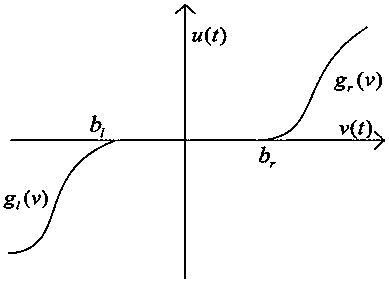Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1248 results about "Deadband" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
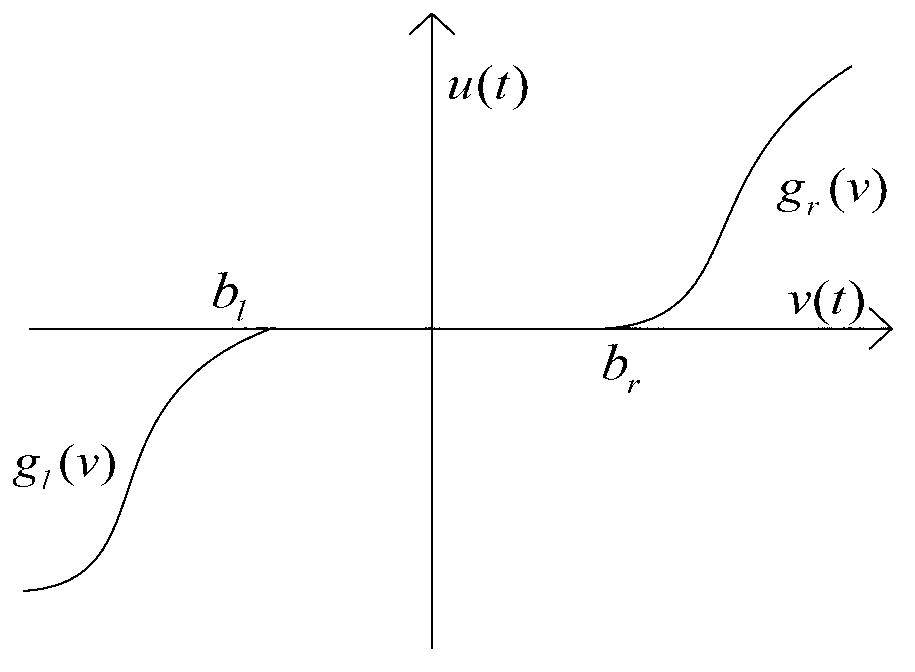
A deadband (sometimes called a neutral zone or dead zone) is a band of input values in the domain of a transfer function in a control system or signal processing system where the output is zero (the output is 'dead' - no action occurs). Deadband regions can be used in control systems such as servoamplifiers to prevent oscillation or repeated activation-deactivation cycles (called 'hunting' in proportional control systems). A form of deadband that occurs in mechanical systems, compound machines such as gear trains is backlash.
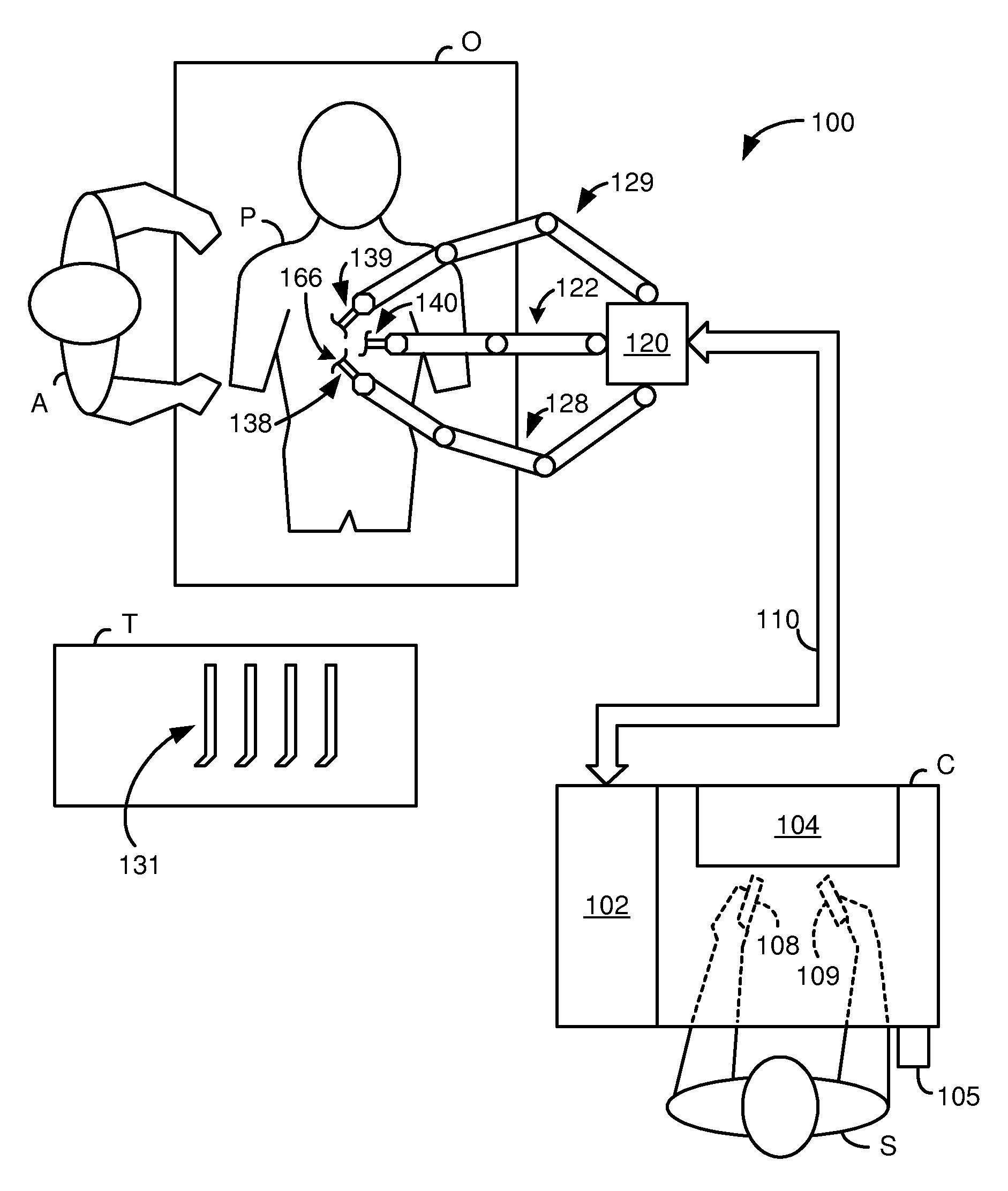
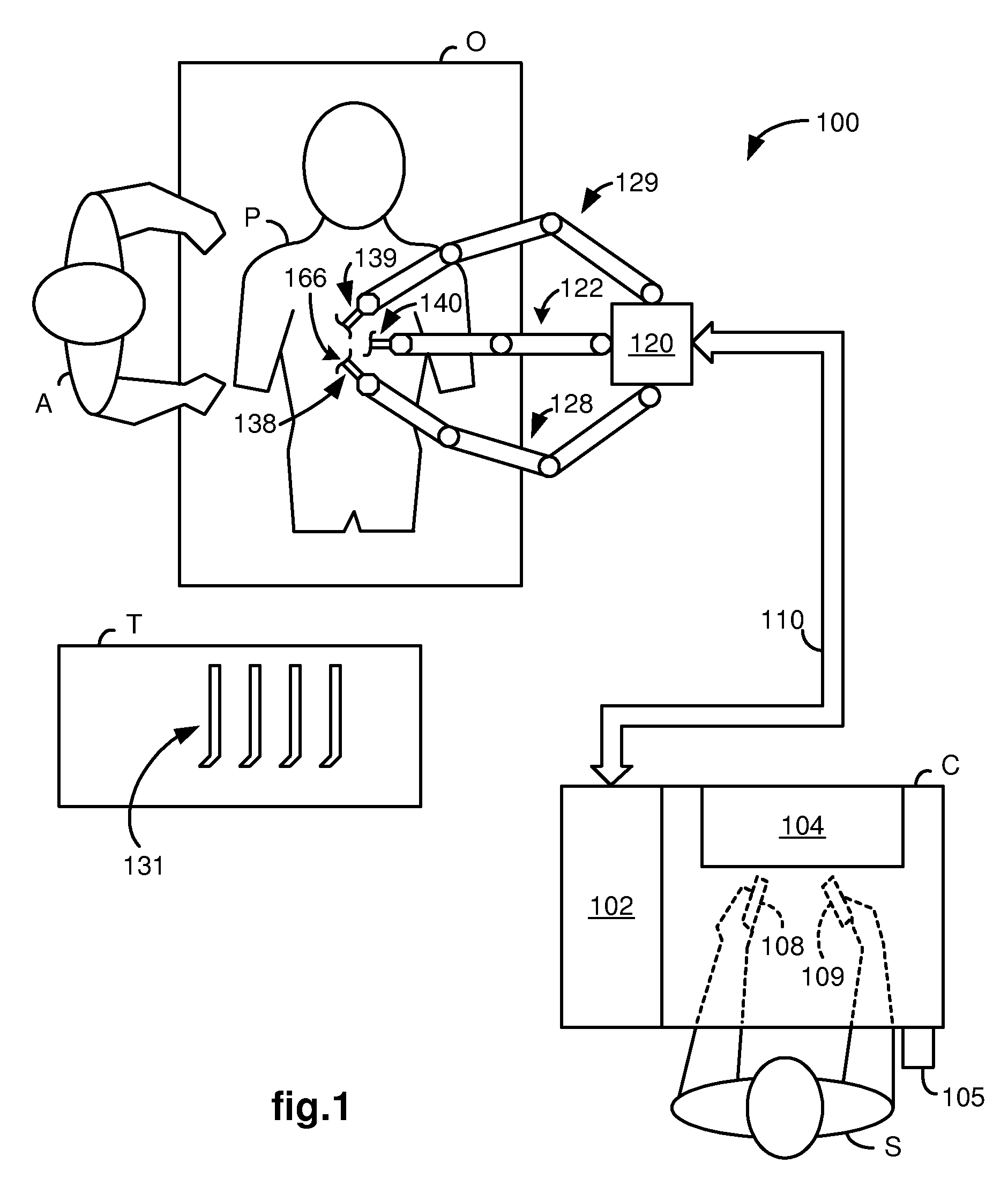
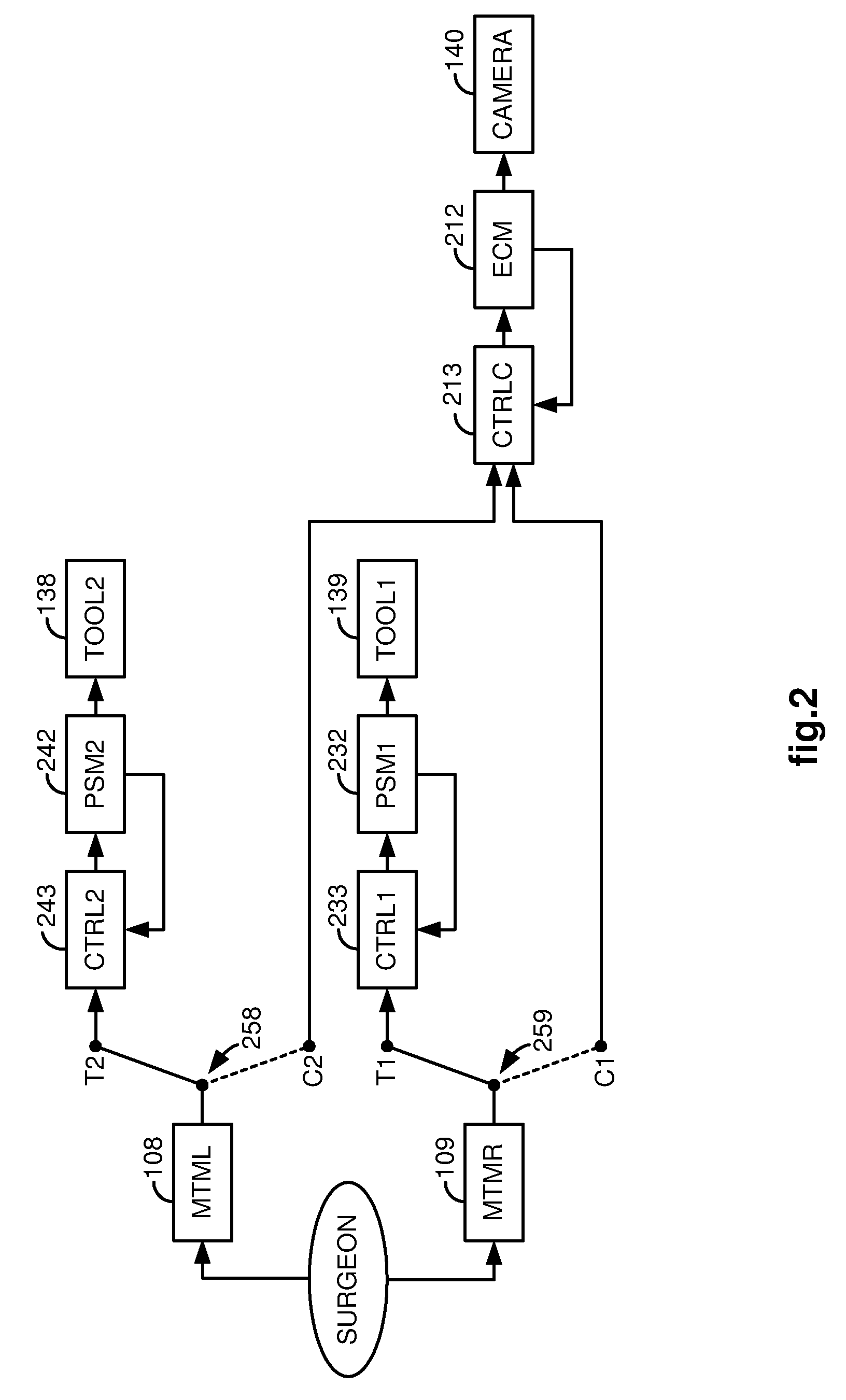
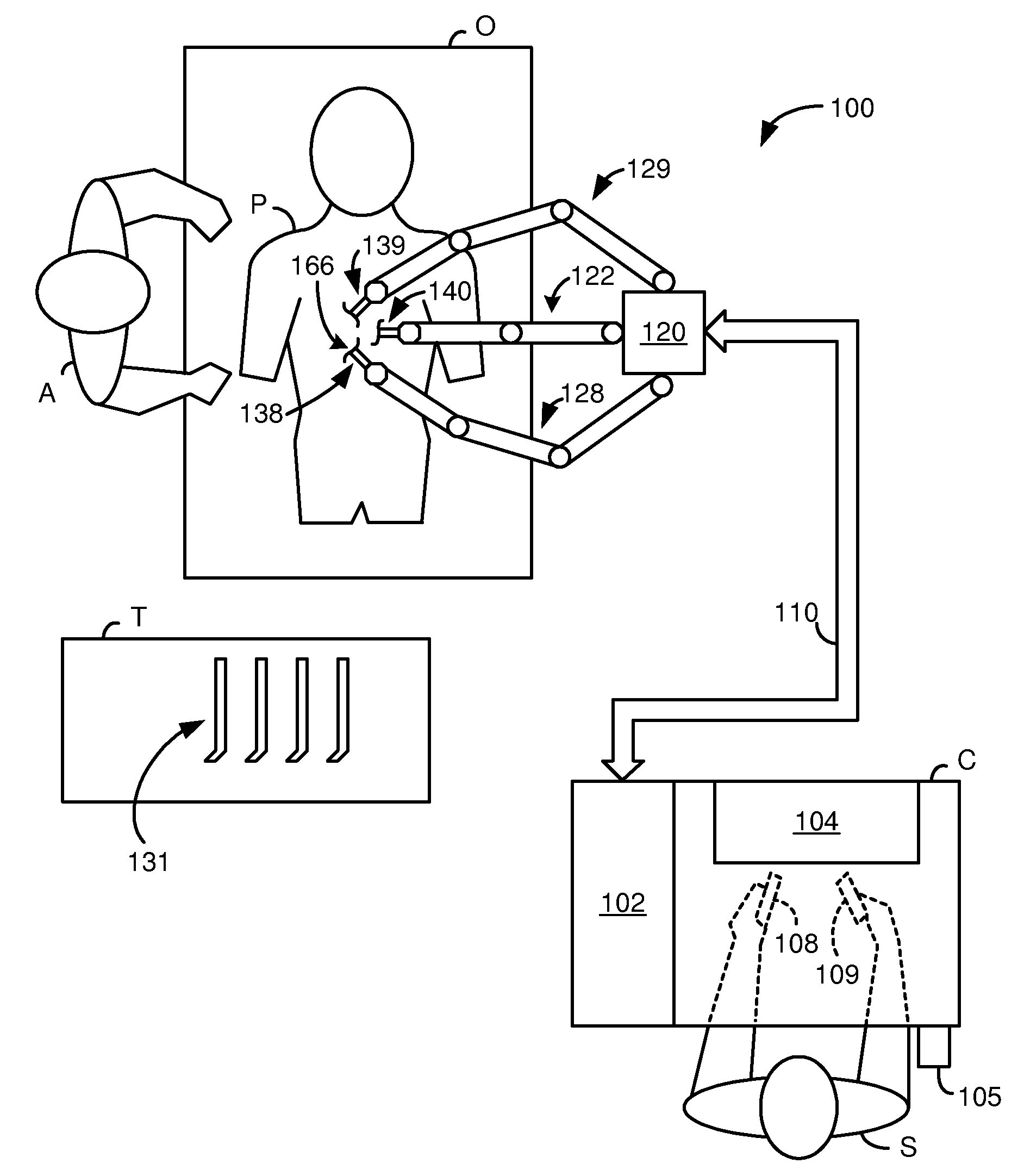
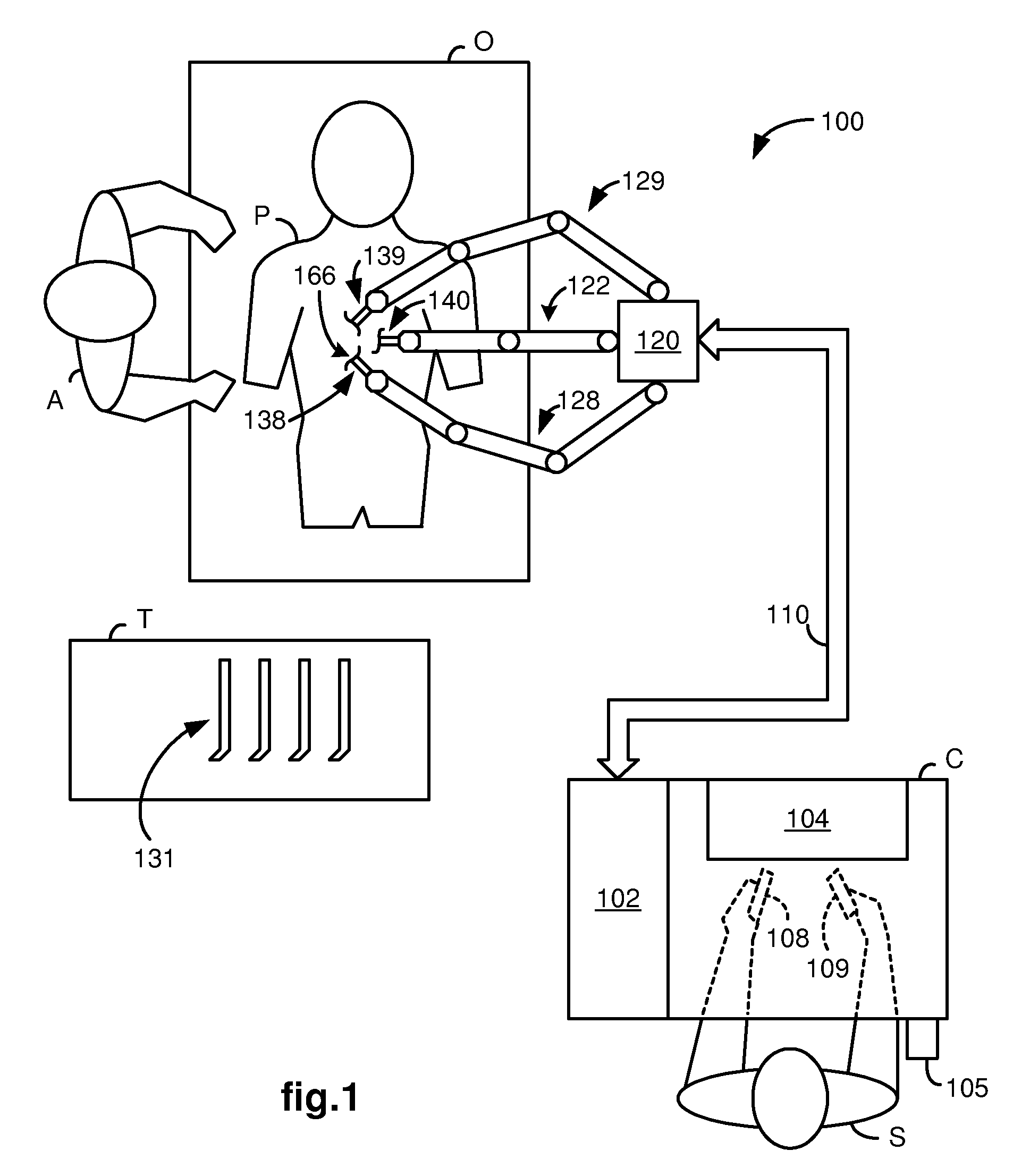
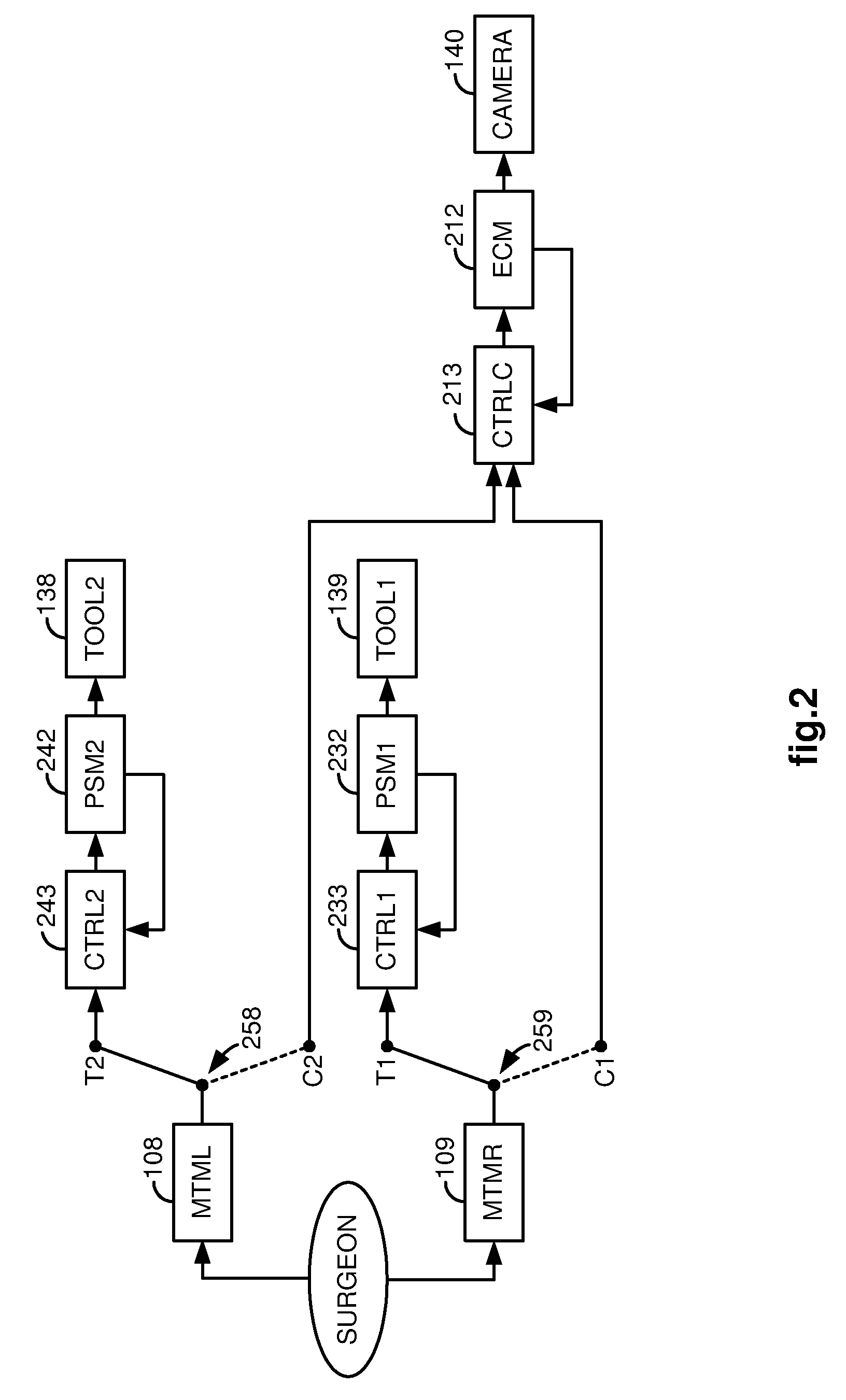
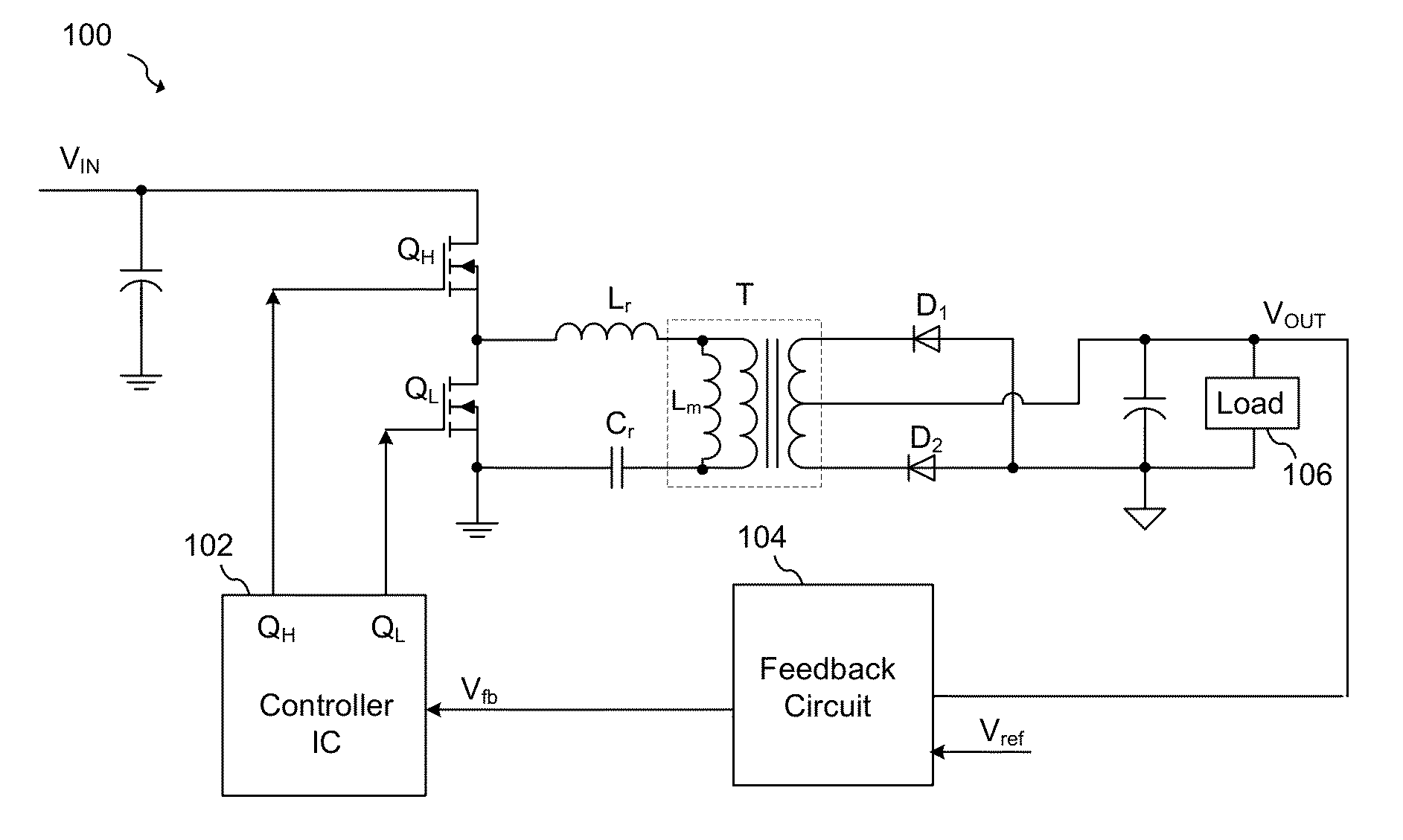
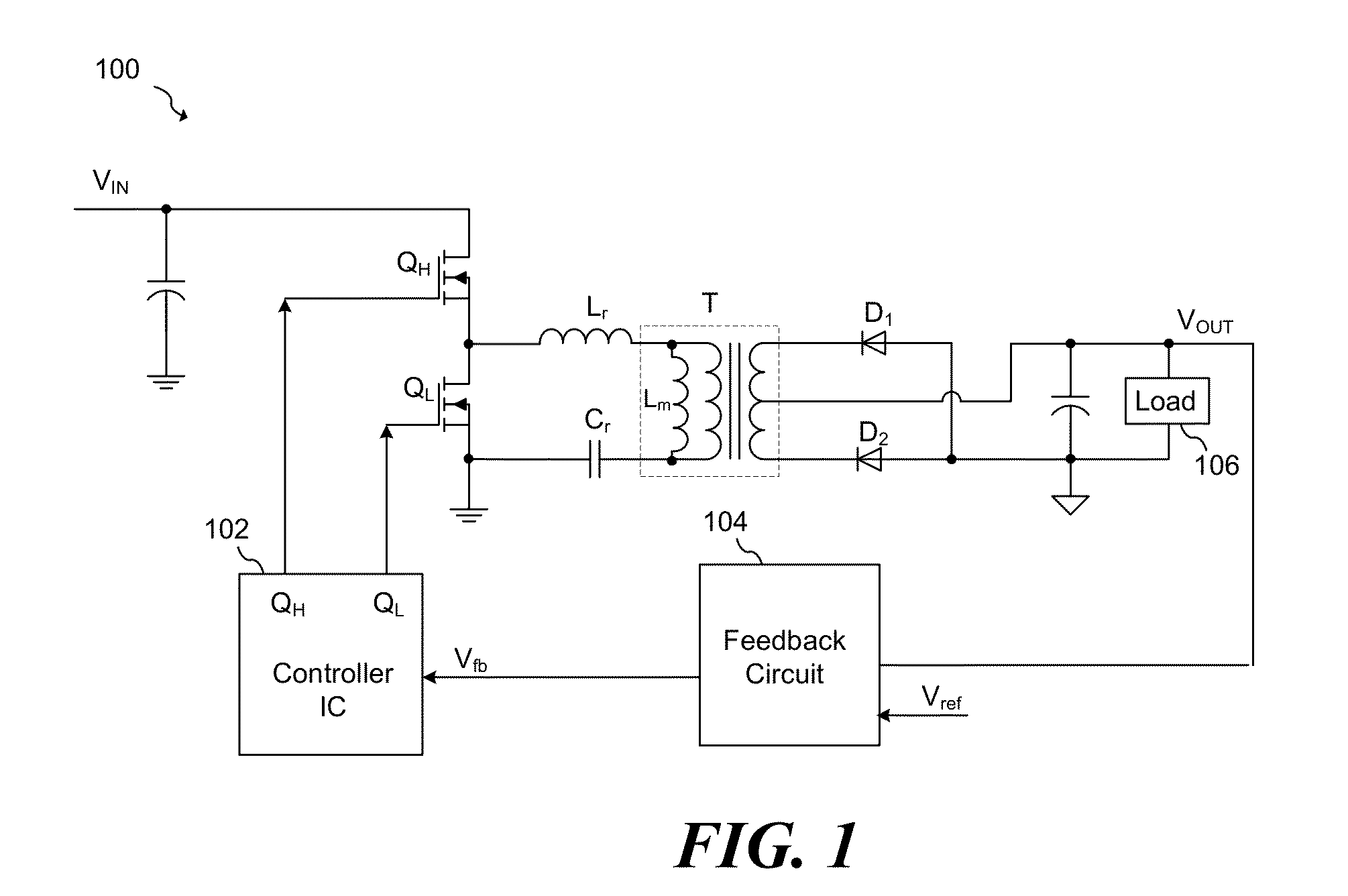
System and method for adjusting an image capturing device attribute using an unused degree-of-freedom of a master control device
ActiveUS8335590B2Sampled-variable control systemsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDevice PropertiesControl engineering
An image capturing device is robotically positioned and oriented in response to operator manipulation of a master control device. An unused degree-of-freedom of the master control device is used to adjust an attribute such as focusing of the image capturing device relative to a continually updated set-point. A deadband is provided to avoid inadvertent adjusting of the image capturing device attribute and haptic feedback is provided back to the master control device so that the operator is notified when adjusting of the attribute is initiated.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
System and method for adjusting an image capturing device attribute using an unused degree-of-freedom of a master control device
ActiveUS20100161129A1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl engineeringDegrees of freedom
An image capturing device is robotically positioned and oriented in response to operator manipulation of a master control device. An unused degree-of-freedom of the master control device is used to adjust an attribute such as focusing of the image capturing device relative to a continually updated set-point. A deadband is provided to avoid inadvertent adjusting of the image capturing device attribute and haptic feedback is provided back to the master control device so that the operator is notified when adjusting of the attribute is initiated.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
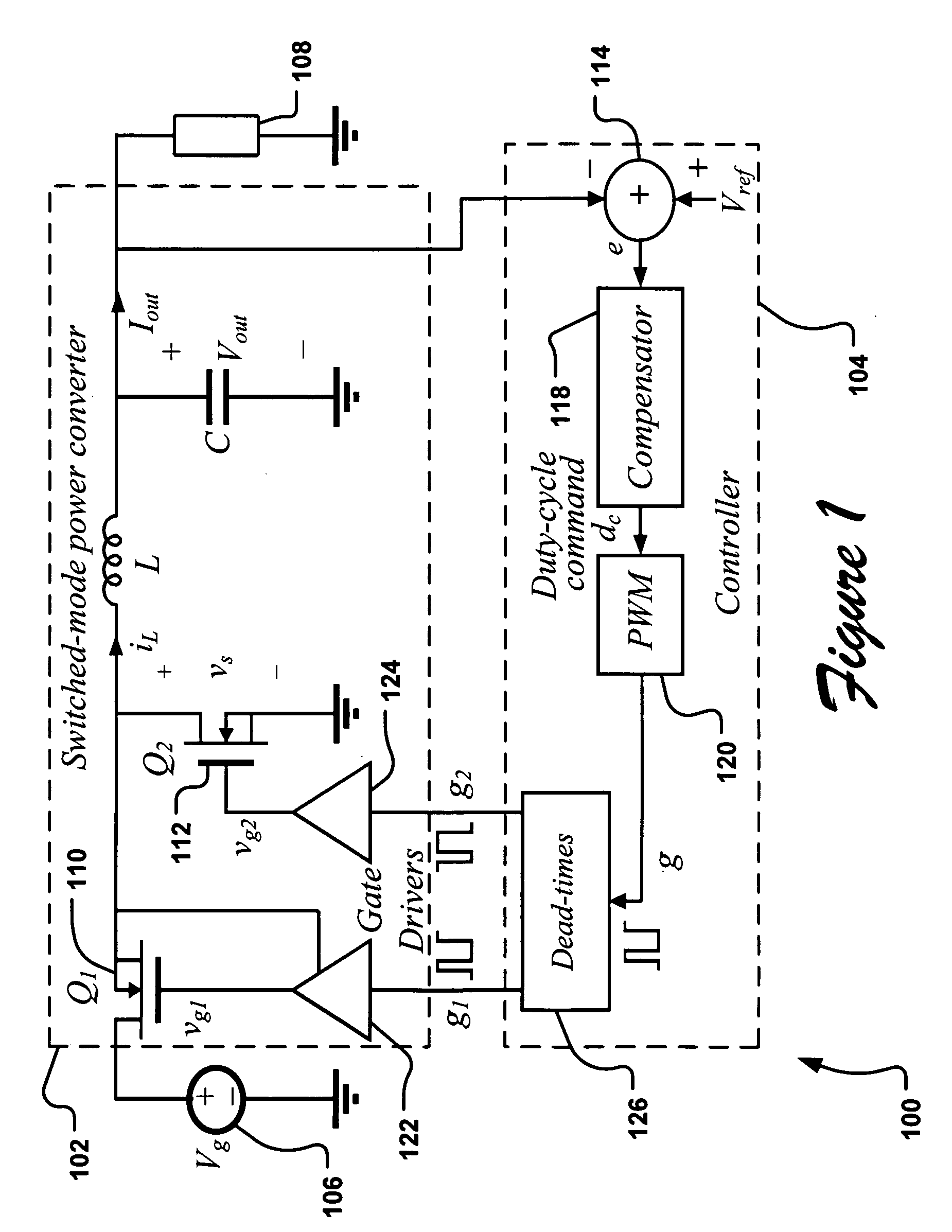
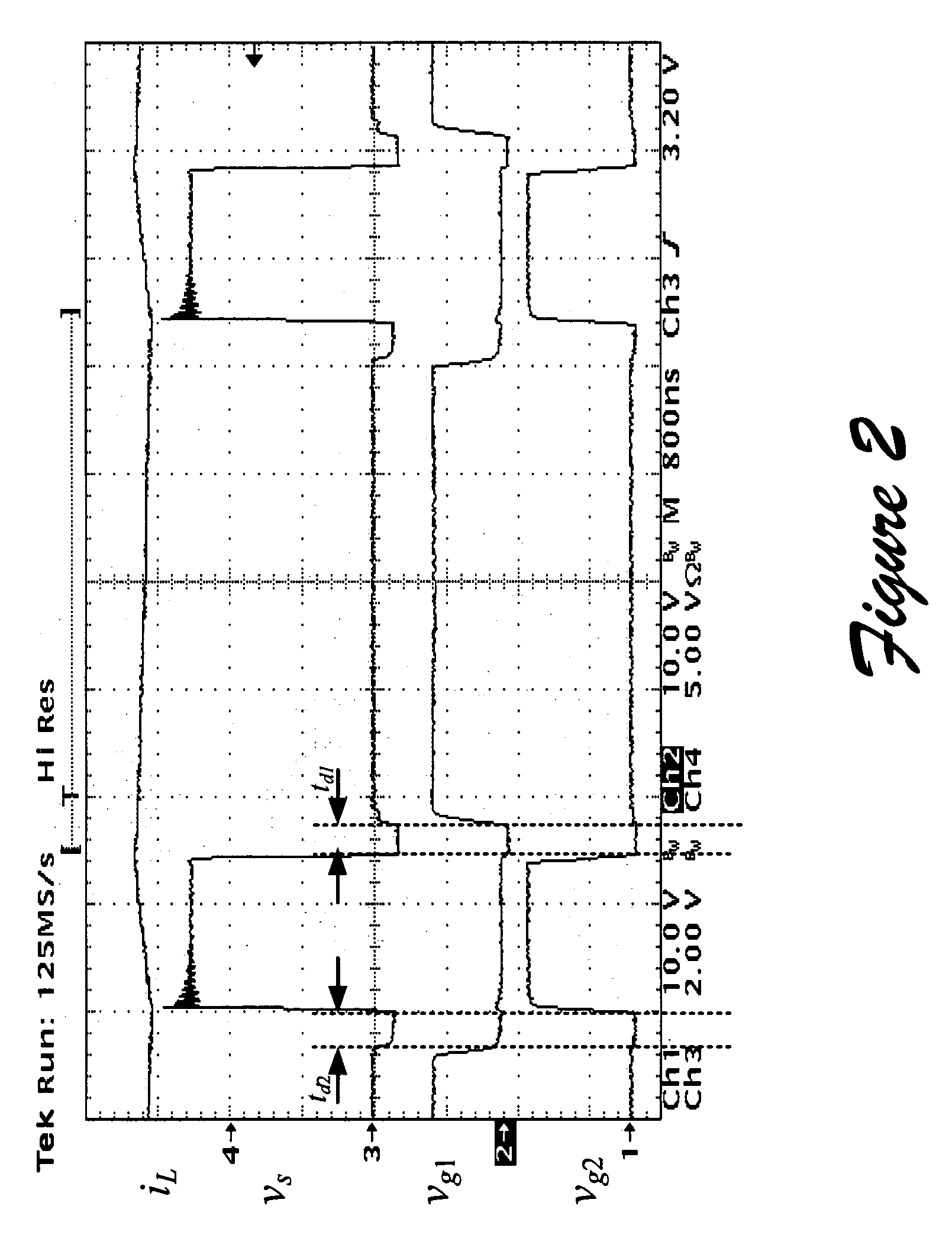
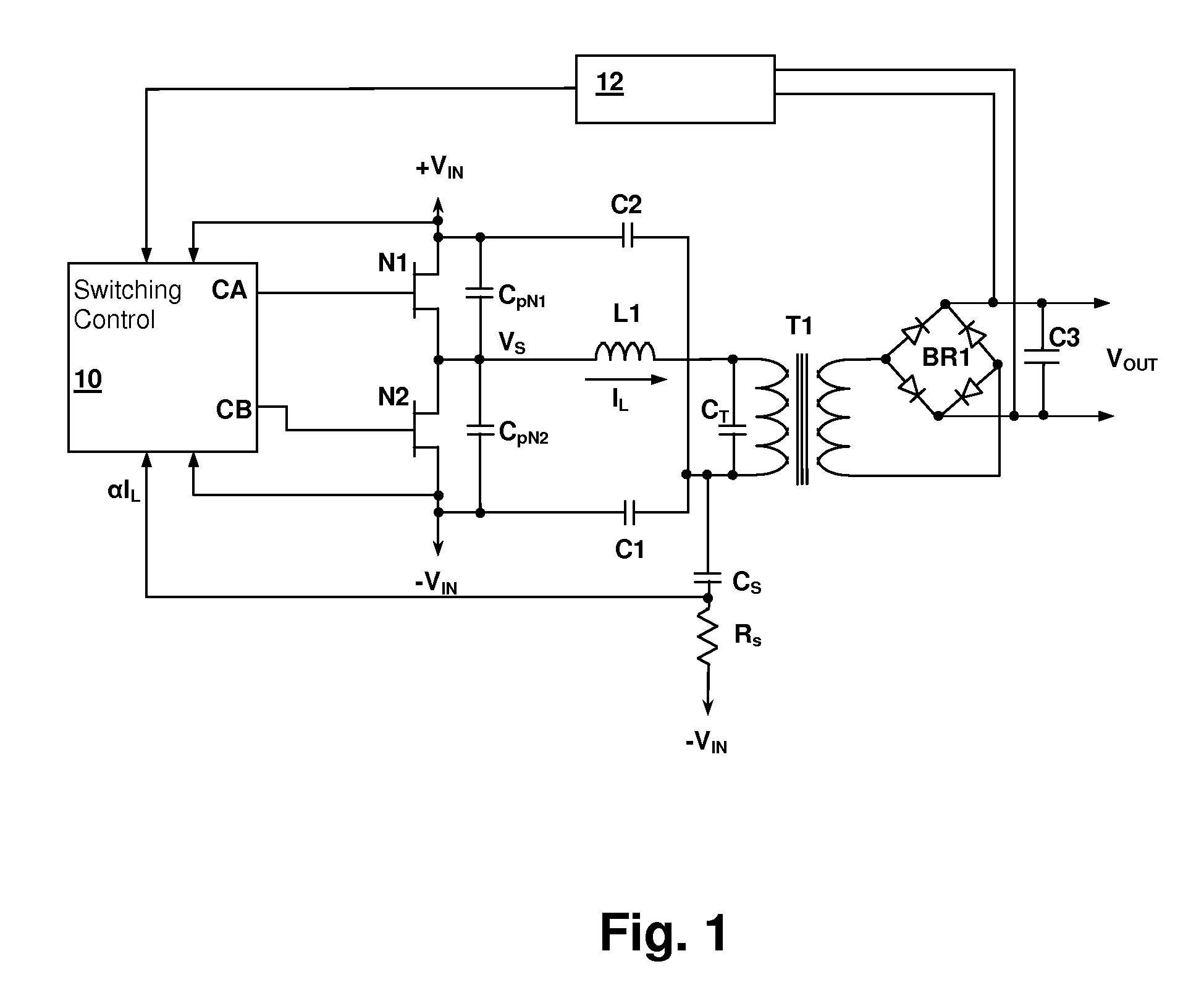
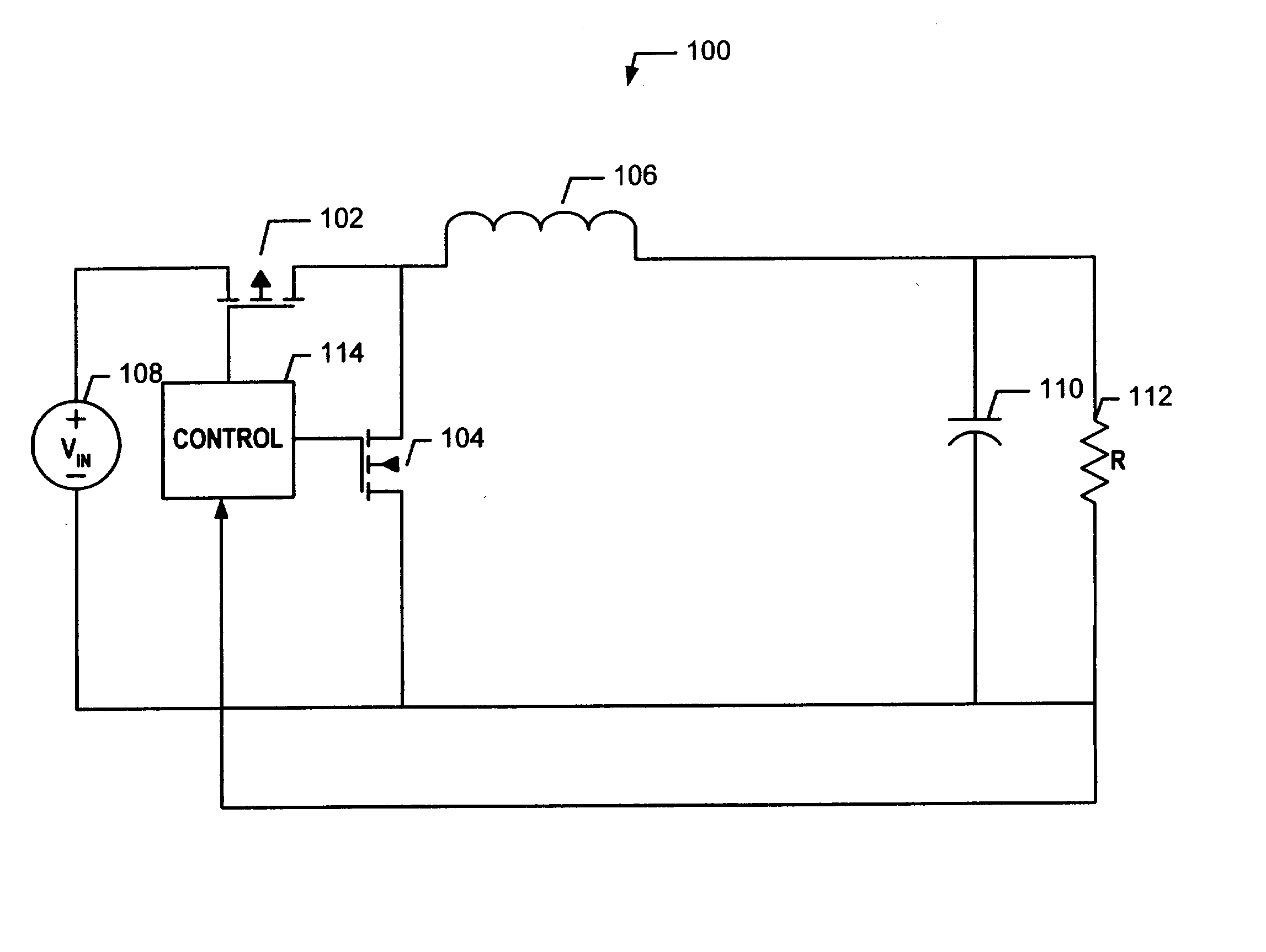
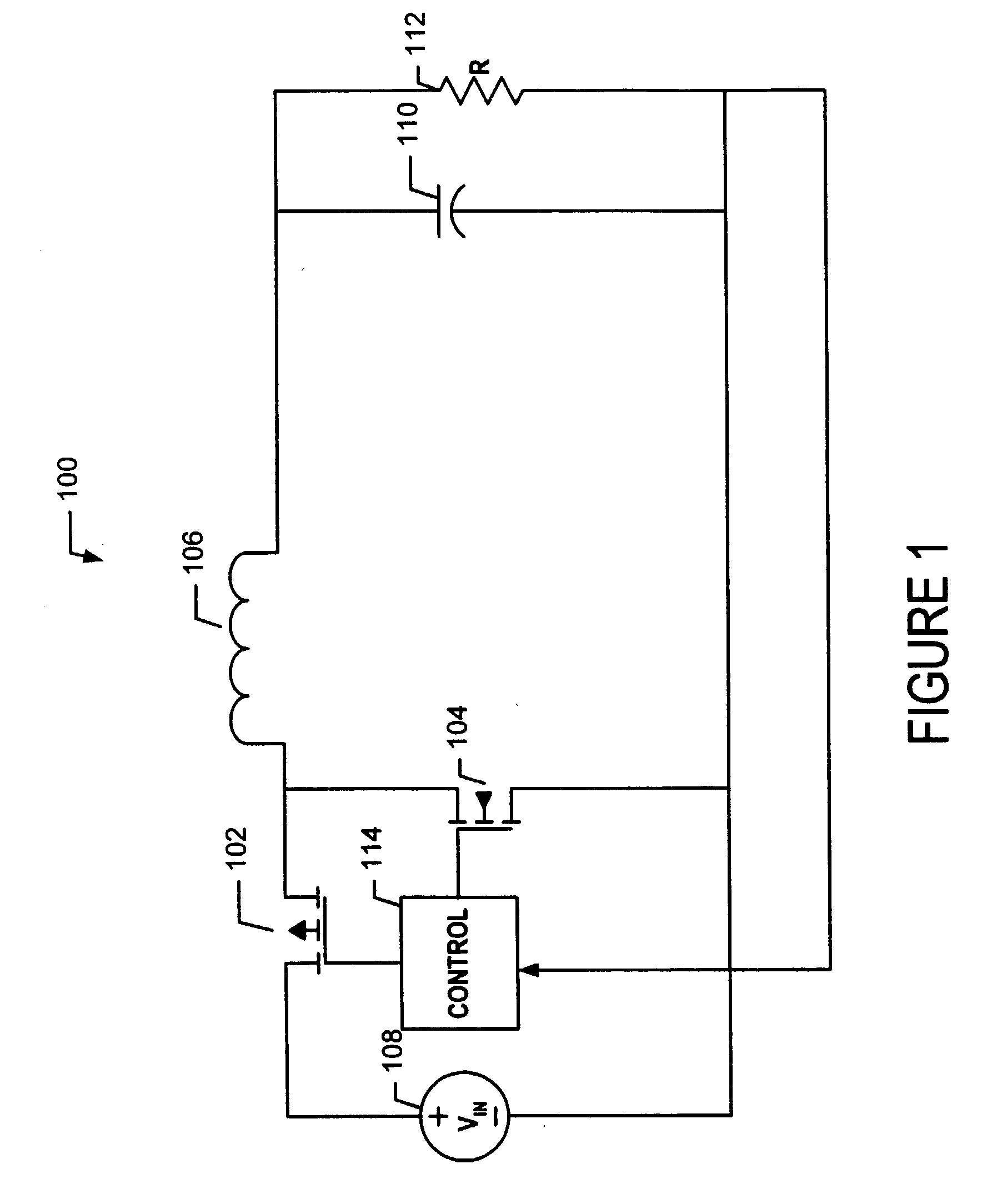
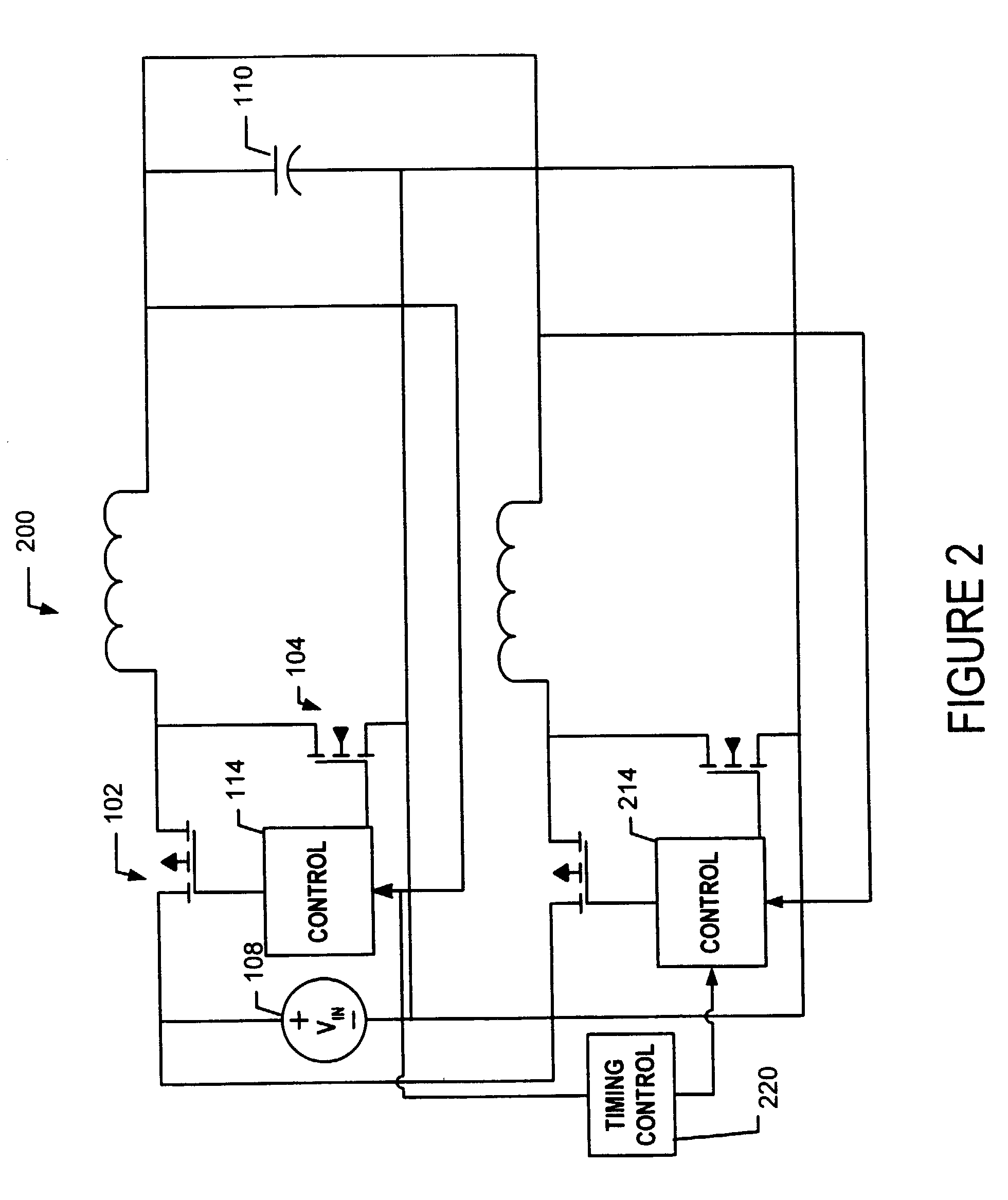
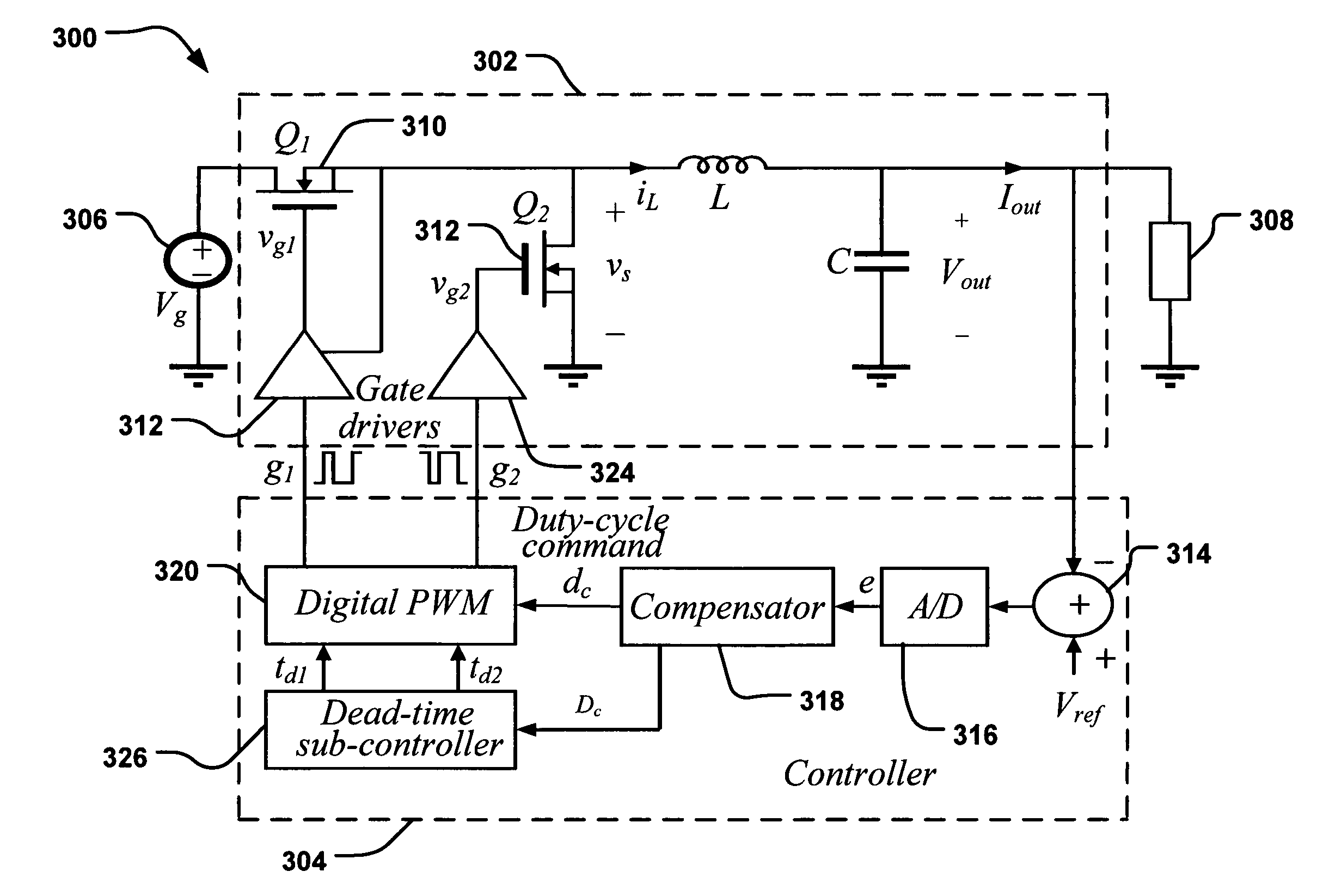
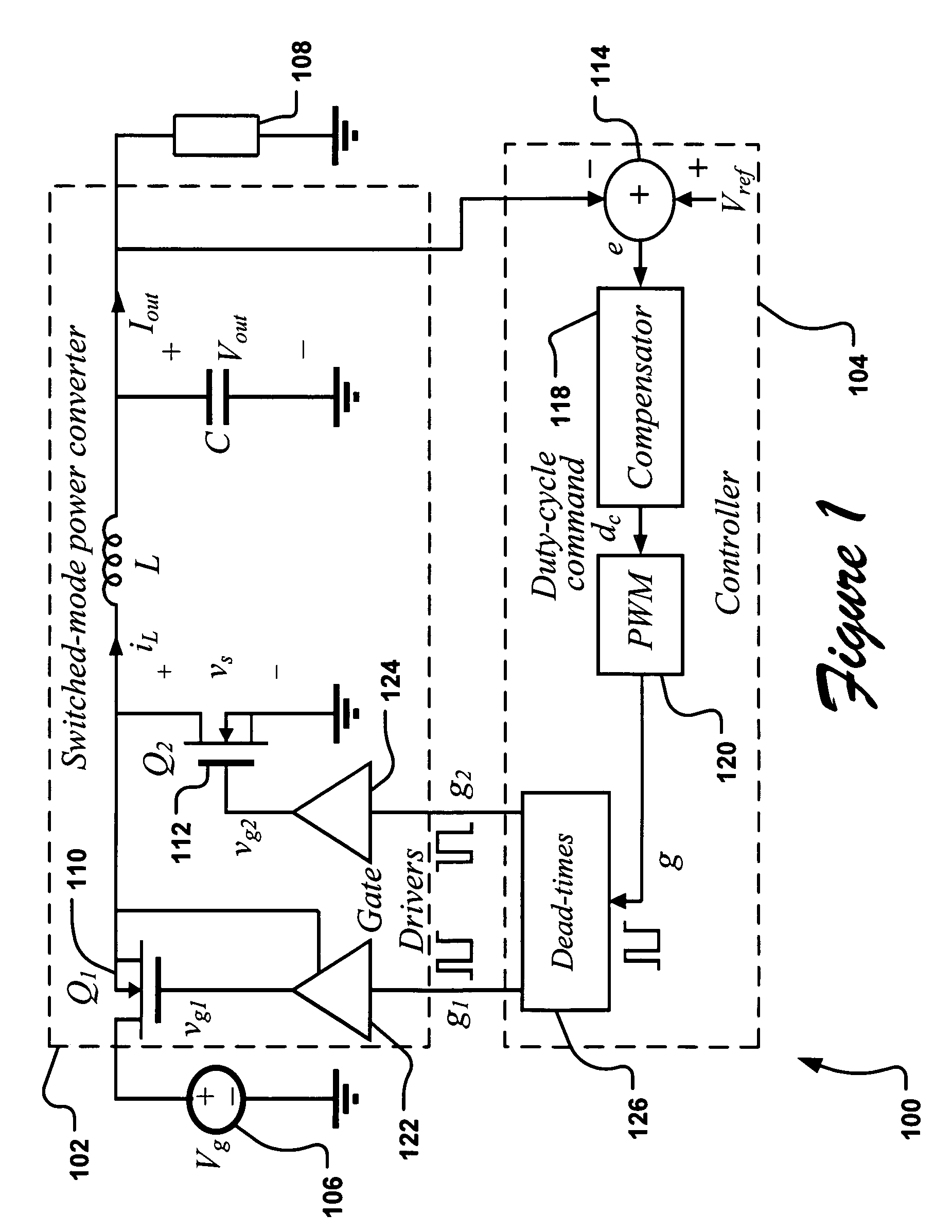
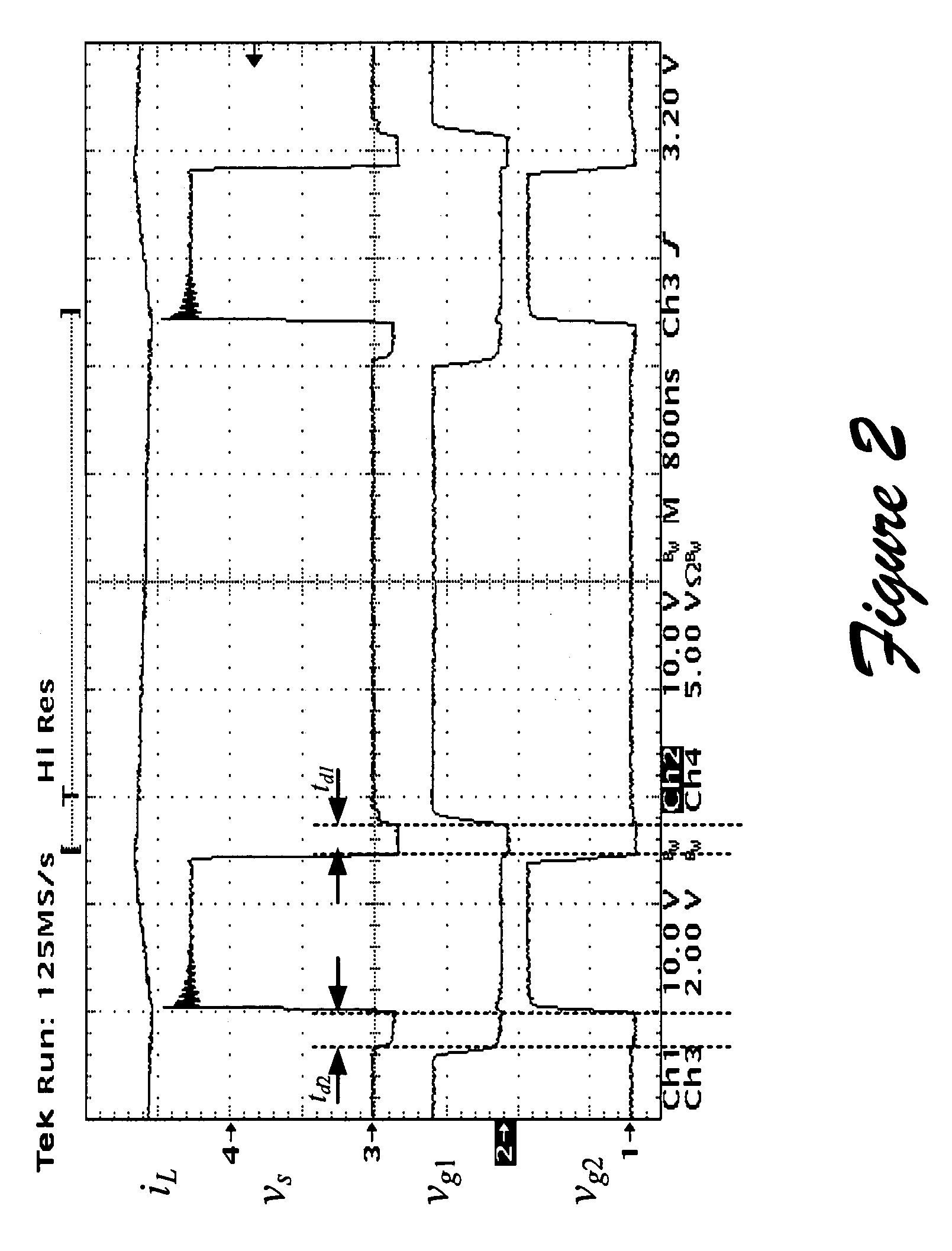
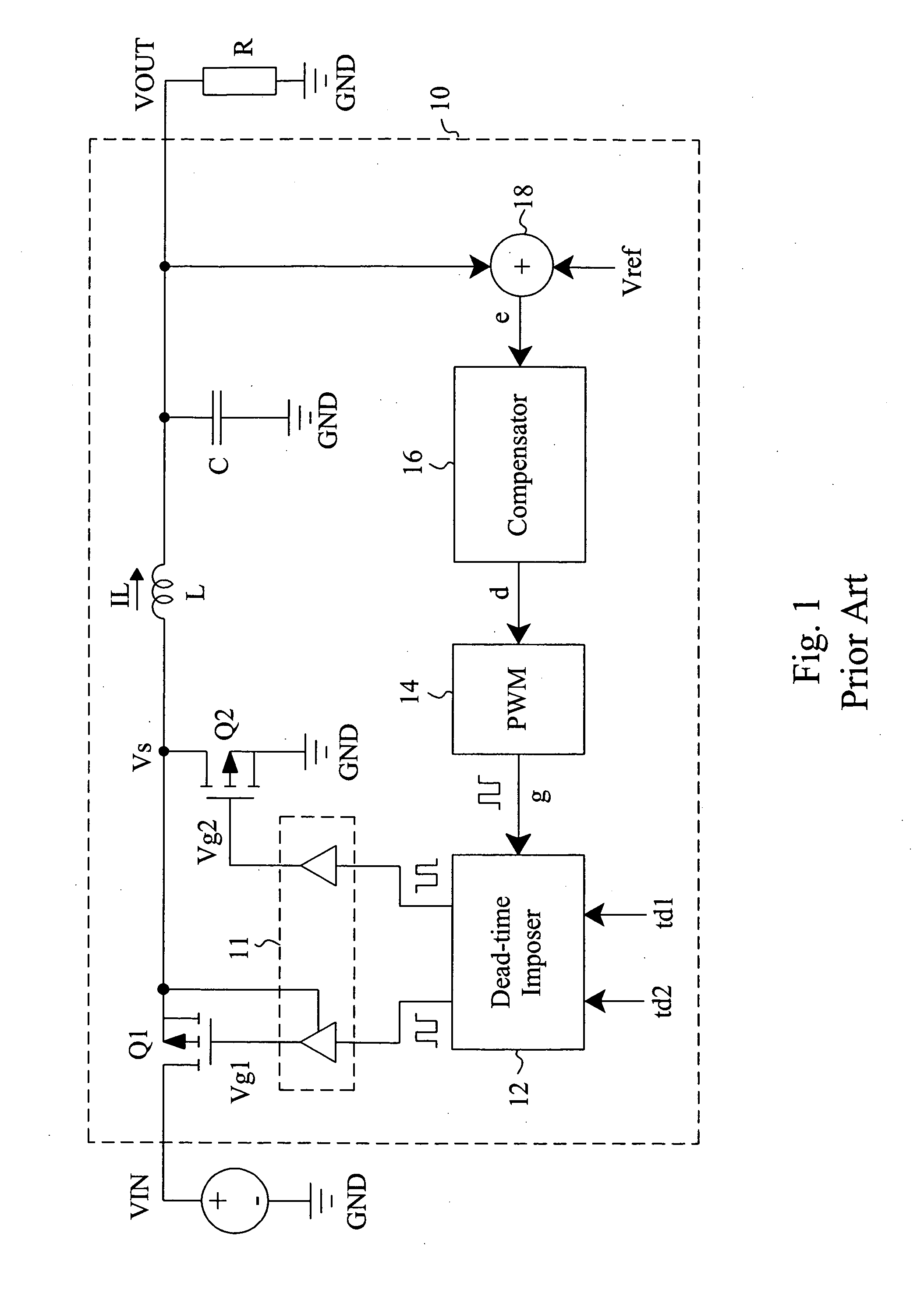
Determining dead times in switched-mode DC-DC converters
ActiveUS20060152204A1Improve efficiencySimpler and faster and accurate implementationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterDead time
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are disclosed for determining dead-times in switched-mode DC-DC converters with synchronous rectifiers or other complementary switching devices. In one embodiment, for example, a controller for a DC-DC converter determines dead-times for switching devices of a synchronous rectifier or other complementary switching device of the converter in which a dead-time is derived from an output voltage or current that is already sensed and used in the output regulation of the converter. In another embodiment, a controller is provided for controlling a switched-mode DC-DC converter comprising a pair of power switches. The controller comprises an input, a reference generator, a comparator, a compensator, a dead-time sub-controller, and a modulator. In another embodiment, the controller may adjust the dead-times during the operation of the converter to adjust periodically and / or in response to changes in operating conditions. In addition, methods of determining dead-times of control signals for a switched-mode DC-DC converter comprising a pair of power switches and of controlling a DC-DC converter are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Multi-Mode Operation and Control of a Resonant Converter
ActiveUS20130229829A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionNormal modeResonant converter
In accordance with an embodiment, a method of controlling a switched-mode power includes generating a feedback signal proportional to an output of the switched-mode power supply, and operating the switched-mode power supply in a normal mode. If the feedback signal crosses a first threshold, the switched-mode power operates in a second operating mode. In the first operating mode the pulse modulated signal is adjusted to regulate a feedback signal to a first signal level, and in the second operating mode, a dead-time of the pulse modulated signal is adjusted to signal to regulate a feedback signal to a second signal level different from the first signal level. The method further includes driving a switch of the switched-mode power supply with the pulse modulated signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
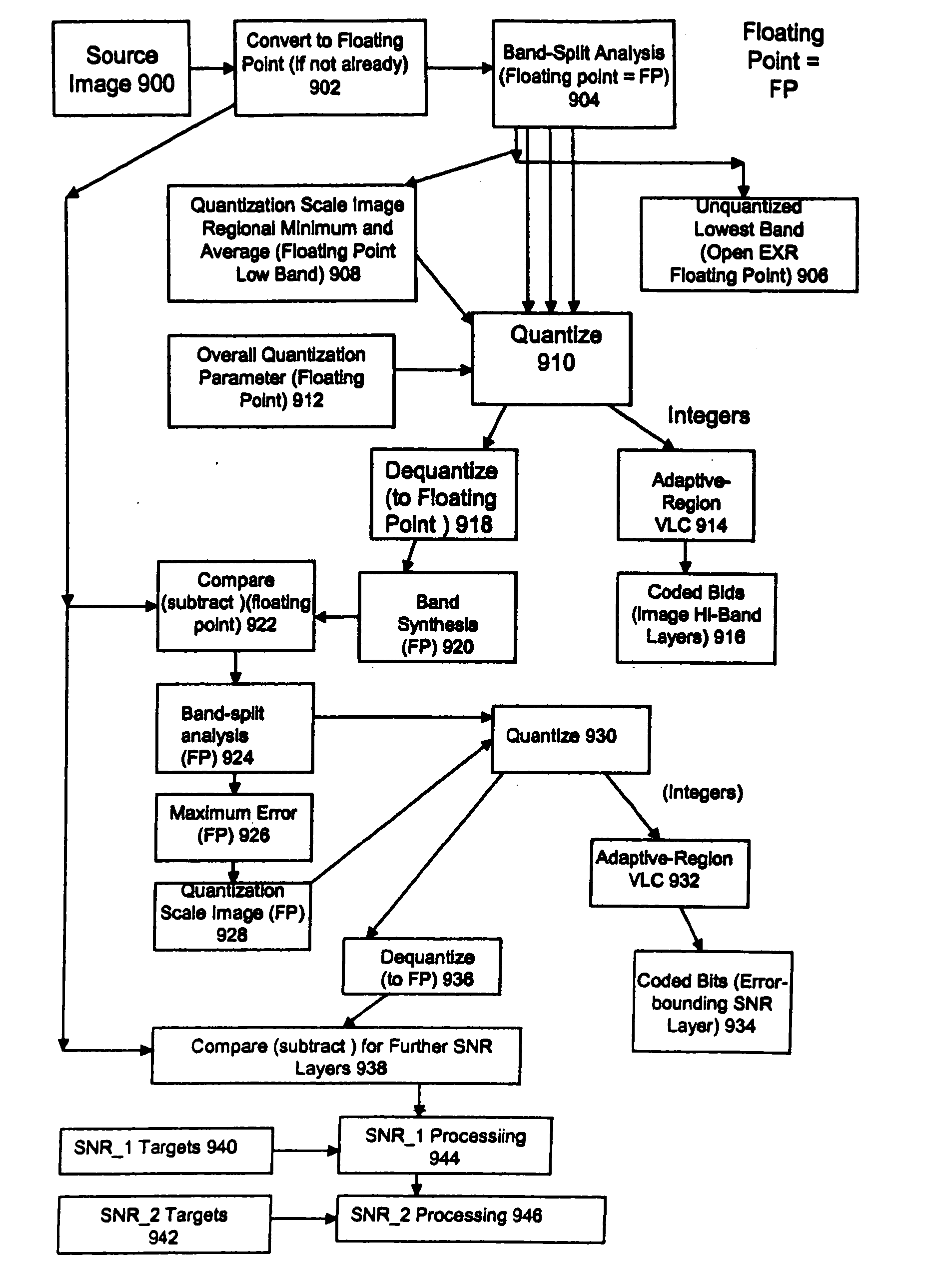
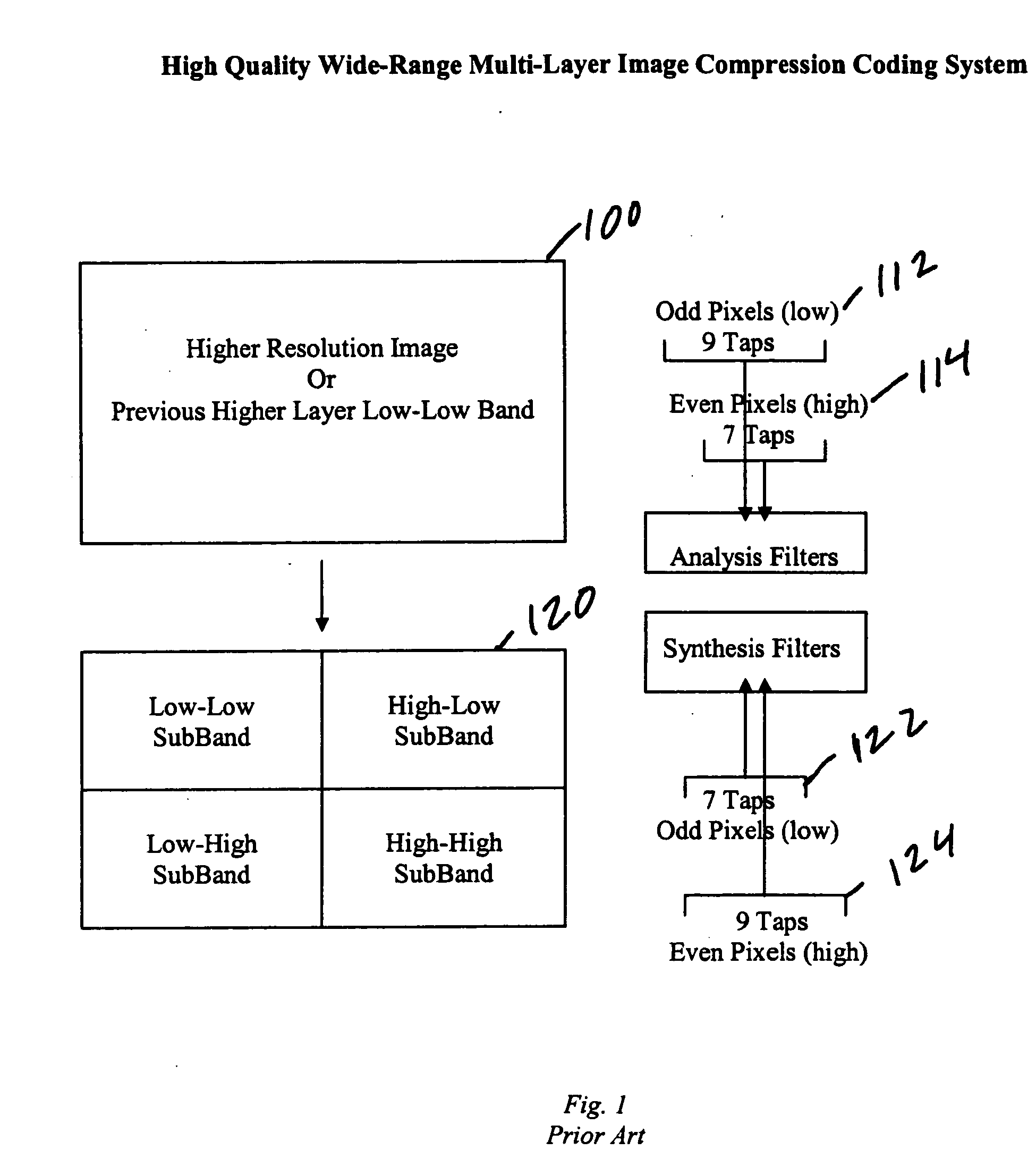
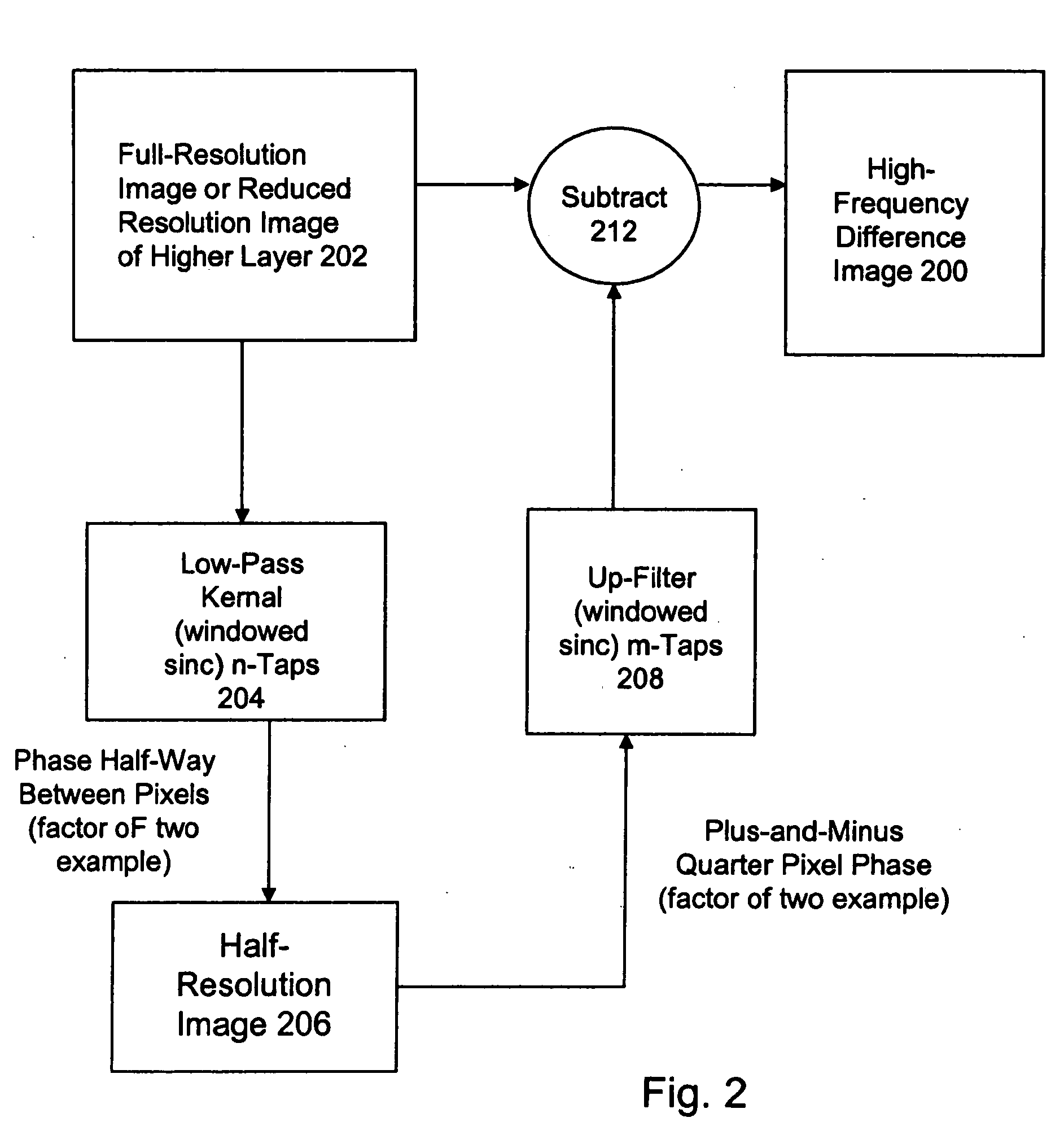
High quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding system
ActiveUS20060071825A1Reduce sharpnessReduce detailsCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionFloating pointImage compression
Systems, methods, and computer programs for high quality wide-range multi-layer image compression coding, including consistent ubiquitous use of floating point values in essentially all computations; an adjustable floating-point deadband; use of an optimal band-split filter; use of entire SNR layers at lower resolution levels; targeting of specific SNR layers to specific quality improvements; concentration of coding bits in regions of interest in targeted band-split and SNR layers; use of statically-assigned targets for high-pass and / or for SNR layers; improved SNR by using a lower quantization value for regions of an image showing a higher compression coding error; application of non-linear functions of color when computing difference values when creating an SNR layer; use of finer overall quantization at lower resolution levels with regional quantization scaling; removal of source image noise before motion-compensated compression or film steadying; use of one or more full-range low bands; use of alternate quantization control images for SNR bands and other high resolution enhancing bands; application of lossless variable-length coding using adaptive regions; use of a folder and file structure for layers of bits; and a method of inserting new intra frames by counting the number of bits needed for a motion compensated frame.
Owner:DEMOS GARY
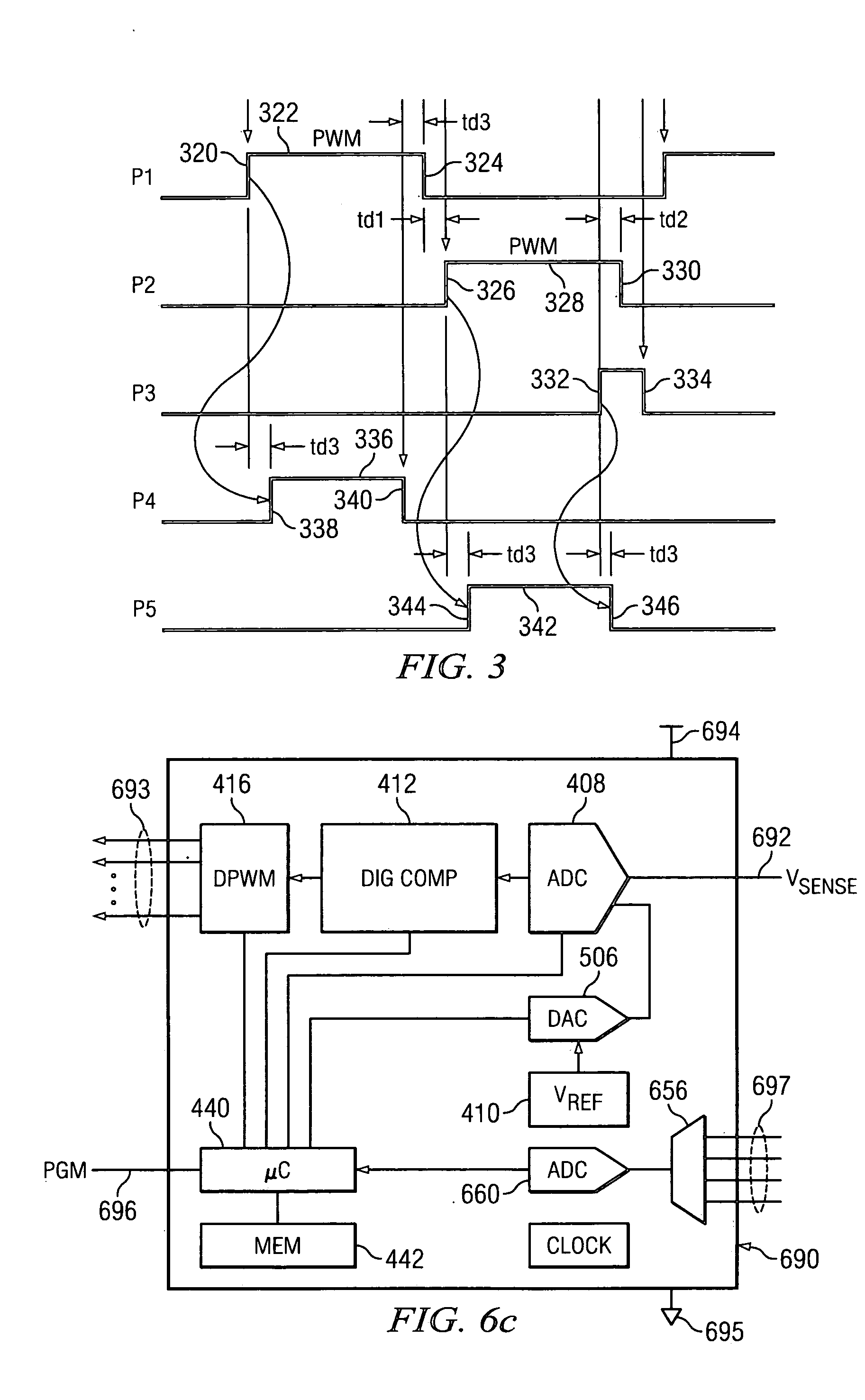
Digital PWM controller for digital power supply having programmable dead times
A system for controlling a switching power converter and includes a digital controller that receives an analog signal representing the output DC voltage of the power converter for comparison to a desired output voltage level and generates switching control signals to control the operation of the power supply to regulate the output DC voltage to said desired output voltage level. At least two of the switching control signals having a dead time between a first edge of a first control signal and a second edge of a second control signal. The dead time is programmable such that the second edge of the second control signal may occur at a selected point in time either before or after the first edge of the first control signal.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Programmable quantization dead zone and threshold for standard-based H.264 and/or VC1 video encoding
ActiveUS20060126724A1Improve visual qualityReduce pulsingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingControl circuit
A video encoder comprising an encoder circuit, a quantizer circuit and a control circuit. The encoder circuit may be configured to generate a number of coefficient values in response to a video stream and a number of quantized values. The quantizer circuit may be configured to generate the number of quantized values in response to the coefficient values, two or more quantization dead zones and two or more offsets. The control circuit may be configured to set the two or more quantization dead zones and the two or more offsets to different values. The two or more quantization dead zones and the two or more offsets are independently programmable.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
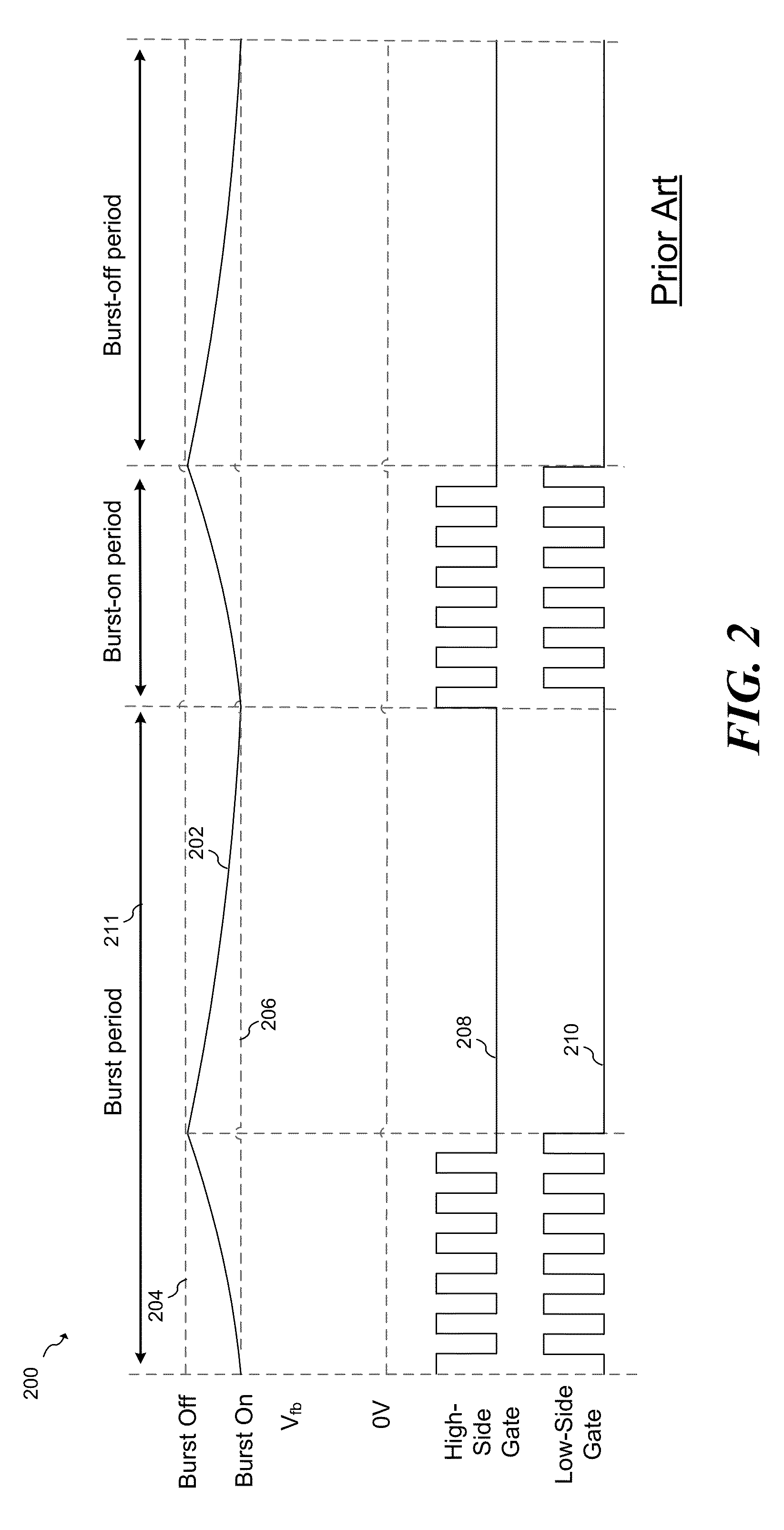
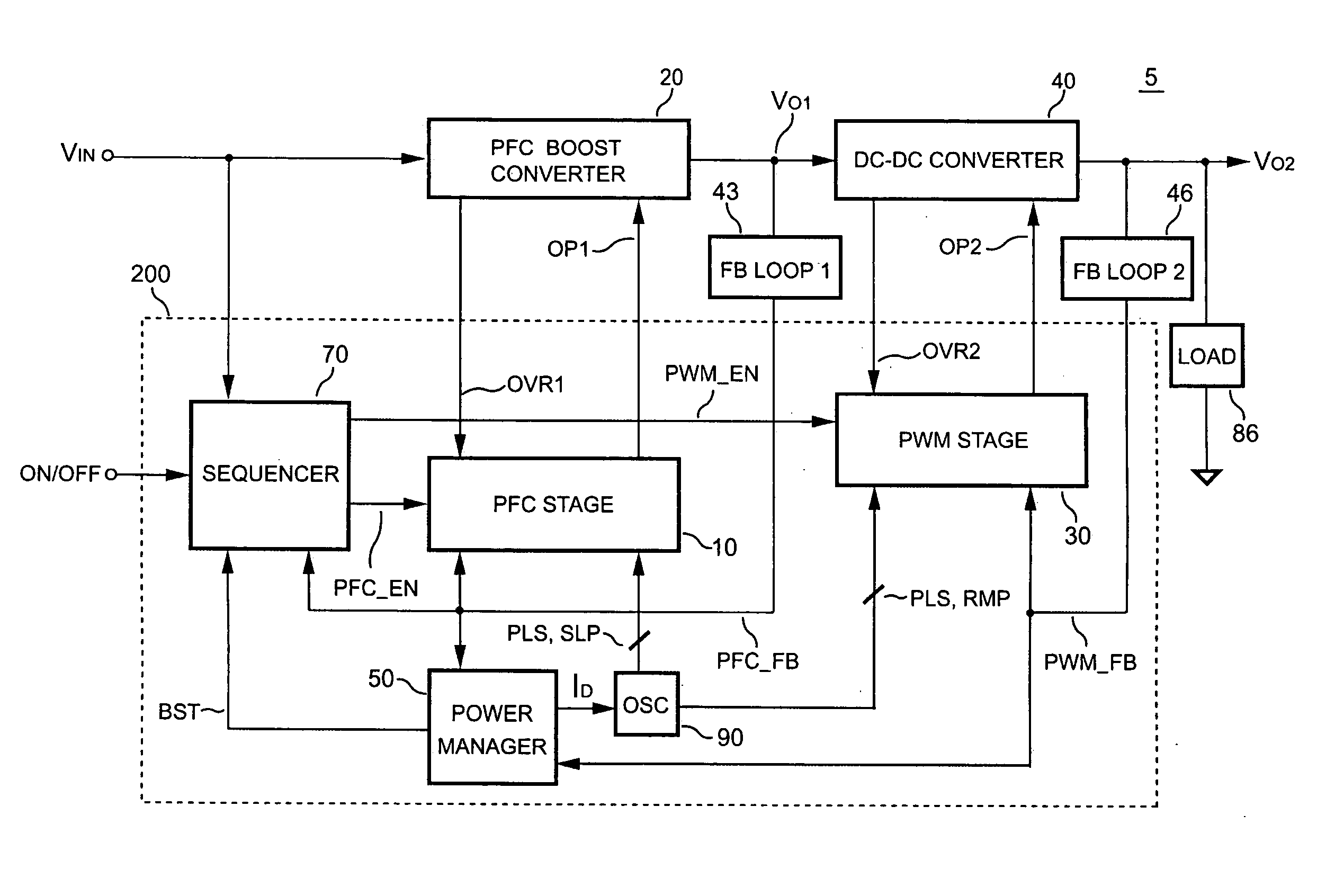
Pfc-pwm controller having interleaved switching
ActiveUS20050099164A1Reduce switching noiseImproper operationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringPwm signals
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
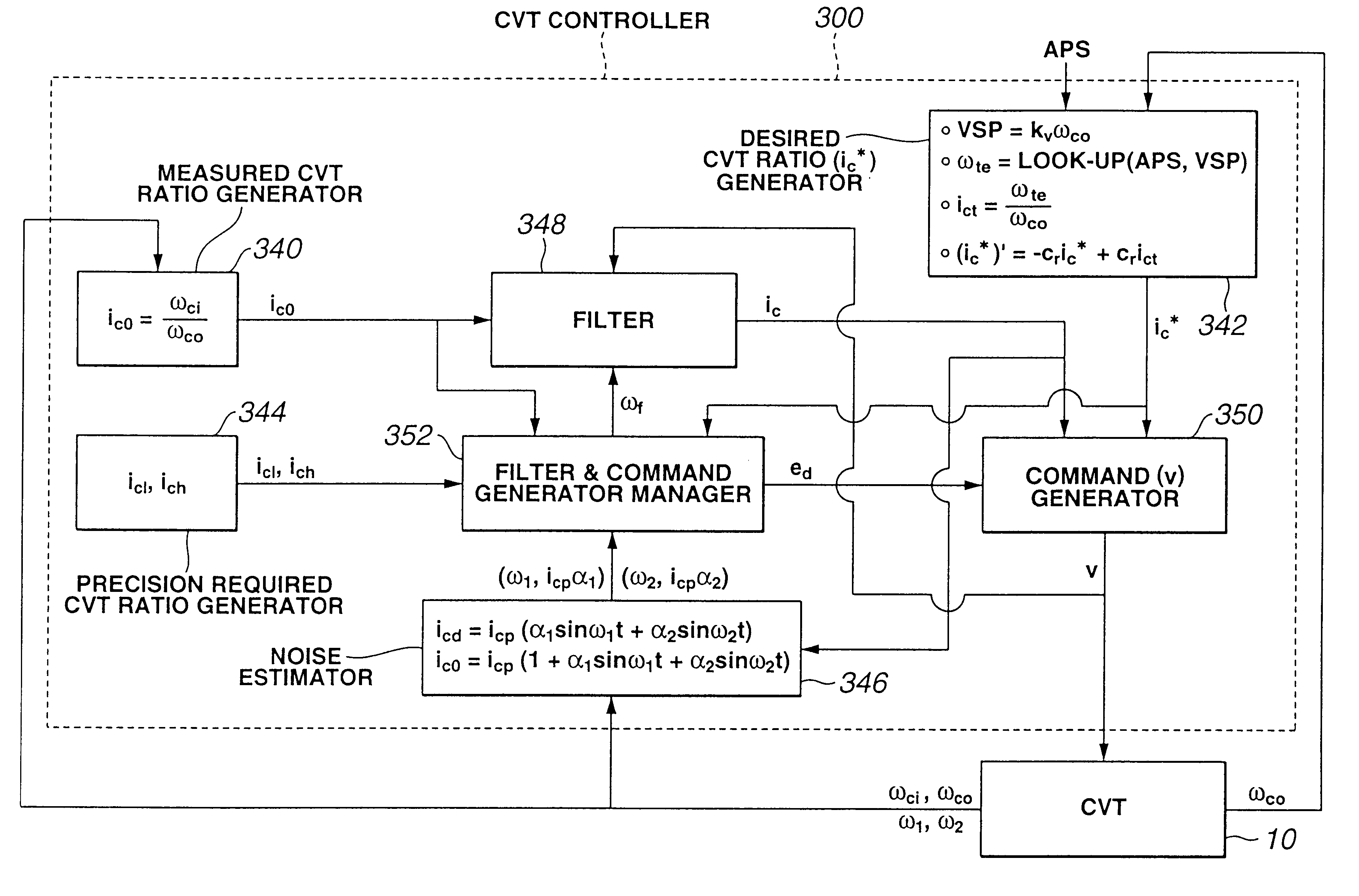
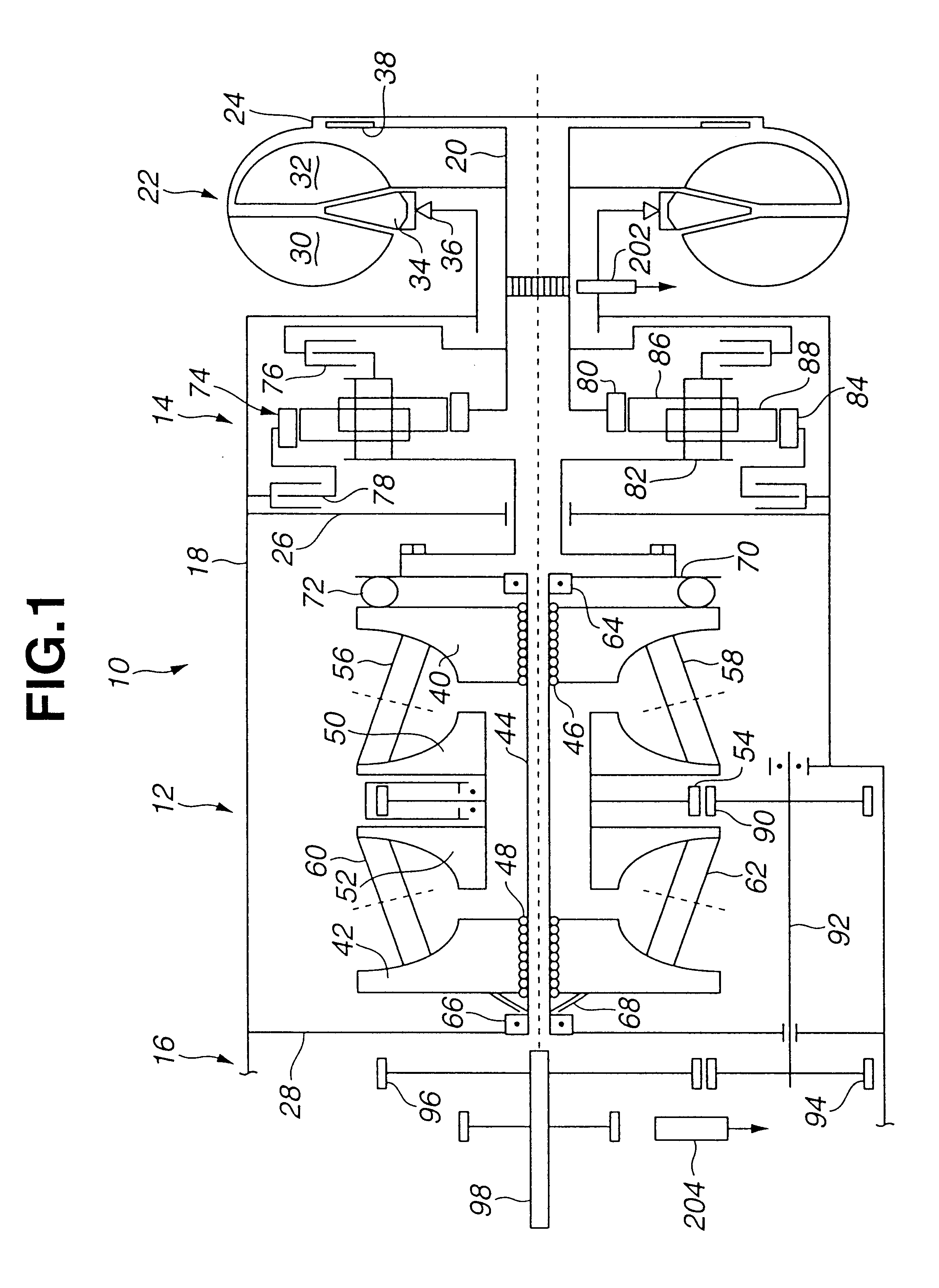
Enhanced ratio control to establish CVT ratio with excellent precision
A system for enhanced ratio control in a continuously variable transmission (CVT) includes a ratio control element positionable by an actuator in response to an actuator command to establish various CVT ratios in the CVT. At least one sensor generates a train of pulses indicative of speed of rotation of a predetermined rotary member of the CVT. A measured CVT ratio generator derives information of an actual CVT ratio out of at least the train of pulses to give a measured value of CVT ratio. A filter processes the measured value of CVT ratio in a manner to refine the information of the actual CVT ratio to give an estimated value of CVT ratio. A command generator determines the actuator command such that the actuator command remains unaltered when a deviation of the estimated value of CVT ratio from a desired value of CVT ratio stays within a dead zone. A filter and command generator manager narrows the dead zone to meet precision requirement upon determination that the desired value of CVT ratio has been accomplished and adjusts filter gain at the filter in a manner to keep amplitude at frequency of noise that is contained in the measured value of CVT ratio within the narrowed dead zone.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for intelligently setting dead time
ActiveUS7098640B2Minimize powerConvenient and cost-effectiveEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMemory addressDead time
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Apparatus and Method for Controlling Vehicle Motion
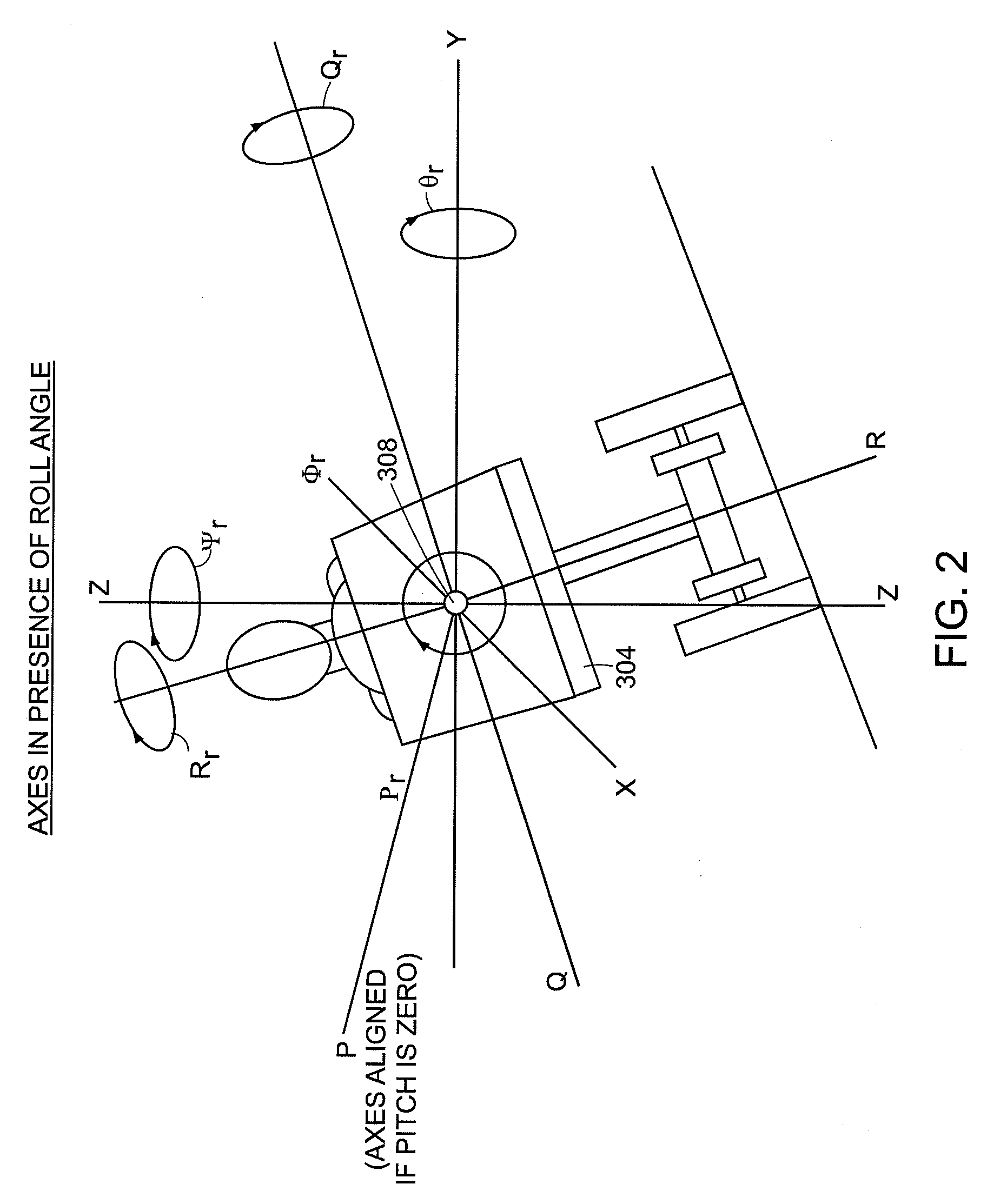
InactiveUS20090105908A1Digital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlControl theoryDeadband
An apparatus and method for controlling a steering command of a vehicle is provided. A deadband value based on a current state of a transporter is applied to a roll compensated steering command to control steering of the vehicle. A gain is applied to a steering command to control steering of the vehicle.
Owner:SEGWAY INC
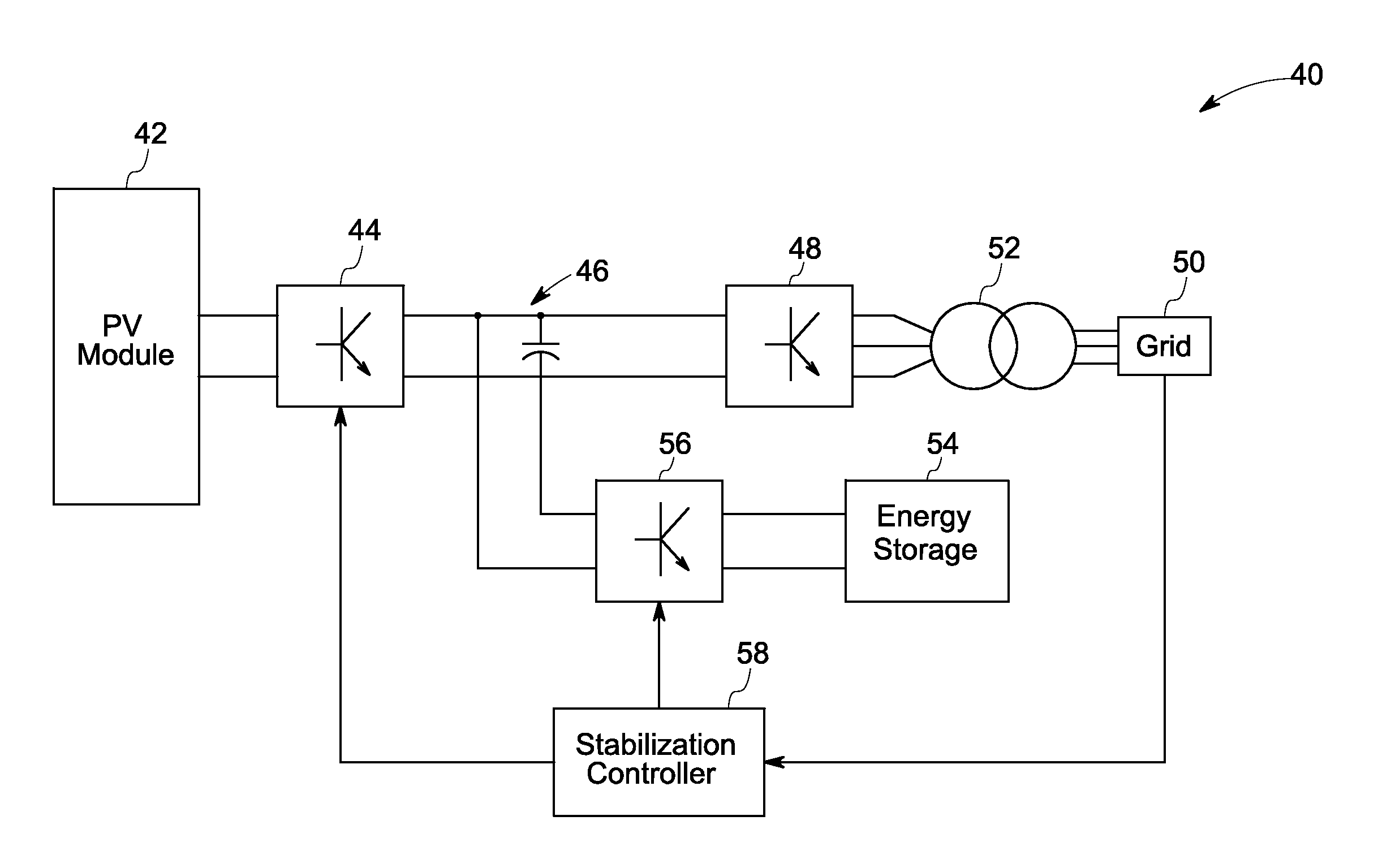
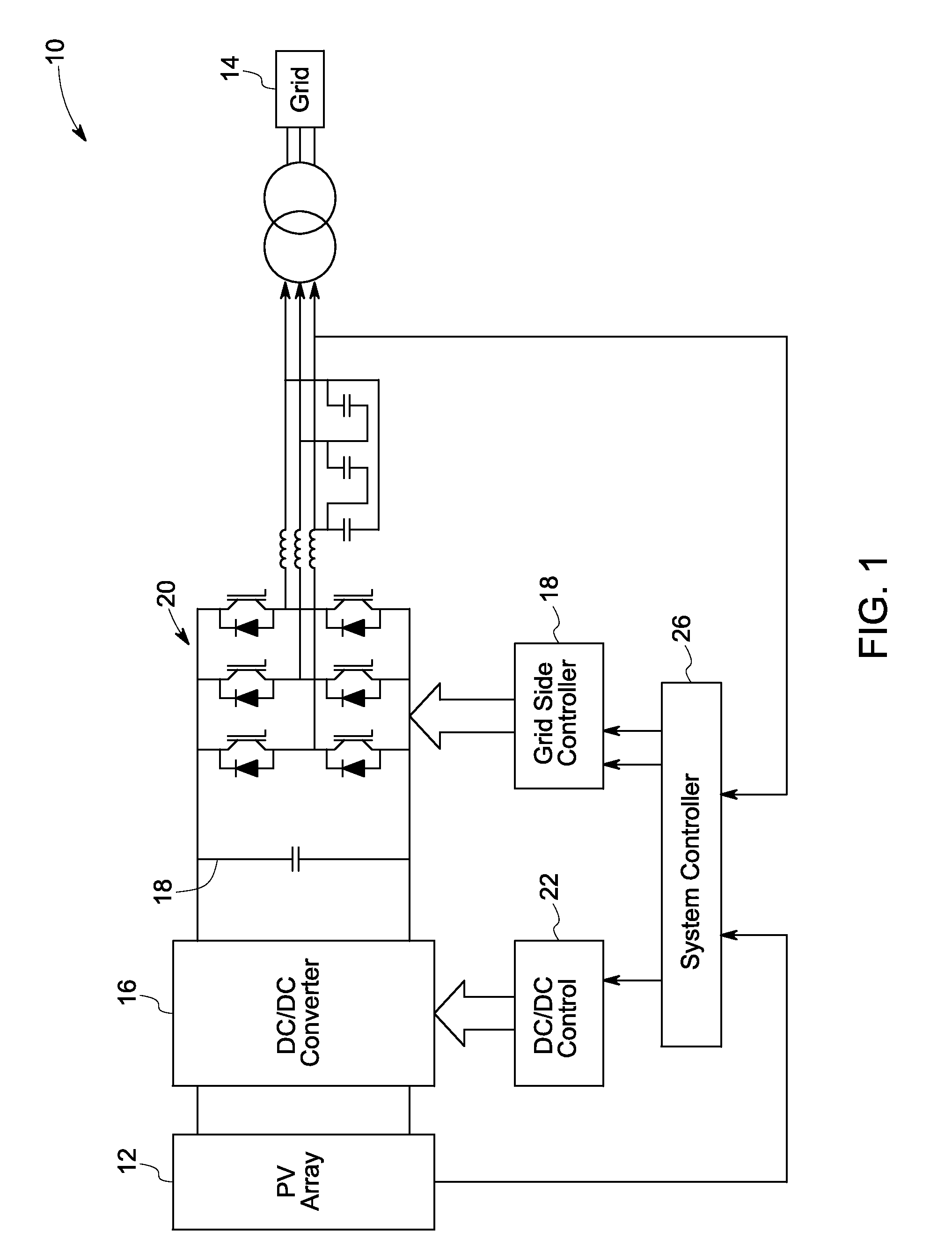
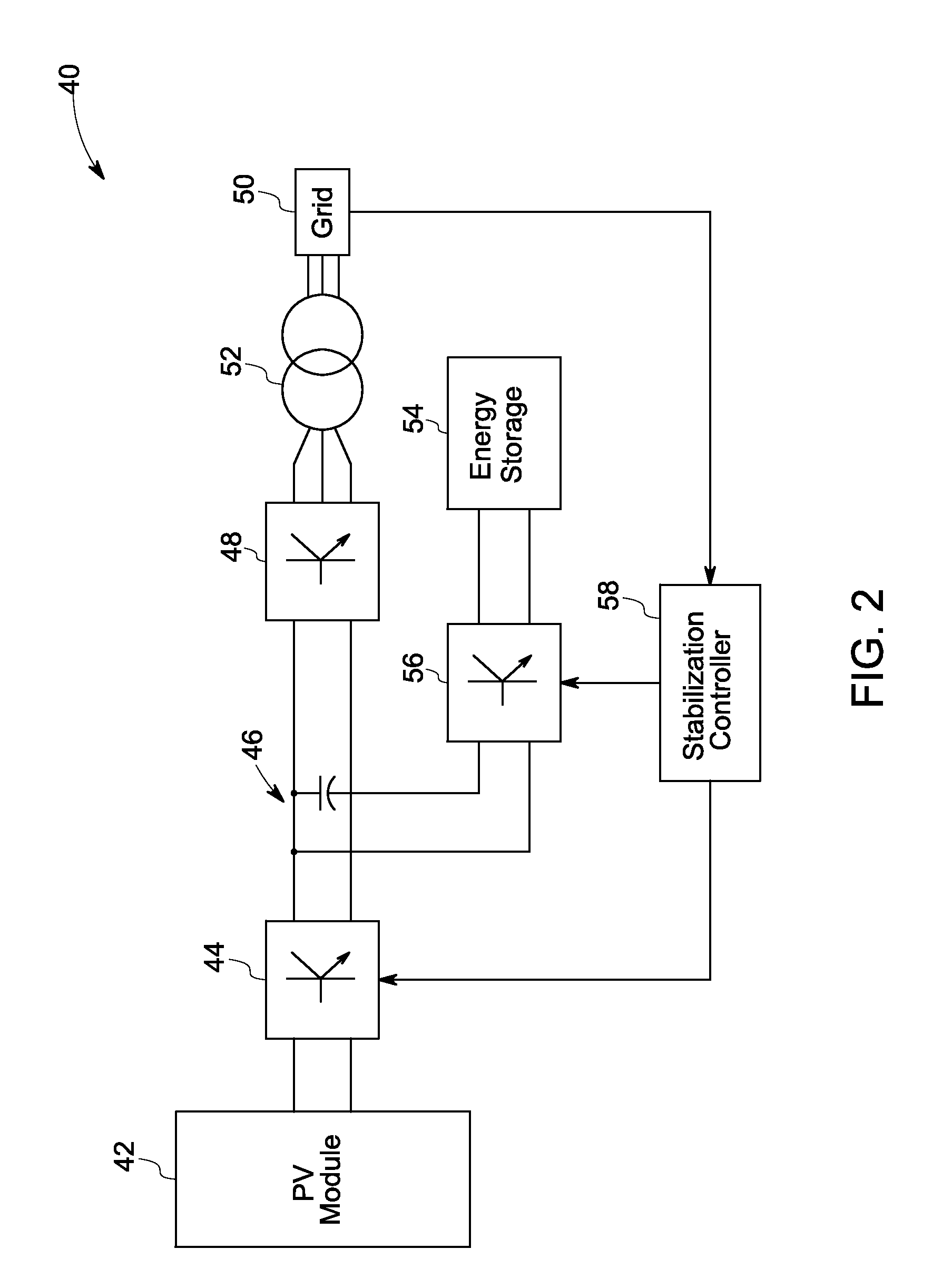
Solar power generation stabilization system and method
ActiveUS20100008119A1Operational constraintBatteries circuit arrangementsSwitch power arrangementsState of chargePower grid
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Resonant switching power converter with adaptive dead time control
InactiveUS20100020569A1Improve efficiencyRelieve pressureTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterEngineering
A resonant switching power converter having adaptive dead time control provides improved efficiency along with reduced EMI / audible noise and component stresses. A dead time between pulses generated by a switching circuit is adaptively set in conformity with a value of the input voltage to the resonant switching power converter and an indication of a magnitude of the current passing through inductive element of the resonant tank of the converter. The indication of the current magnitude may be the switching frequency of the converter, or a measure of line or load current levels. The dead time can be obtained from a look-up table or computed from the current magnitude and input voltage values.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
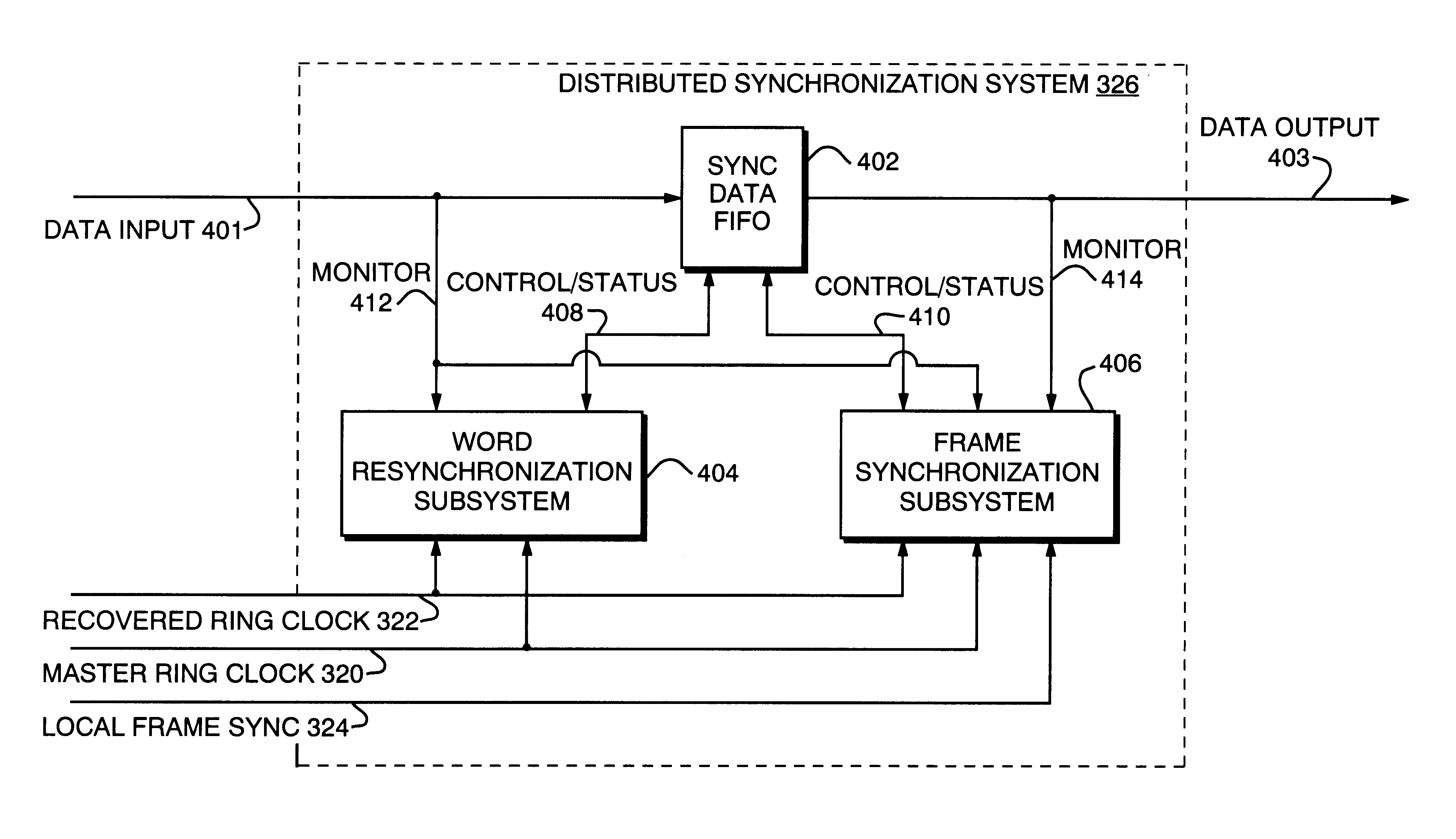
Distributed network synchronization system
InactiveUS6278718B1Effective absorptionOptimization rangeTime-division multiplexLoop networksAsynchronous communicationTelecommunications network
A distributed synchronization system for use in each node of a distributed asynchronous telecommunications network system that continually monitors and controls the flow of data through an implementing node to prevent dataflow errors due to phase and frequency differences in source and destination nodal clocks, and to control inter-nodal network latency so as to support the transmission of synchronous data. A synchronization data FIFO buffers predetermined fields or portions of fields of a unique frame packet received from a source node before retransmission to a destination node on the network. The frame packet includes a frame synchronization field indicating the beginning of a new frame packet; a payload field containing valid data; and a dead zone field providing bandwidth during which the present invention performs synchronization functions. A frame synchronization subsystem, implemented in a designated master node, guarantees that a frame is released at the beginning of an independently-determined frame regardless of network latency. A word resynchronization subsystem manages the flow of data through the data FIFO of each non-master node, receiving and storing data at the source node's clock rate and transmitting the data according to its own clock, thereby guaranteeing the efficient receipt and transmission of data between asynchronously-communicating nodes.
Owner:EXCEL SWITCHING
Multislice DC-DC converter
InactiveUS20030090244A1Energy efficient ICTEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceDead time
A novel monolithic step-down dc-dc buck converter that uses two or more ("n") parallel slices to achieve a high output current with a small filter capacitor is provided. Each of the n slices may be operated with a phase difference of 360° / n. Each of the converter slices may be based on a synchronous rectifier topology to avoid the excessive power losses introduced by the diode component of conventional step-down buck converters. Hysteretic control may be used (with or without pulse-width modulation and pulse-frequency modulation) to provide an internal gate-drive waveform without the need to provide a dedicated clock signal or oscillator circuit. The hysteretic control is further refined using digital control techniques to enforce a brief dead time between the activation of each slice such that undesirable circulating currents are prevented. A significant advantage of the proposed multi-slice step-down dc-dc buck converter and its associated control is that the semiconductor switches, filter inductors and capacitor, and the control circuit may be fabricated as part of a single monolithic integrated circuit.
Owner:SHAKTI SYST
Control System For Modulating Water Heater
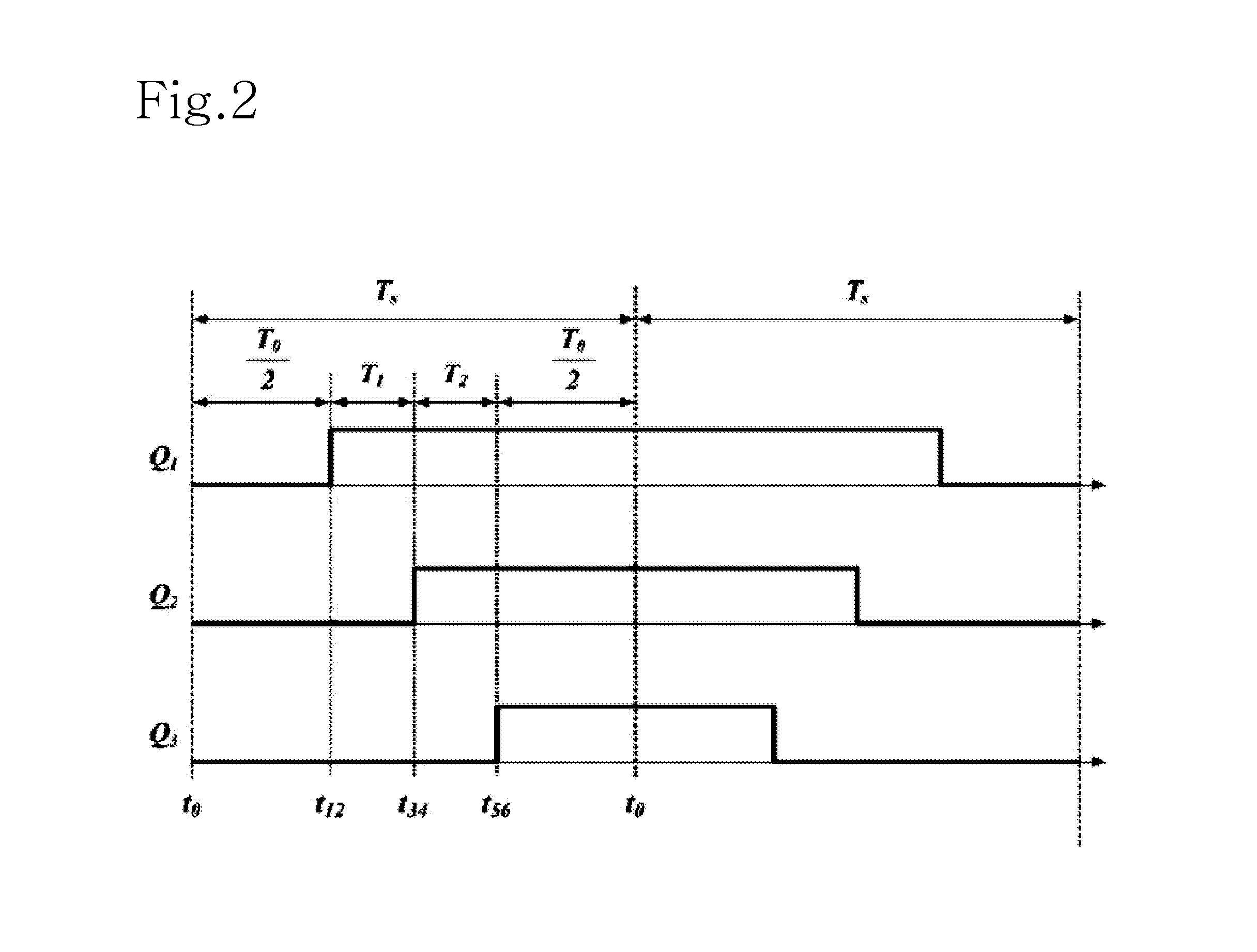
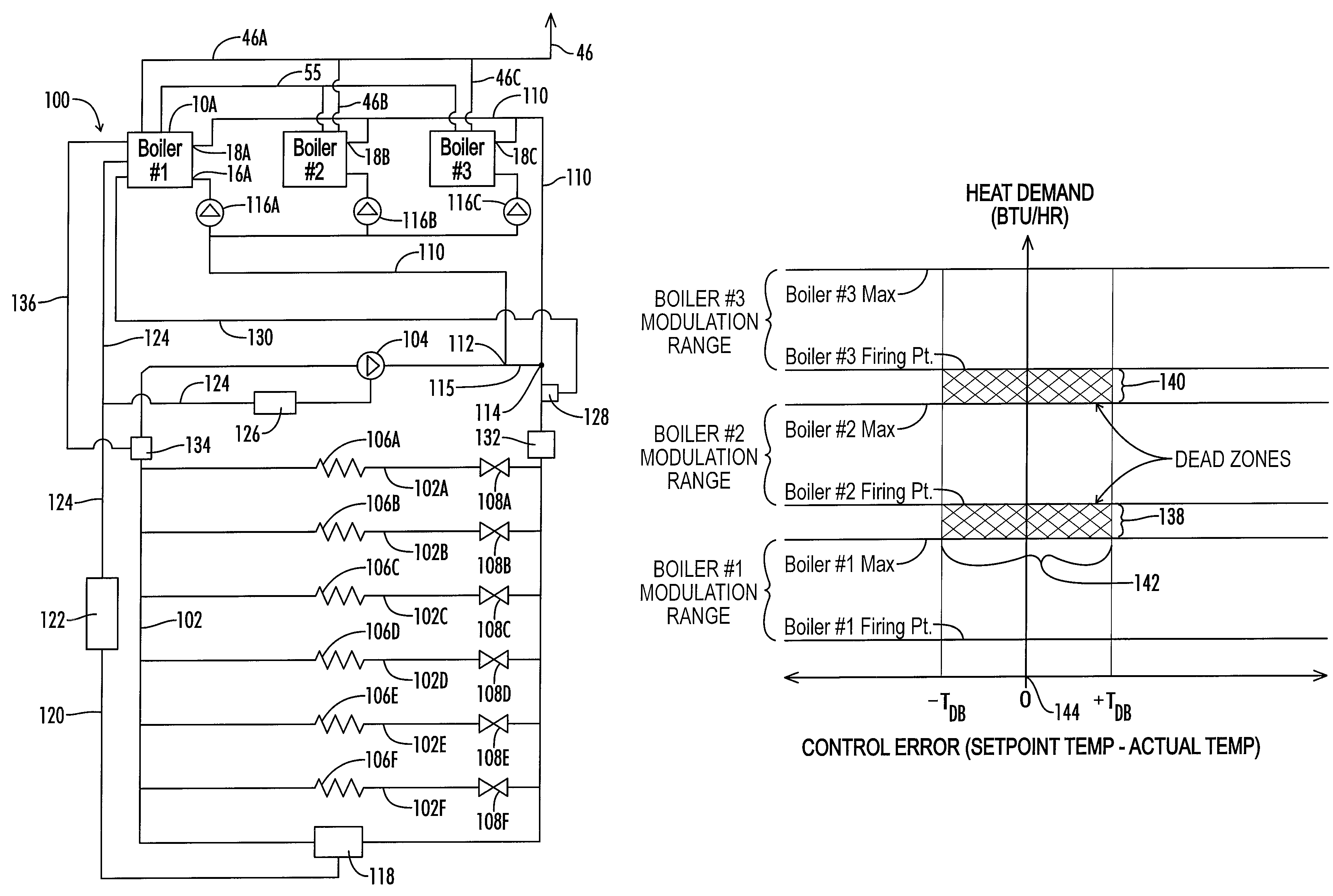
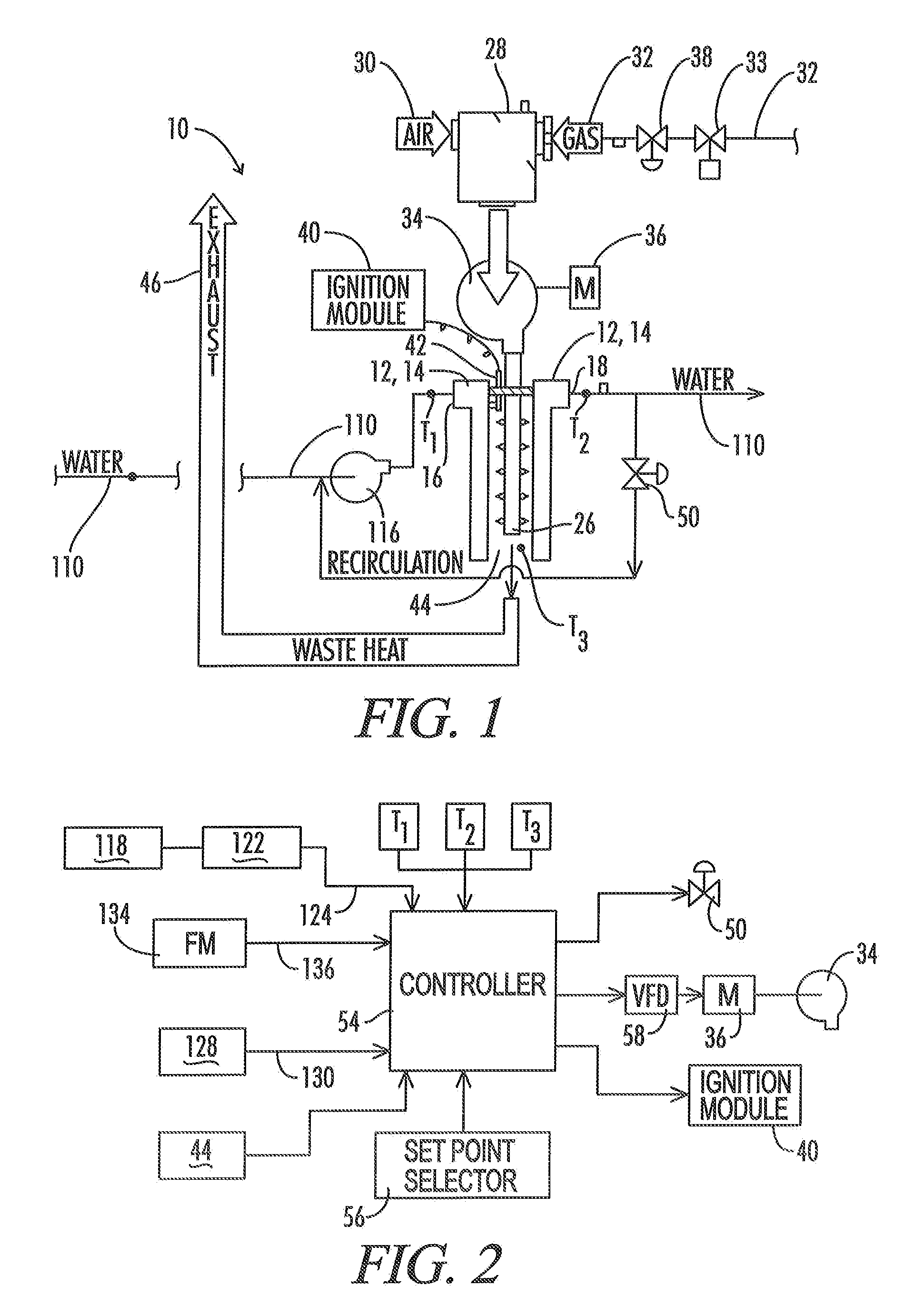
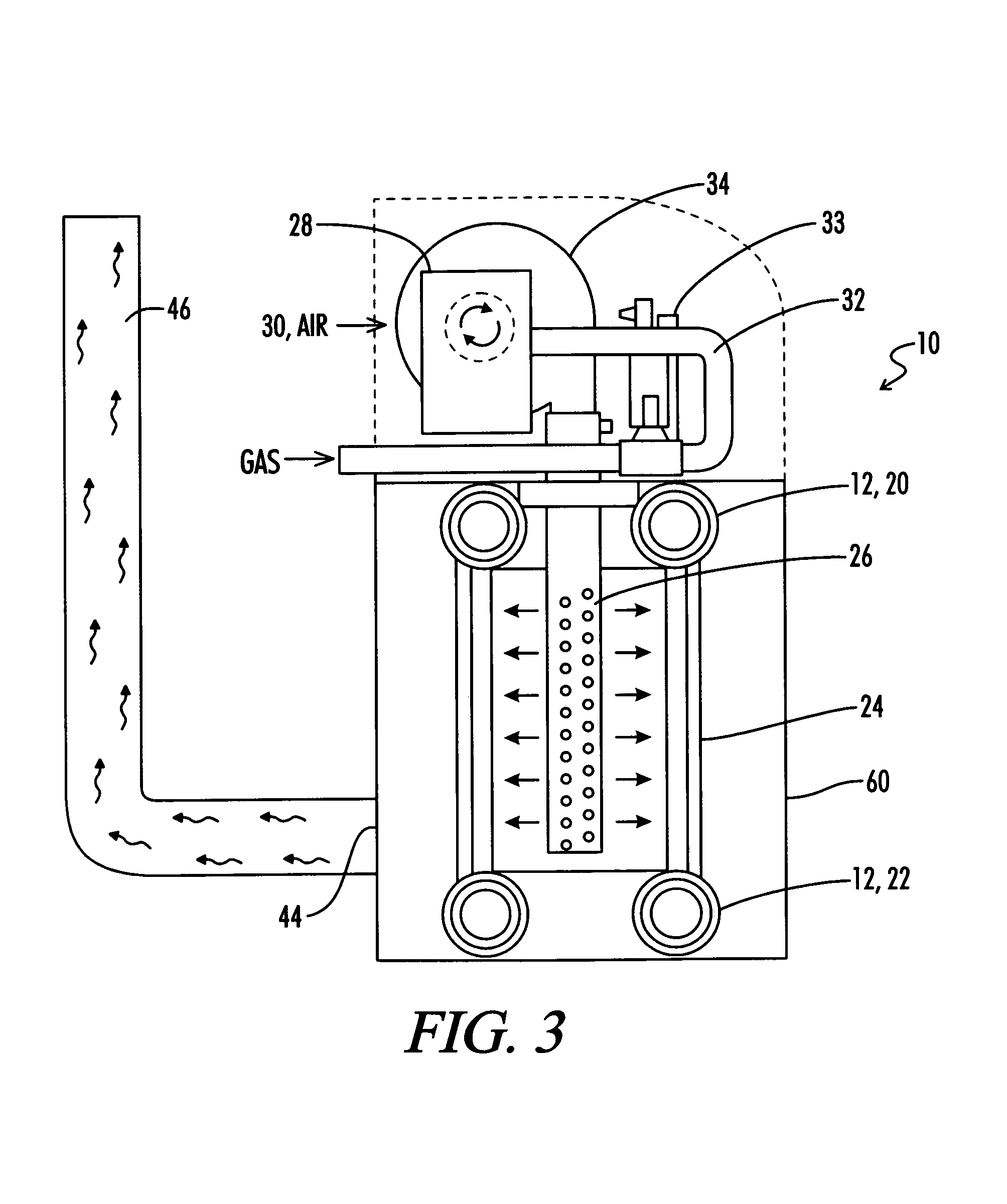
ActiveUS20080216771A1Shorten the overall cycleEarly detectionFluid heatersFuel supply regulationDeadbandHeating system
A control system is provided for a modulated heating system including a plurality of modulating water heaters, which may be modulating boilers. A deadband control scheme provides for reduced cycling of the modulating heater when total system heat demand falls between the maximum output of one heater and the sum of the maximum output of that one point and the minimum firing point of the next subsequent heater.
Owner:LOCHINVAR
Determining dead times in switched-mode DC-DC converters
ActiveUS7456620B2Improve efficiencyIncreased complexityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterDead time
Systems, methods, and apparatuses are disclosed for determining dead-times in switched-mode DC-DC converters with synchronous rectifiers or other complementary switching devices. In one embodiment, for example, a controller for a DC-DC converter determines dead-times for switching devices of a synchronous rectifier or other complementary switching device of the converter in which a dead-time is derived from an output voltage or current that is already sensed and used in the output regulation of the converter. In another embodiment, a controller is provided for controlling a switched-mode DC-DC converter comprising a pair of power switches. The controller comprises an input, a reference generator, a comparator, a compensator, a dead-time sub-controller, and a modulator. In another embodiment, the controller may adjust the dead-times during the operation of the converter to adjust periodically and / or in response to changes in operating conditions. In addition, methods of determining dead-times of control signals for a switched-mode DC-DC converter comprising a pair of power switches and of controlling a DC-DC converter are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Dead-time compensation algorithm for 3-phase inverter using svpwm
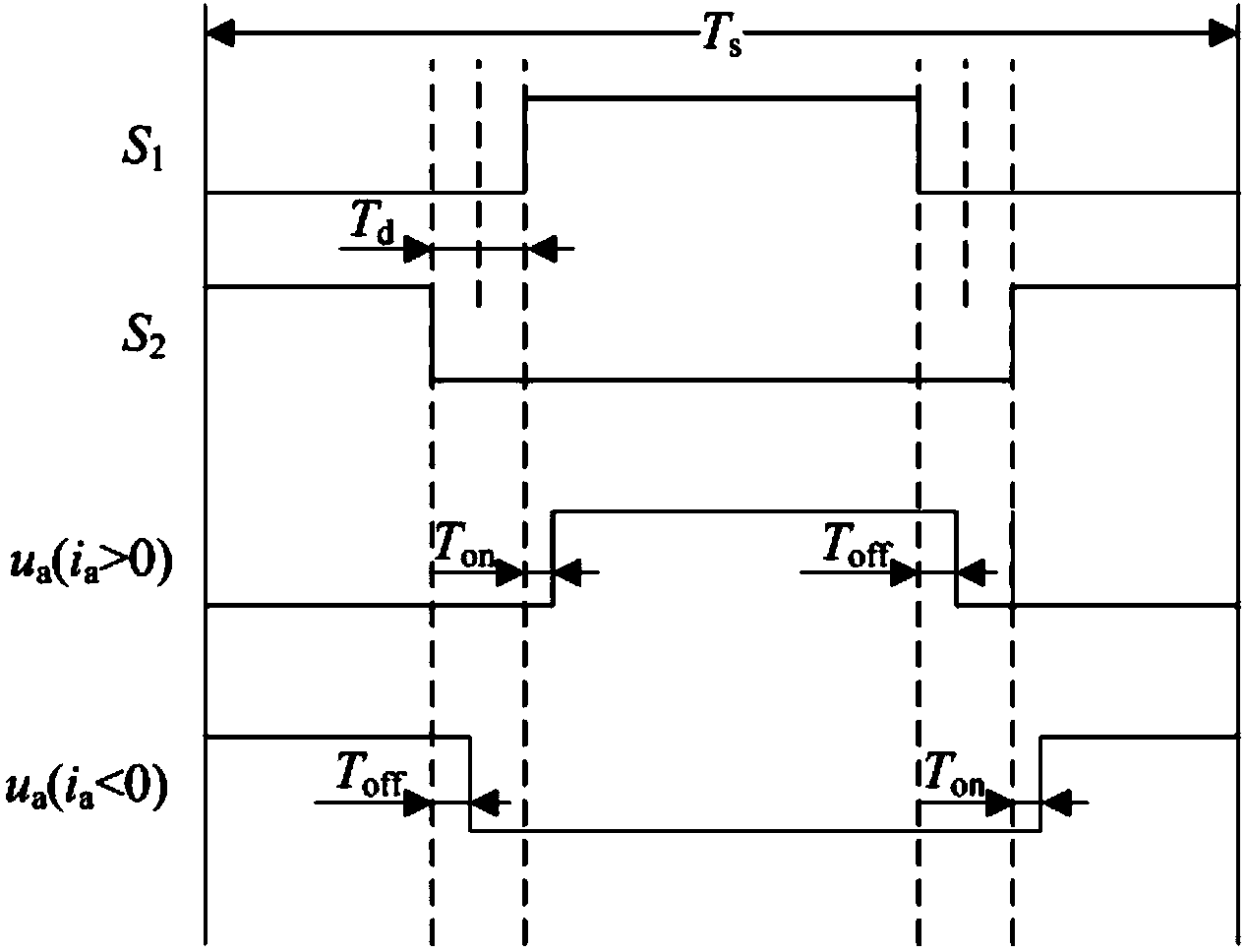
InactiveUS20130088905A1Minimizing distortion of output voltageReduce voltageDc-ac conversion without reversalPhase currentsSwitching signal
Disclosed is a dead-time compensation method of a 3-phase inverter using an SVPWM scheme. The dead-time compensation method includes generating a switching signal having dead-time with respect to the power semiconductor switches of the upper and lower arms in order to obtain a predetermined output through the SVPWM scheme, detecting medium phase current from each phase current output through the switching signal, determining polarity of the medium phase current, and generating a switching signal by calculating switching time in order to compensate for time to apply effective voltage according to the polarity of the medium phase current. Through the dead-time compensation method, the distortion of the output voltage and the reduction of voltage having a fundamental wave in the output voltage, which are caused by the dead-time, are minimized through the switching of compensating for the time to apply effective voltage based on the polarity of the load current.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Control system for modulating water heater
ActiveUS7506617B2Reduce temperature fluctuationsReact much more quicklyMechanical apparatusTemperatue controlDeadbandHeating system
A control system is provided for a modulated heating system including a plurality of modulating water heaters, which may be modulating boilers. A deadband control scheme provides for reduced cycling of the modulating heater when total system heat demand falls between the maximum output of one heater and the sum of the maximum output of that one point and the minimum firing point of the next subsequent heater.
Owner:LOCHINVAR
Compensation device and compensation method of current filtering and dead zone of permanent magnet synchronous motor
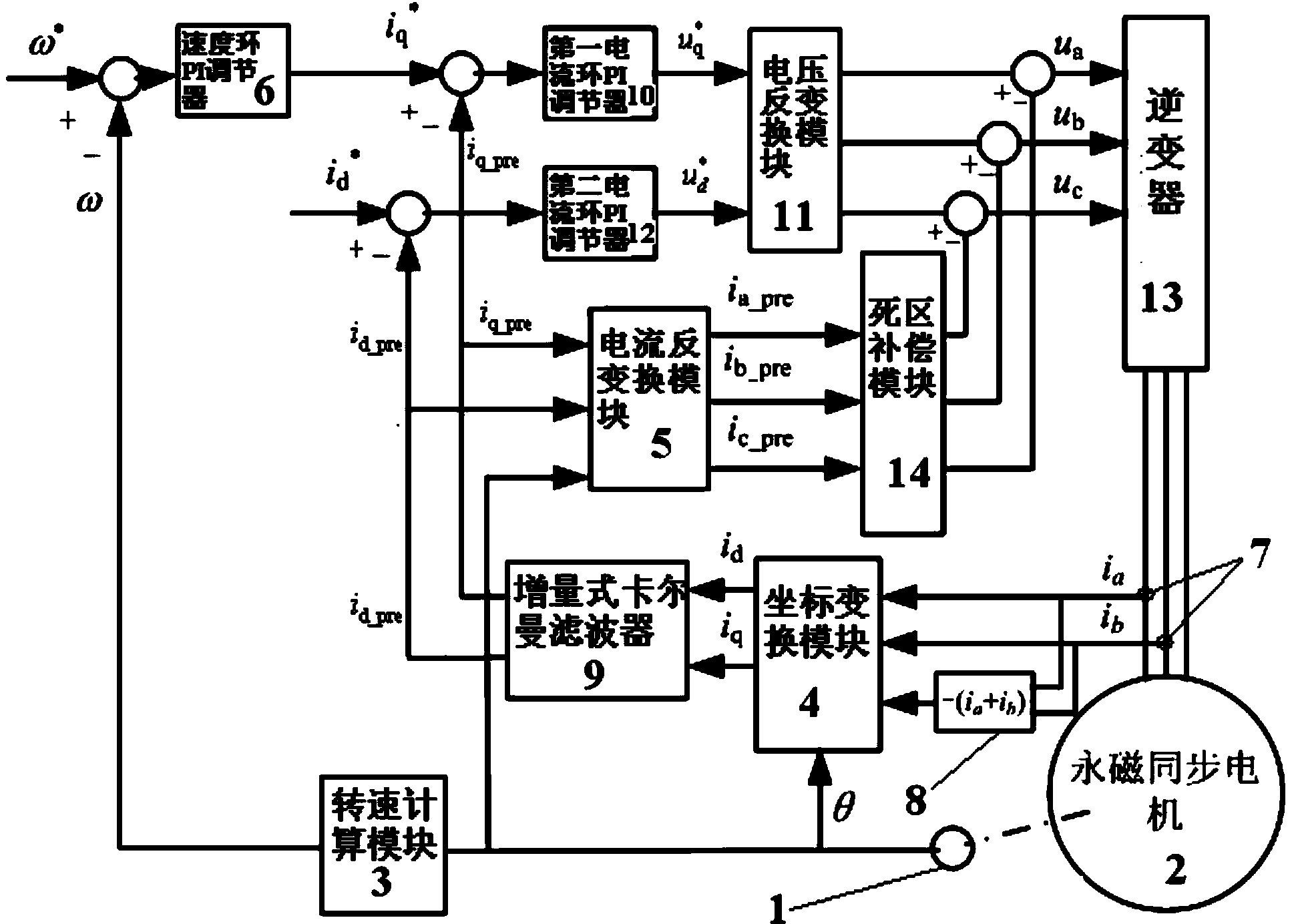
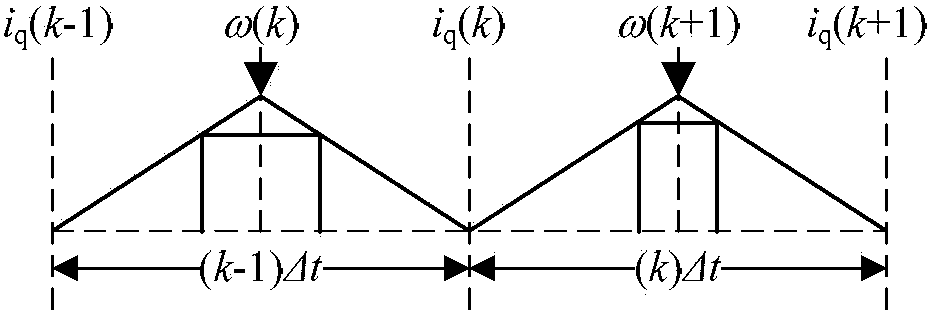
ActiveCN103684179AReduce voltage rippleAvoid the estimation processTorque ripple controlVector control systemsPhase currentsKaiman filter
The invention relates to a compensation device and a compensation method of current filtering and the dead zone of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The input end of a position sensor is connected with the output end of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the output end of the position sensor is connected with a rotating speed calculation module, a coordinate transformation module and a current inverse transformation module respectively. The output value of the rotating speed calculation module is used as the input of a speed ring PI adjuster. A current sensor inputs the detected two-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to the coordinate transformation module through a summation module, meanwhile the two-phase current is input into the coordinate transformation module, the coordinate transformation module transforms the coordinate of three-phase currents and then inputs the currents to an incremental kalman filter, and the output end of the incremental kalman filter is connected with the current inverse transformation module, a q-axis current ring and a d-axis current ring. The output end of a first current ring PI adjuster and the output end of a second current ring PI adjuster are connected with an inverter through a voltage inverse transformation module, the output end of the current inverse transformation module is connected with the input end of a dead zone compensation module, the output end of the dead zone compensation module is connected with the input end of the inverter, and the output end of the inverter is connected with the input end of the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
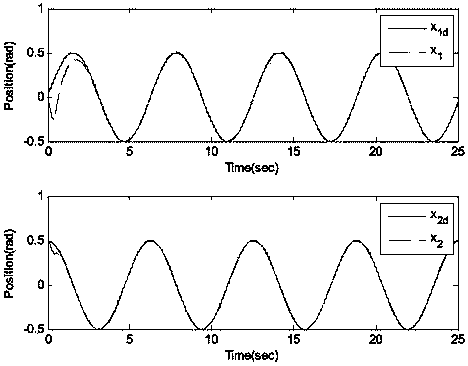
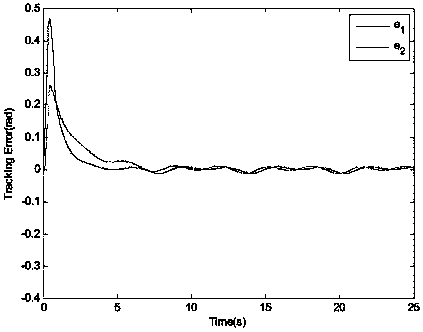
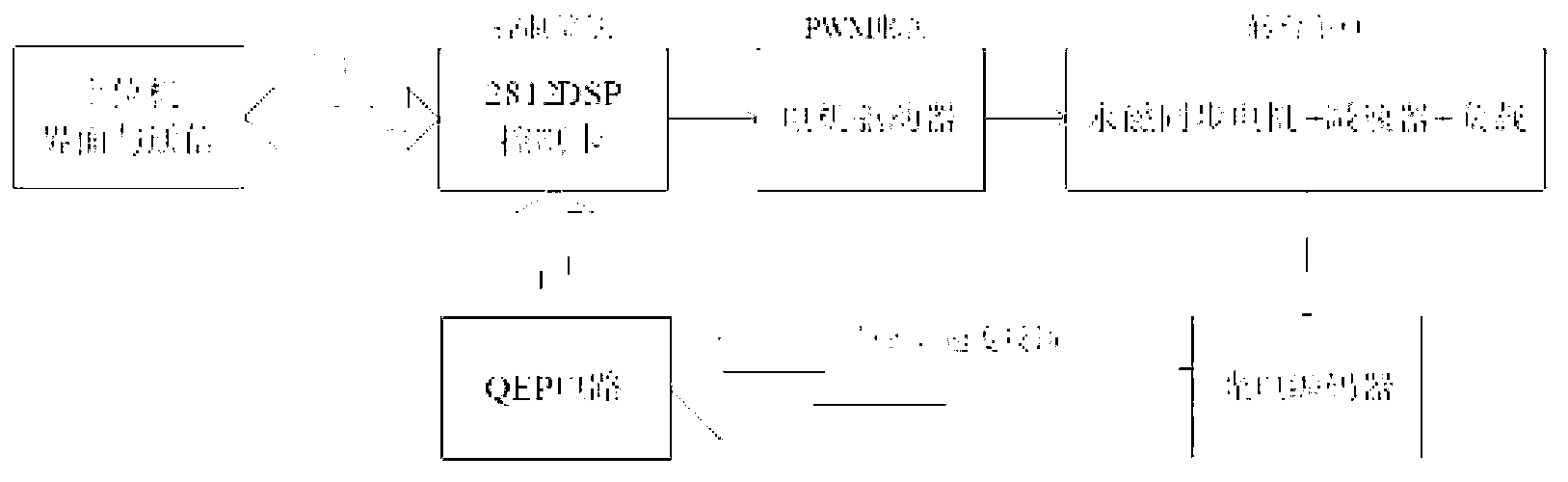
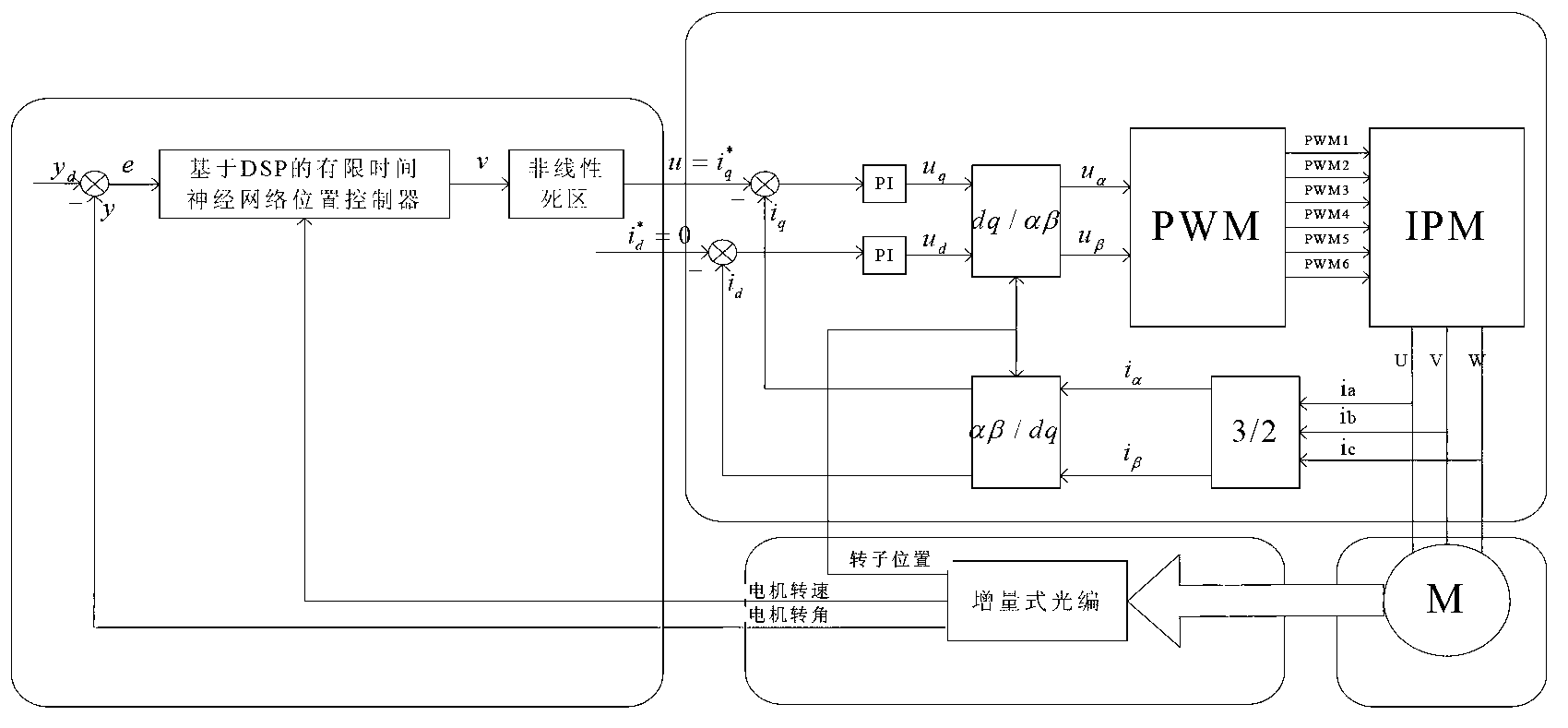
Limit time cooperative control method of mechanical arm servo system
InactiveCN104216284AAvoid Dead Zone Additional Inverse CompensationAvoid High Frequency ChatteringAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime-variant system
A limit time cooperative control method of a mechanical arm servo system includes: building the dynamic model of the mechanical arm servo system, and initiating the system state, sampling time and related control parameters; approximating the nonlinear input dead zone linearity in the system into a simple time-varying system according to the differential mean value theorem, and deriving a mechanical arm servo system model with an unknown dead zone; calculating the tracking error, the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface and the first derivative of a control system; selecting a neural network approximation unknown function on the basis of the mechanical arm servo system model with the unknown dead zone, designing a neural network limit time cooperative controller according to the system tracking error and the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface, and updating a neural network weight matrix. By the method, additional inverted compensation of a nonlinear dead zone can be avoided, sliding model high-frequency buffeting is reduced, and limit time fast tracking of the mechanical arm servo system is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
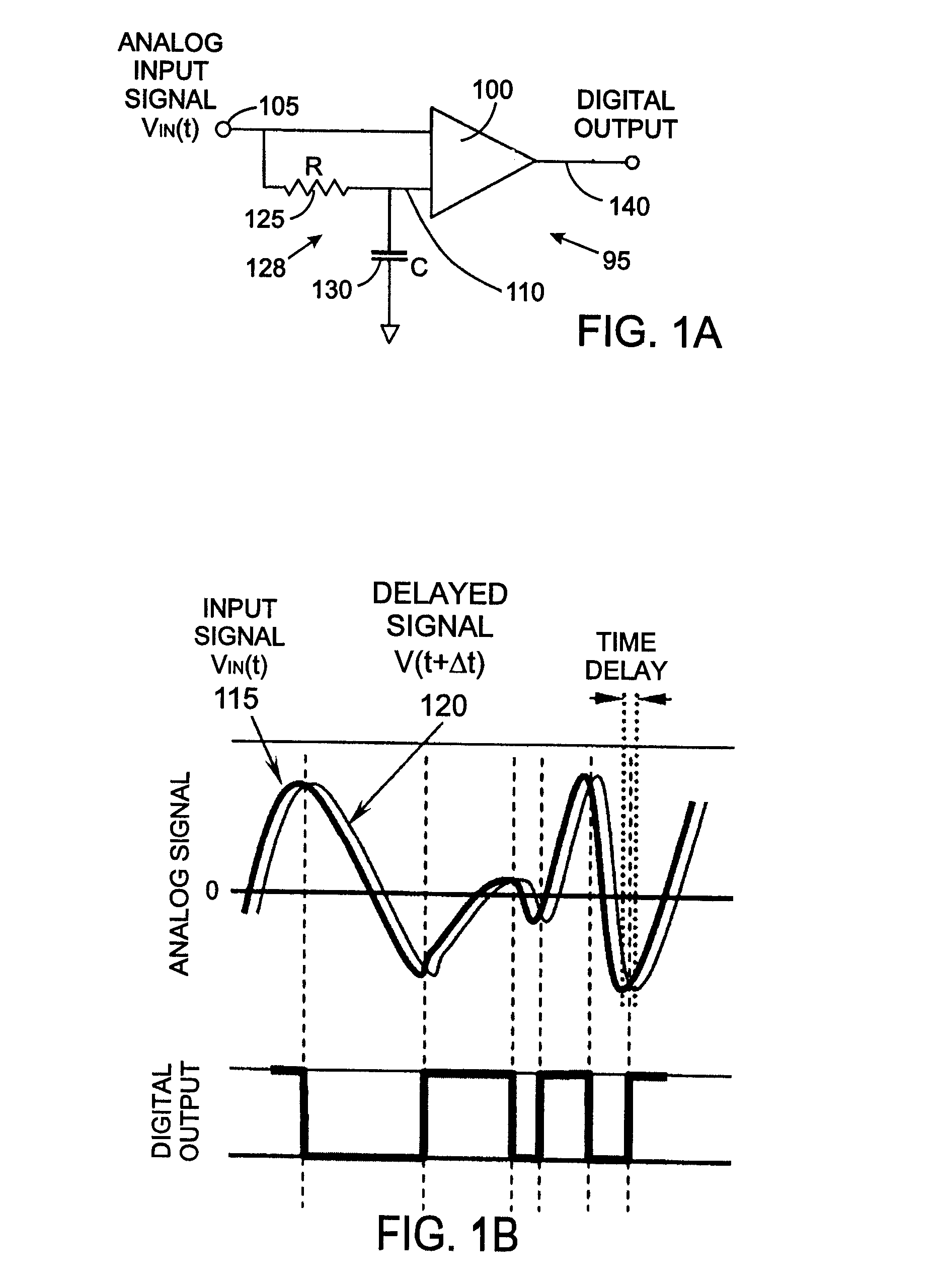
Analog signal transition detector
InactiveUS20070288183A1ElectrocardiographyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHysteresisAnalog signal
An apparatus configured to detect transitions between relatively rising and falling amplitudes of an input signal Vin(t) arriving at a input node comprises a comparator having a first input, a second input, and an output for providing a two state output signal Vout(t) wherein state changes in the output signal Vout(t) correspond to the relatively rising amplitude of the input signal Vin(t) and the relatively falling amplitude of the input signal Vin(t). A delay circuit provides a shifted signal Vin(t+Δt) to the second input of the comparator, and a hysteresis circuit provides hysteretic deadband appended input signal Vin+ΔV to the first input of the comparator.
Owner:KENERGY INC
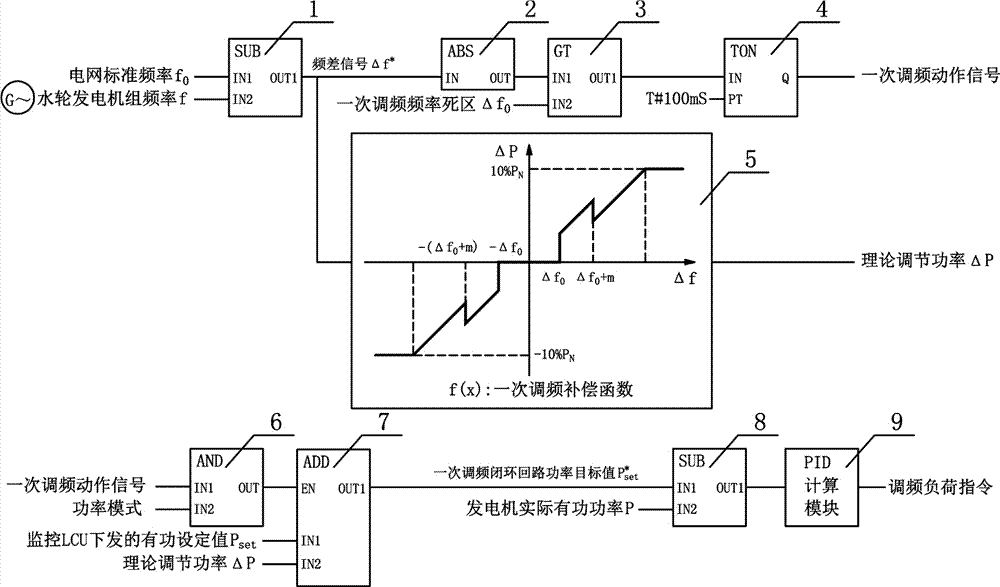
Primary frequency modulation electric quantity compensation refined control method and apparatus under giant hydroelectric generating set power mode
ActiveCN107453375AFulfil requirementsIncrease the amount of power actionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionPower qualityClosed loop
The invention discloses a primary frequency modulation electric quantity compensation refined control method and apparatus under a giant hydroelectric generating set power mode. The control method comprises the steps of obtaining a frequency difference signal between a power grid standard frequency and an actual power grid frequency obtained in real time; judging whether the frequency difference signal is outside a primary frequency modulation frequency dead zone or not, if the frequency difference signal exceeds the primary frequency modulation frequency dead zone, delaying for 0.1second and then outputting a primary frequency modulation action signal; using the frequency difference signal, and enabling a giant hydroelectric generating set speed regulator to be in a power mode; if the actual power grid frequency obtained in real time exceeds the primary frequency modulation frequency dead zone and is within in a range of a superposition value between the primary frequency modulation frequency dead zone and power dead zone equivalent power, performing superposition between a frequency compensation coefficient and the corresponding function of a frequency modulation load according to the frequency difference signal to obtain corresponding theoretical frequency modulation power; obtaining corresponding theoretical regulation power according to the frequency difference signal and the corresponding function of the frequency modulation load; and forming a PID closed loop by a new active given value and the actual power value of the giant hydroelectric generating set, and outputting a corresponding frequency modulation load instruction. By virtue of the primary frequency modulation electric quantity compensation refined control method and apparatus, the primary frequency modulation contribution rate of the giant hydroelectric generating set can be accurately controlled, the primary frequency modulation percent of pass is improved, and the electric energy quality can be improved.
Owner:CHINA YANGTZE POWER
Rotary-table servo system neural network control method
ActiveCN103197562AAvoid complex calculationsImprove algorithm efficiencyAdaptive controlDynamic modelsNetwork approach
A rotary-table servo system neural network control method comprises (1) building a mechanical dynamic model of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotary-table servo system, and initializing the system state, sampling time and relative control parameters; (2) according to the differential mean value theorem, enabling a non-linear input dead zone in the system to linearly approximate to a simple time-varying system, avoiding complex calculation of dead-zone inverse compensation, and finally inferring a rotary-table servo system model provided with an unknown dead zone; (3) at each sampling moment, calculating and controlling a system tracking error, a fast terminal sliding mode surface and a first-order derivative of the system; (4) based on the rotary-table servo system model provided with the unknown dead zone, selecting a neural network approaching unknown trend, designing an adaptive robust finite-time neural network controller according to the system tracking error, the fast terminal sliding mode surface and the first-order derivative of the system, and updating a neural network weight matrix; and (5) entering the next sampling moment, and repetitively executing the steps from (3) to (5).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device
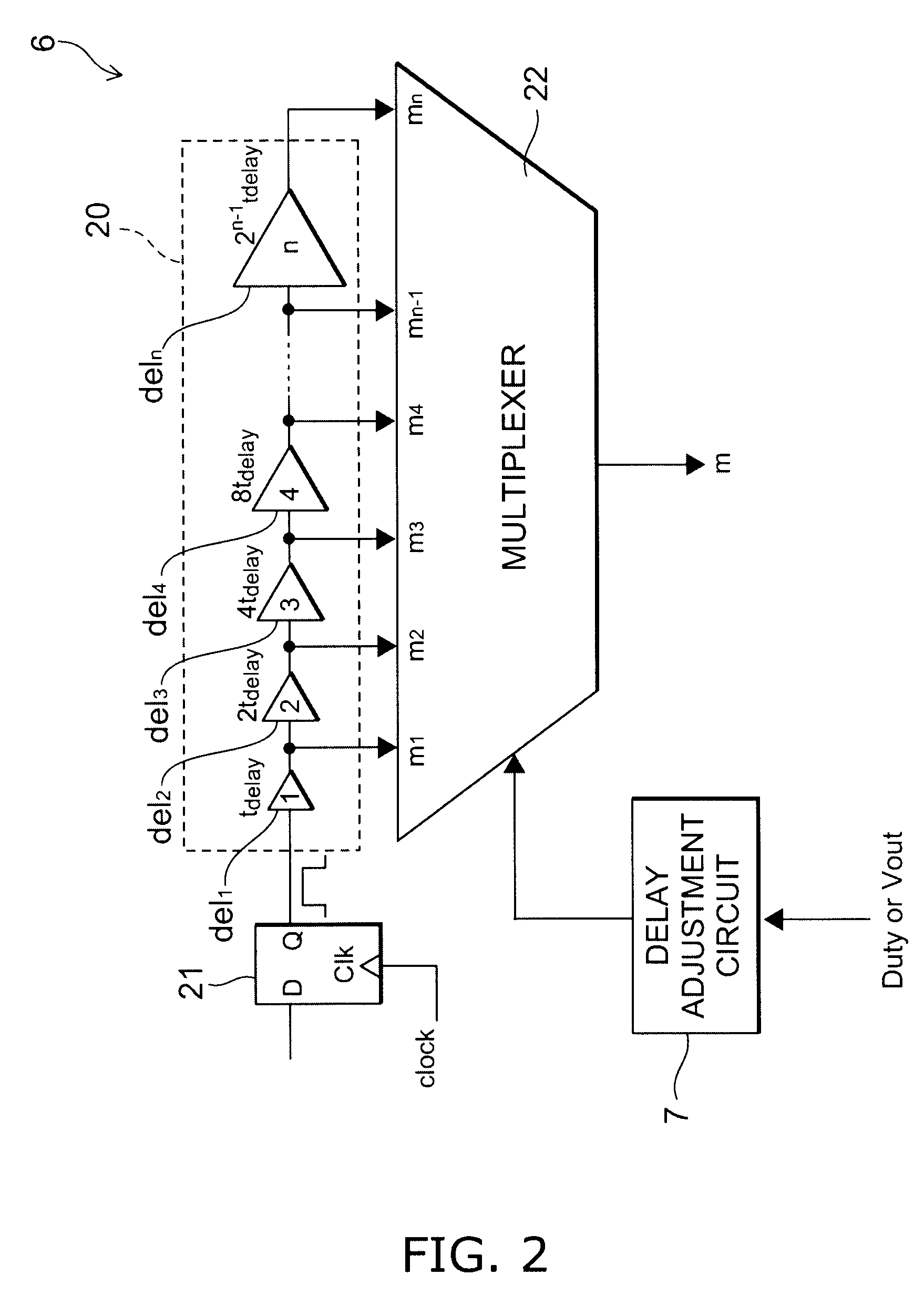
A semiconductor device includes: a digital control circuit configured to supply two semiconductor switching elements connected in series in a switching power supply circuit with a pulse signal for turning on / off the semiconductor switching elements; and a dead time setting circuit configured to set a dead time in which the two semiconductor switching elements are both turned off. The dead time setting circuit includes: a delay generation circuit including a plurality of delay elements connected in series and having mutually different delay values; and a delay adjustment circuit configured to adjust the delay values of the delay generation circuit so that a setting value of the dead time is determined on basis of correlation between the dead time and the duty cycle of the pulse signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Frequency control strategy for multiple DC (Direct Current) send-out island power grid
ActiveCN103633638AEfficient frequency control strategyEfficient frequency control meansDc network circuit arrangementsFrequency stabilizationIslanding
The invention relates to a frequency control strategy for a multiple DC (Direct Current) send-out island power grid. The frequency control strategy comprises the following steps of: 1, for the multiple DC send-out island power grid of which the system frequency is risen or reduced due to a fault, firstly, starting a first defense line and utilizing a DC system frequency limiting function to control the system frequency; 2, when the frequency exceeds a frequency operated dead zone of a dynamo governor, starting another measure in the first defense line, i.e. carrying out primary frequency modulation control by the dynamo governor; 3, when the frequency exceeds a range of 49.0 to 50.6Hz, starting a second defense line, i.e. cutting off a generator or a load according to a control strategy; 4, when the frequency exceeds 50.6Hz, starting a third defense line and carrying out high-frequency cut-off protection to cut off a generating set; 5, when the frequency exceeds 51.5Hz, enabling the generator to execute the overspeed protection action and cutting off the generating set. The frequency control strategy can be used as an actual control strategy for stabilizing the frequency of a large-scale multiple DC send-out island system to be applied to production and operation of the power grid and also can be applied to emulation calculation of related research.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
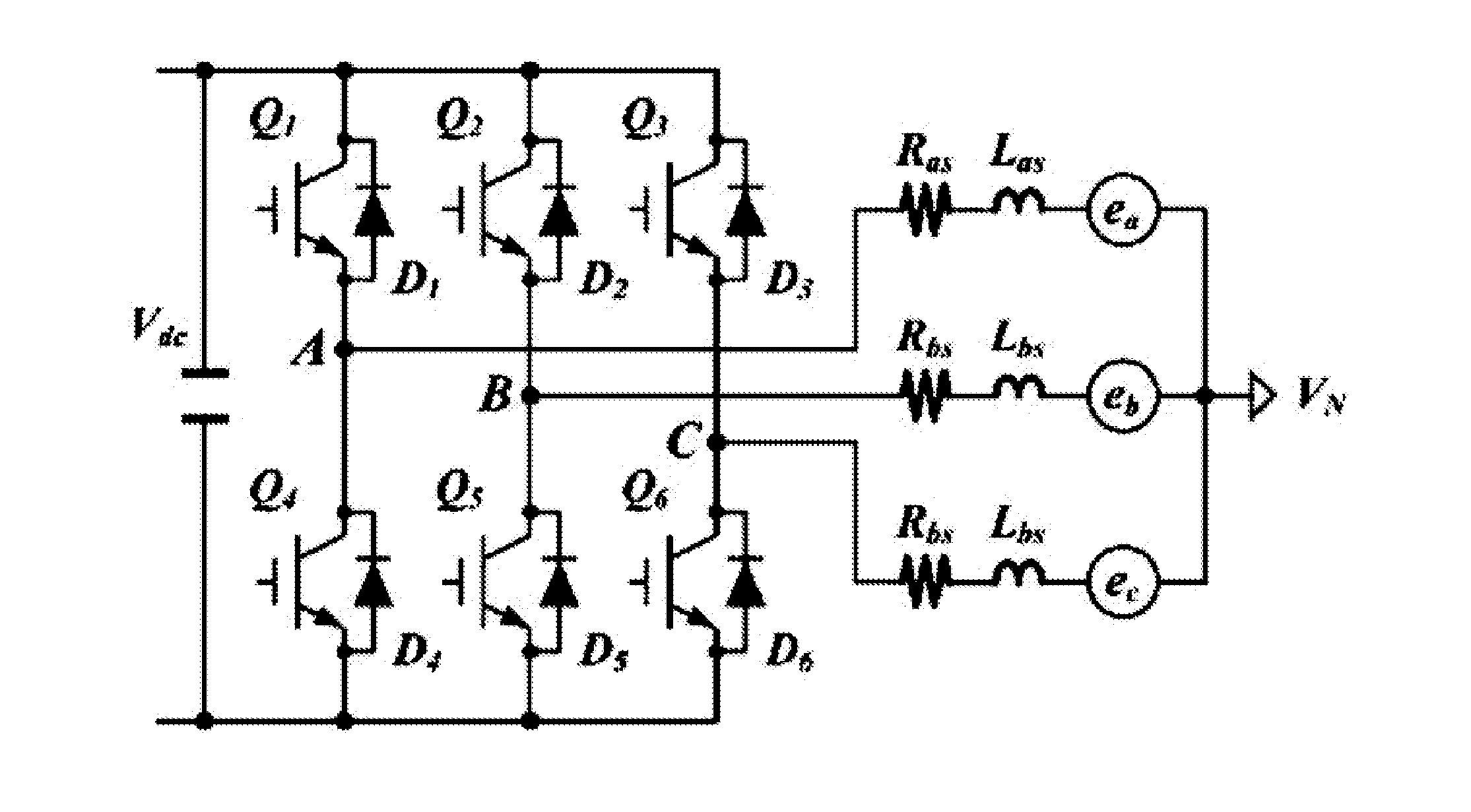
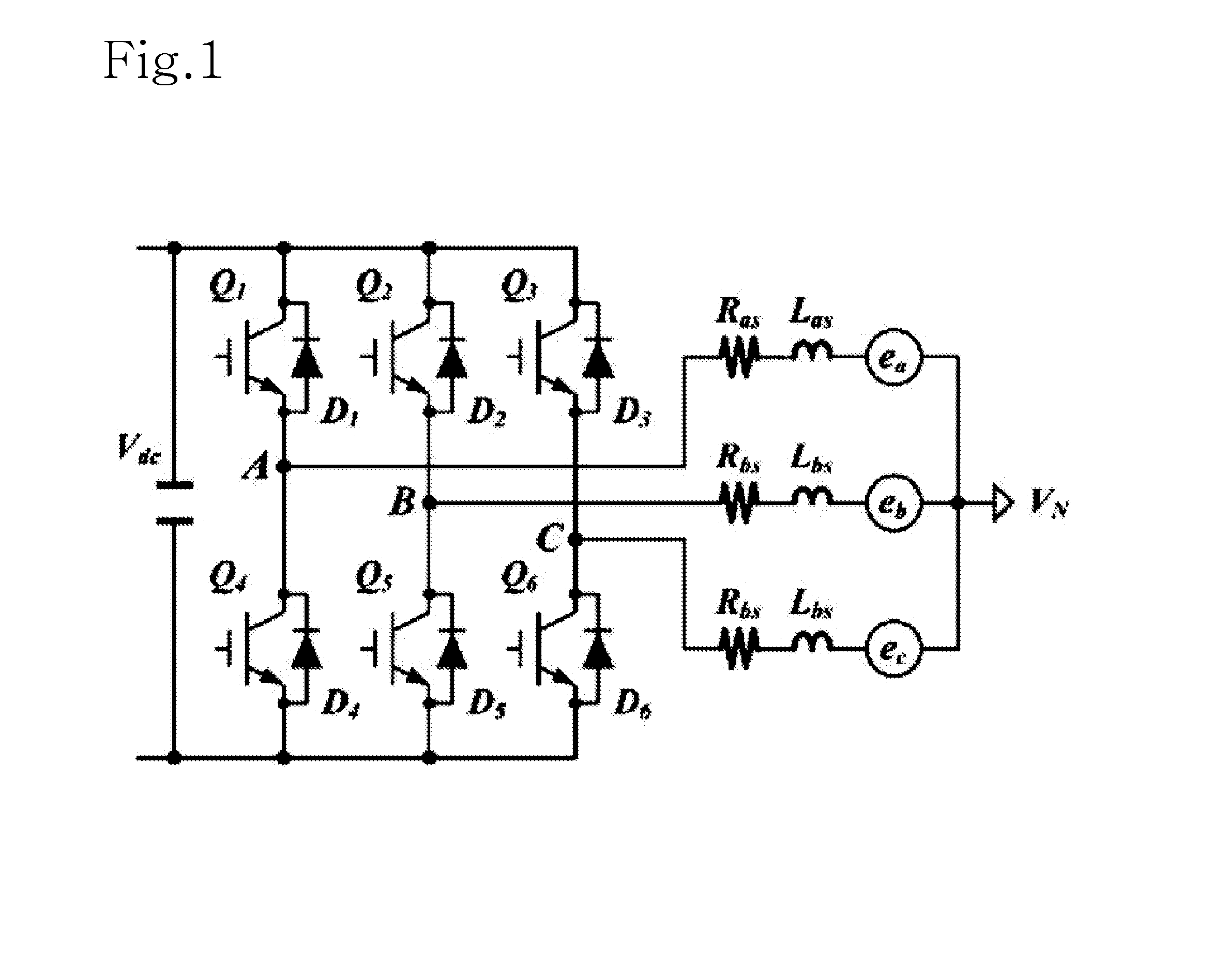
Three-level inverter dead time compensation control method
InactiveCN103236798AImproved output current waveformActual output line voltage risesAc-dc conversionThree levelVoltage vector
A three-level inverter dead time compensation control method is used for compensating the decrease of system performance caused by dead time. According to the topological structure of a three-phase three-level PWM (pulse width modulation) inverter, the method first sets corresponding dead time and determines the on-off delays of power elements in the inverter; the method then considers the tube voltage drops of the power transistors of the inverter and the tube voltage drops of clamping diodes of the inverter and calculates the common voltage expression of the output neutral point of the inverter; afterwards, according to the sector with three-phase current value and a reference voltage vector, the method determines the relational coefficient between voltage error caused by the tube voltage drops of the power transistors, the tube voltage drops of the clamping diodes and the on-off delays of the power transistors and current, and thereby the total dead time compensation time of each phase of the three-level PWM inverter is worked out. The method takes the dead time, the on-off delays of the power elements and the tube voltage drops into full consideration, solves the problem of voltage and current distortion caused by the dead time effect in the three-level inverter, and enhances system performance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
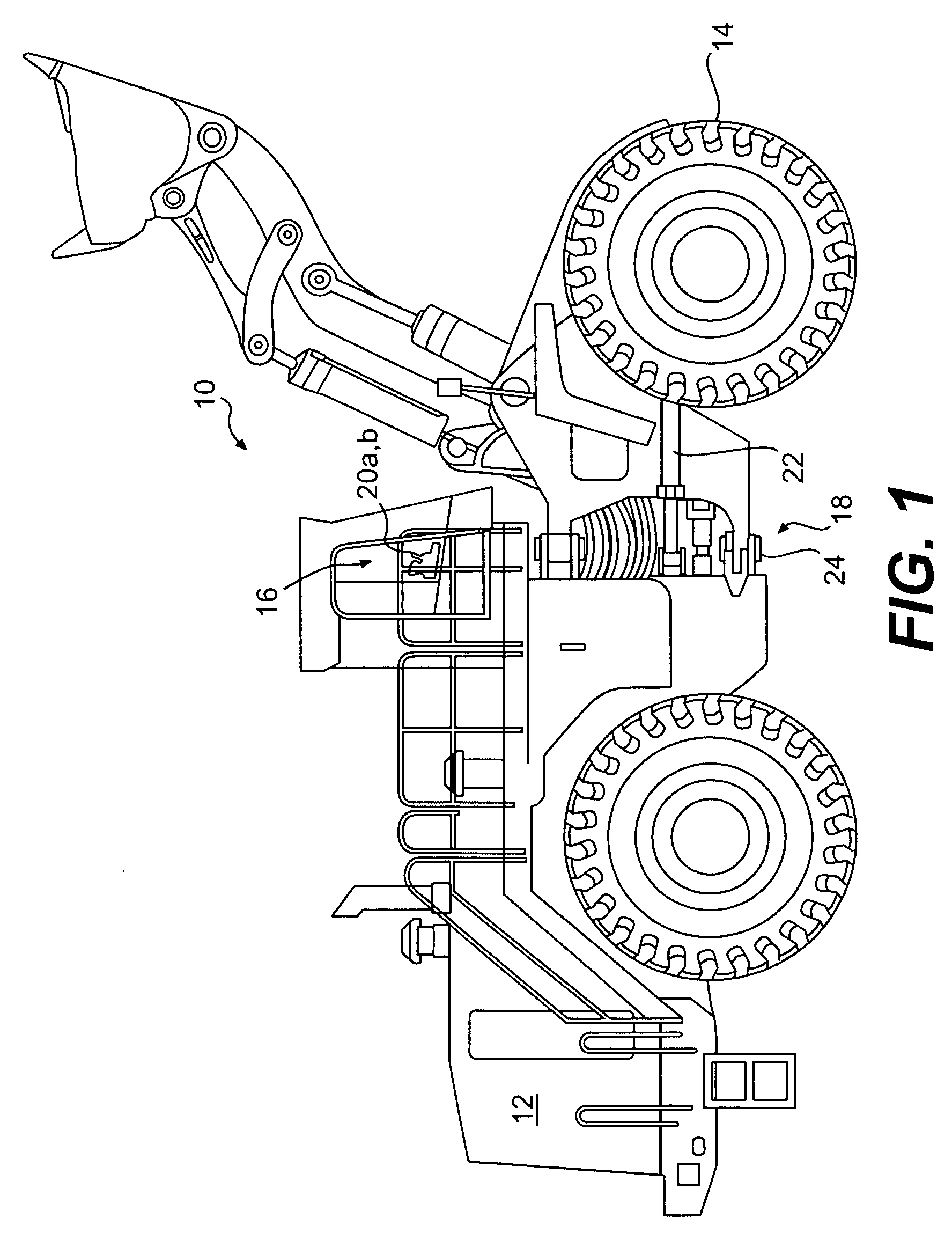
Steering system having multiple strategies and variable deadzone
A steering system for a machine having at least one steerable traction device is disclosed. The steering system may have a steering actuator operatively connected to the at least one steerable traction device, and a travel speed sensor configured to generate a signal indicative of a travel speed of the machine. The steering mechanism may also have an operator input device having a deadzone. The deadzone may vary in response to the signal. The steering system may also have a controller in communication with the steering actuator, the operator input device, and the travel speed sensor. The controller may be configured to affect operation of the steering actuator in response to operation of the operator input device only when the operation of the operator input device deviates from the deadzone.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
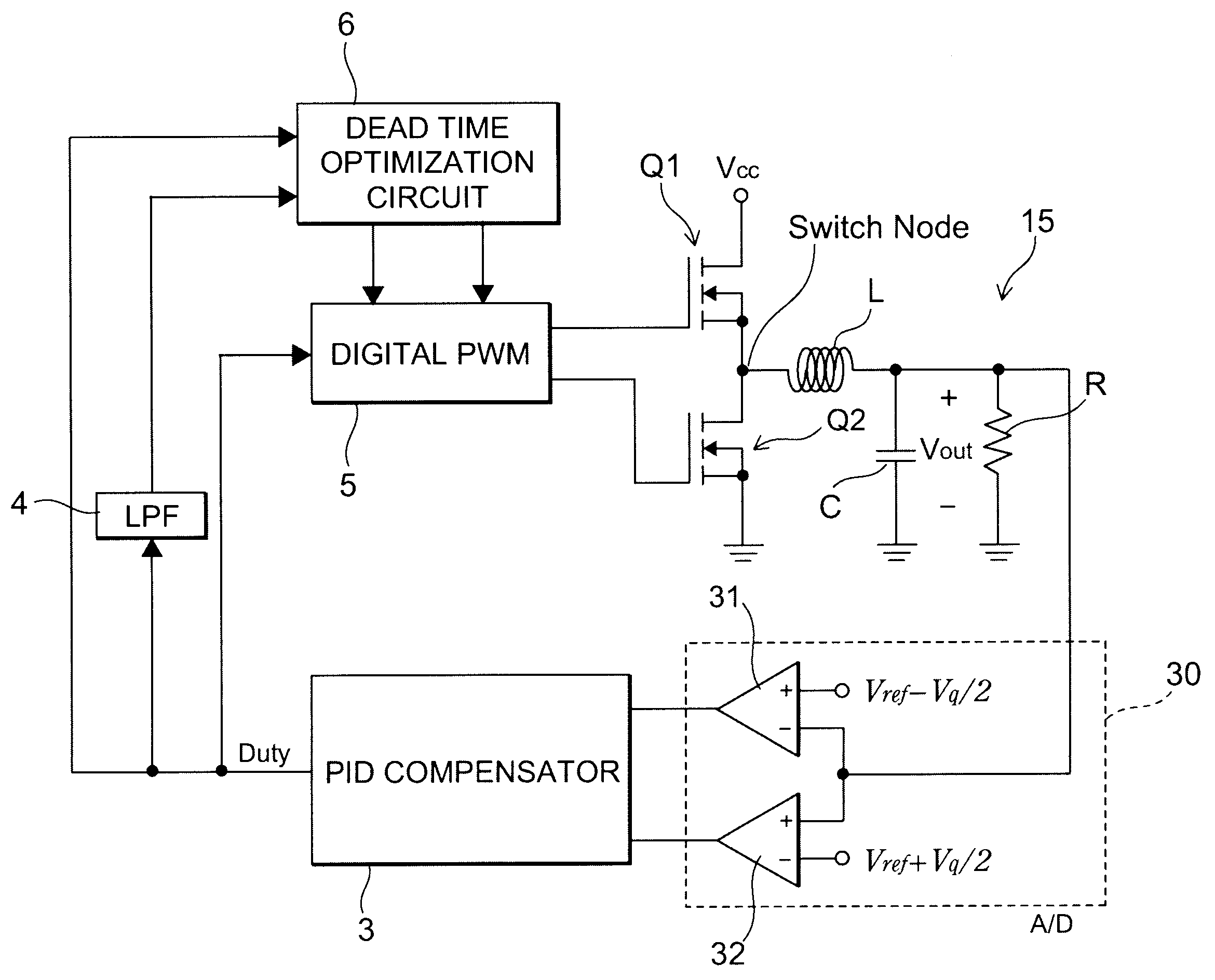
Control circuit and method for a digital synchronous switching converter
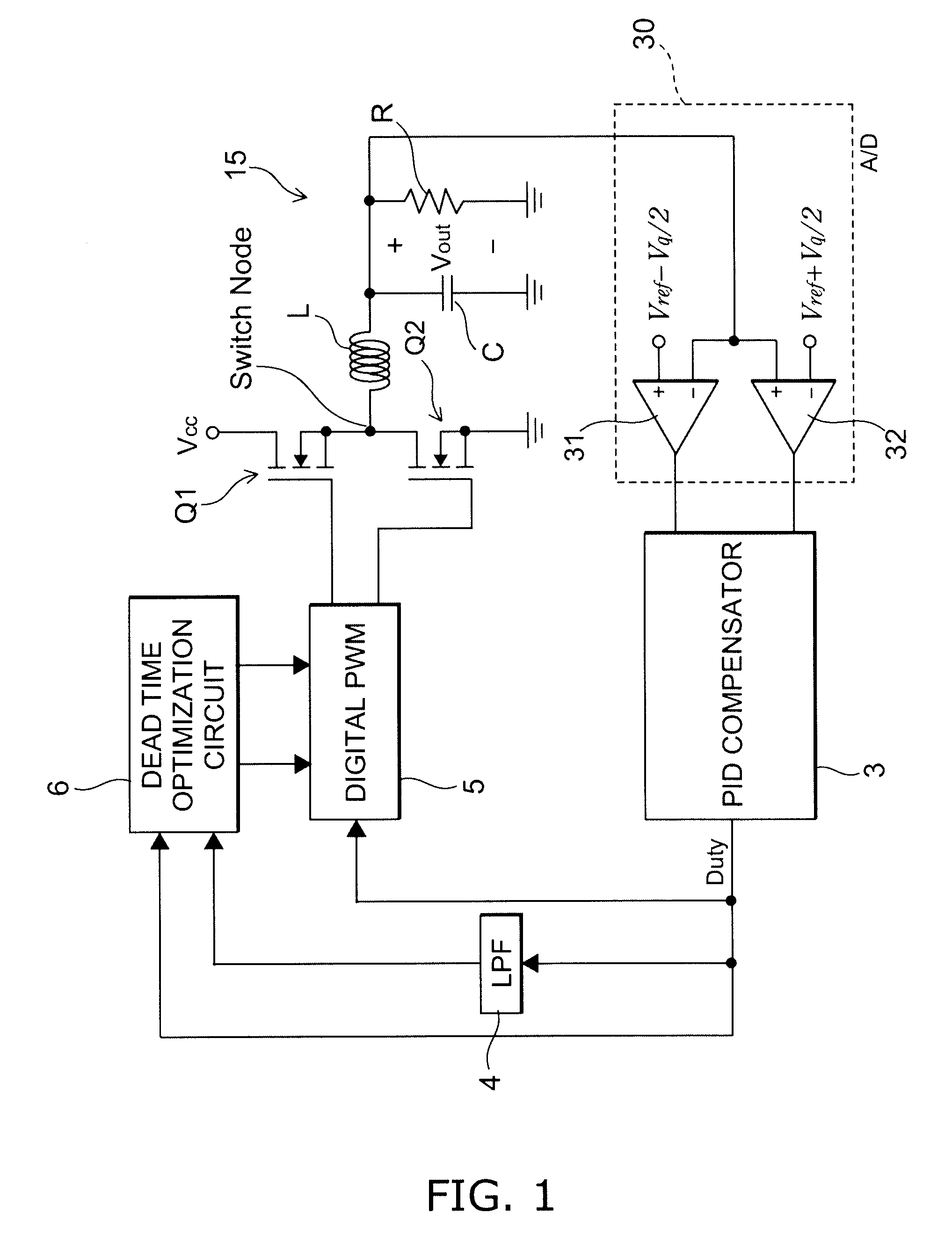
ActiveUS20100156376A1Improve efficiencyElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsStable stateDead time
In addition to an output voltage control loop, a dead-time optimization loop is provided for a digital synchronous switching converter to dynamically adjust the dead-time for the power switches of the converter. It is extracted a minimal feedback signal at a steady state while the output voltage remains under a specification, and a maximal efficiency of the digital synchronous switching converter is thus obtained.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
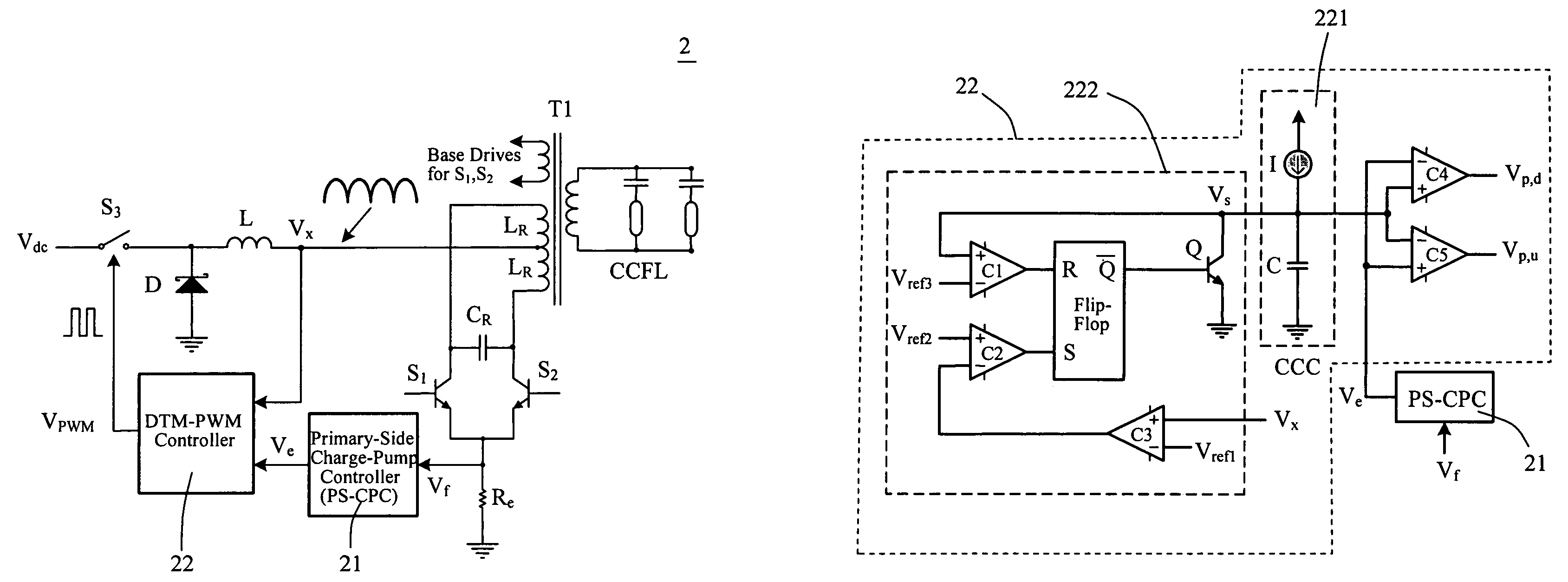
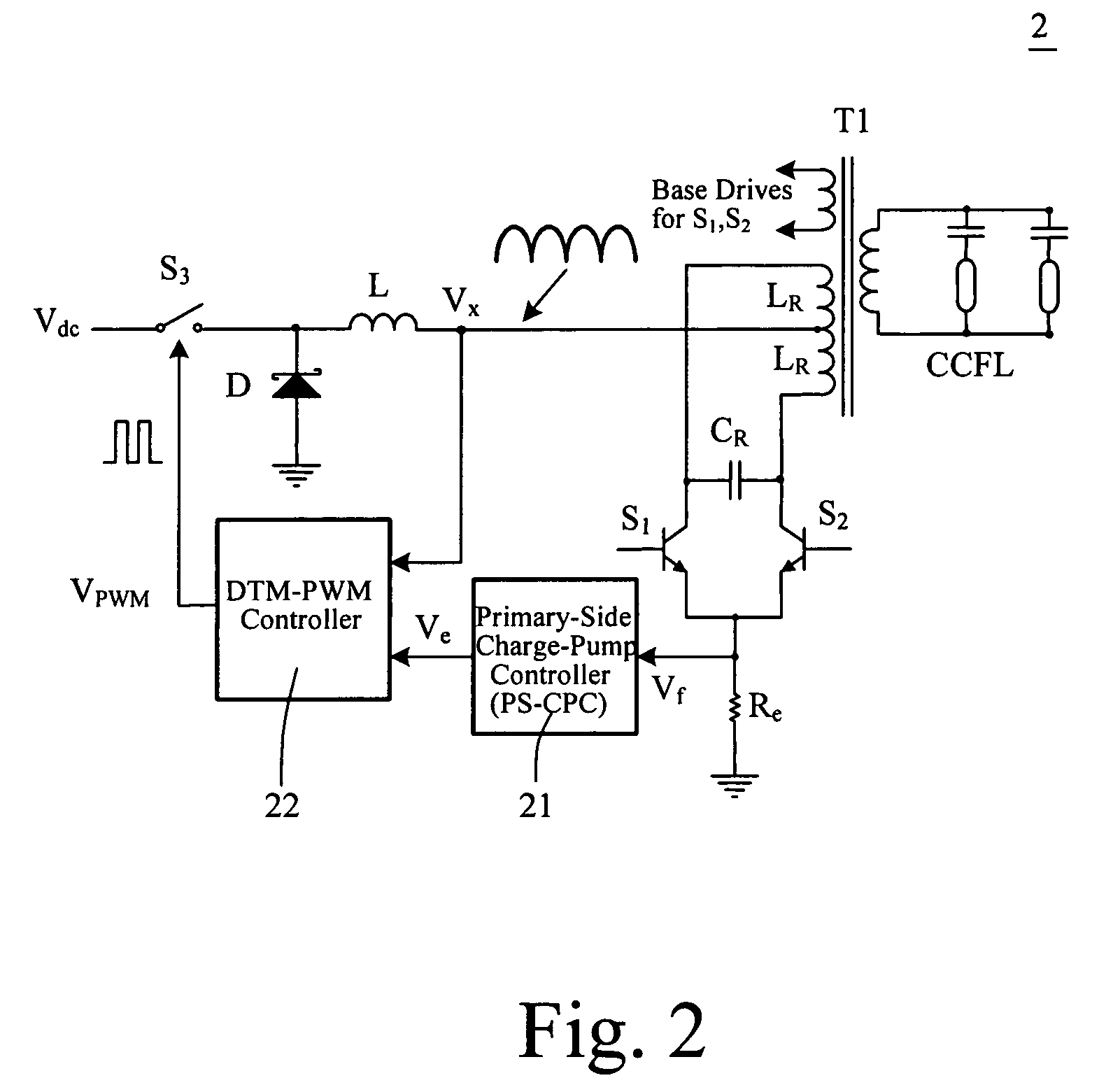
Dead-time-modulated synchronous PWM controller for dimmable CCFL royer inverter
InactiveUS7064497B1Electric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageSelf-oscillationFrequency modulation
A Synchronous PWM controller realized by dead-time modulation is provided for applying to the self-oscillation Royer inverter. The proposed dead-time-modulated PWM (DTM-PWM) controller is composed of a monostable circuit and a constant-current charger (CCC). The presented switching period for the buck regulation consists of a referred sawtooth having a constant-period and a dead-time. The synchronizing strategy is conducted by modulating the dead-time according to the resonant frequency of the Royer inverter. Two kinds of the control strategies in DTM-PWM controller are explored including the down-going and up-going error voltage controls. A DTM-PWM controlled dimmable Royer inverter with two-CCFL having primary-side control is designed and realized. Two kinds of the existing controllers for the Royer inverter are also experimented and compared with the proposed DTM-PWM controller. The results of the analysis and the theoretical prediction are verified with the experiments.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com