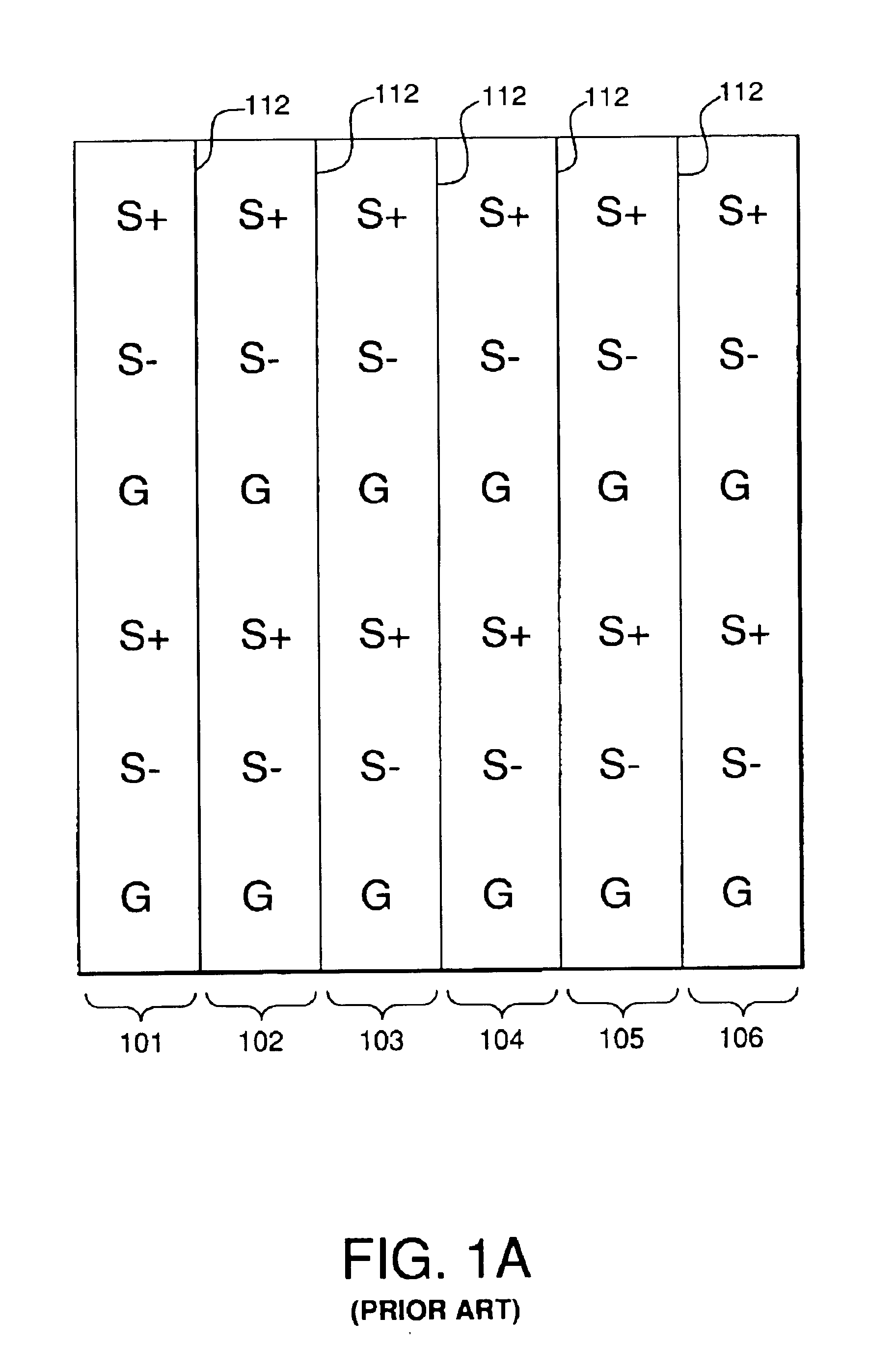
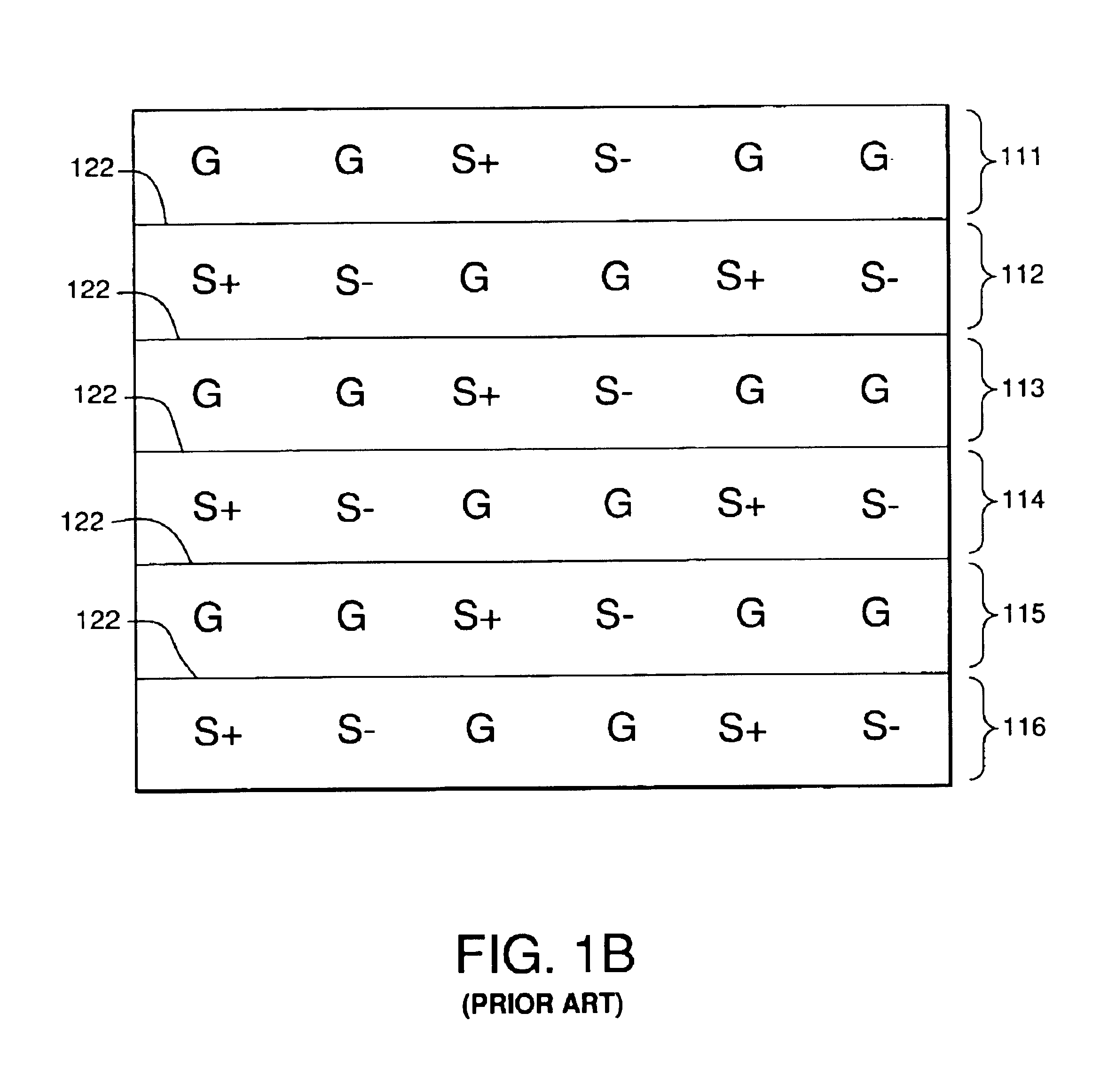
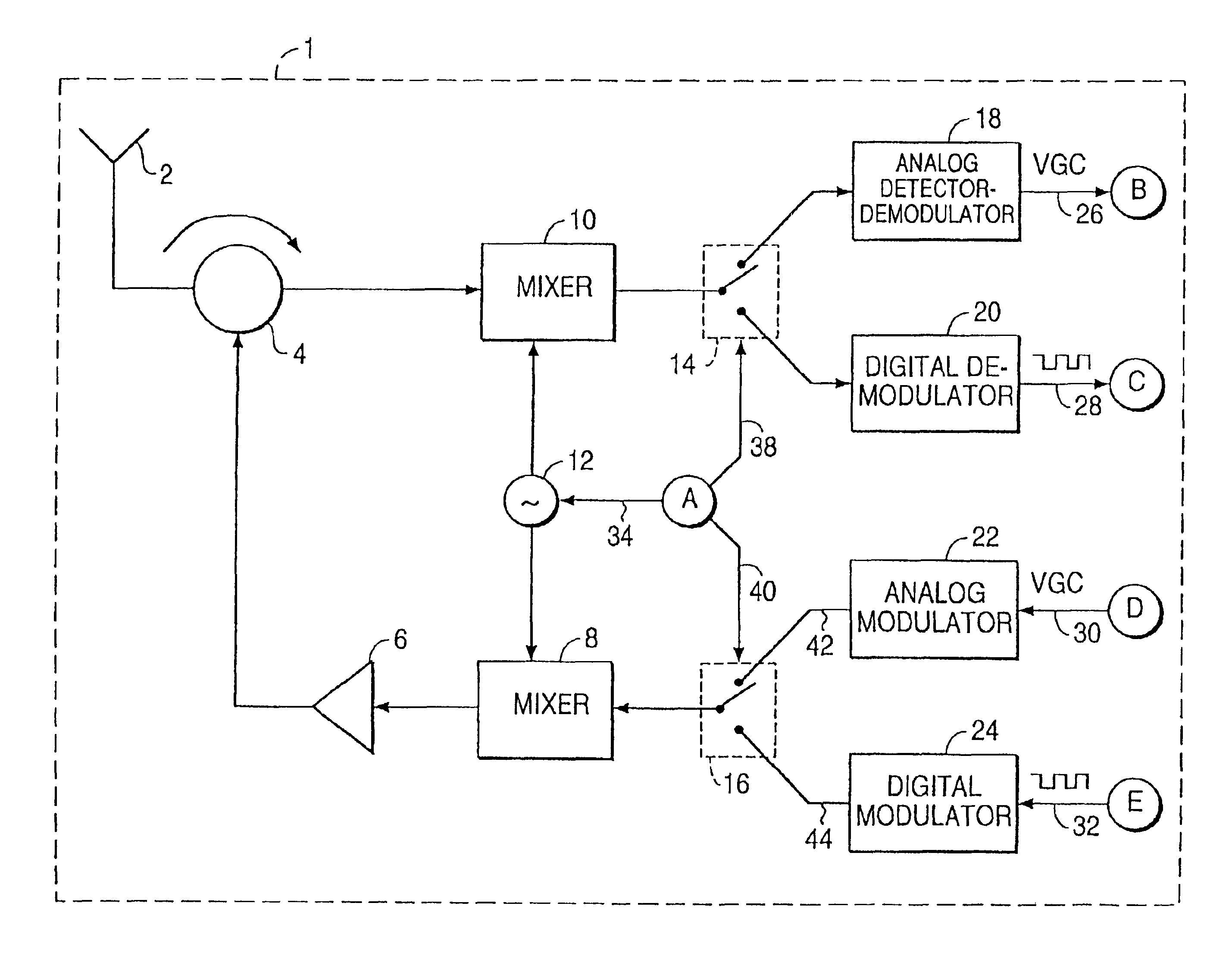
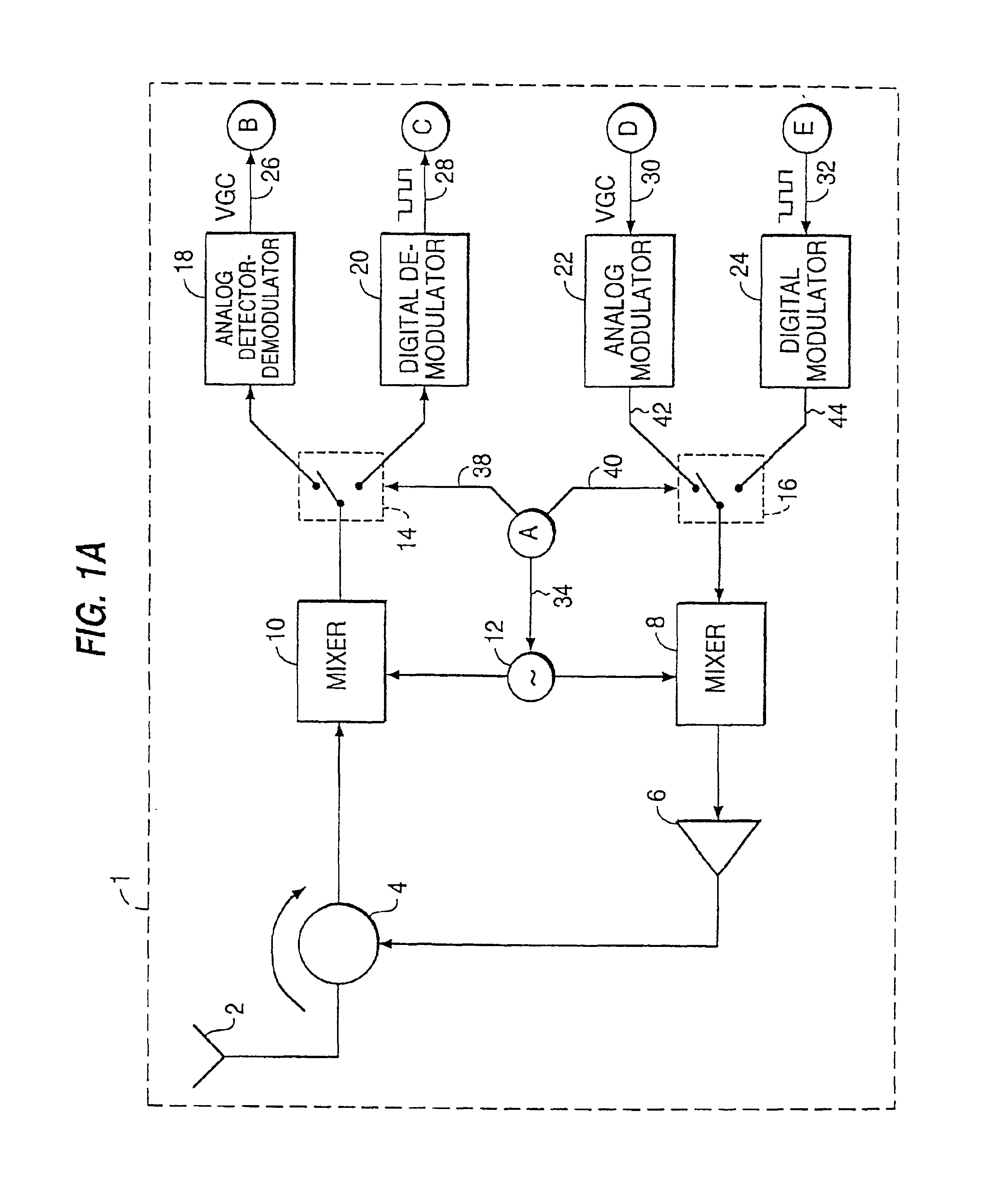
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7354 results about "Interference (communication)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
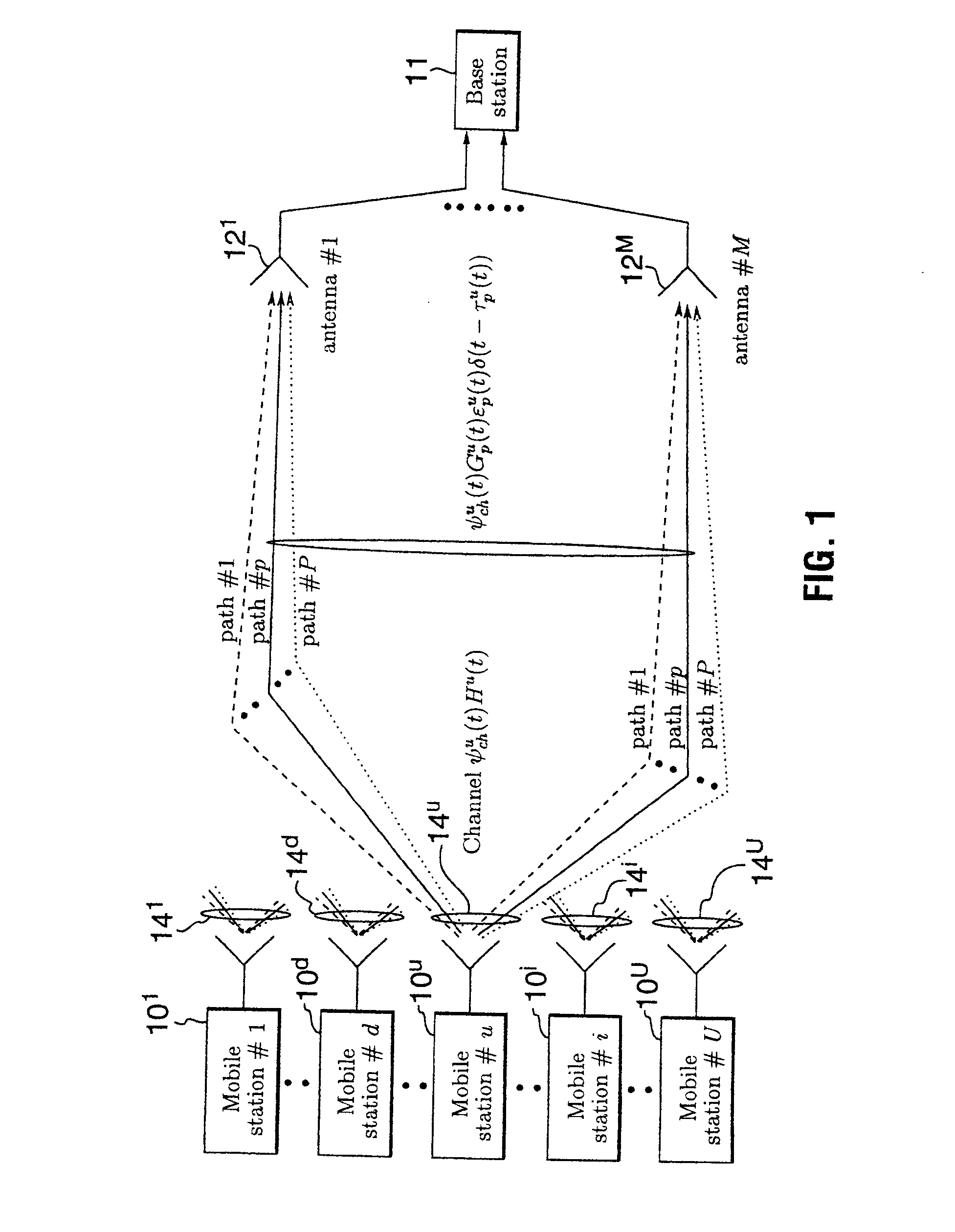
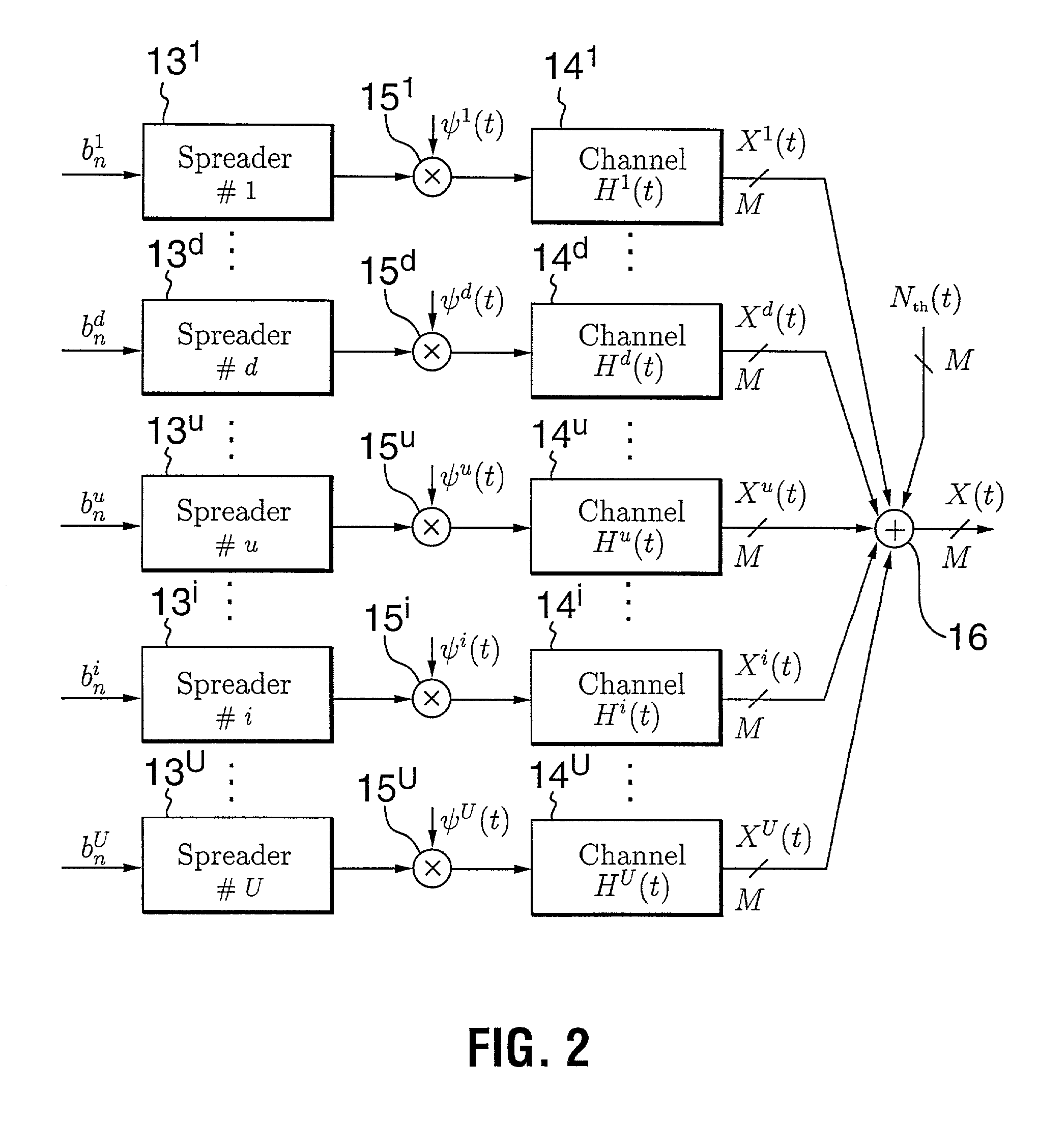
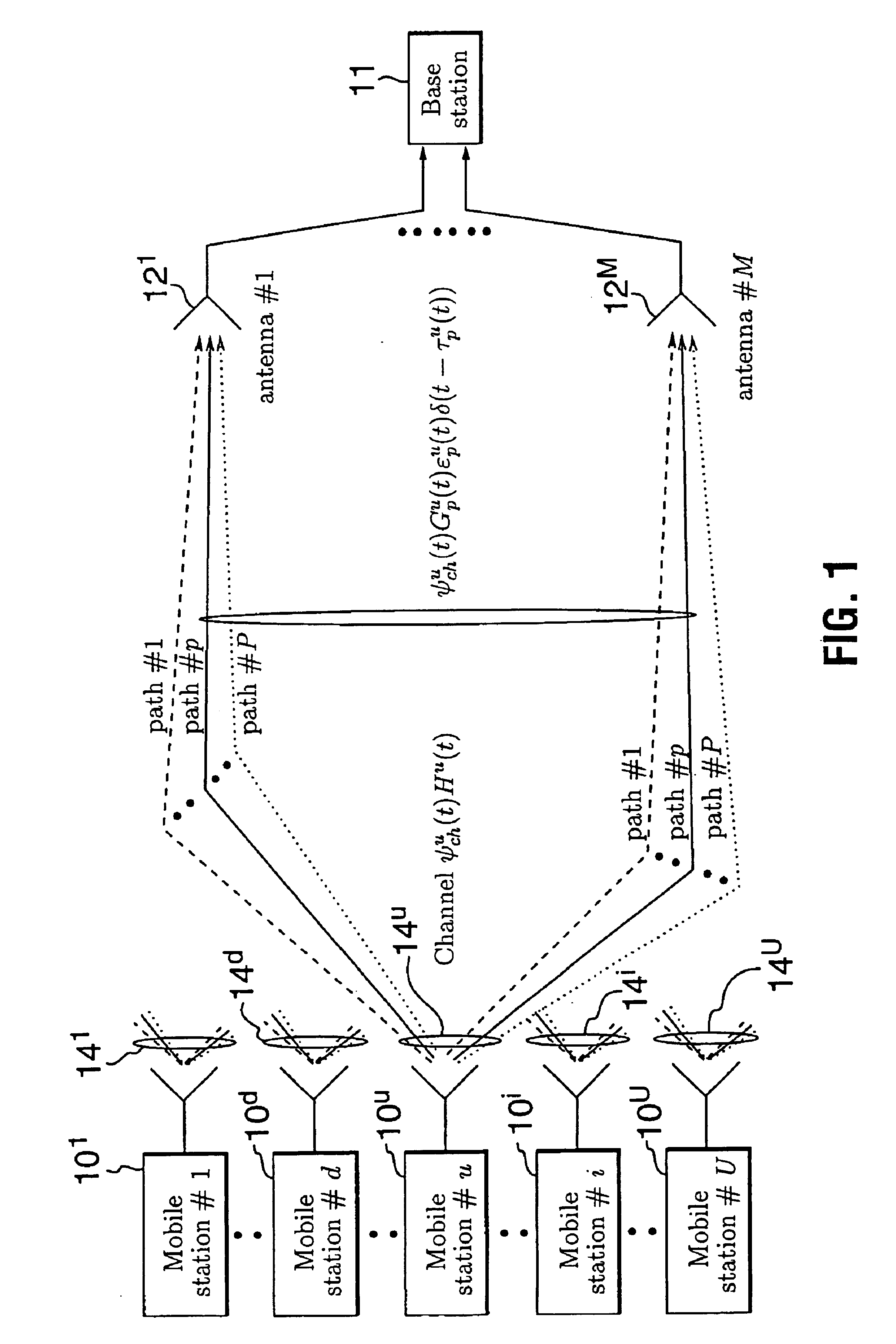
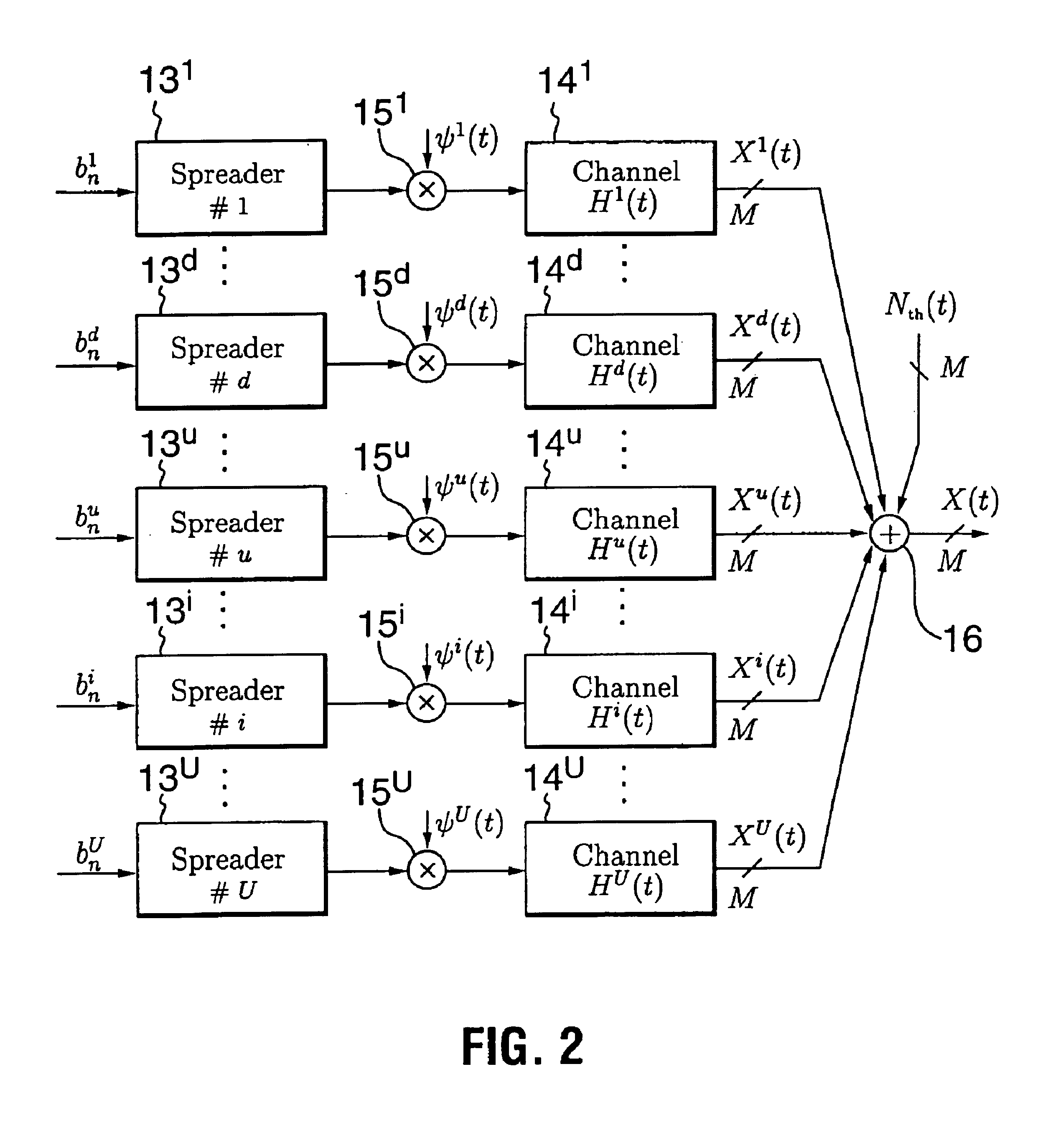
In electronic communications, especially in telecommunications, an interference is that which modifies a signal in a disruptive manner, as it travels along a channel between its source and receiver. The term is often used to refer to the addition of unwanted signals to a useful signal.
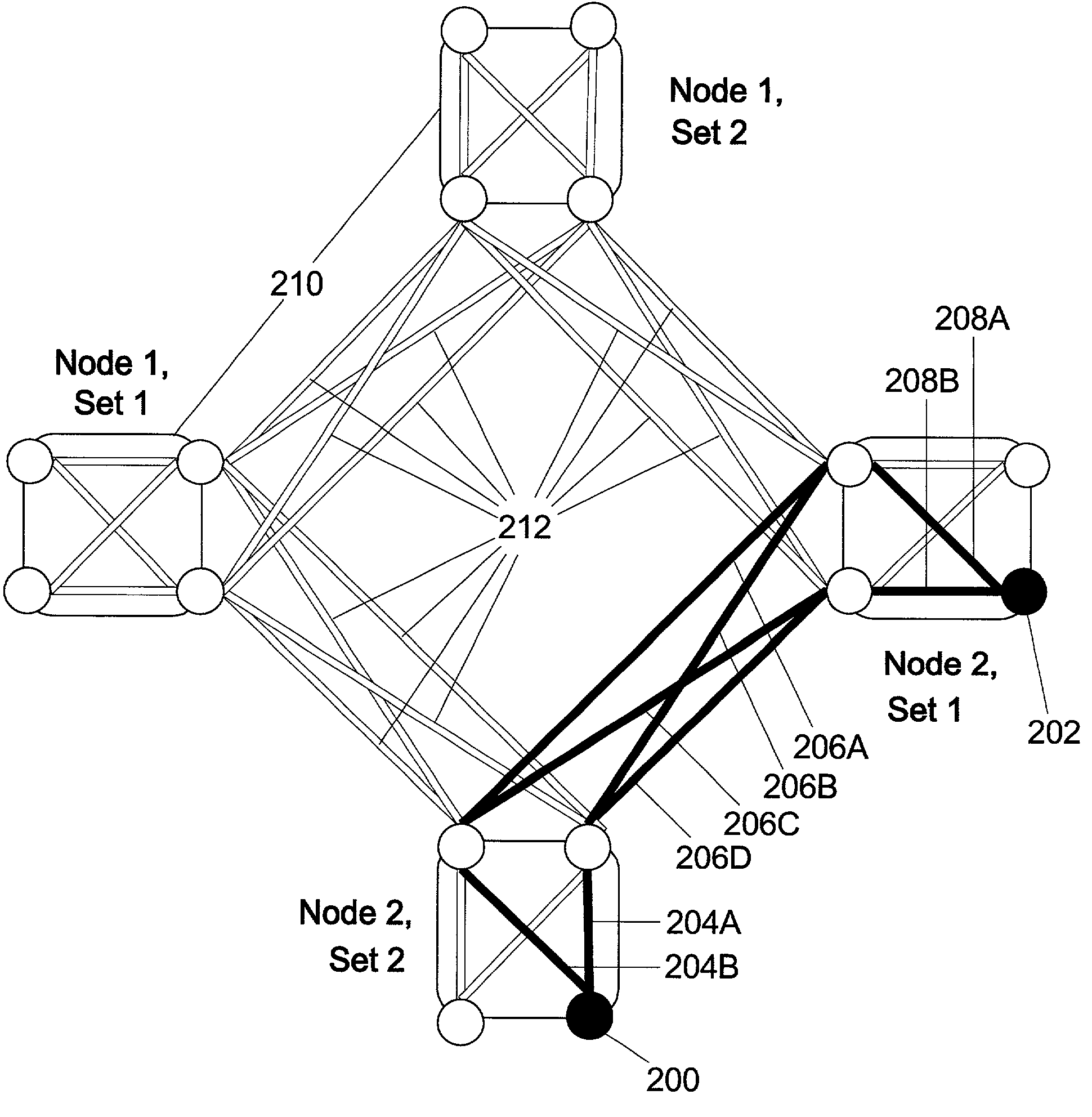
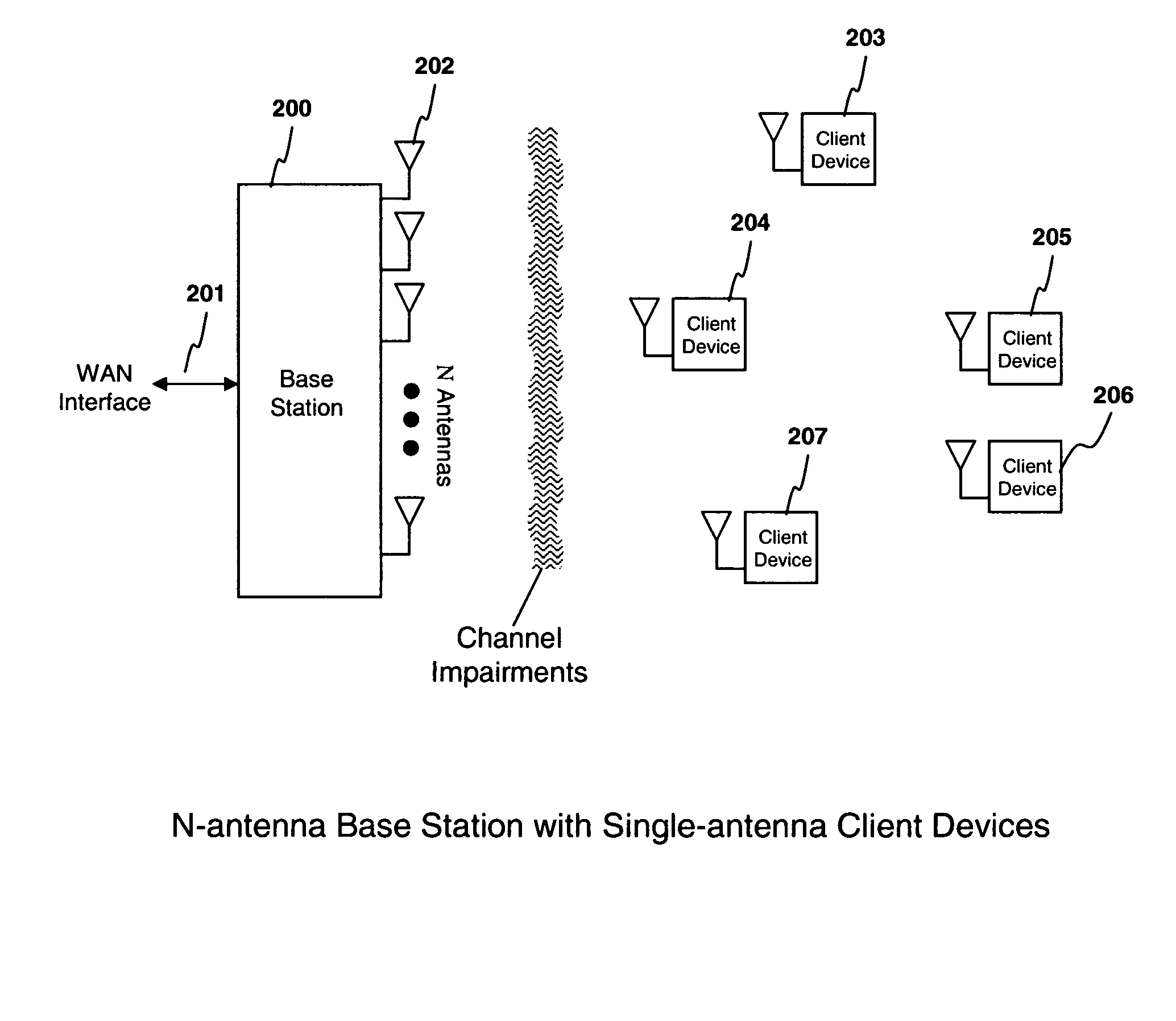
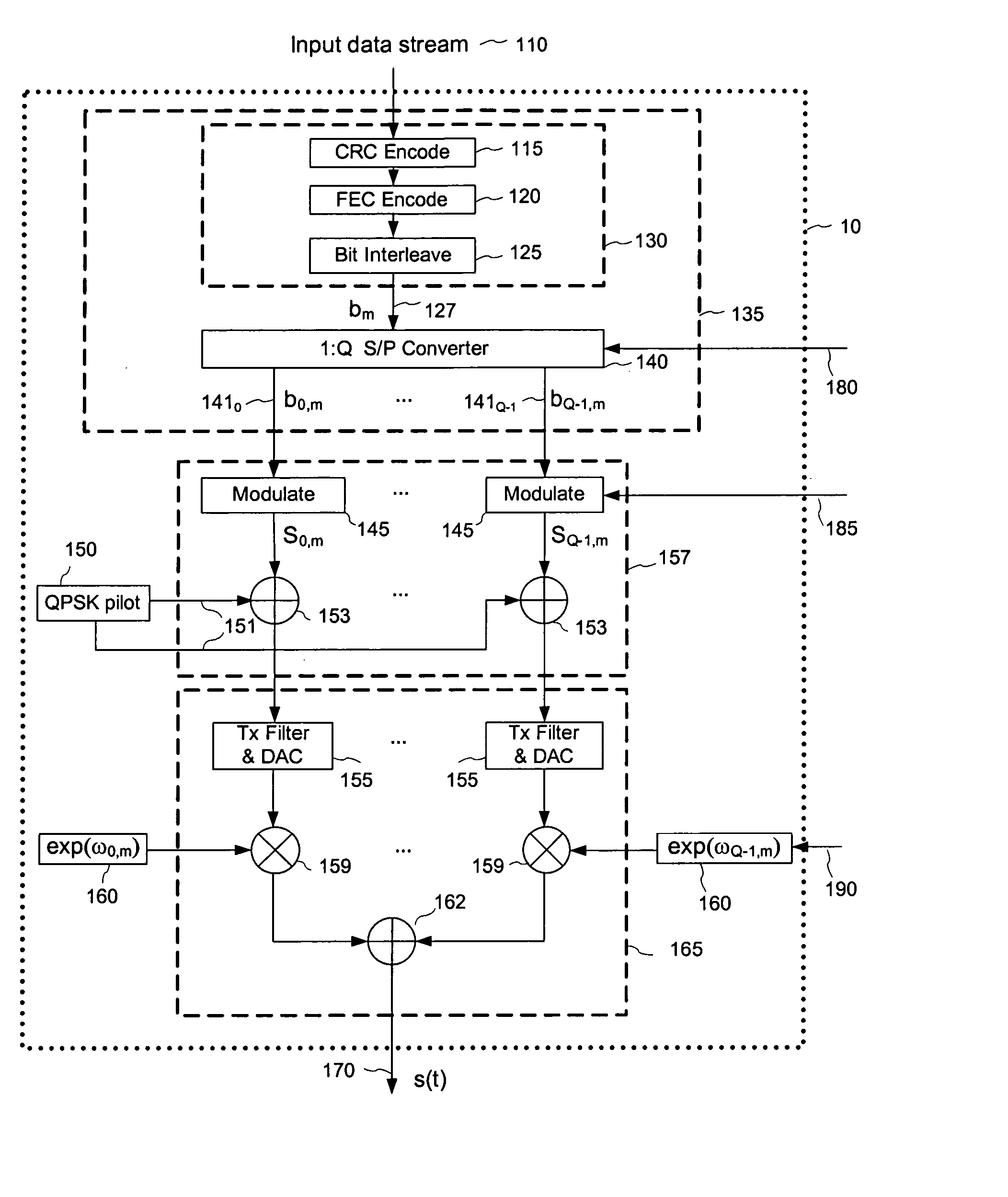
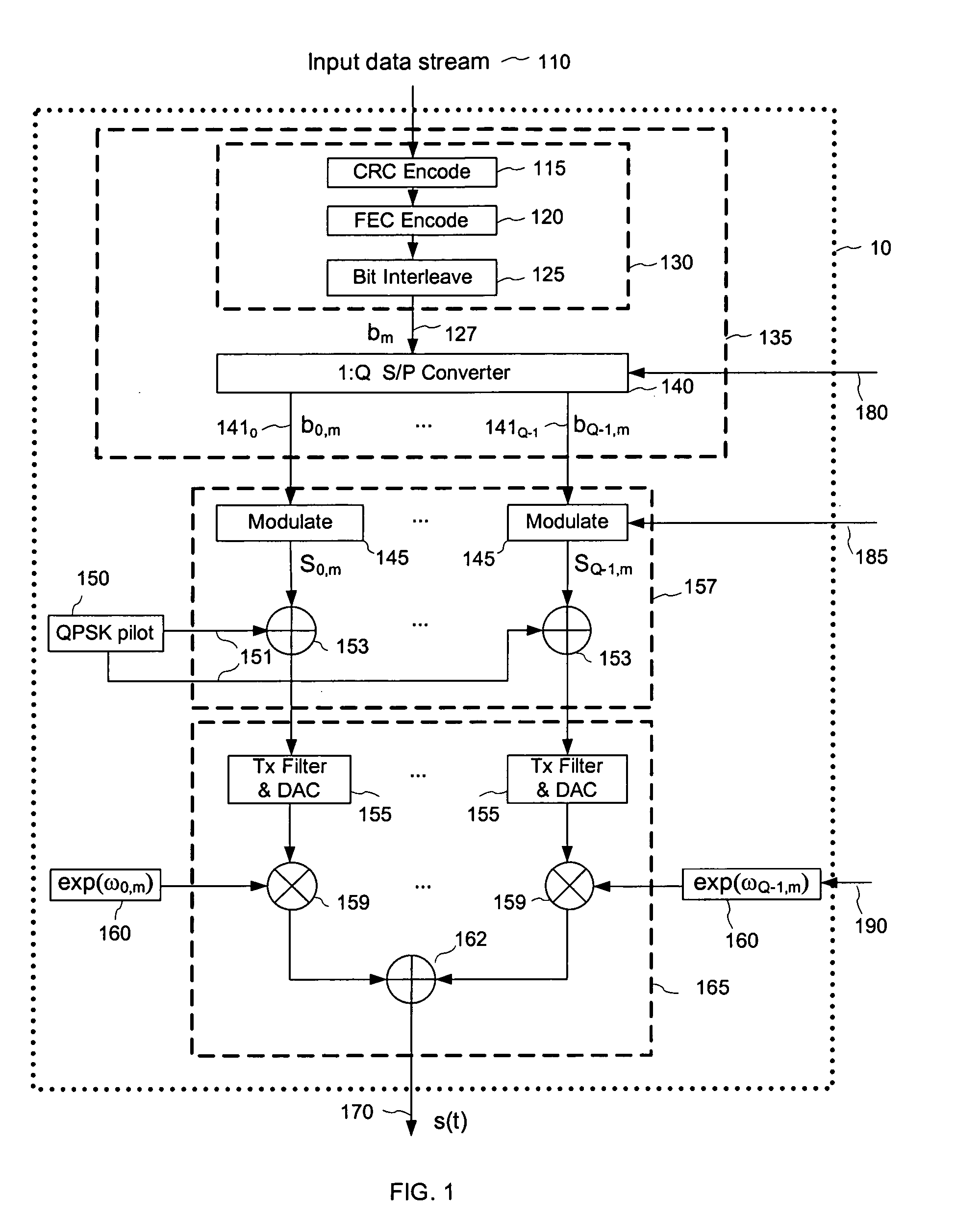
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS20040095907A1Improve signal qualityReduce interference energyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationDiversity scheme
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitione encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Interference suppression in CDMA systems
ActiveUS20020051433A1Improved interference suppressionSuppresses any sensitivitySpatial transmit diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
A receiver of the present invention addresses the need for improved interference suppression without the number of transmissions by the power control system being increased, and, to this end, provides a receiver for a CDMA communications system which employs interference subspace rejection to tune a substantially null response to interference components from selected signals of other user stations. Preferably, the receiver also tunes a substantially unity response for a propagation channel via which a corresponding user's signal was received. The receiver may be used in a base station or in a user / mobile station.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
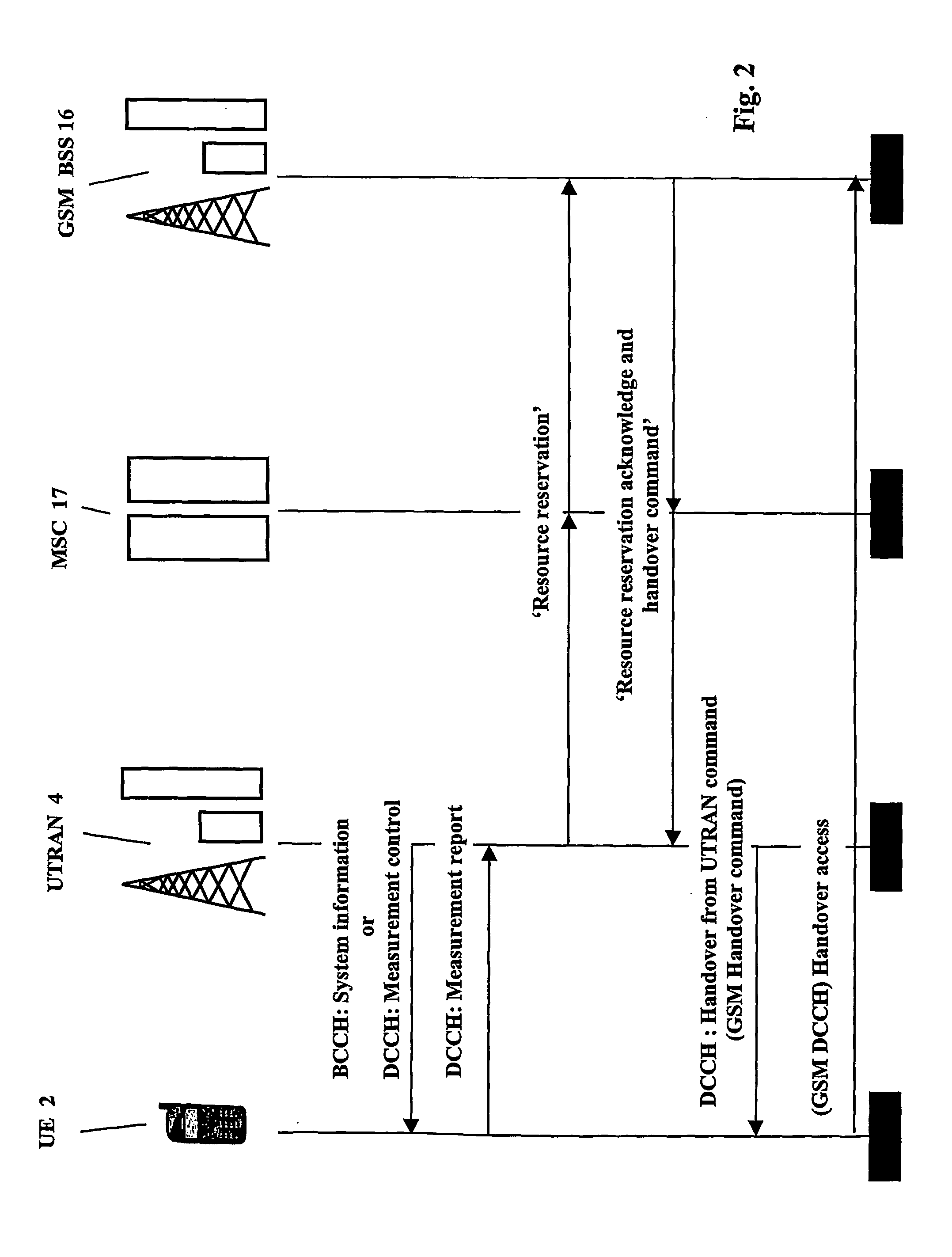
System and method for message redirection between mobile telecommunication networks with different radio access technologies
InactiveUS20040147262A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyCommunications system
Communication systems and methods are provided allowing a single mode mobile terminal to support mobile assisted signal strength measurement operations in both a fixed frequency reuse based communication network and an adaptive channel allocation based communication network. Candidate base station signal strength measurements are requested by a fixed frequency reuse type network, measured by the mobile terminal and provided to the fixed frequency reuse type network which is seeking to identify a strongest signal for mobile assisted handover operations. In addition, interference signal strength measurements are requested by an adaptive channel allocation type network, measured by the mobile terminal and provided to the adaptive channel allocation type network by the mobile terminal. No redundant circuitry is required in the mobile terminal. Instead, the mobile terminal executes the same operations using the same hardware regardless of whether the requested measurement is of a candidate signal strength or an interference signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method utilizing a cognitive transceiver for ad hoc networking
InactiveUS20060084444A1Network topologiesBroadcast service distributionBroadcast channelsCommunications system
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for utilizing unused portions of an allocated frequency spectrum in a wireless communications system that broadcasts content to wireless stations. A first wireless station may communicate with a second wireless station on an idle broadcast channel while keeping the resulting interference level below an acceptable maximum limit at the other wireless stations. Using interference level information that are measured at the wireless stations, the wireless station can negotiate with the other wireless station on an establishment channel for subsequent communications on one or more broadcast channels. The wireless station may receive broadcast content on a time slice that corresponds to a broadcast channel and that is further processed by the wireless station. Otherwise, the wireless station can utilize the corresponding time to measure an interference level for the corresponding channel or to transmit or receive data to / from another wireless station.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks
InactiveUS6404386B1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCellular communication systems
An antenna apparatus which can increase capacity in a cellular communication system. The antenna operates in conjunction with a mobile subscriber unit and provides a plurality of antenna elements, each coupled to a respective signal control component such as a switch. The switch position of each antenna element is programmed for optimum reception during, for example, an idle mode which receives a pilot signal. The antenna array creates a beamformer for signals to be transmitted from the mobile subscriber unit, and a directional receiving array to more optimally detect and receive signals transmitted from the base station. By directionally receiving and transmitting signals, multipath fading is greatly reduced as well as intercell interference. Various techniques for determining the proper arrangement of signal control components for each antenna element are accommodated.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
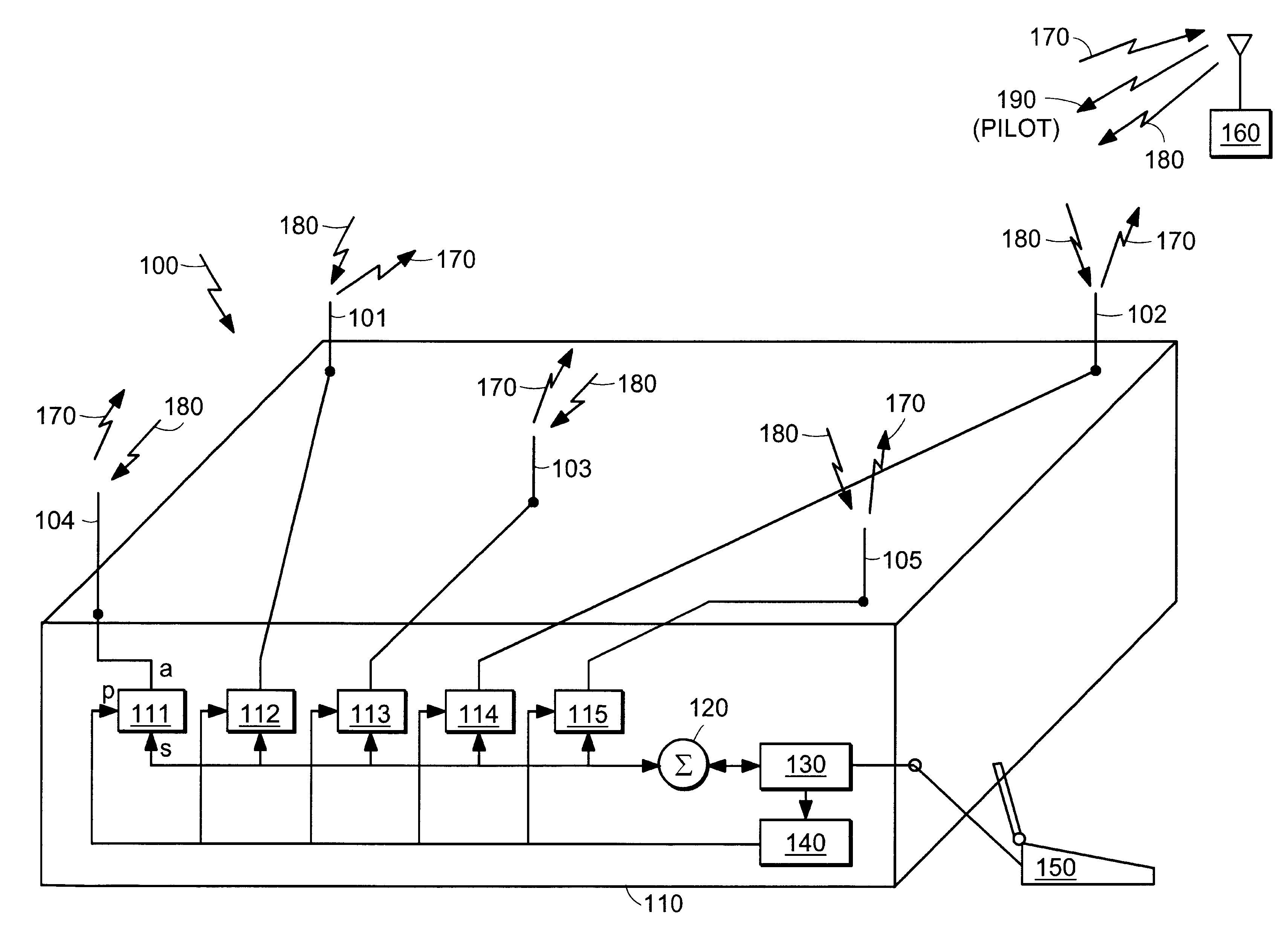
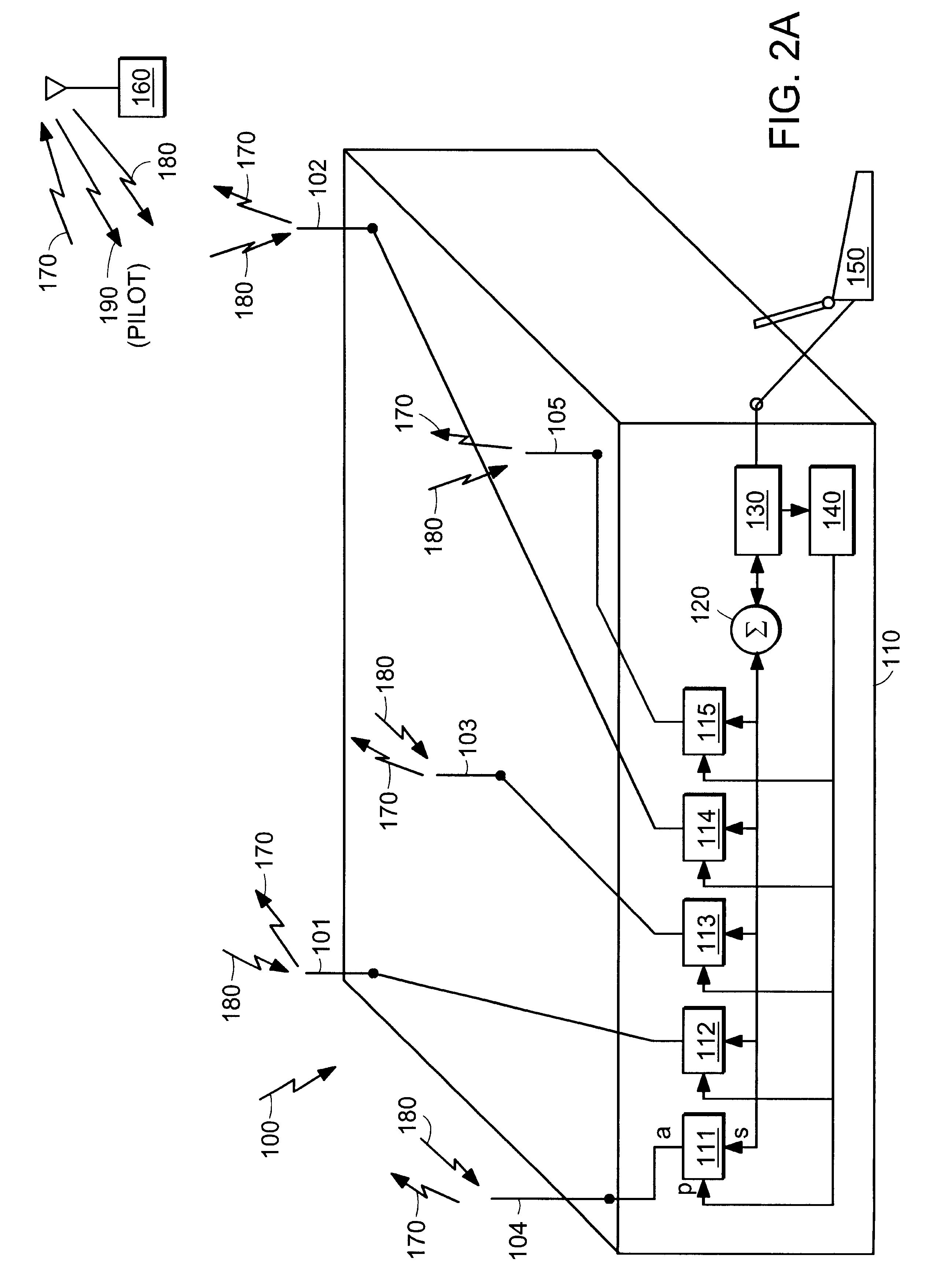
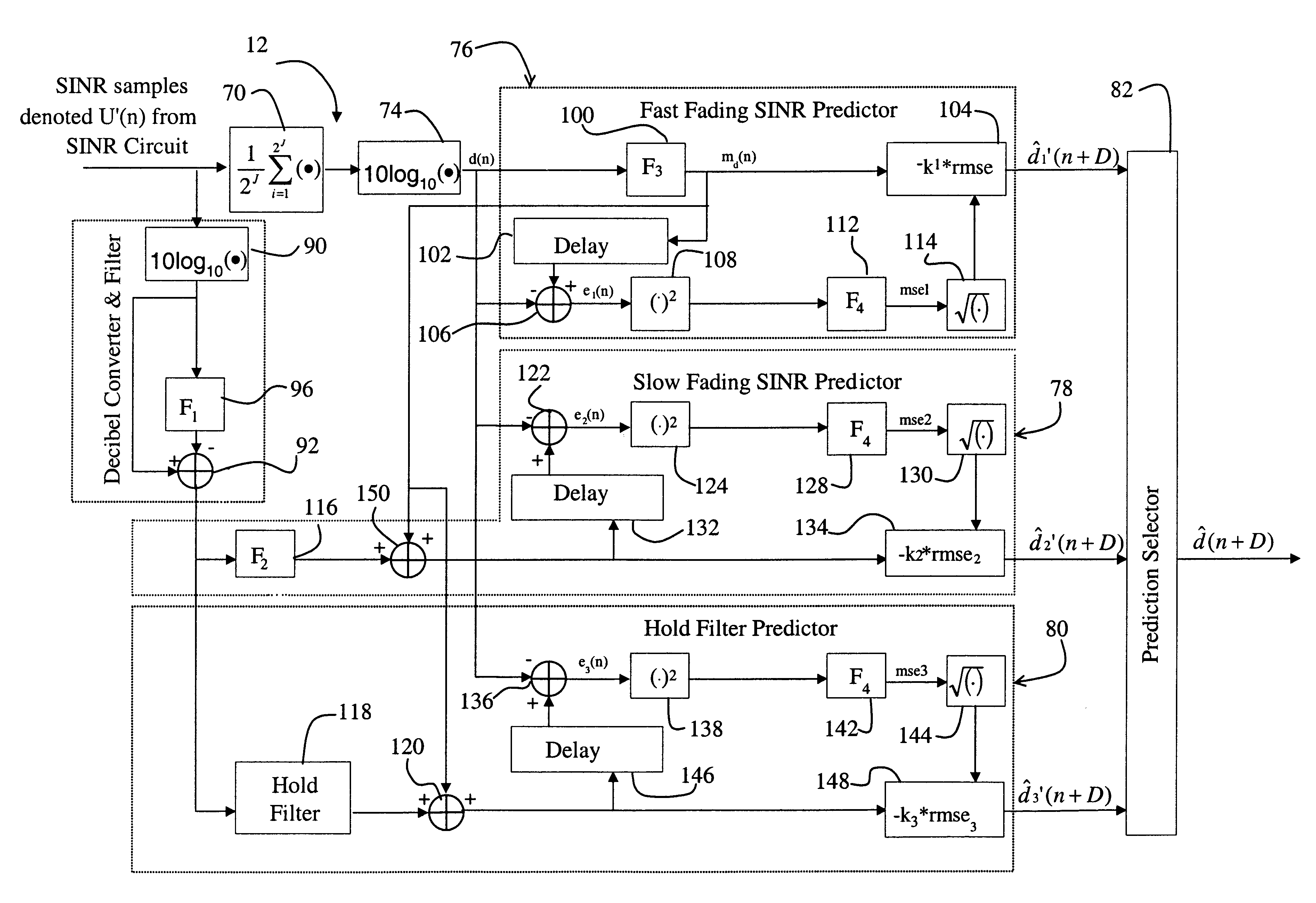
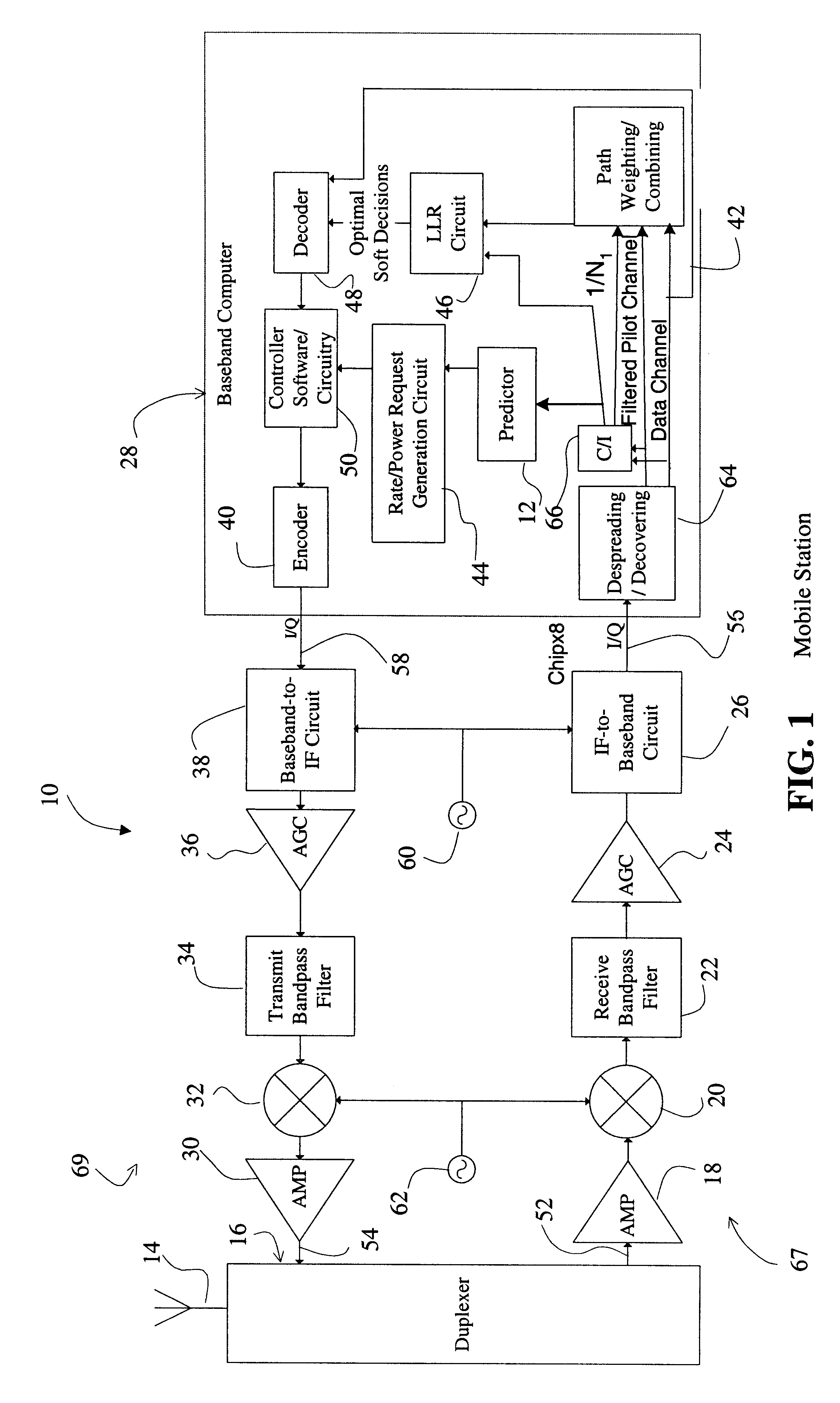
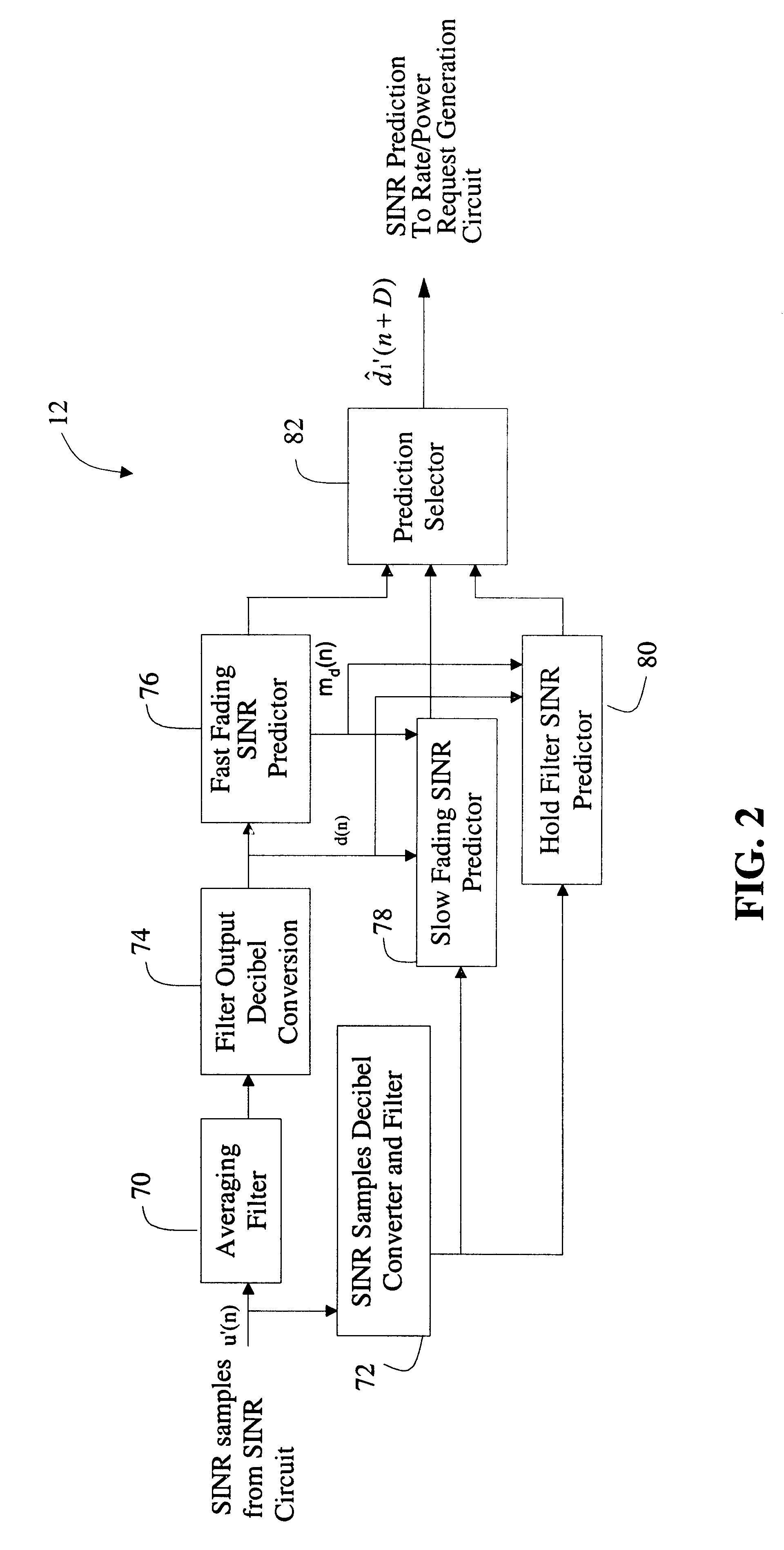
System and method for accurately predicting signal to interference and noise ratio to improve communications system performance
InactiveUS6426971B1Energy efficient ICTError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFinite impulse responseEngineering
A system for providing an accurate prediction of a signal-to-interference noise ratio is described. The system includes a first circuit for receiving a signal transmitted across a channel via an external transmitter. A second circuit generates a sequence of estimates of signal-to-interference noise ratio based on the received signal. A third circuit determines a relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates. A fourth circuit employs the relationship to provide a signal-to-interference noise ratio prediction for a subsequently received signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the inventive system further includes a circuit for generating a data rate request message based on the signal-to-noise ratio prediction. A special transmitter transmits the data rate request message to the external transmitter. In the specific embodiment, the relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates is based on an average of the elements of the sequence of estimates. The third circuit includes a bank of filters for computing the average. The bank of filters includes finite impulse response filters. Coefficients of the transfer functions associated with each filter in the bank of filters are tailored for different fading environments. The different fading environments include different Rayleigh fading environments, one environment associated with a rapidly moving system, a second environment associated with a slow moving system, and a third system associated with a system moving at a medium velocity. A selection circuit is connected to each of the filter banks and selects an output from one of the filters in the filter bank. The selected output is associated with a filter having a transfer function most suitable to a current fading environment.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive control system for interference rejections in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6934340B1Improved interference rejectionImprove robustnessSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemControl system
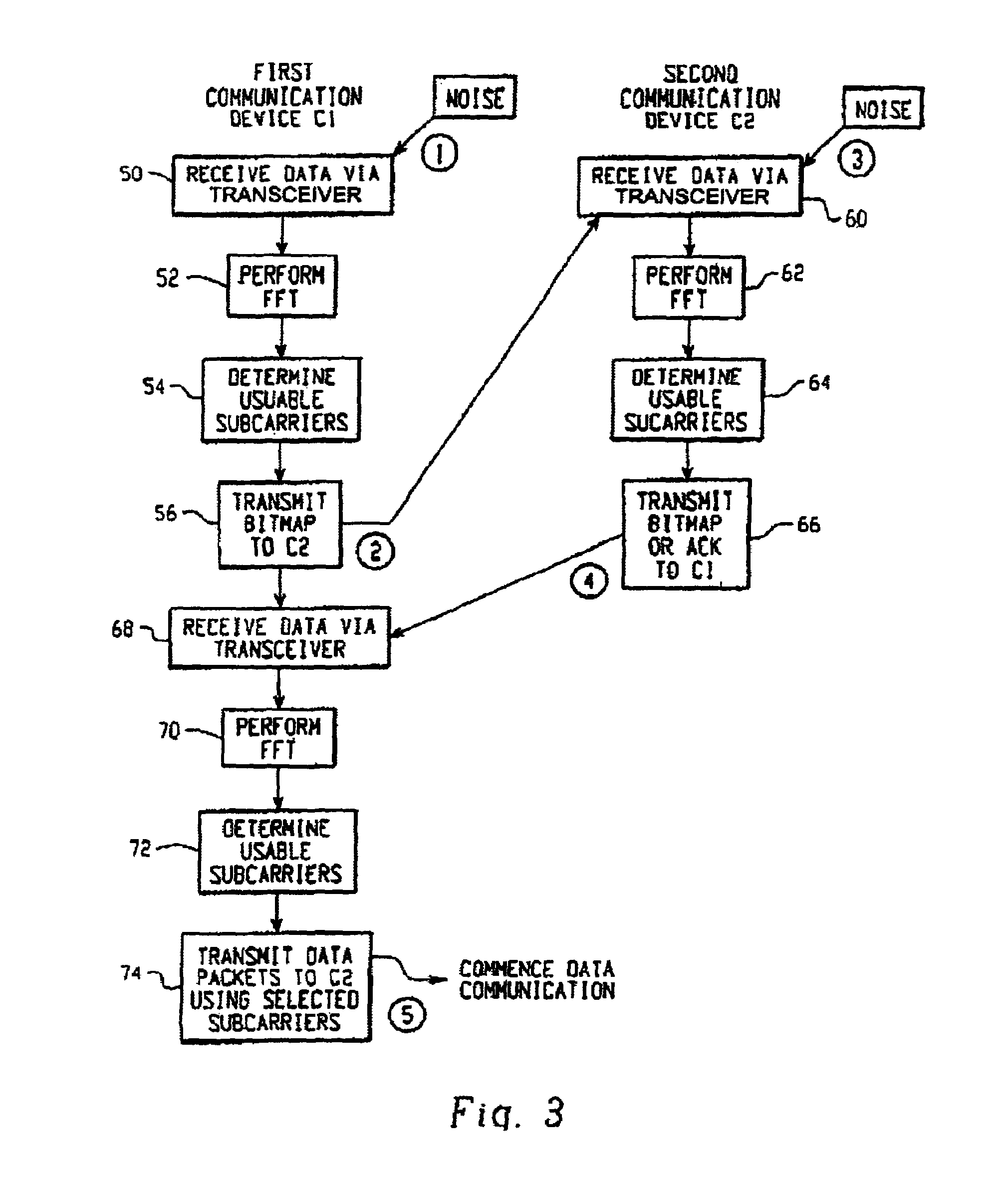
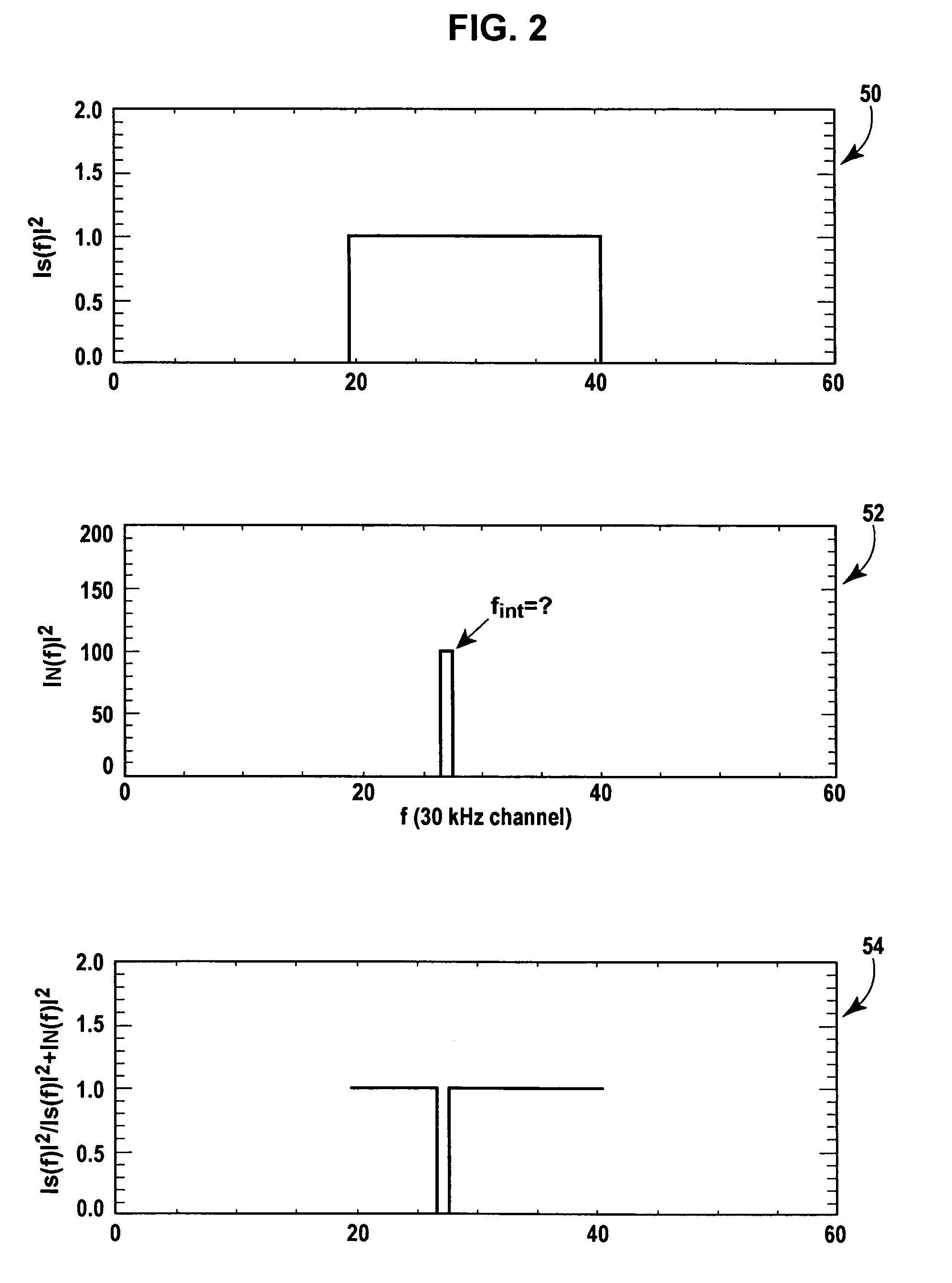
An adaptive control system for controlling the effects of narrow to medium bandwidth interferers in a wireless communications system (e.g., wireless LAN devices) by identifying which sub-carriers in a multi-carrier system are located on frequencies that are subject to interfering signals, and using only those sub-carriers that are not subject to interference for communications between wireless communications devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for detecting interference using correlation
ActiveUS7525942B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemInterference (communication)
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
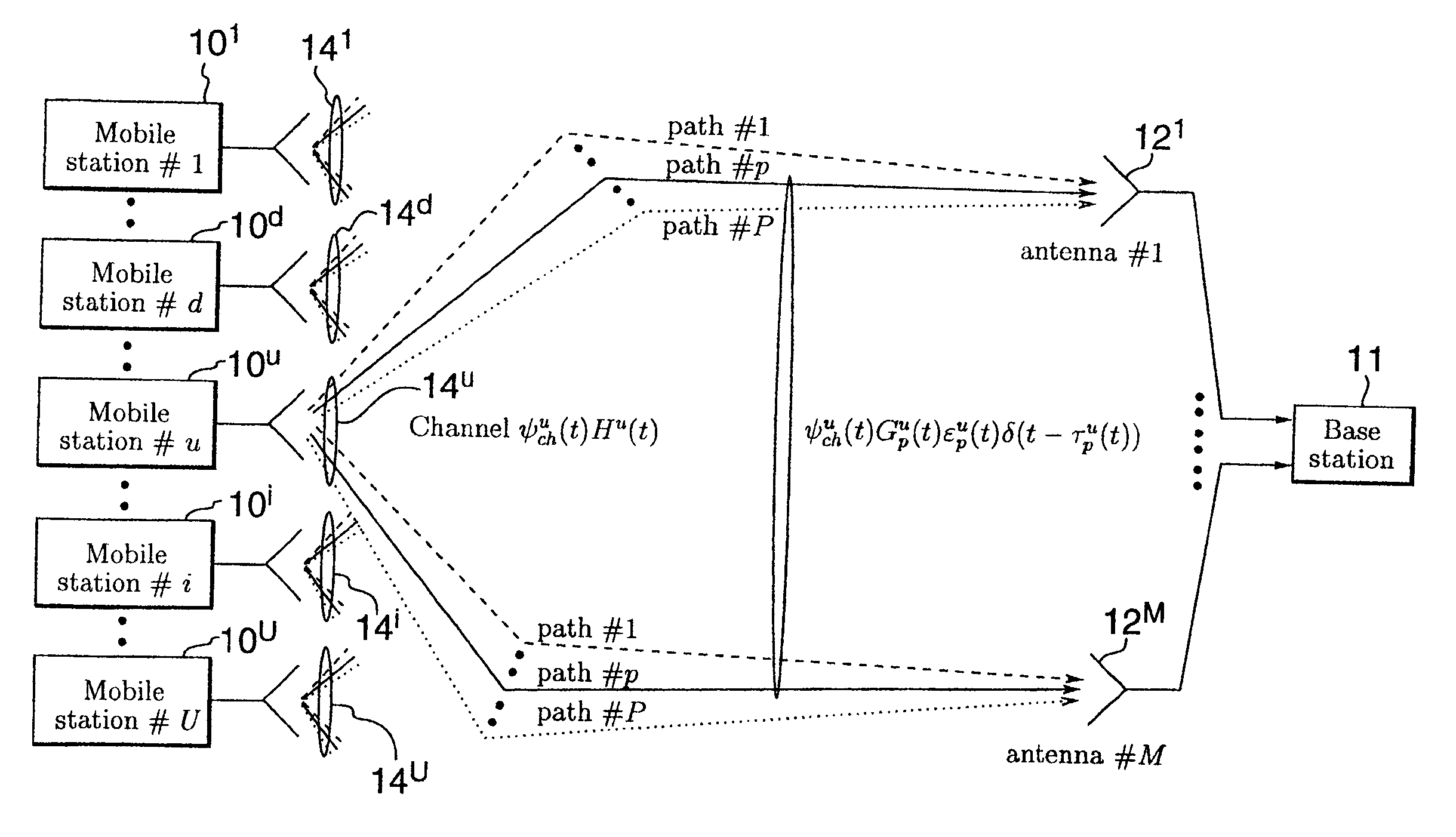
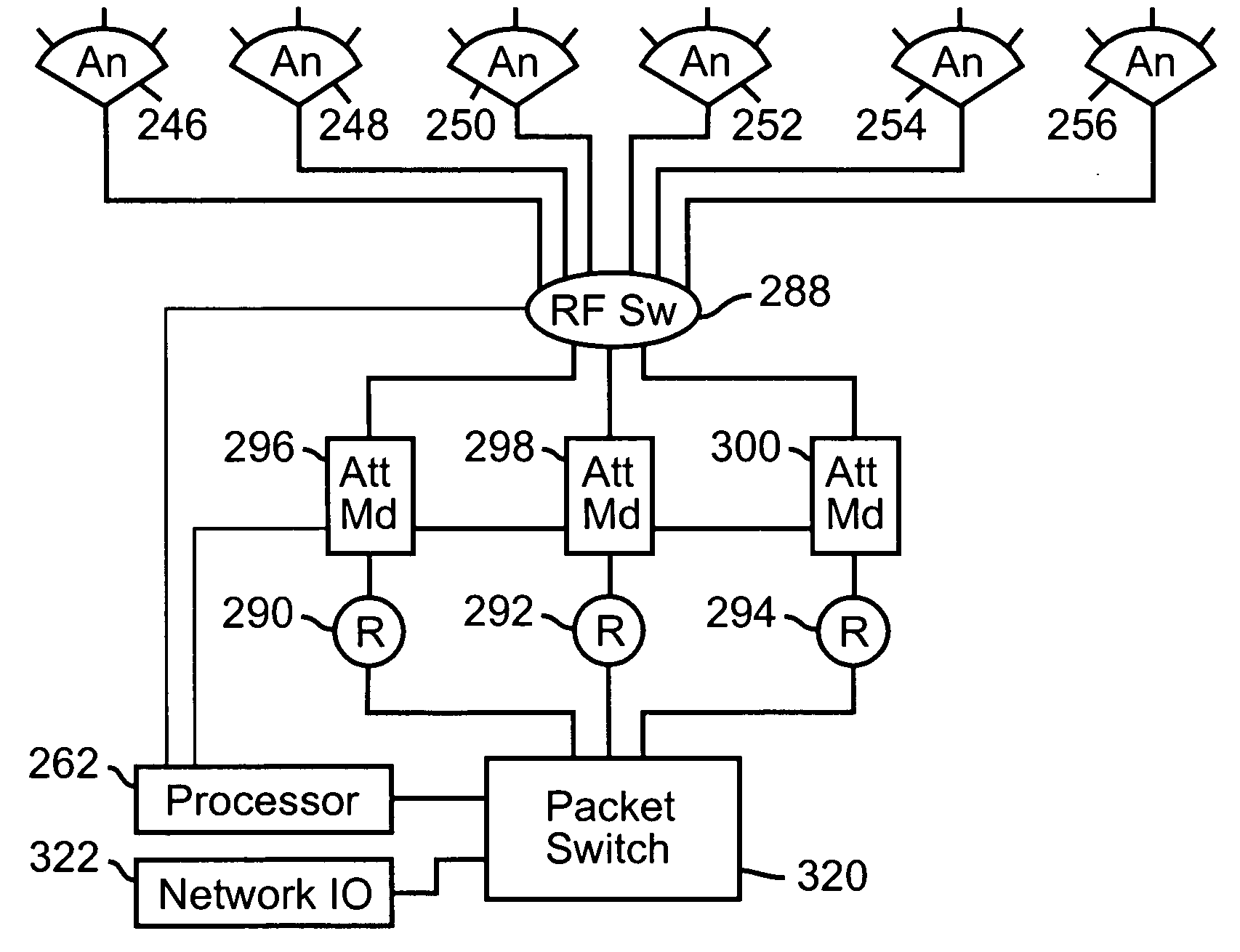
System and method for distributed input distributed output wireless communications
A system and method are described for compensating for frequency and phase offsets in a multiple antenna system (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (“MU-MAS”). For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to one or each of a plurality of wireless client devices, one or each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate frequency offset compensation data, and receiving the frequency offset compensation data at the base station; computing MU-MAS precoder weights based on the frequency offset compensation data to pre-cancel the frequency offset at the transmitter; precoding training signal using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded training signals for each antenna of the base station; transmitting the precoded training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of wireless client devices, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and receiving the channel characterization data at the base station; computing a plurality of MU-MAS precoder weights based on the channel characterization data, the MU-MAS precoder weights calculated to pre-cancel frequency and phase offset and / or inter-user interference; precoding data using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN
RFID reader for a security system
InactiveUS7057512B2Improve reliabilityBurglar alarm by openingFrequency-division multiplex detailsSecurity systemEmbedded system
An RFID reader for use in a security system based upon RFID techniques. The RFID reader can use power line carrier communications to communicate with the controllers in the security system. The RFID reader of the security system can be provided with multiple modulation techniques, multiple antennas, and the capability to vary its power level and carrier frequency. The controller of the security system determines which RFID readers may transmit, at what times, and the parameters with which to transmit. The RFID reader can detect interference or jamming, and respond. The RFID reader can transmit RF energy useful for detecting motion or for charging the batteries in RFID transponders. The RFID reader can receive wireless communications from active transmitters or from other RFID readers.
Owner:LIFESHIELD LLC
Radio communication apparatus and radio communication method
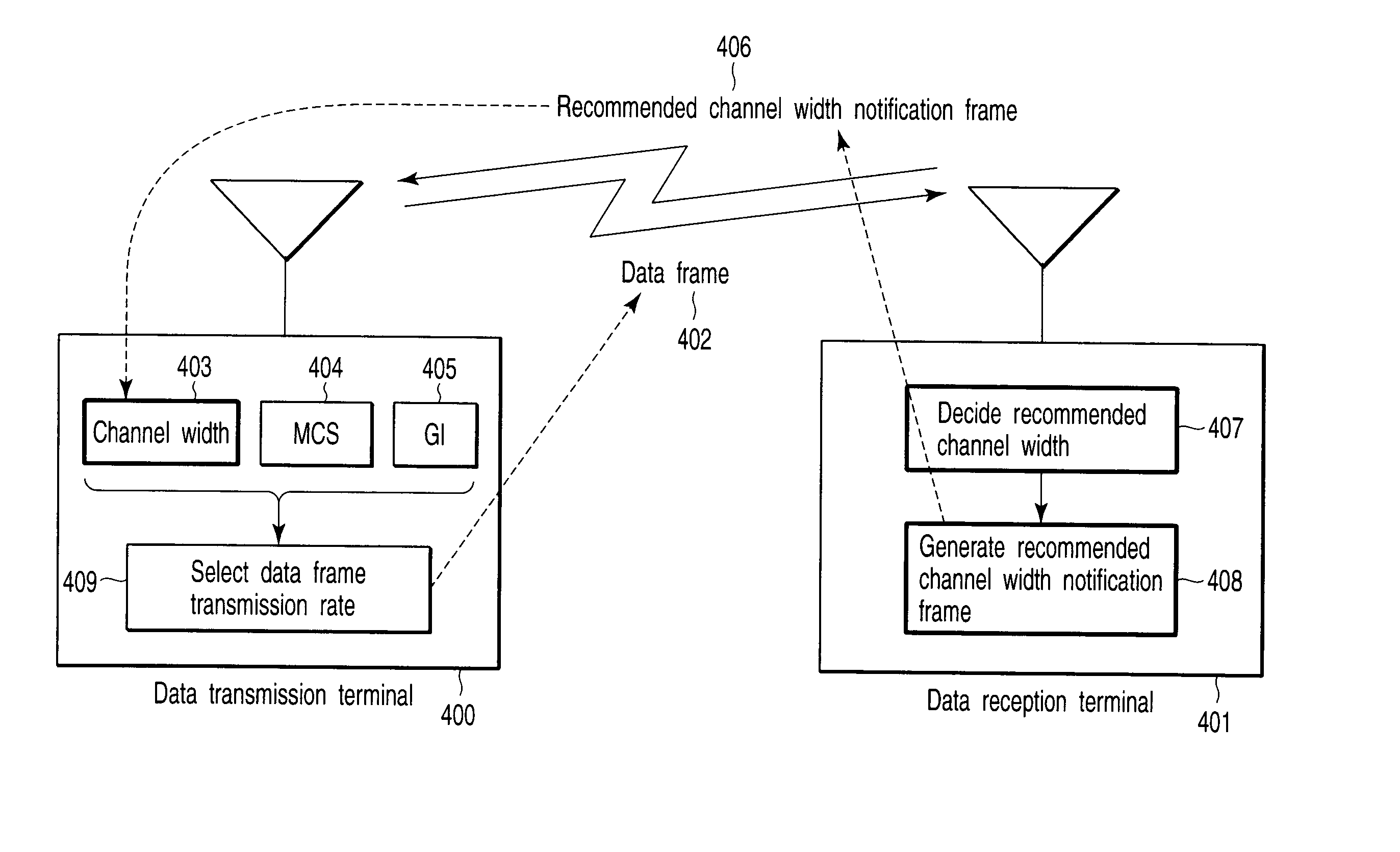
A radio communication apparatus that performs first radio communication using a first channel among two first channels each having a first channel width, and second radio communication using a second channel having a second channel width that is wider than the first channel width and also having a channel width overlapping with the two first channels. The apparatus includes an interference detection device which detects that interference occurs in the first channel among the two first channels, and a frame generation unit which generates a notification frame that recommends the use of only the first channel width. An instruction unit instructs the frame generation unit to generate the notification frame when the occurrence of interference is detected by the interference detection device. A frame transmission unit transmits the notification frame generated from the frame generation unit in response to the instruction from the instruction unit.
Owner:PALMIRA WIRELESS AG
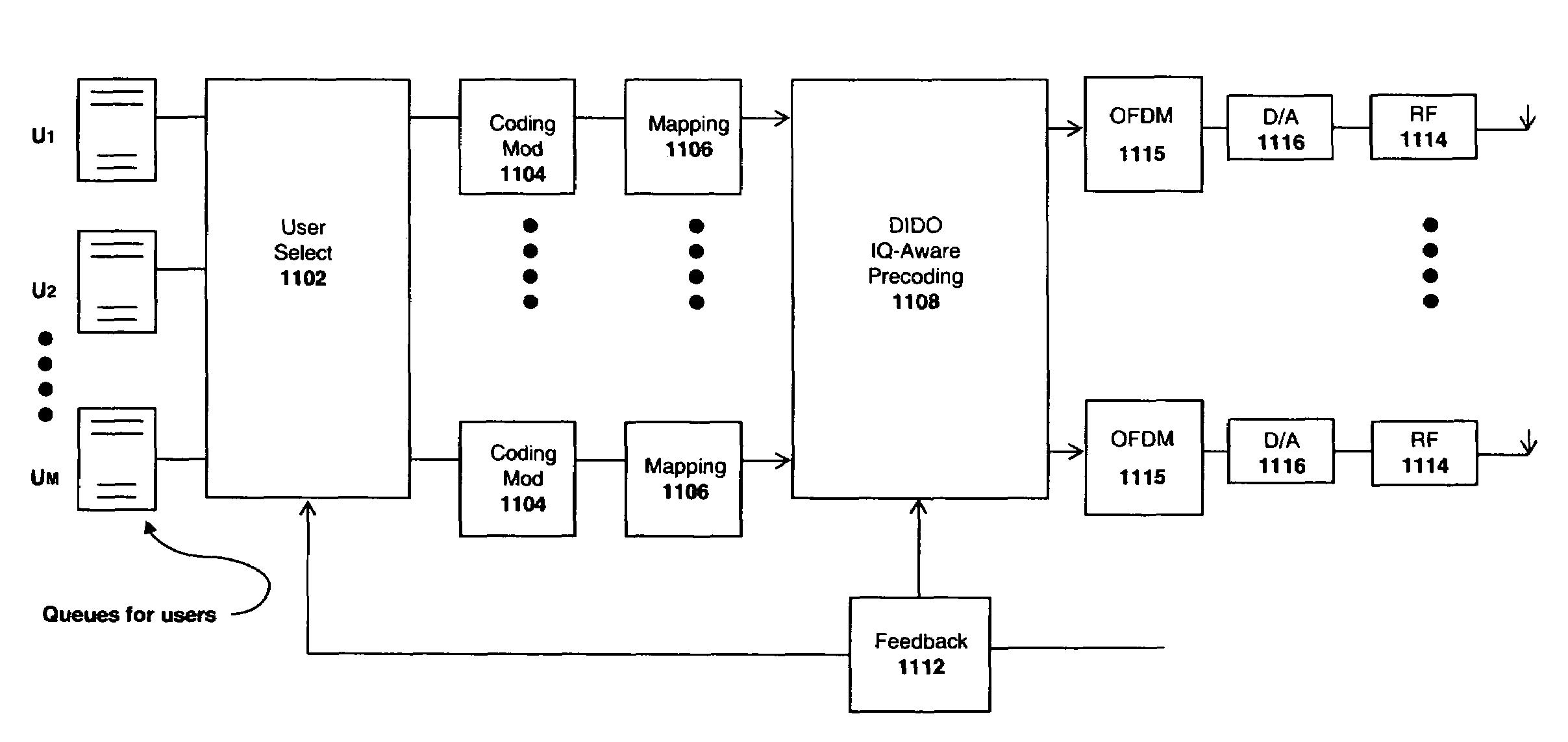
System and method for distributed input-distributed output wireless communications
A system for compensating for in-phase and quadrature (I / Q) imbalances for multiple antenna systems (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (defined with the acronym MU-MAS), such as distributed-input distributed-output (DIDO) communication systems, comprising multicarrier modulation, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). For example, one embodiment of the system comprises one or more coding modulation units to encode and modulate information bits for each of a plurality of wireless client devices to produce encoded and modulated information bits; one or more mapping units to map the encoded and modulated information bits to complex symbols; and a MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding unit to exploit channel state information obtained through feedback from the wireless client devices to compute MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding weights, the MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware preceding unit precoding the complex symbols obtained from the mapping units using the weights to pre-cancel interference due to I / Q gain and phase imbalances and / or inter-user interference.
Owner:REARDEN
Unified multi-carrier framework for multiple-access technologies
InactiveUS7406261B2Reduce the impactReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsOptical multiplexTransmission protocolCarrier signal
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Orthogonality is provided by carrier interference, which causes a narrow pulse in the time domain corresponding to each transmitted data symbol. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Equivalently, pulse waveforms may be generated from an appropriate selection of polyphase sub-carrier codes. Time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers may be employed for multiple access. Received signals are processed by combining frequency-domain components corresponding to a desired user's allocated carriers. Individual data symbols are processed by providing polyphase decoding, matched filtering, or time-domain shifting the received carriers. Carrier Interferometry components may be used to build various signals corresponding to other transmission protocols.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
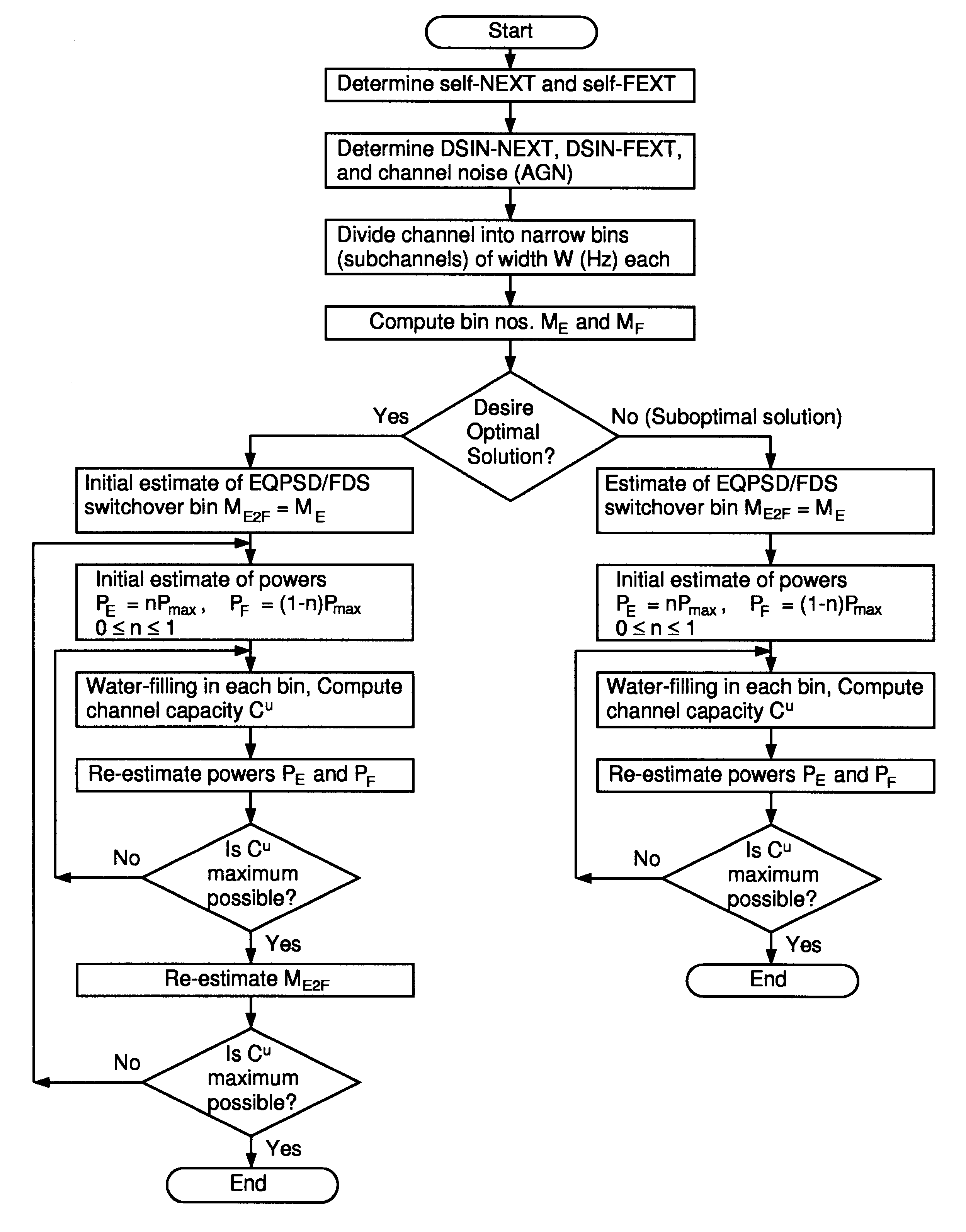
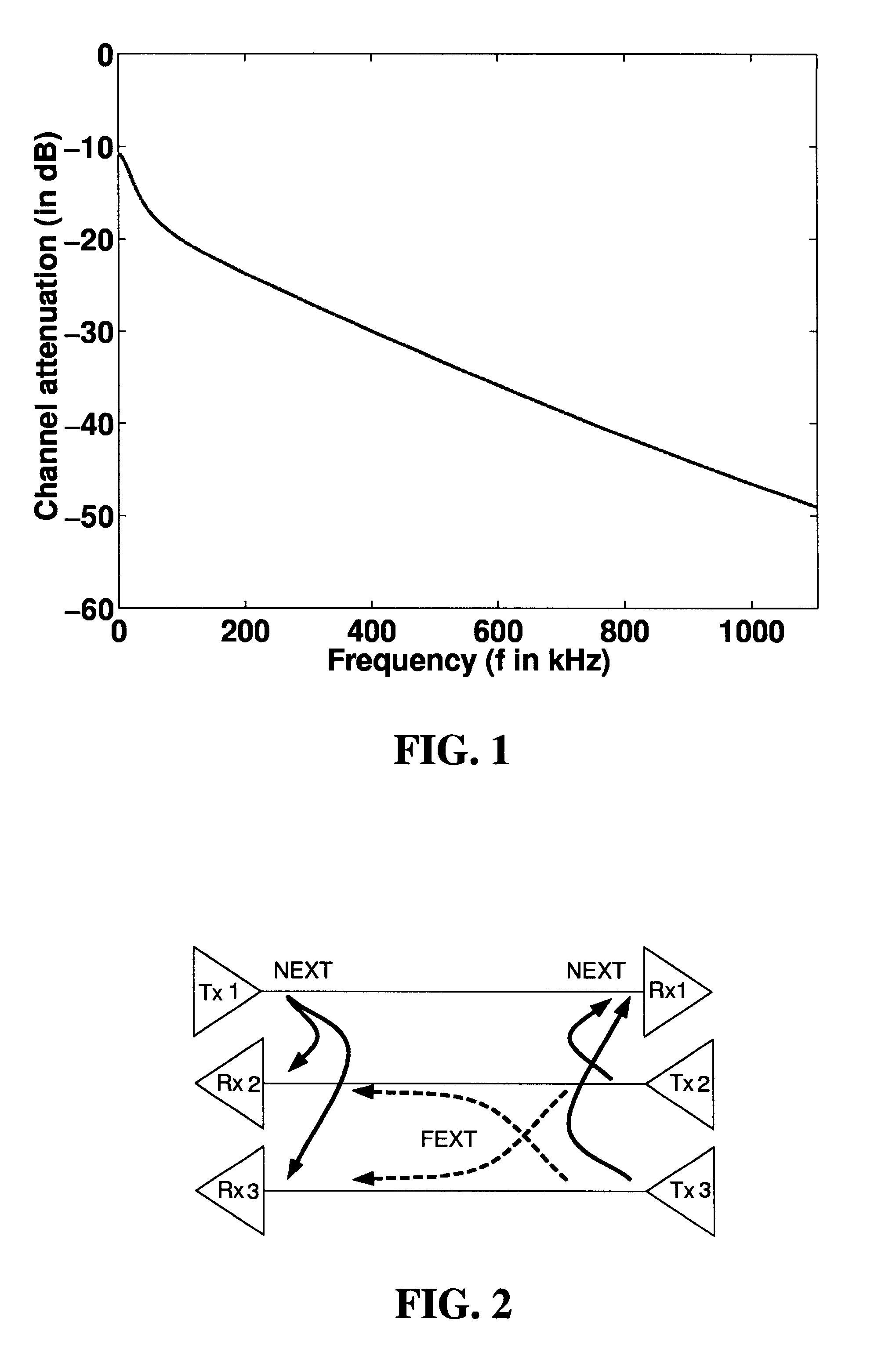
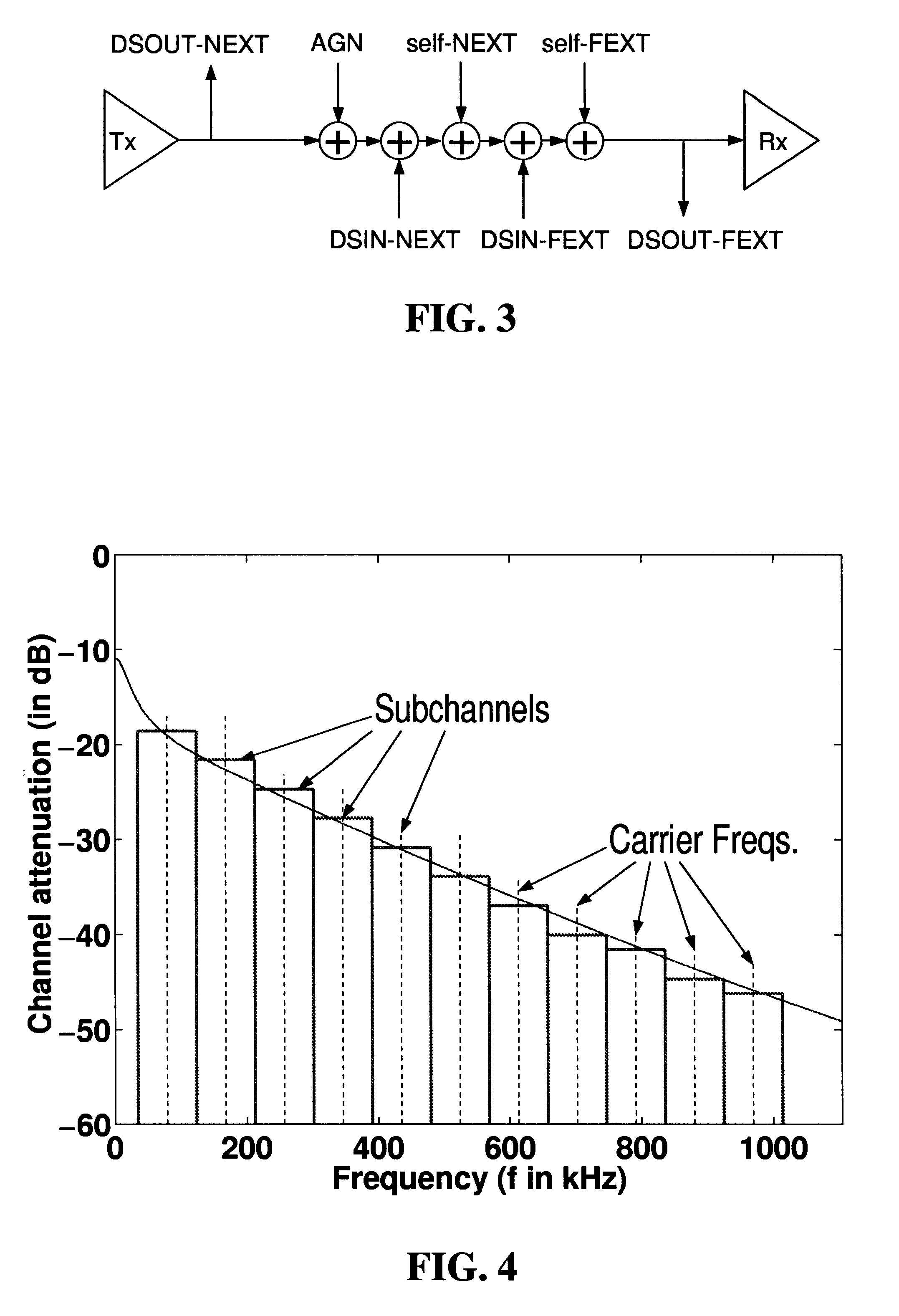
Spectral optimization and joint signaling techniques with upstream/downstream separation for communication in the presence of crosstalk
InactiveUS6292559B1Power managementSubstations coupling interface circuitsChannel transfer functionChannel capacity
A system and method for determining transmission characteristics for a communications channel and for transmitting data on the communications channel. In one embodiment, the method starts by determining the channel's transfer function and determining interference characteristics for the channel. The interference characteristics preferably include transfer functions describing the channel's susceptibility to cross talk from neighboring channels. The channel transfer function and the interference characteristics are then examined and a transmit spectrum (or power spectral density function) is constructed for the channel. The transmit spectrum preferably uses orthogonal separation of upstream and downstream communications to increase channel capacity. This method is useable in communicating data when the channel is subject to interference from one or more other communications channels, including near-end cross talk (NEXT) and far-end cross talk (FEXT), from other channels carrying the same service and / or different services. The present invention may be used in digital subscriber-line (xDSL) communications or in a variety of other applications, such as in well-logging and in systems involving multiple interfering radio transmitters.
Owner:RICE UNIV
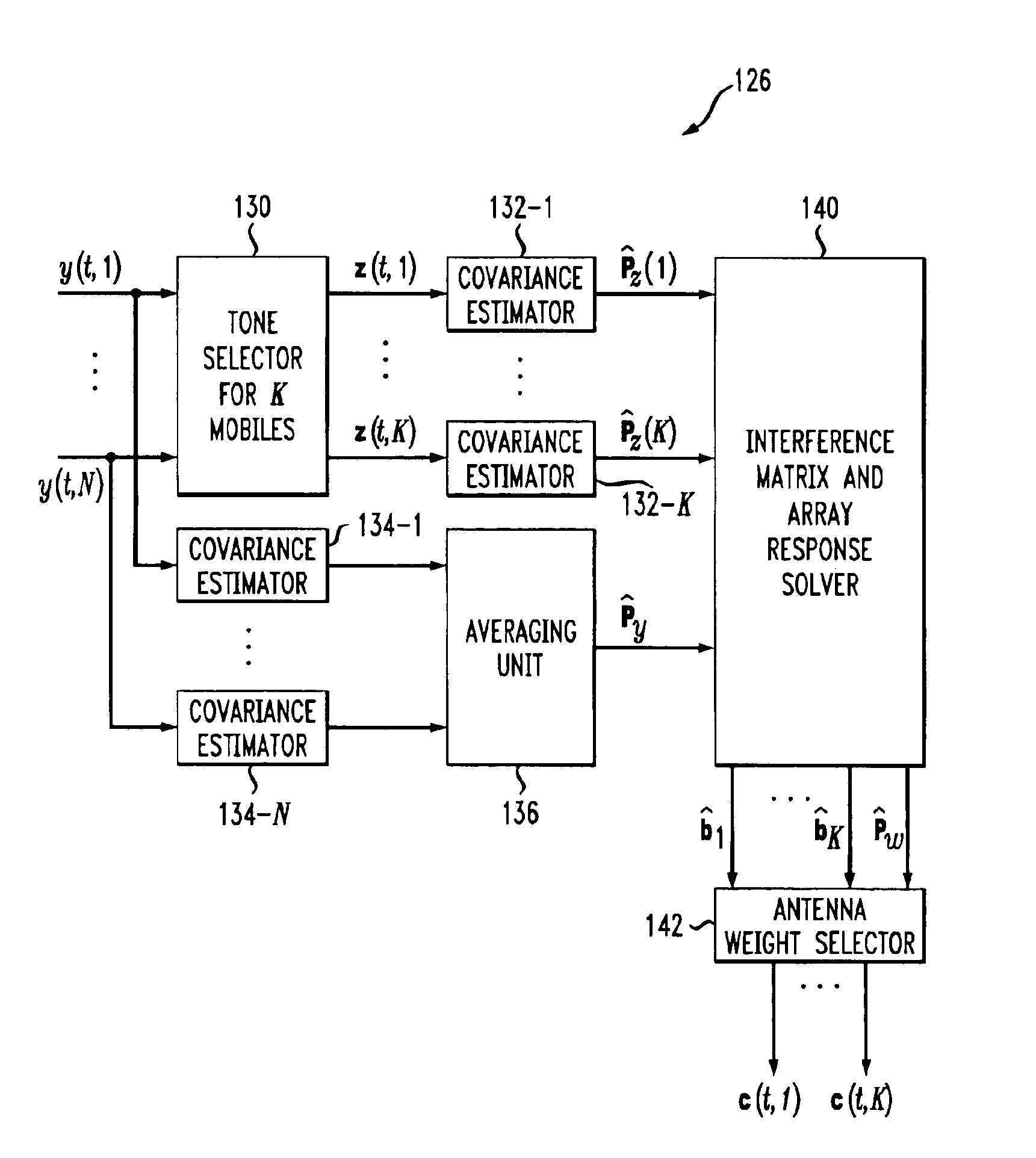
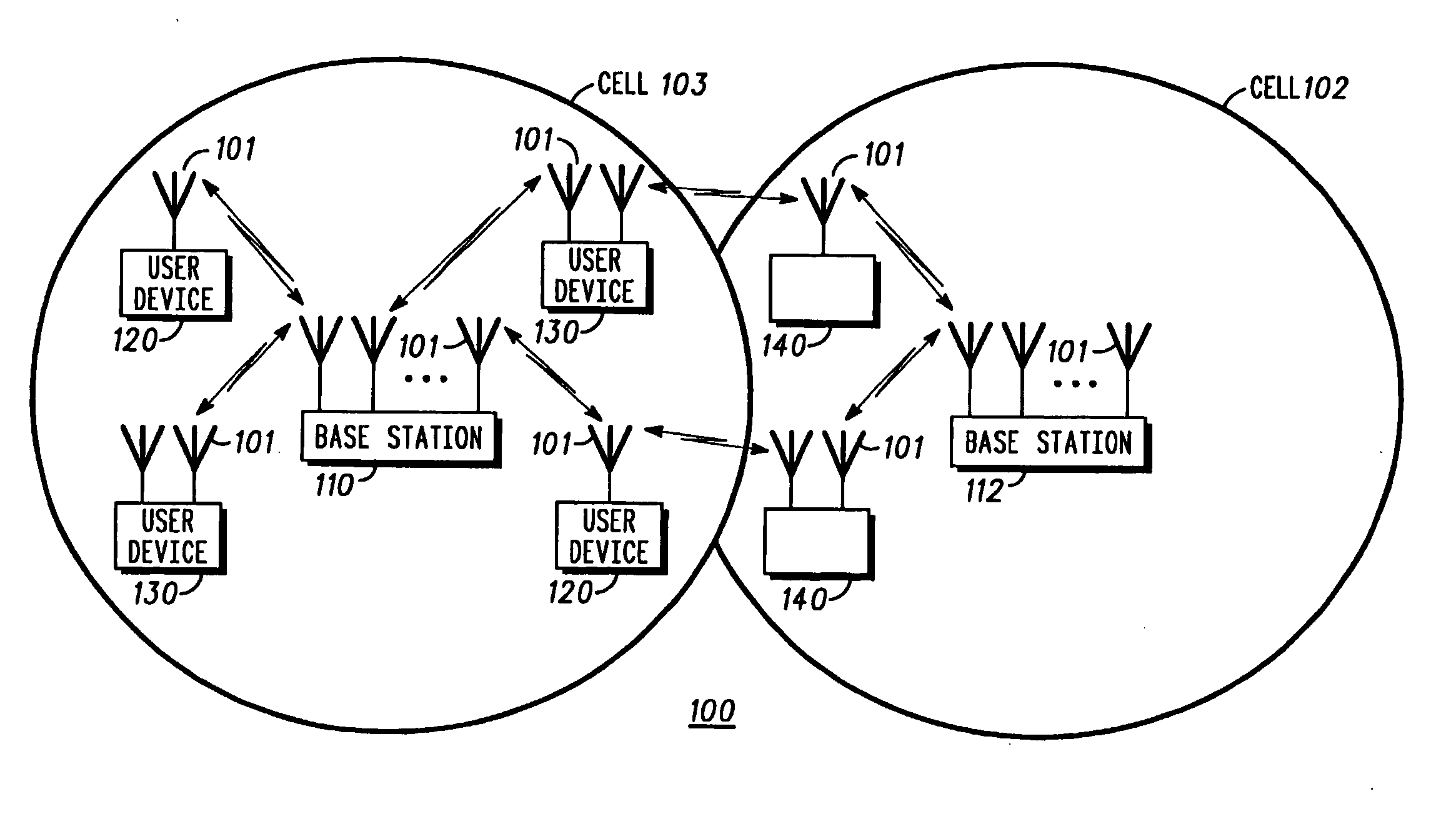
Adaptive antenna array methods and apparatus for use in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6920192B1Fast convergenceReduce computing costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
Adaptive antenna array techniques for use in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed spread-spectrum multi-access (OFDM-SSMA) cellular wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. A base station of the system includes an antenna array and a base station receiver. The base station receiver implements an adaptive antenna gain algorithm which estimates a spatial covariance matrix for each of K mobile stations communicating with the base station. The spatial covariance matrix for a given one of the mobile stations is determined at least in part based on a unique hopping sequence of the mobile station, and provides a correlation between signals received from the mobile station at different antenna elements within the antenna array. An average spatial covariance matrix for a set of received signals is also generated. The individual spatial covariance matrices and the average spatial covariance matrix are processed to generate an estimate of an interference matrix for the K mobile stations, and the estimate of the interference matrix is further processed to generate array responses for each of the mobile stations. The array response for a given mobile station is processed to determine an antenna weighting which is applied to a signal received from the given mobile station in order to facilitate detection of a corresponding transmitted symbol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Non-directional transmitting from a wireless data base station having a smart antenna system
InactiveUS6982968B1Reduce distractionsSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInterference (communication)Communications system
A method, communication apparatus, and machine-readable medium to transmit a downlink signal in a substantially non directional manner from a first communication station of a communication system on a first downlink conventional channel. The first communication station includes a smart antenna system having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes providing a first set of sequential time intervals for the communication device for communication with its remote communication devices. One or more remote communication devices of the communication system known to the first communication station to be undesired remote communication devices transmit a signal on a first uplink conventional channel. The signals transmitted are received. In one version, they are received at the first communication station, and in another version, by another communication station of the communication system. The signal received are used to configure the smart antenna system for transmitting a downlink signal in a non-directional manner that includes mitigating interference towards the undesired remote communication devices on the first downlink conventional channel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Intercell interference mitigation
ActiveUS20090264142A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceImprove coordinationTransmission path divisionSignal allocationFrequency reuseInterference (communication)
Methods and apparatus are described for mitigating intercell interference in wireless communication systems utilizing substantially the same operating frequency band across multiple neighboring coverage areas. The operating frequency band may be shared across multiple neighboring or otherwise adjacent cells, such as in a frequency reuse one configuration. The wireless communication system can synchronize one or more resource allocation regions or zones across the multiple base stations, and can coordinate a permutation type within each resource allocation zone. The base stations can coordinate a pilot configuration in each of a plurality of coordinated resource allocation regions. Subscriber stations can be assigned resources in a coordinated resource allocation region based on interference levels. A subscriber station can determine a channel estimate for each of multiple base stations in the coordinated resource allocation region to mitigate interference.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Orthogonal resource reuse with SDMA beams
ActiveUS20070249402A1Frequency-division multiplexSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaCommunications system
A wireless communication system can implement beamforming across multiple omni-directional antennas to create beams at different spatial directions. The communication system can arrange the beams in sets, with each set arranged to provide substantially complete coverage over a predetermined coverage area. The communication system can arrange the multiple SDMA beam sets to support substantially complementary coverage areas, such that a main beam from a first set provides coverage to a weak coverage area of the second beam set. The wireless communication system assigns or otherwise allocates substantially orthogonal resources to each of the beam sets. The wireless communication system allocates resources to a communication link using a combination of beam sets and substantially orthogonal resources in order to provide improved coverage without a corresponding increase in interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Cross talk reduction and impedance-matching for high speed electrical connectors
InactiveUS6976886B2Reduce weightReduced insertion lossTwo-part coupling devicesPrinted circuitsGround contactInterference (communication)
Lightweight, low cost, high density electrical connectors are disclosed that provide impedance controlled, high-speed, low interference communications, even in the absence of shields between the contacts, and that provide for a variety of other benefits not found in prior art connectors, such as low insertion loss. Signal contacts and ground contacts within the connectors can be scaled and positioned relative to one another such that a differential signal in a first differential signal pair produces a high field in the gap between the contacts that form the signal pair and a low field near an adjacent signal pair. Consequently, cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to acceptable levels for the particular application. In such connectors, the level of cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to the point that the need for (and cost of) shields between adjacent contacts is unnecessary, even in high speed, high signal integrity applications.
Owner:FCI USA LLC
Adaptive omni-modal radio apparatus and methods
InactiveUS6934558B1Easily and conveniently identifyIntense competitionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesTransmission protocolTransceiver
A frequency and protocol agile wireless communication product, and chipset for forming the same, including a frequency agile transceiver, a digital interface circuit for interconnecting the radio transceiver with external devices, protocol agile operating circuit for operating the radio transceiver in accordance with one of the transmission protocols as determined by a protocol signal and an adaptive control circuit for accessing a selected wireless communication network and for generating the frequency control signal and the protocol control signal in response to a user defined criteria Among the possible user defined criteria would be (1) the cost of sending a data message, (2) the quality of transmission link (signal strength, interference actual or potential), (3) the potential for being bumped off of the system (is service provider at near full capacity), (4) the security of transmnission, (5) any special criteria which the user could variably program into his omni-modal wireless product based on the user's desires or (6) any one or more combinations of the above features that are preprogrammed, changed or overridden by the user. The disclosed invention allows wireless service providers to broadcast electronically as part of any “handshaking” procedure with a omni-modal wireless product information such as (1) rate information and (2) information regarding system operating characteristics such as percent of system capacity in use and / or likelihood of being dropped. The disclosed invention creates a user oriented source enrollment and billing service in the wireless data market by establishing uniform standard for “handshakes” to occur between cell service providers and omni-modal wireless products. In addition, the disclosed invention can be implemented on a standard chip or chipset including a radio transceiver specifically designed to be used in all types of omni-modal wireless products.
Owner:ANTON INNOVATIONS INC
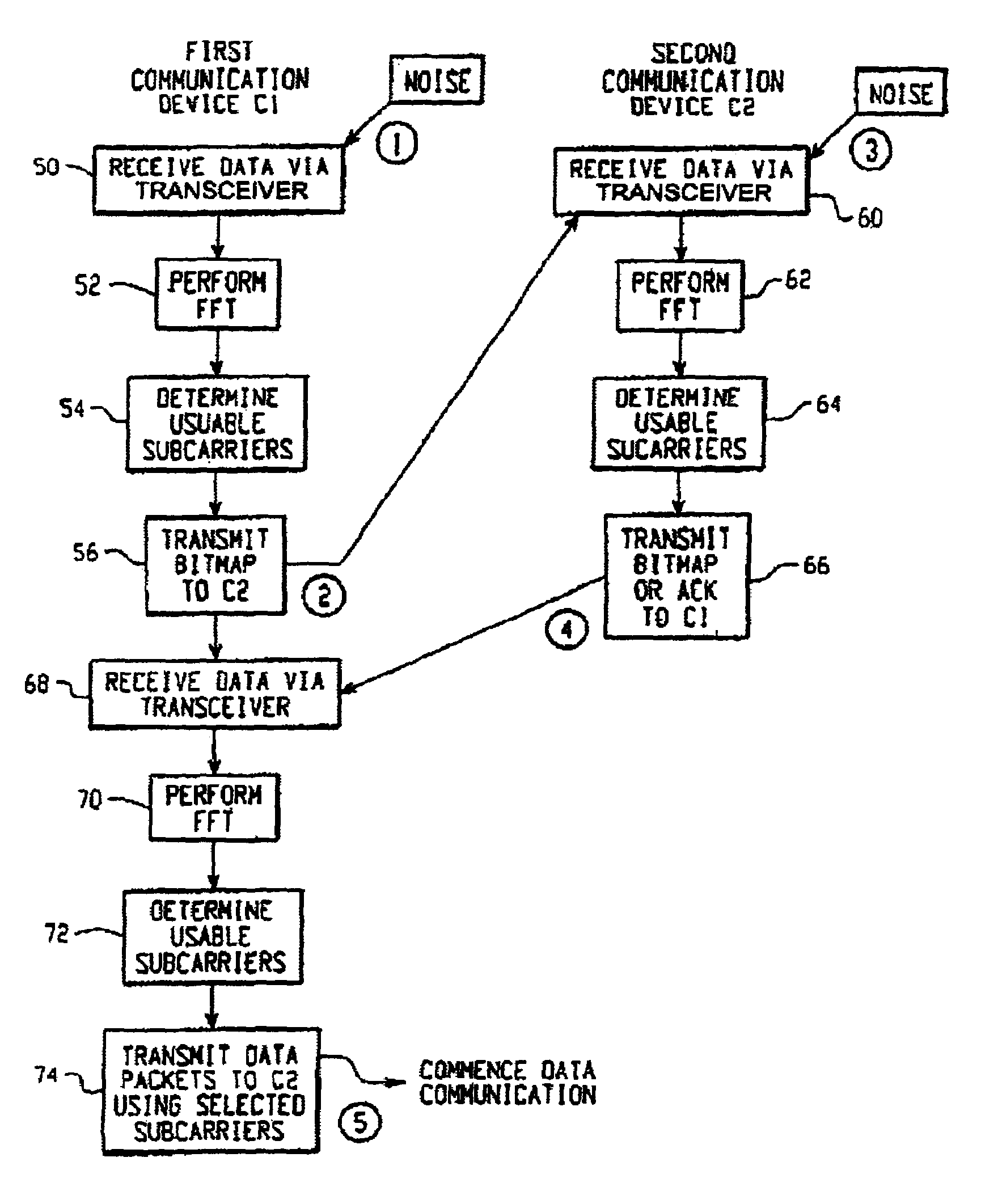
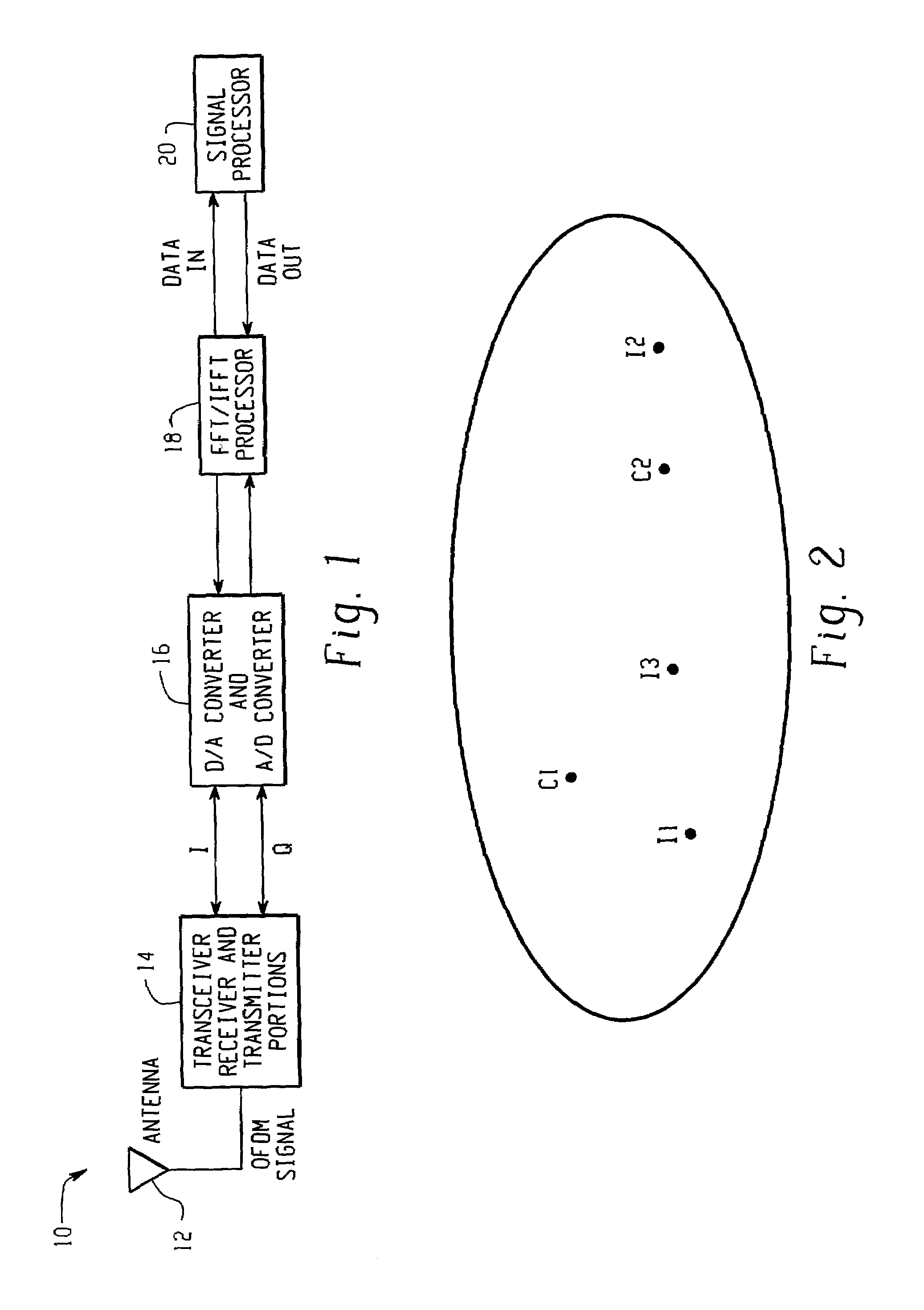
Wireless communication system, wireless communication device, and wireless communication method
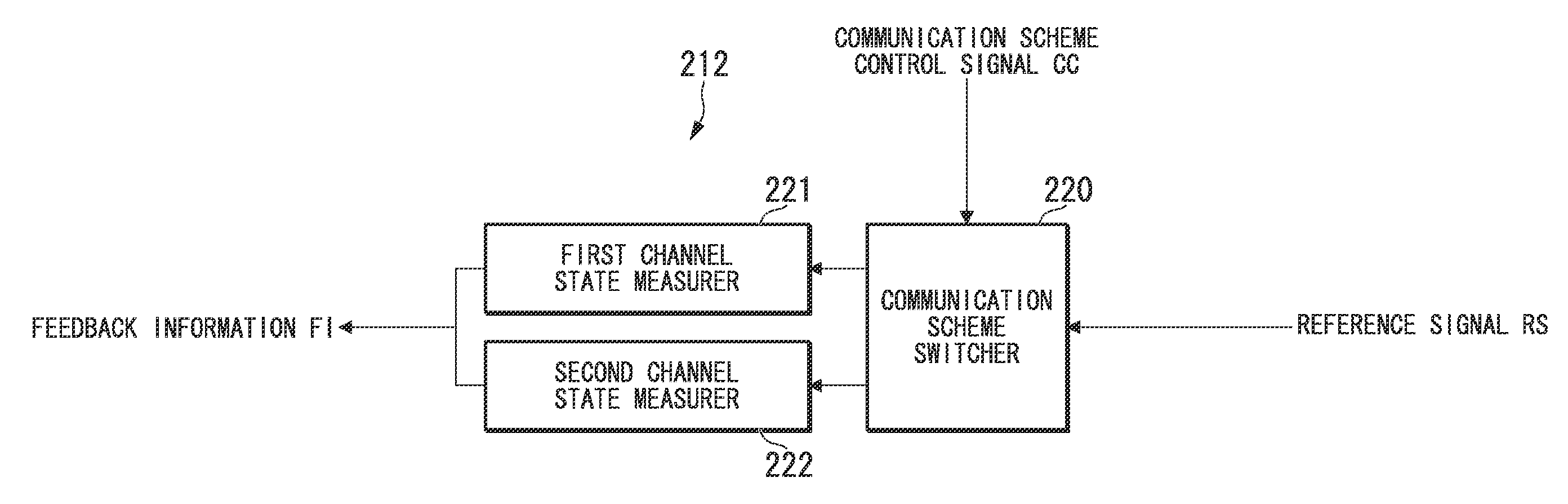
ActiveUS20120033571A1Site diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemInterference (communication)
A wireless communication system includes a first channel state measurer and a second channel state measurer. When a second communication device measures a state of a channel between the second communication device and a first communication device using reference signals transmitted from the first communication device, the first channel measurer is configured to measure a state of the channel including an interference due to a signal transmitted from another first communication device. When measuring the state of the channel between the second communication device and the first communication device using the reference signals transmitted from the first communication device, the second channel state measurer measures the state of the channel while suppressing the interference due to the signal transmitted from the another first communication device. Accordingly, the wireless communication system can generate adequate feedback information both when cooperative communication is performed and when cooperative communication is not performed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
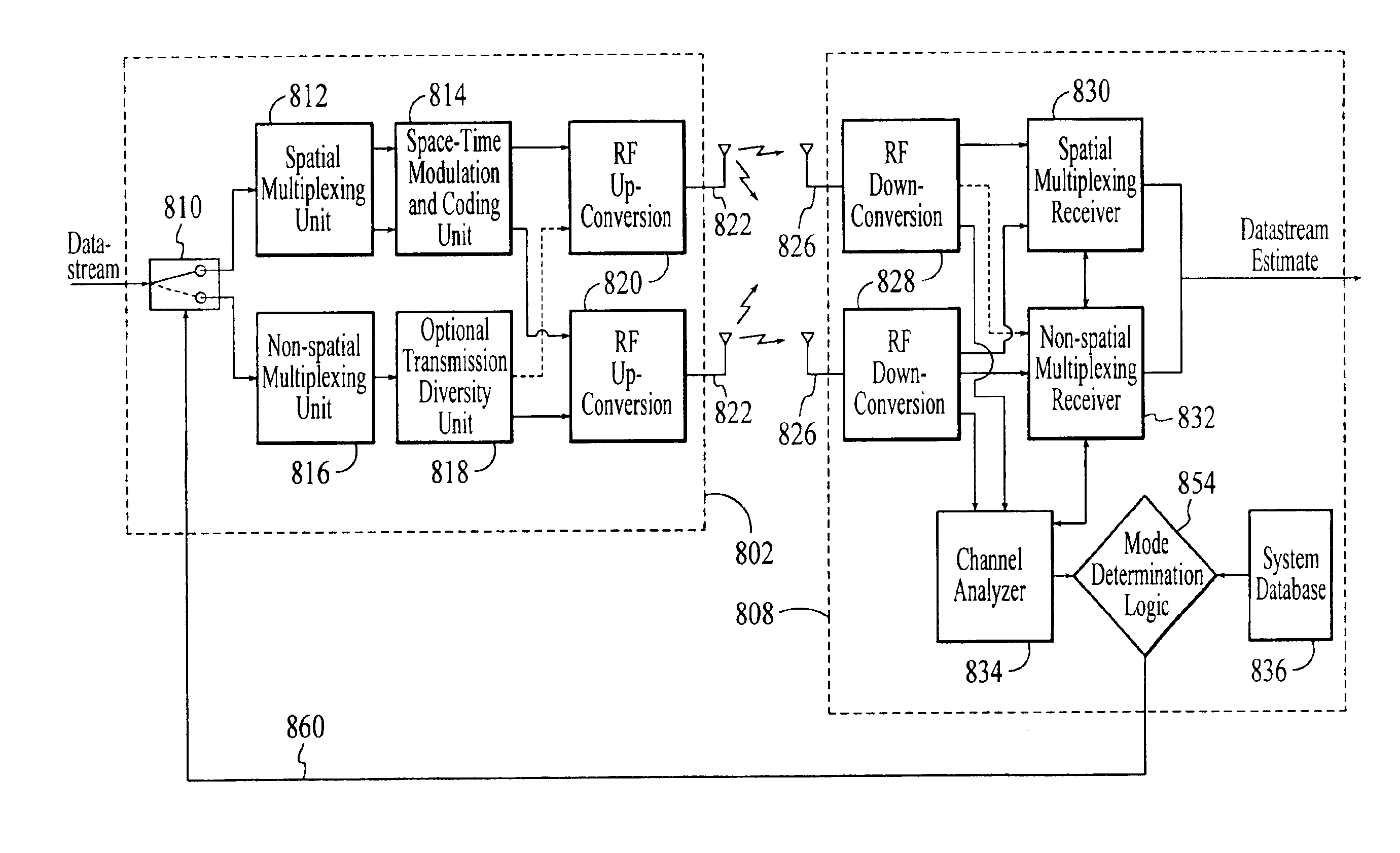
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
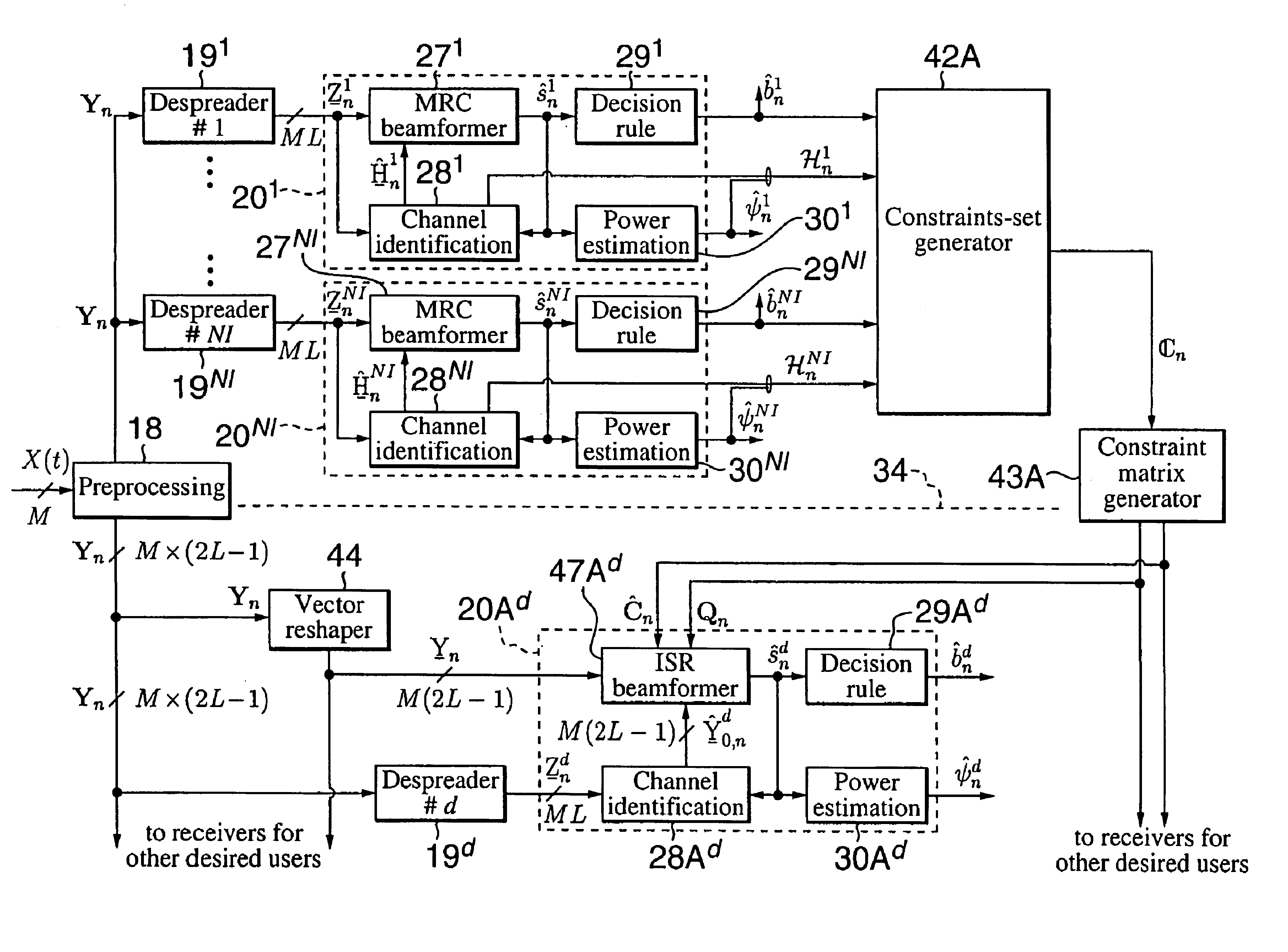
Interference suppression in CDMA systems
InactiveUS6975666B2Suppresses any sensitivityReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversitySignal responseInterference (communication)
A receiver of the present invention addresses the need for improved interference suppression without the number of transmissions by the power control system being increased, and, to this end, provides a receiver for a CDMA communications system which employs interference subspace rejection to tune a substantially null response to interference components from selected signals of other user stations. Preferably, the receiver also tunes a substantially unity response for a propagation channel via which a corresponding user's signal was received. The receiver may be used in a base station or in a user / mobile station.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
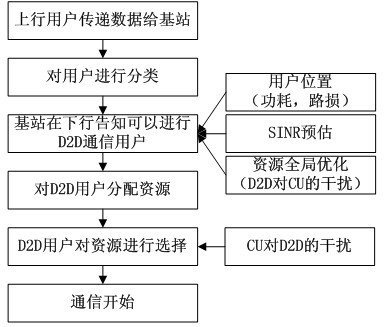
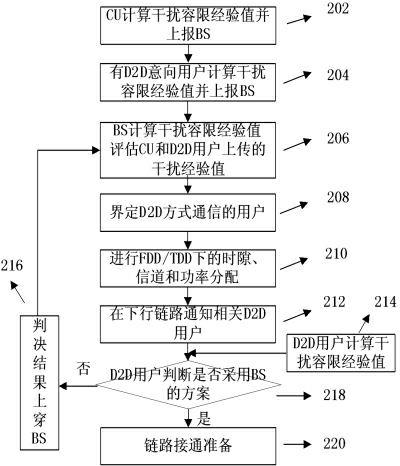
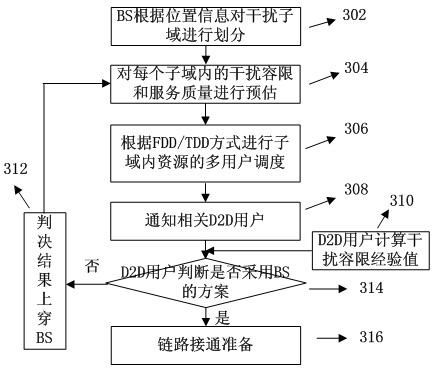
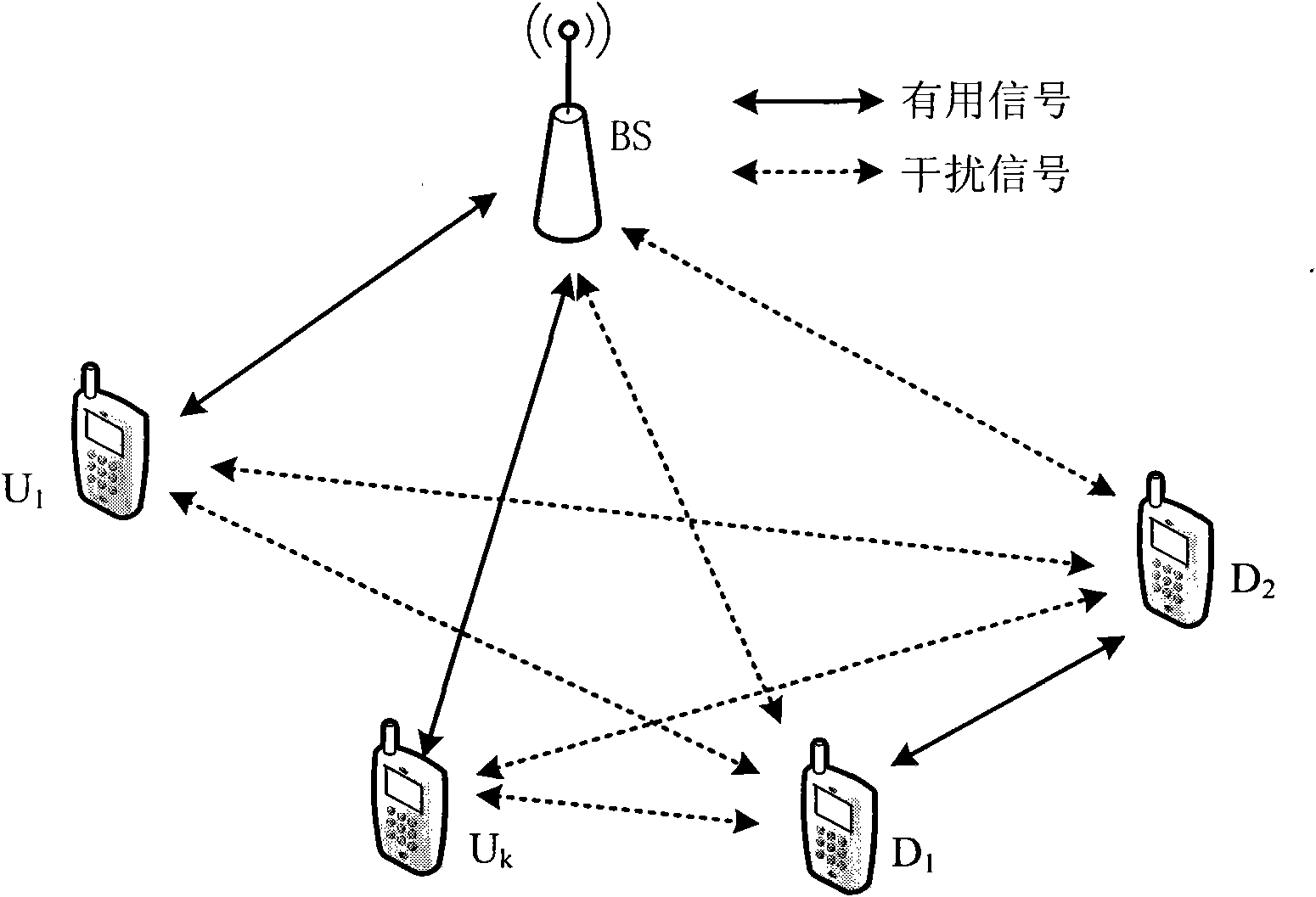
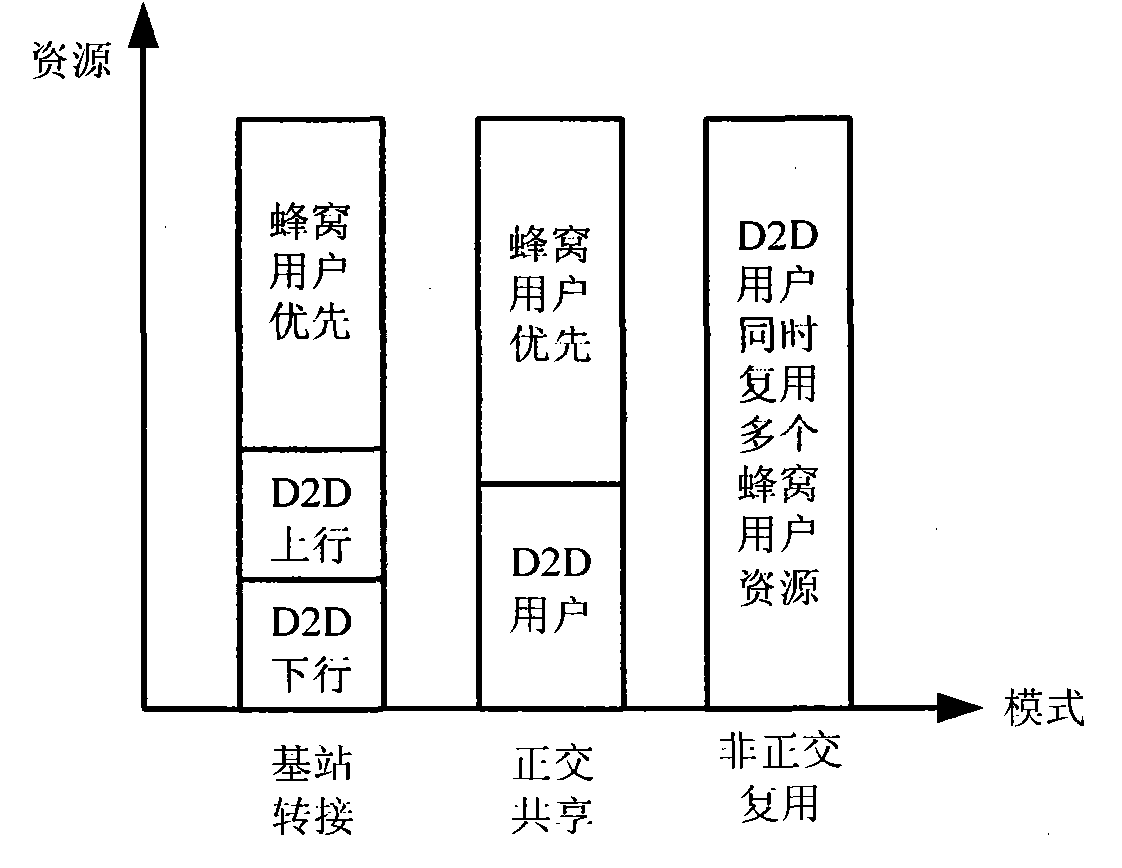
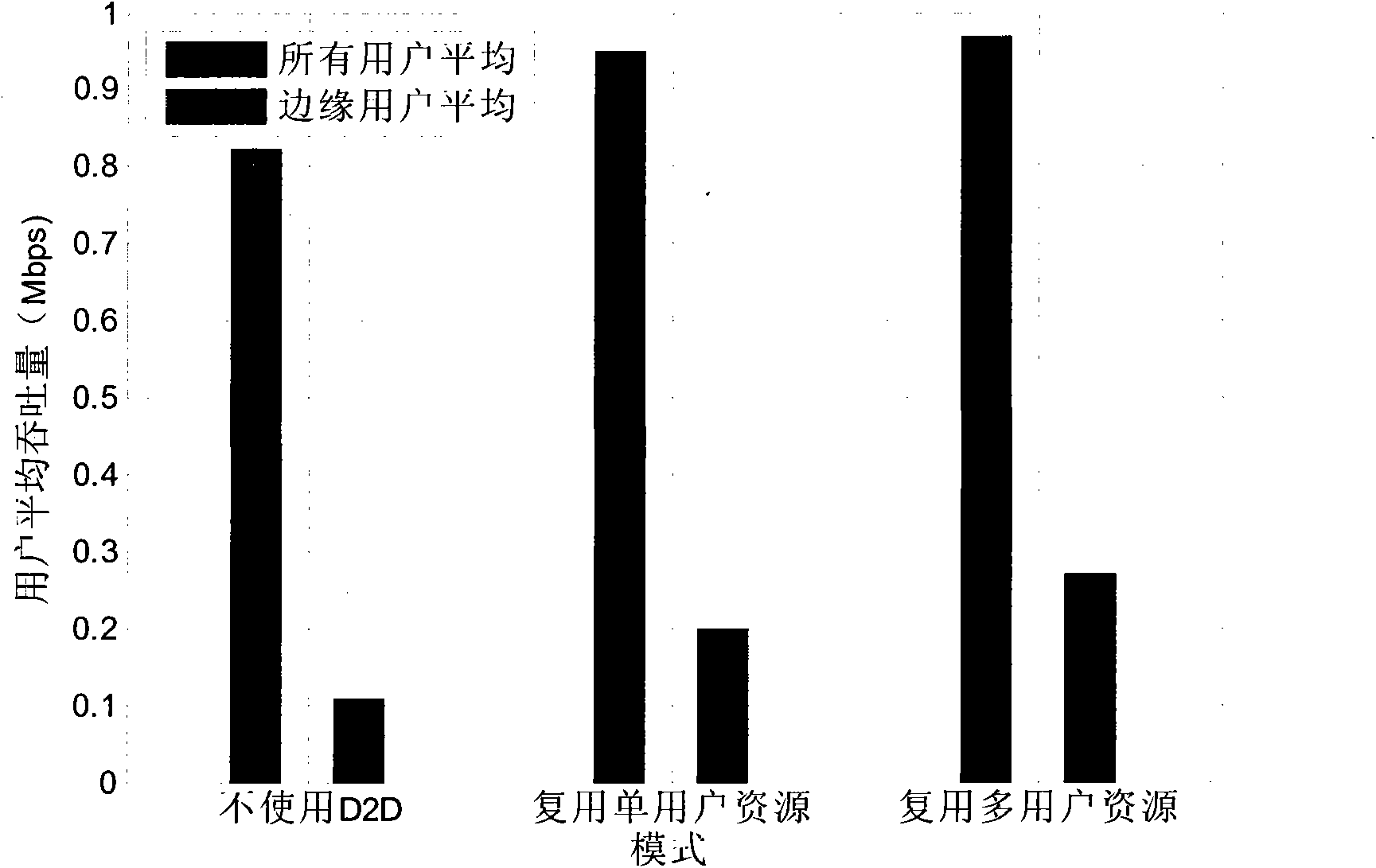
Base-station (BS)-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in direct-through cellular system
ActiveCN102638893AImprove resource utilizationImprove effectivenessWireless communicationMultiplexingQuality of service
The invention provides a base-station (BS)-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in a direct-through cellular system. In order not to interrupt the normal communication of traditional cellular subscriber links and obtain effective gain brought by device-to-device (D2D) direct-through technology, D2D subscribers are allowed to adopt a resource allocation manner that resources are selected by a D2D subscriber end when uplink and downlink resources of the cellular system are shared; at this time, the D2D subscribers only need to consider the interference to other cellular subscribers (CUs) arising from signals of the D2D subscribers; and meanwhile, a BS centralized-control manner is adopted to carry out resource allocation, the centralized-control advantage of a BS is exerted, a BS and D2D terminal combined optimization manner is fully utilized, and the advantages of the two allocation manners are exerted. The BS-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in the direct-through cellular system has the advantages that the resource utilization ratio and availability of a coexistent system which is provided with the D2D direct-through technology are sufficiently improved, the multiplexing gain of the resources are maximally developed, the system capacity is increased, the service types are increased, and the quality of service is ensured; and many chances for resource multiplexing are developed under the condition of limited resources from a novel resource allocation viewing angle.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Methods and apparatus for characterizing noise in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20080013500A1Reduce distractionsPower managementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSignal on
Improved pilot signal sequences which facilitate multiple channel quality measurements, e.g., through the use of different signal pilot transmission power levels, are described. In various implementations the transmitted pilot sequences facilitate determining the contribution of interference from other sectors of a cell using the same tones, e.g., in a synchronized manner, as the sector in which the pilot signal measurements are being made. To measure noise contributions from neighboring sectors a sector NULL pilot, e.g., a pilot with zero power, is transmitted in an adjacent sector at the same time a pilot signal with a pre-selected, and therefore known, non-zero power is transmitted in the sector where the received pilot signal measurement is made. To facilitate background noise measurements, a cell NULL is supported in some embodiments. In the case of a cell NULL, all sectors of a cell transmit a Null pilot, on a tone that is used to measure background noise. Since no power is transmitted in the cell on the tone during the measurement, any measured signal on the tone is attributable to noise, e.g., background noise which may include inter-cell interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for simultaneously multiplexing multiple cellular user resources by D2D (Device-to-Device) user pair
ActiveCN102083138AHigh data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementInterference (communication)Frequency spectrum
The invention provides a technical scheme which is applied to a cellular network for mobile communication. A D2D (Device-to-Device) technology is applied to the cellular network, and thereby a D2D user pair is allowed to simultaneously multiplex multiple cellular network user resources to communicate. In addition, a mode for maximizing system data rate is selected from the scheme and a traditional scheme to realize resource sharing. The scheme proposed by the invention cannot cause great interference to certain cellular user and is easy to realize and relatively flexible to apply in actuality. The invention provides a method for simultaneously multiplexing multiple cellular user resources by single D2D user pair in the cellular network with D2D communication, which can be used for increasing the frequency spectrum efficiency of a system whole (including cellular communication and D2D communication) under the condition of guaranteeing the lowest communication rate of a cellular user. The method provided by the invention has strong actual operability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
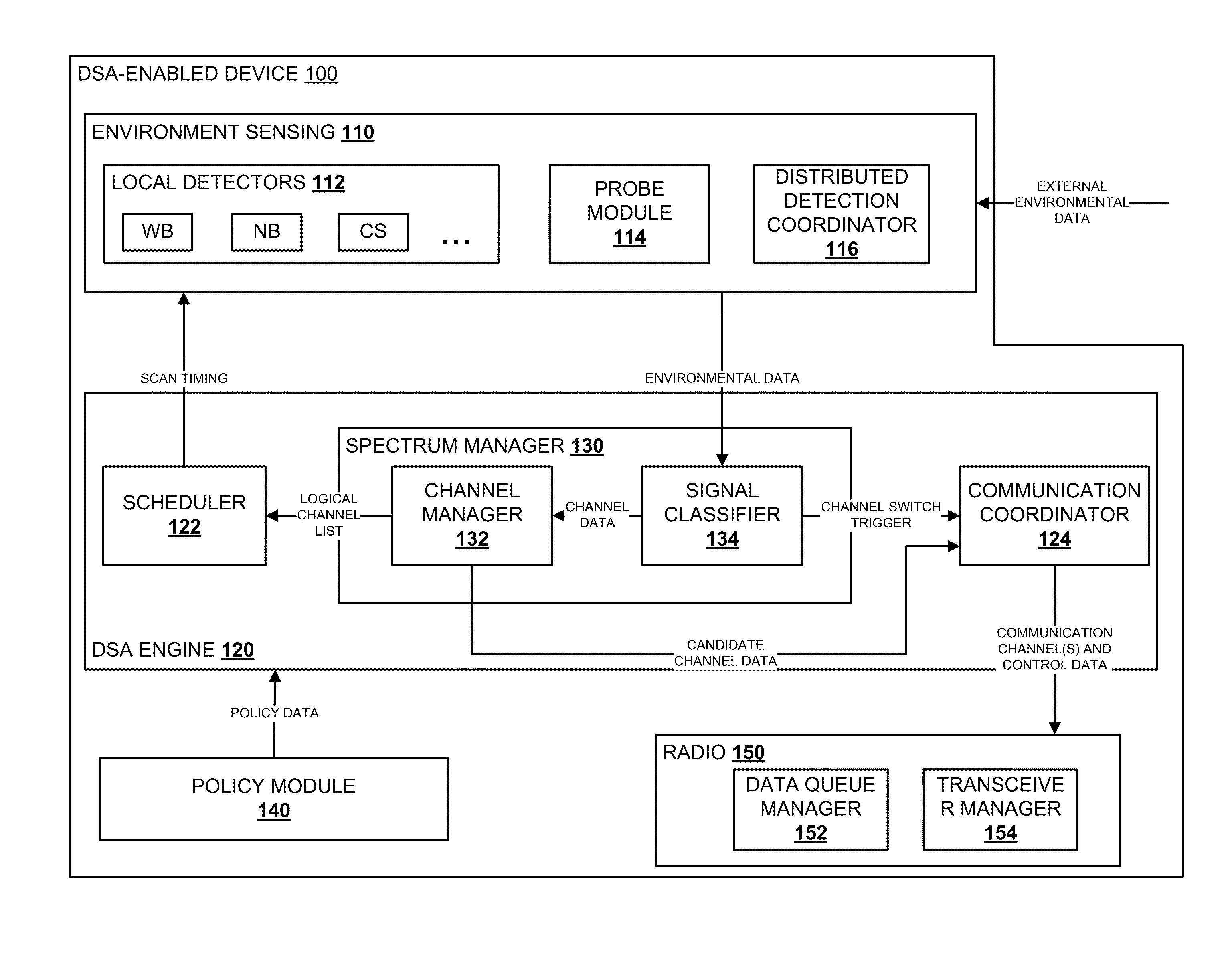
Method and System for Dynamic Spectrum Access Using Detection Periods
InactiveUS20100105332A1Reduce the valueReduce valueSynchronisation arrangementTransmission control/equalisingComputer networkFrequency spectrum
Methods and systems for dynamic spectrum access (DSA) in a wireless network are provided. A DSA-enabled device may sense spectrum use in a region and, based on the detected spectrum use, select one or more communication channels for use. The devices also may detect one or more other DSA-enabled devices with which they can form DSA networks. A DSA network may monitor spectrum use by cooperative and non-cooperative devices, to dynamically select one or more channels to use for communication while avoiding or reducing interference with other devices.
Owner:SHARED SPECTRUM
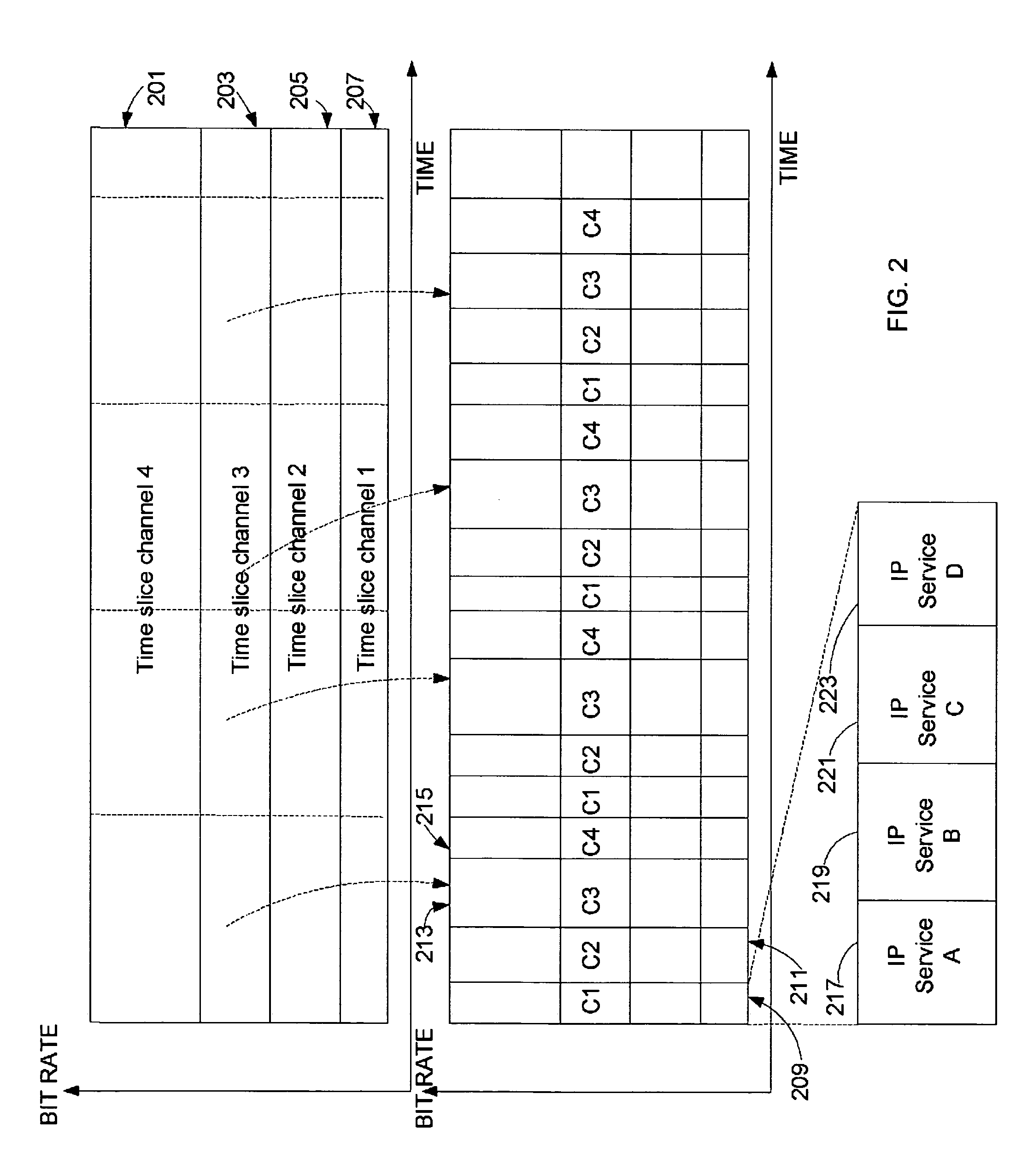
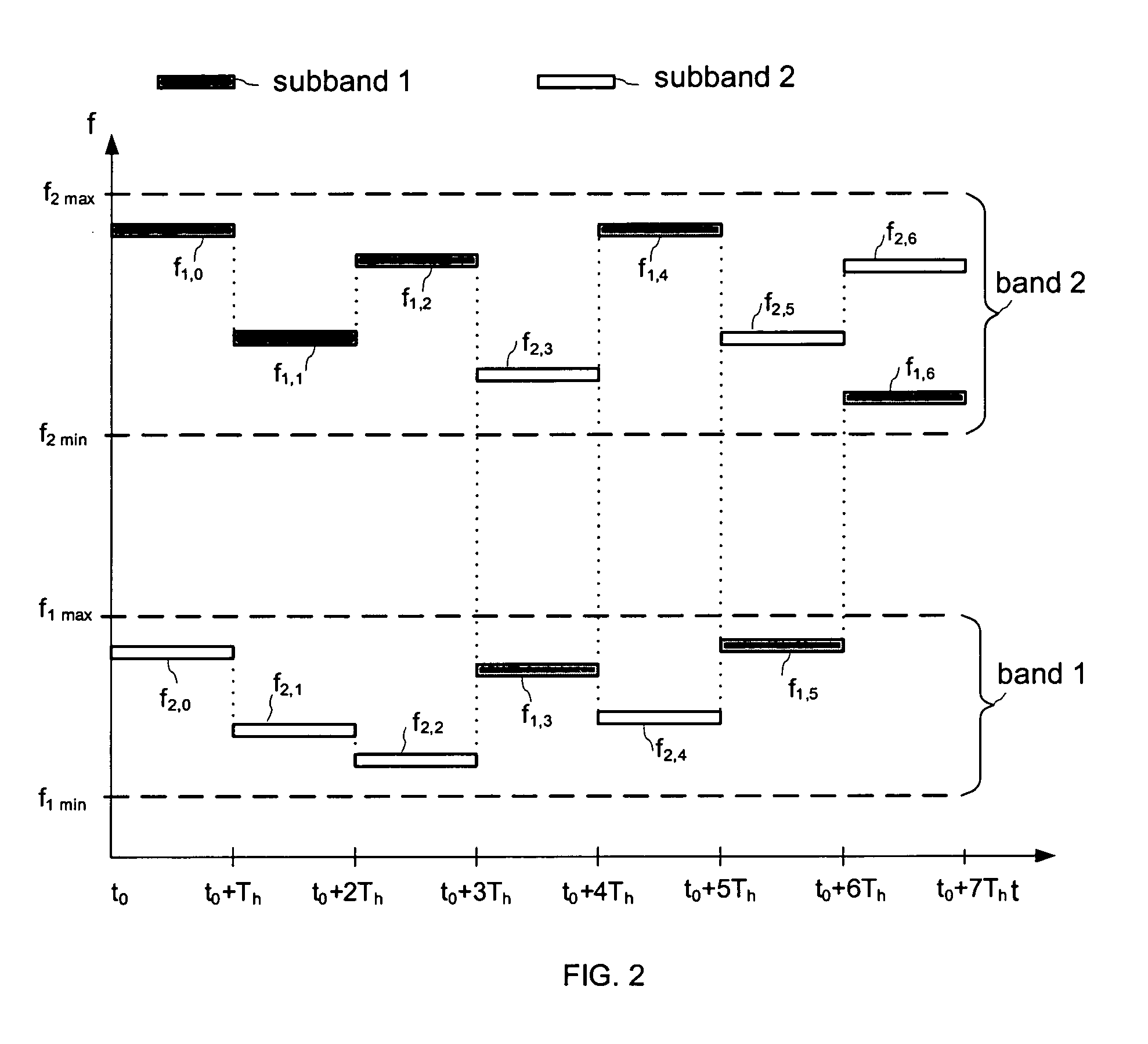
Multi-subband frequency hopping communication system and method
InactiveUS20050249266A1Transmission control/equalisingCode division multiplexCarrier signalBand width
The invention provides an adaptive frequency hopping spread-spectrum (FHSS) transmission system and method, which efficiently utilizes available transmission bandwidth, whilst providing robustness to jamming techniques in wireless communication systems. The proposed technique operates by transmitting a wide-band signal over multiple, single-carrier, parallel transmission subbands, which may occupy non-contiguous frequency regions. The proposed scheme exhibits significant gain in error rate performance, as compared to a data rate equivalent single-subband system in the presence of signal jamming and / or interference without a reduction in the transmission data rate nor an increase in transmitter power. In addition, the proposed system and method are adaptive and enable more efficient use of the available bandwidth for communicating, thus increasing the overall bandwidth utilization of the system.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
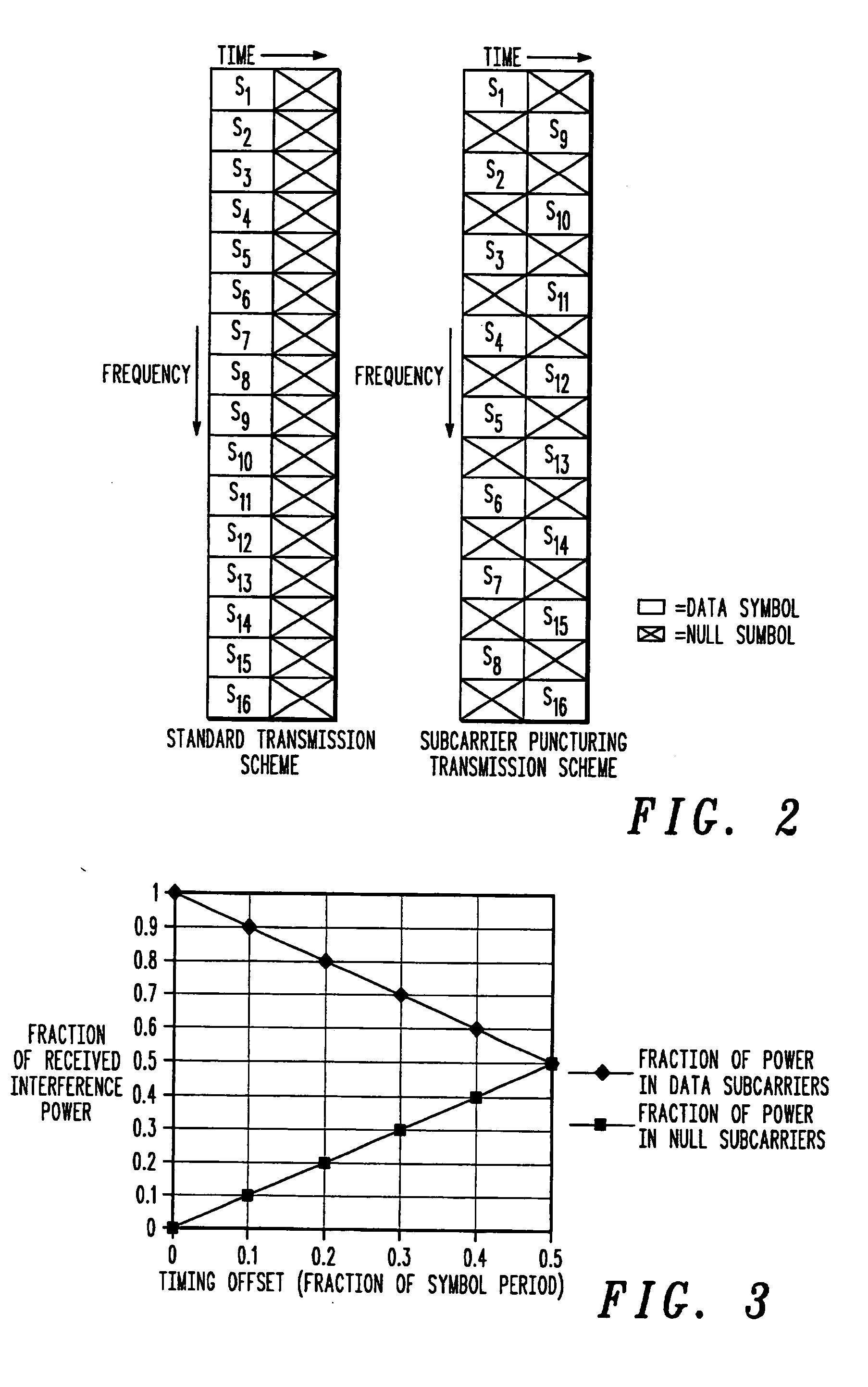
Method and system for interference averaging in a wireless communication system
A family of methods for interference averaging in multicarrier systems, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. The methods can provide interference averaging in situations where an interfering co-channel is either partially or fully loaded. For partially loaded systems, subcarrier puncturing, frequency domain repetition, time domain repetition, and hybrid time-frequency repetition schemes are provided. For systems using adaptive modulation / coding rates, lower rates and transmit power can be selected in order to perform interference averaging in time-spread and frequency-spread OFDM schemes. In systems with downlink power control, frequency domain mixing can be used to perform interference averaging.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Methods and apparatus for high throughput multiple radio wireless cells and networks
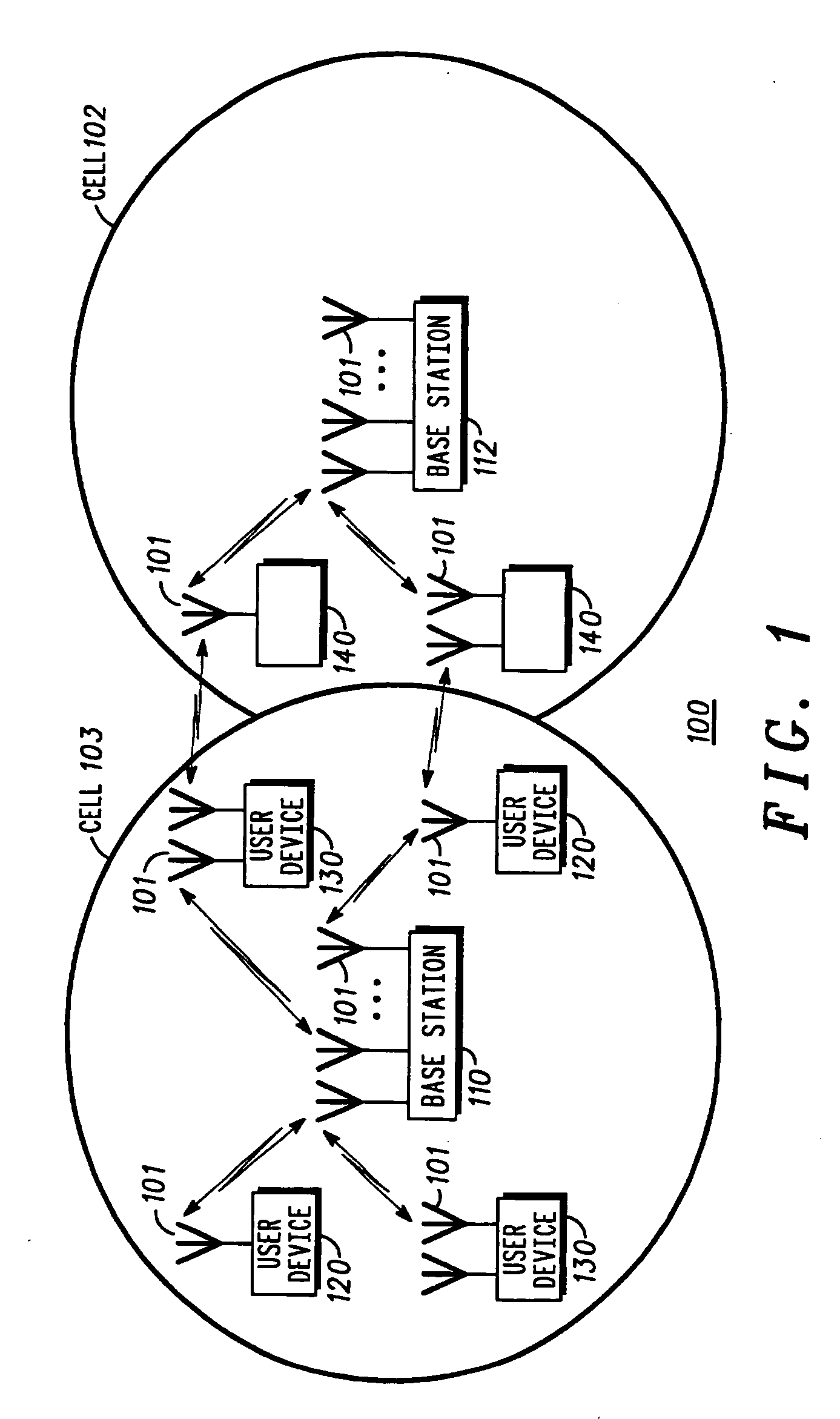
InactiveUS20050003763A1Minimize interferenceImprove data throughputSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityUltrasound attenuationWireless
Methods and apparatus for high throughput wireless cells and networks are described. The wireless cells may be equipped with multiple radios. Antennas may be arranged into overlapping and non-overlapping patterns. Channels may be assigned to foster servicing clients, and inter-cell communication. Attenuation may be used to decrease interference. Networks may be formed using a variety of methods and apparatus.
Owner:ROTANI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com