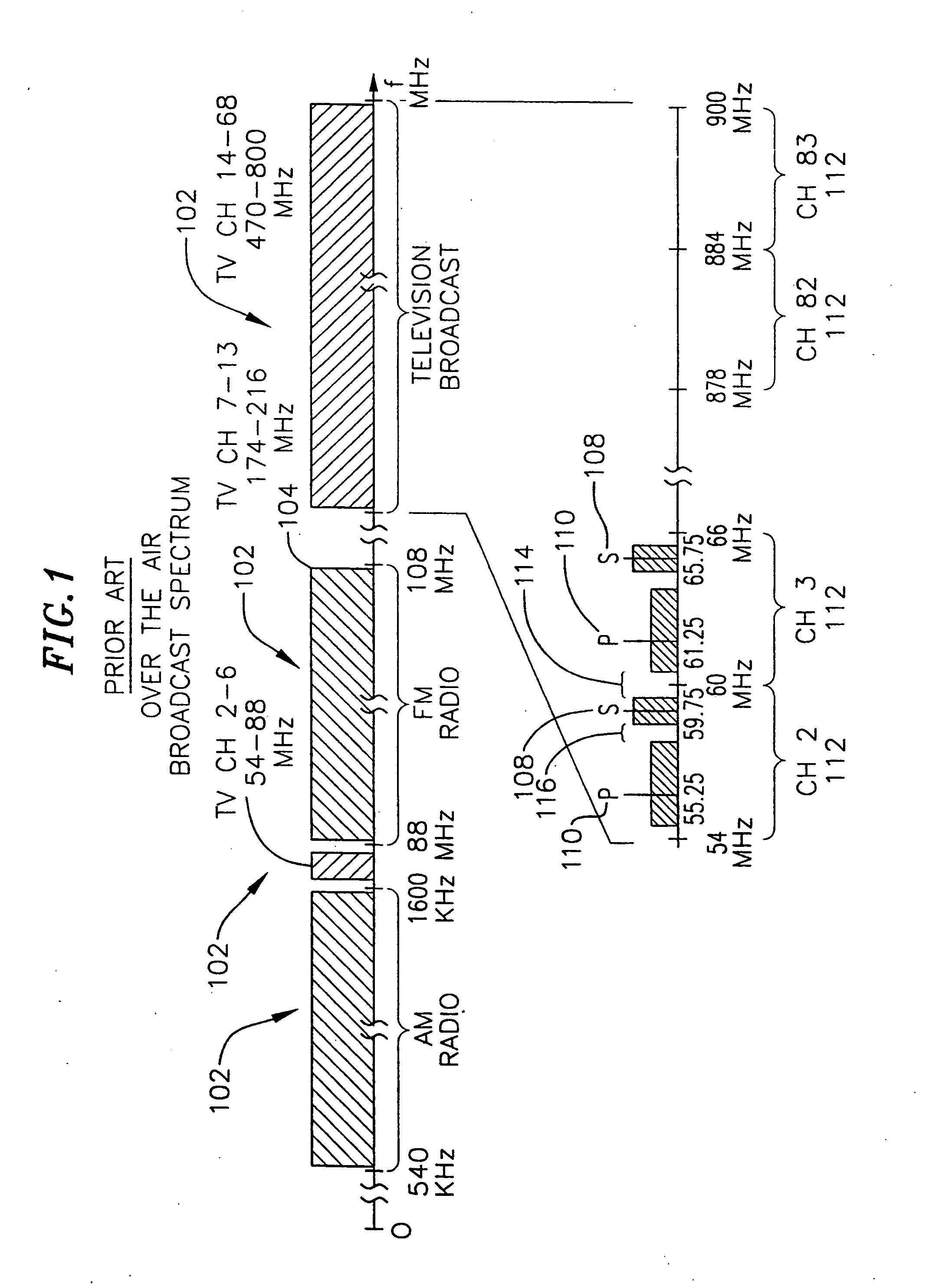
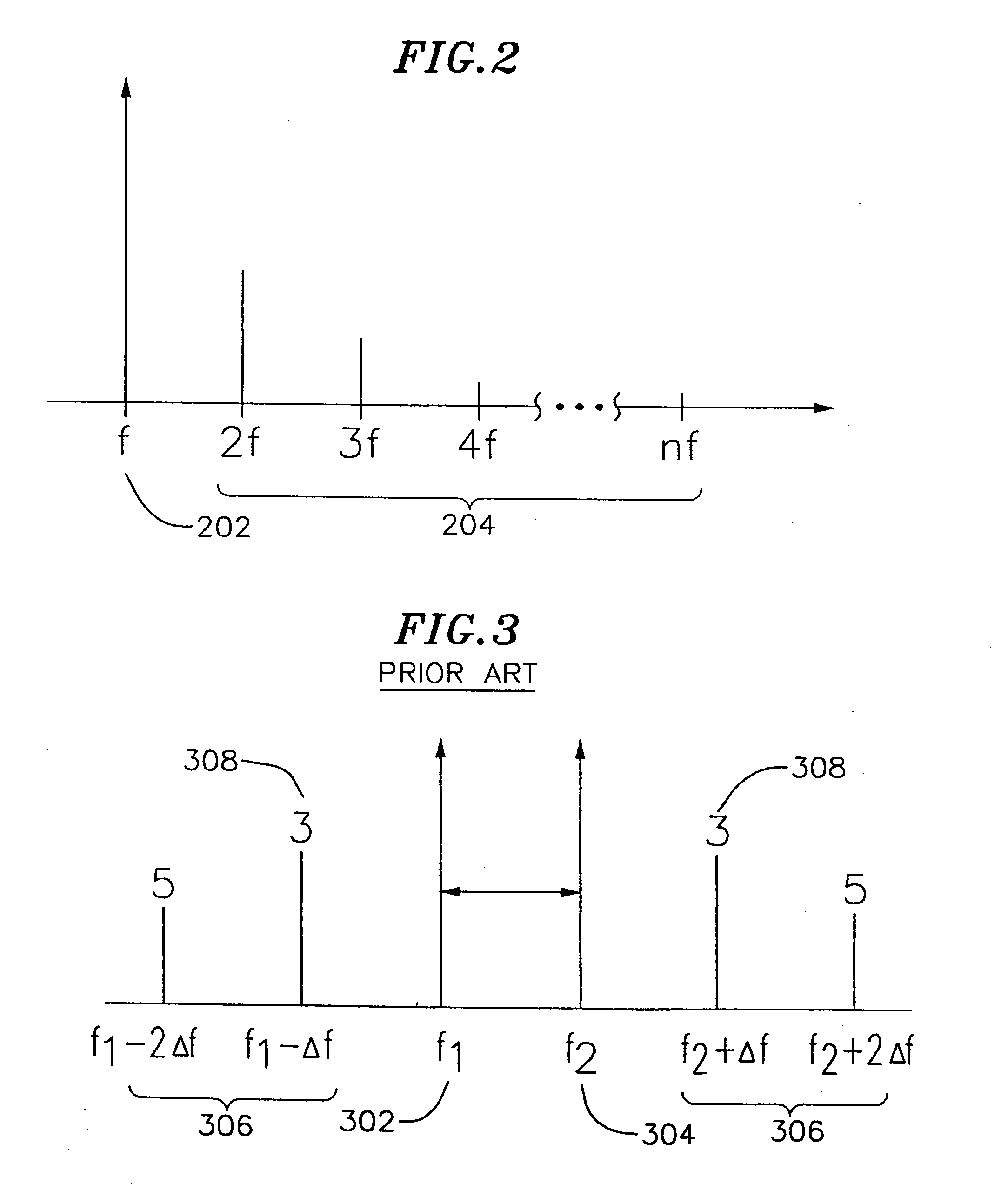
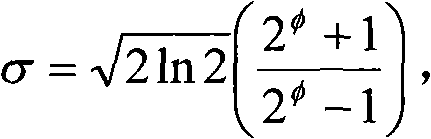Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
598 results about "Frequency scaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
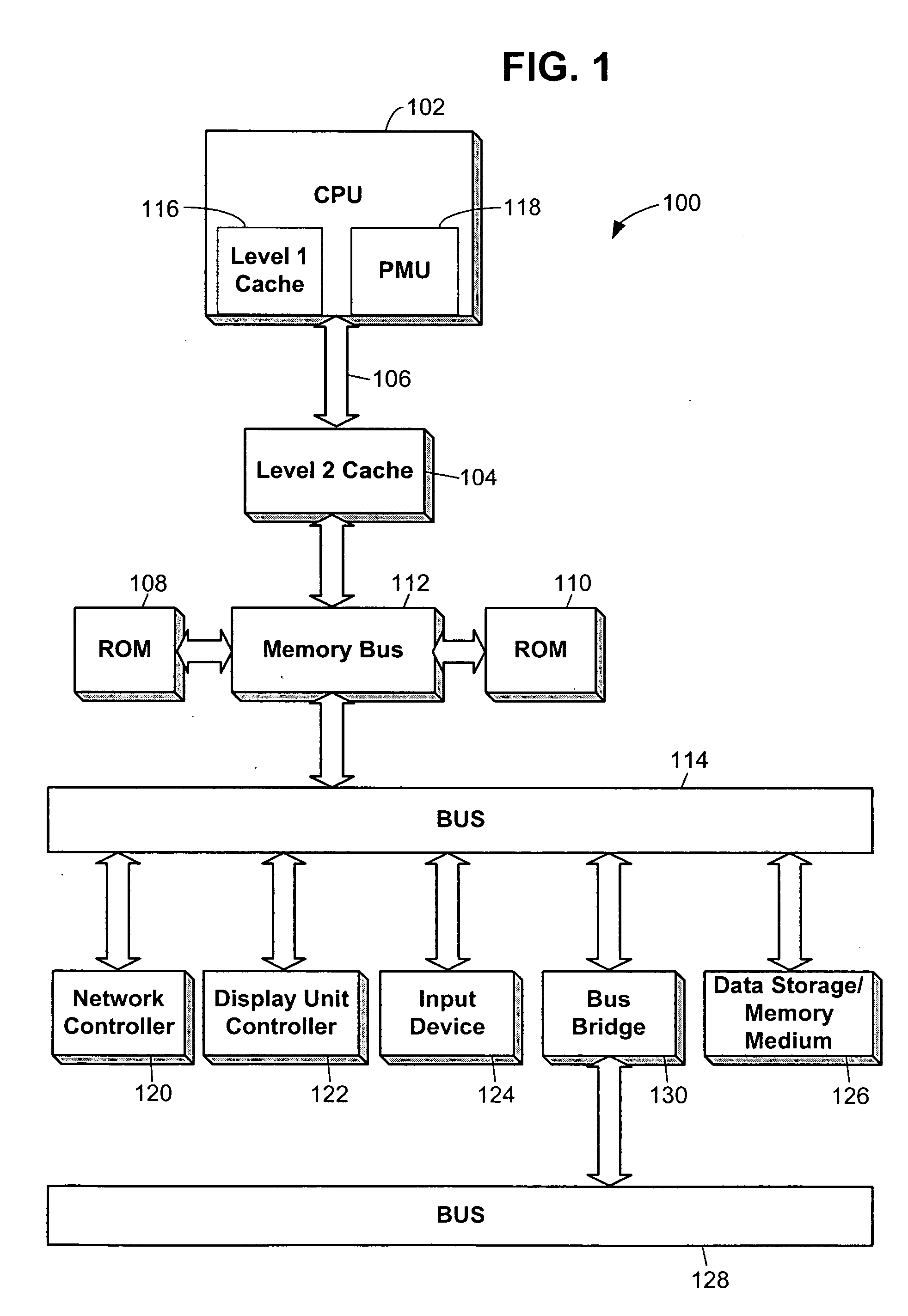
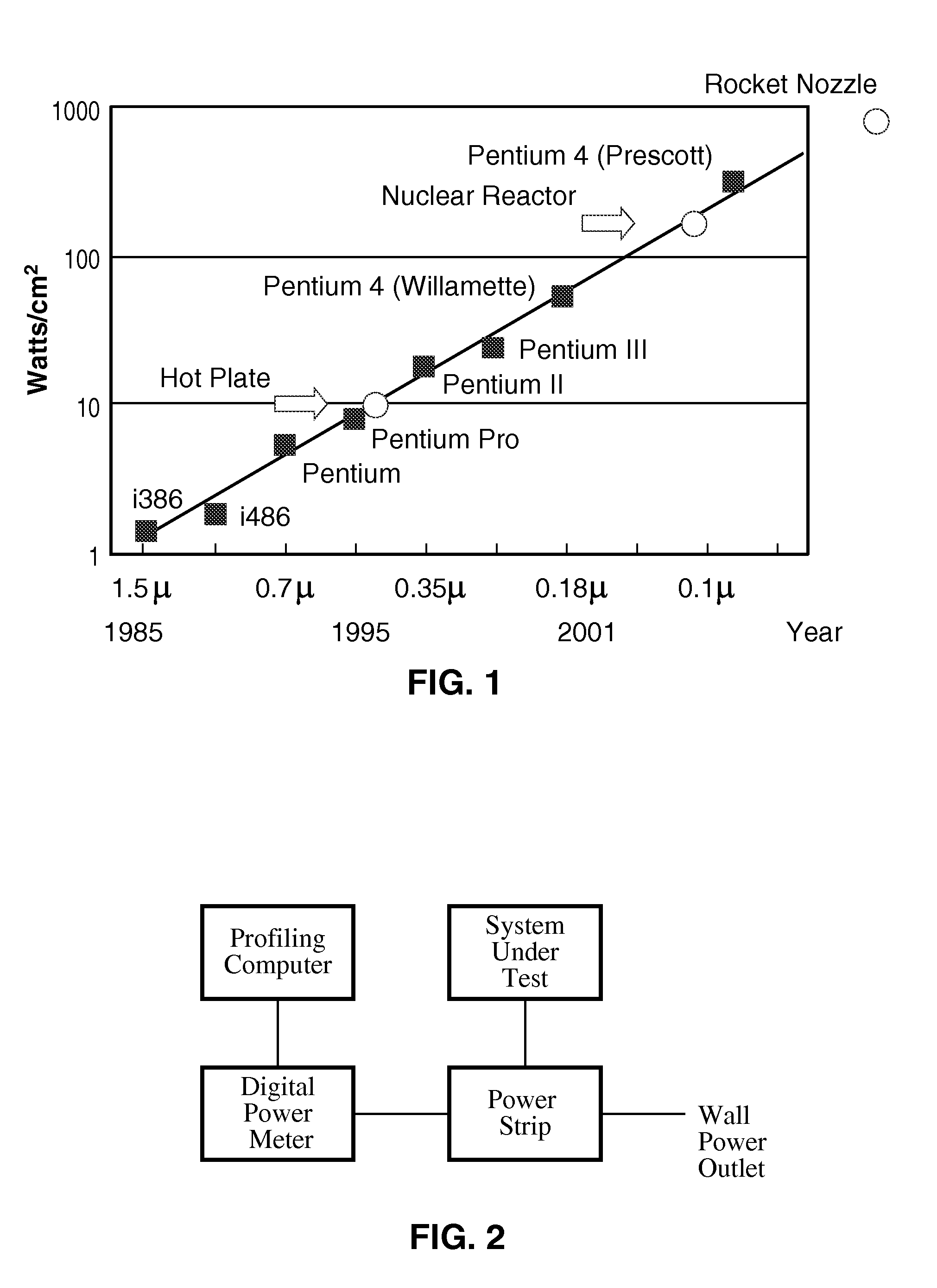
In computer architecture, frequency scaling (also known as frequency ramping) is the technique of increasing a processor's frequency so as to enhance the performance of the system containing the processor in question. Frequency ramping was the dominant force in commodity processor performance increases from the mid-1980s until roughly the end of 2004. The effect of processor frequency on computer speed can be seen by looking at the equation for computer program runtime: Runtime=Instructions/Program×Cycles/Instruction×Time/Cycle, where instructions per program is the total instructions being executed in a given program, cycles per instruction is a program-dependent, architecture-dependent average value, and time per cycle is by definition the inverse of processor frequency.
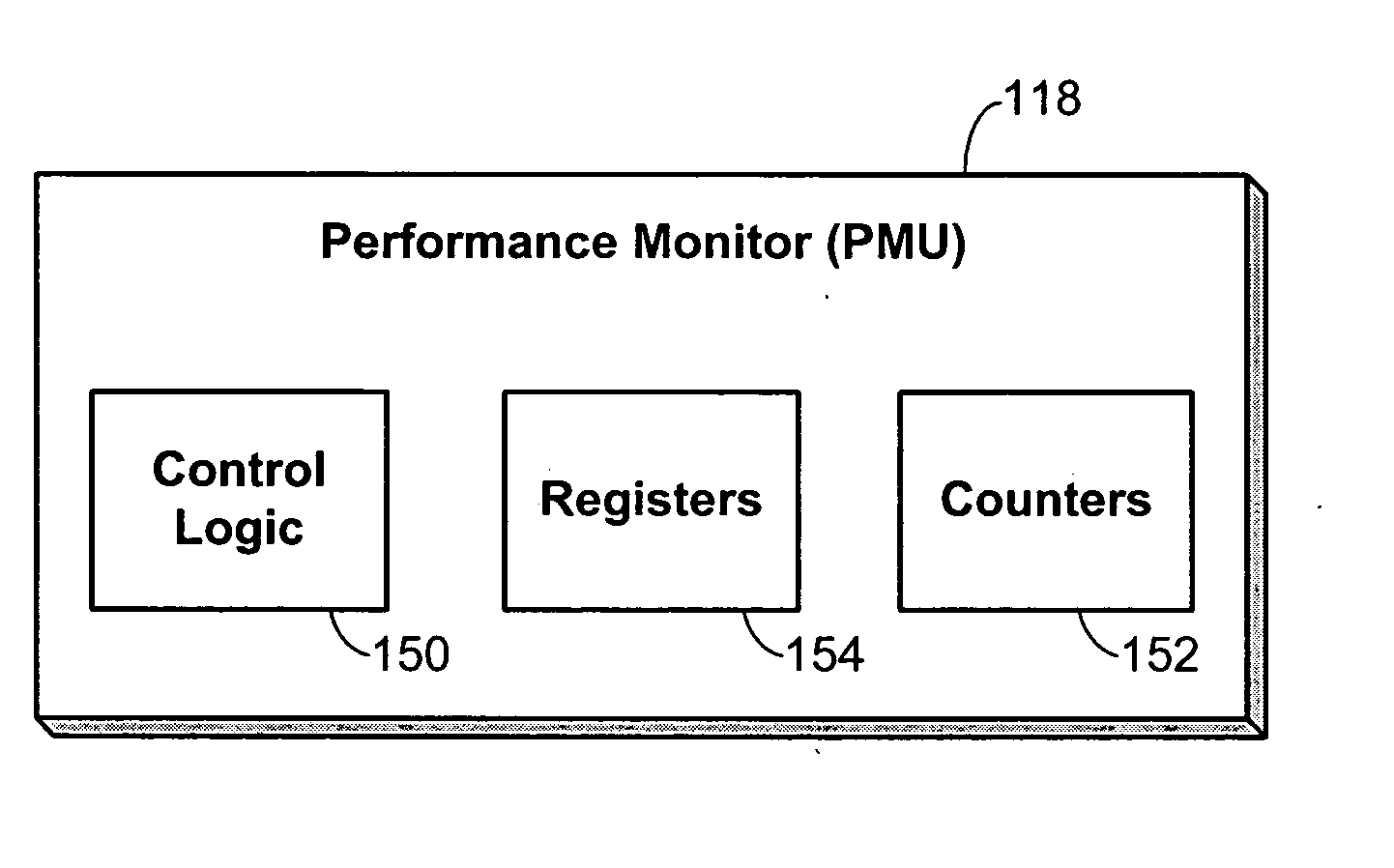
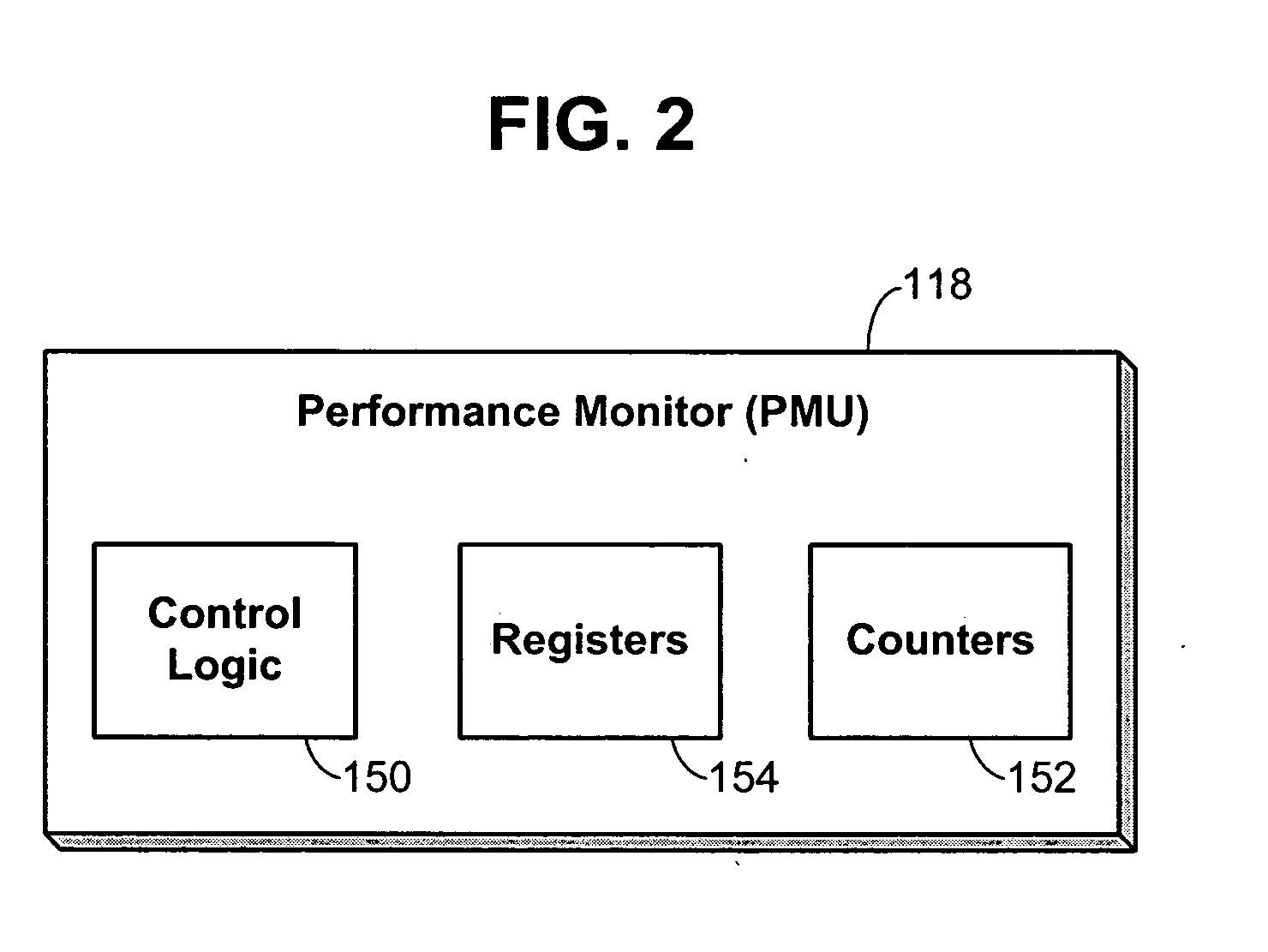
Performance monitoring based dynamic voltage and frequency scaling
Voltage and frequency scaling techniques that are based upon monitored data are provided. The techniques may be used to better manage the power and energy consumption of a processor in an embedded system, such as a cellular telephone, personal data assistant, smart device, or the like. The techniques may be used with processors that offer a performance monitoring capability. The performance monitor may monitor thread-level utilization at runtime. Instructions per cycle and memory references per cycle are example metrics that may be monitored by the performance monitor. The voltage and frequency scaling techniques may adjust the operating voltage and operating frequency of the processor based on the values of these two metrics. For example, the techniques may include accessing a voltage and frequency scheduler lookup table. The techniques may be employed with non-embedded systems, as well, embedded systems.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
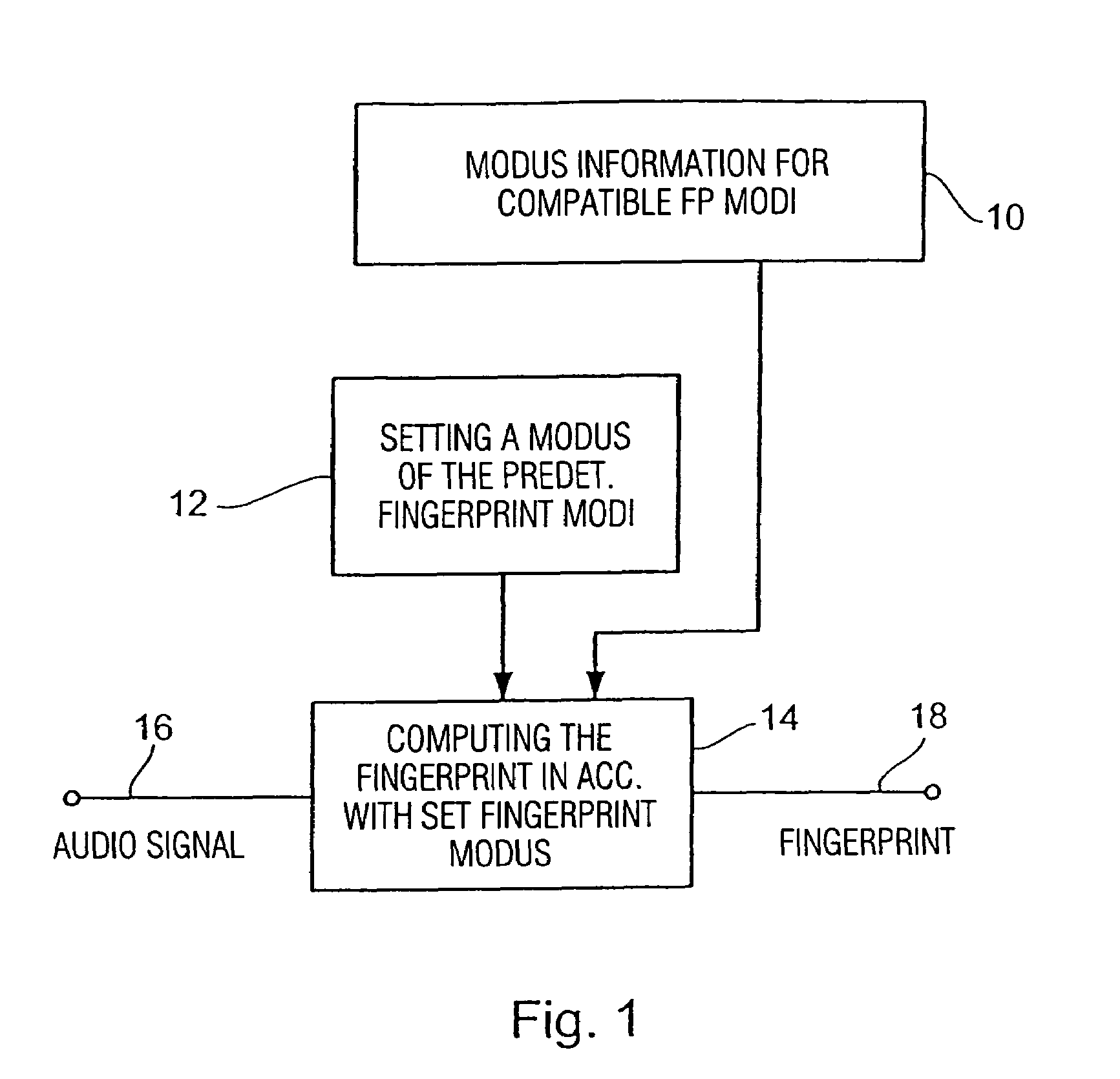
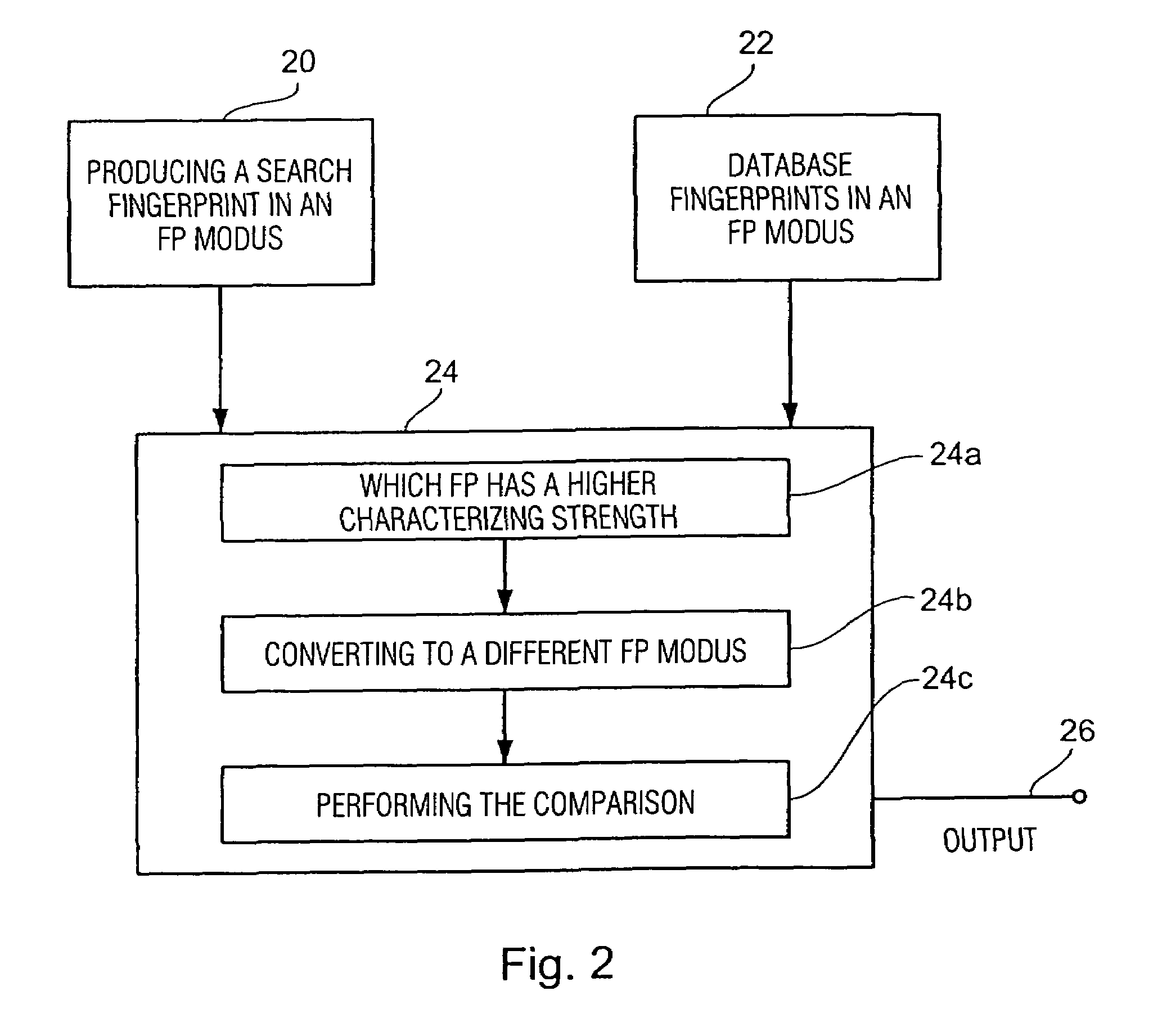
Method and apparatus for producing a fingerprint, and method and apparatus for identifying an audio signal
InactiveUS7460994B2Meet different requirementsHigh strengthDigital data information retrievalUsing non-detectable carrier informationPattern recognitionUltimate tensile strength
Owner:M2ANY
Face recognition method based on Gabor wavelet transform and local binary pattern (LBP) optimization
InactiveCN102024141AReduce distractionsShort storage timeCharacter and pattern recognitionGabor wavelet transformHigh dimensional
The invention relates to a face recognition method based on Gabor wavelet transform and local binary pattern (LBP) optimization. Two-dimensional Gabor wavelet transform can associate pixels of adjacent areas so as to reflect the change conditions of image pixel gray values in a local range from different frequency scales and directions. The feature extraction and the classification recognition are carried out on the basis of a face image two-dimensional Gabor wavelet transform coefficient. For a high-dimensional Gabor wavelet transform coefficient, overall histogram features are extracted by adopting the LBP, and then the image is blocked by utilizing priori knowledge to extract the features of each piece of LBP local histogram. The method has better recognition rate, better robustness to illumination and wide using prospect in the fields of biometric recognition and public security monitoring.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
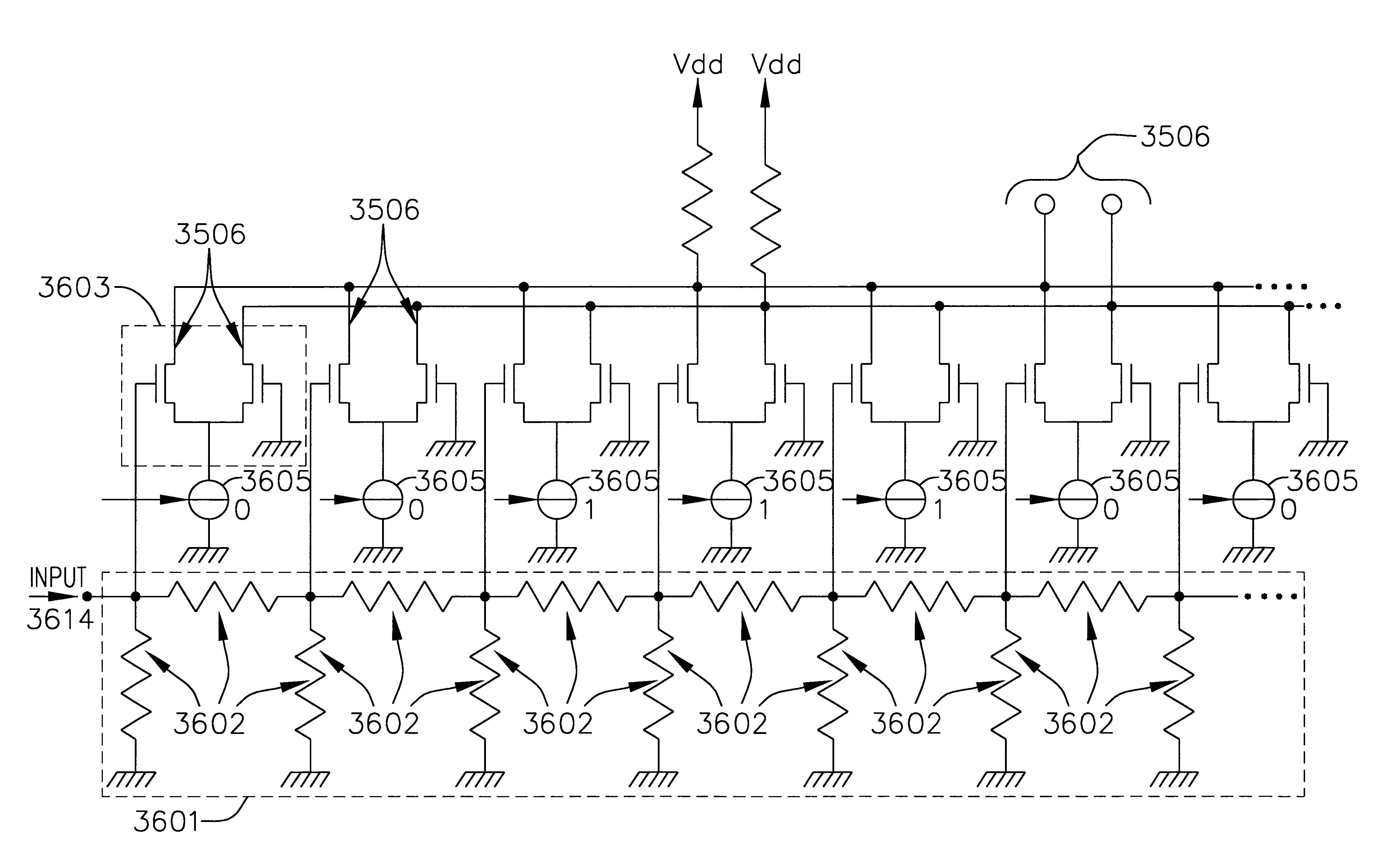
Integrated switchless programmable attenuator and low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6879816B2Multiple-port active networksSwitched capacitor networksCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method for Autonomous Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling of Microprocessors
ActiveUS20080098254A1Improve performanceSave energyEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionComputerized systemWorkload
A method for autonomous dynamic voltage (v) and frequency (f) scaling (DVFS) of a microprocessor, wherein autonomous detection of phases of high microprocessor workload and prediction of their duration is performed (PID). The microprocessor frequency (f) will be temporarily increased (LUT) to an appropriate safe value (even beyond its nominal frequency) consistent with technological and ambient constraints in order to improve performance when the computer system comprising the microprocessor benefits most, while during phases of low microprocessor workload its frequency (f) and voltage (v) will be decreased to save energy. This technique exploits hidden performance capabilities and improves the total performance of a computer system without compromising operational stability. No additional hardware such as service processors is needed for contemporary computer systems supporting performance counters and DFVS already. The invention allows significantly increasing the total computer system performance with only minimal impact on power (PMAX, PACTUAL) consumption.
Owner:IBM CORP
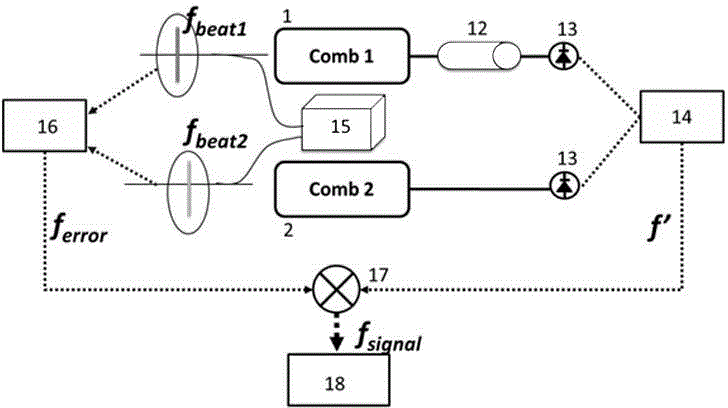
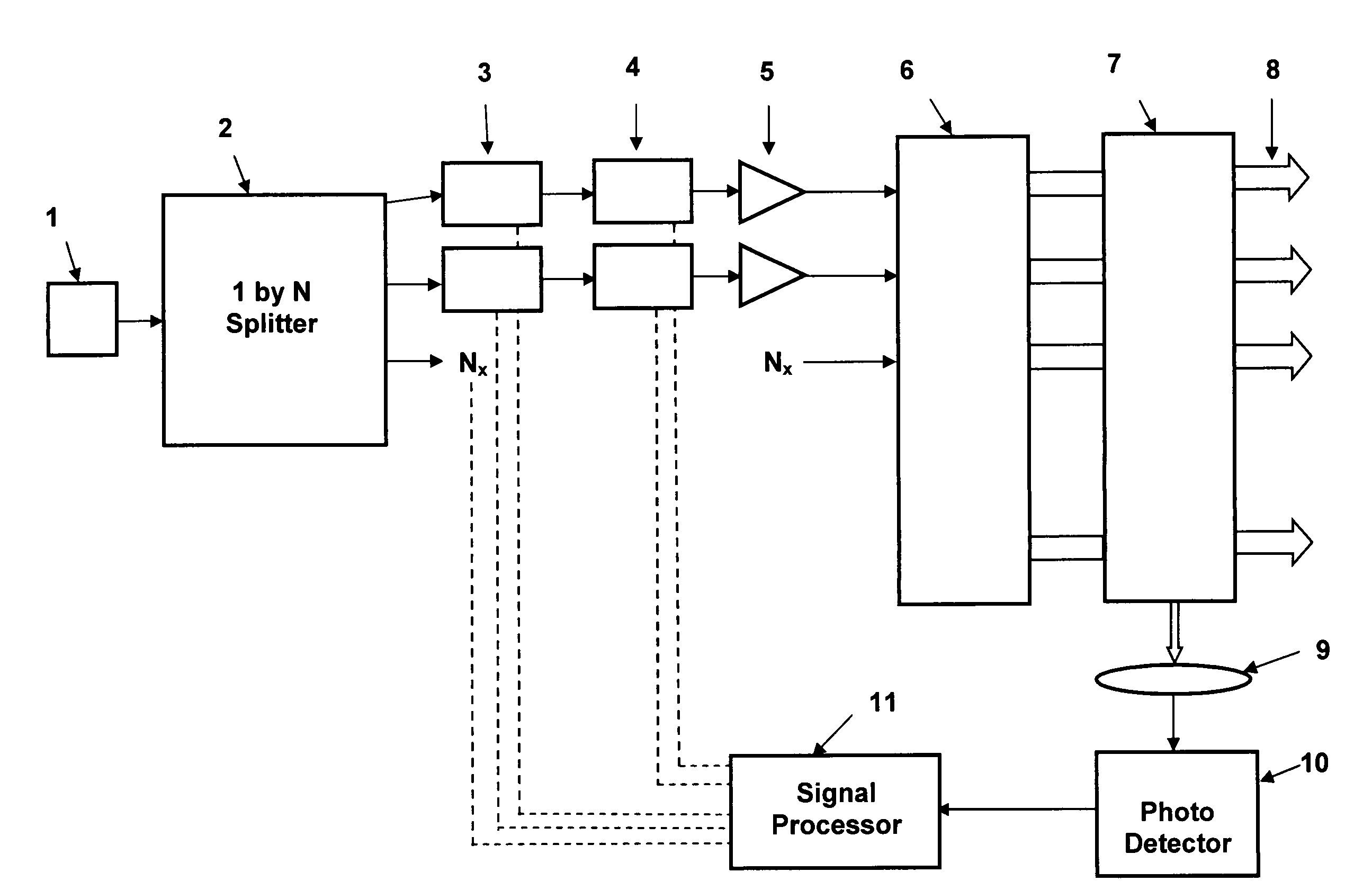
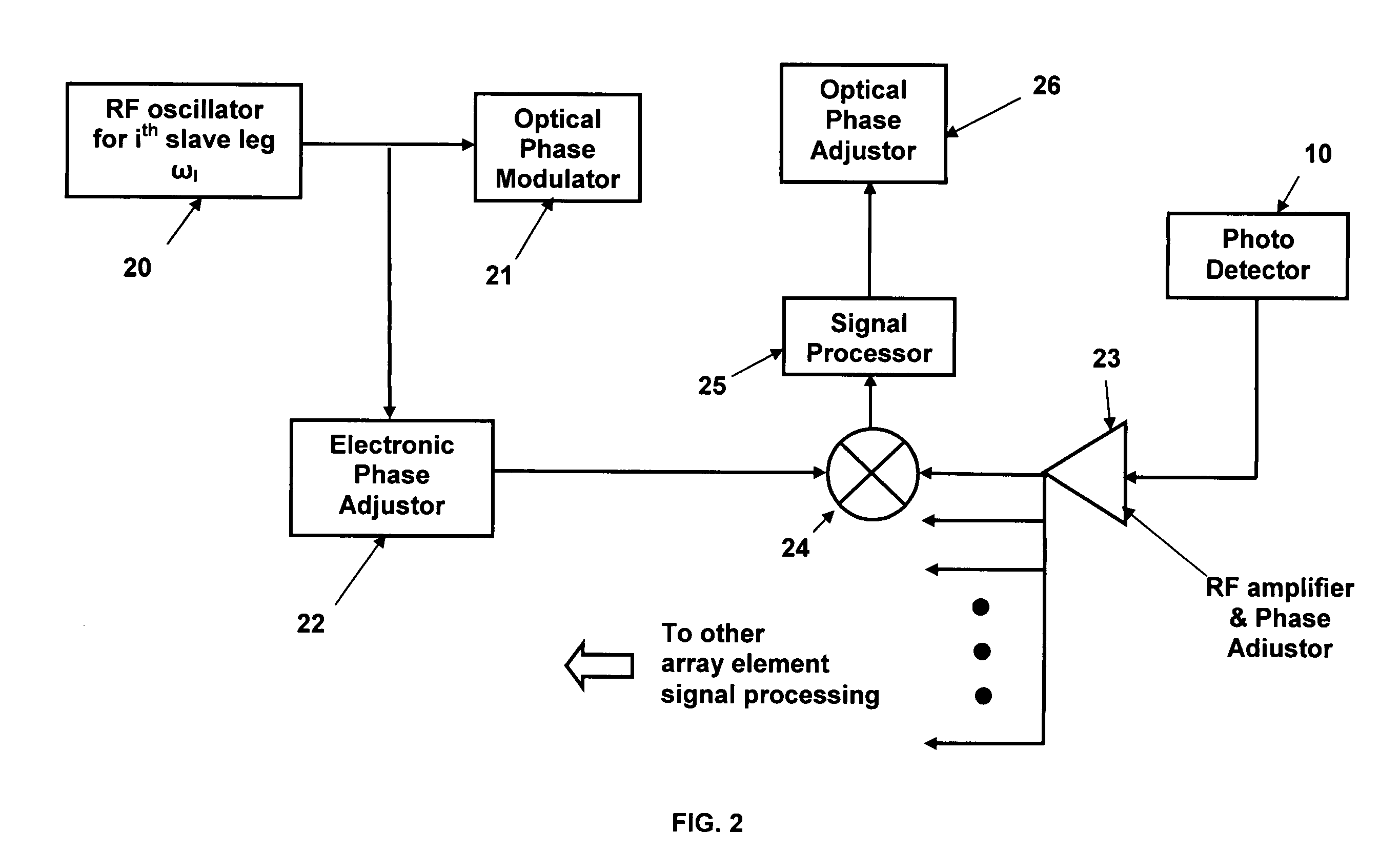
Self-referenced locking of optical coherence by single-detector electronic-frequency tagging
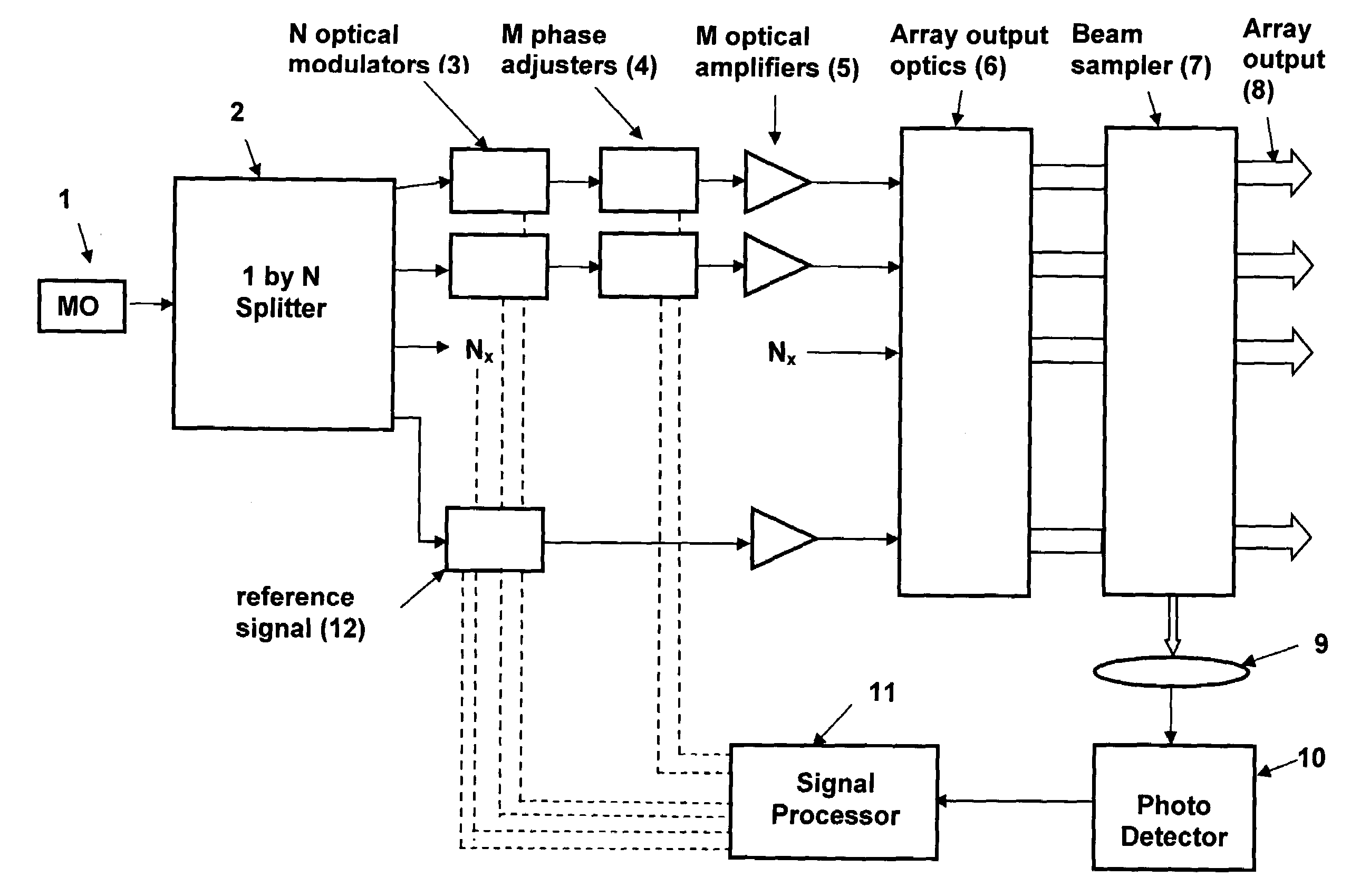
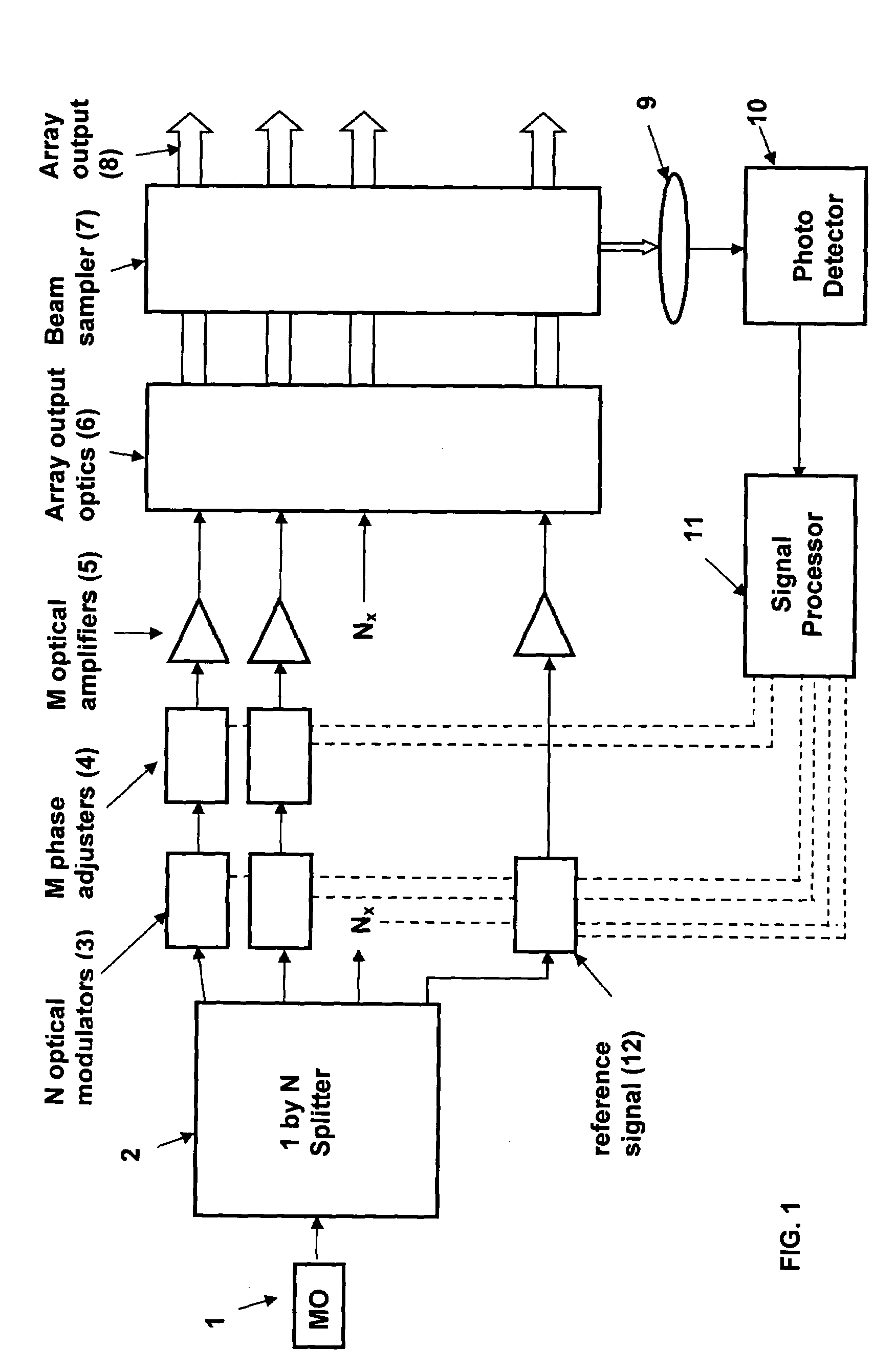
A coherent laser beam combining system wherein the output of a single master oscillator is split into a plurality of signals, the signals are electronically modulated at unique frequencies. One signal is designated a reference signal while the remaining signals are passed through phase adjusters. All signals are optically amplified, aligned and passed through a beam splitter to split off a small sample that is imaged onto a photodetector. The photodetector output is fed to a signal processor that produces phase error signals that drive the phase adjusters resulting in a high-powered optically coherent output signal.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPSESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
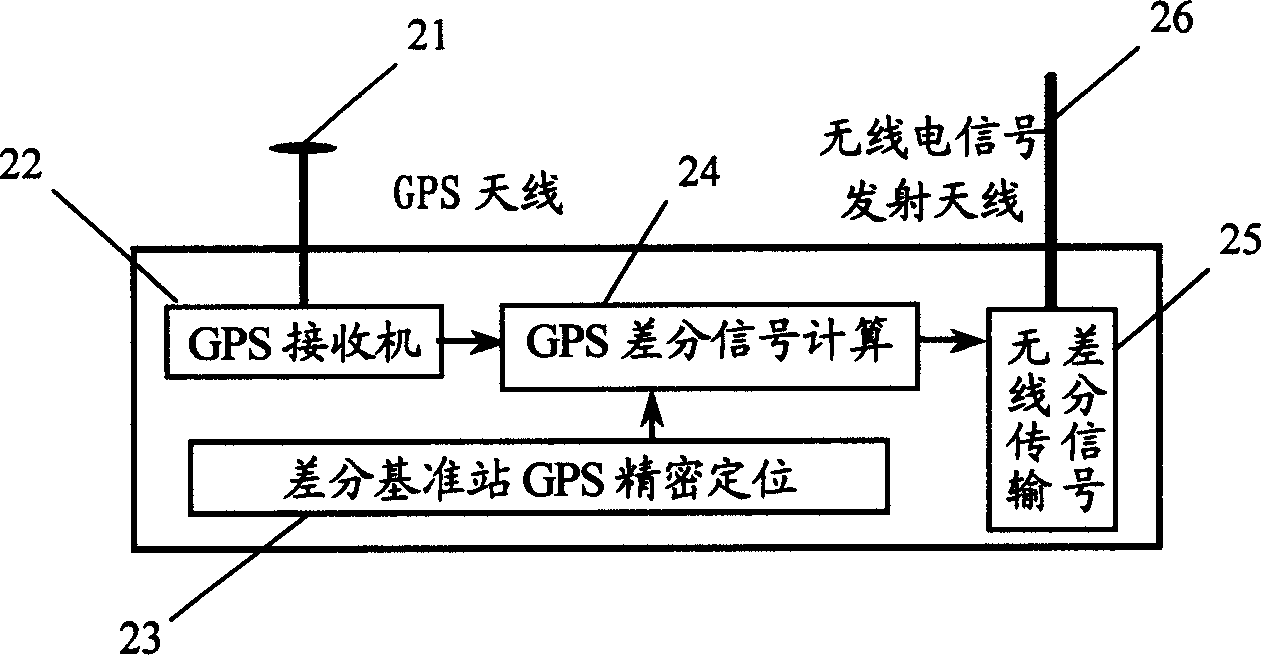
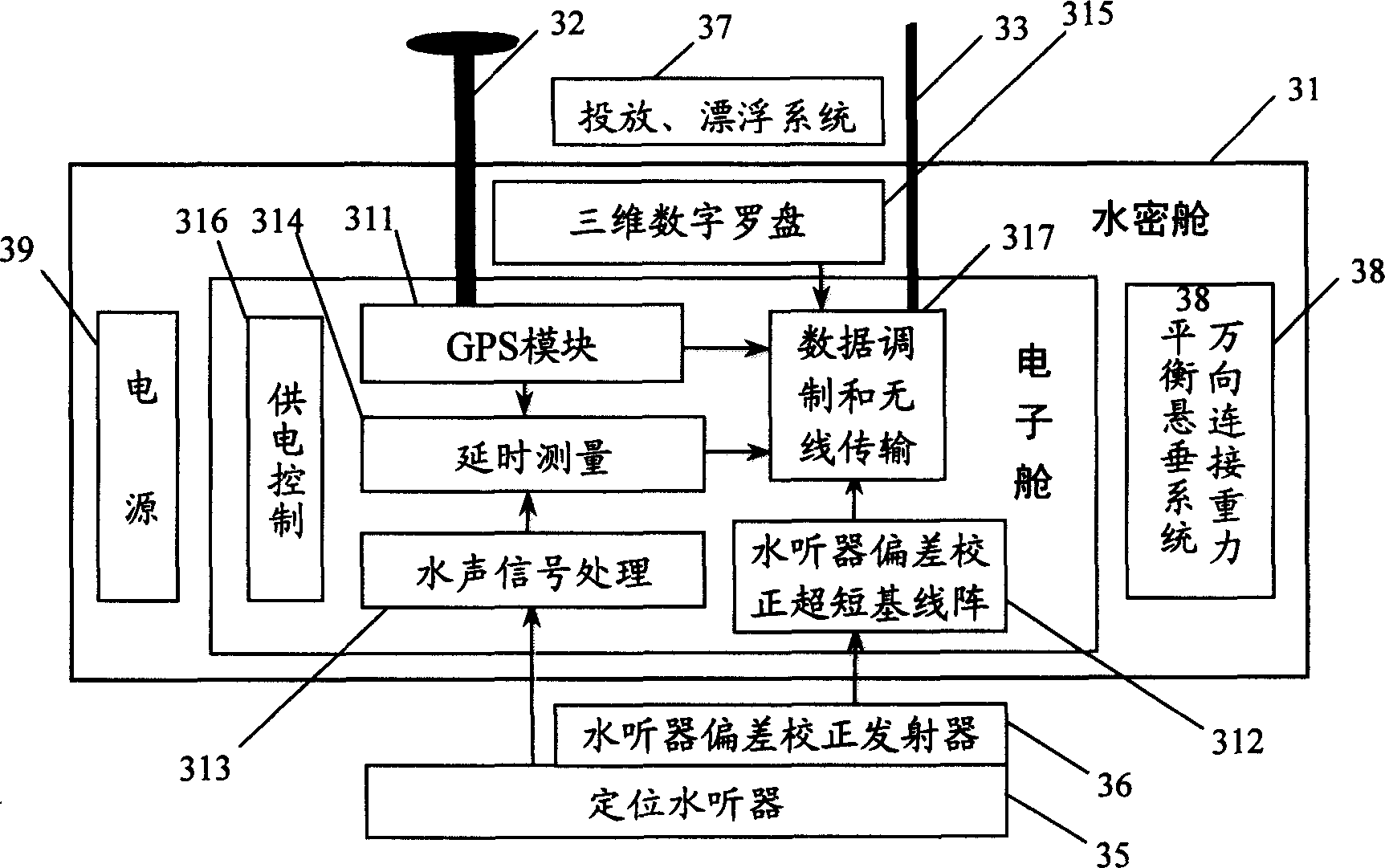
Underwater GPS positioning navigation method and system without high stable frequency scale
InactiveCN1547039AFlexible network layoutLighten the Burden of Underwater Acoustic Data TransmissionPosition fixationTransceiverDifferential signaling
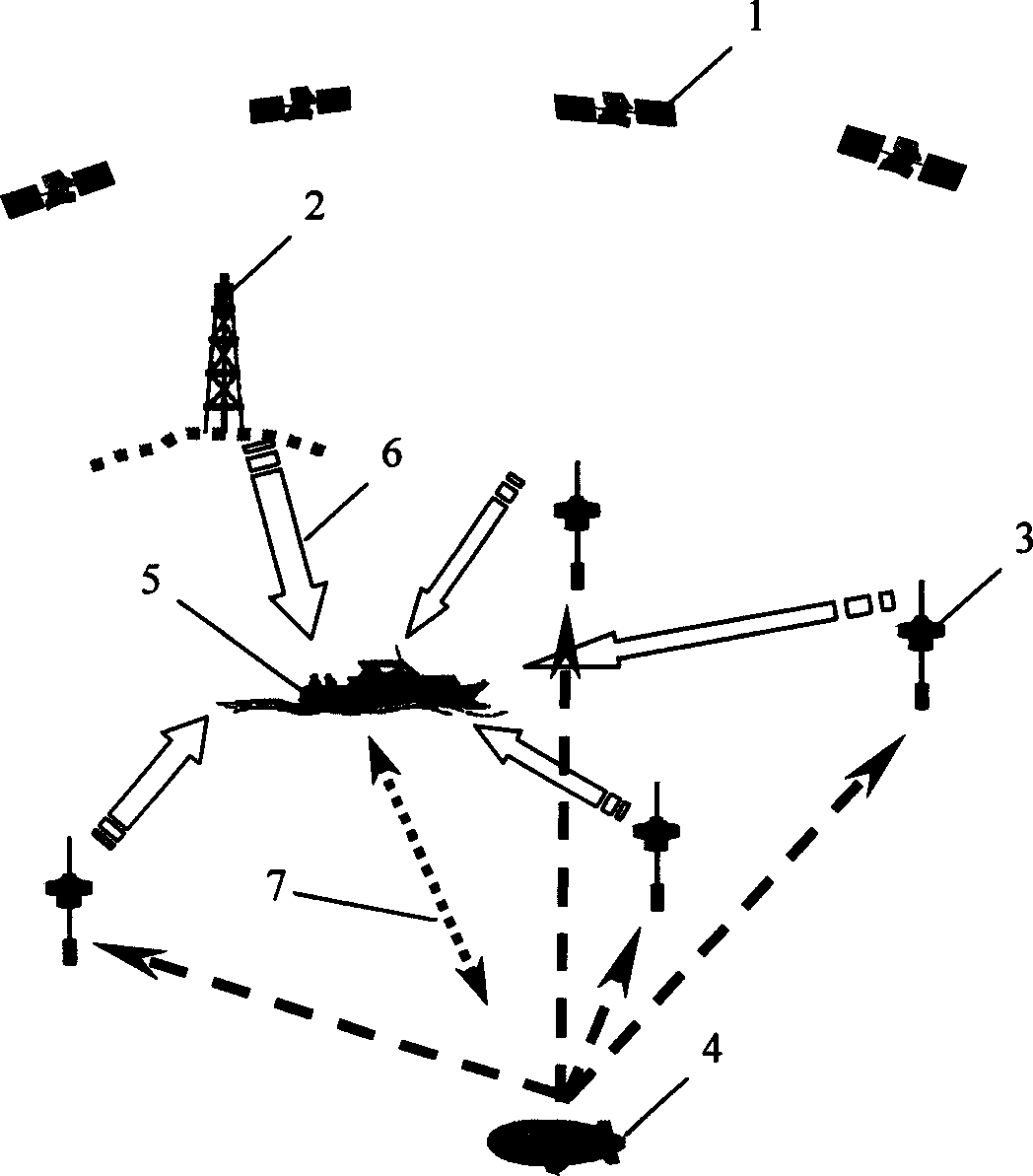
The invention discloses a kind of underwater GPS allocation and navigation system and method without high stable frequency scale. The system is made up of GPS satellite constellation, four or more GPS floating marks, underwater navigation transceiver, data control centre, sea level wireless communication loop and hydroacoustics communication loop. The method is: when the object underwater needed to be located, the underwater navigation transceiver sends out hydroacoustics localization signal to the GPS floating mark, the floating mark transmits the hydroacoustics localization signal, the GPS signal and the posture calibration data wirelessly to the data control centre, and the data are processed with the difference signal, works out the position and time sending out the localization signal of the underwater object, the position and time data are transmitted to the underwater navigation transceiver by the hydroacoustics communication system, it can carry on navigation or time service. The invention can be applied to underwater object tracing, underwater localization and navigation, underwater precise timer service, measuring project control and project structure sample, it needs no high stable frequency scale.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING +1
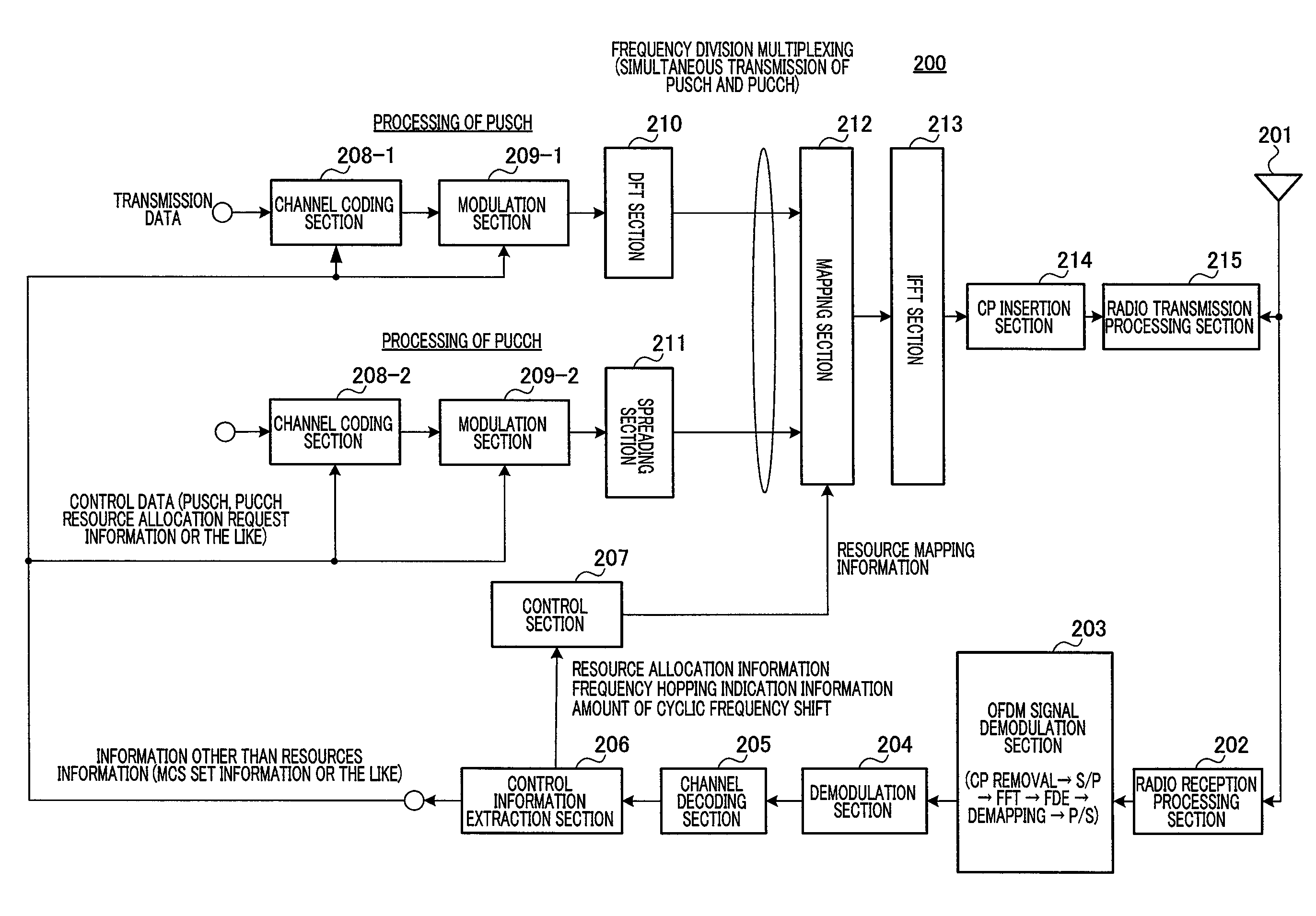
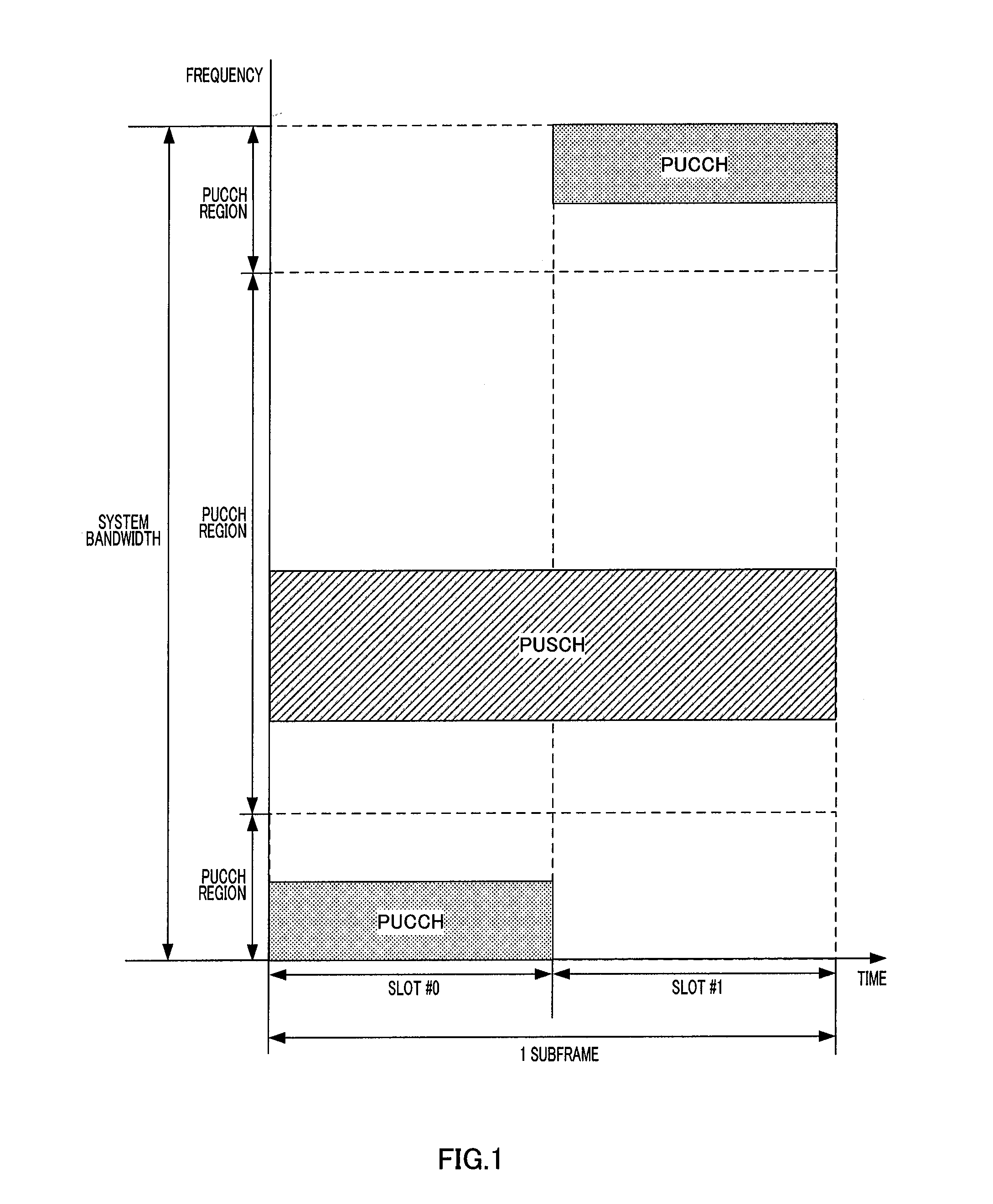
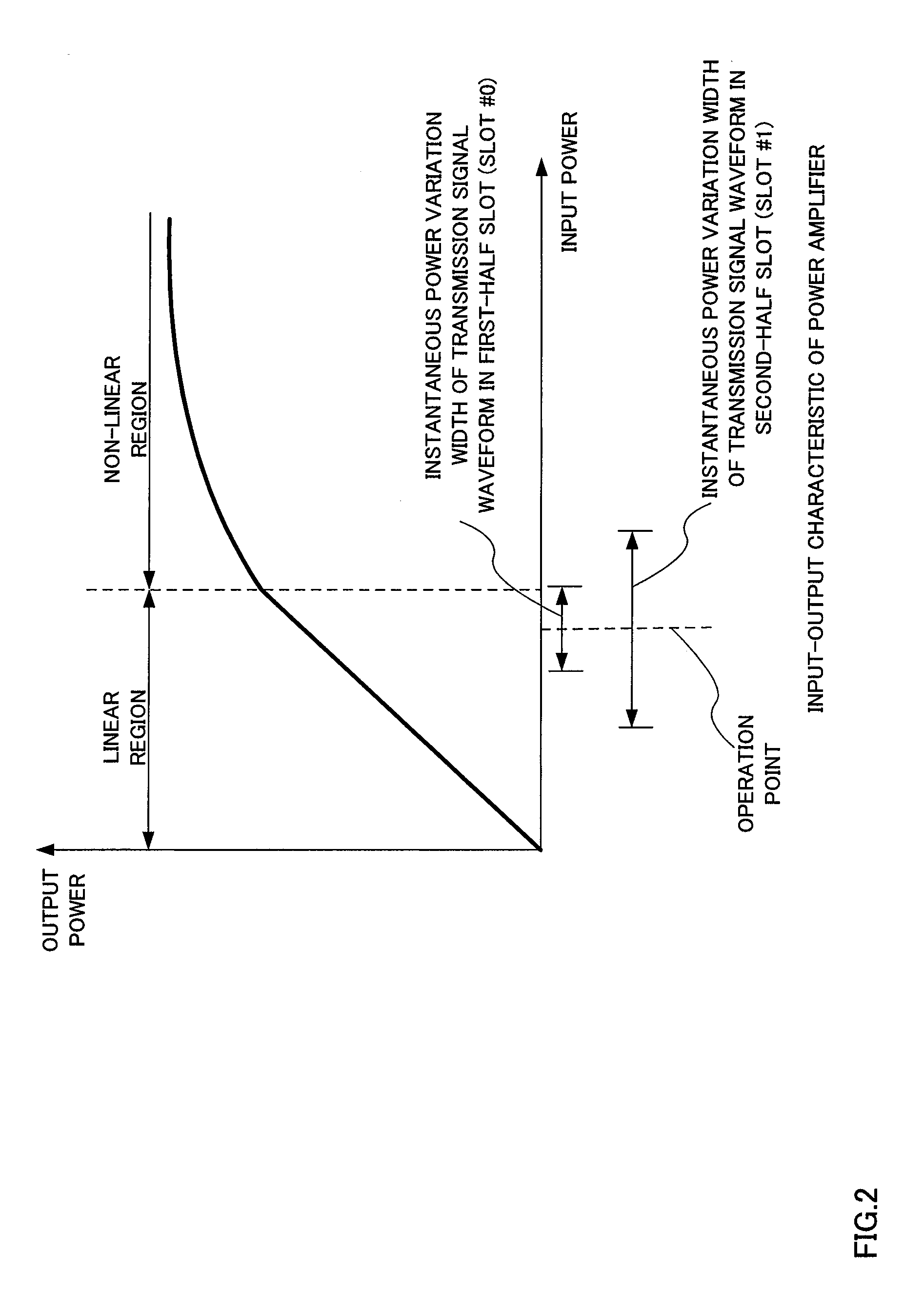
Wireless communication apparatus and frequency hopping method
ActiveUS20120057449A1Inhibit deteriorationFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingDistribution characteristic
Disclosed are a wireless communication apparatus and frequency hopping method which minimize the change in the instantaneous power distribution characteristics of the time waveform of transmission signals when a plurality of channels are multiplexed by frequency division. At a terminal (200), a mapping unit (212) maps the PUCCH to frequency resources of a first slot, maps the PUSCH to frequency resources, among the frequency resources of the first slot, separated exactly by predetermined frequency spacing (B) from the frequency resources to which the PUCCH is mapped, and cyclically shifts the frequencies so as to map the PUCCH and PUSCH to frequency resources, within an IDFT or IFFT bandwidth, of a second slot while maintaining the predetermined frequency spacing (B), thereby allowing frequency hopping of the PUCCH and PUSCH between the first slot and the second slot.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
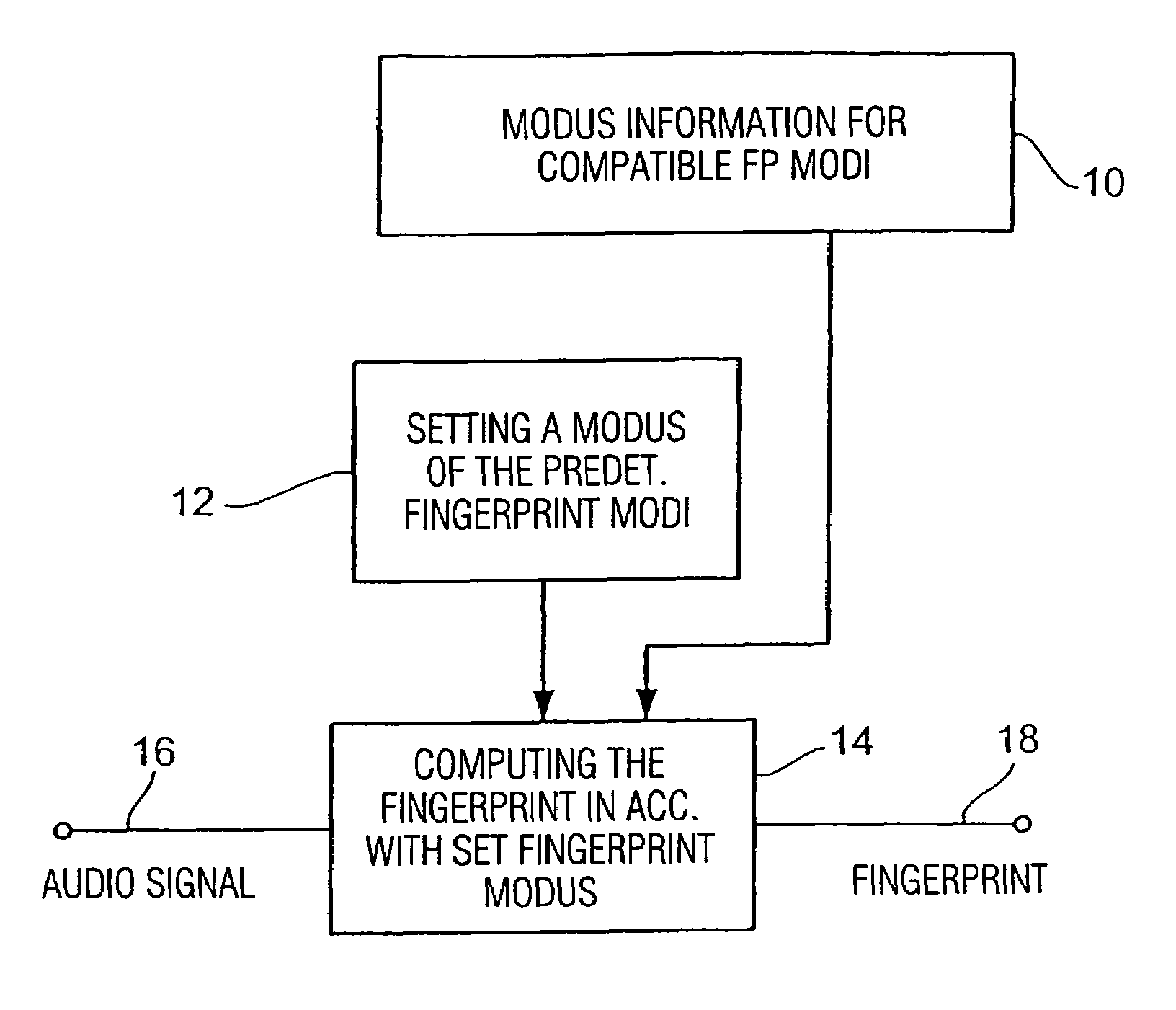
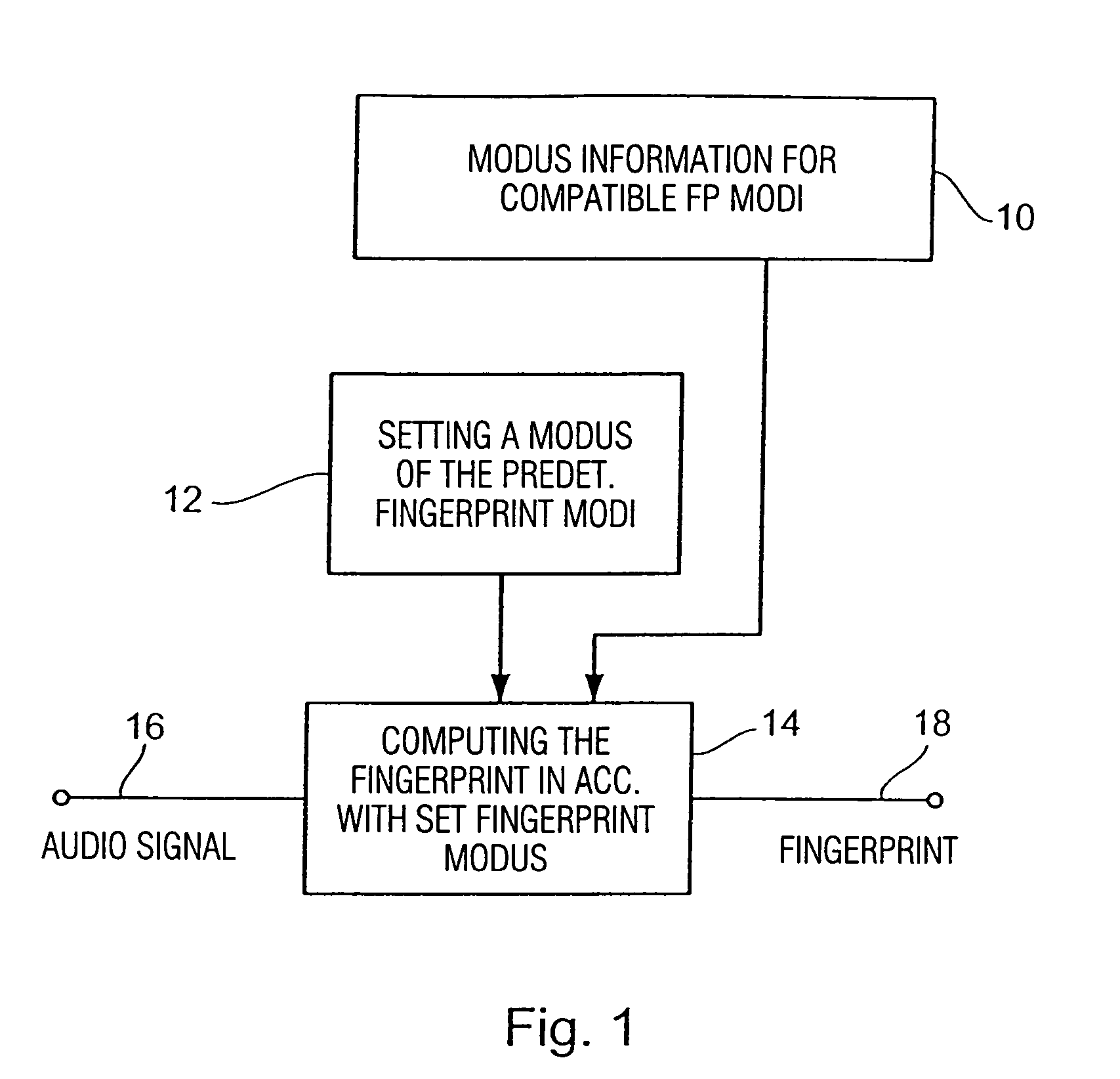
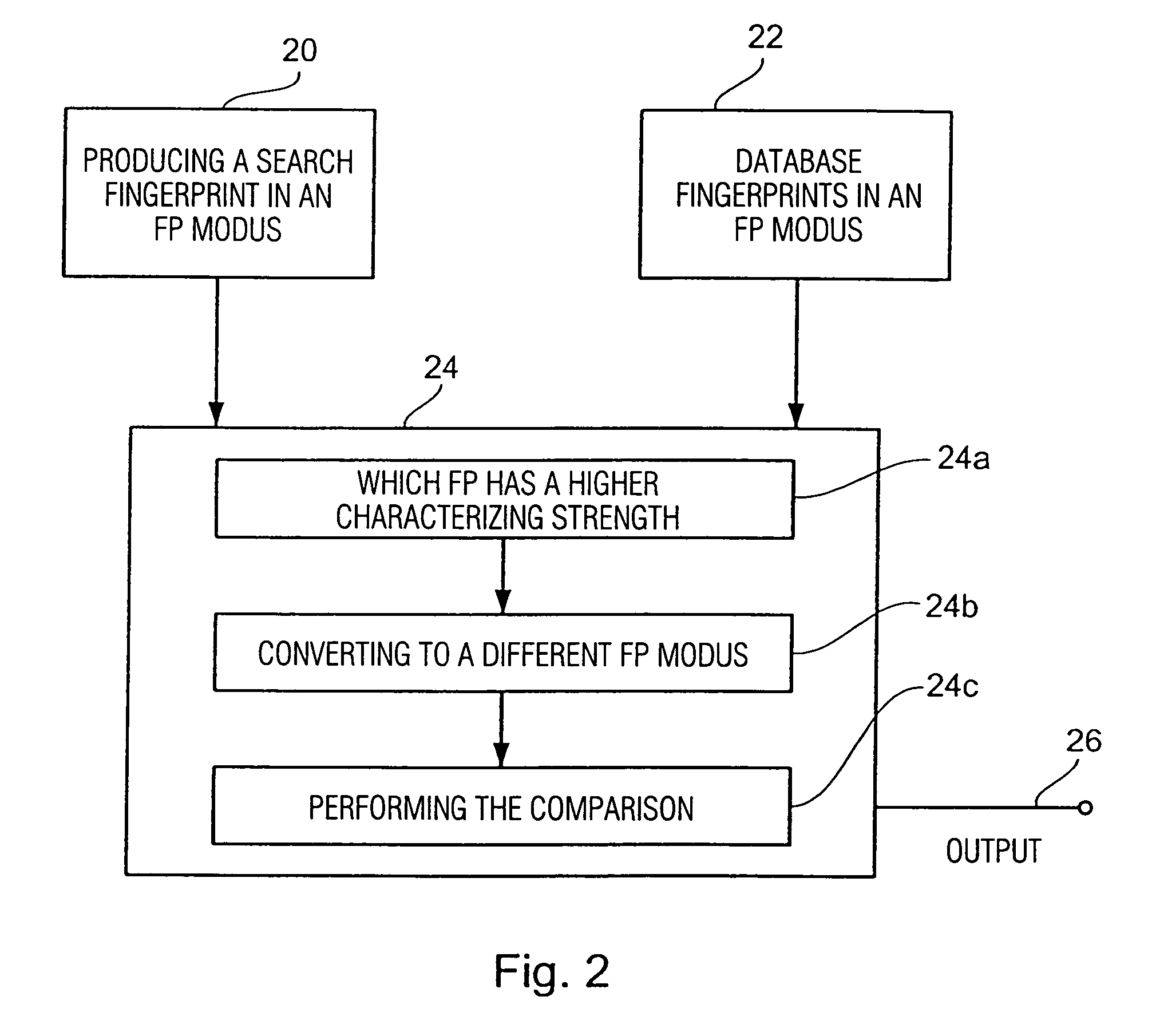
Method and device for producing a fingerprint and method and method and device for identifying an audio signal
InactiveUS20040172411A1High strengthReduced strengthDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPattern recognitionAudio signal flow
For producing a fingerprint of an audio signal, use is made of information defining a plurality of predetermined fingerprint modi, all of the fingerprint modi relating to the same type of fingerprint, the fingerprint modi, however, providing different fingerprints differing from each other with regard to their data volume, on the one hand, and to their characterizing strength for characterizing the audio signal, on the other hand, the fingerprint modi being predetermined such that a fingerprint in accordance with a fingerprint modus having a first characterizing strength is convertible to a fingerprint in accordance with a fingerprint modus having a second characterizing strength, without using the audio signal. A predetermined fingerprint modus of the plurality of predetermined fingerprint modi is set and subsequently used for computing a fingerprint using the audio signal. The convertibility feature of the fingerprints having been produced by the different fingerprint modi enables setting a flexible compromise between the data volume and the characterizing strength for certain applications without having to re-generate a fingerprint database with each change of the fingerprint modus. Fingerprint representations scaled with regard to time or frequency may readily be converted to a different fingerprint modus.
Owner:M2ANY
Spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs
ActiveCN104316186AReduce volumeReduce maintenance difficultyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsFourier analysisVIT signals
The invention discloses a spectral measurement method based on optical frequency combs. The measurement method is characterized in that firstly, an annular laser resonant cavity based on a phase modulator is actively modulated by use of a first optical frequency comb controllable in time domain and frequency domain so that the annular laser resonant cavity is converted into a second optical frequency comb having tiny difference in repetition frequency with the first optical frequency comb, and spectrum detection is performed on the two optical frequency combs to obtain an interference signal carrying the information of a sample to be tested, and meanwhile, frequency beating is performed on the two optical frequency combs and continuous frequency stabilized laser, respectively, the difference frequency signal of two obtained beat frequency signals is mixed with the interference signal, and a signal obtained by virtue of detection mixing is taken as a spectral signal for Fourier analysis so as to reduce the optical information of the sample to be tested. The spectral measurement method has the advantages that the error of the spectral detection due to own phase drift of a dual-optical comb system can be eliminated, and therefore, the resolution and the detection accuracy of the spectral measurement can be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Multiband antenna
InactiveUS6473056B2Increase electrical lengthFacilitates suitableLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorResonance
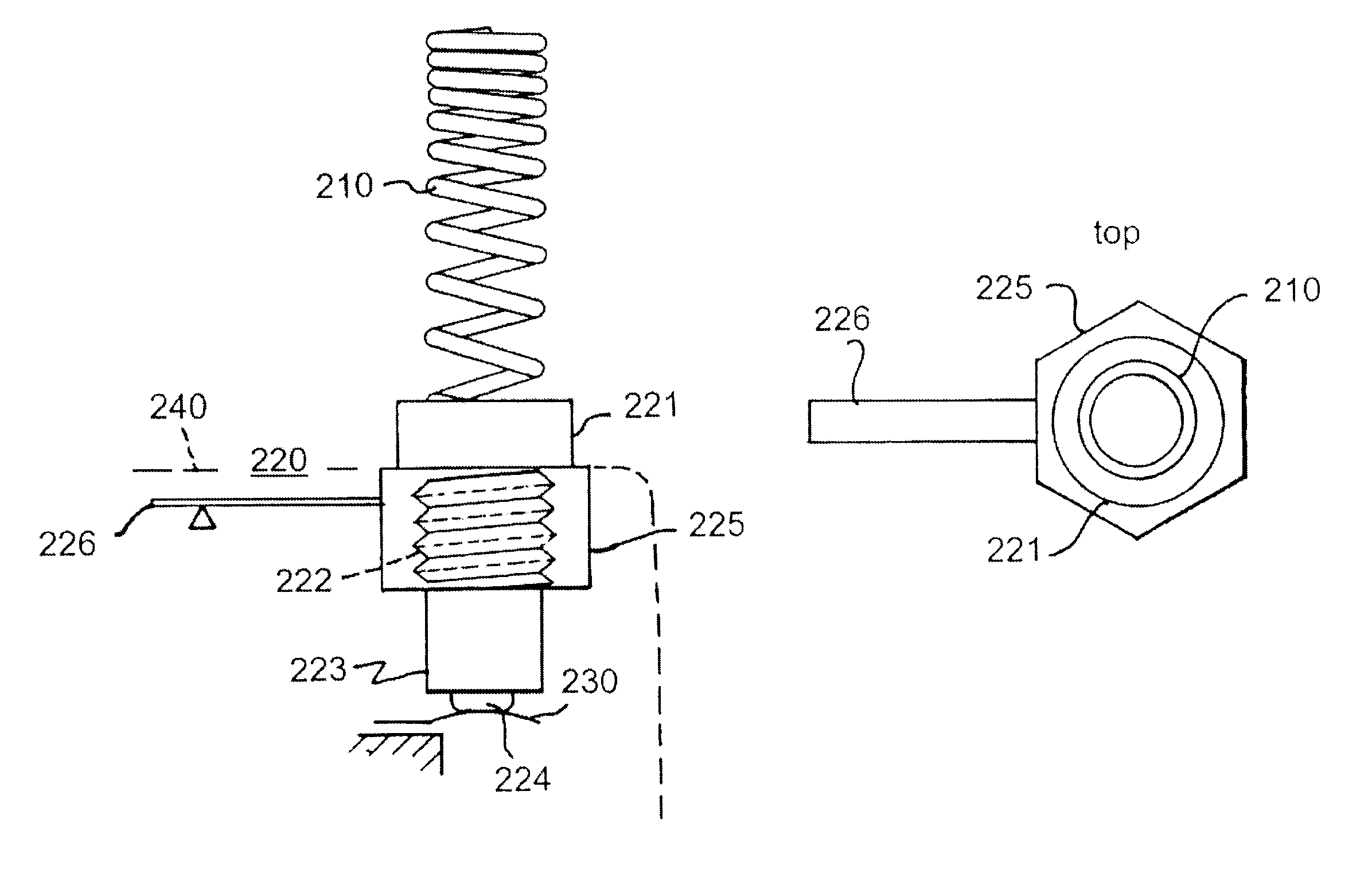
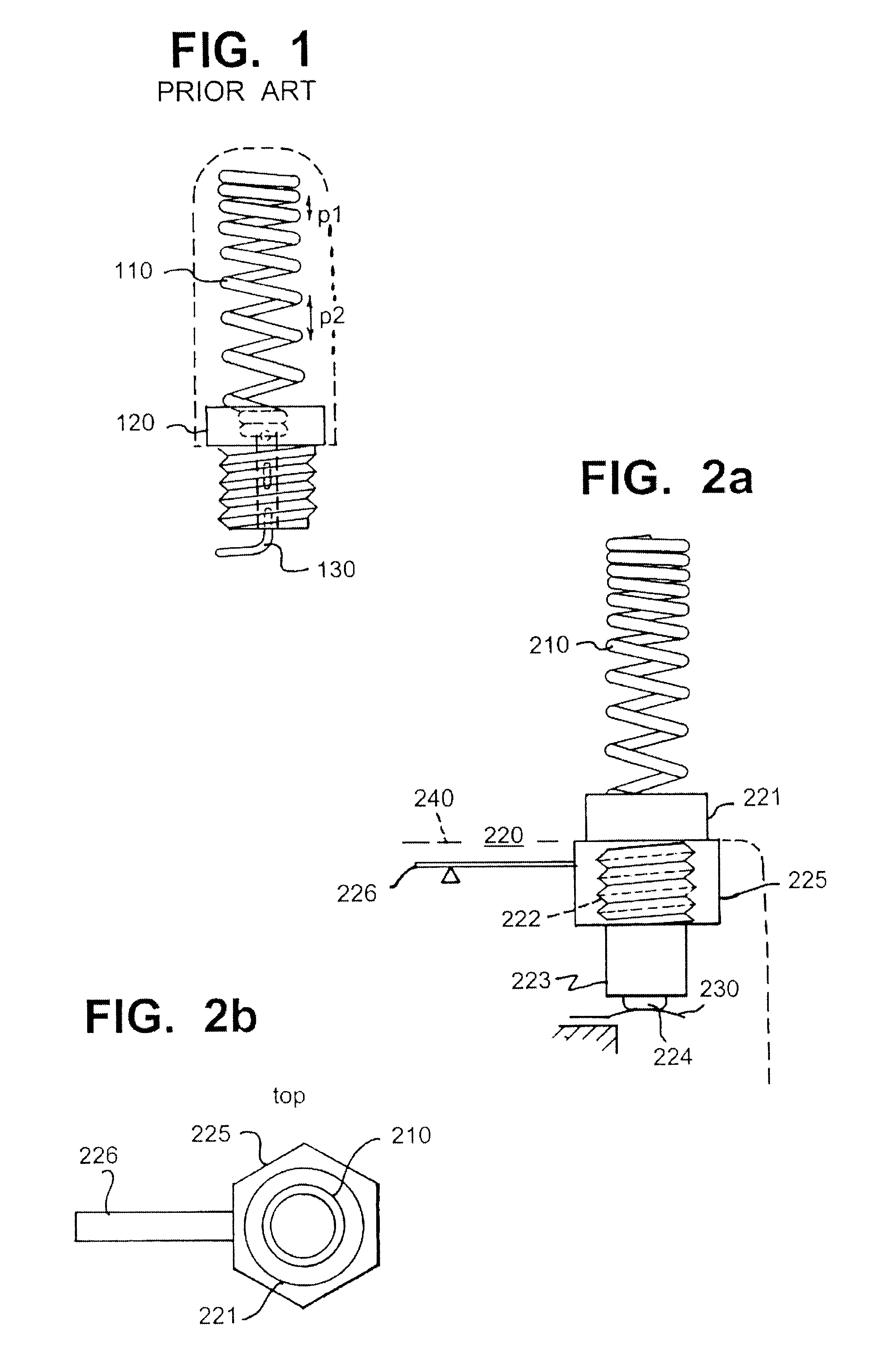
The invention relates to a multiband antenna structure suitable for mobile stations in particular. The radiating elements of the antenna include not only a helix (210) but also the joining piece (220) that attaches the helix to the apparatus. The helix is shaped such that the distance between its conductor turns varies. The electrical length of the joining piece is increased e.g. by means of a conductive projection (226) that remains within the covering of the apparatus. By suitably dimensioning the parts, at least five of the resonances that the helix and joining piece have together and separately are arranged at useful points on the frequency scale. The structure according to the invention is despite the several bands simple and relatively low in production costs.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
4G antenna with metal frame
InactiveCN104300215AExpand low frequency bandwidthEfficient use ofSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceFeed line
A 4G antenna with a metal frame comprises the metal frame, a PCB and an antenna part. The PCB comprises a clearance area and a metal area, the antenna part is located in the clearance area, and comprises a feed supply, a grounding point and a line part, the grounding point and the feed supply are arranged on the PCB, the grounding point is connected with the metal area, a feed line is led out of the feed supply, and the feed supply horizontally extends from the end, close to the metal frame, of the feed line to form a high-frequency line and a low-frequency line which are opposite in direction. First low-frequency resonance is generated by a first low-frequency branch, a second low-frequency branch and a second frame body. First high-frequency resonance is generated by the first low-frequency branch, the second low-frequency branch and a first frame body radiation loop. A first high-frequency branch and the second frame body are coupled to generate second high-frequency resonance. A parasitic branch is used for generating third high-frequency resonance. The method that the front part of the low-frequency line is bent in the reverse height direction is utilized, and the low-frequency bandwidth of the antenna is expanded. Each high-frequency resonance is generated by the radiation of the metal frame, and the problem that the metal frame shields high-frequency antenna radiation is solved.
Owner:HUIZHOU SPEED WIRELESS TECH CO LTD
Cpu/gpu dcvs co-optimization for reducing power consumption in graphics frame processing
ActiveUS20150317762A1Minimize power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTStatic indicating devicesGraphicsComputational science
Systems, methods, and computer programs are disclosed for minimizing power consumption in graphics frame processing. One such method comprises: initiating graphics frame processing to be cooperatively performed by a central processing unit (CPU) and a graphics processing unit (GPU); receiving CPU activity data and GPU activity data; determining a set of available dynamic clock and voltage / frequency scaling (DCVS) levels for the GPU and the CPU; and selecting from the set of available DCVS levels an optimal combination of a GPU DCVS level and a CPU DCVS level, based on the CPU and GPU activity data, which minimizes a combined power consumption of the CPU and the GPU during the graphics frame processing.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Adaptive real-time methodology for optimizing energy-efficient computing
Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) is an effective way to reduce energy and power consumption in microprocessor units. Current implementations of DVFS suffer from inaccurate modeling of power requirements and usage, and from inaccurate characterization of the relationships between the applicable variables. A system and method is proposed that adjusts CPU frequency and voltage based on run-time calculations of the workload processing time, as well as a calculation of performance sensitivity with respect to CPU frequency. The system and method are processor independent, and can be applied to either an entire system as a unit, or individually to each process running on a system.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Integrated spiral inductor
InactiveUS20050156700A1Resonant circuit detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceShunt Device
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programable attenuation and a programable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure that maintains signal integrity. Also provided are shunts at each pin to discharge ESD build up. The shunts utilize a gate boosting structure to provide sufficient small signal RF performance, and minimal parasitic loading.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
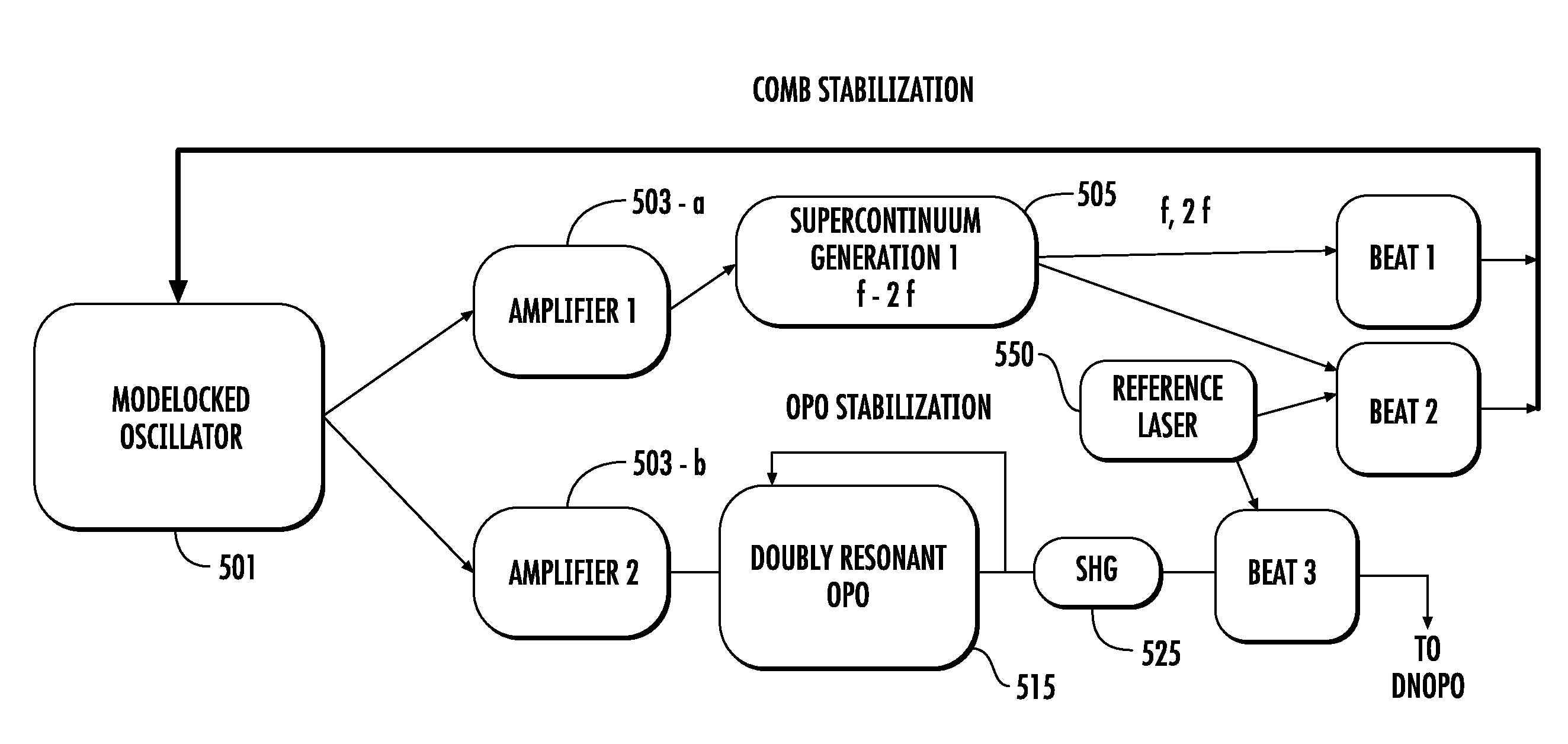
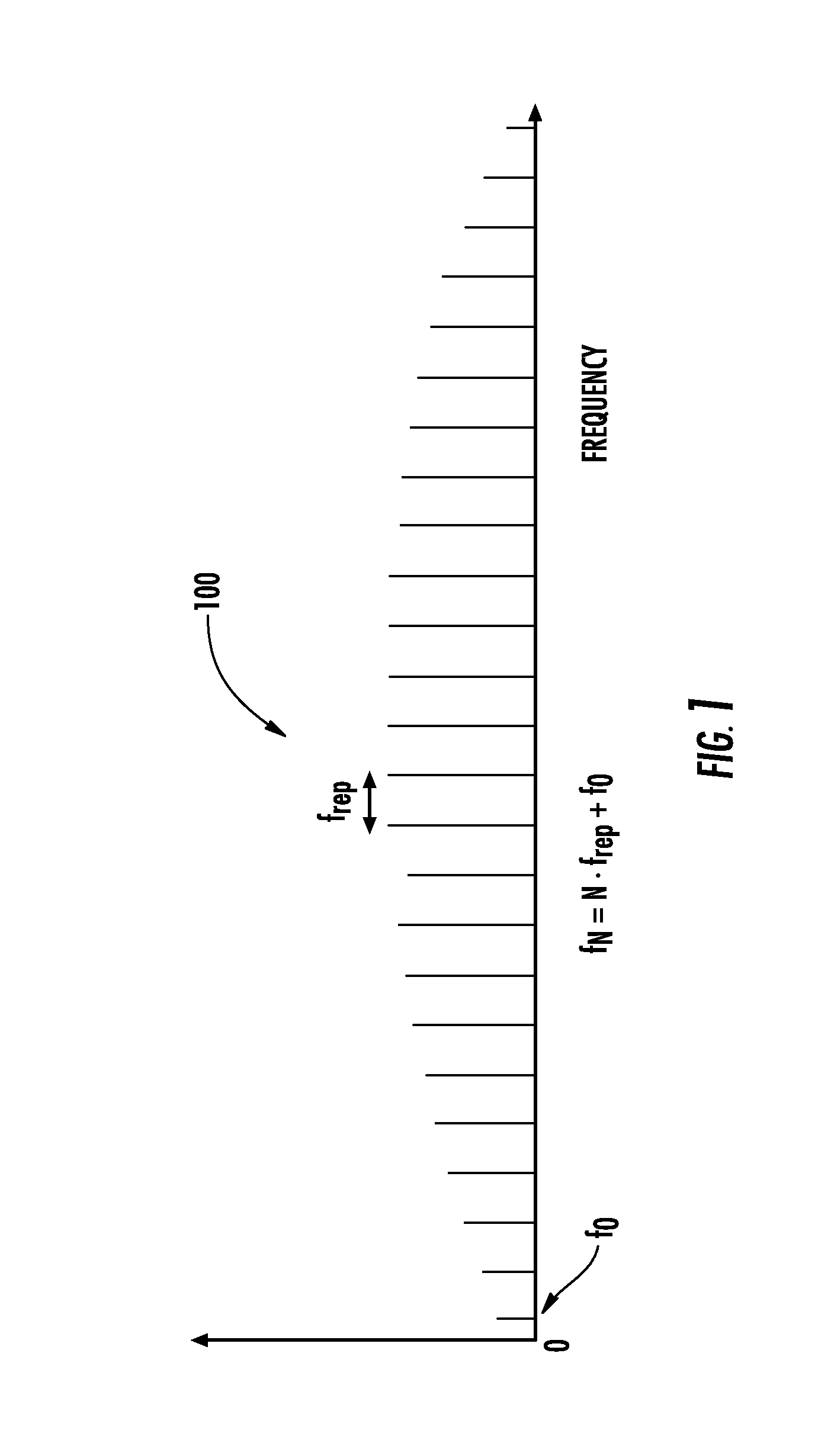
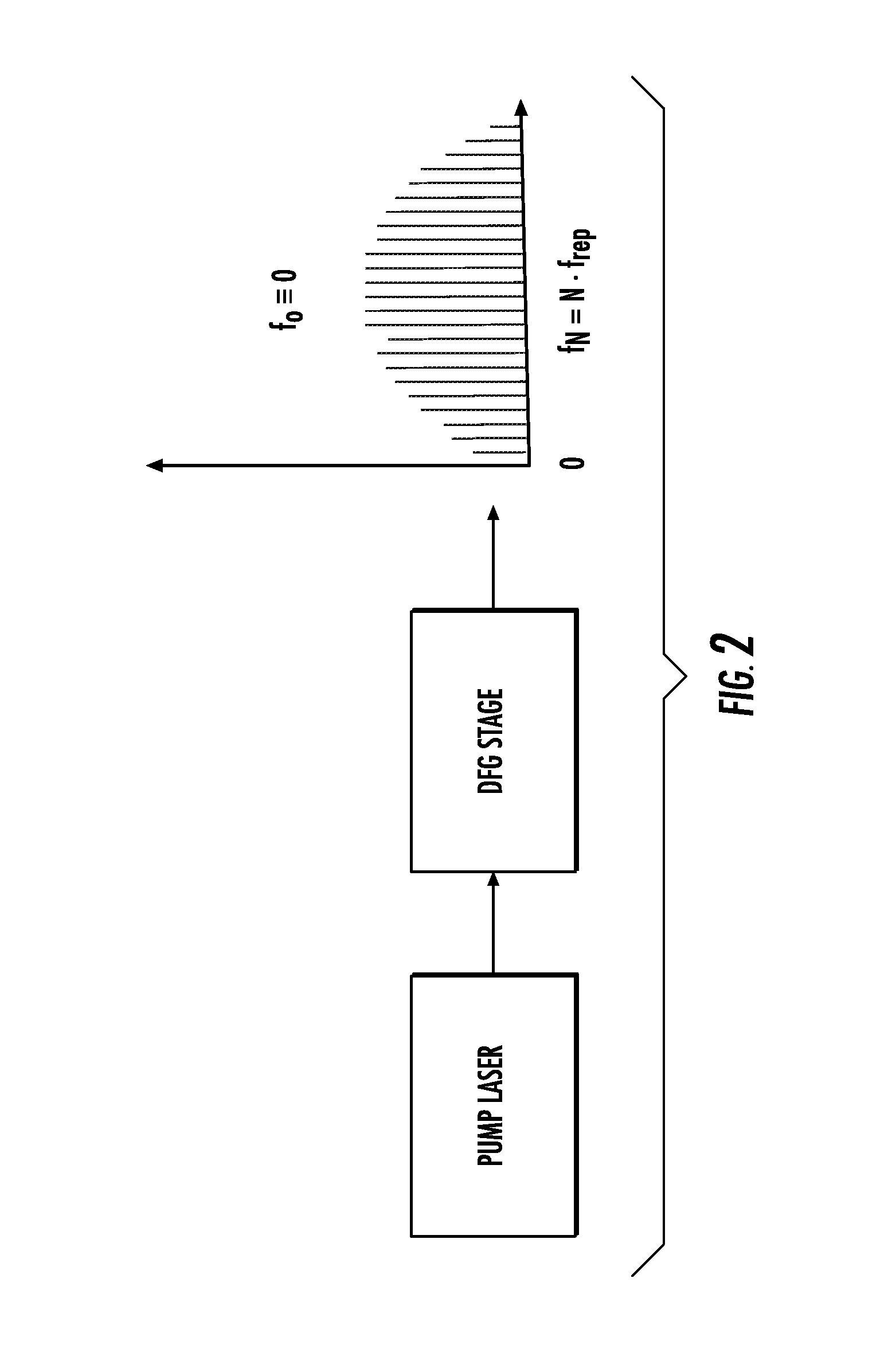
Optical frequency ruler
The present invention relates to frequency rulers. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked pump source operated at pulse repetition rate, and a pump output having a pump carrier envelope offset frequency. A nonlinear optical system outputs a frequency ruler spectrum comprising individual frequency modes. The frequency modes may be characterized by a frequency spacing which is an integer multiple of the repetition rate and by distinct ruler carrier envelope offset frequencies which exhibit at least one discontinuity across the frequency output. The ruler carrier envelope offset frequencies are substantially locked to the carrier envelope offset frequency of the pump laser. One preferred embodiment includes a frequency doubled, doubly resonant, non-degenerate OPO (DNOPO), a supercontinuum generation (SC) stage and at least one reference laser arranged downstream from a Tm fiber-based pump source. A plurality of beat signals generated therefrom provide for stabilization of the system.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Self-synchronous locking of optical coherence by single-detector electronic-frequency tagging
InactiveUS7058098B1Power maximizationEasy to scaleOptical devices for laserBeam splitterSmall sample
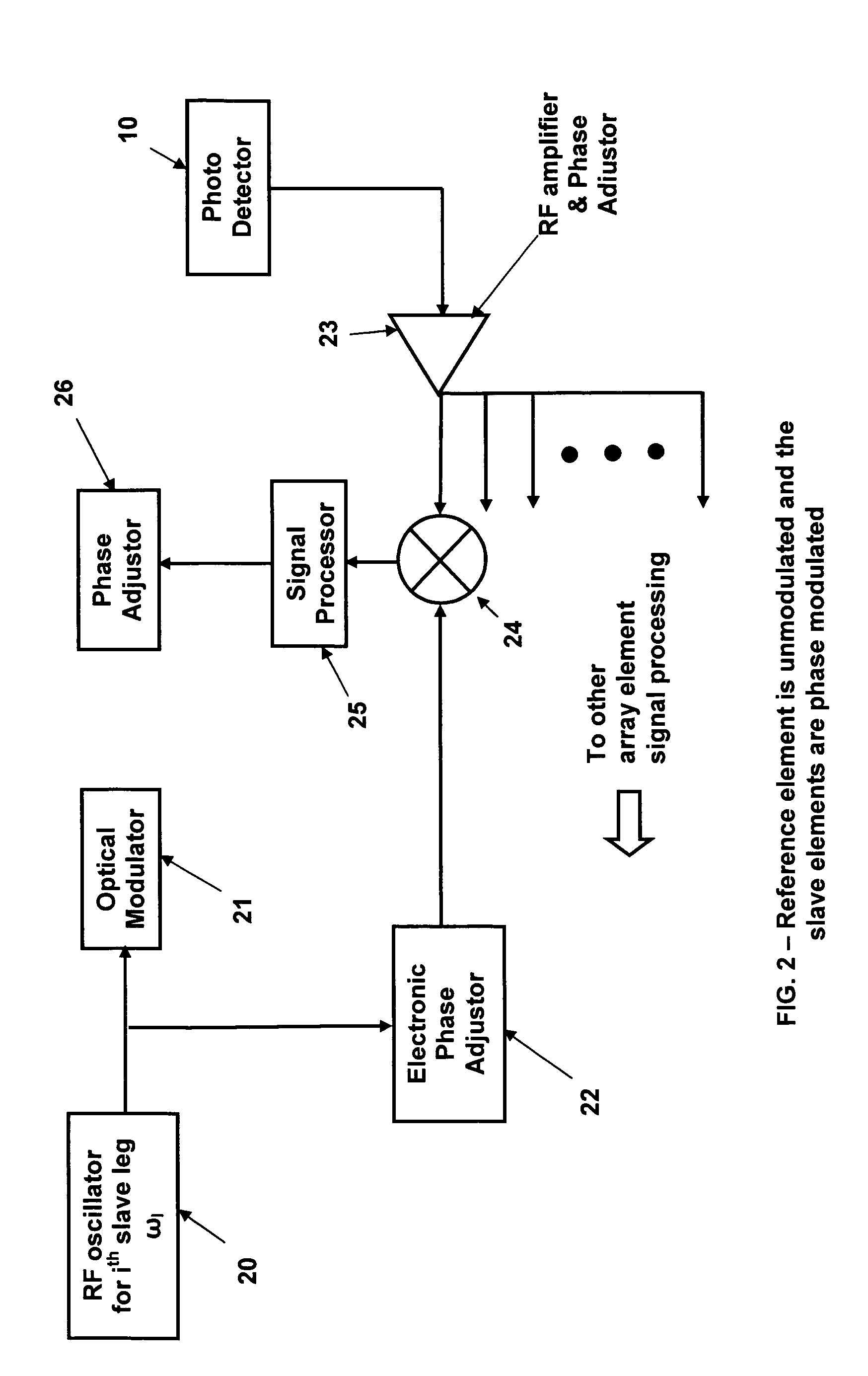
A coherent laser beam combining system wherein the output of a single master oscillator is split into a plurality of N signals, and the N signals are electronically modulated at unique frequencies. There is no reference signal and all of the signals are passed through phase adjusters. All N signals are optically amplified, aligned and passed through a beam splitter to split off a small sample that is imaged onto a photodetector. The photodetector output is fed to a signal processor that separates the N signals and produces N phase error signals that drive the N phase adjusters resulting in a high-powered optically coherent output signal.
Owner:AIRFORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Job scheduling to balance energy consumption and schedule performance
ActiveUS20130139170A1Energy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsJob shop schedulingParallel computing
An energy-aware backfill scheduling method combines overestimation of job run-times and processor adjustments, such as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling, to balance overall schedule performance and energy consumption. Accordingly, some scheduled jobs are executed in a manner reducing energy consumption. A computer-implemented method comprises identifying job performance data for a plurality of representative jobs and running a simulation of backfill-based job scheduling of the jobs at various combinations of run-time over-estimation values and processor adjustment values. The simulation generates data including energy consumption and job delay. The method further identifies one of the combinations of values that optimizes the mathematical product of an energy consumption parameter and a job delay parameter using the simulation generated data for the plurality of jobs. Jobs submitted to a processor are then scheduled using the identified combination of a run-time over-estimation value and a processor adjustment value.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
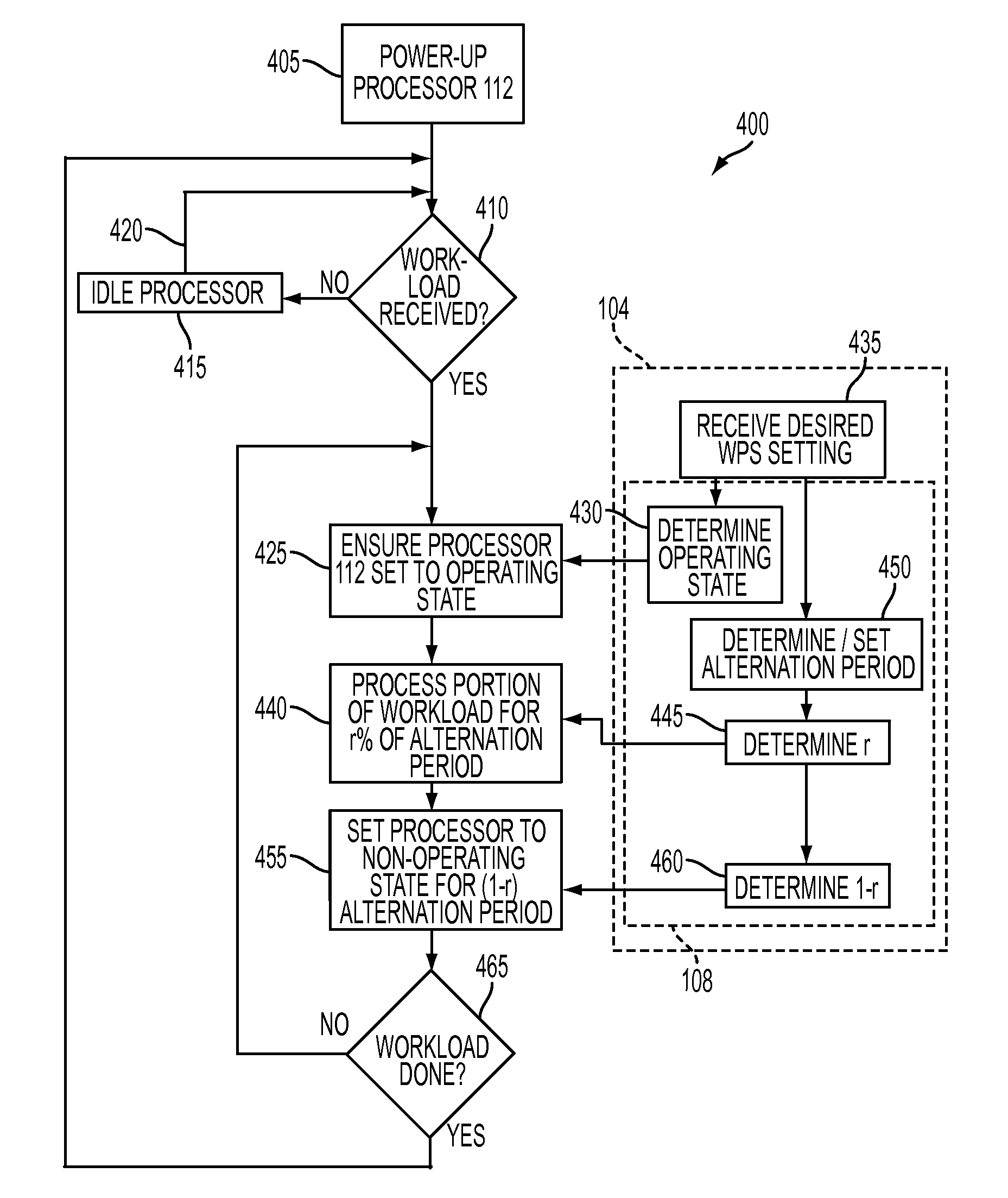
Systems and Methods for Managing Power Consumption and Performance of a Processor
Processor-management techniques that purposely alternate a processor between an operating state and a non-operating state while the processor is executing the workload. The techniques leverage the “ultra-low-power” non-operating states of many processors to provide predictable power and / or frequency control of the processor. These techniques can provide better performance than known clock-throttling and dynamic voltage and frequency scaling schemes for controlling processors.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
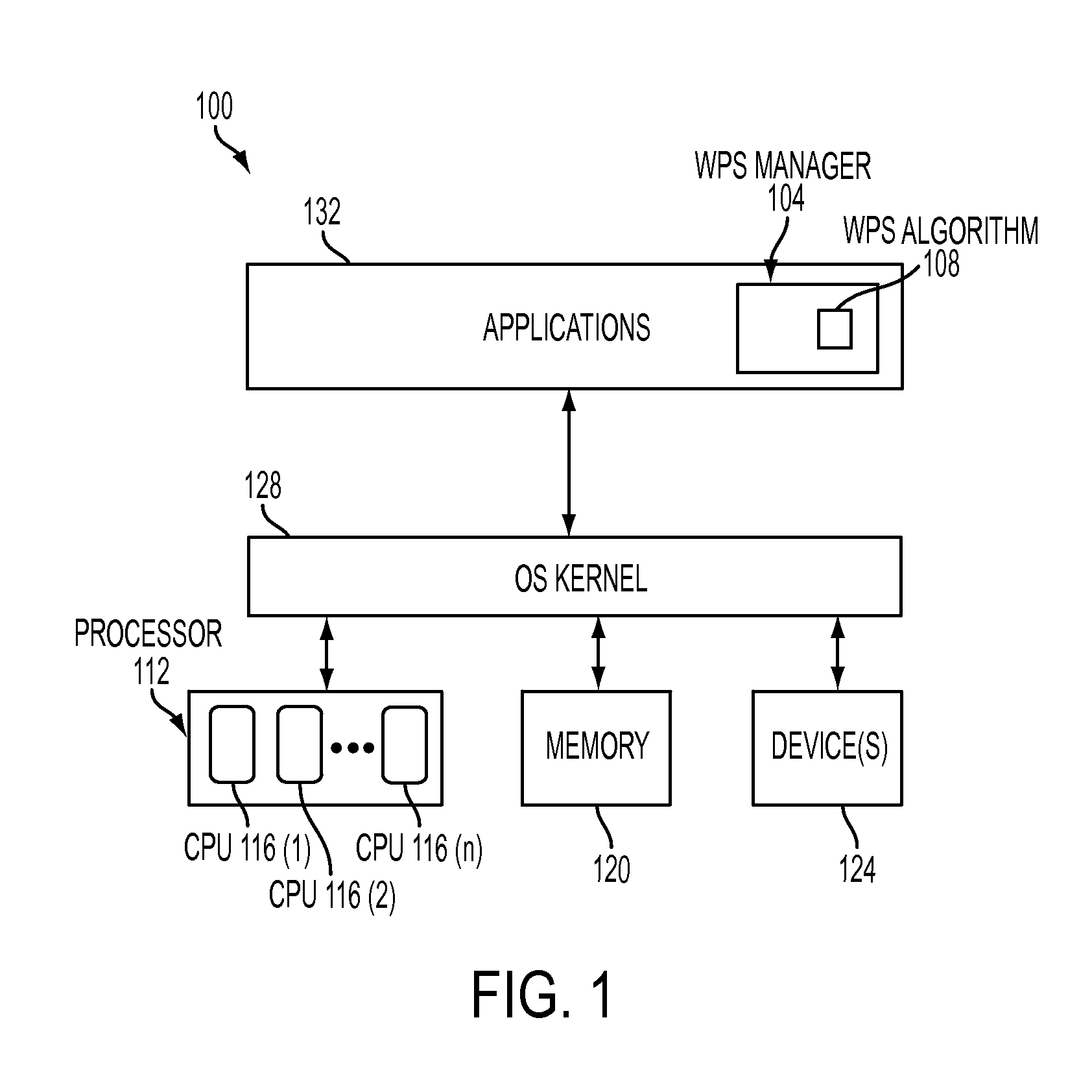
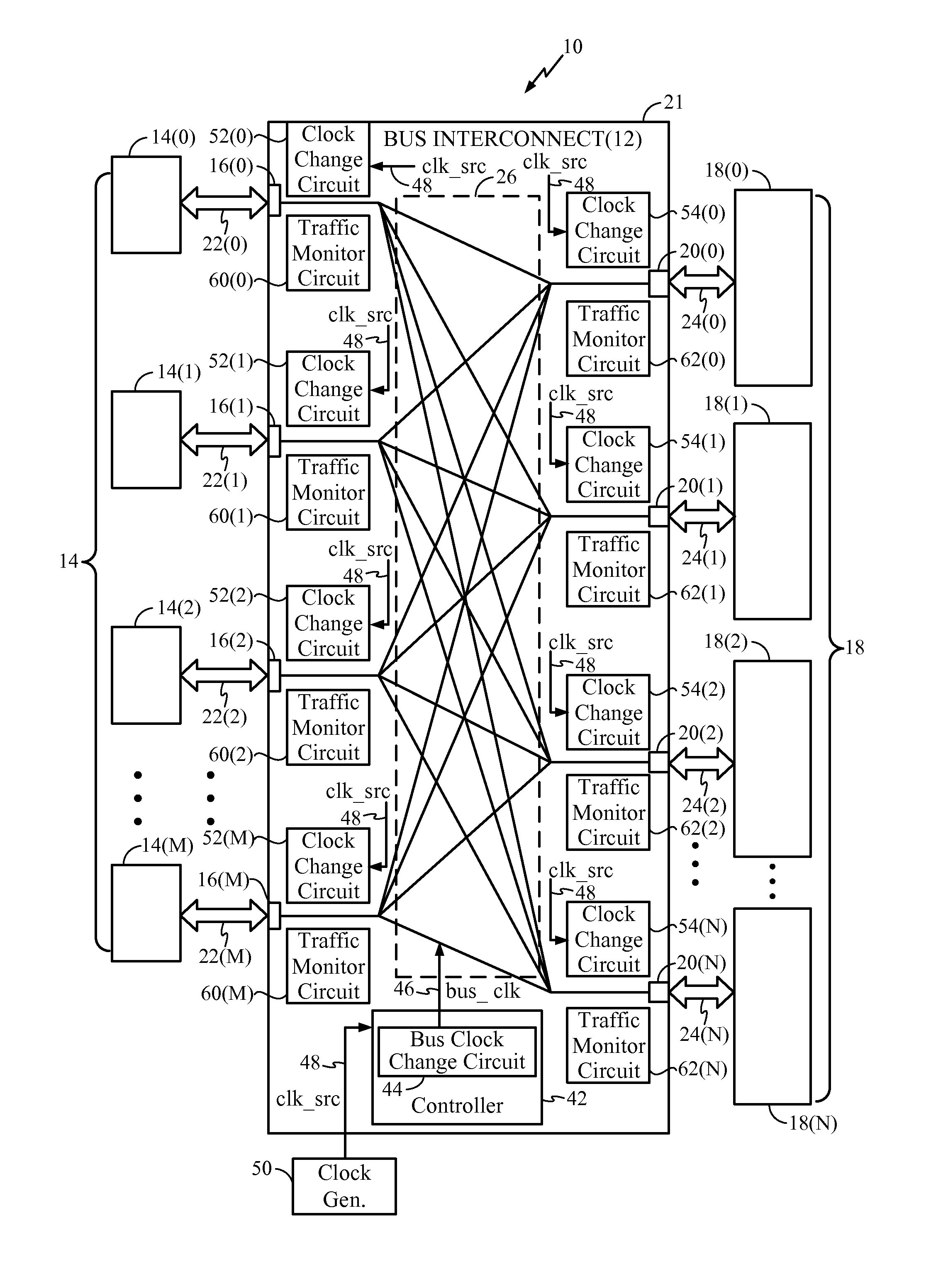
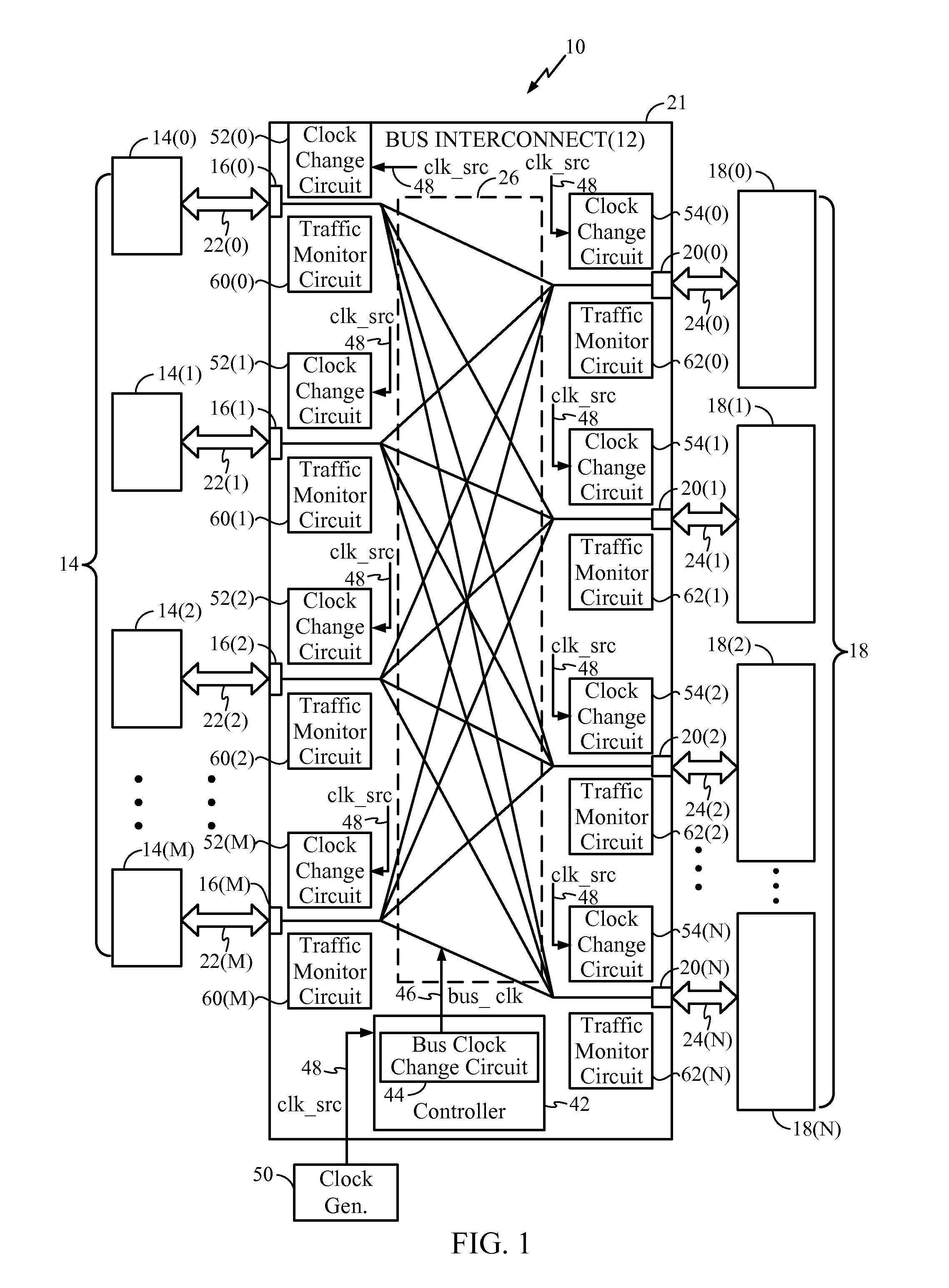
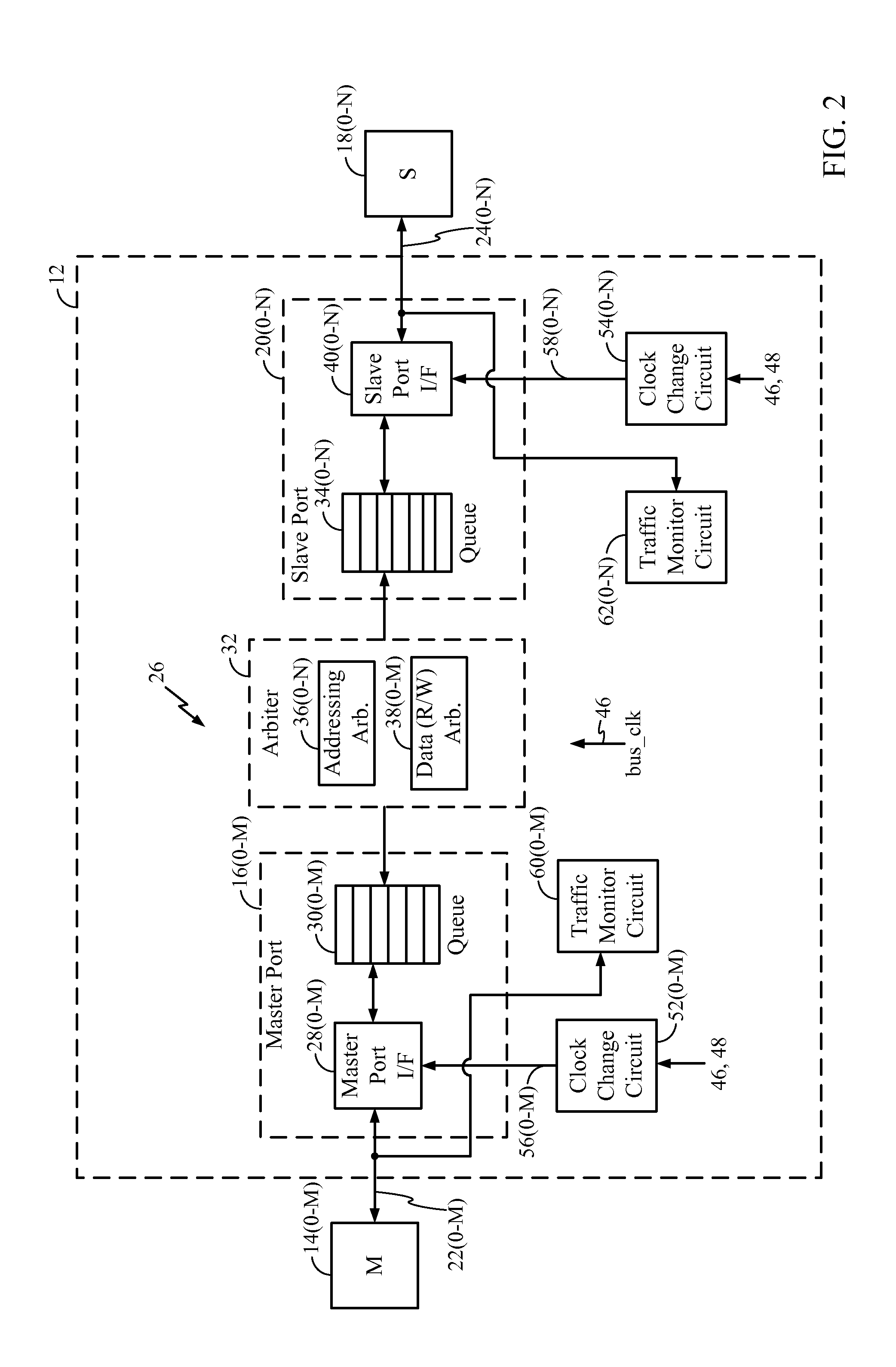
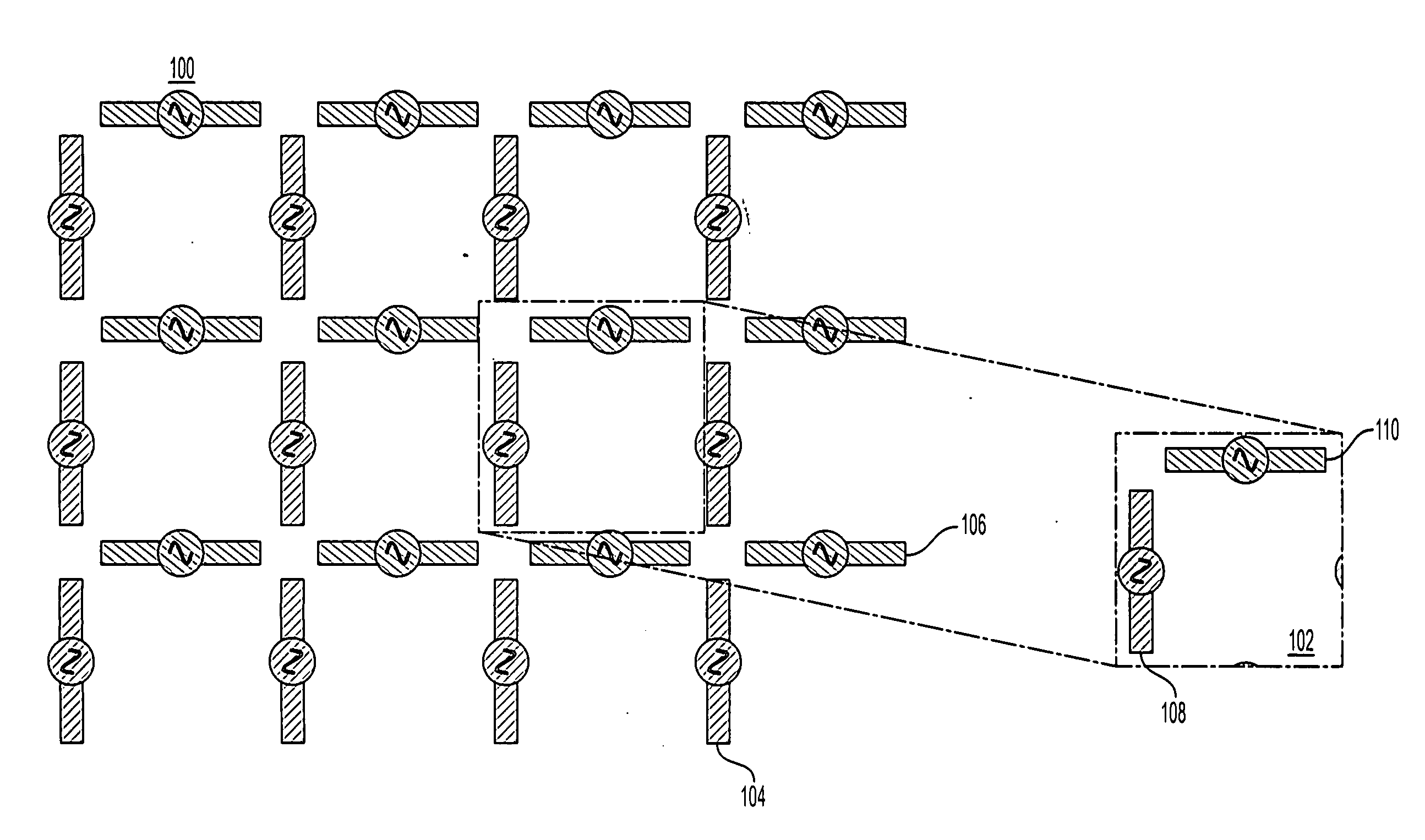
Bus Clock Frequency Scaling for a Bus Interconnect and Related Devices, Systems, and Methods
ActiveUS20120198266A1Reduce frequencyHigh frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingClock rateBand width
Bus clock frequency scaling for a bus interconnect and related devices, systems, and methods are disclosed. In one embodiment, the bus interconnect comprises an interconnect network configurable to connect a master port(s) to a slave port(s). A bus interconnect clock signal clocks the interconnect network. The controller is configured to receive bandwidth information related to traffic communicated over the master port(s) and the slave port(s). The controller is further configured to scale (e.g., increase or decrease) the frequency of the bus interconnect clock signal if the bandwidth of the master port(s) and / or the slave port(s) meets respective bandwidth condition(s), and / or if the latency of the master port(s) meets a respective latency condition(s) for the master port(s). The master port(s) and / or slave port(s) can also be reconfigured in response to a change in frequency of the bus interconnect clock signal to optimize performance and conserve power.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for ESD protection
InactiveUS6963110B2Reduce areaReduce capacitanceResonant circuit detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceCapacitance
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programable attenuation and a programable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure that maintains signal integrity. Also provided are shunts at each pin to discharge ESD build up. The shunts utilize a gate boosting structure to provide sufficient small signal RF performance, and minimal parasitic loading.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Methods and systems for digitally controlled multi-frequency clocking of multi-core processors
ActiveUS20090106576A1Convenient power managementEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsLocal oscillatorEngineering
A method and system for digitally controlled multi-frequency clocking are provided. The method includes receiving a system reference oscillator clock frequency at a microprocessor including multiple cores. The system reference oscillator clock frequency provides a reference frequency to a local oscillator. The local oscillator supplies a core clock frequency to at least one of the cores. The method further includes adjusting the local oscillator to output the core clock frequency at a frequency greater than the system reference oscillator clock frequency as a function of digital frequency characteristic data associated with the core or cores. The method supports extendibility to larger systems and may support enhanced power management through frequency adjustments at the core level.
Owner:IBM CORP
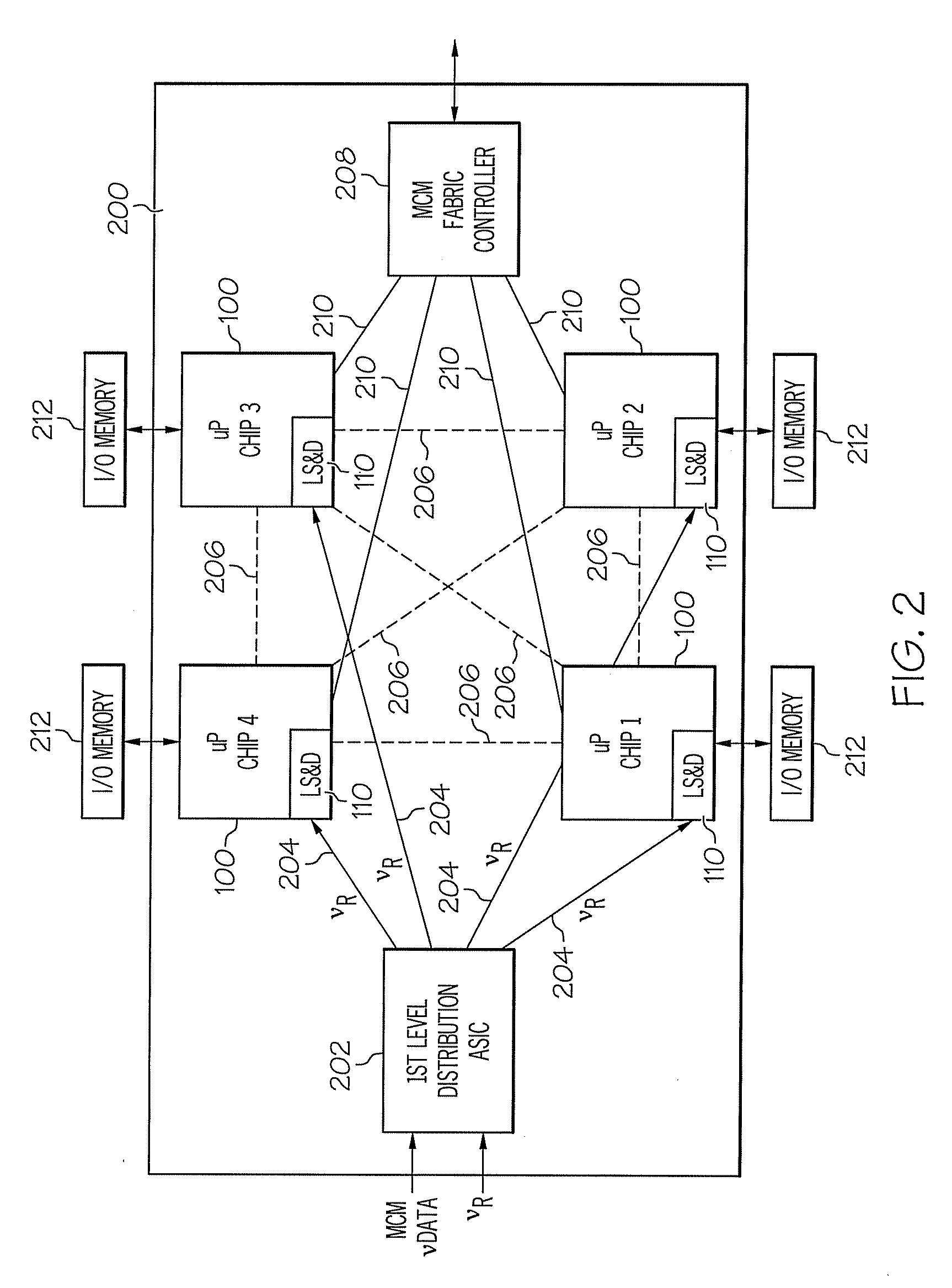
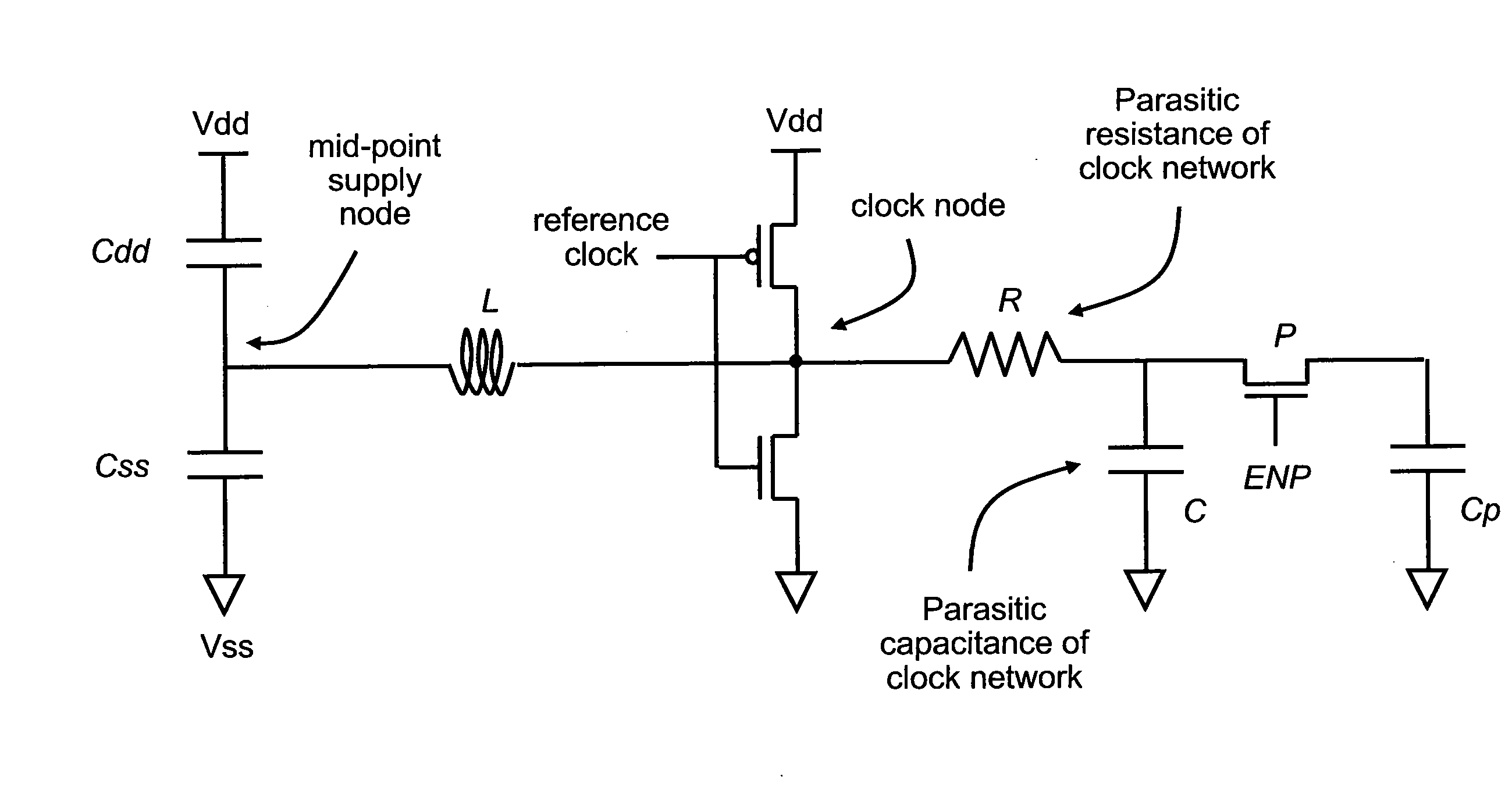
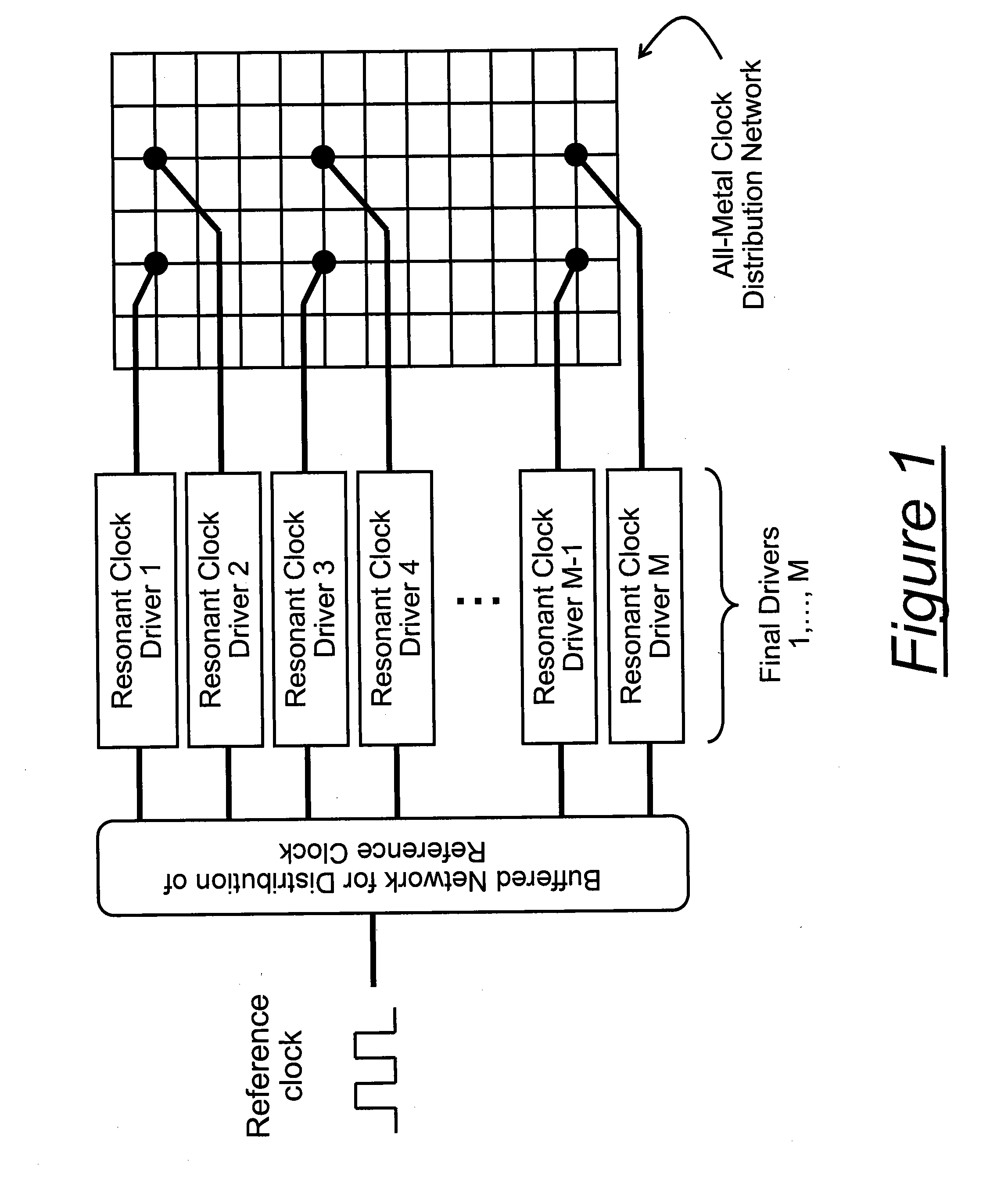
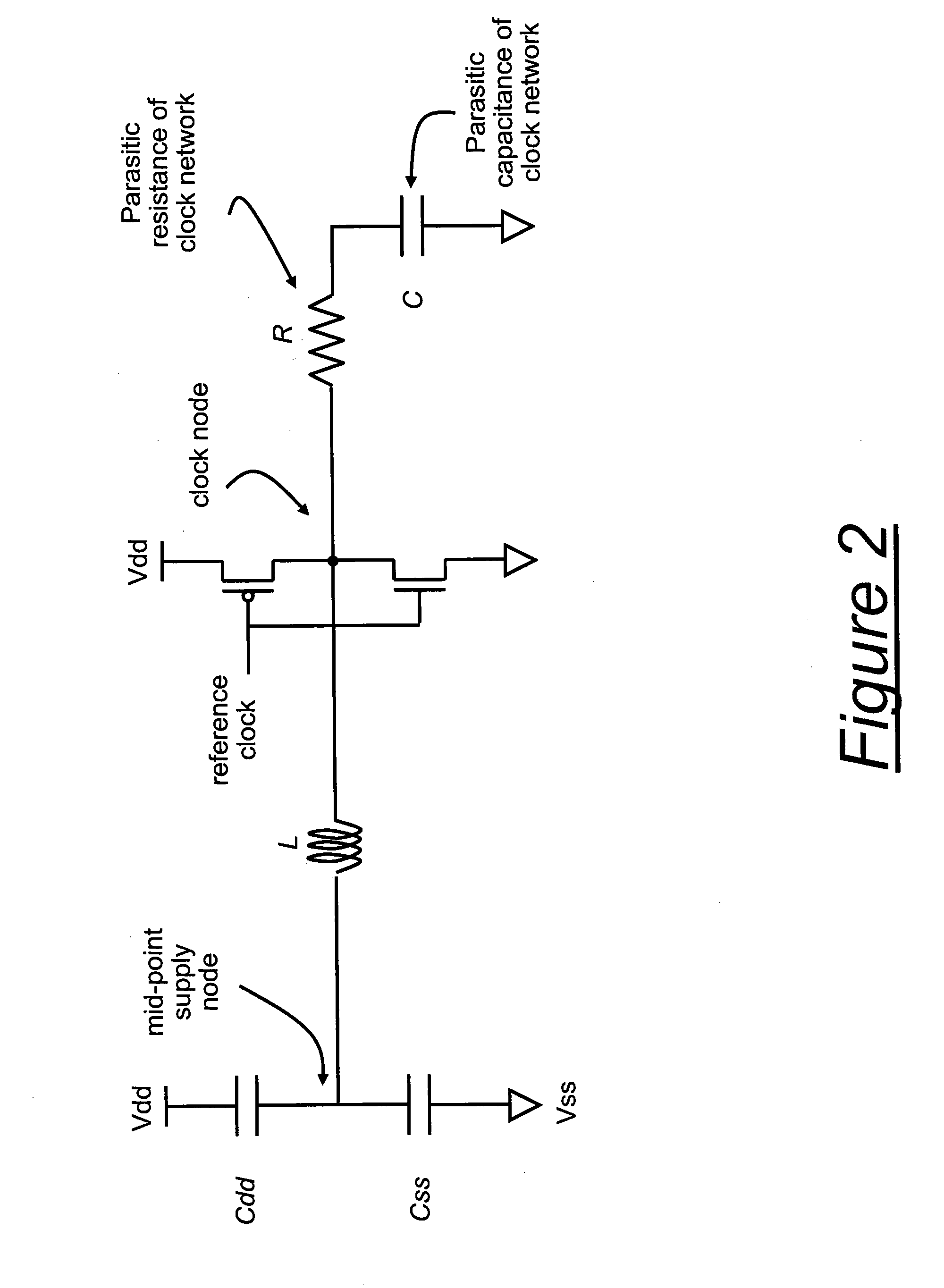
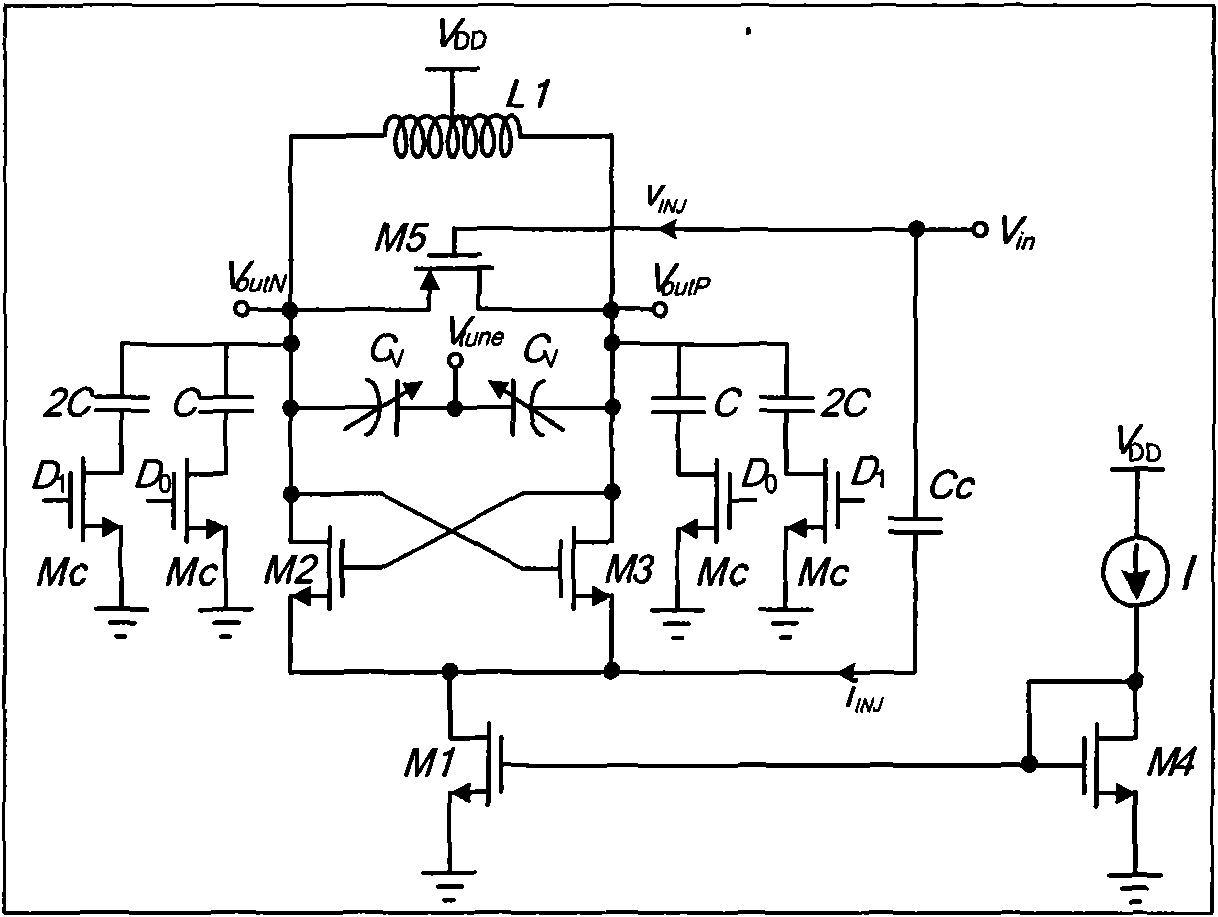
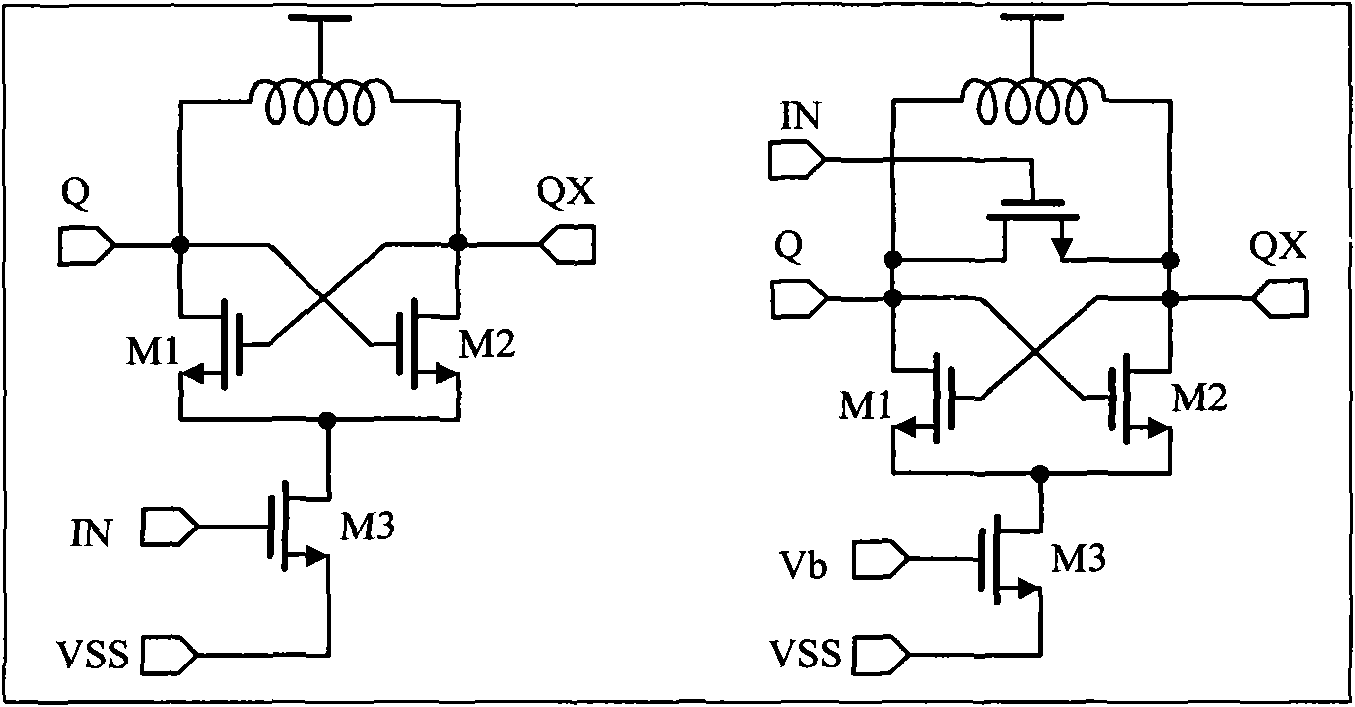
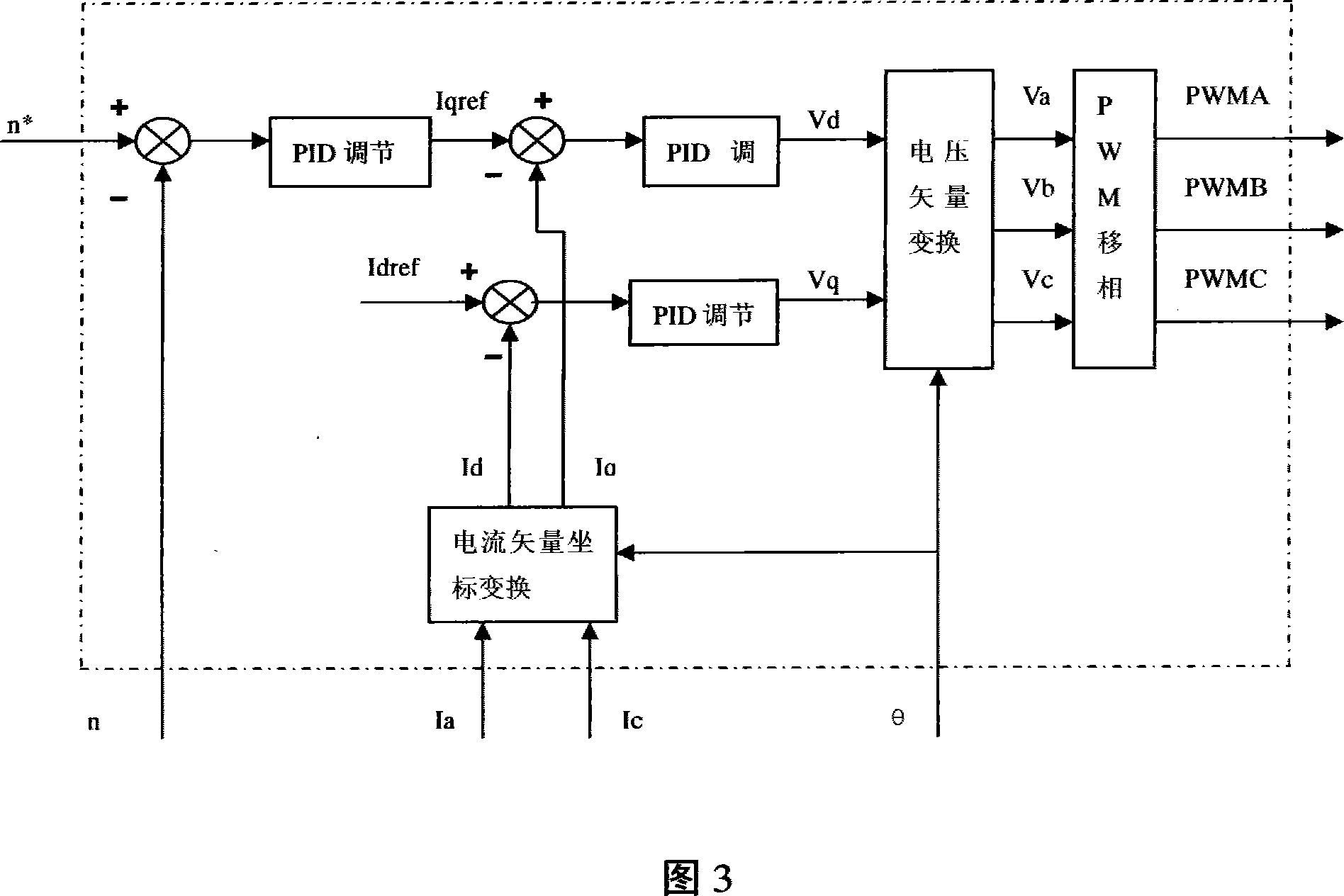
Architecture for frequency-scaled operation in resonant clock distribution networks
An architecture for resonant clock distribution networks is proposed. This architecture allows for the energy-efficient operation of a resonant clock distribution network at multiple clock frequencies through the deployment of flip-flops that can be selectively enabled. The proposed architecture is primarily targeted at the design of resonant clock networks with integrated inductors and exhibits no inductor overheads. Such an architecture is generally applicable to semiconductor devices with multiple clock frequencies, and high-performance and low-power clocking requirements such as microprocessors, ASICs, and SOCs. Moreover, it is applicable to the binning of semiconductor devices according to achievable performance levels.
Owner:CYCLOS SEMICON
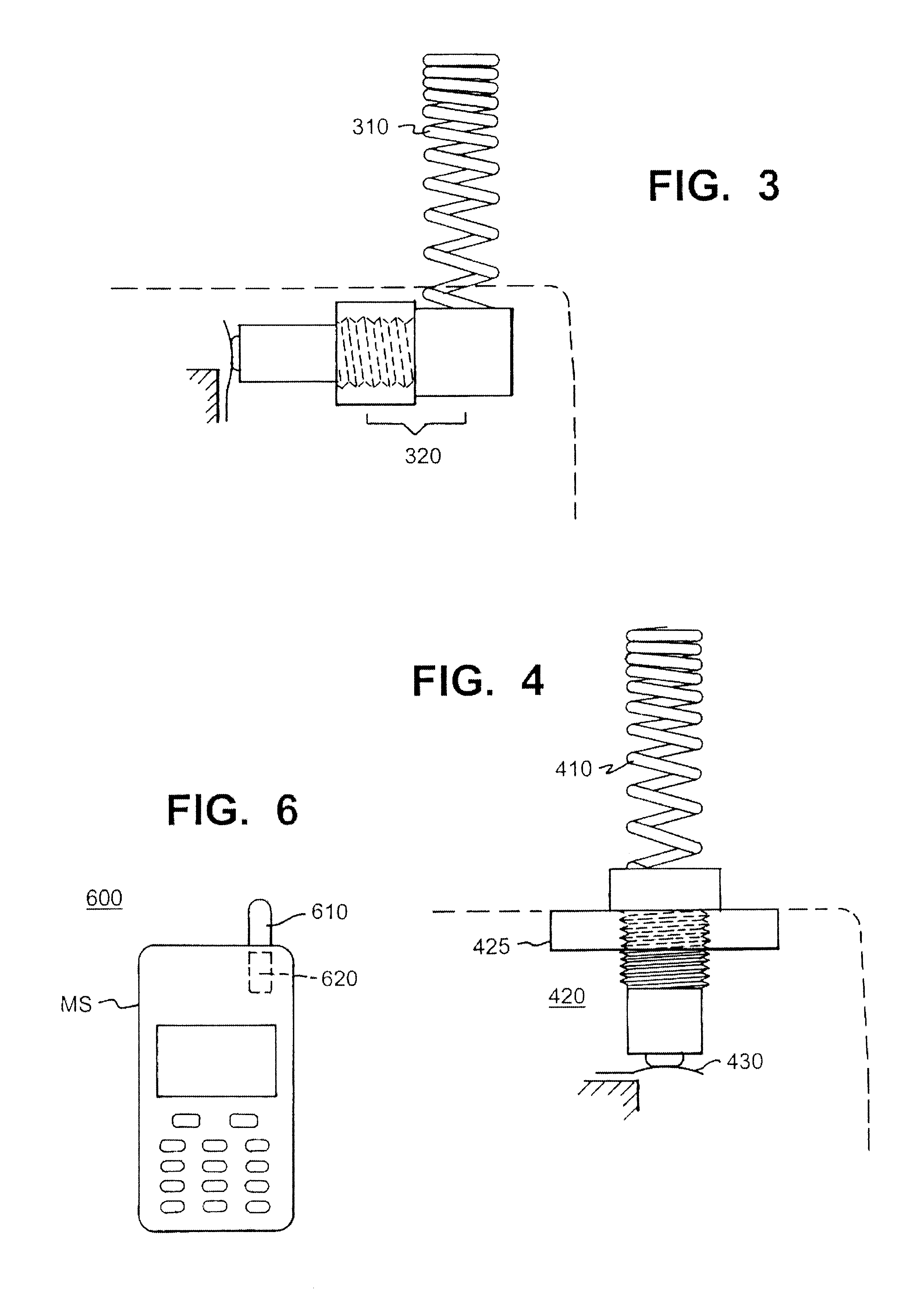
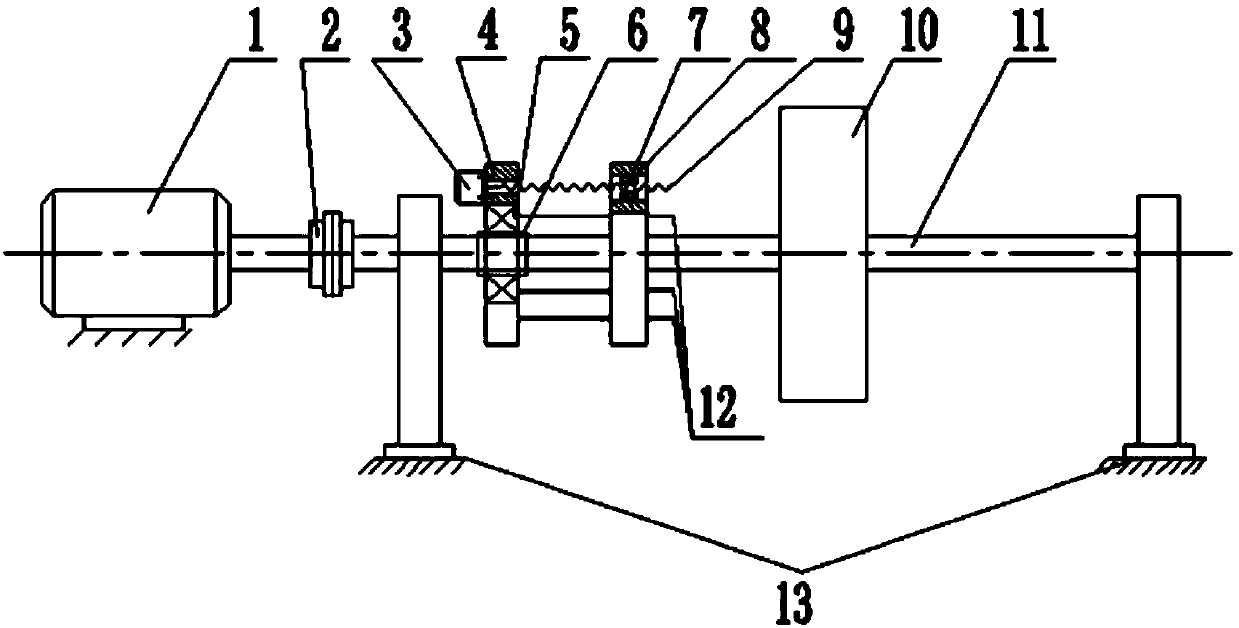
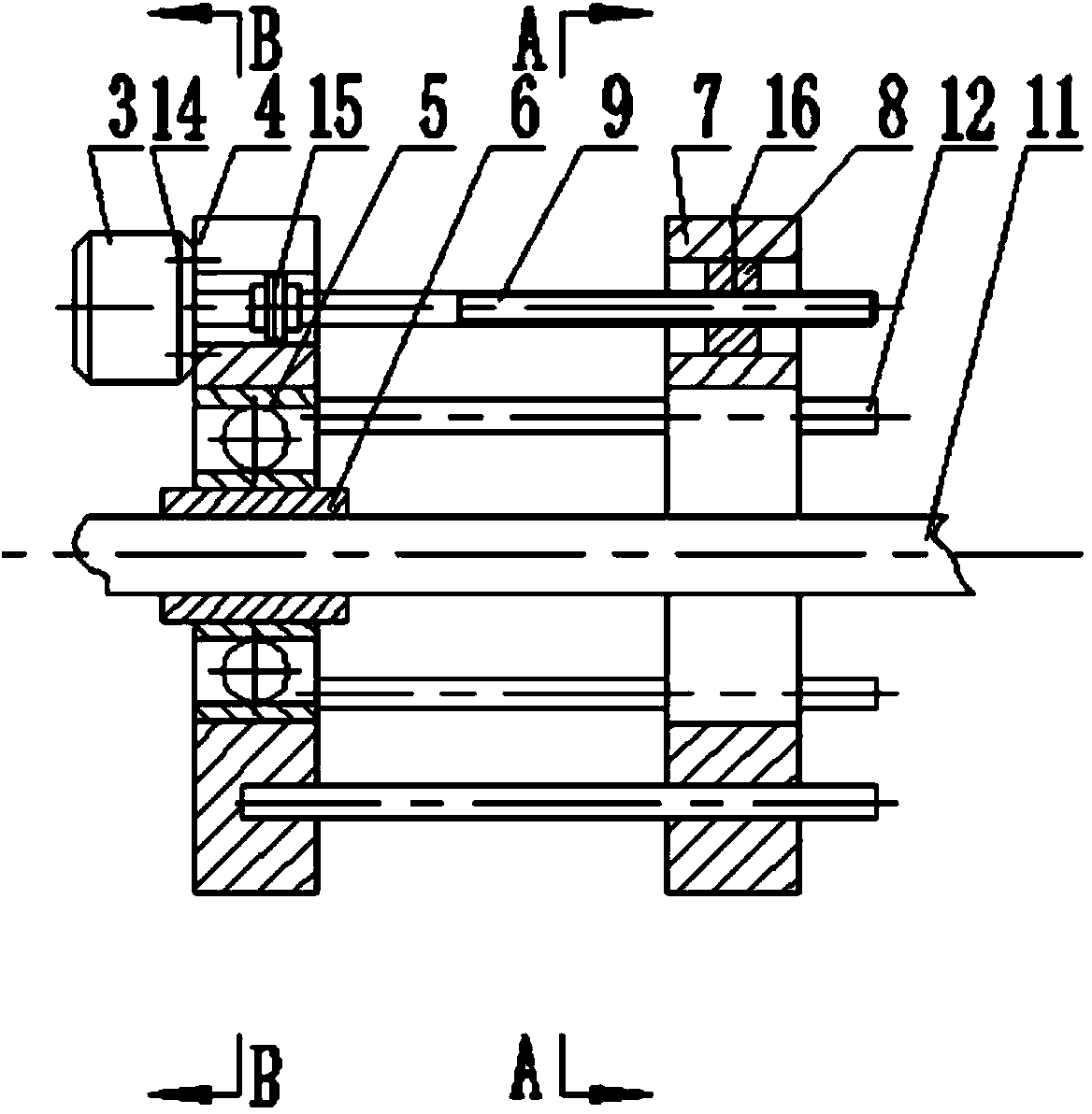
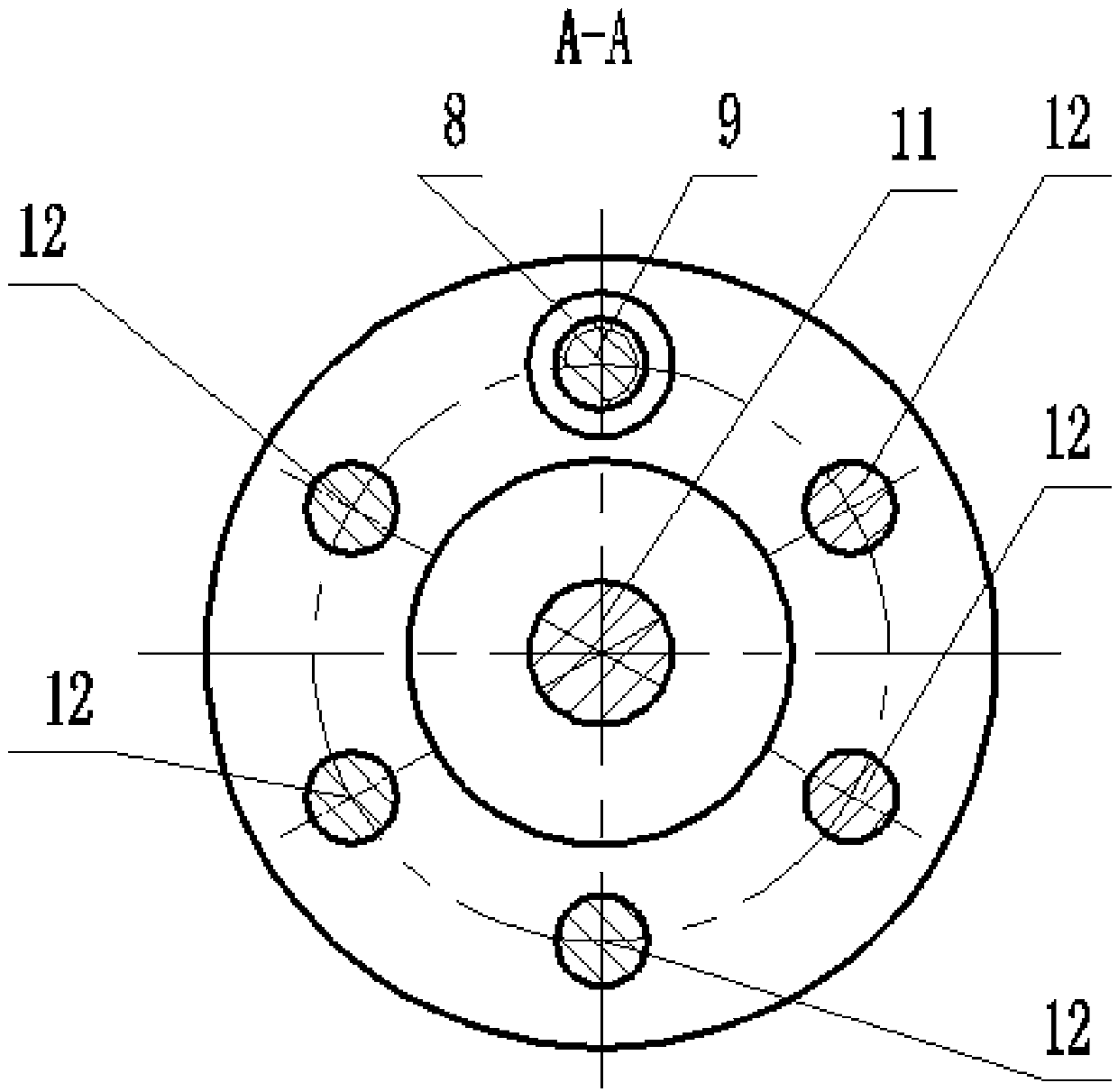
Rotor adaptive continuous frequency shifting tuned mass damper (TMD) for rotary machinery
InactiveCN103742591ADoes not affect normal workPlay the role of vibration energy transferRotating vibration suppressionControl systemSnubber
Disclosed is a rotor adaptive continuous frequency TMD for rotary machinery. The TMD is in a cage structure and comprises a mechanical structure and a control system. The mechanical structure comprises a connection transmission mechanism and a rigidity continuous adjustable tuning mass mechanism. According to the damper, a screw is driven by a stepping motor to rotate, an annular mass block is pulled by a nut matched with the screw to reciprocate to adjust the frequency of the TMD to achieve real-time tracking continuous adjustment of the inherent frequency of a TMD subsystem, so that the frequency of the subsystem is consistent with the main vibration frequency of the rotor to be adapted to the frequency changes of the rotor in the actual condition. The TMD is adaptable to vibration of various frequency components of rotary machinery and has the advantages of being apparent in damping effect, compact in structure, small in required space, high in reliability, large in rigidity adjusting range and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Injection locking frequency divider
InactiveCN101777871AThe injection method increasesIncreased injected energyOscillations generatorsInjection lockedCapacitance
The invention relates to an injection locking frequency divider used in the integrated circuit of a radio receiver, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuits of radio frequency radio receivers. The injection locking frequency divider is formed by an inductance-capacitance oscillator, a tuning circuit, a signal injection circuit and a current source biasing circuit, wherein the tuning circuit comprises a numerical control capacitor array tuner and a varactor tuner. Under the condition of no external input excitation, the inductance-capacitance oscillator self-oscillates by certain frequency. The tuning circuit tunes the self-oscillating frequency through varying the load of the resonant cavity of the oscillator. The signal injection circuit injects input signals into the resonant cavity of the oscillator to realize the traction and the locking of the self-oscillating frequency of the oscillator and to further the frequency halving of the input signals. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the circuit can realize high working frequency under low power consumption and the working frequency range is wide.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
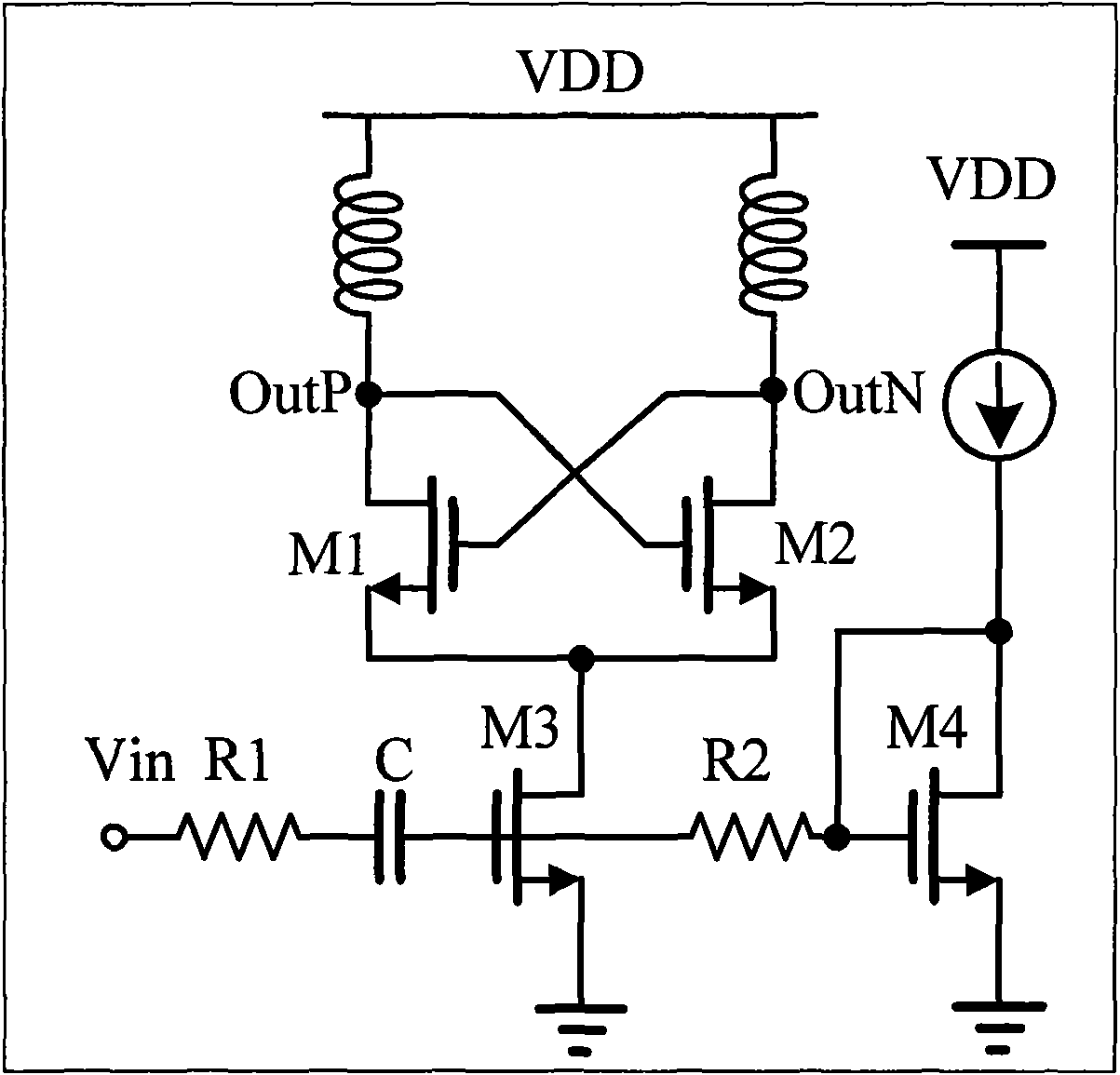
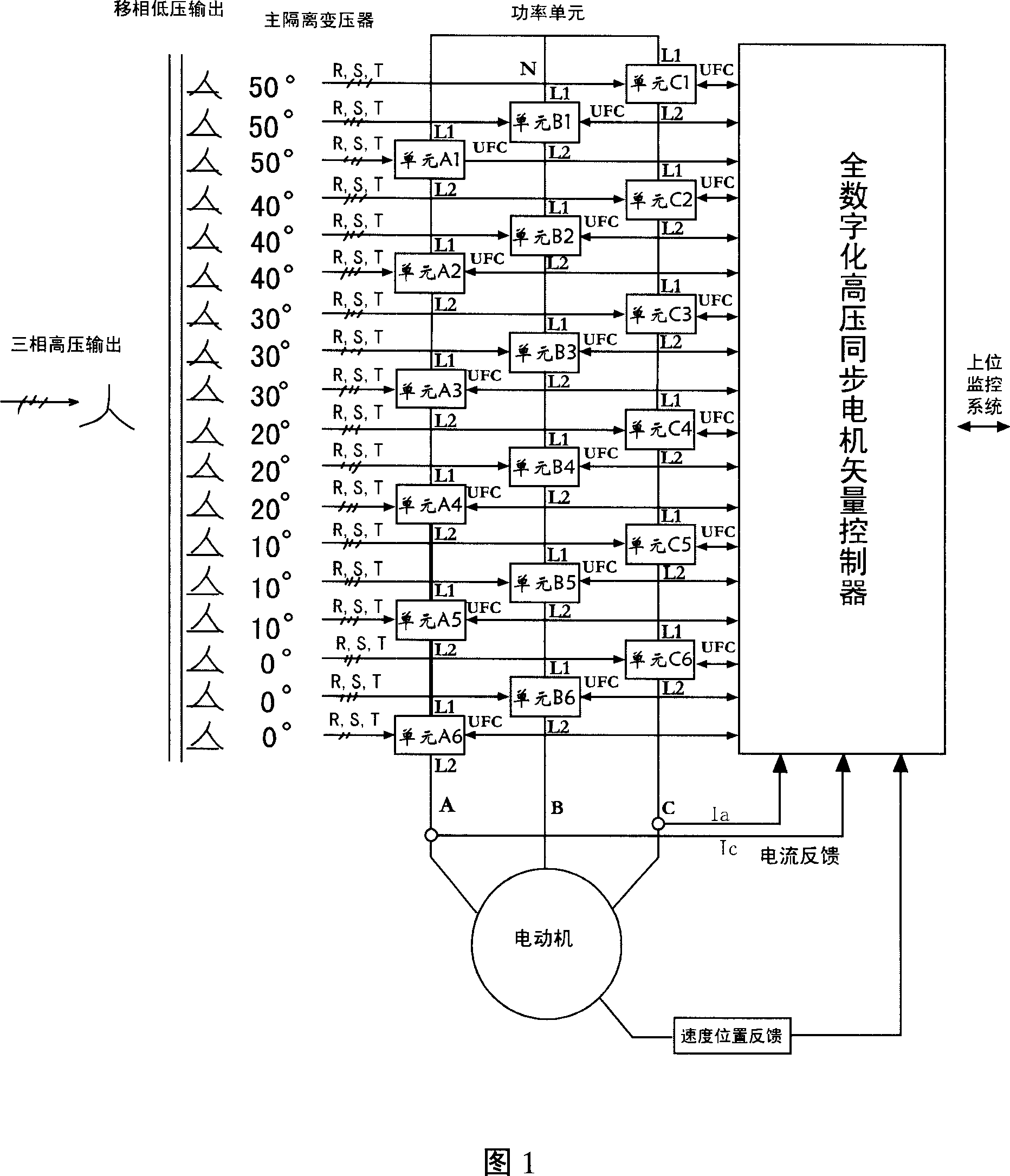
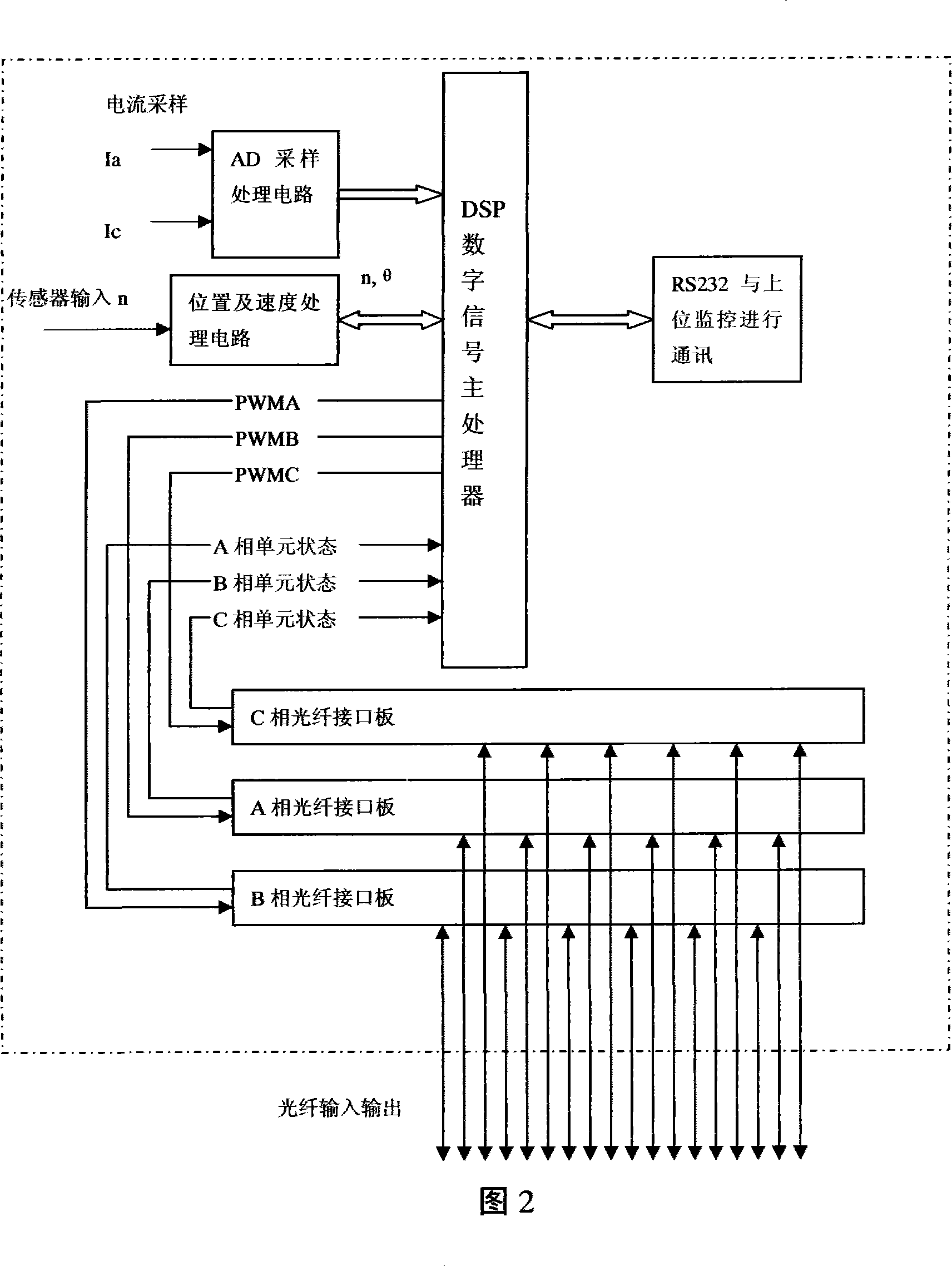
High voltage synchronous machine whole digitization vector control device
ActiveCN101119090AAddress unattainable featuresSolve Harmonic PollutionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFrequency changerSynchronous motor
The present invention is a high voltage synch motor digitalized vector control device which comprises a high voltage input dephasing isolating transformer and a power unit module that is provided with energy feedback. The two units are connected in series to form a three-phase high voltage variable frequency output. The present invention also consists of a digital processor, a programmable logic component, a digital high voltage synchronous machine vector controller that is formed by relative surrounding circuit, a rotor position and speed feedback encoder that is connected with the controlled synchronous motor with the same axle and a monitor transducer of the output current of the frequency changer; the surrounding circuit consists of an optical fiber connector and an upper monitor system that gives frequency. The present invention has the advantages of less pollution to the grid, needless of reactive-load compensation equipment, fast response, wide range of speed regulation ratio, actuated by constant torque and quadrant operating power.
Owner:北京合康新能变频技术有限公司
Adaptive real-time methodology for optimizing energy-efficient computing
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Frequency-scaled ultra-wide spectrum element
ActiveUS20170025767A1Low costEasy to manufactureIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna earthingsEngineeringAntenna element
An antenna element including a base plate, a first ground clustered pillar projecting from the base plate, a second ground clustered pillar projecting from the base plate and spaced apart from a first side of the first ground clustered pillar, a first ground member projecting from the base plate between the first ground clustered pillar and the second ground clustered pillar, wherein a distal end of the first ground member is configured to capacitively couple to the second ground clustered pillar, and a first signal member projecting from the base plate between the first ground clustered pillar and the first ground member, wherein the first signal member is electrically insulated from the base plate, the first ground clustered pillar, and the first ground member, and a distal end of the first signal member is configured to capacitively couple to the first ground clustered pillar.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Pronunciation quality evaluation method of computer auxiliary language learning system
ActiveCN101246685AImprove robustnessImprove performanceSpeech analysisTeaching apparatusSpoken languageComputer-aided
The present invention belongs to voice field of technology, pronunciation quality evaluation method of computer Computer Aided Language Learning system includes: calculation of the matching fraction, calculation of the sensing fraction based on Mel frequency scale, calculation of the segment length fraction and calculation of the keynote fraction, and processing fusion after mapping the above fractions; the pronunciation quality evaluation method of the invention has better robustness, high pertinency with the expert evaluation, used for interactive language learn and automatic spoken language test.
Owner:北京华控智加科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com