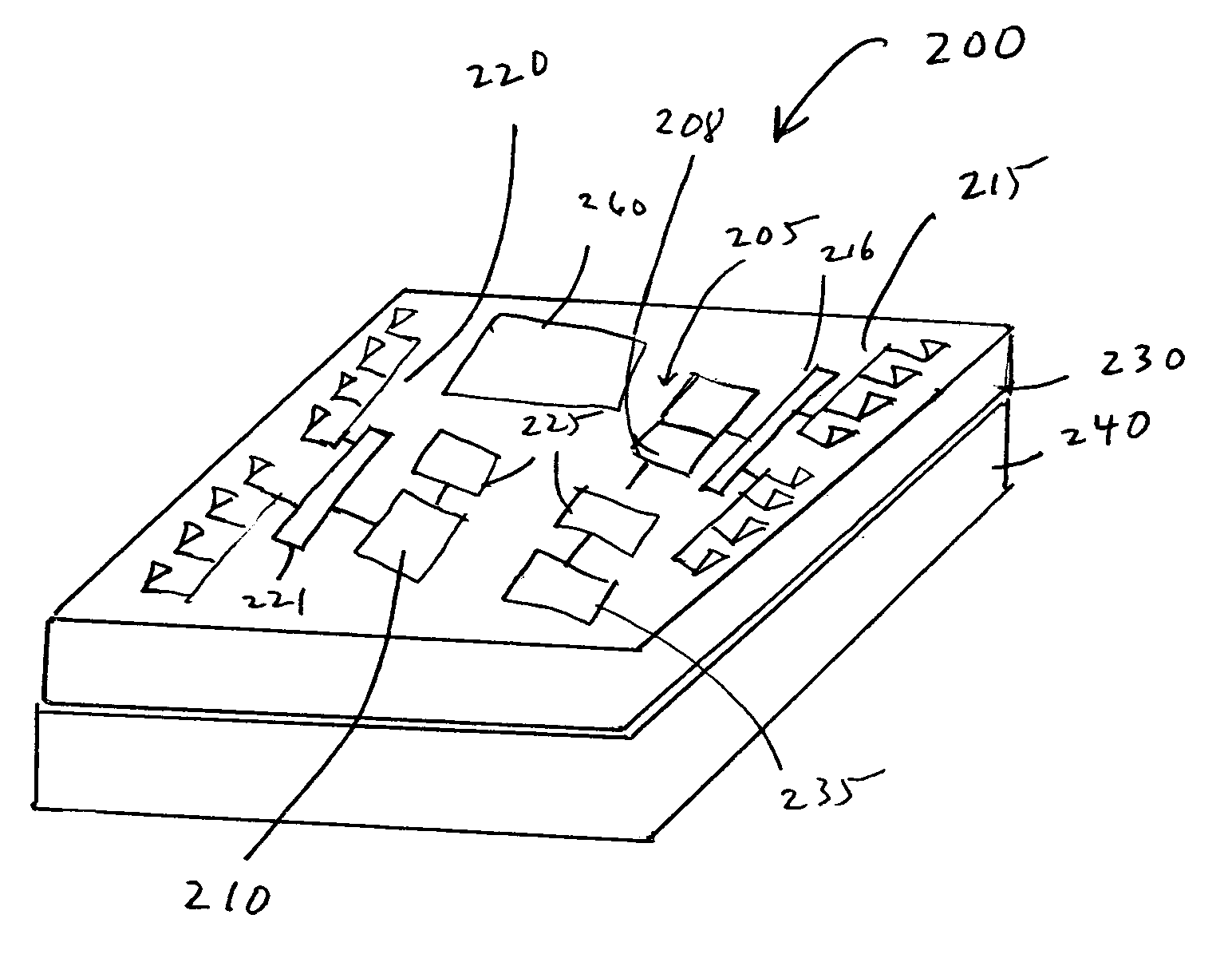
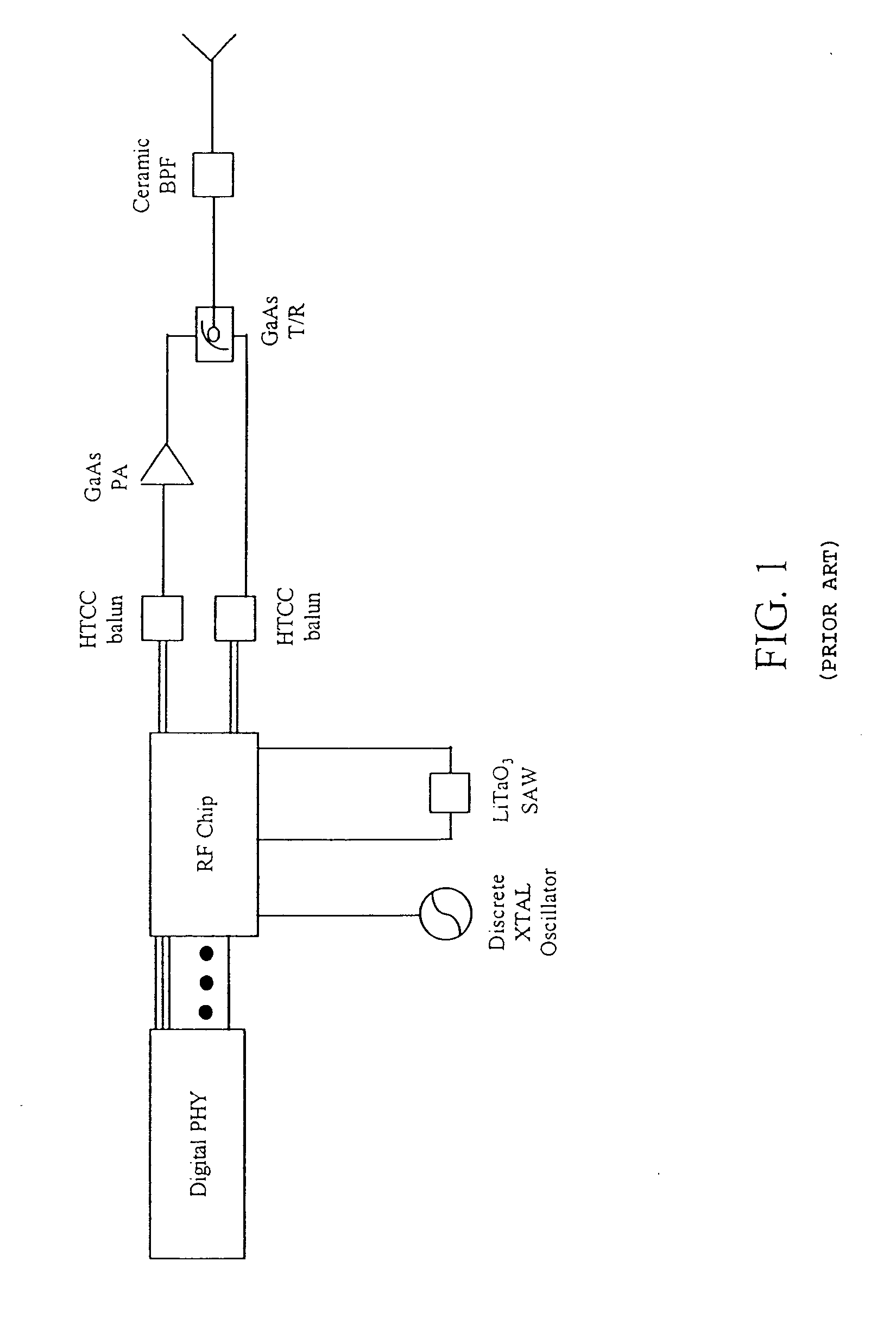
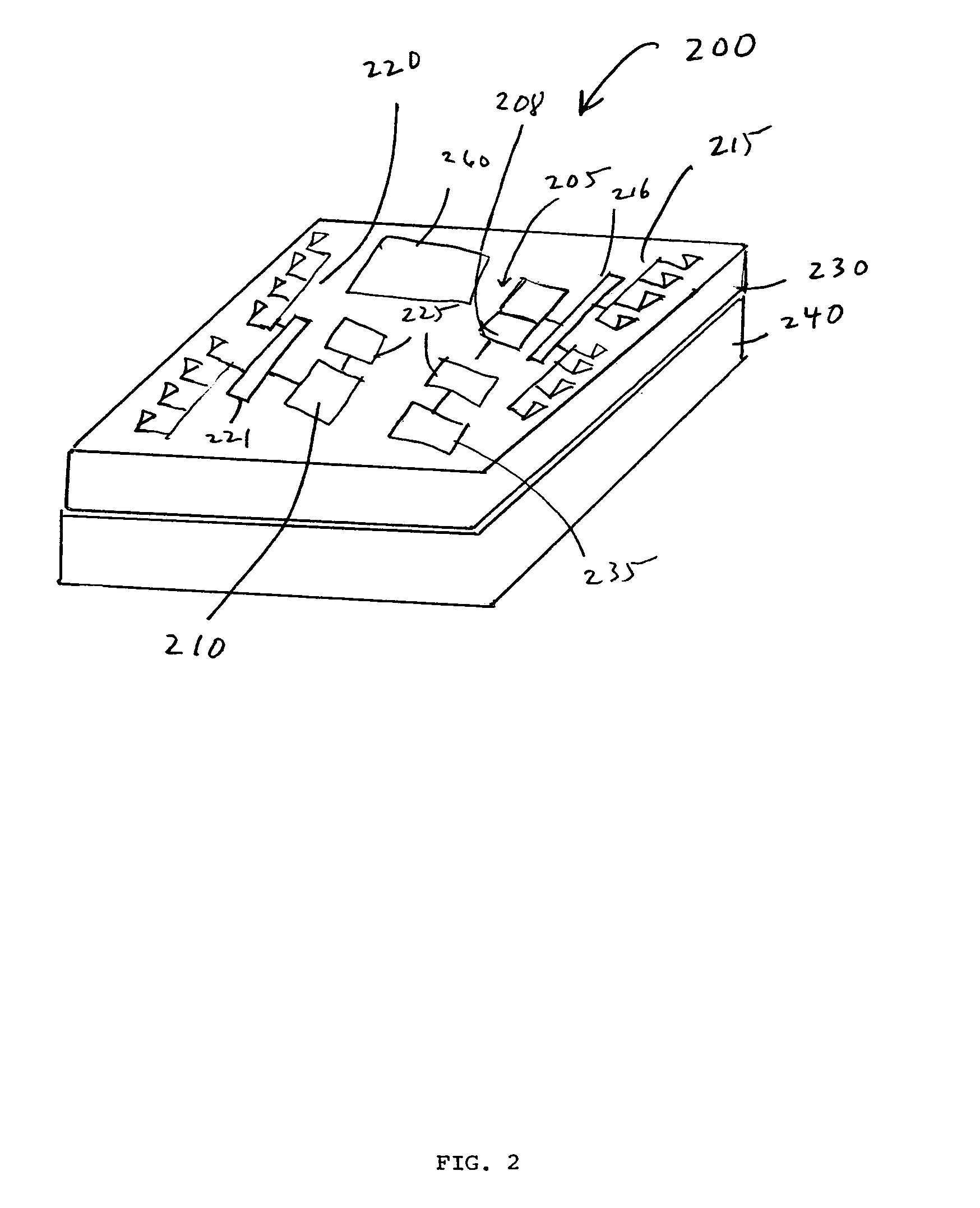
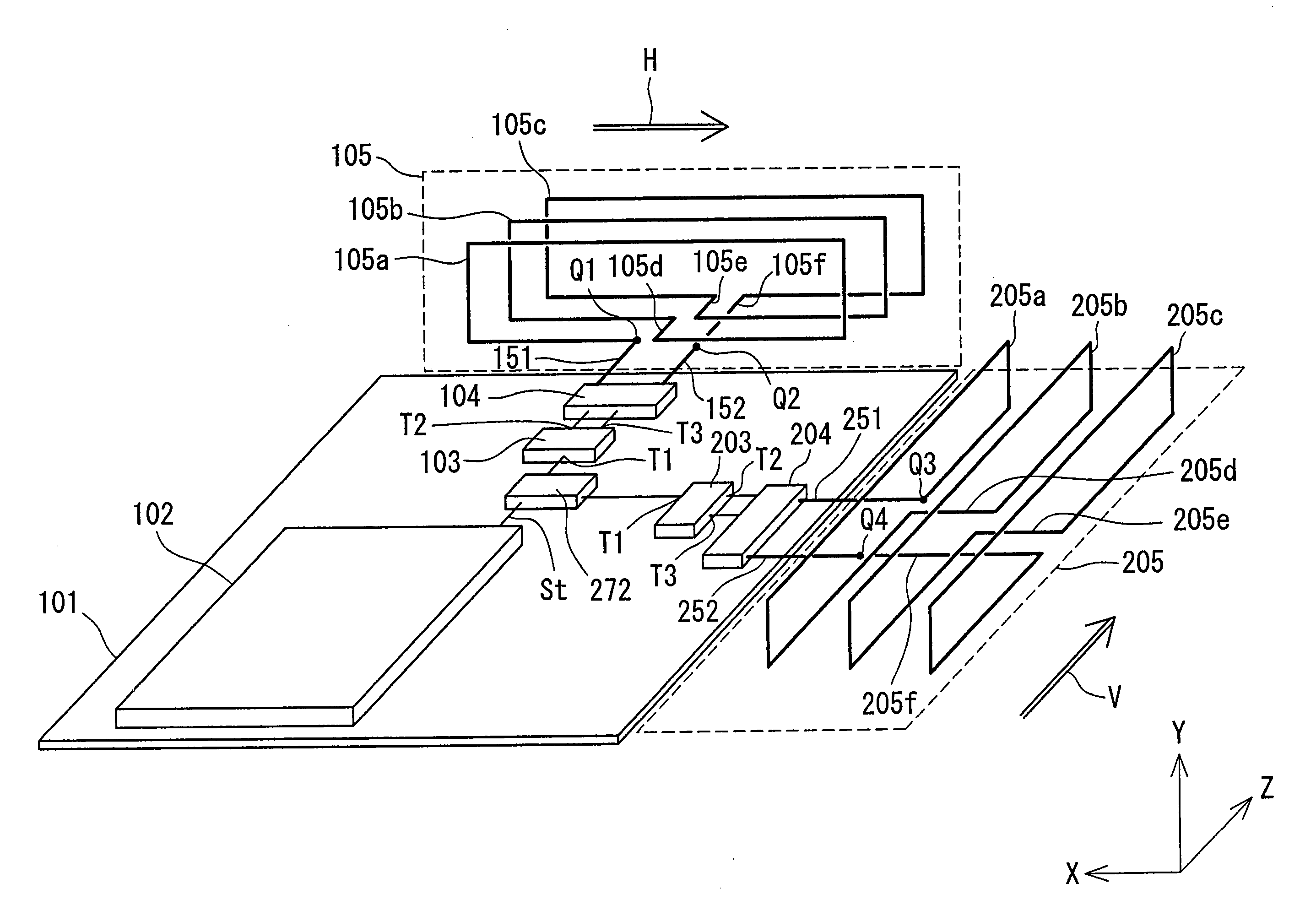
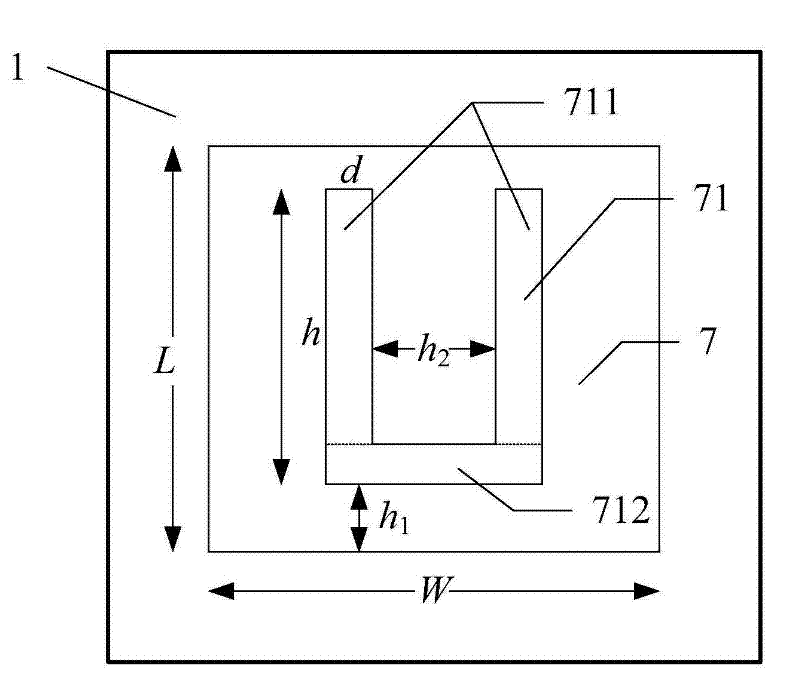
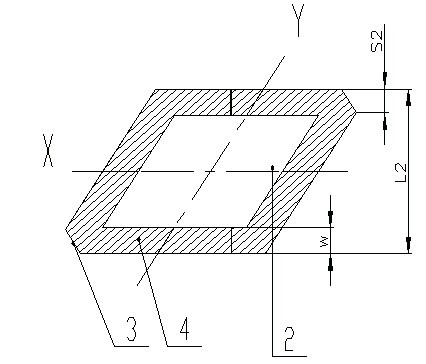
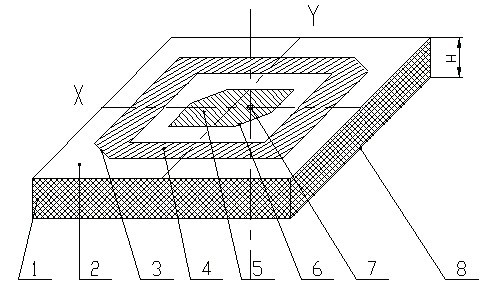
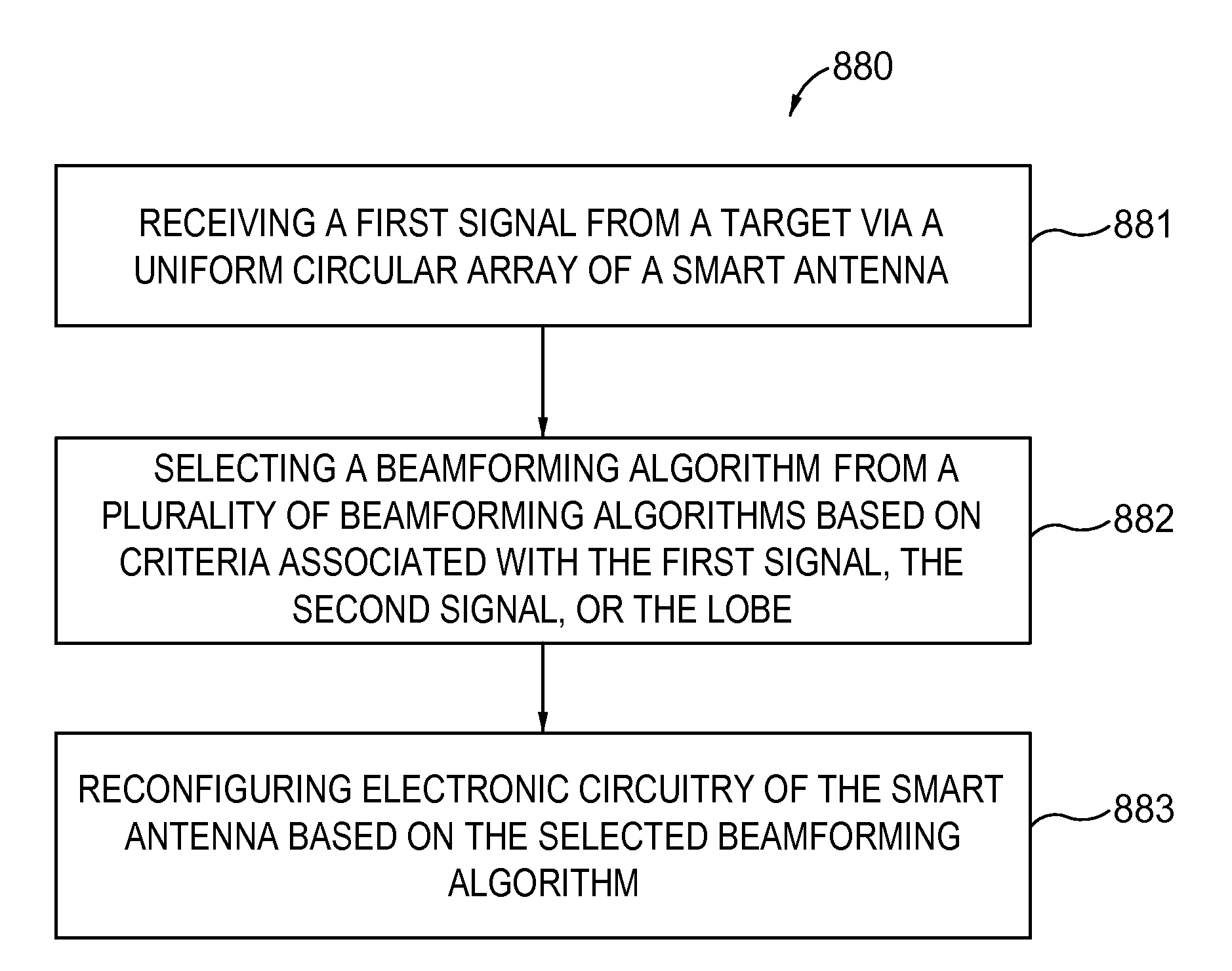
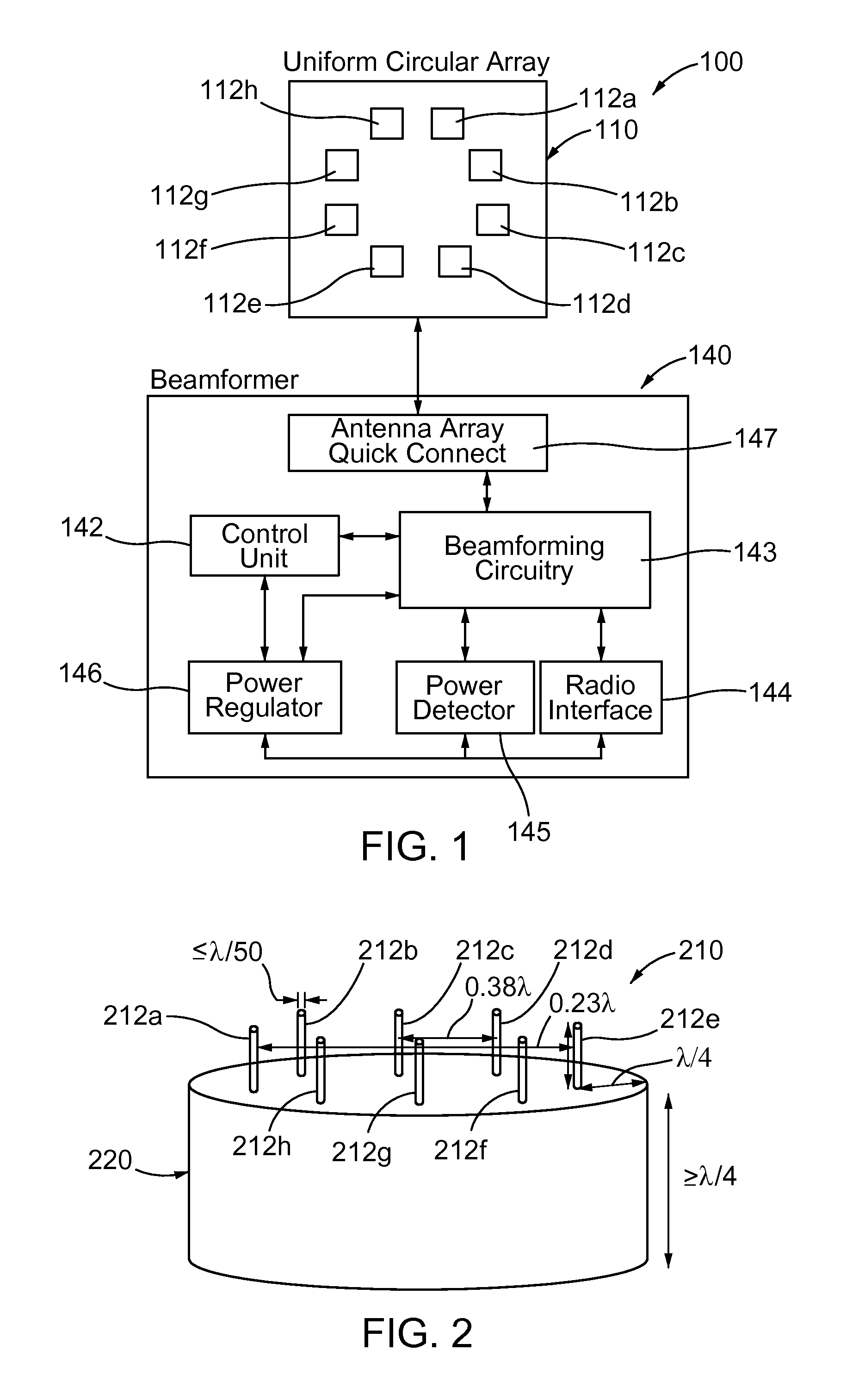
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1331 results about "Antenna gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
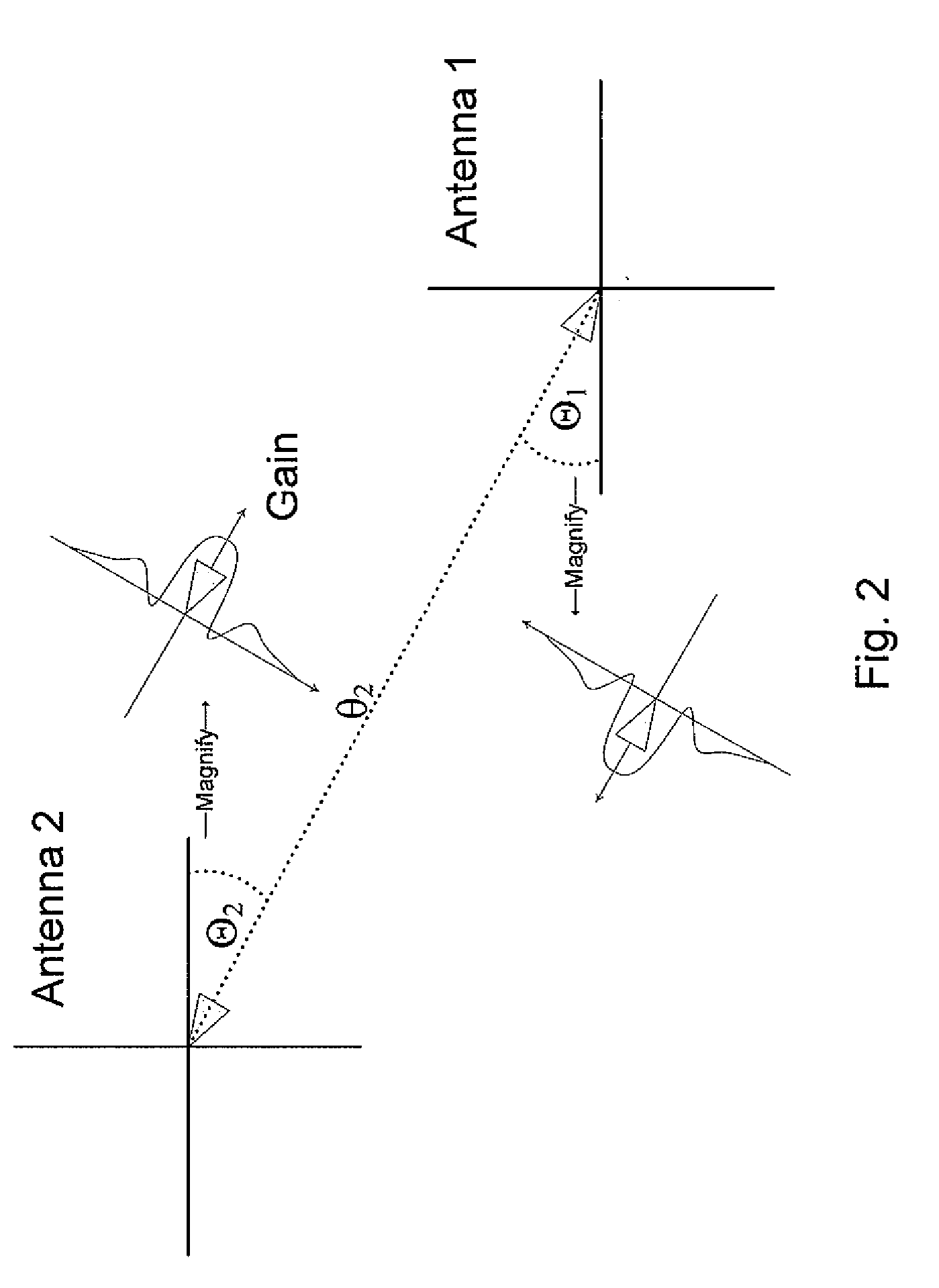
In electromagnetics, an antenna's power gain or simply gain is a key performance number which combines the antenna's directivity and electrical efficiency. In a transmitting antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction. In a receiving antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts radio waves arriving from a specified direction into electrical power.
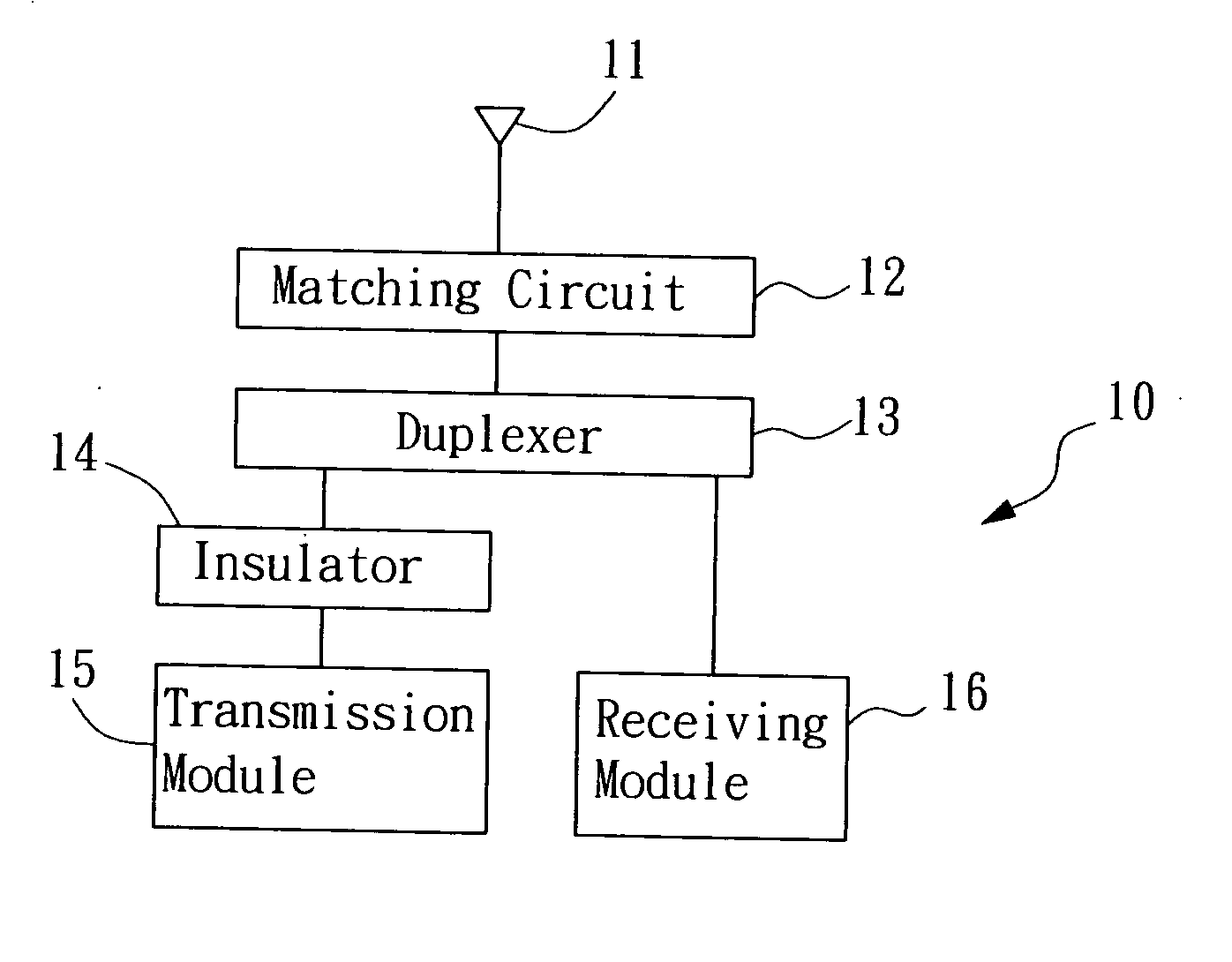
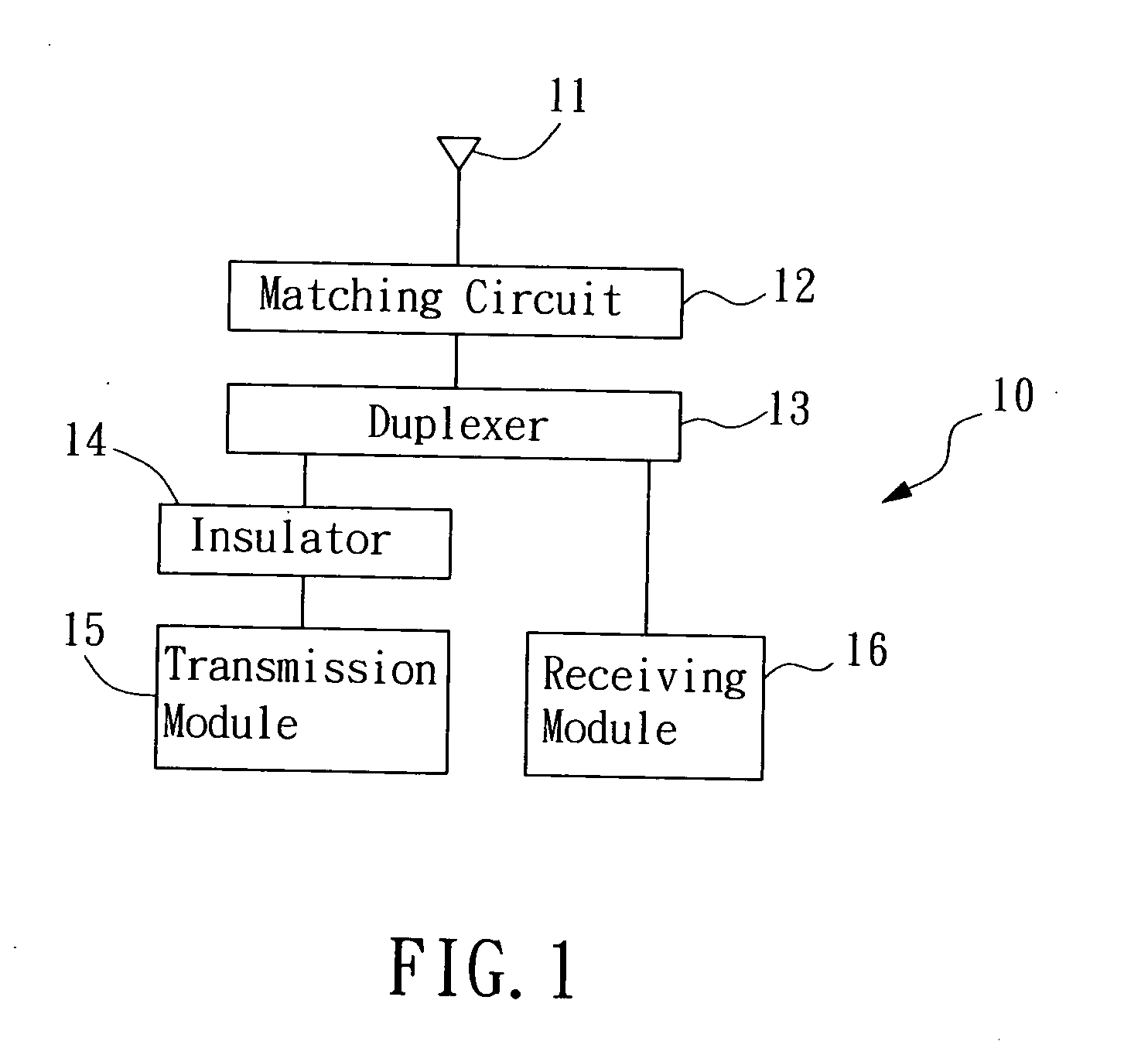
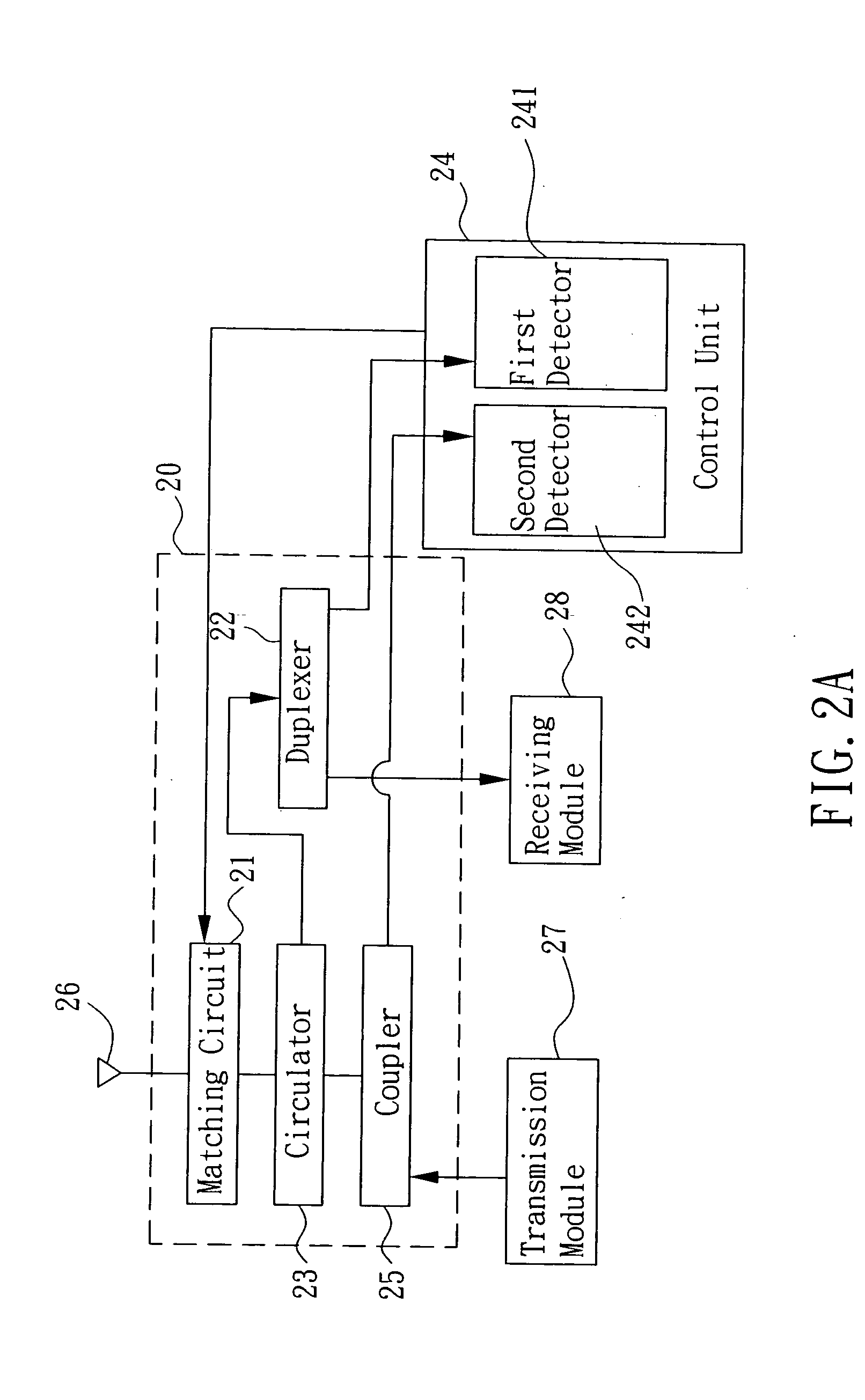
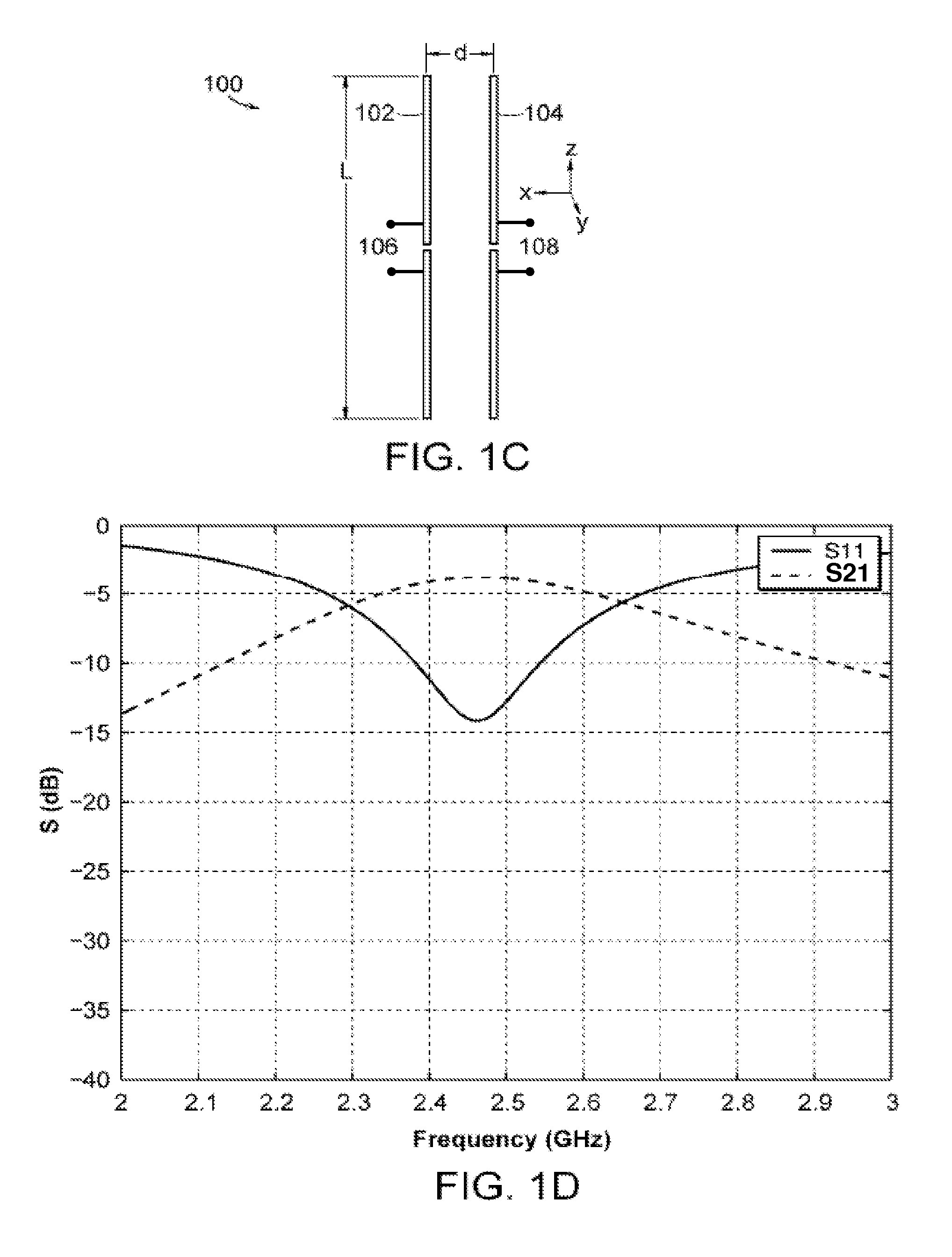
Device and method for antenna matching
InactiveUS20050042989A1Maximizing intensityIntensity of maximizedTransmissionTransceiverAntenna gain
The present invention provides a device and method for antenna matching applied in a transceiver. Wherein, the transceiver has a transmission module and a receiving module. The antenna matching device includes a matching circuit, a duplexer, a circulator, a control unit, and a coupler. Wherein, the matching circuit adjusts the matching impedance according to an adjusting signal and generates a reflection signal. The duplexer receives the reflection signal and a receiving signal and respectively sent the received two signals to the control unit and the receiving module according to their frequencies. The control unit, according to the reflection signal, estimates the adjusting signal for adjusting the matching circuit to an optimal state of the load impedance of the matching antenna, such that the antenna gain may is maximized, and a best efficiency is obtained no matter during receiving or transmission.
Owner:BENQ CORP
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
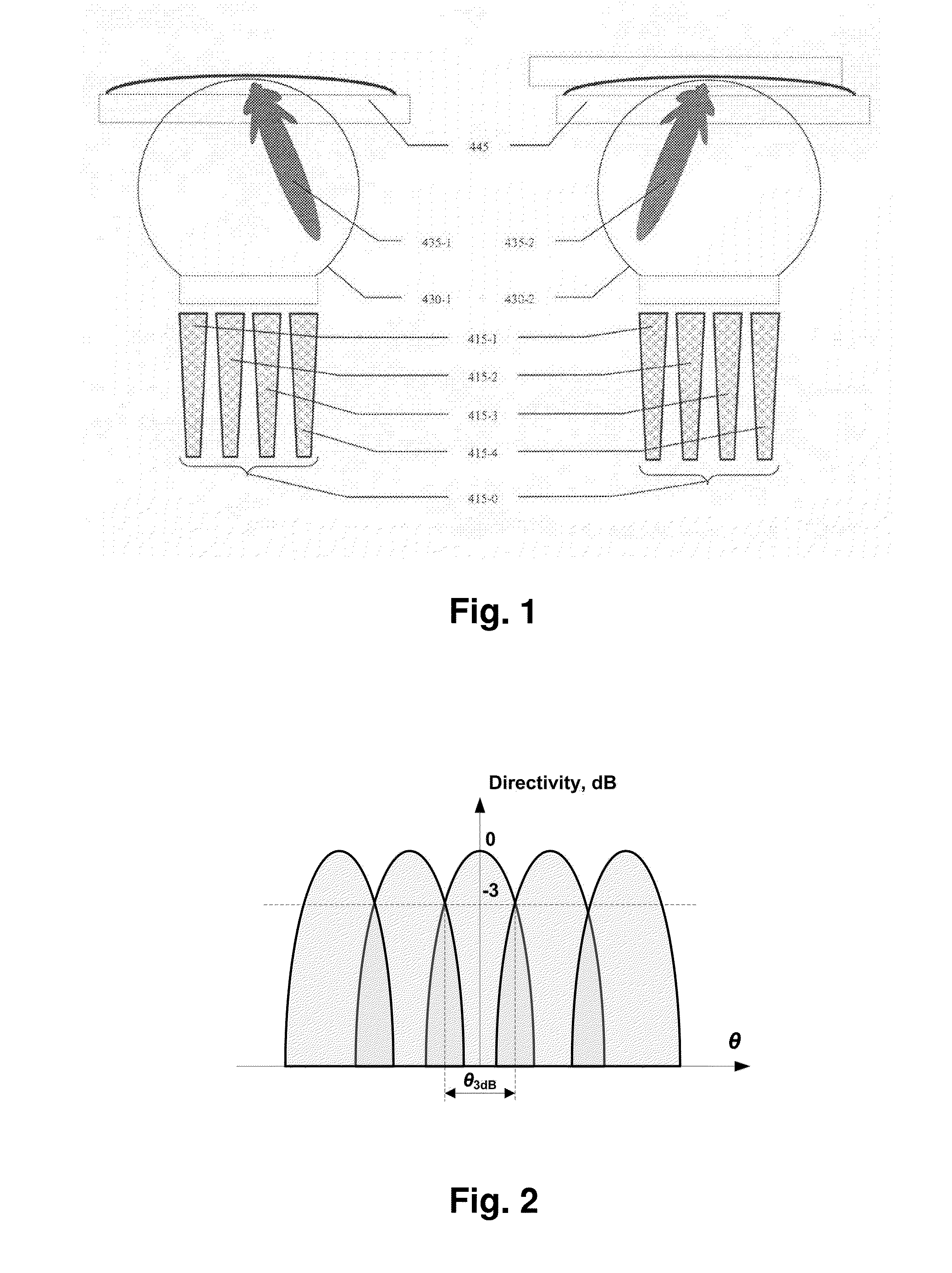
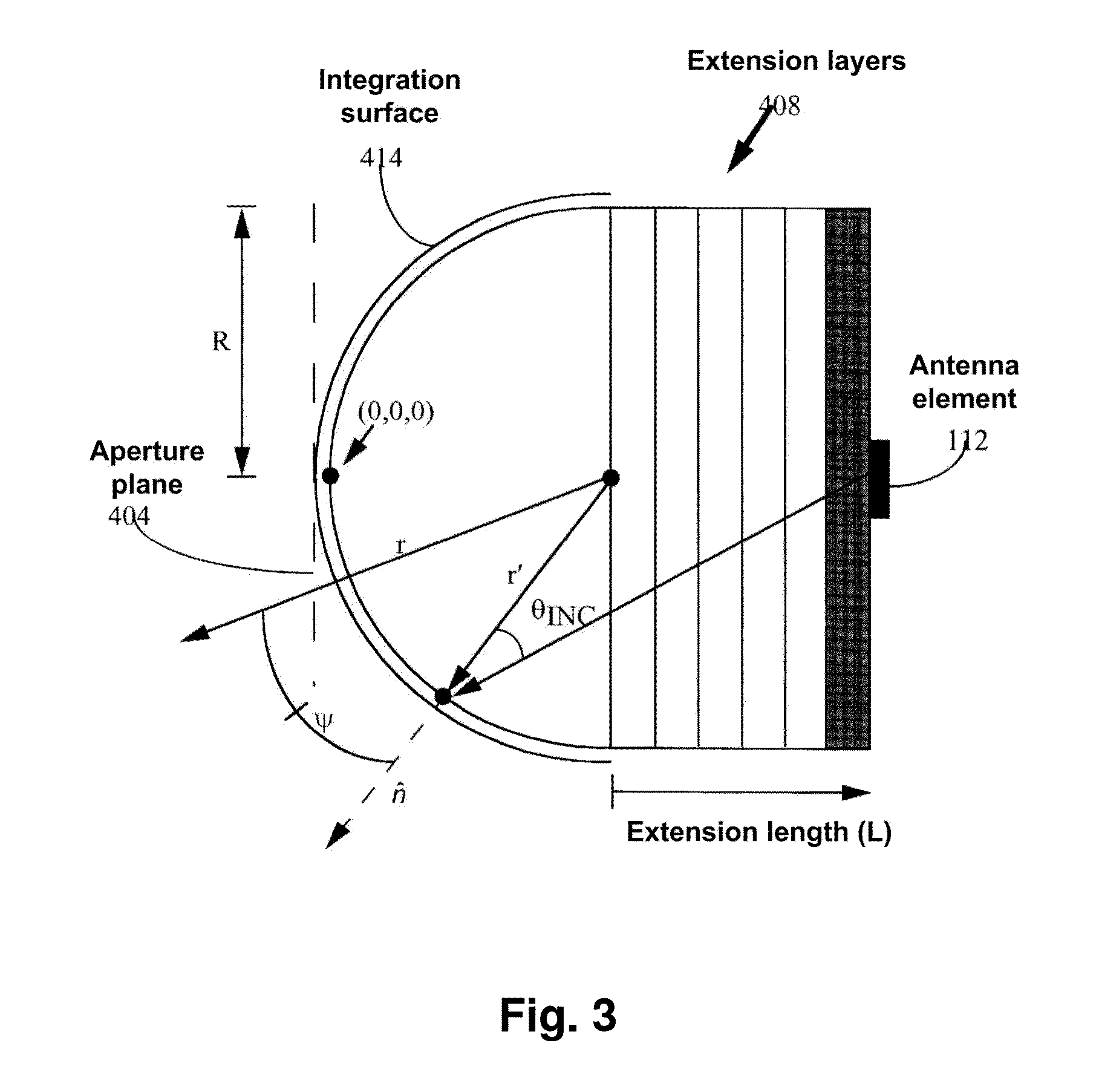
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Multi-Input Multi-Output antenna with multi-band characteristic
InactiveUS20120319904A1Improve isolationAvoid lostSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsMulti inputMulti band
The present invention relates to a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) antenna with a multi-band characteristic which includes a plurality of MIMO antenna, each having a pair of antenna elements, to support multiple bands, and is capable of guaranteeing high antenna efficiency for different bands by minimizing an interference between antenna elements of each MIMO antenna to improve an isolation characteristic. The MIMO antenna system having a multi-band characteristic, which includes two pairs of antenna patterns to support different band and coupling antenna parts separated from and coupled with the pairs of antenna patterns, can improve an isolation through the coupling antenna parts and guarantee an antenna gain. Moreover, since signal interference caused by the coupling effect can be cancelled to guarantee a band width with no change in antenna characteristics, it is possible to constructing two or more antennas to support a multi-band while guaranteeing stable operation of the antennas.
Owner:KIM BOBAE
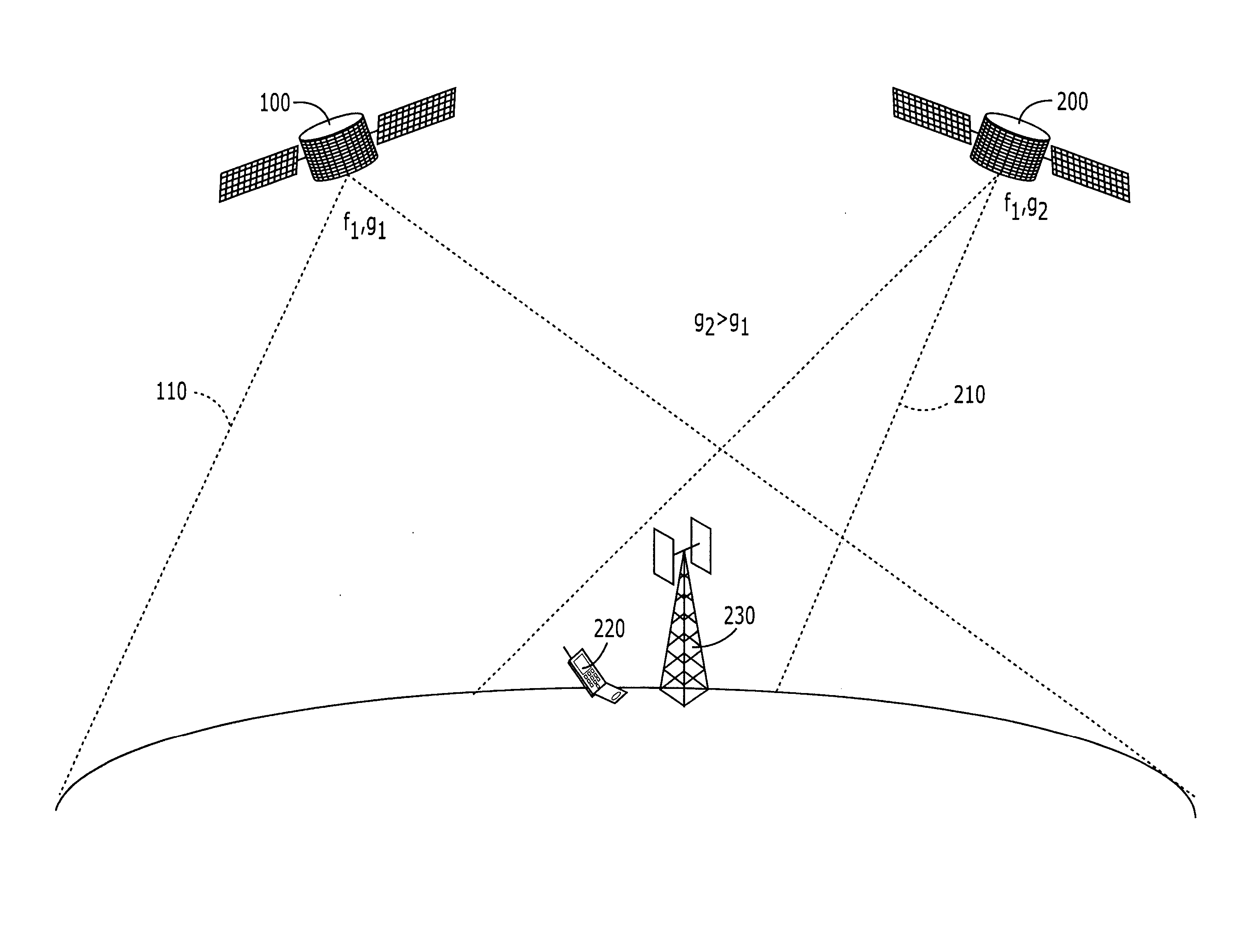
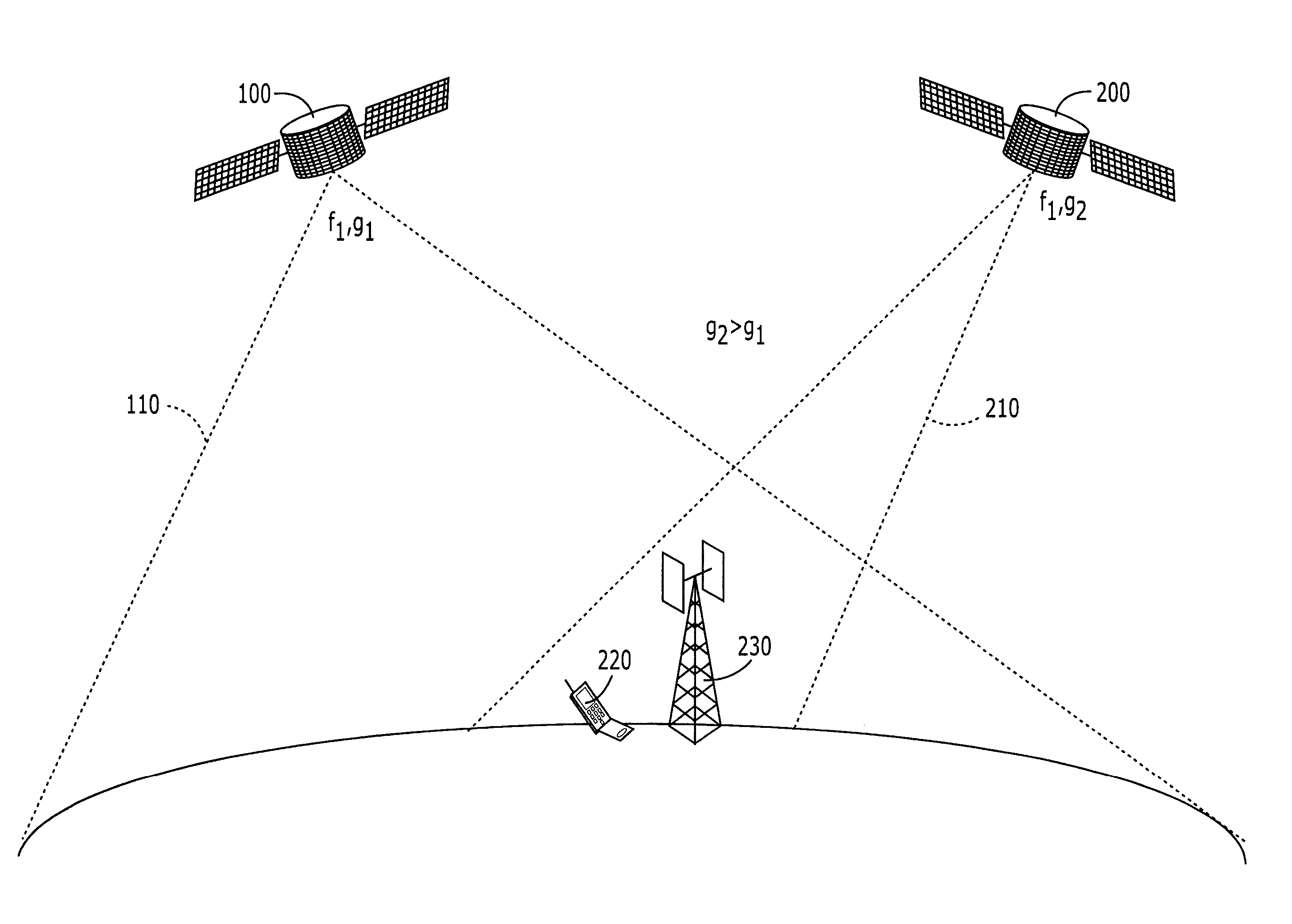
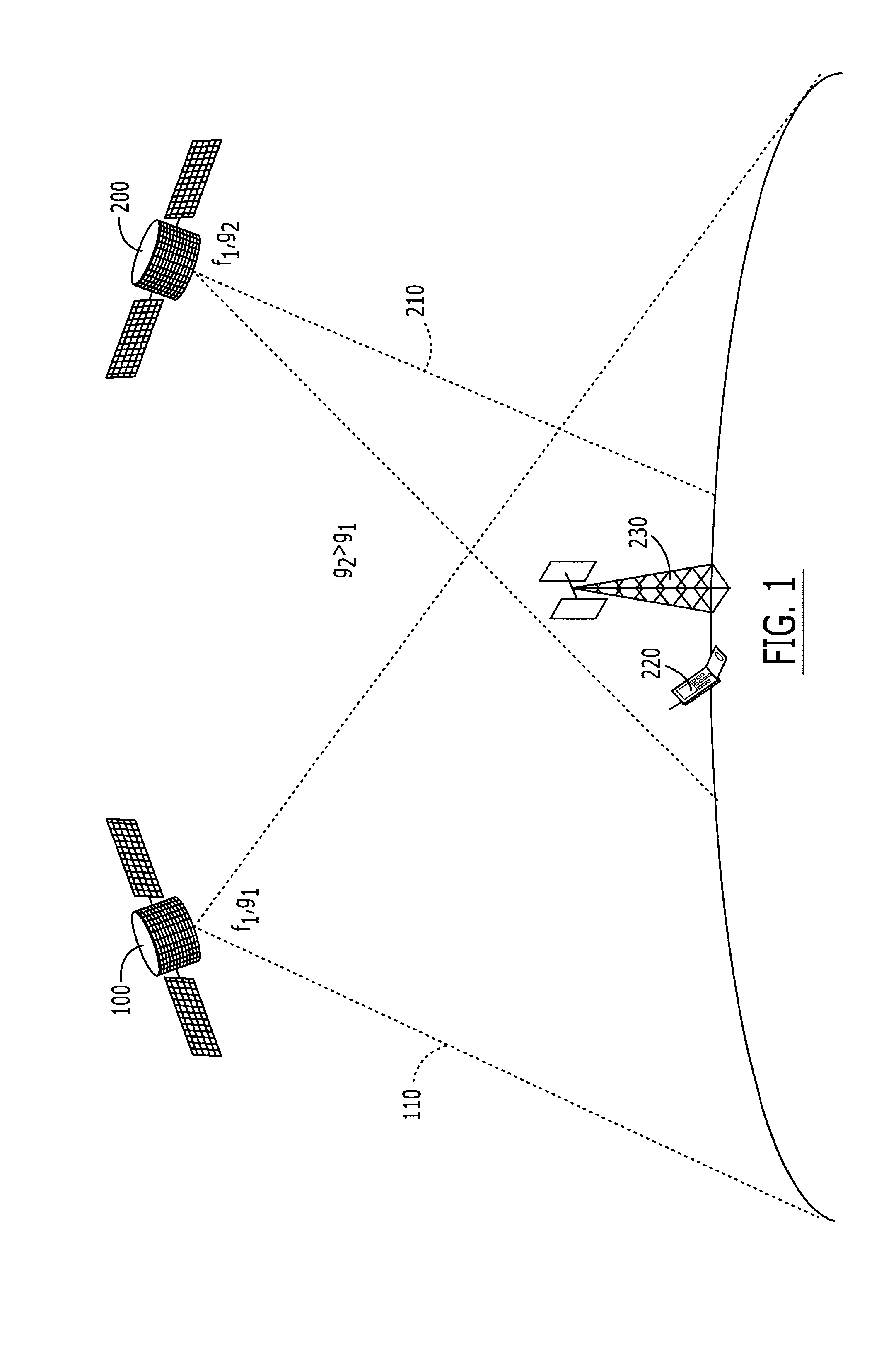
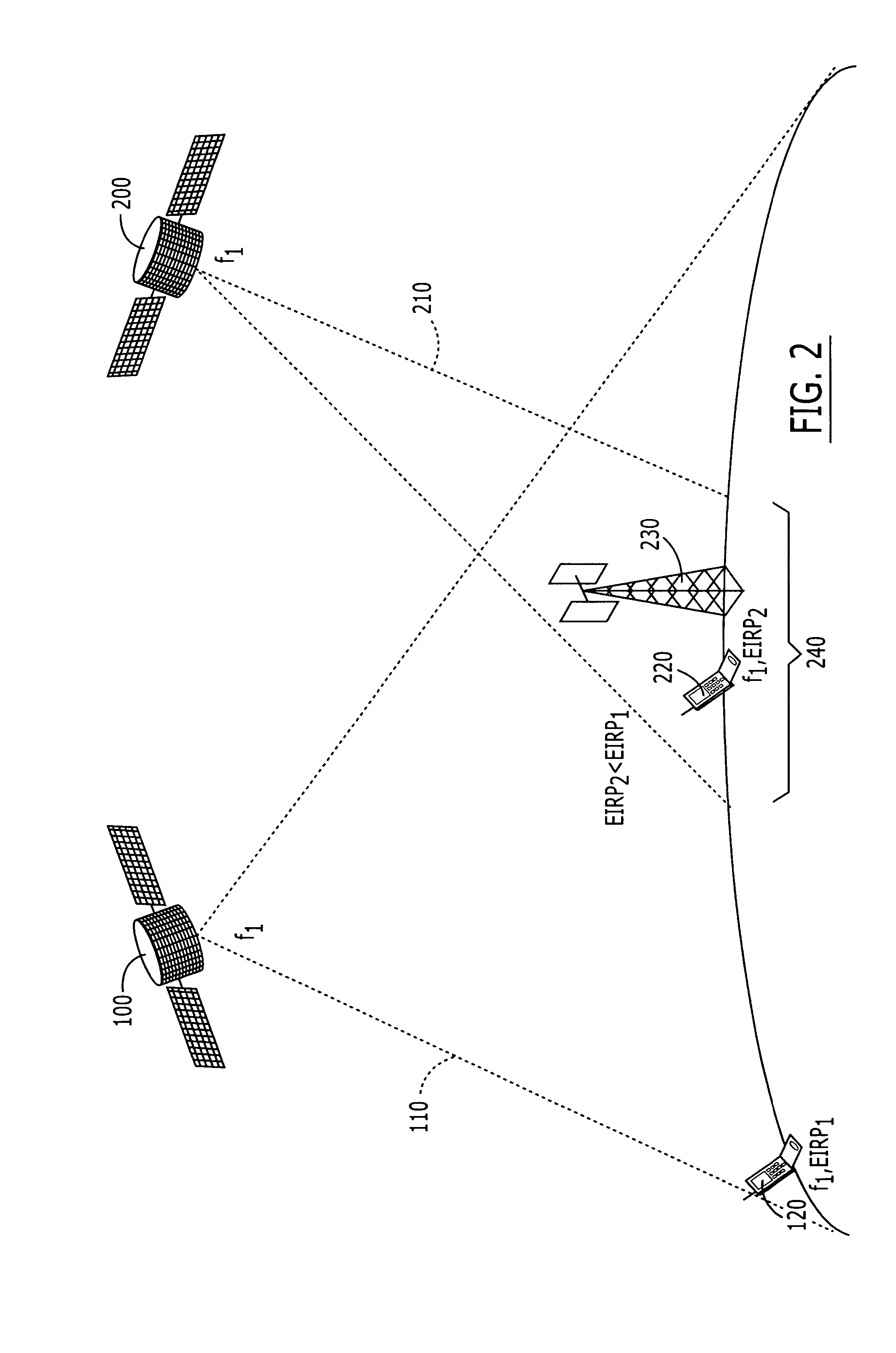
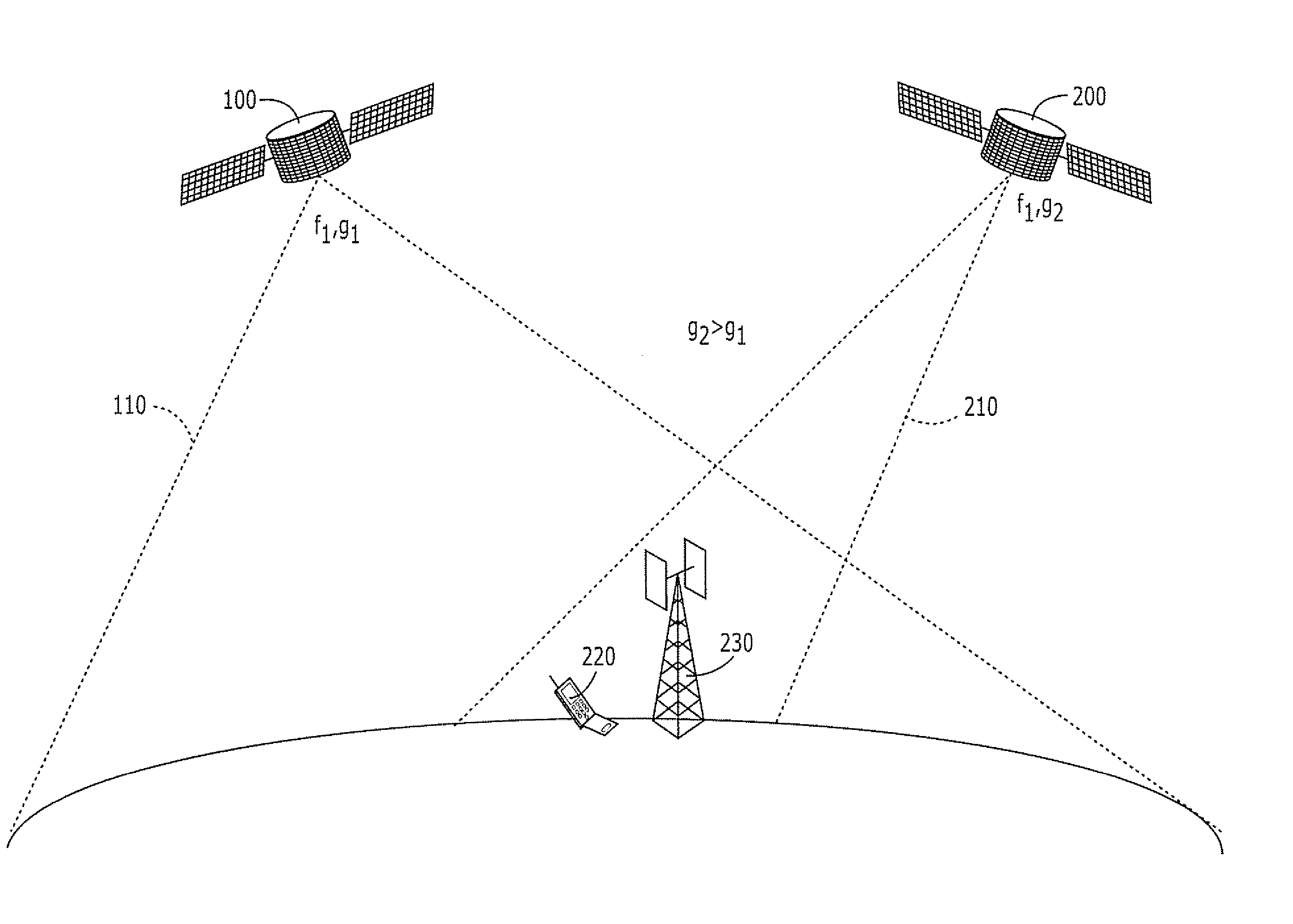
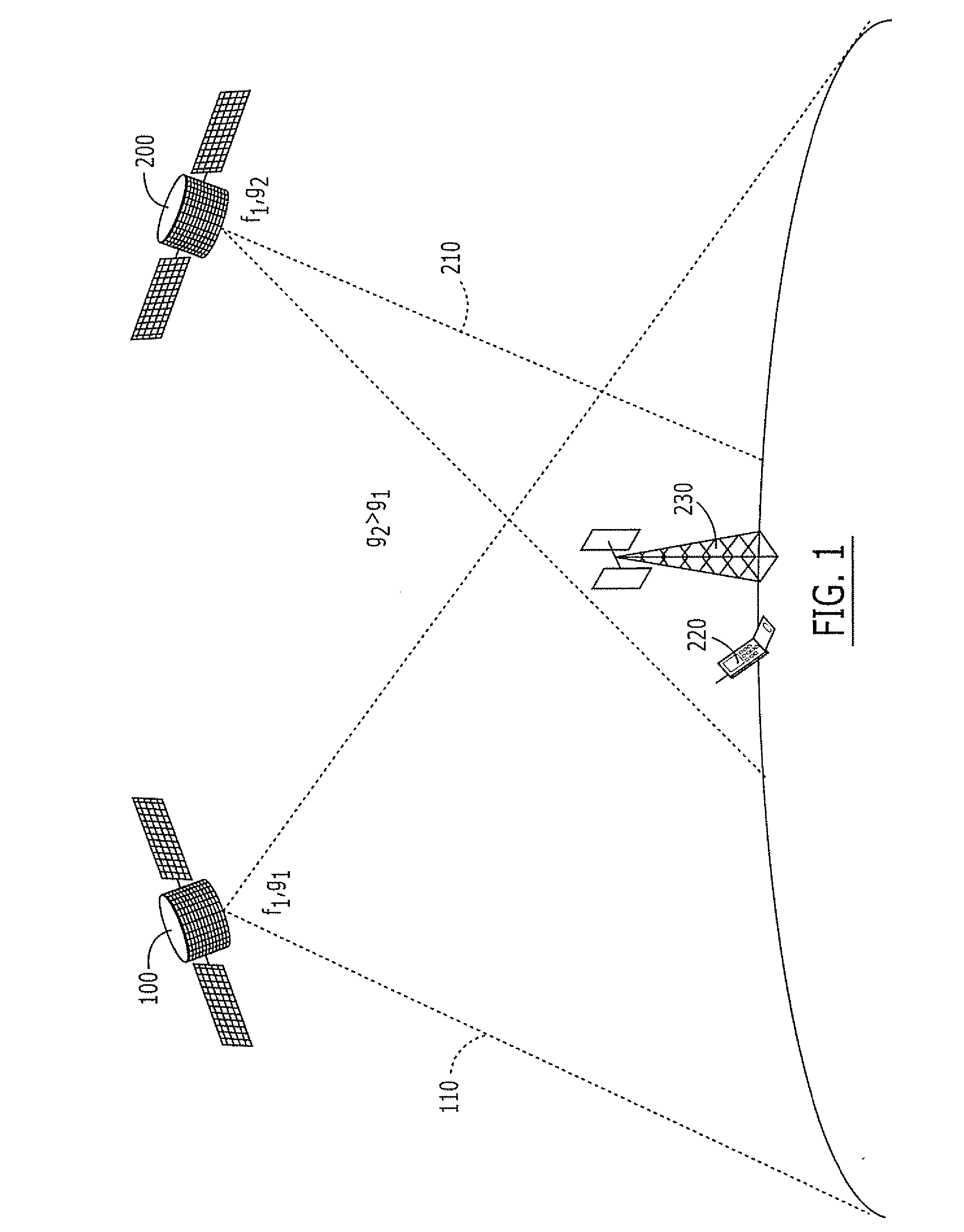
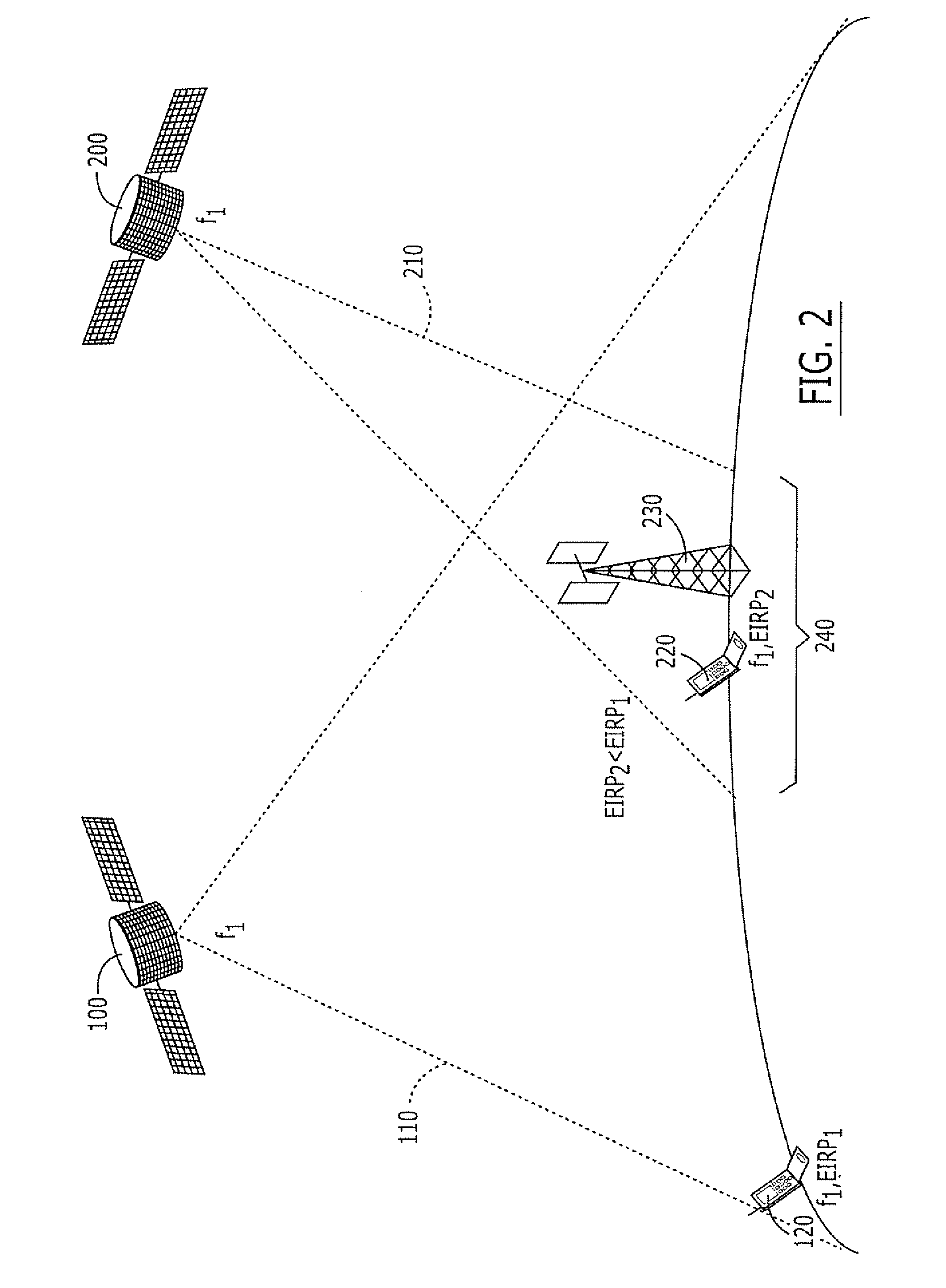
Systems and methods for inter-system sharing of satellite communications frequencies within a common footprint
ActiveUS20050064813A1Improve noiseIncrease aggregate noiseActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
Two satellite communications systems can use the same frequency or frequencies in geographically overlapping footprints, without creating undue interference in a given system that is caused by the same frequency signal(s) that is / are used by the other system. In particular, an aggregate Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of the radioterminals and / or ancillary terrestrial components of a second satellite communications system in the common footprint is sufficiently low, and / or the receive antenna gain of a first satellite communications system is sufficiently low compared to the receive antenna gain of the second satellite communications system, so as to increase an aggregate receiver noise that is seen by the first satellite system receivers by an amount that does not substantially change a Quality of Service (QoS) of the first satellite communications system.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
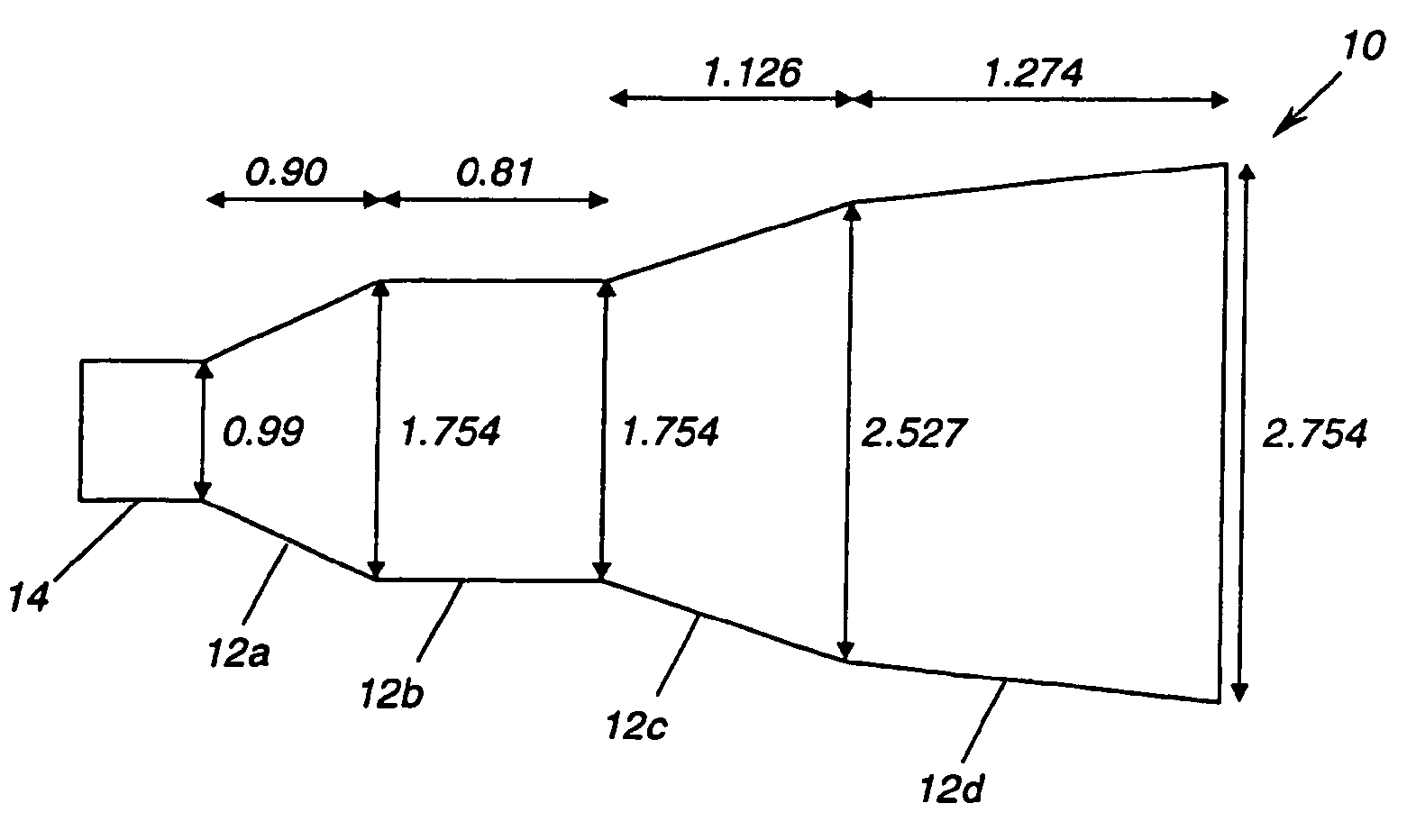
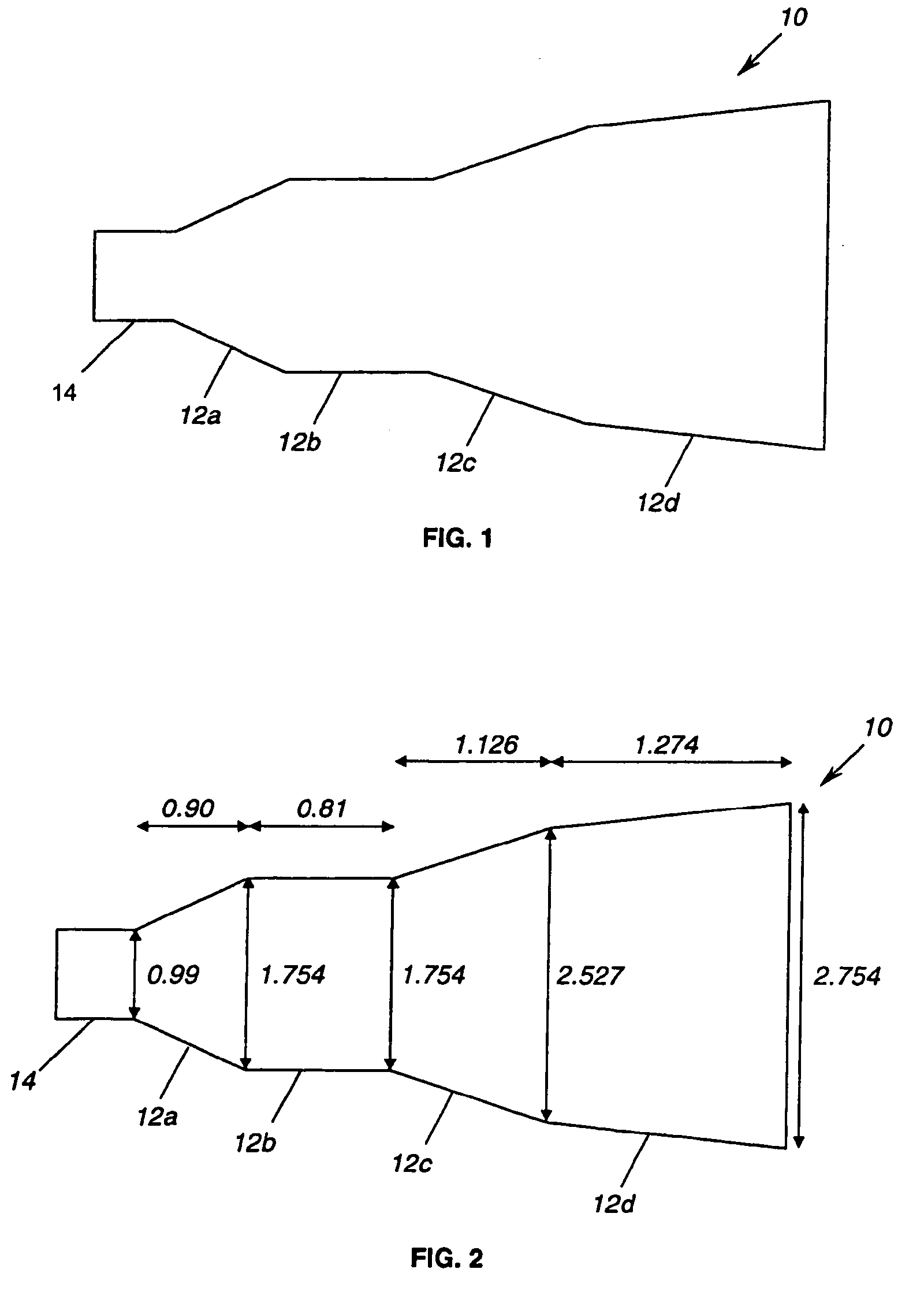
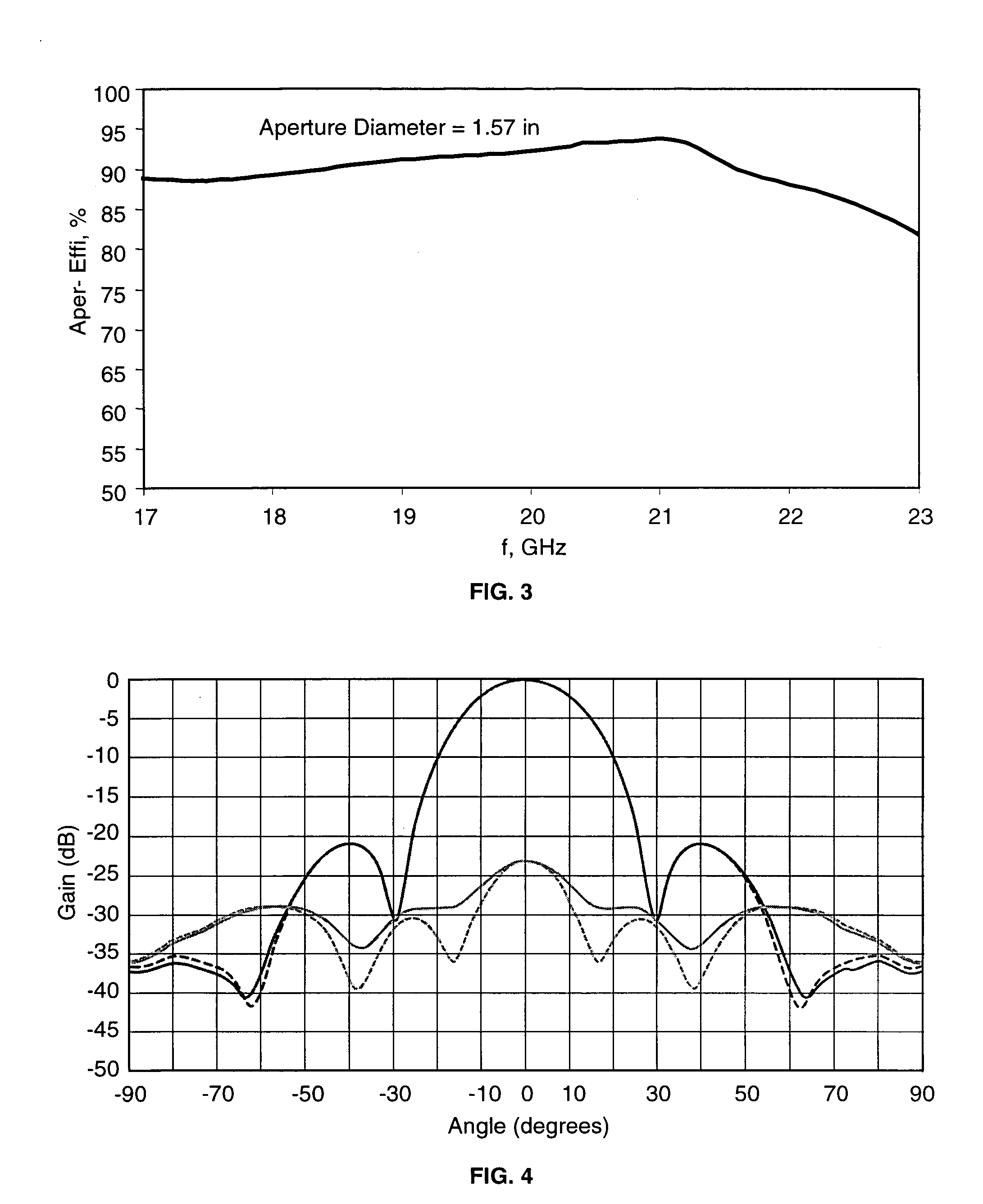
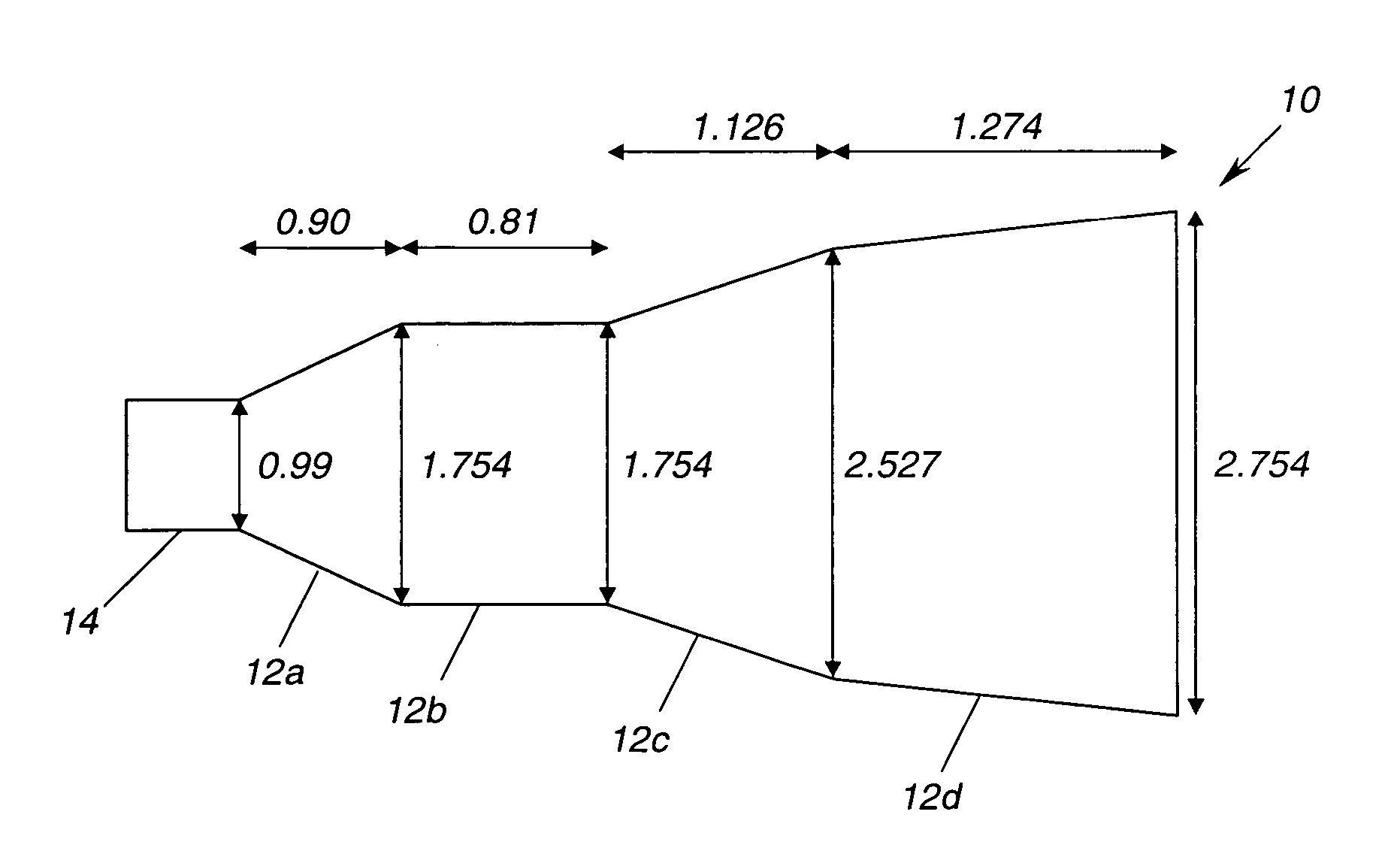
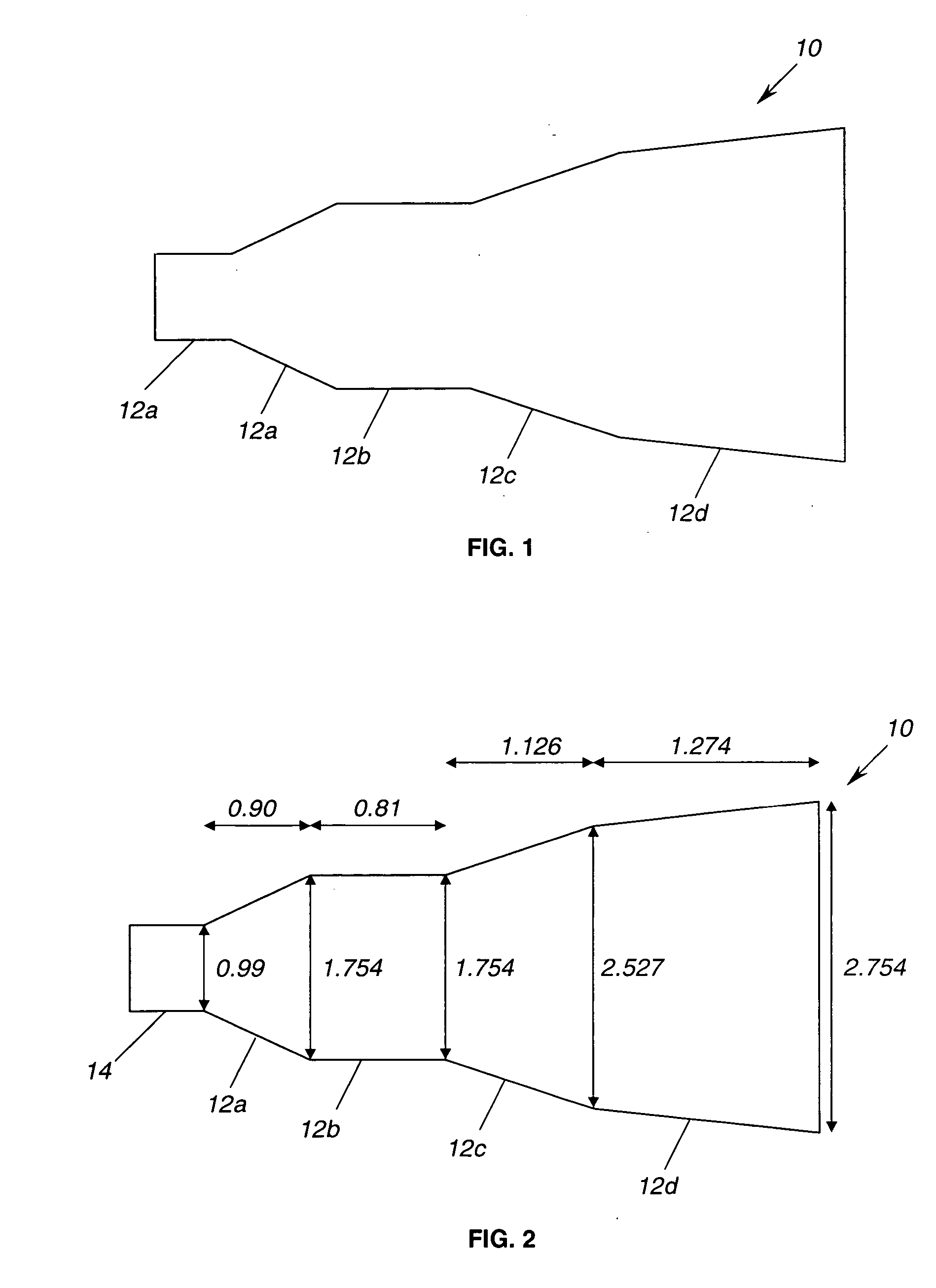
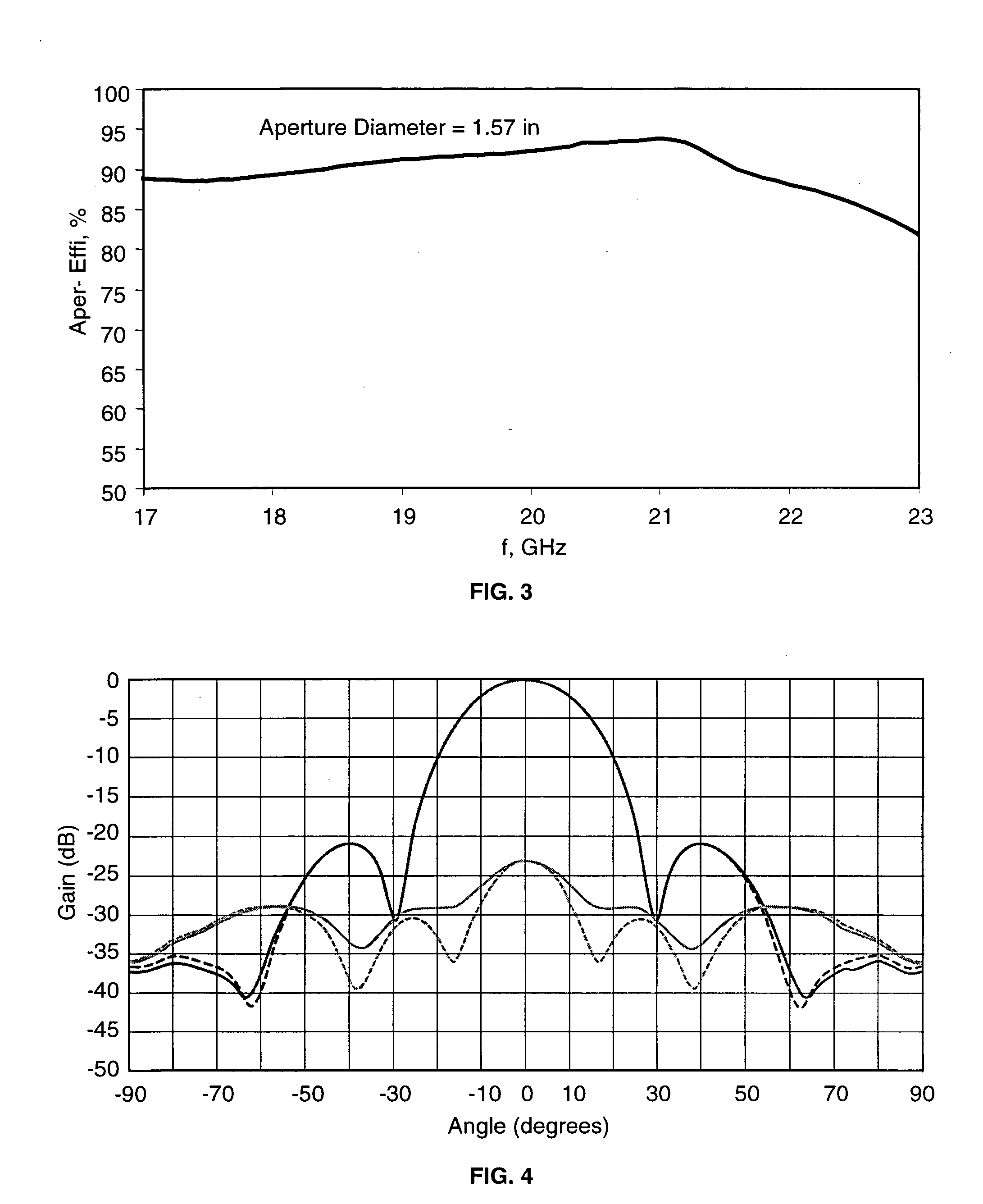
Multiple flared antenna horn with enhanced aperture efficiency
ActiveUS7183991B2Improve efficiencyEnhance desirable electromagnetic modesAntennasAntenna gainElectromagnetic mode
An antenna horn having multiple flared sections with their slopes and lengths selected to enhance desirable electromagnetic modes and to suppress undesirable modes at the horn aperture, thereby increasing the aperture efficiency and antenna gain.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Multiple flared antenna horn with enhanced aperture efficiency
An antenna horn having multiple flared sections with their slopes and lengths selected to enhance desirable electromagnetic modes and to suppress undesirable modes at the horn aperture, thereby increasing the aperture efficiency and antenna gain.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Wireless network-based location approximation
The invention pertains to location approximation of devices, e.g., wireless access points and client devices in a wireless network. Location estimates may be obtained by observation / analysis of packets transmitted or received by the access point. For instance, data rate information associated with a packet is used to approximate the distance between a client device and the access point. This may be coupled with known positioning information to arrive at an approximate location for the access point. Confidence information and metrics about whether a device is an access point and the location of that device may also be determined. Accuracy of the location determination may be affected by factors including propagation and environmental factors, transmit power, antenna gain and diversity, etc. A location information database of access points may employ measurements from various devices over time. Such information may identify the location of client devices and provide location-based services to them.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Telemetry antennas for medical devices and medical devices including telemetry antennas
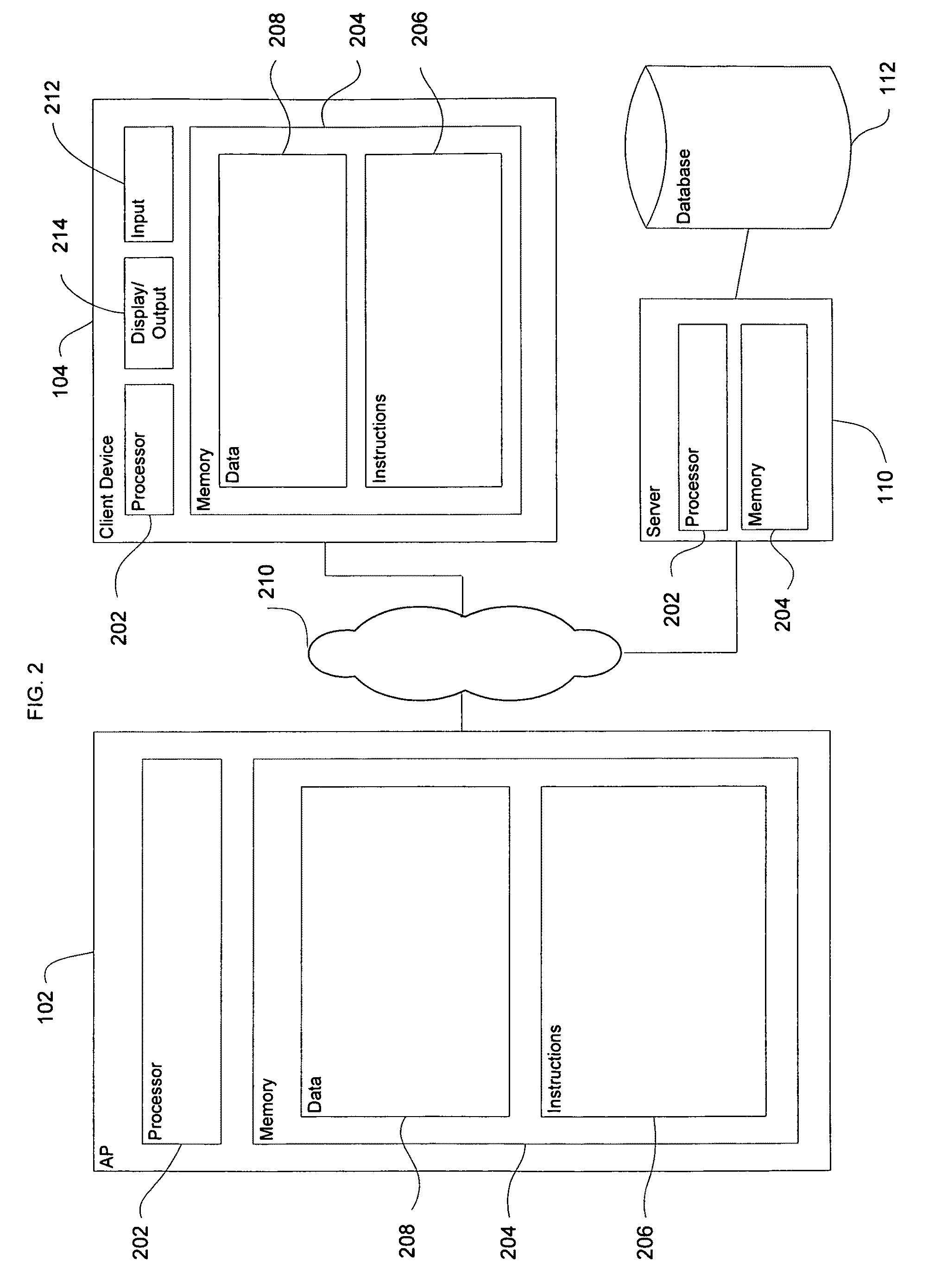
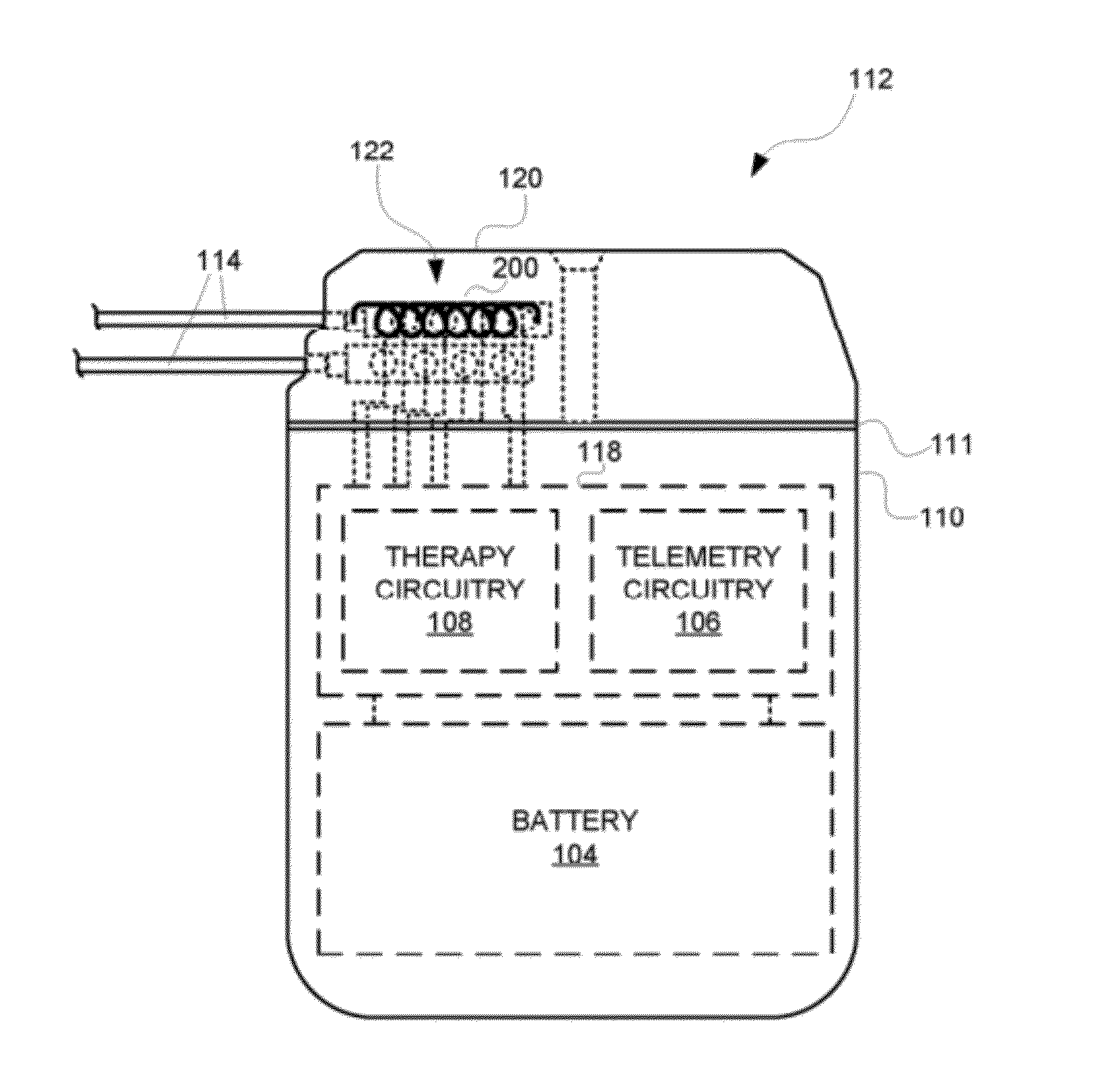
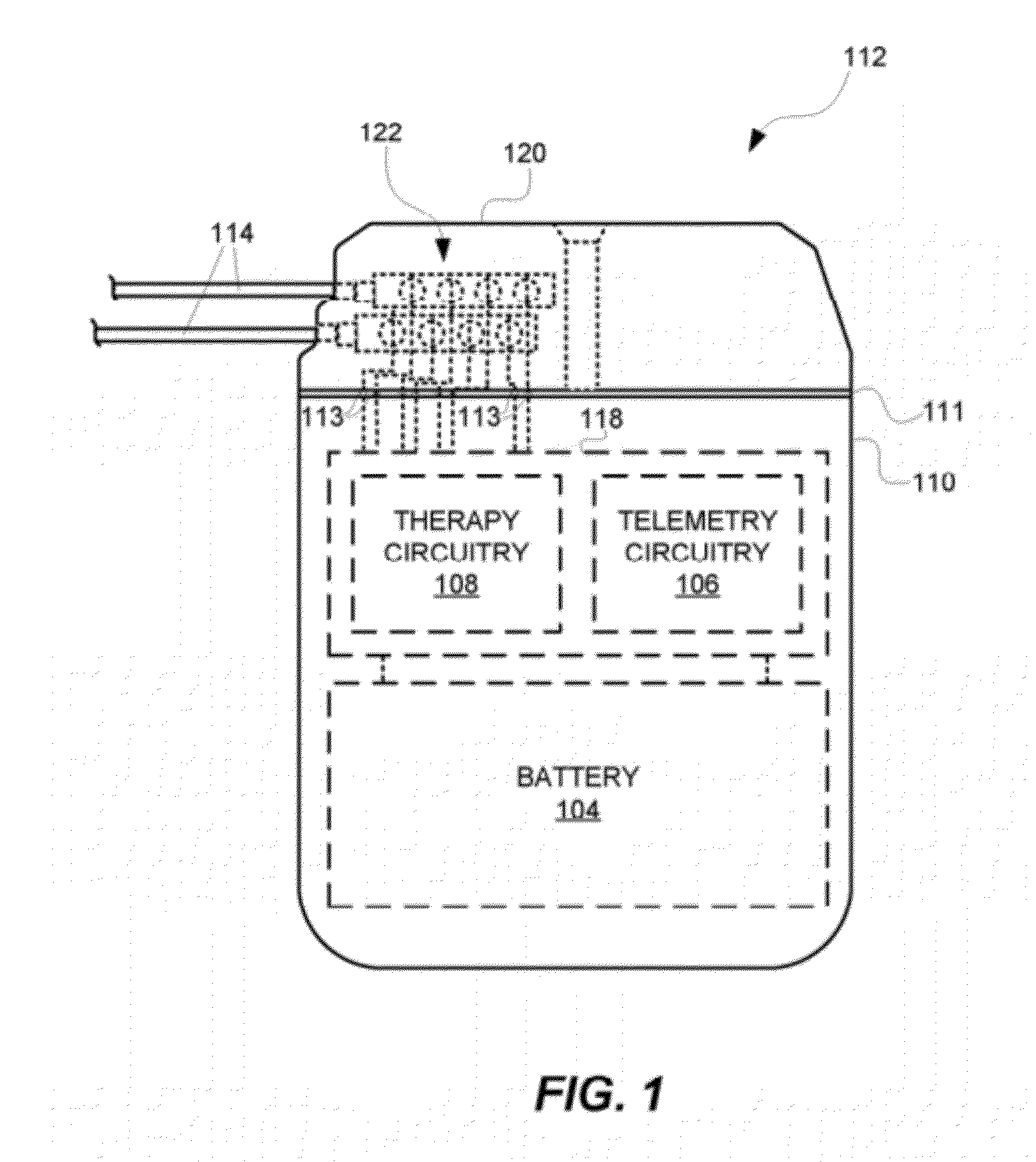
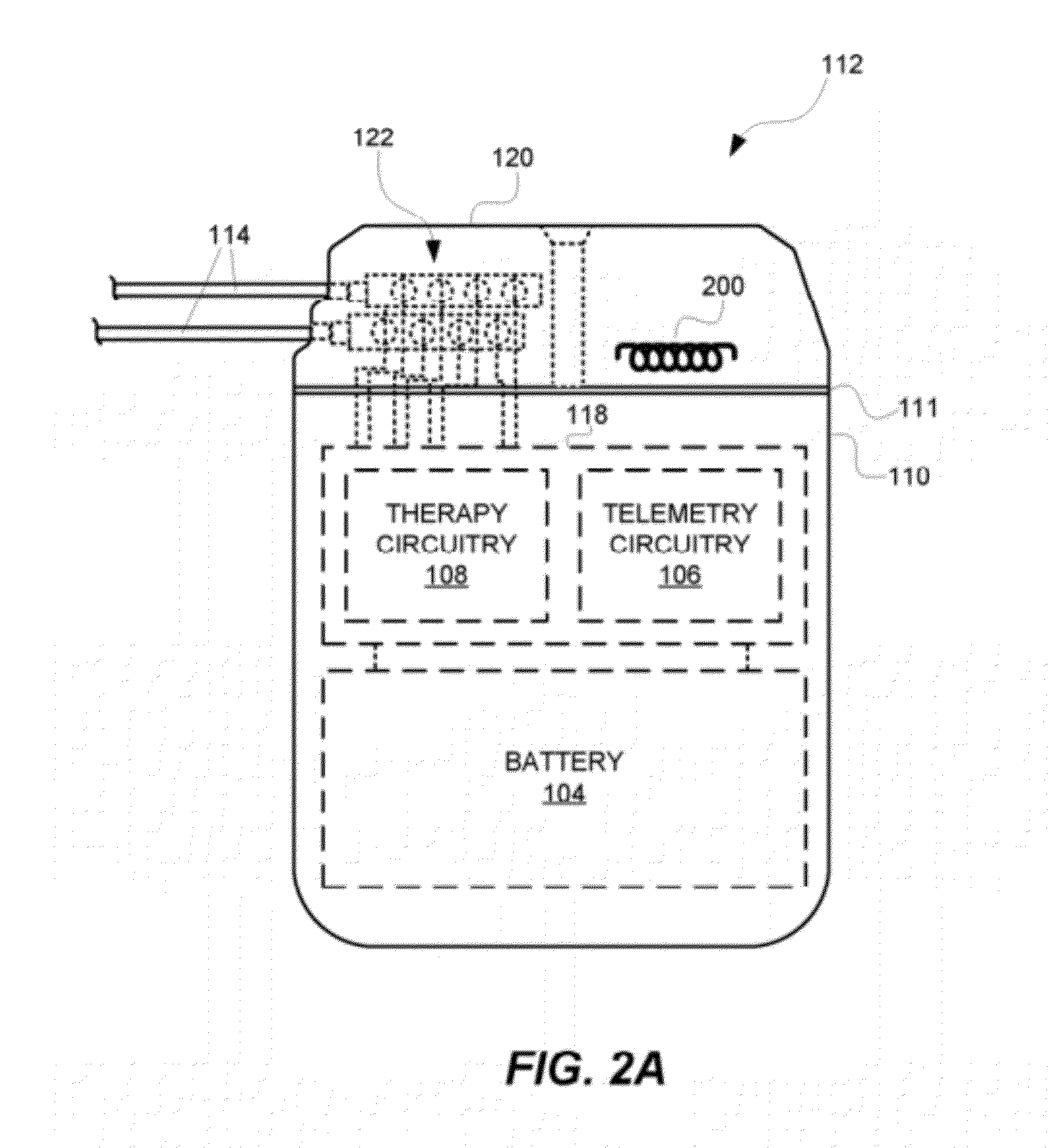
ActiveUS20120265272A1Increase in sizeGreat antenna gain antennaElectrotherapyHelical antennasAntenna bandwidthAntenna gain
In an embodiment, an antenna for a medical device, e.g., an implantable medical device (IMD), comprises an electrically conductive wire that spirals to form a three-dimensional shape of a rectangular cuboid. In another embodiment, the antenna comprises an electrically conductive wire that spirals to form a three-dimensional shape of an elliptical cylinder, an oval cylinder, an elongated pentagonal prism, an elongated hexagonal prism, or some other shape where the longitudinal diameter of the antenna is greater than the lateral diameter of the antenna. The antennas are sized to fit within a portion of a header of the medical device. Such antennas are designed to provide increased antenna gain and antenna bandwidth.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Adaptive antenna array methods and apparatus for use in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6920192B1Fast convergenceReduce computing costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
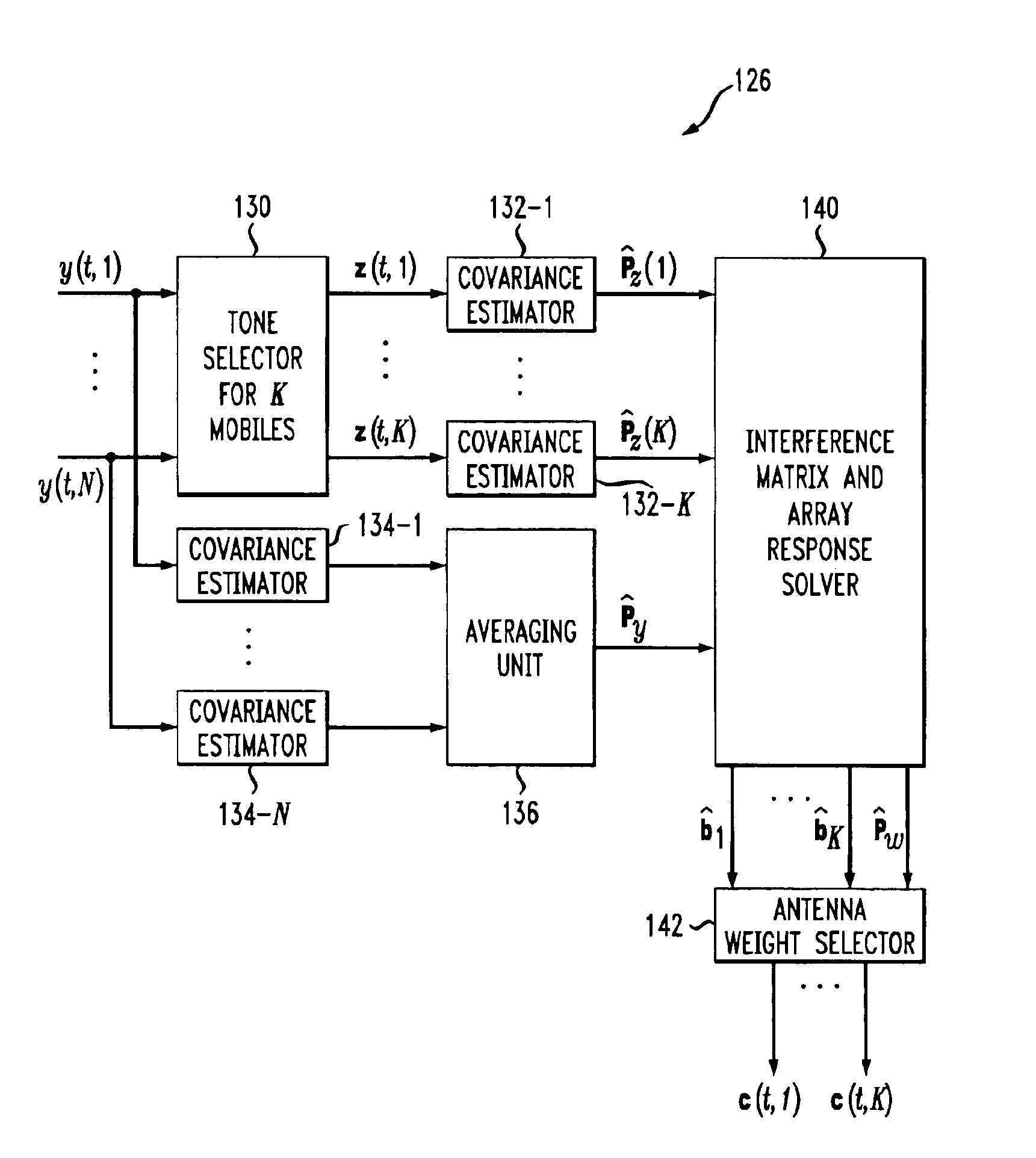
Adaptive antenna array techniques for use in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed spread-spectrum multi-access (OFDM-SSMA) cellular wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. A base station of the system includes an antenna array and a base station receiver. The base station receiver implements an adaptive antenna gain algorithm which estimates a spatial covariance matrix for each of K mobile stations communicating with the base station. The spatial covariance matrix for a given one of the mobile stations is determined at least in part based on a unique hopping sequence of the mobile station, and provides a correlation between signals received from the mobile station at different antenna elements within the antenna array. An average spatial covariance matrix for a set of received signals is also generated. The individual spatial covariance matrices and the average spatial covariance matrix are processed to generate an estimate of an interference matrix for the K mobile stations, and the estimate of the interference matrix is further processed to generate array responses for each of the mobile stations. The array response for a given mobile station is processed to determine an antenna weighting which is applied to a signal received from the given mobile station in order to facilitate detection of a corresponding transmitted symbol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
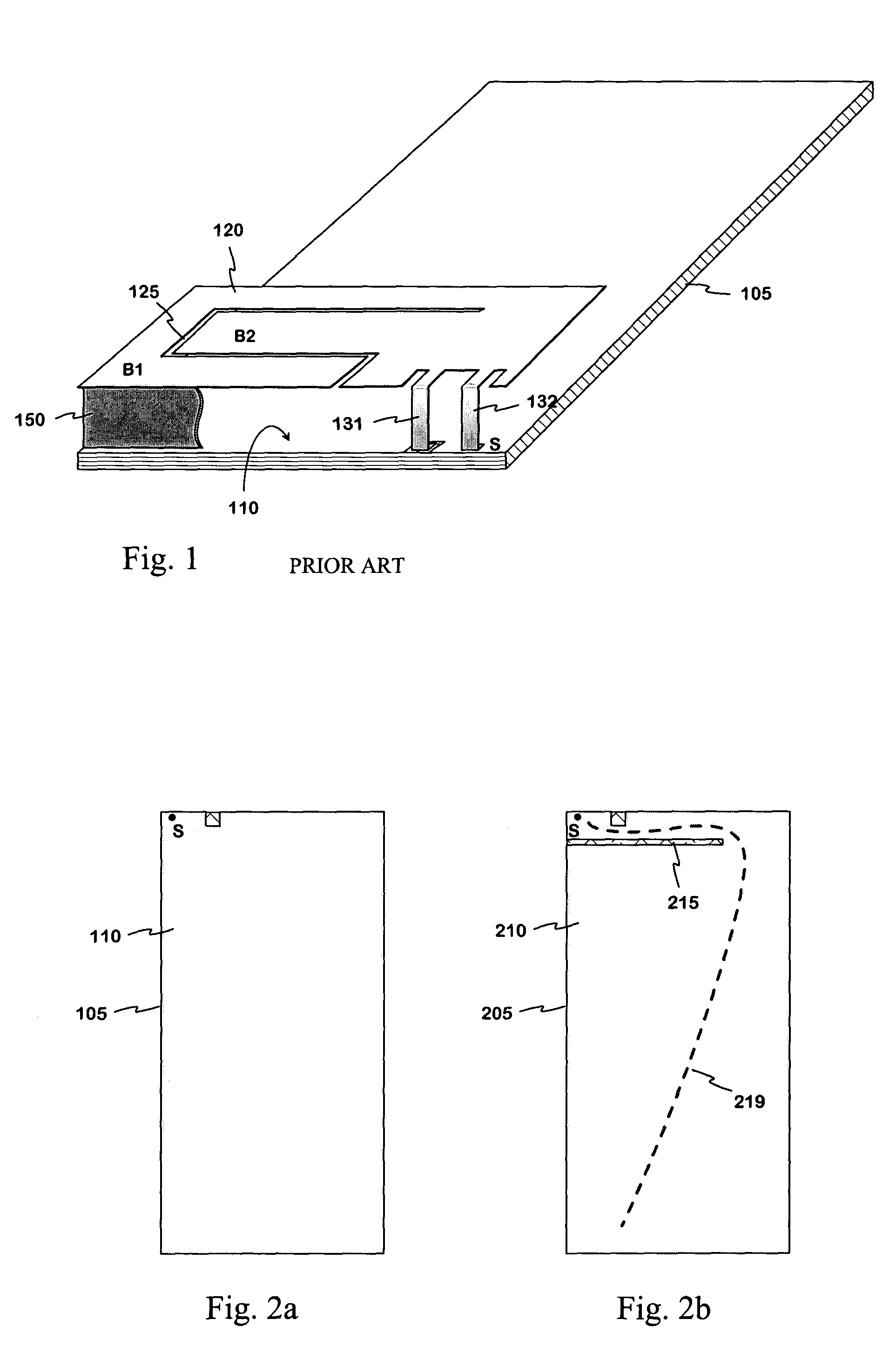
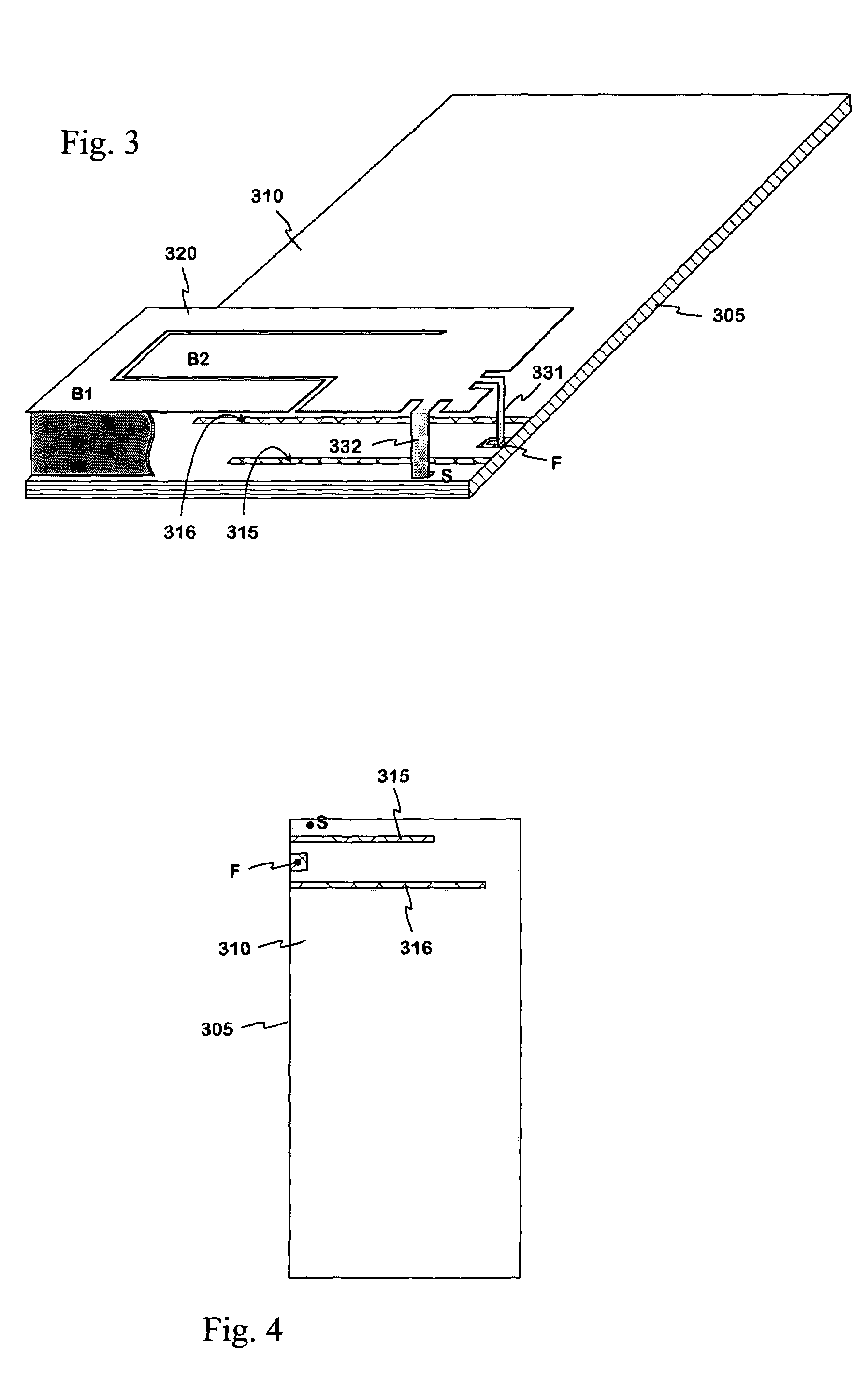
Internal antenna
InactiveUS6985108B2Reduce distanceImprove matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyAntenna gain
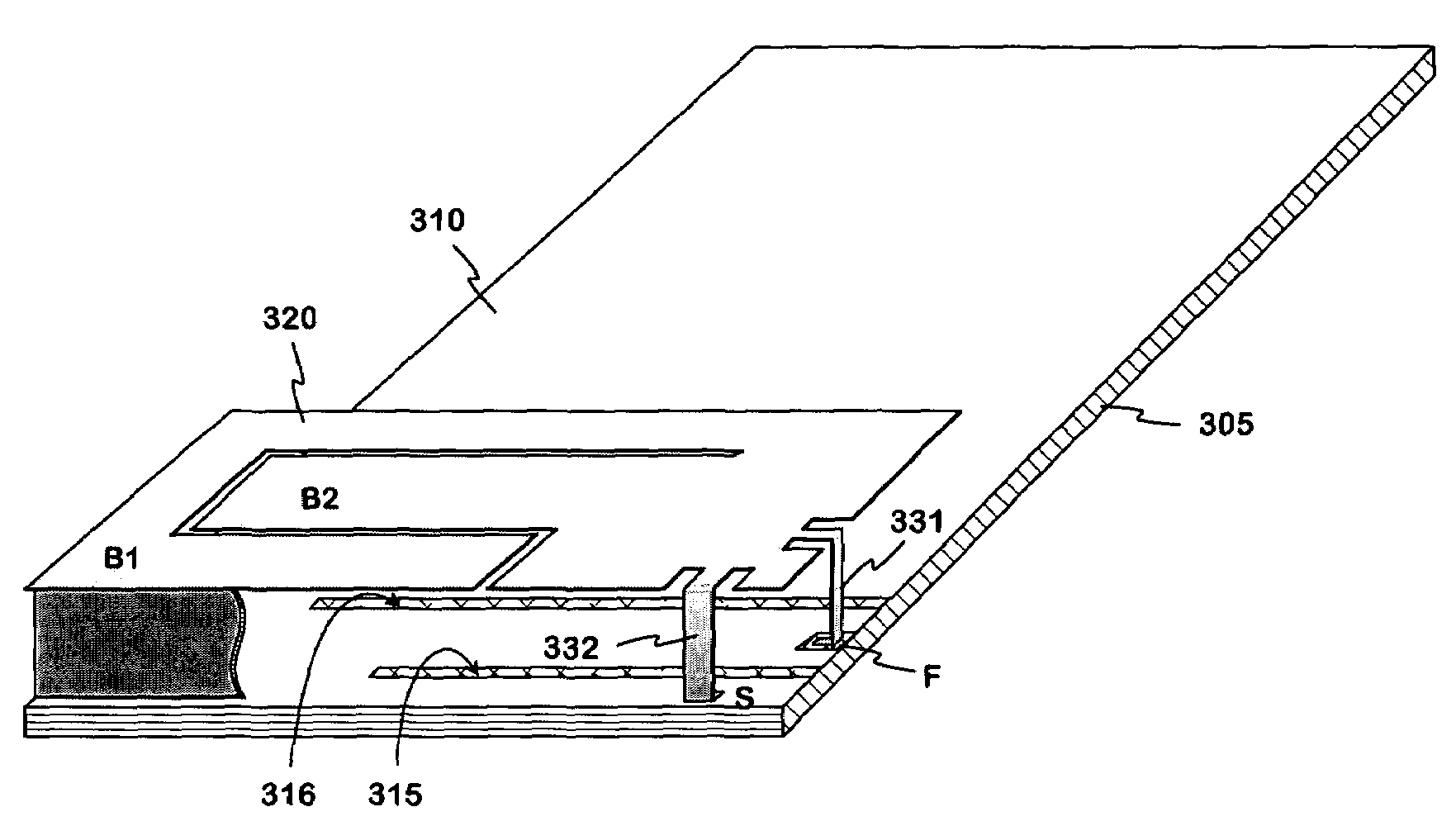
An internal planar antenna for small radio apparatuses. The ground plane (310) of the planar antenna is shaped such that it improves the matching of the antenna. The shaping may be done by means of one or more slots (315, 316) in the ground plane. The slot suitably changes the electrical length of the ground plane as viewed from the short-circuit point (S) so that the ground plane will function as a radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Also the slot (331) in the ground plane can be arranged to function as an additional radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Antenna gain will increase as the matching is improved, and the upper band of a dual band antenna, for example, can be made broader.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
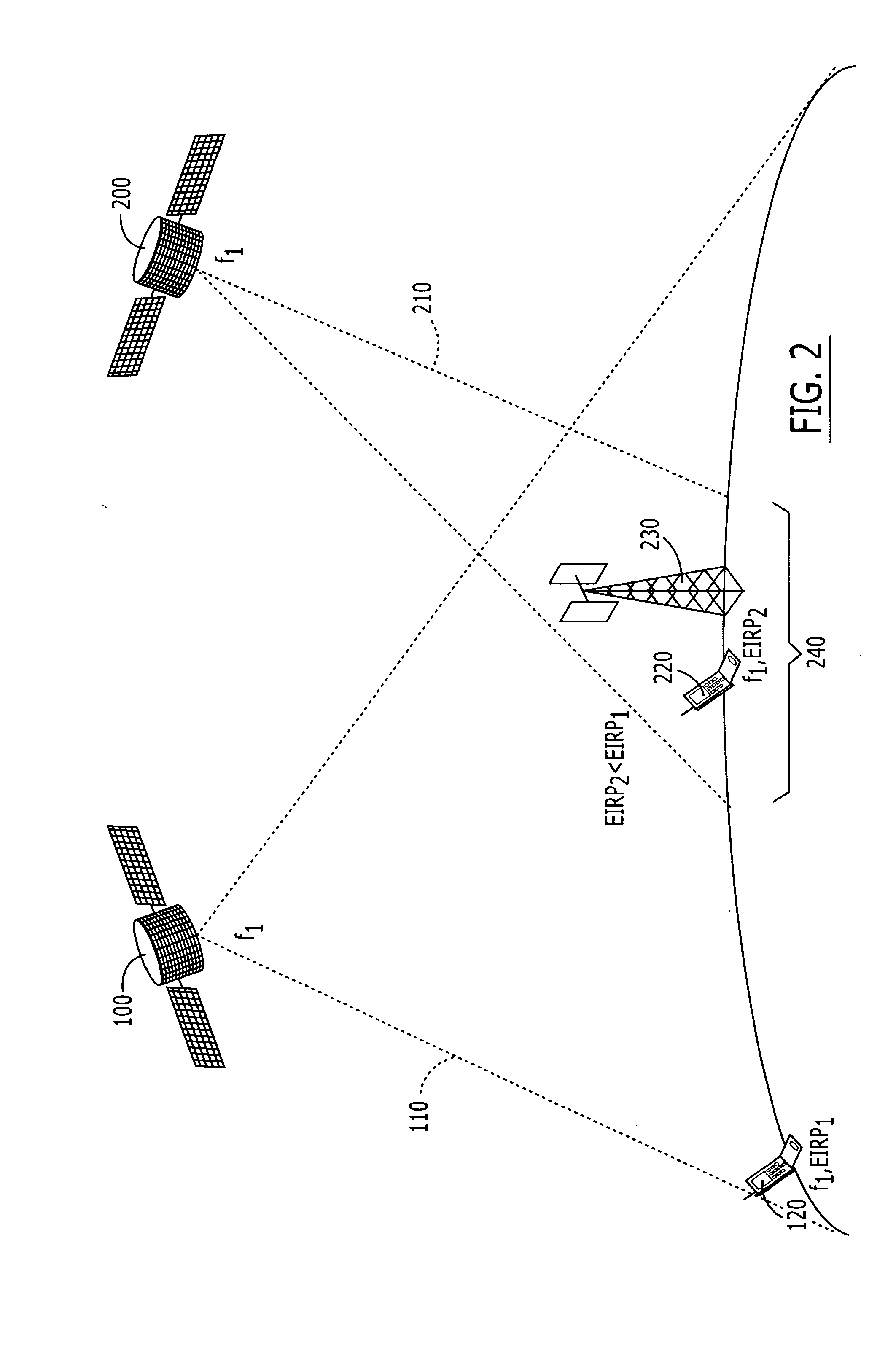
Systems and methods for inter-system sharing of satellite communications frequencies within a common footprint
ActiveUS7113743B2Improve noiseReduce aggregationActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
Two satellite communications systems can use the same frequency or frequencies in geographically overlapping footprints, without creating undue interference in a given system that is caused by the same frequency signal(s) that is / are used by the other system. In particular, an aggregate Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of the radioterminals and / or ancillary terrestrial components of a second satellite communications system in the common footprint is sufficiently low, and / or the receive antenna gain of a first satellite communications system is sufficiently low compared to the receive antenna gain of the second satellite communications system, so as to increase an aggregate receiver noise that is seen by the first satellite system receivers by an amount that does not substantially change a Quality of Service (QoS) of the first satellite communications system.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Antenna structures and methods thereof for selecting antenna configurations
A system incorporating the subject disclosure may include, for example, a method including determining, by a communication device comprising a processor, a usage state of the communication device. The communication device includes selectable antennas, and the usage state includes an orientation of the communication device. The method also includes selecting a set of antennas according to the usage state, and obtaining an antenna gain pattern for an antenna in the selected set of antennas. The method further includes evaluating an expected performance of an antenna configuration corresponding to the selected set of antennas, relative to a performance of an existing antenna configuration. The method also includes initiating usage of the antenna configuration in accordance with improved performance relative to the existing antenna configuration. The antenna configuration comprises a polarization configuration, and the selected set of antennas comprises elements in different planes. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:SKYCROSS INC
Power control for devices having multiple antennas
Power control for devices having multiple transmit antennas are disclosed, including power control methods for Physical Uplink Control Channel (PUCCH) and Sounding Reference Signal (SRS) transmissions for a wireless transmit / receive unit (WTRU). The PUCCH and SRS power control methods include selecting a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) mode and changing the power of the PUCCH or SRS transmission based on the selected MIMO mode. Another power control method estimates an antenna gain imbalance (AGI) for a WTRU having at least two transmit antennas. The AGI is based on measuring a Reference Signal Received Power (RSRP) on each transmit antenna. Each transmit antenna is then scaled by an AGI scaling factor based on the estimated AGI.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
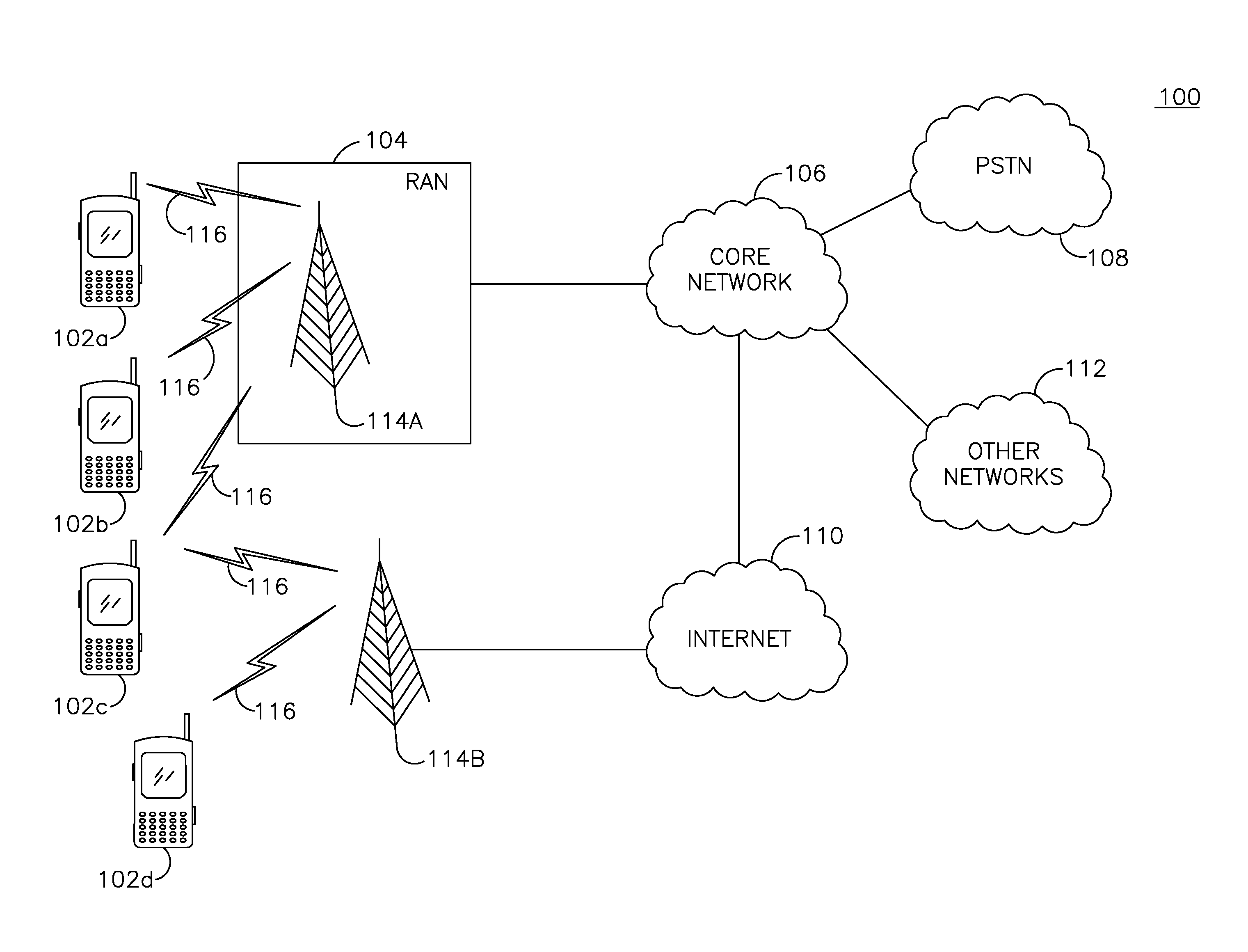
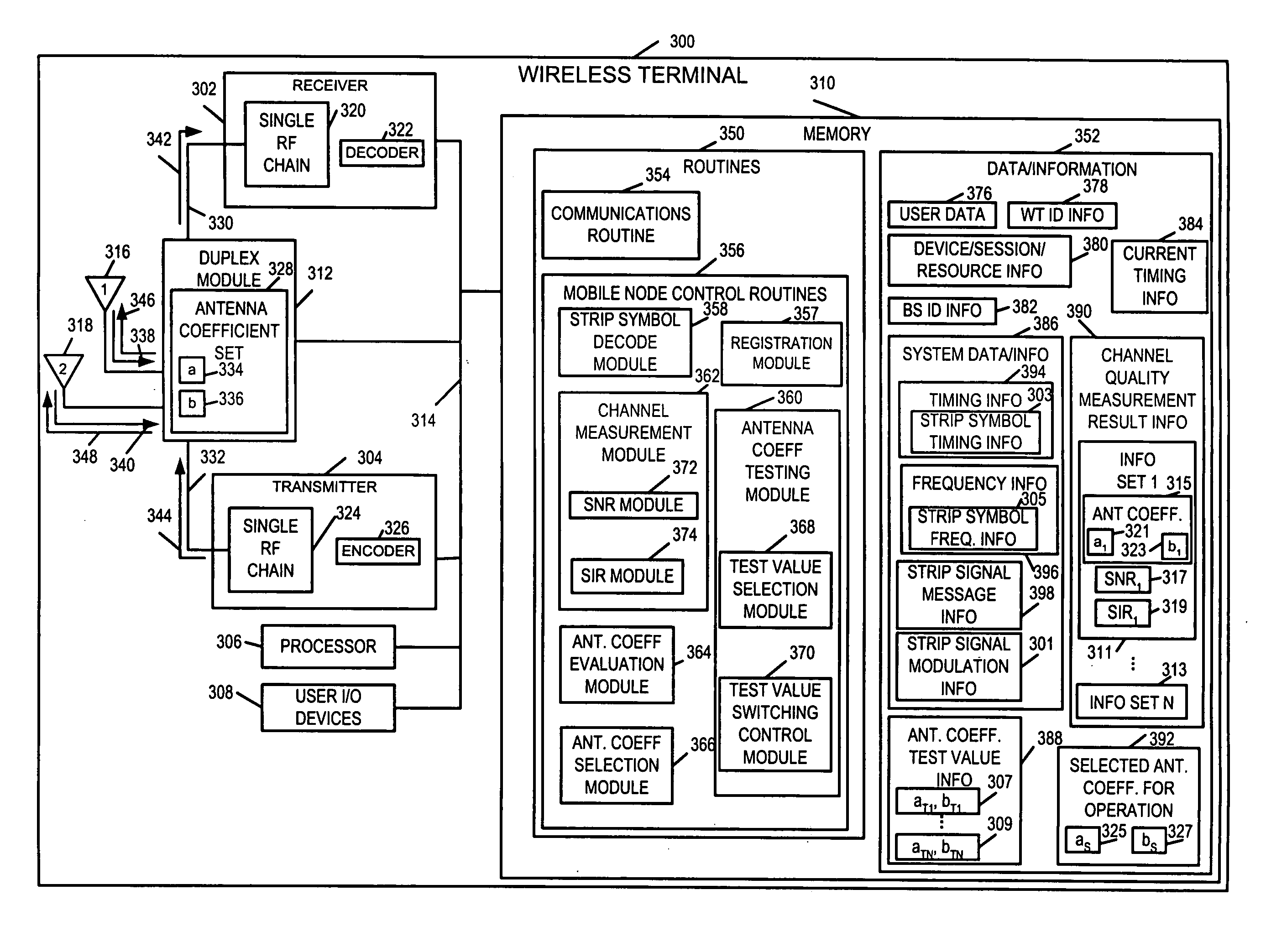
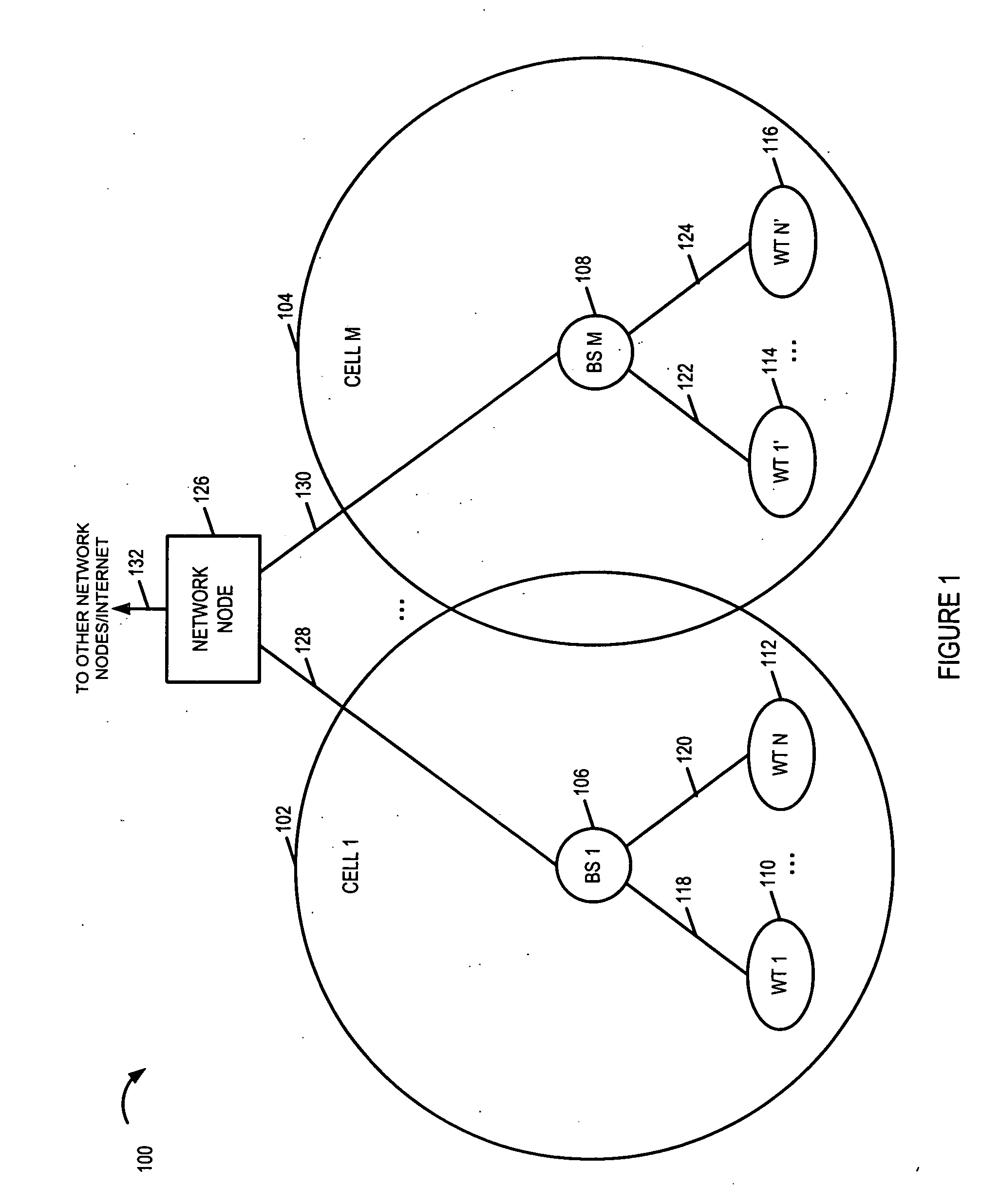
Methods and apparatus for antenna control in a wireless terminal
ActiveUS20060205356A1Increase communication channelsGood coefficientResonant long antennasDiversity/multi-antenna systemsBand shapeAntenna gain
Base stations transmit strip signals using strip signal segments and self supporting modulation scheme techniques facilitating rapid channel estimate. A strip segment occupies one OFDM symbol time interval and uses a set of downlink tones; some, e.g., half, of the tones are left unused facilitating SIR measurement. The strip segments are advantageously timed to correspond to uplink access intervals in which connected wireless terminals do not typically transmit uplink signals. Connected wireless terminals including: multiple antennas used in combination, an antenna duplex module, single RF receiver chain and single RF transmitter chain, switch antenna coefficient combinations based on strip signal segment timing. The wireless terminal determines an independent downlink channel quality measurement, e.g., SNR and / or SIR for each strip signal segment and for on-going non-strip signaling. The wireless terminal compares channel quality measurements and selects an antenna coefficient combination to be used during non-strip signaling intervals obtaining very good antenna gain.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
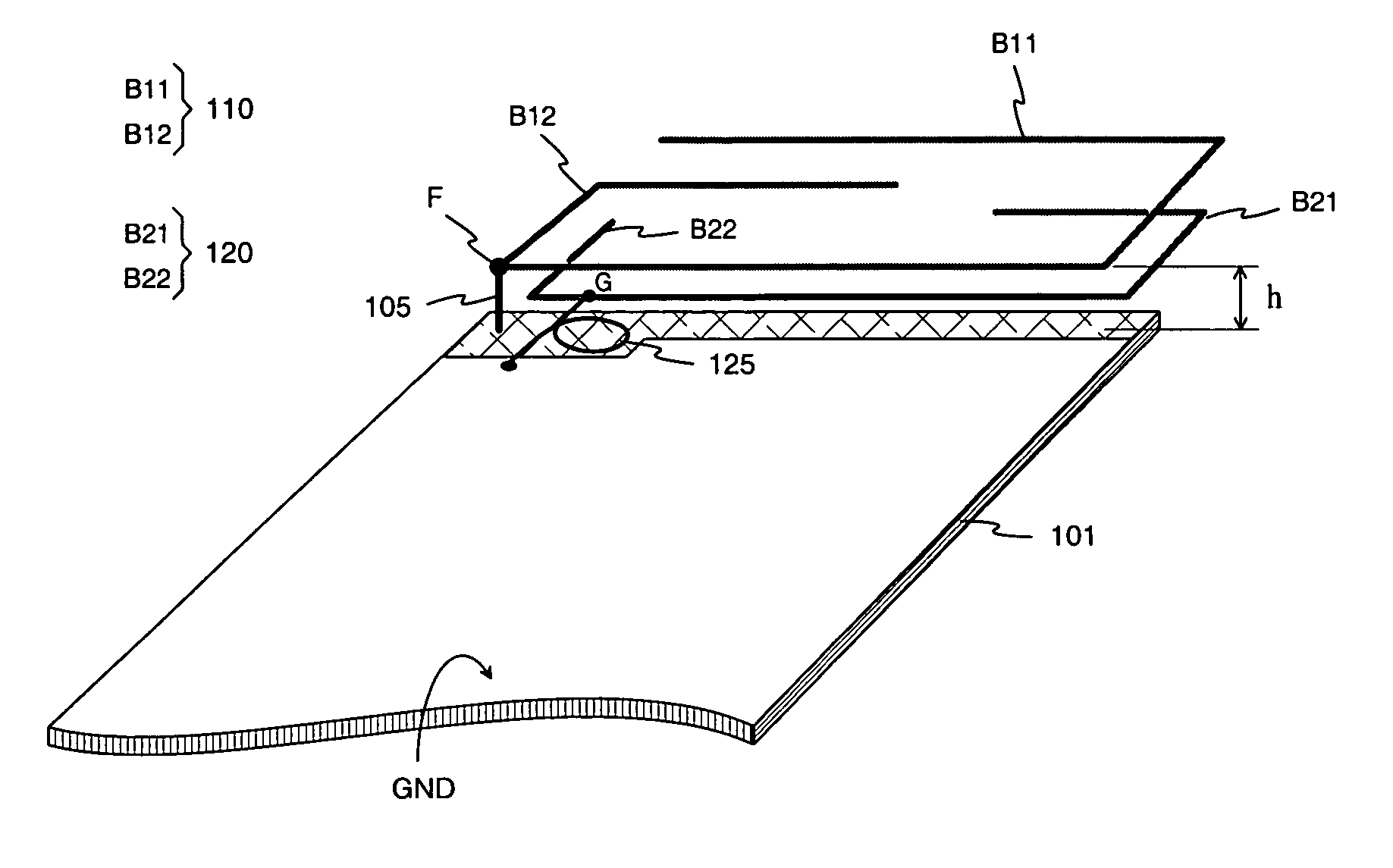
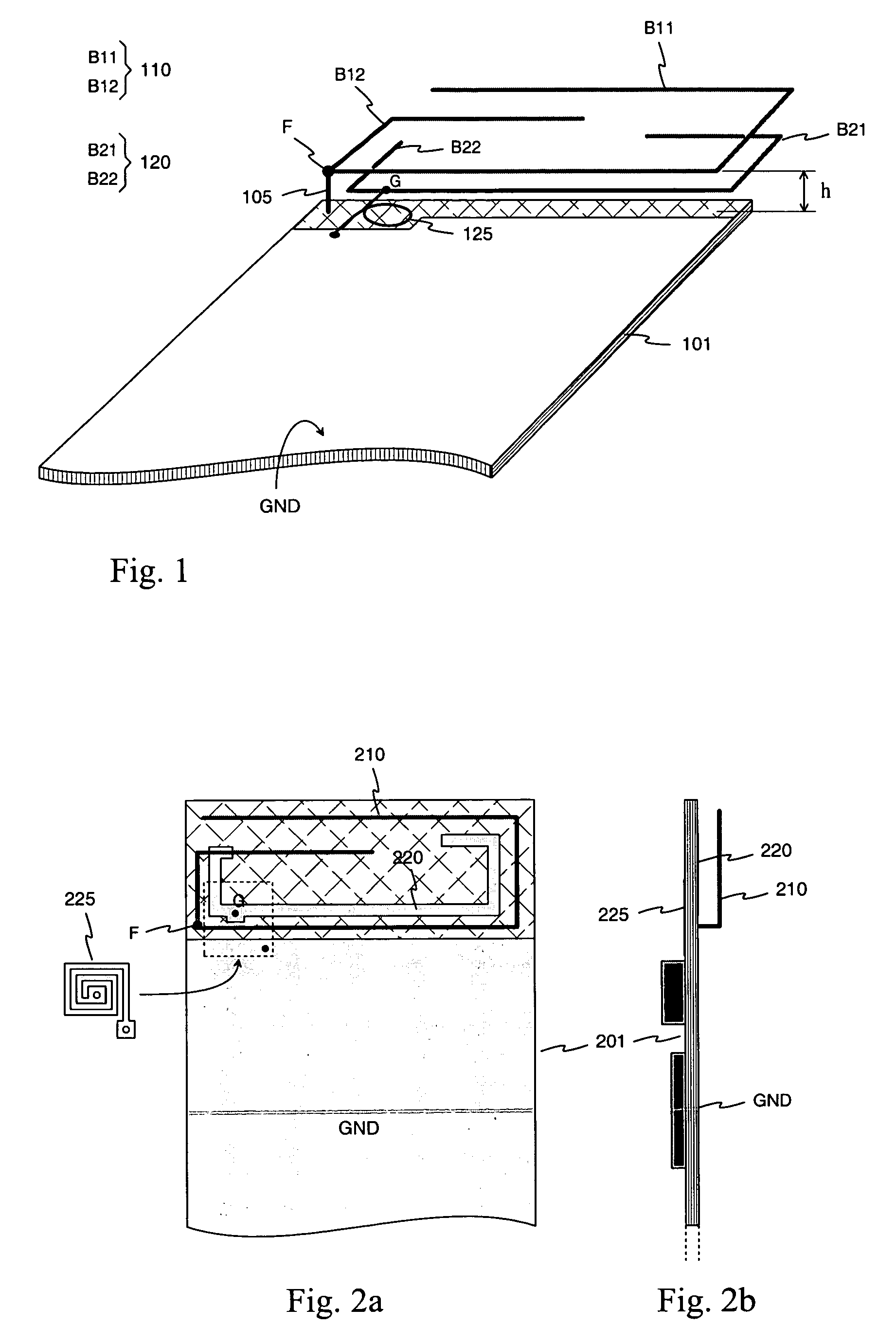
Antenna for flat radio device
InactiveUS7136019B2Antenna gain significantly higherAntenna gain is betterSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentElectrical conductor
An antenna intended to be used in a small-sized and flat radio device, and to a radio device which has an antenna according to the invention. The base element of the antenna is a monopole-type conductor (110) internal to the device. This conductor may be designed such that the harmonic nearest to the fundamental resonating frequency can be utilized in providing an upper operating band. In addition to the base element the antenna structure comprises a parasitic element (120) which functions as both an auxiliary radiator and antenna matching element. Matching is optimized using an inductive component (125) which connects the parasitic element to signal ground. The antenna gain achieved is considerably higher than that of known antenna structures occupying the same space (h), and the antenna matching is improved, compared to known internal monopole antennas.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
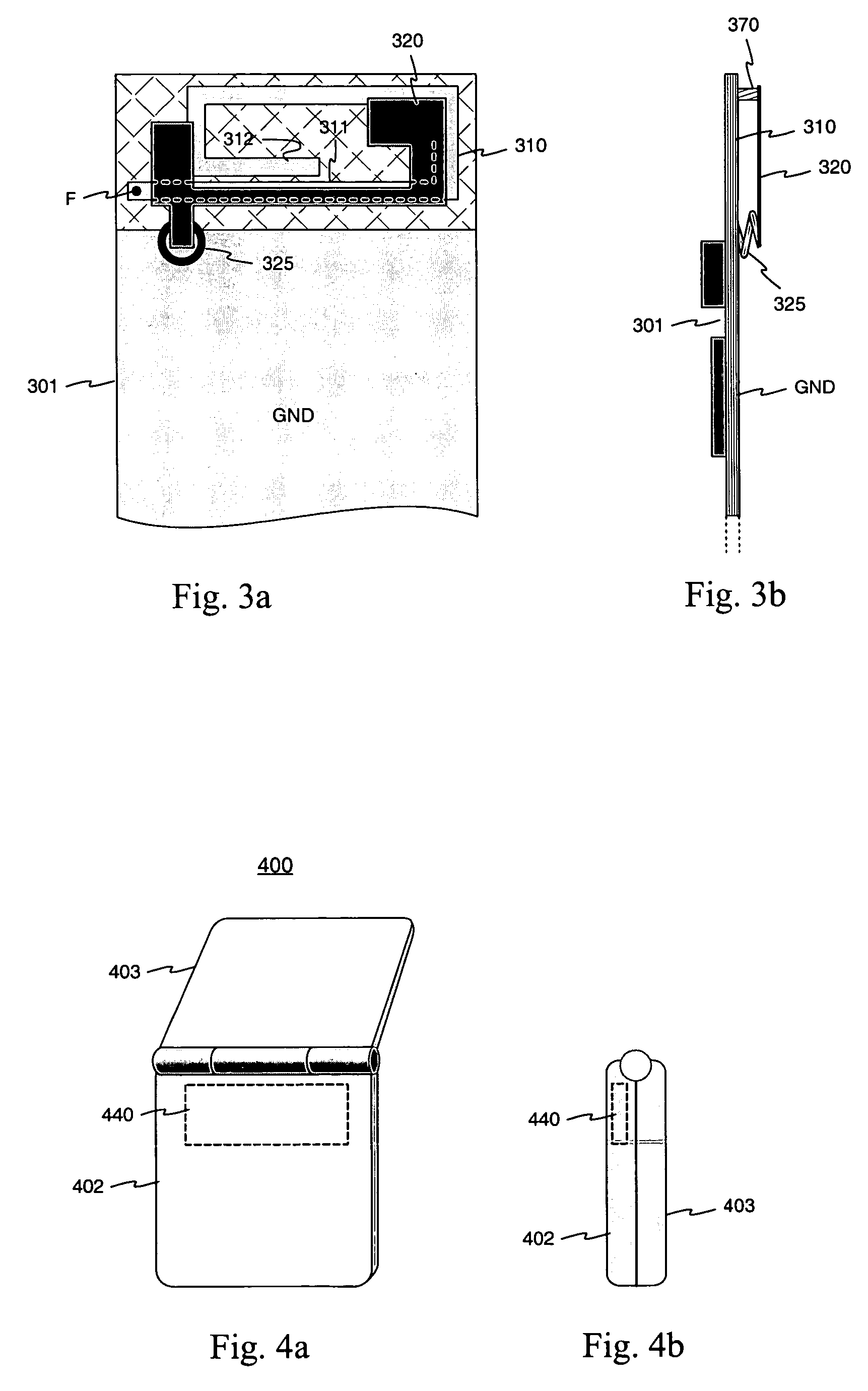
Systems and methods that employ a dualband IFA-loop CDMA antenna and a GPS antenna with a device for mobile communication
InactiveUS20050041624A1Reduce antenna sizeReduce componentsAntenna supports/mountingsBeacon systemsCapacitanceAntenna gain
The present invention comprises systems and methods for cellular, PCS, GPS and / or Bluetooth mobile communication (e.g., a mobile telephone). The systems and methods employ a fully integrated dual band IFA / loop CDMA antenna for cellular and PCS communication. Fully integrating the CDMA antenna within a PWB provides for mitigation of lumped elements to establish dual banding, and can provide for reduced antenna size, device size, cost and interference form a user's hand. The IFA antenna is configured to transmit and receive within the cellular frequency band via a capacitive tap, and the loop antenna is configured to transmit and receive within the PCS frequency band via an impedance matching stub and ground location. The system and methods further employ a firewall to mitigate antenna coupling, and a metal reflector to reduce the electromagnetic reflection, and improve antenna gain and efficiency.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Single chip radio with integrated antenna
InactiveUS7088964B2Eliminate needReduce interactionSimultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRadio equipmentTransceiver
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Antenna apparatus utilizing small loop antenna element having munute length and two feeding points
InactiveUS20090315792A1Constant gainReduce communication qualityResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorAntenna gain
The small loop antenna element of the antenna apparatus includes loop antenna portions that have a predetermined loop plane and radiate a first polarized wave component parallel to the loop plane, and at least one connecting conductor that is provided in a direction orthogonal to the loop plane and connects the plurality of loop plane portions to radiate a second polarized wave component orthogonal to the first polarized wave component. In the case of the antenna apparatus located adjacent to a conductor plate, by making the maximum value of the antenna gain of the first polarized wave component and the maximum value of the antenna gain of the second polarized wave component substantially identical when the distance between the antenna apparatus and the conductor plate is changed, a composite component of the first and second polarized wave components are made substantially constant regardless of the distance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multilayer Broadband Microstrip Antenna
InactiveCN102299418ADirectionalHigh bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsBroadband microstrip antennaAntenna gain
The invention discloses a multilayer broadband microstrip antenna, comprising an upper dielectric baseplate, a middle dielectric baseplate, a lower dielectric baseplate, an upper low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a lower low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a reflection plate and a feed probe, wherein rectangle radiators of metallic copper pasters are arranged on the lower surface of the upper dielectric baseplate and the upper surface of the middle dielectric baseplate and provided with U-shaped slot structures with different sizes respectively. Due to a special double-layer inverted U-shaped slot coupling feed way, the symmetry of directional diagrams on an E surface or H surface of the antenna is good, thus ensuring that the antenna has more consistent performances in more directions, and having more actual meanings as an exploration antenna and a communication antenna. The reflection plate with an EBG (electromagnetic band gap) structure can preferably restrain backward radiation in the specified frequency relative to a traditional metal reflection plate, thus improving the directivity of the antenna, thereby further improving the gain of theantenna.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Systems and Methods for Inter-System Sharing of Satellite Communications Frequencies Within a Common Footprint
ActiveUS20060246838A1Improve noiseReduce aggregationRadiating elements structural formsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
High gain antenna for wireless applications
An antenna having a central active element and a plurality of passive dipoles surrounding the active element is disclosed. The passive dipoles increase the antenna gain by increasing the radiated energy in the azimuth direction. In another embodiment a plurality of parasitic directing elements extend radially outward from the passive dipoles.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT CORP
Location positioning in wireless networks
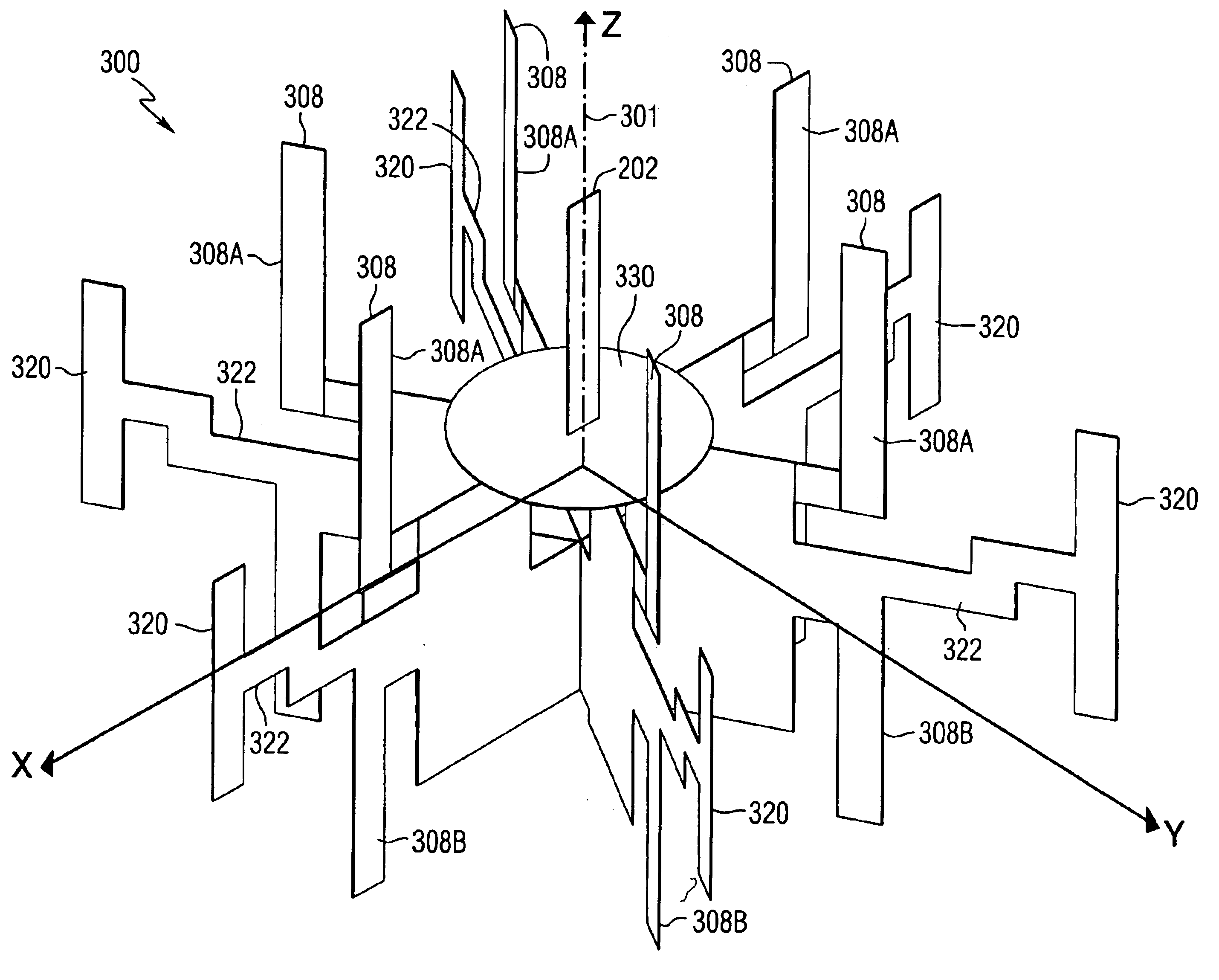
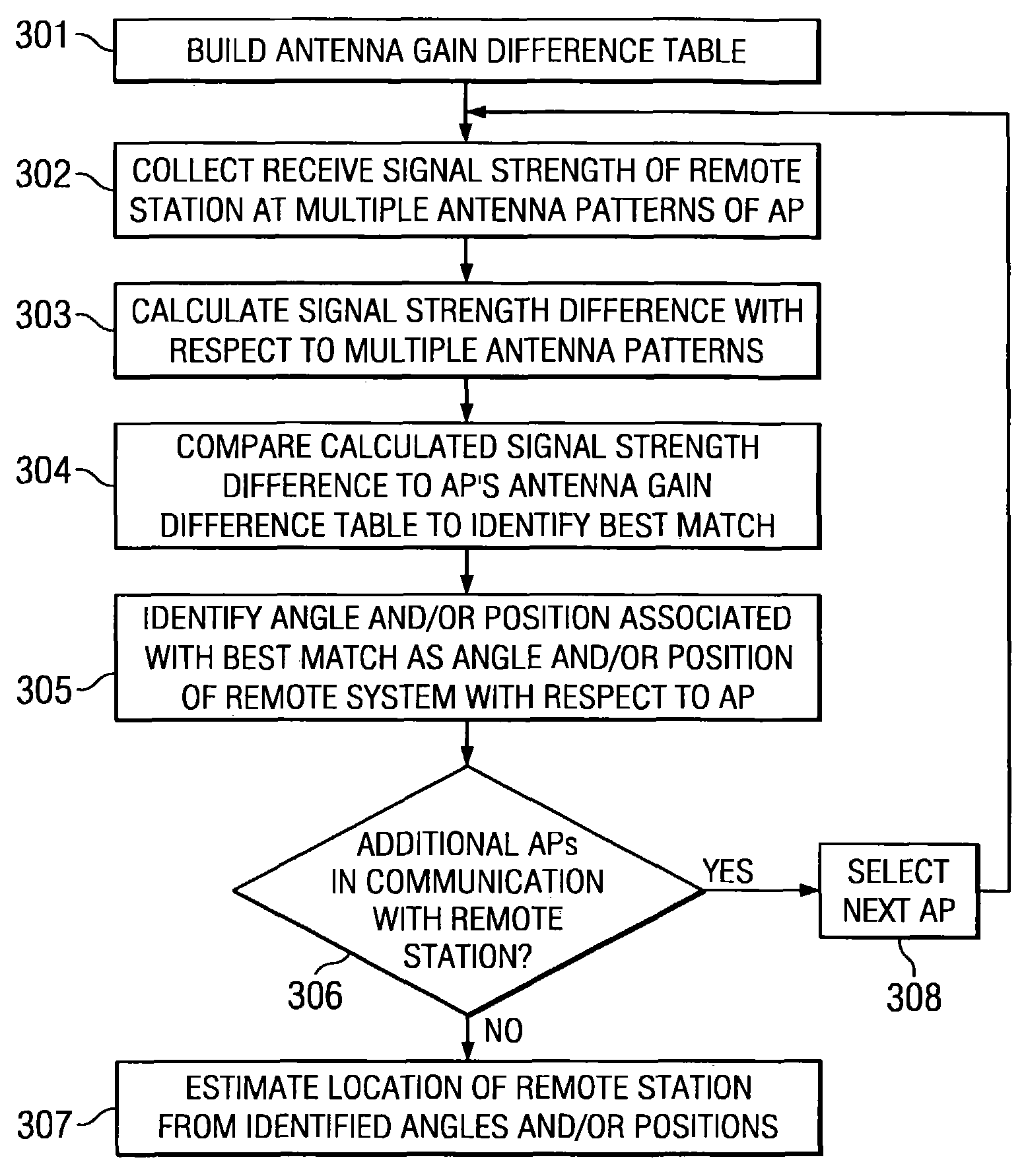
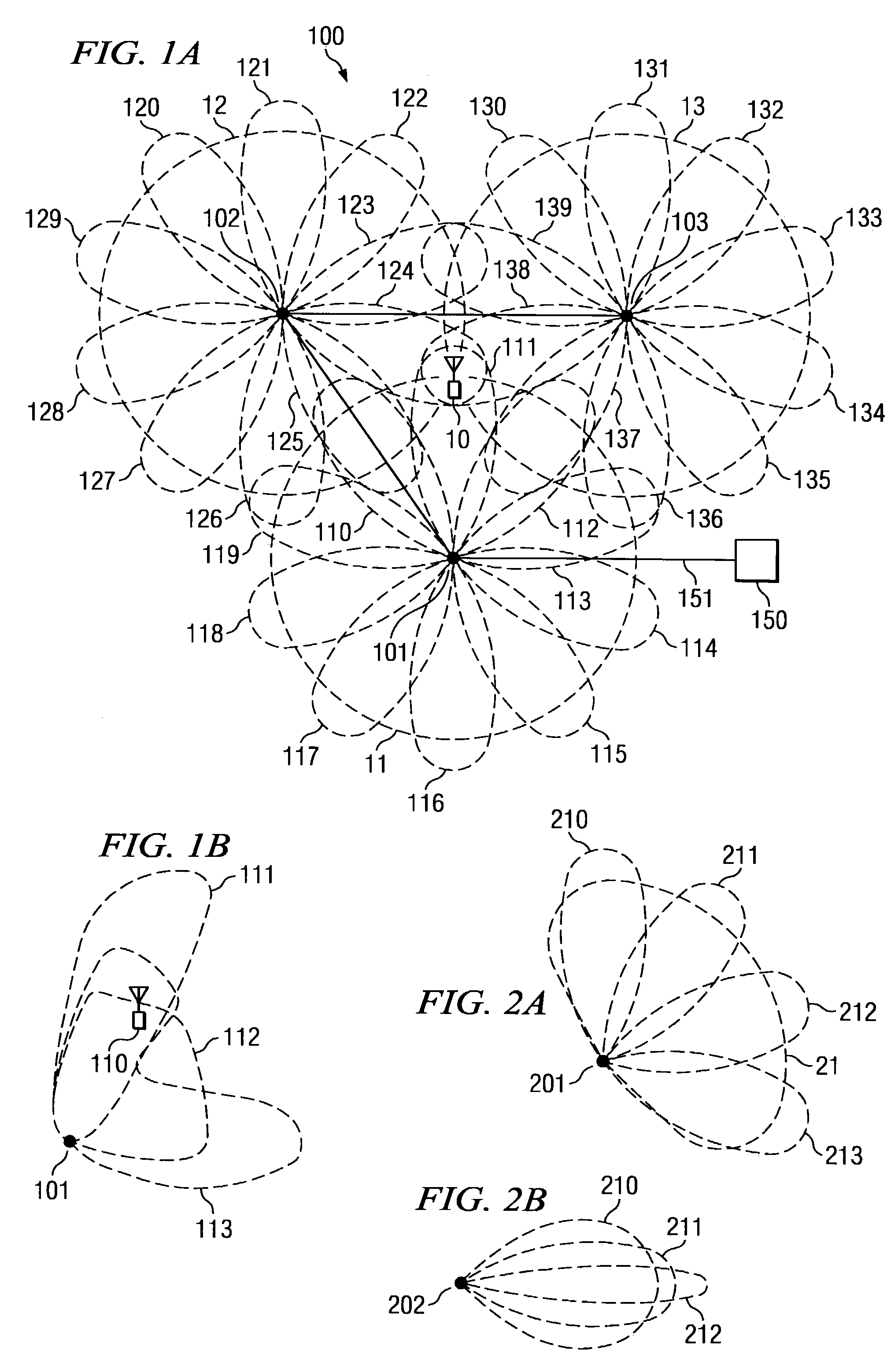
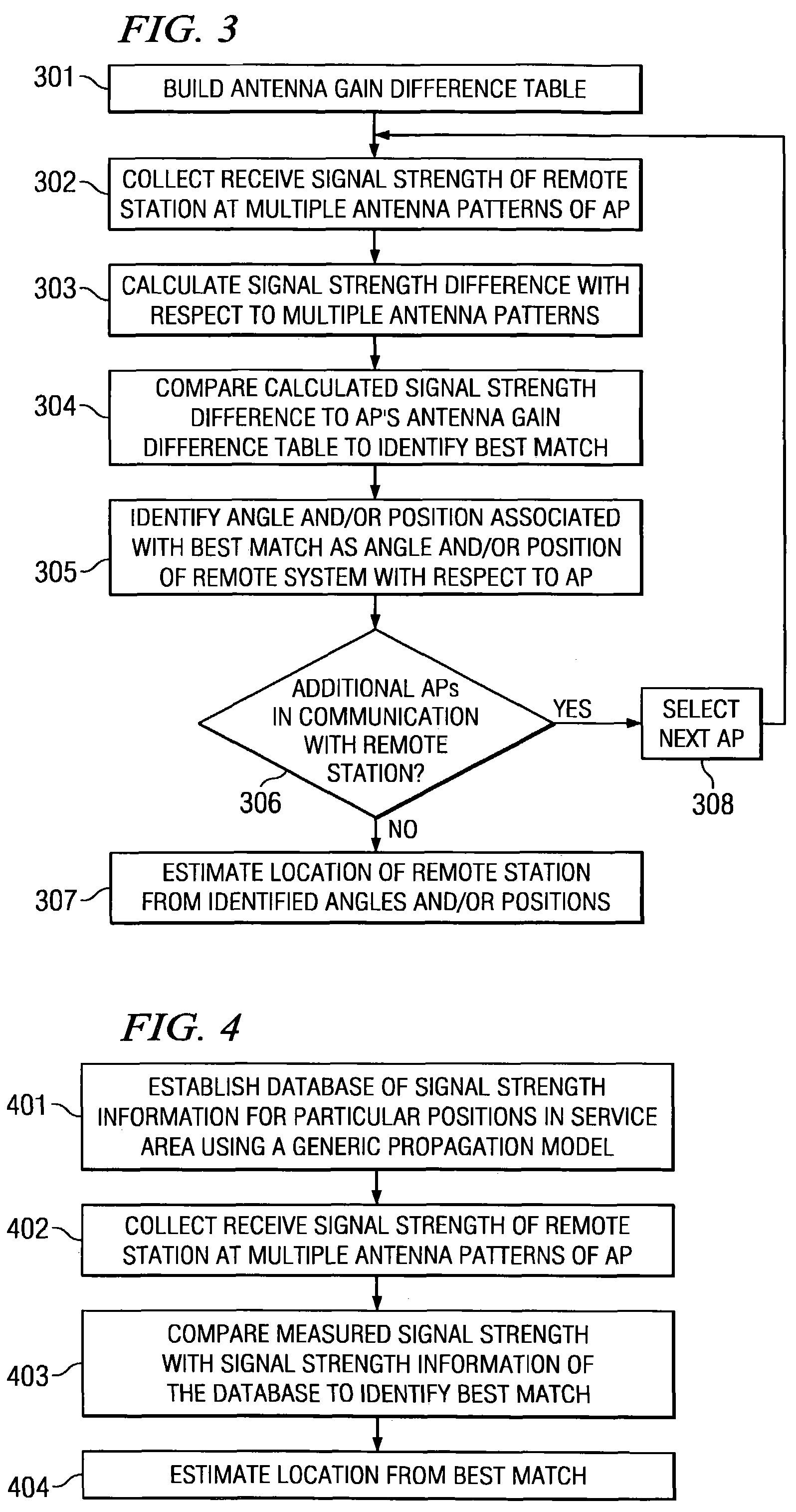
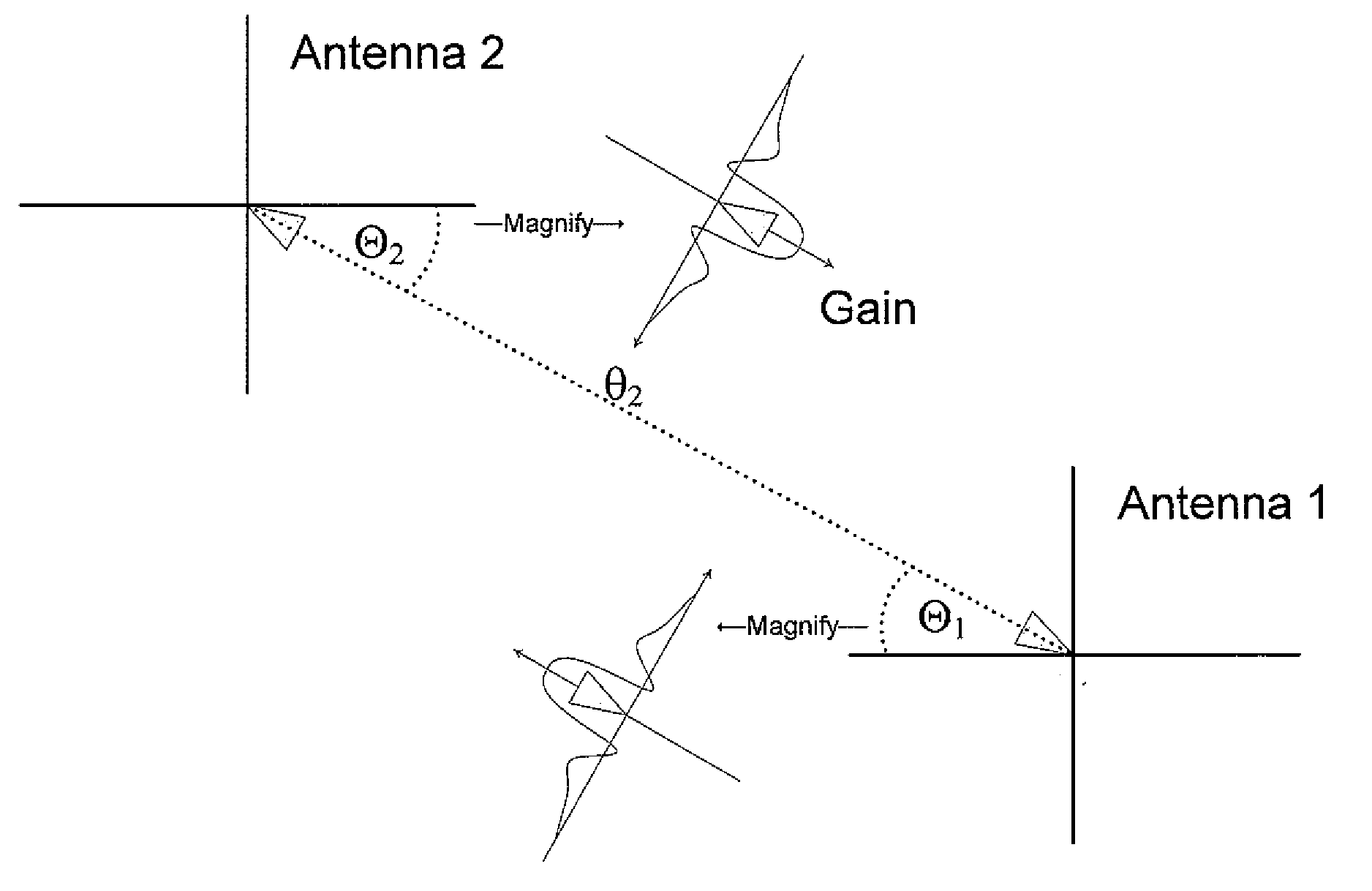
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide for location positioning in wireless networks using techniques which are adapted to provide reliable location determinations even in complex topological environments. Embodiments utilize multiple antenna patterns, such as may be provided using phased array antennas, and implement location positioning techniques which do not require alteration of remote stations in providing location positioning. Various techniques for determining location may be implemented, including a channel model independent approach, a channel model based approach, or combinations thereof. A channel model independent approach used in providing location positioning may compare receive signal strength differences to an antenna gain difference table to determine an angle in the azimuth that a remote station is located. A channel model based approach used in providing location positioning may compare receive signal strength measurements to a database of signal strengths created using a wireless channel model.
Owner:TCL COMM TECH HLDG
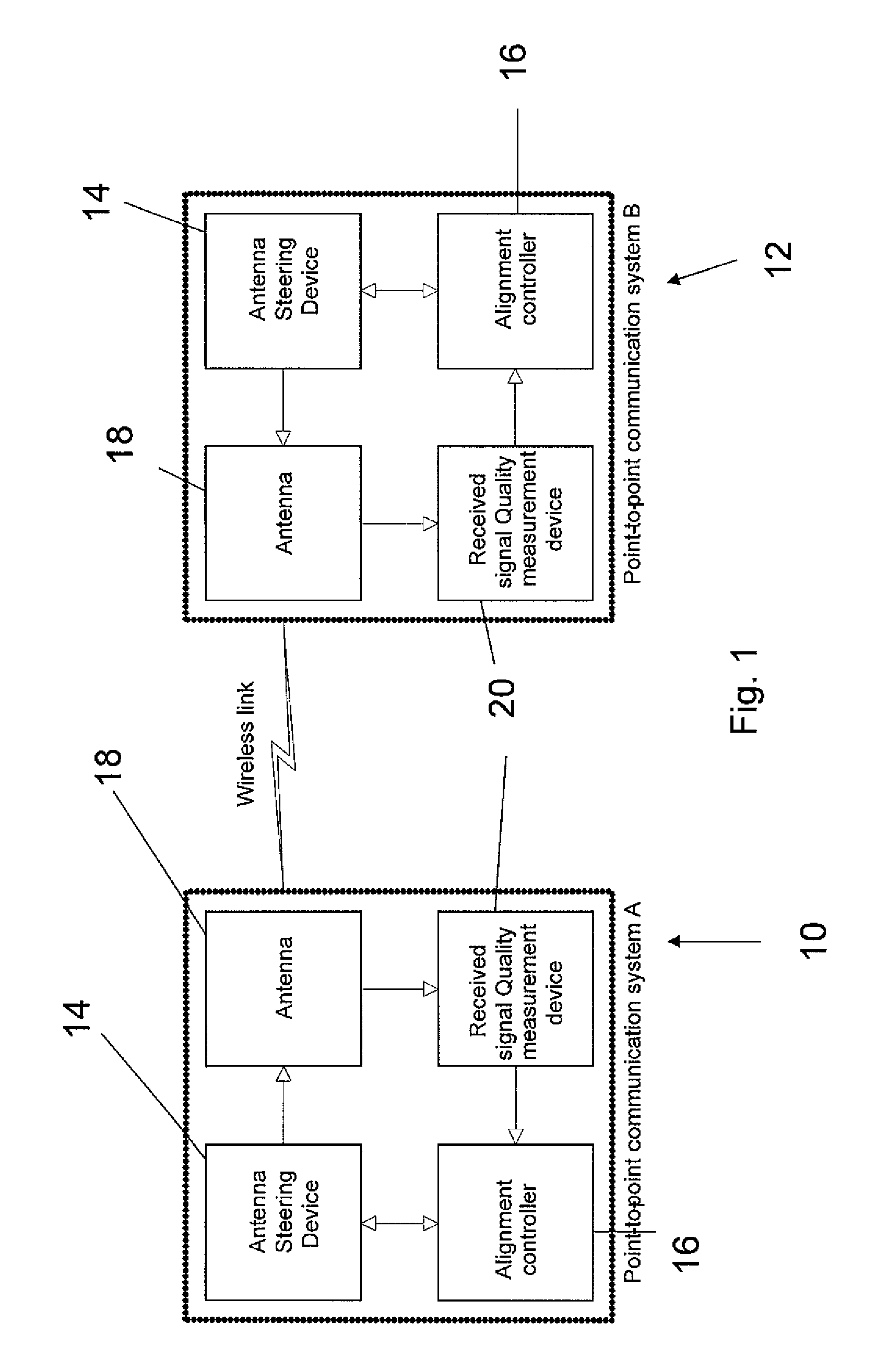
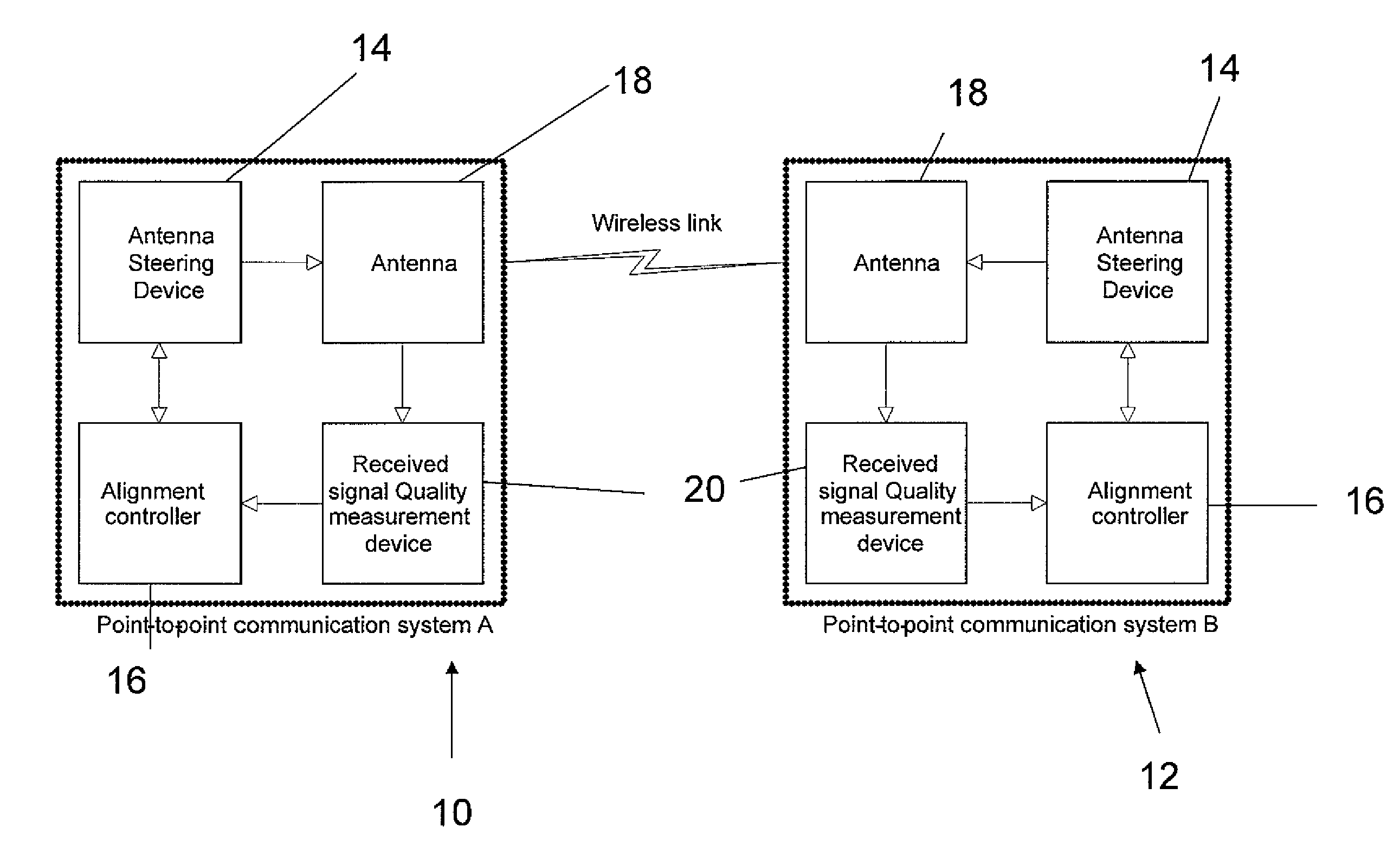
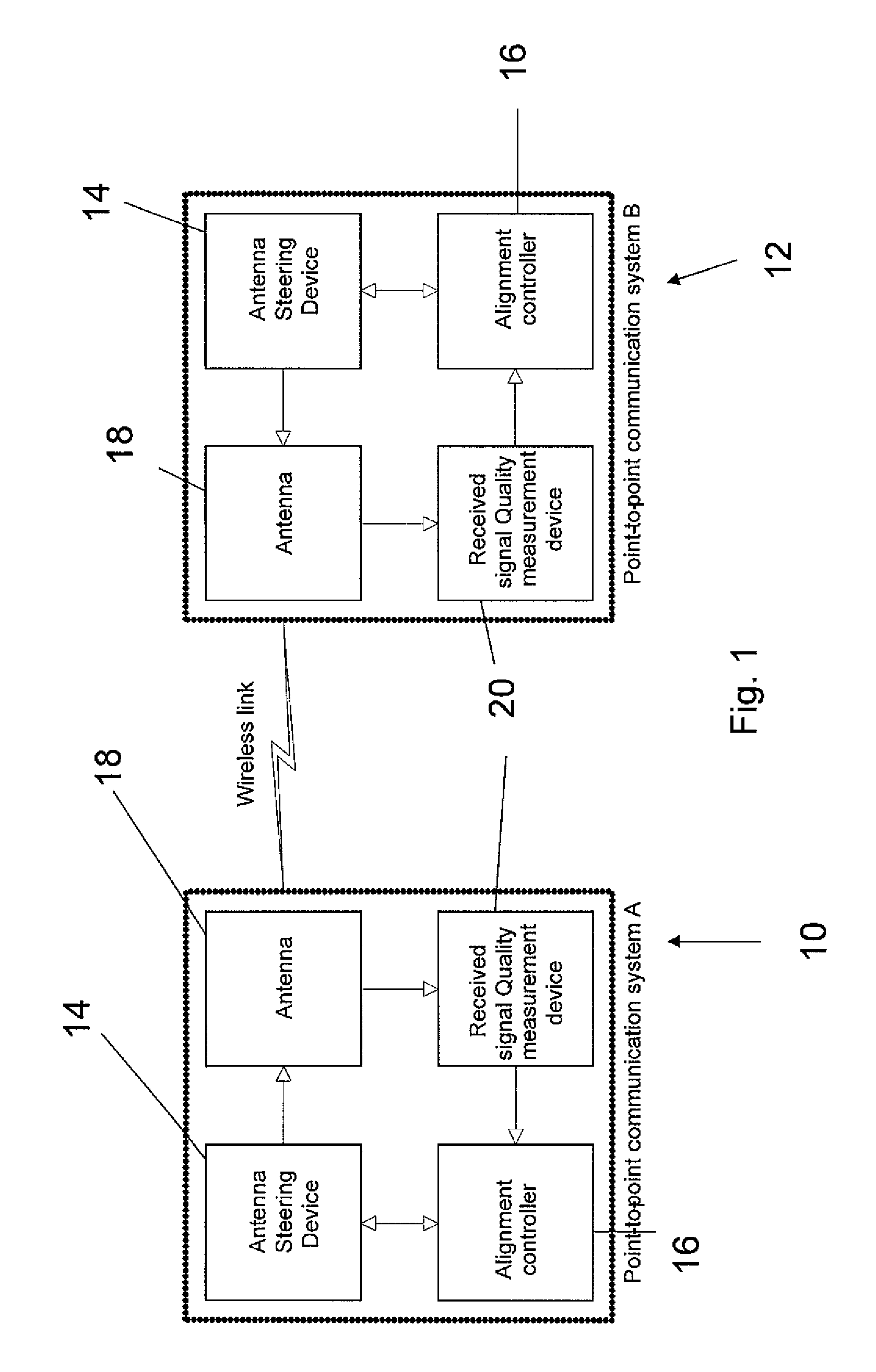
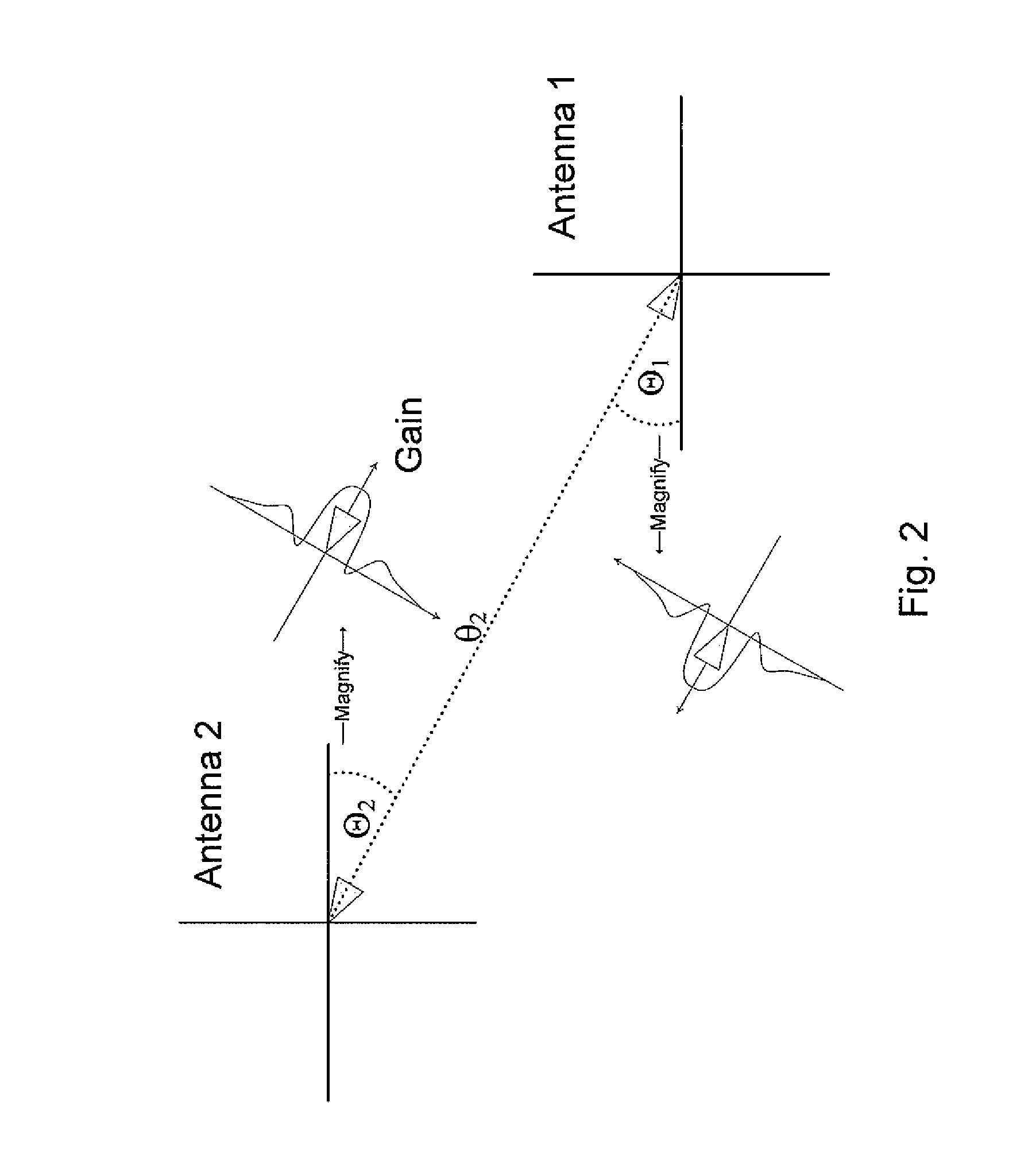
Antenna alignment method and apparatus
ActiveUS20100302101A1Maximize qualityDetectable connectionRadio transmissionAntenna detailsUltrasound attenuationRegular pattern
A method of automatic alignment of two directional beams having a known path attenuation, and an antenna gain pattern, for mutual transmission, comprises: determining a beam width between two angles of minimal detectable connection on either side of a beam maximum; then mapping points onto a scan field in a regular pattern, the pattern based on the beam width, such that a beam with the determined beam width is detected once if the beam is in the scan field at all; scanning the first antenna over the mapped scan points; and for each point allowing the second antenna to scan over all of its own set of mapped scan points, thereby providing a coarse alignment of the two antennas to achieve at least a minimal mutual connection. The coarse alignment may be followed by a fine alignment to maximize the signal.
Owner:SIKLU COMM
Improved free space optical bus
InactiveUS20060251421A1Quality improvementImprove transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementPolarisation/directional diversityCross-linkAntenna gain
A method and apparatus for improving the transmission quality of a free space optical bus between circuitry elements in high speed computing, communication and signal processing systems. Use is made of an adaptive algorithm that learns the transmission properties of the bus, and selects or adjusts transmission paths or characteristics to provide optimum bus performance. Each transmitter on the bus transmits a signal which is generally measured by all of the receivers on the bus, and the measured signals are used to generate a matrix which maps desired transmission along information links, and cross-link interference. Transmission quality is optimized by adjusting one or more characteristics associated with transmission along the bus, including emitted power, beam divergence, wavelength, beam polarization, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the transmitters, and power sensitivity, gain, equalizer coefficients, field of view, polarization sensitivity, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the receivers. Novel bus configurations are described, including use of different wavelengths for different bus functions.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
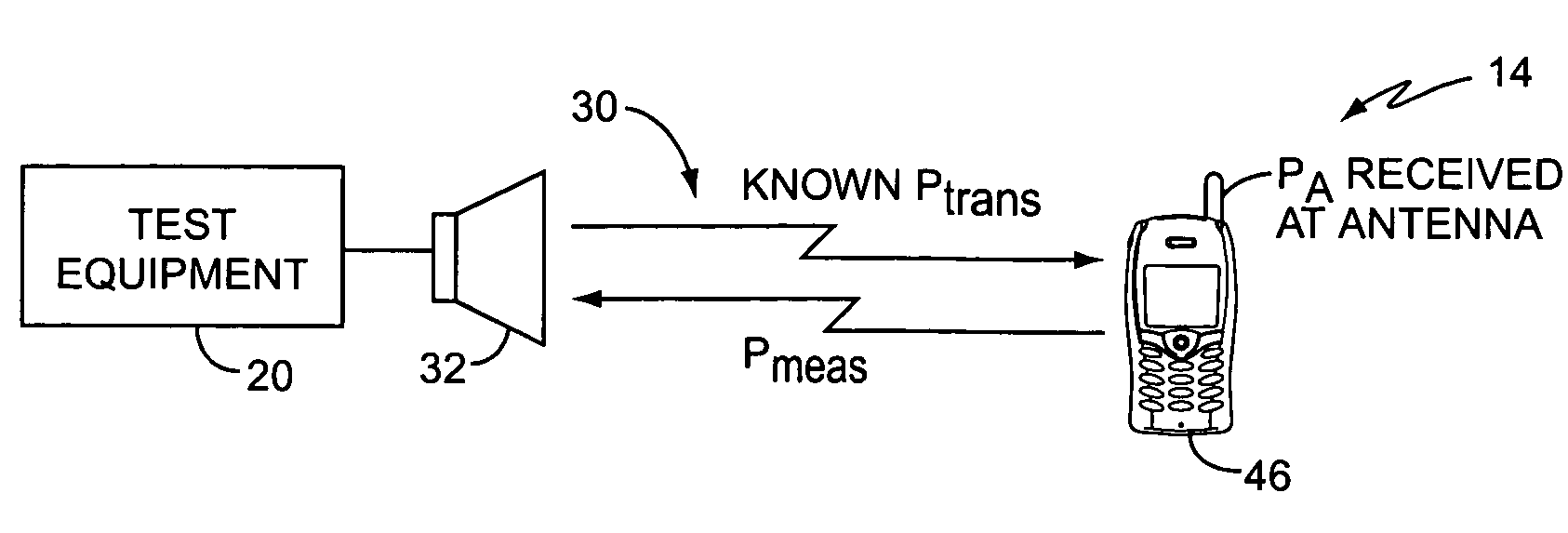
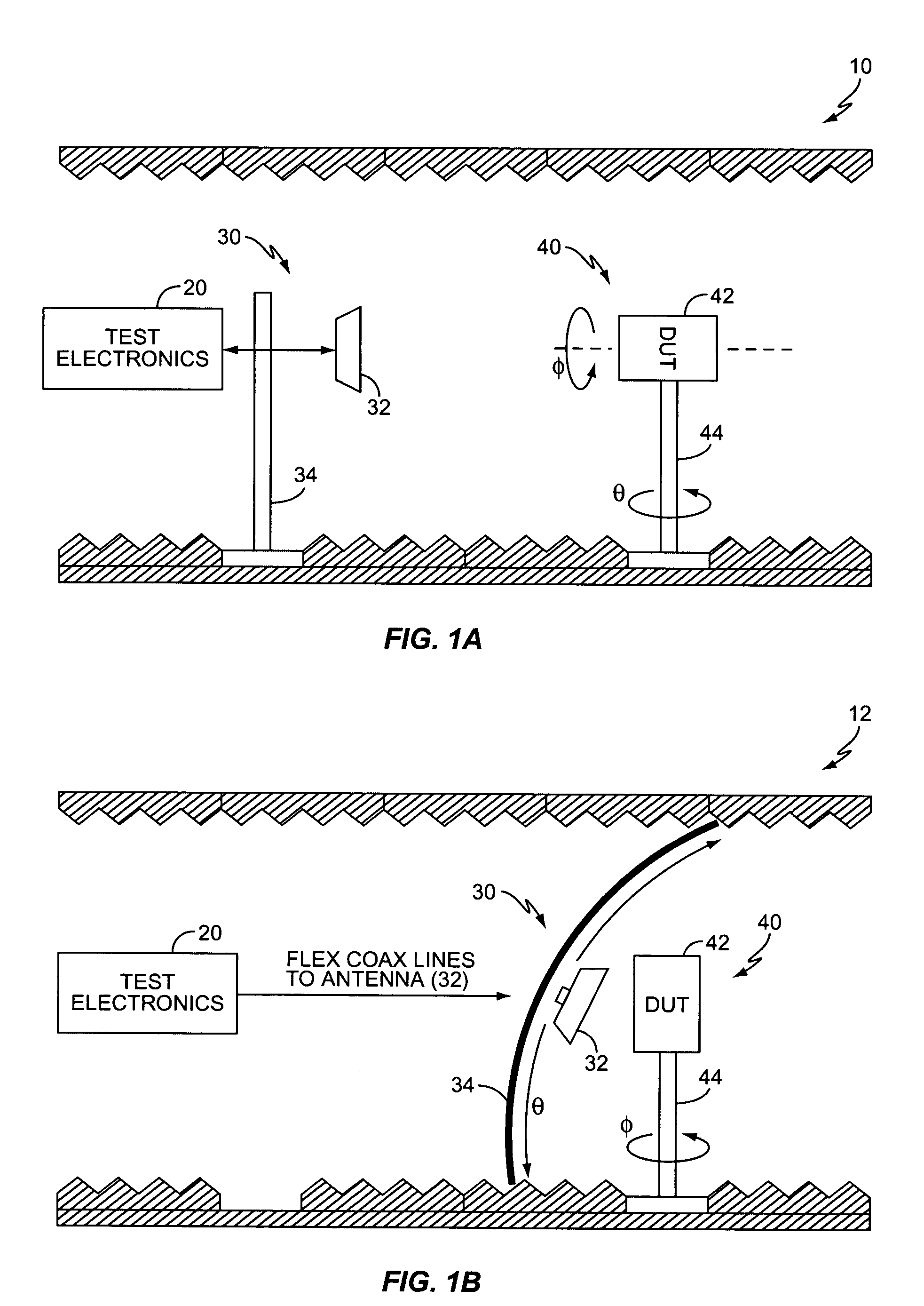
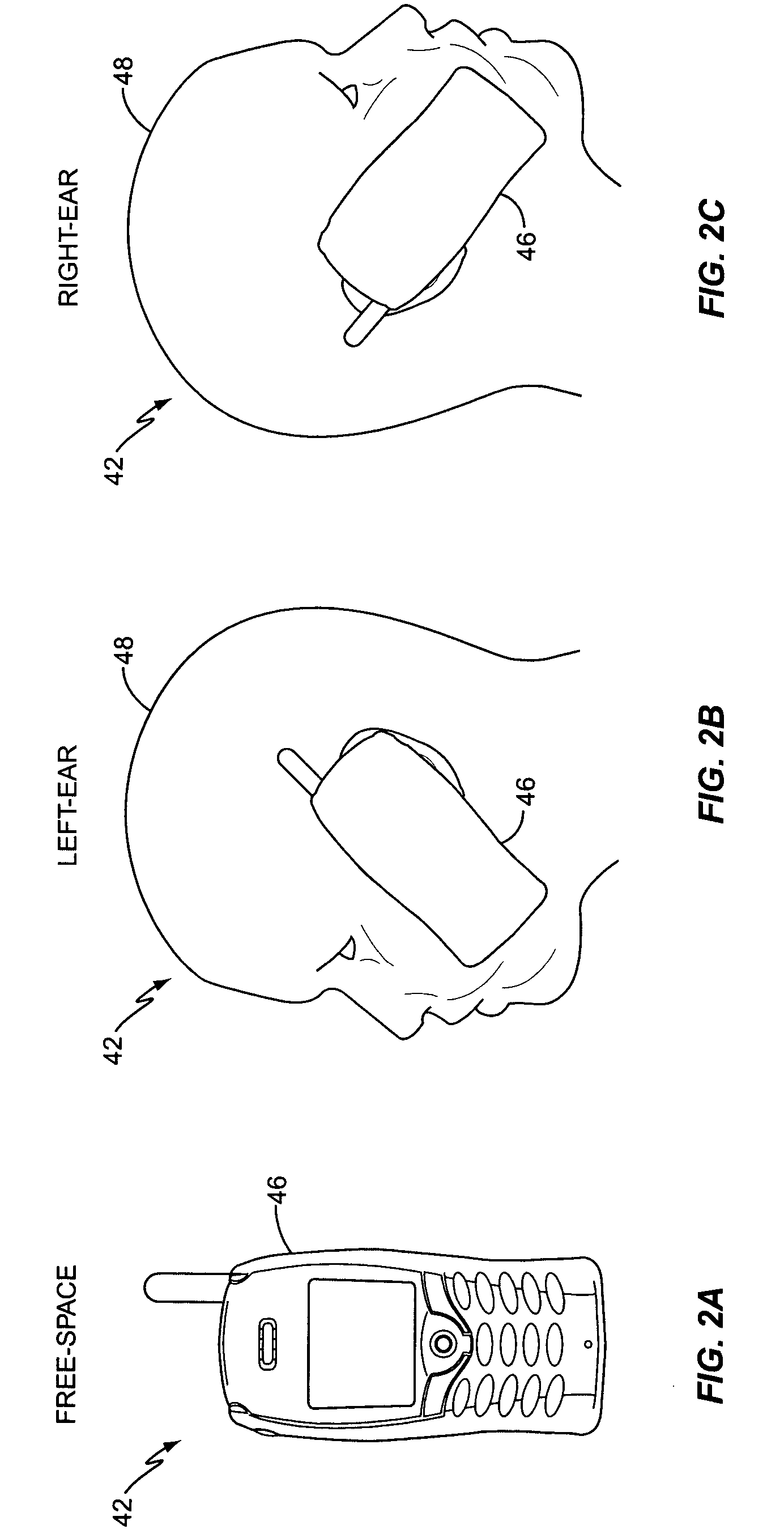
GSM radiated sensitivity measurement technique
A method and apparatus for calculating the radiated sensitivity of a mobile terminal positioned in multiple test orientations for multiple combinations of frequency channel and mobile terminal configuration is described herein. Test equipment measures a reference sensitivity of the mobile terminal when the mobile terminal is positioned in a reference orientation. Further, the test equipment estimates an antenna gain associated with a mobile terminal antenna when the mobile terminal is positioned in a test orientation. The test equipment then adjusts the reference sensitivity, based on the estimated antenna gain, to calculate the sensitivity of the mobile terminal positioned in the test orientation.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Miniature high-gain single-feed-point dual-band dual-polarized microstrip antenna
InactiveCN102148428AAchieve dual-frequency circular polarizationRealize dual-frequency circular polarization characteristicsRadiating elements structural formsResonant antennasAntenna gainEngineering
The invention discloses a miniature high-gain single-feed-point dual-band dual-polarized microstrip antenna, which comprises a substrate, wherein the upper surface of the substrate is provided with a first radiation sticker and a second radiation sticker; the first radiation sticker is positioned in the annular hollow of the second radiation sticker, and the first and second radiation stickers have the same center; the lower surface of the substrate is provided with a conductive grounding plate; a coaxial probe feeder vertically passes through the substrate; the upper end of the coaxial probe feeder is coupled with the first radiation sticker, and the lower end of the coaxial probe feeder is connected with a coaxial radio frequency joint; the coaxial probe feeder is directly connected with the first radiation sticker for electrical coupling; the second radiation sticker is electromagnetically coupled with the first radiation sticker; and the sidewall of the substrate is encased with electrodes which are connected with the conductive grounding plate to form back cavity electrodes. The gain of the dual-band dual-polarized microstrip antenna is increased, and the problem that the antenna gain and volume of the antenna are mutually restricted is solved by increasing the back cavity electrodes connected with the ground plane of the antenna on the premise of not increasing the volume of the dual-band antenna, and the thickness and sectional area of the substrate.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
Compact smart antenna for mobile wireless communications
InactiveUS20120299765A1Suppress interferenceJam suppressionRadio transmissionIndividually energised antenna arraysLow noiseBand-pass filter
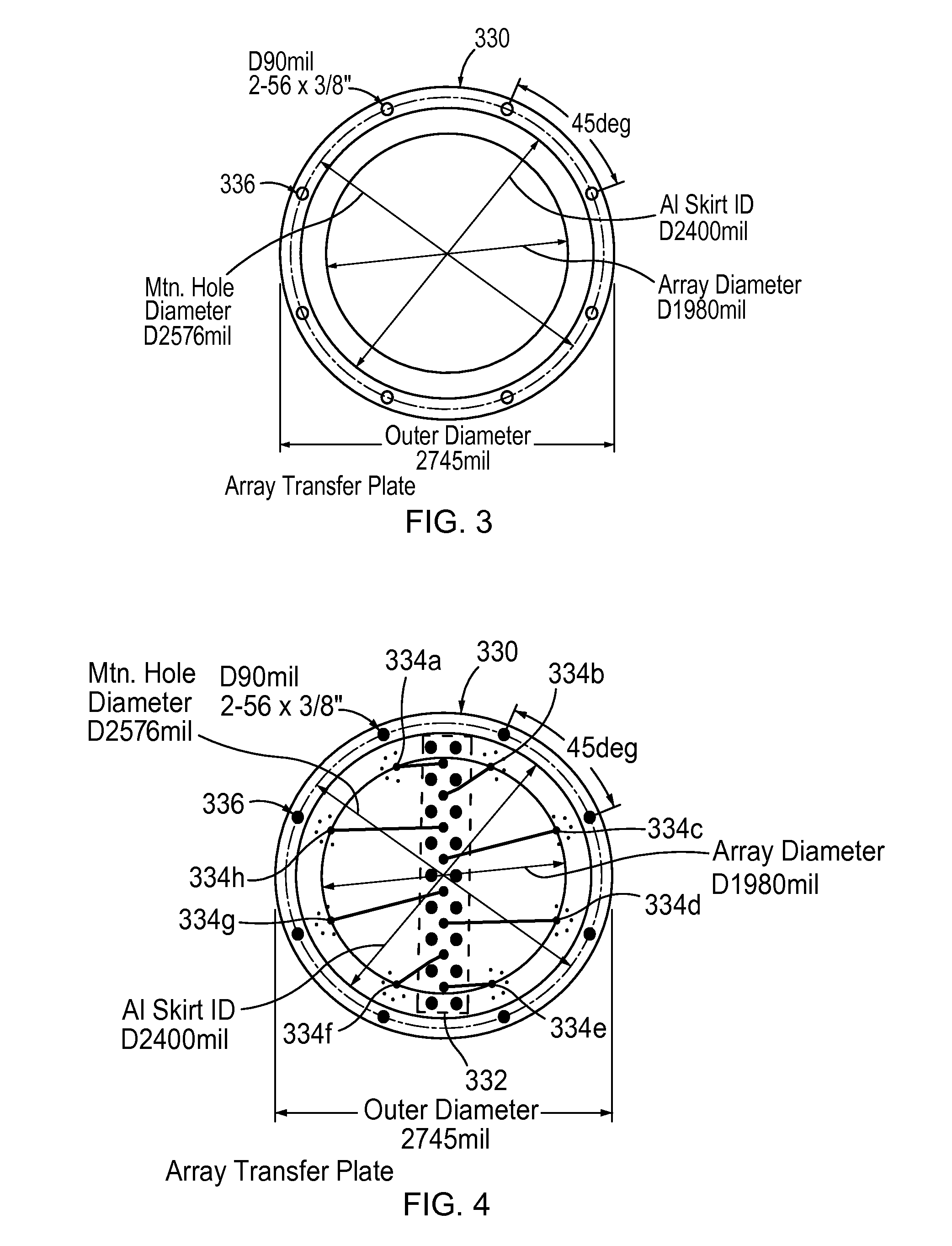
A compact, high gain 8-element circular smart antenna is able to scan a beam azimuthally through 360°. The 8-element array is placed on a ground skirt and connected to an 8-channel beamforning board via a transfer plate. Each channel has two T / R switches, one band pass filer, one power amplifier, two low noise amplifiers, one phase shifter, and one attenuator. The 8-channel-signal is combined through power splitters / combiners and then sent to a connected radio. An FPGA chip controls the digital phase shifters, attenuators and switches for signal searching, beamforming and tracking. The smart antenna can be operated as a compact switched beam system or with an additional processor as an adaptive array system. The smart antenna is capable of tracking mobile targets, directionally communicating with desired users, suppressing interference and jamming, and enabling long range communications with high throughput and reliable connection because of its high antenna gain.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Auto hang tag with radio transponder
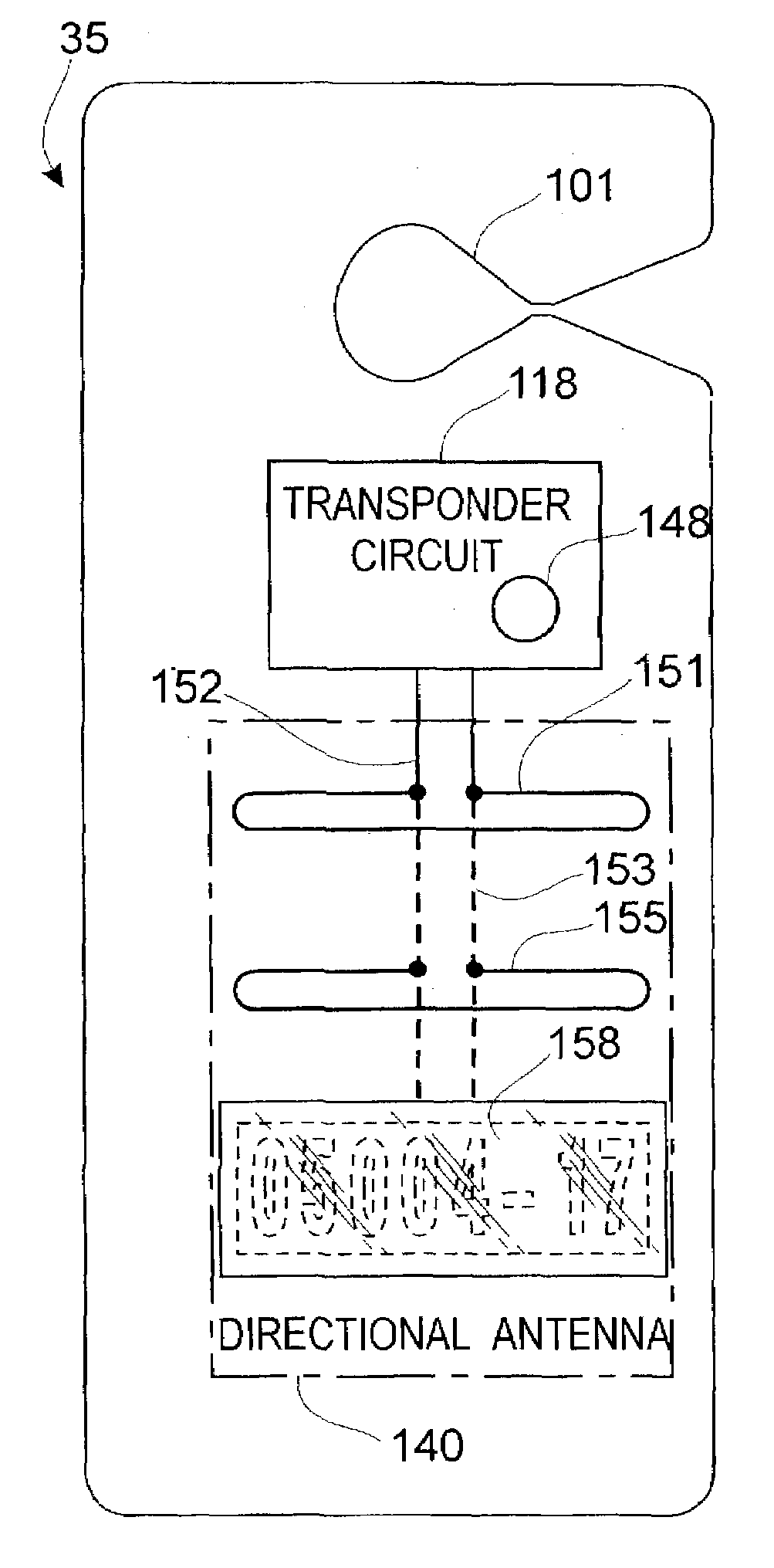
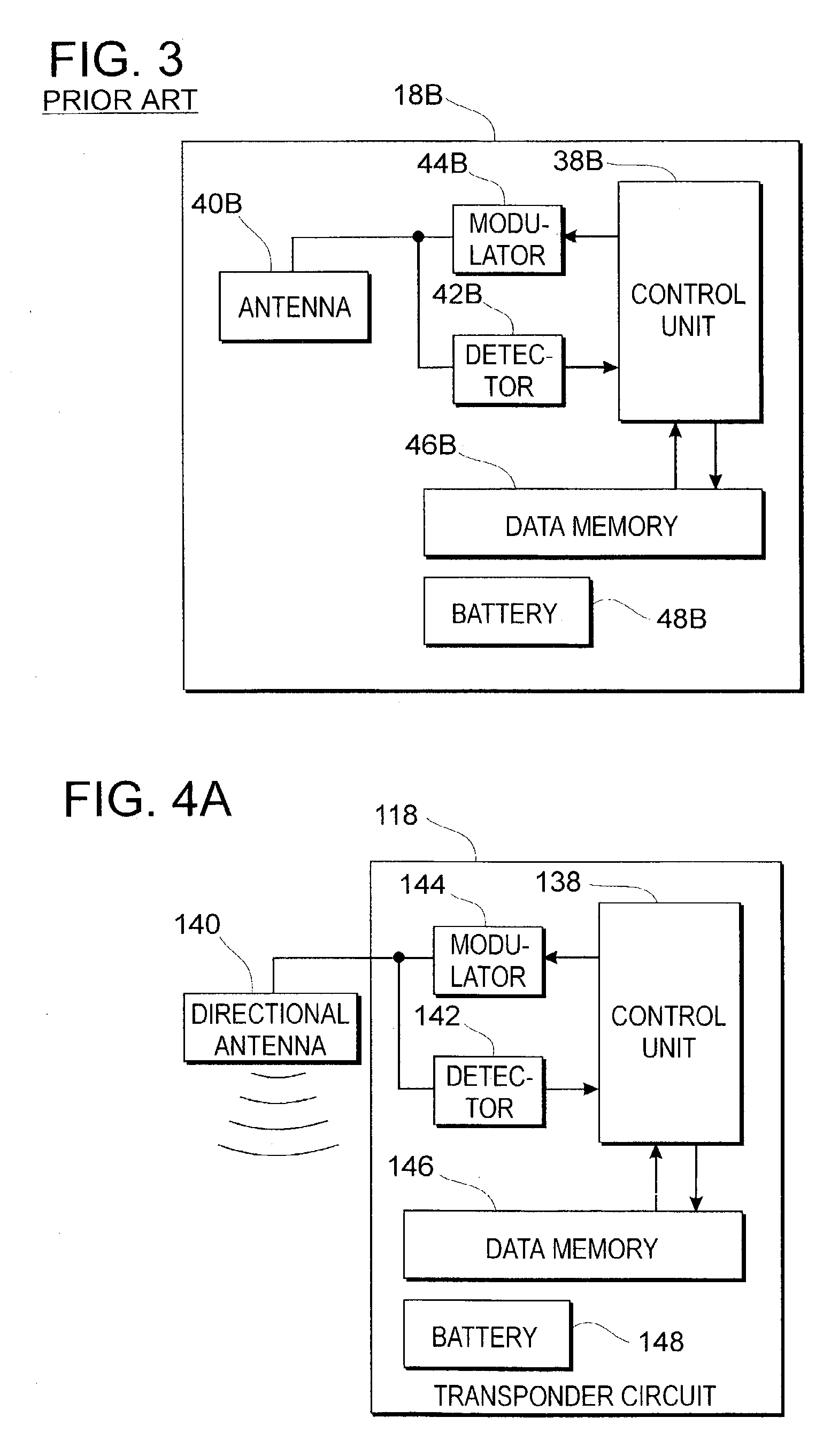
InactiveUS6956472B1Increase rangeImprove reliabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlRadiating elements structural formsMobile vehicleDirectional antenna
There is disclosed an automobile hang tag for use in parking control and the like with an integral radio transponder, together with interrogator apparatus associated therewith in a system for parking control or other purposes. The detection range for the RFID interrogator and transponder is at least about six meters (20 feet) to enable rapid control monitoring of parking facilities from a moving vehicle through the back window or front windshield of parked vehicles. Reliable and trouble-free monitoring of the hang tags in a customary rear view mirror location is facilitated by employing directional antennas in the RFID hang tags, increasing the antenna gain while suppressing false signals and noise and improving the range-to-power ratio for the system. The RFID hang tags may be battery powered but are preferably unpowered RFID transponders. Suitable directional antennas employed may include Yagi antennas, log periodic antennas, stacked dipole antennas, spiral or slot antennas or other monodirectional or bidirectional antennas, preferably those suitable for selected frequencies within the 1,000 megahertz to 10,000 megahertz range.
Owner:WELDON WILLIAMS & LICK
Single chip radio with integrated antenna
InactiveUS20050113035A1Eliminate needReduce chip areaMicrobiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRadio equipmentTransceiver
A true single-chip radio for bidirectional wireless communications includes a bulk substrate, at least one integrated antenna, at least one transceiver, baseband circuitry and at least one filter all integrally formed in or on the substrate. The radio preferably includes a low-loss dielectric propagating layer disposed beneath the substrate to improve antenna gain. The integrated antenna can be an adaptive array for beamforming.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Antenna alignment method and apparatus
ActiveUS8487813B2Detectable connectionRadio transmission for post communicationAntenna detailsUltrasound attenuationRegular pattern
A method of automatic alignment of two directional beams having a known path attenuation, and an antenna gain pattern, for mutual transmission, comprises: determining a beam width between two angles of minimal detectable connection on either side of a beam maximum; then mapping points onto a scan field in a regular pattern, the pattern based on the beam width, such that a beam with the determined beam width is detected once if the beam is in the scan field at all; scanning the first antenna over the mapped scan points; and for each point allowing the second antenna to scan over all of its own set of mapped scan points, thereby providing a coarse alignment of the two antennas to achieve at least a minimal mutual connection. The coarse alignment may be followed by a fine alignment to maximize the signal.
Owner:SIKLU COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com