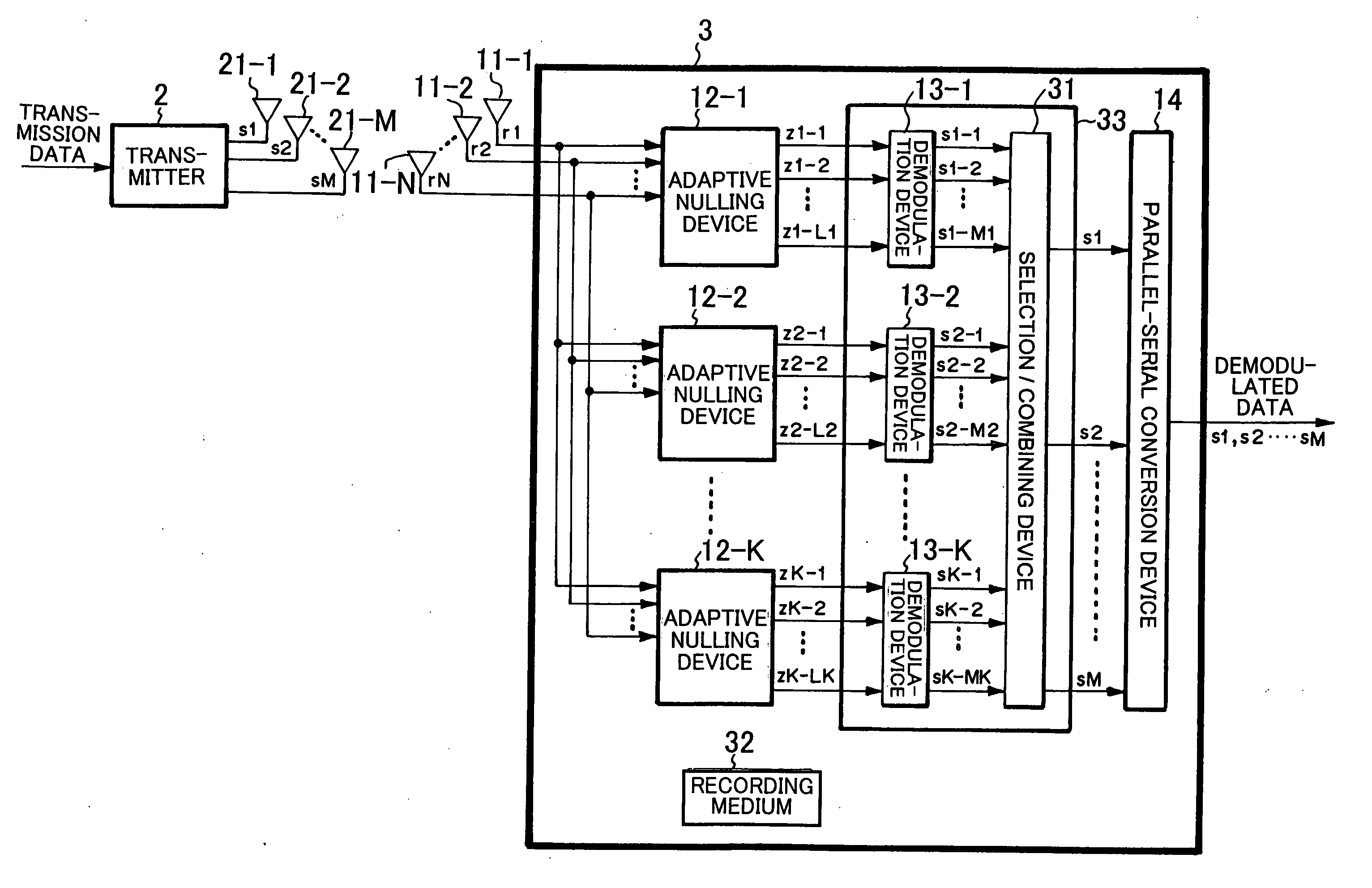
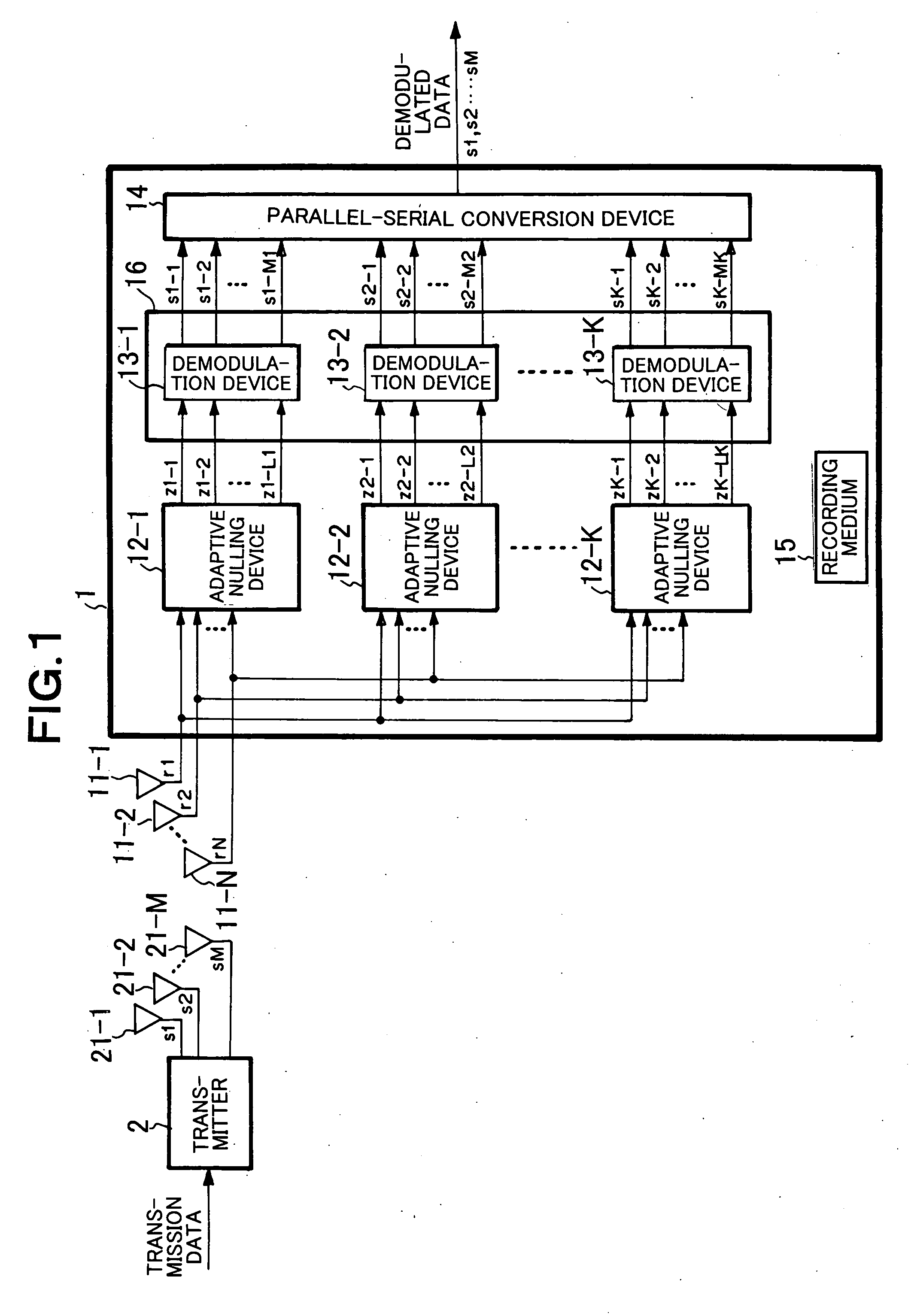
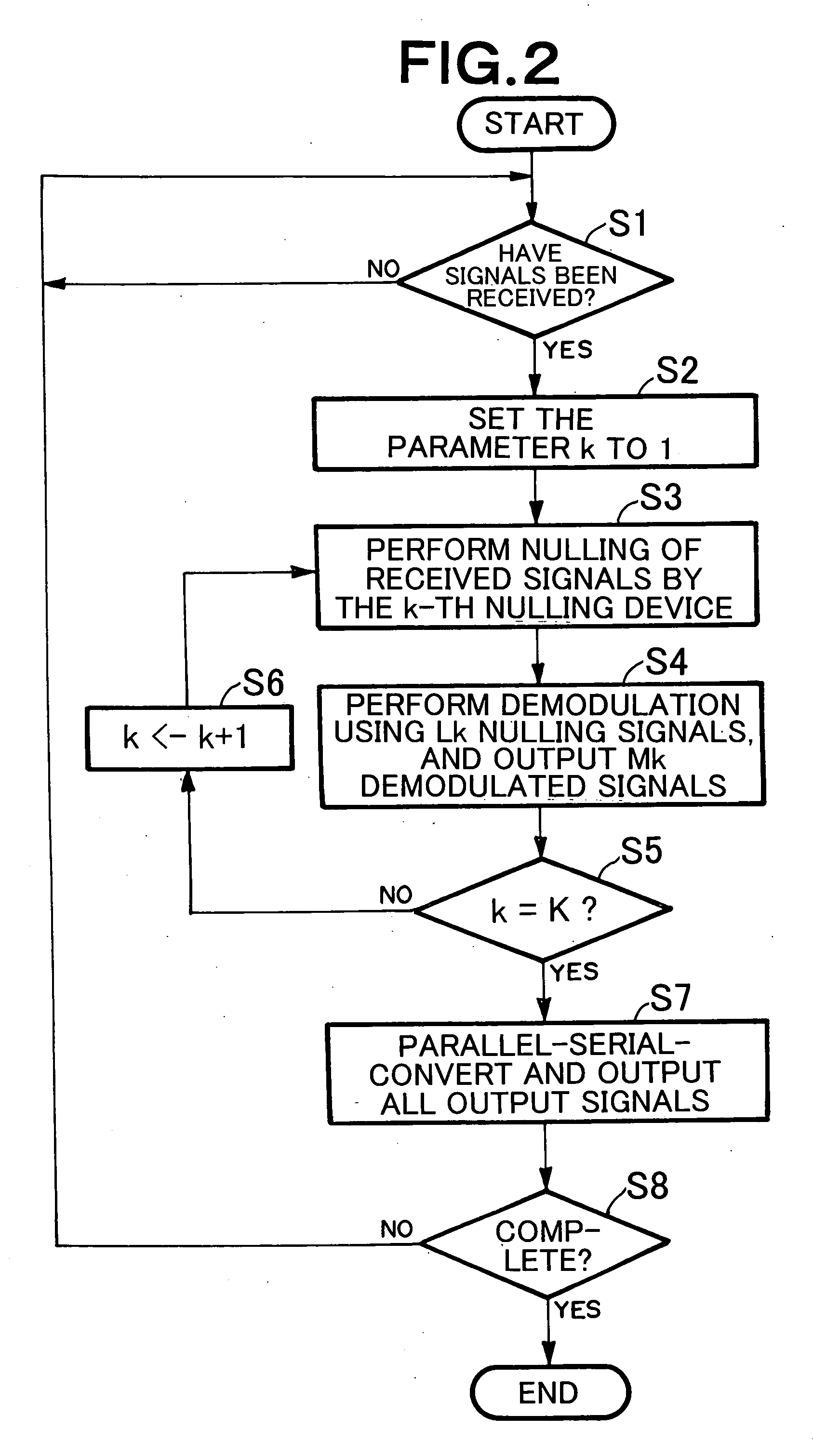
In a wireless communication system having a receiver which receives, through plural reception antennae, signals transmitted from plural transmission antennae, bit likelihood can be surely calculated without requiring a selection processing. A transmitter has M transmission antennae, and transmits signals through the transmission antennae, respectively. A receiver has N reception antennae, and receives signals. K nulling devices perform nulling with use of signals received, and output part of nulling signals. K demodulation devices are inputted with nulling signals, demodulate signals, and output demodulated signals. A parallel-serial conversion device is inputted with demodulated signals, converts the parallel format thereof into a serial format, and outputs the result as demodulated data.
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods of unsupervised anomaly detection using a geometric framework
InactiveUS9306966B2Easy to operateSemi-structured data mapping/conversionTransmissionFir systemFrequency spectrum
A method for unsupervised anomaly detection, which are algorithms that are designed to process unlabeled data. Data elements are mapped to a feature space which is typically a vector space d. Anomalies are detected by determining which points lies in sparse regions of the feature space. Two feature maps are used for mapping data elements to a feature apace. A first map is a data-dependent normalization feature map which we apply to network connections. A second feature map is a spectrum kernel which we apply to system call traces.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
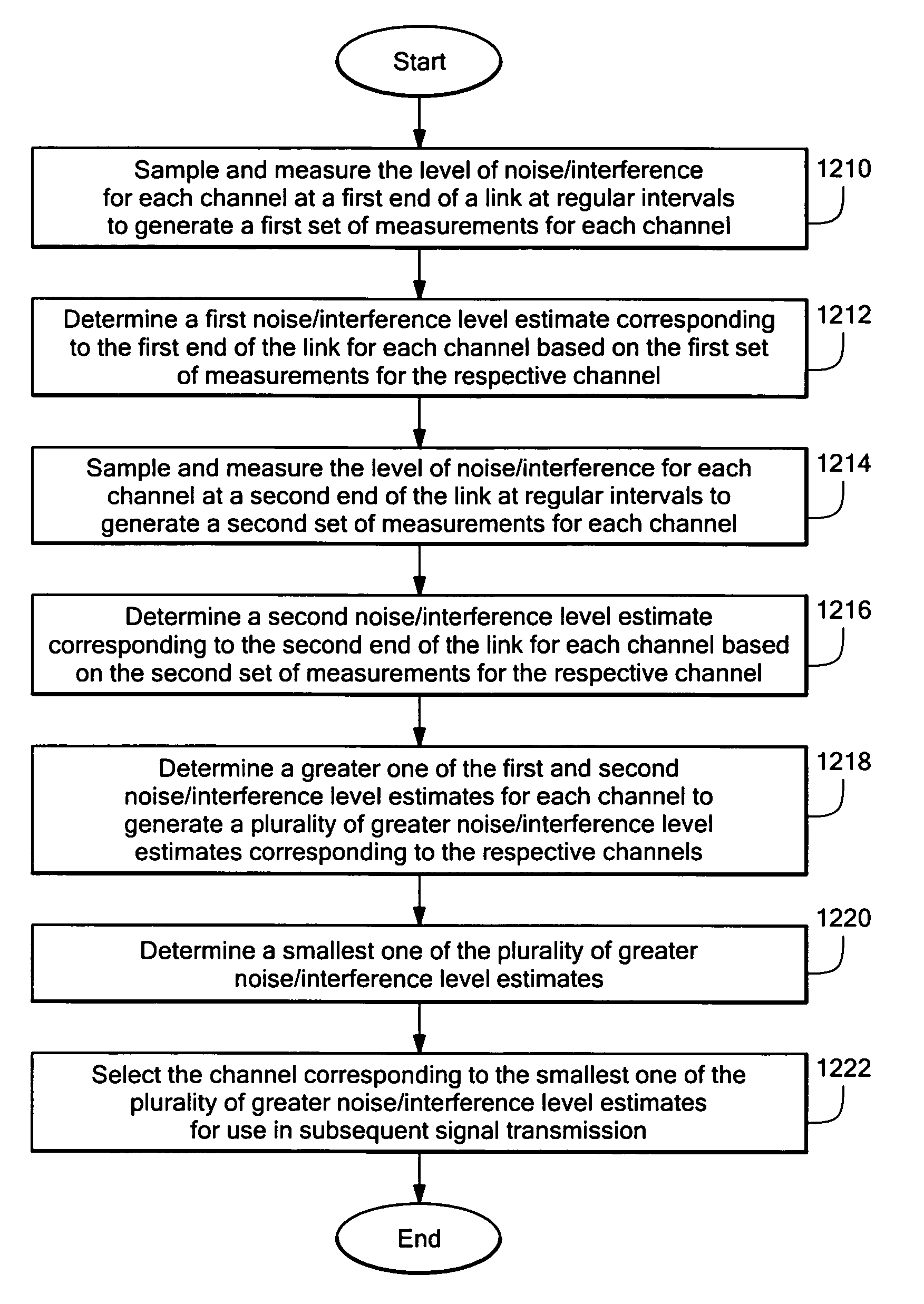
Installation technique for a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications systems
ActiveUS7330697B1Reduce dispersionLow costRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringFir systemTransceiver
Techniques for facilitating and reducing the costs associated with the installation of a wireless broadband communications system. In one mode of operation, the system employs a first transceiver to identify n channels having the n lowest levels of noise and interference associated therewith by a spectrum management technique. Next, the first transceiver transmits a predetermined code over the n channels to a second transceiver, which attempts to identify the predetermined code within a captured transmission. In the event the code is correctly identified, the second transceiver measures a noise and / or interference level associated with the corresponding channels. The channel having the lowest measured noise and interference level is then selected for use in system installation.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com