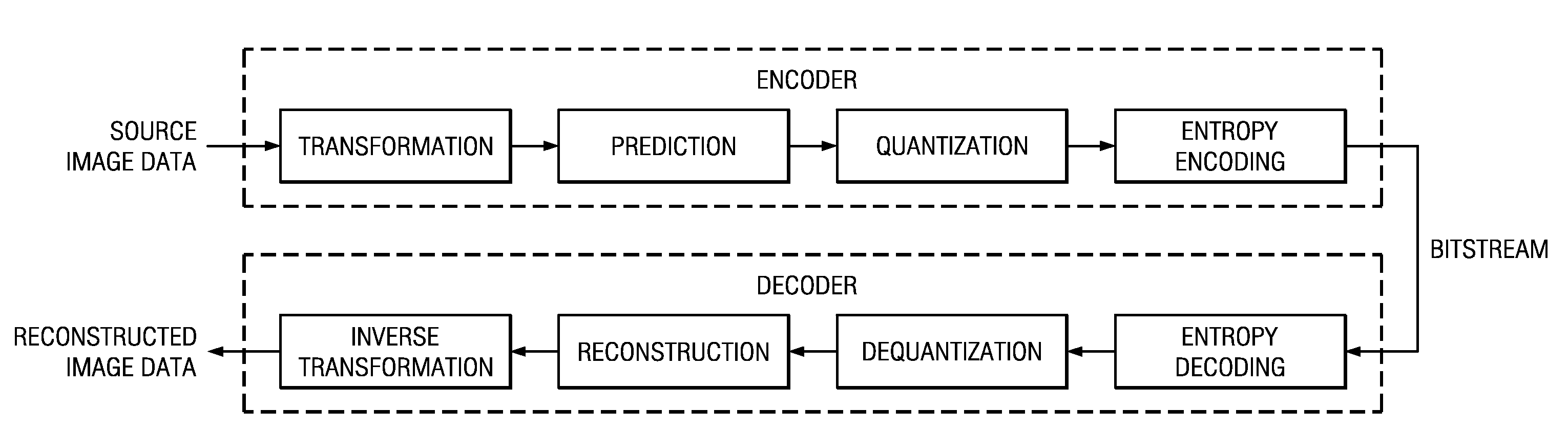
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3447 results about "Image compression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior results compared with generic data compression methods which are used for other digital data.
Digital security multimedia sensor
InactiveUS20050207487A1Ensure effective disseminationEfficient routingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage compressionBiological activation
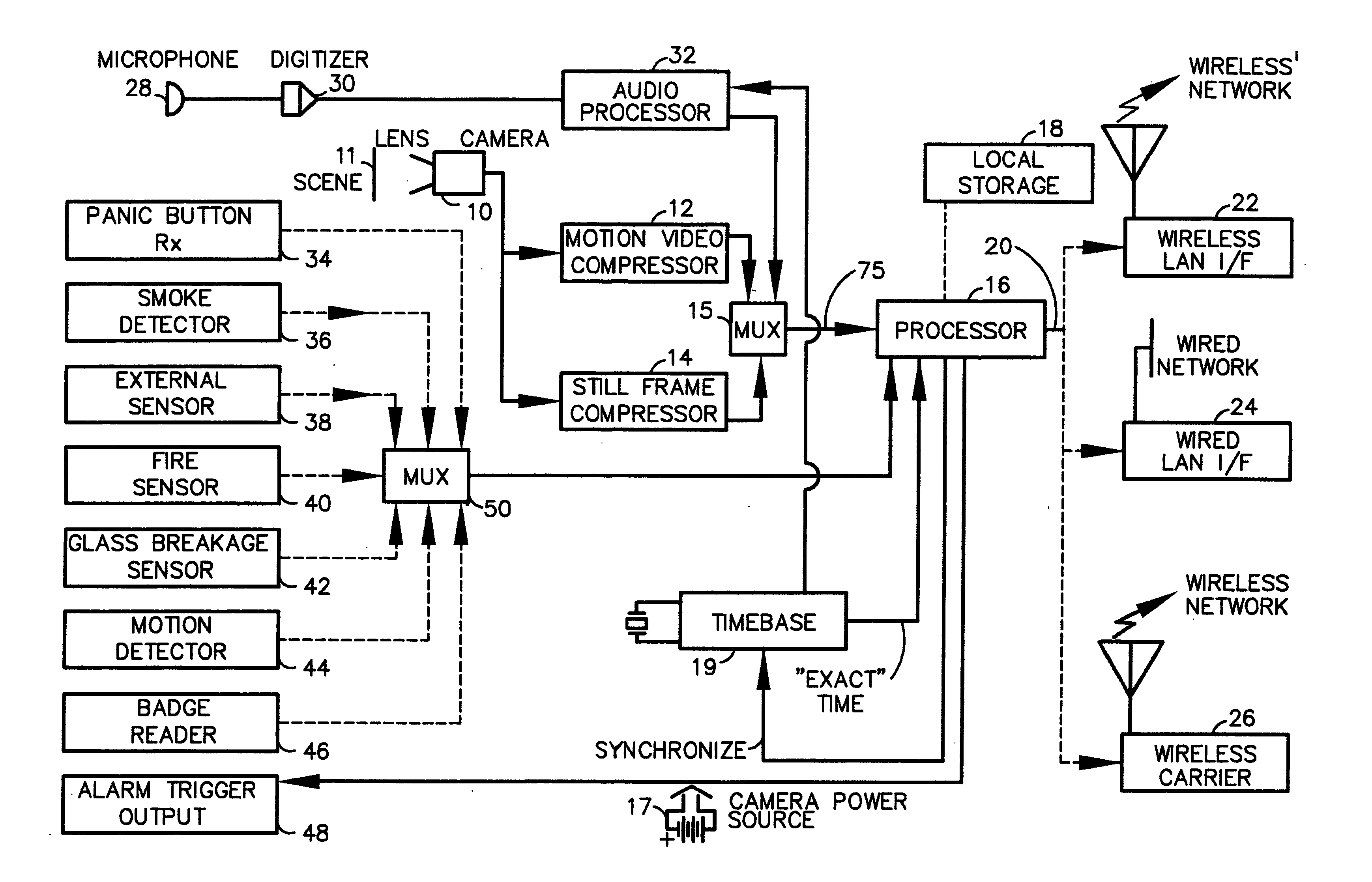
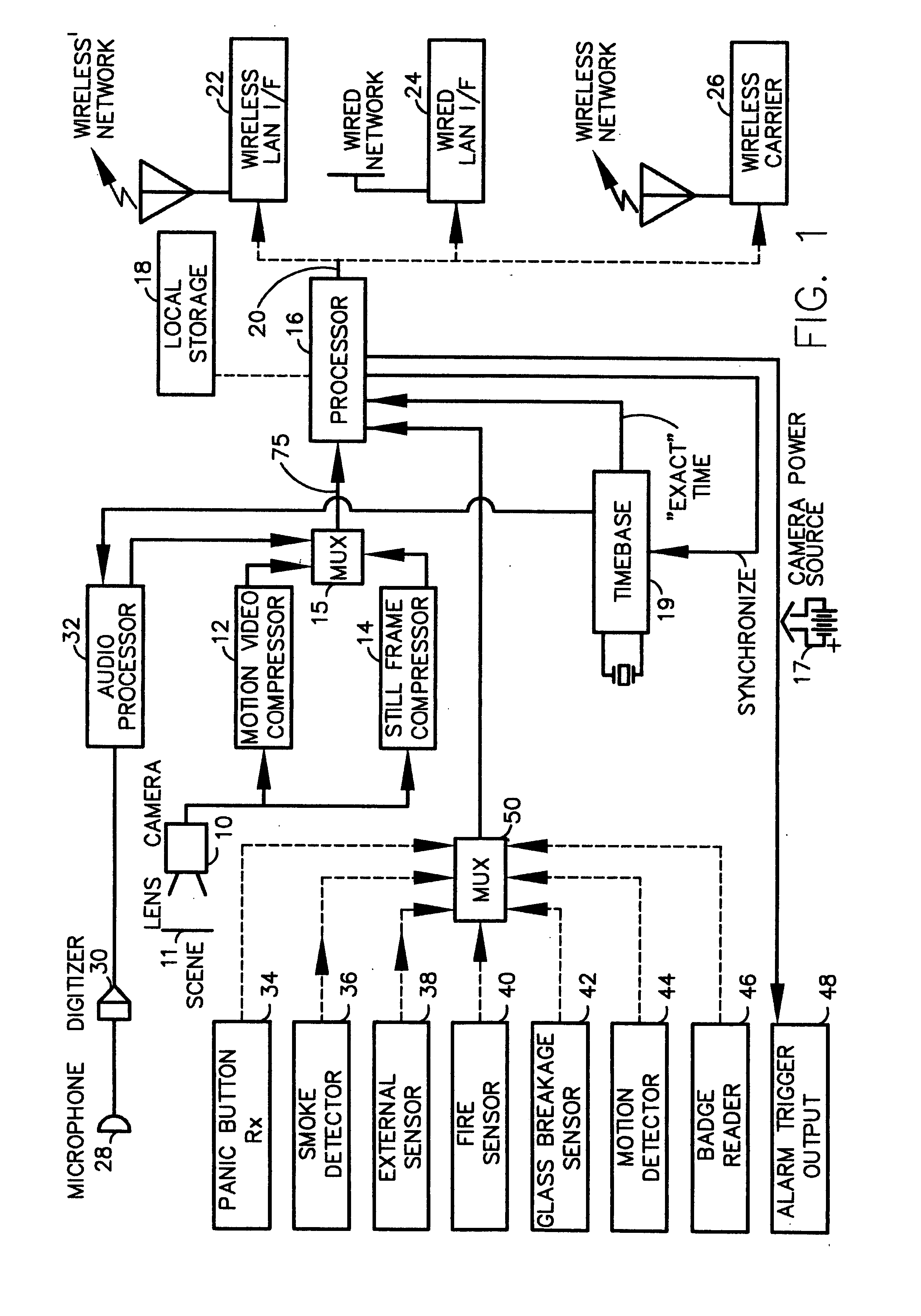
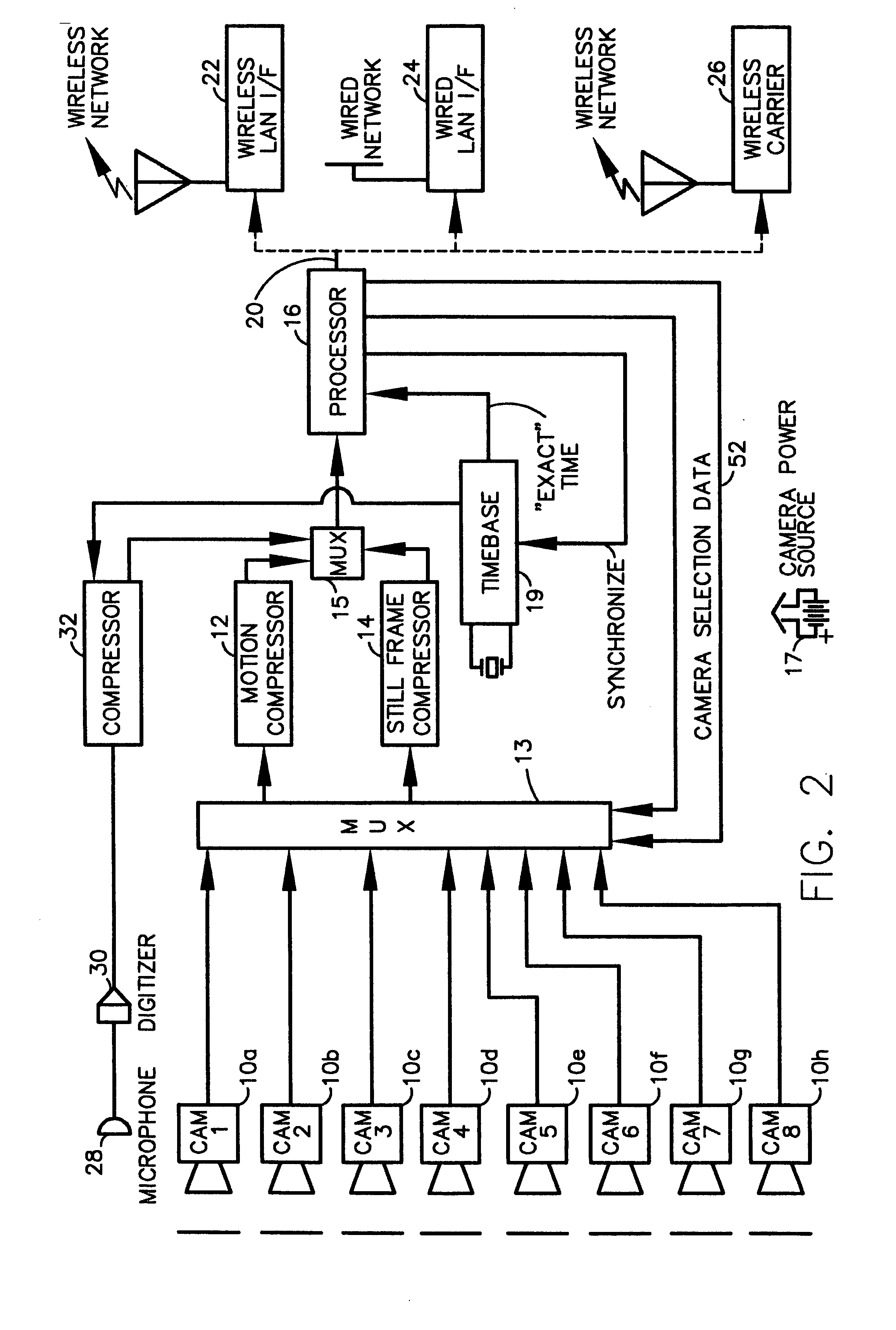
A fully digital camera system provides high-resolution still image and streaming video signals via a network to a centralized, server supported security and surveillance system. The digital camera for collects an image from one or more image transducers, compressing the image and sending the compressed digital image signal to a receiving station over a digital network. A plurality of image transducers or sensors may be included in a single camera unit, providing array imaging such as full 360 degree panoramic imaging, universal or spherical imaging and field imaging by stacking or arranging the sensors in an array. The multiple images are then compressed and merged at the camera in the desired format to permit transmission of the least amount of data to accomplish the desired image transmission. The camera also employs, or connects to, a variety of sensors other than the traditional image sensor. Sensors for fire, smoke, sound, glass breakage, motion, panic buttons, and the like, may be embedded in or connected to the camera. Data captured by these sensors may be digitized, compressed, and networked to detect notable conditions. An internal microphone and associated signal processing system may be equipped with suitable signal processing algorithms for the purpose of detecting suitable acoustic events and their location. In addition, the camera is equipped with a pair of externally accessible terminals where an external sensor may be connected. In addition, the camera may be equipped with a short-range receiver that may detect the activation of a wireless ‘panic button’ carried by facility personnel. This ‘panic button’ may employ infrared, radio frequency (RF), ultrasonic, or other suitable methods to activate the camera's receiver.
Owner:PR NEWSWIRE
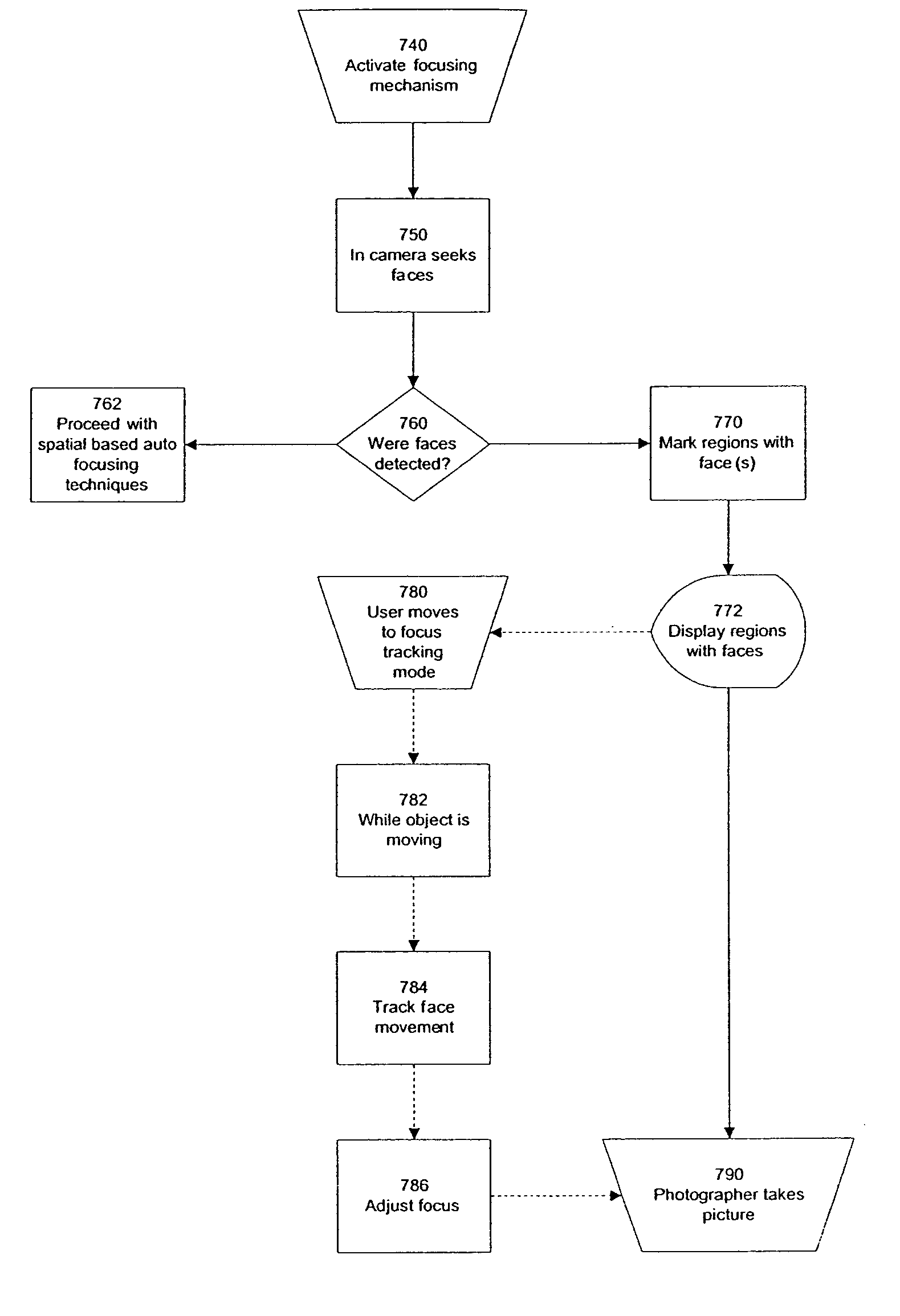
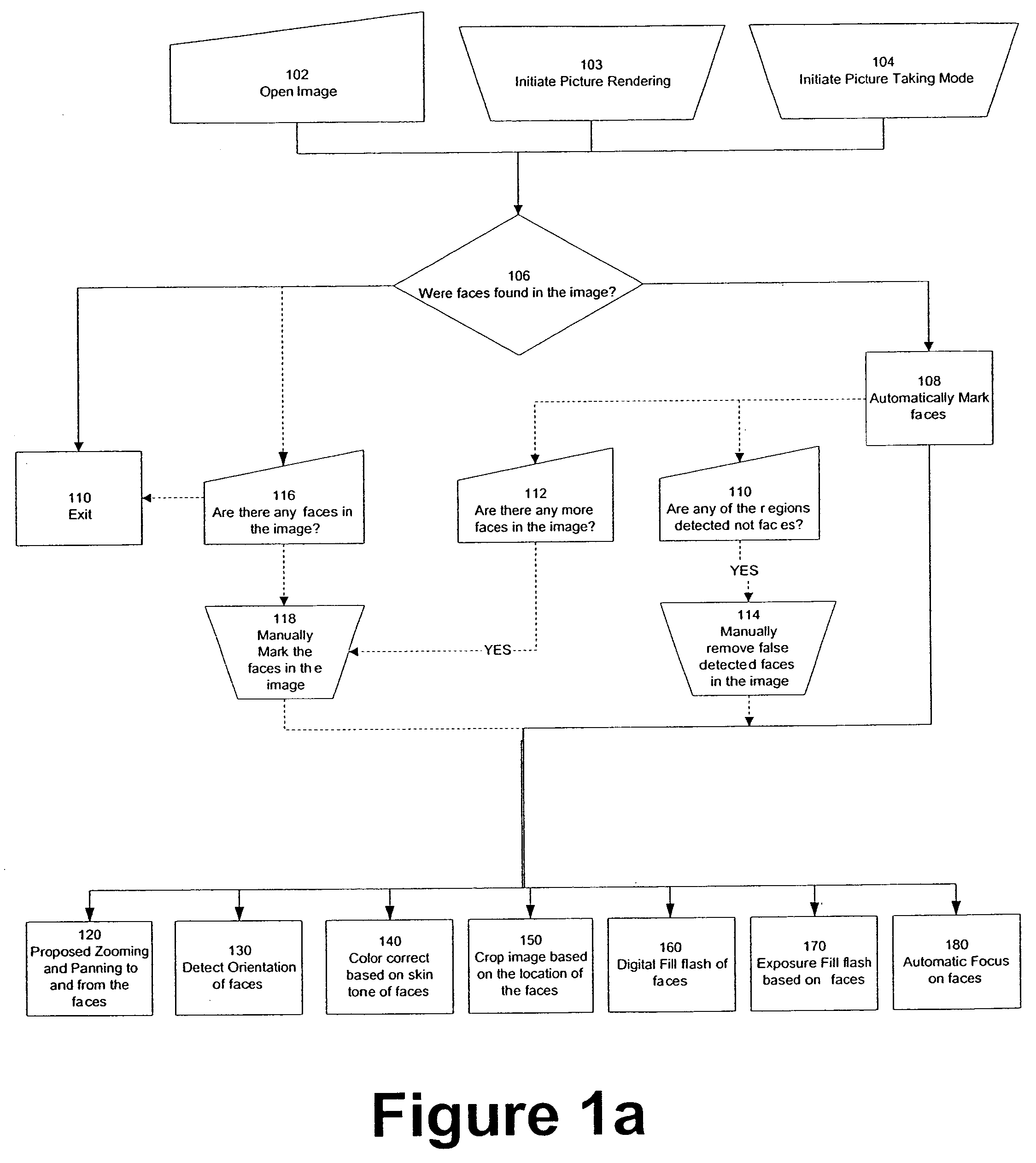
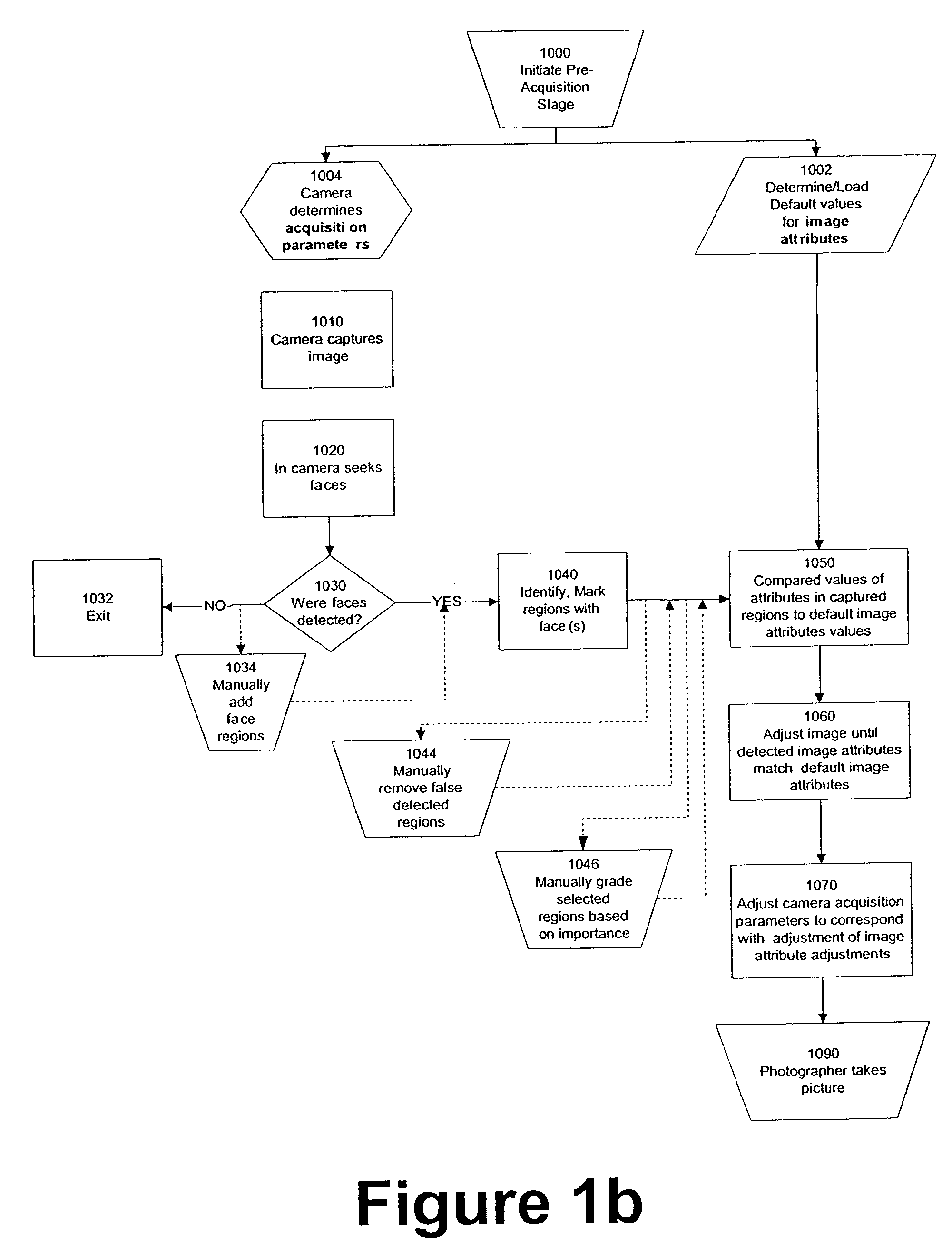
Digital image adjustable compression and resolution using face detection information
ActiveUS7269292B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImage resolution
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Method and apparatus for parallelization of image compression encoders
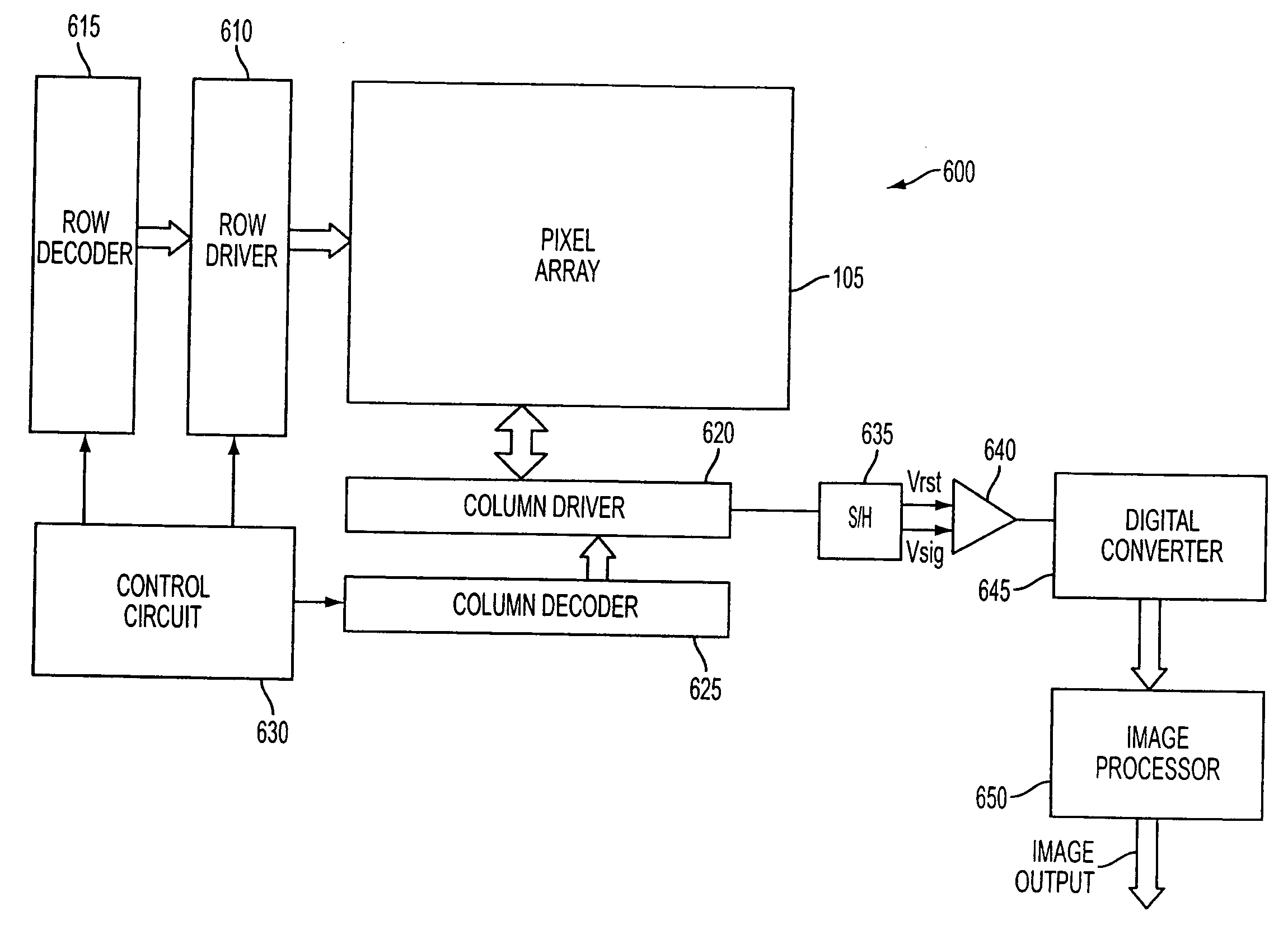
ActiveUS20080247653A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData streamImage compression
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Autonomous inspector mobile platform
ActiveUS20060290779A1Streamlined and low cost inspectionInexpensive and easily deployed/operatedPipe elementsColor television detailsCommunications systemMeasurement device
An autonomous inspector mobile platform robot that is used to inspect a pipe or network of pipes. The robot includes a locomotion device that enables the device to autonomously progress through the pipe and accurately track its pose and odometry during movement. At the same time, image data is autonomously captured to detail the interior portions of the pipe. Images are taken at periodic intervals using a wide angle lens, and additional video images may be captured at locations of interest. Either onboard or offboard the device, each captured image is unwarped (if necessary) and combined with images of adjacent pipe sections to create a complete image of the interior features of the inspected pipe. Optional features include additional sensors and measurement devices, various communications systems to communicate with an end node or the surface, and / or image compression software.
Owner:REDZONE ROBOTICS
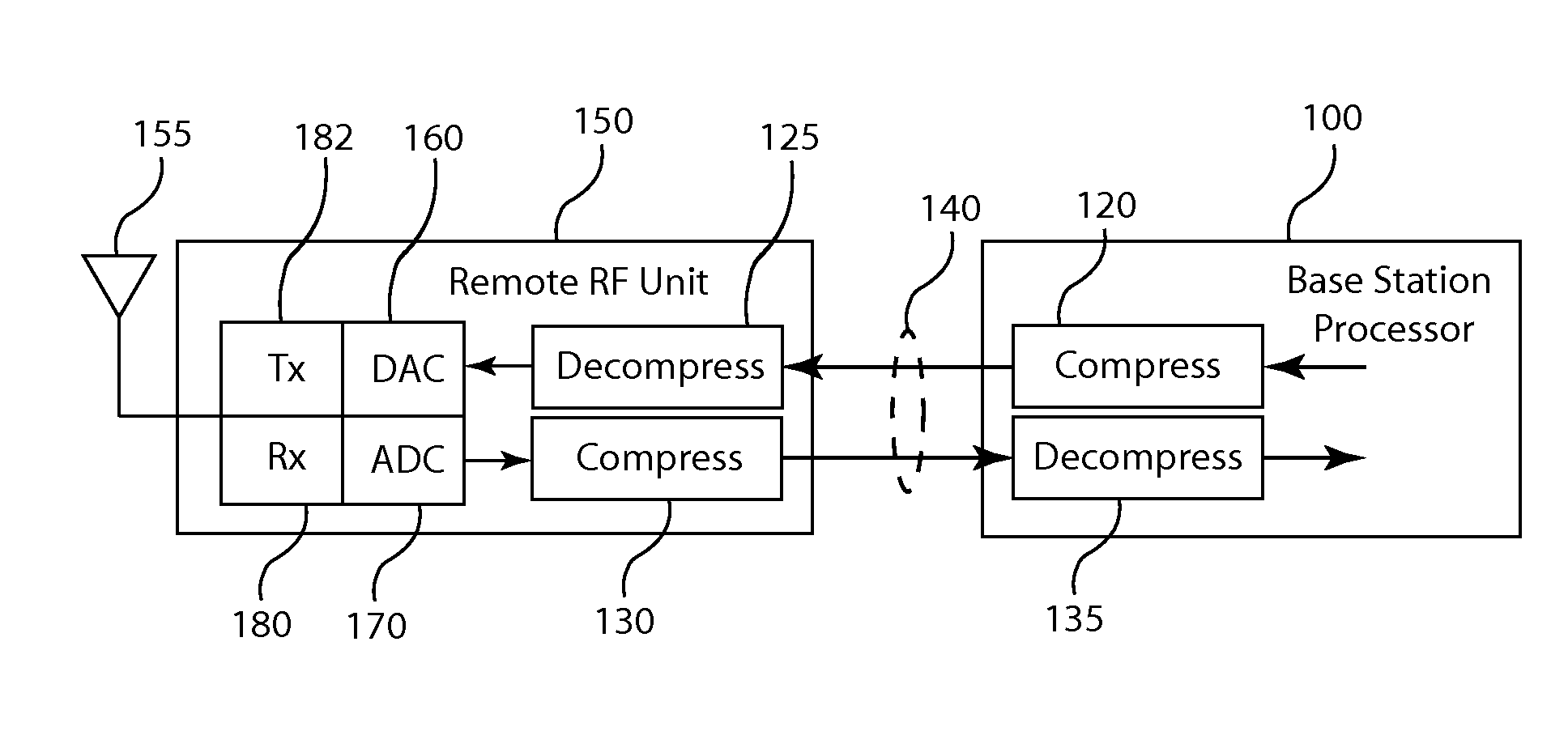
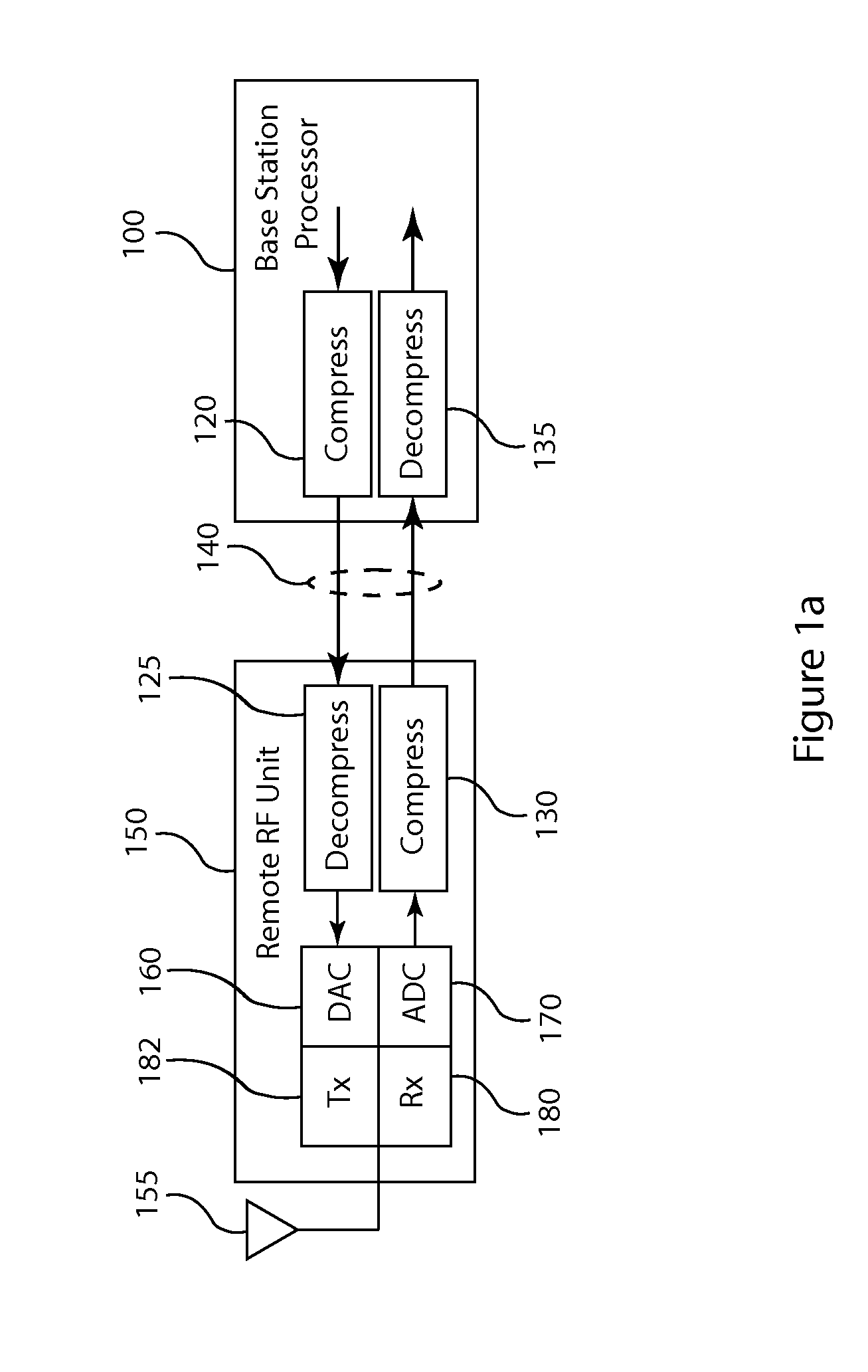
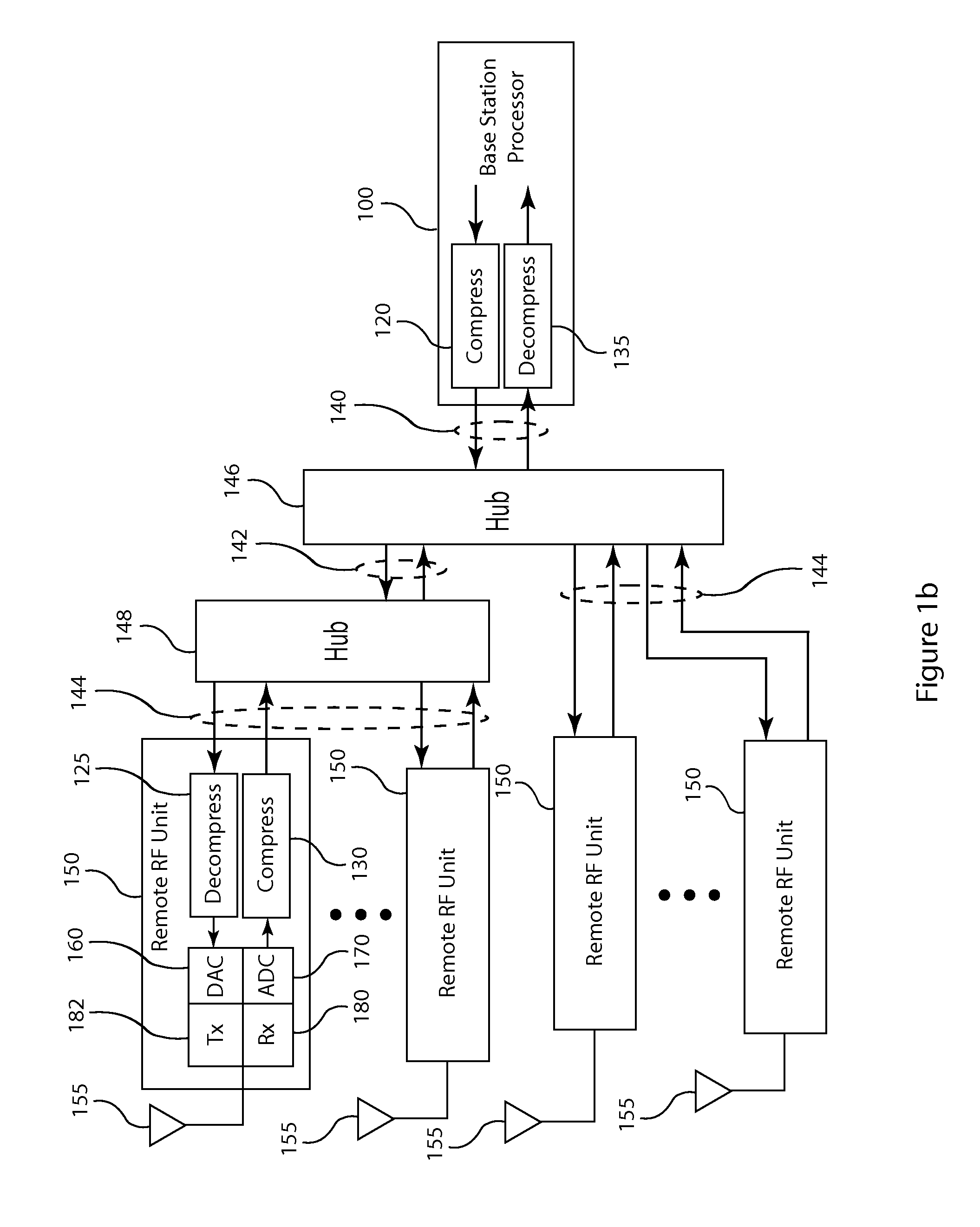
Frequency domain compression in a base transceiver system
ActiveUS20120176966A1Significant compressionReduce processing overheadModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTransceiverImage compression
A method and apparatus provide signal compression for transfer over serial data links in a base transceiver system (BTS) of a wireless communication network. For the uplink, an RF unit of the BTS applies frequency domain compression of baseband signal samples, resulting from analog to digital conversion of received analog signals followed by digital downconversion, forming compressed coefficients. After transfer over the serial data link, the baseband processor then applies frequency domain decompression to the compressed coefficients prior to normal signal processing. For the downlink, the baseband processor applies frequency domain compression of baseband signal samples and transfers the compressed coefficients to the RF unit. The RF unit applies frequency domain decompression to the compressed coefficients prior to digital upconversion and digital to analog conversion, generating the analog signal for transmission over the antenna. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
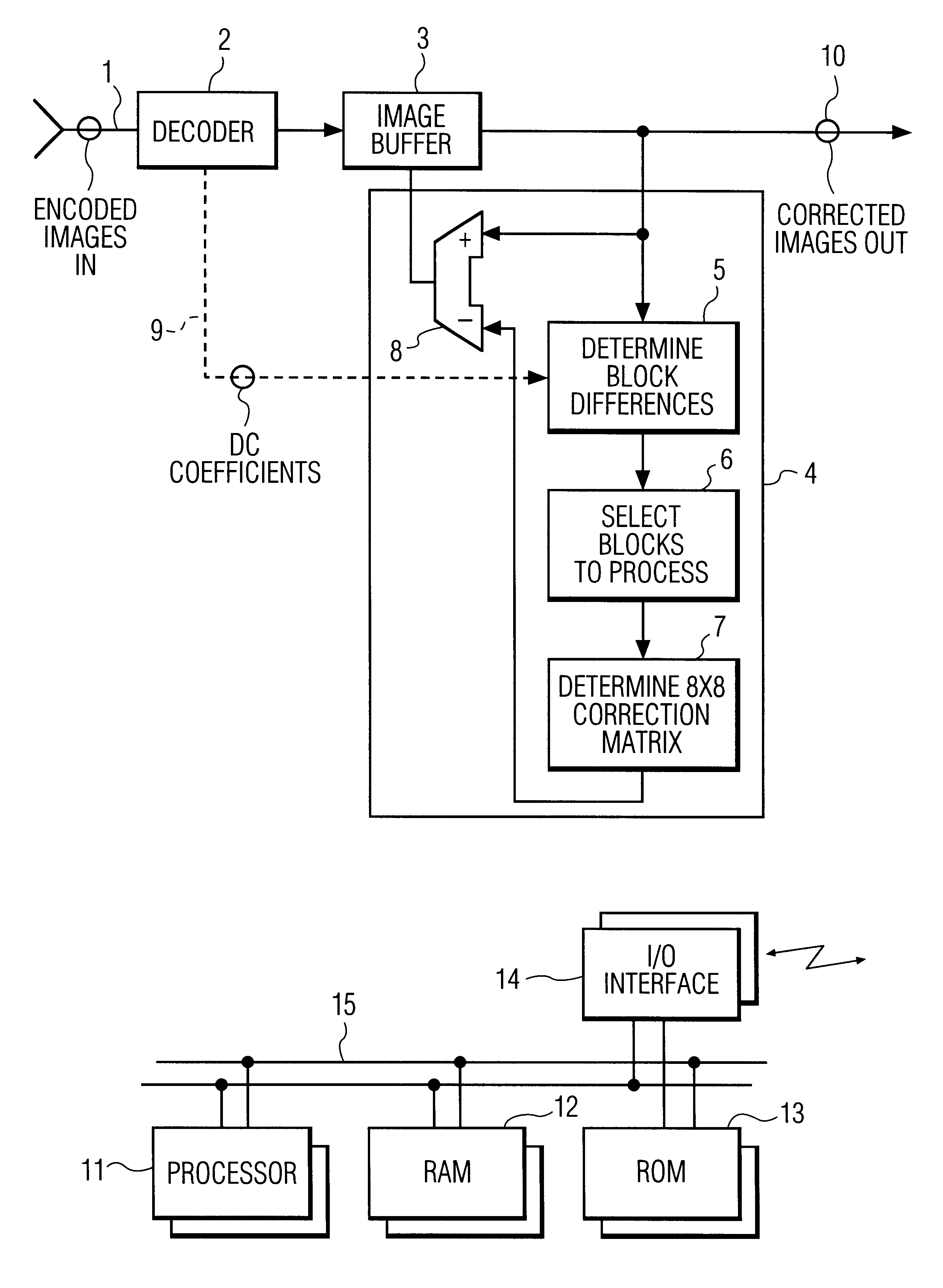
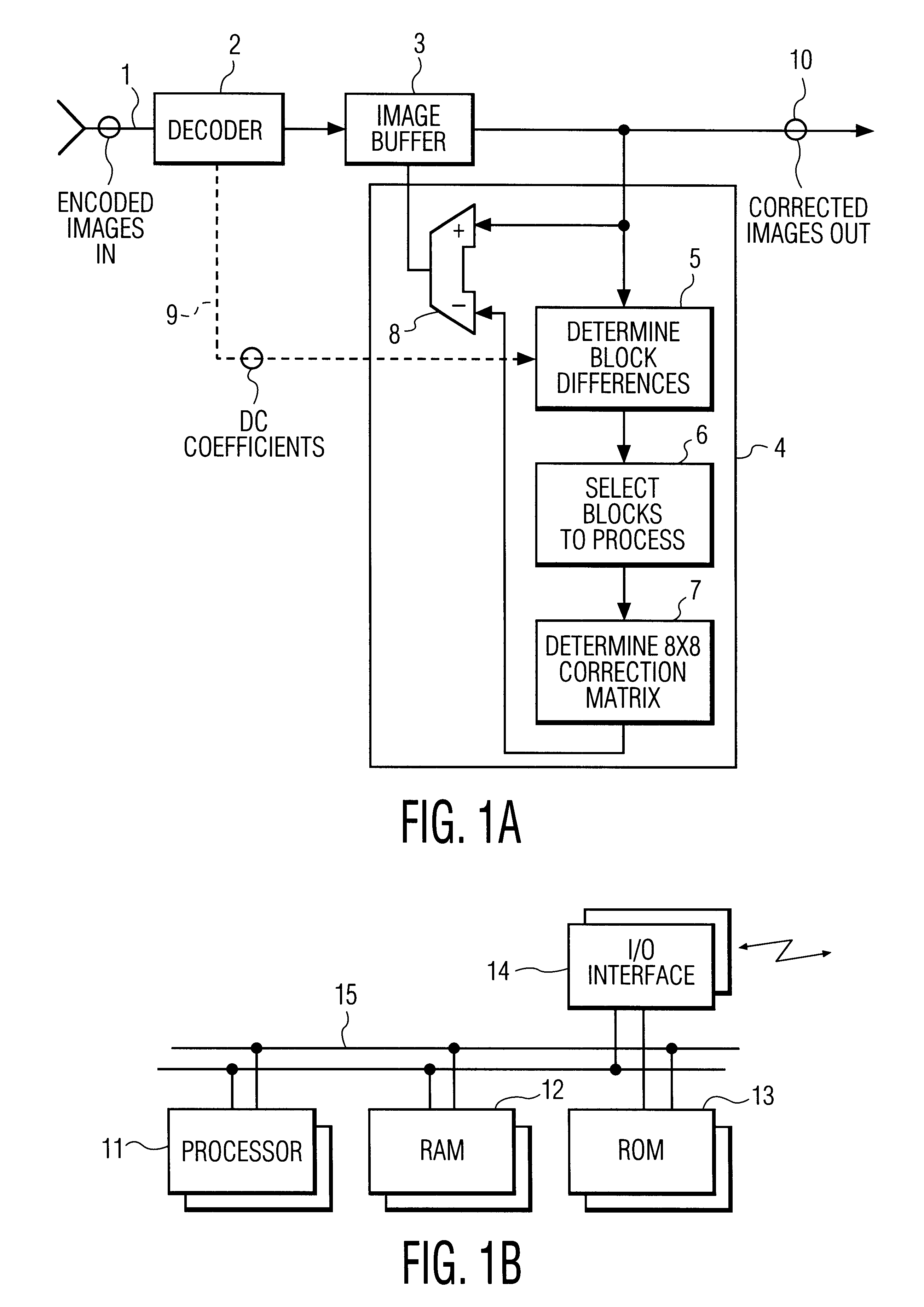
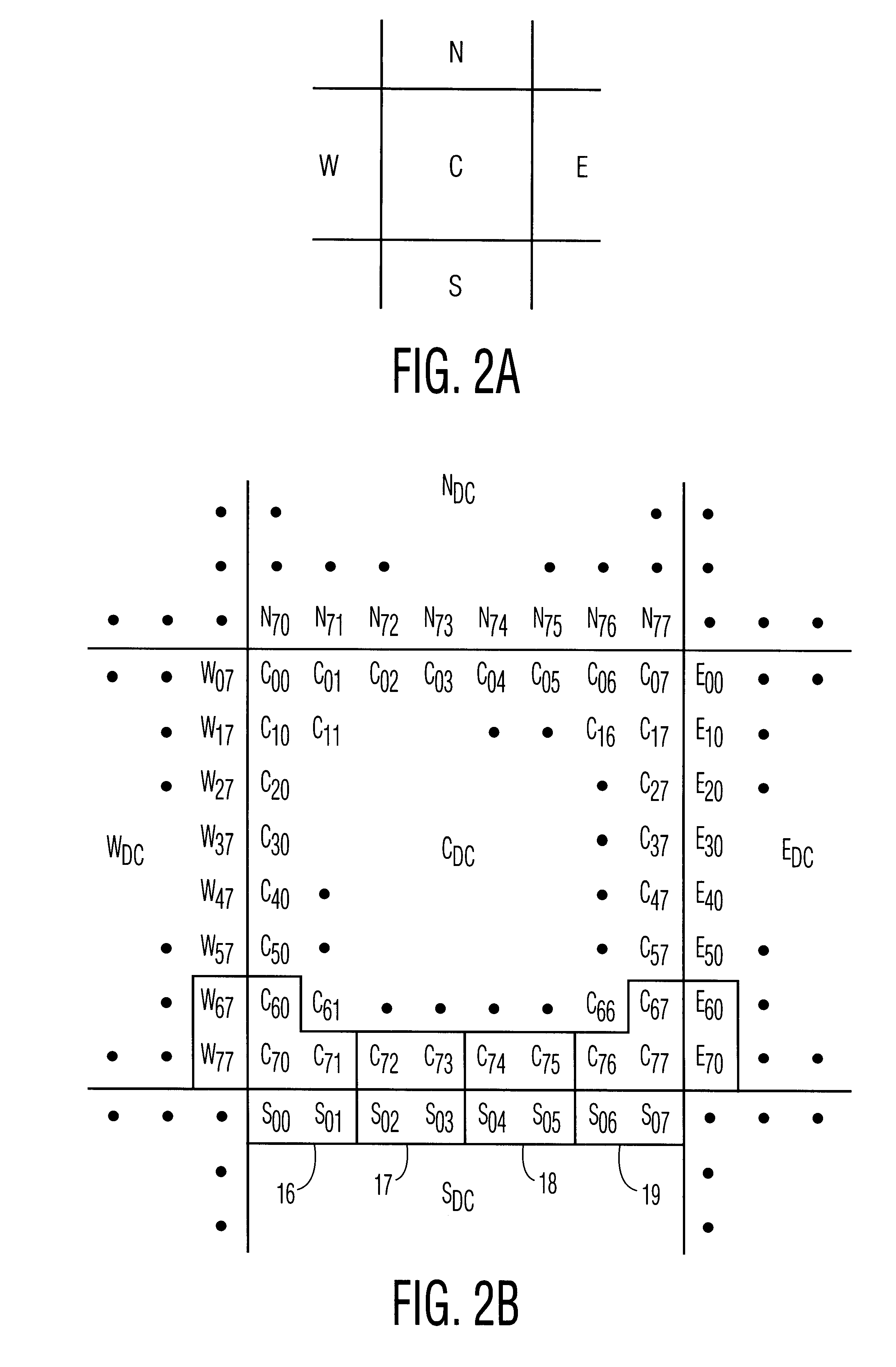
Systems and methods for post-processing decompressed images
This invention relates to a system and method for reducing blocking artifacts introduced by current compression algorithms that compress images as independent blocks of pixels. Preferably, the methods of the invention include determining block-to-block differences in edge pixels or in overall intensities between adjacent pixel blocks, selecting pixel blocks for post-processing that appear to be in relatively featureless regions of the image, interpolating the block-to-block edge differences into a error correction matrix, and then subtracting the error correction matrix from the original pixel block. These methods are preferably implemented in special software routines that execute on micro-processor based systems or on digital signal processor based systems optimized for image decoding.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
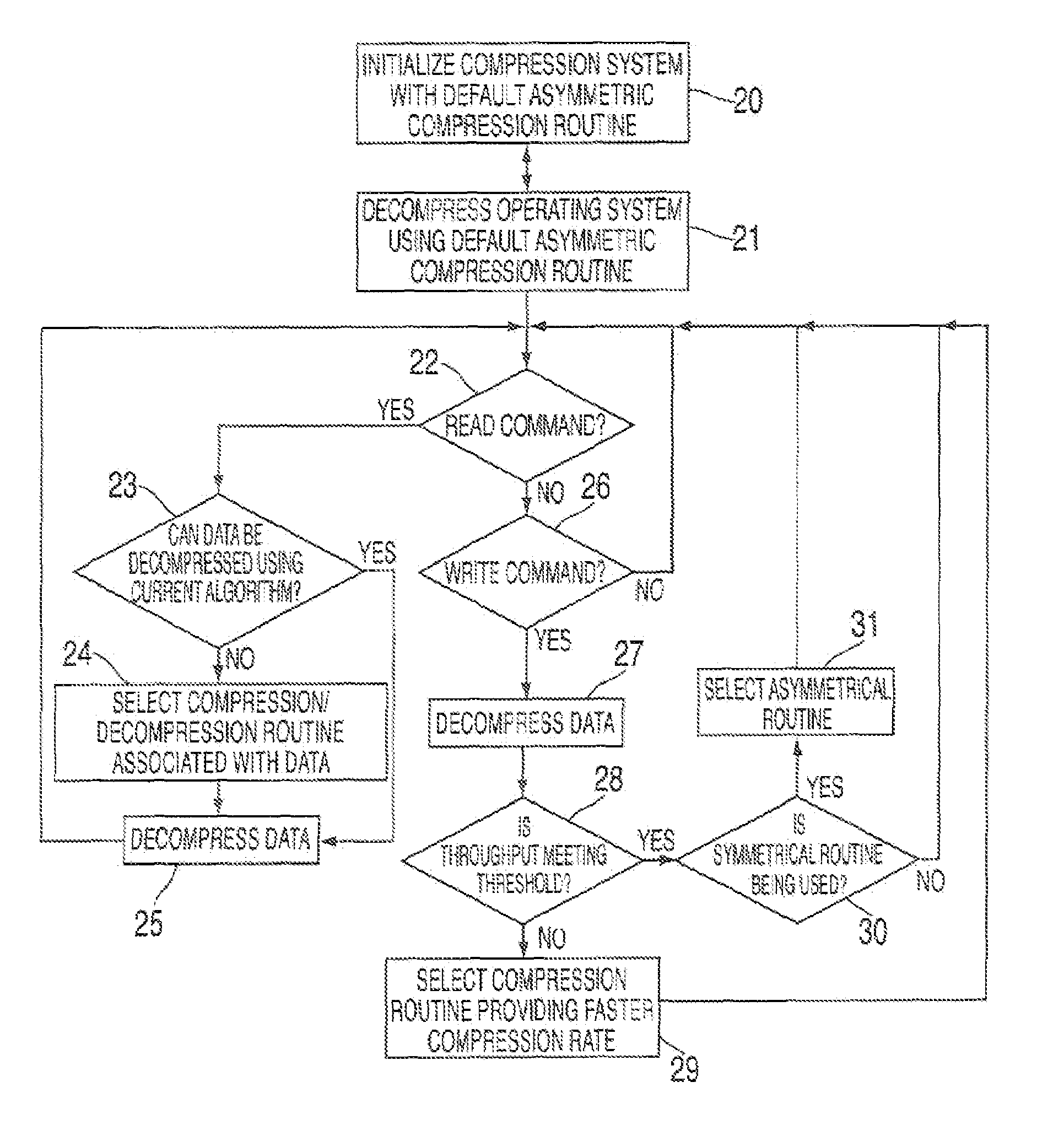
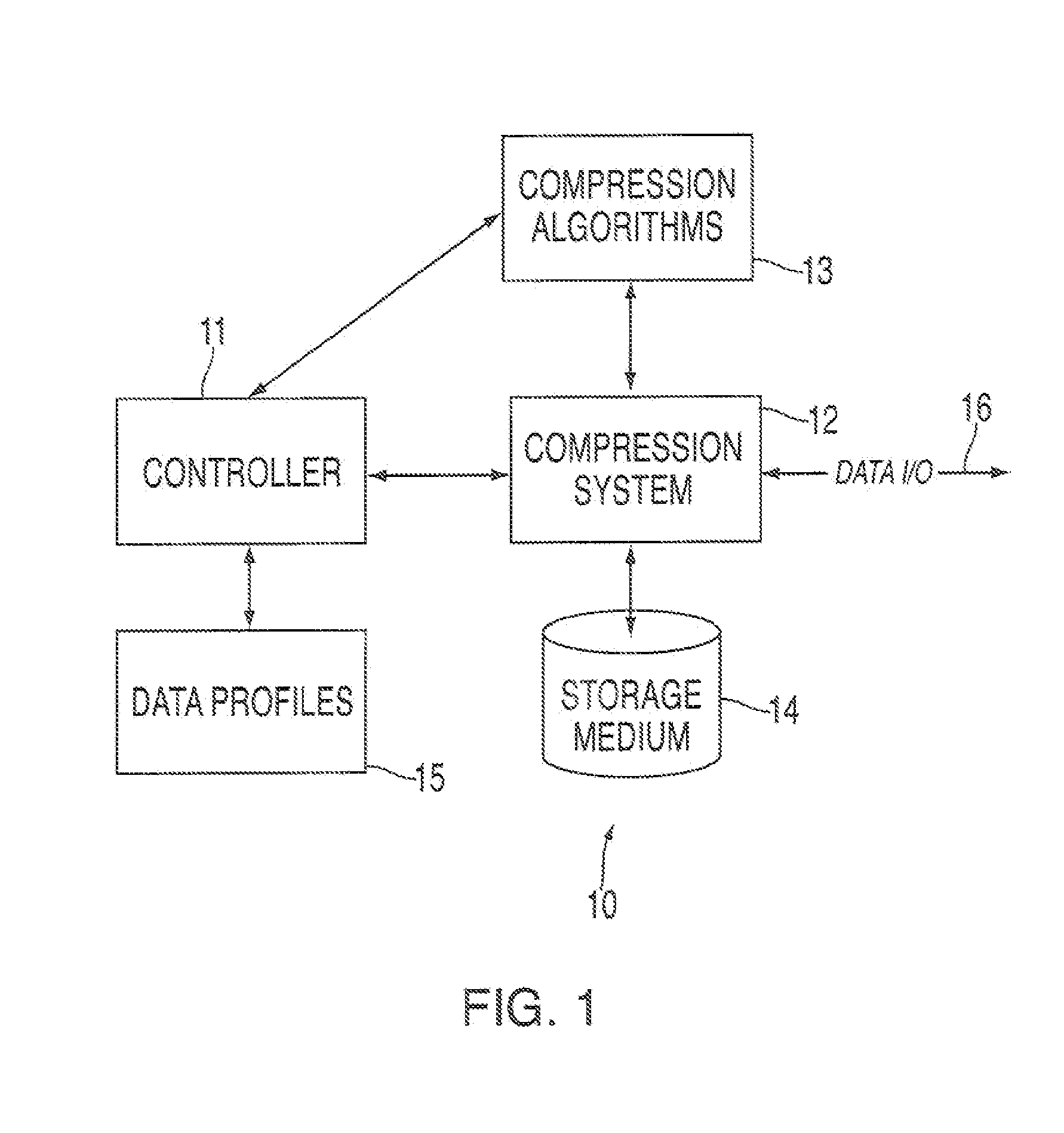
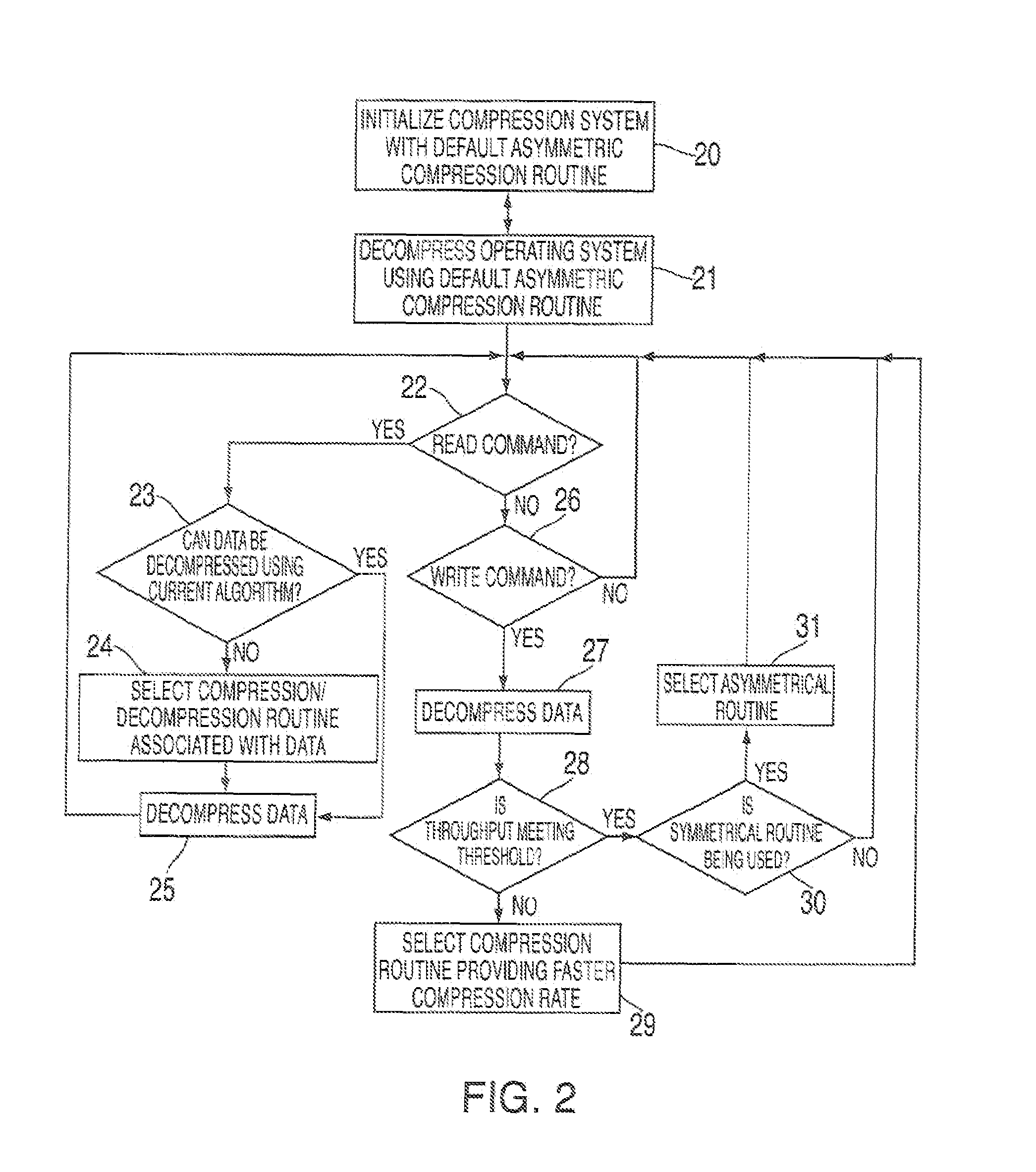
Bandwidth sensitive data compression and decompression
InactiveUS7386046B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionControl signalImage compression
Data compression and decompression methods for compressing and decompressing data based on an actual or expected throughput (bandwidth) of a system. In one embodiment, a controller tracks and monitors the throughput (data storage and retrieval) of a data compression system and generates control signals to enable / disable different compression algorithms when, e.g., a bottleneck occurs so as to increase the throughput and eliminate the bottleneck.
Owner:REALTIME ADAPTIVE STREAMING LLC
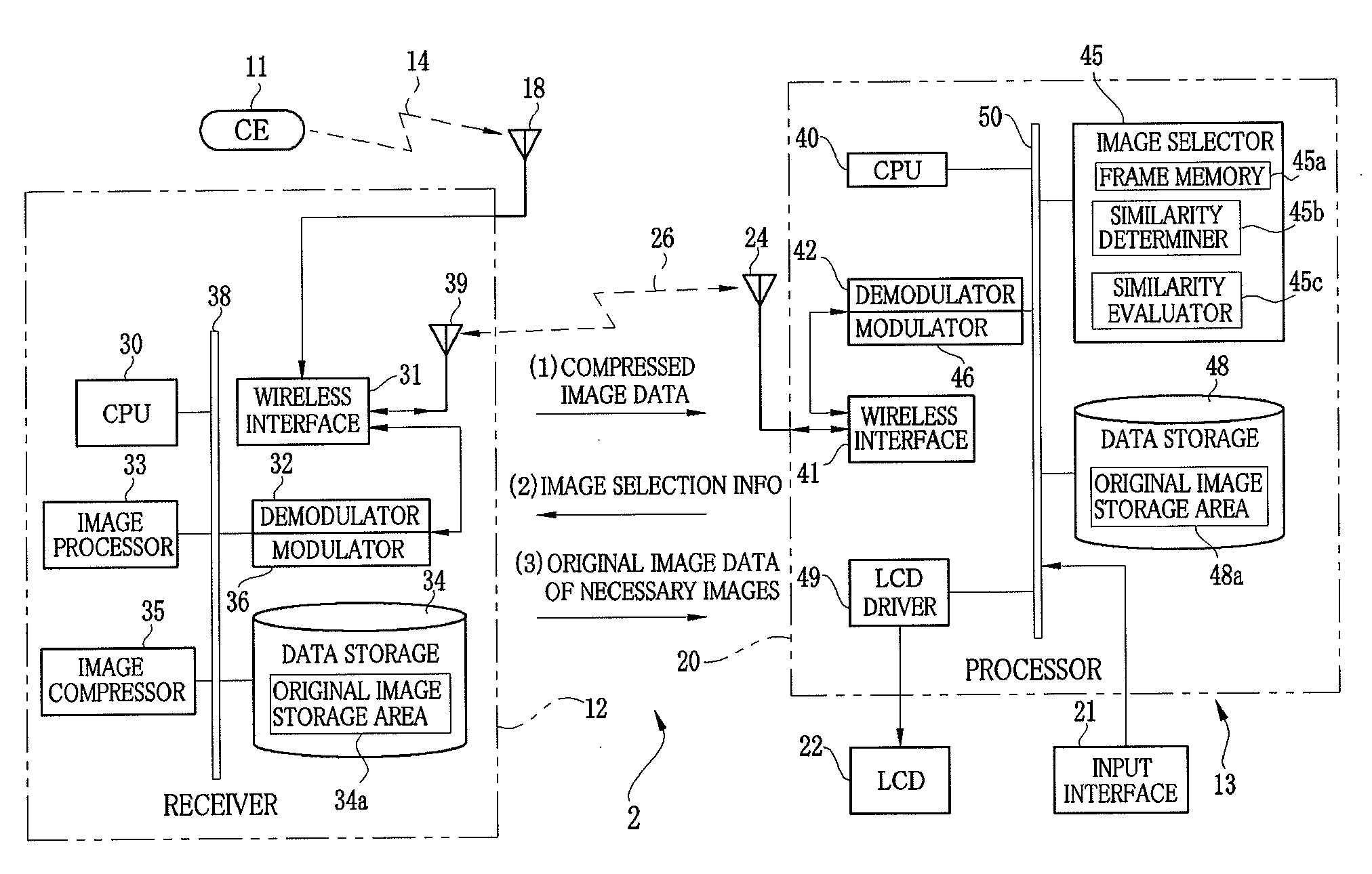
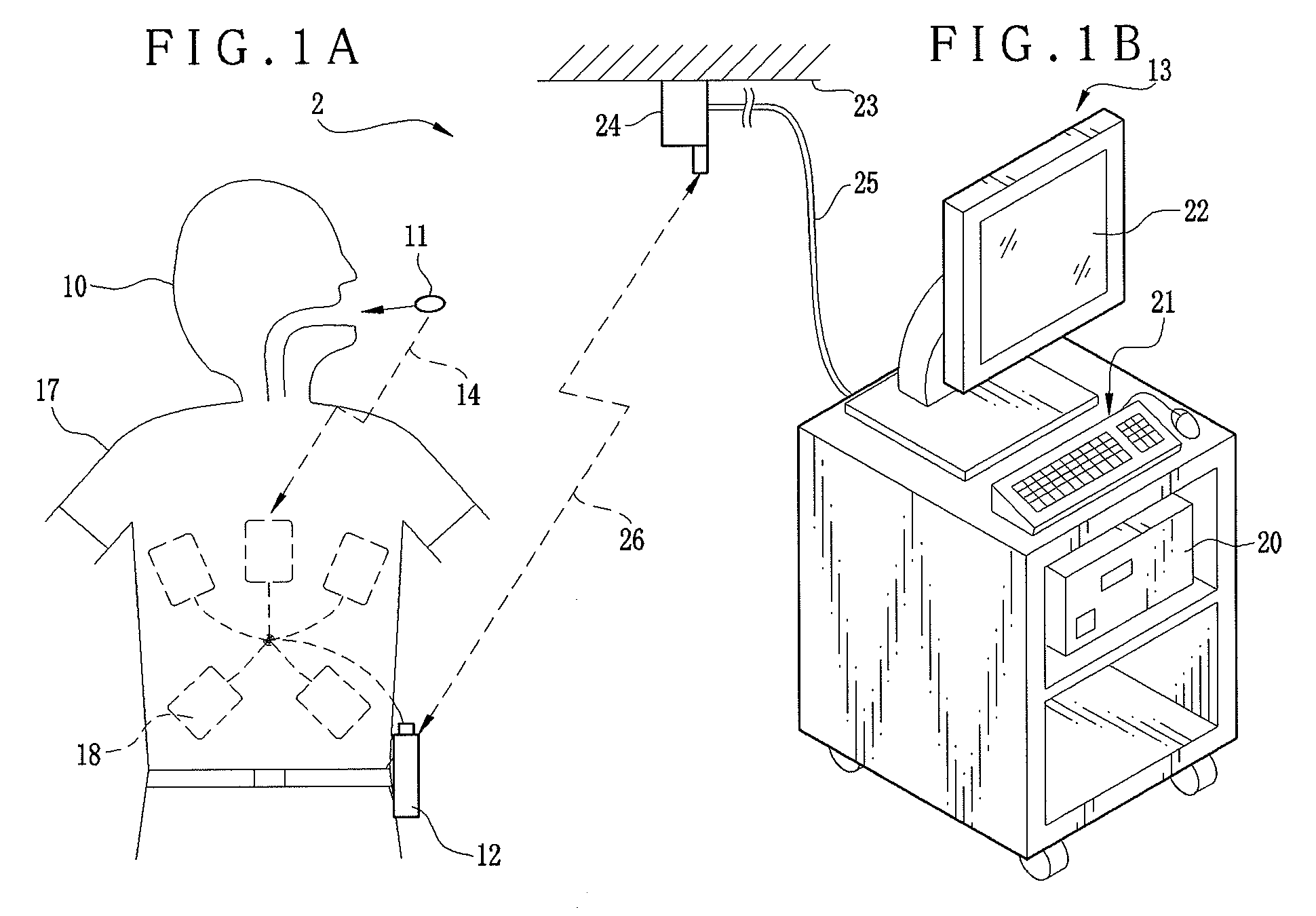
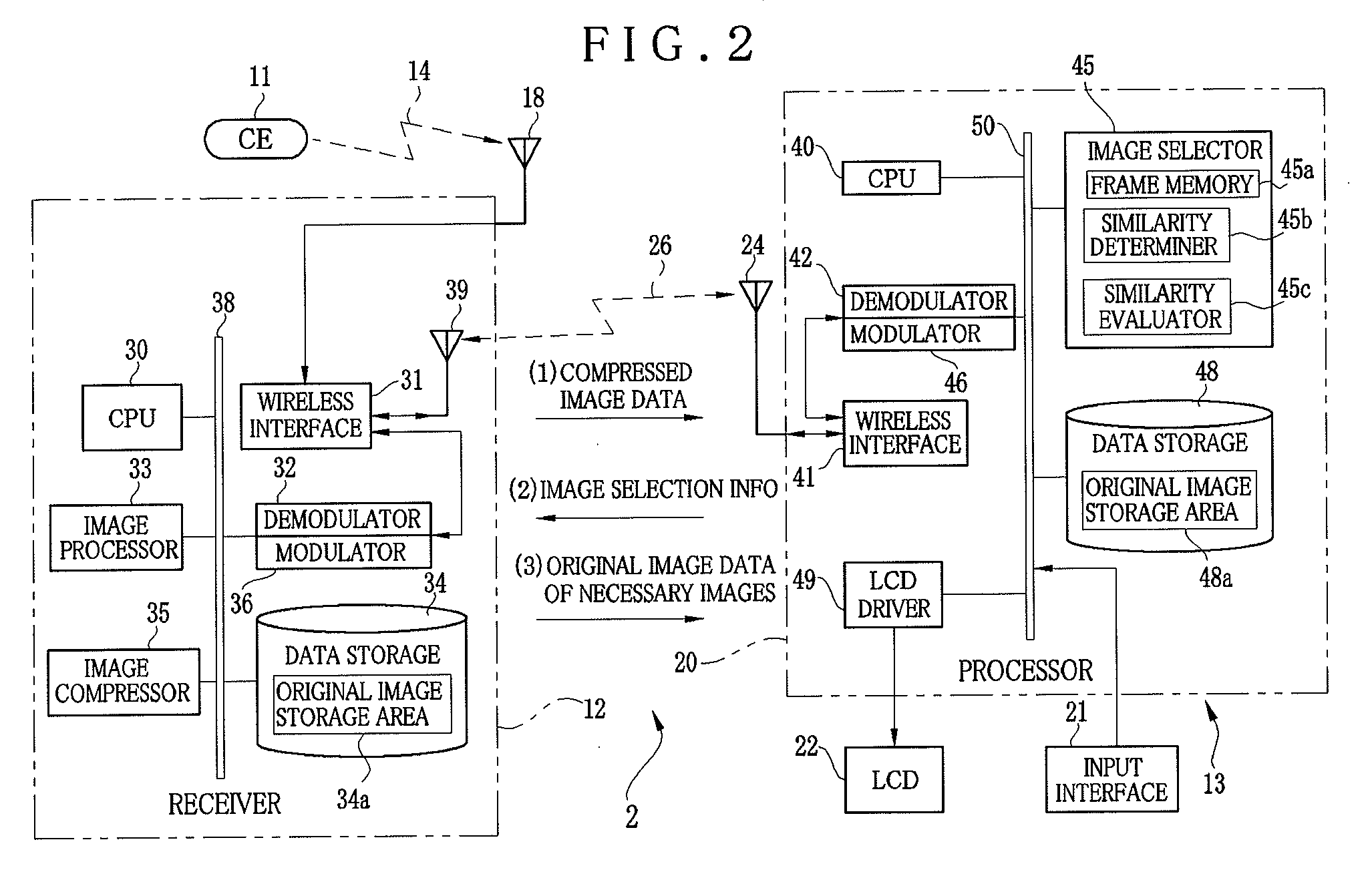
Capsule endoscope system and endoscopic image filing method
InactiveUS20090203964A1Improve efficiencyReduce data sizeSurgeryEndoscopesImage compressionWorkstation
A capsule endoscope system includes a capsule endoscope, swallowable in a body, for forming an image. A receiver is positioned on the body, for wirelessly receiving the image from the capsule endoscope, to store the image. A workstation as information manager operates for image filing of the image from the receiver. A first wireless interface is incorporated in the receiver, for wirelessly transmitting the image during imaging with the capsule endoscope. A second wireless interface is positioned on the workstation, for wirelessly receiving the image from the first wireless interface. Furthermore, an image selector selects the image for image filing in the workstation among plural images received by the receiver. The first wireless interface transmits the selected image to the workstation. The receiver includes an image compressor for reducing a data size of the image received from the capsule endoscope before transmission in the first wireless interface.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of restoring and reconstructing super-resolution image from low-resolution compressed image
InactiveUS20050019000A1Preserving contourRemove image blurImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital videoImage compression
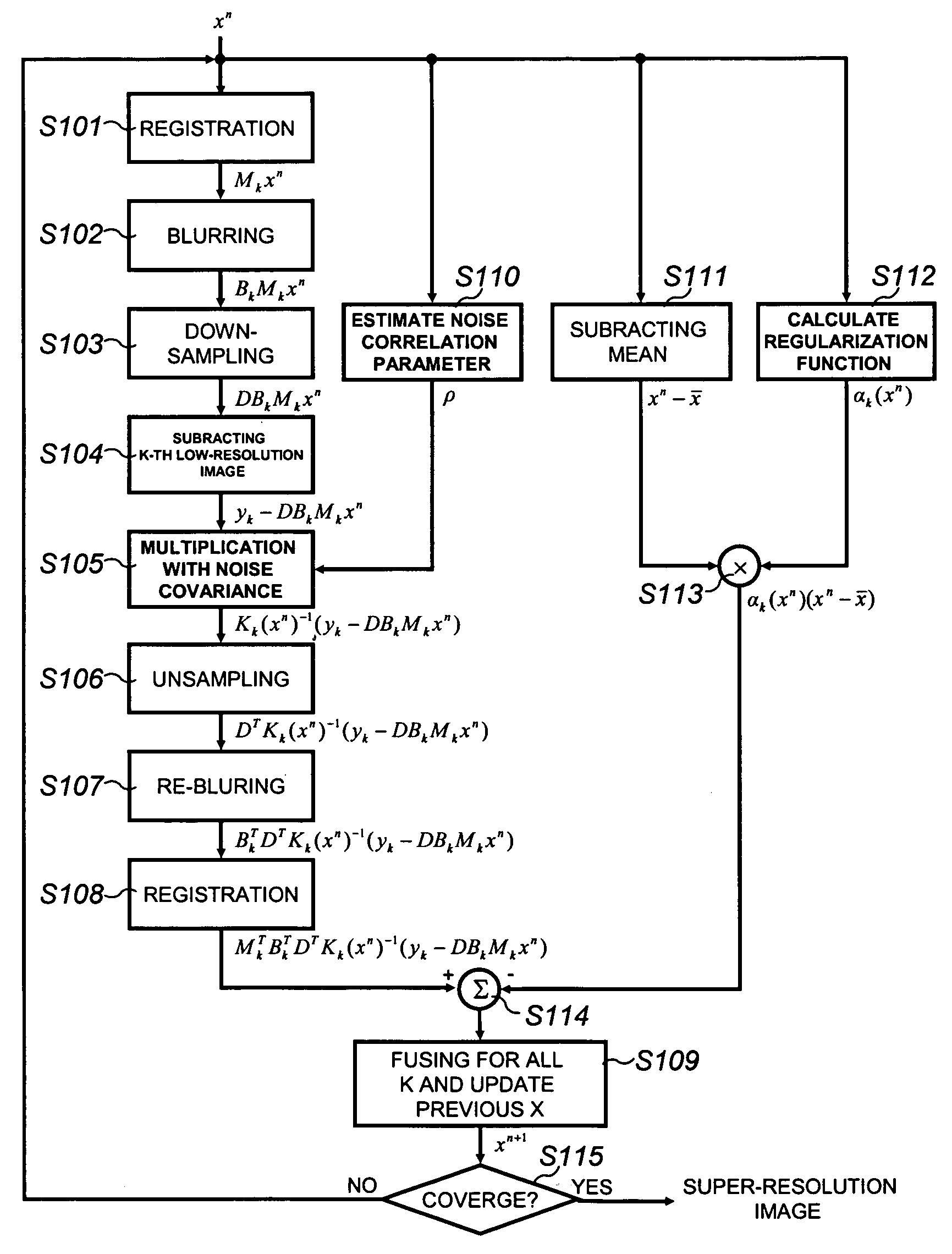
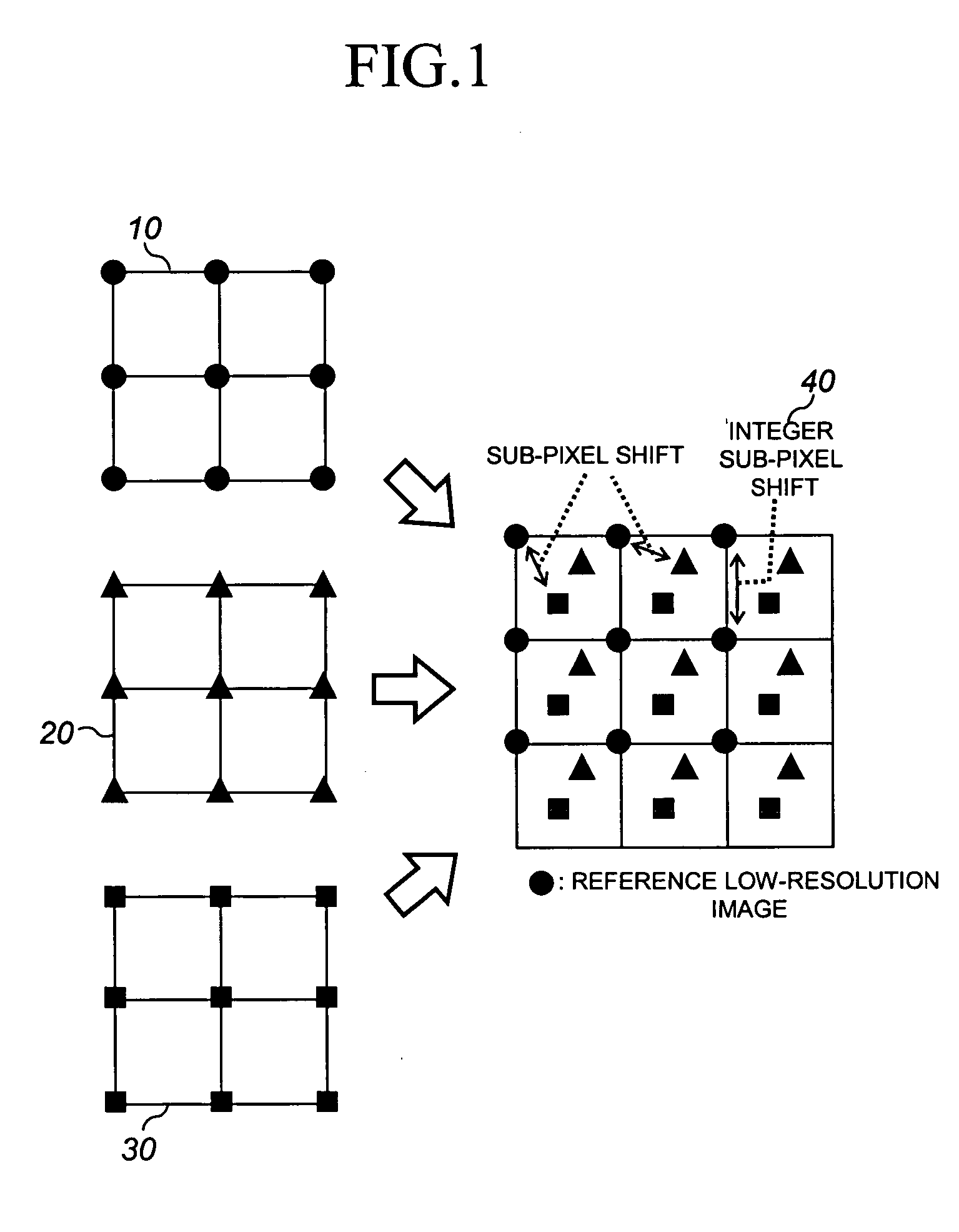
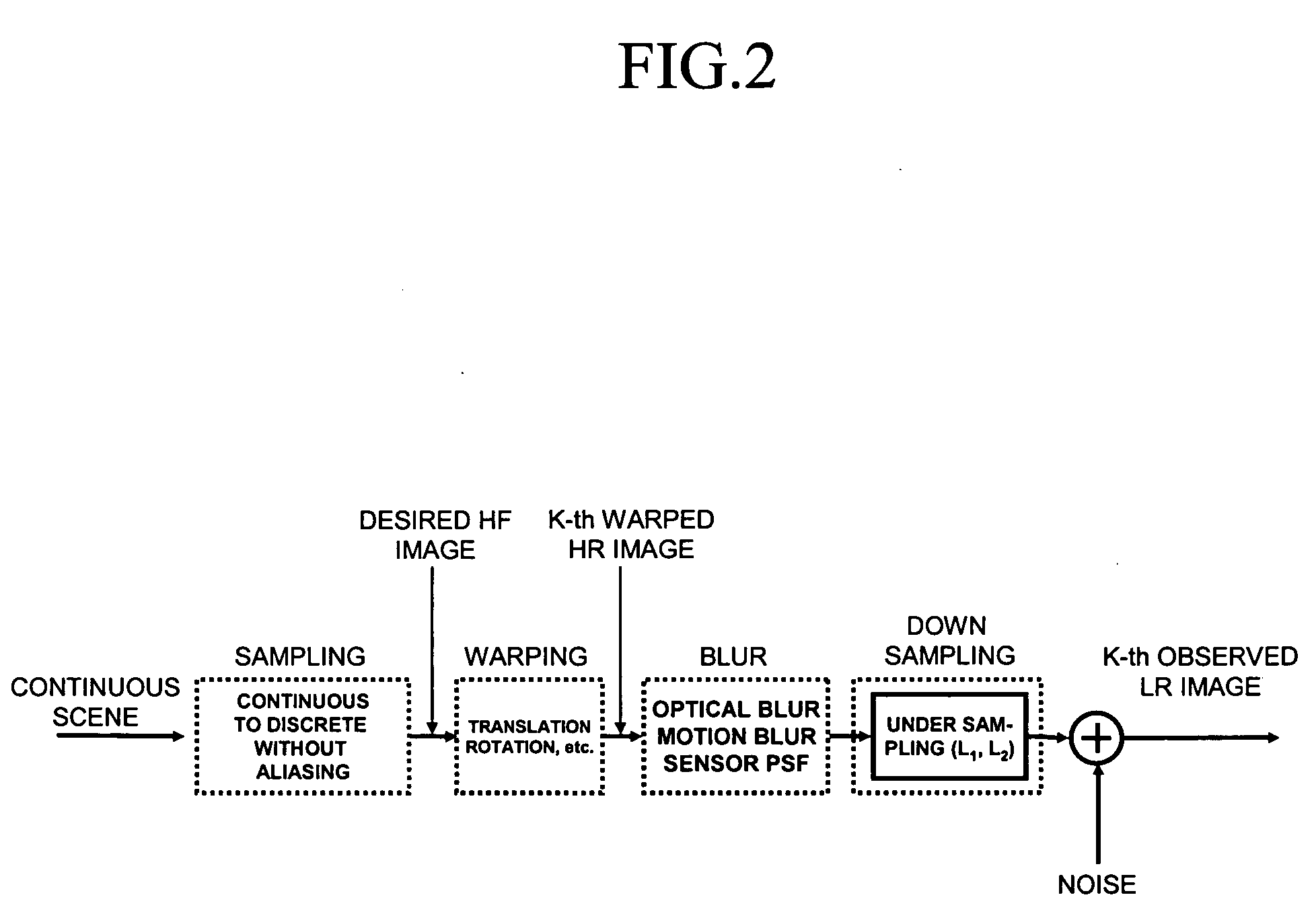
Provided is a method of restoring and / or reconstructing a super-resolution image from low-resolution images compressed in a digital video recorder (DVR) environment. The present invention can remove a blur of a video sequence, caused by optical limitations due to a miniaturized camera of a digital video recorder monitoring system, a limitation of spatial resolution due to an insufficient number of pixels of a CCD / CMOS image sensor, and noises generated during image compression, transmission and storing processes, to restore high-frequency components of low-resolution images (for example, the face and appearance of a suspect or numbers of a number plate) to reconstruct a super-resolution image. Consequently, an interest part of a low-resolution image stored in the digital video recorder can be magnified to a high-resolution image later, and the effect of an expensive high-performance camera can be obtained from an inexpensive low-performance camera.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY +1
Spiking neuron network sensory processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140016858A1Reduce image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesContent distributionNeuron network
Apparatus and methods for detecting salient features. In one implementation, an image processing apparatus utilizes latency coding and a spiking neuron network to encode image brightness into spike latency. The spike latency is compared to a saliency window in order to detect early responding neurons. Salient features of the image are associated with the early responding neurons. A dedicated inhibitory neuron receives salient feature indication and provides inhibitory signal to the remaining neurons within the network. The inhibition signal reduces probability of responses by the remaining neurons thereby facilitating salient feature detection within the image by the network. Salient feature detection can be used for example for image compression, background removal and content distribution.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
System and method using a packetized encoded bitstream for parallel compression and decompression
InactiveUS6862278B1Improve performanceEasy to parallelizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer hardwareParallel compression
A system and method are disclosed for parallel compression and decompression of a bitstream. For compression, the bitstream is separated into a plurality of components, and the components are encoded using a compression algorithm. Packets are then constructed from the encoded components. At least one packet is associated with each encoded component and comprises header information and encoded data. The packets are combined into a packetized encoded bitstream. For decompression, the packets are separated from the packetized encoded bitstream using the header information. The packets are then decoded in parallel using a decompression algorithm to recover the encoded data. The plurality of components are reconstructed from the recovered encoded data and combined to recover the bitstream.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
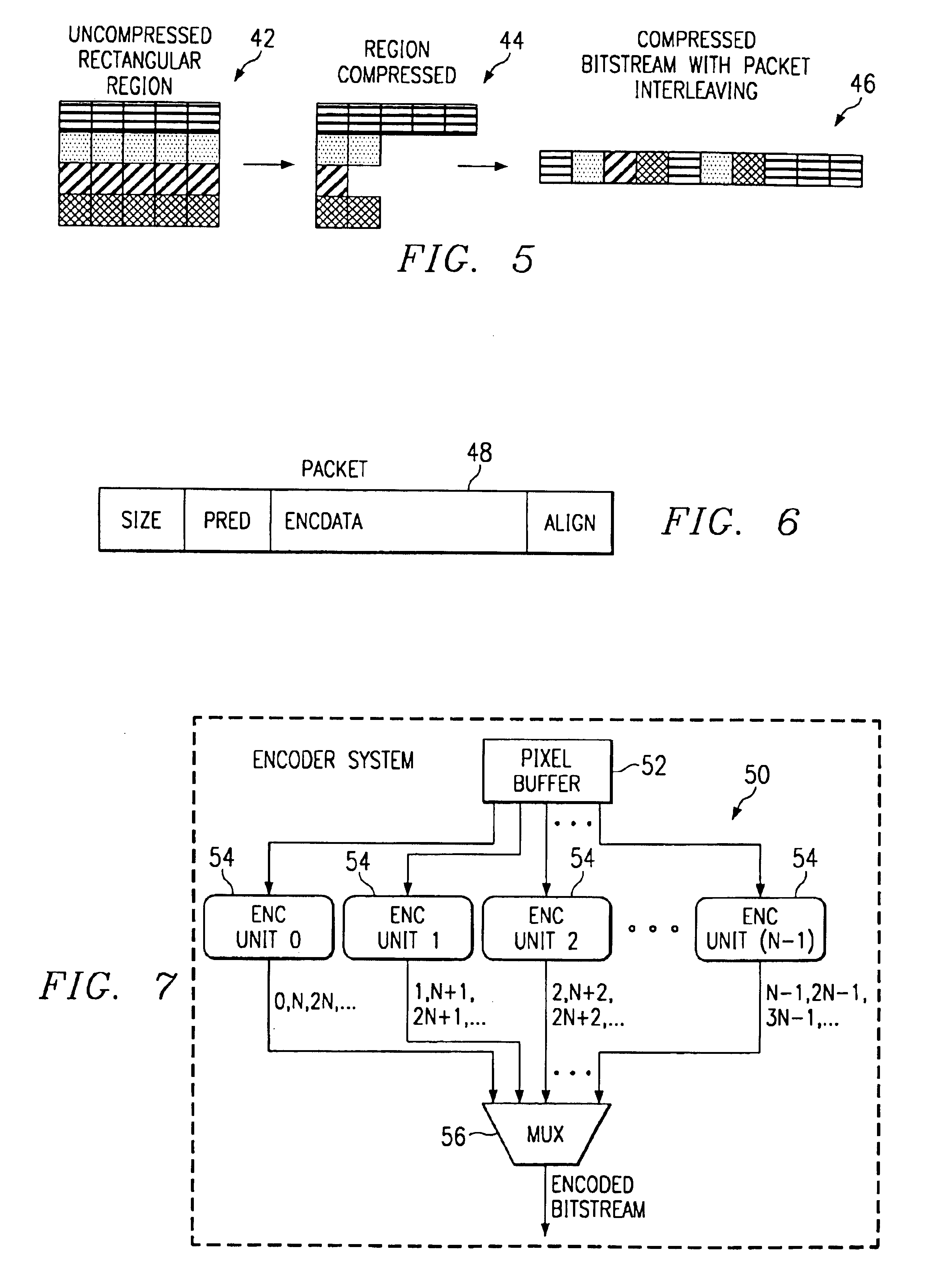
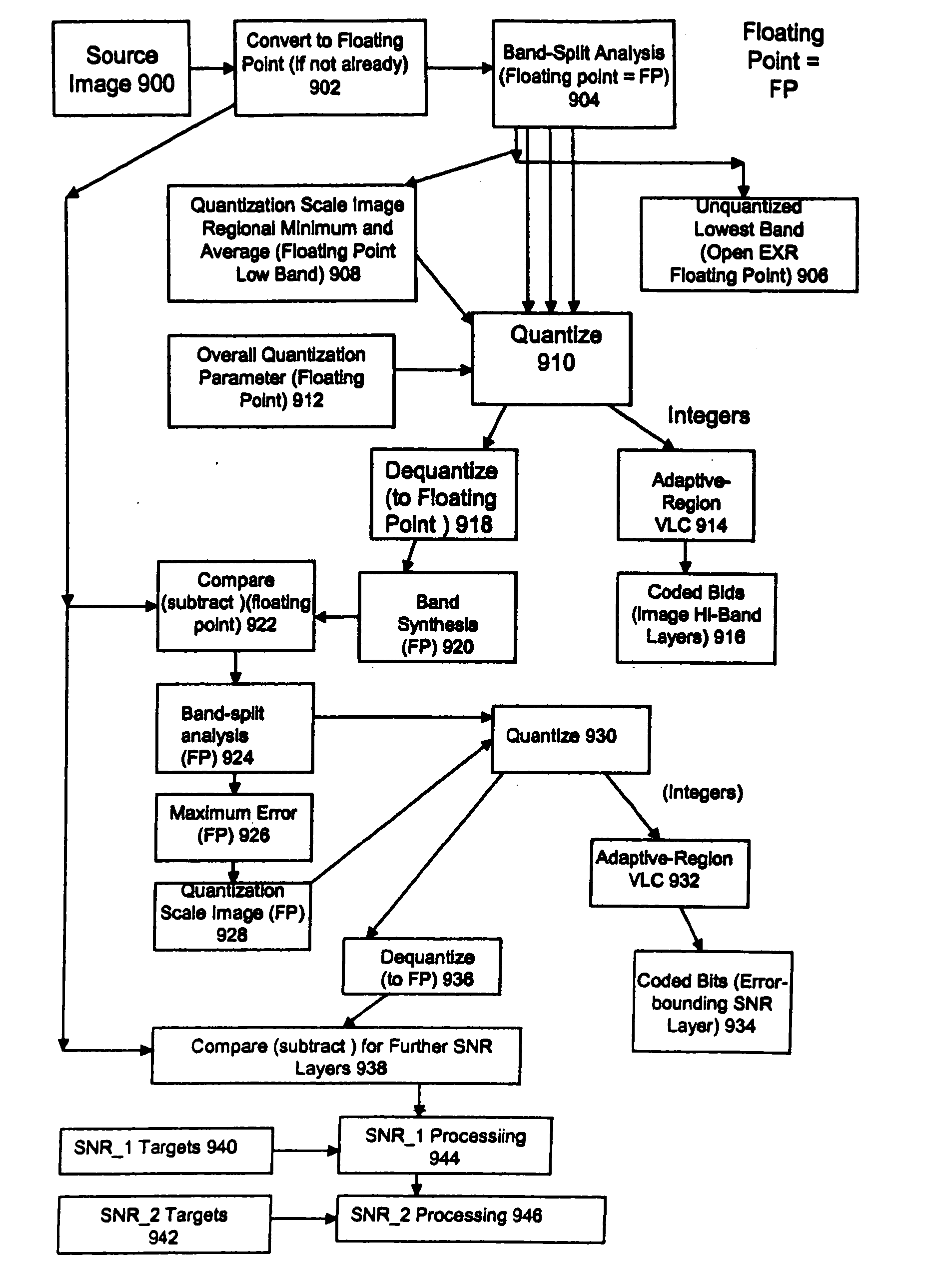
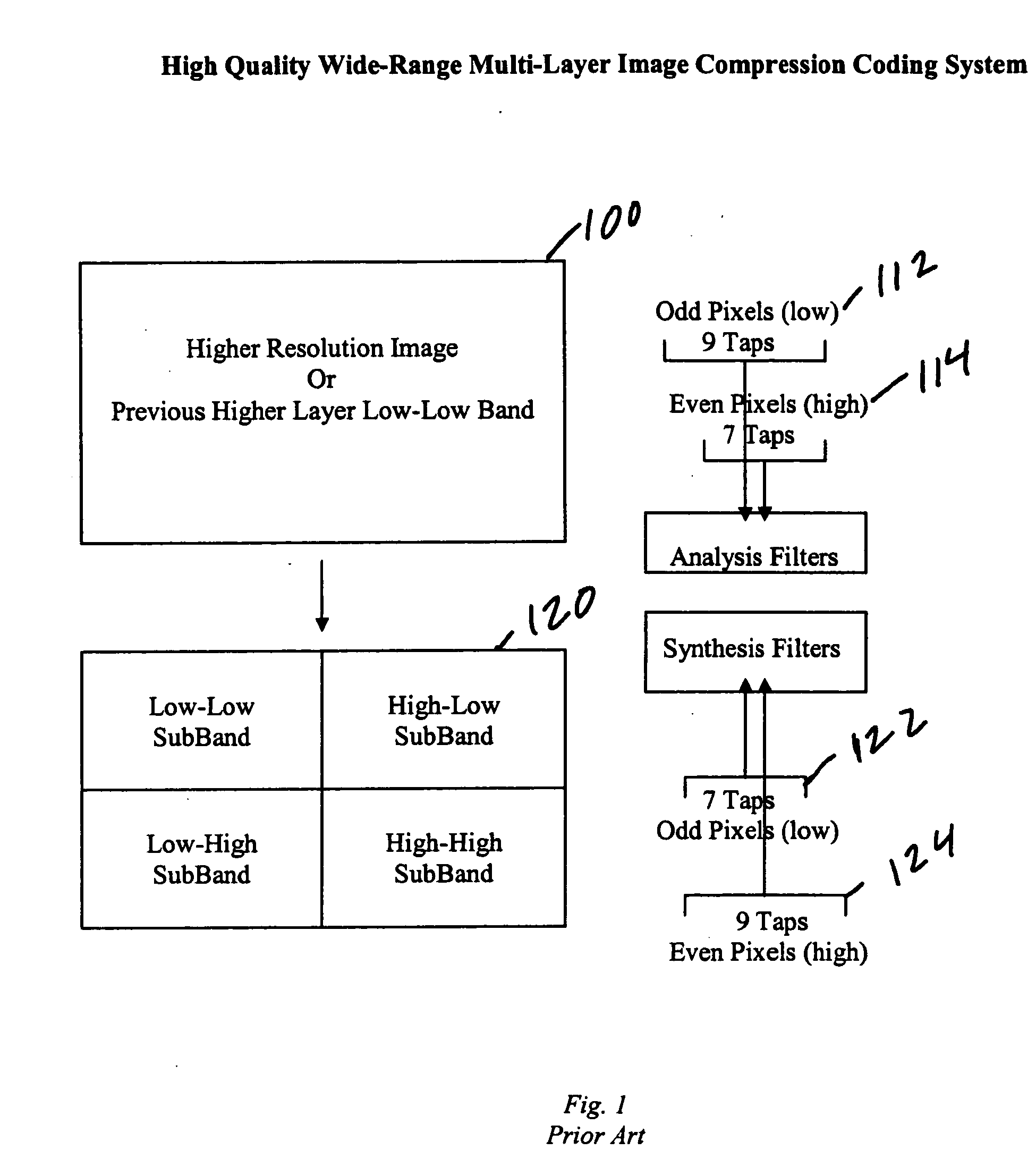
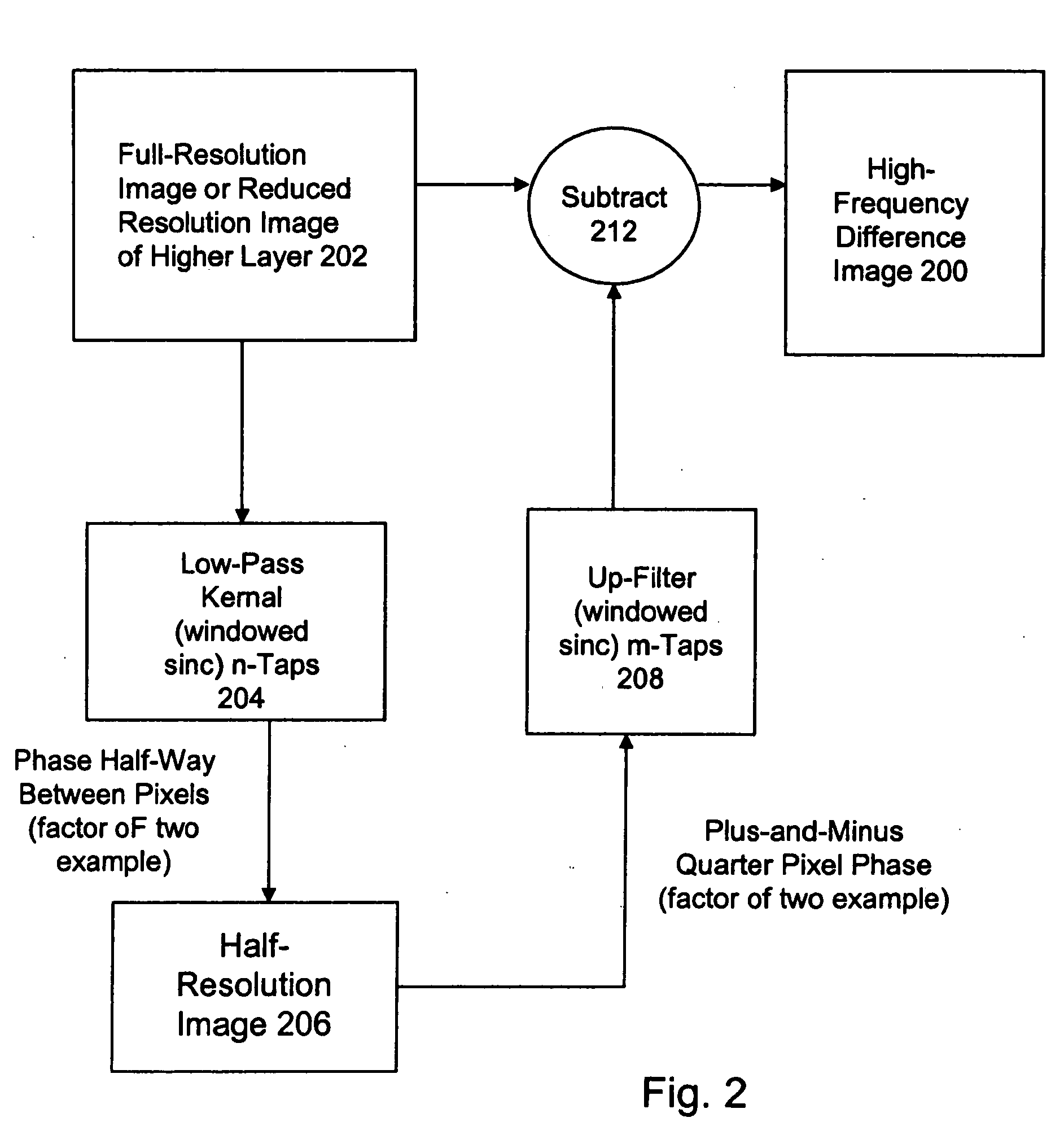
High quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding system
ActiveUS20060071825A1Reduce sharpnessReduce detailsCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionFloating pointImage compression
Systems, methods, and computer programs for high quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding, including consistent ubiquitous use of floating point values in essentially all computations; an adjustable floating-point deadband; use of an optimal band-split filter; use of entire SNR layers at lower resolution levels; targeting of specific SNR layers to specific quality improvements; concentration of coding bits in regions of interest in targeted band-split and SNR layers; use of statically-assigned targets for high-pass and / or for SNR layers; improved SNR by using a lower quantization value for regions of an image showing a higher compression coding error; application of non-linear functions of color when computing difference values when creating an SNR layer; use of finer overall quantization at lower resolution levels with regional quantization scaling; removal of source image noise before motion-compensated compression or film steadying; use of one or more full-range low bands; use of alternate quantization control images for SNR bands and other high resolution enhancing bands; application of lossless variable-length coding using adaptive regions; use of a folder and file structure for layers of bits; and a method of inserting new intra frames by counting the number of bits needed for a motion compensated frame.
Owner:DEMOS GARY
Method of encoding digital signals (variants), method of decoding digital signals (variants), device for implementation thereof (variants), and system for image transmission via limited throughput communication channels (variants)
InactiveUS20100226569A1Quality improvementImprove compression efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionSystematic variationSelf adaptive
The invention relates to systems for a transmission of images via channels of communication with a limited capacity by means of application of compression of the images. The technical result consists in an increase of the compression degree upon encoding, and it allows to fulfill the transmission of such encoded images via the channel of communication with the limited capacity, therewith a high degree of the compression is provided without of increase of computational power of encoding device and without of distortions upon decoding. The result is obtained by the usage of more effective method of interpolation of restored subsamples, in this method there is used an adaptive and applicative set of samples, which restore a quantized signal, and this set of the samples allows to improve an accuracy of the interpolation with a number of the subsamples, which is necessary for the right interpolation that is simultaneously decreased one.
Owner:SIF CODEC
Image processing system, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS7054503B2Easy to processReducing mosquito noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDiscrete cosine transform
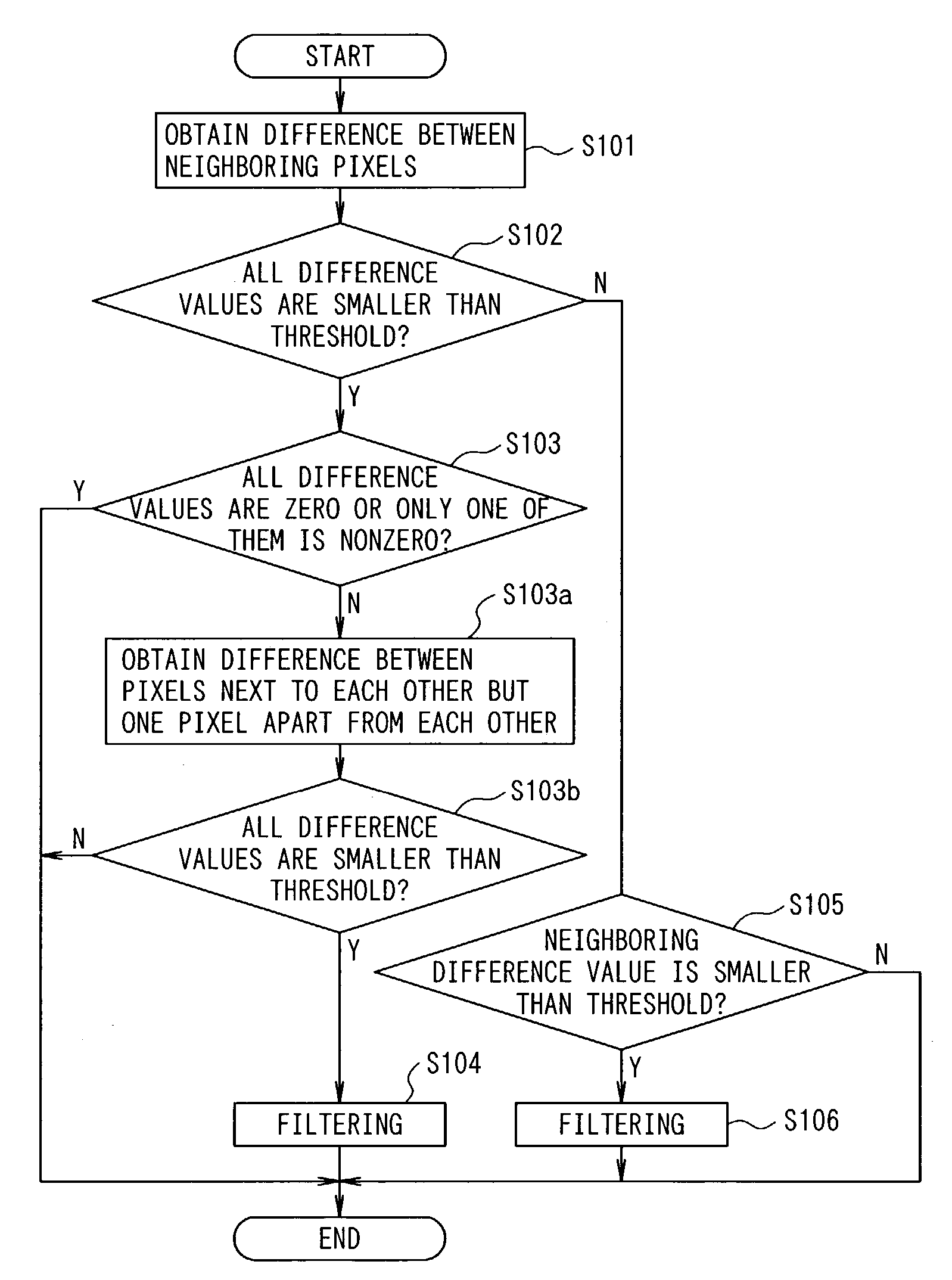
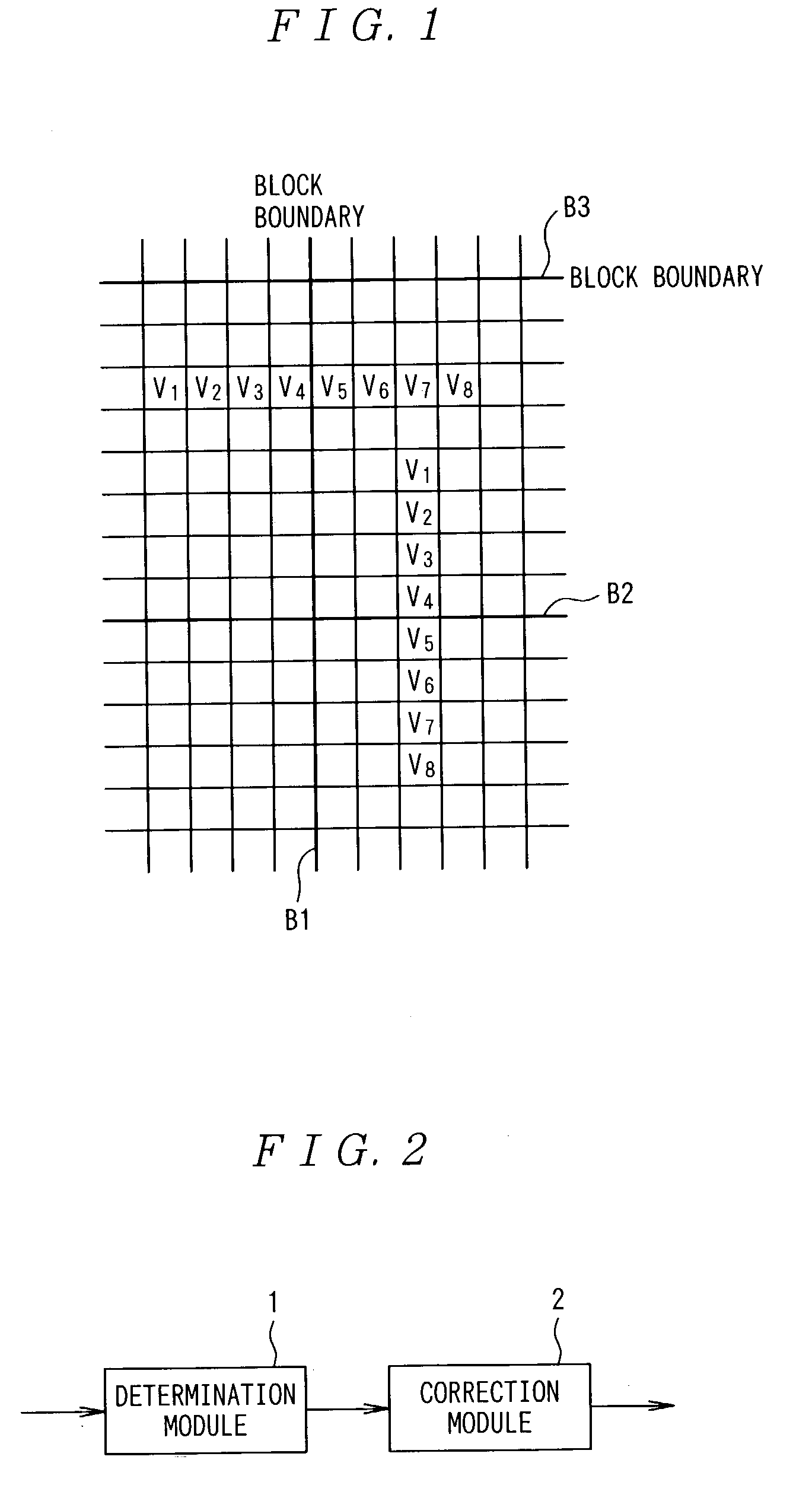
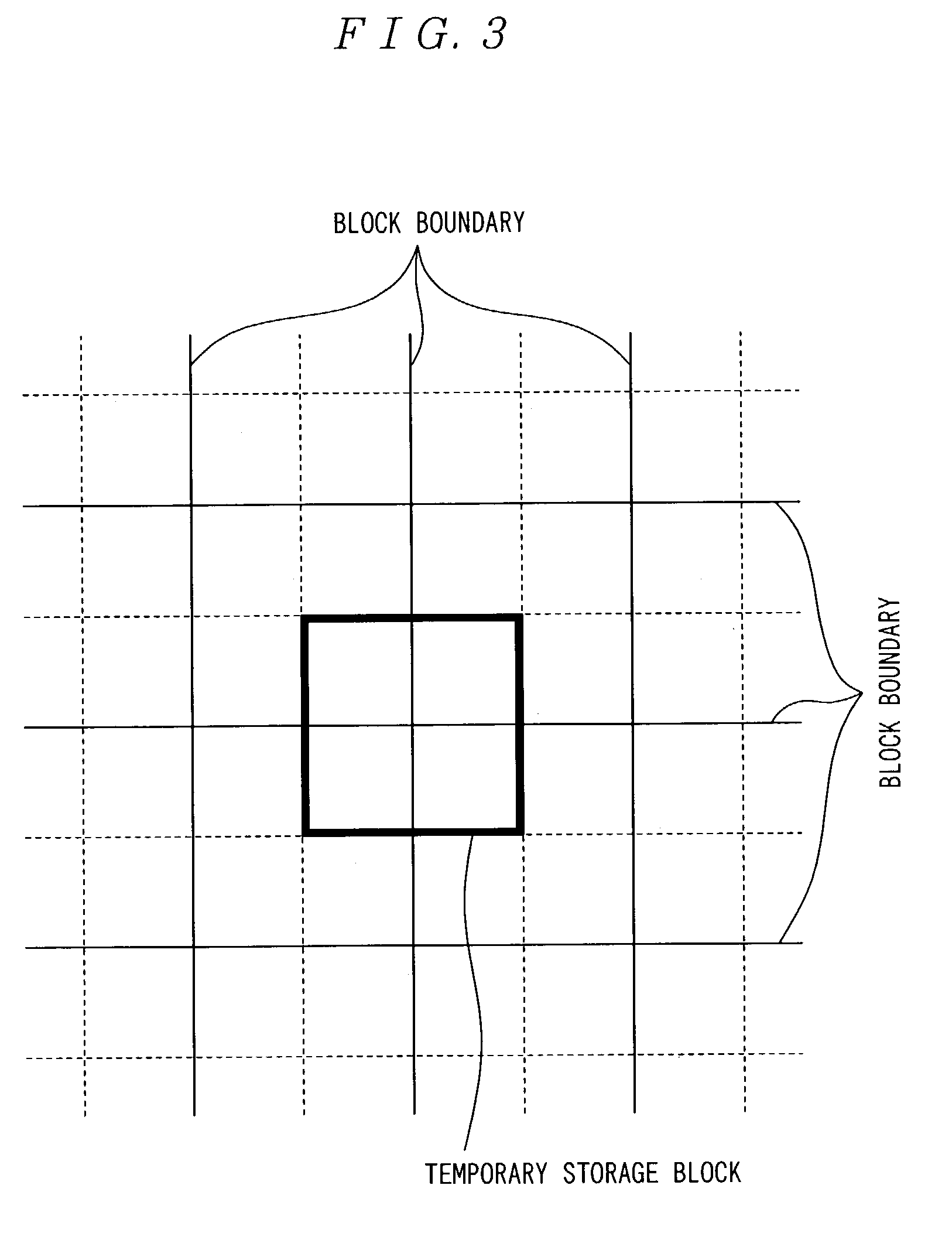
In the present invention, 2N pixels (having signal levels V1 through V8), including a boundary pixel, that consist of N pixels on each side of a boundary and run orthogonally to the boundary are referenced to determine whether correction should be performed or not. If it is determined that the correction should be performed, the boundary pixel and M pixels on each side of the boundary pixel are used to perform the correction. In an image processing system for performing filtering on pixels belonging to a block, which is a unit of discrete cosine transform in image compression, the maximum value of differences between neighboring pixels in at least half, including a pixel of interest, of all the pixels composing a block to be processed is obtained. Differences between neighboring pixels in 2N pixels, including the pixel of interest, that run orthogonally to the boundary between blocks and consist of N pixels on each side of the boundary are calculated. The differences calculated are compared with a threshold corresponding to the maximum value to determine whether filtering should be performed. If it is determined that filtering should be performed, the pixel of interest and M pixels on each side of the pixel of interest are used to perform filtering. N is a positive integer and M is a positive integer smaller than N.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Method and apparatus for processing image data
InactiveUS20060013495A1Small data sizeImage is often very smallImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCommunication unitImaging processing
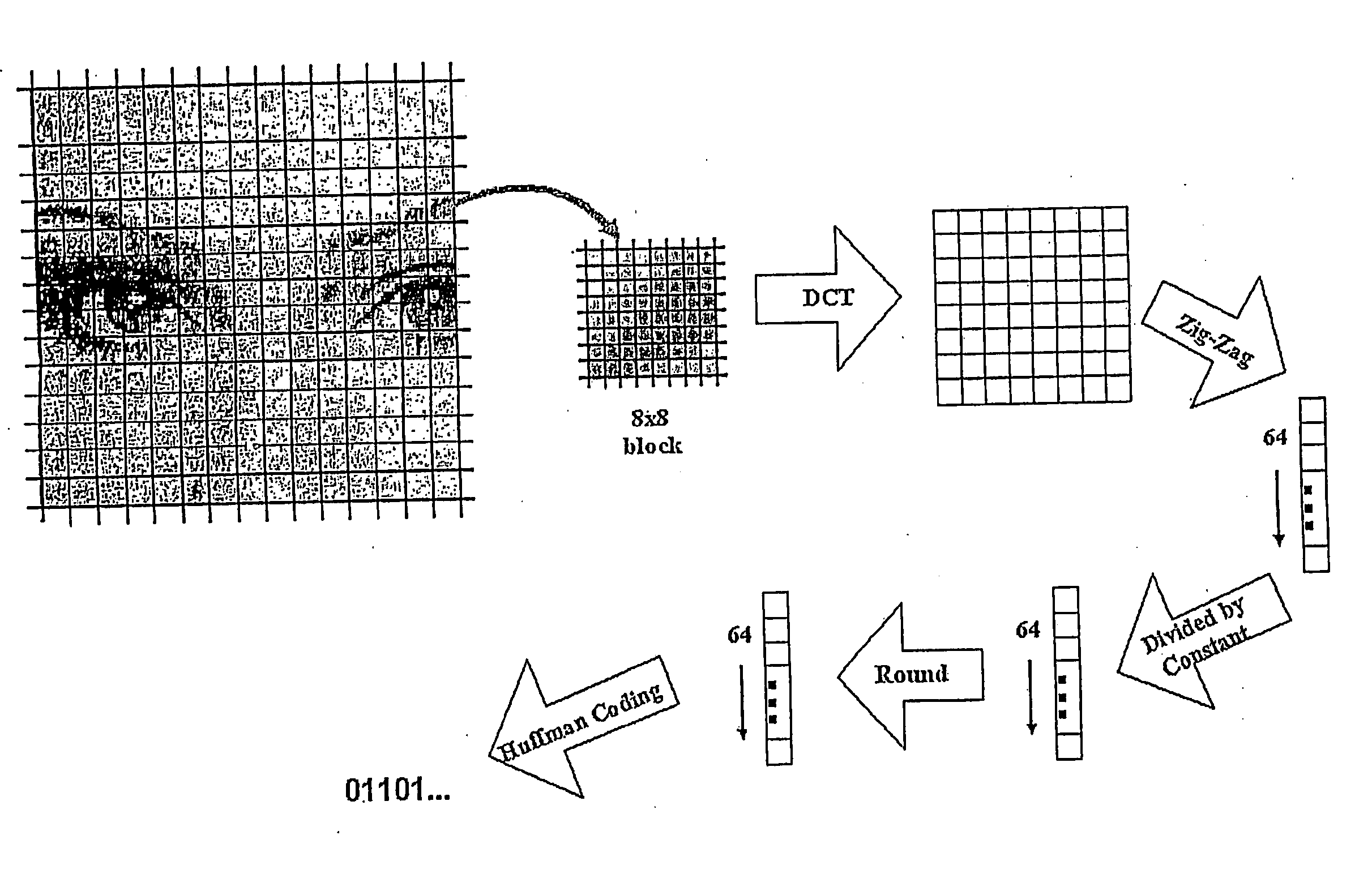
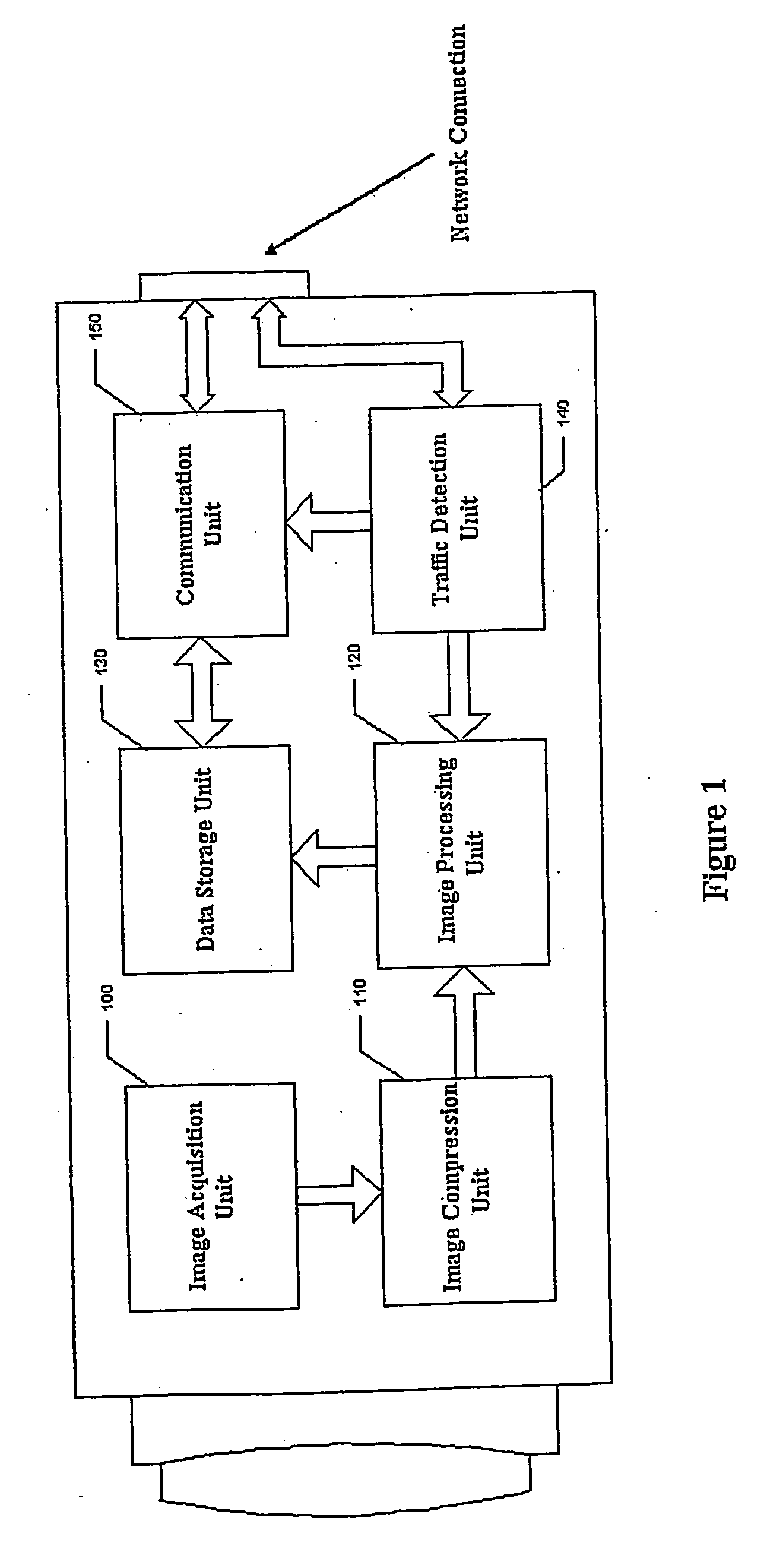
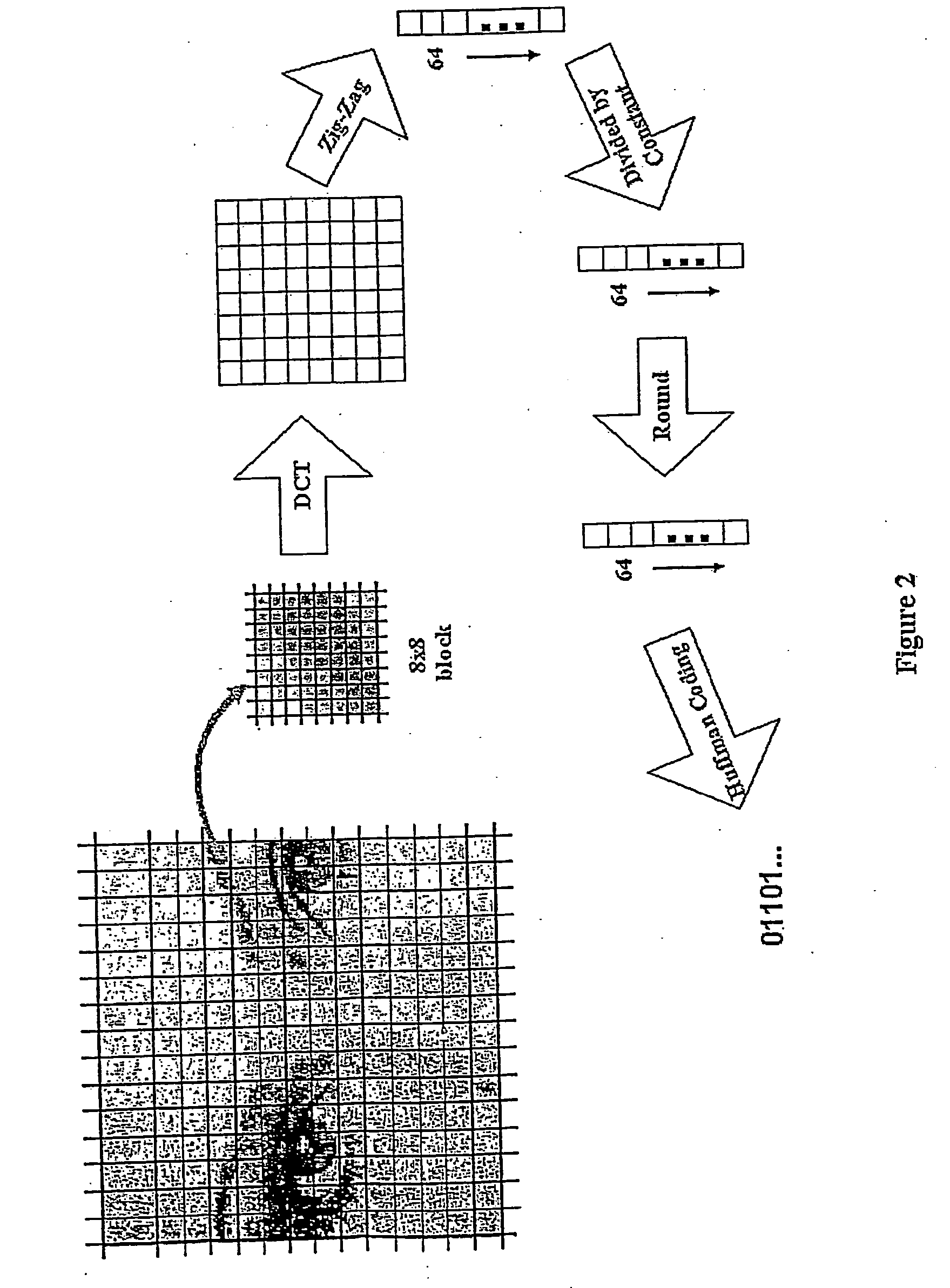
A network camera apparatus is disclosed including an image requisition unit which obtains an analog signal of an image and converts this into digital format; an image compression unit which utilizes standard image compression techniques (JPEG, MJPEG) to decrease the data size; an image processing unit which analyzes the compressed data of each image, detects motion from compressed data, and identifies background and foreground regions for each image; a data storage unit which stores the image data processed by the image processing unit; a traffic detection unit which detects the traffic amount of the network and decides the frame rates of the image data to be transmitted; and a communication unit which communicates with the network to transmit the image data and other signals.
Owner:VISLOG TECH PTE +1
Image decoding device, image decoding method, and image decoding program
InactiveUS8249147B2Improve efficiencyReduce computing costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareImage compression
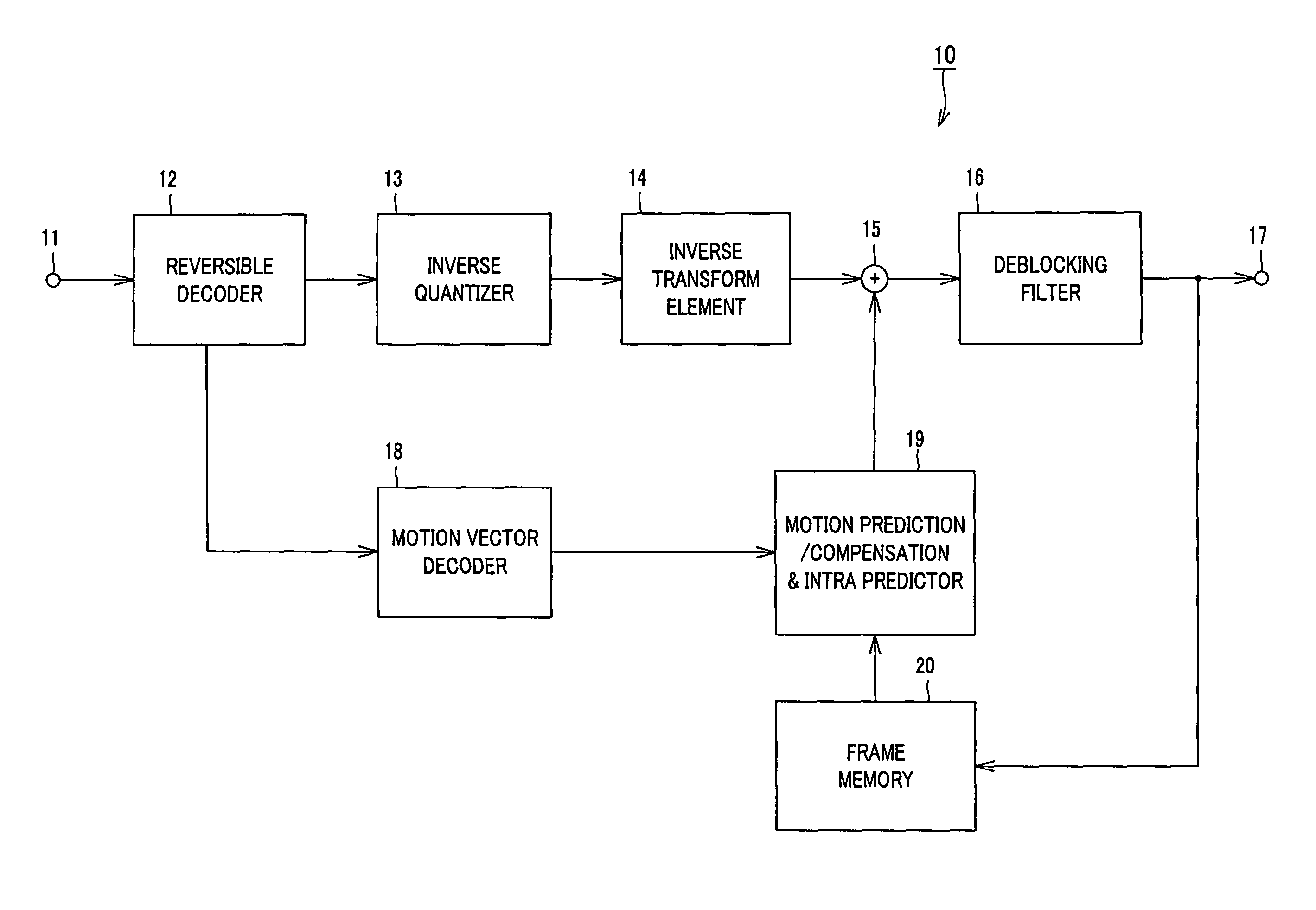
The present invention is directed to an image decoding apparatus adapted for decoding information obtained by implementing inverse quantization and inverse orthogonal transform to image compressed information in which an input image signal is blocked to implement orthogonal transform thereto on the block basis so that quantization is performed with respect thereto, which comprises a reversible decoder (12) for decoding quantized and encoded transform coefficients, an inverse quantizer (13) indicating, as a flag, in inverse-quantizing transform coefficients which have been decoded by the reversible decoder (12), existence of each transform coefficient every processing block of inverse quantization, and an inverse transform element (14) for changing inverse transform processing to be implemented to inverse quantization transform coefficients within processing block by using the flag which has been indicated by the inverse-quantizer (13).
Owner:SONY CORP
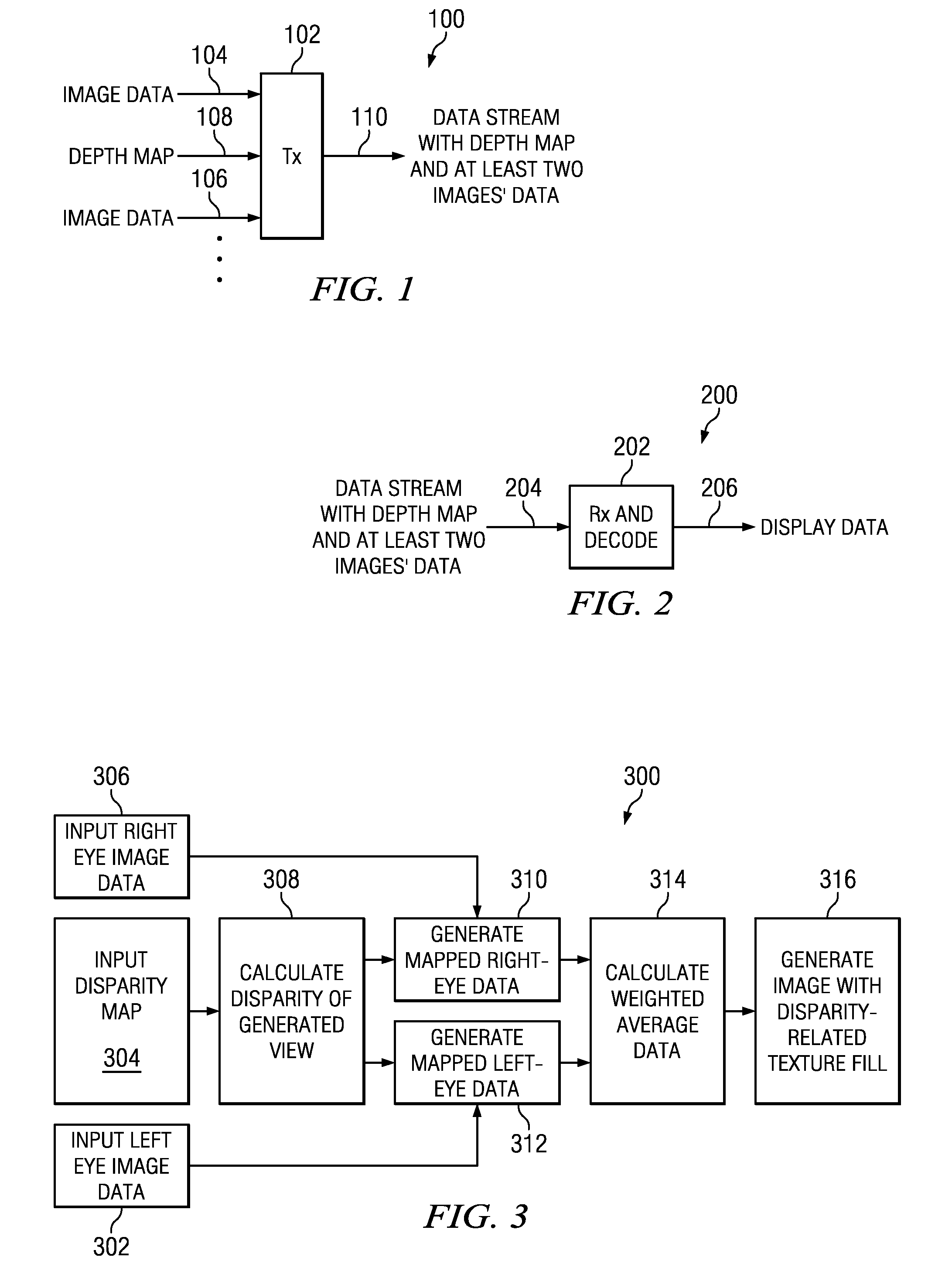
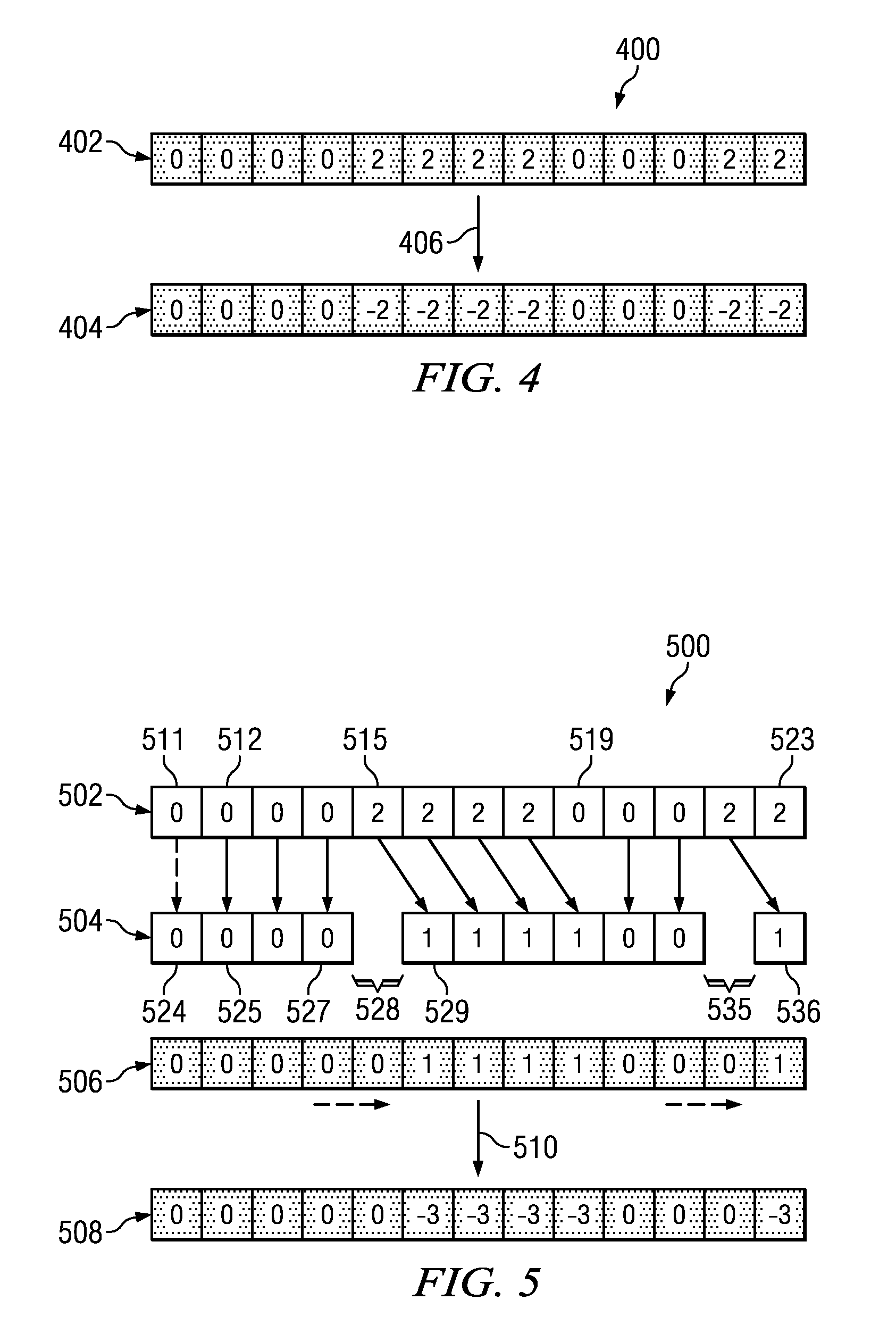
Stereoscopic image format with depth information
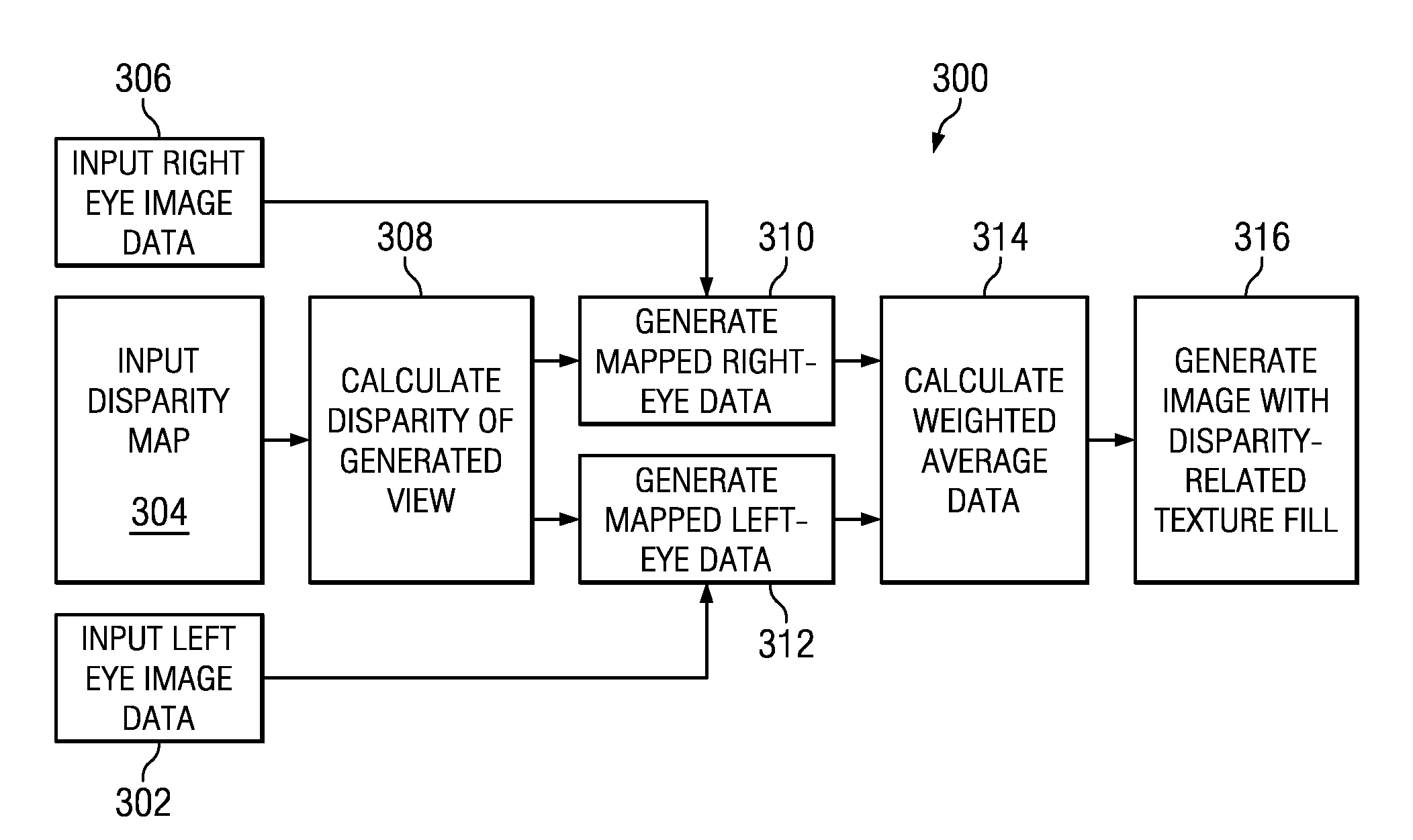
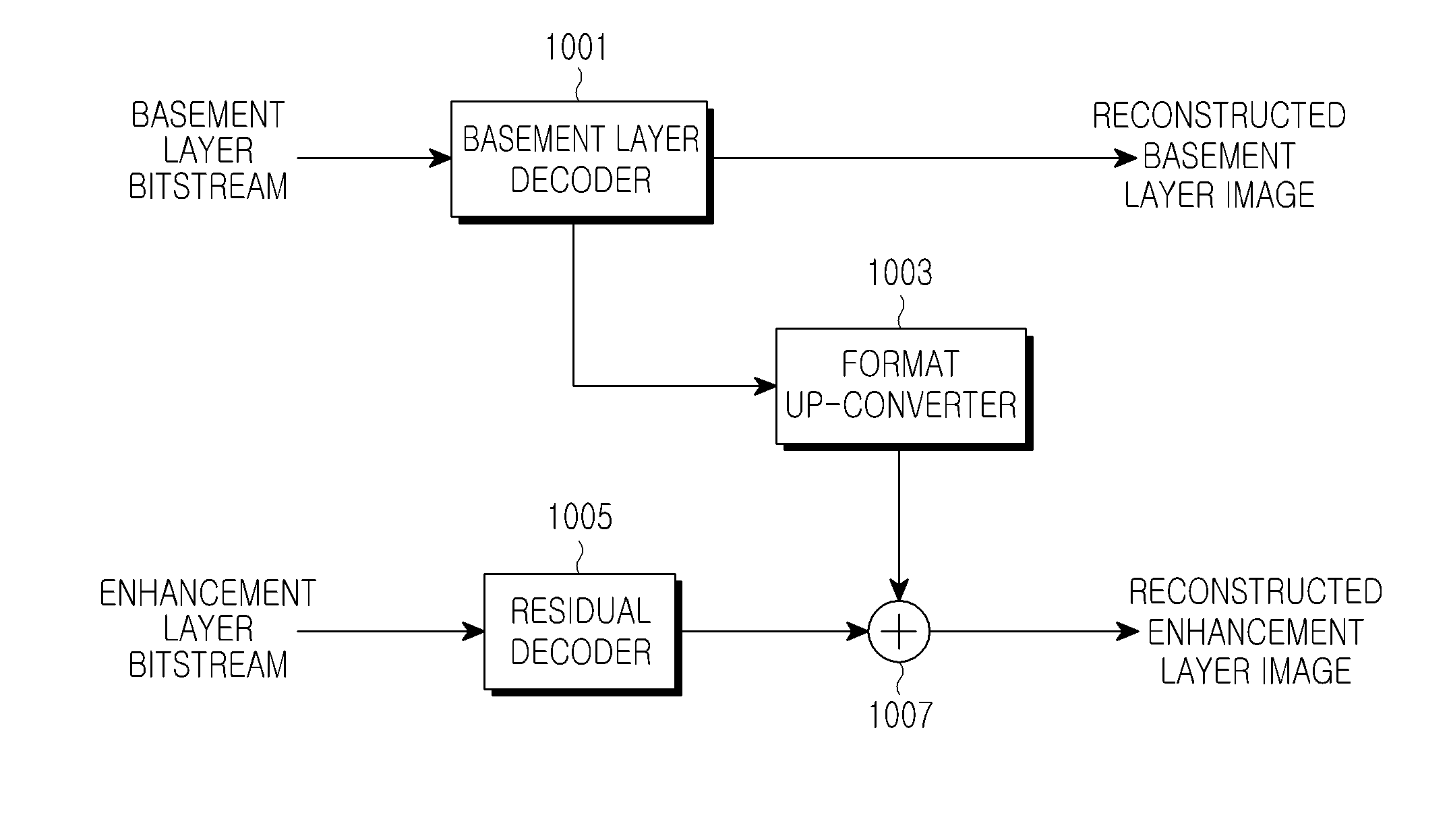
ActiveUS20100103249A1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage compressionDepth map
A multi-view distribution format is described for stereoscopic and autostereoscopic 3D displays. In general, it comprises multi-tile image compression with the inclusion of one or more depth maps. More specifically, it provides embodiments that utilize stereoscopic images with one or more depth maps typically in the form of a compressed grey scale image and, in some instances, incorporates depth information from a second view encoded differentially.
Owner:REAID INC
A mixed image compression method based on block classification
InactiveCN101217668AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioAccurate segmentationImage enhancementTelevision systemsGraphicsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for content driven image compression
InactiveUS20050131660A1Small sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionFiltration
A method with related structures and computational components and modules for modeling data, particularly audio and video signals. The modeling method can be applied to different solutions such as 2-dimensional image / video compression, 3-dimensional image / video compression, 2-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, 3-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, pattern recognition, object meshing / tessellation, audio compression, audio understanding, etc. Data representing audio or video signals is subject to filtration and modeling by a first filter that tessellates data having a lower dynamic range. A second filter then further tessellates, if needed, and analyzes and models the remaining parts of data, not analyzable by first filter, having a higher dynamic range. A third filter collects in a generally lossless manner the overhead or residual data not modeled by the first and second filters. A variety of techniques including computational geometry, artificial intelligence, machine learning and data mining may be used to better achieve modeling in the first and second filters.
Owner:YADEGAR JOSEPH +1
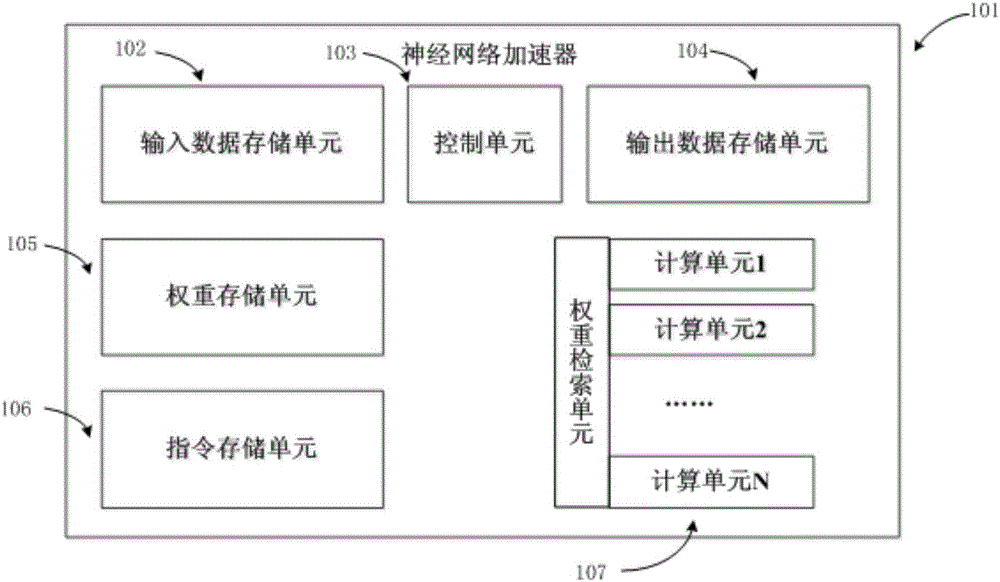
Neural network processor based on weight compression, design method, and chip
ActiveCN106529670AReduce occupancyFast operationPhysical realisationImage compressionNetwork processor
Owner:中科时代(深圳)计算机系统有限公司
Image compression and decompression
ActiveUS20100027686A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce needPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionMotion vector
Clusters of pixels are defined for use in image compression and decompression. The image information used to define the clusters may include pixel values at predetermined positions relative to a pixel or related motion vectors, gradients, texture etc. During compression of images the image information relative to pixels is examined to determine the cluster to which it belongs. Thus pixels can be classified according to the cluster for their image information. In an embodiment the definitions of the clusters are selected dynamically, dependent on image content. For each cluster a control parameter set is computed for a post-processing operation, such as filter coefficients for filtering or statistical data for locally generating texture. The control parameter set is selected dependent on the image content so that, when the post-processing operation is applied to the image after decompression it will improve image quality for the pixels that are classified as belonging to the cluster. The compressed image and the control parameter sets are transmitted to a decompression apparatus. Upon decompression, the image information that represents the decompressed image is examined to classify pixels according to the clusters and the different control parameter sets for the selected clusters are used to control post-processing at the locations of the pixels.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
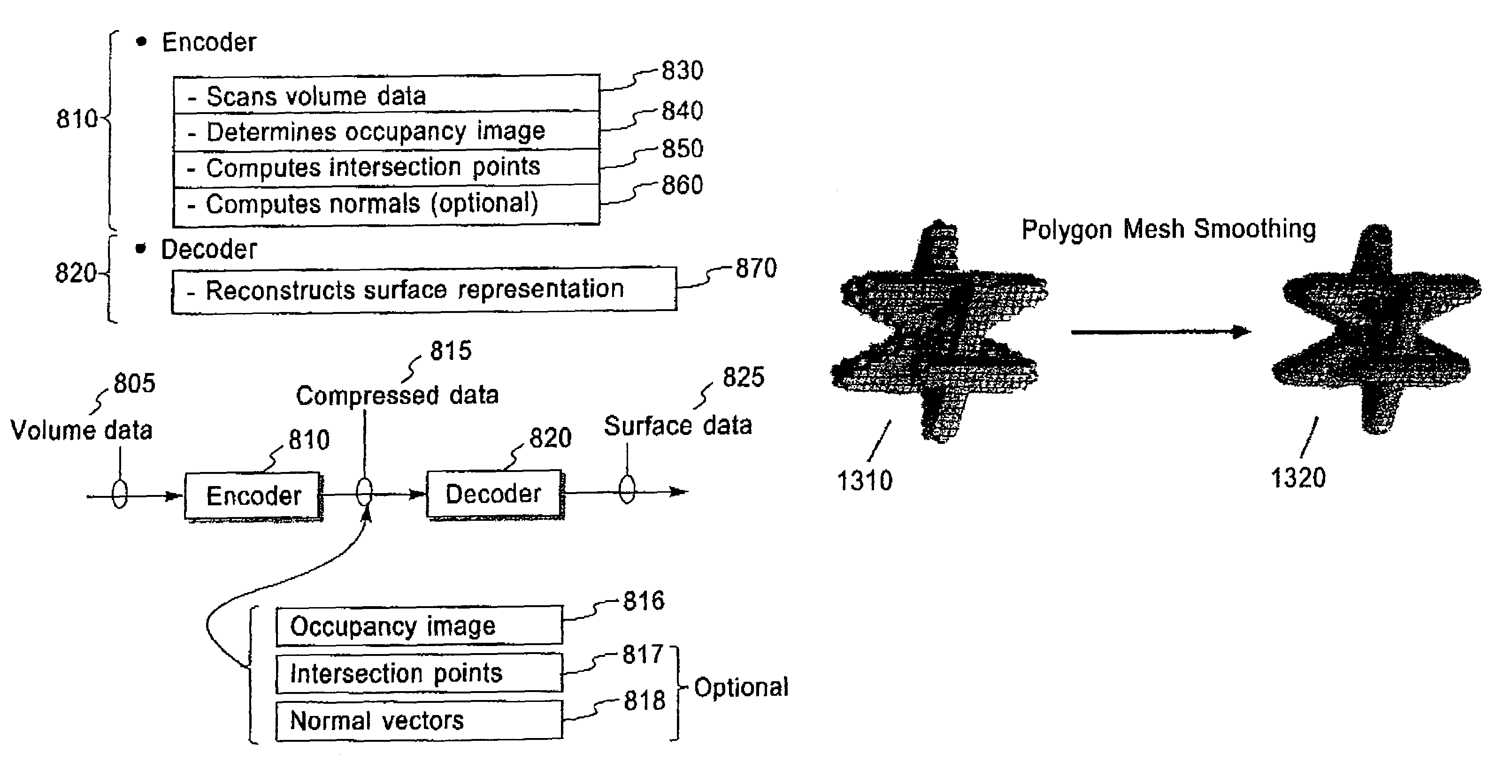
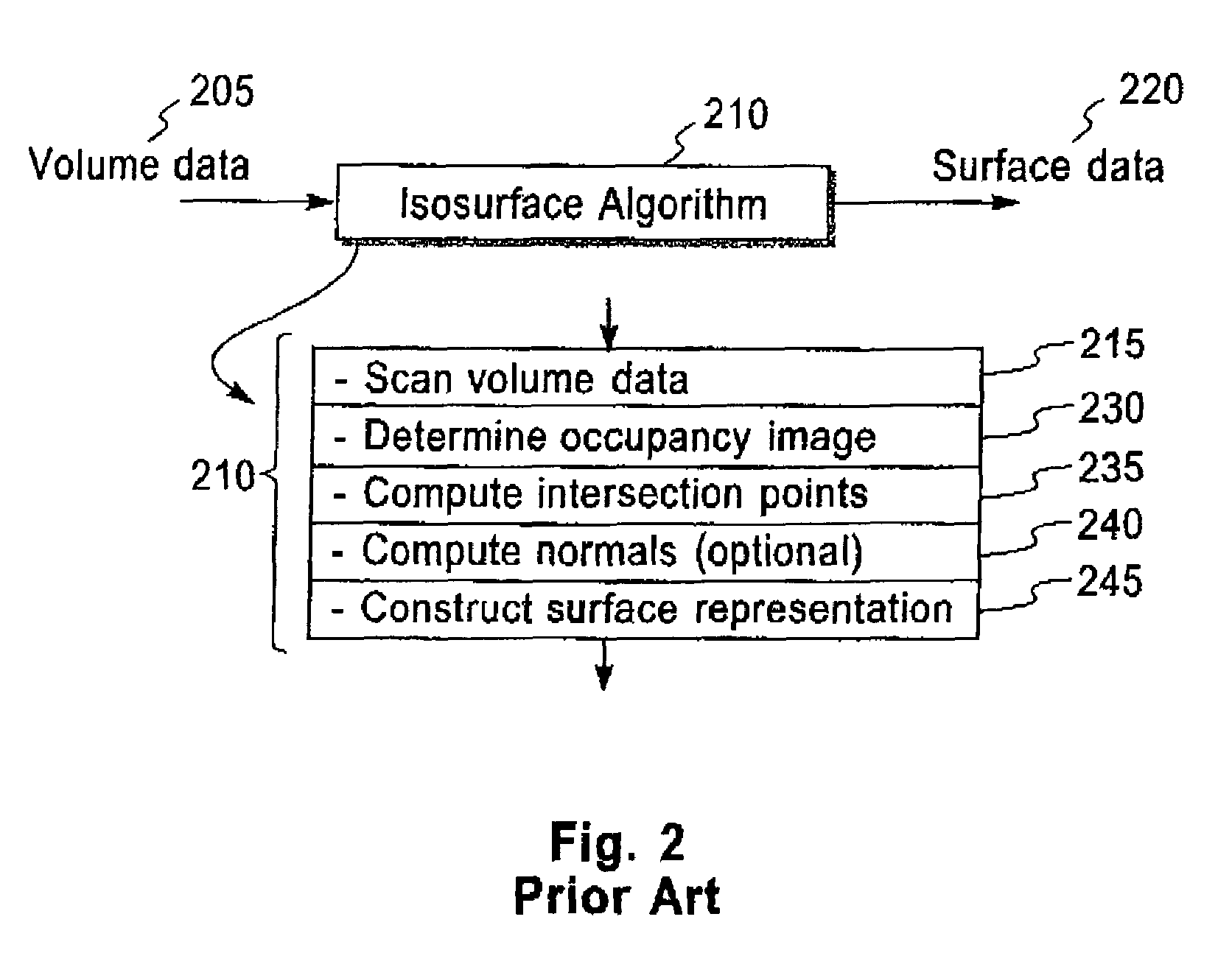
Bi-level iso-surface compression
InactiveUS7230616B2Extreme simplicityIncrease the compression ratioImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmImage compression
Methods, structures and systems for encoding and decoding isosurface data. An encoder process takes volume data and an isolevel as input and produces compressed isosurface data as output. The compressed isosurface data produced by an encoder process is composed of an occupancy image record, an optional intersection points record, and an optional normal vectors record. An occupancy image is compressed with a context-based arithmetic encoder. Compressed isosurface data can be stored in a data storage device or transmitted through a communication medium to a remote computer system, where the decoder process is executed. The decoder processes take compressed surface data as input and produce surface data as output. The decoder processes first reconstructs the occupancy image by decoding the occupancy image record. An in-core isosurface decoder process produces a polygon mesh as a surface representation. An out-of-core isosurface decoder process produces a set of oriented points as a surface representation.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
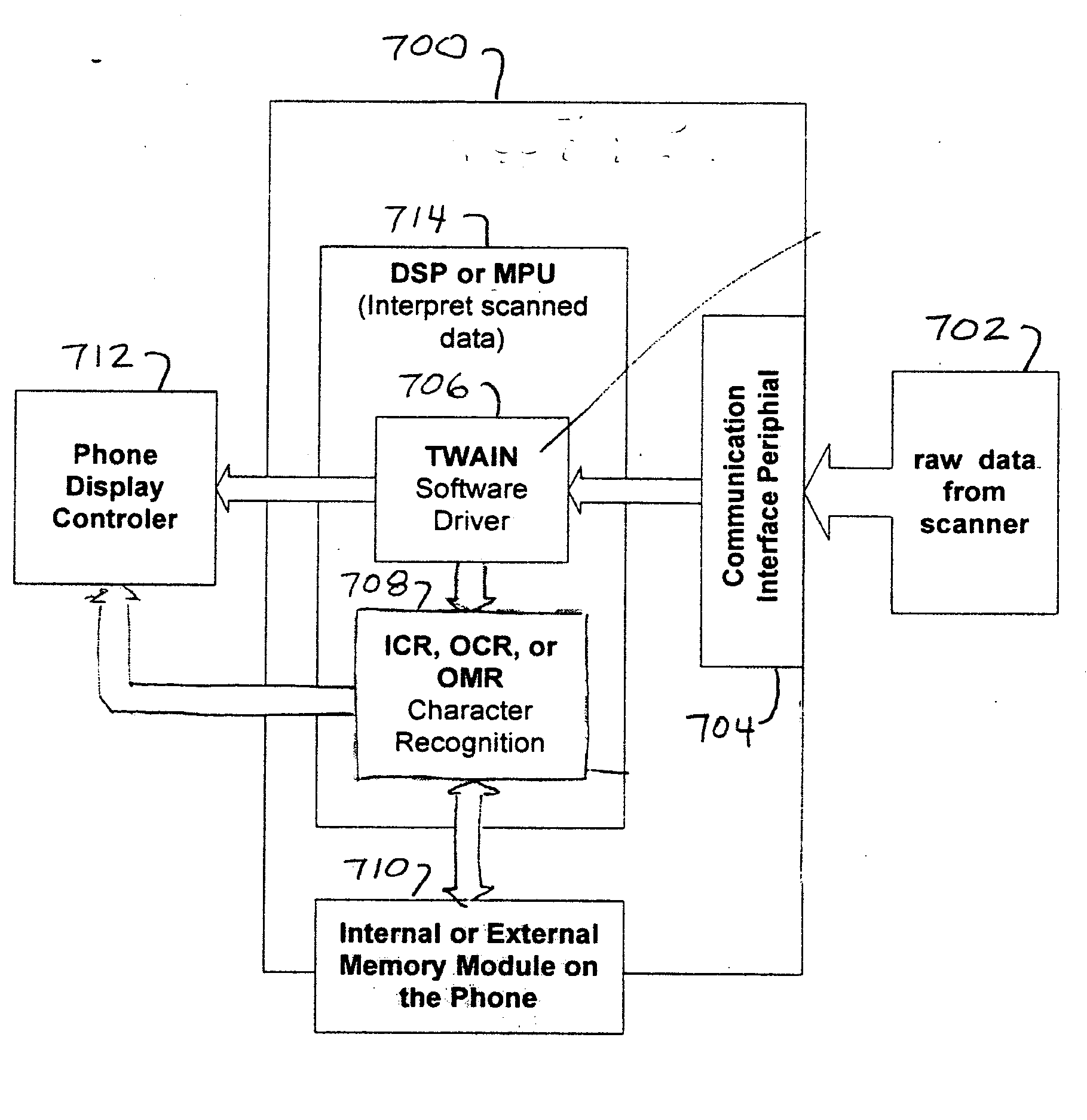
Cellular phone with scanning capability
ActiveUS20050205671A1Improve practicalityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsTicket-issuing apparatusJPEGImage compression
A cellular phone is provided with a media scanning capability. Scanner optics, an optional light source and related scanning circuitry is integrated within a cellular phone to enable image or text scanning, facsimile, text-to-speech conversion, and language translation. Position sensors provide position data as the scanner is manually moved, in one or more passes across the scanned media, to enable a bit-mapped image of the strip to be created in a data buffer. Image data from the strips is processed to remove redundant overlap data and skew position errors, to give a bit-mapped final image of the entire scanned item. Image compression is provided to compress the image into standard JPEG format for storage or transmission, or into facsimile format for transmission of the document to any fax machine. Optical character recognition (OCR) is provided to convert image data to text which may be sent as email, locally displayed, stored for later use, or further processed. Further processing of text data includes language translation and text to speech conversion of either the original or translated text. The resulting speech audio can be heard locally or transmitted over the cellular network.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Feedback scheme for video compression system
InactiveUS7158681B2Character and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsImage compressionComputer vision
The quality of digital images recovered from compressed data in an inter-frame redundancy-removing scheme is enhanced using a self-adaptive feedback scheme in an image compression / decompression system so as to provide for the compensation of the distortion component from prior frame compression in subsequent difference frame compression. Each transmitted frame is stored after a full compress / decompress cycle, and difference data (which includes the inverse of the distortion component from compression of the transmitted frame) representing the difference between the stored frame and the incoming new frame is transmitted. Consequently, the quality of static regions in the recovered images may be improved with each subsequent iteration by taking the distortion component in the prior frame into consideration along with the inter-frame motion information. The feedback loop thus forms a self-adaptive iterative cycle.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
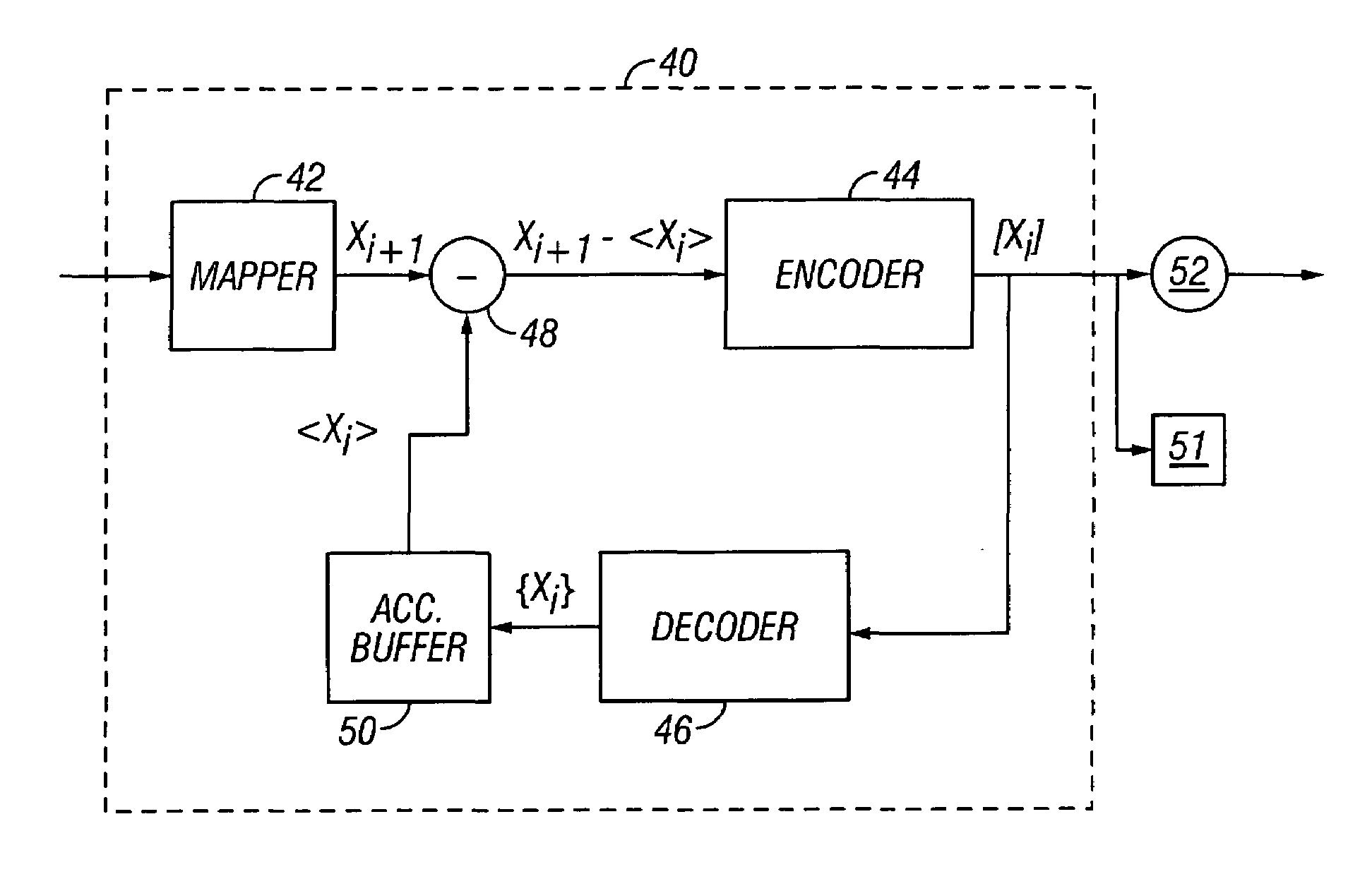
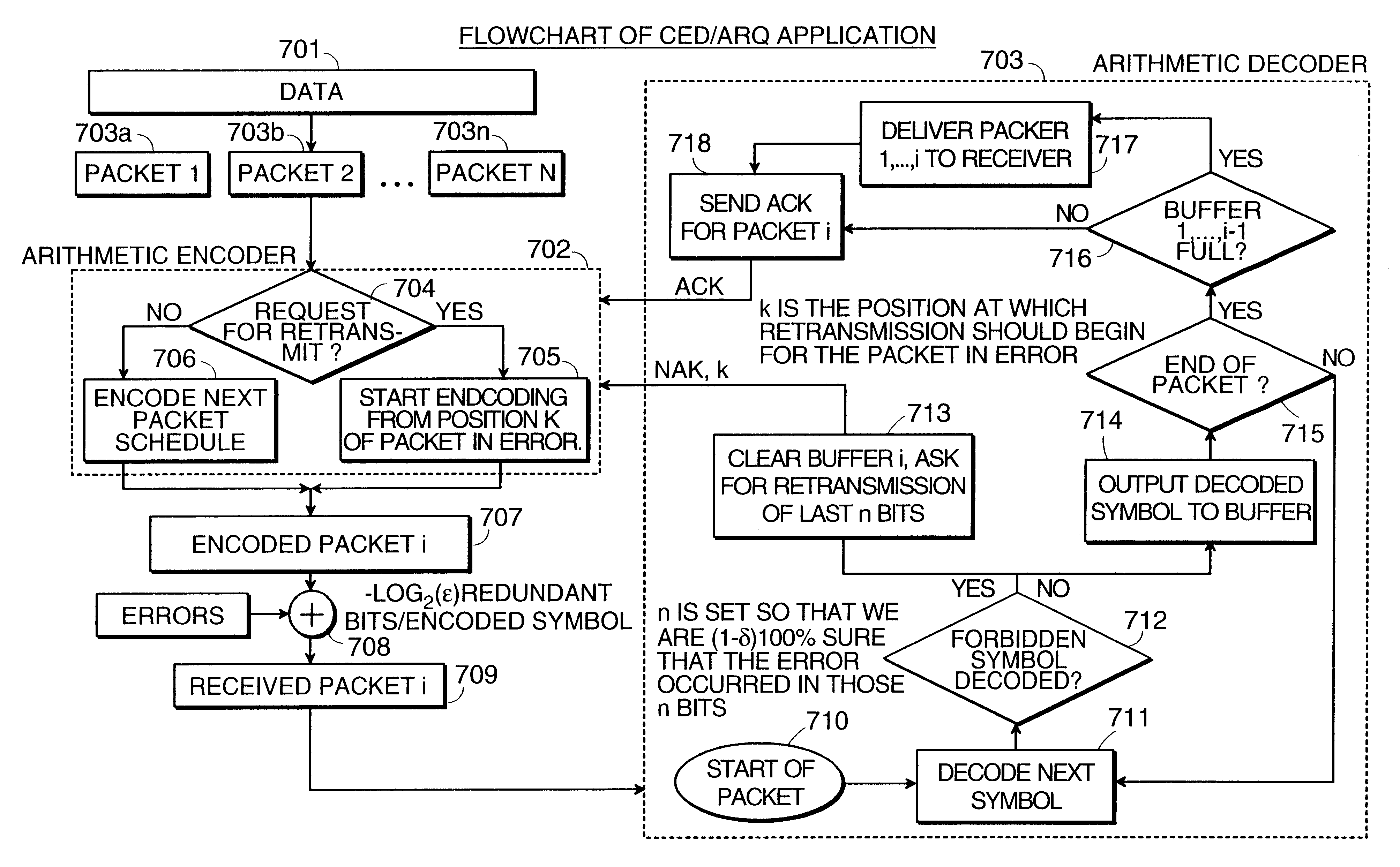
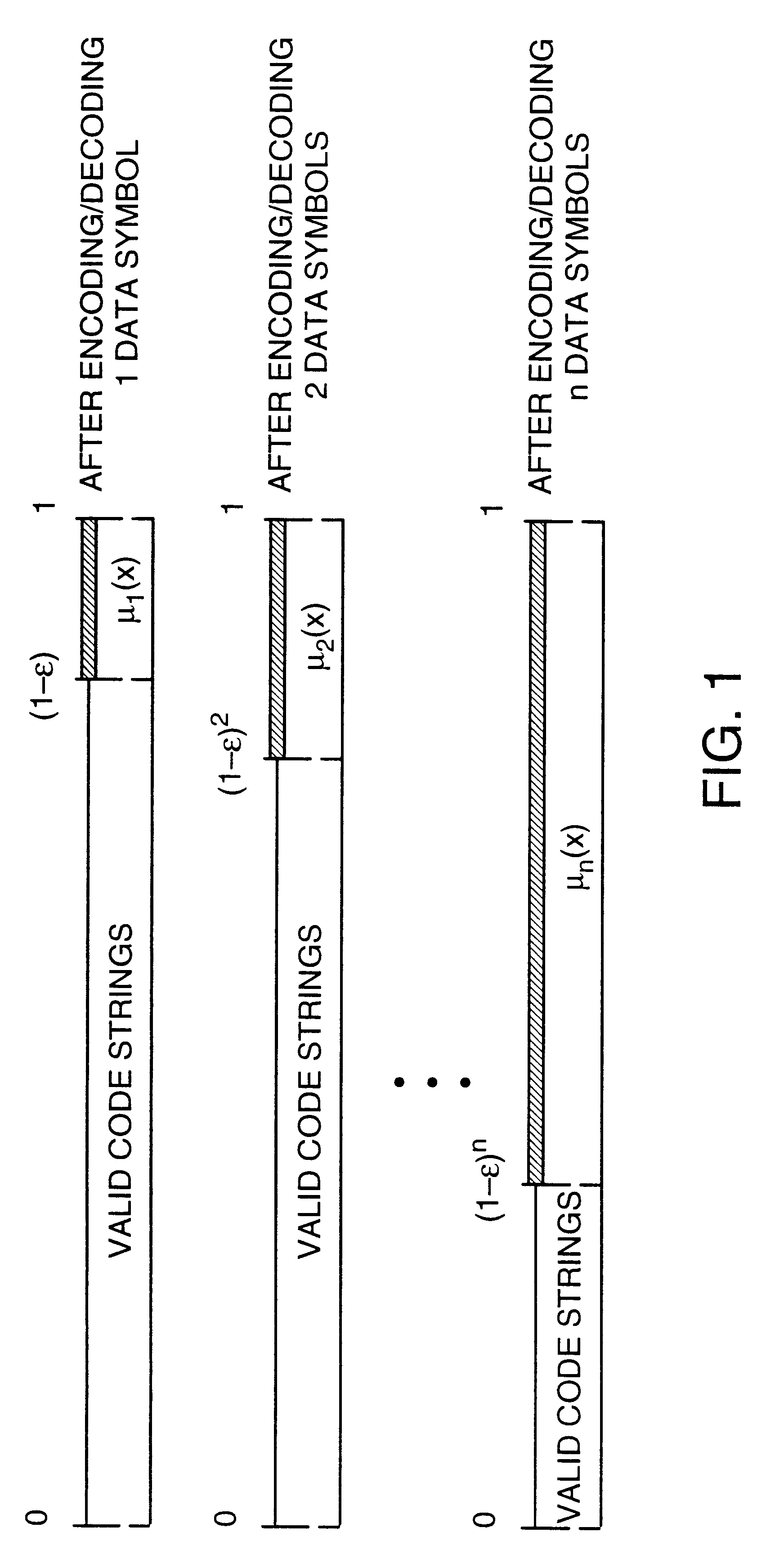
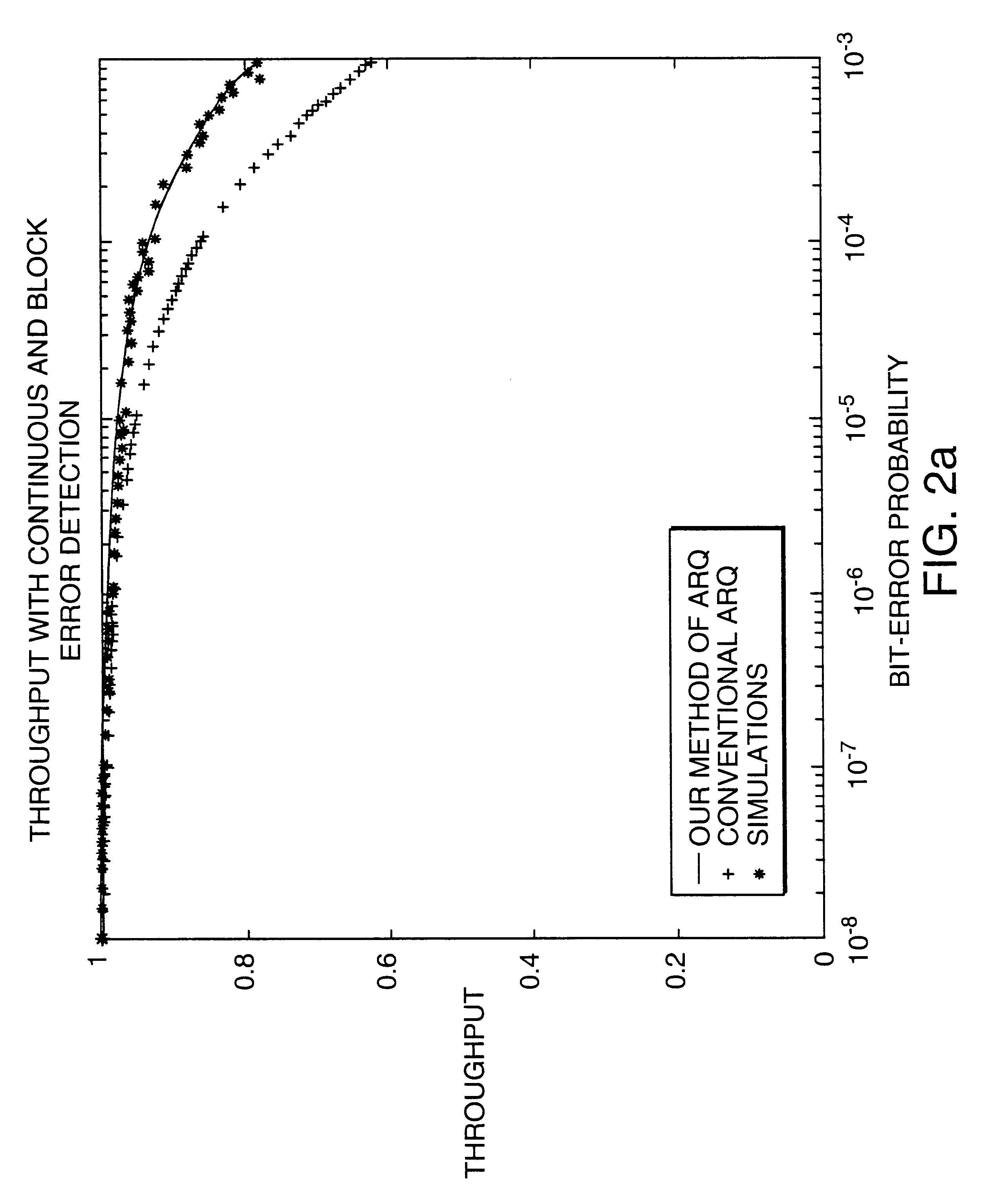
Data transmission using arithmetic coding based continuous error detection
InactiveUS6418549B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsAutomatic repeat requestTrade offs
Method and apparatus for image transmission using arithmetic coding, based on continuous error detection uses a controlled amount of added redundancy. A continuous error detection scheme is provided, wherein there is a trade-off between the amount of added redundancy and the time needed to detect an error once it occurs. Herein, there is no need for the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to wait until an entire block of data has been received and processed before an error can be detected. The invention can be used to great advantage both in the automatic repeat request (ARQ) and other concatenated coding schemes. Errors in the received bit stream are detected by introducing added redundancy, e.g., a forbidden symbol, in the arithmetic coding operation. The forbidden symbol is never intended to be encoded. The redundancy error causes loss of synchronization, which is used to detect errors. If a forbidden symbol gets decoded, it means that an error has occurred. In this invention, there is direct control over the amount of redundancy added vs. the amount of time it takes to detect an error. For image compression systems, by using the invention and ARQ, only one device would suffice both for source compression and channel coding.
Owner:MERU NETWORKS
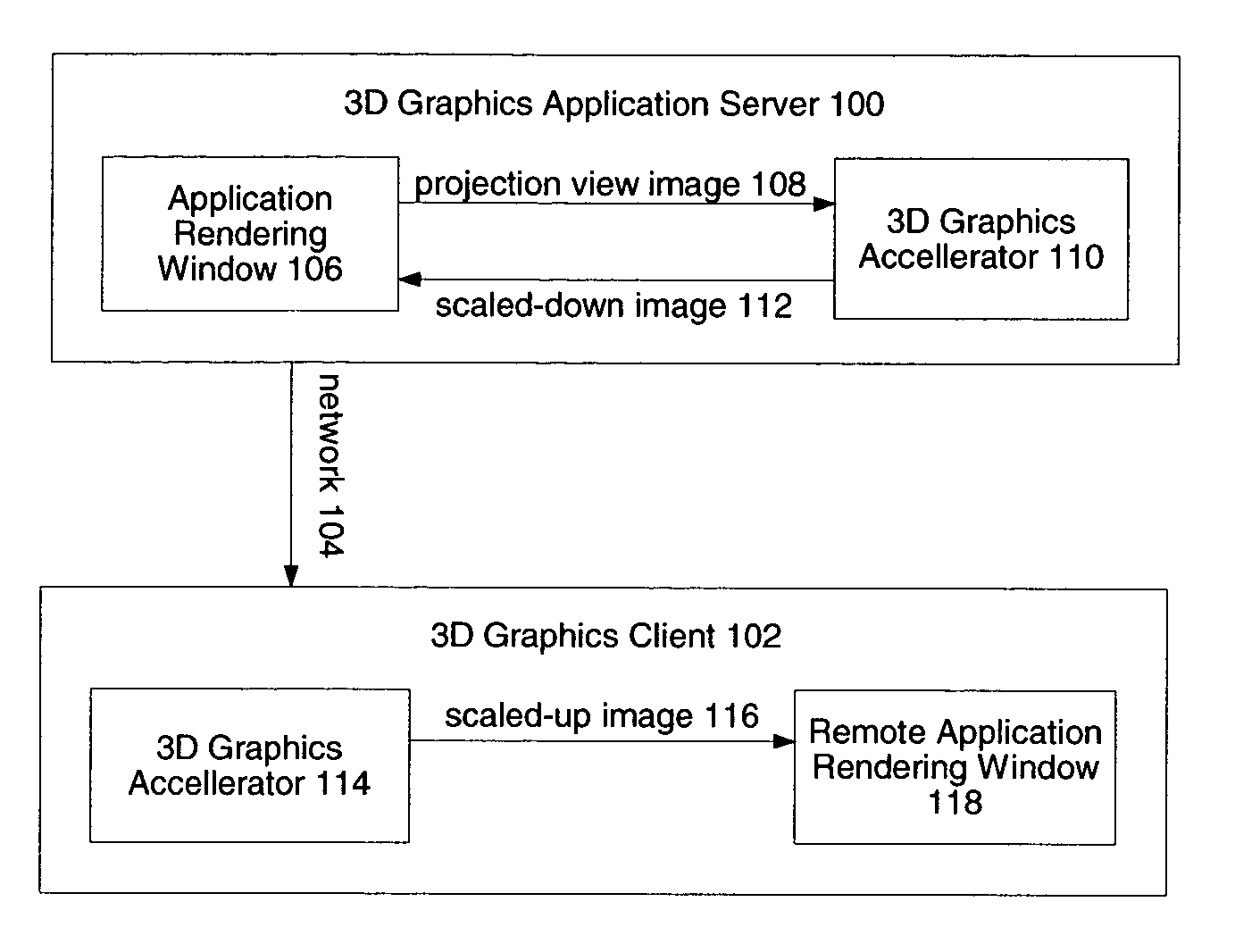
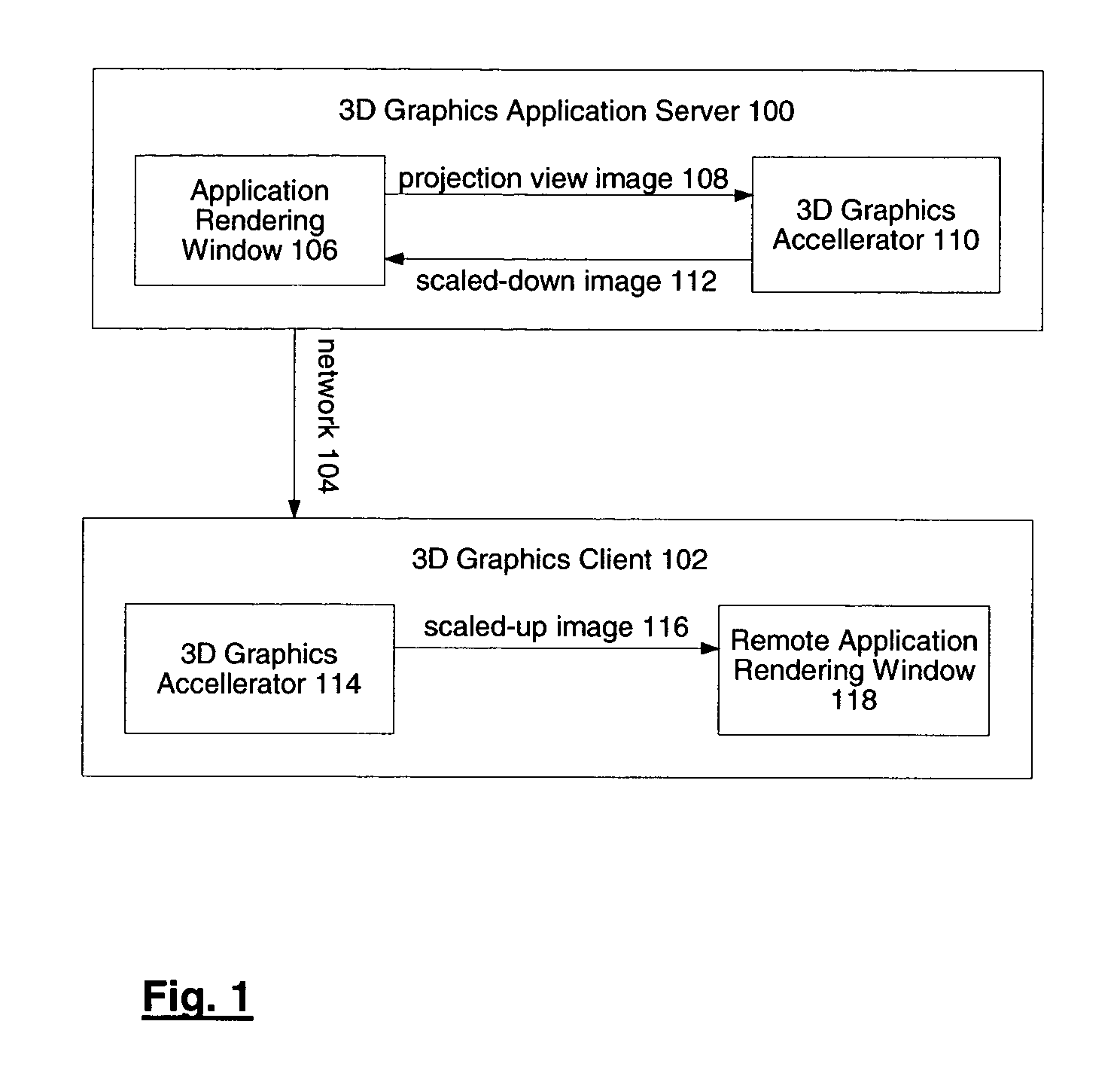
System and method for network transmission of graphical data through a distributed application
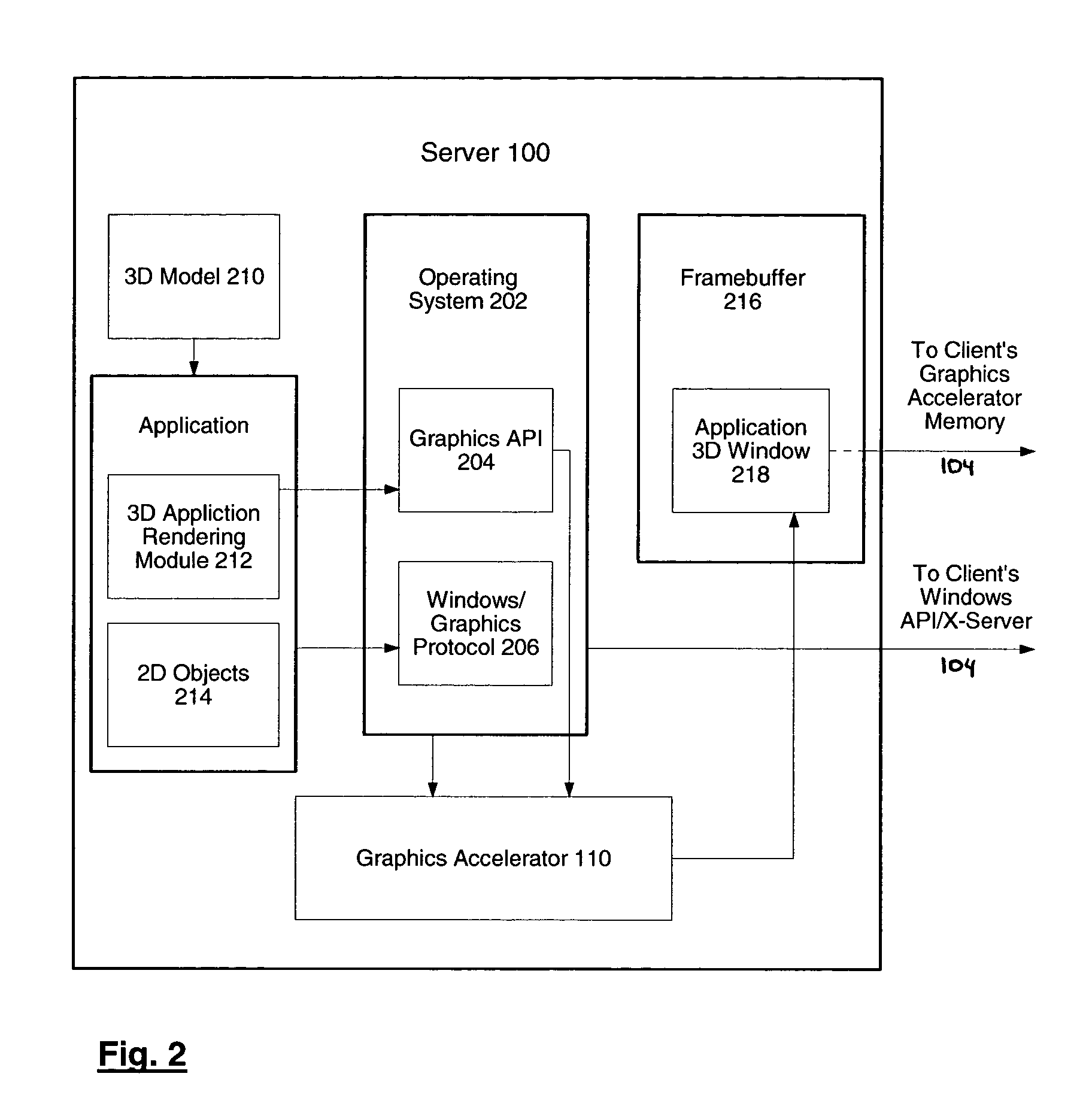
InactiveUS7076735B2Reduce network bandwidth requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsGraphic cardNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
Systems and methods for network transmission of three-dimensional graphical data are disclosed. A single graphical application instance can virtually and efficiently exist on multiple local or remote display systems by directly sharing its raw rendered framebuffer memory information among all local or remote graphics accelerators, thus avoiding the need to re-render any application information again on each node. An internal graphics card is used to scale the rendered data prior to transmission. This graphics scaling eliminates the need for data compression or image compression and achieves an adaptive, hardware-accelerated reduction in network bandwidth. Furthermore, since all memory and remote processing support tasks are performed within the graphics card, the CPU, system bus, and memory bandwidth remain available to the system and other applications.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
Motion vector prediction method, and apparatus and method for encoding and decoding image using the same
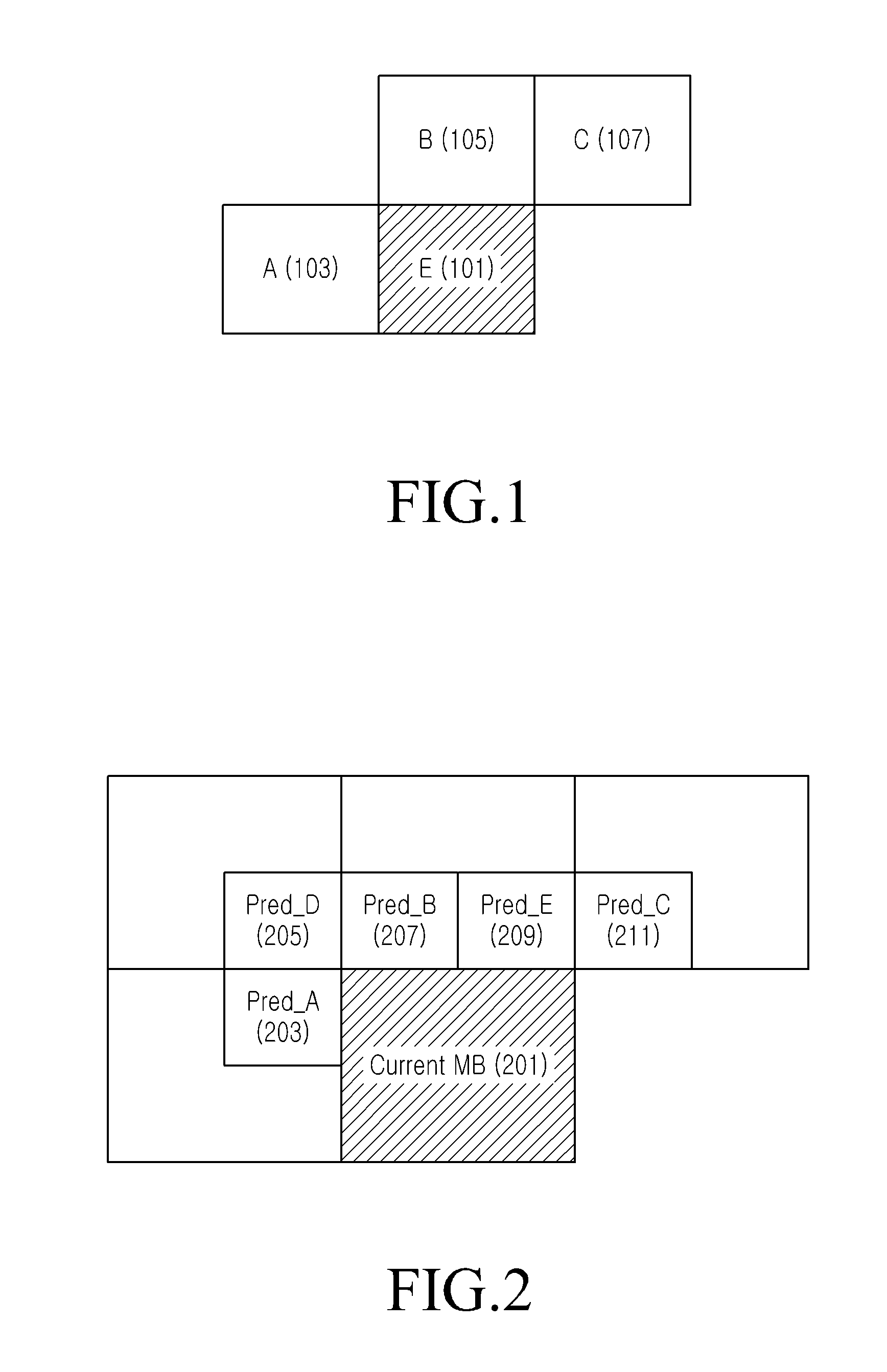
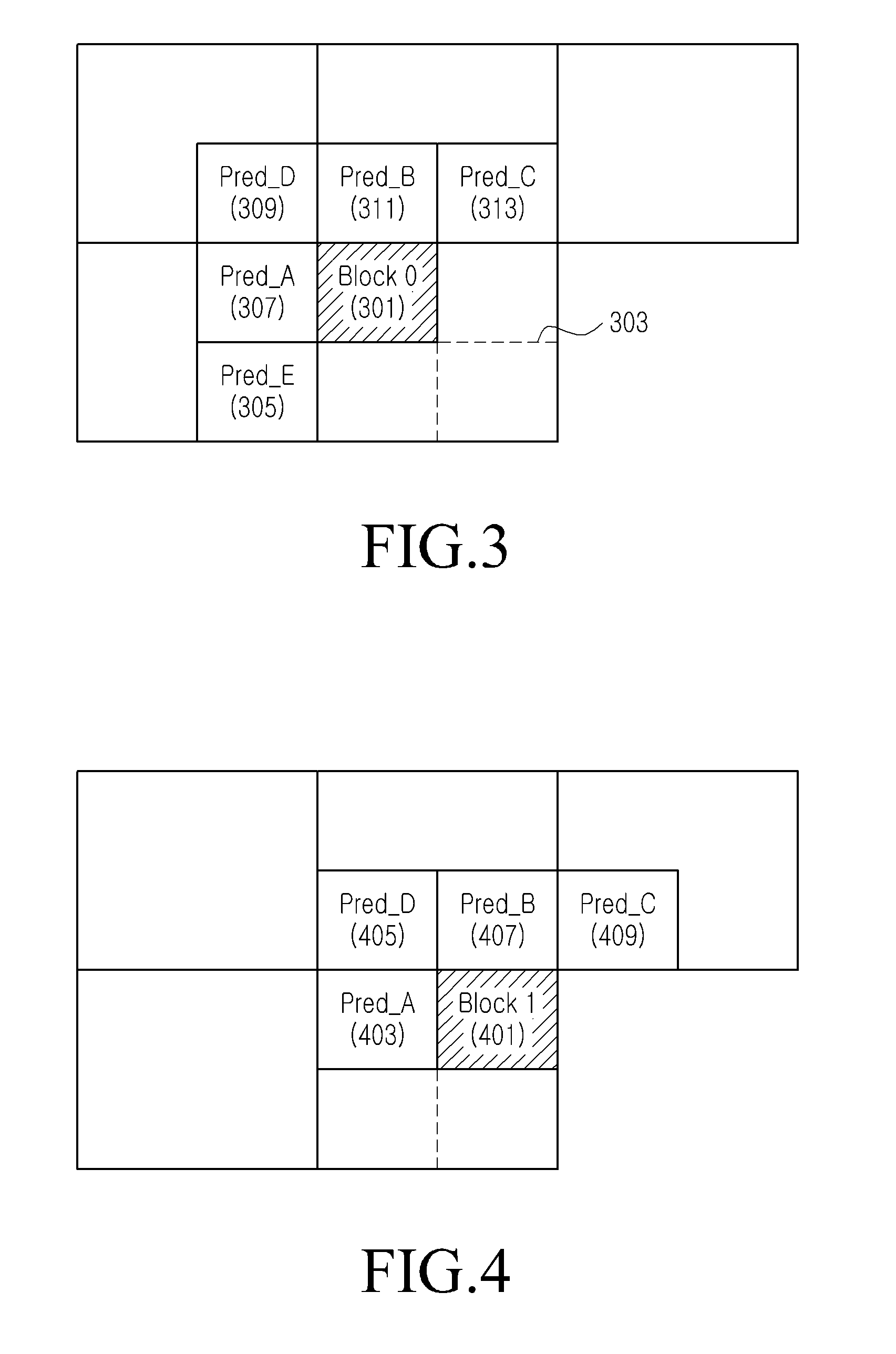
InactiveUS20110013697A1Sure easyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorImage compression
A method for predicting motion vectors to improve compressibility in an image compression codec which processes videos, and an image encoding / decoding apparatus and method using the same. A method for predicting a motion vector used during differential encoding of a motion vector for image encoding, the method including generating a motion vector list with candidate motion vectors for adjacent blocks of a target block, a predictive motion vector of which is to be obtained; calculating each distance between motion vectors included in the motion vector list; and determining a predictive motion vector for the target block by removing motion vectors in order of large distances between the motion vectors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Guaranteed-Rate Tiled Image Data Compression
ActiveUS20110206289A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationImage compressionDigital image data
A method of compressing digital image data is provided that includes, for each image data block in a plurality of image data blocks in the digital image data, transforming image data in the image data block to convert the image data to a low-frequency coefficient and a plurality of high-frequency coefficients, computing a predicted low-frequency coefficient for the image data block based on at least one neighboring image data block in the plurality of image data blocks, computing a residual low-frequency coefficient based on the predicted low-frequency coefficient and the low-frequency coefficient, quantizing the plurality of high-frequency coefficients, and entropy coding the residual low-frequency coefficient and the quantized high-frequency coefficients.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
JPEG2000 self-adapted rate control system and method based on pre-allocated code rate
InactiveCN101106711AAccurate code rate pre-allocationPre-allocated precisionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCoding blockControl system
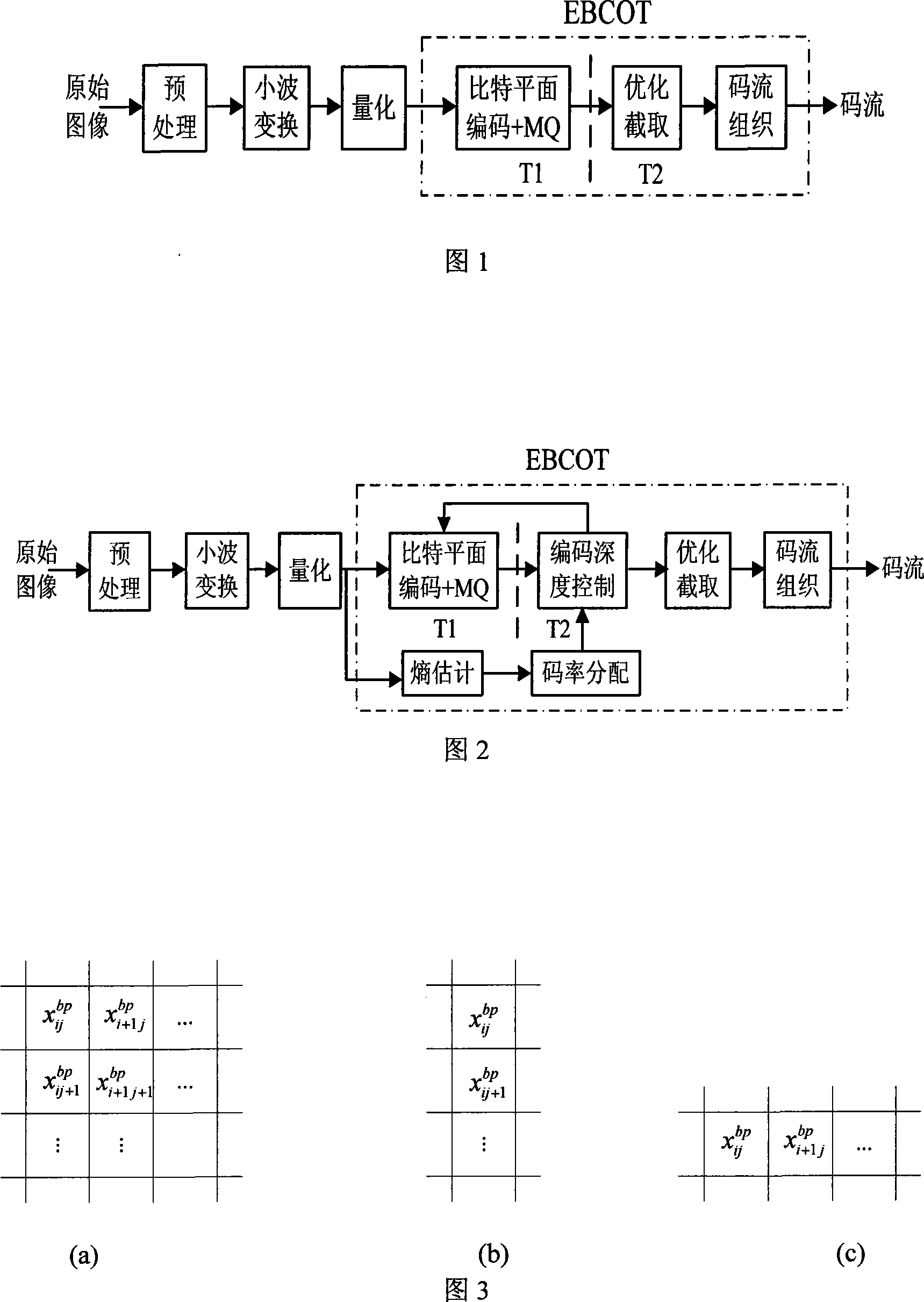
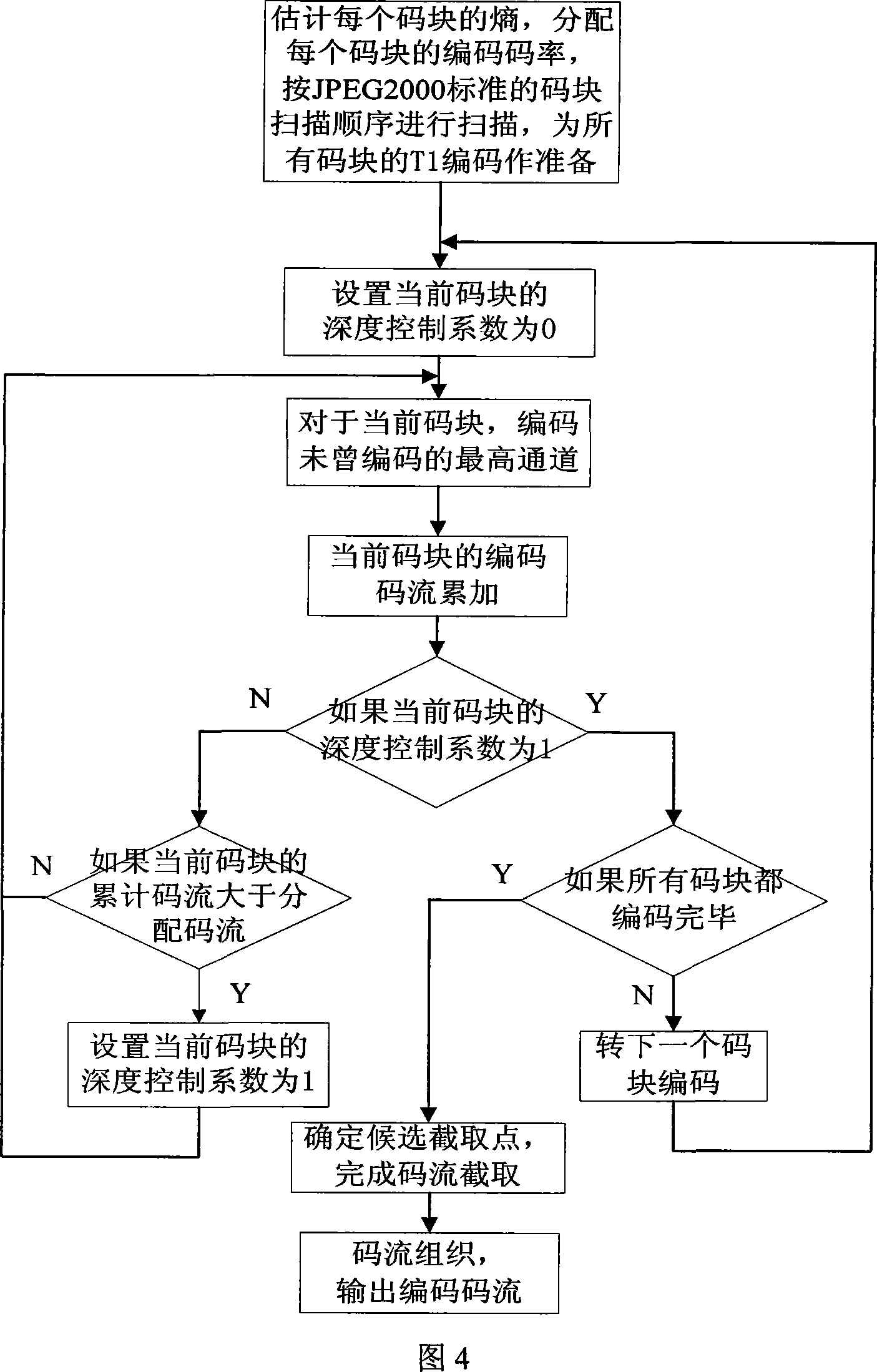
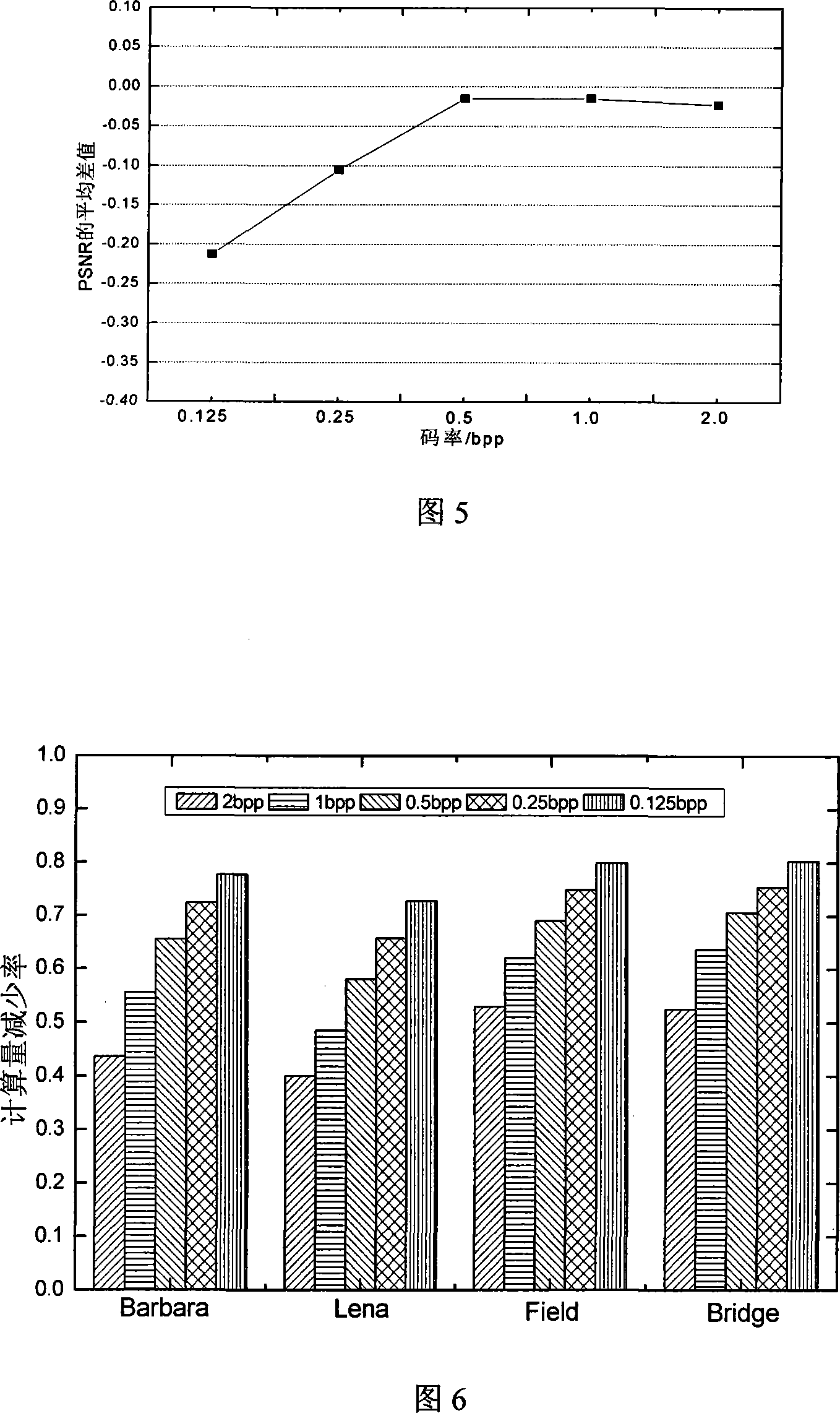
The invention discloses a JPEG2000 self-adapting rate control system and a method based on pre-assignment of code rate, mainly solving the problem of large calculation amount and large memory size of JPEG2000 encoding method. The code block of the original image after pretreatment, wavelet transformation and quantification is output by two lines, one line directly enters the bit plane and MQ coder; for the other line, the entropy of each code block is estimated by the entropy estimate module, sent to the code rate assignment module to assign code rate, and the code rate of each code block is feed back to the bit plane and MQ coder through the encoding depth control module, after the code blocks are encoded by the bit plane, further feed back to the encoding depth control module to determine the output code stream of each encoded code block, and the output code stream is under optimal interception and code stream organization to output the ultimate code stream. At the same time, the invention can change the threshold value of the encoding depth control coefficient as required, to flexibly control the encoding depth in order to improve the image compression quality. The invention has the advantages of low complexity and easiness for hardware implementation, and is suitable for various JPEG2000 image real-time compression systems.
Owner:SHANDONG HUAYU AEROSPACE TECH CO LTD
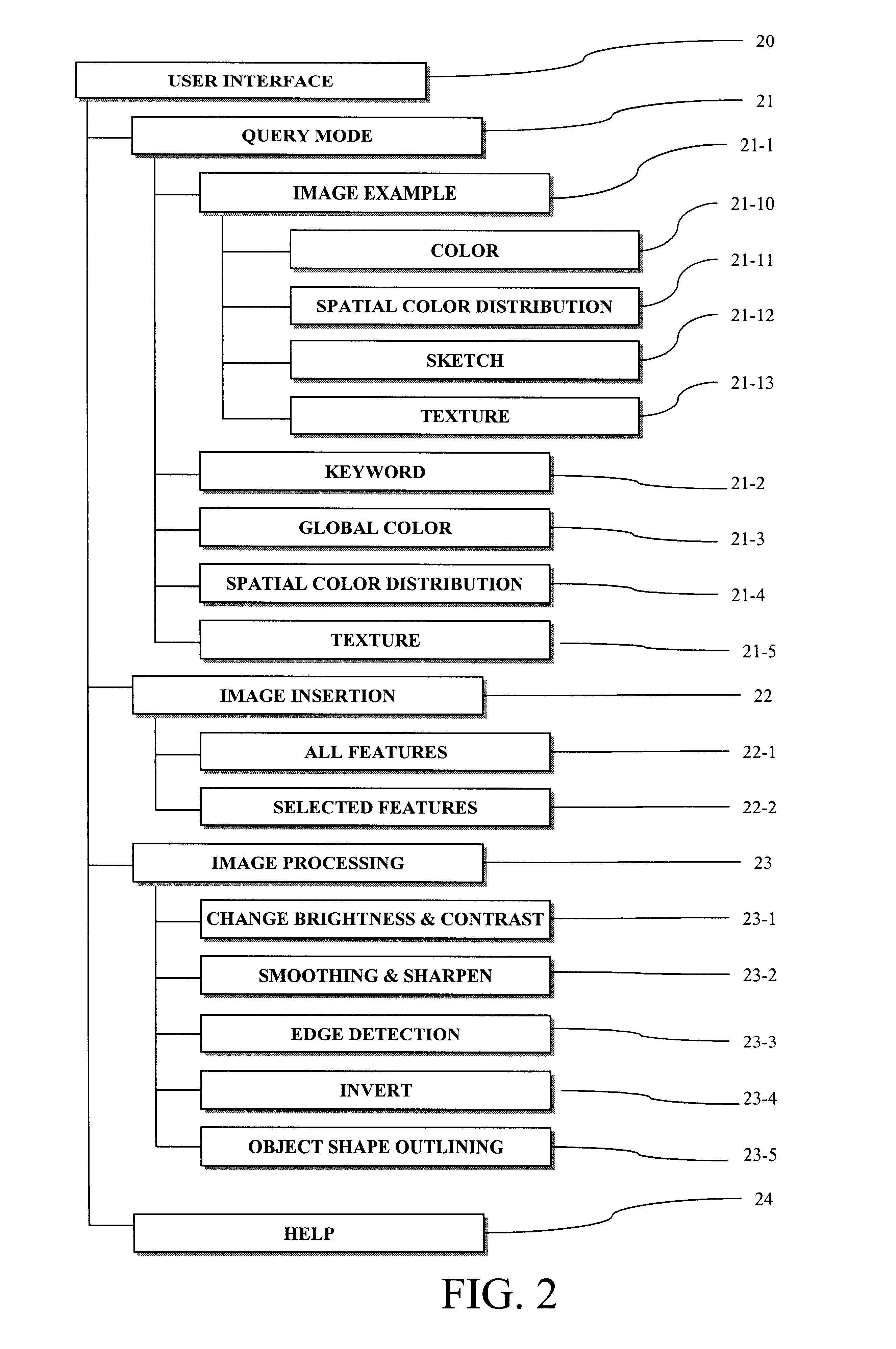
Method for computerized indexing and retrieval of digital images based on spatial color distribution
InactiveUS6594386B1Improve performanceMinimal overheadDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPersonal computerImage compression
In the context of image database systems, a method for indexing and retrieval of images by their color content and the spatial distribution of color is disclosed. The method is implemented as a software tool that runs on a personal computer and enables the computer to find a desired image from an image database. The user interface allows the user to describe the desired image, and the tool searches the repository for any images that satisfy the description. The description of the composite image may include information on shapes, texture, presence or absence of objects, and color. The process of search and retrieval of images makes use of a method that determines whether a specific color, or a combination of colors, is present in an image. Further, the method determines the location where the specific color or color combination can be found. By analyzing the results of comparisons between the features found in the composite image and in the stored images, the tool retrieves those images that satisfy the description of the query, image. Calculation of color-related features makes significant use of the calculations that are made in the process of image compression which is an essential step prior to image storage. The process of search and retrieval on the basis of features relating to color are provided via a library of routines that perform the necessary tasks.
Owner:GOLSHANI FOROUZAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com