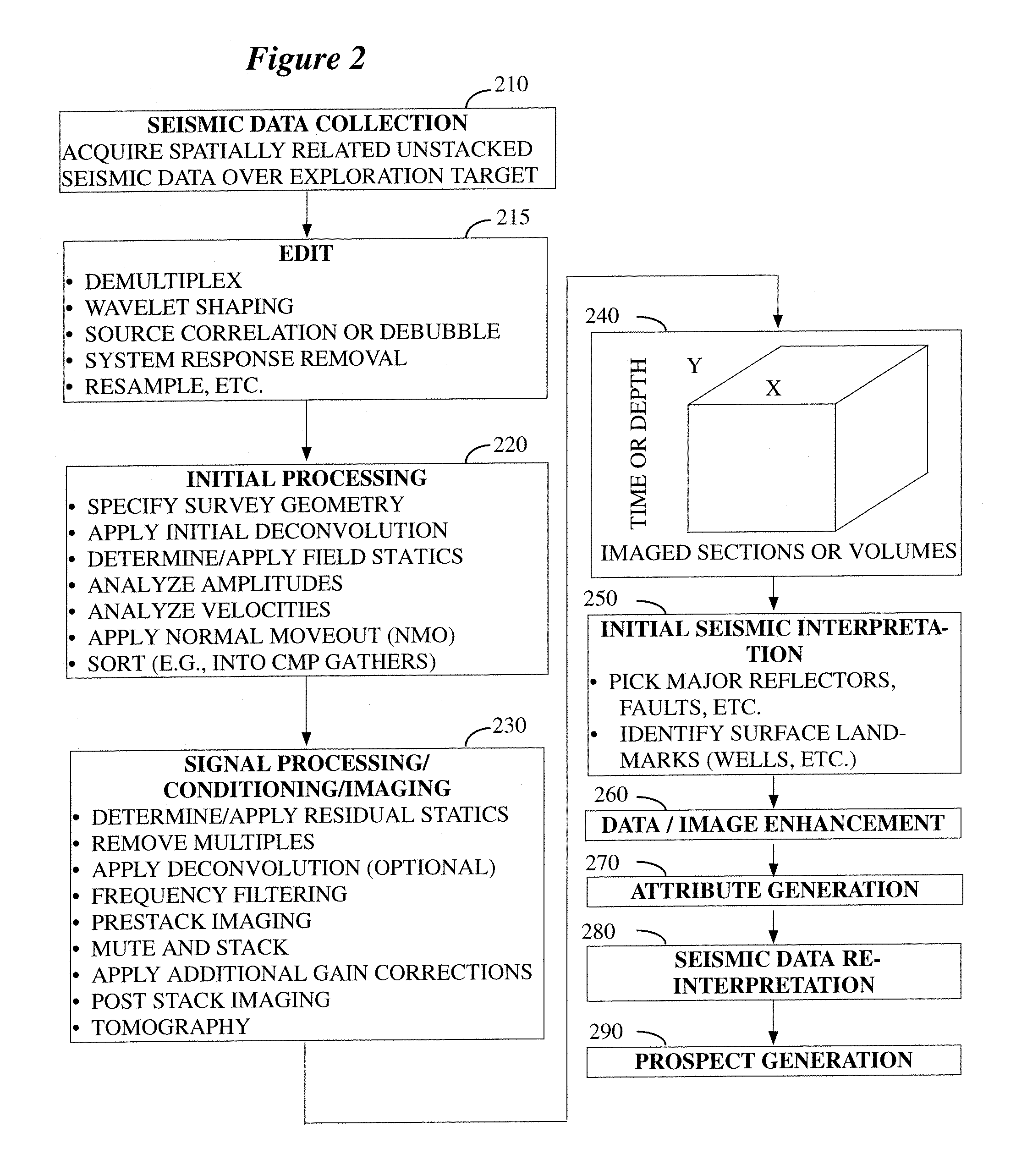
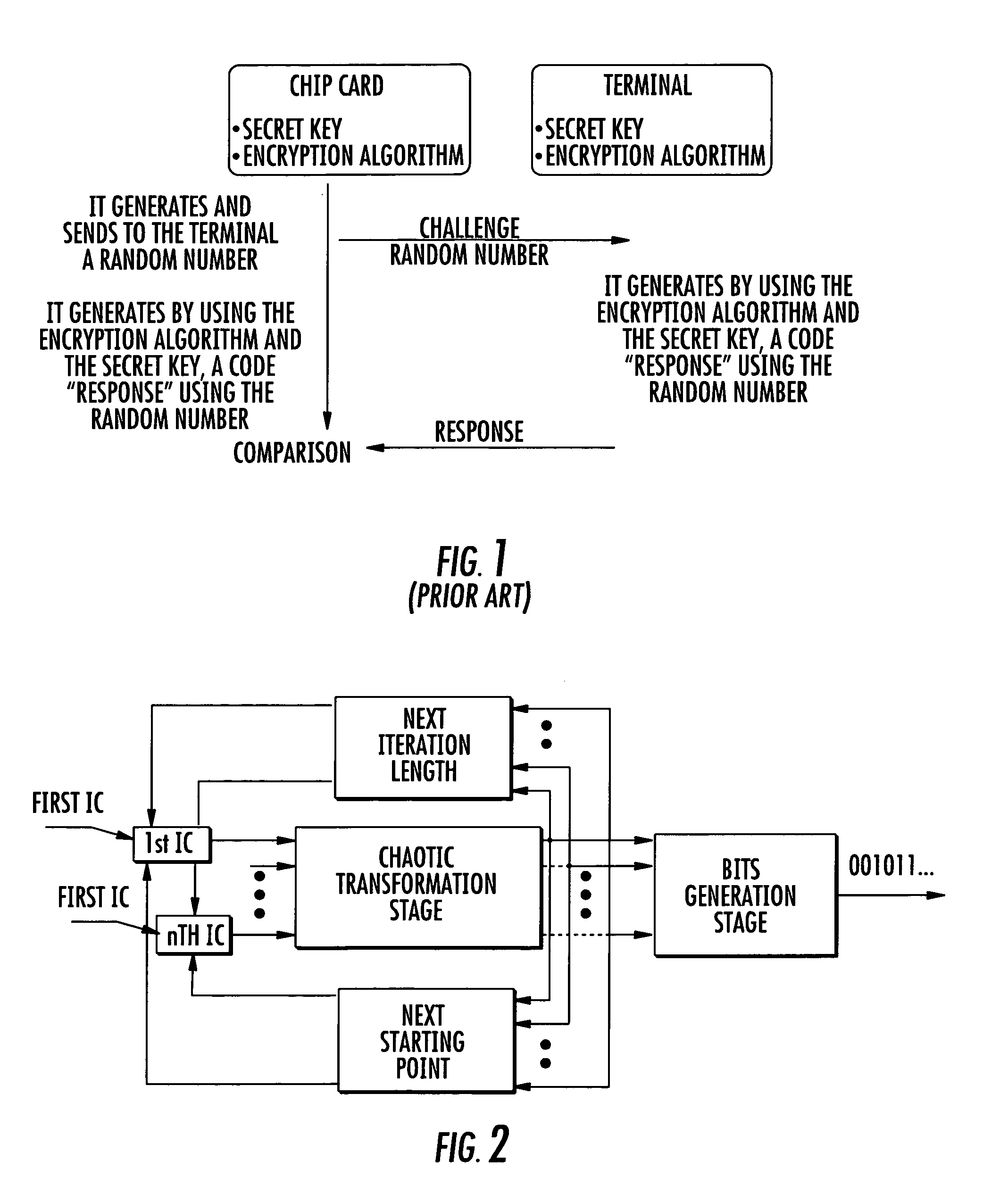
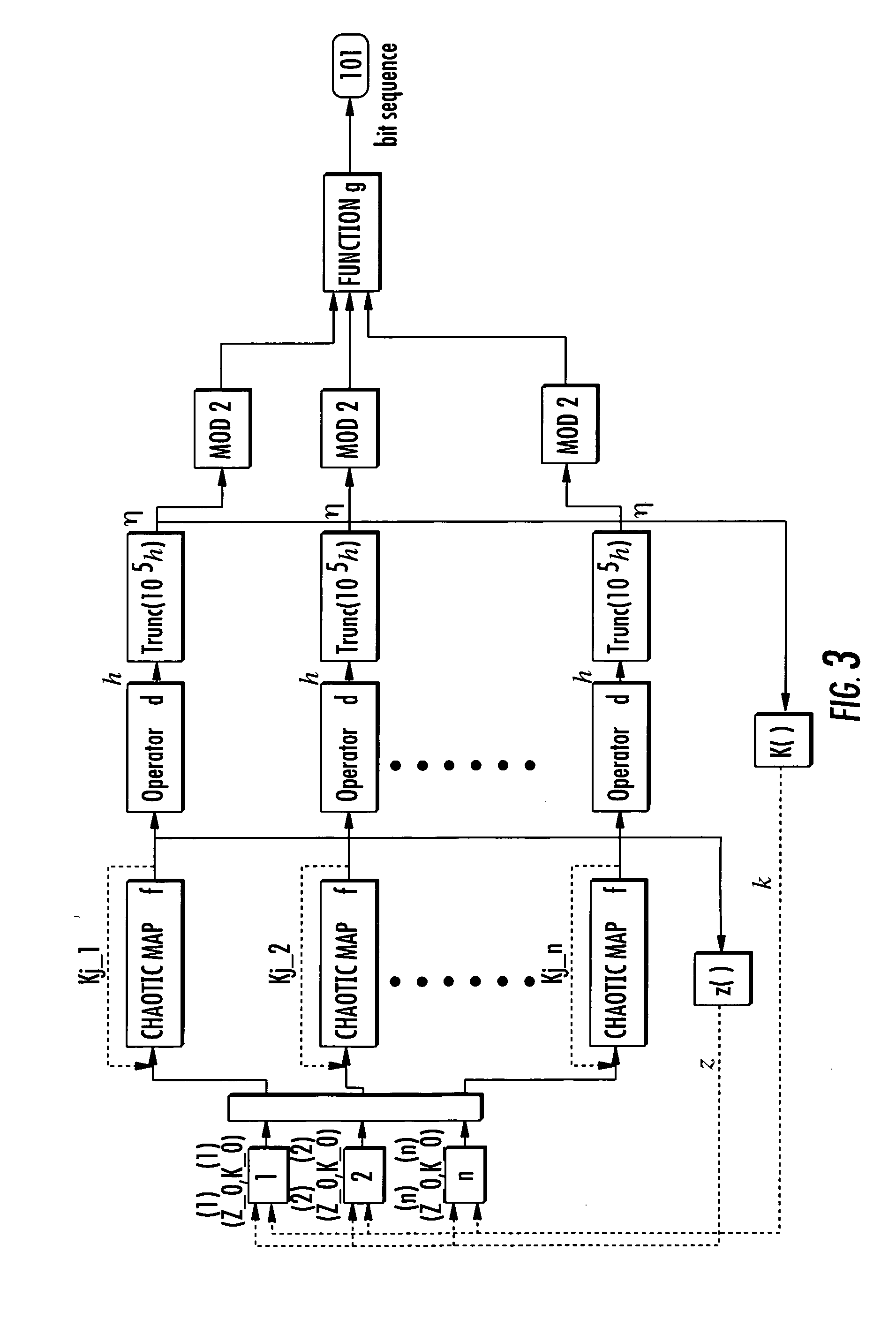
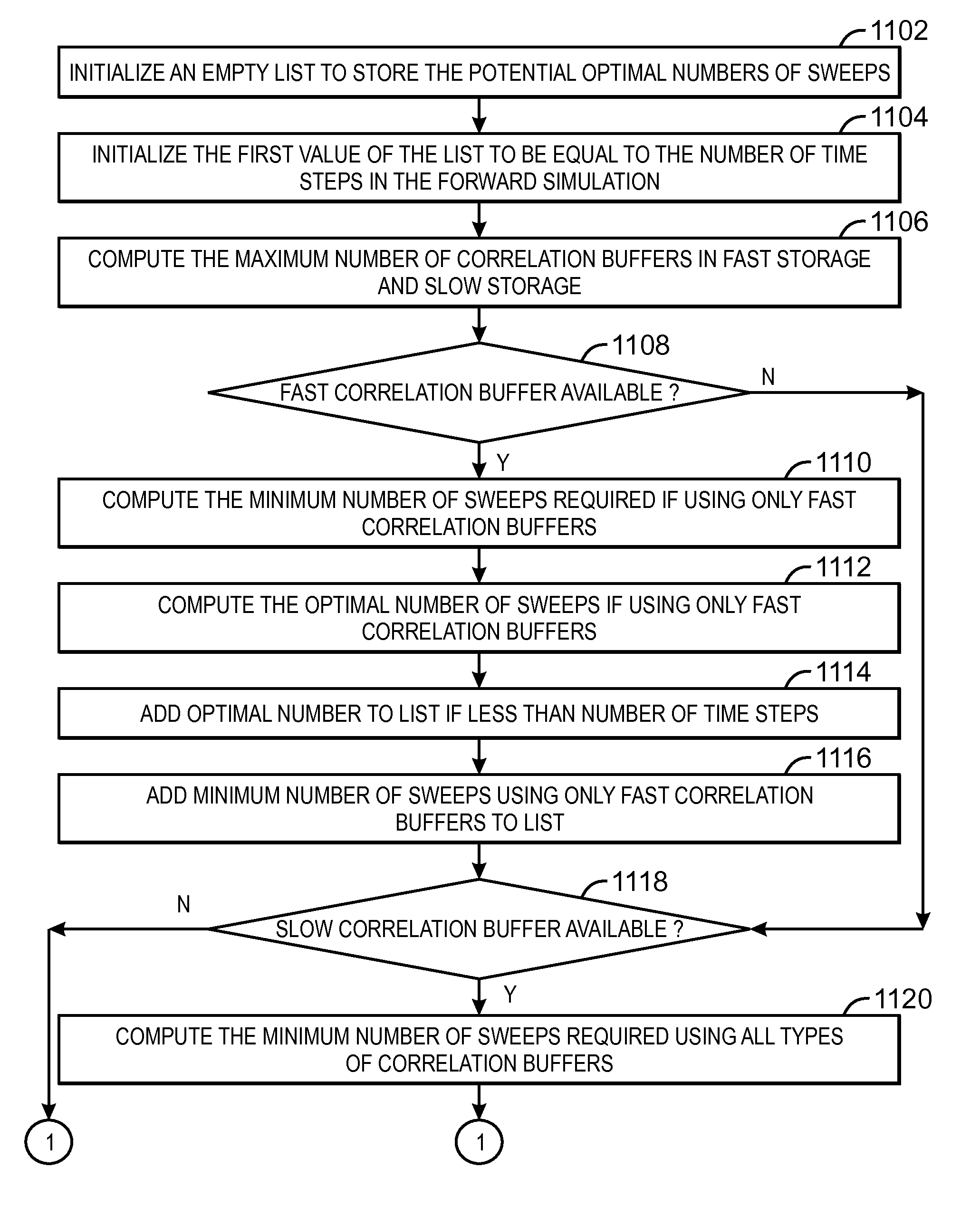
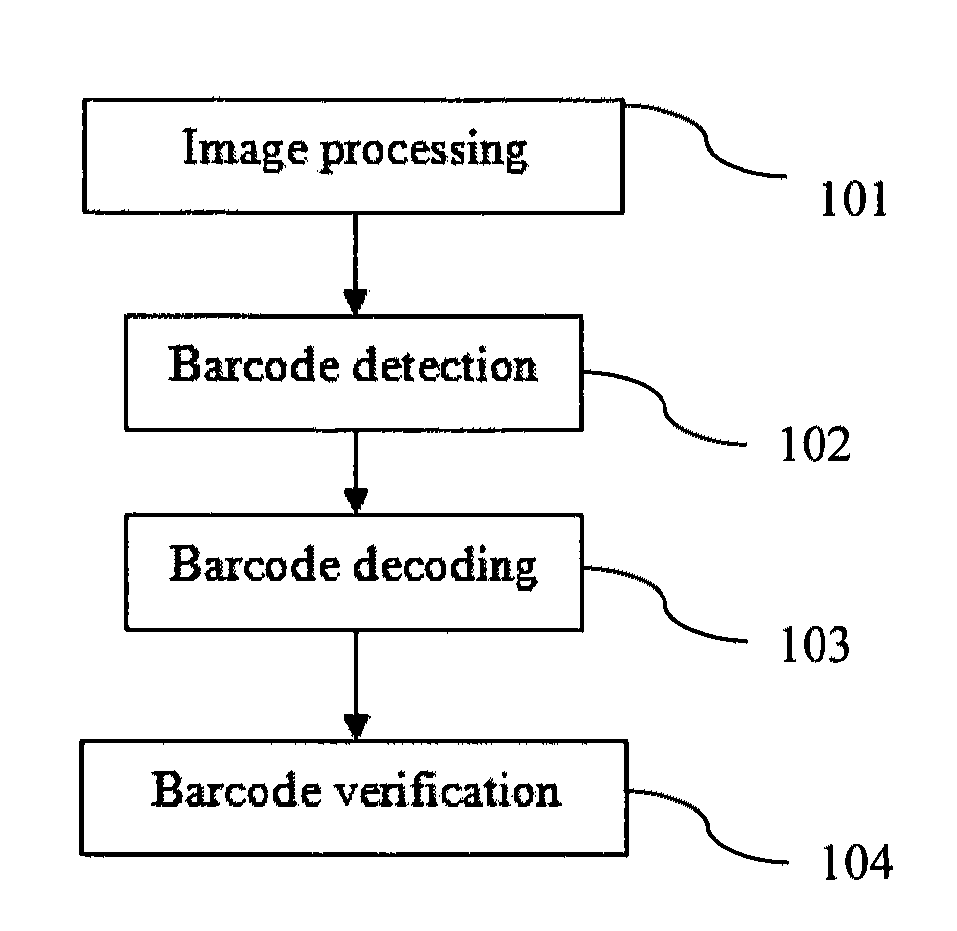
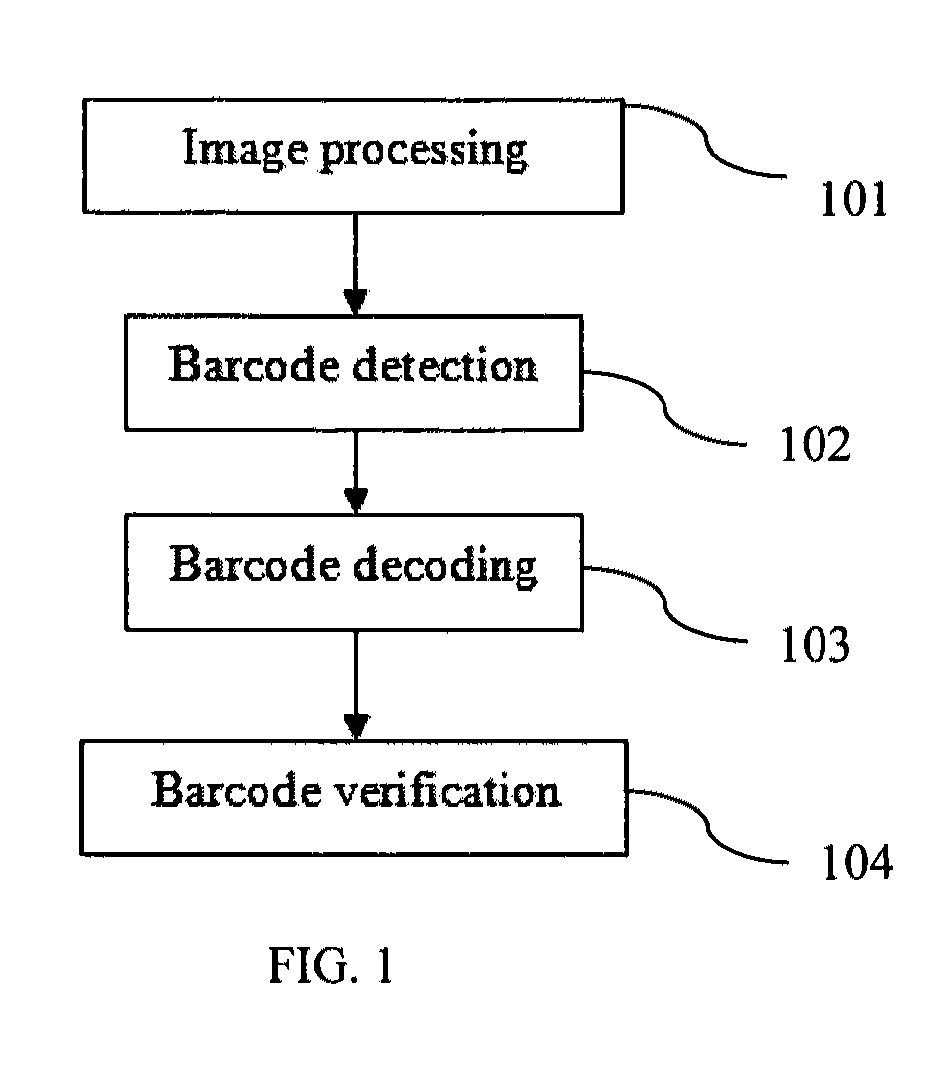
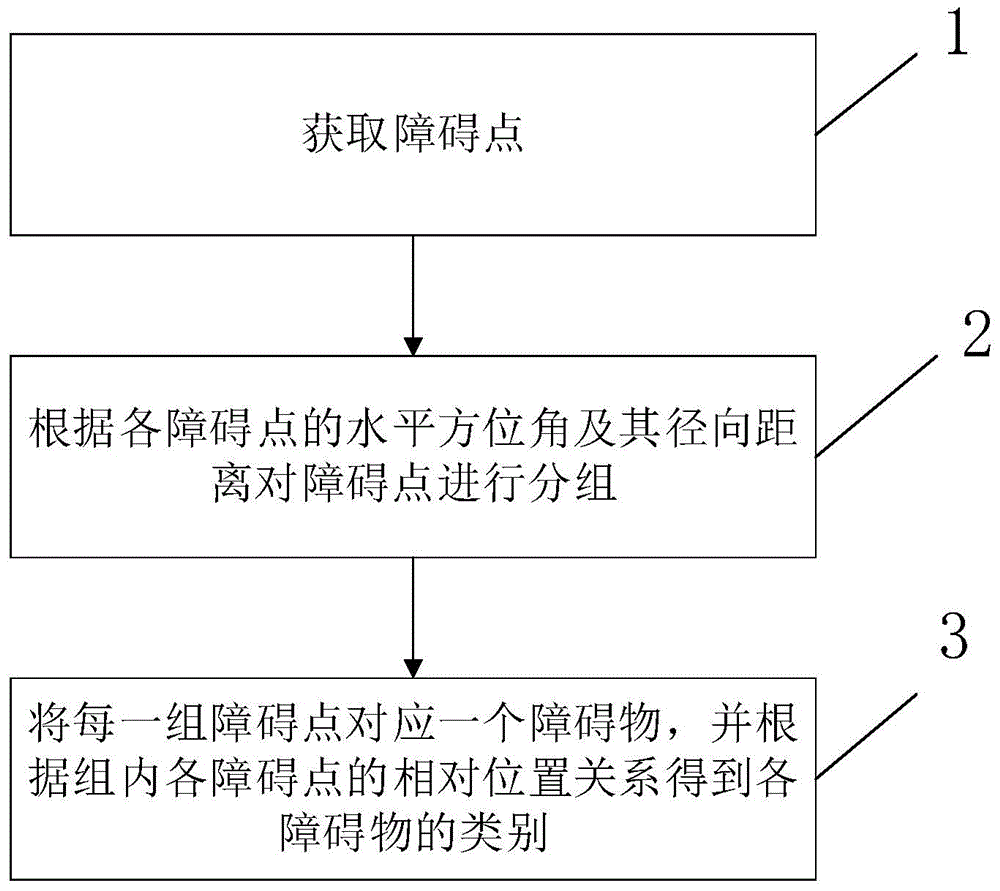
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
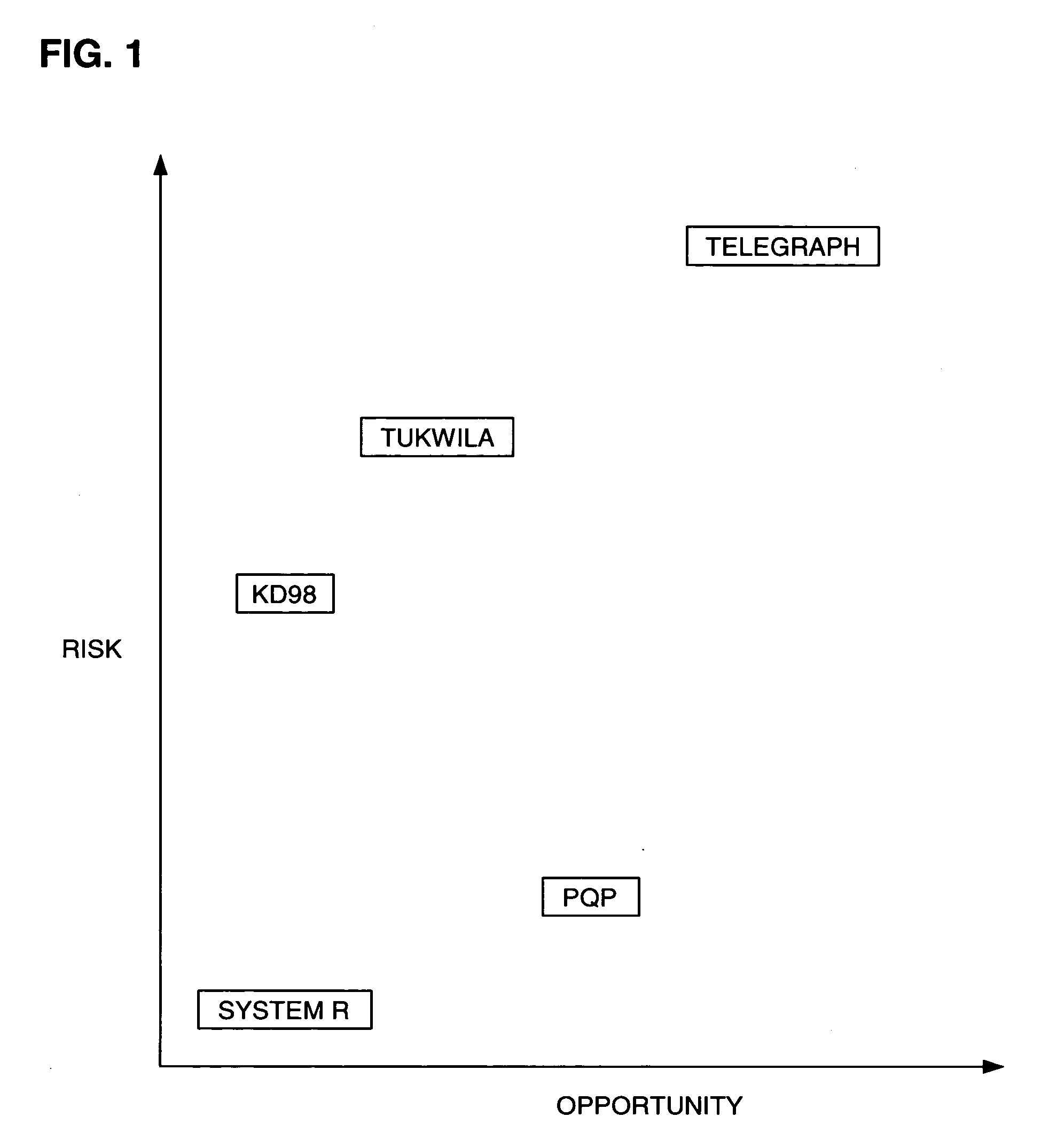
2417results about How to "Reduce computing cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
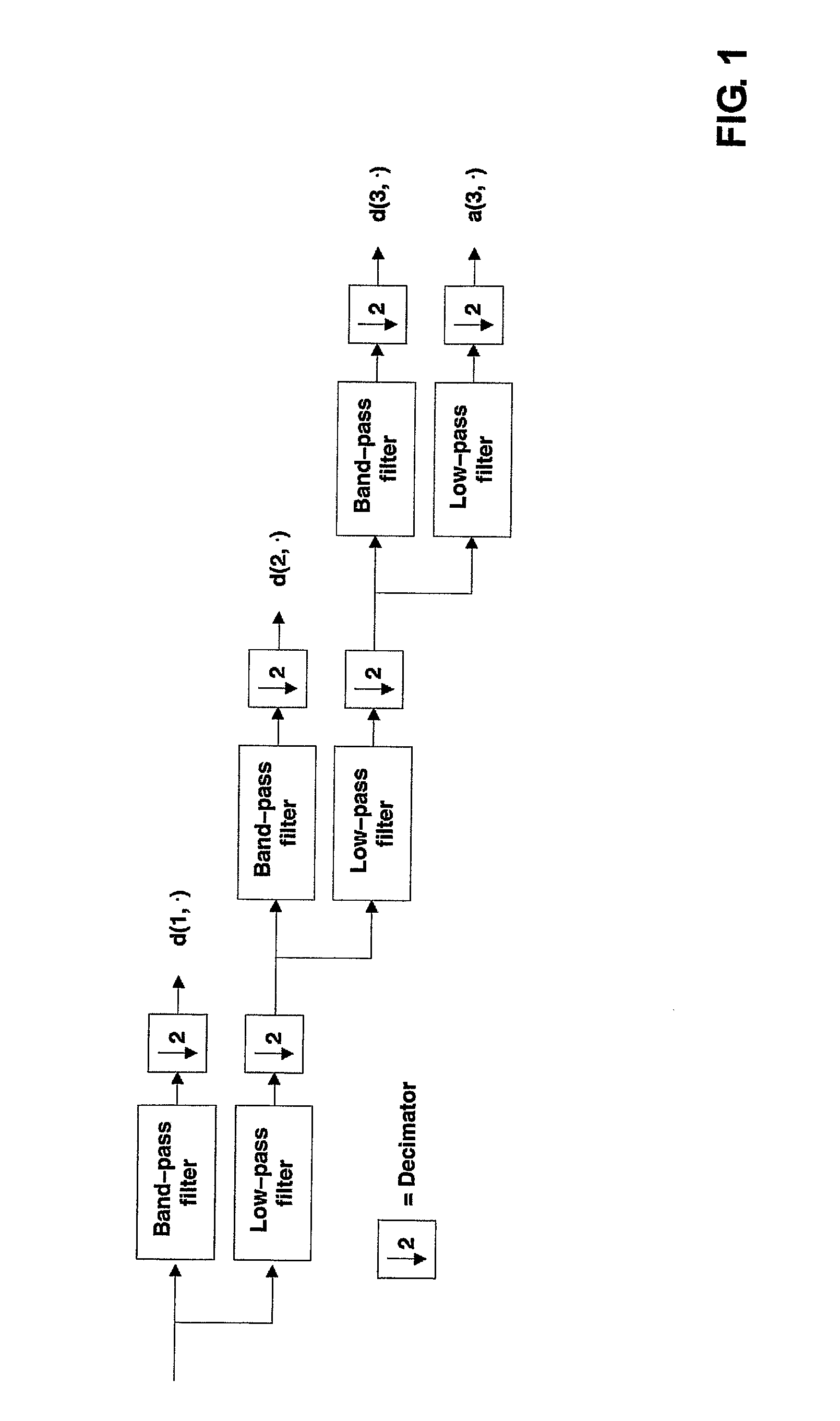
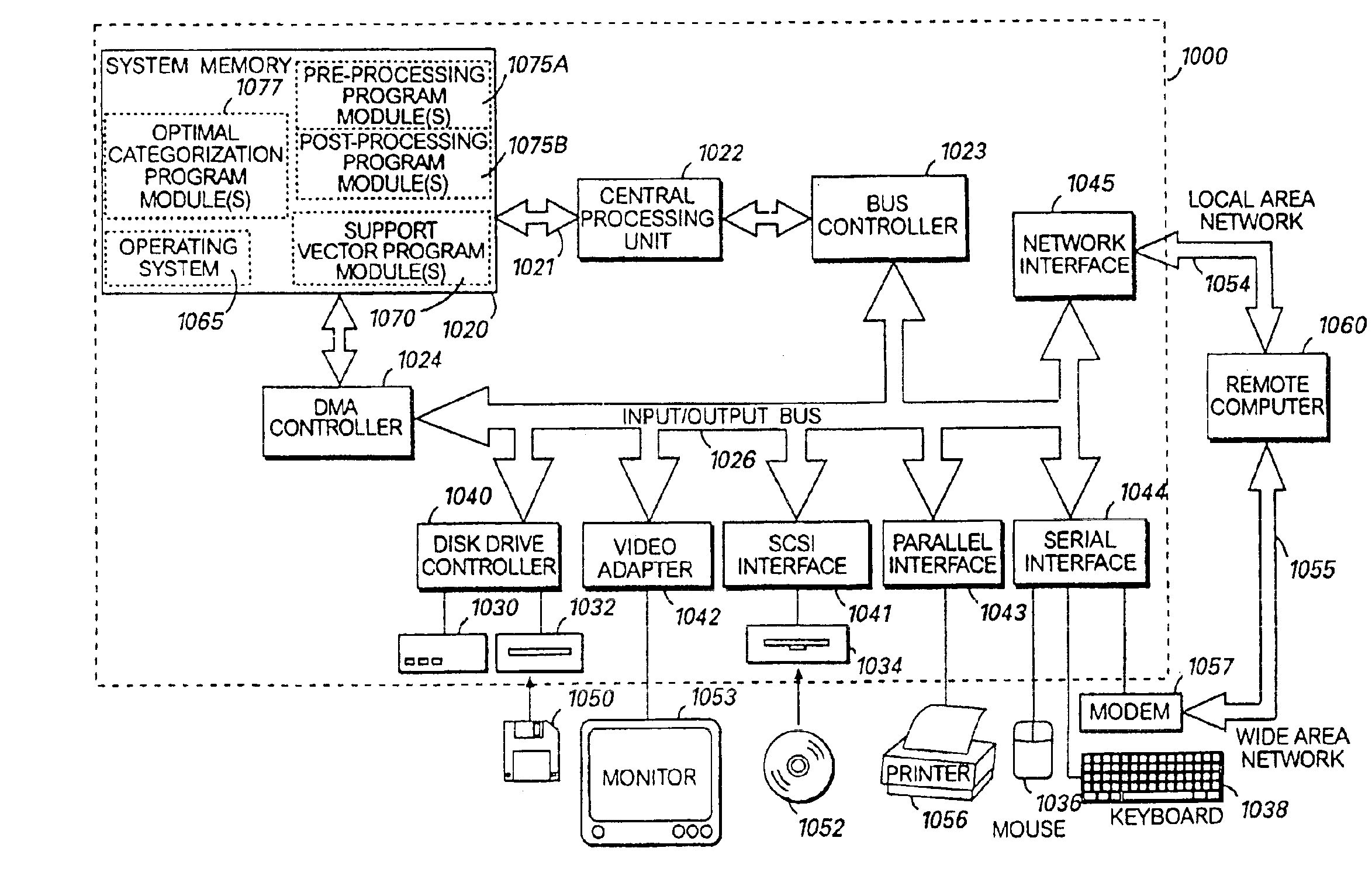
Structured and parameterized model order reduction
InactiveUS20080072182A1Reduce redundancyNon-uniformity is constantDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationStructured modelOrder reduction
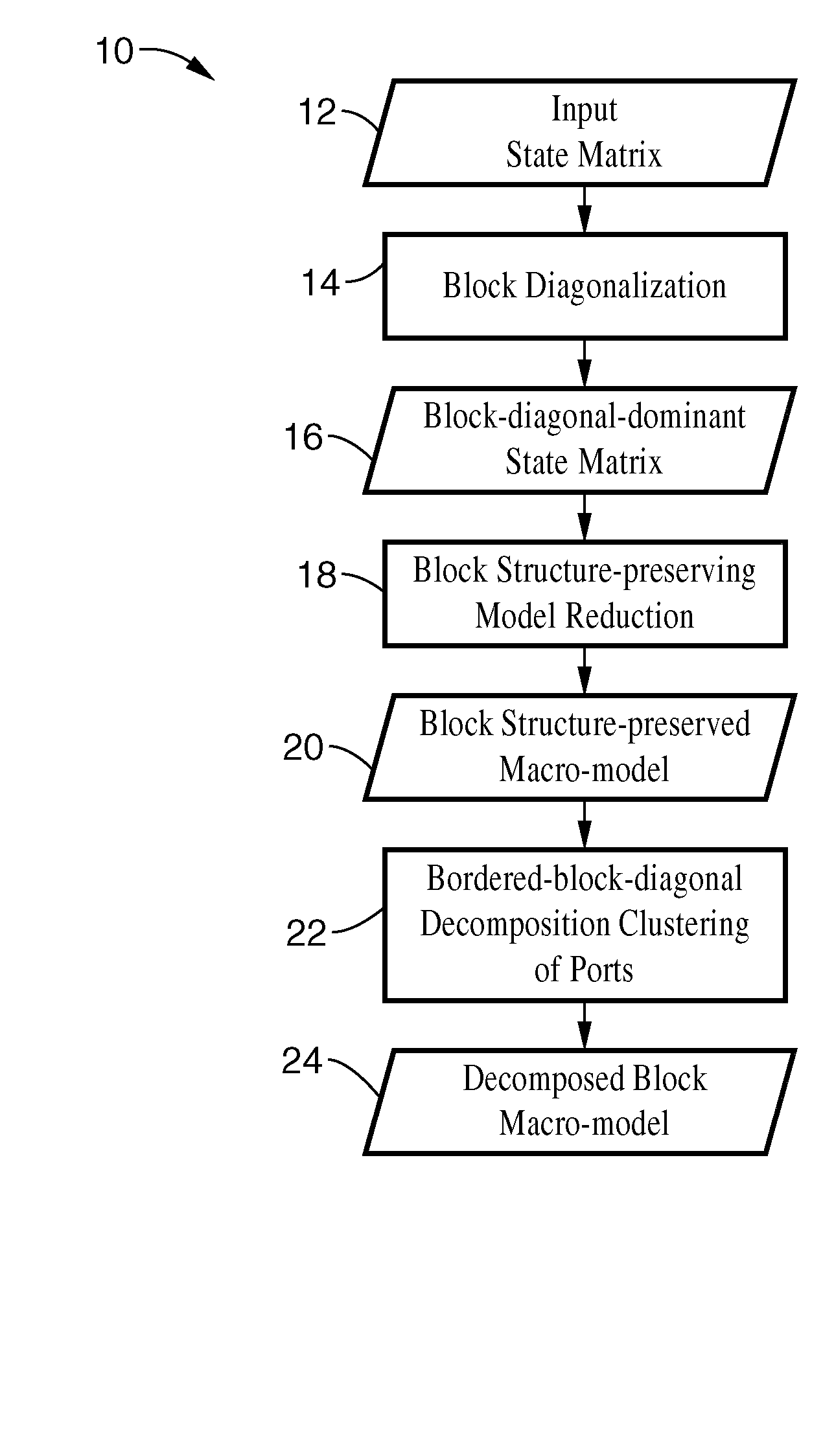
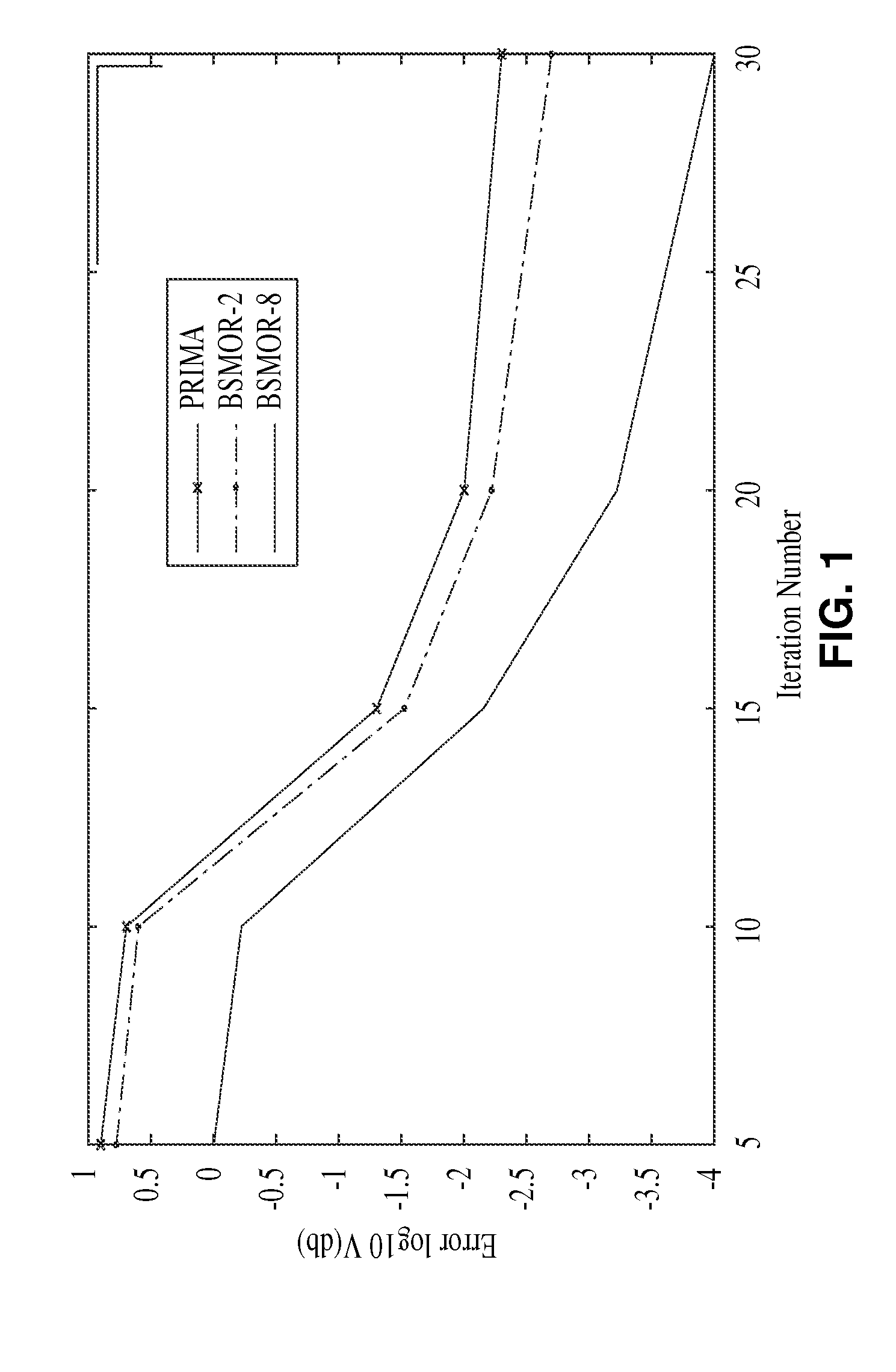
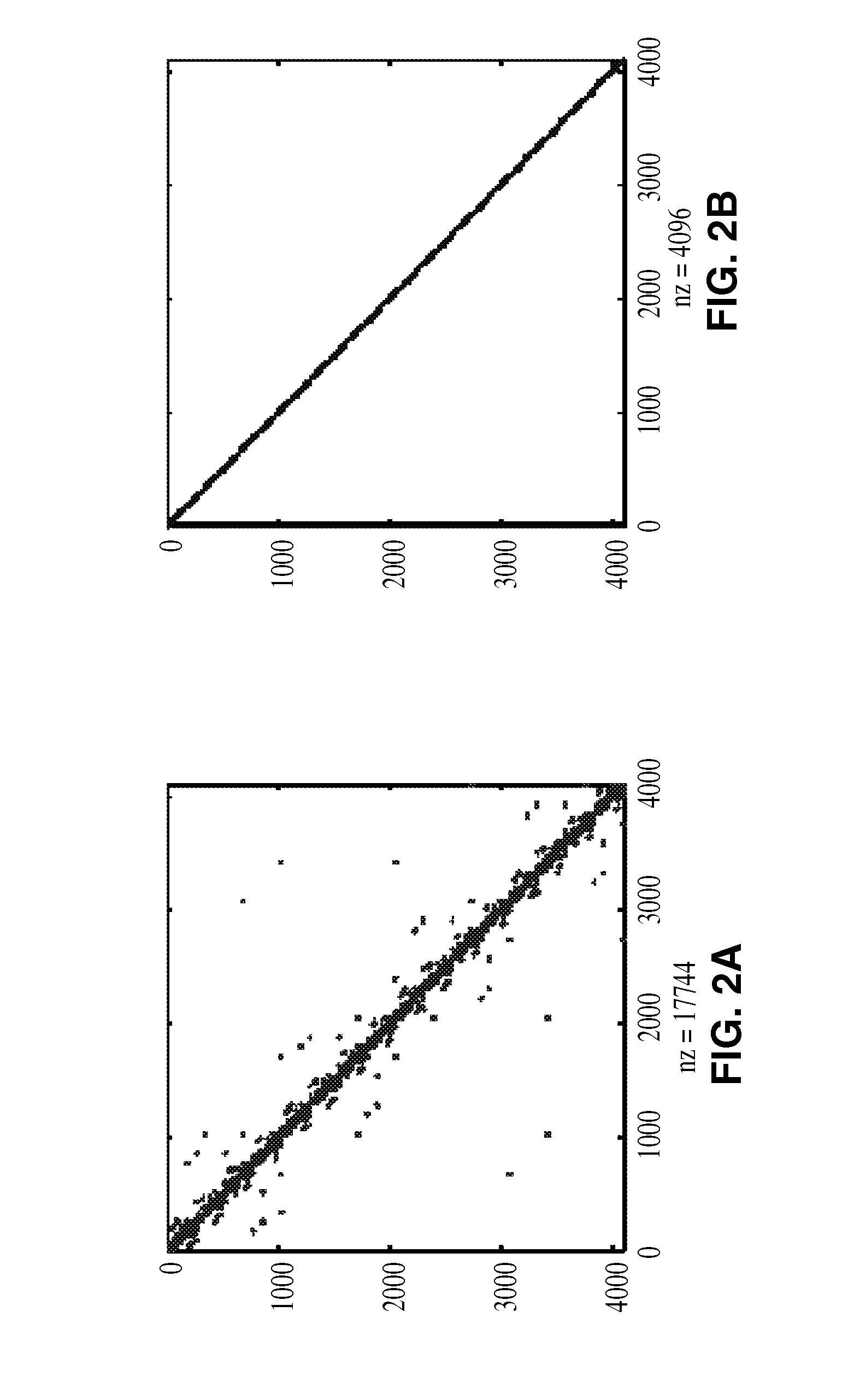
Model-order reduction techniques are described for RLC circuits modeling the VLSI layouts. A structured model order reduction is developed to preserve the block-level sparsity, hierarchy and latency. In addition, a structured and parameterized model order reduction is developed to generate macromodels for design optimizations of VLSI layouts. The applications are thermal via allocation under the dynamic thermal integrity and via stapling to simultaneously optimize thermal and power integrity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System, method, and computer program product for progressive query processing
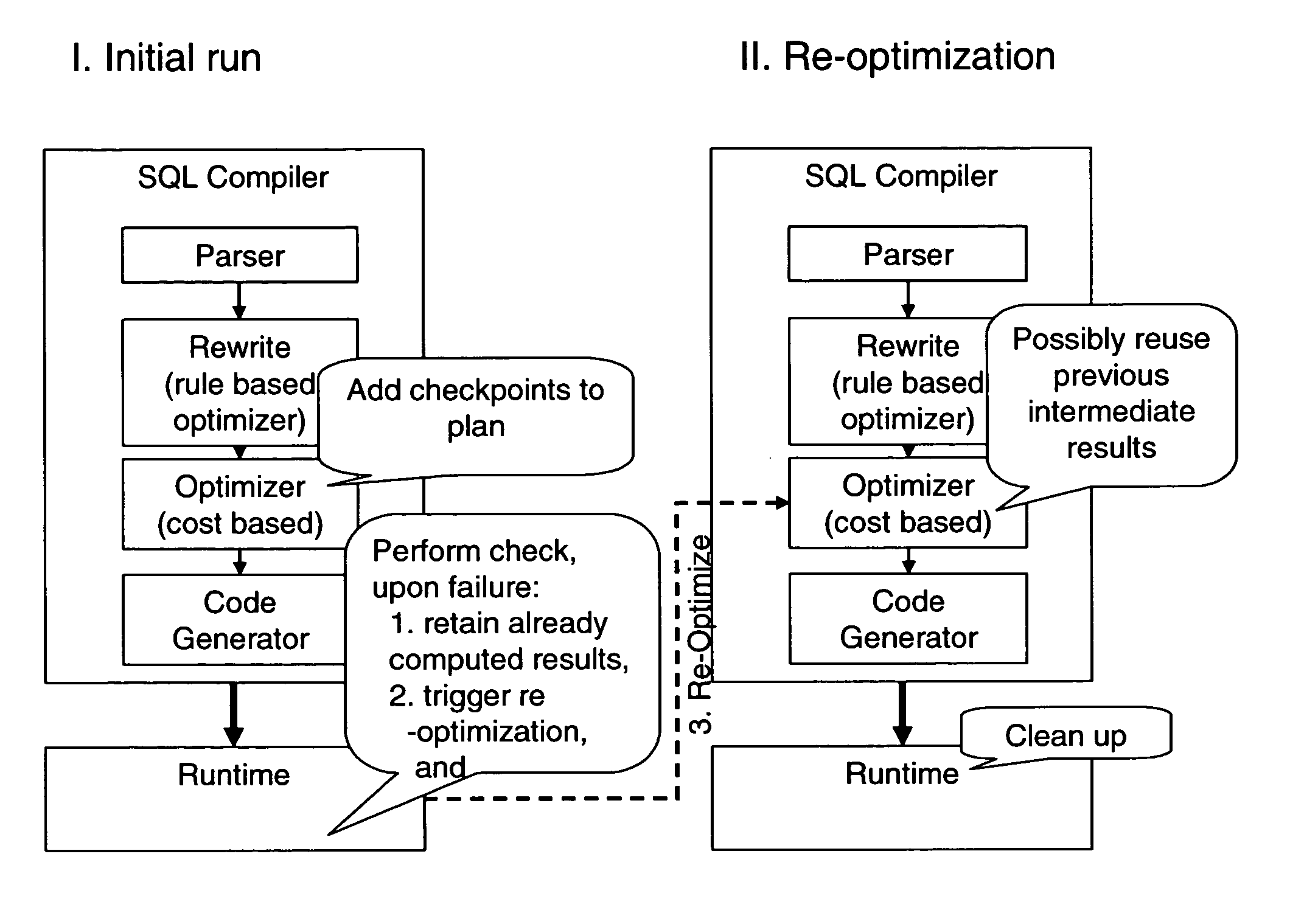
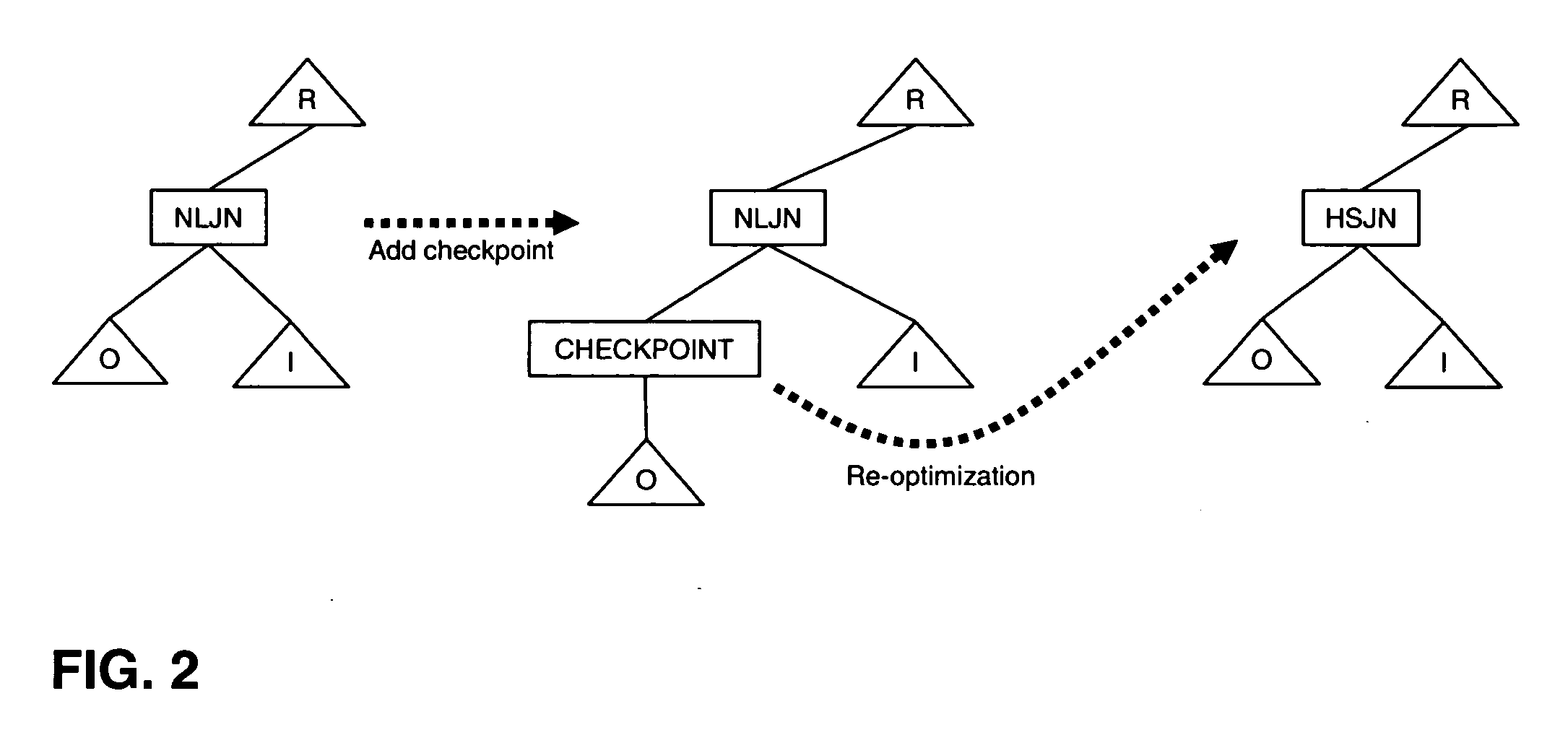
ActiveUS20050097078A1Reduce computing costEliminate duplicationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExecution planView maintenance
A method, system, and computer program product to make query processing more robust in the face of optimization errors. The invention validates the statistics and assumptions used for compiling a query as the query is executed and, when necessary, progressively re-optimizes the query in mid-execution based on the knowledge learned during its partial execution. The invention selectively places a number of CHECK operators in a query execution plan to validate the optimizer's cardinality estimates against actual cardinalities. Errors beyond a threshold trigger re-optimization, and the optimizer decides whether the old plan is still optimal and whether to re-use previously computed results. The invention addresses arbitrary SQL queries whose plans can contain sub-queries, updates, trigger checking, and view maintenance operations. The invention can handle concurrent update transactions or updates of common sub-expressions in a query execution plan without compromising consistency and isolation as locking information is tied to the record ID.
Owner:HULU
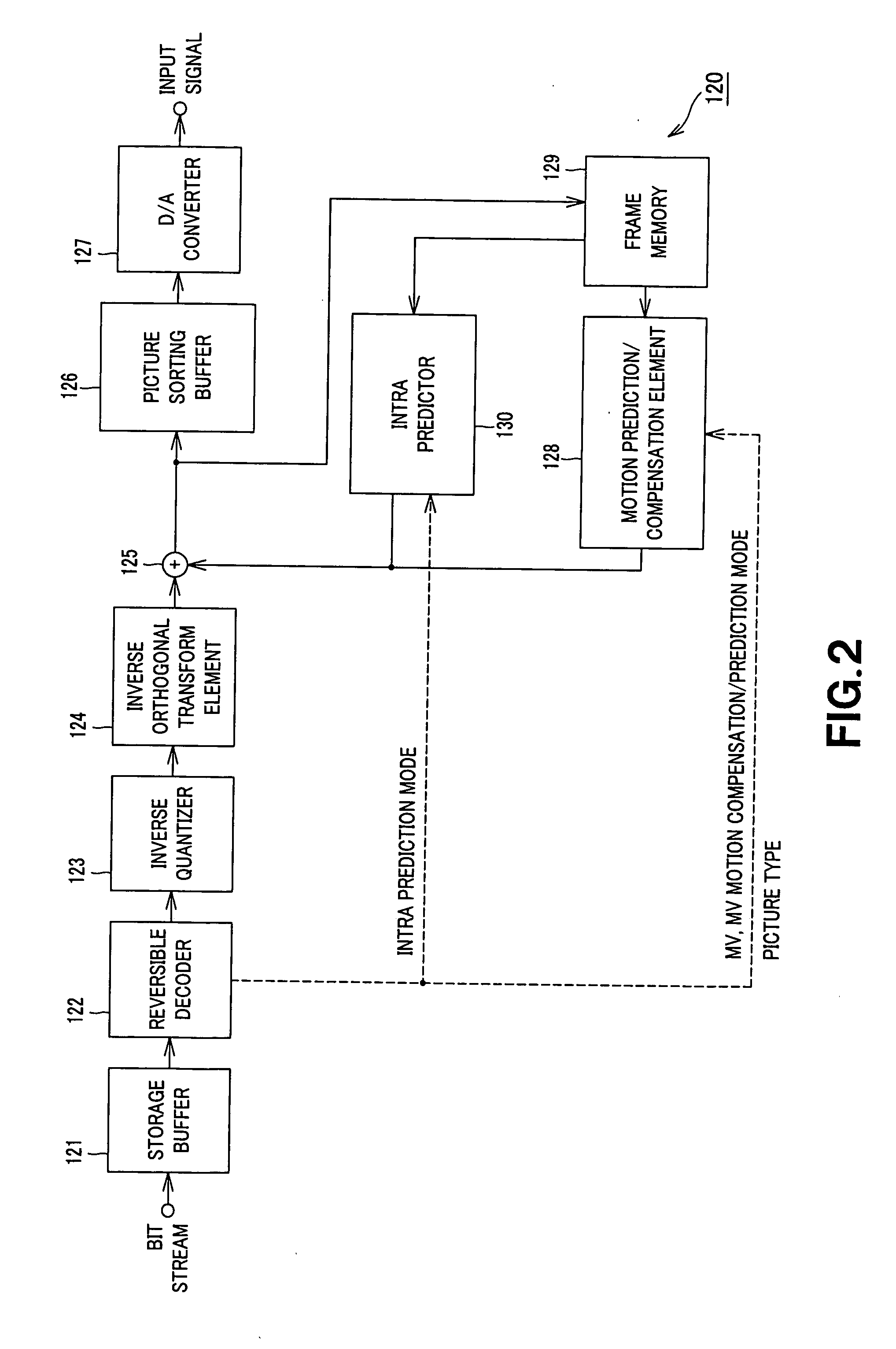
Image decoding device, image decoding method, and image decoding program
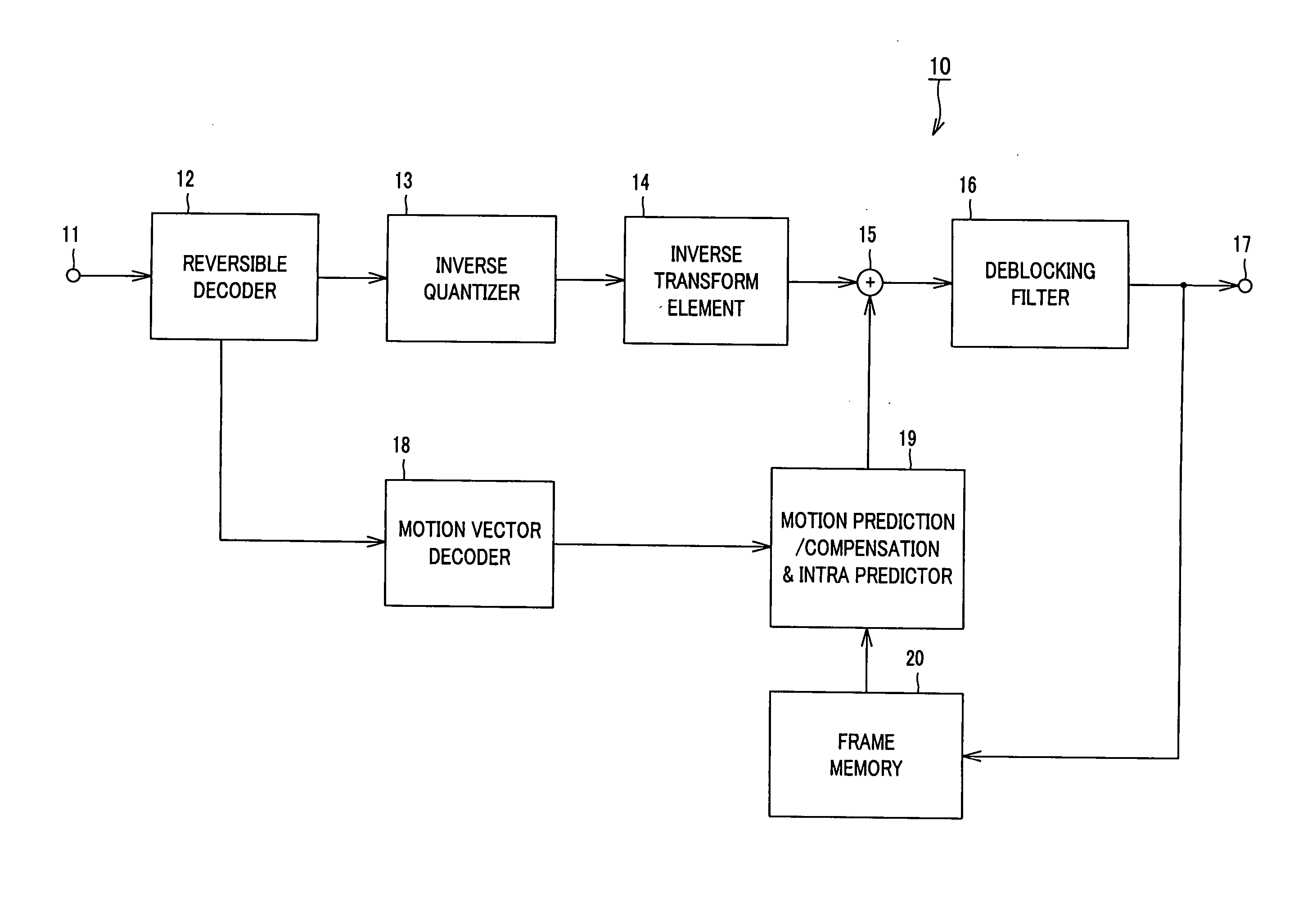
InactiveUS20060291556A1High speed decoding processingUnnecessary to performColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage compressionComputer hardware
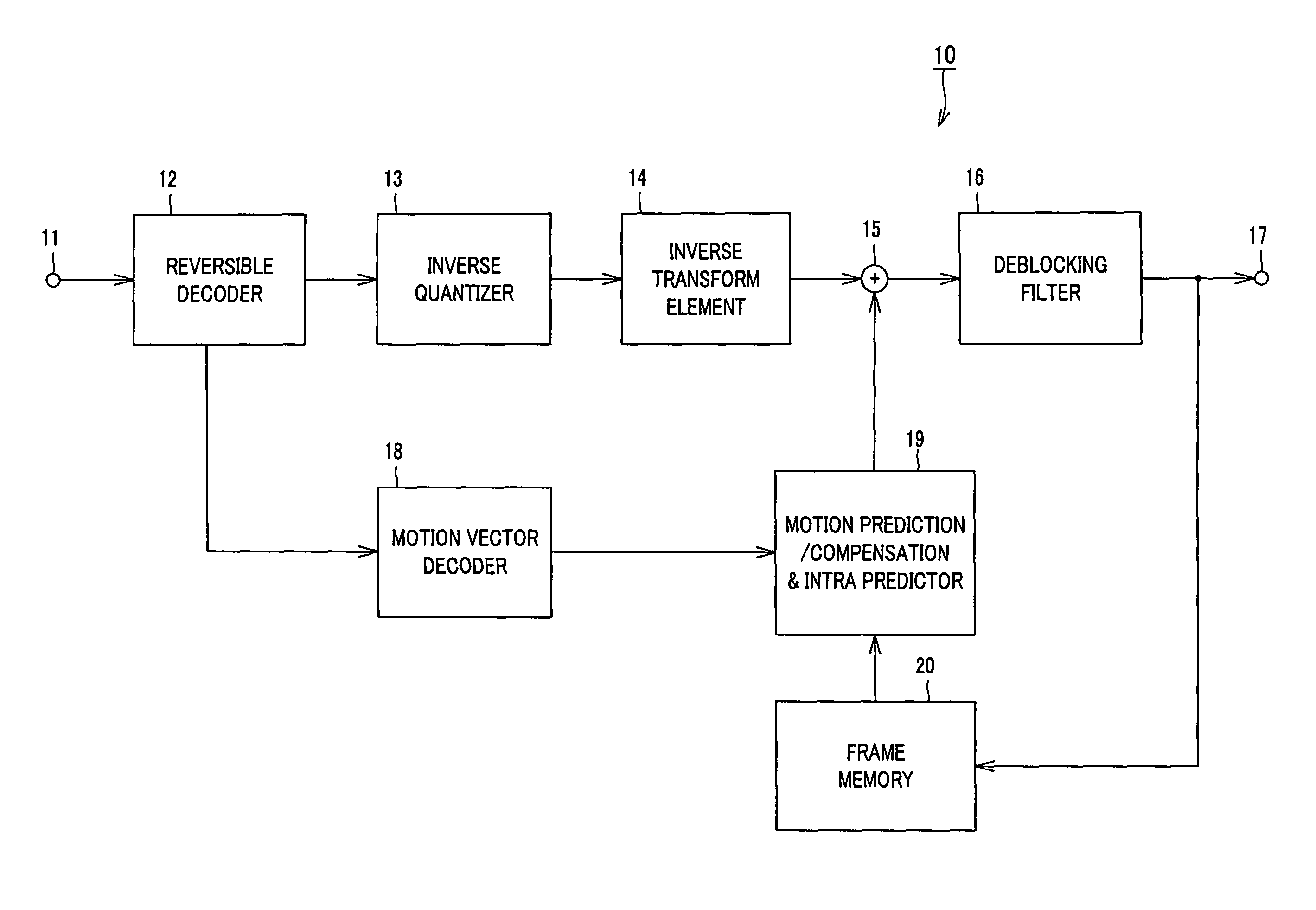
The present invention is directed to an image decoding apparatus adapted for decoding information obtained by implementing inverse quantization and inverse orthogonal transform to image compressed information in which an input image signal is blocked to implement orthogonal transform thereto on the block basis so that quantization is performed with respect thereto, which comprises a reversible decoder (12) for decoding quantized and encoded transform coefficients, an inverse quantizer (13) indicating, as a flag, in inverse-quantizing transform coefficients which have been decoded by the reversible decoder (12), existence of each transform coefficient every processing block of inverse quantization, and an inverse transform element (14) for changing inverse transform processing to be implemented to inverse quantization transform coefficients within processing block by using the flag which has been indicated by the inverse-quantizer (13).
Owner:SONY CORP
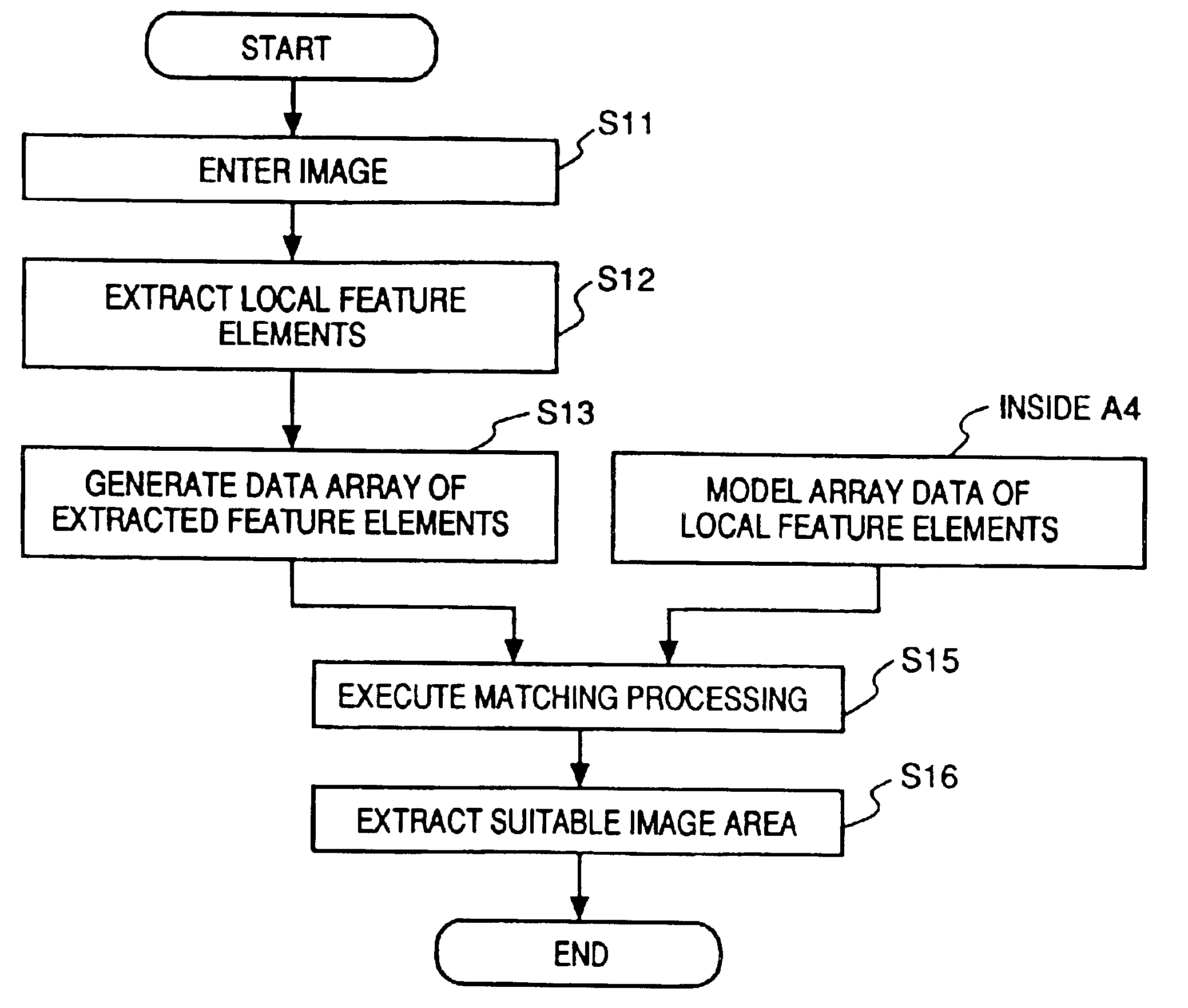
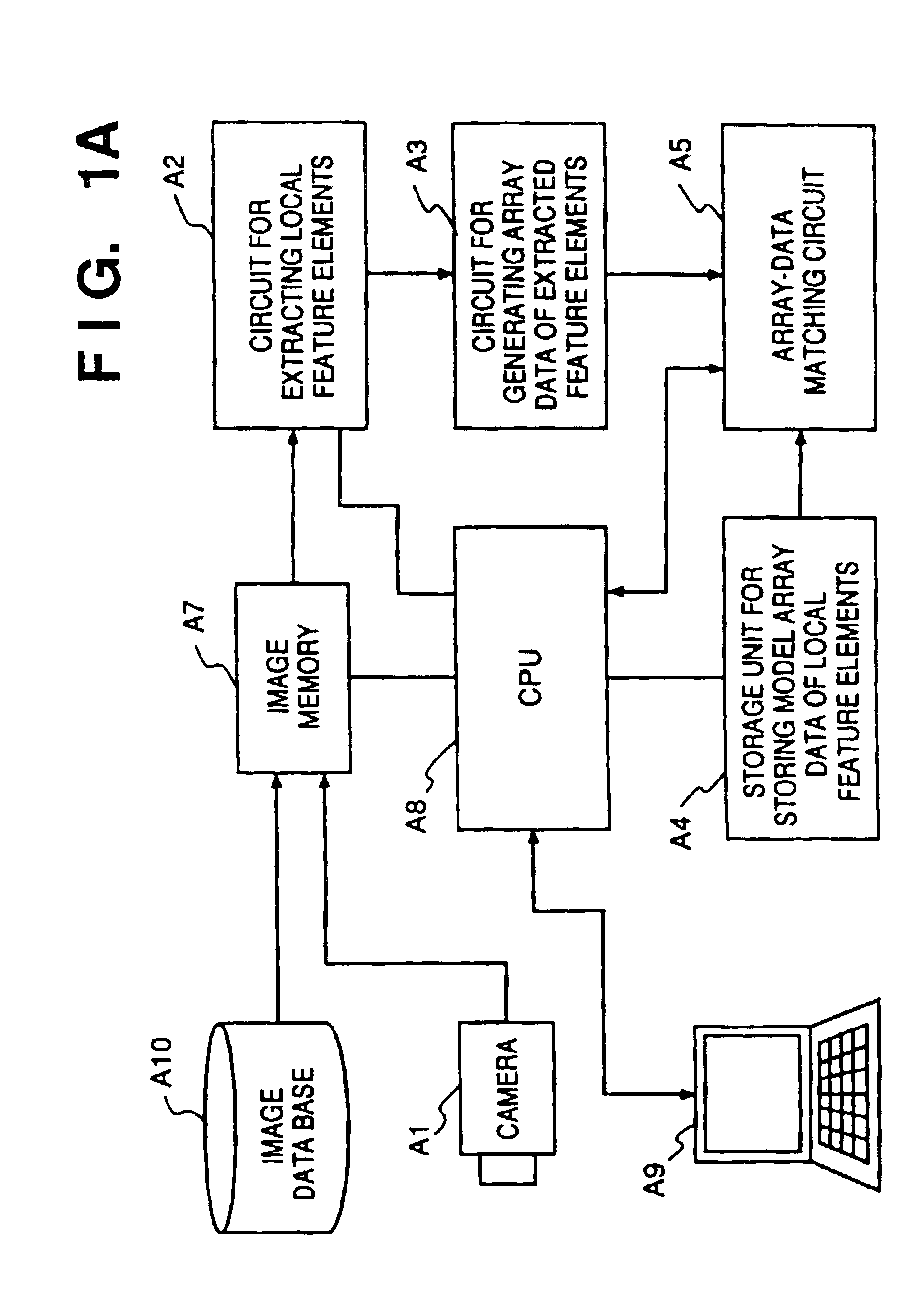
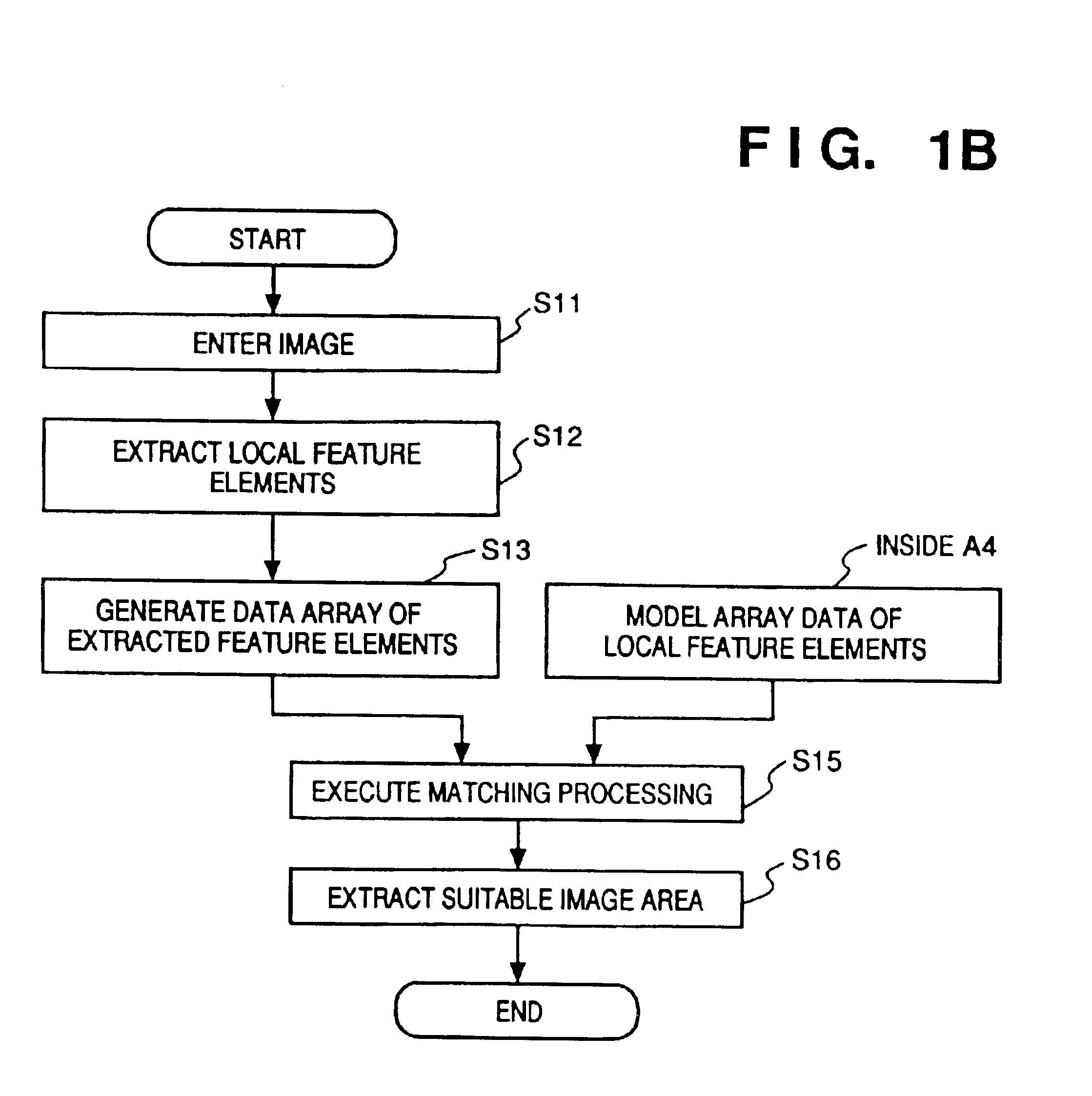
Image recognition/reproduction method and apparatus
InactiveUS6907140B2Reduce computing costShort processing timeCharacter and pattern recognitionEditing/combining figures or textPattern recognitionReproduction
An image recognition / reproduction method includes an extraction step of extracting local feature elements of an image, and a selection step of selecting a pair composed of a prescribed local feature element and position information indicative thereof, this pair being such that the distance between a pair composed of a prescribed local feature element and position information indicative thereof and a pair composed of a local feature element extracted at the extraction step and position information indicative thereof is less than a prescribed distance.
Owner:CANON KK
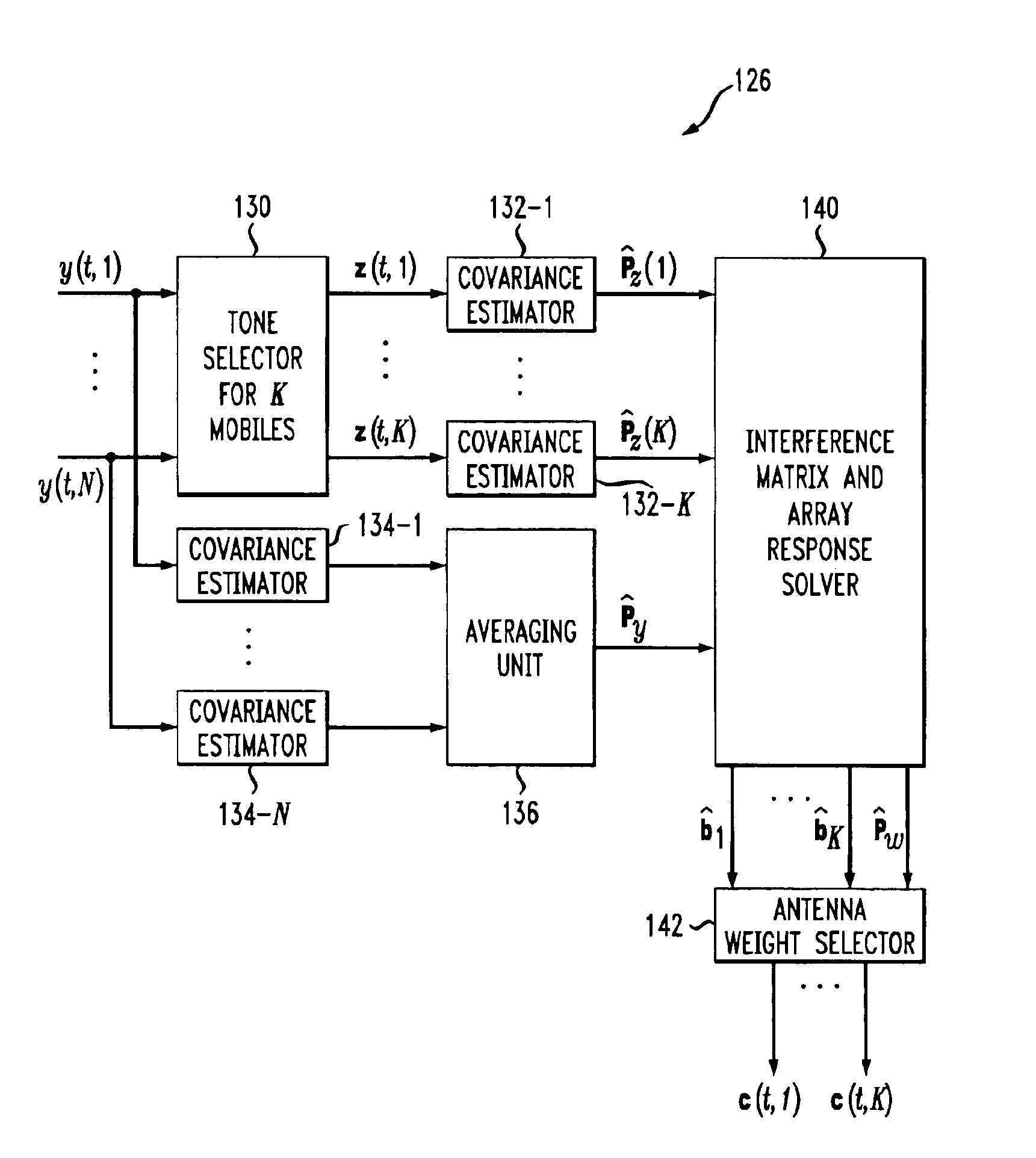
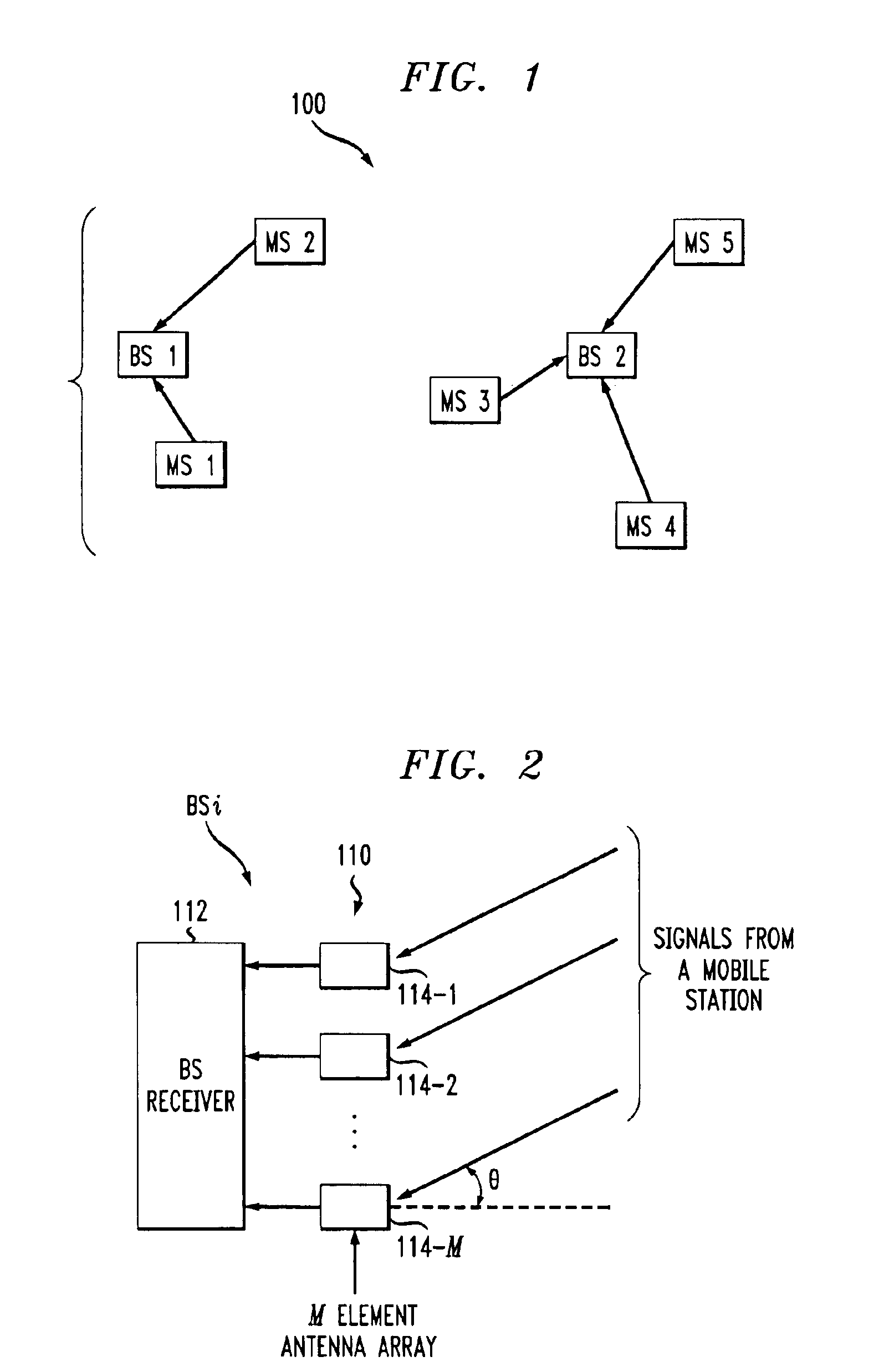
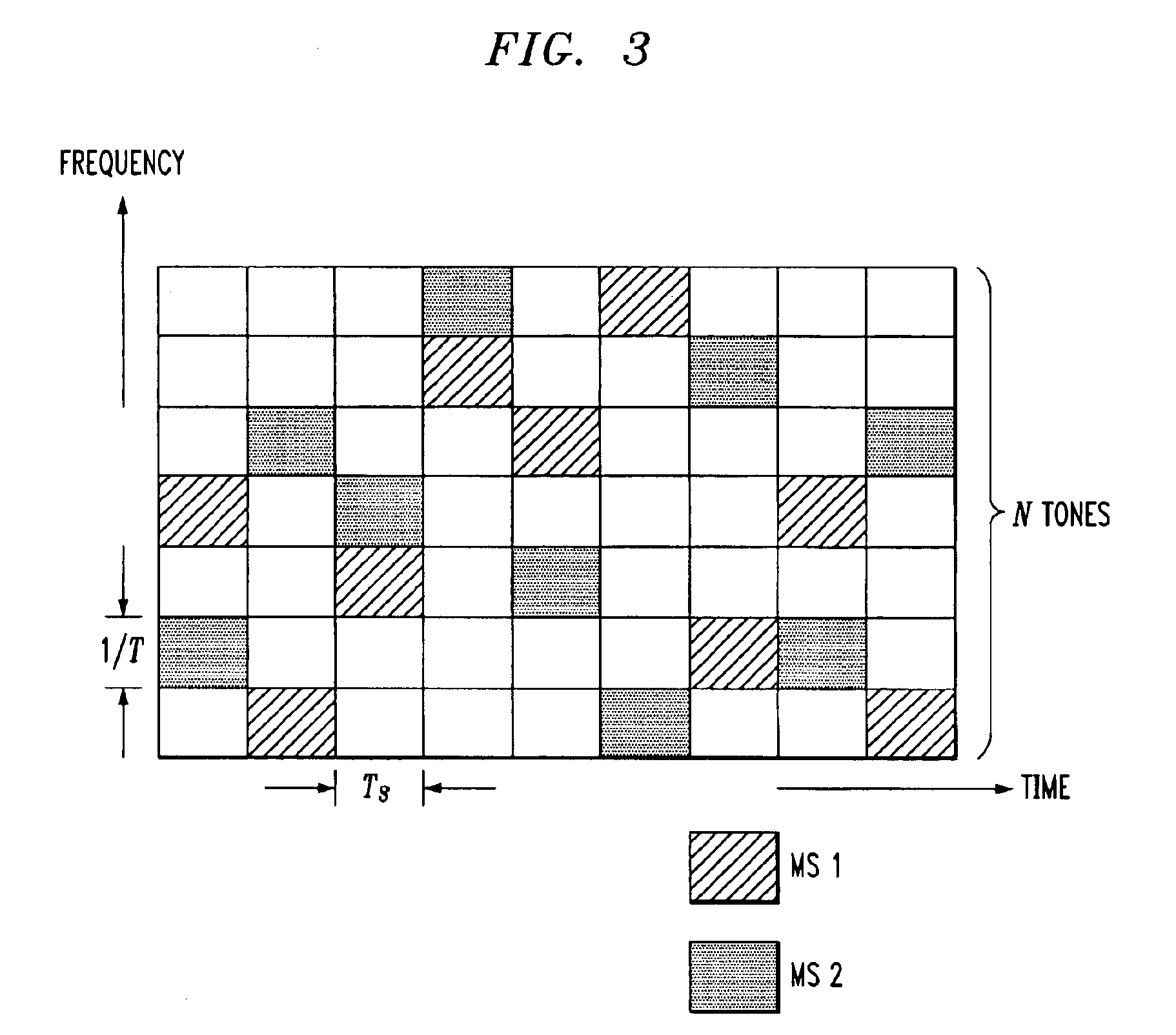
Adaptive antenna array methods and apparatus for use in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6920192B1Fast convergenceReduce computing costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
Adaptive antenna array techniques for use in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed spread-spectrum multi-access (OFDM-SSMA) cellular wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. A base station of the system includes an antenna array and a base station receiver. The base station receiver implements an adaptive antenna gain algorithm which estimates a spatial covariance matrix for each of K mobile stations communicating with the base station. The spatial covariance matrix for a given one of the mobile stations is determined at least in part based on a unique hopping sequence of the mobile station, and provides a correlation between signals received from the mobile station at different antenna elements within the antenna array. An average spatial covariance matrix for a set of received signals is also generated. The individual spatial covariance matrices and the average spatial covariance matrix are processed to generate an estimate of an interference matrix for the K mobile stations, and the estimate of the interference matrix is further processed to generate array responses for each of the mobile stations. The array response for a given mobile station is processed to determine an antenna weighting which is applied to a signal received from the given mobile station in order to facilitate detection of a corresponding transmitted symbol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method for Automatic Speaker Recognition
InactiveUS20070233484A1Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationSpeech recognitionFractional Brownian motionTime segment
It is proposed a text-independent automatic speaker recognition (ASkR) system which employs a new speech feature and a new classifier. The statistical feature pH is a vector of Hurst parameters obtained by applying a wavelet-based multi-dimensional estimator (M dim wavelets) to the windowed short-time segments of speech. The proposed classifier for the speaker identification and verification tasks is based on the multi-dimensional fBm (fractional Brownian motion) model, denoted by M dim fBm. For a given sequence of input speech features, the speaker model is obtained from the sequence of vectors of H parameters, means and variances of these features.
Owner:COELHO ROSANGELO FERNANDES
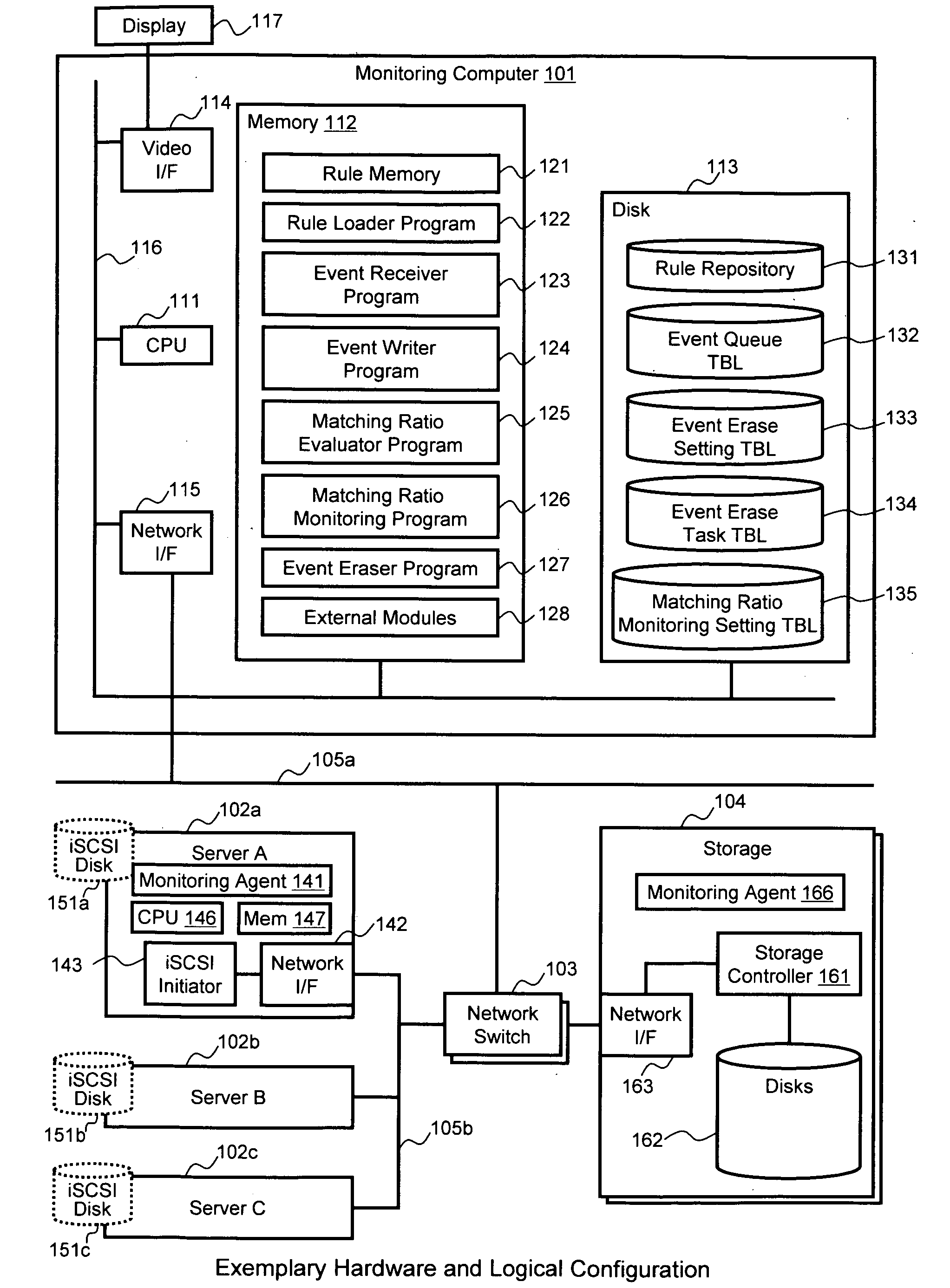
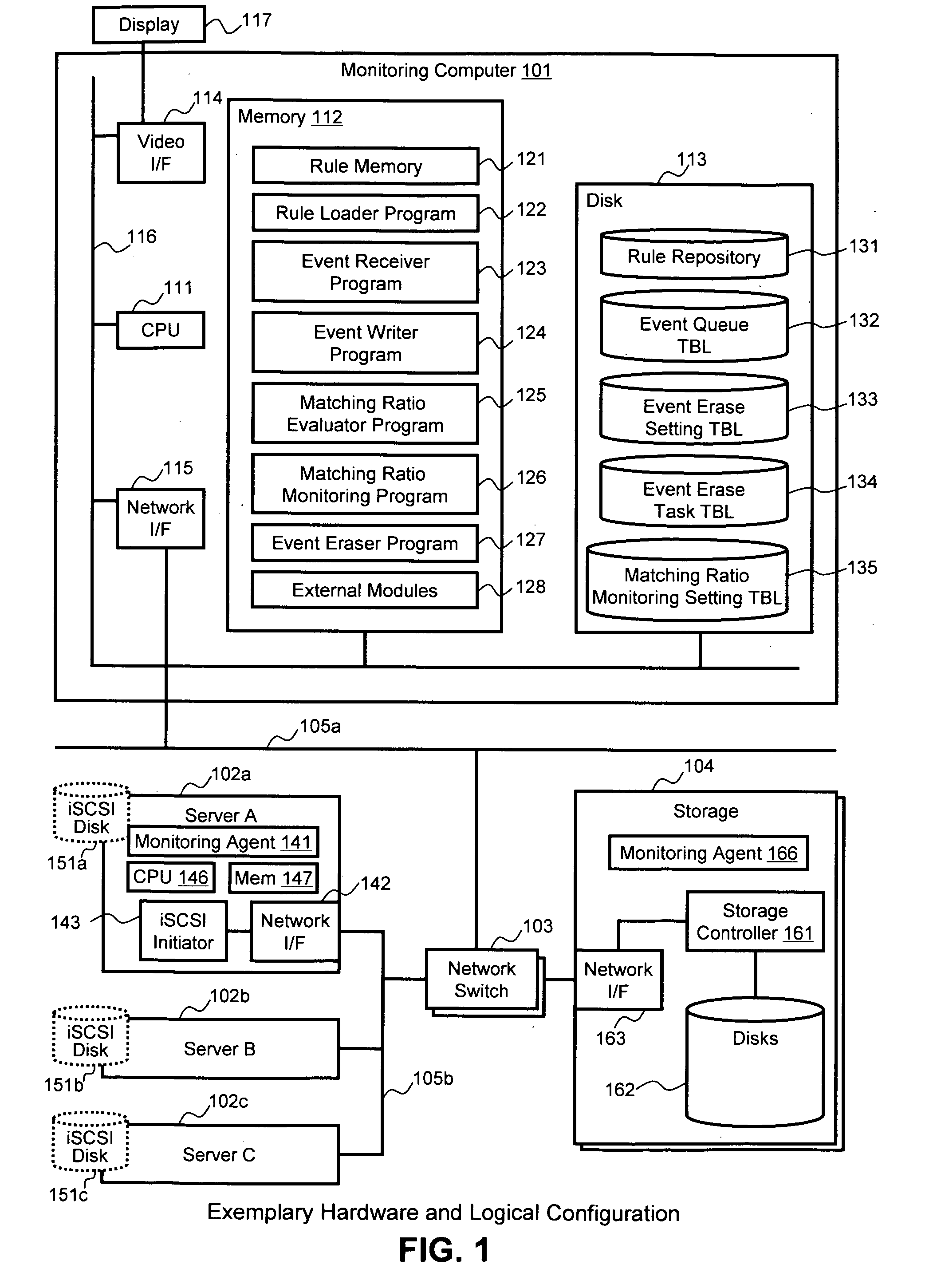
Methods and systems for performing root cause analysis
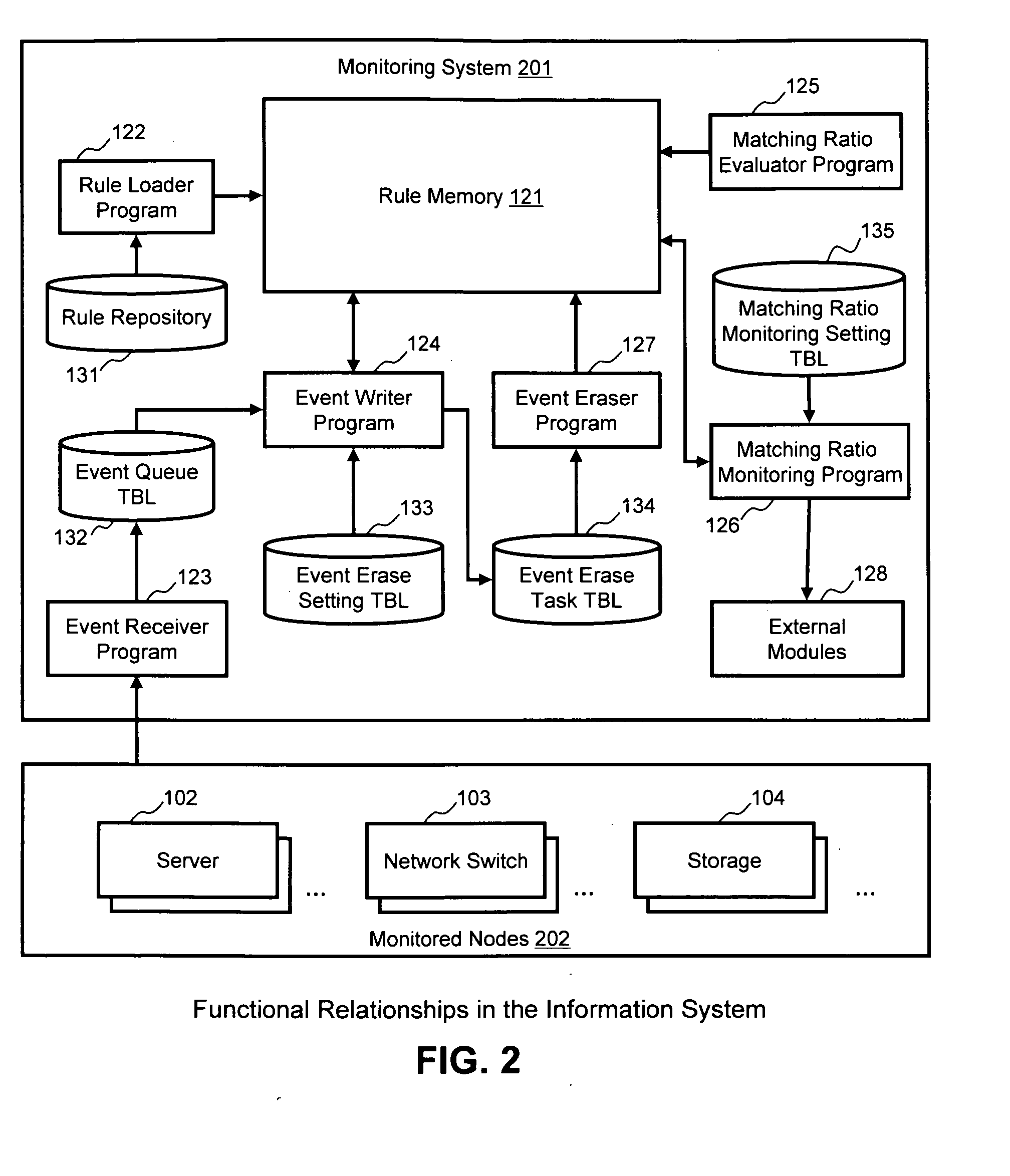
ActiveUS20090313198A1Improve accuracyReduce computing costNon-redundant fault processingKnowledge representationRoot cause analysisData mining
A root cause analysis engine uses event durations and gradual deletion of events to improve analysis accuracy and reduce the number of required calculations. Matching ratios of relevant rules are recalculated every time notification of an event is received. The calculation results are held in a rule memory in the analysis engine. Each event has a valid duration, and when the duration has expired, that event is deleted from the rule memory. Events held in the rule memory can be deleted without affecting other events held in the rule memory. The analysis engine can then re-calculate the matching ratio of each rule by only performing the re-calculation with respect to affected rules related to the deleted event. The calculation cost can be reduced because analysis engine processes events incrementally or decrementally. Analysis engine can determine the most possible conclusion even if one or more condition elements were not true.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
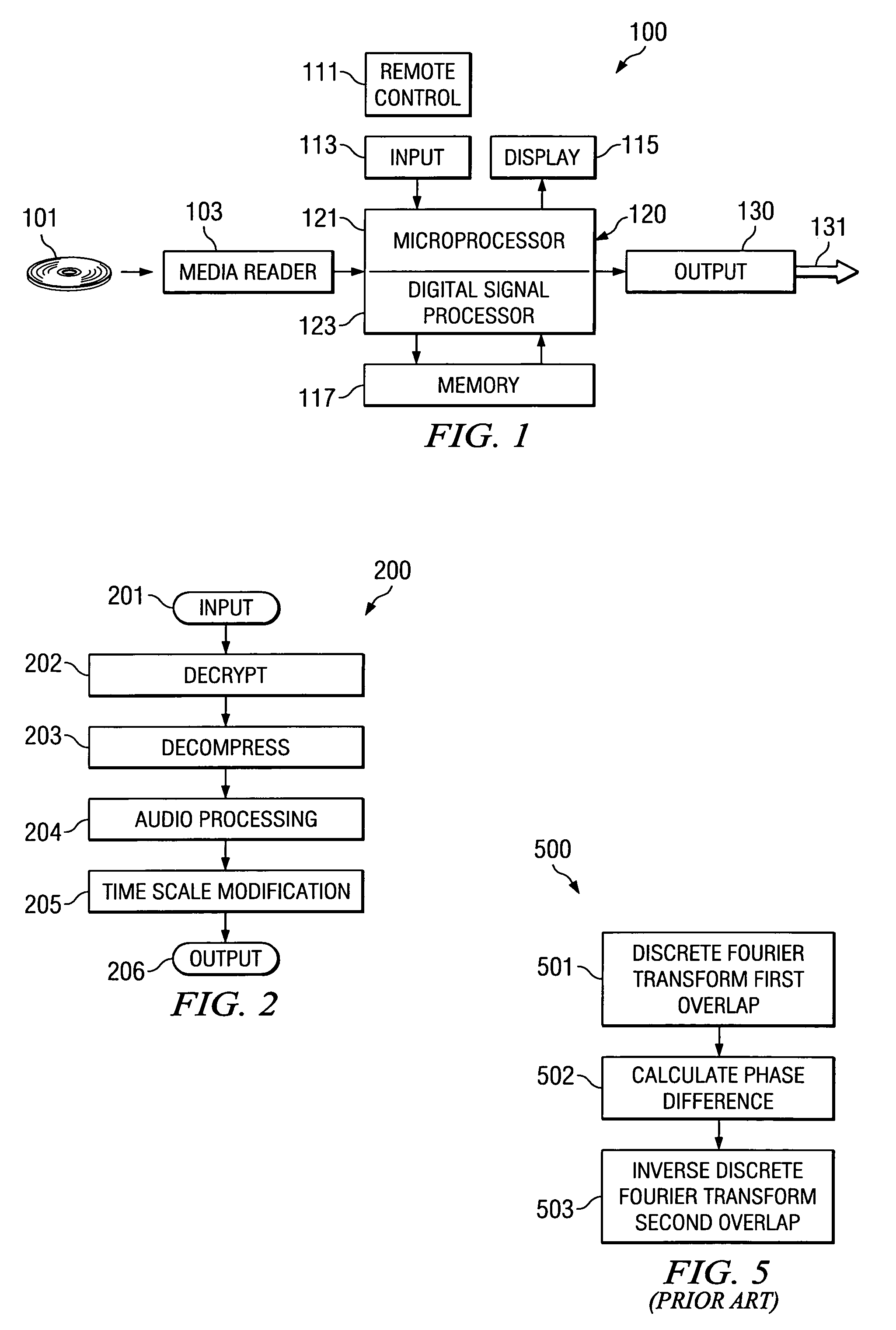
Time-scale modification stereo audio signals
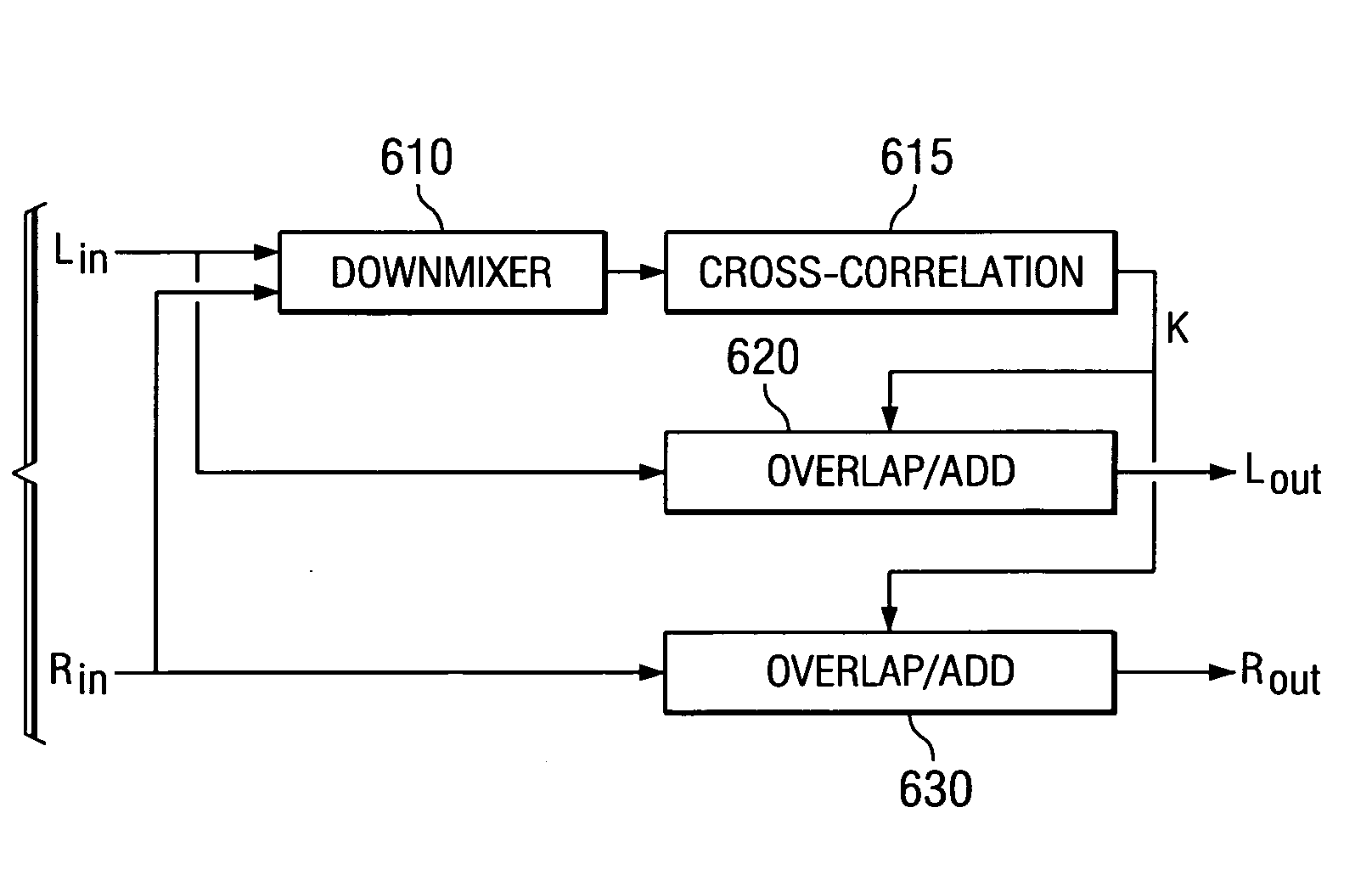
InactiveUS20050137729A1Obviates problemLow computational costSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsStereophonic soundFrame based
An efficient time scale modification (TSM) scheme for stereo signals is proposed where the overlap point is calculated just once per stereo frame based on a downmixed signal. The proposed scheme results in significantly lower computational cost compared with conventional methods: about 1.2 to 1.3 times the amount of computation required by monoaural signals, against 2.0 times the amount of computation required by channel-independent methods. Listening tests indicate that the quality achieved is higher than conventional channel-independent approaches due to the preservation of the spatial localization of the sound.
Owner:SAKURAI ATSUHIRO +1
Method and vehicle with an advanced driver assistance system for risk-based traffic scene analysis
ActiveUS20150344030A1Improve estimateReduce computing costDigital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorEngineering
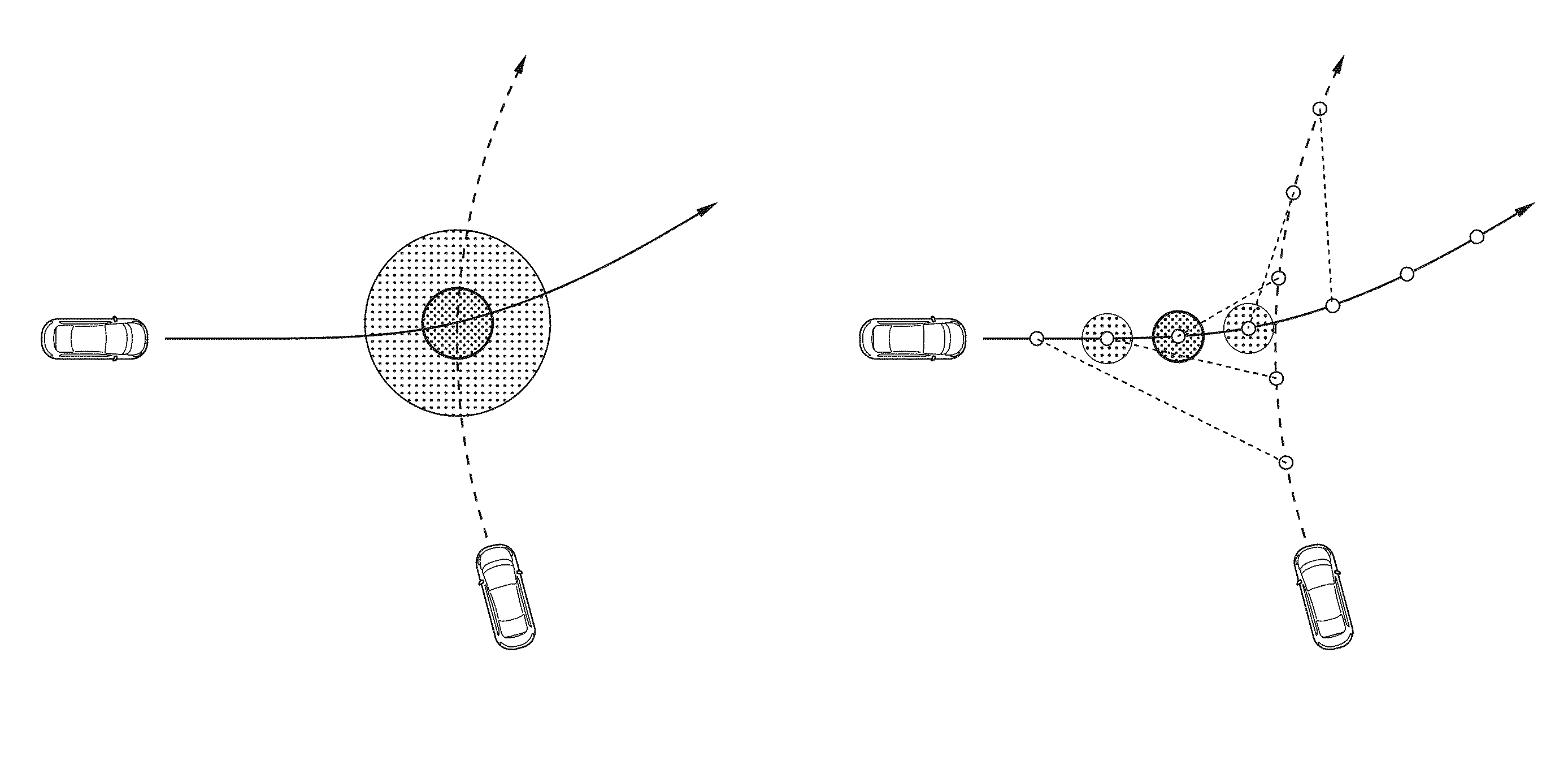
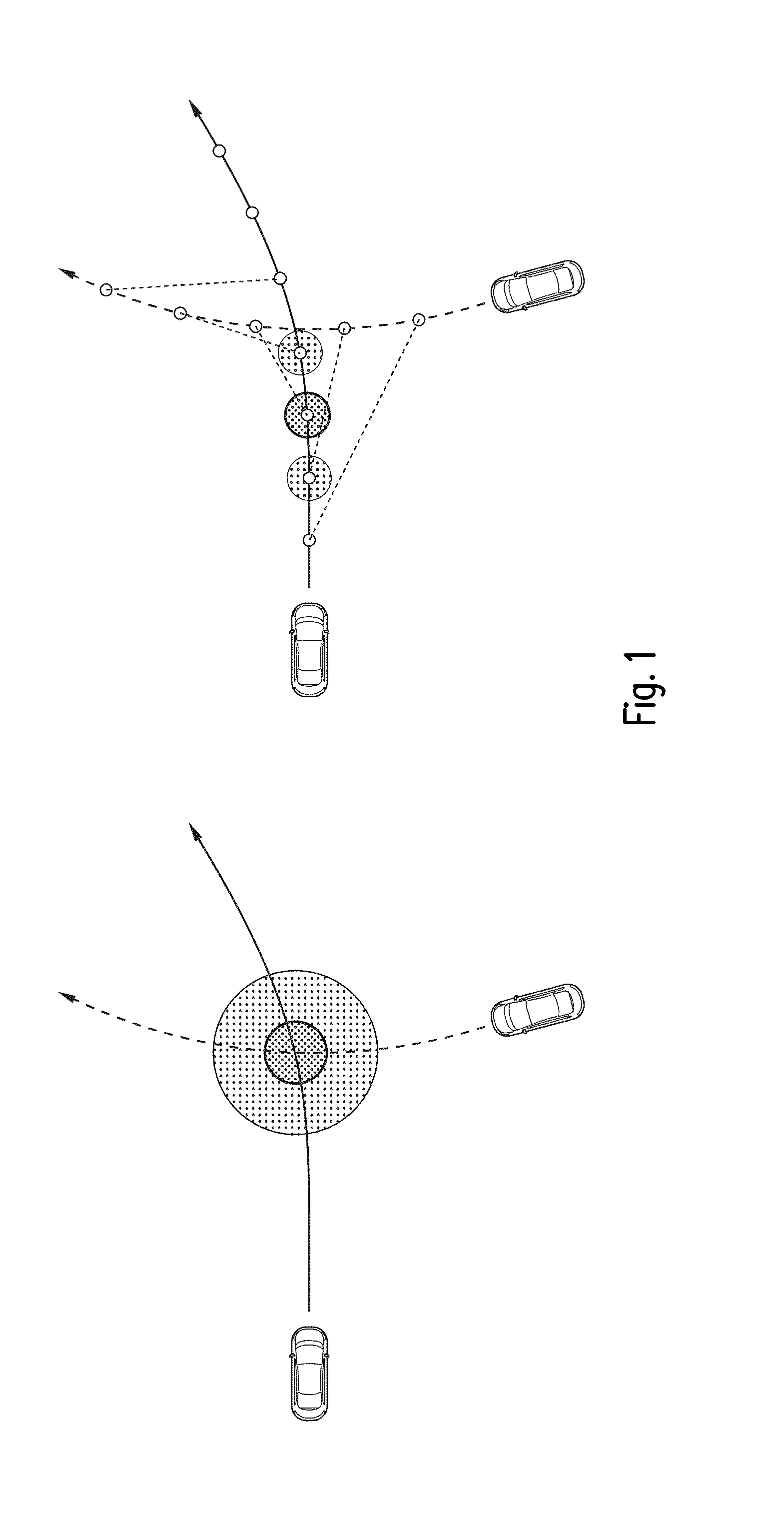
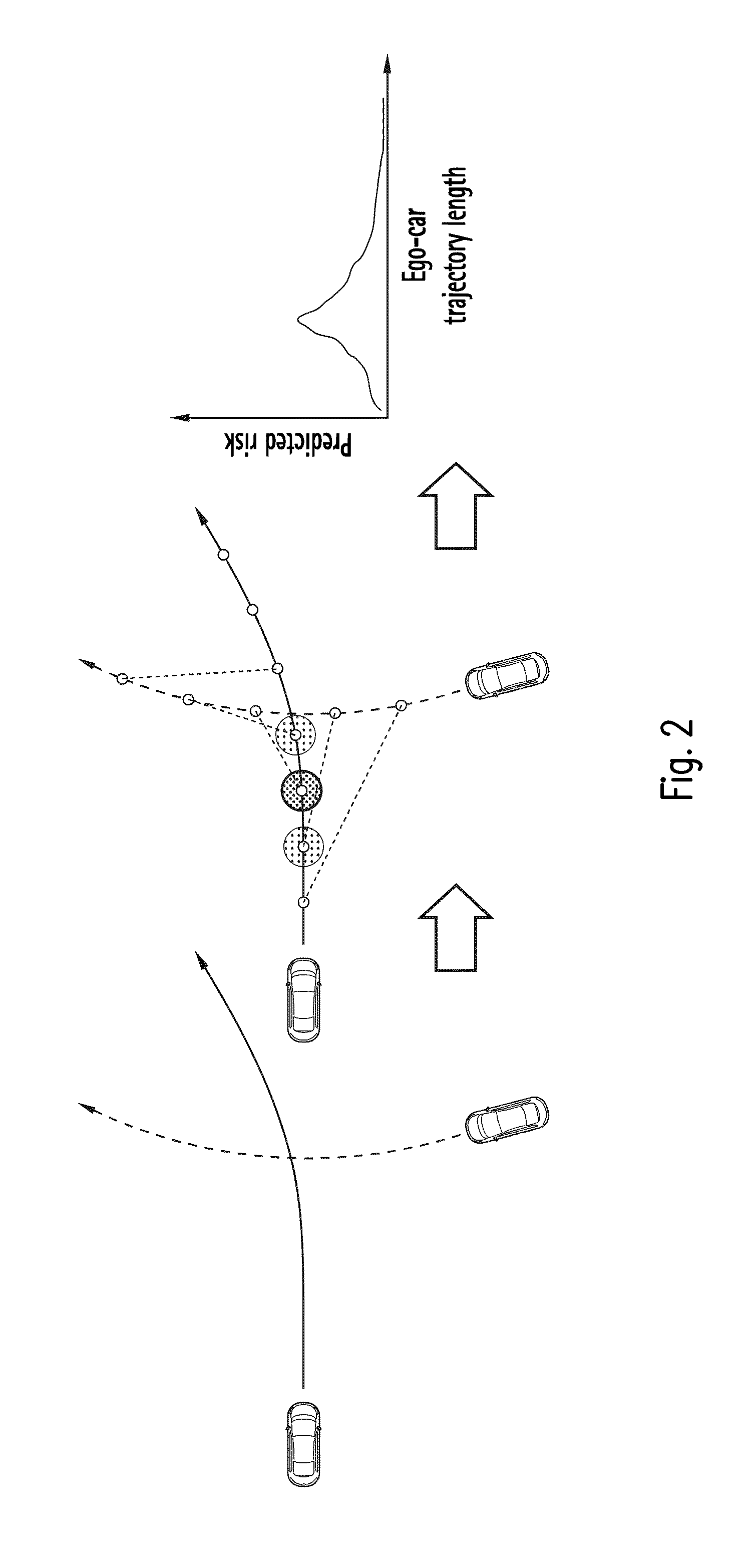
A method supports driving an ego-vehicle including a driver assistance system. A traffic participant or infrastructure element involved in the traffic situation is selected and taken into consideration for traffic scene analysis. A hypothetical future trajectory for the ego-vehicle is predicted by predicting the current state of the ego-vehicle and varied to generate a plurality of ego-trajectory alternatives including the calculated hypothetical future ego-trajectory. A hypothetical future trajectory from another traffic participant gained by predicting the current state of the traffic participant or calculating a hypothetical future state sequence of the infrastructure element is determined. Based upon at least one pair of ego-trajectory plus one other trajectory risk functions over time or along the calculated hypothetical future ego-trajectory alternatives are calculated. One risk function corresponds to one ego-trajectory alternative. The risk functions are combined into a risk map. From an analysis result a control signal is generated.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Controlling unmanned aerial vehicles to avoid obstacle collision
ActiveUS20170193830A1Simple and efficientObstacle collisionScene recognitionRemote controlled aircraftApparent SizeDistance sensors
A method, device, framework, and system provide the ability to control an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to avoid obstacle collision. Range data of a real-world scene is acquired using range sensors (that provide depth data to visible objects). The range data is combined into an egospace representation (consisting of pixels in egospace). An apparent size of each of the visible objects is expanded based on a dimension of the UAV. An assigned destination in the real world scene based on world space is received and transformed into egospace coordinates in egospace. A trackable path from the UAV to the assigned destination through egospace that avoids collision with the visible objects (based on the expanded apparent sizes of each of the visible objects) is generated. Inputs that control the UAV to follow the trackable path are identified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
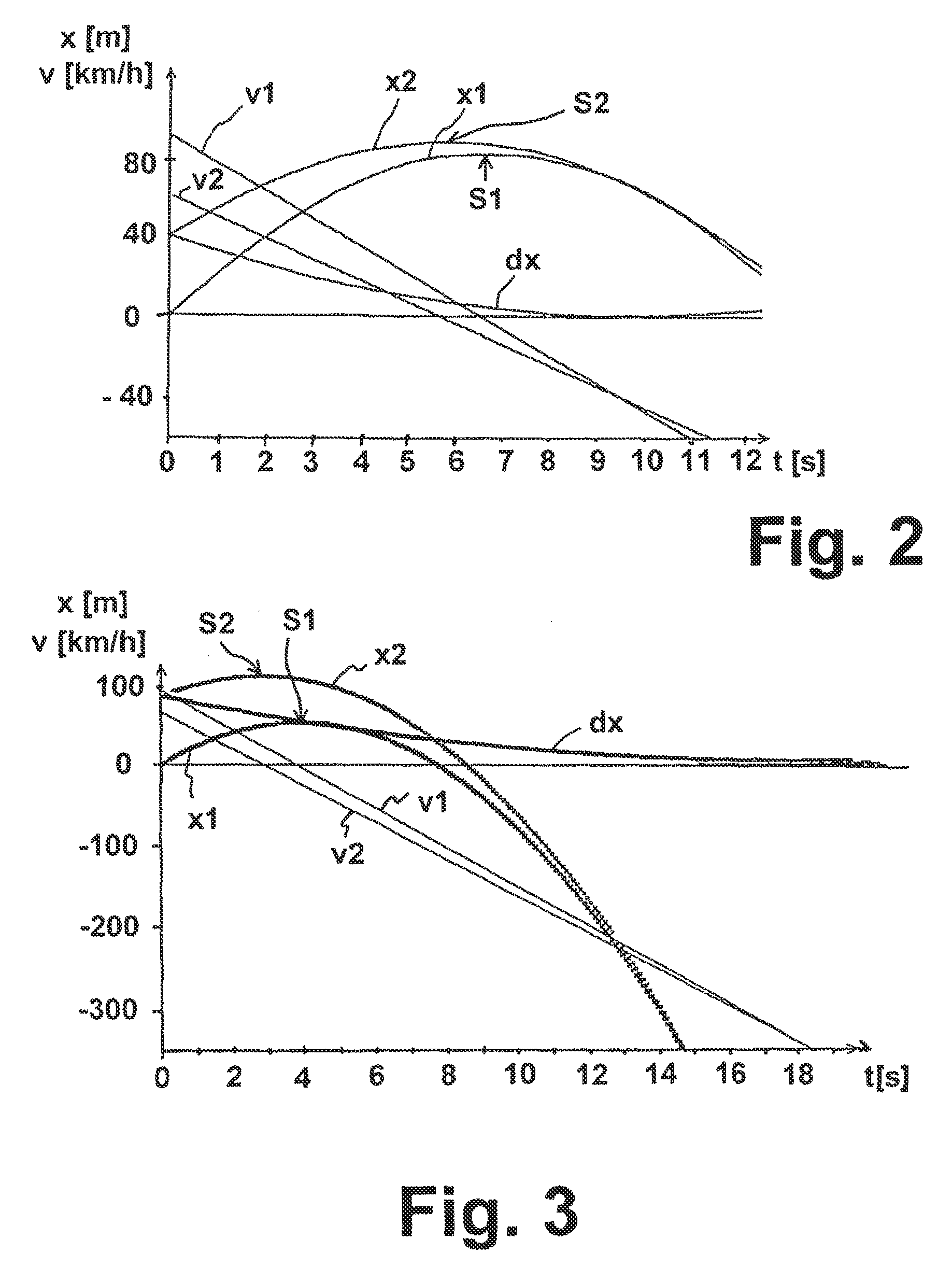
Method for determining an emergency braking situation of a vehicle
ActiveUS9566959B2Reliable recognitionReduce the possibilityVehicle fittingsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementControl theoryComputer science
To determine whether an emergency braking situation exists for a vehicle, the vehicle determines at least the following state variables: its own velocity, its own longitudinal acceleration, its relative distance from an object in front, and the speed and acceleration of the object in front. A suitable evaluation method to assess whether an emergency braking situation is present is determined as a function of these state variables from a plurality of evaluation method options, including at least a movement equation evaluation method in which a movement equation system of the vehicle and of the object in front is determined, and an evaluation method in which a braking distance of the vehicle is determined.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
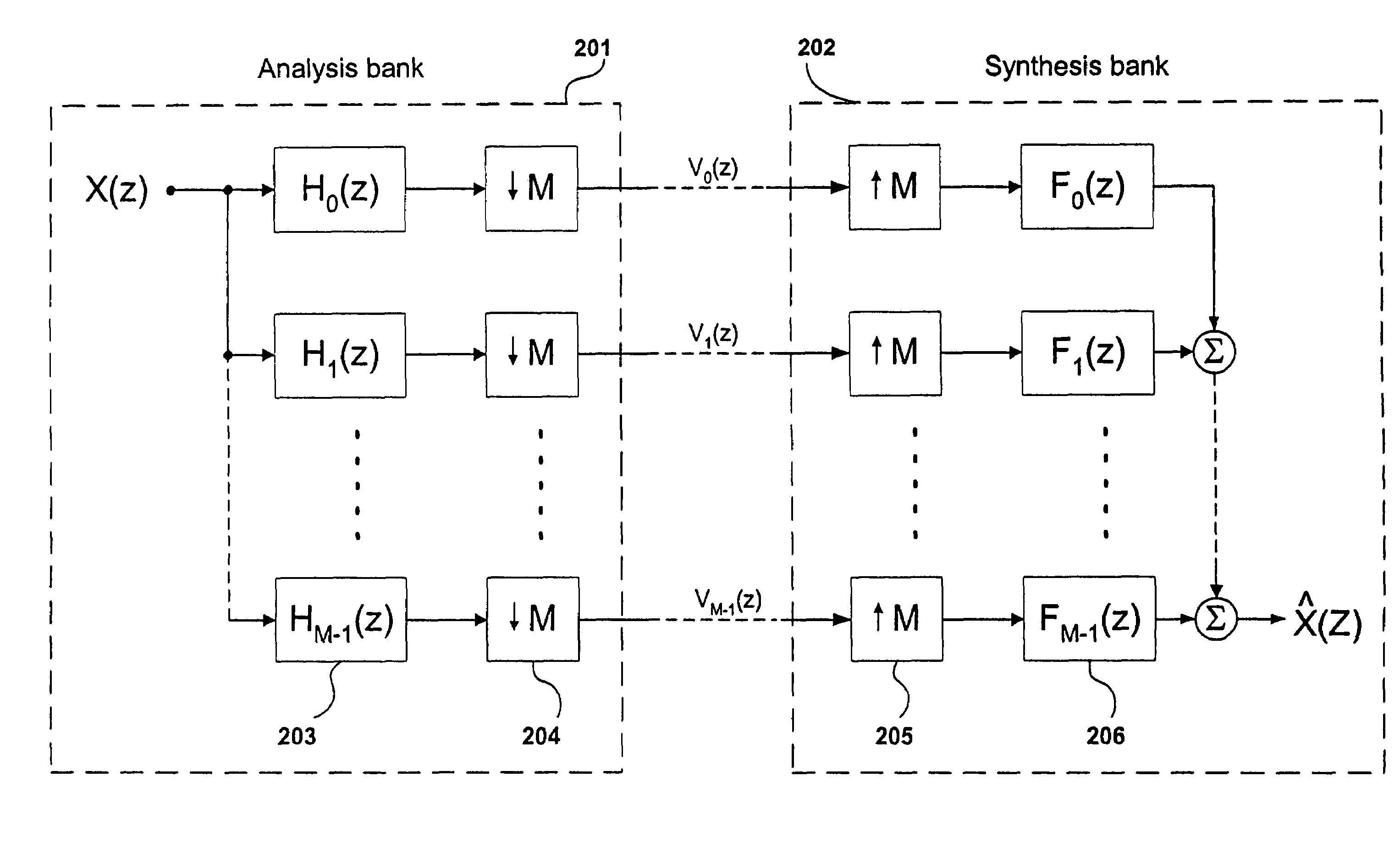
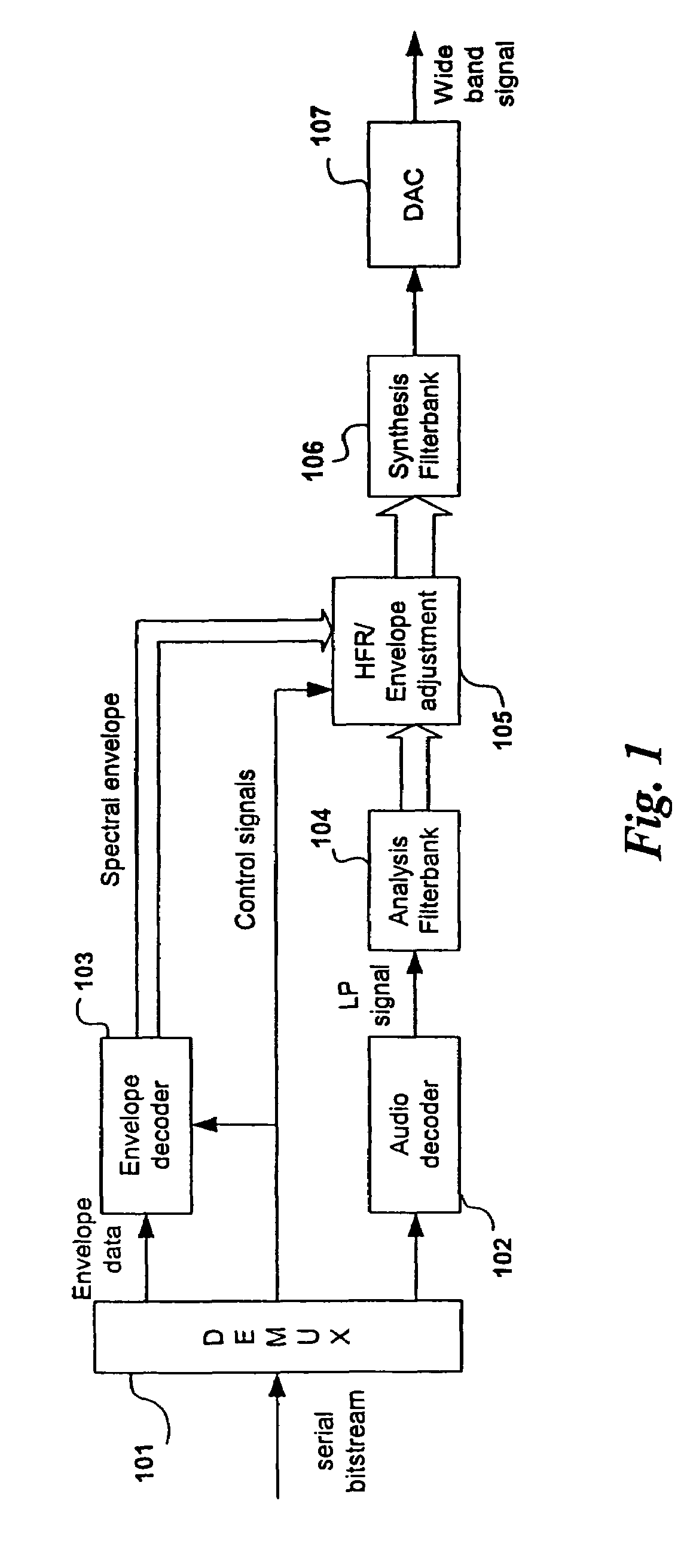
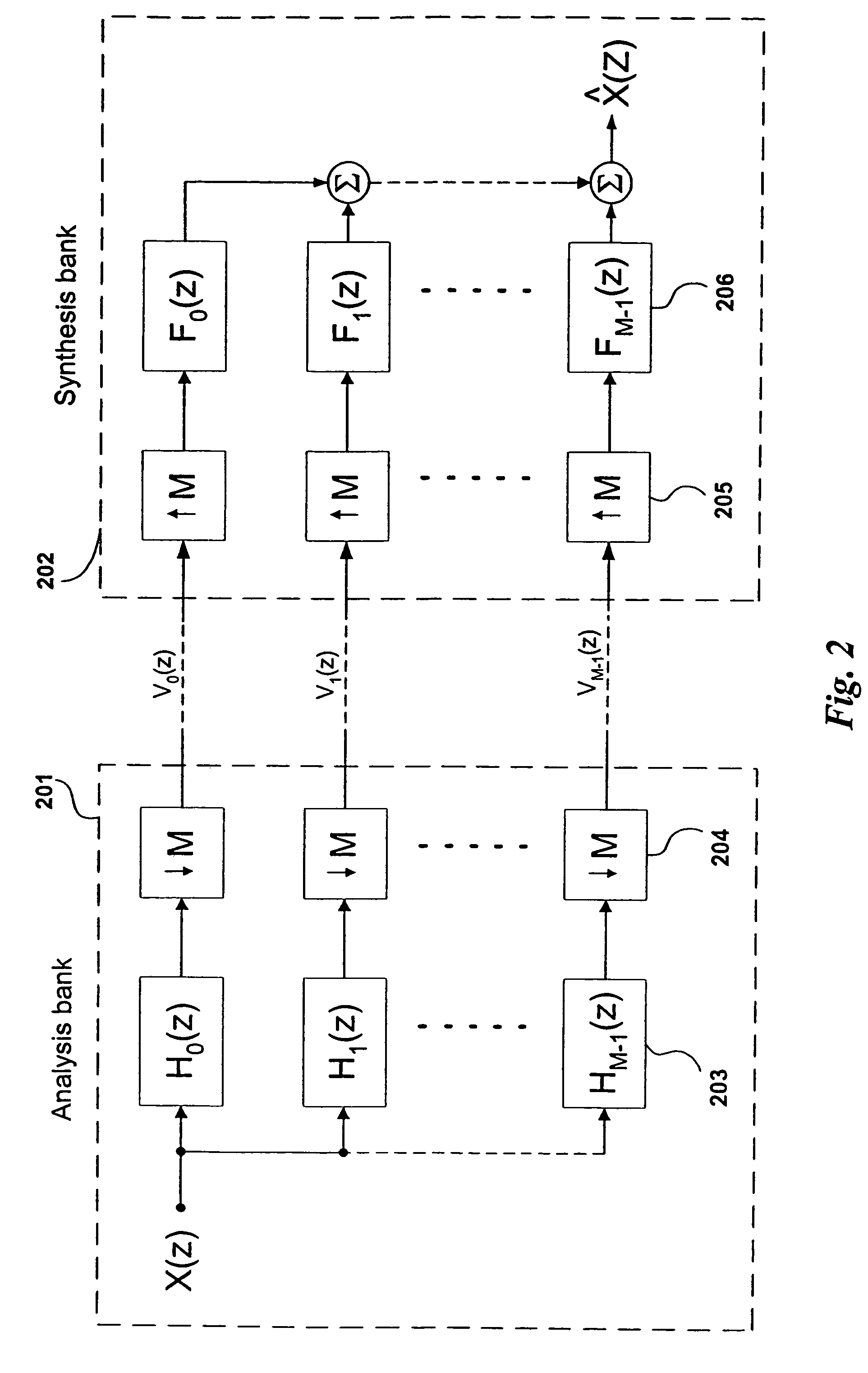
Spectral translation/folding in the subband domain
ActiveUS7483758B2Reduce complexityImproved crossover accuracyGain controlSpeech analysisSpectral envelopeLow complexity
The present invention relates to a new method and apparatus for improvement of High Frequency Reconstruction (HFR) techniques using frequency translation or folding or a combination thereof. The proposed invention is applicable to audio source coding systems, and offers significantly reduced computational complexity. This is accomplished by means of frequency translation or folding in the subband domain, preferably integrated with spectral envelope adjustment in the same domain. The concept of dissonance guard-band filtering is further presented. The proposed invention offers a low-complexity, intermediate quality HFR method useful in speech and natural audio coding applications.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Image decoding device, image decoding method, and image decoding program
InactiveUS8249147B2Improve efficiencyReduce computing costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareImage compression
The present invention is directed to an image decoding apparatus adapted for decoding information obtained by implementing inverse quantization and inverse orthogonal transform to image compressed information in which an input image signal is blocked to implement orthogonal transform thereto on the block basis so that quantization is performed with respect thereto, which comprises a reversible decoder (12) for decoding quantized and encoded transform coefficients, an inverse quantizer (13) indicating, as a flag, in inverse-quantizing transform coefficients which have been decoded by the reversible decoder (12), existence of each transform coefficient every processing block of inverse quantization, and an inverse transform element (14) for changing inverse transform processing to be implemented to inverse quantization transform coefficients within processing block by using the flag which has been indicated by the inverse-quantizer (13).
Owner:SONY CORP
Anonymous authentication system and anonymous authentication method
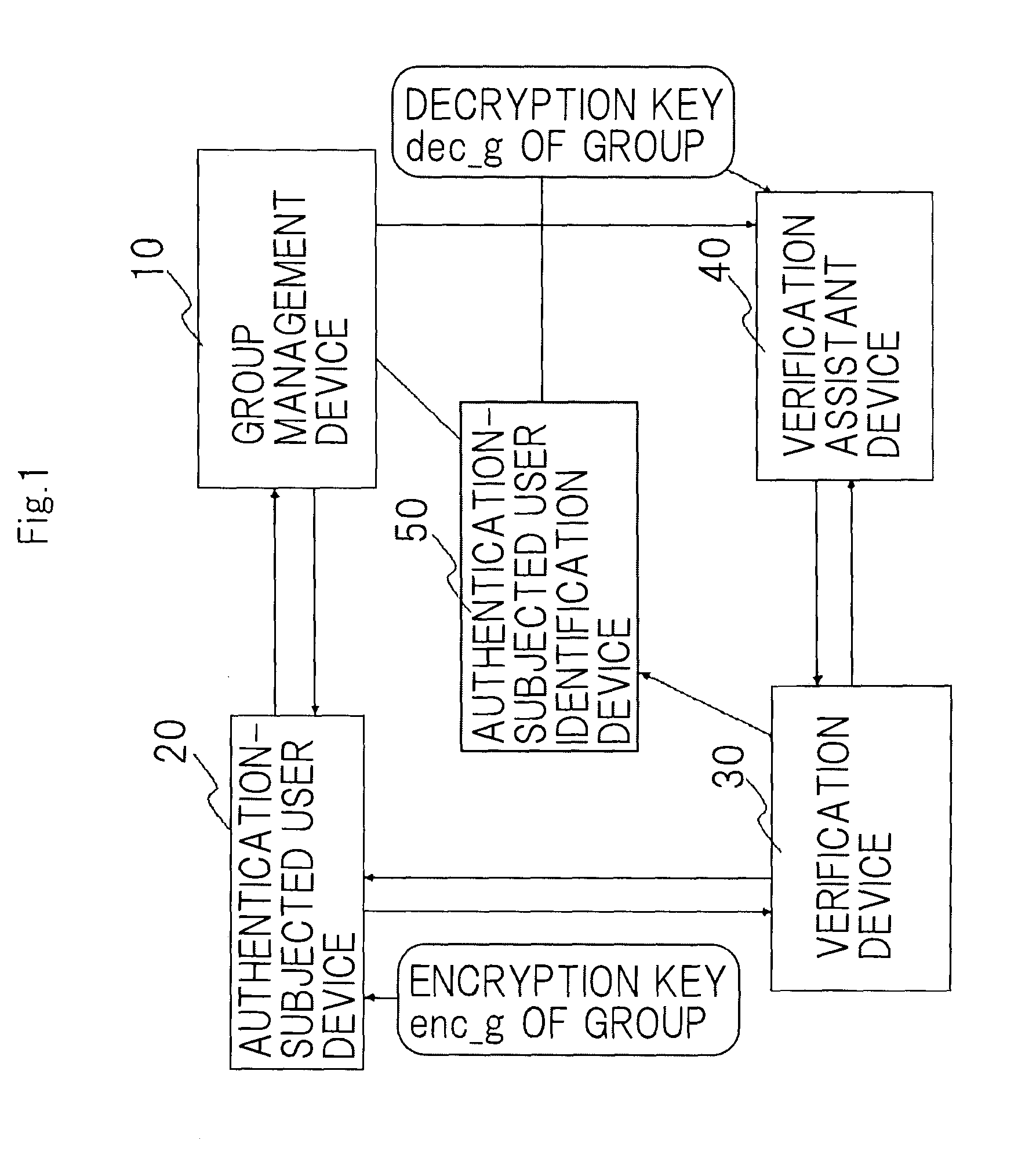
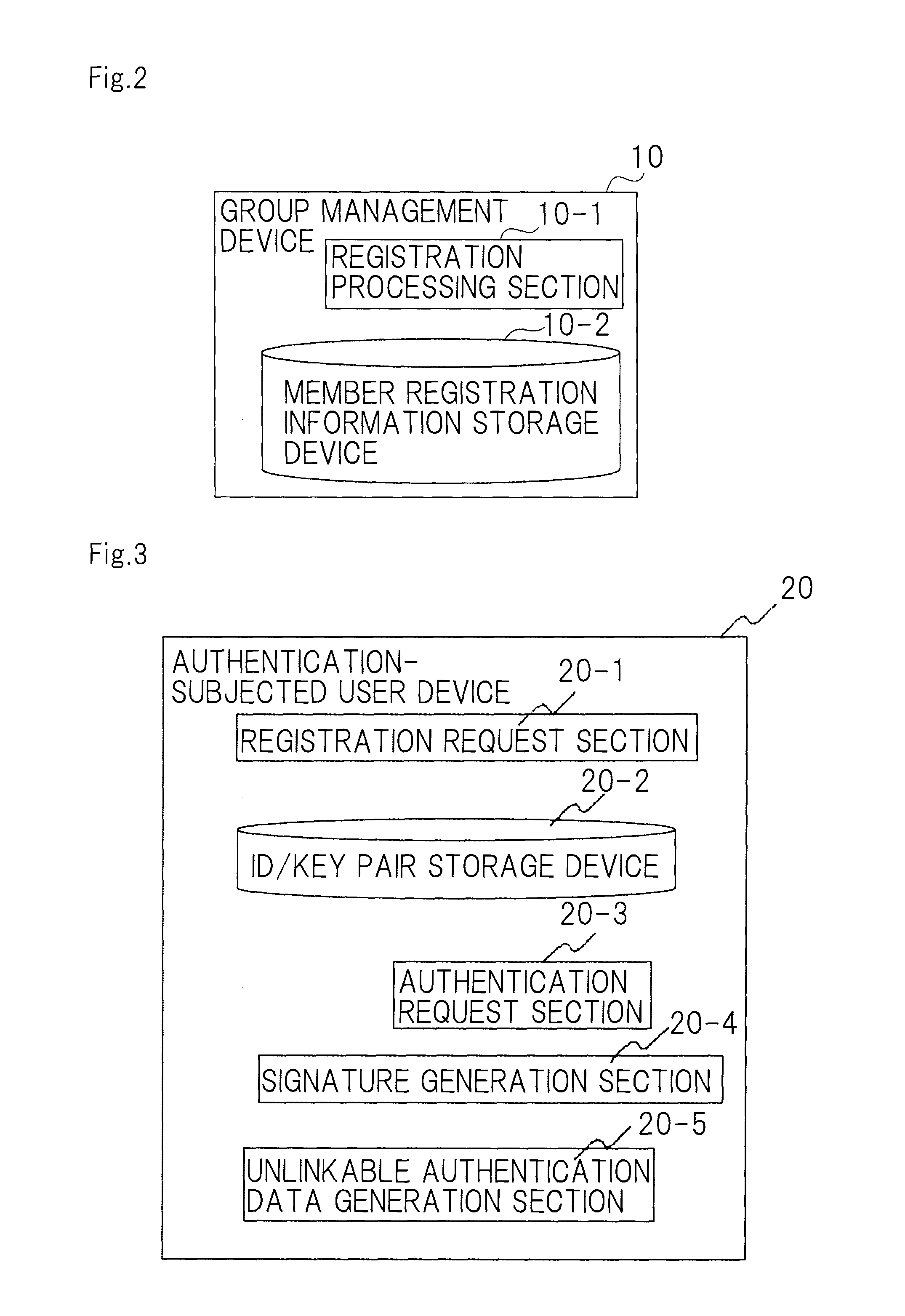
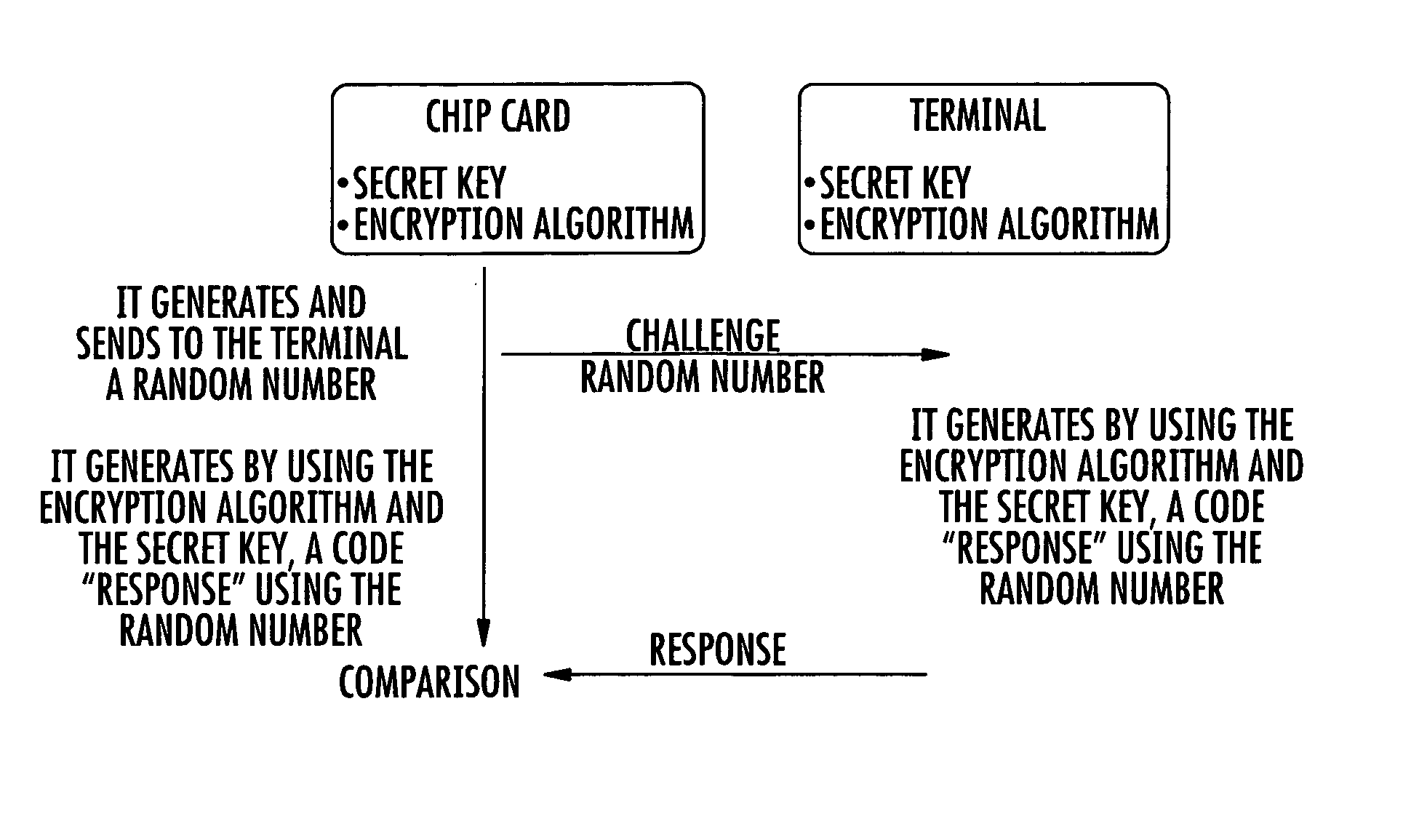
InactiveUS20100174911A1Privacy protectionPrevented excessively chargingDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationData validationUser device
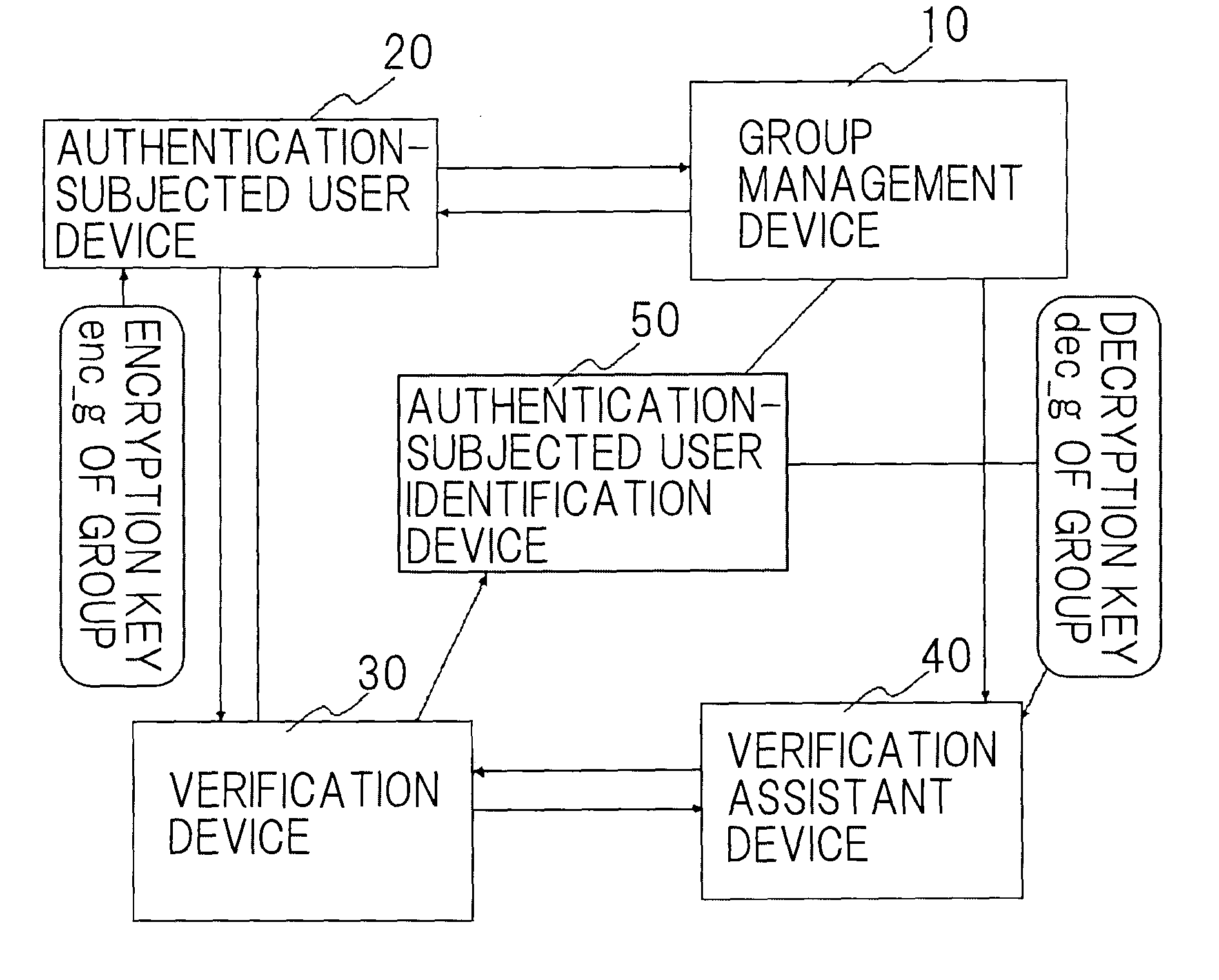
A disclosed anonymous authentication system comprises a group management device, an authentication-subjected user device, a verification device and an authentication-subjected user identification device. A user previously registers a verification key in the group management device such that his signature can be verified. For authentication, the user generates his or her own signature using the authentication-subjected user device, and encrypts the signature using an encryption key of the group to generate authentication data. The verification device authenticates the signature in collaboration with a verification assistant who has a decryption key of the group. The authentication-subjected user identification device that has the decryption key of the group decrypts the authentication data as required to identify a user who is to be authenticated.
Owner:NEC CORP
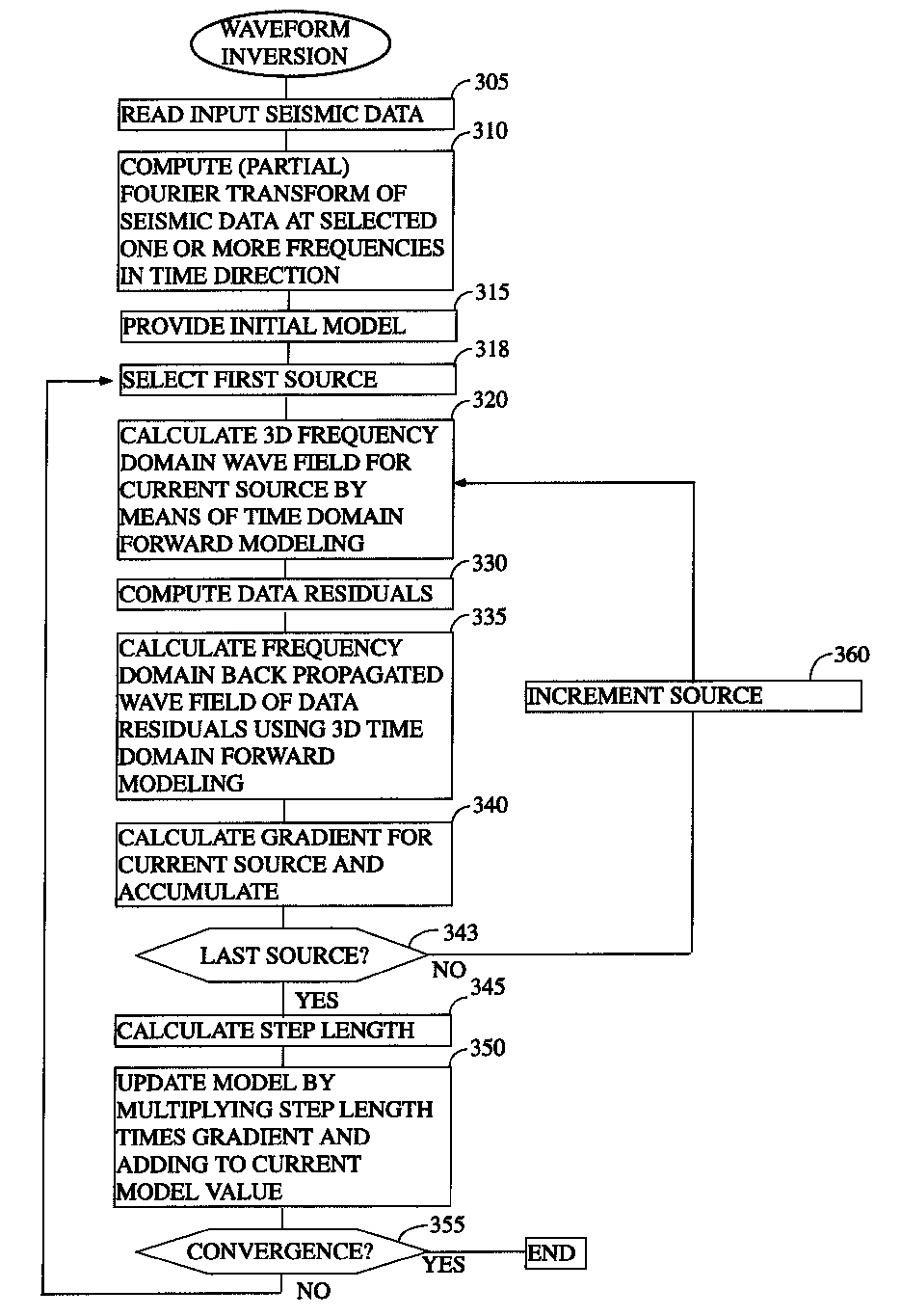
System and method for 3D frequency domain waveform inversion based on 3D time-domain forward modeling
ActiveUS7725266B2Reduce computing costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyTime domainData set
According to a first preferred aspect of the instant invention, there is provided an efficient method of computing a 3D frequency domain waveform inversion based on 3D time domain modeling. In the preferred arrangement, 3D frequency domain wavefields are computed using 3D time-domain modeling and a discrete Fourier transformation that is preferably computed “on the fly” instead of solving the large systems of linear equations that have traditionally been required by direct frequency domain modeling. The instant invention makes use of the theory of gradient-based waveform inversion that estimates model parameters (for example velocities) by matching modeled data to field data sets. Preferably the modeled data are calculated using a forward modeling algorithm.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
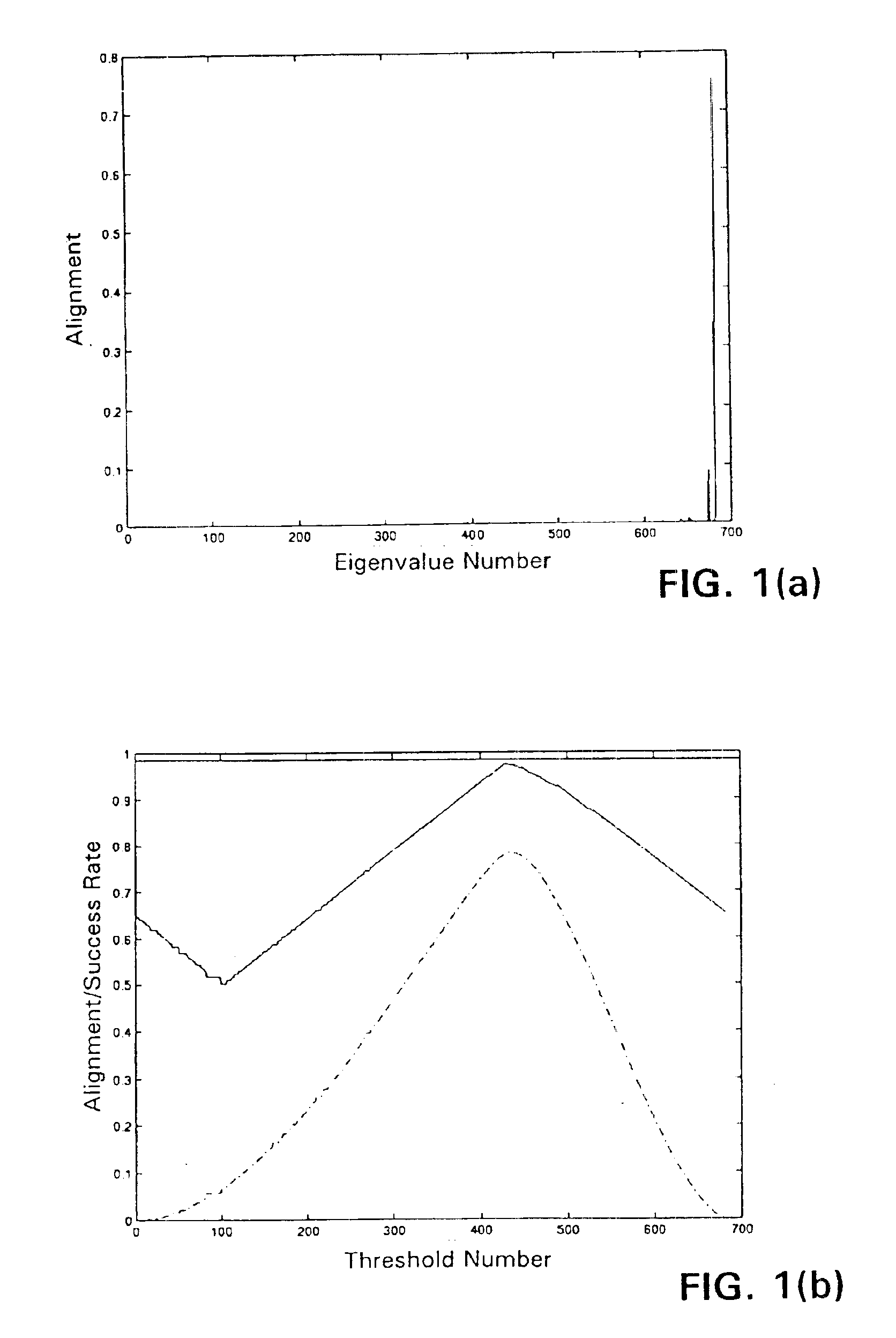
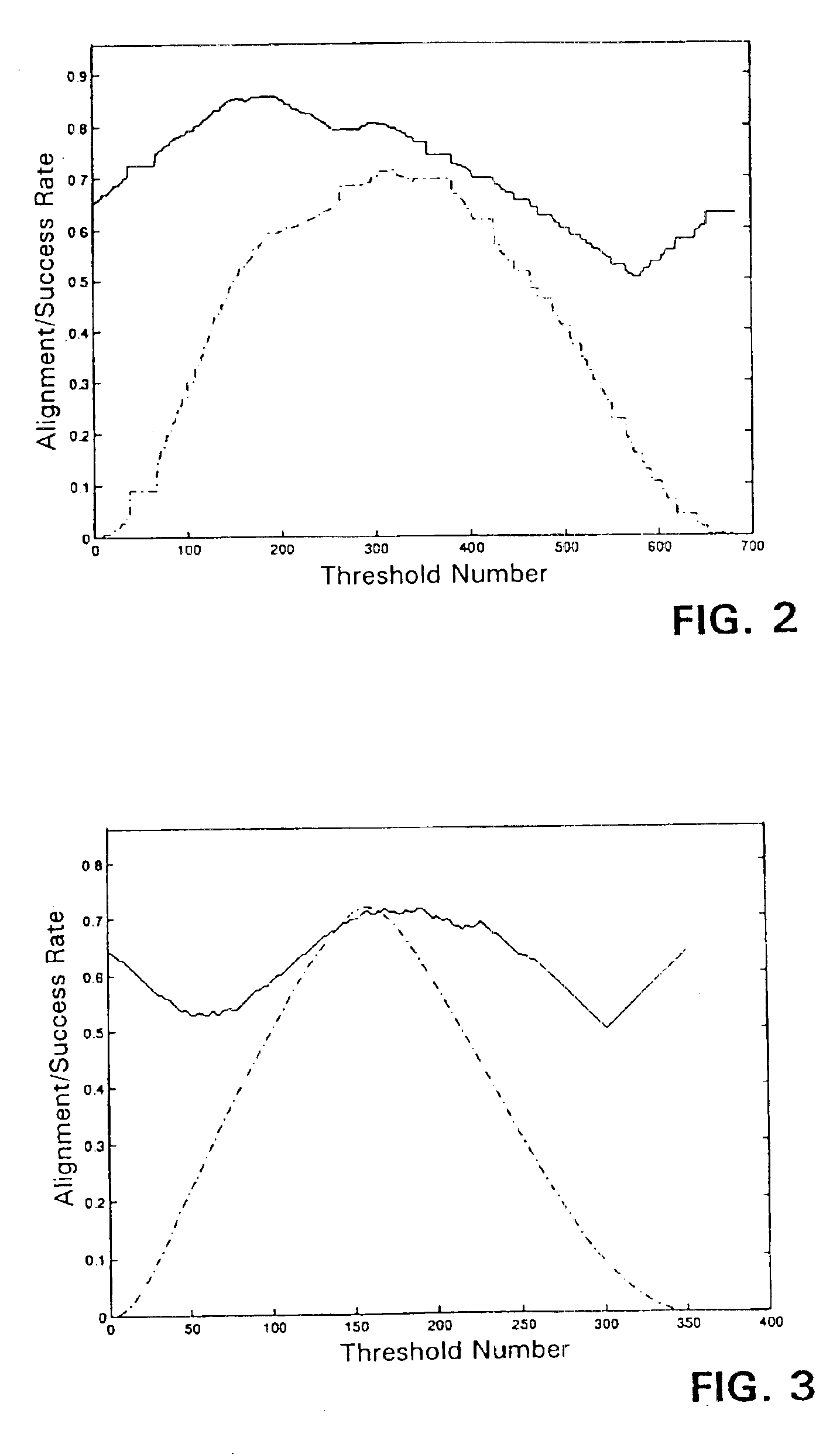
Spectral kernels for learning machines
InactiveUS6944602B2Reduce computing costLow costKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature vector
The spectral kernel machine combines kernel functions and spectral graph theory for solving problems of machine learning. The data points in the dataset are placed in the form of a matrix known as a kernel matrix, or Gram matrix, containing all pairwise kernels between the data points. The dataset is regarded as nodes of a fully connected graph. A weight equal to the kernel between the two nodes is assigned to each edge of the graph. The adjacency matrix of the graph is equivalent to the kernel matrix, also known as the Gram matrix. The eigenvectors and their corresponding eigenvalues provide information about the properties of the graph, and thus, the dataset. The second eigenvector can be thresholded to approximate the class assignment of graph nodes. Eigenvectors of the kernel matrix may be used to assign unlabeled data to clusters, merge information from labeled and unlabeled data by transduction, provide model selection information for other kernels, detect novelties or anomalies and / or clean data, and perform supervised learning tasks such as classification.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
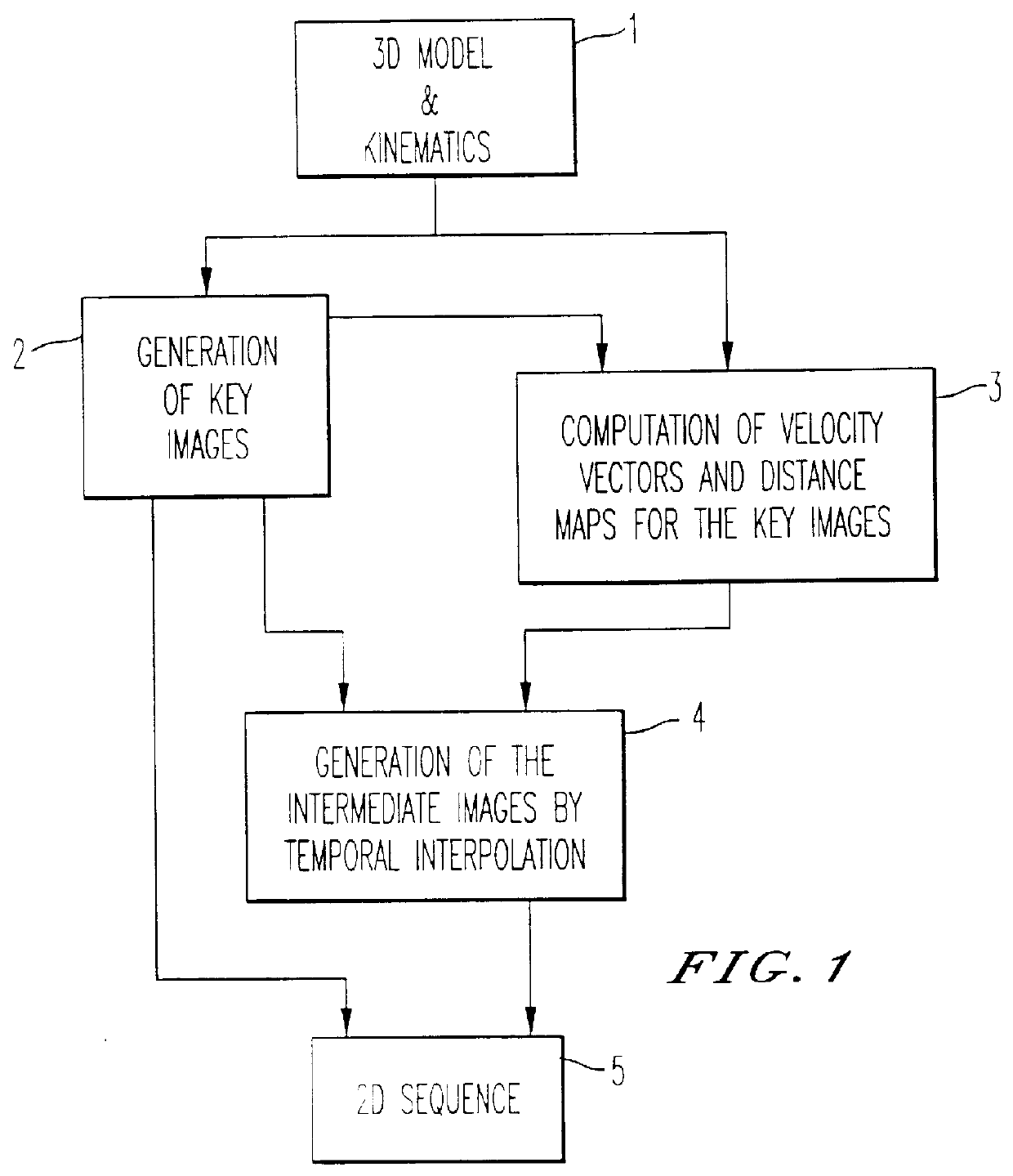
Method for the generation of synthetic images
InactiveUS6031538AHigh realismReduce computing costImage enhancementImage analysisCo ordinateComputer science
PCT No. PCT / FR95 / 01019 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 9, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 9, 1996 PCT Filed Jul. 28, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 07162 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 7, 1996The generation of images is done by the computation of the motion vectors representing the evolution from one image 2D to the other, directly from the co-ordinates and coefficients of geometrical transformation, of associated points in the 3D scene. The applications relate to the generation of monocular sequences by temporal interpolation and of stereoscopic sequences by extrapolation.
Owner:THOMSON BROADCAST SYST CERGY PONTOISE
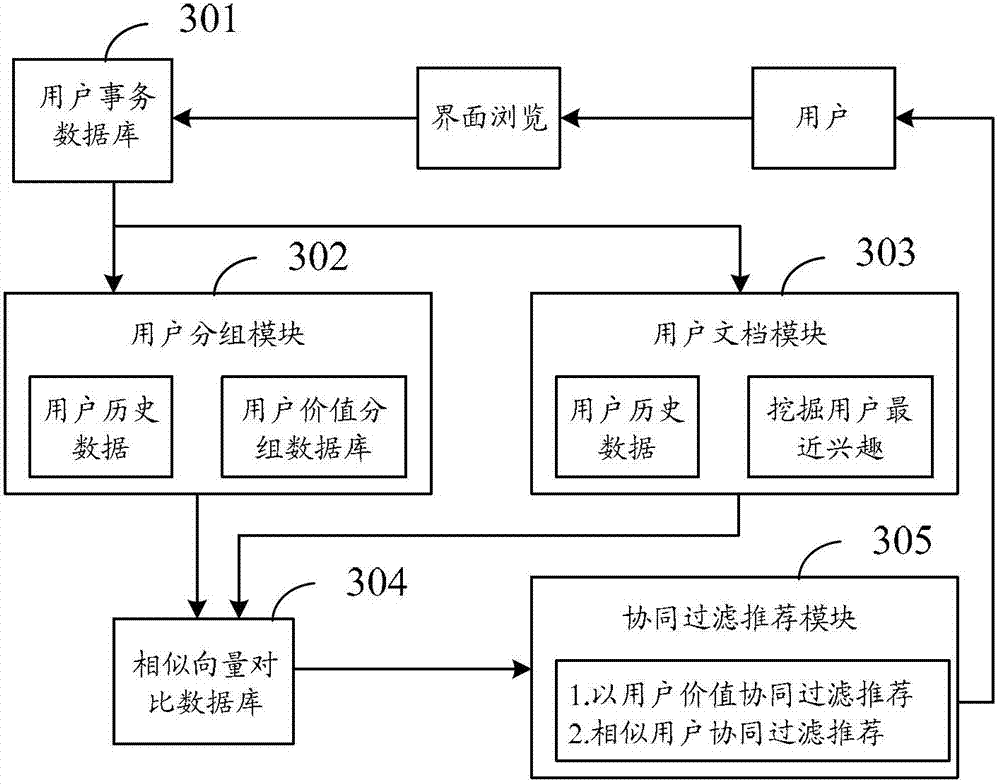
Application recommendation method and application recommendation system
InactiveCN103198418AReduce occupancySimplified recommended stepsMarketingData miningMultiple applications
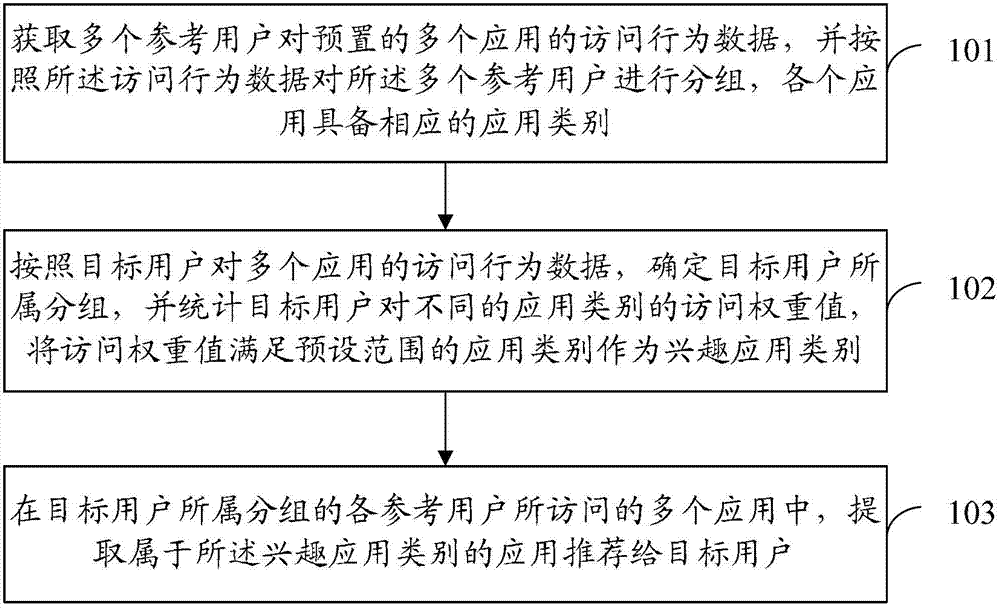
The invention provides an application recommendation method and an application recommendation system. The application recommendation method includes the following steps: access behavior data of multiple reference users to preset multiple applications are obtained, the multiple reference users are subjected to grouping according to the access behavior data, and each of the multiple applications has a corresponding application class; a group which a target user belongs to is determined according to access behavior data of the target user to the multiple applications, access weighted values of the target user to different application classes are subjected to statistics, and the application classes with the access weighted values which are in a preset range are regarded as interest application classes; and the applications which belong to the interest application classes are extracted from the multiple applications which are accessed by all the reference users and are in the group which the target user belongs to, and then the applications are recommended to the target user. The application recommendation method and the application recommendation system can occupy fewer system resources when the applications are recommended.
Owner:BEIJING IZP NETWORK TECH CO LTD
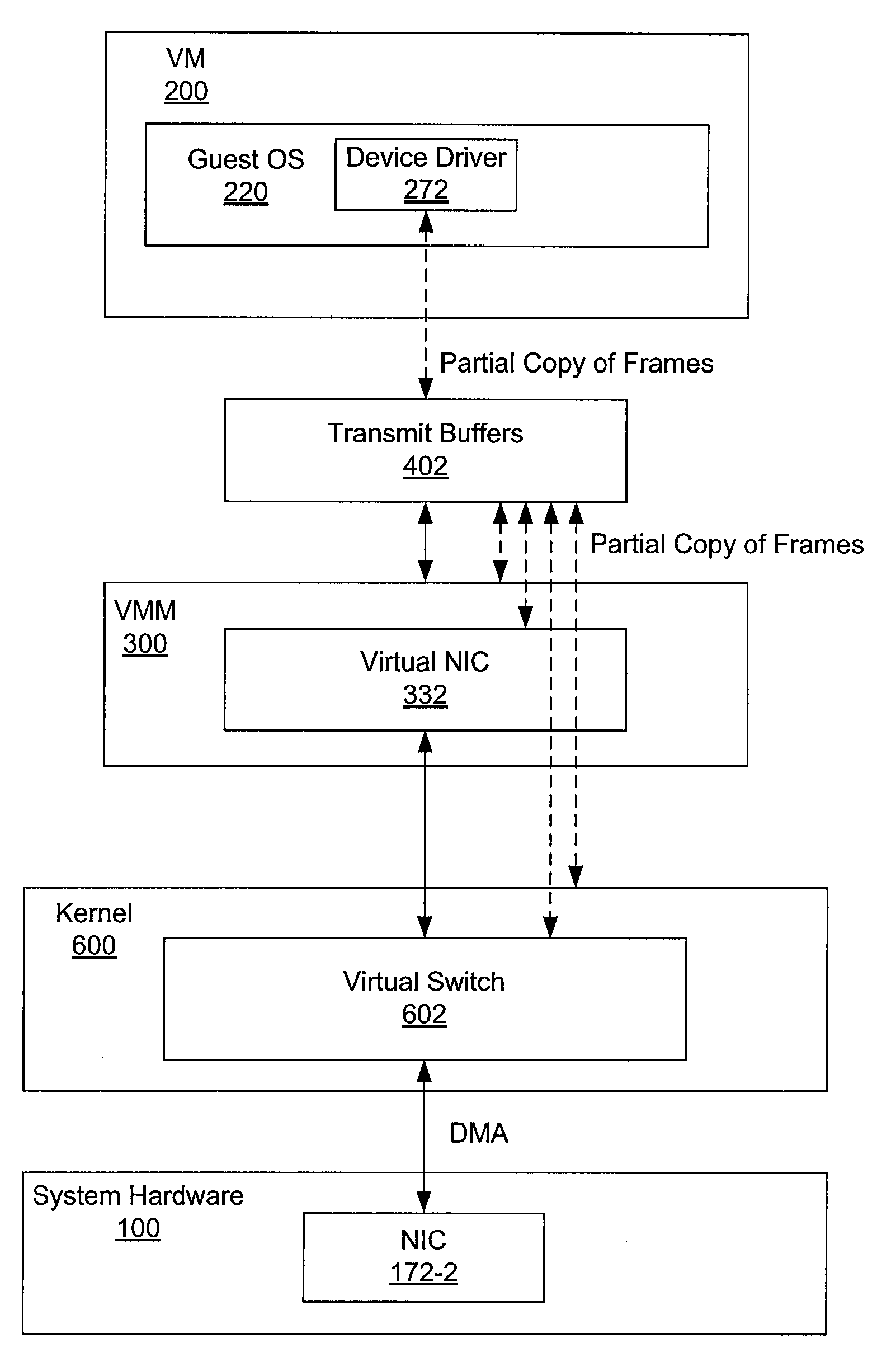
Partial copying of data to transmit buffer for virtual network device
ActiveUS7657659B1Increased computational burdenLighten the computational burdenTime-division multiplexComputer security arrangementsVirtualizationComputer hardware
In a virtualized computer system, a network frame is transmitted from a virtual machine using a network interface device, possibly through a virtual switch, by copying only a part of the network frame to the transmit buffers that have pre-translated mappings from guest physical addresses to hypervisor virtual addresses and to machine addresses. The length of the part of the network frame that is copied to the transmit buffers may be variable.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Method and system for adaptive direct volume rendering
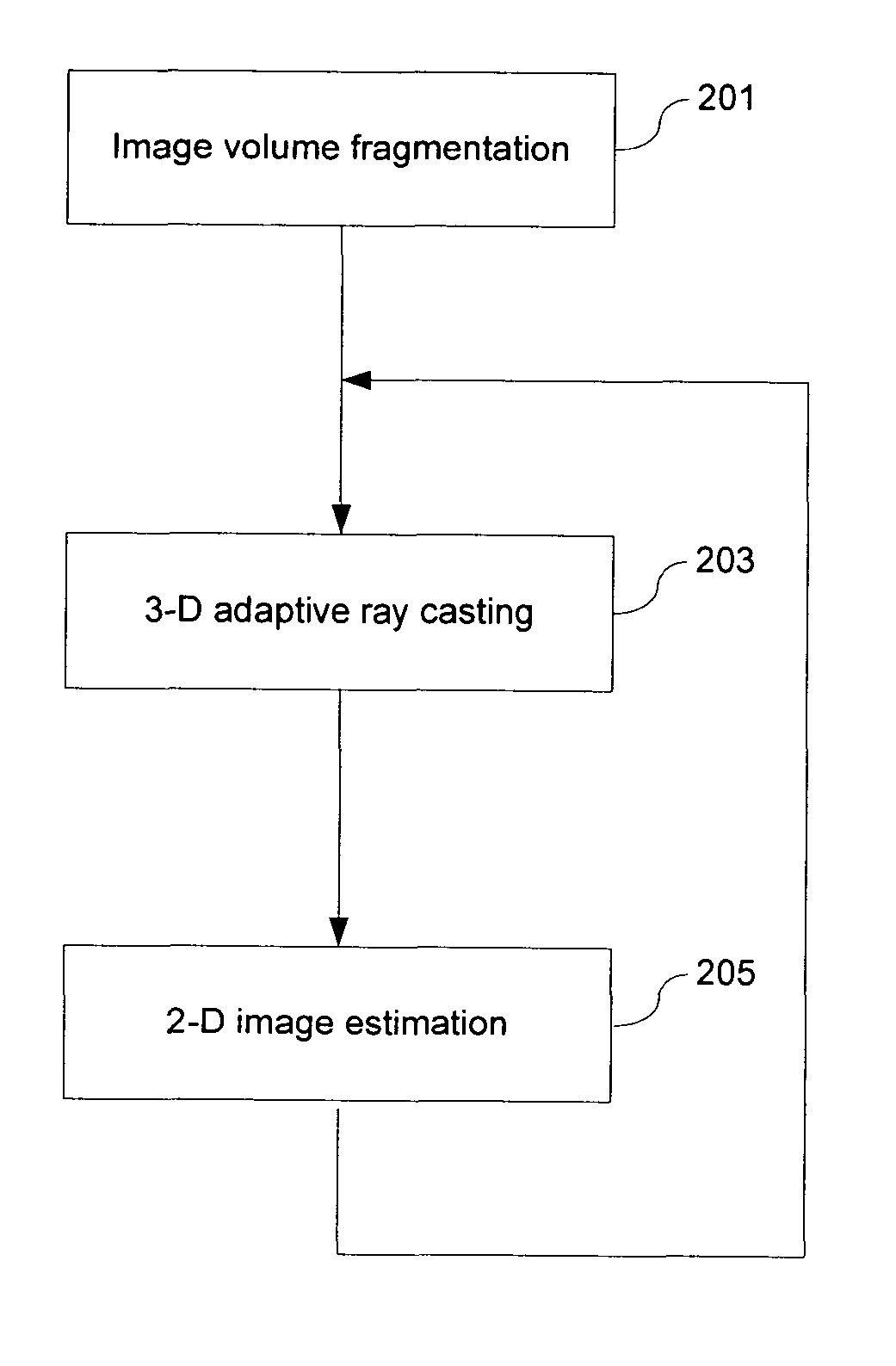
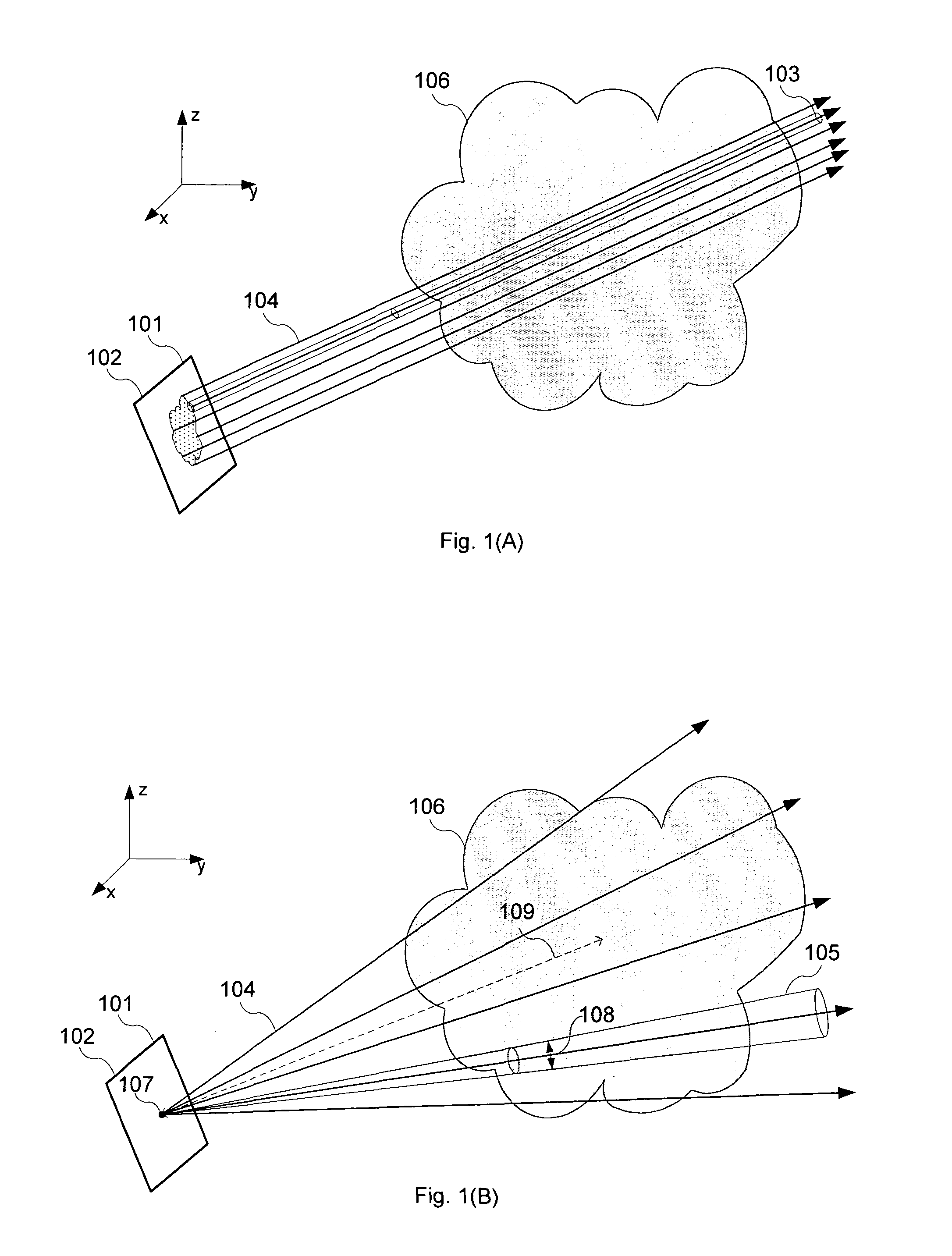
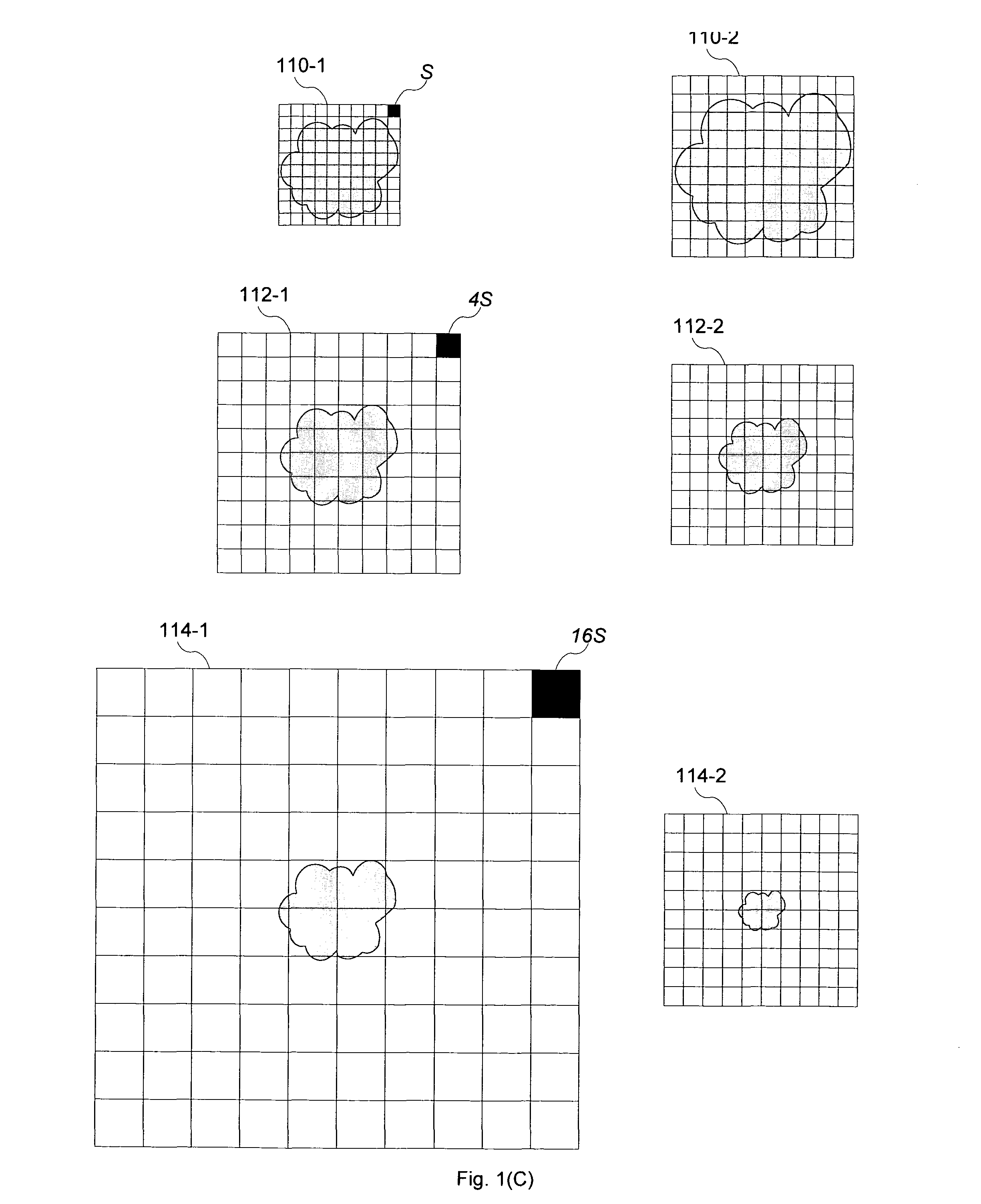
ActiveUS20060274065A1High-qualityReduce computing costCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingVolume renderingSelf adaptive
An adaptive image volume rendering system first fragments a 3-D dataset into multiple sub-volumes and constructs an octree structure, wherein each sub-volume is associated with one node on the octree. The system then establishes a 2-D image plane and selectively launches a plurality of rays towards the 3-D dataset, each ray adaptively interacting with a subset of the sub-volumes. The ray energy reflected by each sub-volume is estimated using a modified Phong illumination model, constituting a pixel value at the ray origin on the 2-D image plane. Finally, the system interpolates pixel values at a plurality of selected locations and generates a 2-D image of the 3-D dataset.
Owner:FOVIA
Method of generating successions of pseudo-random bits or numbers
InactiveUS20060251250A1Conveniently implementedReduce computing costSecuring communication by chaotic signalsTheoretical computer scienceChaotic map
A method for generating a succession of pseudo-random numbers includes choosing at least one chaotic map, and choosing a seed for the chaotic map and a number of iterations for the chaotic map. The succession of pseudo-random numbers are generated by executing iteratively generating a pseudo-random number as a function of a final state reached by the chaotic map iterated for the current number of iterations starting from the current seed, and generating a new seed for the chaotic map or a new number of iterations as a function of the final state.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and system for checkpointing during simulations
ActiveUS20110288831A1Reduce computing costMinimal costAcoustic presence detectionSeismic data acquisitionParallel computingComputer memory
Method and system for more efficient checkpointing strategy in cross correlating (316) a forward (328) and backward (308) propagated wave such as in migrating (326) or inverting seismic data. The checkpointing strategy includes storing in memory forward simulation data at a checkpointed time step, wherein the stored data are sufficient to do a cross correlation at that time step but not to restart the forward simulation. At other checkpoints, a greater amount of data sufficient to restart the simulation may be stored in memory (314). Methods are disclosed for finding an optimal combination, i.e. one that minimizes computation time (1132), of the two types of checkpoints for a given amount of computer memory (1004), and for locating a checkpoint at an optimal time step (306, 1214, 1310). The optimal checkpointing strategy (1002) also may optimize (1408) on use of fast (1402) vs. slow (1404) storage.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Real-time barcode recognition using general cameras
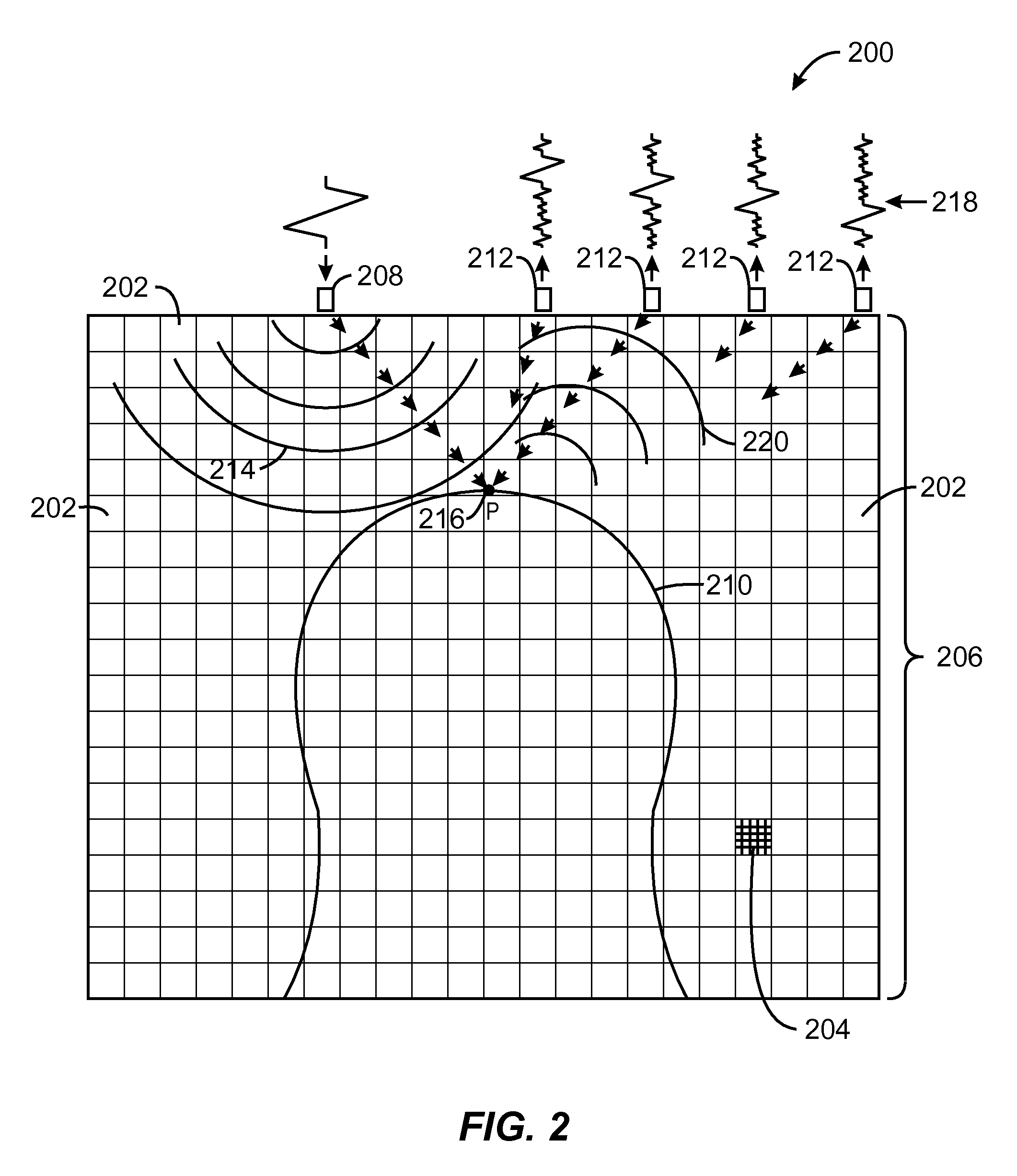
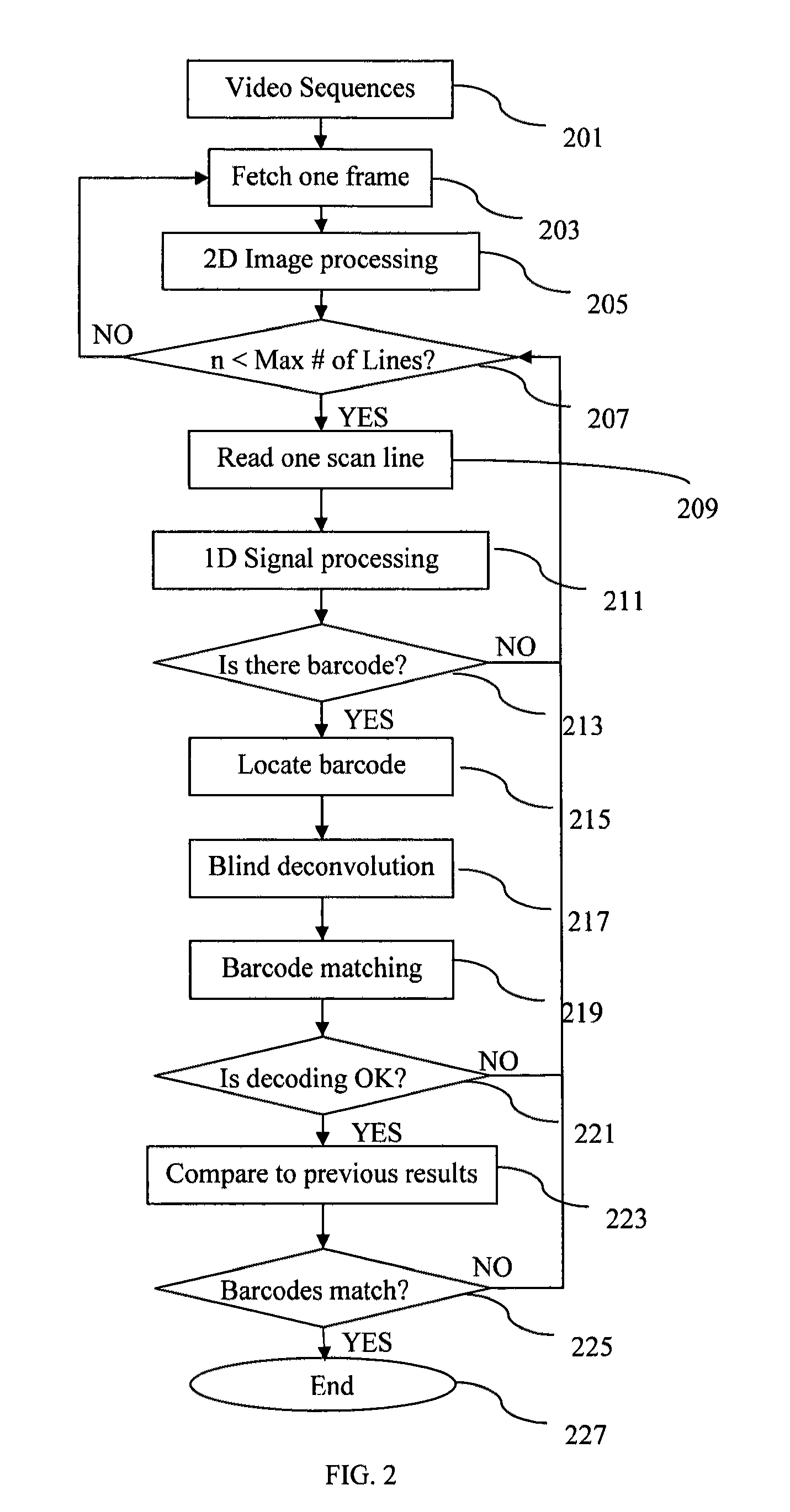
ActiveUS20120091204A1Reduce computing costEasy to measureSensing record carriersVerifying markings correctnessPattern recognitionPoint spread
A method, apparatus, and system for decoding and recognizing barcode information by using a general camera such as one in a mobile device is disclosed. The invention uses a set of compact point spread functions (PSF) with a squared-shape distribution to restore blurred barcode image for quick and efficient decoding and recognition. Image pre-processing methods are applied to reduce noise and normalize pixel grayscale. On each normalized image, the invention checks if the image contains barcode lines. If there is a barcode, the invention tries to identify the beginning and ending positions of the barcode. The invention selectively decodes multiple scan lines across the barcode and match against predefined barcode models. The best matched barcodes are saved in the history buffer.
Owner:SHI JIAZHENG +1
Touch surface with two-dimensional compensation
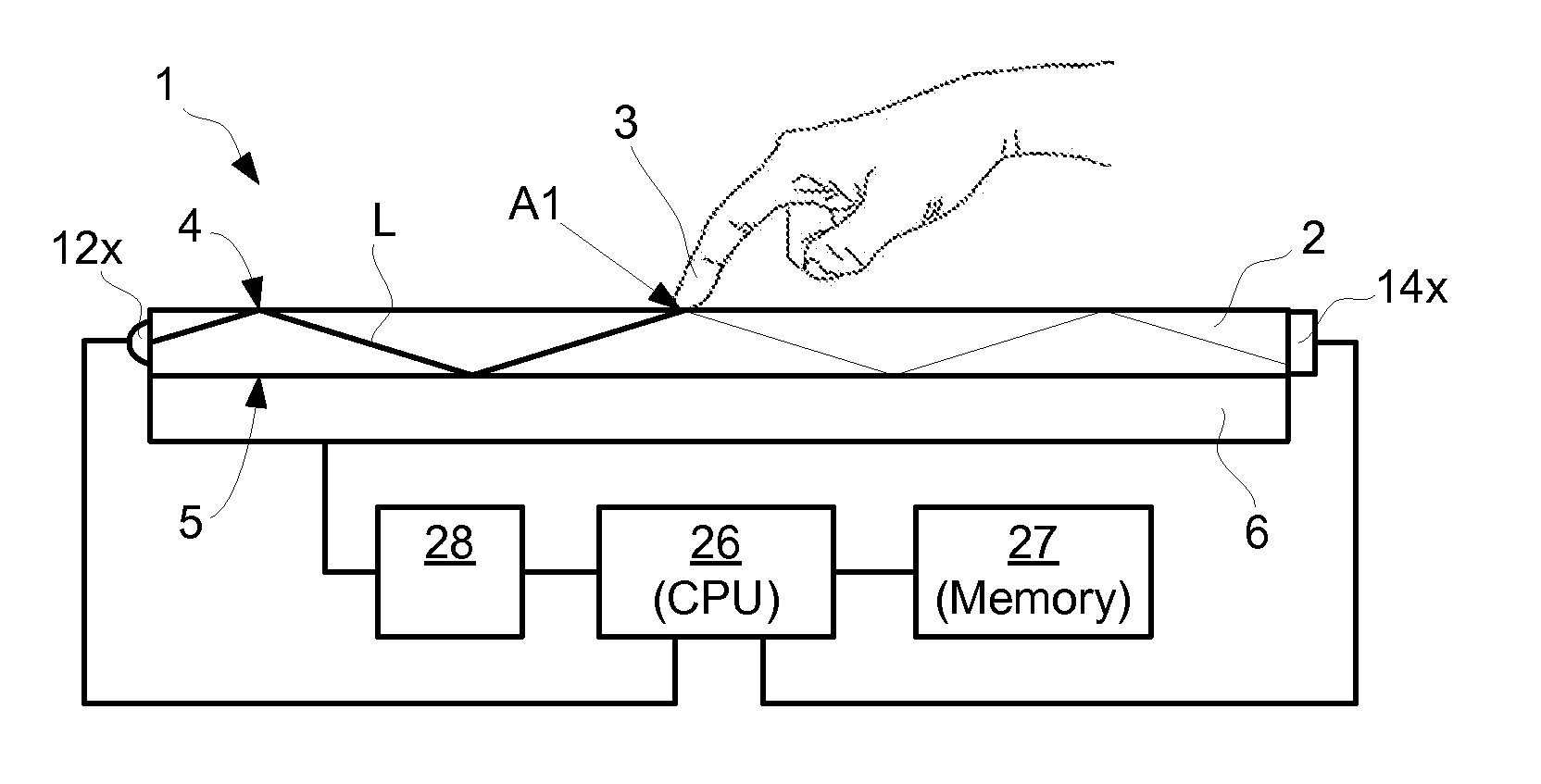
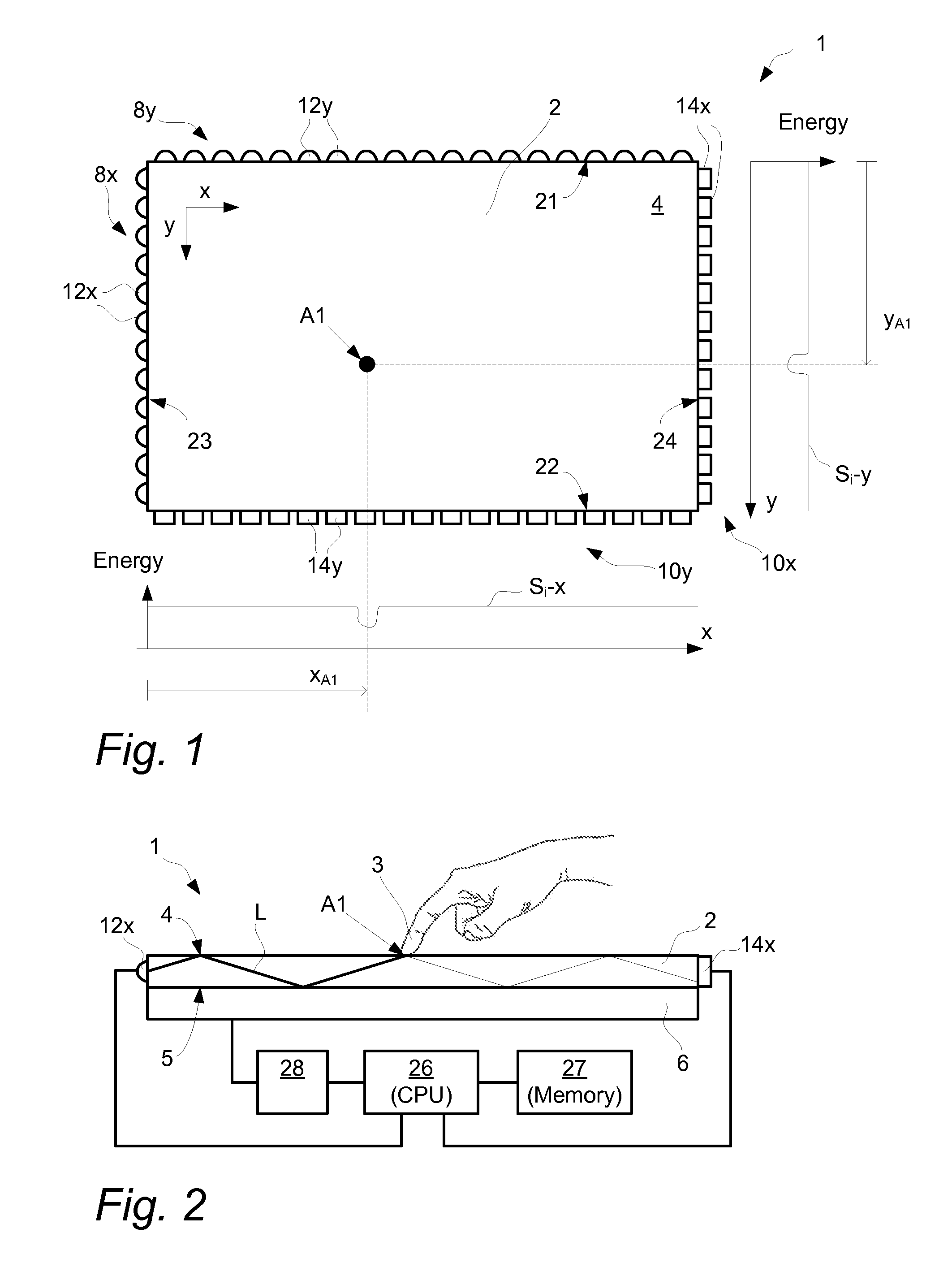
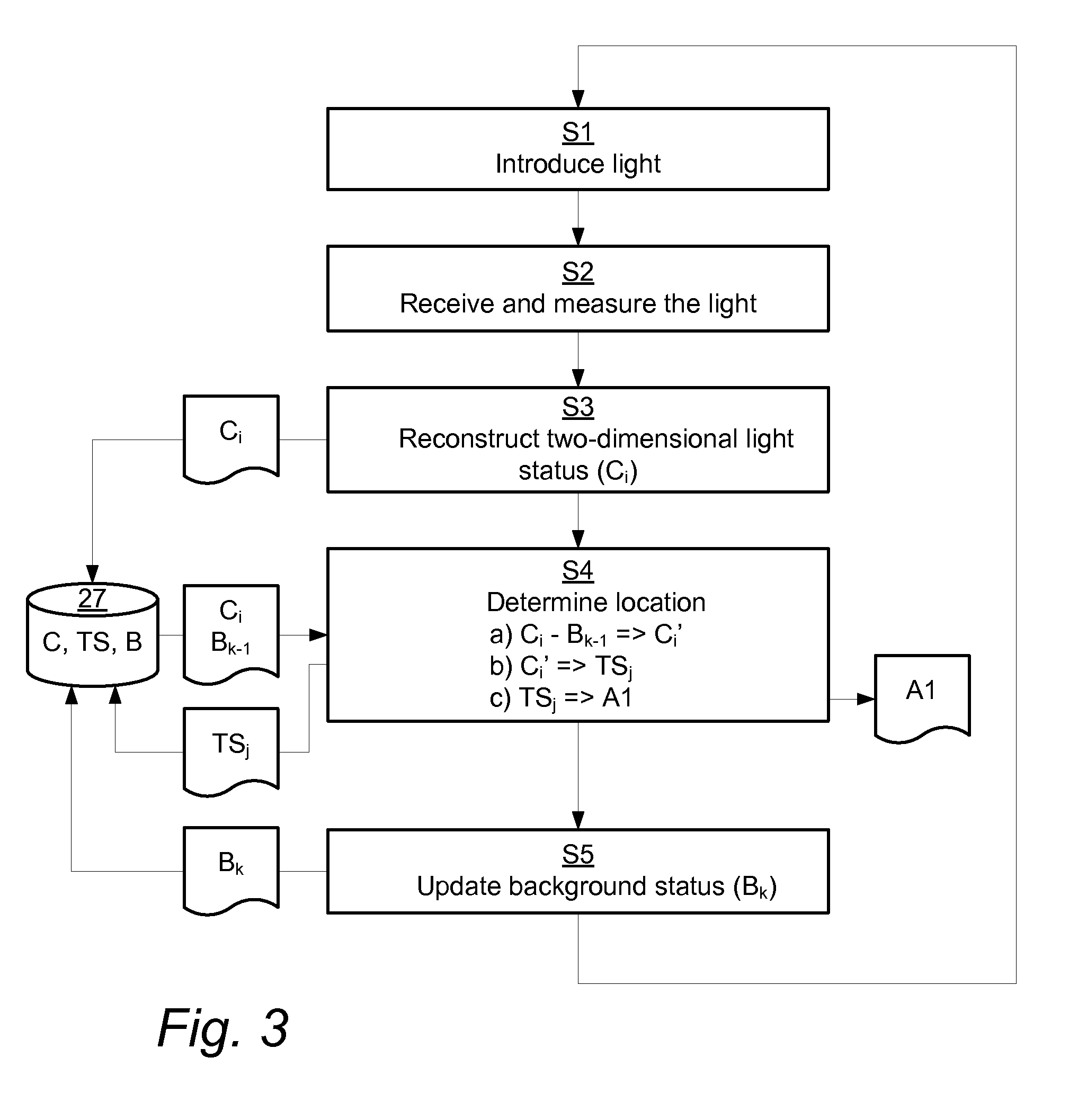
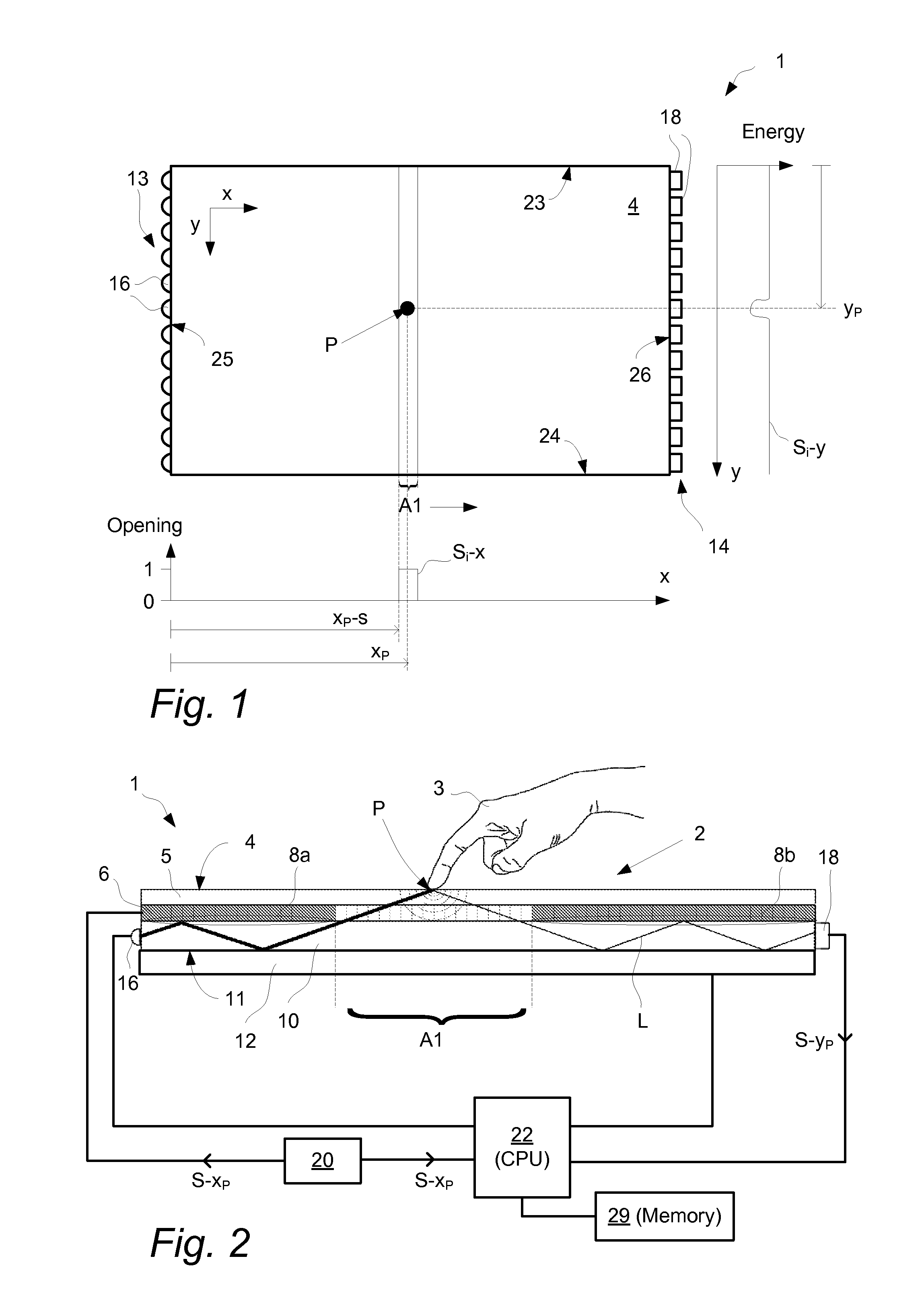
InactiveUS20120200538A1Overcome limitationsAccurate measurementInput/output processes for data processingContaminationOptics
An apparatus for determining an interaction between an object and a touch surface of a panel. An illumination arrangement introduces light into the panel for propagation by internal reflection between the touch surface and an opposite surface and towards a receiving light detection arrangement. A processor unit is configured to iteratively i) determine, based on the received light, a current light status representing a two-dimensional distribution of light in the panel, ii) determine the interaction with the object as a function of the current light status and a previously updated background status representing a two-dimensional distribution of light in the panel caused by contaminations, and iii) update the background status as a function of the interaction. A method and computer readable medium are also described.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Touch surface with variable refractive index
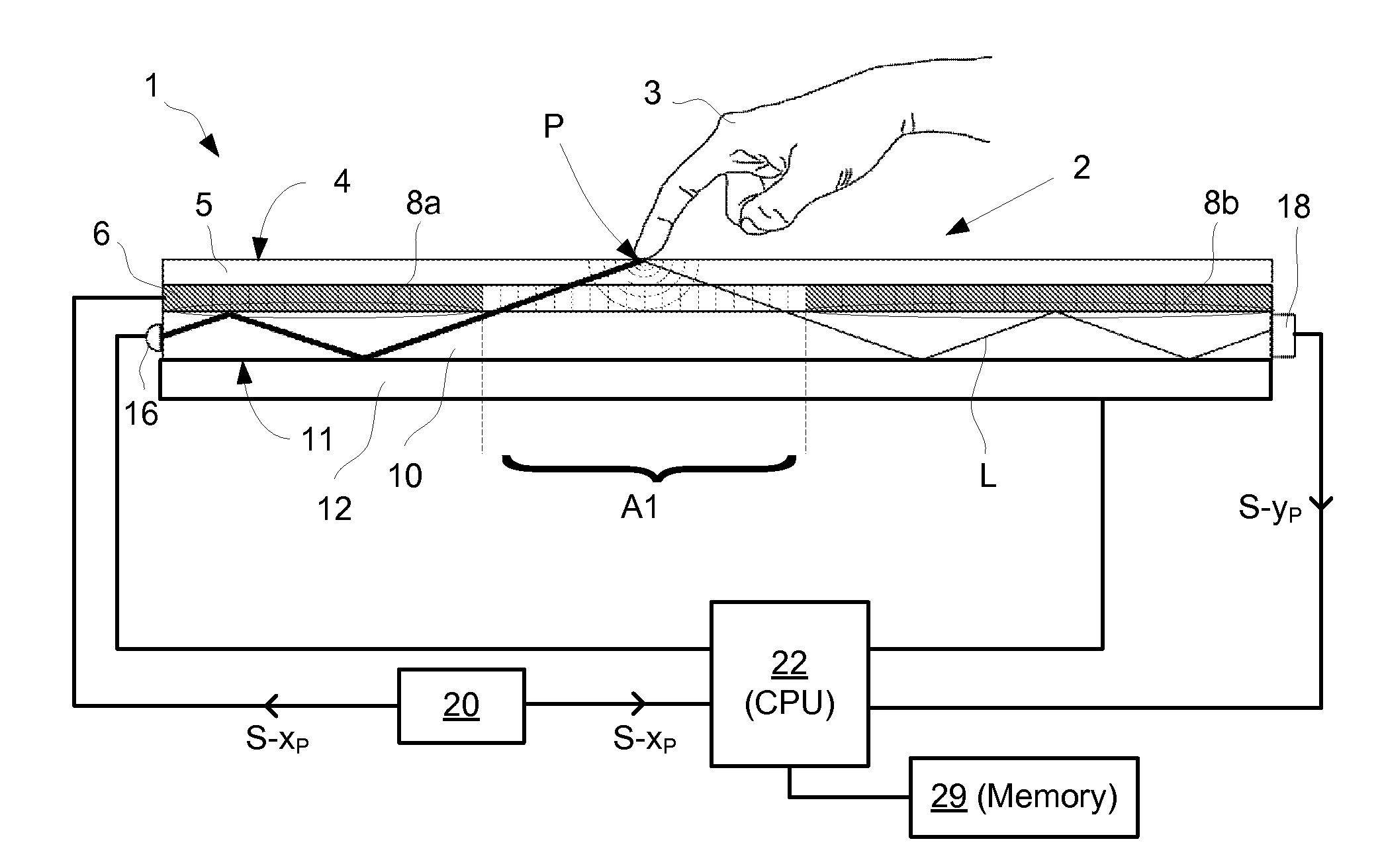
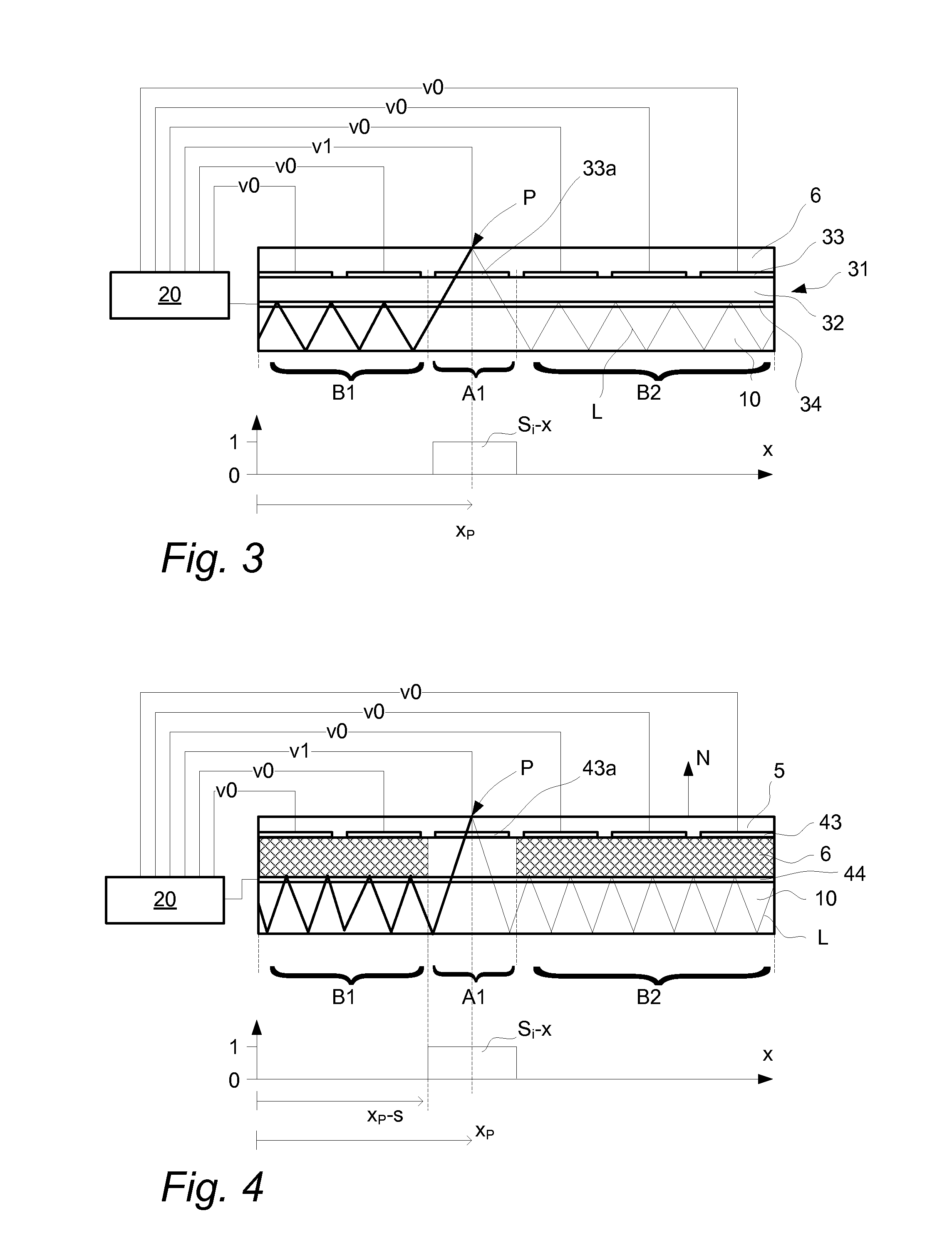
InactiveUS20120169672A1Reduce the numberOvercome limitationsInput/output processes for data processingRefractive indexSelective control
An apparatus for determining a location of at least one object on a touch surface, comprising: a light transmissive panel defining the touch surface and including a controllable reflective boundary; an illumination arrangement configured to introduce light into the panel; a control device configured to selectively control the reflective boundary such that the light may pass between a first layer and a second layer via an opening in the reflective boundary; a light detection arrangement configured to measure the light passed via the opening and impinged on the touch surface; and a processor unit configured to determine the location as a function of the measured light passed via the opening and the selective control of the reflective boundary. A method and computer readable medium is also described.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
System and method for real-time whiteboard capture and processing
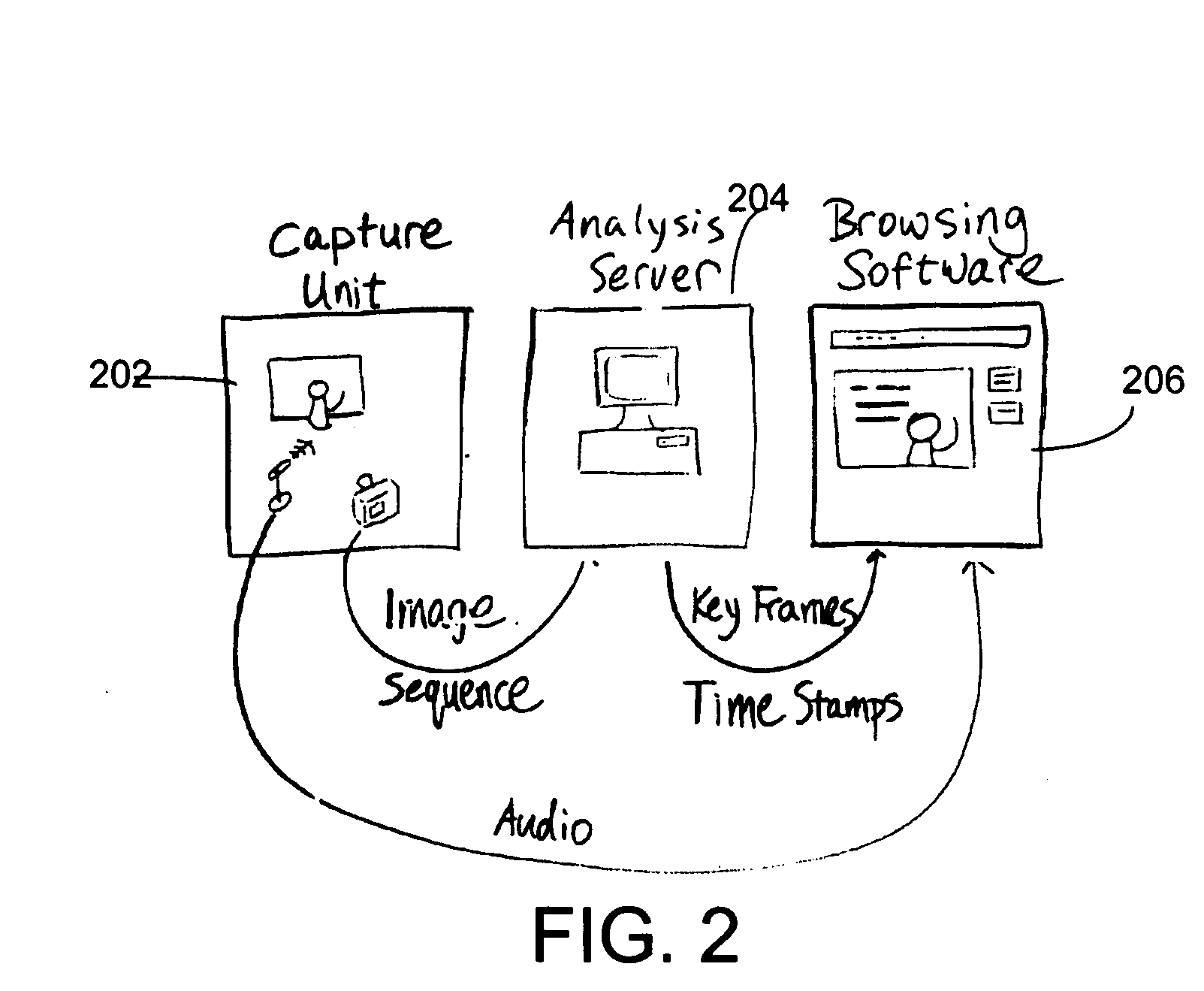
InactiveUS20050104864A1Save memoryQuality improvementInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementWhiteboardOff the shelf
A system that captures both whiteboard content and audio signals of a meeting using a video camera and records or transmits them in real-time. The Real-Time Whiteboard Capture captures pen strokes on whiteboards in real time using an off-the-shelf video camera. Unlike many existing tools, the RTWCS does not instrument the pens or the whiteboard. It analyzes the sequence of captured video images in real time, classifies the pixels into whiteboard background, pen strokes and foreground objects (e.g., people in front of the whiteboard), and extracts newly written pen strokes. This allows the RTWCS to transmit whiteboard contents using very low bandwidth to remote meeting participants. Combined with other teleconferencing tools such as voice conference and application sharing, the RTWCS becomes a powerful tool to share ideas during online meetings.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Obstacle identification method for smart vehicles
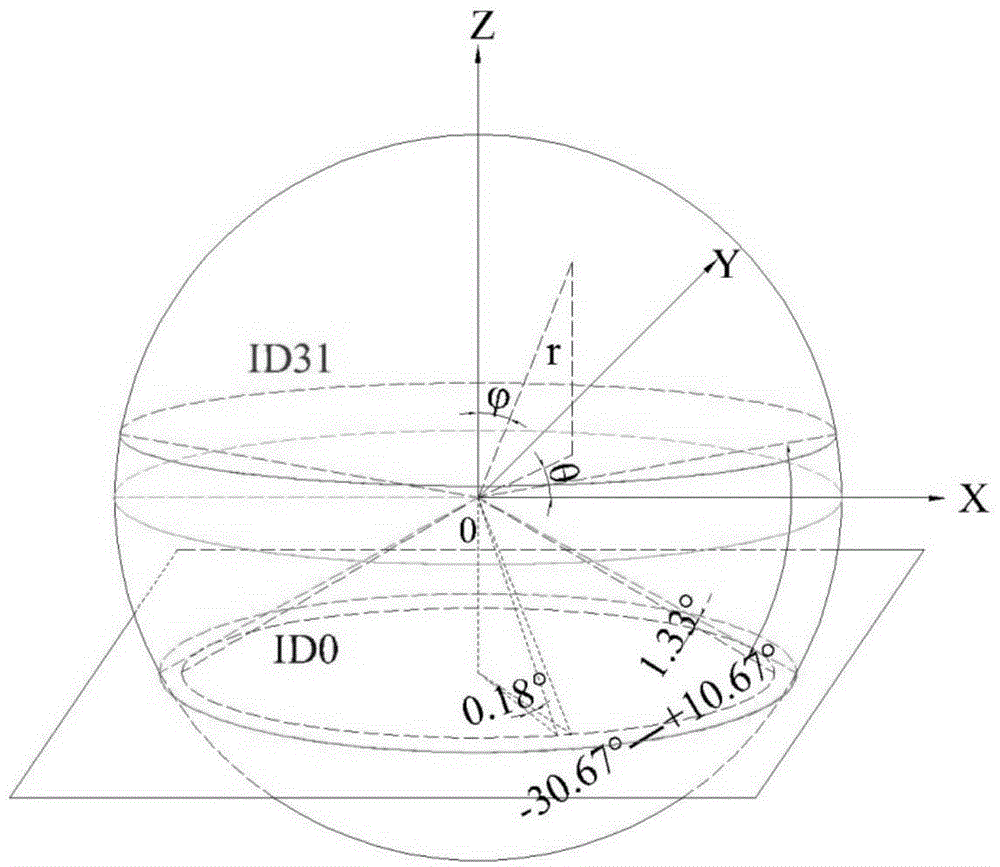
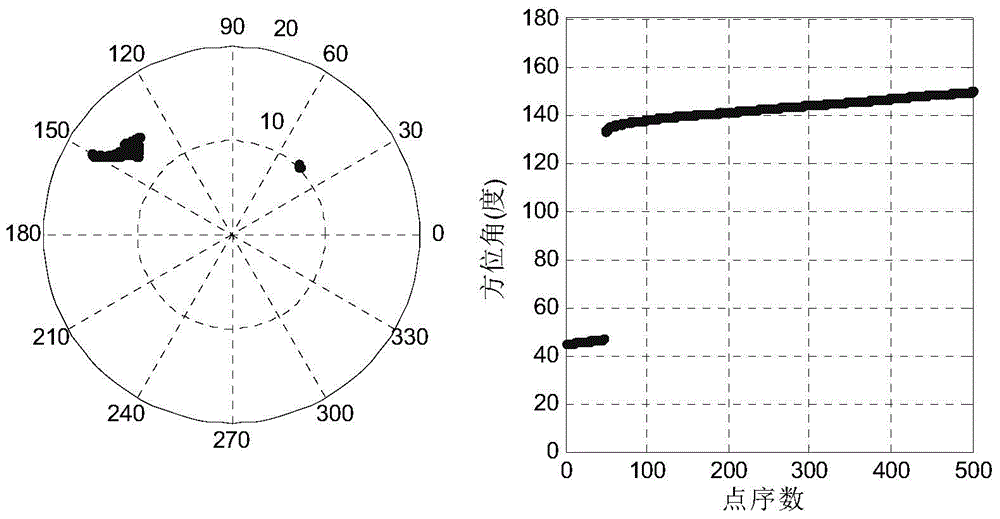
InactiveCN104931977AImprove processing efficiencyAvoid under-segmentation problemsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
The invention relates to an obstacle identification method for smart vehicles. The obstacle identification method includes the following steps that: 1) data points of original scanning point cloud three-dimensional laser radar of surrounding environment of the vehicles under a spherical coordinate system are obtained, and obstacle points are screened out from all the data points; 2) the obstacle points are grouped according to the horizontal azimuth angles of the obstacle points and the radial distances of the obstacle points relative to a three-dimensional laser radar sensor; and 3) each group of obstacle points correspond to one obstacle, and the categories of the obstacles can be obtained according to the relative position relationships of the obstacle points in each group. Compared with the prior art, and according to the obstacle identification method for the smart vehicles of the invention, the intrinsic unity of the measurement principles of the a three-dimensional laser radar and a point cloud data spherical coordinate representation method is utilized; it is point cloud data that are analyzed based on spherical coordinates, and the Cartesian coordinates of the point cloud data are not analyzed, and therefore, high efficiency can be realized; and at the same time, the original data of point cloud are directly analyzed, and grid division is not needed to perform on the point cloud, and therefore, processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
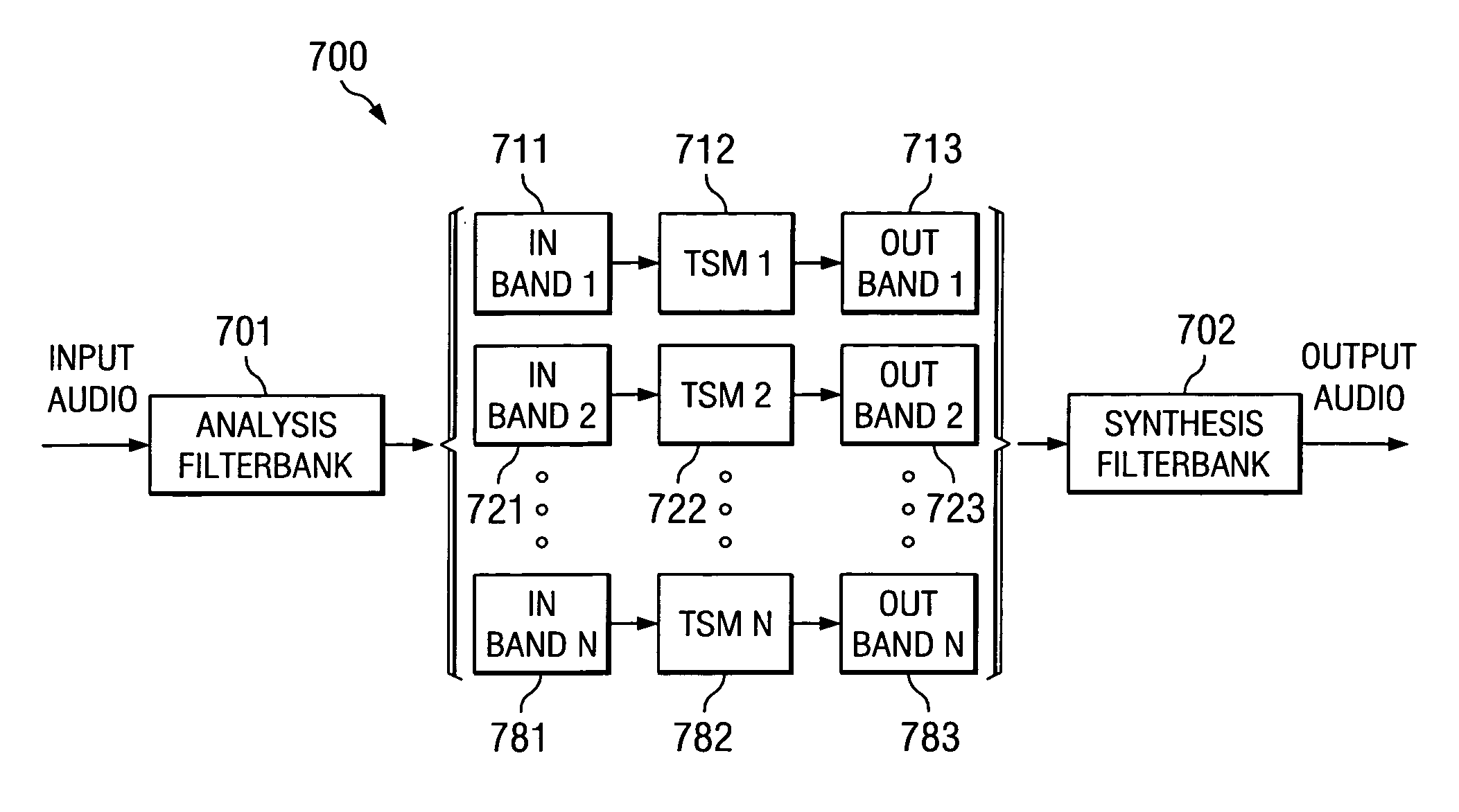
Time-scale modification of music signals based on polyphase filterbanks and constrained time-domain processing
ActiveUS6982377B2Reduce computing costElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisTime domainCombined use
A time scale modification method employs separate bands obtained through an analysis polyphase filter bank with separate time-scale modification processing for the bands. The outputs are combined using a synthesis filter bank. Some constraints are imposed on the time-scale modification processing, such a limitation of the range of overlap adjustment values for bands other than the greatest energy band, to eliminate noise due to aliasing and inter-channel phase mismatch. This invention produces output quality considerably higher than conventional time-domain time-scale modification methods for general music signals with computational requirements comparable to those of conventional time-domain time-scale modification methods.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
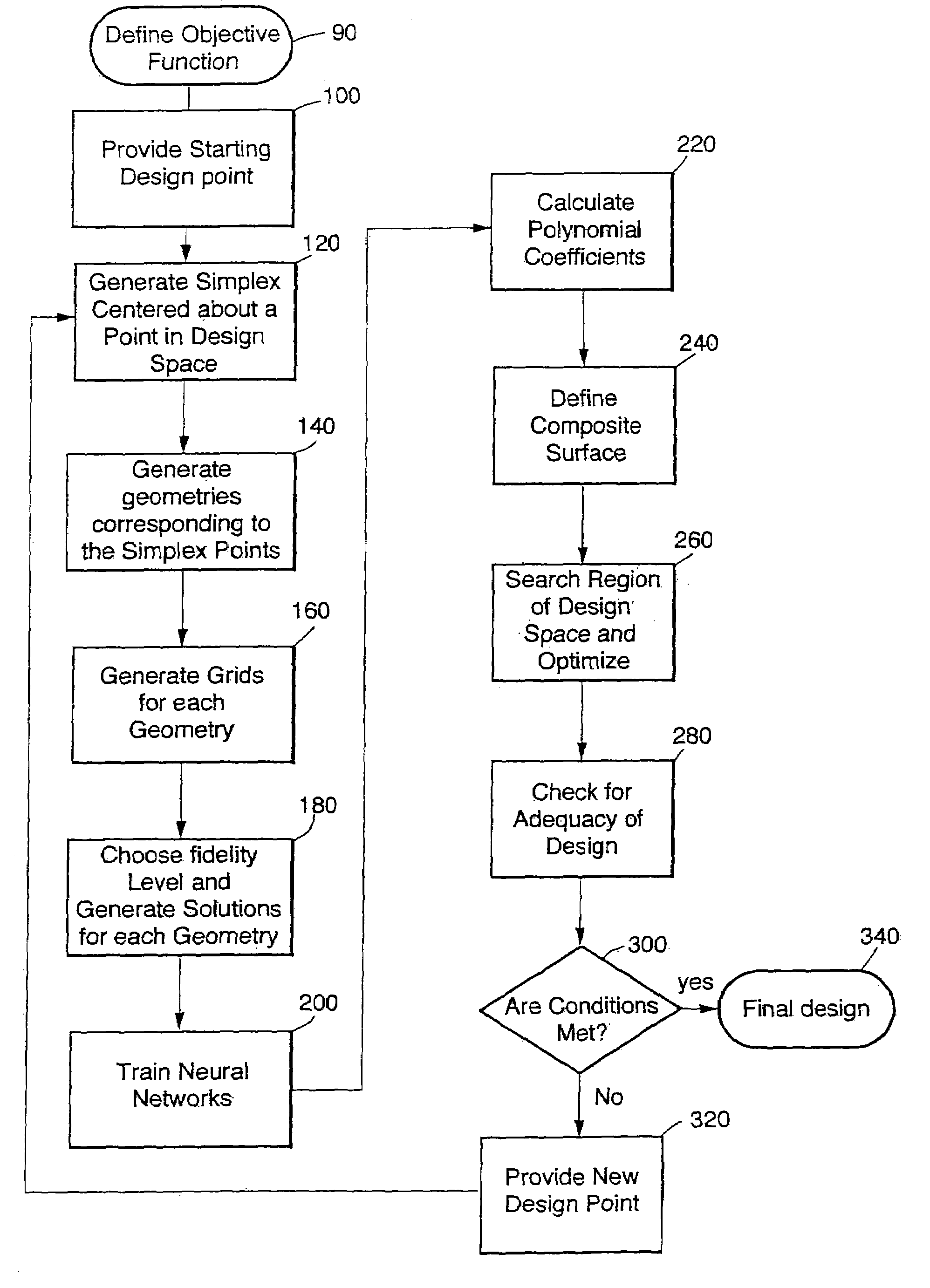
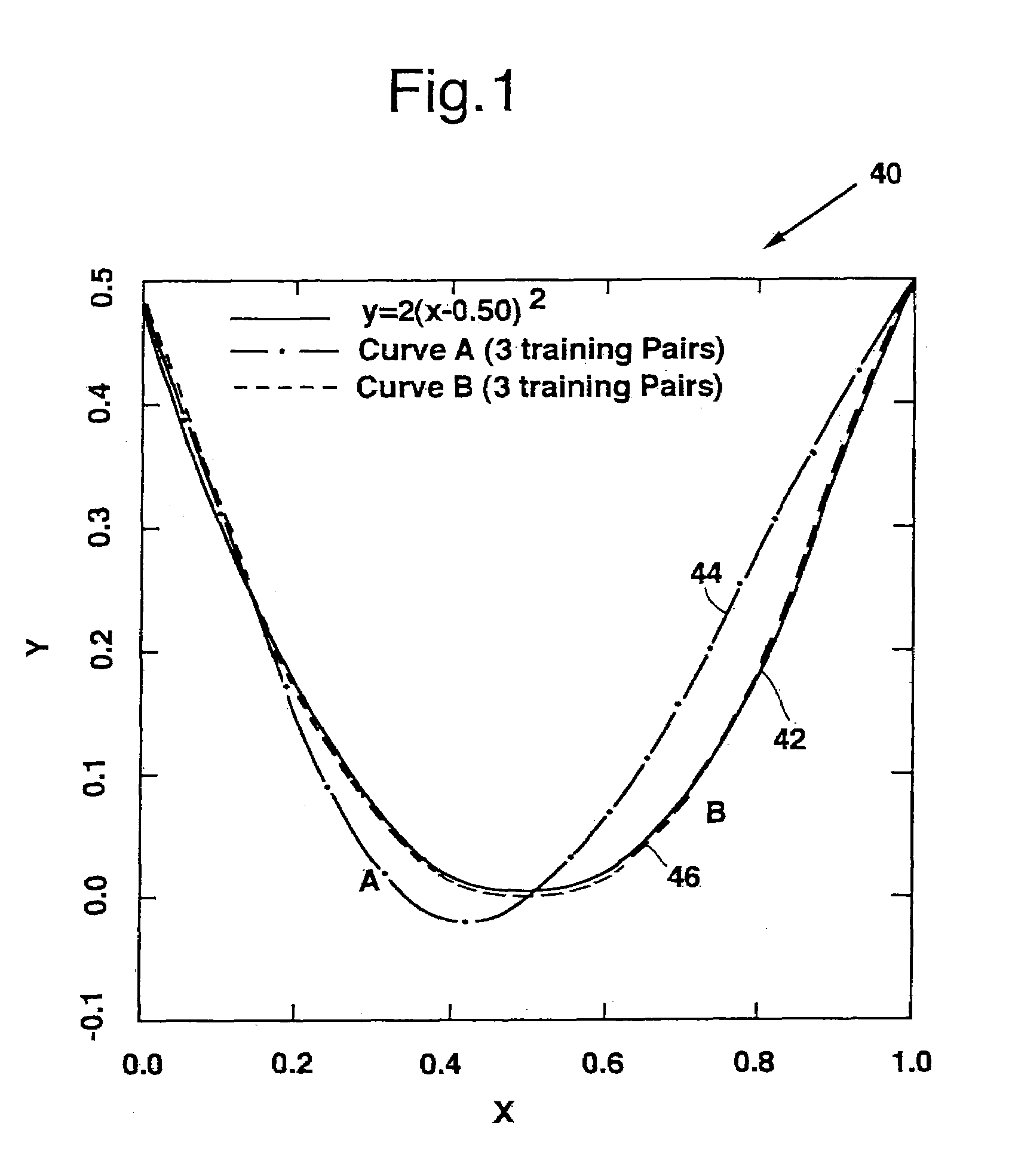
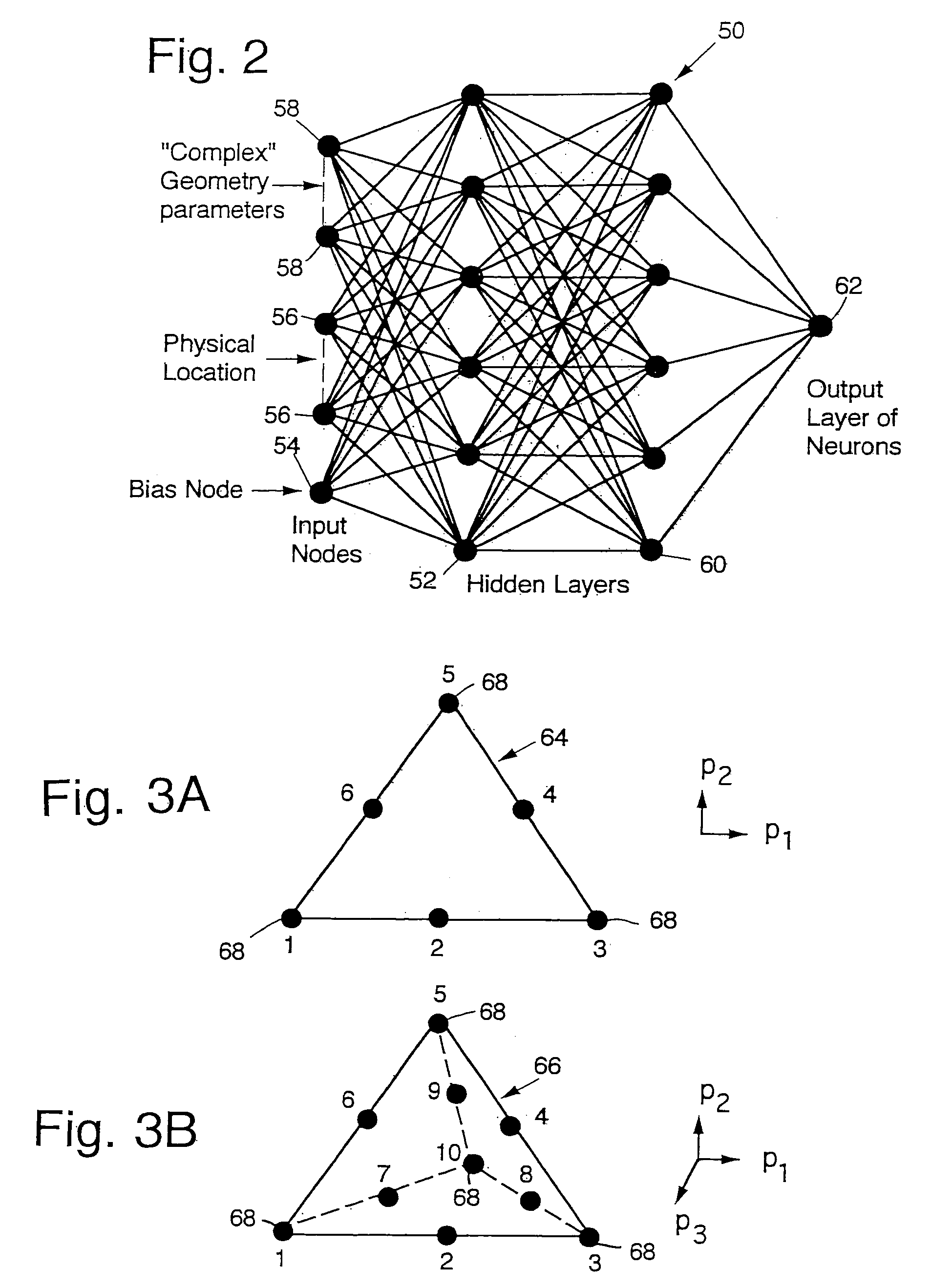
Method for constructing composite response surfaces by combining neural networks with polynominal interpolation or estimation techniques
InactiveUS7191161B1Reduce computing costPerformance trade-offDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkNeural network analysis
A method and system for data modeling that incorporates the advantages of both traditional response surface methodology (RSM) and neural networks is disclosed. The invention partitions the parameters into a first set of s simple parameters, where observable data are expressible as low order polynomials, and c complex parameters that reflect more complicated variation of the observed data. Variation of the data with the simple parameters is modeled using polynomials; and variation of the data with the complex parameters at each vertex is analyzed using a neural network. Variations with the simple parameters and with the complex parameters are expressed using a first sequence of shape functions and a second sequence of neural network functions. The first and second sequences are multiplicatively combined to form a composite response surface, dependent upon the parameter values, that can be used to identify an accurate model.
Owner:NASA
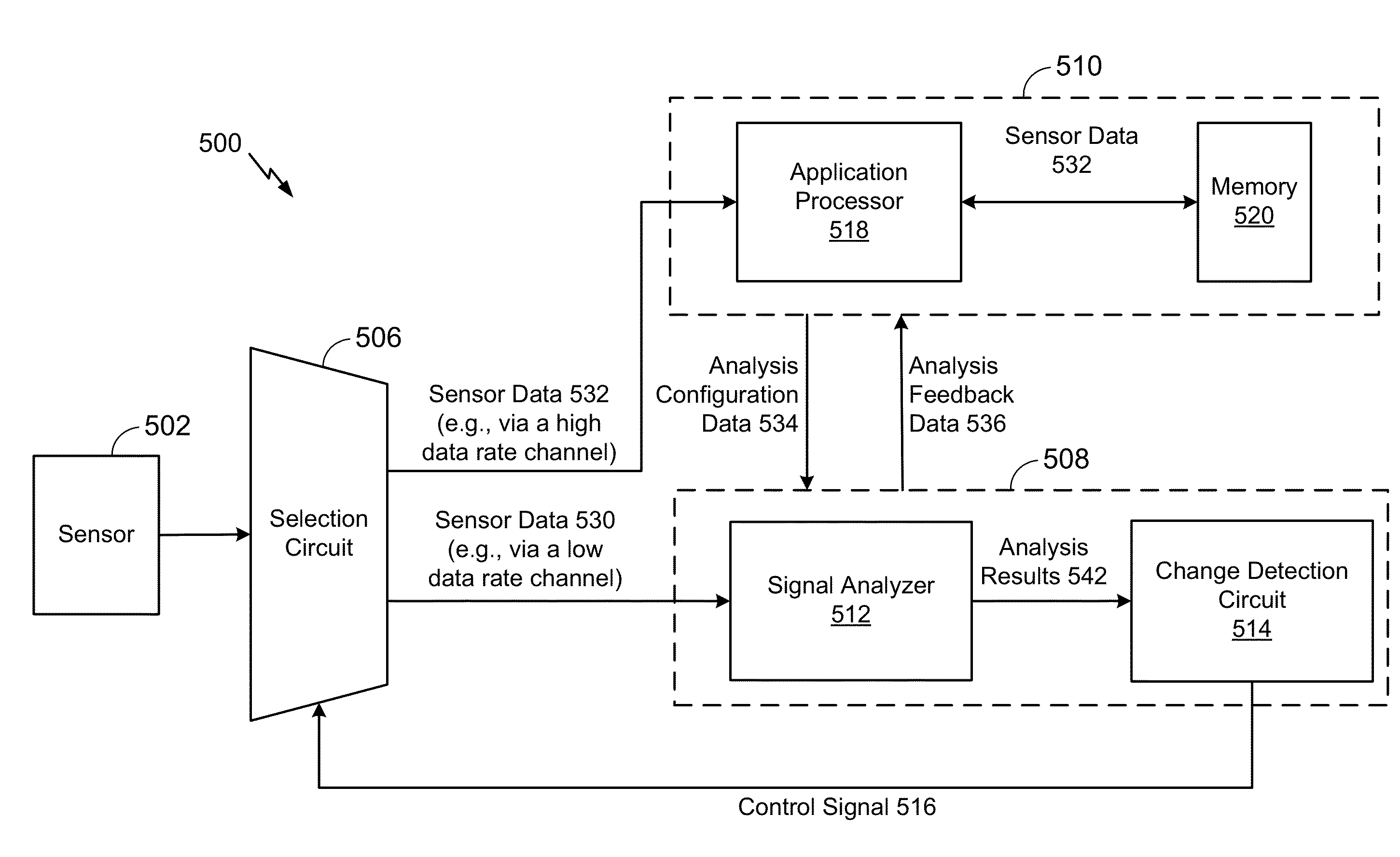
Computer vision application processing
ActiveUS20140368626A1Reduce the amount of powerSave battery powerTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsProcess efficiencyComputer vision
Methods, systems, and techniques to enhance computer vision application processing are disclosed. In particular, the methods, systems, and techniques may reduce power consumption for computer vision applications and improve processing efficiency for computer vision applications.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com