Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2066 results about "Frame synchronization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication, frame synchronization or framing is the process by which, while receiving a stream of framed data, incoming frame alignment signals (i.e., a distinctive bit sequences or syncwords) are identified (that is, distinguished from data bits), permitting the data bits within the frame to be extracted for decoding or retransmission.
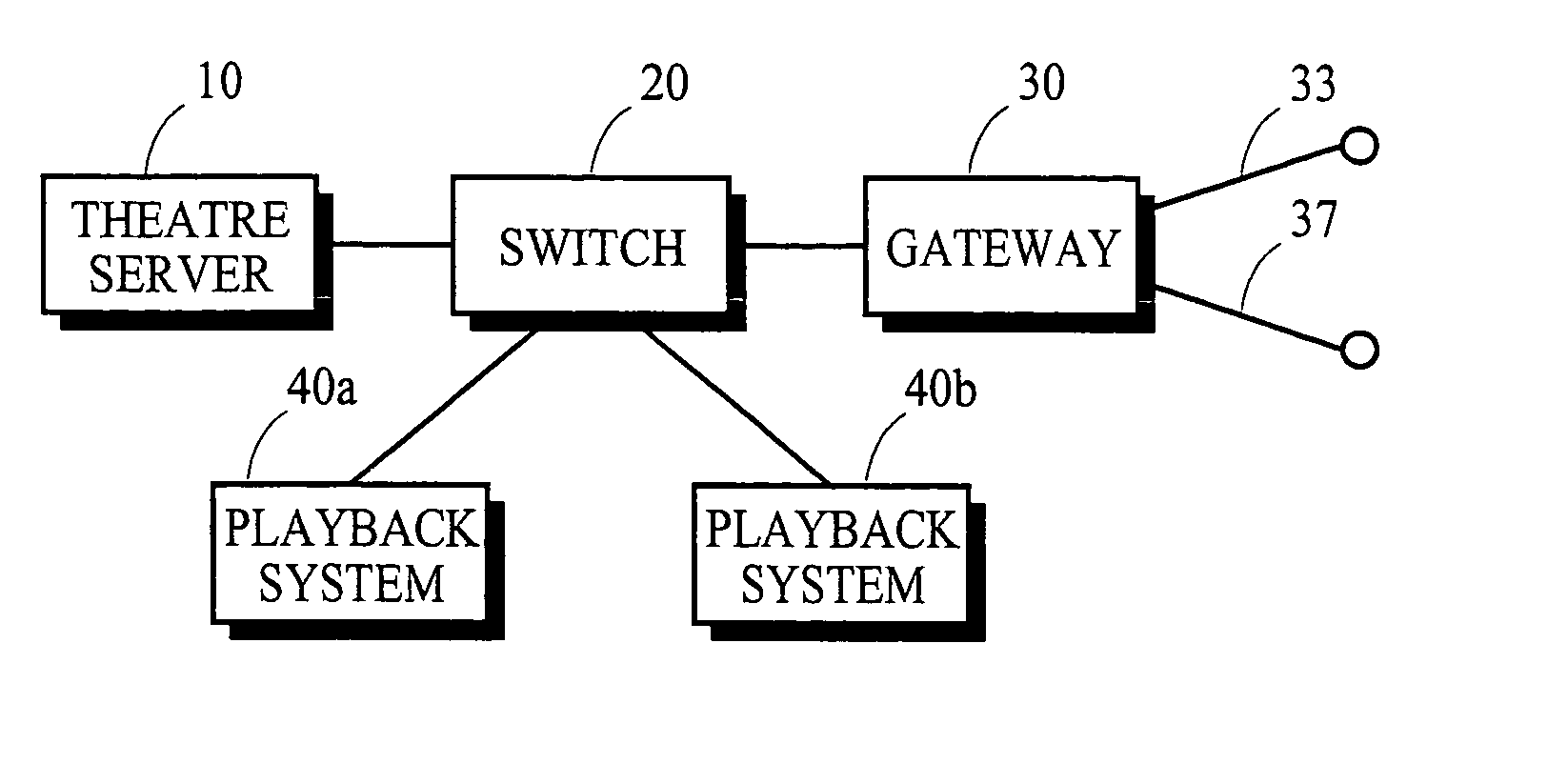
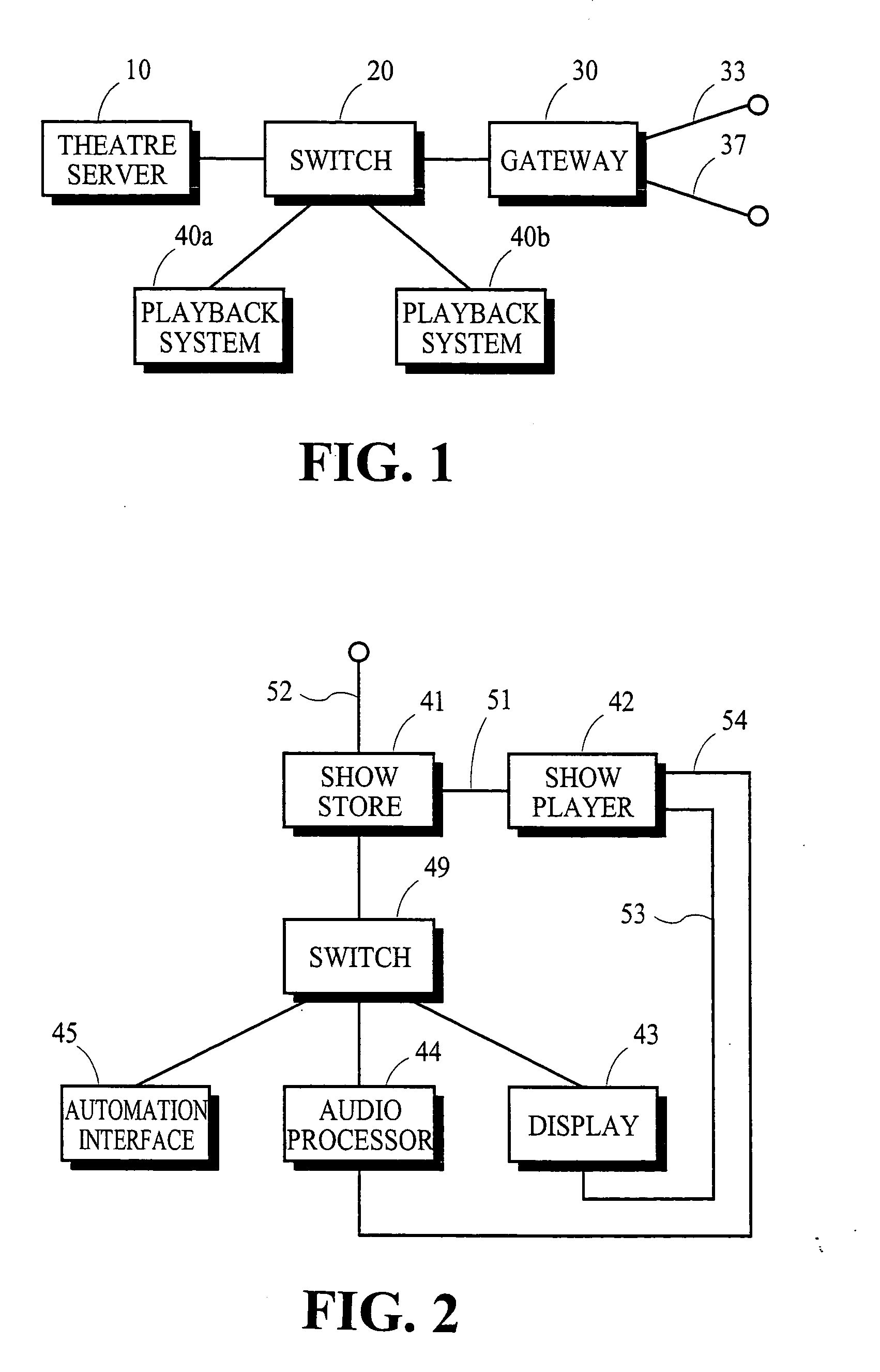
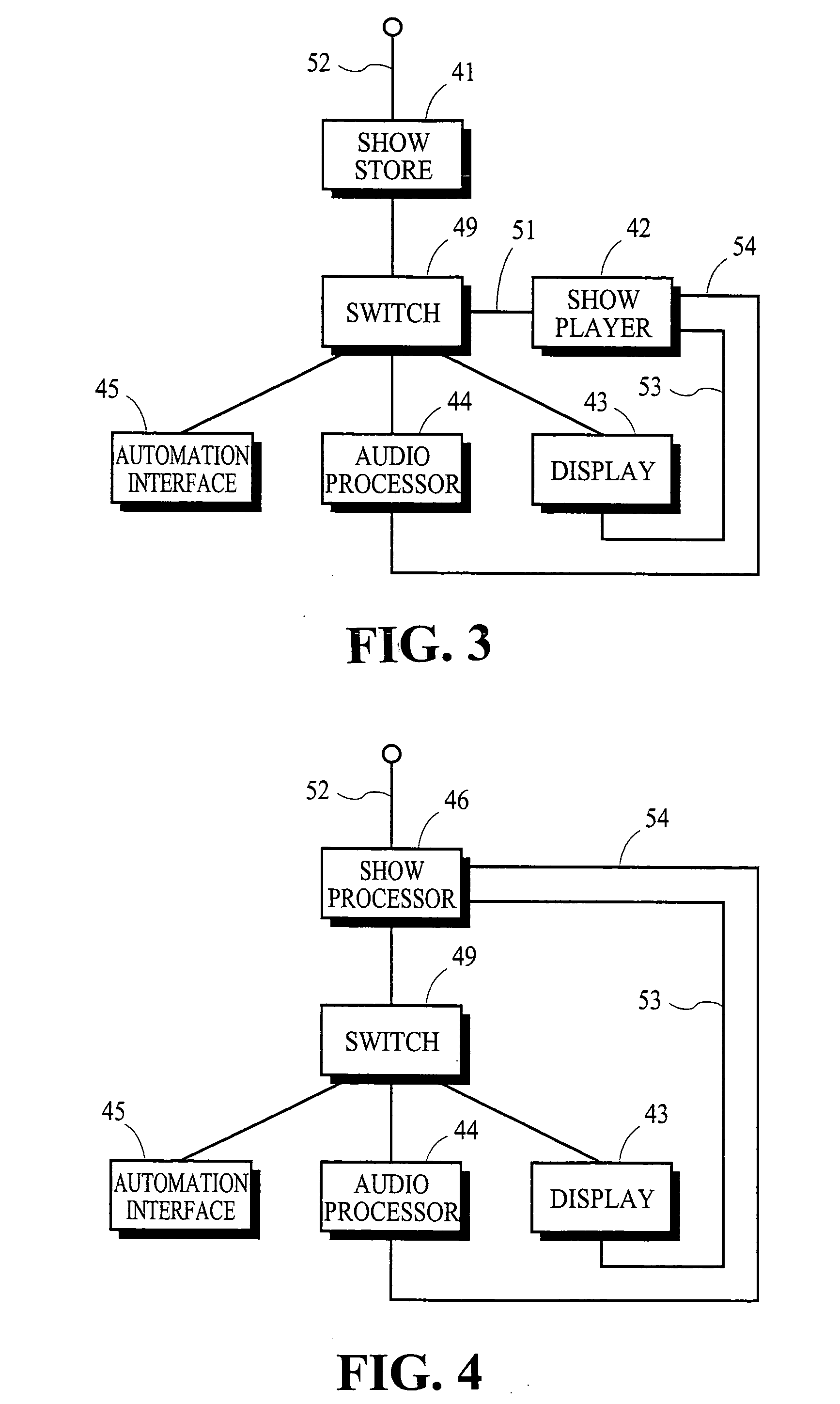
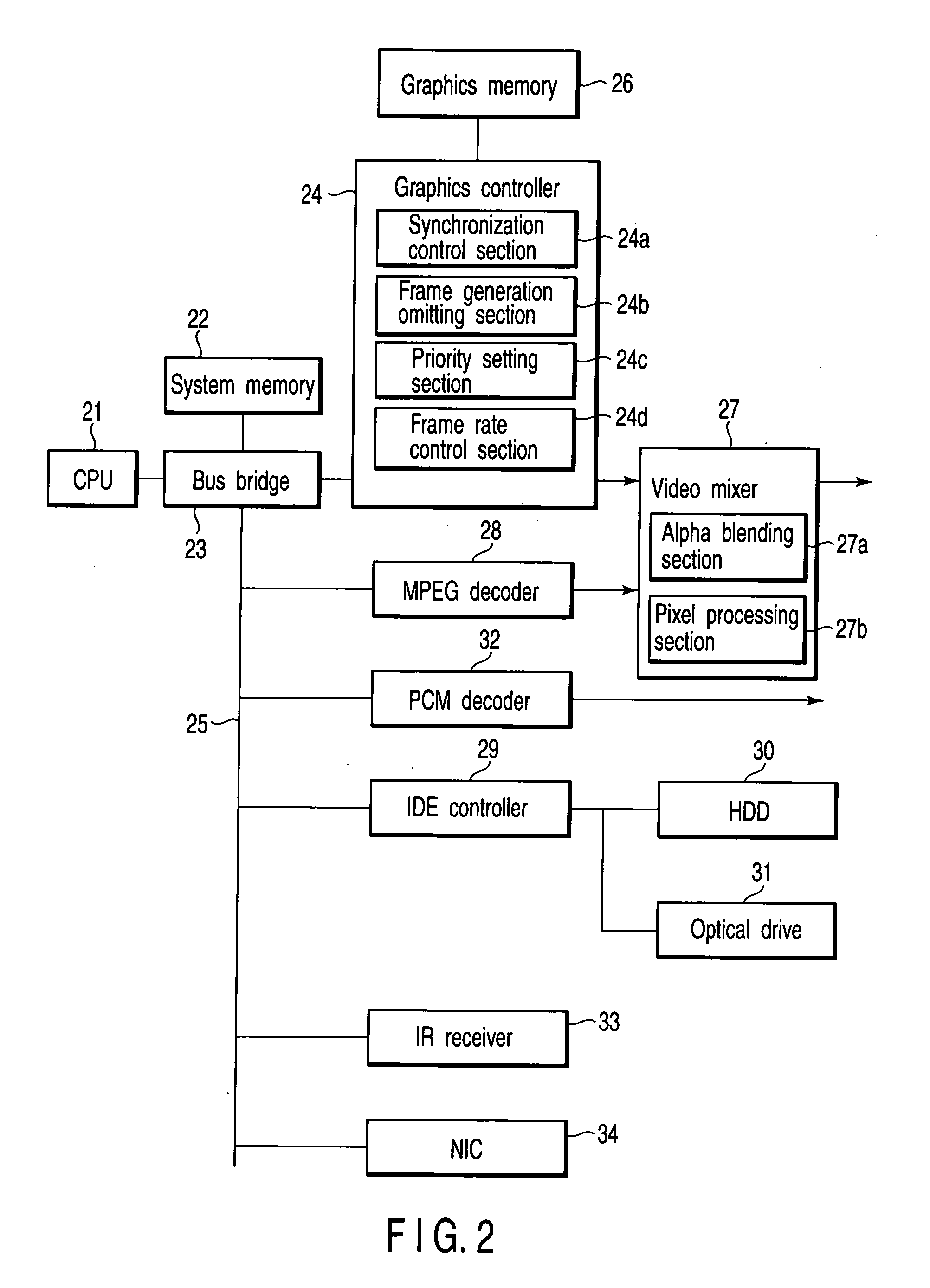
Frame synchronization in an ethernet NTP time-keeping digital cinema playback system
ActiveUS20050283820A1Highly accurateHighly stableTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideo decodingEthernet
In a digital cinema network of NTP-timekeeping devices in which one of the devices decodes video information, the scheduling of future instructions takes into account the differences between the nominal and actual frame rates of the video decoding device and the network's NTP latency.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for embodying and synchronizing downlink signal in mobile communication system and method for searching cell using the same
InactiveUS20060114812A1Solve the excessive calculationSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationCell searchCyclic prefix
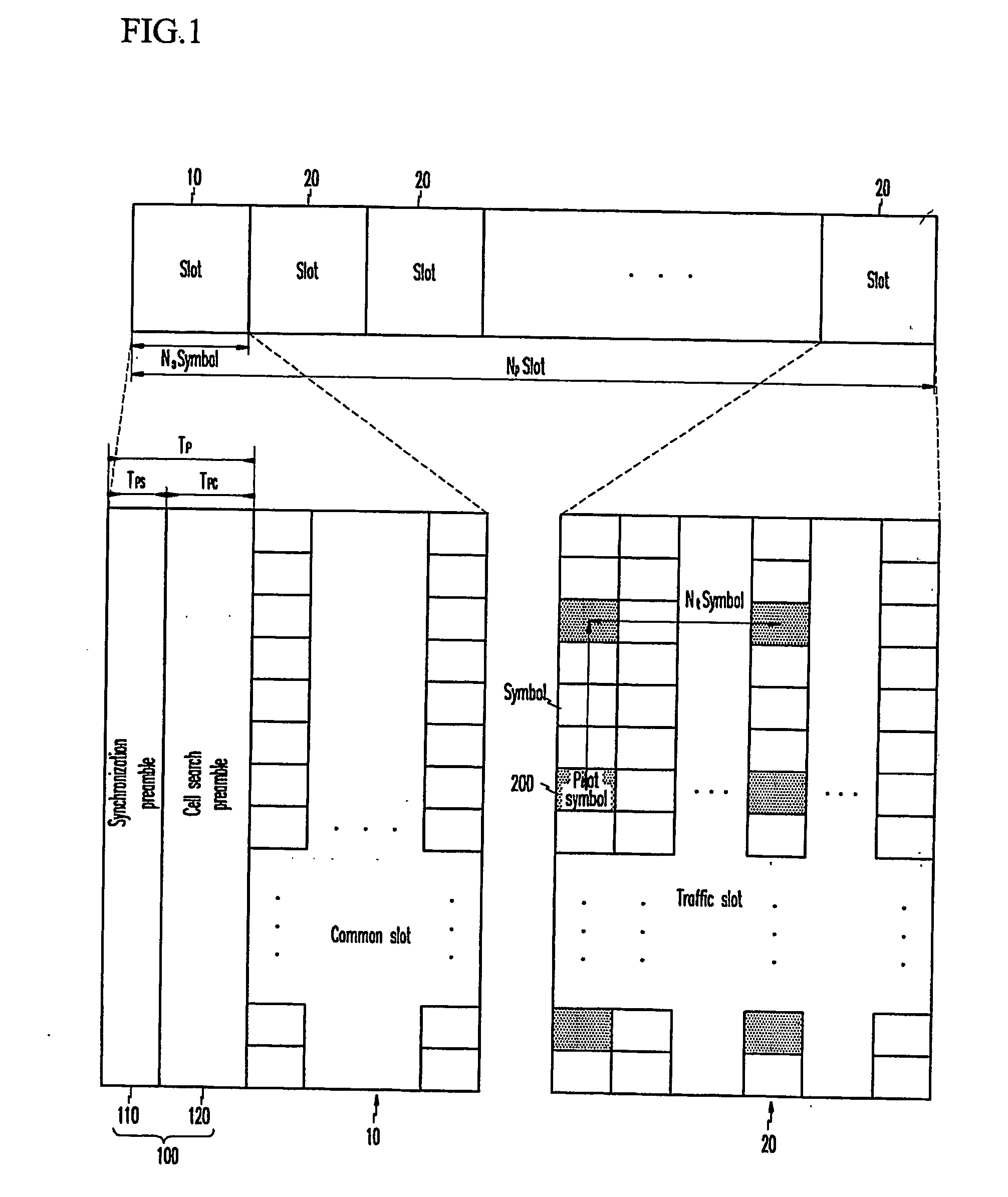
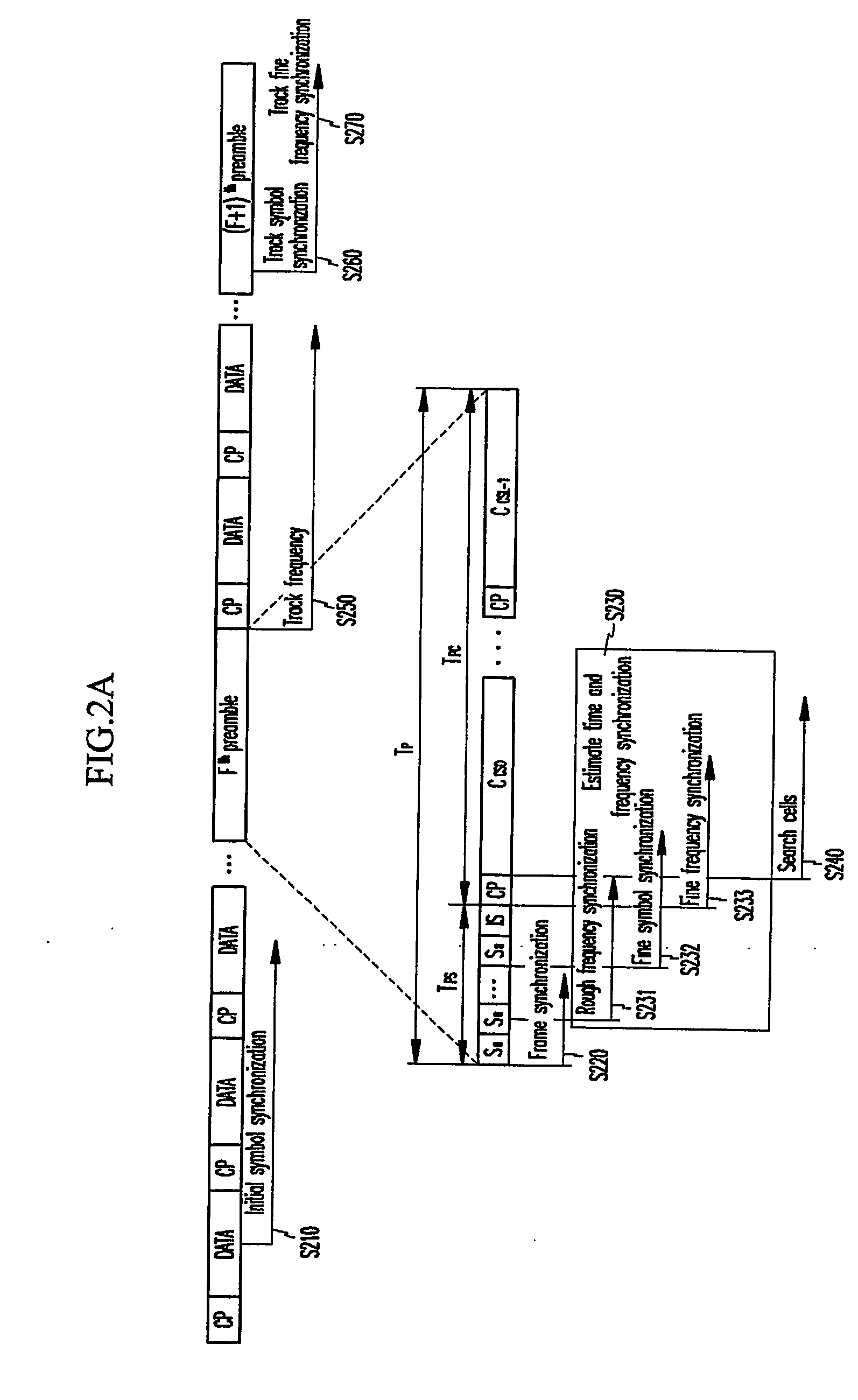
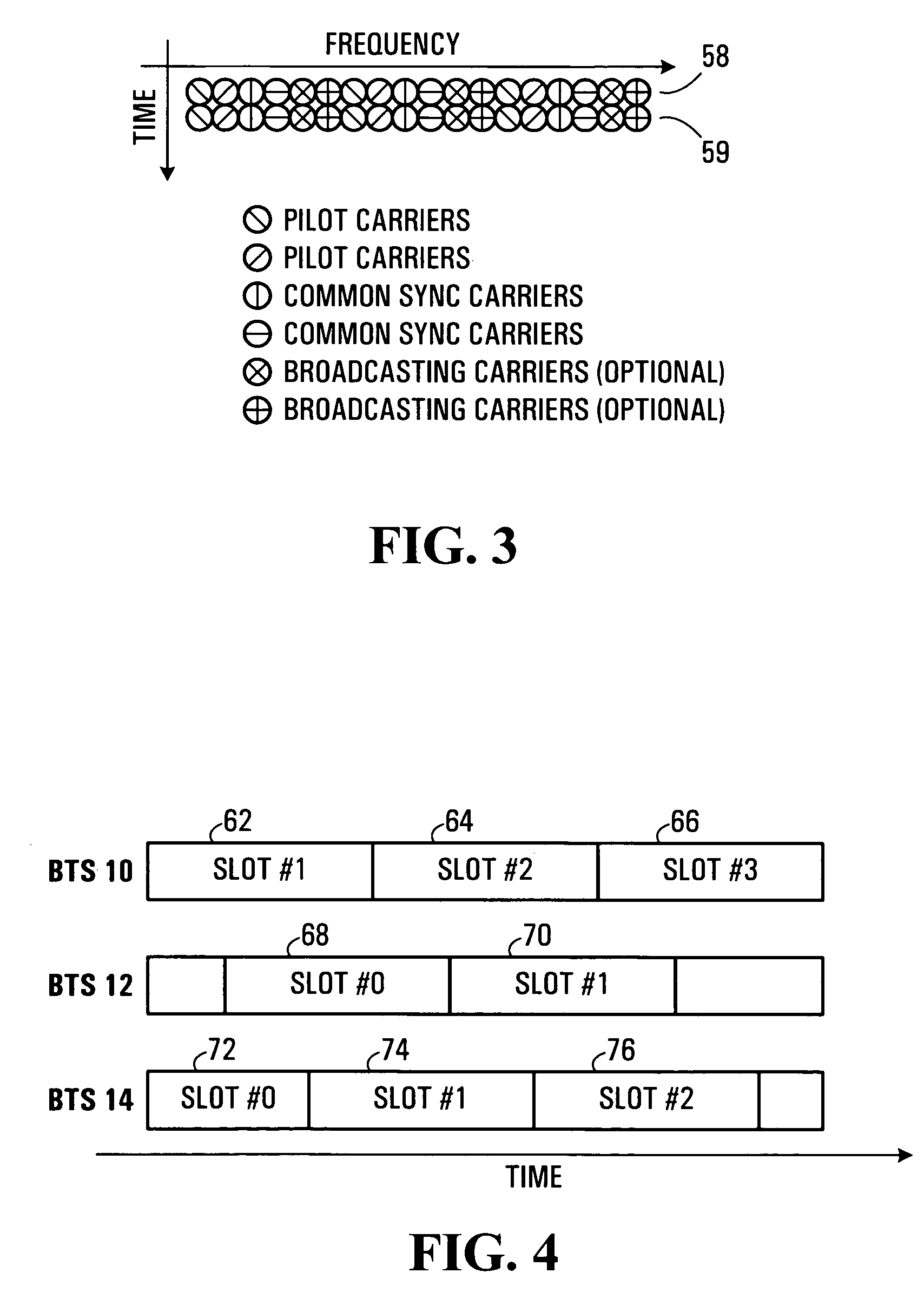
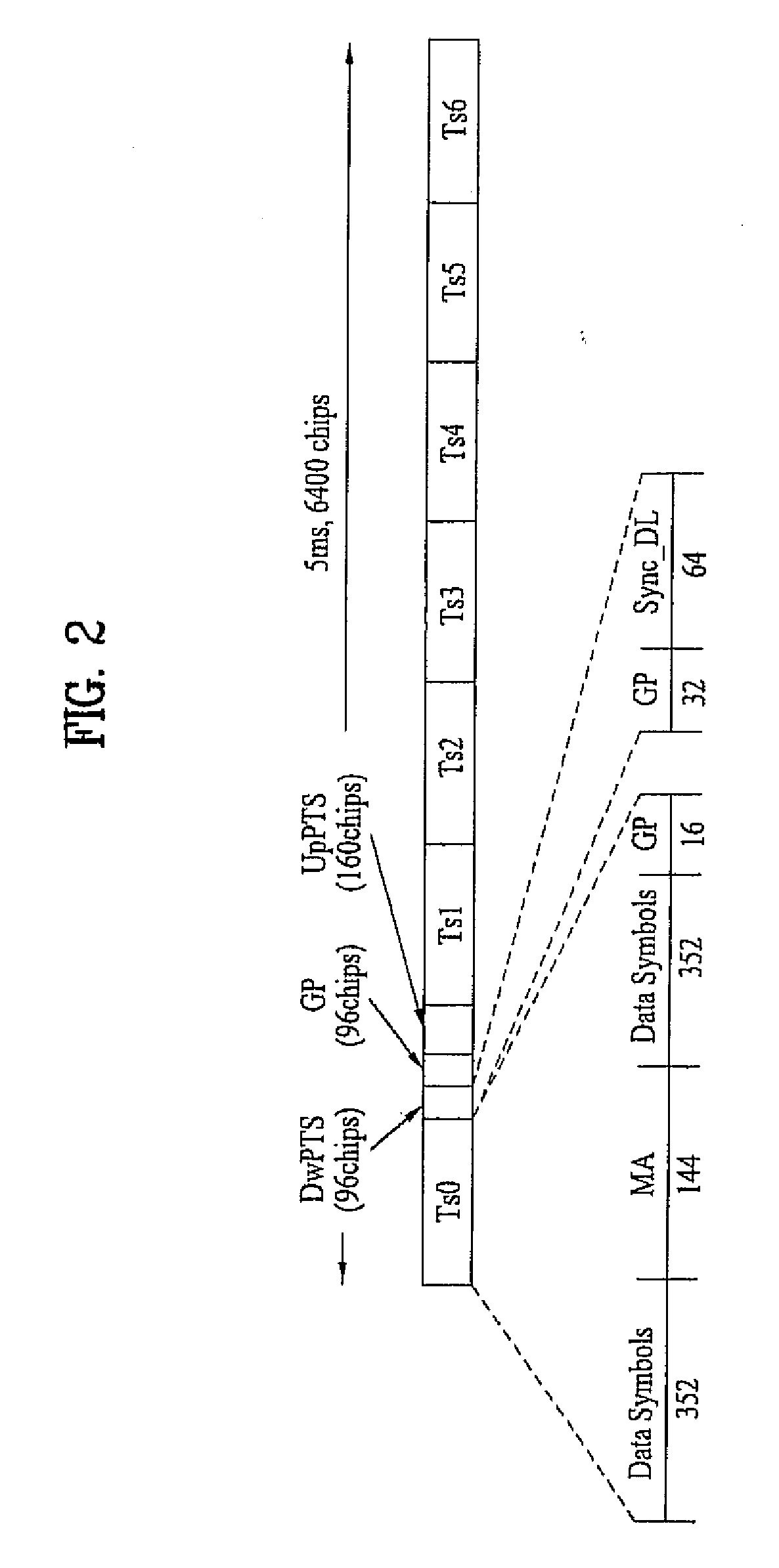
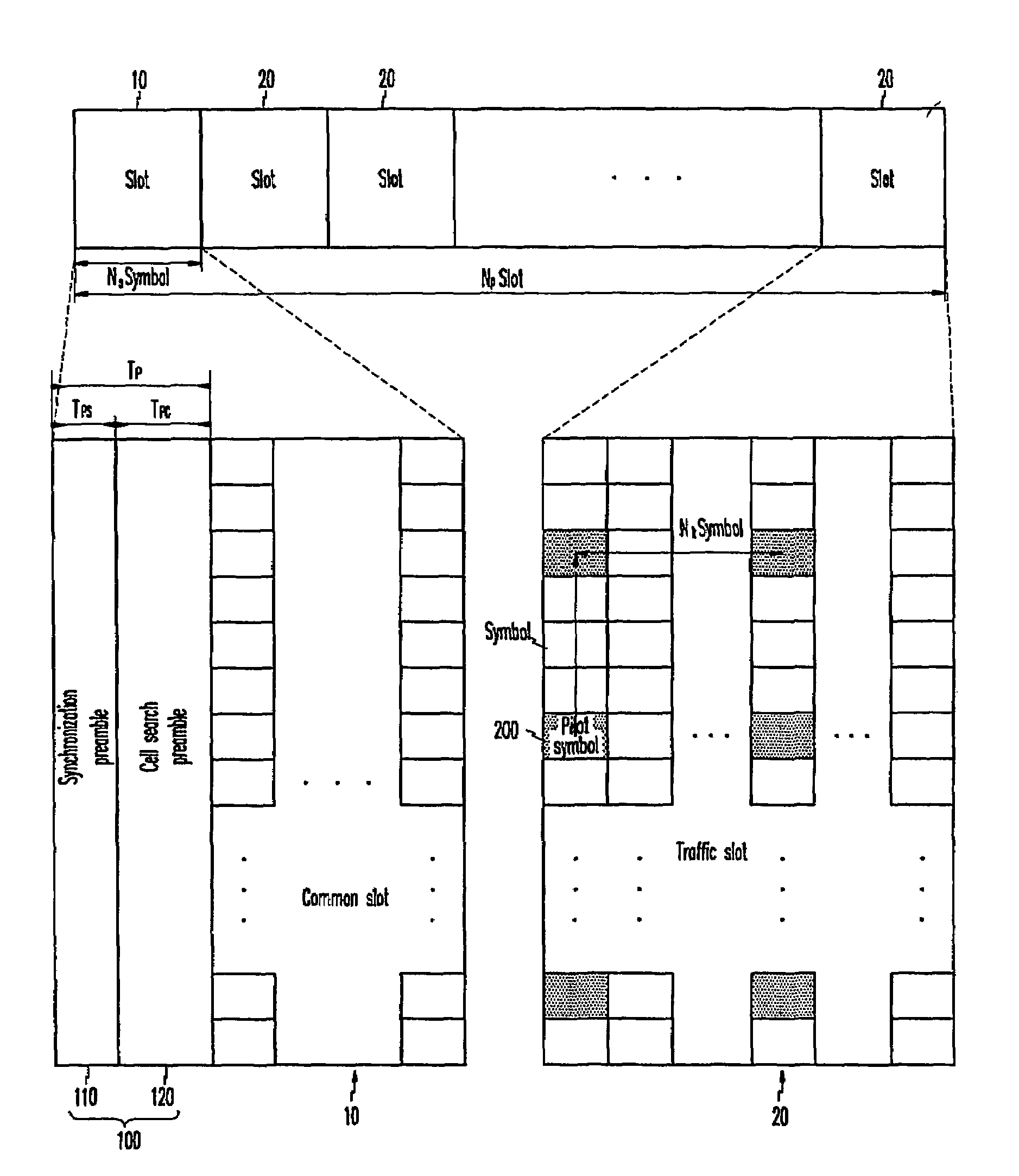
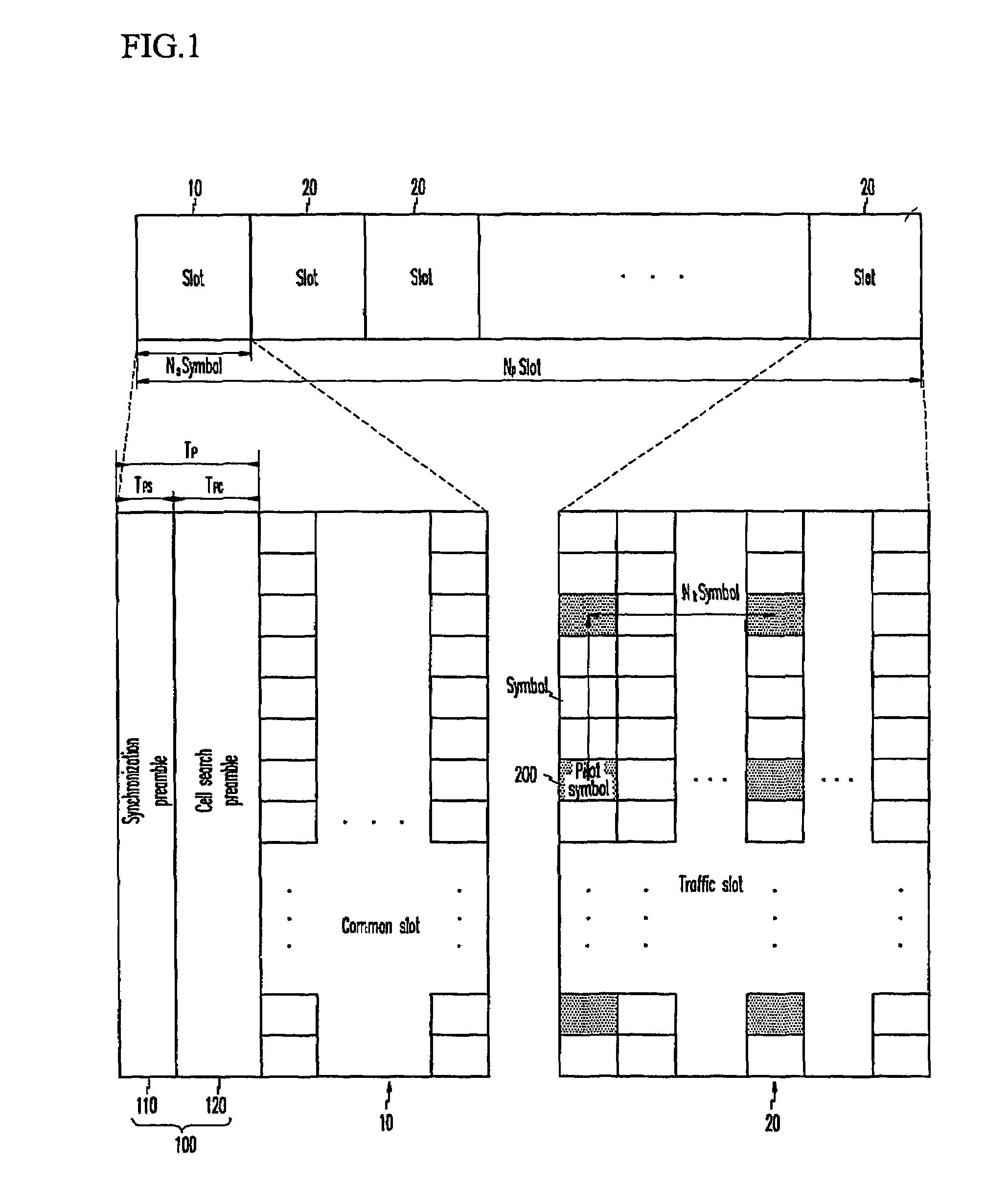
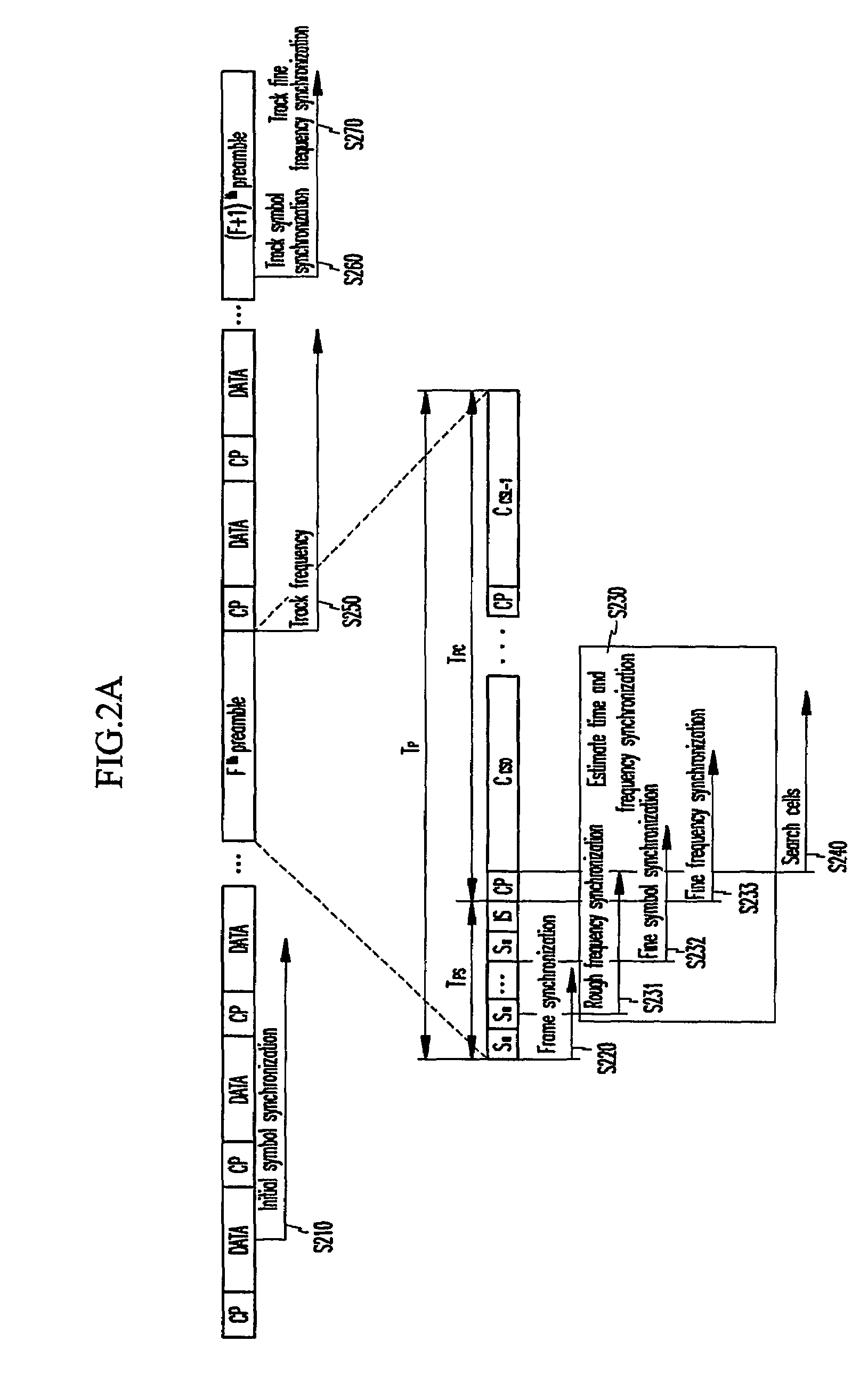
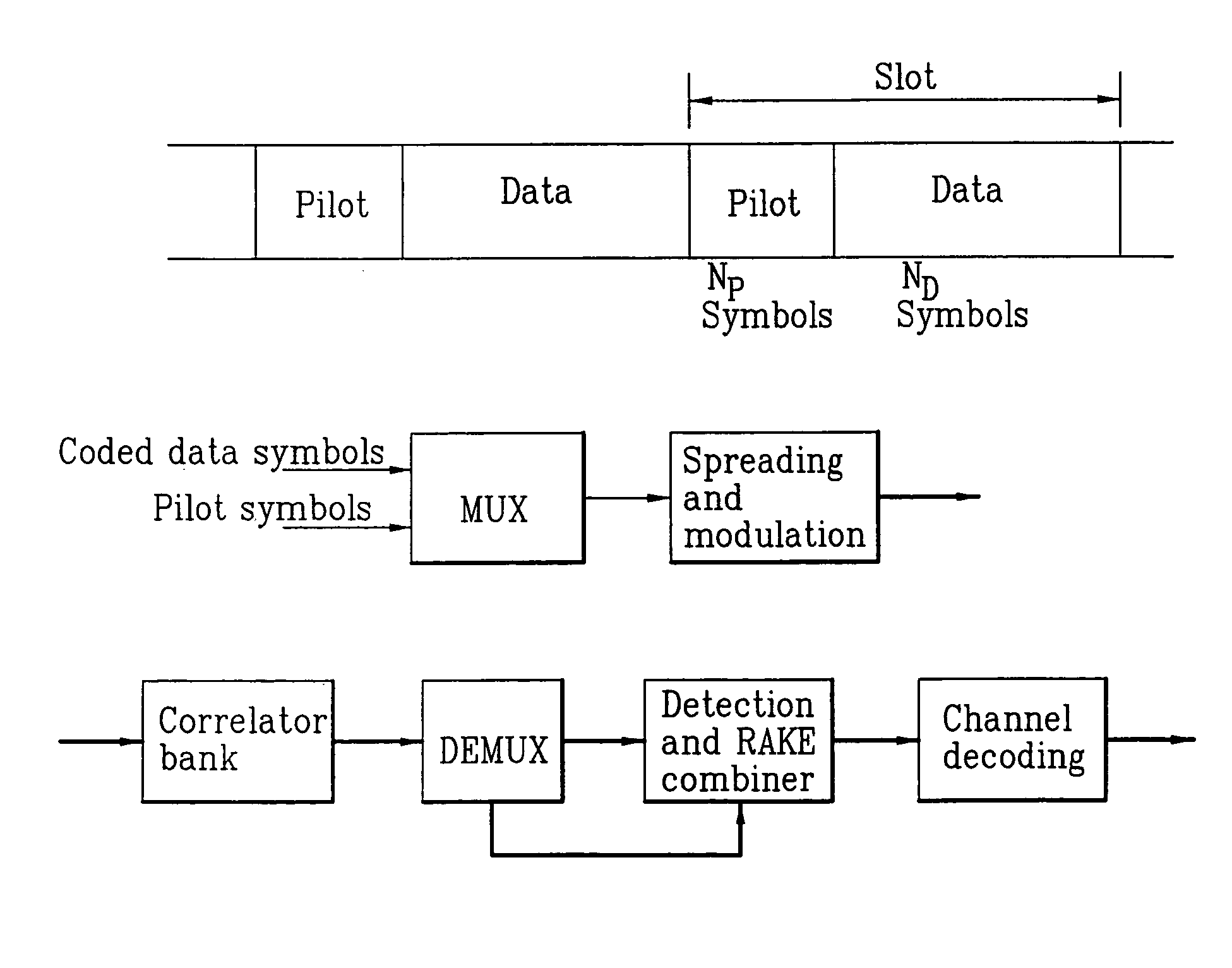
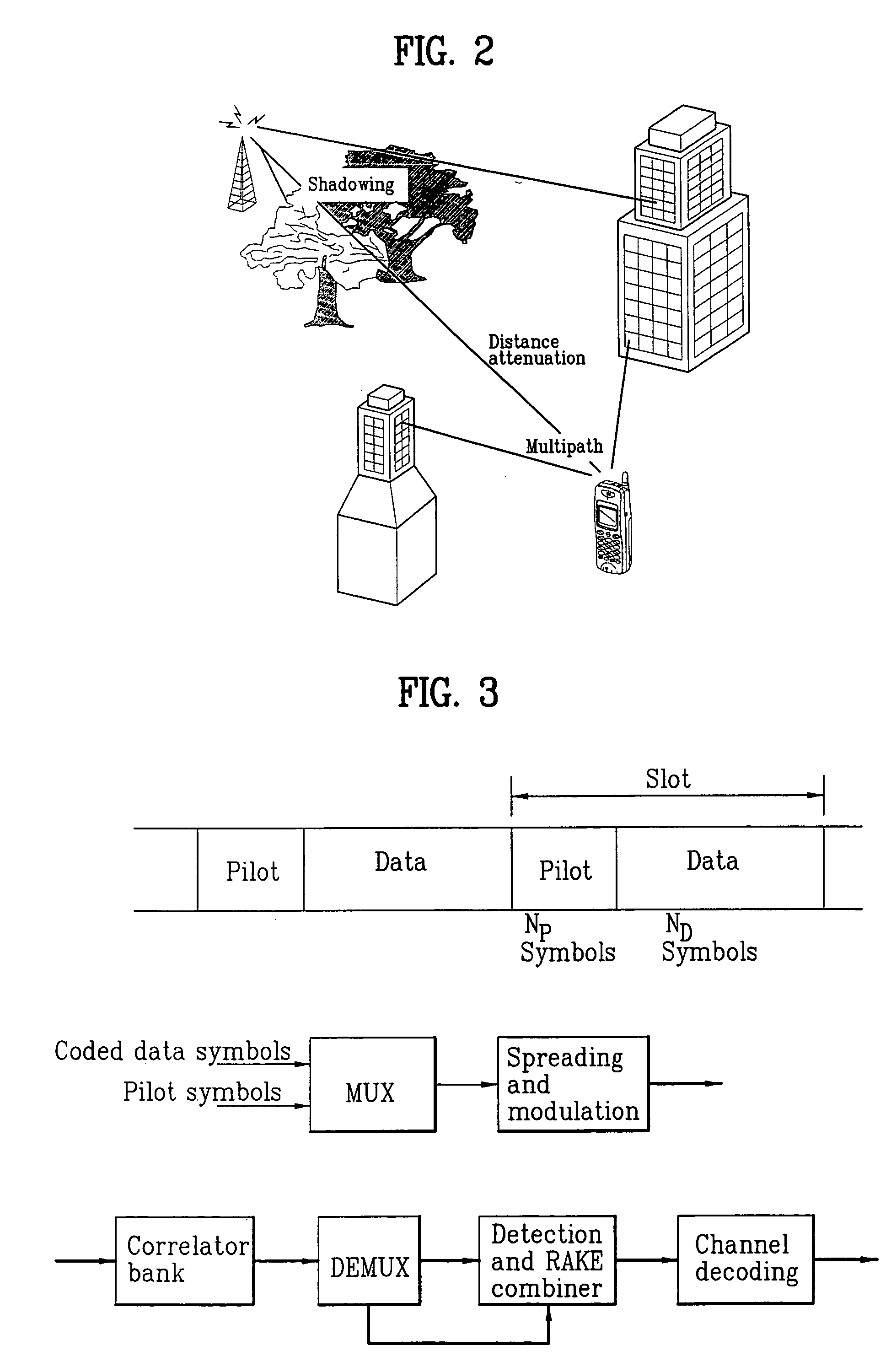
In an OFDMA-based cellular system, a frame of a downlink signal includes a common slot and traffic slots. The common slot includes a synchronization preamble and a cell search preamble. The synchronization preamble has a structure for synchronizing time and frequency, and the cell search preamble has a cell search structure. The traffic slot includes pilot symbols provided on the time and frequency axes. A cyclic prefix is used to estimate initial symbol synchronization, and the initial symbol synchronization and the synchronization preamble are used to synchronize the frame. The synchronization frame and the cell search preamble are used to estimate time and frequency synchronization. The cell search preamble is used to search cells. When the initial synchronization is performed, the cyclic prefix is used to track the frequency, the synchronization preamble is used to track symbol synchronization, and the cell search preamble is used to track fine frequency synchronization.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
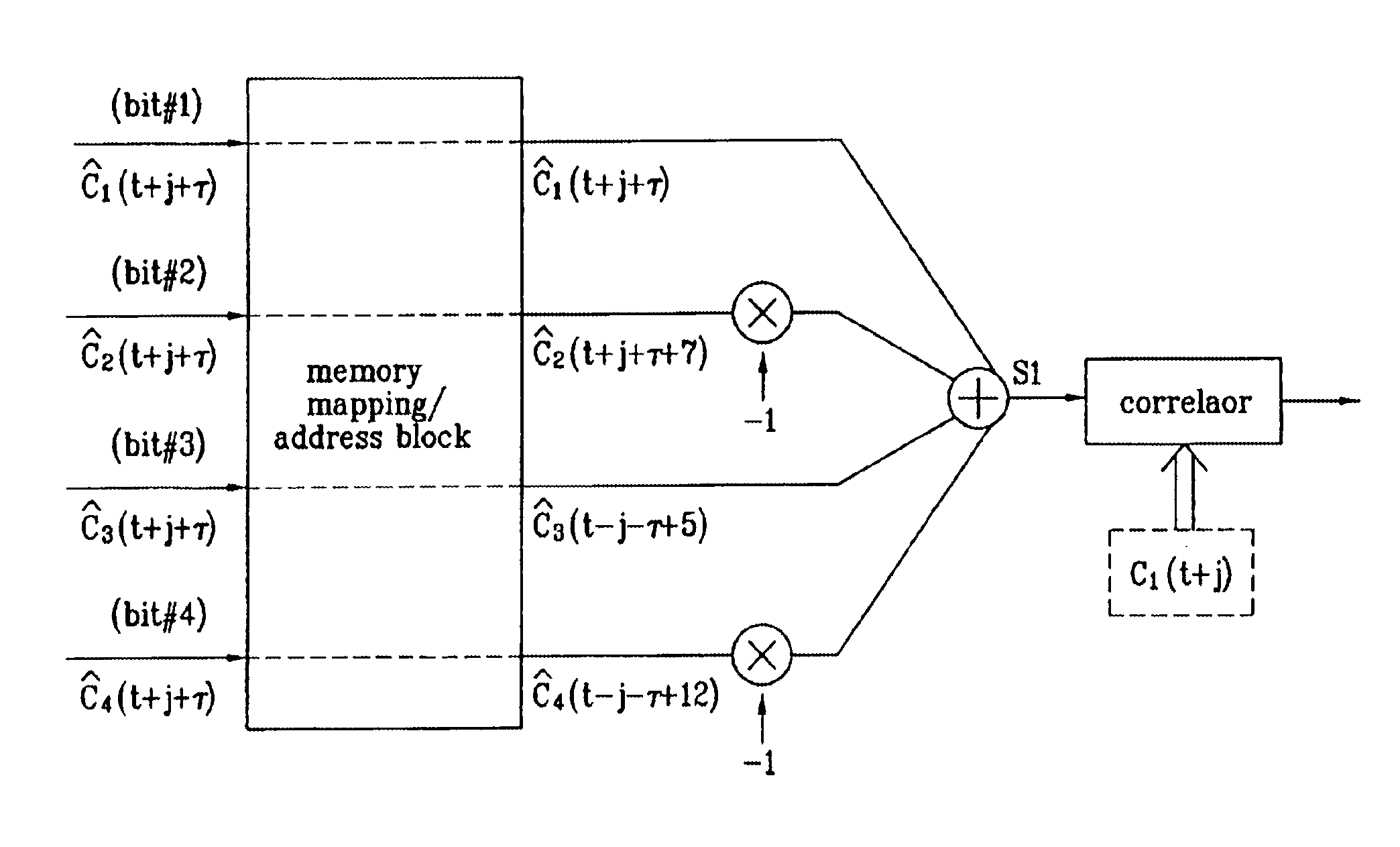
InactiveUS6987746B1Optimal autocorrelation resultEliminate and prevent sidelobesSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexCode division multiple accessCorrelation function
The frame words of the preferred embodiment are especially suitable for frame synchronization and / or channel estimation. By adding the autocorrelation and cross-correlation functions of frame words, double maximum values equal in magnitude and opposite polarity at zero and middle shifts are obtained. This property can be used to slot-by-slot, double-check frame synchronization timing, single frame synchronization and / or channel estimation and allows reduction of the synchronization search time. Further, the present invention allows a simpler construction of a correlator circuit for a receiver. A frame synchronization apparatus and method using an optimal pilot pattern is used in a wide band code division multiple Access (W-CDMA) next generation mobile communication system. This method includes the steps of storing column sequences demodulated and inputted by slots, in a frame unit, in detecting frame synchronization for upward and downward link channels; converting the stored column sequences according to a pattern characteristic related to each sequence by using the pattern characteristic obtained from the relation between the column sequences; adding the converted column sequences by slots; and performing a correlation process of the added result to a previously designated code column.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
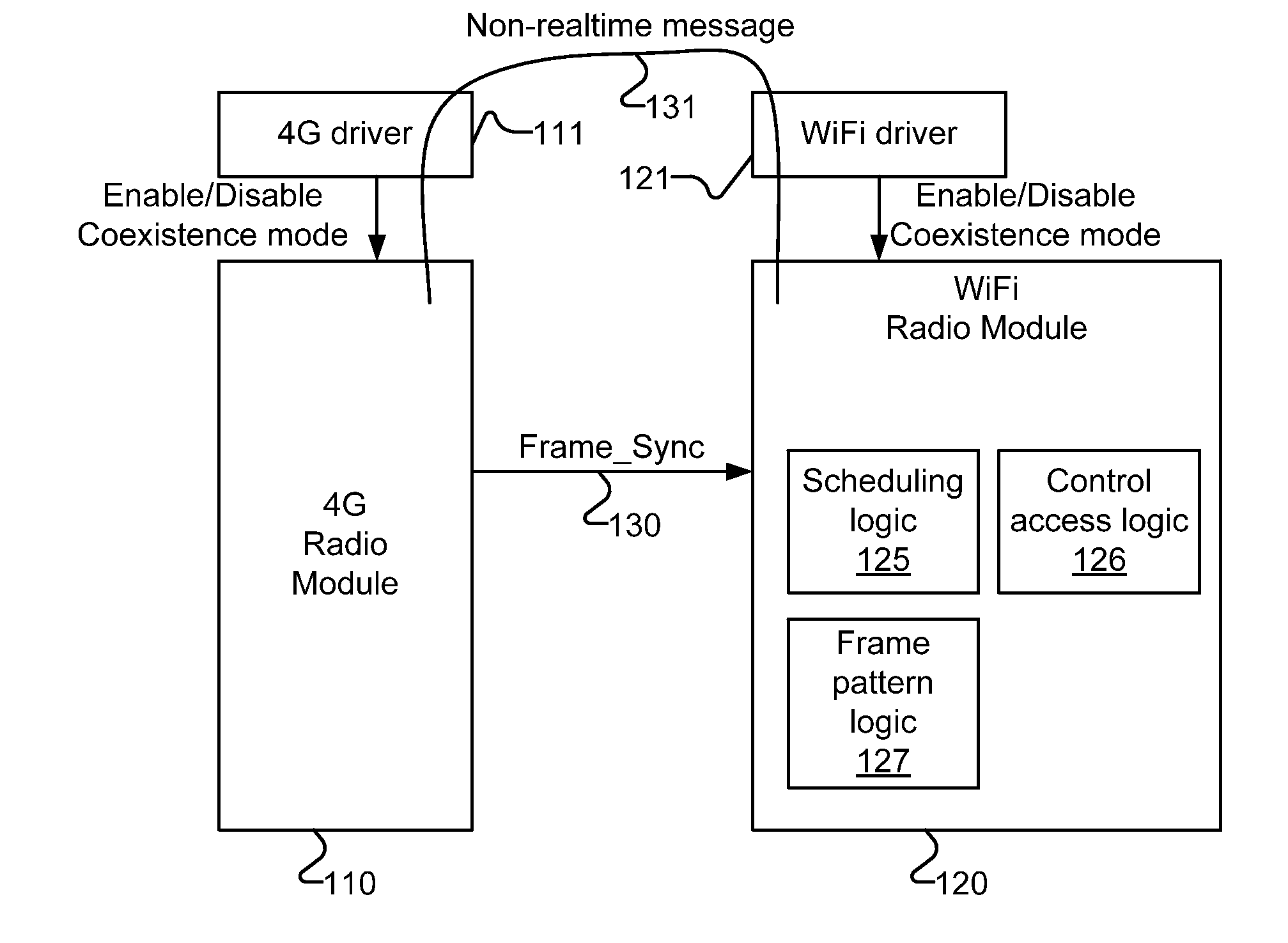
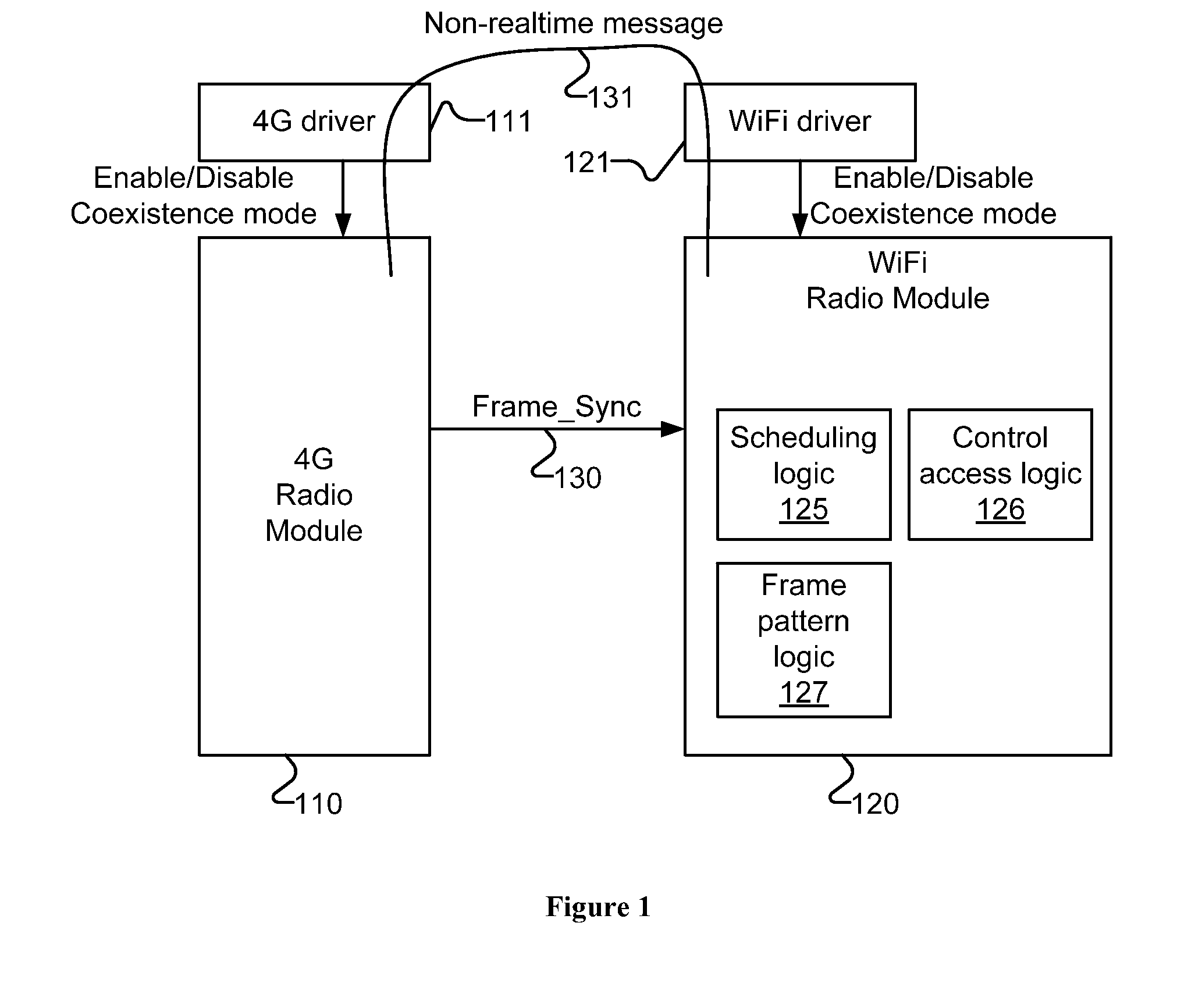
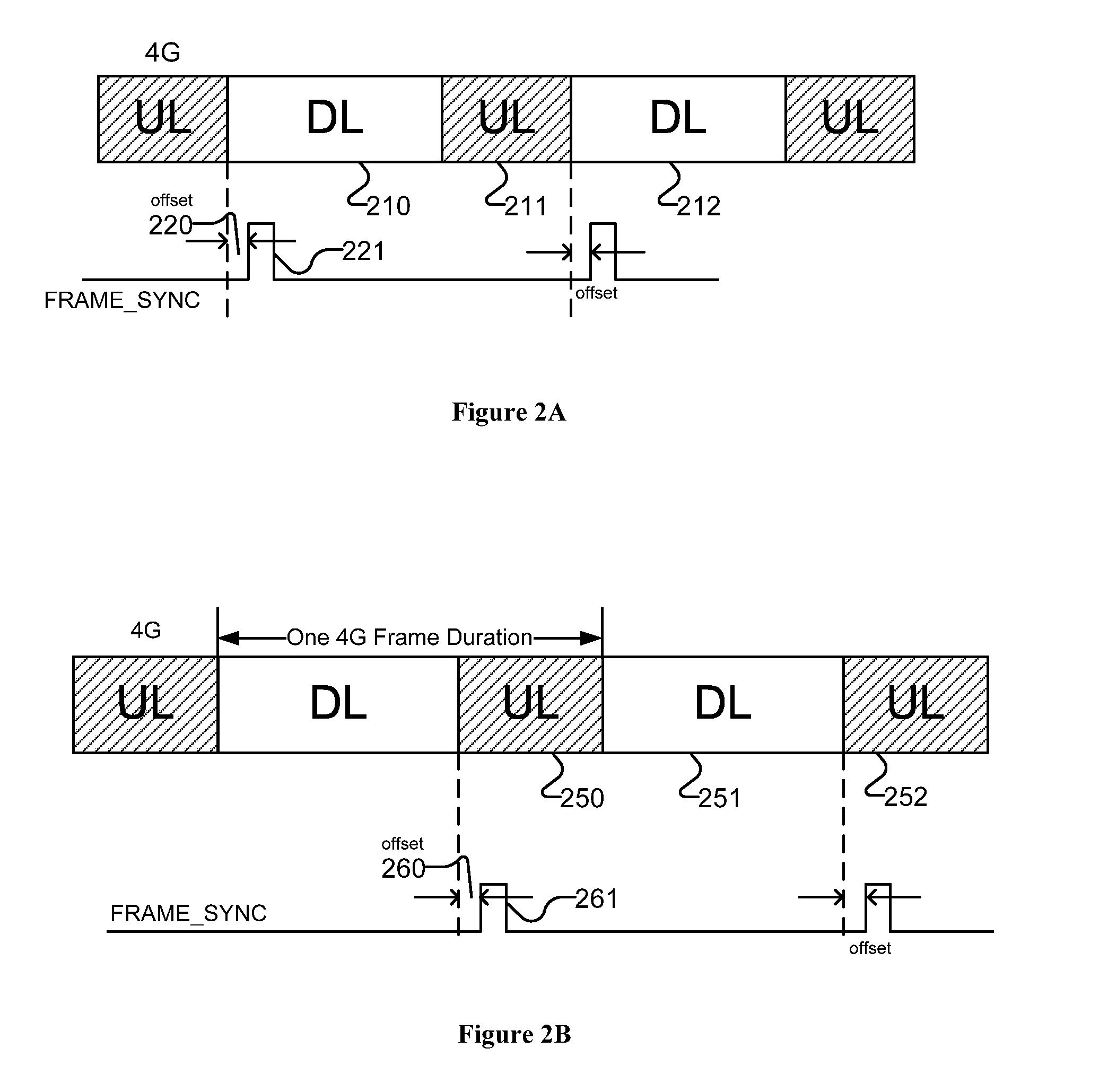
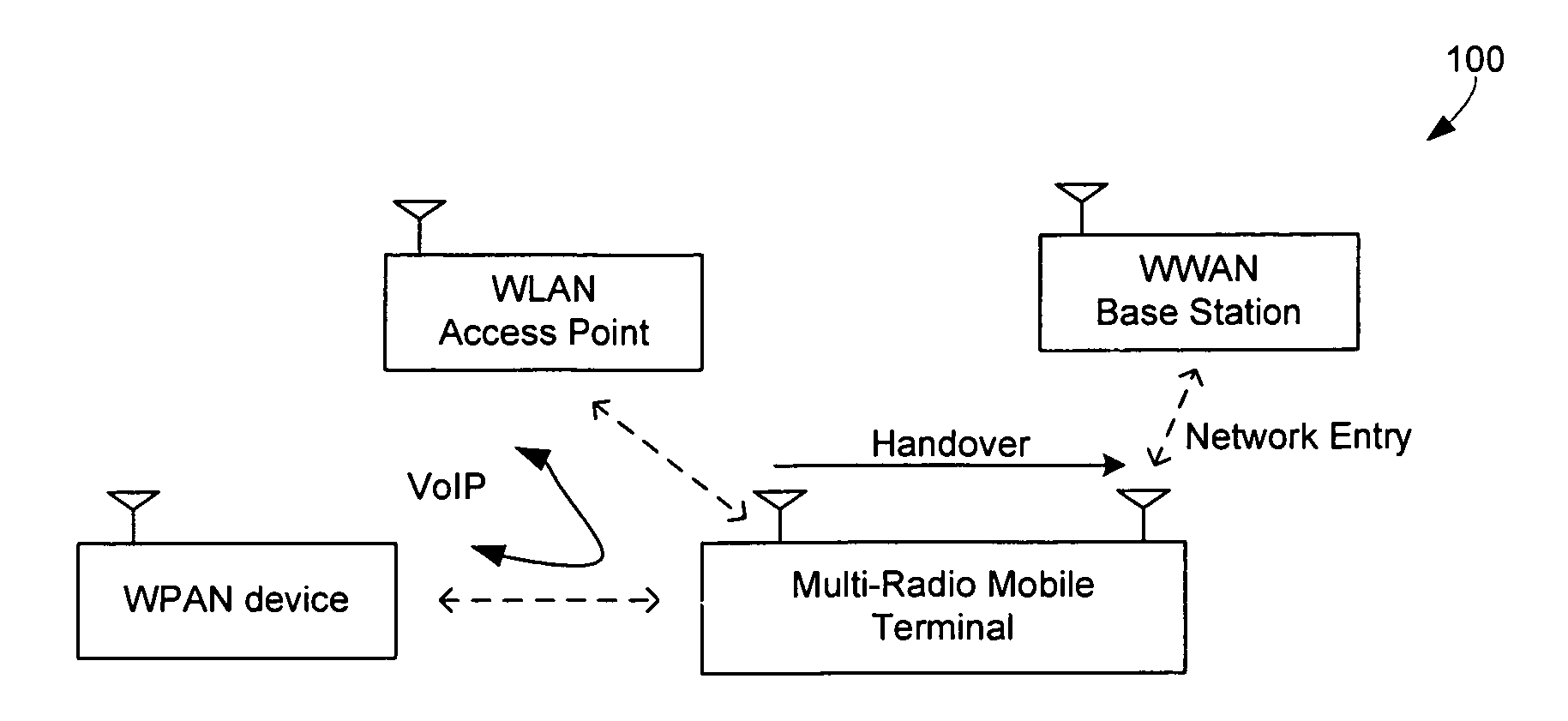
Methods and apparatuses for multi-radio coexistence
InactiveUS20120120944A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemVIT signals
A method for coexistence radio communication systems is presented. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a realtime frame synchronization signal and receiving one or more frame parameters. The method further includes determining, based at least on the frame synchronization signal and the frame parameters, estimated frame timing information and scheduling transmission based on the estimated frame timing information to avoid collision of the transmission and reception.
Owner:INTEL CORP
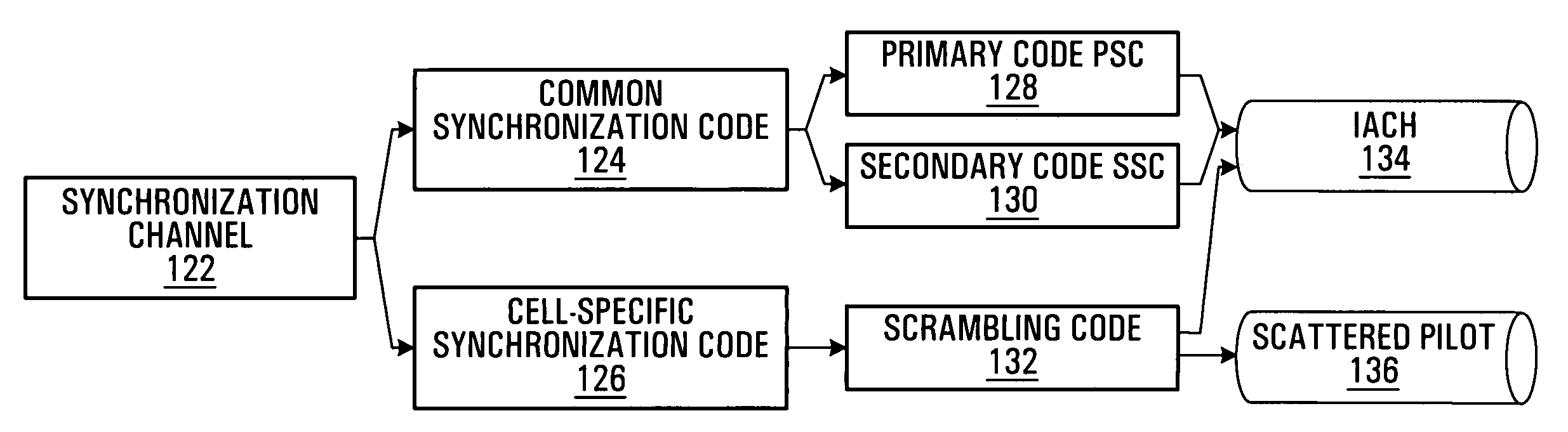
Physical layer structures and initial access schemes in an unsynchronized communication network
Physical layer structures and related access schemes for unsynchronized communication networks are provided. Access channel information, preferably including a common synchronization code associated with all transceiver stations in a communication network and a cell-specific synchronization code uniquely associated with one of the transceiver stations, is modulated onto at least one set of time-continuous signal components of a communication signal. In order to access the communication network, communication terminals search for the access channel information in one or more sets of time-continuous signal components and synchronization parameters are then determined based on a location of the access channel information in the sets of time-continuous signal components. Some embodiments of the invention provide for joint frame synchronization and coarse timing synchronization. In further embodiments, the communication signal also includes a scattered pilot channel onto which a portion of the access channel information, preferably the cell-specific synchronization code, is modulated. The pilot channels may then be re-used for initial access operations in addition to its conventional uses for such operations as channel estimation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of transmitting preamble for synchronization in a MIMO-OFDM communication system
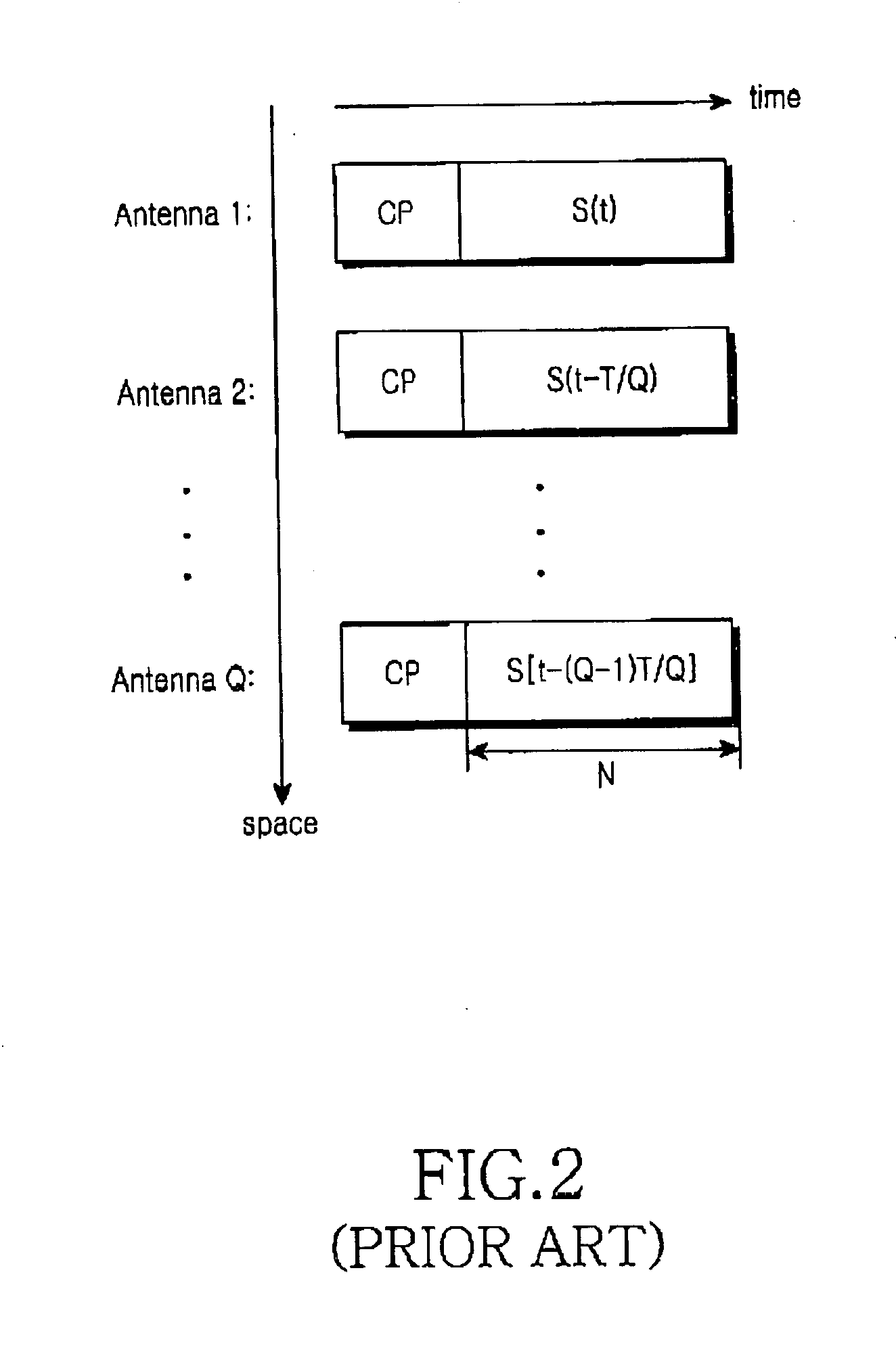
ActiveUS20050084030A1Effective structureEfficient methodSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsCommunications systemOrthogonal sequence
A method and apparatus for transmitting a preamble for frame synchronization and channel estimation in a MIMO-OFDM communication system are provided. An OFDM communication system using Q transmit antennas generates a base preamble sequence including a CP and an orthogonal sequence. If Q≦a predetermined number M, a preamble sequence for a kth antenna is S(t−(k−1)T / Q). If Q>M and k≦M, the preamble sequence transmitted for the kth antenna is S(t−(k−1)T / Q). If Q>M and k>M, the preamble sequence for the kth antenna is (−1)(ps−1)S(t−(k−1)T / Q). Here, S(t) is the orthogonal sequence, T is the period of the orthogonal sequence, and PS is an index indicating a transmission period of the preamble sequence. The preamble sequences are at least twice transmitted from the Q transmit antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Embedded chirp signal for position determination in cellular communication systems
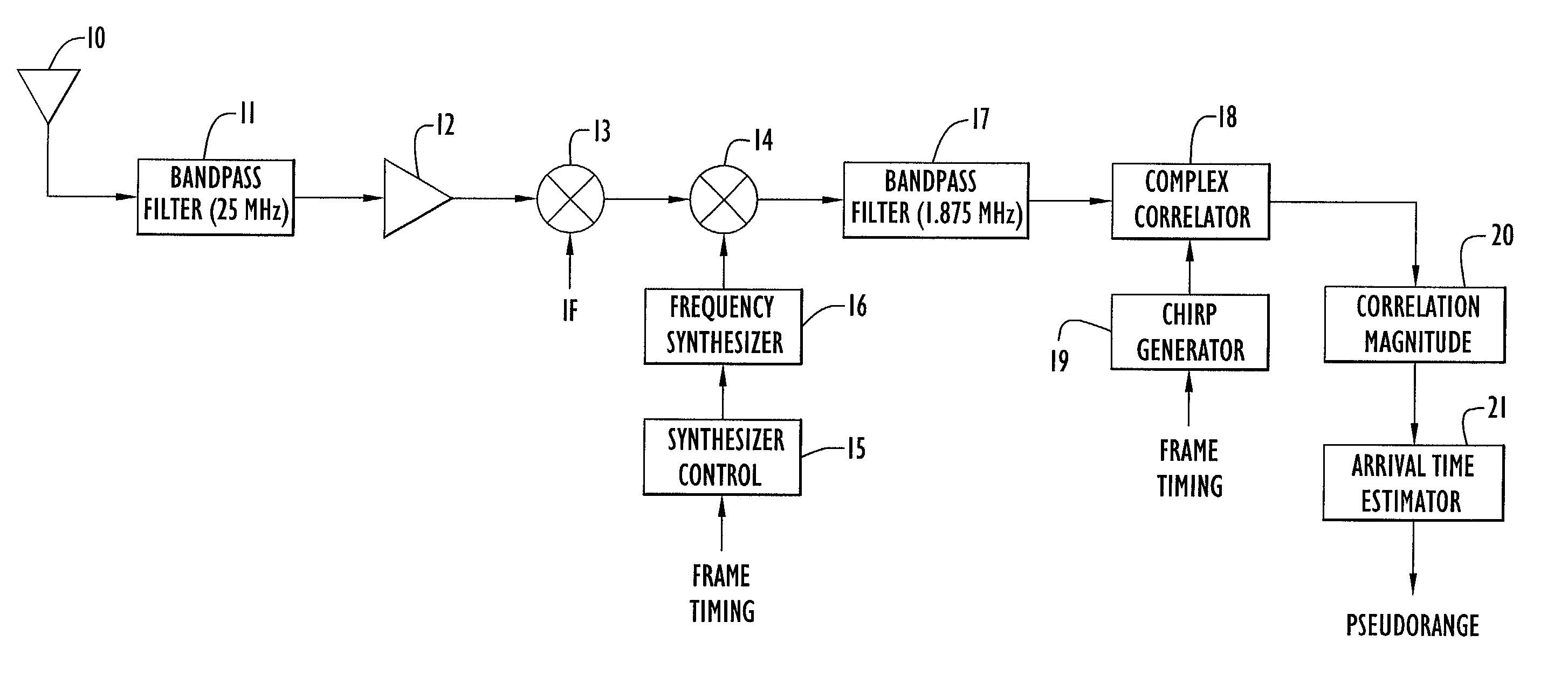
ActiveUS7068704B1Precise positioningEnergy efficient ICTPosition fixationCommunications systemCellular communication systems
Systems and methods are described here for locating the position of a mobile terminal in a cellular communications system. A base station in the cellular communication system broadcasts a communication signal having embedded therein a navigation signal. The navigation signal uses a chirp technique in which the chirp signal includes two portions, an up-chirp portion and a down-chirp portion. Each portion of the chirp signal is synchronized with a frame in the communication signal. The chirp navigation signal is at a power level much lower than the communication signal so as not to interfere with the communication signal. A mobile terminal generates a corresponding chirp signal to correlate with the incoming signal and to extract the navigation signal. The mobile terminal uses the detected navigation signal to determine a time of arrival of the communication signal for use in determining the position of the mobile terminal either at the terminal or to send to a network center for location processing.
Owner:ITT CORP
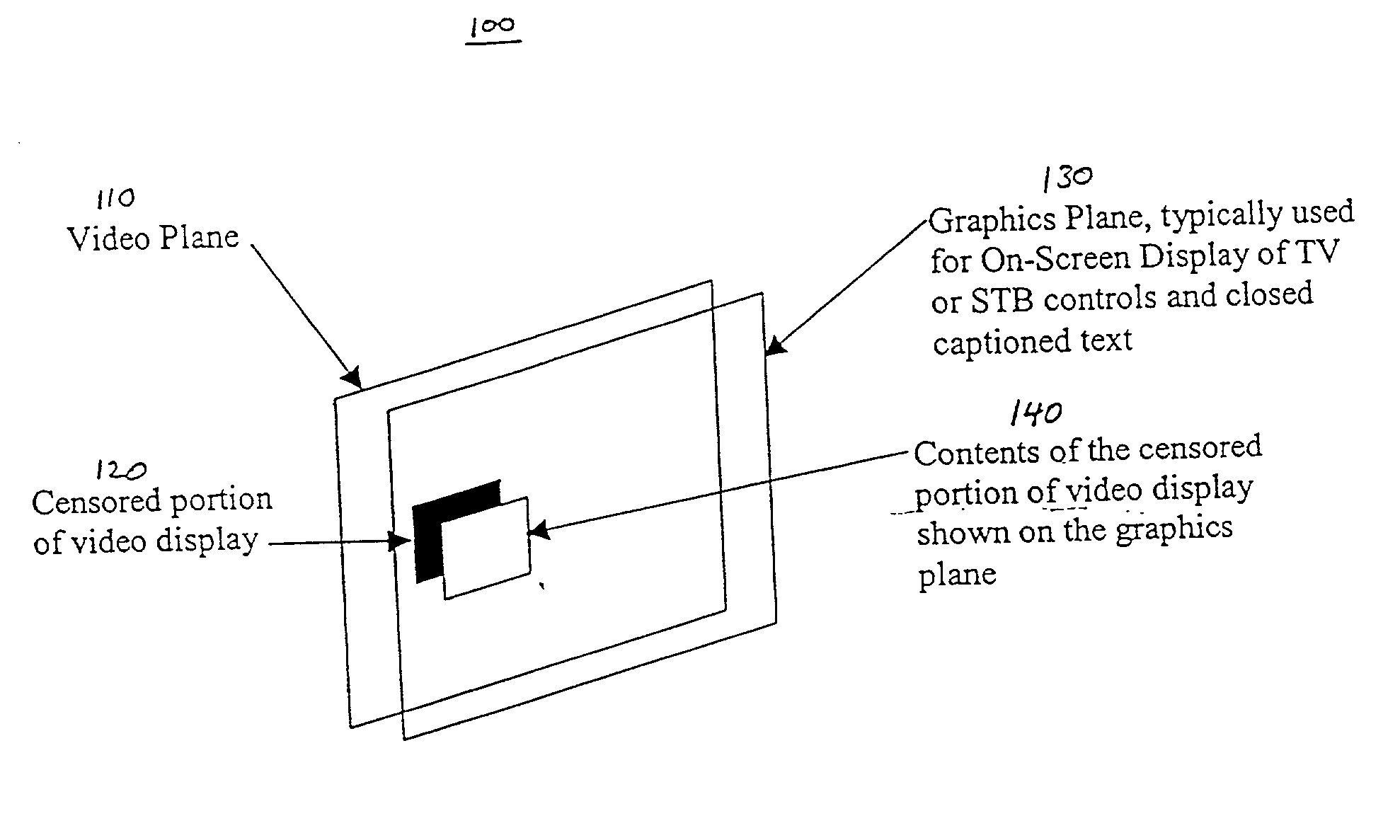
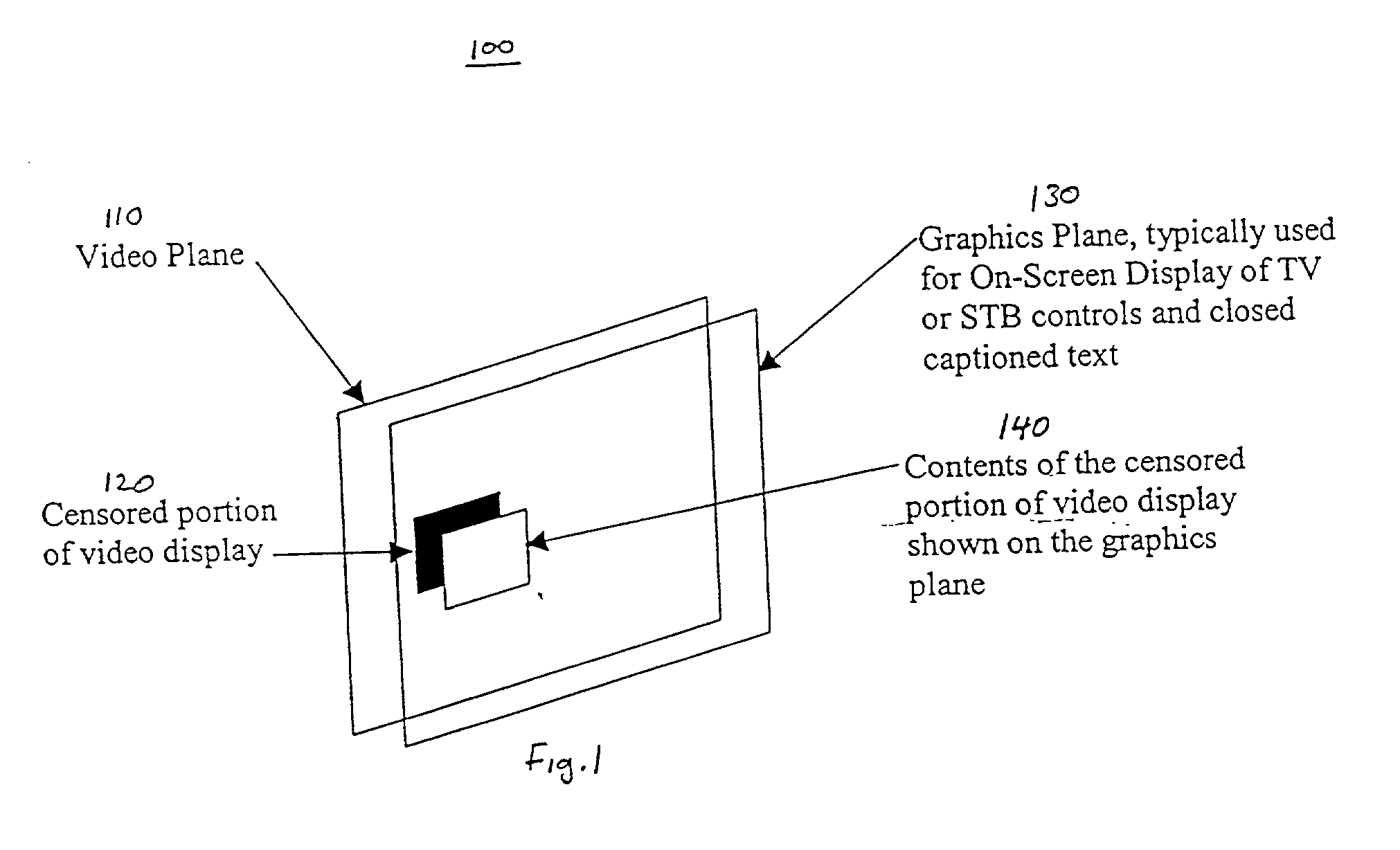
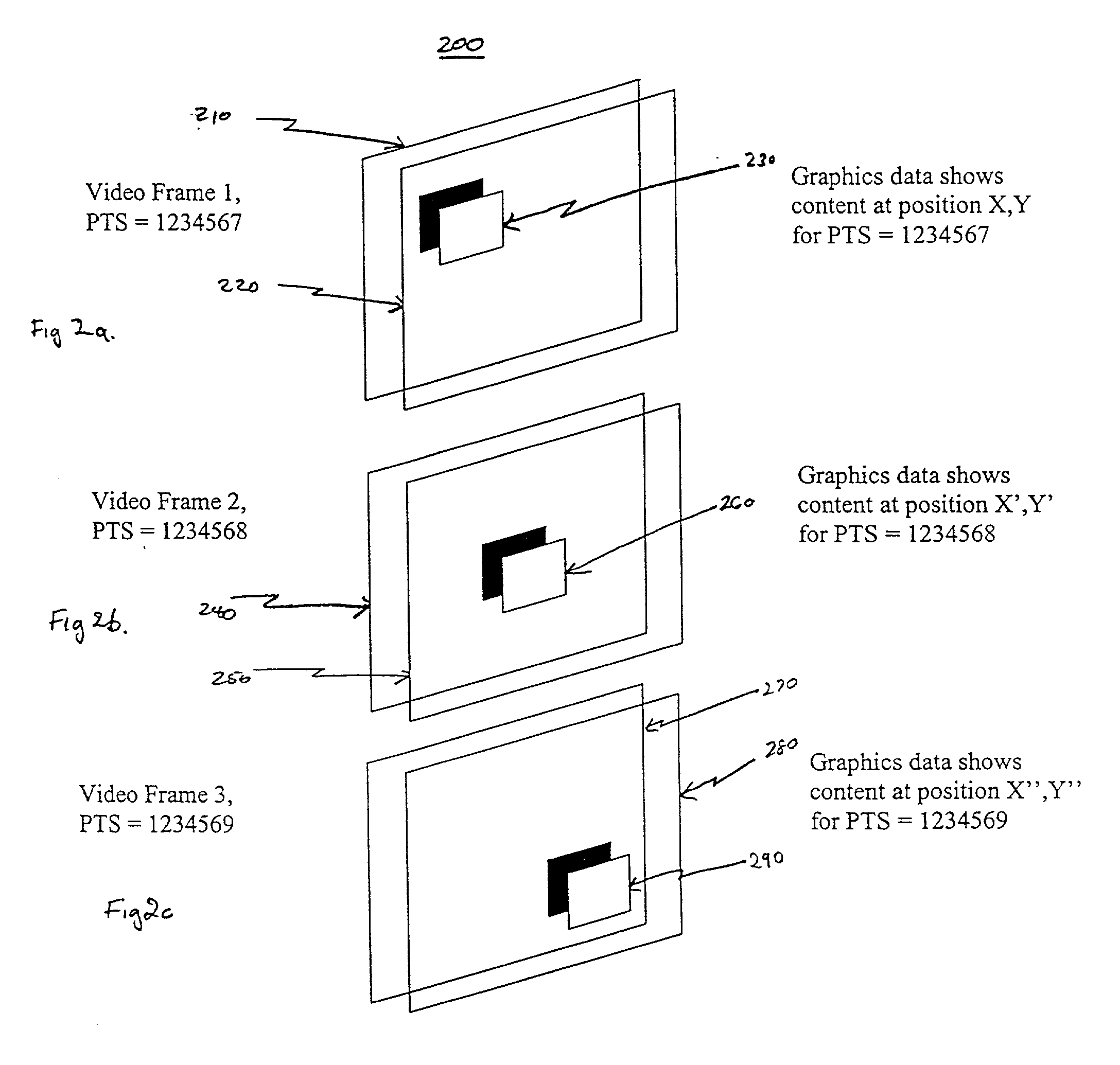
Method and apparatus for synchronizing dynamic graphics
An apparatus and a method for overlaying parts of a displayed presentation of a video by using graphic content rendered by a receiving device such as a set top box or television to complete a displayed presentation of the video. The apparatus receiving frame synchronizing information from a content provider and then conveying the frame synchronizing information as a graphic overlay to the video. The frame synchronizing information comprises frame starting identifier data, frame ending identifier and positional information for describing frame locations and frame timing for overlaying the graphic content and positional information to indicate were to place the graphic content to be overlaid. The frame synchronizing information provides the information necessary to place graphic content, such as a graphic image or graphic animation, at specified positions that are synchronized to the displayed presentation. The same method also enables audio information to be synchronized. The graphic content supplied may include a block of pixel data, an image, an animation or an audio clip.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Configuring method, configuring system, apparatus, receiving method, receiving system, and terminal
ActiveCN104968052AEasy to detect and receiveAccurately detect and receiveSynchronisation arrangementCriteria allocationComputer terminalComputer science
The invention provides a reference signal configuring method and system, an apparatus with a base station function, a reference signal receiving method, a reference signal receiving system, and a terminal. The reference signal configuring method comprises: setting at least one discovery reference signal (DRS) in DMTC (DRS measurement timing configuration); configuring a sending parameter for the at least one DRS; and sending the sending parameter to a terminal served by the apparatus with a base station function in order that the terminal receives the at least one DRS according to the sending parameter. The reference signal configuring method may reduce DRS detection complexity for UE while increasing DRS sending probability in order to enable the terminal to accurately receive the DRS and achieve frame synchronization and subframe synchronization.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
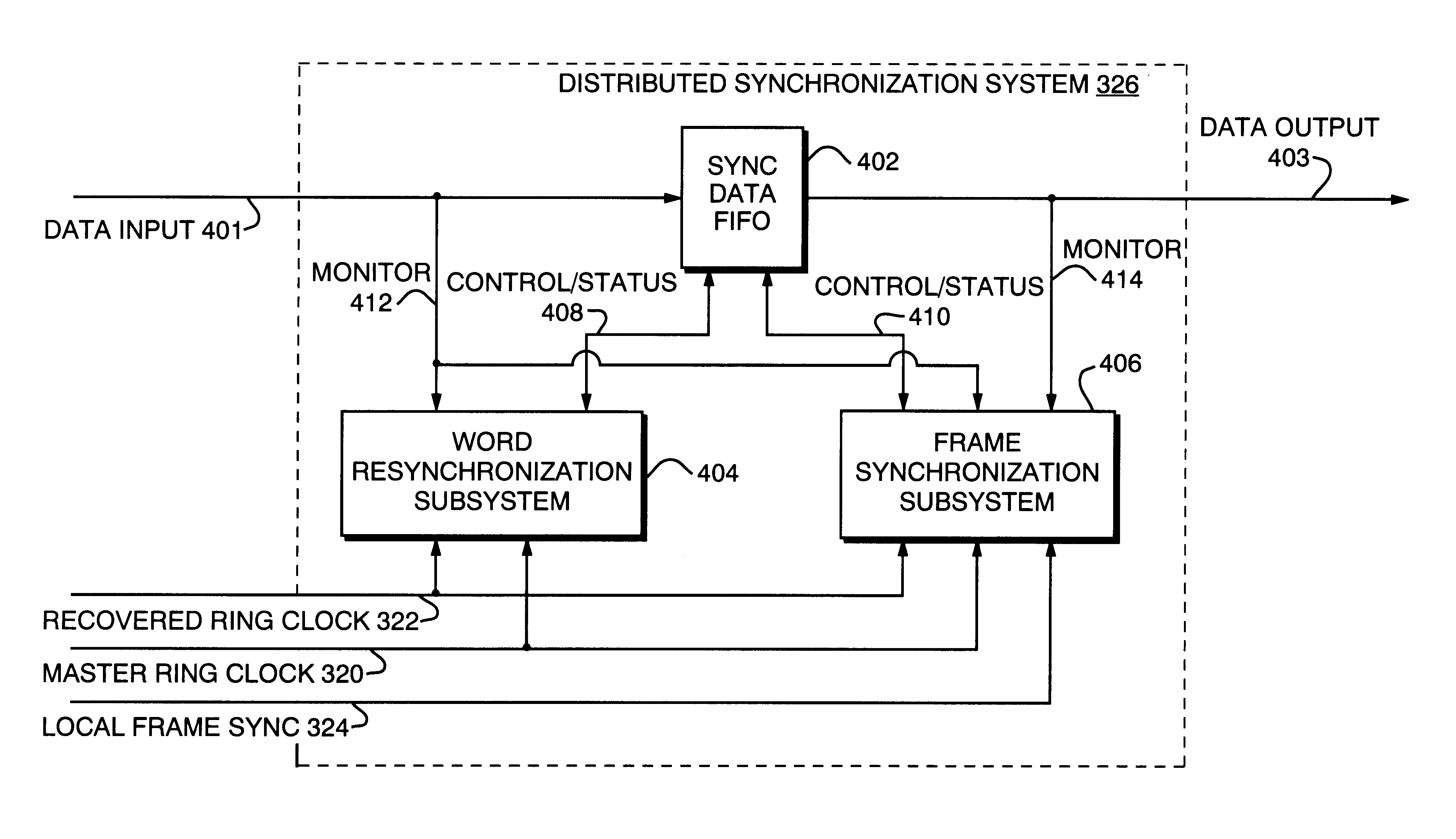
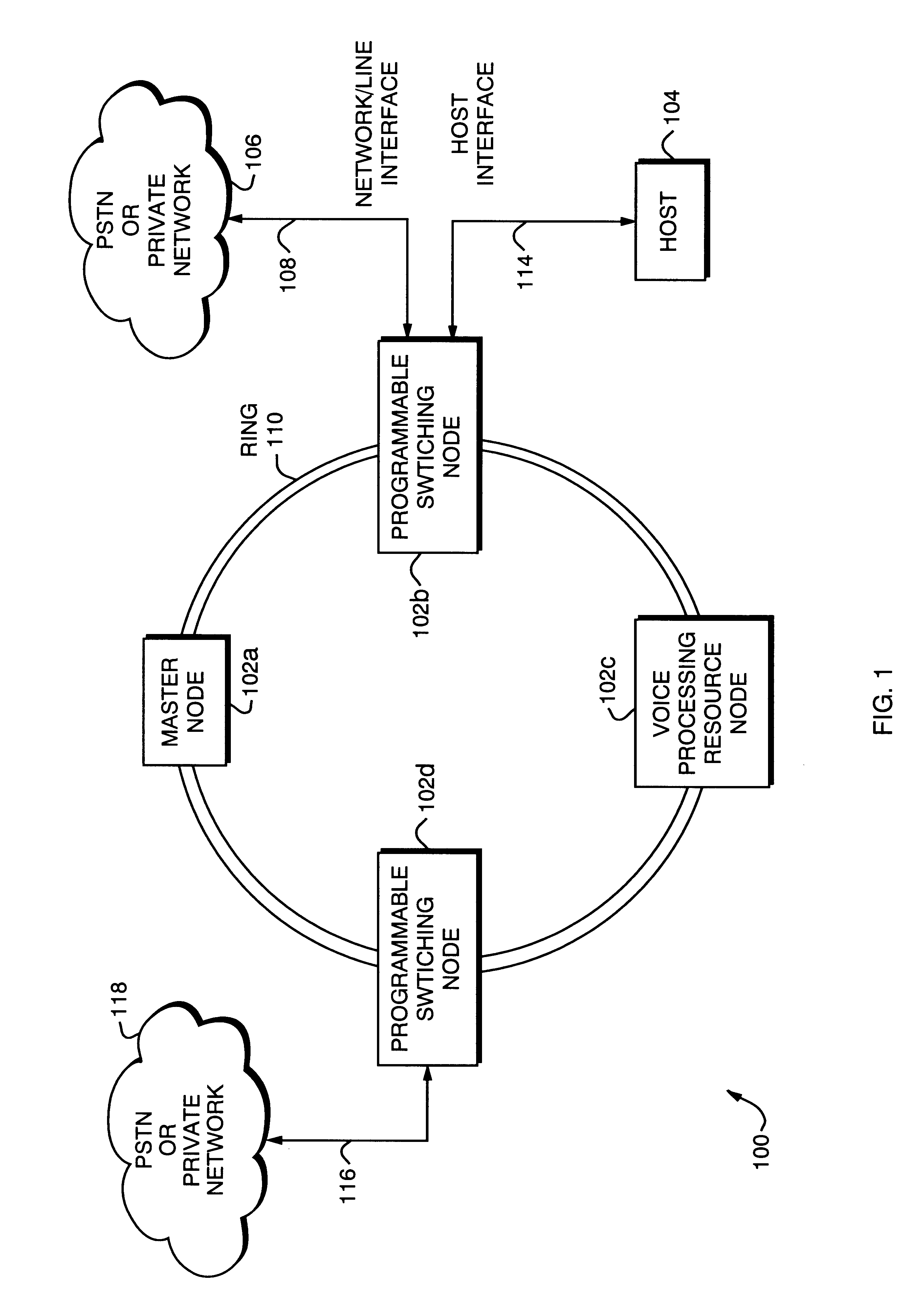
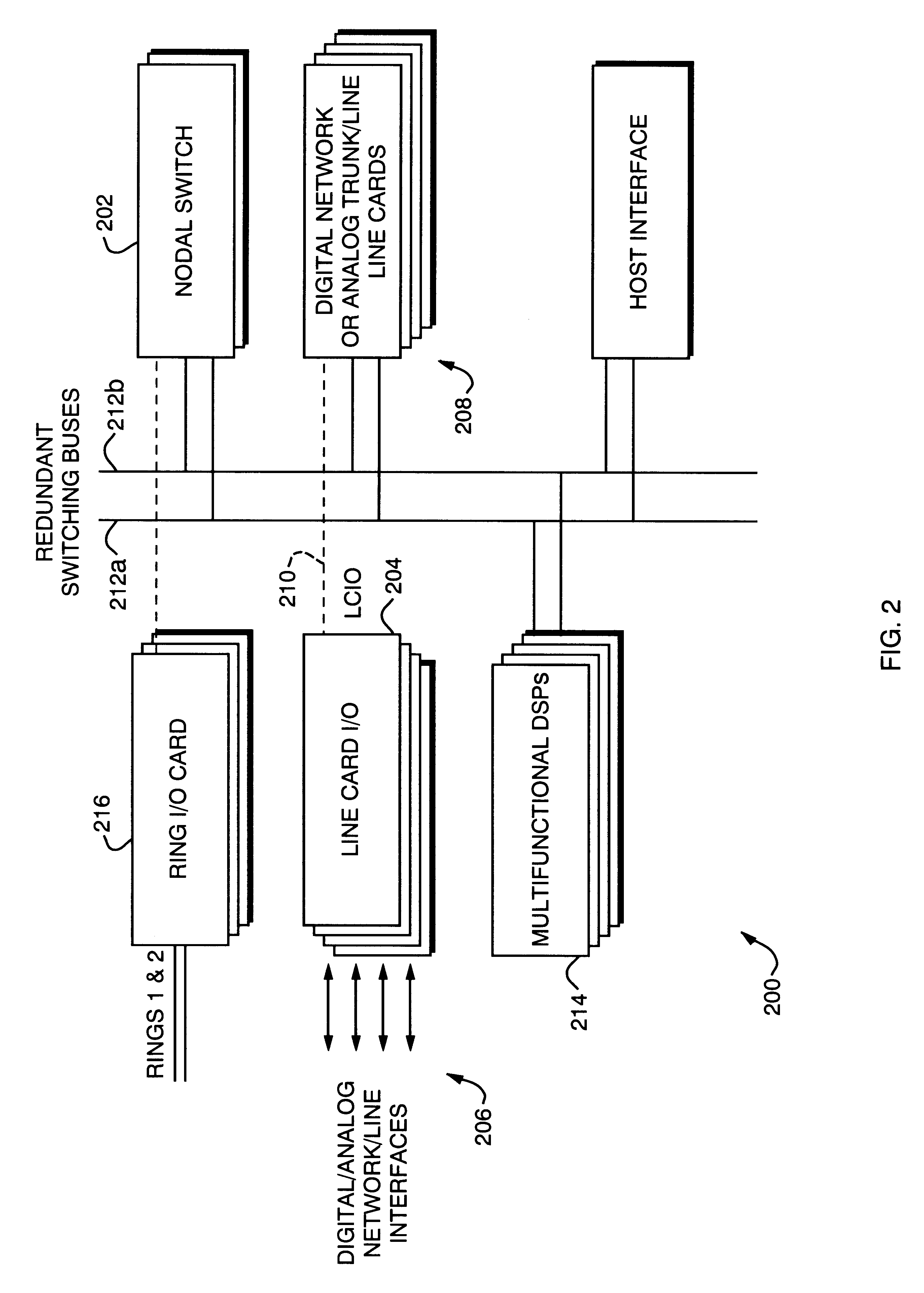
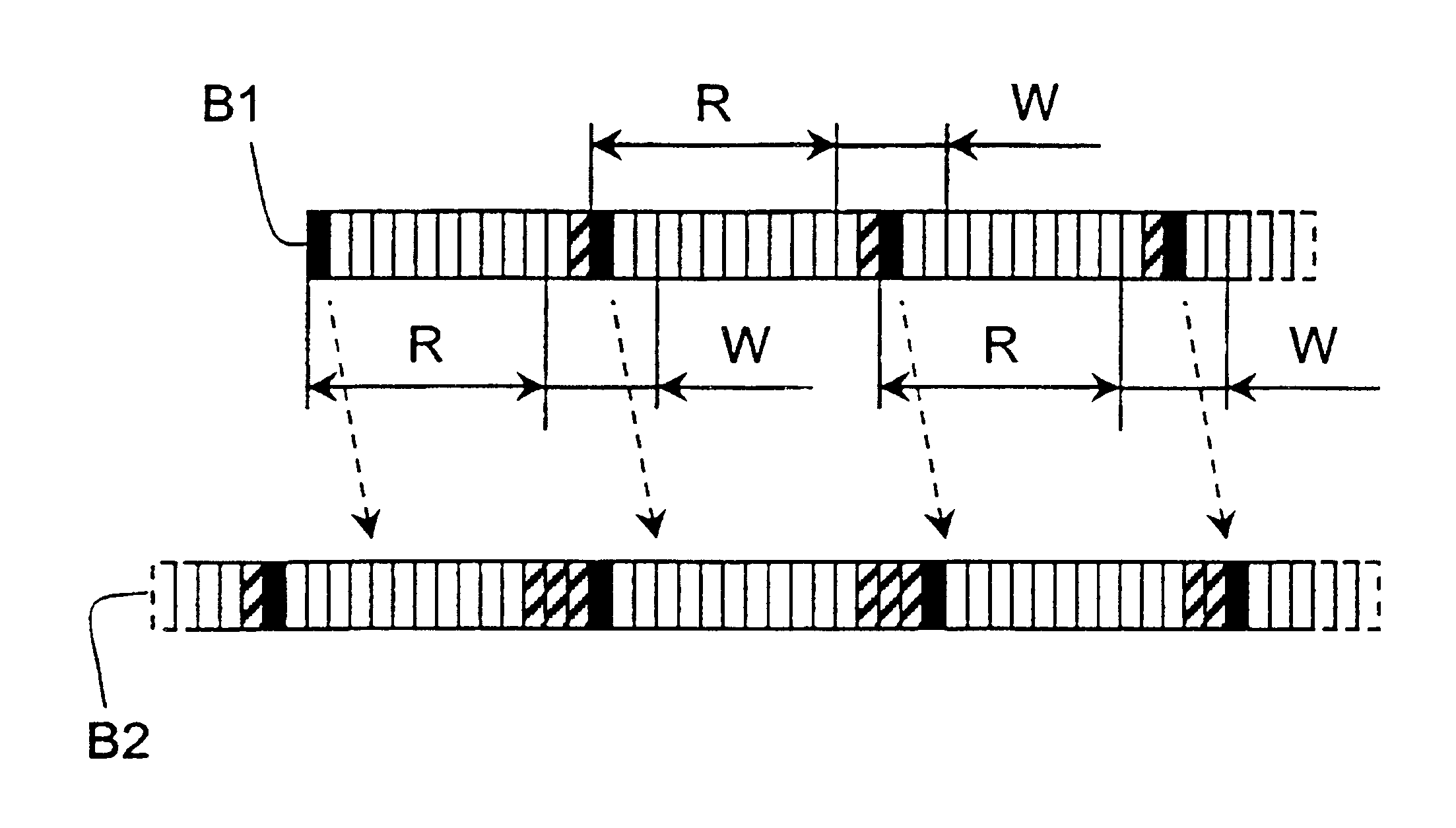
Distributed network synchronization system
InactiveUS6278718B1Effective absorptionOptimization rangeTime-division multiplexLoop networksAsynchronous communicationTelecommunications network
A distributed synchronization system for use in each node of a distributed asynchronous telecommunications network system that continually monitors and controls the flow of data through an implementing node to prevent dataflow errors due to phase and frequency differences in source and destination nodal clocks, and to control inter-nodal network latency so as to support the transmission of synchronous data. A synchronization data FIFO buffers predetermined fields or portions of fields of a unique frame packet received from a source node before retransmission to a destination node on the network. The frame packet includes a frame synchronization field indicating the beginning of a new frame packet; a payload field containing valid data; and a dead zone field providing bandwidth during which the present invention performs synchronization functions. A frame synchronization subsystem, implemented in a designated master node, guarantees that a frame is released at the beginning of an independently-determined frame regardless of network latency. A word resynchronization subsystem manages the flow of data through the data FIFO of each non-master node, receiving and storing data at the source node's clock rate and transmitting the data according to its own clock, thereby guaranteeing the efficient receipt and transmission of data between asynchronously-communicating nodes.
Owner:EXCEL SWITCHING
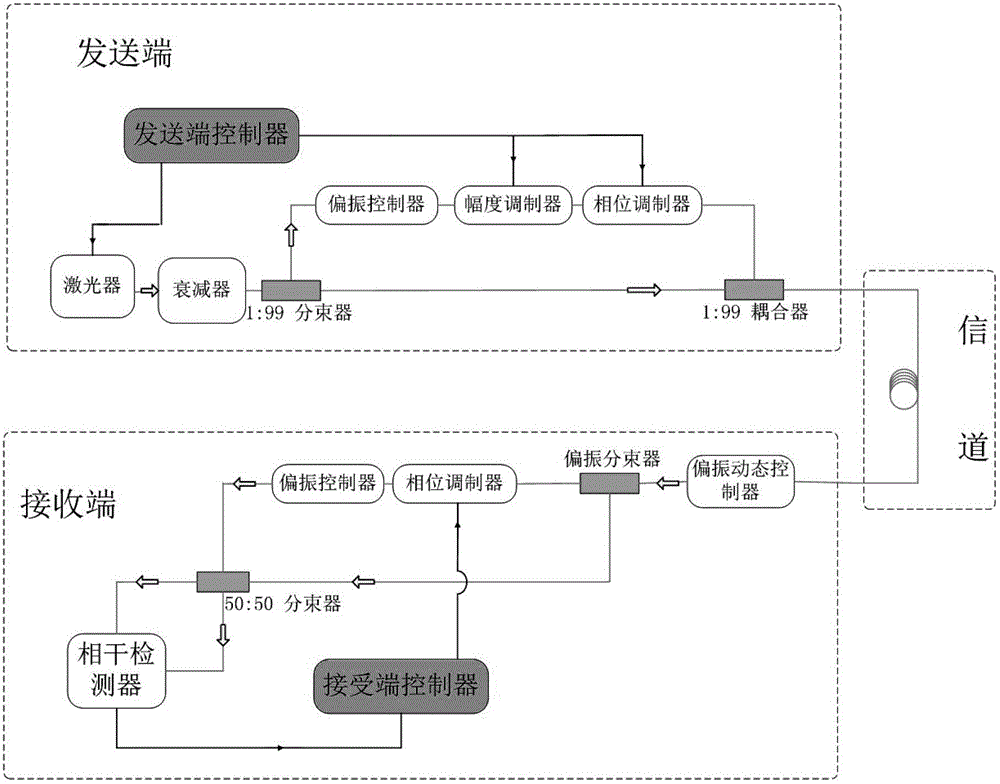
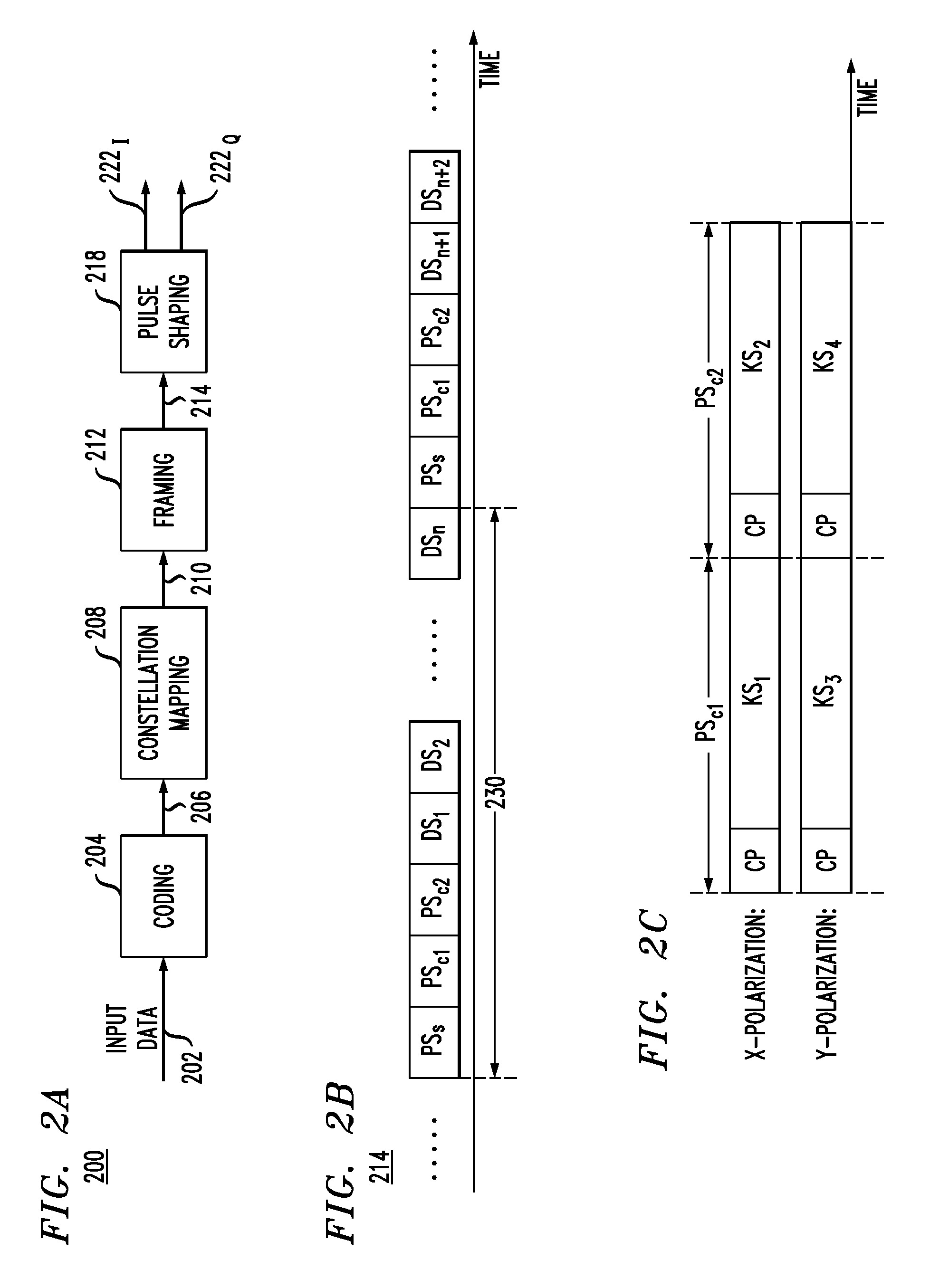
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system and synchronous realization method thereof
ActiveCN102724036AImprove bit error rateAvoid interferenceKey distribution for secure communicationMulti-frequency code systemsBeam splitterAmplitude control
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a synchronous realization method thereof. The continuous quantum key distribution system consists of a light path part and a circuit control part, wherein the light path part mainly consists of a laser, an attenuator, a beam splitter, a polarization controller, am amplitude controller, a phase controller and a coupler. A control part is a transmission end controller module and consists of a true random key generator, an analog voltage output and a trigger clock output. The synchronous method comprises a bit synchronizing step and a frame synchronizing step. The invention provides a completely novel synchronous realization scheme based on properties of continuous variable quantum in an optical fiber, the practical orientation of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system is promoted, and the interference that the continuous variable quantum on the synchronous realization in the optical communication process also can be effectively overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
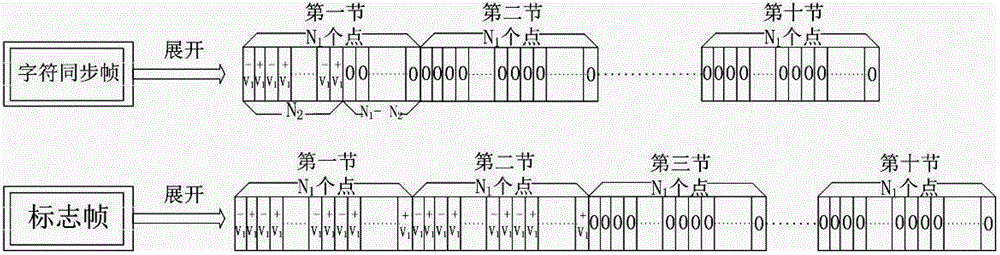
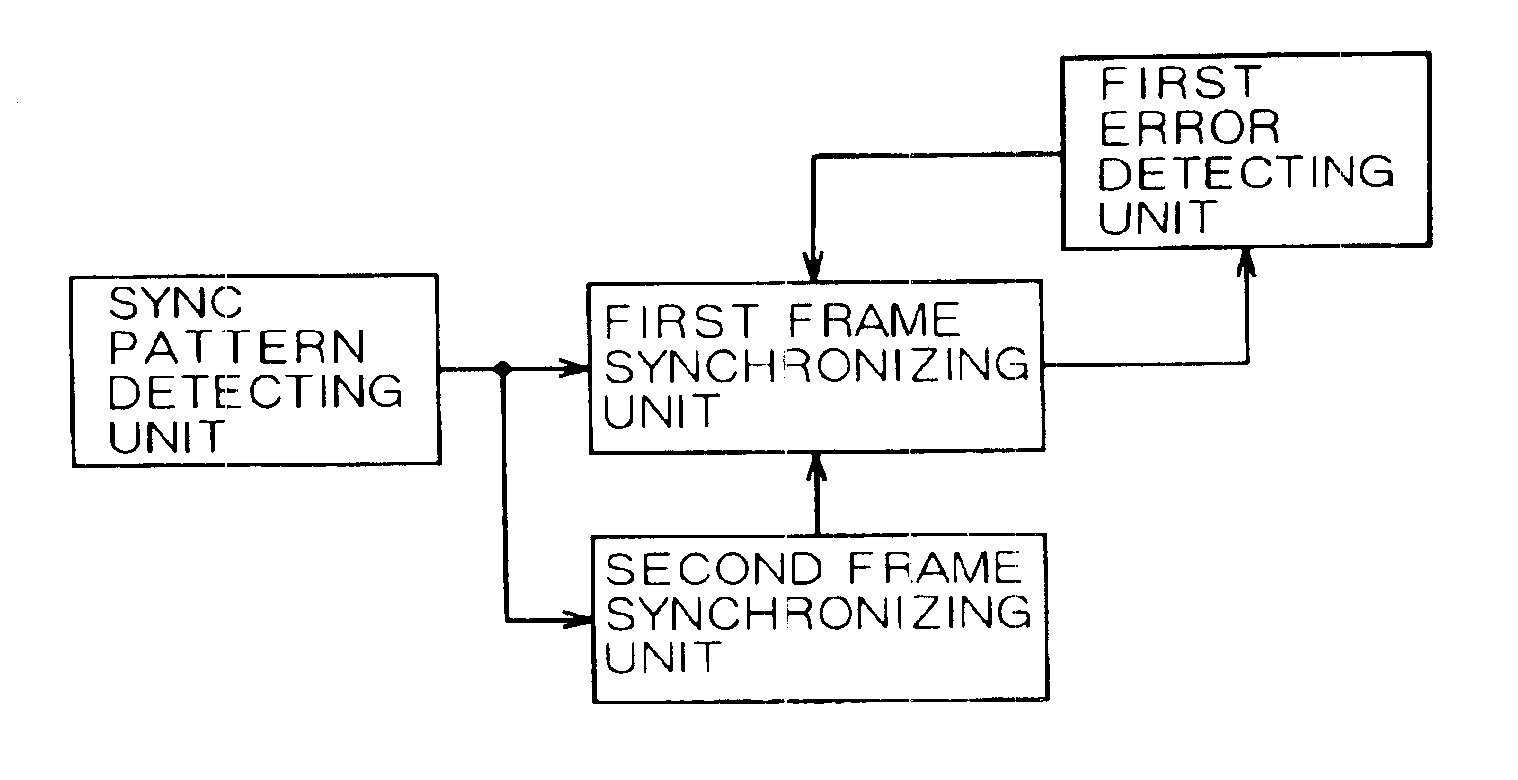
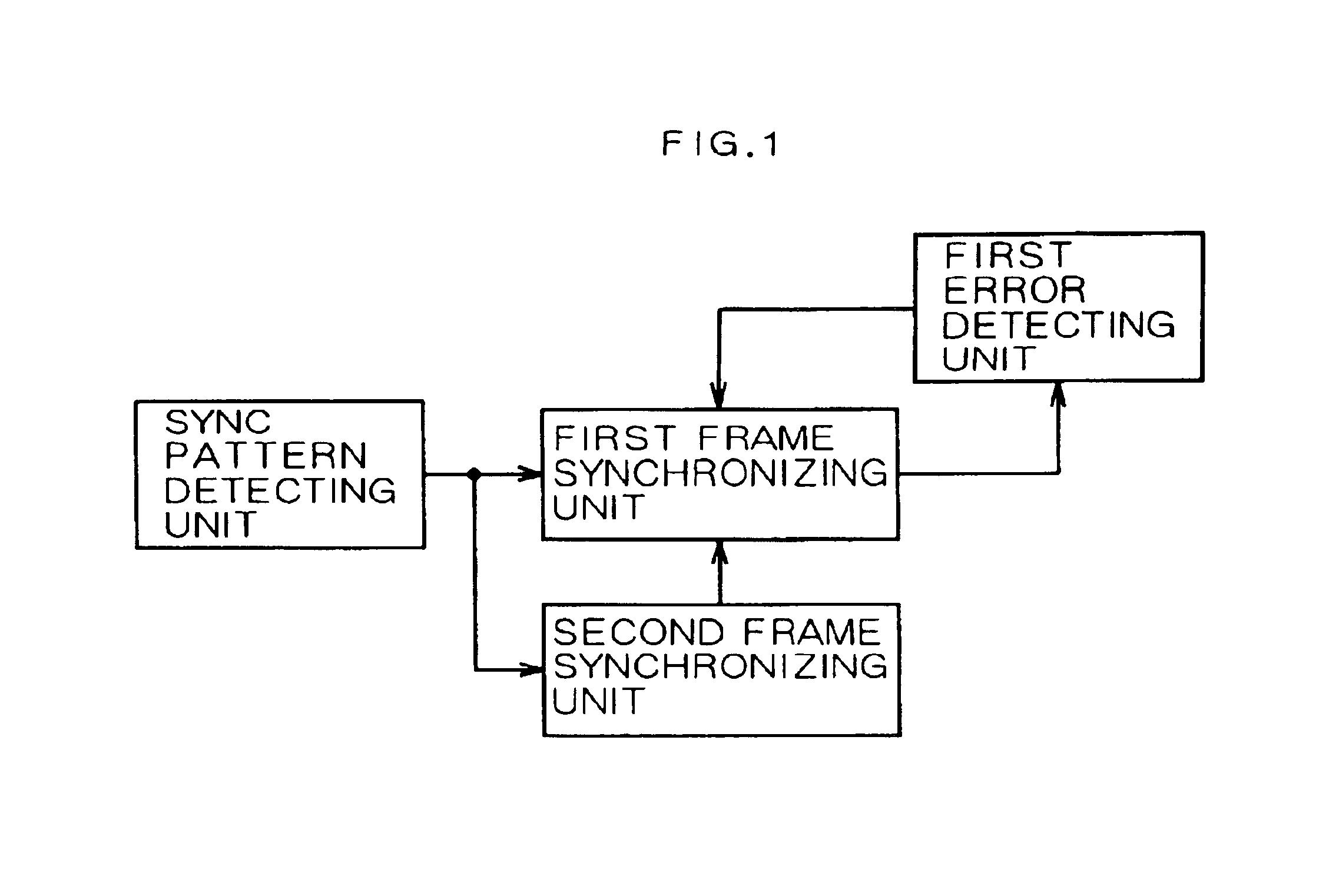
Frame synchronizing circuit
InactiveUS6865240B1Shorten the timeData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionSynchronizingReal-time computing
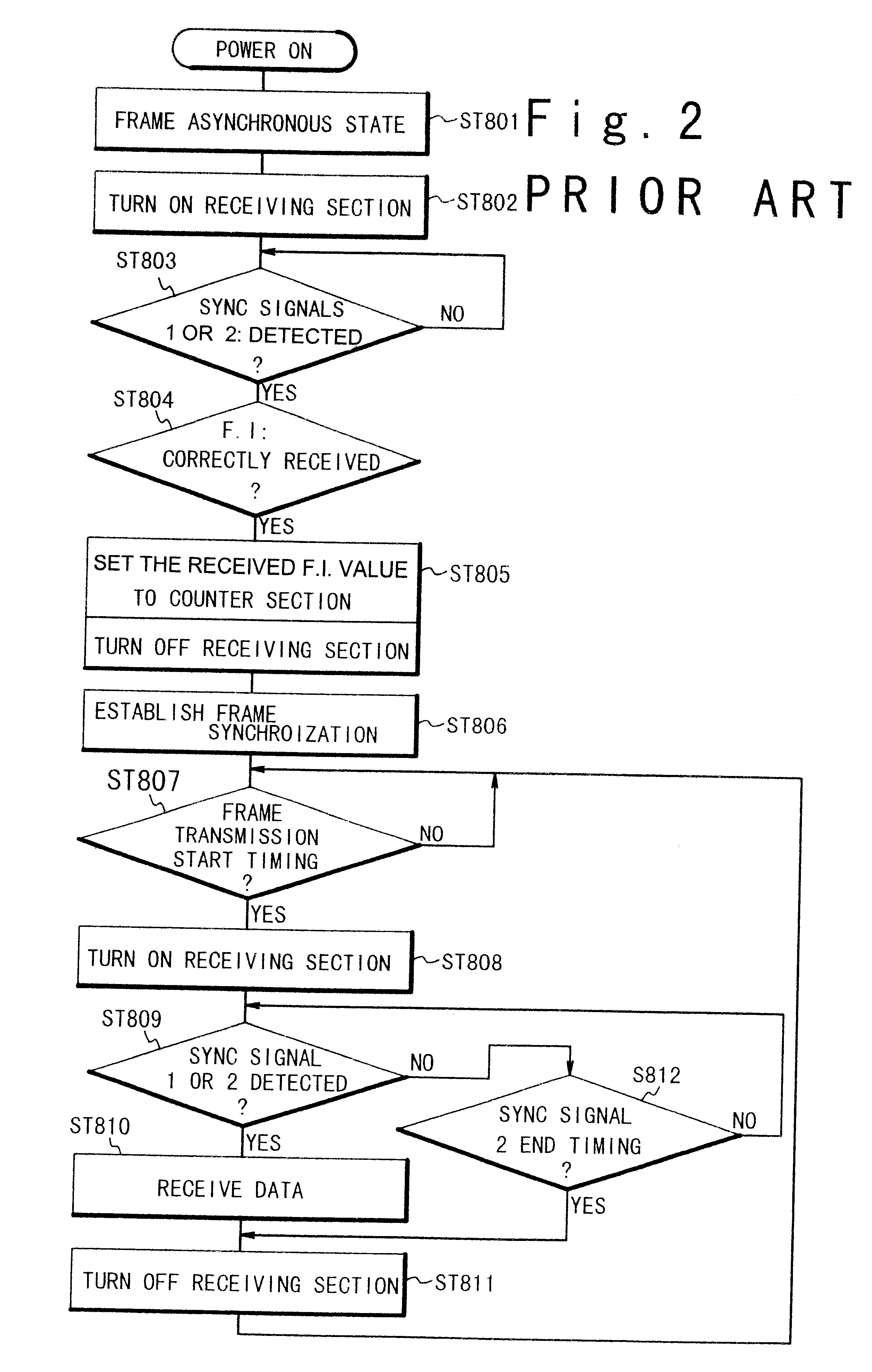
The frame synchronizing circuit establishes frame synchronization by detecting a sync pattern laid in an incoming frame. The frame synchronization circuit comprises a first frame synchronizing unit and a second frame synchronizing unit. The first and second synchronizing units synchronize with a first pattern, a second pattern at a first position and a second position, respectively. Thereafter, when the first position used for the synchronization by the first frame synchronizing unit is found to be in error, the first frame synchronizing unit synchronizes with the second pattern at the second position used by the second frame synchronization unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
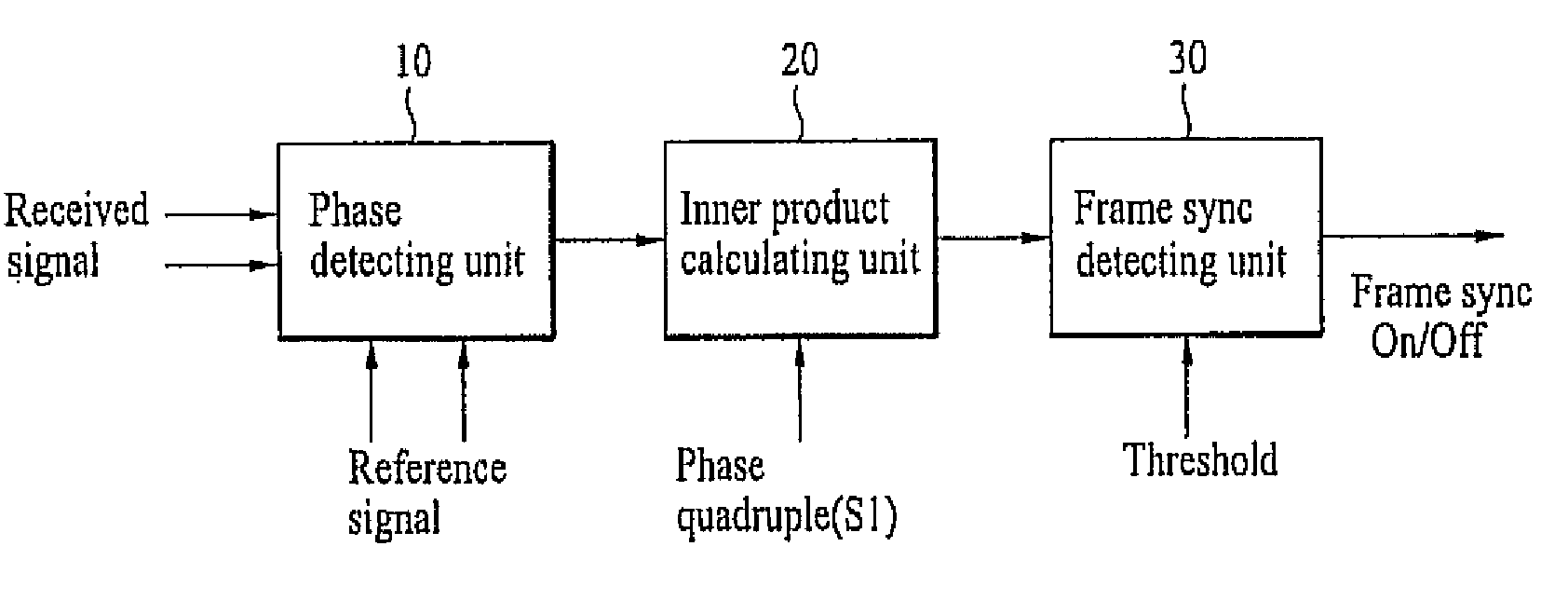
Apparatus for performing initial synchronization and frame synchronization in mobile communications system and method thereof
InactiveUS20070098116A1Without increasing excessive memoryDetection errorAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCommunications systemReference vector
An apparatus for performing initial synchronization and frame synchronization in a mobile communications system and method thereof are disclosed. First of all, a method and apparatus for performing frame synchronization in a mobile communications system using a correlation value between a received signal and a reference vector for a phase according to one embodiment of the present invention are disclosed. Secondly, a method and apparatus for performing frame synchronization by considering all phase modulation possibility and frequency offsets according to another embodiment of the present invention are disclosed. Thirdly, a method and apparatus for performing initial estimation in a manner of dividing at least one subframe received from a base station by a UE in the course of cell search into at least two areas, calculating a correlation for each of the at least two areas and using a maximum value of the calculated correlation value per area are disclosed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
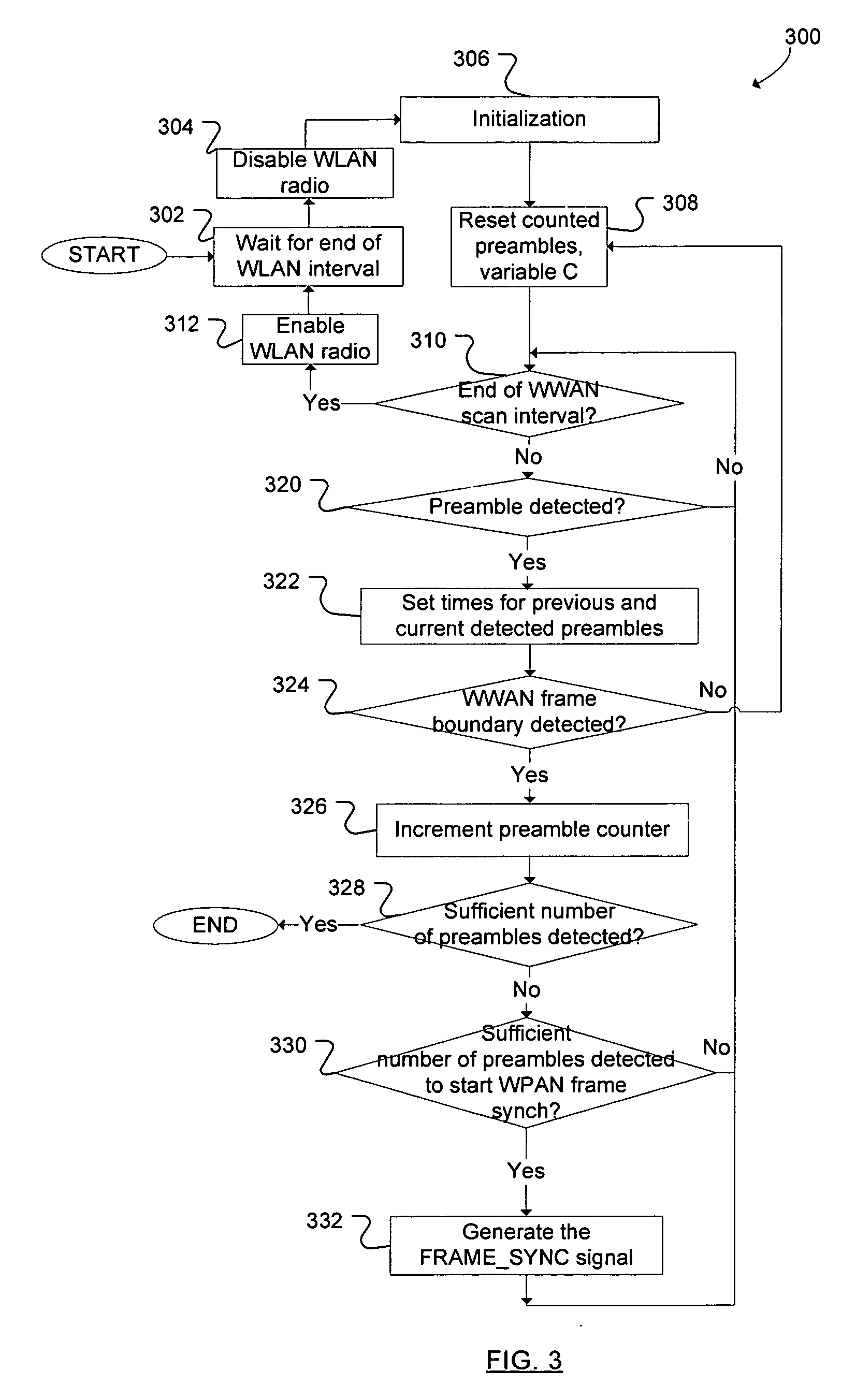
Techniques to improve co-existence among multiple radios
ActiveUS20100027525A1Synchronisation arrangementSynchronisation information channelsFrame synchronizationReal-time computing
Techniques are described that can be used to permit coexistence of different radios. Preambles of frames from a first radio are detected. If the preambles occur within a prescribed period of one another, then a frame synchronization signal is transmitted. Based on the timing of the frame synchronization signal, a second radio adjusts the timing of transmit and receive time slots.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Wireless transmitting apparatus, wireless receiving apparatus, wireless transmission method, wireless reception method, wireless communication system, and wireless communication method
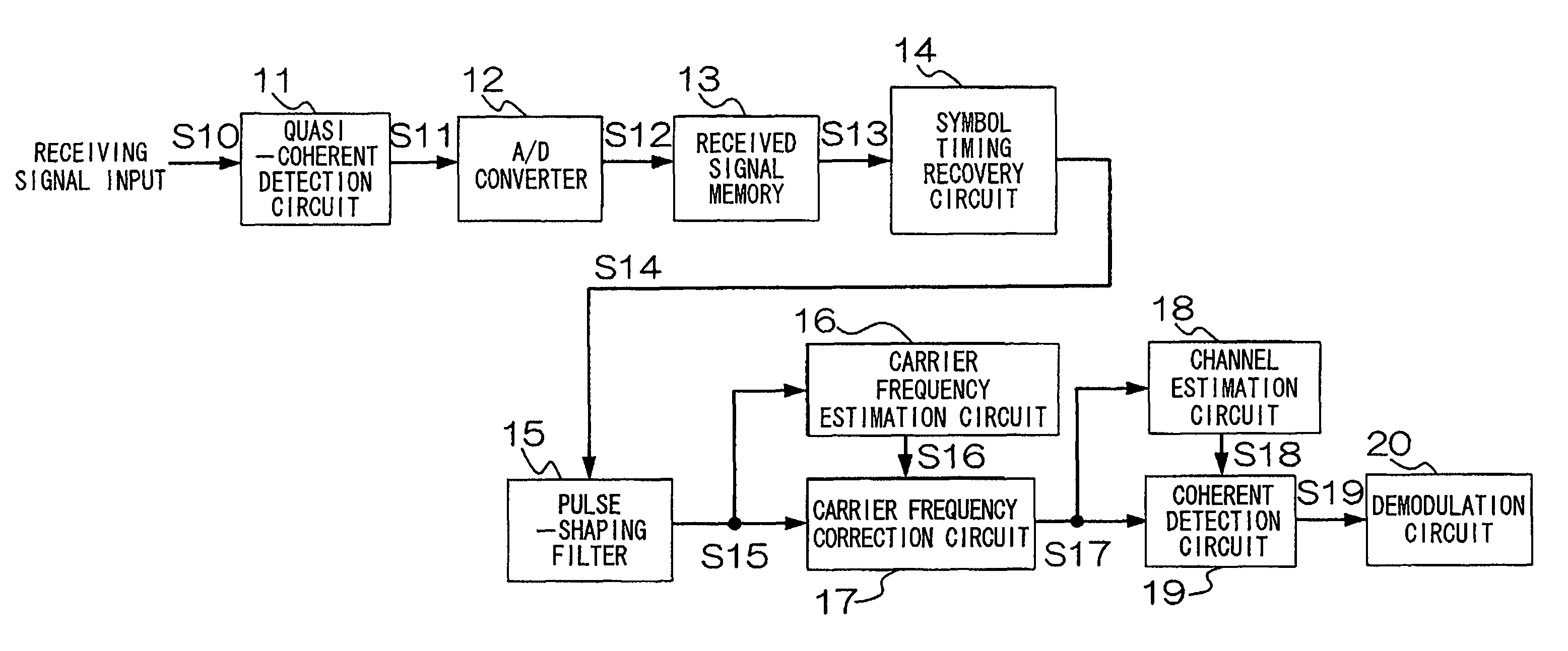
ActiveUS8248975B2Improve efficiencyAccurate performancePhase-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionWireless transmissionCommunications system
A wireless transmitting apparatus inserts a training signal into a transmission burst at fixed symbol intervals as a pilot signal, a wireless receiving apparatus performs AD conversion of a received burst signal, performs symbol timing recovery, performs frame position detection and pilot signal extraction from the received burst signal for which symbol timing was established, performs frame synchronization, and performs a carrier frequency estimation using pilot signal. A carrier frequency estimation is also performed with respect to a received burst signal for which frame synchronization was established, and channel distortion is estimated and output based on a frequency-corrected received burst signal. Channel distortion estimation is then performed with respect to a frequency-corrected received burst signal, and a data symbol sequence of the channel-compensated received burst signal is converted to a received data bit stream.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and apparatus for embodying and synchronizing downlink signal in mobile communication system and method for searching cell using the same
In an OFDMA-based cellular system, a frame of a downlink signal includes a common slot and traffic slots. The common slot includes a synchronization preamble and a cell search preamble. The synchronization preamble has a structure for synchronizing time and frequency, and the cell search preamble has a cell search structure. The traffic slot includes pilot symbols provided on the time and frequency axes. A cyclic prefix is used to estimate initial symbol synchronization, and the initial symbol synchronization and the synchronization preamble are used to synchronize the frame. The synchronization frame and the cell search preamble are used to estimate time and frequency synchronization. The cell search preamble is used to search cells. When the initial synchronization is performed, the cyclic prefix is used to track the frequency, the synchronization preamble is used to track symbol synchronization, and the cell search preamble is used to track fine frequency synchronization.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
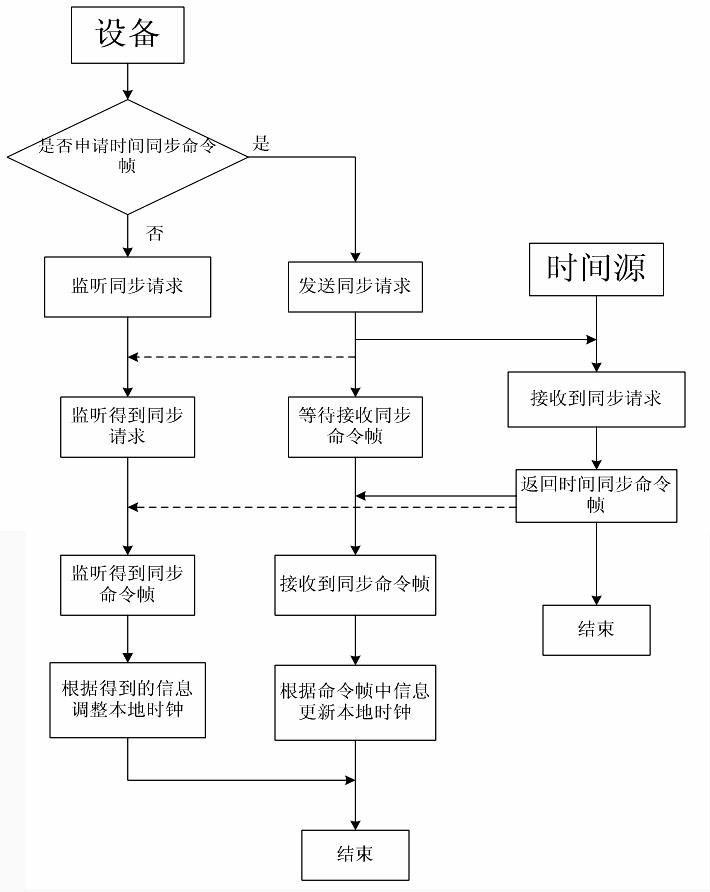
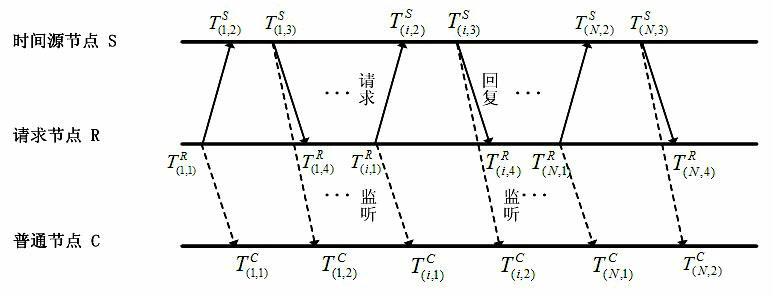
Time synchronization method applicable to wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102118849AImprove time synchronization accuracyCurb free growthSynchronisation arrangementTime deviationBeacon frame
The invention requests to protect a time synchronization method applicable to a wireless sensor network and relates to a wireless network communication technology. The time synchronization method comprises the steps: time source equipment generates beacon frames and broadcasts and sends the beacon frames periodically; non-time source equipment obtains time stamps in the transmitting and receiving process of the beacon frames, obtains frequency deviation and time deviation of an equipment clock and a time source equipment clock according to calculation of a plurality of collected time stamps, compensates a local clock and realizes synchronization with a time source; and time synchronization is carried out step by step, and finally the time synchronization of the whole network is realized. Considering the application environment of the equipment and different requirements for time synchronization, a multi-stage and multilevel synchronization mechanism for combining broadcast synchronization, matching synchronization and monitoring synchronization is adopted. The non-time source equipment can apply synchronization of time synchronization command frames according to different requirements, the equipment without applying the time synchronization command frames can monitor and receive the time synchronization command frames similarly and finish synchronization, so that the whole communication overhead and energy consumption of the network are reduced and the normal operation of the network is guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
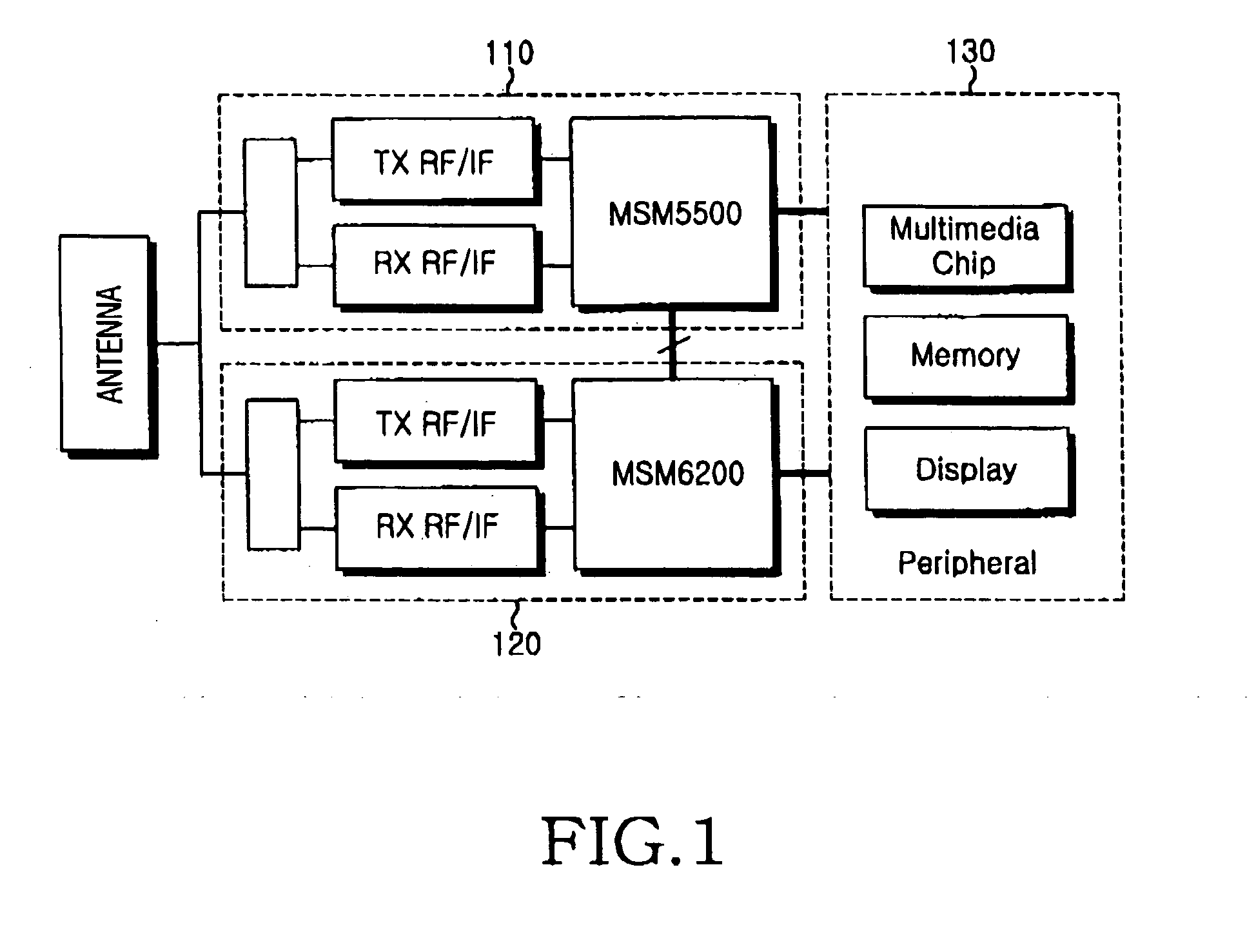
Radio communication apparatus with power consumption reduced
InactiveUS6633753B1Timely controlCordless telephonesPower managementElectric power systemElectric power
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Handover procedures in radio communication system
InactiveCN1451250AHigh switching processing speedEliminate bottlenecksSynchronisation arrangementCode division multiplexTransport systemCommunications system
Intercell handover method in UMTS mobile systems in TDMA-SCDMA technique (and also FDMS-SDMA) with full duplexing of the TDD type. The complexity of the technique adopted requires a frame synchronization mechanism employing a downlink pilot signal, broadcasting transmitted by the base station, echoed by signature sequences transmitted by the single Mobile units in the procedures foreseeing an uplink access. The above, together with the high cipher speed (1.28 Mchip) imposed by the CDMA technique, makes inappropriate the addition of other fields to the sequence of the downlink pilot, which shall remain a pure synchronization sequence. Contrarily to the GSM, a field is missing in the synchronism burst for the transport of the system frame number FSN, absolutely necessary for the iperframe synchronism and the starting of ciphering on the channel. The information on SFN is included in the common signalling channel as other broadcasting information.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
System and method for GPS navigation before signal bit synchronization
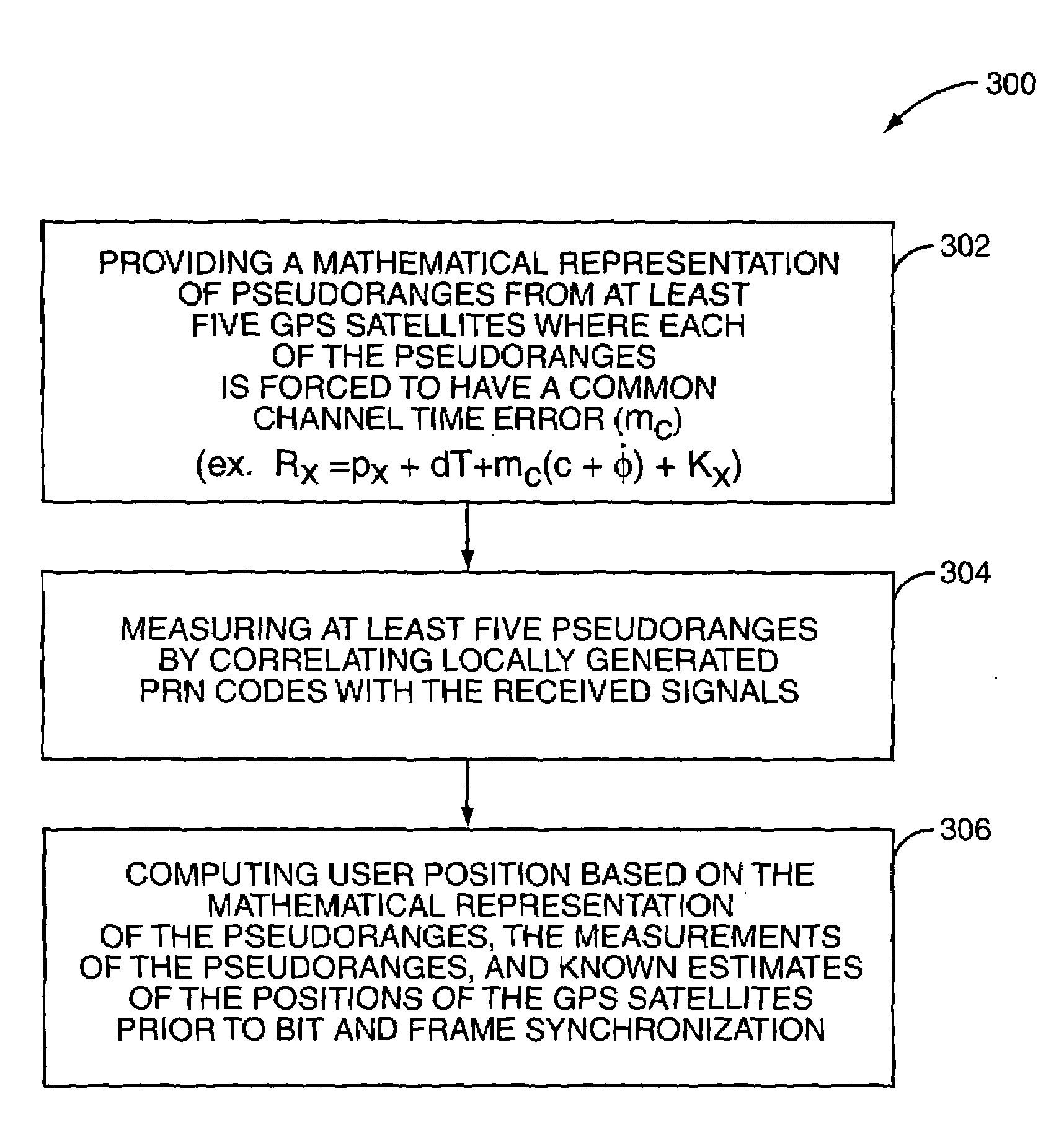
InactiveUS7064709B1Not substantially improve time-to-first-fixTime-to-first-fix is substantially reducedPosition fixationRadio transmissionTime errorTime to first fix
A system and method are provided for determining a position of a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver prior to bit and frame synchronization. As such, the time-to-first-fix is substantially reduced. More specifically, pseudoranges to five GPS satellites are measured by correlating locally generated Pseudo-Random Number (PRN) codes with signals received from the GPS satellites. After correlation, the pseudorange measurements are correct with an unknown integer number of milliseconds error, which is different for each of the pseudorange measurements. Using the measurements of the pseudoranges and a mathematical model where each of the pseudorange measurements is forced to have a common channel time error, the user position and the common channel time error are determined prior to bit and frame synchronization.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
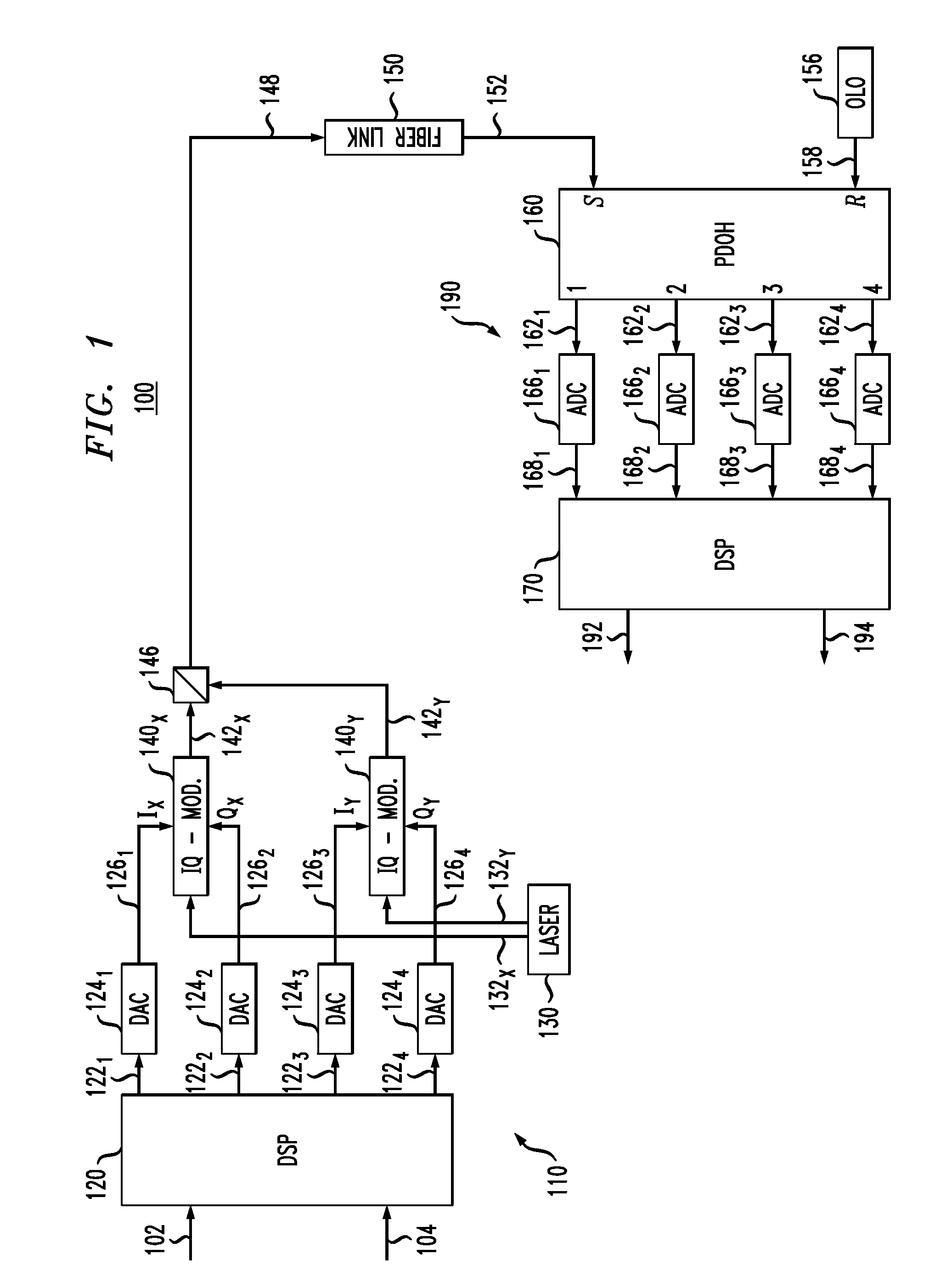
Coherent optical receiver for pilot-assisted data transmission
InactiveUS20120148264A1Cancel adverse effectSave powerPolarisation multiplex systemsMulti-frequency code systemsSlide windowGuard interval
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Apparatus and method for identifying a neighboring cell boundary in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050153695A1Synchronisation arrangementCode division multiplexCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A mobile terminal identifies a cell boundary of a mobile communication network supporting an asynchronous scheme for handover between different communication systems. For this, a boundary indication base station newly defines boundary indication codewords distinguished from existing codewords used for acquisition of frame synchronization, and transmits one of the boundary indication codewords over a secondary synchronization channel every frame. Upon receiving the boundary indication codeword over the secondary synchronization channel, the mobile terminal recognizes that it is located in a boundary of the mobile communication network supporting the asynchronous scheme, and performs handover to a mobile communication network supporting a synchronization scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and apparatuses for providing synchronization in a communication network
InactiveUS6868093B1Promote recoveryTime-division multiplexCircuit switching systemsEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
The present invention refers to methods and apparatuses for providing synchronization in a time division multiplexed network, wherein data is transferred on multi-access bitstreams in circuit-switched channels that are defined by respective time slots of regularly recurrent frames of said bitstreams, said frames being defined by regularly recurrent frame synchronization signals transferred on said bitstreams. According to the invention an auxiliary regularly recurrent frame synchronization signal is generated and selected as a basis for defining said frames on a bitstream if the frame synchronization signal that is used as a basis for synchronizing said frames during normal operation is not detected in accordance with an expected frame rate.
Owner:NET INSIGHT INTPROP
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS20050018754A1Avoid poor resultsEliminate and prevent sidelobesBaseband system detailsTime-division multiplexCorrelation functionSelf correlation
The frame words of the preferred embodiment are especially suitable for frame synchronization and / or channel estimation. By adding the autocorrelation and cross-correlation functions of frame words, double maximum values equal in magnitude and opposite polarity at zero and middle shifts are obtained. This property can be used to slot-by-slot, double-check frame synchronization timing, single frame synchronization and / or channel estimation and allows reduction of the synchronization search time. Further, the present invention allows a simpler construction of a correlator circuit for a receiver.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
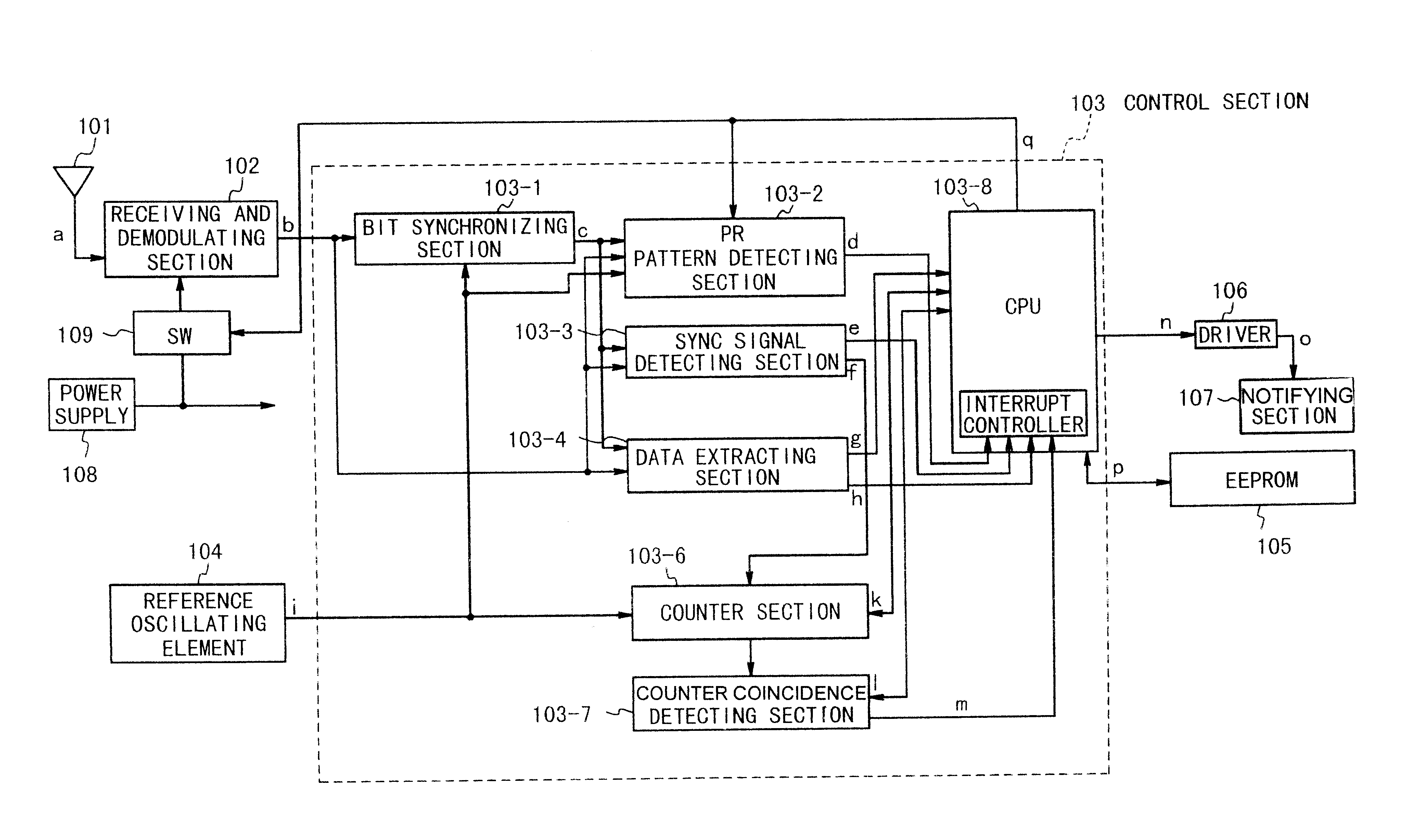
Optical signal reception device and method of controlling optical signal reception
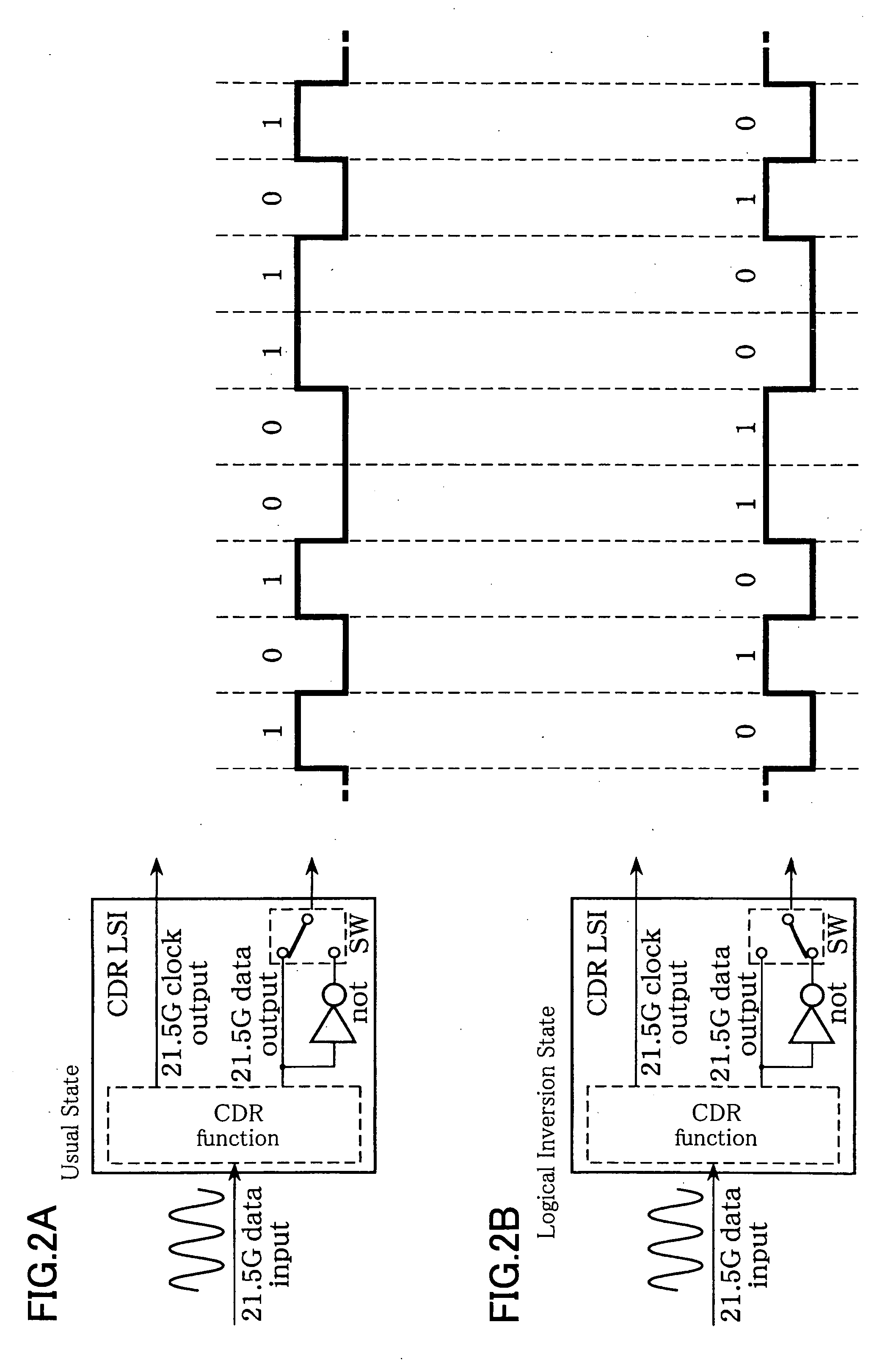
ActiveUS20070065157A1Quickly identify the signal reception statePerform the frame synchronization pull-in operations quicklyModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingMultiplexer
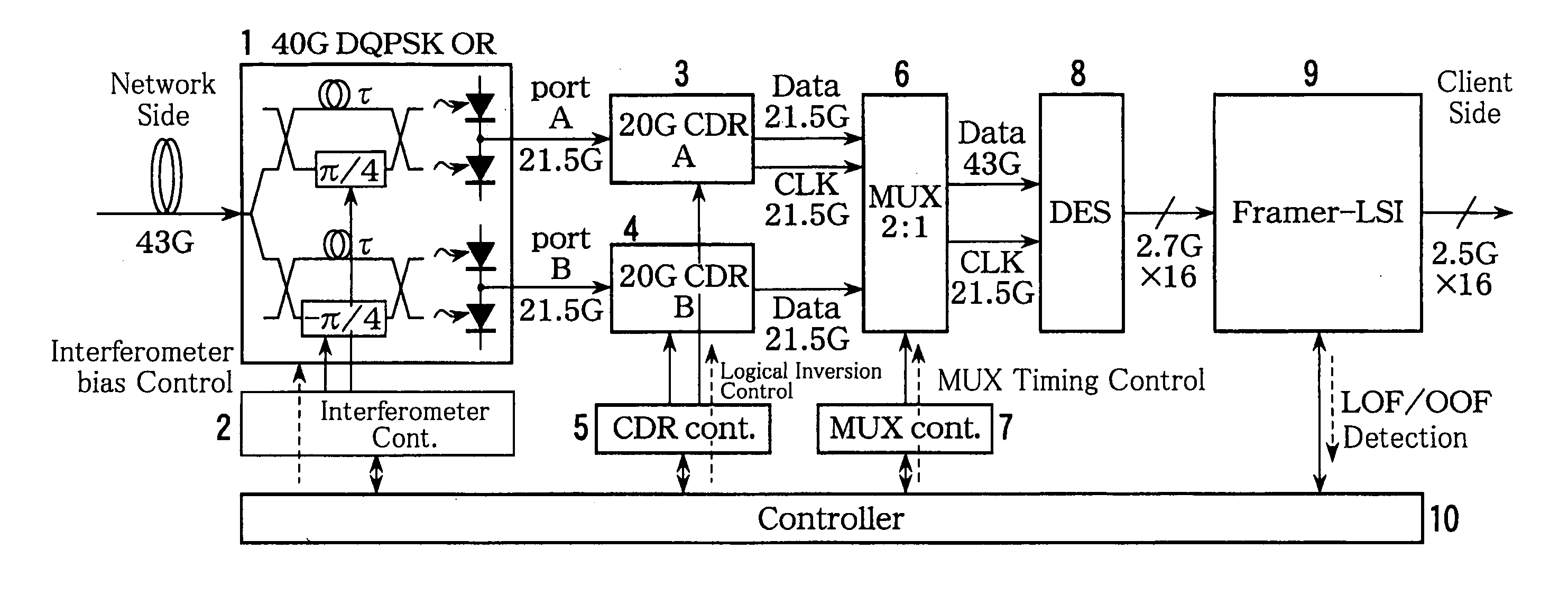
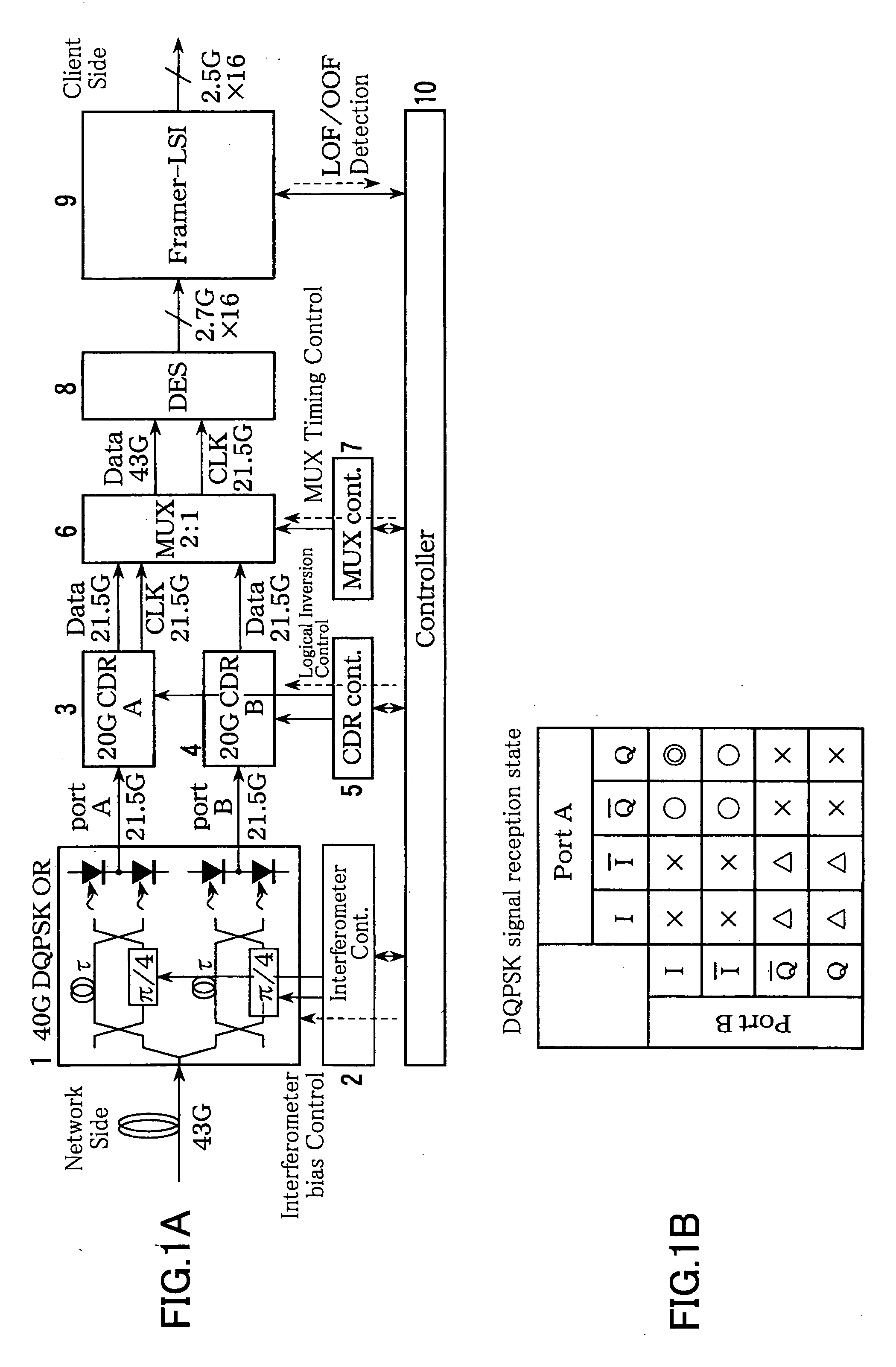
An optical signal reception device is disclosed that receives and demodulates an optical signal modulated by DQPSK and performs logical inversion and other controls to transit to the object reception state. The signal reception device includes a front end including a delay interferometer and an opto-electric conversion element that receive the DQPSK optical signal and convert it into an in-phase signal and a quadrature-phase signal, a clock regenerator that regenerates a clock signal based on the in-phase signal and the quadrature-phase signal, a multiplexer that multiplexes the in-phase signal and the quadrature-phase signal, a reception frame processing unit that detects frame synchronization based on the signal multiplexed by the multiplexer and de-maps the received frames, and a controller that, based on out-of-frame-synchronization information (LOF / OOF) from the reception frame processing unit, performs logical inversion control in the clock regenerator, multiplexing timing control in the multiplexer, and controls the delay interferometer in the front end so as to transit to the object reception state.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
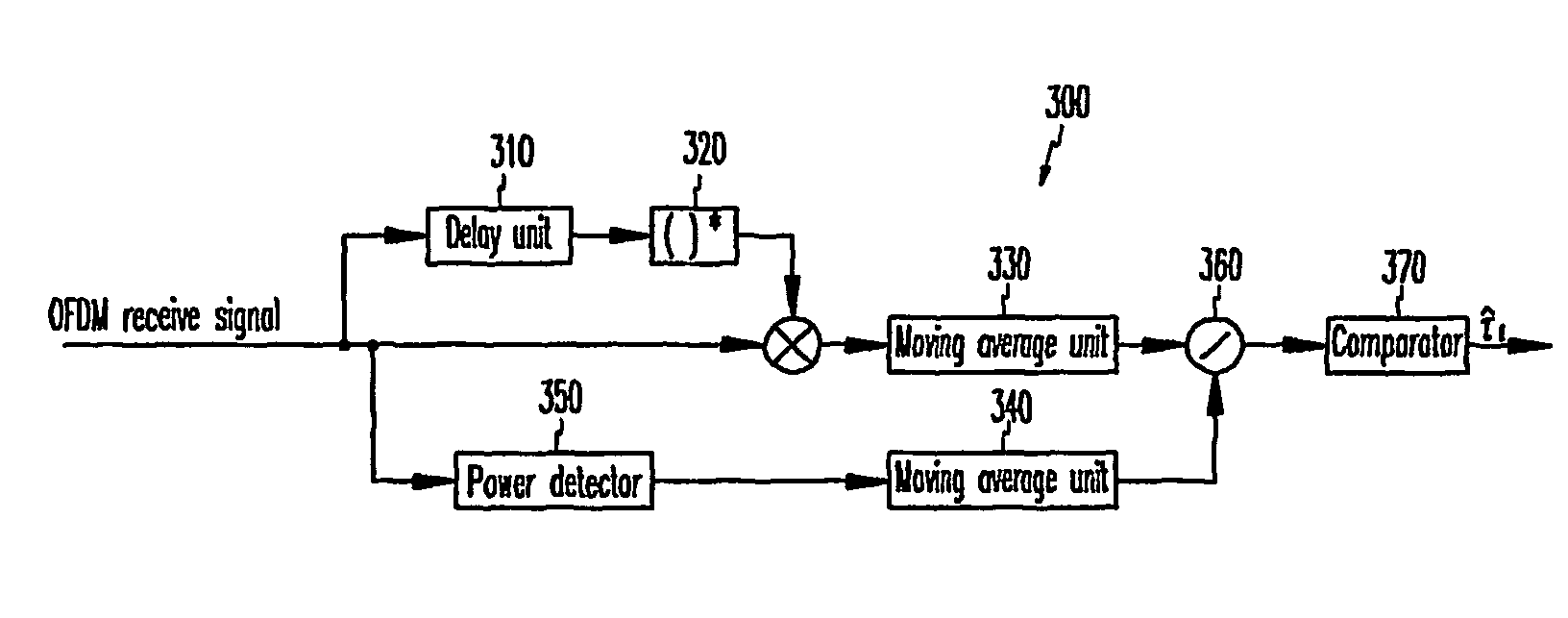
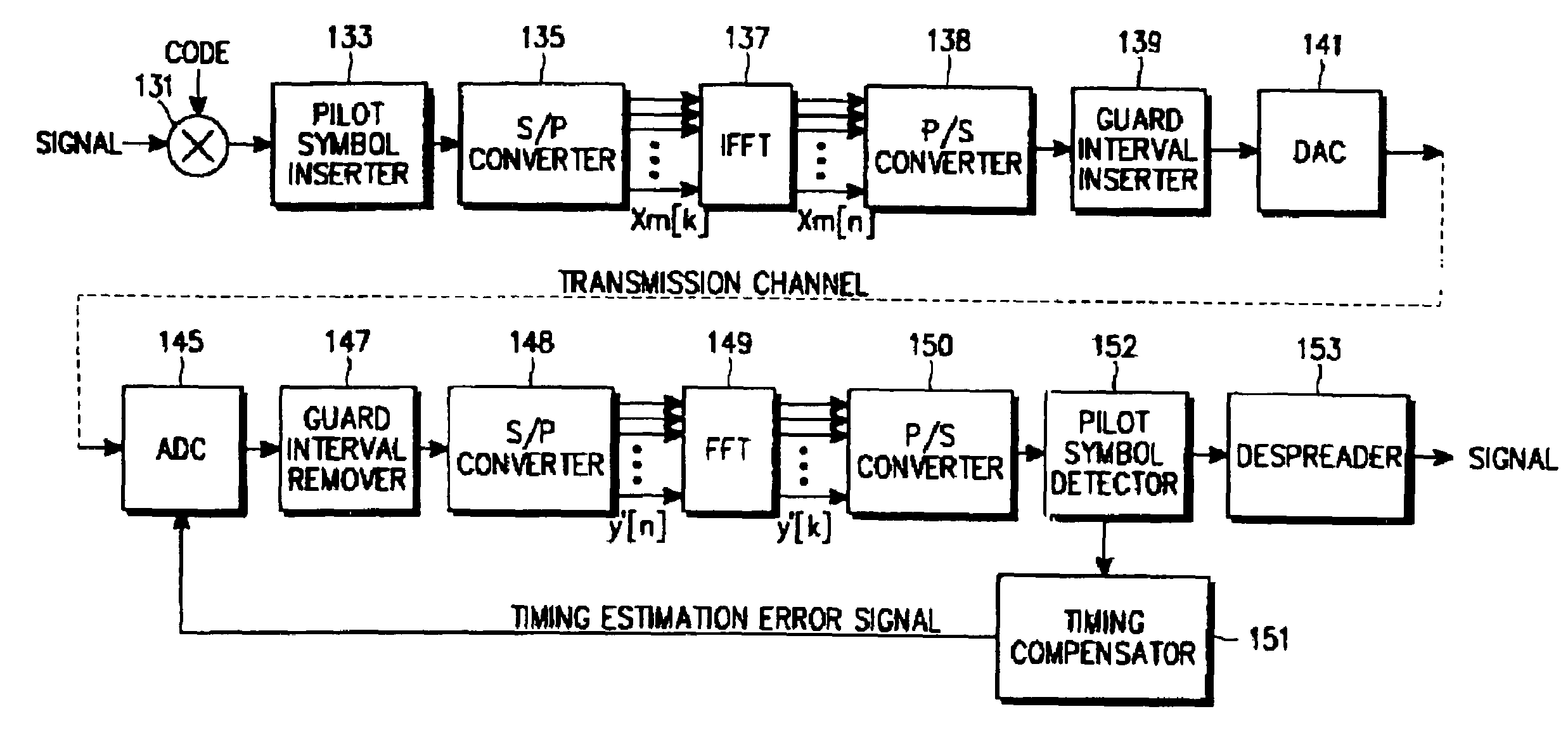
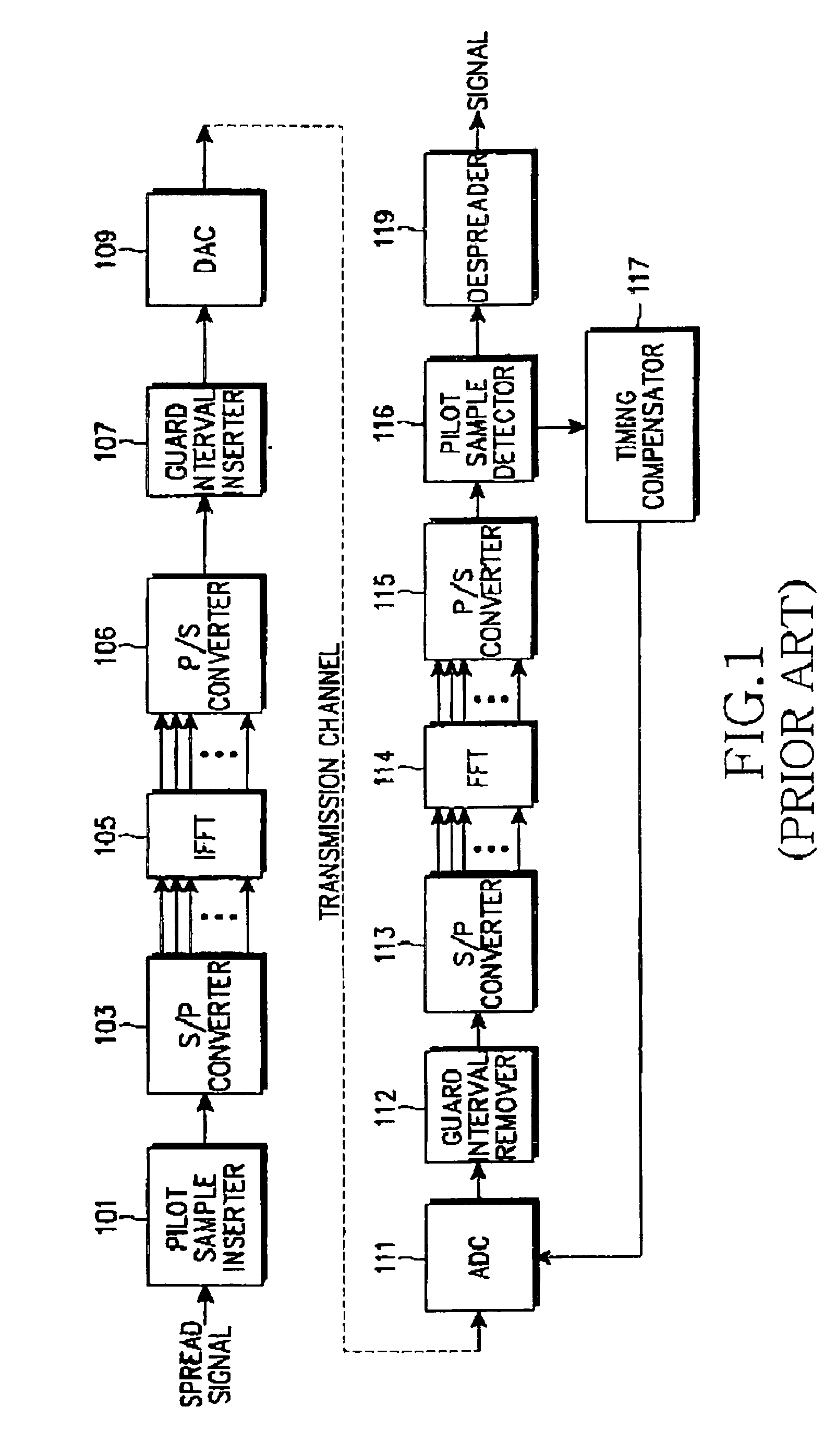
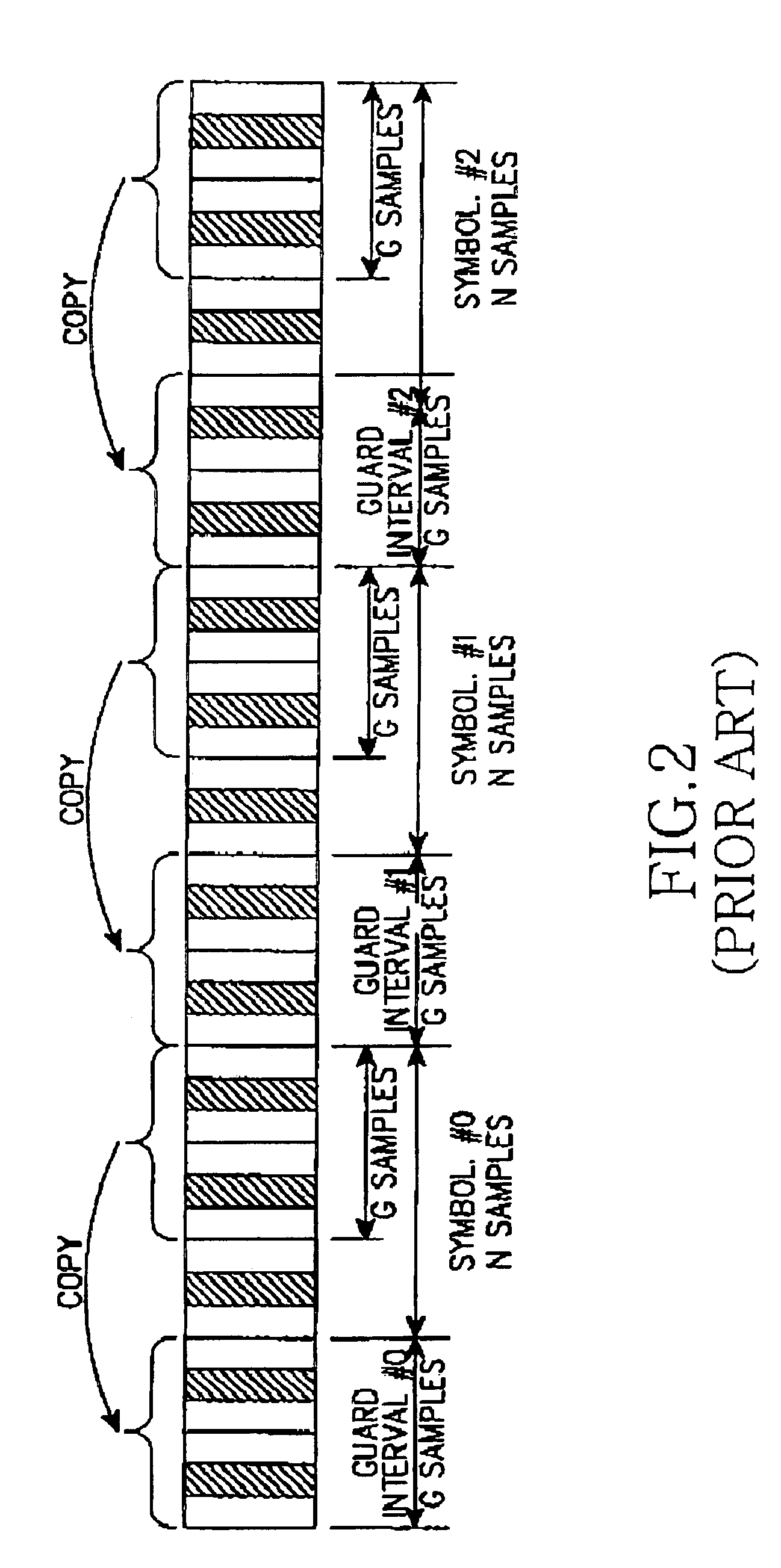
System and method for compensating timing error using pilot symbol in OFDM/CDMA communication system
InactiveUS7110387B1Frequency-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTime errorAnalog-to-digital converter
A timing error compensation system in an OFMD / CDMA communication system includes an analog-to-digital converter for converting an OFDM signal, comprised of a data symbol stream in which a pilot symbol is inserted at intervals of a prescribed number of data symbols, received from a transmitter, to a digital OFDM symbol stream by prescribed sampling synchronization, a guard interval remover for removing a guard interval inserted in the OFDM symbol by prescribed frame synchronization, and a fast Fourier transform (FFT) device for performing fast Fourier transform on the guard interval-removed OFDM symbol and outputting a data symbol stream. In the time error compensation system, a pilot symbol detector receives the data symbol stream and detects the pilot symbols inserted in the data symbol stream at prescribed intervals. A timing compensator determines a linear phase difference line for the detected pilot symbol, generates a timing error estimation signal according to the determined linear phase difference line, and provides the timing error estimation signal to the analog-to-digital converter and the guard interval remover so as to determine the sampling synchronization and the frame synchronization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Frame synchronization system between base stations of mobile radio communication system and base station device employing this system
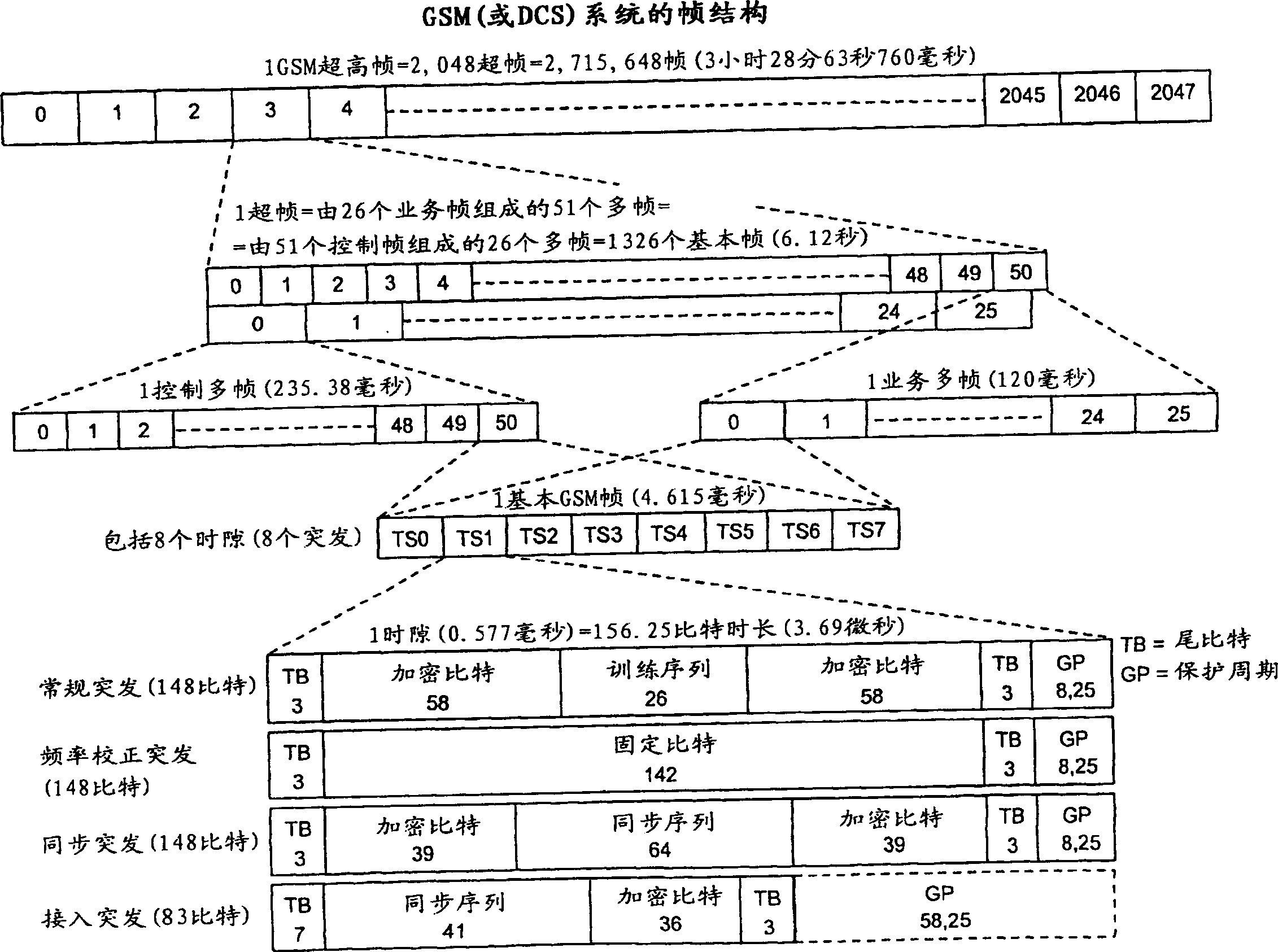
InactiveUS6480483B2Little influenceShorten the timeSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexBase station identity codeCommunications system
The disclosure concerns an inter-base station frame synchronization system for use in a mobile communication system having at least one master base station and a plurality of slave base stations. The master base station is arranged to transmit a control channel signal to the slave base stations located around the master base station in synchronization with a reference frame timing. The slave base stations set a control channel signal observation period. The slave base stations are arranged to generate frame timing based on timings of a received control channel signal from the master base station or other slave base stations when the received control channel signal is received during the control channel signal observation period.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
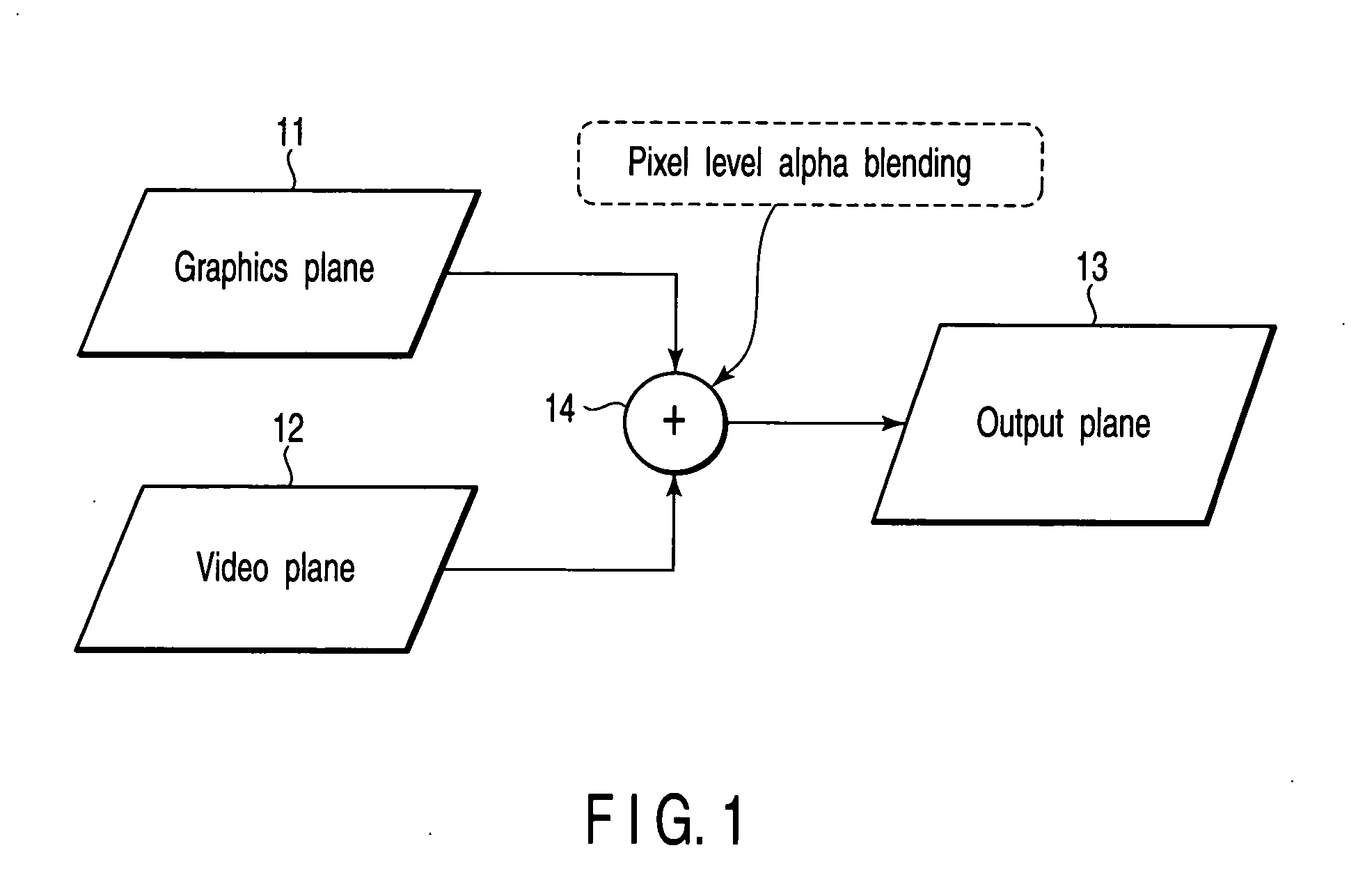
Video data processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050265688A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Synchronous control
When one video image (e.g., second video image) is blended or synthesized to video image (e.g., main video image), time base correction is made between both video data. A video data processing apparatus comprising a first video generator generating a first video data having an arbitrary frame rate, a second video generator generating a second video data having an arbitrary frame rate different from the first video data, and a synchronization controller using video reproduction time managed by the first video generator as a reference time, and correcting video reproduction time of the second video generator shifted from the reference time by repeatedly using the second video data to obtain frame synchronization.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
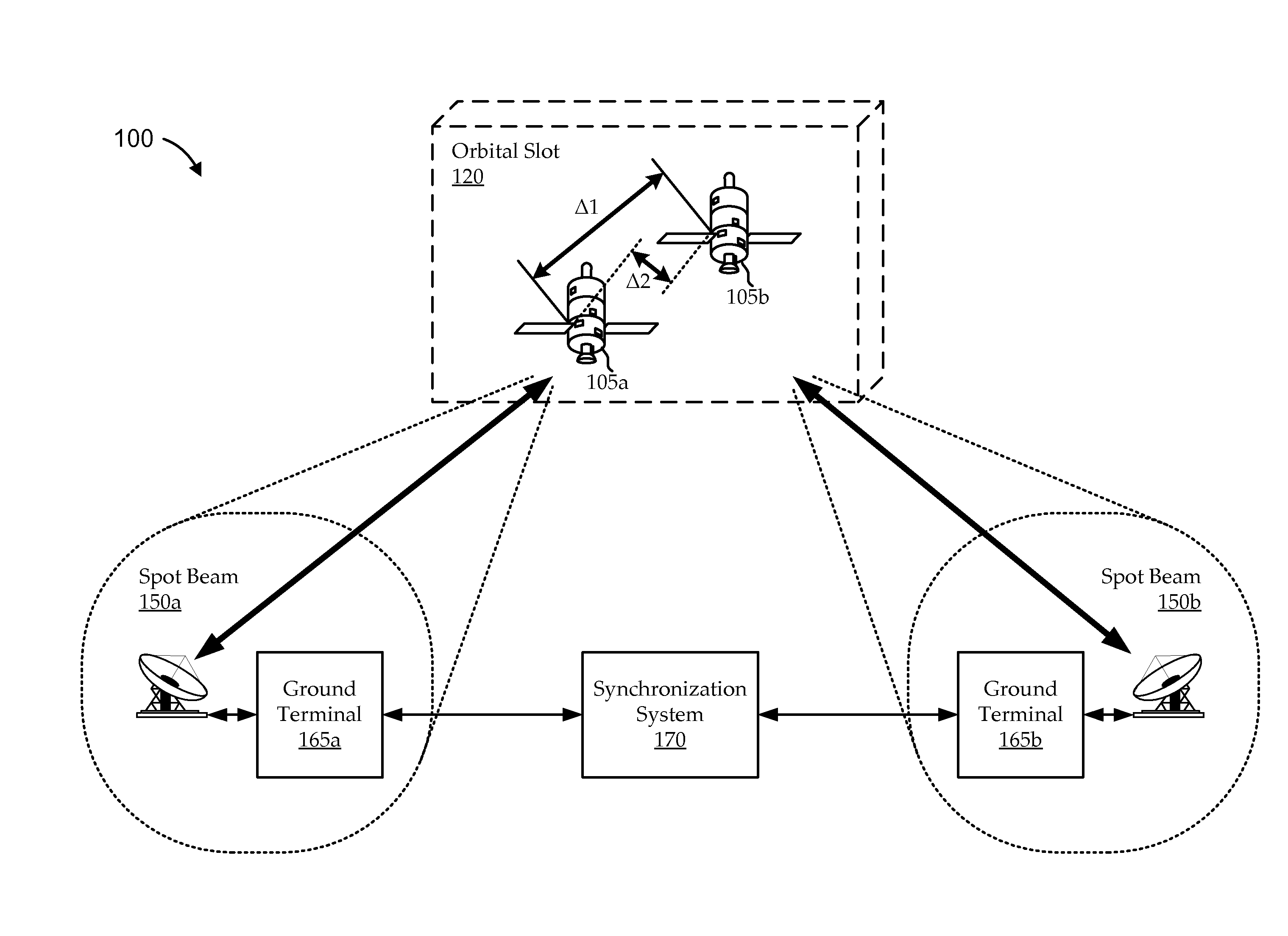
Tandem satellite frame synchronization
Systems and methods are described synchronizing communications frames and their respective time slots for satellite communications architectures having multiple satellites in the same orbital slot in such a way that addresses inter-satellite inter-beam interference. In some embodiments, the first and second satellites communicate with a respective number of ground terminals (e.g., gateway and user terminals) according to first and second satellite time slots, respectively. The satellites maintain relative positions in their orbital slot to manifest a maximum path delay difference between first and second path delays, the first path delay being between the first ground terminals and the first satellite, and the second path delay being between the first ground terminals and the second satellite. A synchronization system can offset the first satellite time slots from the second satellite time slots as a function of the maximum path delay difference.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Synchronized method of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system
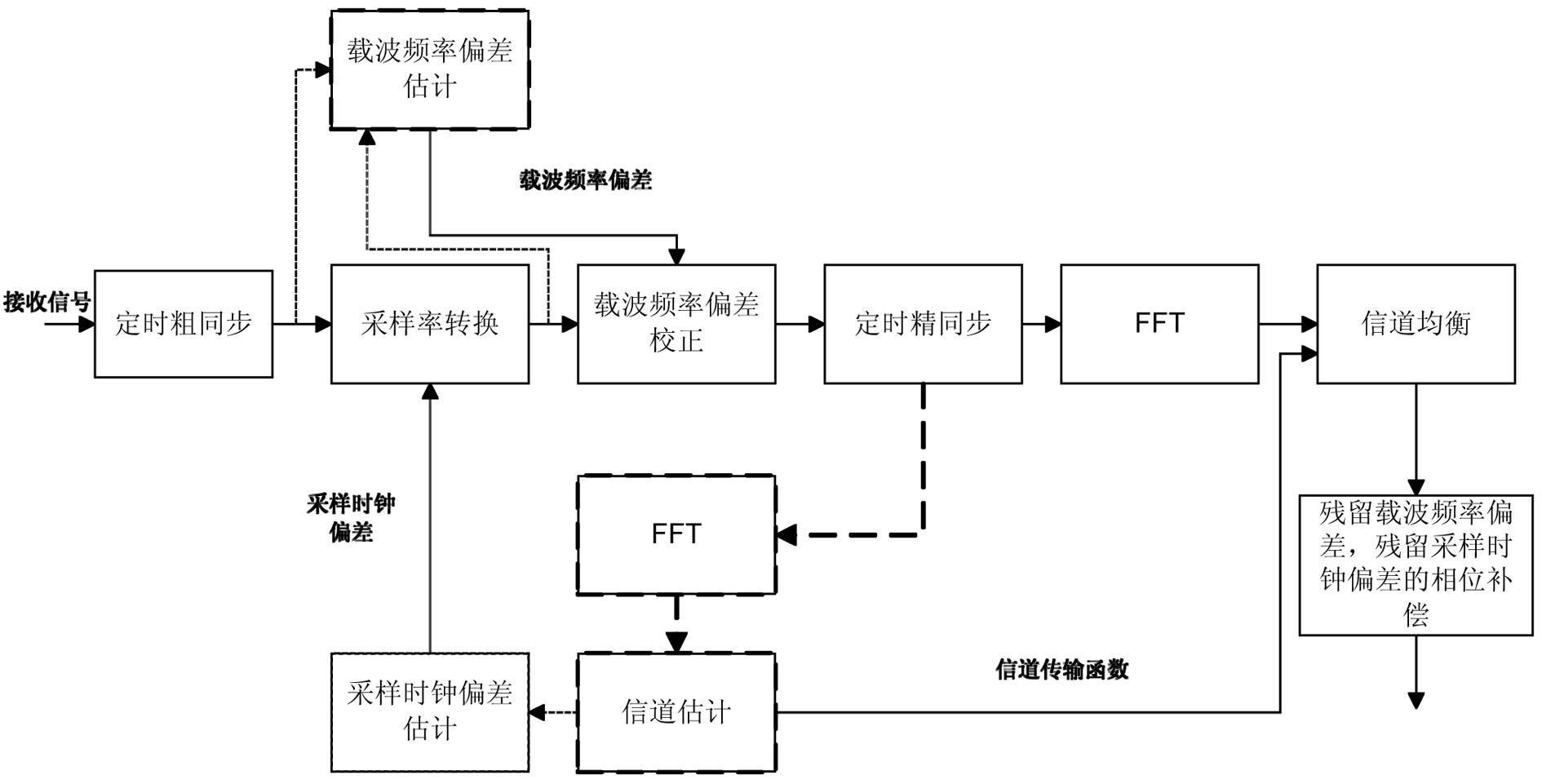
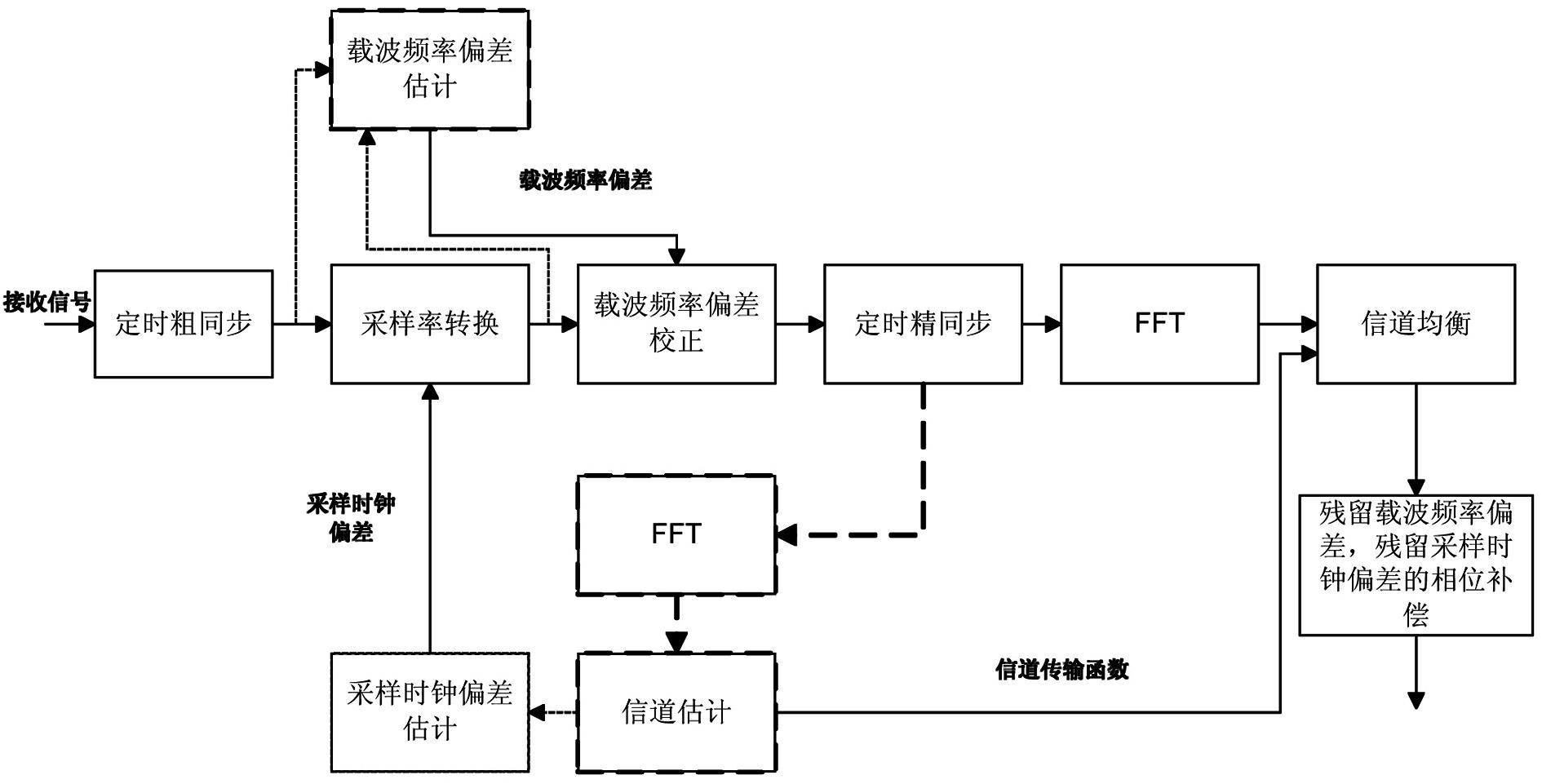
InactiveCN102075486AAvoid the impact of timing fine synchronizationMeet needsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier frequency offsetCarrier signal
The invention provides a synchronized method of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. The invention discloses an associated synchronized method of frame synchronization, carrier frequency synchronization and sampling clock synchronization. Carrier frequency offset estimation, channel estimation and fine estimation of symbol timing offset are performed again after sampling clock offset correction is finished, thereby avoiding influences of sampling clock offset on the carrier frequency offset estimation, the channel estimation and the fine estimation of the symbol timing offset, compensating phase deflection caused by the residual carrier frequency offset and the sampling clock offset simultaneously, greatly improving the synchronized performance, and meeting the demands of a high-order modulated system. In addition, due to aiming at a low time-varying channel, the channel estimation is required to be performed once only, thereby reliving the complexity of the system.
Owner:深圳市阿派斯实业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com