Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
847 results about "Electrical length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications and electrical engineering, electrical length (or phase length) refers to the length of an electrical conductor in terms of the phase shift introduced by transmission over that conductor at some frequency.
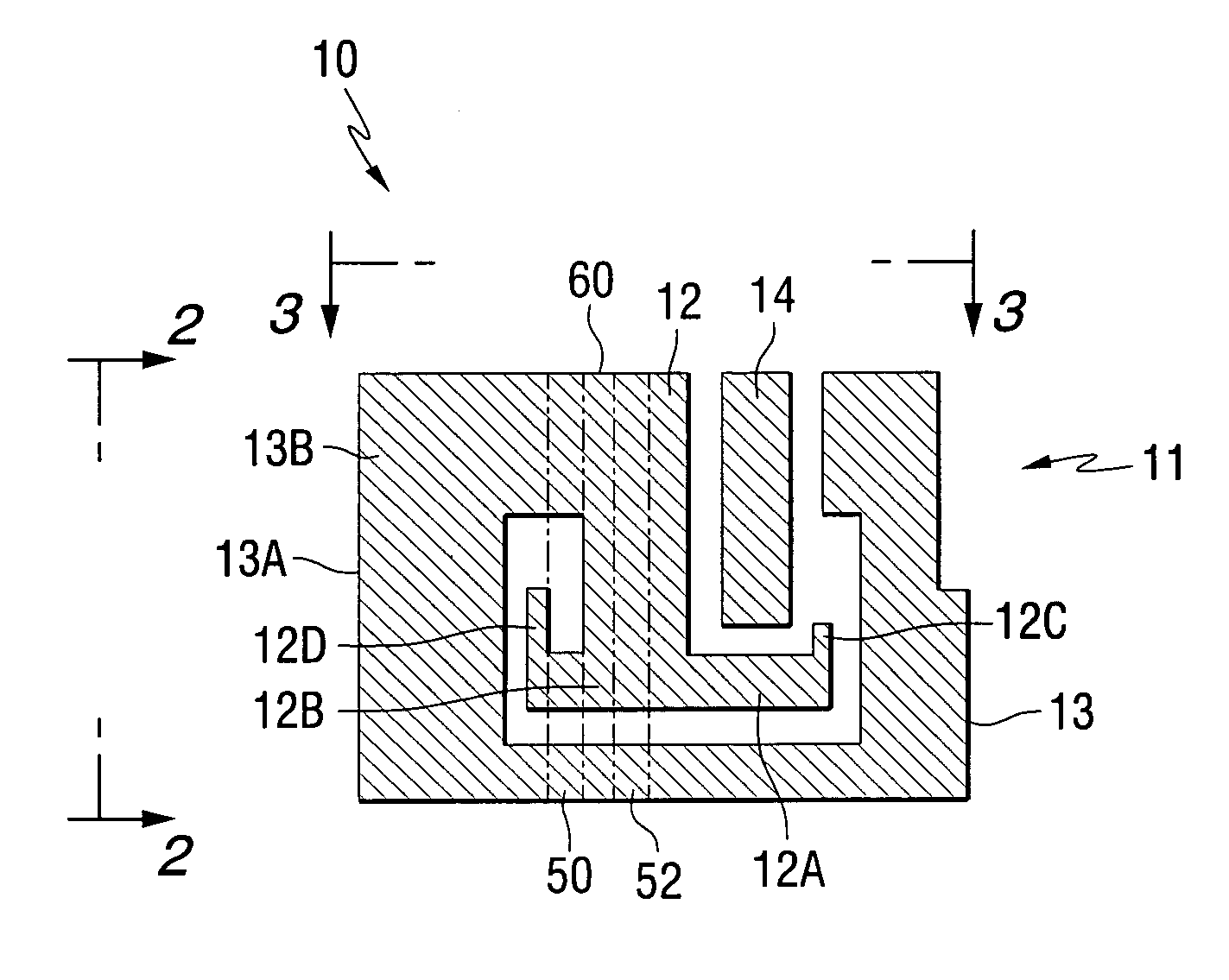
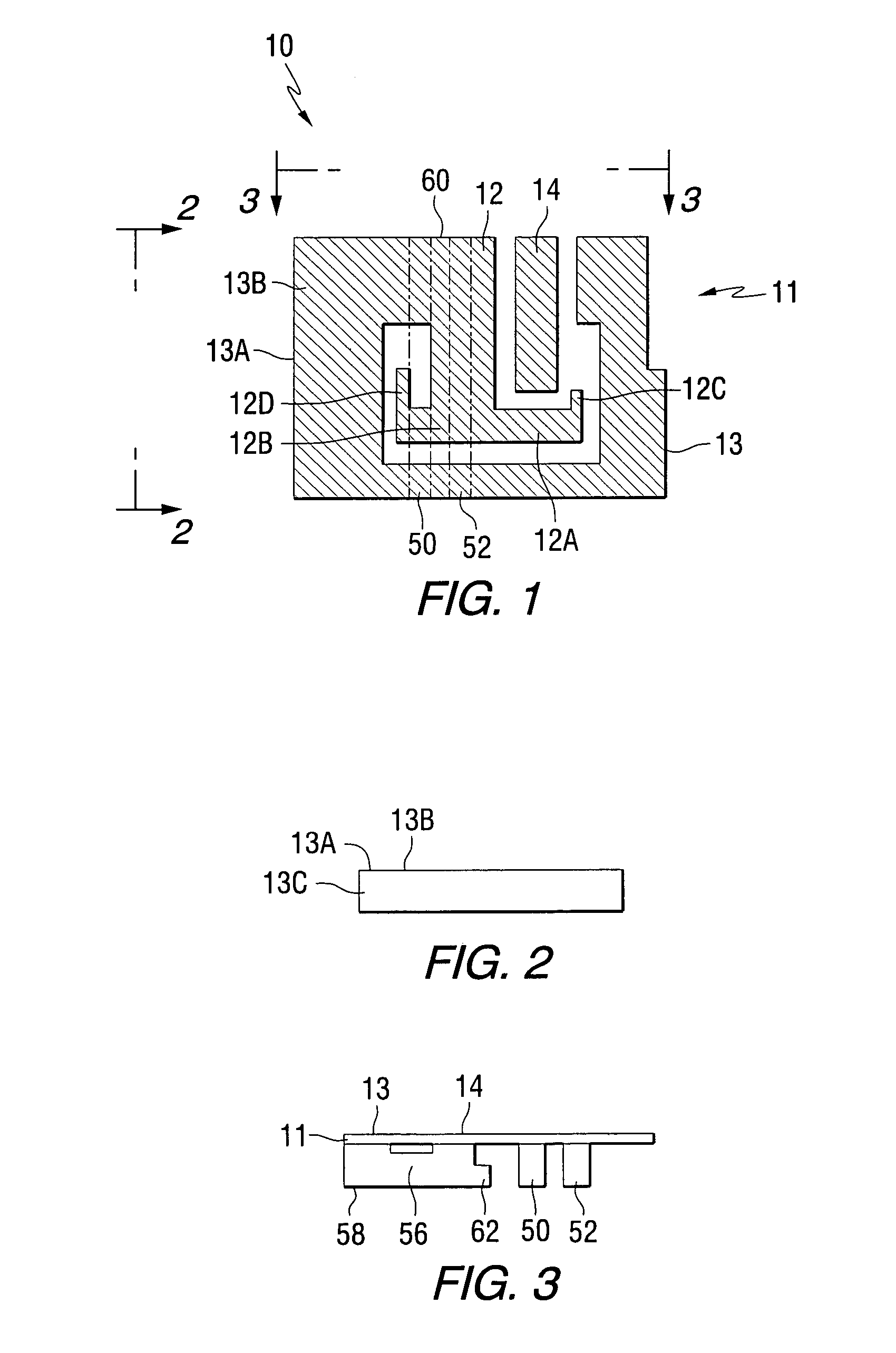
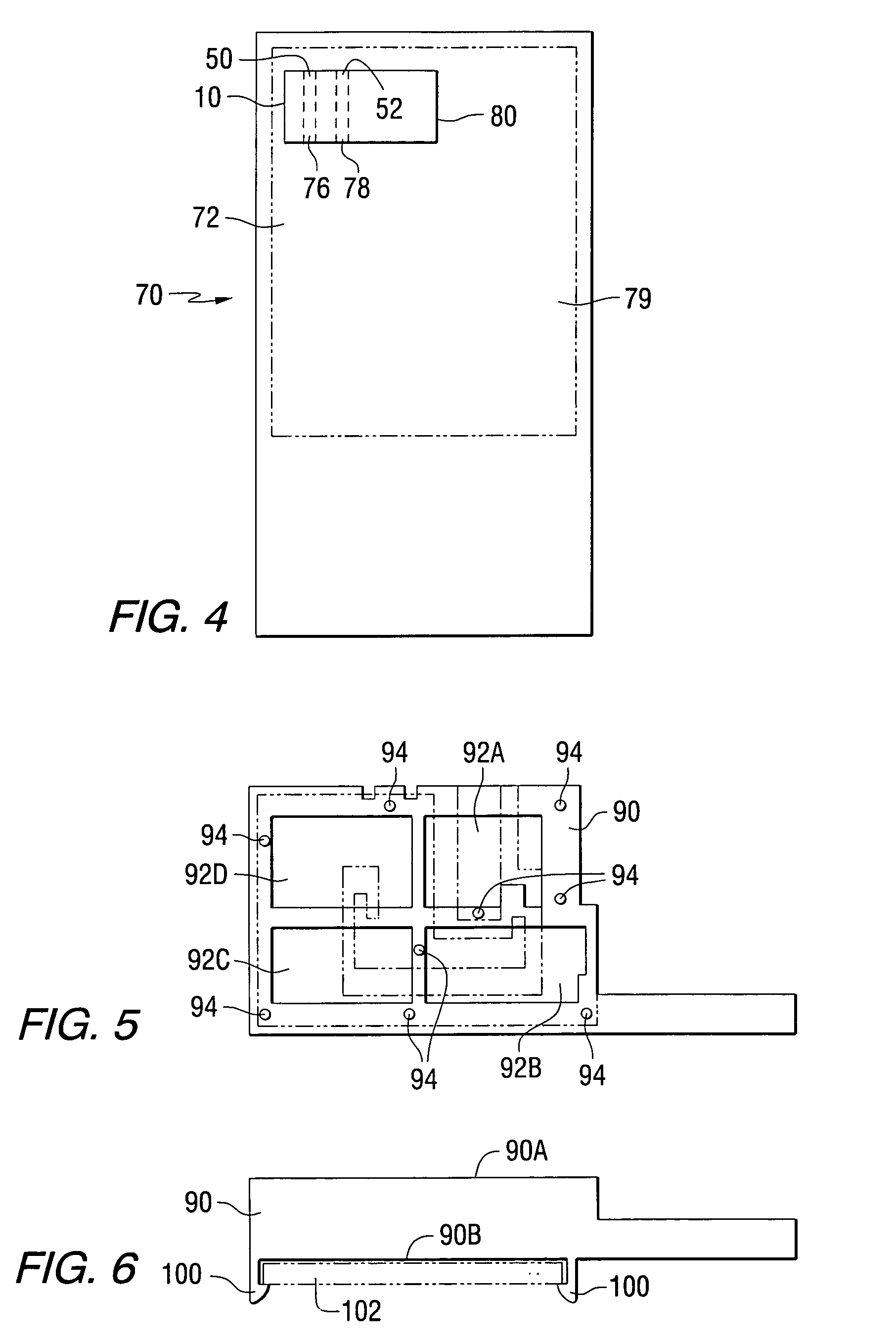
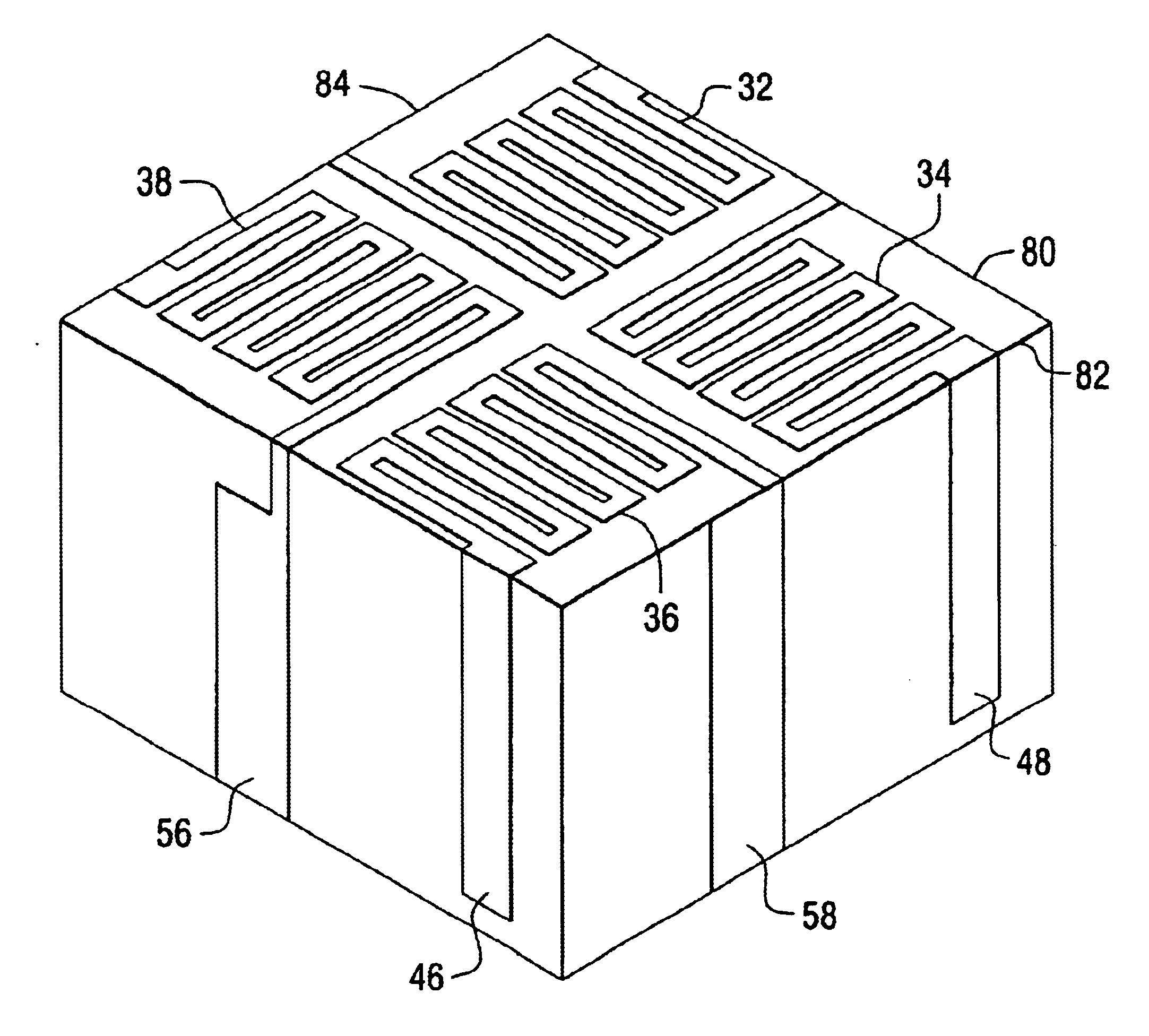
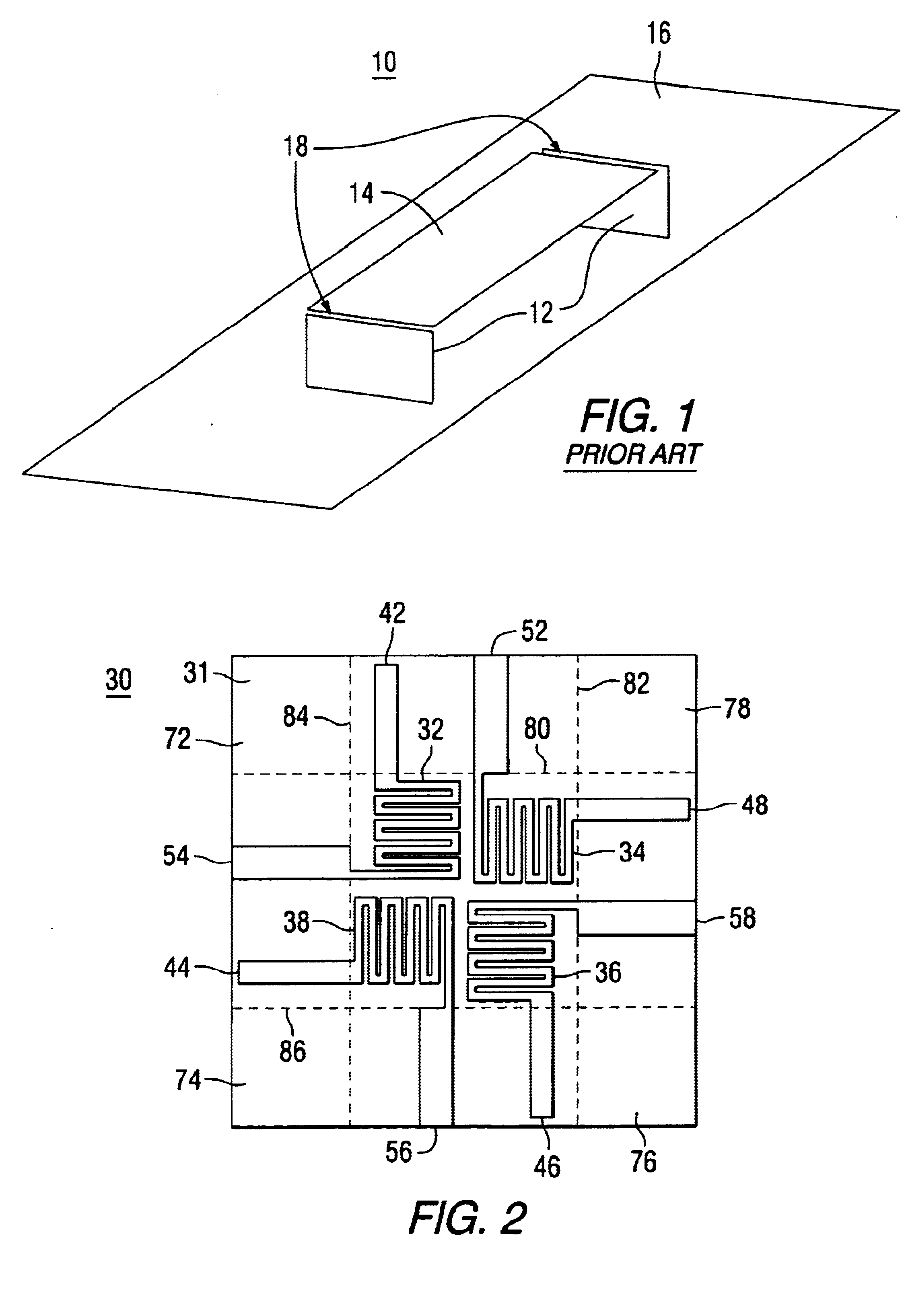
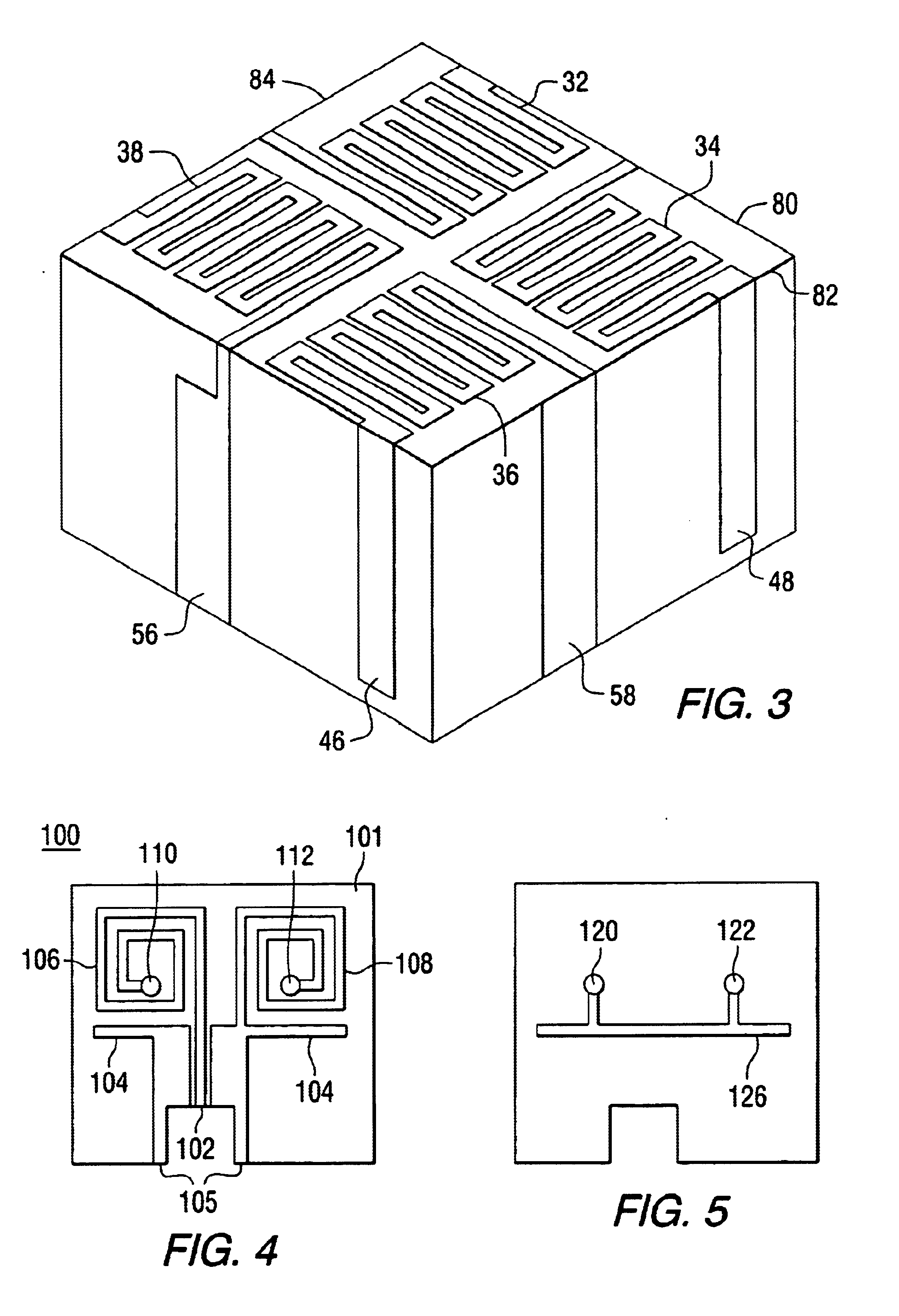
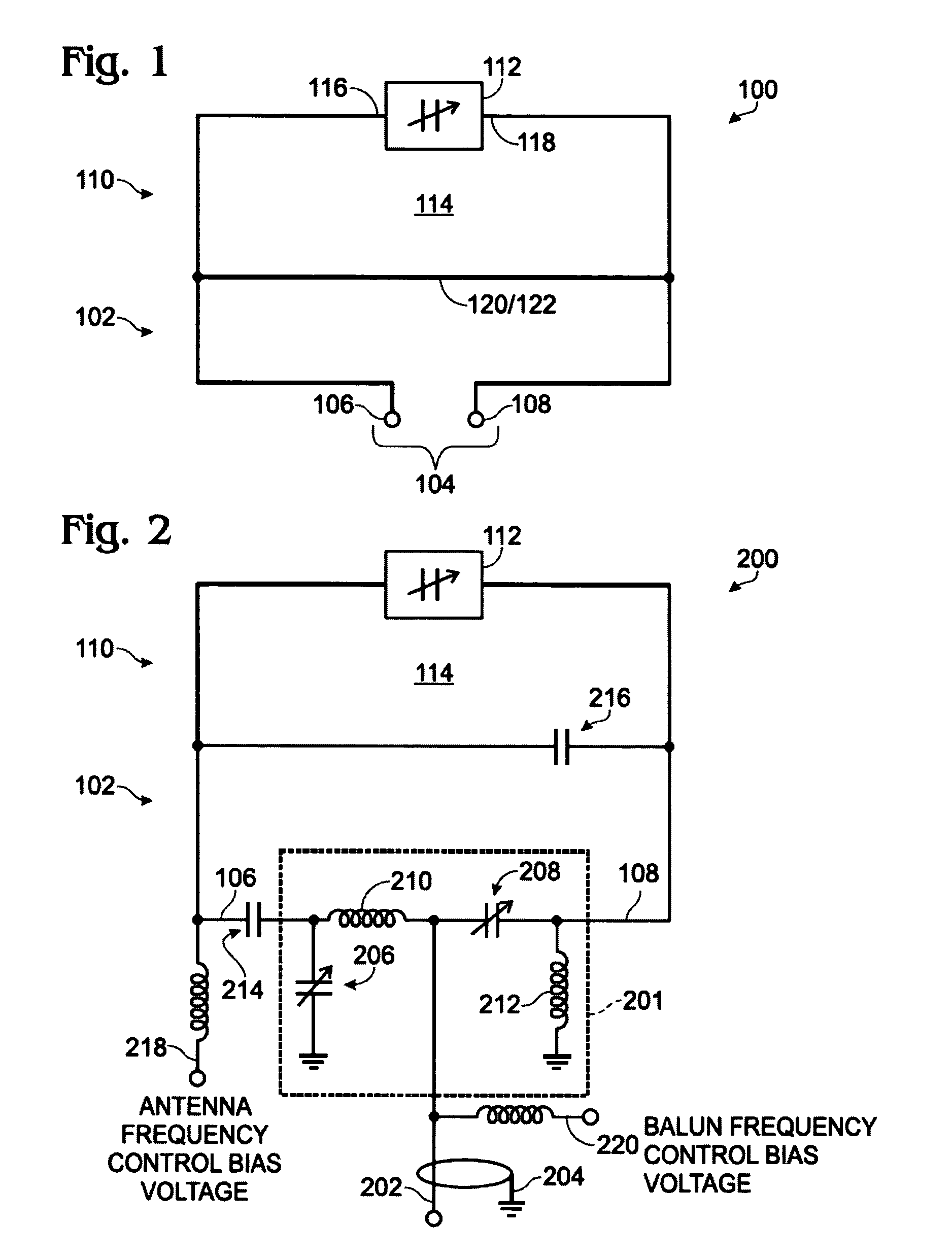
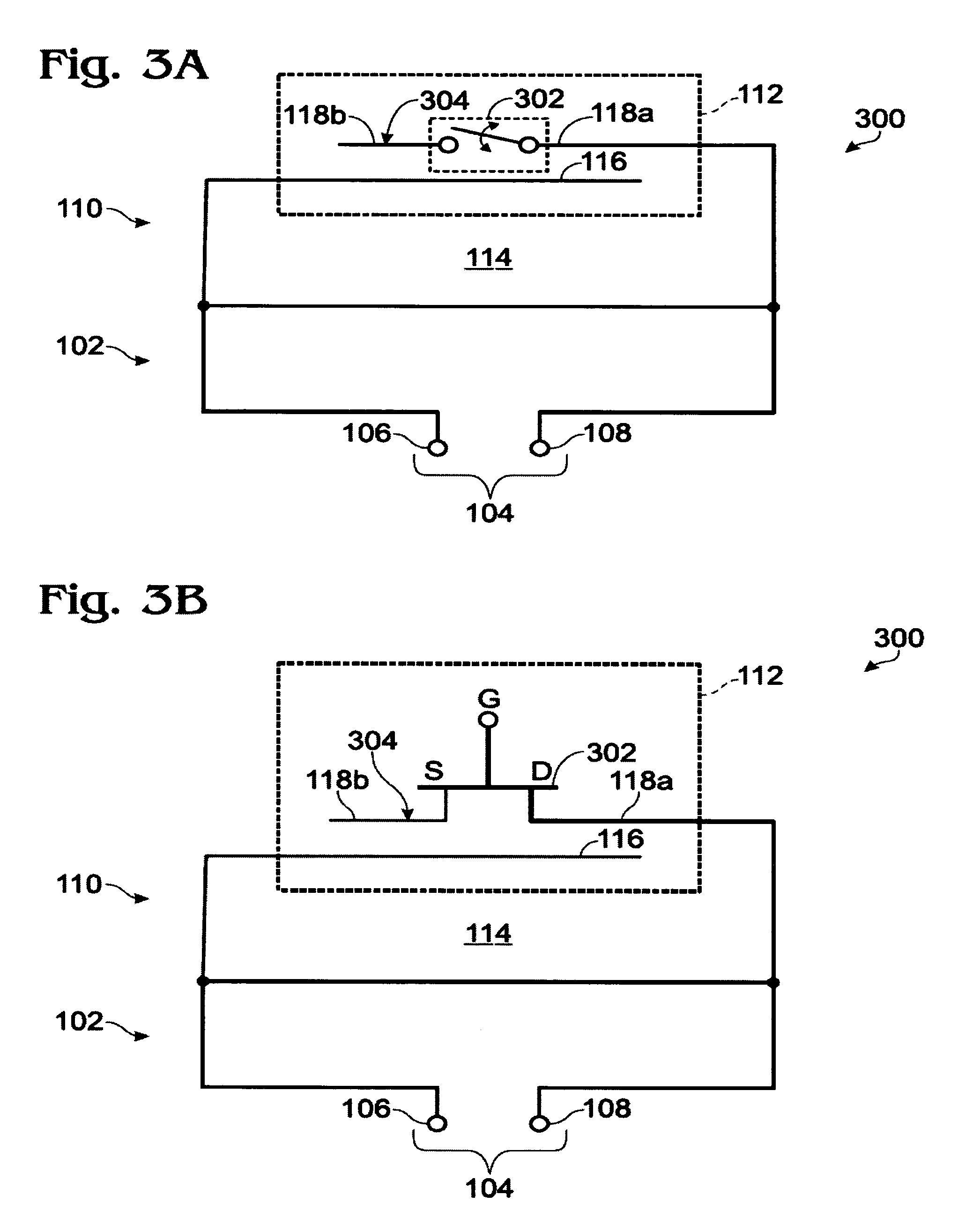
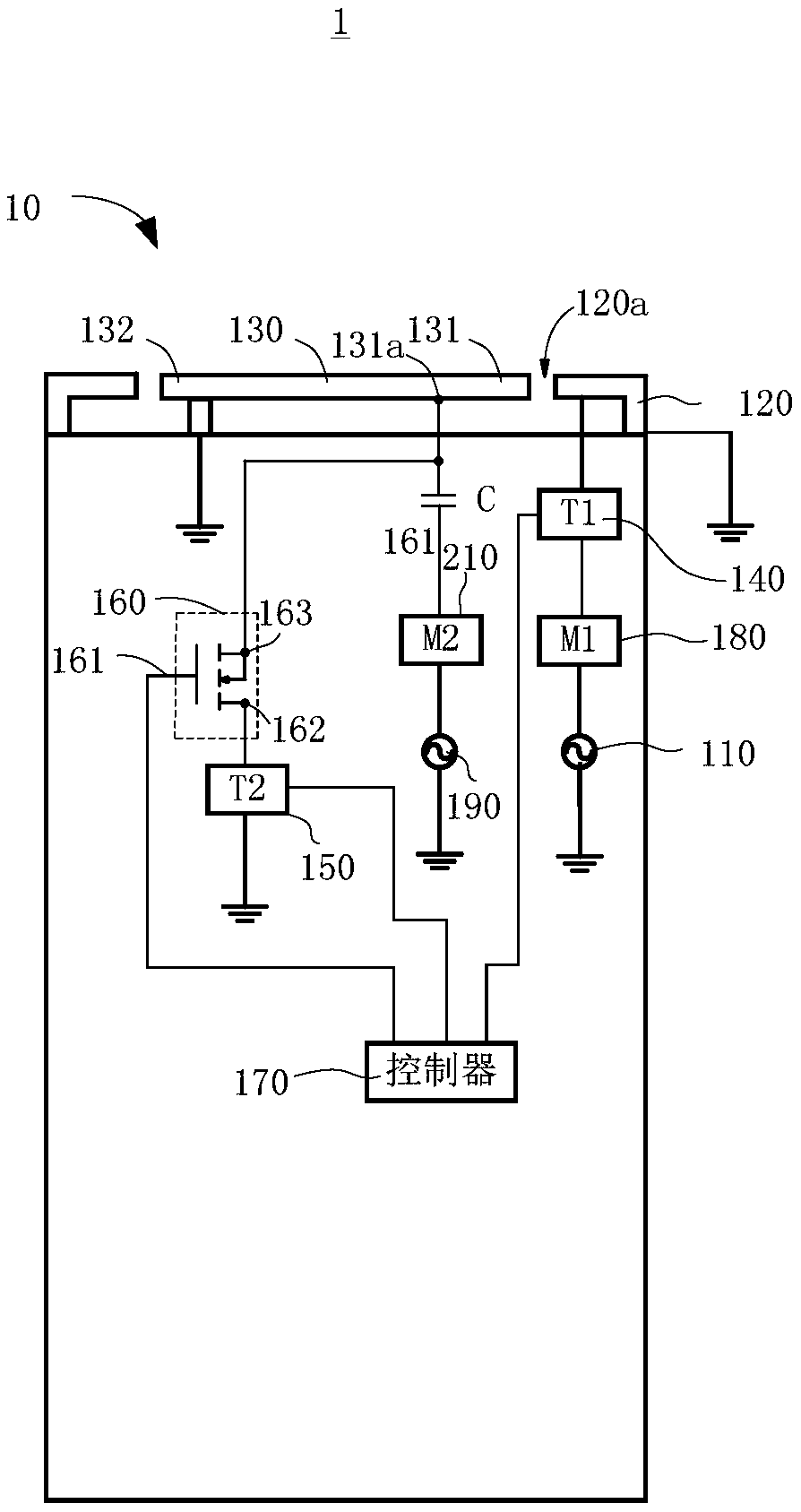
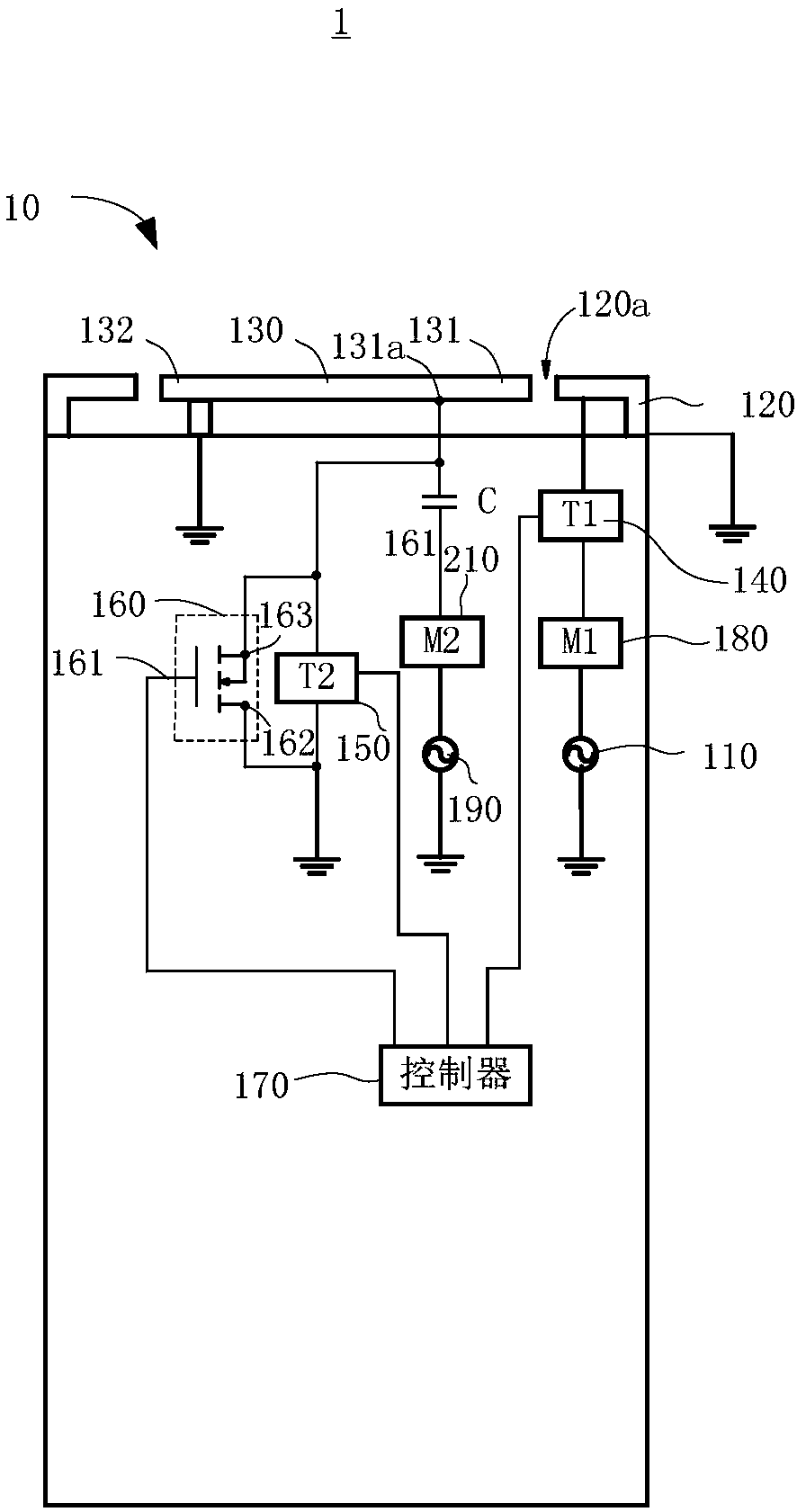
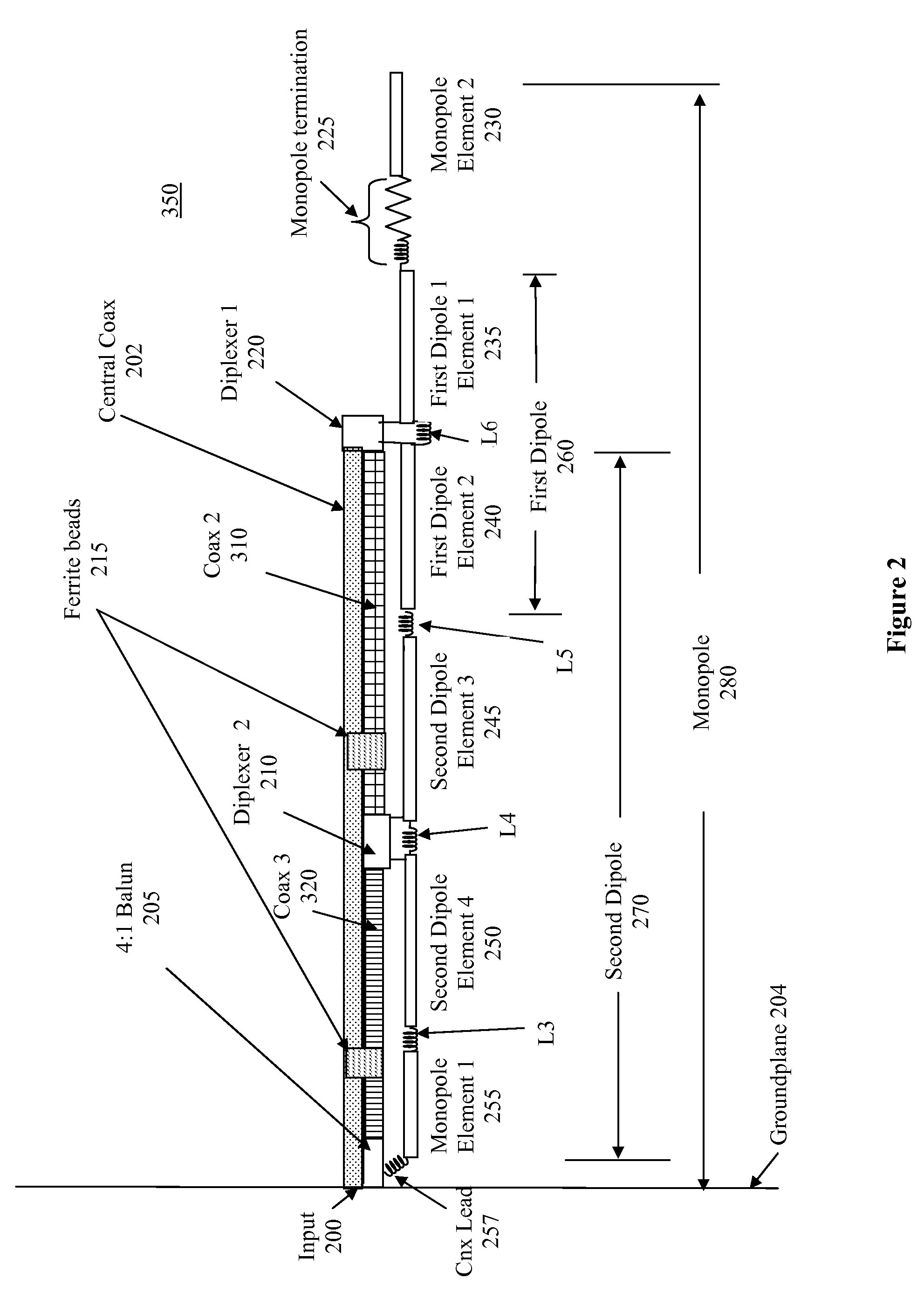
Low profile compact multi-band meanderline loaded antenna
InactiveUS7079079B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
An antenna for transmitting and receiving radio frequency energy. The antenna comprises a conductive radiator comprising a first and a second conductive region for providing a first and a second current path length. A feed conductor and a ground conductor operate as meanderline (or slow wave) elements to provide an electrical length longer than a physical length.
Owner:SKYCROSS INC
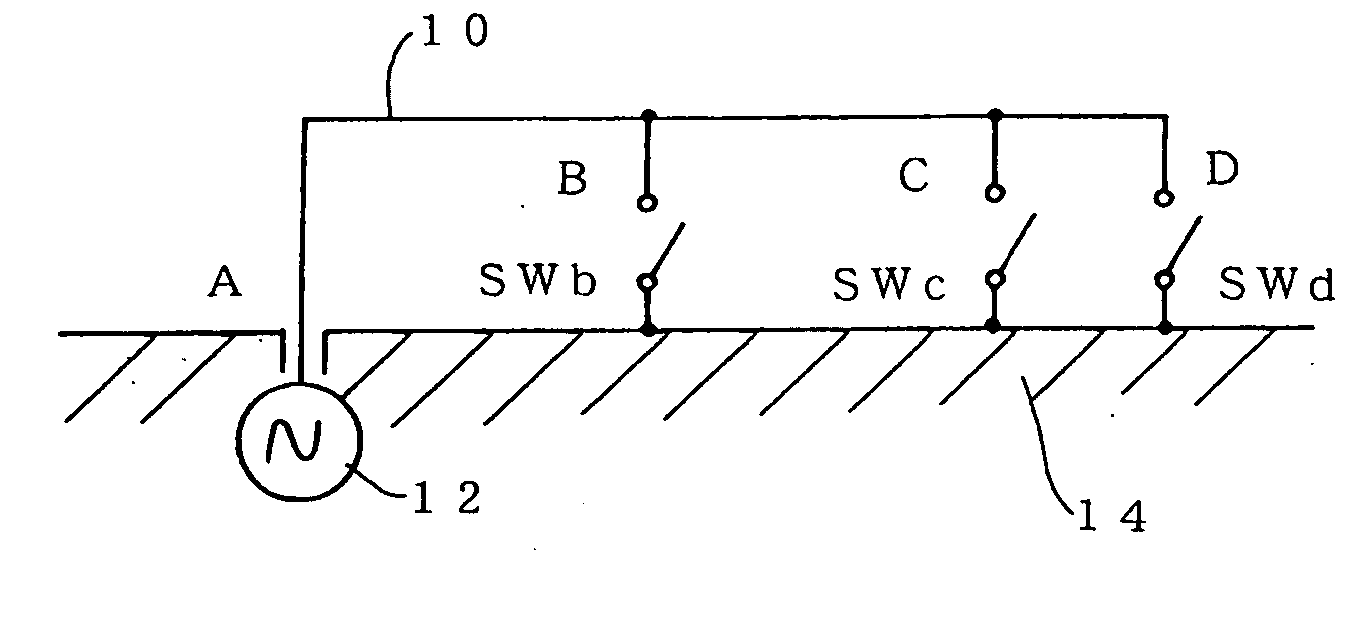
Antenna for a plurality of bands
InactiveUS20060097918A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringMultiple frequency
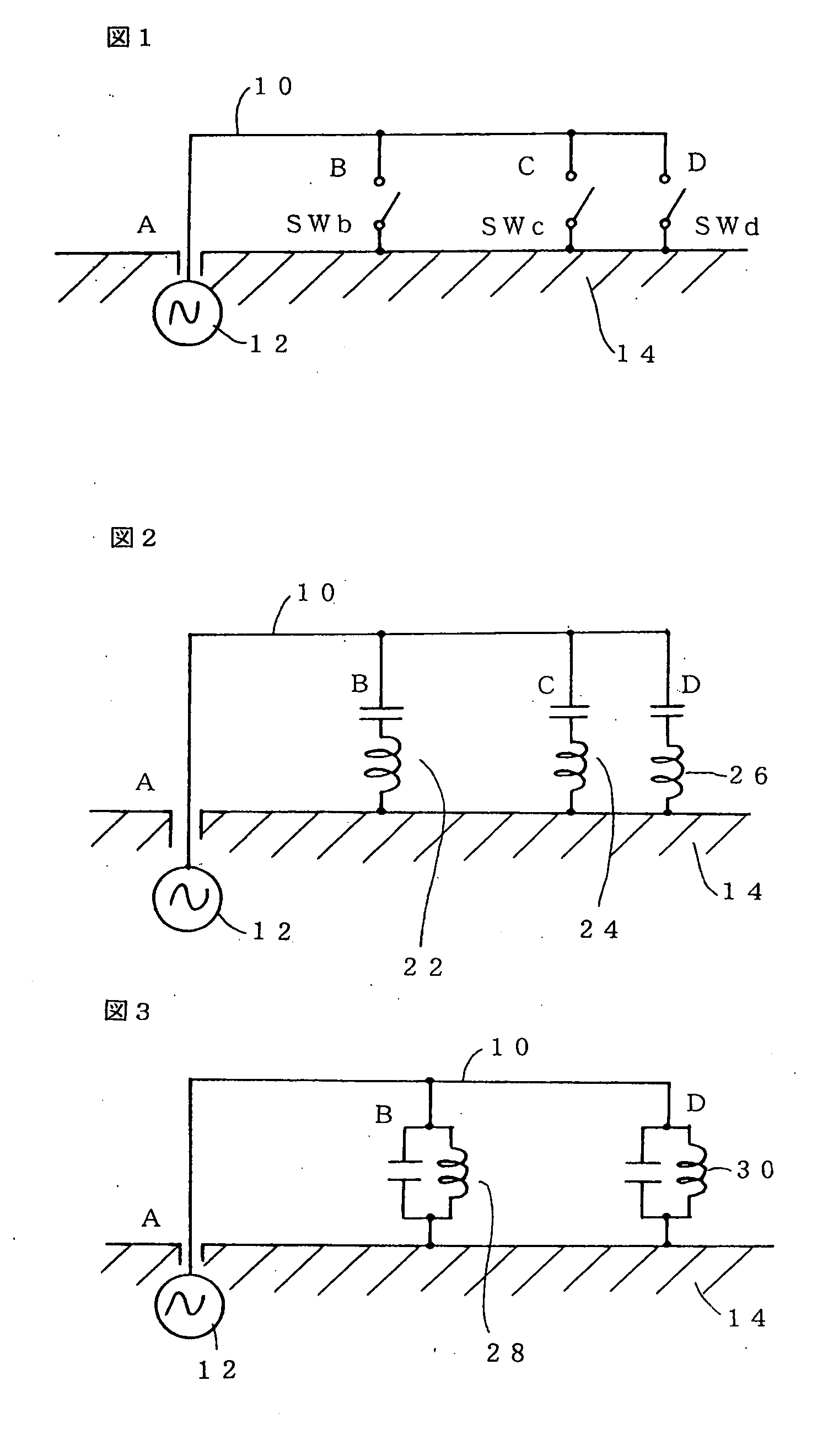
The present invention provides an antenna for multiple bands employing a single antenna element 10, capable of operating in multiple frequency bands, and ideal for size reduction purposes. One end A of an antenna element 10 is electrically connected to a feeding point 12 and intermediate points B and C and the other end thereof is electrically connected via switches SWb, SWc, and SWd to a ground conductor 14. The electrical lengths of the antenna element 10 from the terminal to the intermediate points B and C plus connection lines from these points via the switches SWb and SWc to the ground conductor 14 and the electrical length from the one end A to the other end D plus a connection line from the other end via the switch SWd to the ground conductor 14 are set to be capable of resonating different desired frequency bands. By closing one of the switches SWb, SWc, and SWd, one of the desired frequencies can be selected and the antenna can resonate with that frequency. Thus, the antenna employing the single antenna element 10 can operate in multiple frequency bands.
Owner:YOKOWO CO LTD
Array antenna apparatus having at least two feeding elements and operable in multiple frequency bands
ActiveUS20080174508A1Simple configurationEnsure adequate isolationSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsCouplingResonance
An array antenna apparatus includes a first feeding element having a first feed point, a second feeding element having a second feed point, and a first parasitic element electrically connected to the respective first and second feeding elements. In a first frequency band, respective resonances in the feeding elements occur independent of each other, by eliminating electromagnetic mutual coupling between the feeding elements, and exciting the first feeding element through the first feed point as well as exciting the second feeding element through the second feed point. In a second frequency band lower than the first frequency band, a loop antenna having a certain electrical length is formed by the first and second feeding elements and the first parasitic element, and a resonance of the loop antenna substantially occurs by exciting the first feeding element through the first feed point.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Internal antenna
InactiveUS6985108B2Reduce distanceImprove matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyAntenna gain
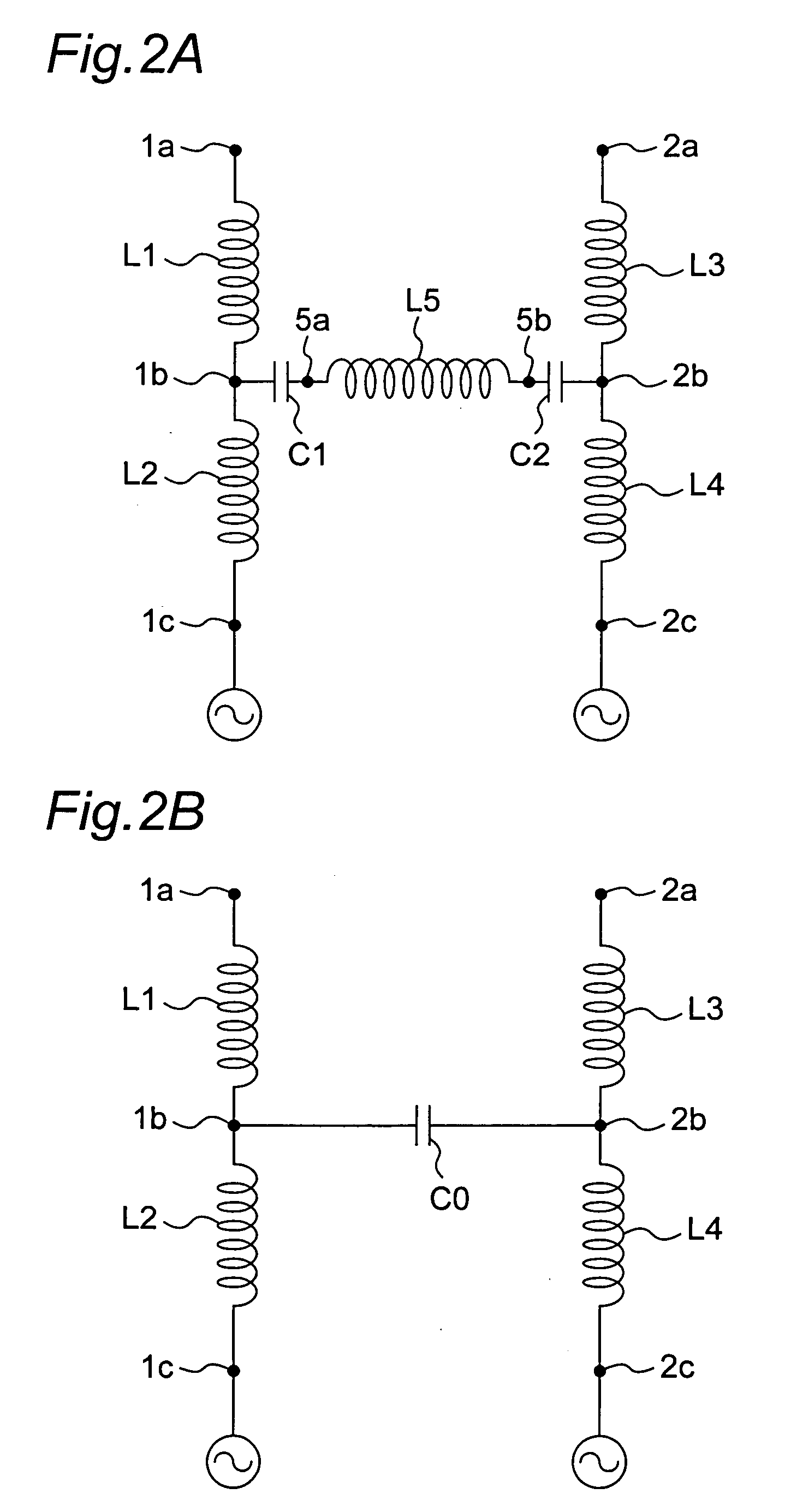
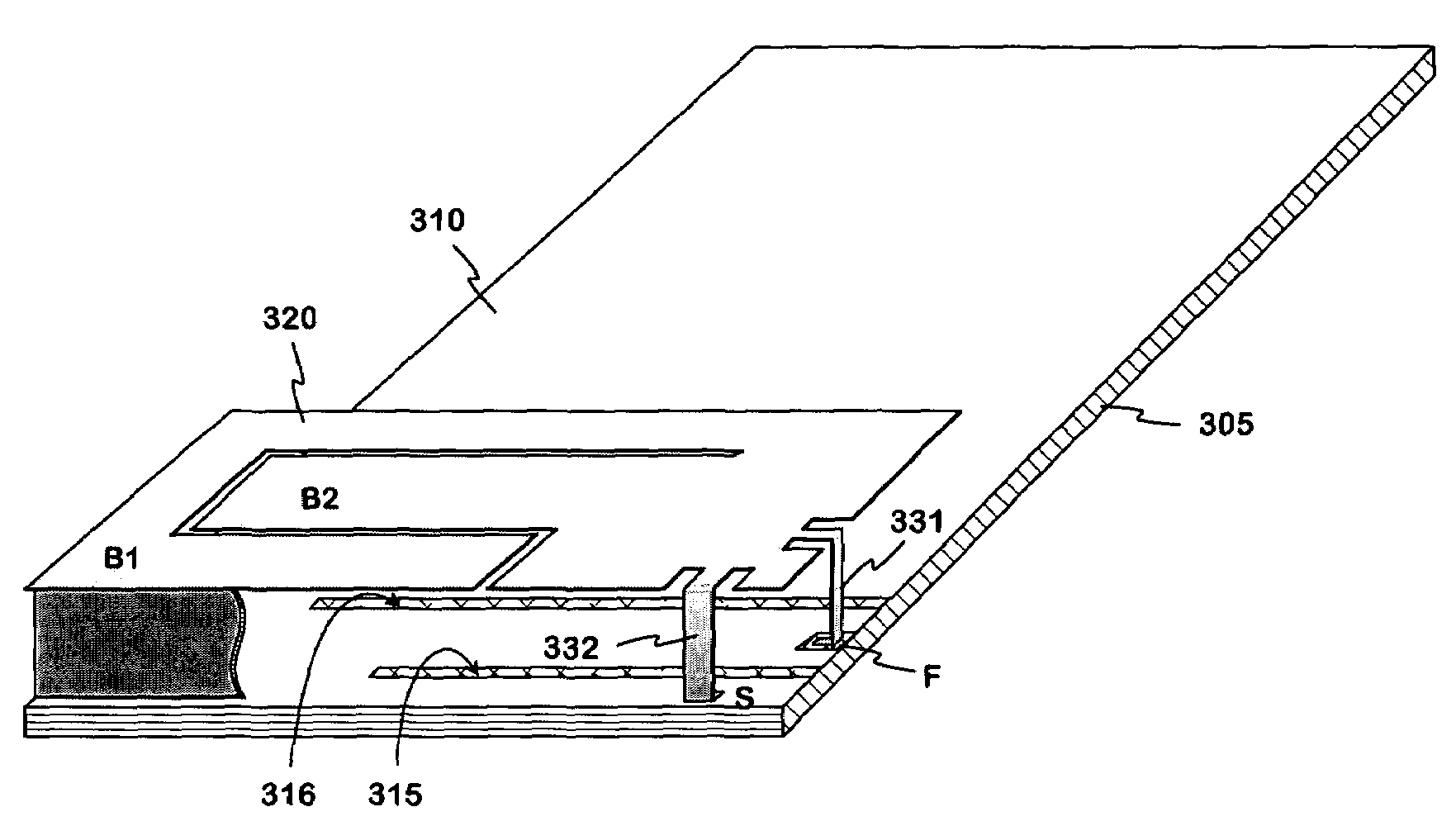
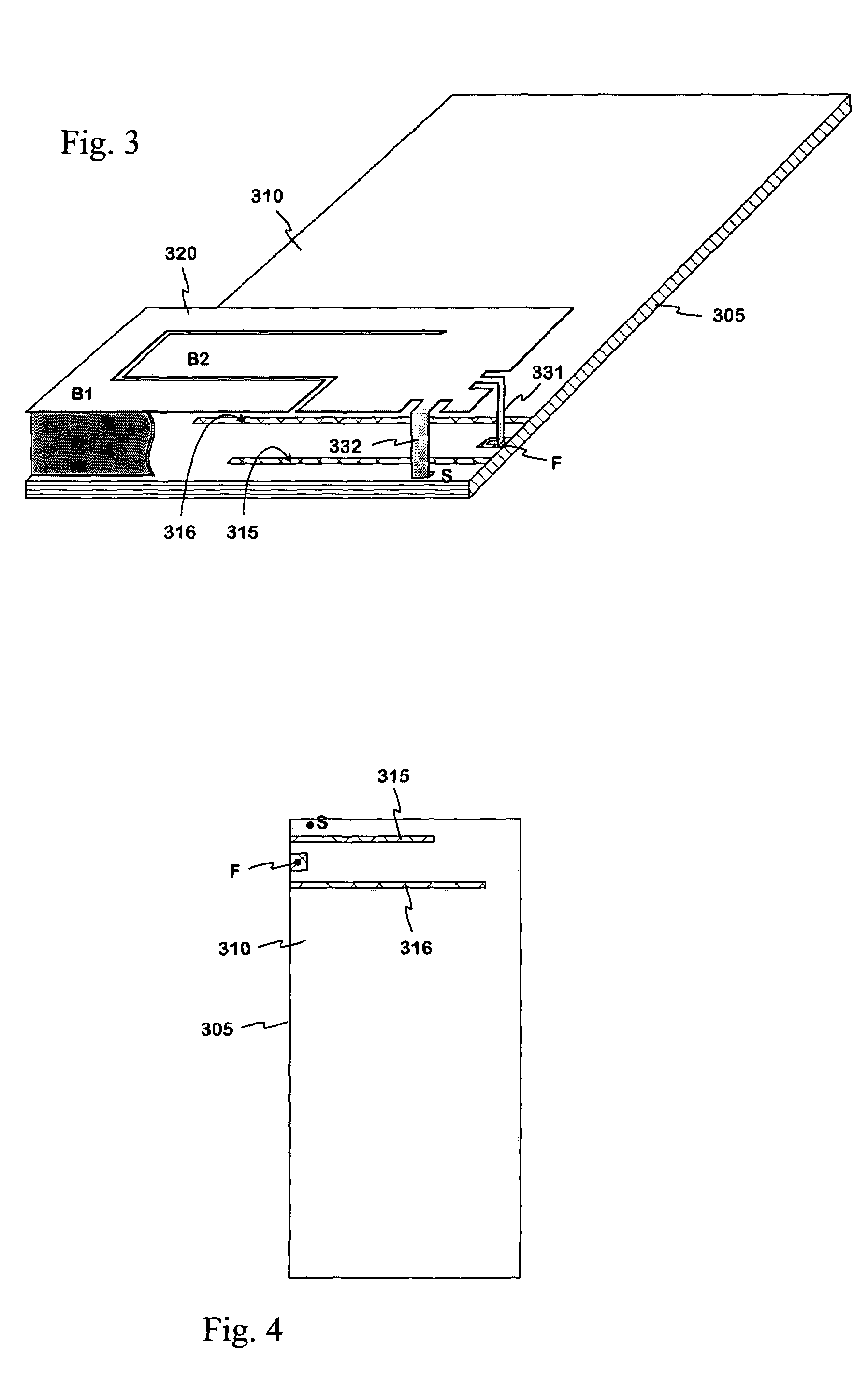
An internal planar antenna for small radio apparatuses. The ground plane (310) of the planar antenna is shaped such that it improves the matching of the antenna. The shaping may be done by means of one or more slots (315, 316) in the ground plane. The slot suitably changes the electrical length of the ground plane as viewed from the short-circuit point (S) so that the ground plane will function as a radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Also the slot (331) in the ground plane can be arranged to function as an additional radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Antenna gain will increase as the matching is improved, and the upper band of a dual band antenna, for example, can be made broader.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Internal digital TV antennas for hand-held telecommunications device
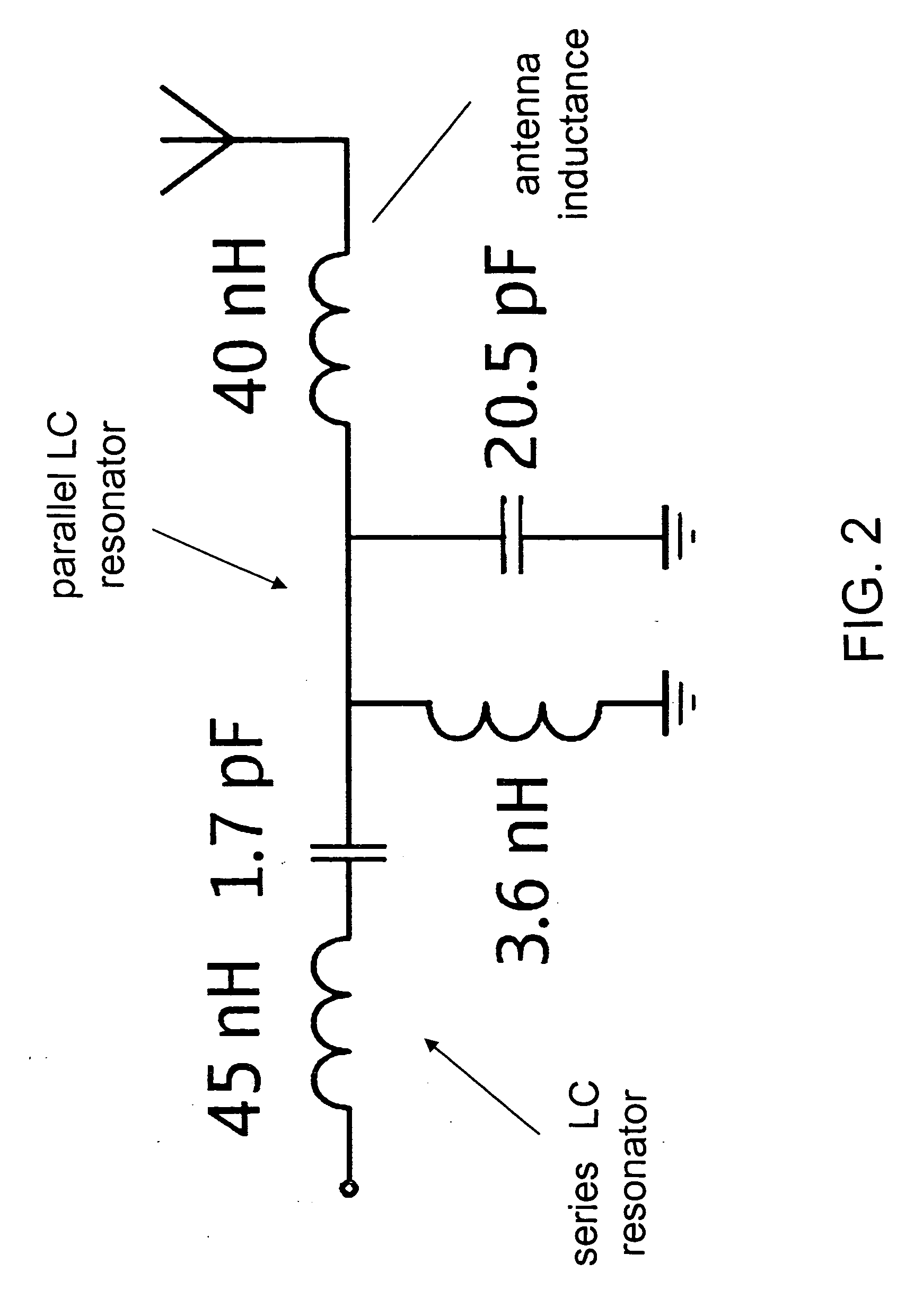
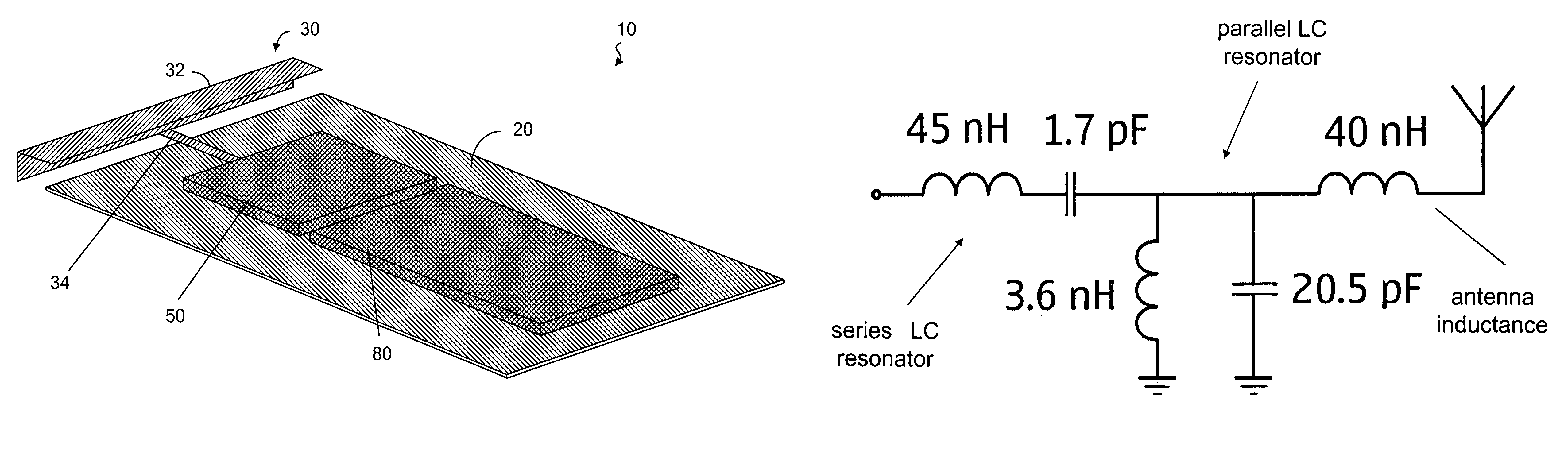
An antenna structure comprises an unbalanced antenna for receiving digital video broadcasting signals. The antenna is dimensioned to fit within an electronic device, such as a mobile phone. The unbalanced antenna has a radiative element and a feed line connected to a matching circuit so as to achieve two or more resonances within a DVB-H frequency range, such as 470 to 702 MHz. The physical length of the radiative element is always smaller than λ / 4 at the frequencies of interest (470-702 MHz), but the electrical length can be smaller or substantially equal to λ / 4. The matching circuit can comprise one or more LC resonators depending on the number of resonances. The resonators can be series or parallel connected between the feed line and RF circuitry for processing the broadcasting signals. The antenna can be tuned to other bands above the DVB-H frequencies for use as a diversity or MIMO antenna.
Owner:RPX CORP
Resonance modifying connector
ActiveUS20110300757A1Improve anti-interference abilityHigh frequencyContact member assembly/disassemblyCoupling device detailsResonanceOperating frequency
A connector assembly is provided that is suitable for modifying the resonant frequency of ground terminals used in conjunction with high data rate signal terminals. Ground terminals may be interconnected with a conductive bridge so as to provide ground terminals with a predetermined maximum effective electrical length. Reducing the effective electrical length of the ground terminal can move the resonance frequencies of the connector outside the operational range of frequencies at which signals will be transmitted.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Dielectrically-loaded antenna
InactiveUS6914580B2High bandwidthReduced insertion lossResonant long antennasLogperiodic antennasResonanceEngineering
A dielectrically-loaded loop antenna with a cylindrical dielectric core, a feeder structure passing axially through the core, a sleeve balun encircling one end portion of the core and helical antenna elements extending from a feed connection with the feeder structure at the other end of the core to the rim of the balun. The antenna elements are arranged as a pair of laterally opposed groups of conductive elongate helical elements each having at least first and second conductive elements of different electrical lengths to form a plurality of looped conductive paths. By forming at least one of the conductive elements in each group as a conductive strip with one or both edges meandered, such that the edges of the strip are non-parallel and have different electrical lengths, additional modes of resonance arc created, yielding an improvement in bandwidth.
Owner:SARANTEL LTD
MRI tunable antenna and system
InactiveUS7088104B2Reduce couplingImprove performanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorLength wave
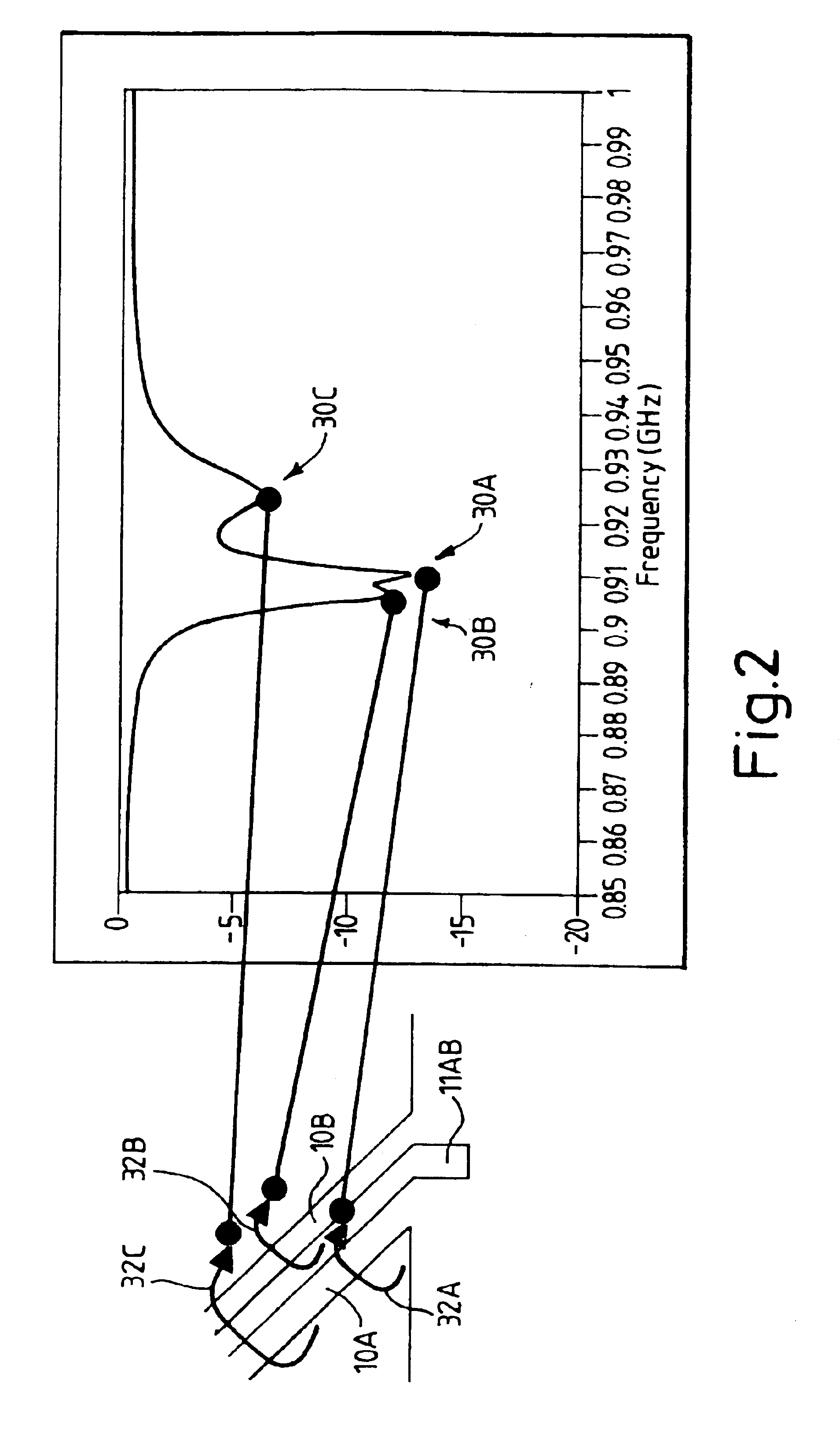
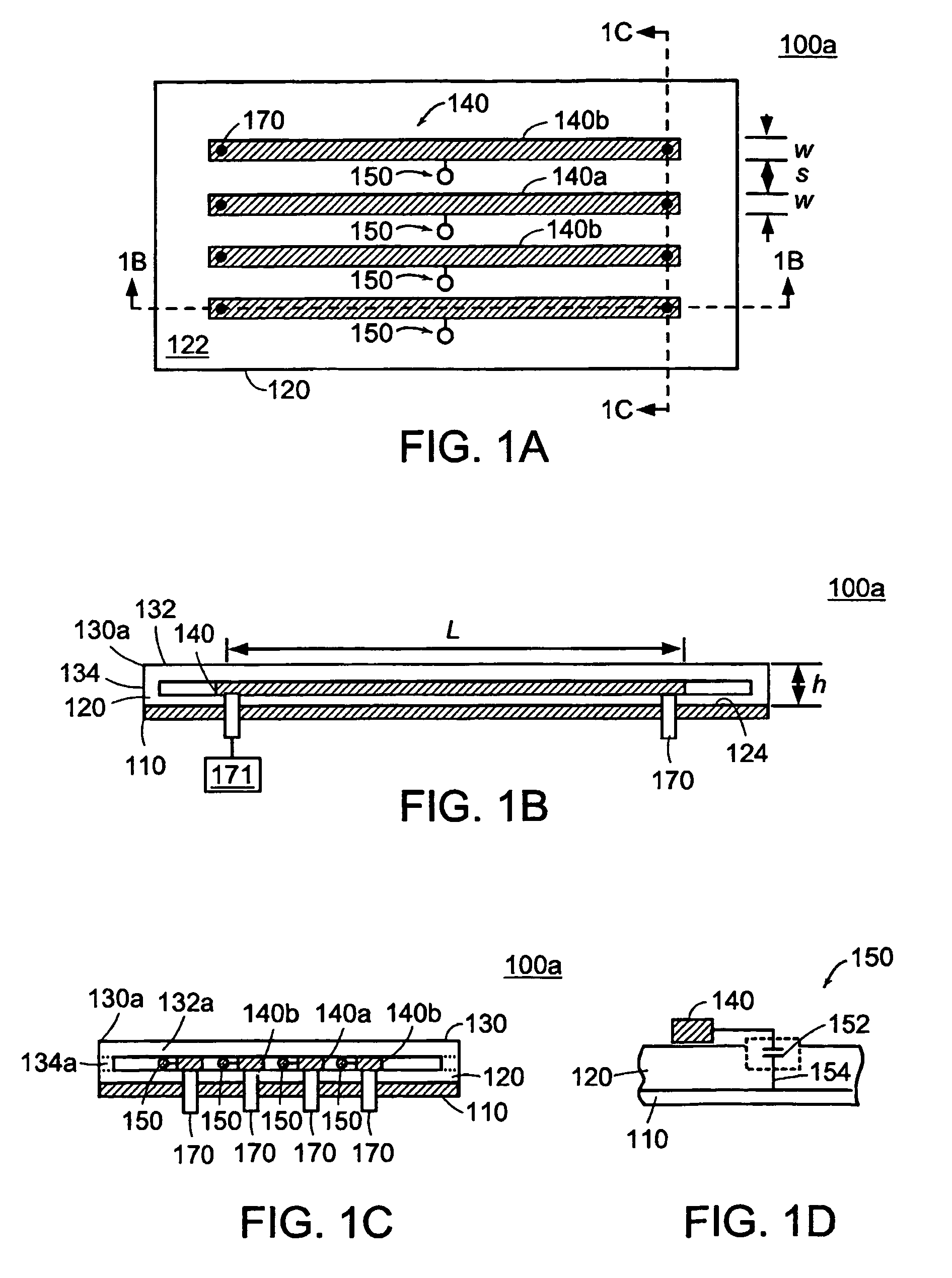
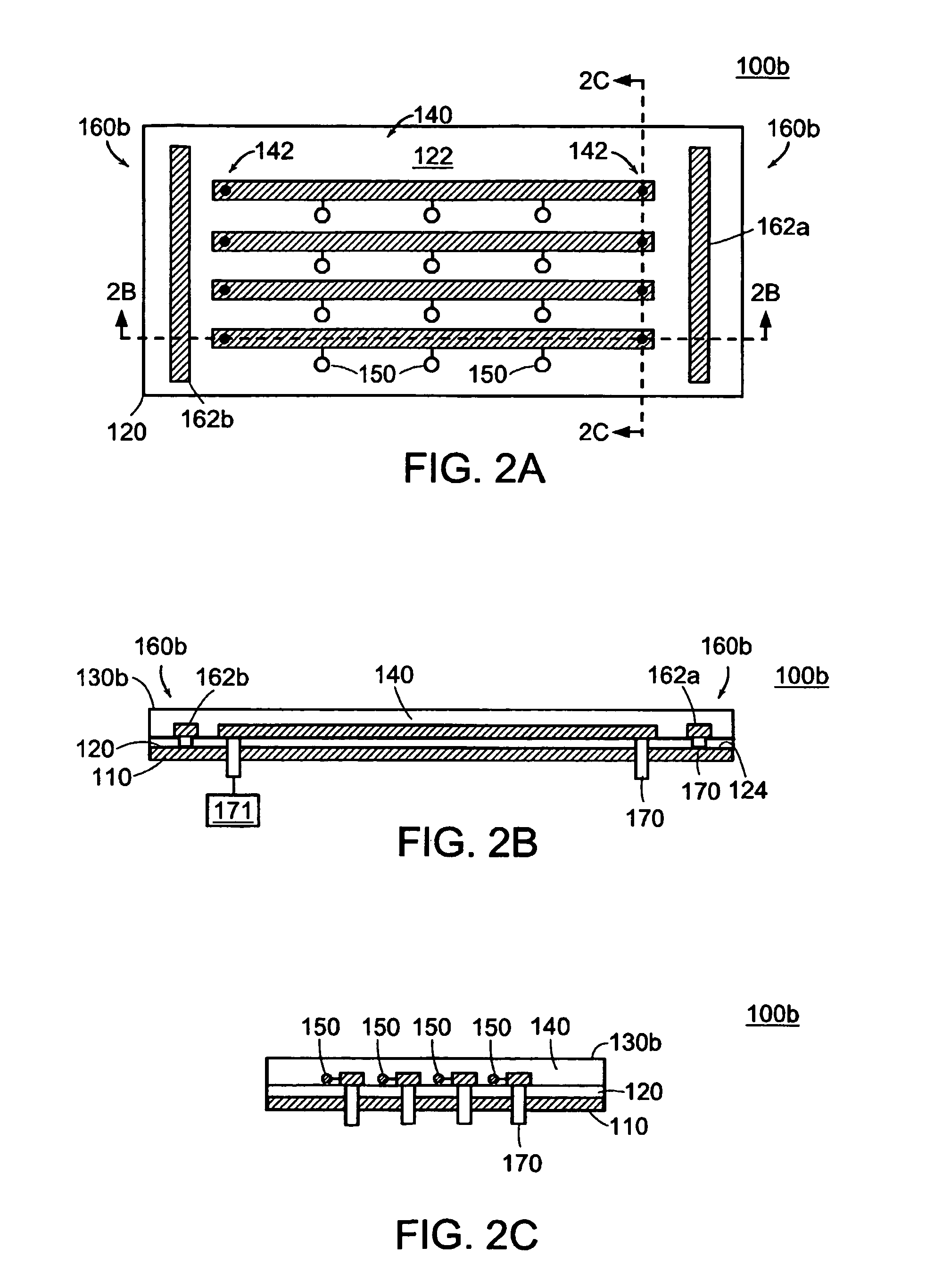
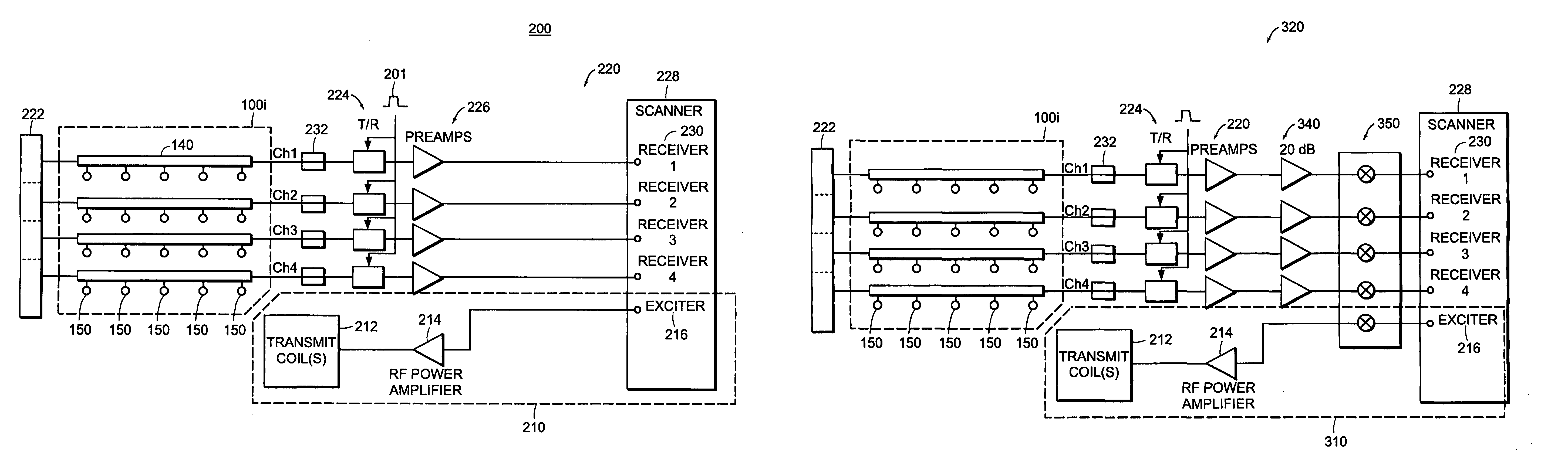
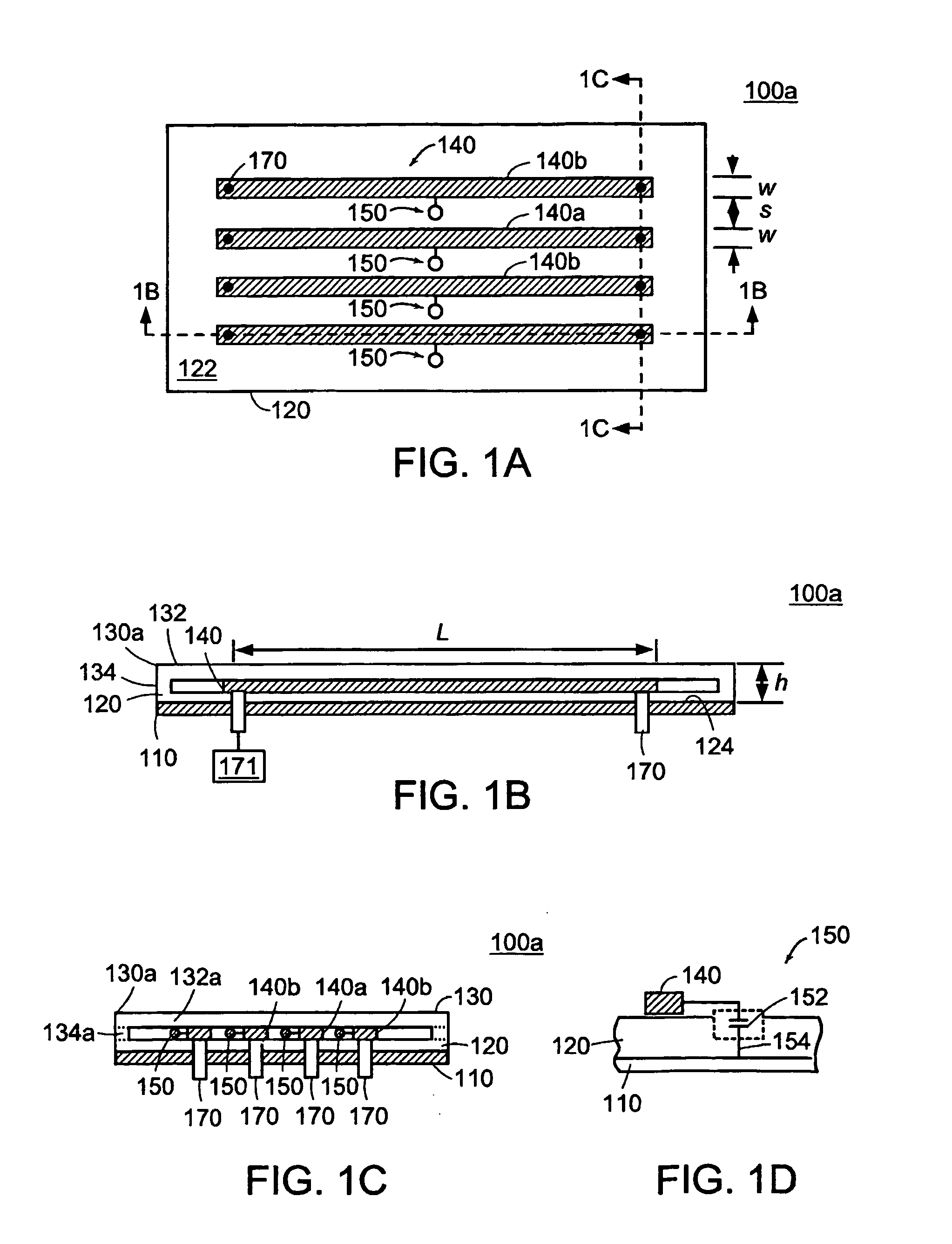
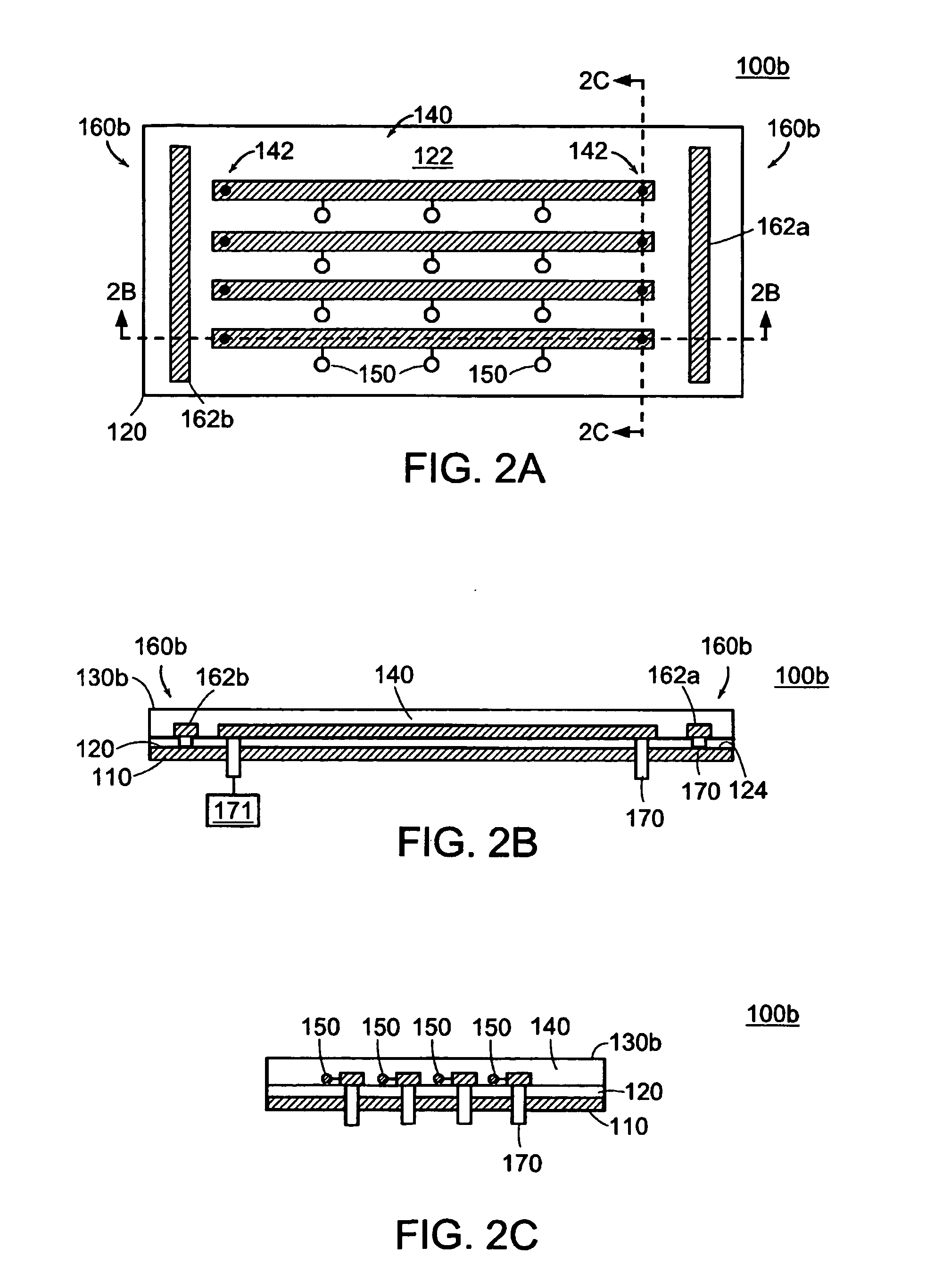
A strip array antenna including a number of conductors (14) that are connected to ground or virtual ground though at least one reactive component (150). The apparent electrical length of conductors (140) is tuned so that it equals an integer multiple of a quarter wavelength at the operating frequency.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Resonance modifying connector
ActiveUS8540525B2Improve anti-interference abilityHigh frequencyContact member assembly/disassemblyCoupling device detailsResonanceOperating frequency
A connector assembly is provided that is suitable for modifying the resonant frequency of ground terminals used in conjunction with high data rate signal terminals. Ground terminals may be interconnected with a conductive bridge so as to provide ground terminals with a predetermined maximum effective electrical length. Reducing the effective electrical length of the ground terminal can move the resonance frequencies of the connector outside the operational range of frequencies at which signals will be transmitted.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Internal digital TV antennas for hand-held telecommunications device
InactiveUS7760146B2Antenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedLc resonatorTelecommunications link
An antenna structure comprises an unbalanced antenna for receiving digital video broadcasting signals. The antenna is dimensioned to fit within an electronic device, such as a mobile phone. The unbalanced antenna has a radiative element and a feed line connected to a matching circuit so as to achieve two or more resonances within a DVB-H frequency range, such as 470 to 702 MHz. The physical length of the radiative element is always smaller than λ / 4 at the frequencies of interest (470-702 MHz), but the electrical length can be smaller or substantially equal to λ / 4. The matching circuit can comprise one or more LC resonators depending on the number of resonances. The resonators can be series or parallel connected between the feed line and RF circuitry for processing the broadcasting signals. The antenna can be tuned to other bands above the DVB-H frequencies for use as a diversity or MIMO antenna.
Owner:RPX CORP
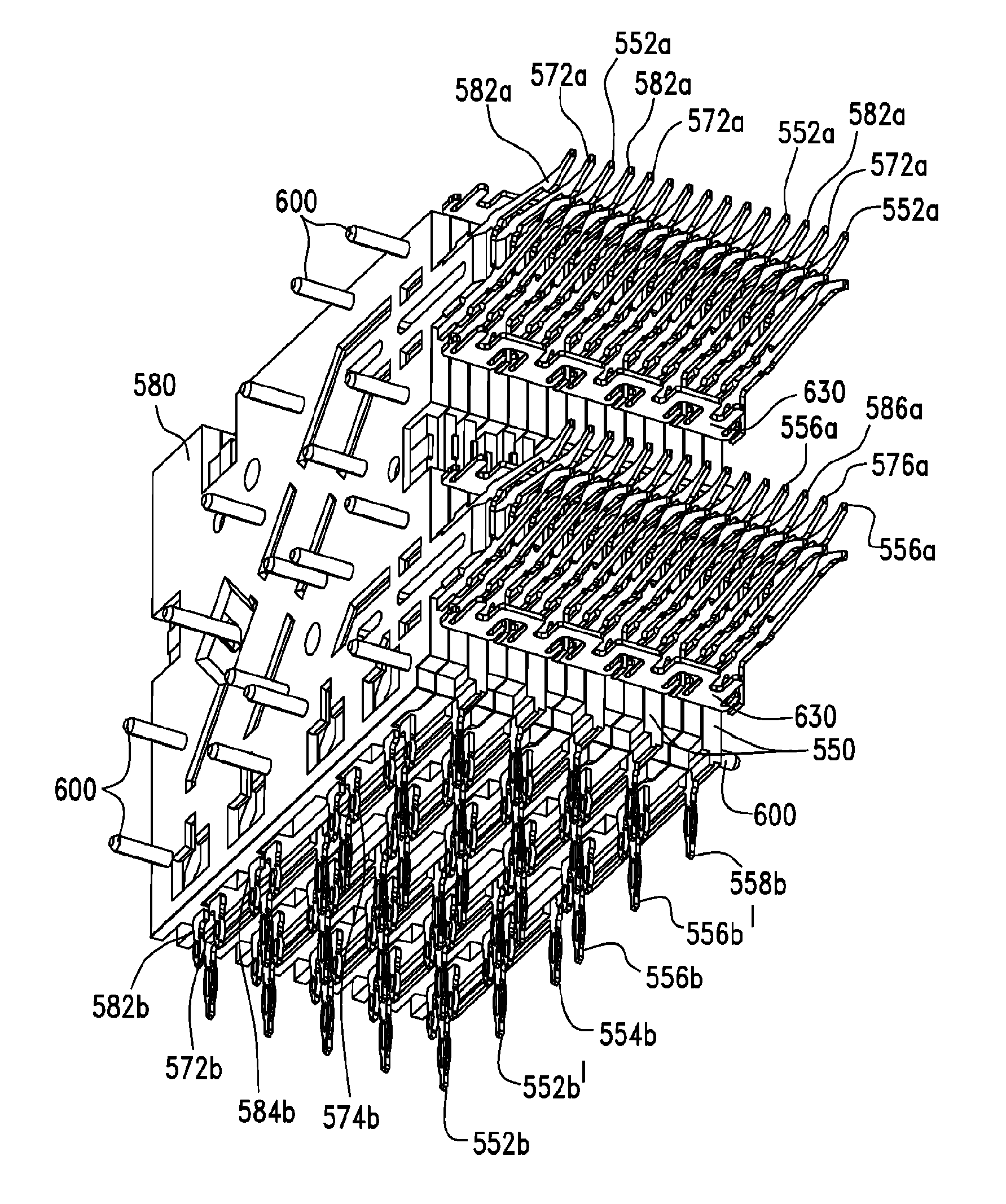
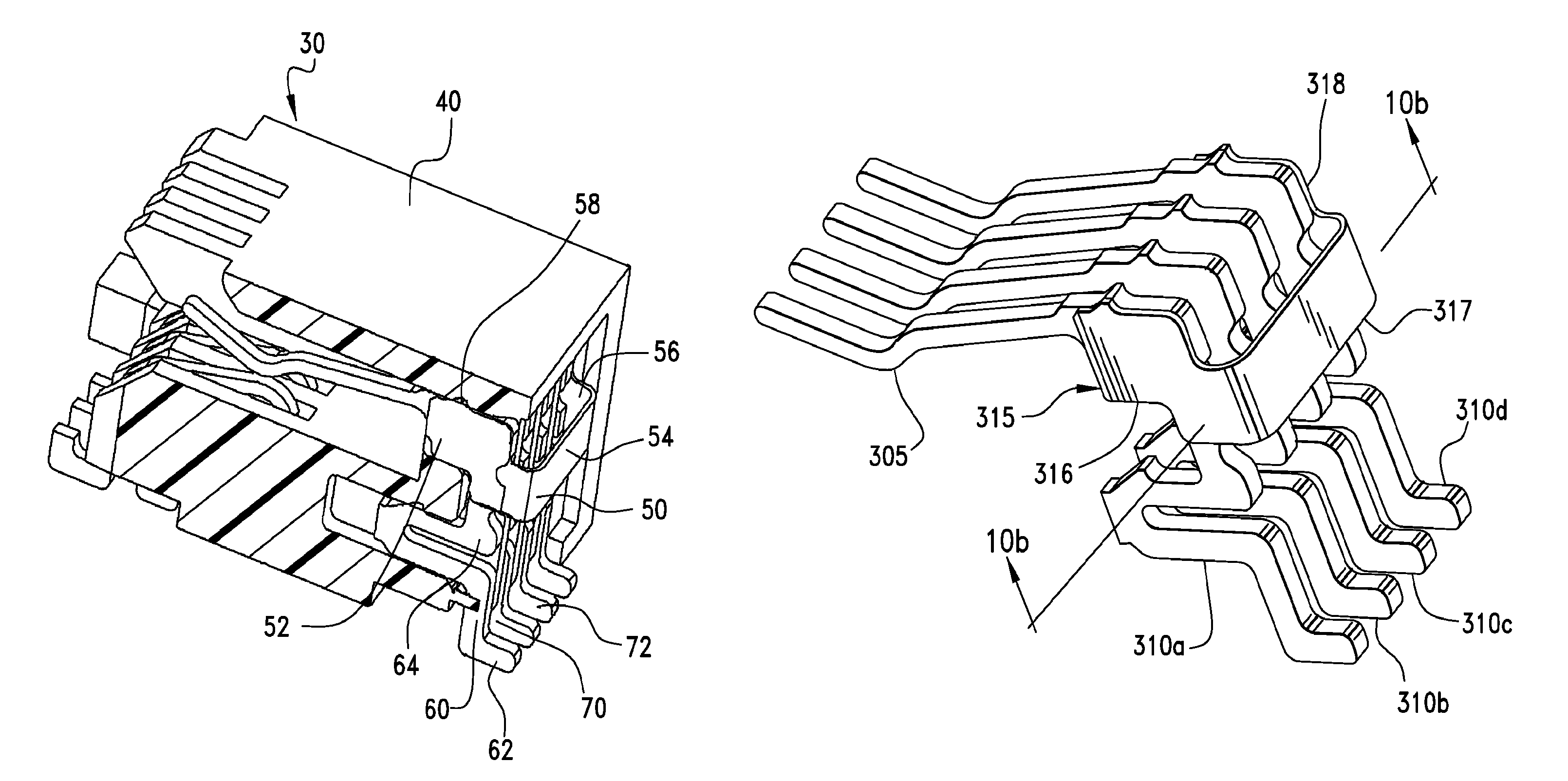
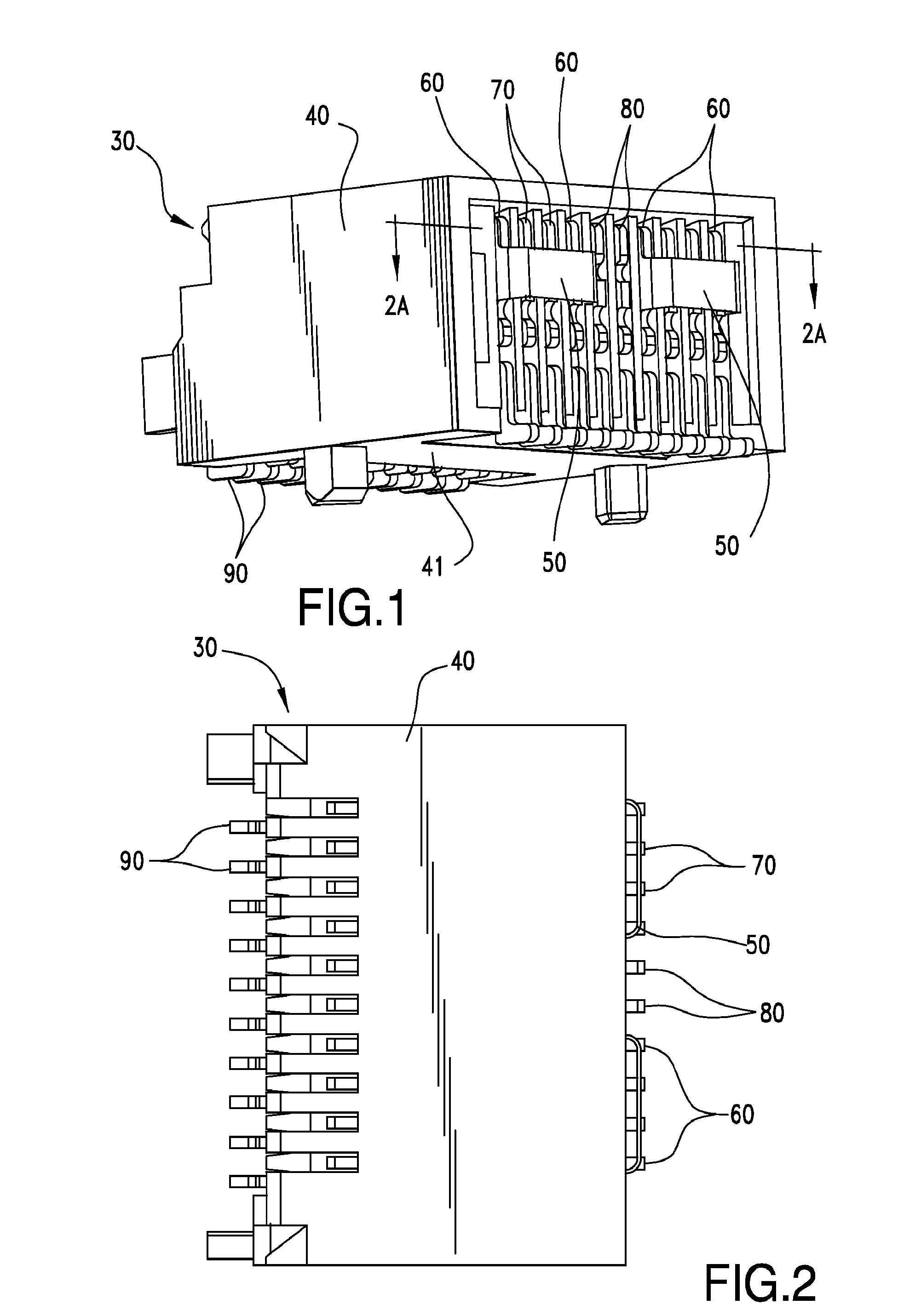
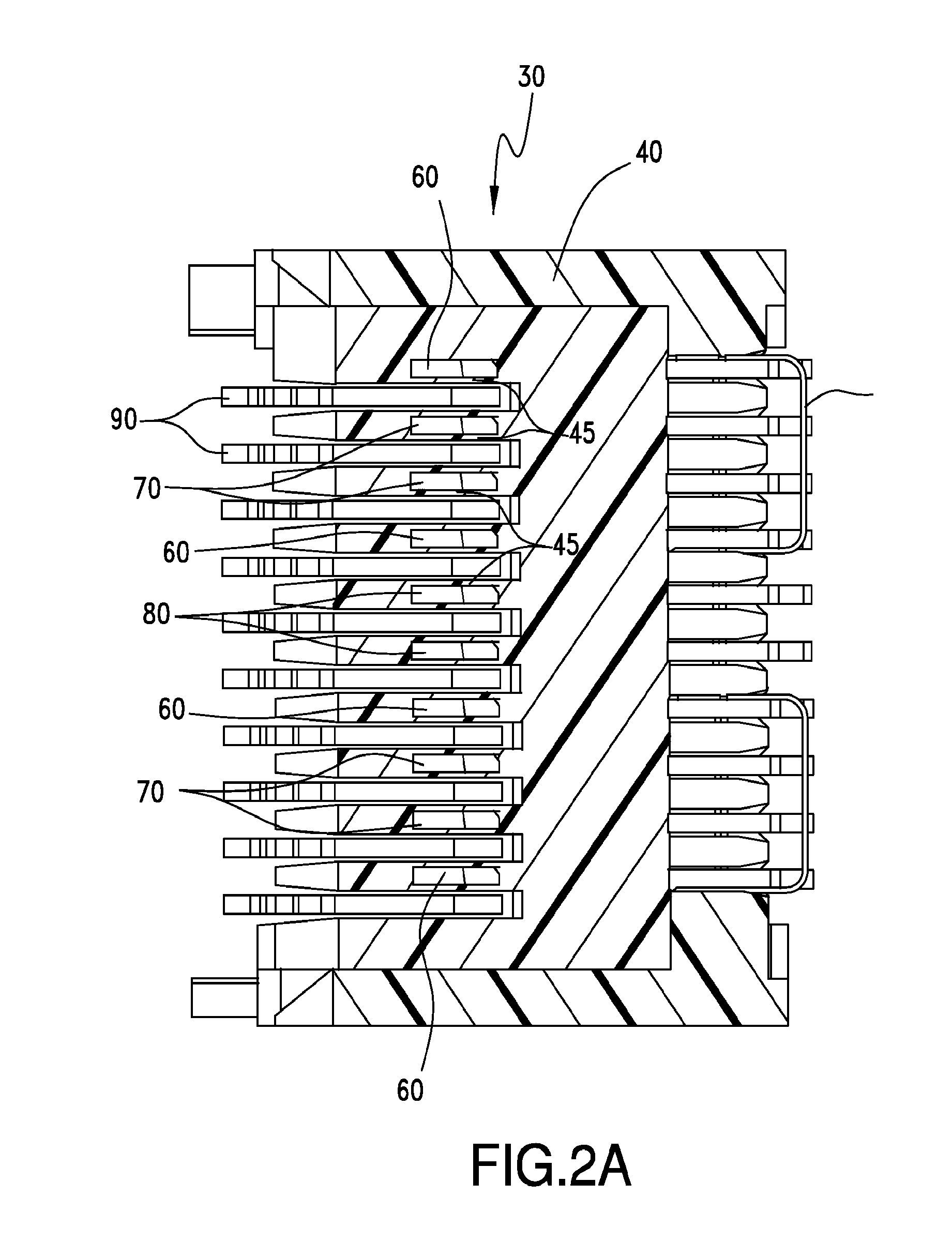
Differential electrical connector with improved skew control
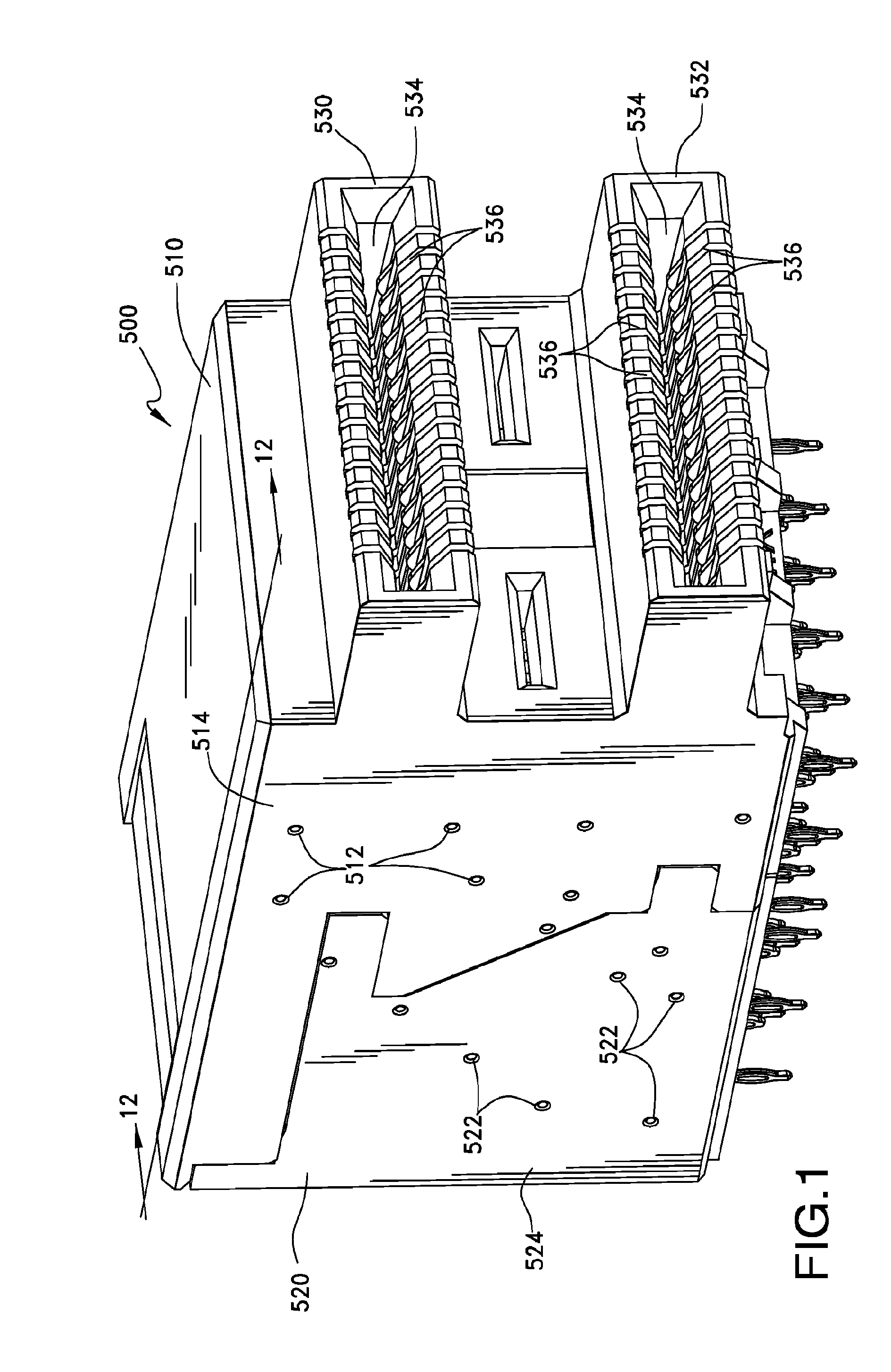
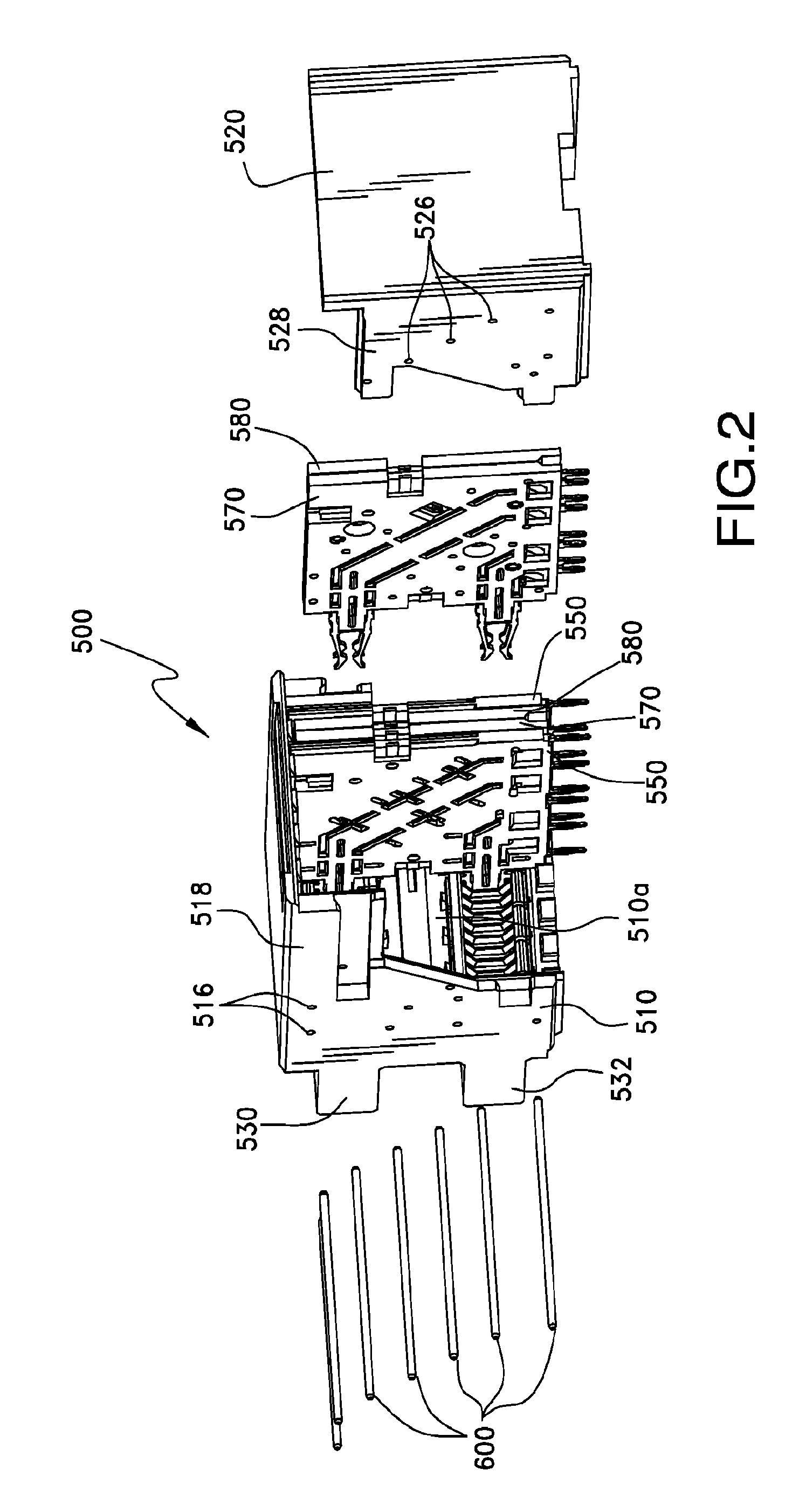
ActiveUS20100291803A1Reduce skewIncrease electrical lengthElectric discharge tubesTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityEngineering
An electrical interconnection system with high speed, differential electrical connectors. The connector is assembled from wafers each containing a column of conductive elements, some of which form differential pairs. Skew control is provided for at least some of the pairs by providing a profile on an edge of the shorter signal conductor of the pair. The profile may contain multiple curved segments that effectively lengthen the signal conductor without significantly impacting its impedance. For connectors in which ground conductors are included between adjacent pairs of signal conductors, patterned segments of varying parameters may be included on edges of the signal conductors and ground conductors to equalize electrical lengths of all edges in a set of edges for which there is common mode or differential mode coupling as a signal propagates along each pair. Such features for skew control may be used in combination with other skew control features. The features used may vary depending on the location of the pair within the column.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Mri tunable antenna and system
InactiveUS20050062472A1Minimize EMMinimizes interactionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorLength wave
A strip array antenna including a number of conductors (14) that are connected to ground or virtual ground though at least one reactive component (150). The apparent electrical length of conductors (140) is tuned so that it equals an integer multiple of a quarter wavelength at the operating frequency.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High frequency switch
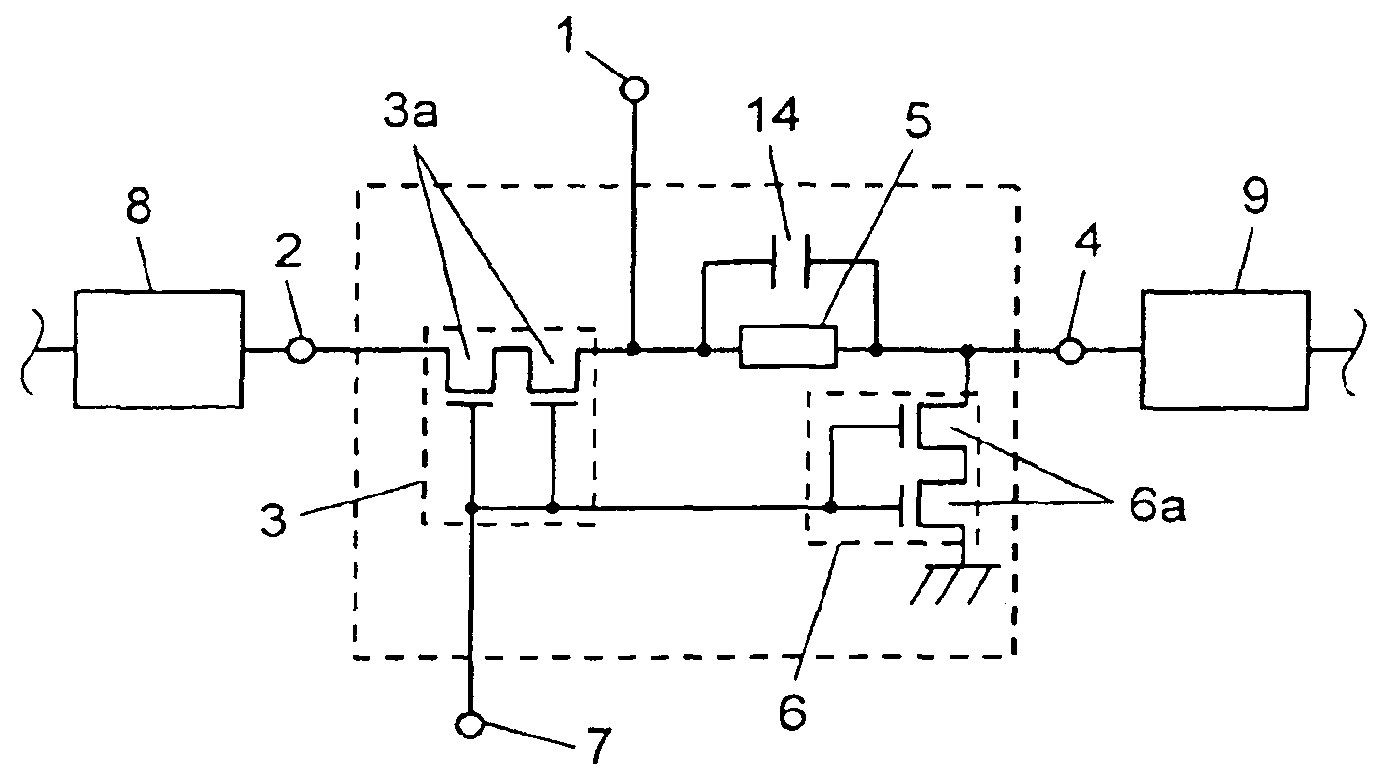
A high frequency switch configured particularly with FET switches. One end of second FET switch is connected between I / O port and reception port and the other end is ground. A parallel unit of strip line and capacitor is connected between second FET switch and I / O port. This parallel unit has the electrical length equivalent to ¼ wavelength of the high frequency signal input from transmission port.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multiband antenna
InactiveUS6473056B2Increase electrical lengthFacilitates suitableLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorResonance
The invention relates to a multiband antenna structure suitable for mobile stations in particular. The radiating elements of the antenna include not only a helix (210) but also the joining piece (220) that attaches the helix to the apparatus. The helix is shaped such that the distance between its conductor turns varies. The electrical length of the joining piece is increased e.g. by means of a conductive projection (226) that remains within the covering of the apparatus. By suitably dimensioning the parts, at least five of the resonances that the helix and joining piece have together and separately are arranged at useful points on the frequency scale. The structure according to the invention is despite the several bands simple and relatively low in production costs.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
Reflected wave clock synchronization
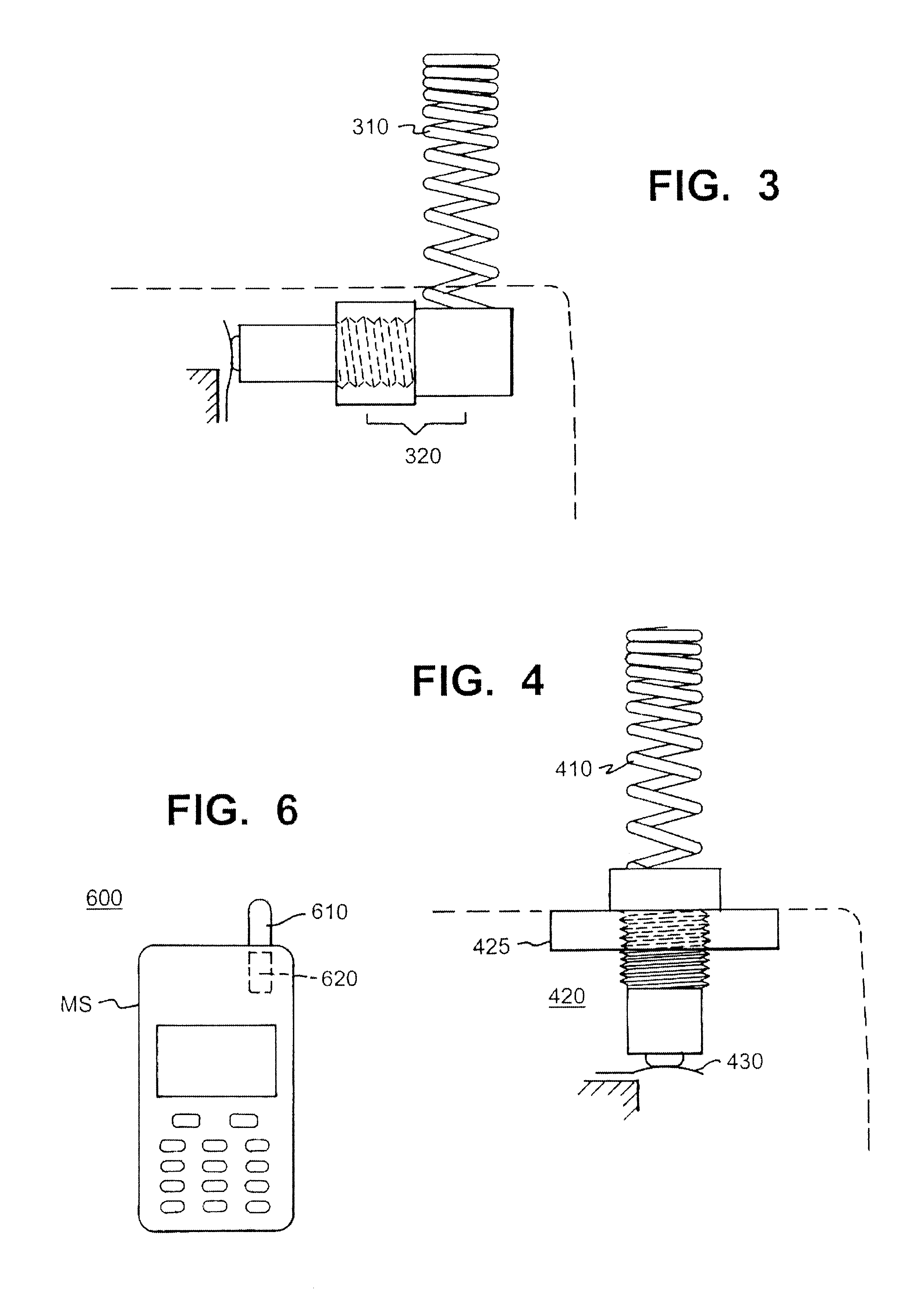
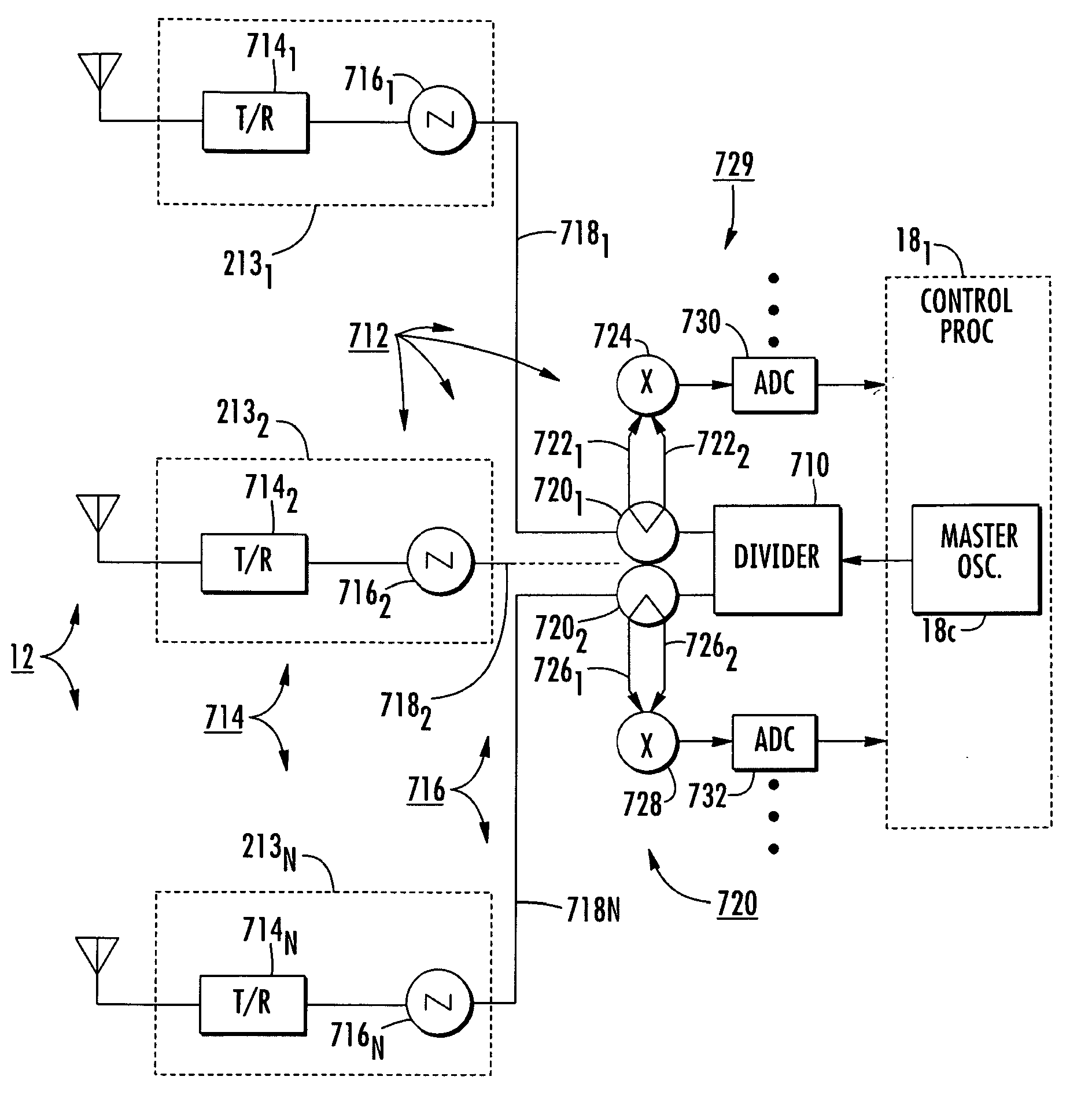
A radar system has a phased-array antenna and plural local oscillators for controlling local transmit / receive units. The local oscillators are slaved to a master oscillator. The analog clock signal paths are subject to relative changes in electrical length. The electrical lengths of the signal paths are measured by phase-detecting forward- and reverse-direction clock signal flows. The phase-detected information for each signal path is a measure of the time delay. The radar command processor receives the measure of time delay and corrects the radar operation in response thereto.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Wireless communications device pseudo-fractal antenna
InactiveUS6975277B2Reduce overall form factorCooperate effectivelyLogperiodic antennasRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorDipole antenna
A pseudo-fractal antenna is provided comprising a dielectric, and a radiator proximate to the dielectric having an effective electrical length formed in a pseudo-fractal geometry. That is, the radiator includes at least one section formed in a fractal geometry and at least one section formed in a non-fractal geometry. The antenna can be either a monopole or a dipole antenna. For use in a wireless communication telephone, the antenna operating frequency can be approximately 1575 megahertz (MHz), to receive global positioning satellite (GPS) information. In one aspect, the radiator has a fractal geometry section formed as a Koch curve. When the antenna is a dipole, the counterpoise can also be a pseudo-fractal geometry with a section formed in Koch curve fractal geometry section. The radiator can be a conductor embedded in the dielectric. Alternately, the radiator is a conductive line overlying a dielectric layer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
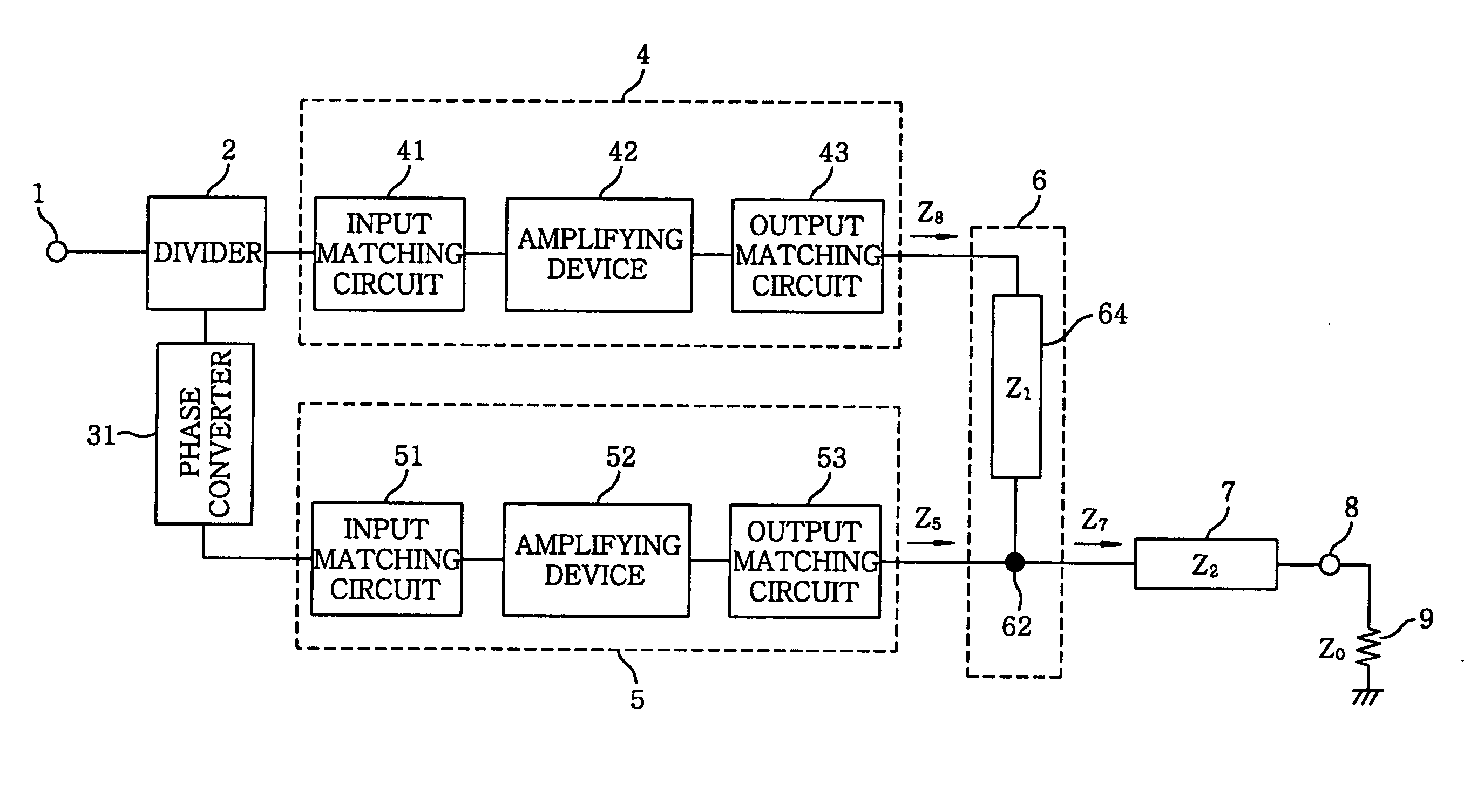
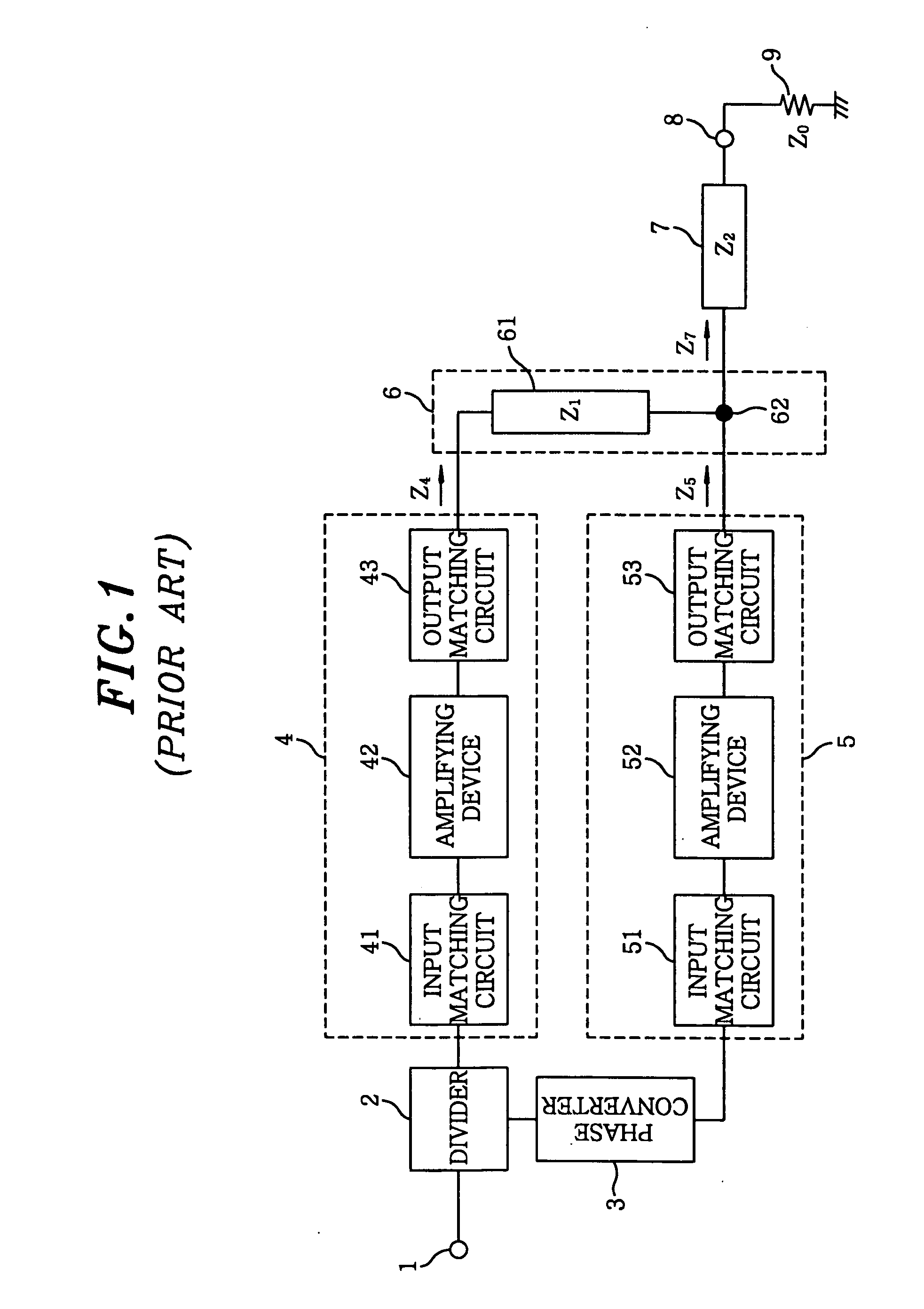
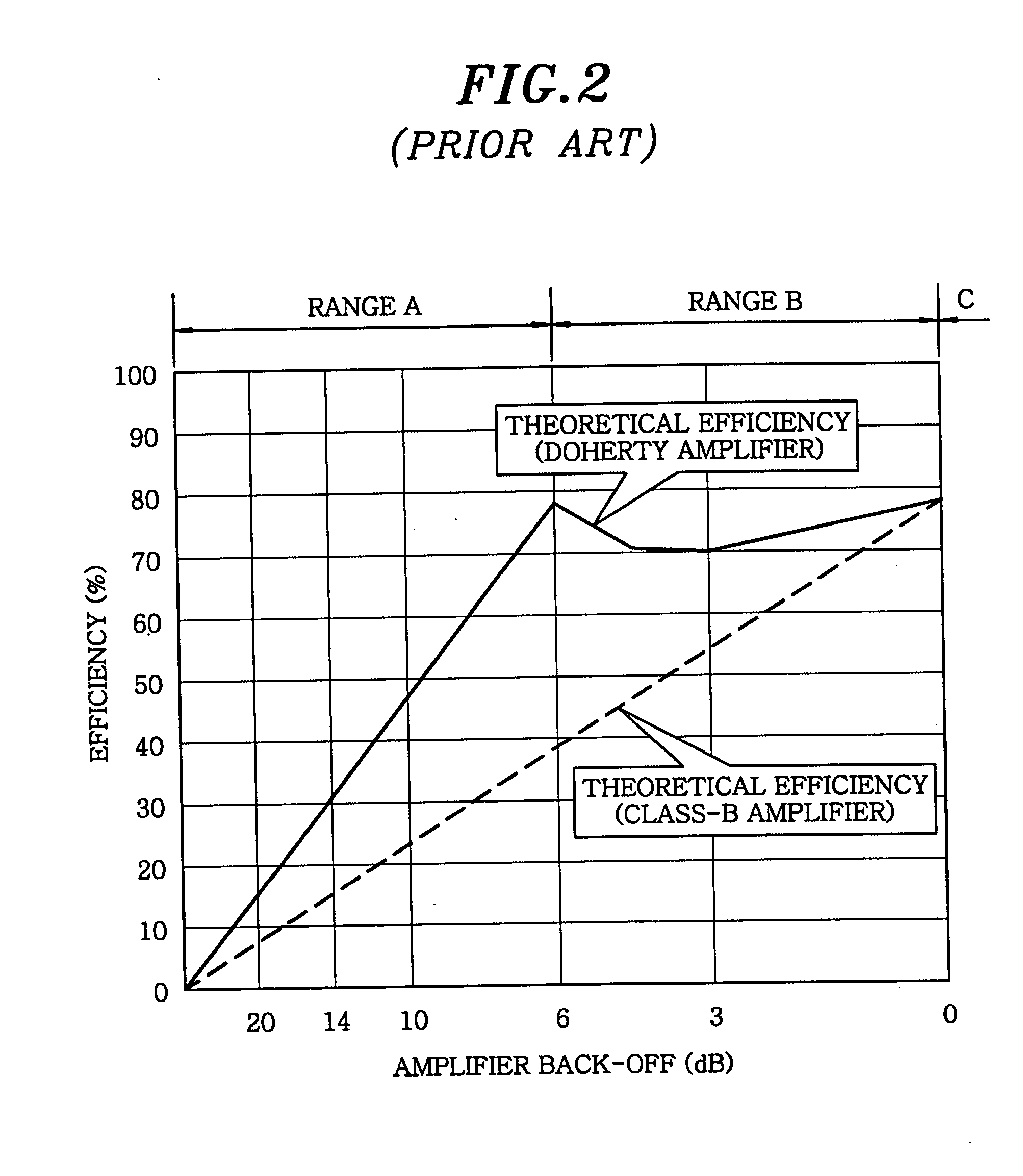
Amplifier
InactiveUS20060097783A1Improve performanceGain is largeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierImpedance transformer
There is provided an amplifier for combining outputs of a plurality of amplifying circuits to generate an amplifier output. The amplifier includes a first amplifying circuit for operating a first amplifying device in class-AB, wherein the first amplifying circuit is one among the plurality of the amplifying circuits; a second amplifying circuit for operating a second amplifying device in class-B or class-C, wherein the second amplifying circuit is one among the plurality of the amplifying circuits; and a summing node at which an output of the first amplifying circuit is combined with an output of the second amplifying circuit via a first impedance transformer containing a transmission line of an electrical length other than λ / 4. The second amplifying device is connected to the summing node via an output matching circuit and a second impedance transformer containing a transmission line.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Fabrication method and apparatus for antenna structures in wireless communications devices
InactiveUS6842148B2Comparable and enhanced performanceMinimum footprintAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsPlanar substrateConductive materials
There is disclosed a meanderline loaded antenna formed by applying a conductive ink or other conductive material to a flexible substrate. The substrate is then shaped by removing regions and folding other regions along perforated or scored lines to fit the antenna within the available space of a wireless device. In lieu of folding regions of a planar substrate to form a three-dimensional structure, the substrate can be vacuum formed over a mandrel after the antenna elements have been formed thereon. The antenna can also be formed by printing on existing enclosure surfaces of a wireless device or on the surfaces of components within the device. Thus the advantages offered by a meanderline antenna where the effective electrical length is greater than the actual physical length are achieved in conjunction with a space-saving physical structure for the antenna.
Owner:SKYCROSS INC
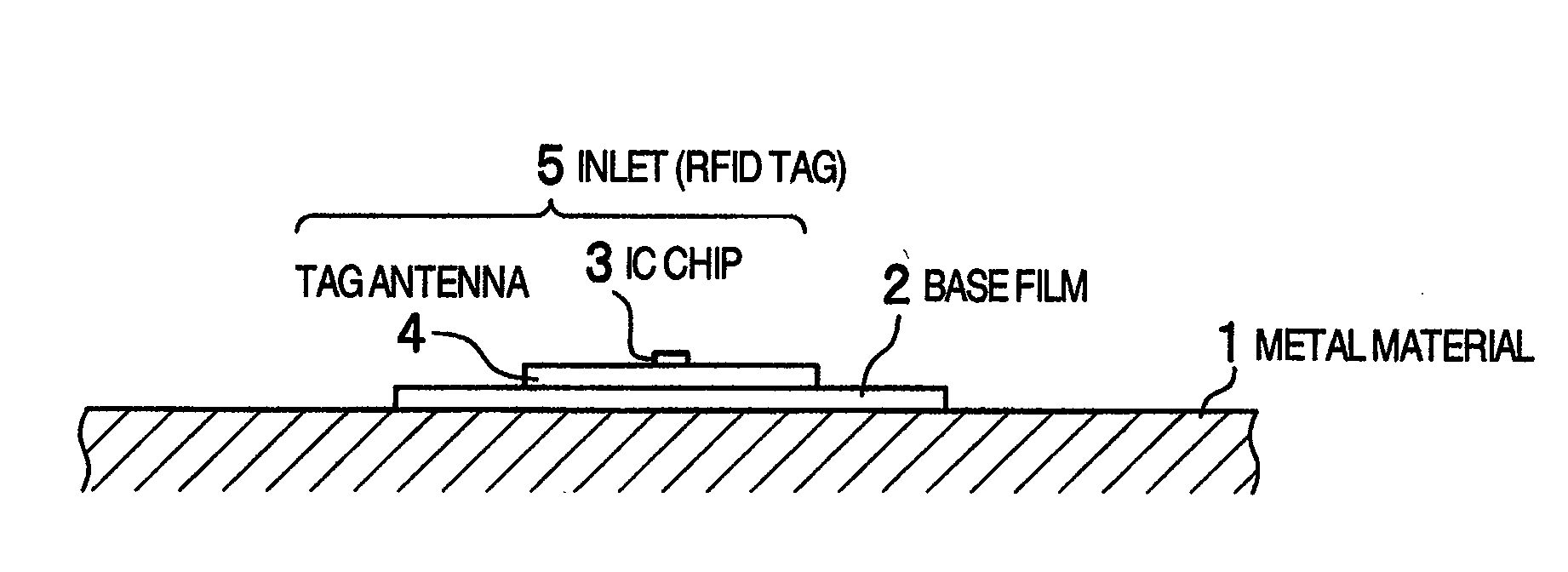
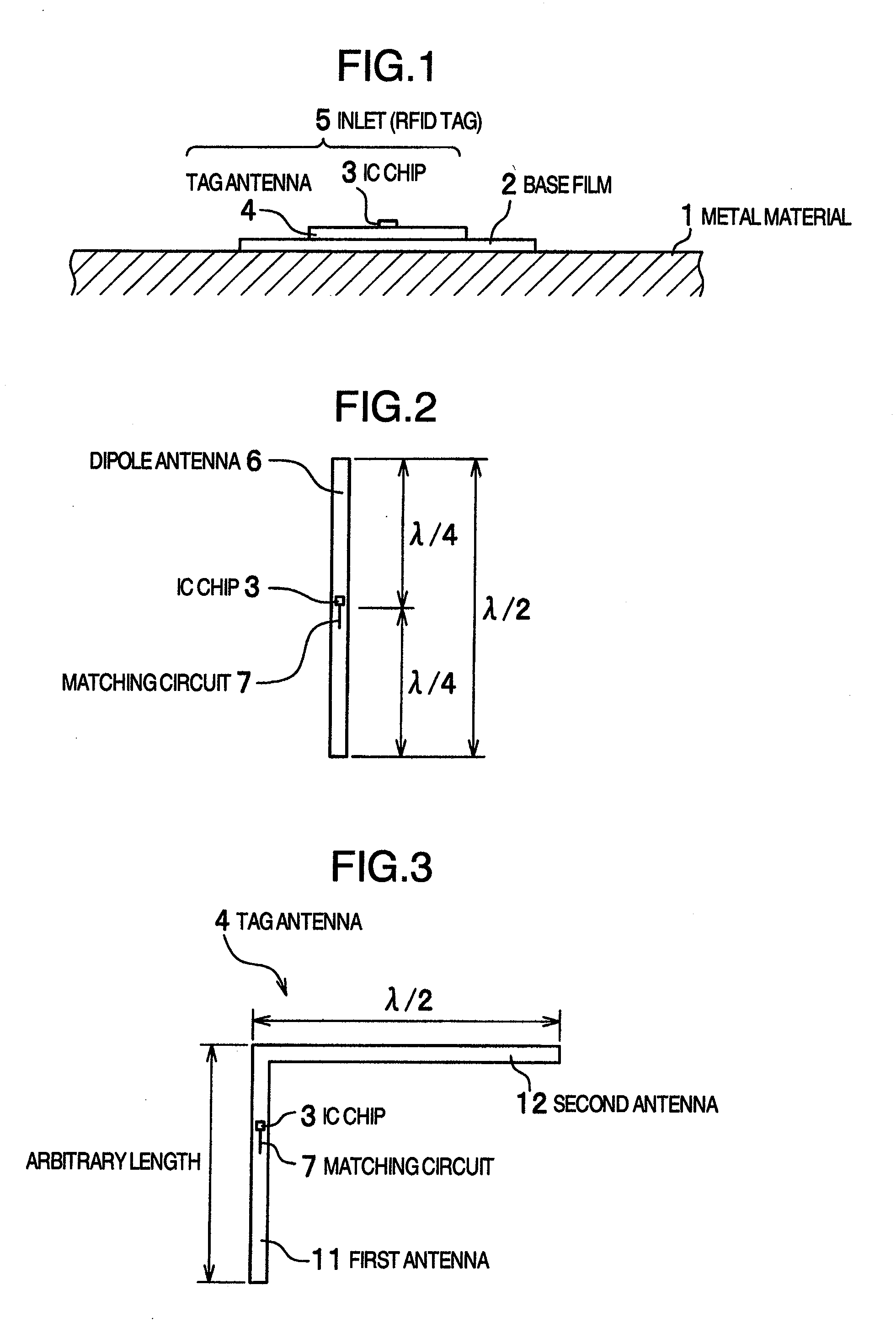
RFID tag
InactiveUS20080252462A1Slow changeReduce variationSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesTag antennaElectrical length
An RFID tag according to the present invention includes a first antenna on which an IC chip is mounted and a second antenna extending from an end of the first antenna in a direction at right angles to the first antenna. The first antenna has an arbitrarily electrical length and the second antenna has an electrical length of λ / 2 or an integral multiple of λ / 2. A resin base film having a thickness of approximately 50 μm is disposed on the back side of the first antenna and the second antenna. With this configuration of a tag antenna, the second antenna resonates with the first antenna to exhibit a radio wave amplifying effect. Therefore, a long communication distance can be achieved even if the electrical length of the first antenna is chosen to be short or the thickness of the base film is chosen to be thin.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
UTP cable apparatus with nonconducting core, and method of making same
InactiveUS20050045367A1Improve signal qualityReduce crosstalkCables with twisted pairs/quadsEngineeringAnalog signal
An unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable minimizes skew delay of analog signals by enforcing a common electrical length among twisted pairs that carry those analog signals. By applying a different lay length and lay direction to the twisted pair that carries the digital signal, cross-talk from the digital signal onto the analog signals is minimized. A nonconductive filler provides a central core about which the twisted pairs are wound during the bundling process. The presence of the nonconductive core ensures that a minimum distance (i.e., the diameter of the core) is maintained between non-adjacent pairs for the length of the cable.
Owner:RGB SYST INC
Performance improvement of antennas
InactiveUS20090322619A1Increase electrical lengthImprove performanceAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna earthingsGround planeEngineering
The present invention relates to an antenna arrangement, an adaptive system comprising such arrangement, a portable electronic device comprising such arrangement or adaptive system, a method of manufacturing such an arrangement, and a computer-readable storage medium encoded with instructions for performing such method. The antenna arrangement can comprise at least one antenna element (110) configured to supply a current, at least one ground plane element (120) configured to conduct the current, and at least one magnetic element (130) configured to influence at least a part of the current in order to modify an electrical length of the at least one ground plane element (120). It enables to increase the electrical length of a terminal chassis, which may increase the operation bandwidth of the antenna-chassis combination. This effect can be further increased when combining at least one slot and at least one magnetic element covering the same at least partially.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Surface mount antenna and communication device including the same
InactiveUS6452548B2Increase electrical lengthChange frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandCommunication device
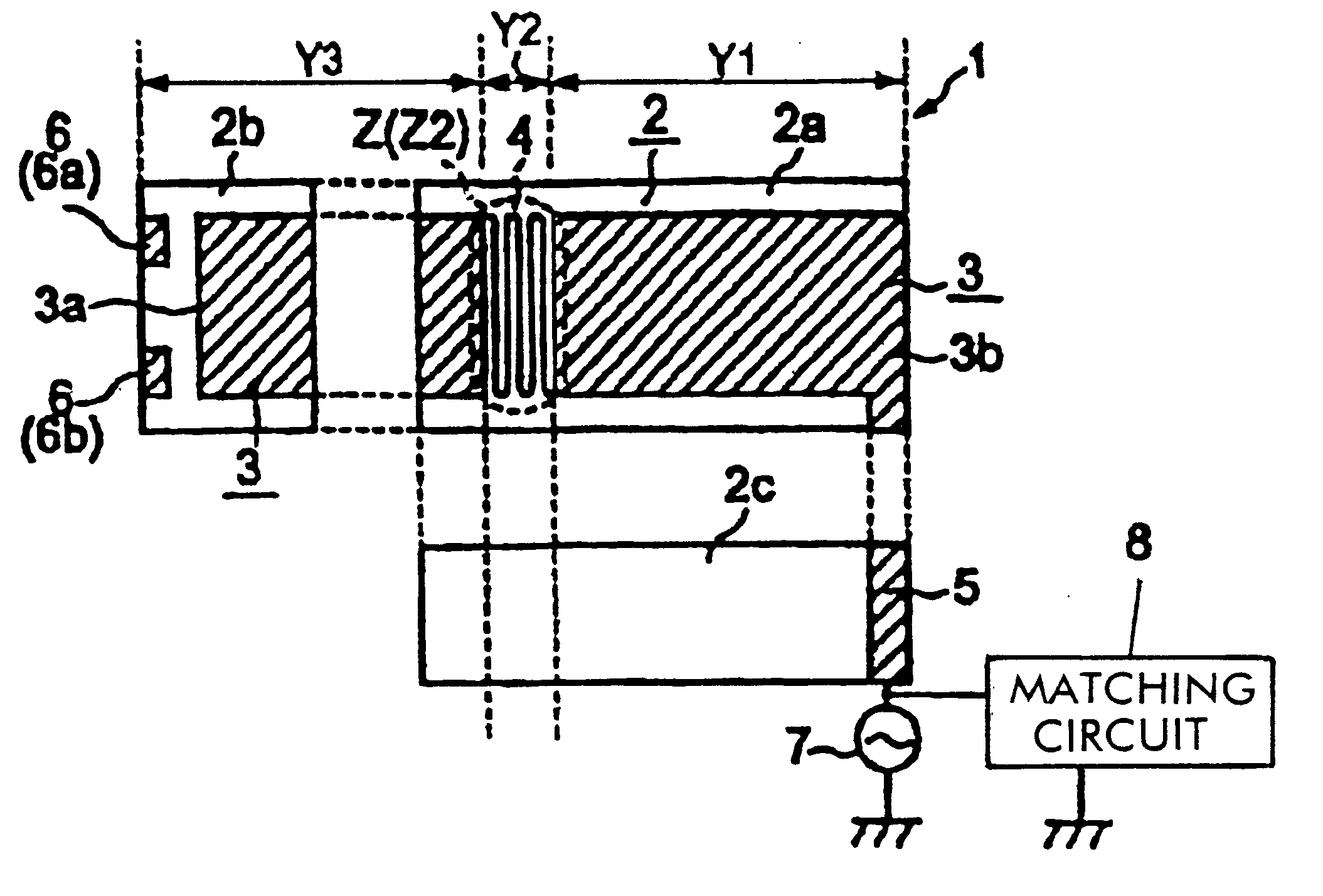
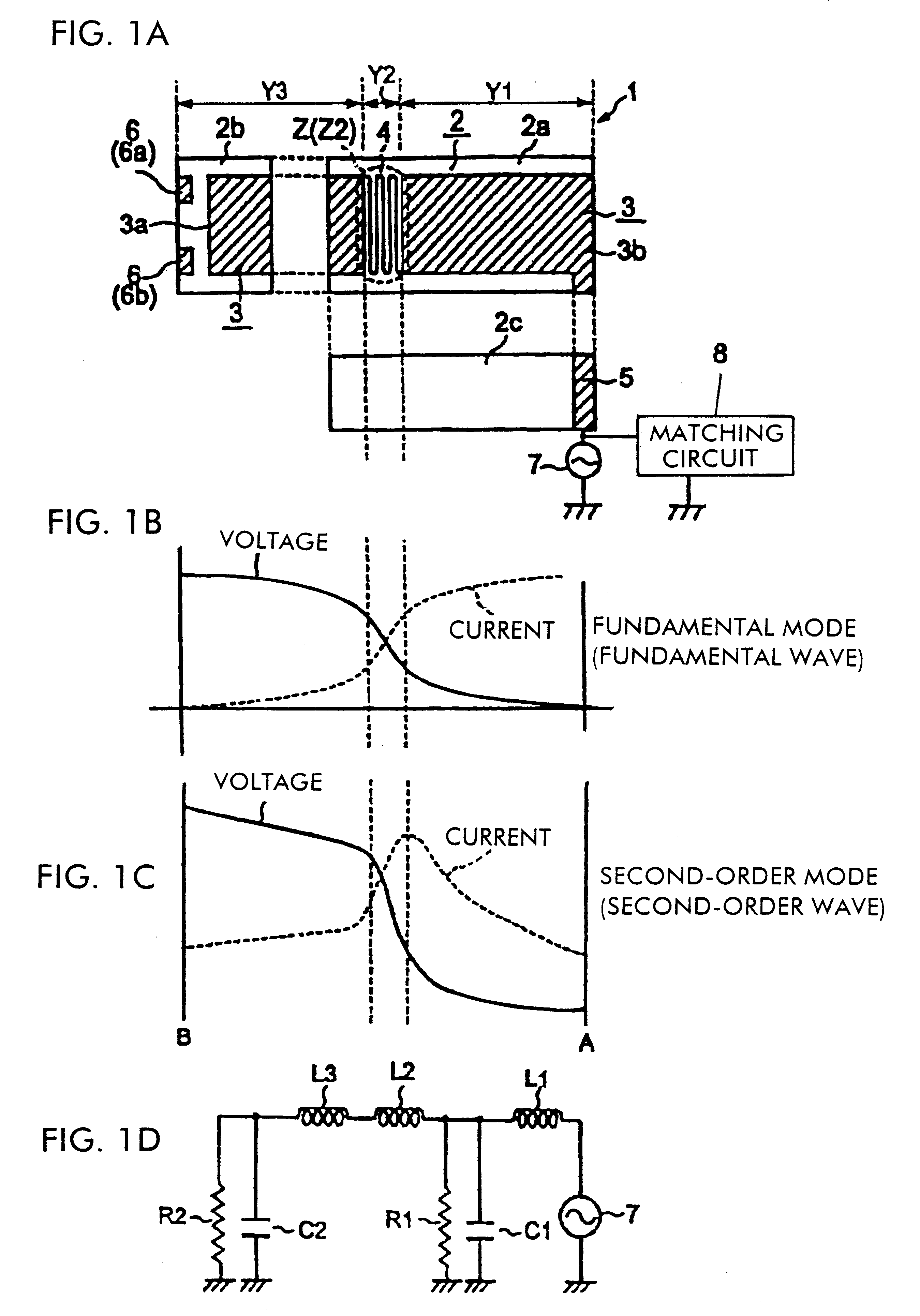
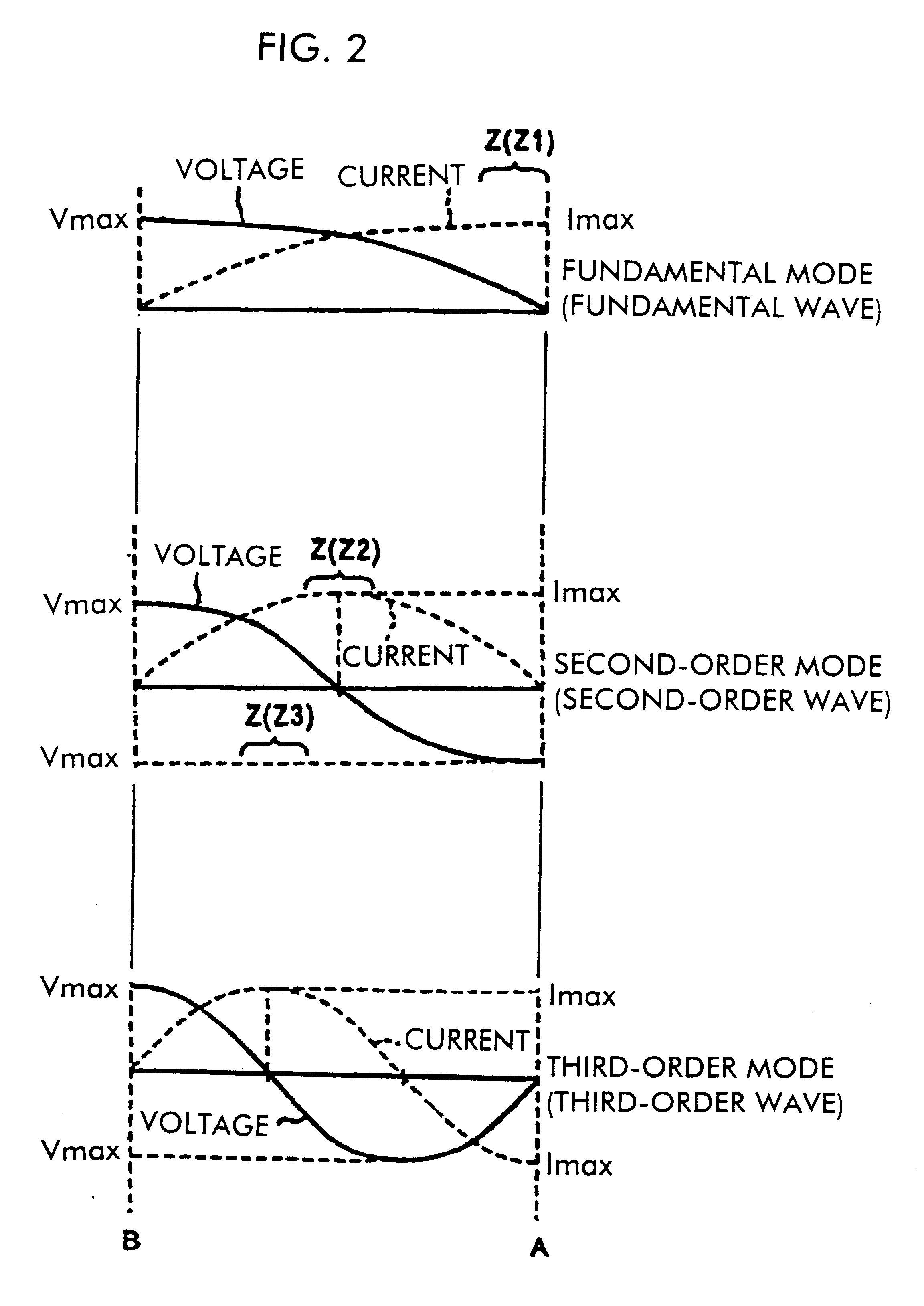
In a feeding radiation electrode of a surface mount antenna, a series inductance component such as a meander pattern is formed locally in a maximum resonance current part in a high-order mode (second-order mode) so as to locally form a series inductance component therein thereby making the maximum resonance current part have a greater electrical length per unit physical length than the other parts. This makes it possible to control the difference between the resonance frequency in a fundamental mode and the resonance frequency in the high-order mode over a large range. Furthermore, it is possible to vary the resonance frequency in the second-order mode independently of the resonance frequency in the fundamental mode by varying the number of lines or the line-to-line distance of the meander pattern thereby varying the value of the series inductance component. Thus, it is possible to easily and efficiently design a surface mount antenna having a frequency characteristic which satisfies requirements needed in multi-band applications without having to change the basic design.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Tunable capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole antenna
InactiveUS7408517B1Minimize susceptibilityLess susceptible to RF noiseResonant long antennasAntenna arraysCapacitanceTransformer
A frequency-tunable capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole antenna includes a transformer loop having a balanced feed interface, and a capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole radiator with a tunable effective electrical length. In one embodiment, the capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole radiator includes a tunable electric field bridge. For example, the capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole radiator may comprise a quasi loop with a tunable electric field bridge interposed between the quasi loop first and second ends. The electric field bridge may be an element such as a ferroelectric (FE) tunable capacitor or a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) capacitor, to name a couple of examples. In certain embodiments, the capacitively-loaded magnetic dipole radiator includes a quasi loop with a loop perimeter. The effective electrical length of the radiator is changed by adjusting the perimeter using an element such as a MEMS switch, or a semiconductor switch.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Resonance modifying connector
ActiveUS20110269346A1Complex transmission structureTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsResonanceElectrical length
A connector assembly is provided that is suitable for controlling the resonance frequency of ground terminals used to shield high-speed differential pairs. Ground terminals may be commonized so as to provide ground terminals with a predetermined maximum electrical length. Reducing the electrical length of the ground terminal can move a resonance frequency of the ground terminals of the connector outside the range of frequencies at which signals will transmitted.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Variable impedance matching circuit
The present invention is directed to a circuit capable of matching variable impedances, and implements the variable impedance matching circuit by varying an electrical length of a transmission line by means of external control signals. In the L or pi type matching circuit using inductance and capacitance as lumped elements, the variable impedance matching circuit is implemented by changing impedance values of the variable inductance and variable capacitance as lumped elements which have been made to be controlled, or by changing a topology of a circuit network by external control signals. Therefore, the variable impedance matching circuit according to the present invention enables it possible to electrically control an impedance of interest from arbitrary impedances, thereby a radio frequency circuit to which the variable impedance matching circuit belongs can be controlled, and the matching circuit can be implemented with arbitrary complex loads from any RF signal sources.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wireless unit antenna apparatus and mobile wireless unit
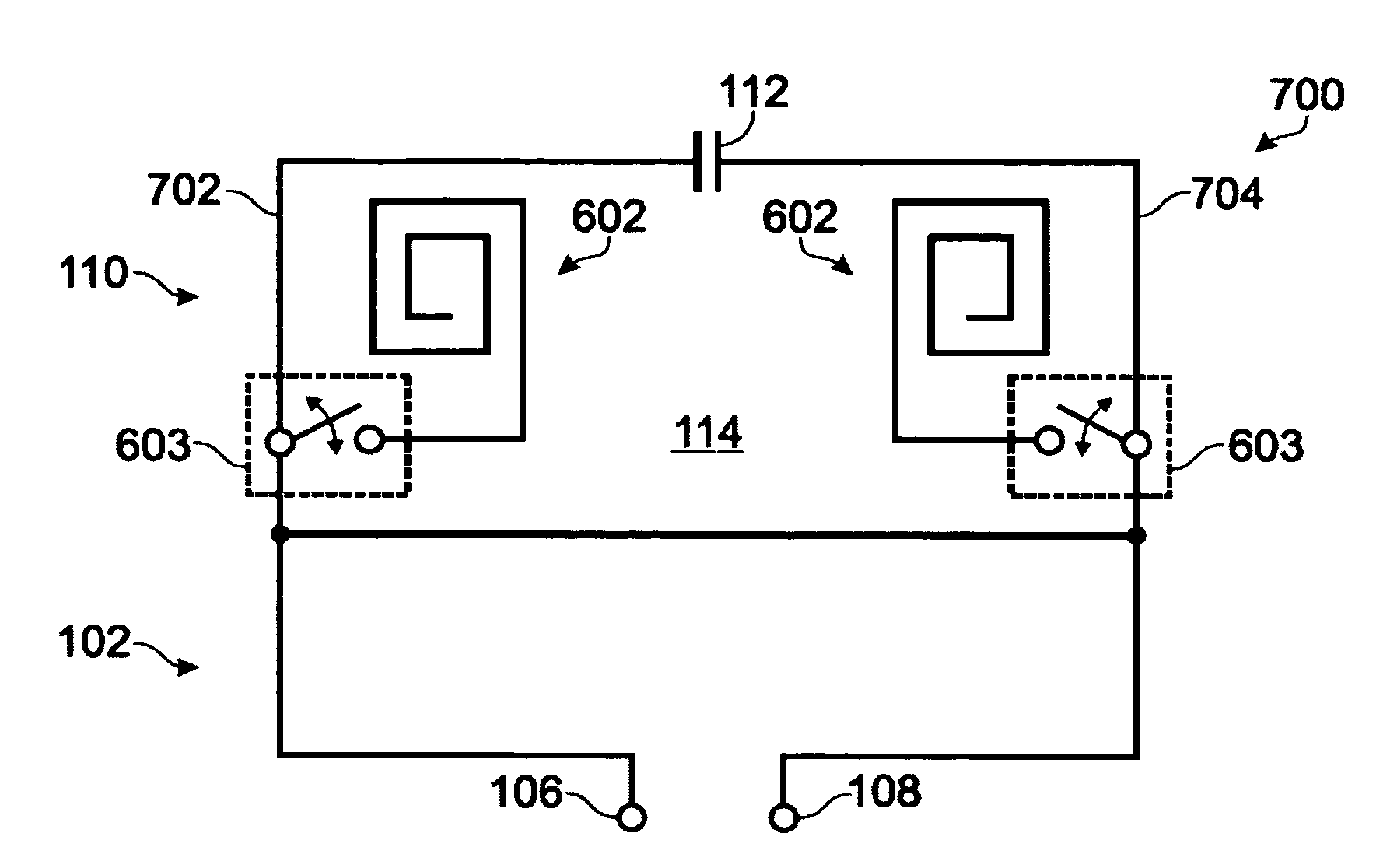
InactiveUS20090102726A1Reduce SARReduce constructionAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna earthingsLength waveAntenna element
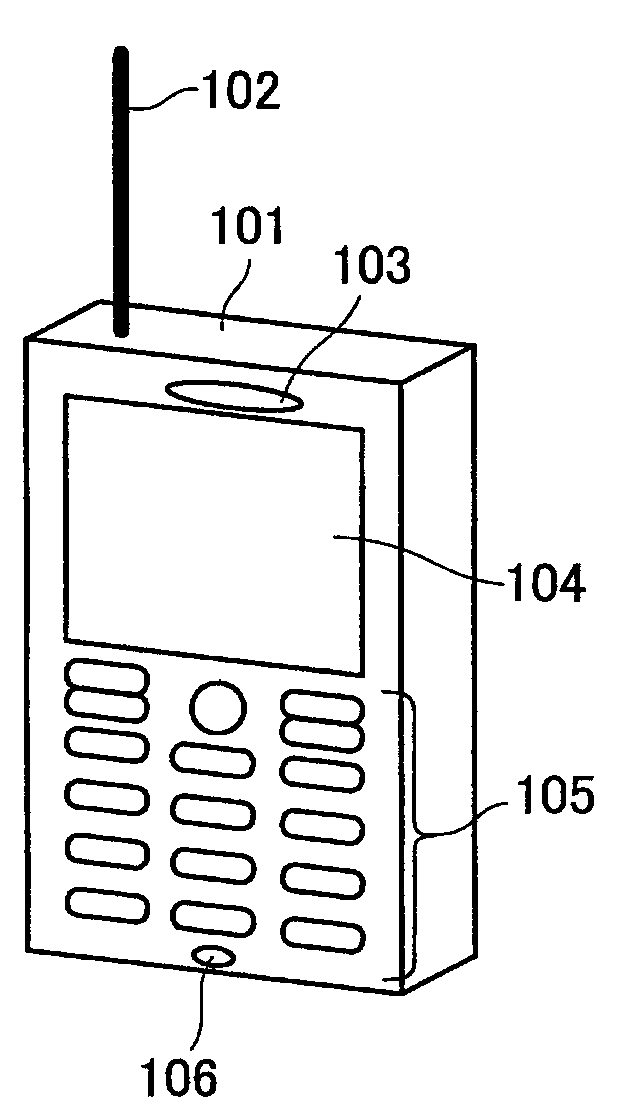
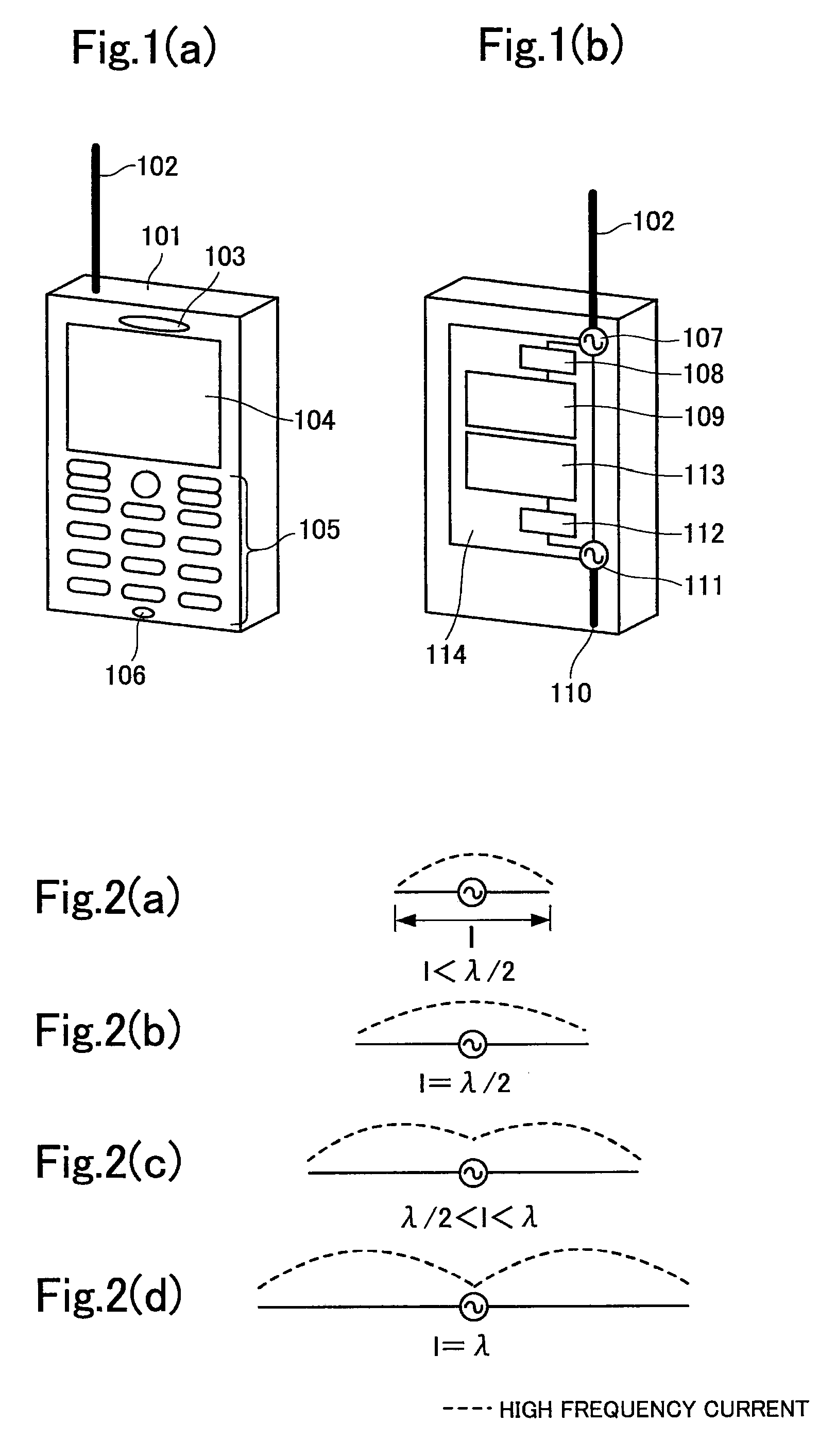
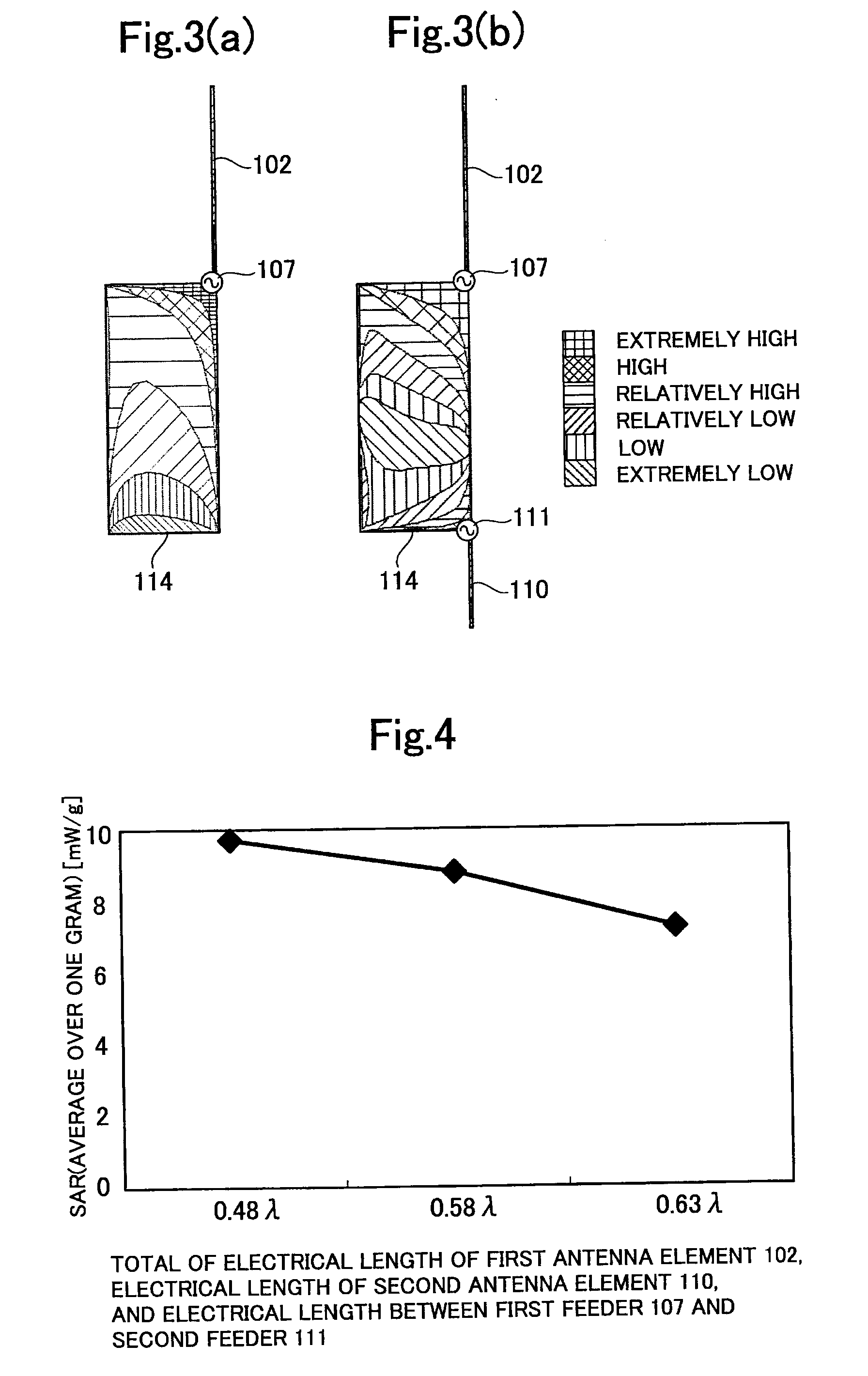
The present invention provides an antenna apparatus for a wireless unit, the antenna apparatus exhibiting a reduced specific absorption rate (SAR) without an additional component for reducing the SAR, which is the amount of energy of an electromagnetic wave absorbed by a human body. The antenna apparatus comprises a board 114 serving as a ground plate of an antenna, a first antenna element 102 transmitting and receiving an electromagnetic wave in a first frequency band and provided on the board 114 through the first feeder 107, and a second antenna element110 transmitting and receiving an electromagnetic wave in a second frequency band and provided on the board 114 through the first feeder 111, wherein the total of an electrical length between the first and second feeders 107 and 111, an electrical length of the first antenna element 102, and an electrical length of the second antenna element 110 is larger than a half wavelength of the first frequency band and equal to or smaller than one wavelength of the first frequency band.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Antenna assembly and electronic device
ActiveCN108631041AImprove communication performanceBand widthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsControl signalRadio frequency signal
The present application provides an antenna assembly and an electronic device. The antenna assembly comprises a first radio frequency signal source, a first antenna radiator, a second antenna radiator, a first adjustment circuit, a second adjustment circuit, a mode switch and a controller, wherein the controller generates first, second and third control signals, the first radio frequency signal source generates a first radio frequency signal, the first adjustment circuit adjusts an equivalent electrical length of the first antenna radiator under the control of the first control signal to generate first electromagnetic wave signals of different bands, the second antenna radiator comprises a first portion arranged at a preset clearance away from the first antenna radiator, the first portioncouples the first electromagnetic wave signals to generate second electromagnetic wave signals, and when the mode switch is in a first state under the control of the second control signal, the secondadjustment circuit is electrically connected with the first portion, and the second adjustment circuit adjusts the equivalent electrical length of the first portion under the control of the third control signal to radiate the second electromagnetic wave signals.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
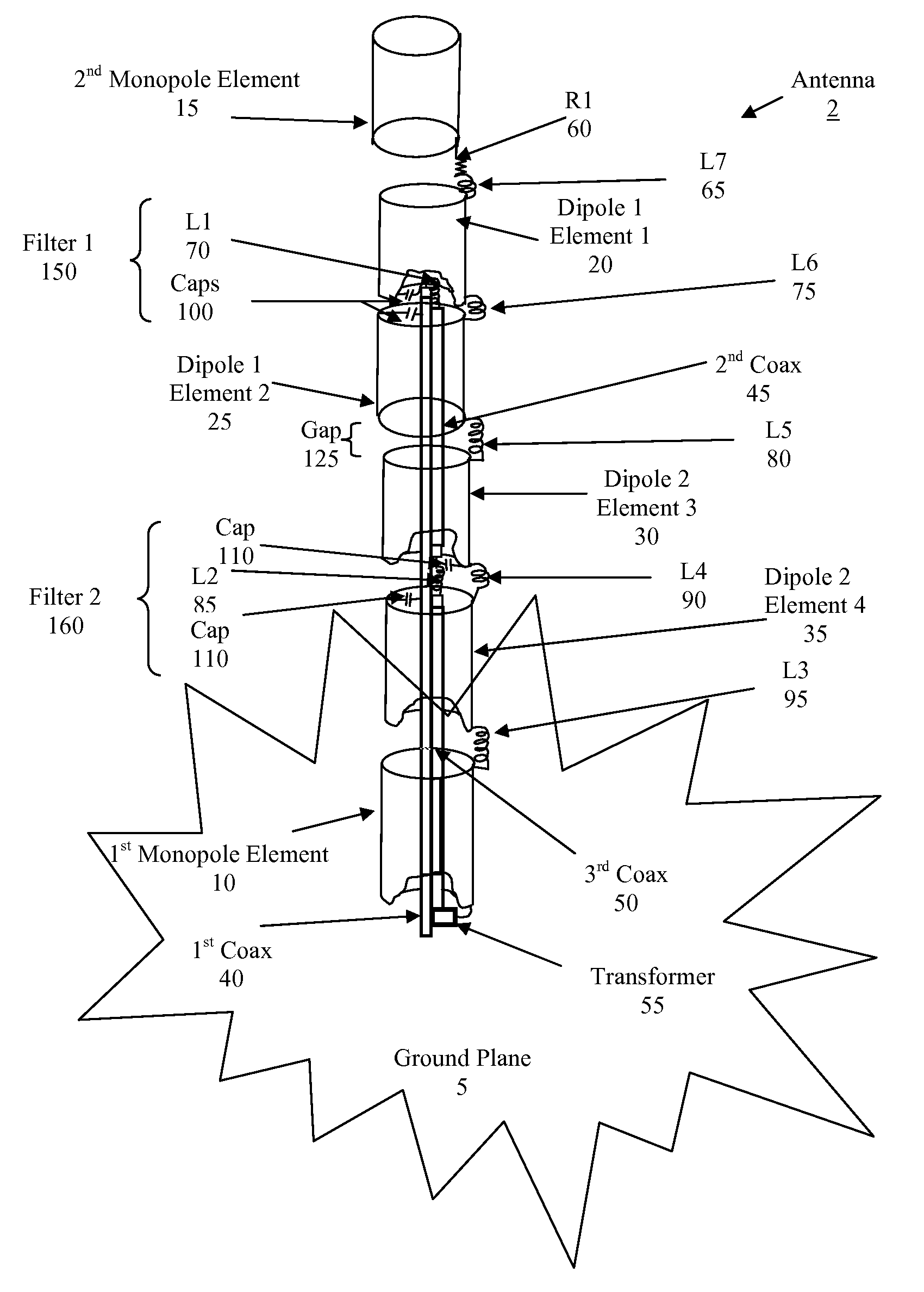
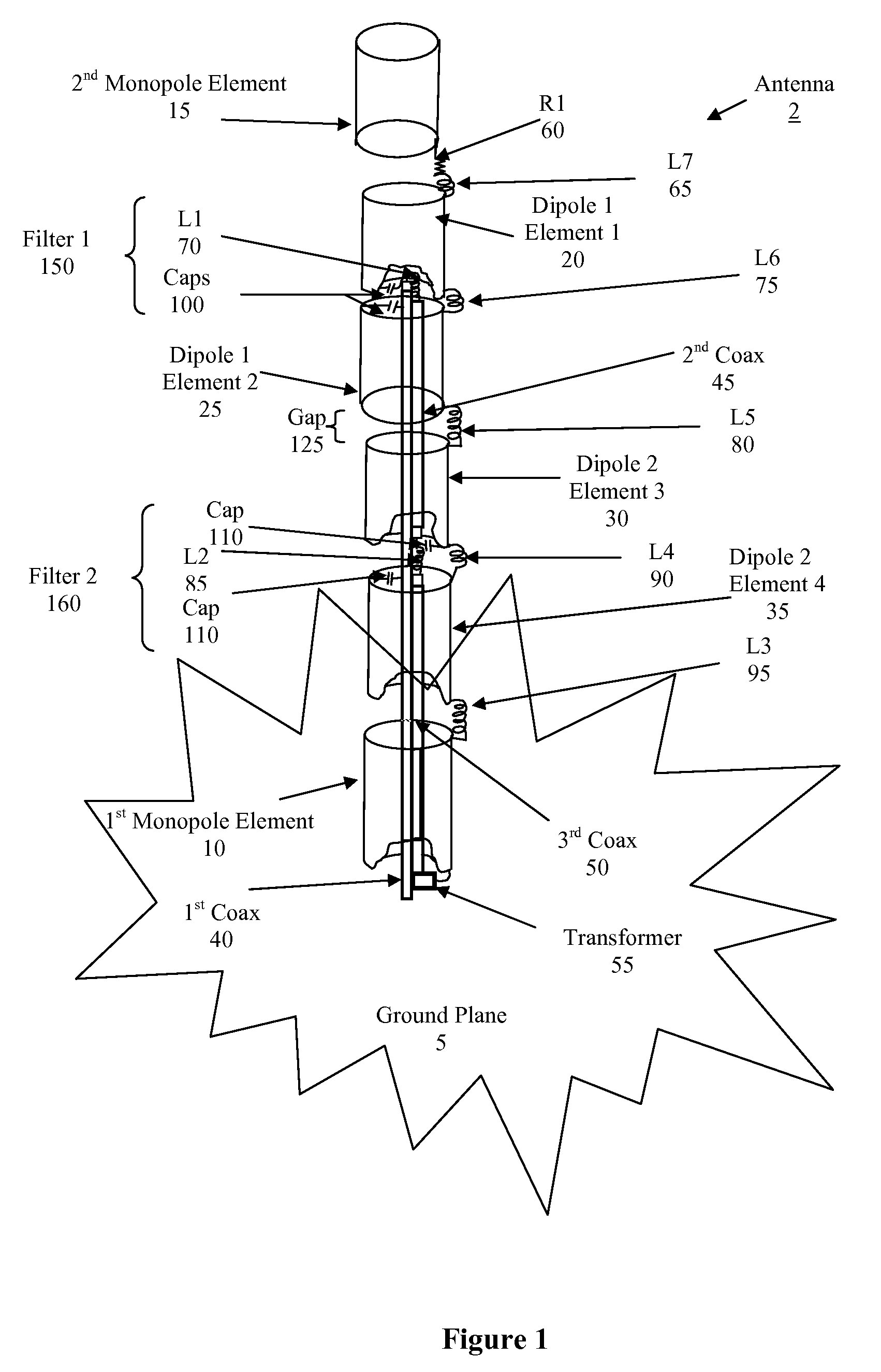
Ultra broadband linear antenna
ActiveUS7289080B1Improve performanceGreat frequency rangeSimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysBroadbandWide band
An antenna of dipole and monopole antenna elements with filtering to achieve a greater bandwidth. The multiple antenna elements are isolated or combined in order to provide a self adjusting electrical length by using multi-terminal filtering.
Owner:CAES SYST LLC
Connector with terminals forming differential pairs
ActiveUS8545240B2Two-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsResonanceEngineering
A connector assembly is provided that is suitable for controlling the resonance frequency of ground terminals used to shield high-speed differential pairs. Ground terminals may be commonized so as to provide ground terminals with a predetermined maximum electrical length. Reducing the electrical length of the ground terminal can move a resonance frequency of the ground terminals of the connector outside the range of frequencies at which signals will transmitted.
Owner:MOLEX INC
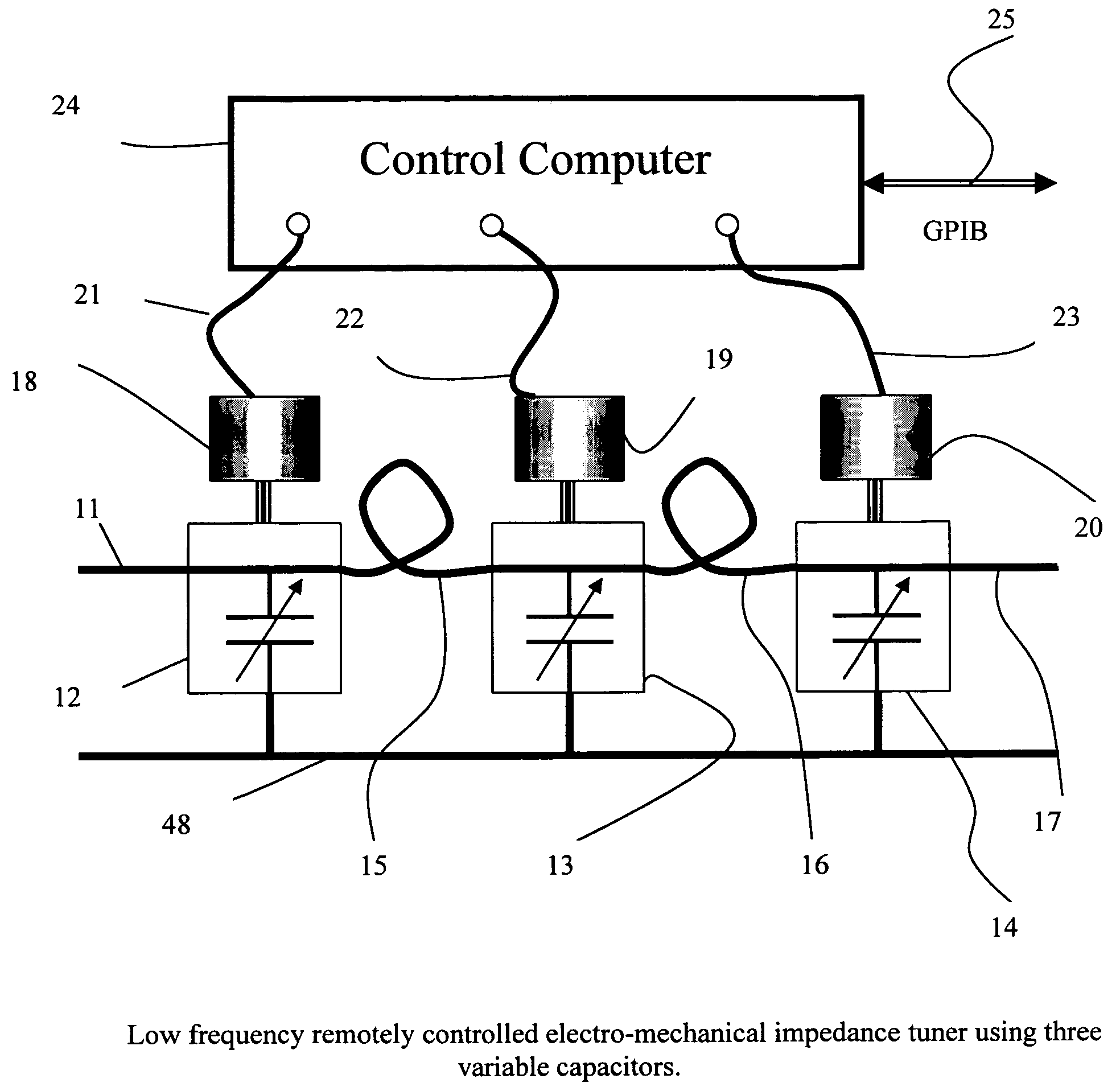
Low frequency electro-mechanical impedance tuner
InactiveUS7646267B1Small sizeEasy to manufactureMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringElectric cables
A segmented, electro-mechanical, remotely controlled programmable impedance tuner for the frequency range between 10 and 200 MHz uses a cascade of three continuously variable mechanical capacitors interconnected by a set of two low loss flexible or semi-rigid cables; the electrical length of the interconnecting cables between the capacitors determines the frequency at which tuning coverage of the entire area of the Smith chart is optimum; for maximum impedance coverage the length is to be chosen such as to generate a transmission phase shift of 60 degrees at the center frequency between each capacitor stage. Remote tuning is possible by changing the value of the capacitors using electrical stepper motors. The tuner is calibrated using a vector network analyzer and the data are saved in the memory of the control computer, which then allows tuning to any user defined impedance within the tuning range. Reflection factor values between 0 and higher than 0.9 can be obtained using this tuner.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com