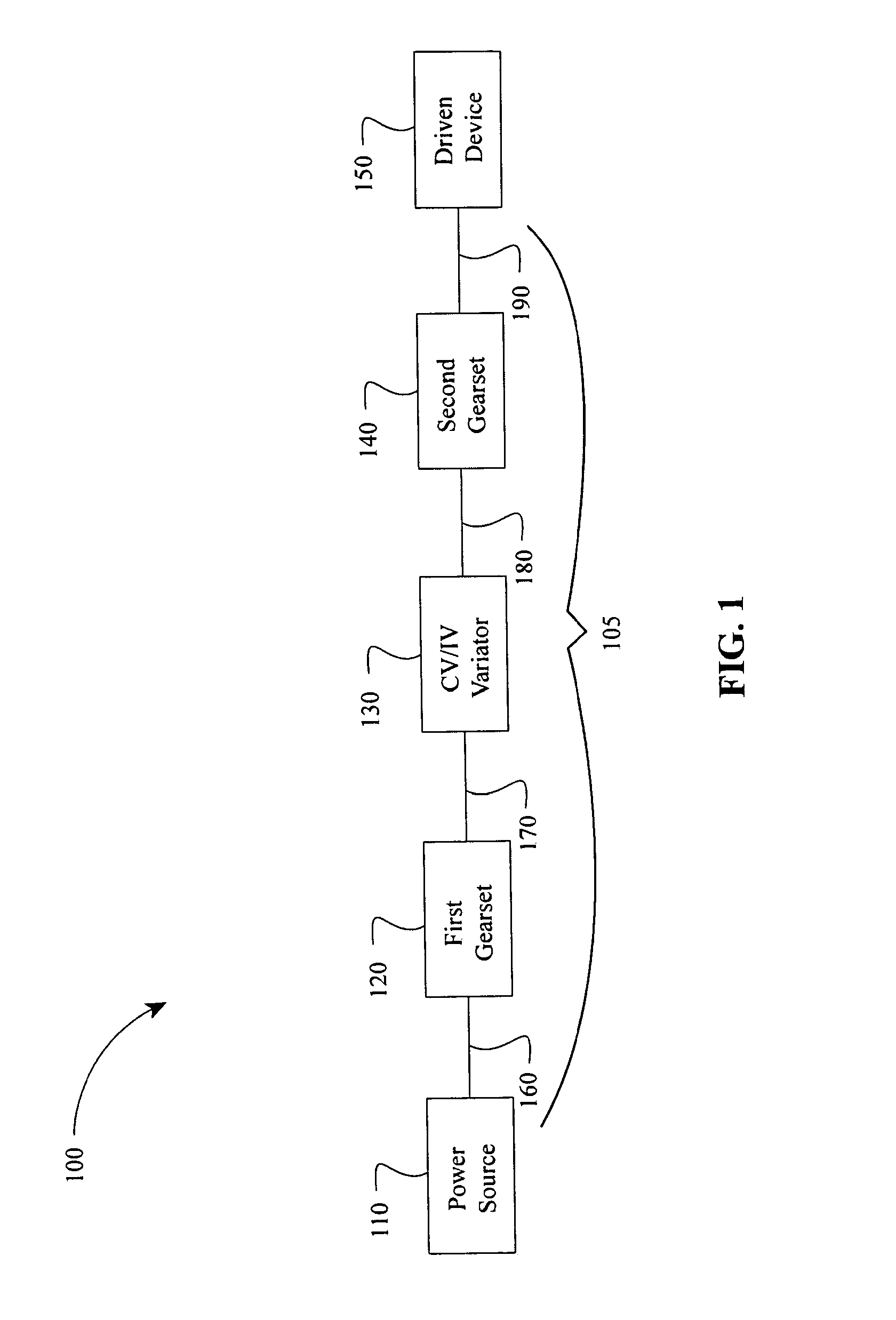
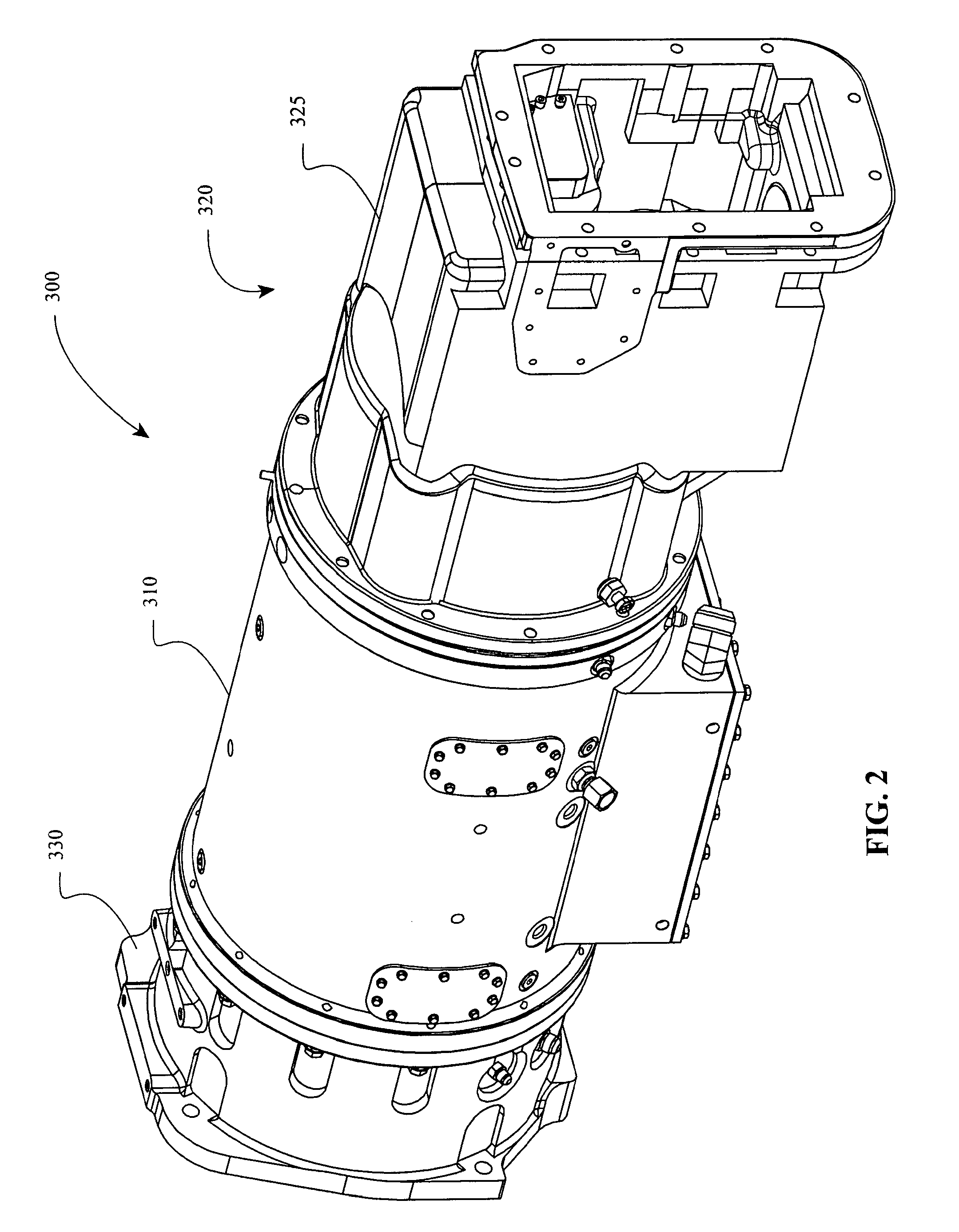
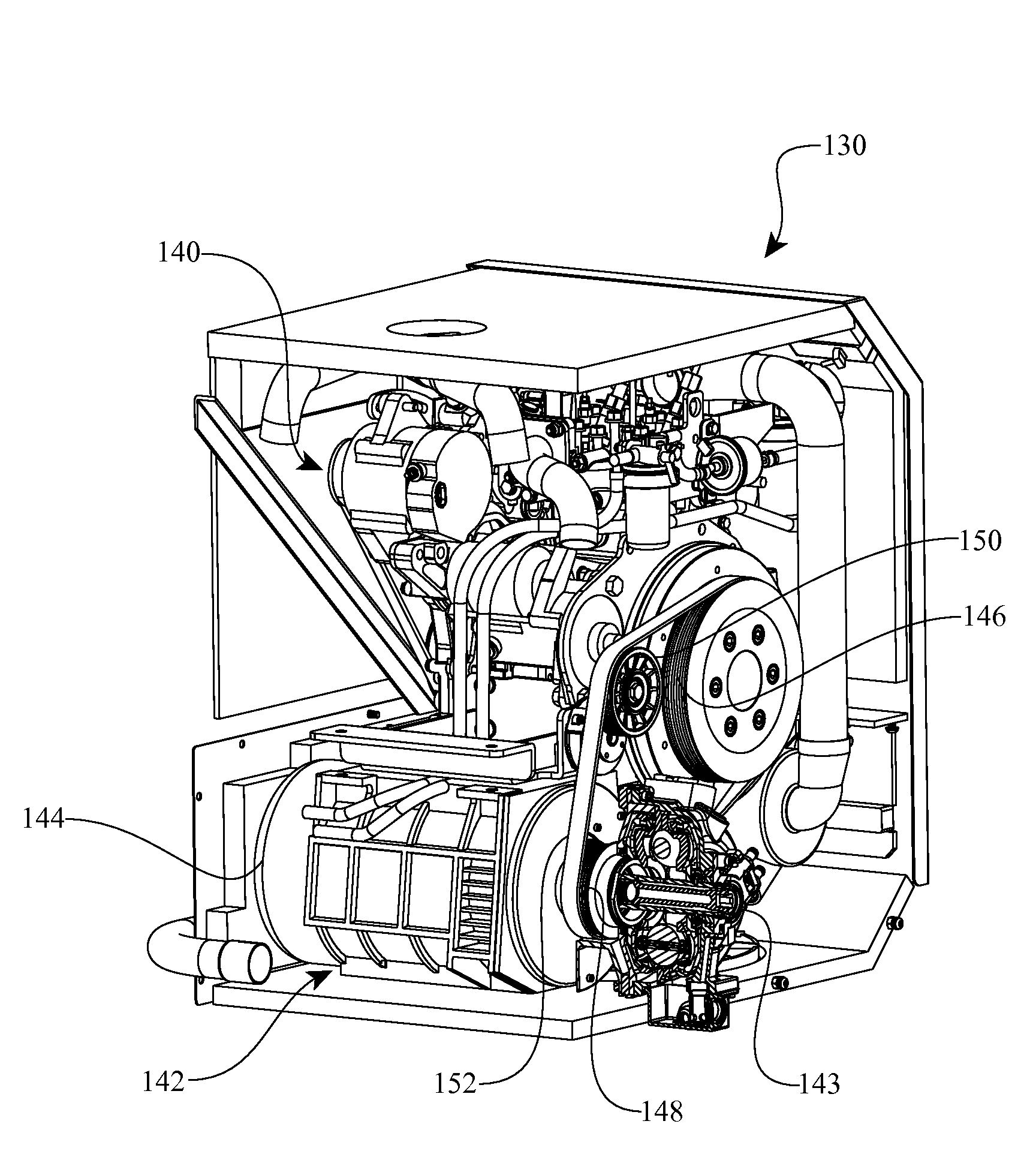
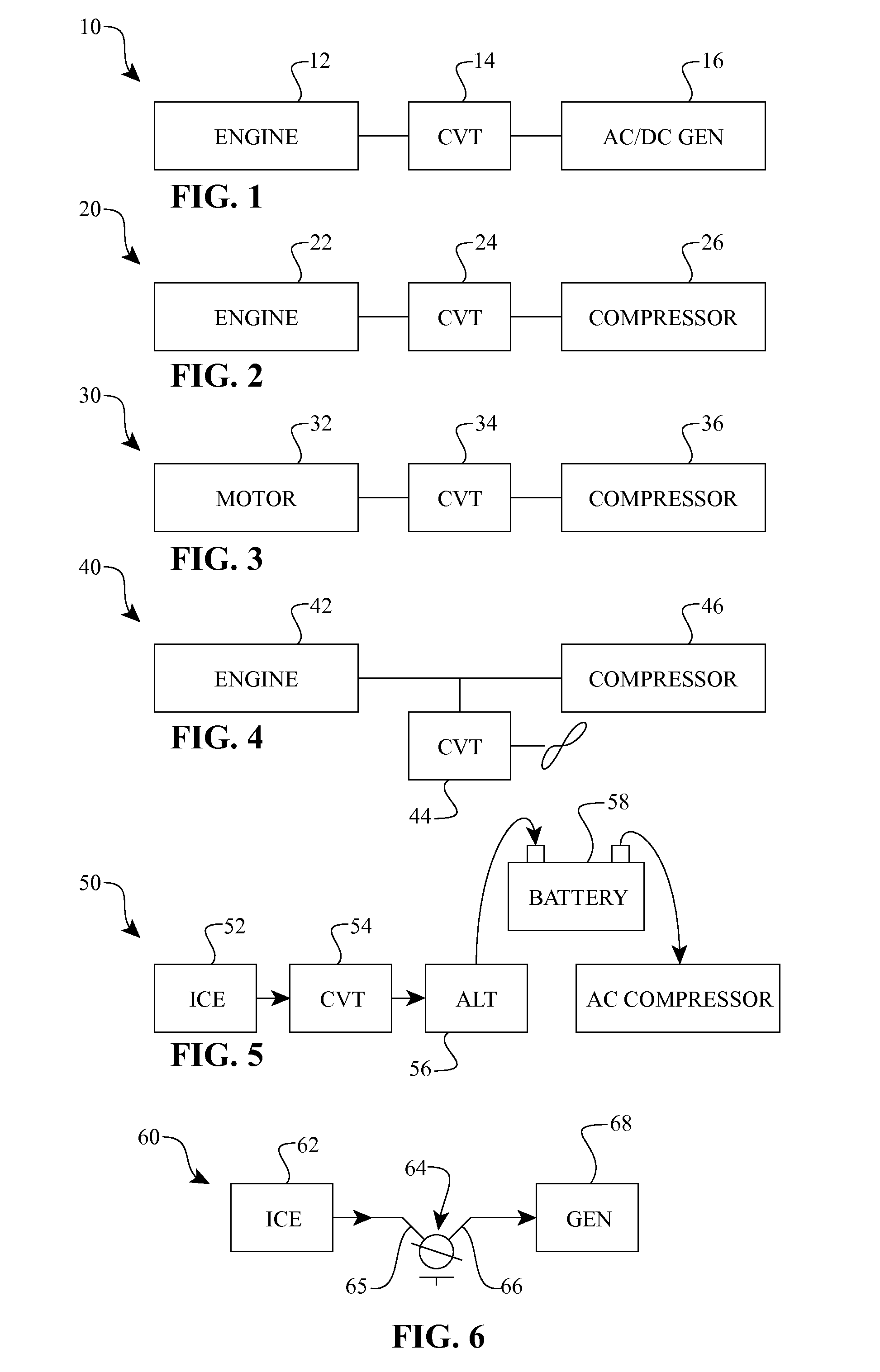
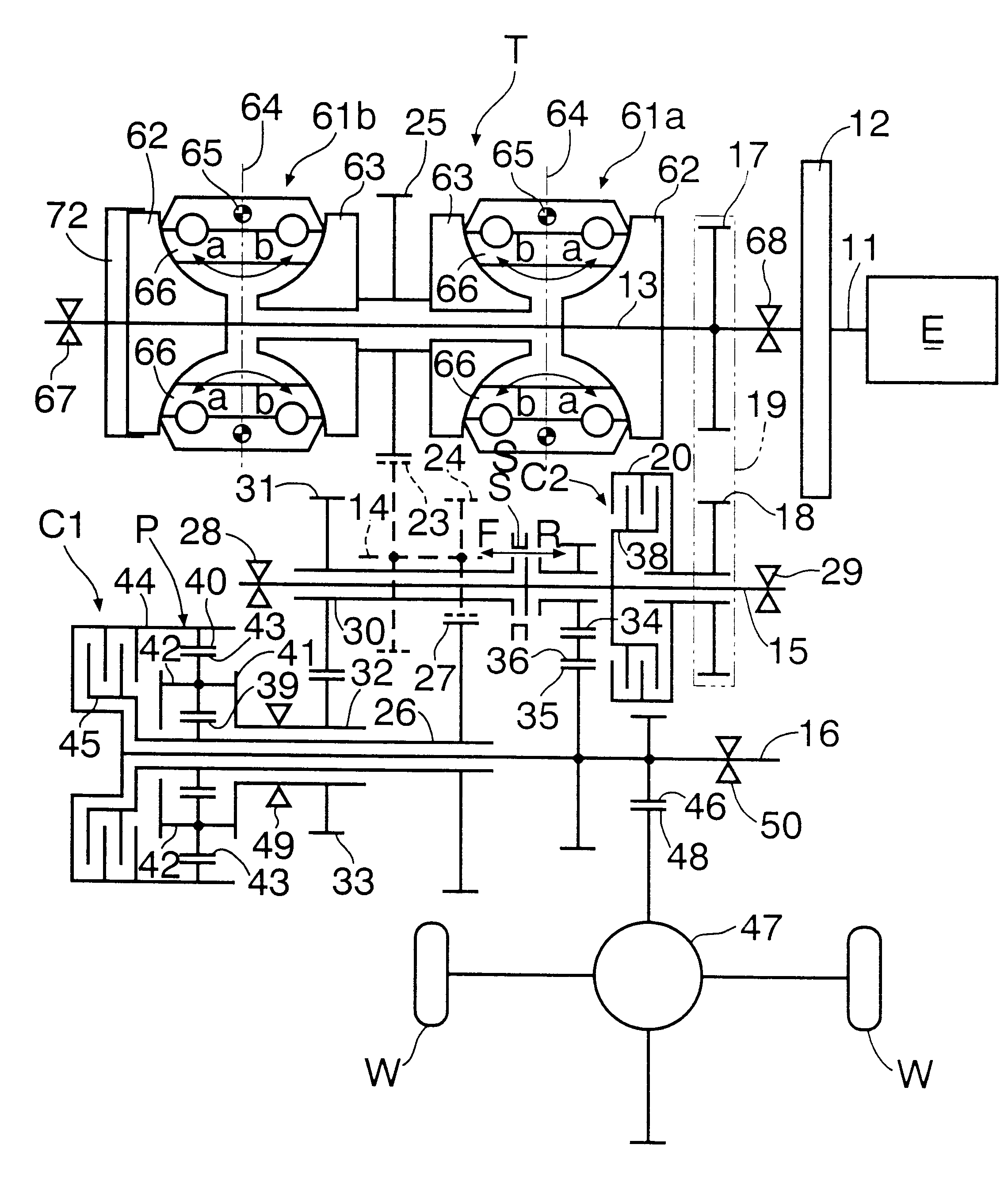
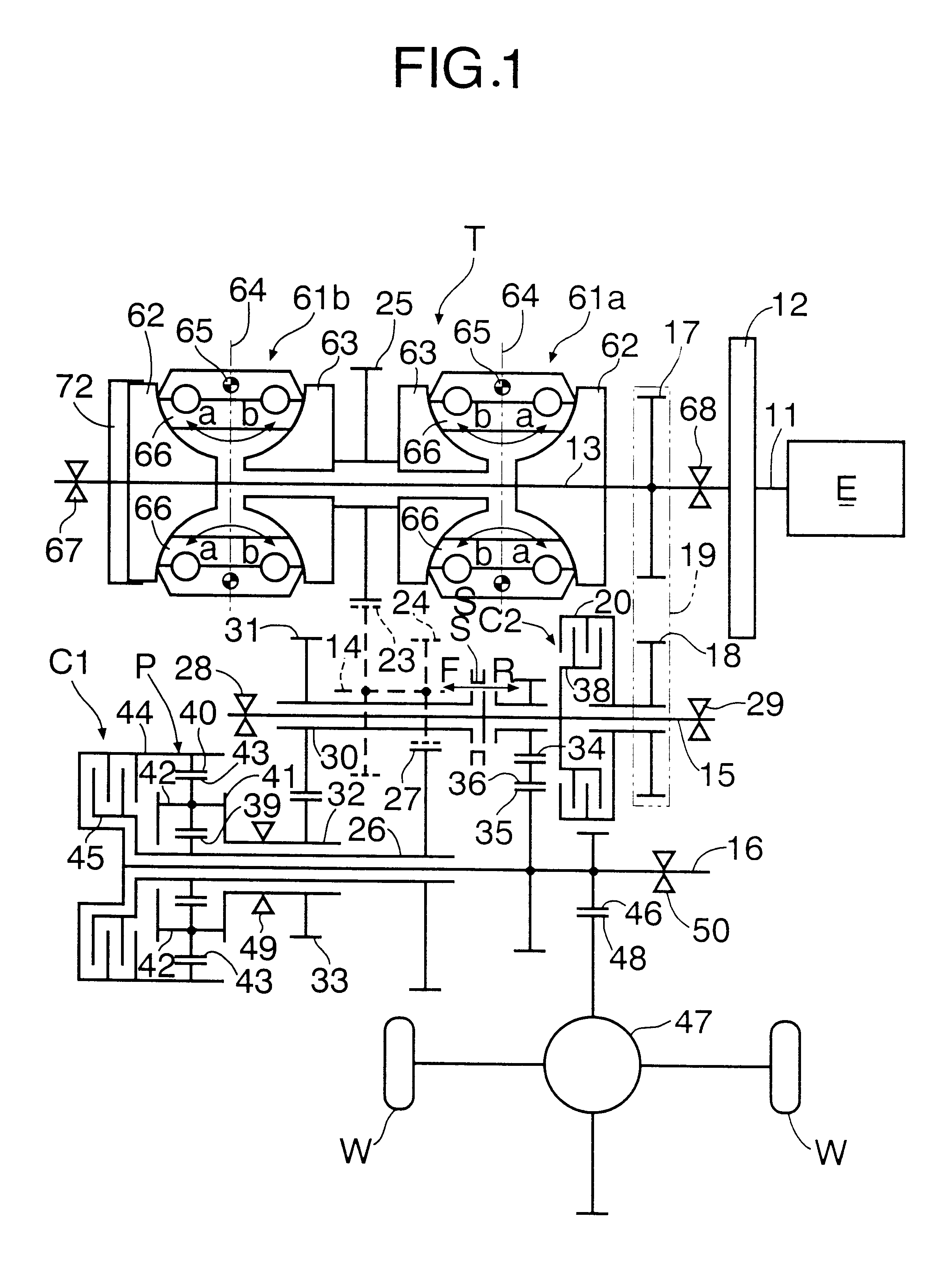
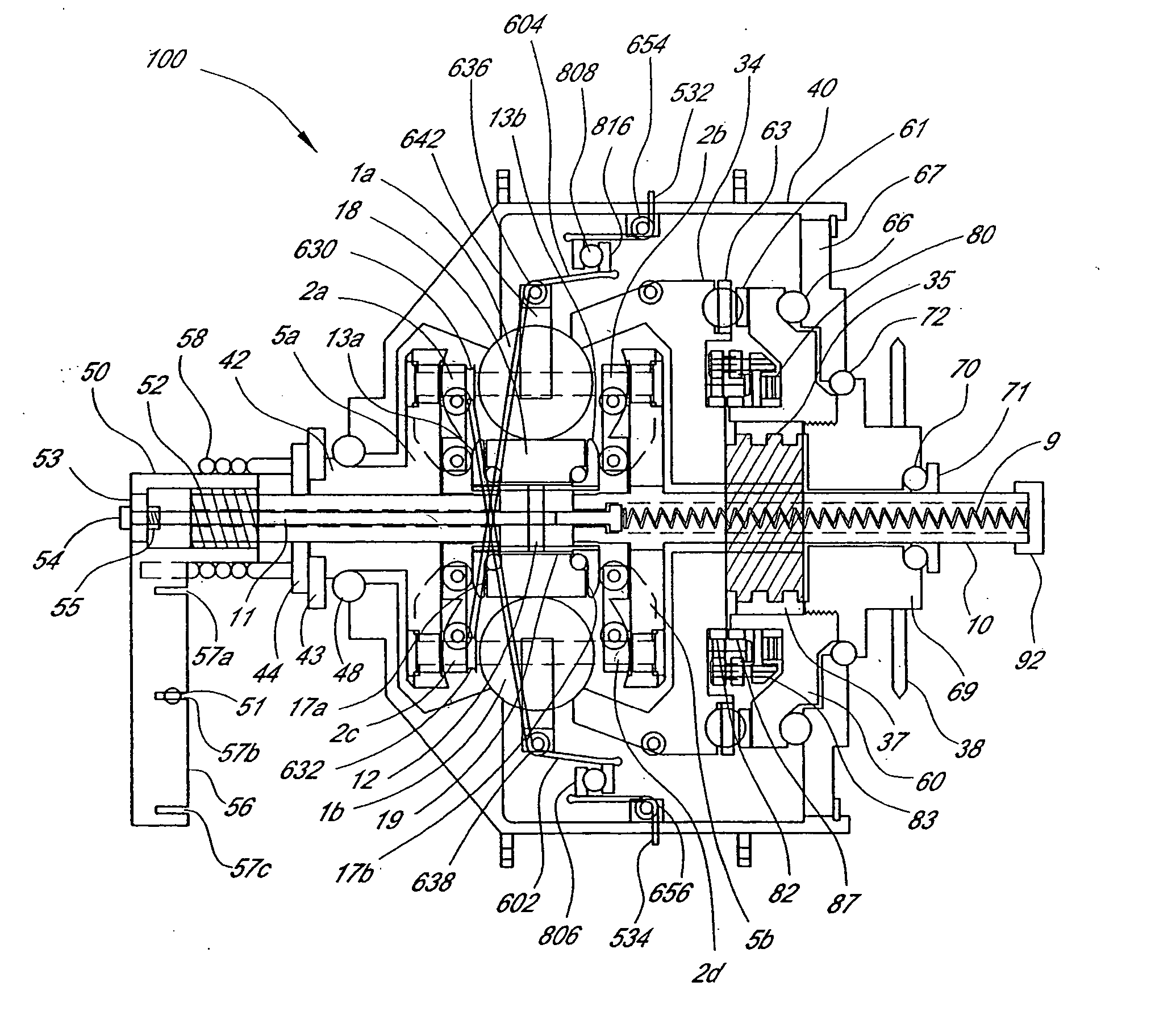
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4256 results about "Continuously variable transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
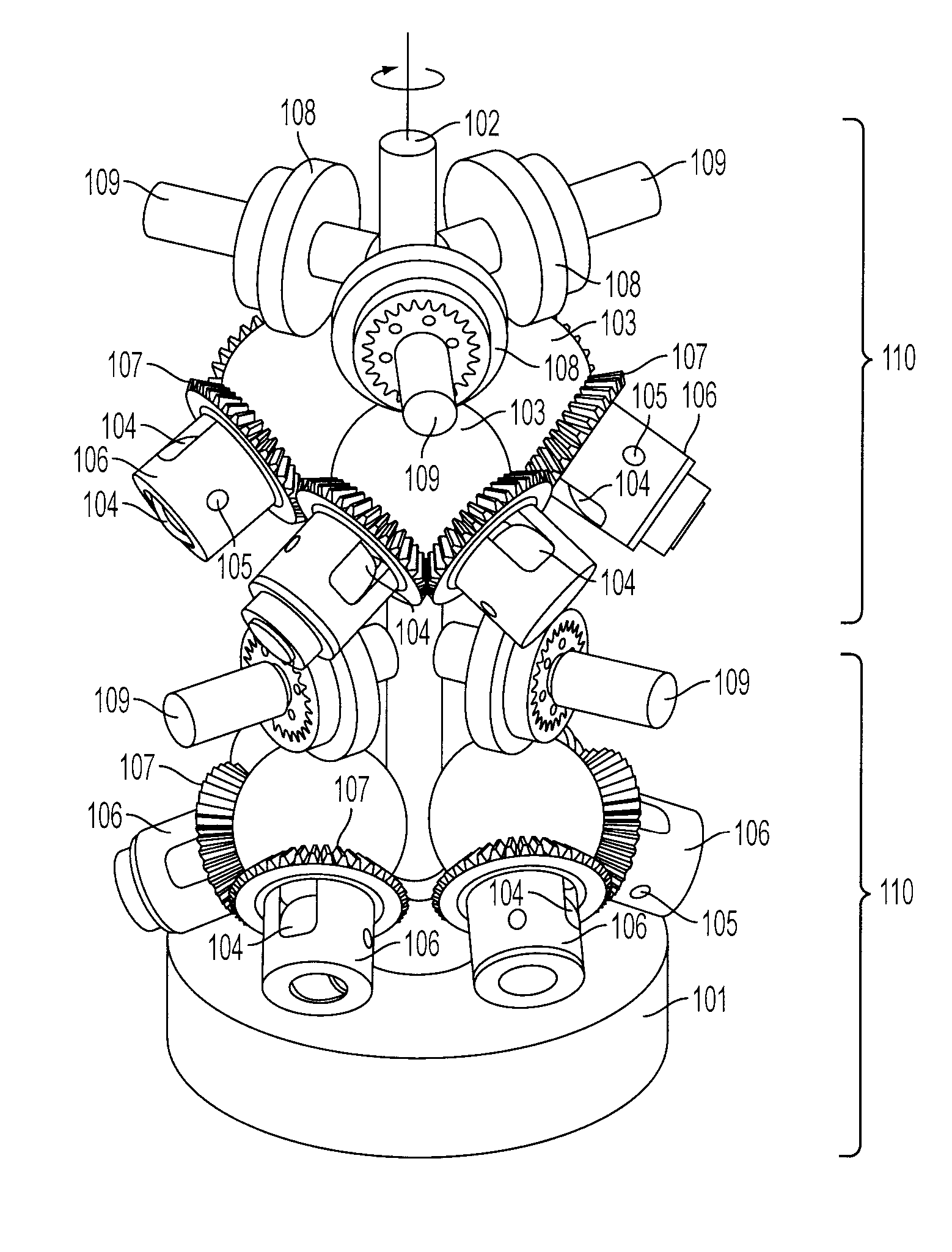
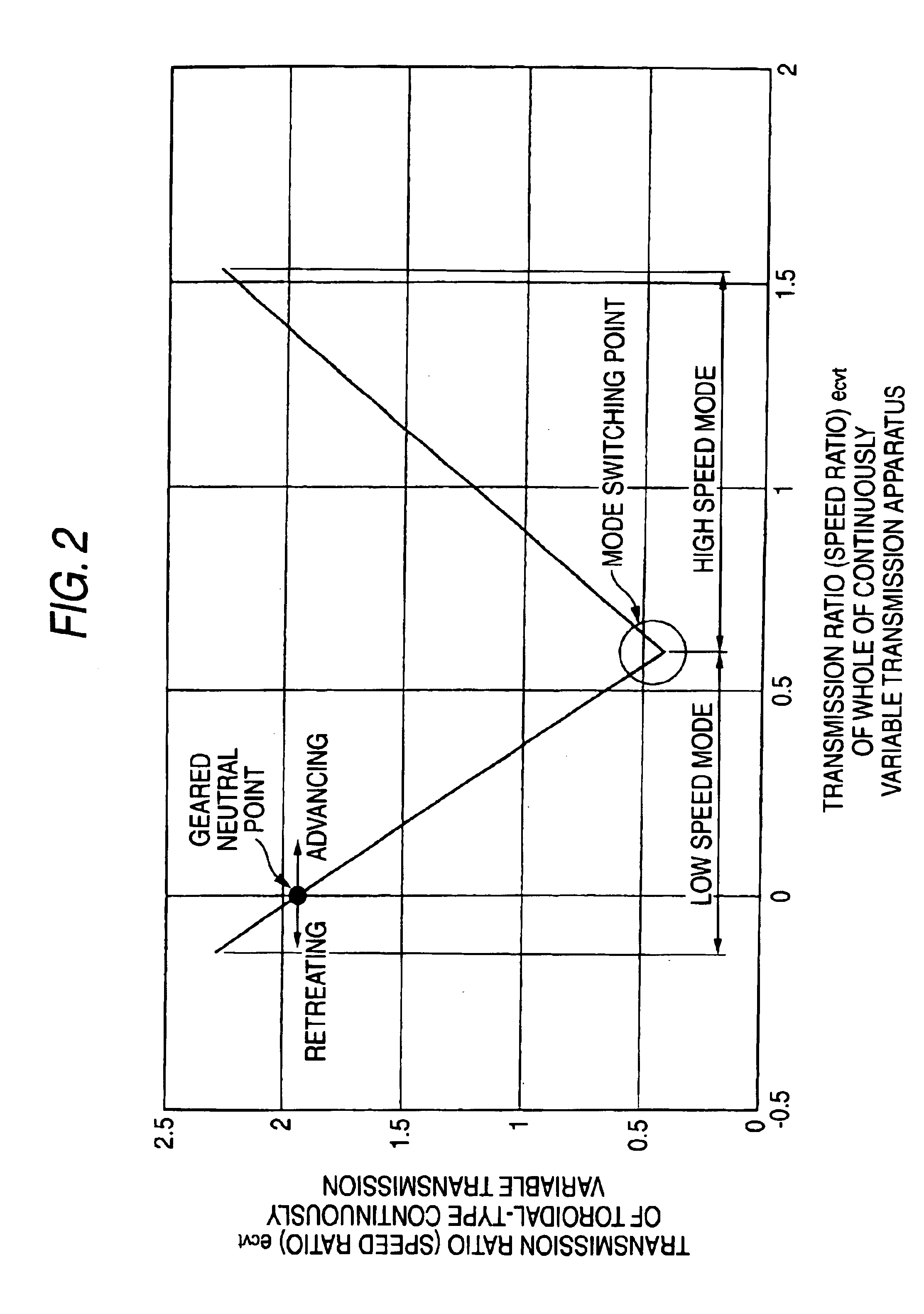
A continuously variable transmission (CVT), also known as a shiftless transmission, single-speed transmission, stepless transmission, pulley transmission, or, in case of motorcycles, a 'twist-and-go', is an automatic transmission that can change seamlessly through a continuous range of effective gear ratios. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios. The flexibility of a CVT with suitable control may allow the input shaft to maintain a constant angular velocity even as the output speed varies.
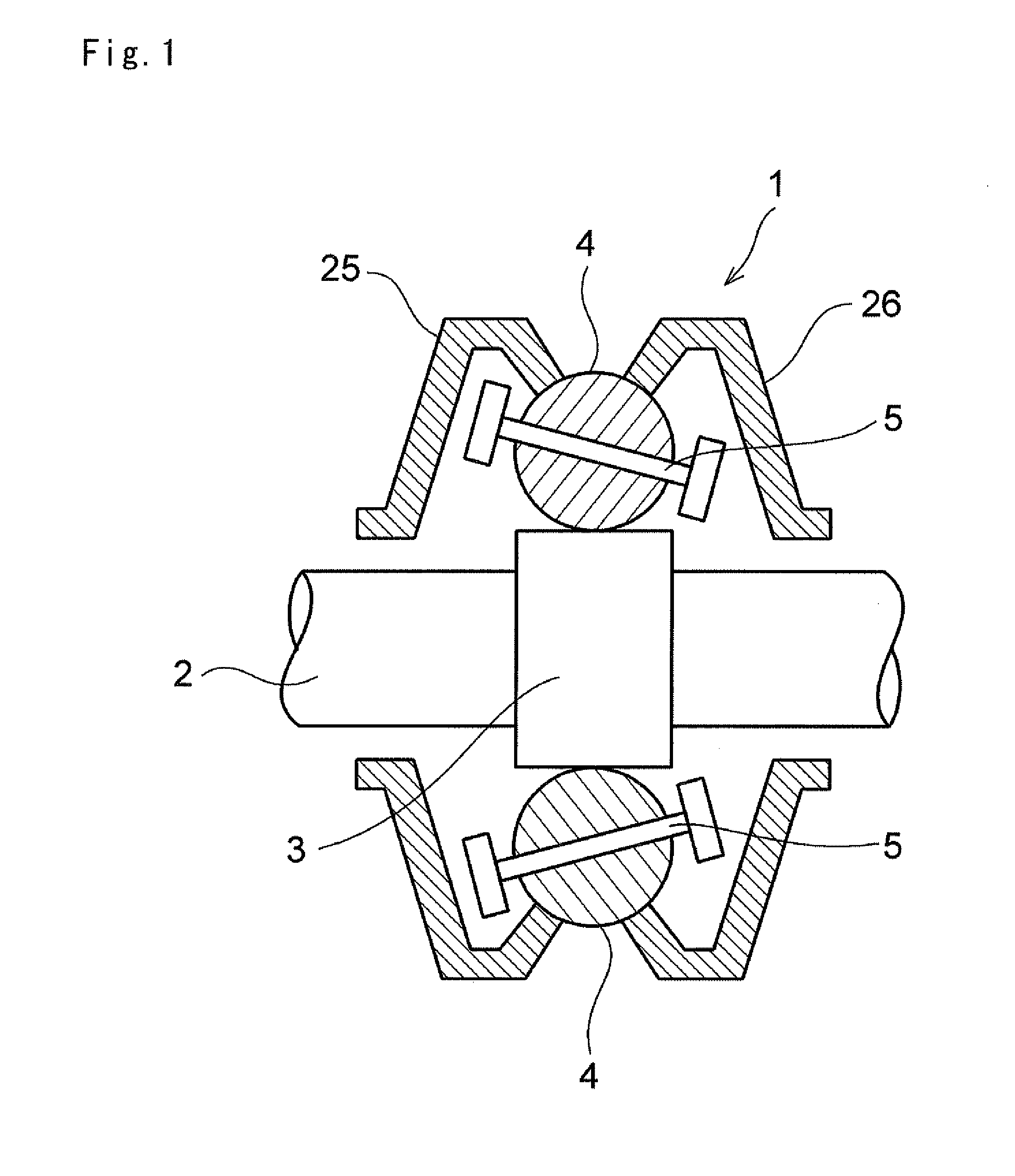
Toroidal type continuously variable transmission
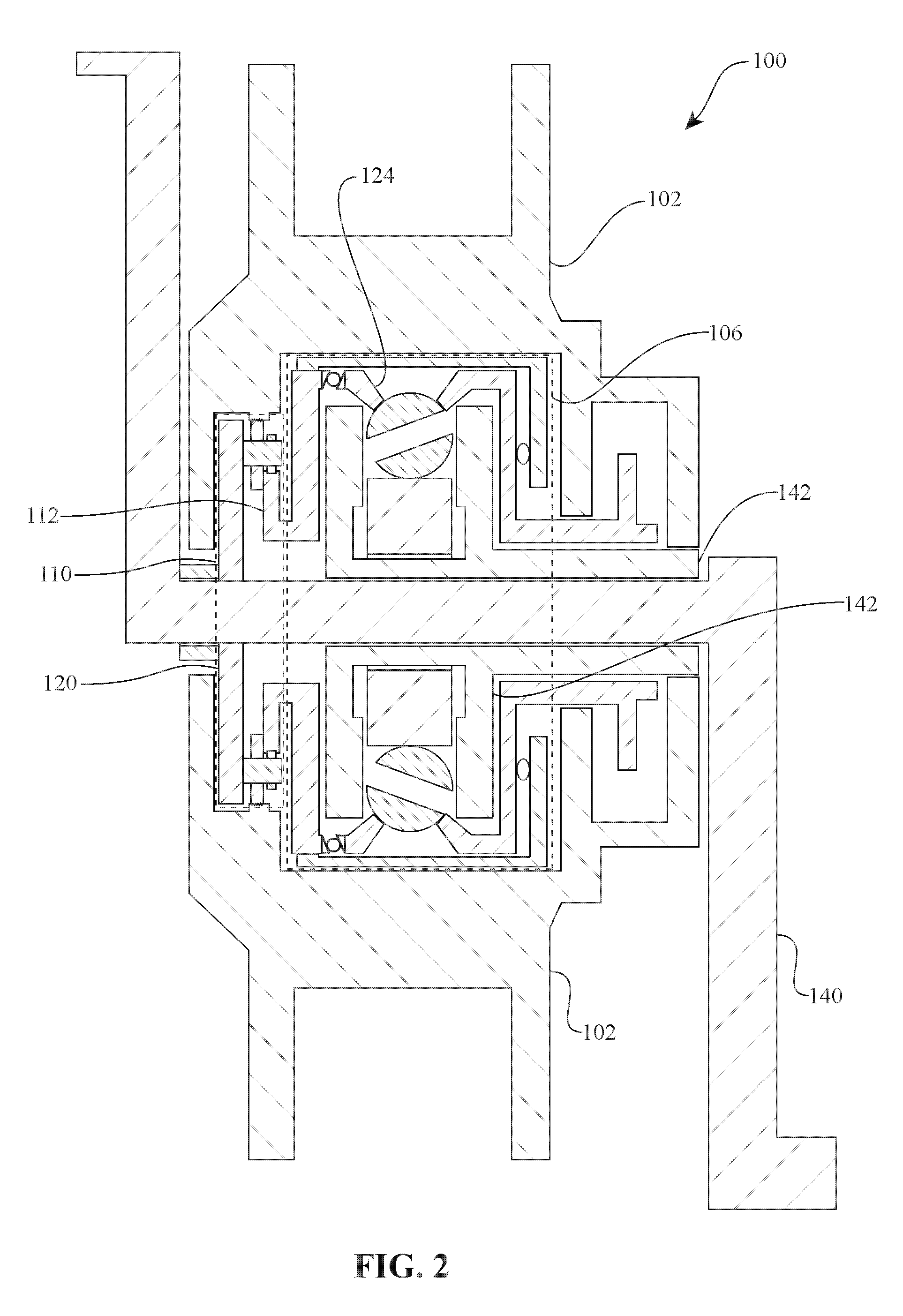
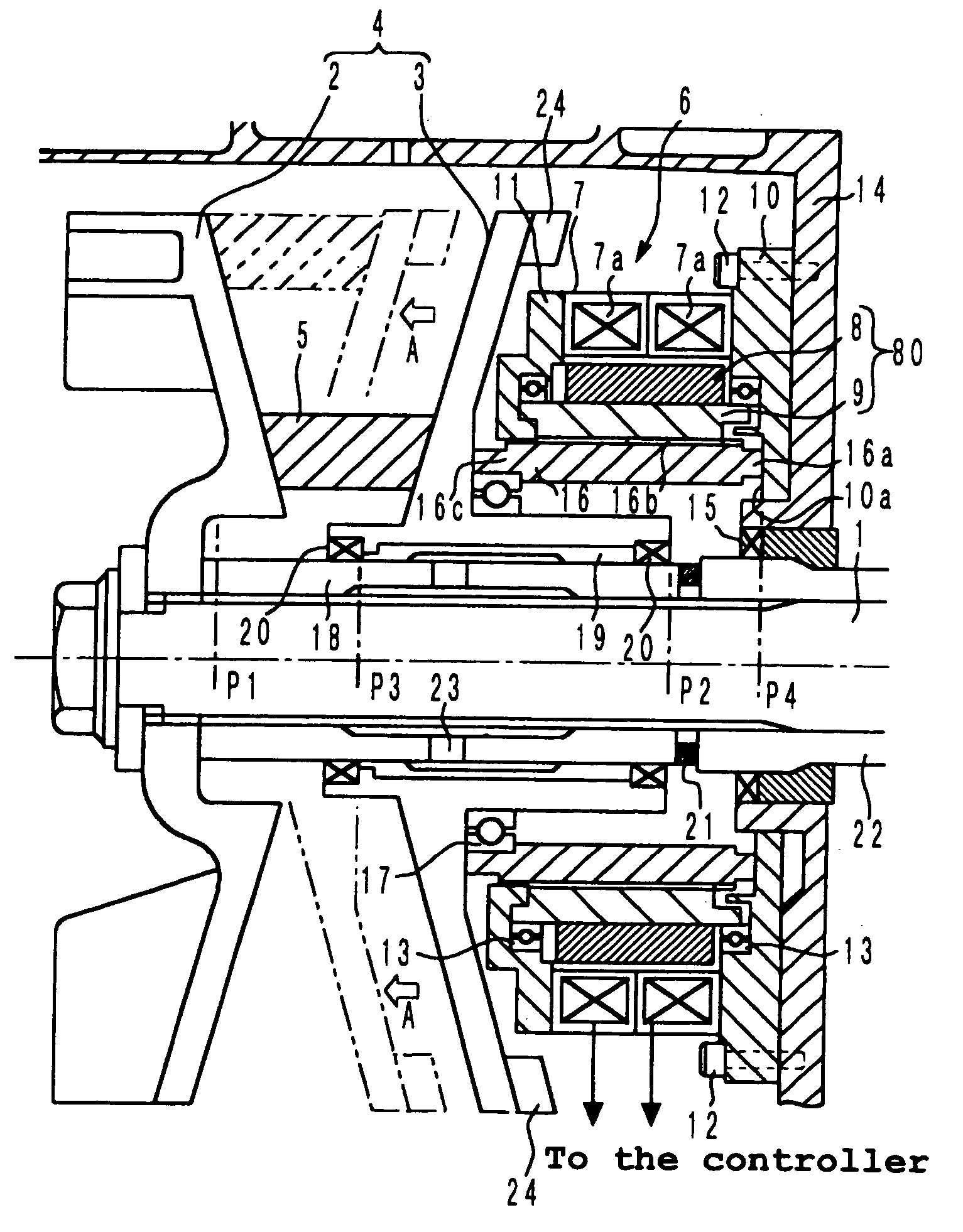
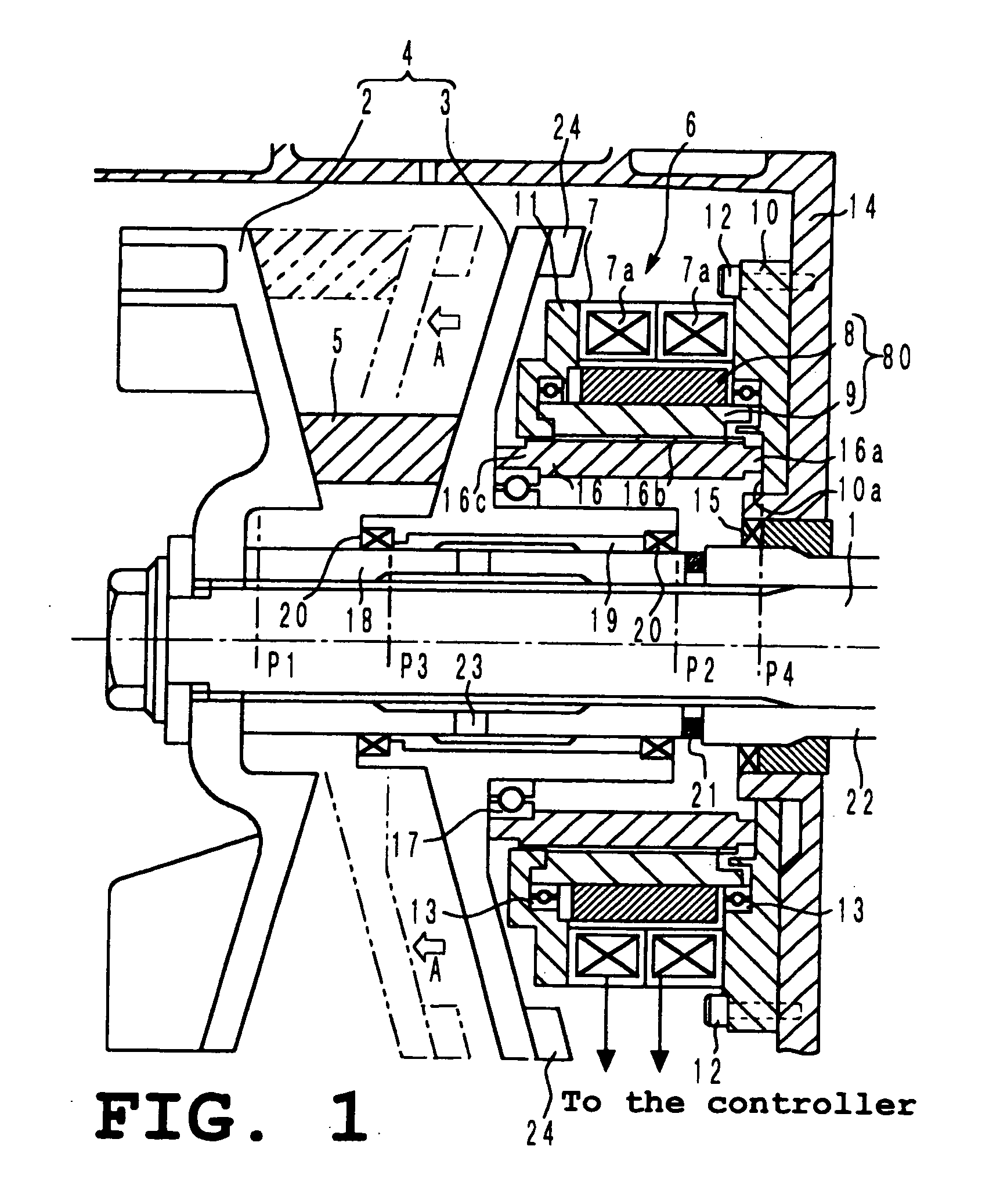
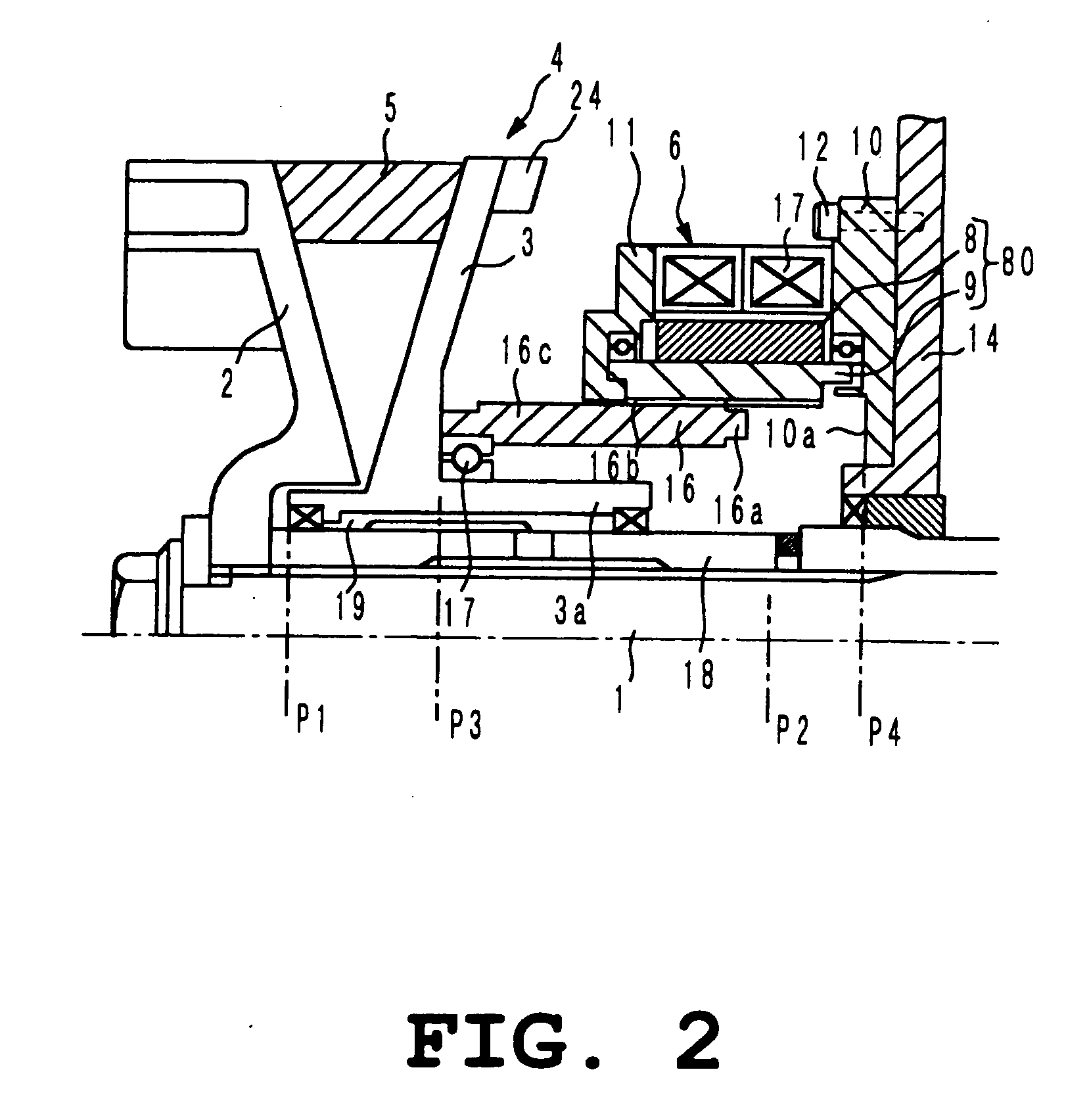
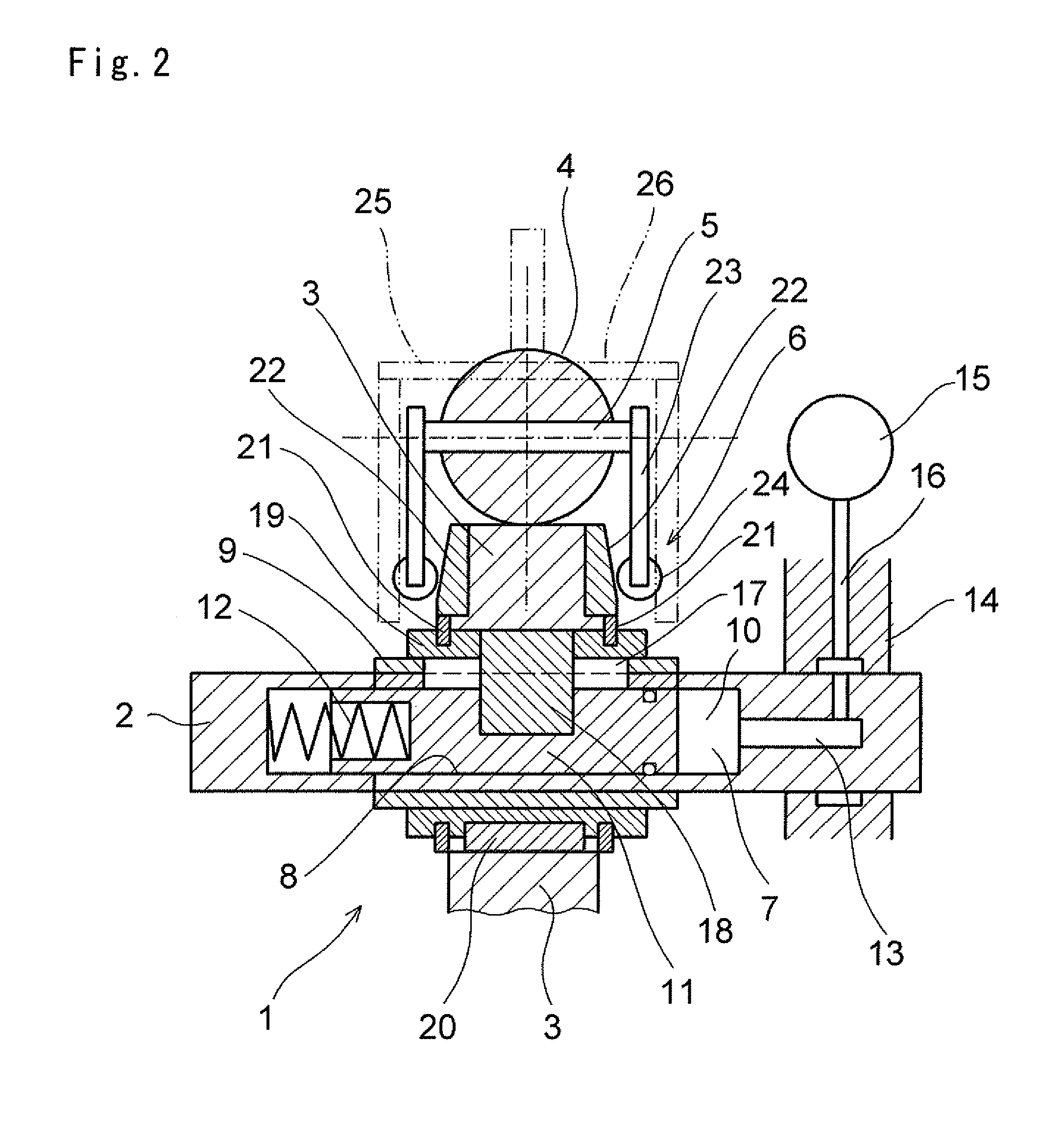
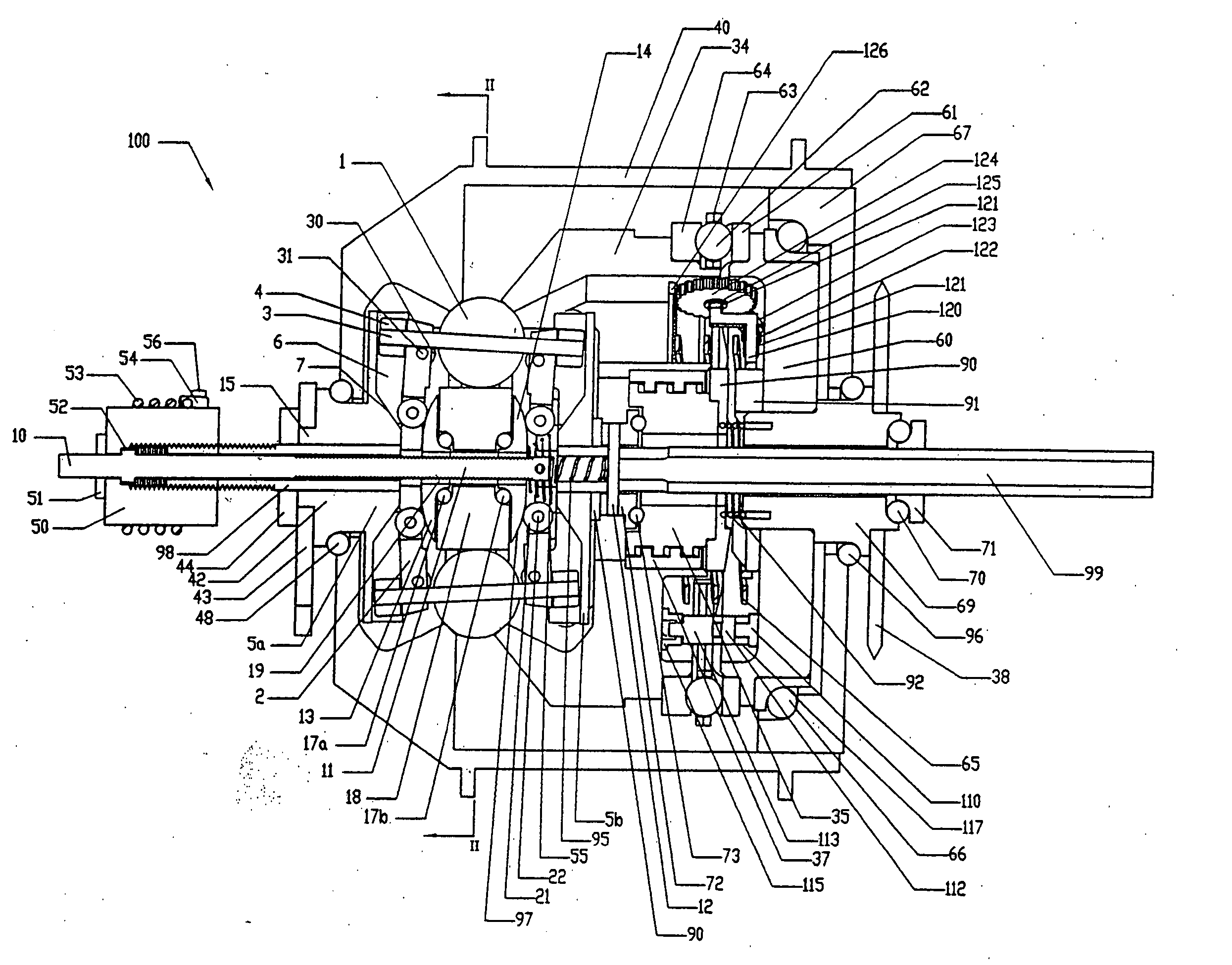
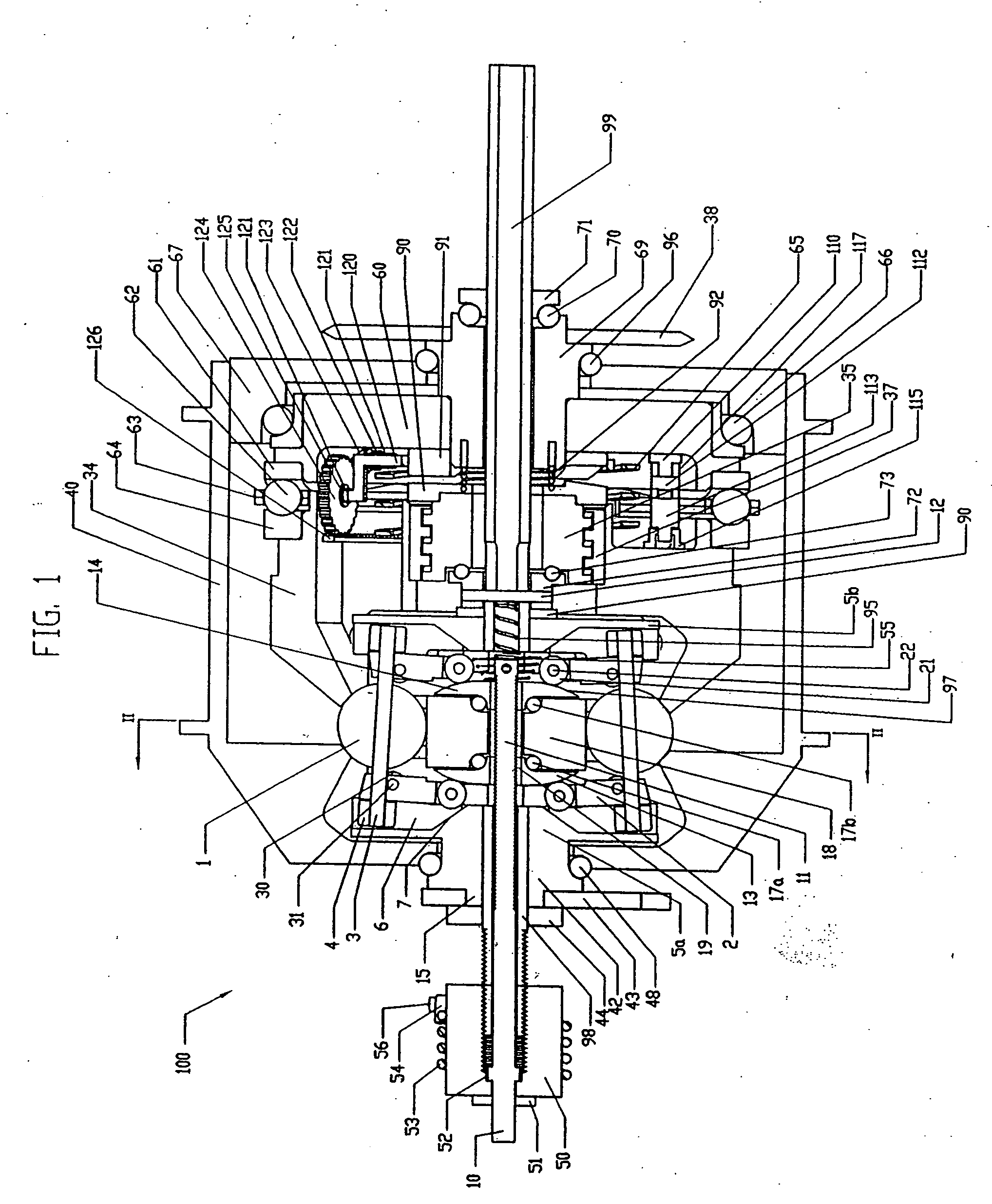
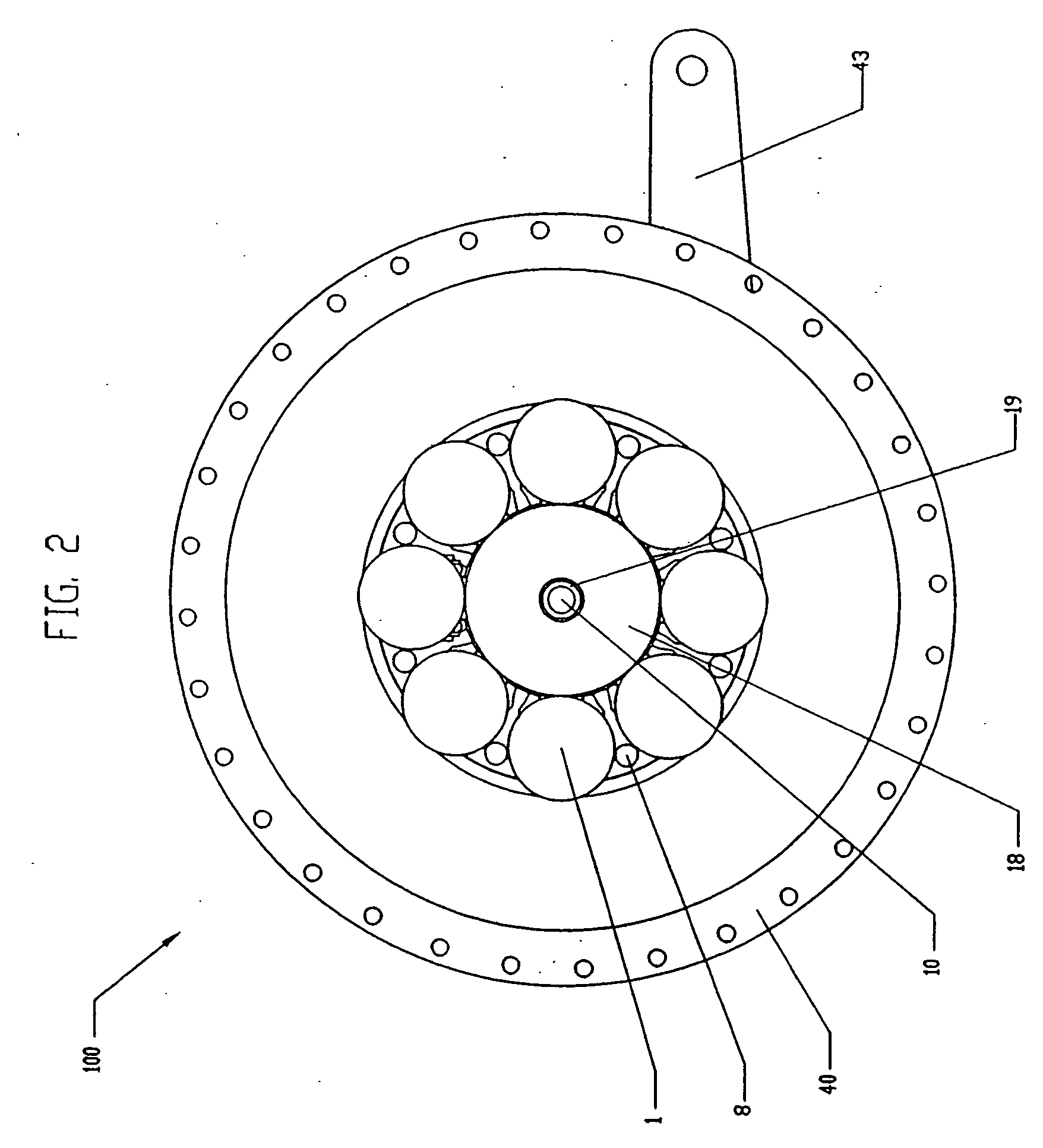
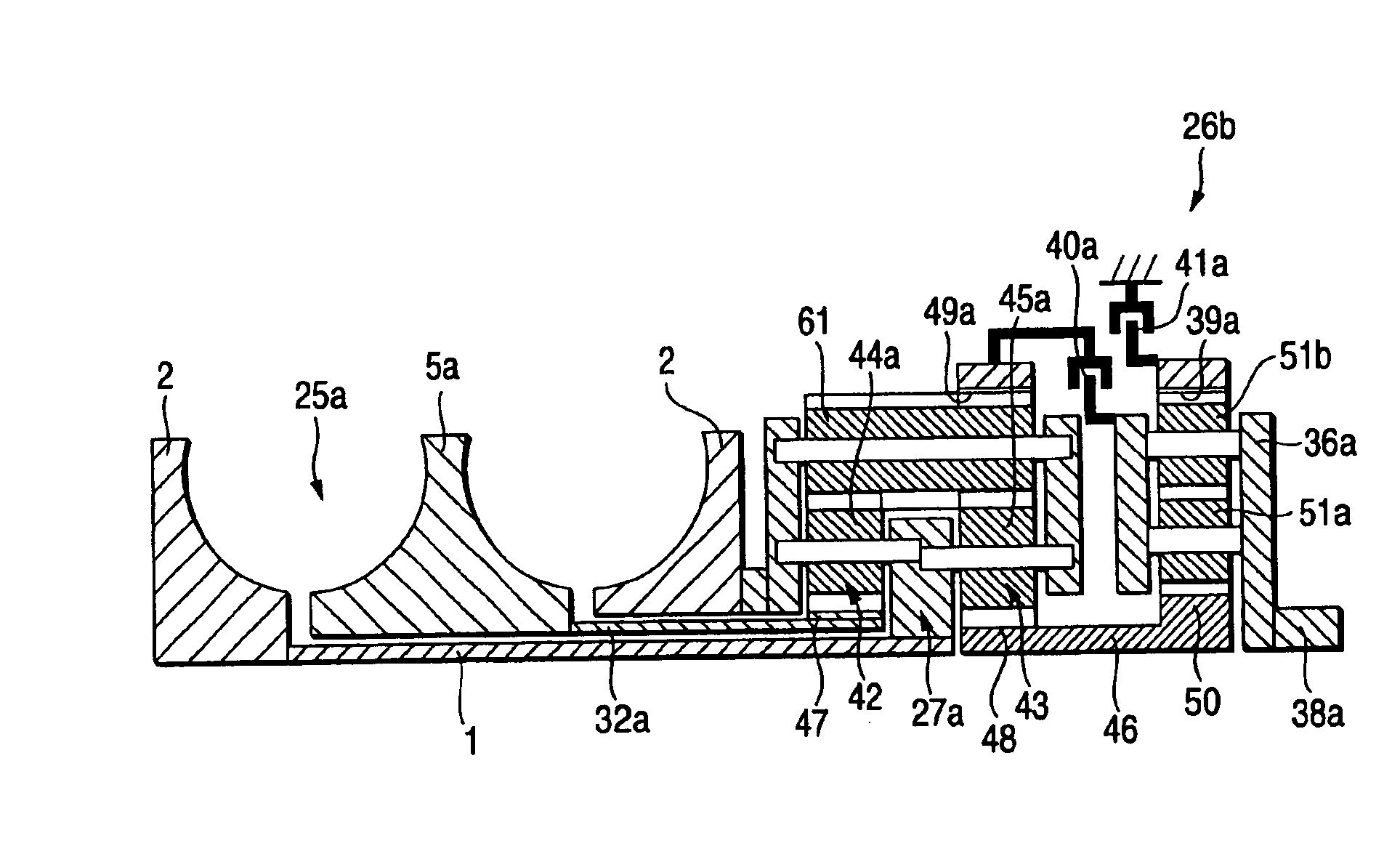
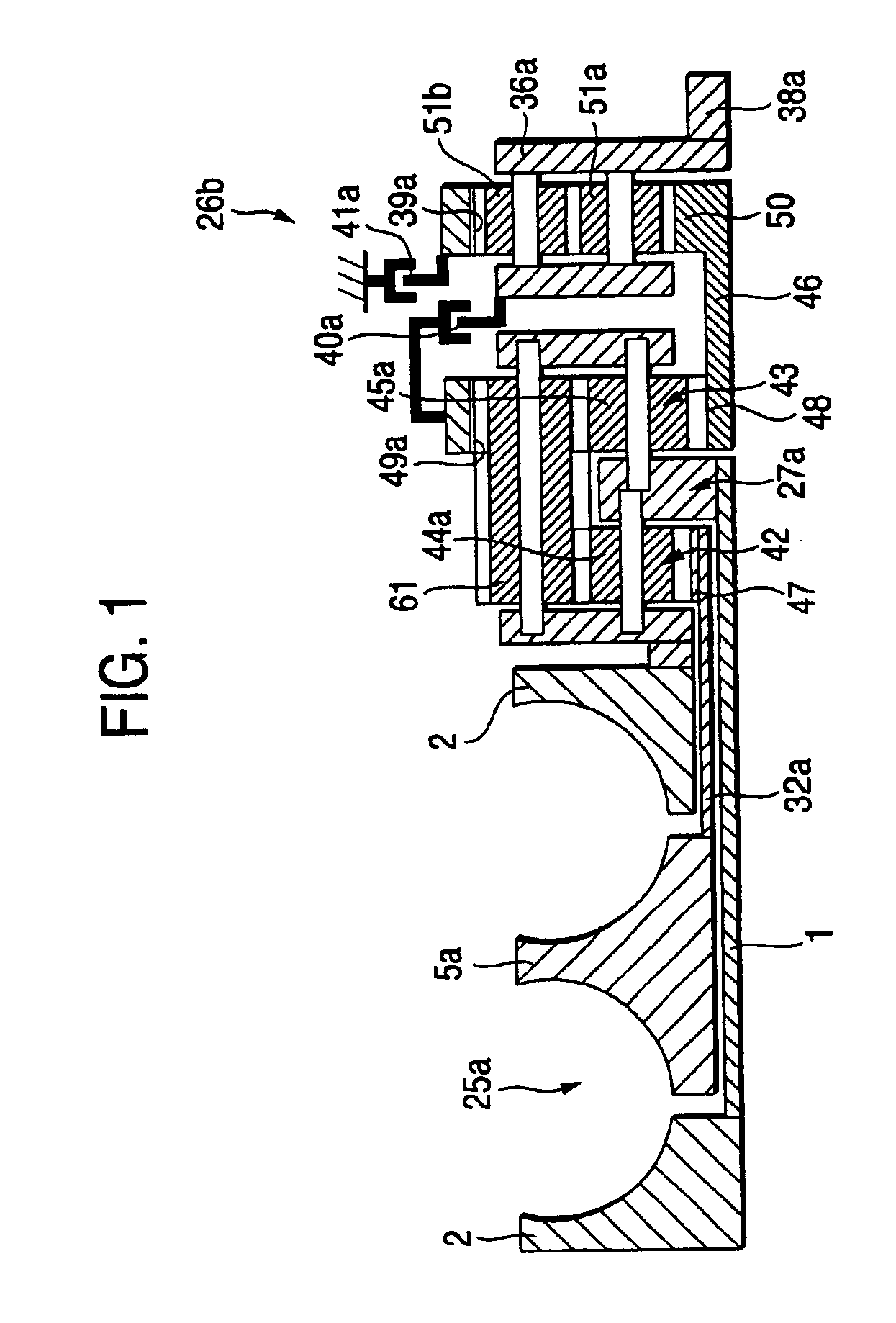
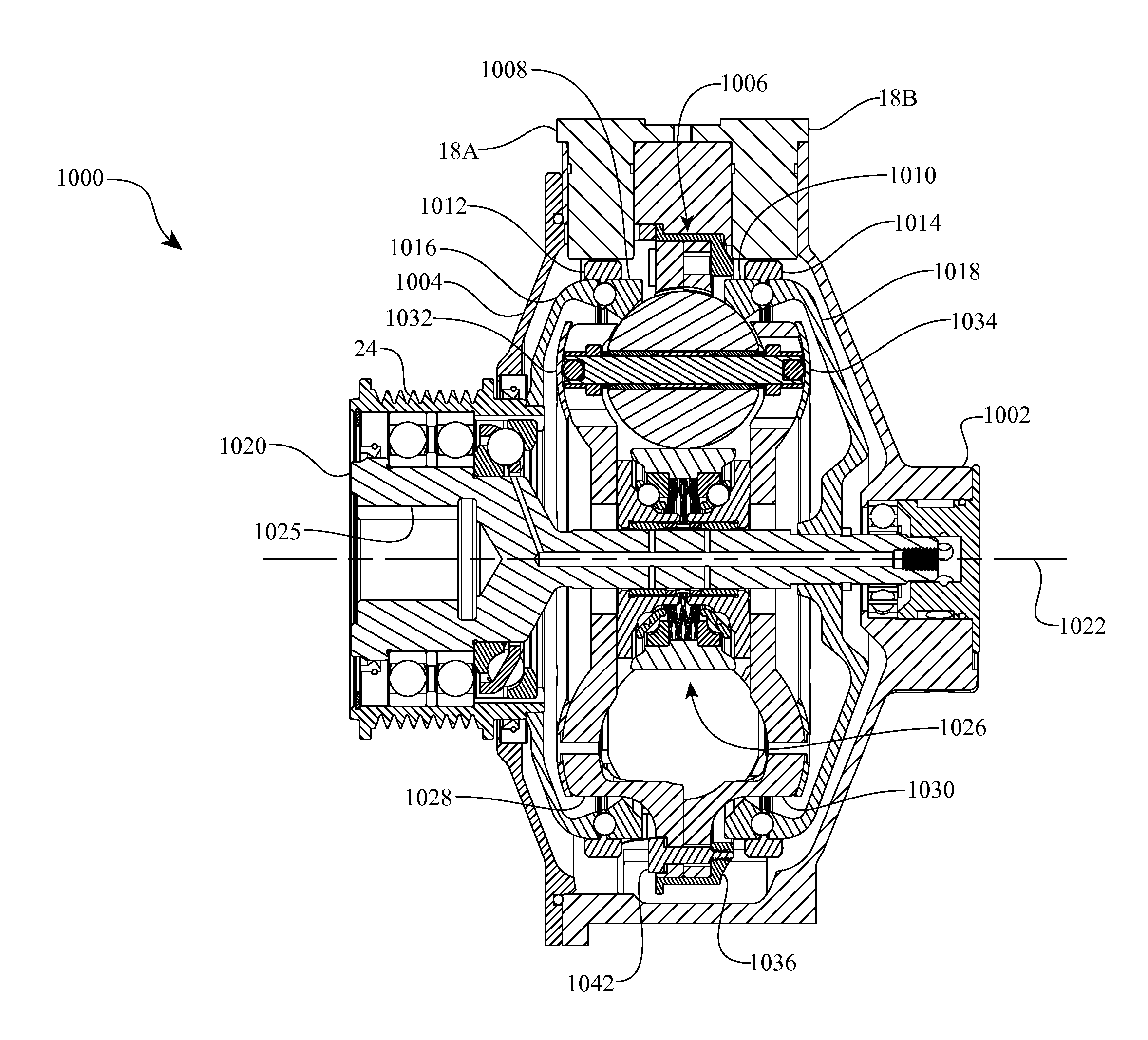
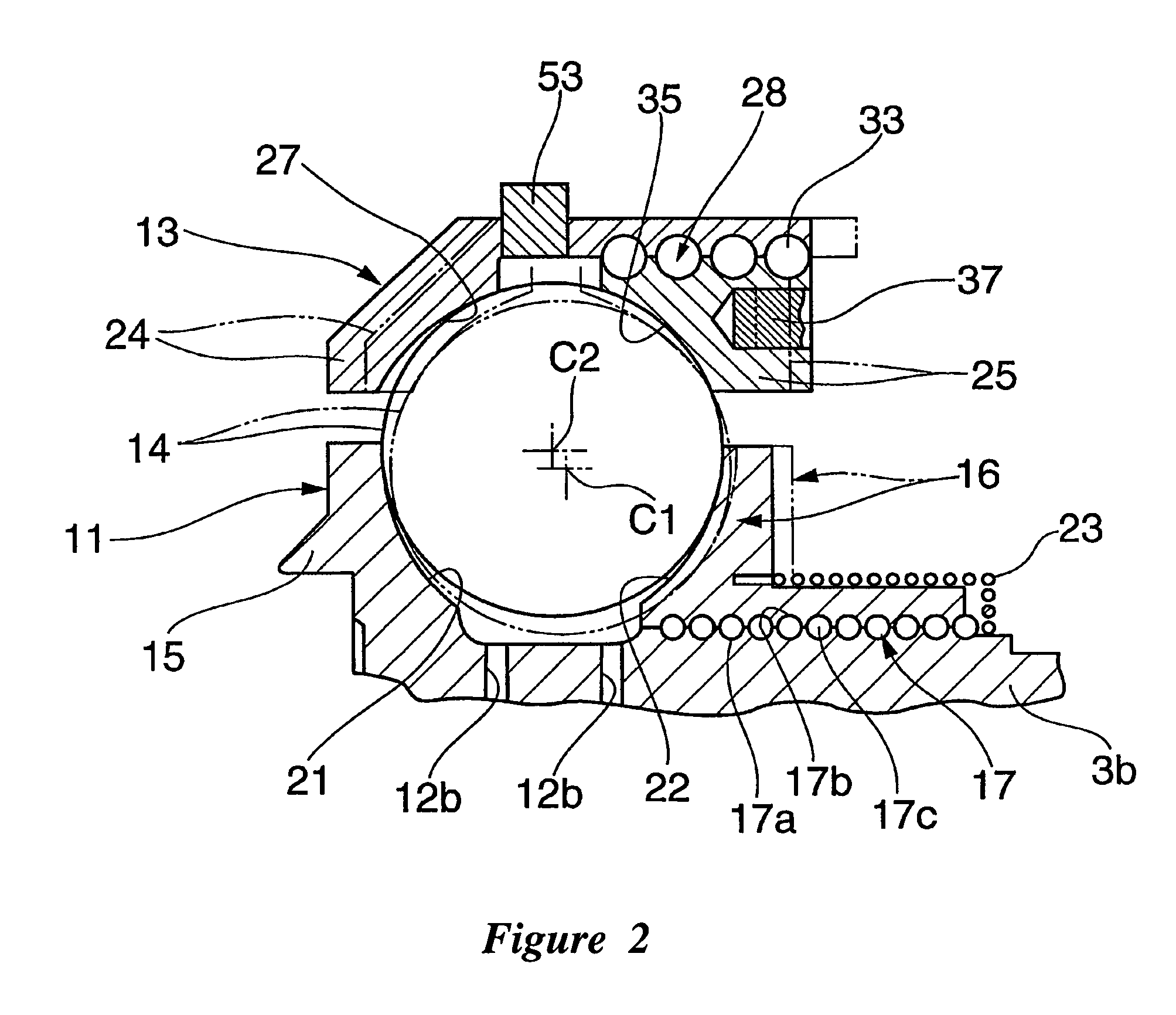
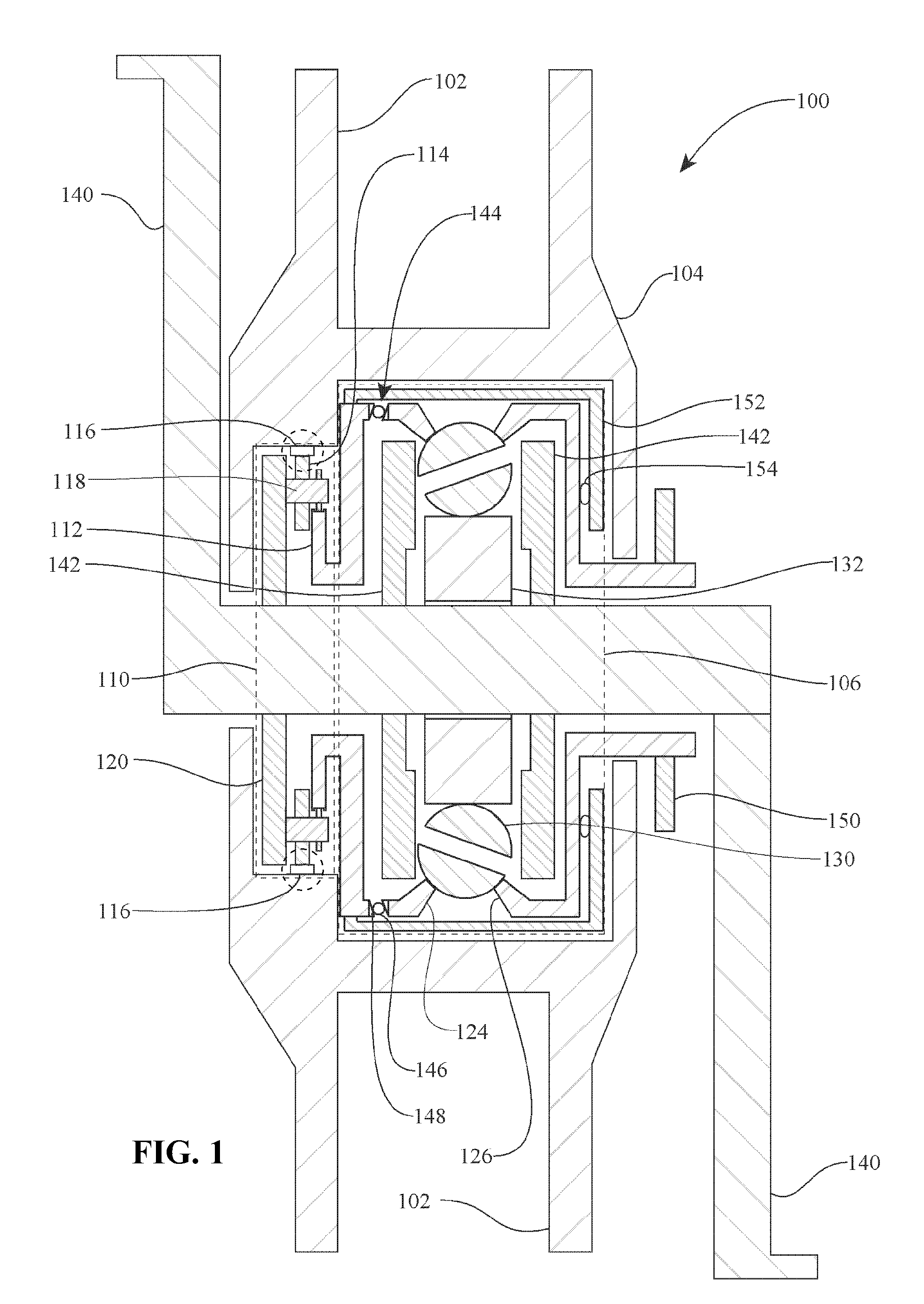
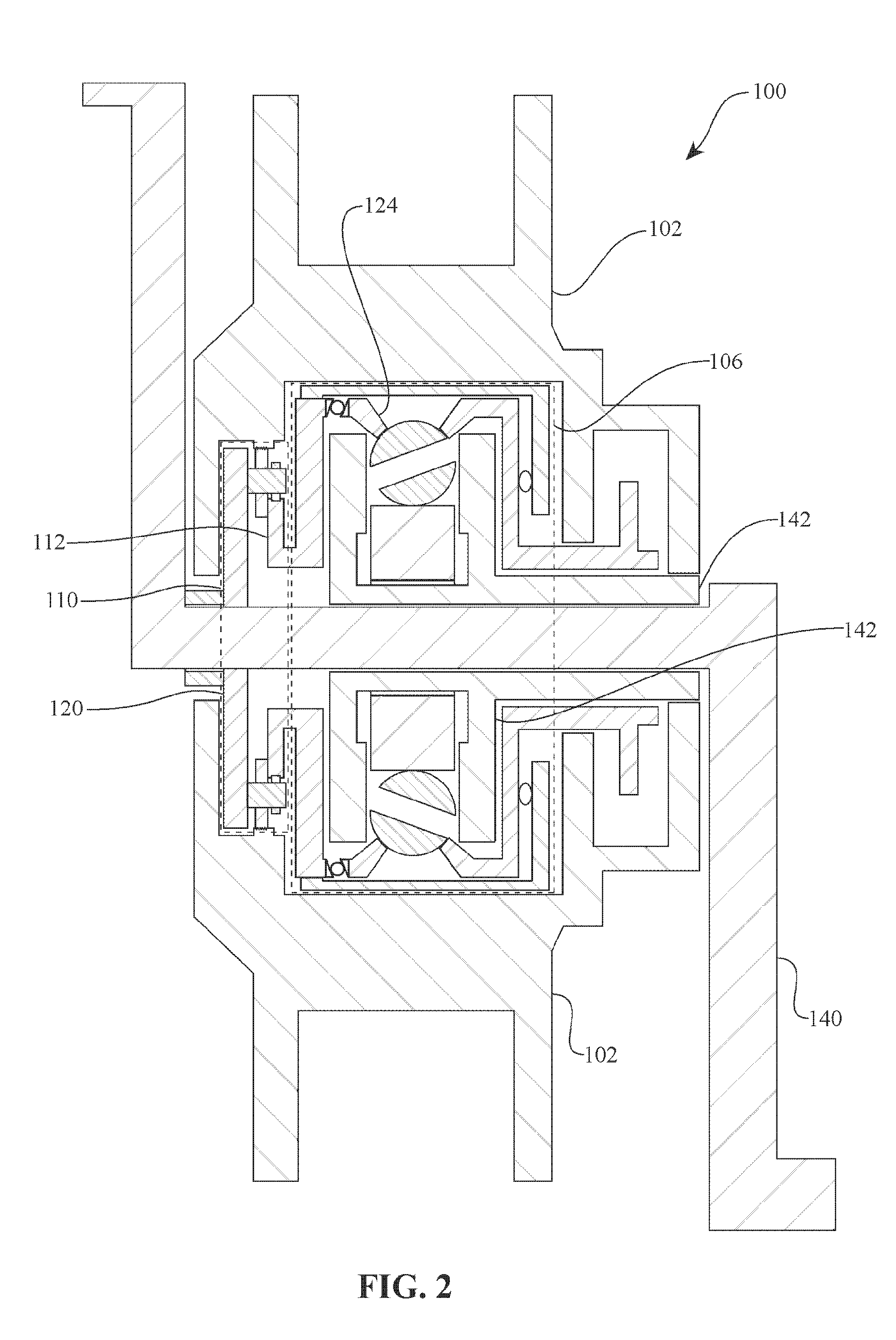
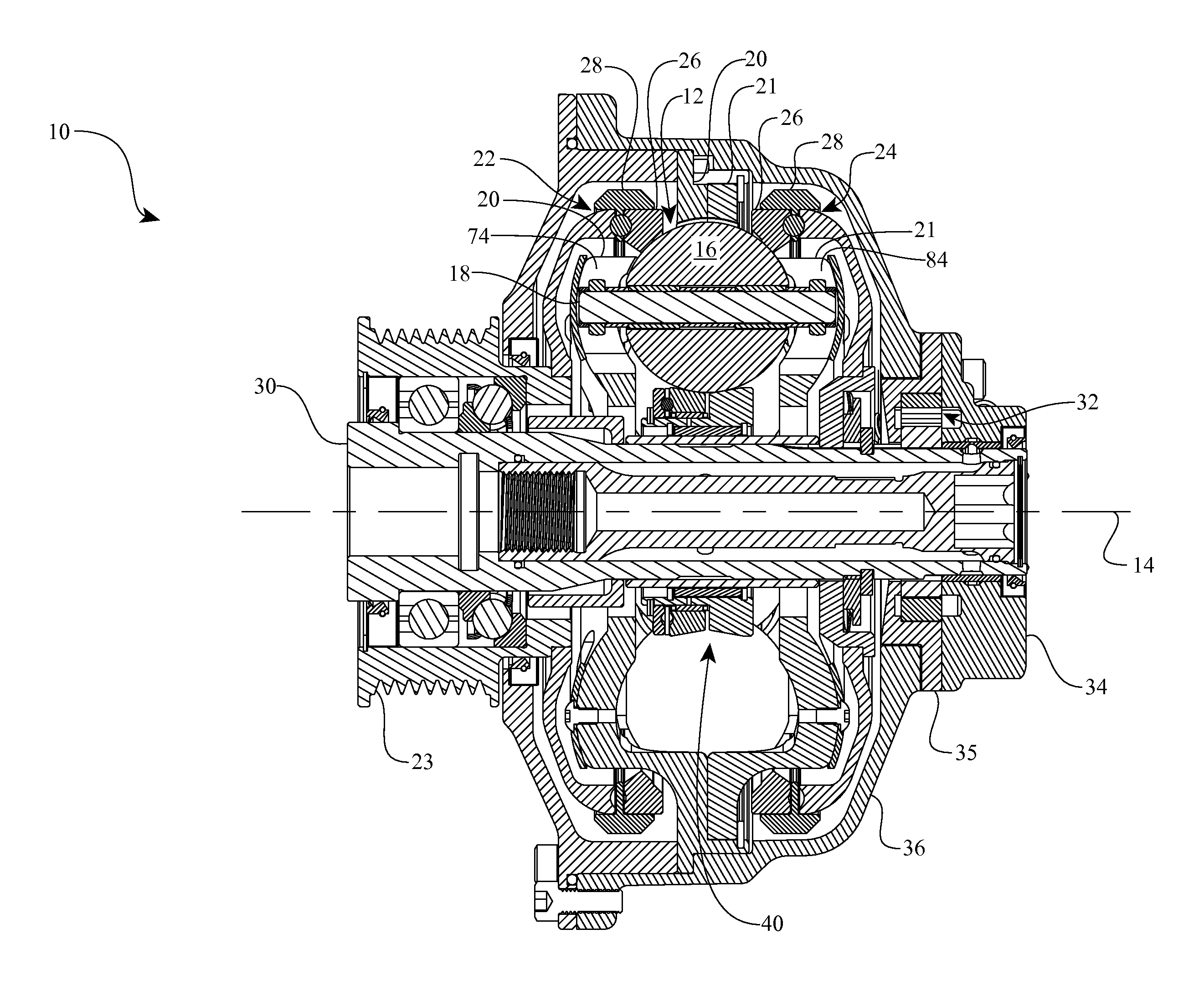
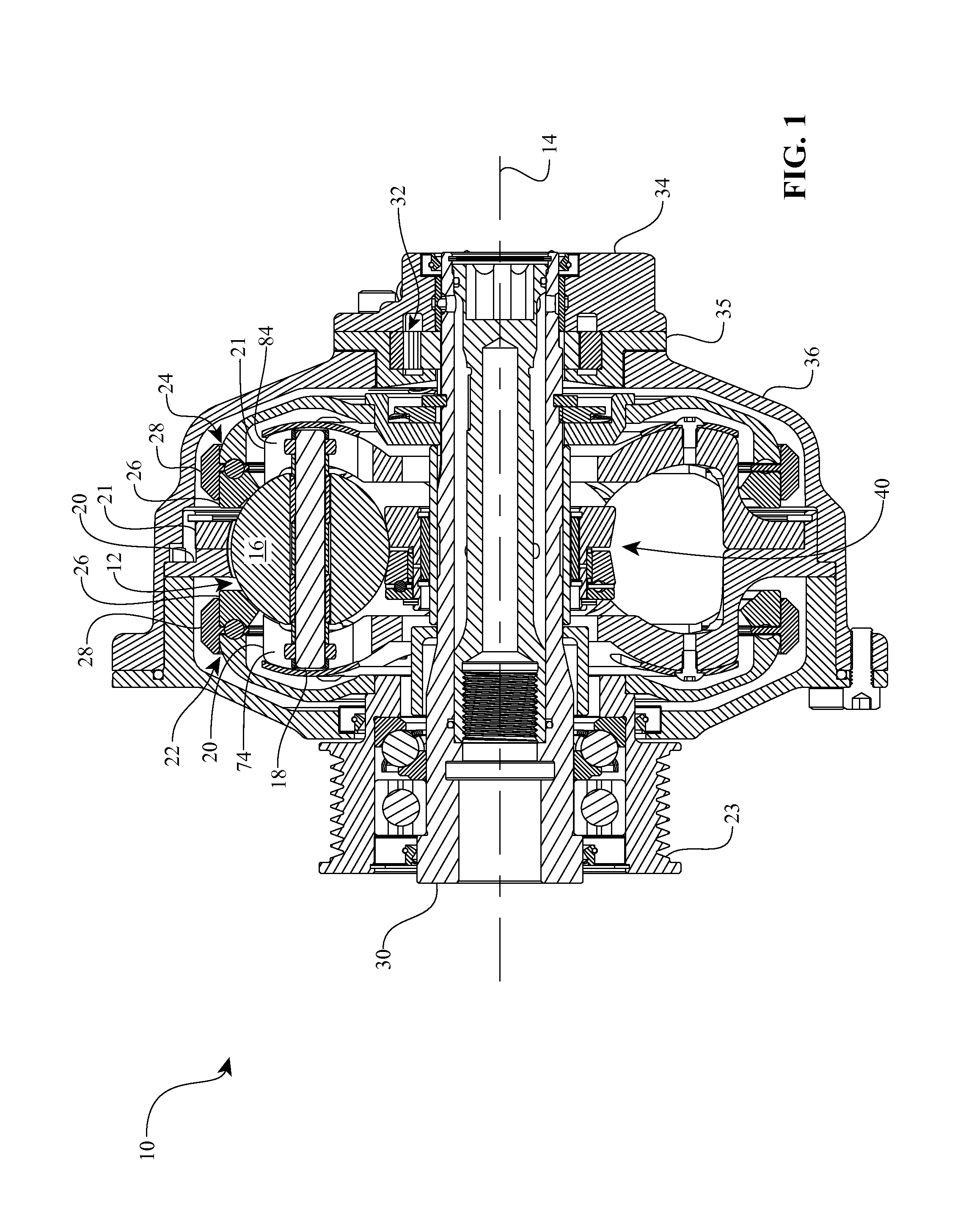
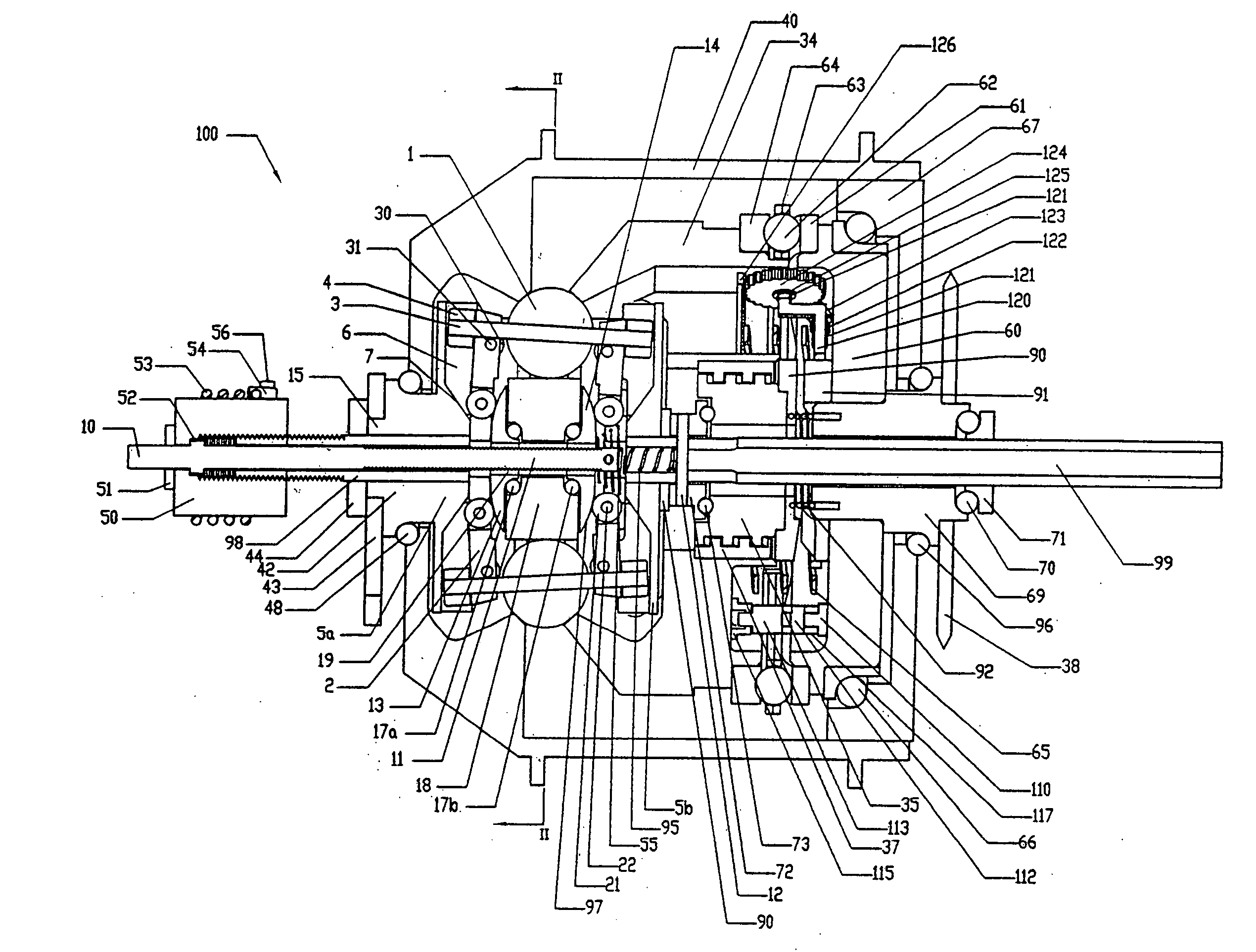
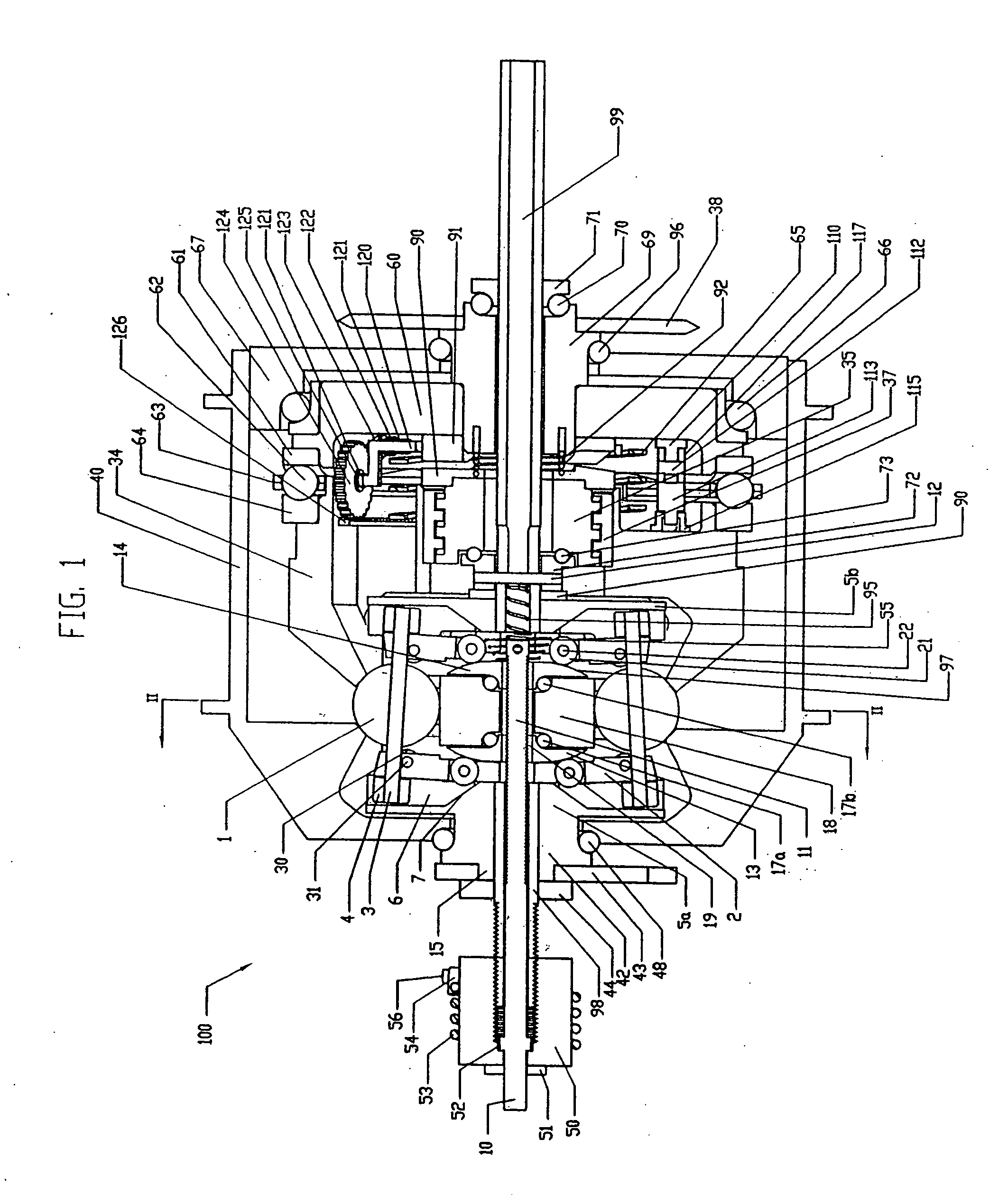
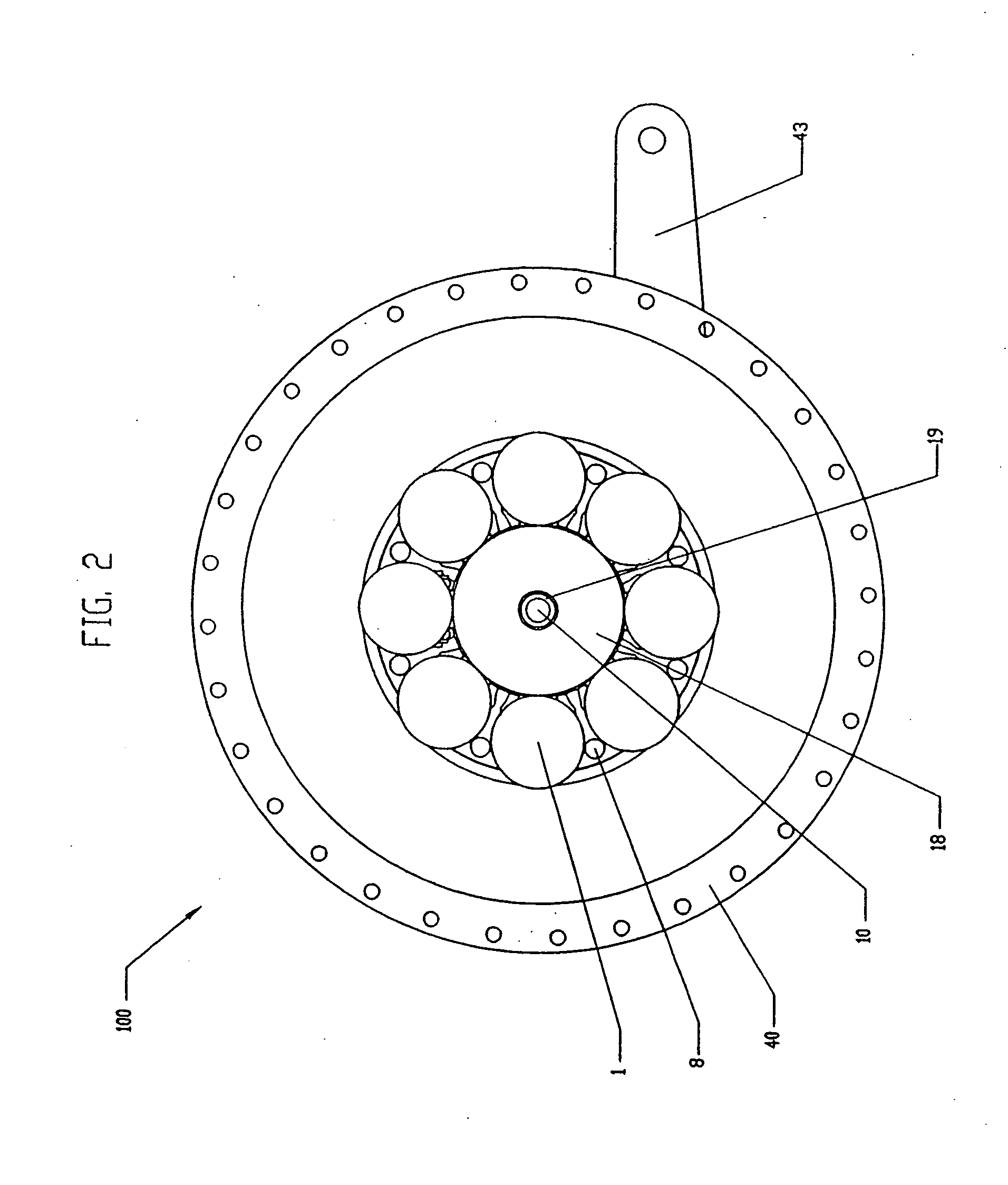
A toroidal type continuously variable transmission having first and second discs supported around a rotating shaft and receiving power rollers therebetween includes a ball spline having a first spline groove formed in an outer circumferential surface of the rotating shaft, a second spline groove formed in an inner circumferential surface of the first disc, and balls provided between the first spline groove and the second spline groove rollably. An axial position of an end portion of an effective groove portion of the first spline groove is located to correspond to an axial position of an inner end portion of the second spline groove or more closely to the second disc than the axial position thereof when a pressing unit, a preload spring and the first disc are installed around the rotating shaft, pressure oil is not fed to the pressing unit, and the preload spring is not elastically deformed.
Owner:NSK LTD
Continuously variable transmissions and methods therefor
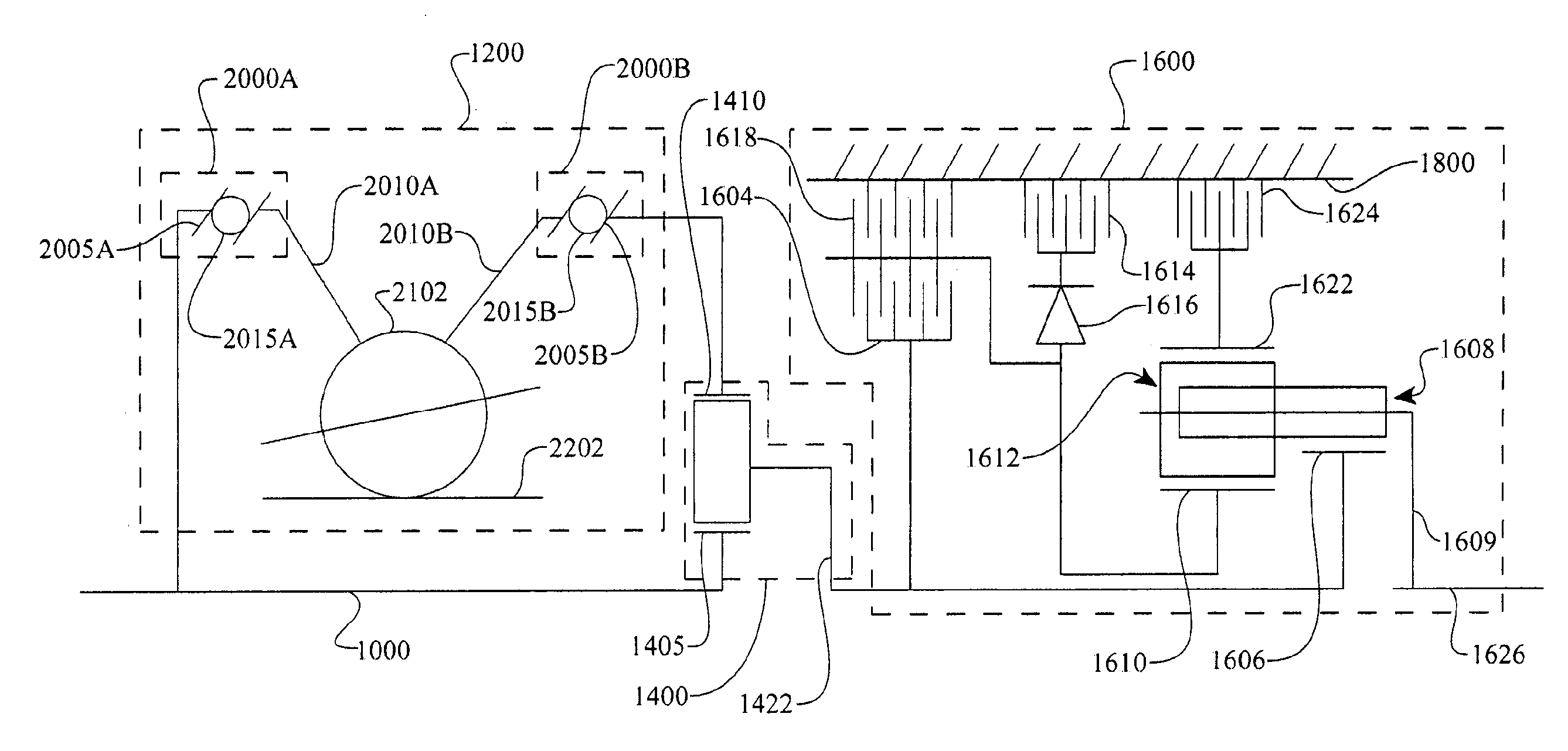
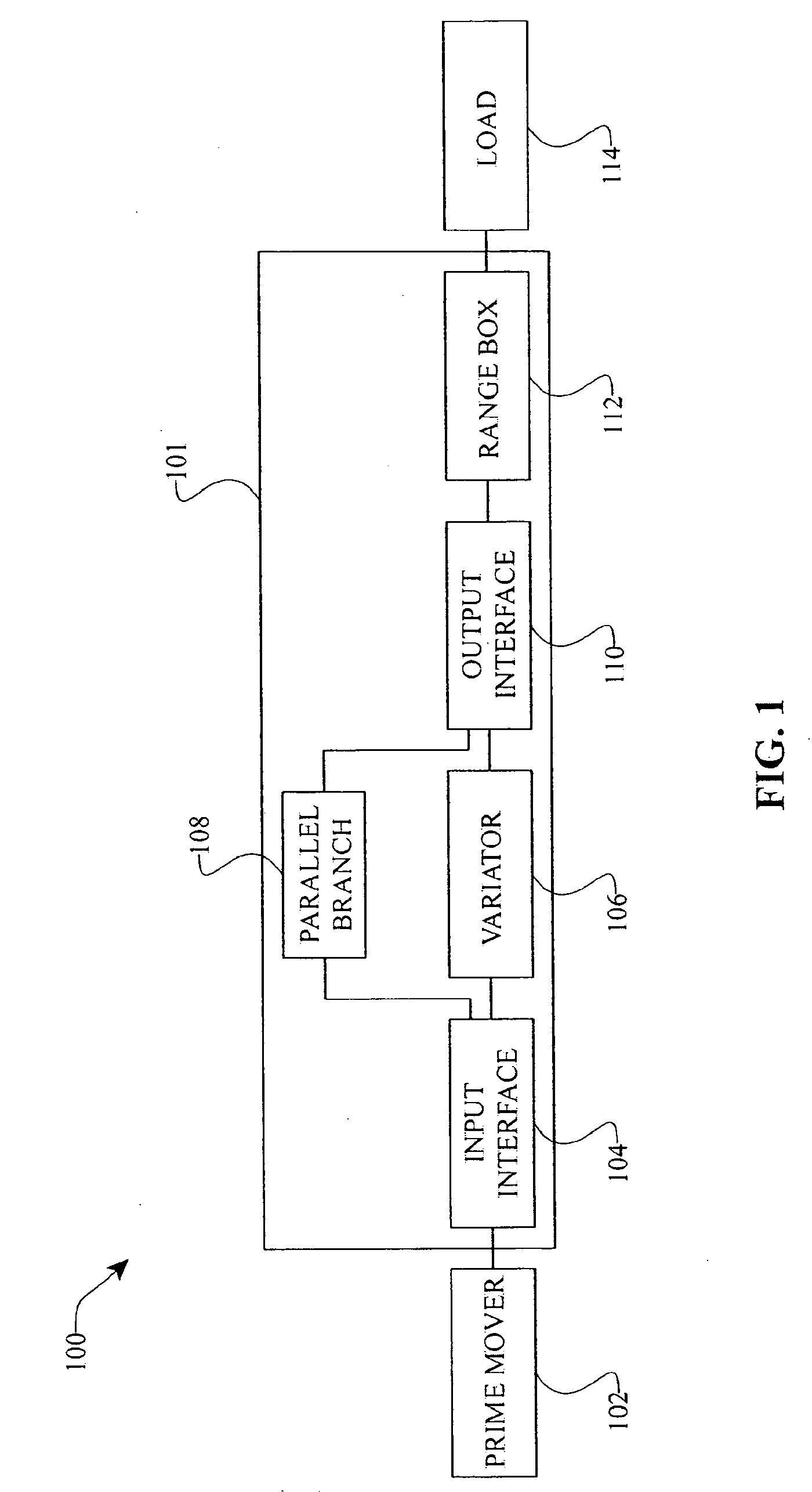
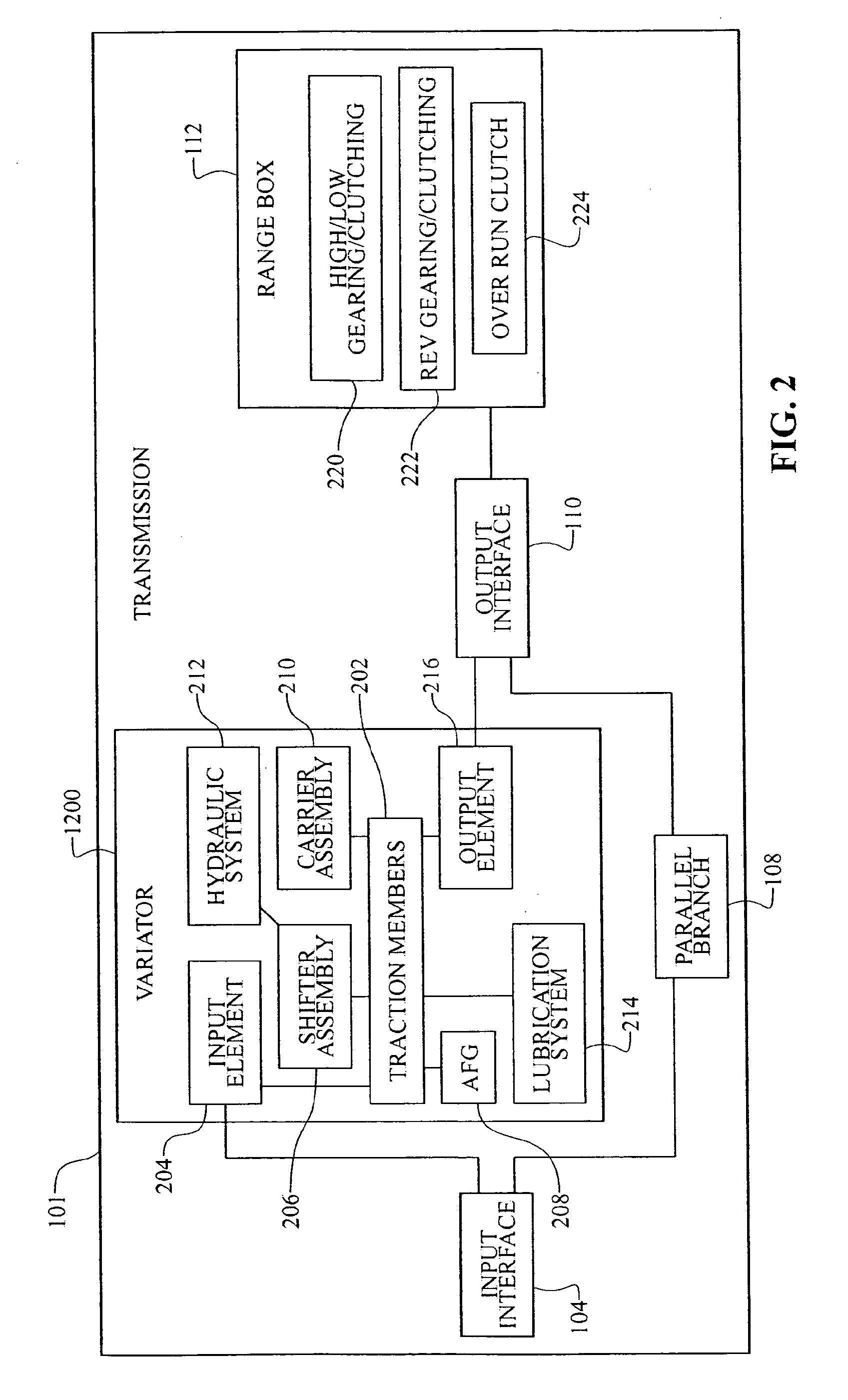
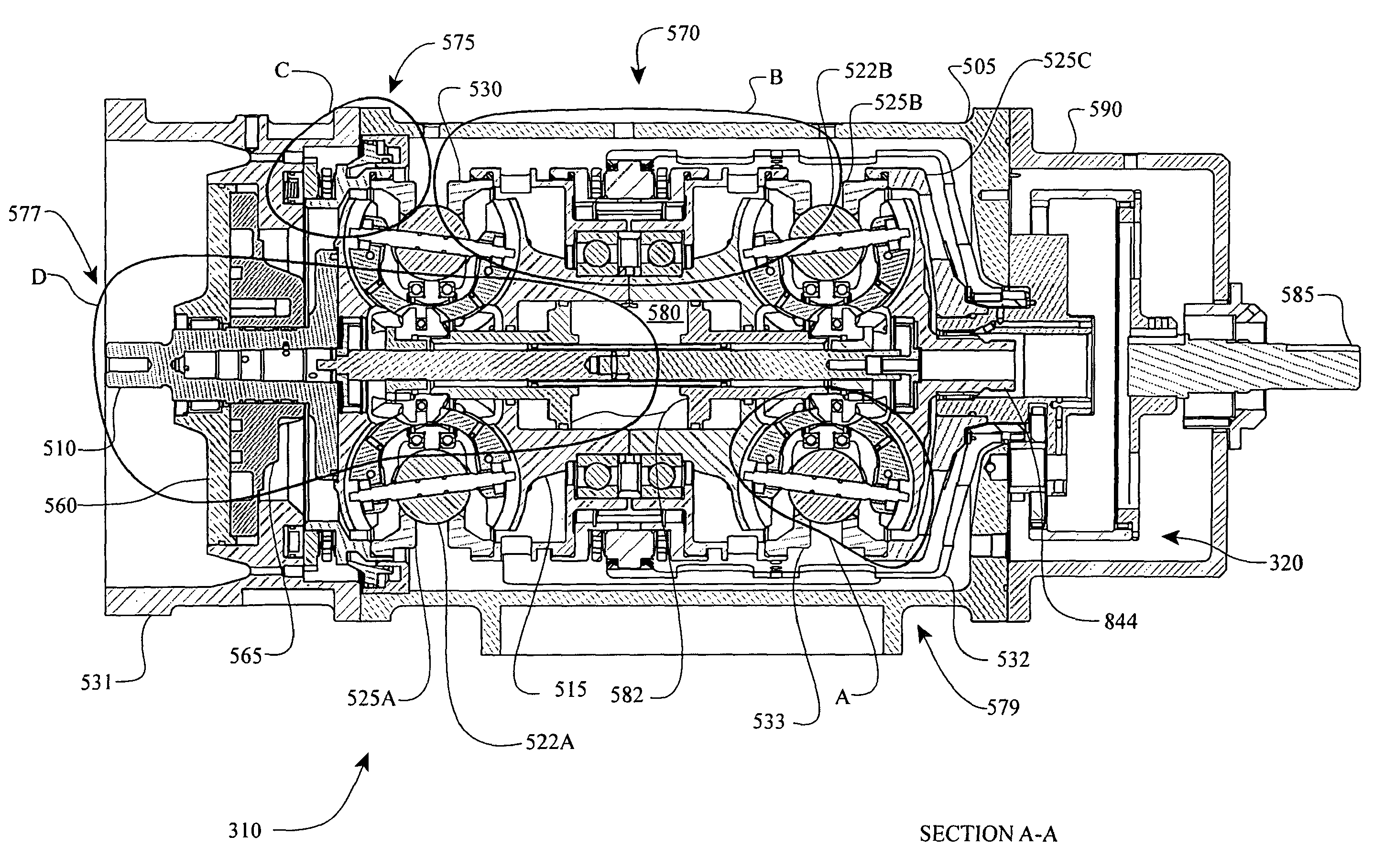
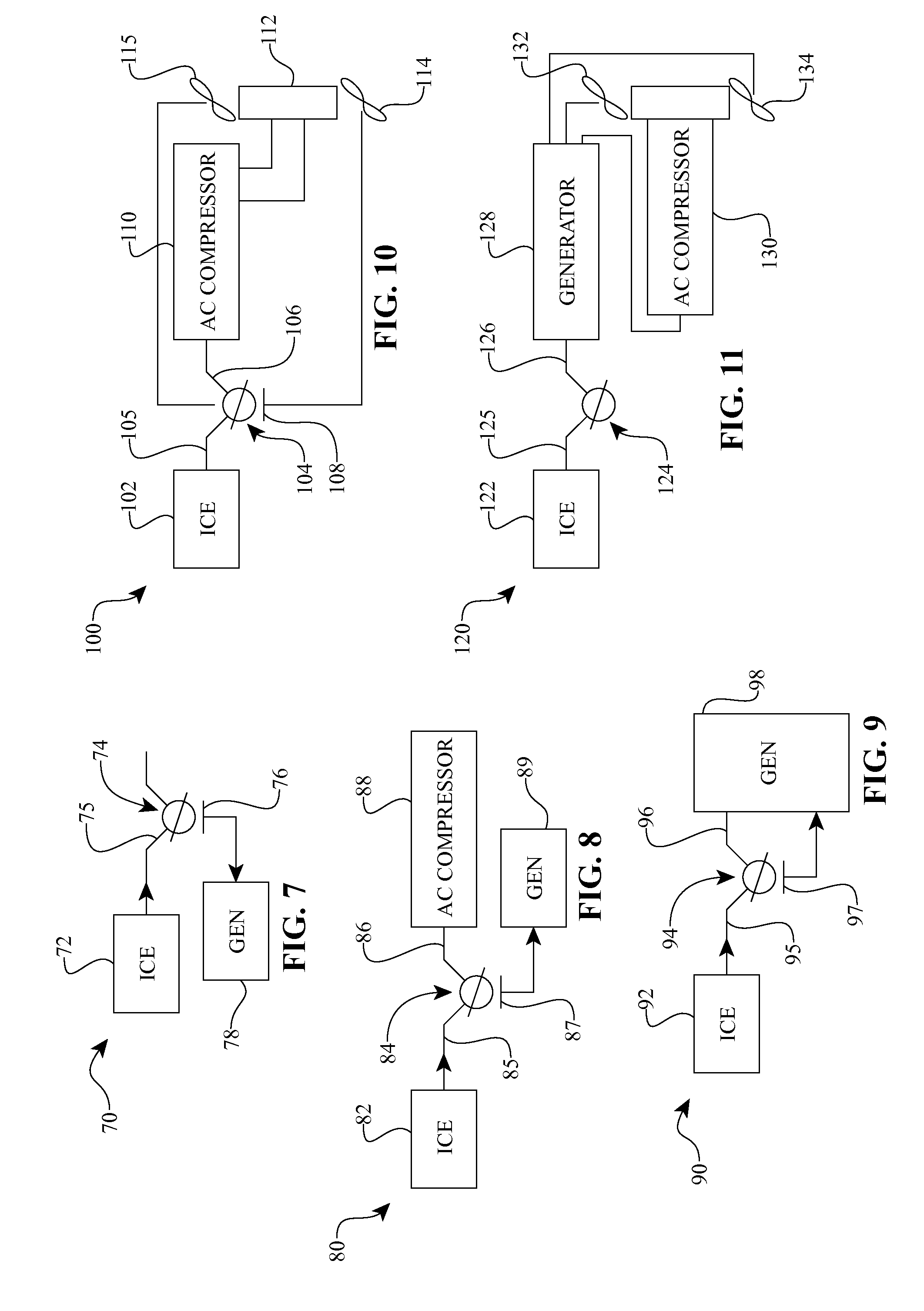
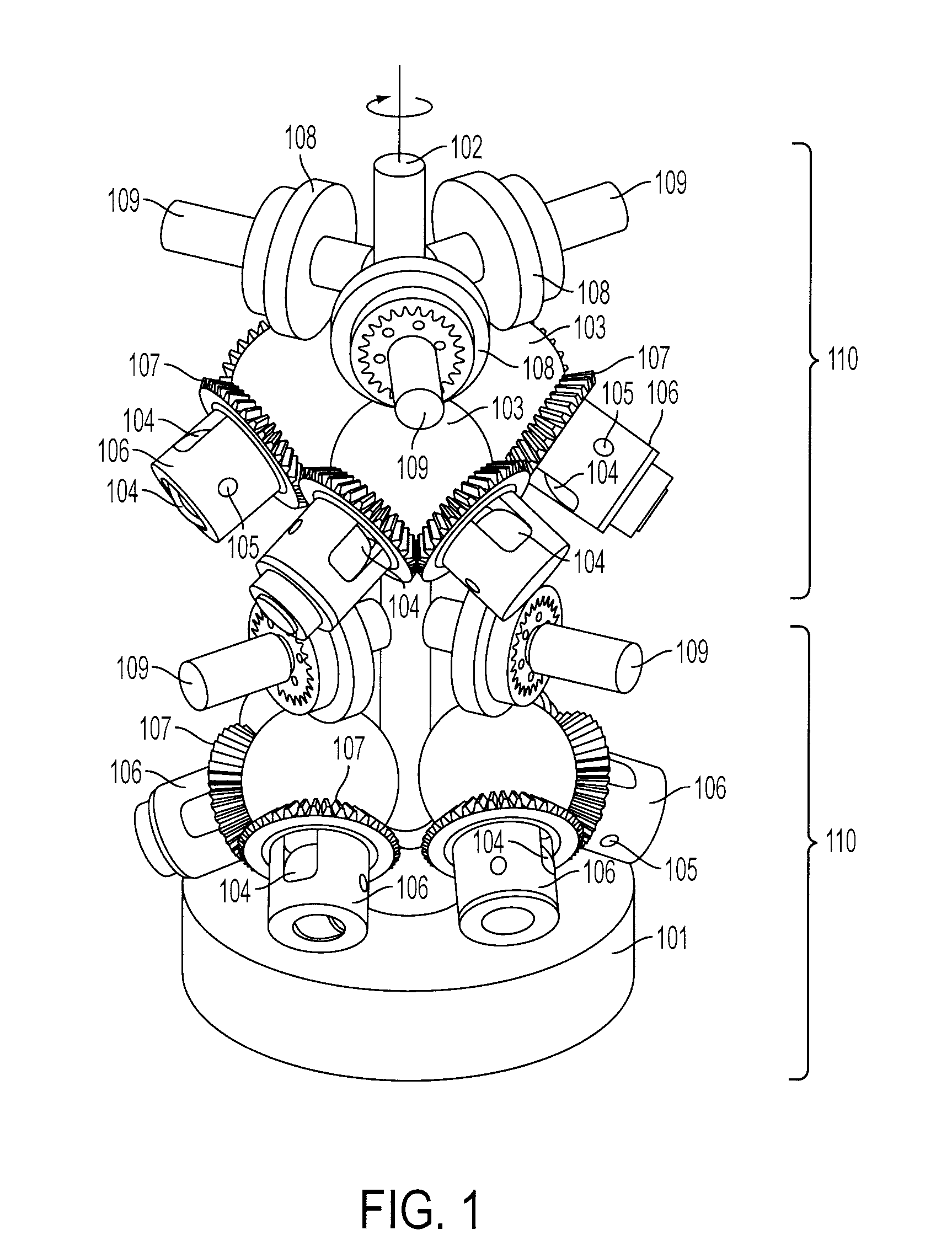
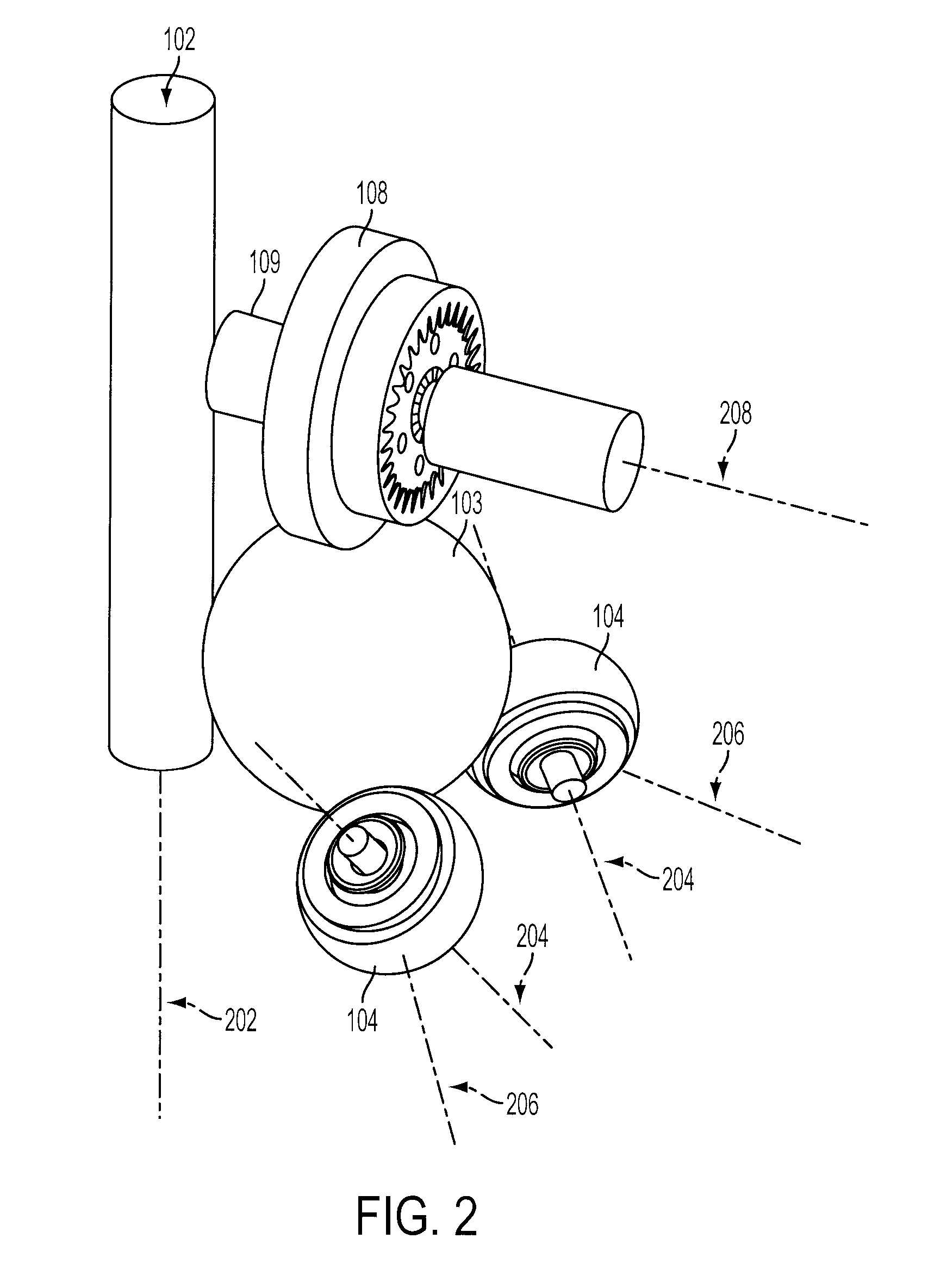
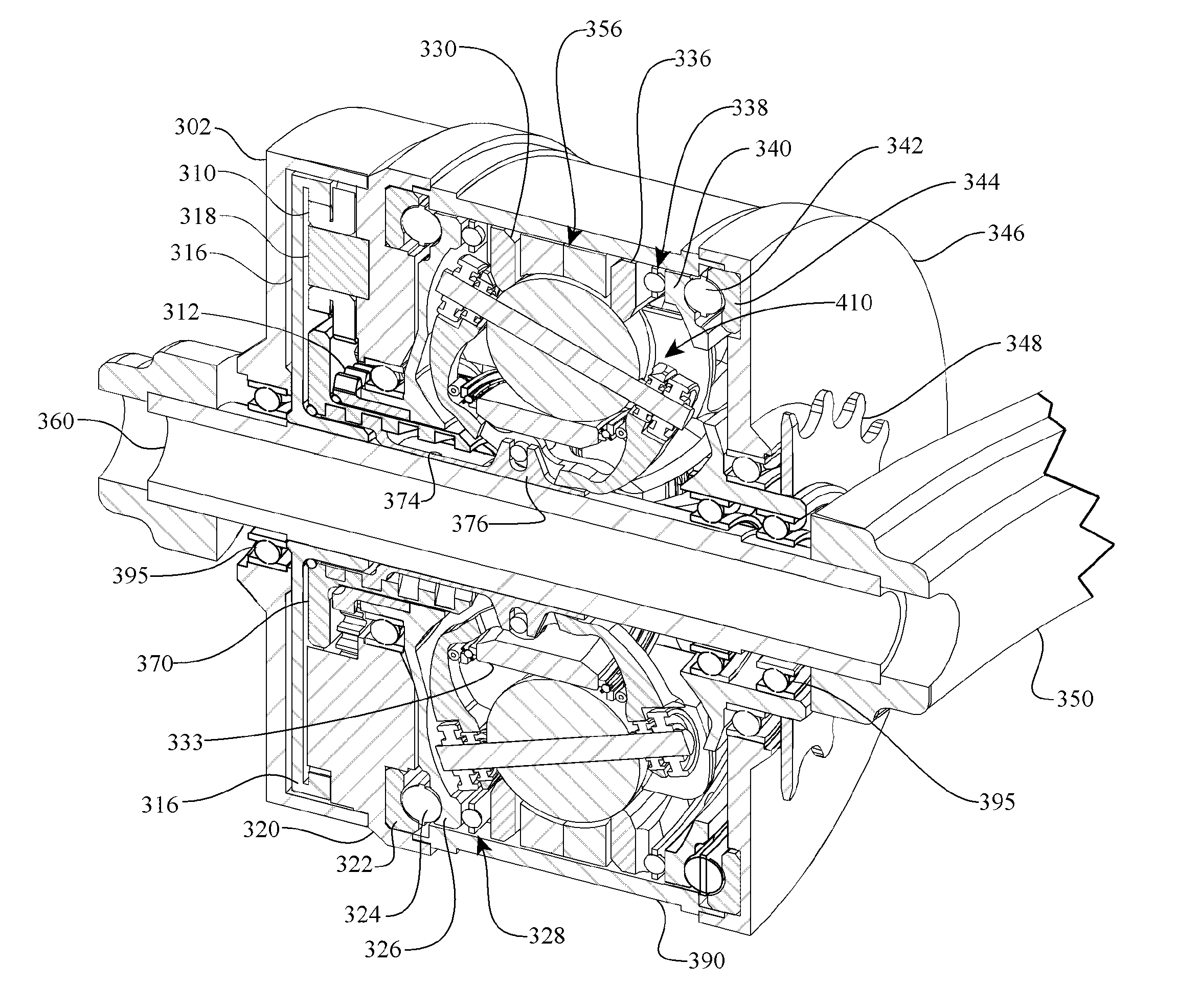
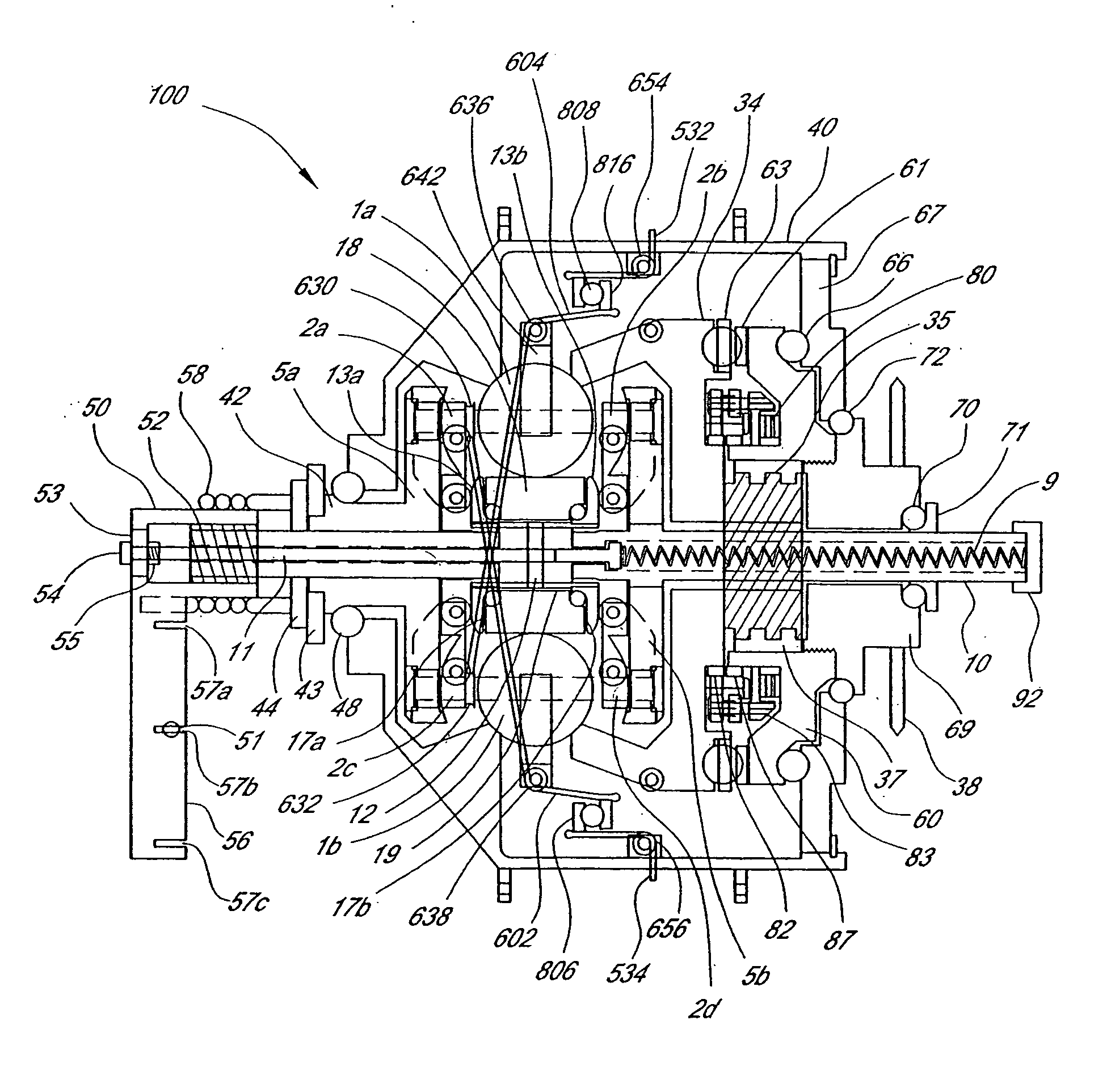
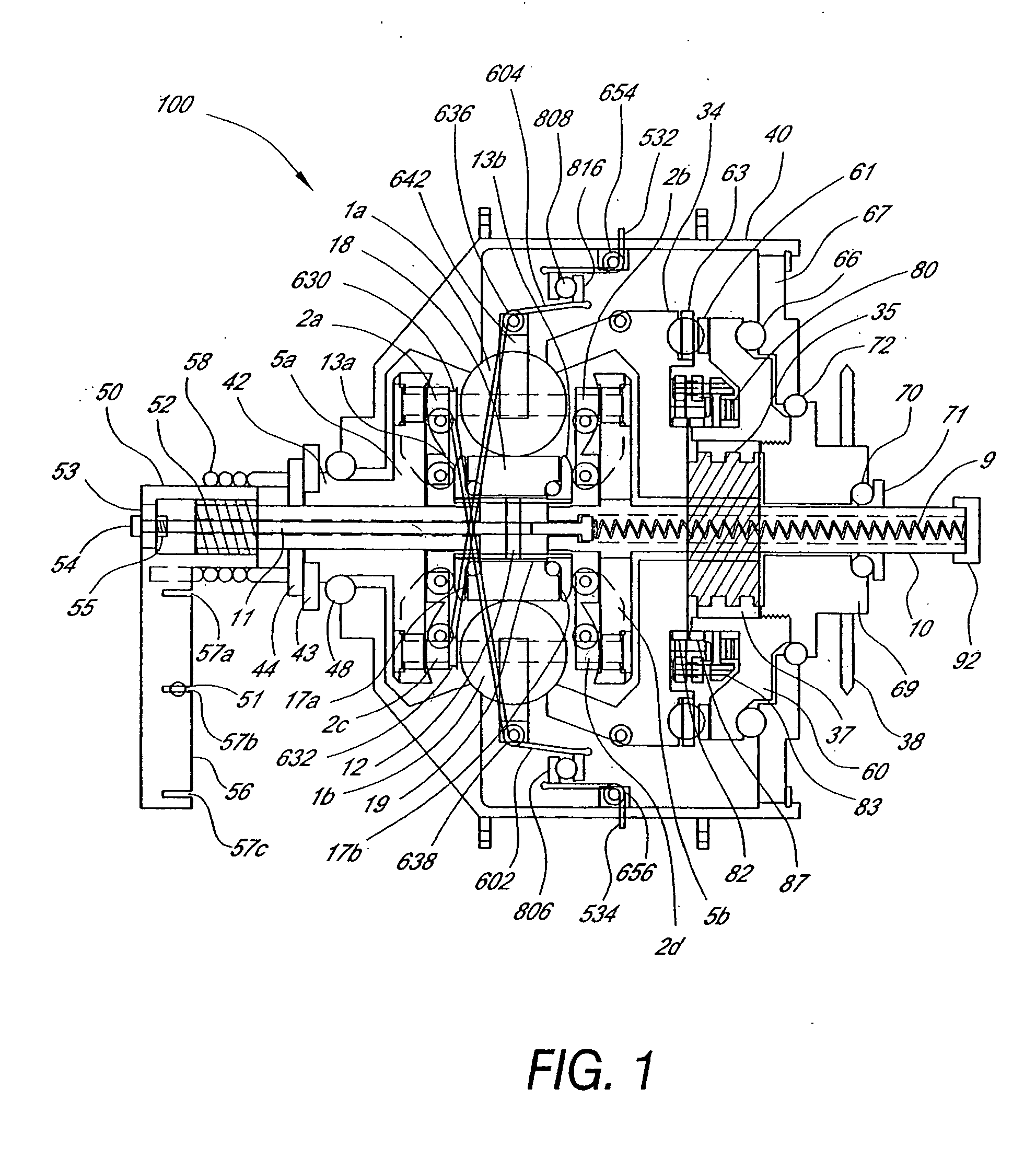
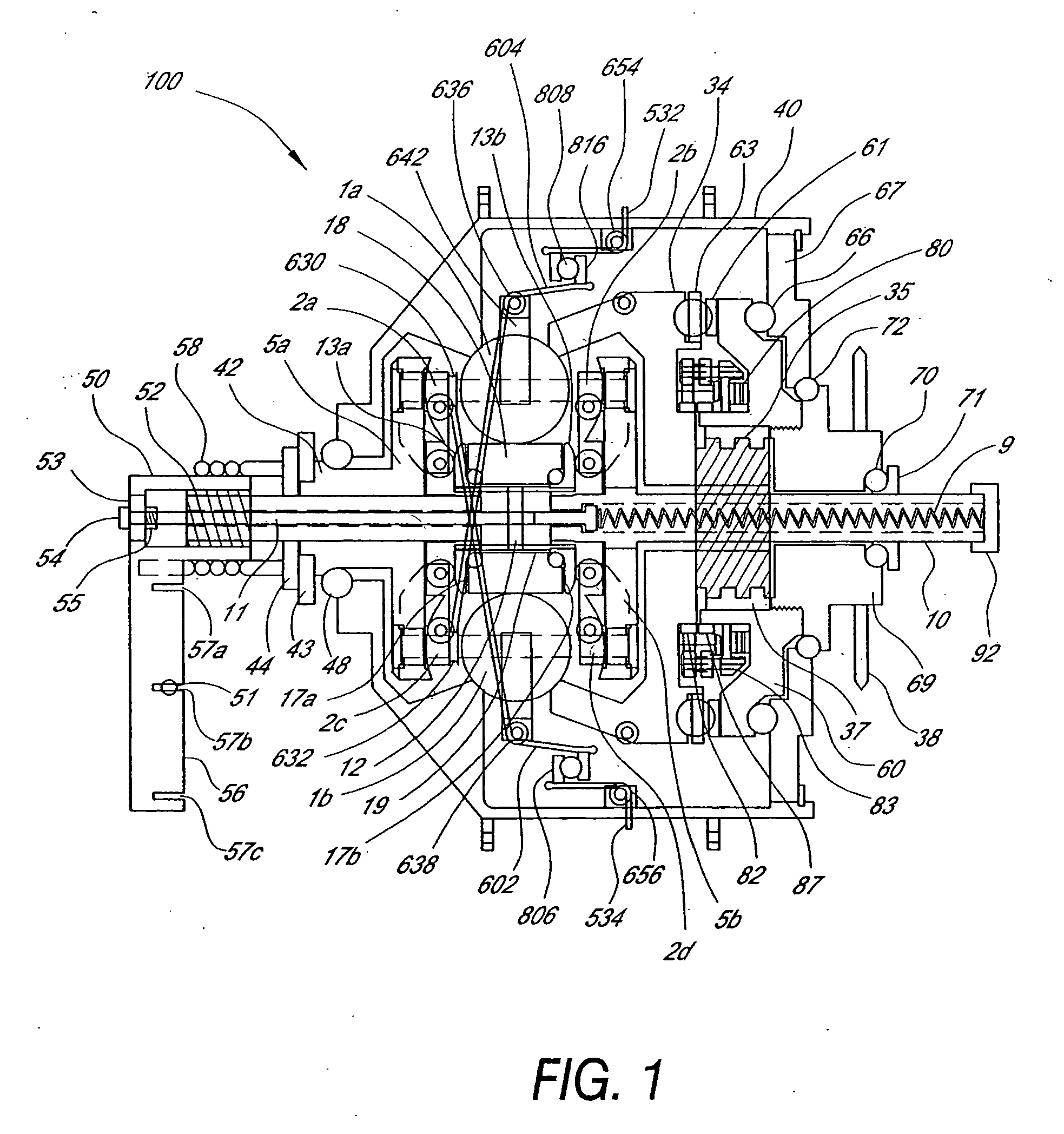
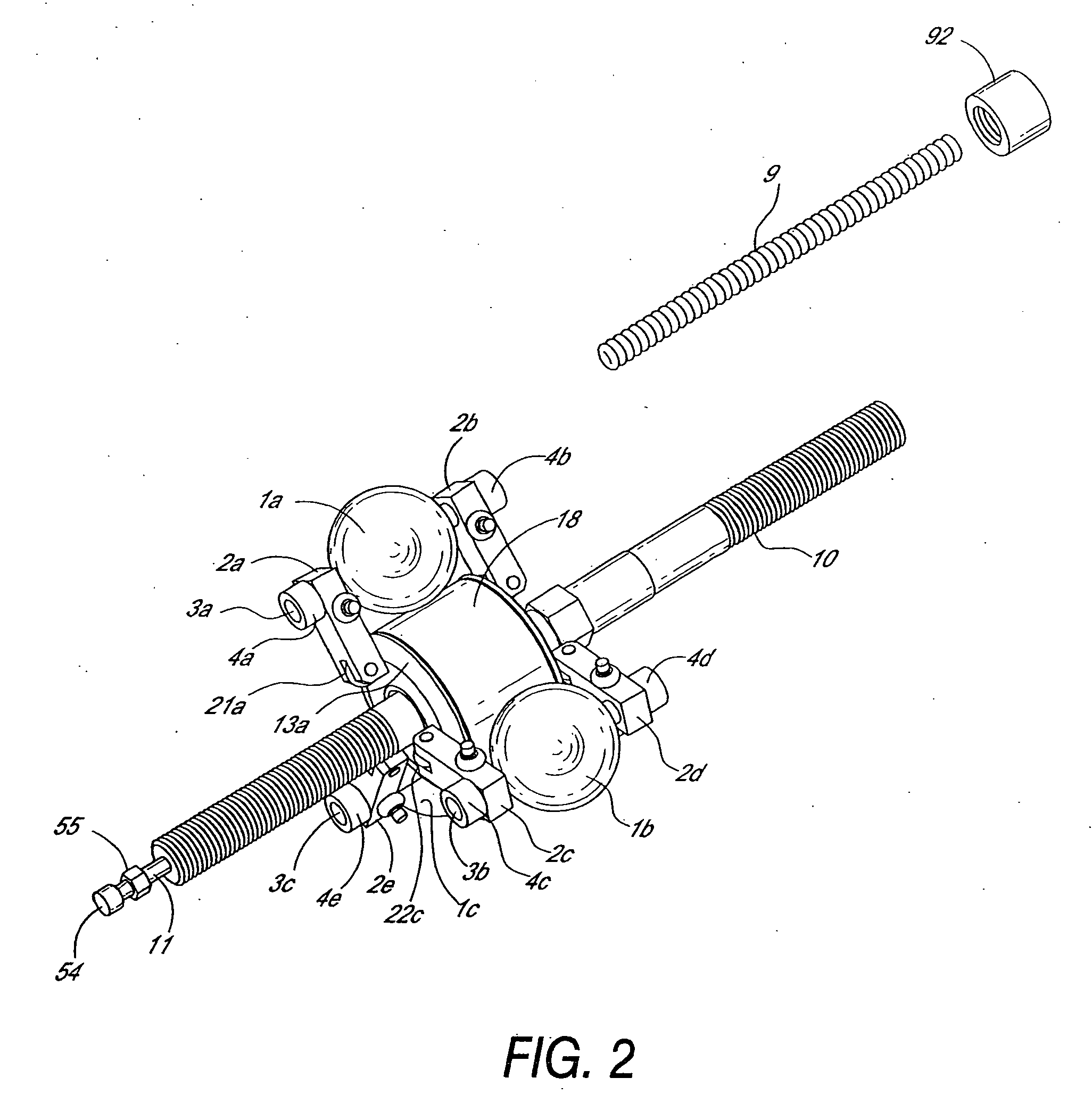
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for continuously variable transmissions (CVT) having a variator provided with a plurality of tilting, traction planets and traction rings. In one embodiment, a variator is coupled to a rangebox to provide multiple operating modes. In another embodiment, a hydraulic system is configured to control the transmission ratio of the variator and the rangebox. Various inventive shift-cam-and-sun subassemblies can be used to facilitate shifting of the transmission ratio of a CVT. Embodiments of a transmission housing and bell housing are adapted to house components of a CVT and, in some embodiments, to cooperate with other components of the CVT to support operation and / or functionality of the CVT. Various related devices include embodiments of, for example, a pivot arm, a control feedback mechanism, axial force generation and management mechanisms, a control valve integral with an input shaft, a pivot pin hub, and a rotatable carrier configured to support planet-pivot arm assemblies. FIG. 72 shows a torque-split ball-type rolling traction CVT with a ball-type rolling traction variator (1200) and planetary gearset (1400) which is followed by a rangebox (1600).
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS20070155567A1Easy to adjustImprove translationWheel based transmissionChain/belt transmissionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Traction planets and traction rings can be operationally coupled to a planetary gearset to provide a continuously variable transmission (CVT). The CVT can be used in a bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on the frame of the bicycle at a location forward of the rear wheel hub of the bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on and supported by members of the bicycle frame such that the CVT is coaxial with the crankshaft of the bicycle. The crankshaft is configured to drive elements of the planetary gearset, which are configured to operationally drive the traction rings and the traction planets. Inventive component and subassemblies for such a CVT are disclosed. A shifting mechanism includes a plurality of pivot arms arranged to pivot about the centers of the traction planets as a shift pin hub moves axially.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission controller
InactiveUS20070004552A1Reduce shift shockReduce update speedDigital data processing detailsGearingThrottle openingControl theory
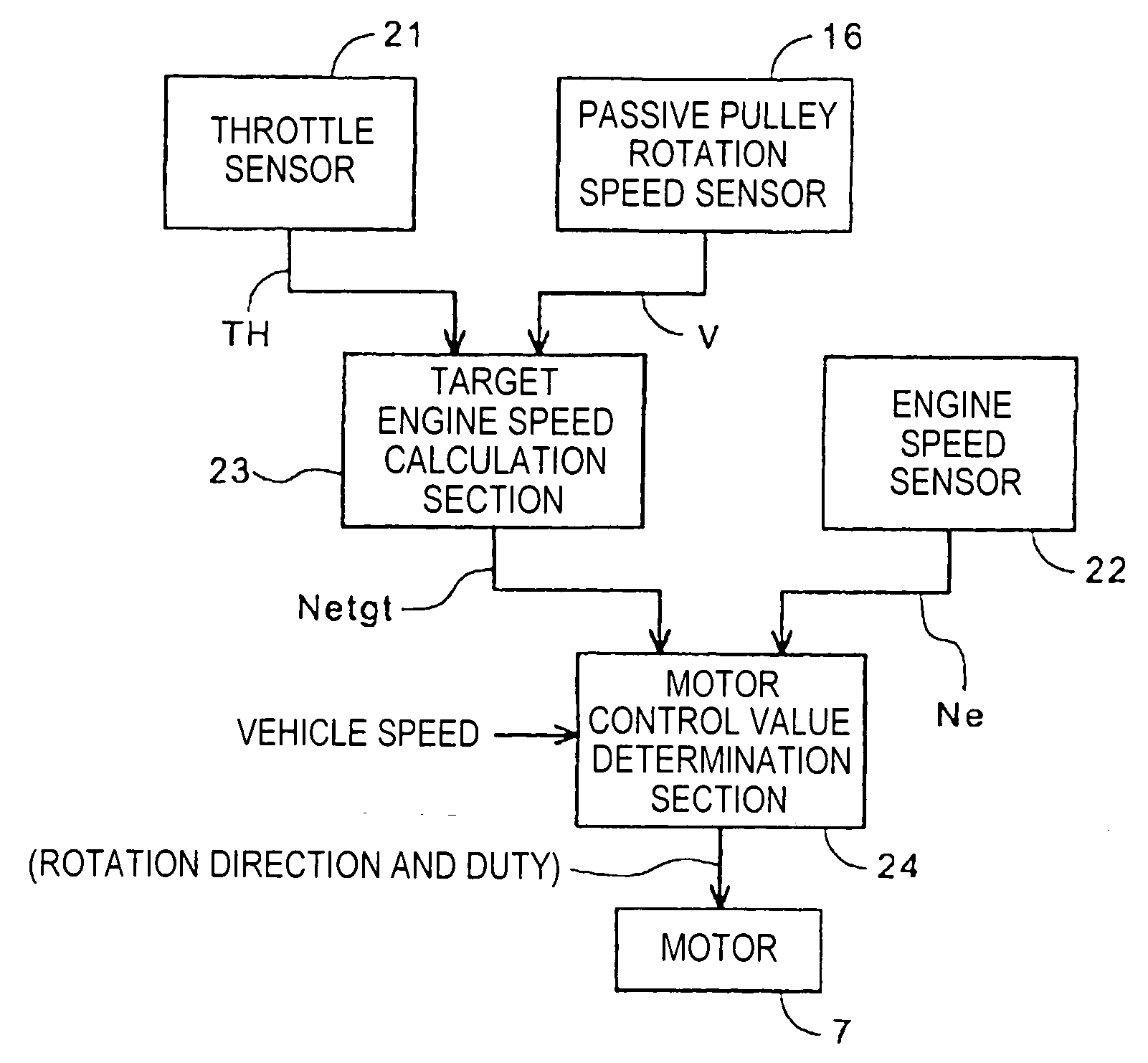
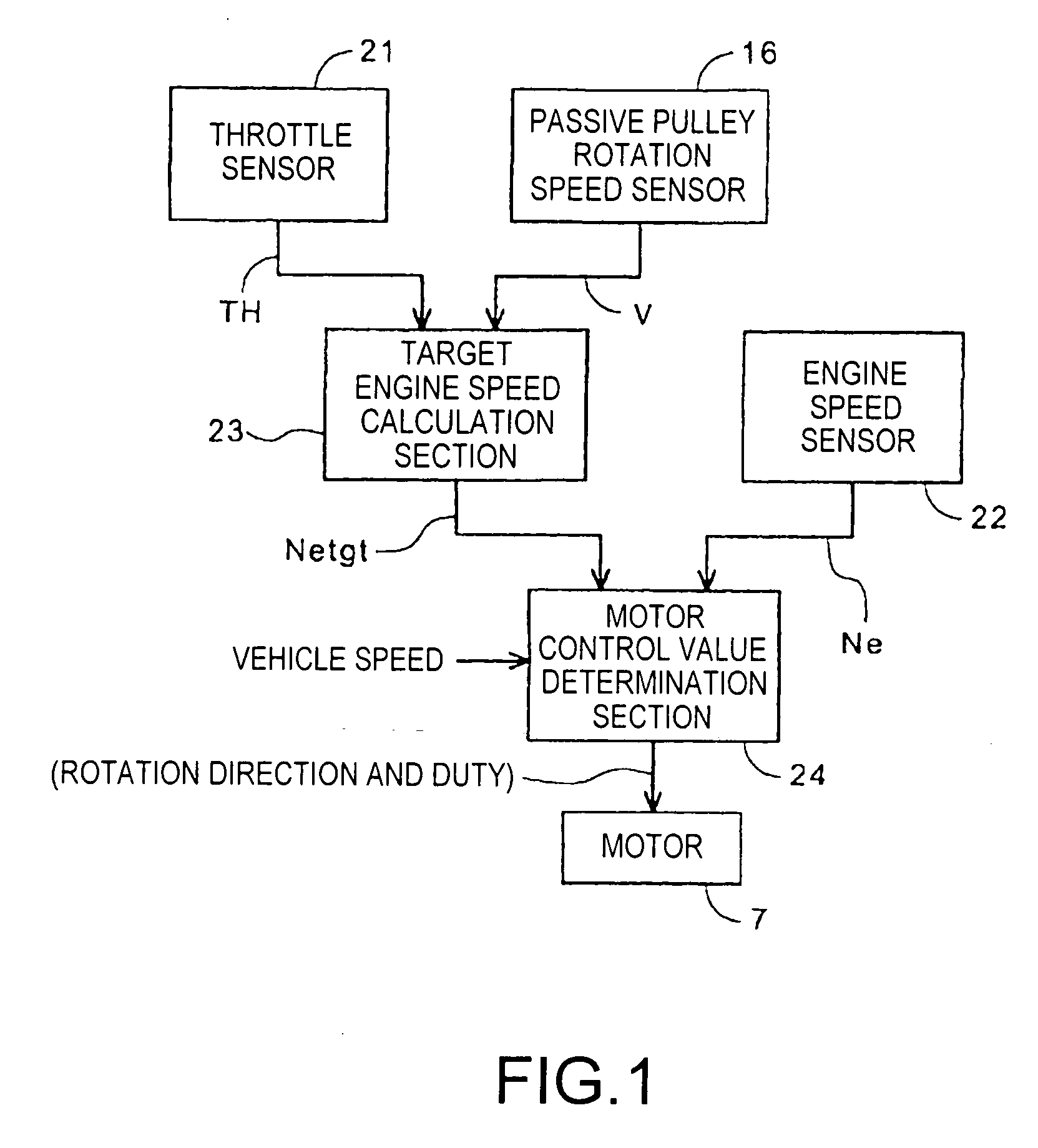
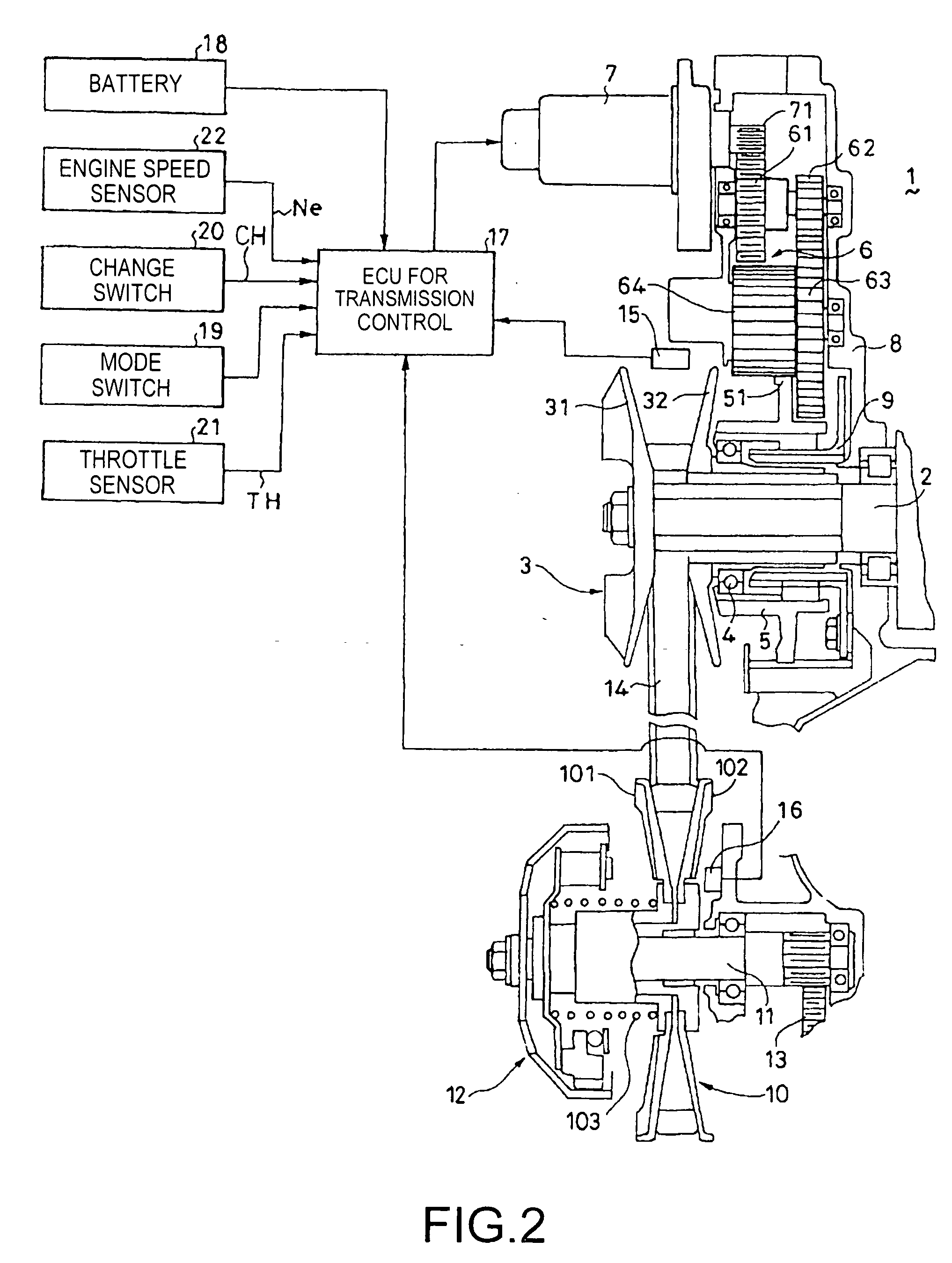
A continuously variable transmission is mounted on a vehicle capable of selecting plural drive modes and changes a target engine speed between drive modes. A pulley ratio is controlled by a motor. An ECU for transmission control includes a calculation section which outputs a target engine speed as a function of throttle opening and vehicle speed, and a motor control value determination section which outputs a control value for controlling the motor based on the target engine speed and an actual engine speed. In a case where, when a drive mode is selected, the current target engine speed changes by an amount exceeding a predetermined judgment value according to vehicle speed, the motor control value determination section updates the current target engine speed in a stepwise manner. The resulting configuration reduces a shift shock caused by a drive mode change.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Continuously variable transmission and method of controlling it
InactiveUS20050037876A1Shorten the axial lengthReduce widthGearingGearing controlRotational axisControl theory
To provide a continuously variable transmission and a control method thereof, allowing for control of the axial position of a movable sheave without a sensor for measuring the axial position of the movable sheave on a rotational shaft and for stable control with the movable sheave being held in position, without the increase in the size of mechanisms and power consumption. A continuously variable transmission in which, on a rotational shaft 1 thereof are mounted a fixed sheave 2 positioned in the axial direction and a movable sheave 3 slidable axially, so as to face each other, a motor is provided for driving the movable sheave, and a slide driving means 16 is provided for sliding the movable sheave 3 axially by the rotation of the motor, characterized in that: the motor is a step motor 6, and the step motor 6 and the slide drive means 16 are mounted coaxially with the rotational shaft 1.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
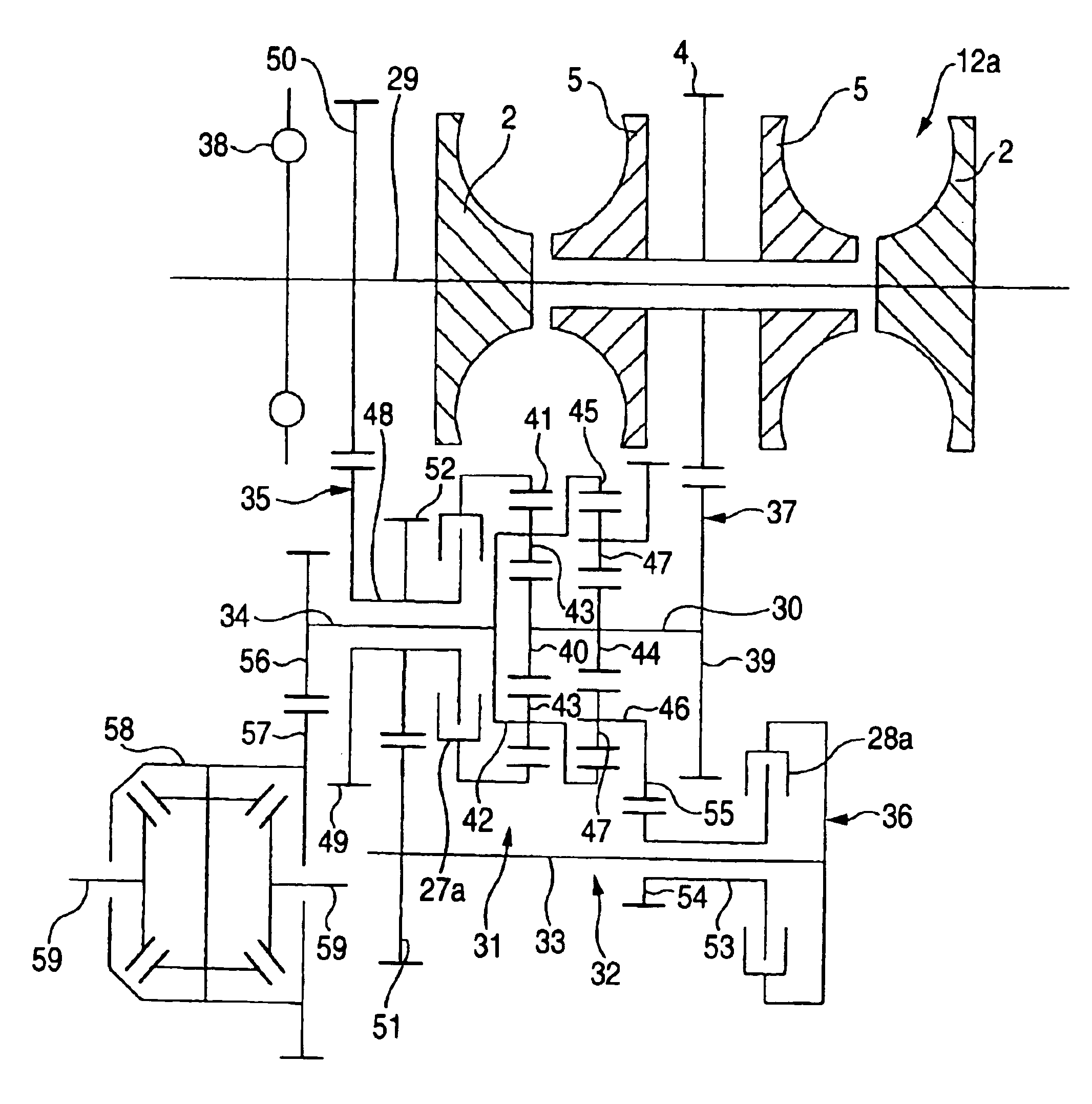
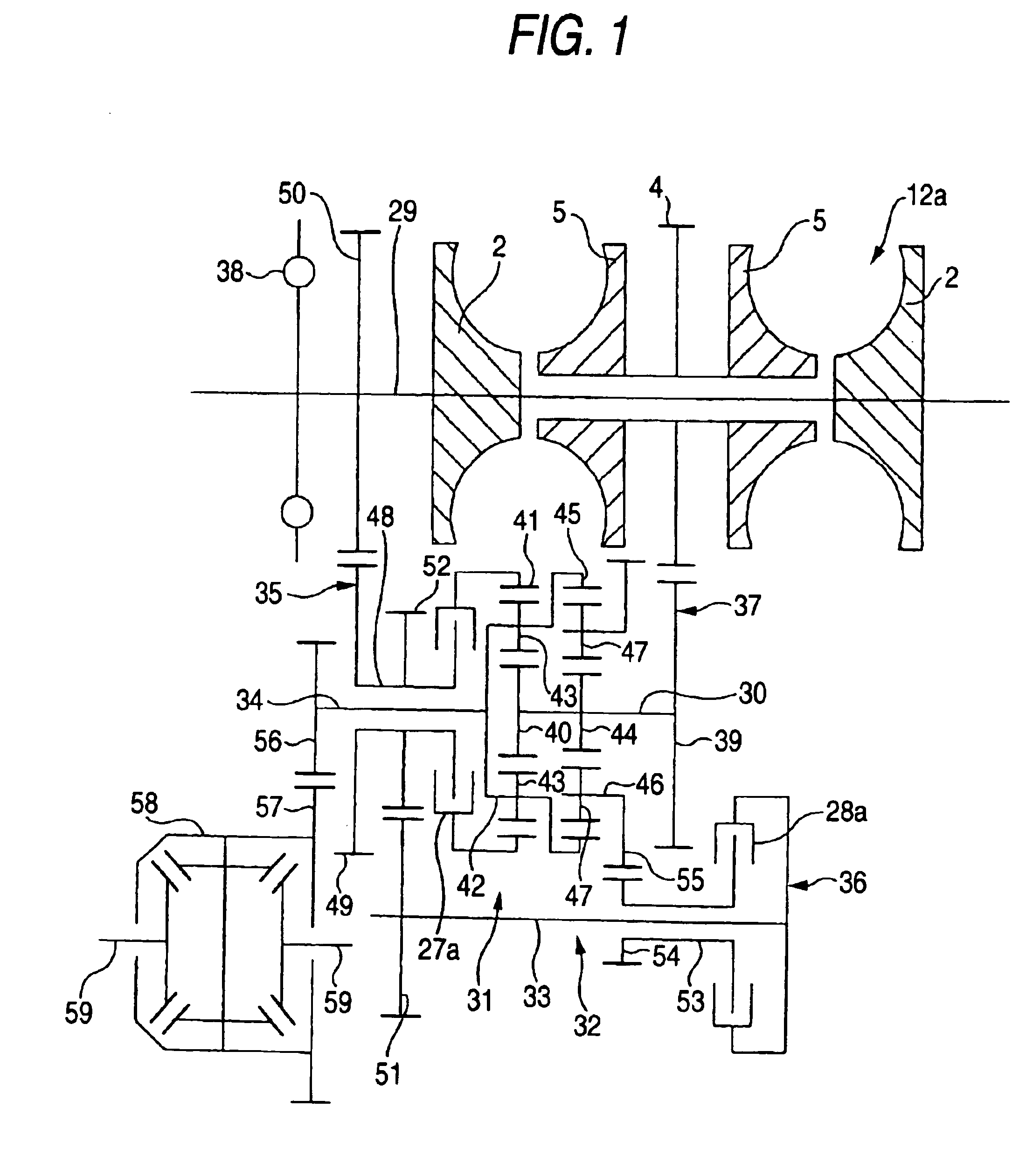
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
InactiveUS7160220B2Avoid feeling uncomfortableGearing controlEngine controllersControl theoryContinuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission apparatus includes: an input shaft, an output shaft, a toroidal continuously variable transmission, a gear-type differential unit including a plurality of gears, and a controller. The controller calculates a torque actually passing through the toroidal continuously variable transmission to obtain a deviation of the torque from a target value and adjusts a transmission ratio of the toroidal continuously variable transmission to eliminate the deviation. The controller stops the adjustment of the transmission ratio when the torque is not stable.
Owner:NSK LTD
Continuously variable transmission mechanism and transmission using the same
InactiveUS20110319222A1Increase rotation speedRotational radiusFriction gearingsRotation velocityControl theory
A continuously variable transmission adapted to set a speed change ratio in accordance with a tilt angle of a rolling member mediating a torque being transmitted, and to transmit a torque among three elements. The transmission mechanism is provided with a rolling member having a smooth outer face and capable of tilting a rotational center axis thereof, and a rotary member arranged to be contacted with a predetermined portion of the outer face of the rolling member in a torque transmittable manner. Specifically, the continuously variable transmission mechanism is configured to vary a rotational speed of the rotary member by changing a rotation radius of a contact point between the rolling member and the rotary member by tilting the rotational center axis of the rolling member.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
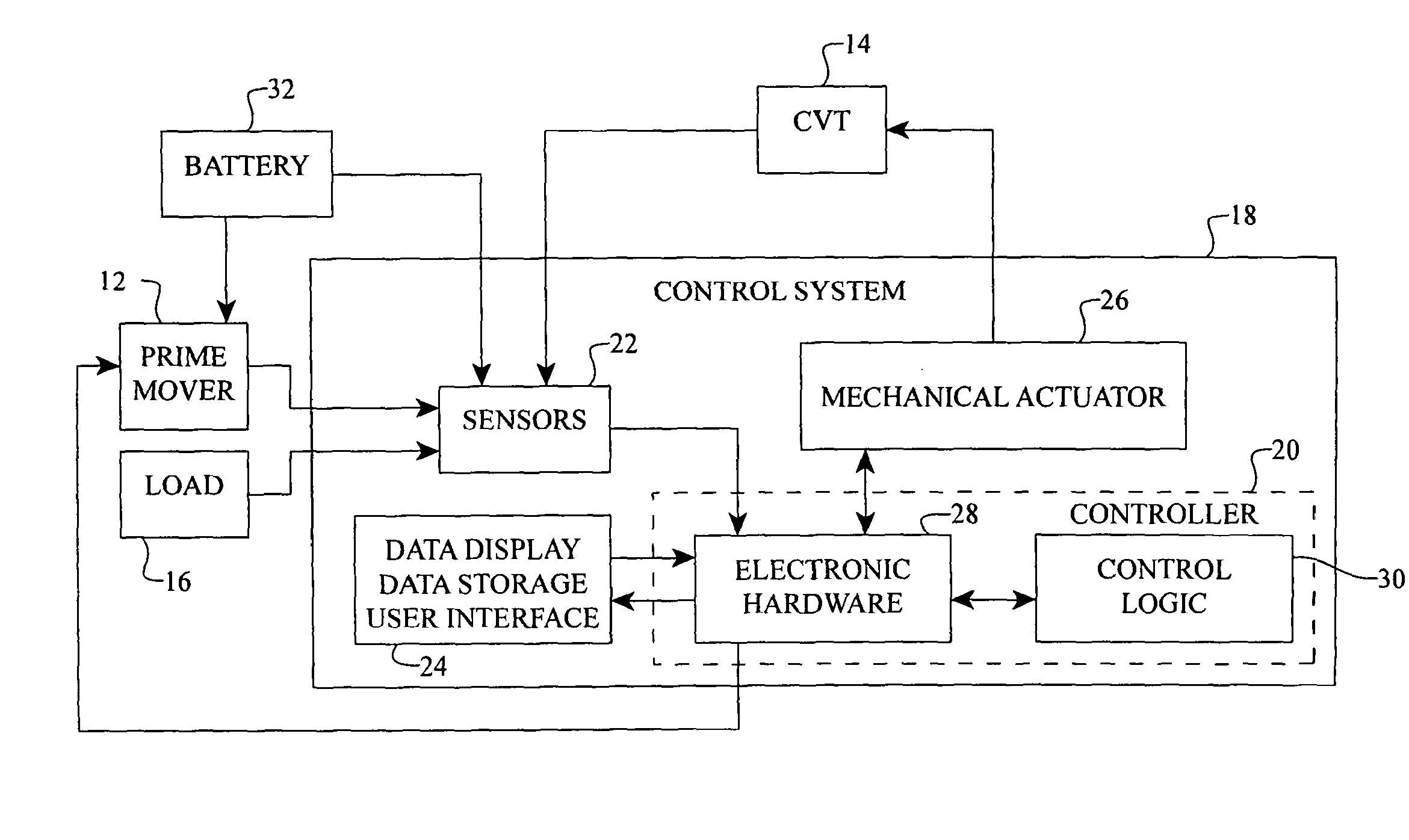
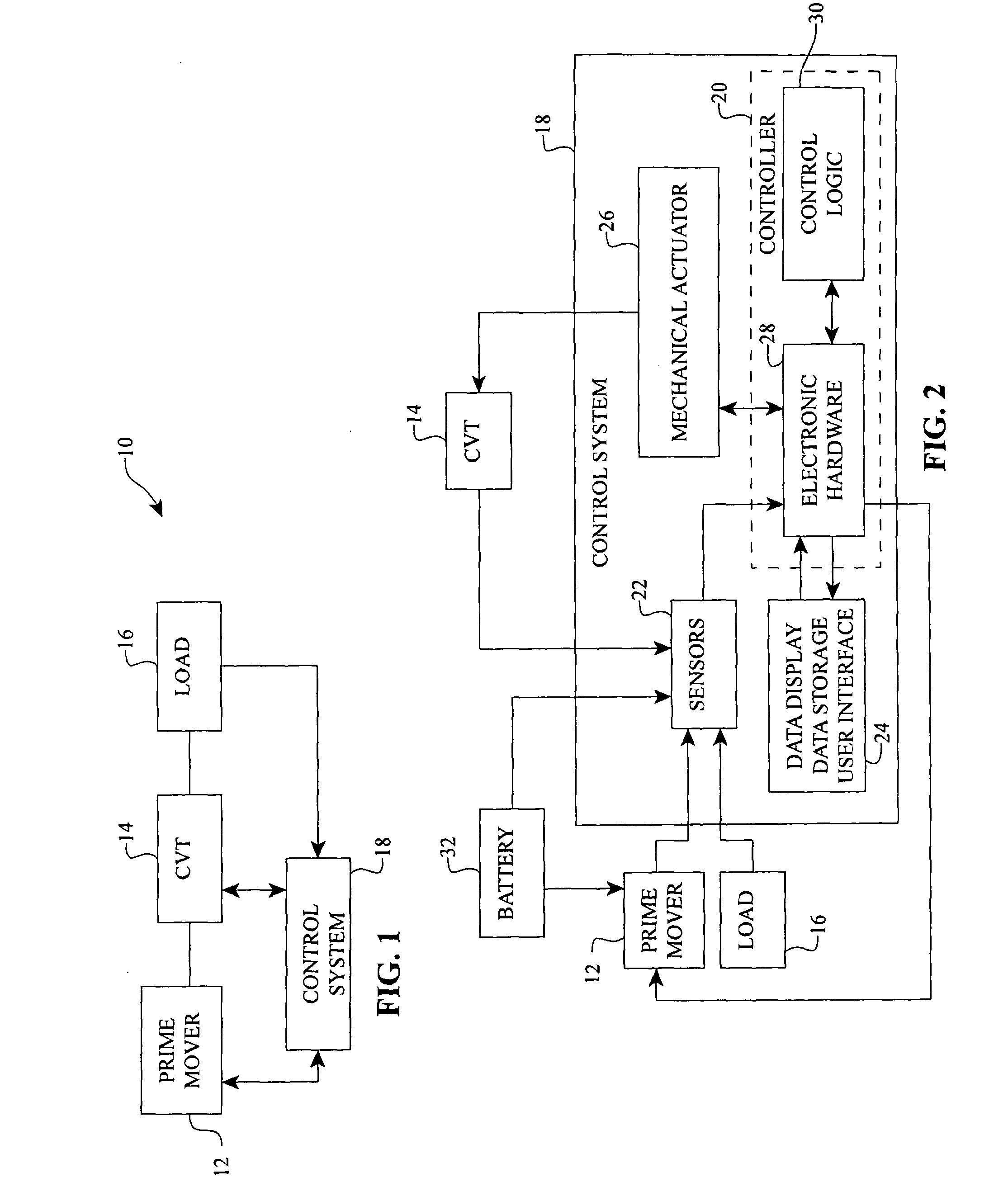
Systems and methods for control of transmission and/or prime mover
Disclosed here are inventive systems and methods for a powertrain of an electric vehicle (EV). In some embodiments, said powertrain includes a continuously variable transmission (CVT) coupled to an electric drive motor, wherein a control system is configured to control the CVT and / or the drive motor to optimize various efficiencies associated with the EV and / or its subsystems. In one specific embodiment, the control system is configured to operate the EV in an economy mode. Operating in said mode, the control system simultaneously manages the CVT and the drive motor to optimize the range of the EV. The control system can be configured to manage the current provided to the drive motor, as well as adjust a transmission speed ratio of the CVT. Other modes of operation are also disclosed. The control system can be configured to manage the power to the drive motor and adjust the transmission speed ratio of the CVT taking into account battery voltage, throttle position, and transmission speed ratio, for example.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
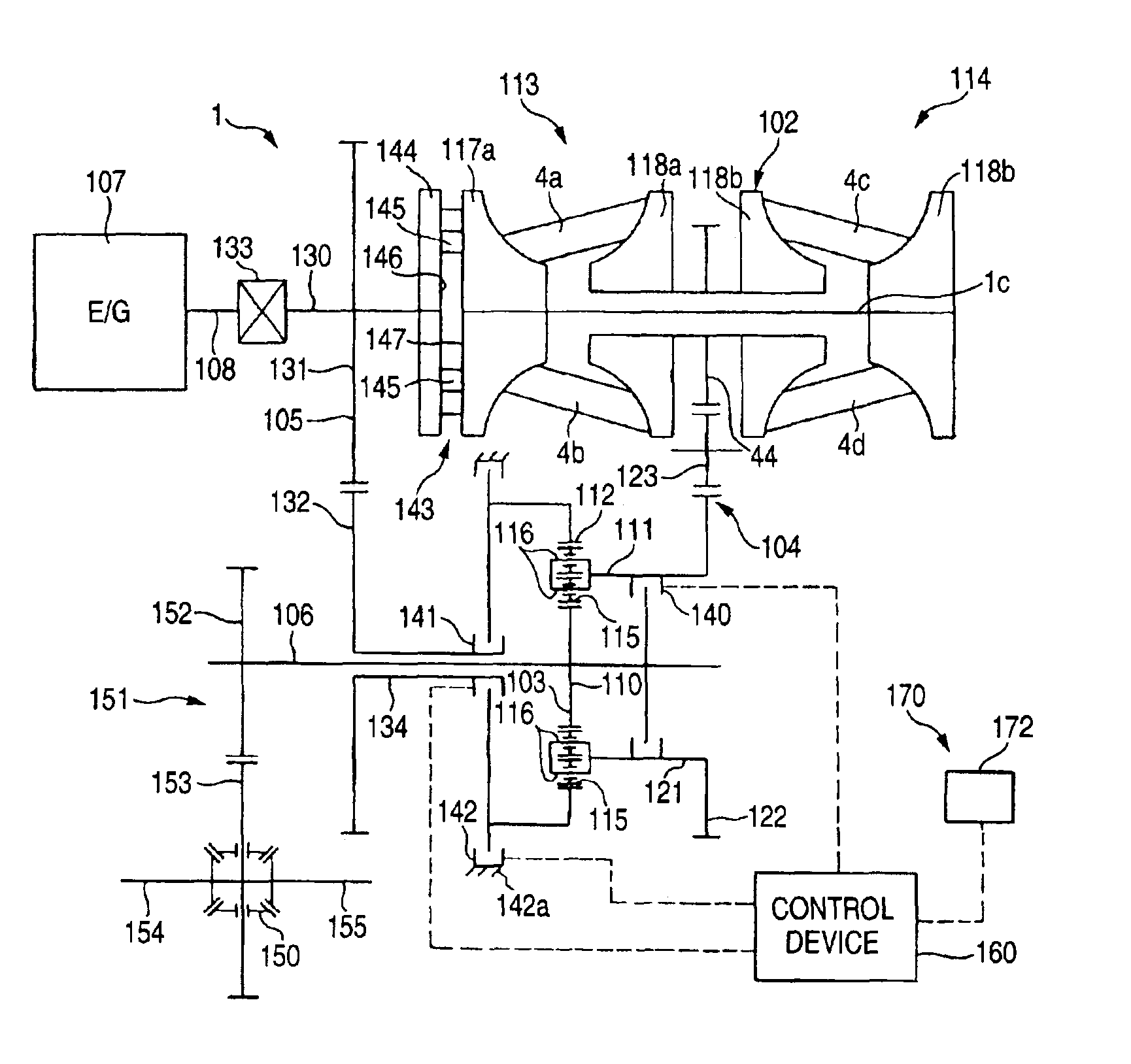
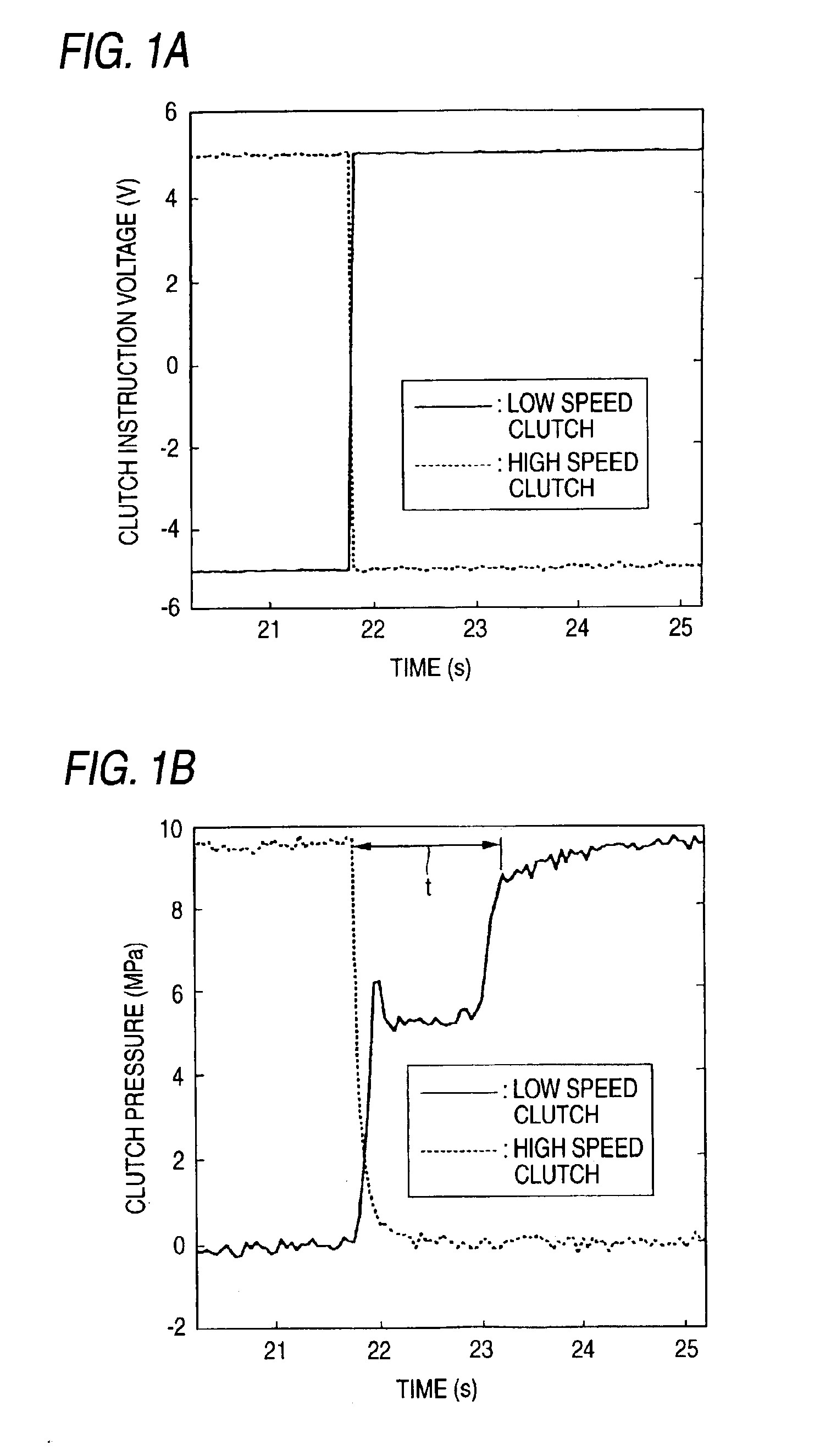
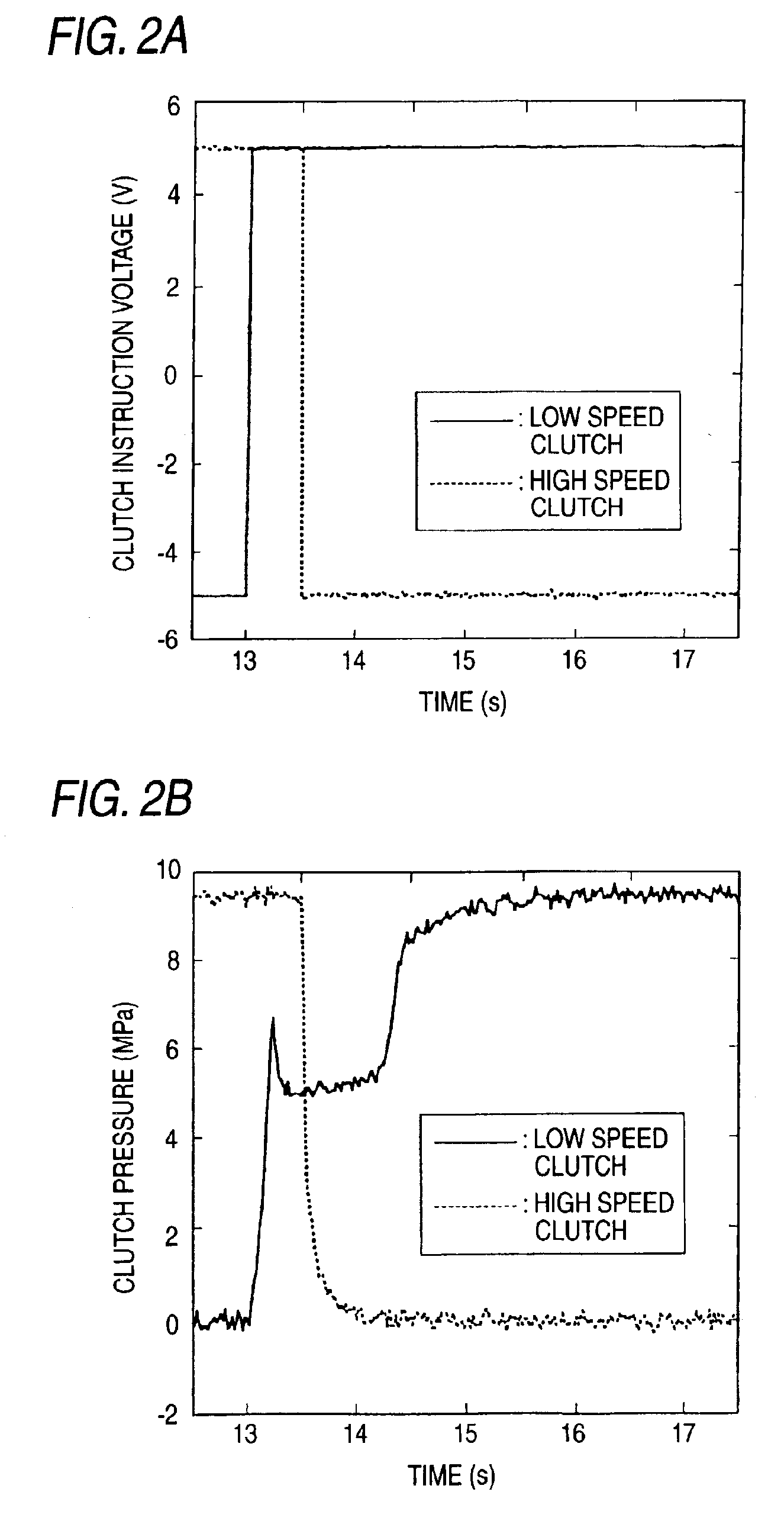
A continuously variable transmission apparatus has clutch device having a low speed clutch; a high speed clutch; and, a controller switching the transmission state into any one of a low speed mode and a high speed mode by connecting any one of the clutches, wherein timings for signaling by the controller for switching the connected and disconnected states of the clutches vary according to the switching directions of the low speed and high speed modes; and, a timing for signaling for connecting the low speed clutch with respect to the moment for signaling for cutting off the connection of the high speed clutch in order to switch the high speed mode over to the low speed mode is set earlier than a timing for signaling for connecting the high speed clutch with respect to the moment for signaling for cutting off the connection of the low speed clutch.
Owner:NSK LTD
Continuously variable transmission
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for continuously variable accessory drives (CVAD). In one embodiment, a skew-based control system is adapted to facilitate a change in the ratio of a CVAD. In another embodiment, a skew-based control system includes a skew actuator coupled to a carrier member. In some embodiments, the skew actuator is configured to rotate a carrier member of a CVT. Various inventive traction planet assemblies can be used to facilitate shifting the ratio of a CVT. In some embodiments, the traction planet assemblies include legs configured to cooperate with the carrier members. In some embodiments, a traction planet assembly is operably coupled to the carrier members. Embodiments of a shift cam and a traction sun are adapted to cooperate with other components of the CVT to support operation and / or functionality of the CVT. Among other things, shift control interfaces for a CVT are disclosed.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Infinitely variable transmissions, continuously variable transmissions, methods, assemblies, subassemblies, and components therefor
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for infinitely variable transmissions (IVT) having a variator provided with a plurality of tilting spherical planets. In one embodiment, a variator is provided with multiple planet arrays. In another embodiment, a hydraulic system is configured to control the transmission ratio of the IVT. Various inventive idler assemblies and planet-pivot arm assemblies can be used to facilitate adjusting the transmission speed ratio of an IVT. Embodiments of a transmission housing and bell housing are adapted to house components of an IVT and, in some embodiments, to cooperate with other components of the IVT to support operation and / or functionality of the IVT. Various related devices include embodiments of, for example, a control feedback mechanism, axial force generation and management mechanisms, a control valve integral with an input shaft, and a rotatable carrier configured to support planet-pivot arm assemblies.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Auxiliary power unit having a continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS20120258839A1Fuel consumption is minimizedIncreased power demandAuxillary drivesVehicle fittingsCombustionControl system
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for auxiliary power units (APU). In one embodiment, the APU includes a source of rotational power such as a combustion engine operably coupled to a continuously variable transmission (CVT). The CVT can be coupled to a load. In some embodiments, the load is provided by a generator. In one embodiment, the APU has a control system configured to control the operation of the engine and the operation of the CVT. The control system can facilitate substantially constant speed operation of the generator in the presence of variable operation of the engine. In another embodiment, the APU includes a continuously variable accessory drive (CVAD) operably coupled to an engine. The CVAD can include a continuously variable transmission operably coupled to a generator. In one embodiment, a skew-based control system is adapted to facilitate a change in the ratio of a CVAD.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
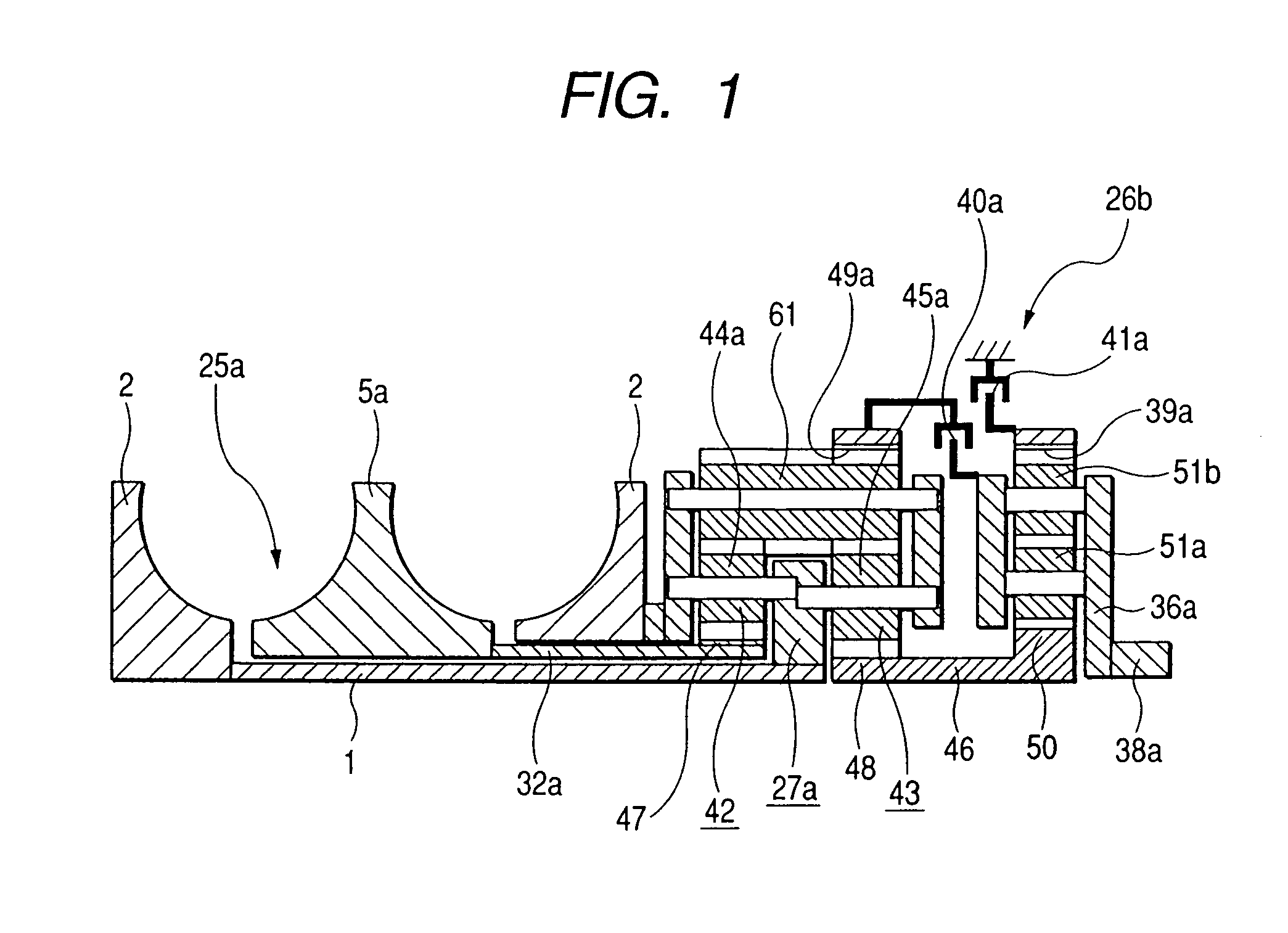
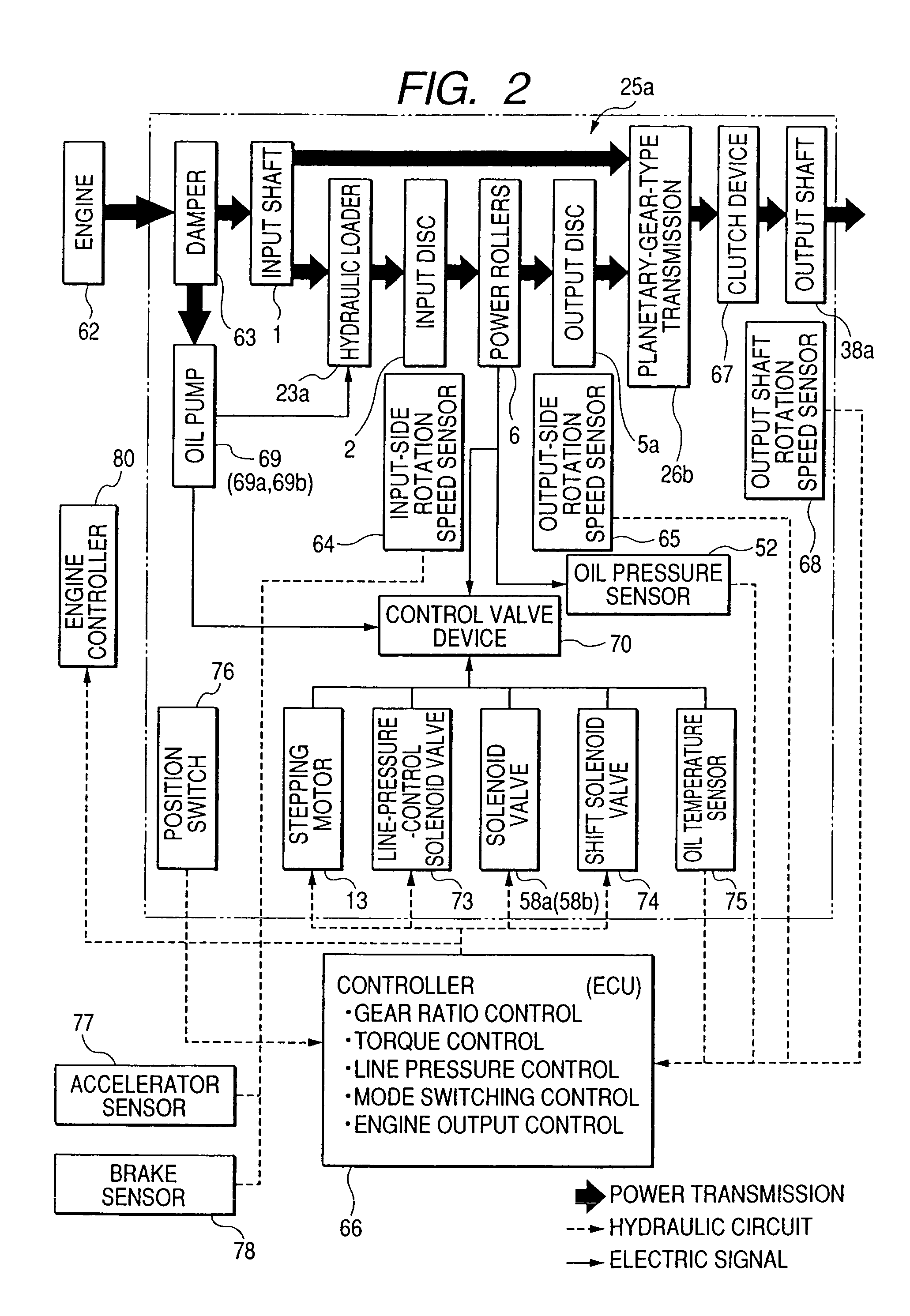
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
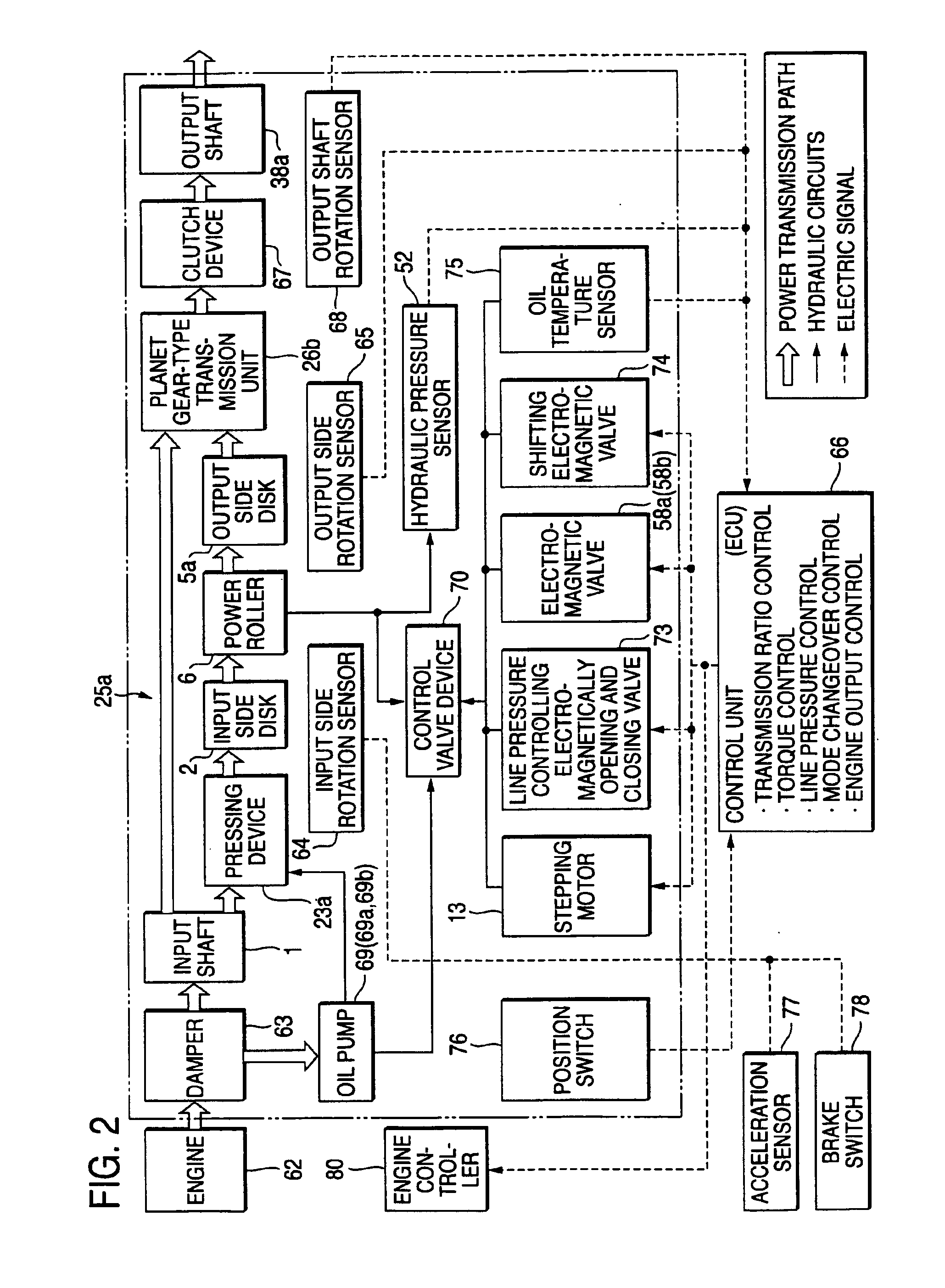
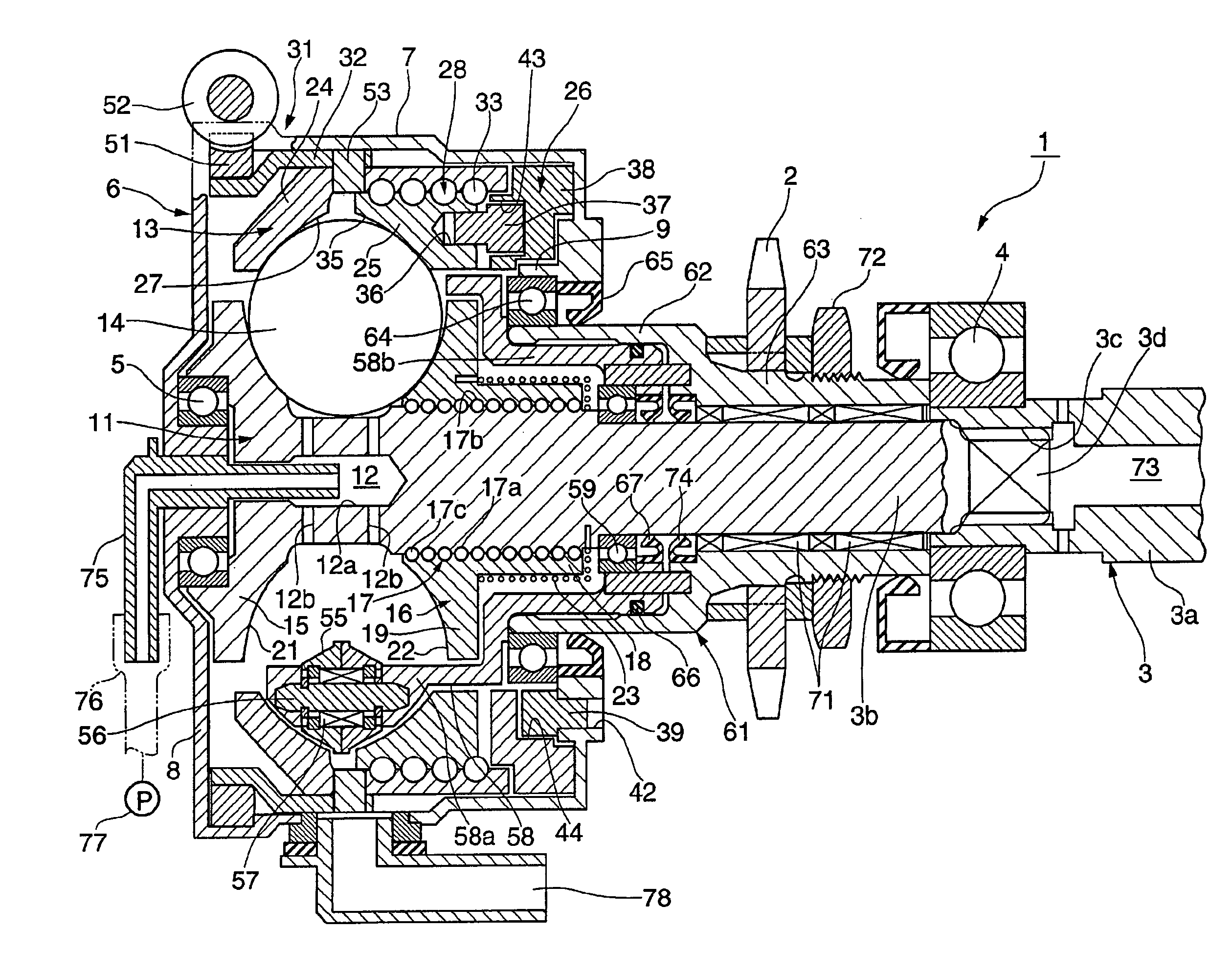
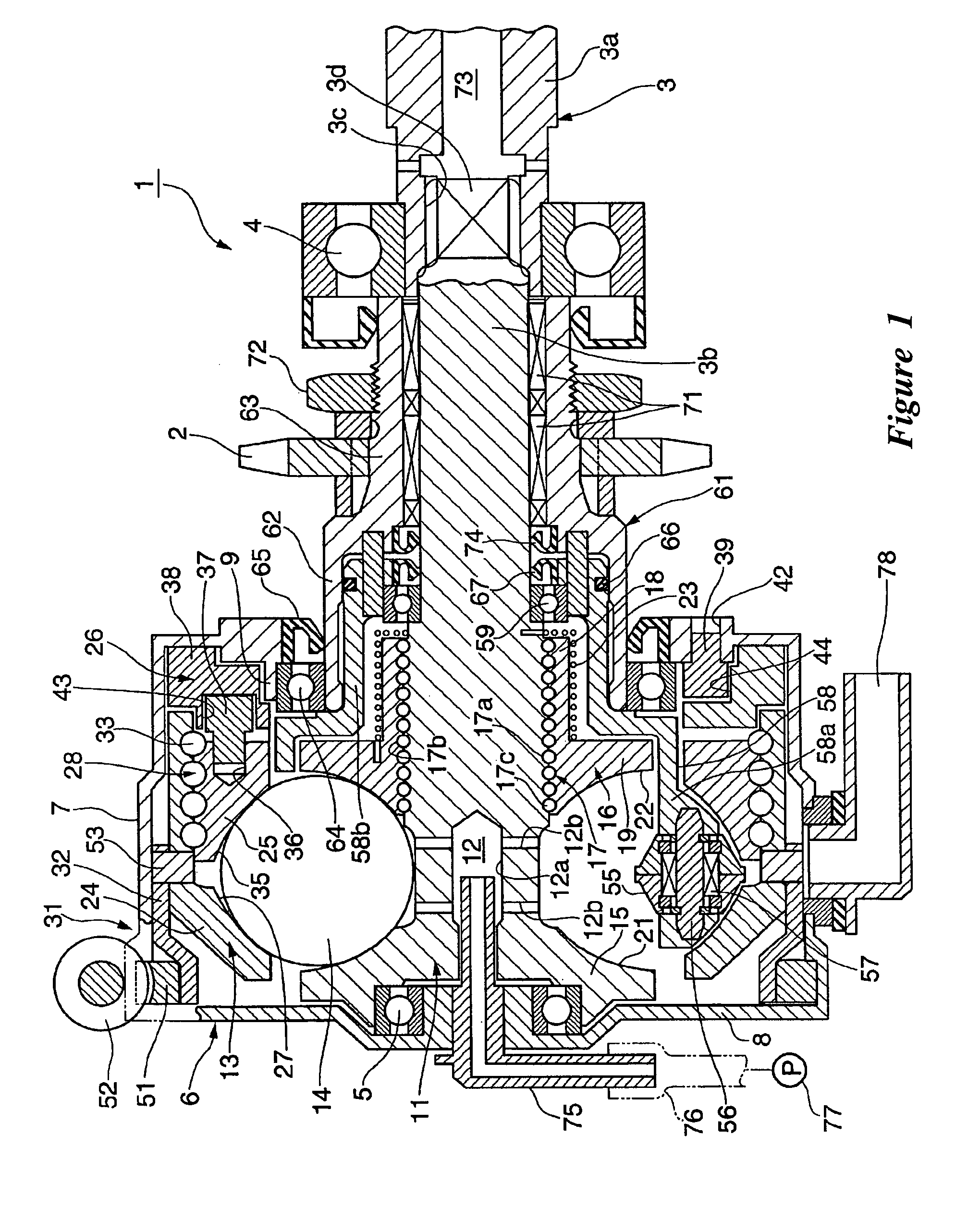
A continuously variable transmission apparatus having input and output shafts, a toroidal-type continuously variable transmission unit (CVT unit), a gear-type differential unit with gears, and a control unit, the CVT unit has; input and output side disks, power rollers, input and output side rotation sensors, wherein the differential unit has; a first input portion and a second input portion, and wherein the control unit regulates the transmission ratio of the CVT unit so as to change relative displacement speeds of the gears of the differential unit to thereby convert the rotational state of the output shaft to forward and backward rotations with a stationary state being interposed therebetween, with the input shaft being kept rotating in one direction, and to calculate a rotational speed of the output shaft based on rotational speeds of the input and output side disks and a gear ratio of the differential unit.
Owner:NSK LTD
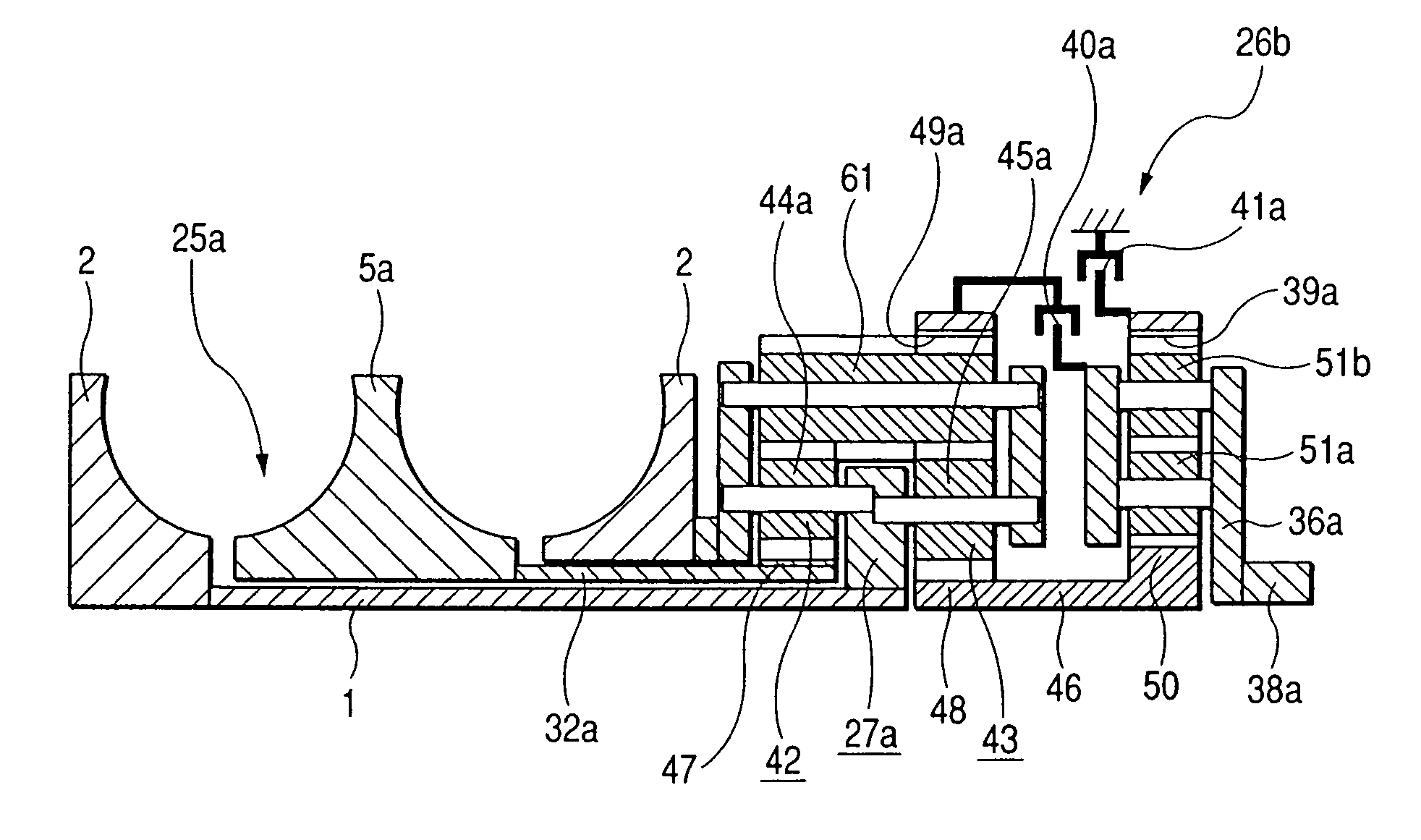
Electromotive drives
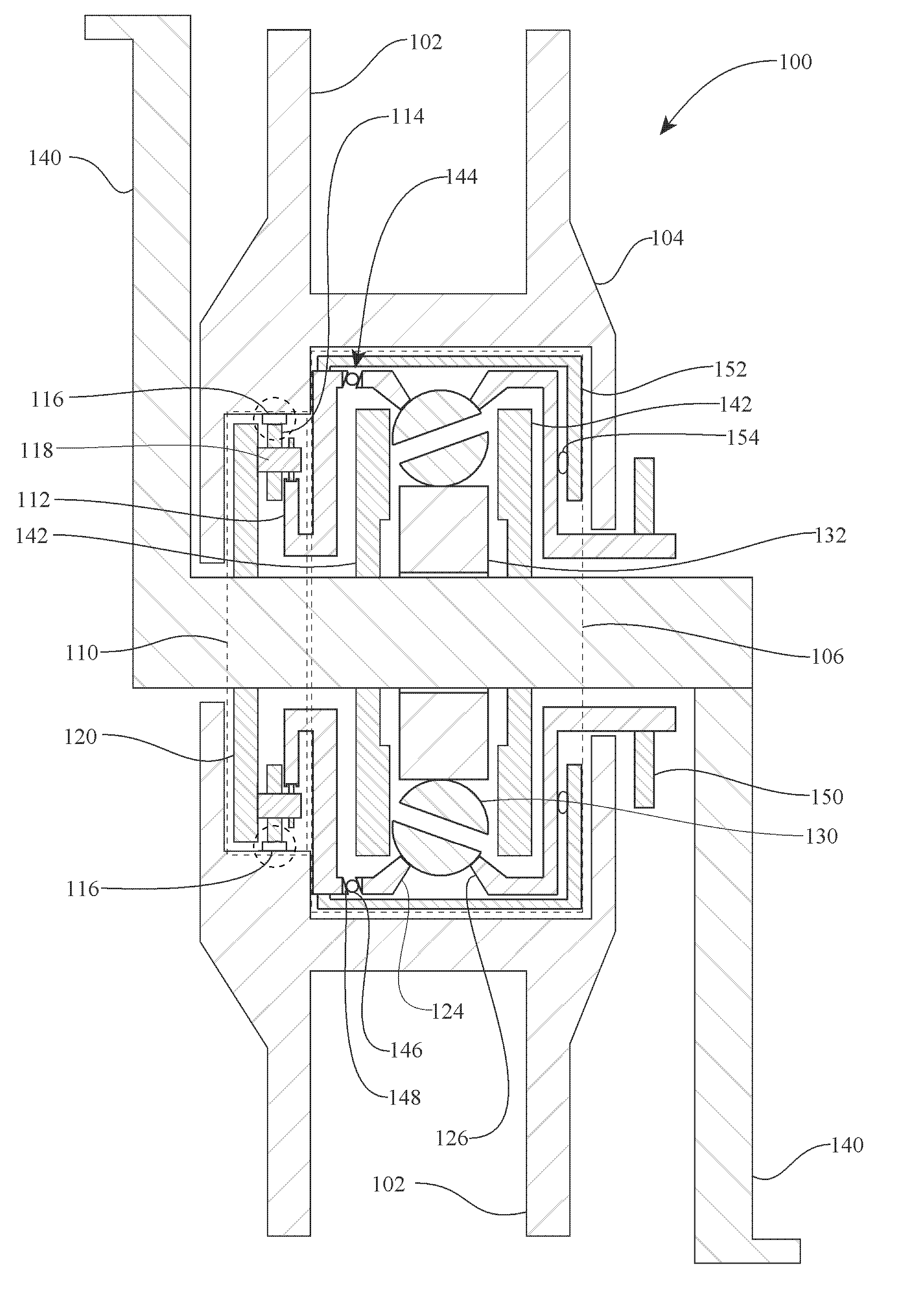
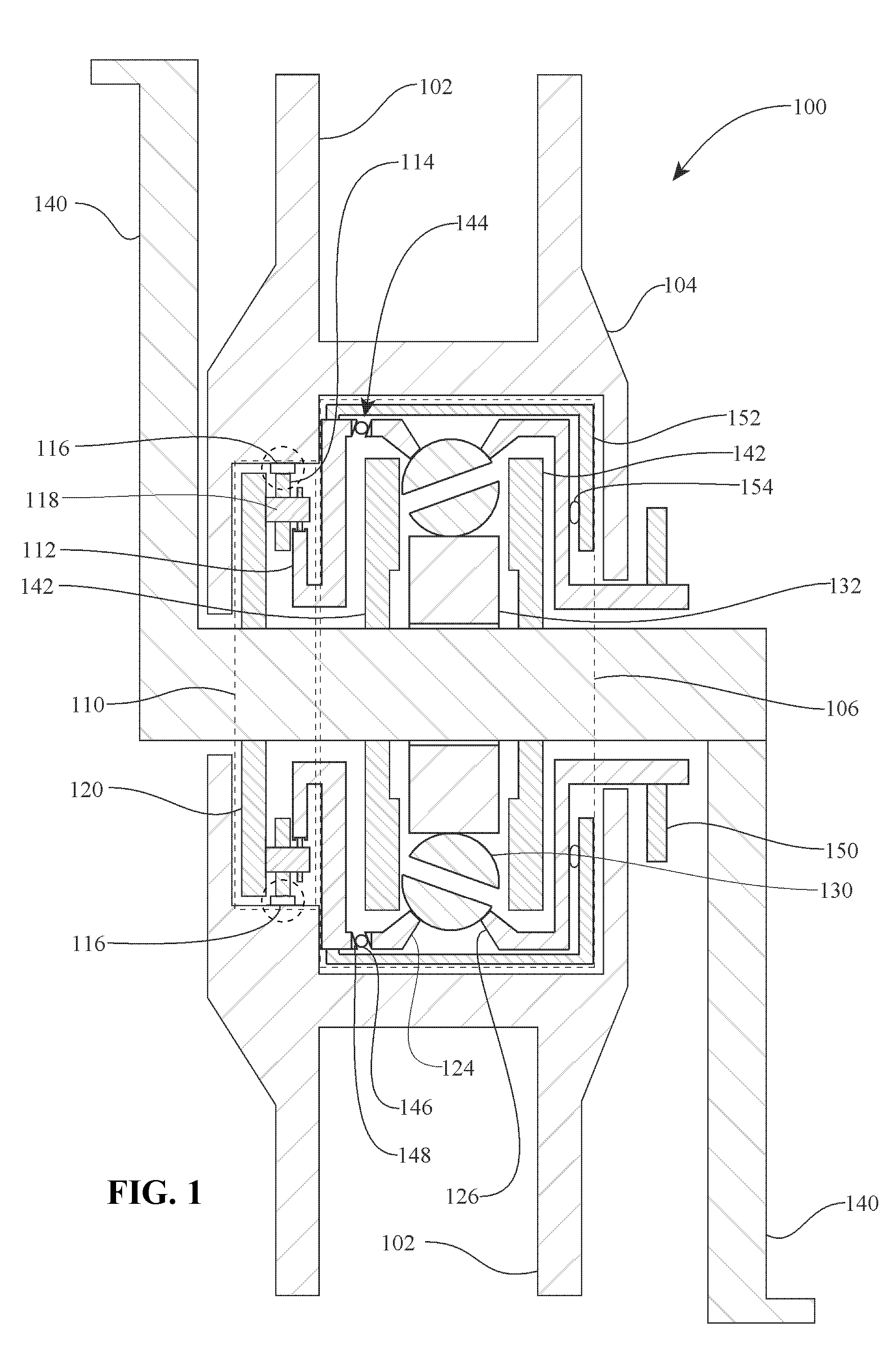
A transmission having a plurality of tilting balls and opposing input and output discs provides an infinite number of speed combinations over its transmission ratio range. The transmission provides multiple powerpaths and can be combined with electrical components to provide motor / generator functionality, which reduces the overall size and complexity of the motor and transmission compared to when they are constructed separately. In one embodiment, rotatable components of a continuously variable transmission are coupled separately to an electrical rotor and to an electrical stator so that the rotor and stator rotate simultaneously in opposite directions relative to one another. In other embodiments, an electrical rotor is configured to transfer torque to or from a disc that is in contact with a plurality of speed adjusters, while an electrical stator is configured to transfer torque to a shaft that is operationally coupled to the speed adjusters via an idler.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
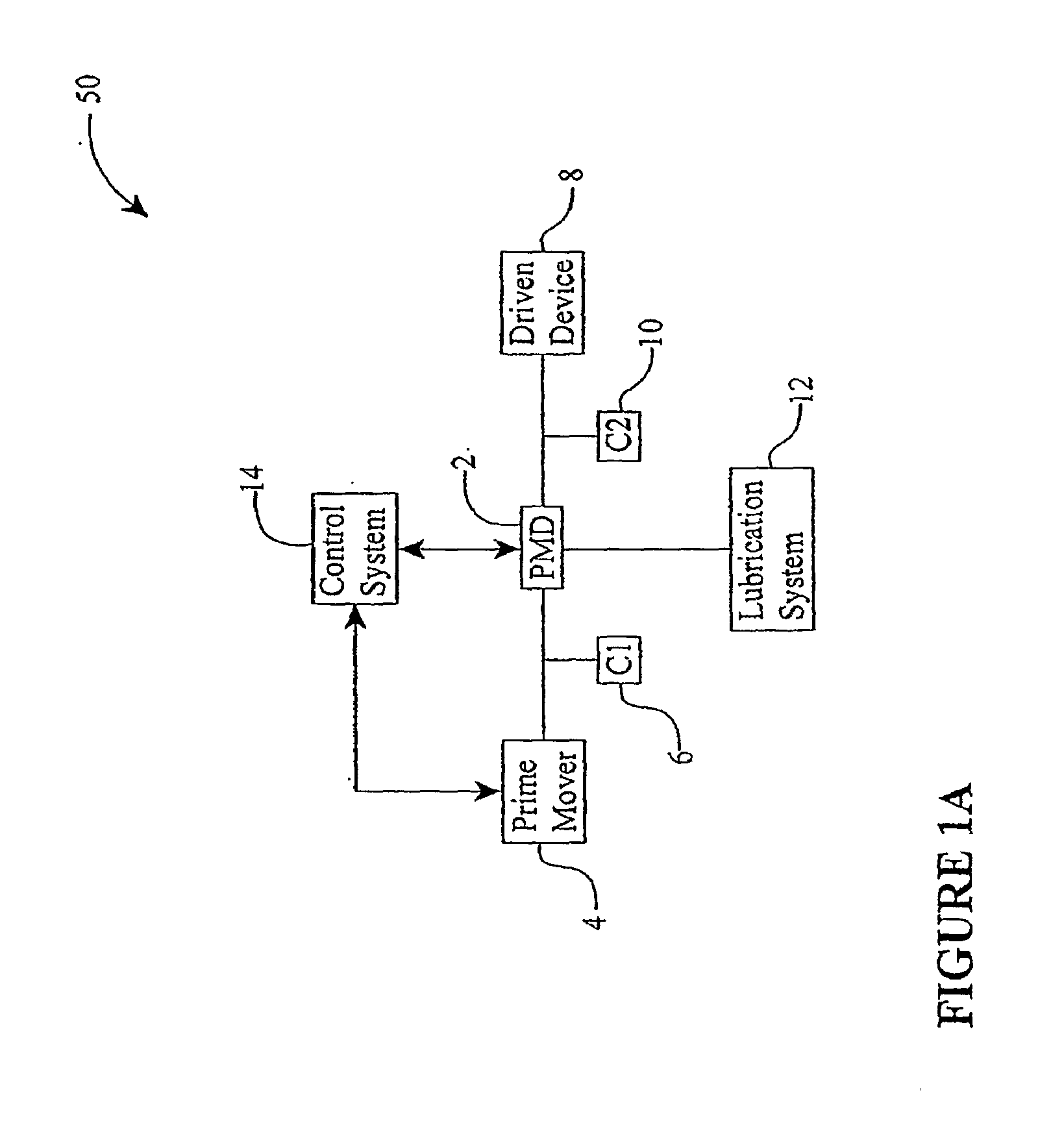
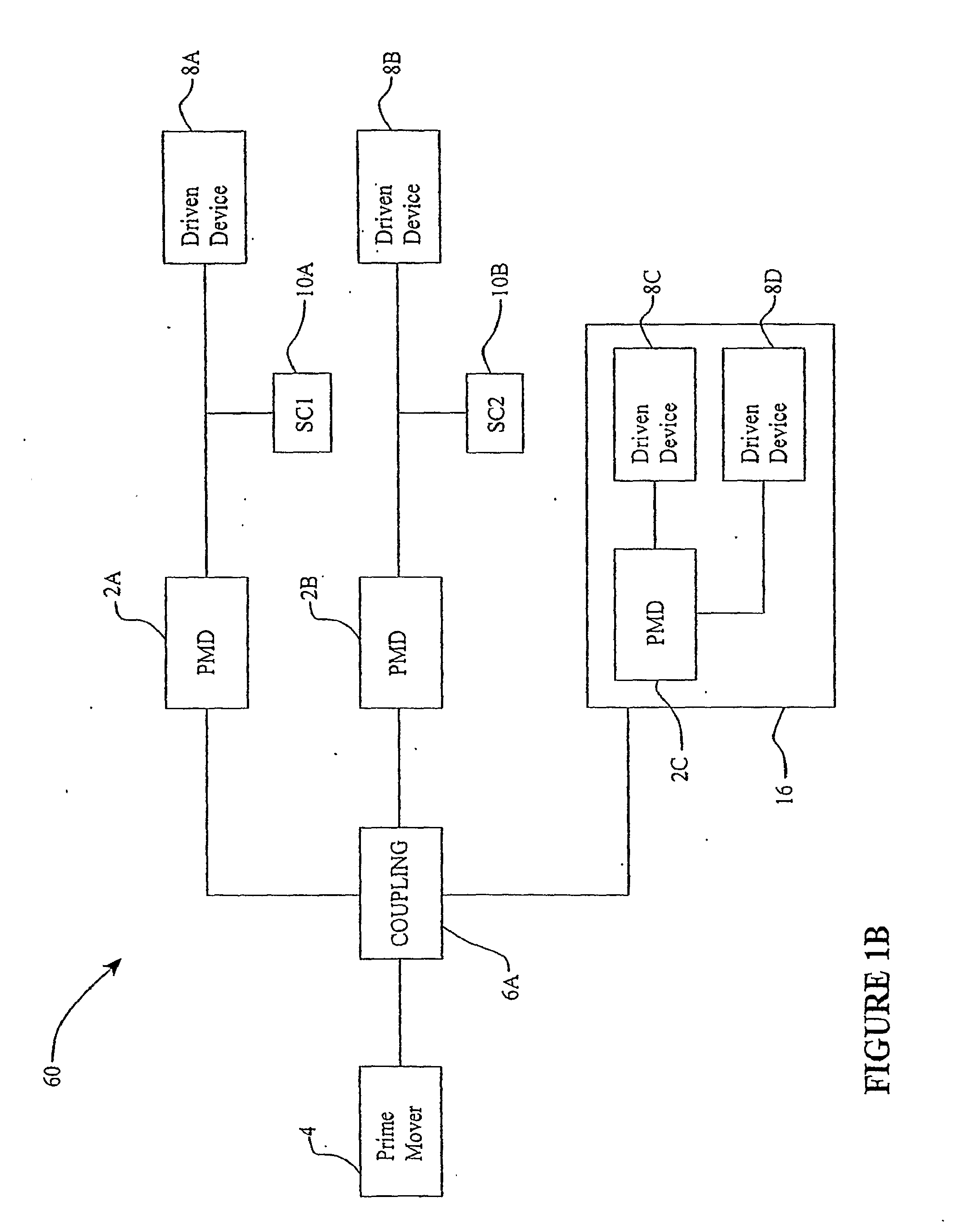
Continuously variable transmission
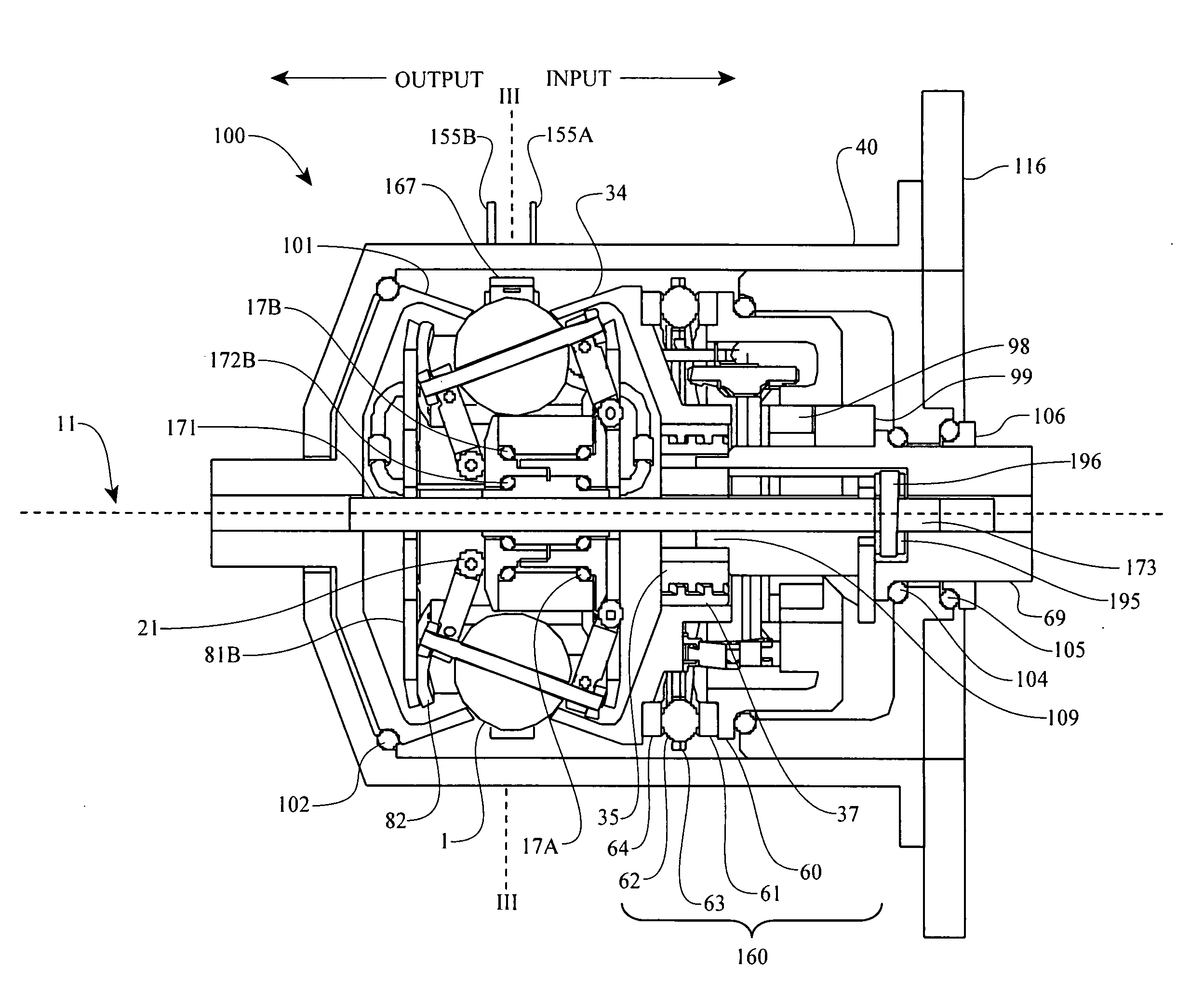
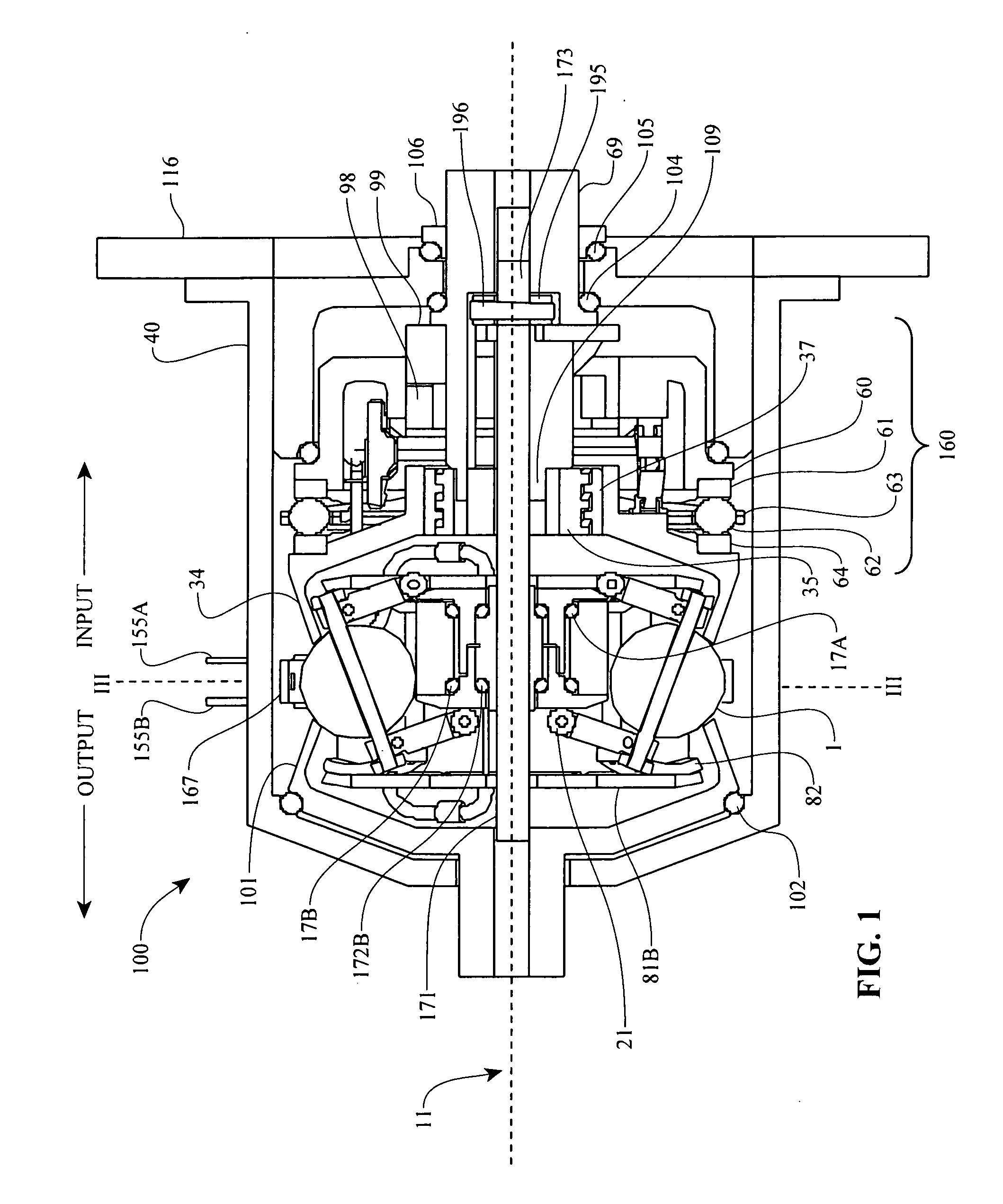
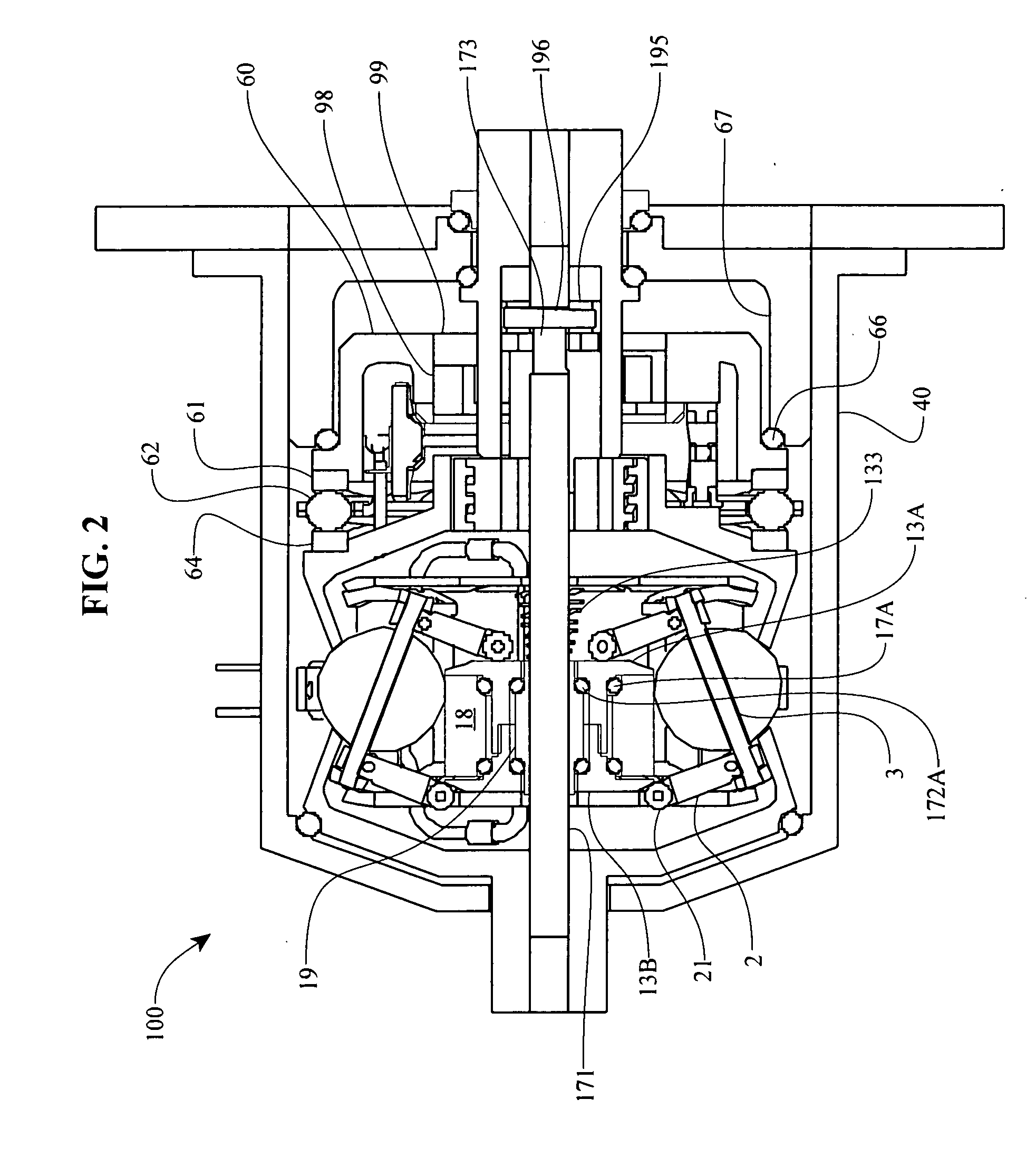
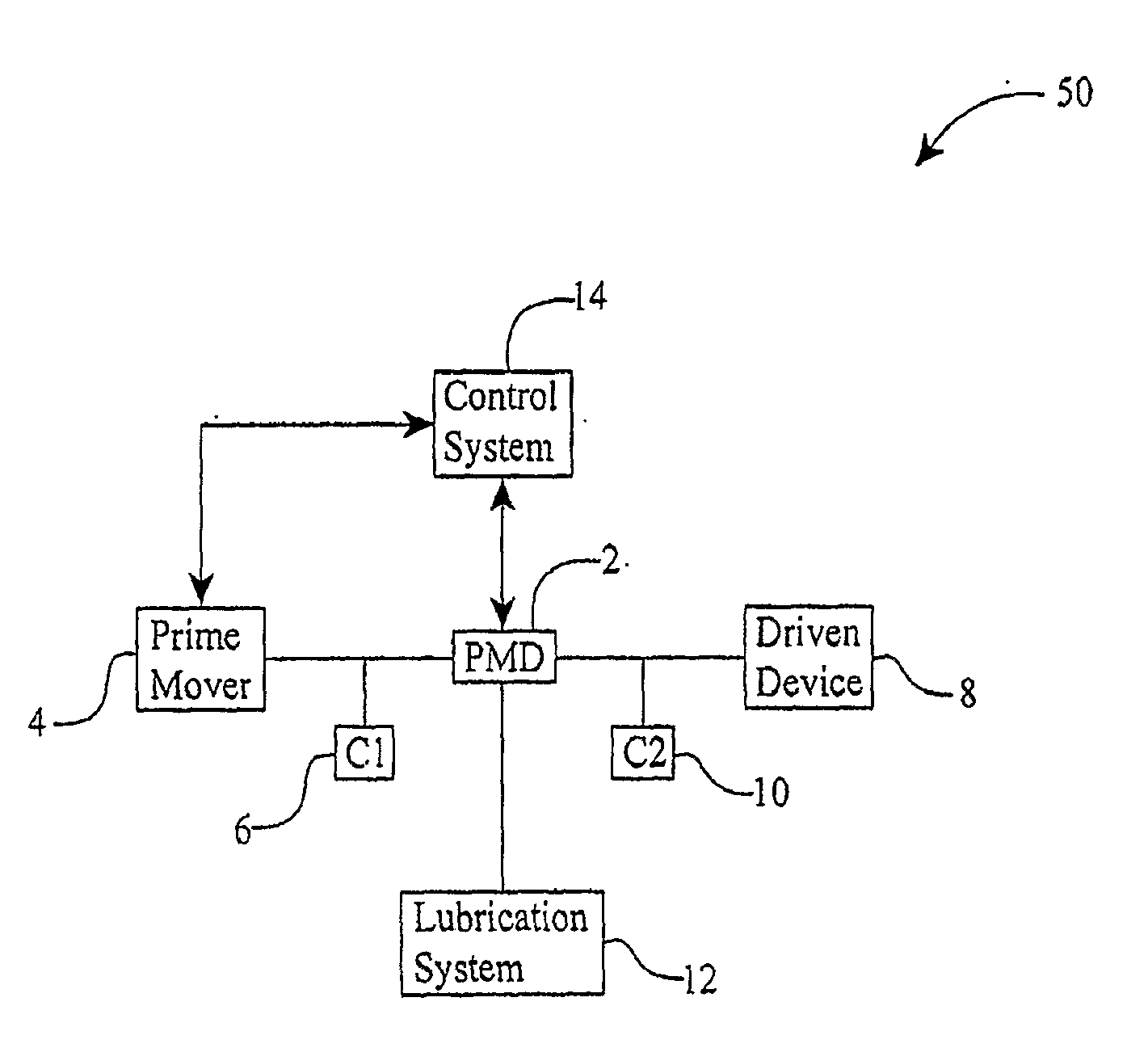
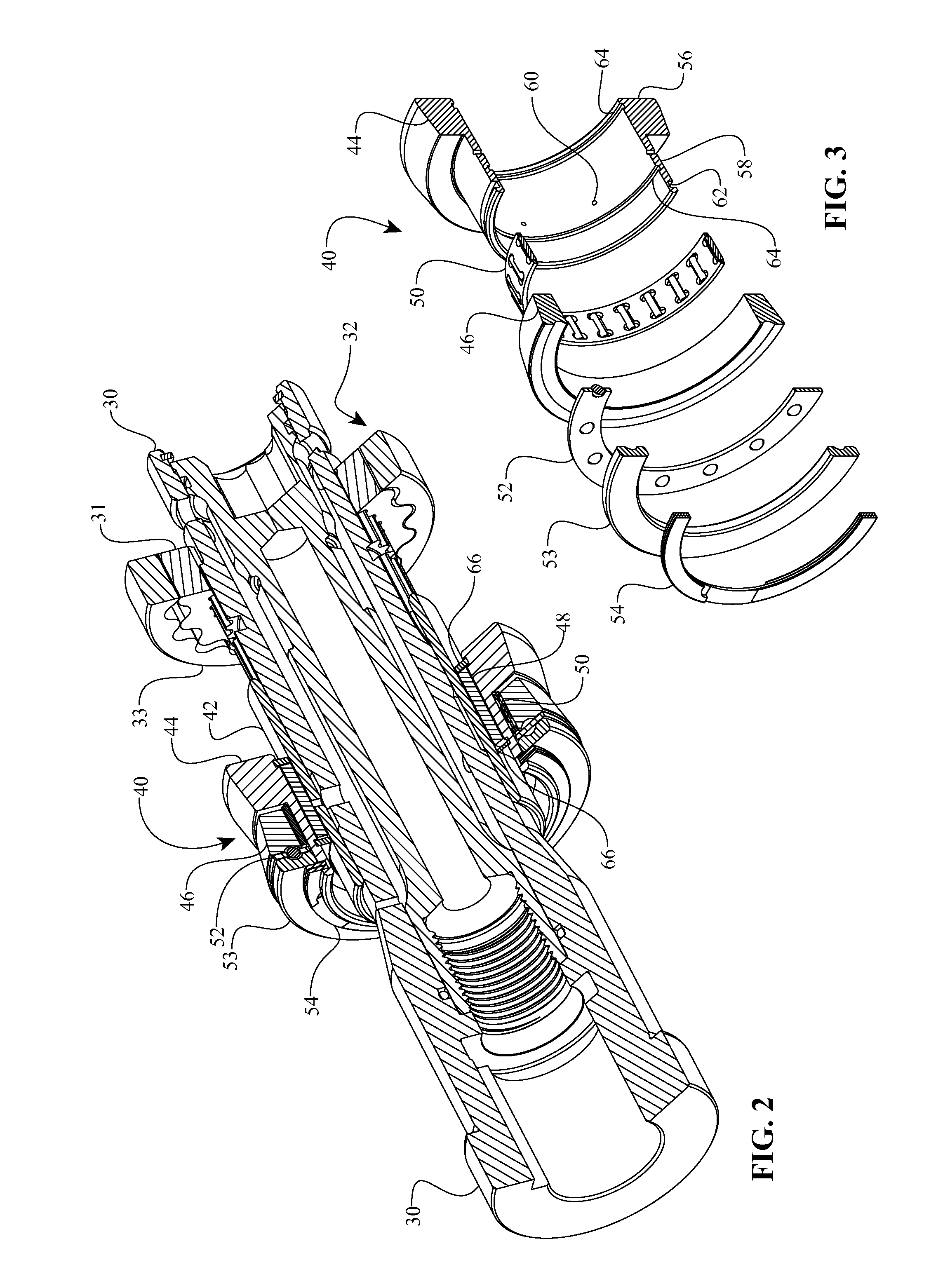
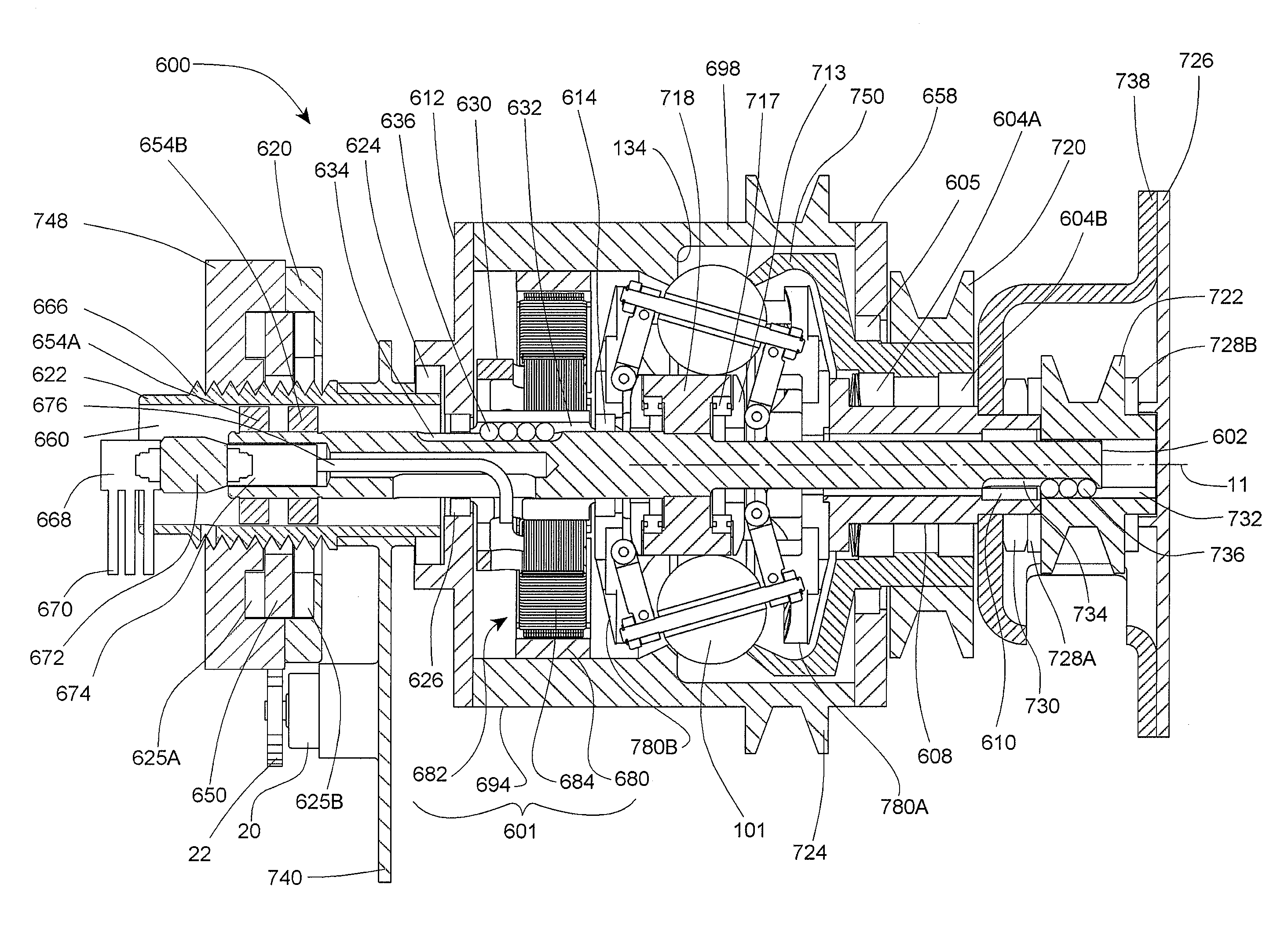
Embodiments are directed to a front end accessory drive (FEAD), subassemblies, and components therefor. Embodiments disclosed cover power modulating devices (PMD) which can be used in a FEAD. In one embodiment, a continuously variable transmission (CVT) is coupled directly to a crankshaft of a prime mover, and the CVT is used to regulate the speed and / or torque delivered to an accessory. A compound drive device includes a motor / generator subassembly cooperating with a CVT subassembly to provide a motor functionality with torque multiplication or division, or alternatively, a generator functionality with torque multiplication or division. In some embodiments, a FEAD includes a PMD having a sun shaft configured to couple to a sun of the PMD and to an electric motor component, such as an electrical armature or an electrical field. In one embodiment, the electrical armature the electrical field are placed concentrically and coaxially and configured to rotate relative to one another in opposite directions.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Toroidal continuously variable transmission
ActiveUS20080305920A1Low costReduce processing costsMetal-working apparatusGear wheelsEngineeringGear ratio
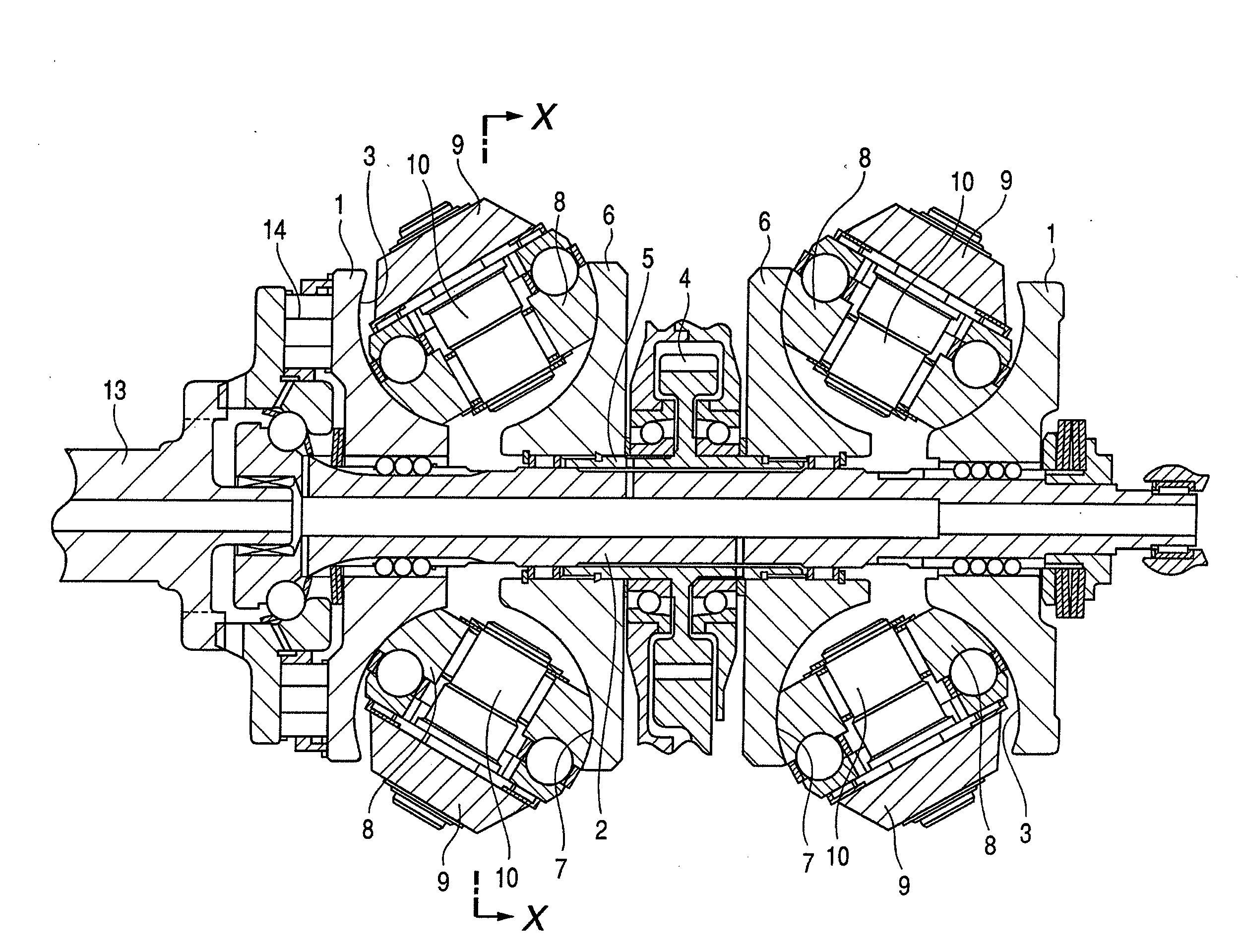
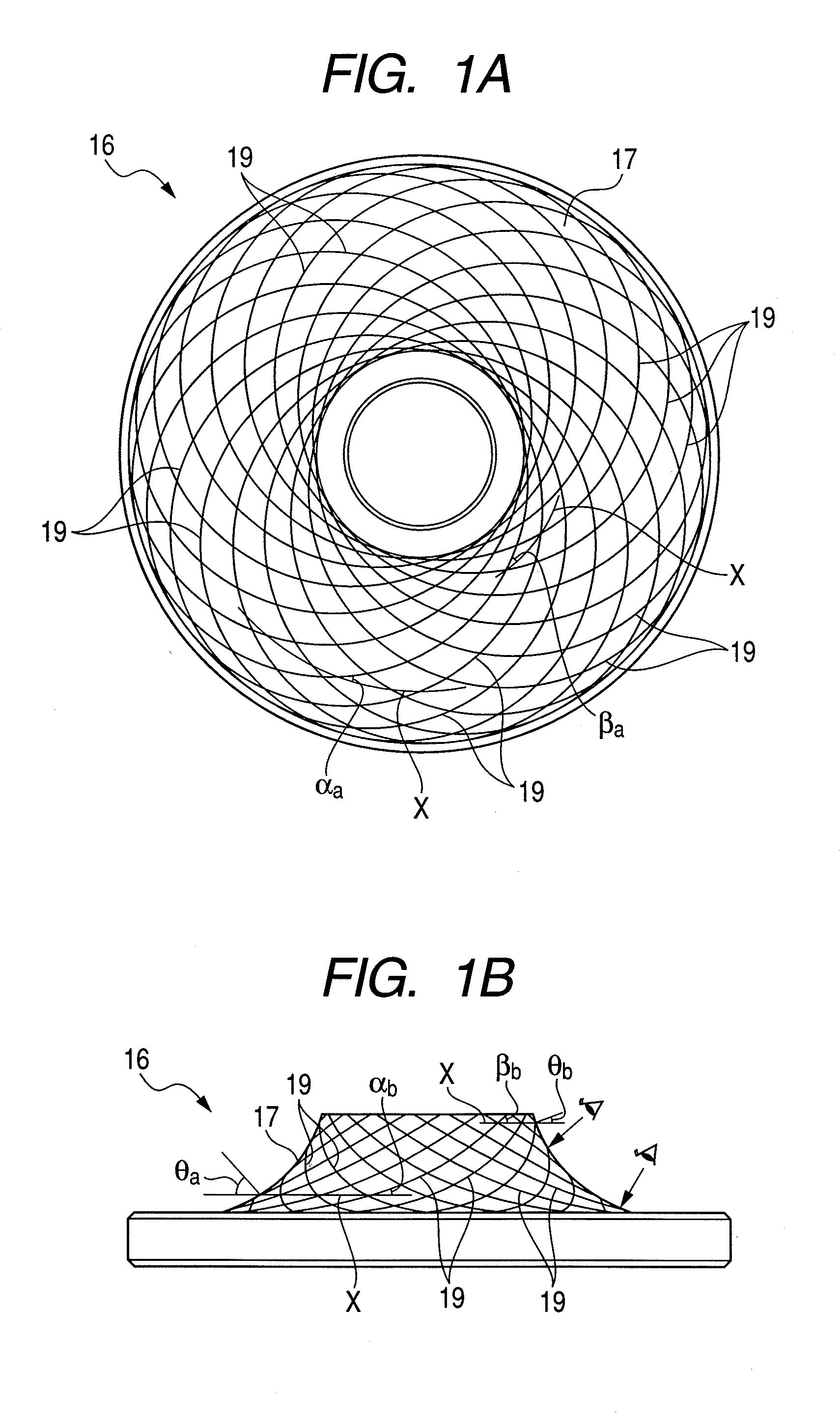
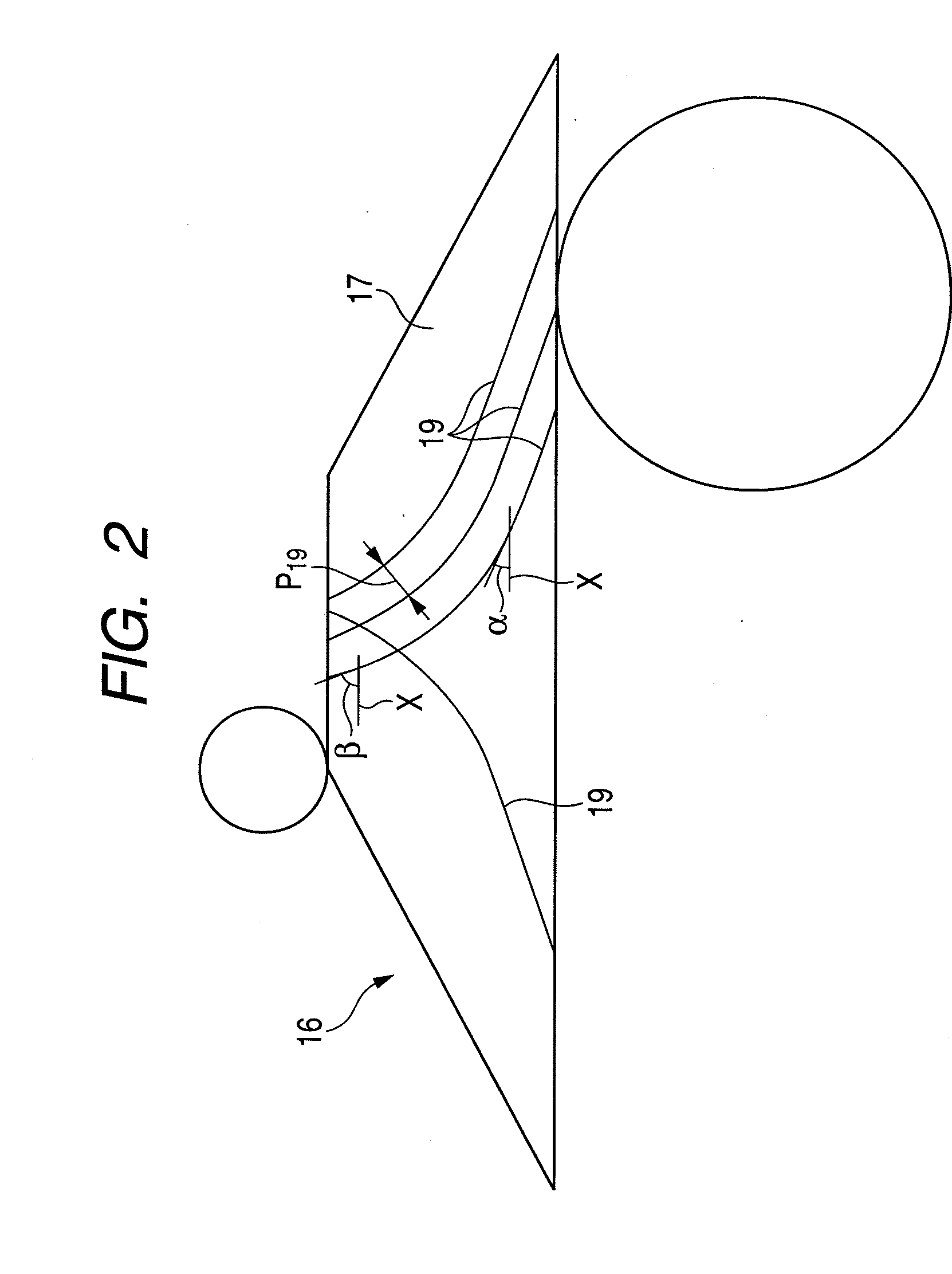
Power roller-side concave grooves are opposed to disk-side concave grooves 19, 19 so as to have angles therebetween in a rolling contact area between a peripheral surface of the power roller and a one-side surface 17 of a disk 16 in an axial direction regardless of a transmission gear ratio of a toroidal continuously variable transmission. Accordingly, the disk-side concave grooves 19, 19 are formed so as to have angles with respect to a circumferential direction of the disk 16 when viewed from a normal direction relative to the one-side surface 17 in the axial direction. Meanwhile, the power roller-side concave grooves are formed into a concentric shape (or a spiral shape) about a central shaft of the power roller. As a result, it is possible to prevent a decrease of a contact area in the rolling contact area regardless of the transmission gear ratio.
Owner:NSK LTD
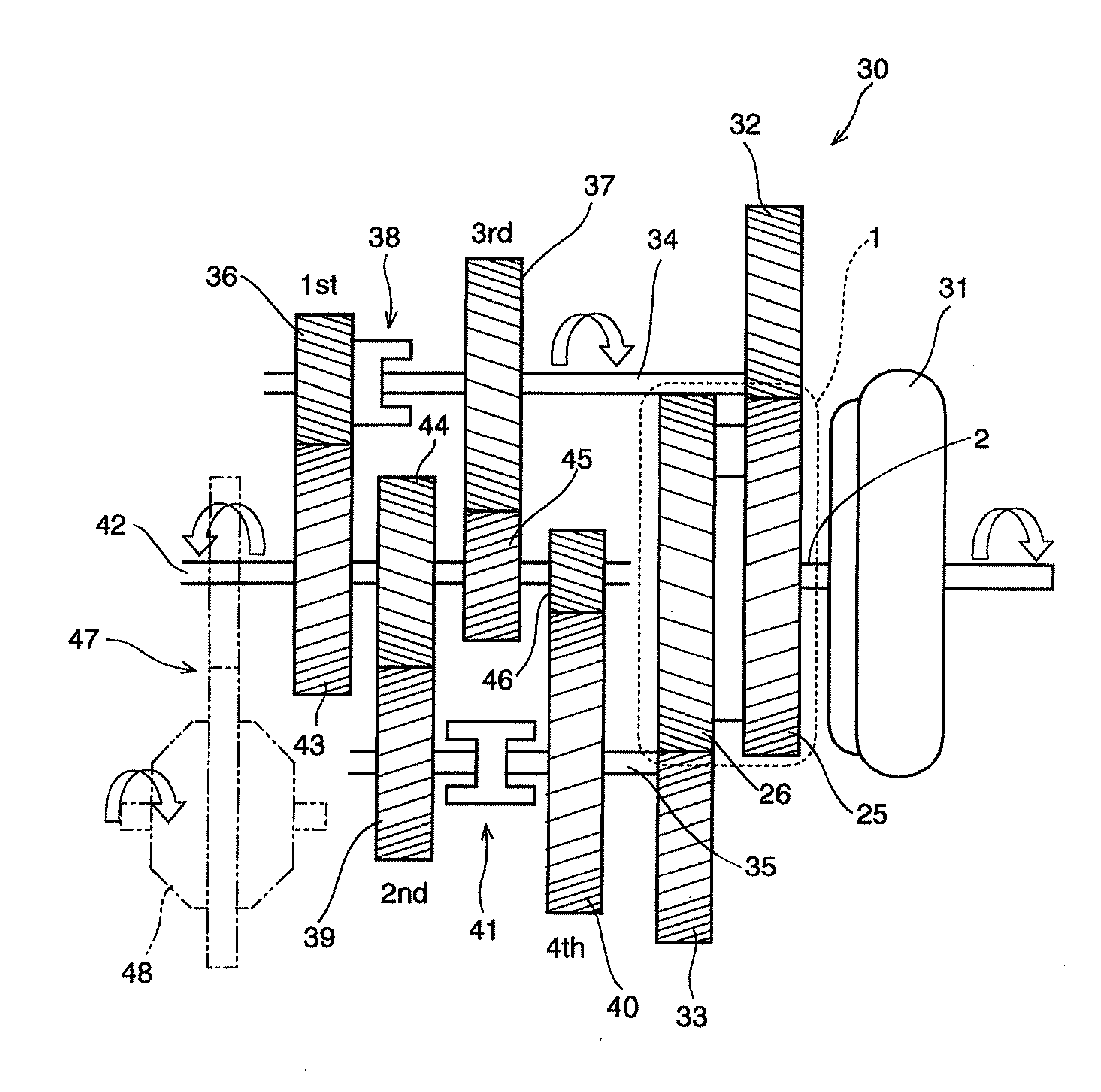
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
ActiveUS7094171B2Save spaceAxial-direction dimension can be reducedFriction gearingsGear wheelDrive shaft
A continuously variable transmission apparatus, has: an input shaft; a toroidal-type continuously variable transmission; a rotation transmission shaft; first, second and third planetary-gear-type transmissions; a first power transmission mechanism; a second power transmission mechanism; a third power transmission mechanism; and, a switching mechanism, wherein the second sun gear and one of the first and third sun gears are rotated together with the rotation transmission shaft to thereby execute the power transmission through the rotation transmission shaft and one of the first and second planetary-gear-type transmissions, and, in a state where the power transmission through the third planetary-gear-type transmission is cut off, in accordance with the control of the transmission ratio of the toroidal-type continuously variable transmission, the output shaft is stopped while the input shaft is rotating.
Owner:NSK LTD
Continuously variable transmission
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for continuously variable accessory drives (CVAD). In one embodiment, a skew-based control system is adapted to facilitate a change in the ratio of a CVAD. In another embodiment, a skew-based control system includes a skew actuator coupled to a carrier member. In some embodiments, the skew actuator is configured to rotate a carrier member of a CVT. Various inventive traction planet assemblies can be used to facilitate shifting the ratio of a CVT. In some embodiments, the traction planet assemblies include legs configured to cooperate with the carrier members. In some embodiments, a traction planet assembly is operably coupled to the carrier members. Embodiments of a shift cam and a traction sun are adapted to cooperate with other components of the CVT to support operation and / or functionality of the CVT. Among other things, shift control interfaces for a CVT are disclosed.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously Variable Transmission with Mutliple Outputs
ActiveUS20080081728A1Efficient power utilizationSaving of weightFriction gearingsManual control with multiple controlling membersEngineeringProsthetic hand
A transmission or actuator offering multiple rotational outputs proportionate in speed to that of a common rotational input, each output according to its own ratio. The ratios are continuously variable between positive and negative values, including zero, and may be varied by electromechanical actuators under computer control. The transmission relates the output speeds one to another under computer control, and thus makes possible the establishment of virtual surfaces and other haptic effects in a multidimensional workspace to which the transmission outputs are kinematically linked. An example of such a workspace is that of a robotic or prosthetic hand.
Owner:HDT EXPEDITIONARY SYST
Continuously variable transmission and engine
A continuously variable transmission features an inner ring and an outer ring. Each of the inner ring and the outer ring is split into a first portion and a second portion. At least two balls are positioned between the inner ring and the outer ring. The at least two balls also are positioned between the first and second portions of the inner and outer ring. The at least two balls rotate with rotation of the input shaft. As the distance between the first and second portions of the outer ring changes, the at least two balls move to a smaller radius of travel or a larger radius of travel. The rotation of the balls is transmitted to an output shaft. The input shaft and the output shaft are directly connectable through a one-way clutch to allow engine braking and / or push starting of the associated engine. A dedicated lubrication system also can be provided.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
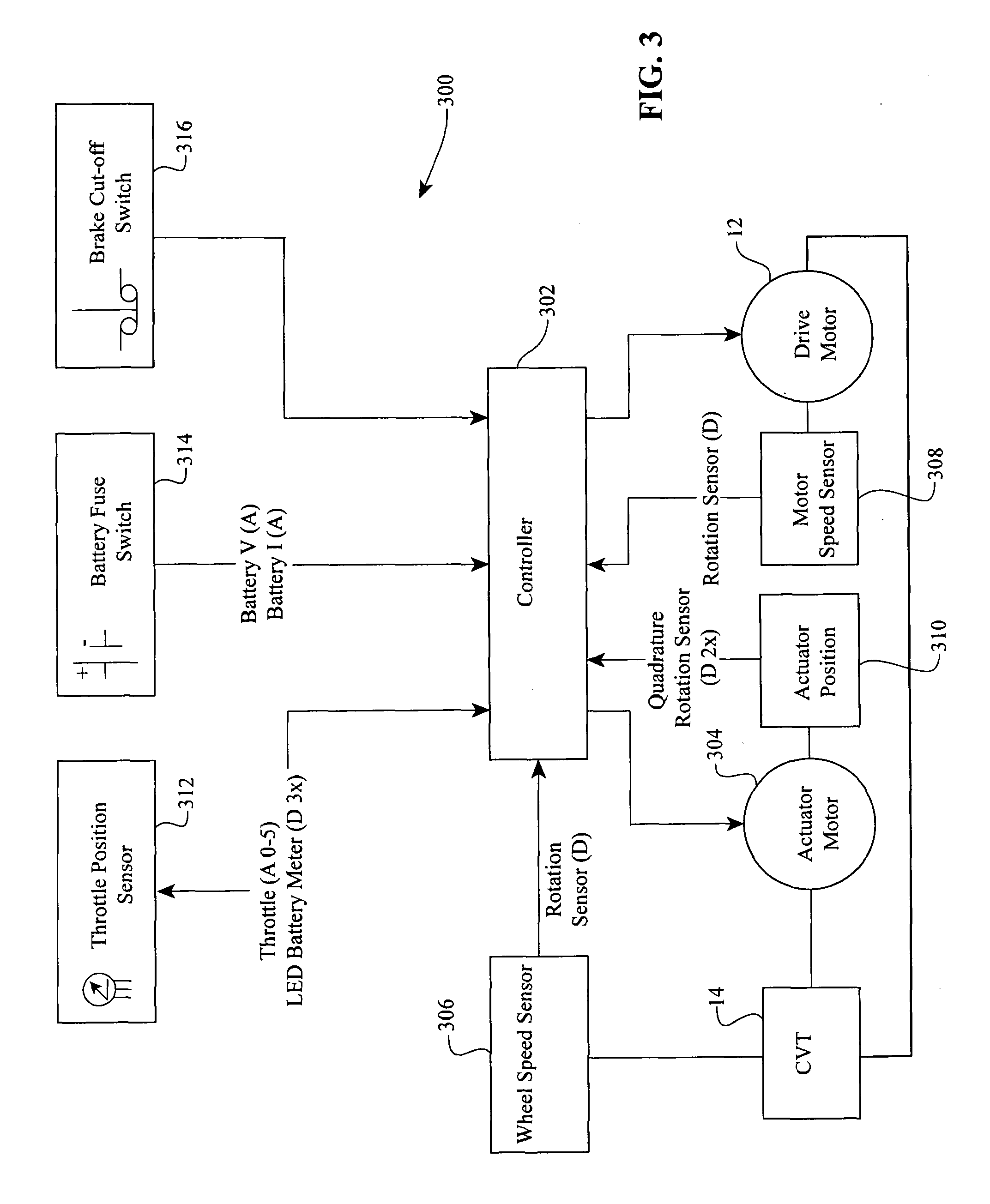
Scooter shifter
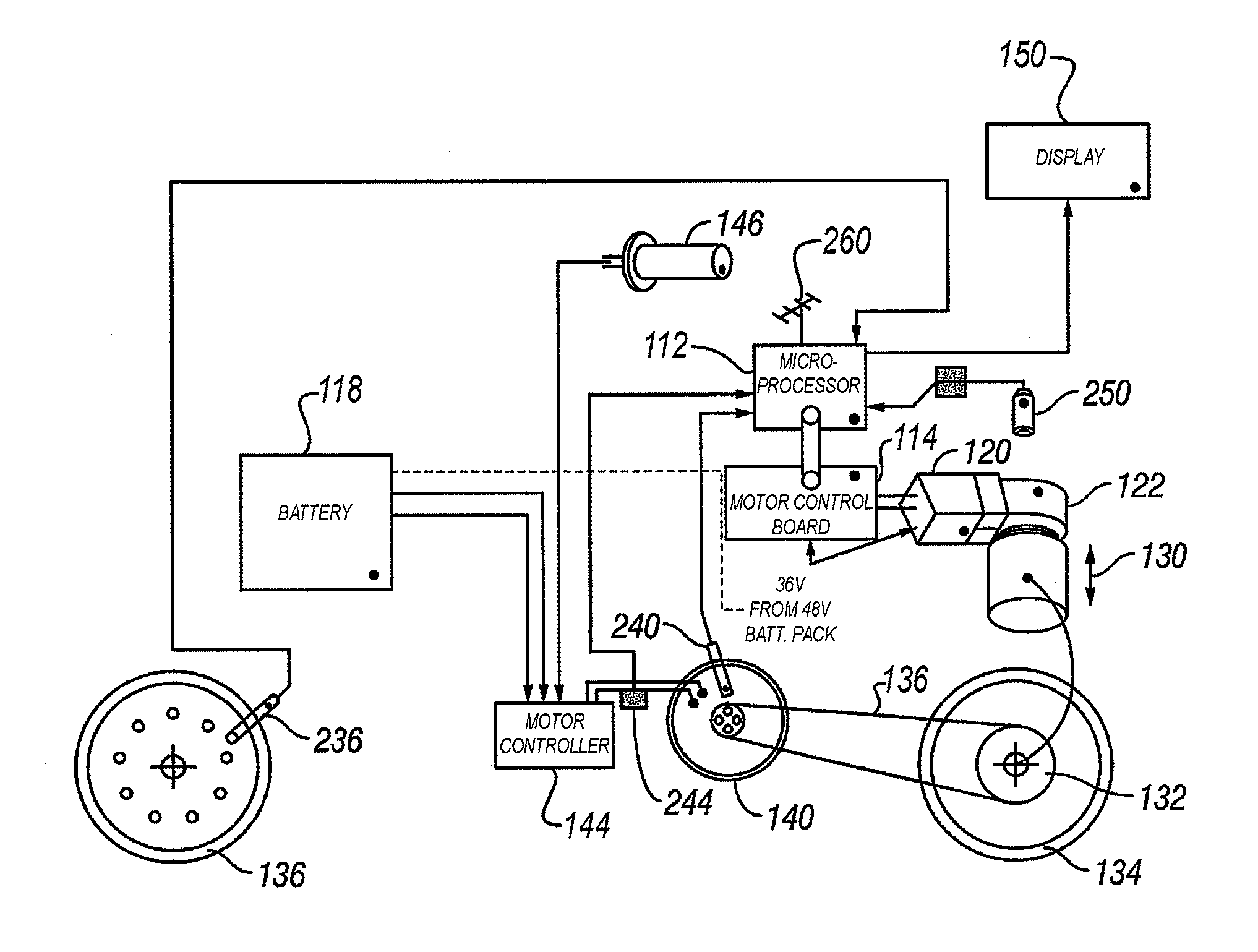
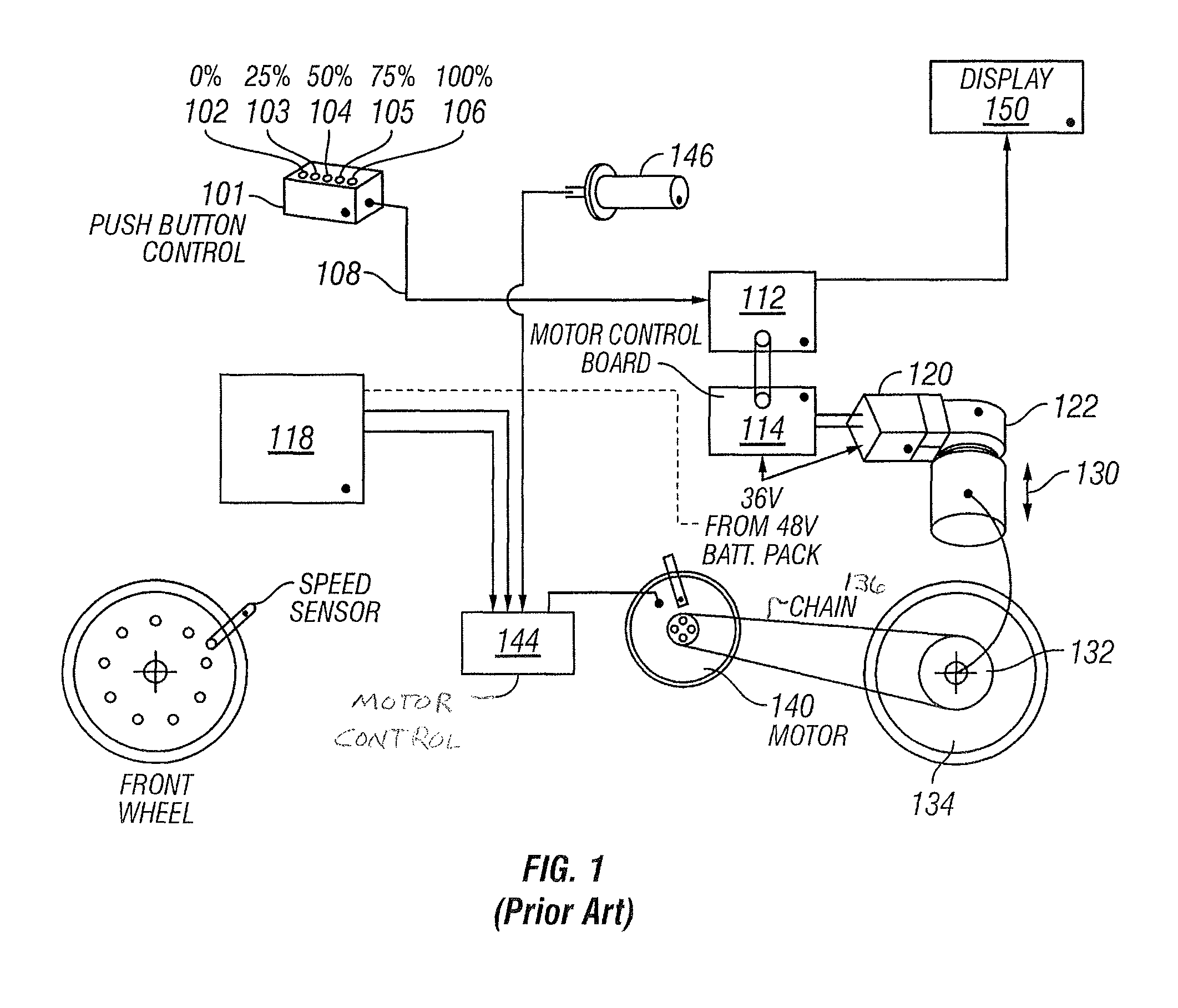
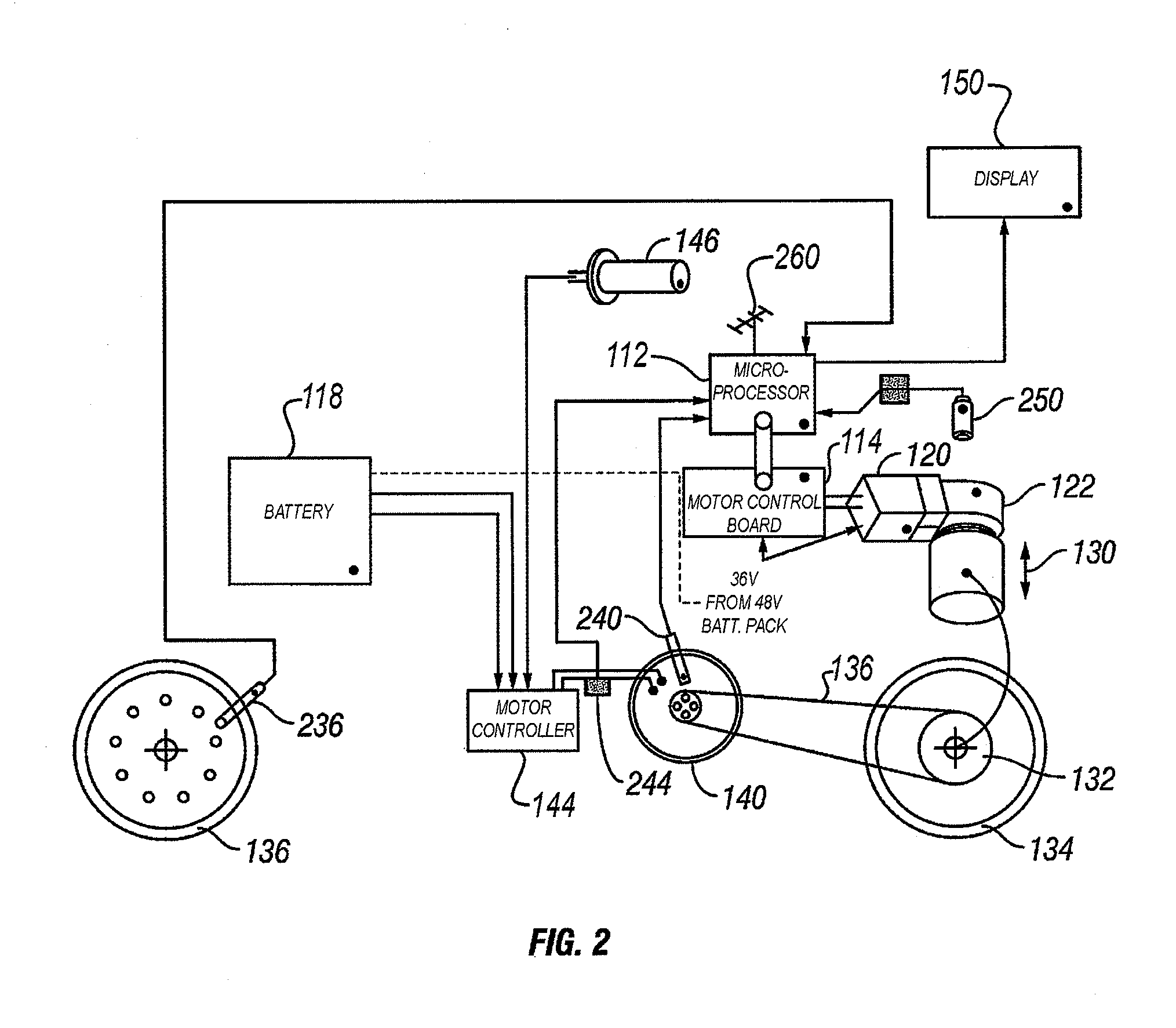
The present invention provides a system and method for automatically adjusting a continuously variable transmission (CVT) in a motorized vehicle. A microprocessor processor in the vehicle receives data about the operating status of the vehicle from a plurality. Examples of vehicle data include vehicle speed, motor speed, throttle position, current draw from a battery, and battery level. A servo motor is in mechanical communication with the CVT and provides an axial force to adjust the CVT. The microprocessor uses lookup tables of optimal set points for vehicle data to instruct the servo motor to adjust the transmission ratio of the CVT according to the vehicle data provided by the sensors.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
A continuously variable transmission apparatus, has: an input shaft; a toroidal-type continuously variable transmission; a first rotation transmission shaft; a first planetary-gear-type transmission; a second planetary-gear-type transmission; a second rotation transmission shaft; an output shaft; a first power transmission mechanism; a second power transmission mechanism; and a switching mechanism, wherein, in a state where the power transmission through the first power transmission mechanism is allowed and the power transmission through the second power transmission mechanism is cut off, in accordance with the control of the transmission ratio of the toroidal-type continuously variable transmission, the output shaft be stopped while leaving the input shaft rotating.
Owner:NSK LTD
Continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS7914029B2Easy to adjustFacilitating axial translationWheel based transmissionChain/belt transmissionEngineeringDriven element
Traction planets and traction rings can be operationally coupled to a planetary gearset to provide a continuously variable transmission (CVT). The CVT can be used in a bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on the frame of the bicycle at a location forward of the rear wheel hub of the bicycle. In one embodiment, the CVT is mounted on and supported by members of the bicycle frame such that the CVT is coaxial with the crankshaft of the bicycle. The crankshaft is configured to drive elements of the planetary gearset, which are configured to operationally drive the traction rings and the traction planets. Inventive component and subassemblies for such a CVT are disclosed. A shifting mechanism includes a plurality of pivot arms arranged to pivot about the centers of the traction planets as a shift pin hub moves axially.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The single axle transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. An additional embodiment is disclosed which shifts automatically dependent upon the rotational speed of the wheel. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The disclosed transmission may be used in vehicles such as automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles. The transmission may, for example, be driven by a power transfer mechanism such as a sprocket, gear, pulley or lever, optionally driving a one way clutch attached at one end of the main shaft.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission system for vehicle
InactiveUS6494805B2Increased durabilityImprove performanceToothed gearingsFriction gearingsDrive wheelGear train
An engine is connected to a sun gear of a planetary gear train via a toroidal type continuously variable transmission. Driven wheels of a vehicle are connected to a ring gear of the planetary gear train. The sun gear and the ring gear are connected to each other by a first clutch. A shifter can connect a second clutch connected to the engine either to a carrier of the planetary gear train or the driven wheels. When the vehicle is started when a failure of the electronic central system has occurred, by engaging the first and second clutches with predetermined engagement forces while the second clutch is connected to the carrier by the shifter, change of the ratio of the toroidal type continuously variable transmission beyond either the LOW ratio or the OD ratio is prevented so as to avoid generating an excessive load.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The single axle transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. An additional embodiment is disclosed which shifts automatically dependent upon the rotational speed of the wheel. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The disclosed transmission may be used in vehicles such as automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles. The transmission may, for example, be driven by a power transfer mechanism such as a sprocket, gear, pulley or lever, optionally driving a one way clutch attached at one end of the main shaft.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
Embodiments are directed to a front end accessory drive (FEAD), subassemblies, and components therefor. Embodiments disclosed cover power modulating devices (PMD) which can be used in a FEAD. In one embodiment, a continuously variable transmission (CVT) is coupled directly to a crankshaft of a prime mover, and the CVT is used to regulate the speed and / or torque delivered to an accessory. A compound drive device includes a motor / generator subassembly cooperating with a CVT subassembly to provide a motor functionality with torque multiplication or division, or alternatively, a generator functionality with torque multiplication or division. In some embodiments, a FEAD includes a PMD having a sun shaft configured to couple to a sun of the PMD and to an electric motor component, such as an electrical armature or an electrical field. In one embodiment, the electrical armature the electrical field are placed concentrically and coaxially and configured to rotate relative to one another in opposite directions.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is disclosed for use in rotationally or linearly powered machines and vehicles. The transmission provides a simple manual shifting method for the user. Further, the practical commercialization of traction roller transmissions requires improvements in the reliability, ease of shifting, function and simplicity of the transmission. The present invention includes a continuously variable transmission that may be employed in connection with any type of machine that is in need of a transmission. For example, the transmission may be used in (i) a motorized vehicle such as an automobile, motorcycle, or watercraft, (ii) a non-motorized vehicle such as a bicycle, tricycle, scooter, exercise equipment or (iii) industrial equipment, such as a drill press, power generating equipment, or textile mill.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com