Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
620 results about "Continuous signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A continuous signal or a continuous-time signal is a varying quantity whose domain, which is often time, is a continuum. That is, the function's domain is an uncountable set. The function itself need not be continuous. To contrast, a discrete time signal has a countable domain, like the natural numbers. A signal of continuous amplitude and time is known as a continuous time signal or an analog signal. This will have some value at every instant of time. The electrical signals derived in proportion with the physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, sound etc. are generally continuous signals. The other examples of continuous signals are sine wave, cosine wave, triangular wave etc. The signal is defined over a domain, which may or may not be finite, and there is a functional mapping from the domain to the value of the signal. The continuity of the time variable, in connection with the law of density of real numbers, means that the signal value can be found at any arbitrary point in time. A typical example of an infinite duration signal is: A finite duration counterpart of the above signal could be: and otherwise.
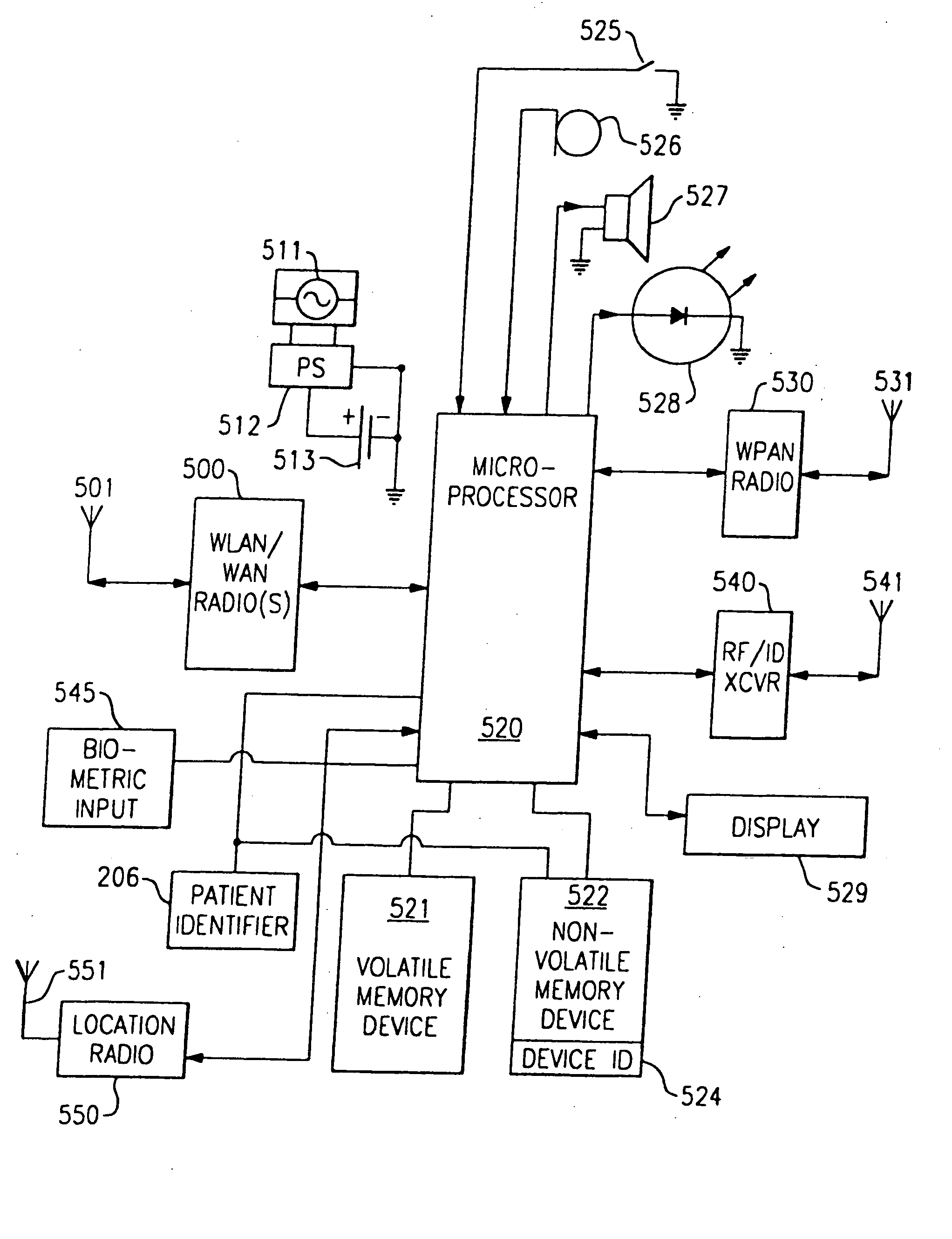
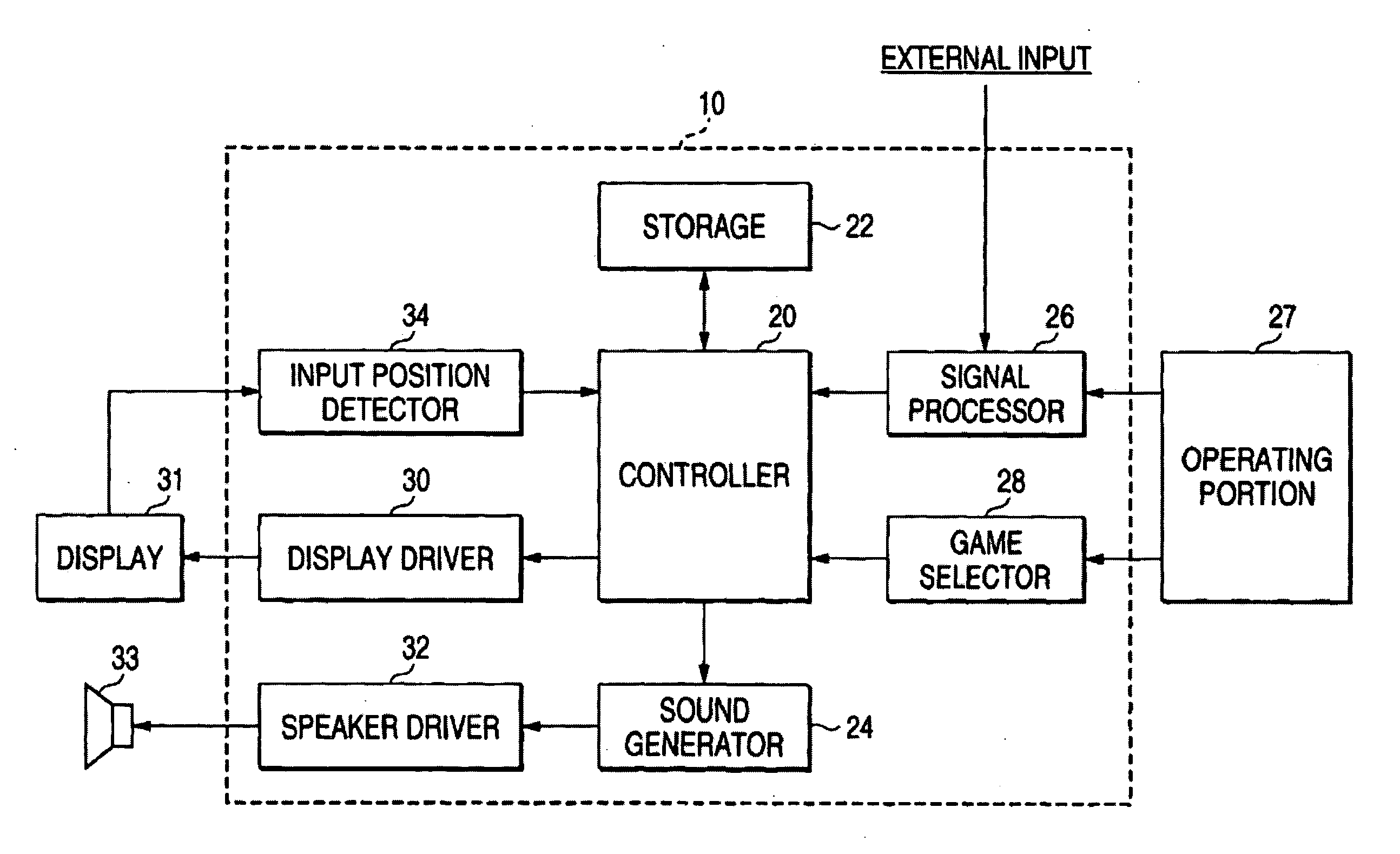
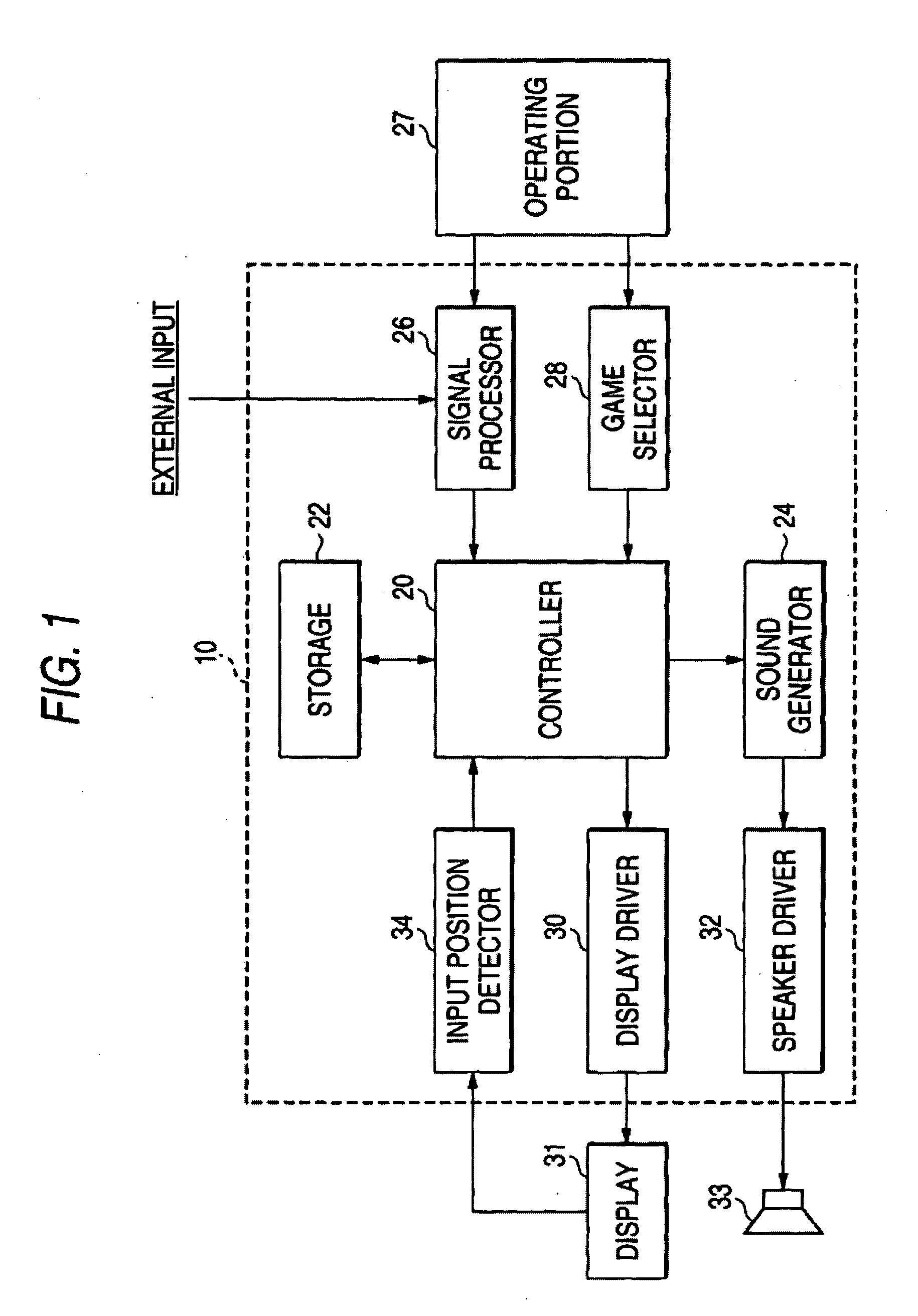
Personal status physiologic monitor system and architecture and related monitoring methods
ActiveUS20060238333A1Preserve battery lifeLow costElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringContext managementContinuous signal
A method for performing context management, said method comprising the steps of: producing a continuous physiologic signal, as detected by a monitoring device; associating at least one unique hardware identifier to said continuous physiologic signal and binding a unique patient identifier to said continuous signal wherein a change in said physiologic signal in which said signal is no longer continuous will cause the unique patient identifier to unbind from said signal.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
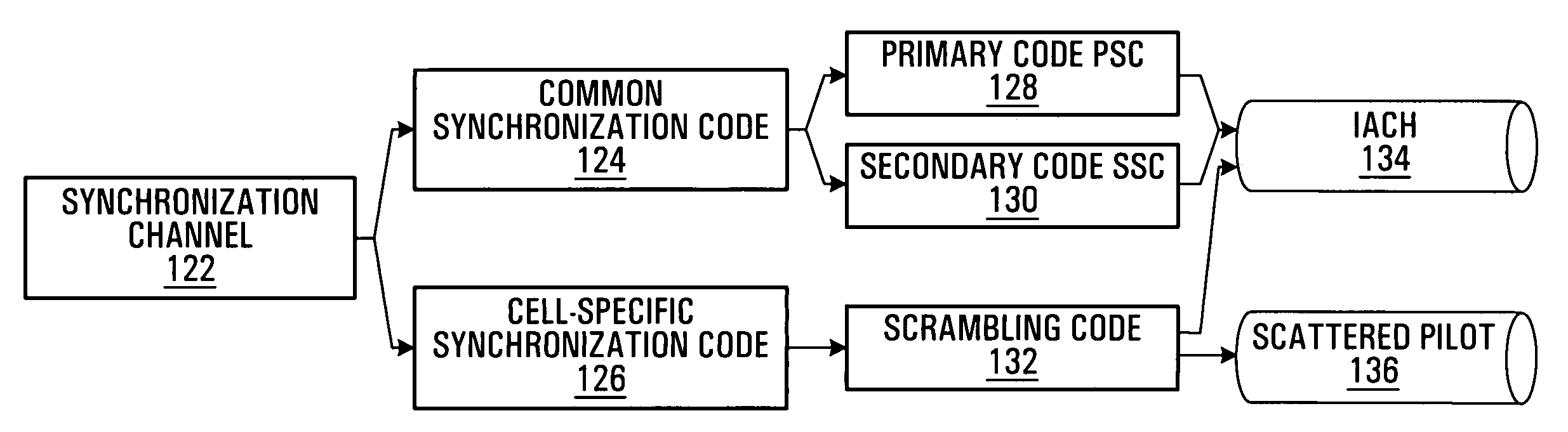
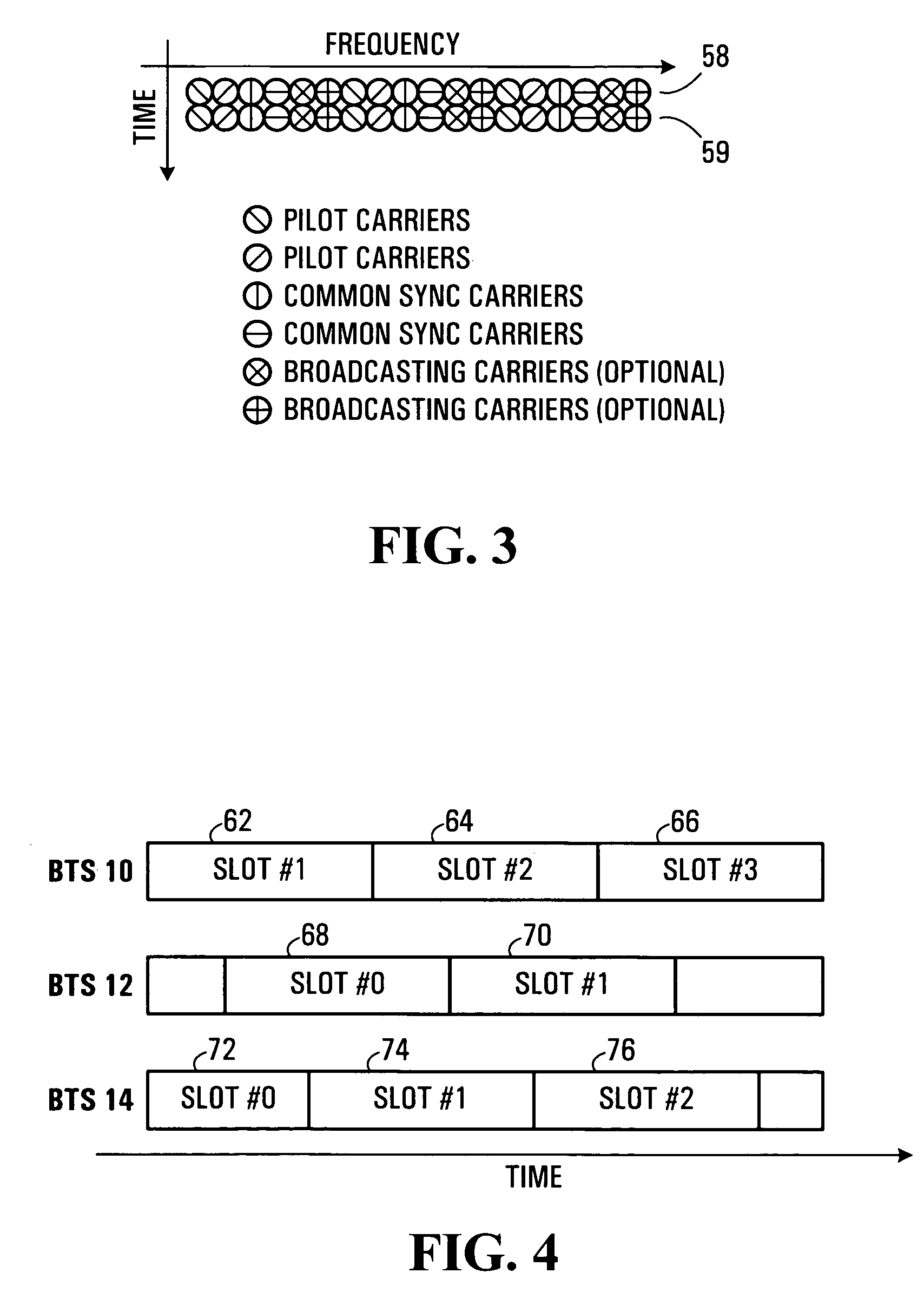
Physical layer structures and initial access schemes in an unsynchronized communication network
Physical layer structures and related access schemes for unsynchronized communication networks are provided. Access channel information, preferably including a common synchronization code associated with all transceiver stations in a communication network and a cell-specific synchronization code uniquely associated with one of the transceiver stations, is modulated onto at least one set of time-continuous signal components of a communication signal. In order to access the communication network, communication terminals search for the access channel information in one or more sets of time-continuous signal components and synchronization parameters are then determined based on a location of the access channel information in the sets of time-continuous signal components. Some embodiments of the invention provide for joint frame synchronization and coarse timing synchronization. In further embodiments, the communication signal also includes a scattered pilot channel onto which a portion of the access channel information, preferably the cell-specific synchronization code, is modulated. The pilot channels may then be re-used for initial access operations in addition to its conventional uses for such operations as channel estimation.
Owner:APPLE INC
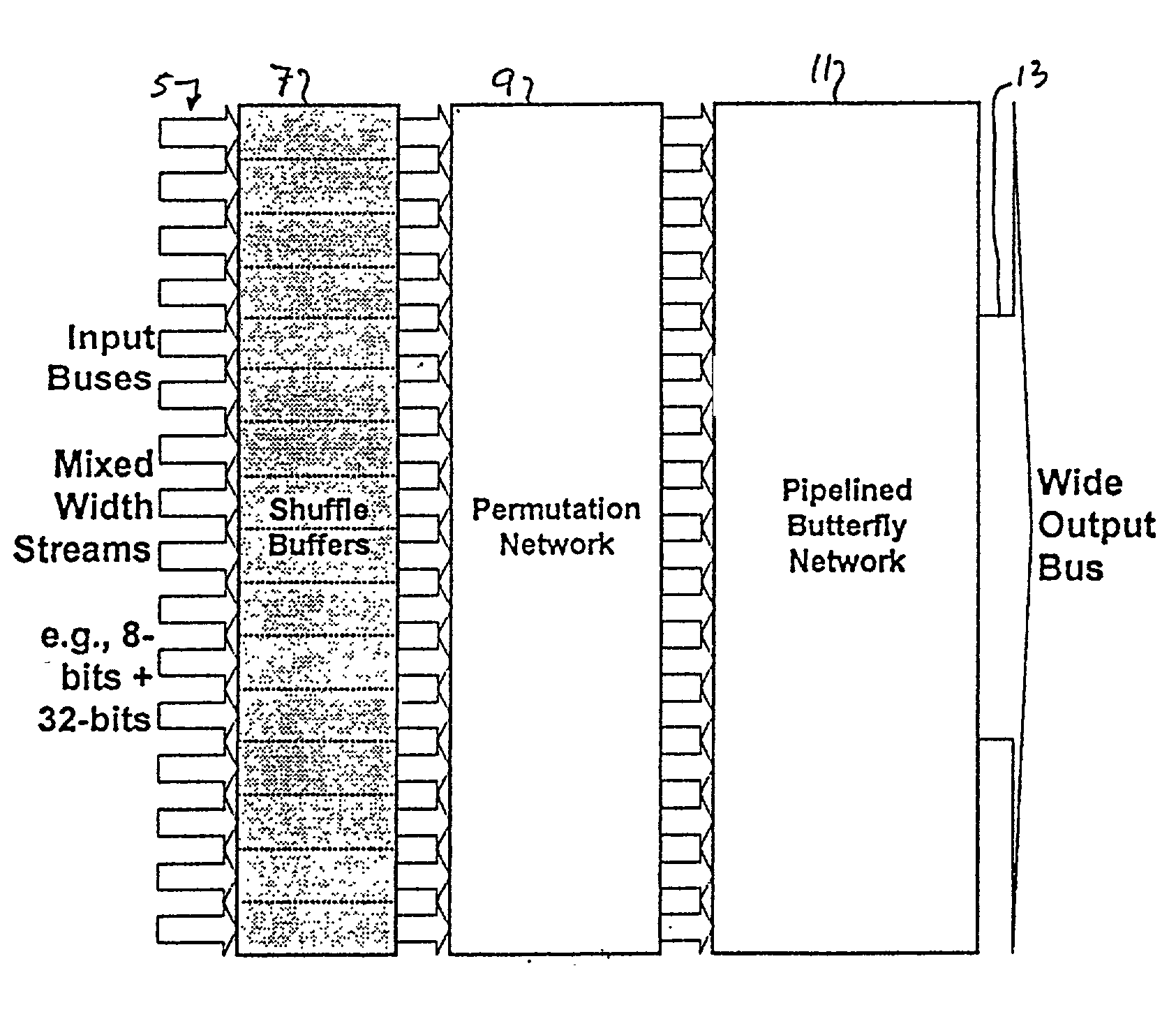
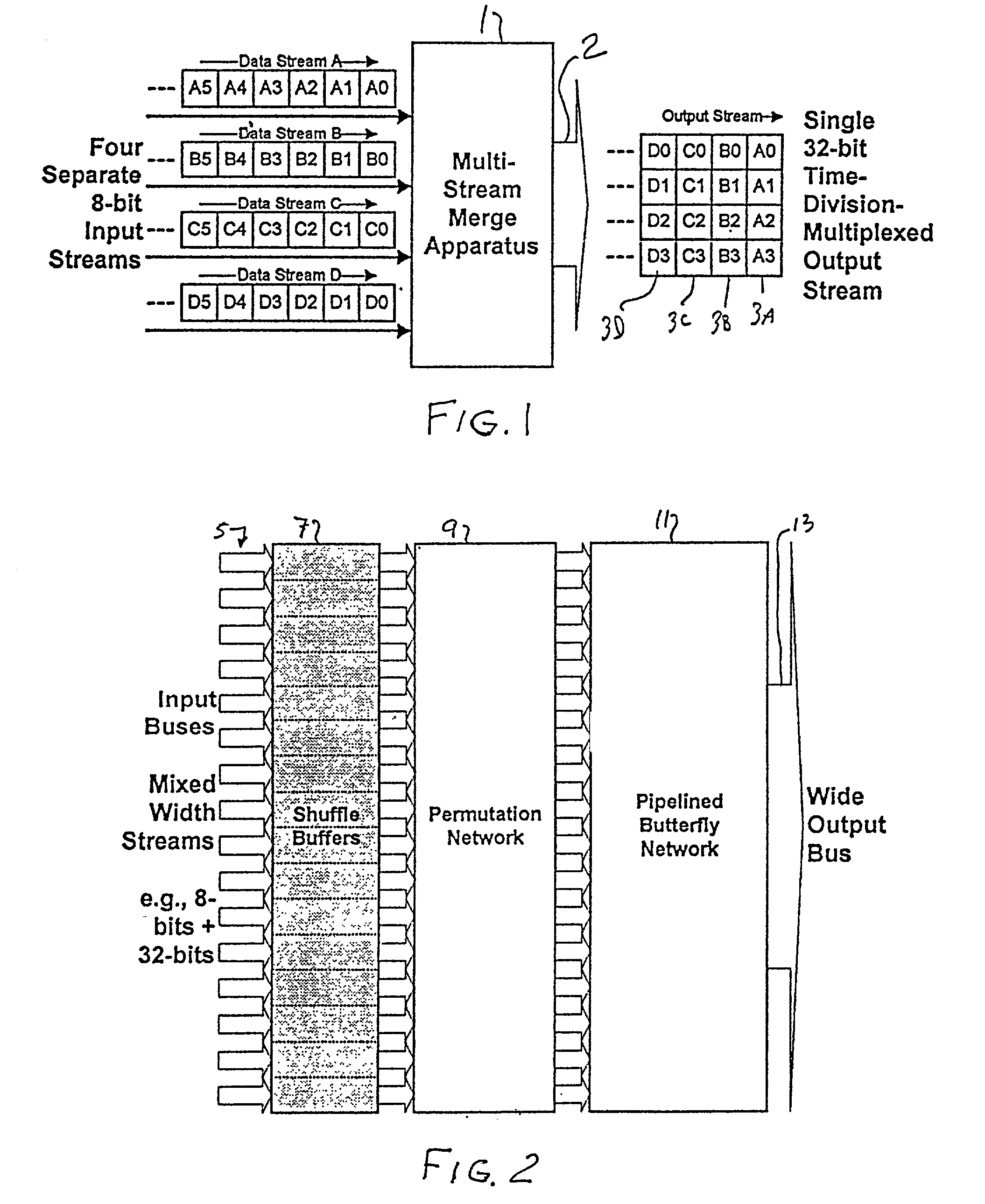
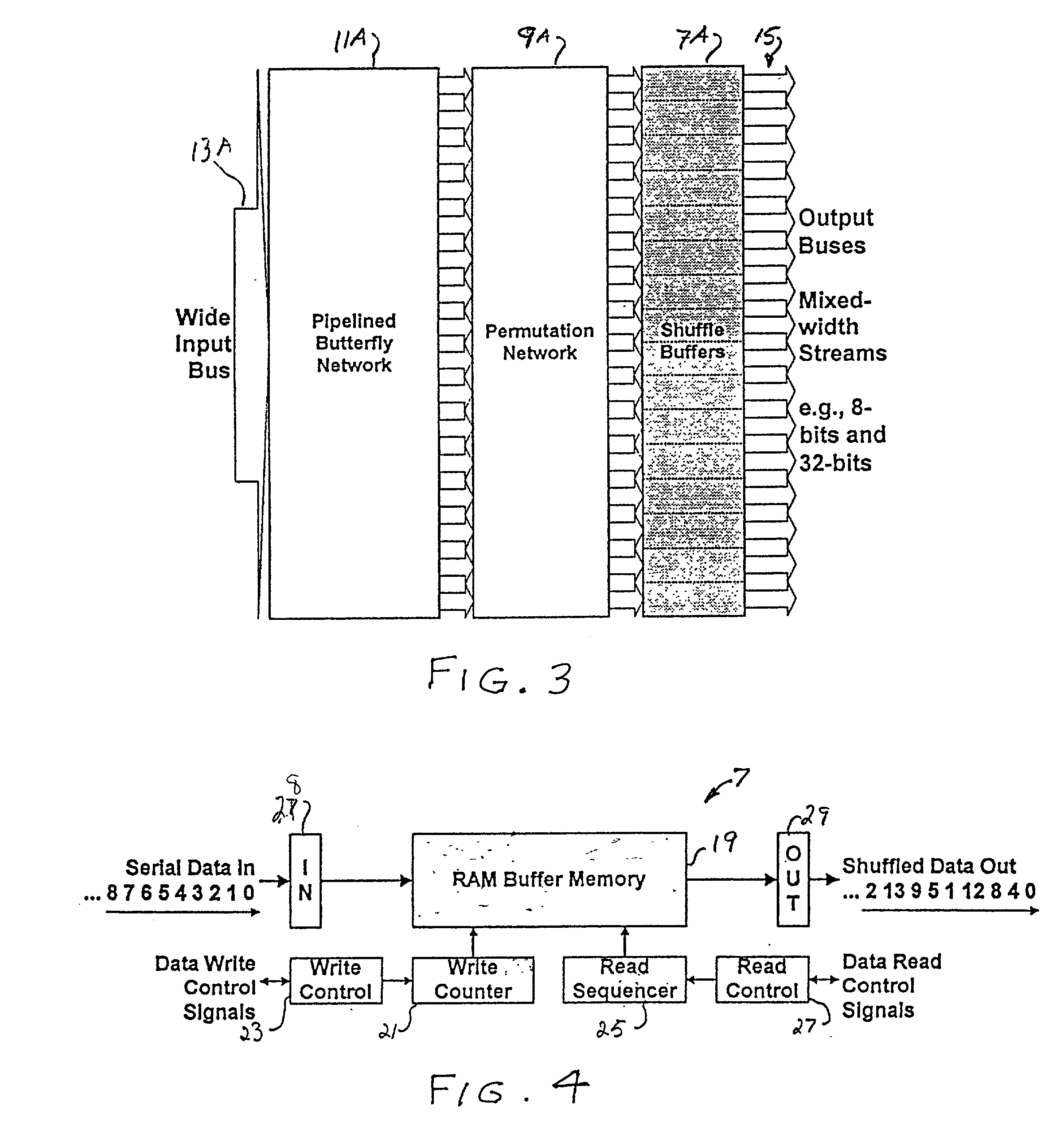
Multi-stream merge network for data width conversion and multiplexing
InactiveUS20030002474A1Less complexParallel/series conversionTime-division multiplexMultiplexingData stream
The present invention relates to a merging network for multiple data streams comprising a pipelined butterfly network. The pipelined butterfly network comprises an input network for receiving a plurality of data streams of mutually constant widths, each data stream having logically related data bits carried on contiguous signal lines, a butterfly network containing suitably interconnected register and multiplexer means for rearranging the received data streams into a time-multiplexed constant-width output data stream, the output data stream having a width equal to or greater than the sum of the widths of the input data streams, and an output network for providing the output data stream interleaved to an output bus.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
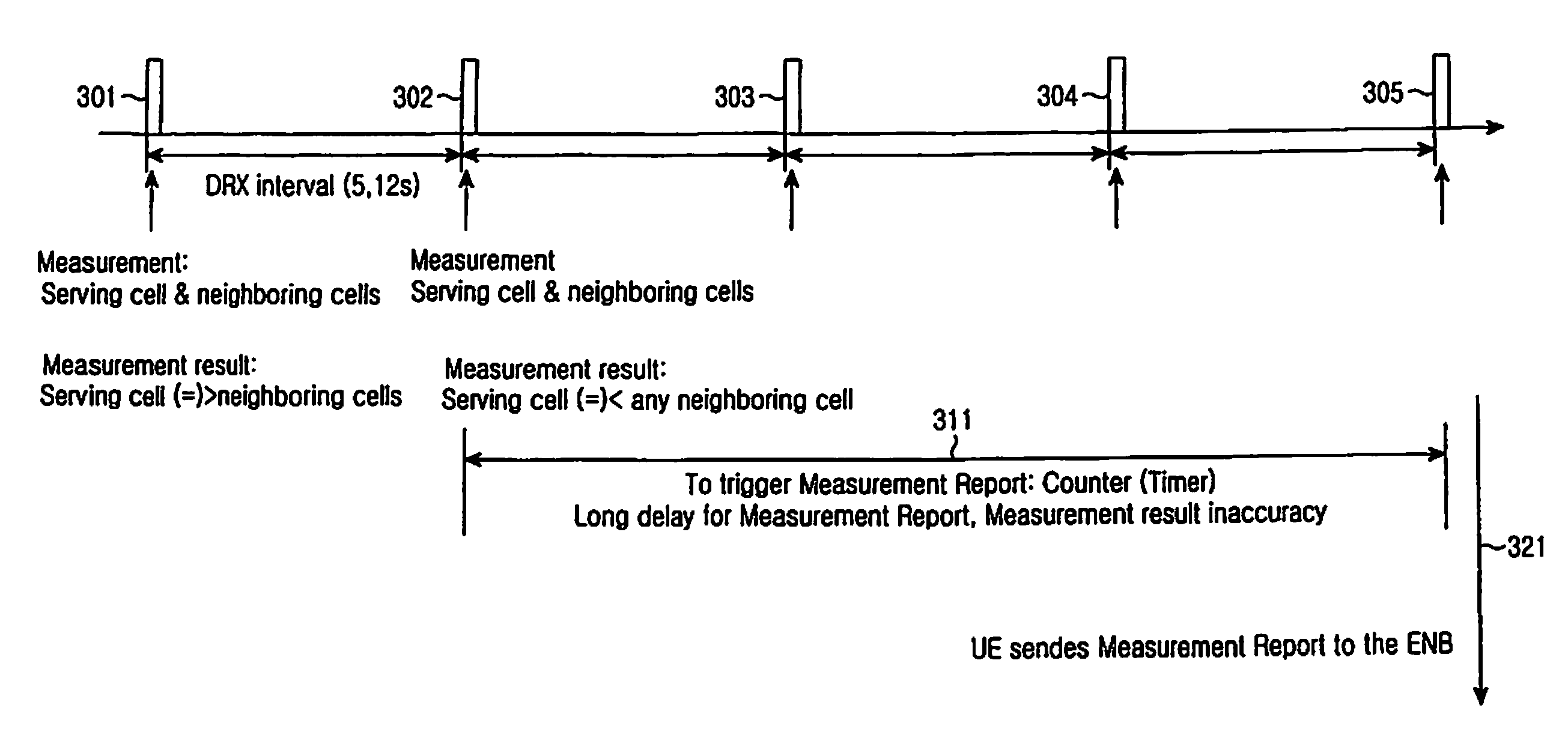
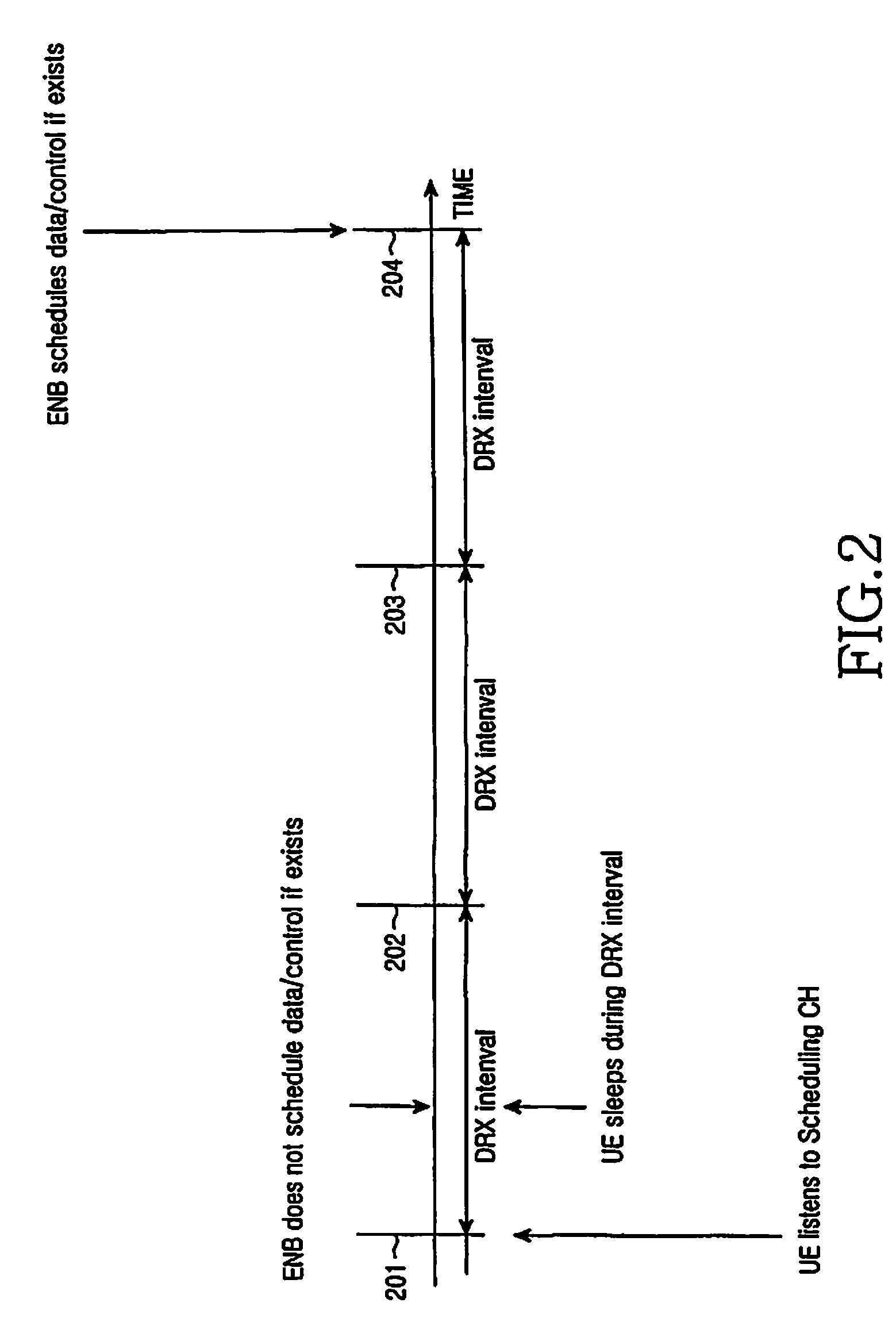
Measurement method and apparatus of user equipment having variable measurement period in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20080160918A1Minimize power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementContinuous measurementContinuous signal
A method and apparatus for performing measurement by a User Equipment (UE) in a mobile communication system are provided. The UE has a Discontinuous Reception (DRX) mode for discontinuously receiving data and a continuous reception mode for continuously receiving data. The mobile communication system also has a serving cell where the UE is located, and a neighboring cell located near the serving cell. Signal strength of the serving cell is measured according to a period of the DRX mode. The signal strength measurement is continuously performed on the serving cell and the neighboring cell, if the measured signal strength of the serving cell is less than or equal to a particular threshold. The continuous signal strength measurement is stopped and signal strength of the serving cell is measured according to the period of the DRX mode, if the continuously measured signal strength of the serving cell is greater than the particular threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar moving target recognizer and recognition method
InactiveCN103529444AImprove ranging accuracyImprove angle measurement accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntermediate frequencyContinuous signal
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar moving target recognizer. The vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar moving target recognizer is characterized in that the recognizer is a frequency synthesizer; a frequency agility continuous signal is modulated into a pulse signal and then is processed into a millimeter-wave signal by up-conversion; after being amplified by a power amplifier, the millimeter-wave signal is transmitted out; an antenna receives a radar echo signal back to a circulator and then the signal is transmitted into a frequency mixer; a high-frequency echo pulse and constant-amplitude high-frequency voltage generated by a high-stability local oscillator are mixed and the signal is reduced to a middle frequency and then is processed by a middle-frequency amplifier; the middle-frequency signal is directly sampled by an A / D (Analogue / Digital) conversion module; after being sampled, echo signals of a whole pulse string are stored into a storage unit; and information of targets, such as quantity, speed and direction, is measured by a signal processing unit and then is transmitted to an alarm executing unit. With the adoption of the structure, the vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar moving target recognizer has the advantages that 1 the distance measuring precision and the angle measuring precision of a moving target are improved; and 2 excessive hardware does not need to be added and the production cost is lower.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Blood pump system and method of operation
A blood pump system includes a blood pump having a motor with a rotor and a stator. The stator has a plurality of stator windings situated therein. A motor controller is coupled to the motor, and a processor has inputs coupled to the motor controller for receiving a time continuous signal from the pump. The processor is programmed to transform the time continuous signal to the frequency domain, and control the pump and detect excess suction in response to the time continuous signal in the frequency domain.
Owner:RELIANTHEART
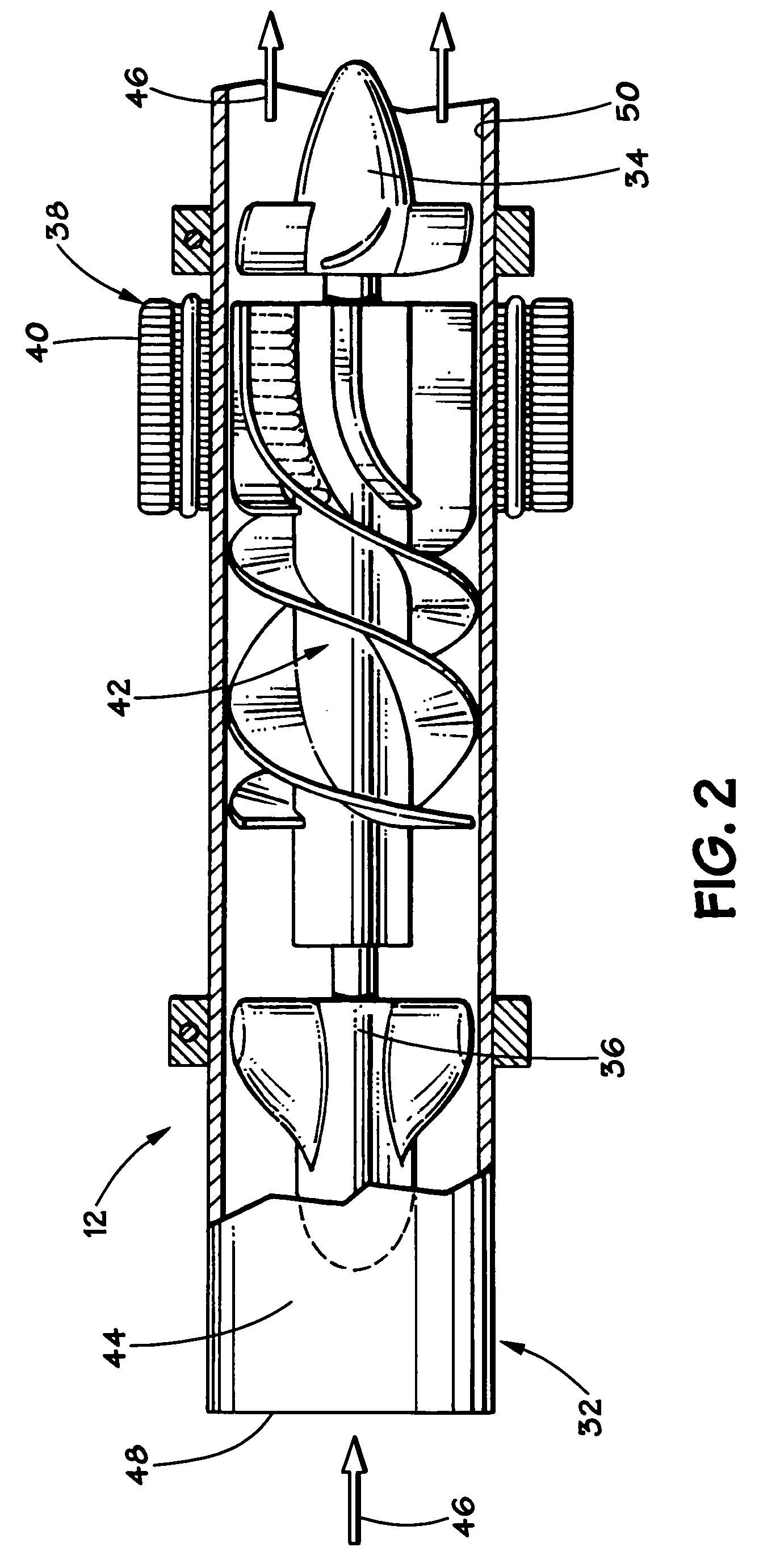
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
ActiveUS20050031322A1Small and cost-efficient packageRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
Apparatus and method for compressing measurement data corelative to machine status
InactiveUS6507804B1Reduce data volumeVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingFrequency spectrumEngineering
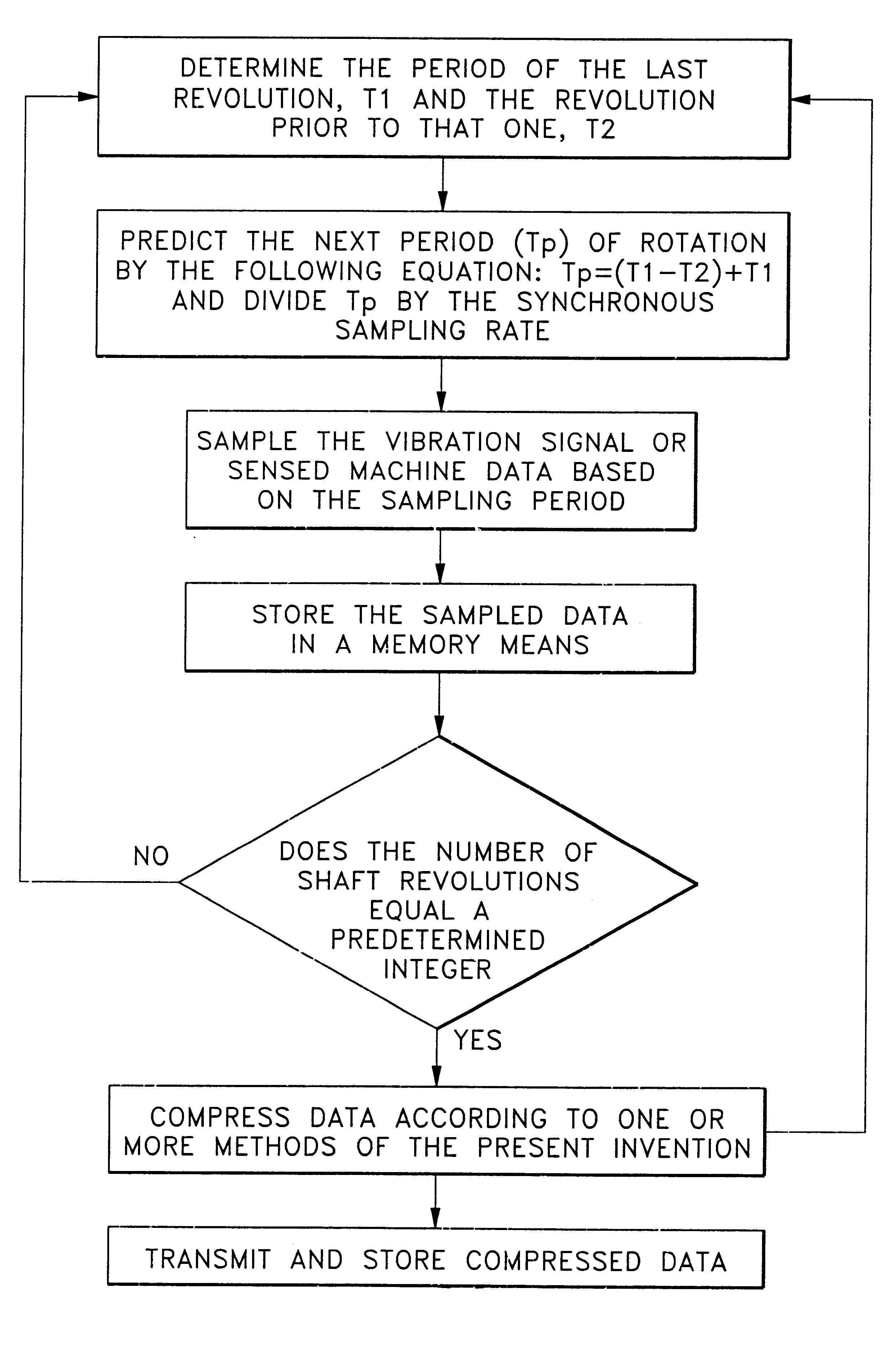
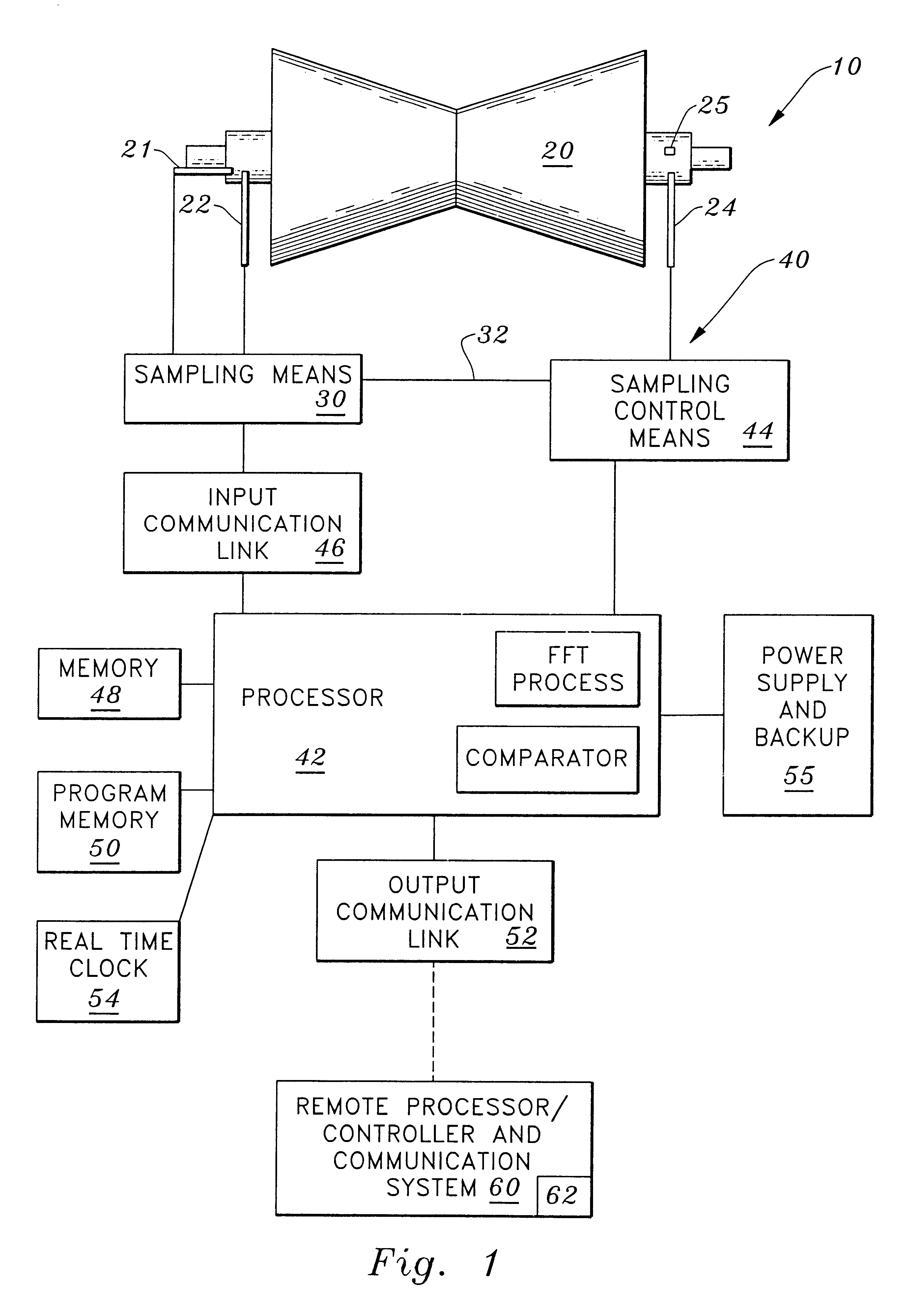
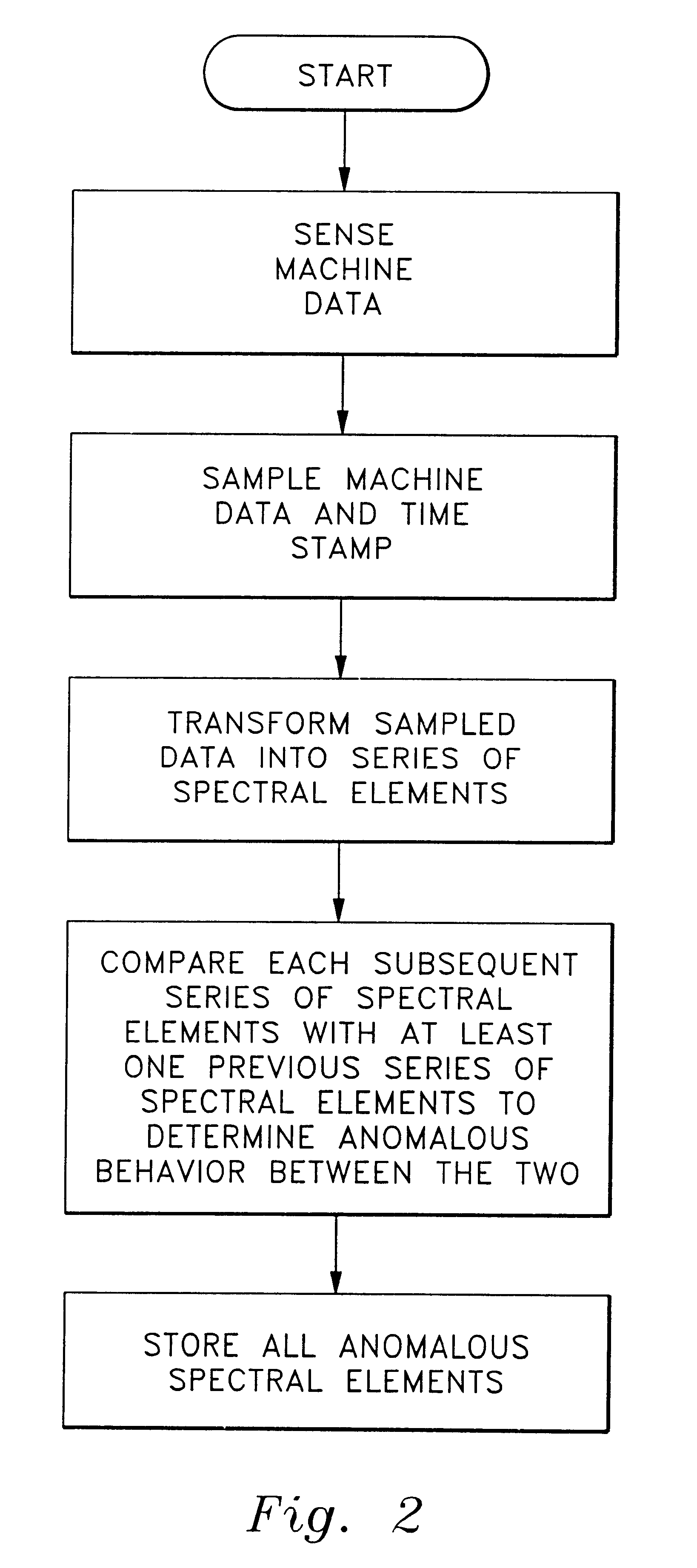
A method and apparatus for compressing, storing and transmitting measurement data correlative to machine status is disclosed in which the measurement data is continuously sensed, sampled and processed to extract significant spectral elements including magnitude and phase information from each successive period of the originally measured data and to store those spectral elements in a memory means from an initial period of significant spectral elements and each successive period of significant spectral elements which have changed since the previous period for developing a compressed data history correlative to a continuous history of the status of the machine being monitored and from which continuous signals can be regenerated and analyzed for any earlier historical time.
Owner:BENTLY NEVADA INC
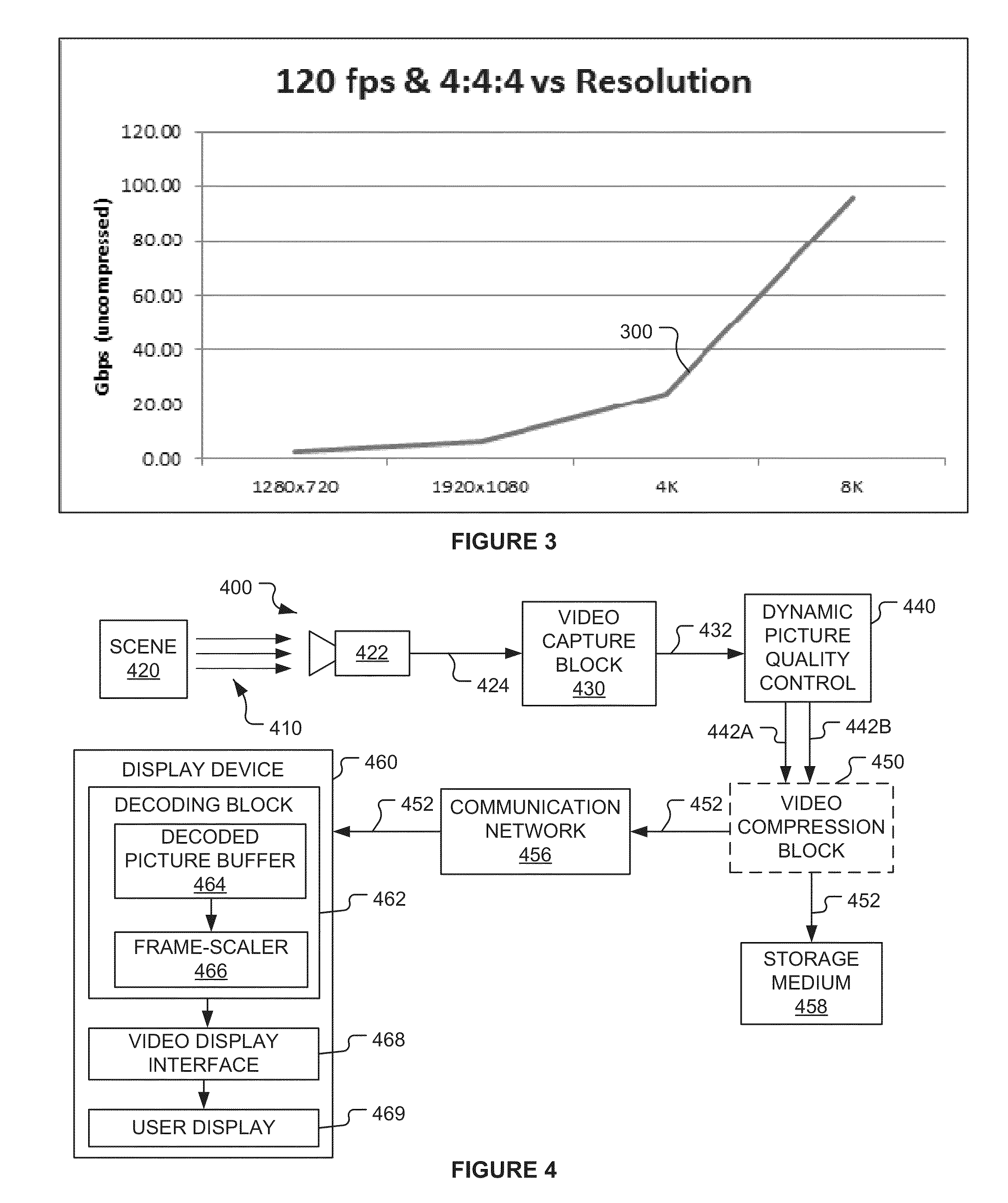
Dynamic picture quality control
A method performed by one or more computing devices. The method includes identifying first and second portions of a digital video signal. First and second values of a plurality of quality metrics are determined for the first and second portions, respectively. The first and second values of the metrics are used to determine first and second values, respectively, of a plurality of picture quality parameters such that a signal transmitted using either the first or second values of the parameters would require at most a maximum output bitrate. The first values of the parameters may differ from the second values of the parameters. The first and second portions are adjusted using the first and second values, respectively, of the parameters. The first and second adjusted portions are transmitted in a continuous signal. Optionally, the first and second adjusted portions are compressed before they are transmitted.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
Communication channel with undersampled interpolative timing recovery
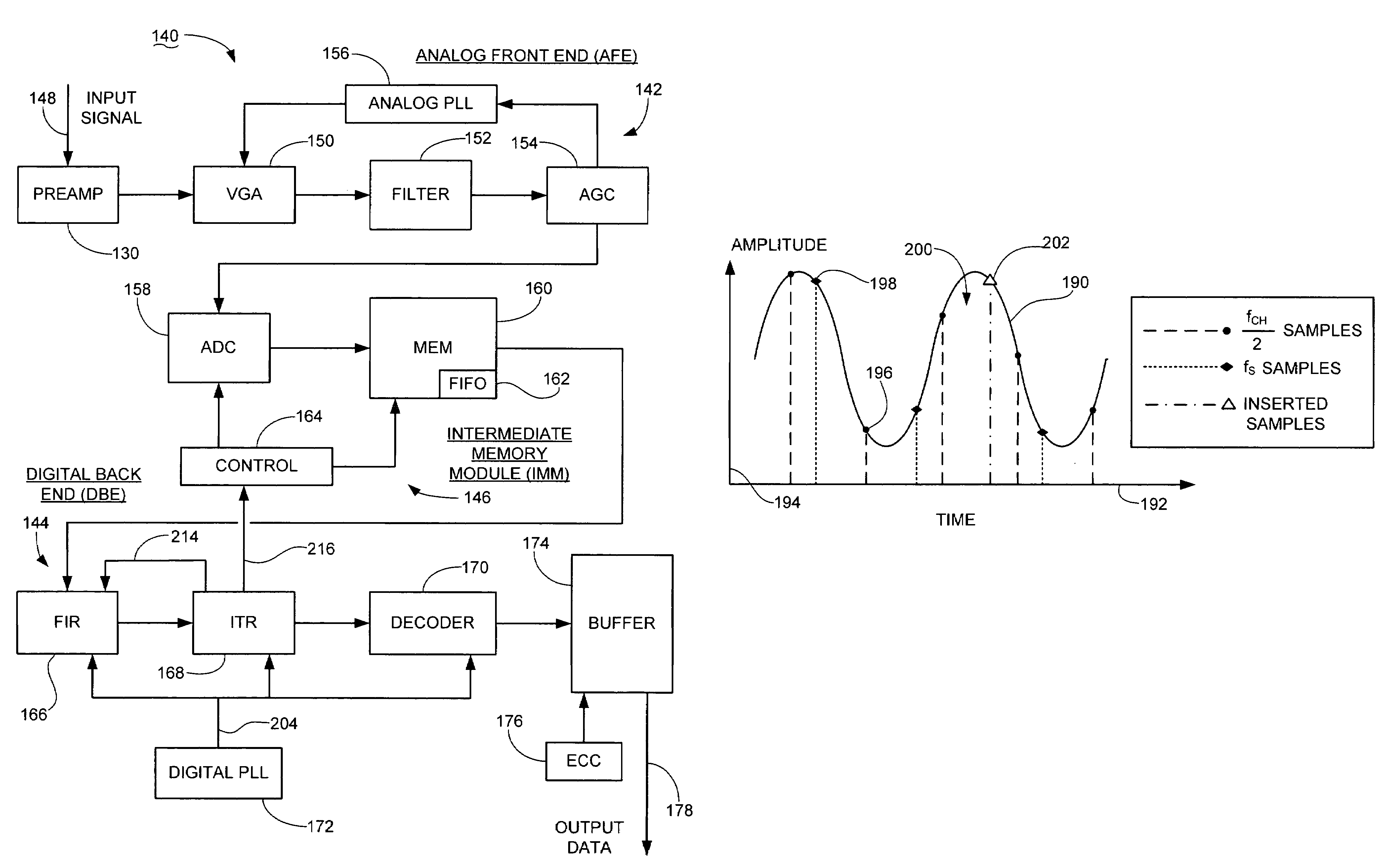
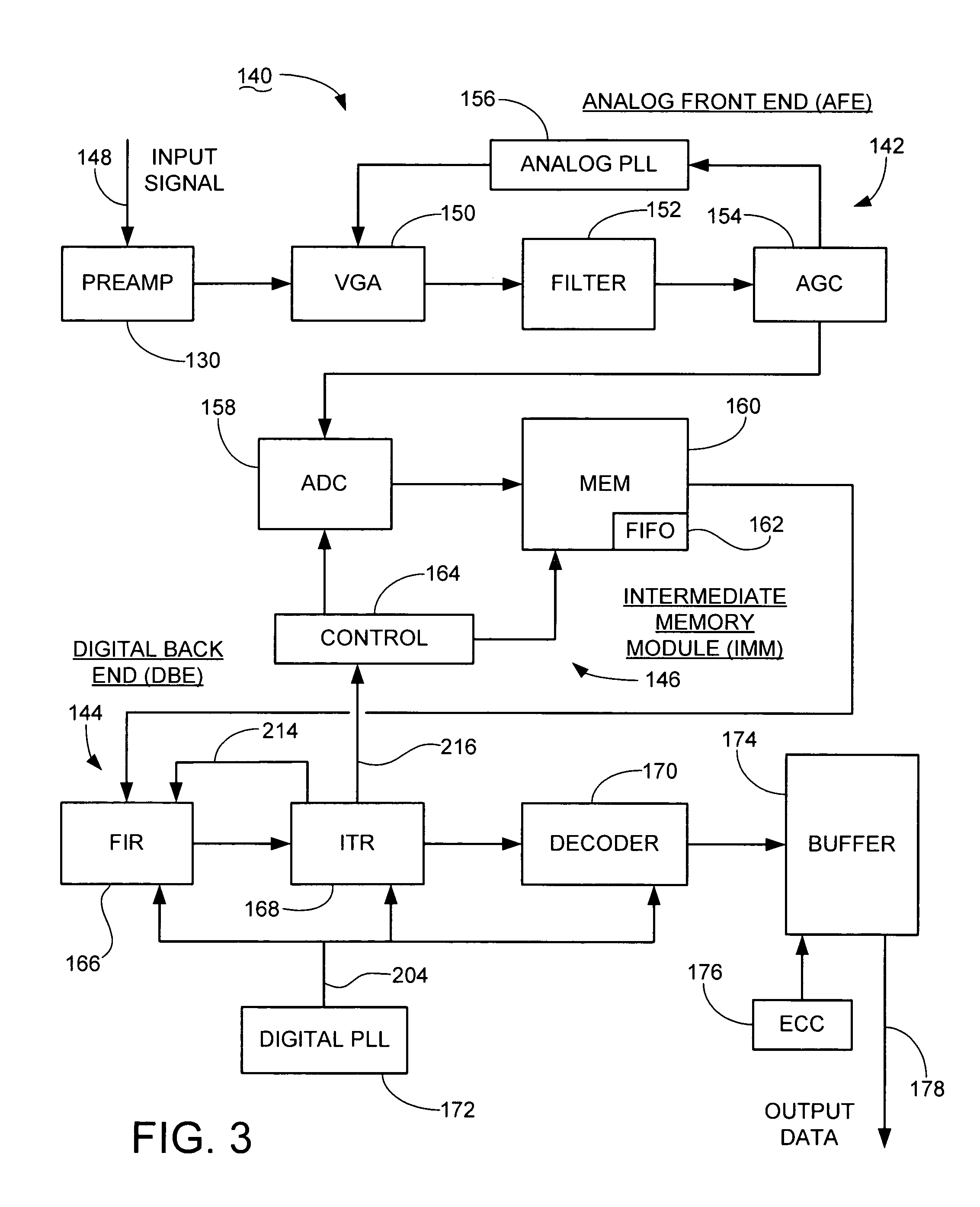
InactiveUS7365671B1Improve efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsModification of read/write signalsRecovery methodContinuous signal
Method and apparatus for processing transmitted data. A sampling circuit preferably performs lossy sampling of a continuous signal to provide a corresponding sequence of discrete samples at a sampling rate less than a Nyquist rate of the continuous signal. A processing circuit reconstructs an informational content of the continuous signal from the discrete samples, and operates to periodically insert additional samples into the sequence, which preferably increases an effective rate of said sampling to match or exceed the Nyquist rate. Preferably, the lossy discrete samples are temporarily stored in a memory space prior to reconstruction by the processing circuit. The sampling circuit preferably comprises an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of an analog front end (AFE). The processing circuit preferably comprises a digital back end (DBE) employing partial-response, maximum-likelihood (PRML) detection. The additional samples are preferably provided by an iterative timing recovery (ITR) block of the DBE.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
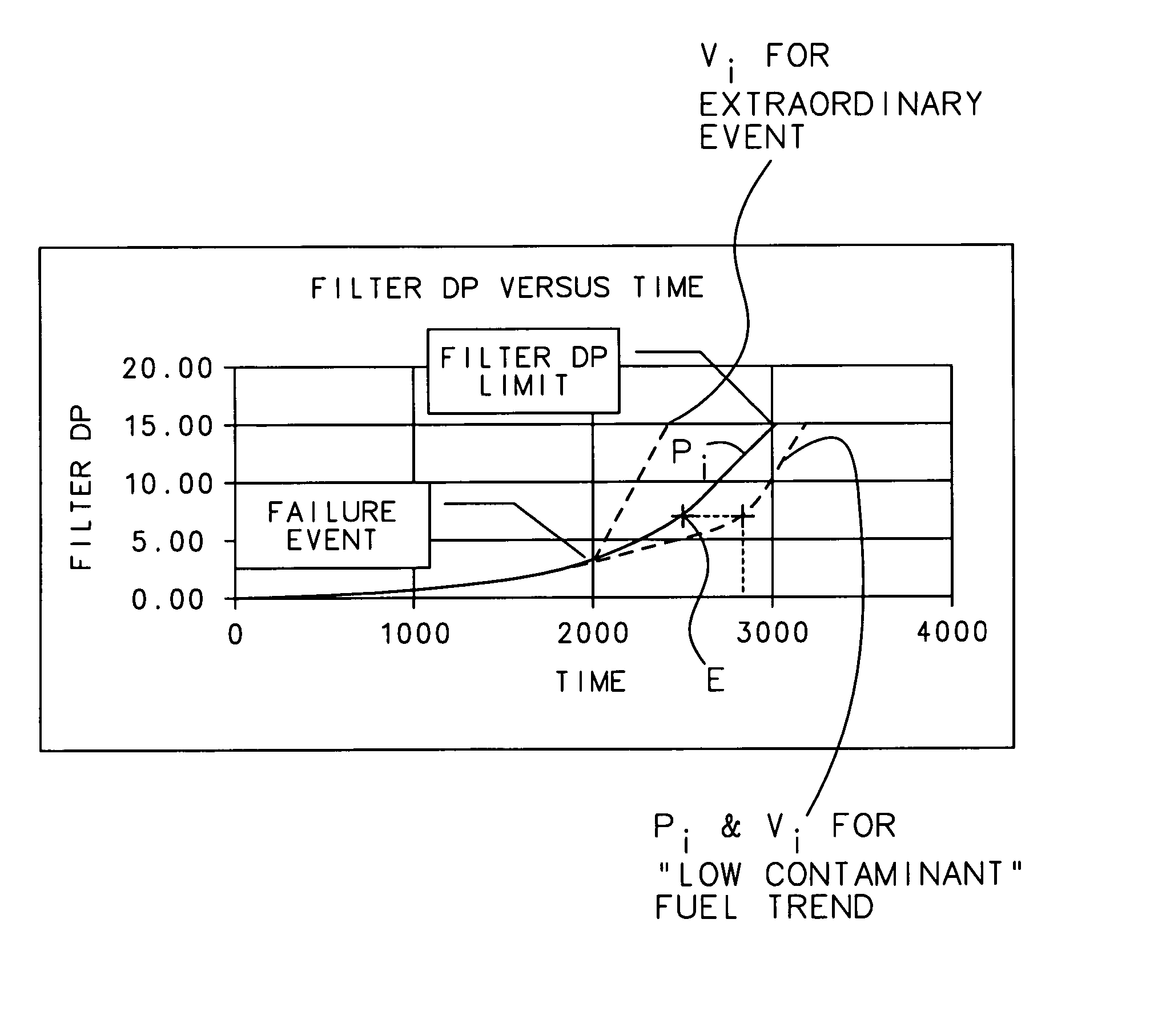
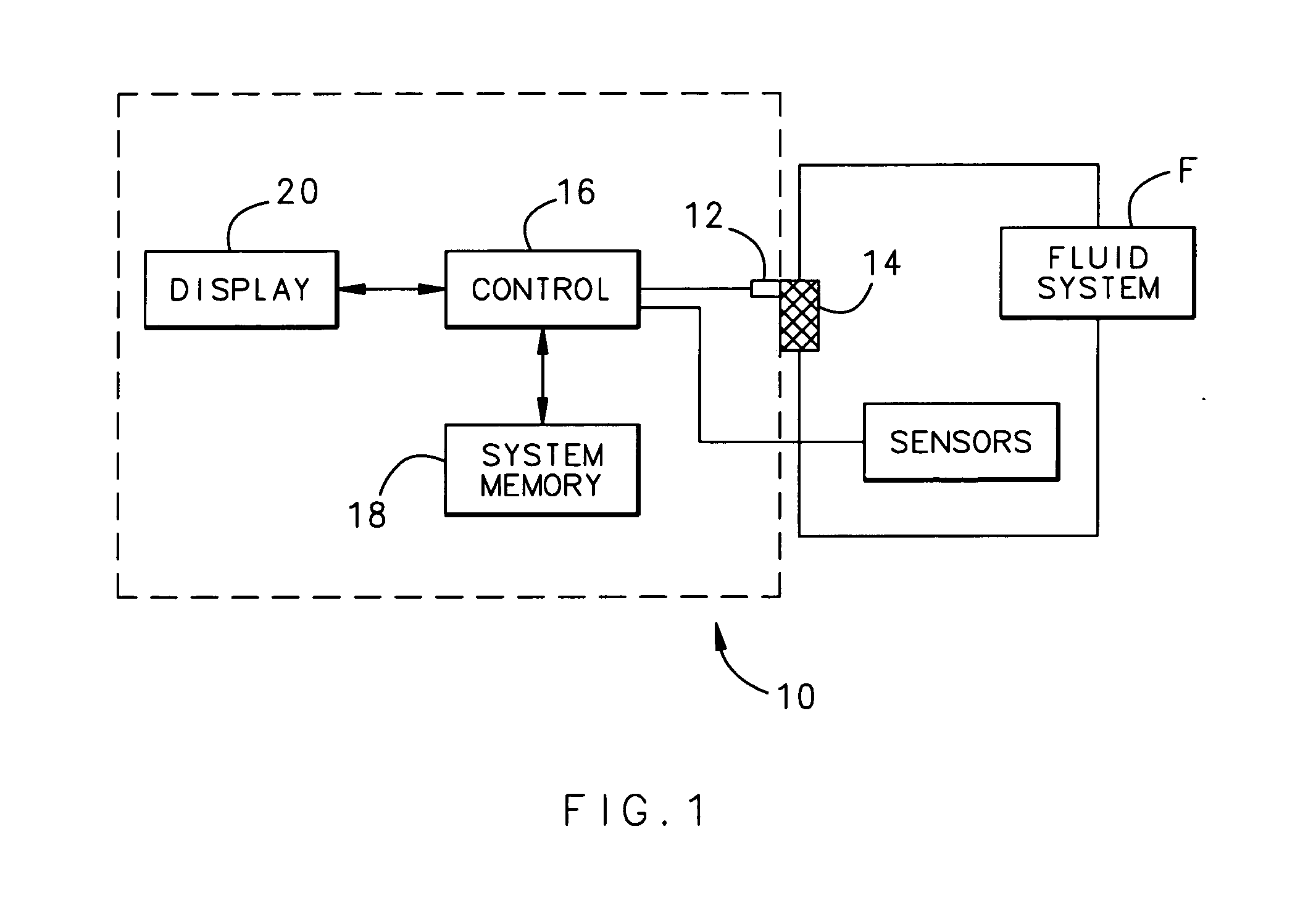
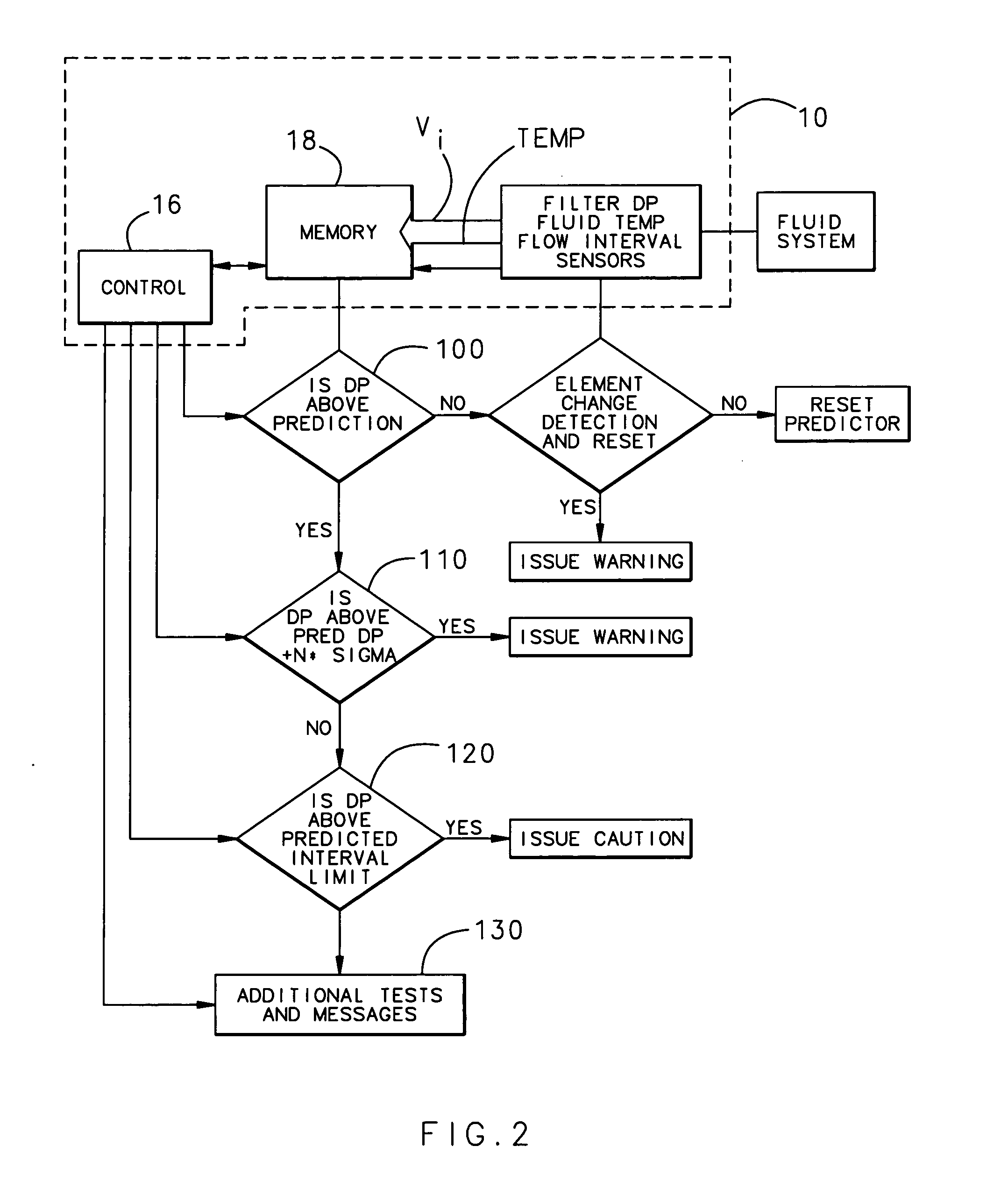
Filter monitoring system
ActiveUS7174273B2Minimizing expenseImprove resource efficiencyDispersed particle filtrationNuclear monitoringDifferential pressureMonitoring system
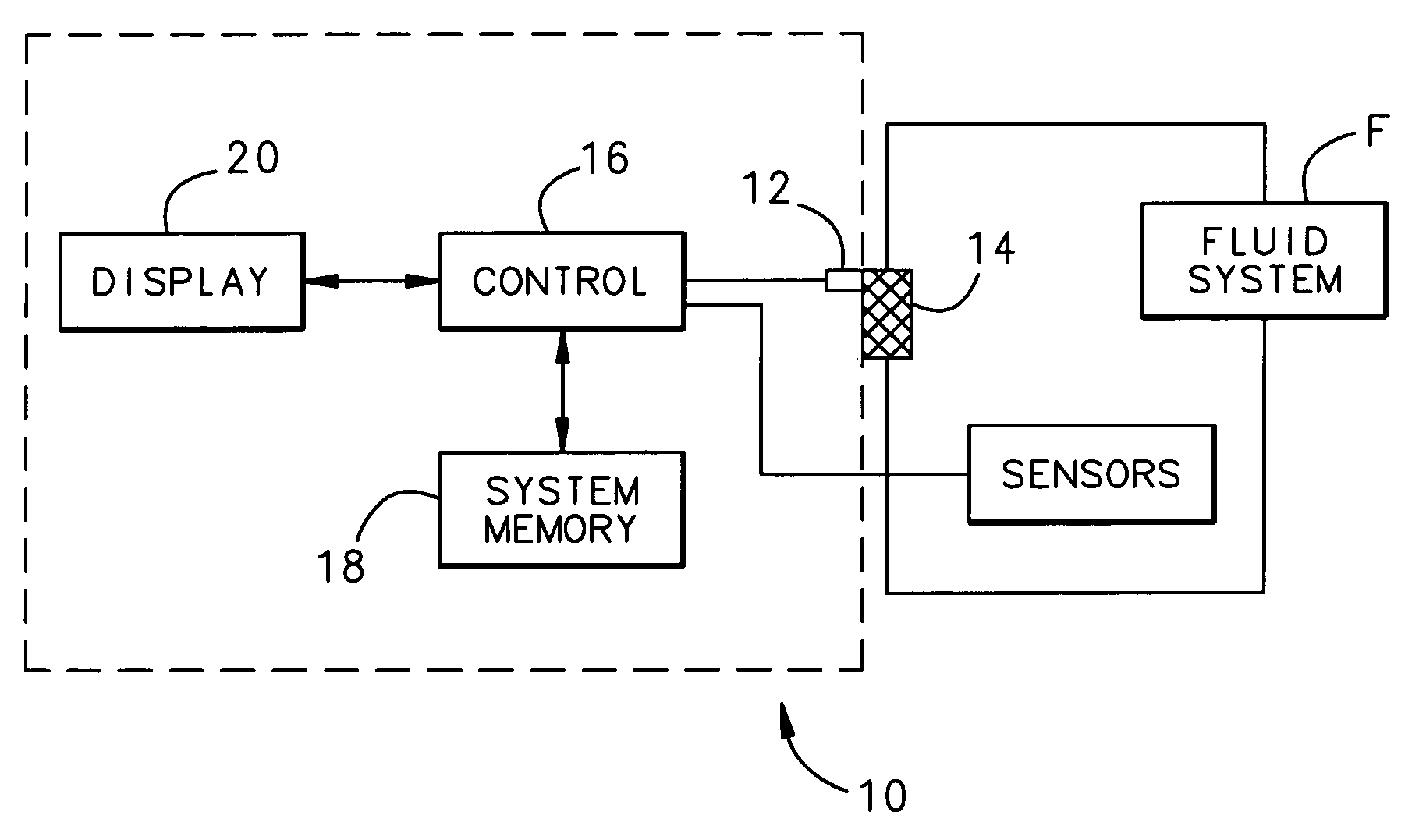
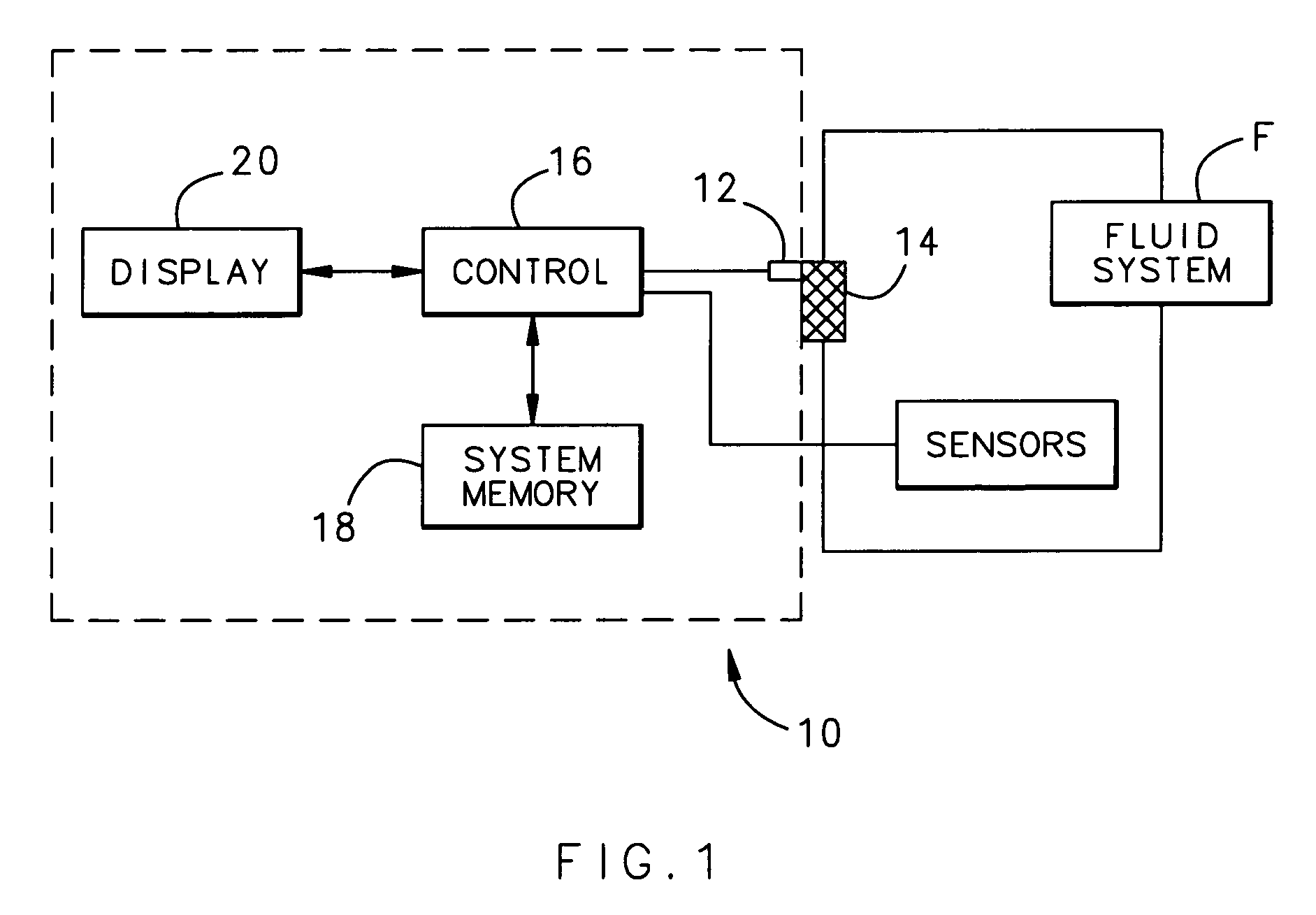
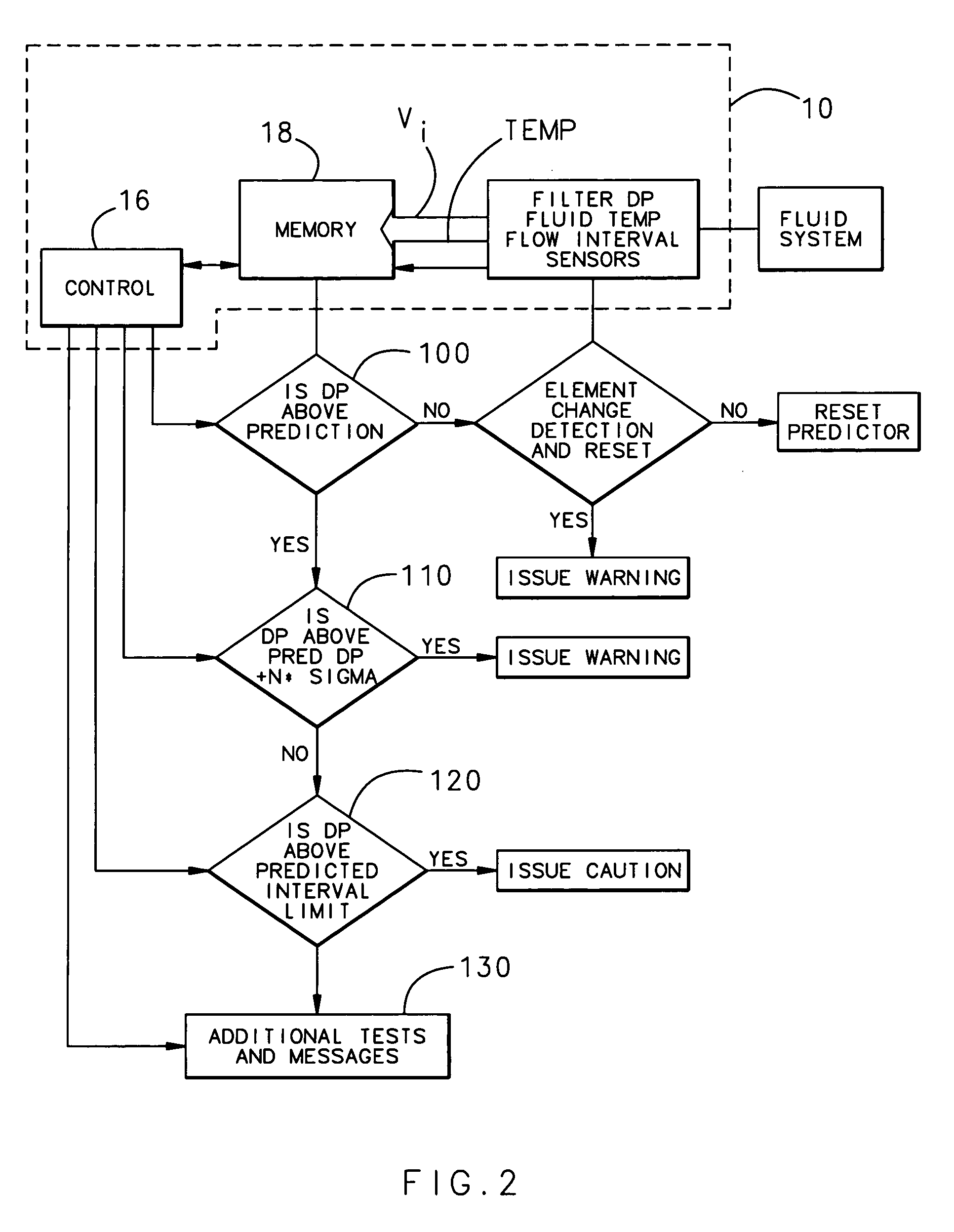
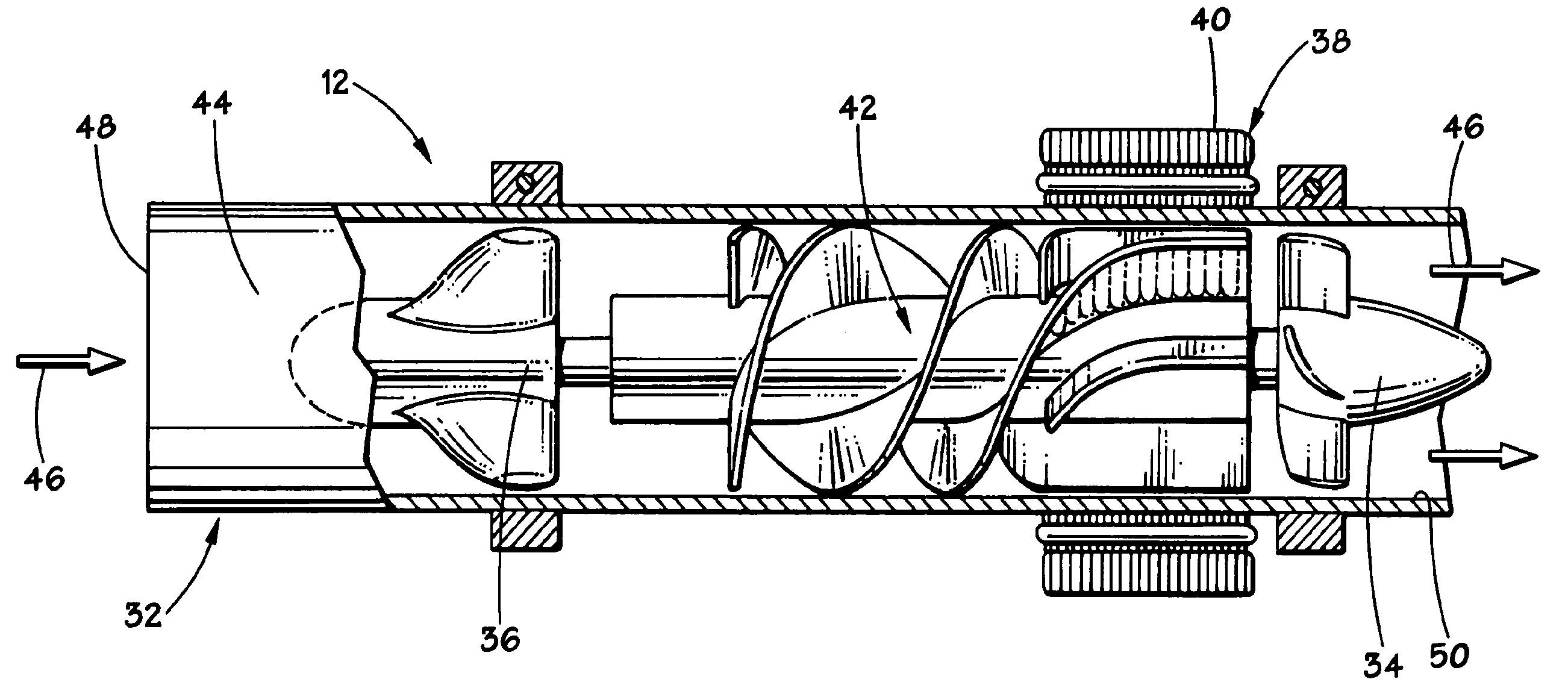
A filter monitoring system employs a differential pressure sensor to provide a continuous signal output proportional to a pressure drop across a filter element. The differential pressure sensor communicates with a controller that provides output signals to indicate that the filter requires replacement and provides advanced warning for when the filter element will reach a predicted filter differential pressure limit value.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Blood pump system and method of operation
A blood pump system includes a blood pump having a motor with a rotor and a stator. The stator has a plurality of stator windings situated therein. A motor controller is coupled to the motor, and a processor has inputs coupled to the motor controller for receiving a time continuous signal from the pump. The processor is programmed to transform the time continuous signal to the frequency domain, and control the pump and detect excess suction in response to the time continuous signal in the frequency domain.
Owner:RELIANTHEART
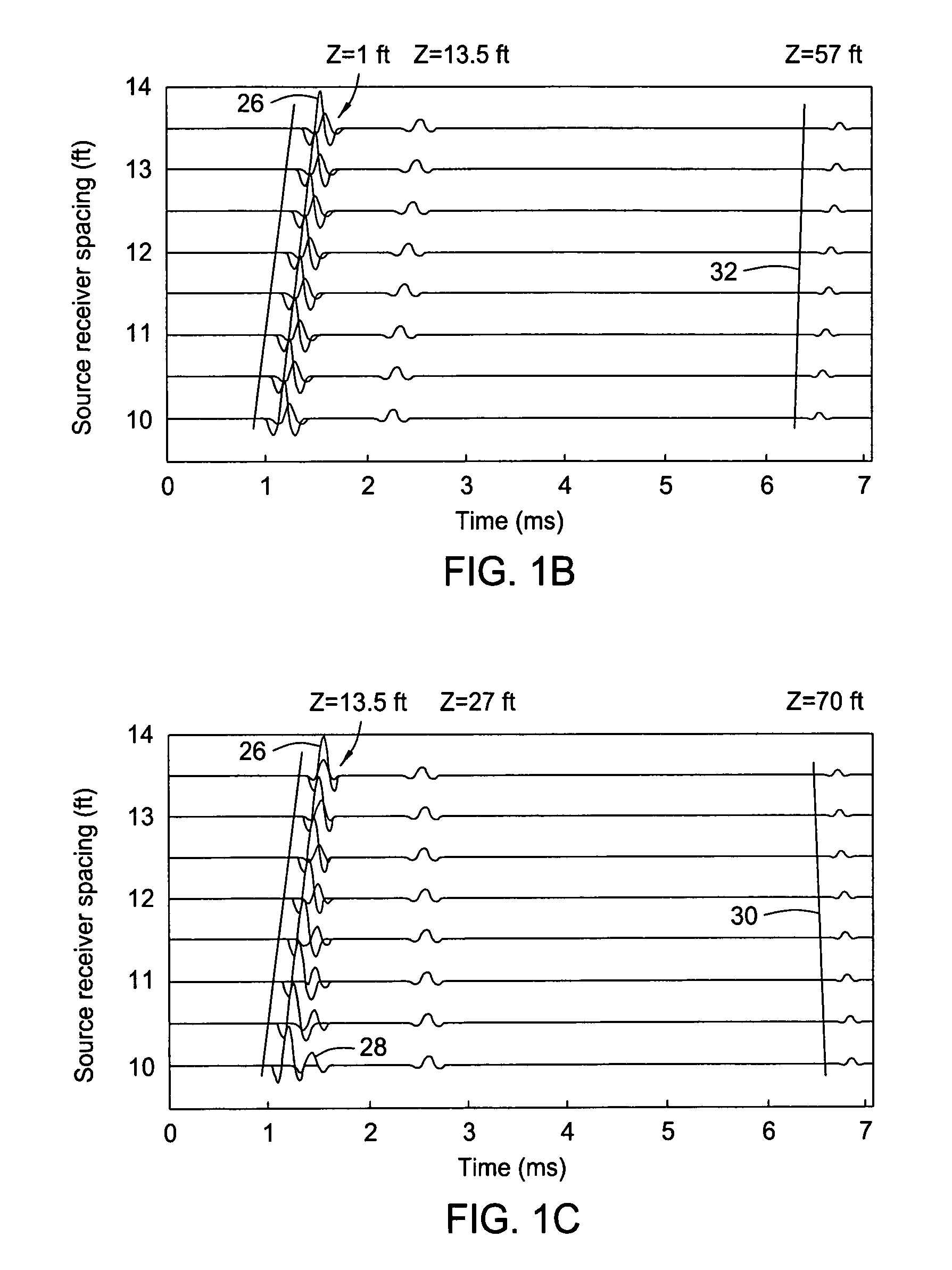
Method for processing acoustic reflections in array data to image near-borehole geological structure
ActiveUS20070097788A1Enhances moveout differenceDistanceSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingReflected wavesContinuous signal
A method and apparatus for enhancing the moveout between a direct wave and a reflected wave. The method involves transmitting imaging signals into a body to be imaged and receiving the resulting signals propagated from the signal source. The step of receiving the propagated signals includes selectively adjusting the distance between the signal source and the signal receivers between successive signals. The method further comprises separating the reflected signals from the total received signals and enhanced stacking of the measured reflected signals.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
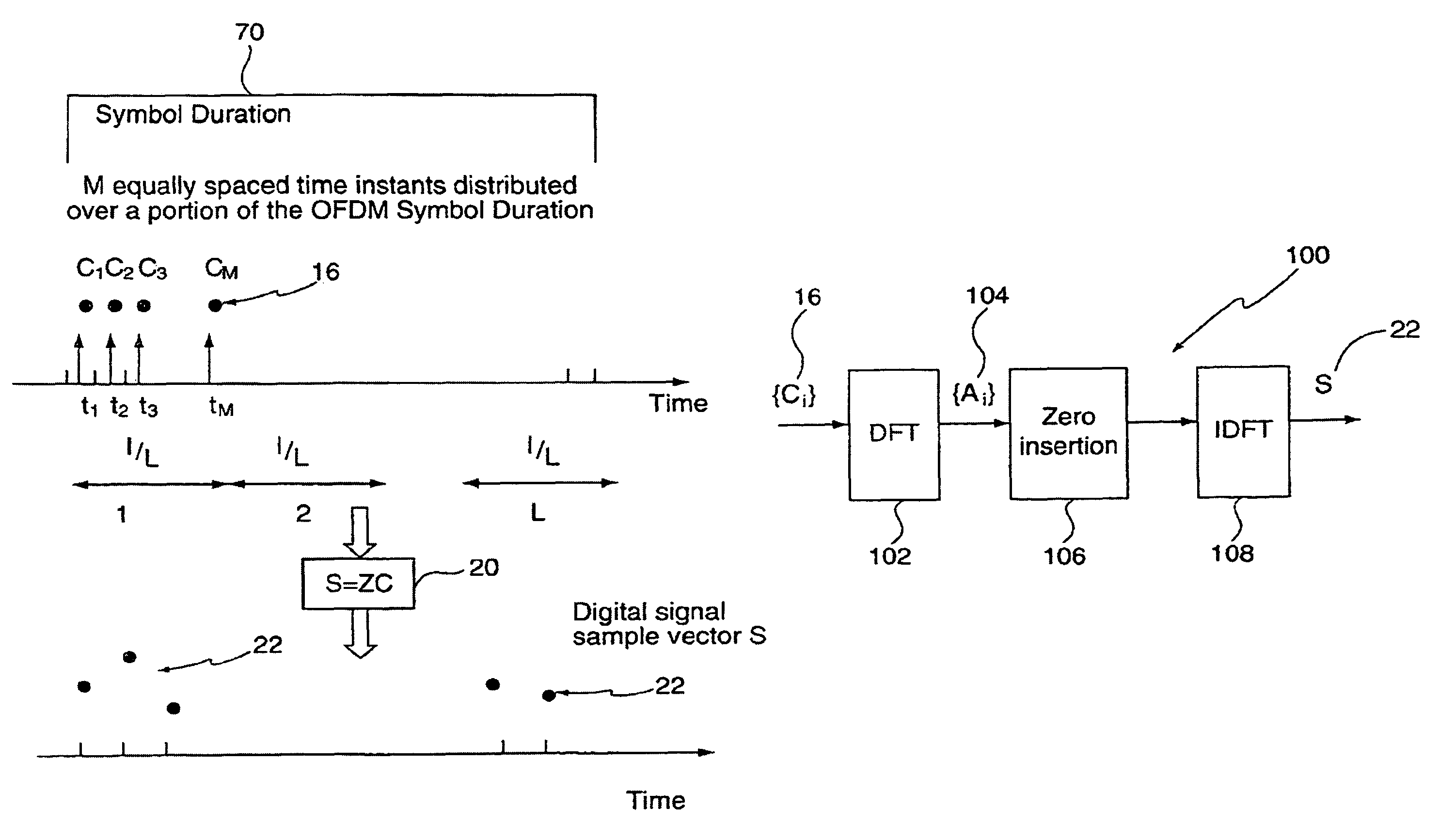
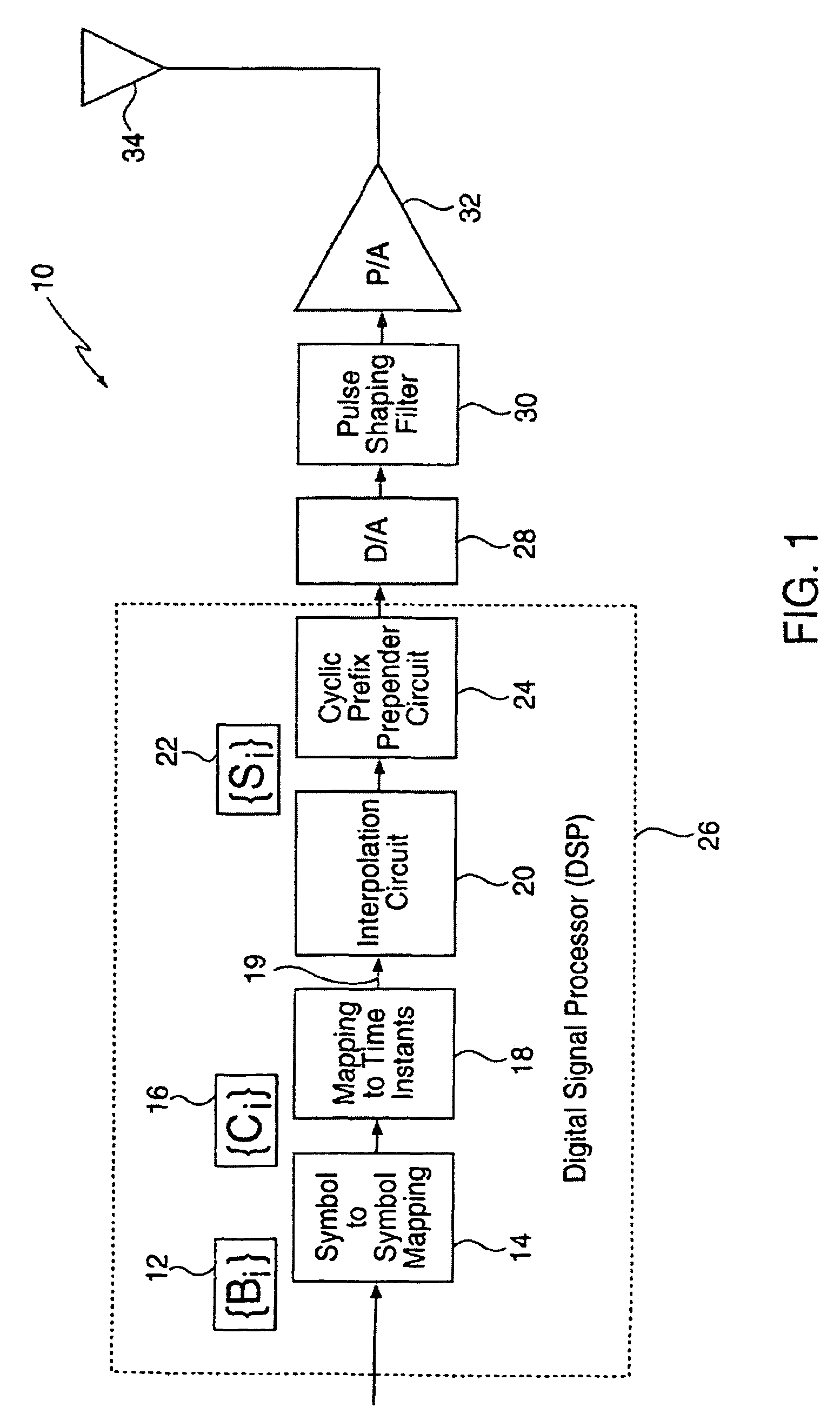
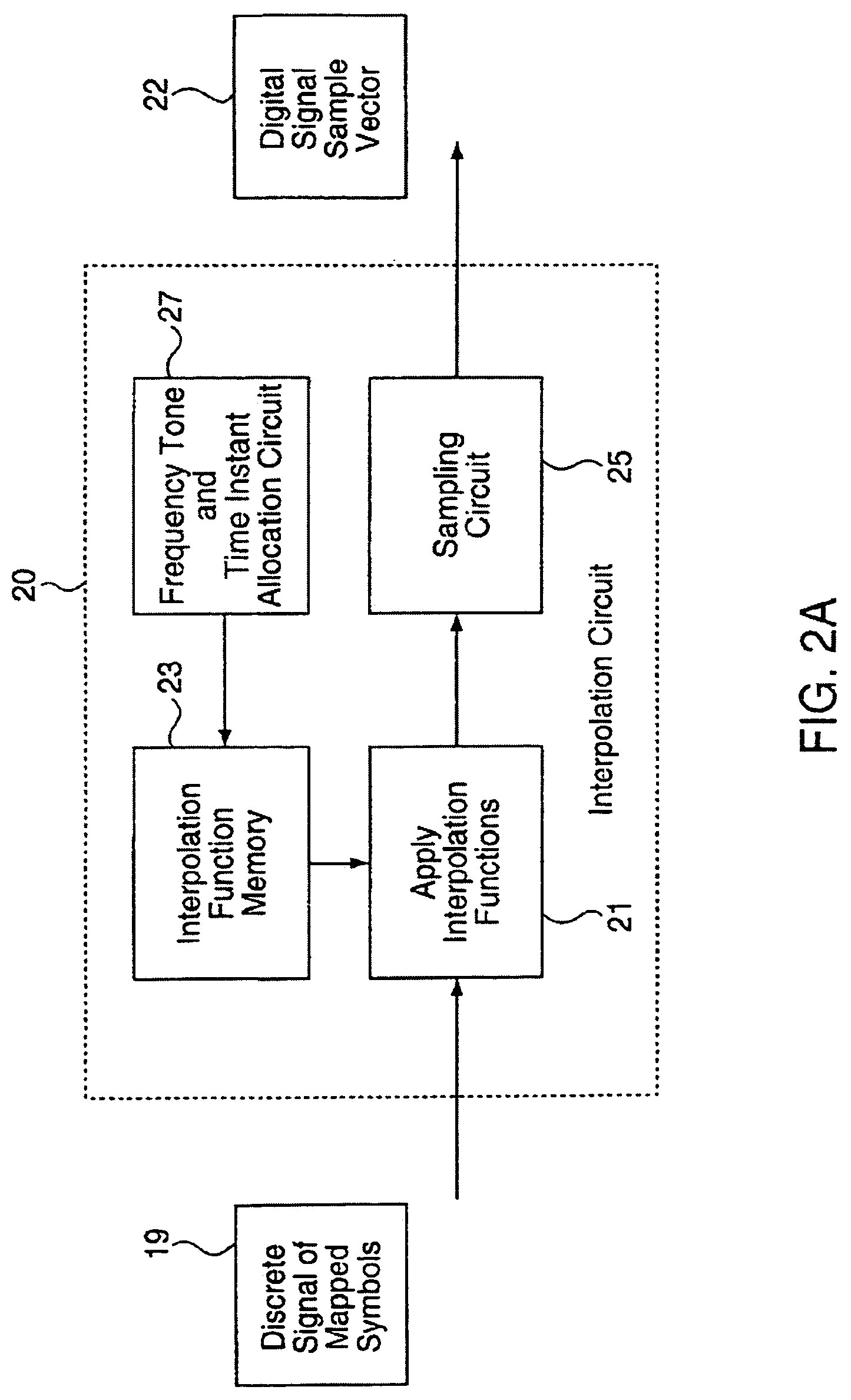
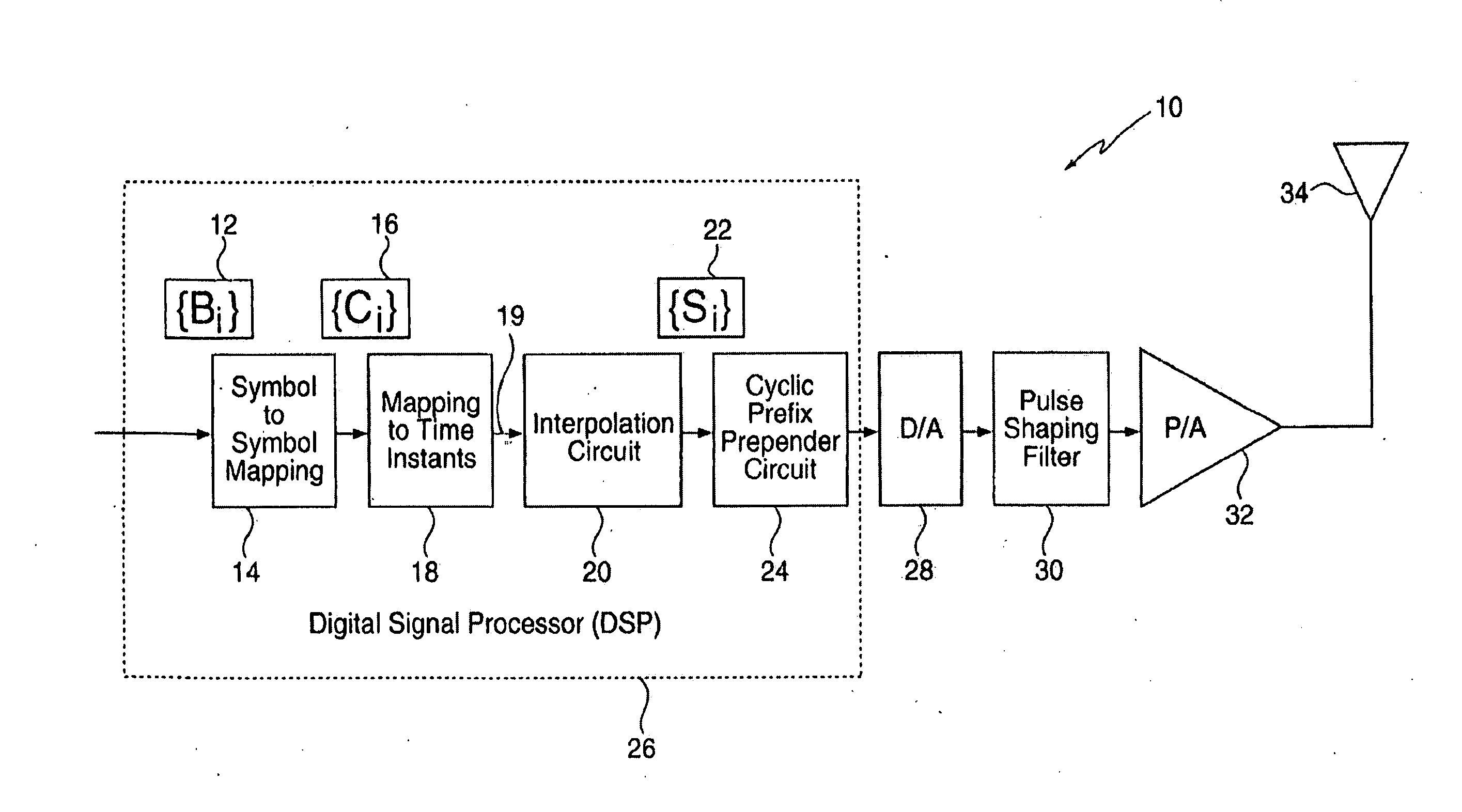
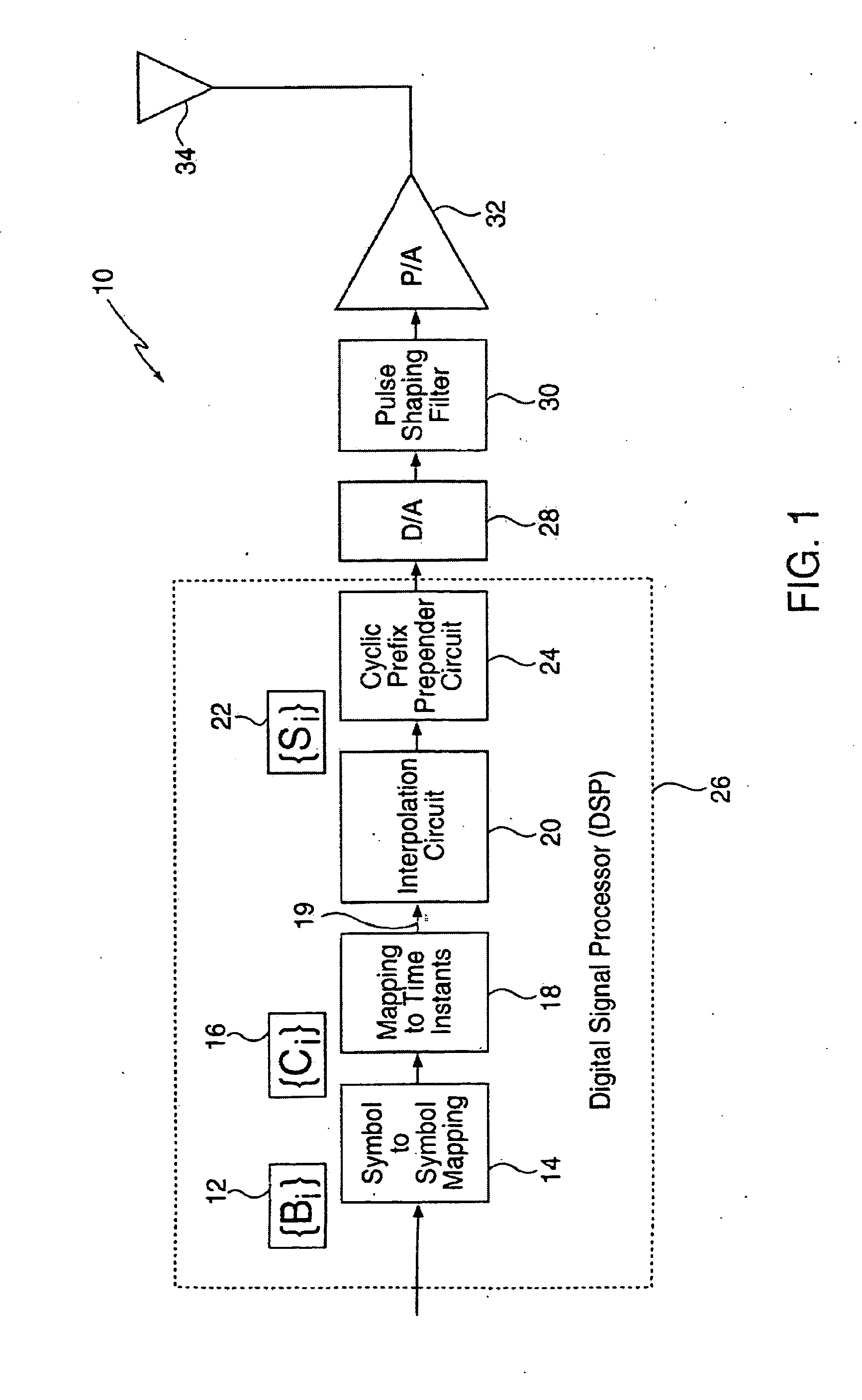
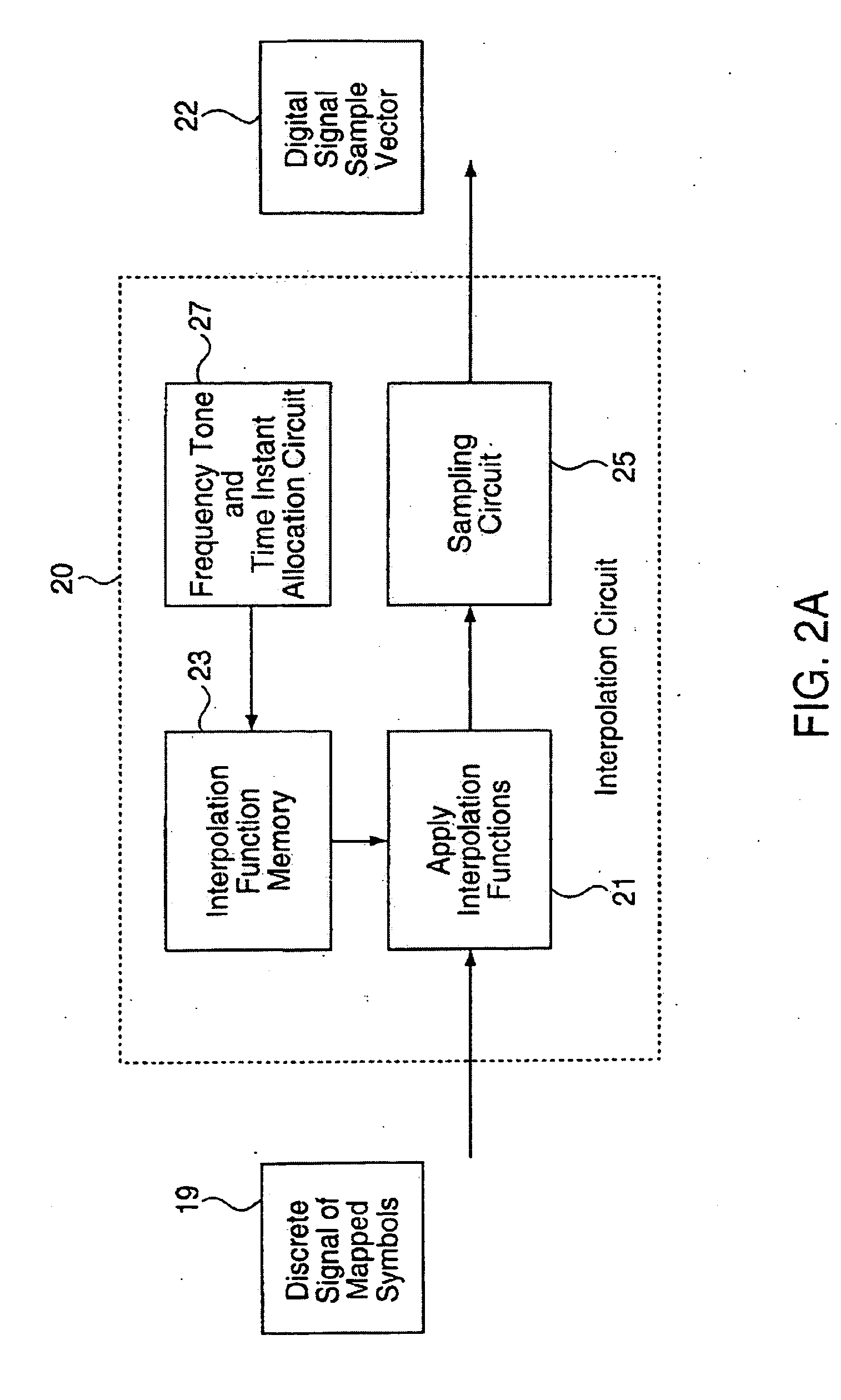
Signaling method in an OFDM multiple access system
InactiveUS8223627B2Good peak-to-average ratio propertyMinimized peak-to-average ratioTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionTime domainContinuous signal
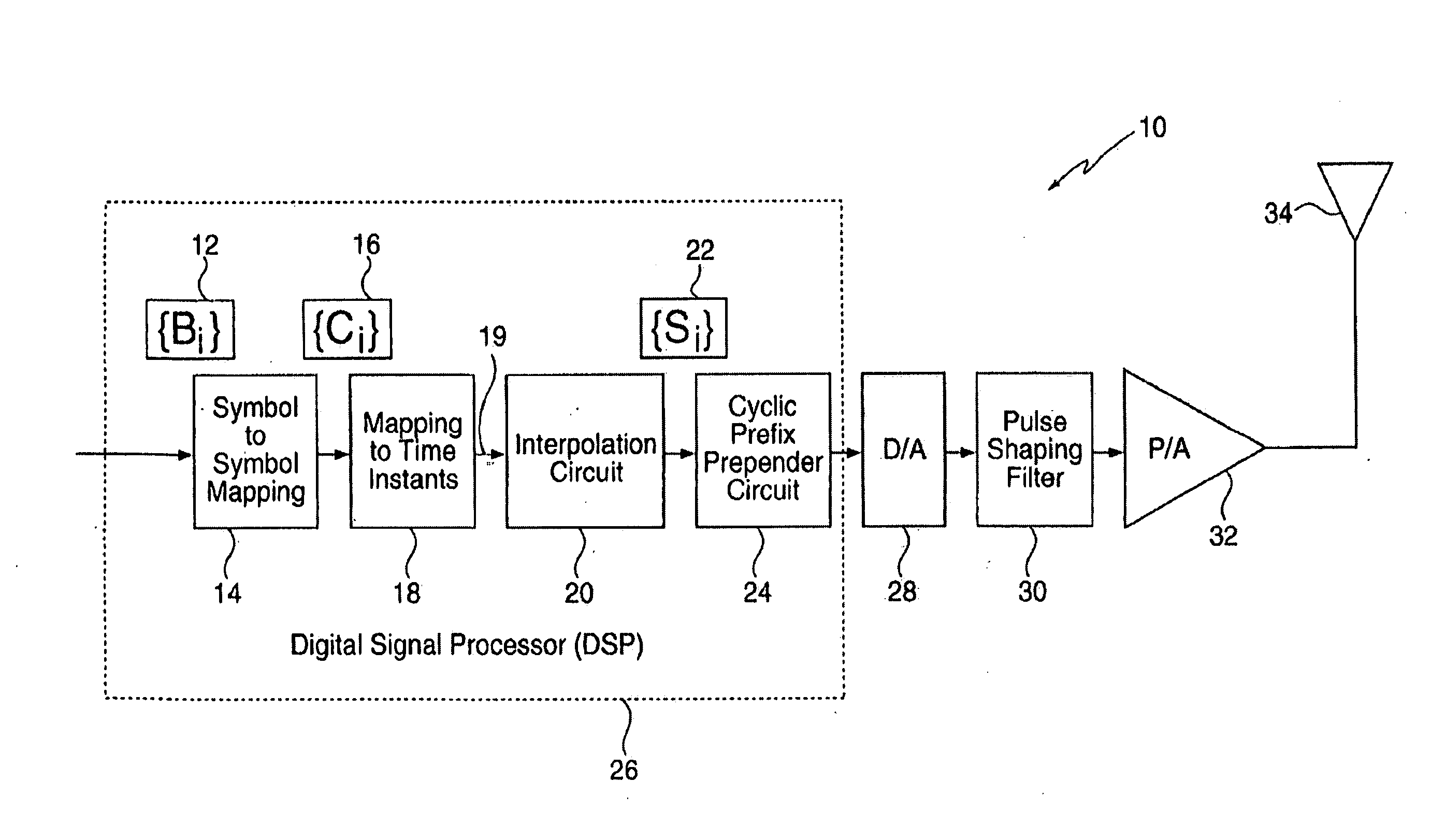
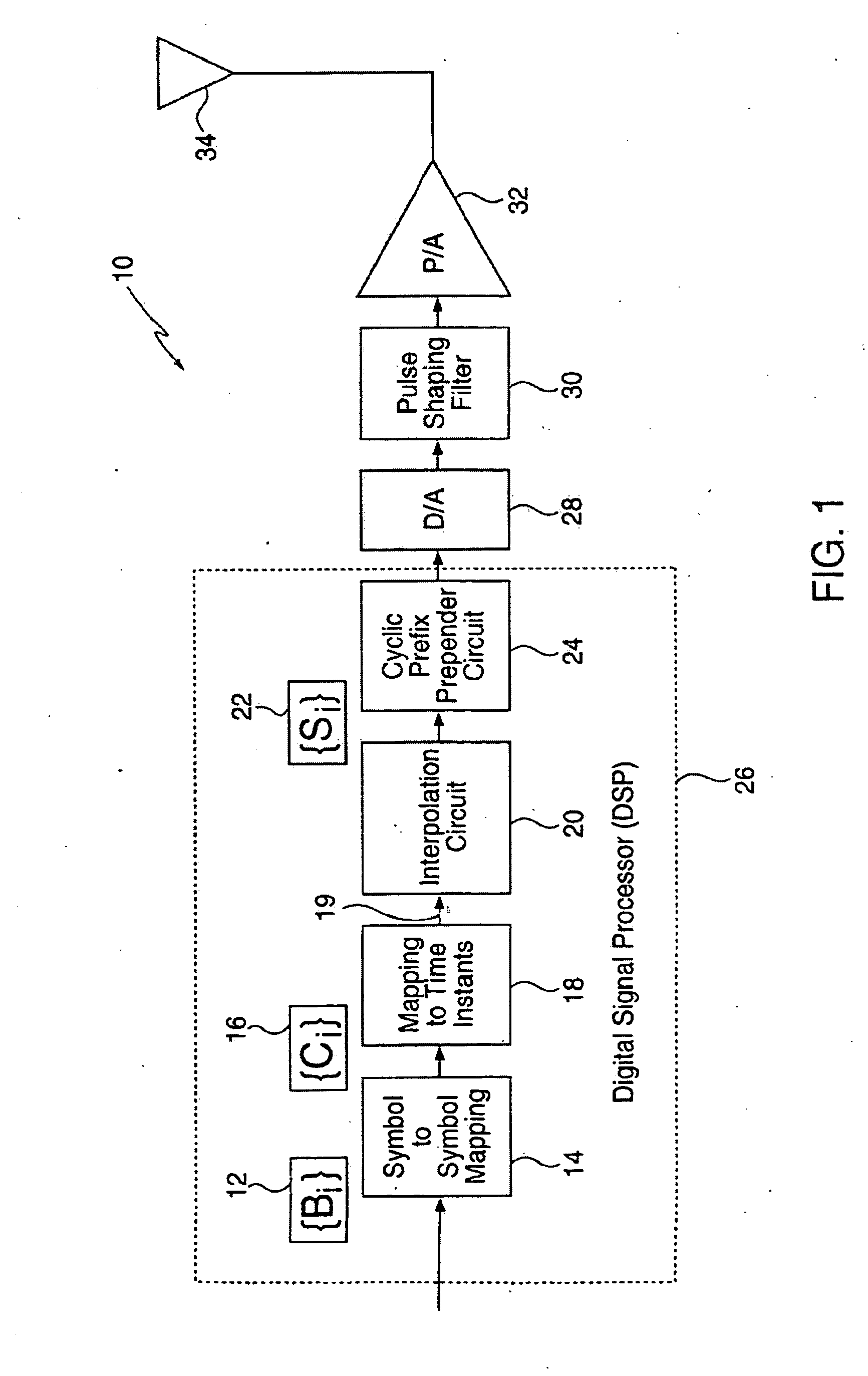
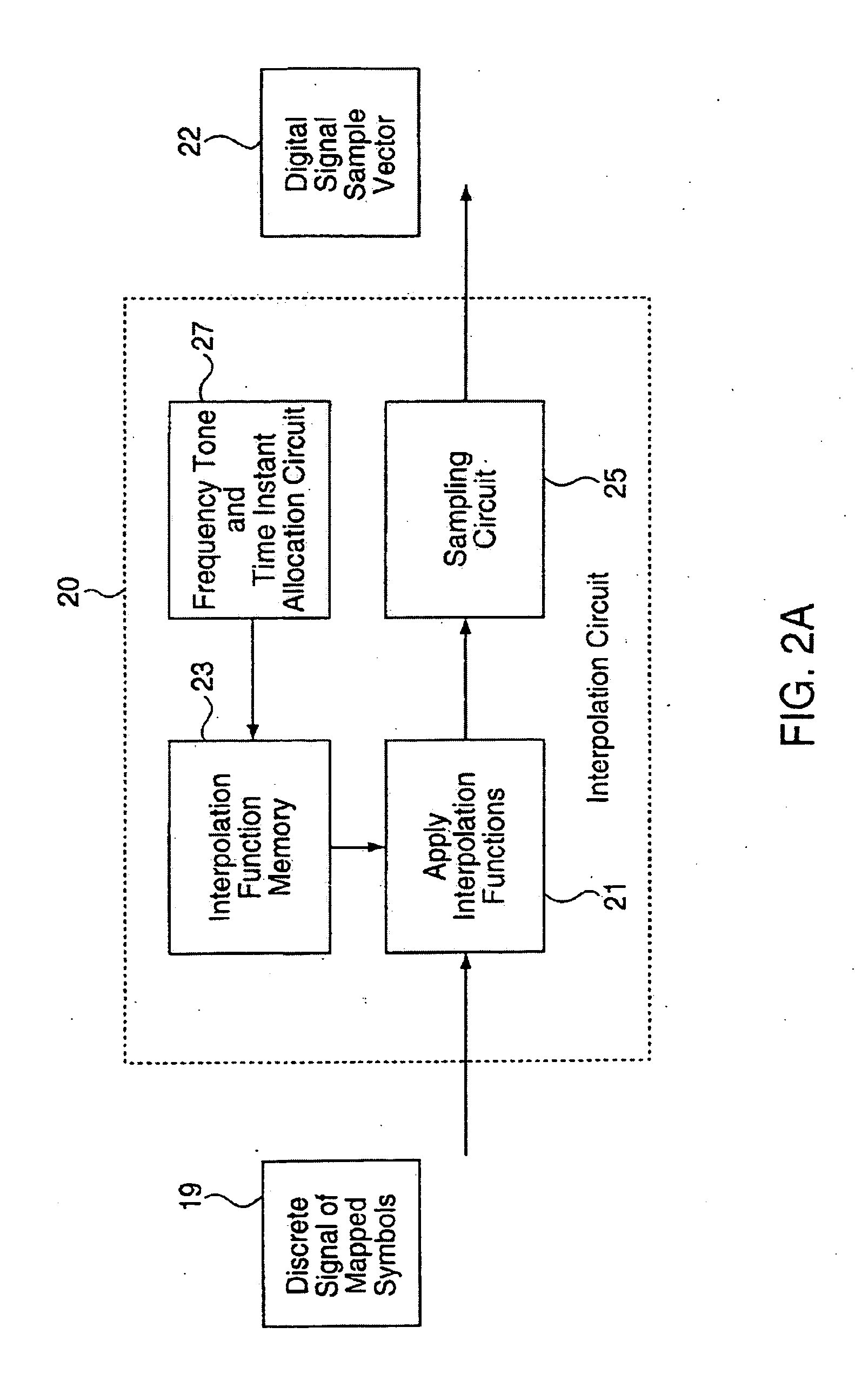
A method for reducing the peak-to-average ratio in an OFDM communication signal is provided. The method includes defining a constellation having a plurality of symbols, defining a symbol duration for the OFDM communication signal, and defining a plurality of time instants in the symbol duration. A plurality of tones are allocated to a particular communication device, and a discrete signal is constructed in the time domain by mapping symbols from the constellation to the time instants. A continuous signal is generated by applying an interpolation function to the discrete signal such that the continuous signal only includes sinusoids having frequencies which are equal to the allocated tones.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Signaling method in an OFDM multiple access system
InactiveUS20110235746A1Good peak-to-average ratio propertyMinimized peak-to-average ratioTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionTime domainContinuous signal
A method for reducing the peak-to-average ratio in an OFDM communication signal is provided. The method includes defining a constellation having a plurality of symbols, defining a symbol duration for the OFDM communication signal, and defining a plurality of time instants in the symbol duration. A plurality of tones are allocated to a particular communication device, and a discrete signal is constructed in the time domain by mapping symbols from the constellation to the time instants. A continuous signal is generated by applying an interpolation function to the discrete signal such that the continuous signal only includes sinusoids having frequencies which are equal to the allocated tones.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
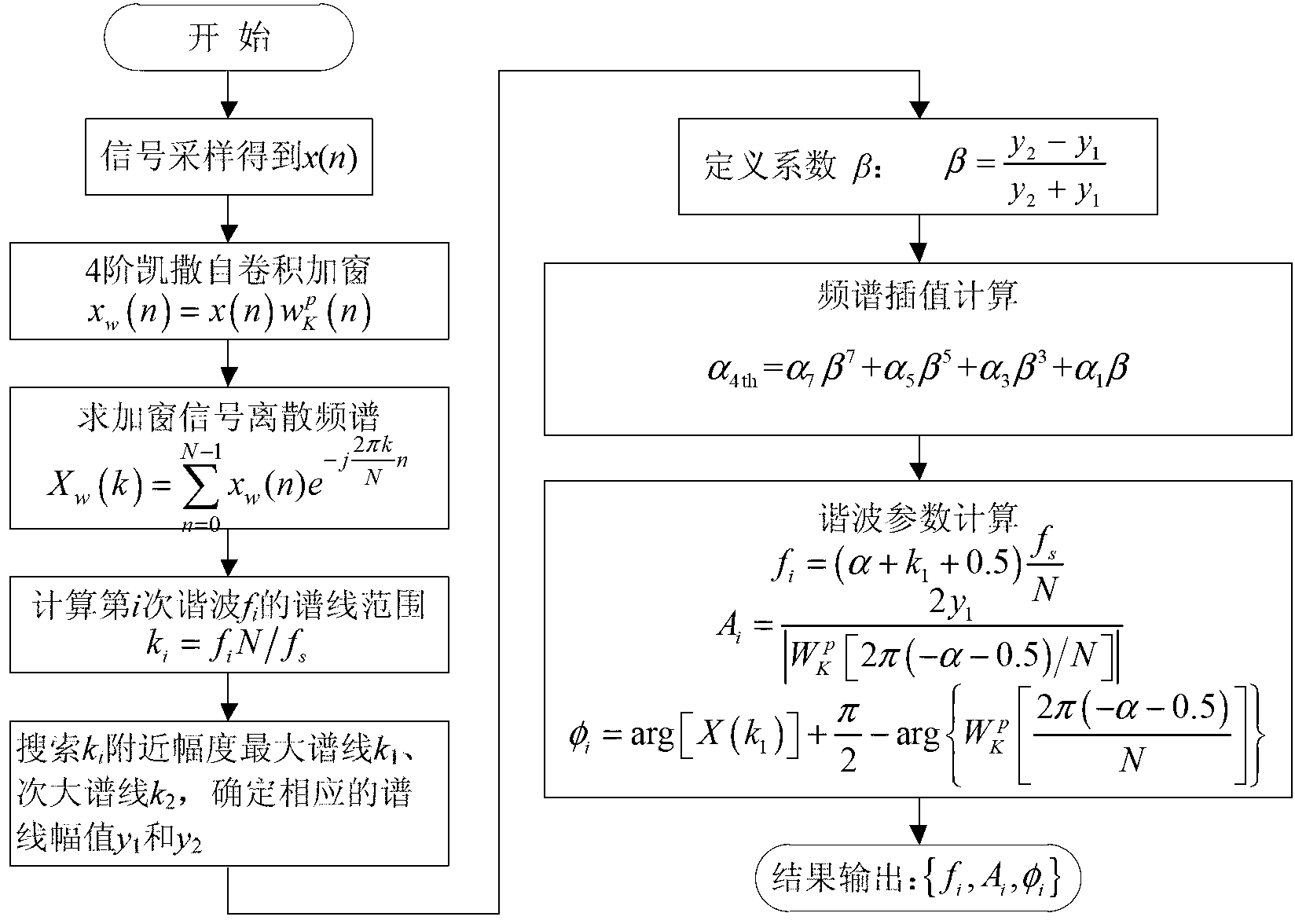
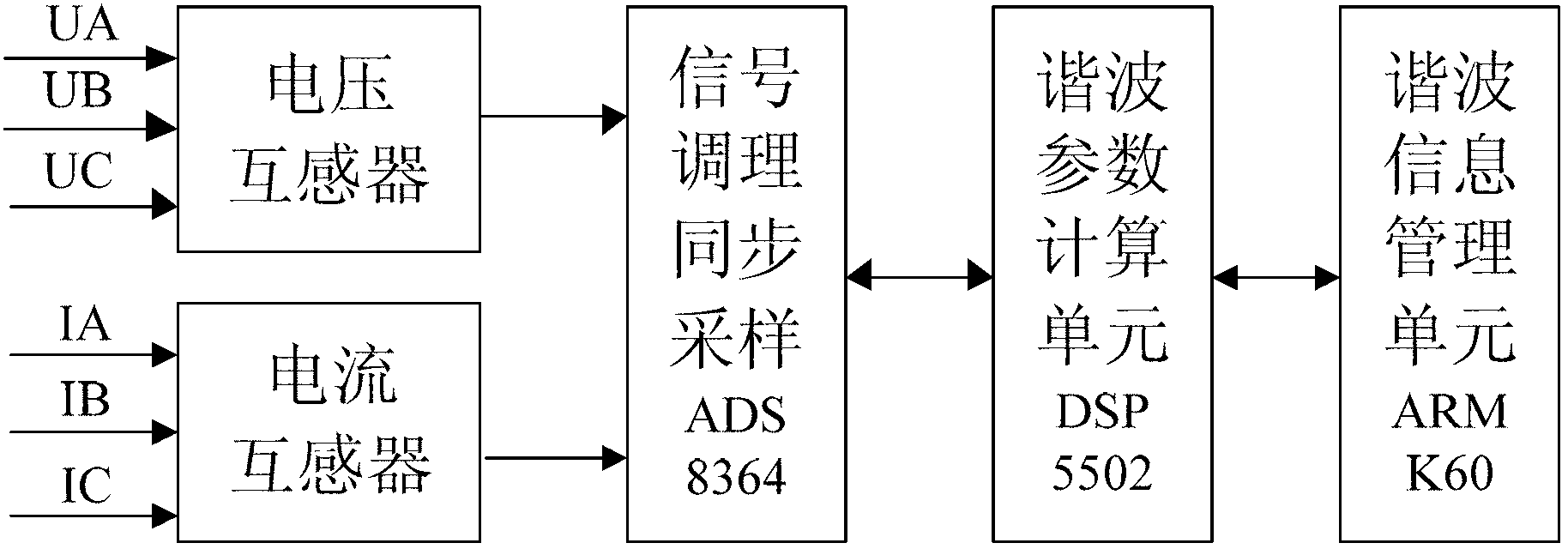
Harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and device thereof
InactiveCN103308766AQuick checkAccurate detectionFrequency analysisFrequency spectrumFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps of sampling a signal: sampling a time-domain continuous signal, and discretizing to obtain an infinitely long discrete sequence; windowing a four-order Kaiser self-convolution window function: performing four-order Kaiser self-convolution window operation on the infinitely long discrete sequence; performing N-point FFT on a windowed and truncated signal to obtain the discrete spectrum of the signal; determining the peak parameter of the discrete spectrum: searching the local spectrum peak of each integer harmonic frequency around the integer harmonic frequency; and calculating a harmonic parameter: solving a coefficient alpha by adopting a discrete spectrum interpolation correction formula based on an LSM (Least Square Method), and calculating parameters such as a harmonic frequency, an amplitude, an initial phase angle and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the fundamental and harmonic components of a tested signal can be detected rapidly and accurately, and accurate frequency measurement is realized; and the method is convenient for implementing an embedded system, and the tested signal can be detected continuously for a long time.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Filter monitoring system
ActiveUS20060259273A1Minimizing expenseImprove resource efficiencyDispersed particle filtrationDigital computer detailsDifferential pressureMonitoring system
A filter monitoring system employs a differential pressure sensor to provide a continuous signal output proportional to a pressure drop across a filter element. The differential pressure sensor communicates with a controller that provides output signals to indicate that the filter requires replacement and provides advanced warning for when the filter element will reach a predicted filter differential pressure limit value.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
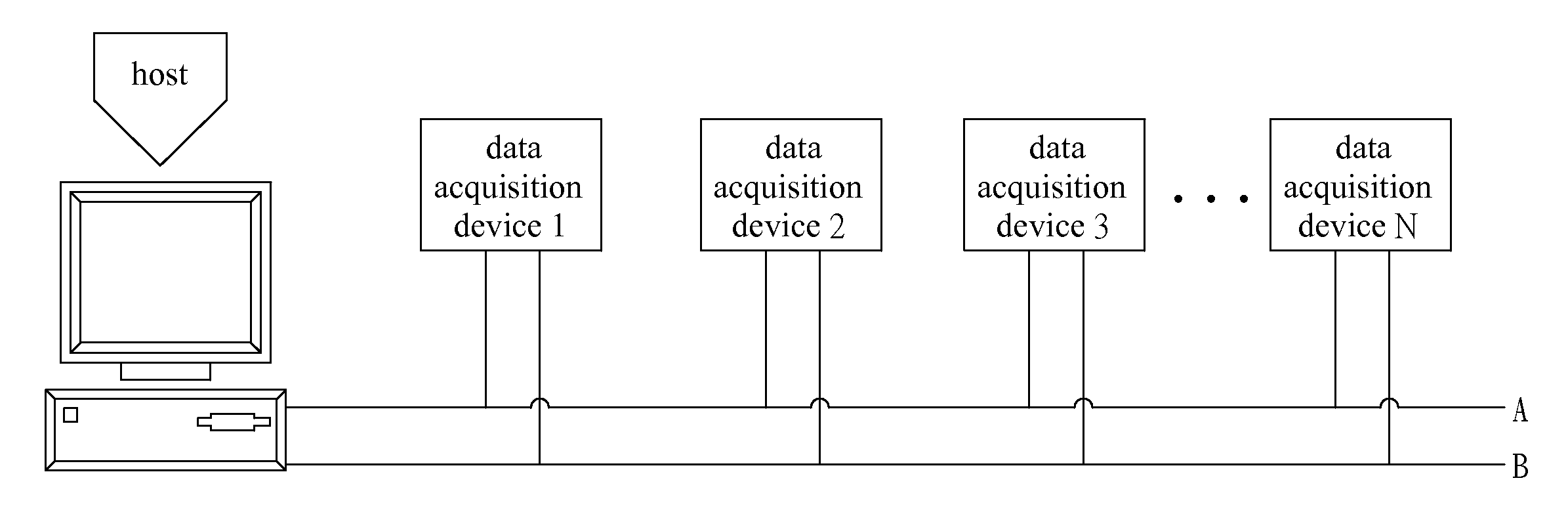
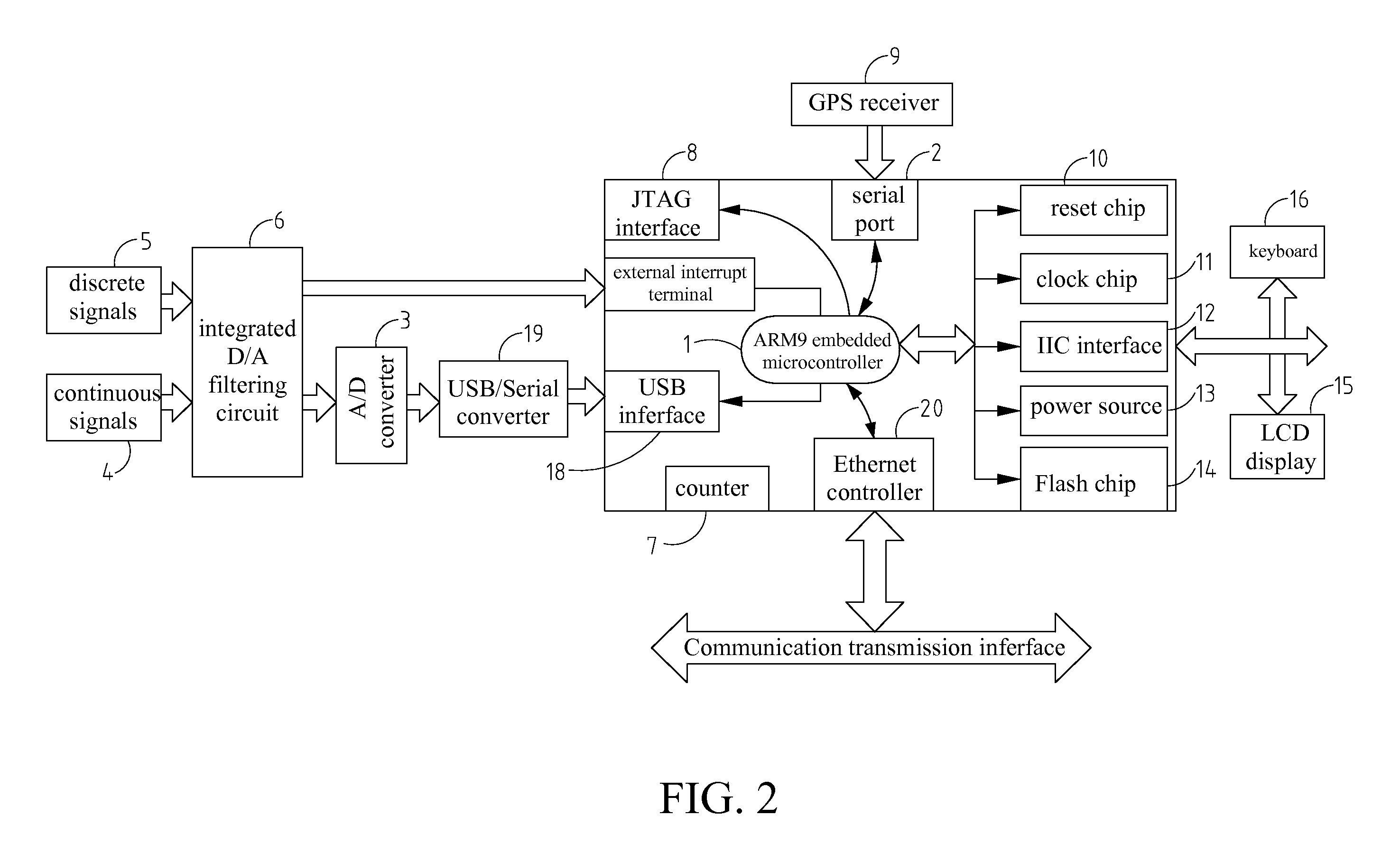
Distributed Networked Data Acquisition Device
InactiveUS20070174451A1Guaranteed synchronizationHigh precision machiningTariff metering apparatusDigital computer detailsGNU/LinuxData acquisition
A distributed networked data acquisition system having distributed networked data acquisition devices based on embedded Linux development platform having an ARM9 CPU is proposed. The system is defined as one or more distributed networked data acquisition devices together with a host. The host could dynamically display data and also coordinate and control the many distributed networked data acquisition devices. Each distributed networked data acquisition device is connected with the host by means of transmission media. The distributed networked data acquisition devices adopts the distributed data acquisition network to implement multi-point data acquisition having many distributed networked data acquisition devices working together and using several UTPs to connect with the distributed networked data acquisition devices in various distribution points. Each distributed networked data acquisition device can connect with different types of sensors, and each sensor can collect different types of continuous signals.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Signaling method in an OFDM multiple access system
InactiveUS20110235747A1Good peak-to-average ratio propertyMinimized peak-to-average ratioTransmission path divisionRadio transmissionTime domainContinuous signal
A method for reducing the peak-to-average ratio in an OFDM communication signal is provided. The method includes defining a constellation having a plurality of symbols, defining a symbol duration for the OFDM communication signal, and defining a plurality of time instants in the symbol duration. A plurality of tones are allocated to a particular communication device, and a discrete signal is constructed in the time domain by mapping symbols from the constellation to the time instants. A continuous signal is generated by applying an interpolation function to the discrete signal such that the continuous signal only includes sinusoids having frequencies which are equal to the allocated tones.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Free running RF identification system with increasing average inter transmission intervals
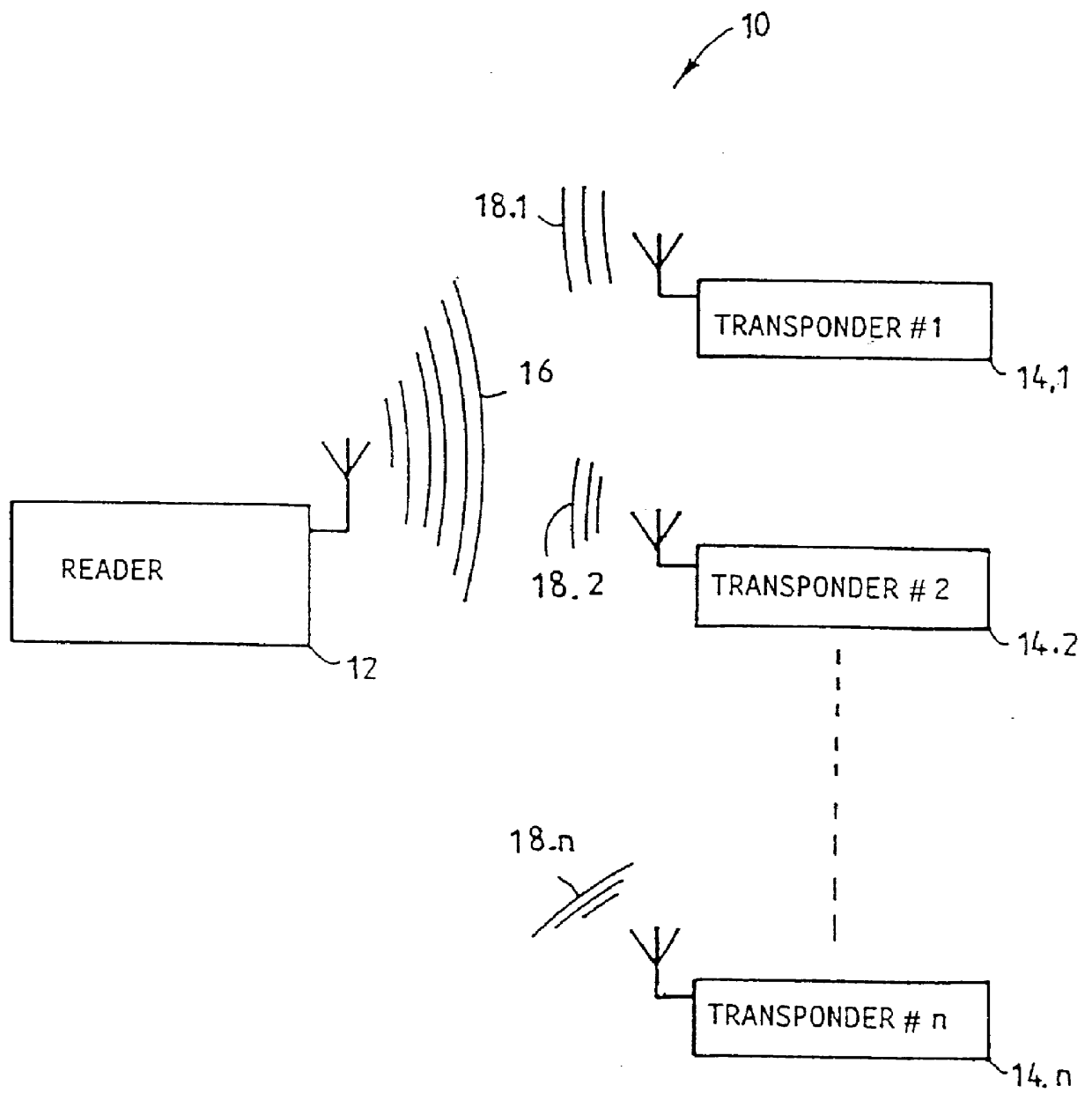
InactiveUS6154136ARaise countMemory record carrier reading problemsSubscribers indirect connectionElectronic identificationContinuous signal
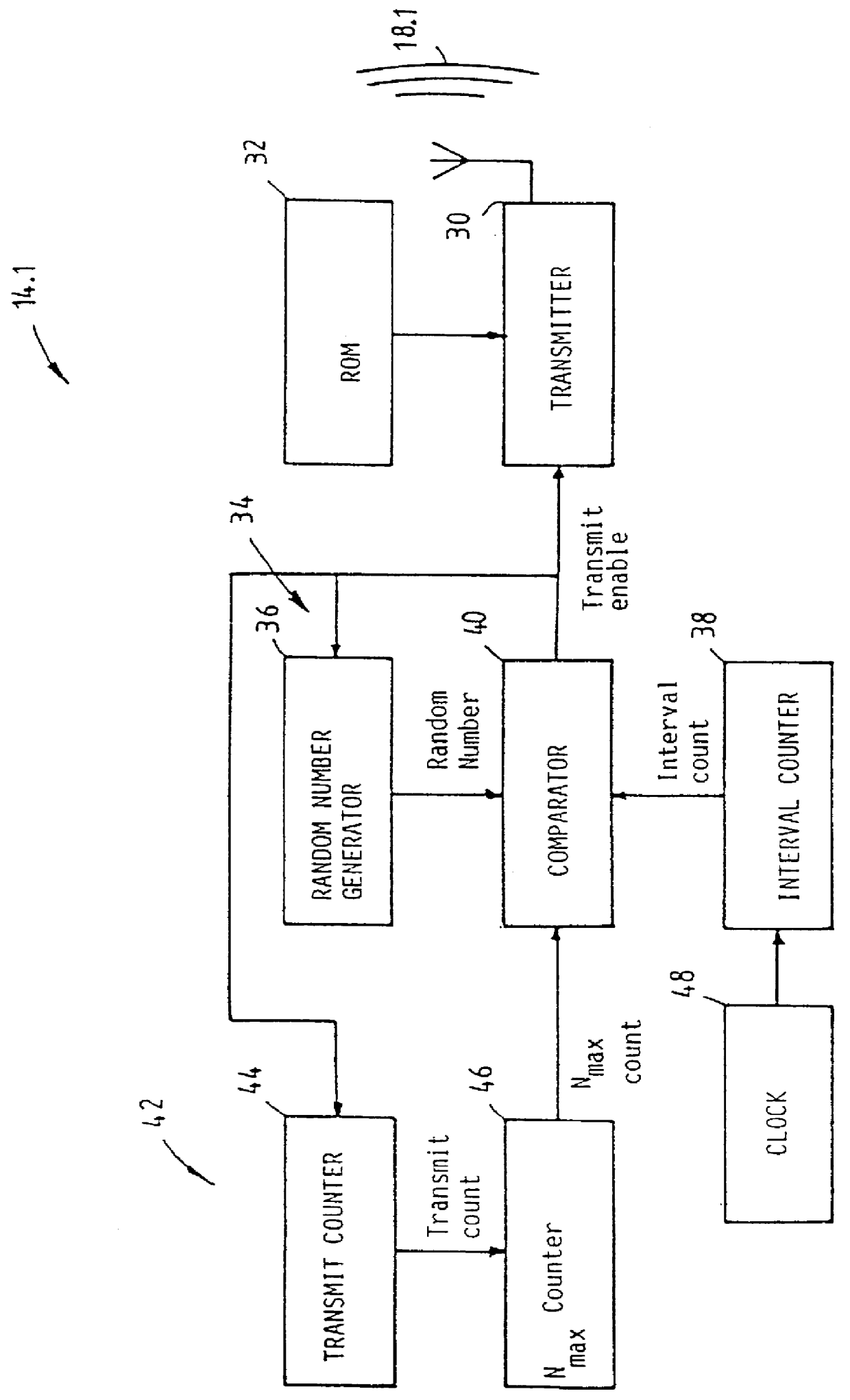
An RF electronic identification system 10 is disclosed and claimed. The system includes a reader 12 and a plurality of transponders 14.1 to 14.n. When energized by an interrogation signal from the reader, each transponder automatically responds by repeatedly retransmitting a signal burst including identification code data associated with the relevant transponder. Each transponder includes circuitry 34 for generating random inter-transmission intervals for separating any two consecutive signal bursts and a controller 42 for the generation circuitry, to cause an average value of the inter-transmission intervals over a period of time to vary, preferably to increase. This feature enhances the probability and speed of reading a transponder population of almost any size.
Owner:ACTIVE NETWORK LLC
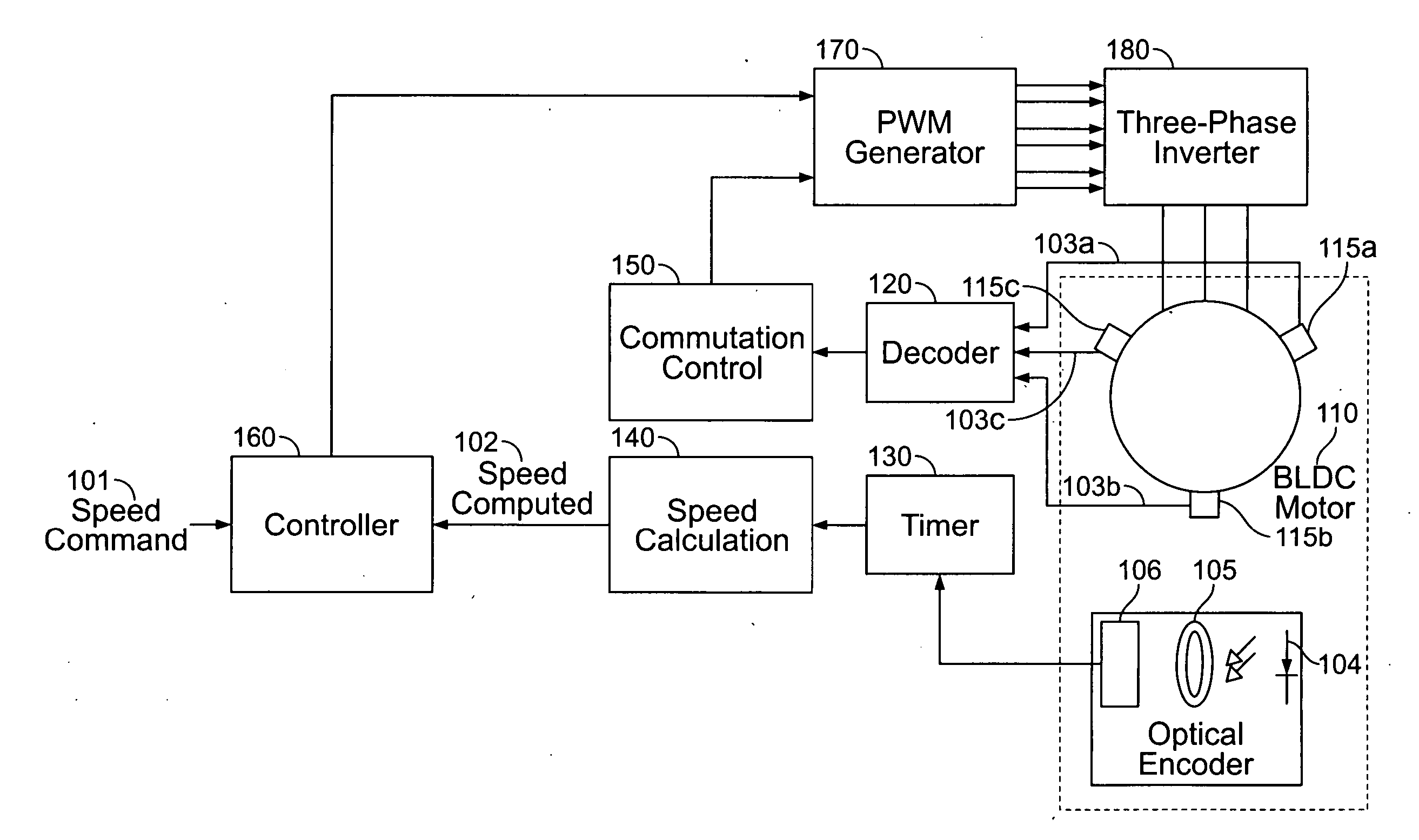
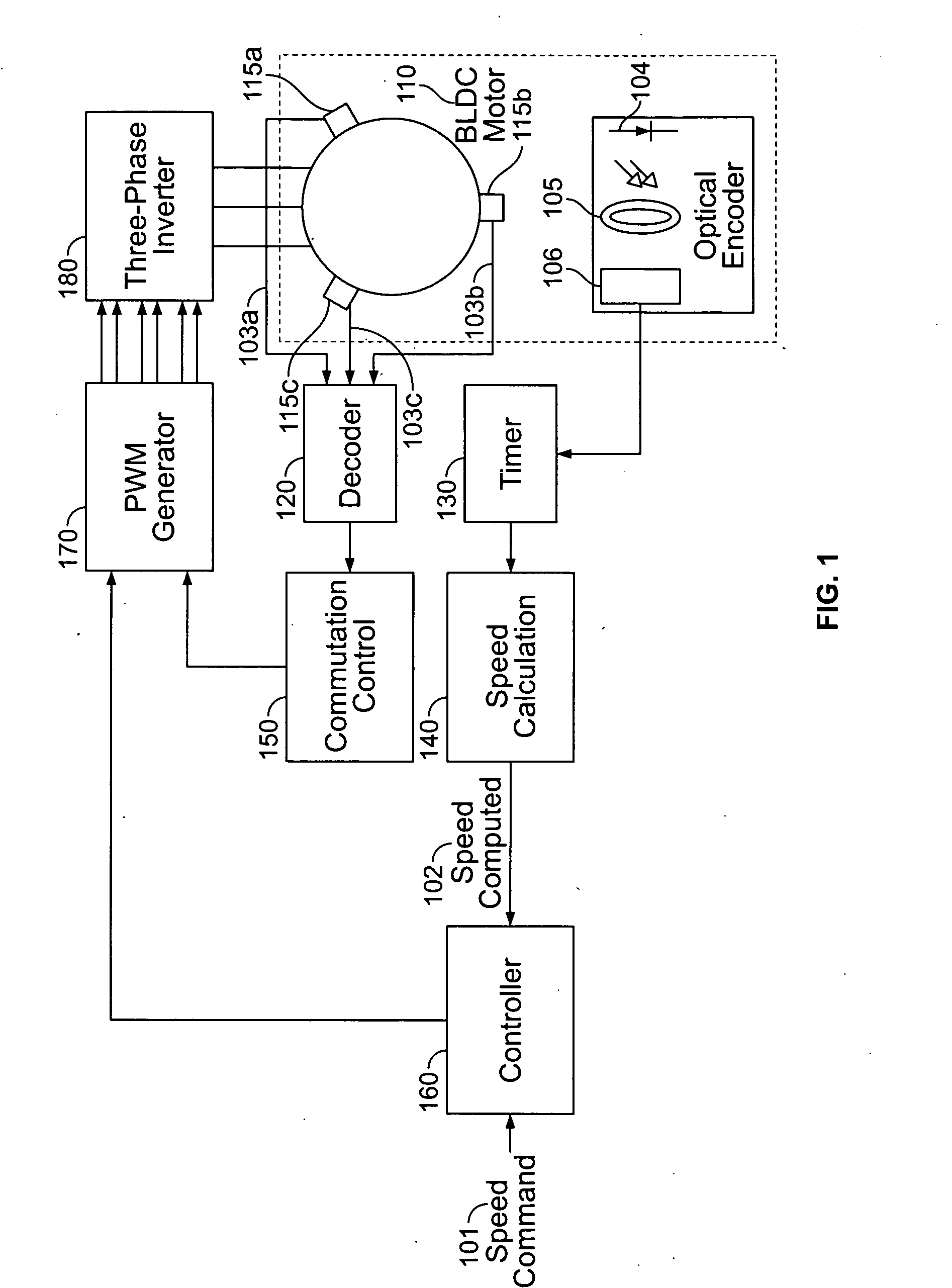
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
InactiveUS20080092893A1RespiratorsDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:CAREFUSION 207 INC
Process for enhancing the existing ambience, imaging, depth, clarity and spaciousness of sound recordings
A process for enhancing ambience in an audio signal output that is derived from an audio signal input in a dual channel audio ambience extraction circuit. The process includes cross-coupling of audio signals in one channel with audio signals in another channel. Each of the cross-coupled signals is attenuated and delayed by an adjustable time period that is within a haas delay time and is then applied in the feedback path to a summing input of an opposite channel. At the summing input, the signals are mixed with subsequent audio signal inputs to that channel. All of the attenuated and delayed signals are continuously applied to outputs of the extraction circuit during the cross-coupling process. The output signals comprise the original signals plus delayed and attenuated reproductions of the original signal along with continuing signals that are submitted to the extraction circuit subsequent to the initial signals.
Owner:KATZ ROBERT A
Cross-correlation timing calibration for wafer-level IC tester interconnect systems
InactiveUS20020049554A1Easy accessDigital circuit testingTesting/calibration apparatusContact padTester device
A timing calibration system for a wafer level integrated circuit (IC) tester is disclosed. The tester includes a set of probes for contacting pads on a surface of an IC and having a plurality of tester channels. Each channel generates a TEST signal at a tip of a corresponding probe in response to a periodic CLOCK signal with a delay adjusted by drive calibration data supplied as input to the tester channel. The TEST signal produced by each channel includes edges occurring in a timing pattern controlled by programming data provided as input to each tester channel. To calibrate test signal timing of all channels, each channel is programmed to generate a test signal having the same repetitive edge timing pattern at the tester channel's corresponding probe tip. The test signal produced at each probe tip is then cross-correlated to a periodic reference signal having the same repetitive edge timing pattern. The drive calibration data of each channel is then iteratively adjusted to determine a value which maximizes the cross-correlation between its output test signal and the reference signal. To maximize the accuracy of the timing calibration, each repetition of the test and reference signal edge pattern provides pseudo-randomly distributed time intervals between successive signal edges.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Data communication via a voice channel of a wireless communication network using discontinuities
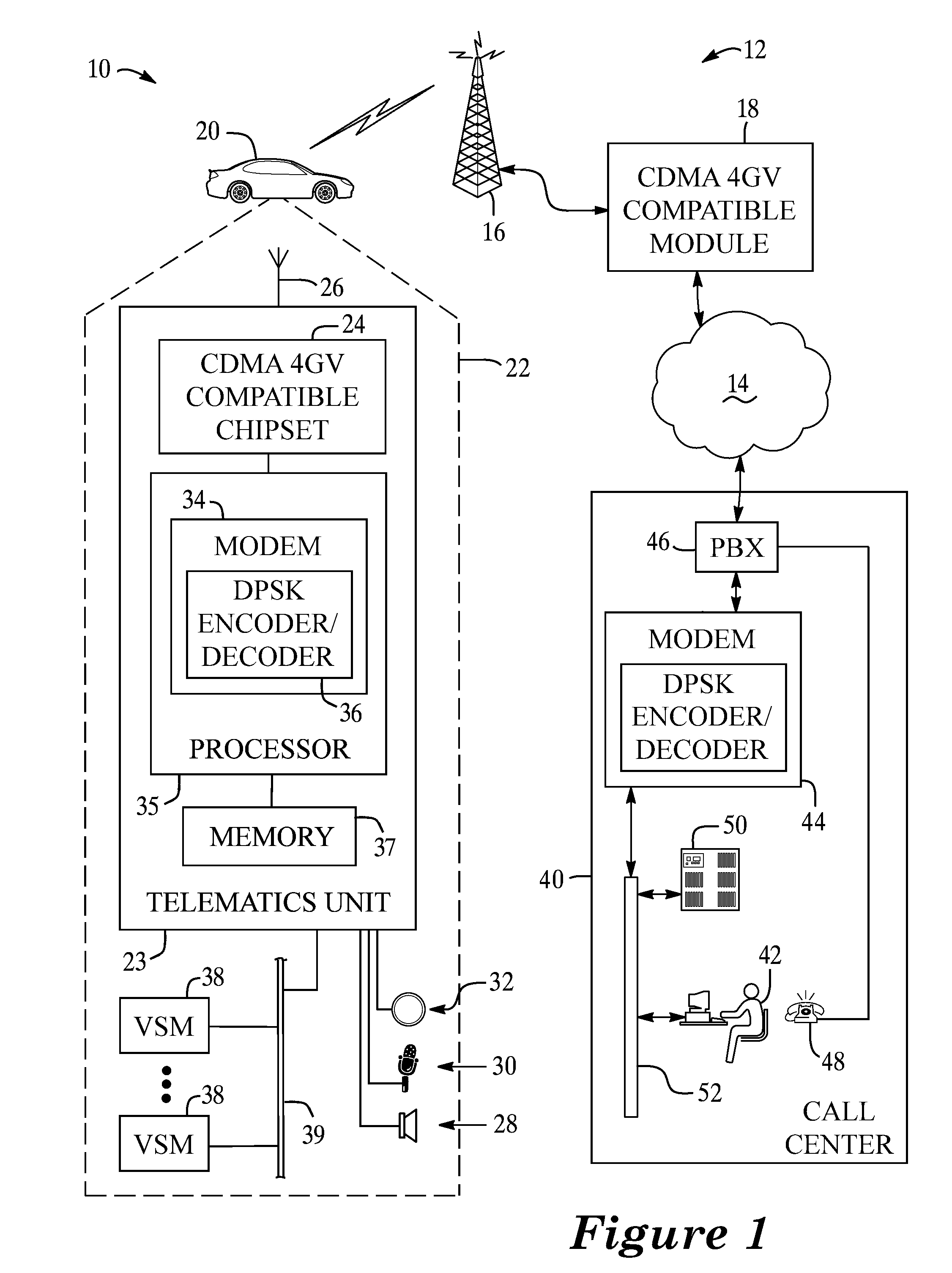
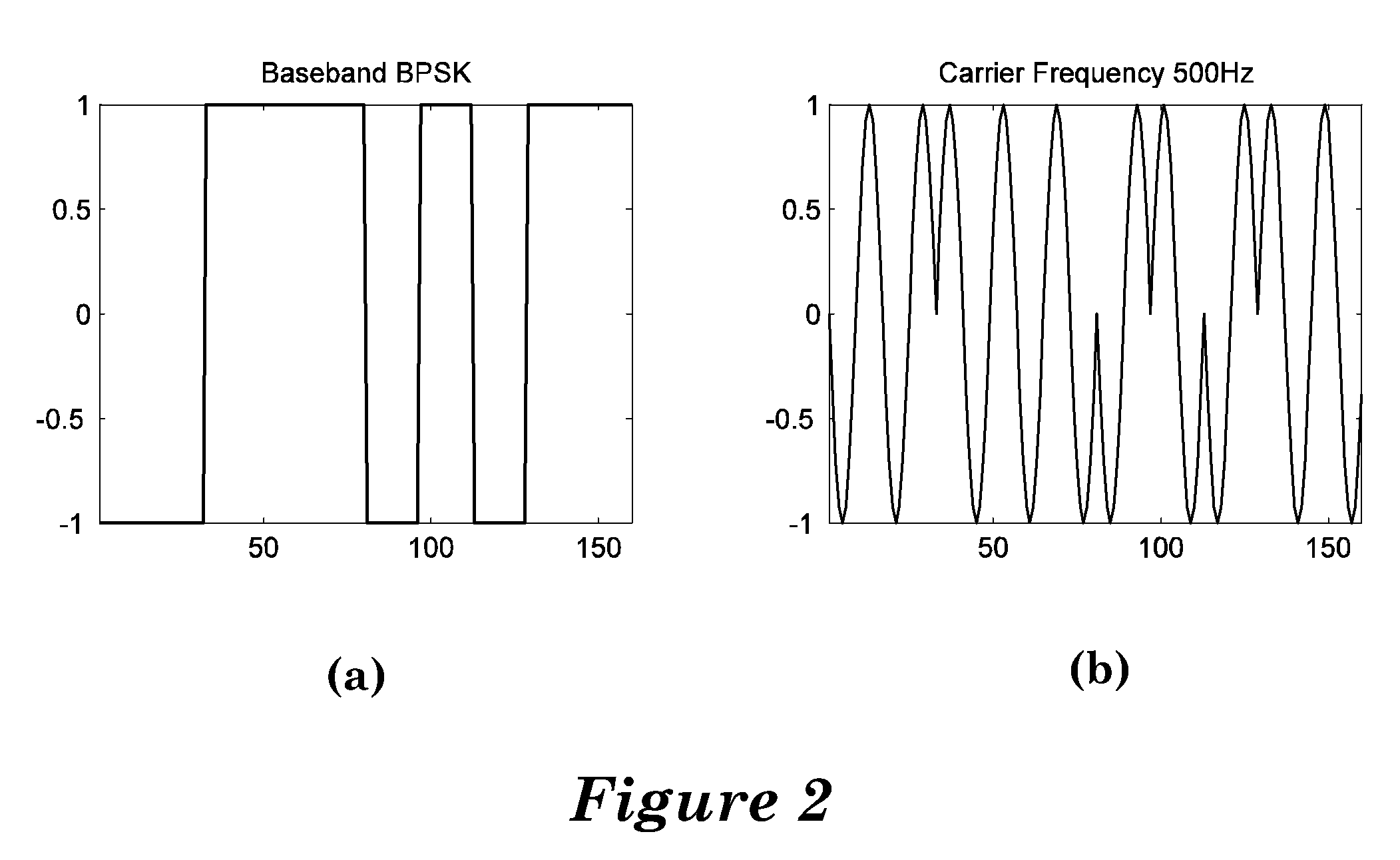
A system and method for data communication over a cellular communications network that allows the transmission of digital data over a voice channel using a vocoder that operates in different modes depending upon characteristics of the inputted signal it receives. To prepare the digital data for transmission, one or more carrier signals are encoded with the digital data using one of a number of modulation schemes that utilize differential phase shift keying to give the modulated carrier signal certain periodicity and energy characteristics that allow it to be transmitted by the vocoder at full rate. The modulation schemes include DPSK using either a single or multiple frequency carriers, combined FSK-DPSK modulation, combined ASK-DPSK, PSK with a phase tracker in the demodulator, as well as continuous signal modulation (ASK or FSK) with inserted discontinuities that can be independent of the digital data.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
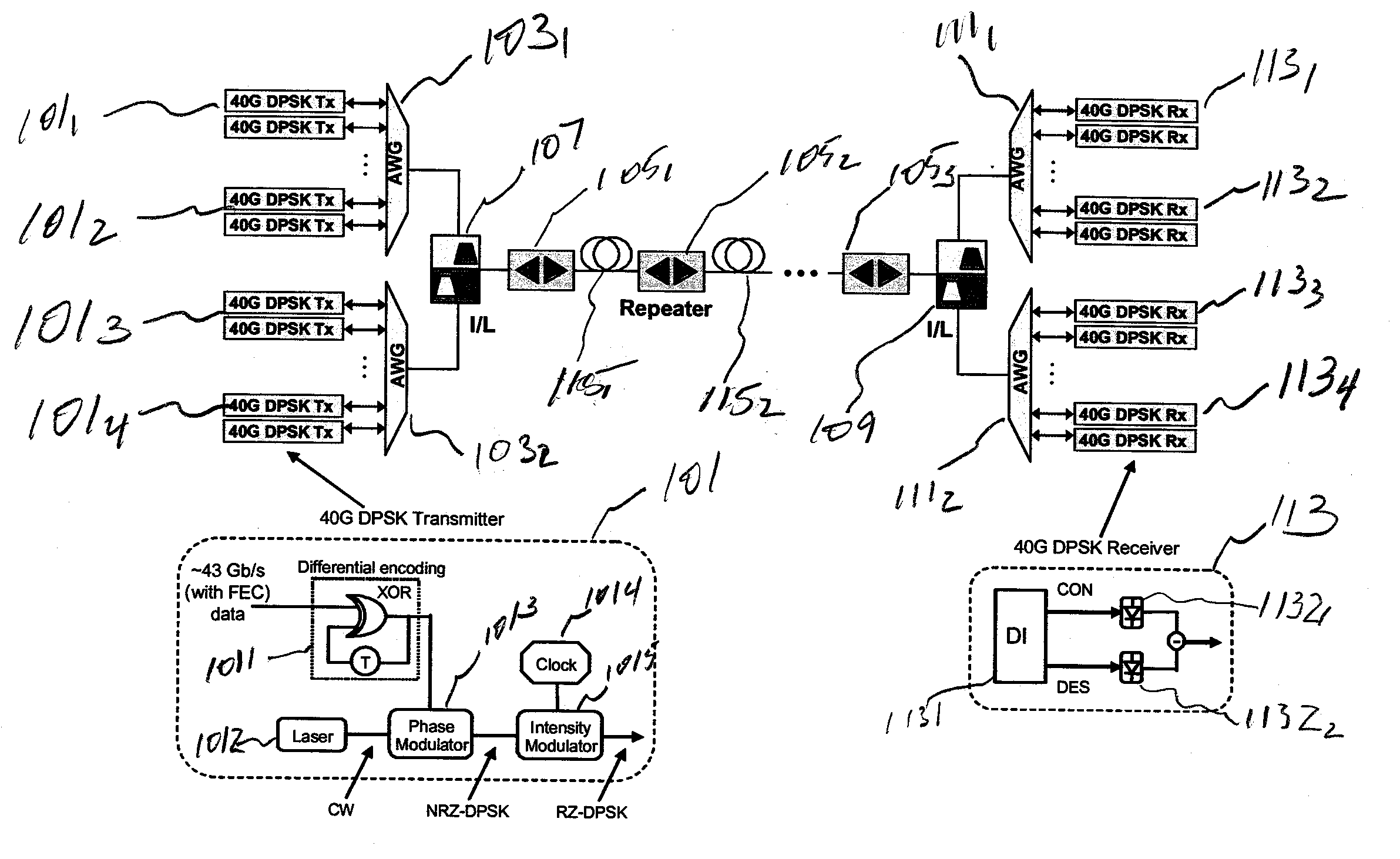
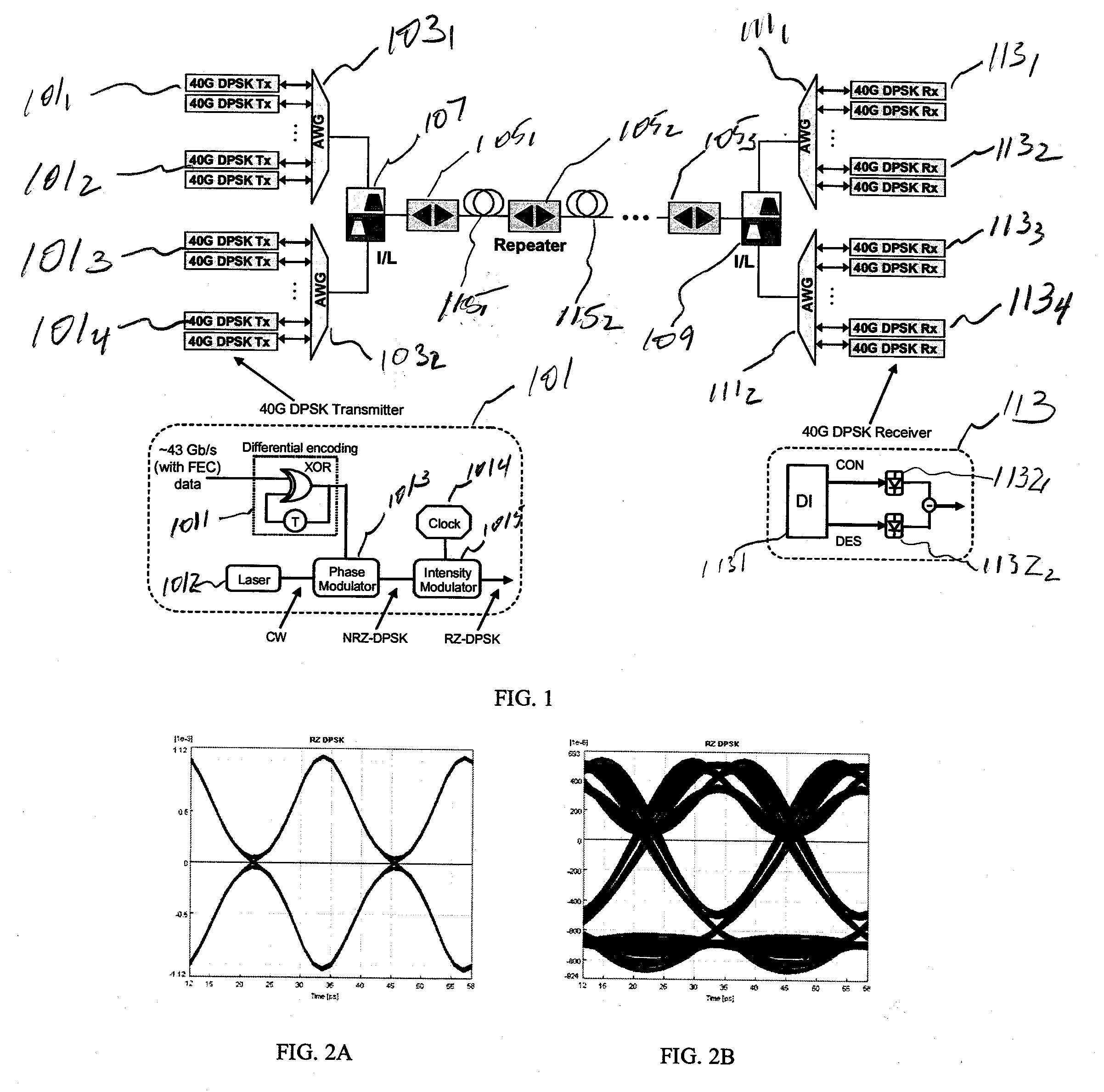
Inter-Symbol Interference-Suppressed Colorless DPSK Demodulation
An optical device includes an interferometer for a received optical differential phase shift keying DPSK signal, and an equalizer integrated with the interferometer in a manner for reducing from optical filtering effects an interference by signal bits of the DPSK signal with signal bits of a contiguous DPSK signal. The interferometer is a Michelson delay interferometer type, but can also be a Mach-Zehnder delay interferometer type on fiber, waveguide or other optical structure. The equalizer is a Fabry-Perot type equalizer, but can be a ring resonator type or a fiber based equalizer.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Method for qulitative evaluation of a digital audio signal
InactiveUS20050143974A1Reduce bitrateReliable estimateSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumIndicator vector
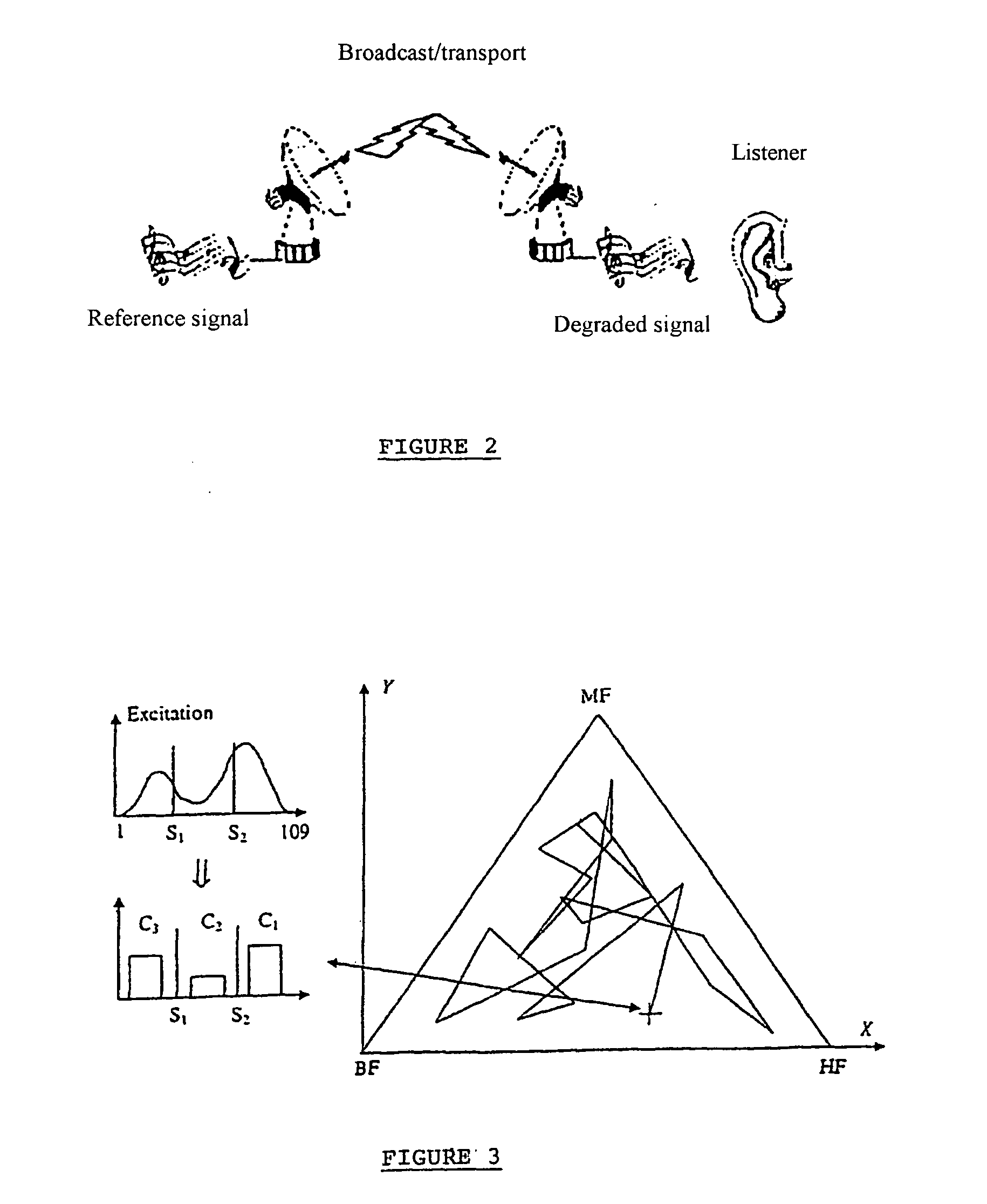
The invention relates to a method of qualitatively evaluating a digital audio signal. It calculates a quality indicator consisting of a vector associated with each time window in real time, in continuous time, and in successive time windows. For example, the generation of a quality indicator vector calculates, for a reference audio signal and for an audio signal to be evaluated, the spectral power density of the audio signal, the coefficients of a prediction filter, using an autoregressive method, a temporal activity of the signal or the minimum value of the spectrum in successive blocks of the signal. To evaluate the deterioration of the audio signal, the method may calculate a distance between the vectors of the reference audio signal and the audio signal to be evaluated associated with each time window.
Owner:TELEDIFFUSION DE FRANCE SA
Distributed stimulated Brillouin temperature strain sensing system based on double-sideband modulation
InactiveCN102680136ACompensation for the Brillouin effectLow costThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansContinuous lightLine width
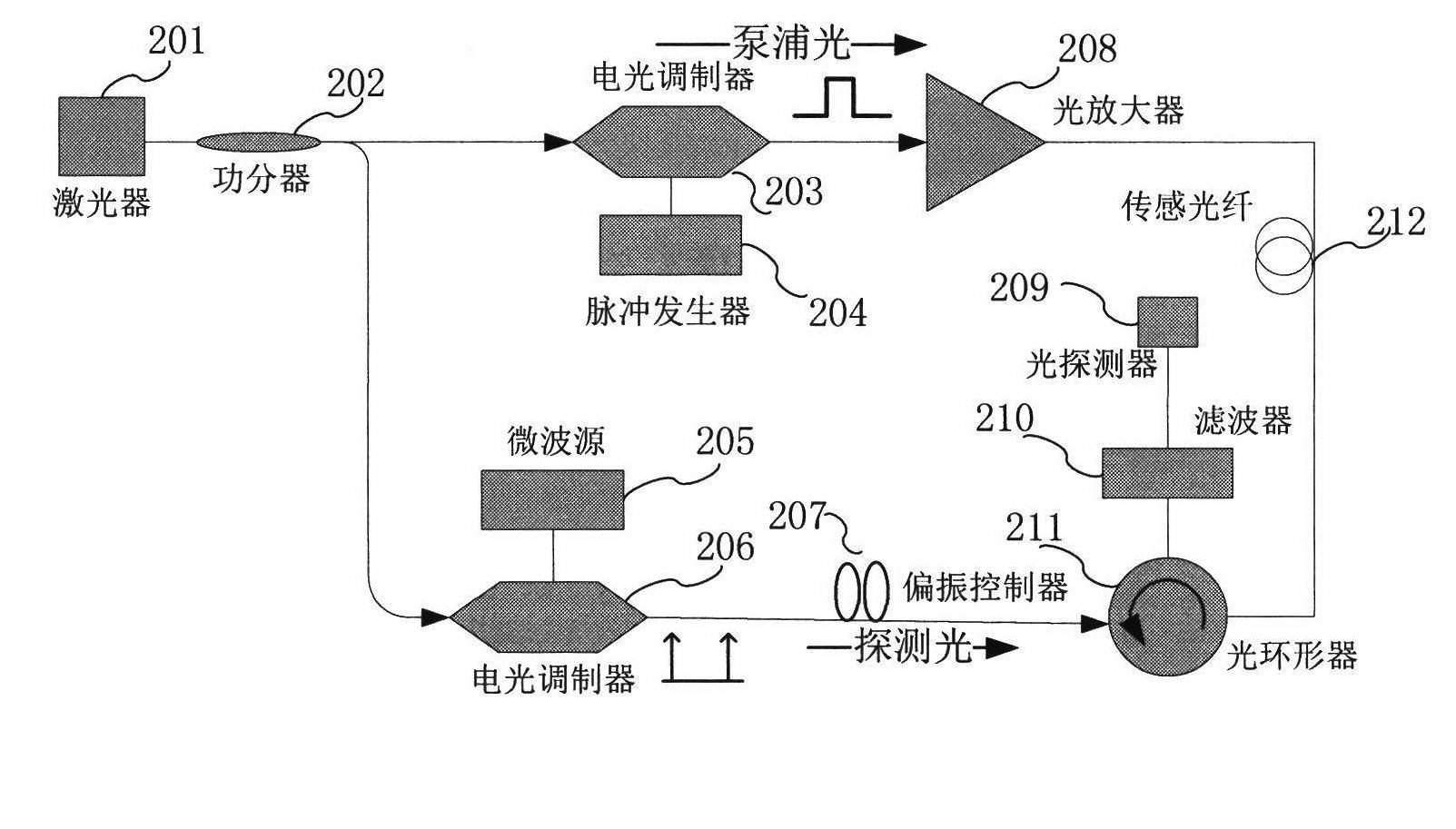
The invention provides a distributed stimulated Brillouin temperature strain sensing system based on double-sideband modulation, which includes a narrow linewidth light source, a power divider, a microwave source, a pulse signal emitter, an optical receiver, an optical amplifier, an electrooptical modulator and a sensing optical fiber, wherein a pulse optical signal and a continuous signal that is modulated by double-sideband are input into the two ends of the sensing optical fiber respectively; the pulse optical signal serves as a pumping optical signal; the double-sideband continuous optical signal serves as a detecting optical signal; the pumping optical and detecting optical signals encounter to produce the stimulated Brillouin; and the continuous light carries the temperature or strain information of the points distributed along the sensing optical fiber. The double-sideband technology can effectively controls the Brillouin consumption of the pumping pulse during transmission, and greatly reduces the system error in measurement. The distributed stimulated Brillouin temperature strain sensing system is applicable to the fields as transmission cable and oil-gas pipeline monitoring and fire control, and is particularly applicable to sensing of long distance more than 50km.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
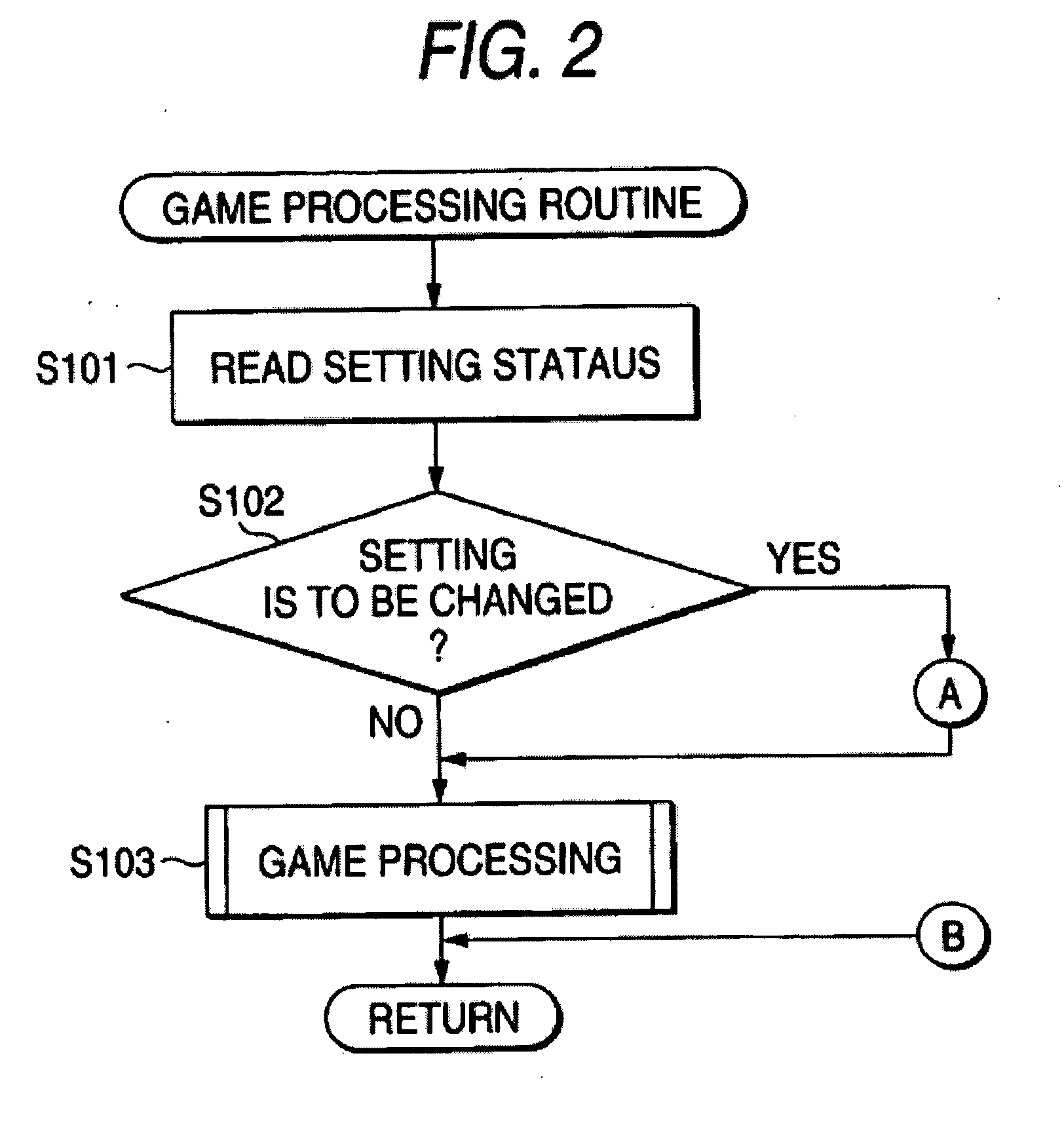
Game machine
InactiveUS20080132328A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesEngineeringContinuous signal
A game machine includes, an operating portion, a signal detector, a prompter, a determination receiver and a speed changer. The operating portion outputs a signal in accordance with a player's operation for proceeding a game. The signal detector detects either a consecutive signal within a predetermined period of time or an intermittent signal within a predetermined period of time from the operating portion. The prompter prompts a player to determine whether to change a speed of progress in the game when either the consecutive signal or the intermittent signal is detected. The determination receiver receives a player's determination regarding the change of the speed of progress in the game. The speed changer changes the speed of progress in the game in accordance with the player's determination when the player's determination is received.
Owner:KONAMI GAMING
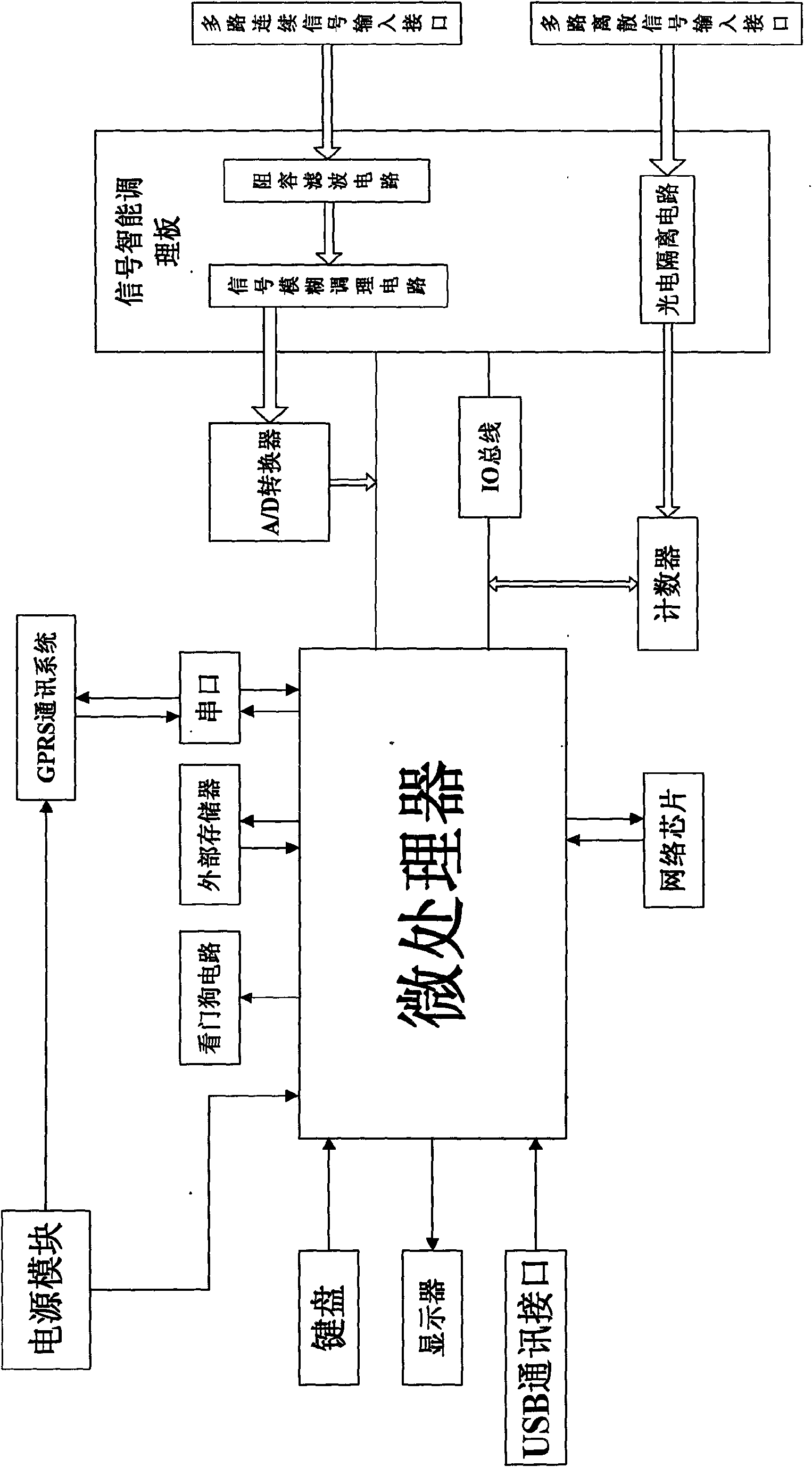
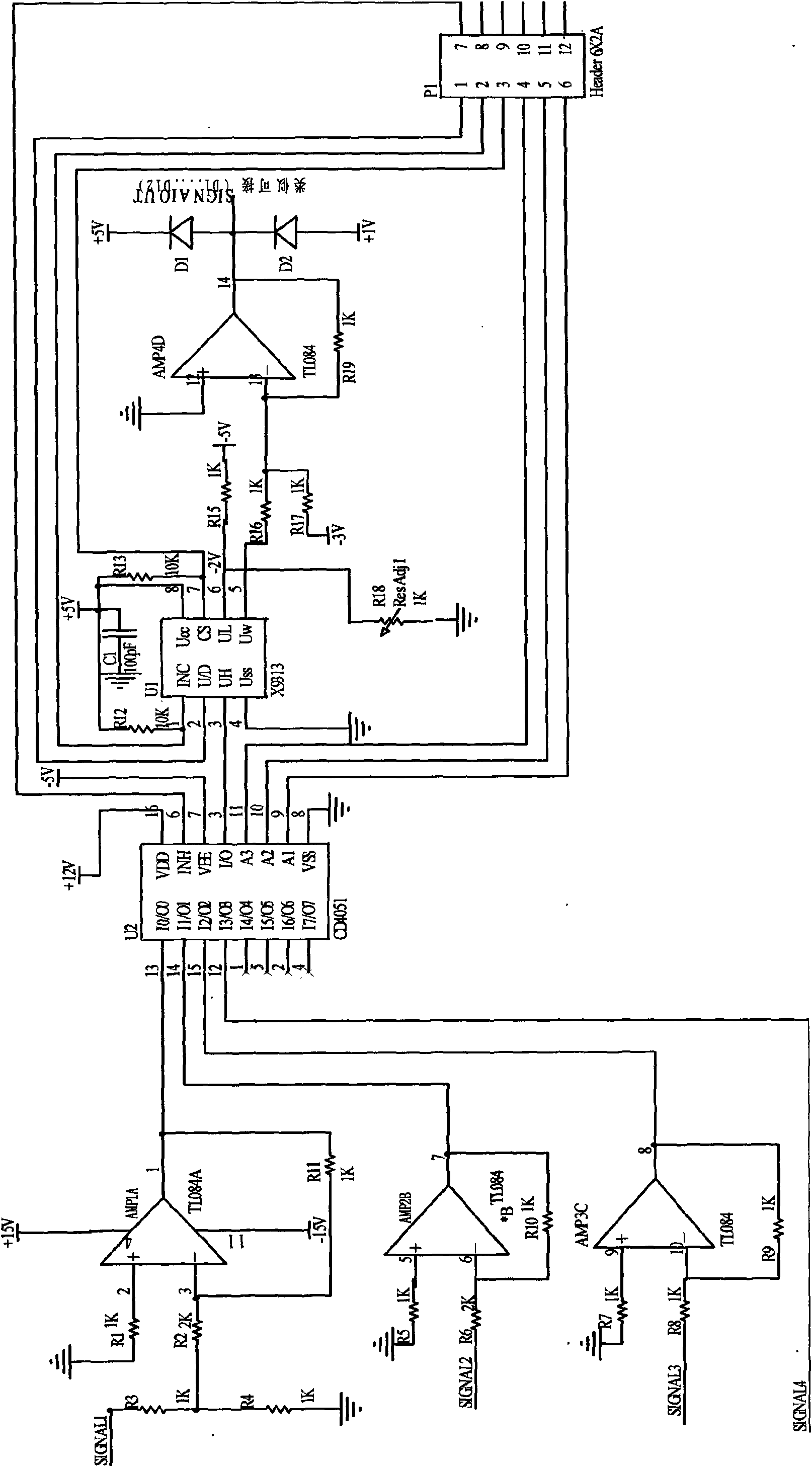
Universal data acquisition unit and data acquisition method thereof
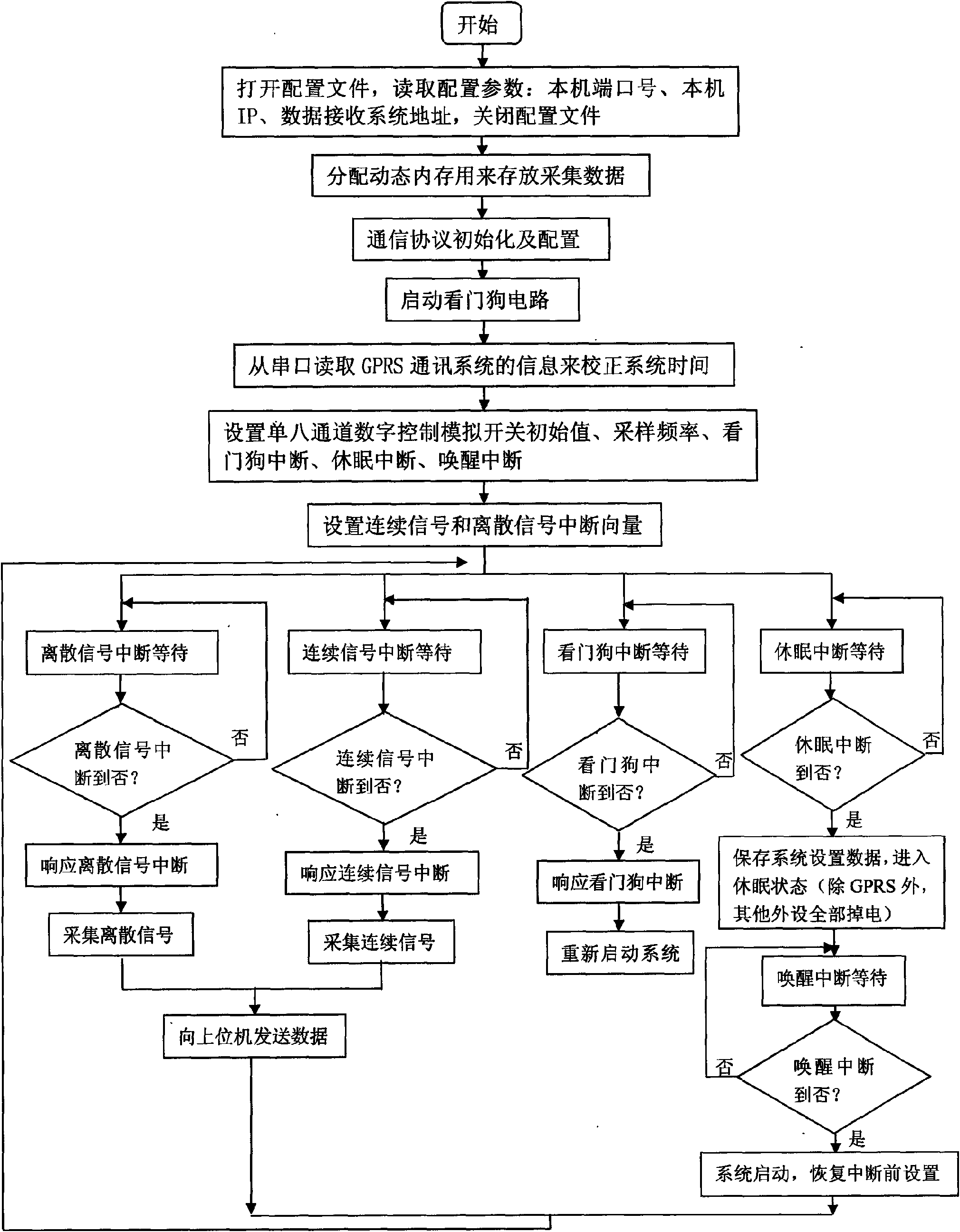
InactiveCN101661276AImprove performanceReduce power consumptionProgramme controlComputer controlData acquisitionContinuous signal
The invention relates to a universal data acquisition unit and a data acquisition method thereof, belonging to the technical field of data acquisition; the universal data acquisition unit comprises amicroprocessor; a multi-path discrete signal input interface is connected with the input end of a counter by a photoelectric isolating circuit, and a multi-path continuous signal input interface is connected with the input end of an A / D converter, and a microprocessor is connected with the input ends of the A / D converter and the counter. The data acquisition method comprises that: system initialization is carried out; continuous and discrete signal interrupt vector is set; interrupt latency is carried out, if the discrete signal is interrupted, the discrete signal is acquired; if the continuous signal is interrupted, the continuous signal is acquired; if a watchdog is interrupted, a system is restarted; if hibernation is interrupted, system setting data is stored, and then a hibernation state is carried out; and then, interrupt latency awaken operation is carried out, if awakening is interrupted, the system is started, and the setting is restored before interruption; if the continuoussignal and the discrete signal are acquired, interrupt latency is continuously carried out after data is transmitted to an upper computer; if not, interrupt latency is carried out directly.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Signal processing method, equipment and system for passive optical network (PON)
InactiveCN102075478AReduce construction costsSimple optical power compensationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission path divisionCarrier signalContinuous signal
The embodiment of the invention relates to a signal processing method, signal processing equipment and a signal processing system for a passive optical network (PON). The signal processing method for the PON comprises the following steps of: performing baseband coding on a received service signal; modulating the service signal subjected to baseband coding to an allocated orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) subcarrier in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation mode; performing digital-to-analog conversion on the modulated OFDMA subcarrier to acquire an electric domain OFDMA signal; modulating the electric field OFDMA signal to an uplink optical signal to acquire an optical domain OFDMA signal; and sending the optical domain OFDMA signal. In the embodiment of the invention, continuous optical signals can be acquired in the OFDMA modulation mode, and can perform optical power compensation so as to support remote transmission; and compared with equipment for transmitting and receiving a burst signal, equipment for transmitting and receiving the continuous signals is low in cost, so that the construction cost of the network is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com